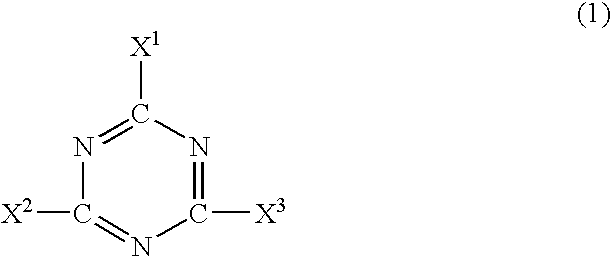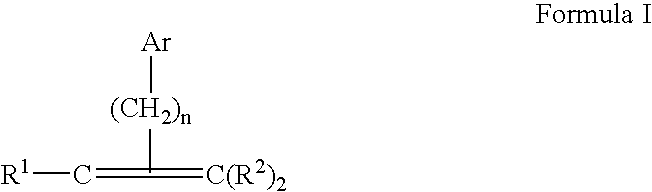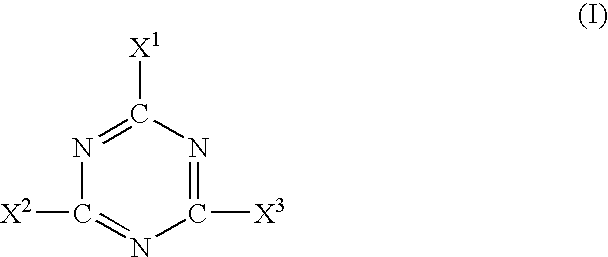Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
538results about "Domestic upholstery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
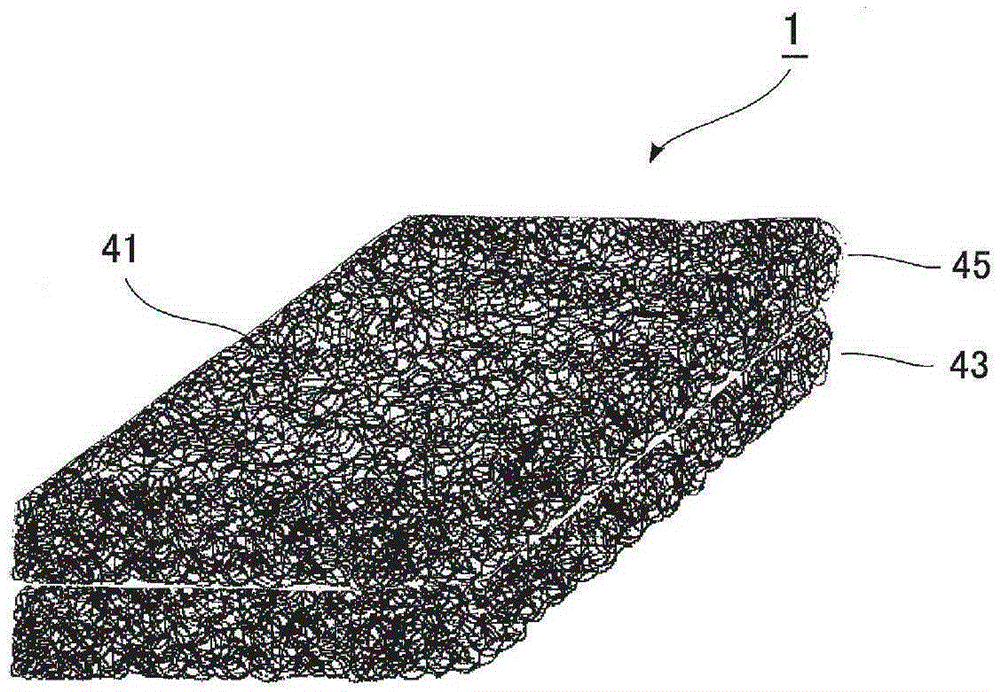
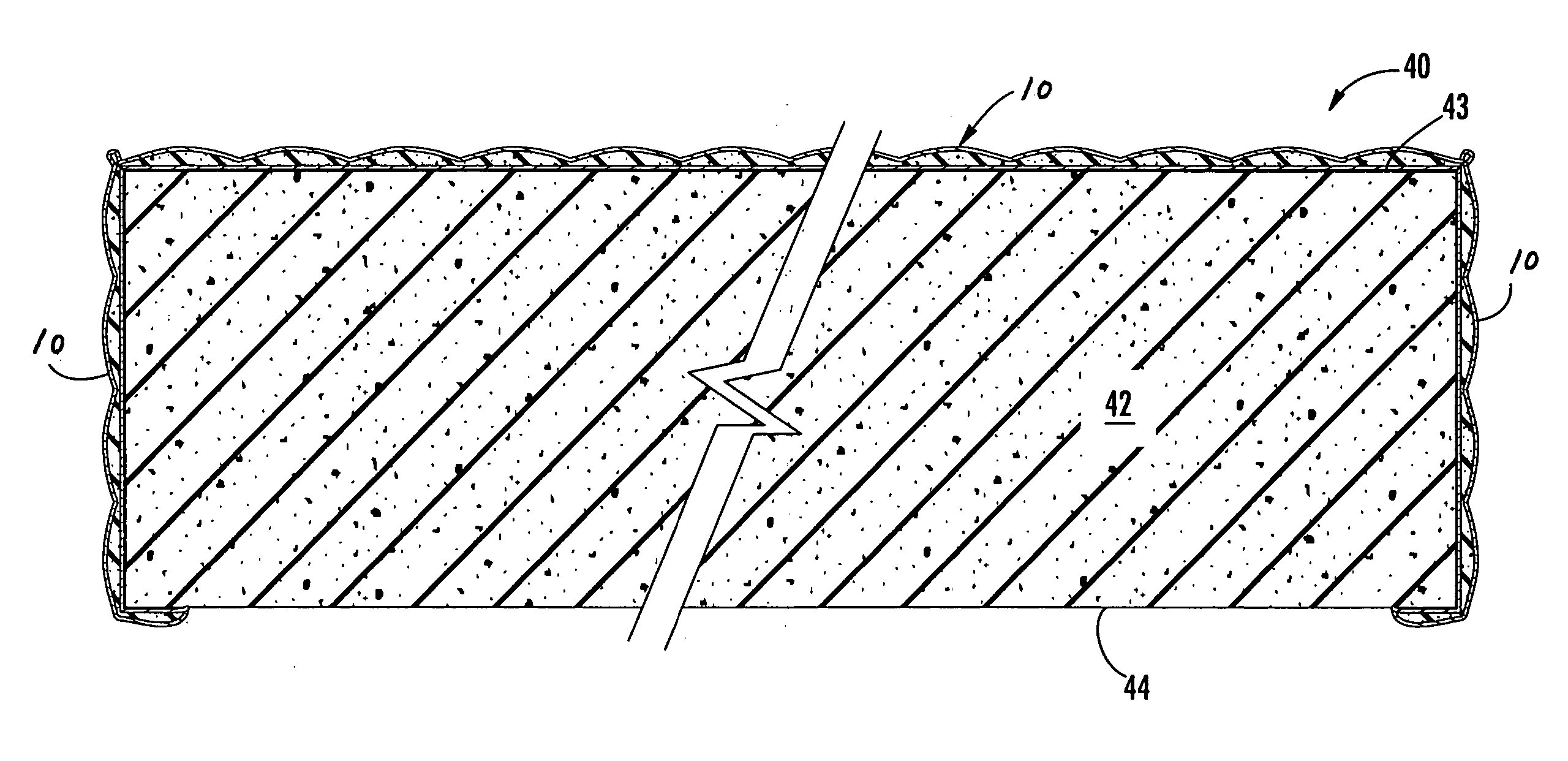
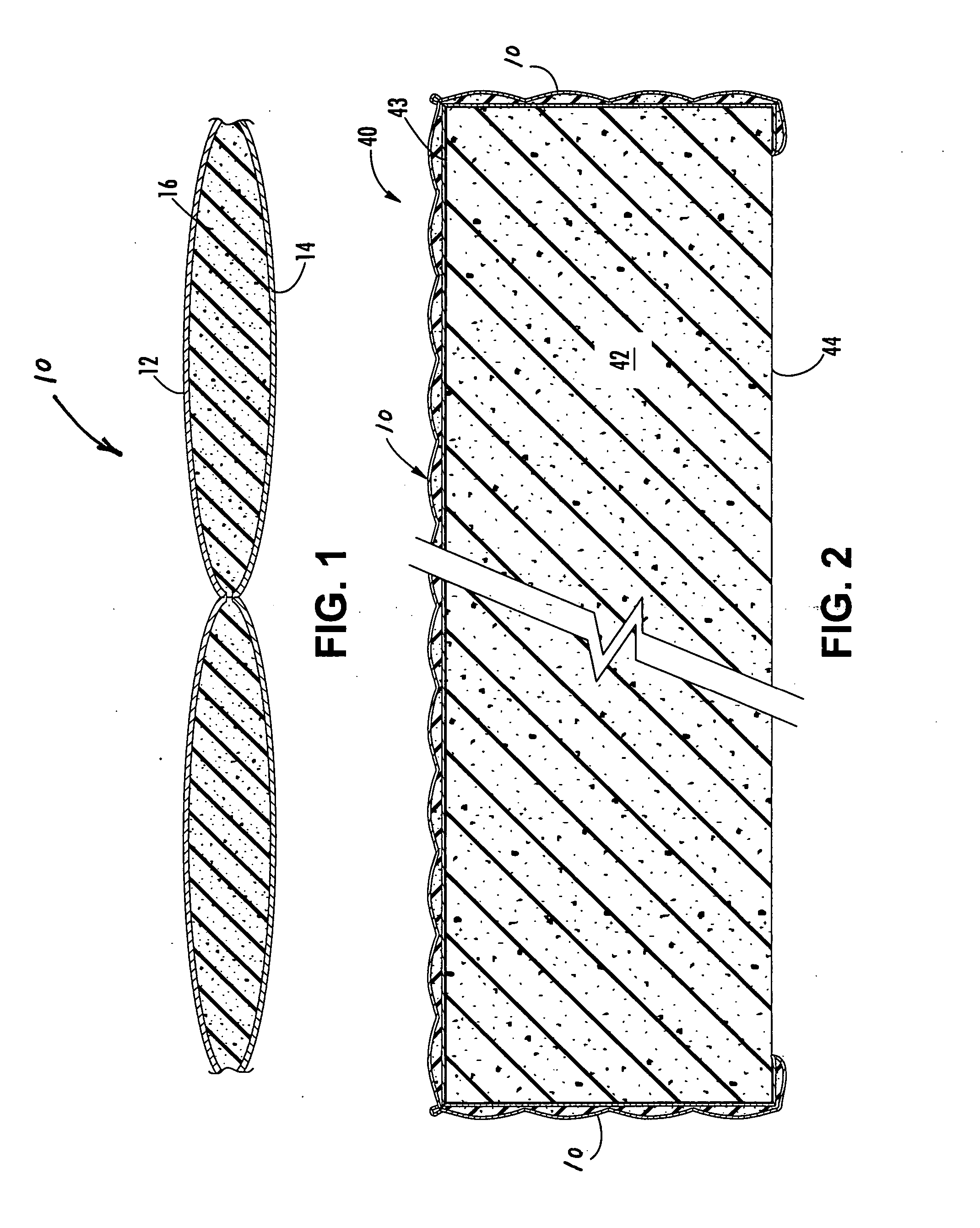
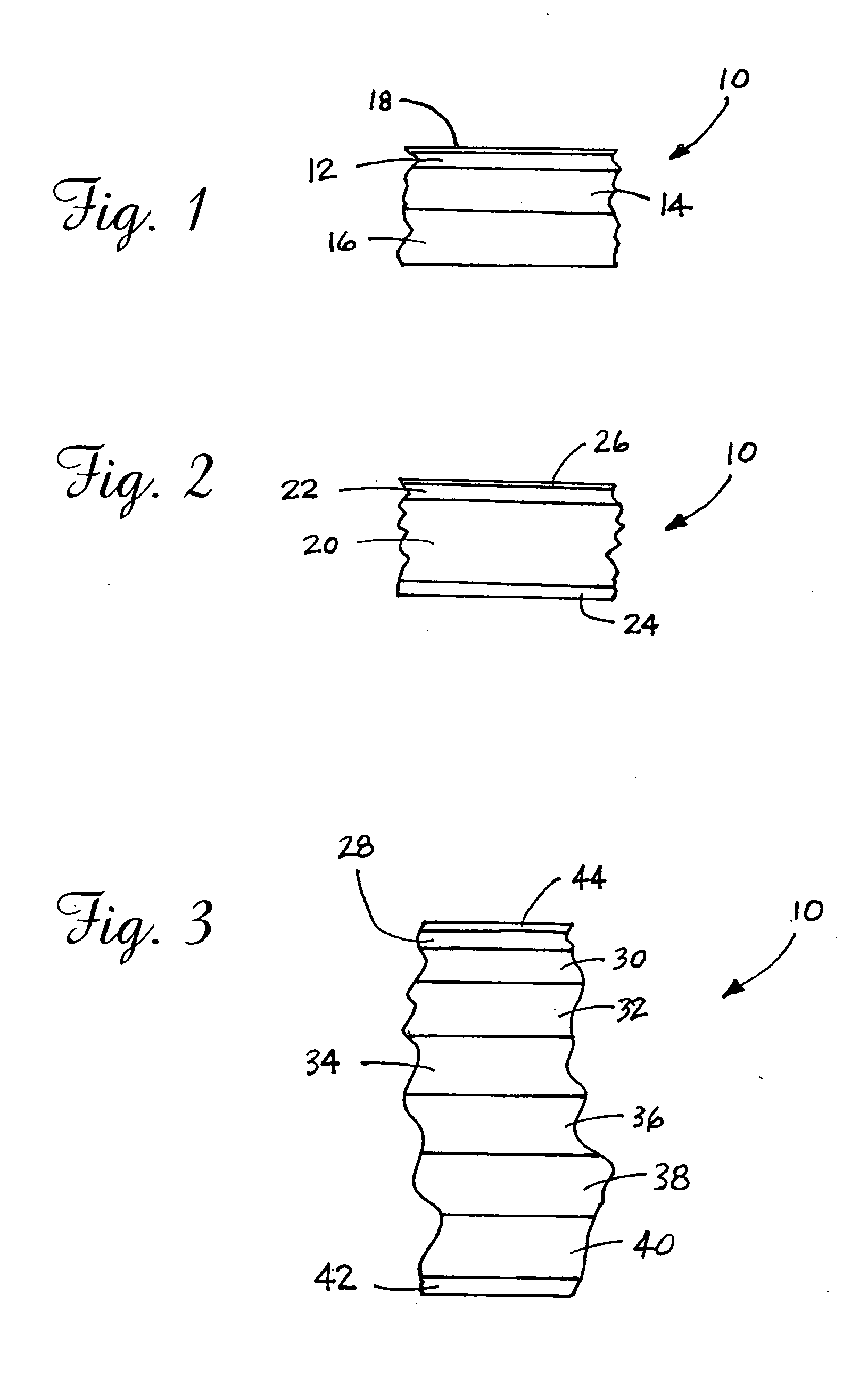
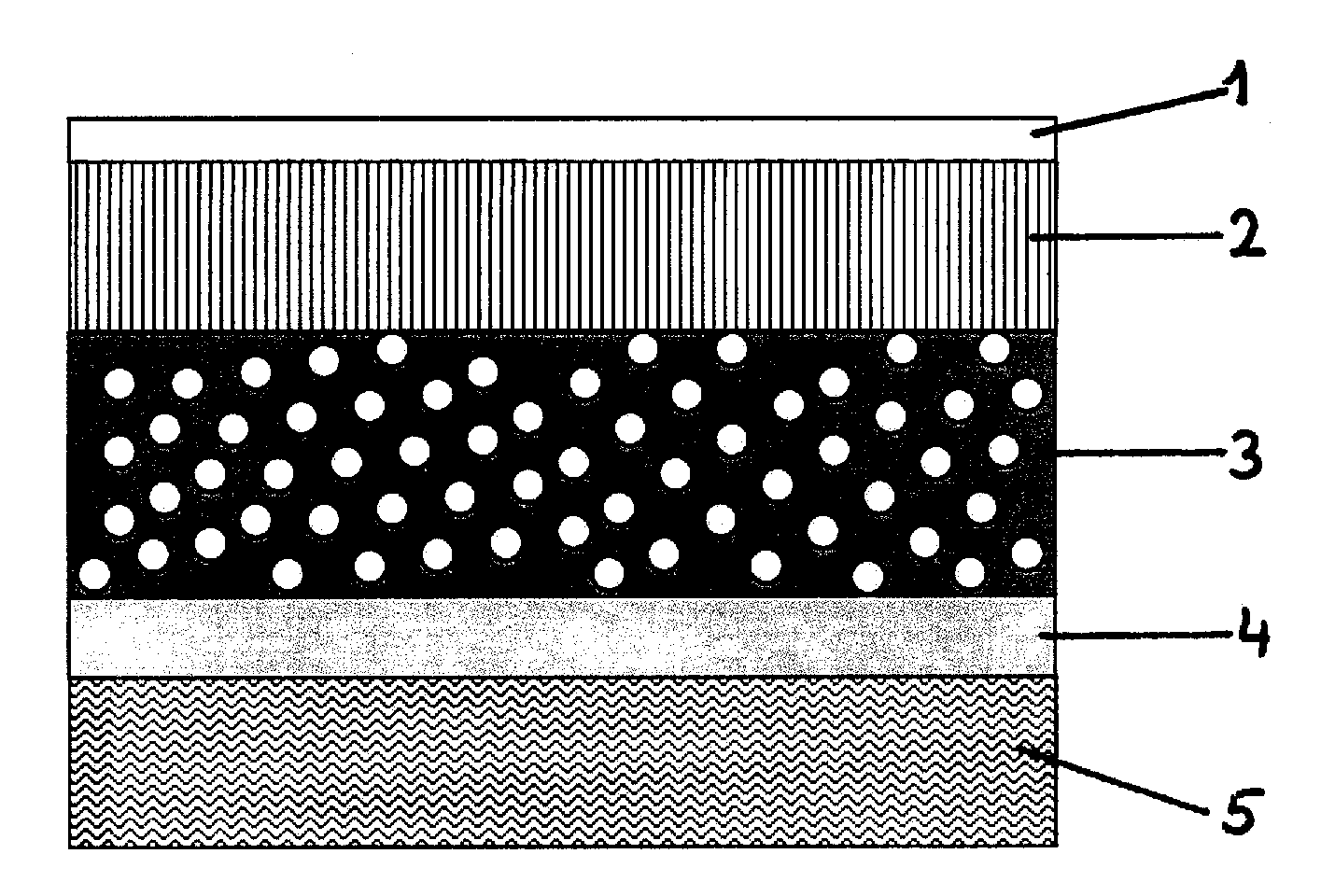
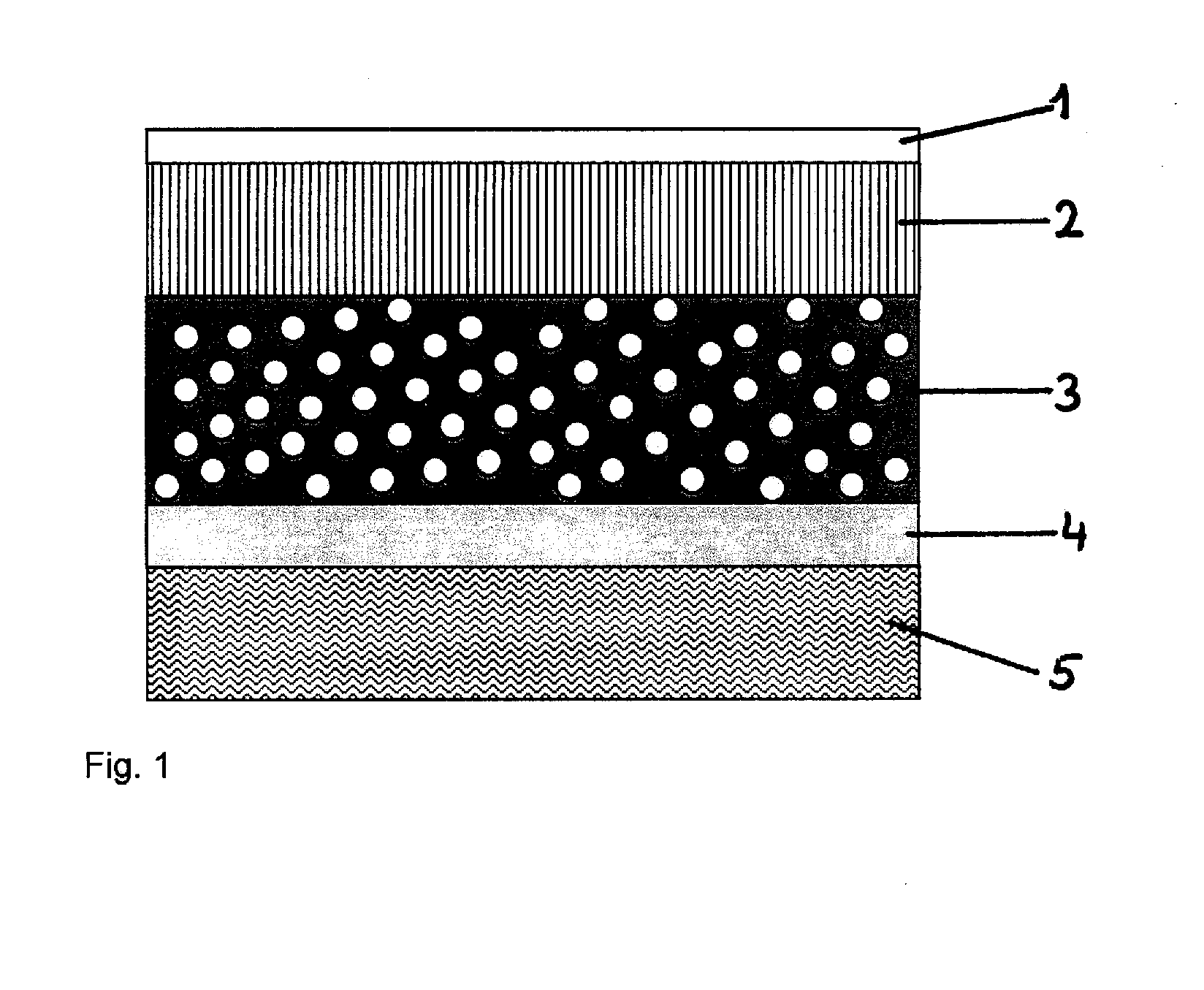
Upholstery panels with fire resistant backing layer
InactiveUS20050095936A1Low costReduce weightStuffed mattressesDomestic upholsteryCushioningEngineering
A composite upholstery panel includes a layer of ticking fabric, a layer of flame and heat-resistant backing fabric, and a layer of resilient flame and heat-resistant cushioning material sandwiched between the layer of ticking fabric and the layer of backing fabric. The composite upholstery panel maintains flame and heat resistant integrity when impinged at any location with a gas flame in accordance with testing protocol set forth in Technical Bulletin 603 of the State of California Department of Consumer Affairs (TB-603). However, individually, the ticking layer, backing layer and cushioning layer would fail to maintain flame and heat resistant integrity when impinged with a gas flame in accordance with testing protocol set forth in TB-603.
Owner:PRECISION FABRICS GROUP
Silicone-impregnated foam product and method for producing same
ActiveUS20090047495A1Low smoke emissionLow toxicityLamination ancillary operationsPersonal carePolymer chemistryPolyurethane
The present invention relates to products having a foam carrier or substrate, and particularly to such products employing a reticulated polyurethane foam carrier impregnated with silicone polymer. The present invention also relates to a method of producing these silicone-impregnated foam products.
