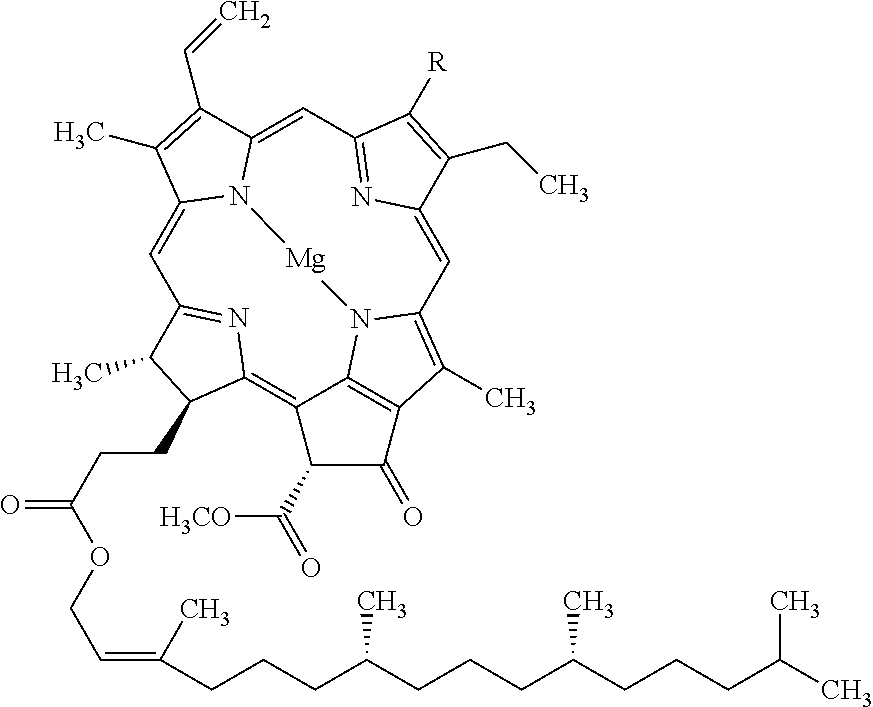
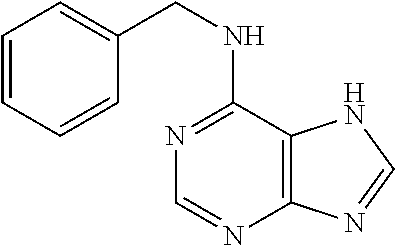
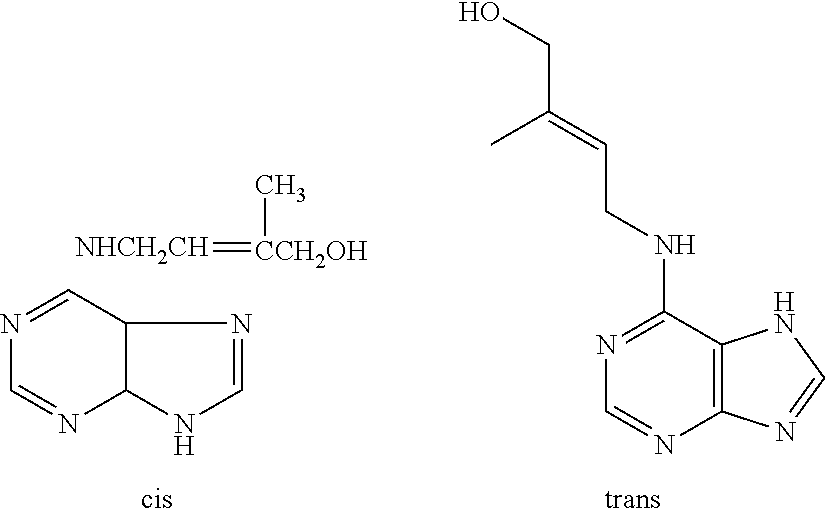
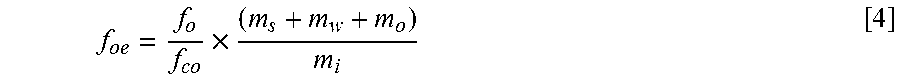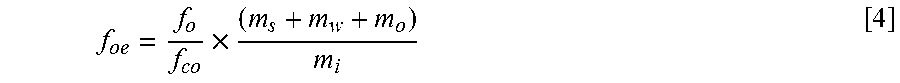Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99results about "Fruits/vegetable preservation by blanching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for the preparation of a crisp food product
A crisp food product is prepared in a first phase from thin food pieces of raw fruit, vegetable or gelatinizable proteins, by blanching them (if necessary) and drying them. A second phase takes place in a vacuum chamber, where the dried thin food pieces are exposed to heat to expand them, are quickly removed from the heat source and are cooled, before being removed from the vaccuum.
Owner:MELNYCZUK TANIA MARIA
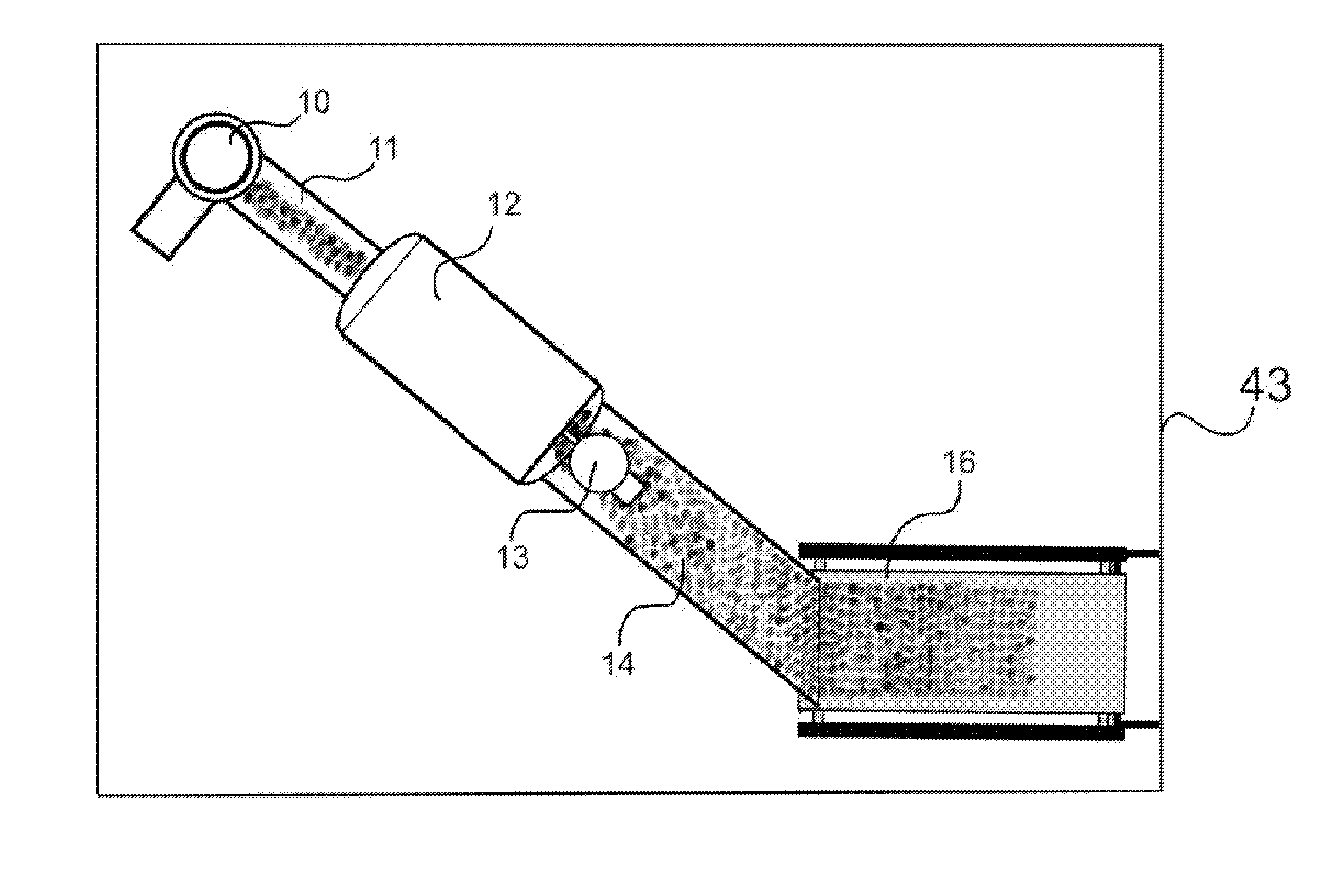
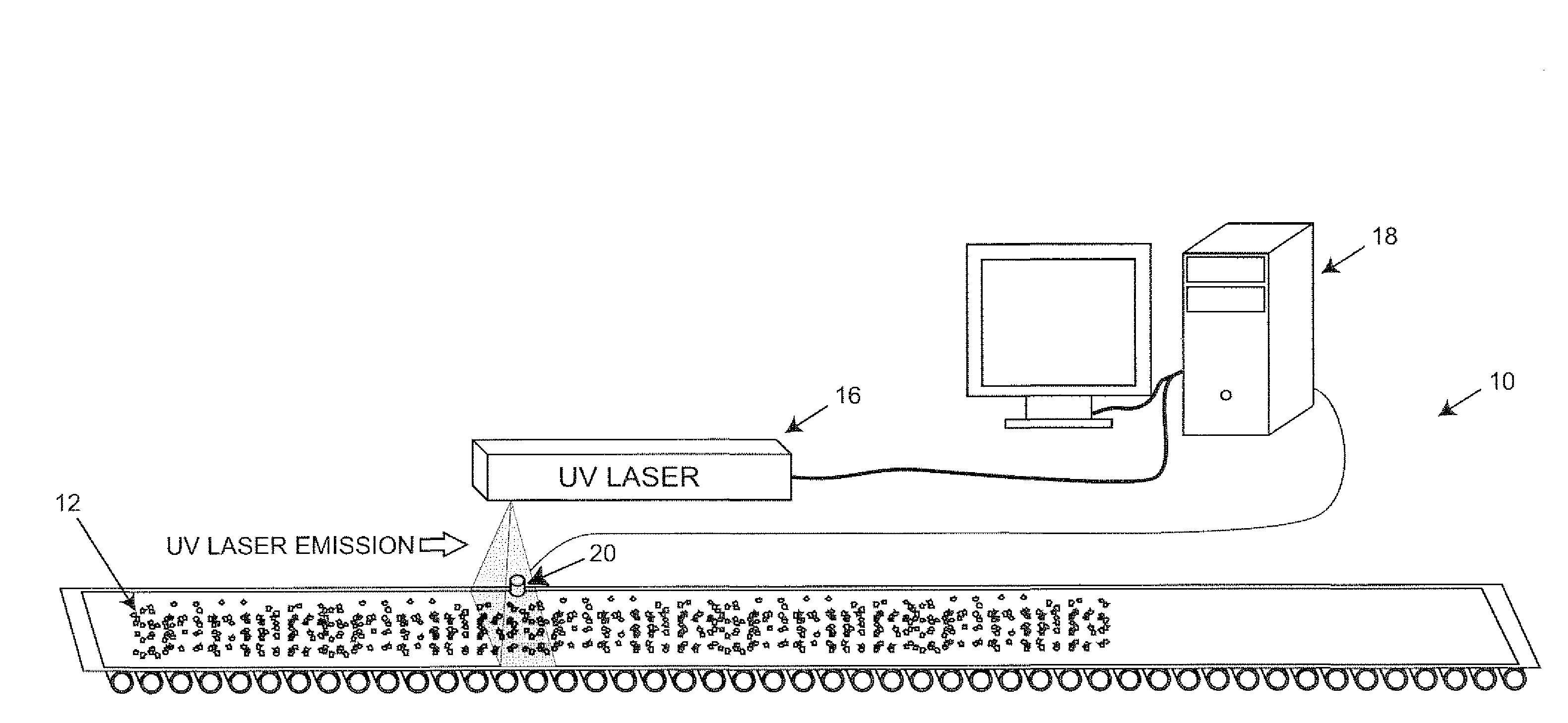
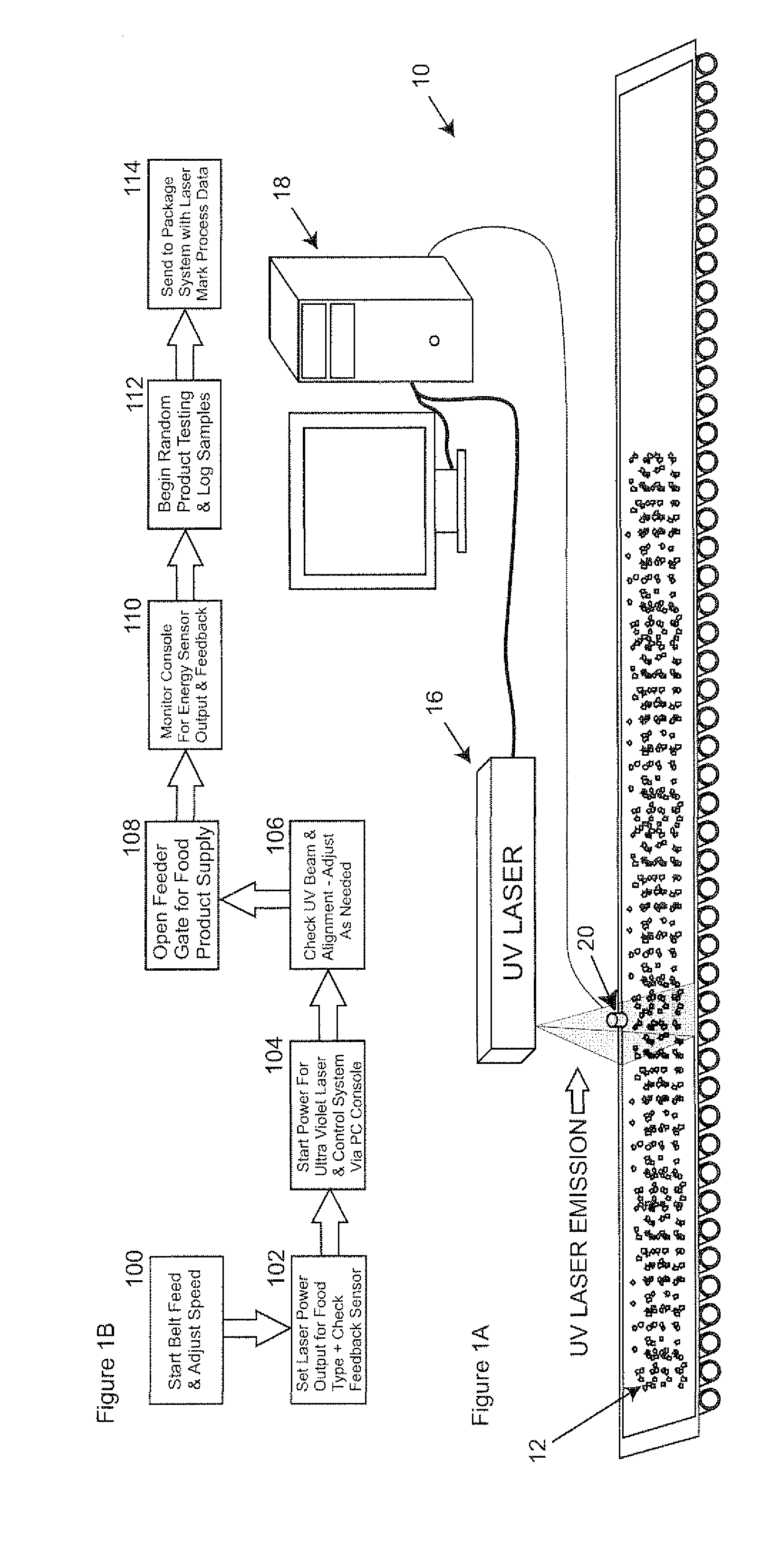
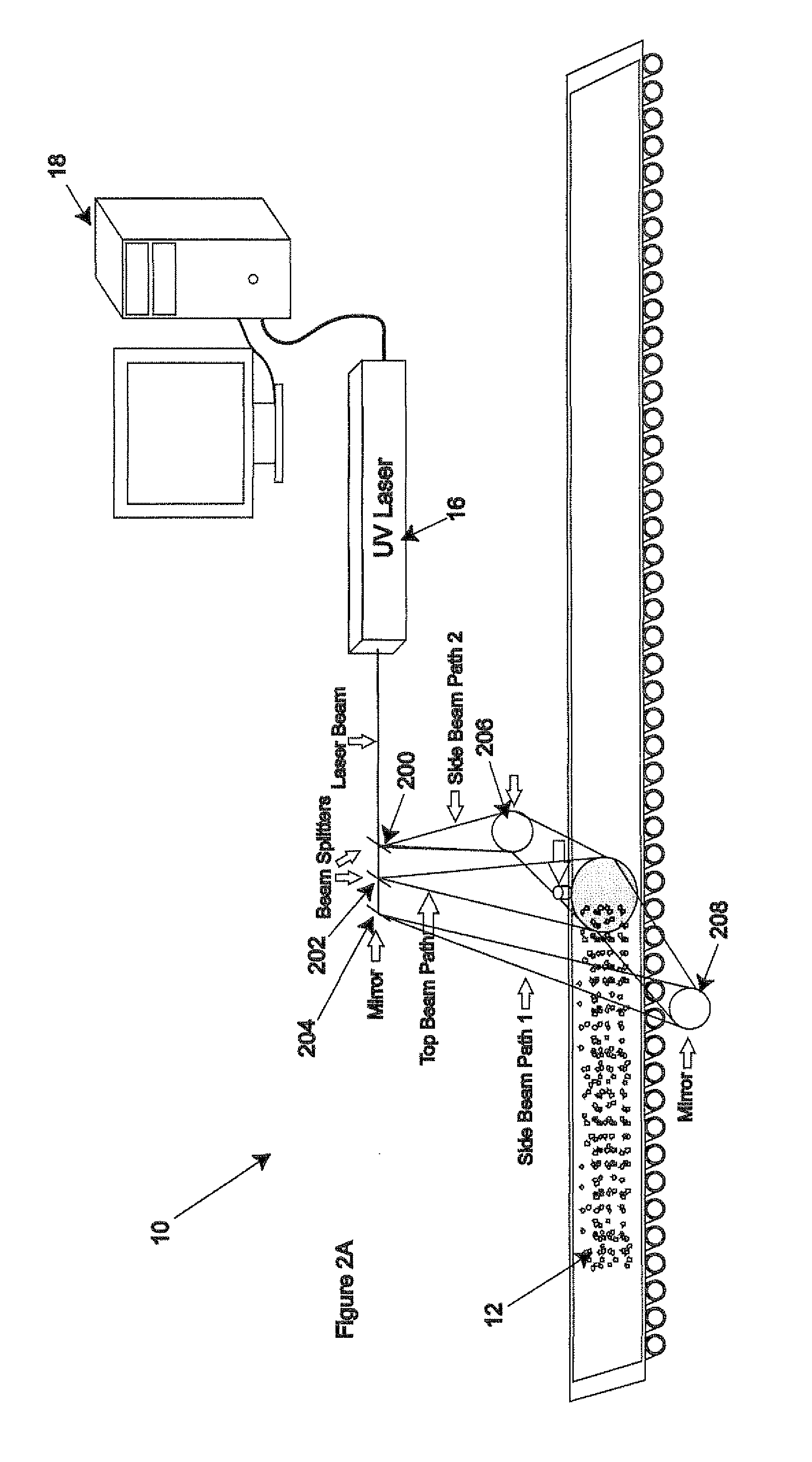
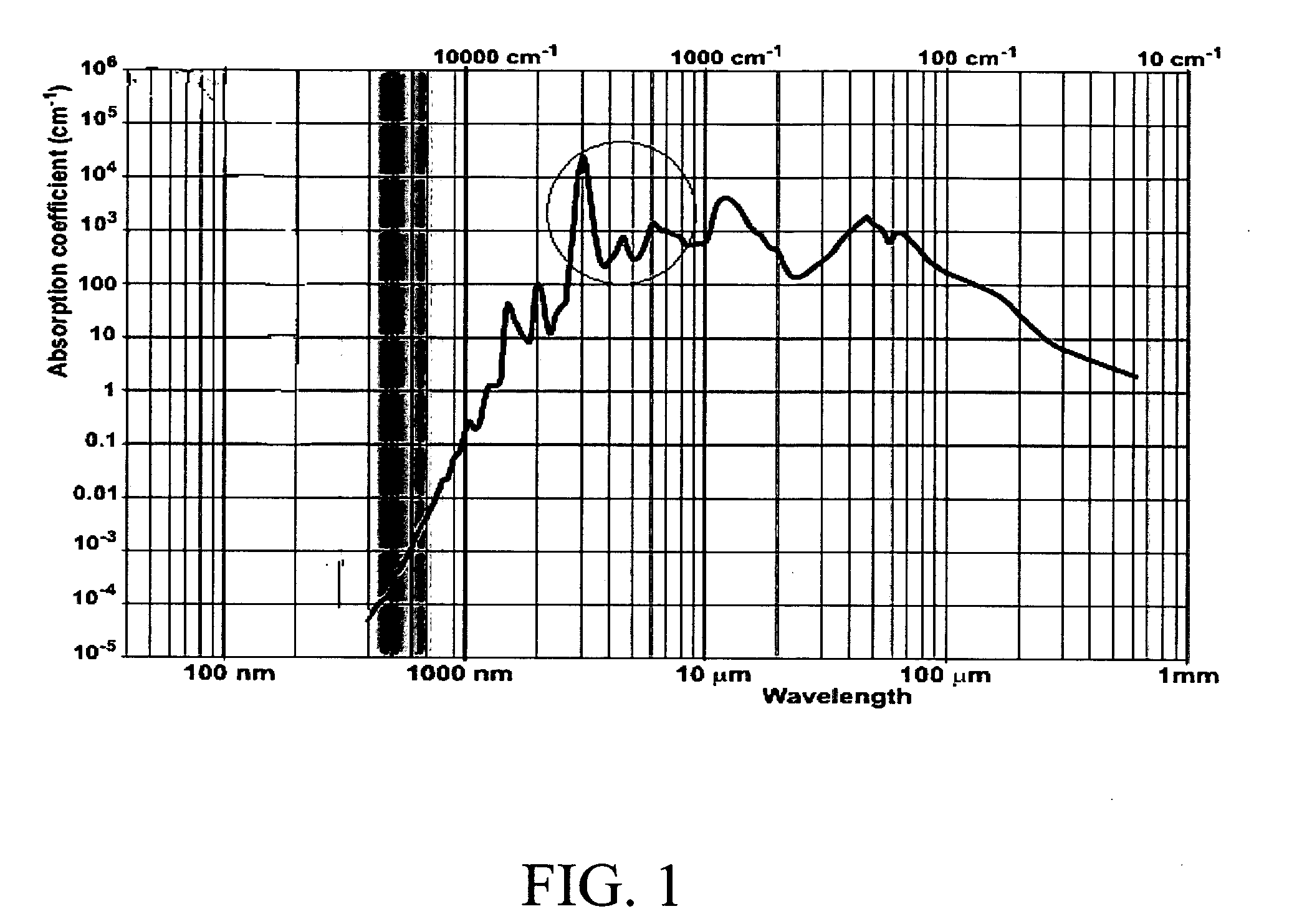
Method and apparatus for sanitizing consumable products using ultraviolet light
A method and apparatus are provided for sanitizing consumable products using ultraviolet light. The consumable products are exposed to the ultraviolet light for a preselected duration of time and at a desired power level to achieve a desired level of sanitization.
