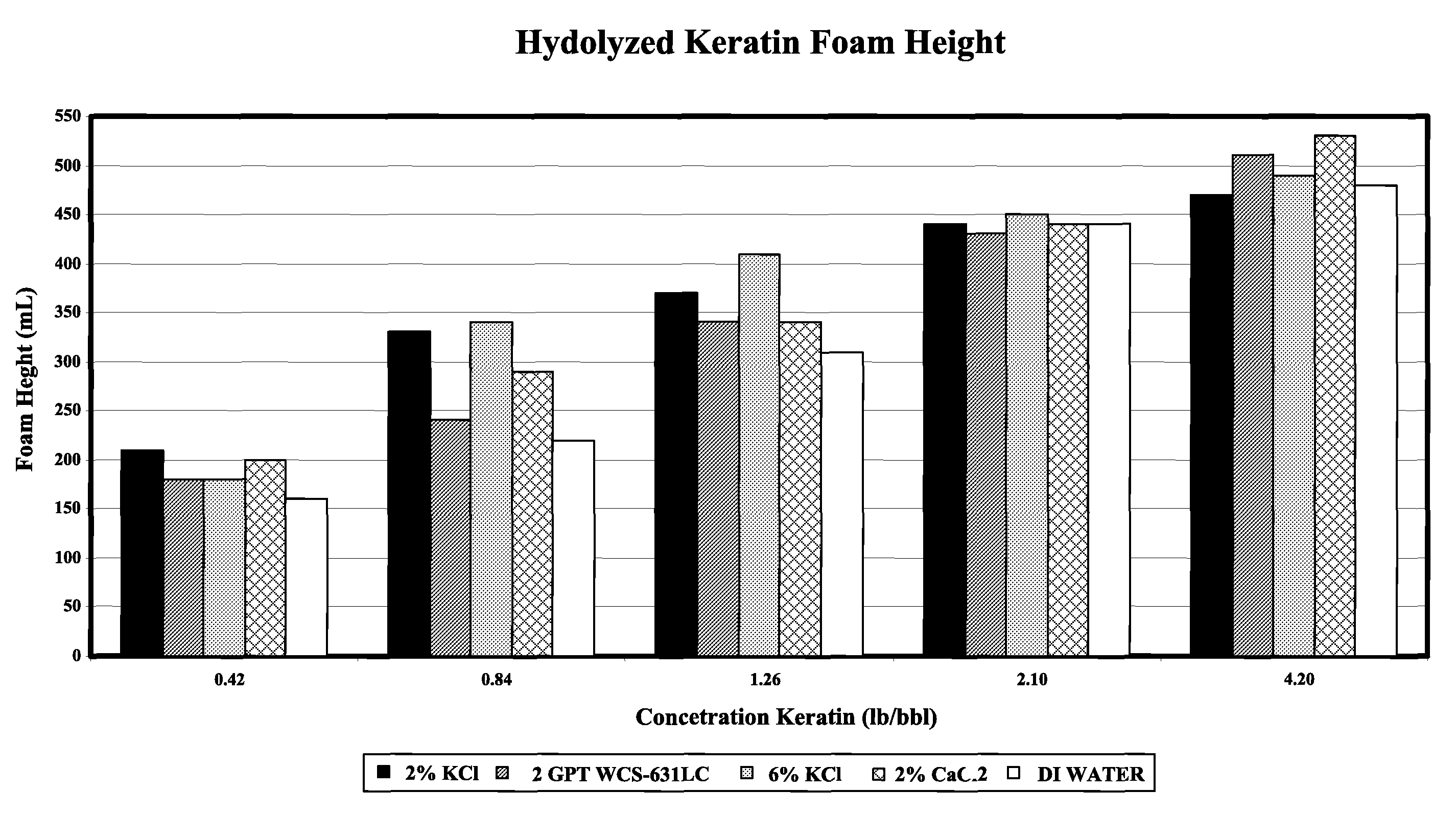
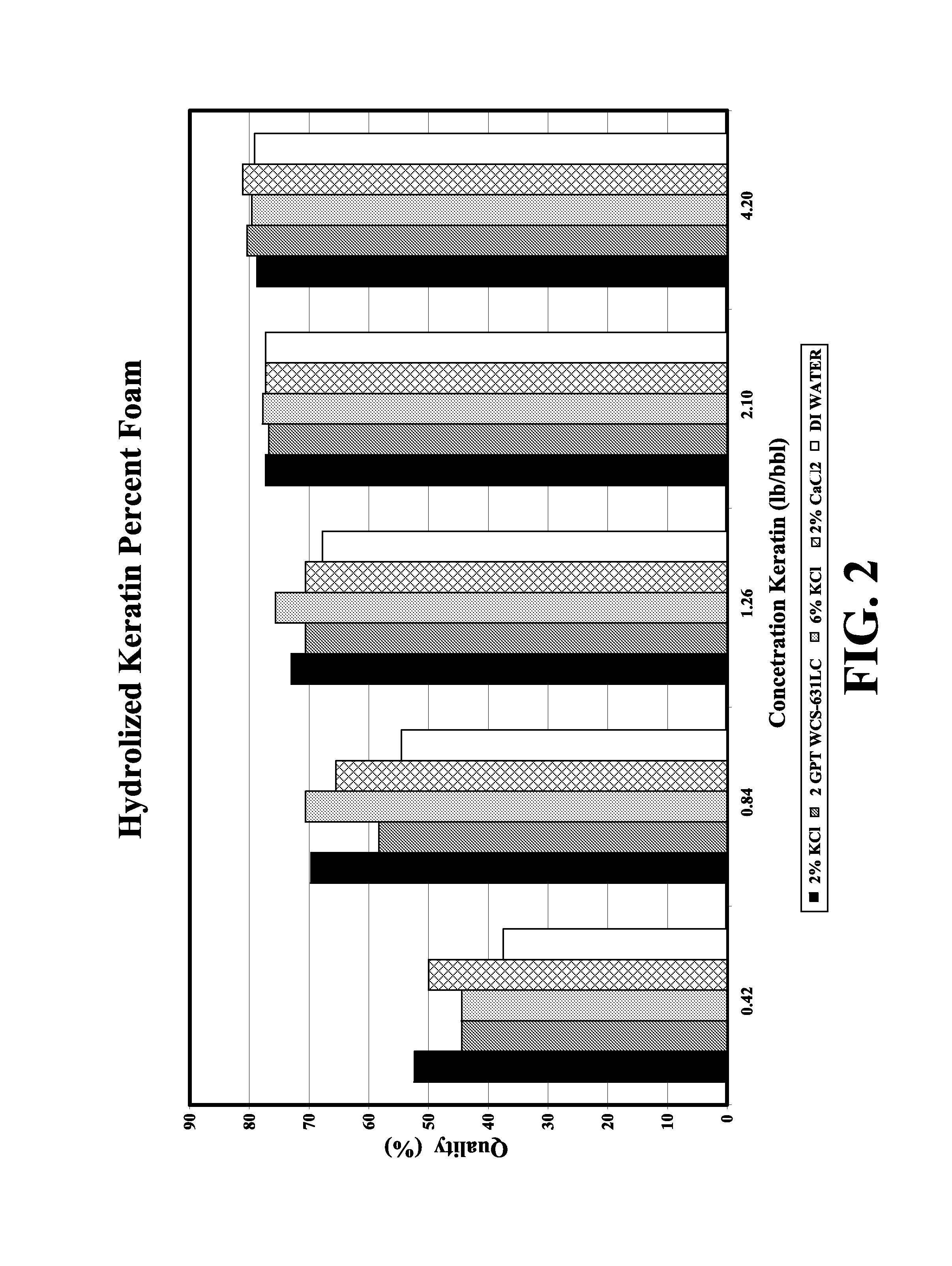
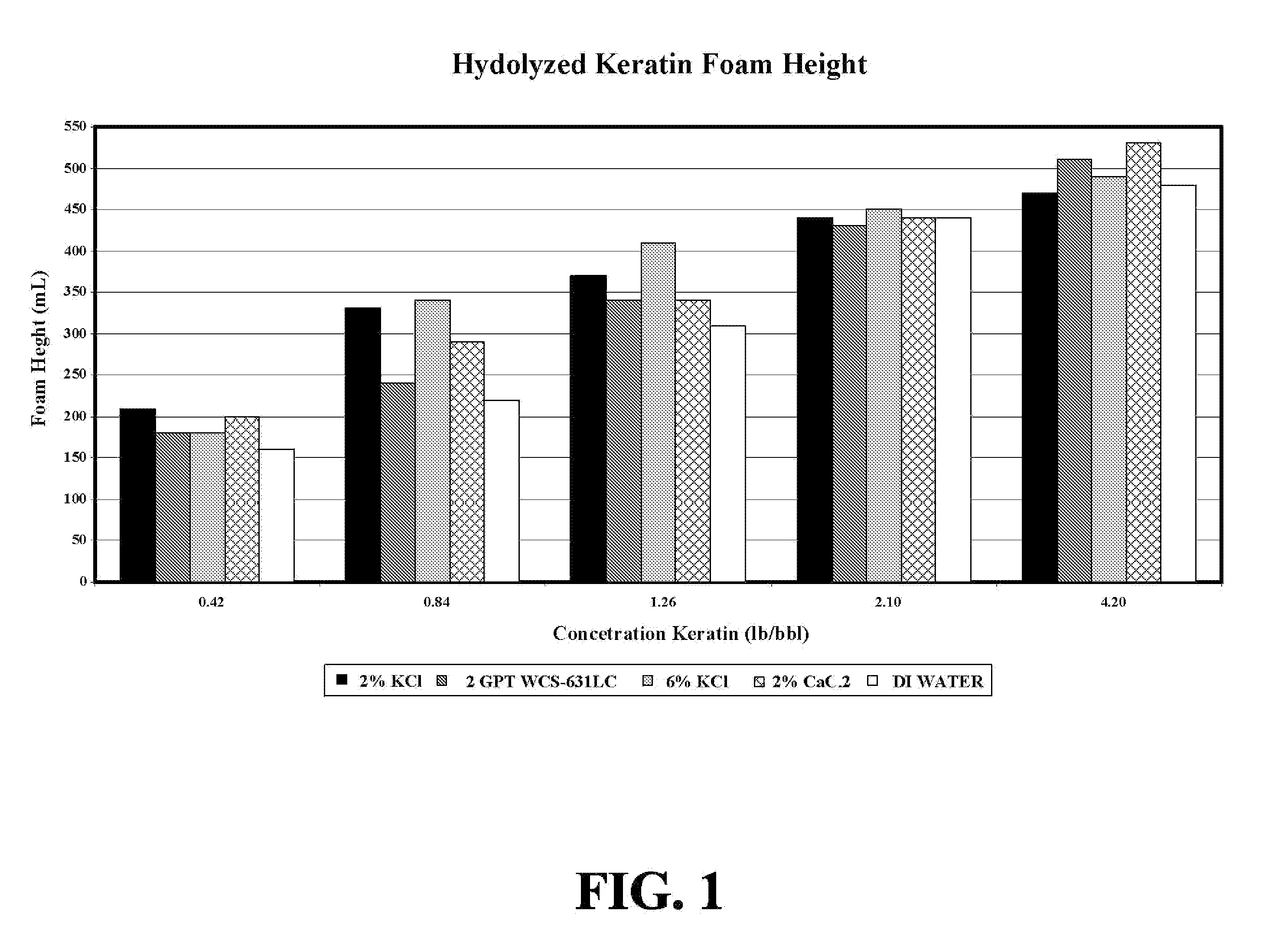
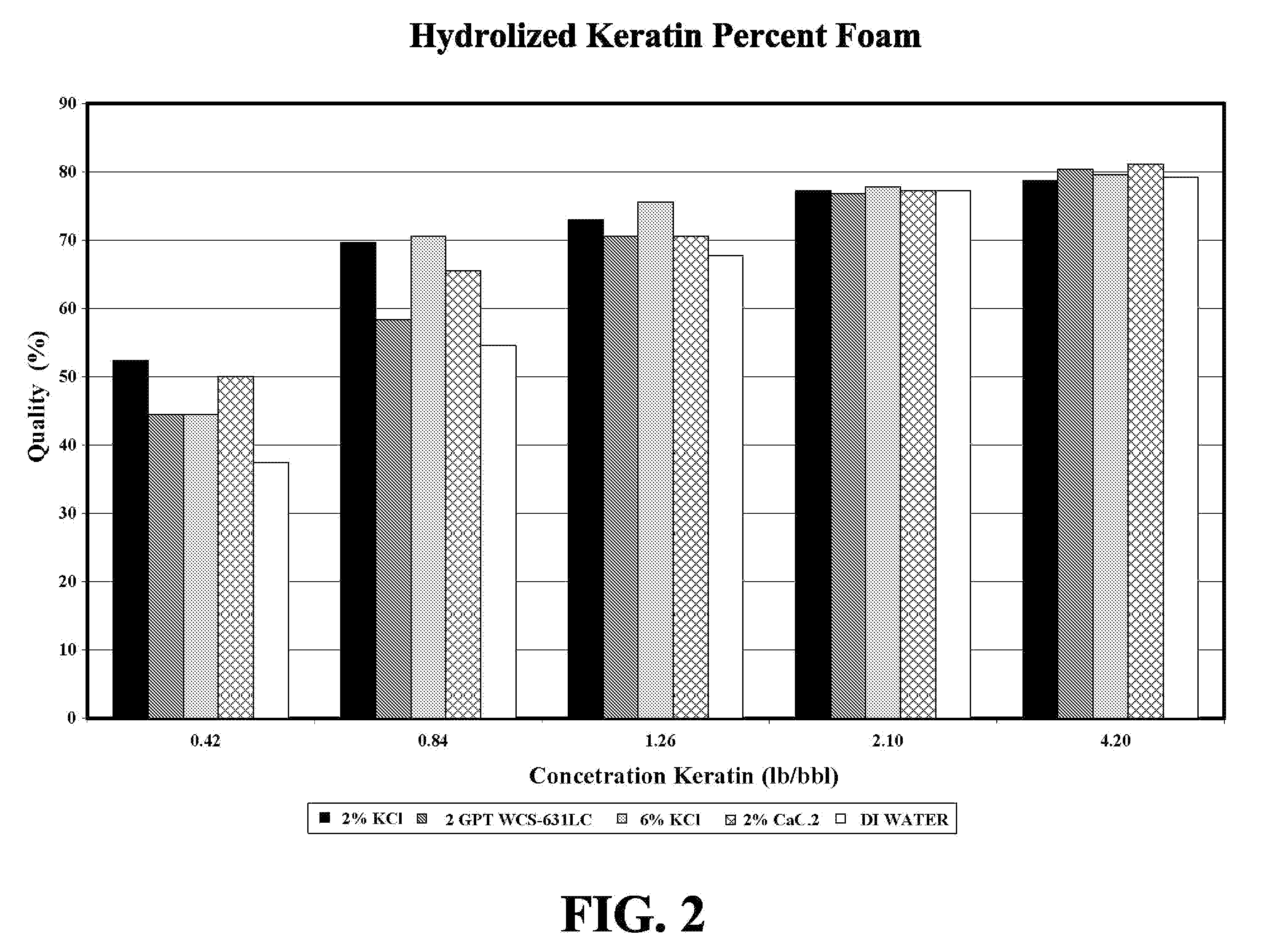
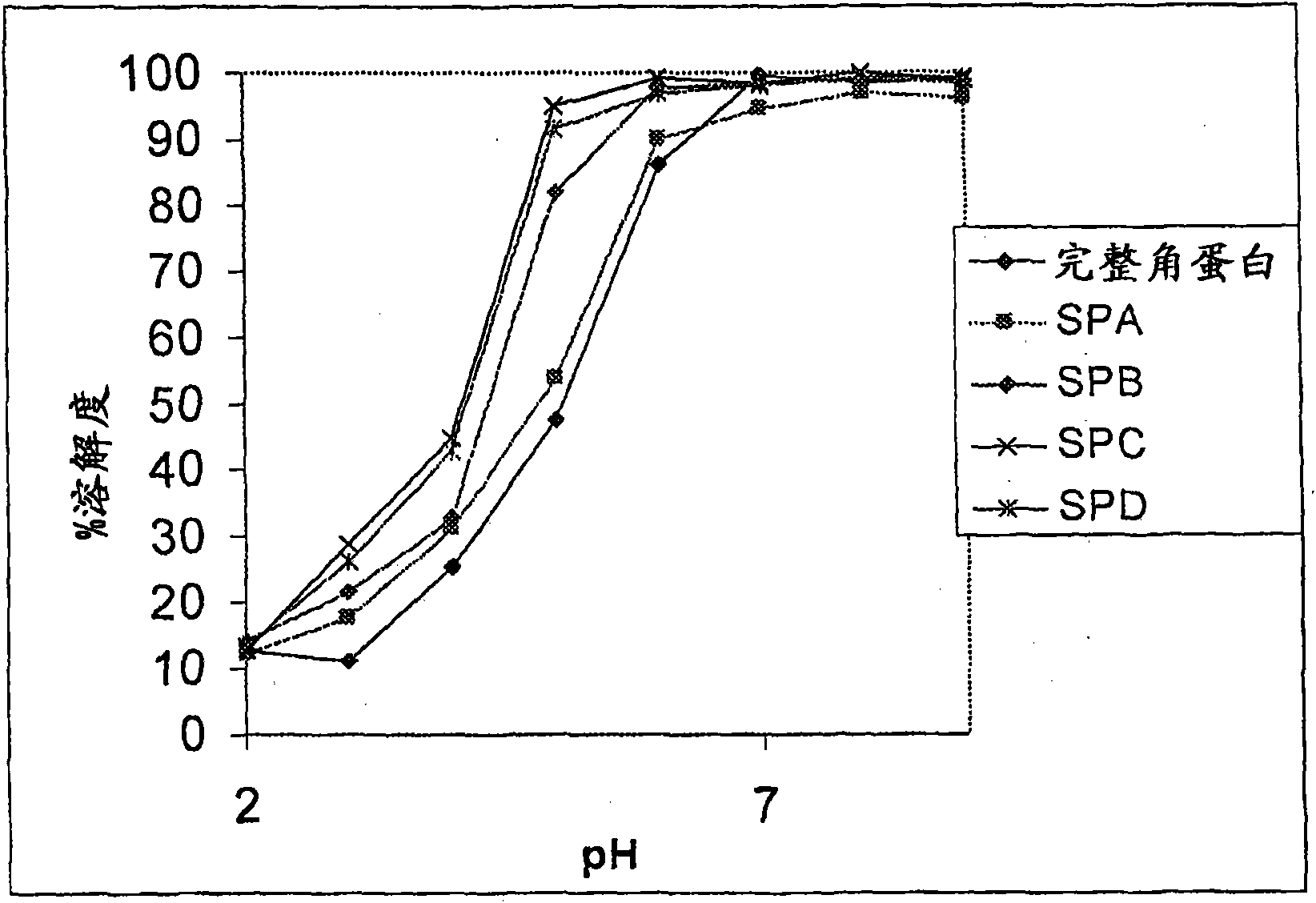
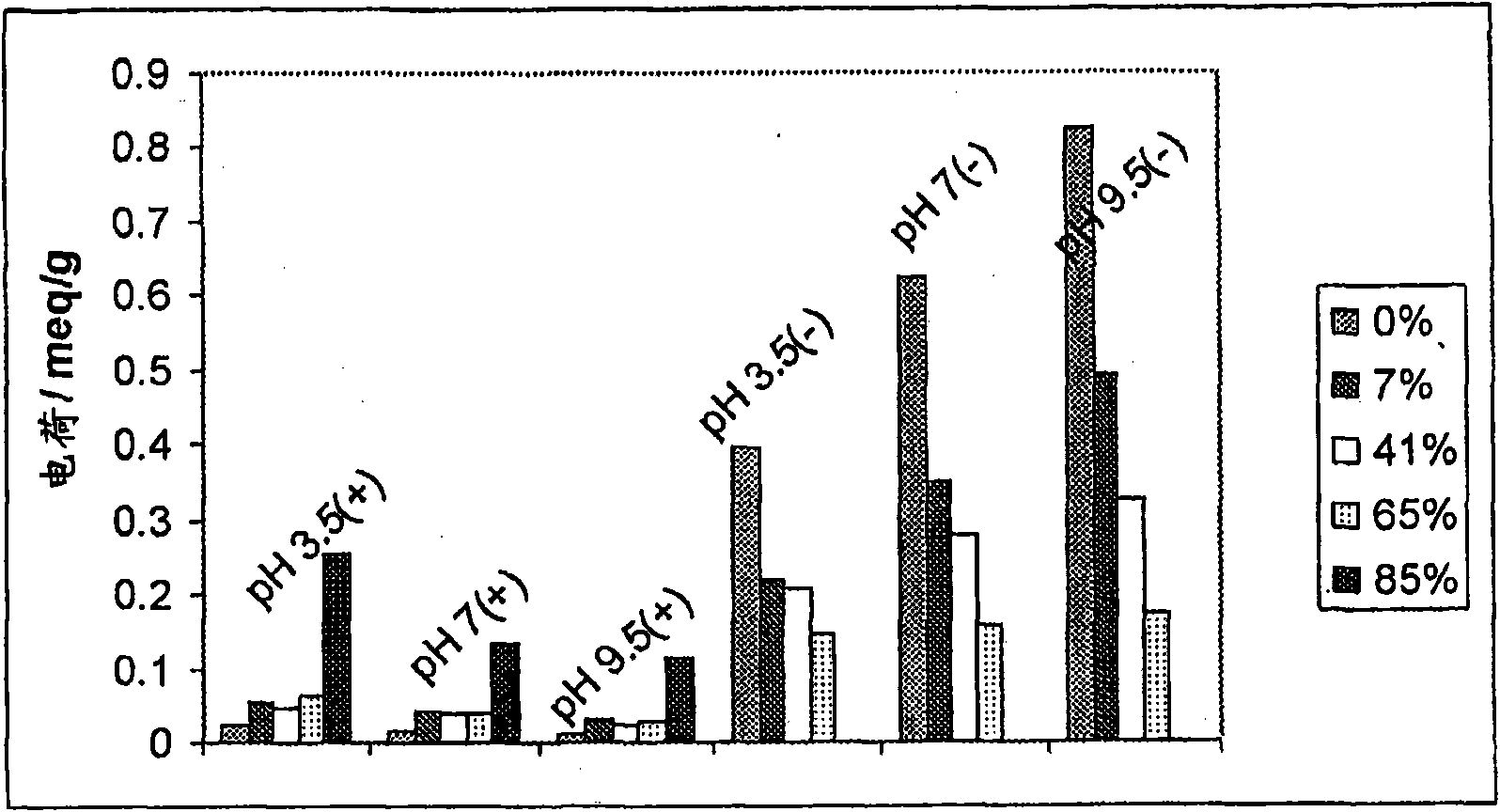
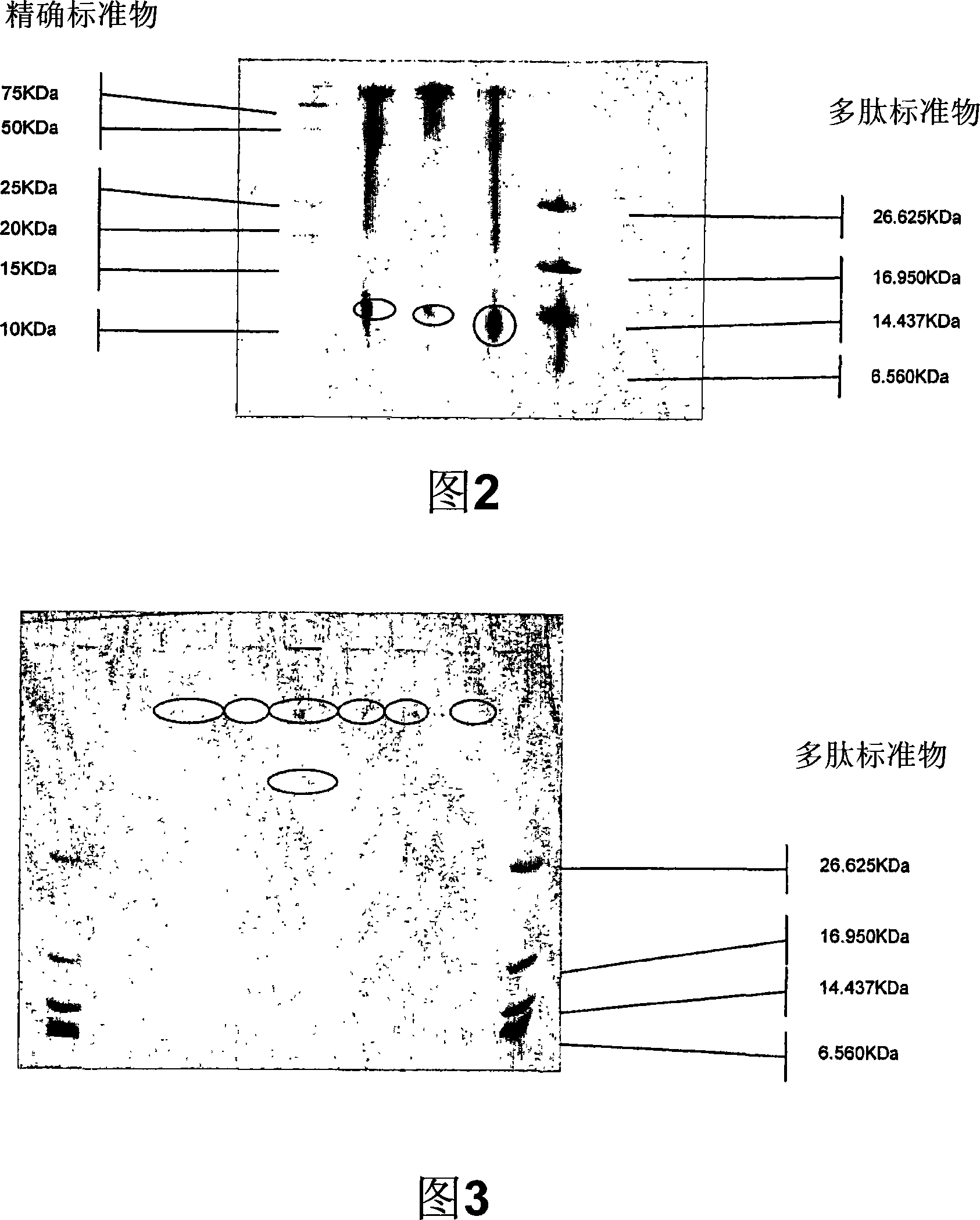
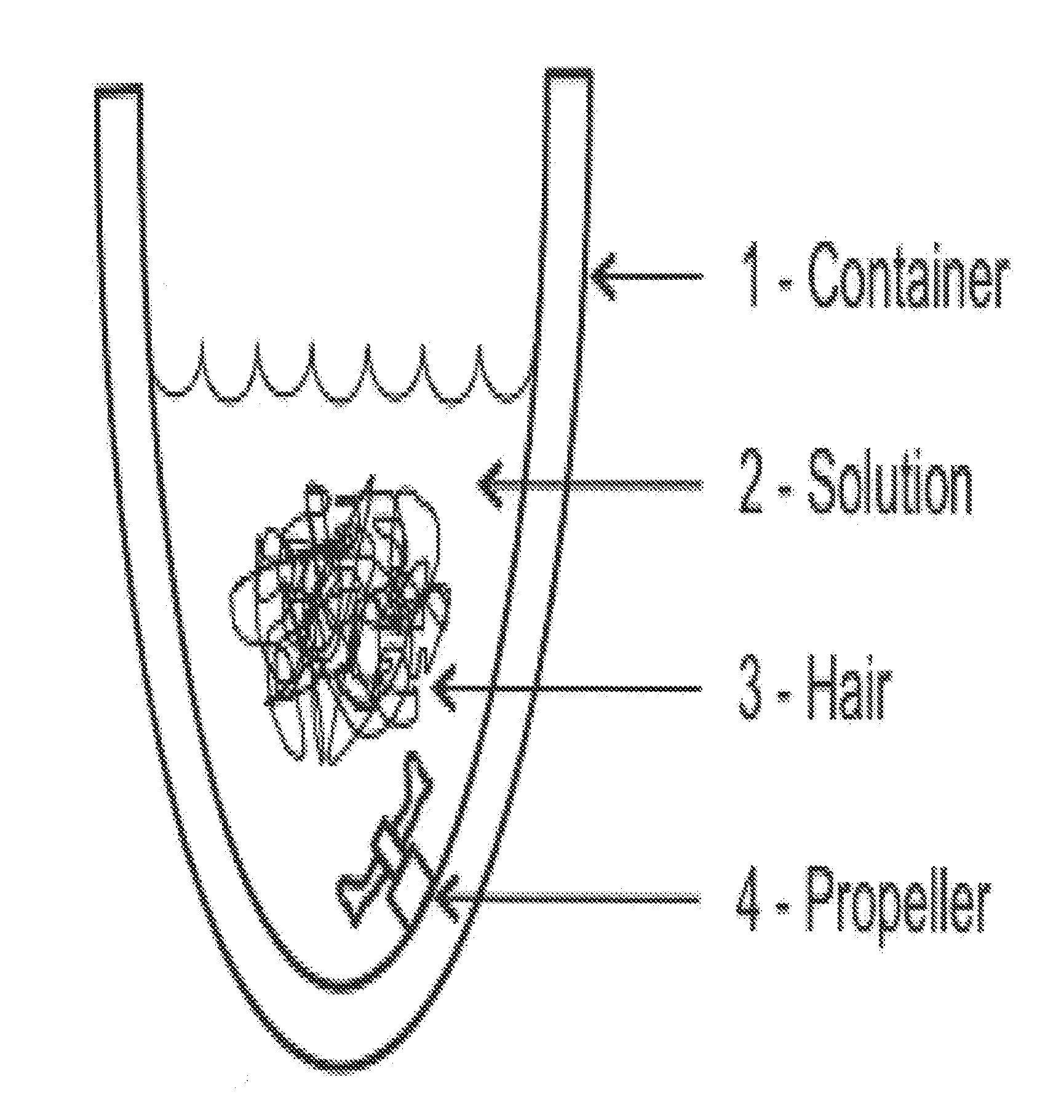
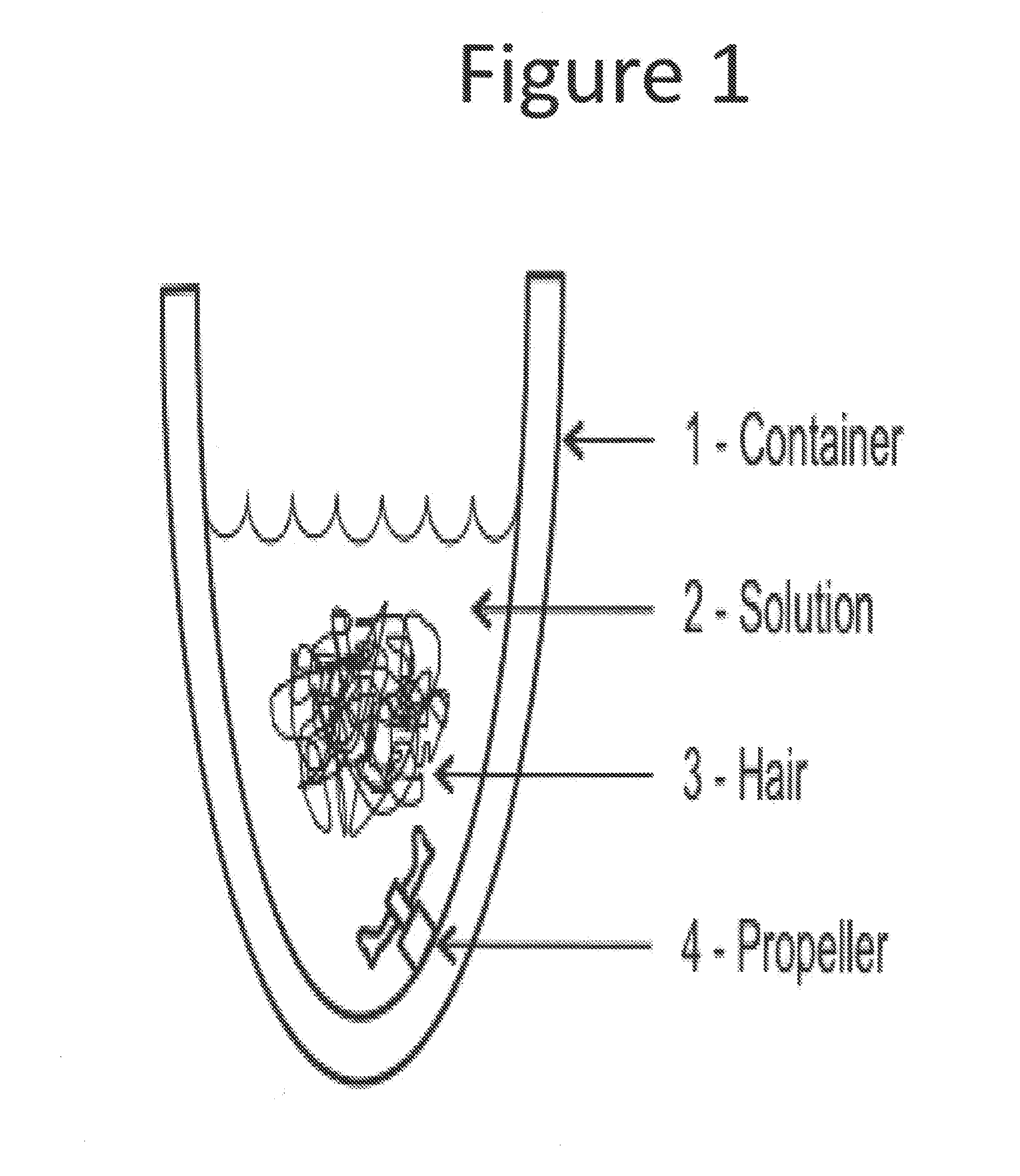
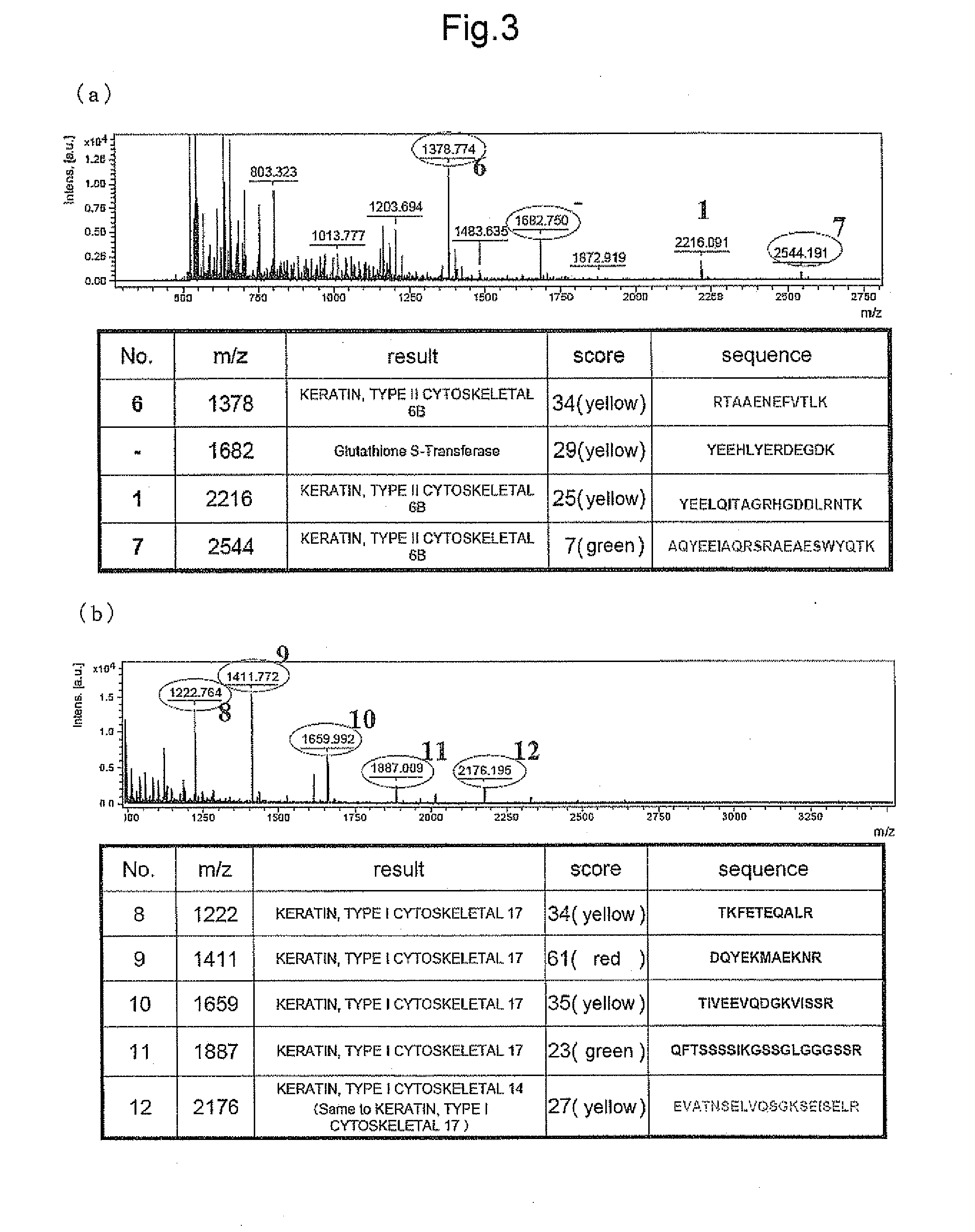
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130results about "Cytokeratin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Production of soluble keratin derivaties
InactiveUS7148327B2Low costReduce impactPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSulfurIntermediate Filament Protein
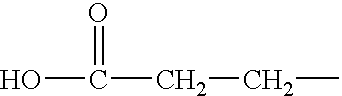
A process for the preparation of soluble proteins of high molecular weight with little or no damage to the structural integrity of the proteins. The process is economically and environmentally acceptable by virtue of the cost of reagents that are used, and the recycling of some of those reagents, and is suitable for the production of soluble proteins on a large scale. The process includes a first stage using oxidative sulfitolysis followed by a second stage using mild conditions to extract the soluble protein. In the case of wool as the protein source the process leads to the production of soluble keratin proteins fractionated into the classes S-sulfonated keratin intermediate filament proteins and S-sulfonated keratin high sulfur proteins.
