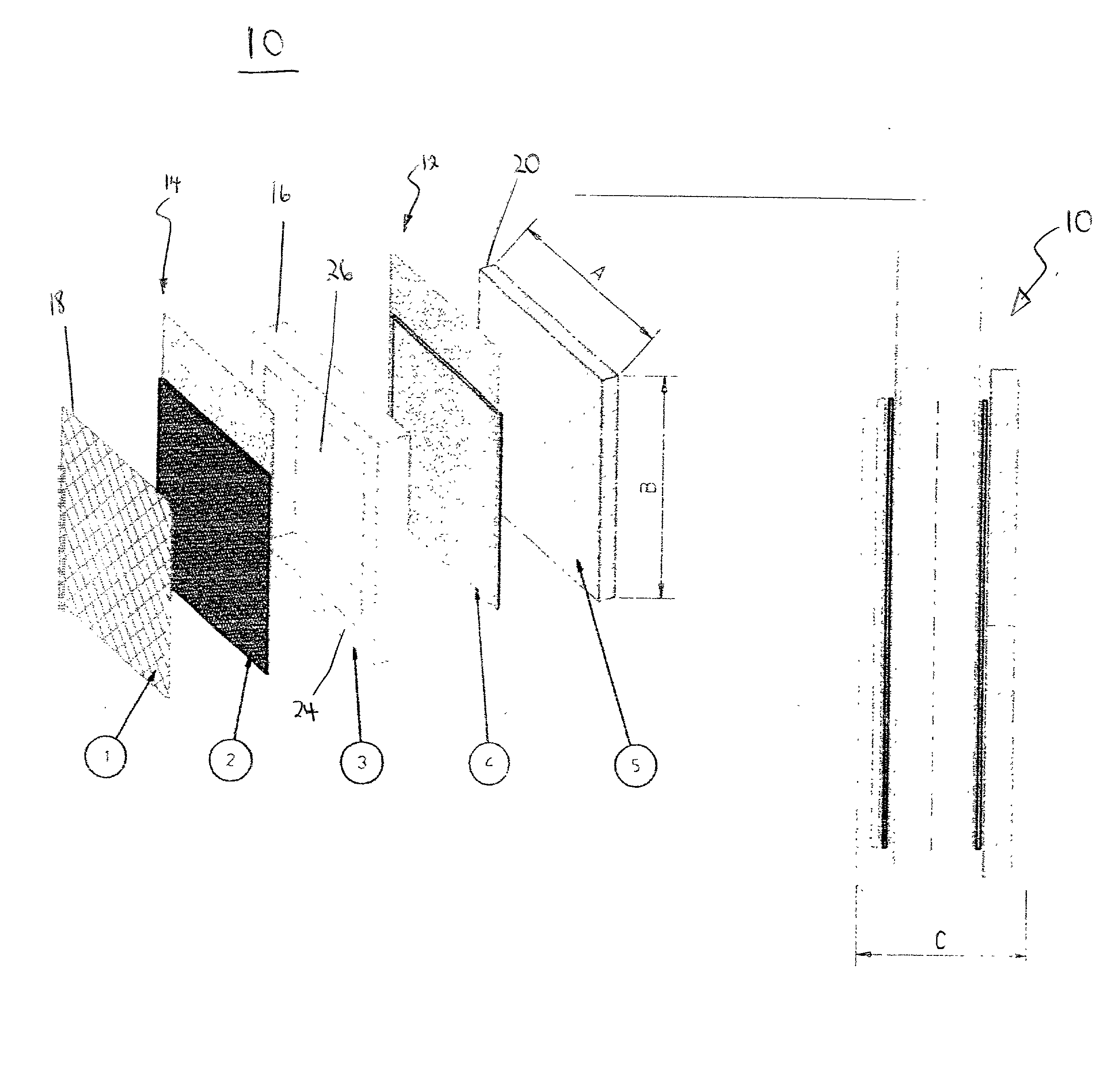
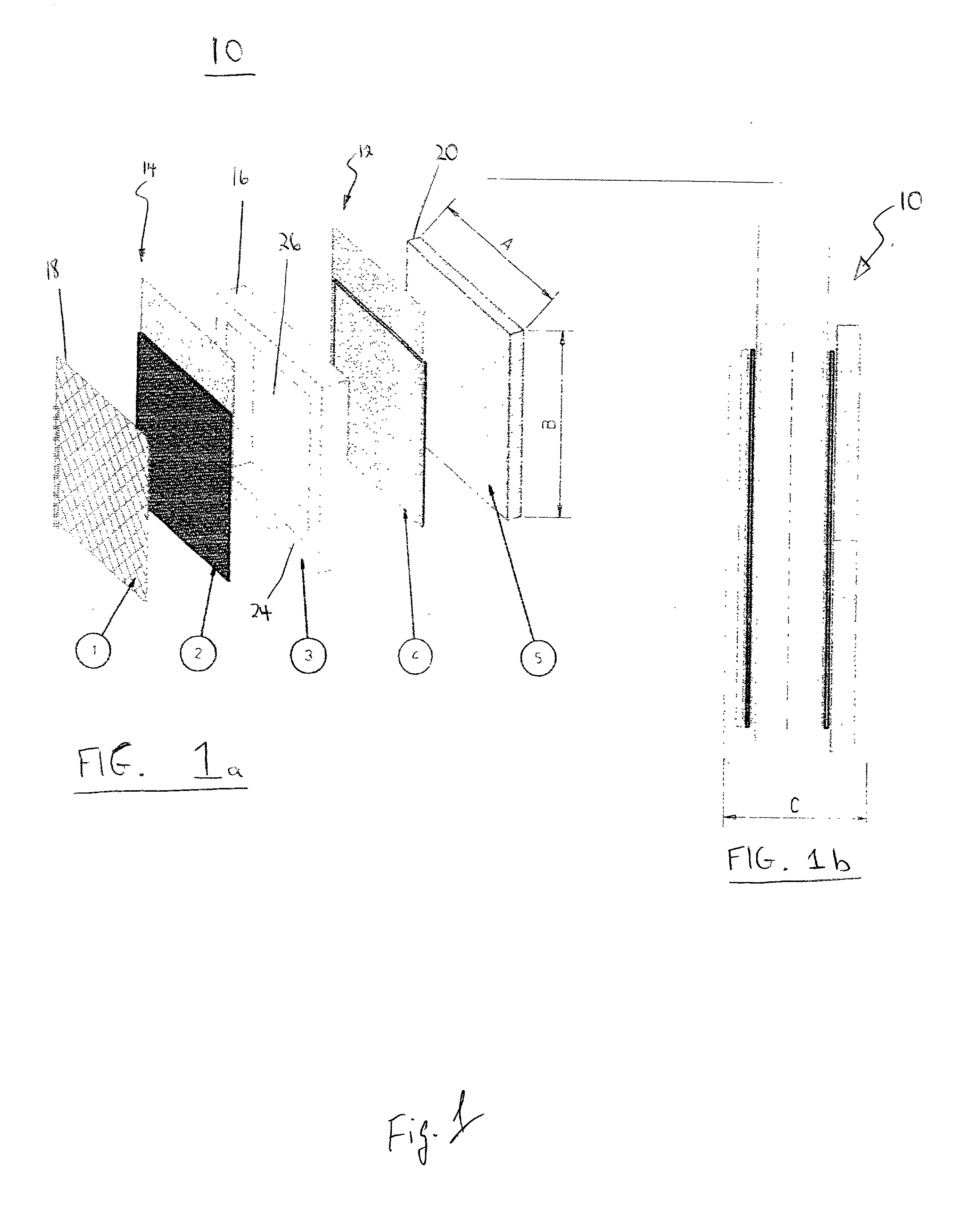
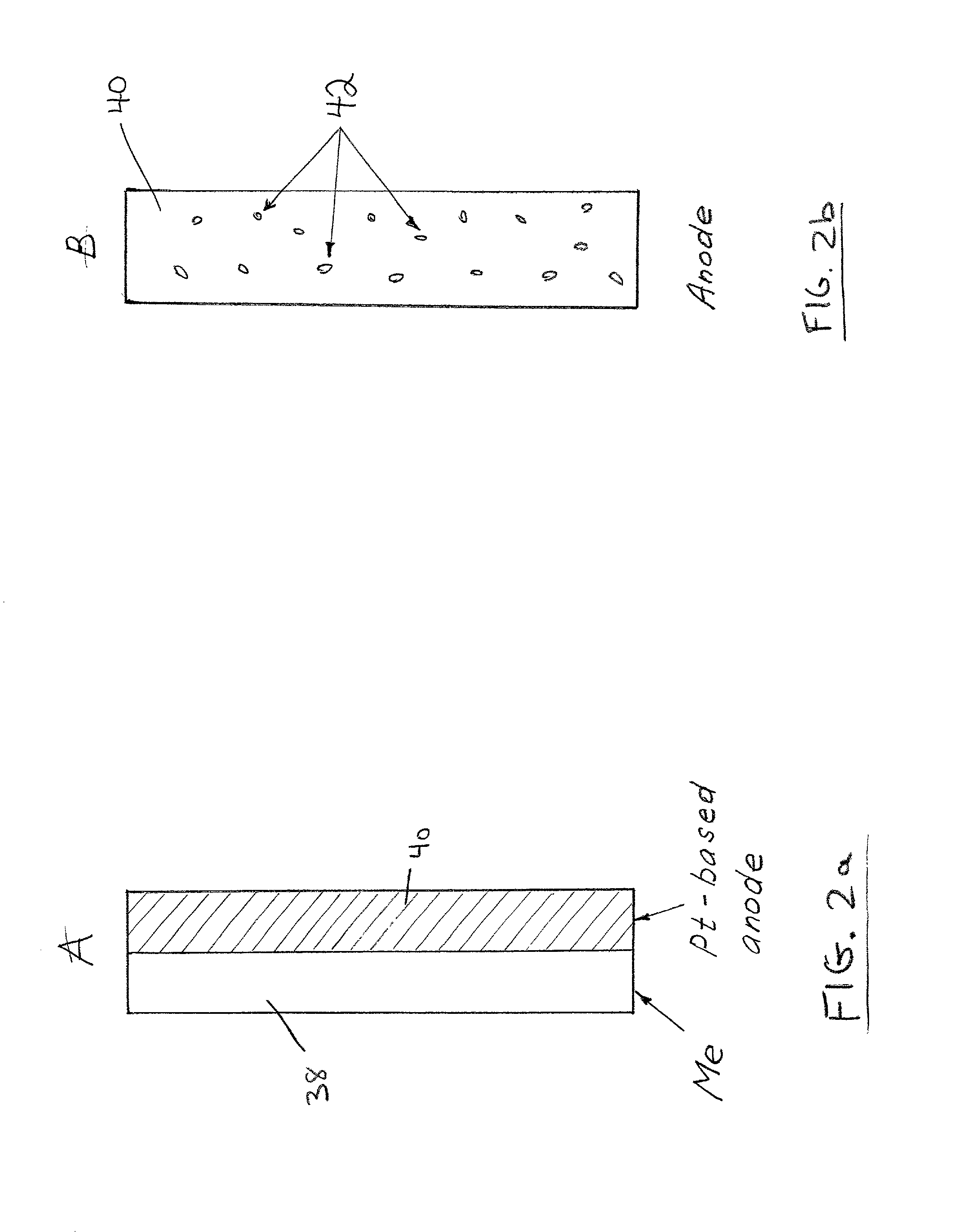
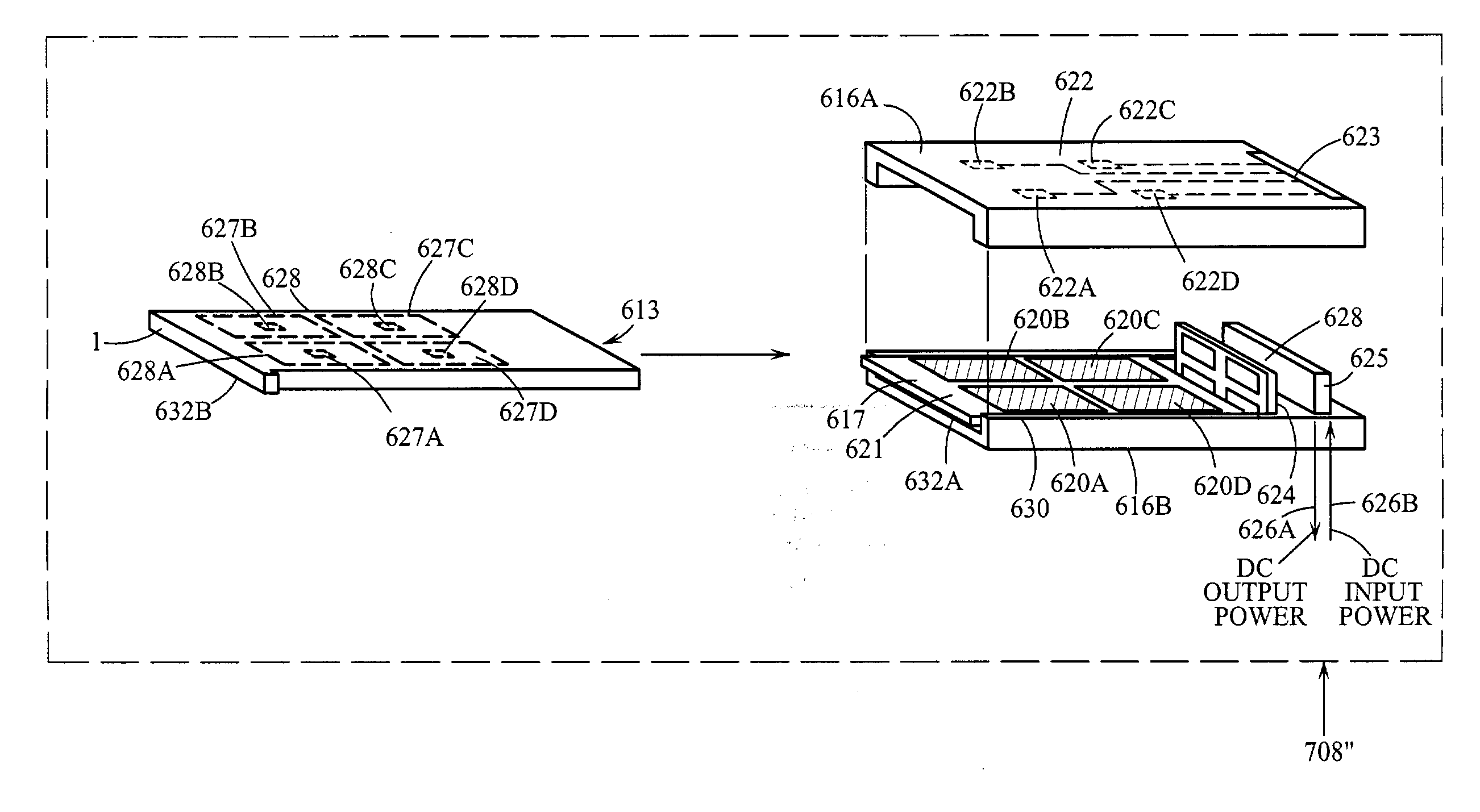
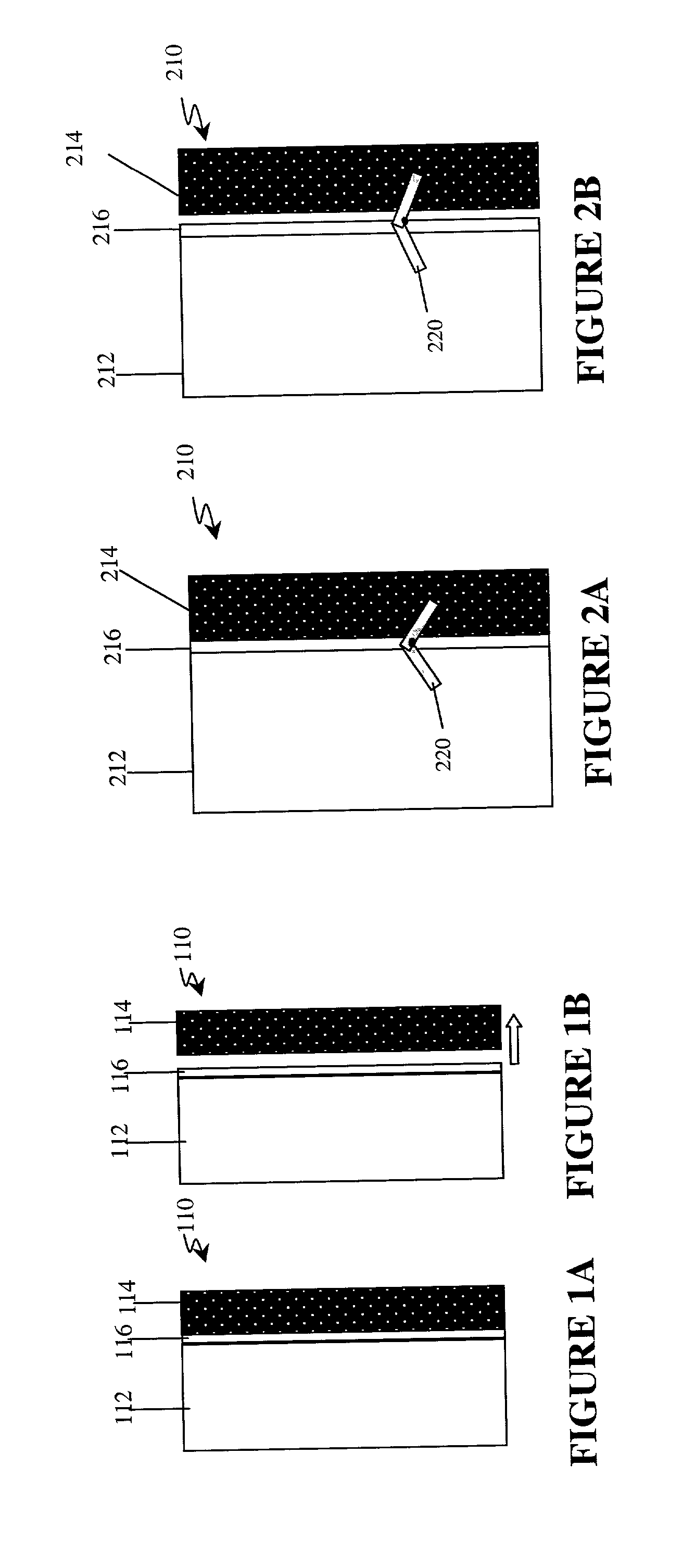
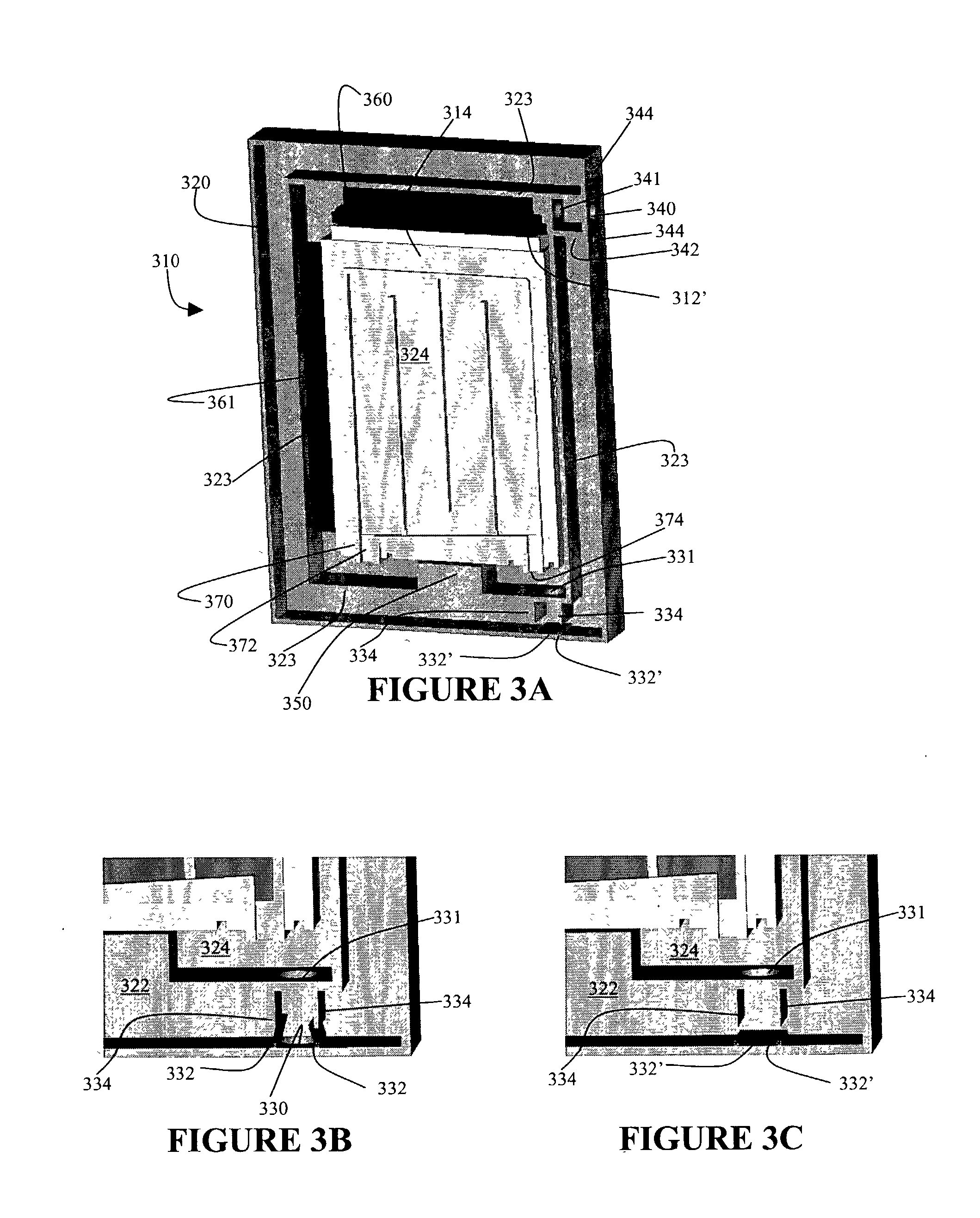
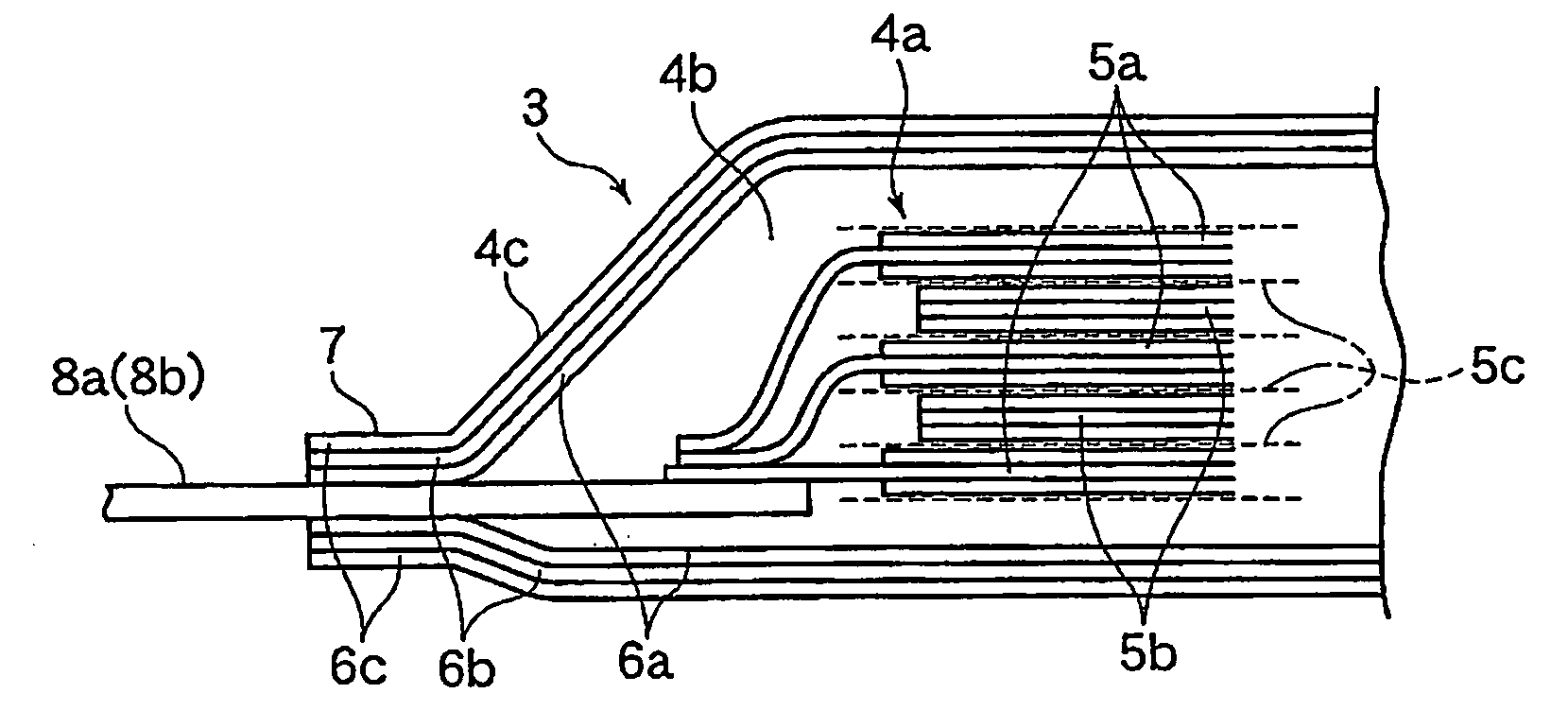
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54results about "Insertable electrodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
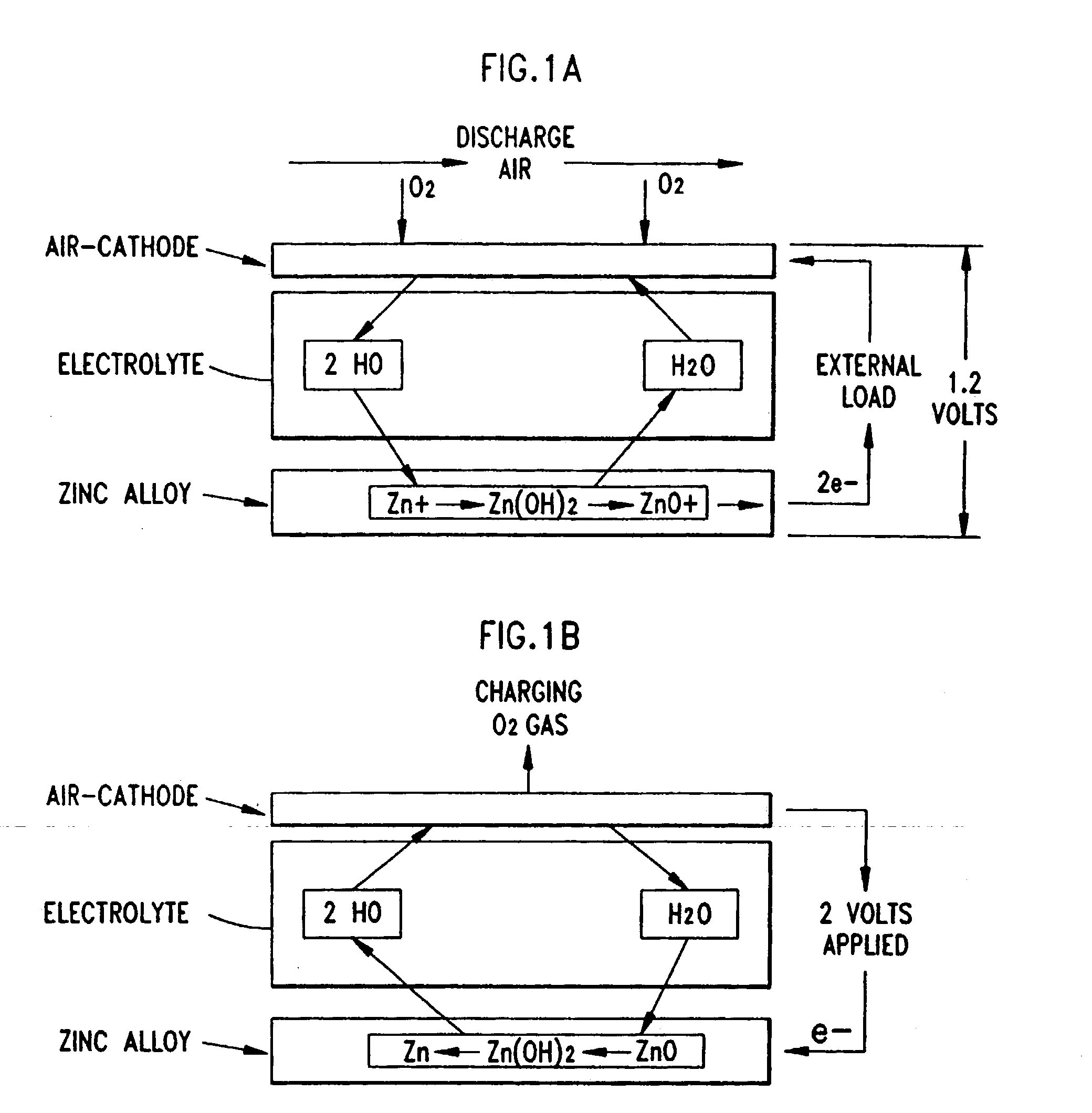
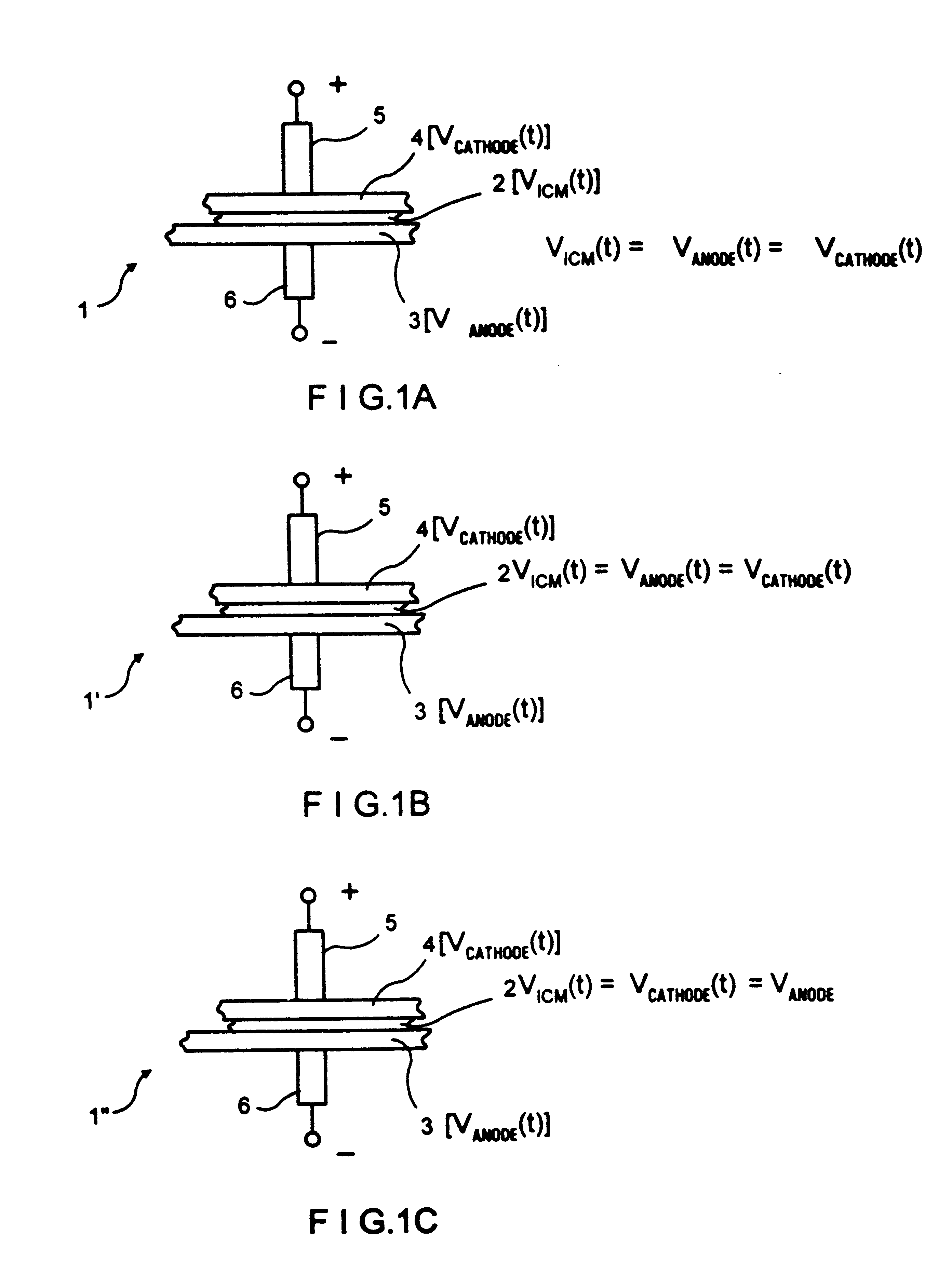
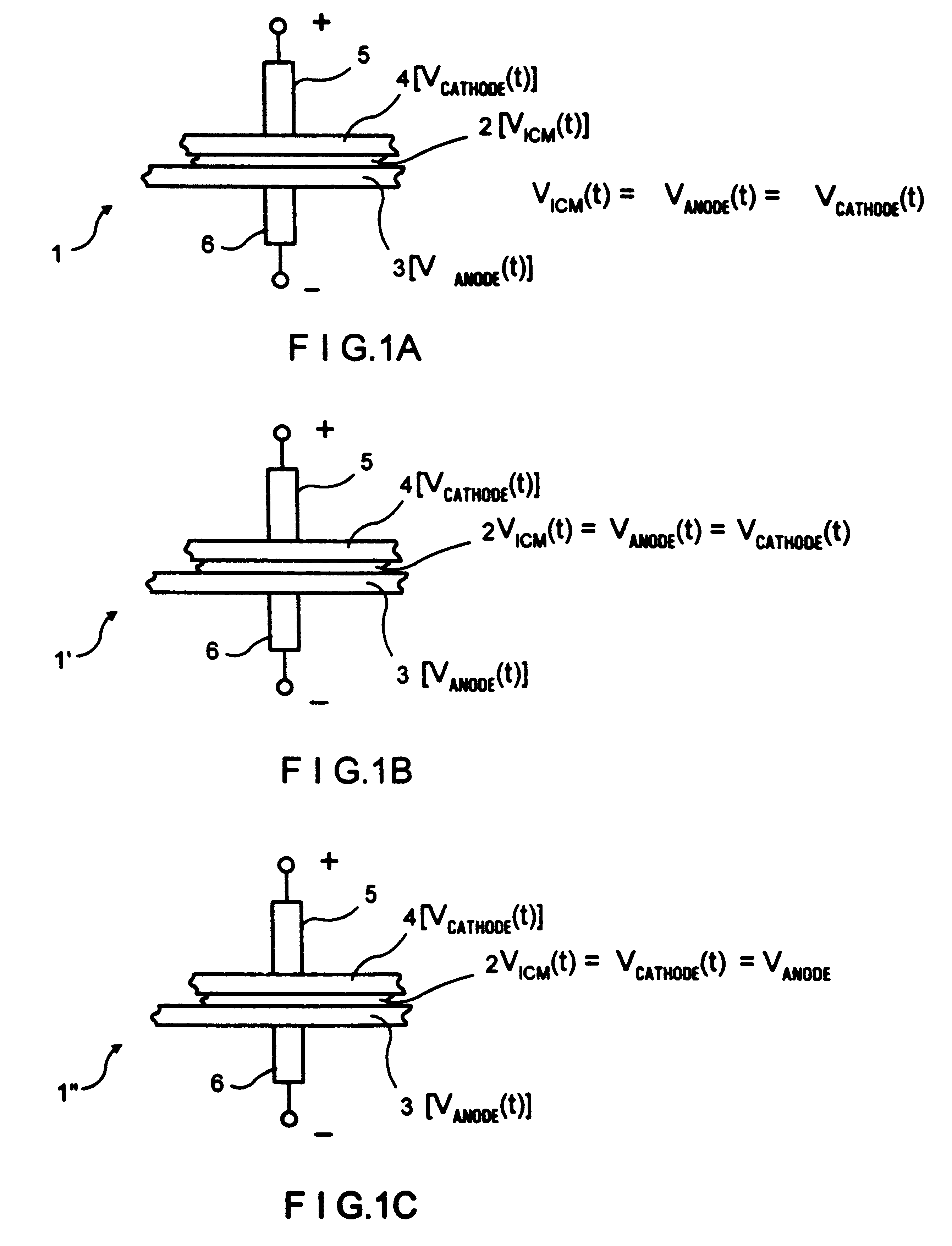
Direct liquid fuel cell and a novel binary electrode therefor
A fuel cell comprising: (a) a binary anode, (b) a cathode, and (c) a liquid electrolyte disposed between and interacting with the binary anode and the cathode, wherein the binary anode includes at least one liquid fuel and at least one solid fuel. Preferably, the electrolyte includes an alcohol such as methanol, and the solid fuel includes aluminum, magnesium and / or zinc.