Owner:FELIX PERRY DEAN
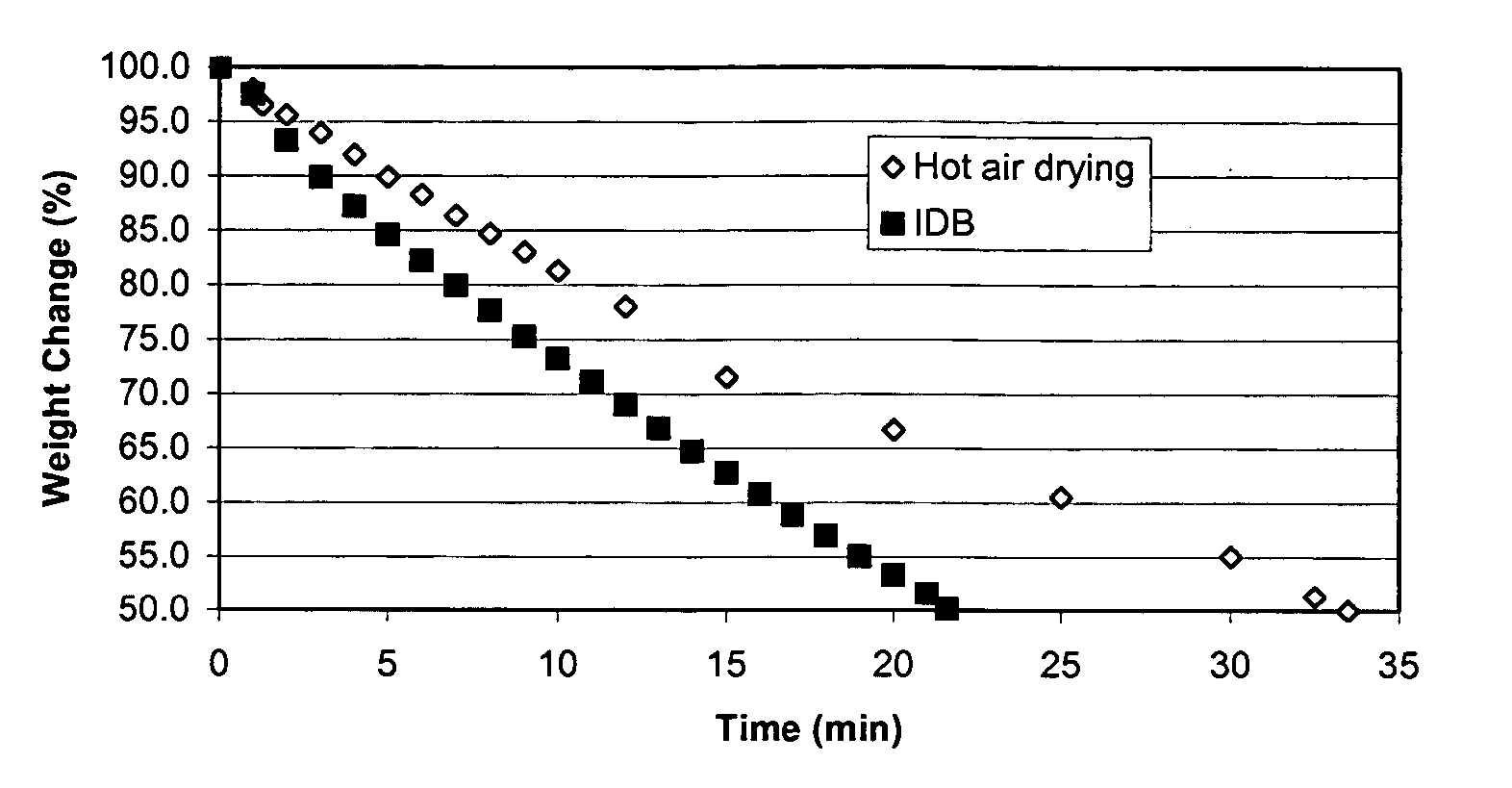
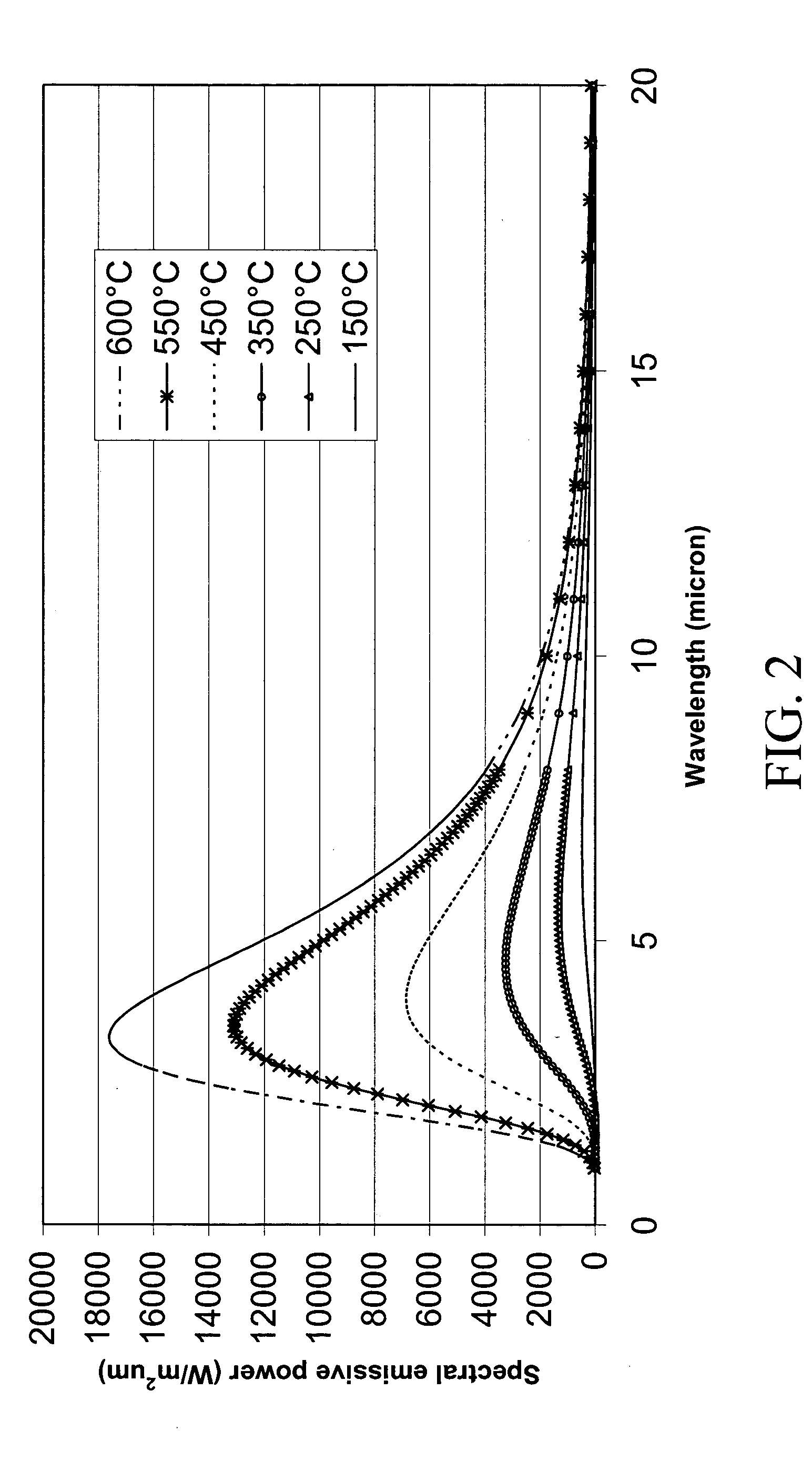
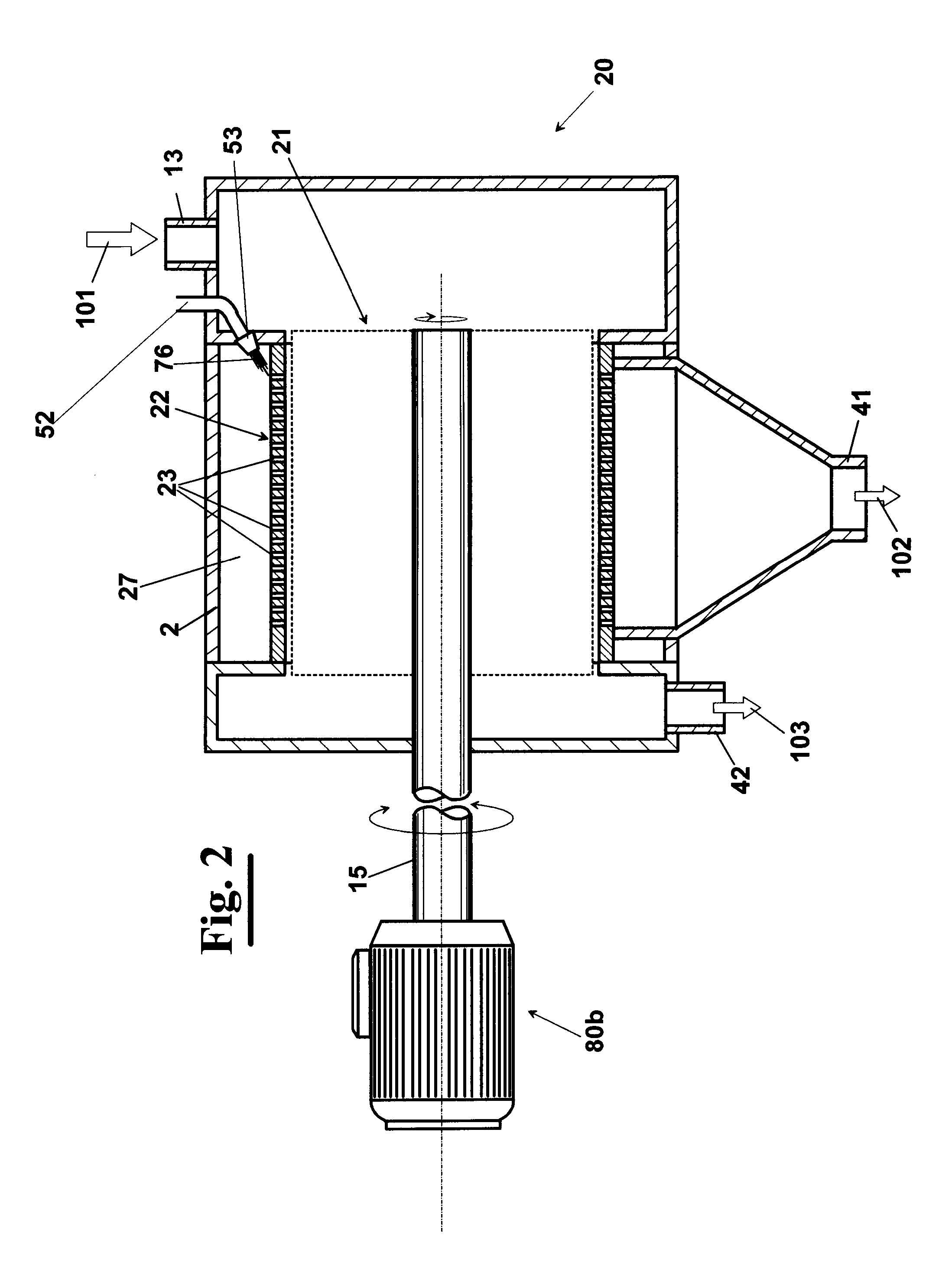
Novel infrared dry blanching (IDB), infrared blanching, and infrared drying technologies for food processing
InactiveUS20060034981A1Simple processShorten the timeMilk preservationDough treatmentSide effectVolumetric Mass Density
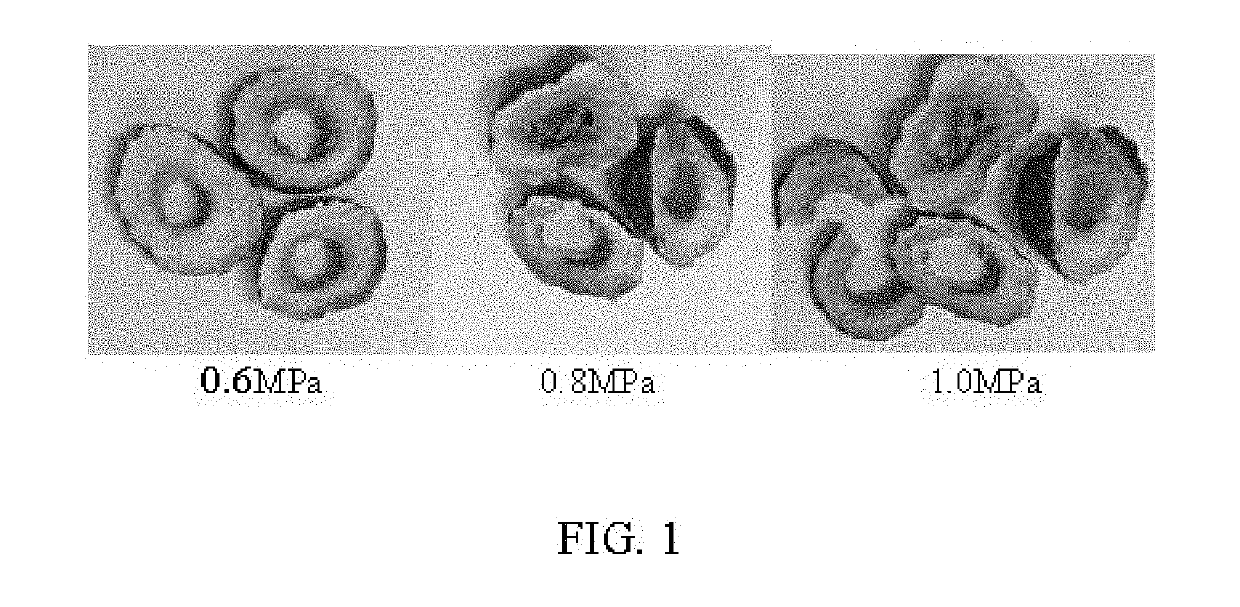
This invention relates to food processing and, in particular, blanching and dehydration of foods. Conventional blanching and dehydration requires use of steam and forced hot air. This invention is the first to effectively use infrared radiation energy to perform simultaneous blanching and dehydration of fruits and vegetables. Since this technology does not involve the addition of steam or water in the process of blanching, it has been named “infrared dry-blanching” (IDB) technology. IDB is intended to be a replacement for current steam, water and / or microwave blanching methods. It can be used to produce many kinds of value-added dried, refrigerated, frozen and dehydrofrozen foods such as fruit and vegetable products. In general, the advantages of IDB include (1) uniform heating which enhances energy efficiency and limits damage from over-heating, (2) capability of zone heating to address differential density, (3) ability to treat large or small lots with the same piece of equipment, (4) portability, since equipment can be built on wheels, and (5) a safe, non-toxic process with no harmful side-effects to humans or the environment.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
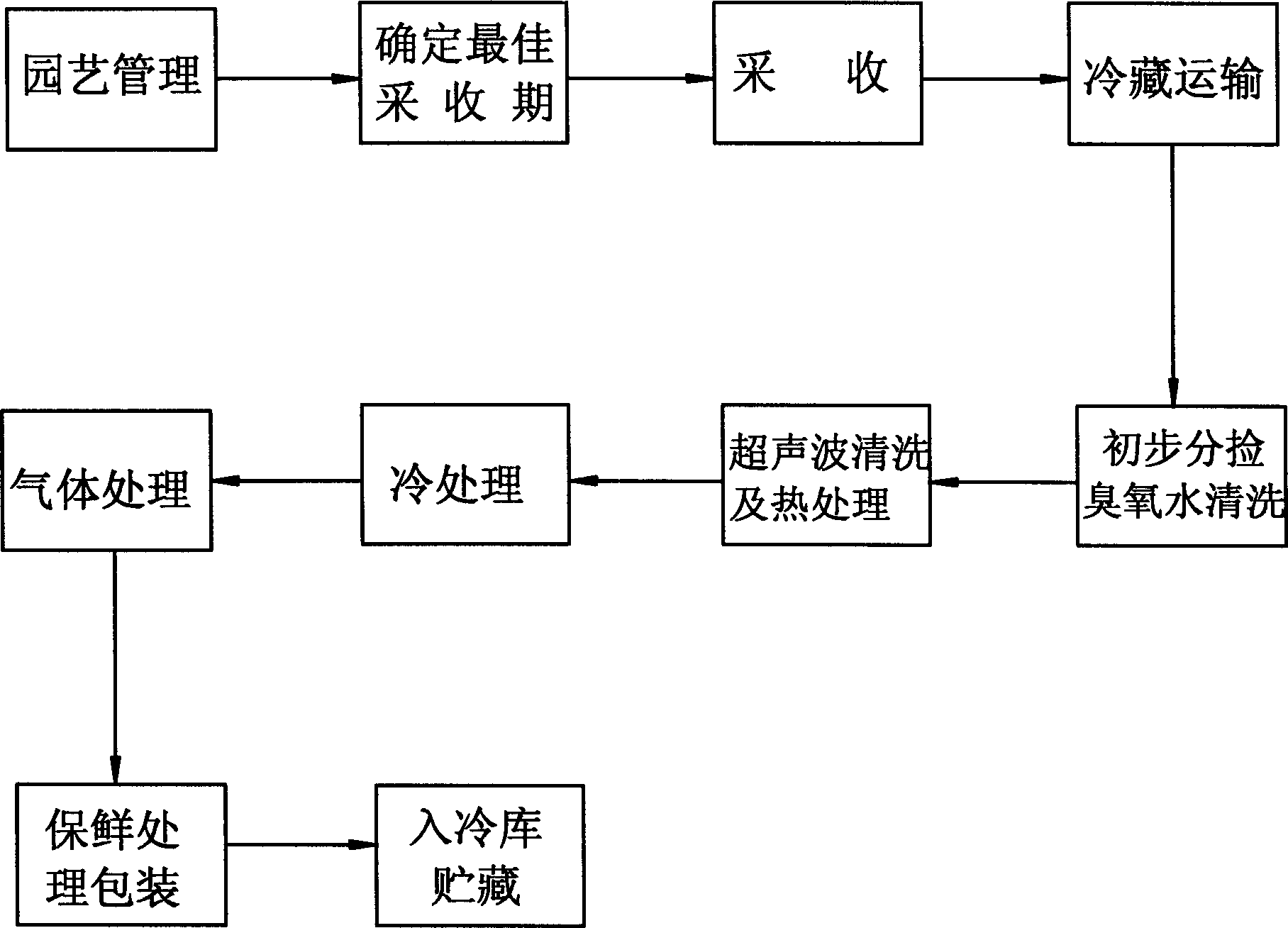
Lychee storage and transportation fresh-retaining method
InactiveCN1401254AGuaranteed good fruit rateExtended shelf lifeFruits/vegetable preservation by blanchingMegasonic cleaningAqueous solution
An anstistaling method for the storage and transportation of fresh litchi includes selection, rinsing in the aqueous solution of ozone, classifying, ultrasonic water washing, high-temp heat treating, cold treating, treating with gas, spraying antistaling agent, packing and cold storage. Its antistaling period can reach 40-50 days.
