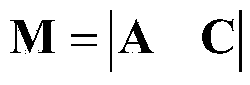Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74 results about "Spectral matching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
To generate a time series using spectral matching in frequency domain, do the following: Use the command Define > Functions > Time History, select type "Matched to a Response Spectrum", and click "Add New Function". Choose method "Spectral Matching in Time Domain". Choose a target response spectrum.
Spectrum matching
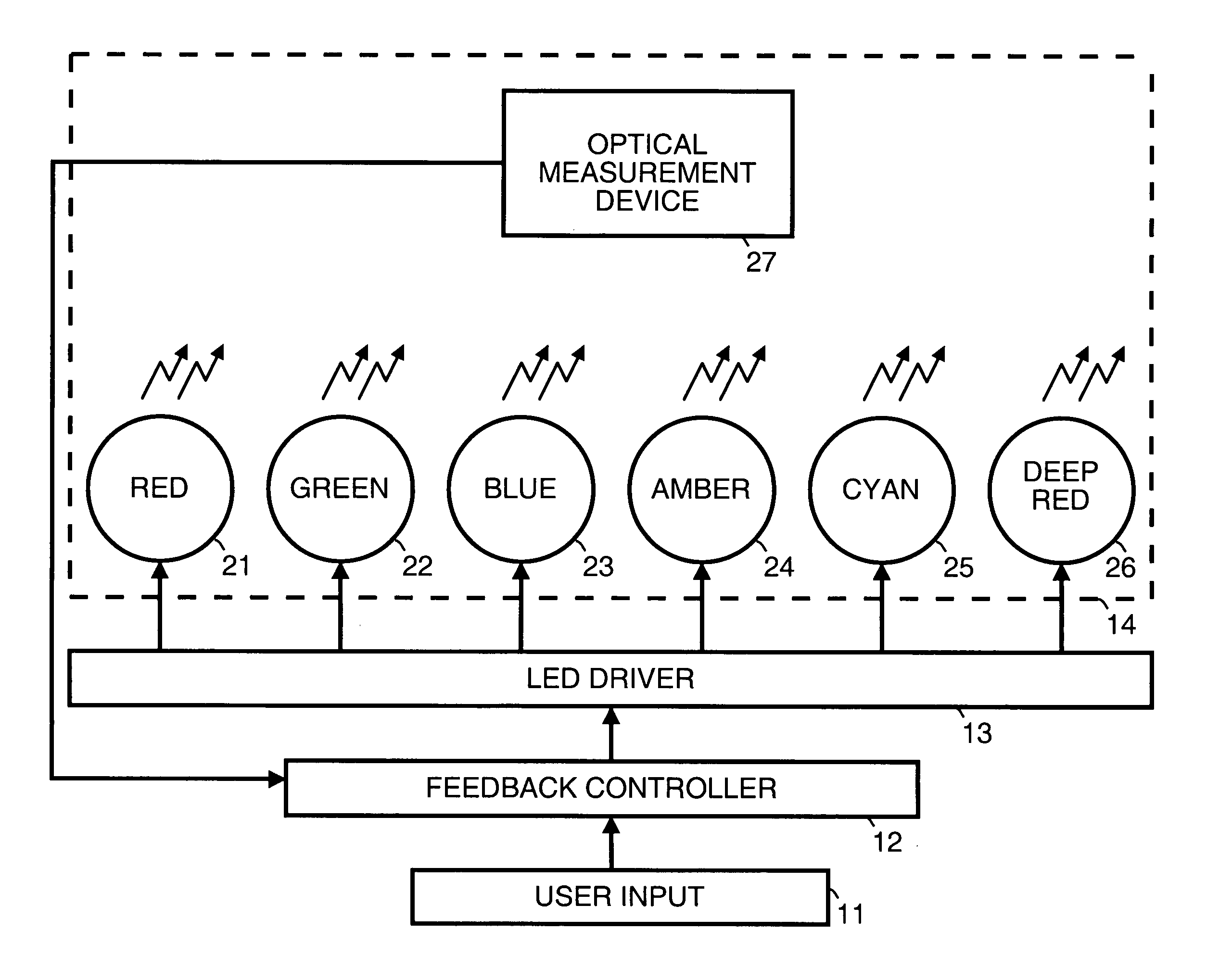
InactiveUS20060018118A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesFrequency spectrumMeasurement device
Light is generated in accordance with a desired spectral power distribution curve. A spectrum of light is generated with a plurality of different light sources. An optical measurement device measures the spectrum of light generated by the plurality of different light sources. The optical measurement device is able to detect light within the entire spectrum of light generated by the plurality of different light sources. The measured spectrum of light is used as feedback to vary the spectrum of light generated with the plurality of different light sources to approximate the desired spectral power distribution curve.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
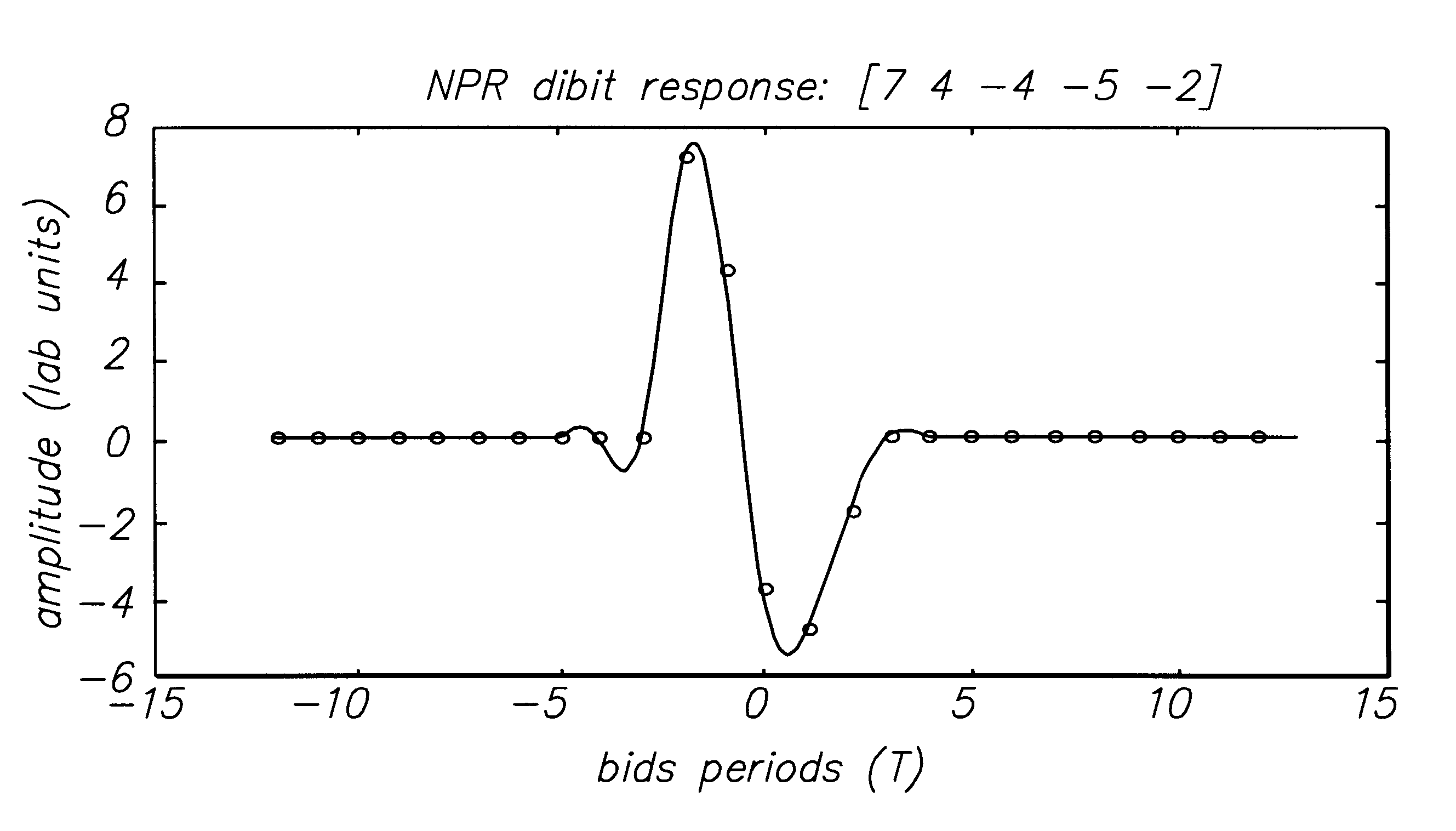
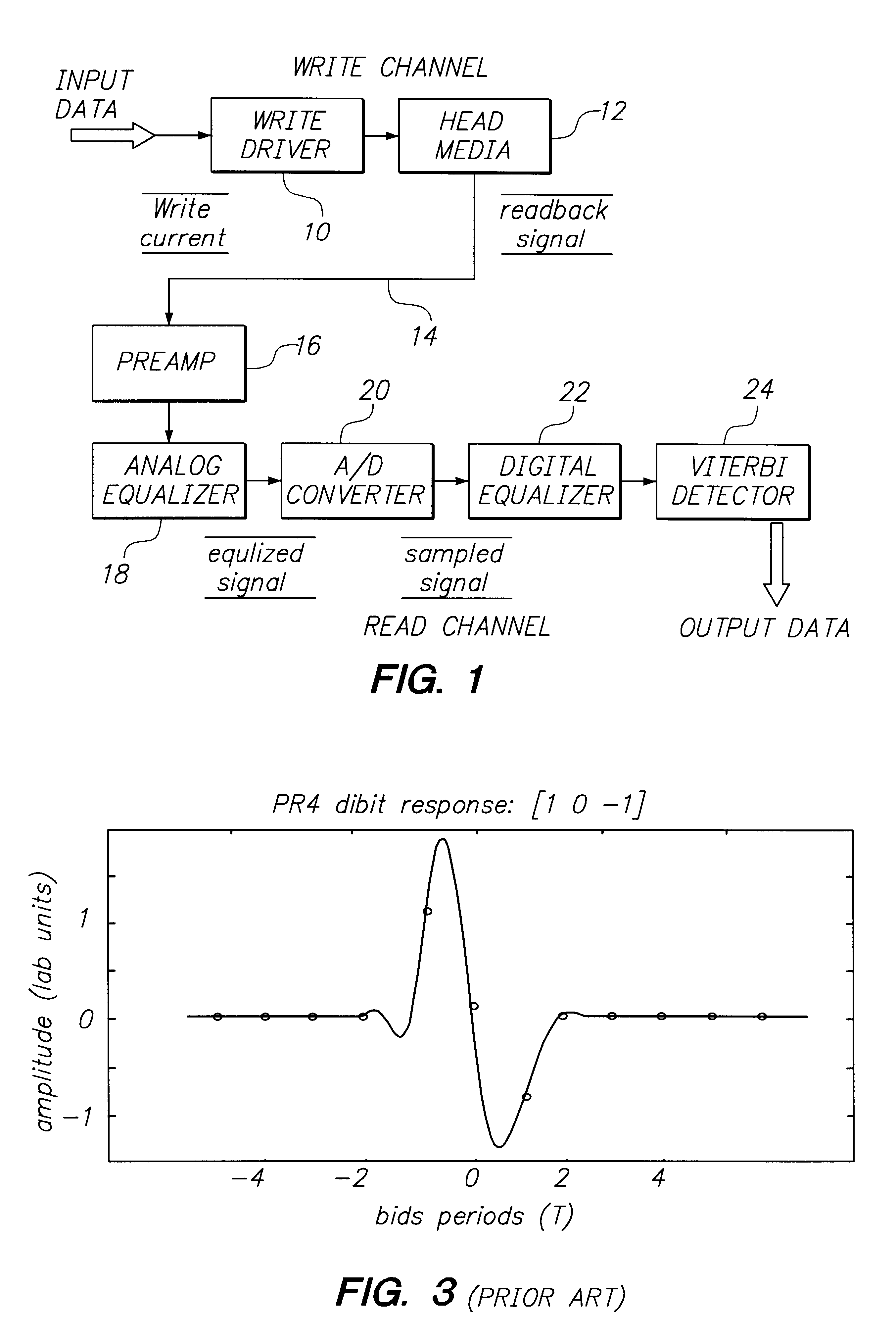
Class of fixed partial response targets in a PRML sampled data detection channel
InactiveUS6249398B1Modification of read/write signalsRecord information storageFrequency spectrumMagnetic media
A new class of fixed partial response targets are disclosed for use in a PRML magnetic medium read channel. The preferred embodiment exhibits an equalization response characterized by the polynomial 7+4*D-4*D2-5*D3-2*D4, where D represents the unit delay operator. This read channel target provides improved matching to the inherent magnetic channel over the known canonical class of targets (1-D)(1+D){circumflex over ( )}N, and thereby reduces equalization losses. The improved spectral matching reduces amplification of noise in the channel, thereby reducing bit-error-rates. The new class of targets also exhibits a spectral null at DC, reducing problems for offset cancellation circuitry and making the disk drive less sensitive to thermal asperities. It also exhibits a spectral depression rather than a spectral null at the Nyquist frequency, making quasi-catastrophic error sequences virtually impossible. The new class of target simplifies coding and allows RLL code ratios that approach unity, improving effective recording densities, while significantly reducing BER.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
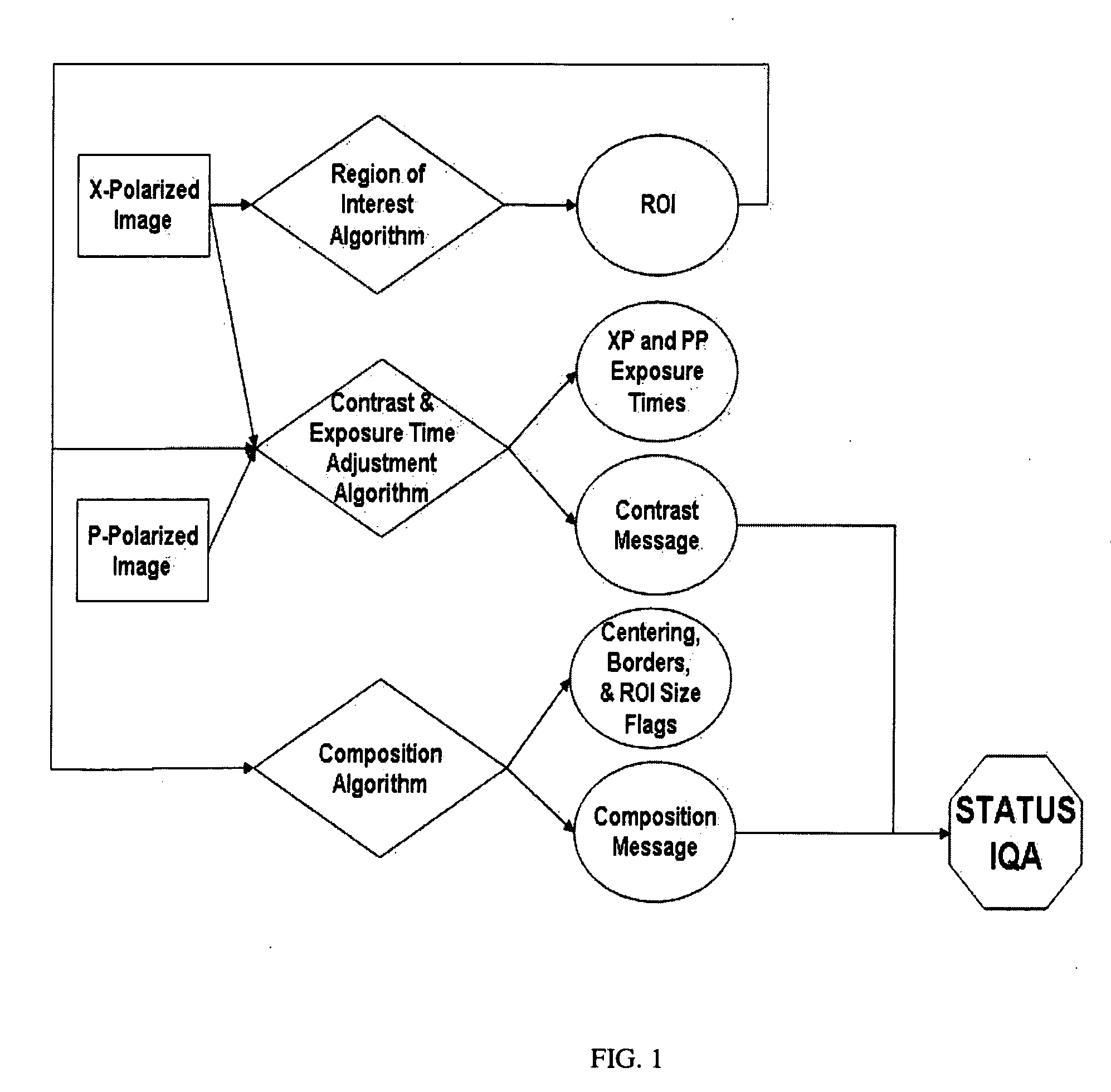
Method to provide automated quality feedback to imaging devices to achieve standardized imaging data
Automated image quality assessment algorithms, which perform the functions of locating a region of interest, maximizing the image contrast, and ensuring the region of interest is properly centered in the image. Wherein the region of interest is located by spectral matching filter using a target spectrum obtained from samples of the image itself.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
High Mass Accuracy Filtering for Improved Spectral Matching of High-Resolution Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Data Against Unit-Resolution Reference Databases
ActiveUS20150340216A1Strong specificityConfidenceParticle separator tubesComponent separationGas chromatography–mass spectrometryUnit resolution
The invention provides methods, systems and algorithms for identifying high-resolution mass spectra. In some embodiments, an analyte is ionized and analyzed using high-resolution mass spectrometry (MS) at high mass accuracy (such as ≦75 ppm or ≦30 ppm) and the obtained mass spectra are matched with one or more prospective candidate molecules or chemical formulas. The invention provide, for example, methods and systems wherein the possible fragments that can be generated from the candidate molecules or chemical formulas are determined as well as the masses of each of these fragments. The invention provide, for example, methods and systems wherein the high-resolution mass spectra are then compared with the calculated fragment masses for each of the candidate molecules or chemical formula, and the portion of the high-resolution mass spectra that corresponds or can be explained by the calculated fragment masses is determined.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Efficient spectral matching, particularly for multicomponent spectra
