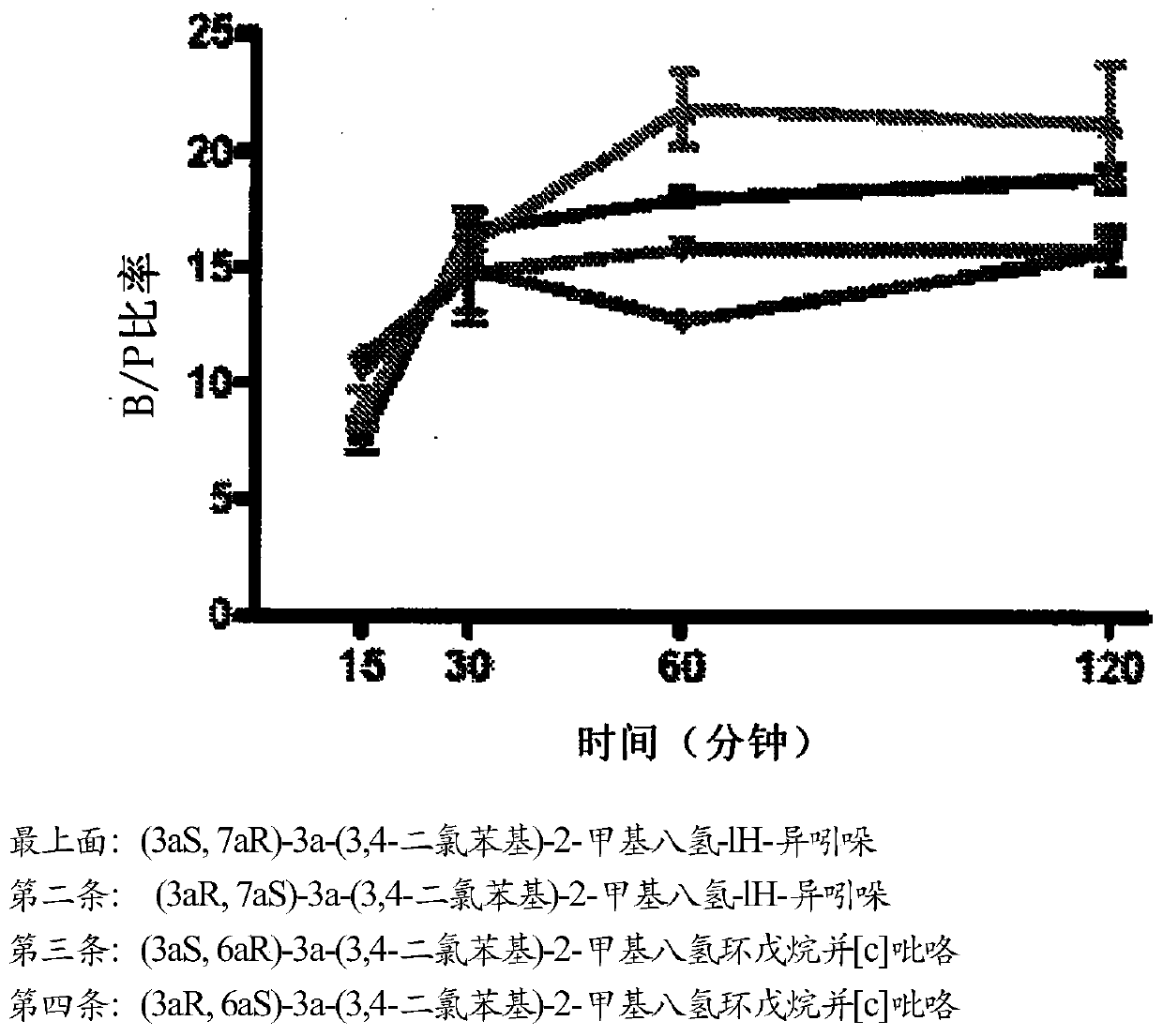
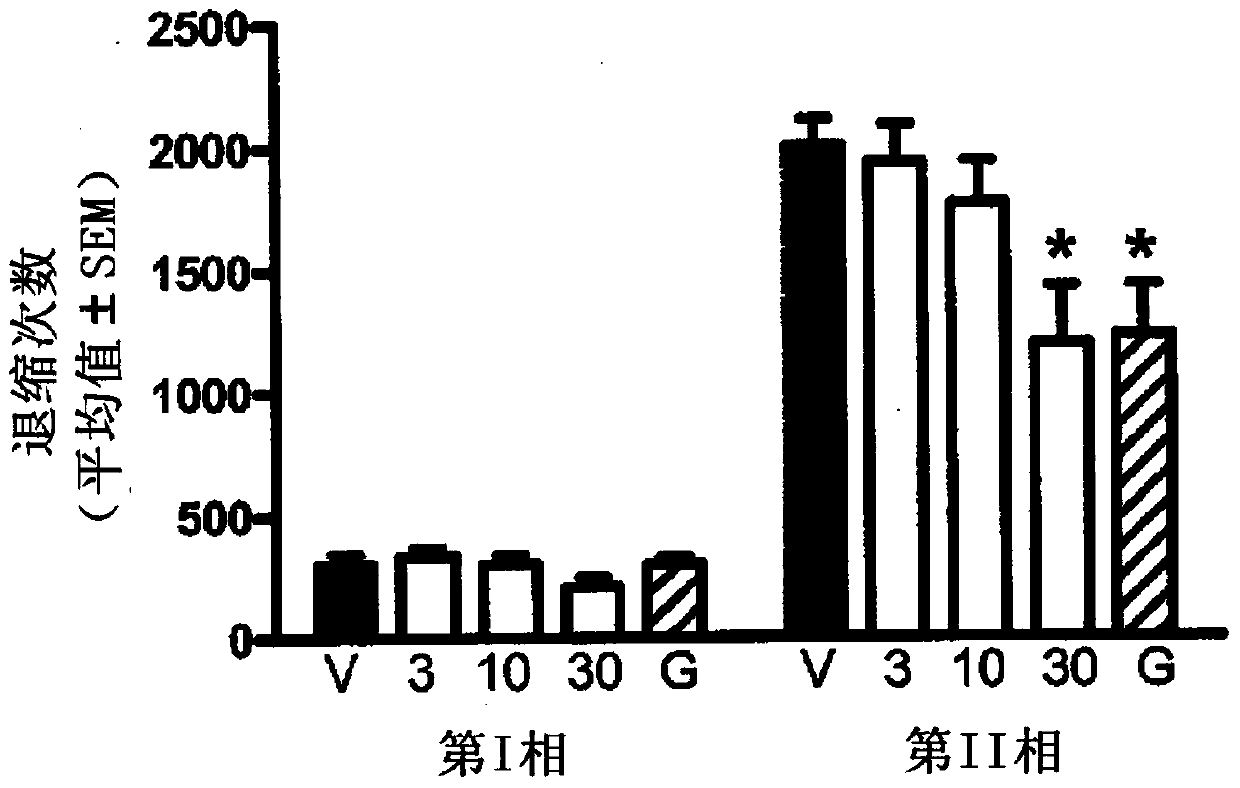
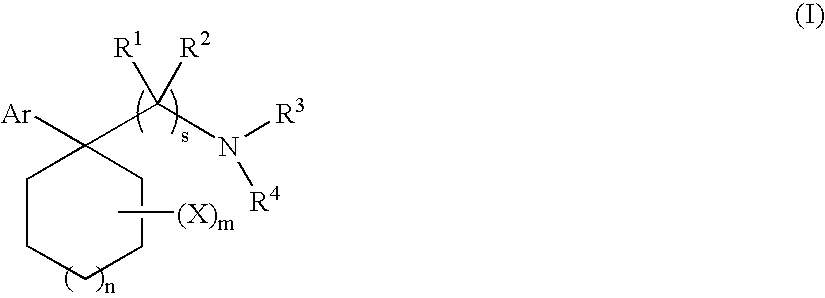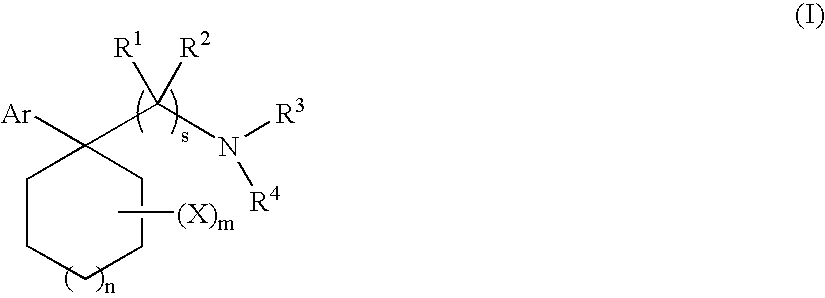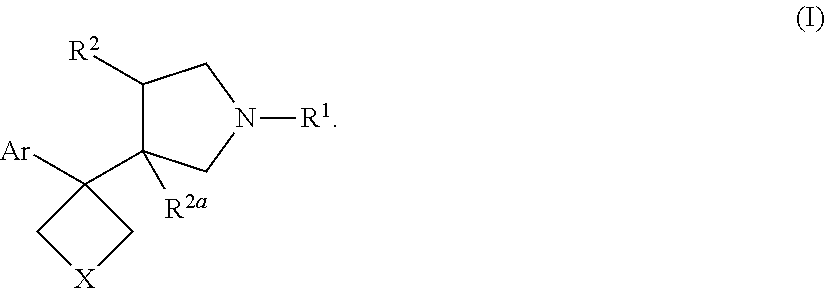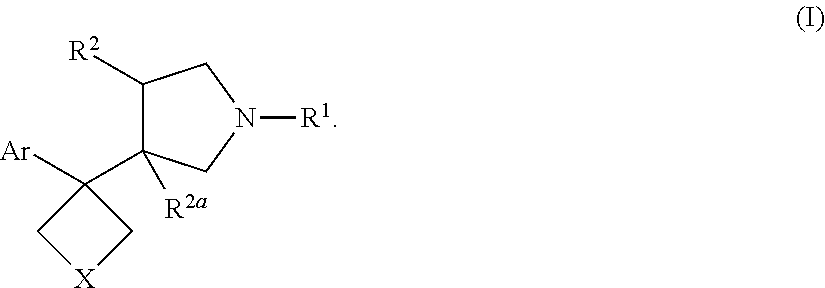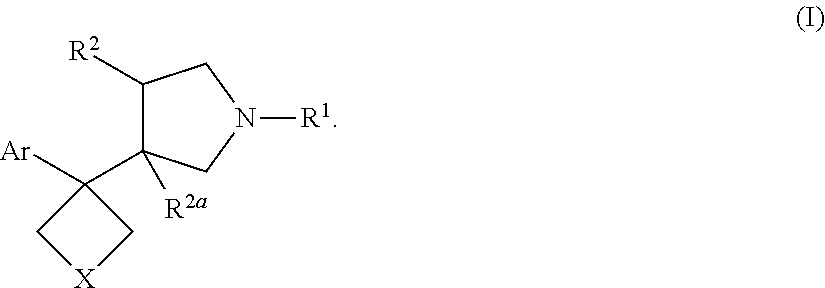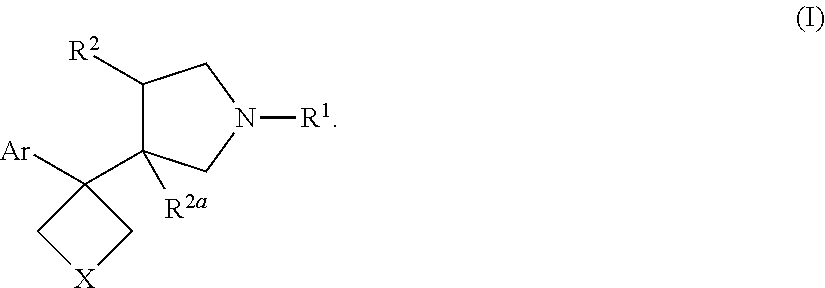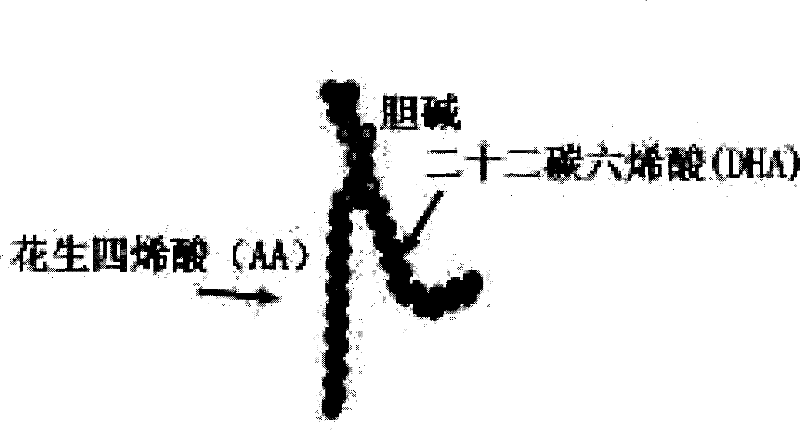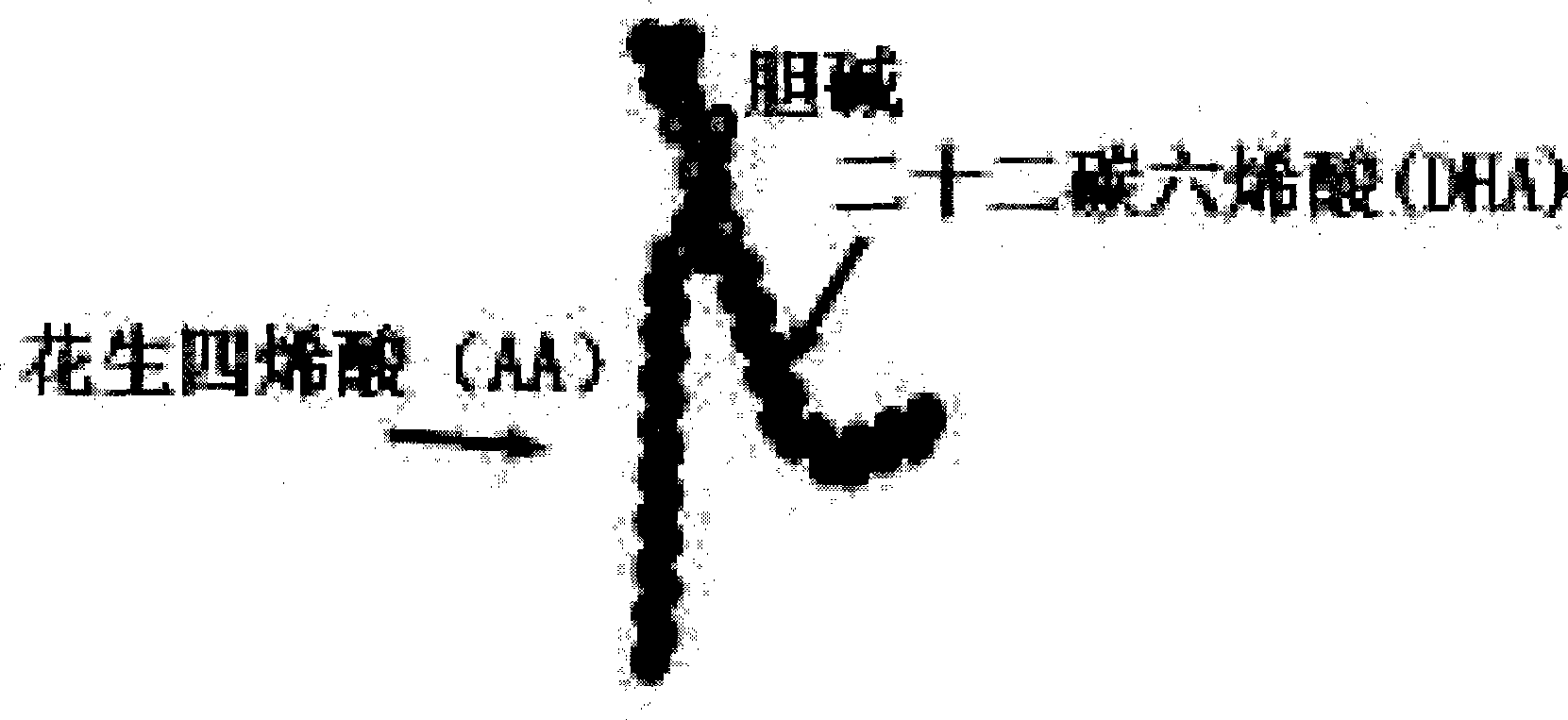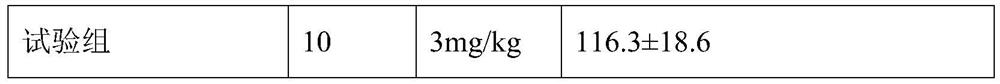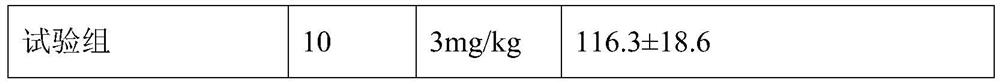Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Synaptic