Owner:钟楚杰 +1
Methods of making snack food products and products made thereby
ActiveUS20090304865A1Lower initial moisture contentReduce moisture contentDough treatmentFood thermal treatmentFlavorSnack food
Methods of making low-fat or fat free snack food products, and products made according to the methods, in which food pieces are subjected to enzyme and / or cation treatment and / or specific cooking and / or drying techniques, to provide for snack food products having the texture, flavor, and other characteristics of conventional full-fat products.
Owner:JIMMYASH
Fresh-keeping bamboo shoot processing method
ActiveCN102805146AExtended shelf lifeEasy to processFruits/vegetable preservation by blanchingVitamin CPre treatment
The invention belongs to a food fresh-keeping processing method, which particularly relates to a fresh-keeping bamboo shoot processing method. The fresh-keeping bamboo shoot processing method is a fresh-keeping treatment technology characterized in that the edible position of the head of the bamboo shoot, used as the raw material, is mixed with vitamin C, bamboo vinegar (edible fermentation), tea polyphenol and CaCl2 at a certain ratio according to the working procedures of taking the raw material, pre-processing, bleaching, cooking, cooling, priming, packaging, and sterilizing, thus obtaining a finished product. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the shelf life can be prolonged for one year, and the product is guaranteed to be safe and healthful. The food fresh-keeping processing method has an important meaning on increasing the bamboo sheet selling amount, prolonging the processing period and the shelf life of the bamboo sheet, solving the long-distance transport problem that the fresh bamboo sheet needs to be refrigerated, and improving the farmer income.
Owner:HUNAN ACAD OF FORESTRY
