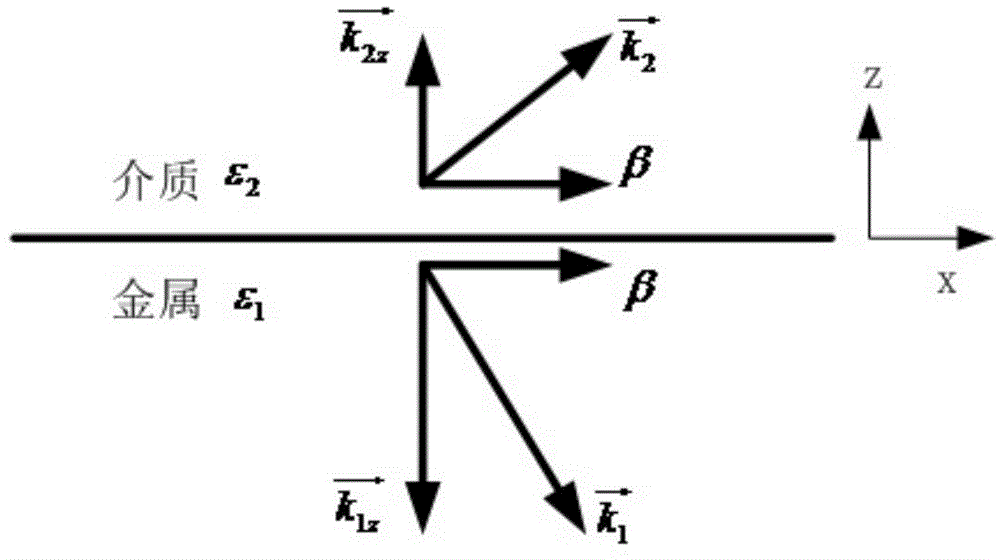
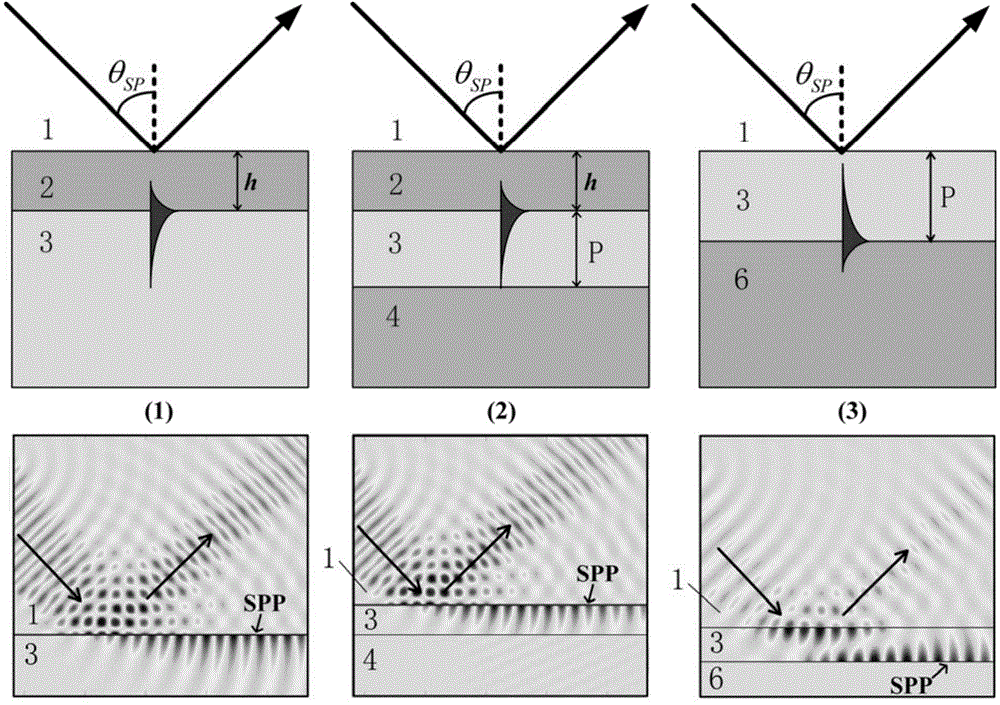
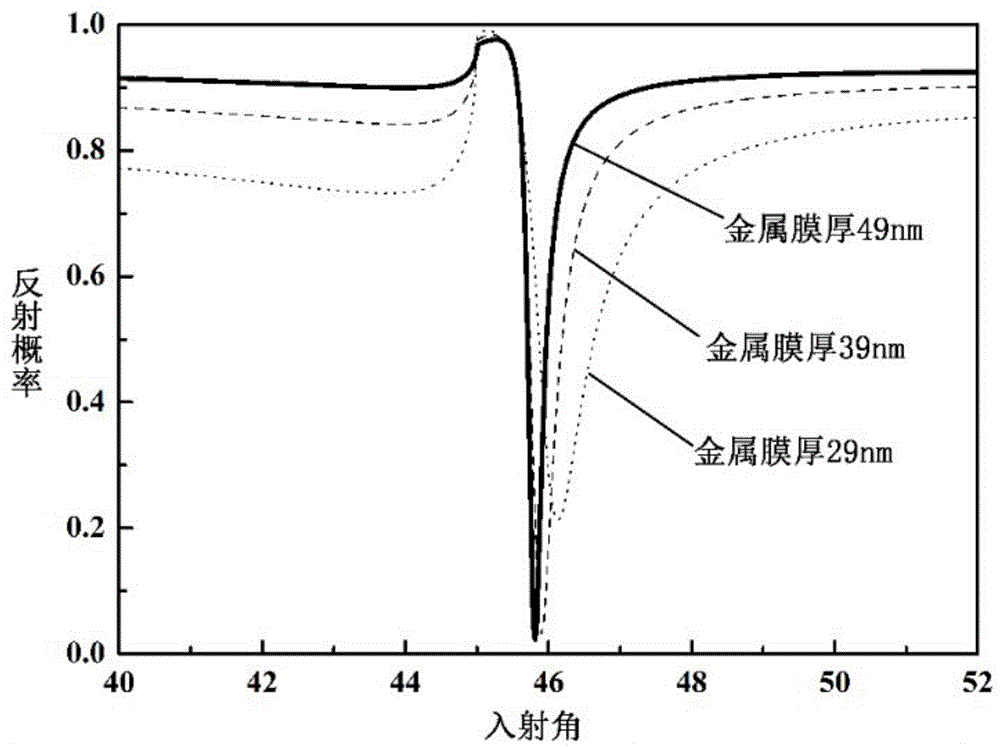
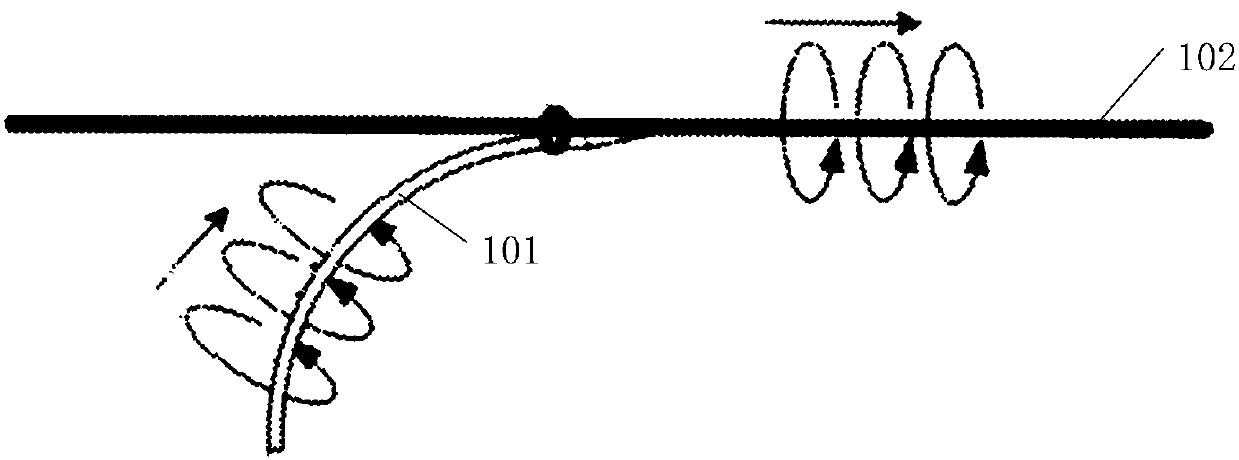
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Surface wave excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
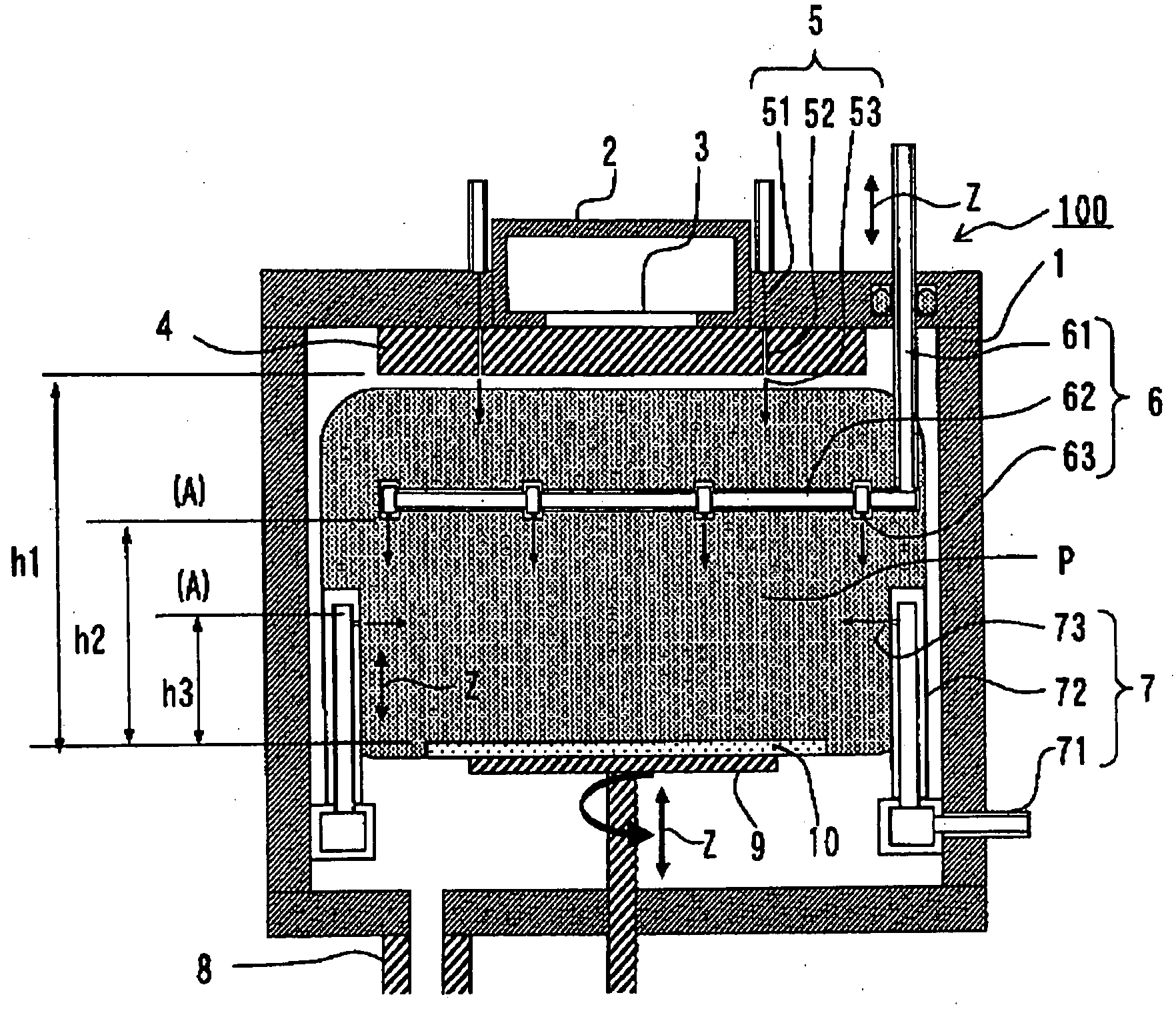
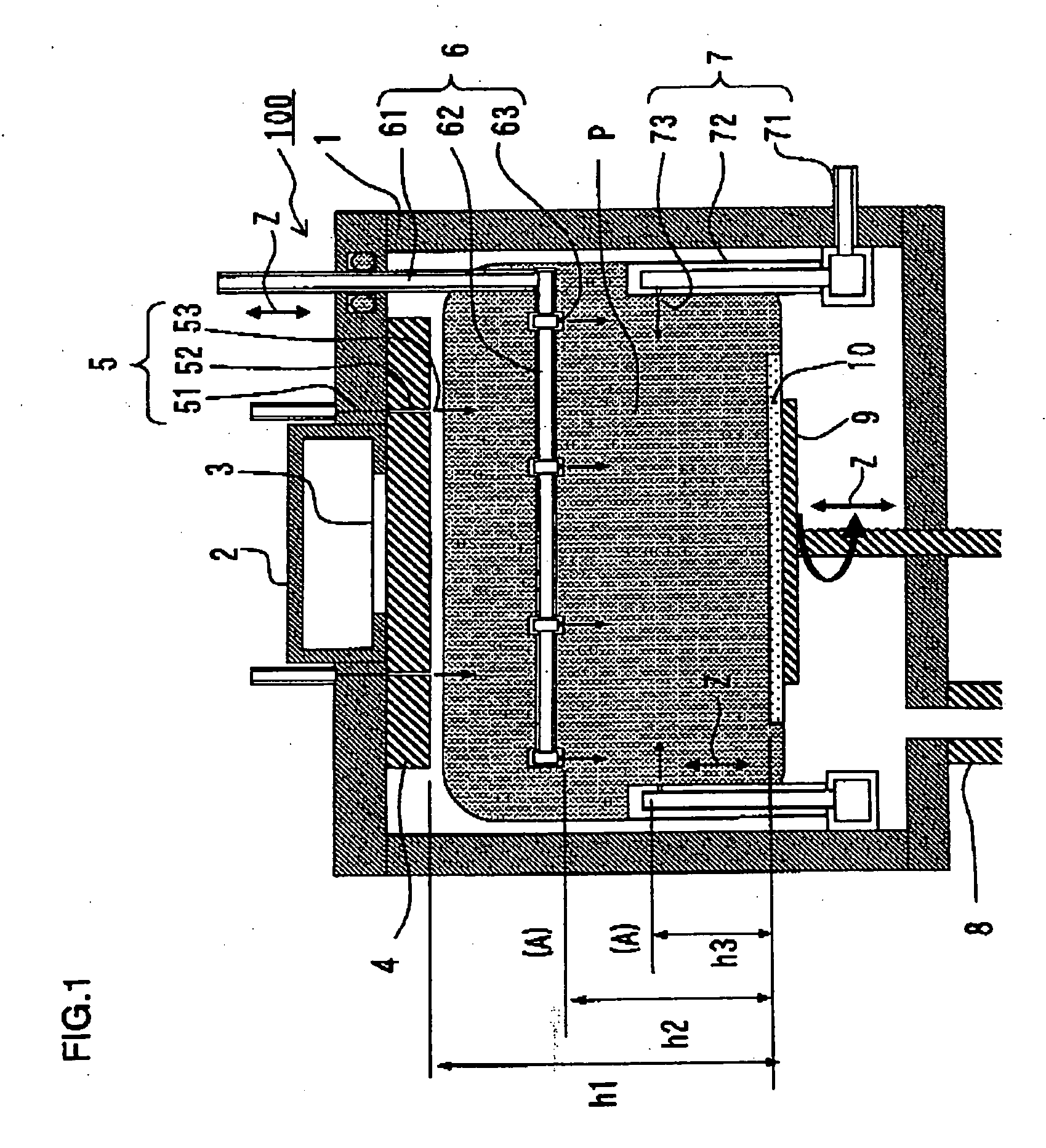
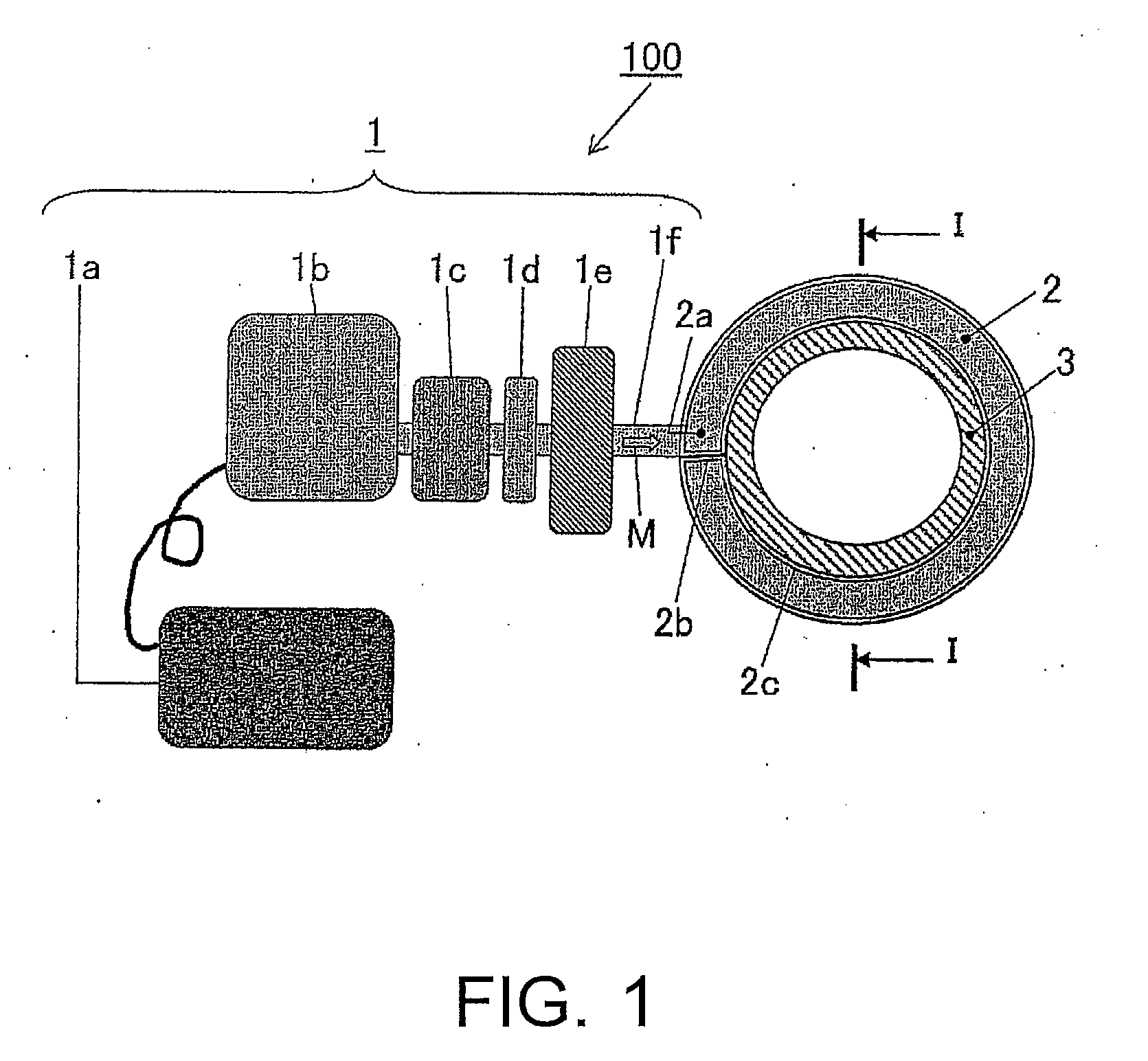
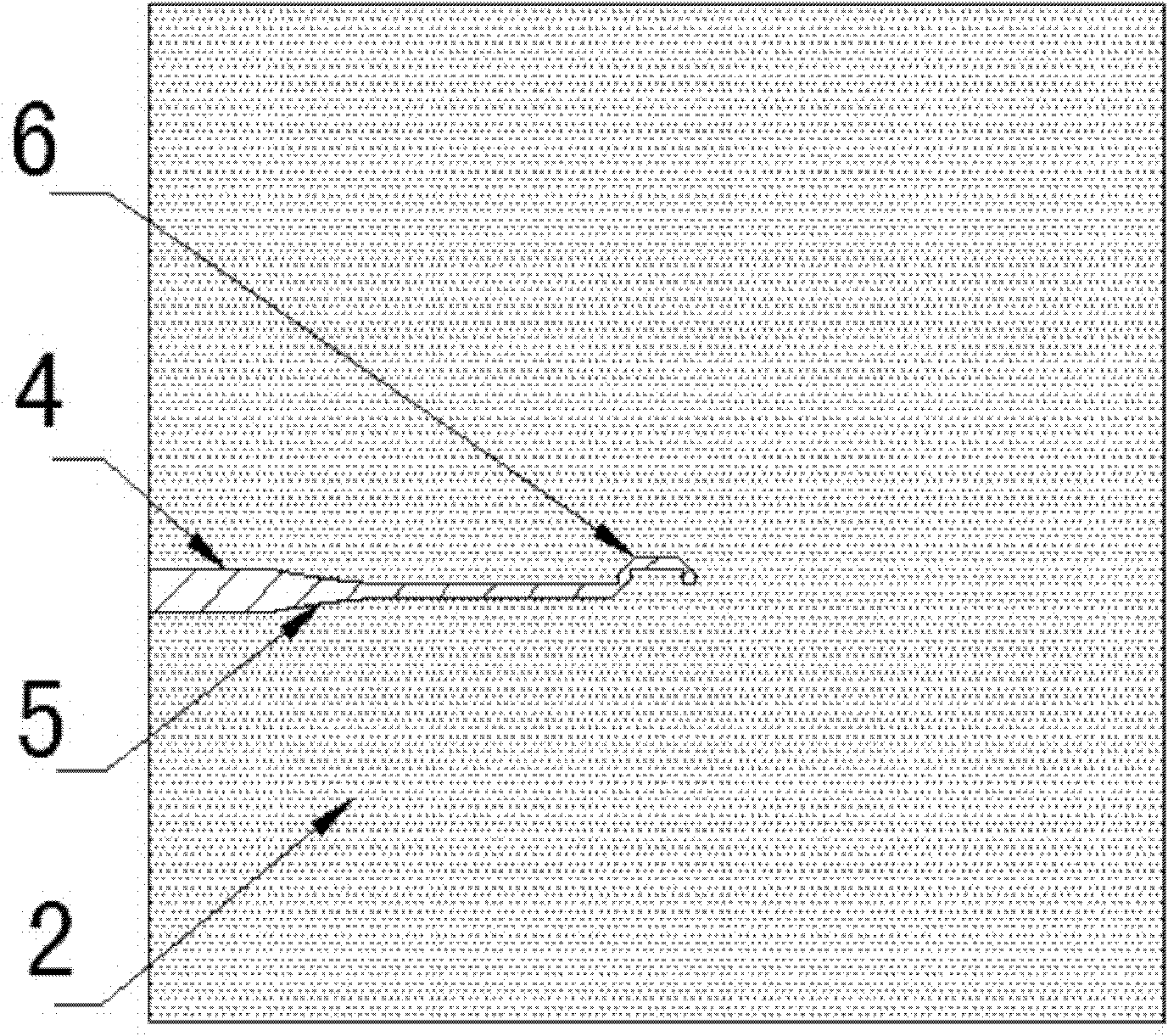
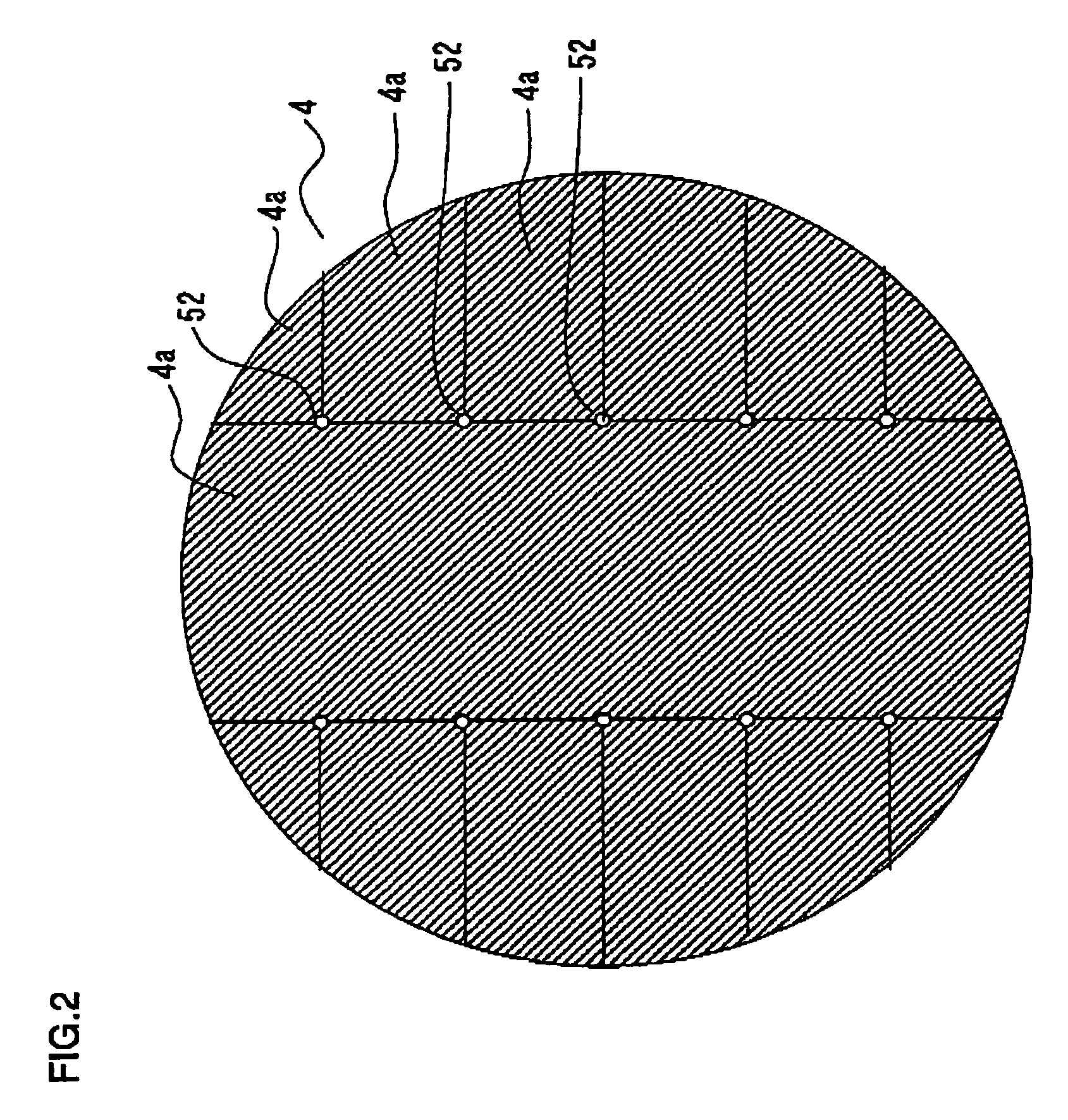
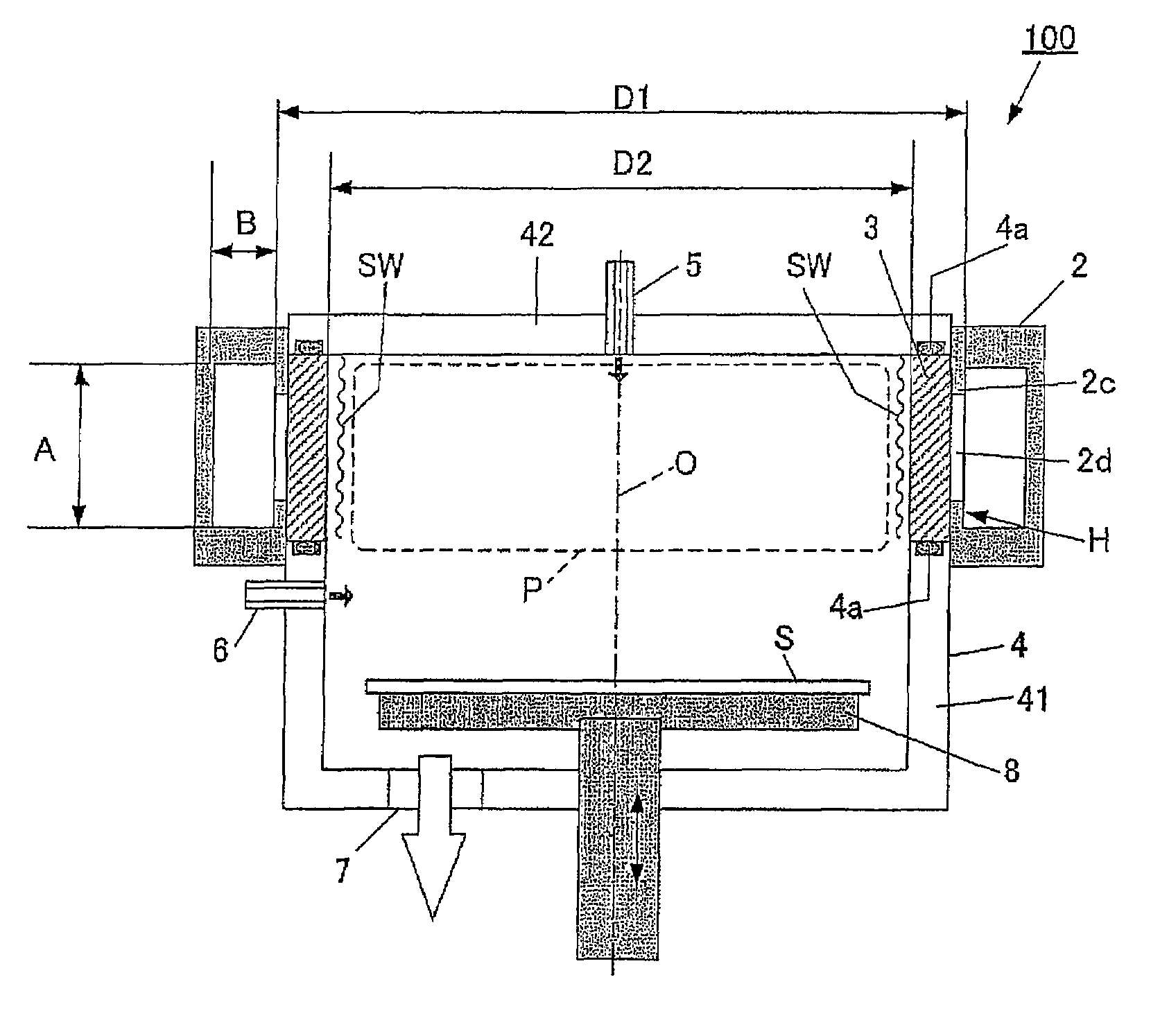
Surface wave excitation plasma CVD system
InactiveUS20050109279A1Increase plasma densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
This surface wave excitation plasma CVD system, along with feeding a material gas including silicon element by feeding the material gas into a chamber 1 from at least one of an upper surface gas introduction conduit and a side surface gas introduction conduit, also activates the material gas with a surface wave excitation plasma and feeds a process gas which initiates chemical reactions within the material gas into the chamber 1 from a process gas introduction conduit 5. A gas feed aperture of the upper surface gas introduction conduit and / or the side surface gas introduction conduit is provided in a position which is closer to the substrate than the gas feed aperture of the process gas introduction conduit.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Laser sonic surface wave stress test system
InactiveCN101281172AFast 2D scanningHigh detection sensitivityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationMetallic materials
The invention discloses a laser acoustic surface wave stress test system, which is mainly comprises an ultrasound surface wave excitation part composed of a short-pulse laser, a spectroscope, a triple prism and a cylindrical convex lens, and an ultrasound surface wave detection part composed of a PVDF piezoelectric film and a high-frequency pre-amplifier. The invention uses the short-pulse laser to generate a high-frequency ultrasound surface wave on the surface of the samples to be tested, a stress value is obtained according to the principle of acoustic elasticity, the PVDF piezoelectric film is served as the receiver of the ultrasound surface wave, fast two-dimensional scanning is realized on the surface of the samples in the way that the PVDF piezoelectric film is fixed, the excitation source and the samples to be tested are in two-dimensional translation motion, the obtained ultrasound surface wave signals are transmitted to an electronic computer, and the measurement of the stress distribution on the surface and the sun-surface of the samples is realized through fast computing and processing by programming according to the principle of acoustic elasticity. The system has the advantages of simple structure and low cost, which can be widely used in the stress distribution measurement on the surface and the sun-surface of metal materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