Owner:MORE ENERGY
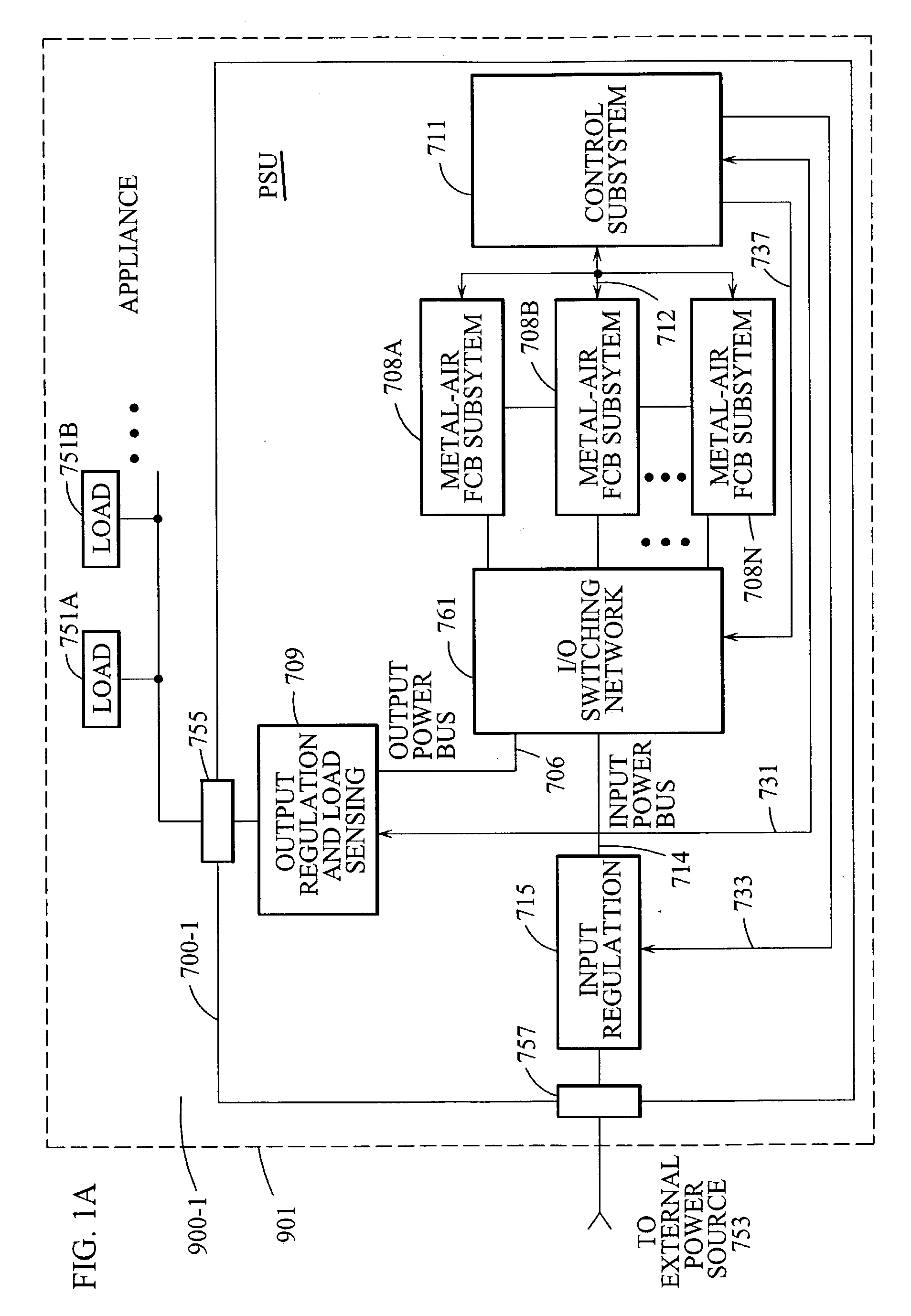
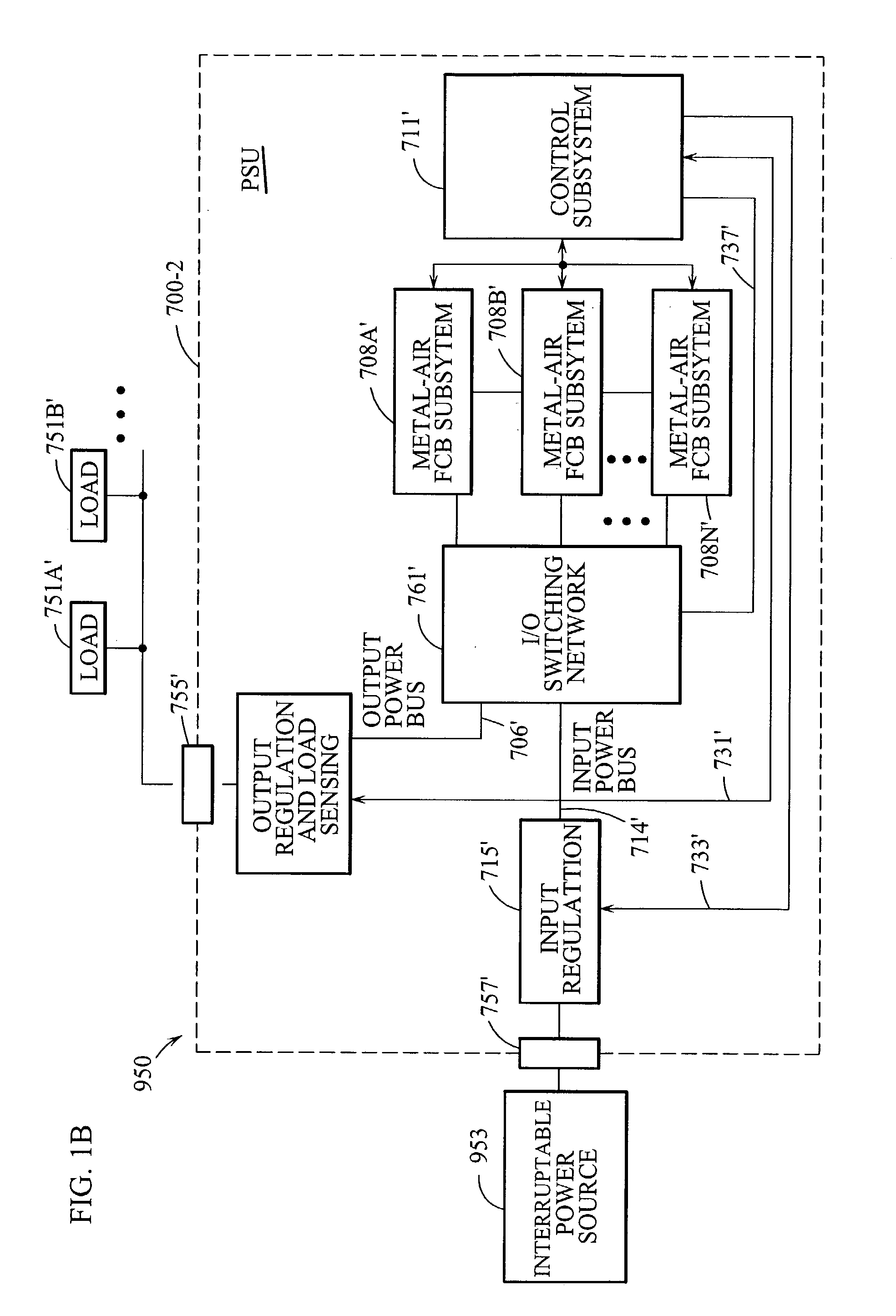
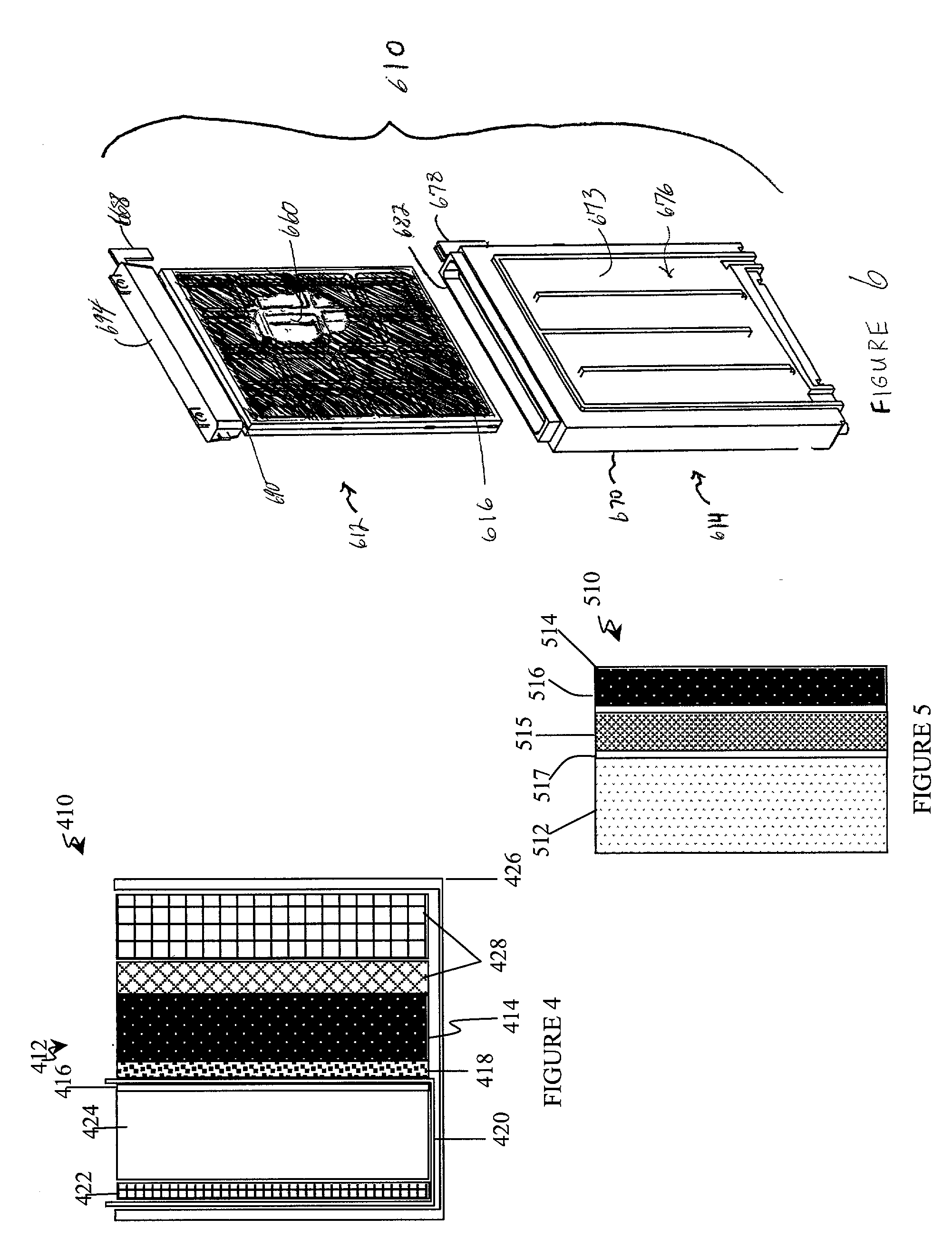
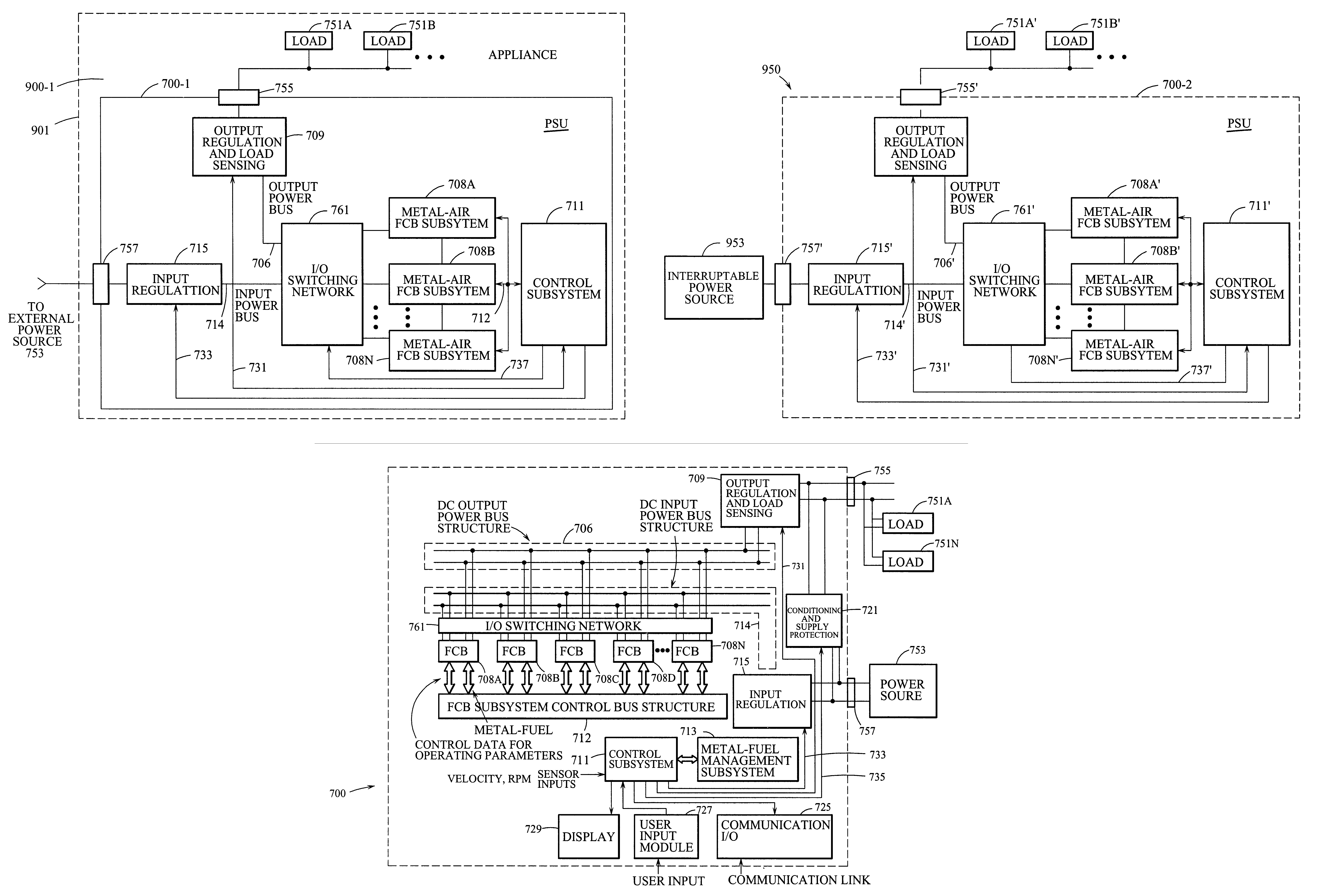
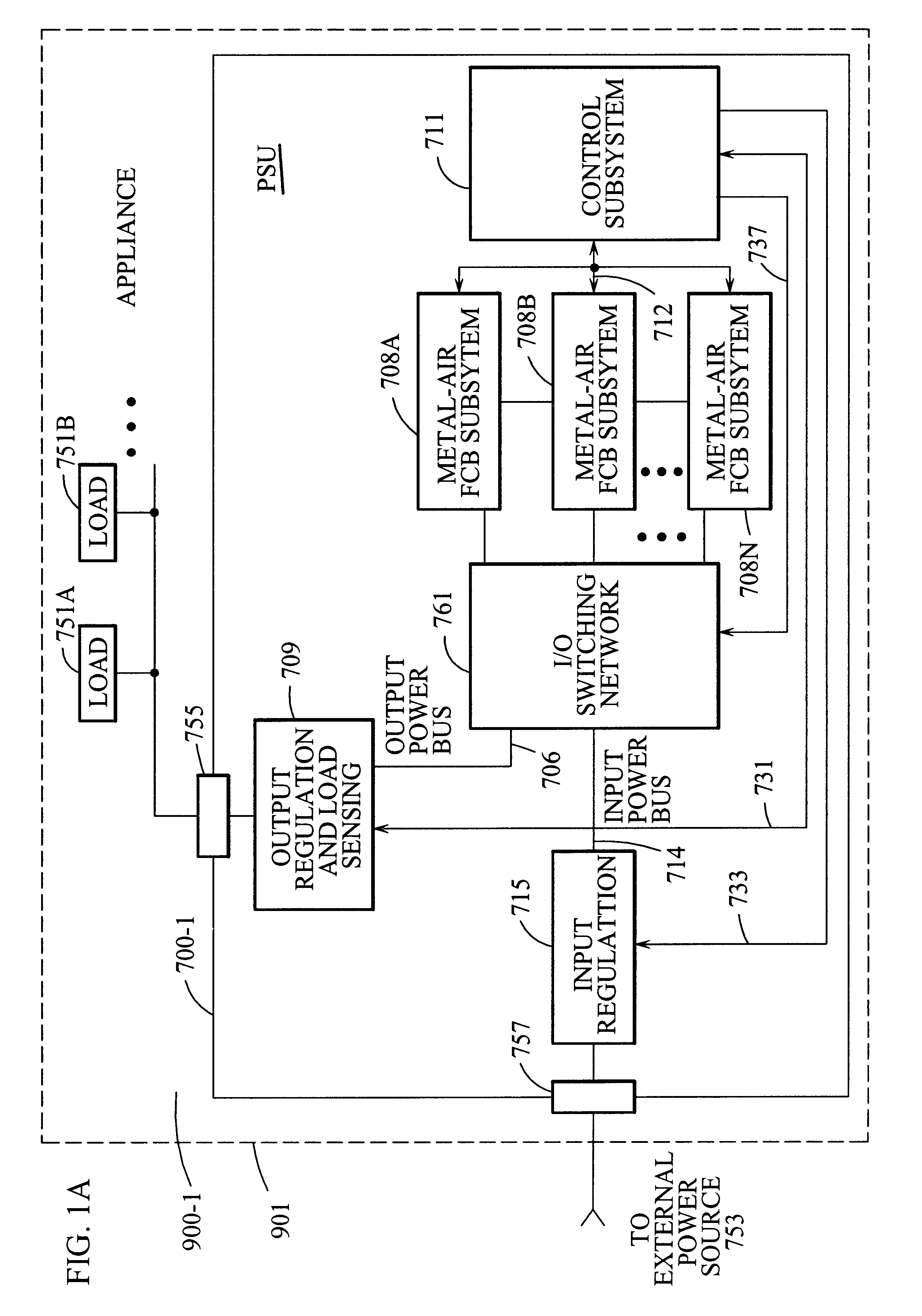
Appliance with refuelable and rechargeable metal-air fuel cell battery power supply unit integrated therein
InactiveUS20040005488A1Without risk and limitationEliminate needPrimary cell to battery groupingFuel and primary cellsElectricityFuel cells
Owner:FARIS SADEG M +1
Refuelable metal air electrochemical cell and refuelabel anode structure for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS20020142203A1Fuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsMetal–air electrochemical cellMetal particle
A refuelable anode structure containing anode paste for a metal air electrochemical cell is provided. The anode paste comprises metal particles, a gelling agent, and a base. The spent anode structure may be removed after discharging. The anode structure may thereafter be electrically recharged to convert oxidized metal into consumable metal fuel, or mechanically emptied and refilled with fresh metal fuel paste.
Owner:EVIONYX INC
Metal air cell system
A metal air cell system is provided. The system includes a cathode having a pair of oxidant sides and anode sides. An anode is provided in two parts, each part having a side complementary each anode side of the cathode. A separator is disposed between the anode and cathode to electrically isolate the anode and the cathode. Electrolyte is disposed between the cathode and the anode, the electrolyte provided within the anode, separately at the interface between the cathode and the anode, or both within the anode and separately at the interface between the cathode and the anode. This configuration generally allows a single oxidant flow to be exposed to both portions of the cathode due to the central passage of the oxidant.
Owner:EVIONYX INC
Appliance with refuelable and rechargeable metal-air fuel cell battery power supply unit integrated therein
InactiveUS6558829B1Without riskWithout limitationPrimary cell to battery groupingFuel and primary cellsElectrical batteryEngineering
A device / system having an integrated refuelable and rechargable metal-air FCB based power supply unit for generating and providing electrical power to at least one electrical-energy-consuming load device disposed therein. An external power source is used to recharge the metal-air FCB subsystems embodied therein. A control subsystem automatically transitions between discharging mode (wherein at least one metal-air FCB subsystem supplies electrical power to the electrical power-consuming load device) and a recharging mode (wherein the external power source is electrically coupled to at least one metal-air FCB subsystem to thereby recharge the metal-air FCB subsystem(s). The metal-air FCB subsystem(s) are refueled by manually loading and unloading metal-fuel from the metal-air FCB subsystem(s). Preferably, electrical power provided to the at least one electrical power-consuming load device is supplied solely by electrical power generated by discharging metal-fuel in the metal-air fuel cell battery subsystem(s). In addition, the metal-air FCB subsystem(s) preferably has a modular architecture that enable flexible and user-friendly operations in loading of metal-fuel, unloading of consumed metal-fuel, replacement of the ionic-conducting medium, and replacement of the cathode.
