Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "TDM Bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
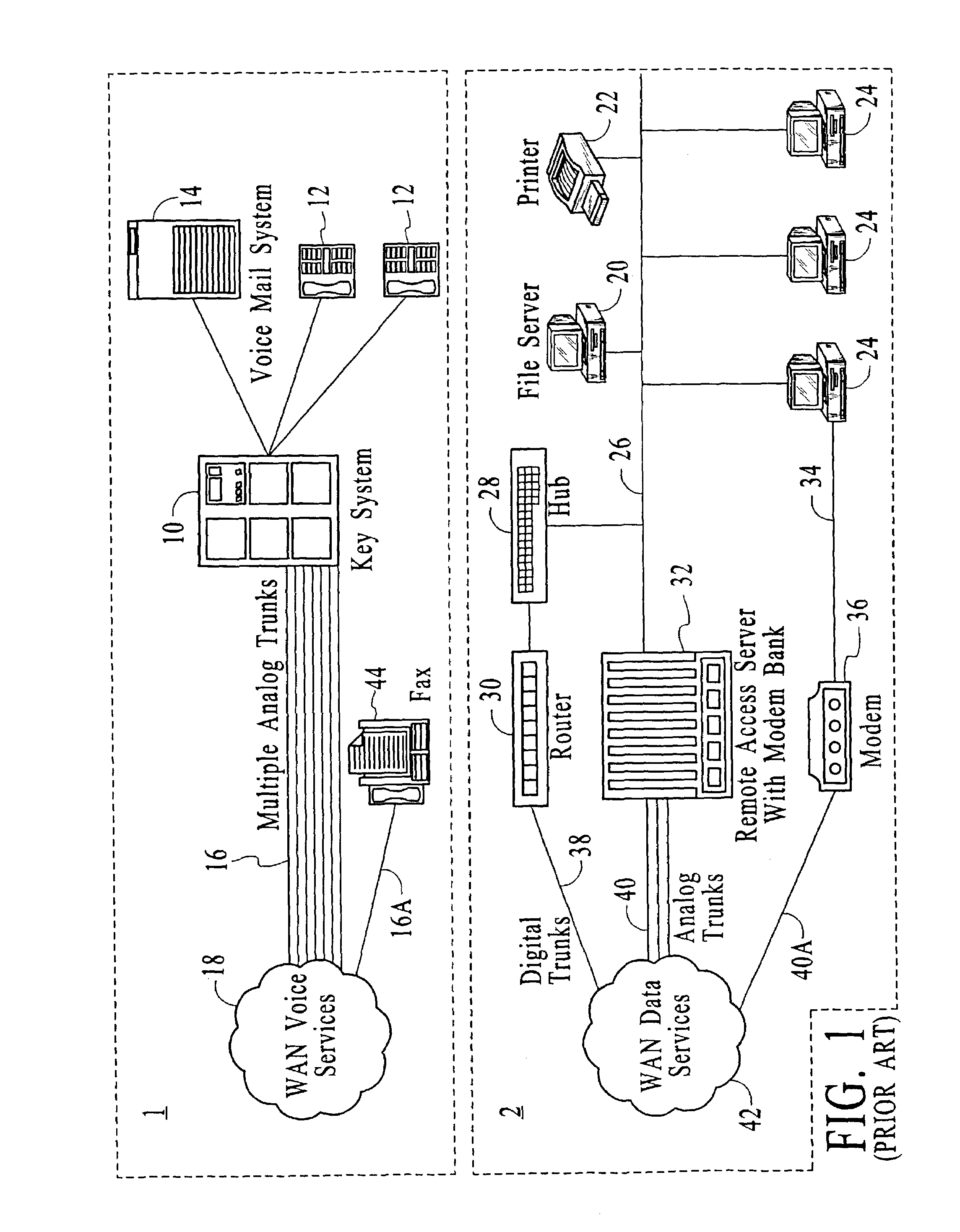
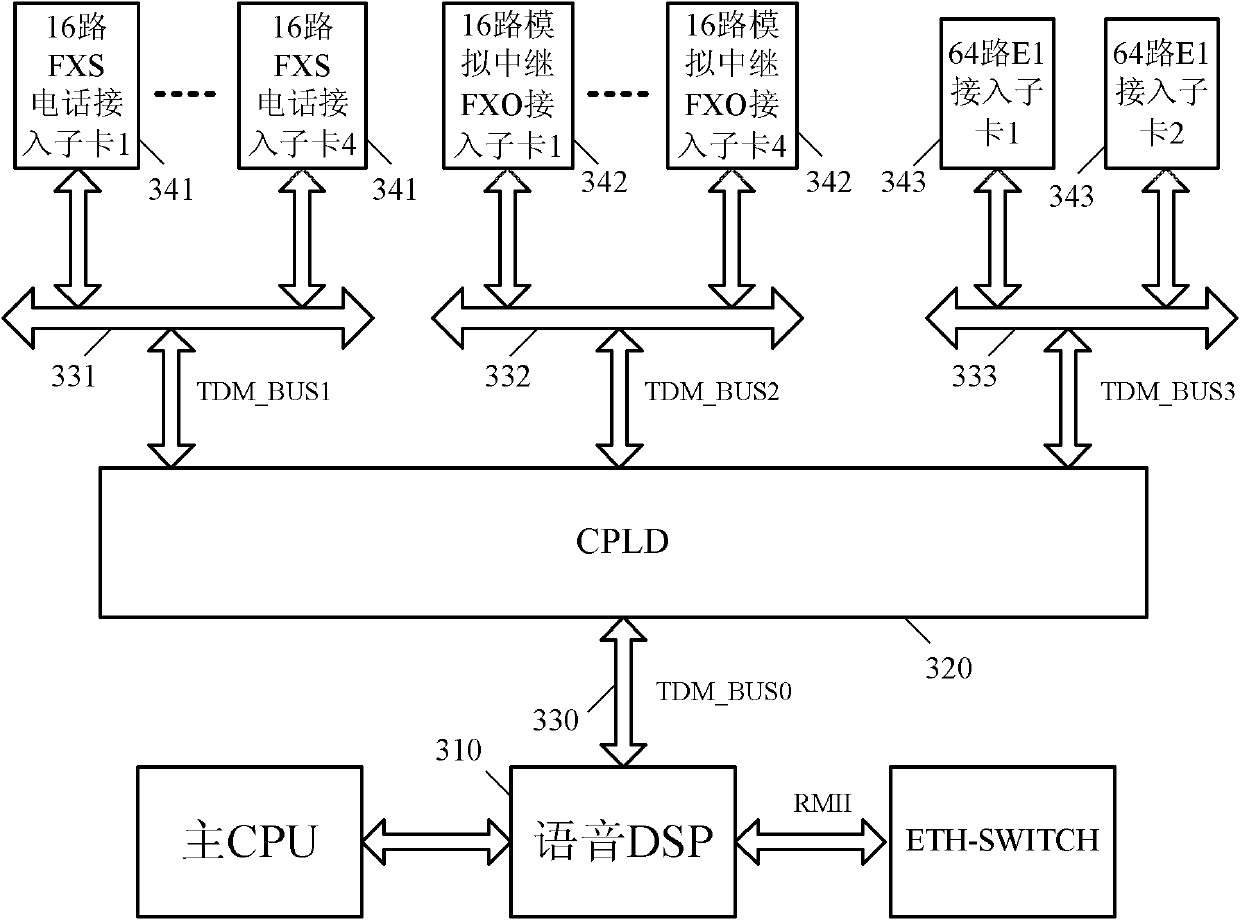
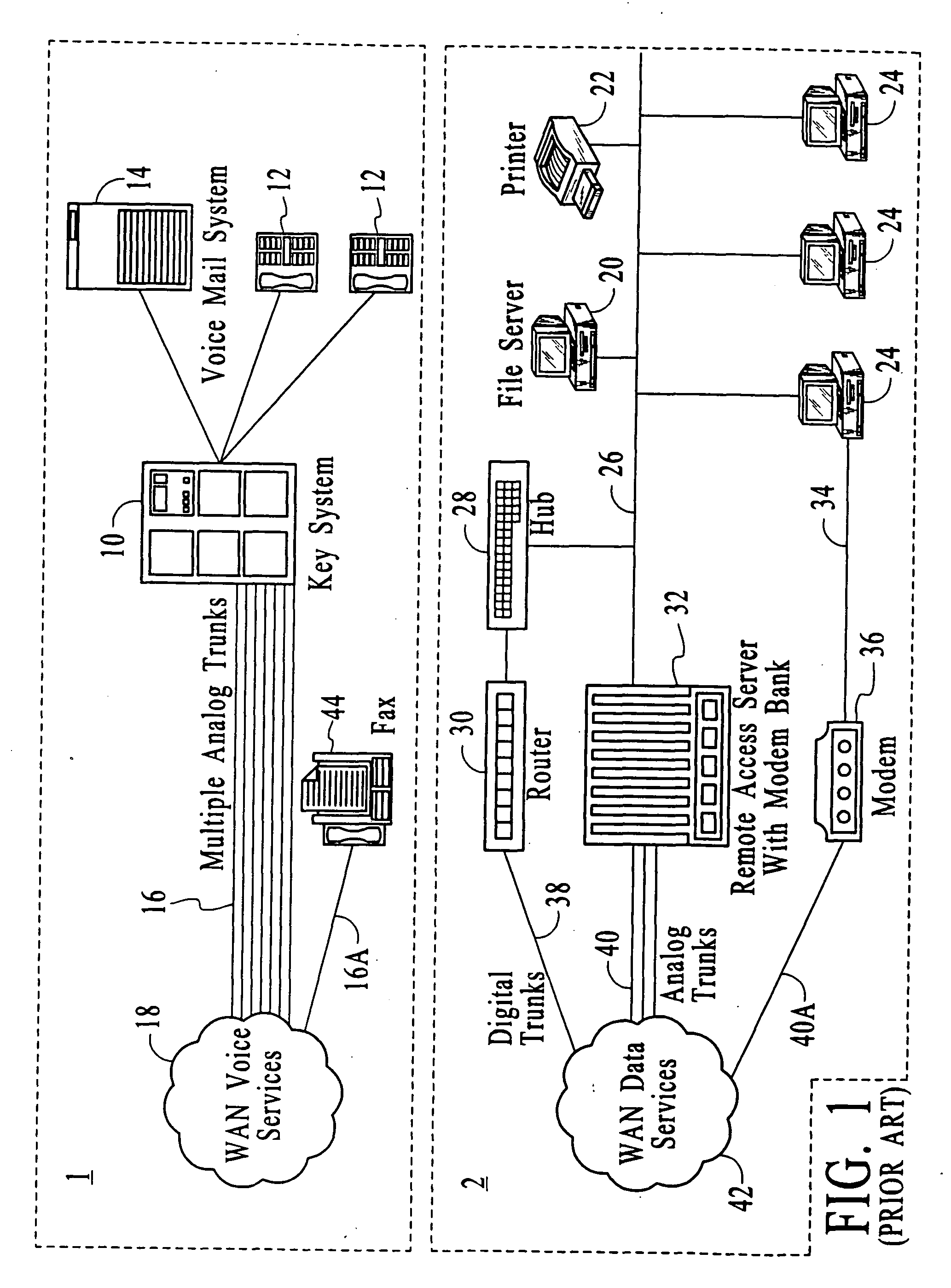
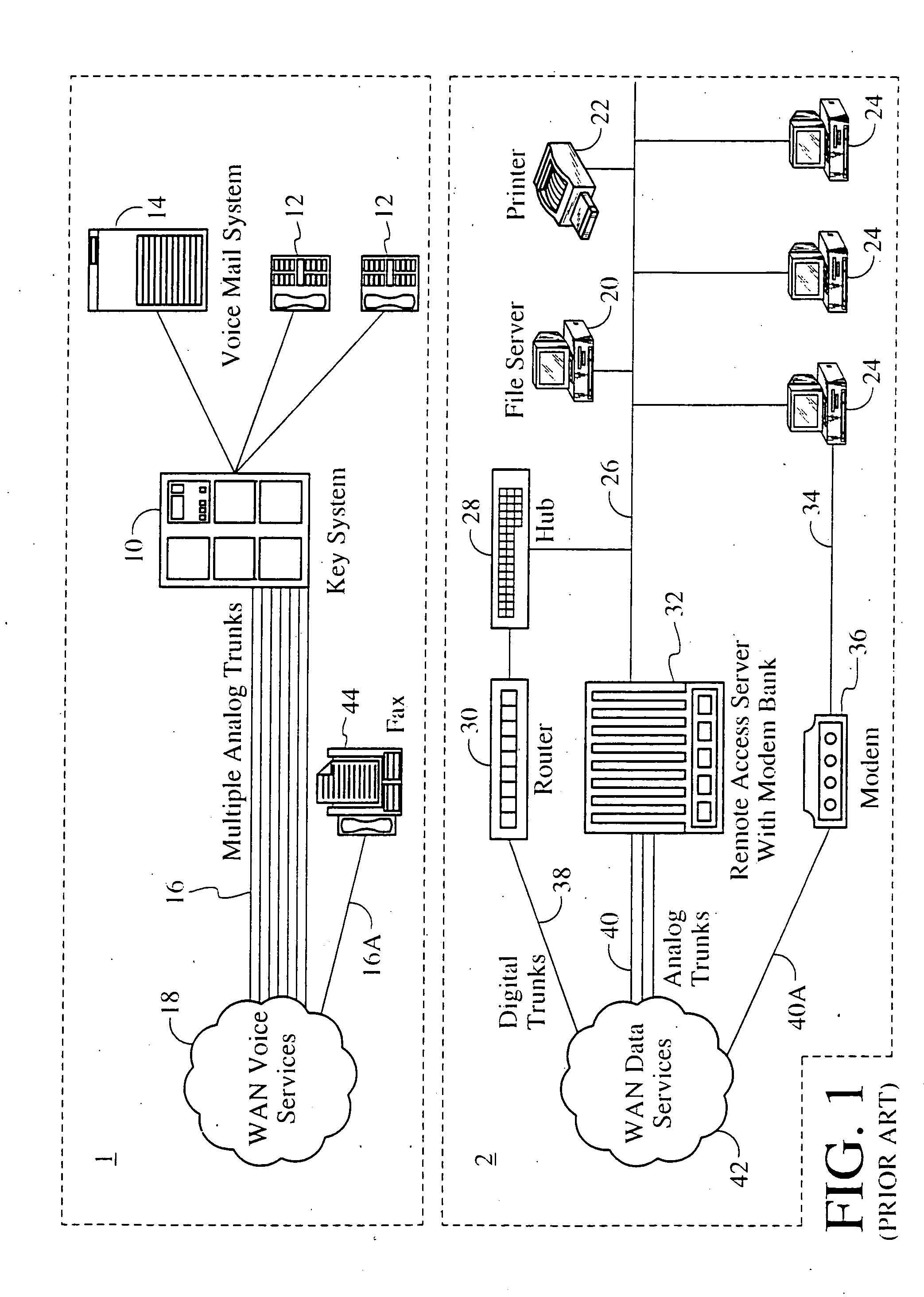
A TDM bus is one application of the principle of Time-Division Multiplexing. In a TDM Bus, data or information arriving from an input line is put onto specific timeslots on a high-speed bus, where a recipient would listen to the bus and pick out only the signals for a certain timeslot.
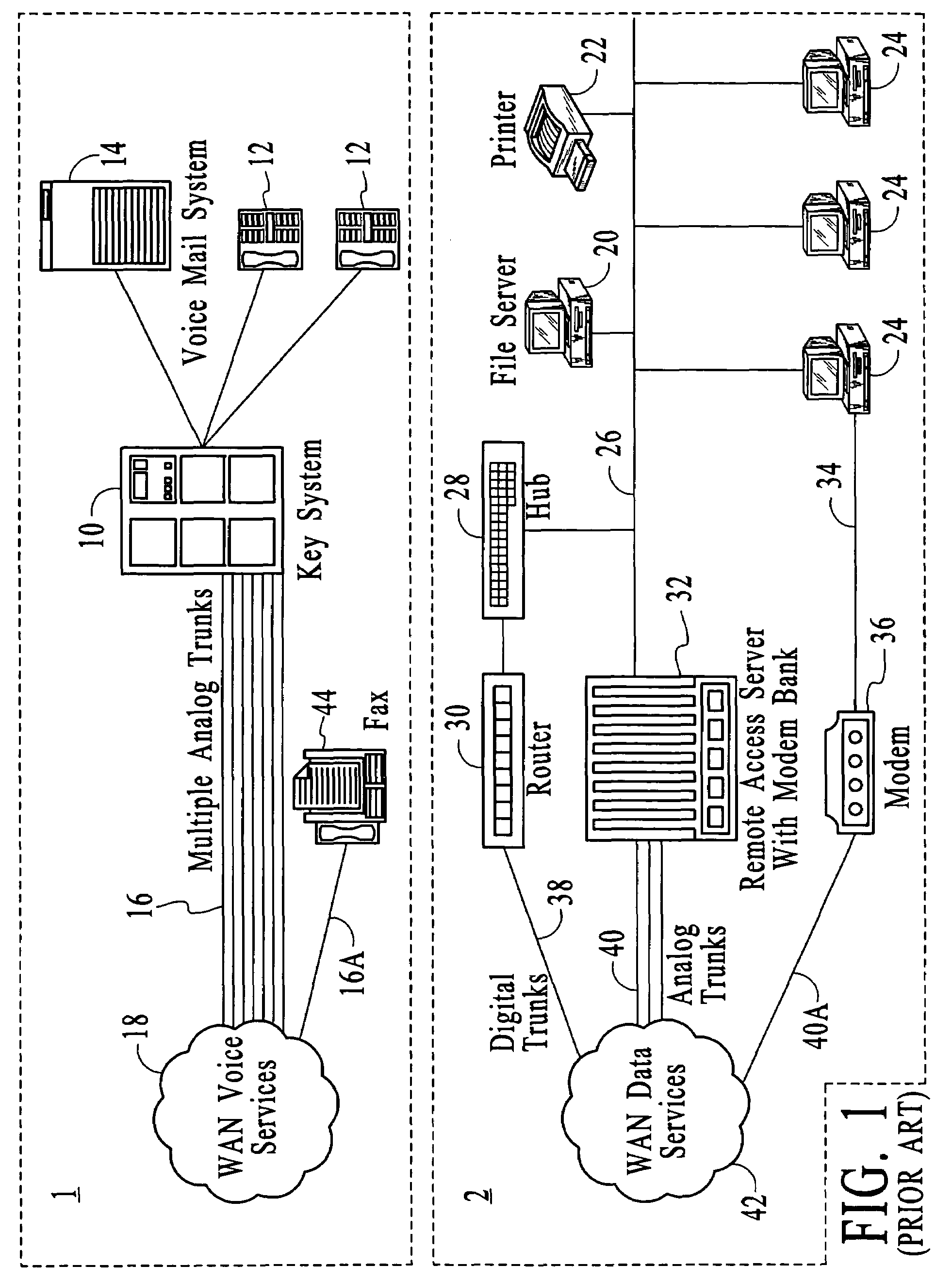
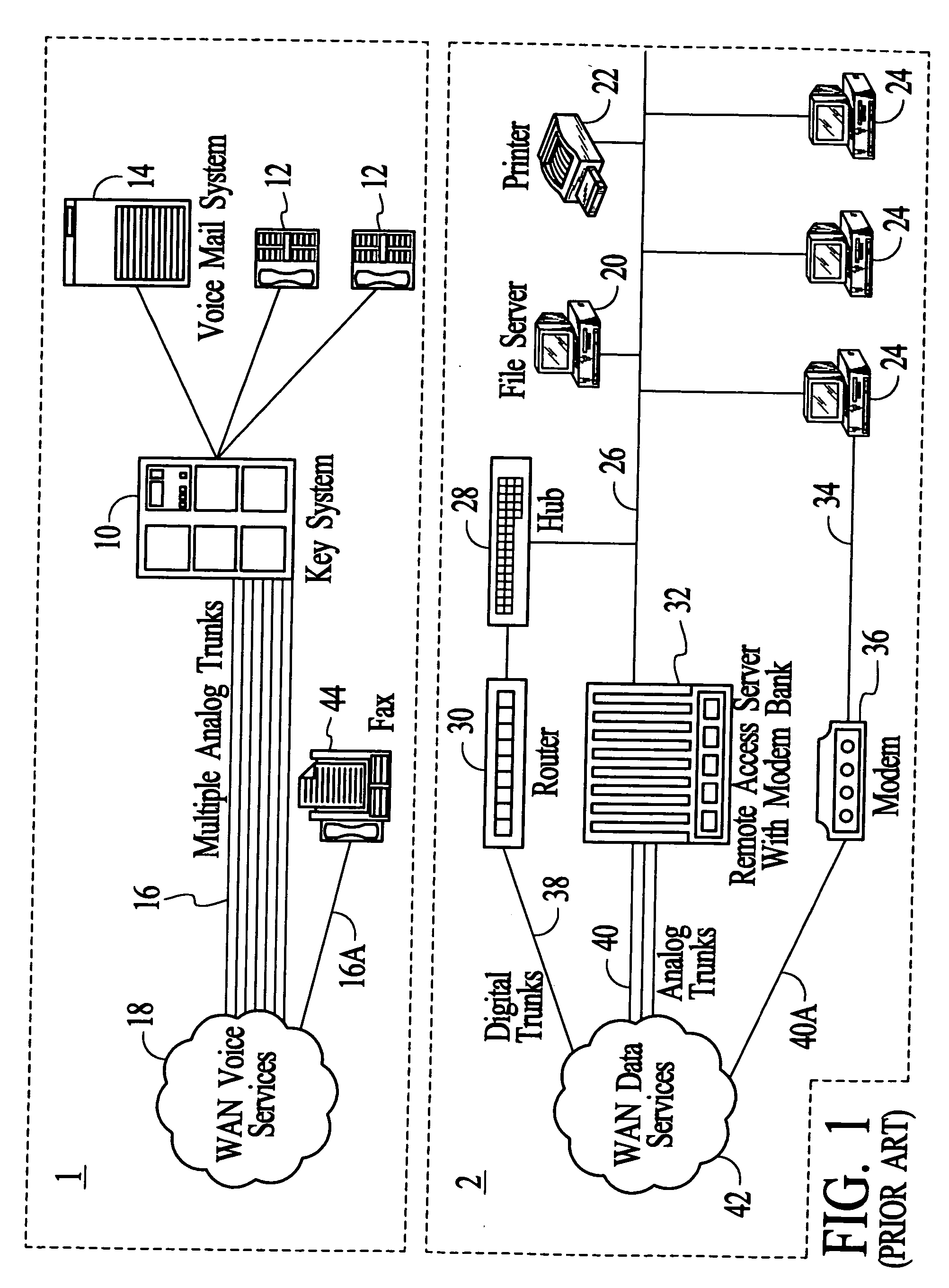
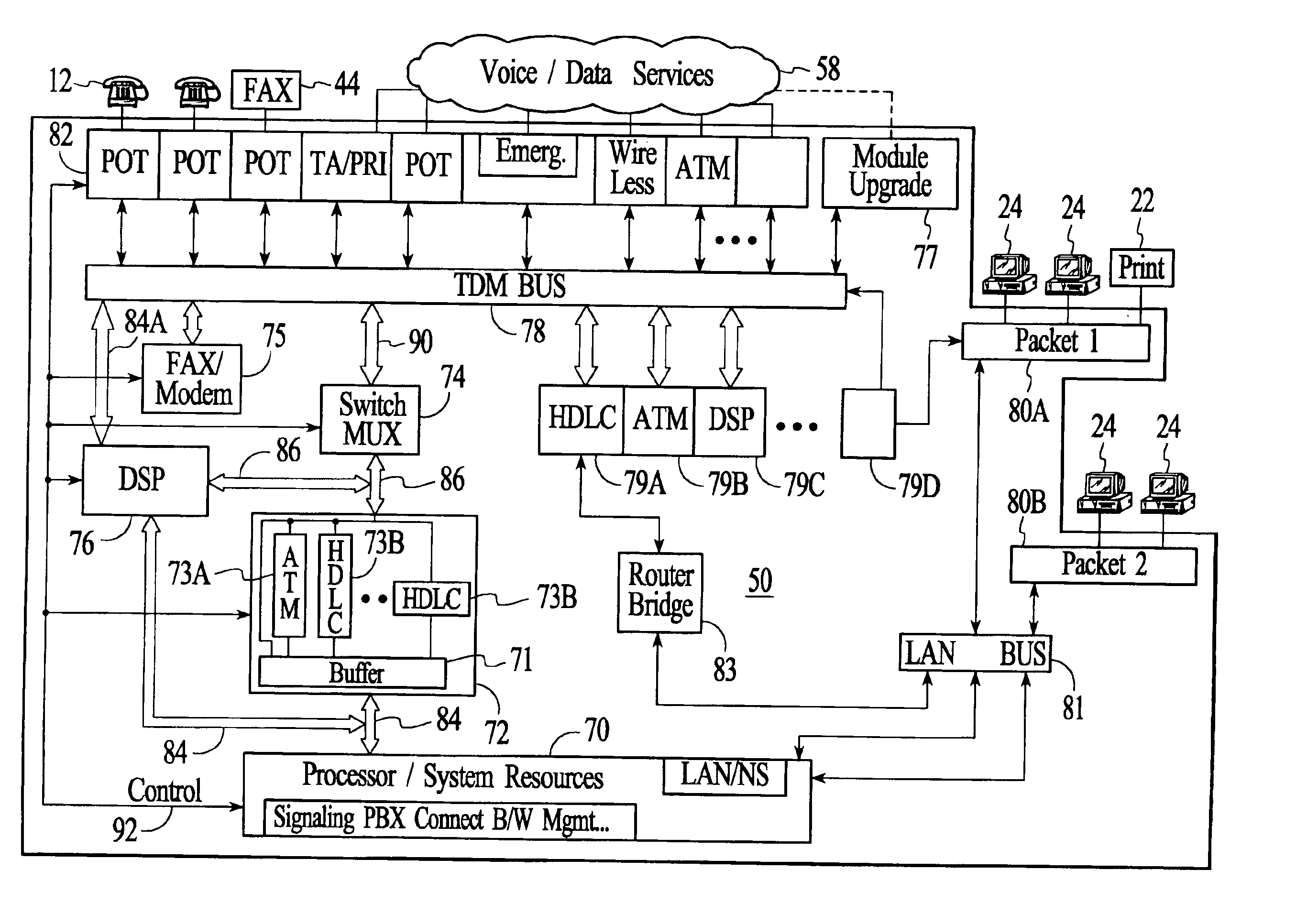
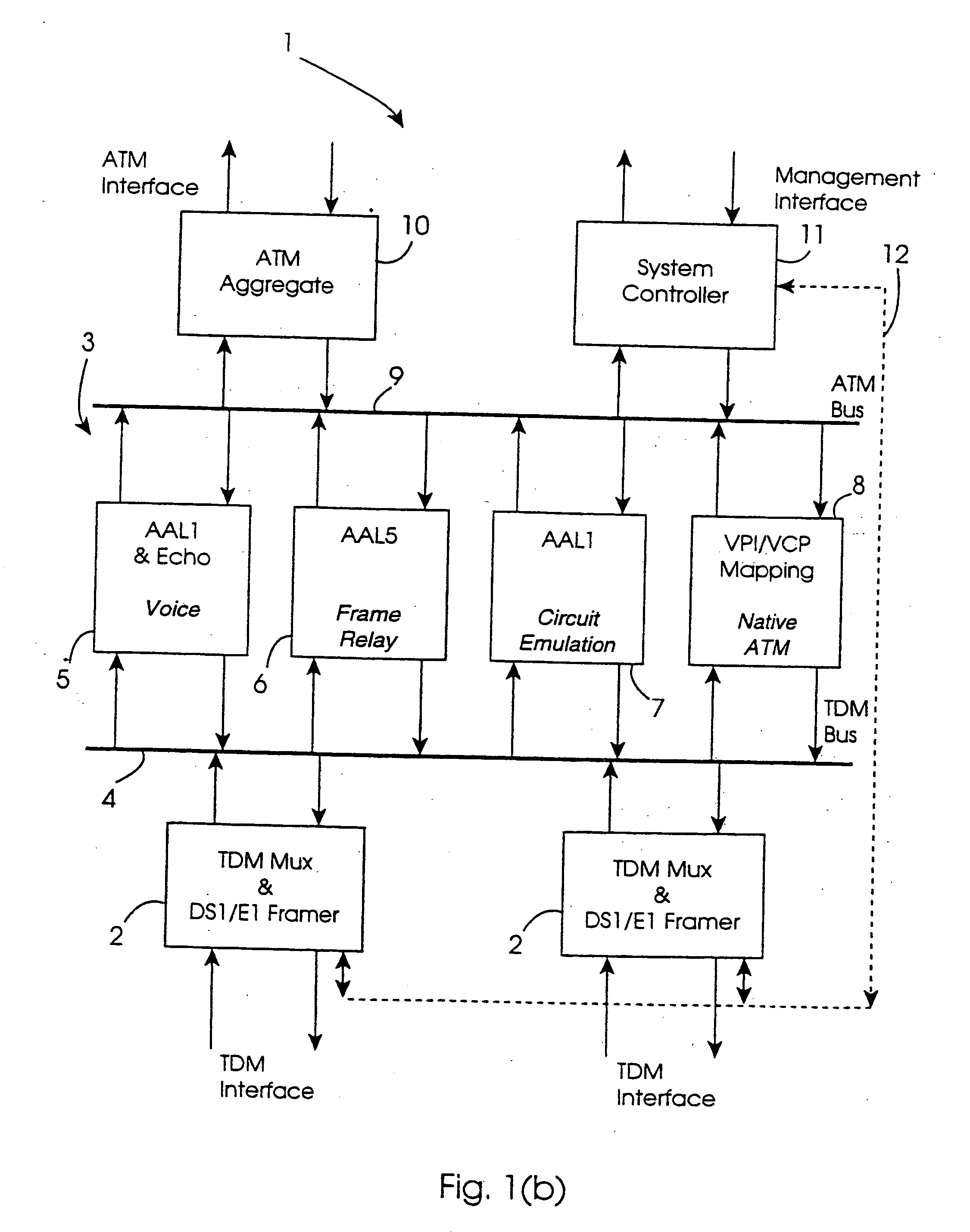
Systems and methods for multiple mode voice and data communications using intelligently bridged TDM and packet buses and methods for implementing language capabilities using the same
InactiveUS20070239429A1Effective supportPerformed conveniently and efficientlyNatural language translationAutomatic exchangesMulti protocolMultiple modes
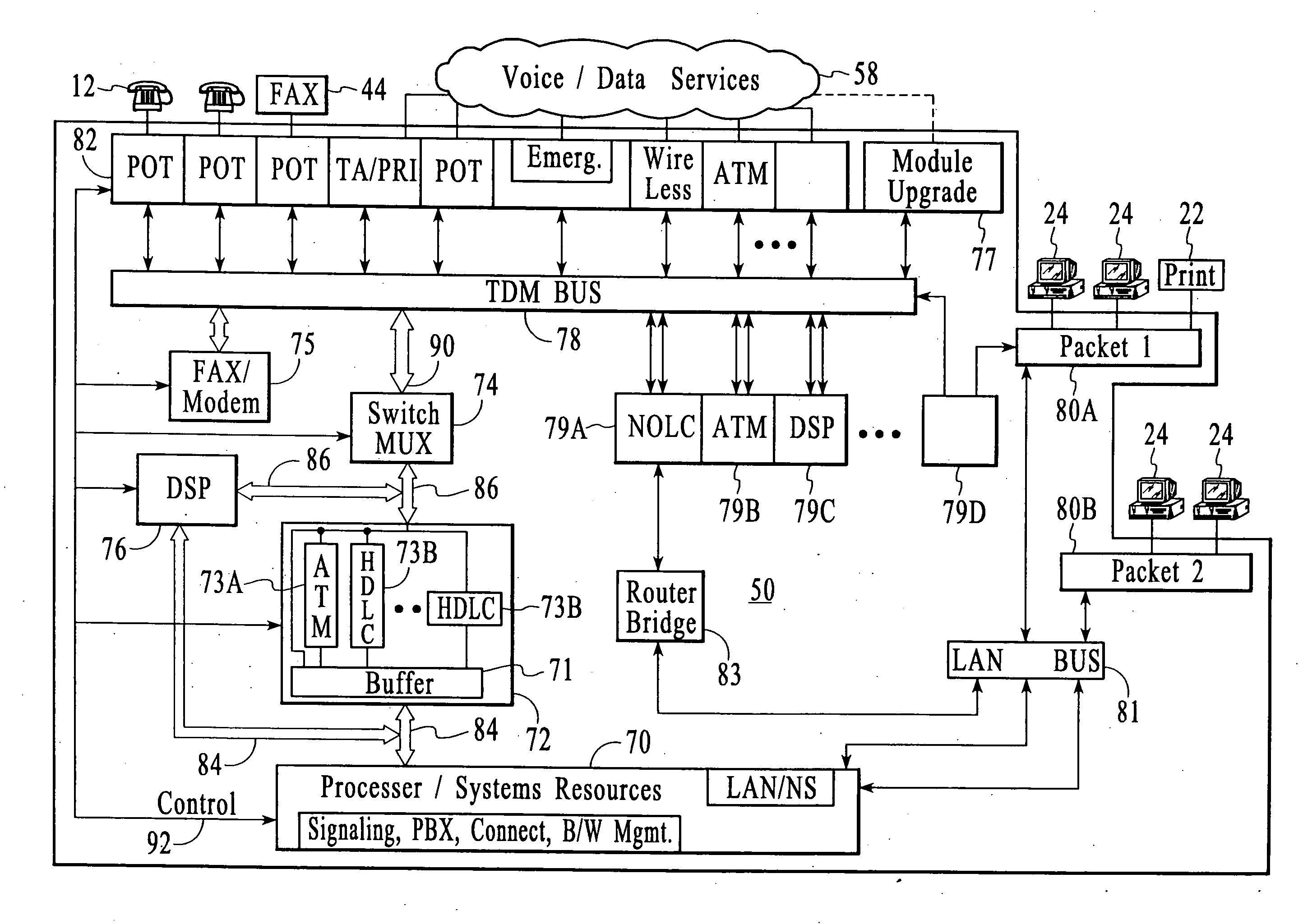
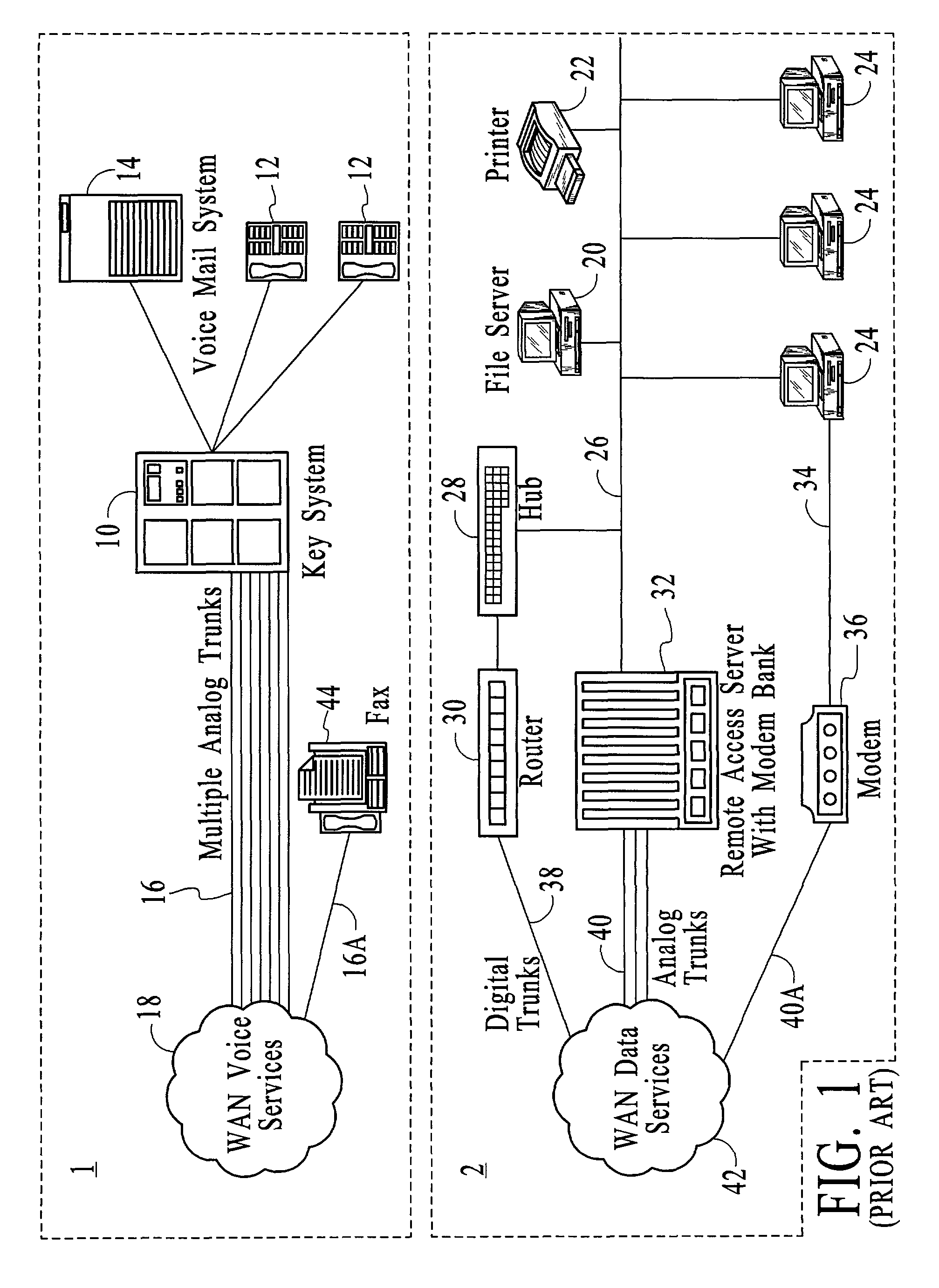
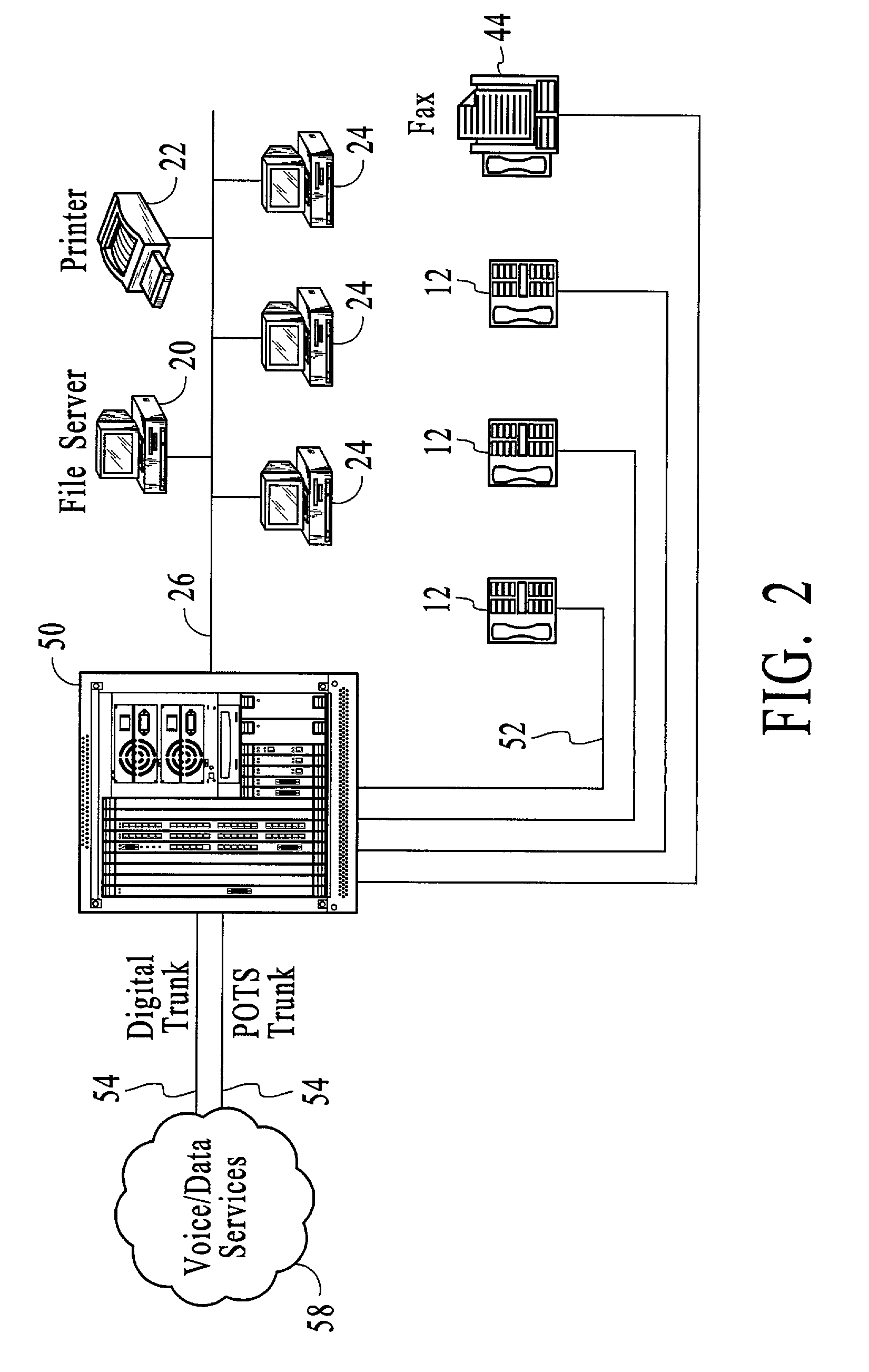
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur in multiple modes / protocols are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided for multiple native mode / protocol voice and data transmissions and receptions with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus, and multi-protocol framing engines. Such systems preferably include subsystem functions such as PBX, voice mail and other telephony functions, LAN hub and data router. In preferred embodiments, a TDM bus and a packet bus are intelligently bridged and managed, thereby enabling such multiple mode / protocol voice and data transmissions to be intelligently managed and controlled with a single, integrated system. A computer or other processor includes a local area network controller, which provides routing and hub(s) for one or more packet networks. The computer also is coupled to a buffer / framer, which serves to frame / deframe data to / from the computer from TDM bus. The buffer / framer includes a plurality of framer / deframer engines, supporting, for example, ATM and HDLC framing / deframing. The buffer / framer is coupled to the TDM bus by way of a switch / multiplexer, which includes the capability to intelligently map data traffic between the buffer / framer and the TDM bus to various slots of the TDM frames. Preferably, a DSP pool is coupled to buffer / framer in a manner to provide various signal processing and telecommunications support, such as dial tone generation, DTMF detection and the like. The TDM bus is coupled to a various line / station cards, serving to interface the TDM bus with telephone, facsimiles and other telecommunication devices, and also with a various digital and / or analog WAN network services. Language support for such systems is accomplished by way of a program / data structure so that additional language support may be readily implemented, for example, by a non-software programmer using grammar and voice prompt files, which are preferably located in a predetermined directory in the system.
