Method and composition for treating neuropathic pain
A neurological, compositional technology, applied in the field of combined treatment regimens, able to solve the problems of not allowing to limit the treatment effect of spinal cord segments, without chronic neuropathic pain, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] Vector delivery in mouse models
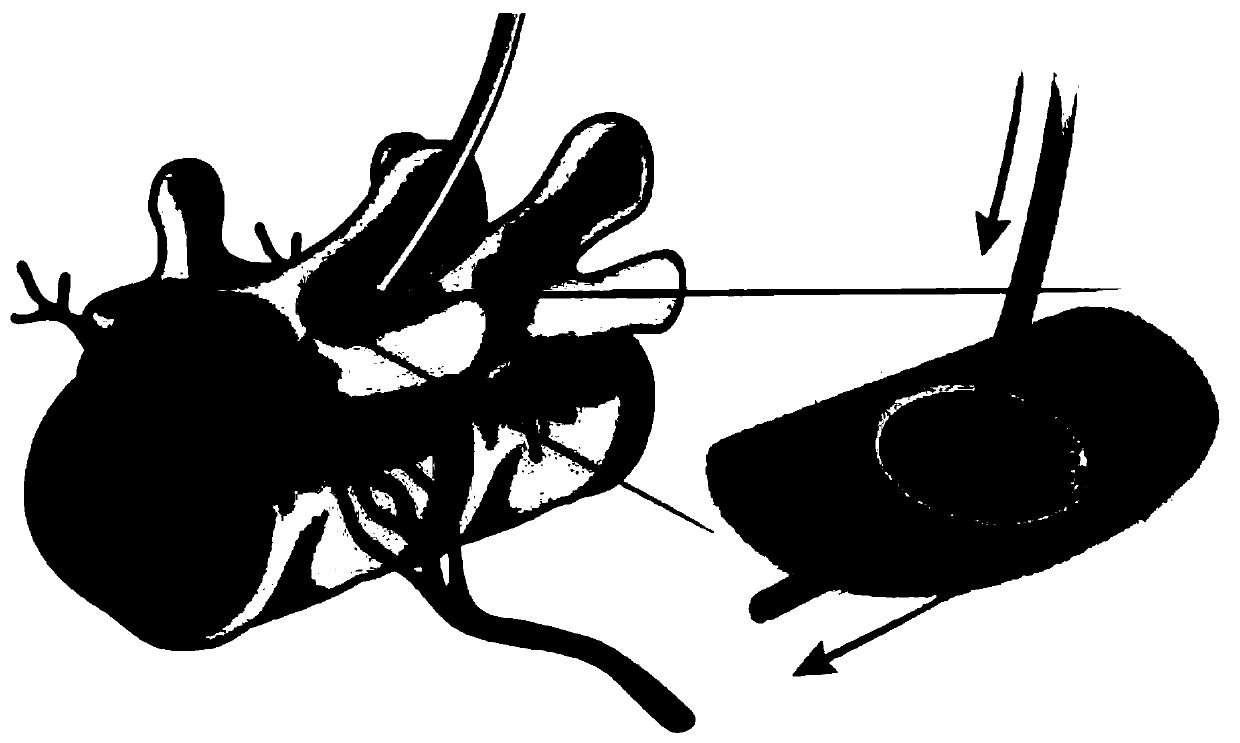
[0138] Figure 1A with Figure 1B The subpial delivery of an AAV9 (or Anc80) vector encoding GAD65 (glutamate decarboxylase 65) and VGAT (vesicular GABA transporter) into the targeting segment is exemplified. One-third to one-half the diameter of the sciatic nerve of blank C57BL6 mice was tightly ligated (unilateral ligation) to induce mechanical allodynia. Animals were tested for changes in tactile nociceptive thresholds using von Frey filaments and brush-induced allodynia over a 10-day period following nerve injury.
[0139] Ten days after induction of sciatic nerve injury, animals received a unilateral subpial injection of AAV9 encoding the GAD65 and VGAT genes under the ubiquitin promoter (UBI). Two control groups were studied. In the first control group, animals with sciatic nerve injury were injected subpially at L2-L3 only with PBS. In another control group (uninjured blank animals), no treatment was given. In a separate grou...
Embodiment 2
[0146] Vector delivery in a porcine model
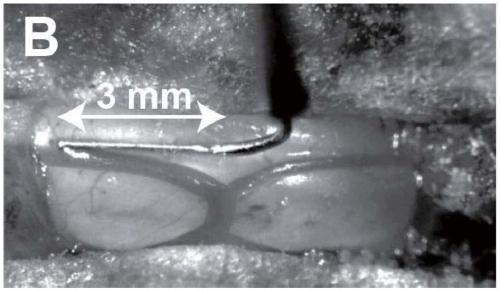
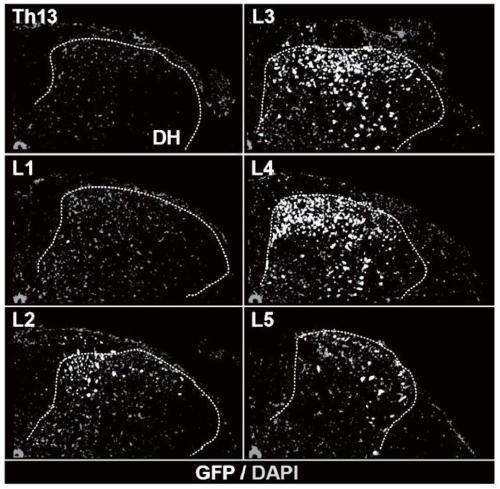
[0147] In this example, an adult pig model is used to demonstrate that subpial delivery of vectors achieves well-targeted transgene expression in an animal species with spinal cord dimensions similar to those of adults. Adult pigs (Yugatan pigs, 15kg to 25kg; n=3) received unilateral subpial (L2-L3) Anc80-UBI-Rpl22-3xHA vector delivery (100 μl; 1.2×10 13 gc / ml). Animals survived for 48 hours after vehicle injection and were then perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde for fixation. Transverse spinal cord sections were then prepared and stained with anti-HA antibody. Stained sections were analyzed by confocal microscopy. Such as Figure 5A to Figure 5D As shown, dorsal horn neuron-specific Rp122 protein expression was observed on the same side as the vector-injected side.
[0148] Another group of adult pigs (Göttingen-Minnesota; 35kg to 45kg; n=3) received unilateral subpial (L2-L3) Anc80-UBI-GAD65 / VGAT (100 μl; 1.2×10 13 gc / ml) to d...
Embodiment 3
[0151] Vector delivery in a rat model of chronic muscle spasticity
[0152] In a rat model of chronic muscle spasticity (ie, rats with spinal cord-induced muscle spasm), vehicle treatment was provided to demonstrate antispasticity following subpial delivery of AAV9-UBI-GAD65 / VGAT. Such as Figure 8A with Figure 8B As shown, muscle spasms measured in animals receiving a control vector (AAV9-GFP) showed a gradual increase in muscle spasms over 8 weeks after virus delivery (compared to baseline measured 2 to 3 months after spinal cord transection). In contrast, a near complete blockade of the spastic response was measured in animals receiving the AAV9-UBI-GAD65 / VGAT vector. Measurements of H-reflex frequency-dependent inhibition (RDD) revealed a significant restoration of RDD in animals treated with the AAV9-UBI-GAD65 / VGAT vector ( Figure 8C with Figure 8D ).
[0153] Bilateral (L2-L4) subpial AAV9-UBI-GAD65 / VGAT delivery induces a mixed inhibitory-excitatory neurotransmi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com