Owner:REVEO
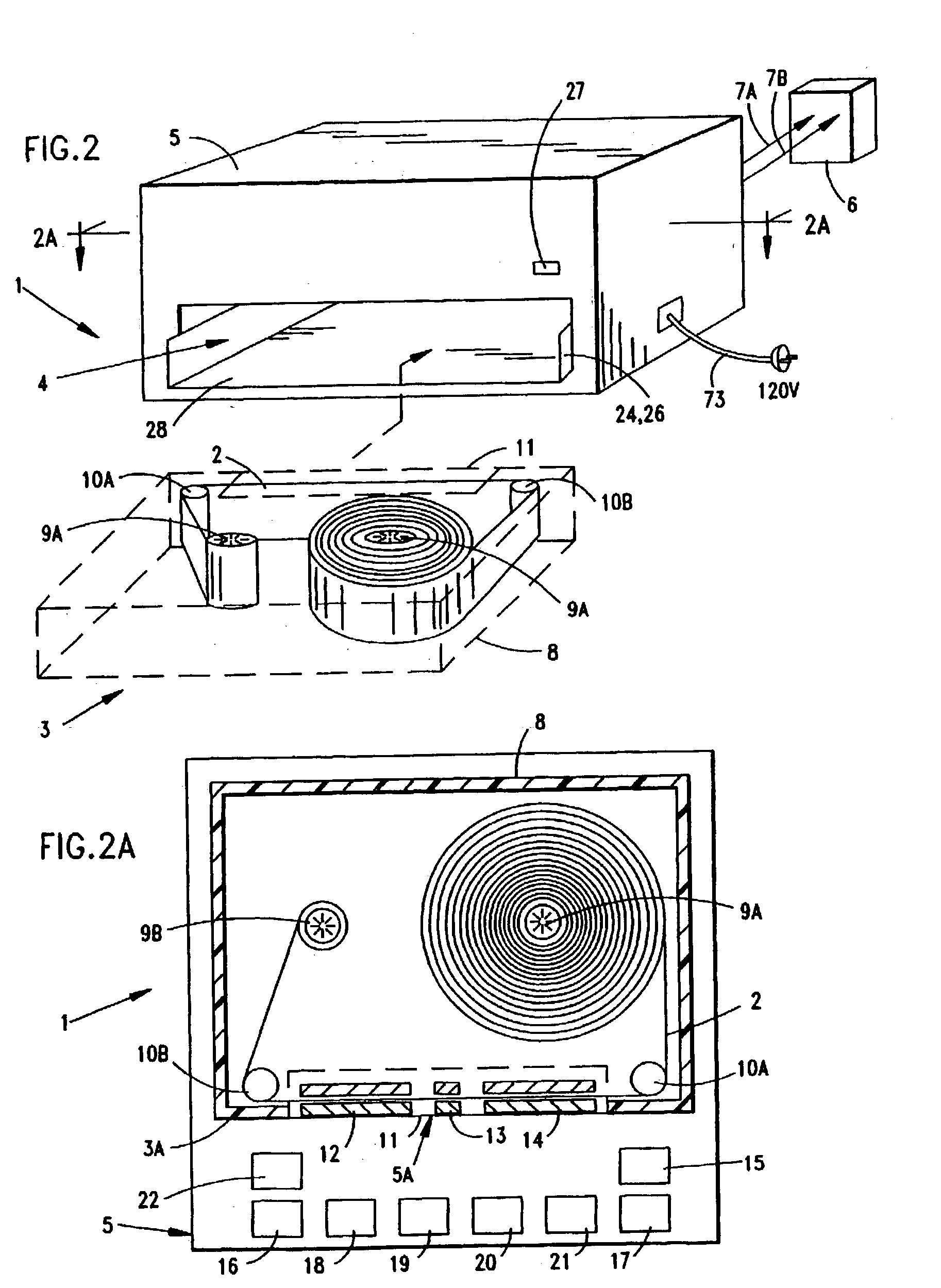
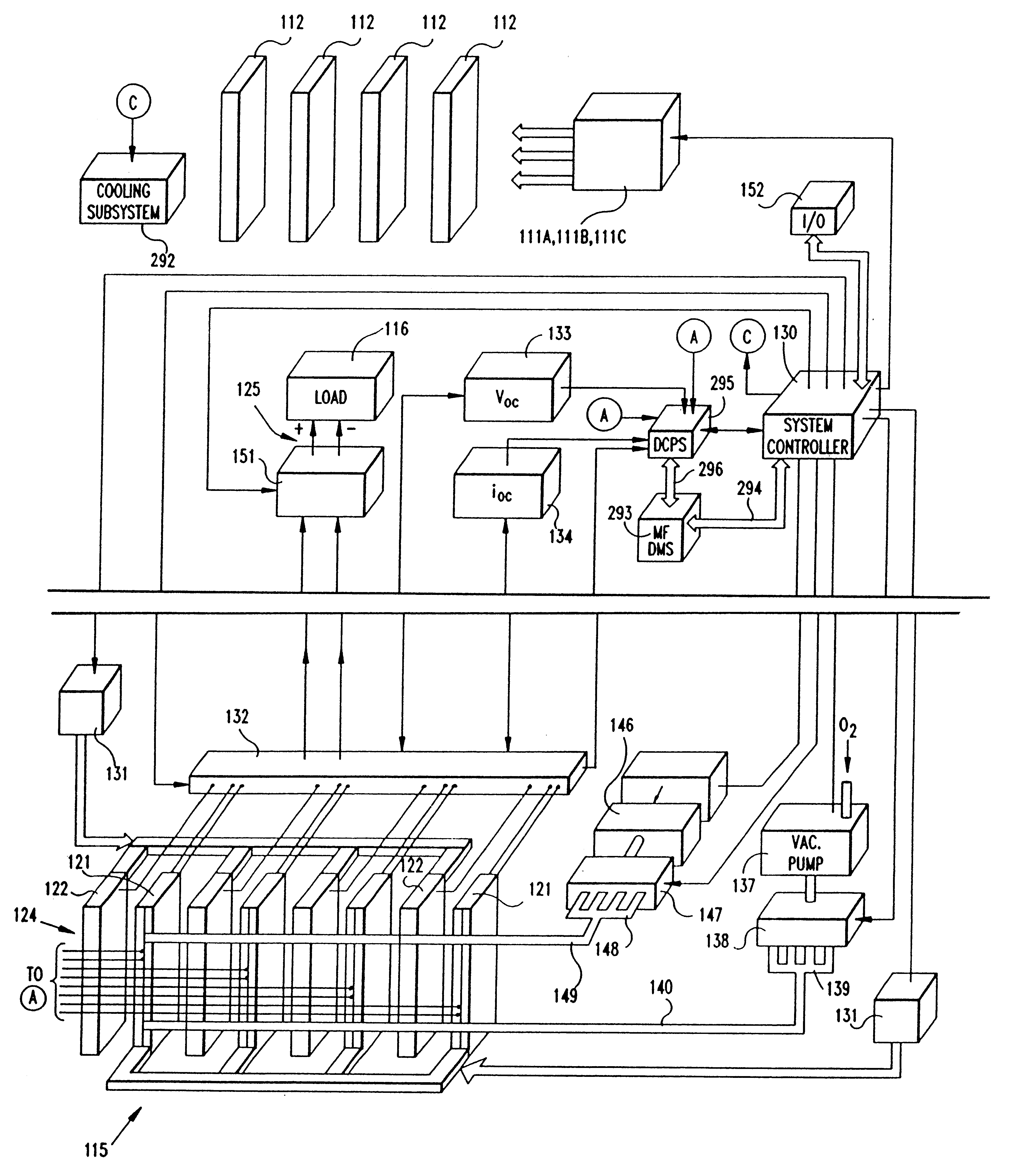
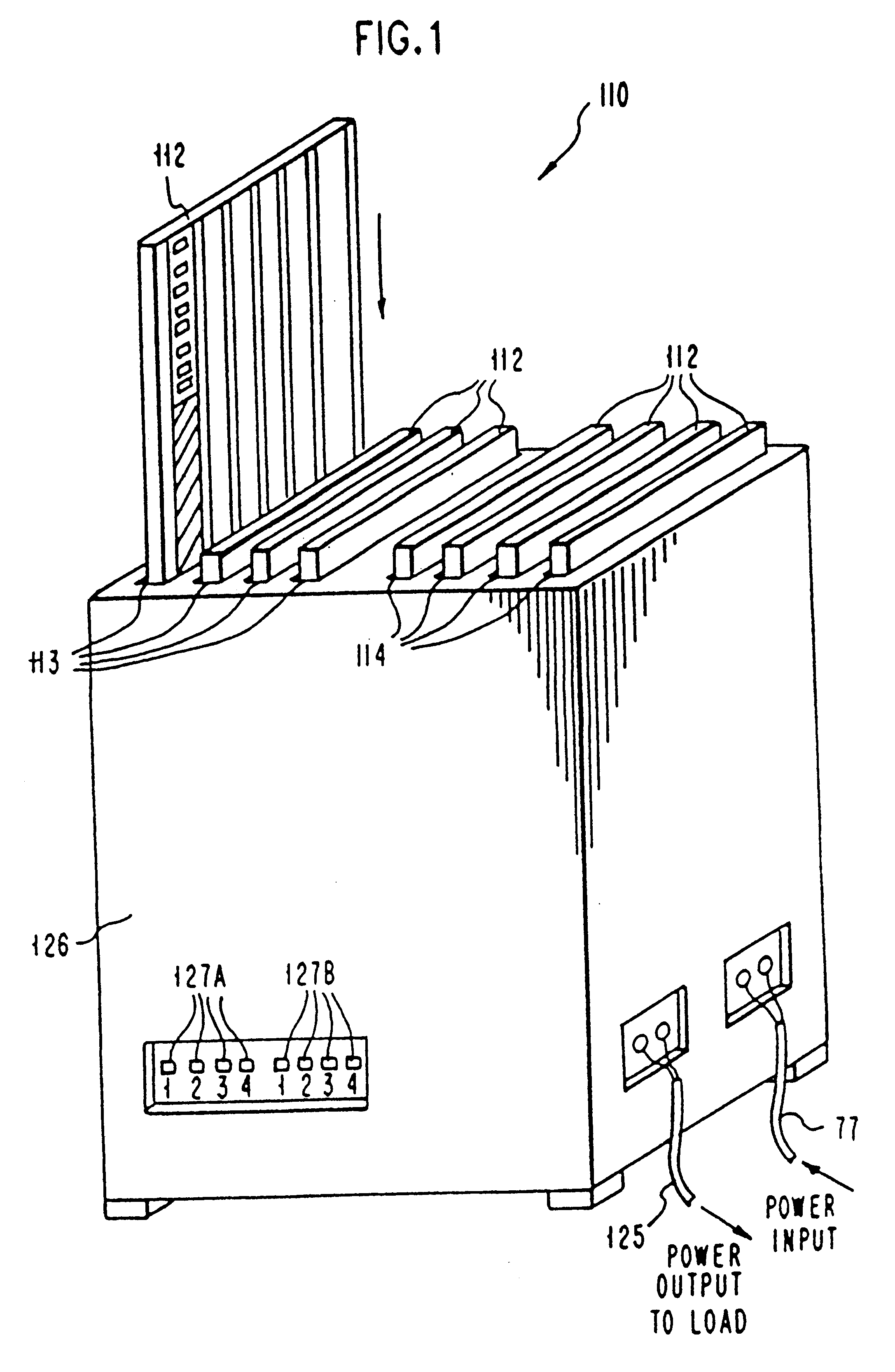
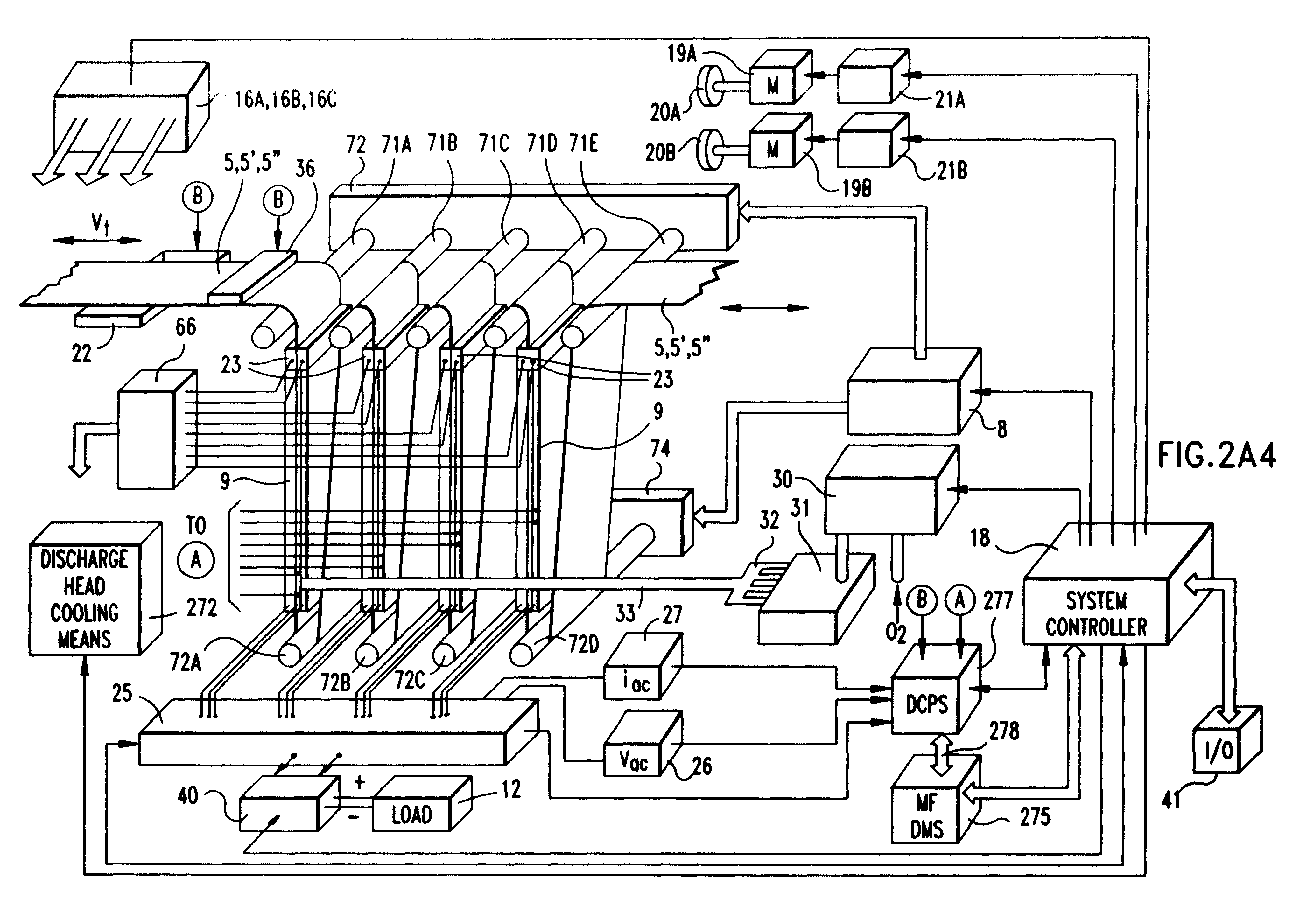
System and method for producing electrical power using metal-air fuel cell battery technology
InactiveUS20040247969A1Fast chargingFuel and primary cellsMoving electrode arrangementsElectricityFuel cells
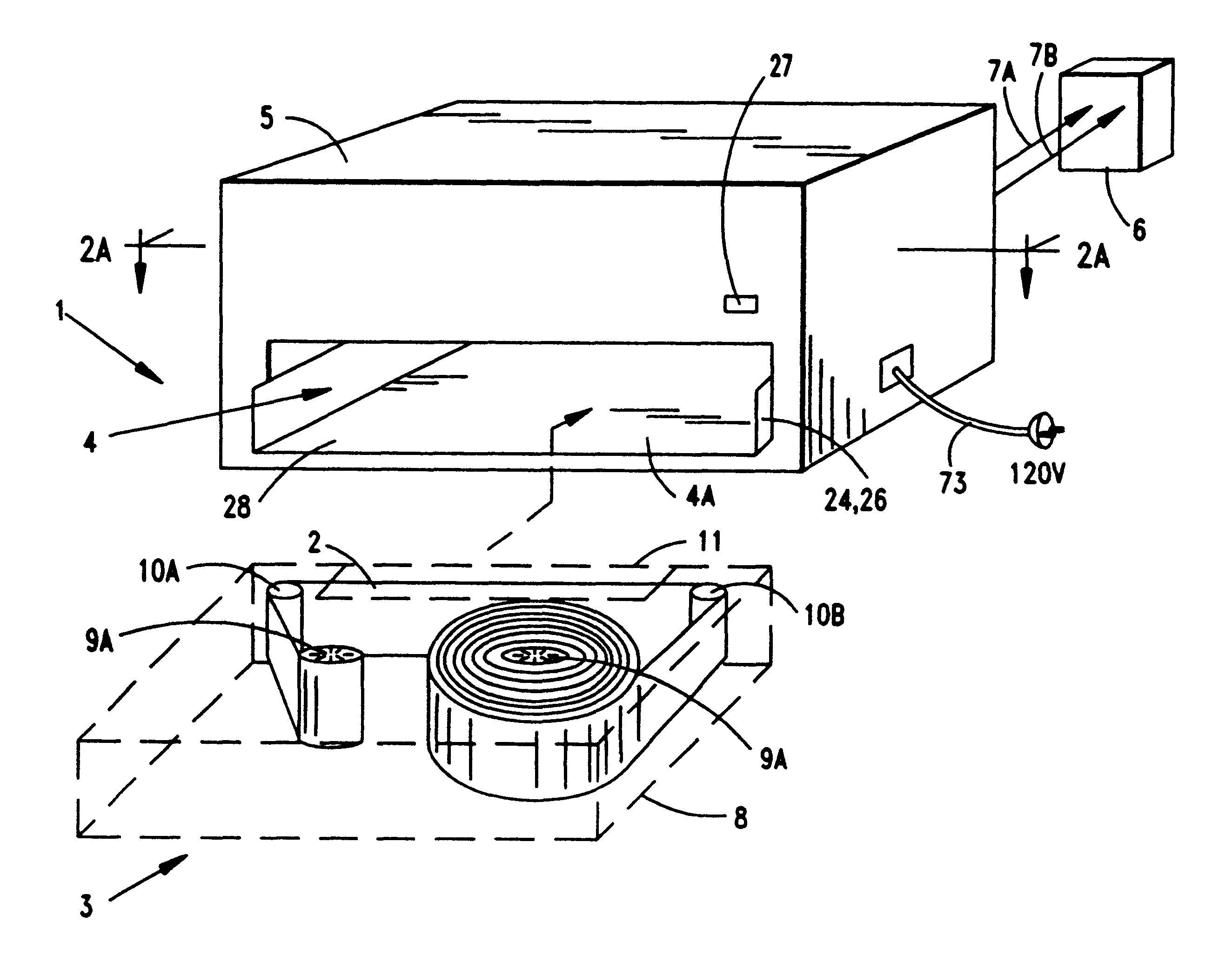
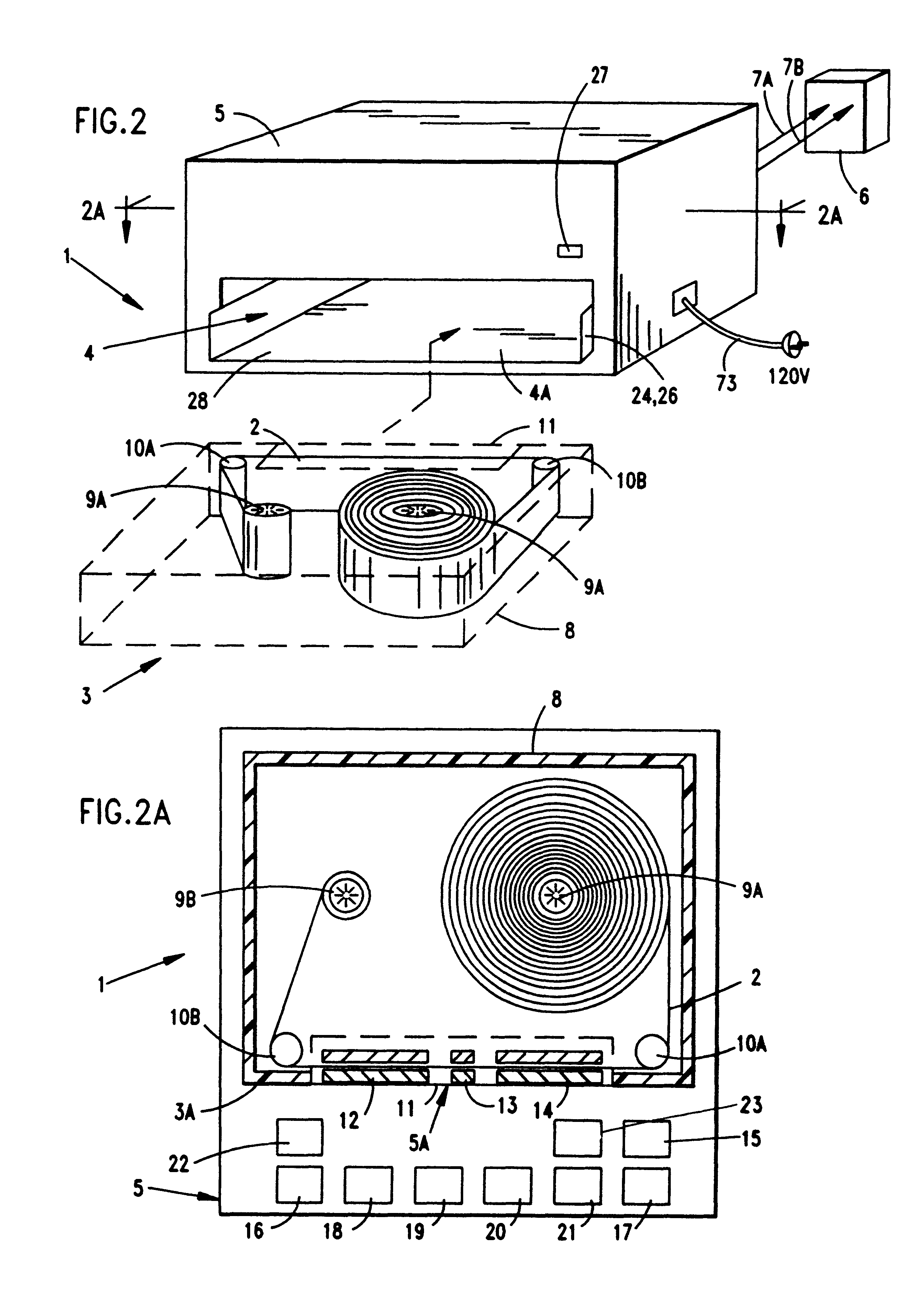
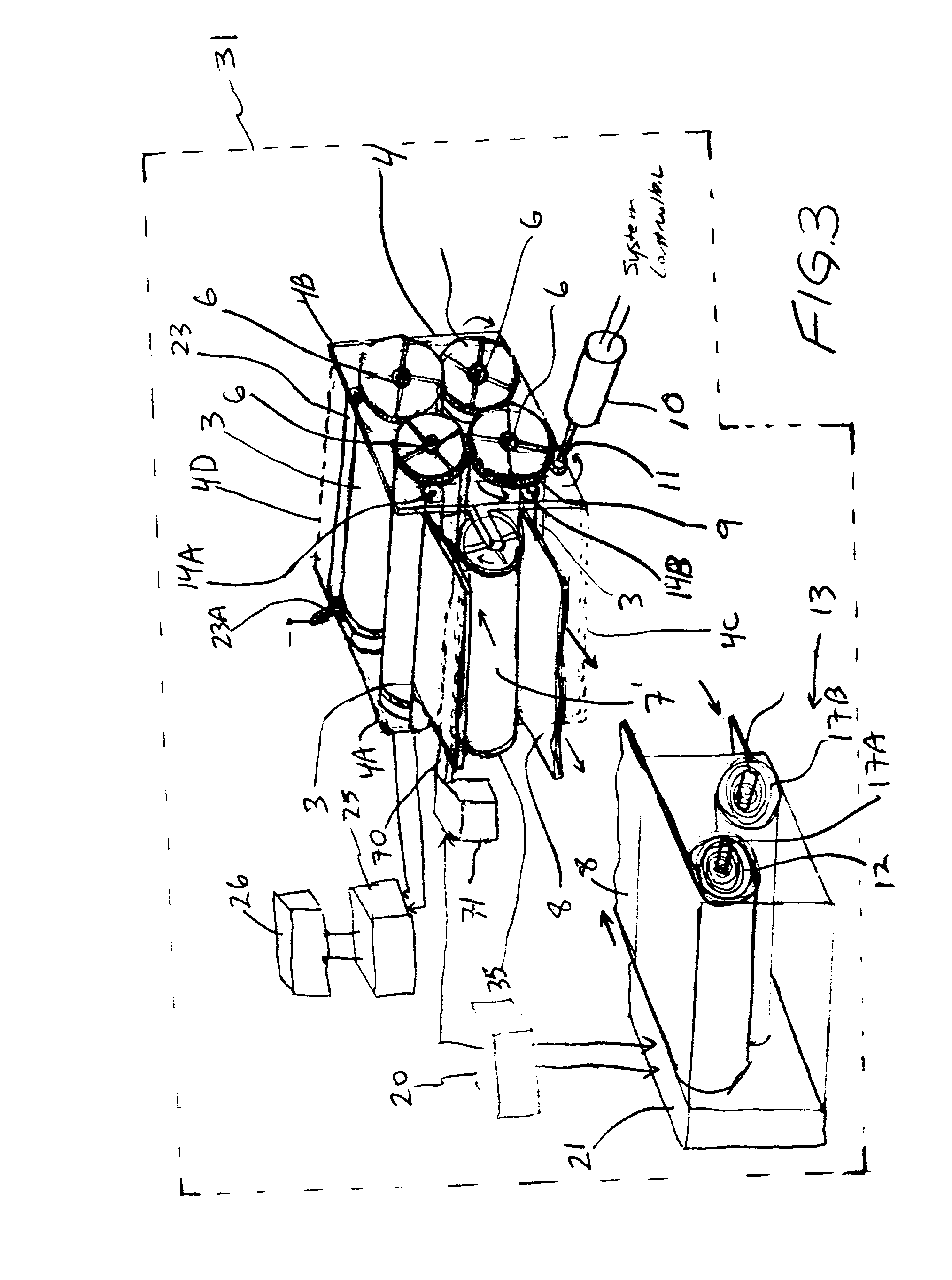
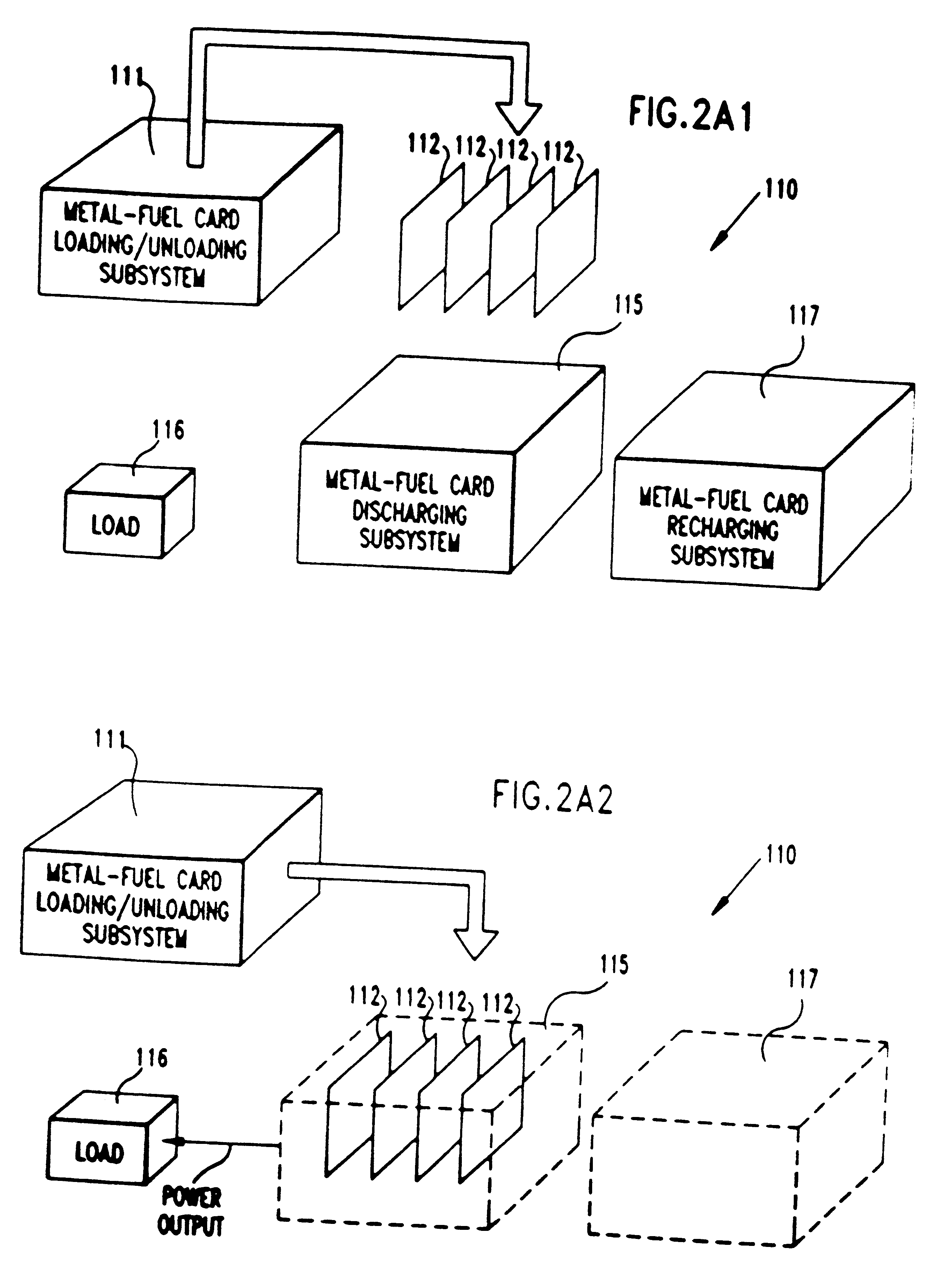
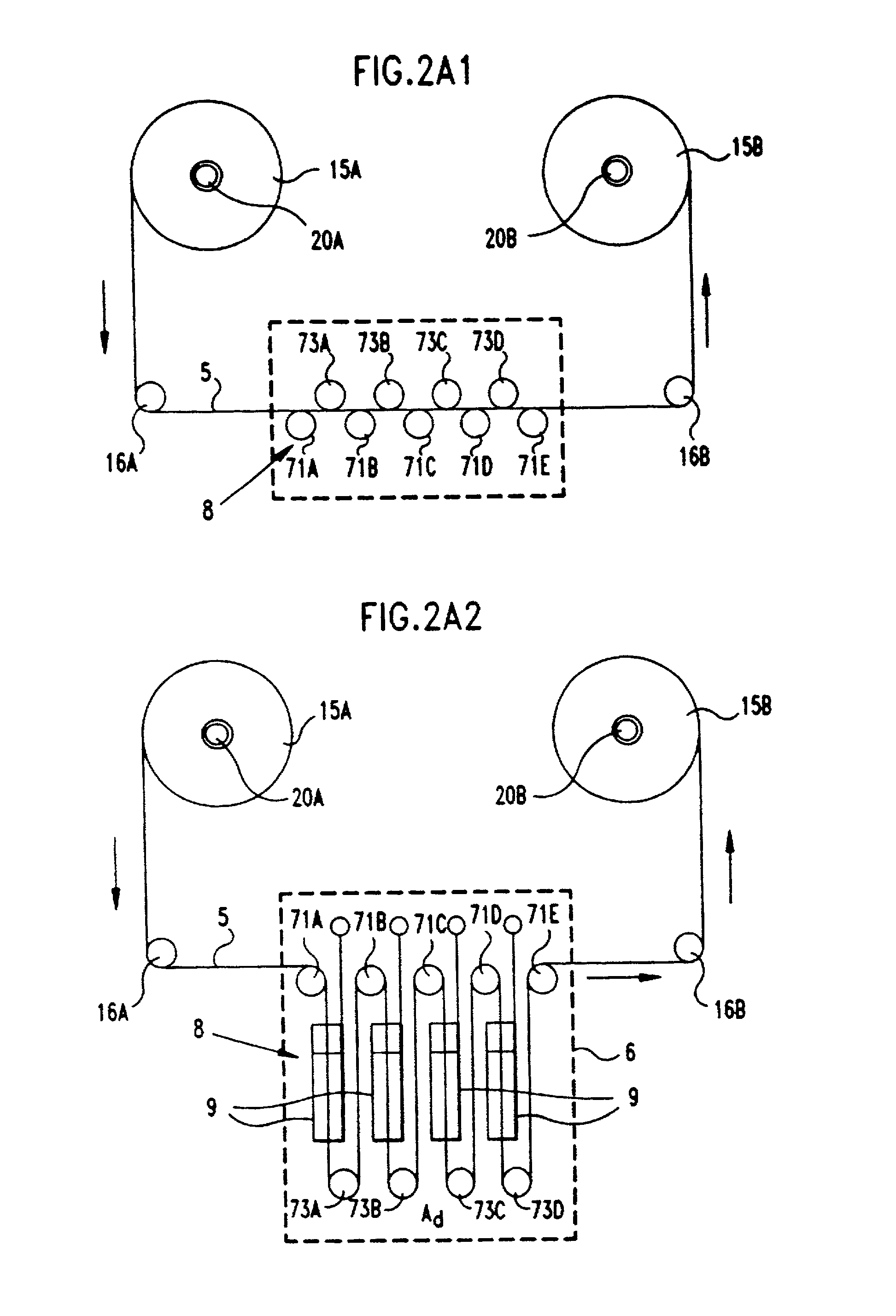
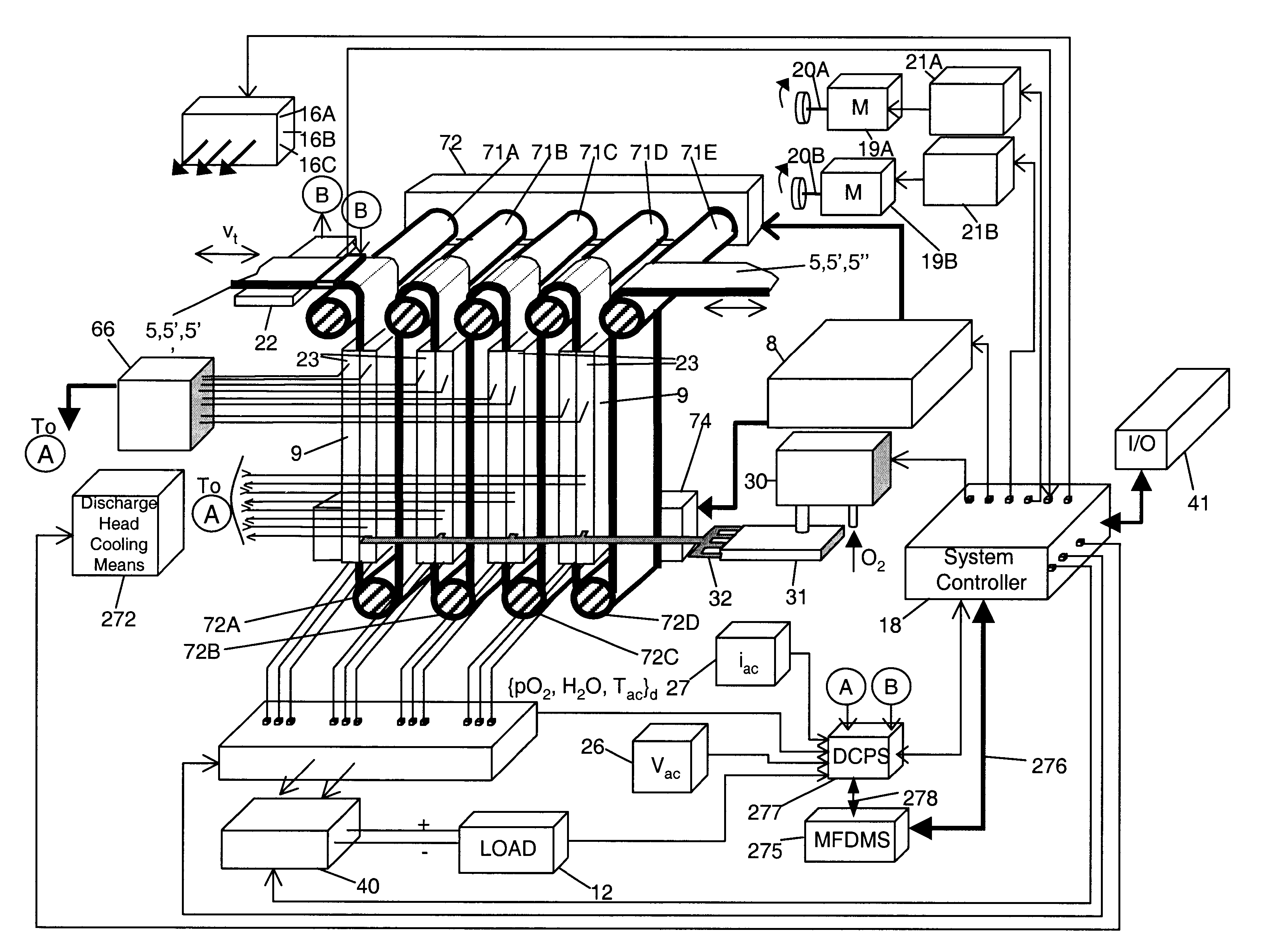
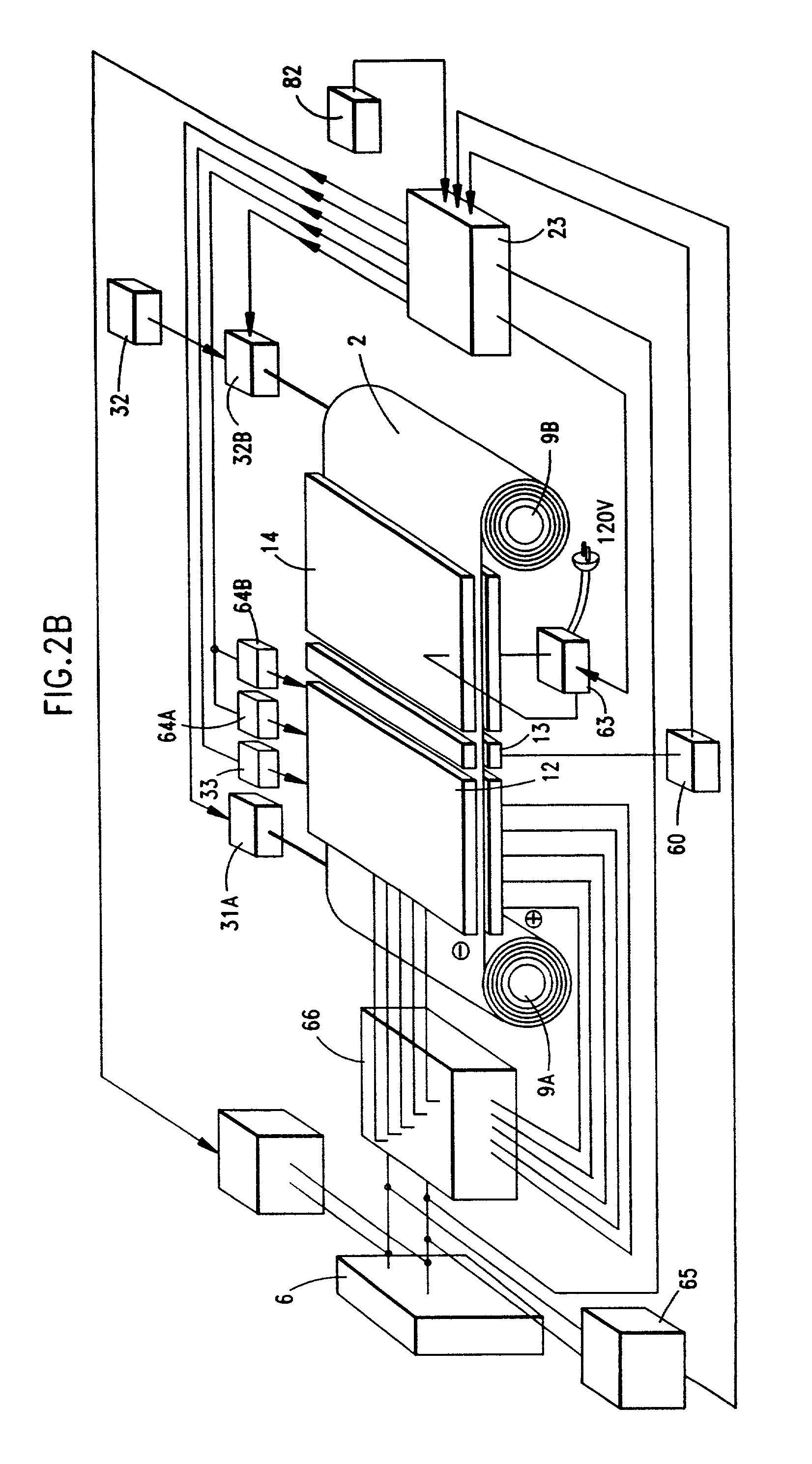
Improved metal-air fuel cell battery systems having metal-fuel realized in the form of metal-fuel tape cartridges and metal-fuel cards, which can be either manually or automatically inserted within the power generation bay of the system. In order to produce a range of output voltages, the metal-fuel tape has a plurality of electrically-isolated metal-fuel tracks and the metal-fuel cards have a plurality of electrically-isolated metal-fuel strips. An output voltage configuration subsystem is provided for configuring the voltages produced by the individual cells to produce a desired output. A subsystem is provided for detecting oxide formation on the metal-fuel tracks and strips so that only metal-fuel that has been oxidized is reduced during recharging operations. A subsystem is also provided for controlling the flow of oxygen into the power generation head in order to control the power output from the system.