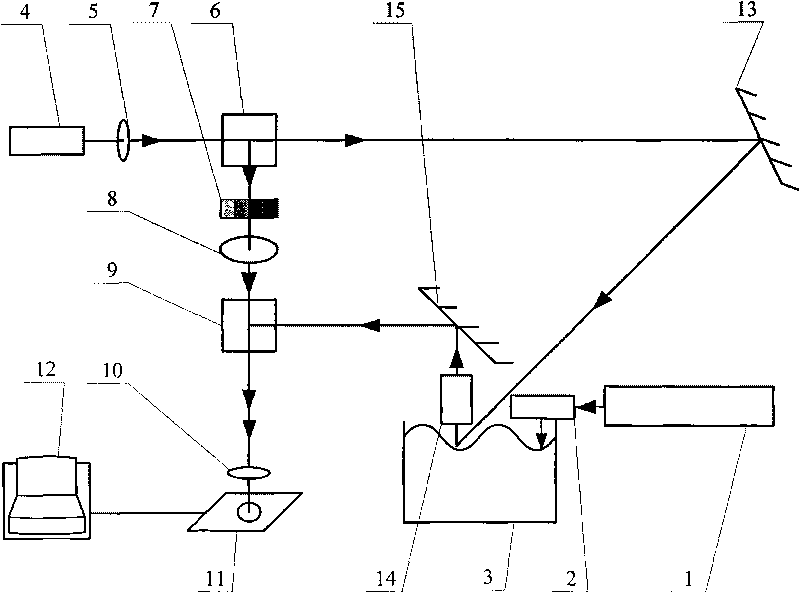
Liquid surface wave detecting method and device based on scattering laser Doppler effect
InactiveCN101710154AAccurate measurementAccurate detectionSpectral/fourier analysisFrequency measurement arrangementData acquisitionAlternating current
The invention relates to liquid surface wave detecting method and device based on a scattering laser Doppler effect, belonging to the field of detection of liquid surface waves. The invention solves the problems of main reflecting light receiving, strict matching of angles of a light path output part and a light path receiving part and large adjusting difficulty in a laser interference technology of the traditional liquid surface wave measurement. In the method, a coherent laser beam irradiates the surface of liquid; after receiving an interference light signal, a photoelectric receiver outputs a time domain oscillogram to obtain an alternating current photoelectric signal, and the alternating current photoelectric signal is demodulated to obtain the frequency of a surface wave; and an amplitude of the liquid surface wave is calculated and obtained by a Doppler frequency shift value on a frequency spectrum analysis chart converted by the time domain oscillogram. The device comprises a low-frequency signal generator, a surface wave excitation machine, a liquid pool, a laser, a quarter of wave sheet, a polarizing spectroscope, an attenuating sheet, a half of wave sheet, a spectroscope, a filter, a photoelectric receiver, a data acquiring and processing system, a first reflecting mirror, a telescopic system and a second reflecting mirror. The invention is used for the detection of the liquid surface wave.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
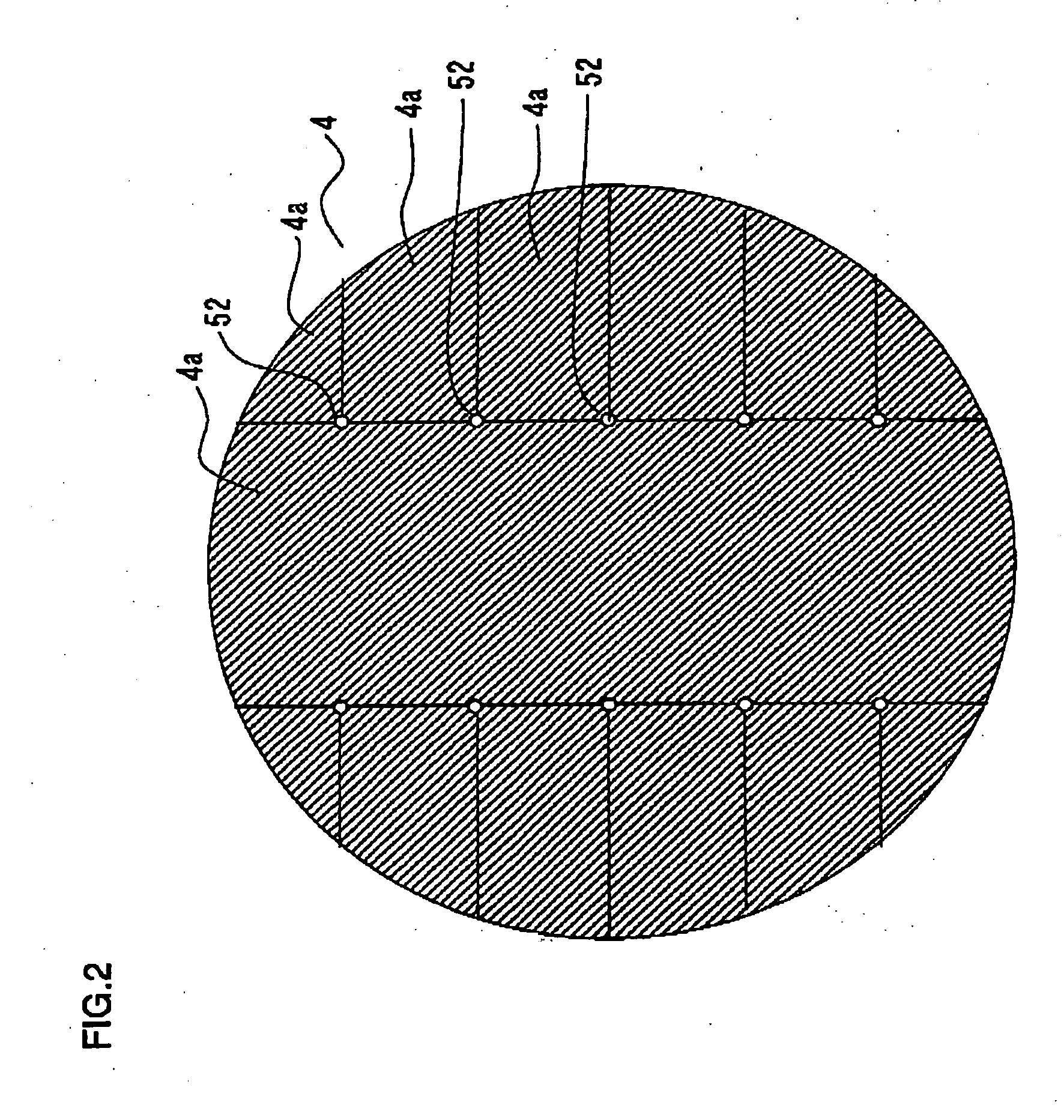
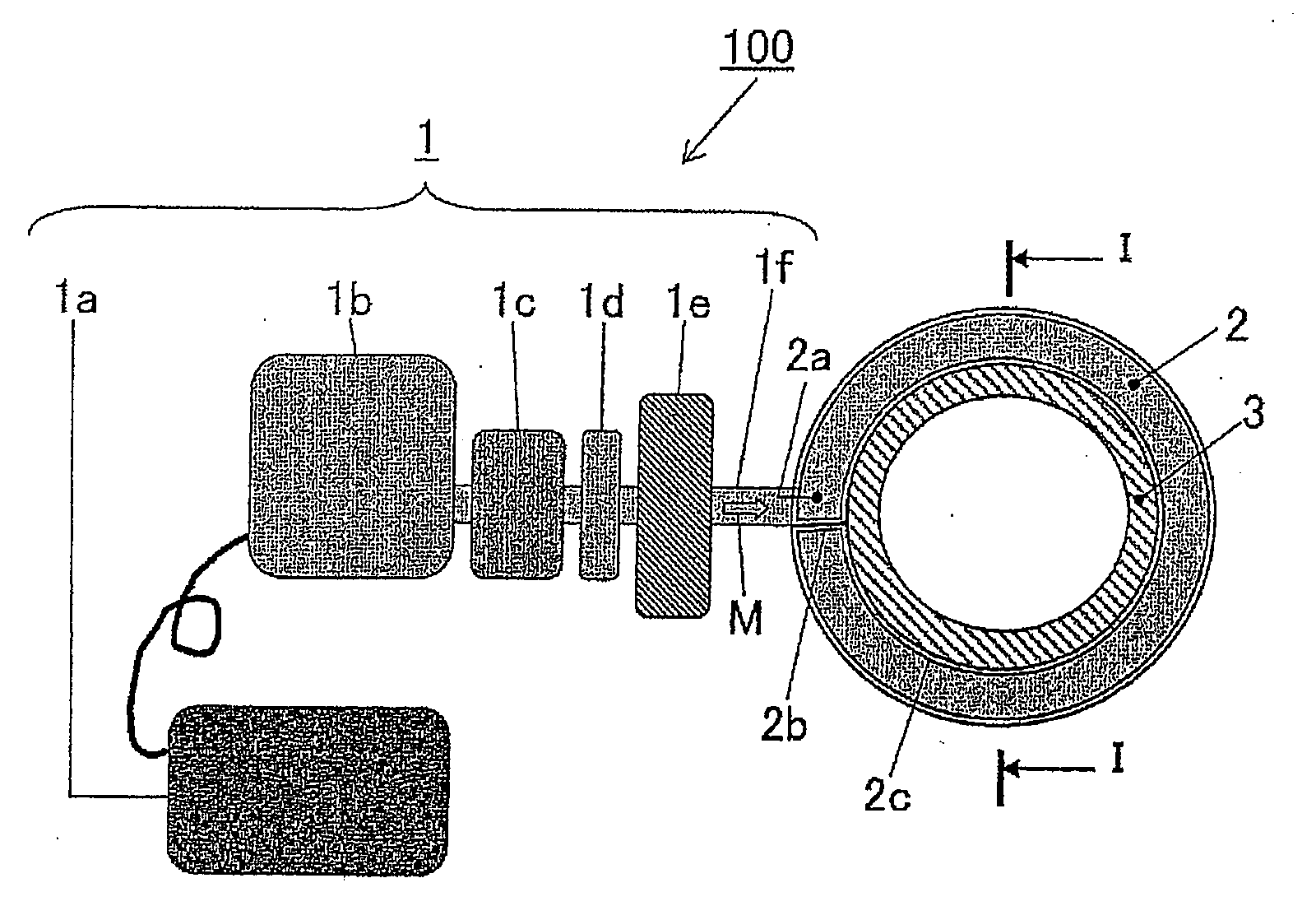
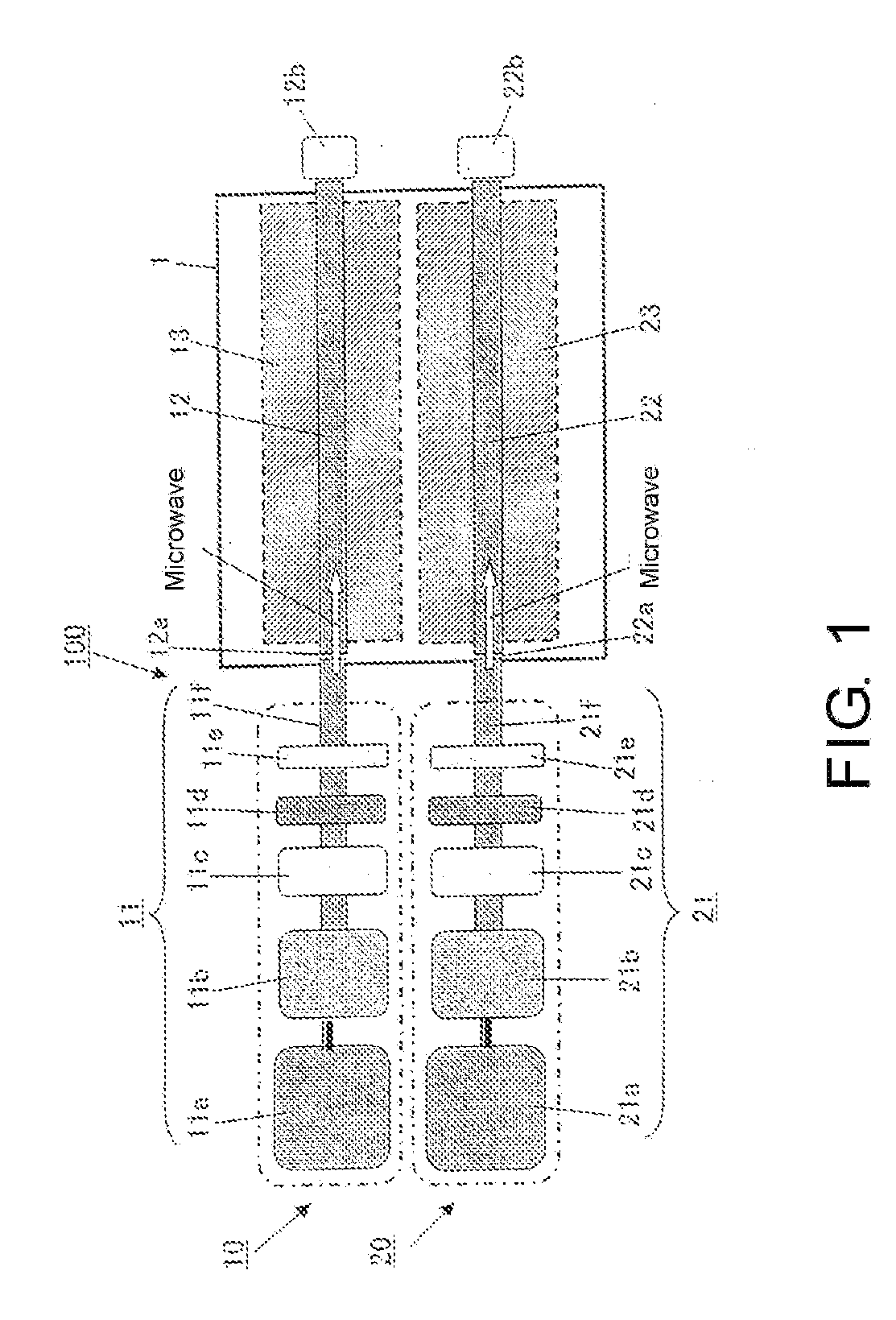
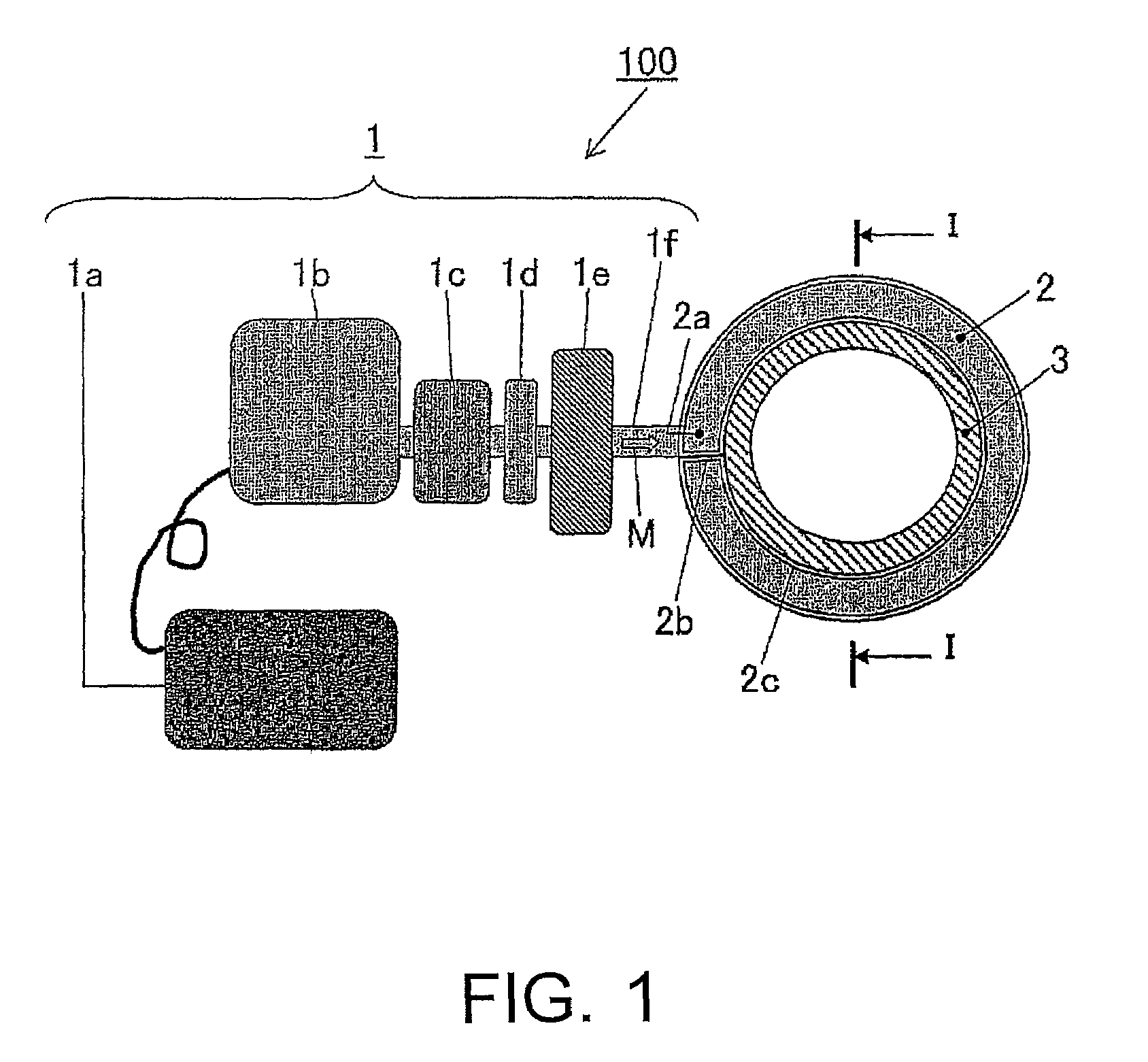
Surface wave excitation plasma generator and surface wave excitation plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20090026963A1Generate efficientlyElectric arc lampsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowavePlasma generator
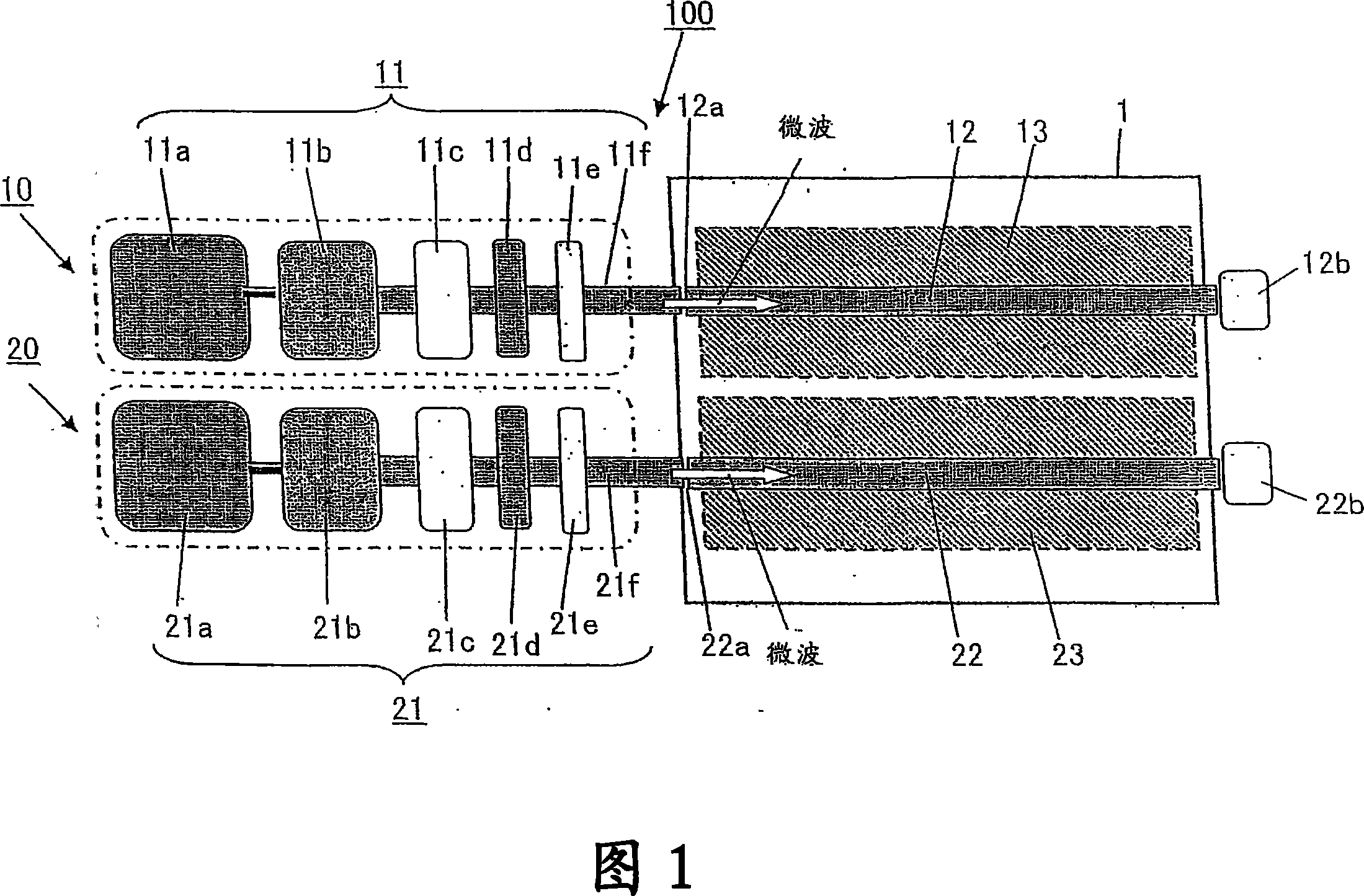
The present invention provides a surface wave excitation plasma generator in which surface wave excitation plasma is efficiently generated. A surface wave excitation plasma generator including an annular waveguide and a dielectric tube is provided. The annular waveguide 2 includes an inlet 2a for introducing a microwave M, an end plate 2b for reflecting the microwave M introduced and propagating within the waveguide, and a bottom plate 2c on which slot antennas 2d are formed at a predetermined interval. When the wavelength of the microwave M in the waveguide is λg, the length from position b through positions c, d, e to position f on the bottom plate 2c, i.e. the circumferential length (π×D1) of the annular waveguide, is set as 2 λg, and the positions b, c, d, e, f are spaced apart at an interval of λg / 2. Since the slot antennas 2d are arranged at two positions c and e, the interval between these two slot antennas 2d is equal to the wavelength λg in the waveguide.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