Owner:KERATEC LTD
Foamed fluid additive for underbalance drilling
A method of drilling or gas-lifting is disclosed where the methods including the use of a foaming agent and a gas, where the foaming agent is a keratin and the hydrostatic pressure of the fluid in the well is for a portion of the drilling or gas-lift operation less than an hydrostatic pressure of the formation being drilled or under production.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Foamed fluid additive for underbalance drilling
A method of drilling or gas-lifting is disclosed where the methods including the use of a foaming agent and a gas, where the foaming agent is a keratin and the hydrostatic pressure of the fluid in the well is for a portion of the drilling or gas-lift operation less than an hyrdrostatic pressure of the formation being drilled or under production.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Polytetrafluoroethylene binding peptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20080207872A1Cosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding peptideComputational chemistry
Combinatorially generated peptides are provided that have binding affinity for Polytetrafluoroethylene (NY). The peptides may be used to deliver benefit agents to various PTFE surfaces.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Polytetrafluoroethylene binding peptides and methods of use
InactiveUS7700716B2Cosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding peptideComputational chemistry
Combinatorially generated peptides are provided that have binding affinity for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The peptides may be used to deliver benefit agents to various PTFE surfaces.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Coatings and Biomedical Implants Formed From Keratin Biomaterials
ActiveUS20090004242A1Inhibit blood coagulationPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgeryFractionationBlood coagulations
Methods are provided to produce optimal fractionations of charged keratins that have superior biomedical activity. Also provided are medical implants coated with these keratin preparations. Further provided are methods of treating blood coagulation in a patient in need thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Novel hair keratin-associated proteins
InactiveUS20050170366A1Promoting and suppressing expressionPromoting and suppressing expression of proteinCosmetic preparationsBacteriaKeratin-Associated ProteinsProteome
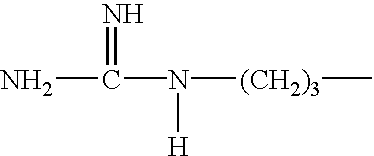
The present invention relates to provide a protein group binding to keratin which is the major component of body hair, or genes encoding the same, particularly to keratin-associated proteins (KAP) which bind specifically and strongly to hair keratin or genes encoding the same. The base sequence of eurochromtic region of approximately 33.5 Mb of human chromosome 21 was determined, a dot-matrix analysis of the base sequence of the long arm region of chromosome 21 (21q22.3) was carried out, homology search was made to low frequency repetitive sequences and 16 KAP genes being expressed only in hair root cells were found. Moreover, the high frequency repetitive sequences present in the sequence spanning for approximately 1 Mb between CLDN8 gene and TIAM1 gene in the long arm region of chromosome 21 (21q22.11) were masked, the presence or absence of short low frequency repetitive sequence was searched, and 22 KAP genes were found. Moreover, a group of functional peptide was designed from the above mentioned KAPs.
Owner:SHIMIZU NOBUYOSHI
Keratin derivatives and methods of making the same
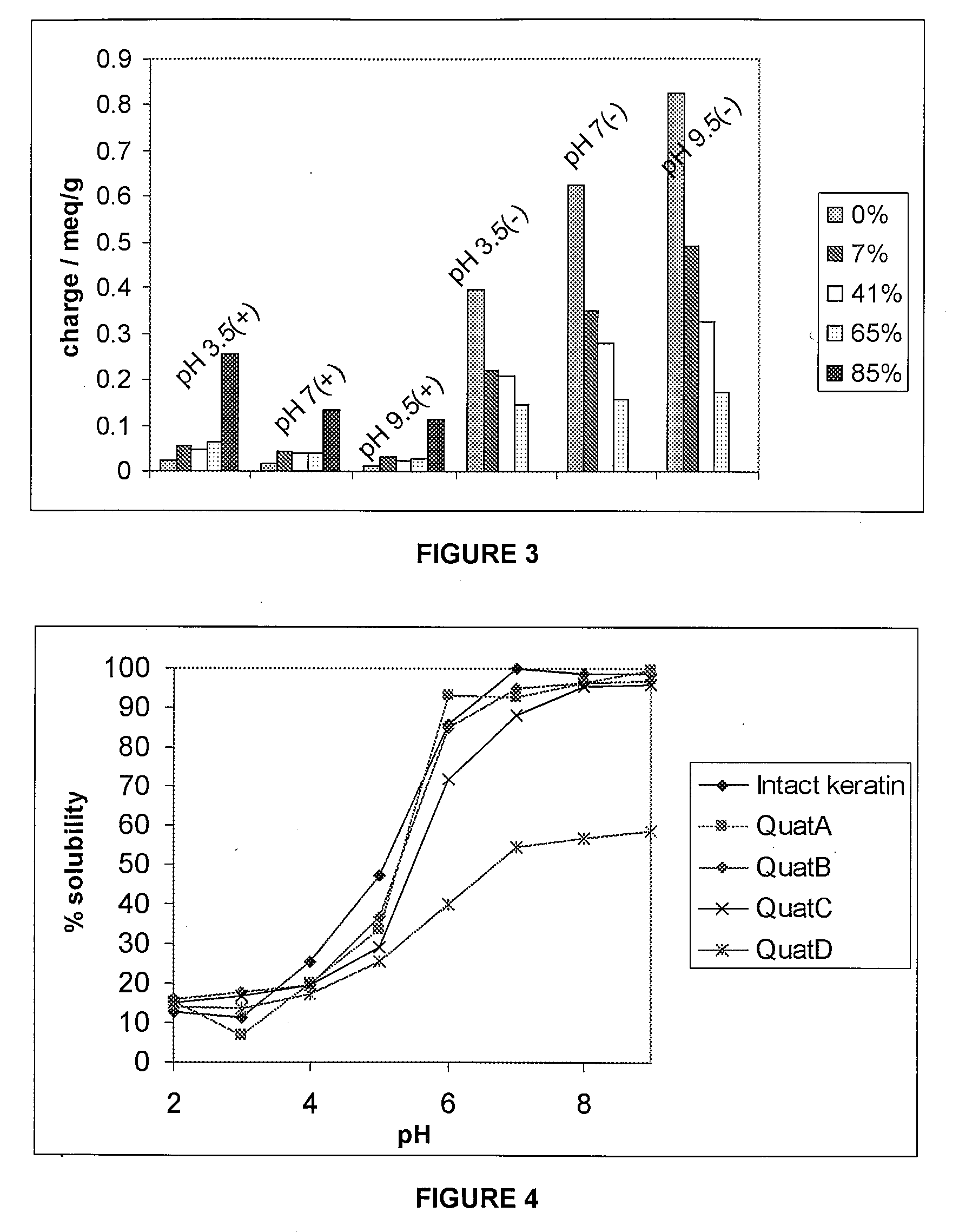
InactiveUS20090111750A1Excessive chargingNegatively chargedCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsPersonal careSuccinylation
Soluble keratin derivatives are disclosed. The soluble keratin derivatives may include a soluble keratin protein having at least one substituted chemical group at a lysine group, terminal amine group and / or hydroxyl amino acid group of a soluble keratin protein. Soluble keratin derivatives may be formed by succinylation or quaternisation, or by reaction with fatty acid derivatives. The soluble keratin derivatives may be used in personal care formulations, and may also comprise mixtures of several different soluble keratin derivatives.
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Process For Producing Solubilized Keratin
InactiveUS20070207111A1Increase valueEfficient hydrolysisCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsHydrolysisWater content
A process for producing a solubilized keratin of utility value easily with high yield while suppressing coloration and smelling occurring in the hydrolysis of keratin. There is provided a process for producing a solubilized keratin, characterized in that it comprises regulating the water content of keratin raw material to a hydrous state of 20 to 80%, hydrolyzing the same in an alkali solution, neutralizing the hydrolyzate liquid, and extracting a keratin hydrolyzate from the supernatant.
Owner:NOKODAI TLO KK
Methods for producing, films comprising, and methods for using heterogeneous crosslinked protein networks
InactiveUS6989437B2Efficiently formedCosmetic preparationsHydrolysed protein ingredientsProtein networkSilicone
Methods for producing biocompatible heterogeneous proteinaceous networks crosslinked with a heterogeneous crosslinking agent, and novel heterogeneous crosslinked networks. Preferred heterogeneous crosslinking agents are silicone-based.
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Methods for producing, films comprising, and methods for using heterogenous crosslinked protein networks
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Bioactive keratin peptides
Compositions containing biologically active peptides are disclosed. Active peptides are isolated fragments derived from human hair or sheep wool keratin proteins. Compositions may be prepared for pharmaceutical or topical administration or for use in cosmetic preparations.
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Monoclonal antibody against CK8 protein and cell strain, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112940118AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisAntigenWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a monoclonal antibody capable of recognizing a human leukocyte differentiation antigen CK8, a secretory cell strain, a preparation method thereof and application in immunodetection. According to the technical scheme, 340-365 amino acid sequences at the C tail end of CK8 protein are selected as antigen peptides, and the antigen peptides are coupled with KLH carrier protein to obtain the immunogen; the amino acid sequence of the antigen peptide is shown as SEQID1, a mouse is immunized, and the mouse hybridoma cell strain 14C2 capable of efficiently secreting the anti-CK8 protein monoclonal antibody and the anti-CK8 protein monoclonal antibody secreted by the cell strain are obtained through cell fusion, screening and subcloning. The antibody obtained by the scheme has high specificity and sensitivity, can specifically recognize cells expressing the CK8 protein, and is suitable for immunological detection, especially immunohistochemical detection.