Owner:FARIS SADEG M +3
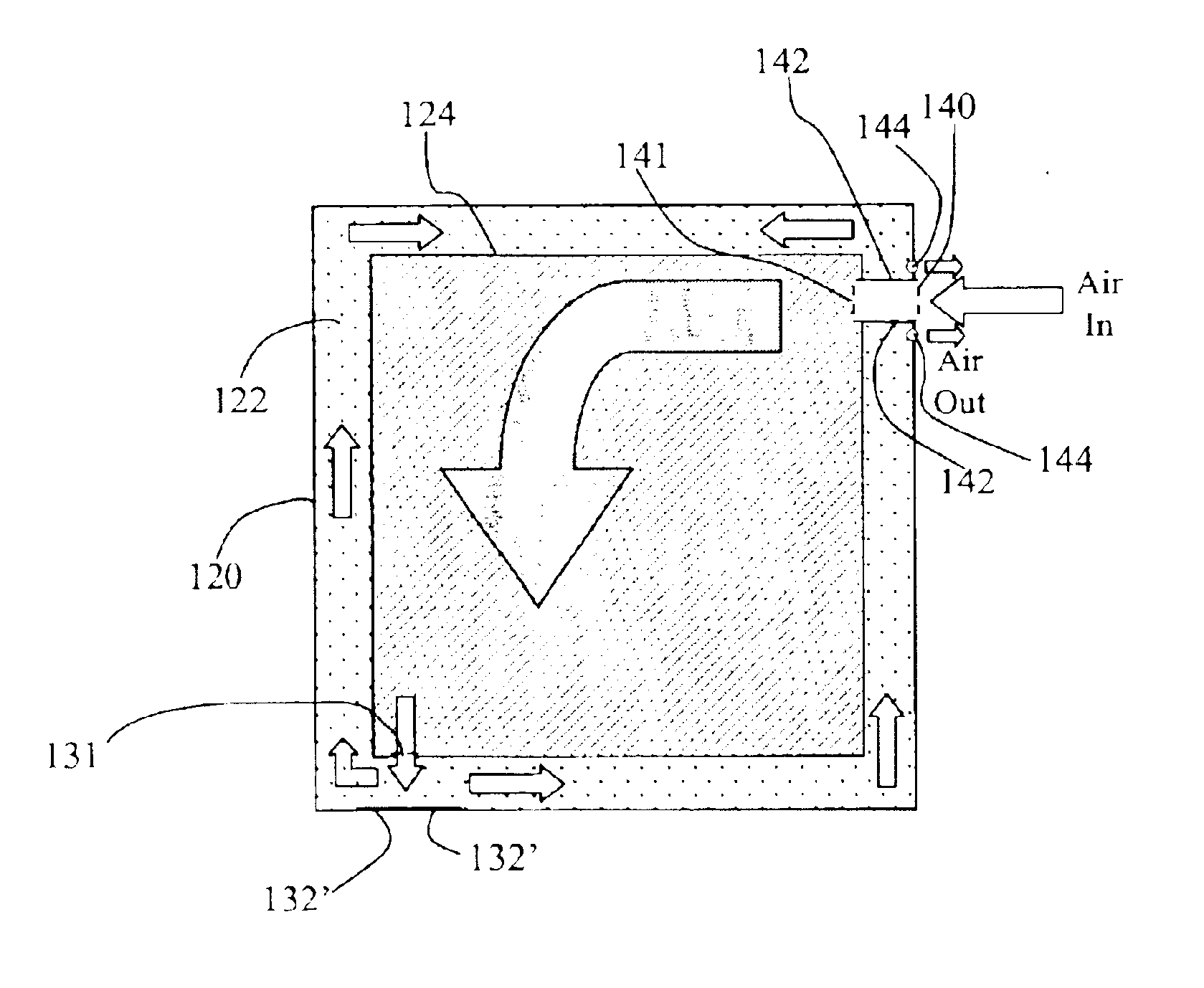
Metal air cell incorporating air flow system
A metal air cell system comprises a frame structure configured with variable airflow paths. The variable airflow paths provide alternatives between direct open loop airflow and semi-closed loop air flow, wherein air is at least partially circulated around the cell components. This is particularly useful for operation in different temperature environments. The open loop mode is useful for high temperature environments, and the semi-closed loop mode is useful for low temperature environments.
Owner:EVIONYX INC
System and method for producing electrical power using metal-air fuel cell battery technology
InactiveUS6296960B1Improve performance parametersIncrease energy densityFuel and primary cellsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityFuel cells
Improved metal-air fuel cell battery systems having metal-fuel realized in the form of metal-fuel tape cartridges and metal-fuel cards, which can be either manually or automatically inserted within the power generation bay of the system. In order to produce a range of output voltages, the metal-fuel tape has a plurality of electrically-isolated metal-fuel tracks and the metal-fuel cards have a plurality of electrically-isolated metal-fuel strips. An output voltage configuration subsystem is provided for configuring the voltages produced by the individual cells to produce a desired output. A subsystem is provided for detecting oxide formation on the metal-fuel tracks and strips so that only metal-fuel that has been oxidized is reduced during recharging operations. A subsystem is also provided for controlling the flow of oxygen into the power generation head in order to control the power output from the system.
Owner:REVEO