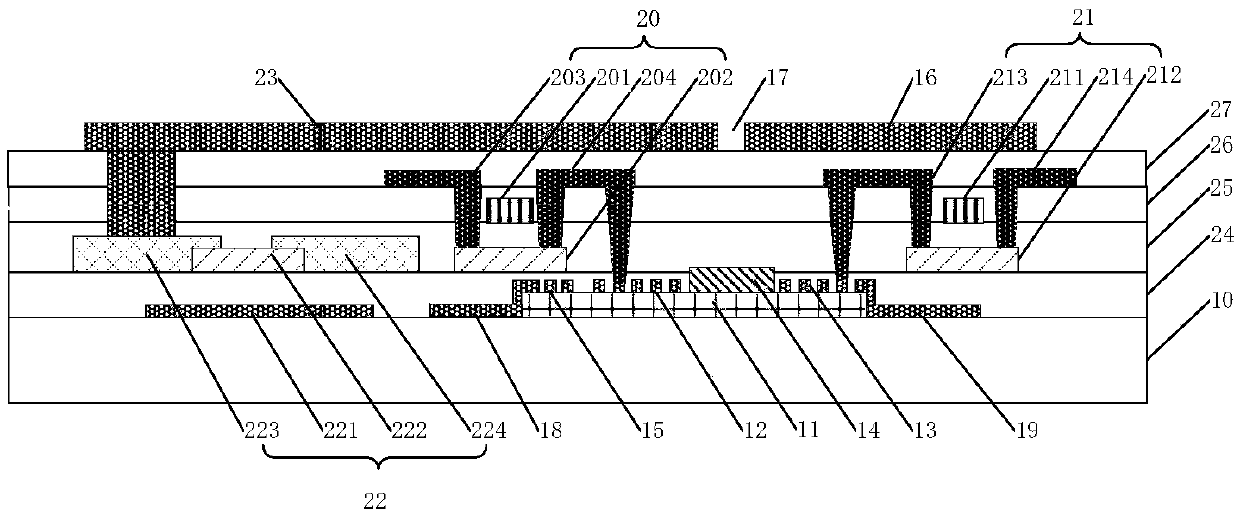
Array substrate and manufacturing method thereof, display panel and display device thereof
ActiveCN108052930AQuick responseHigh sensitivityPrint image acquisitionDisplay deviceSurface wave excitation
The invention discloses an array substrate. The array substrate comprises a substrate body, a piezoelectric induction layer which is formed on the substrate body, an acoustic surface wave excitation electrode and an acoustic surface wave receiving electrode which are formed on the piezoelectric induction layer and a photosensitive resistance layer which is formed on the piezoelectric induction layer, and the photosensitive resistance layer is located between the acoustic surface wave excitation electrode and the acoustic surface wave receiving electrode. The invention further discloses a display panel and a display device which comprise the array substrate. The array substrate, the display panel and the display device use the acoustic surface wave excitation electrode and the acoustic surface wave receiving electrode with fast response, high sensitivity and small volume to realize a fingerprint recognition function, and can improve the fingerprint recognition speed and sensitivity.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Trace element detection device based on plasma surface wave excitation
PendingCN107422025ASolve the problem that the sample tolerance is too lowSimple instrument systemMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhysicsSurface wave
The invention provides a trace element detection device based on plasma surface wave excitation and belongs to the field of trace element detection. The trace element detection device comprises a plasma excitation source generation system, an atomization system, a spectrum detection system and a cooling system. Working gas is injected from the upstream of a discharge tube, an energy coupling area of a surface wave plasma exciter generates plasma, and the generated surface wave plasma can extend to an outlet end of the discharge tube; a to-be-detected liquid sample after being treated by a pneumatic atomizing device forms a gaseous-phase sample, the gaseous-phase sample is led into the surface wave plasma by a lead-in port through a quartz lead-in tube, elements in the to-be-detected sample are excited by the surface wave plasma to generate feature spectra which are received by an optical fiber probe at an observation window for spectrum detection and transmitted to a spectrograph, and a computer analyzes feature excitation lines of the to-be-detected sample to realize qualitative and quantitative analysis of to-be-detected trace elements in the to-be-detected sample. The trace element detection device can improve bearing capacity of microwave plasma to the gaseous-phase sample and is simple in structure and convenient to operate.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