Owner:DEVINE INNOVATIONS
Wet-lay flame barrier
InactiveUS20060068675A1Increase speedExtension of timeDomestic upholsteryLayered productsFiberGlass fiber
Nonwoven wet-lay flame barrier of the invention comprises a blend of water dispersible fibers, that are inherently fire resistant and nonshrinking to direct flame, along with water dispersible fibers extruded from polymers made with halogenated monomers and optionally including fiberglass and wood pulp, being together thermally bonded with a binder resin in a wet-lay manufacturing process to provide a relatively thin, but dense, durable flame barrier with excellent tensile, and durability properties in the end use application. The wet-lay flame barrier of this invention also allows for the manufacture of open flame resistant composite articles, while also permitting the continued use of conventional non-flame retardant dress cover fabrics, conventional non-flame retardant fiberfills and conventional non-flame retardant polyurethane foams.
Owner:HANDERMANN ALAN C +3
Matte film
InactiveUS20070160782A1Adequate film-forming stabilityQuality improvementAgricultural articlesWrappersPolymer chemistryPolylactic acid
A polylactic acid resin film or sheet which can be satisfactorily and stably formed and has excellent matte properties. It is a single-layer matte film or sheet which comprises a polylactic acid resin composition containing a particulate substance and at least one side of which has a surface gloss as measured in accordance with ASTM-D2457-70 (45° gloss) of 60% or lower.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI LIFE & LIVING CORP
Articles containing bimodal ionomer compositions
Provided are partially or fully neutralized mixtures of carboxylate functionalized ethylene high copolymers or terpolymers (Mw between 80,000 and 500,000 Da) with carboxylate functionalized ethylene low copolymers (Mw between 2,000 and 30,000 Da). The compositions are used in films, multilayer structures and other articles of manufacture. The compositions are preferably used on a surface of the articles.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
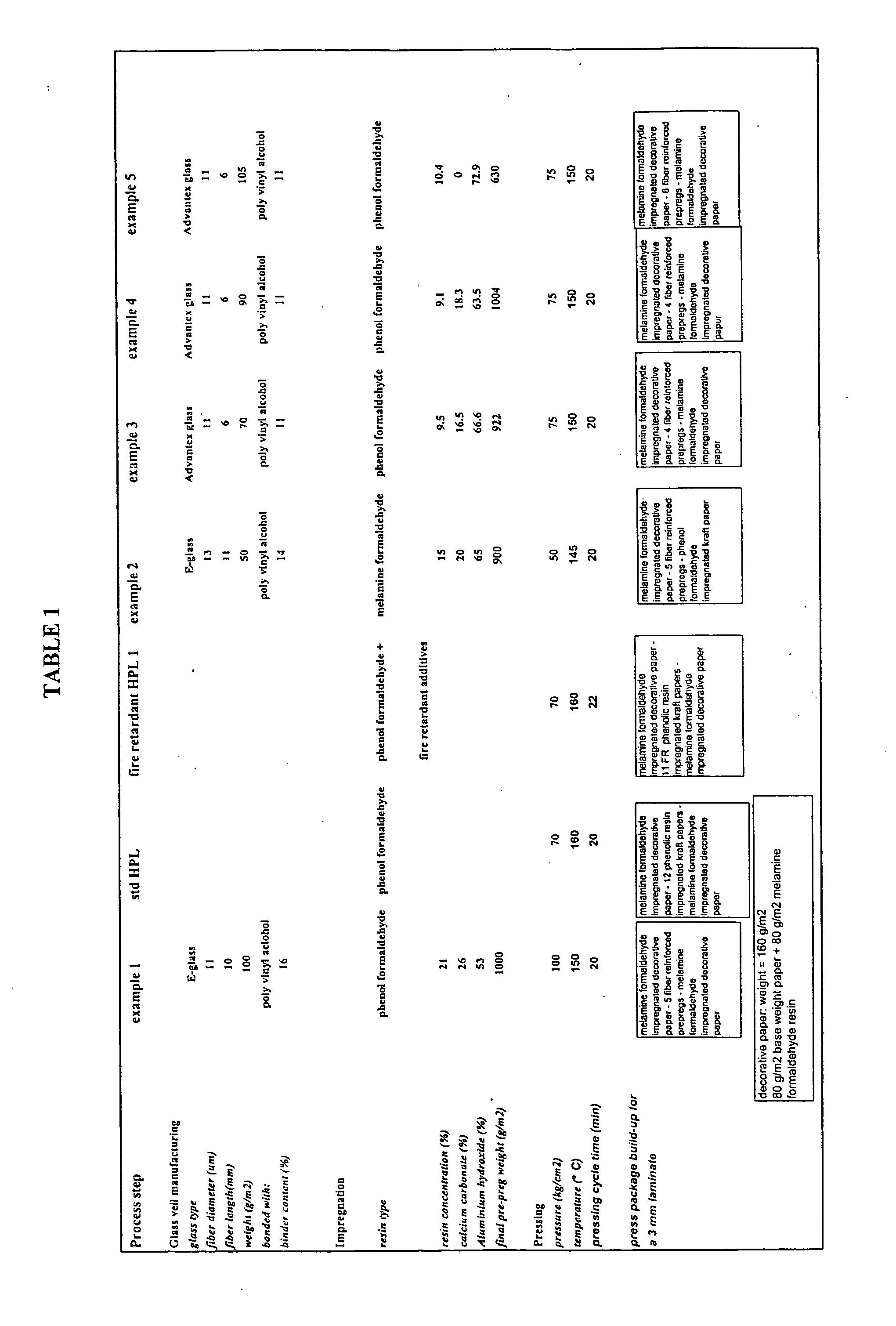
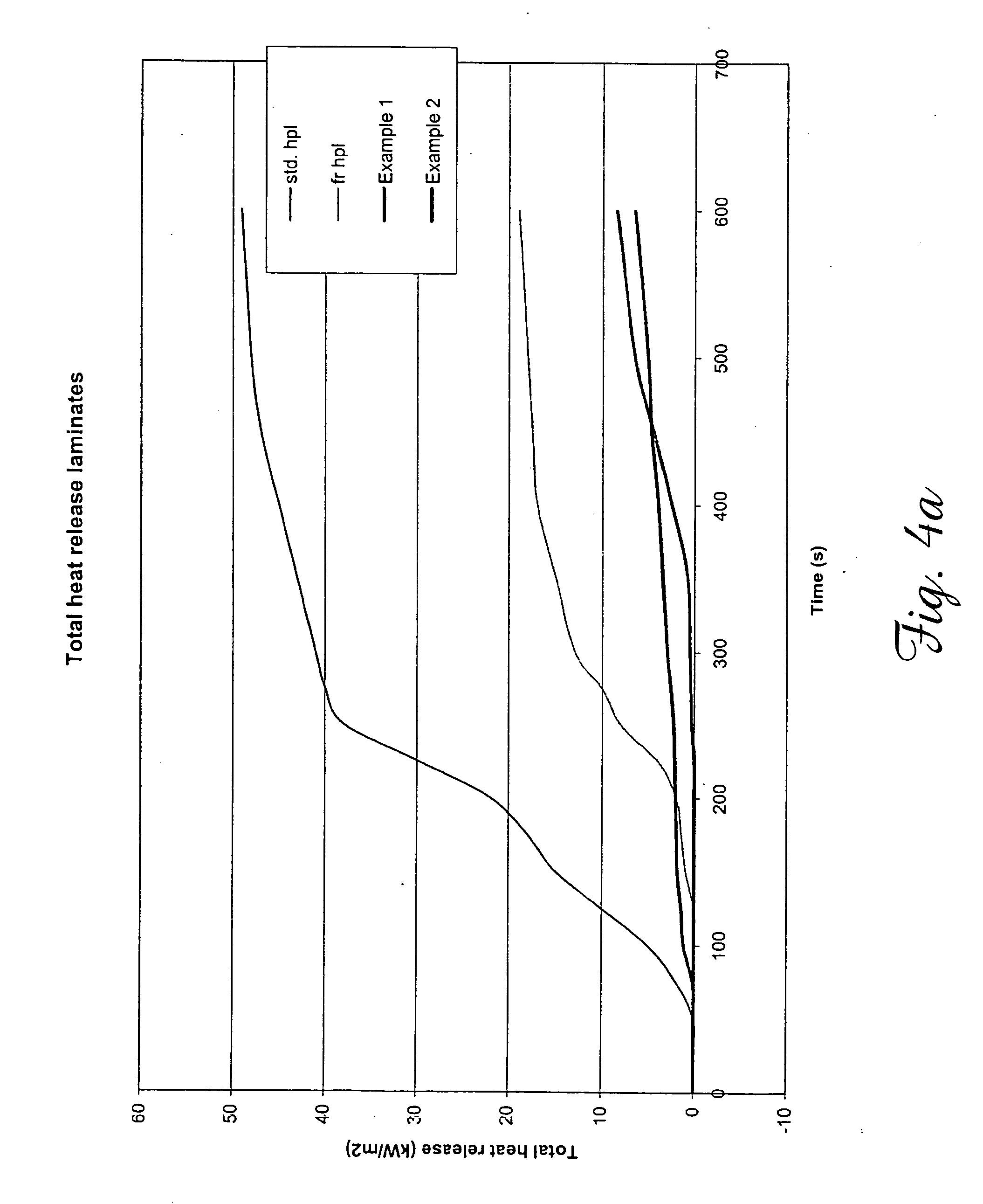
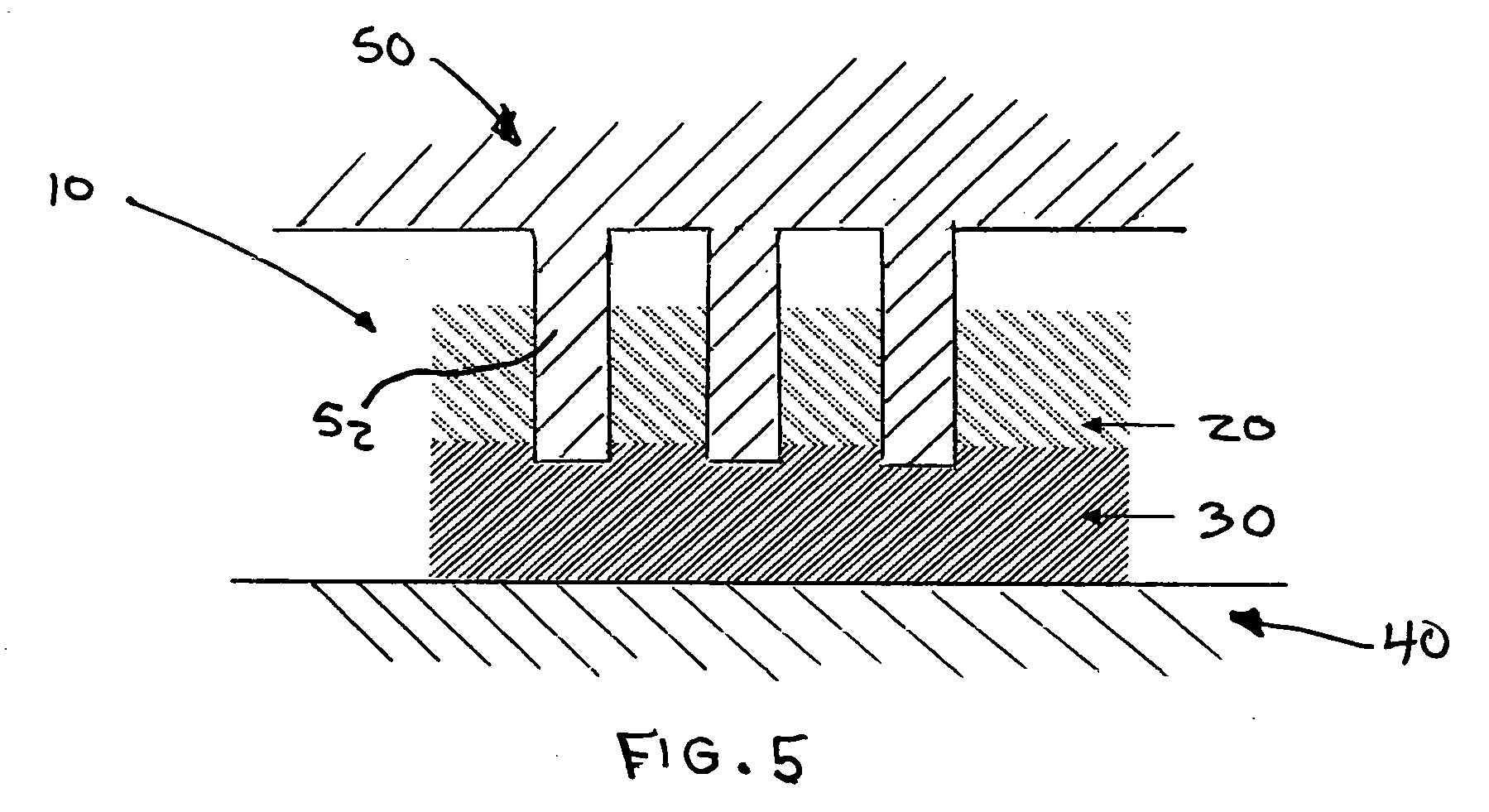
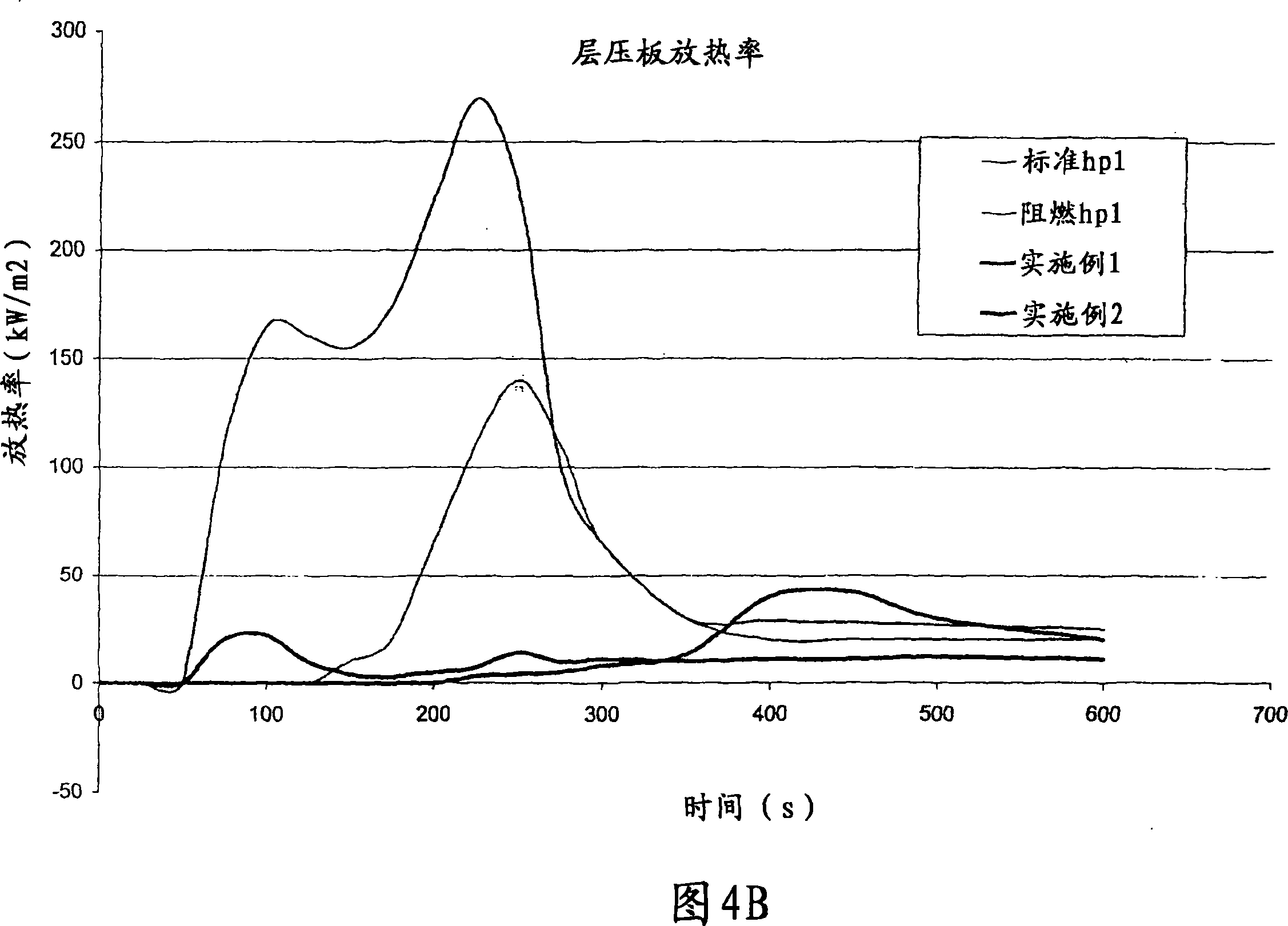
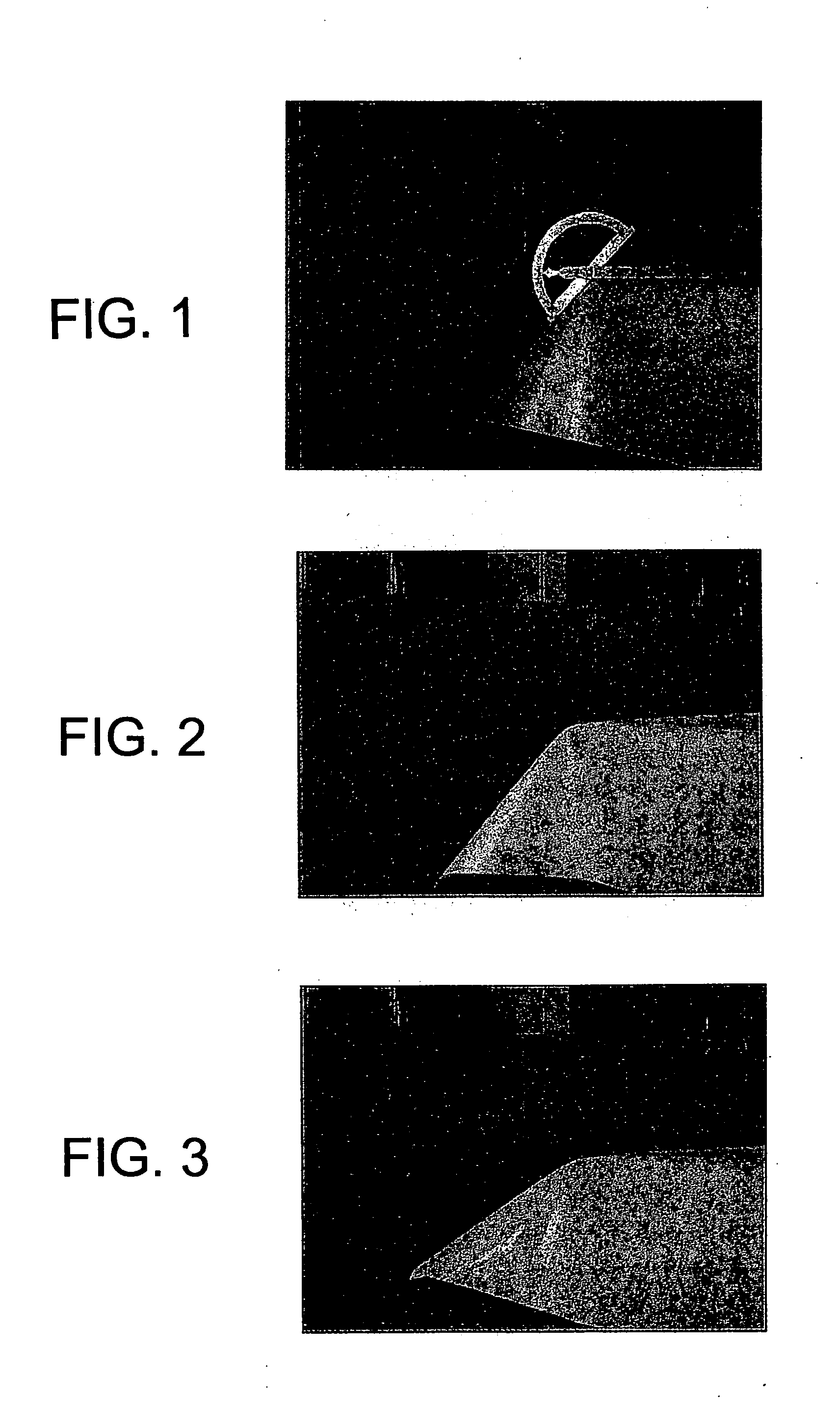
Non-combustible high pressure laminate