cleft" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
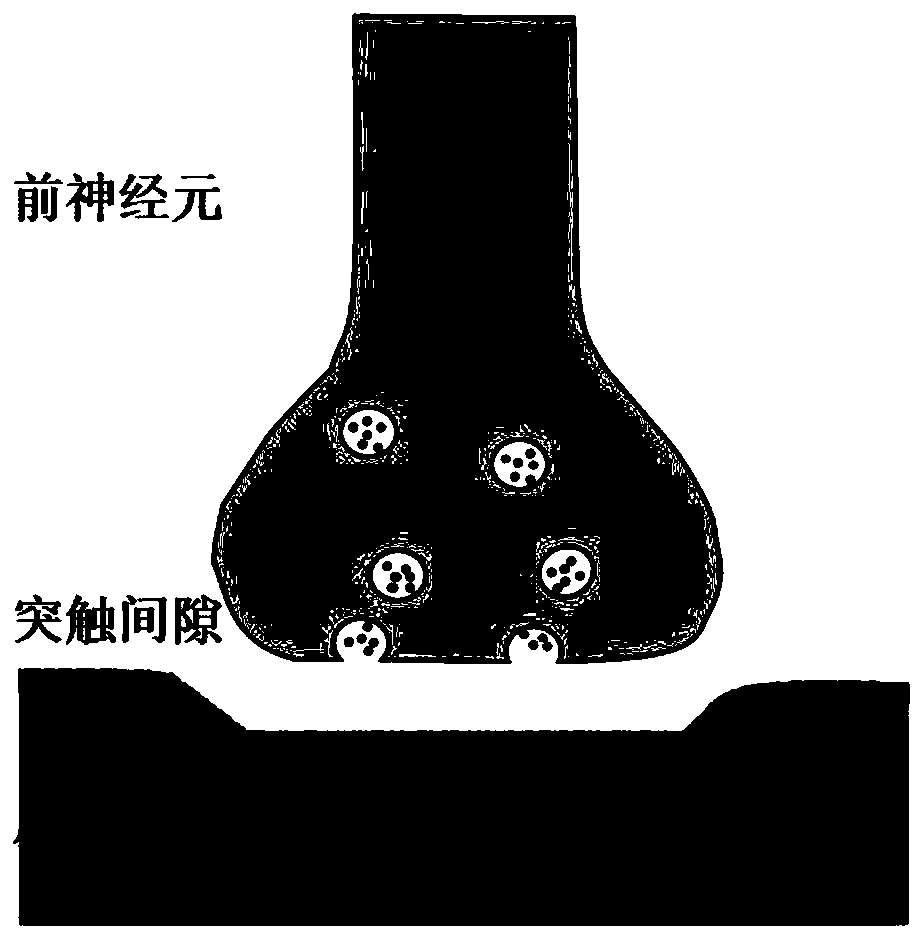
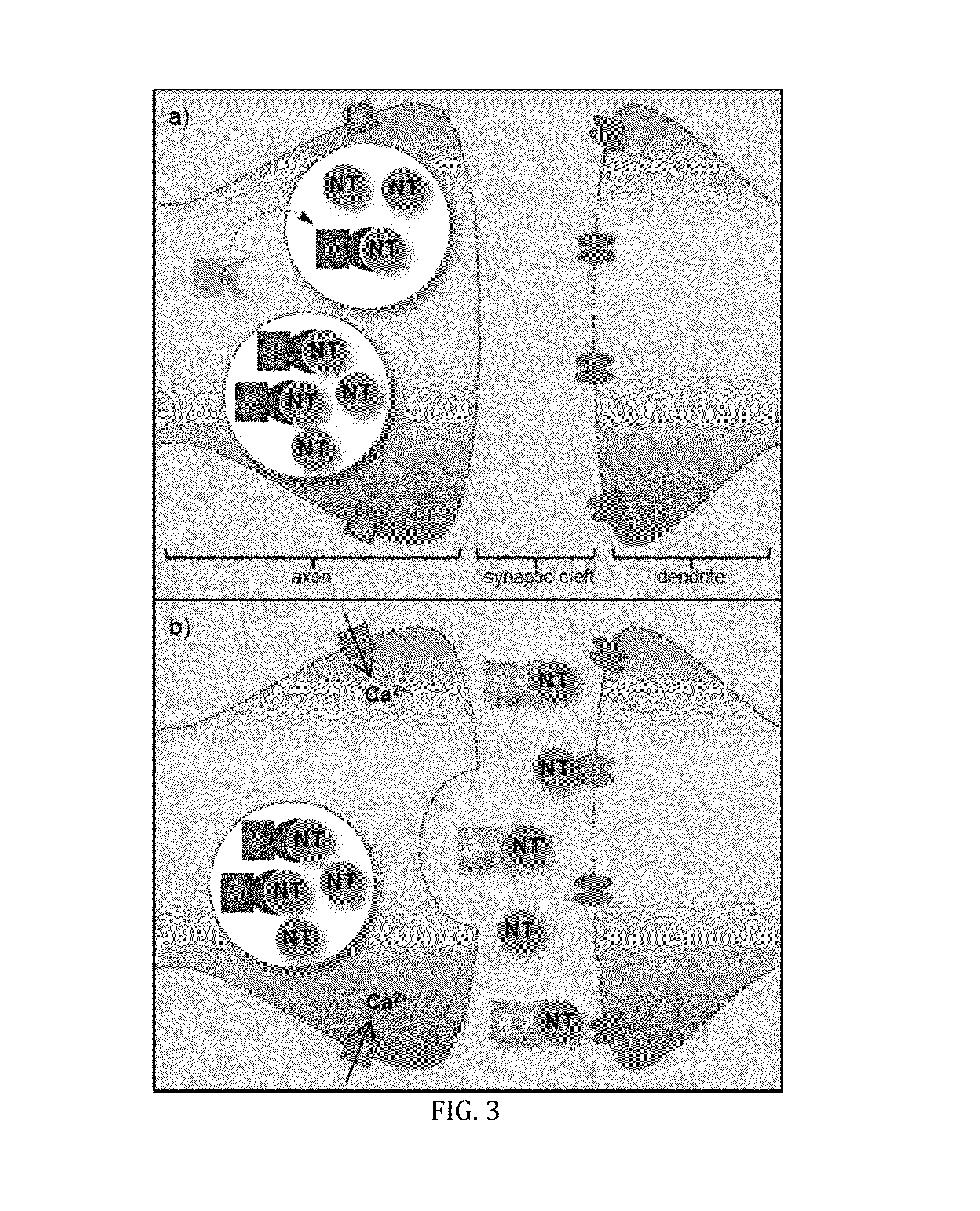
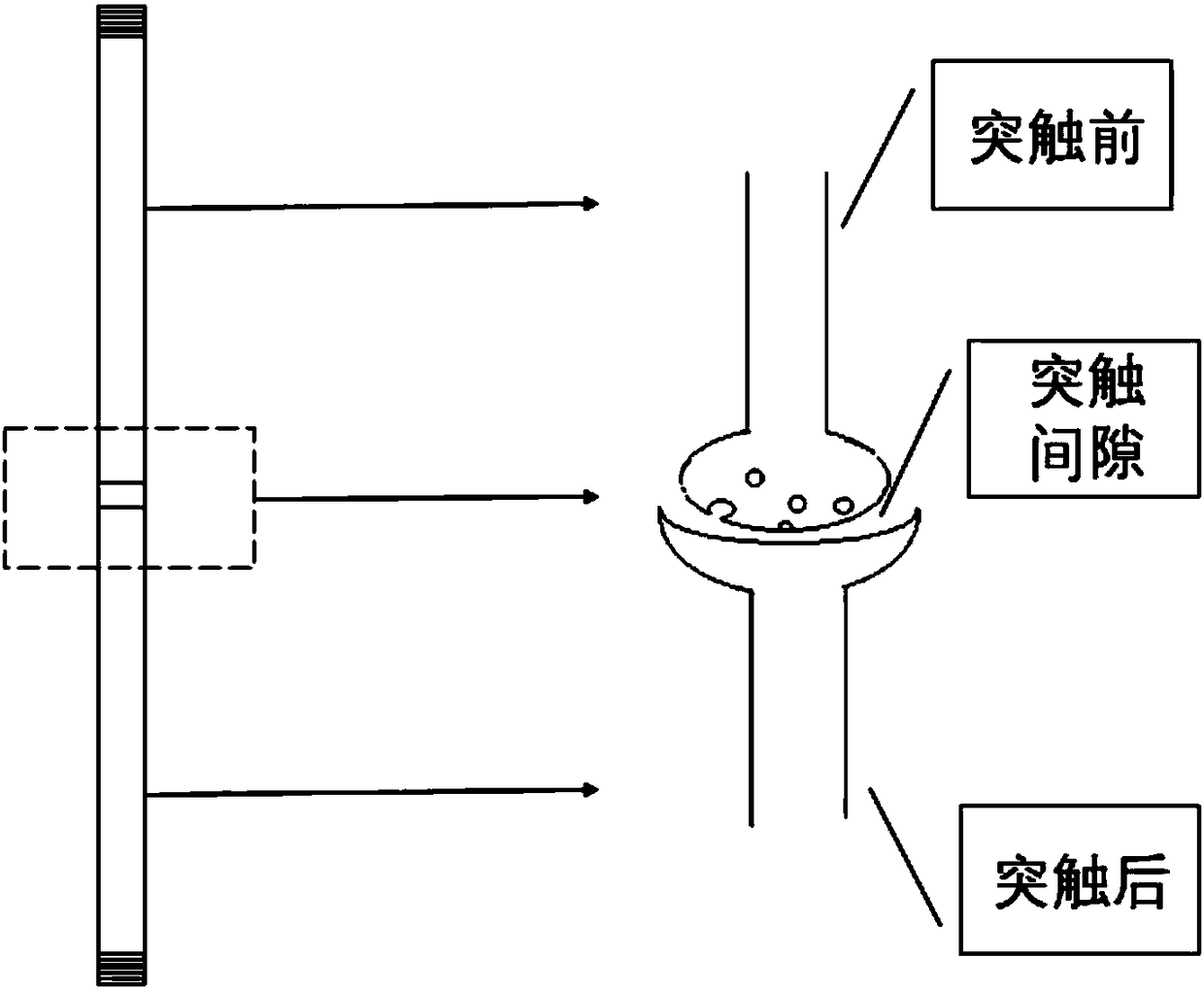
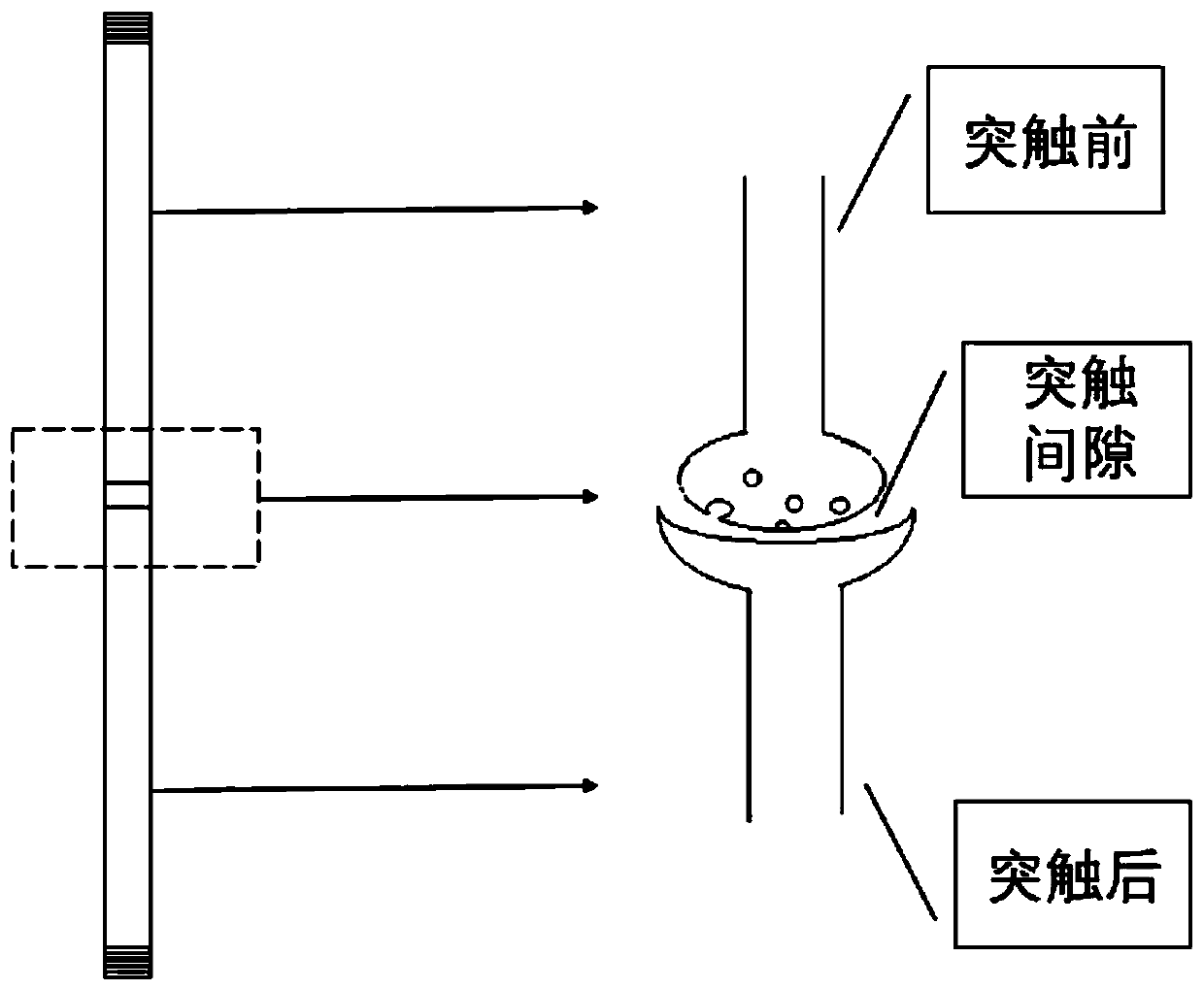
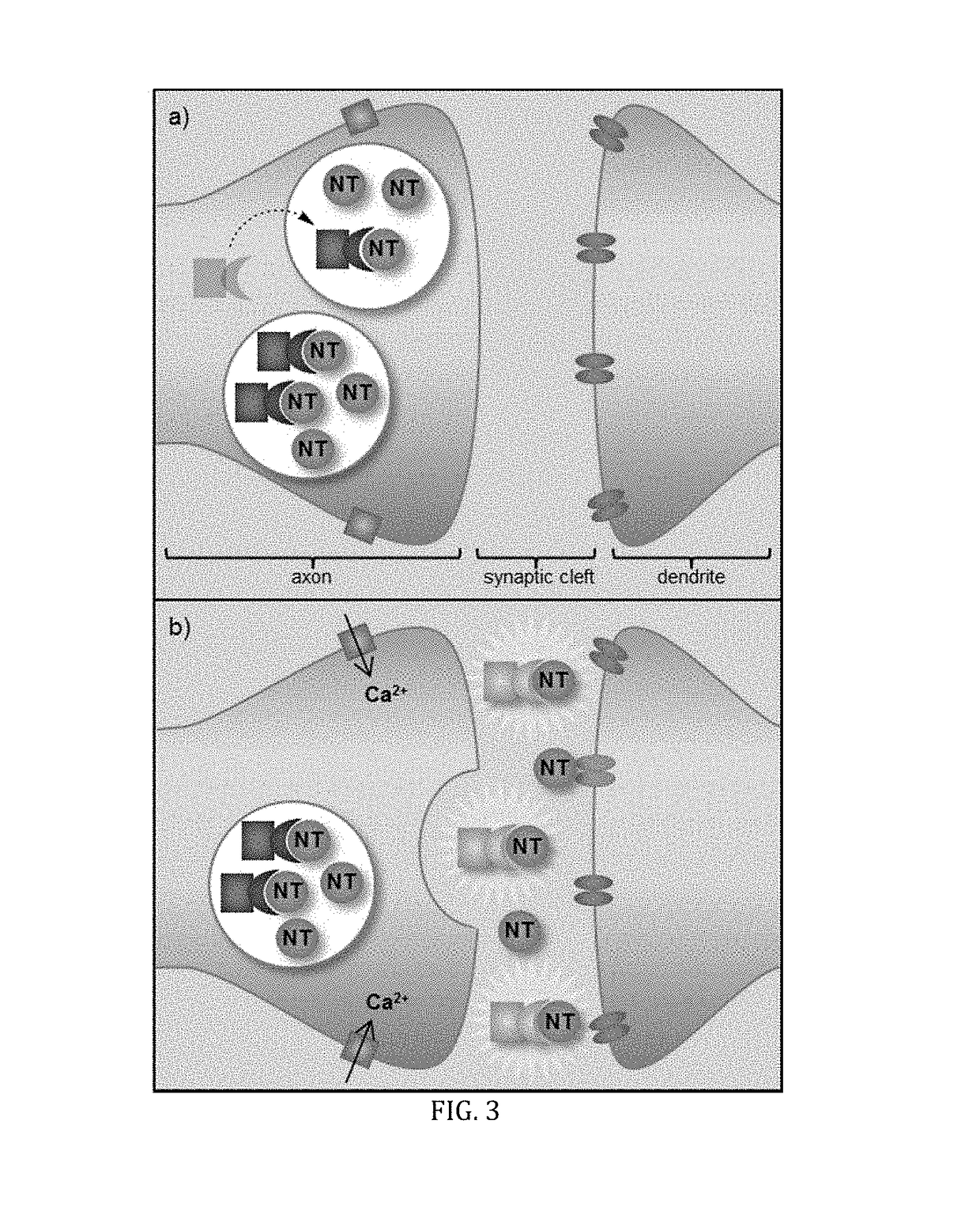
The synaptic cleft —also called synaptic gap— is a gap between the pre- and postsynaptic cells that is about 20 nm (0.02 μ) wide. The small volume of the cleft allows neurotransmitter concentration to be raised and lowered rapidly.
