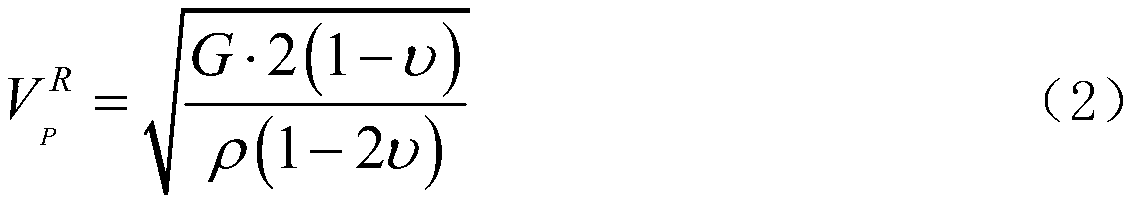Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
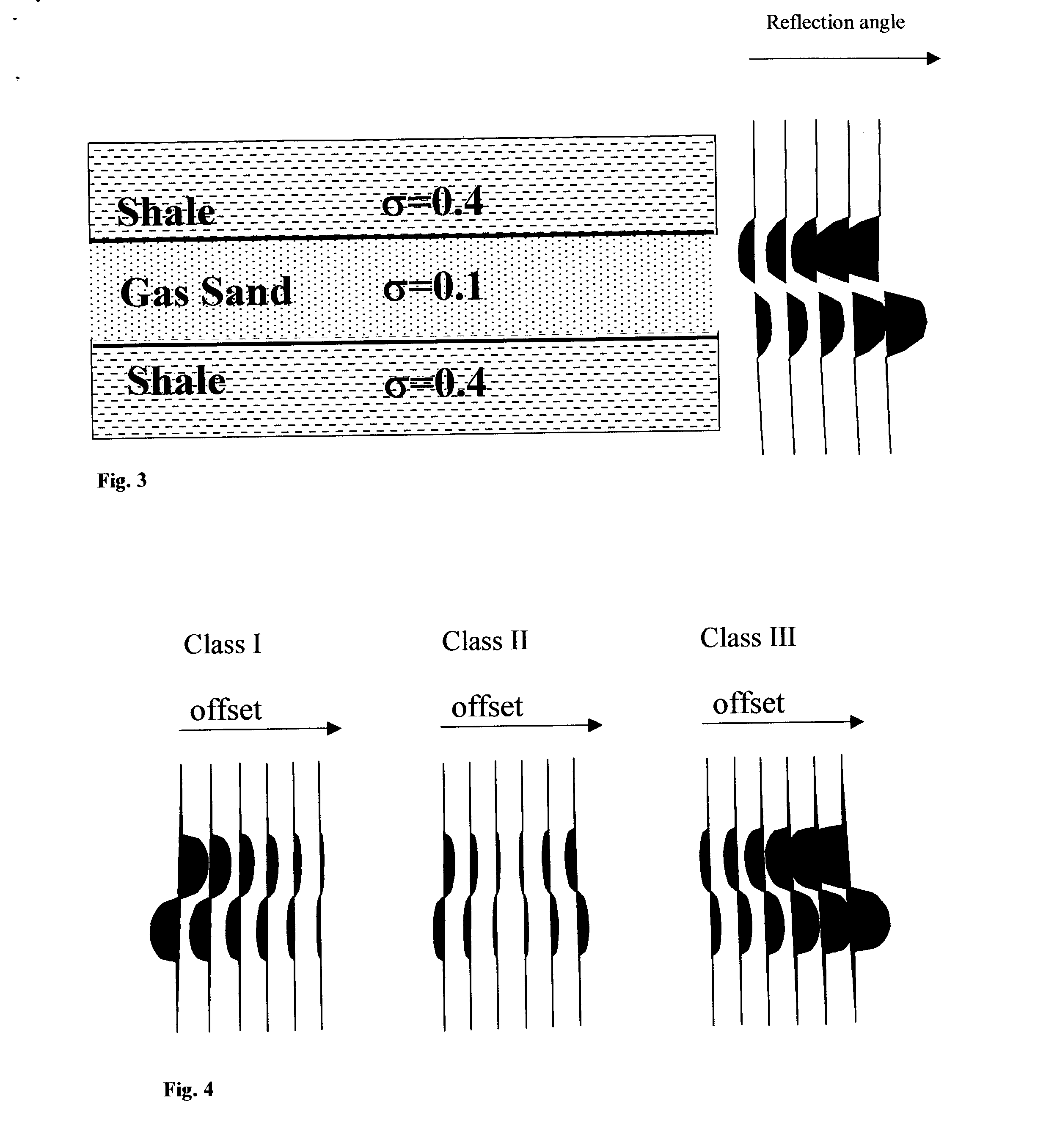
137 results about "Seismic analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Seismic analysis is a subset of structural analysis and is the calculation of the response of a building (or nonbuilding) structure to earthquakes. It is part of the process of structural design, earthquake engineering or structural assessment and retrofit (see structural engineering) in regions where earthquakes are prevalent.
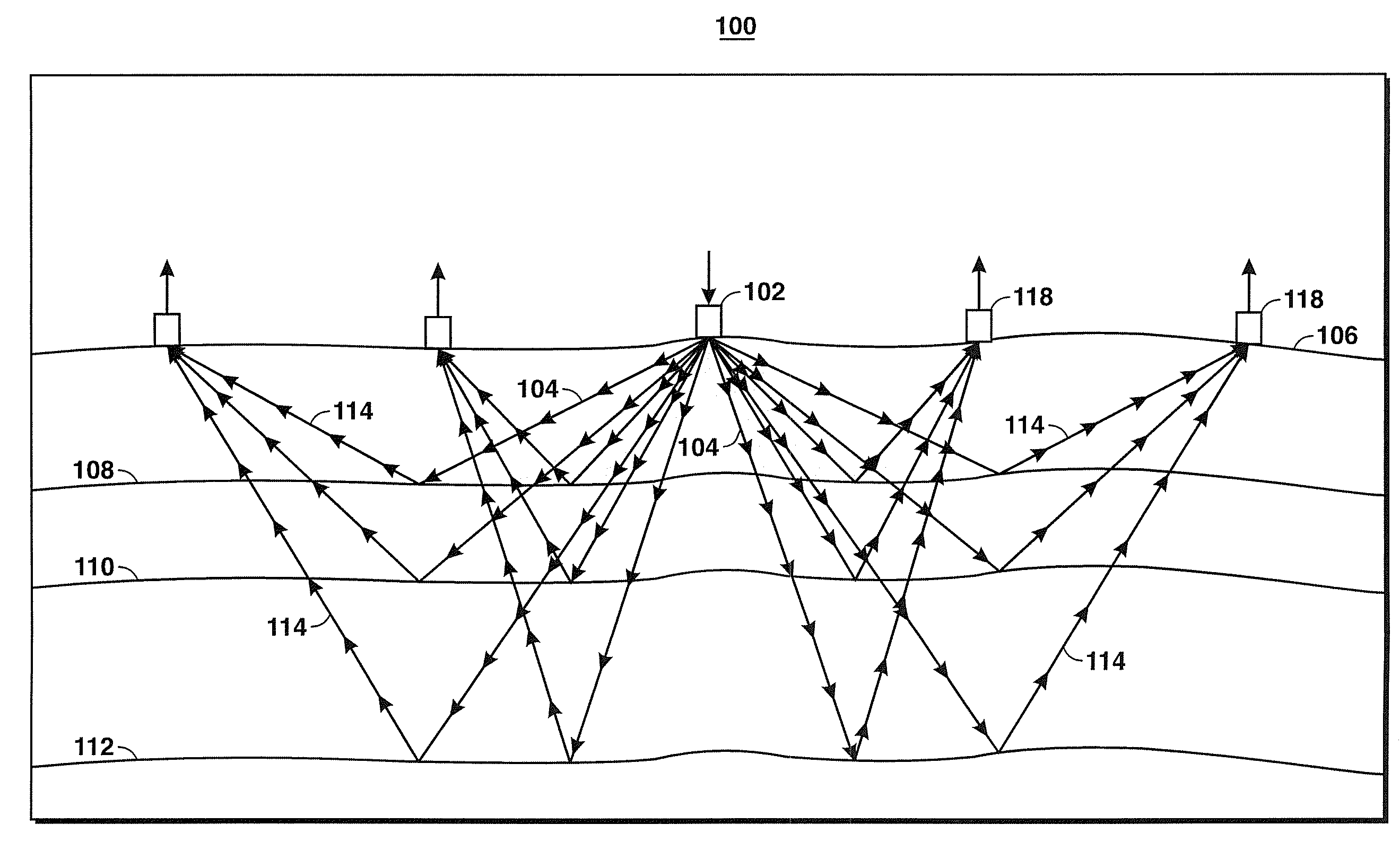
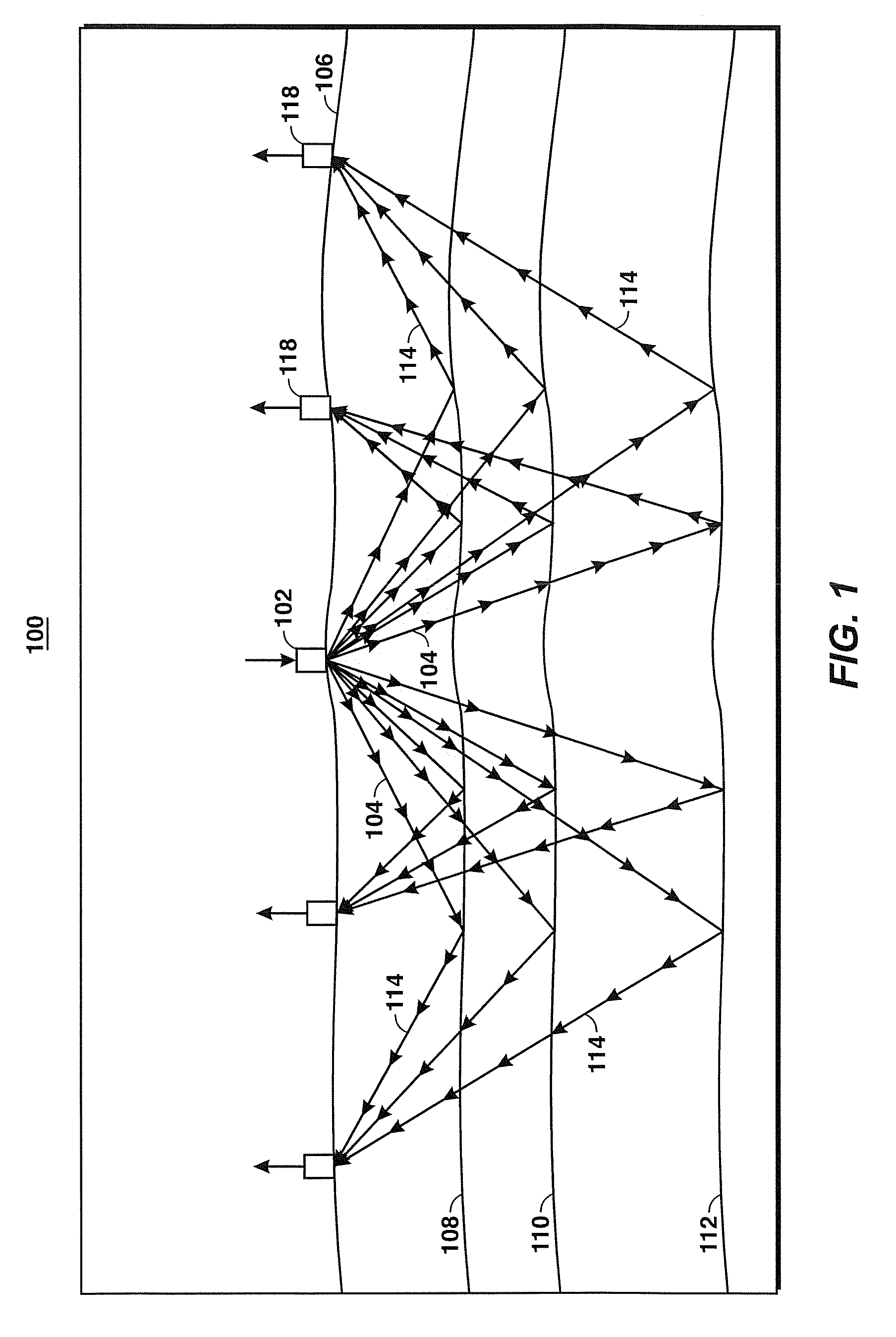
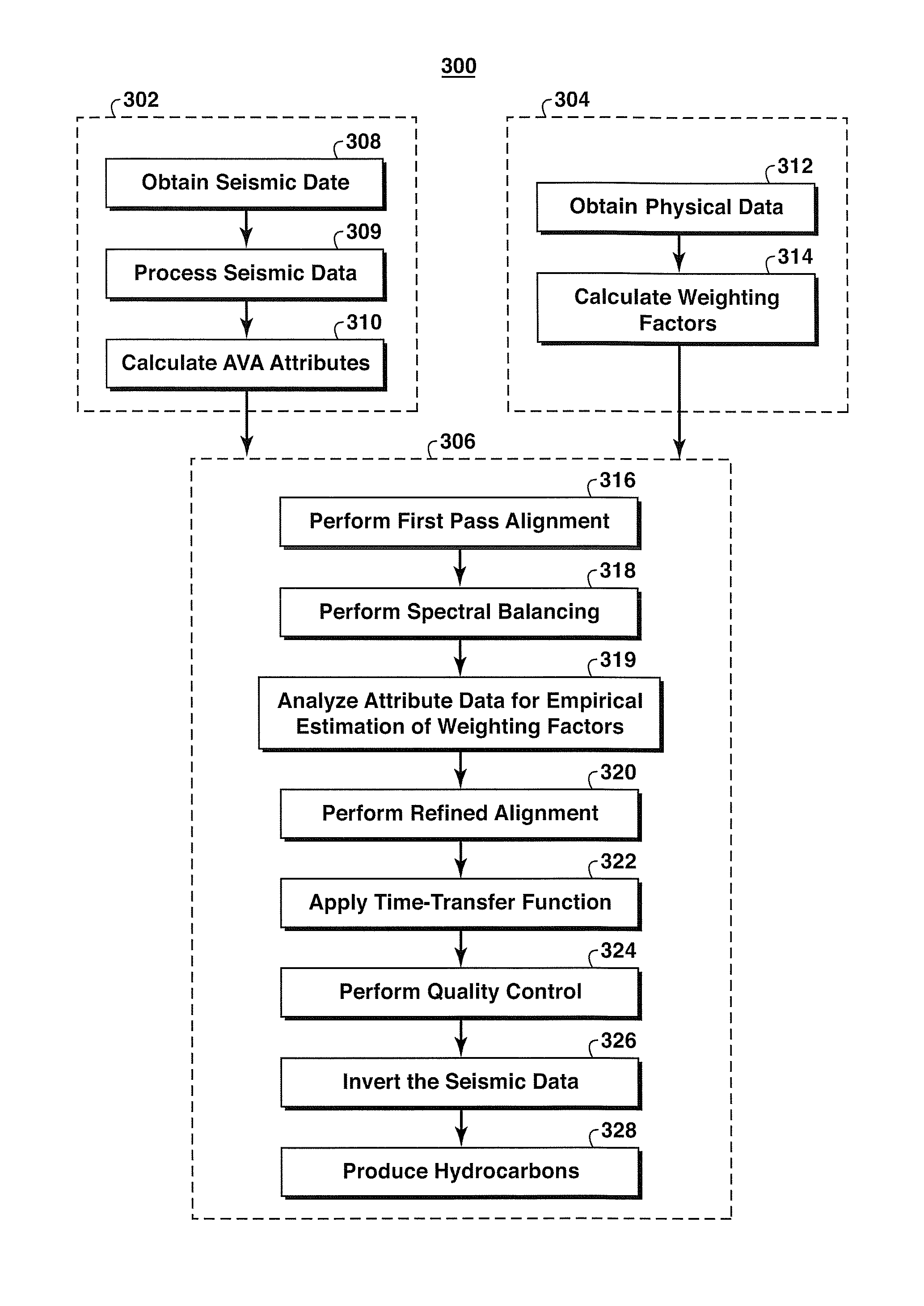
Using Seismic Attributes for Data Alignment and Seismic Inversion In Joint PP/PS Seismic Analysis
Method for aligning converted wave seismic reflection data (PS data) with conventional PP seismic reflection data so that both data types may be used to more accurately image the subsurface for hydrocarbon exploration or field development. Amplitude vs. angle (AVA) or amplitude vs. offset (AVO) attributes of PP and PS seismic data are identified and defined, which attributes are theoretically expected to be in phase and optimize seismic resolution in the data. In one embodiment of the invention, such attributes are calculated (310), then the same horizons are identified in a series of PP attributes and in a series of PS attributes, then the second series is aligned with the first at the horizon locations (316, 320), then a time transfer function is generated and applied to the PS mode data (322), and the aligned joint-mode data are inverted (326) using, for example, AVA attributes.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Dip guided full waveform inversion
InactiveUS20110131020A1Reduce difficultyLow costSeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationImaging qualityFull waveform