Owner:RPX CORP
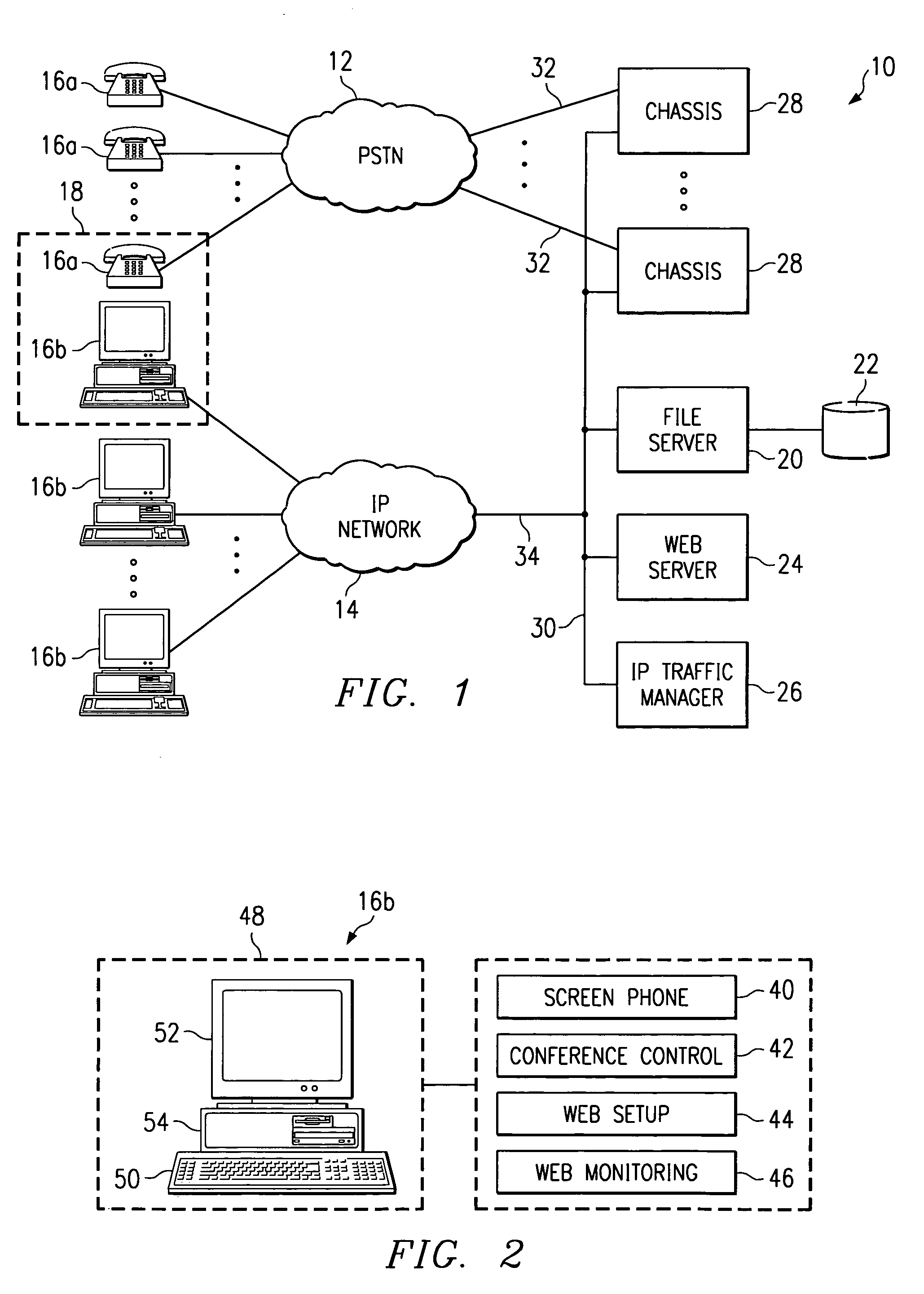
Internet-enabled conferencing system and method accommodating PSTN and IP traffic
InactiveUS6961416B1Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedReducing and eliminating conferee limitationInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersTraffic capacityProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A system for conferencing callers includes a time division multiplexed (TDM) bus. A public switched telephone network (PSTN) interface node that is coupled to the TDM bus receives PSTN signals from a PSTN caller and communicates corresponding information in a first timeslot using the TDM bus. An Internet Protocol (IP) interface node coupled to the TDM bus receives IP packets from an IP caller and communicates corresponding information in a second timeslot using the TDM bus. Also coupled to the TDM bus is a conference bridge node that receives the information for the IP caller and communicates it to the PSTN interface node in a first conference timeslot, using the TDM bus. The conference bridge node also receives the information for the PSTN caller and communicates it to the IP interface node in a second conference timeslot, using the TDM bus.
Owner:EMEETING NET
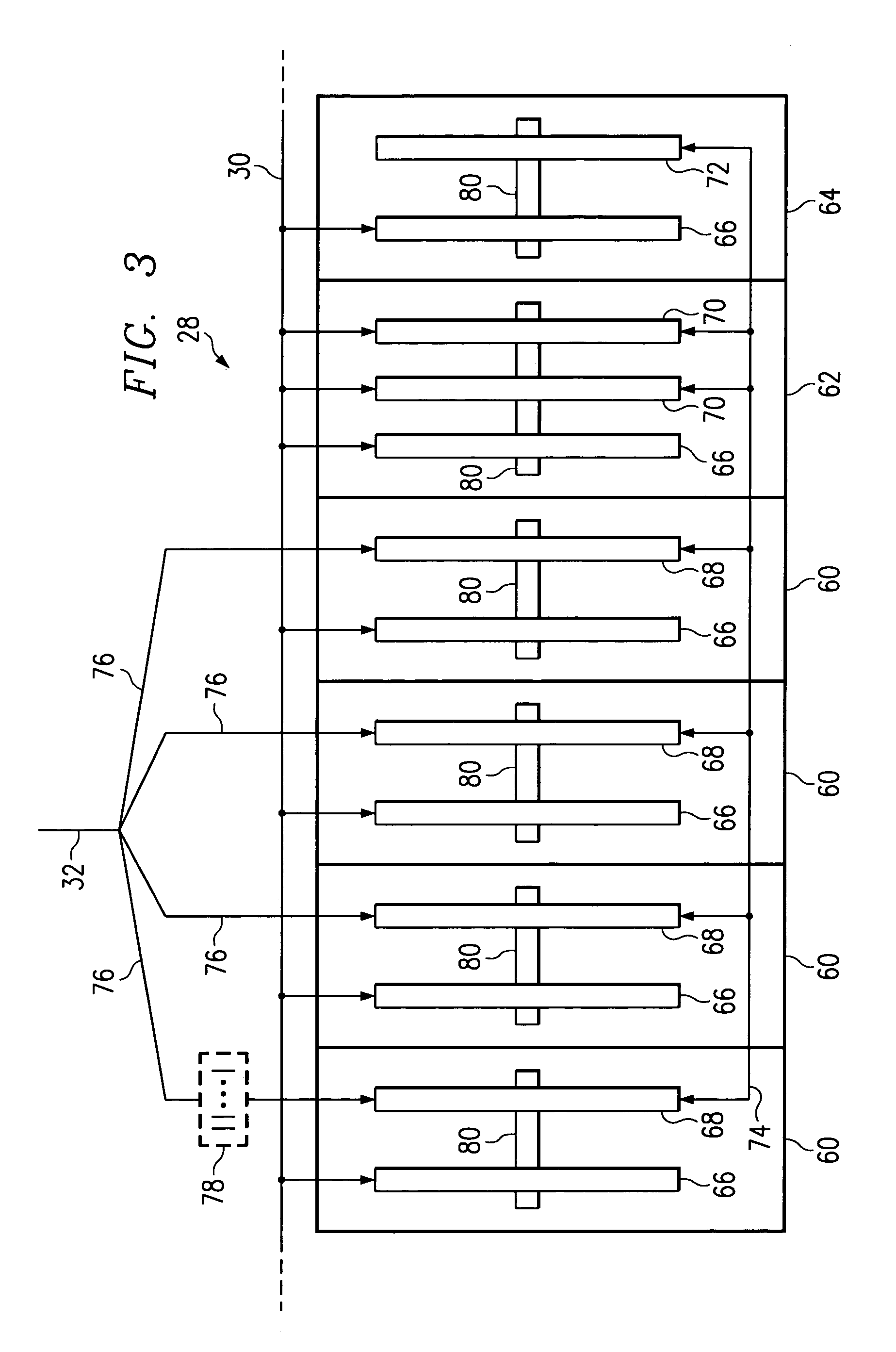
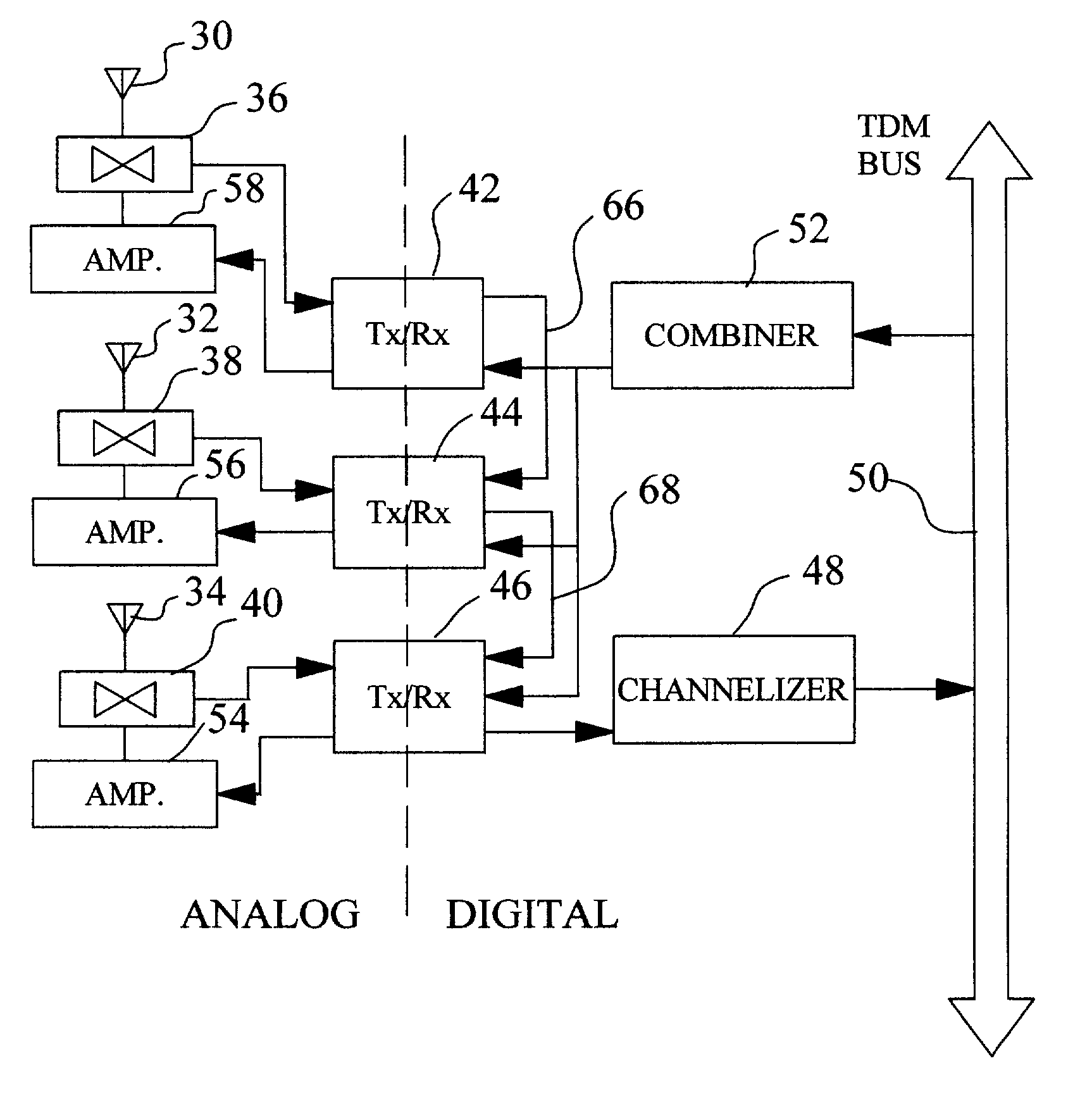
Sectorized cell having non-redundant broadband processing unit
InactiveUS6253094B1Low costReduce power levelMultiplex system selection arrangementsEnergy efficient ICTDigital dataTransceiver
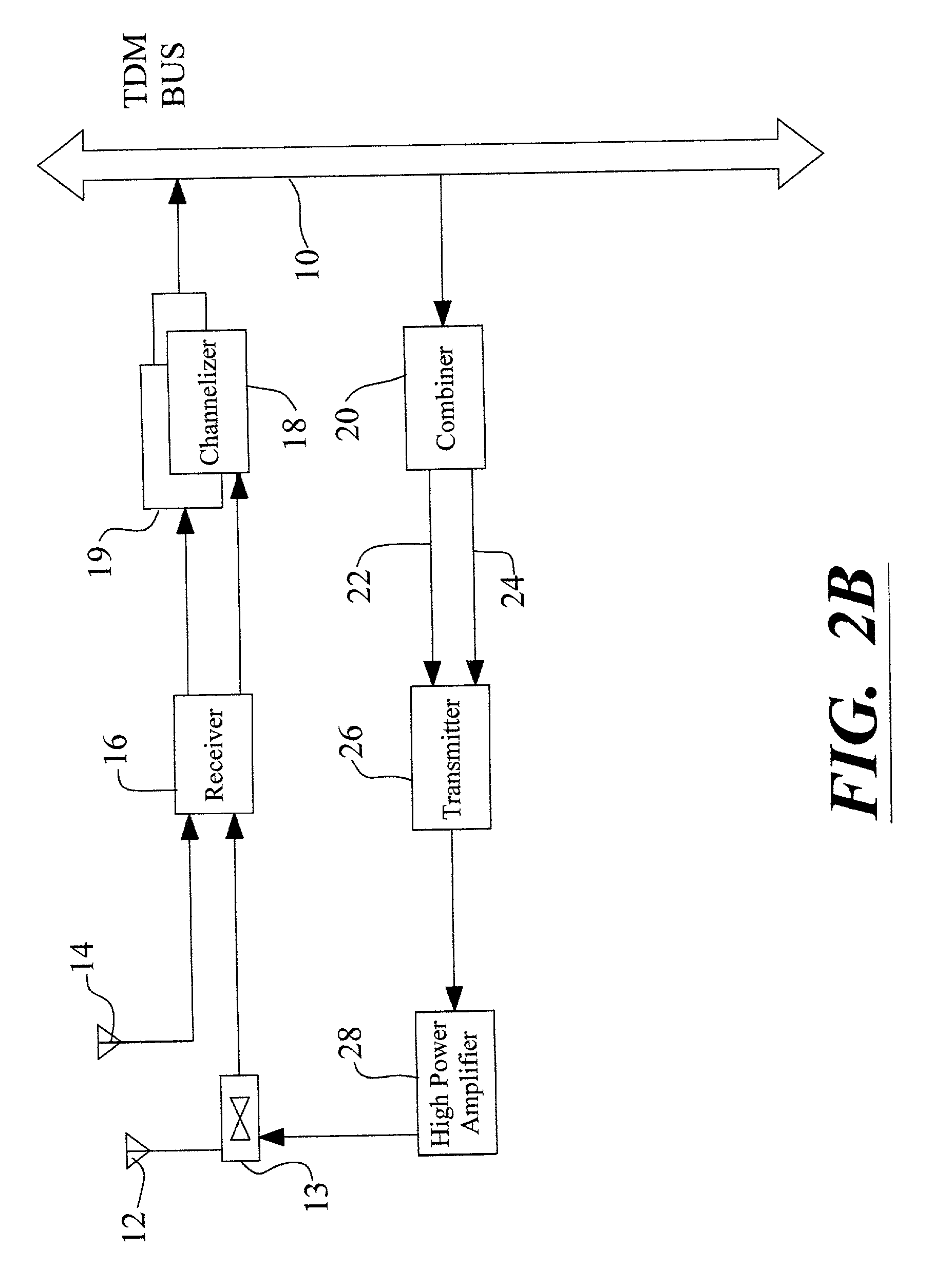
A technique for converting a non-sectorized cell to a sectorized cell having multiple sectors utilizing a single broadband processing unit. The spectrum of a given frequency band having a center frequency 'OMEGAo is divided into multiple bands (three, for example) having center frequencies 'OMEGAo, 'OMEGAo-alpha and 'OMEGAo+alpha. In the receive path, respective sub-bands are used to convey analog RF signals from a subscriber in respective sectors to an associated transceiver. Each of the transceivers includes a front end for receiving incoming RF signals and an analog-to-digital converter for converting the analog signal to a digital data stream. The digital data streams from transceivers are combined, i.e., processed by digitally adding, and supplied to a single channelizer which, in turn, supplies the data to a TDM bus for transmission to a PSTN network. In the reverse path from the PSTN network, TDM digital data signals emanating from a TDM bus are supplied to a combiner which feeds each of the respective transceivers which select the appropriate data from the combiner by digital filtering or processing. The transceivers convert the digital signal to analog form. After conversion, power amplifiers associated with the respective sectors effect emission of radiated power in the respective sectors. Advantageously, amplifiers in the sectorized improvement operate at lower power levels than the single high power amplifier of a non-sectorized cell, thereby providing substantial cost savings. More importantly, instead of deploying multiple broadband processing units the improved sectorized cell requires only a single broadband processing unit, thereby providing further economies.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Timed division multiplex bus connection controller
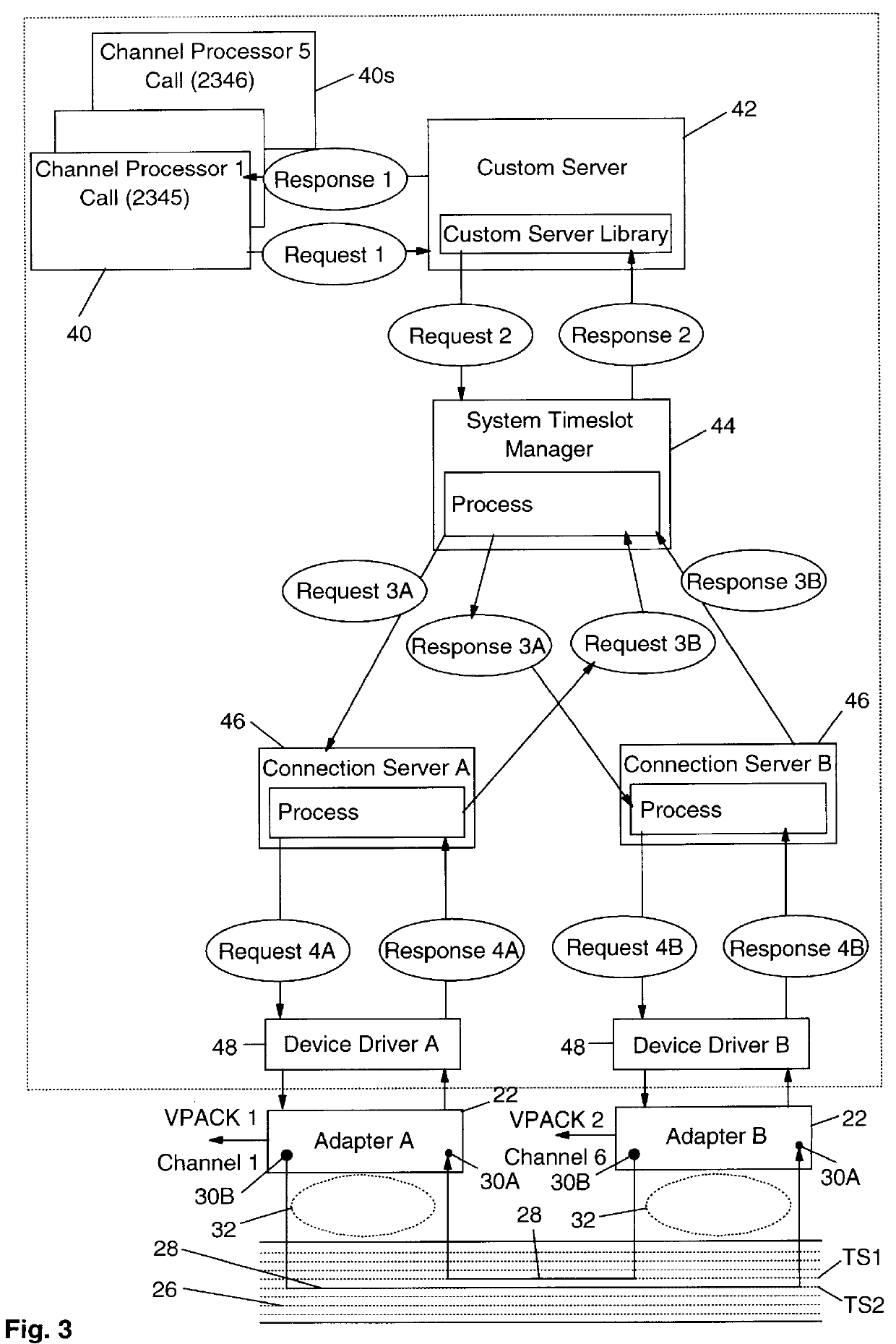
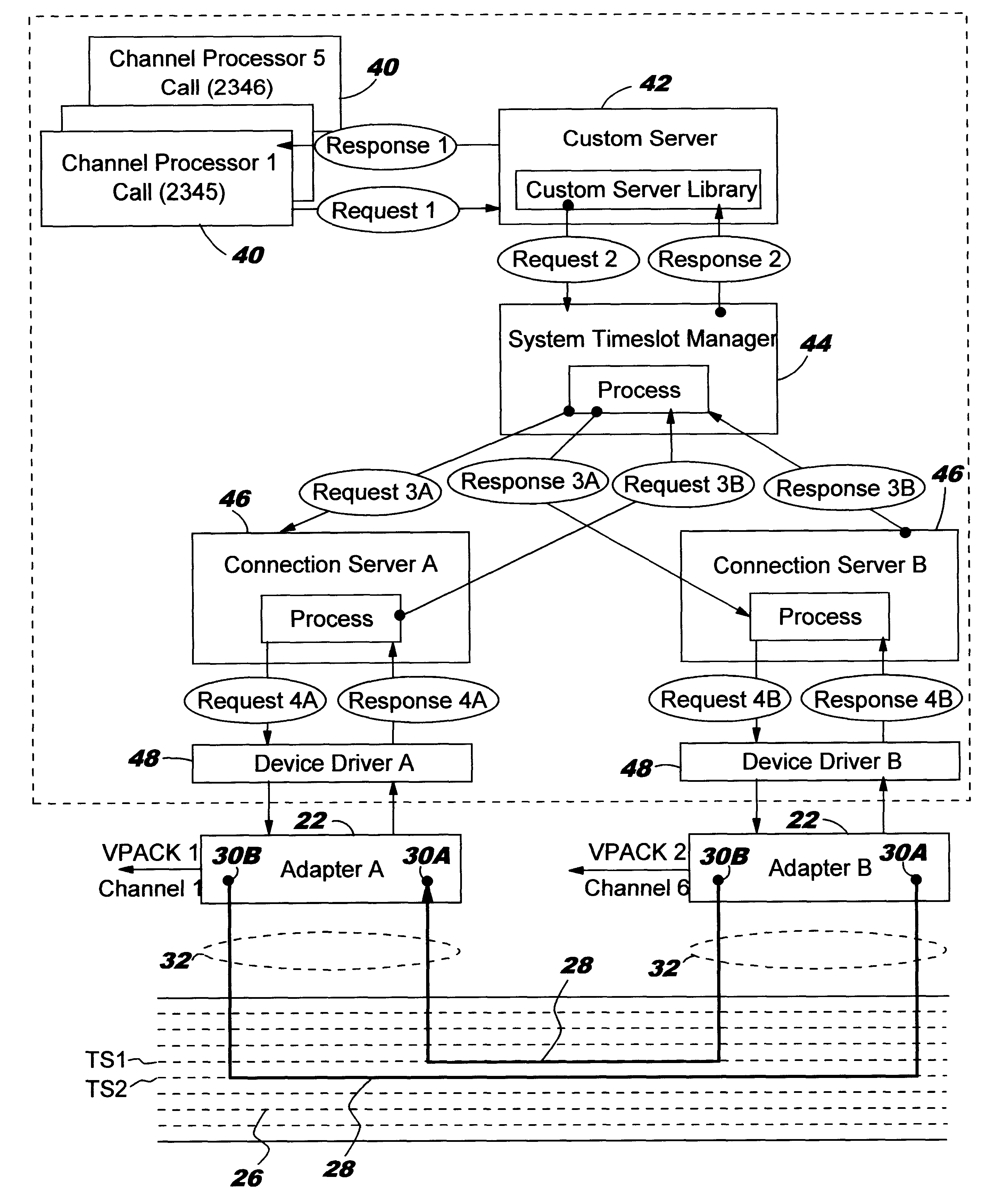
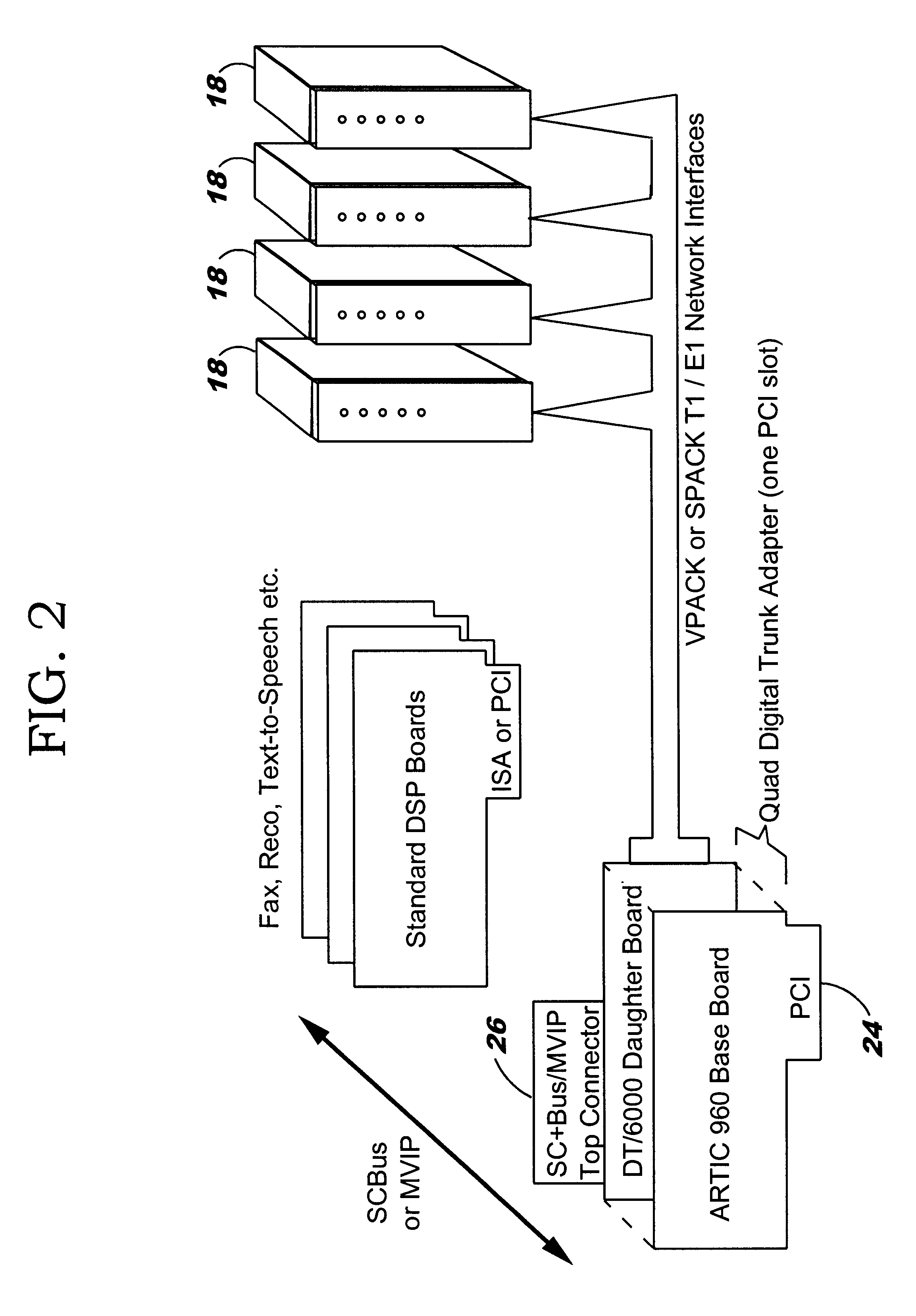
A bus connection controller in a voice processing is for managing the connection of a timeslot on a time-division multiplex (TDM) bus to a port on an adapter. The voice processing system includes basic time-division multiplex (TDM) connection management to enable the coordination of connections between resources such as channels on line cards (SPacks or VPacks), and channels on digital signal processor (DSPs) cards that provide, amongst others things, voice recognition, text-to-speech, fax capabilities and so on. One of the problems with known voice processing systems having a TDM bus is that there is no facility to allow the use of third party devices without modifications being made to the TDM connection controller. The bus controller comprises: a custom server 42 for sending a first request including a port identifier and using a first protocol for connection or disconnection of a port indicated by said port identifer on an adapter to the TDM bus 26; a timeslot manager for analyzing the first request to determine the port availability and state and for making a second request; device driver means (48), corresponding to the particular adapter, for sending the appropriate signals to the adapter to connect or disconnect the port on the adapter to a time slot 28 on the TDM; and a connection server 46, corresponding to a particular adapter, for analyzing the second request and for making a third request to the device driver means (48) using a second protocol for connection or disconnection of the port on that adapter to the TDM bus 26.