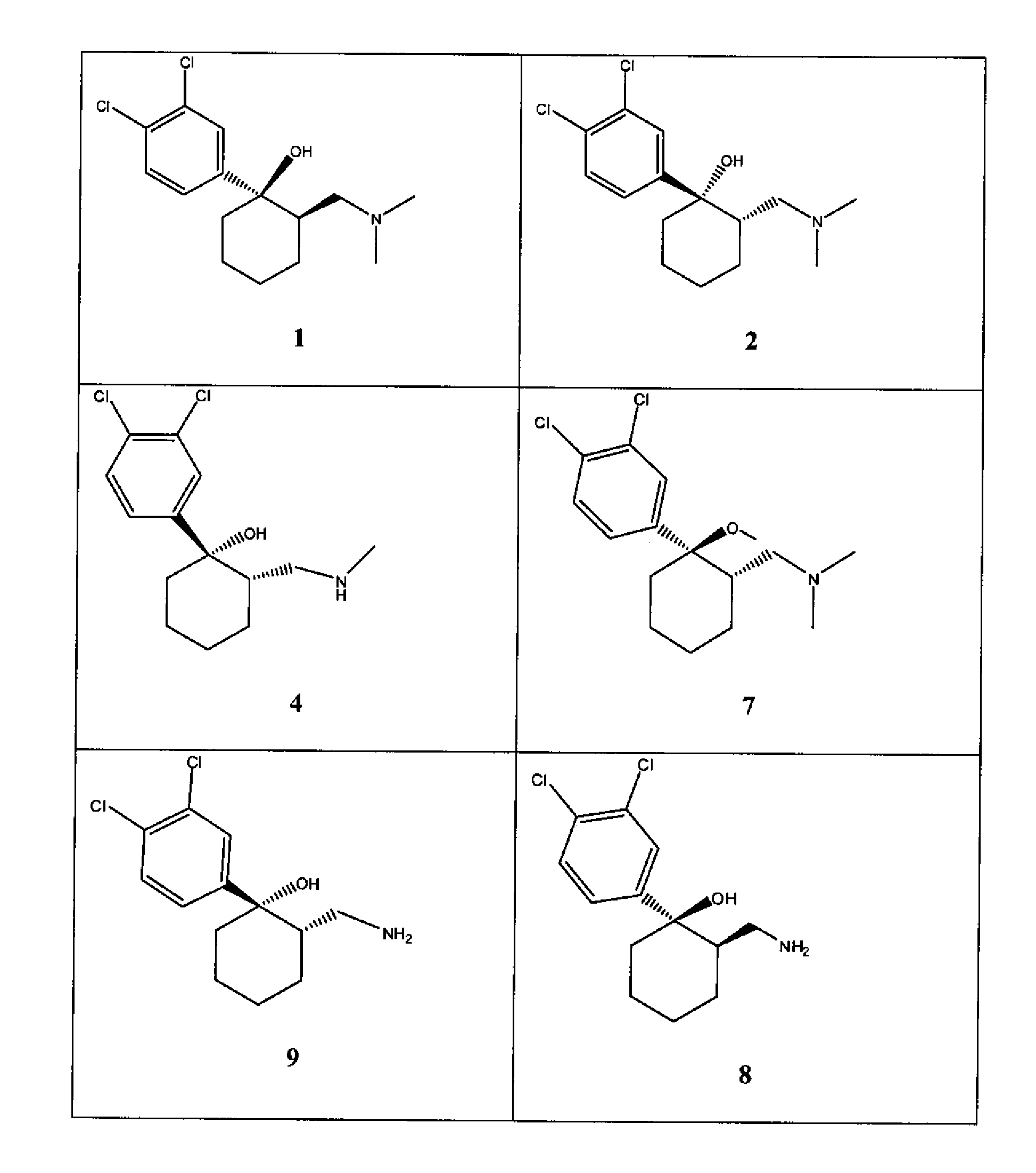
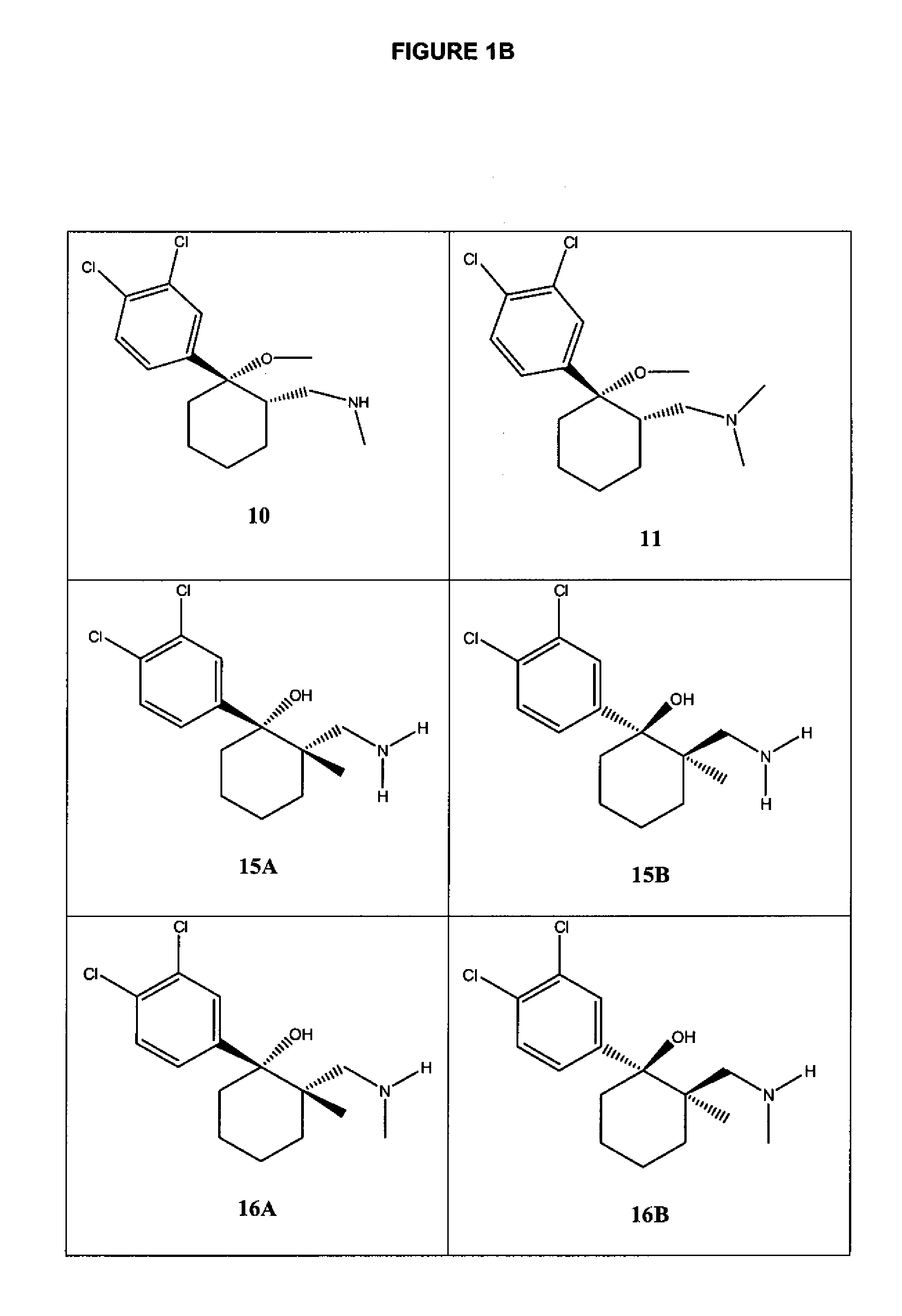
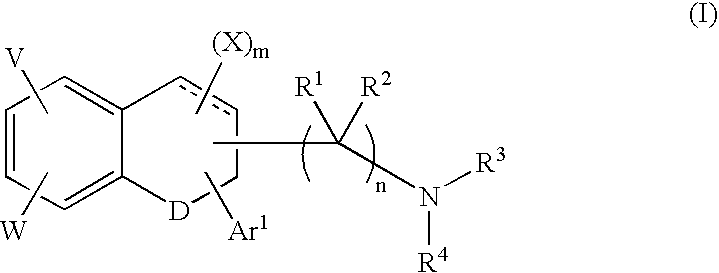
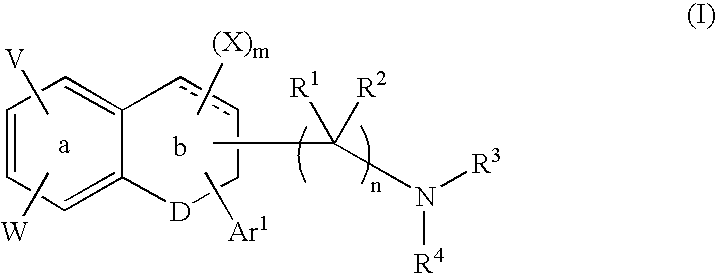
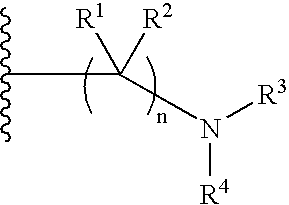
Cycloalkylamines as monoamine reuptake inhibitors
InactiveUS20070203111A1Inhibit bindingInhibitory activityBiocideNervous disorderSynaptic cleftAdrenergic
The invention relates to novel cyclohexylamine derivatives and their use in the treatment and / or prevention of central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia and sleep disorder as well as methods for their synthesis. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the invention, as well as methods of inhibiting reuptake of endogenous monoamines, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft and methods of modulating one or more monoamine transporter.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Phenyl substituted cycloalkylamines as monoamine reuptake inhibitors
ActiveUS20090005456A1Improve usabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSynaptic cleftPharmaceutical formulation
Phenyl-substituted cyclohexylamine derivatives and method for their synthesis and characterization are disclosed. Use of these compounds to treat / prevent neurological disorders as well as methods for their synthesis are set forth herein. Exemplary compounds of the invention inhibit reuptake of endogenous monoamines, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine (e.g., from the synaptic cleft) and modulate one or more monoamine transporter. Pharmaceutical formulations incorporating compounds of the invention are also provided.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
Tetralone-based monoamine reuptake inhibitors
ActiveUS8053603B2Increase synaptic availabilityImprove usabilityBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseSynaptic cleft
The invention relates to novel tetralone based amines and their use in the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and Parkinson's disease. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds and compositions of the invention as well as methods of inhibiting reuptake of one or more monoamine, such as such as dopamine and norepinephrine, from the synaptic cleft, and methods of modulating one or more monoamine transporter.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
Tetralone-based monoamine reuptake inhibitors
ActiveUS20070197588A1Increase synaptic availabilityImprove usabilityBiocideNervous disorderSynaptic cleftTetralone
The invention relates to novel tetralone based amines and their use in the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and Parkinson's disease. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds and compositions of the invention as well as methods of inhibiting reuptake of one or more monoamine, such as such as dopamine and norepinephrine, from the synaptic cleft, and methods of modulating one or more monoamine transporter.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
Floating gate memristor
InactiveCN107068708AEliminate the effects ofStrong process controllabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesSynaptic cleftNervous system
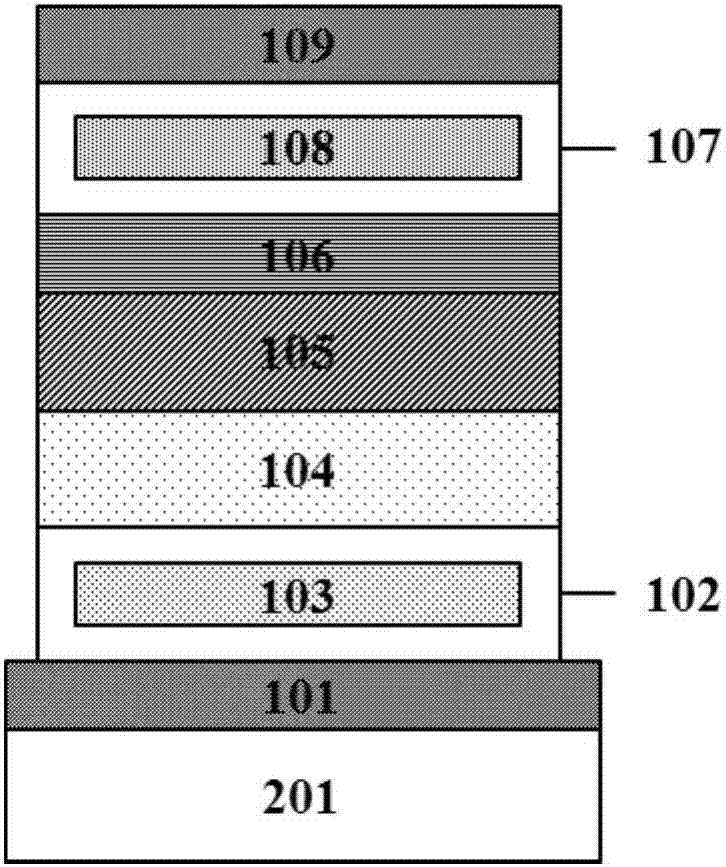
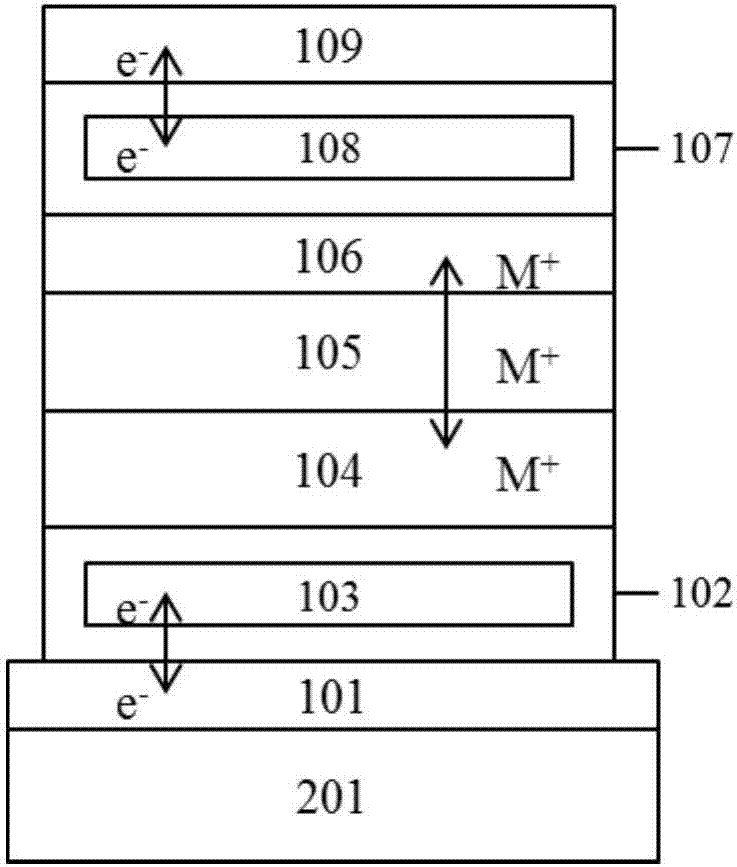
The invention relates to a floating gate memristor. The basic structure of the floating gate memristor successively includes a front electrode, a front dielectric layer, a front floating gate layer, a nanometer battery anode, a nanometer battery electrolyte, a nanometer battery cathode, a rear floating gate layer, a rear dielectric layer and a rear electrode, wherein the front electrode, the front dielectric layer, the front floating gate layer and the nanometer battery anode simulate a presynaptic membrane which converting electronic signals to ion signals by utilizing electronic tunnel transfer and field effect; the nanometer battery electrolyte serves an ion channel simulating a synaptic cleft; the nanometer battery cathode, the rear floating gate, the rear dielectric layer and the rear electrode simulate a subsynaptic membrane which converts the ion signals to electronic signals. The floating gate memristor is stable in reading and writing, good in controllability, simple in structure, compatible to CMOS, easy to integrate, suitable for large scale production and commercialization and capable of promoting development of nervous system calculation and encephaloid calculation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Novel compositions comprising a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor and their use in methods of treatment
InactiveUS20130296324A1Enhance health and appearanceFacilitating accelerating healingBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseSynaptic cleft
The invention relates generally to novel pharmaceutical methods for the treatment of various conditions. Compositions comprising: at least one phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitor in combination with one or more of the following medications: a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; a cholinesterase inhibitor; a dopamine agonist; or a medication suitable to increase the chemical concentrations of the neurotransmitters, selected from amino acids, monoamines, neuropeptides and other agents capable of primary neurotransmission in the synaptic clefts, and their use for treating a neurodegenerative disease in a subject. The invention also relates to: Compositions comprising: at least one phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitor in combination with one or more of the following medications: a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; or a cholinesterase inhibitor, and their use for treating damaged skin in a subject.