A method of determining seismic data velocity models comprising dip-guided full waveform inversion that obtains a better velocity model with less computational requirements. DG-FWI quickly converges to provide a better image, obtains better amplitudes, and relies less on lower frequencies. Improved image quality allows detailed seismic analyses, accurate identification of lithological features, and imaging near artifacts and other anomalies.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Method and system for utilizing string-length ratio in seismic analysis
InactiveUS20050288863A1Facilitates visual recognitionSimple processCharacter and pattern recognitionSeismic signal processingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesVisual recognition
An apparatus and method for analyzing known data, storing the known data in a pattern database (“PDB”) as a template is provided. Additional methods are provided for comparing new data against the templates in the PDB. The data is stored in such a way as to facilitate the visual recognition of desired patterns or indicia indicating the presence of a desired or undesired feature within the new data. Data may be analyzed as fragments, and the characteristics of various fragments, such as sting length, may be calculated and compared to other indicia to indicate the presence or absence of a particular substance, such as a hydrocarbon. The apparatus and method is applicable to a variety of applications where large amounts of information are generated, and / or if the data exhibits fractal or chaotic attributes.
Owner:CHROMA ENERGY
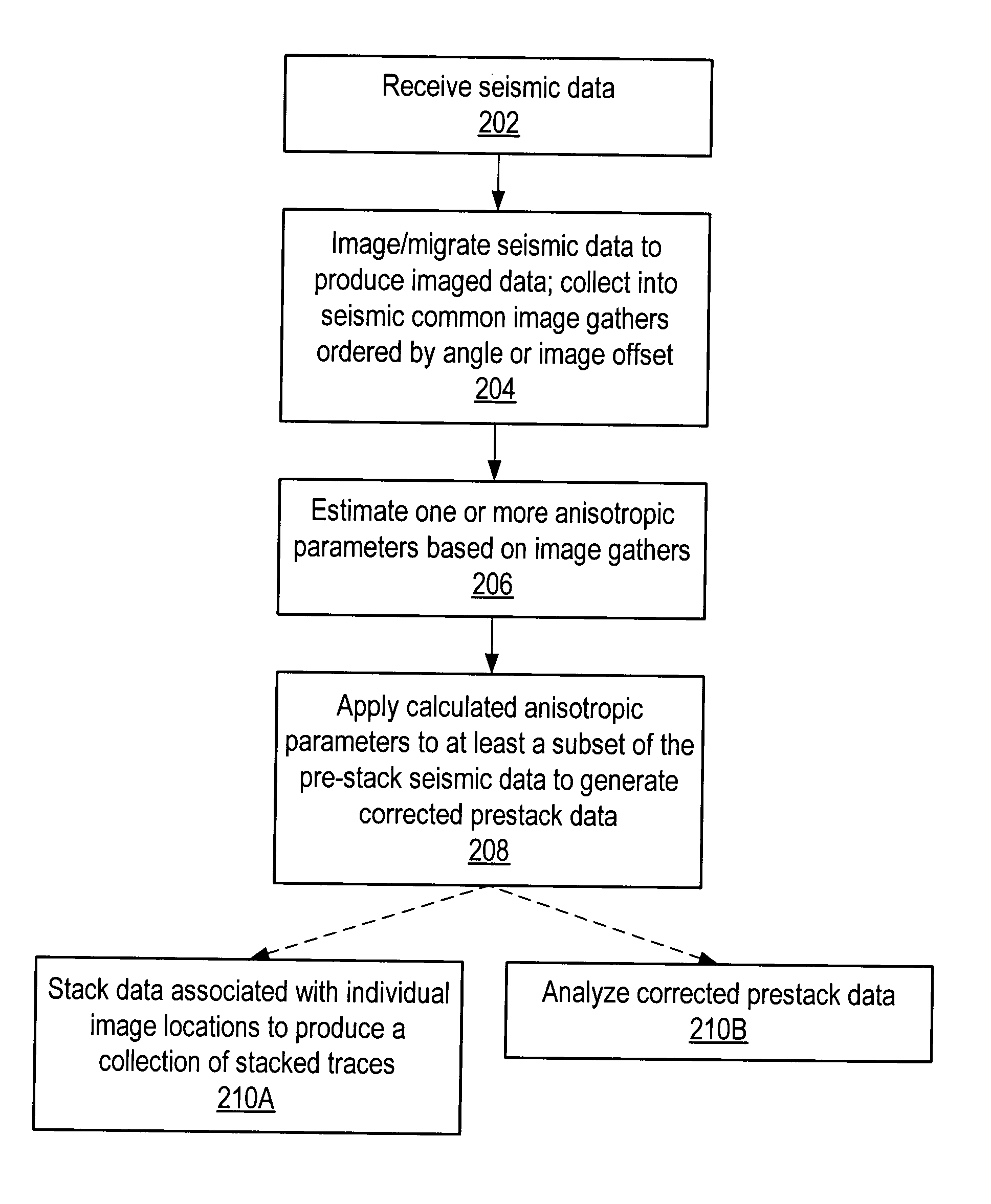
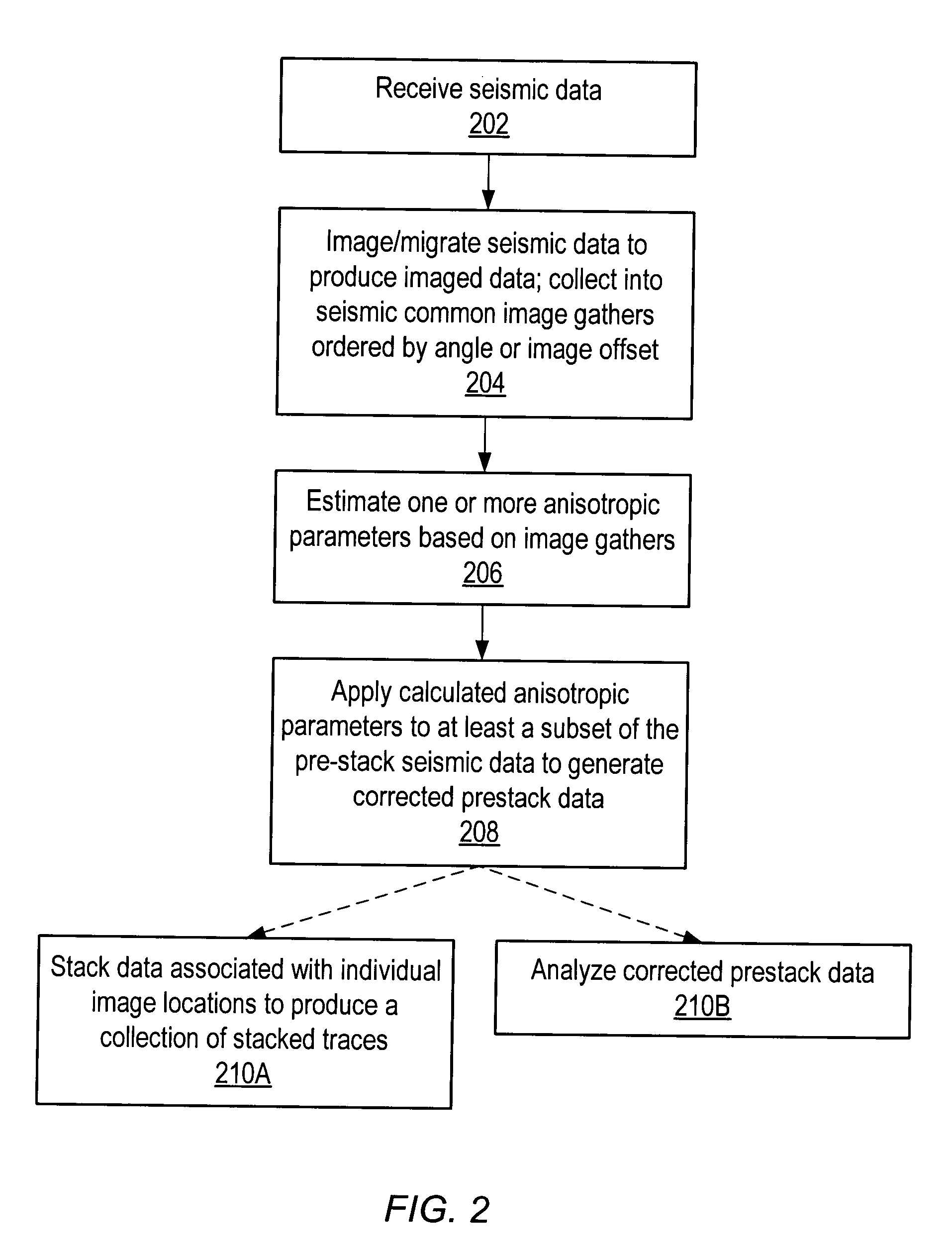
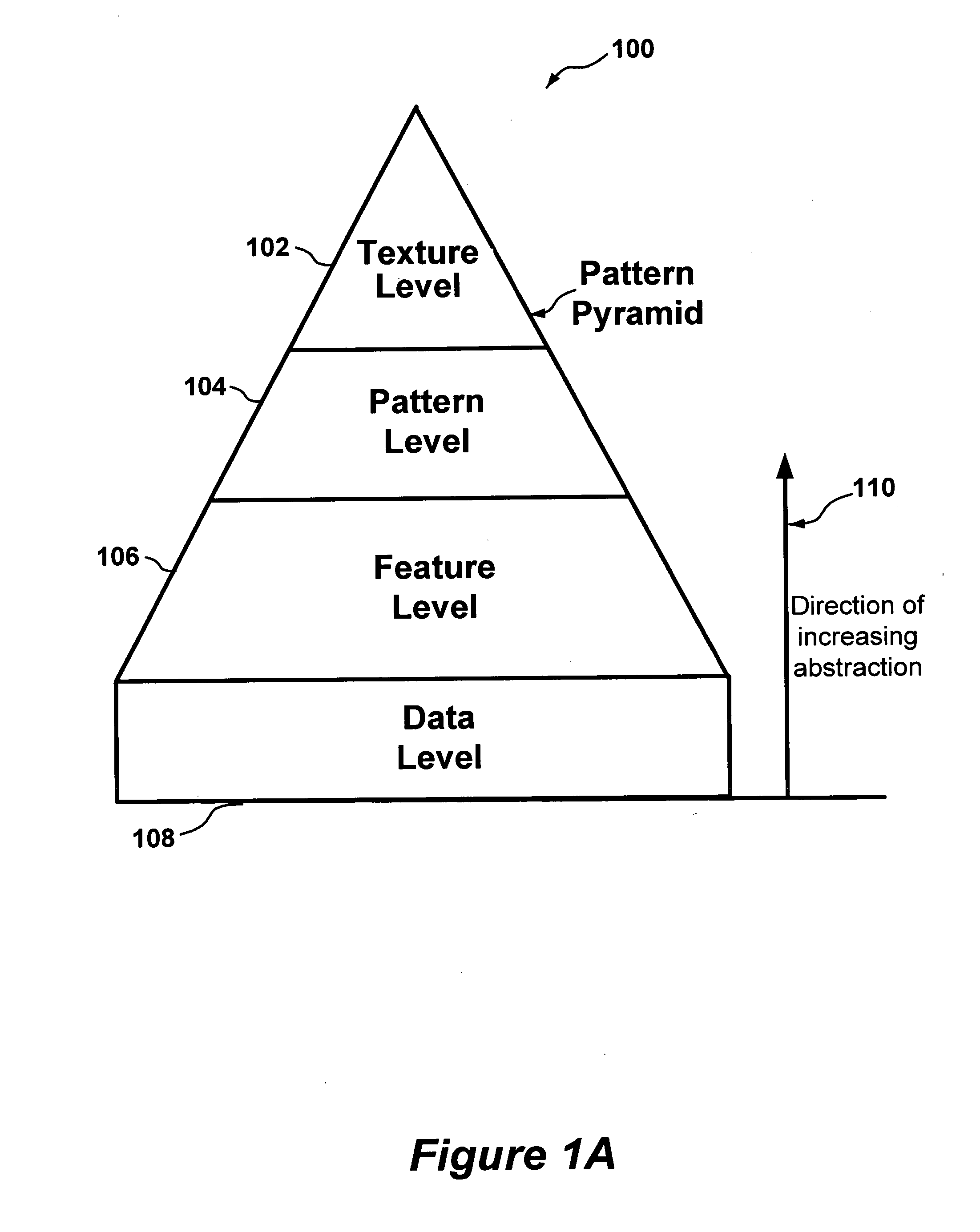
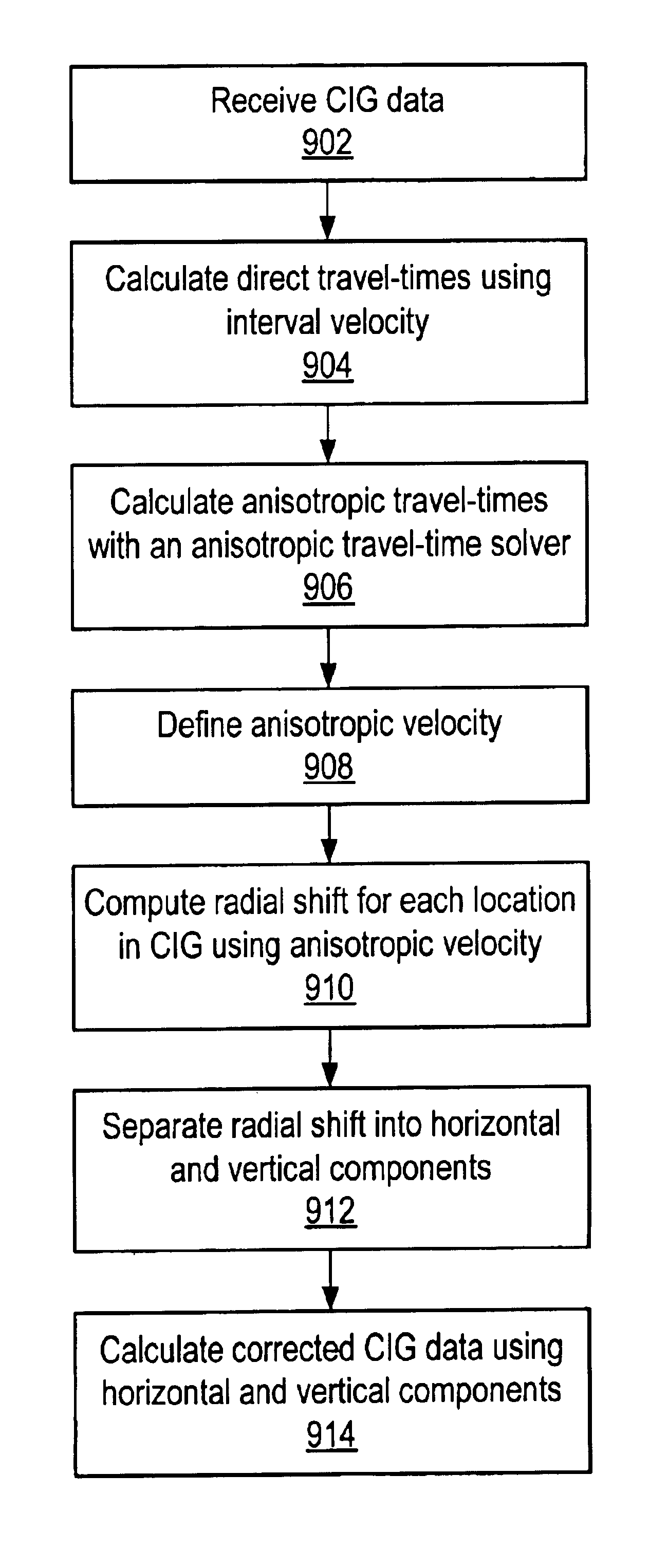
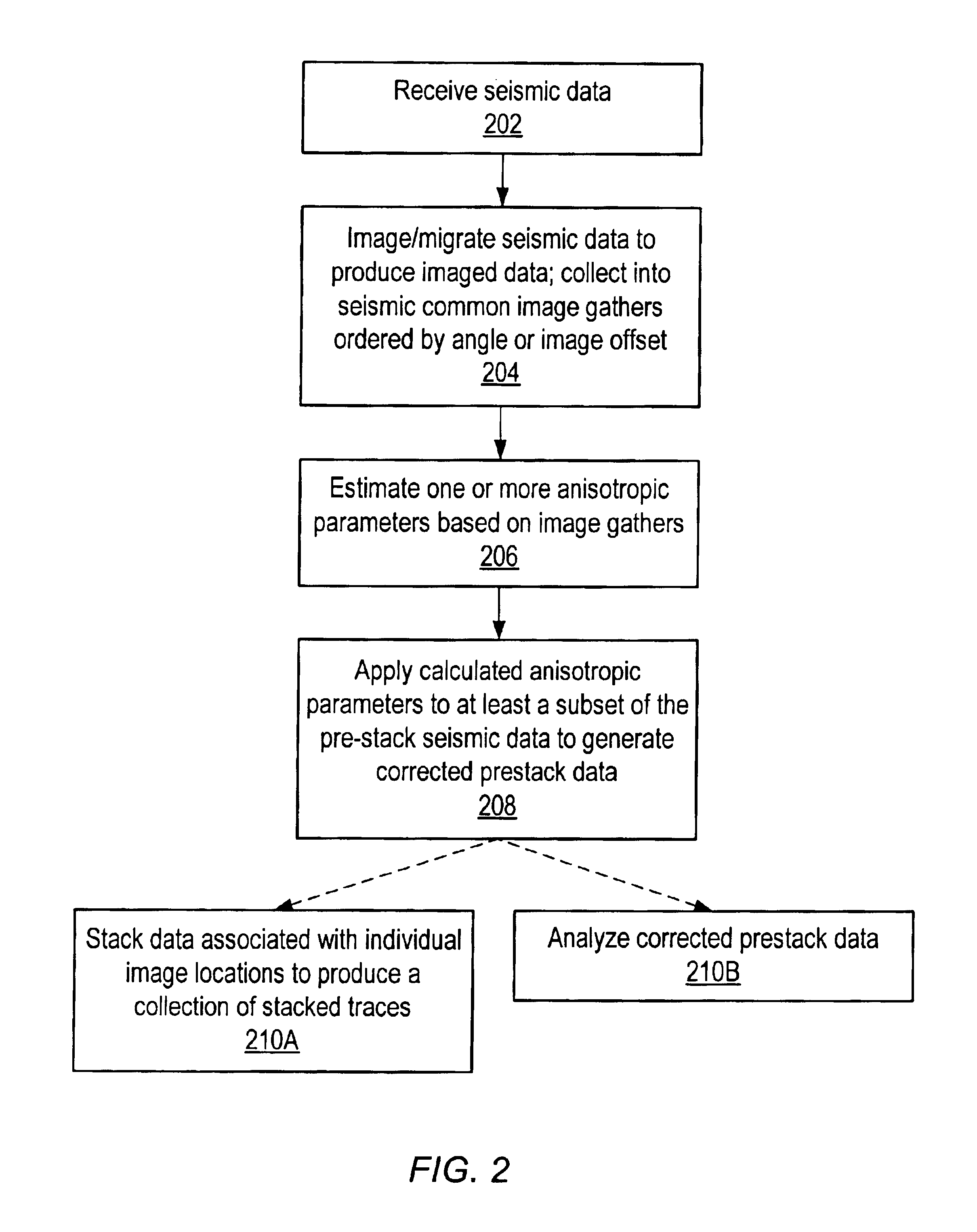
Seismic analysis using post-imaging seismic anisotropy corrections
ActiveUS20040093163A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic anisotropySeismic analysis
System and method for performing anisotropy corrections of post-imaging seismic data for a subsurface formation. The method may receive seismic data, preferably pre-stack seismic data comprising a plurality of traces, e.g., collected from a plurality of source and receiver locations. The seismic data may be imaged / migrated to produce imaged seismic data, which is organized into an