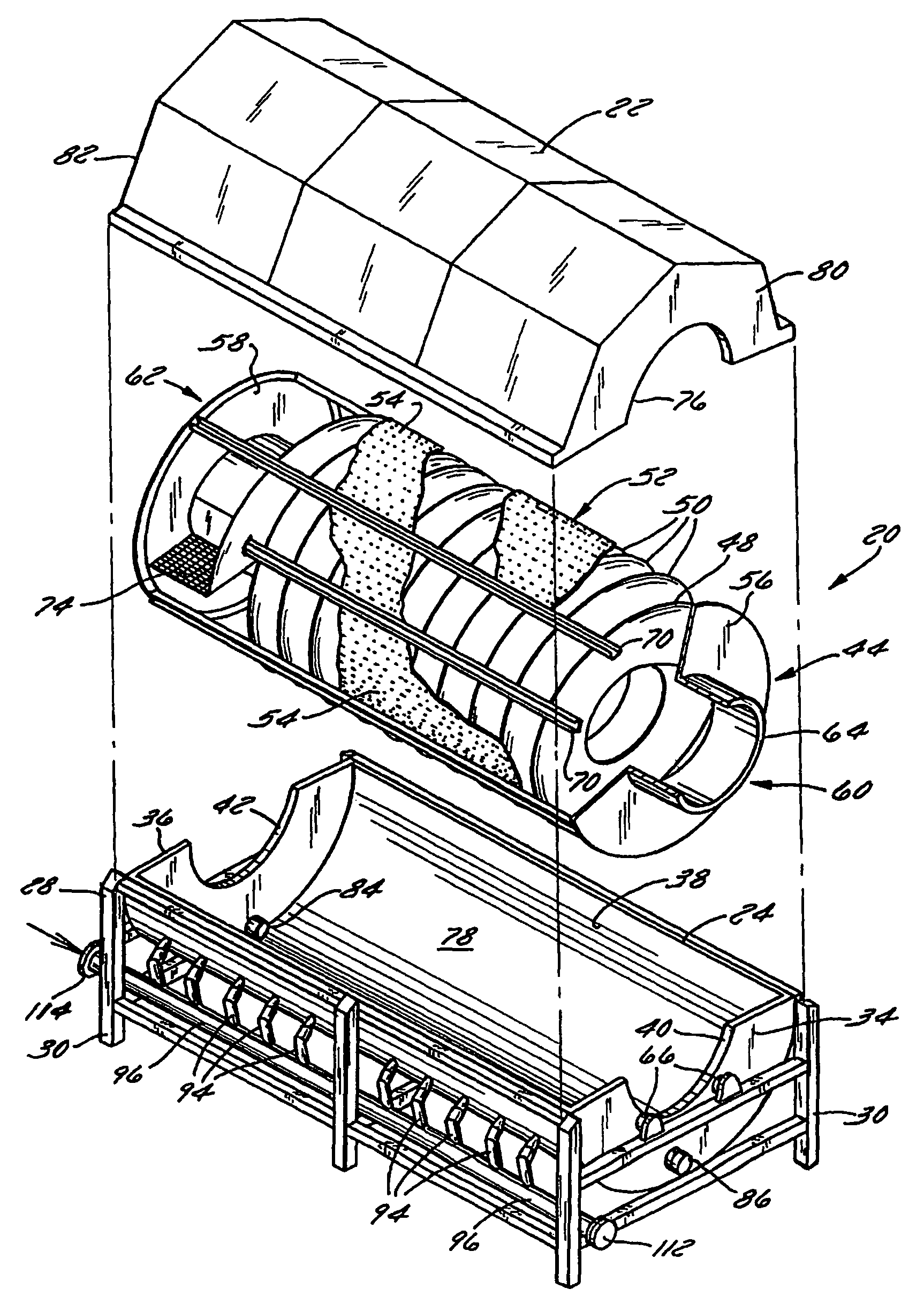
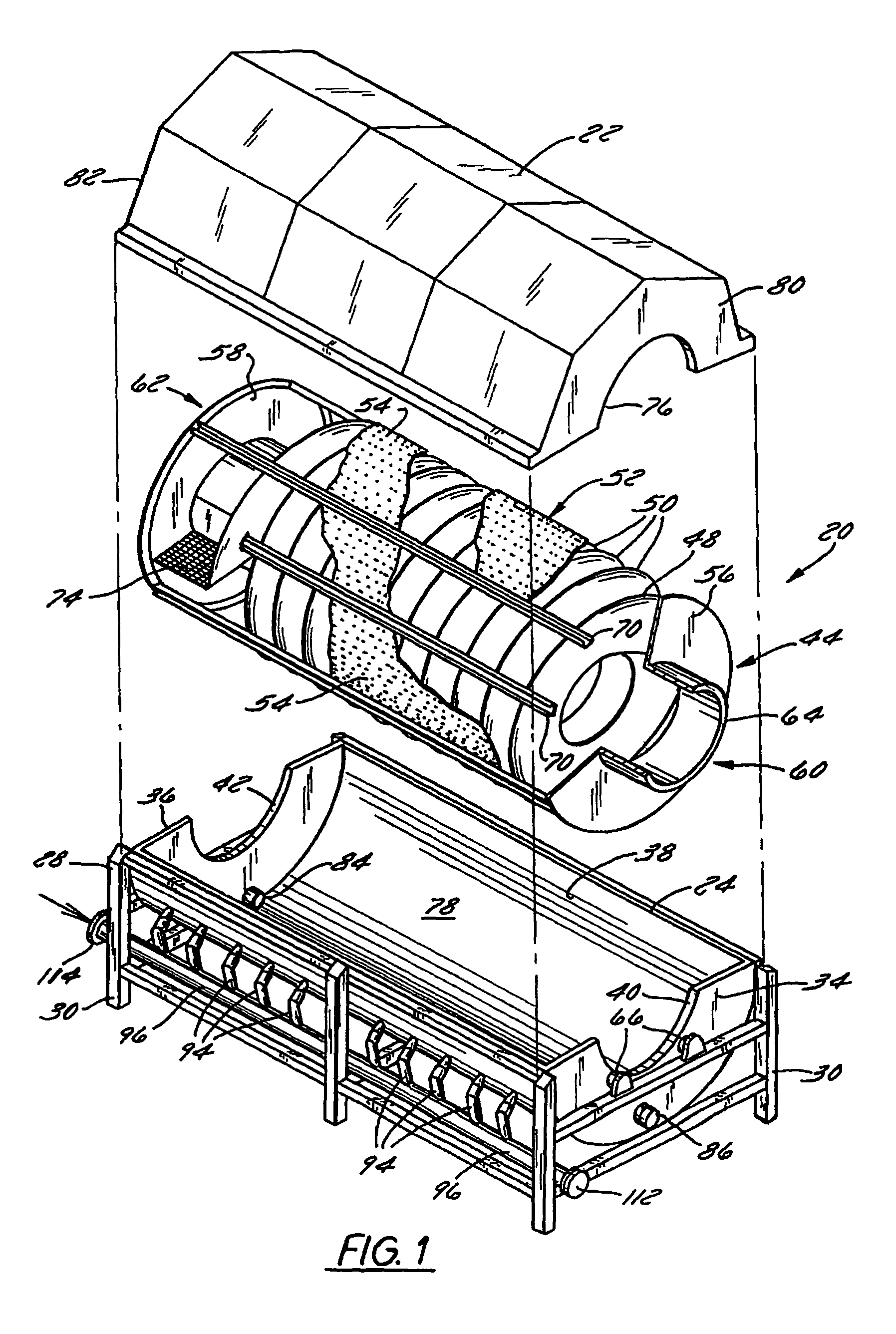
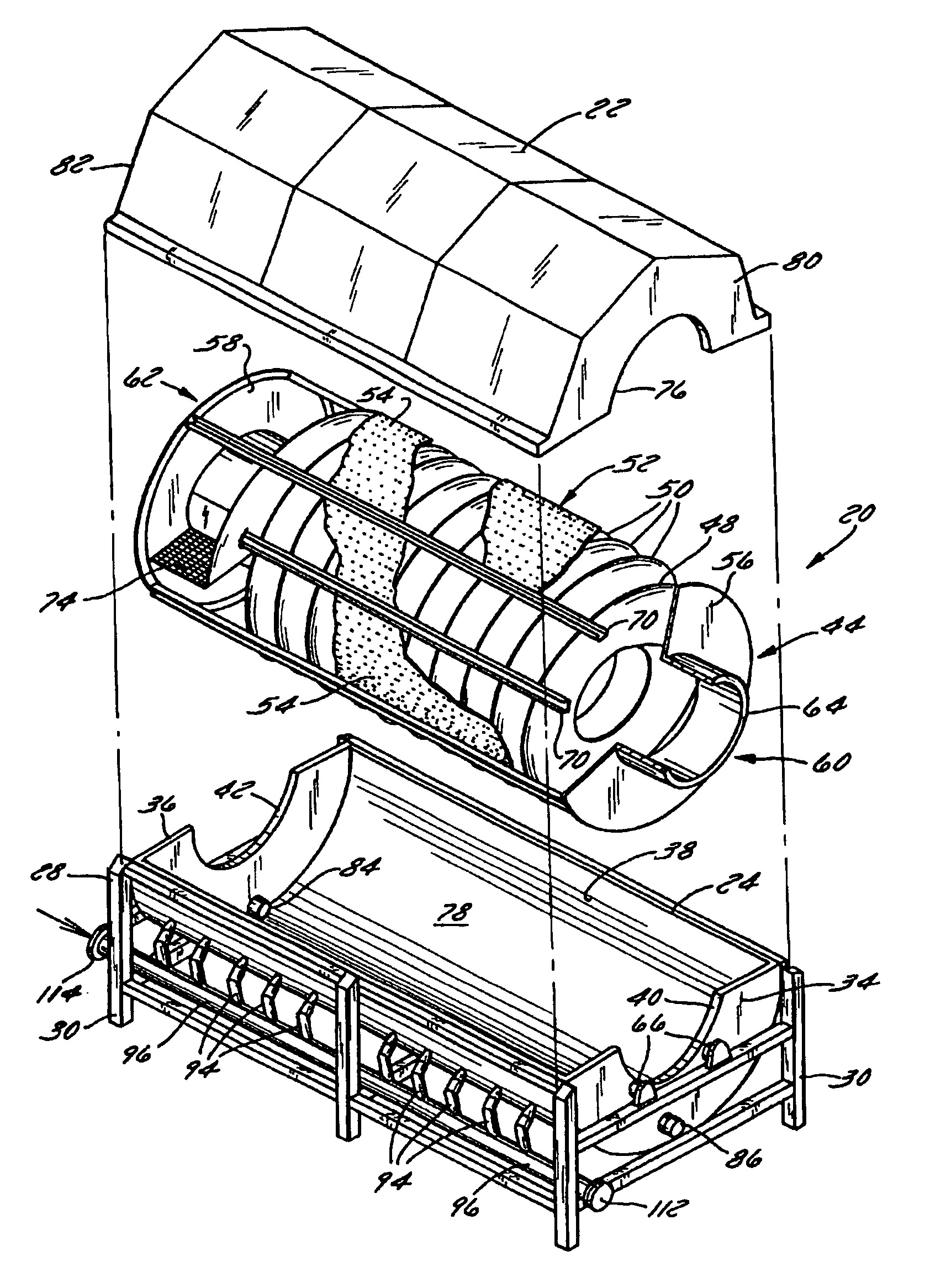
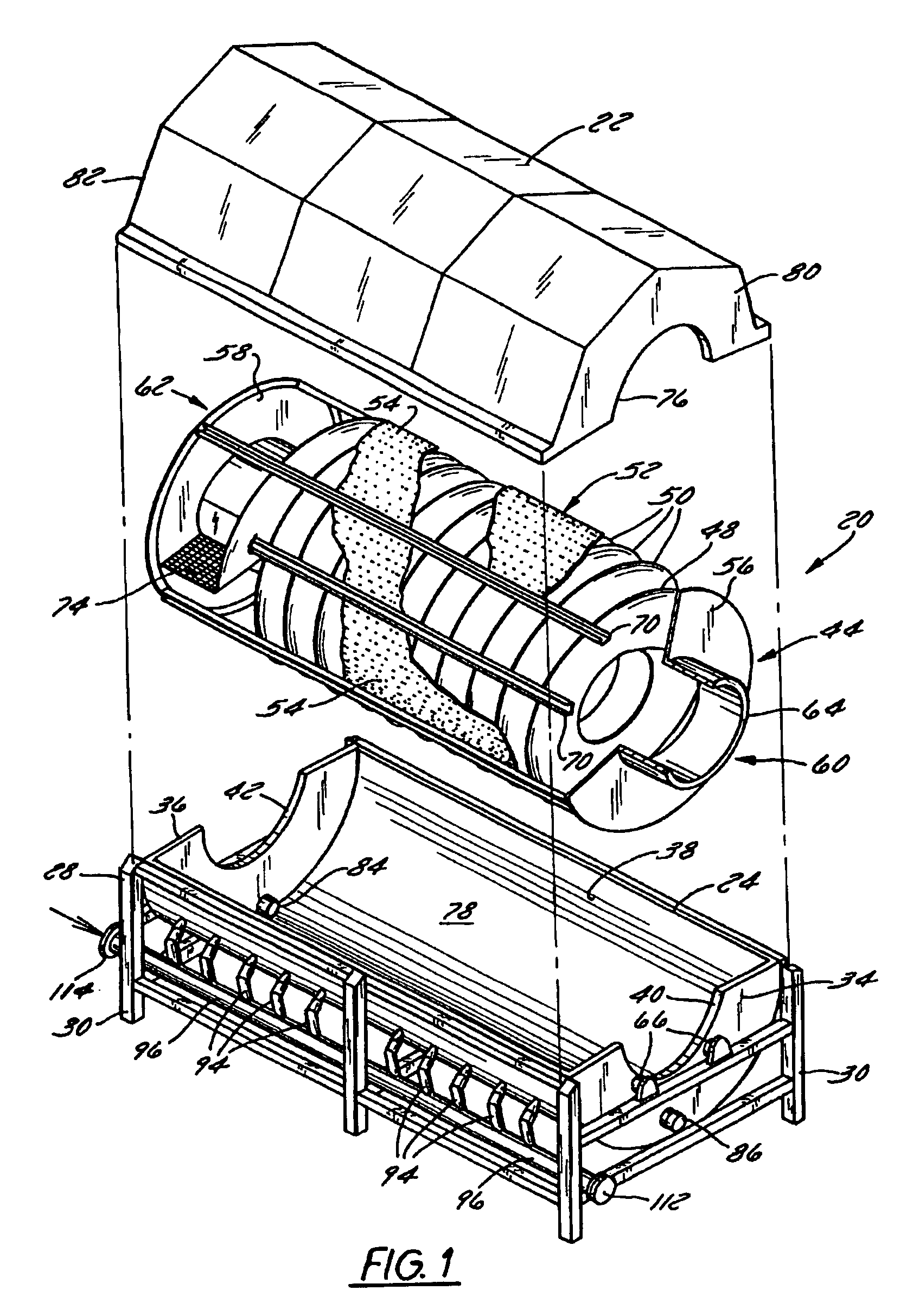
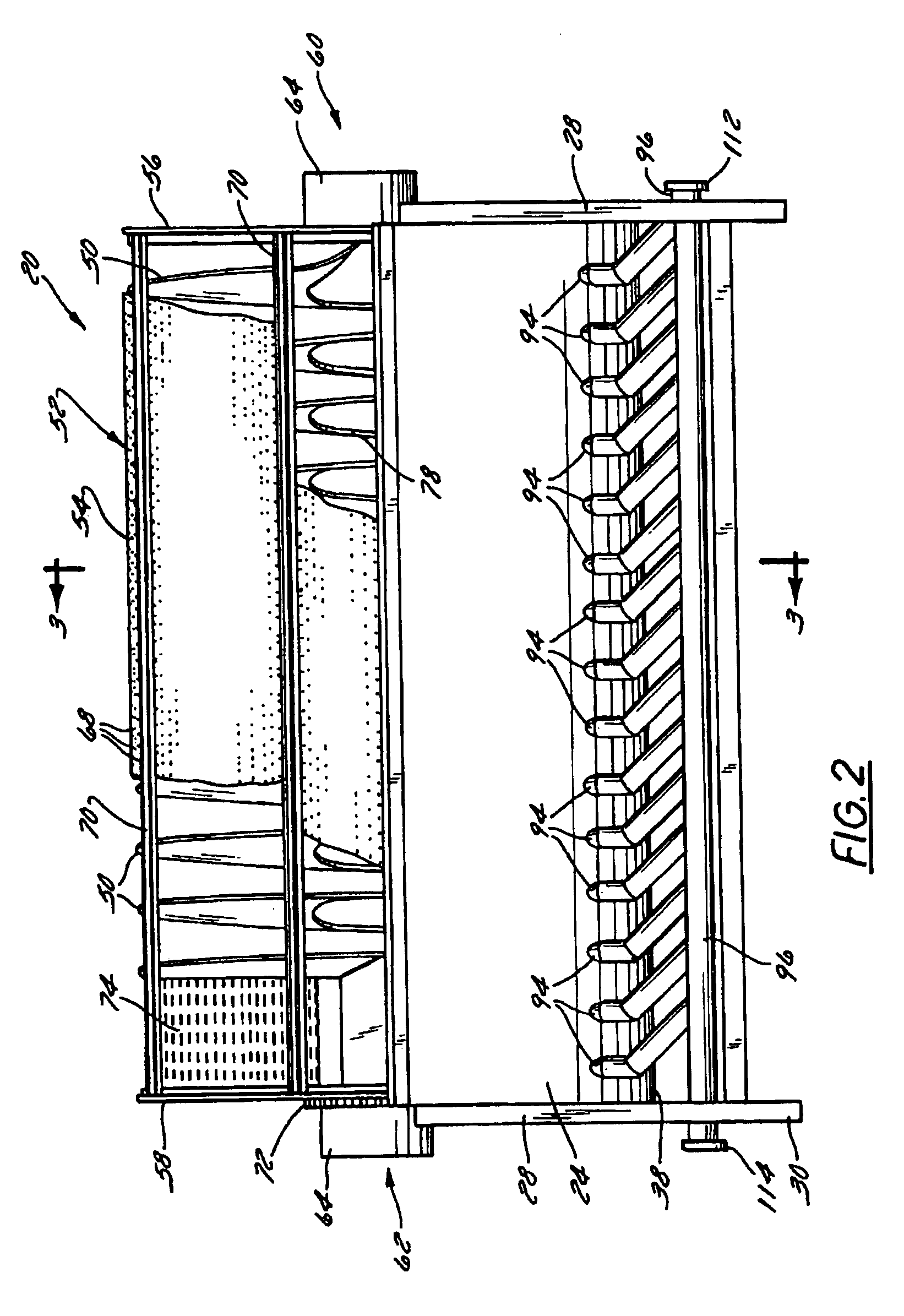
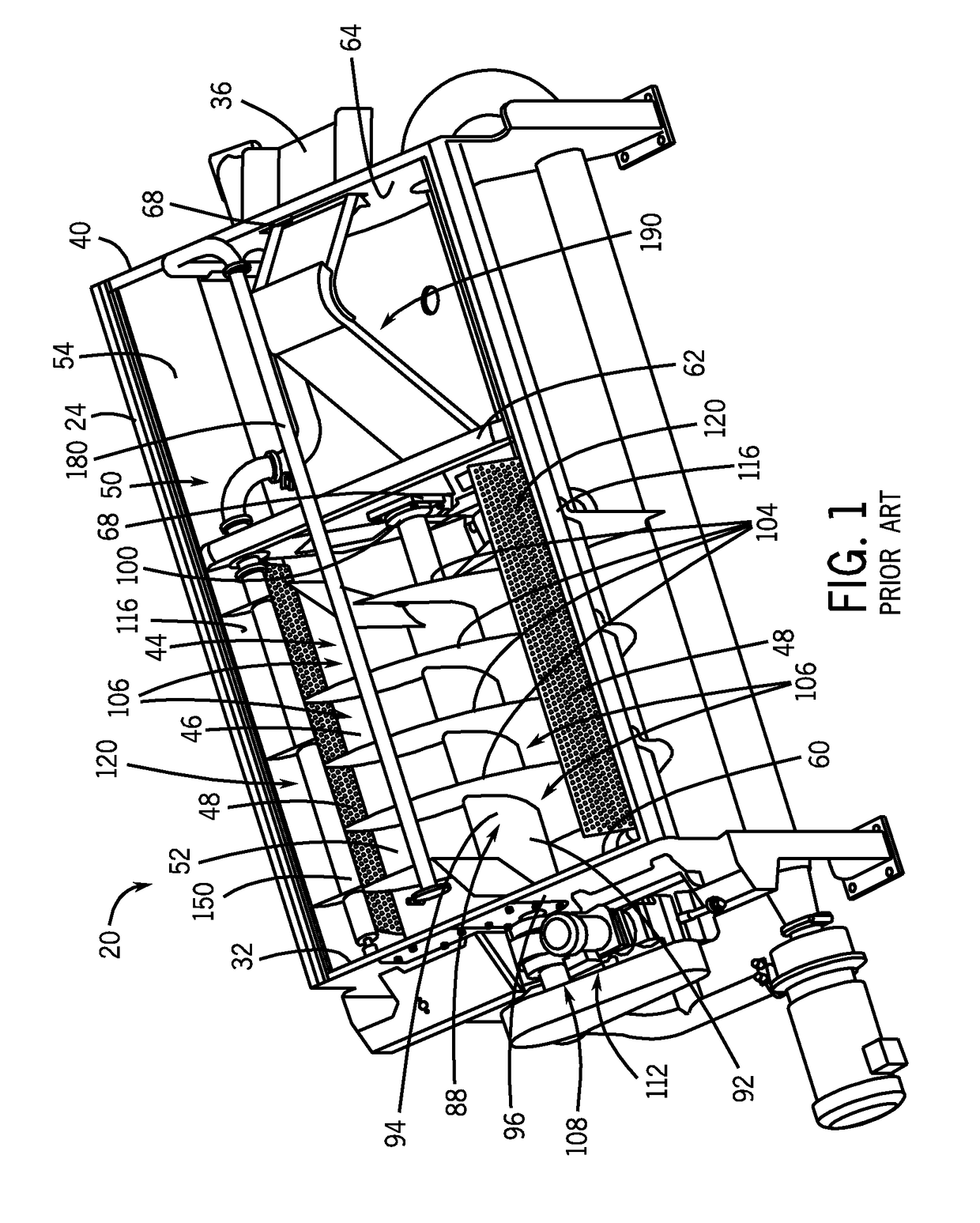
Rotary blancher for processing food product
InactiveUSRE42732E1Increase buoyancyAvoid gatheringMeat/fish preservationLighting and heating apparatusThermodynamicsPasteurization
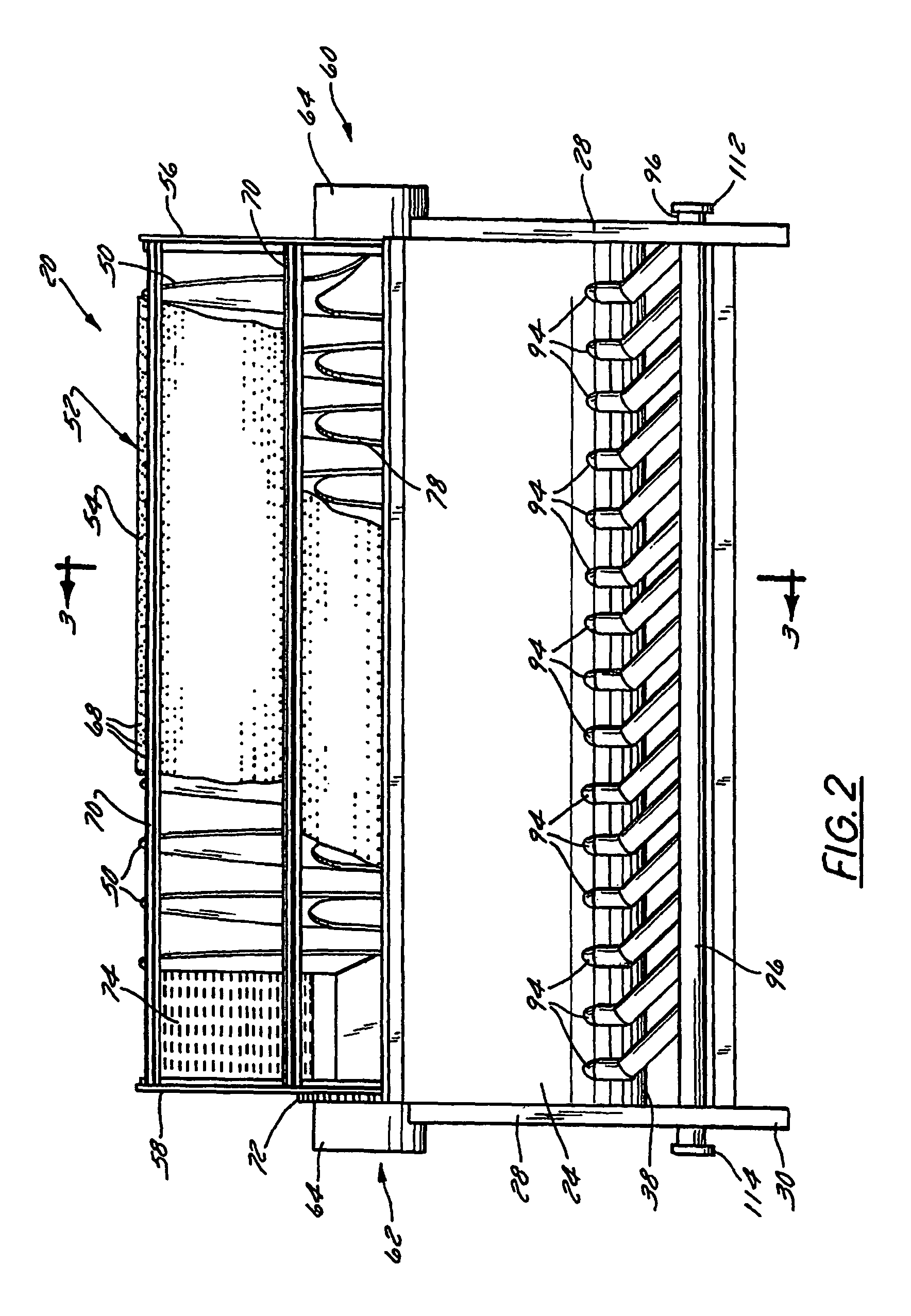
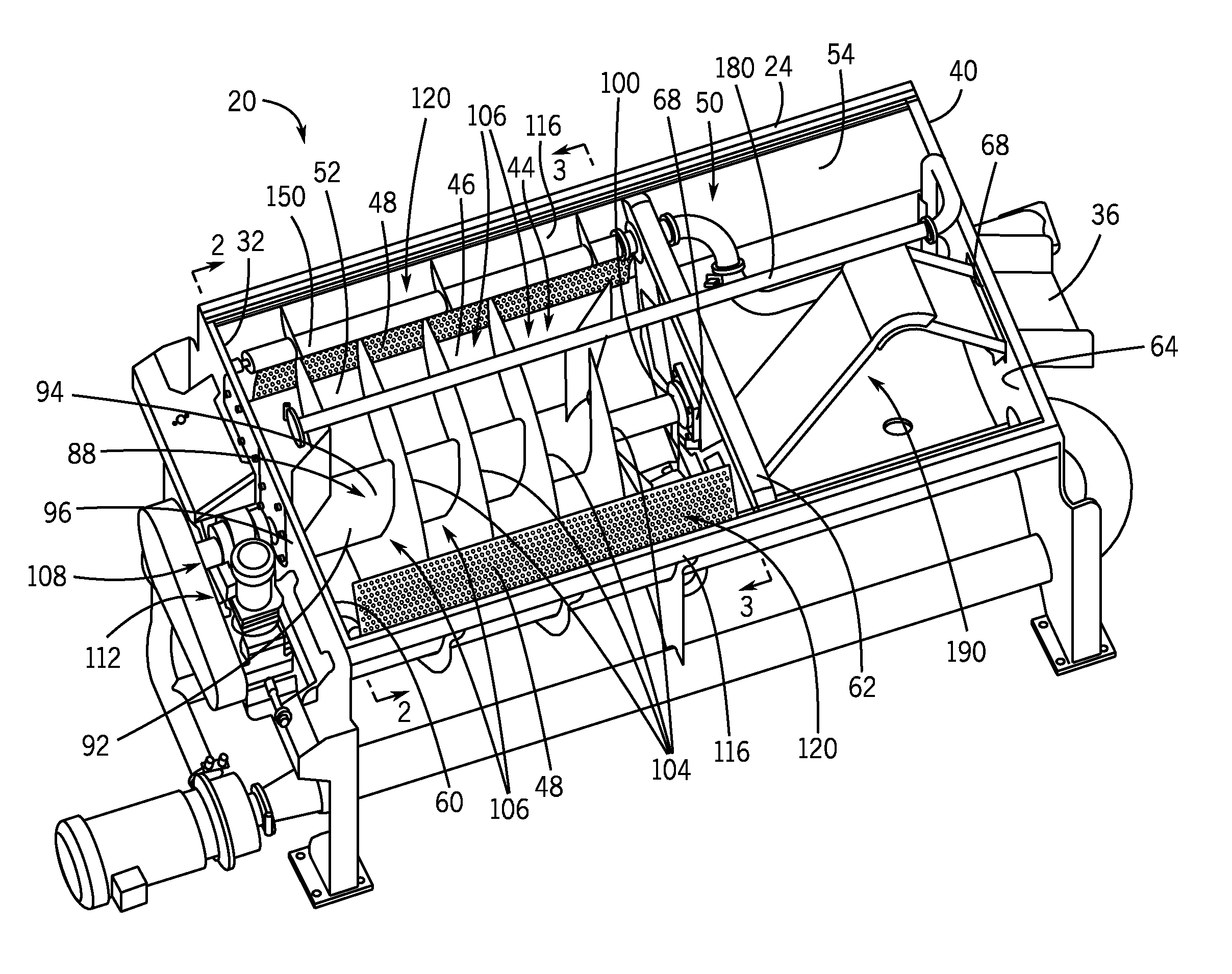
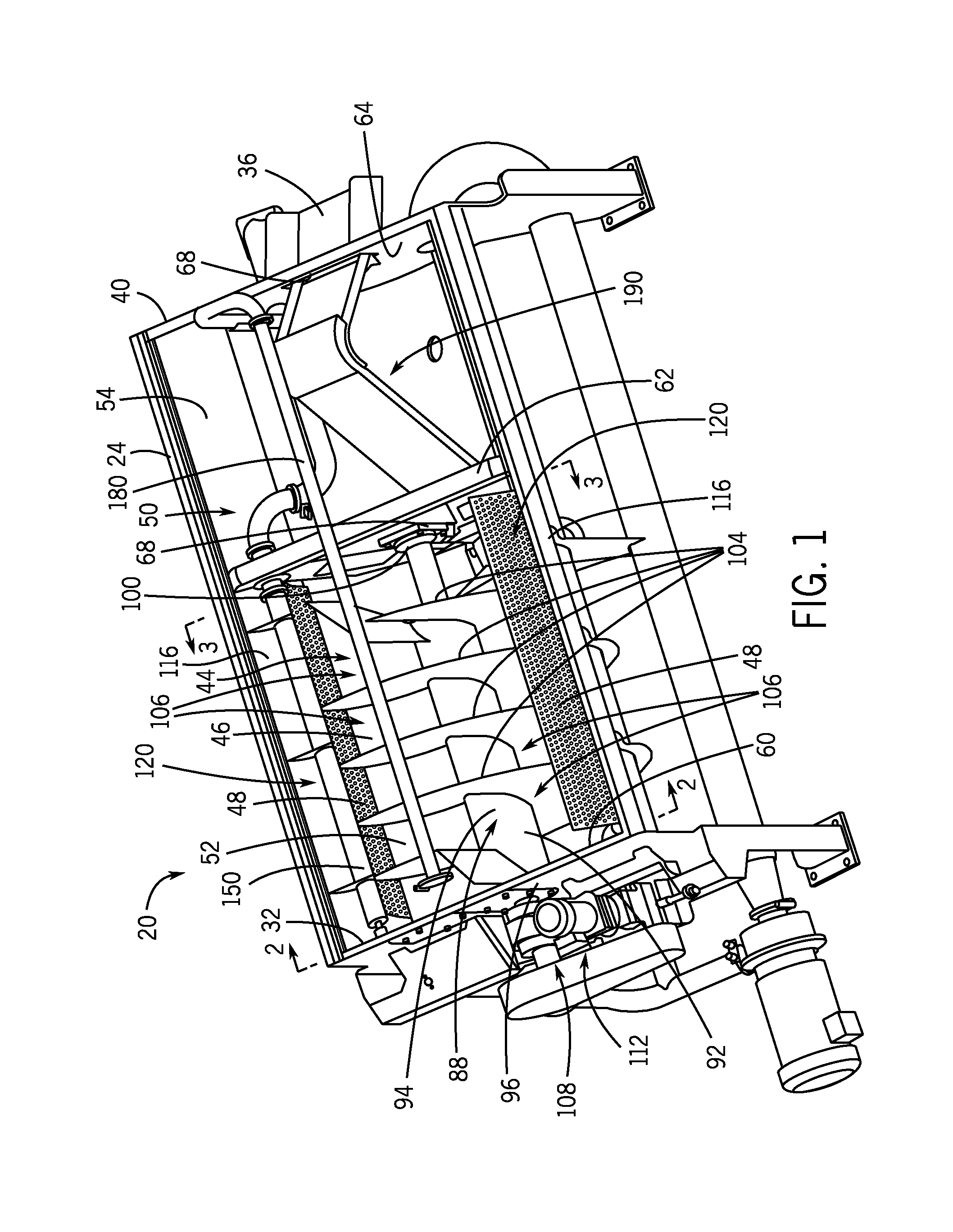
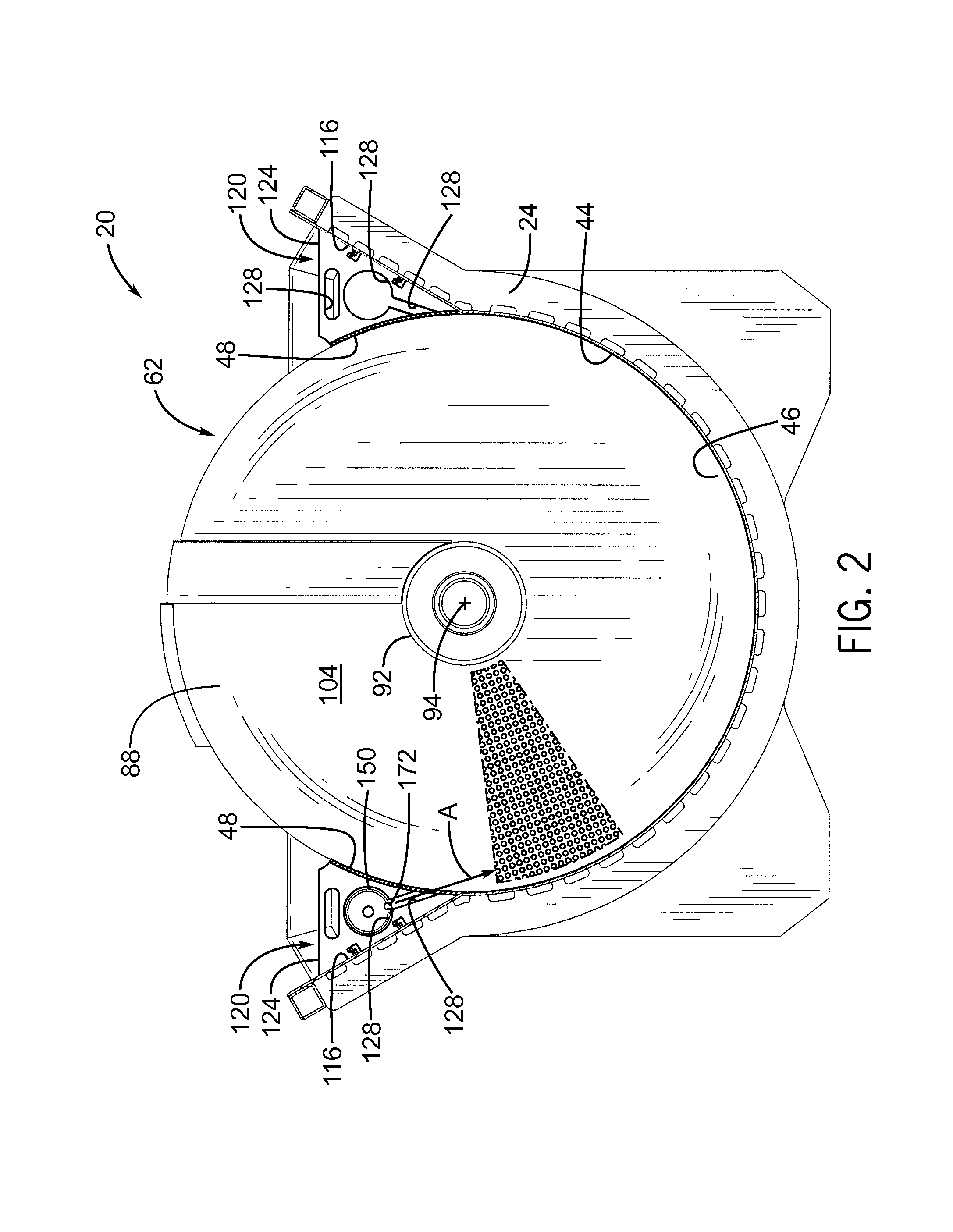
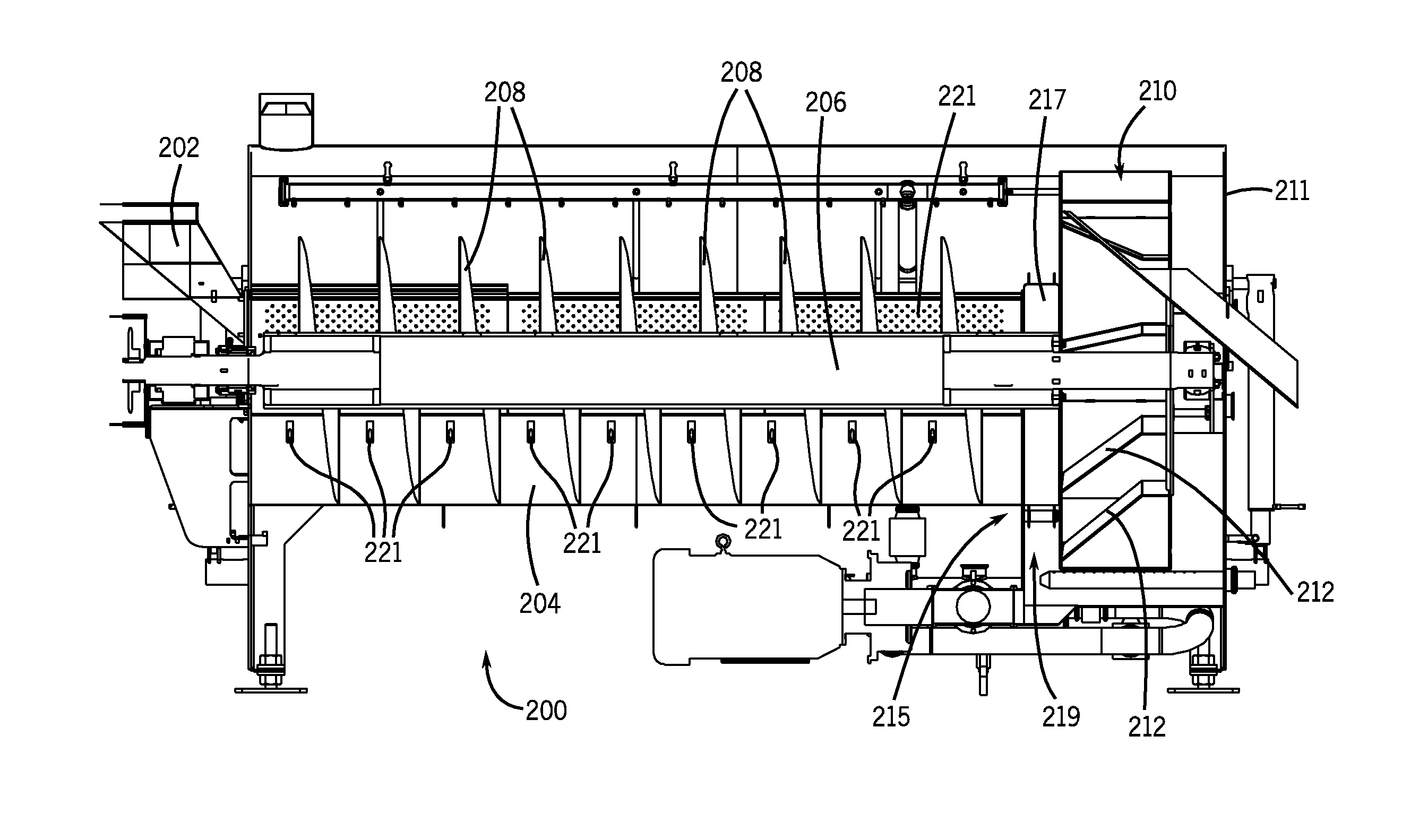
A method and rotary blancher for processing food product using a heat transfer medium and directed flows of a fluid that can comprise a liquid, a gas, a vapor or a combination thereof. The directed flows can be discharged from orifices or banks of orifices that are distributed around the food products in the blancher. The flows are discharged at a high flow rate, a high pressure, or a combination of both. Where a liquid is discharged, it preferably is discharged at a flow rate of at least 20 gpm and at least 30 psi. Where a gas is discharged, it is discharged at a flow rate of at least 60 CFM at a pressure of at least 2 psi or at a flow rate of at least 10 CFM at a pressure of at least 80 psi. If desired, discharged fluid can be recirculated to save energy. To help increase agitation and help break up clumps of food products in the blancher, direct-contact mechanical agitation devices, such as baffles, can be used. Such a blancher and method can be used to process food product by blanching, cooking and pasteurizing, is suited for processing relatively heavy food products having a density of at least 55 lbs / ft3 using discharged liquid and gas, and is suited for processing food products having a lesser density using only discharged gas.