Owner:HELD JERRY M
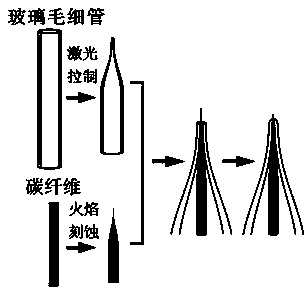
Novel carbon fiber nanocone electrode as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103399068AIncrease consumptionEasy to makeMaterial electrochemical variablesSynaptic cleftLow noise
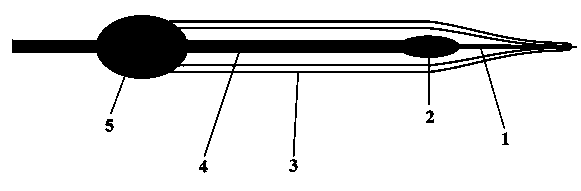
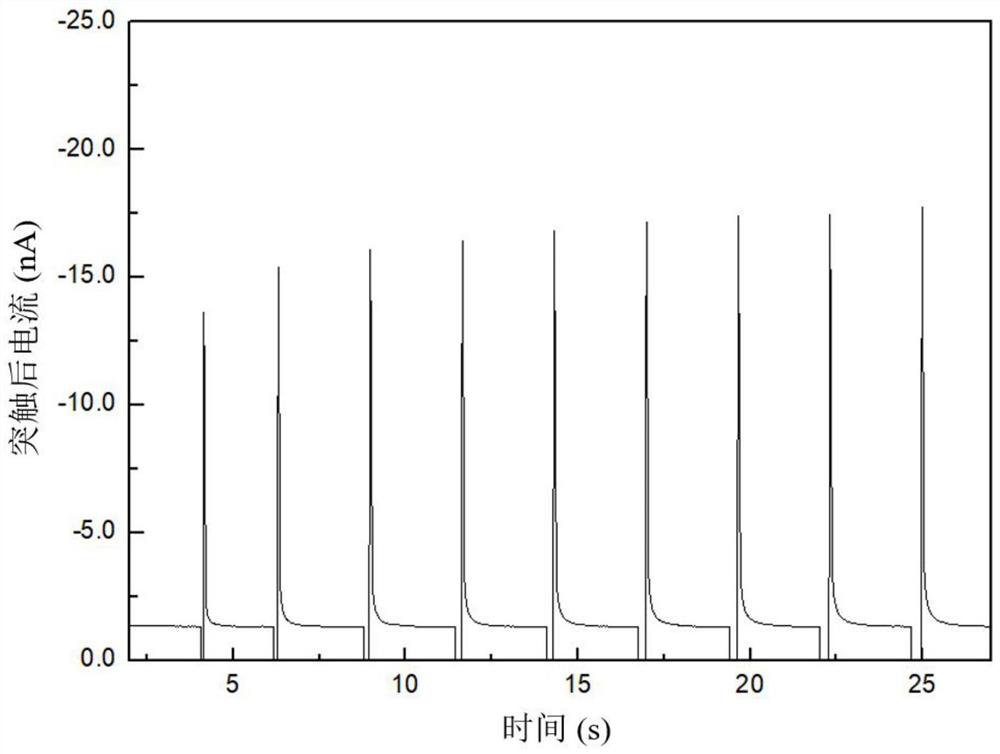
The invention discloses a novel carbon fiber nanocone electrode as well as a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of electrochemistry and material science. The novel carbon fiber nanocone electrode comprises a carbon fiber, an electrode lead and a glass capillary tube, wherein the carbon fiber is connected with the electrode lead through a conductive adhesive; the front part, as long as 50-100 microns, of the carbon fiber is etched to be of a needle shape, and the tip end of the needle-shaped part has the diameter of 100nm-300nm; one end of the glass capillary tube is pulled to form a tip end with the diameter less than or equal to 1micron; the carbon fiber connected with the electrode lead penetrates into the pulled tip of the glass capillary tube, and is exposed out of the tip end of the glass capillary tube; the electrode lead is exposed out of the other end of the glass capillary tube, and the end is sealed by an AB adhesive. According to the invention, the problem that after a nano electrode is insulated, the tip end cannot be exposed easily is solved radically. The carbon fiber nanocone electrode provided by the invention has the advantages of low noise, high sensitivity and high temporal-spatial resolution, and can be applied to real-time detection on neurotransmitter in synaptic cleft in neuroscience research.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Cycloalkylamines as monoamine reuptake inhibitors
ActiveUS20100190861A1Increase synaptic availabilityImprove usabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSynaptic cleftNervous system
The invention relates to novel cyclohexylamine derivatives and their use in the treatment and / or prevention of central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia and sleep disorder as well as methods for their synthesis. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the invention, as well as methods of inhibiting reuptake of endogenous monoamines, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft and methods of modulating one or more monoamine transporter.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
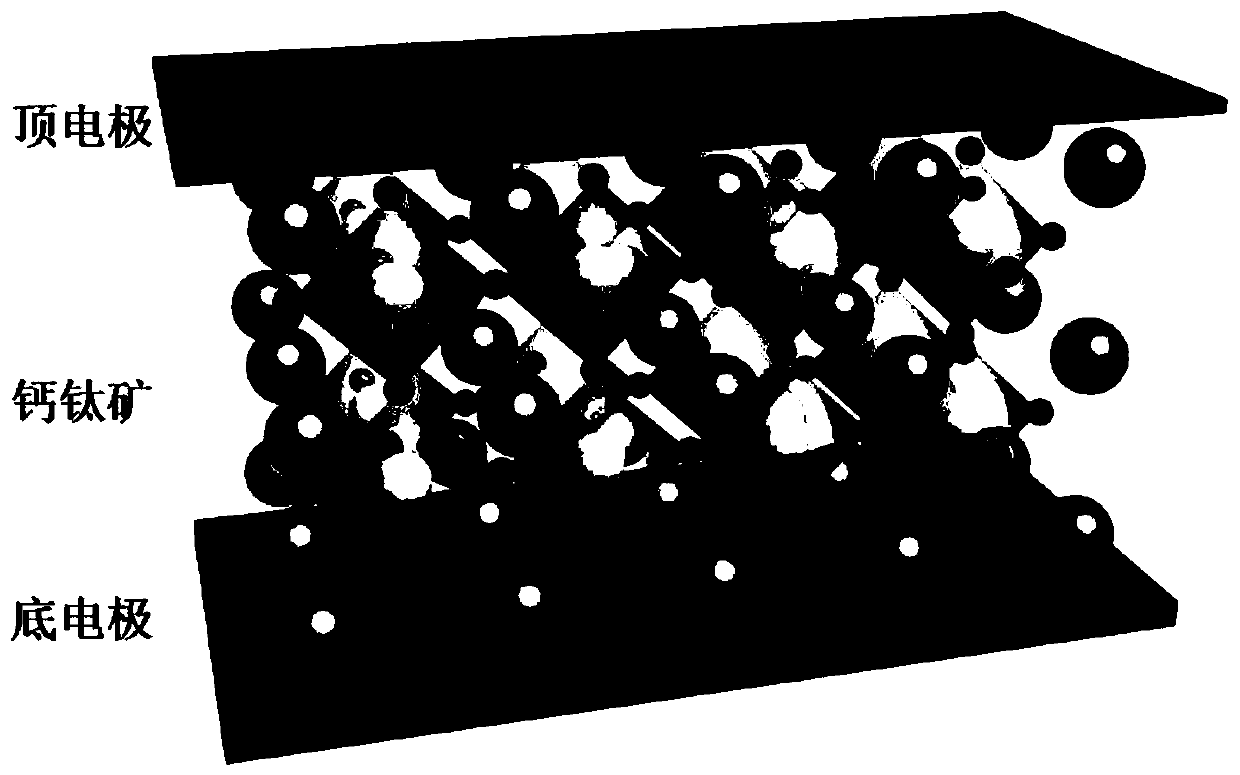
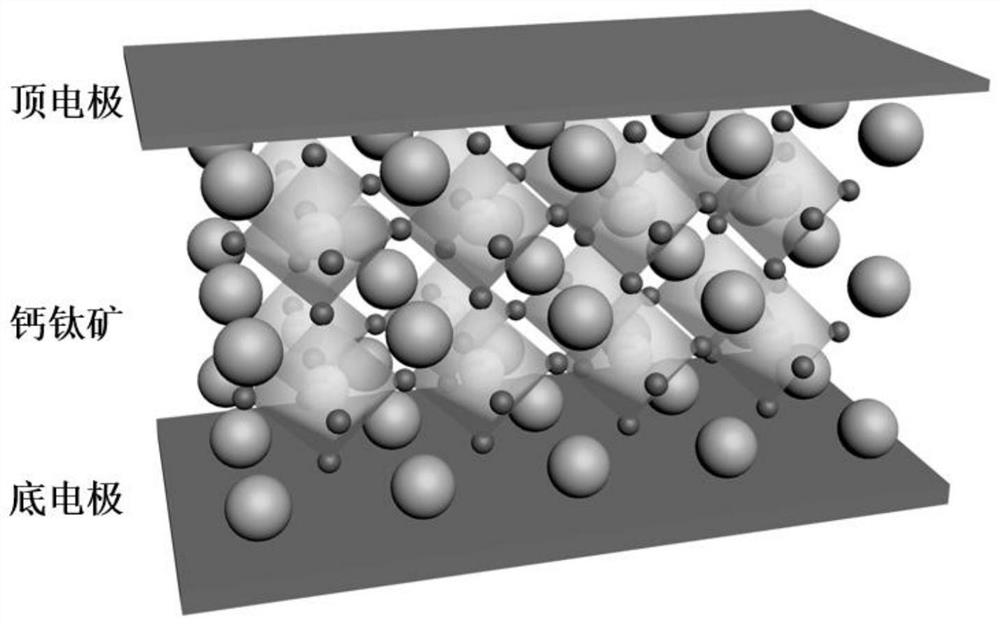
Preparation method of electronic device with artificial synapsis at two ends based on organic/inorganic hybrid perovskite
ActiveCN109920914AImprove qualityReduce manufacturing costNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSynaptic cleftEngineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of an electronic device with artificial synapsis at two ends based on organic / inorganic hybrid perovskite, and belongs to the field of the electronic device. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pre-treating a high-doped silicon substrate, spinning-coating a configured perovskite solution on a substrate, performing annealing treatment to obtain a perovskite thin film with good crystallinity; and then evaporating a metal top electrode to obtain the electronic device with perovskite artificial synapsis at two ends. Since the top electrode simulates the biological synapsis cephacoria, a perovskite active layer simulates the synaptic cleft, and a bottom electrode simulates synapsis caudacoria, the perovskite artificial synapsis hascomparatively high sensitivity (100mA), and the dual-pulse facilitation, the peak voltage dependence plasticity, peak persistent dependence plasticity and peak frequency dependence plasticity are realized. The preparation method disclosed by the invention not only can effectively simplify the basic structures of the perovskite artificial synapsis at two ends, the sensitivity is improved, the energy consumption is reduced, and the preparation method has significance for the development of the neuromorphic engineering and the human-like robot.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Novel combinations comprising a phoshodiesterase-5 inhibitor and their use
InactiveUS20110034471A1Reduces unwanted side effectEnhance health and appearanceBiocideNervous disorderPhosphodiesteraseSynaptic cleft
The invention relates generally to novel pharmaceutical methods for the treatment of various conditions. Compositions comprising: at least one phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitor in combination with one or more of the following medications: a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; a cholinesterase inhibitor; a dopamine agonist; or a medication suitable to increase the chemical concentrations of the neurotransmitters, selected from amino acids, monoamines, neuropeptides and other agents capable of primary neurotransmission in the synaptic clefts, and their use for treating a neurodegenerative disease in a subject. The invention also relates to: Compositions comprising: at least one phosphodiestersa-5-inhibitor in combination with one or more of the following medications: a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; or a cholinesterase inhibitor, and their use for treating damaged skin in a subject.