arrangement that preserves aspects of the relative seismic propagation angle in the subsurface. One or more anisotropic parameters and corresponding corrections may be determined by analyzing the organized imaged seismic data. The determined parameters or corrections may be used to correct at least a subset of the imaged seismic data, thereby producing corrected seismic data which is useable in analyzing the formation. The corrected data may then optionally be stacked to produce a collection of corrected stacked traces, and / or analyzed as desired. The pre-stack data and / or the corrected seismic data may optionally be displayed.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Method and system for trace aligned and trace non-aligned pattern statistical calculation in seismic analysis
InactiveUS20060184488A1Facilitates visual recognitionComparison process is enhancedCharacter and pattern recognitionSeismic signal processingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesVisual recognition
An apparatus and method for analyzing known data, storing the known data in a pattern database (“PDB”) as a template is provided. Additional methods are provided for comparing new data against the templates in the PDB. The data is stored in such a way as to facilitate the visual recognition of desired patterns or indicia indicating the presence of a desired or undesired feature within the new data. Data may be analyzed as fragments, and the characteristics of various fragments, such as string length, may be calculated and compared to other indicia to indicate the presence or absence of a particular substance, such as a hydrocarbon. The length and / or character of each fragment are a product of the cutting criteria in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Modifying the cutting criteria can have a beneficial effect on the results of the analysis and / or in the amount of time necessary to achieve useful results. The apparatus and method is applicable to a variety of applications where large amounts of information are generated, and / or if the data exhibits fractal or chaotic attributes.