Owner:IBM CORP
Bus connection set up and tear down
A bus connection controller in a voice processing is for managing the connection of a timeslot on a time-division multiplex (TDM) bus to a port on an adapter. The voice processing system includes basic time-division multiplex (TDM) connection management to enable the coordination of connections between resources such as channels on line cards (SPacks or VPacks), and channels on digital signal processor (DSPs) cards that provide, amongst others things, voice recognition, text-to-speech, fax capabilities and so on. Problems are encountered when a telephone call in a voice processing system ends suddenly because one of the callers hangs up. If the telephony channel has connections with other channels or resources via a TDM bus, callers may hear spurious data. To address this problem each call is associated with its corresponding connection on the TDM bus and each connection is associated with its connection details including the adapters and ports involved in connecting the calls. When one of the calls ends all the relevant ports involved with the connection are immediately disconnected.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods for generating voice prompts using grammatical rules in a system proving TDM voice communications and VOIP communications
InactiveUS7181401B2Telephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersVoice communicationMulti protocol
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur in multiple modes / protocols are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided for multiple native mode / protocol voice and data transmissions and receptions with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus, and multi-protocol framing engines. Such systems preferably include subsystem functions such as PBX, voice mail and other telephony functions, LAN hub and data router. In preferred embodiments, a TDM bus and a packet bus are intelligently bridged and managed, thereby enabling such multiple mode / protocol voice and data transmissions to be intelligently managed and controlled with a single, integrated system. A computer or other processor includes a local area network controller, which provides routing and hub(s) for one or more packet networks. The computer also is coupled to a buffer / framer, which serves to frame / deframe data to / from the computer from TDM bus. The buffer / framer includes a plurality of framer / deframer engines, supporting, for example, ATM and HDLC framing / deframing. The buffer / framer is coupled to the TDM bus by way of a switch / multiplexer, which includes the capability to intelligently map data traffic between the buffer / framer and the TDM bus to various slots of the TDM frames. Preferably, a DSP pool is coupled to buffer / framer in a manner to provide various signal processing and telecommunications support, such as dial tone generation, DTMF detection and the like. The TDM bus is coupled to a various line / station cards, serving to interface the TDM bus with telephone, facsimiles and other telecommunication devices, and also with a various digital and / or analog WAN network services. Language support for such systems is accomplished by way of a program / data structure so that additional language support may be readily implemented, for example, by a non-software programmer using grammar and voice prompt files, which are preferably located in a predetermined directory in the system.
Owner:RPX CORP
Systems and methods for multiple mode voice and data communications using intelligenty bridged TDM and packet buses and methods for performing telephony and data functions using the same
InactiveUS7586908B2Effective supportPerformed conveniently and efficientlyFrequency-division multiplex detailsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingTelecommunications networkVoice data
Owner:RPX CORP
Systems and methods for voice and data communications including a scalable TDM switch/multiplexer
InactiveUS20110200034A1Effective supportPerformed conveniently and efficientlyTime-division multiplexNetwork connectionsCommunications systemMultiplexer
Integrated communications systems having a scalable or upgradable TDM switch fabric (i.e., e.g., TDM-controlling switch / MUX) are disclosed. At a first point in time a system is first sold, installed and utilized with a first TDM capacity, using a first TDM switch / MUX controlling a first set of TDM streams operating at a first frequency. A first set of line and other cards (e.g., DSP resources) are provided to provide or receive the first set of TDM streams. At a second point in time the system is upgraded by installation of a second TDM switch / MUX; the second TDM switch MUX controls the first set of TDM streams operating at the first frequency and also controls a second set of TDM streams operating at second frequency, which is a frequency different and preferably higher as compared to the first frequency. With at least some of the first cards coupled to the TDM bus, the second TDM switch / MUX couples TDM streams to and from the first cards using the first streams at the first frequency, while concurrently coupling TDM streams to and from the second cards using the second streams at the second frequency. The first switch / MUX preferably operates concurrently with the second switch / MUX to couple streams to and from the TDM bus (e.g., from an HDLC or multi-protocol framing engine, etc.), while the first switch / MUX does not operate to control the TDM bus, as this function is carried out by the second switch / MUX.
Owner:RPX CORP
Systems and methods for voice and data communications including a network drop and insert interface for an external data routing resource
InactiveUS7706359B2Effective supportPerformed conveniently and efficientlyData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionTelecommunications linkVoice data
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus. An integrated communication system is coupled to a digital telecommunications link, the communication system providing voice and data communications to a plurality of users. At least a first packet bus is coupled to one or more packet-based devices and adapted for transferring packetized data to and from the system. One or more time division multiplex (TDM) buses are coupled to one or more telephony devices. Data routing resources are provided internal to the integrated system. A network interface module couples data to and from a data router external to the integrated system. The data router external to the integrated system is coupled to the first packet bus. Data is routed via the external data router through the network interface module and coupled to data channels of the digital telecommunications link, while voice data is selectively coupled to voice channels of the digital telecommunications link.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
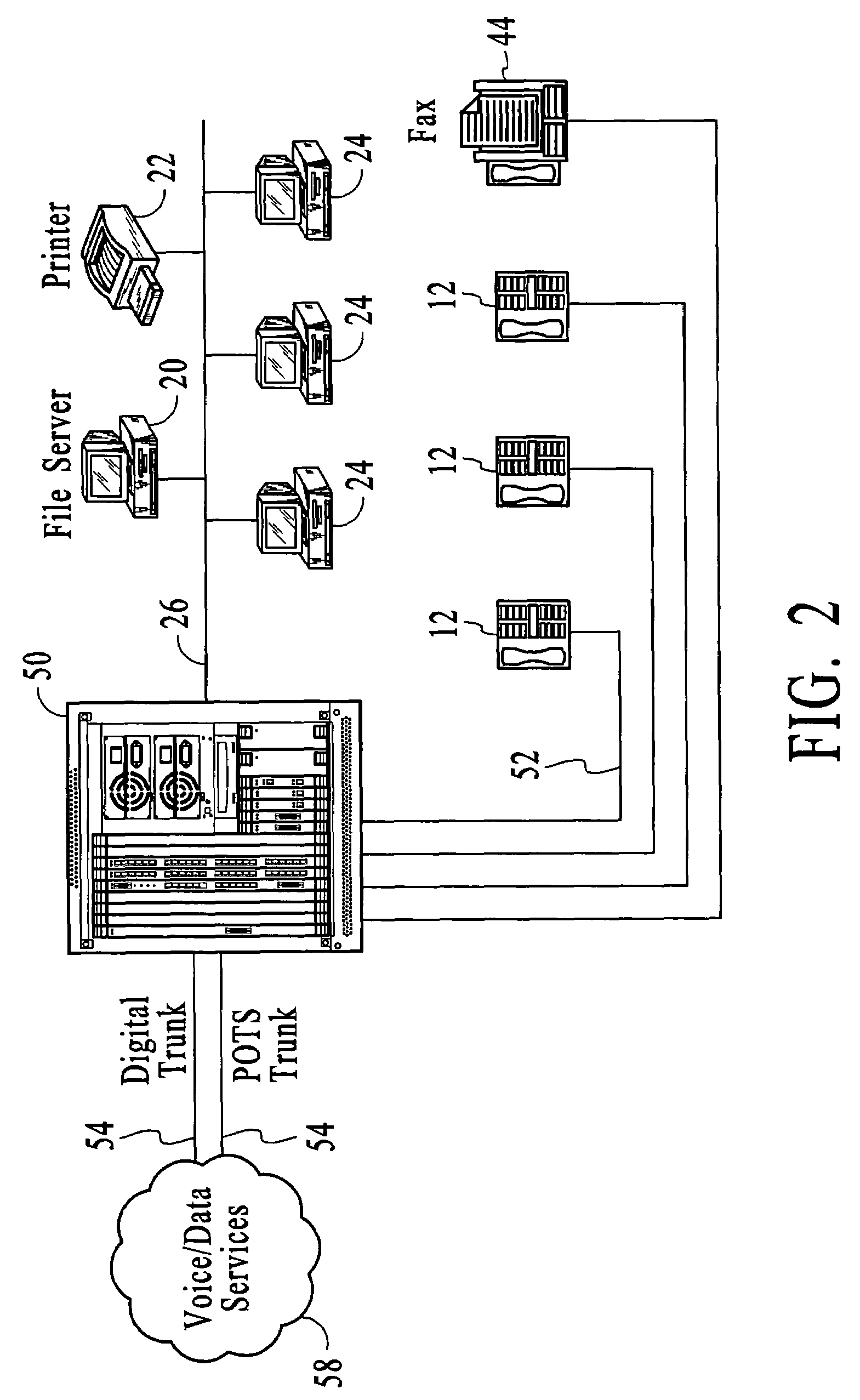
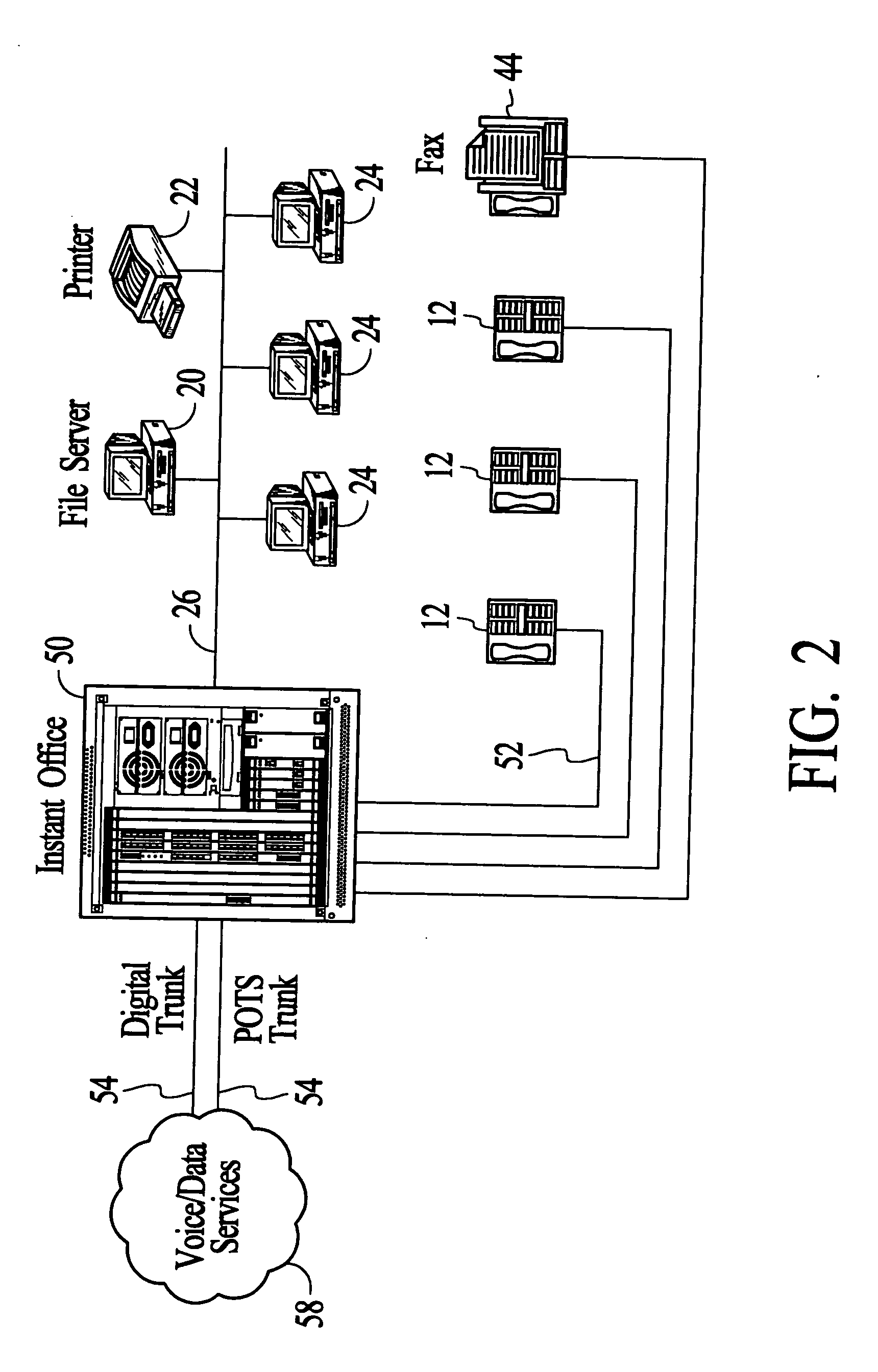
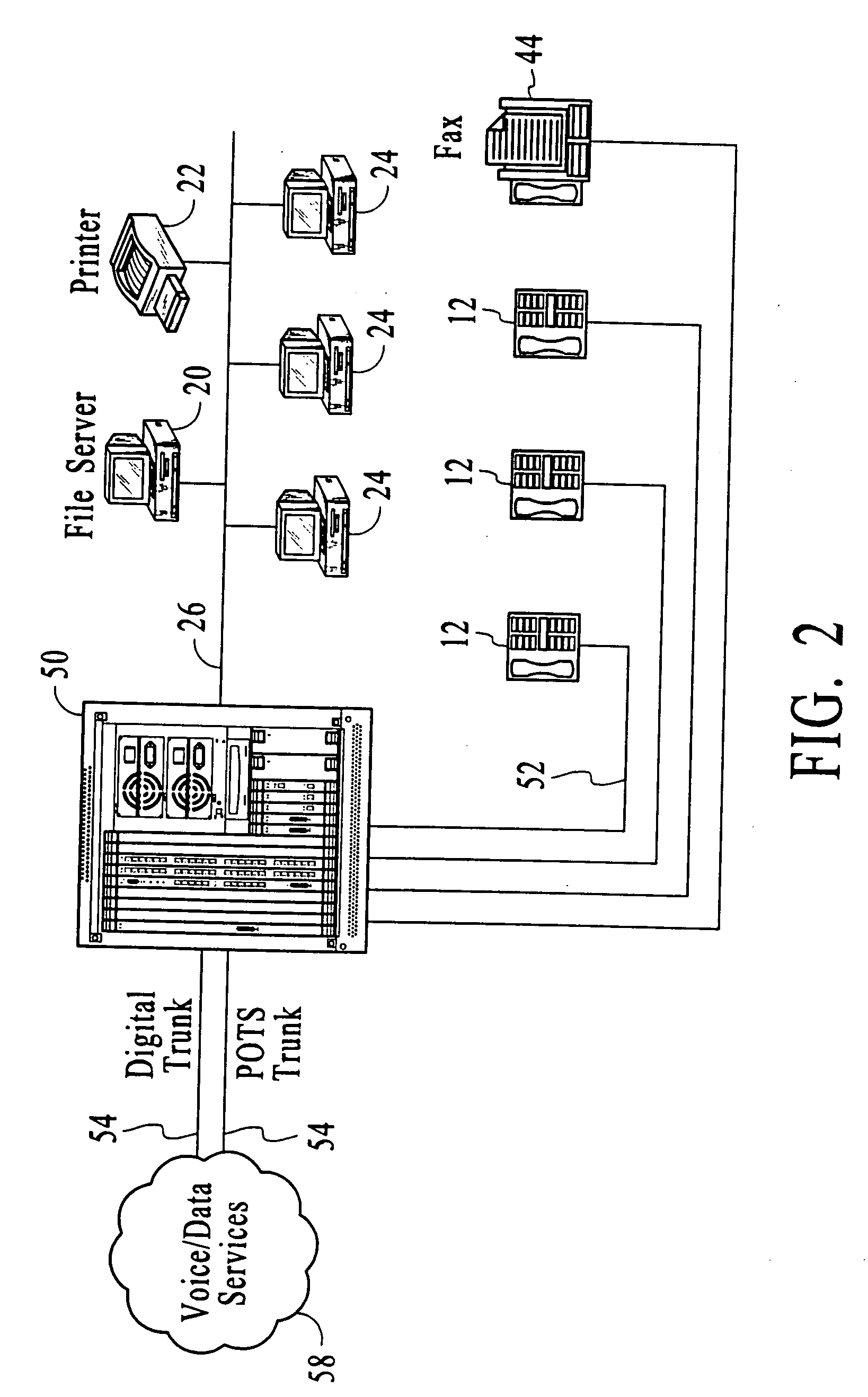
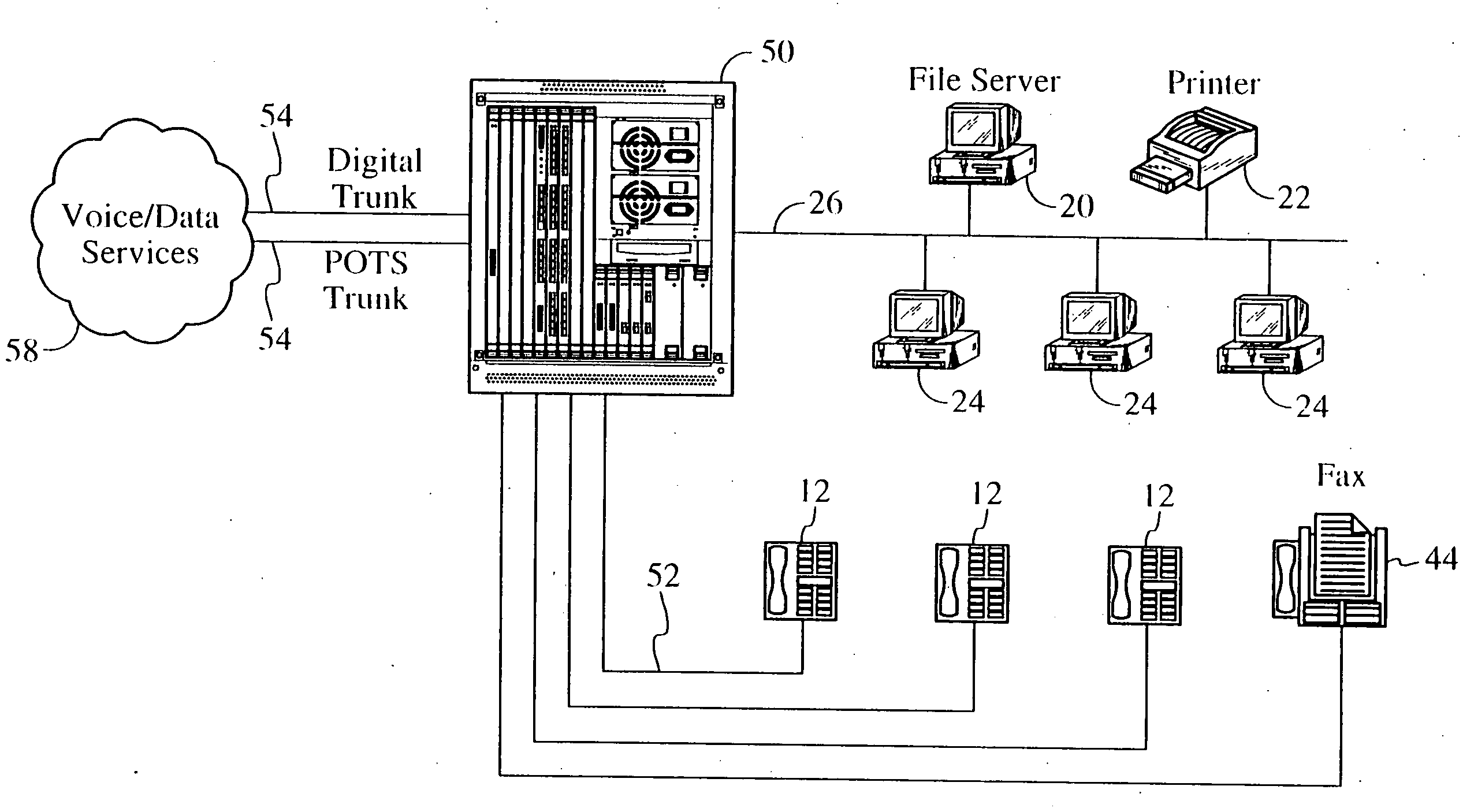
Systems and methods for TDM/packet communications using telephony station cards including voltage generators
InactiveUS20070036150A1Effective supportEasy to upgradeHybrid switching fabricsSpecial service for subscribersPacket communicationMulti protocol
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur in multiple modes / protocols are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided for multiple native mode / protocol voice and data transmissions and receptions with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus, and multi-protocol framing engines. Such systems preferably include subsystem functions such as PBX, voice mail and other telephony functions, LAN hub and data router or switch functions. In preferred embodiments, a TDM bus and a packet bus are intelligently bridged and managed, thereby enabling such multiple mode / protocol voice and data transmissions to be intelligently managed and controlled with a single, integrated system. In particular, systems and methods for generating required telephony voltages directly on station cards, rather than on the basis of a large, central ringing or other power supply that supply such telephony voltages to each of the station cards, are disclosed. In accordance with the present invention, a plurality of station cards are provided in the telephony or communications system. One or more DC power supplies provide a source of DC voltage, such as 12 volts, to each of the station cards. The station cards are coupled to a processor of the system. The station cards may support a plurality of analog and / or digital telephony devices, such as telephones facsimile, voice mail, recording, speakerphone, conferencing or other type telephony devices.