Owner:FUZHOU MAIXIN BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for preparing keratin by dissolving wool with deep-eutectic solvent
ActiveCN108467427AWide variety of sourcesLow pricePeptide preparation methodsCytokeratinOrganic acidFiltration
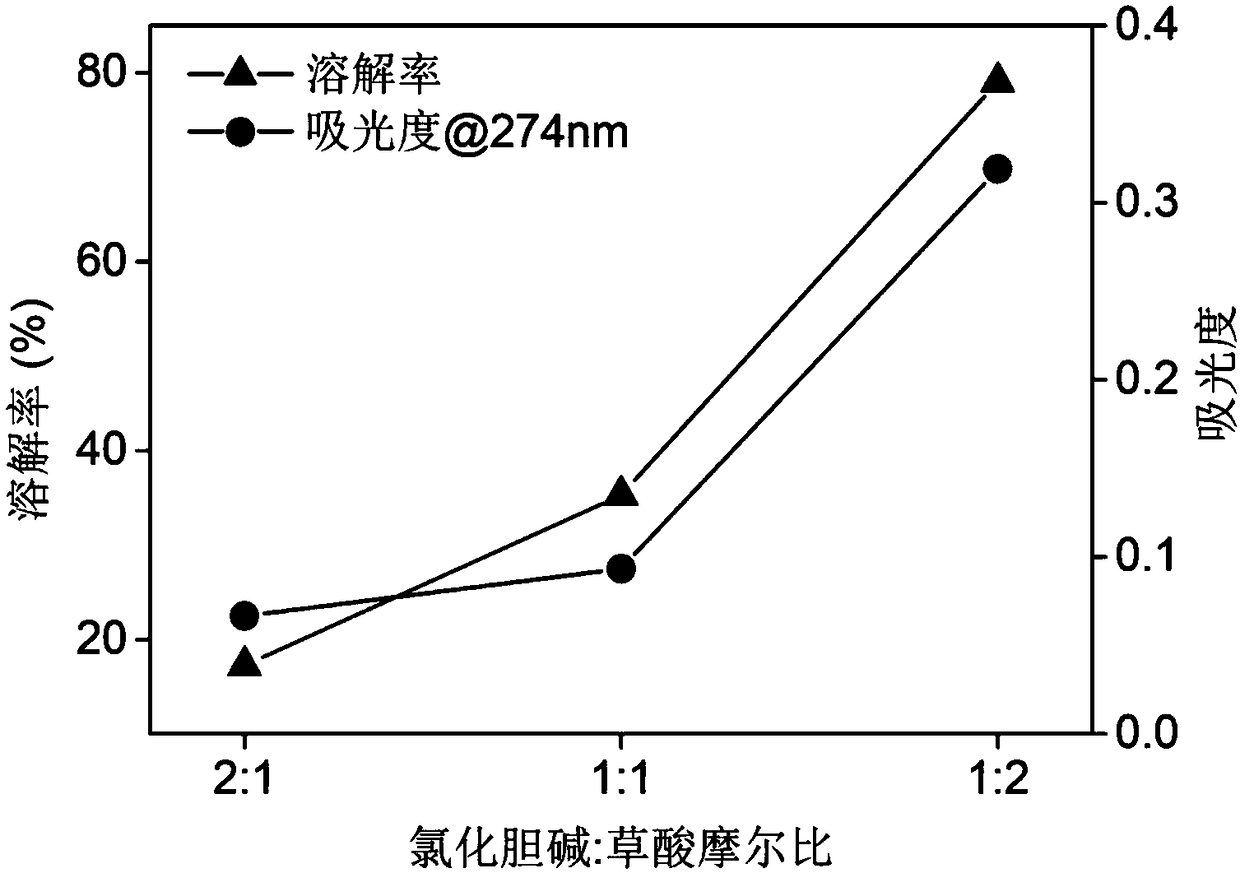
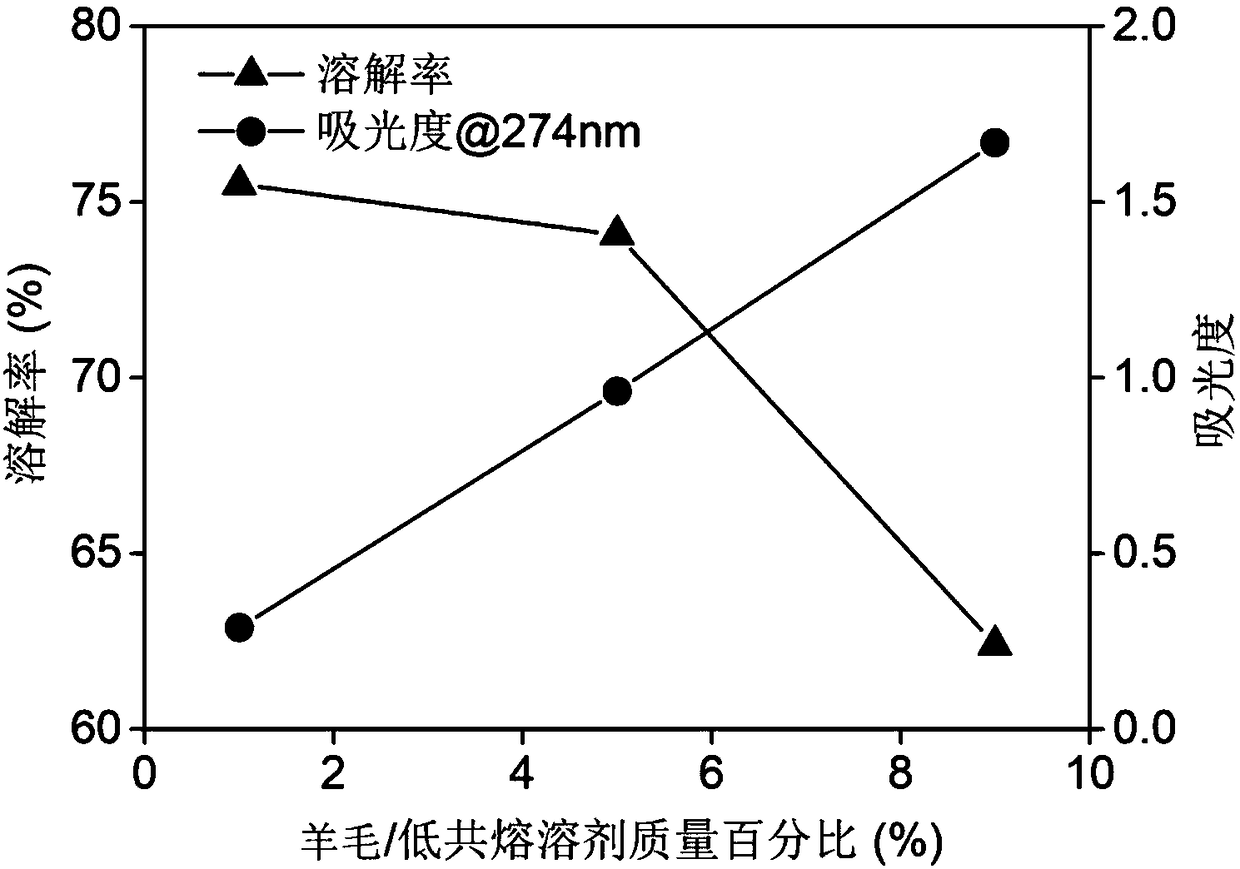
The invention relates to a method for preparing keratin by dissolving wool with a deep-eutectic solvent, the method comprises the steps of adding the wool to a choline eutectic solvent, dissolving at80 to 130 DEG C for 0.5 to 3 hours, and performing dialysis and filtration to obtain keratin contained in filtrate, wherein the choline eutectic solvent comprises a choline salt and an organic acid, and the molar ratio of the choline salt to the organic acid is 1:1-2. The deep eutectic solvent used in the method is a green additive, conforms to the concept of green environmentally-friendly chemistry, and the method has a short time for dissolving the wool and a high dissolution rate of the wool.
Owner:NANTONG TEXTILE & SILK IND TECH RES INST +1
Soluble human keratin and application thereof
ActiveCN110117323ADoes not damage the structurePreparation Method Green MildBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman bodyWound healing
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and particularly relates to soluble human keratin and application thereof. The soluble keratin is obtained through the following process of cloning amiddle sequence of a human gene K37, constructing a recombinant vector, transforming bacteria, inducing expression of the recombinant protein and purifying the recombinant protein to obtain the soluble keratin. The soluble keratin has the characteristic of rapid swelling and can promote mitosis and migration of epidermal cells, and therefore the soluble keratin can be used for preparing biologicalmaterials or medicaments for promoting cell proliferation or migration, and plays a role in hemostasis and wound healing. Moreover, the soluble keratin causes no rejection phenomenon when being usedfor the human body, is safe to use and thus has a wide application prospect in the field of biomedicine.
Owner:海默斯(重庆)医学生物技术有限公司
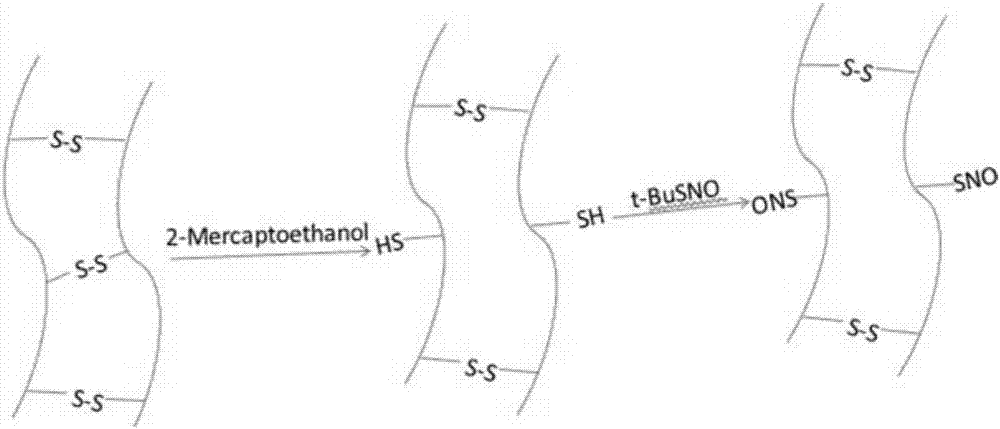
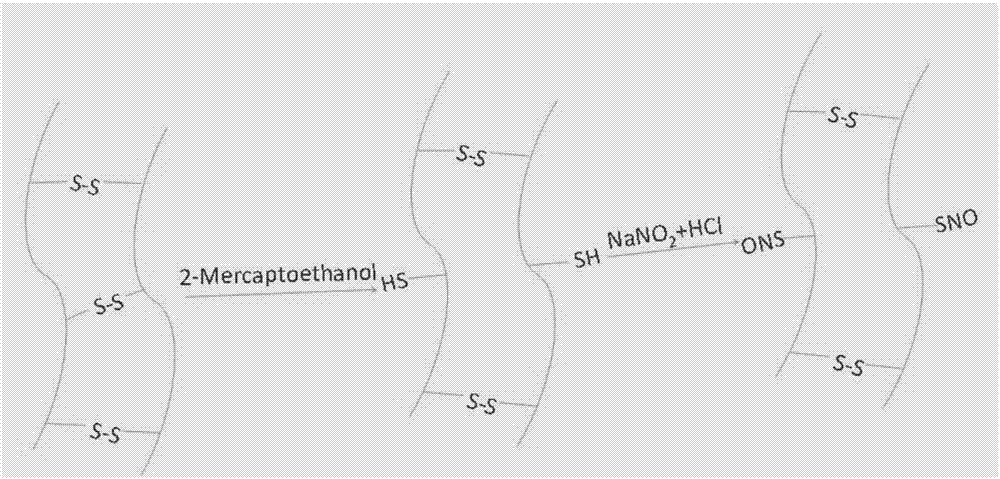
Keratin biomacromolecular nitric oxide donor and synthesis and application thereof
ActiveCN107141345AHigh molecular weightStable storageSurgeryPeptide preparation methodsReduction treatmentNitrite
The invention discloses a keratin biomacromolecular nitric oxide donor. The keratin biomacromolecular nitric oxide donor contains reduced keratin obtained through reduction treatment on keratin, and SNO groups are formed on the sulfydryl groups of the reduced keratin. The keratin biomacromolecular nitric oxide donor is an S-nitrosated keratin and is synthesized and prepared through reaction between the reduced kertin and tert-butyl nitrite or sodium nitrite. The keratin biomacromolecular nitric oxide donor is high in molecular weight, stable in storage and capable of releasing nitric oxide under certain conditions. The keratin biomacromolecular nitric oxide donor can directly serve as a nitric oxide donor as well as be compounded with other polymers to prepare nitric oxide releasing materials to give play to a controllable nitric oxide releasing function, thereby being applicable to preparing materials such as artificial blood vessels, intravascular stent and wound dressings.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for controlling peptide solubility, chemically modified peptides, and stable solvent systems for producing same
ActiveUS20030119089A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSolubilityChemical modification
Methods for chemically modifying peptides, preferably keratinaceous feedstocks, to achieve desired solubility characteristics; stable solvent systems for preparing the modified peptides; and, the resulting chemically modified peptides.