Owner:IKON SCI AMERICAS
Seismic analysis using post-imaging seismic anisotropy corrections
InactiveUS6904368B2The result is accuratePrecise positioningSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic anisotropySeismic analysis
System and method for performing anisotropy corrections of post-imaging seismic data for a subsurface formation. The method may receive seismic data, preferably pre-stack seismic data comprising a plurality of traces, e.g., collected from a plurality of source and receiver locations. The seismic data may be imaged / migrated to produce imaged seismic data, which is organized into an arrangement that preserves aspects of the relative seismic propagation angle in the subsurface. One or more anisotropic parameters and corresponding corrections may be determined by analyzing the organized imaged seismic data. The determined parameters or corrections may be used to correct at least a subset of the imaged seismic data, thereby producing corrected seismic data which is useable in analyzing the formation. The corrected data may then optionally be stacked to produce a collection of corrected stacked traces, and / or analyzed as desired. The pre-stack data and / or the corrected seismic data may optionally be displayed.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
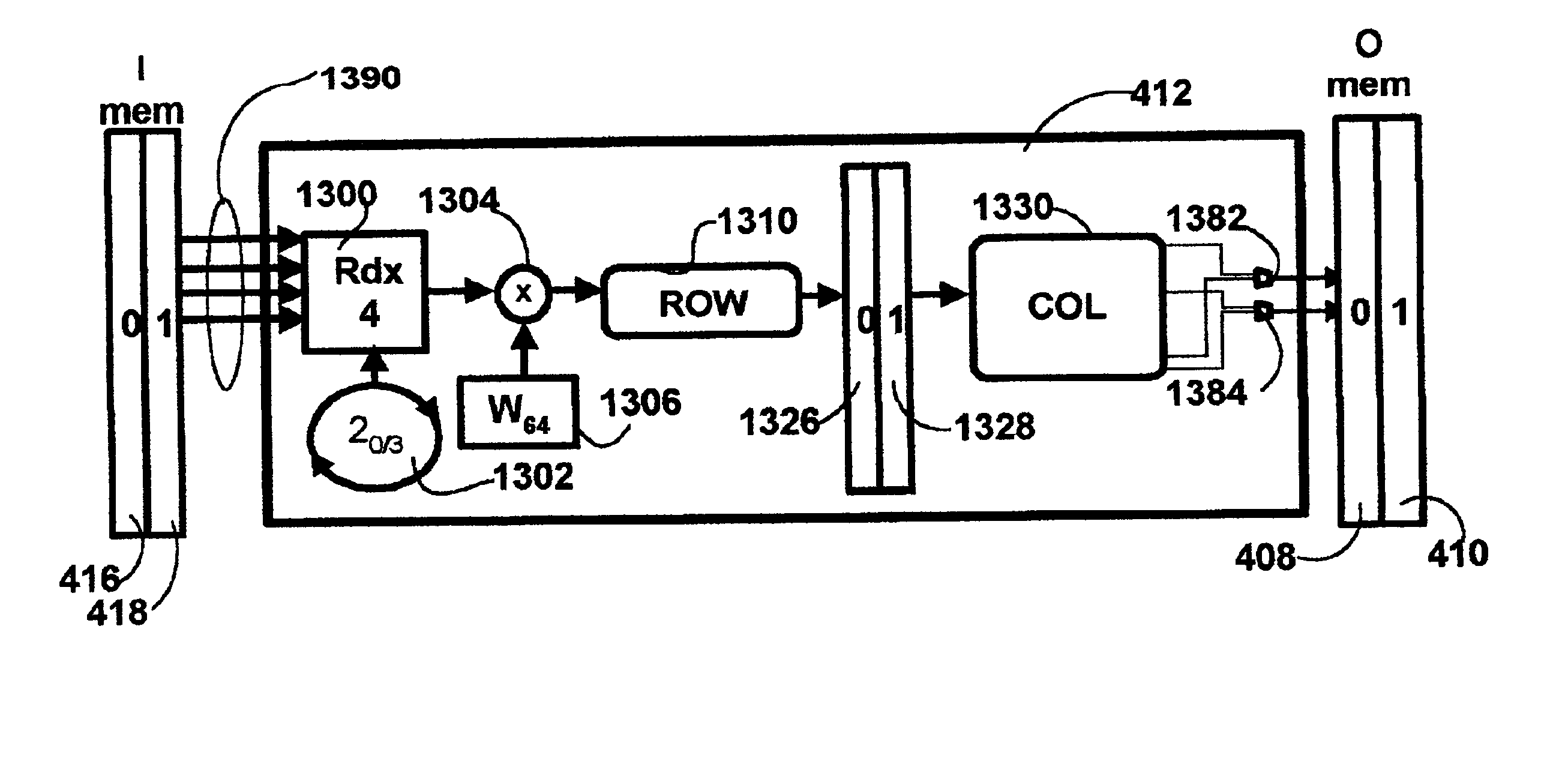
Method and apparatus for a X-DSL communication processor
InactiveUS6940807B1Rapid responseModulated-carrier systemsPower distribution line transmissionComputer hardwareExtensibility
The current invention provides a DSP which accommodates multiple current X-DSL protocols and is further configurable to support future protocols. The DSP is implemented with shared and dedicated hardware components on both the transmit and receive paths. The DSP implements both the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) portions across a wide range of sample sizes and X-DSL protocols. Multiple channels, each with varying ones of the X-DSL protocols can be handled in the same session. The DSP offers the speed associated with hardware implementation of the transforms and the flexibility of a software only implementation. Traffic flow is regulated in the chip using a packet based schema in which each packet is associated with a specific channel of upstream and downstream data. Header and control information in each packet is used to govern the processing of each packet as it moves along either the transmit path or receive path. The DSP of the current invention may advantageously be utilized in fields other than communications, such as: medical and other imaging, seismic analysis, radar and other military applications, pattern recognition, signal processing etc. The present invention provides a signal processing architecture that supports scalability of CO / DLC / ONU resources, and allows a significantly more flexible hardware response to the evolving X-DSL standards without over committing of hardware resources. As standards evolve hardware may be reconfigured to support the new standards.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
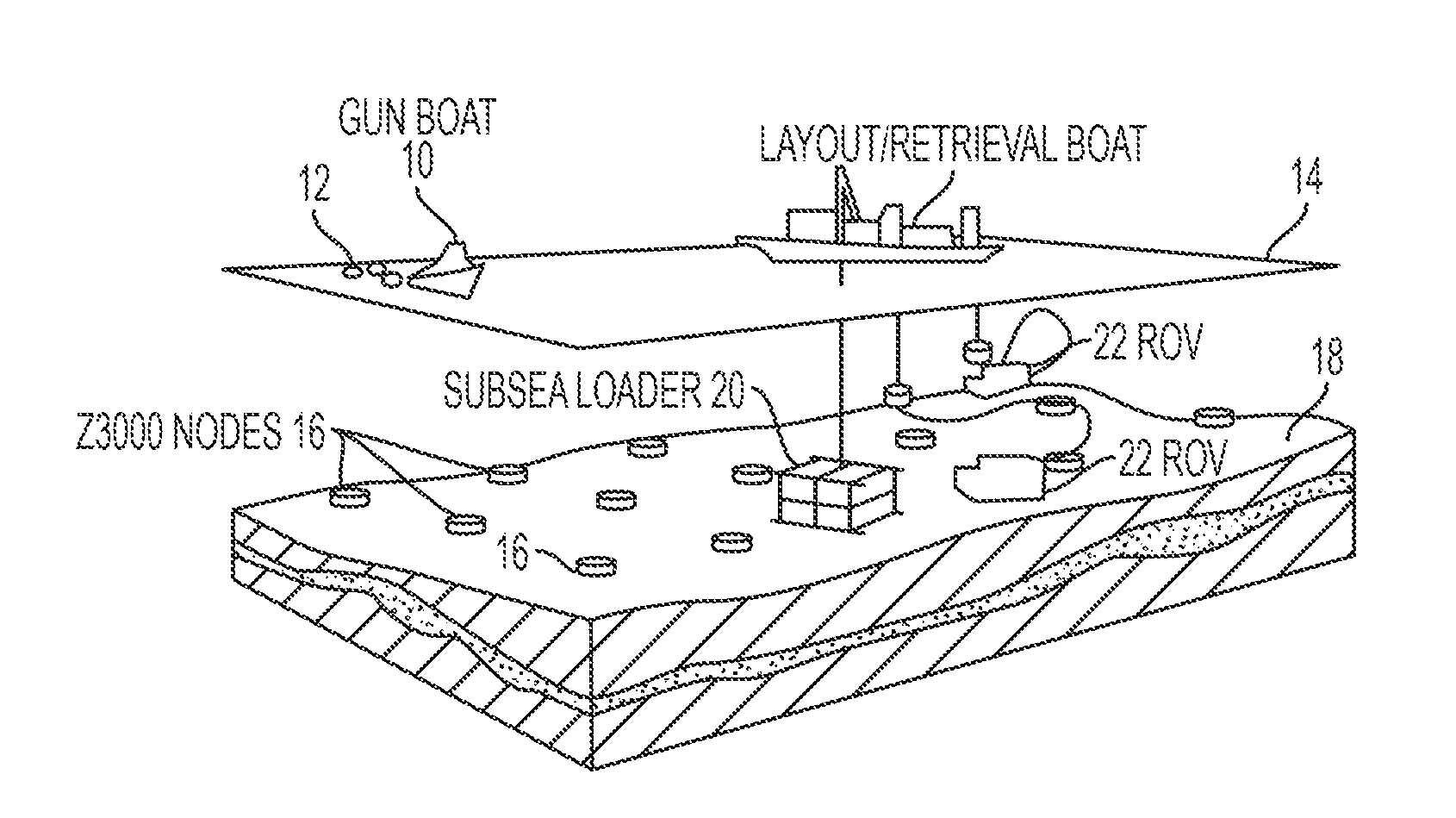
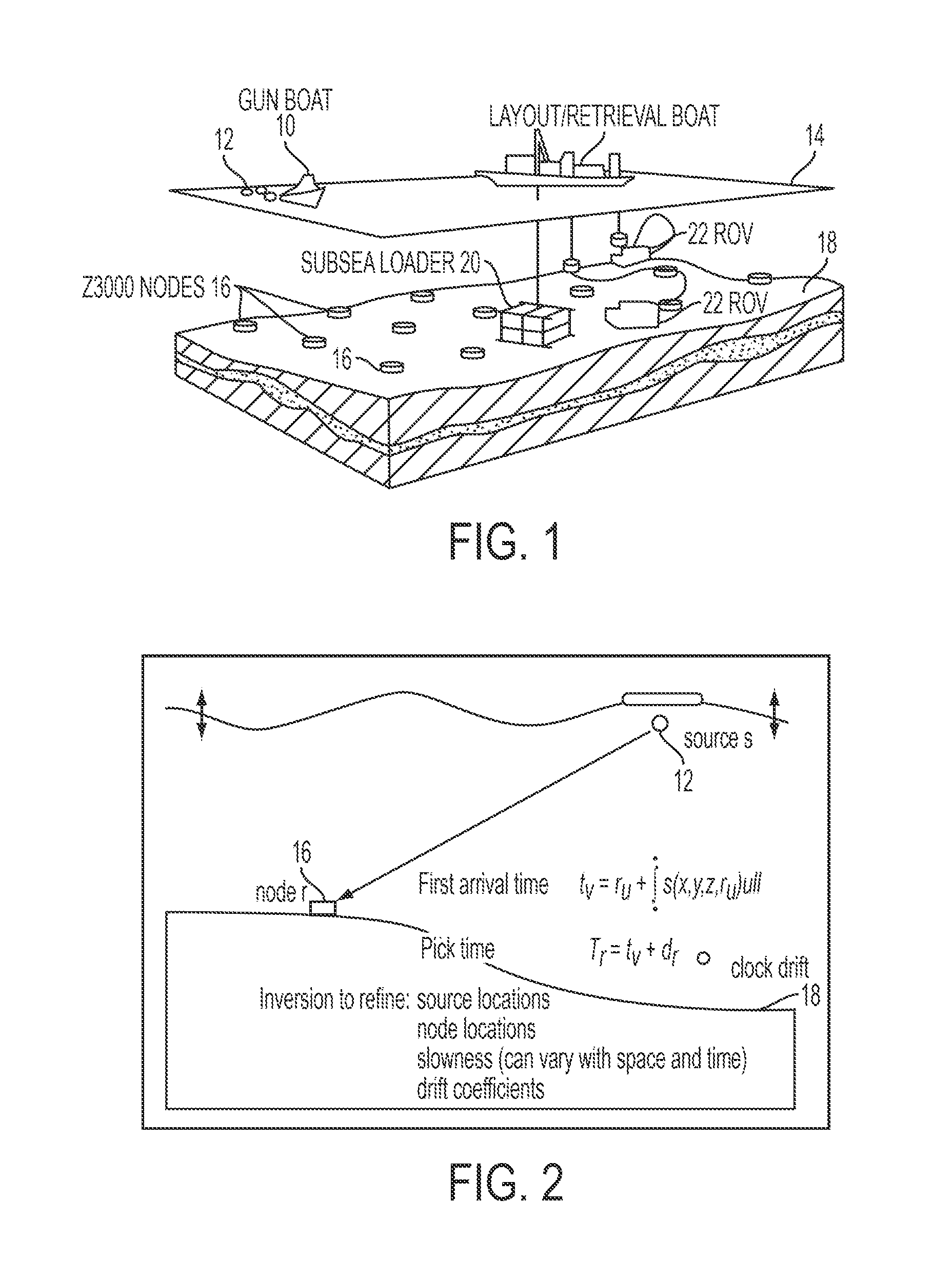
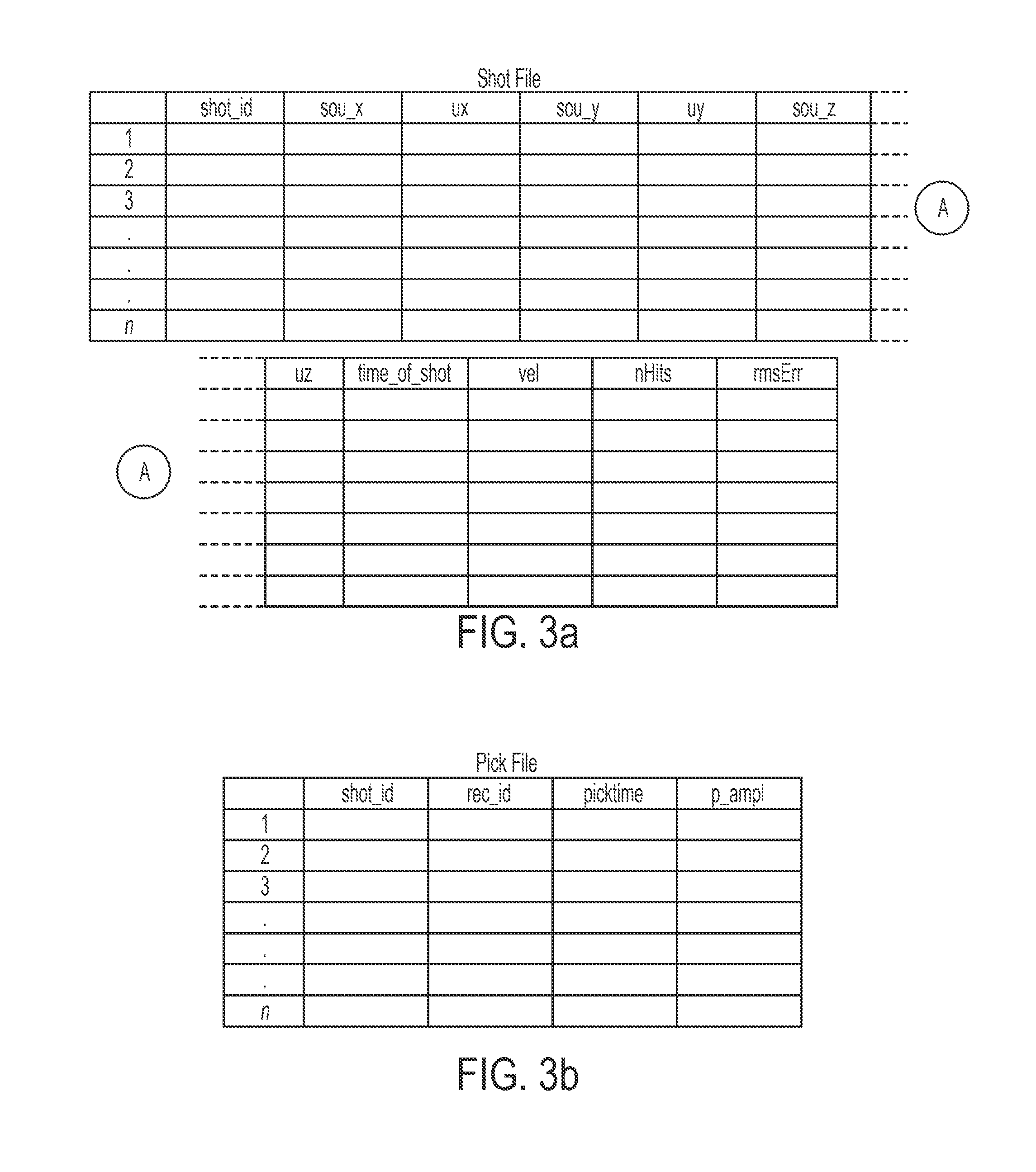
Seismic data analysis using ocean bottom node data collection
ActiveUS20150168576A1Error minimizationSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasOcean bottomTime error
The present invention permits RMS traveltime error in a seismic data acquisition to be minimized. Field measurements of source and receiver coordinates, speed of sound in water as a function of depth and time, receiver timing, and clock drift are first collected. The seismic data is then examined to measure travel time from each source to each reciever. A model travel time can then be computed based on the field measurements. By iteratively perturbing at least one of the field measured data using a look-up table and calculating the travel time after each perturbation until an acceptable RMS error has been achieved, conditioned seismic data that takes into account the dynamic nature of the water column will provide the basis for creating an accurate seismic map that is unaffected by the changing water conditions.