Owner:LYCO MFG
Freezing vegetables
InactiveUS20040065094A1Limit softeningQuality improvementLighting and heating apparatusCooling fluid circulationCore temperatureFrozen vegetables
A process for the production of a frozen vegetable or part thereof, wherein said process comprises the steps: (i) subjecting a vegetable or part thereof to a firming treatment selected from: a) immersing the vegetable or part thereof in a solution of a calcium salt. b) heating the vegetable or part thereof to a temperature in the range 50 to 70° C., and c) a combination of a) and b); (ii) under-cooling to a core temperature of less than or equal to -5° C.; (iii) reducing the temperature to less than or equal to -18° C. The frozen vegetables, when thawed, possess a texture and appearance which closely resembles that of fresh vegetables.
Owner:UNILEVER BESTFOODS NORTH AMERICA DIV OF CONOPCO
Method for improving reheated texture of frozen prepared tuberous vegetables
InactiveCN106857802AReduce contentHigh glass transition temperatureFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingFruits/vegetable preservation by blanchingAdditive ingredientGlass transition
The invention relates to a method for improving the reheated texture of frozen prepared tuberous vegetables, belonging to the technical field of agricultural product processing. The whole reheated texture improvement process of the frozen prepared tuberous vegetables is completed by combining raw material pretreatment and low-frequency ultrasonic-assisted osmotic dehydration with blanching, quick-freezing, glass state freezing storage and reheating. By adopting the low-frequency ultrasonic-assisted osmotic dehydration, the method increases the glass-transition temperature of the tuberous fruits and vegetables, reduces the damage of ice crystal formation to cell structures in a freezing process, can be used for freezing at the glass-transition temperature, and maintains the sensory quality and nutritional ingredients of the vegetables to a greater extent. Furthermore, multiple methods are adopted for cooperative reheating at the later period, so that the materials can be rapidly and stably reheated, and the change of the reheated texture and nutritional quality of the vegetables can be improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Dried fresh jujube slices and energy-saving process technology for differential pressure expansion drying
PendingUS20190269160A1Difficult to chewIncrease investmentFood coatingFood shapingFreeze-dryingDifferential pressure
A method for processing dried fresh jujube slices includes the following steps: preparing jujube slices, coring and removing stems, quick-freezing and retaining freshness of the jujube slices, thawing frozen jujube slices, protecting color treatment, expanding jujube slices under differential pressure, preparing superfine mixed seasoning powder, and coating of the superfine mixed seasoning powder. For one hand, this method solves problems that the dried fresh jujube slices will be deeply oxidized and brown when dried by the hot air at a high temperature of 90-110° C., the jujube slices with compacted cells will become harder and be difficult to chew because of 6-8 h rapid dehydration. On the other hand, it solves problems that exist in freeze drying at a vacuum degree of 1.3-13 Pa, and at a low temperature of −10-50° C., such as high energy consumption, long processing cycle, high equipment investment, small size of slices, and poor taste.
Owner:NINGXIA ZHONGXI JUJUBE IND LTD LTD +1
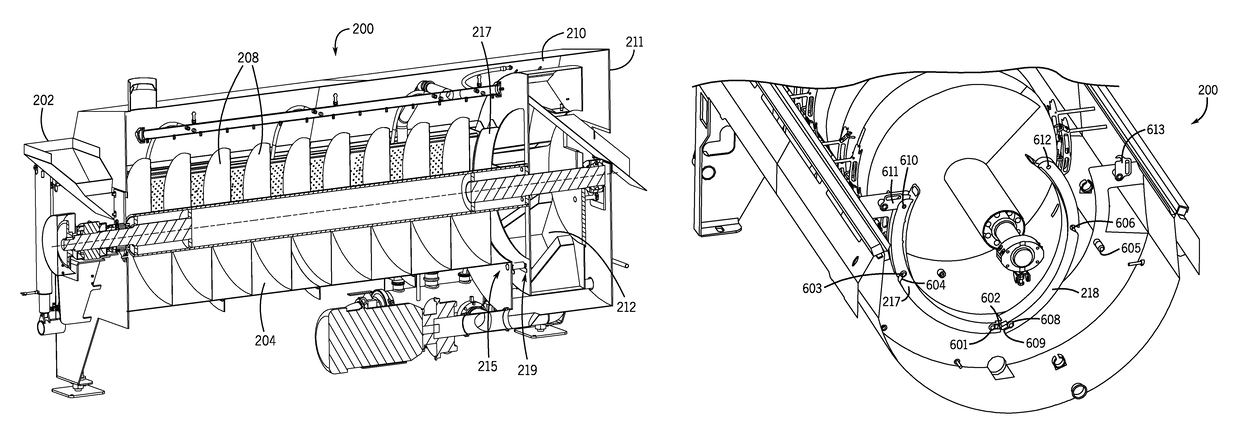
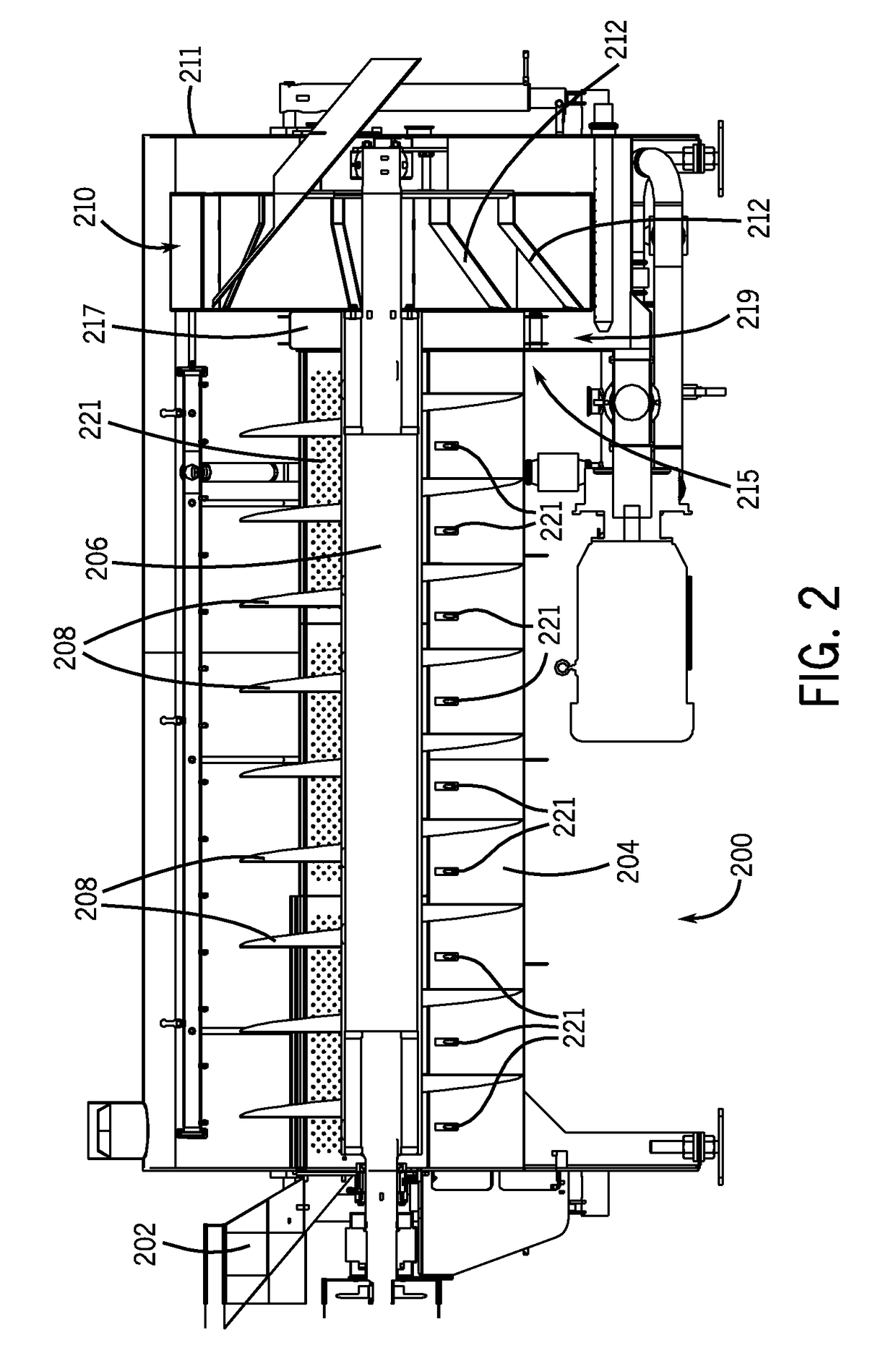
Rotary screw blancher with fluid passage and fluid agitation
ActiveUS8800435B2Reduce heat lossEasy to cleanMeat/fish preservation using liquidsBaking plantsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A food processing apparatus including a tank having an inlet end for receiving food product and an outlet end for discharging food product, the tank having an inner wall defining a compartment and including a solid, imperforate wall portion, fluid being contained in the compartment, and a rotatable auger mounted in the compartment, the auger for advancing food product within the compartment from the inlet end toward the outlet end, the auger including flights having a flight wall with a radial edge, a clearance space being defined between the radial edge of the flights and the solid, imperforate wall portion of the inner wall. Flow of fluid through the clearance space may be inhibited. One of the inner wall and the flight wall may include a perforated wall portion. Flow of fluid between the first auger section and the second auger section may be provided through the perforated wall portion.
Owner:LYCO MFG
Methods of making snack food products and products made thereby
Methods of making low-fat or fat free snack food products, and products made according to the methods, in which food pieces are subjected to enzyme and / or cation treatment and / or specific cooking and / or drying techniques, to provide for snack food products having the texture, flavor, and other characteristics of conventional full-fat products.
Owner:JIMMYASH
Process for improving shelf-life of fresh cut vegetables and food products produced thereby
ActiveUS10492507B2Extended shelf lifeIncrease cell structure permeabilityFruits/vegetable preservation by heatingFruits/vegetable preservation using acidsProcessing aidFood products
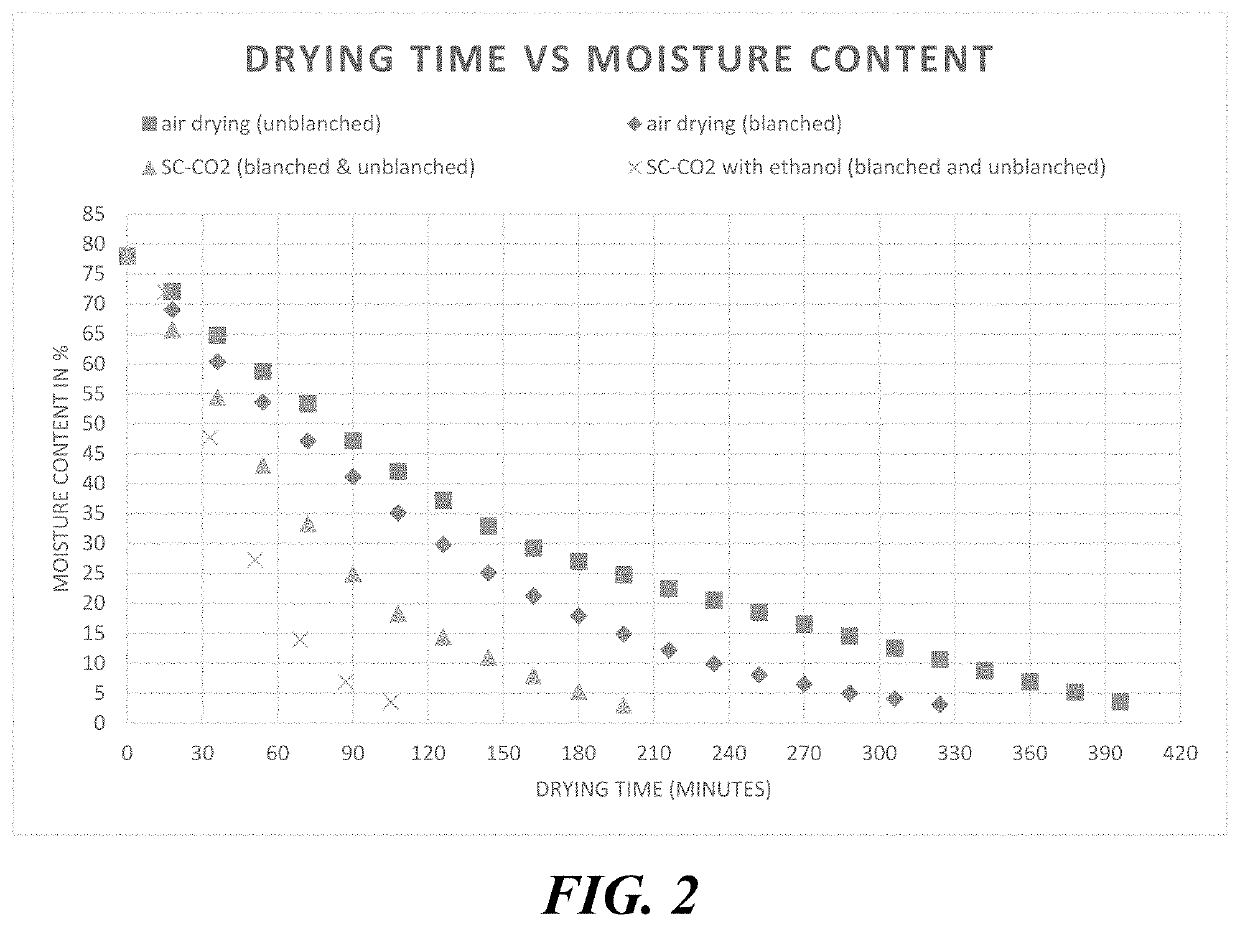
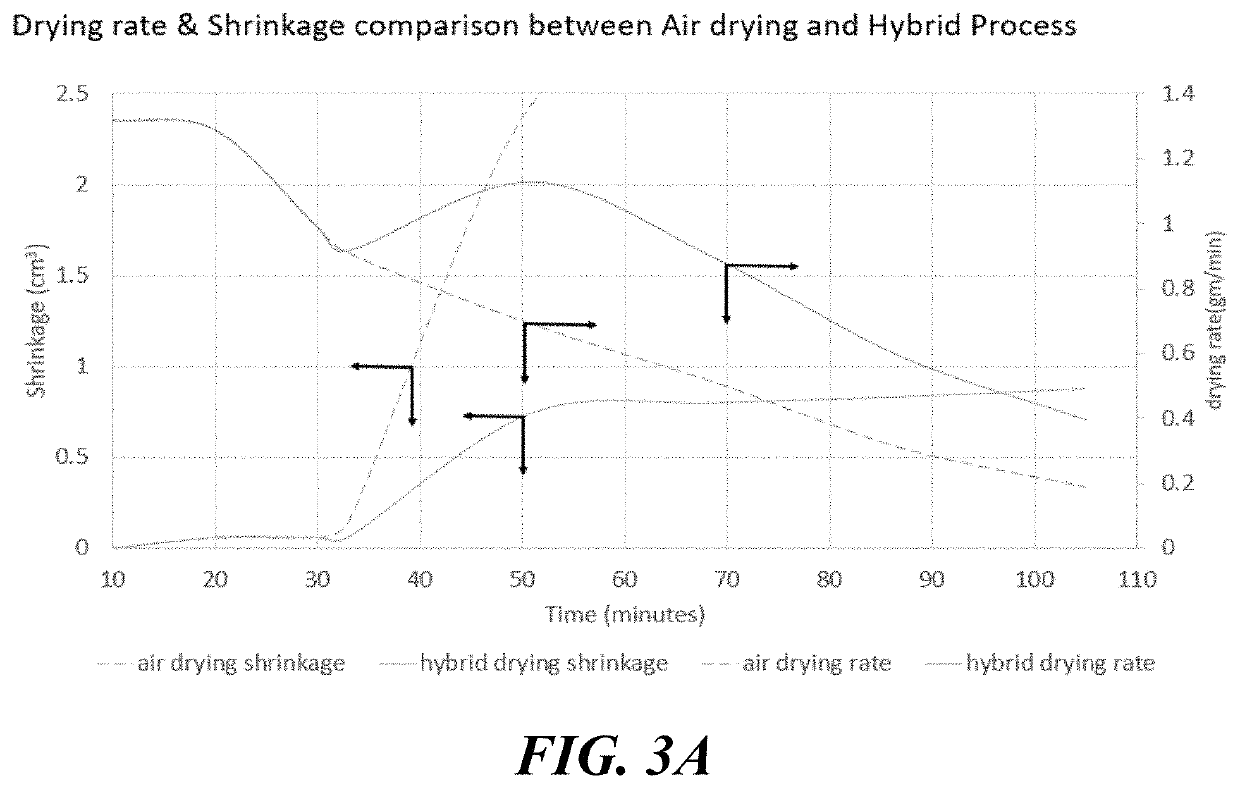
The present disclosure relates to, inter alia, processes for improving shelf-life and flavoring of fresh-cut / fresh vegetables, as well as food products produced by these processes. In accordance with the present disclosure, the processes generally include various new combinations of steps such as blanching, air drying, supercritical fluid processing with and without a processing aid, pressurization, de-pressurization, and packaging. The present disclosure further relates to methods of preparing edible food products that incorporate the processed fresh-cut vegetables, as well as the food products produced by these methods.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Nutrient-fortified, reduced-calorie fruit and/or vegetable food product and processes for making same
InactiveUS20070128332A1Reduced caloric contentReduced reducing sugar contentFruits/vegetable preservation by heatingAnimal feeding stuffNutritive valuesCompound (substance)
A reduced-calorie fruit and / or vegetable spread product, optionally fortified with additional nutrients, including whole, natural fruit(s) and / or vegetable(s), or combinations thereof, having improved flavor, texture (e.g., mouth feel), color, and nutritional value as compared to fruit and / or vegetable spread products made with conventional processes. More particularly, the present invention includes a fruit and / or vegetable spread product having reduced caloric and carbohydrate content and having increased soluble dietary fiber content, optionally fortified with vitamins, minerals and other nutrients, and processes for making, or preparing, the same.