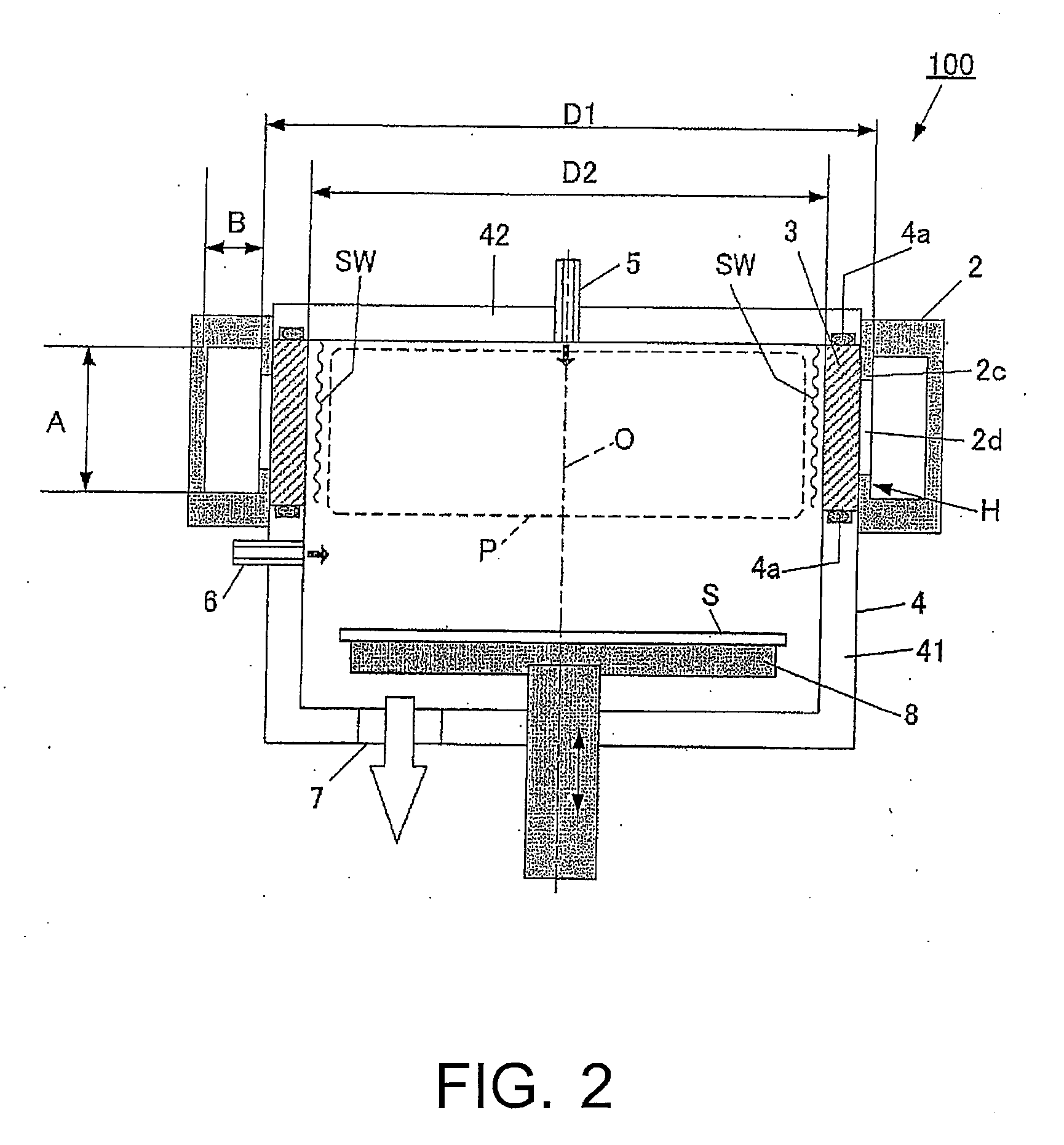
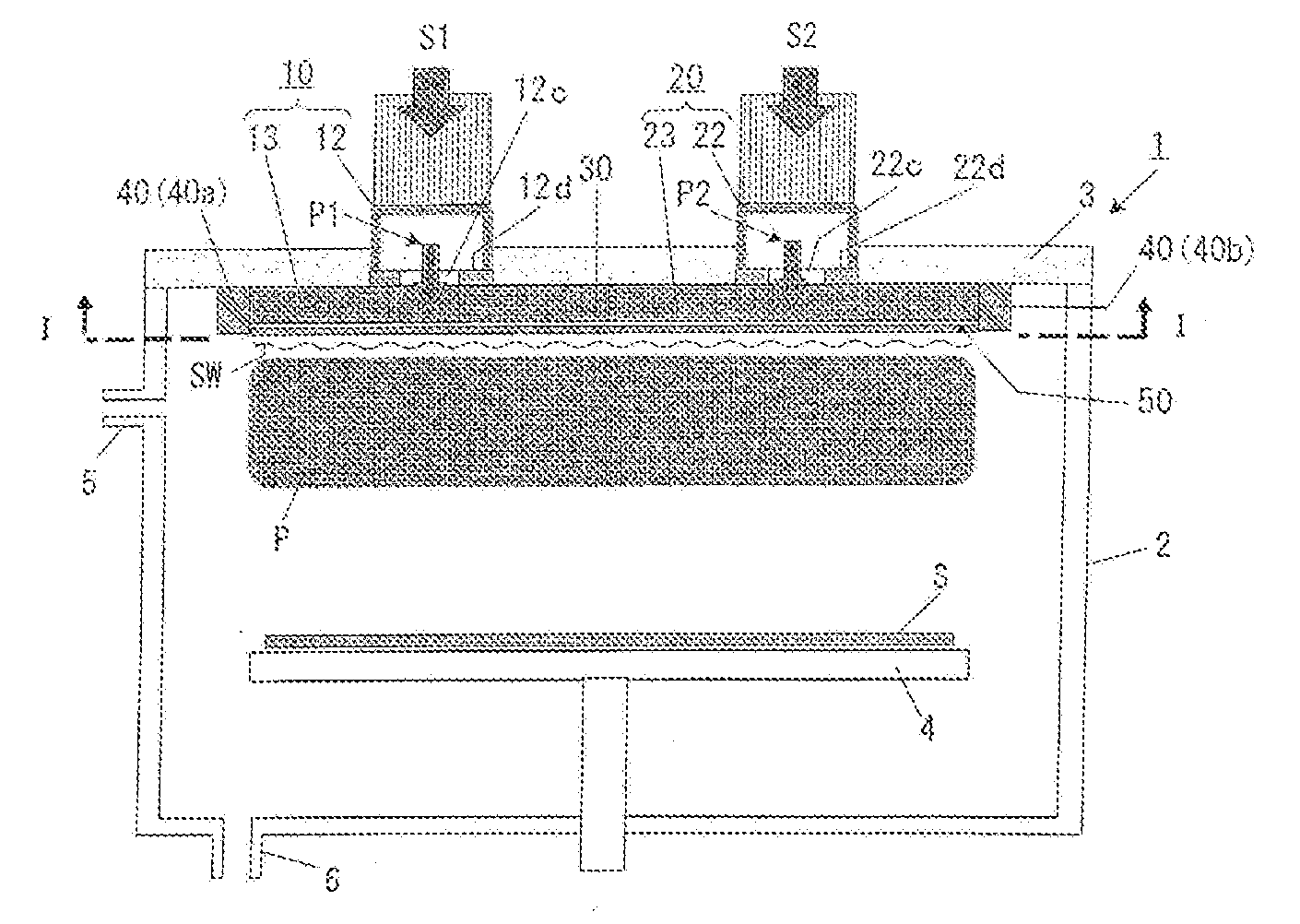
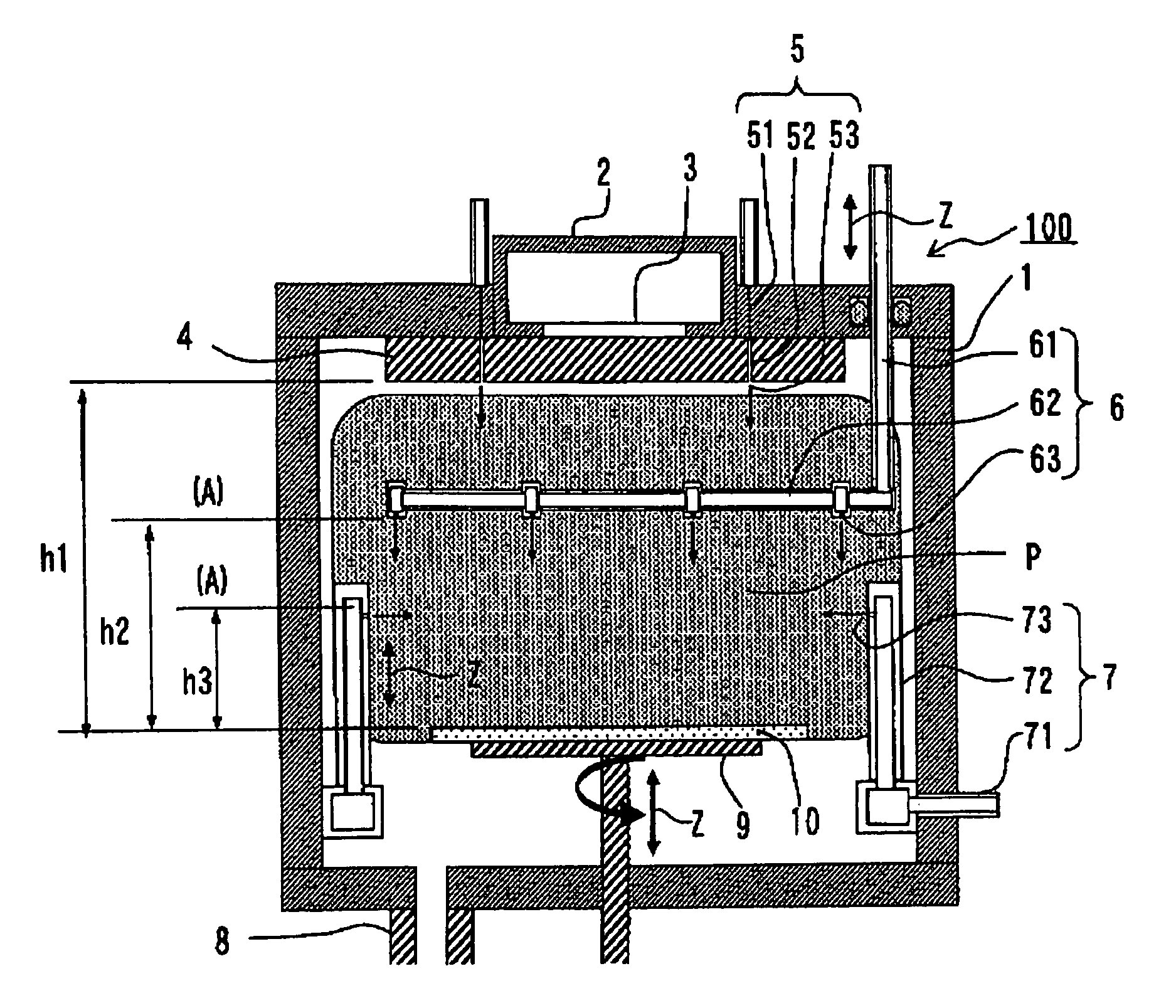
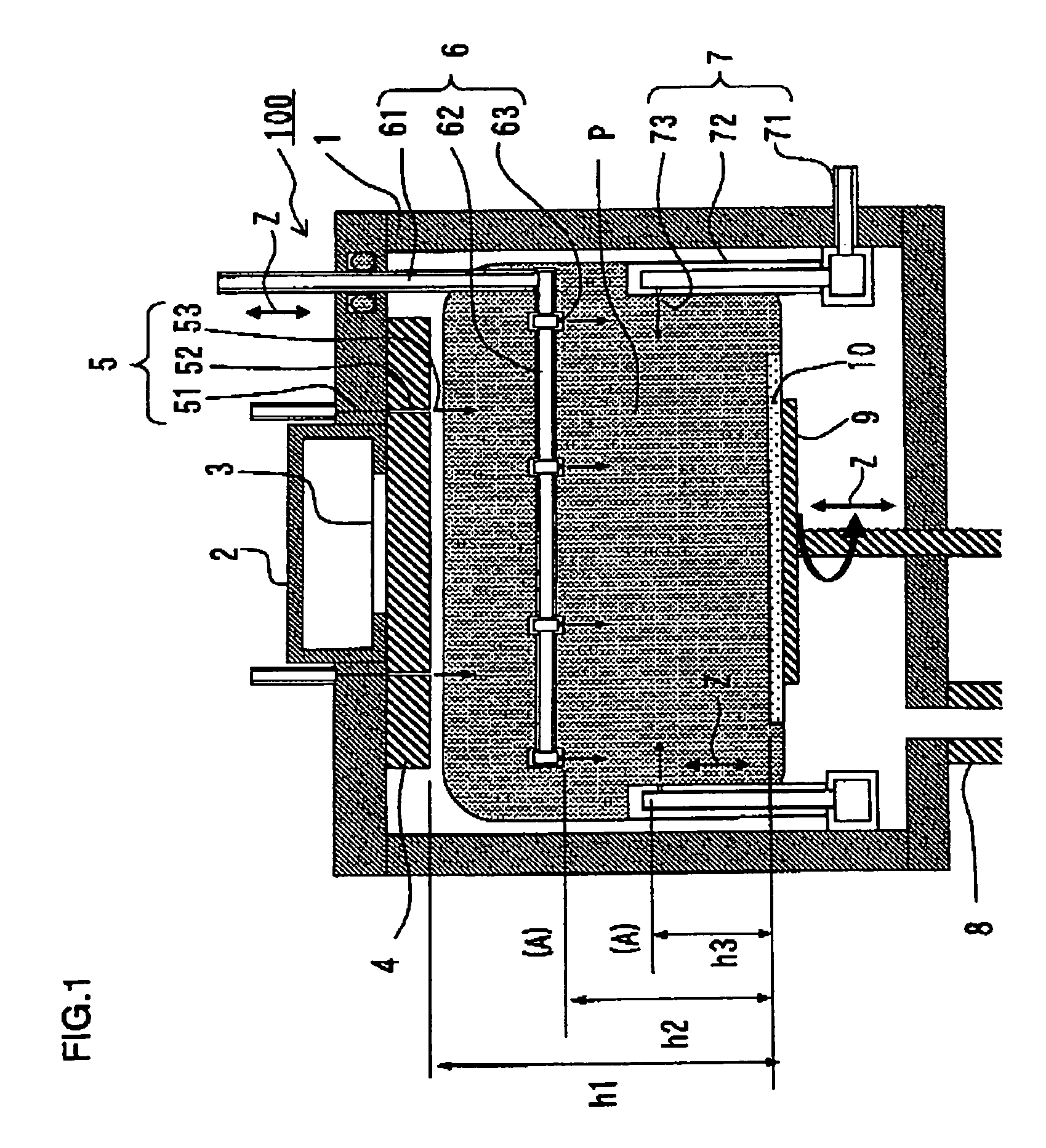
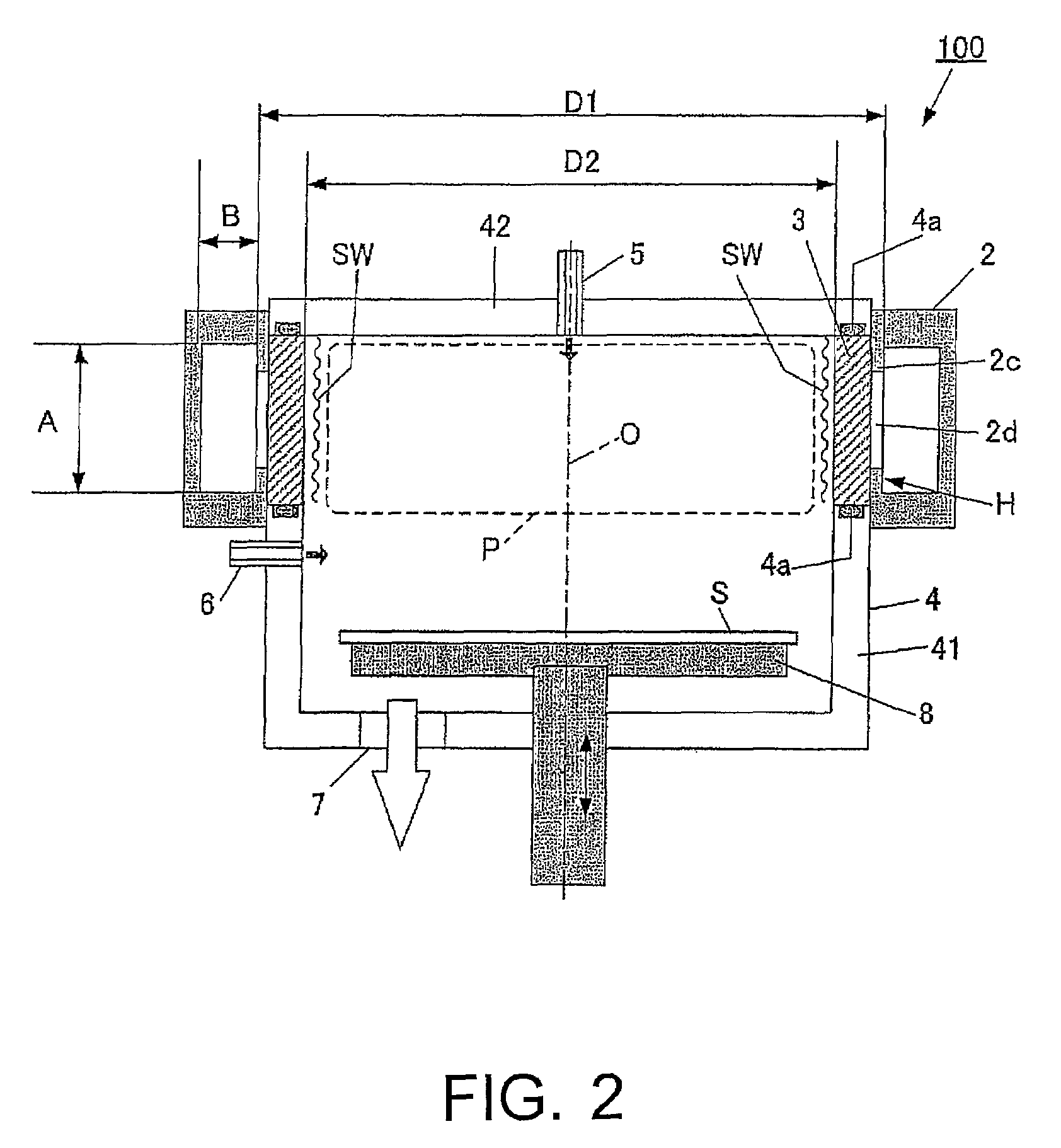
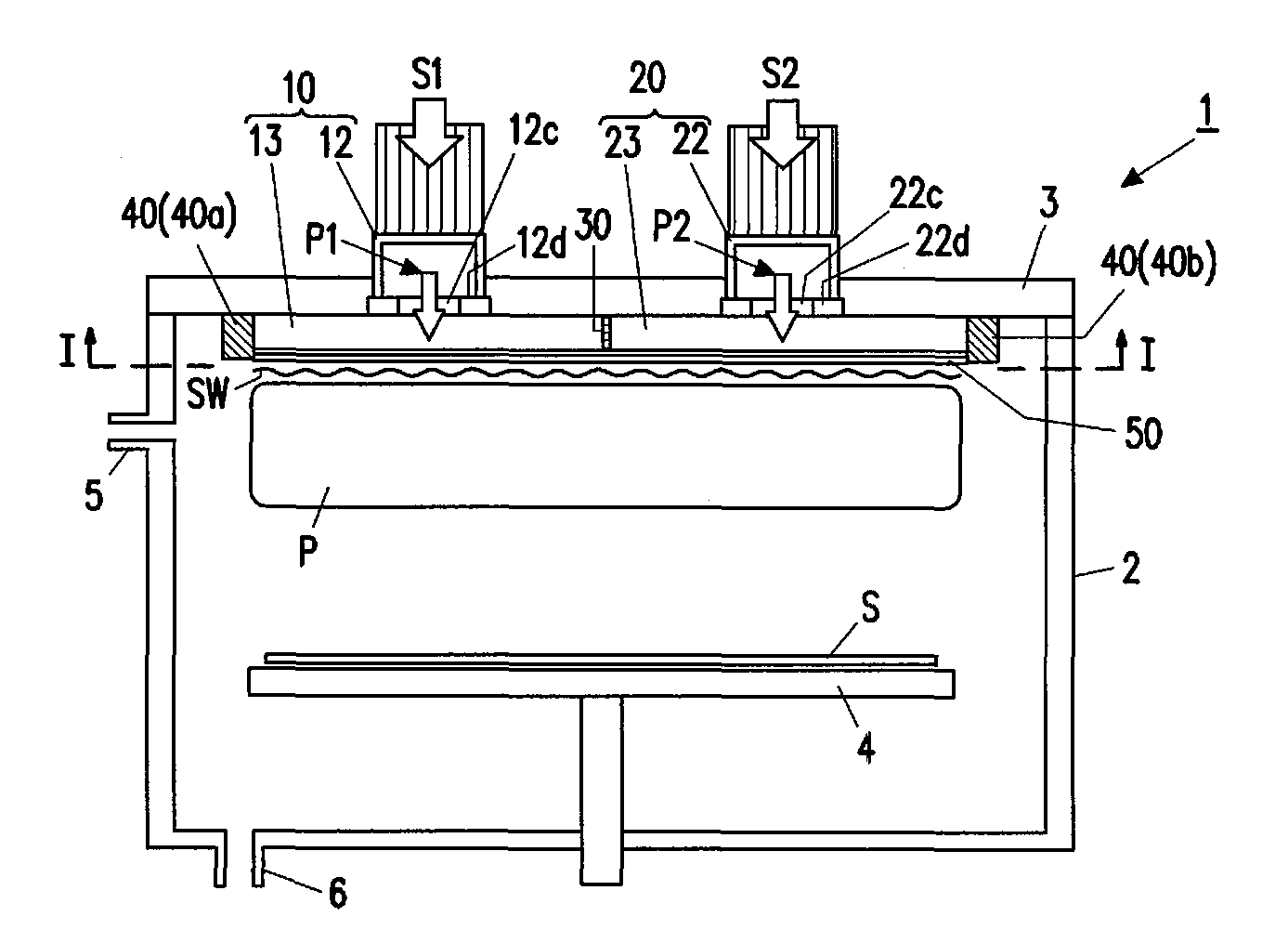
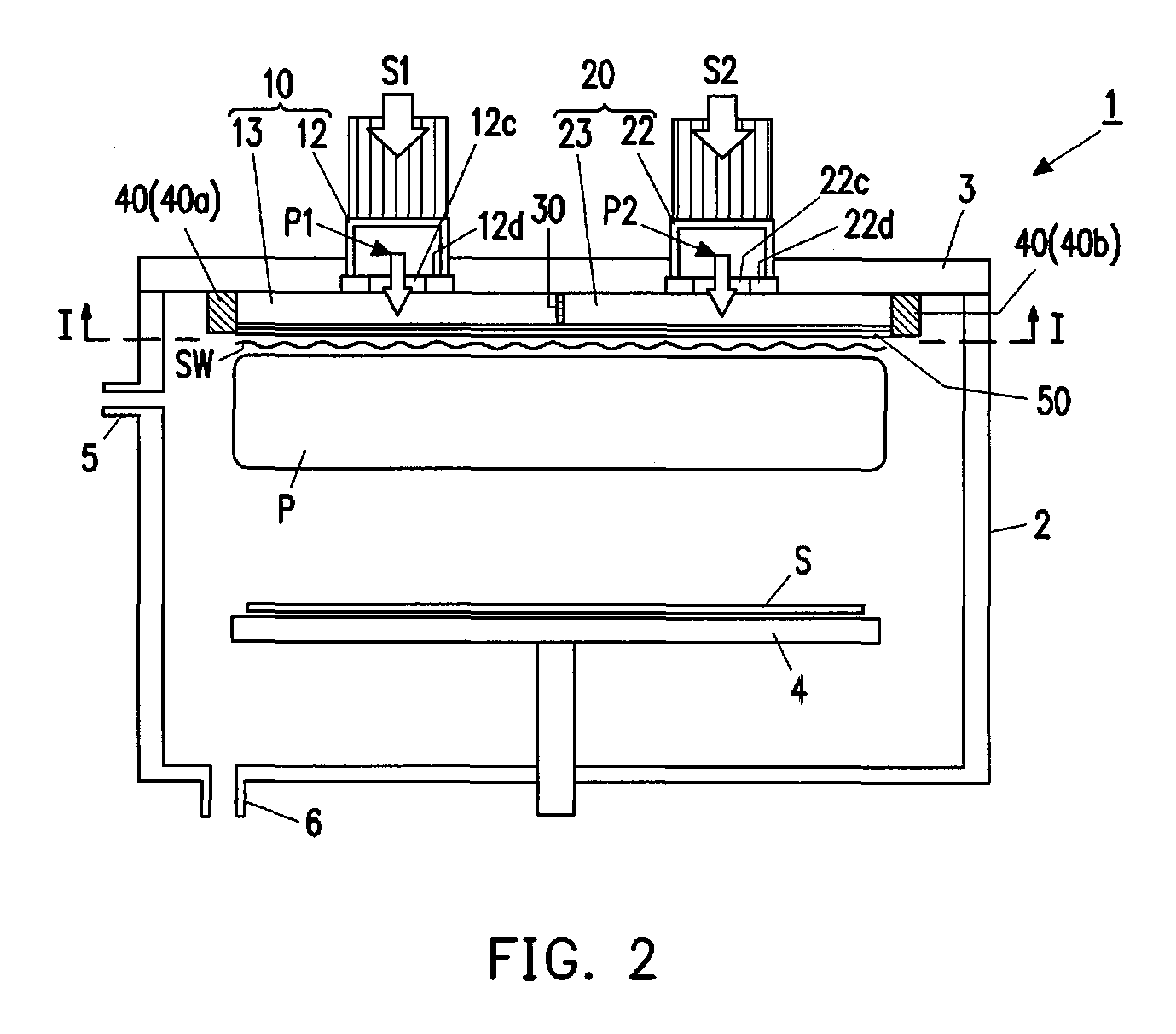
Surface wave excitation plasma processing system
InactiveCN101099419AGenerate uniformAvoid mutual interferenceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMicrowave
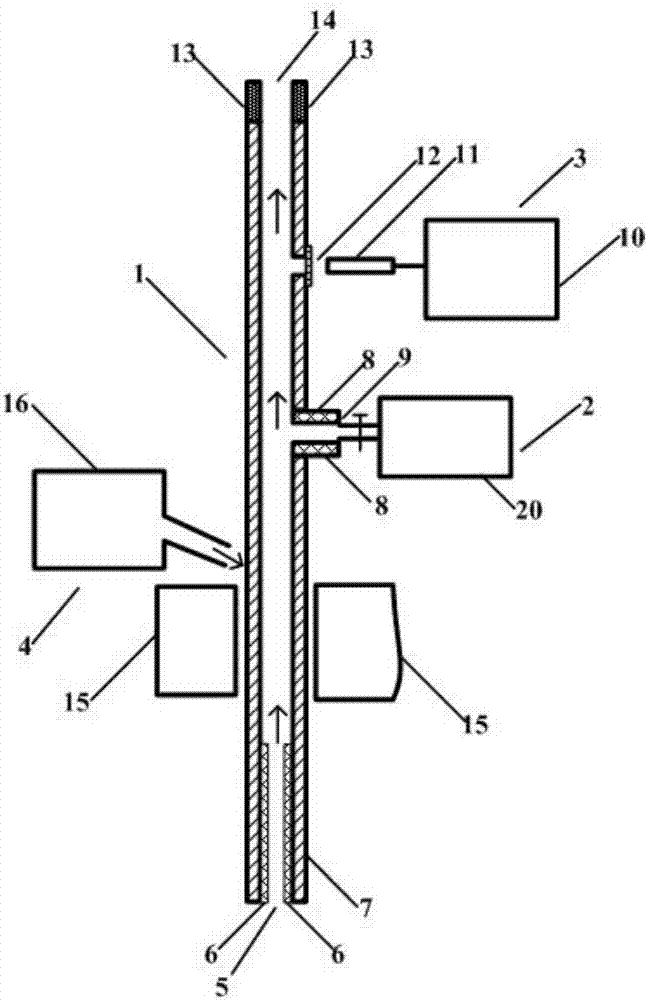
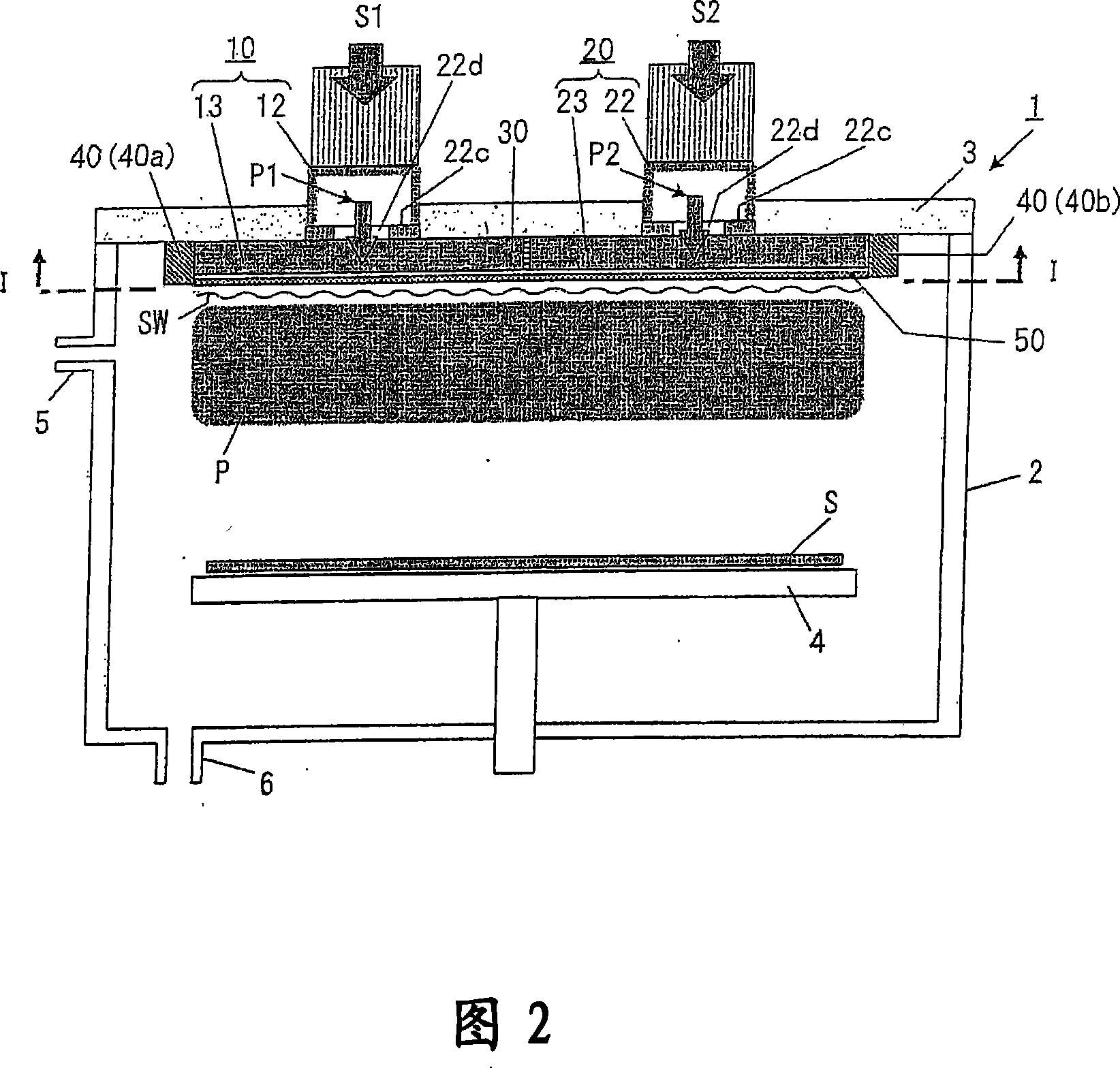
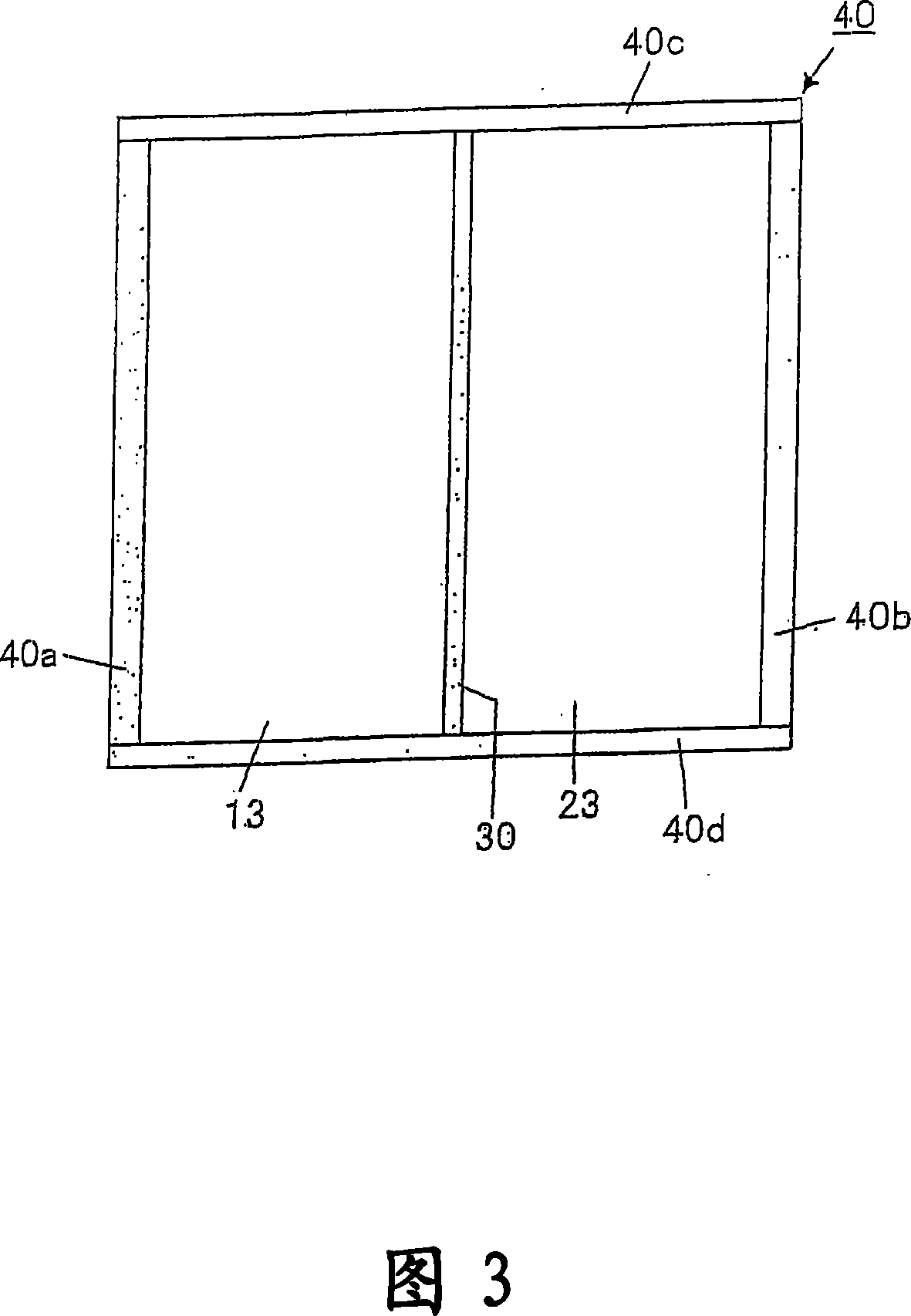
To sustain uniform generation of plasma constantly over a large area. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] A plasma source (10) comprises a microwave generator, a microwave waveguide (12) and a dielectric block (13), and a plasma source (20) also comprises a microwave generator, a microwave waveguide (22) and a dielectric block (23) similarly. The lid (3) of a chamber (1) is fixed with the microwave waveguides (12, 22) in parallel, and the dielectric blocks (13, 23) are arranged in the chamber (1). A reflector (30) is interposed between the dielectric blocks (13, 23) so that electromagnetic waves (microwaves) propagating through the dielectric blocks (13, 23) are prevented from advancing into counterpart dielectric blocks as reflection waves. Consequently, the plasma sources (10, 20) are controlled independently. Furthermore, a side reflector (40) is arranged at the outer circumference of each of dielectric blocks (23, 13) so that a standing wave of the electromagnetic wave propagating through the dielectric blocks (13, 23) is formed thus forming a large-area standing wave mode of surface wave SW uniformly.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
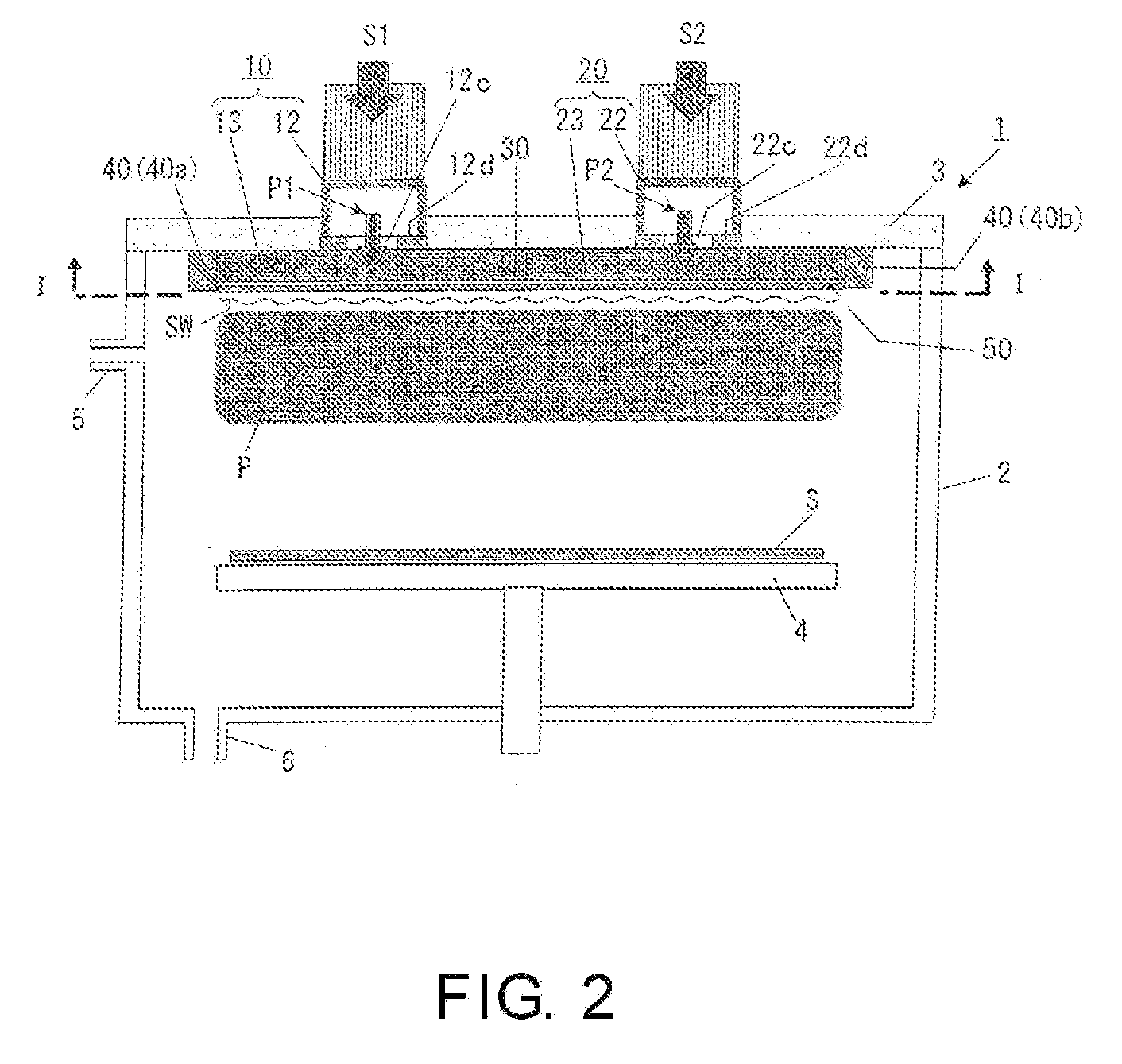
Surface wave excitation plasma processing system
InactiveUS20090232715A1InterferenceAvoid interferenceElectric discharge tubesEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesDielectricMicrowave
To sustain uniform generation of plasma constantly over a large area. In the surface wave excitation plasma processing device, a plasma source includes: a microwave generator, a microwave waveguide and a dielectric block; and a plasma source also includes: a microwave generator, a microwave waveguide and a dielectric block. The lid of a chamber is fixed onto the microwave waveguides in parallel, and the dielectric blocks disposed in the chamber. A reflecting plate is disposed between the dielectric