ActiveUS20090210194A1Short timeRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpectroscopyComputational physics
An unknown spectrum obtained from infrared or other spectroscopy can be compared to spectra in a reference library to find the best matches. The best match spectra can then each in turn be combined with the reference spectra, with the combinations also being screened for best matches versus the unknown spectrum. These resulting best matches can then also undergo the foregoing combination and comparison steps. The process can repeat in this manner until an appropriate stopping point is reached, for example, when a desired number of best matches are identified, when some predetermined number of iterations has been performed, etc. This methodology is able to return best-match spectra (and combinations of spectra) with far fewer computational steps and greater speed than if all possible combinations of reference spectra are considered.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRON SCI INSTR
Efficient spectral matching, particularly for multicomponent spectra
ActiveUS7698098B2Short timeRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpectroscopySpectral matching
An unknown spectrum obtained from infrared or other spectroscopy can be compared to spectra in a reference library to find the best matches. The best match spectra can then each in turn be combined with the reference spectra, with the combinations also being screened for best matches versus the unknown spectrum. These resulting best matches can then also undergo the foregoing combination and comparison steps. The process can repeat in this manner until an appropriate stopping point is reached, for example, when a desired number of best matches are identified, when some predetermined number of iterations has been performed, etc. This methodology is able to return best-match spectra (and combinations of spectra) with far fewer computational steps and greater speed than if all possible combinations of reference spectra are considered.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRONICS SCI INSTR LLC
Spectral matching guide for spot color print applications
ActiveUS20110149312A1Raise the possibilityDigitally marking record carriersRadiation pyrometryPattern recognitionSpectral matching
What is disclosed is a novel system and method for generating a spectral matching guide for spot color print applications. Spectral matching values are determined for spot colors obtained from a library of spot colors. A spectral matching guide is created from the spot colors and their respective spectral matching values in a manner more fully disclosed herein. Thereafter, when a user desires to render a job in a particular spot color, the associated spectral matching value for that spot color can be obtained from the spectral matching guide. In other embodiments, recommendations in the form of a suggested printer to use, a media type, a halftone screen, and other meaningful assistance can be provided for selection of spot colors for a given print / copy job that are less sensitive to varying illuminations. The present spectral matching guide provides meaningful extensions in spectral color reproduction in print / copy job environments.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Active camouflage using real-time spectral matching
ActiveUS20070034774A1Reduce intensityHigh strengthPhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationSpectral matchingElectromagnetic radiation
An invention is provided for concealing an object. The invention includes a plurality of electromagnetic radiation sources that generate an electromagnetic radiation spectrum, and a controller in communication with the plurality of electromagnetic radiation sources. The controller includes logic that compares the electromagnetic radiation spectrum generated from the plurality of electromagnetic radiation sources with an electromagnetic radiation spectrum from an environment surrounding the object. In operation, the controller adjusts the plurality of electromagnetic radiation sources to generate an electromagnetic radiation spectrum that matches the electromagnetic radiation spectrum of the environment surrounding the object.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Near-infrared spectrum imaging system and method for diagnosis of depth and area of burn skin necrosis