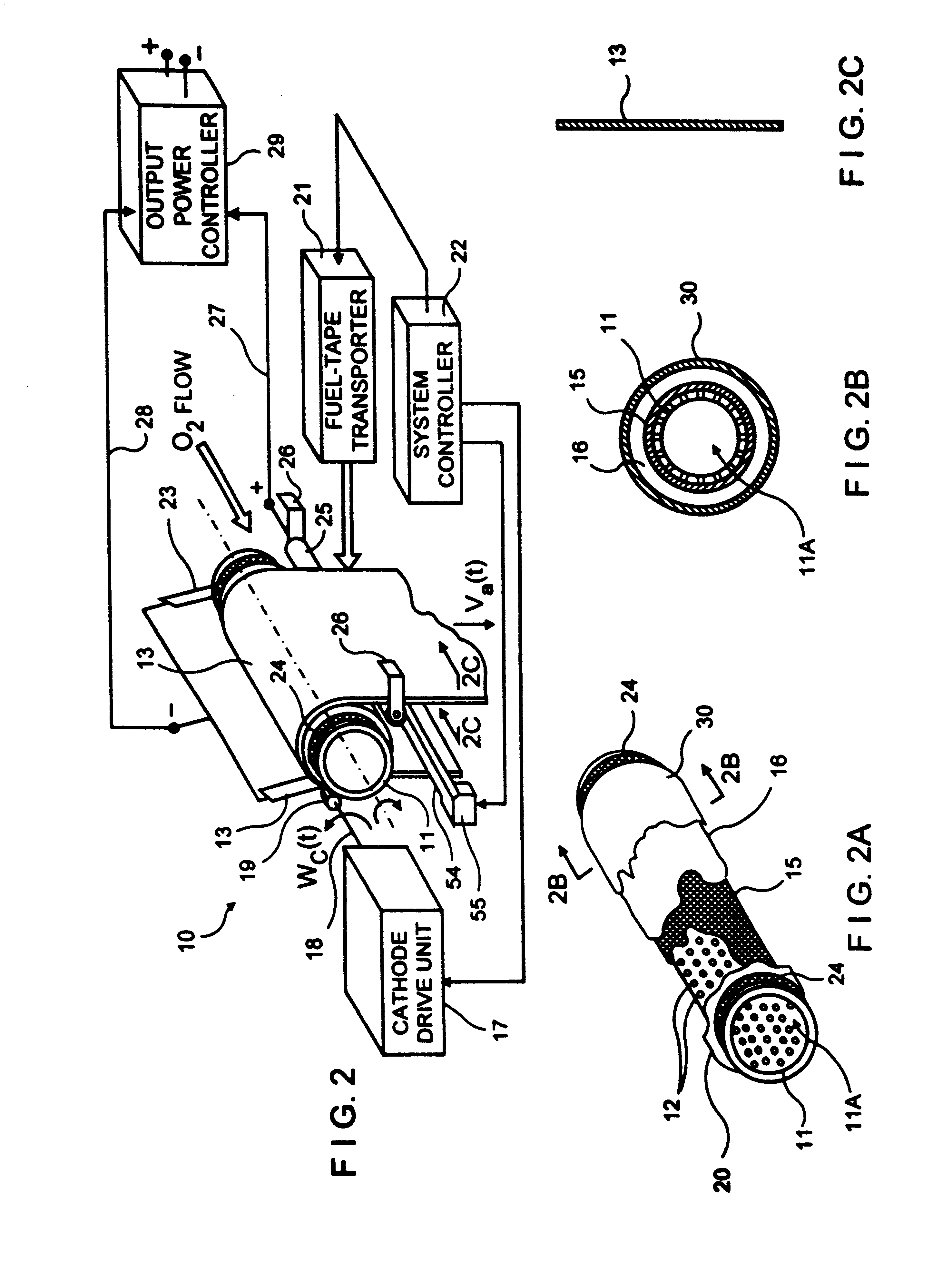
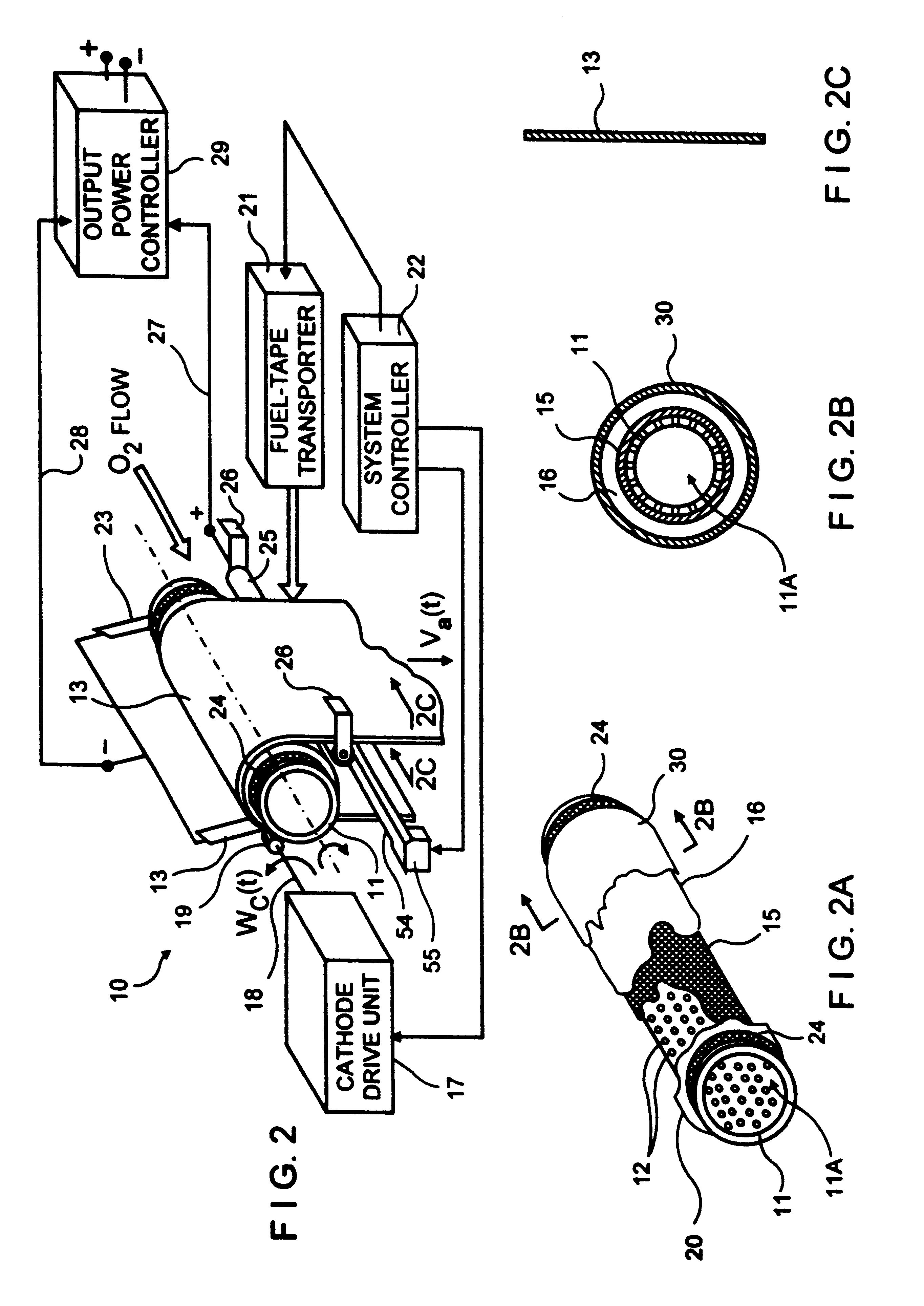
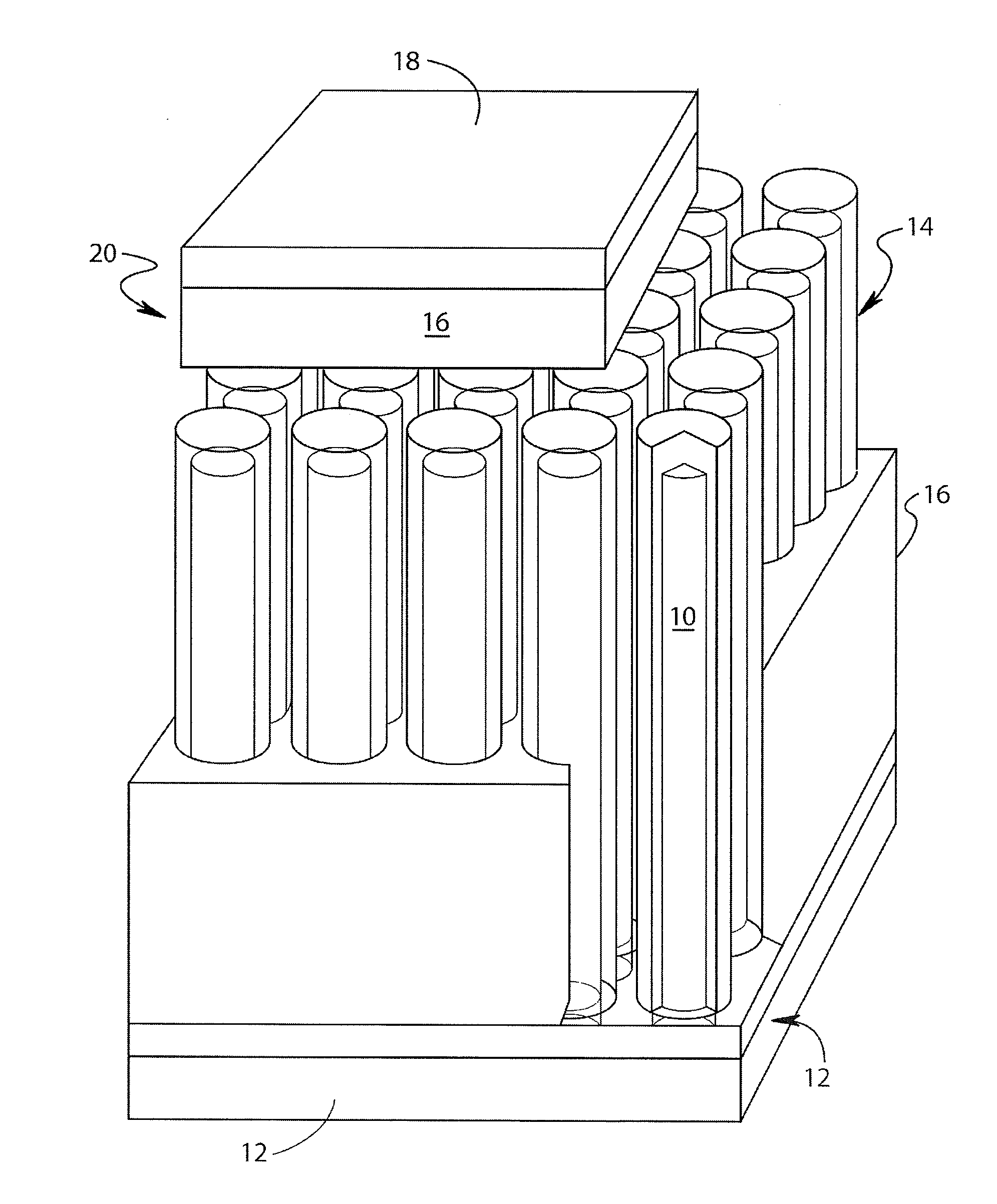
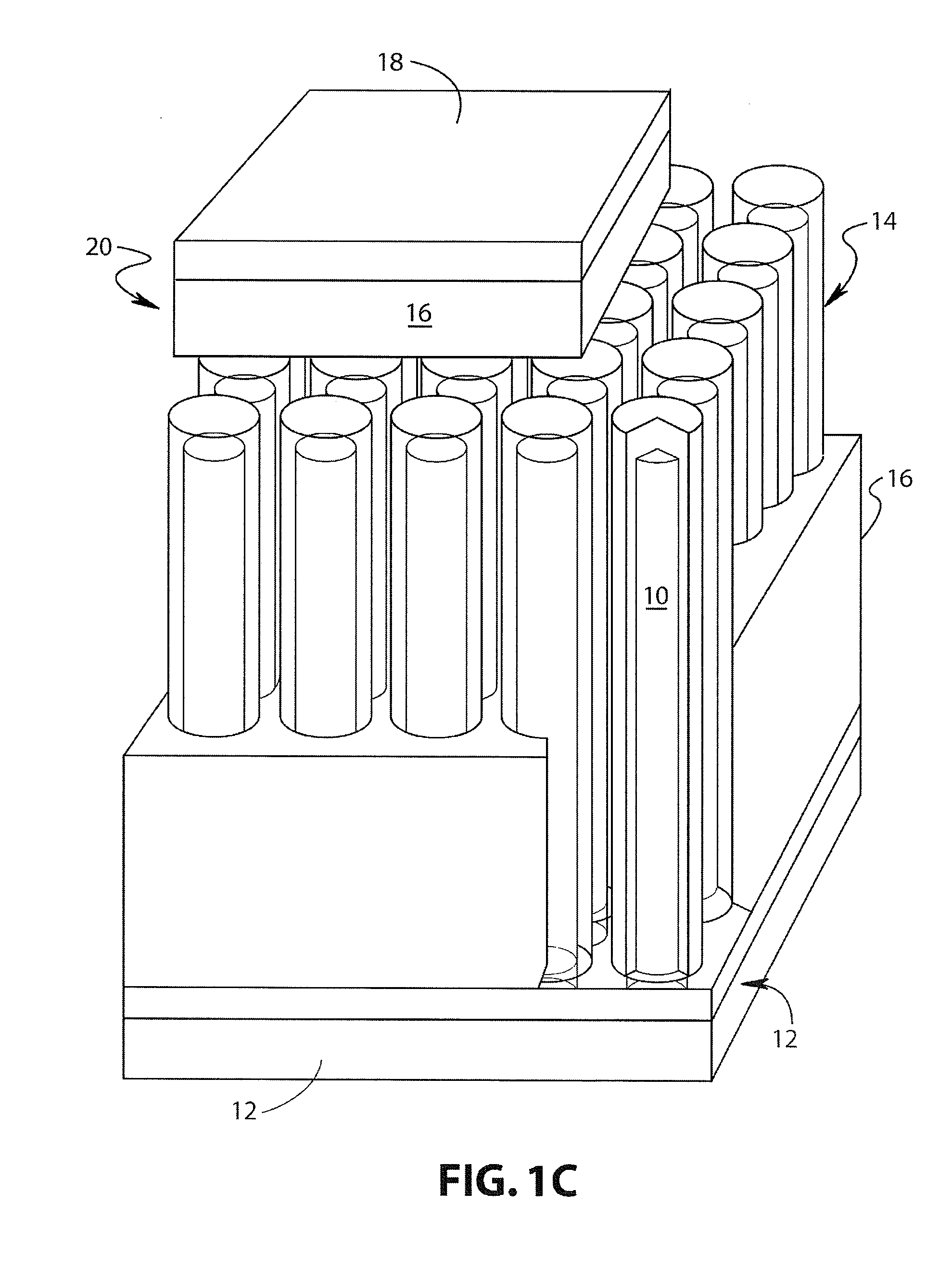
Metal-air fuel cell battery system employing a plurality of moving cathode structures for improved volumetric power density
InactiveUS20010007725A1High densityFriction is generatedFuel and primary cellsBatteries circuit arrangementsFuel cellsBattery system
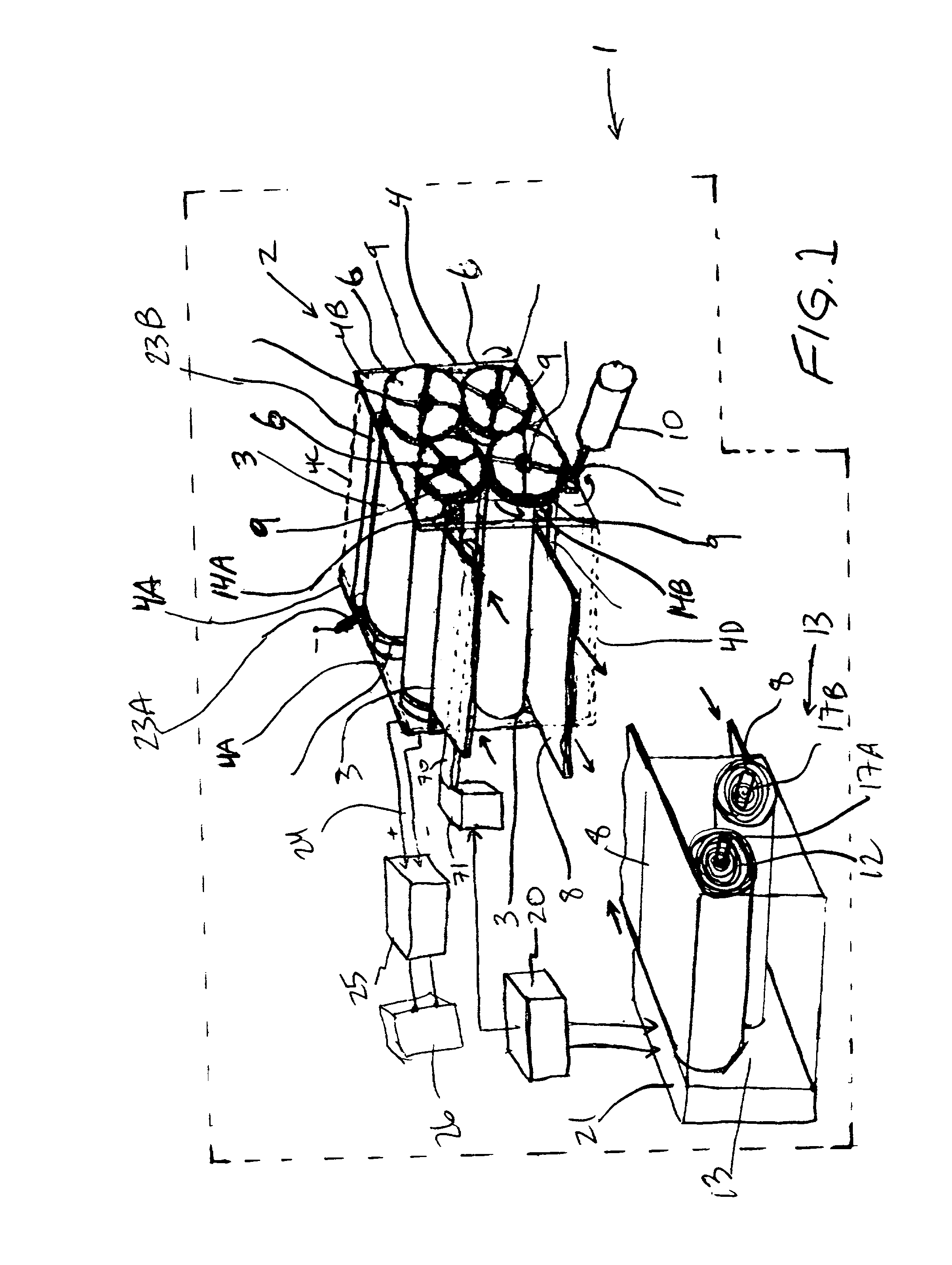
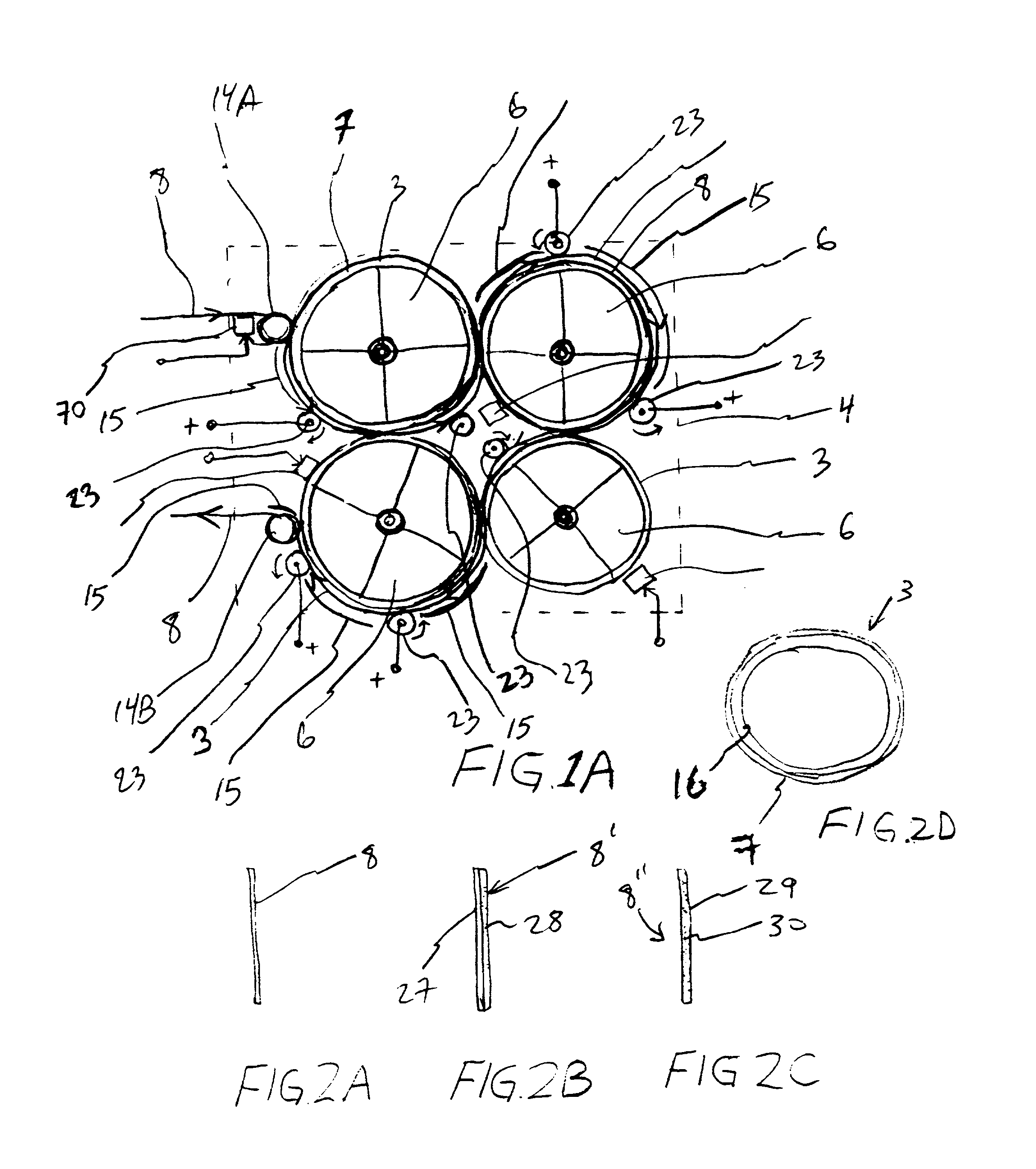
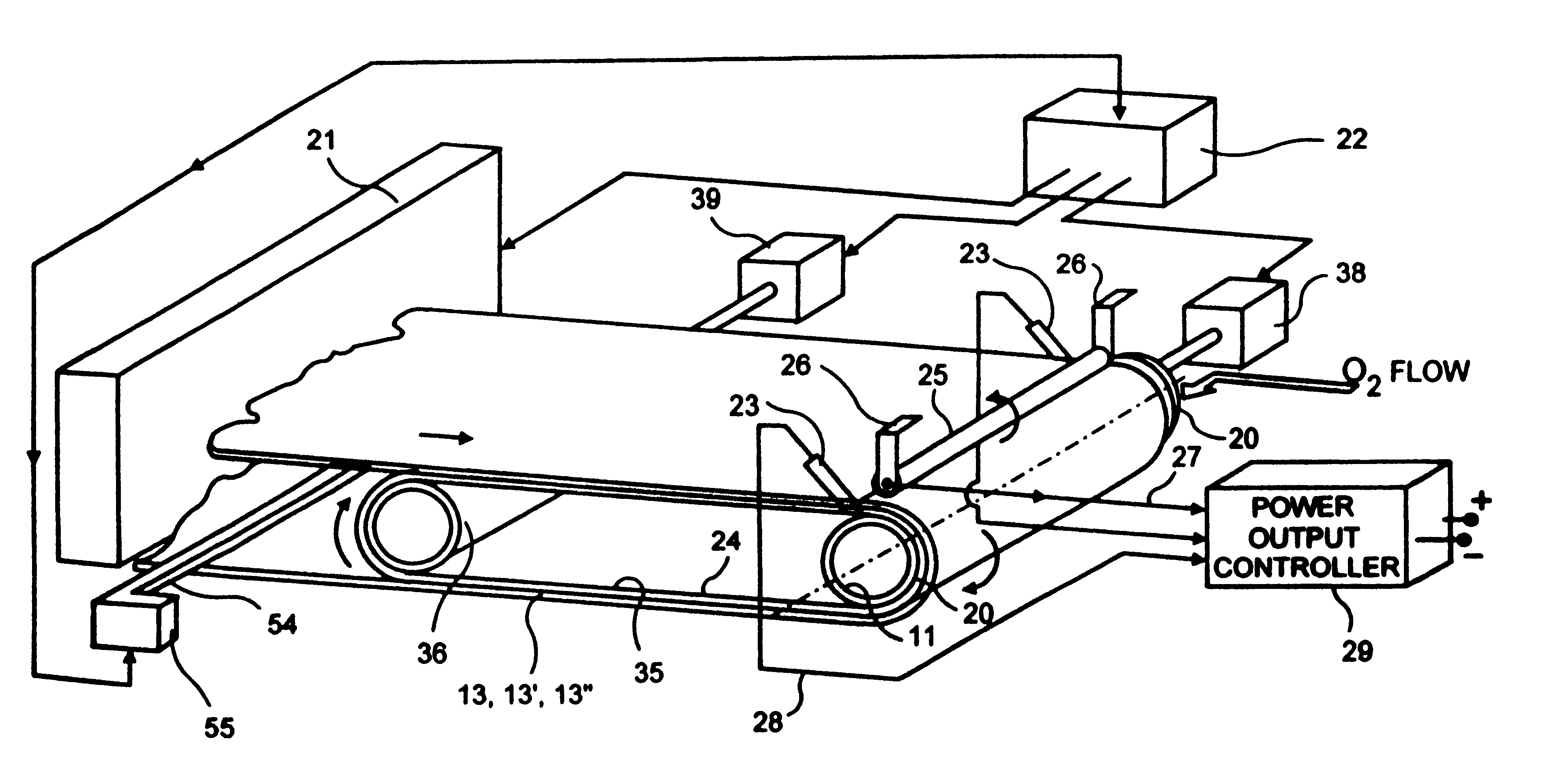
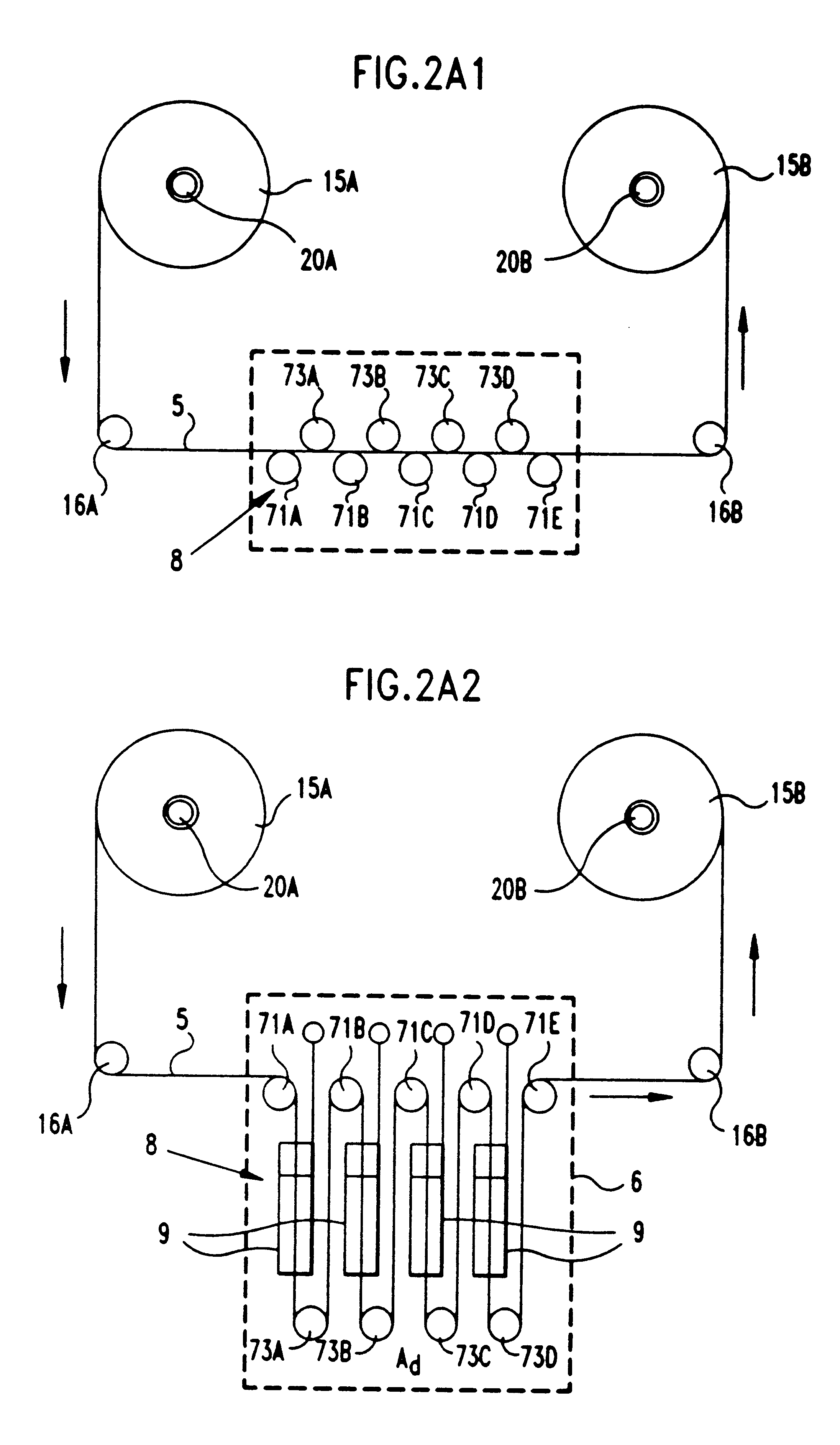
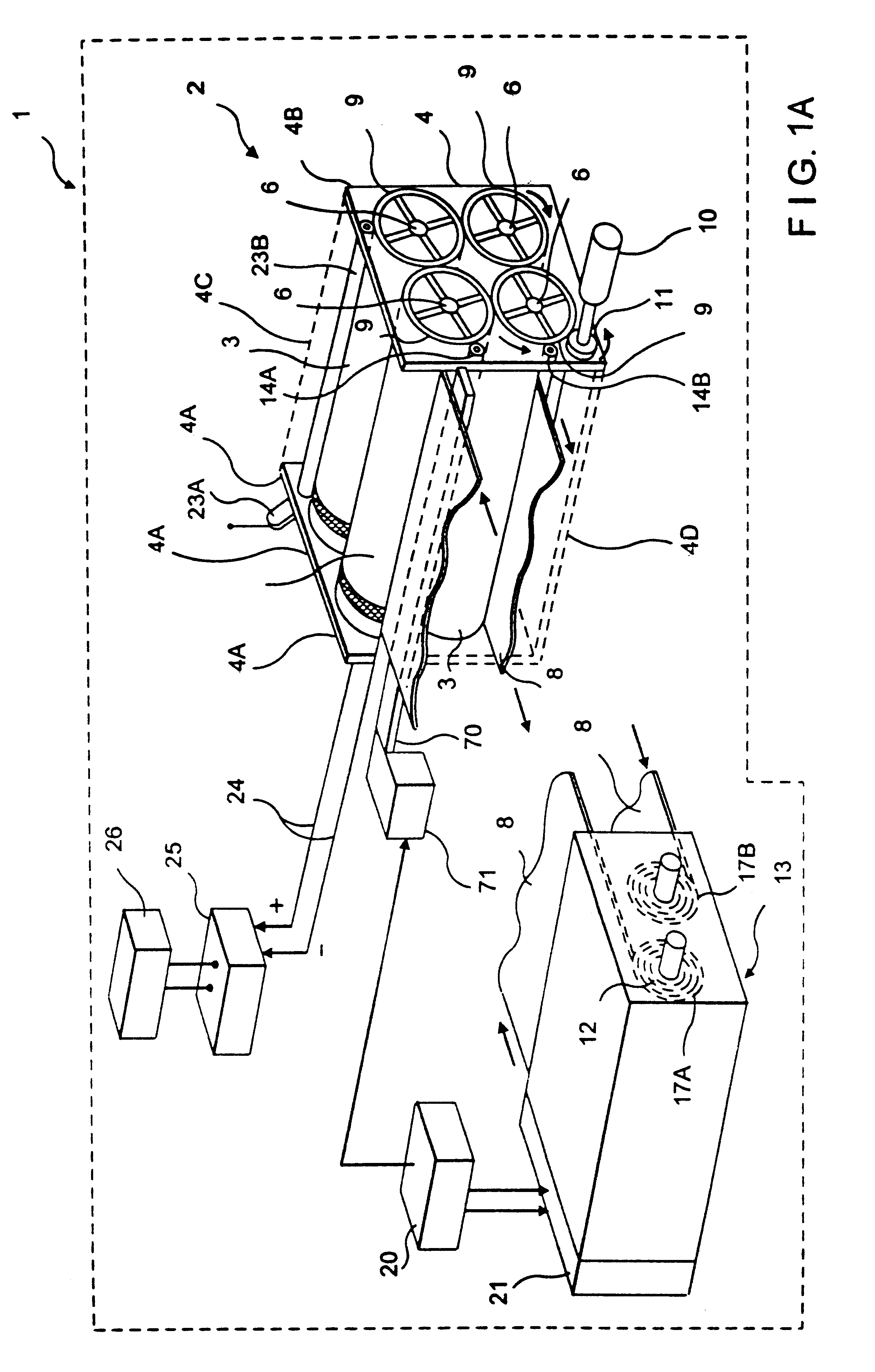
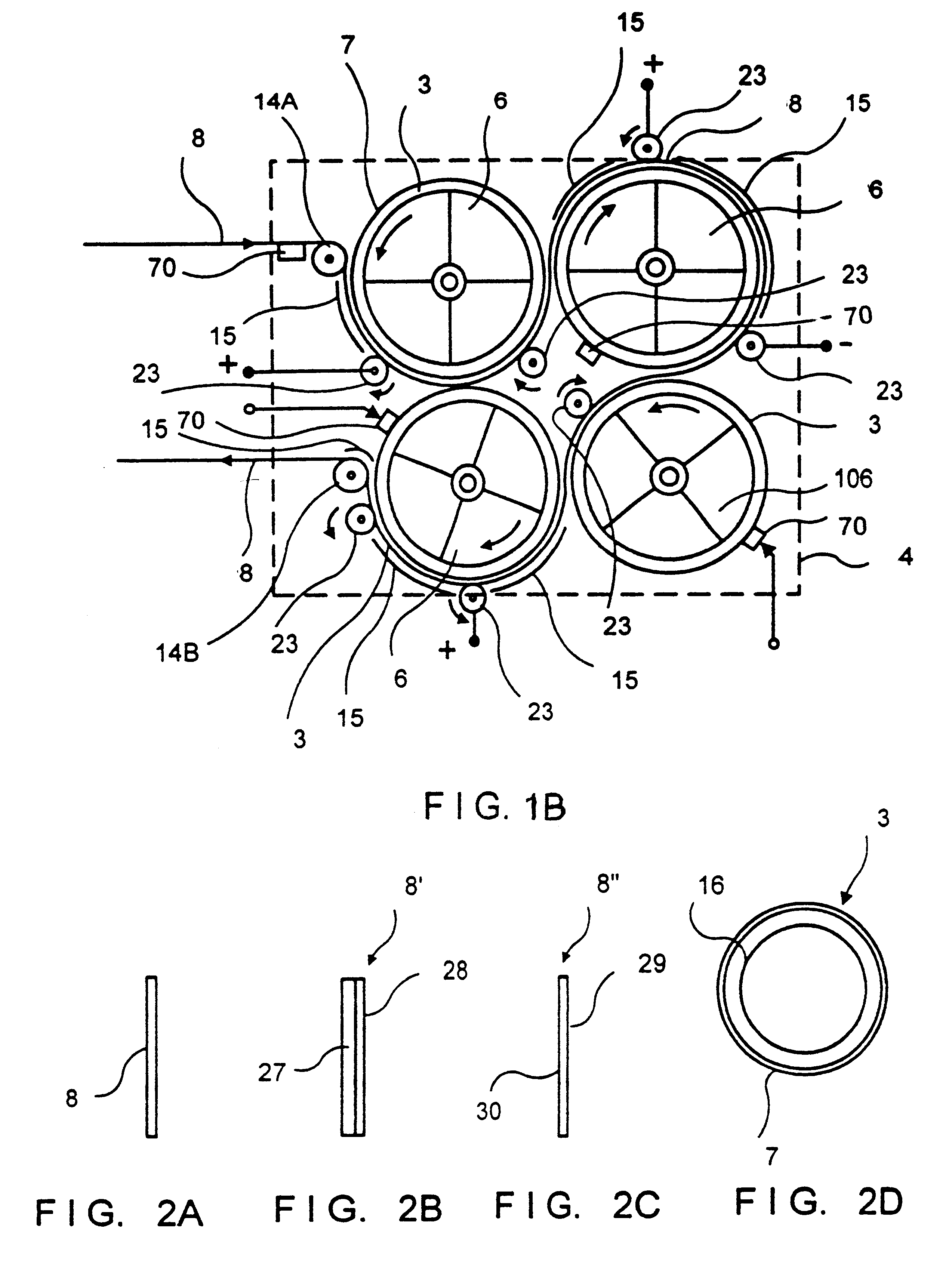
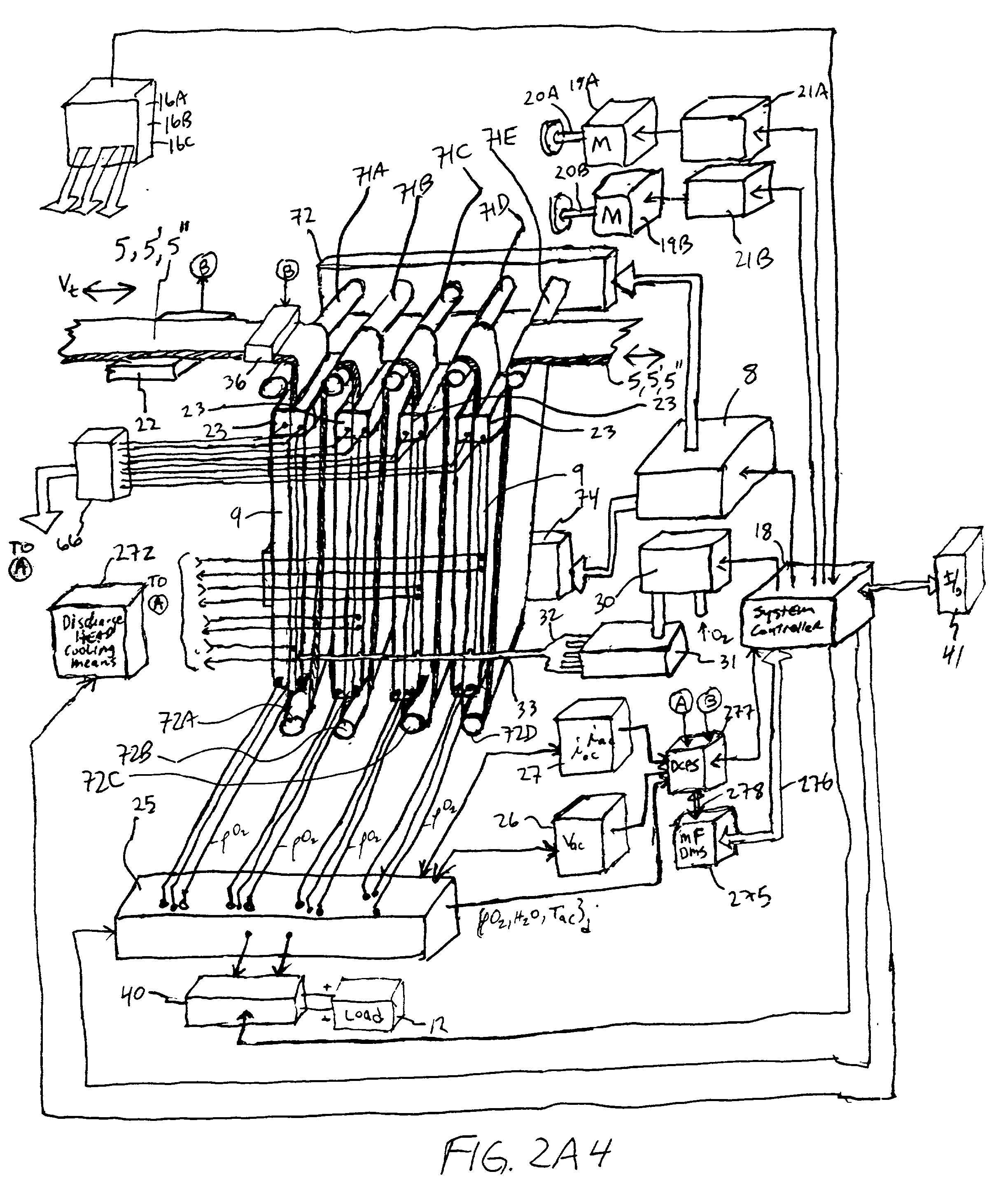
In an air-metal fuel cell battery (FCB) system, wherein a plurality of movable cathode structures are mounted within a compact housing through which metal-fuel tape is transported along a predetermined path while an ionically-conductive medium is disposed between the metal-fuel tape and each movable cathode structure at points of contact. In illustrative embodiments, the movable cathode structures are realized as rotatable cathode cylinders, and transportable cathode belts. The ionically-conductive medium is realized as a solid-state ionically-conductive film applied to the cathode structures and / or metal-fuel tape, as well as ionically-conductive belt structures transported at the same velocity as corresponding cathode structures (e.g. cathode cylinders or belts) at the locus of points at which the ionically-conductive medium contacts the moving cathode structure and the moving metal-fuel tape. By virtue of the present invention, the volumetric power density characteristics of FCB systems can be significantly improved, while the likelihood of damage to the cathode structures and metal-fuel tape is substantially reduced.