blocks so that electromagnetic waves propagating through the dielectric blocks are prevented from advancing into the counterpart dielectric blocks as reflected waves. Consequently, the plasma sources are controlled independently. Furthermore, a side reflector is disposed at outer circumference of each of the dielectric blocks so that a standing waves of the electromagnetic waves propagating through the dielectric blocks is formed thus forming a large area standing wave mode of surface waves uniformly.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Micro-strip scoop-type feed slit surface wave excitation antenna
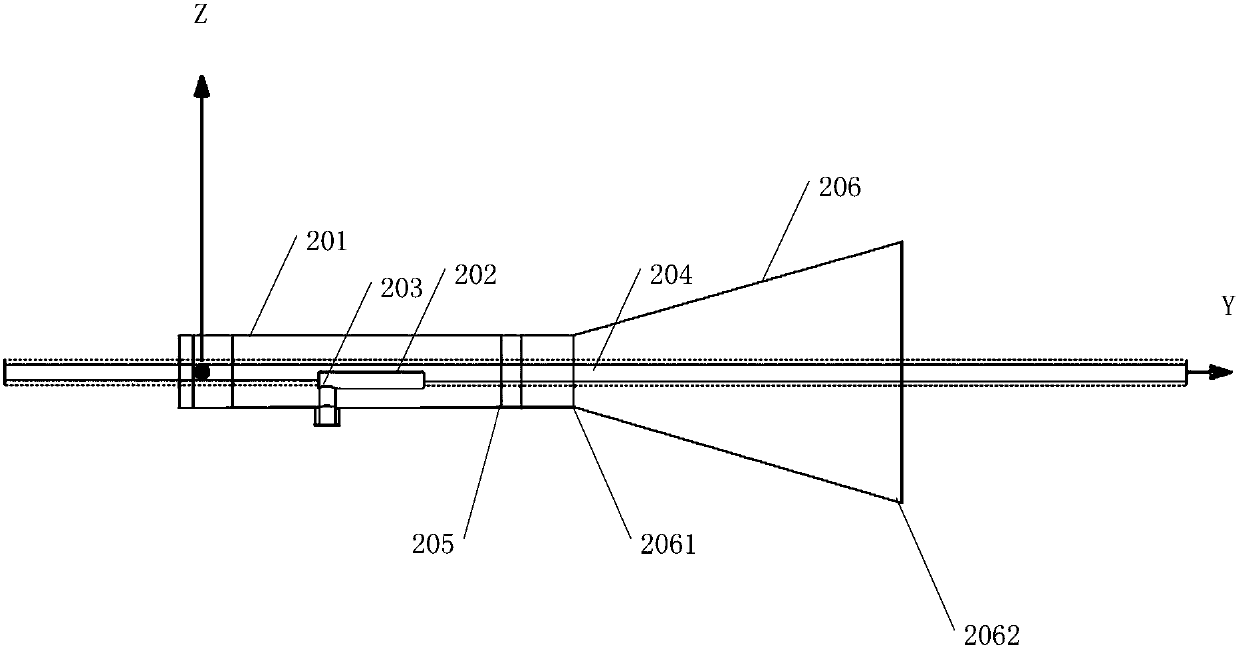
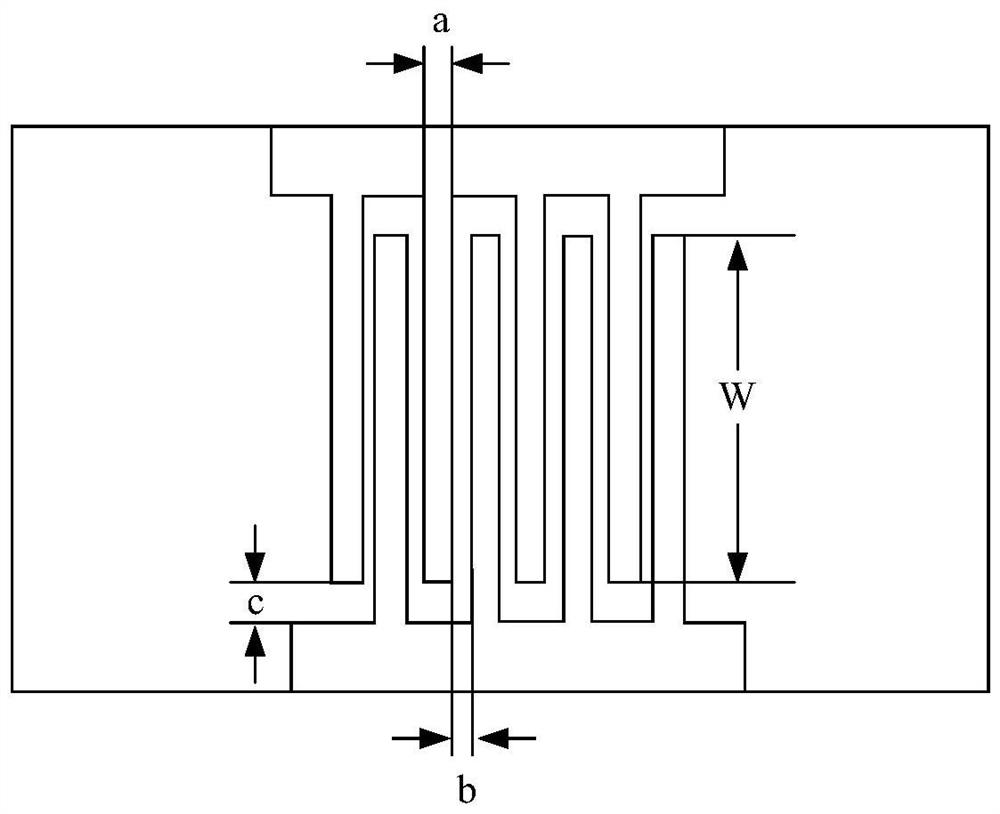
InactiveCN102694265ACompact structureReduce weightRadiating elements structural formsLeaky-waveguide antennasElectricityImpedance matching
The invention discloses a micro-strip scoop-type feed slit surface wave excitation antenna. The antenna is characterized in that: the surface wave excitation antenna contains a feed unit and a radiation unit; the surface wave excitation antenna is divided into three layers, and an upper layer and a lower layer are metal layers (1) and (3), and a middle part is a dielectric layer (2); the upper metal layer (1) is a micro-strip feed structure of the antenna; a micro-strip feed unit is formed by connection between a 50 omega first micro-strip line (4) and a scoop-type micro-strip (6) through an index gradient micro-strip structure (5); starting from the 50 omega first micro-strip line (4), an excitation signal realizes impedance matching through the index gradient micro-strip structure (5); the scoop-type micro-strip (6) carries out feed on a radiation unit (7) of a rear metal layer, wherein the radiation unit (7) sets three yagi slits in a grounding metal layer (3) so as to realize directed radiation.
Owner:吕清
Surface wave excitation plasma CVD system
InactiveUS8307781B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical reactionSurface wave excitation
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Microwave antenna applicator
InactiveUS20170077609A1Minimised sideways excitation of surface waveHigh dielectric constantDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrowave therapyElectricityPermittivity
A new and comparatively small type of open-ended microwave applicators has been disclosed. They are for example suitable for transmission into and reception from contacting objects such as protruding human bodyparts for inhomogeneity detection by tomographic methods. The applicators according to the invention are of the dielectric-filled open-ended ridged rectangular TE10 type, with an insert filling the ridge and having a higher permittivity than the surrounding space. The shape of the insert can be as a frustrum pyramid towards the opening. The overall design promotes narrow beamwidths and minimises nearfields and surface wave excitation.