ActiveUS10278636B2High resolutionImprove efficiencyDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical sensorsBurned skinInfrared
Owner:BEIJING HEFENGLIANKANG INVESTMENT MANAGEMENT LTD
Paired optically variable security element
Disclosed is a paired optically variable security element which comprises first and second optically variable thin-film multilayer interference devices in the form of optically variable foils or of printings made with inks comprising optically variable interference pigments, wherein said first and second interference devices exhibit spectral matching at a determined angle of incidence. Sets of optically variable devices and of coating compositions comprising optically variable pigments for the production of said paired optically variable security element are also disclosed, as well as the use of said security element for the protection of documents and goods, and security documents and goods carrying same.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
Rapid automatic target compound confirmation using deconvolution and spectral matching
ActiveUS20050273276A1Component separationSpecial data processing applicationsSpectral matchingDeconvolution
A method for automatically verifying the existence of a target compound comprises generating a total ion chromatogram. The total ion chromatogram comprises a plurality of peaks, each peak representing one or more compounds in a sample matrix, each peak comprising at least two compounds. The method also comprises deconvoluting each peak to isolate each target compound present in the peak, and automatically verifying the identity of each target compound against a target compound library.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Printing ink color matching method based on spectral matching
ActiveCN103612483AMatching has low impactGood visual matching effectColor measuring devicesPrinting press partsPattern recognitionSpectral matching
The invention relates to a printing ink color matching method based on spectral matching. The printing ink color matching method aims to achieve the optimal spectral matching of printing ink colors. The Lab color values of splines of a database and the spectral reflectivity of visible spectrums of the splines are measured and obtained; the corresponding relation of the spectral reflectivity of the visible spectrums, the Lab color values and a formula and each spline is built; the Lab value of target colors and the spectral reflectivity of visible spectrums of the target colors are measured; data points are extracted from the database according to the Lab color values of the target colors, wherein the color difference between the data points and the target colors is 0-5; the spectral reflectivity of each extracted data point in the database is regulated, and the mean value of the spectral reflectivity of samples is made to correspond to the mean value of the spectral reflectivity of the target colors; the spectrum difference index of each data point and the target colors is calculated and extracted; the point with the smallest difference index is found out from the extracted data points, and the optimal printing ink formula of the target colors is given according to the printing ink formula, corresponding to the point, in the database.
Owner:中国印刷科学技术研究所
Spectral line inflexion multi-scale optimizing segmentation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of hyperspectral remote sensing application and in particular relates to a spectral matching and recognition method. The invention overcomes the defects that the conventional spectral matching and recognition method only considers the whole similarity measurement between spectral lines but neglects the local difference measurement between the spectral lines, and provides a spectral segmentation-based matching and recognition method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing transformation processing on the spectral lines by adopting the multi-scale wavelet transform taking a second-order Gaussian derived function as a wavelet function; secondly, extracting an optimized