Owner:RPX CORP
Systems and methods for voice and data communications including a scalable TDM switch/multiplexer
InactiveUS7869424B2Effective supportPerformed conveniently and efficientlyTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionCommunications systemMultiplexer
Integrated communications systems having a scalable or upgradable TDM switch fabric (i.e., e.g., TDM-controlling switch / MUX) are disclosed. At a first point in time a system is first sold, installed and utilized with a first TDM capacity, using a first TDM switch / MUX controlling a first set of TDM streams operating at a first frequency. A first set of line and other cards (e.g., DSP resources) are provided to provide or receive the first set of TDM streams. At a second point in time the system is upgraded by installation of a second TDM switch / MUX; the second TDM switch MUX controls the first set of TDM streams operating at the first frequency and also controls a second set of TDM streams operating at second frequency, which is a frequency different and preferably higher as compared to the first frequency. With at least some of the first cards coupled to the TDM bus, the second TDM switch / MUX couples TDM streams to and from the first cards using the first streams at the first frequency, while concurrently coupling TDM streams to and from the second cards using the second streams at the second frequency. The first switch / MUX preferably operates concurrently with the second switch / MUX to couple streams to and from the TDM bus (e.g., from an HDLC or multi-protocol framing engine, etc.), while the first switch / MUX does not operate to control the TDM bus, as this function is carried out by the second switch / MUX.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
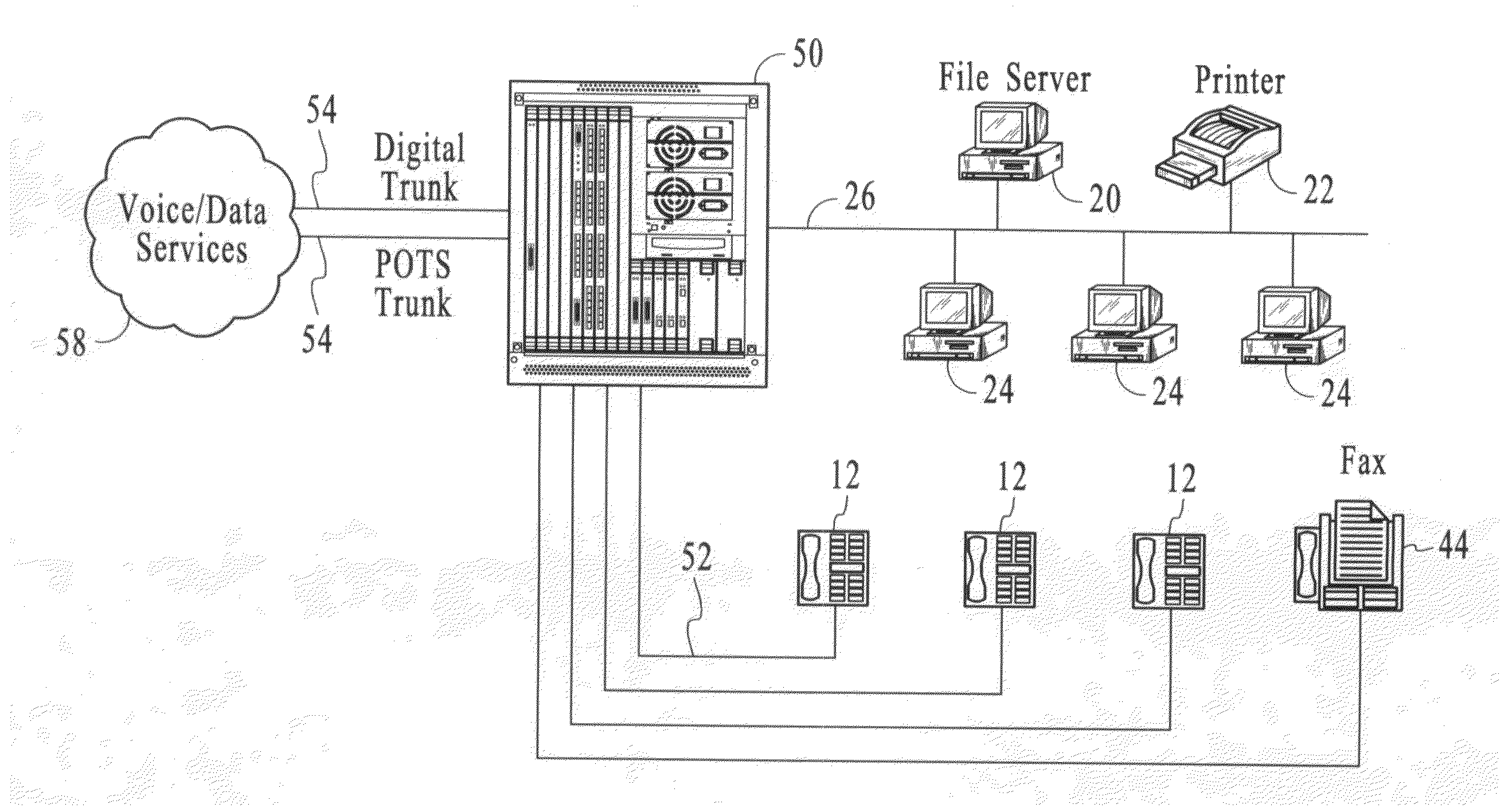
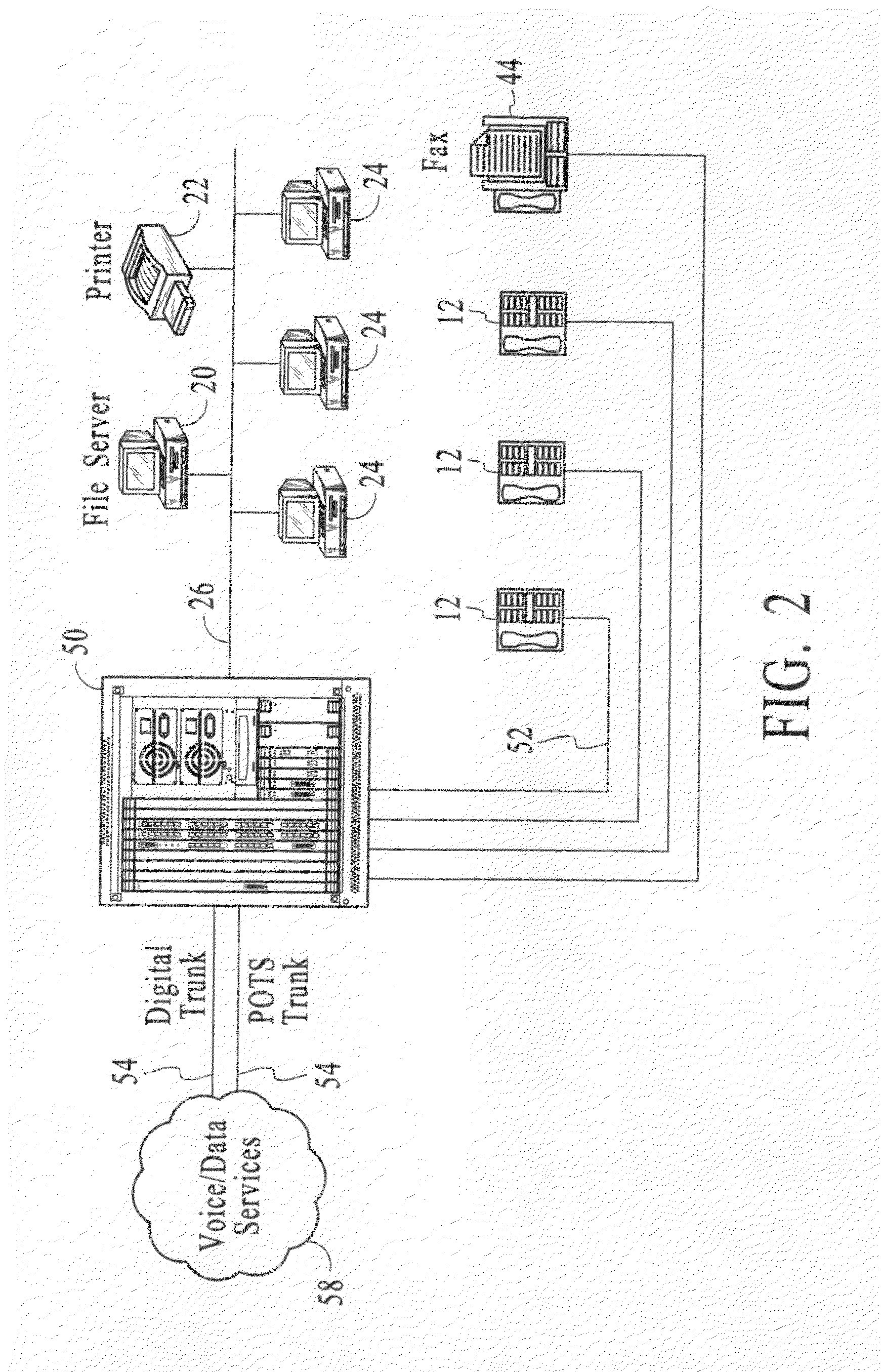
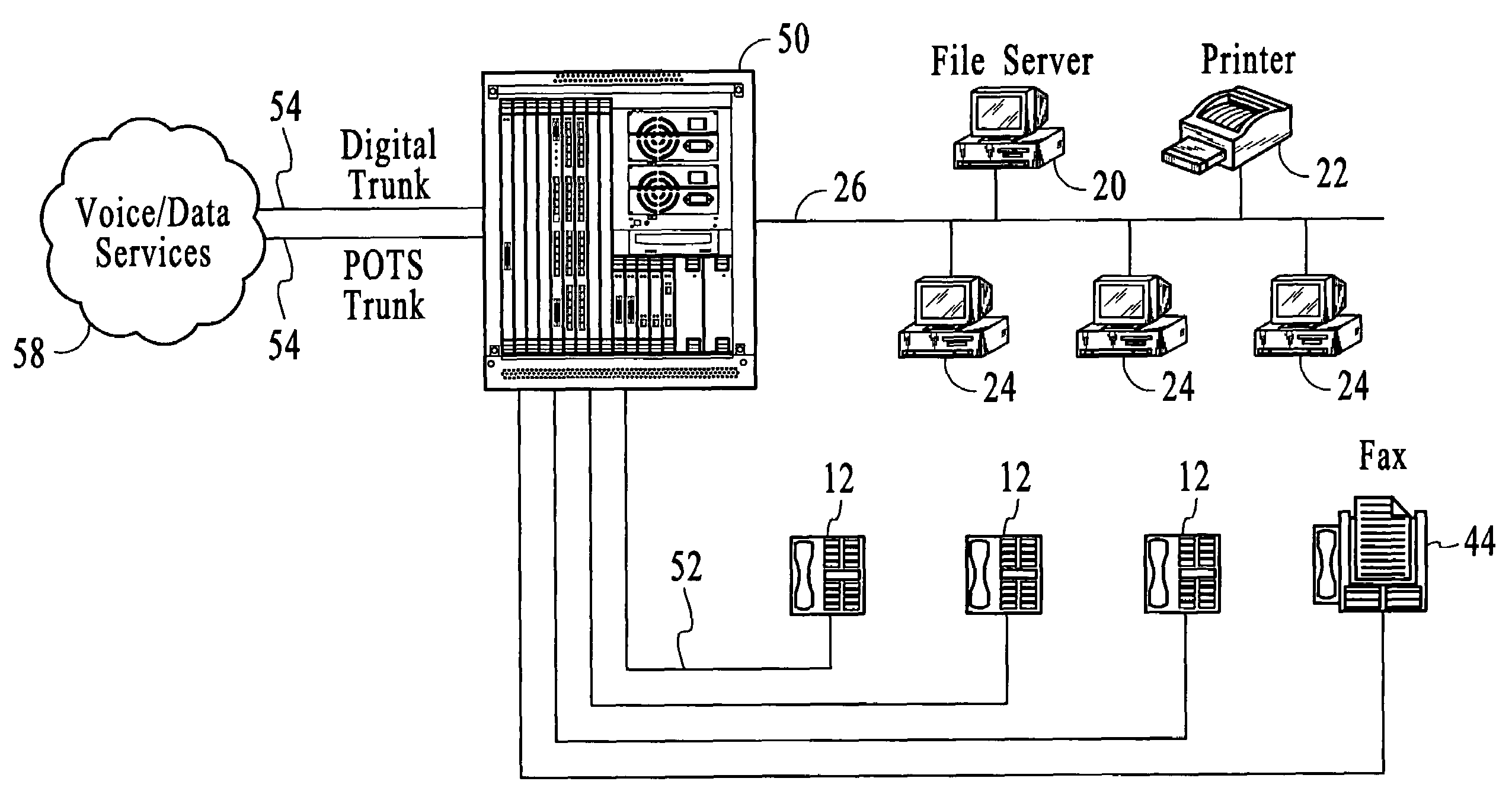
Method and apparatus for interfacing multiple communication devices to a time division multiplexing bus
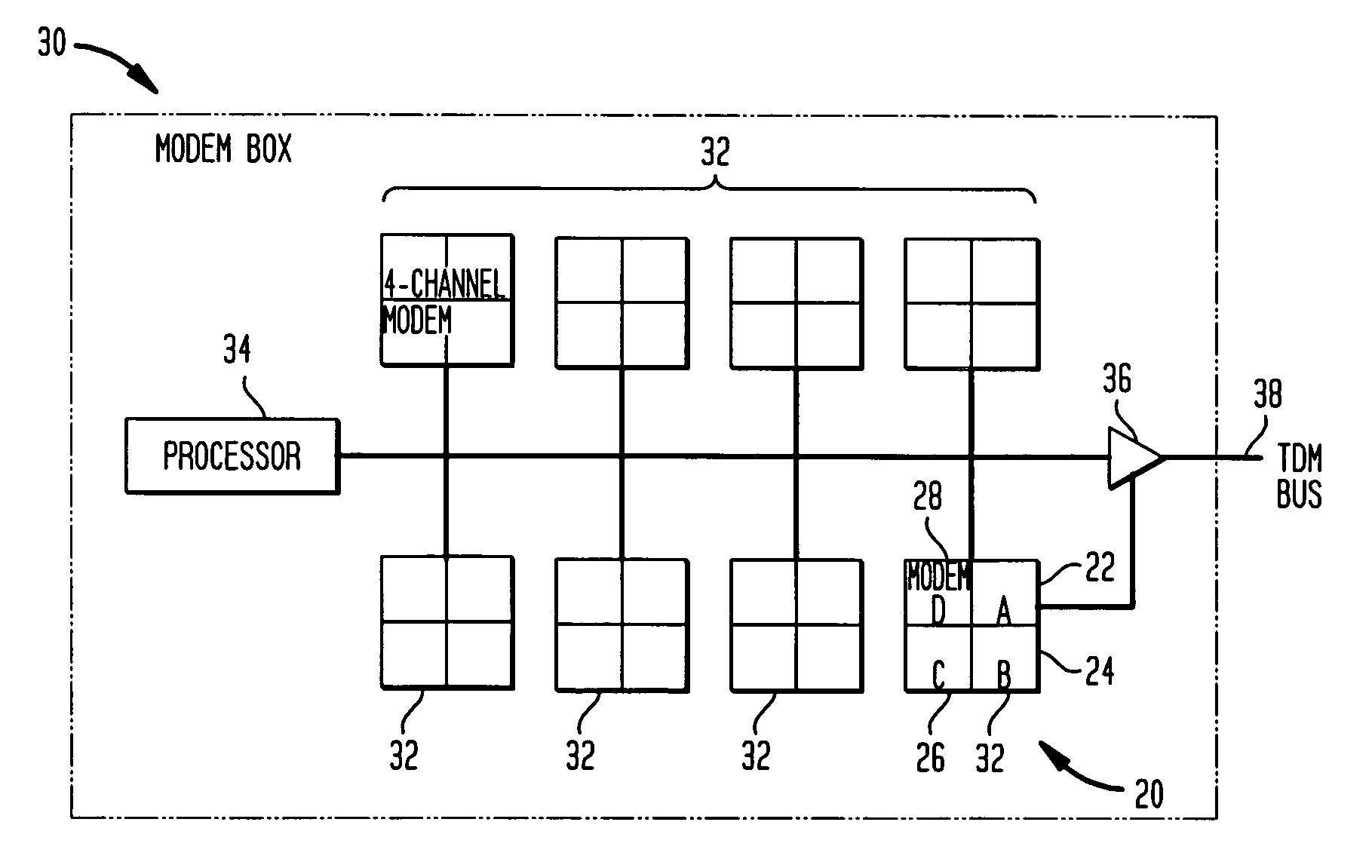
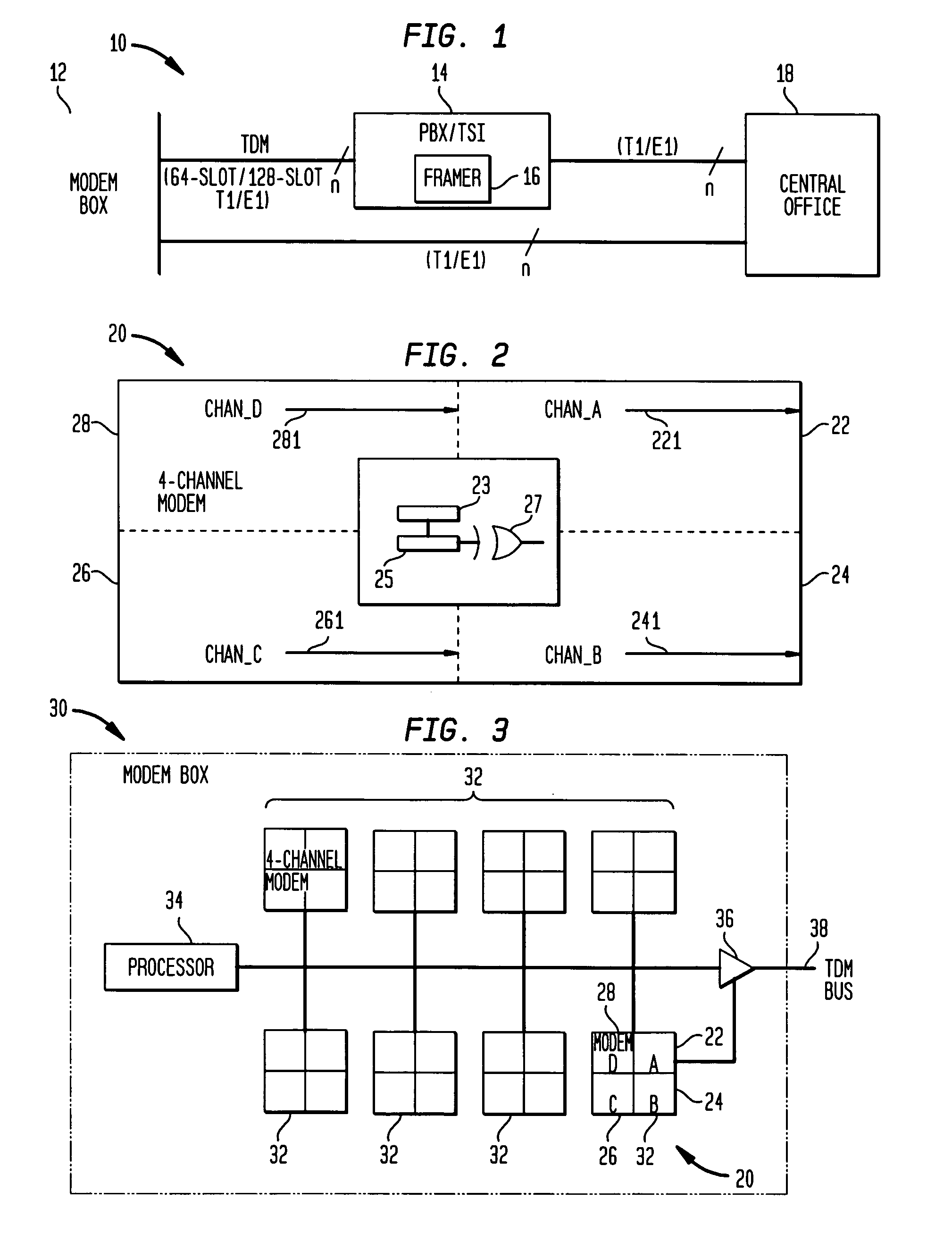
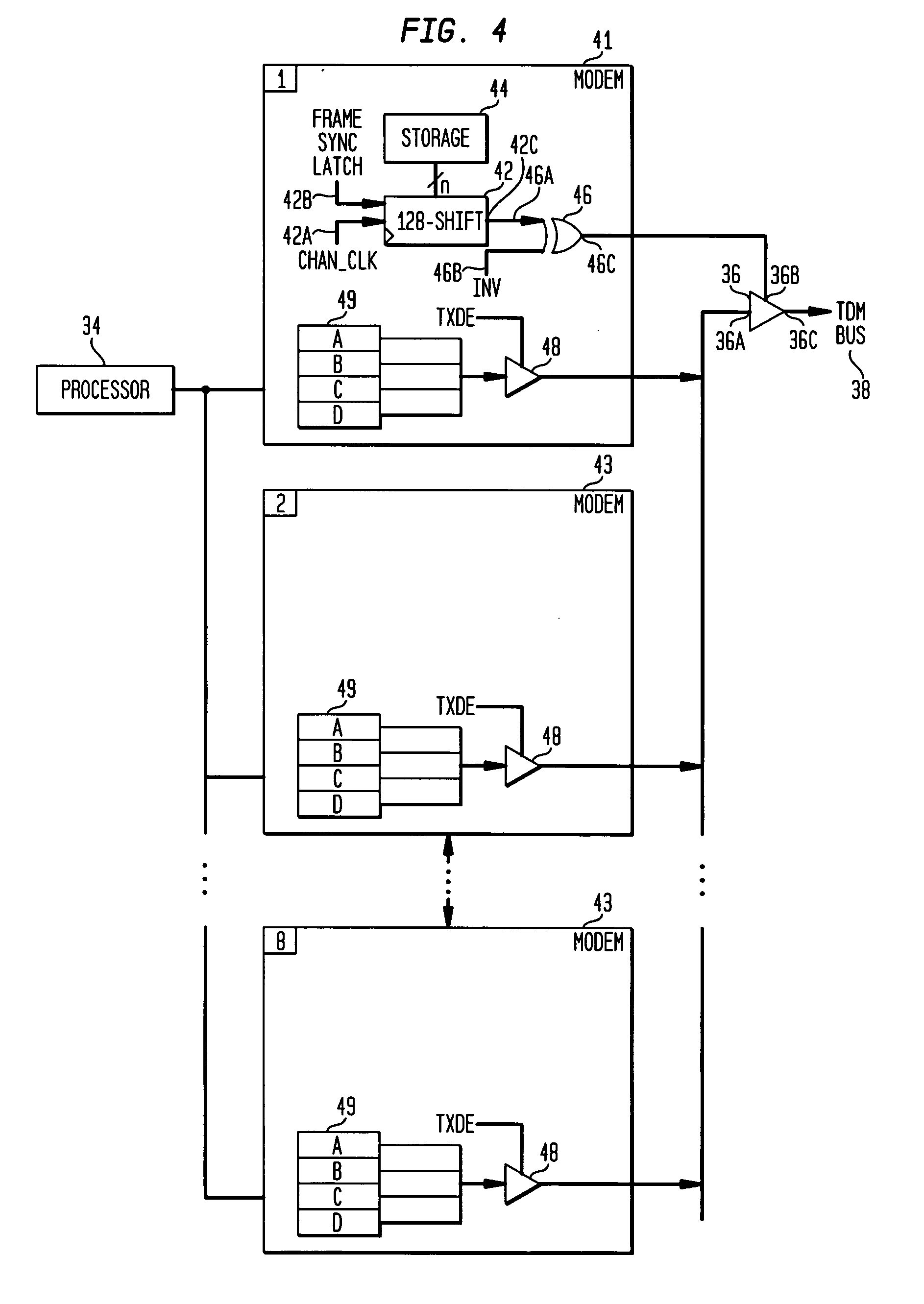
A time division multiplexing (TDM) method and apparatus for interfacing data from communication channels to a TDM bus. The TDM arrangement uses a shift register to control a tri-state buffer. The shift register regulates the tri-state buffer based on a data bit pattern loaded into the shift register. The data bit pattern corresponds to the status of the individual channels. Each channel is assigned a bit which indicates whether the channel is active or inactive. As the shift register shifts out data, the tri-state buffer allows data to flow onto the TDM bus when a bit indicating an active channel is present and insulates the TDM bus from the communication channels when a bit representing an inactive channel is present. A processor is used to control the interrelationship of the multiple communication channels and to generate the status bits to be loaded into the shift register. The processor fills the shift register through the use of a storage register. In a preferred embodiment, the shift register is capable of shifting out a sufficient number of bits to fill an entire transmission frame operating in T1 (24 channels), E1 (32 channels), 64-slot (64 channels), and 128-slot (128 channels) transmission modes. In addition, the tri-state buffer may perform the additional function of level shifting the voltage level of the data from the multiple communication channels to a level compatible with the TDM bus.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Microcomputer relay protection device based on serial bus technology
ActiveCN102437550AWith data verification functionThe connection relationship is simpleEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric digital data processingMicrocomputerArea network
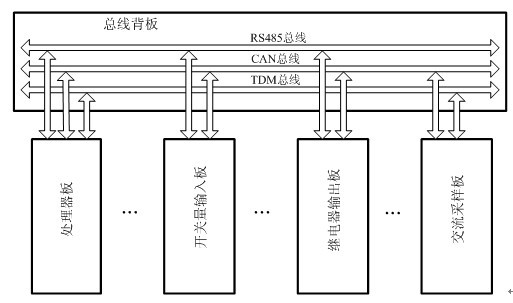
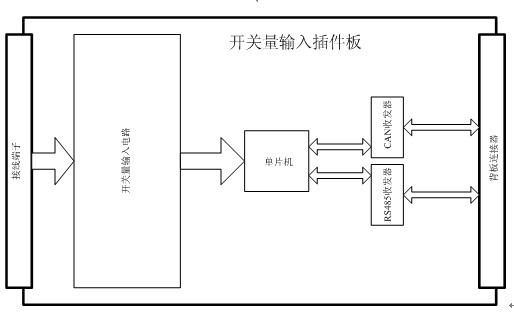
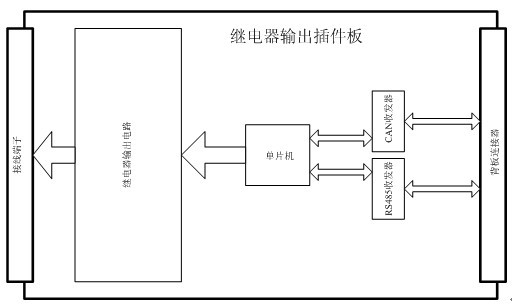
The invention discloses a microcomputer relay protection device based on a serial bus technology. On the basis of a design mode of backplanes and plug-in boards, the microcomputer relay protection device mainly comprises a master processor plug-in board, an on-off input plug-in board, a relay output plug-in board and an analog input plug-in board, wherein, the plug-in boards are connected through serial backplane buses. In the microcomputer relay protection device, a CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, an RS485 bus and a TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) bus are utilized as connecting channels of board cards. The microcomputer relay protection device has the advantages that as the serial buses are adopted instead of special connecting lines and parallel buses, the connecting lines for the backplanes are reduced, the flexibility and reliability are enhanced and the complexity of the device is lowered; and meanwhile by adopting the serial buses, a self-check function and a heartbeat return function are added for all I / O (input / output) board cards so that the device can monitor the working state in real time and an alarm can be timely sent in case of an internal fault.