Owner:FAIRFIELD INDUSTRIES INC
Methods and systems for determining signatures for arrays of marine seismic sources for seismic analysis
InactiveUS7440357B2Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasSurface oceanOcean bottom
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for deriving a source signature for an array of seismic sources for marine seismic analysis, wherein the systems and methods include factors for determining the source signature taking into consideration both sea-surface and sea-floor reflections of signals produced by the seismic sources. In certain aspects, reflection coefficients of the sea-surface and the sea-floor and relative lengths of paths between a seismic source image and a detector are applied to a series of simultaneous equations that are solved using measurements of the pressure field produced by the array at a plurality of known locations to determine individual source signatures for each seismic source in the array and these individual source signatures may then be superposed to provide a source signature for the array that accounts for sea-floor reflections of outputs from the seismic sources.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Methods and systems for determining signatures for arrays of marine seismic sources for seismic analysis
InactiveUS20070258322A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasOcean bottomSimultaneous equations
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for deriving a source signature for an array of seismic sources for marine seismic analysis, wherein the systems and methods include factors for determining the source signature taking into consideration both sea-surface and sea-floor reflections of signals produced by the seismic sources. In certain aspects, reflection coefficients of the sea-surface and the sea-floor and relative lengths of paths between a seismic source image and a detector are applied to a series of simultaneous equations that are solved using measurements of the pressure field produced by the array at a plurality of known locations to determine individual source signatures for each seismic source in the array and these individual source signatures may then be superposed to provide a source signature for the array that accounts for sea-floor reflections of outputs from the seismic sources.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Method, system and device for reminding data traffic
ActiveCN102480578APrecisely control consumer behaviorAvoid problems such as inaccurate remindersTelephonic communicationWireless communicationTraffic capacityCommunications system
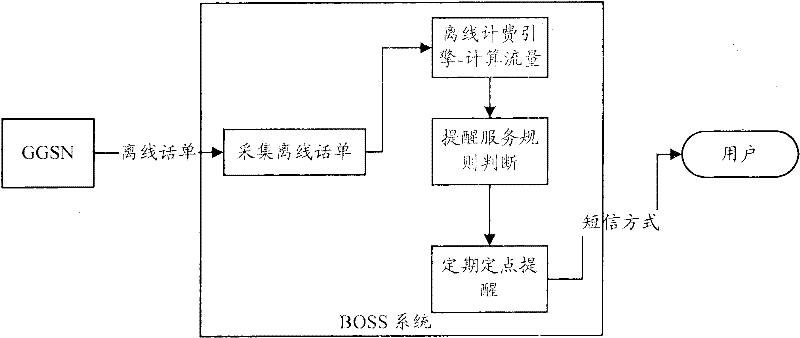
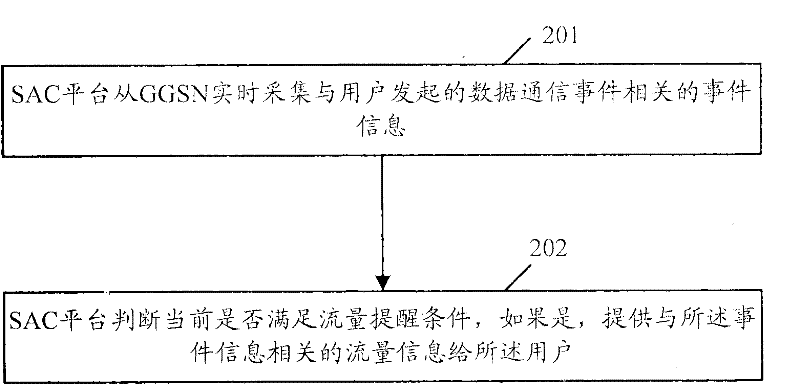
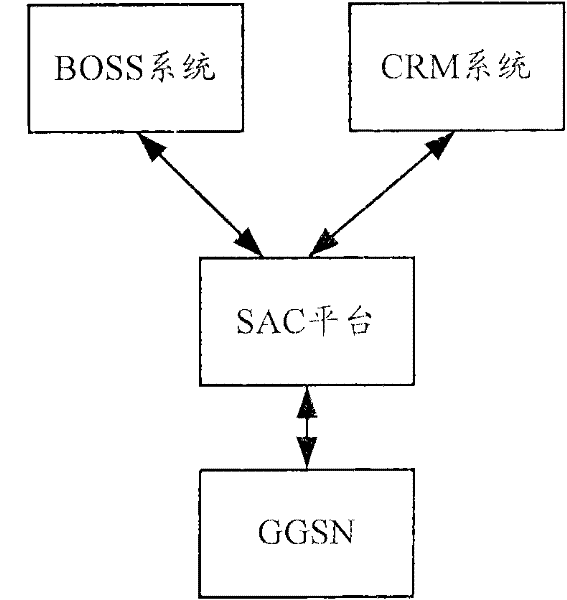