Owner:RISMAN PER OLOV +2
Surface wave excitation and long-distance transmission structures based on metamaterials
The invention discloses surface wave excitation and long-distance transmission structures based on metamaterials. The first structure, the second structure and the third structure are free space coupling structures, and the fourth structure is an end face coupling structure. All the four structures do not need to coupled through lenses high in refractive index, integration of optical elements is facilitated, meanwhile, the propagation distance of light can reach millimeter magnitude, and the structures can be widely used in the optical elements. The structures are simple, SPPs are easily coupled under the circumstance that no lens high in refractive index is used, integration of the optical elements is facilitated, meanwhile, the propagation distance of the light can reach the millimeter magnitude, and the structures can be widely used in the optical elements.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Surface wave excitation device
ActiveCN109802235AAntennas earthing switches associationWaveguidesRadiation lossElectrical conductor
The embodiment of the application discloses a surface wave excitation device. The surface wave excitation device in the embodiment of the application includes a metal waveguide, a coupling part, a feeding part and a transmission line. The metal waveguide sleeves the transmission line. The coupling part is arranged inside the metal waveguide. The metal waveguide and the transmission line are coaxial. The feeding part is connected with the coupling part. The coupling part is arranged in parallel with the transmission line. A gap is formed between the coupling part and the conductor of the transmission line. Electromagnetic waves are propagated from the feeding part to the coupling part and coupled through the coupling part to the surface of the transmission line, so as to transmit surface waves. The surface wave excitation device in the embodiment of the application is used to reduce the radiation loss of surface waves.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
High-frequency heating device
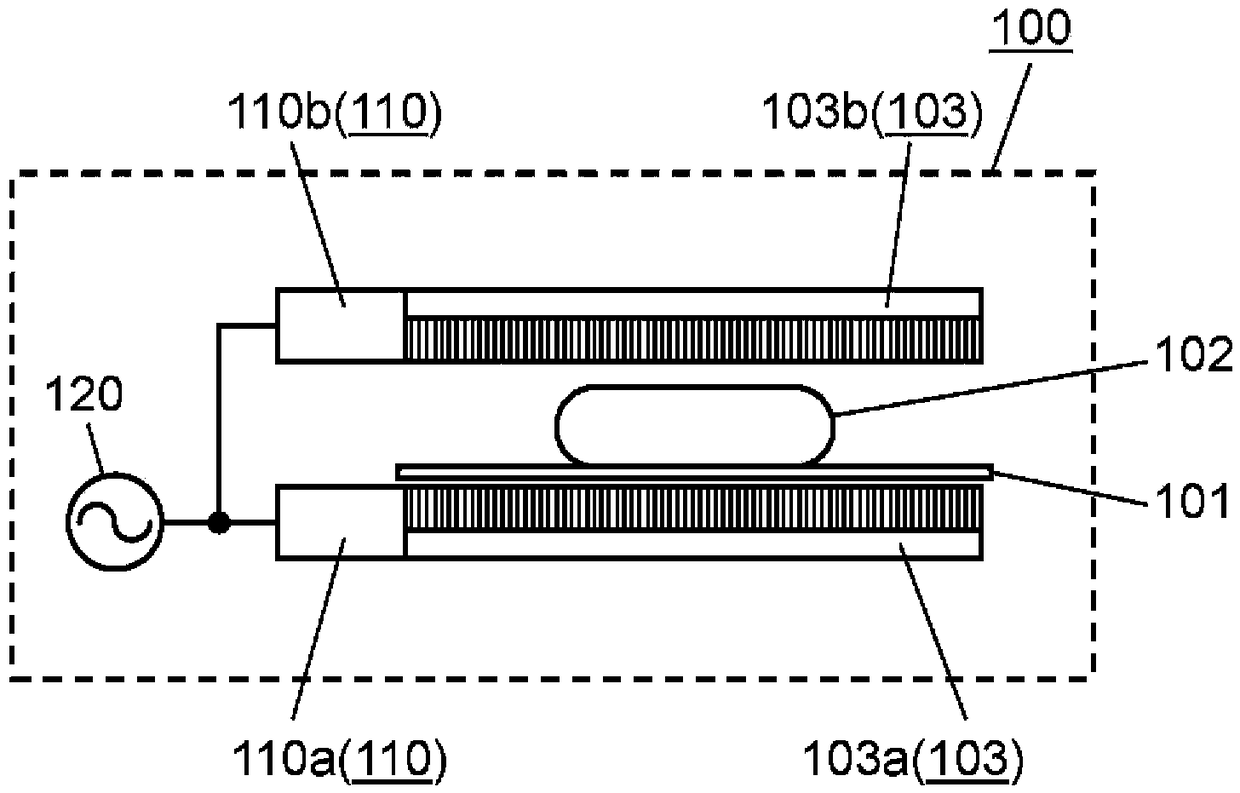
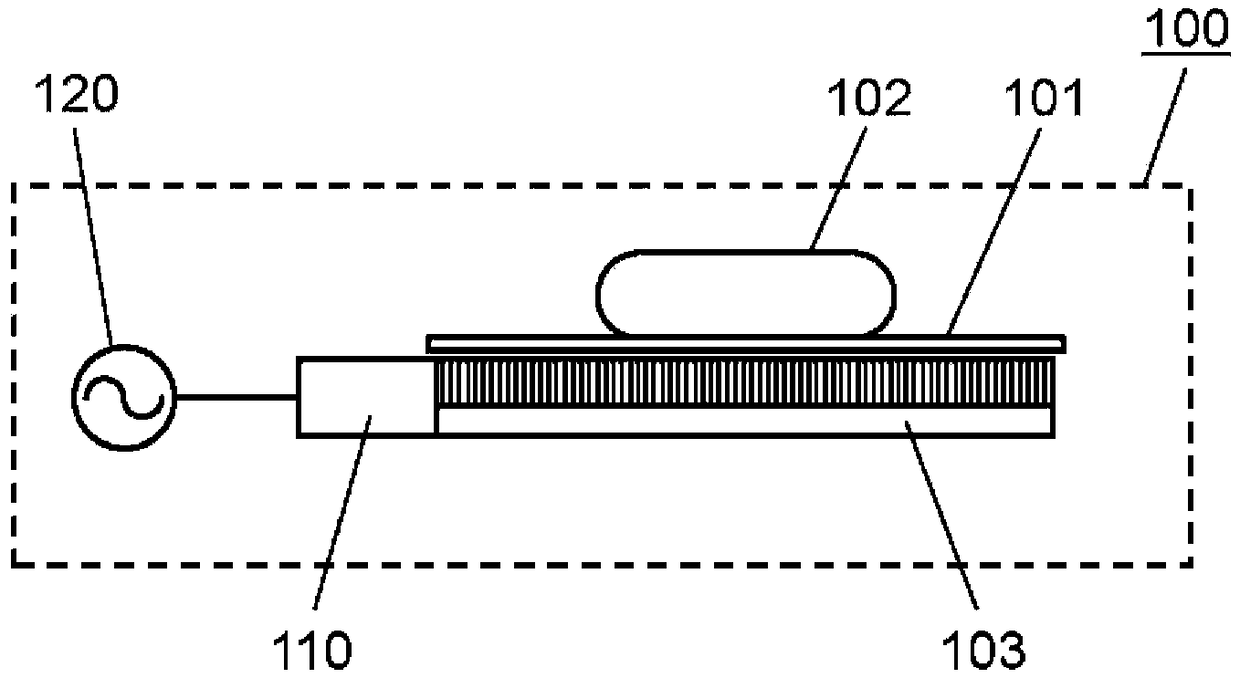
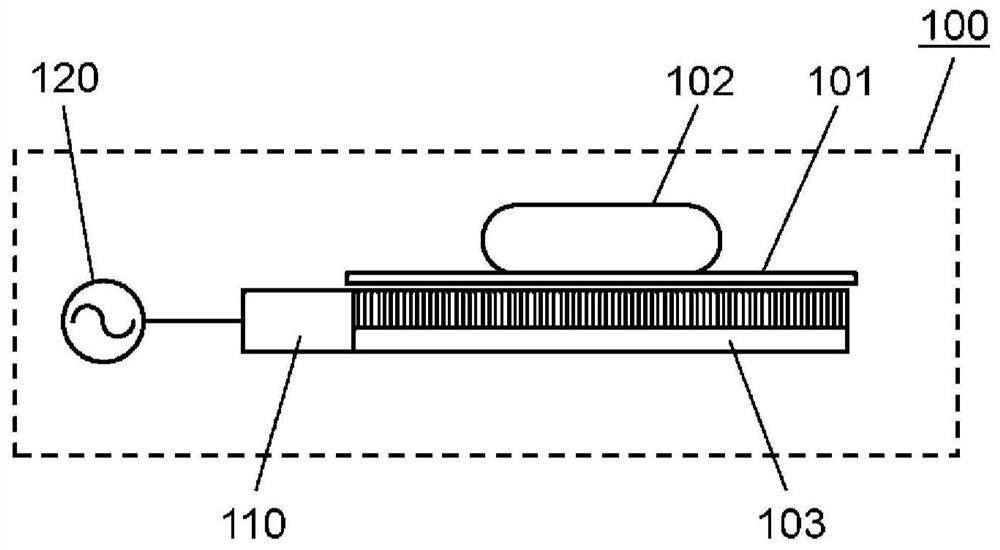
A high-frequency heating device (100) that comprises: a first surface wave excitation body (103a) and a second surface wave excitation body (103b); a first high-frequency power supply part (110a) anda second high-frequency power supply part (110b); and a high-frequency power generation part (120). The first surface wave excitation body (103a) and the second surface wave excitation body (103b) face each other so as to sandwich an object to be heated (102). The high-frequency heating device (100) can thereby heat and scorch both surfaces of the object to be heated (102) without using a heater or the like.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Surface wave excitation plasma generator and surface wave excitation plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS7640887B2Generate efficientlyElectric arc lampsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowavePlasma generator
The present invention provides a surface wave excitation plasma generator in which surface wave excitation plasma is efficiently generated. A surface wave excitation plasma generator including an annular waveguide and a dielectric tube is provided. The annular waveguide 2 includes an inlet 2a for introducing a microwave M, an end plate 2b for reflecting the microwave M introduced and propagating within the waveguide, and a bottom plate 2c on which slot antennas 2d are formed at a predetermined interval. When the wavelength of the microwave M in the waveguide is λg, the length from position b through positions c, d, e to position f on the bottom plate 2c, i.e. the circumferential length (π×D1) of the annular waveguide, is set as 2 λg, and the positions b, c, d, e, f are spaced apart at an interval of λg / 2. Since the slot antennas 2d are arranged at two positions c and e, the interval between these two slot antennas 2d is equal to the wavelength λg in the waveguide.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Directional broadband efficient surface wave excitation device
ActiveCN105141276AHigh Surface Wave Excitation EfficiencyFlexible accessImpedence networksWireless transmissionSurface wave excitation
The invention provides a directional broadband efficient surface wave excitation device. The directional broadband efficient surface wave excitation device comprises an input matching section, an excitation section and a cover plate, wherein the input matching section comprises a coaxial connector, a coaxial-ridge waveguide switch and a ridge waveguide-waveguide switch; the excitation section comprises a downwards excitation section and an upwards excitation section. Non-contact between an inner core of the coaxial connector and the single ridge waveguide can be realized by opening a pore on a ridge of the single ridge waveguide. The excitation section adopts a two-stage structure to realize the broadband efficient surface wave excitation. Compared with the existing excitation device, the excitation device provided by the invention obviously improves the bandwidth performance and excitation efficiency, and can flexibly move on the surface of the surface wave and enhance the flexibility of application. The directional broadband efficient surface wave excitation device provided by the invention is wide in frequency band, high in surface wave excitation efficiency, compact in structure, easy in processing and low in cost; a surface wave wireless transmission system is formed by the directional broadband efficient surface wave excitation device and the surface of the surface wave, so that the excitation device can flexibly access and remove from the surface of the surface wave, thus the wireless fast transmission application requirement for high speed big data by the millimeter wave frequency band in the future can be satisfied.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
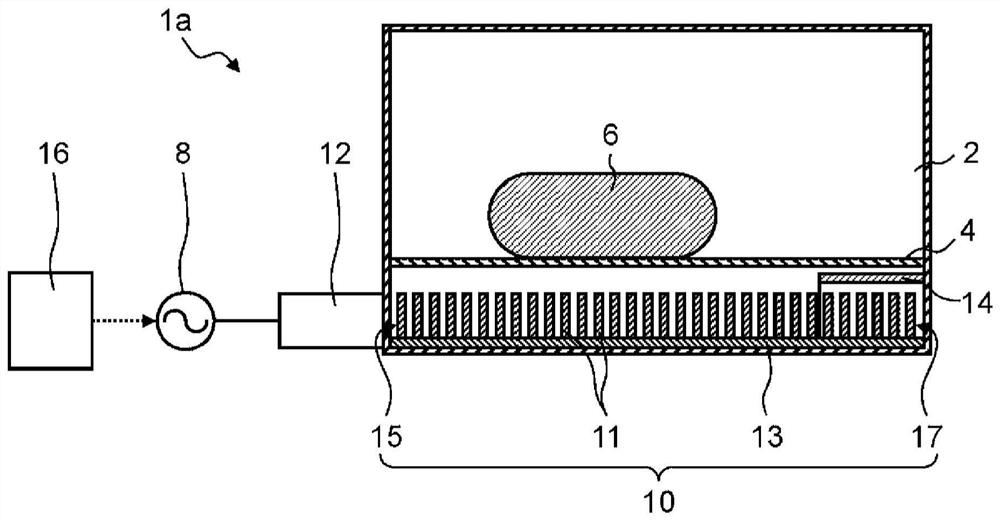
High frequency heating device
ActiveCN109156054BHeating evenlyDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusMicrowaveEngineering
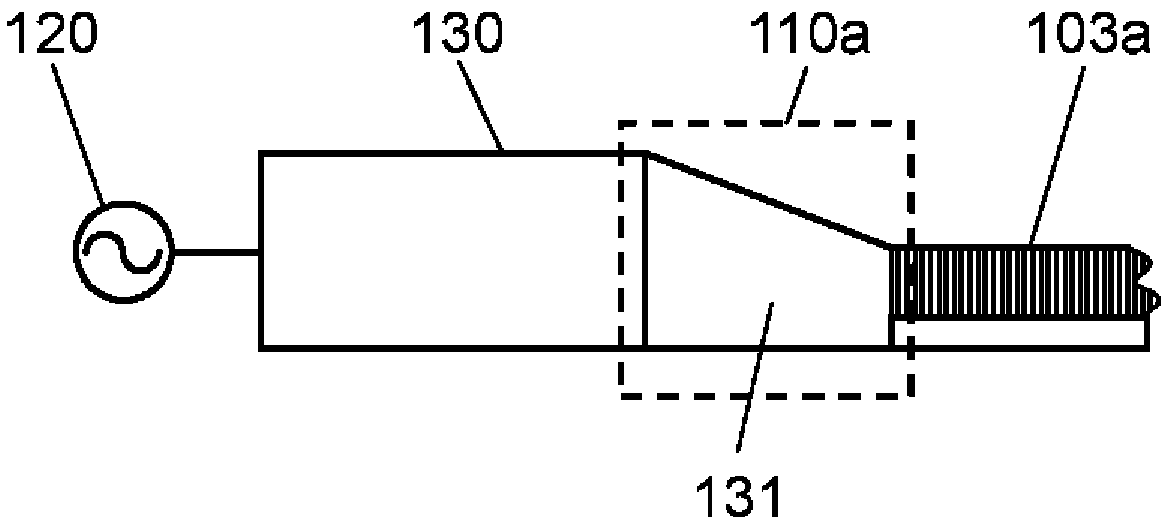
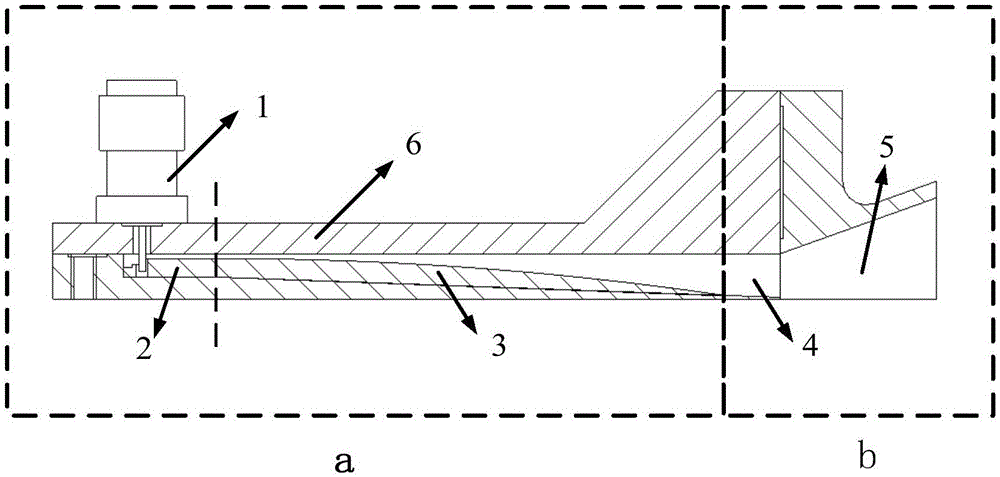
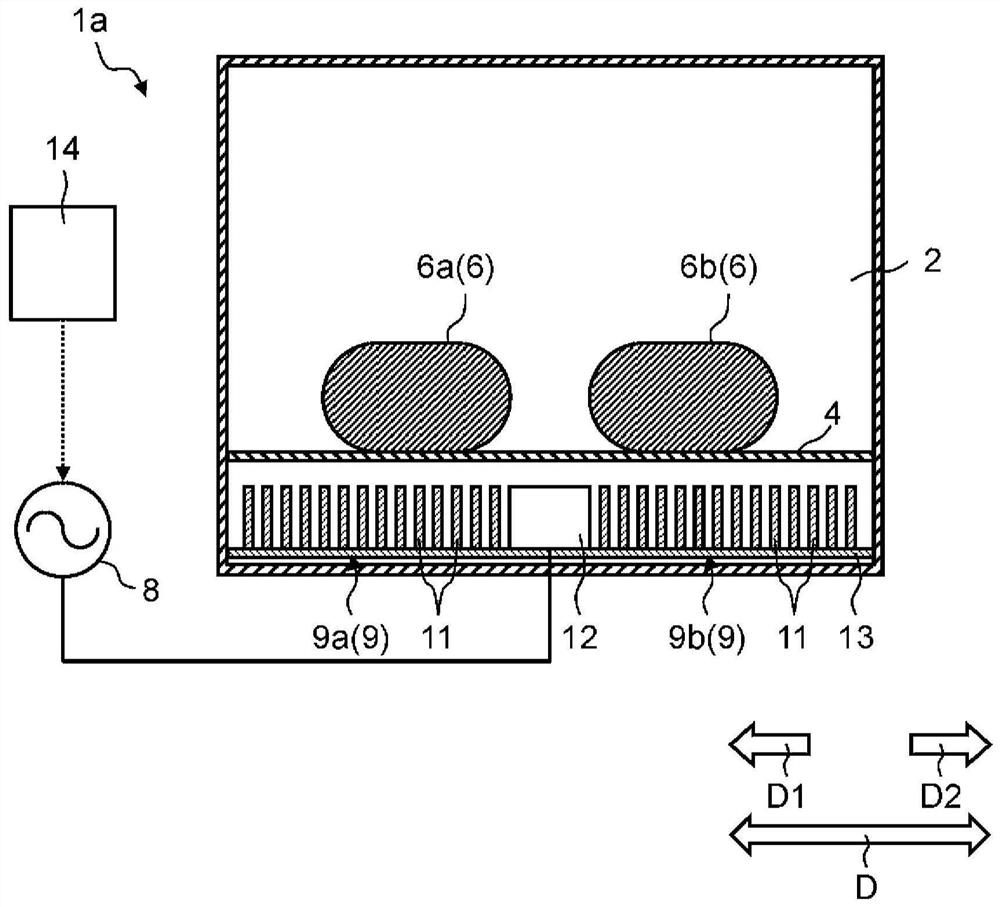
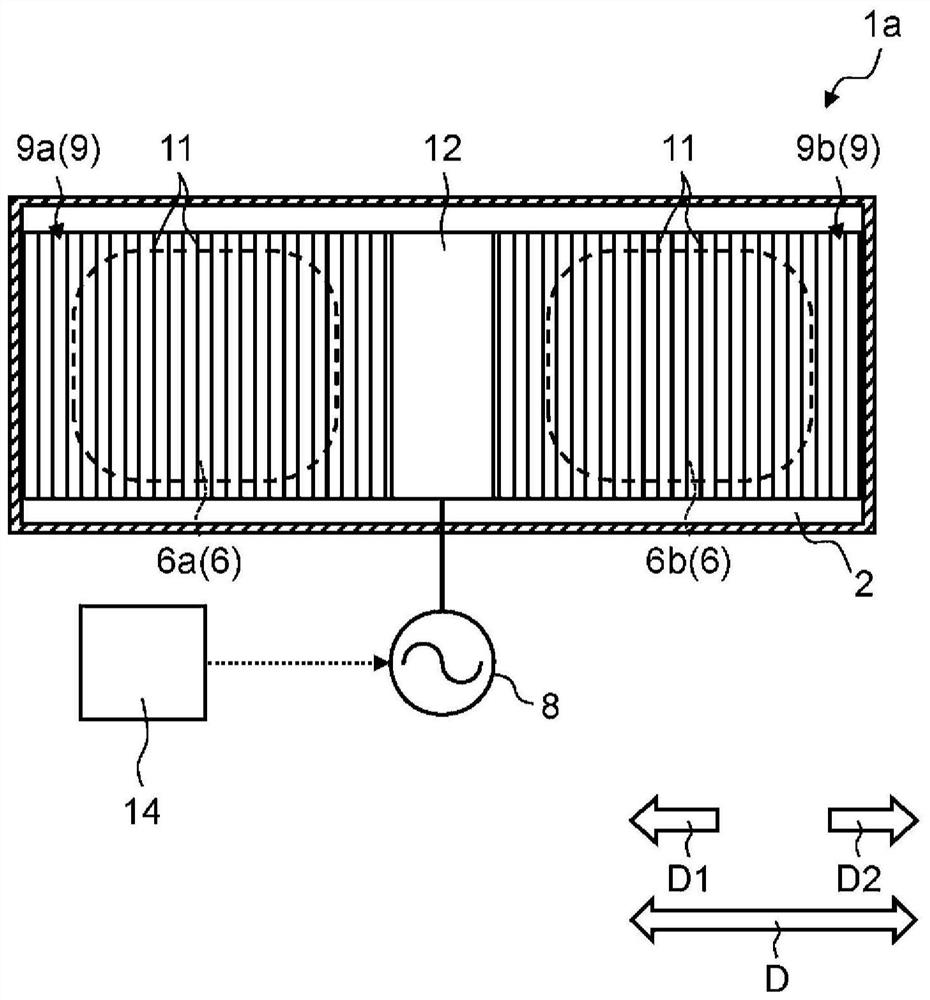
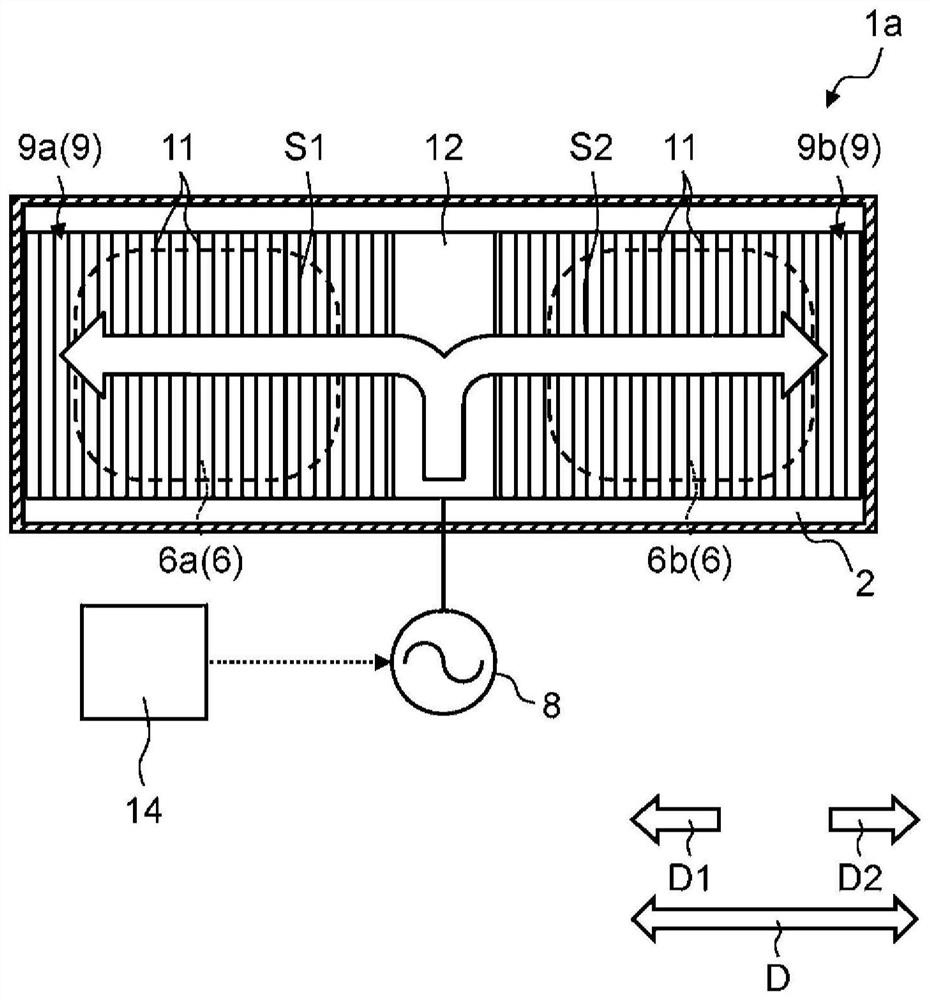