Owner:HELD JERRY M
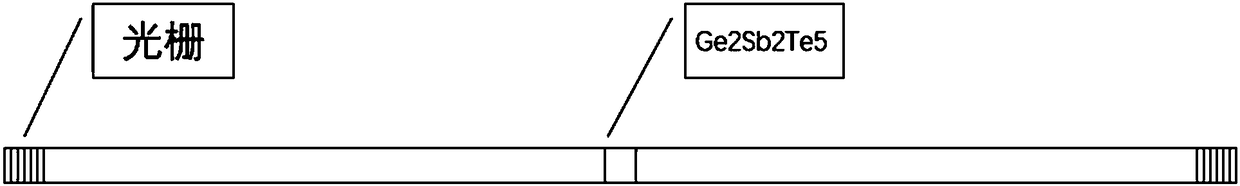
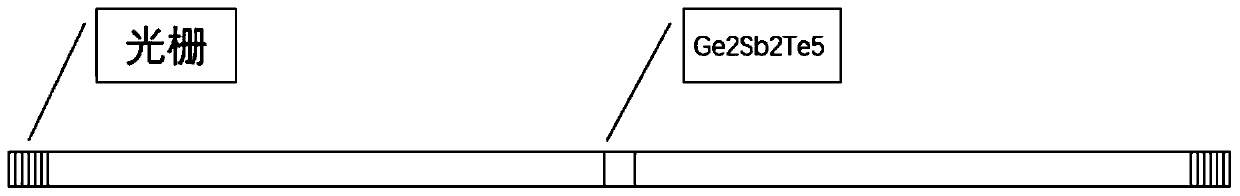
Neuron-like all-optical memory device based on Ge2Sb2Te5
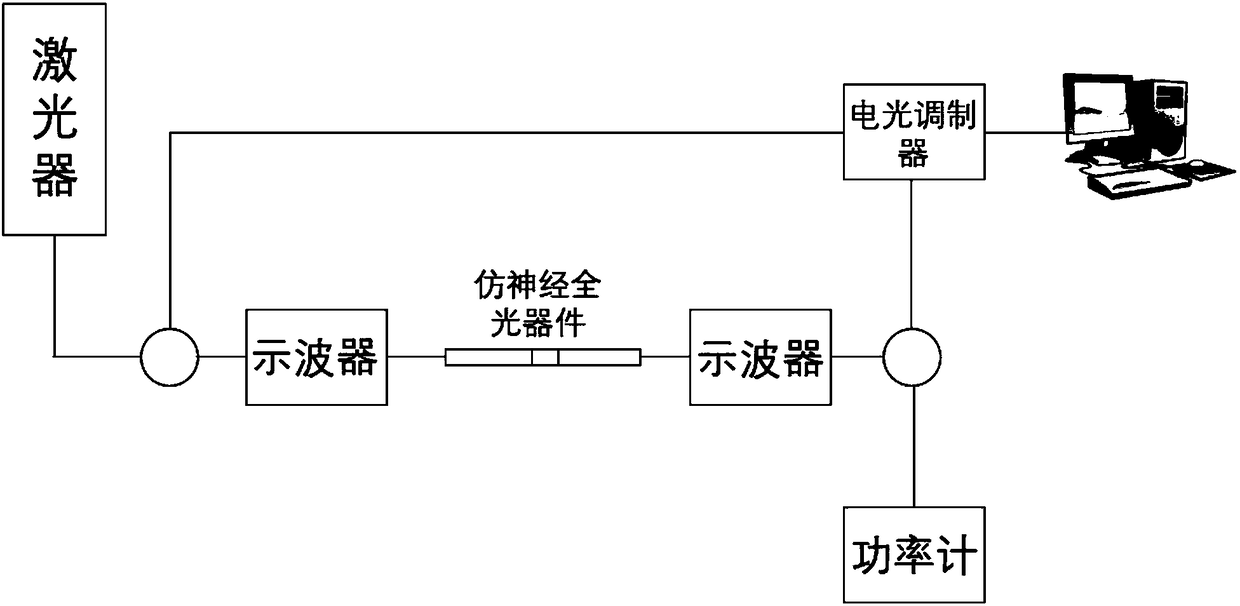
The invention discloses a neuron-like all-optical memory device based on Ge2Sb2Te5, and belongs to the technical field of picosecond laser application. The neuron-like all-optical memory device is based on a multi-pulse action and an STDP neural memory theory. The amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5 is coupled with optical waveguide. Ge2Sb2Te5 is attached to the optical waveguide by a way of magnetron sputtering,and a coupling region is a bionic neural synaptic cleft. The device can realize the reading, memory and erasing processes of the device through all-optical signals. Moreover, the refractive index ofcrystalline Ge2Sb2Te5 is higher than that of amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5, so the material after crystallization is easier to deflect to the direction of Ge2Sb2Te5 than that of amorphous light, the informationretention in the memory region is facilitated, and the device continuously strengthens recording in use.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Pyrrolidine triple reuptake inhibitors
In various embodiments, the present invention provides cycloalkyl pyrrolidine compounds and methods for their use in the treatment and / or prevention of various diseases, conditions and syndromes, including central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia and sleep disorder as well as methods for their synthesis. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the invention, as well as methods of inhibiting reuptake of endogenous monoamines, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft and methods of modulating one or more monoamine transporter.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
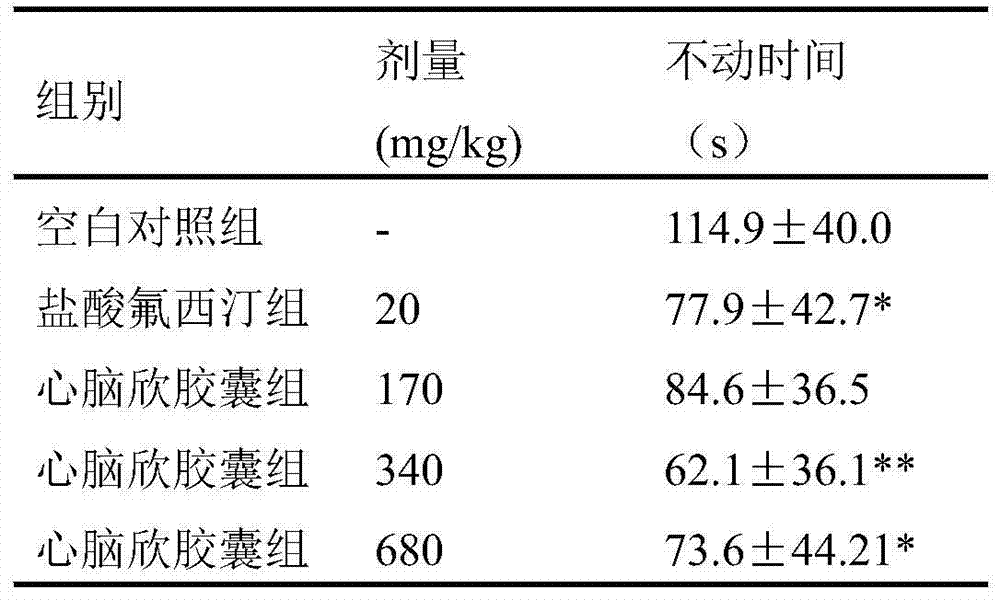
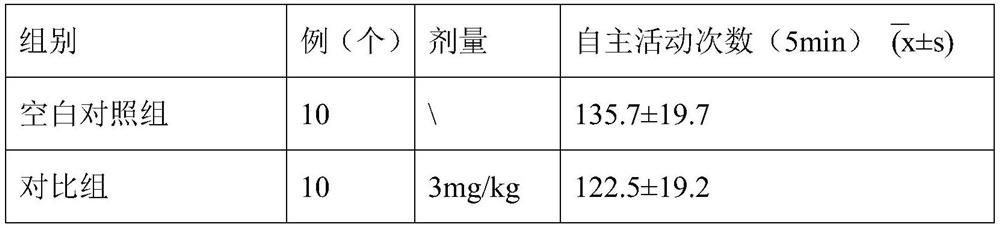
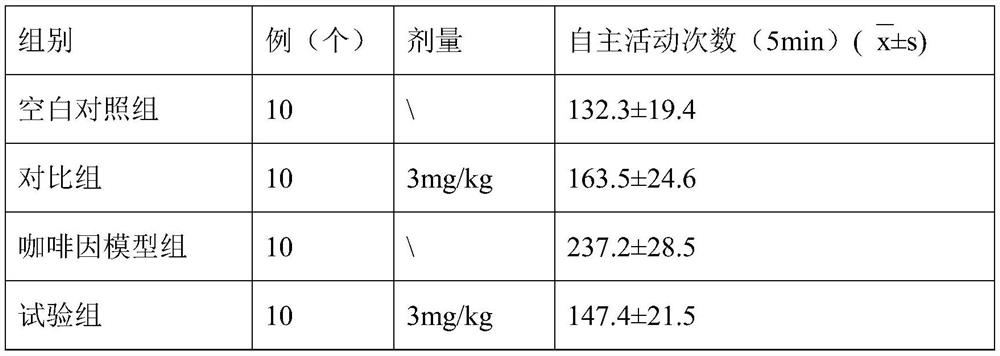
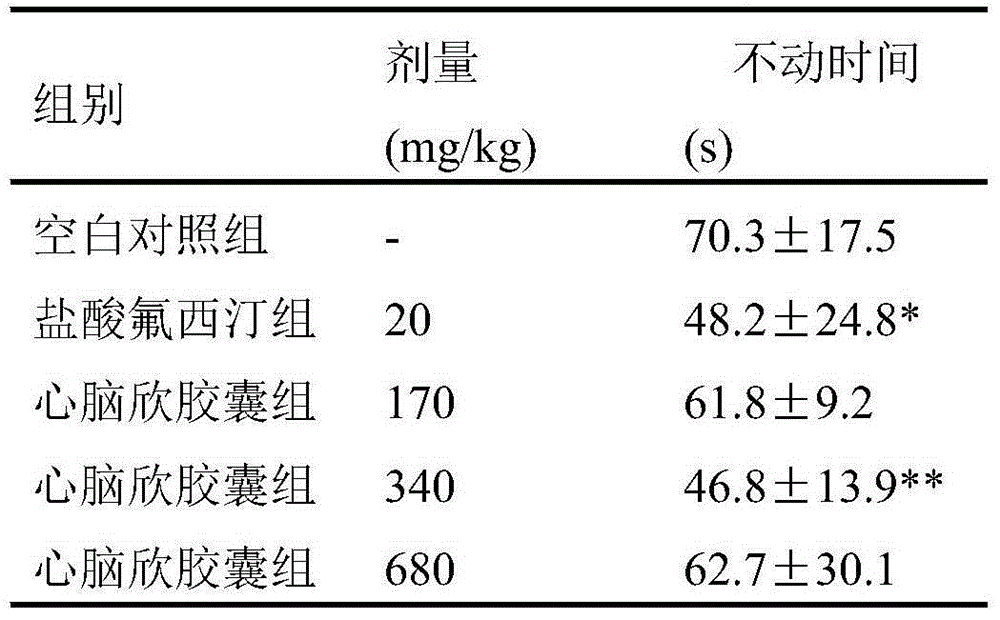
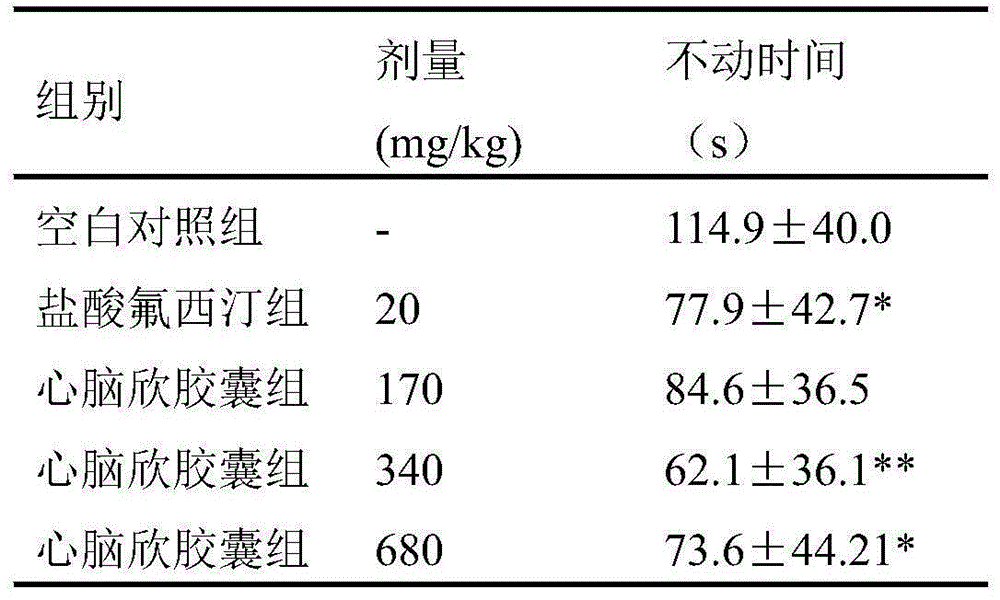
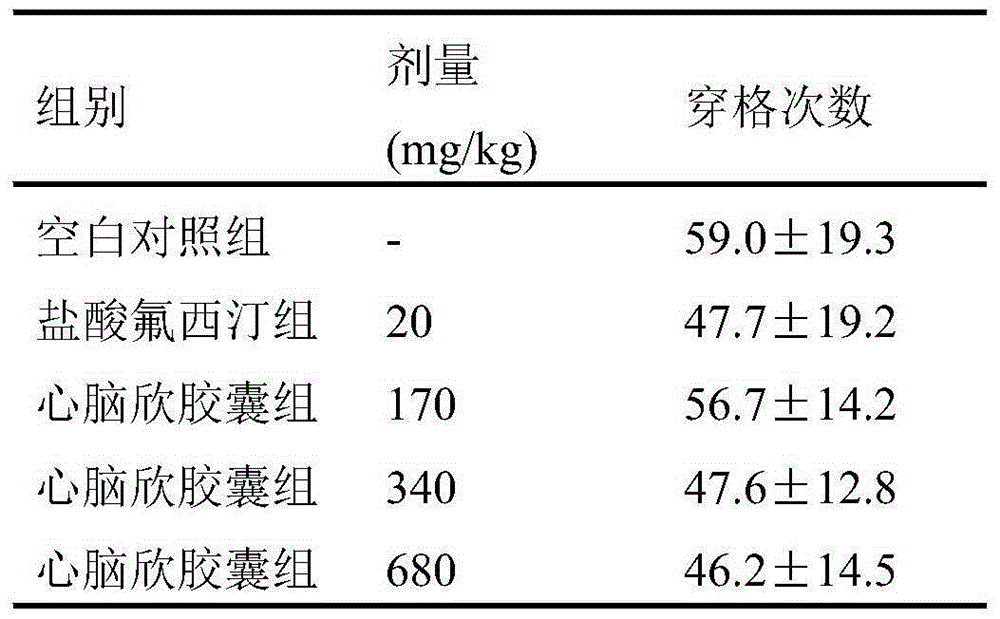
Application of Xinnaoxin capsule in preparation of antidepressant
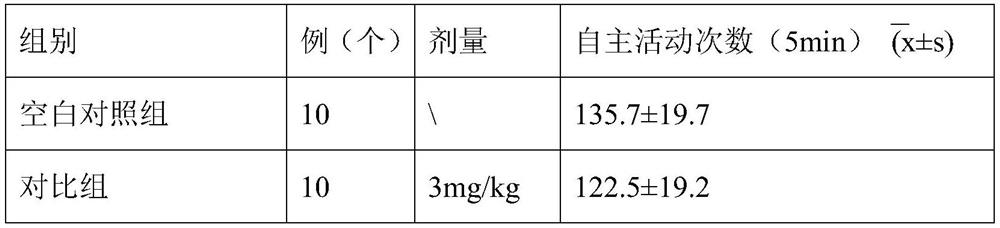
ActiveCN103494946AAntidepressantDoes not interfere with spontaneous activityNervous disorderCapsule deliverySynaptic cleftMedicine
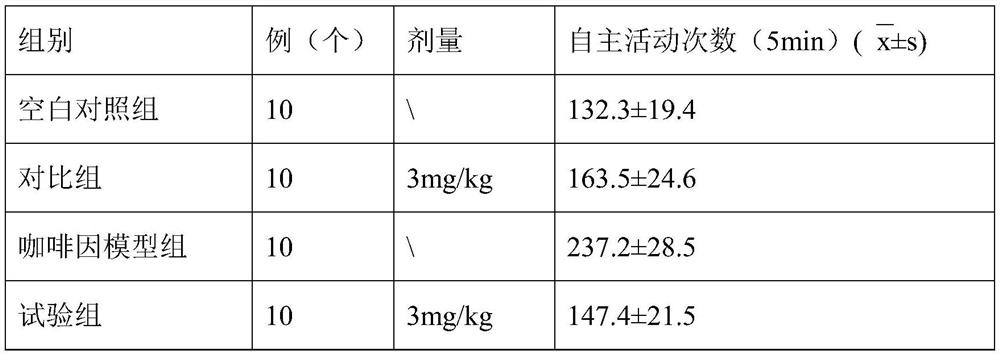
The invention discloses application of a Xinnaoxin capsule in preparation of an antidepressant. According to experimental studies, the Xinnaoxin capsule can substantially reduce dead time during tail suspension and forced swimming of behavioral despair model mice; according to open field experiments, spontaneous activities of the mice are not influenced while dead time is substantially decreased, which prompts that the Xinnaoxin capsule has a certain anti-depression effect. Meanwhile, the Xinnaoxin capsule can substantially inhibit activity of monoamine oxidase and increase the content of a monoamine neurotransmitter in a synaptic cleft, which proves that the Xinnaoxin capsule has the anti-depression effect. Moreover, the Xinnaoxin capsule can substantially antagonize decrease of body temperature of the mice caused by reserpine and apomorphine and increase exogenous toxicity given to NE, which reveals that the capsule has the anti-depression effect. The anti-depression effect of the capsule is realized through improvement of the level of the monoamine neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft.