Owner:REVEO
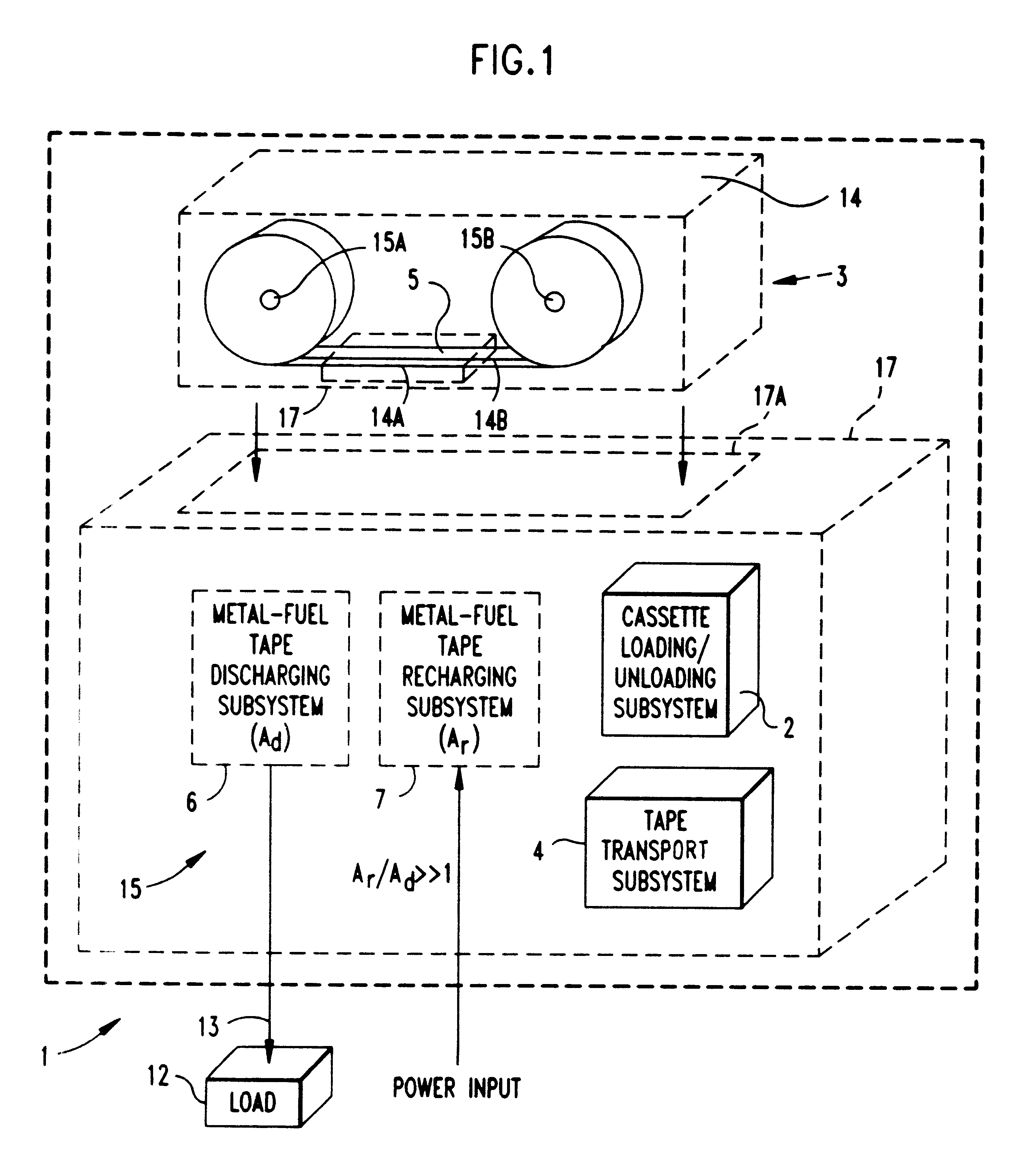
Metal-air fuel cell battery systems employing means for discharging and recharging metal-fuel cards
InactiveUS6306534B1Several cell simultaneous arrangementsFuel and primary cellsElectrochemical responseChemical reaction
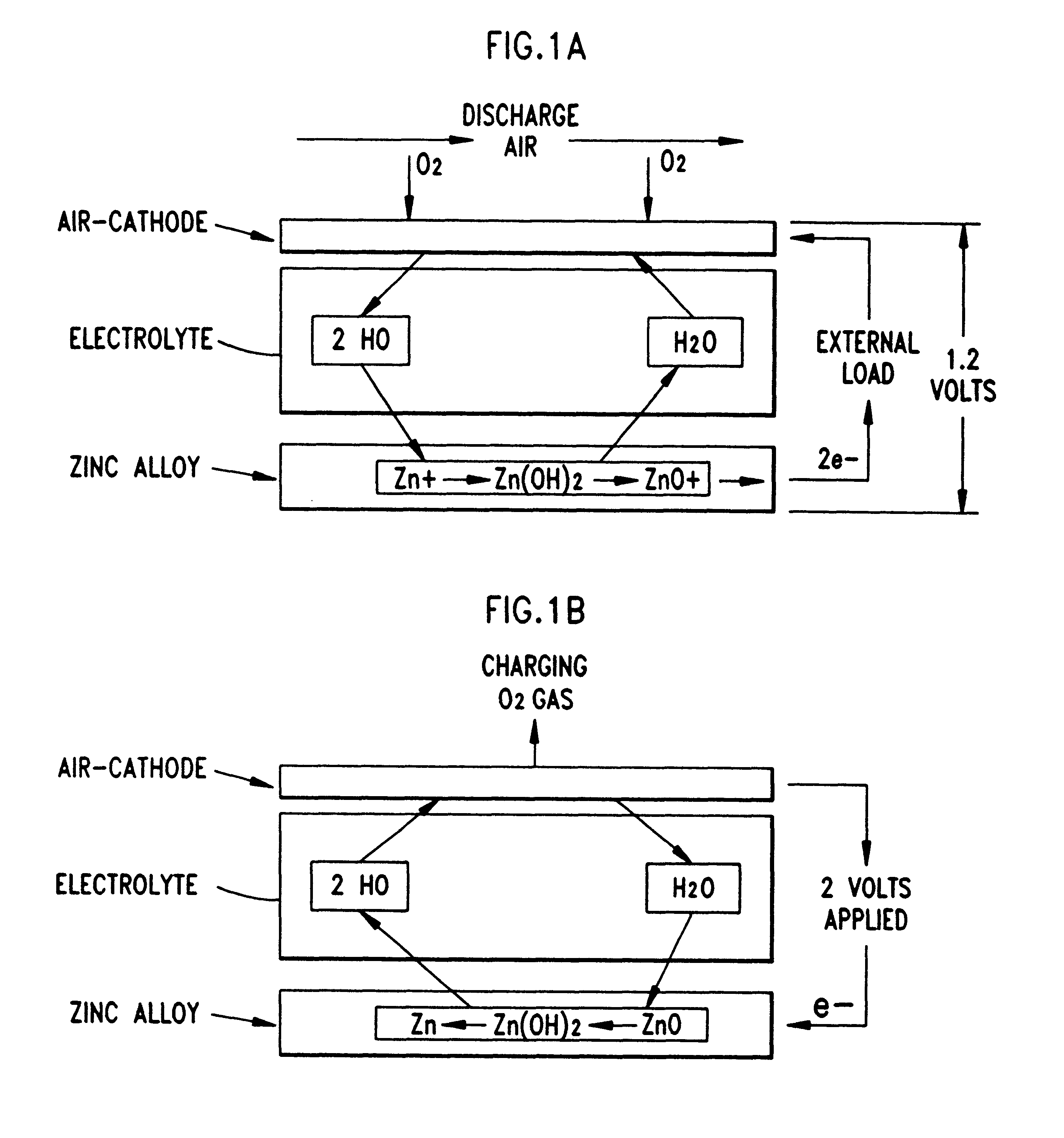
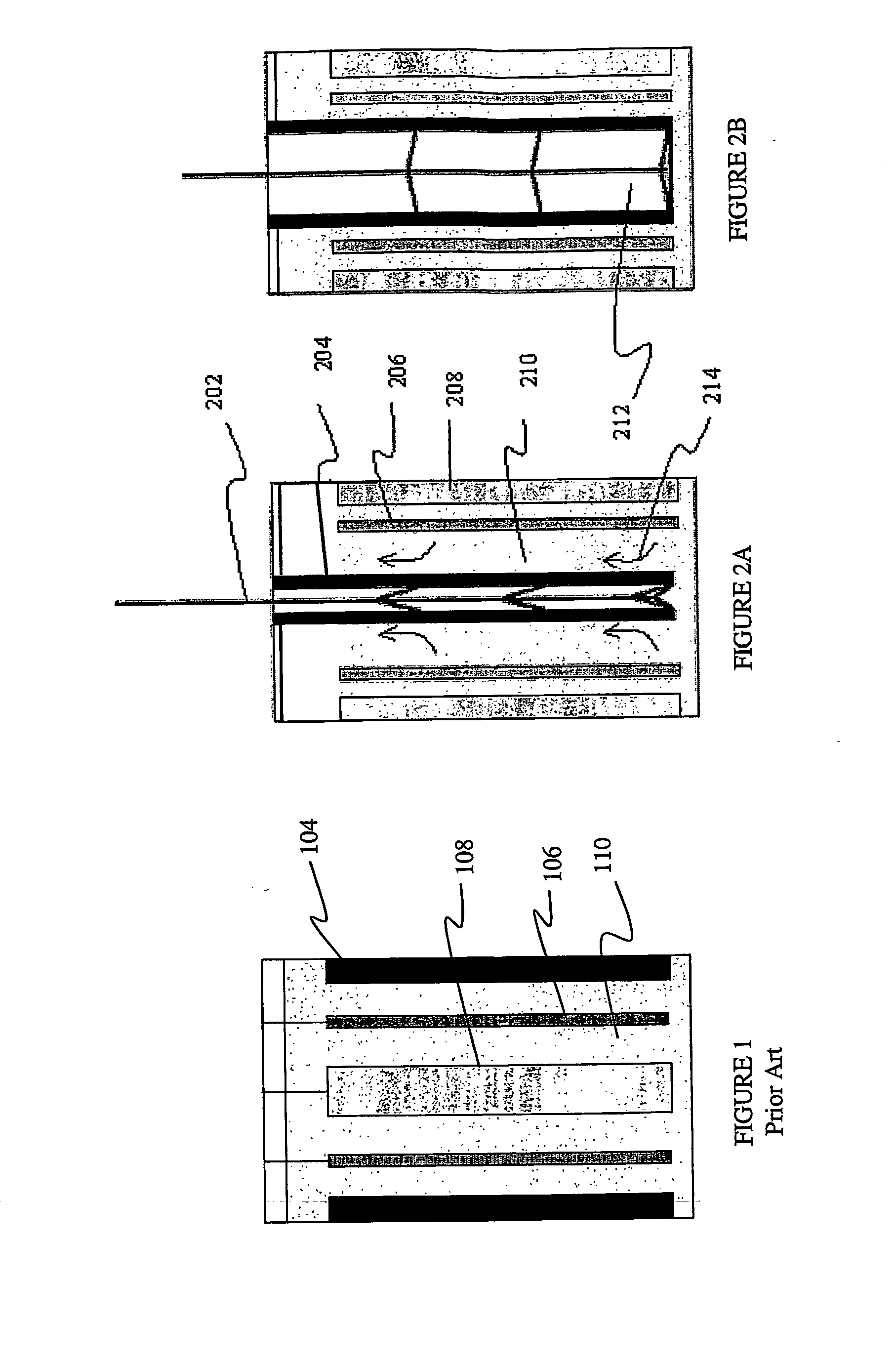
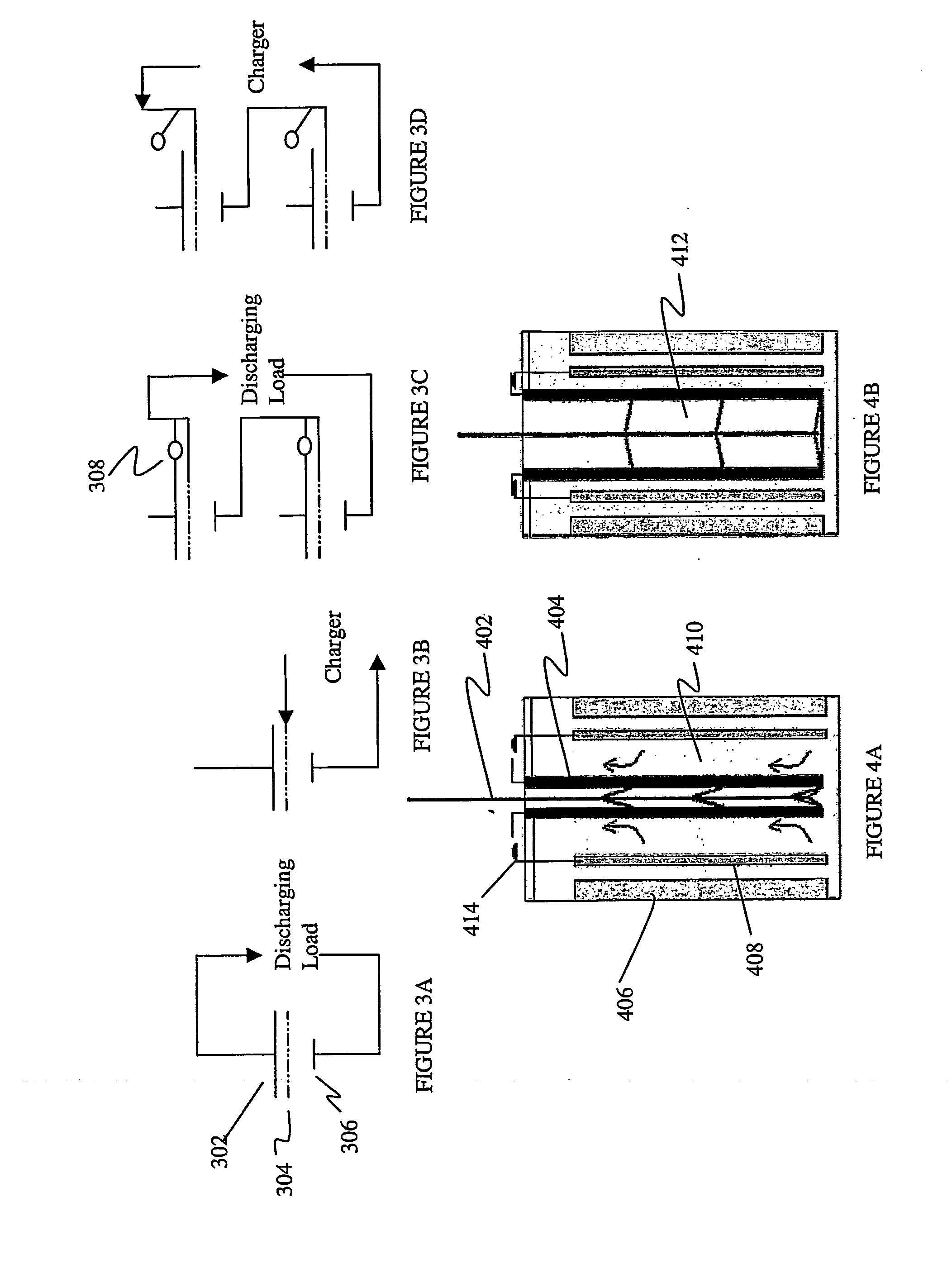
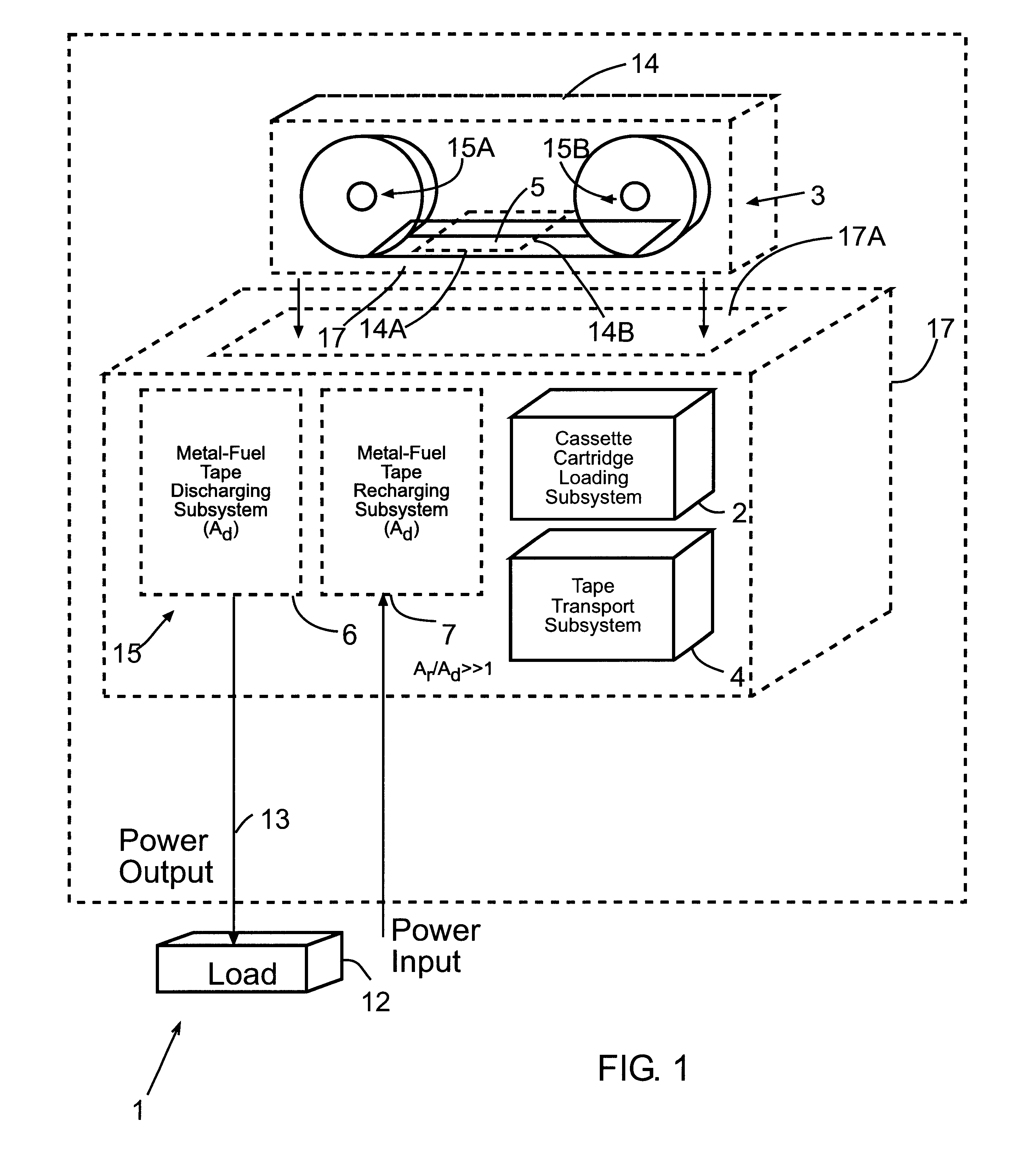
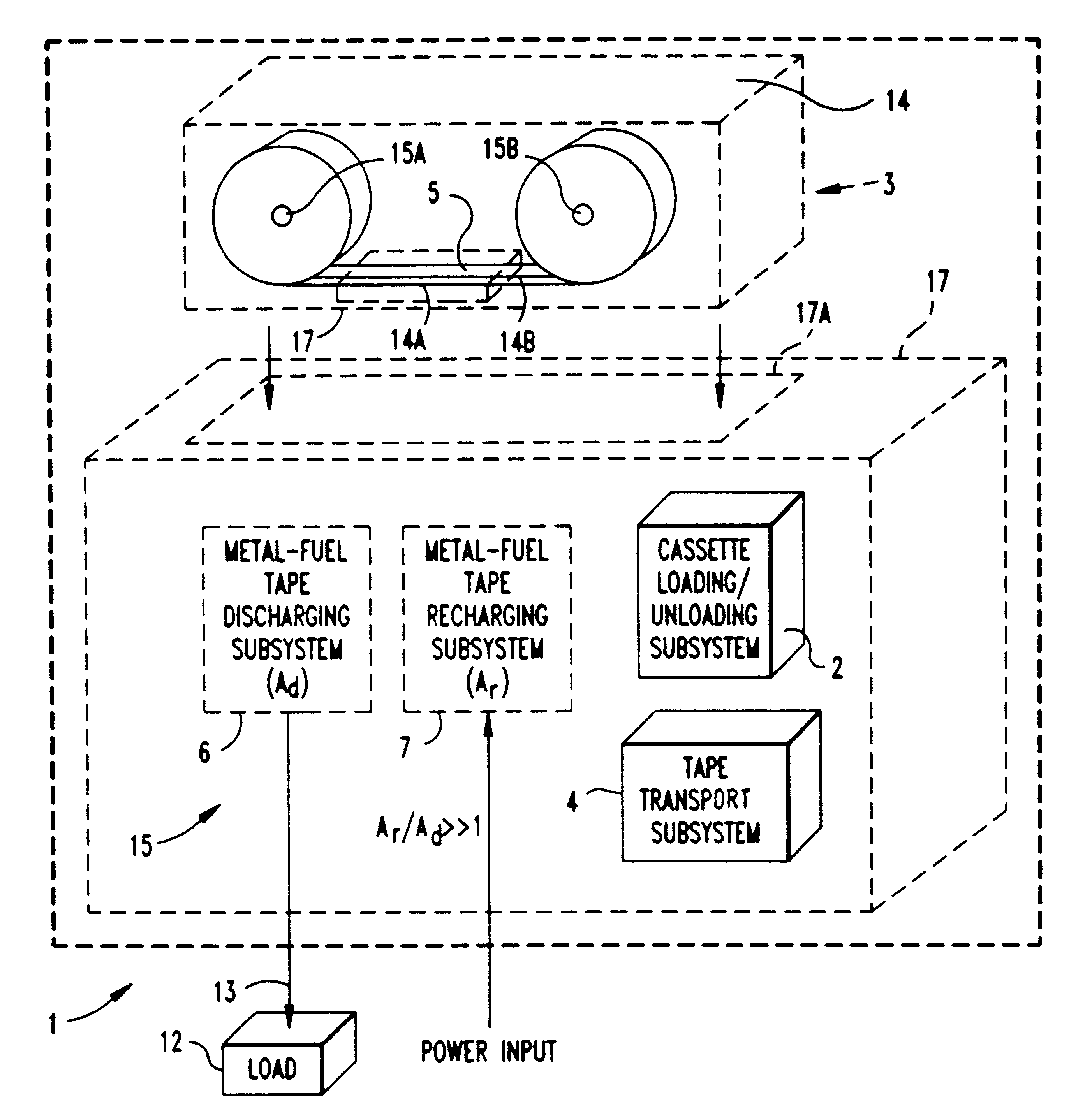
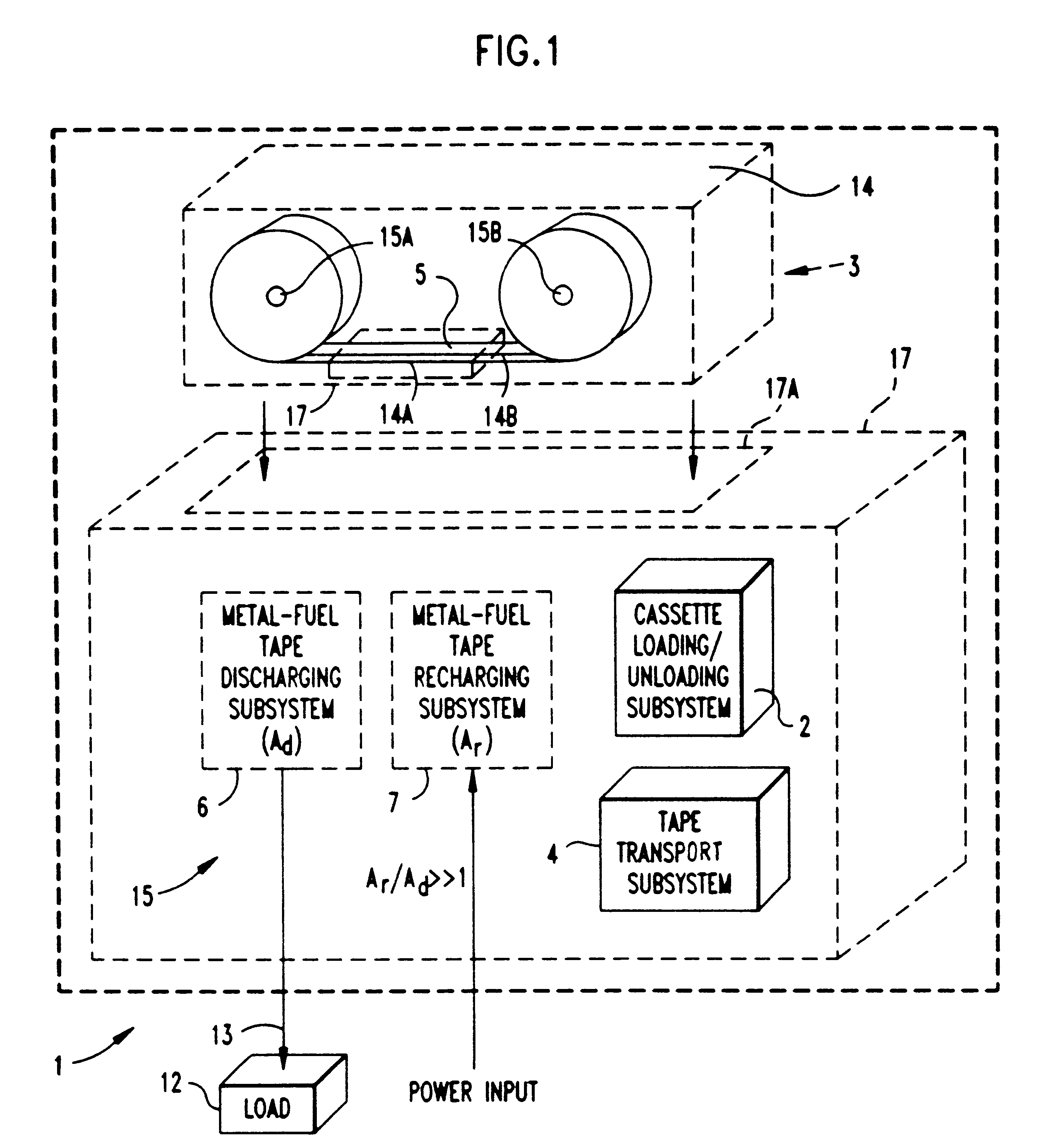
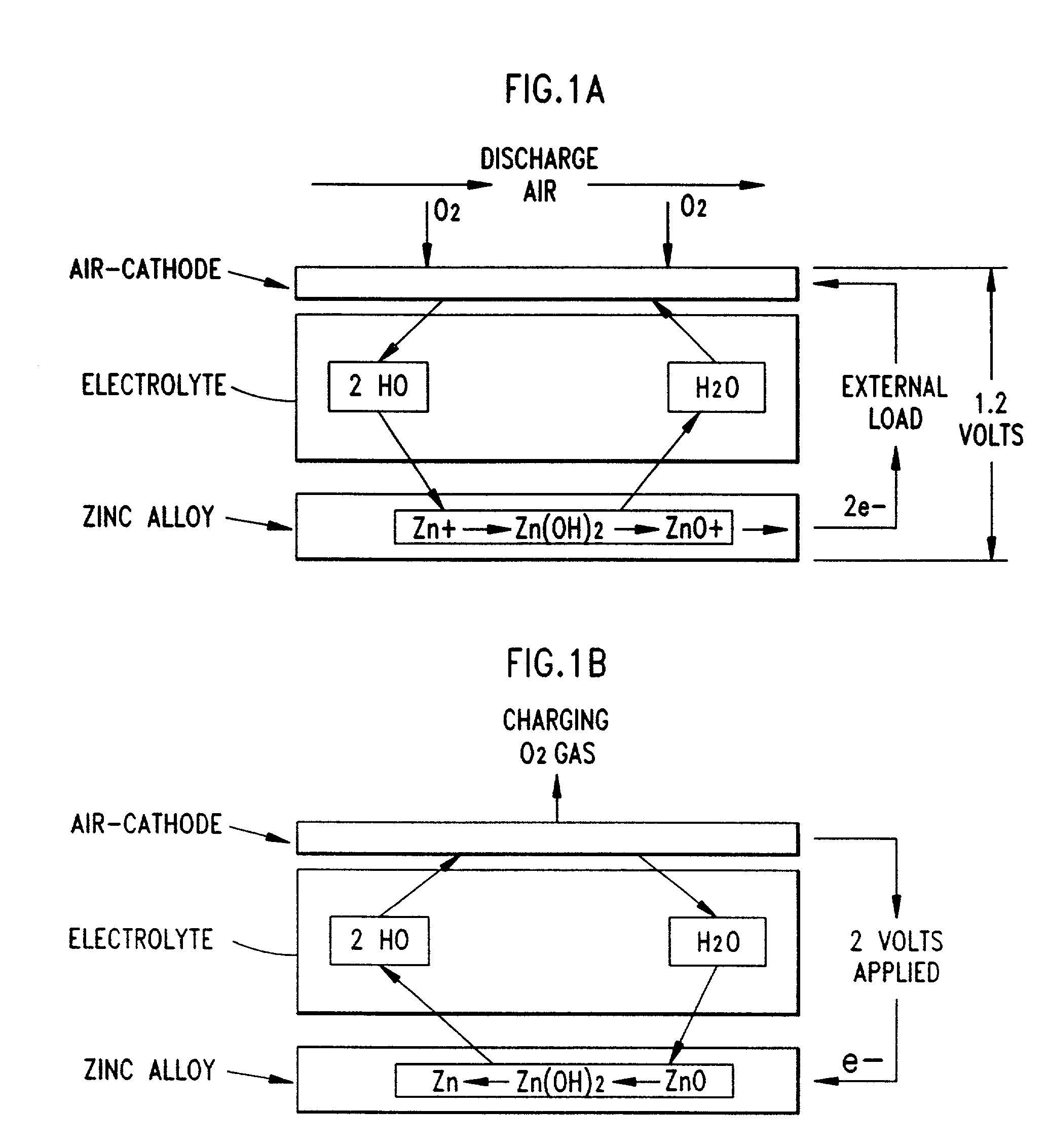
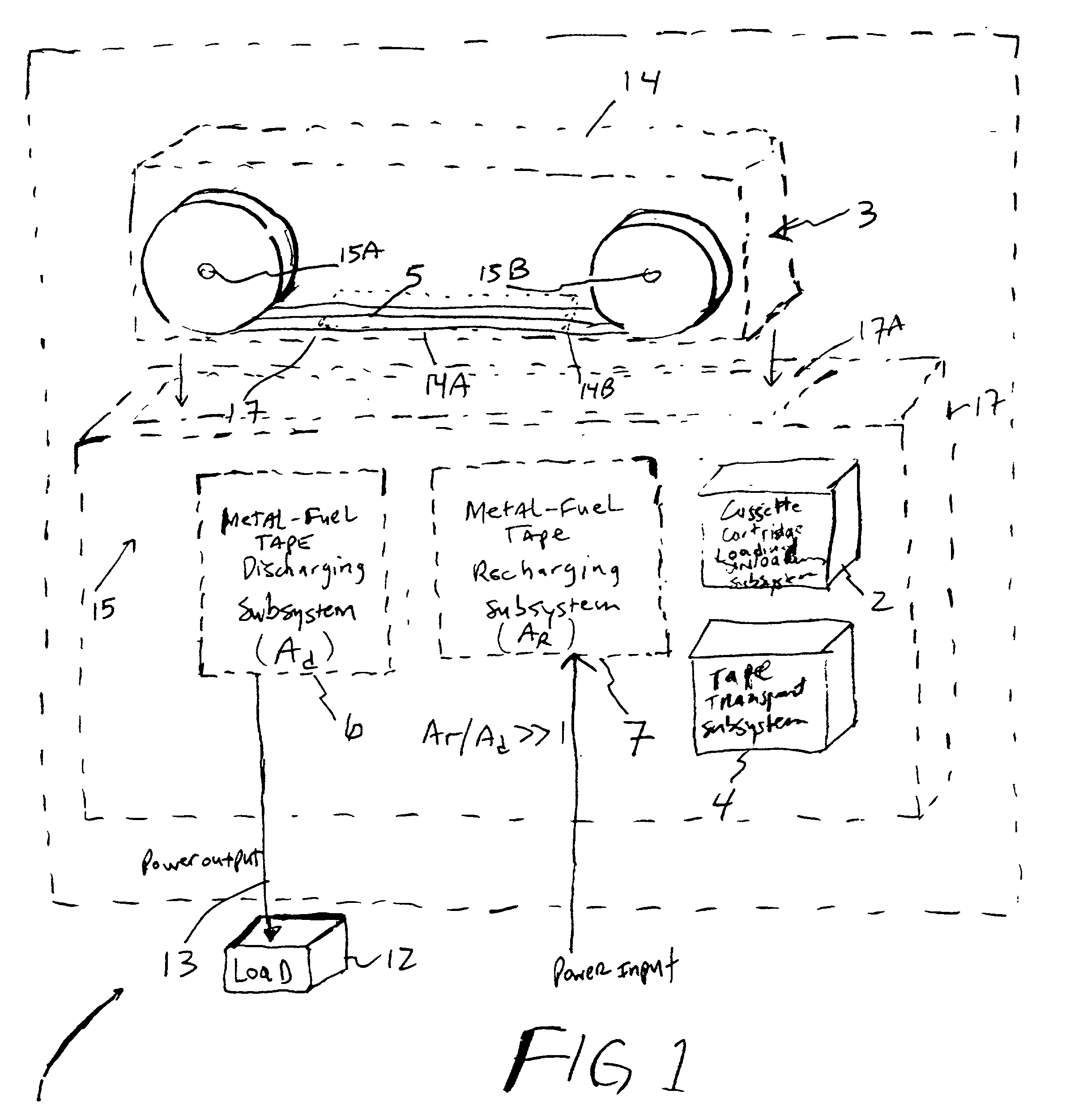
Disclosed are various types of metal-air FCB-based systems comprising a Metal-Fuel Transport Subsystem, a Metal-Fuel Discharging Subsystem, and a Metal-Fuel Recharging Subsystem. The function of the Metal-Fuel Transport Subsystem is to transport metal-fuel cards or sheets to the Metal-Fuel Discharge Subsystem, or the Metal-Fuel Recharge Subsystem, depending on the mode of the system selected. When transported to or through the Metal-Fuel Discharge Subsystem, each metal-fuel card is discharged by (i.e. electro-chemically reaction with) one or more discharging heads in order produce electrical power across an electrical load connected to the subsystem while H2O and O2 are consumed at the cathode-electrolyte interface during the electro-chemical reaction. When transported to or through the Metal-Fuel Recharging Subsystem, discharged metal-fuel is recharged by one or more recharging heads in order to convert the oxidized metal-fuel material into its source metal material suitable for reuse in power discharging operations, while O2 is released at the cathode-electrolyte interface during the electro-chemical reaction. In the illustrative embodiments, various forms of metal fuel cards can be discharged and recharged in an efficient manner to satisfy a broad range of electrical loading conditions.