A high pressure laminate includes a first layer of resin impregnated paper and at least one layer of fiber reinforced veil. Each layer of fiber reinforced veil includes binder and filler. The laminate is characterized by having a caloric value of lower than 3.0 MJ / kg when tested in accordance with ISO 1716. A method for producing this high pressure laminate is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Method of forming multi-colored composite by pinsonic embossing
ActiveUS20060089071A1Lamination ancillary operationsDomestic upholsteryBiological activationNonwoven fabric
A method of forming a multi-colored multi-layered non-woven composite includes the application of ultrasonic energy to the top layer to displace a portion of that layer in a predetermined pattern such that openings are formed through which any underlying layer may be visible. In related embodiments, the use of pinsonic or ultrasonic embossing of a non-woven layer provides a three-dimensional colored pattern due to melting and densification of the fibers and / or the activation of heat activatable pigments or dyes used to color the non-woven.
Owner:FREUDENBERG VLIESSTOFFE
Slickened or siliconized flame resistant fiber blends
InactiveUS20060160454A1Extinguish any residual flameMinimal shrinkageDomestic upholsteryFibre treatmentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to slickened or siliconized flame resistant fiber blends that are well suited for use in mattresses, boxsprings, upholstered furniture, fiber-filled bed clothing, transportation seating or any end use application where a soft materials are desired for flame resistant (FR) purposes. Some of the fibers in the blend are slickened. The FR fibers incorporated into these blends include both char forming FR fibers and oxygen depleting FR fibers. FR char-forming fibers are those which exhibit little shrinkage when exposed to direct flame and are not spun from polymers manufactured with halogenated monomers. Oxygen depleting FR fibers are spun from polymers manufactured with halogenated monomers.
Owner:BEIJING CARINAE MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Method of delivering a thermoplastic and/or crosslinking resin to a composite laminate structure
The present invention provides a process for producing a prepreg of high modulus reinforcing fibers, the process comprising the steps of: a) providing a reinforcing fiber bundle layer wherein such bundle contains a thermoplastic and / or crosslinking resin within the fiber bundle; b) providing a layer of a thermoplastic and / or crosslinking material layer on at least one side of the high modulus fiber layer of step a); c) compressing the layers from step b) under an appropriate amount of heat and pressure, and thereby producing a prepreg of high modulus reinforcing fibers.