Owner:GANSU CHEEZHENG TIBETAN MEDICINE CO LTD
Pyrrolidine triple reuptake inhibitors
In various embodiments, the present invention provides cycloalkyl pyrrolidine compounds and methods for their use in the treatment and / or prevention of various diseases, conditions and syndromes, including central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia and sleep disorder as well as methods for their synthesis. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the invention, as well as methods of inhibiting reuptake of endogenous monoamines, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine from the synaptic cleft and methods of modulating one or more monoamine transporter.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
Phenyl substituted cycloalkylamines as monoamine reuptake inhibitors
ActiveUS8669291B2Improve usabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSynaptic cleftPharmaceutical formulation
Phenyl-substituted cyclohexylamine derivatives and method for their synthesis and characterization are disclosed. Use of these compounds to treat / prevent neurological disorders as well as methods for their synthesis are set forth herein. Exemplary compounds of the invention inhibit reuptake of endogenous monoamines, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine (e.g., from the synaptic cleft) and modulate one or more monoamine transporter. Pharmaceutical formulations incorporating compounds of the invention are also provided.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
Pharmaceutical uses of polyene phosphatidyl choline for treating cognitive impairment
InactiveCN101366720BEasy to useFair priceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSynaptic cleftFunctional disturbance
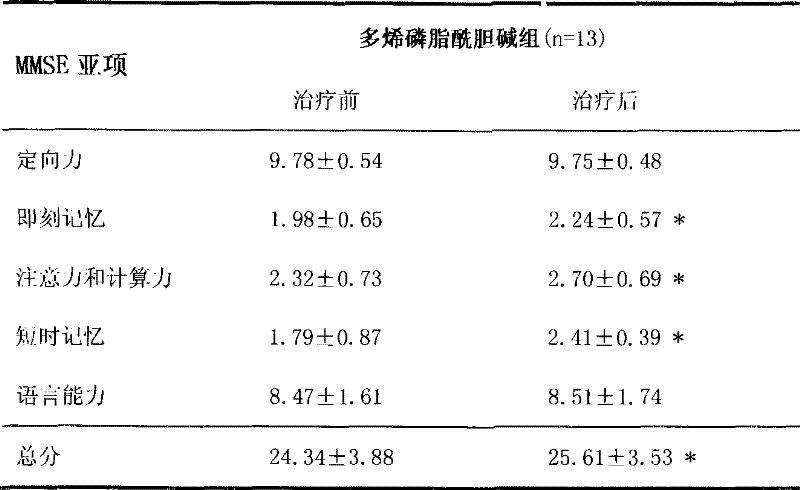
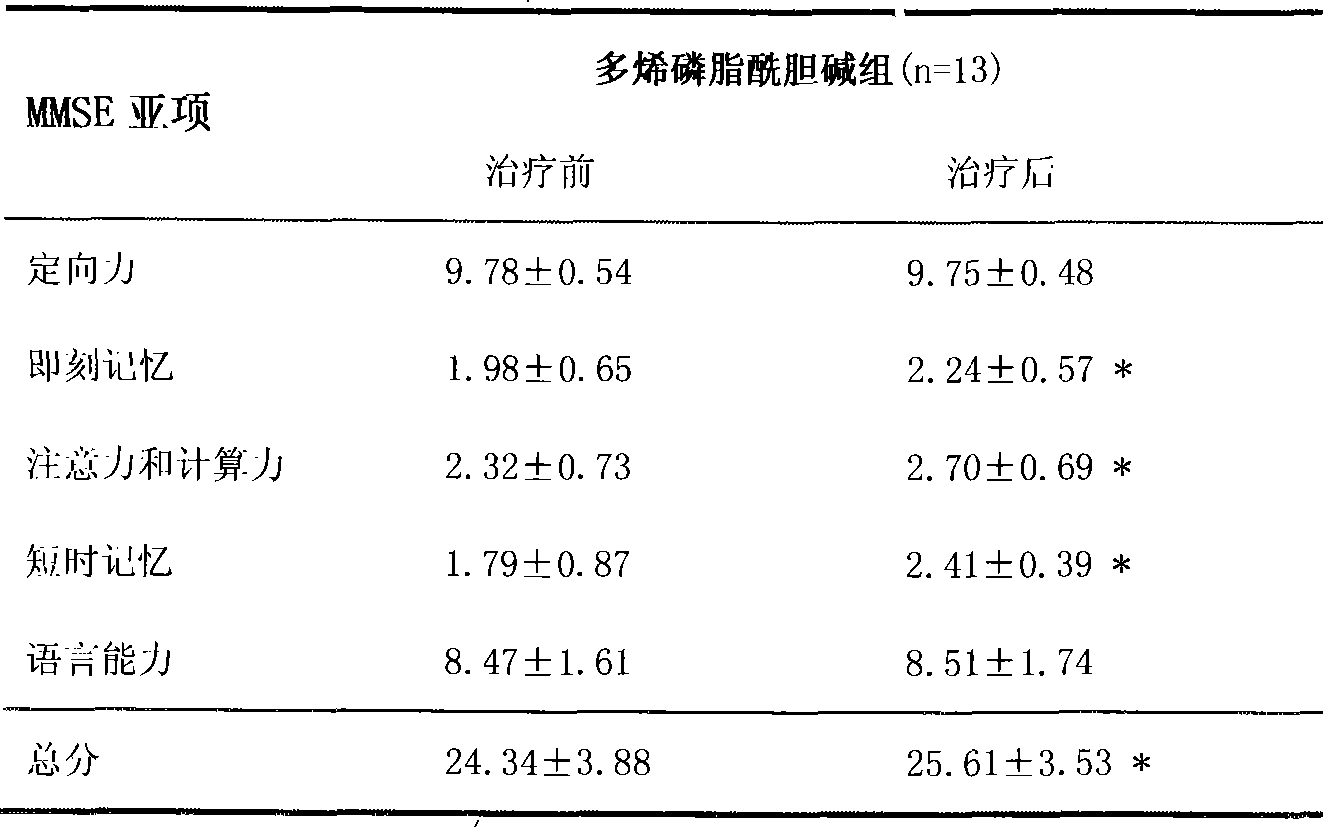
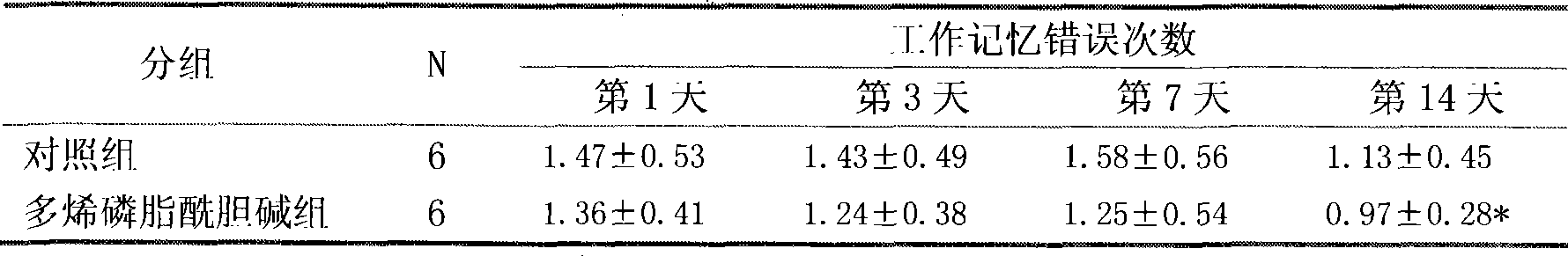
The invention provides medicinal application of polyene phosphatidylcholine in treating cognitive functional disorder, which adopts a clinically commonly used medicine for protecting the liver - the polyene phosphatidylcholine to be a novel medicine for treating the cognitive functional disorder. As proved by clinical application and animal experiments, the polyene phosphatidylcholine has influence on improving the cognitive functional disorder and the memory function and has good effect of treating the cognitive functional disorder. Due to introduction of 'polyene' radicals which are more fat-soluble, the polyene phosphatidylcholine is more favorable to pass through blood-brain barriers and can be completely taken by neurons; and choline products produced by decomposition of the polyene phosphatidylcholine by the neurons can be further synthesized into acetylcholine in the neurons, thereby compensating for choline exhausted by synaptic clefts. The polyene phosphatidylcholine can generate the choline, DHA and an arachidonic acid during the process of metabolism, is a medicine for treating the cognitive functional disorder which has moderate price and small toxic and side effect, and is safe and reliable, and can also become a medicine for improving intelligence.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Pharmaceutical uses of polyene phosphatidyl choline for treating cognitive impairment
InactiveCN101366720AEasy to useFair priceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSynaptic cleftFunctional disturbance
The invention provides medicinal application of polyene phosphatidylcholine in treating cognitive functional disorder, which adopts a clinically commonly used medicine for protecting the liver - the polyene phosphatidylcholine to be a novel medicine for treating the cognitive functional disorder. As proved by clinical application and animal experiments, the polyene phosphatidylcholine has influence on improving the cognitive functional disorder and the memory function and has good effect of treating the cognitive functional disorder. Due to introduction of 'polyene' radicals which are more fat-soluble, the polyene phosphatidylcholine is more favorable to pass through blood-brain barriers and can be completely taken by neurons; and choline products produced by decomposition of the polyene phosphatidylcholine by the neurons can be further synthesized into acetylcholine in the neurons, thereby compensating for choline exhausted by synaptic clefts. The polyene phosphatidylcholine can generate the choline, DHA and an arachidonic acid during the process of metabolism, is a medicine for treating the cognitive functional disorder which has moderate price and small toxic and side effect, and is safe and reliable, and can also become a medicine for improving intelligence.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions comprising a phoshodiesterase-5 inhibitor and their use in methods of treatment
InactiveUS8440671B2Enhance health and appearanceFacilitating accelerating healingBiocideNervous disorderSynaptic cleftAmino acid
Owner:HELD JERRY M
Method and composition for treating neuropathic pain
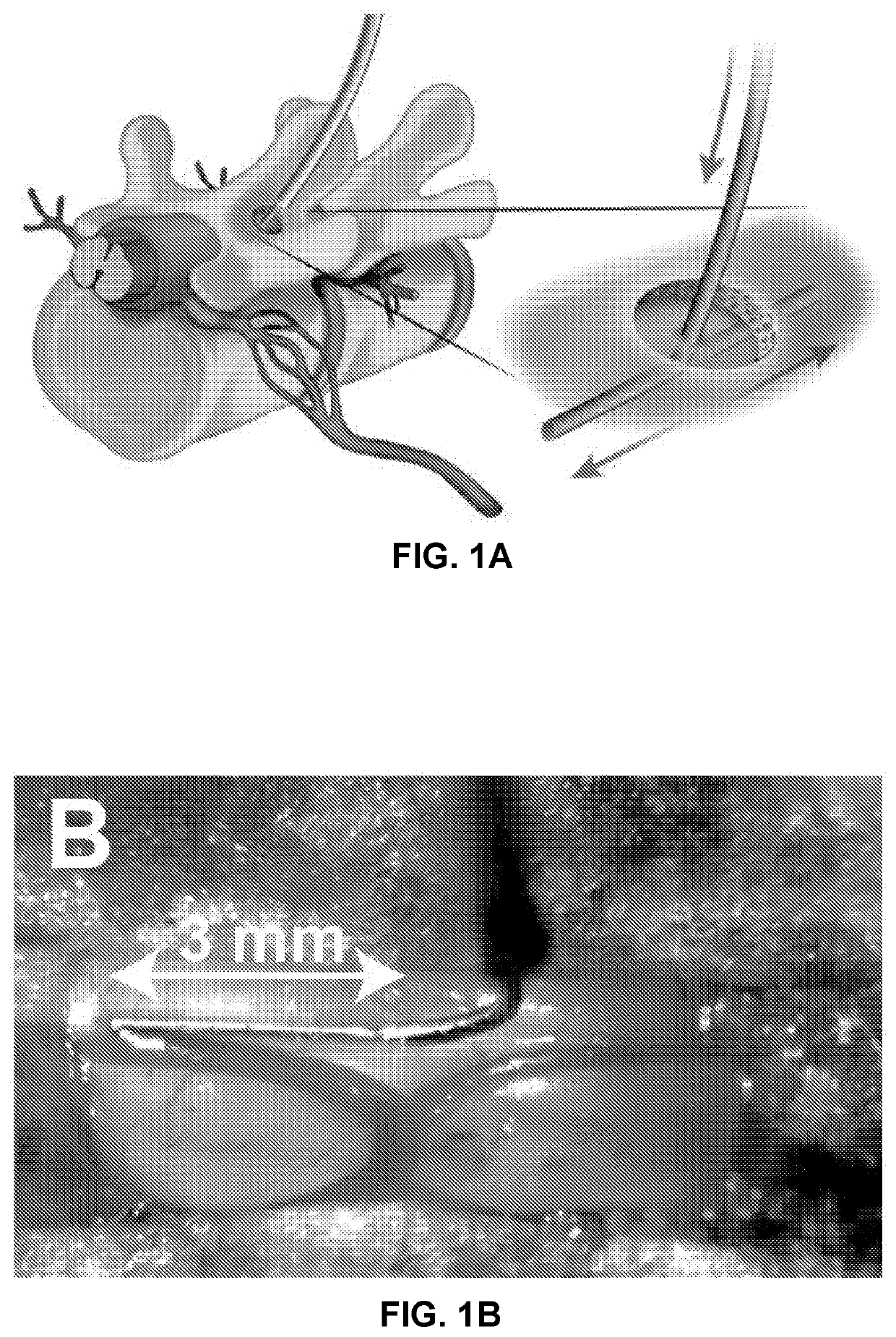
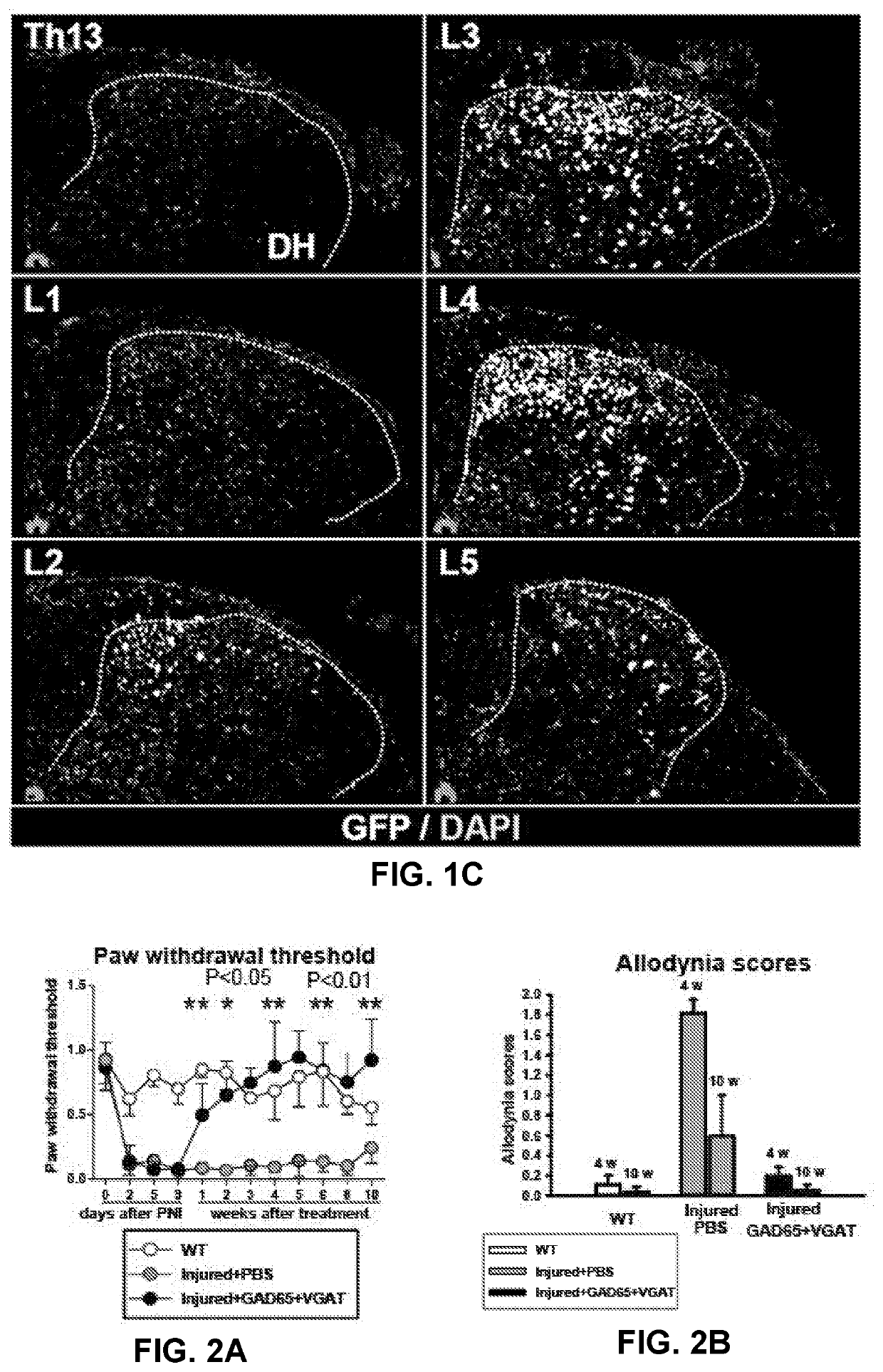
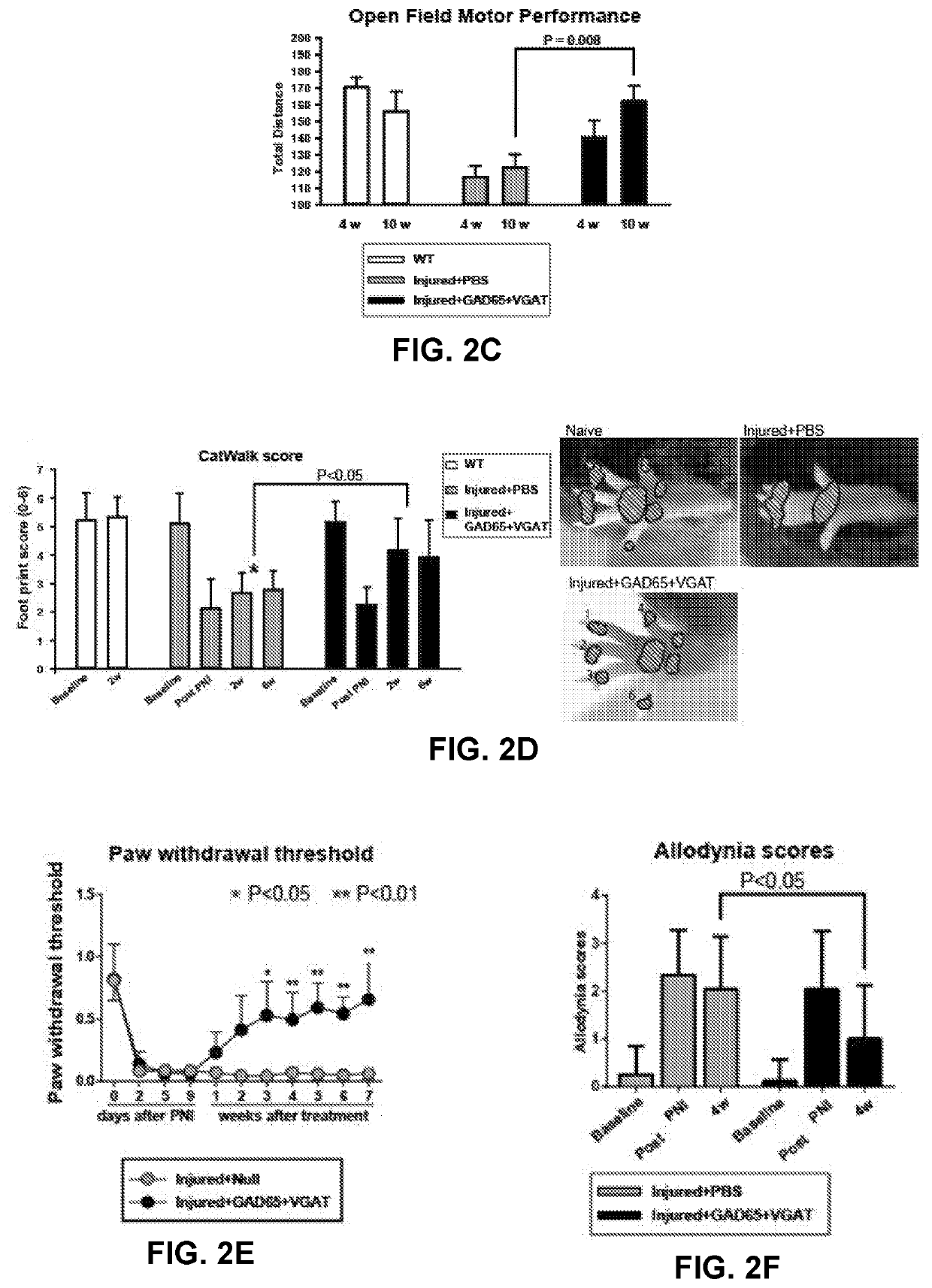
ActiveUS20210353775A1Efficient inductionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSynaptic cleftSpinal column
The present invention provides a therapy for treating neuropathic pain by subpial administration of small quantities of a composition for spinal segment-specific upregulation of GAD65 (glutamatedecarboxylase) gene and VGAT (vesicular GABA transporter) gene, which is effective for induction of nociceptive effects by potentiating release of vesicular GABA from infected dorsal horn neurons into the synaptic cleft.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
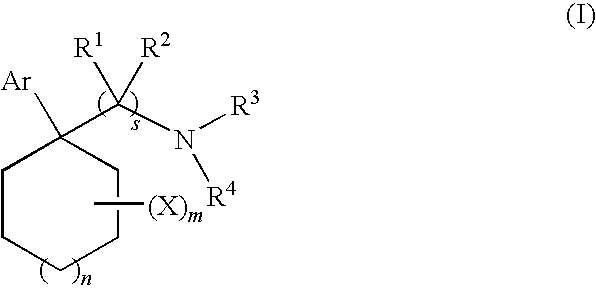
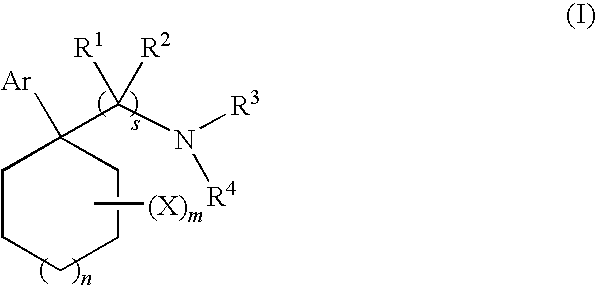
A kind of medicine with neuroprotective effect and its application
ActiveCN111821294BNo obvious toxic side effectIncrease neurotransmitter concentrationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSynaptic cleftGallate
The invention provides a kind of medicine with neuroprotective effect and application thereof. The medicine is theaflavin-3'-gallate, and its structure is shown in formula (I). Described compound of formula (I) has obvious effect in terms of depressive neurosis, and the antidepressant effect of theaflavin-3'-gallate is mainly by increasing the content of 5-HT and DA in the brain, improving the synaptic cleft nerve. The concentration of the transmitter can be achieved, which can obviously relieve and treat nervous symptoms. The theaflavin-3'-gallate of the present invention also has a good curative effect in the aspect of cardiac neurosis.