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Wool keratin extraction method
ActiveCN105399809AAvoid damageHigh molecular weightPeptide preparation methodsCytokeratinBuffer solutionIonic liquid
The invention relates to a wool keratin extraction method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, immersing wool in a compounded ionic liquid, adding loose wool to the compounded ionic liquid, and heating the ionic liquid under vacuum conditions to 80-100DEG C for 2h while stirring until the wool is dissolved to form a beige liquid; 2, adding the treated liquid obtained in step 2 to a buffer solution; 3, centrifuging the treated solution obtained in step 2 to obtain wool keratins; and 4, adding the buffer solution to a centrifuged liquid obtained in step 3, circulating the step 2 and the step 3, repeatedly extracting 4-10 times, and mixing all the separated wool keratins.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
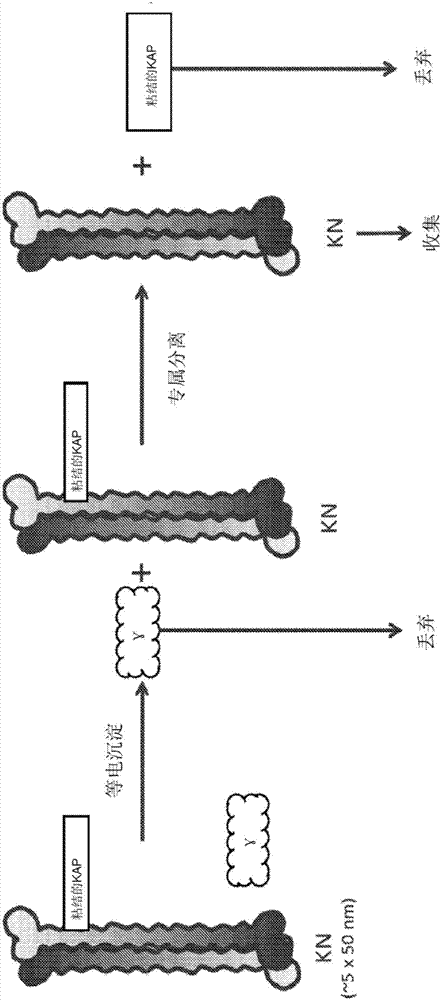
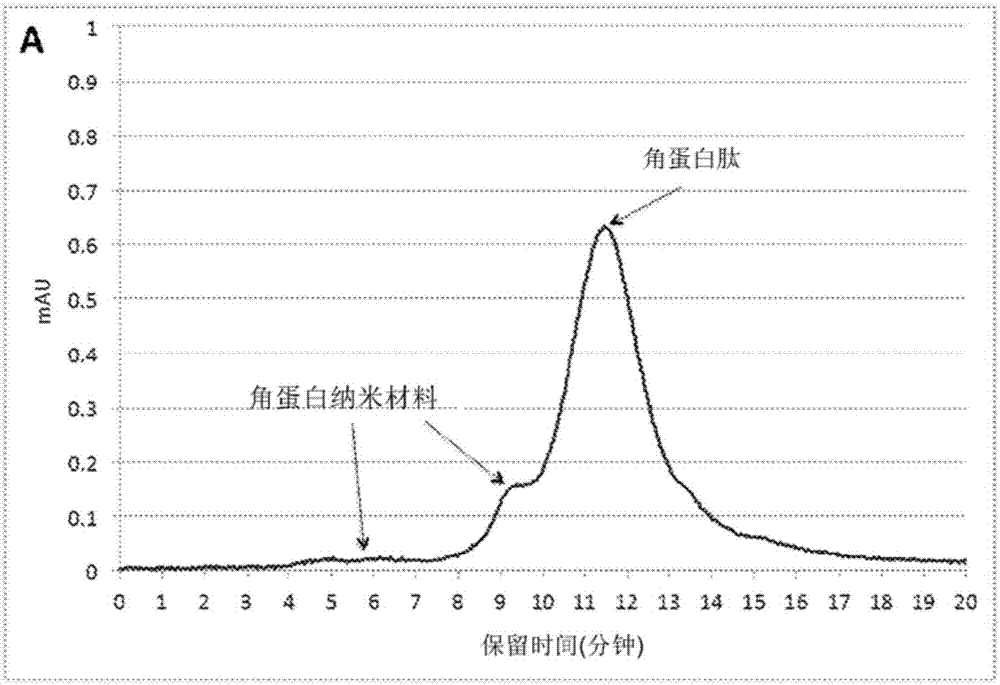
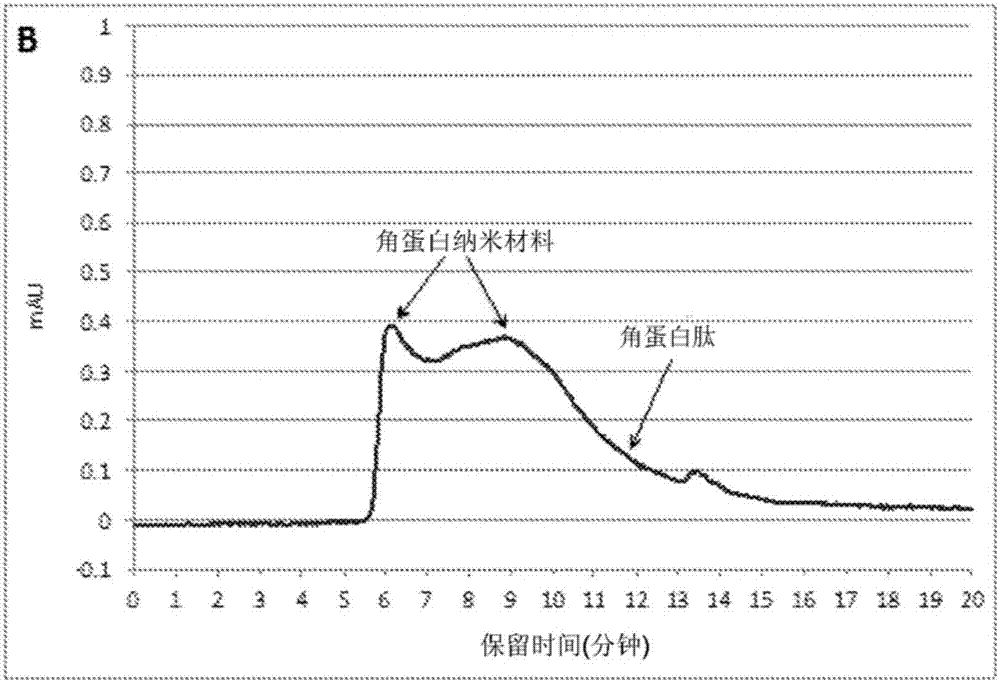
Keratin nanomaterials and methods of production
The present disclosure relates to keratin nanomaterials, methods for obtaining keratin nanomaterials, and biomaterials made from keratin nanomaterials. In particular, keratin nanomaterials comprising Type I and Type II monomer pairs are disclosed as well as a method for obtaining keratin nanomaterials comprising obtaining a solution of keratin and processing the solution by ultrafiltration with buffer solution containing phosphate.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
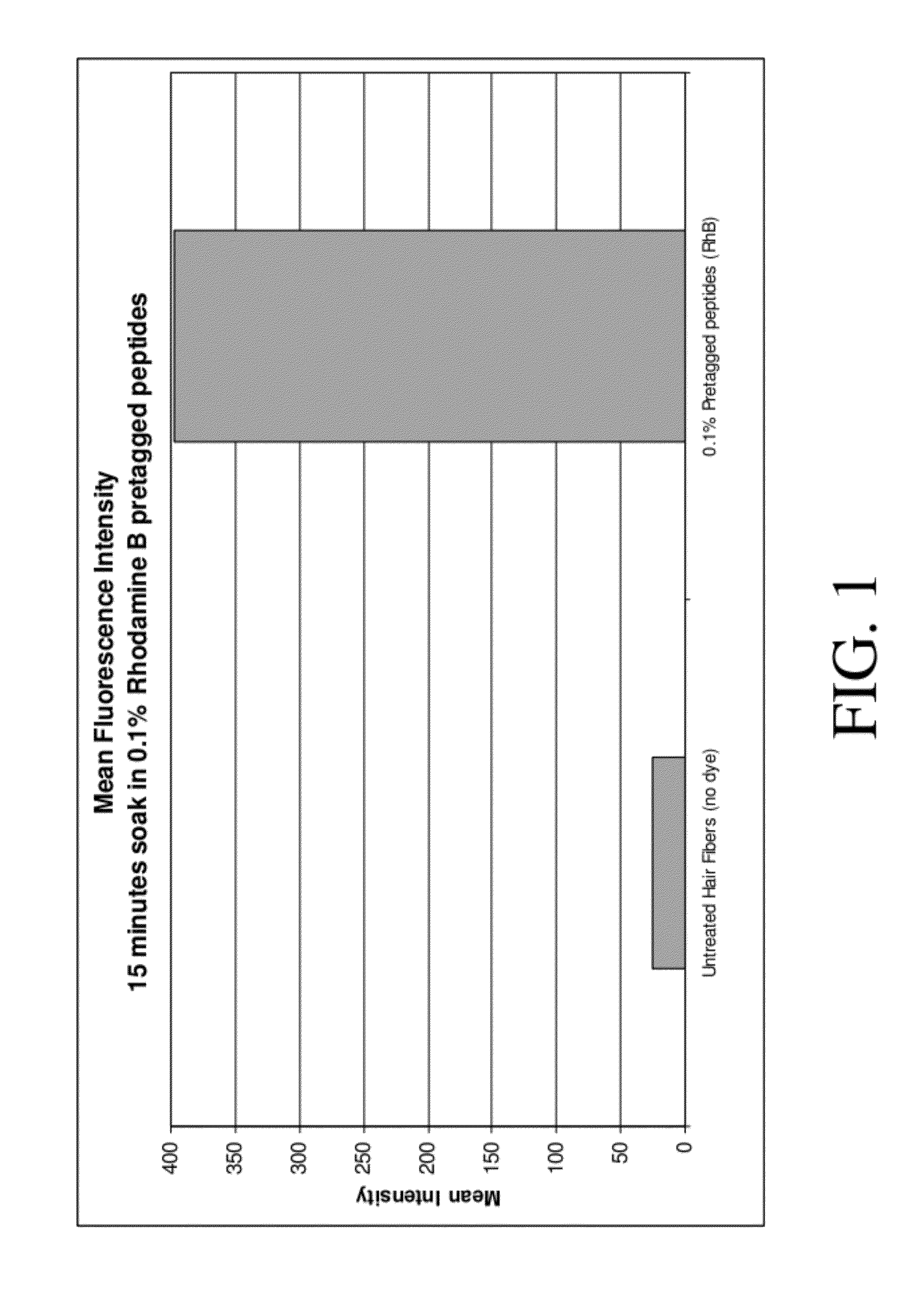
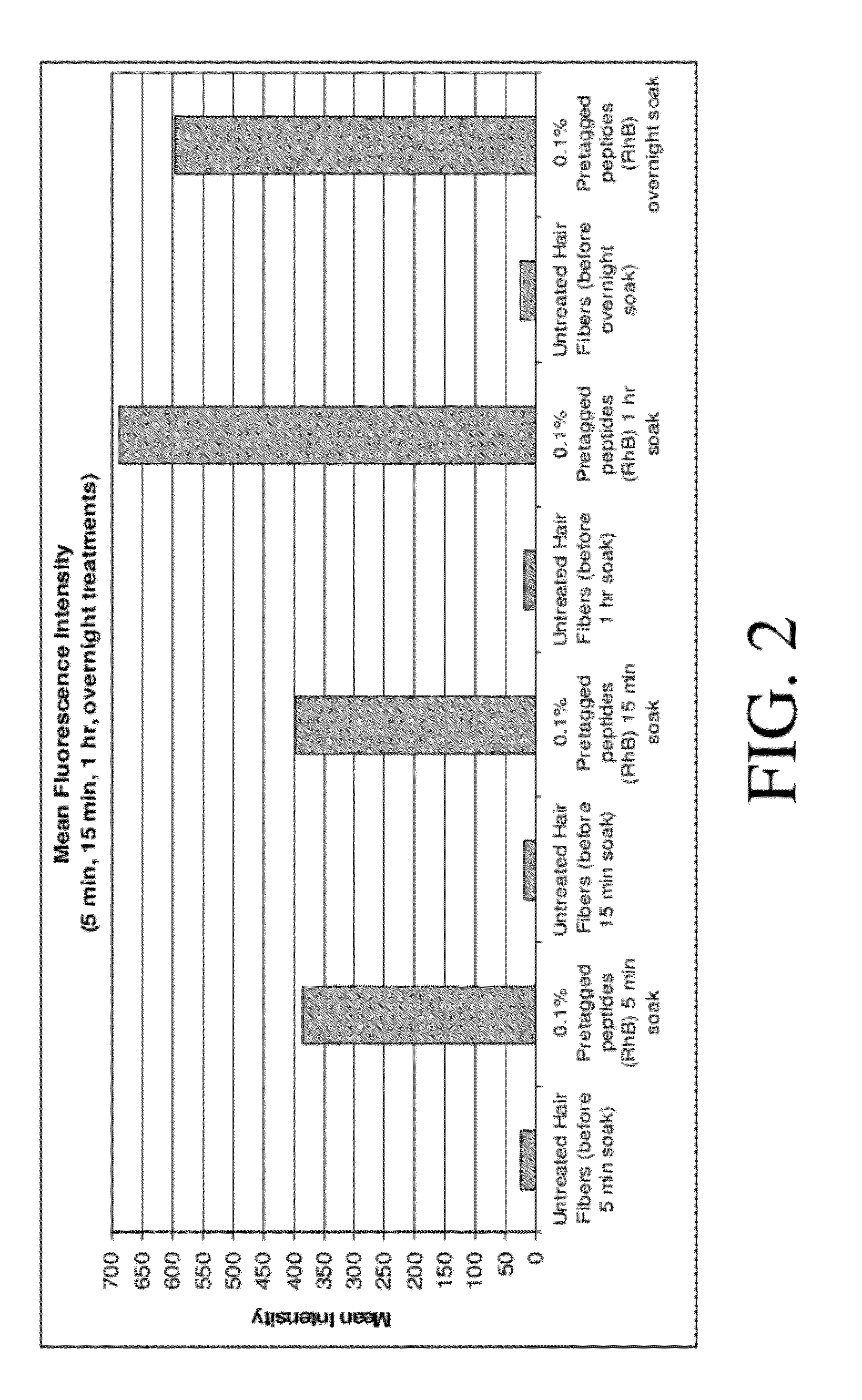
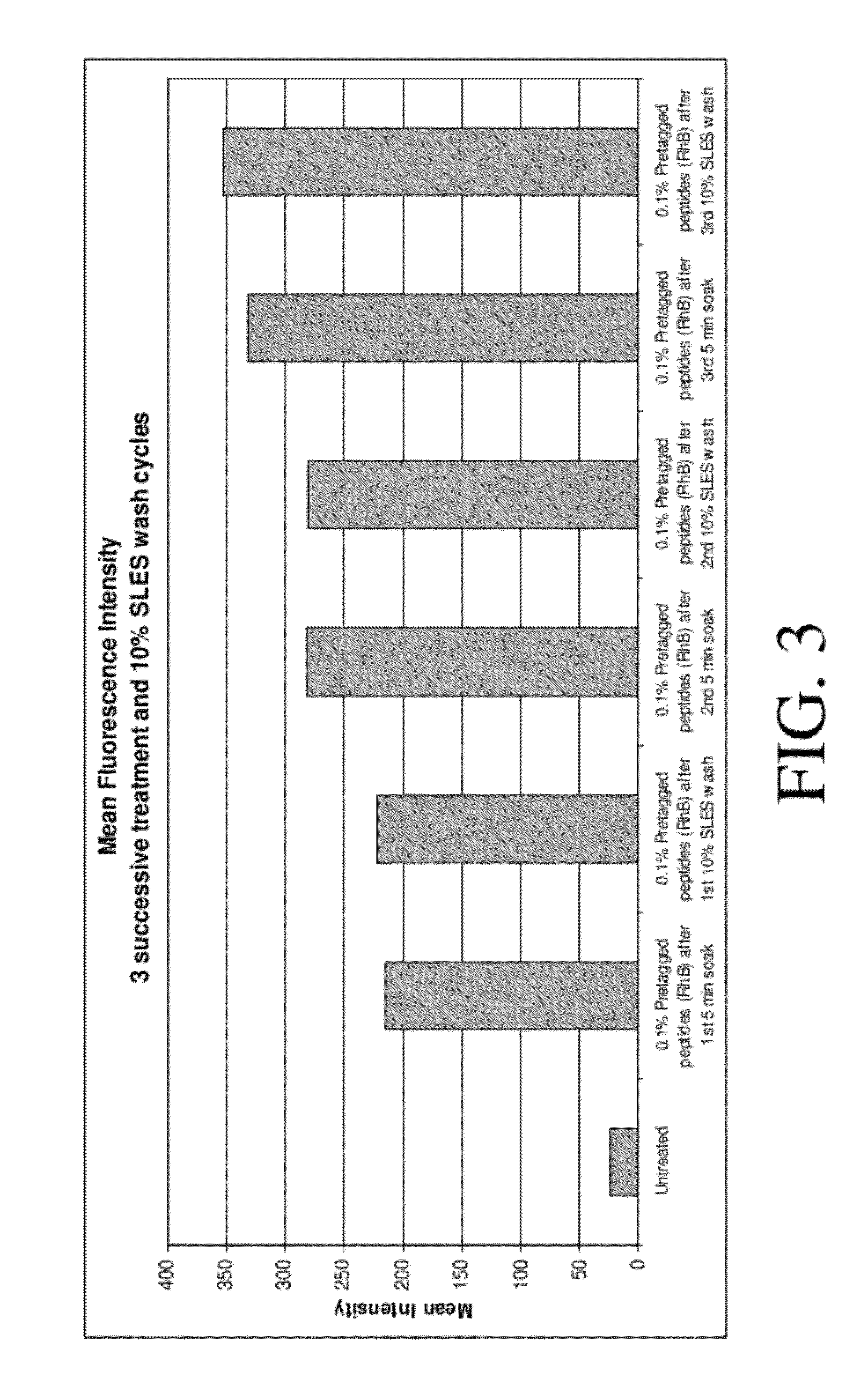
Hair treatment composition with naturally - derived peptide identical to human hair
ActiveUS20120052034A1Improve rigidityHigh strengthCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsAmino acid synthesisMedicine
A hair treatment composition containing at least one peptide identical to human hair, where preferably the peptide is synthesized from naturally-derived amino acids and can serve as a natural alternative to the commonly used human or animal derived (wool) keratin peptides.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Method for separating keratinous proteins from materials
InactiveUS20090209738A1Eliminate riskMaximising molecular weightDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsLiquid mediumSulfide
A process for separating keratinous proteins from a keratin-containing material, the process comprising the steps of: subjecting the keratin-containing material to reduction in a liquid medium to solubilise the keratinous proteins under conditions that minimise hydrolysis of the keratinous proteins, to yield a solution of keratinous proteins and undissolved solids; subjecting the solution of keratinous proteins to peroxide oxidation, without any intervening keratin precipitation step; and separating the solution of keratinous proteins from the undissolved solids prior to, at the same time as, or following the oxidation step. Preferred conditions for performing the reduction step involve contacting the