Owner:KEUCHEL KENNETH HERBERT
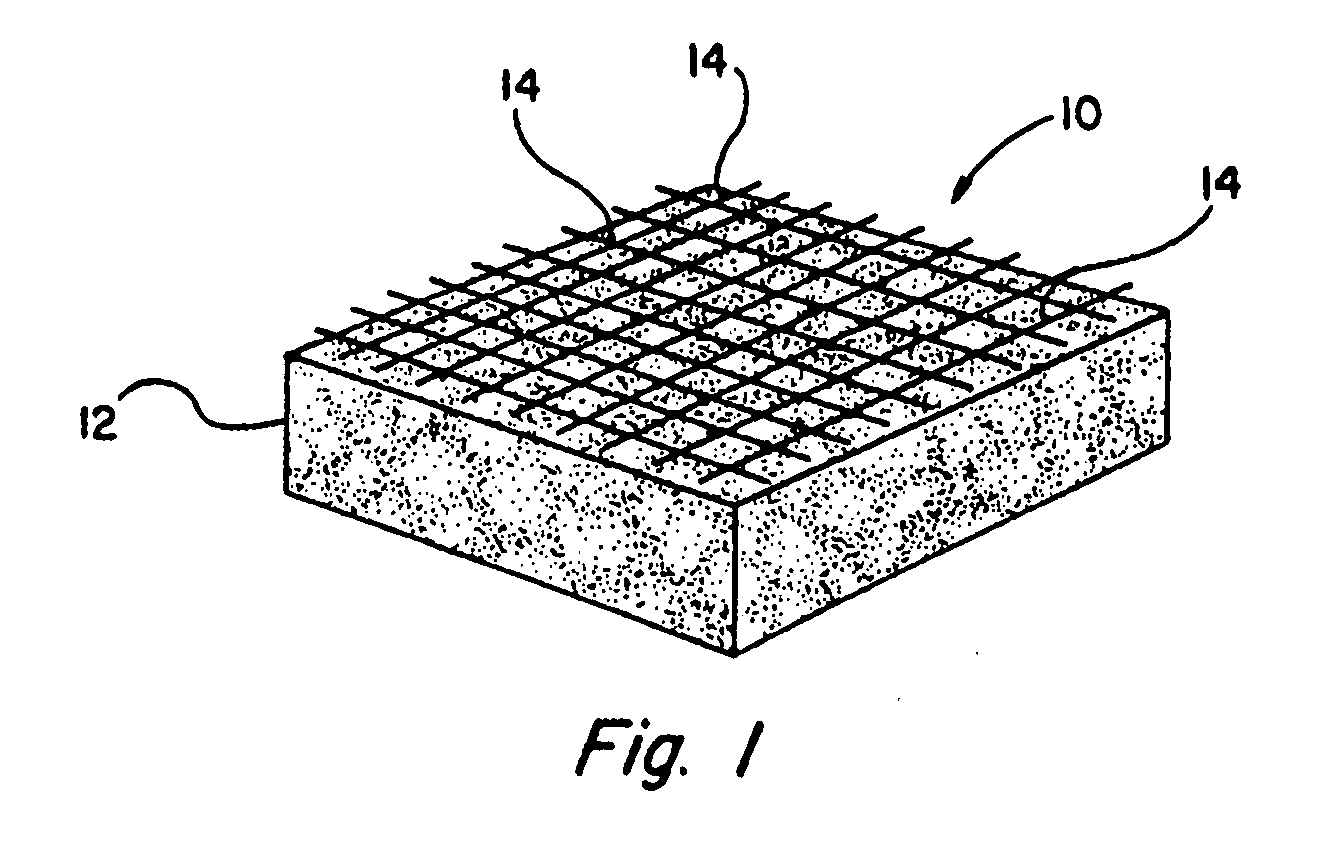
Non-combustible high pressure laminate
A high pressure laminate includes a first layer (12) of resin impregnated paper and at least one layer (14,16) of fiber reinforced veil. Each layer of fiber reinforced veil includes binder and filler. The laminate is characterized by having a caloric value of lower than 3.0 MJ / kg when tested in accordance with ISO 1716. A method for producing this high pressure laminate is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Multilayer structures
InactiveUS20050106965A1Domestic upholsteryPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAlkeneOrganic chemistry
A multilayer structure comprising (A) a fabric and (B) a polymeric layer comprising a substantially random interpolymer comprising in polymerized form i) one or more α-olefin monomers and ii) one or more vinyl or vinylidene aromatic monomers and / or one or more sterically hindered aliphatic or cycloaliphatic vinyl or vinylidene monomers, and optionally iii) other polymerizable ethylenically unsaturated monomer(s); layer (B) being free from a substantial amount of tackifier. The multilayer structure has desirable haptics and surprisingly good drape properties. It is useful in many applications, for example as water-impermeable clothes, tablecloths, tents, water-impermeable covers, curtains, artificial leather or upholstery.
Owner:WEVERS RONALD +8
Panel with paper honeycomb cores using as a table top
InactiveUS20090324872A1Highly strongCost-effectiveDomestic upholsterySynthetic resin layered productsHoneycombPulp and paper industry
The present invention relates to a panel with paper honeycomb cores, which is usable as a table top. The panel comprises a top panel, a bottom panel, paper honeycomb cores and an internal fixed part, in which the paper honeycomb cores are filled in the closed space which is enclosed by the top panel and the bottom panel, and are fixed with the top panel and the bottom panel. The peripheries of the paper honeycomb cores are completely or partially surrounded by the internal fixed part, or the internal fixed part is installed in the suited position of the panel, and the internal fixed part serves as the stiffening art of the panel. The edge of the bottom panel and the lower edge of the top panel, which is formed by ending the top panel downwards are cohered together, and the flection of the top panel forms the side edge of the panel. The top panel and the bottom panel may be formed by suction moulding process or contour machining process directly. The panel having the structure described above can connect with other parts of the table.
Owner:LENG LUHAO
Composite leather material
InactiveUS20070184742A1Improve propertiesHigh strengthDomestic upholsteryLeather websNatural rubber latexCalcium carbonate
Engineered leather substrates, methods of making the substrates, engineered leather composites including the substrates, and articles of manufacture which include the engineered leather substrates or composites are disclosed. The substrate includes leather, non-leather fibers, a binding agent and one or more additional components such as cushioning agents, softeners, processing aids, and colorants. A composite material can be formed including the substrate and one or more additional layers, such as top coat layers, reinforcing layers, and cushioning layers. The substrate and or the composite can be chemically or mechanically embossed. The leather used to form the engineered leather substrate can be derived from post-industrial and / or post-consumer materials. The non-leather fibers can be organic or inorganic, and the composition can also include inorganic fillers, such as calcium carbonate, and clays. The cushioning agents can include polymeric microbubbles, foam, rubber particles, and other low density cushioning agents. The binding agents can be synthetic or natural, such as synthetic latex, natural latex, PVA, and starch.
Owner:MALLARD CREEK POLYMERS
Biofabricated leather articles, and methods thereof
Owner:MODERN MEADOW INC
Core material for cushion, and cushion
ActiveUS20160174725A1Solve the lack of resistanceSuppress shrinkage of the cushion and wrinkles of the coverStuffed mattressesDomestic upholsteryThermoplasticPolyester