inflexion of a spectral curve by using the designed inflexion multi-scale optimizing algorithm; and finally, segmenting the spectral lines based on the extracted optimized inflexion information, and recognizing the spectral lines by adopting a segmentation matching method. The spectral matching and recognition method has the advantages that: wave bands with larger ground object spectrum difference and wave bands with smaller spectrum difference can be segmented into different segmentations through the inflexion segmentation so as to protrude the wave bands with the larger spectrum difference and enhance the effectiveness of spectral matching and recognition.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
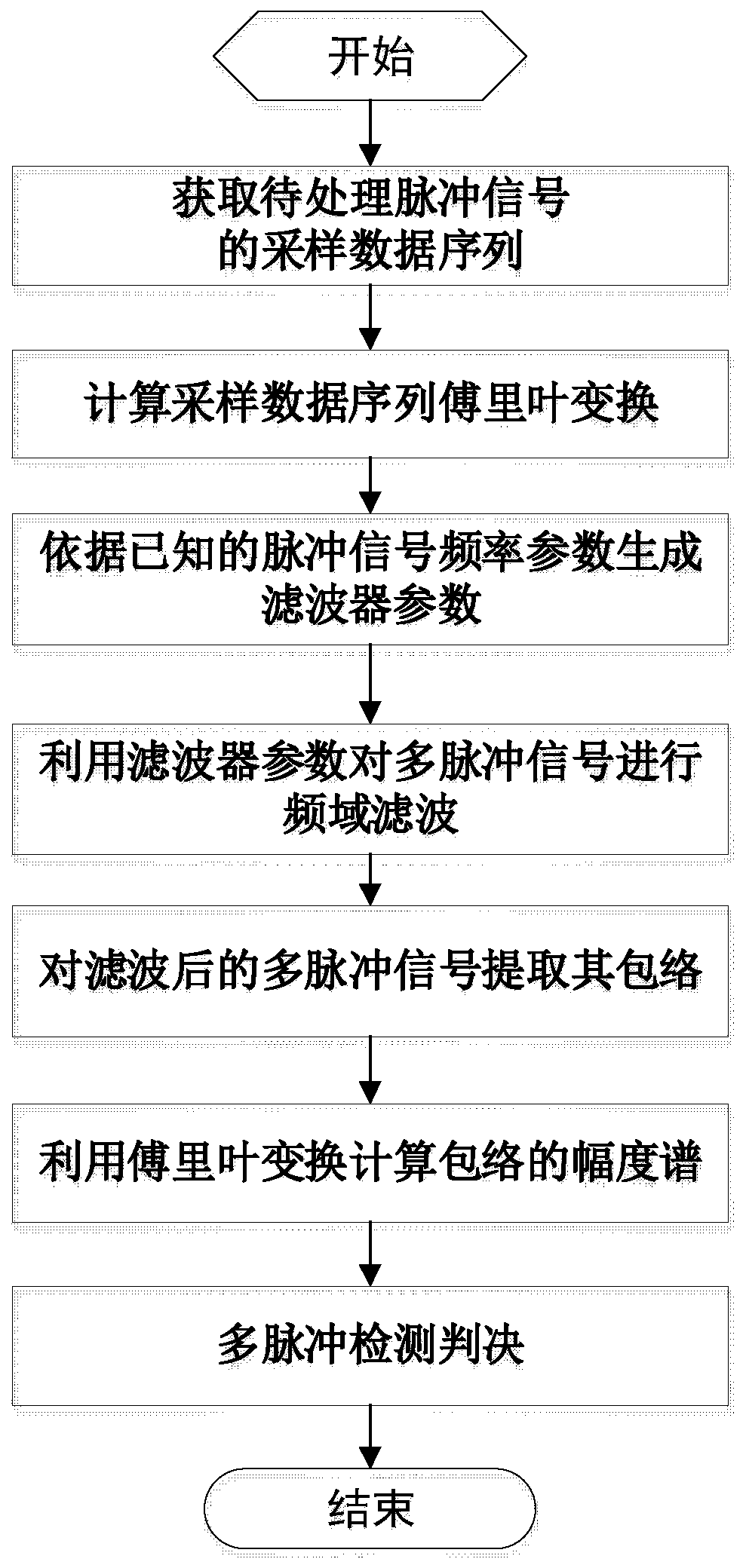
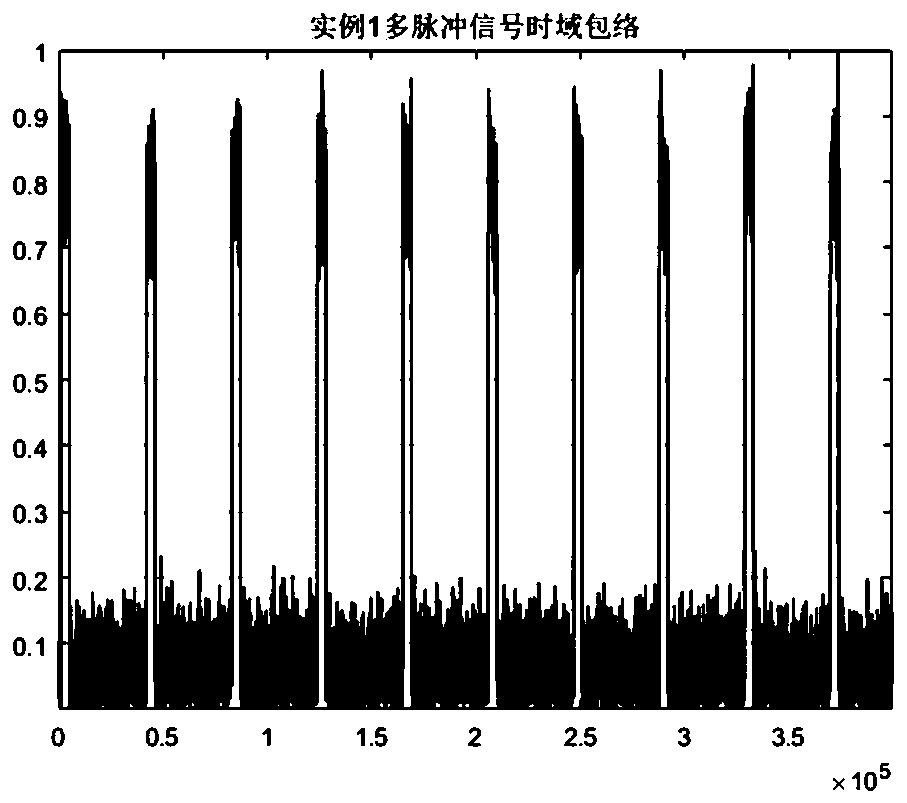
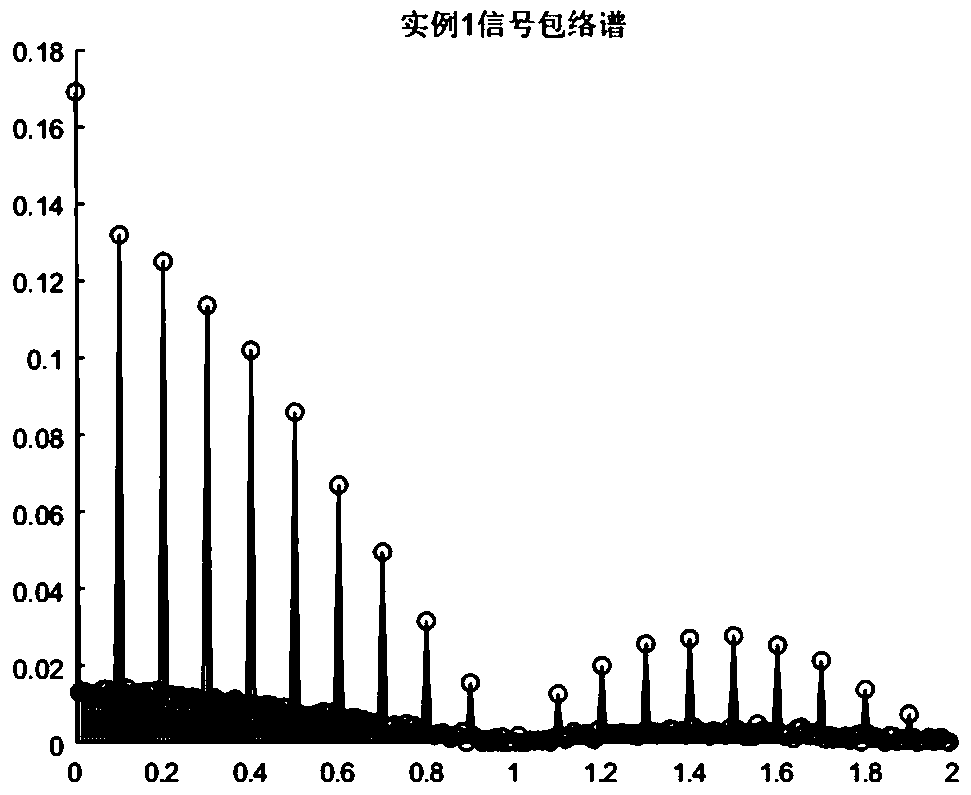
Pulse signal detection method based on multi-pulse envelope spectrum matching
ActiveCN110852201AGreat impactInhibition effectCharacter and pattern recognitionAcoustic wave reradiationPulse envelopeFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a pulse signal detection method based on multi-pulse envelope spectrum matching. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring a sampling data sequence of a to-be-processed pulse signal; 2, calculating discrete Fourier transform of a sampling data sequence; 3, generating filter parameters according to known pulse signal frequency parameters; 4, performing frequency domain filtering on the multi-pulse signal by utilizing the generated filter parameters; 5, extracting an envelope of the multi-pulse signal after frequency domain filtering; 6, calculating theamplitude spectrum of the envelope by using Fourier transform; and 7, carrying out detection judgment on the pulse signal by utilizing the multi-pulse signal envelope spectrum. According to the multi-pulse detection method, the pulse string signal envelope is extracted through frequency domain filtering, high signal-to-noise ratio gain can be obtained, the envelope spectrum of the multi-pulse signal is matched with the ideal periodic rectangular signal frequency spectrum, the matching result is detected and judged, the detection probability of the pulse signal can be improved, and the false alarm probability can be reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
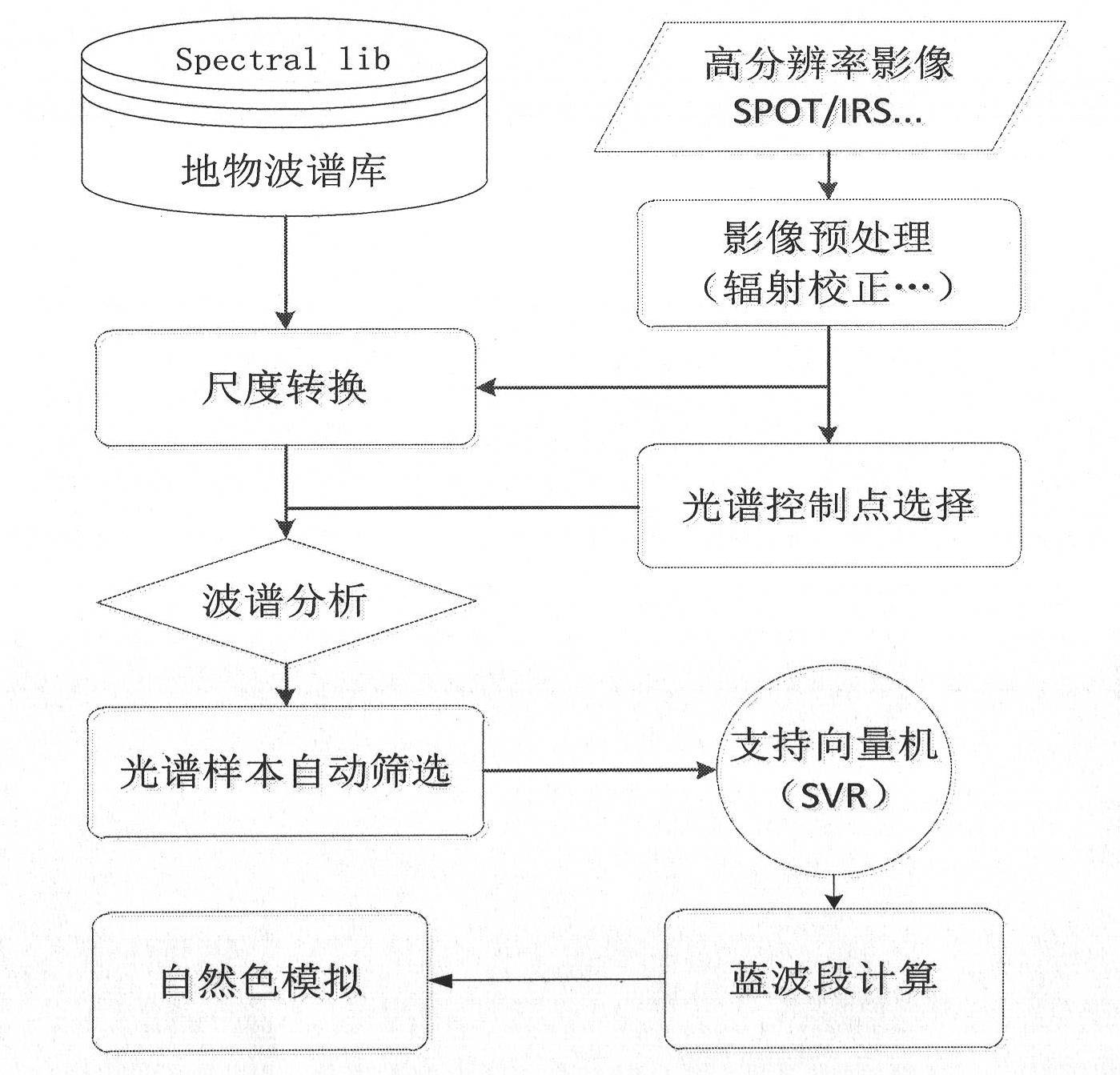
Automatic simulation method of natural-color products of high-space-resolution remote sensing images
InactiveCN102222238ARich Spectral InformationTrue colorCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageData pre-processing
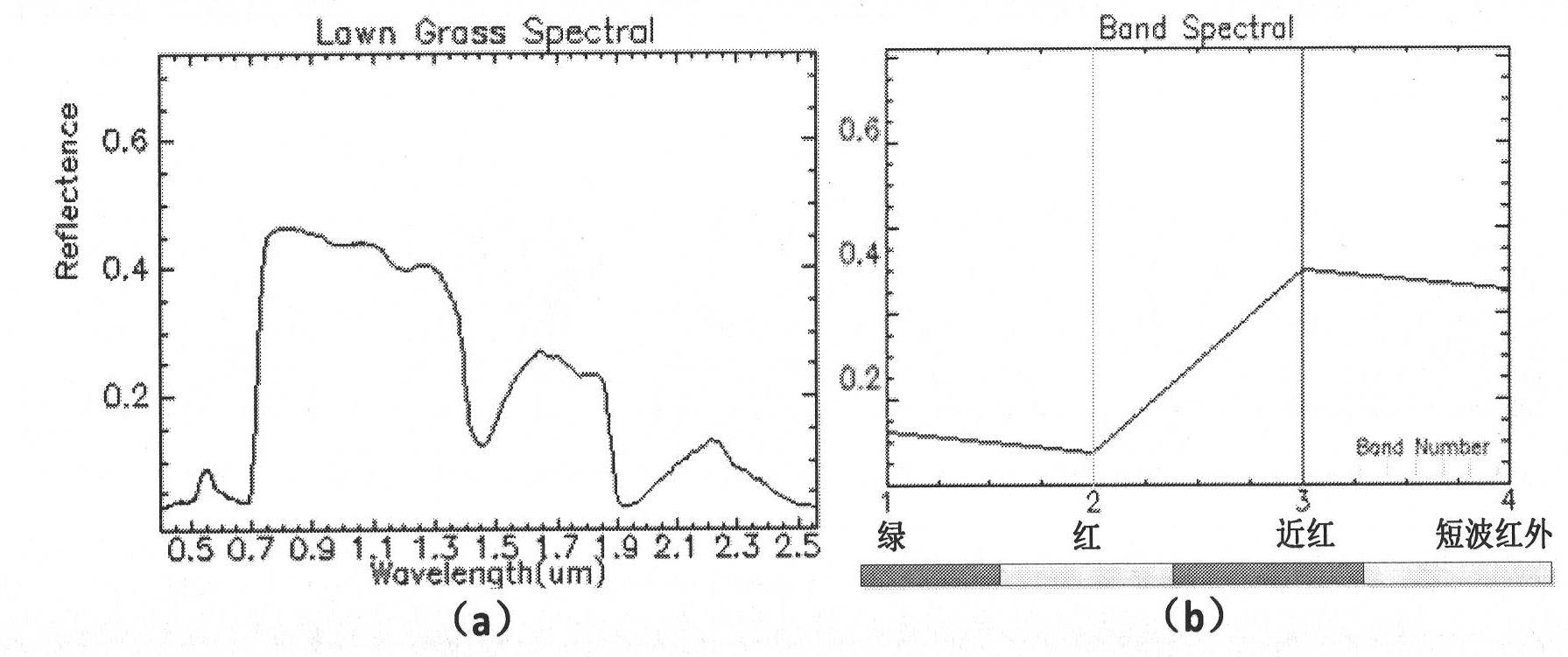
The invention provides a simulation method of natural colors of high-resolution remote sensing images based on field spectroscopic data; especially for high-resolution remote sensing images without blue-light waveband (such as SPOT, IRS and the like), the difficulty of natural color synthesis of the images can be solved by simulation of the blue-light wave band. The simulation method comprises the steps of: firstly, preprocessing the field object wave spectrum data according to wavelength bandwidth setting of images to be simulated and a spectrum response function; then selecting control points of spectrum samples automatically according to the cluster result of ISODATA (iterative self-organizing data) algorithm, and selecting spectrum candidate samples by a spectral matching algorithm; next, learning and training by using a support vector machine to construct a nonlinear relation model among the blue-light wavebands to be simulated and known wavebands; and finally, realizing calculation of the blue-light wavebands according to the nonlinear relation model (SVM). The simulated natural-color image product is natural in color tone and real in color, and can be used in multiple fields, the automatic simulation of the missing blue-light wavebands of the high-space-resolution remote sensing images and the making of natural-color images are realized and the workload of manual image adjustment is greatly reduced.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantum dot light-emitting thin film enhanced ultraviolet imaging detector