Owner:TOVES FRANCES A
Rotary screw blancher
A food processing apparatus including a tank having an inlet end for receiving food product and an outlet end for discharging food product, the tank having a rotatable auger mounted in a compartment, the auger for advancing food product within the compartment from the inlet end toward the outlet end, the auger including flights having a flight wall with a radial edge, a clearance space being defined between the radial edge of the flights and a solid, imperforate wall portion of an inner wall. One of the inner wall and the flight wall may include a perforated wall portion. A transition zone includes a moveable surface to contain food product while in use.
Owner:LYCO MFG
Chilled dishes and process for preparing same
InactiveUS20080317920A1Food shapingPackaging protectionCarbohydrate compositionRefrigerated temperature
The present invention is directed to a process for making a microwavable dish comprising vegetables, sauce and a carbohydrate, wherein the dish is Refrigerator-stable after packaging and prior to microwaving, even at a pH of greater than or equal to about 5. The vegetables are provided fresh and / or IQF, heated in water, and steamed. The steamed vegetables are mixed with sauce and carbohydrate components, refrigerated after packaging and prior to microwaving, and maintain good textural, visual and taste characteristics. Specifically, the vegetable component has a Just About Right / Acceptable Texture and a Firmness of at least about 5.46 Kg force.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
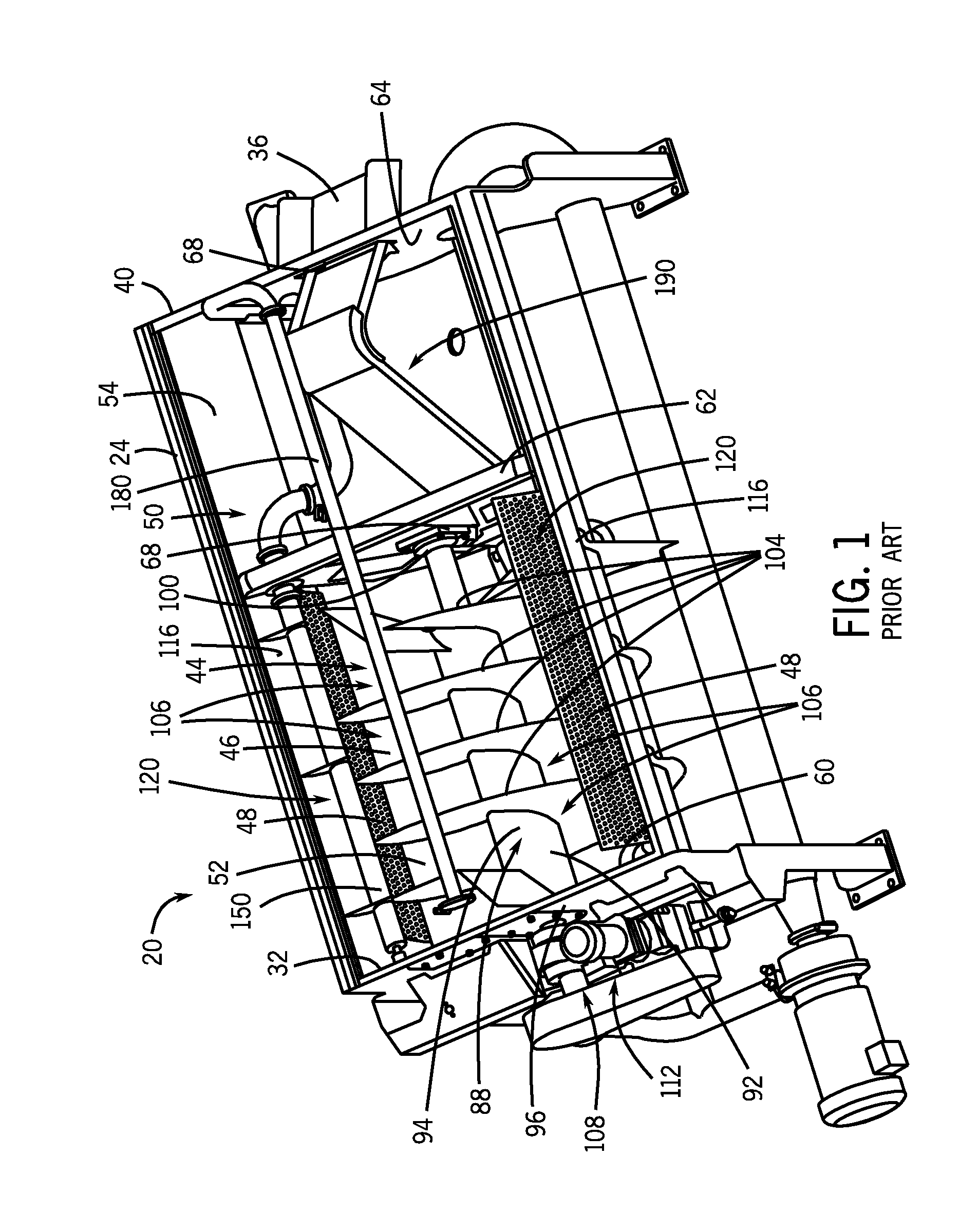
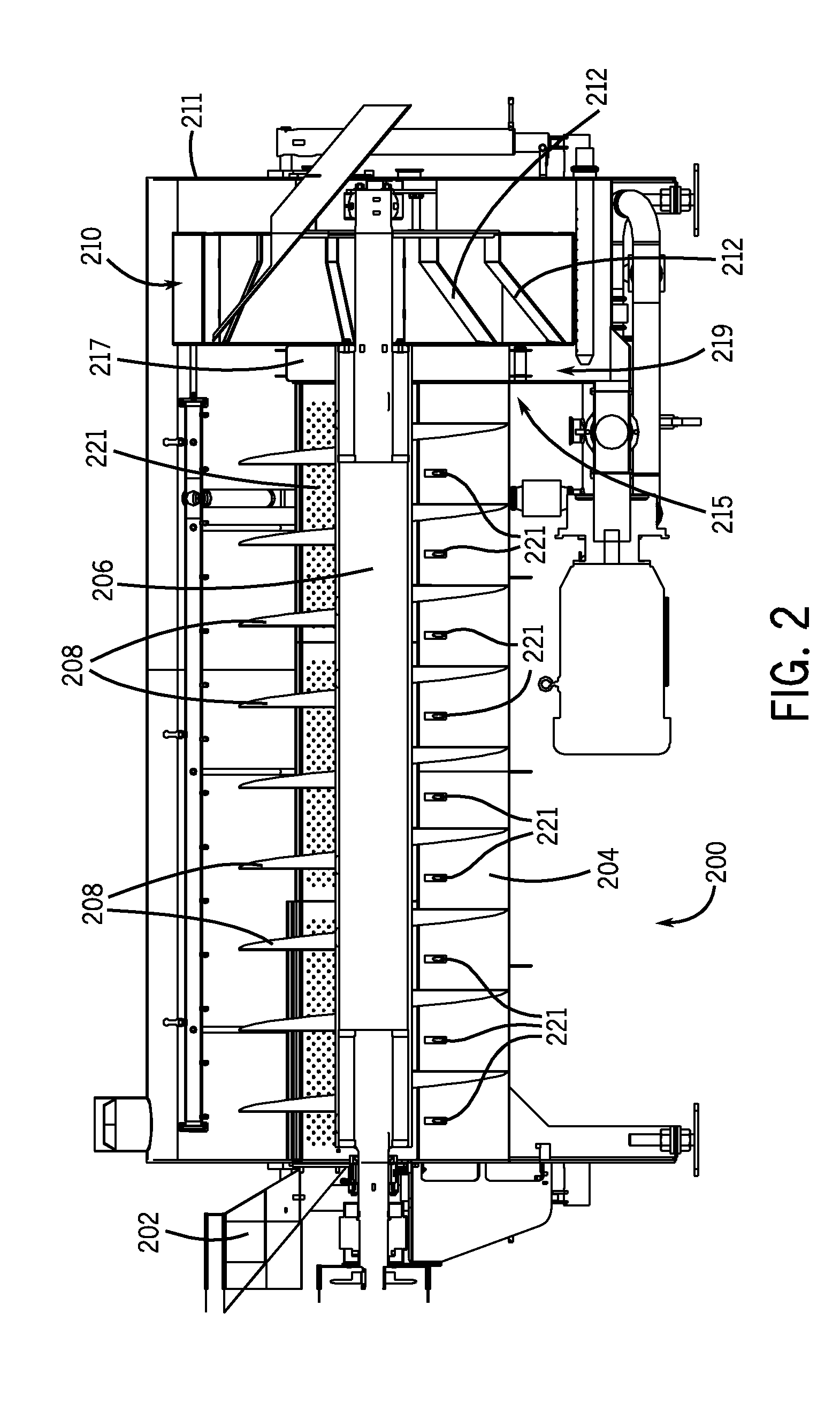
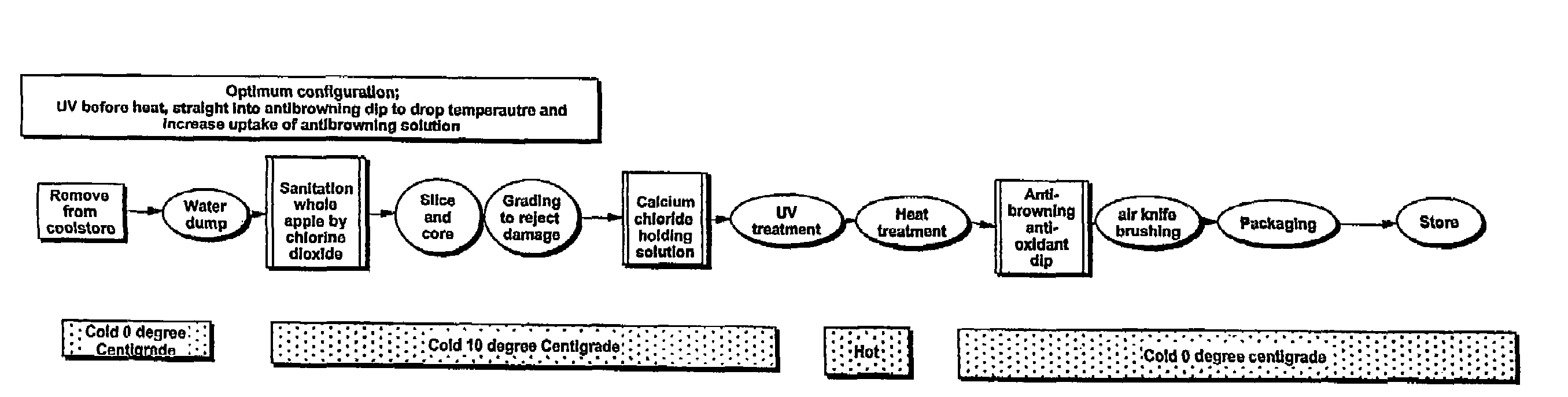
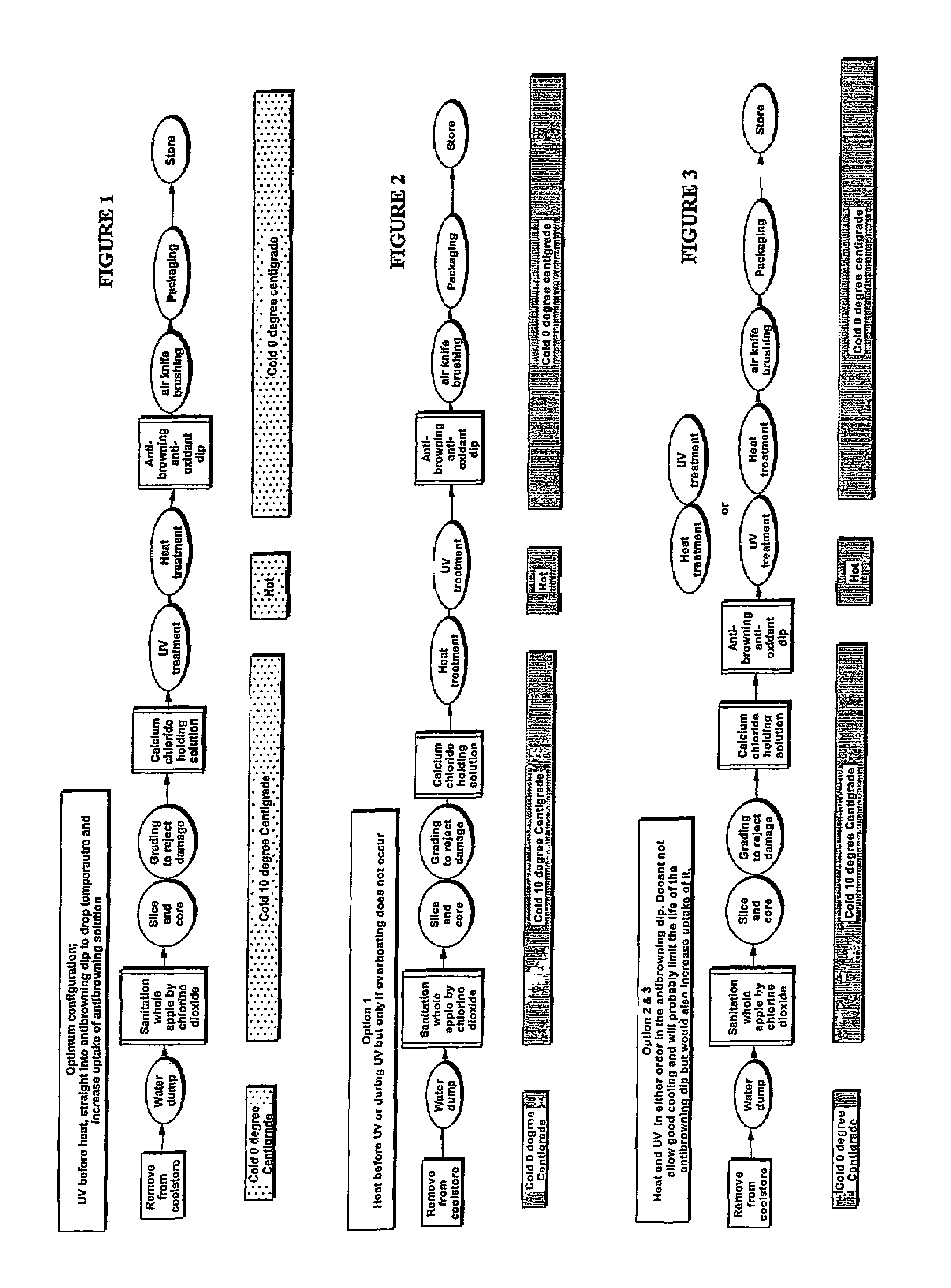
Preservation of produce
InactiveUS7601376B2Inhibited visible microbial spoilageLow TPC levelMilk preparationMilk preservationCellular DebrisLight irradiation
Food safety and longevity of still respiring fruit or vegetable pieces are enhanced reliant on a treatment process where the cut surfaces (preferably cleaned of cell debrit) are subjected to both UV light irradiation and heating so as, in concert, render the surfaces more sterile. The heating also has the effect of reducing ethylene production and at least depressing respiration. Such a process is preferably in addition to an anti-oxidant impregnation. The overall process in its preferred forms significantly extends the life and apparent freshness of, for example, apple slices when kept post treatment (eg; 25 days) over the temperature range of from 0° C. to 8° C.
Owner:THE NEW ZEALAND INST FOR PLANT & FOOD RES LTD
Process for the controlled introduction of oil into food products
ActiveUS20150335047A1Reduce moisture contentWide and precisely controllable rangeTea extractionAnimal feeding stuffSufficient timeOil water emulsion
A process for the application of a predetermined amount of oil to food pieces comprises: (a) providing or receiving a plurality of cut or shaped food pieces; (b) applying an oil-water emulsion to the food pieces for a time sufficient to provide a predetermined amount of oil to the food pieces and so that the food pieces have an initial moisture level after applying the oil-water emulsion; and (c) reducing the initial moisture level, in the absence of frying in oil, to a moisture level of from about 0.2 to about 80% by weight to provide a cooked food product, comprising said predetermined amount of oil, wherein step (c) does not comprises frying the food pieces in hot oil.
Owner:JIMMYASH
Method for processing food product
InactiveUSRE40232E1Increase buoyancyIncrease flow rateMeat/fish preservation by heatingFood processingEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
A method and rotary blancher for processing food product using a heat transfer medium and directed flows of a fluid that can comprise a liquid, a gas, a vapor or a combination thereof. The directed flows can be discharged from orifices or banks of orifices that are distributed around the food products in the blancher. The flows are discharged at a high flow rate, a high pressure, or a combination of both. Where a liquid is discharged, it preferably is discharged at a flow rate of at least 20 gpm and at least 30 psi. Where a gas is discharged, it is discharged at a flow rate of at least 60 CFM at a pressure of at least 2 psi or at a flow rate of at least 10 CFM at a pressure of at least 80 psi. If desired, discharged fluid can be recirculated to save energy. To help increase agitation and help break up clumps of food products in the blancher, direct-contact mechanical agitation devices, such as baffles, can be used. Such a blancher and method can be used to process food product by blanching, cooking and pasteurizing, is suited for processing relatively heavy food products having a density of at least 55 lbs / ft3 using discharged liquid and gas, and is suited for processing food products having a lesser density using only discharged gas.
Owner:LYCO MFG
Process for the controlled introduction of oil into food products
ActiveUS9615601B2Reduce moisture contentWide and precisely controllable rangeFood coatingFruits/vegetable preservation by dehydrationSufficient timeEngineering
A process for the application of a predetermined amount of oil to food pieces comprises: (a) providing or receiving a plurality of cut or shaped food pieces; (b) applying an oil-water emulsion to the food pieces for a time sufficient to provide a predetermined amount of oil to the food pieces and so that the food pieces have an initial moisture level after applying the oil-water emulsion; and (c) reducing the initial moisture level, in the absence of frying in oil, to a moisture level of from about 0.2 to about 80% by weight to provide a cooked food product, comprising said predetermined amount of oil, wherein step (c) does not comprises frying the food pieces in hot oil.