An object is to provide a hygienic cushion that has an adequate thickness to provide the repulsive force of or above a specified level and the body-holding property, is light in weight, has excellent air permeability and is washable with water. The core material for cushion 1 comprising the three-dimensional net-like structure, which is comprised of a polyethylene thermoplastic resin, a polyester thermoplastic elastomer or a mixture of a polyethylene thermoplastic resin and a polyethylene thermoplastic elastomer. The three-dimensional net-like structure has a first layer that includes a thermoplastic resin and a second layer that is stacked on a single surface or both surfaces of the first layer and includes a thermoplastic resin different from the thermoplastic resin of the first layer. The three dimensional net-like structure has an impact resilience of not lower than 13 cm, a hysteresis loss of not higher than 34% and not lower than 13%, and a thermal expansion rate of 0 to 8% in the longitudinal direction before and after a hot-air drying test that is performed at a temperature of 90° C. for 30 minutes with regard to the polyethylene thermoplastic resin, that is performed at a temperature of 130° C. for 30 minutes with regard to the polyester thermoplastic elastomer and that is performed at a temperature of 90° C. for 30 minutes with regard to the mixture of the polyethylene thermoplastic resin and the polyethylene thermoplastic elastomer.
Owner:C ENG CO LTD
Multilayer spunlaced nonwoven fire blocking composite
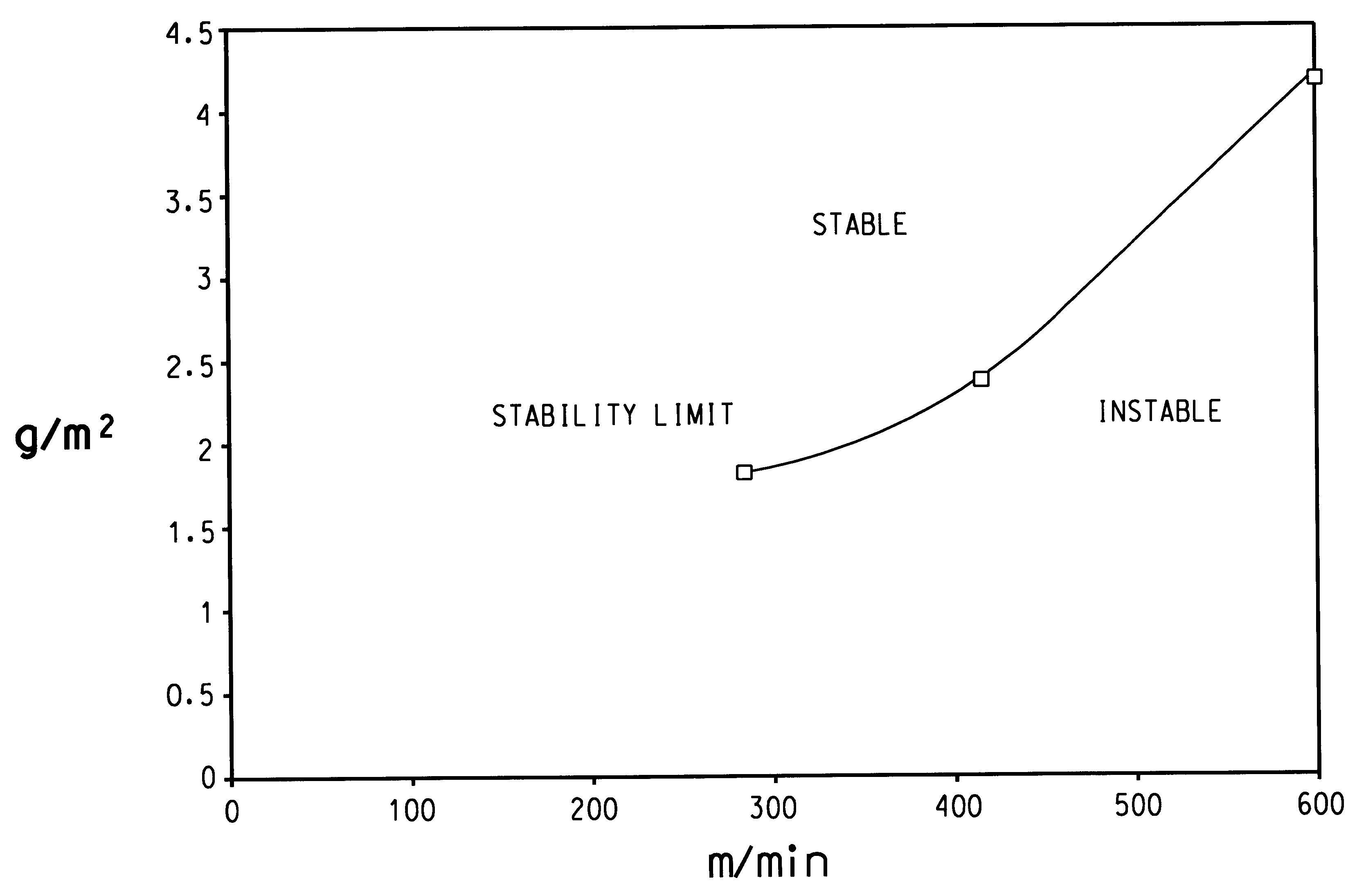
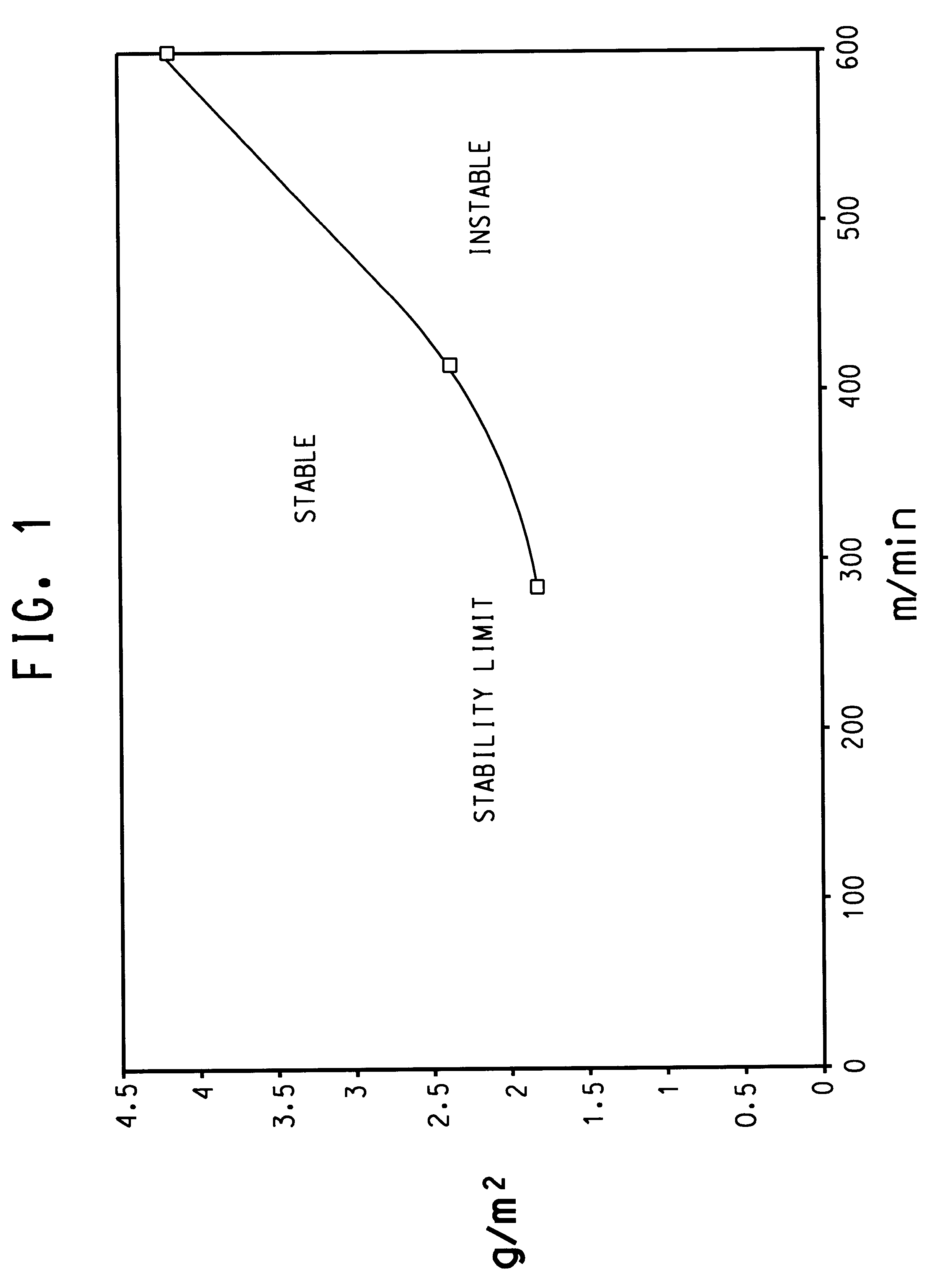
This invention relates to a mulilayer spunlaced nonwoven composite useful as a fire blocking component for an article, an article such as furniture or a mattress comprising the nonwoven composite, and processes for making the nonwoven composite and fire blocking an article with the nonwoven composite. The multilayer nonwoven composite comprises a first layer comprising 75 to 25 weight percent regenerated cellulosic fiber that retains at least 10 percent of its fiber weight when heated in air to 700° C. at a rate of 20 degrees C. per minute and 25 to 75 weight percent heat-resistant fiber, said first layer having a basis weight of from 1 to 5 ounces per square yard (34 to 170 grams per square meter); and a second layer comprising up to 75 weight percent of a regenerated cellulosic fiber that retains at least 10 percent of its fiber weight when heated in air to 700° C. at a rate of 20 degrees C. per minute, and 25 to 100 weight percent of a modacrylic fiber, said second layer having a basis weight of from 1 to 5 ounces per square yard (34 to 170 grams per square meter), the nonwoven composite having a total basis weight of from 2 to 7 ounces per square yard (68 to 237 grams per square meter).
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Exhaust valve apparatus and gas filled cushion
InactiveUS20160058218A1Easy dischargeEasy to usePaper/cardboard articlesDomestic upholsteryCushioningExhaust valve
A gas cushioning material preserved by easily discharging a gas from a bag part and used by filling the bag part with the gas when used again is provided. Gas cells are disposed in parallel in a gas cell row by forming heat-fusion parts in the transverse direction. A discharge valve part for discharging gas is formed at an end portion of each gas cell row. A narrowed discharge passage is formed in the discharge valve part. When the bag part is filled with a gas, the discharge valve part is bent to close the discharge passage, and in the state in which the discharge valve part is bent, a first surface fastener and a second surface fastener formed on a front surface and a rear surface of the discharge valve part are coupled to each other to maintain a closed state of the discharge passage.
Owner:YOSHIFUSA KATSUTOSHI +3
Multi-layer sheet suitable as sealable sheet
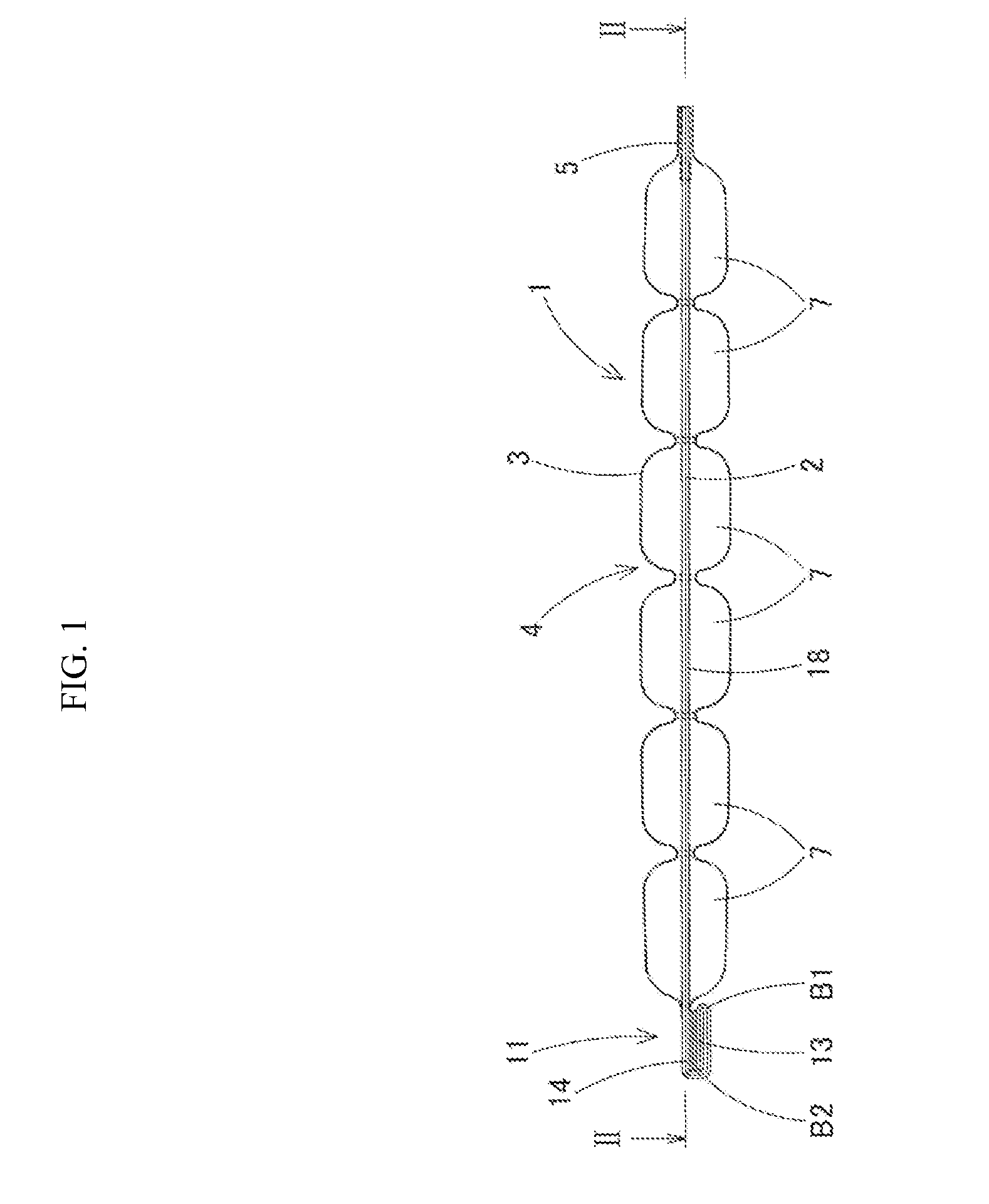
A multi-layer sheet suitable as sealable or peelable sheet specially used for closing foodstuff containers or blisters. This multi-layer sheet comprises a tie-layer between a substrate layer and a seal or a peel-seal layer comprising a polyolefin with acid or anhydride, grafted or copolymerized. The tie-layer has a thickness equivalent to 1-7 g / m2. The seal layer comprises a polyolefin. The total thickness of the combination of tie-layer and seal layer is equivalent to 3-20 g / m. This multilayer sheet is prepared by extrusion or coextrusion coating.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
Ticking Layers that Reduce Flame Propagation and Upholstered Articles Incorporating Same
InactiveUS20110283458A1Prevent and reduce flame propagationReduce riskLiquid surface applicatorsStuffed mattressesFlame propagationGas phase
A method of producing a ticking includes laminating a flame retardant backer to film material, wherein the backer releases flame retardant in the vapor phase that reduces the rate of flame propagation along the film material, when the ticking layer is exposed to flame. The backer is laminated in direct contact with the film material. In some embodiments, the laminated ticking is configured to release less than 15 MJ of heat in the first ten minutes when exposed to a flame in accordance with the testing protocol set forth in 16 CFR 1633. Upholstered articles, such as mattresses, mattress foundations, and articles of furniture, may incorporate the ticking layer.