The invention discloses a quantum dot light-emitting thin film enhanced ultraviolet imaging detector, comprising a silicon-based surface array device of which the photosensitive area surface is of a pixel-level grid structure, a quantum dot light-emitting thin film and a micro-nano optical structure, wherein the micro-nano optical structure is used for reflecting visible light and increasing the permeability of ultraviolet radiation; the quantum dot light-emitting thin film is used for converting ultraviolet light to the visible light; the quantum dot light-emitting thin film is made of a quantum dot material or a quantum dot composite material; the silicon-based surface array device with the pixel-level grid structure is used for detecting the visible light emitted by the quantum dot light-emitting thin film; and the quantum dot light-emitting thin film and the silicon-based surface array device implement pixel-level coupling and spectral matching through the micro-nano optical structure. The detector disclosed by the invention has the advantages of adjustable and controllable response wave bands, relatively high sensitivity, fast response, large surface array, low cost and high image definition.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Active camouflage using real-time spectral matching
ActiveUS7199344B2Photometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationSpectral matchingElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:THE BOEING CO
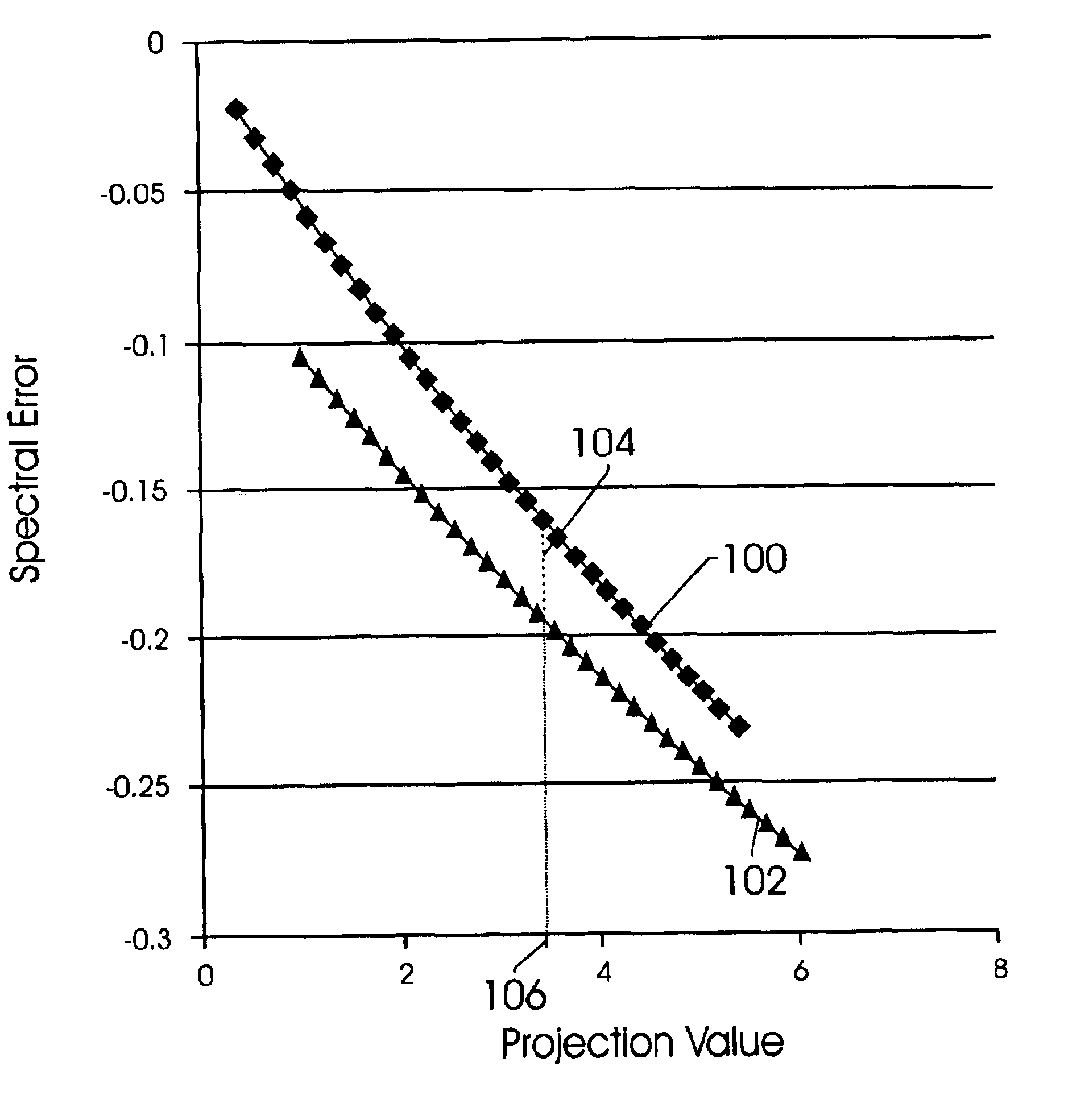
Spectral Matching Based Calibration
ActiveUS20130132021A1Improve measurement consistencyDifference can not be correctedRadiation pyrometryTesting/calibration apparatusSpectral matchingErrors and residuals
Methods and systems for calibrating system parameter values of a target inspection system are presented. Spectral Error Based Calibration (SEBC) increases consistency among inspection systems by minimizing differences in the spectral error among different inspection systems for a given specimen or set of specimens. The system parameter values are determined such that differences between a spectral error associated with a measurement of a specimen by the target inspection system and a spectral error associated with a measurement of the same specimen by a reference inspection system are minimized. In some examples, system parameter values are calibrated without modifying specimen parameters. Small inaccuracies in specimen parameter values have little effect on the calibration because the target system and the reference system both measure the same specimen or set of specimens. By performing SEBC over a set of specimens, the resulting calibration is robust to a wide range of specimens under test.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Multi-strategy image fusion method under compressed sensing framework
InactiveCN102096913AReduce data volumeReduce computational complexityImage enhancementFrequency spectrumComputation complexity
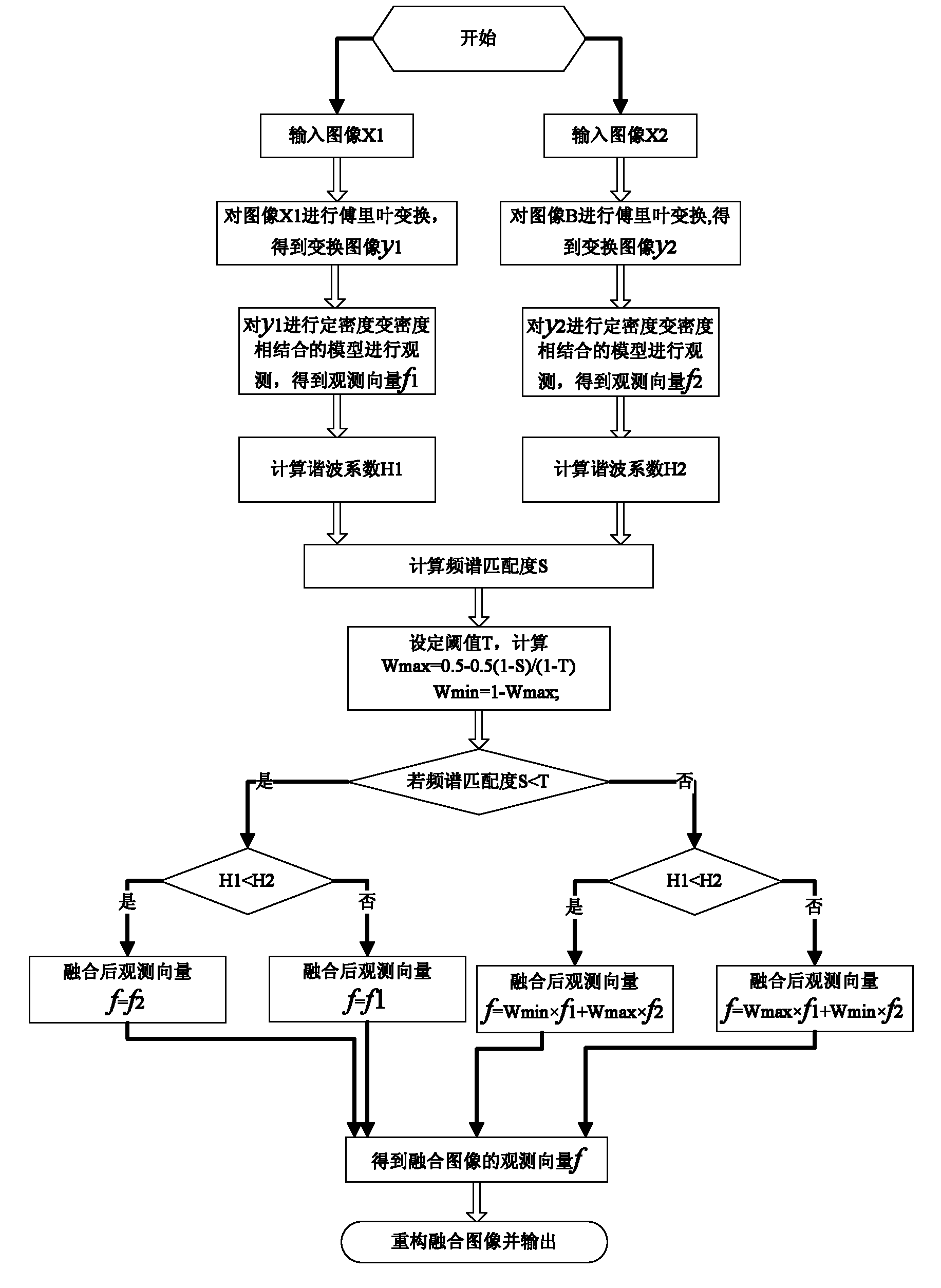
The invention discloses a multi-strategy image fusion method under a compressed sensing framework, mainly solving the problems of large calculated amount, high time complexity and large storage space of the traditional image fusion method. The multi-strategy image fusion method comprises the following implementation processes: inputting original images A and B and dividing the original images A and B into local images X1 and X2 of C*C in size; respectively carrying out Fourier transformation on X1 an X2 to obtain coefficient matrixes y1 and y2; observing y1 and y2 respectively by adopting a Fourier coefficient low-frequency full variable-density observing model to obtain observation vectors f1 and f2; calculating harmonic coefficients H1 and H2 and frequency-spectrum matching degree S according to f1 and f2; selecting a threshold T and calculating a weighting coefficient; comparing the weighting coefficient, the threshold and the frequency-spectrum matching degree to calculate a fused observation vector f; and iterating the observation vector f for twenty times by using a Split Bregman reconfiguration algorithm to finally obtain a required fused image. Compared with the traditional fusion method, the multi-strategy image fusion method provided by the invention has the advantages of low calculation complexity and good fusion effect, and can be used for video tracking, target recognition and computer vision.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
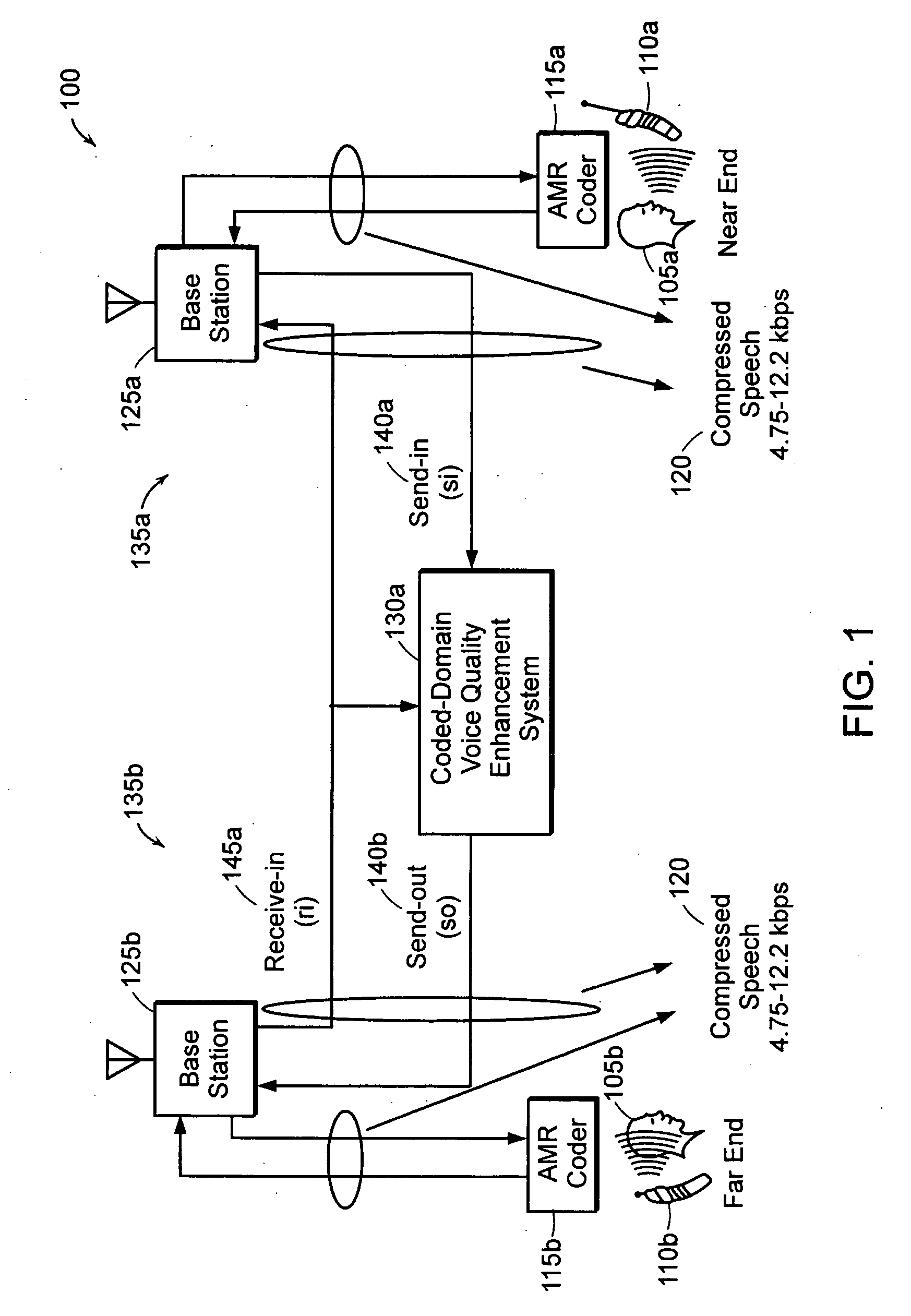