The invention provides a method and system for reminding data traffic and an SAC (Seismic Analysis Code) platform. The method is applied to a data communication system which at least comprises a GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node) and the method comprises the following steps of: A, collecting event information related to a data communication event from the GGSN in time by the SAC platform, wherein the data communication event is started by a user; and B, judging whether the current data traffic meets a data traffic reminding condition by the SAC platform; and if so, supplying data traffic information related to the event information to the user. With the adoption of the invention, the accurate data traffic information can be reminded.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SICHUAN
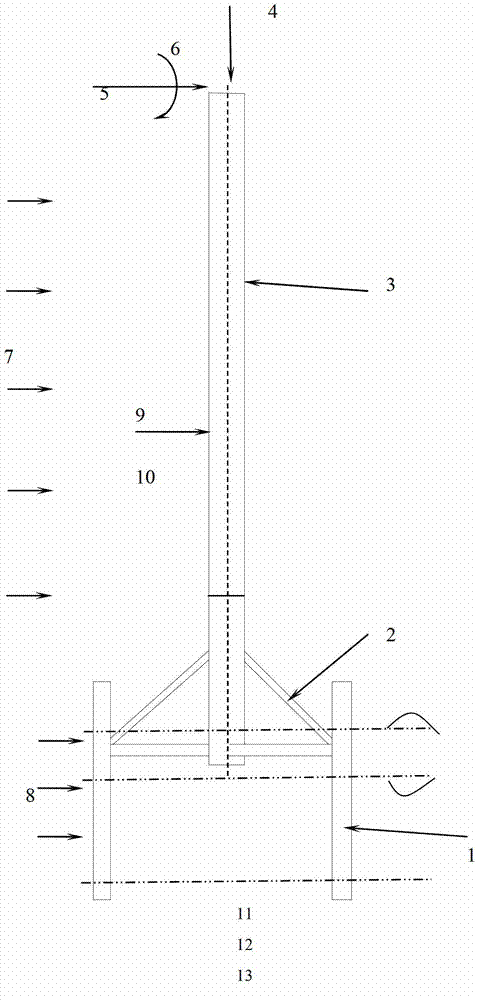
Offshore fan pile foundation design method and application thereof
ActiveCN102926399AReasonable designReasonable design methodFoundation engineeringStructural analysisEngineering
The invention discloses an offshore fan pile foundation design method and application thereof. According to the offshore fan foundation design specifications and the offshore fixed platform design specifications, design calculation analysis is carried out based on ocean engineering design analysis software structural analysis computer system (SACS). The design calculation analysis comprises a fundamental analysis, a modal analysis, a seismic analysis, an ice load analysis, a hoisting analysis, a transportation analysis and an installation analysis. Through the method, actual environmental conditions of offshore fans are totally considered in the method, the analyses are accurate, results are reliable and design efficiency is high. Meanwhile, all aspects of foundation design, hoisting, transportation and installation of the offshore fans are considered in the design method. Therefore, the offshore fan pile foundation design method has the advantages of systematicness and comprehensiveness, and can be applied to intertidal belt fan pile foundation design.
Owner:GUODIAN UNITED POWER TECH
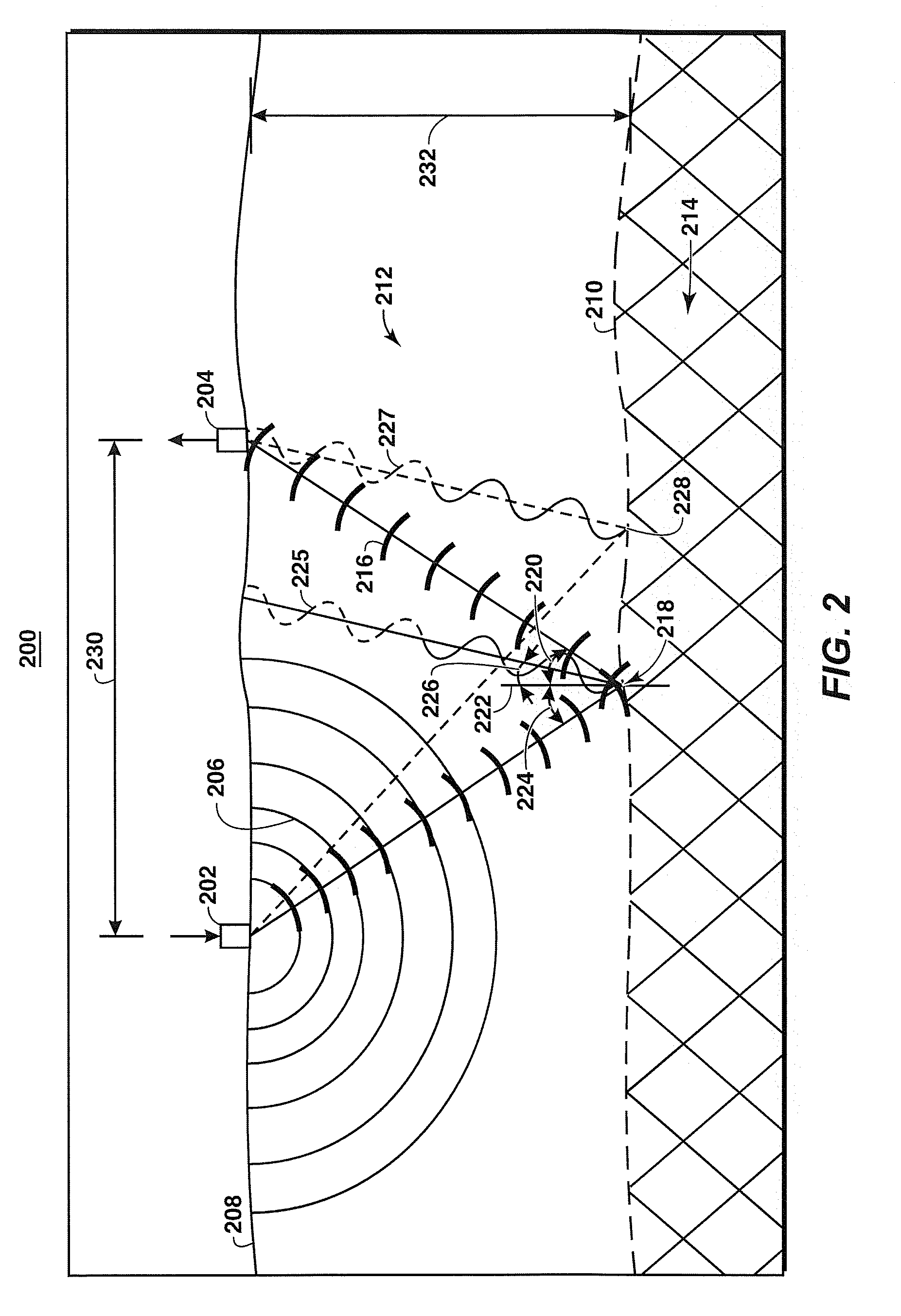
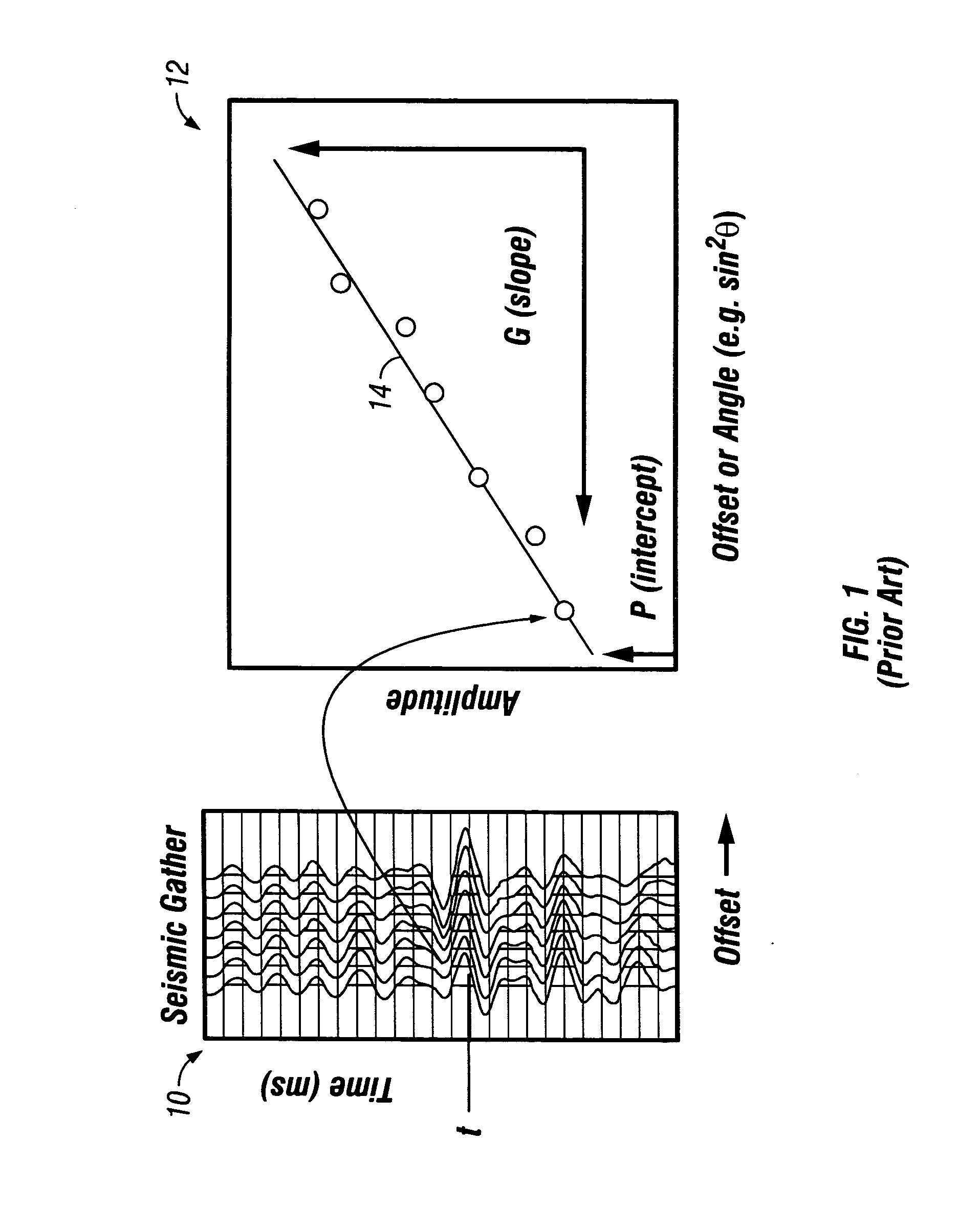
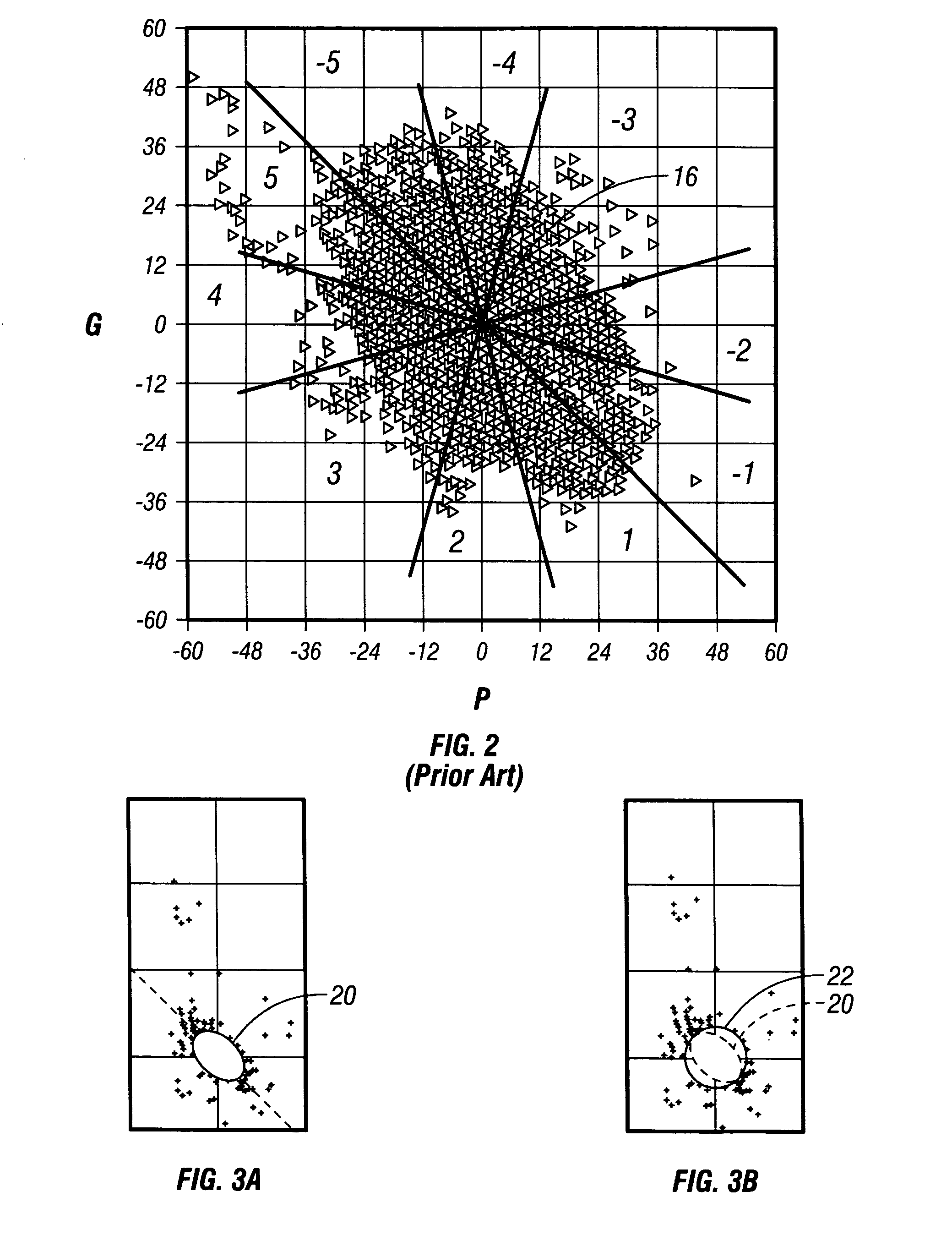
Crossplot analysis of A.V.O. anomolies in seismic surveying
ActiveUS20040240321A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic attributeAnalysis method
A method of seismic data analysis to provide clustering of A.V.O. data into A.V.O. anomaly types, the method comprising: obtaining successive values of a plurality of seismic attributes, each seismic attribute comprising a respective property of a seismic reflection event, grouping said values using a running window of a predetermined size into a plurality of groups, for each group identifying first and second parameters corresponding to said first and second attributes, and plotting each group as a single event based on said group parameters, said group parameters having been selected to cause clustering of said seismic reflection events on said plot according to the presence or absence of A.V.O. anomalies.
Owner:ASPEN PARADIGM HLDG LLC
Seismic data analysis
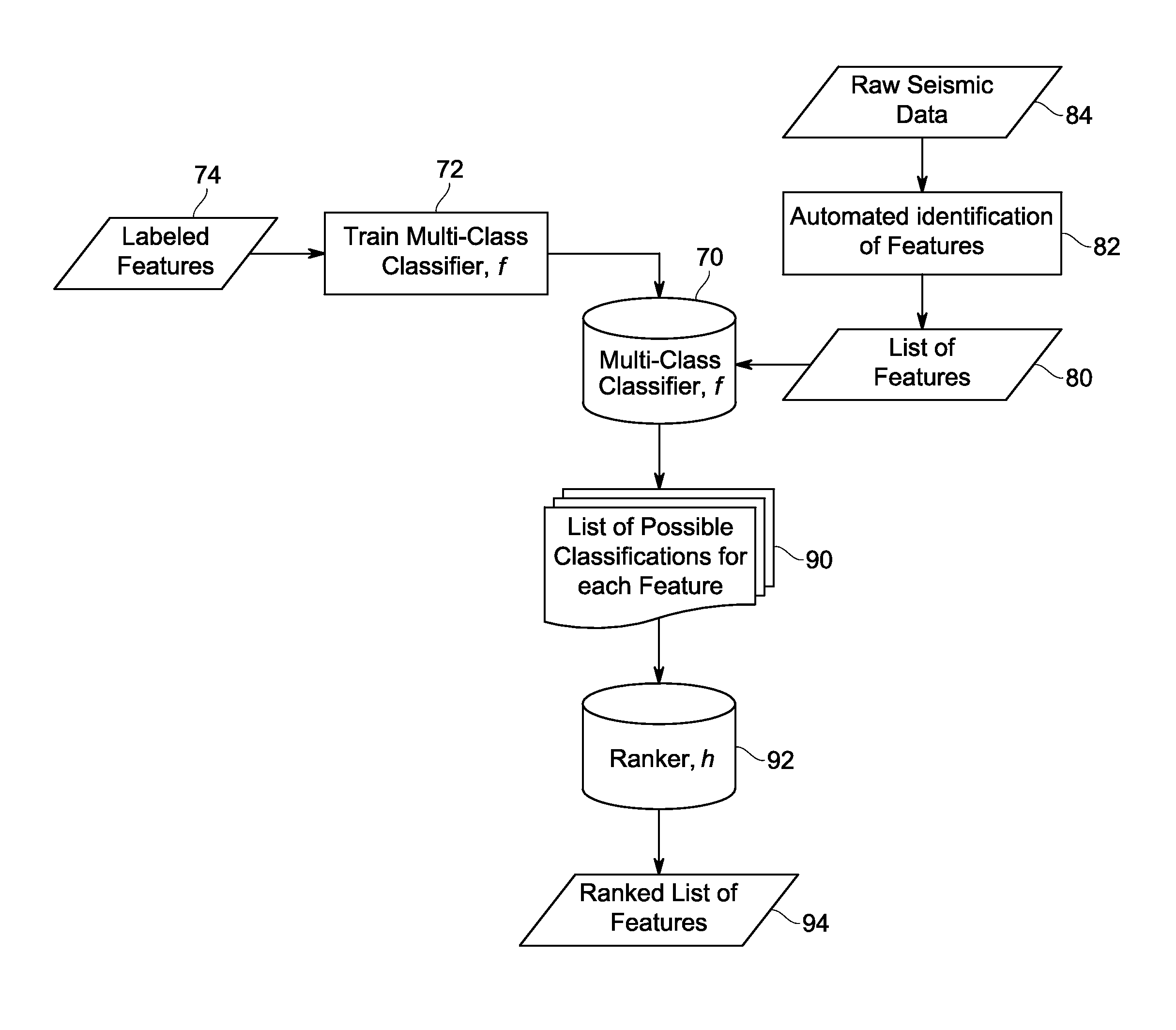
ActiveUS20140188769A1Reduce varianceDigital computer detailsSeismologySorting algorithmProactive learning
An approach for seismic data analysis is provided. In accordance with various embodiments, the active learning approaches are employed in conjunction with an analysis algorithm that is used to process the seismic data. Algorithms that may employ such active learning include, but are not limited to, ranking algorithms and classification algorithms.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC +1