Owner:JIMMYASH
Preparation of vegetable material and food products
InactiveUS20120128860A1Improve protectionReduce the amount of solutionAnimal feeding stuffFood preparationVegetable materialFood products
The present invention relates to a method for preparation of a vegetable material, wherein a living plant is treated with a cytokinin prior to harvest. The invention also relates to a method for preparation of food products, as well as food products comprising the vegetable material. The advantage of the method is that the vegetable material remains green longer during storage of the food product.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Method of Preserving Ipomoea Aquatica, Method of Preserving Vegetables and Processed Food
InactiveUS20080044529A1Suppression of qualityEnlarge regionFruits/vegetable preservation by heatingSolid waste disposalLeaf baseIpomoea aquatica
Effective utilization of vegetable called Ipomoea aquatica that although exhibiting high nutritional value and excellent antioxidant capability and ensuring huge supply capacity, is poor in distribution preservability and is notable in discoloration and quality degeneration attributed to processing, thereby disenabling merchandization of relevant processed food. There is provided a method of cultivating Ipomoea aquatica, characterized in that Ipomoea aquatica having been broadly classified as per flower color and leaf width is minutely classified as per whole leaf shape, leaf configuration appearing within a radius of equal to or less than 5.0 cm from leaf base and configurational difference among leaves from the same stem, and that an appropriate one is selected from among the resultant classes and cultivated. By virtue of this method, the distribution enduring period in fresh condition can be prolonged, and the discoloration by heating can be suppressed. Ipomoea aquatica can be resistant to discoloration by heating or freezing.
Owner:SYNAPSE LINK CORP
Process for the Preparation of Ready to Eat and Ready to Cook Food Snacks
InactiveUS20100159106A1Prevent rancidityAnimal feeding stuffOther dairy technologyReady to eatFlavor
A process for preparation of food snack comprising steps of soaking raw cereals in water, boiling, freeze drying followed by addition of dry ingredients. A process for preparation of vegetable preparation comprising steps of boiling of vegetable / cereal followed by freeze drying and addition of dry ingredients. A process for preservation of vegetables comprising steps of soaking, blanching / boiling and freeze drying followed by application of a layer. Further, this invention is directed to paneer preparation comprising of paneer, vegetable, spices and flavourings. A curry masala preparation comprising of vegetable, spices and flavourings. A KOFTA preparation comprising of KOFTA, vegetable, spices and flavourings. The ingredients are freeze, dried wherever required.
Owner:AGRAWAL GHANSHYAM DAS
Apparatus for producing parboiled rice
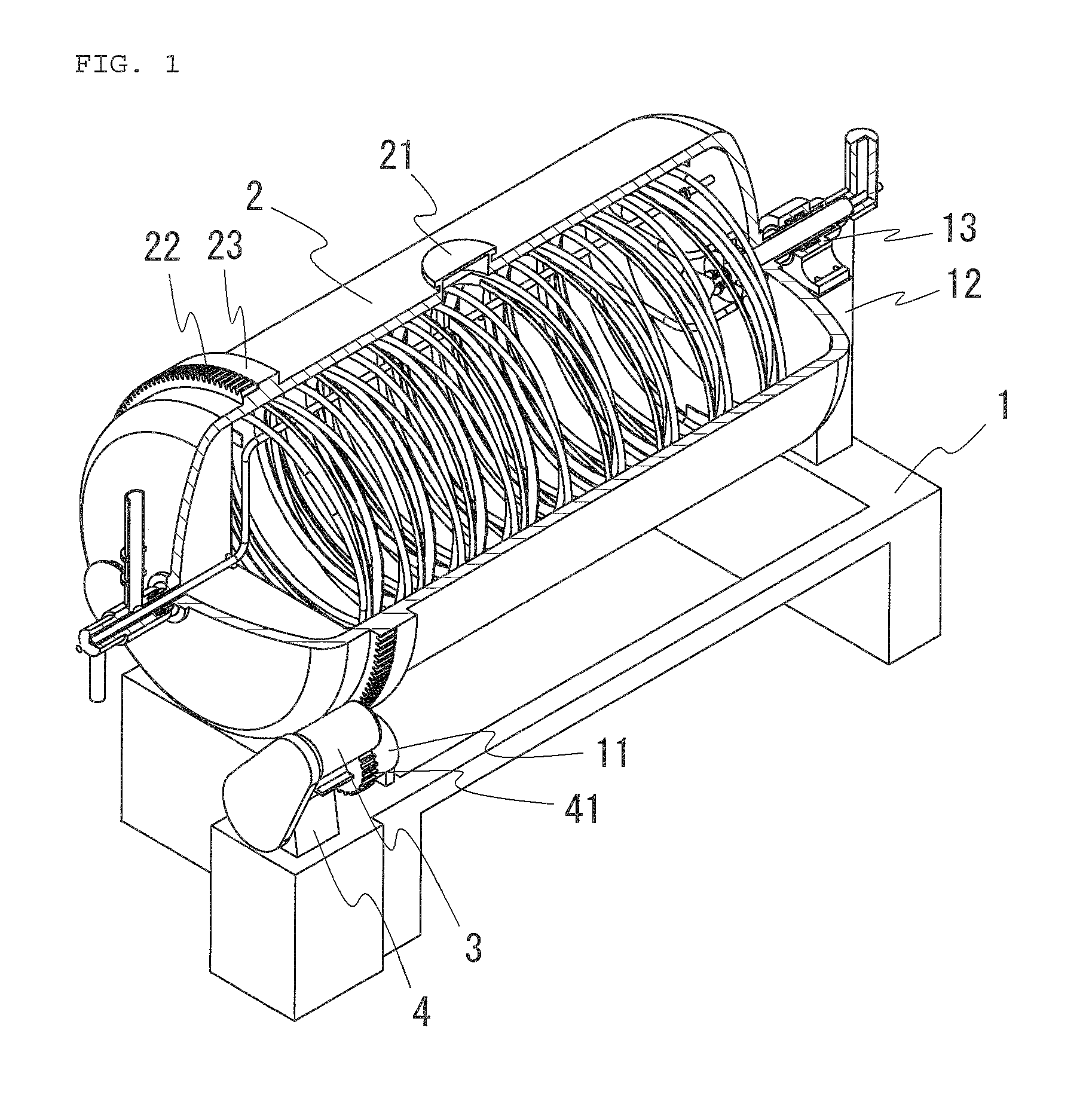
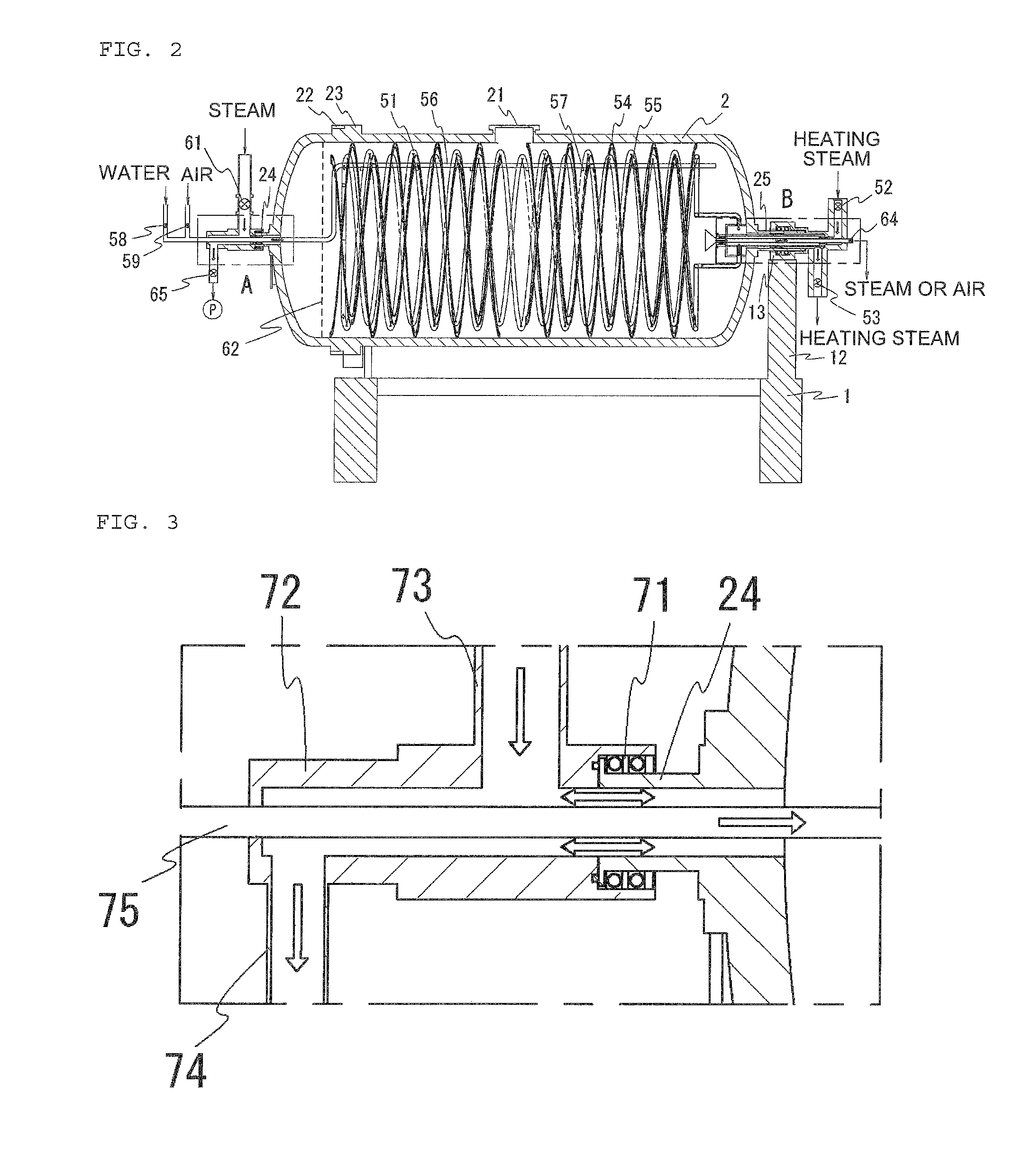
ActiveUS20140251161A1Eliminate needIncrease in sizeDrying solid materials without heatSteam cooking vesselsHorizontal axisEngineering
An object of this invention is to provide a parboiled rice manufacturing apparatus capable of efficiently manufacturing good-quality parboiled rice without increasing the overall size of the apparatus.A parboiled rice manufacturing apparatus according to this invention includes a drum which has a raw material hatch provided at a peripheral surface and is disposed to be rotatable about a horizontal axis, a heating unit which is disposed inside the drum and heats an interior of the drum, an agitation unit which is disposed inside the drum and agitates a raw material charged through the raw material hatch into the drum, a steam supply unit which supplies steam into the drum, a pressure adjustment unit which has a valve allowing communication of the interior of the drum with outside air and allows increase of pressure inside the drum with steam supplied from the steam supply unit by closing the valve at the time of processing of the raw material through the pressurized steam-boiling treatment, a water addition unit which is disposed inside the drum and adds water to the raw material inside the drum, and a drying unit which dries the raw material by reducing the pressure inside the drum.
Owner:SATAKE CORP
Method for reducing oil content of oil-fried potato strips
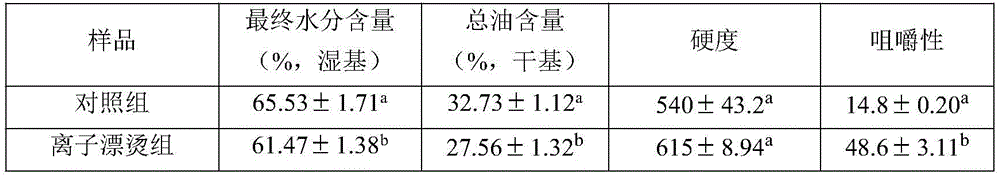
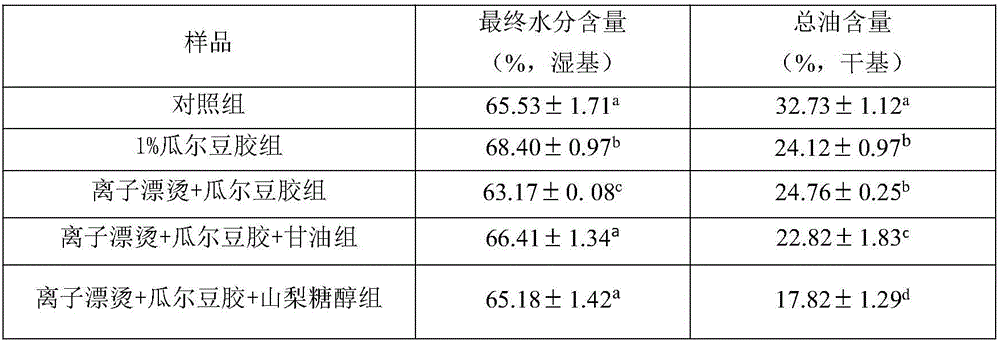
InactiveCN106722534ASimple structureHinder entryFood coatingFood ingredient as coating agentBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention discloses a method for reducing oil content of oil-fried potato strips, and belongs to the technical filed of fine and deep processing of foods. The method for reducing the oil content of the oil-fried potato strips comprises the following steps: taking potatoes as raw materials; carrying out washing, peeling, strip-cutting and ion-blanching; carrying out coating by using a mixed solution adopting guar gum and sorbitol as basis; and then, carrying out oil-frying. Bridged structures form due to chemical reactions between calcium ions in the blanching liquid and low-methoxyl pectin in the potato strips; moreover, the calcium ions and the guar gum may also interact so as to facilitate escape of moisture and block entry of oil when the samples are being oil-fried. For pores produce on the guar gum coating due to the high-temperature oil-frying, oil will enter the foods through the pores, so that the sorbitol is added in order to further improve the coating structure; thus, the final moisture content can be controlled from obvious increasing, and the oil content of the product can be effectively reduced. Moreover, no significant impact is caused on the other qualities of the product.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