Method and apparatus for injecting comfort noise in a communications system
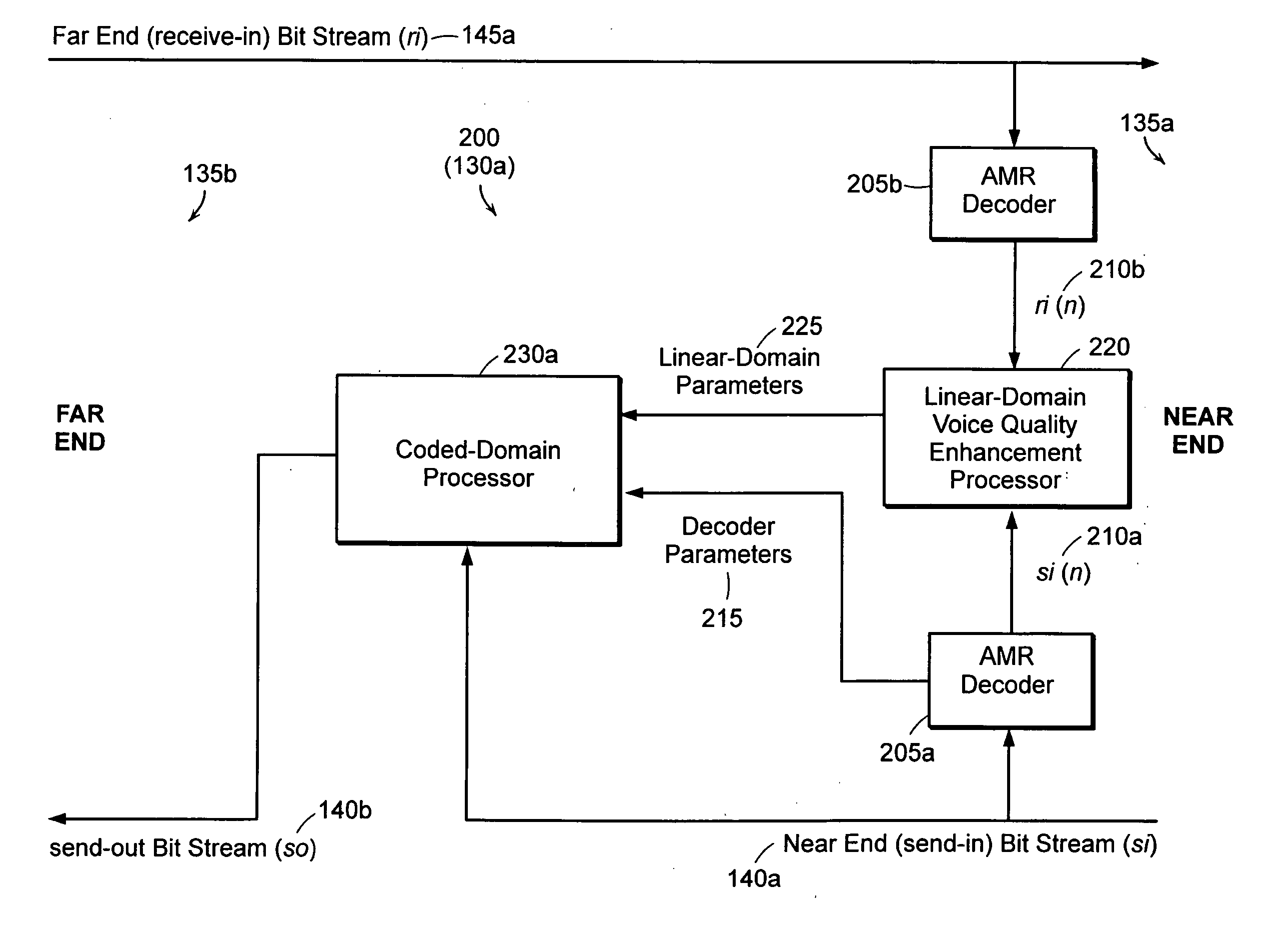
Background noise, optionally spectrally matched, is performed directly in a coded domain. A Coded Domain Spectrally Matched Noise Injection (CD-SMNI) system modifies at least one parameter of a first encoded signal, resulting in corresponding modified parameter(s). The CD-SMNI system replaces the parameter(s) of the first encoded signal with the modified parameter(s), resulting in a second encoded signal. In a decoded state, the second encoded signal approximates background noise in the first encoded signal in a decoded state. Thus, the first encoded signal does not have to go through intermediate decode / re-encode processes, which can degrade overall speech quality. Computational resources required for a complete re-encoding are not needed. Overall delay of the system is minimized. The CD-SMNI system can be used in any network in which signals are communicated in a coded domain, such as a Third Generation (3G) wireless network.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Light conversion film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a light conversion film which is characterized by comprising a film base body, a red light conversion agent and a first addition agent, wherein the weight of the red light conversion agent is 0.1-10% of the weight of the film; the weight of the first addition agent is 0.1%-10% of the weight of the film; the balance is the film base body; and a composition general formula of the red light conversion agent is Cal-xMxS:TM, wherein the x is less than 1 and is larger than or equal to 0, the M is one kind or more kinds of Mg, Ba, Sr, Zn, Cd, and Hg, and the TM is one kind or more kinds of Sm, Ce, Y, Gd, La, Pr, Eu, Cu, and Mn. The light conversion agent is mixed into a film especially an agricultural film, the film has light conversion effects, and application of the light conversion agent is convenient. The light conversion film is good in spectral matching with plant photosynthesis. A planting method that the light conversion film is used and meanwhile carbon dioxide is added is used, great effects on plant production and quality increase are achieved, diseases, pests, chemical pesticides do not exist, quality is good, the yield and others are increased, effects are remarkable, high economic value is provided, and a large-scale popularization prospect is achieved.
Owner:FOSHAN ONMILLION NANO MATERIALS
Photoetching projection objective wave aberration detection method based on space image frequency spectrum
ActiveCN102236268AAvoid lossSimplify the centering processPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusFrequency spectrumPrincipal component analysis
The invention relates to a photoetching projection objective wave aberration detection method based on a space image frequency spectrum, which is characterized in that the space image centering and the wave aberration solving are carried out through frequency spectrum matching. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: 1) computing the simulation space images corresponding to different Zernike aberration combinations by utilizing photoetching simulation software PROLITH and carrying out the Fourier transform on each space image; 2) carrying out the principal component analysis on simulation space image frequency spectrum sets and establishing a regression matrix between the principal component coefficients and the Zernike coefficients through linear regression analysis; 3) operating the space image acquisition program of a photoetching machine and finishing the acquisition of actual-measurement space images; 4) centering the actual-measurement space images by utilizing a frequency spectrum centering method and modifying the frequency spectrum of the actual-measurement space images into the frequency spectrum corresponding to ideal position space images; and 5) computing the wave aberration of a projection objective. The photoetching projection objective wave aberration detection method provided by the invention can avoid the errors caused by space image difference values, simplifies the testing procedures and improves the testing accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
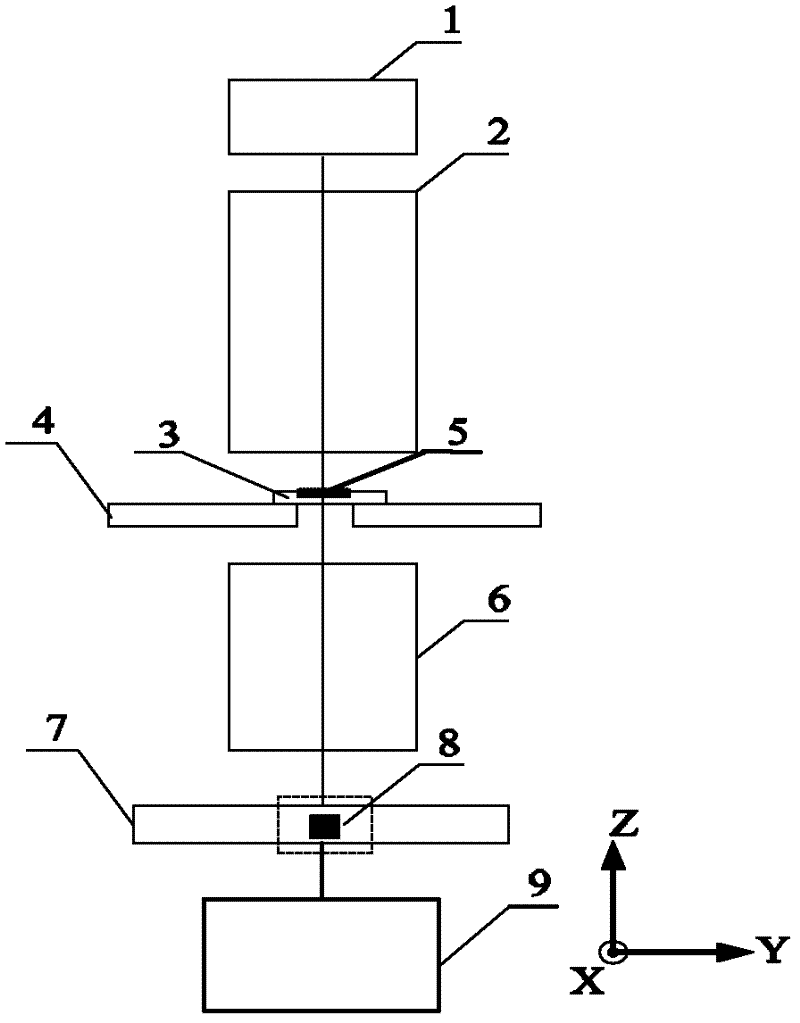
Method and apparatus for correcting bone induced spectral artifacts