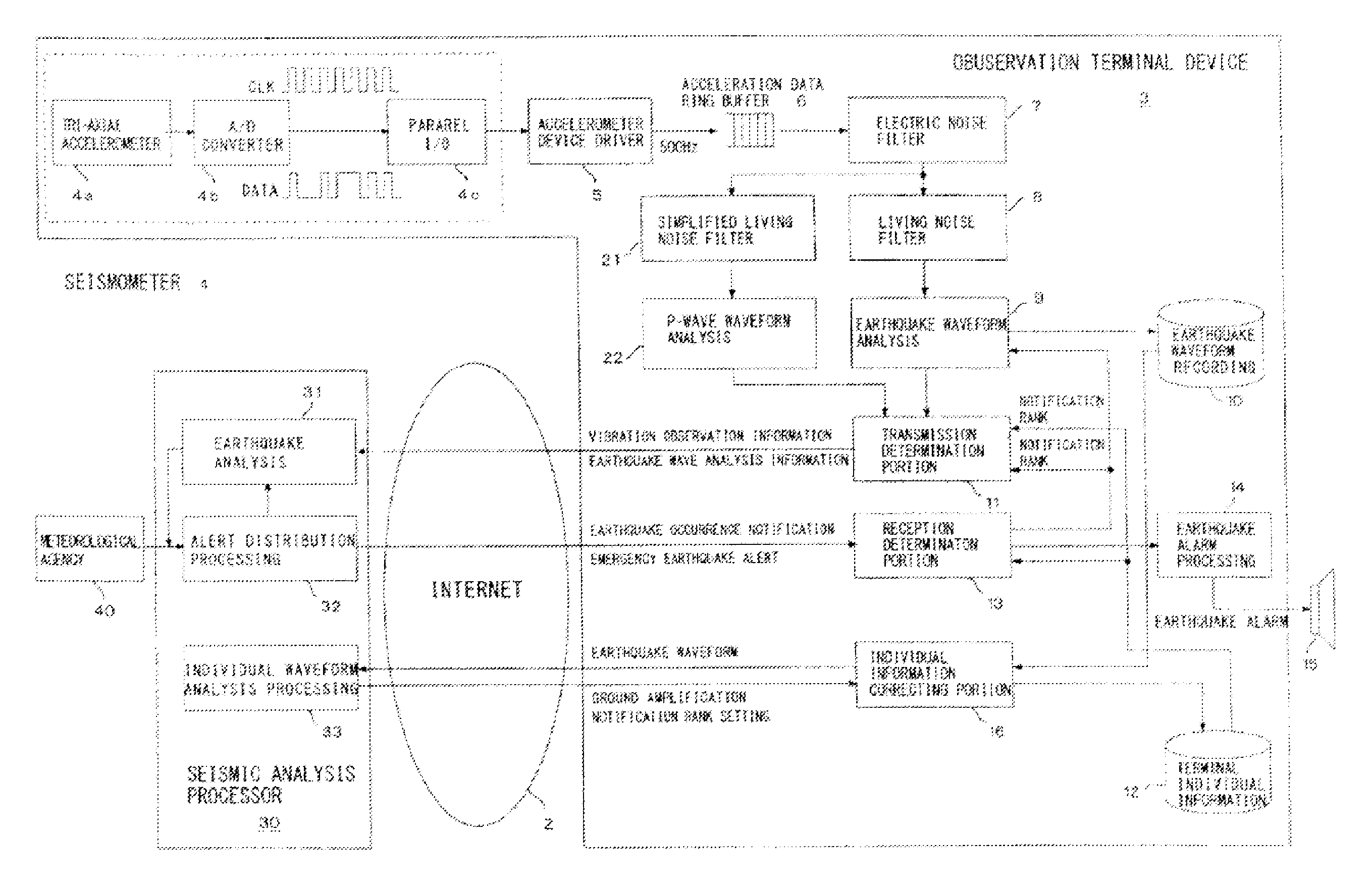
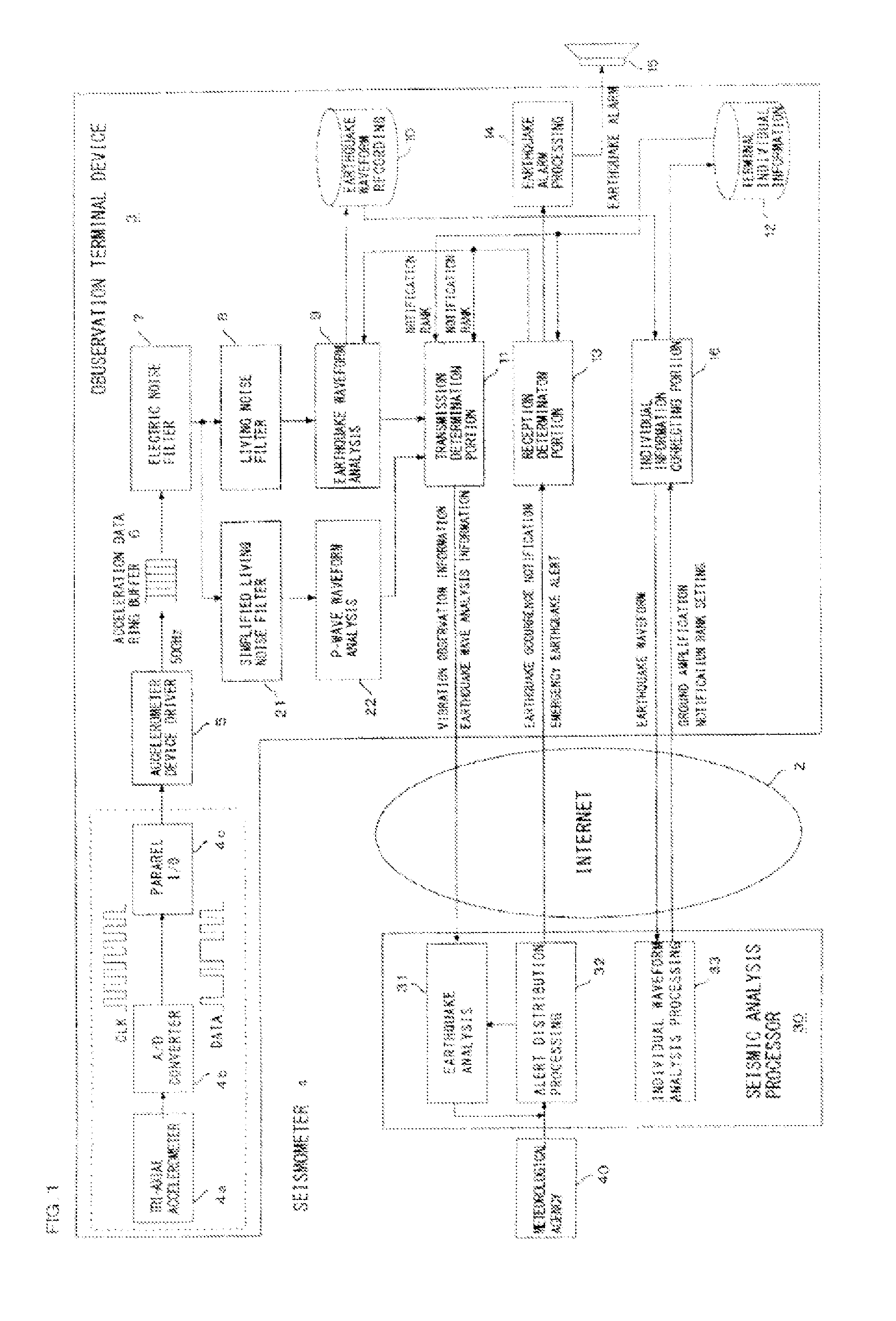
Earthquake determination system and seismic analysis method
ActiveUS20120078520A1Increase probabilityEarthquake measurementSeismic signal processingTerminal equipmentSeismic analysis
An earthquake determination system which includes a plurality of observation terminal devices are connected by a communication network. When estimated P-wave detection information is received from the plurality of the observation terminal devices, a distance D between the observation terminal devices and a time interval δ between detection times are acquired and when transmission limit distance of local vibration energy is DSL, the minimum propagation speed of the earthquake P waves is SP, and the maximum detection error between detection times by the pair of observation terminal devices is Δt, the seismic analysis processor determines occurrence of an earthquake, if the both of the two pairs of the observation terminal devices satisfy the relationships of 2DSL<D and δ<D / SP+Δt.
Owner:A2 CO LTD
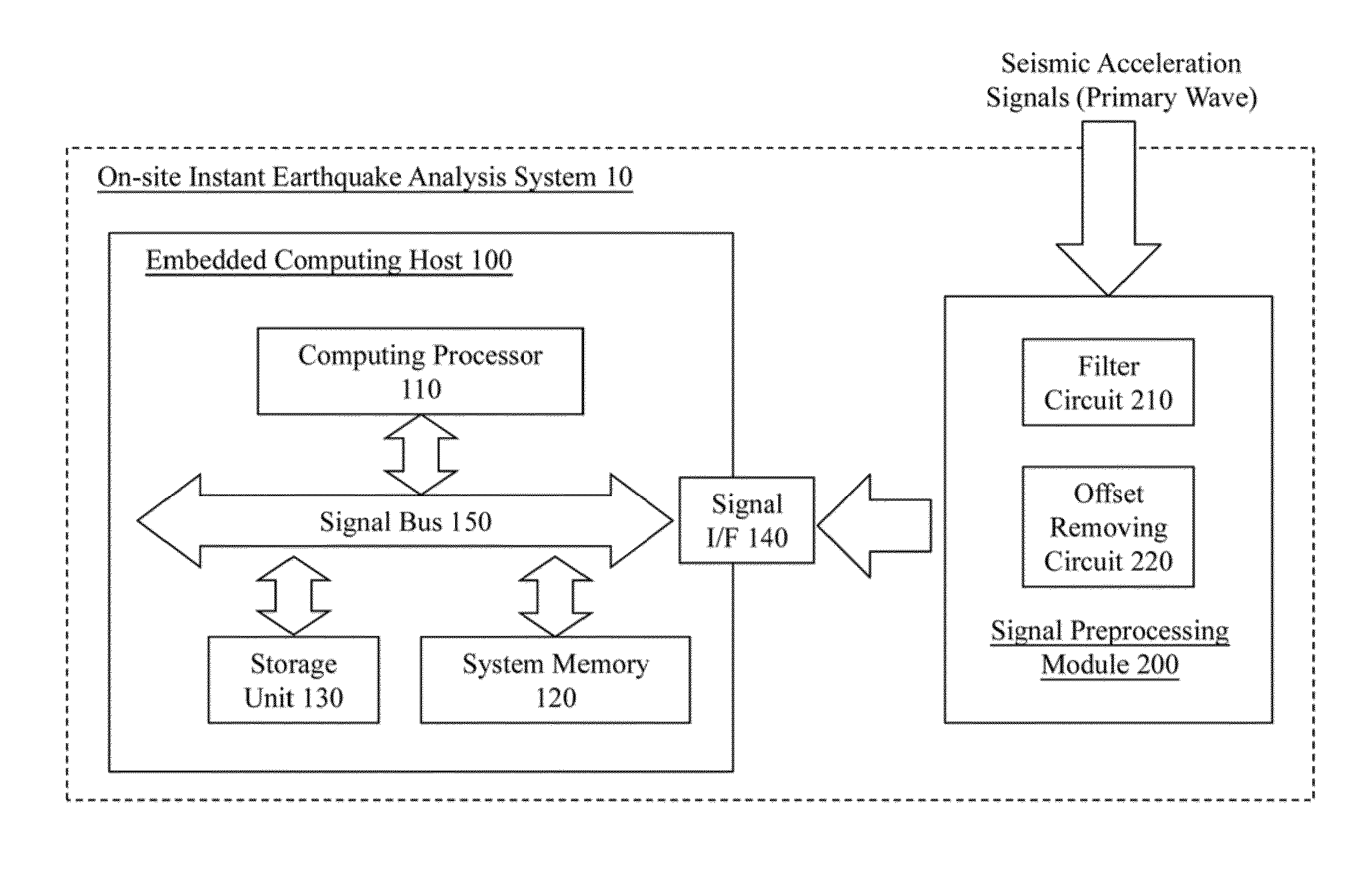
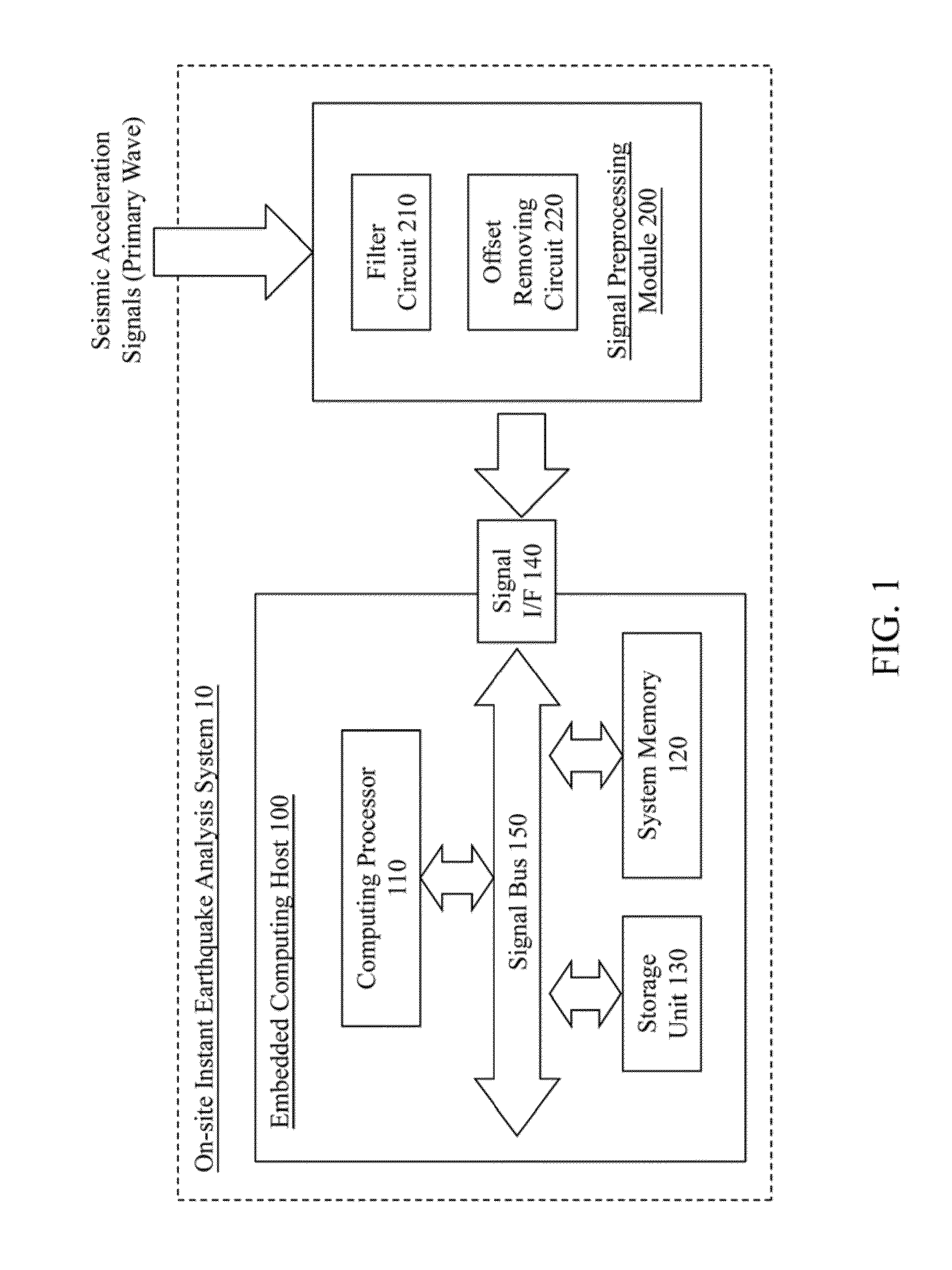
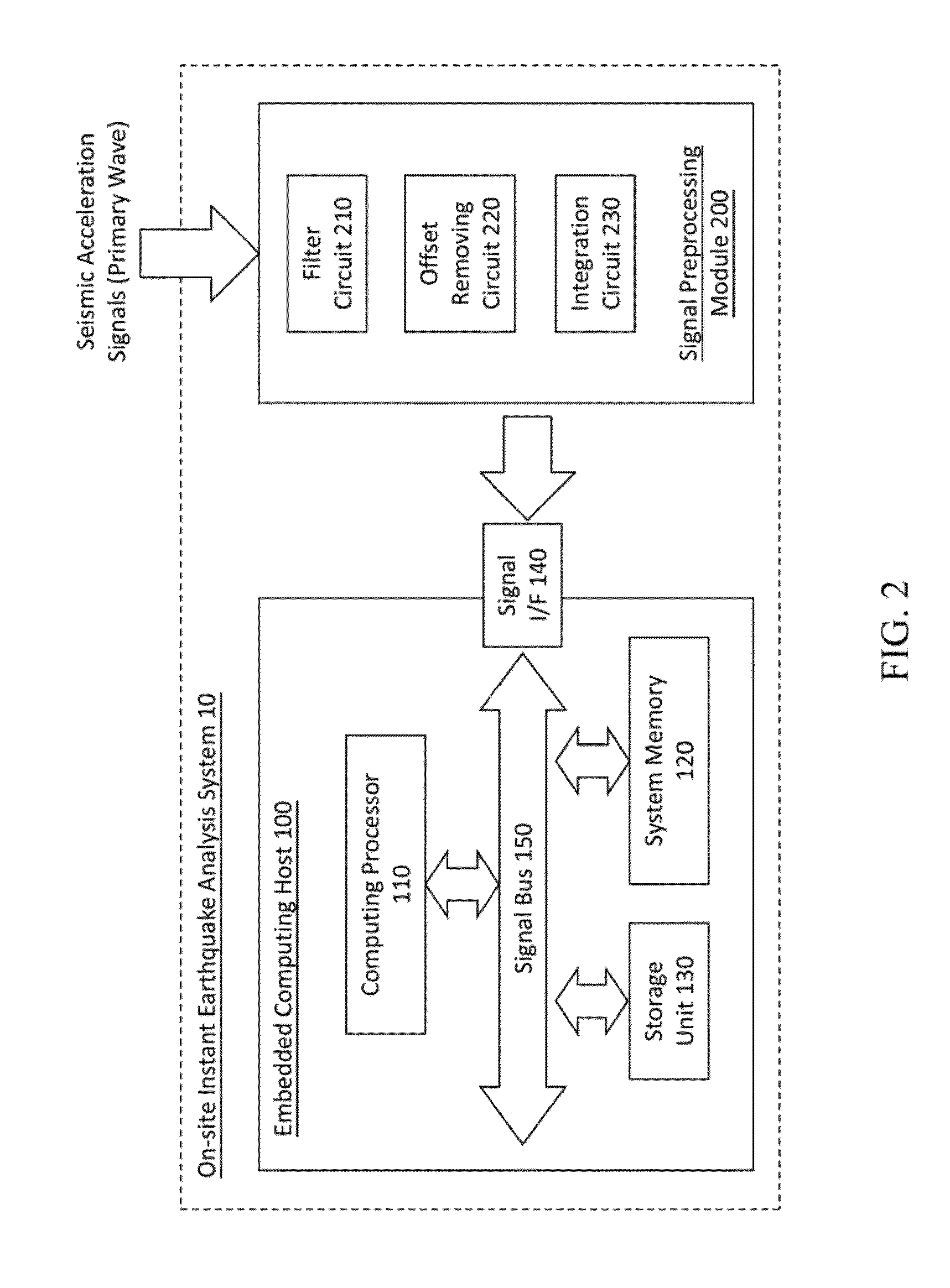
System and method for on-site instant seismic analysis
ActiveUS20130046475A1Seismic data acquisitionEarthquake measurementPeak ground accelerationSpot analysis
A system and method instantly on-site analyze seismic acceleration signals measured from a primary wave of an earthquake and at a detecting site. The system includes an embedded computing host and a signal preprocessing module. Hardware preprocessing is executed on the seismic acceleration signals; and whether the earthquake is a seismic event is able to be determined according to a seism determining logic. Seismic acceleration signals are converted into ground velocities and ground displacements to obtain a peak ground displacement. A seismic fracture time parameter is calculated through the ground velocities and ground displacements and then a seismic magnitude of the earthquake is obtained. According to the peak ground displacement and the seismic magnitude, an epicentral distance is further calculated. Then a peak ground acceleration of the earthquake's shear wave at the detection site is able to be obtained through the seismic magnitude and the epicentral distance.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Using seismic attributes for data alignment and seismic inversion in joint PP/PS seismic analysis