Owner:NANJING INTELLIGENT APP
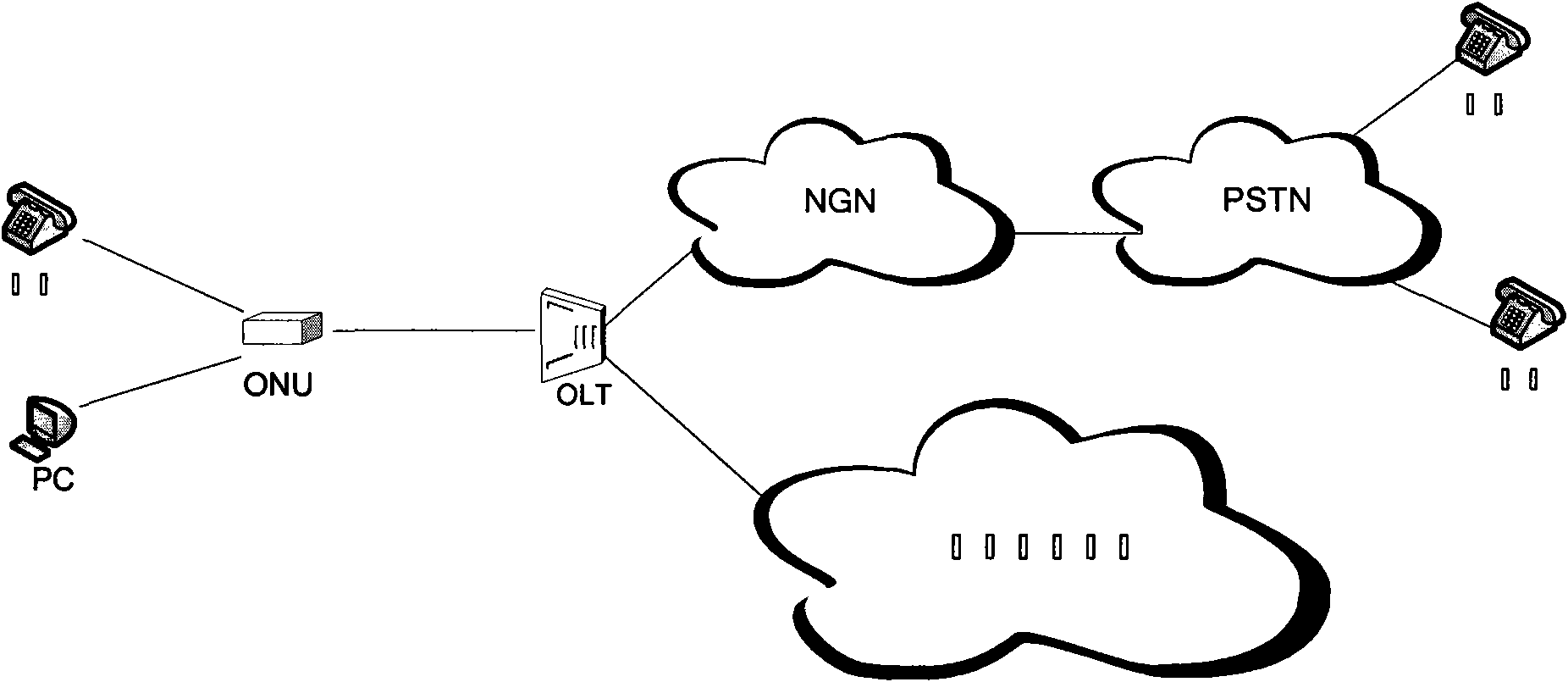
Plugboard type FTTB (Fiber To The Building) type ONU (Optical Network Unit) and method for realizing voice service
InactiveCN101841747ASolve the problem of resource bottleneckEasy to handleMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionDigital signal processingFiber
The invention discloses a plugboard type FTTB (Fiber To The Building) type ONU (Optical Network Unit) and a method for realizing a voice service. The plugboard type FTTB type ONU comprises a backboard, a main control disk and a plurality of service disks, wherein at least one of the service disks is a voice service disk; and the main control disk and a plurality of service disks are respectively inserted into the backboard and are mutually connected through an IP (Internet Protocol) bus on the backboard. In the invention, a DSP (Digital Signal Processing) module is placed on the voice servicedisk, so that the main control disk is connected with the voice service disk through the IP bus; the invention changes the traditional mode of TDM (Time Division Multiplex) bus communication and simplifies a backboard circuit and a system structure; and according to the proportion for provisioning the voice service, DSP resources can be flexibly allocated, the processing capacity of the system onthe voice service can be improved, and the problem of the bottleneck of the DSP resources can be solved.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
High voltage DC control protection system board card testing device
InactiveCN108051726AFlexible configurationSupport online Hibug functionElectronic circuit testingElectric testing/monitoringHuman–machine interfaceInformation access
The invention discloses a high voltage DC control protection system board card testing device comprising a man-machine interface, a control unit, an analog quantity generator, a switching value generator, a communication module and a physics interface module; the control unit and the physics interface module are kept in a CAN bus, TDM bus and Ethernet connection through the communication module, wherein the CAN bus transmits the switching value information, the TDM bus transmits the analog quantity information, and the Ethernet transmits the board card information; the control unit obtains theboard card information accessing the physics interface module through the communication module, starts a corresponding testing flow according to the board card information, and uses the analog quantity generator and the switching value generator to send a test signal to the physics interface module according to the testing flow; the control unit uses the communication module to obtain the test result of the to-be-tested board card, and displays the test result on the man-machine interface. The testing device can test a plurality of board cards of the same or different types in one time, and the detection steps are simple and direct, thus effectively finishing the test works of the high voltage DC control protection system board card.
Owner:国网河南省电力公司超高压公司 +1
Systems for voice and data communications having TDM and packet buses and telephony station cards including voltage generators
InactiveUS7072330B2Effective supportEasy to upgradeHybrid switching fabricsSpecial service for subscribersMulti protocolMultiple modes
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur in multiple modes / protocols are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided for multiple native mode / protocol voice and data transmissions and receptions with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus, and multi-protocol framing engines. Such systems preferably include subsystem functions such as PBX, voice mail and other telephony functions, LAN hub and data router or switch functions. In preferred embodiments, a TDM bus and a packet bus are intelligently bridged and managed, thereby enabling such multiple mode / protocol voice and data transmissions to be intelligently managed and controlled with a single, integrated system. In particular, systems and methods for generating required telephony voltages directly on station cards, rather than on the basis of a large, central ringing or other power supply that supply such telephony voltages to each of the station cards, are disclosed. In accordance with the present invention, a plurality of station cards are provided in the telephony or communications system. One or more DC power supplies provide a source of DC voltage, such as 12 volts, to each of the station cards. The station cards are coupled to a processor of the system. The station cards may support a plurality of analog and / or digital telephony devices, such as telephones facsimile, voice mail, recording, speakerphone, conferencing or other type telephony devices.