Owner:REVEO
Electrochemical Device
ActiveUS20090246612A1Improve securityEasy to adjust resistance valueHybrid capacitor separatorsProtecting/adjusting hybrid/EDL capacitorElectrical resistance and conductanceControl layer
An electrochemical device having an electrode matrix including a multilayer structure laminating positive and negative electrodes with a separator interposed therebetween; wherein at least one of the positive and negative electrodes has a resistance control layer at least at an edge part exposed when the separator thermally shrinks on a surface on the separator side; and wherein the resistance control layer has a resistance value as a total resistance value of the electrode matrix falling in such a range that an estimated internal short circuit current between the positive and negative electrodes is equivalent to 0.09 C to 1 C.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
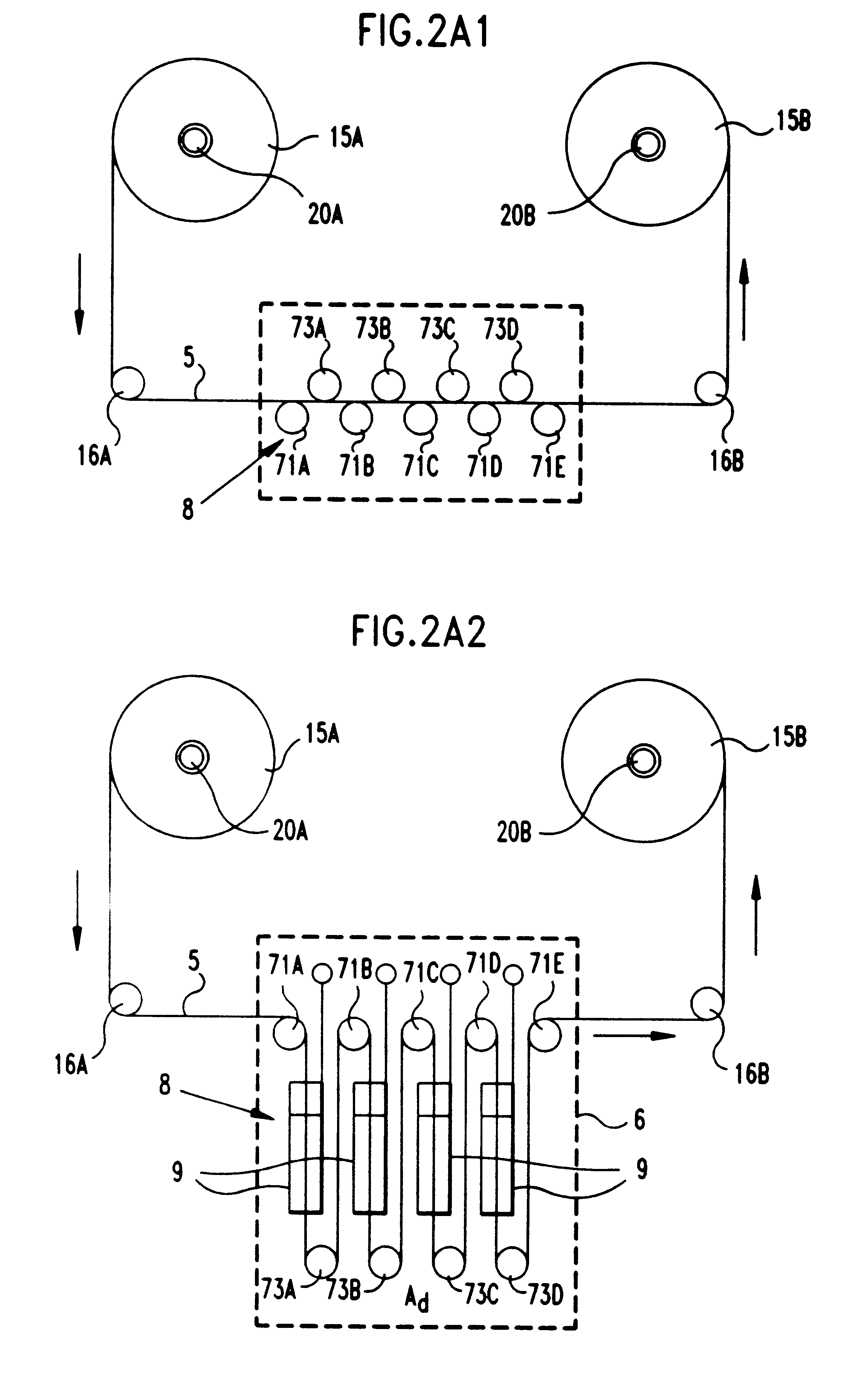
Metal-air fuel cell battery systems having mechanism for extending the path length of metal-fuel tape during discharging and recharging modes of operation
InactiveUS20020022168A1Fast chargingFuel and primary cellsSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsFuel cellsPath length
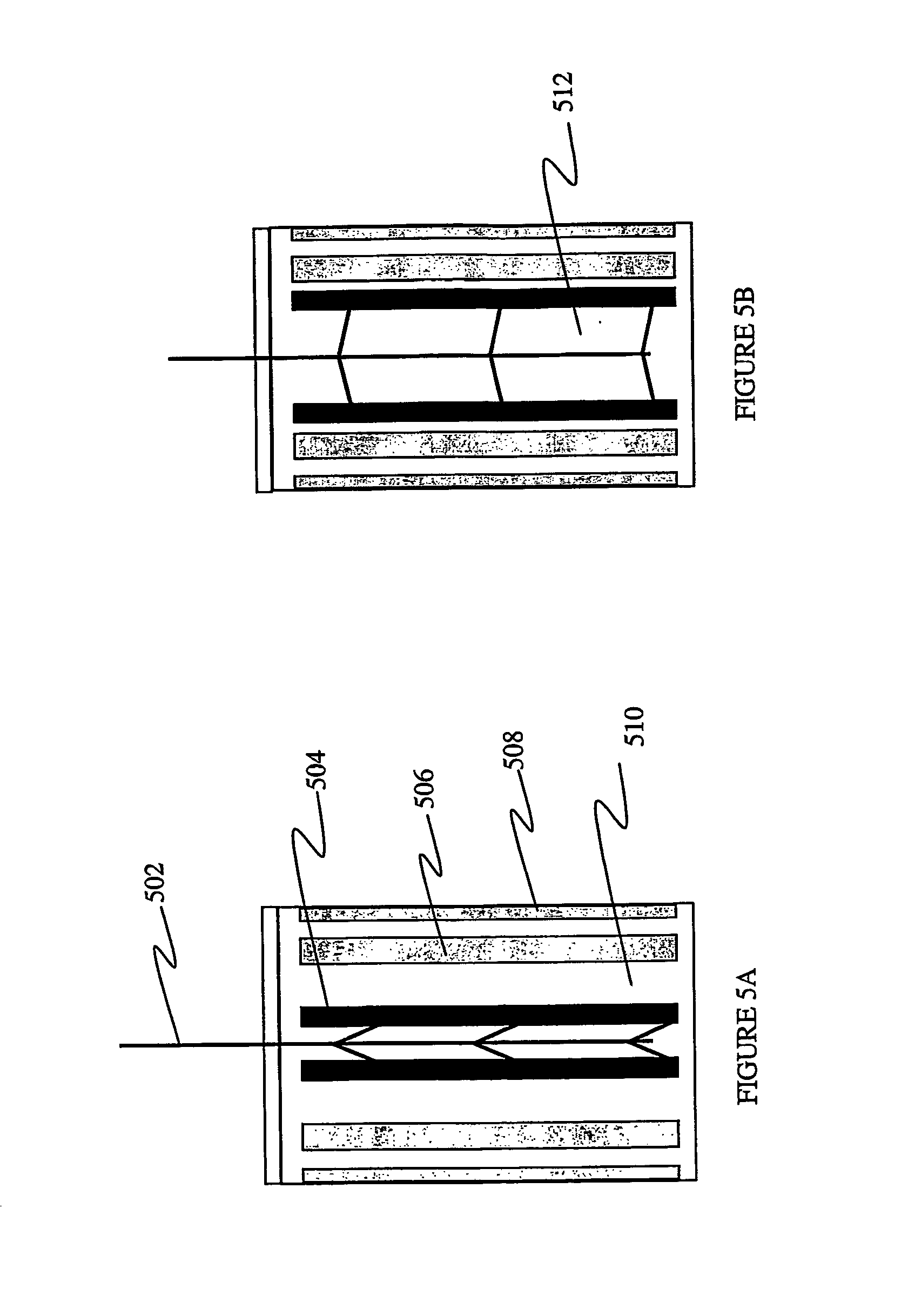
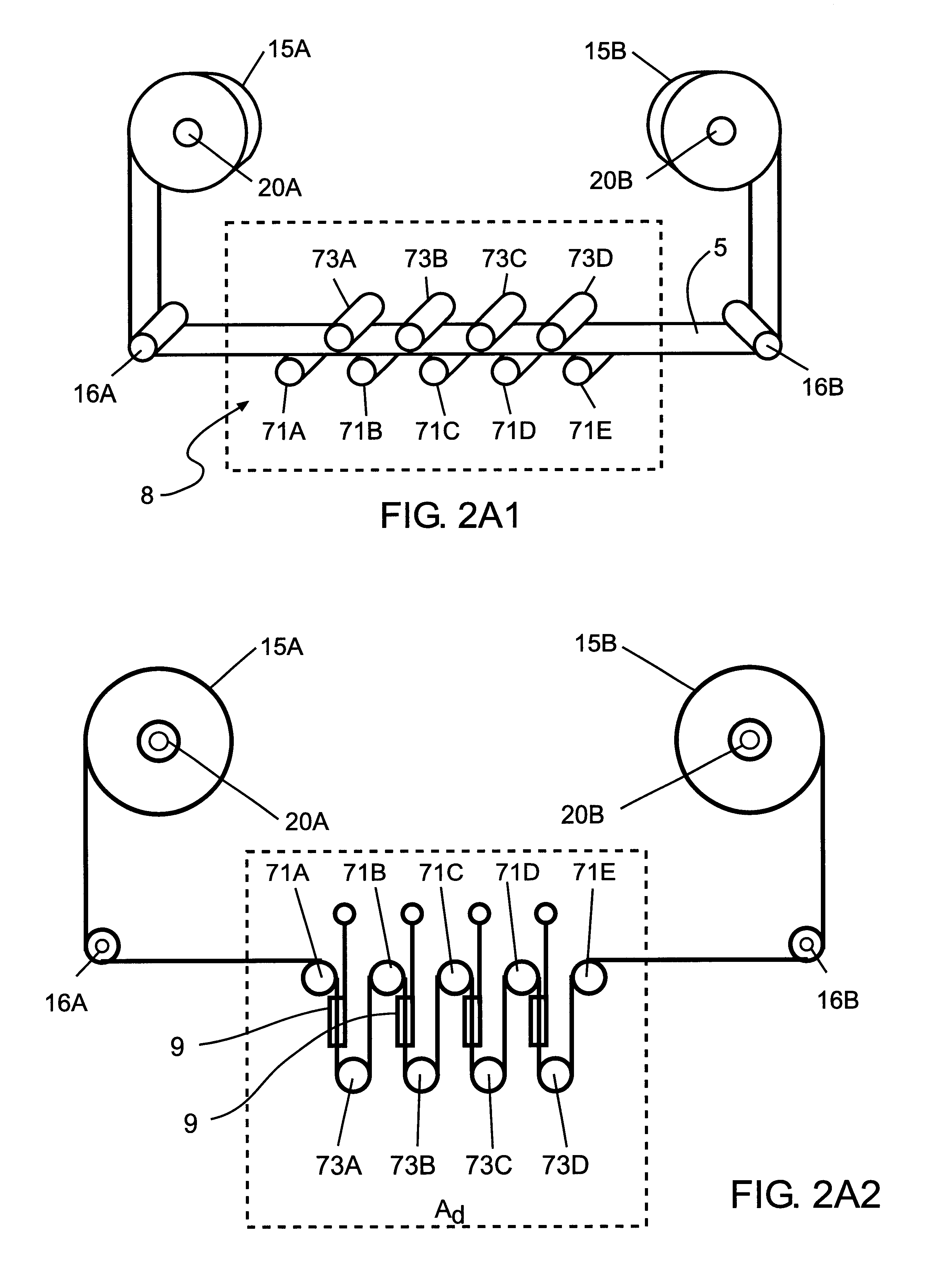
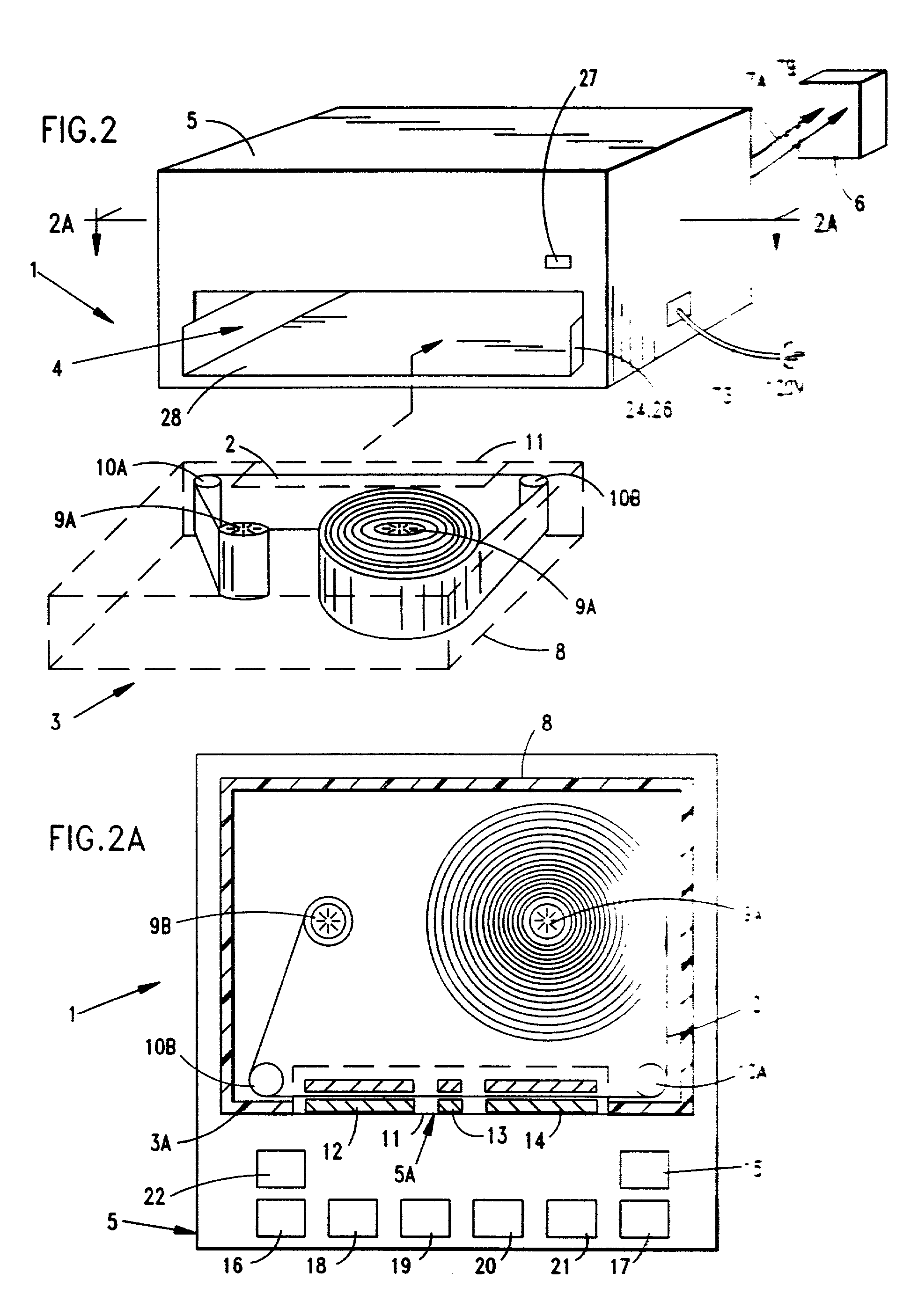
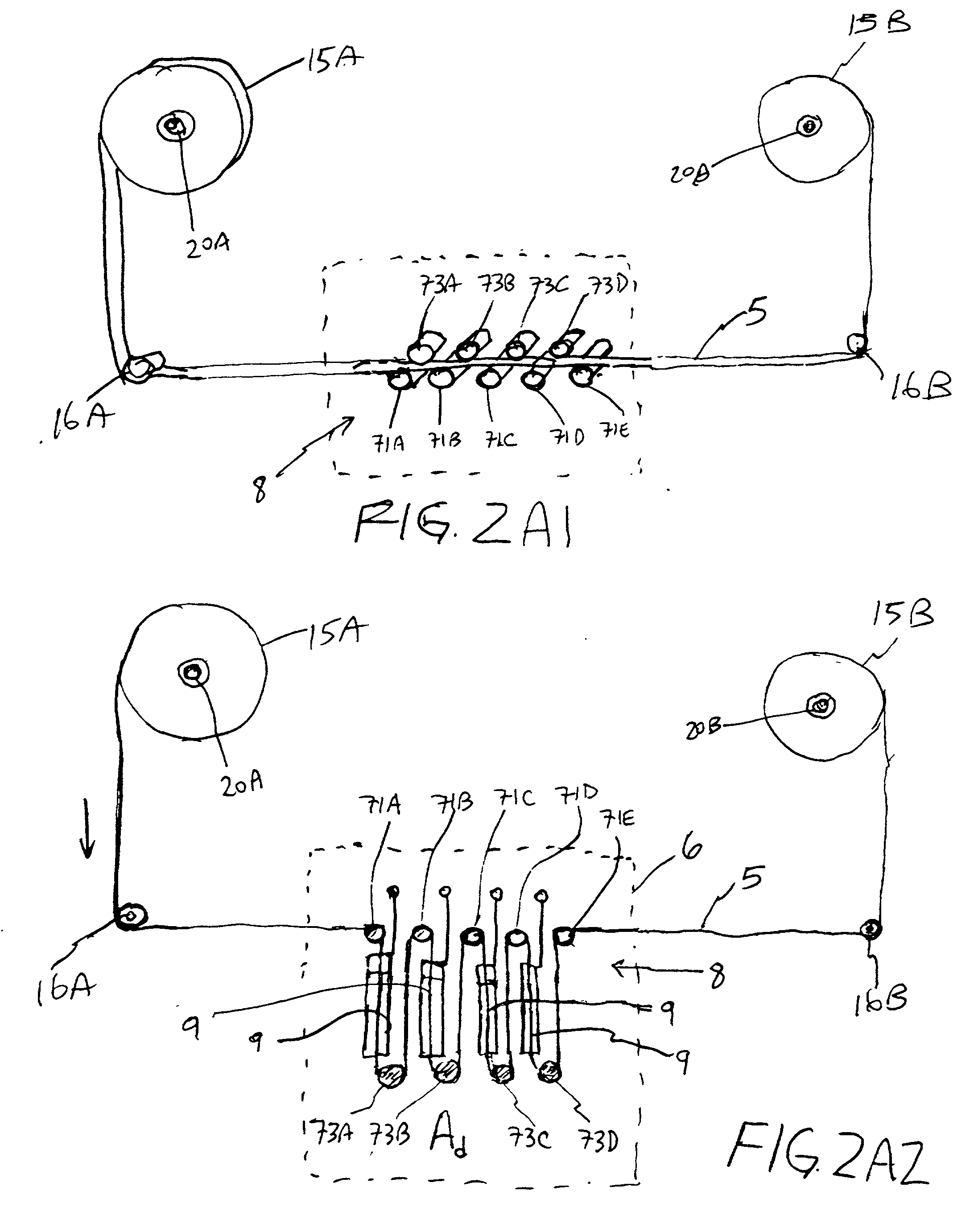
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for extending path-length of metal-fuel tape during discharging and / or recharging operations so that a supply of metal-fuel tape contained within a cassette device or on a supply reel can be rapidly discharged and / or recharged in an improved manner. During discharging operations, a plurality of discharging heads are selectively arranged about the extended path-length of metal-fuel tape so as increase the rate at which electrical power is powered from the system. During recharging operations, a plurality of recharging heads are selectively arranged about the extended path-length of metal-fuel tape to decrease the time required to recharge the metal-fuel tape transported through the system.
Owner:REVEO
Rechargeable metal air electrochemical cell incorporating collapsible cathode assembly
InactiveUS20050019651A1Promotes Oxygen RemovalExtended service lifeFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsMetal–air electrochemical cellEngineering
The rechargeable metal air electrochemical cell generally includes a pair of air cathode portions centrally disposed and attached to each other with a collapsible mechanism. Anodes are disposed in ionic communication with each air cathode portions via a suitable electrolyte. For recharging, a pair of third charging electrodes is provided ionic communication with the anode portions.
Owner:EVIONYX INC
Metal-air fuel cell battery system having means for bi-directionally transporting metal-fuel tape and managing metal-fuel available therealong
InactiveUS6410174B1Improve system performanceImprove performanceFuel and primary cellsSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsFuel cellsBattery system
Disclosed is a metal-air fuel cell battery system, wherein metal-fuel tape can be transported through its discharging head assembly as well as its recharging head assembly in a bi-directional manner while the availability of metal-fuel therealong is automatically managed in order to improve the performance of the system.
Owner:REVEO
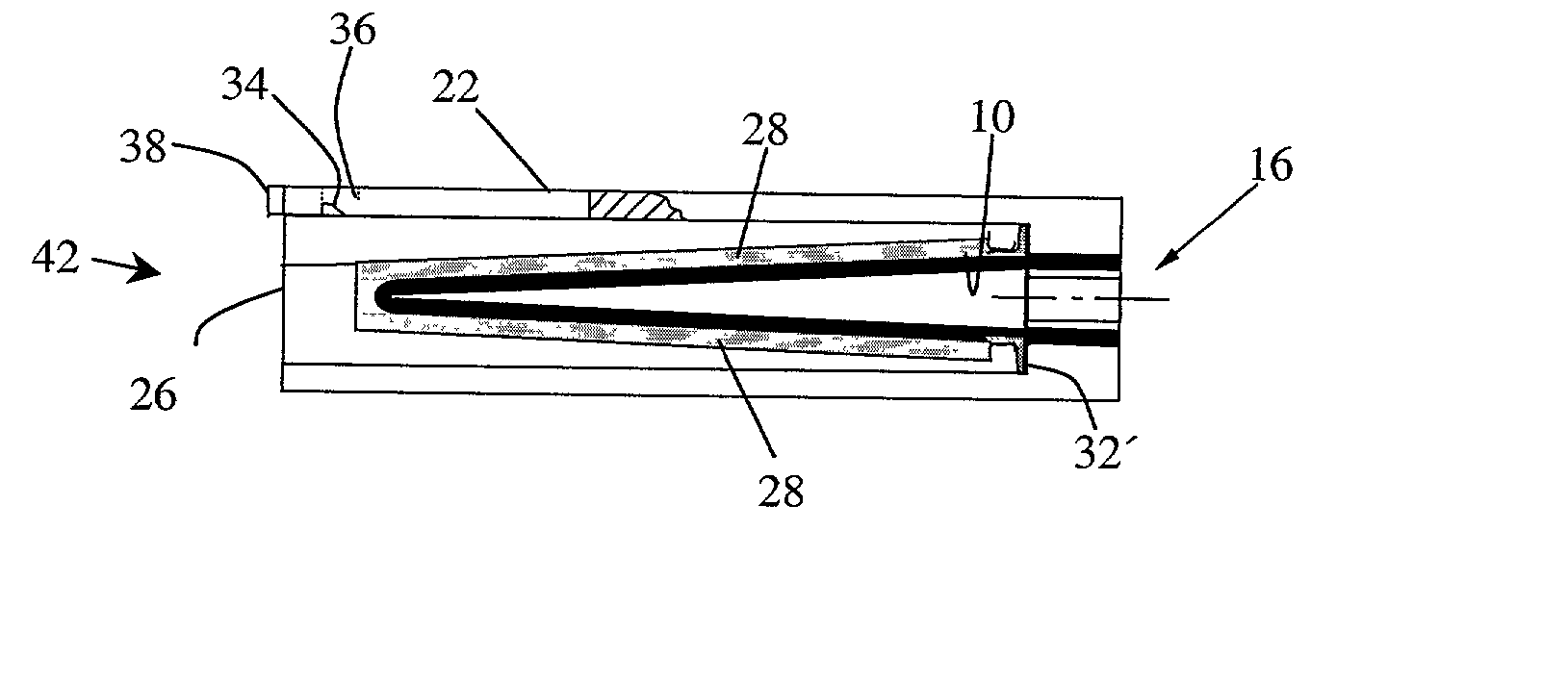
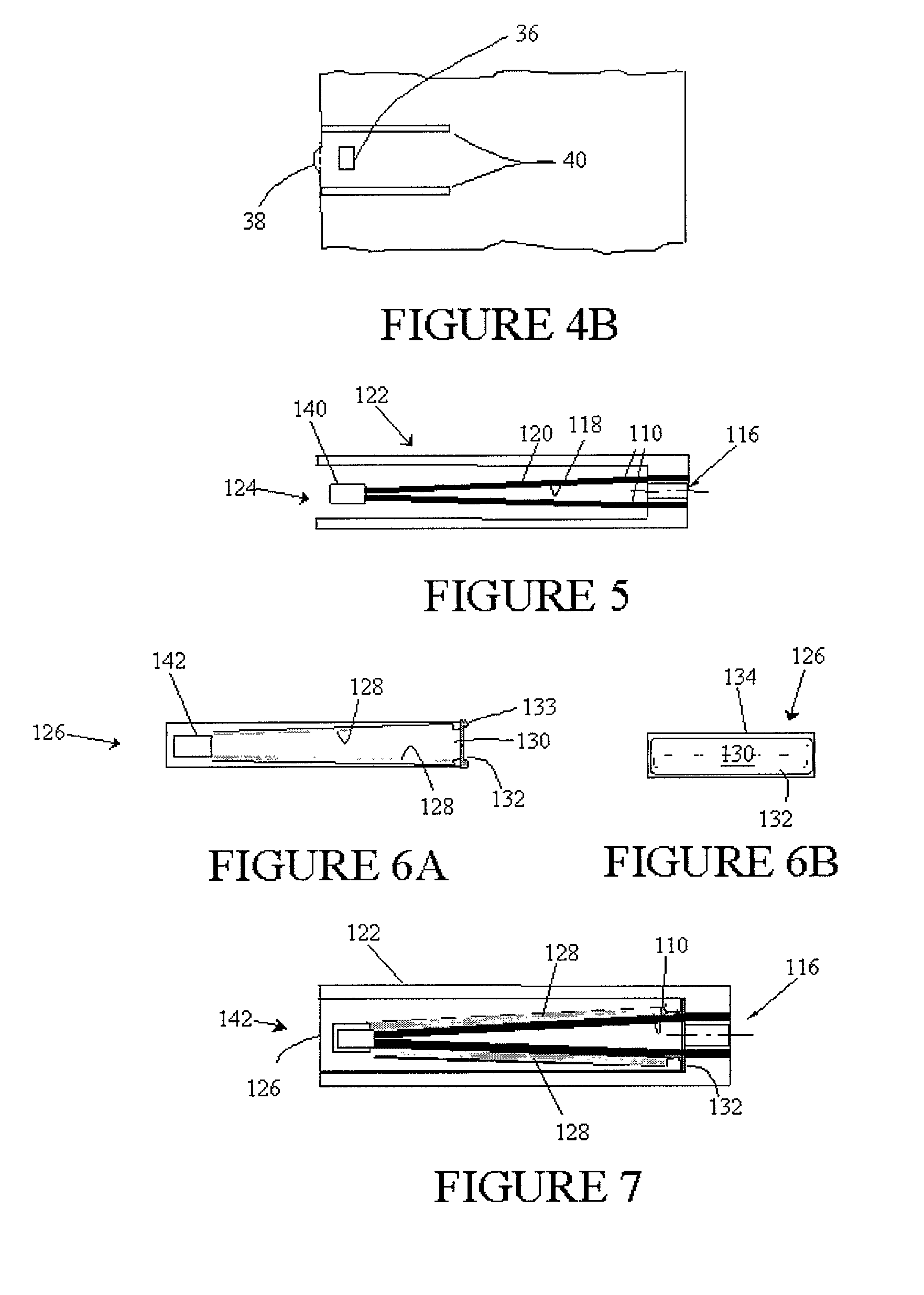
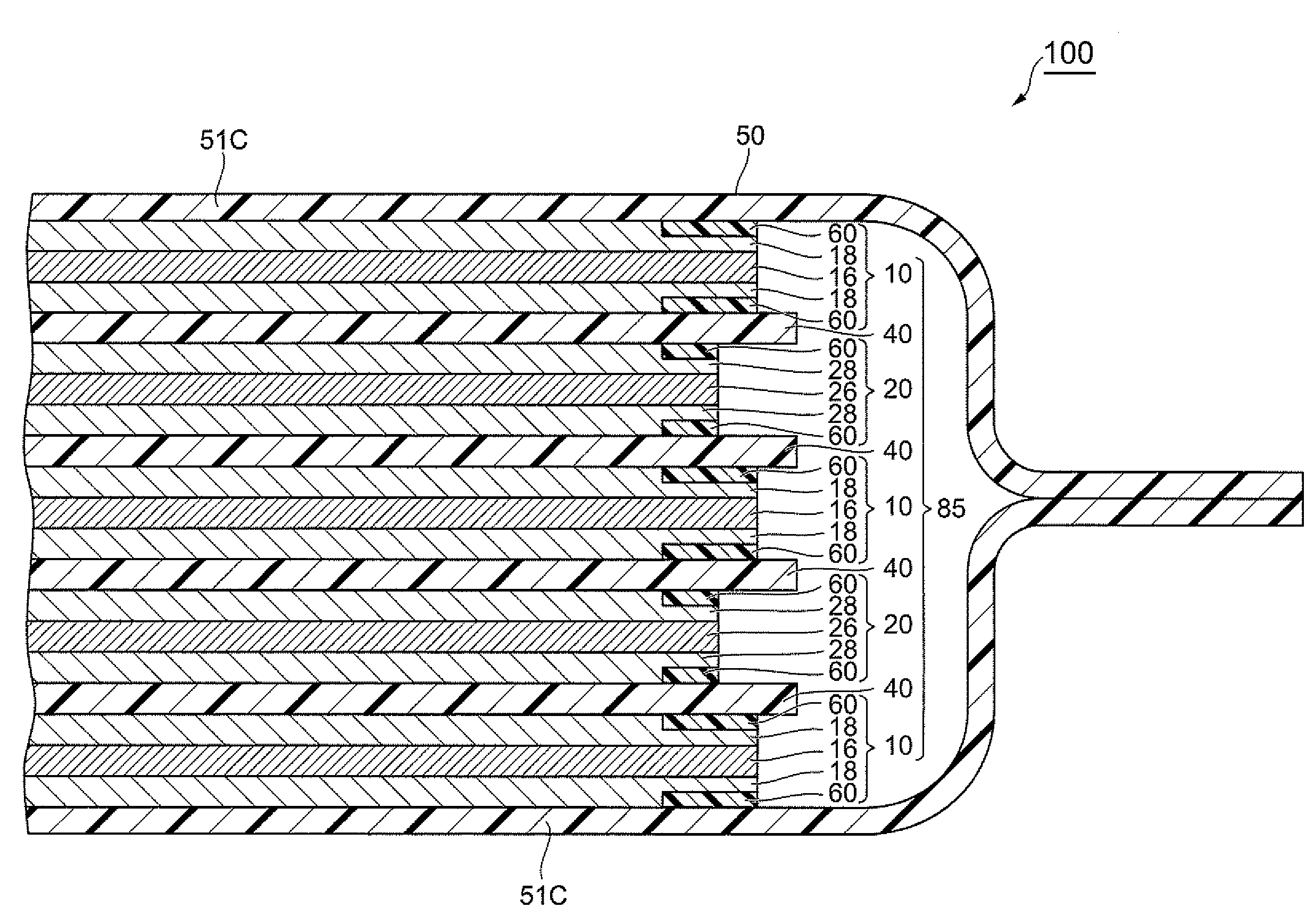
Cathode cylinder for use in metal-air fuel cell battery systems and method of fabricating the same
In an air-metal fuel cell battery (FCB) system, wherein metal-fuel tape, the ionically-conductive medium and the cathode structures are transported at substantially the same velocity at the locus of points at which the ionically-conductive medium contacts the moving cathode structure and the moving metal-fuel tape during discharging and recharging modes of operation. In a first generalized embodiment of the present invention, the ionically-conductive medium is realized as an ionically-conductive belt, and the metal-fuel tape, ionically-conductive belt, and movable cathode structure are transported at substantially the same velocity at the locus of points which the ionically-conducing belt contacts the metal-fuel tape and the cathode structure during system operation. In a second generalized embodiment of the present invention, the ionically-conductive medium is realized as a solid-state (e.g. gelatinous) film layer integrated with the metal-fuel tape. In a third generalized embodiment of the present invention, the ionically-conductive medium is realized as a solid-state film layer integrated with the movable cathode structure. By transporting the movable cathode structure, ionically contacting medium and metal-fuel tape within the system as described above, generation of frictional forces among such structures are minimized during system operation, and thus the damage to the cathode structure and metal-fuel tape is substantially reduced.