Owner:PRECISION FABRICS GROUP
Cellular structures with fourteen-cornered cells
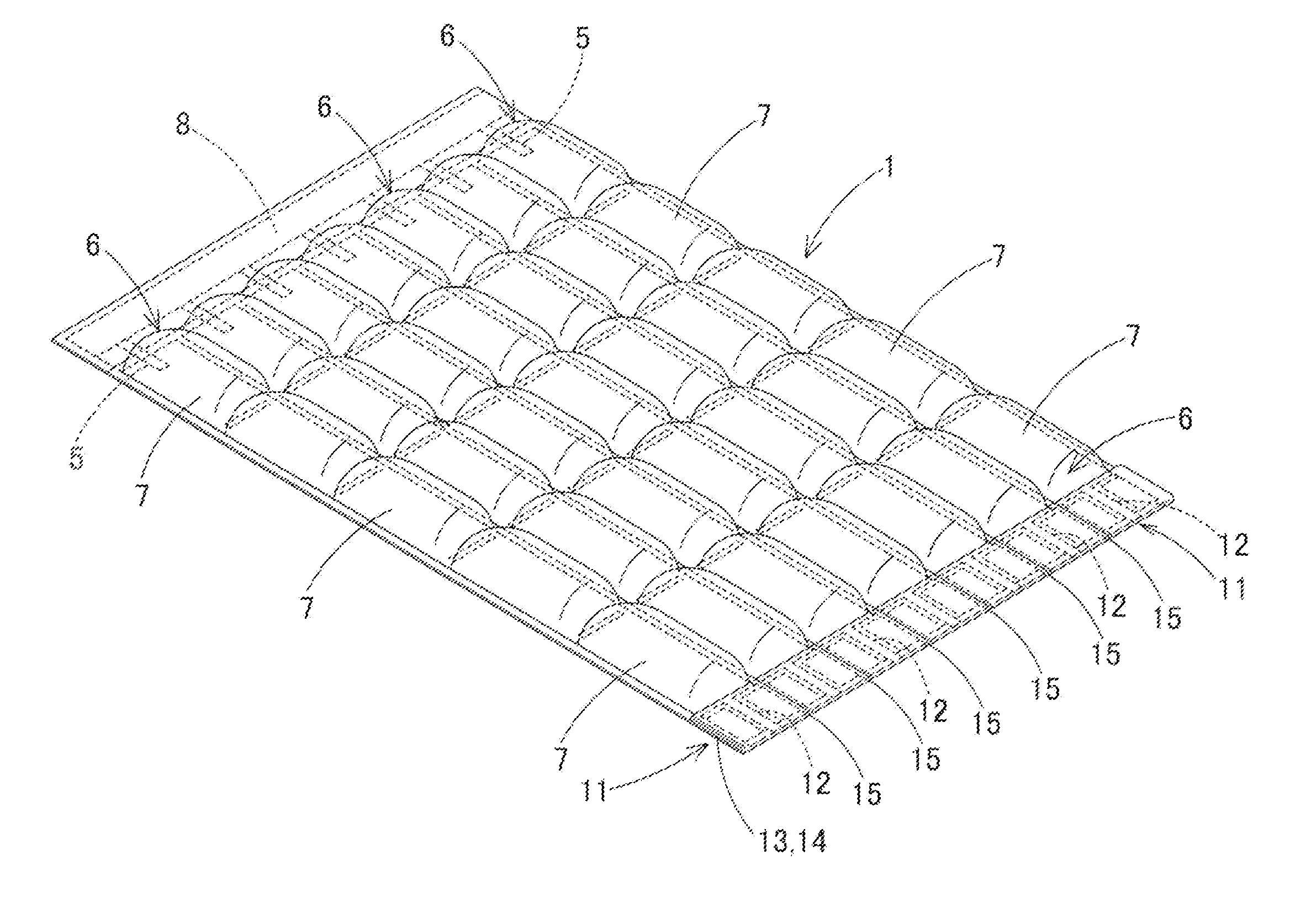
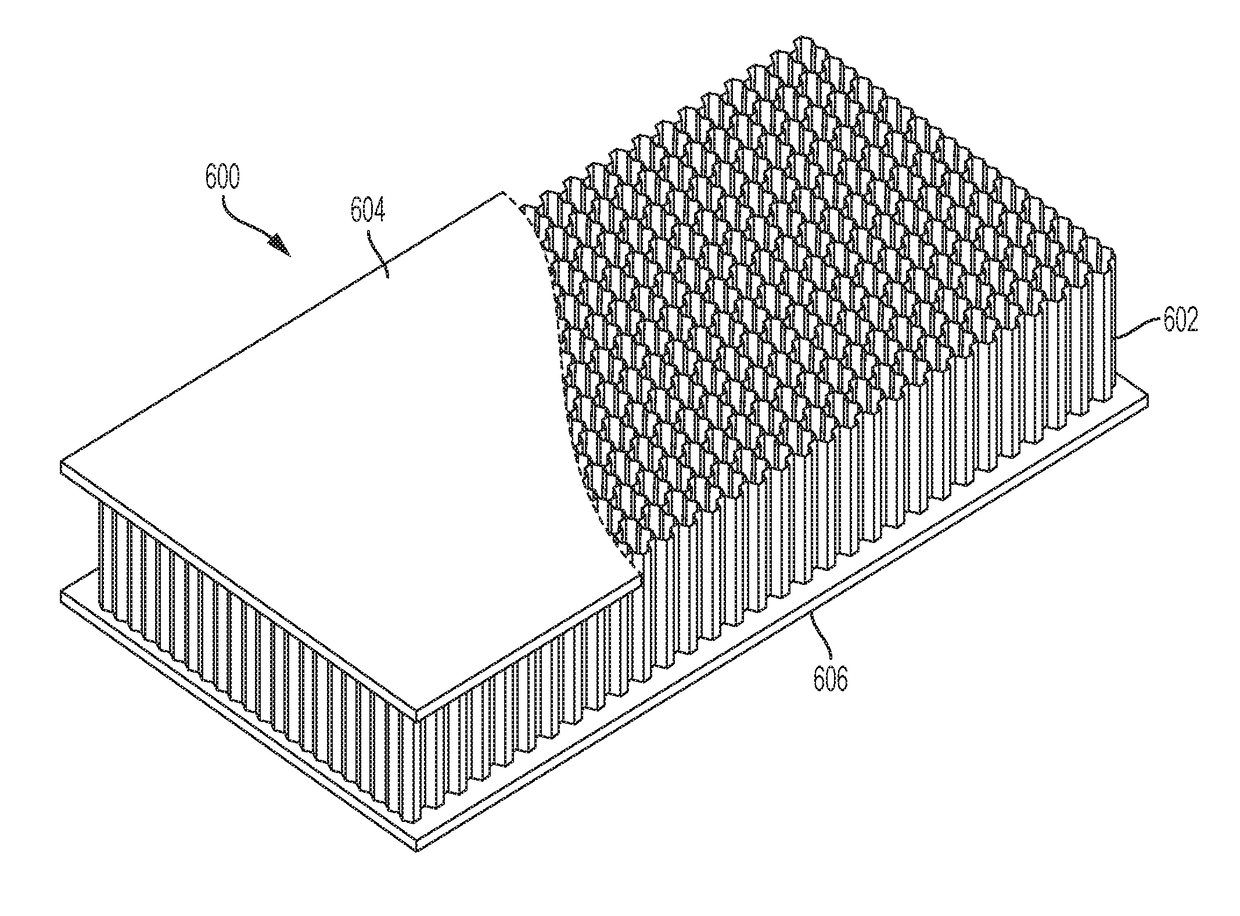
ActiveUS20180057060A1Reduce distanceImprove energy absorptionDomestic upholsteryUnderstructuresEngineeringCell structure
A cellular structure may include a plurality of cells each cell of the plurality of cells having a fourteen-cornered cross section. The fourteen-cornered cross section may include fourteen sides and fourteen corners. Each cell may include a plurality of longitudinal walls extending between a top and a bottom of the cell, the longitudinal walls intersecting to create corners of the cell.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Engineered toweling
The present invention is directed to articles of manufacture for drying or wiping a surface or protecting a surface from soiling. In one embodiment, a seat cover is described. In another embodiment, a fishing chap is described. In still another embodiment, a wiping and cleaning article is described.
Owner:KATSIN DANIEL H
Composite material
A composite material comprising a first layer which comprises a surfactant component, surfactant-generated microcells, a gel catalyst component and a binder component, and a second layer which comprises a metallic component is provided. The first layer may further comprise a filler component. In addition, the composite material may further comprise a substrate to which the first layer is adhered. The composite materials have heat insulating and fire resistant characteristics and are particularly suited for use in building materials and mattresses.
Owner:ELCOR CORP
Multi-Layer Sheet Material and Method for the Production thereof
InactiveUS20120258303A1Reduced tendency toward yellowingImprove the immunityLamination ancillary operationsDomestic upholsteryCalcium hydroxidePlasticizer
A multi-layer sheet material includes at least one textile substrate layer, at least one foamed layer made of polyvinyl chloride containing plasticizer, at least one cover layer made of polyvinyl chloride containing plasticizer, and at least one coating layer facing outward on the cover layer. The invention further relates to a method for producing the multi-layer sheet material and to an interior trim part made of a sheet material for a vehicle. For a reduced tendency to yellow under high-temperature aging and for greater color fastness, the polyvinyl chloride fraction in the cover layer is based at least 50 wt% on a polyvinyl chloride that was produced according to the method of suspension polymerization (S-PVC), and the composition for the cover layer comprises a calcium hydroxide stabilizer and / or a Ca / Zn stabilizer that contains 1 to 3 wt% calcium and 1 to 2 wt% zinc.
Owner:BENECKE-KALIKO
Reinforced nonwoven fire blocking fabric having ridges and grooves and articles fire blocked therewith
ActiveUS7247585B2Increasing the thicknessStuffed mattressesDomestic upholsteryPolymer scienceFire-retardant fabric
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Flame resistant matelasse fabrics utilizing spun and filament flame resistant yarns
InactiveUS20070004302A1Efficient use ofReduce flammabilityWeft knittingDomestic upholsteryConus californicusUpholstered furniture
The invention relates to the use of a flame resistant (FR) three-layer double-knit fabric, also know as a matelasse fabric. The top layer is of standard non-FR face yarn, the middle layer is of a FR filler spun yarn and the bottom layer is of a FR spun yarn or FR filament yarn. This FR matelasse fabric can be used to protect a mattress, foundation, upholstery cushion, pillow, office panel, transportation seat or any other article requiring FR protection. In this invention, a matelasse fabric is formed by circular double knitting a FR spun or FR filament yarn into the bottom portion of the fabric, utilizing a heavy cotton count FR filler spun yarn for the middle layer and using conventional non-FR yarns for the top layer. The invention has particular applicability in the formation of FR mattresses and foundations that require passage of large open flame tests such as CPSC's 16 CFR Part 1633, California's Test Bulletin 603 and Test Bulletin 129 and in the formation of FR upholstered furniture that requires passage of California's Test Bulletin 133 or British Standard 5852 using the crib 5 ignition source or higher.