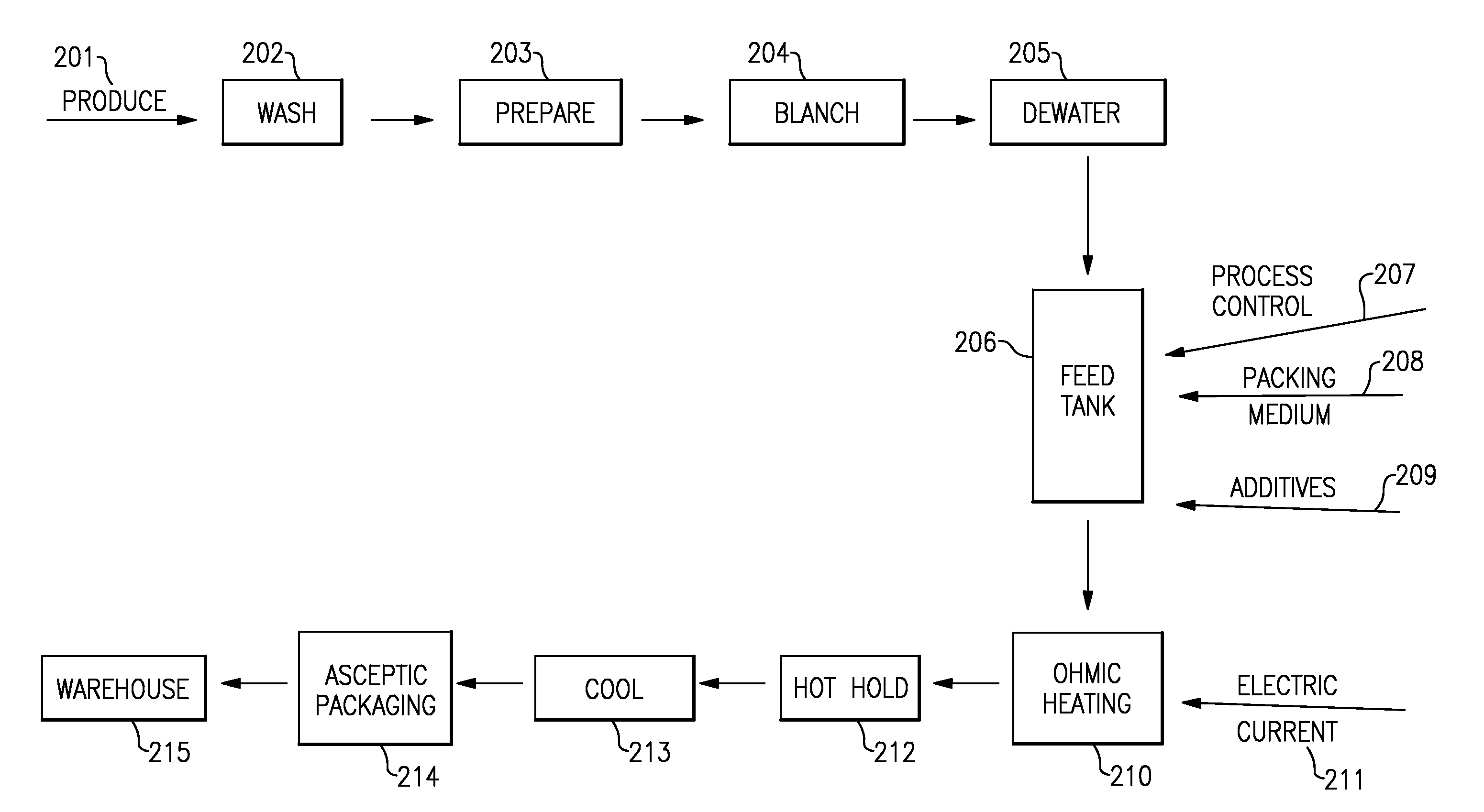
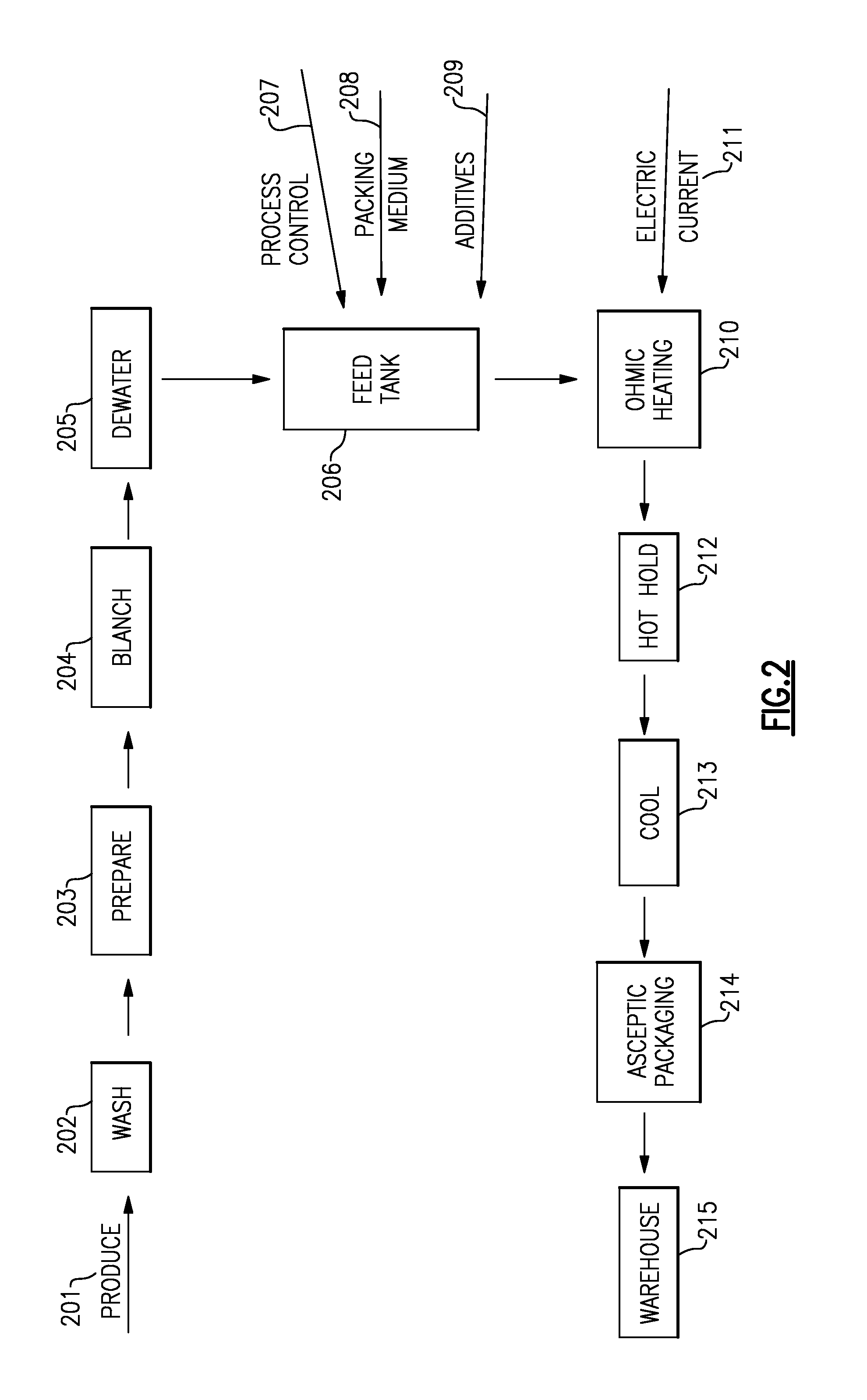
Methods for Sterilizing, Stabilizing and Packaging Harvested Produce
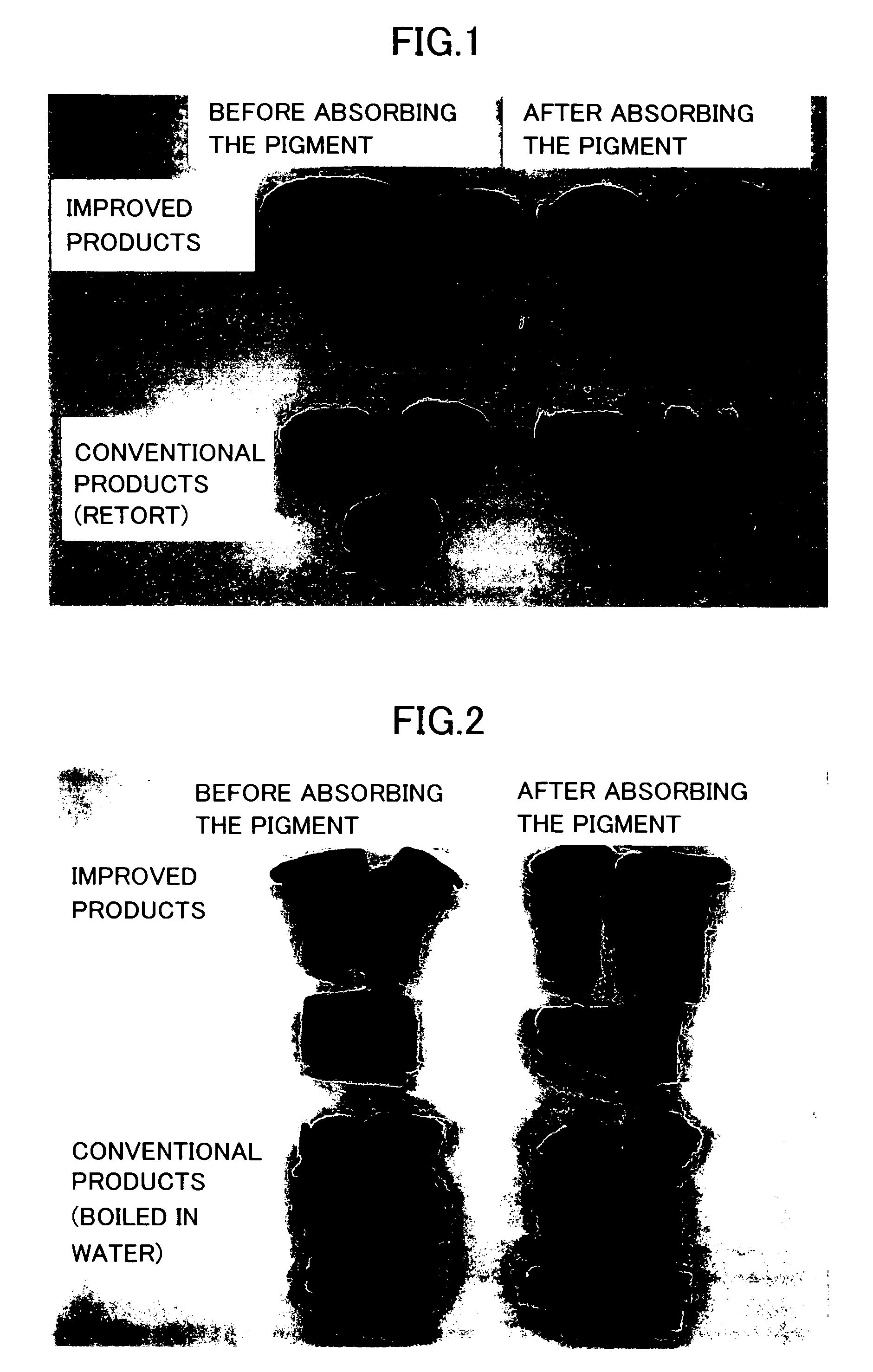
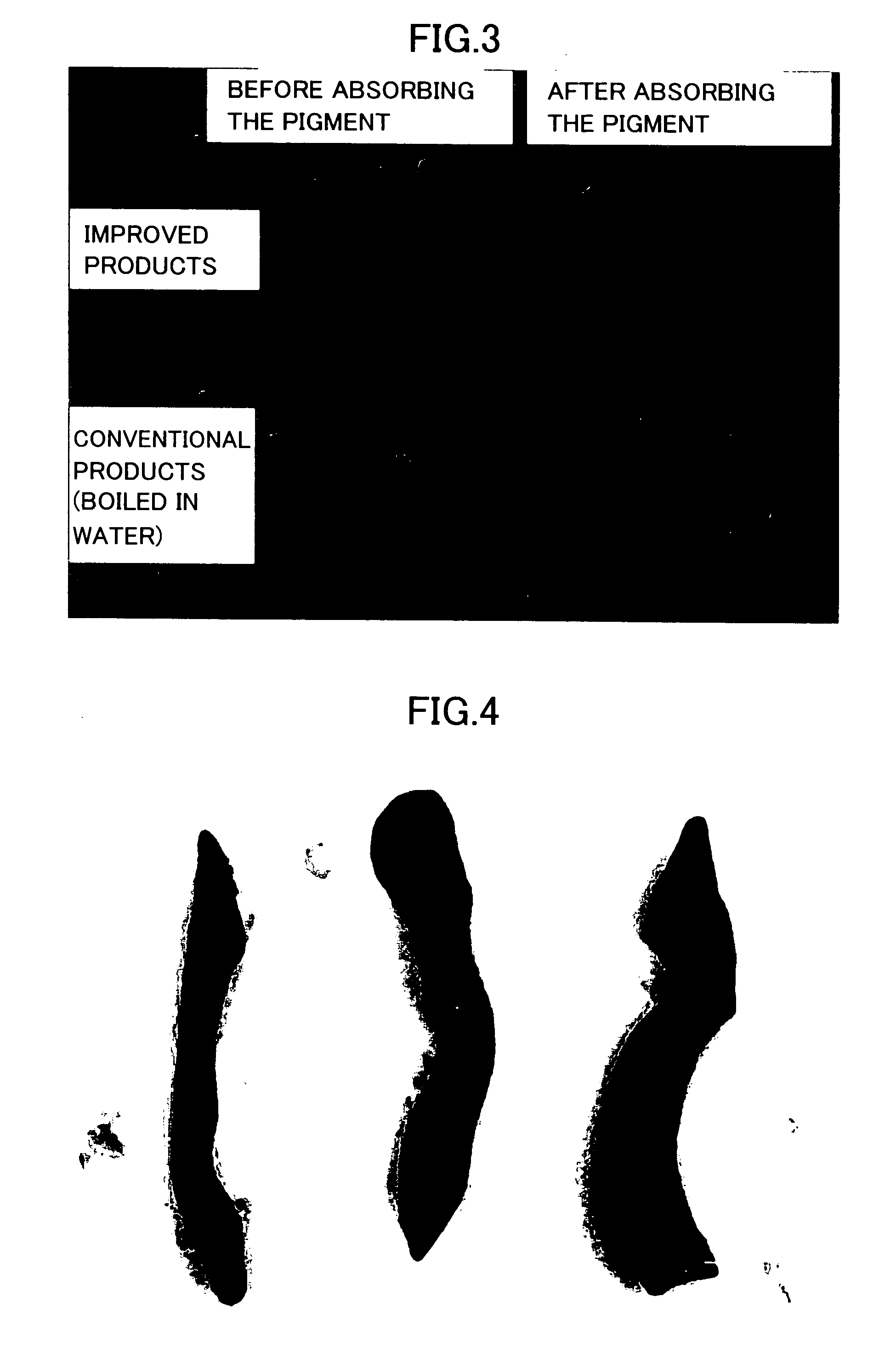
Disclosed are methods for processing harvested produce such as fruits and vegetables, where the sterilization, stabilization and packaging is done in such a manner that it allows for longer retention of freshness, texture, flavor and overall quality than is possible with conventional retort processes and packaging. One specific embodiment discusses sterilizing and packaging harvested produce into a bulk storage container, comprising the steps of cleaning, dicing and blanching said produce, thereby creating pre-processed produce; adding water, at least one acid or salt, and at least one carbohydrate, to said pre-processed produce to form a mixture of pre-processed produce and a liquid packing medium; processing said mixture in an ohmic processing vessel to form a sterilized mixture suitable for aseptic packaging in said container, without first packaging said mixture.
Owner:DEL MONTE FOODS
Process for making a reduced-calorie fruit and/or vegetable spread
A process for making, or preparing, a reduced-calorie fruit and / or vegetable spread product including whole, natural fruit(s) and / or vegetable(s), or combinations thereof, having improved flavor, texture (e.g., mouth feel), color, and nutritional value as compared to fruit and / or vegetable spread products made with conventional processes. More particularly, the process of the present invention includes a pasteurization step, using a swept-surface heat exchanger, for making fruit and / or vegetable spread products having reduced caloric and sugar content and having increased soluble dietary fiber content. The minimal processing of the present process enables the produced fruit and / or vegetable spread products to retain flavor, texture, color, vitamins and other nutrients which are, typically, lost in traditionally-processed fruit and / or vegetable spread products. The process' preferable use of squeeze tube packaging eliminates the need for cutlery in order to use or consume the fruit and / or vegetable spread products and serves to make the products more portable.
Owner:BOCABEAR FOODS
Processed foods containing fungi for cooking by heating with a microwave oven
InactiveUS20060188624A1Easily burstFruits/vegetable preservation by heatingFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingAbsorption ratioMicrowave oven
The present invention provides a processed food for cooking by heating with a microwave oven, containing edible fungi which do not make the sound of burst at the time of cooking by heating with the microwave oven due to treatments after harvesting them, and a processed food for cooking by heating with a microwave oven, containing edible fungi wherein the water absorption ratio of parts corresponding to those that are lightly stained in the caramel staining test is 15 weight % or more.
Owner:HOUSE FOOD IND CO LTD
Apparatus for enzymatic inactivation of puree, or juice, obtained by vegetable or animal food, and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20130220146A1Minimizing residence timeMinimize timeJuice extractionMilk preservationAnimal foodFruit juice
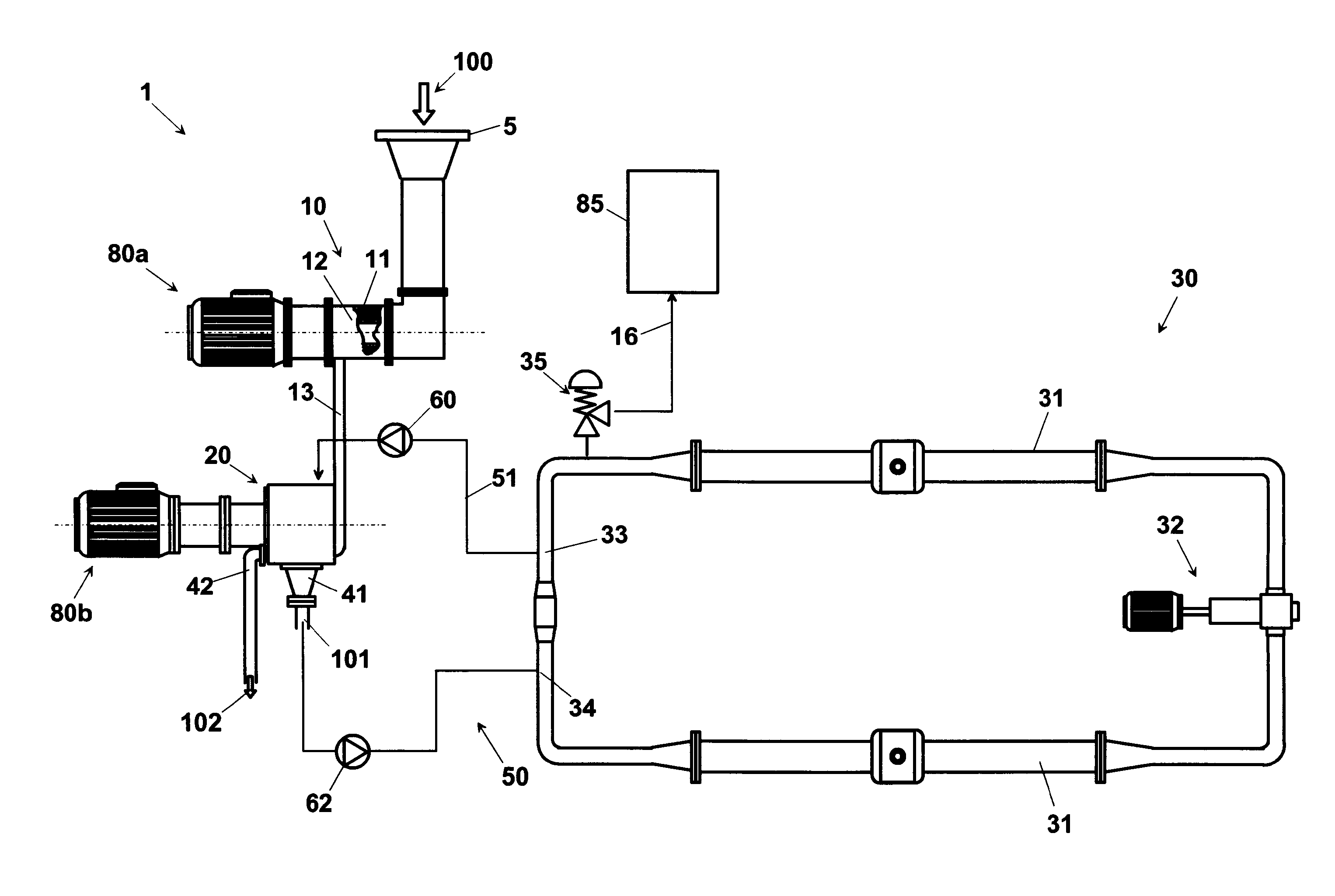
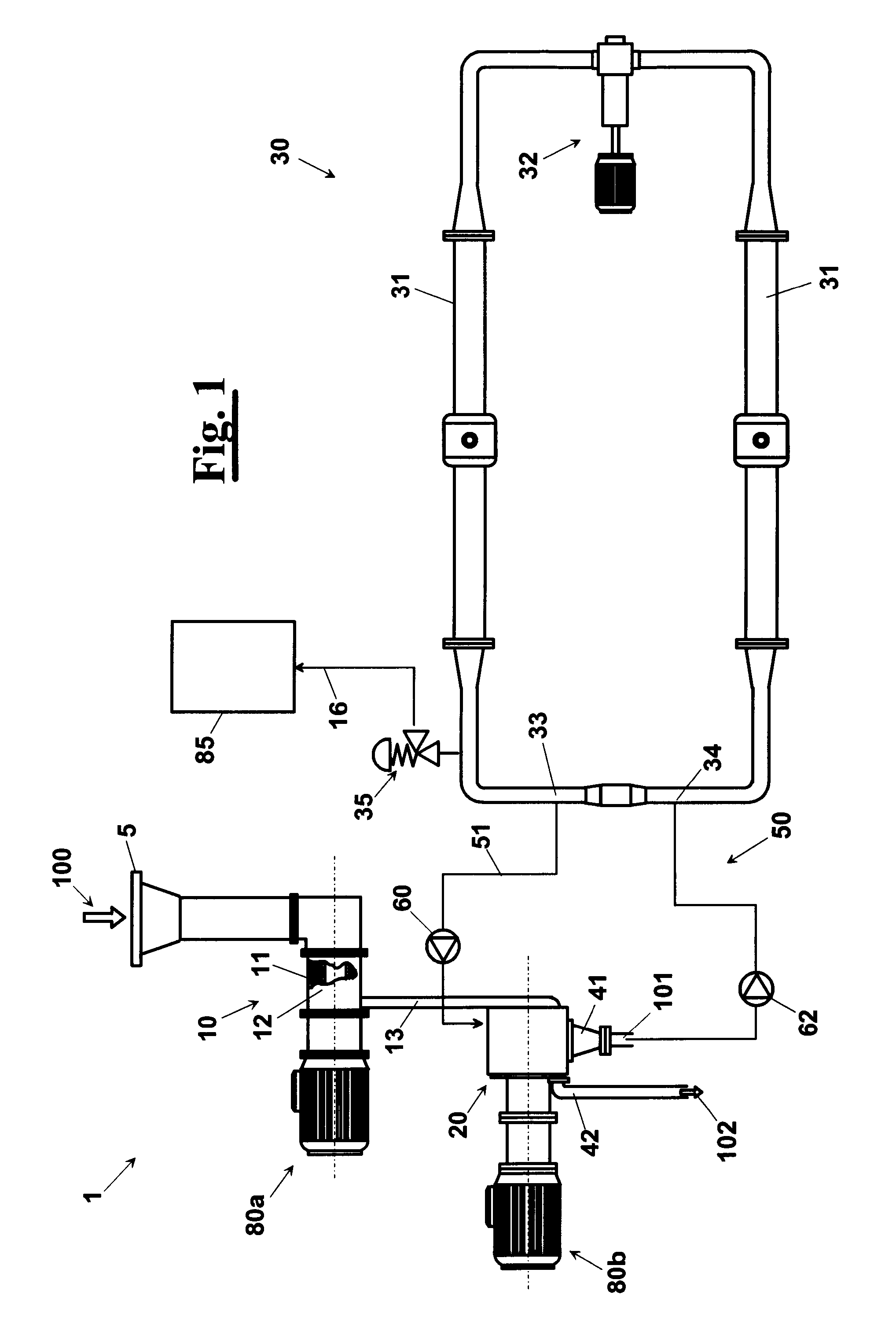
An apparatus (1), for enzymatic inactivation of puree, or juice, from vegetable or animal food, comprises a treatment section (10) of food (100) of vegetable origin obtaining a treated product. The treated product exiting from the treatment section (10) is then directed, for example through a duct (13), towards an extraction section (20). More precisely, the treated product enters the extraction section (20) at a temperature T0, for example set between about −25° C. and about +30° C. The apparatus (1) is further provided with a storage and recirculation section (30), comprising, in particular, an enzymatic inactivation circuit crossed by a hot product at a temperature T2, higher than the enzymatic inactivation temperature T*, normally is about 85° C.-90° C., of the main product. The main product present in the extraction section (20) is struck, near the sieve (22), or directly on its surface, by a flow of hot product coming from the enzymatic inactivation section (30). The mixture so obtained in the extraction section (20) comprises at least one part of inactivated product and is then discharged through an outlet (41).
Owner:BERTOCCHI ALESSANDRO
Rotary screw blancher
A food processing apparatus including a tank having an inlet end for receiving food product and an outlet end for discharging food product, the tank having a rotatable auger mounted in a compartment, the auger for advancing food product within the compartment from the inlet end toward the outlet end, the auger including flights having a flight wall with a radial edge, a clearance space being defined between the radial edge of the flights and a solid, imperforate wall portion of an inner wall. One of the inner wall and the flight wall may include a perforated wall portion. A transition zone includes a moveable surface to contain food product while in use.
Owner:LYCO MFG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com