Owner:MUDANJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
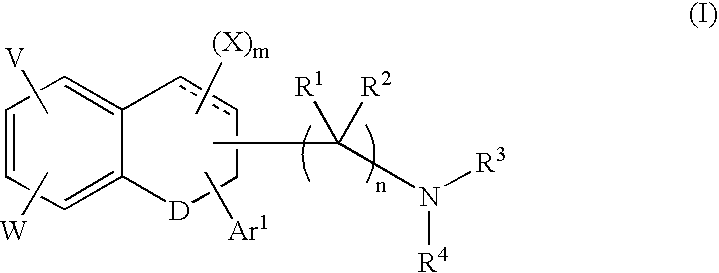
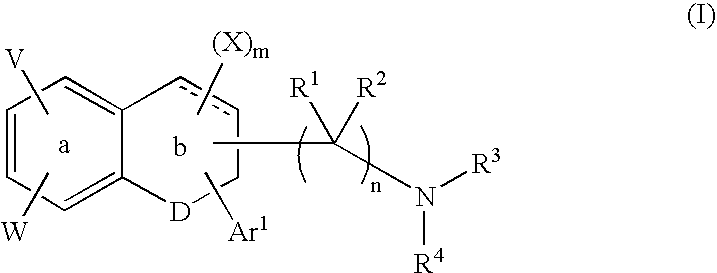
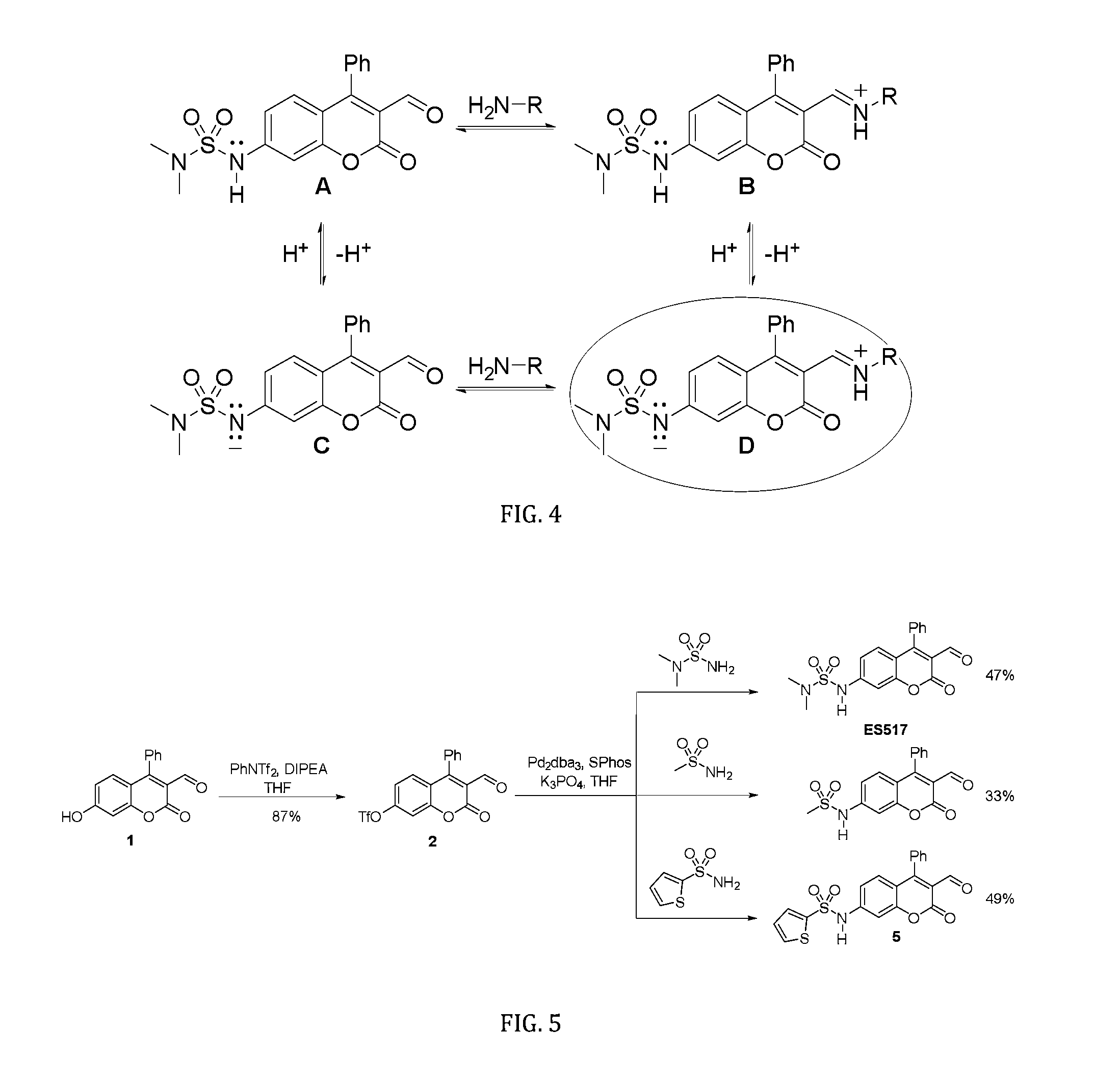
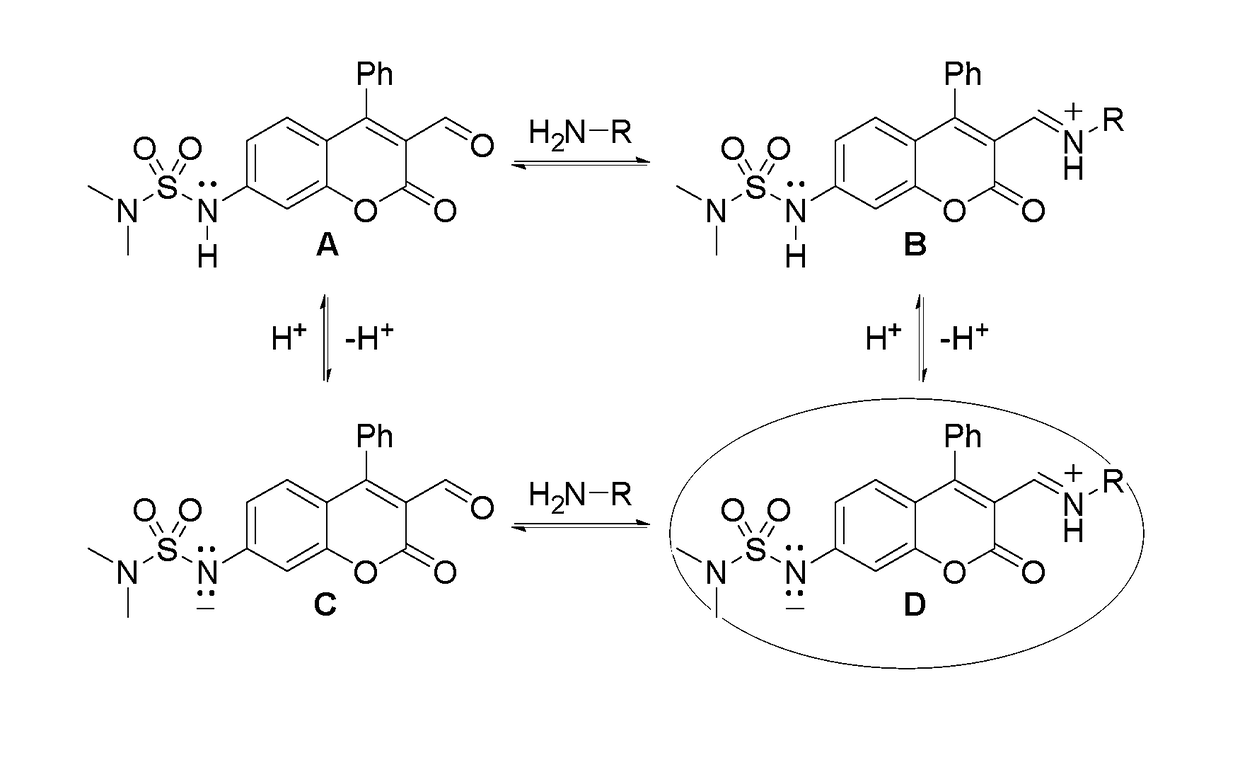
Fused ring compound and preparation method and application thereof
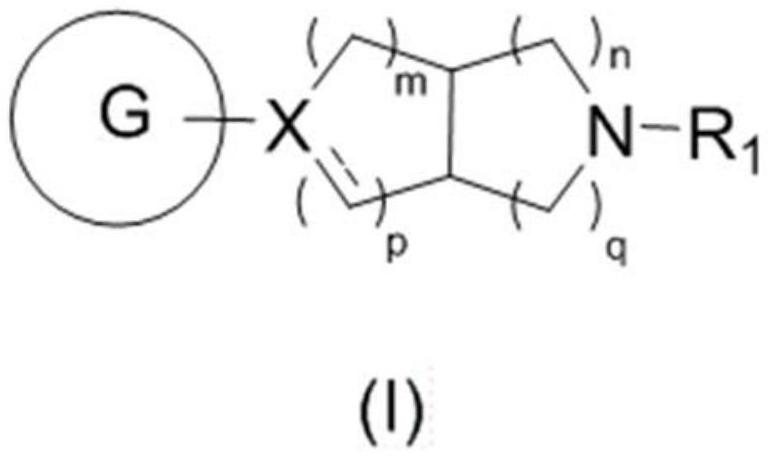
ActiveCN112010859AHigh affinityHigh activityNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySynaptic cleftNeurological problems
The present invention relates to a fused ring compound represented by general formula (I), a stereoisomer thereof or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a preparation method therefor, a pharmaceutical composition, and a use thereof. The compound is used for treating, preventing and / or controlling various nervous system disorders. The compound provided herein modulates one or more monoaminetransporters, inhibits reuptake of endogenous monoamines such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine (e.g., from synaptic clearances), and / or modulates the 5-HT3 receptor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and composition for treating neuropathic pain
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ionic two-end bionic memristor and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114005936AExcellent scalingHigh density integrationElectrical apparatusPhysical realisationSynapseSynaptic cleft
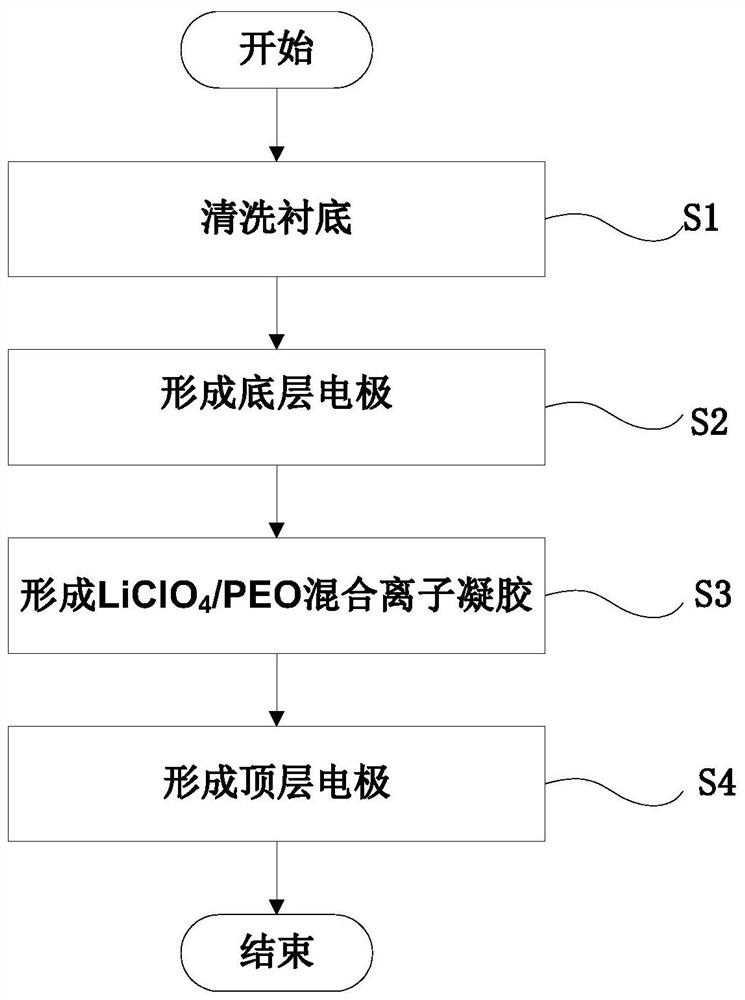
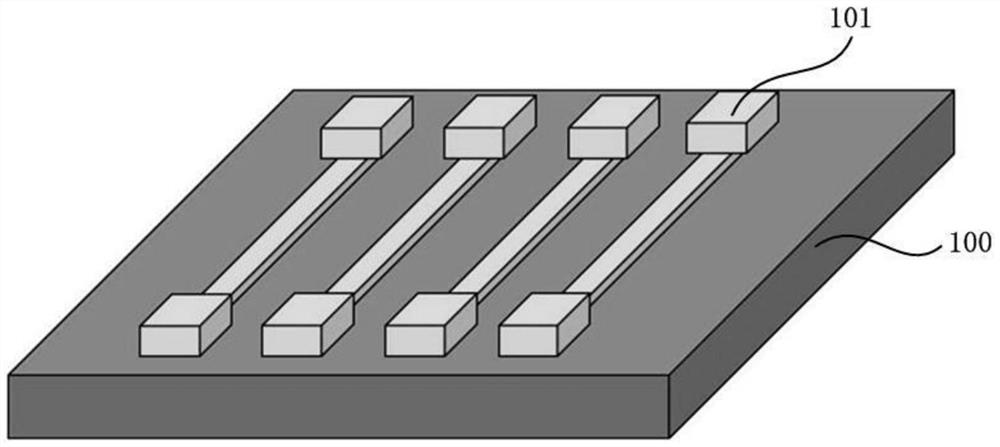
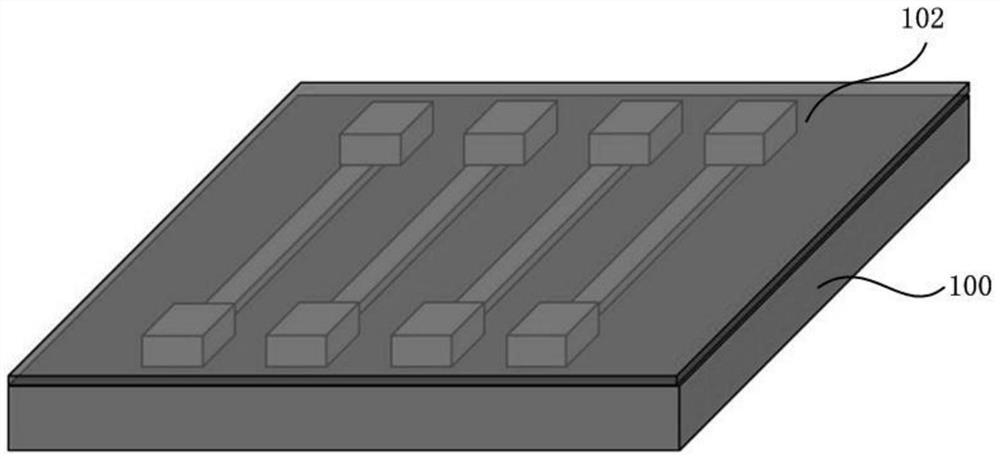
The invention discloses an ionic two-end bionic memristor and a preparation method thereof. The ionic two-end bionic memristor device comprises a substrate, bottom electrodes which are formed on the substrate, are arranged in parallel along a first direction at certain intervals and serve as one end of the memristor, ionic gel which is formed on the bottom layer electrode and serves as a functional layer of the memristor, and top electrodes which are formed on the ionic gel, are arranged in parallel along a second direction at certain intervals, are in a cross array structure with the bottom electrodes, and serve as the other end of the memristor, wherein two ends of the memristor respectively correspond to a synaptic front end and a synaptic rear end, a functional layer of the memristor corresponds to a synaptic gap, ion migration in brain-like nerve synapses is simulated by utilizing diffusibility of ions in the ionic gel, information transmission of a conductive channel is realized, an ion channel effect in a similar organism is simulated, and a nerve synapse weight modulation process is completed.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Triple reuptake inhibitors and methods of use thereof
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
Neuro-inspired all-optical memory device based on ge2sb2te5
The invention discloses a neuron-like all-optical memory device based on Ge2Sb2Te5, and belongs to the technical field of picosecond laser application. The neuron-like all-optical memory device is based on a multi-pulse action and an STDP neural memory theory. The amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5 is coupled with optical waveguide. Ge2Sb2Te5 is attached to the optical waveguide by a way of magnetron sputtering,and a coupling region is a bionic neural synaptic cleft. The device can realize the reading, memory and erasing processes of the device through all-optical signals. Moreover, the refractive index ofcrystalline Ge2Sb2Te5 is higher than that of amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5, so the material after crystallization is easier to deflect to the direction of Ge2Sb2Te5 than that of amorphous light, the informationretention in the memory region is facilitated, and the device continuously strengthens recording in use.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
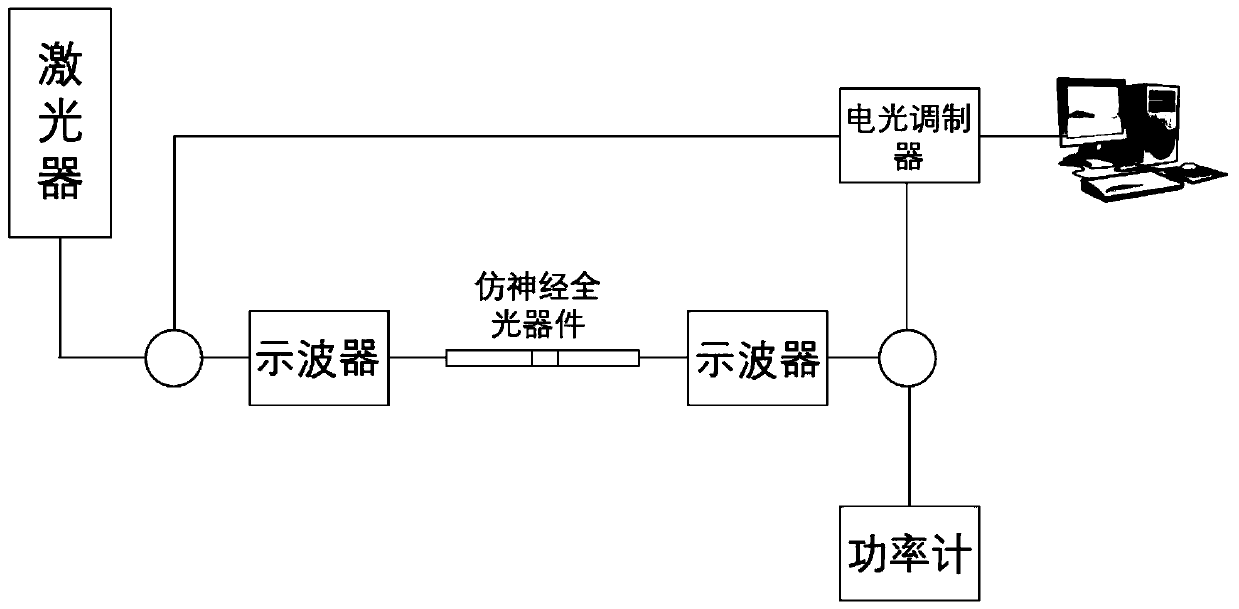
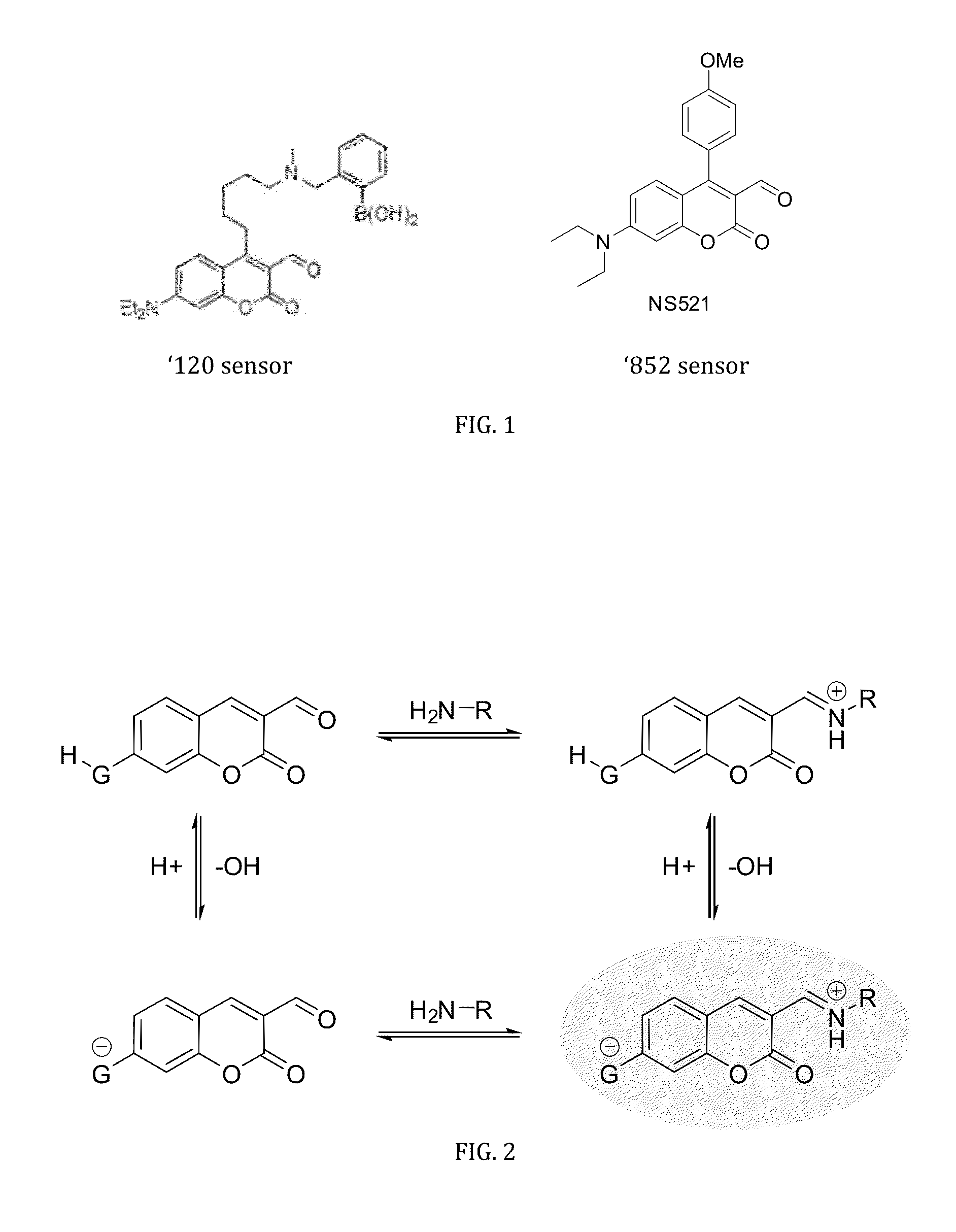
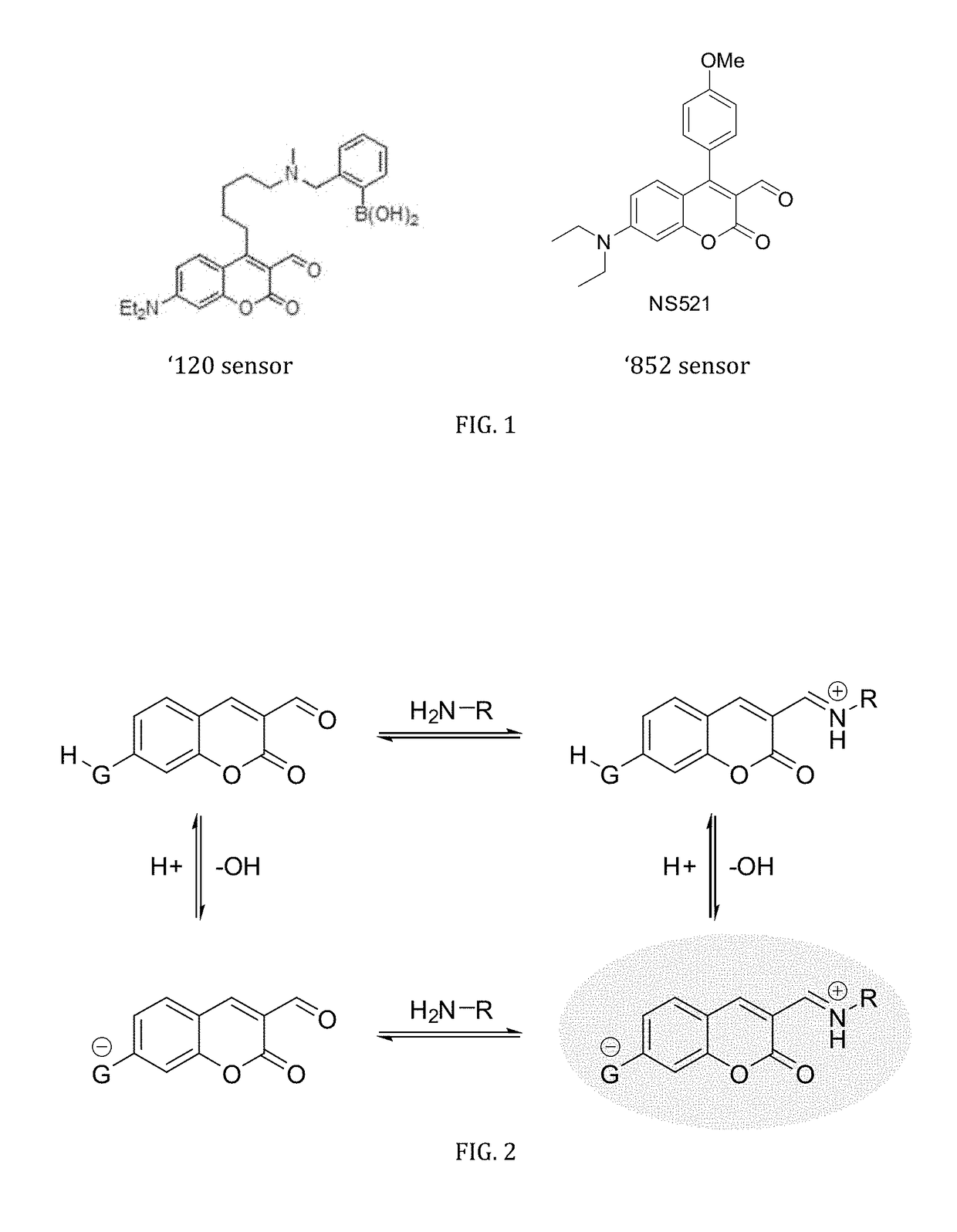
ph-sensitive fluorescent sensors for biological amines
The invention is directed to dual-analyte fluorescent chemosensors for the direct detection and visualization (imaging) of neurotransmitters released upon exocytosis. The inventive sensor exploits the high concentration of neurotransmitters (e.g., glutamate, norepinephrine, and dopamine) and capitalizes upon the pH gradient between the vesicle and synaptic cleft.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