Owner:RPX CORP
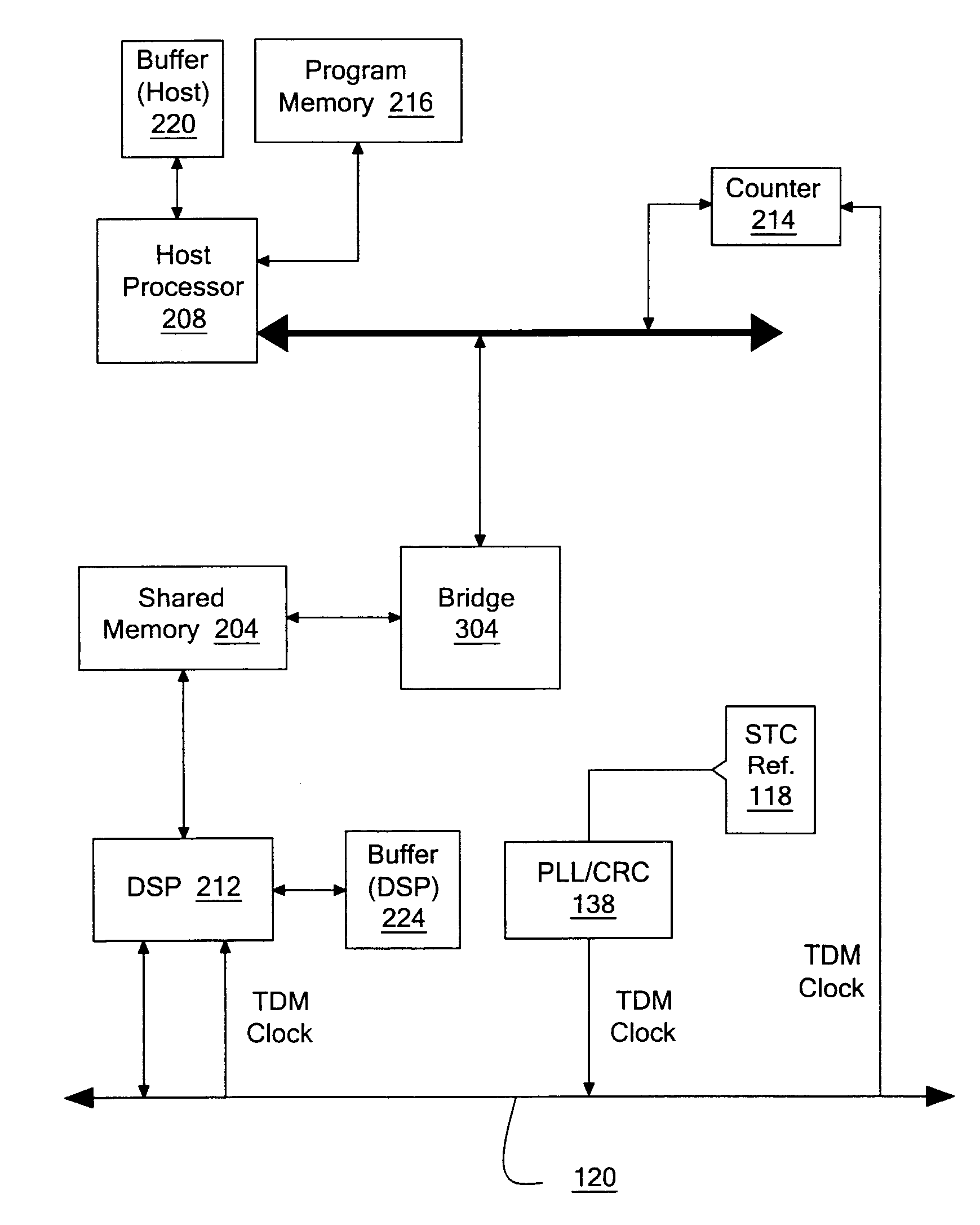
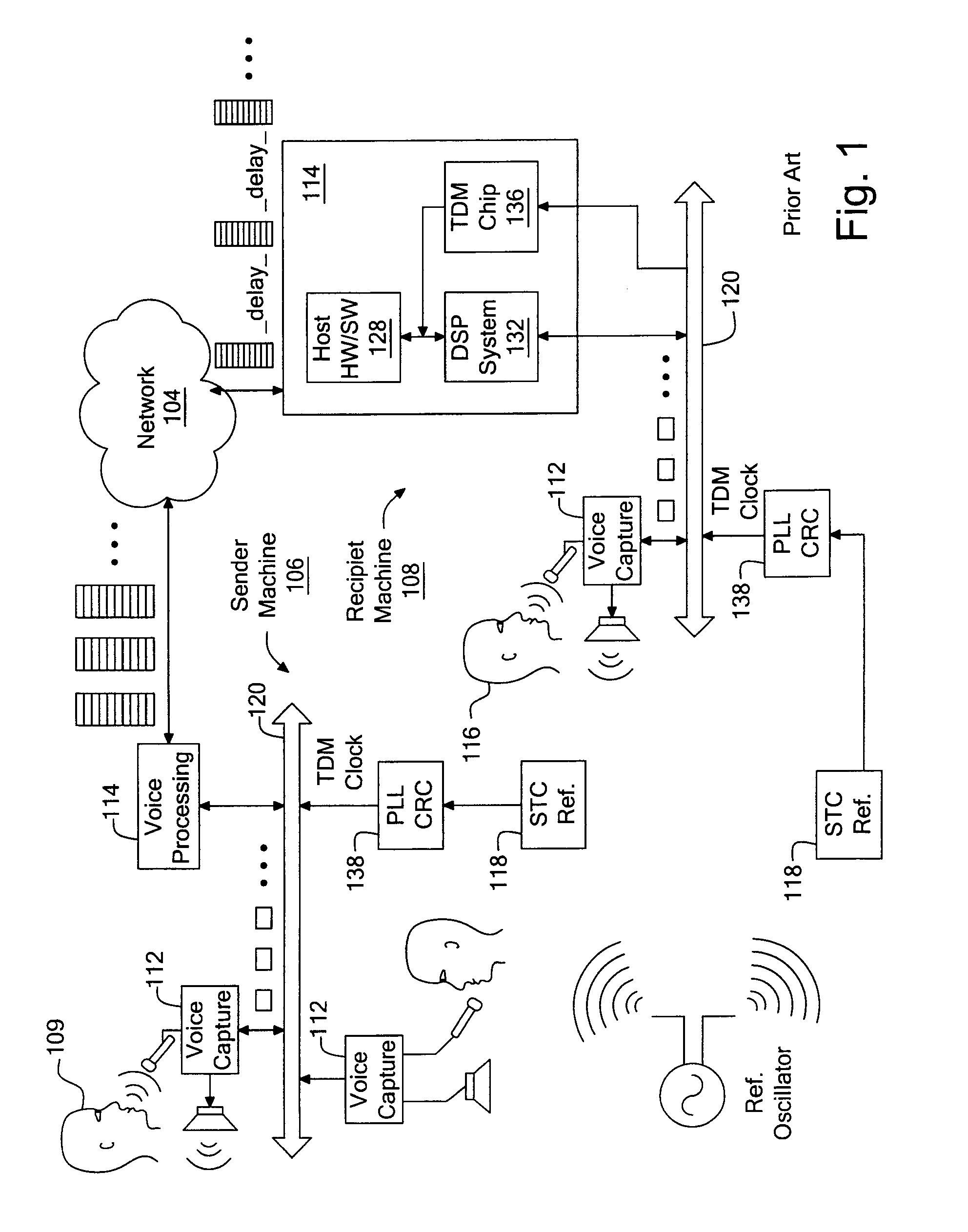
Stratum traceable clock driver for voice dejittering and control
InactiveUS6856615B1Low costImprove design flexibilityTime-division multiplexNetwork connectionsNetwork packetSpeech sound
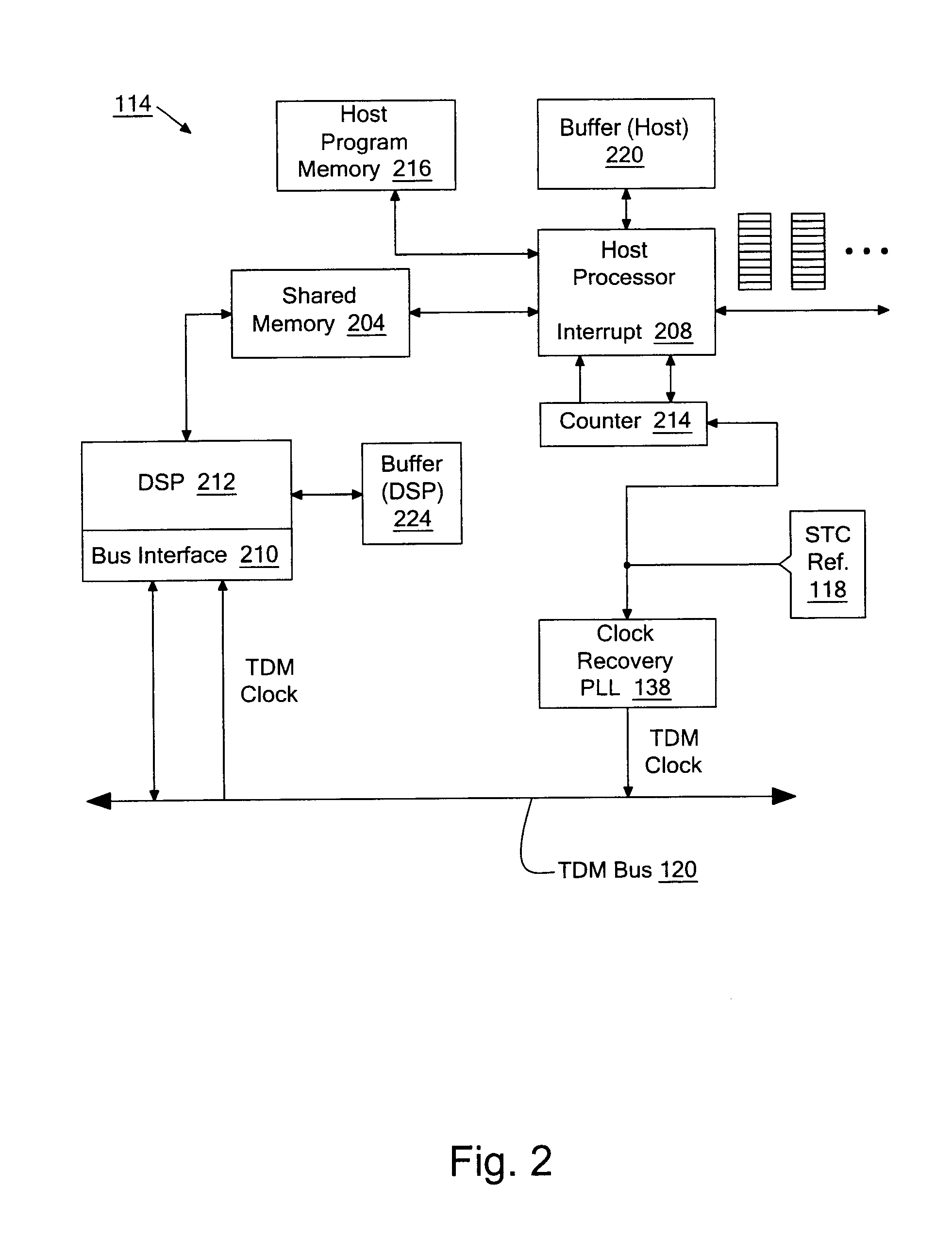
According to an embodiment of the invention, the voice processing logic for a node in a packet-based network includes a shared memory, a counter to be clocked by a signal derived from a stratum traceable clock (STC) reference, a processor, a digital signal processor (DSP) system, and an interface to a time division multiplexed (TDM) bus. The processor is to execute a number of instructions stored in program memory, to thereby process voice payload into a number of voice packets, where the voice payload has been obtained from a number of network packets sent by the sender machine through the network. The host system buffers the voice packets before writing them to the shared memory. One or more voice packets are written in response to a processor interrupt received from the counter. The DSP system is to read the voice packets from the shared memory before processing them, while the TDM bus interface transmits voice data of one or more channels, from the packets processed by the DSP system, over the TDM bus and according to a TDM bus clock. This bus clock is also derived from the STC reference. In this way, the transfer of packets from the host to the DSP is controlled to correspond to the STC reference, so that the delivery and pickup of the voice stream at the TDM bus occurs at essentially the same rate as their counterparts in the sender machine. Such an effect may be achieved without requiring a dedicated TDM controller chip.
Owner:CALIX
Telecommunication systems
InactiveUS20050249205A1Simple methodFlexibility rangeMultiplex communicationData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsSignal on
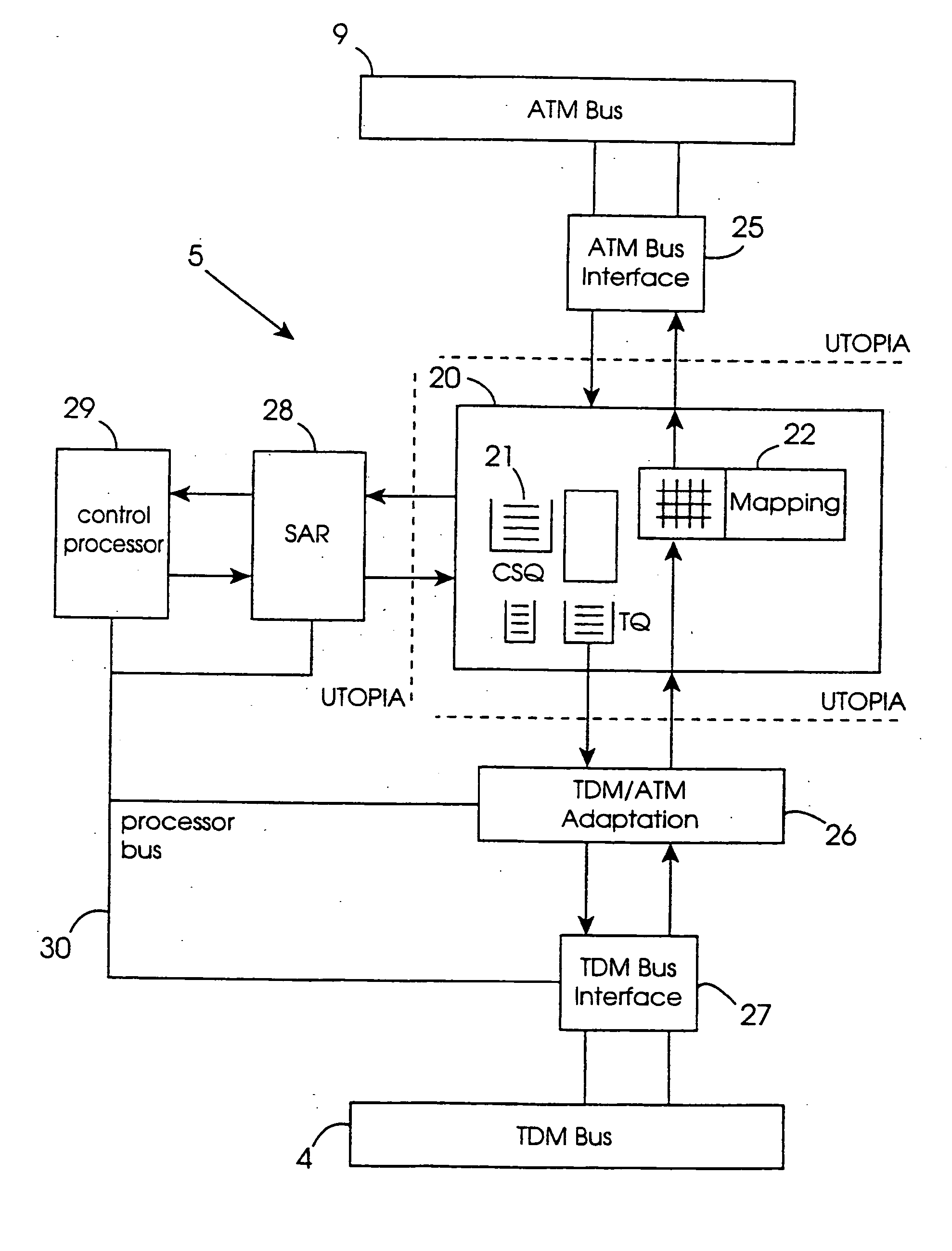
A telecommunication system (1) provides bi-directional communication between TDM signals on one side and ATM signals on the other. An ATM aggregate (10) receives and transmits ATM signals, and a TDM interface (2) receives and transmits TDM signals. A format converter has an ATM bus (9) and a TDM bus (4) connected to their respective interfaces. Service-specific adapters (5-8) are connected between the buses.
Owner:TELLABS EMEA HLDG
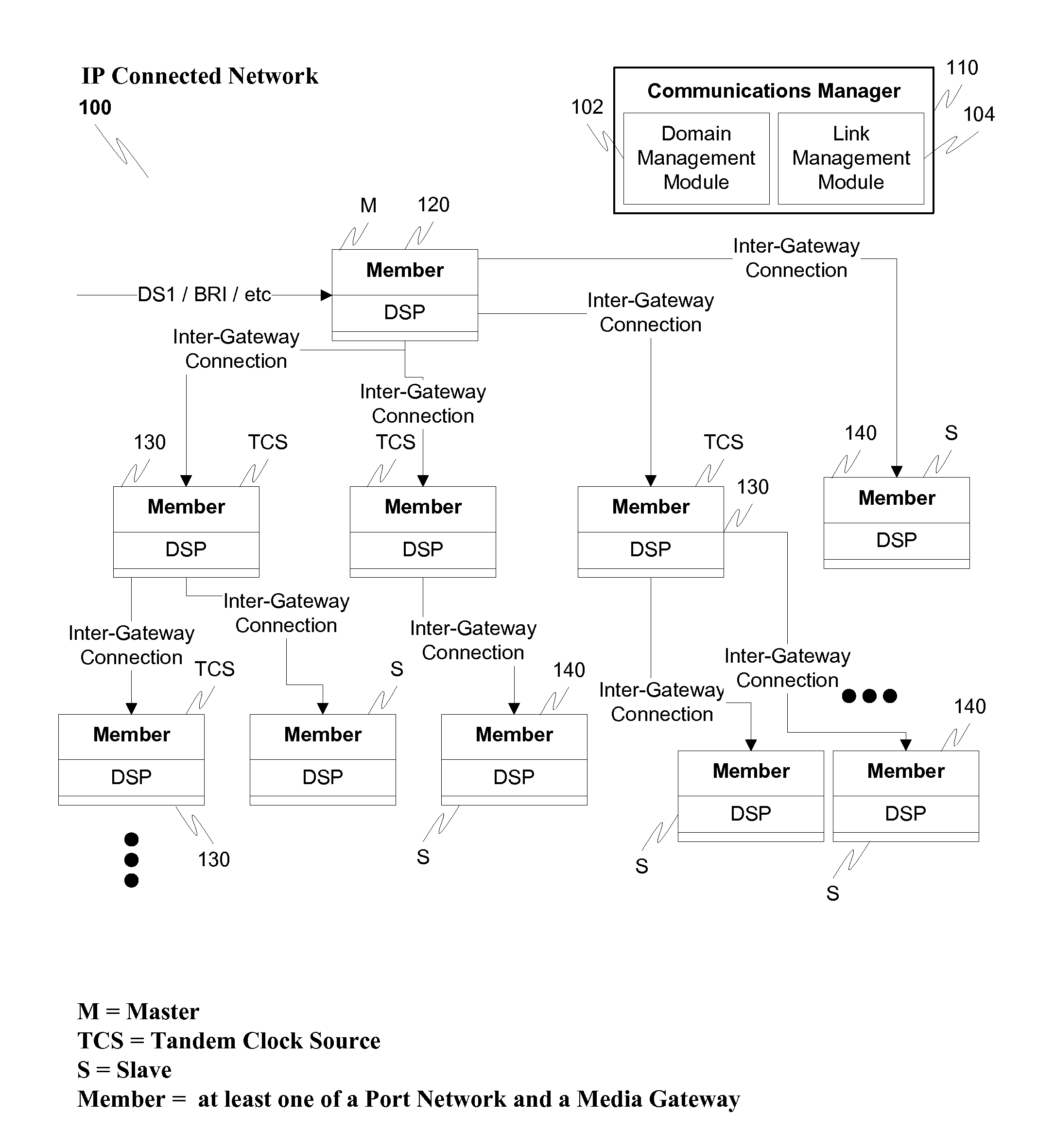
Network synchronization over IP networks
Owner:AVAYA INC
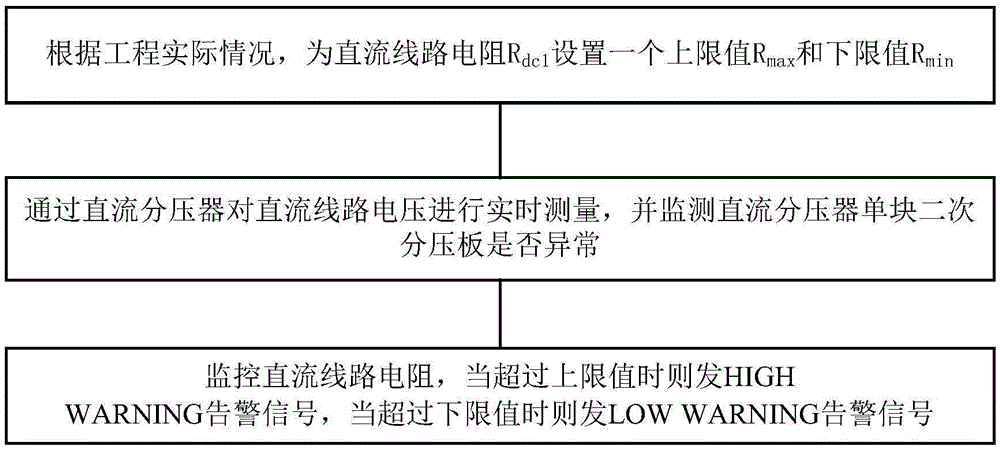
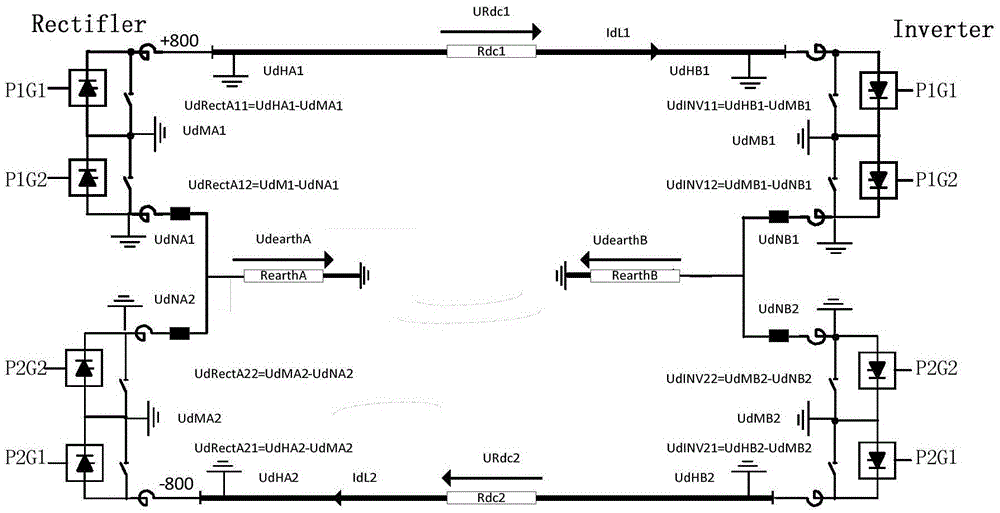
Method for monitoring extra high voltage DC power transmission system DC line voltage fluctuation
ActiveCN105548661AFlexible limit settingPrevent failure from expandingElectric power transfer ac networkVoltage measurements onlyLimit valueHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for monitoring extra high voltage DC power transmission system DC line voltage fluctuation, comprising steps of setting an upper limit value and a lower limit value for a DC line resistor according to a practical construction condition, performing real-time measurement on the DC line voltage through a DC voltage divider and monitoring whether a secondary voltage dividing plate of the DC voltage divider is normal, monitoring the resistor of the DC line, generating a HIGH WARNING alarm signal when the DC line resistance exceeds the upper limit value, generating a LOW WARNING alarm signal when the DC line resistance exceeds the lower limit value, adding a TDM bus data analysis module on the DC voltage divider for analyzing the data of two sets of the TDM measurement buses, obtaining a absolute value after subtracting the DC line voltage of two sets of the measurement systems , converting the absolute value to a per unit value which is compared with a set value, and emitting an EXCEED WARNING alarm signal when the set value is exceeded. The method disclosed by the invention can perform sensitive, rapid and comprehensive monitoring on the line voltage fluctuation of the HVDC power transmission system, can promptly perform early warning and prevents the expansion of the fault range caused by abnormal voltage fluctuation.
Owner:CSG EHV POWER TRANSMISSION
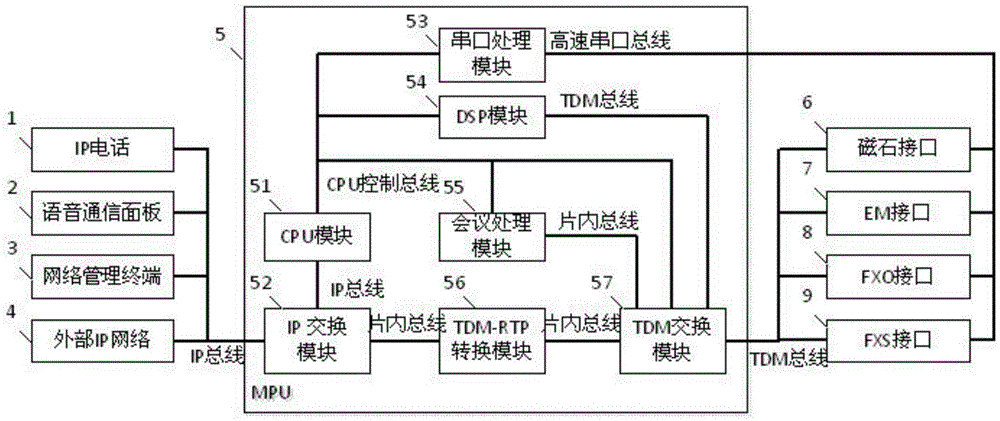
Voice communication control system based on TDM and IP buses
ActiveCN105472187AImprove access capabilitiesImprove real-time performanceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpecial service for subscribersComputer hardwareVoice communication
The invention discloses a voice communication control system based on TDM and IP buses, comprising an IP telephone, a voice communication panel, a network management terminal, an external IP network, an MPU unit, a magnet interface, an EM interface, an FXO interface and an FXS interface. The IP telephone, the voice communication panel, the network management terminal and the external IP network are on the IP side, and are connected with the MPU unit through an IP bus. The magnet interface, the EM interface, the FXO interface and the FXS interface are on the TDM side, and are connected with the MPU unit through a TDM bus. The voice communication panel is a communication terminal. The network management terminal is used for monitoring and managing the system. The external IP network is used for realizing external connection of the system. The magnet interface, the EM interface, the FXO interface and the FXS interface are analog user interfaces based on the TDM bus.