A high-frequency heating device (1a) has a first generating unit (8), a surface wave exciter (9), and a first coupling unit (12). The first generation unit (8) generates microwaves. A surface wave exciter (9) has a plurality of metal plates (11) periodically arranged at predetermined intervals in a microwave propagation direction, and heats a heating object (6) by propagating microwaves in a surface wave mode. The first coupling part (12) is arranged in the middle part of the surface wave excitation body (9) in the propagation direction (D) of the microwave, so that the microwave generated by the first generating part (8) passes through the first coupling part (12) It is supplied to the surface wave exciter (9). According to this aspect, the object to be heated can be heated more uniformly.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
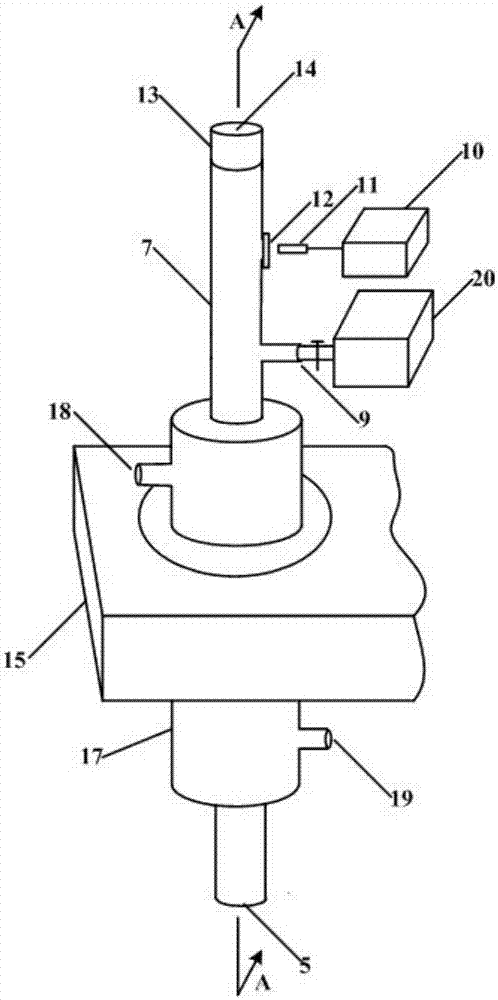
A shape memory alloy microvalve based on surface acoustic wave and its control method
ActiveCN106247006BAchieve closureIncrease in sizeValve arrangementsShape-memory alloySurface acoustic wave sensor
The invention discloses a shape memory alloy micro valve based on acoustic surface waves and a control method of the shape memory alloy micro valve. The shape memory alloy micro valve comprises a PCB, an acoustic surface wave excitation device, a PDMS coagulating body with a micro-channel and a shape memory alloy line formed by a first crooked section at the indoor temperature and a second straight section at the indoor temperature; the acoustic surface wave excitation device and the PDMS coagulating body are installed on the PCB, a groove is formed in the PDMS coagulating body, and the other end of the shape memory alloy line is connected with the PCB; the section, stretching across a propagation path of the acoustic surface waves excited by the acoustic surface wave excitation device and located on the propagation path, of the shape memory alloy line is covered with paroline micro liquid on the propagation path; and the second section of the shape memory alloy line is sleeved with a guide pipe connected with the PCB, and a plastic sheet is connected to the other end of the second section of the shape memory alloy line and extrudes a part, located between the groove and the micro-channel, of the PDMS coagulating body and the under pushing force to deform so as to block the micro-channel. The shape memory alloy micro valve has the beneficial effects of being simple in structure, small in size and easy to integrate.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Central surface acoustic wave heating element
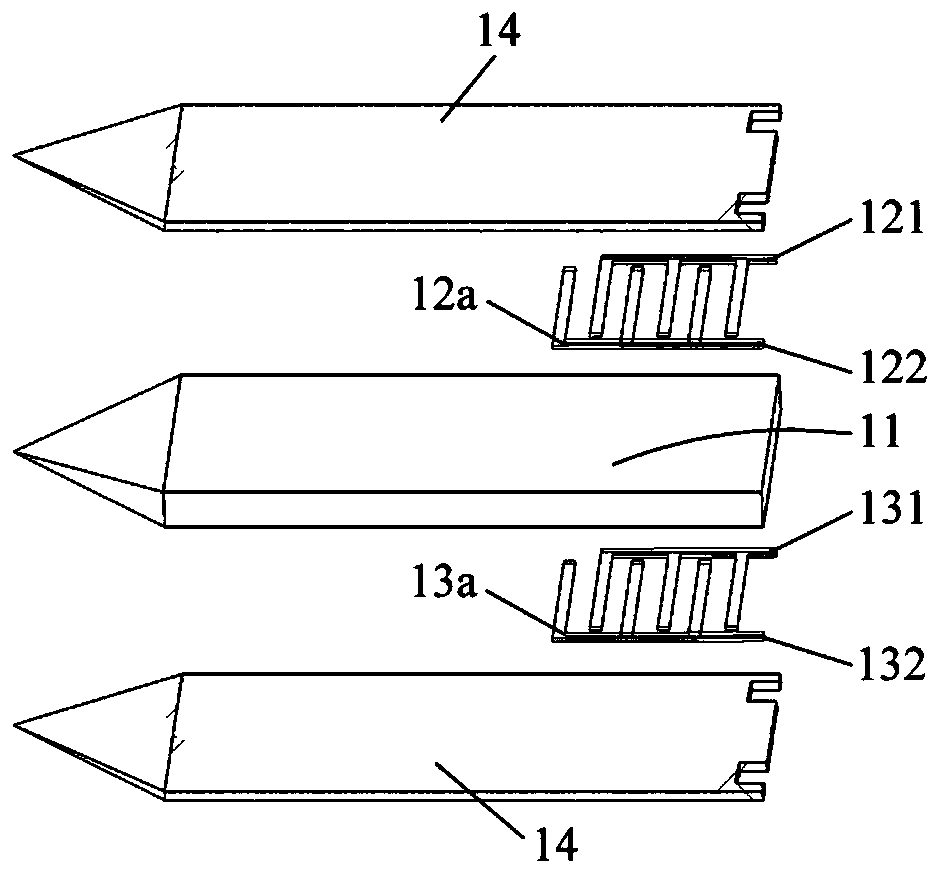
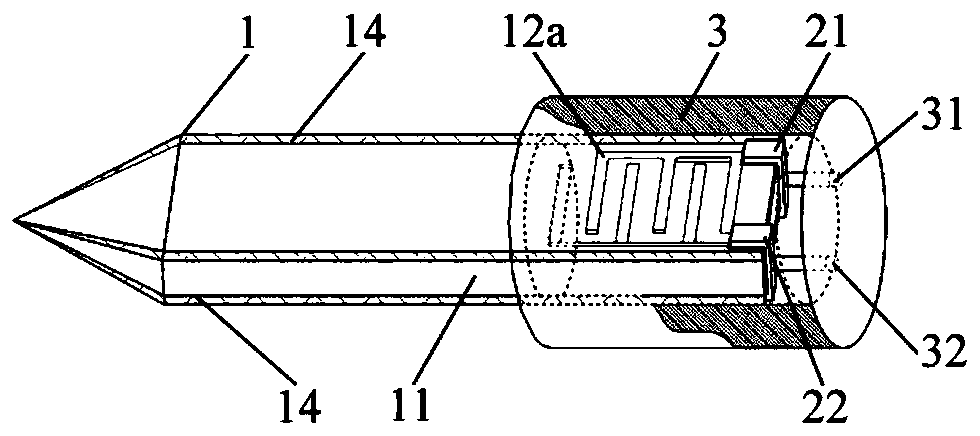
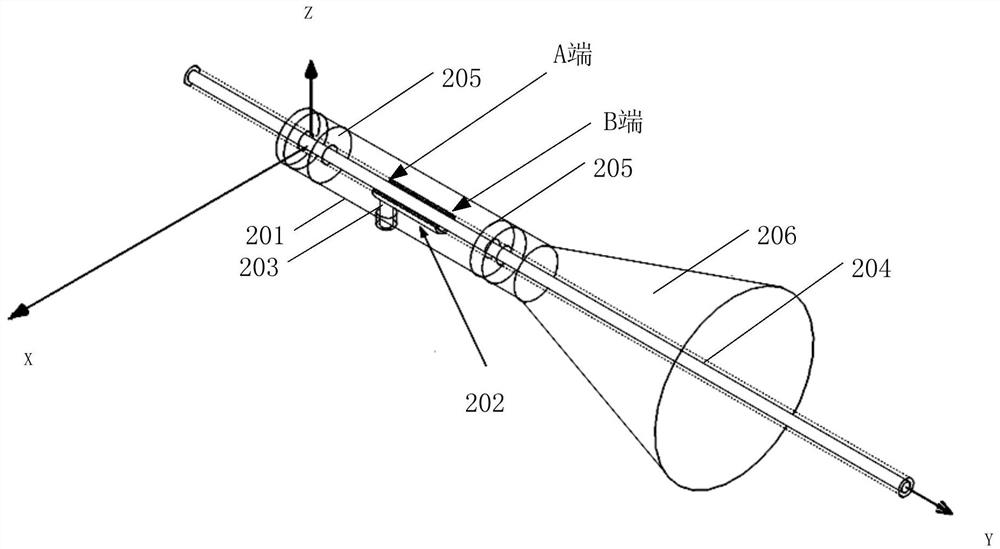
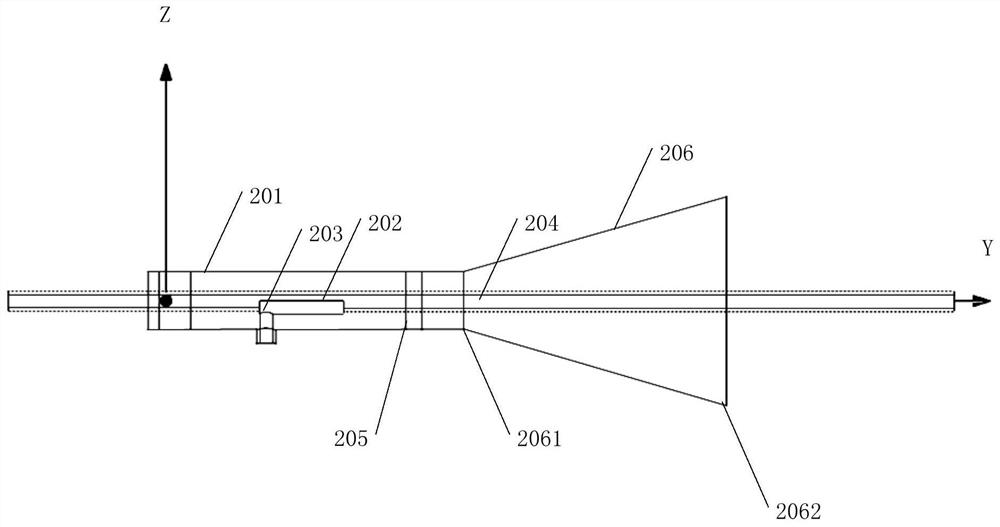
PendingCN111567897AIncrease energy densityImprove heating efficiencyTobaccoElectrical connectionSurface wave excitation
The invention discloses a central surface acoustic wave heating element, which mainly comprises a piezoelectric substrate (11), interdigital electrode structures and a sleeve base (3), wherein the front end of the piezoelectric substrate (11) is tip-shaped, and one or more interdigital electrode structures are arranged on the wall of the rear end of the piezoelectric substrate (11); the sleeve base (3) is sleeved at the rear end of the piezoelectric substrate (11), and the interdigital electrode structuresarepositioned in the sleeve base (3); and two electrodes are arranged at the bottom end of the sleeve base (3) and are electrically connected with bus bars of the interdigital electrode structures respectively. The central type acoustic surface wave heating element is used for heating non-combustible cigarettes and has the advantages of being high in heating efficiency, good in heat uniformity, high in safety coefficient and the like, and an acoustic surface wave excitation source does not make contact with a cigarette core.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
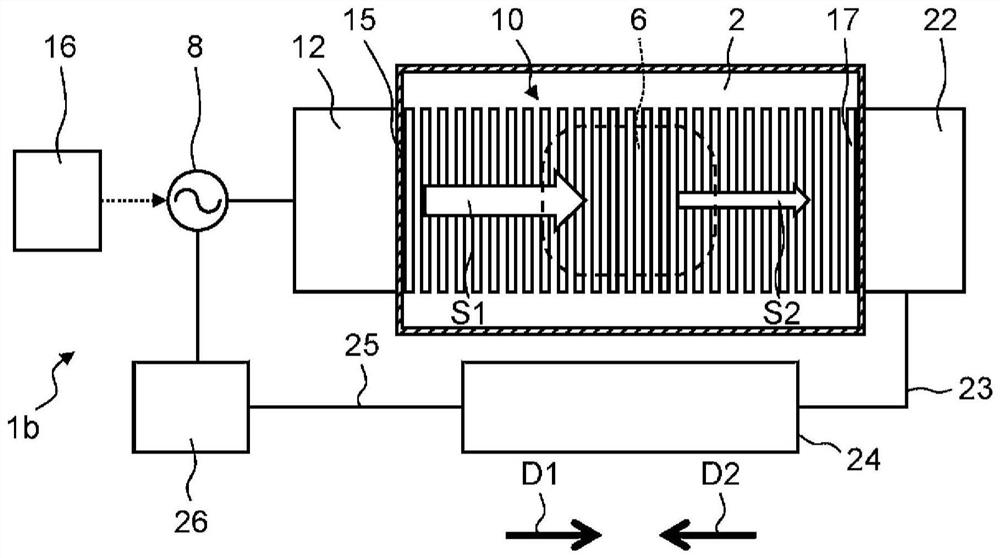
High-frequency heating device
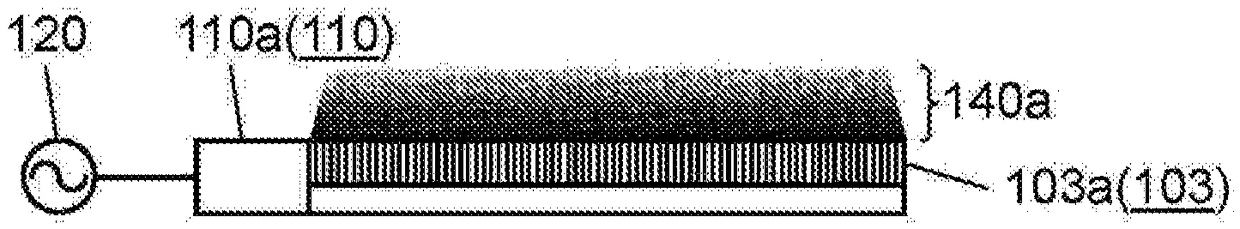
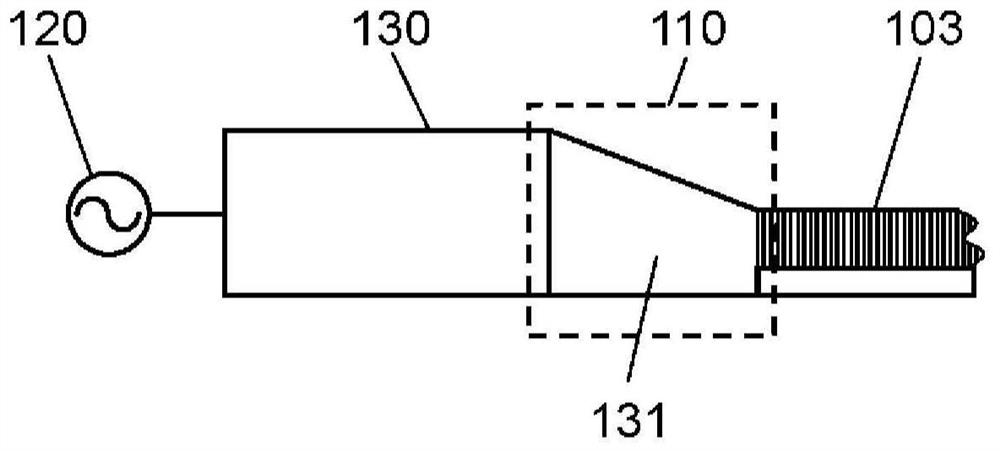
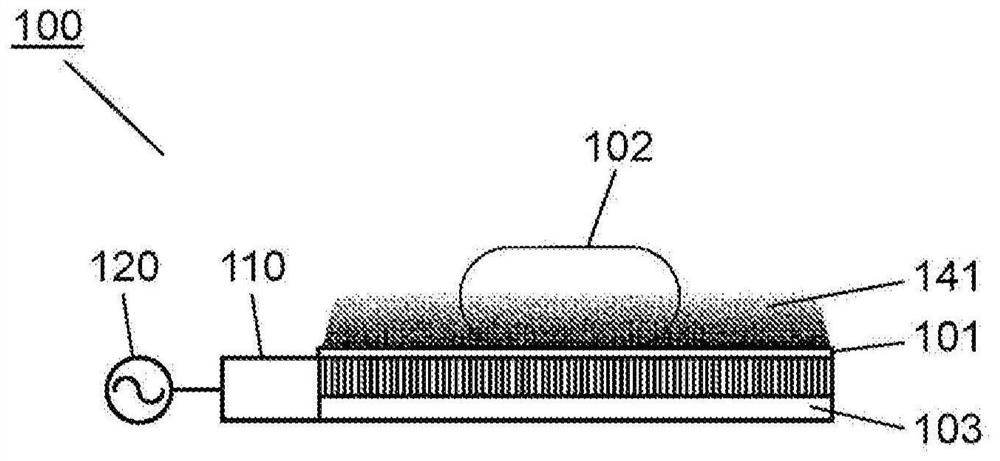
The present invention comprises: a high-frequency power generation part (120) that generates high-frequency power; a surface wave excitation body (103) that uses surface waves to propagate the high-frequency power and thereby heats an object to be heated (102); a high-frequency power supply part (110) that supplies the high-frequency power to the surface wave excitation body (103); and a mountingstand (101) for mounting the object to be heated (102). In accordance with the surface concentration desired for the high-frequency power near the surface wave excitation body (103), the high-frequency power generation part (120) establishes a magnitude correlation between the frequency of the high-frequency power supplied to the surface wave excitation body (103) and the excitation frequency of the surface wave excitation body (103) and heats the object to be heated (102). The present invention thereby provides a high-frequency heating device (100) that can change the thickness-direction heating state of the object to be heated (102).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
High frequency heating device
The high-frequency heating device (100) has: a high-frequency power generating part (120), which generates high-frequency power; a surface wave exciter (103), which uses surface waves to propagate high-frequency power to the heated object (102) heating; a high-frequency power supply unit (110), which supplies high-frequency power to the surface wave excitation body (103); and a setting table (101), which sets the object to be heated (102). The high-frequency power generator (120) sets the frequency and surface area of the high-frequency power supplied to the surface wave exciter (103) according to the desired surface concentration of the high-frequency power near the surface wave exciter (103). The object to be heated (102) is heated according to the size relationship between the excitation frequency of the wave excitation body (103). Thereby, there is provided a high-frequency heating device (100) capable of changing the heating state in the thickness direction of an object to be heated (102).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Microwave antenna applicator
InactiveUS10186780B2Improve stabilityMinimised sideways excitation of surface waveDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrowave therapyEngineeringPermittivity
A new and comparatively small type of open-ended microwave applicators has been disclosed. They are for example suitable for transmission into and reception from contacting objects such as protruding human bodyparts for inhomogeneity detection by tomographic methods. The applicators according to the invention are of the dielectric-filled open-ended ridged rectangular TE10 type, with an insert filling the ridge and having a higher permittivity than the surrounding space. The shape of the insert can be as a frustrum pyramid towards the opening. The overall design promotes narrow beamwidths and minimizes nearfields and surface wave excitation.