Owner:REVEO
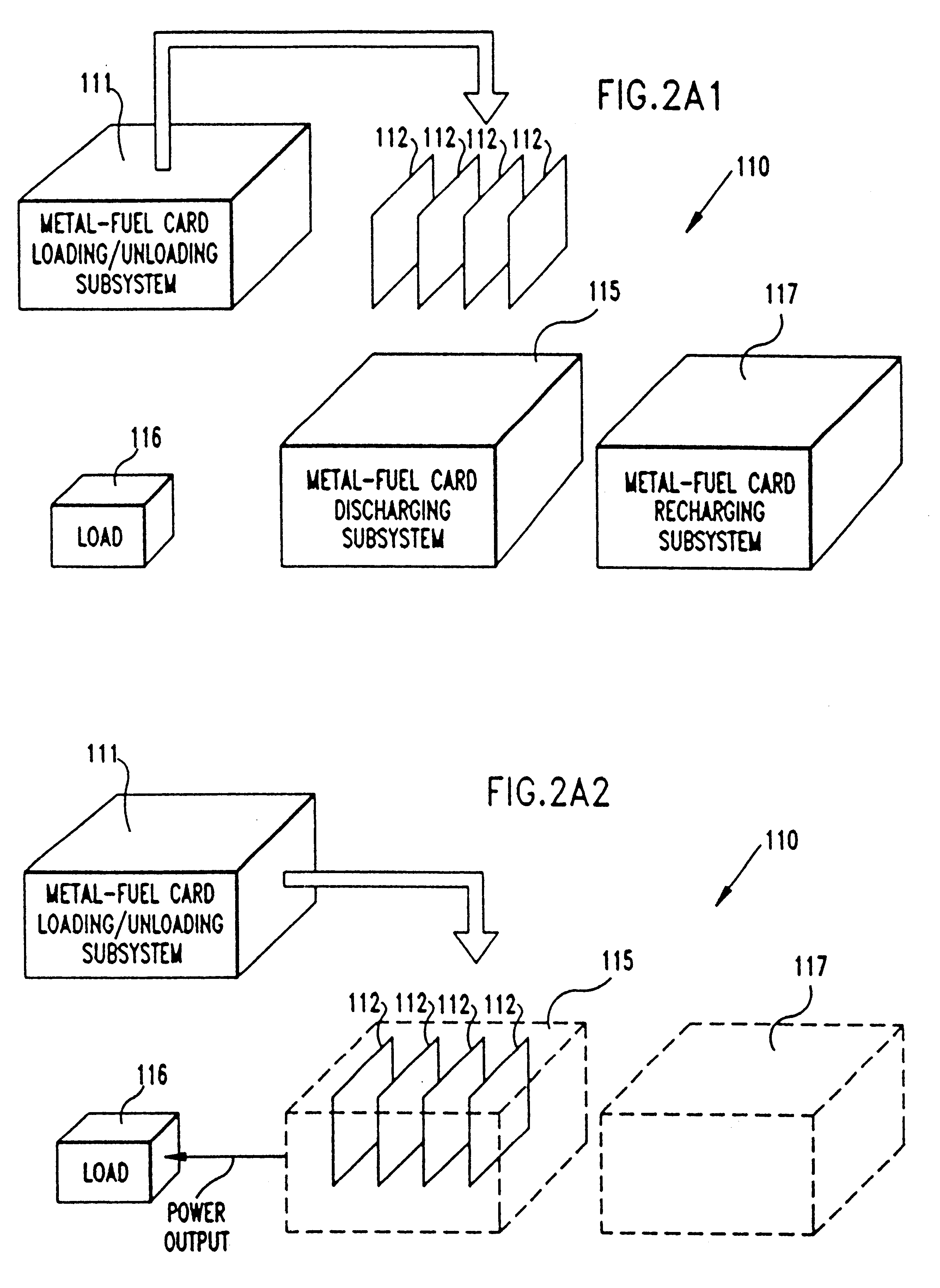
Method of and system for producing and supplying electrical power to an electrical power consuming device using a metal-air fuel cell battery (FCB) module and a supply of metal-fuel cards
InactiveUS6348277B1Compact structureHousing compactFuel and primary cellsBatteries circuit arrangementsFuel cellsEngineering
An improved metal-air fuel cell battery (FCB) system and a method of producing and supplying electrical power to an electrical power consuming device. The method involves packaging and distributing together (i) a metal-air FCB module for producing electrical power using a metal-fuel card insertable within the metal-air FCB module, and (ii) a supply of metal-fuel cards, available as metal-fuel consumable within the metal-air FCB module. The metal-air FCB module includes a cathode structure and an anode contacting structure wherebetween a metal-fuel card can be inserted during a metal-fuel card loading operation, when electrical power is required from the metal-air FCB module. By virtue of the present invention, consumers can now quickly and easily refuel a metal-air FCB module used to power electrical power consuming devices, without wasting or otherwise replacing the typically massive, expensive, and non-consumed components of the metal-air FCB module.
Owner:REVEO
Metal-air fuel cell battery systems having mechanism for extending the path length of metal-fuel tape during discharging and recharging modes of operation
InactiveUS6228519B1Easy dischargeFast chargingFuel and primary cellsSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsFuel cellsPath length
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for extending path-length of metal-fuel tape during discharging and / or recharging operations so that a supply of metal-fuel tape contained within a cassette device or on a supply reel can be rapidly discharged and / or recharged in an improved manner. During discharging operations, a plurality of discharging heads are selectively arranged about the extended path-length of metal-fuel tape so as increase the rate at which electrical power is powered from the system. During recharging operations, a plurality of recharging heads are selectively arranged about the extended path-length of metal-fuel tape to decrease the time required to recharge the metal-fuel tape transported through the system.
Owner:REVEO
Metal air cell incorporating ionic isolation systems
InactiveUS20020177036A1Fuel and primary cellsMoving electrode arrangementsElectrochemical cellHydration control
Electrochemical cell systems are disclosed herein that are capable of selective ionic isolation, oxidant isolation, oxidant removal, moisture control, and combinations thereof. Selective ionic isolation is generally effectuated by selectively eliminating or minimizing ionic communication between an anode and a cathode of the electrochemical cell.
Owner:REVEO
Metal air cell incorporating air flow system
A metal air cell system comprises a frame structure configured with variable airflow paths. The variable airflow paths provide alternatives between direct open loop airflow and semi-closed loop air flow, wherein air is at least partially circulated around the cell components. This is particularly useful for operation in different temperature environments. The open loop mode is useful for high temperature environments, and the semi-closed loop mode is useful for low temperature environments.
Owner:EVIONYX INC
Thin-type secondary battery and method of producing the same, and secondary battery module
ActiveUS20050170243A1Fuel efficiency deterioratesIncrease freedomFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsEngineeringElectrode pair
To provide a high capacity thin-type secondary battery suitably formed into a module and having no thickness fluctuation, excellent quality stability, and excellent heat radiation properties, by using a sheet-like separator having expansion anisotropy due to penetration of an electrolytic solution. A method of producing a thin-type secondary battery includes the steps of: sandwiching a sheet-like separator having expansion anisotropy due to penetration of an electrolytic solution, by a sheet-like electrode pair; inserting the separator sandwiched by the electrode pair and injecting the electrolytic solution, into a thin-type outer wrapper having an opened portion; penetrating the electrolytic solution into the separator without fixing motion of the separator in a maximum expanding direction and in a state where the maximum expanding direction of the separator and a penetrating direction of the electrolytic solution are substantially parallel to each other; and sealing the opened portion into a tightly sealed state.
Owner:ENVISION AESC JAPAN LTD
Electrostatic discharge device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120224285A1Less prone to macrophase separationEasy to storeShielding materialsNanostructure manufactureOptoelectronicsViscosity
The invention is achieved by applying a layer of the mixture that contains polymer and conductive particles over a first surface, when the mixture has a first viscosity that allows the conductive particles to rearrange within the layer. An electric field is applied over the layer, so that a number of the conductive particles are aligned with the field and thereafter the viscosity of the layer is changed to a second, higher viscosity, in order to mechanically stabilise the layer. This leads to a stable layer with enhanced and anisotropic conductivity that can be used in the manufacture of ESD devices.
Owner:CONDALIGN AS
Metal-air fuel cell battery system employing a plurality of moving cathode structures for improved volumetric power density
InactiveUS6335111B1High densityFriction is generatedFuel and primary cellsBatteries circuit arrangementsFuel cellsEngineering
In an air-metal fuel cell battery (FCB) system, wherein a plurality of movable cathode structures are mounted within a compact housing through which metal-fuel tape is transported along a predetermined path while an ionically-conductive medium is disposed between the metal-fuel tape and each movable cathode structure at points of contact. In illustrative embodiments, the movable cathode structures are realized as rotatable cathode cylinders, and transportable cathode belts. The ionically-conductive medium is realized as a solid-state ionically-conductive film applied to the cathode structures and / or metal-fuel tape, as well as ionically-conductive belt structures transported at the same velocity as corresponding cathode structures (e.g. cathode cylinders or belts) at the locus of points at which the ionically-conductive medium contacts the moving cathode structure and the moving metal-fuel tape. By virtue of the present invention, the volumetric power density characteristics of FCB systems can be significantly improved, while the likelihood of damage to the cathode structures and metal-fuel tape is substantially reduced.
Owner:REVEO
Metal-air fuel cell battery system employing metal-fuel cards
Improved metal-air fuel cell battery systems having metal-fuel realized in the form of metal-fuel tape cartridges and metal-fuel cards, which can be either manually or automatically inserted within the power generation bay of the system. In order to produce a range of output voltages, the metal-fuel tape has a plurality of electrically-isolated metal-fuel tracks and the metal-fuel cards have a plurality of electrically-isolated metal-fuel strips. An output voltage configuration subsystem is provided for configuring the voltages produced by the individual cells to produce a desired output. A subsystem is provided for detecting oxide formation on the metal-fuel tracks and strips so that only metal-fuel that has been oxidized is reduced during recharging operations. A subsystem is also provided for controlling the flow of oxygen into the power generation head in order to control the power output from the system.
Owner:REVEO
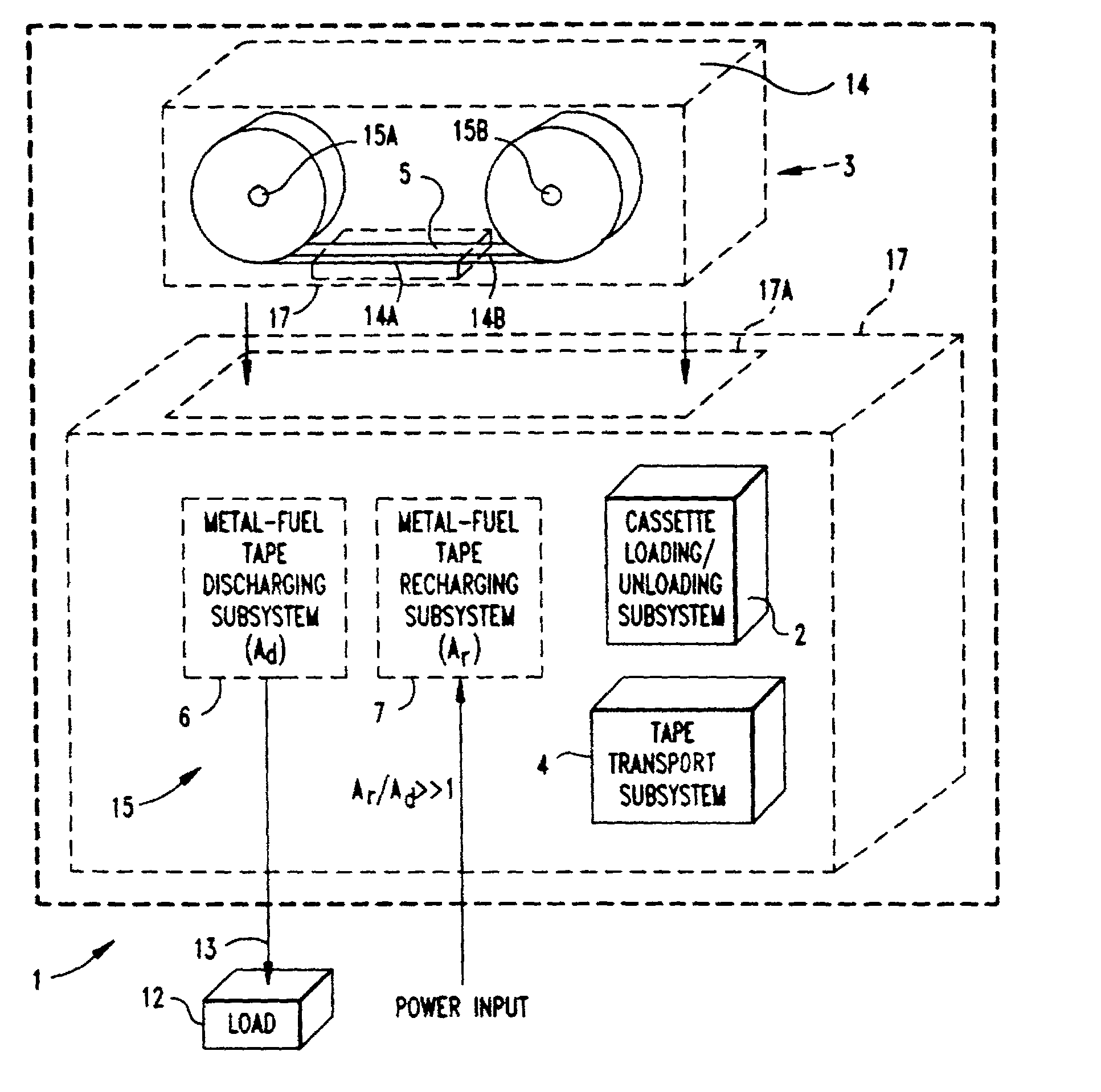
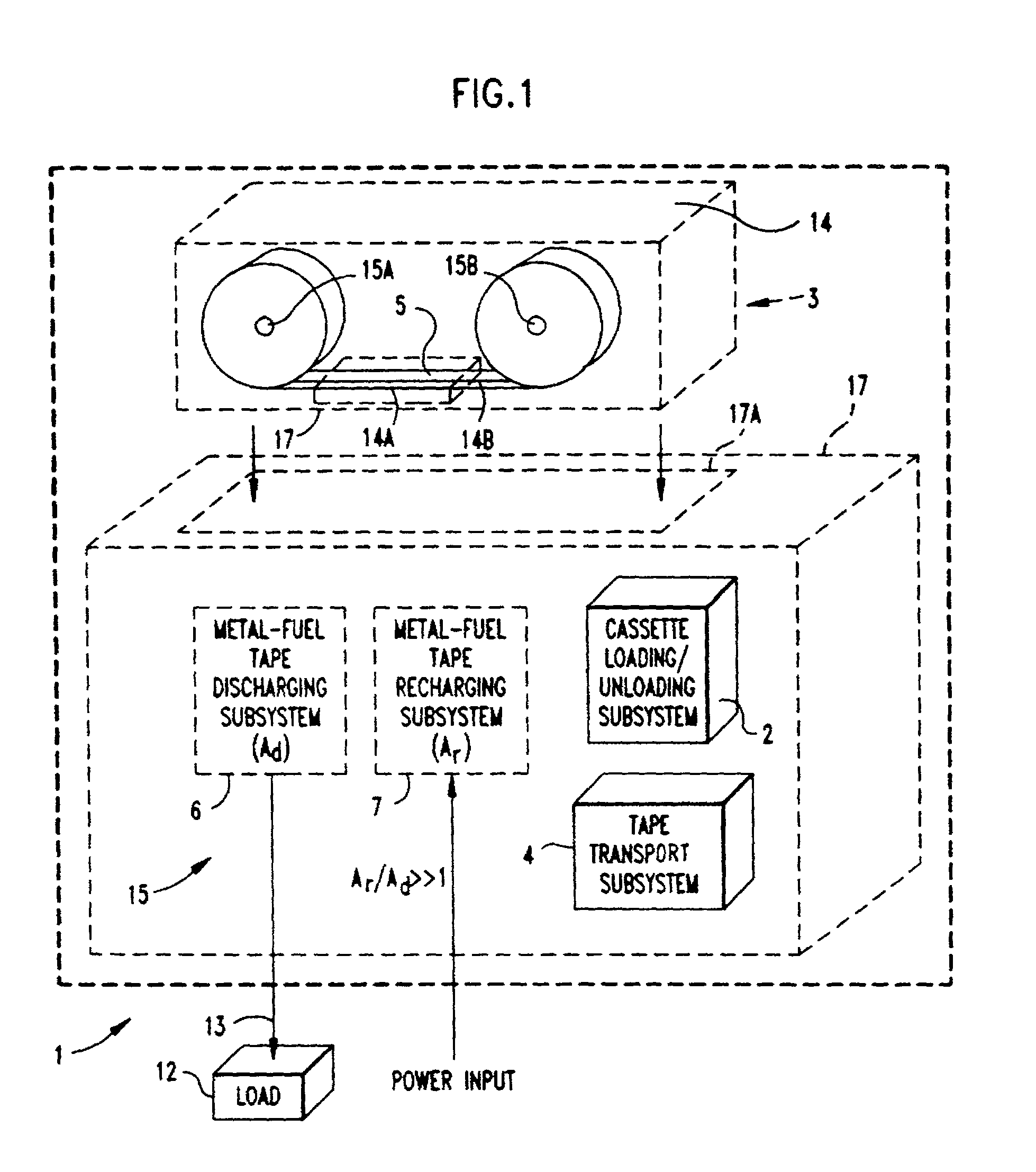
Metal-air fuel cell battery systems having a metal-fuel card storage cassette, insertable within a port in a system housing, containing a supply of substantially planar discrete metal-fuel cards, and fuel card transport mechanisms therein
InactiveUS20010014416A1Fuel and primary cellsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrochemical responseChemical reaction
Disclosed are various types of metal-air FCB-based systems comprising a Metal-Fuel Transport Subsystem, a Metal-Fuel Discharging Subsystem, and a Metal-Fuel Recharging Subsystem. The function of the Metal-Fuel Transport Subsystem is to transport metal-fuel material, in the form of tape, cards, sheets, cylinders and the like, to the Metal-Fuel Discharge Subsystem, or the Metal-Fuel Recharge Subsystem, depending on the mode of the system selected. When transported to or through the Metal-Fuel Discharge Subsystem, the metal-fuel is discharged by (i.e. electro-chemically reaction with) one or more discharging heads in order produce electrical power across an electrical load connected to the subsystem while H2O and O2 are consumed at the cathode-electrolyte interface during the electro-chemical reaction. When transported to or through the Metal-Fuel Recharging Subsystem, discharged metal-fuel is recharged by one or more recharging heads in order to convert the oxidized metal-fuel material into its source metal material suitable for reuse in power discharging operations, while O2 is released at the cathode-electrolyte interface during the electro-chemical reaction. In the illustrative embodiments, various forms of metal fuel can be discharged and recharged in an efficient manner to satisfy a broad range of electrical loading conditions.
Owner:REVEO
System for synthesis of electrode array
InactiveUS20050089626A1Electrochemical processing of electrodesInsertable electrodesElectrolysisElectrode array
Systems and methods for preparing electrocatalysts are disclosed. The system includes-a high temperature synthesis device for preparing an array of electrocatalysts as electrolytic surfaces of working electrodes. At least a portion of the electrolytic surfaces are defined by different materials. The device includes a plurality of openings for receiving the array of working electrodes and a mask having a plurality of openings configured for exposing at least a portion of each of the working electrodes for forming the electrolytic surfaces thereon.
Owner:FREESLATE +1
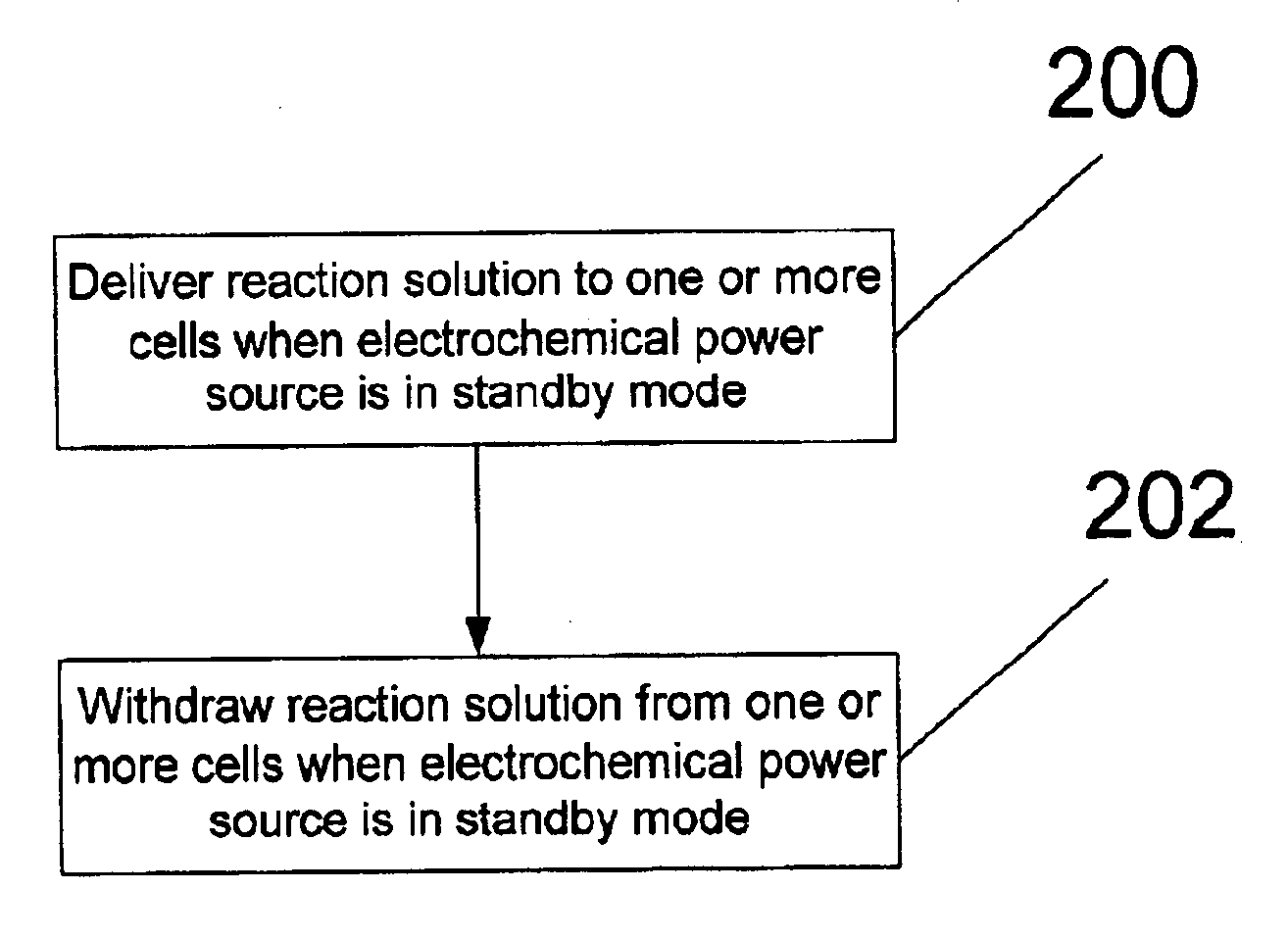
Method of and system for flushing one or more cells in a particle-based electrochemical power source in standby mode
A method of and system for flushing one or more cells or components thereof in a particle-based electrochemical power source is provided. Reaction solution is delivered to and withdrawn from the one or more cells when the electrochemical power source is in a standby mode of operation.
Owner:METALLIC POWER INC
Cathode cylinder for use in metal-air fuel cell battery systems and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS6218034B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce the possibilitySeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsFuel and primary cellsFuel cellsEngineering
In an air-metal fuel cell battery (FCB) system, wherein metal-fuel tape, the ionically-conductive medium and the cathode structures are transported at substantially the same velocity at the locus of points at which the ionically-conductive medium contacts the moving cathode structure and the moving metal-fuel tape during discharging and recharging modes of operation. In a first generalized embodiment of the present invention, the ionically-conductive medium is realized as an ionically-conductive belt, and the metal-fuel tape, ionically-conductive belt, and movable cathode structure are transported at substantially the same velocity at the locus of points which the ionically-conducing belt contacts the metal-fuel tape and the cathode structure during system operation. In a second generalized embodiment of the present invention, the ionically-conductive medium is realized as a solid-state (e.g. gel-like) film layer integrated with the metal-fuel tape, and the metal-fuel tape, ionically-conductive film layer and movable cathode structure are transported at substantially the same velocity at the locus of points which the ionically-conducing film layer contacts the metal-fuel tape and the cathode structure during system operation. In a third generalized embodiment of the present invention, the ionically-conductive medium is realized as a solid-state film layer integrated with the movable cathode structure, and the metal-fuel tape, ionically-conductive film layer and movable cathode structure are transported at substantially the same velocity at the locus of points which the ionically-conducing film layer contacts the metal-fuel tape and the cathode structure during system operation. By transporting the movable cathode structure, ionically contacting medium and metal-fuel tape within the system as described above, generation of frictional forces among such structures are minimized during system operation, and thus the damage to the cathode structure and metal-fuel tape is substantially reduced.
Owner:REVEO
Metal-air fuel cell battery system having means for controlling discharging and recharging parameters for improved operating efficiency
InactiveUS6287715B1Fast and efficient operationFuel and primary cellsSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsElectrochemical responseChemical reaction
Disclosed are various types of metal-air FCB-based systems comprising a Metal-Fuel Transport Subsystem, a Metal-Fuel Discharging Subsystem, and a Metal-Fuel Recharging Subsystem. The function of the Metal-Fuel Transport Subsystem is to transport metal-fuel material, in the form of tape, cards, sheets, cylinders and the like, to the Metal-Fuel Discharge Subsystem, or the Metal-Fuel Recharge Subsystem, depending on the mode of the system selected. When transported to or through the Metal-Fuel Discharge Subsystem, the metal-fuel is discharged by (i.e. electro-chemically reaction with) one or more discharging heads in order produce electrical power across an electrical load connected to the subsystem while H2O and O2 are consumed at the cathode-electrolyte interface during the electrochemical reaction. When transported to or through the Metal-Fuel Recharging Subsystem, discharged metal-fuel is recharged by one or more recharging heads in order to convert the oxidized metal-fuel material into its source metal material suitable for reuse in power discharging operations, while O2 is released at the cathode-electrolyte interface during the electro-chemical reaction. In the illustrative embodiments, discharge and recharge parameters are detected and processed in order to generate control data signals that are used to control discharging and recharging parameters so that discharging and recharging operations and metal-fuel / metal-oxide management operations are carried out in an efficient manner.
Owner:REVEO
Lithium-ion battery
ActiveUS8795885B2Improve diffusivityNanotechElectrolytic inorganic material coatingSolid state electrolytePhosphate
A lithium-ion battery having an anode including an array of nanowires electrochemically coated with a polymer electrolyte, and surrounded by a cathode matrix, forming thereby interpenetrating electrodes, wherein the diffusion length of the Li+ ions is significantly decreased, leading to faster charging / discharging, greater reversibility, and longer battery lifetime, is described. The battery design is applicable to a variety of battery materials. Methods for directly electrodepositing Cu2Sb from aqueous solutions at room temperature using citric acid as a complexing agent to form an array of nanowires for the anode, are also described. Conformal coating of poly-[Zn(4-vinyl-4′methyl-2,2′-bipyridine)3](PF6)2 by electroreductive polymerization onto films and high-aspect ratio nanowire arrays for a solid-state electrolyte is also described, as is reductive electropolymerization of a variety of vinyl monomers, such as those containing the acrylate functional group. Such materials display limited electronic conductivity but significant lithium ion conductivity. Cathode materials may include oxides, such as lithium cobalt oxide, lithium magnesium oxide, or lithium tin oxide, as examples, or phosphates, such as LiFePO4, as an example.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Anisotropic conducting body and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20120231178A1Fast curing timeHigh bonding strengthShielding materialsNanostructure manufactureOptoelectronicsViscosity
A layer of the mixture that contains polymer and conductive particles is applied over a first surface, when the mixture has a first viscosity that allows the conductive particles to rearrange within the layer. An electric field is applied over the layer, so that a number of the conductive particles are aligned with the field and thereafter the viscosity of the layer is changed to a second, higher viscosity, in order to mechanically stabilise the layer. This leads to a stable layer with enhanced and anisotropic conductivity.
Owner:CONDALIGN AS
Popular searches
Fuel cell auxillaries Aqueous electrolyte fuel cells Cell component details Solid electrolyte fuel cells Regenerative fuel cells Secondary cells servicing/maintenance Primary cell electrodes Non-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodes Electrolyte immobilisation/gelification Cell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacers
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com