InactiveUS6904120B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX ray spectraSpectral matching
The present technique provides for the estimation and correction of bone induced spectral (BIS) artifacts. Spectral matching is employed to approximate the incident X-ray spectrum attenuated by bone and water with an X-ray spectrum attenuated by water alone. A table can be built to express the amount in apparent projection value shift for objects containing bone and water compared with water-like object when their corresponding normalized spectra match. The BIS error may thereby be determined from existing spectral error data obtained from spectral calibration. A corresponding correction factor may be determined from the shift value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
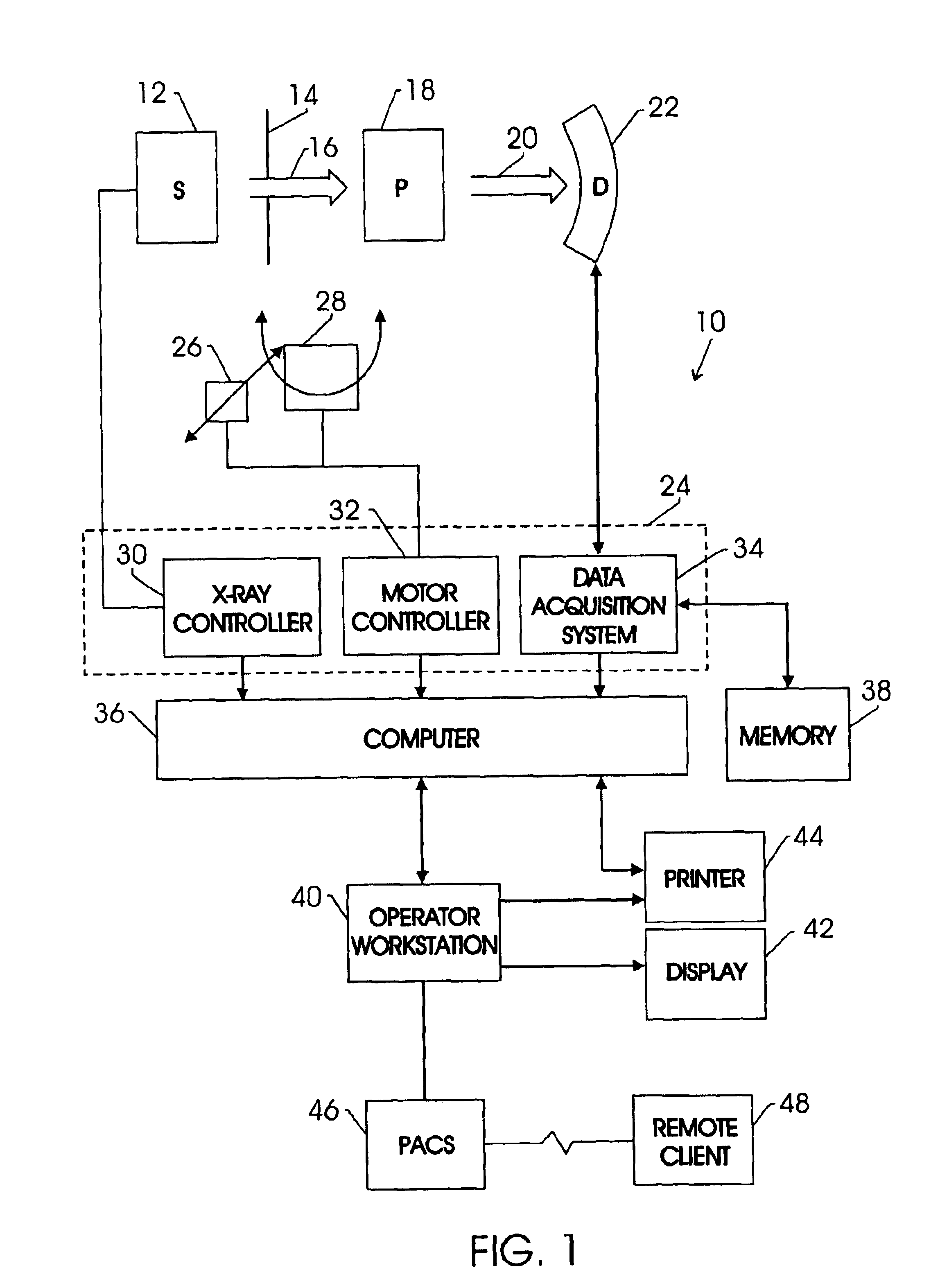
Remote emissions sensing system and method incorporating spectral matching by data interpolation
InactiveUS7400398B2Improve matchRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric discharge tubesSpectral matchingLength wave
A system and method for correcting for “wavelength drift” in an RES system. One advantage provided by the invention includes the ability to correct for offset amounts of “wavelength drift” that are not divisible by an integer number of pixels (e.g., fraction pixel offset amounts) in an optical detector used in the RES system. Correction of fractional pixel offset amounts may enhance spectral matching, enable substantially continuous calibration of an RES system, and / or other benefits.
Owner:ENVIROTEST SYST HLDG CORP
Double-pass absorption spectral matching laser amplifier and amplifying method thereof
InactiveCN103560387AEfficient conversionOptical resonator shape and constructionAudio power amplifierCoupling
The invention discloses a double-pass absorption spectral matching laser amplifier and an amplifying method thereof. The laser amplifier comprises a pump light focusing lens, a double-color coupling mirror, a polarization selecting mirror, a gain medium, a curve face double-color coupling mirror, a one fourth wave plate, a curve face total reflection mirror, a seed laser focusing lens and a total reflection mirror, wherein the polarization selecting mirror, the gain medium, the curve face double-color coupling mirror, the one-fourth wave plate and the curve face total reflection mirror are sequentially distributed on the same optical axis, and the seed laser focusing lens and the total reflection mirror are arranged in the direction parallel to the optical axis. Polarization seed laser and pump light are respectively emitted into the focus lens and enter to optical structure to be subjected to double-pass absorption and laser amplification, and after the seed laser is amplified, output laser with different seed laser polarization states is output. The amplifier and the amplifying method effectively utilize the pump light, and light-laser converting efficiency is improved.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Method and apparatus for correcting bone induced spectral artifacts
InactiveUS20050002484A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-raySpectral matching
The present technique provides for the estimation and correction of bone induced spectral (BIS) artifacts. Spectral matching is employed to approximate the incident X-ray spectrum attenuated by bone and water with an X-ray spectrum attenuated by water alone. A table can be built to express the amount in apparent projection value shift for objects containing bone and water compared with water-like object when their corresponding normalized spectra match. The BIS error may thereby be determined from existing spectral error data obtained from spectral calibration. A corresponding correction factor may be determined from the shift value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for monitoring irrigation area of irrigation area based on high-resolution satellite data
ActiveCN110288647AHigh precisionEfficient extractionImage enhancementImage analysisSensing dataSatellite data