Owner:RISMAN PER OLOV +2
Bloch surface wave exciter, nano-particle spectrometer and measuring method of nano-particle spectrometer
PendingCN113418604ALow costSimple requirementsRadiation pyrometryMirrorsOptical spectrometerNanoparticle
The invention relates to a Bloch surface wave exciter based on nano-particles, used for a spectrograph. The Bloch surface wave exciter comprises a glass substrate and a Bragg reflection unit arranged on the glass substrate, the Bragg reflection unit is formed by alternately stacking high-refractive-index dielectric layers and low-refractive-index dielectric layers, the top layer of the Bragg reflection unit is a defect layer, and nanoparticles are arranged on the surface of the top layer. The invention also provides a corresponding spectrometer and a measuring method thereof. According to the Bloch surface wave exciter, the in-plane size of a spectrograph can reach the nanoscale, and small light source signals can be measured. In addition, the preparation method is simple and low in cost. In addition, when the spectrometer is used, the requirement for the incident spectrum is simple, and the requirement for polarization of the incident spectrum does not exist. Meanwhile, the back focal plane image only needs to be shot once, so that the operation is simple, and the time is saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Excitation and long-distance transport structures of surface waves based on metamaterials
The invention discloses surface wave excitation and long-distance transmission structures based on metamaterials. The first structure, the second structure and the third structure are free space coupling structures, and the fourth structure is an end face coupling structure. All the four structures do not need to coupled through lenses high in refractive index, integration of optical elements is facilitated, meanwhile, the propagation distance of light can reach millimeter magnitude, and the structures can be widely used in the optical elements. The structures are simple, SPPs are easily coupled under the circumstance that no lens high in refractive index is used, integration of the optical elements is facilitated, meanwhile, the propagation distance of the light can reach the millimeter magnitude, and the structures can be widely used in the optical elements.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
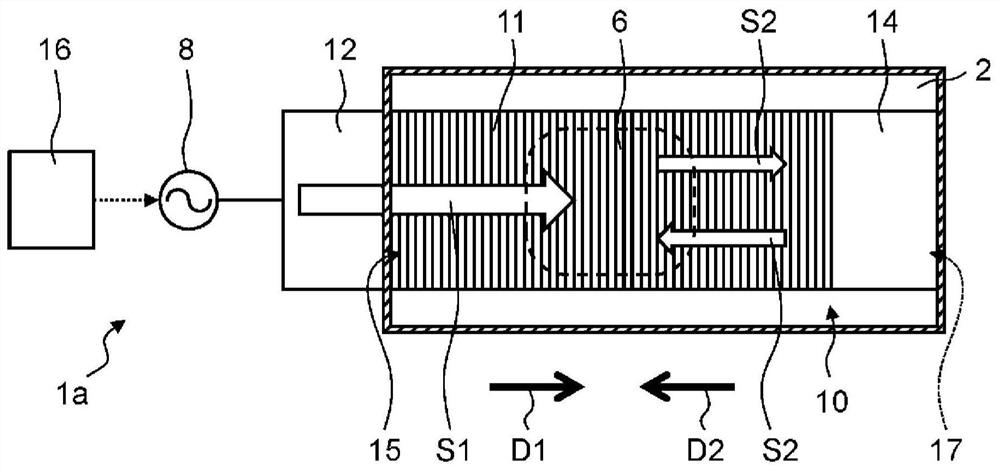
High frequency heating device
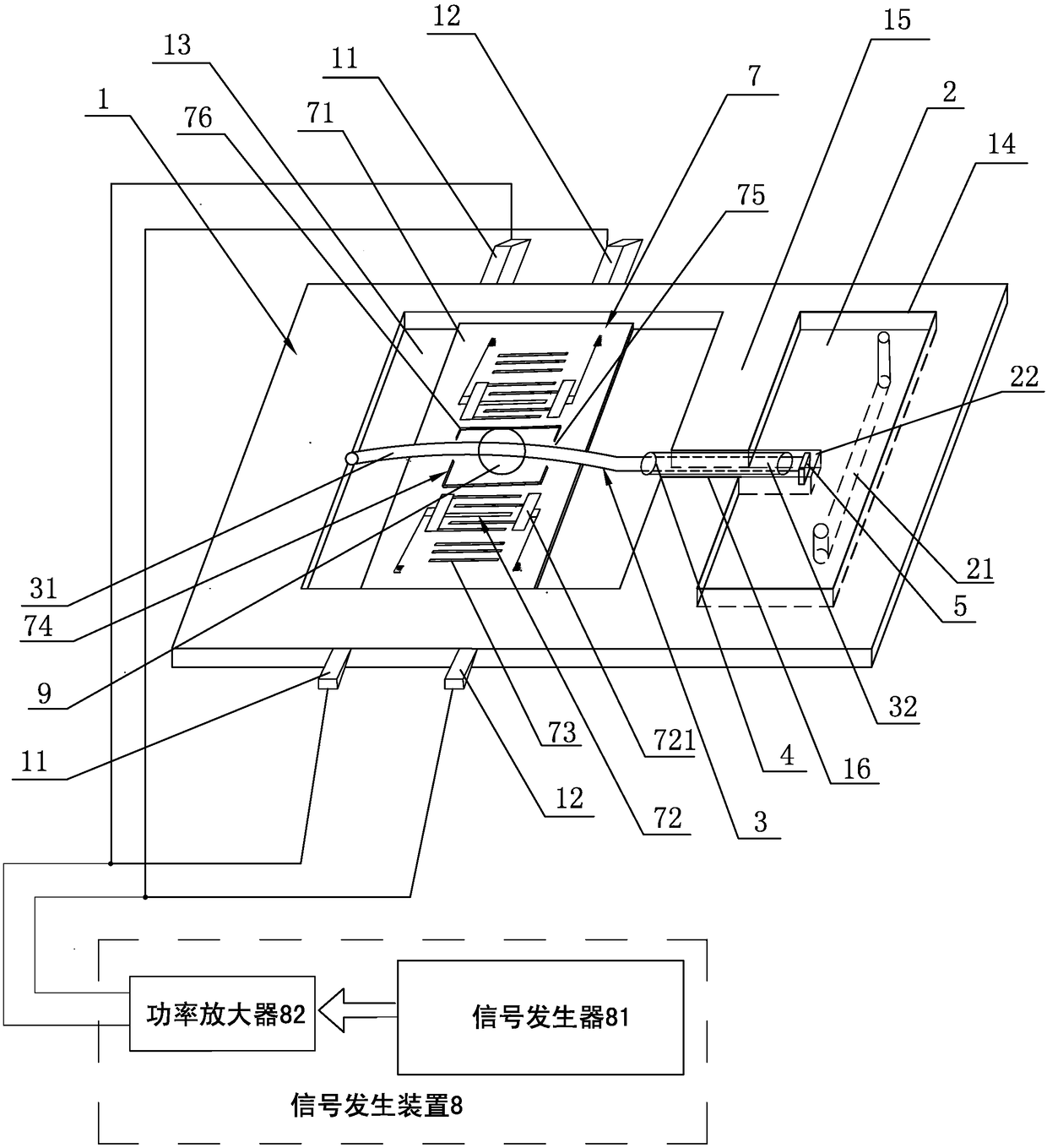
A high-frequency heating device (1a) has a generating unit (8), a surface wave exciter (10), a first coupling unit (12), and a recycling unit (14). A generating unit (8) generates microwaves. The surface wave exciter (10) has a periodic structure, and heats the object to be heated (6) by propagating microwaves in a surface wave mode. The first coupling part (12) is arranged at one end part (15) of the surface wave excitation body (10). The microwave generated by the generating unit (8) is supplied to the surface wave exciter (10) via the first coupling unit (12). The reuse unit (14) recycles microwaves that have reached the other end (17) of the surface wave excitation body (10) in the microwave propagation direction from one end (15) of the surface wave excitation body (10). It is used for heating the object to be heated (6). According to this aspect, microwaves not absorbed by the object to be heated can be reused for heating the object to be heated.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
A surface wave excitation device
ActiveCN109802235BAntennas earthing switches associationWaveguidesRadiation lossElectrical conductor
The embodiment of the present application discloses a surface wave excitation device. The surface wave excitation device in the embodiment of the present application includes: a metal waveguide, a coupling part, a feeding part and a transmission line, the metal waveguide sleeve is placed outside the transmission line, the coupling part is placed inside the metal waveguide, and the metal waveguide It is a coaxial structure with the transmission line; the feeding part is connected to the coupling part, and the coupling part is arranged in parallel with the transmission line, and there is a gap between the coupling part and the conductor of the transmission line; so that the electromagnetic wave Propagated from the feeding part to the coupling part, coupled to the surface of the transmission line through the coupling part to transmit the surface wave. The surface wave excitation device in the embodiment of the present application is used to reduce surface wave radiation loss.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Array substrate, manufacturing method thereof, display panel and display device
The invention discloses an array substrate, comprising a base substrate; a piezoelectric induction layer formed on the base substrate; a surface acoustic wave exciting electrode and a surface acoustic wave receiving electrode formed on the piezoelectric induction layer; The photosensitive resistance layer formed on the piezoelectric sensing layer, the photosensitive resistance layer is located between the surface acoustic wave excitation electrode and the surface acoustic wave receiving electrode, and the invention also discloses a display panel and a display device including the array substrate , the present invention uses surface acoustic wave excitation electrodes and receiving electrodes with fast response speed, high sensitivity and small volume to realize the fingerprint recognition function, which can improve the speed and sensitivity of fingerprint recognition.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Method for determining medium properties and device for determining medium properties
ActiveCN108496075BAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementBiological propertyEngineering
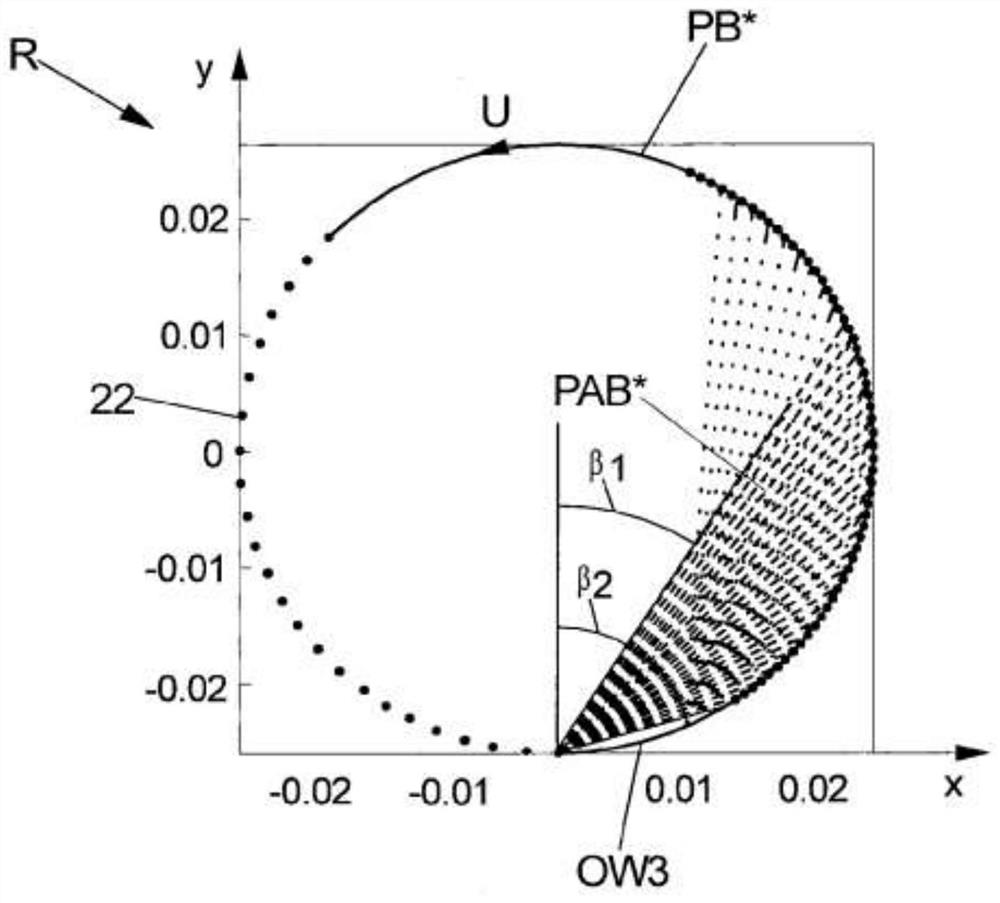
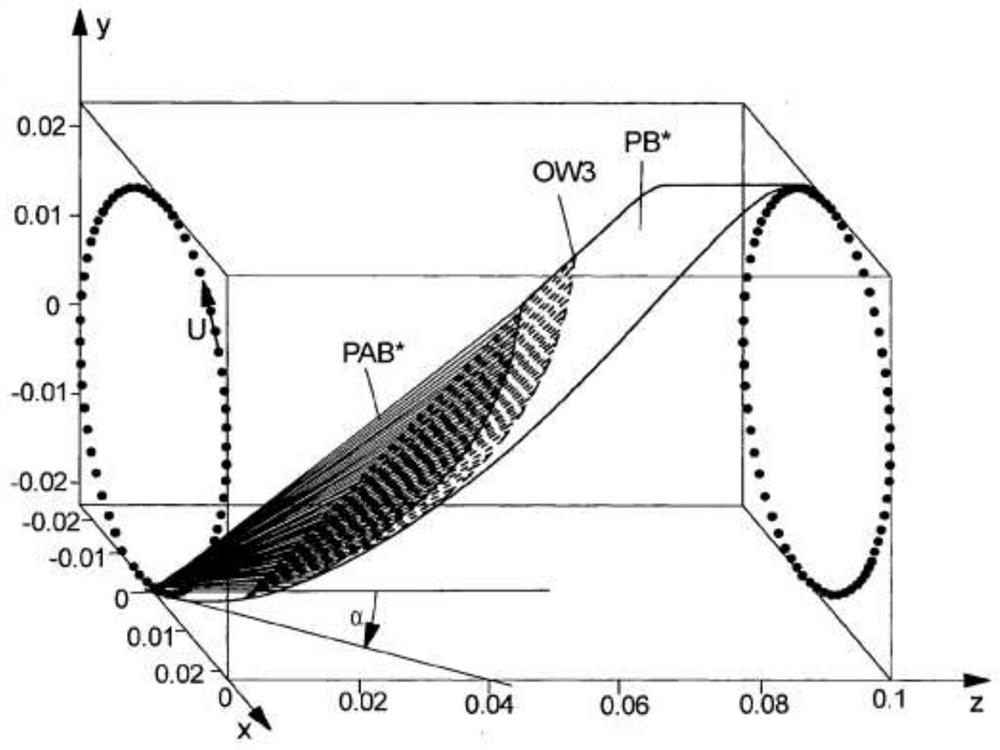
The invention relates in particular to a method for determining physical, chemical and / or biological properties of a medium (M) by means of a first and a second transmitter-receiver pair (SE1, SE2; SE1, SE3) The receivers (SE2, SE3) of the receivers (SE2, SE3) receive surface waves (OW1, OW2, OW3) originating at least in part from the first or second acoustic waves (VW1, VW2, ...), which are passed through the guiding element ( The acoustic surface waves (OW1, OW2, OW3) propagating at the shell surfaces (11, 12, 21, 22) of R) are excited, propagate in the medium (M) and at least partially in turn act as surface waves (OW1, OW2, OW3) ) is coupled into the guide element, eg the tube (R) or the shell surface (11, 12, 21, 22) of the tube section. According to the invention, it is proposed: - Excitation of surface waves (OW1, OW2) by the transmitter (SE1) of the first transmitter-receiver pair (SE1, SE2), the propagation direction of said surface waves being parallel to the direction of the guide element (R) The longitudinal extension direction (z) extends, and the surface wave (OW3) is excited by the transmitter (SE1) of the second transmitter-receiver pair (SE1, SE3), the propagation direction of the surface wave being set relative to the guide The longitudinal extension (z) of the element (R) has a defined angle α, where 0°
Owner:ENDRESSHAUSER FLOW DEUTSCHLAND AG
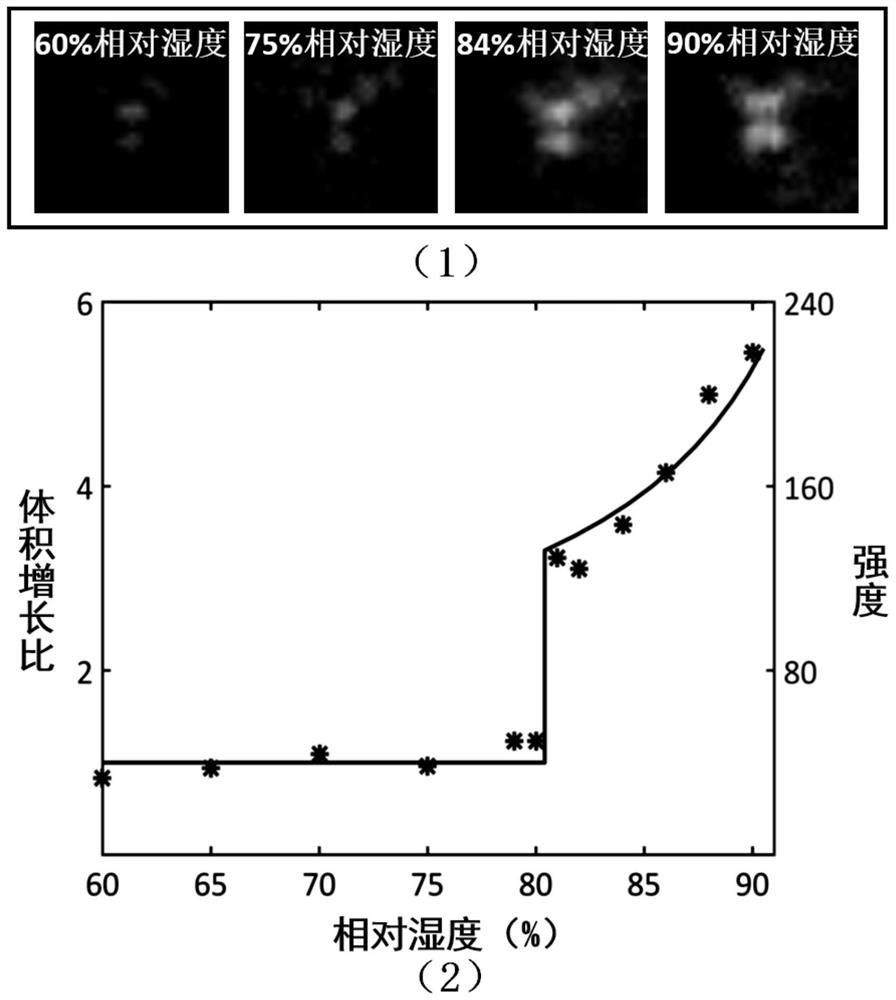
Atmospheric ultrafine particulate matter moisture absorption growth detection device based on surface wave imaging
PendingCN113533142AEffective constraintsSensitive to environmental changesParticle size analysisMicro imagingMoisture absorption
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Surface wave excitation plasma processing system
InactiveUS8018162B2InterferenceUniform generation of the plasma over a large area stablyElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsDielectricMicrowave
To sustain uniform generation of plasma constantly over a large area. In the surface wave excitation plasma processing device, a plasma source includes: a microwave generator, a microwave waveguide and a dielectric block; and a plasma source also includes: a microwave generator, a microwave waveguide and a dielectric block. The lid of a chamber is fixed onto the microwave waveguides in parallel, and the dielectric blocks disposed in the chamber. A reflecting plate is disposed between the dielectric blocks so that electromagnetic waves propagating through the dielectric blocks are prevented from advancing into the counterpart dielectric blocks as reflected waves. Consequently, the plasma sources are controlled independently. Furthermore, a side reflector is disposed at outer circumference of each of the dielectric blocks so that a standing waves of the electromagnetic waves propagating through the dielectric blocks is formed thus forming a large area standing wave mode of surface waves uniformly.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com