keratin-containing material with a solution of an alkali metal sulfide reducing agent at a temperature of between 25 C and 50 C for a time of between 30 and 90 minutes, assuming atmospheric pressure. The peroxide oxidation is suitably carried out within not more than 4 hours after the reduction step, and involves reducing the pH of the solution to a level not less than pH 10, although pH 11.3 is most preferred. The product is demonstrated to have a principal fraction that has a molecular weight above 10 kDa, reflecting that the disulfide bonds in the keratinous proteins are broken without hydrolysis of the proteins.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN WOOL INNOVATION +1
Method for the degradation of keratin and use of the keratin hydrolysate produced
The present invention relates to a method of producing keratin hydrolysate comprising the steps of: i) reacting keratin material with a protease; and ii) reacting keratin material with a chemical oxidant; wherein step ii occurs: a) after step i); b) during step i) when the selected protease hydrolyses under the pH conditions used for the chemical reaction and / or c) prior to step i) when the selected protease hydrolyses under the reaction conditions used for the chemical reaction; keratin hydrolysate so produced and uses thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Keratin derivatives and methods of making the same
Soluble keratin derivatives are disclosed. The soluble keratin derivatives may include a soluble keratin protein having at least one substituted chemical group at a lysine group, terminal amine group and / or hydroxyl amino acid group of a soluble keratin protein. Soluble keratin derivatives may be formed by succinylation or quaternisation, or by reaction with fatty acid derivatives. The soluble keratin derivatives may be used in personal care formulations, and may also comprise mixtures of several different soluble keratin derivatives.
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Keratin-chitosan composite medical dressing and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106421888AAvoid painFree from painPeptide preparation methodsCytokeratinCarboxymethyl celluloseBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a keratin-chitosan composite medical dressing and a preparation method thereof; the dressing is prepared from, by weight, 2-8% of keratin, 0.6-1% of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 0.3-0.9% of chitosan, 6-8% of glycerol, and the balance of water. The preparation method comprises: adding keratin and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose into water, adding chitosan and glycerol, mixing well, and performing first lyophilizing; soaking sequentially in CaCl2 solution and NaOH solution, and performing second lyophilizing after soaking is complete; soaking in glycerol aqueous solution, and performing third lyophilizing after soaking is complete. The keratin-chitosan composite medical dressing prepared herein has no immunogenicity, is good in hemostatic effect and high in air permeability, and also has the advantages, such as good biocompatibility and the ability to promote cell growth.