Owner:NANJING LES ELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Large-scale call center trunk circuit access system
InactiveCN103269461AIncrease profitLow input costTransmissionSelection arrangementsSession managementOperating system
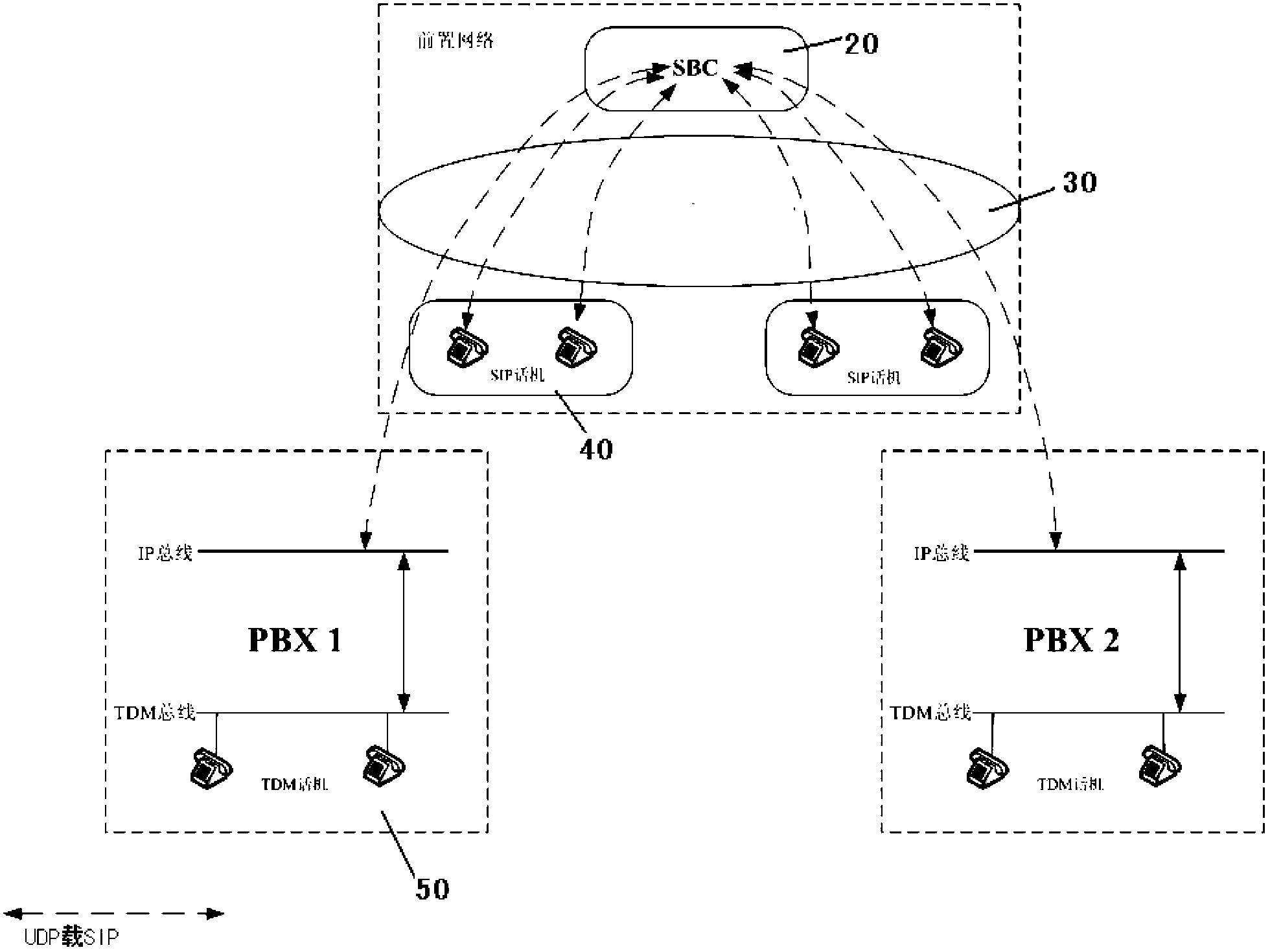
The invention relates to a large-scale call center trunk circuit access system which comprises a session manager and a PBX server, wherein the session manager and an SIP relay accessing which is interconnected with at least one trunk gateway trunk gateway and is parallelly accessed are routed, the PBX server is interconnected with the session manager in an SIP mode and provides exchange of an internal IP bus and a TDM bus for the SIP trunk accessing accessed from the session manager. The large-scale call center trunk circuit access system has the advantages of providing a system separated from a PBX and being capable of accessing a trunk circuit in the call center SIP front-end processor environment, wherein the accessing method has an important significance in simplifying call center trunk accessing, improving the circuit utilization ratio and reducing hardware invested costs.
Owner:CTRIP COMP TECH SHANGHAI
Sectorized cell having non-redundant broadband processing unit
InactiveUS20010004592A1Low costEnergy efficient ICTRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDigital dataTransceiver
A technique for converting a non-sectorized cell to a sectorized cell having multiple sectors utilizing a single broadband processing unit. The spectrum of a given frequency band is divided into multiple bands. In the receive path, respective sub-bands are used to convey analog RF signals from a subscriber in respective sectors to an associated transceiver. Each of the transceivers includes a front end for receiving incoming RF signals and an analog-to-digital converter for converting the analog signal to a digital data stream. The digital data streams from transceivers are combined, and supplied to a single channelizer which, in turn, supplies the data to a TDM bus for transmission to a PSTN network. In the reverse path from the PSTN network, TDM digital data signals emanating from a TDM bus are supplied to a combiner which feeds each of the respective transceivers with appropriate data from the combiner. The transceivers convert the digital signal to analog form. After conversion, power amplifiers associated with the respective sectors effect emission of radiated power in the respective sectors.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Method for expanding time division multiplexing (TDM) bus
InactiveCN102567267AReduce work speedUnlimited quantityElectric digital data processingCommunications systemEmbedded system
The invention discloses a method for expanding a time division multiplexing (TDM) bus, which comprises the following steps that: the TDM bus is divided into m plus 1 groups of sub buses, wherein a media processor is hooked with one group of sub bus, and a TDM interface of the media processor is connected with a corresponding input / output (IO) port on a programmable device through the sub bus; and the corresponding numbers of media processors are respectively hooked onto the residual m groups of sub buses, and the TDM interfaces of all the media objects are respectively connected with the corresponding IO ports on the programmable device through the sub buses which are hooked with the media objects. The number of the media objects which are hooked with a communication system which is constructed by the method is not limited, the practicability is strong, and the working speed of the communication system cannot be reduced due to the reconstruction of the buses. The method is easy to realize, is low in cost, can simply program the programmable device, and is particularly suitable for high-capacity backplane switching systems.
Owner:BEIJING DATANG GOHIGH DATA NETWORKS TECH CO LTD
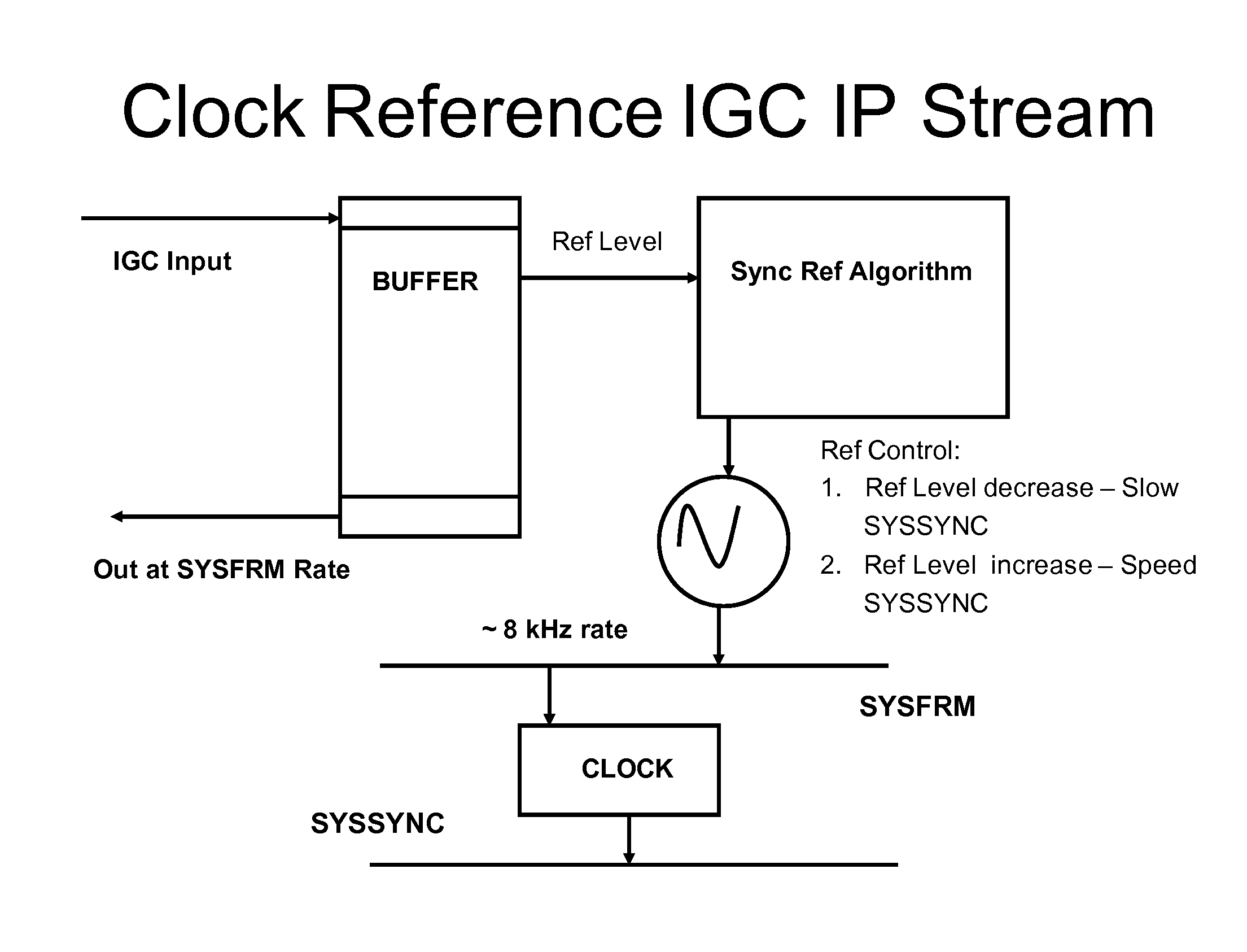
Network synchronization over IP networks
ActiveUS20100254499A1Digital computer detailsTime-division multiplexSpeech soundDigital signal processor
Network timing is derived from the PSTN and distributed through the network to gateways capable of deriving timing from the incoming UDP stream. The derived timing has the correct frequency for voice telephony without using external timing sources or extraneous hardware components. For example, a digital signal processor (DSP) can derive the timing from a timed TDM bus and distribute messages, such as IP messages, to other gateways or port networks. The other gateways and port networks use the incoming stream to extract the timing which is then used to time their TDM bus. The port networks and gateways can also distribute other streams to other gateways in a fan-out type of arrangement. This internally generated timing can be used, for example, for Circuit Emulated Services (CES).
Owner:AVAYA INC
Systems and methods for voice and data communications including a network drop and insert interface for an external data routing resource
InactiveUS20110038365A1Effective supportPerformed conveniently and efficientlyNetwork connectionsTelecommunications linkVoice data
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus. An integrated communication system is coupled to a digital telecommunications link, the communication system providing voice and data communications to a plurality of users. At least a first packet bus is coupled to one or more packet-based devices and adapted for transferring packetized data to and from the system. One or more time division multiplex (TDM) buses are coupled to one or more telephony devices. Data routing resources are provided internal to the integrated system. A network interface module couples data to and from a data router external to the integrated system. The data router external to the integrated system is coupled to the first packet bus. Data is routed via the external data router through the network interface module and coupled to data channels of the digital telecommunications link, while voice data is selectively coupled to voice channels of the digital telecommunications link.
Owner:RPX CORP
Round-robin bus protocol
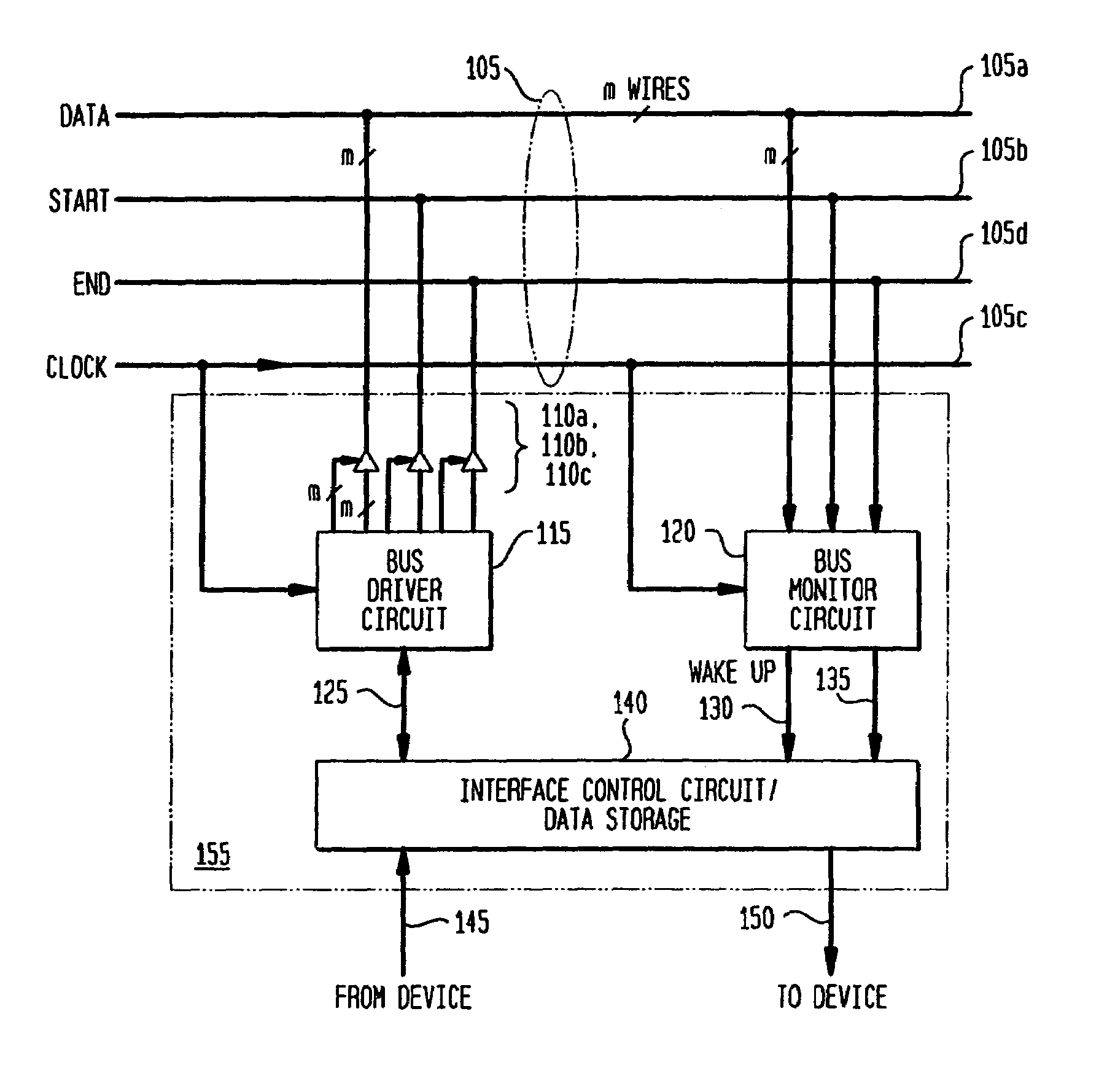
A low-latency, peer-to-peer TDM bus including one or more data lines and one or more control lines is provided. Attached devices access the bus sequentially in order of their bus addresses. During a device's access period, if the device has data to transmit, the device places its address on the data lines, asserts a START signal on the bus, and proceeds to transmit data to the other devices on the bus. When the data transmission is completed, the device asserts an END signal on the bus, thus passing control of the bus to the next device in the sequence. If the device has no data to transmit, the device simply places its address on the data lines, asserts the START signal, and asserts the END signal, and control passes directly to the next device in line. In this manner, each device has an opportunity to transmit on the bus.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Using hot swap logic in a communication system
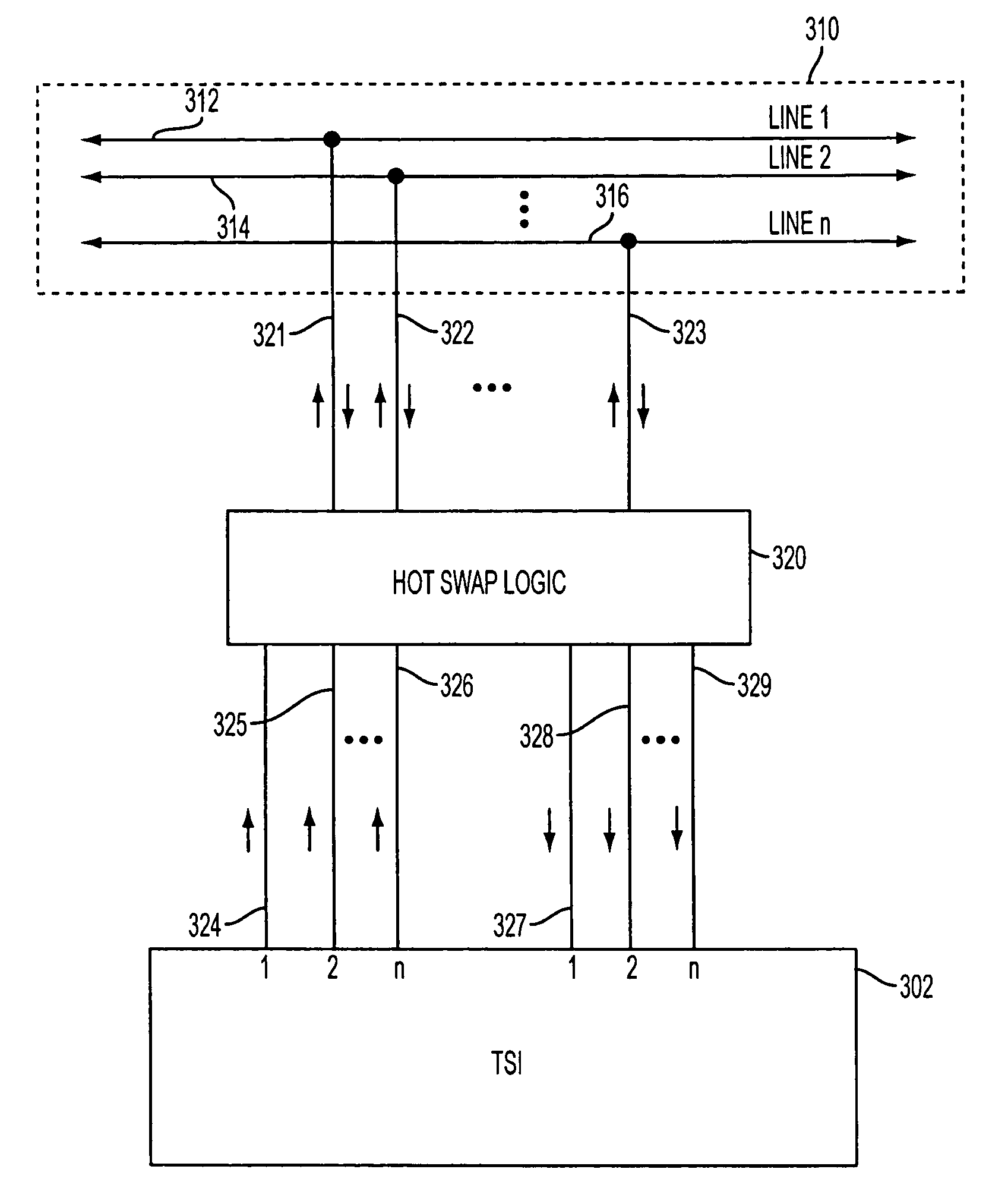
InactiveUS7620038B1Improve performanceEnhances various aspectTime-division multiplexCircuit switching systemsCommunications systemEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for providing hot swapability of TSIs in a TDM system using FPGA hot swap logic. The hot swap logic is used to provide isolation for the TSIs from a system TDM bus in the TDM system. Moreover, the hot swap logic is capable of improving the performance of the TDM system. For example, the hot swap logic is capable of compensating for clock distortion associated with the distribution of a common clock signal to various TSIs in the TDM system. Additionally, for example, the hot swap logic is capable of compensating for the limitations imposed in conventional TDM systems due to the relatively high clock-to-out times of conventional TSIs.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and methods for multiple mode voice and data communications using intelligenty bridged TDM and packet buses and methods for performing telephony and data functions using the same
InactiveUS20100157852A1Effective supportPerformed conveniently and efficientlySpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexing selectionMulti protocolMultiple modes
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur in multiple modes / protocols are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided for multiple native mode / protocol voice and data transmissions and receptions with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus, and multi-protocol framing engines. Such systems preferably include subsystem functions such as PBX, voice mail and other telephony functions, LAN hub and data router. In preferred embodiments, a TDM bus and a packet bus are intelligently bridged and managed, thereby enabling such multiple mode / protocol voice and data transmissions to be intelligently managed and controlled with a single, integrated system. A computer or other processor includes a local area network controller, which provides routing and hub(s) for one or more packet networks. The computer also is coupled to a buffer / framer, which serves to frame / deframe data to / from the computer from TDM bus. The buffer / framer includes a plurality of framer / deframer engines, supporting, for example, ATM and HDLC framing / deframing. The buffer / framer is coupled to the TDM bus by way of a switch / multiplexer, which includes the capability to intelligently map data traffic between the buffer / framer and the TDM bus to various slots of the TDM frames. Preferably, a DSP pool is coupled to buffer / framer in a manner to provide various signal processing and telecommunications support, such as dial tone generation, DTMF detection and the like. The TDM bus is coupled to a various line / station cards, serving to interface the TDM bus with telephone, facsimiles and other telecommunication devices, and also with a various digital and / or analog WAN network services.
Owner:RPX CORP
Systems and methods for multiple mode voice and data communications using intelligenty bridged TDM and packet buses
InactiveUS20080228972A1Effective supportTelephone data network interconnectionsHybrid switching fabricsMulti protocolMultiple modes
Systems and methods by which voice / data communications may occur in multiple modes / protocols are disclosed. In particular, systems and methods are provided for multiple native mode / protocol voice and data transmissions and receptions with a computing system having a multi-bus structure, including, for example, a TDM bus and a packet bus, and multi-protocol framing engines. Such systems preferably include subsystem functions such as PBX, voice mail and other telephony functions, LAN hub and data router. In preferred embodiments, a TDM bus and a packet bus are intelligently bridged and managed, thereby enabling such multiple mode / protocol voice and data transmissions to be intelligently managed and controlled with a single, integrated system. A computer or other processor includes a local area network controller, which provides routing and hub(s) for one or more packet networks. The computer also is coupled to a buffer / framer, which serves to frame / deframe data to / from the computer from TDM bus. The buffer / framer includes a plurality of framer / deframer engines, supporting, for example, ATM and HDLC framing / deframing. The buffer / framer is coupled to the TDM bus by way of a switch / multiplexer, which includes the capability to intelligently map data traffic between the buffer / framer and the TDM bus to various slots of the TDM frames. Preferably, a DSP pool is coupled to buffer / framer in a manner to provide various signal processing and telecommunications support, such as dial tone generation, DTMF detection and the like. The TDM bus is coupled to a various line / station cards, serving to interface the TDM bus with telephone, facsimiles and other telecommunication devices, and also with a various digital and / or analog WAN network services.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com