The invention discloses a method for monitoring the irrigation area of an irrigation area based on high-resolution satellite data. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, obtaining and preprocessing satellite remote sensing data; step 2, actually measuring sample point data; step 3, extracting an end member spectrum according to the real sample point data obtained in the step 2; step 4, calculating spectral similarity by adopting a statistical algorithm and a spectral waveform feature algorithm in a spectral matching method, and quantitatively analyzing the matching degree of the end member spectrum of the main crops in the research area and the target spectrum through three indexes; and step 5, calculating an SSV segmentation threshold value by adopting an OTSU adaptive threshold value algorithm to judge whether the irrigation area is an irrigation area, and if the SSV segmentation threshold value is smaller than the SSV segmentation threshold value, identifying the irrigation area spatial distribution condition of the research area, and finally obtaining the irrigation area range. The method is suitable for high-resolution satellite remote sensing data, meets the requirement for extracting small plot irrigation information, and can improve the accuracy of an irrigation area monitoring result.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Rapid automatic target compound confirmation using deconvolution and spectral matching
ActiveUS7117103B2Component separationSpecial data processing applicationsSpectral matchingDeconvolution
A method for automatically verifying the existence of a target compound comprises generating a total ion chromatogram. The total ion chromatogram comprises a plurality of peaks, each peak representing one or more compounds in a sample matrix, each peak comprising at least two compounds. The method also comprises deconvoluting each peak to isolate each target compound present in the peak, and automatically verifying the identity of each target compound against a target compound library.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Hyperspectral curve matching method based on absorption peak characteristic
The present invention provides a hyperspectral curve matching method based on an absorption peak characteristic. Firstly, a hyperspectral curve is subjected to enveloping line elimination and a spectral characteristic parameter matrix is extracted, then the matching vector of an absorption peak is searched one by one according to the cosine distance-Euclidean distance between a standard characteristic parameter matrix and each vector of a characteristic parameter matrix to be measured, and then the spectral matching is carried out according to a selected absorption peak characteristic parameter matrix. According to the method, an optimal characteristic parameter vector can be searched, thus the selection of the absorption peak is realized, and after the characteristic parameter matrix of the selected absorption peak is used to carry out hyperspectral matching, the a matched error is reduced to a certain extent.
Owner:奥谱天成(厦门)光电有限公司
Target spectral matching method
ActiveCN104573732AUnaffected by fixed measurement deviationsImprove noise immunityCharacter and pattern recognitionSystem matrixSpectral matching
The invention relates to a target spectral matching method. The target spectral matching method sequentially comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring a reference spectrum A={a1, a2, ..., an|ai>= 0, i epsilon 1, ...n} <T>, wherein ai is the spectral value of the reference spectrum A, n is the band number of the reference spectrum, and the band number of a test spectrum B is equal to that of the reference spectrum; 2, building a vector C={c1, c2, ..., cn|ci is not equal to 0, ci=c1, i epsilon 1, ...n} <T>, wherein ci is a real number constant; 3, building a linear equation system matrix M: M=|A C| or M=|C A|; 4, building a linear equation system: Mx=B; 5, solving a linear equation system: x=(M<T>M)<-1>M<T>B, wherein the solution corresponding to A is the content of the reference spectrum in the test spectrum B or the similarity degree of the test spectrum and the reference spectrum; the solution corresponding to C is the noise mean value and the system droop in the test spectrum. According to the invention, the calculation result is free from limitation on the value range, and the value is subject to linear variation according to the content of the reference spectrum in a target spectrum. The target spectral matching method has stronger anti-noise performance and the calculation result is free from influence of gaussian noise.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com