Owner:北京东方艾美生物技术股份有限公司
Method for Inhibiting HIV Replication in Mammal and Human Cells
ActiveUS20130130971A1Avoids viral resistanceReduce probabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusADAMTS Proteins
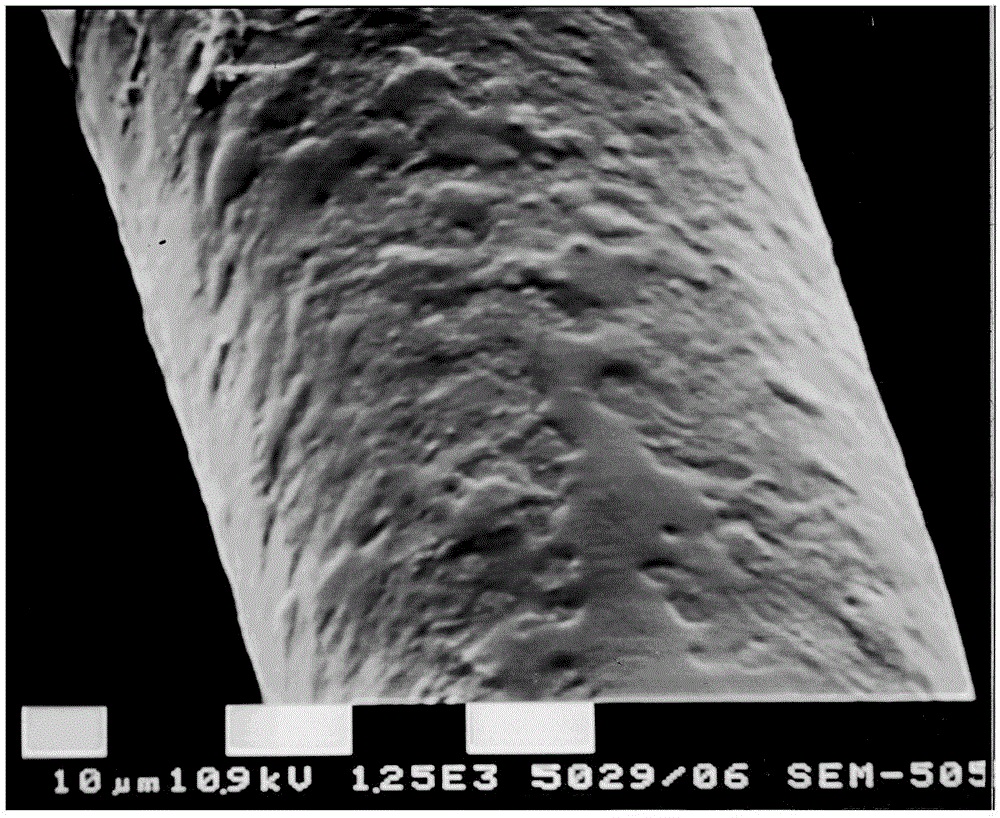
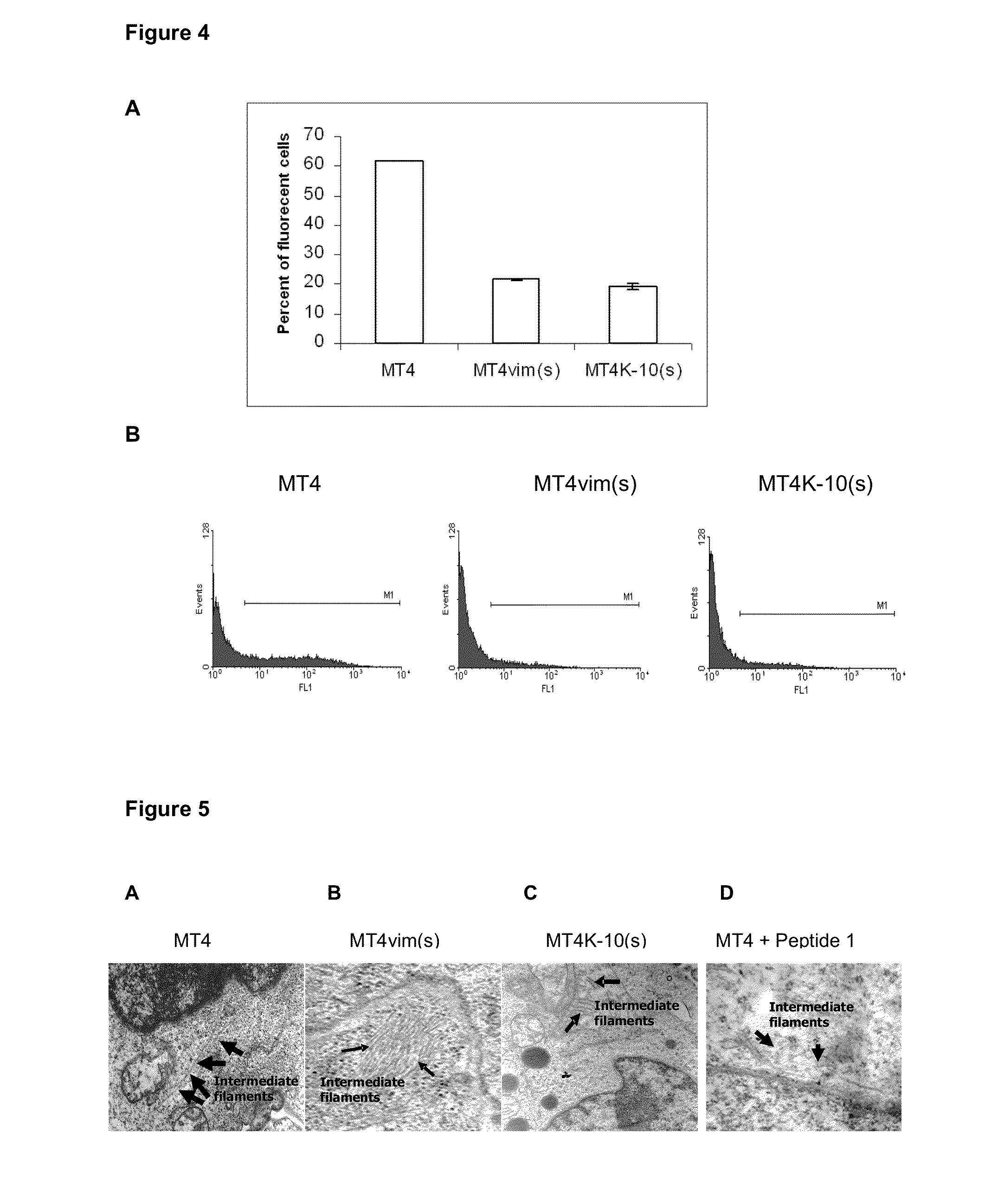
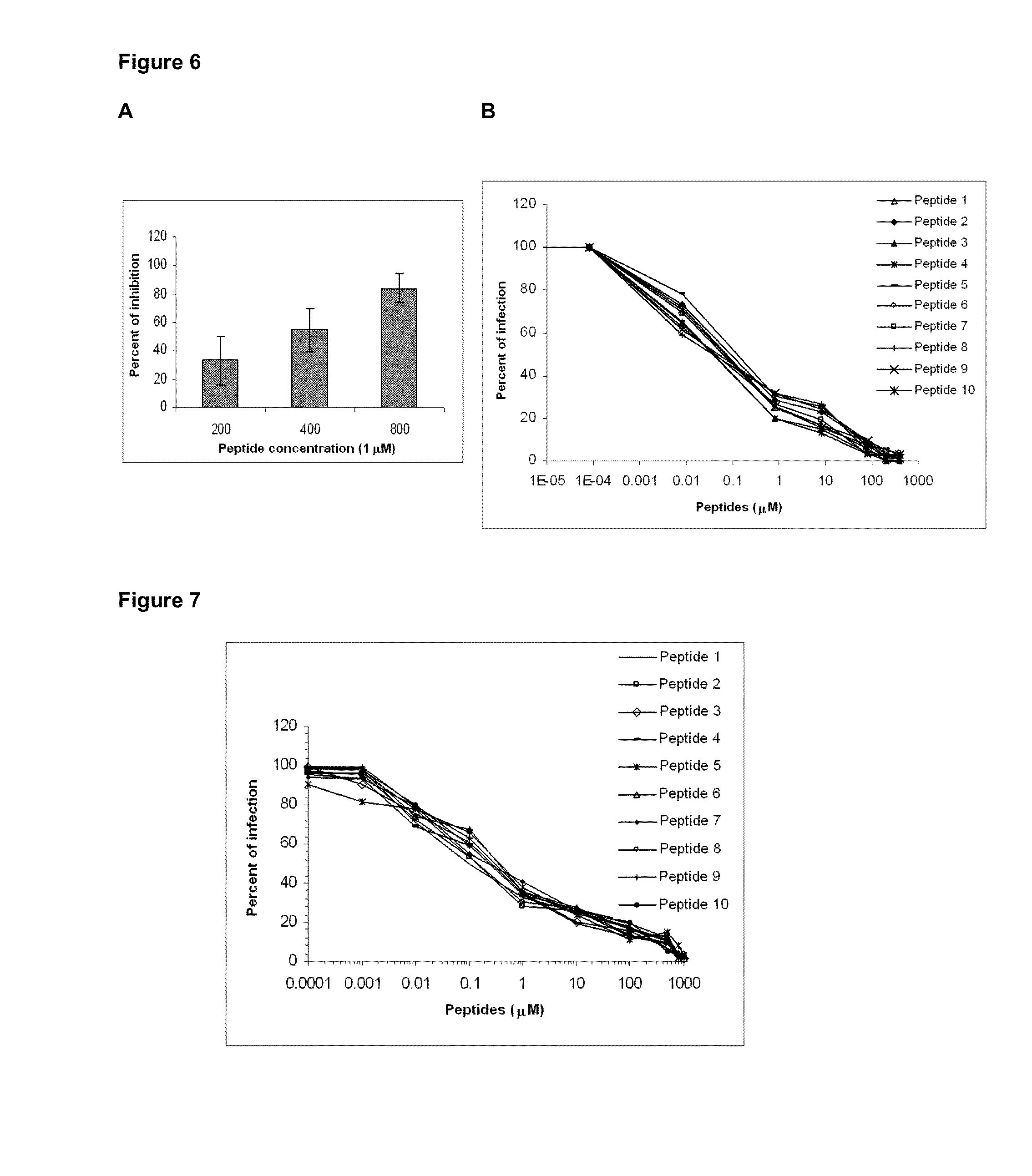
The present invention describes a method to inhibit replication of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) by negatively modulating or altering the cytoskeleton, more precisely the proteins forming the intermediate cytoskeletal filaments, wherein the said proteins are vimentin and / or keratin-10. The replication of the virus is inhibited in human cells by intervening in the structure of these proteins. The present invention is also related to the use of agents, which comprise peptides and / or interfering RNA and / or lipidic compounds, said agents producing a negative modulation or alteration of the cytoskeleton to prevent or to treat the HIV infection. The invention provides means and methods for altering the cytoskeleton / filament structure of cells, as a result of which the infection of human cells by HIV is disturbed and can even be completely inhibited. The cytoskeleton is altered by reducing the amount of vimentin and / or keratin (e.g. by transcriptional control using interfering RNA) or by using peptides that disrupt the cytoskeleton.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
Method for separating keratinous proteins from materials
A process for separating keratinous proteins from a keratin-containing material, the process comprising the steps of: subjecting the keratin-containing material to reduction in a liquid medium to solubilise the keratinous proteins under conditions that minimise hydrolysis of the keratinous proteins, to yield a solution of keratinous proteins and undissolved solids; subjecting the solution of keratinous proteins to peroxide oxidation, without any intervening keratin precipitation step; and separating the solution of keratinous proteins from the undissolved solids prior to, at the same time as, or following the oxidation step. Preferred conditions for performing the reduction step involve contacting the keratin-containing material with a solution of an alkali metal sulfide reducing agent at a temperature of between 25 C and 50 C for a time of between 30 and 90 minutes, assuming atmospheric pressure. The peroxide oxidation is suitably carried out within not more than 4 hours after the reduction step, and involves reducing the pH of the solution to a level not less than pH 10, although pH 11.3 is most preferred. The product is demonstrated to have a principal fraction that has a molecular weight above 10 kDa, reflecting that the disulfide bonds in the keratinous proteins are broken without hydrolysis of the proteins.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN WOOL INNOVATION +1
Methods for extracting keratin proteins
ActiveUS20150080552A1Minimize degradationPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesParticulatesMineralogy
Owner:KERANETICS
Repeat sequence protein polymer active agent congjugates, methods and uses
InactiveUS7691806B2Improve utilizationImprove applicabilityCosmetic preparationsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsActive agentChemistry
Biomolecular conjugates are provided which comprise the conjugation product of a repeat sequence protein polymer and at least one active agent. Additional aspects provide methods for their manufacture and various industrial and consumer applications.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Method for extracting keratins from rabbit hair
InactiveCN103497244AShorten the dissolution timeReduce consumptionPeptide preparation methodsCytokeratinDistilled waterPre treatment
The invention relates to a method for extracting keratins from rabbit hair. The method comprises the following steps: 1, performing hydrogen peroxide pretreatment and drying to obtain dry rabbit hair; 2, performing enzymatic treatment and drying to obtain dry rabbit hair; 3, performing ZnCl2 treatment to obtain a solution of the rabbit hair; 4, extracting the keratins from the rabbit hair to obtain precipitates by adopting an isoelectric precipitation method; 5, flushing the precipitates for multiple times by using distilled water, and performing drying and grinding to obtain keratin powder. The method has the beneficial effects that a three-step treatment method comprising hydrogen peroxide pretreatment, enzymatic treatment and 40 percent ZnCl2 treatment is adopted, and compared with a purer ZnCl2 treatment method, has the advantages that the dissolution time of the rabbit hair is remarkably shortened, and energy consumption in an extraction process is reduced; the precipitates are washed for multiple times by using the distilled water, so that the concentration of Zn<2+> can be remarkably reduced, impurities can be reduced, and the purity of the keratins in the rabbit hair can be improved; the method is simple in process, low in treatment cost and high in rabbit hair keratin extraction rate.
Owner:KUNSHAN WANFENG GARMENT
Periodontal-disease-specific peptide, and treatment and diagnosis of periodontal disease using same
ActiveUS20130086703A1Production can be suppressedAvoid attackCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAutoimmune responsesGingival epithelium
The present invention provides an inhibitor of an autoimmune response to a periodontal bacterial enzymatic degradation product of keratin in gingival epithelium in a mammal having a periodontal bacterium in the oral cavity, containing a substance having affinity to the keratin or a degradation product thereof and / or a substance having affinity to an autoantibody to the degradation product, an agent for the prophylaxis and / or treatment of a periodontal disease and / or a complication thereof; a RANKL expression inhibitor containing a substance having affinity to the keratin or a degradation product thereof; and a method of diagnosing a periodontal disease including detecting the keratin or a degradation product thereof and / or an autoantibody thereto.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com