pH-sensitive fluorescent sensors for biological amines
The invention is directed to dual-analyte fluorescent chemosensors for the direct detection and visualization (imaging) of neurotransmitters released upon exocytosis. The inventive sensor exploits the high concentration of neurotransmitters (e.g., glutamate, norepinephrine, and dopamine) and capitalizes upon the pH gradient between the vesicle and synaptic cleft.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
A preparation method of two-terminal artificial synapse electronic device based on organic/inorganic hybrid perovskite
ActiveCN109920914BImprove qualityReduce manufacturing costNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSynaptic cleftPerovskite (structure)
The invention discloses a preparation method of an electronic device with artificial synapsis at two ends based on organic / inorganic hybrid perovskite, and belongs to the field of the electronic device. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pre-treating a high-doped silicon substrate, spinning-coating a configured perovskite solution on a substrate, performing annealing treatment to obtain a perovskite thin film with good crystallinity; and then evaporating a metal top electrode to obtain the electronic device with perovskite artificial synapsis at two ends. Since the top electrode simulates the biological synapsis cephacoria, a perovskite active layer simulates the synaptic cleft, and a bottom electrode simulates synapsis caudacoria, the perovskite artificial synapsis hascomparatively high sensitivity (100mA), and the dual-pulse facilitation, the peak voltage dependence plasticity, peak persistent dependence plasticity and peak frequency dependence plasticity are realized. The preparation method disclosed by the invention not only can effectively simplify the basic structures of the perovskite artificial synapsis at two ends, the sensitivity is improved, the energy consumption is reduced, and the preparation method has significance for the development of the neuromorphic engineering and the human-like robot.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Drug with neuroprotective effect and application of drug
ActiveCN111821294ANo obvious toxic side effectIncrease neurotransmitter concentrationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSynaptic cleftTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a drug with a neuroprotective effect and application of the drug. The drug is theaflavin-3'-gallate, and a structure of the drug is shown as a formula (I). A compound of the formula (I) has obvious effects on depressive neurosis, the antidepressant effect of theaflavin-3'-gallate is mainly realized by increasing the content of 5-HT and DA in brain and increasing the concentration of synaptic cleft neurotransmitter, and theaflavin-3'-gallate has obvious relieving and therapeutic effects on nervous tension symptoms. The theaflavin-3'-gallate further has a good curative effect on cardiac neurosis.
Owner:MUDANJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Application of Xinnaoxin Capsules in Preparation of Antidepressants
ActiveCN103494946BAntidepressantDoes not interfere with spontaneous activityNervous disorderCapsule deliverySynaptic cleftMorphine
The invention discloses application of a Xinnaoxin capsule in preparation of an antidepressant. According to experimental studies, the Xinnaoxin capsule can substantially reduce dead time during tail suspension and forced swimming of behavioral despair model mice; according to open field experiments, spontaneous activities of the mice are not influenced while dead time is substantially decreased, which prompts that the Xinnaoxin capsule has a certain anti-depression effect. Meanwhile, the Xinnaoxin capsule can substantially inhibit activity of monoamine oxidase and increase the content of a monoamine neurotransmitter in a synaptic cleft, which proves that the Xinnaoxin capsule has the anti-depression effect. Moreover, the Xinnaoxin capsule can substantially antagonize decrease of body temperature of the mice caused by reserpine and apomorphine and increase exogenous toxicity given to NE, which reveals that the capsule has the anti-depression effect. The anti-depression effect of the capsule is realized through improvement of the level of the monoamine neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft.
Owner:GANSU CHEEZHENG TIBETAN MEDICINE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com