Owner:MCKINNON LAND
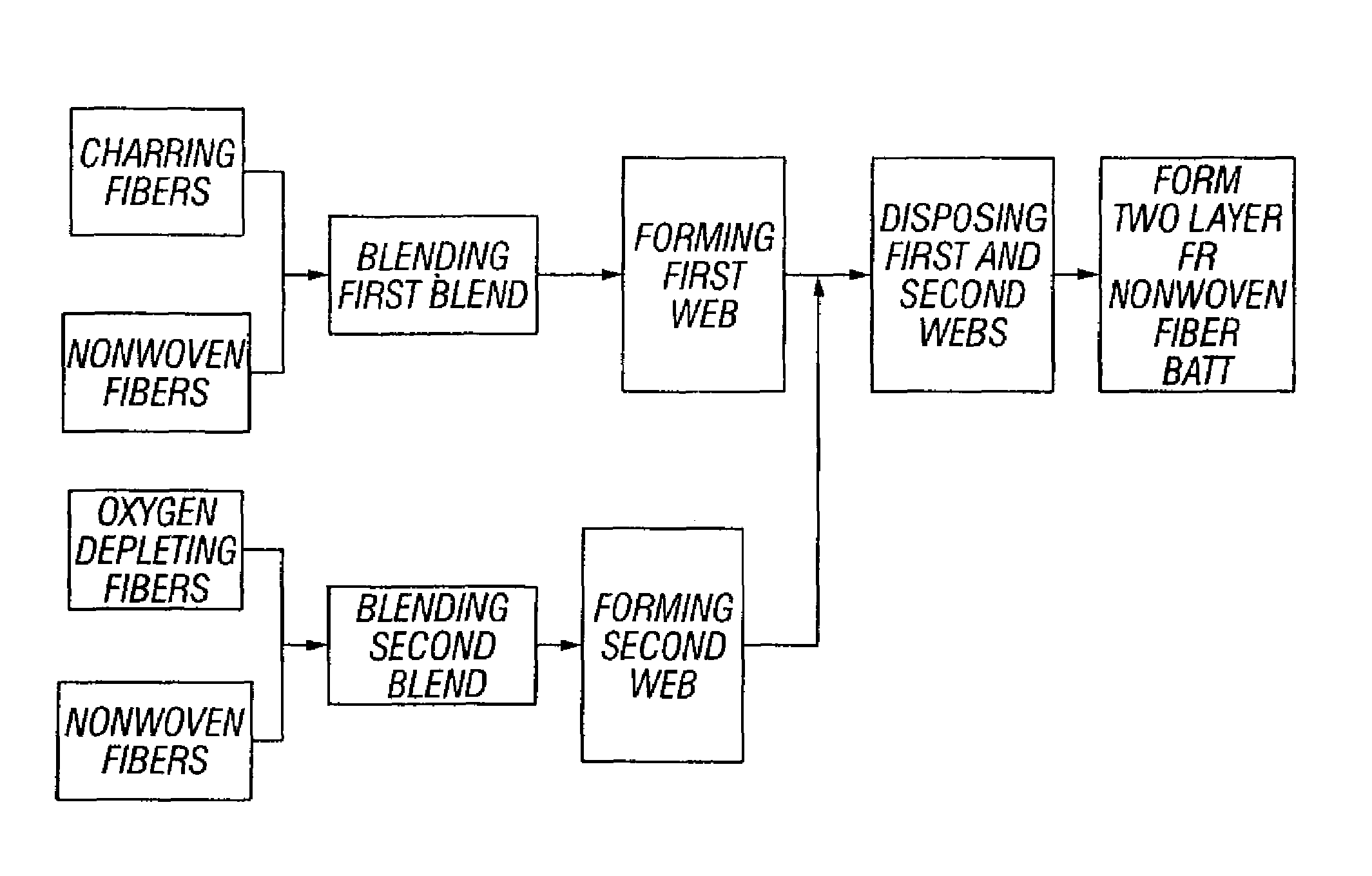
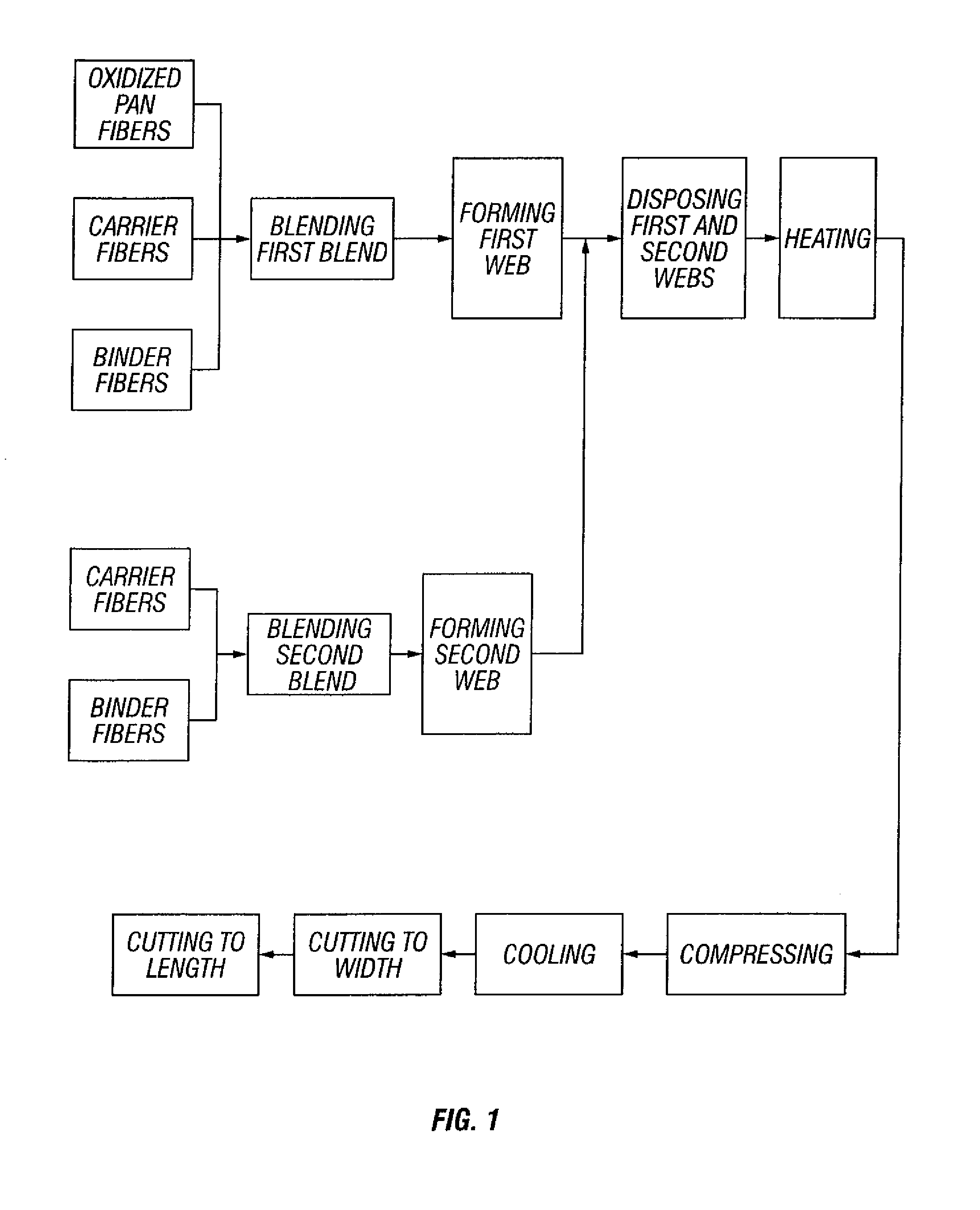
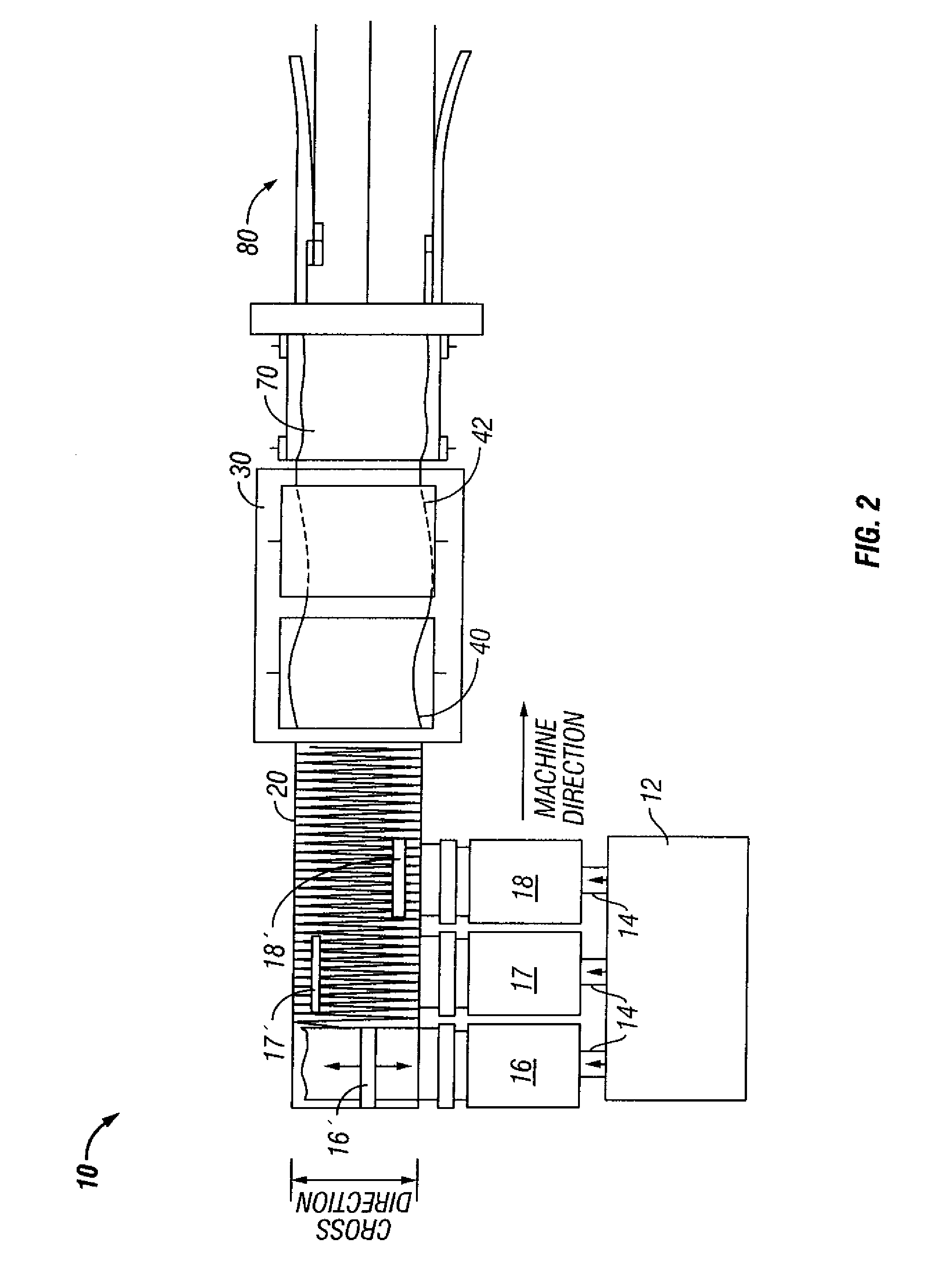
Fire resistant nonwoven batt having both charring and oxygen-depleting fibers
Owner:POLYESTER FIBERS LLC
Slickened or siliconized flame resistant fiber blends
InactiveUS7589037B2Desirable soft and comfortable propertyLess testingDomestic upholsteryFibre treatmentFiberPolymer science
Owner:BEIJING CARINAE MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Core material for cushion, and cushion
ActiveCN105377083AInhibition of contractionHigh Thermal Expansion PropertiesStuffed mattressesDomestic upholsteryHysteresisPolyester
The present invention provides a hygienic cushion which can be washed in water, exhibits excellent air permeability, and is light while exhibiting body-shape retention and exerting a resiliency force no less than a given standard at an appropriate thickness. A core material (1) for a cushion, wherein: one surface or both surfaces of a first layer in a three-dimensional mesh structure, said first layer being formed from a polyethylene-based thermoplastic resin, a polyester-based thermoplastic elastomer, or a mixture of a polyethylene-based thermoplastic resin and a polyethylene-based thermoplastic elastomer, is / are laminated with a second layer containing a thermoplastic resin that is different from that of the first layer; the three-dimensional mesh structure has an impact resilience of 13cm or greater and a hysteresis loss of 13-34%; and the thermal elongation rate of the three-dimensional mesh structure in the lengthwise direction before and after a hot-air drying test is 0-8% after 30 minutes at 90 DEG C in the case of a polyethylene-based thermoplastic resin, after 30 minutes at 130 DEG C in the case of a polyester-based thermoplastic elastomer, or after 30 minutes at 90 DEG C in the case of a mixture of a polyethylene-based thermoplastic resin and a polyethylene-based thermoplastic elastomer.
Owner:C ENG CO LTD
Active self-transformable textiles
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Phase change material (PCM) compositions for thermal management
InactiveUS8333903B2Domestic upholsteryHeat-exchange elementsLow-density polyethyleneVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to a Phase Change Material (PCM) composition comprising a) from 20 to 80 wt % of a PCM; and b) from 20 to 80 wt % of one or more polymers chosen from the group consisting of b1) Very Low Density Polyethylene (VLDPE) having a density equal or lower than 0.910 g / cm3 measured according to ASTM 792; b2) Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) having a density equal or lower than 0.900 g / cm3 measured according to ASTM 792; b3) Styrene Ethylene Butadiene Styrene (SEBS) copolymers; and b4) Styrene Butadiene Styrene (SBS) copolymers. The PCM composition of the present invention can be used in applications where thermal management is needed, like for example in building, automotive, packaging, garments and footwear.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com