Method for aligning converted wave seismic reflection data (PS data) with conventional PP seismic reflection data so that both data types may be used to more accurately image the subsurface for hydrocarbon exploration or field development. Amplitude vs. angle (AVA) or amplitude vs. offset (AVO) attributes of PP and PS seismic data are identified and defined, which attributes are theoretically expected to be in phase and optimize seismic resolution in the data. In one embodiment of the invention, such attributes are calculated (310), then the same horizons are identified in a series of PP attributes and in a series of PS attributes, then the second series is aligned with the first at the horizon locations (316, 320), then a time transfer function is generated and applied to the PS mode data (322), and the aligned joint-mode data are inverted (326) using, for example, AVA attributes.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Depth domain phase-control inversion method
ActiveCN106707339AAvoid lossGuaranteed high resolution featuresSeismic signal processingIntermediate frequencyWell logging
The invention provides a depth domain phase-control inversion method. The depth domain phase-control inversion method comprises the steps of: A, carrying out seismic phase analysis; B, matching sample wells having similar waveforms; C, filtering in a range higher than a seismic frequency band to filter out a high frequency band, so as to find cut-off frequency of the similar waveforms having common structures; D, performing interpolation to establish an initial model, and carrying out phase control by combining with a seismic phase analysis result during the interpolation process; E, performing frequency analysis on seismic data, determining a low-pass frequency and a high-pass frequency, and filtering the initial model to filter out the low-pass frequency and the high-pass frequency, so as to obtain a band-notched initial model; F, combining with colored inversion, and merging an intermediate-frequency portion of colored inversion with low-frequency and high-frequency portions of the band-notched initial model by utilizing a frequency domain to obtain an absolute wave impedance or velocity invertomer, thereby completing depth domain reservoir inversion. The depth domain phase-control inversion method overcomes the high-frequency information loss caused by resampling during the well-logging curve time-depth conversion process, and effectively guarantees the high resolution feature of the seismic data.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
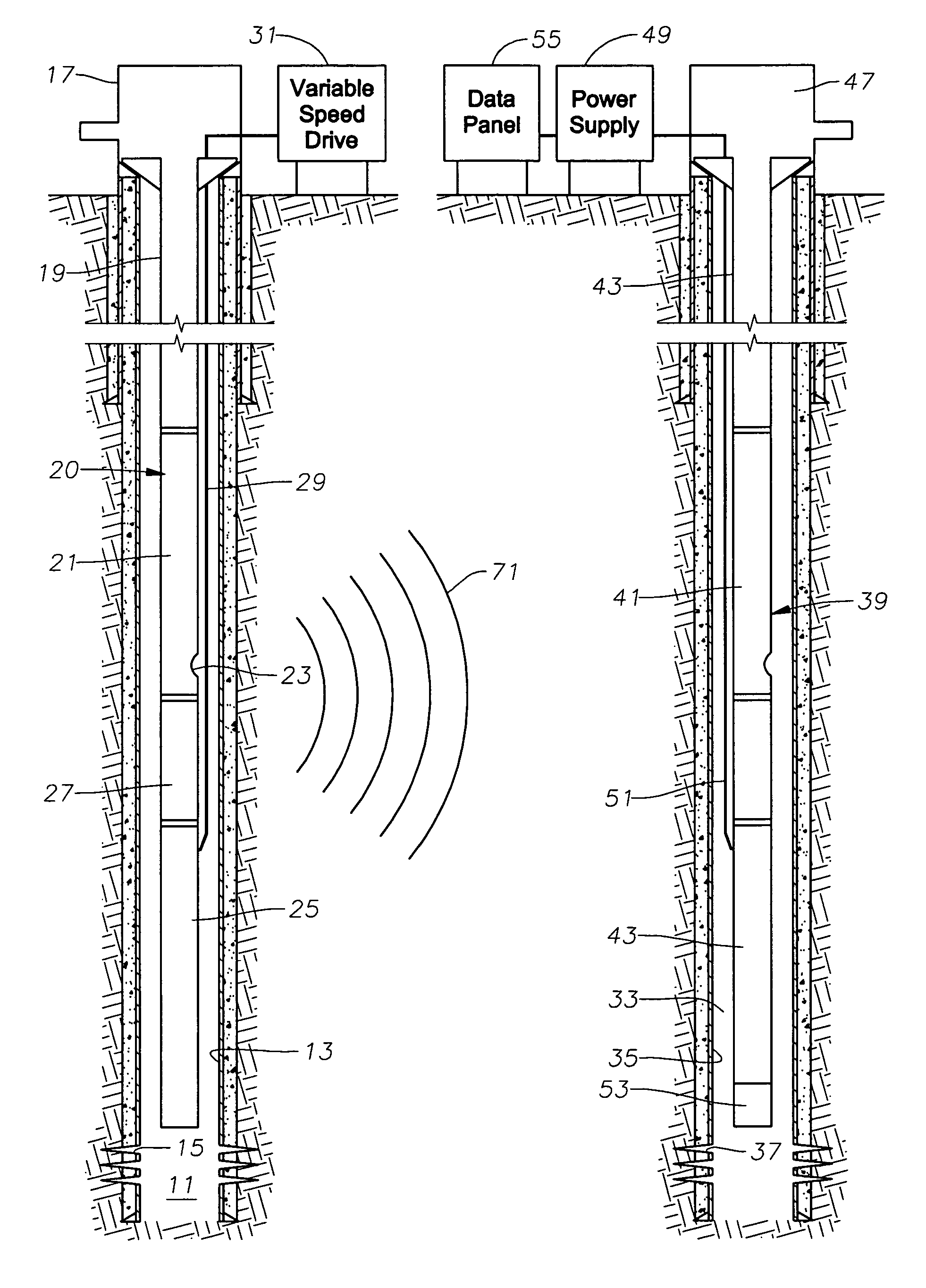
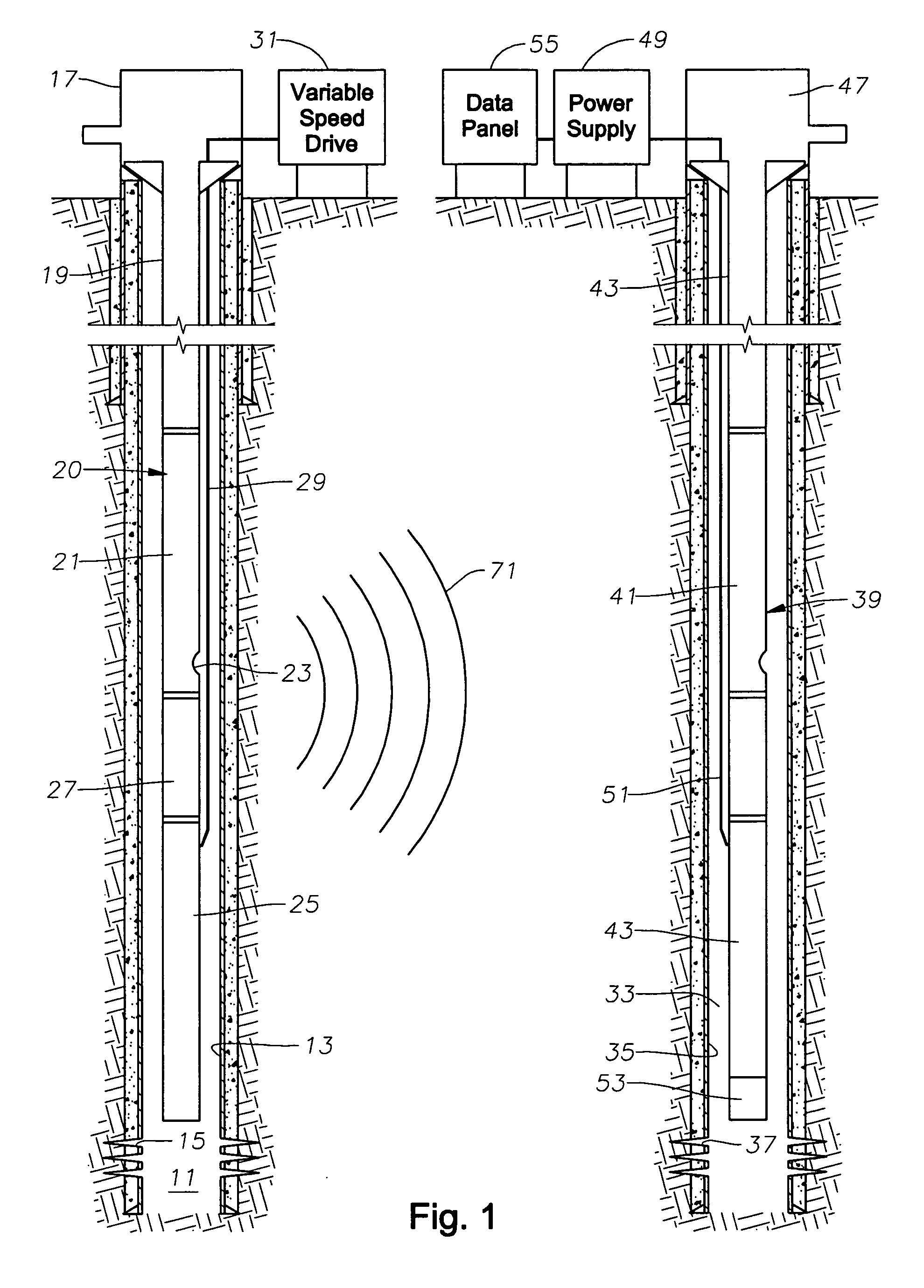
Seismic analysis using electrical submersible pump
ActiveUS20060247861A1Little interferenceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingPower cableSeismic survey
Seismic data is collected by using an electrical submersible pump assembly in a well that is producing well fluid. By sweeping the rotational speed of the pump assembly through a selected range at selected intervals, seismic waves of varying frequency are emitted. These seismic waves are then picked up with a seismic sensor located at the surface or located in another well. If the seismic sensors are located in another well, the signal from the sensor may be transmitted to the surface by superimposing the data onto the power cable leading to the pump located in that other well. The seismic survey may be repeated at regular intervals, and the results will reveal the changes that have taken place over time in the reservoir.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
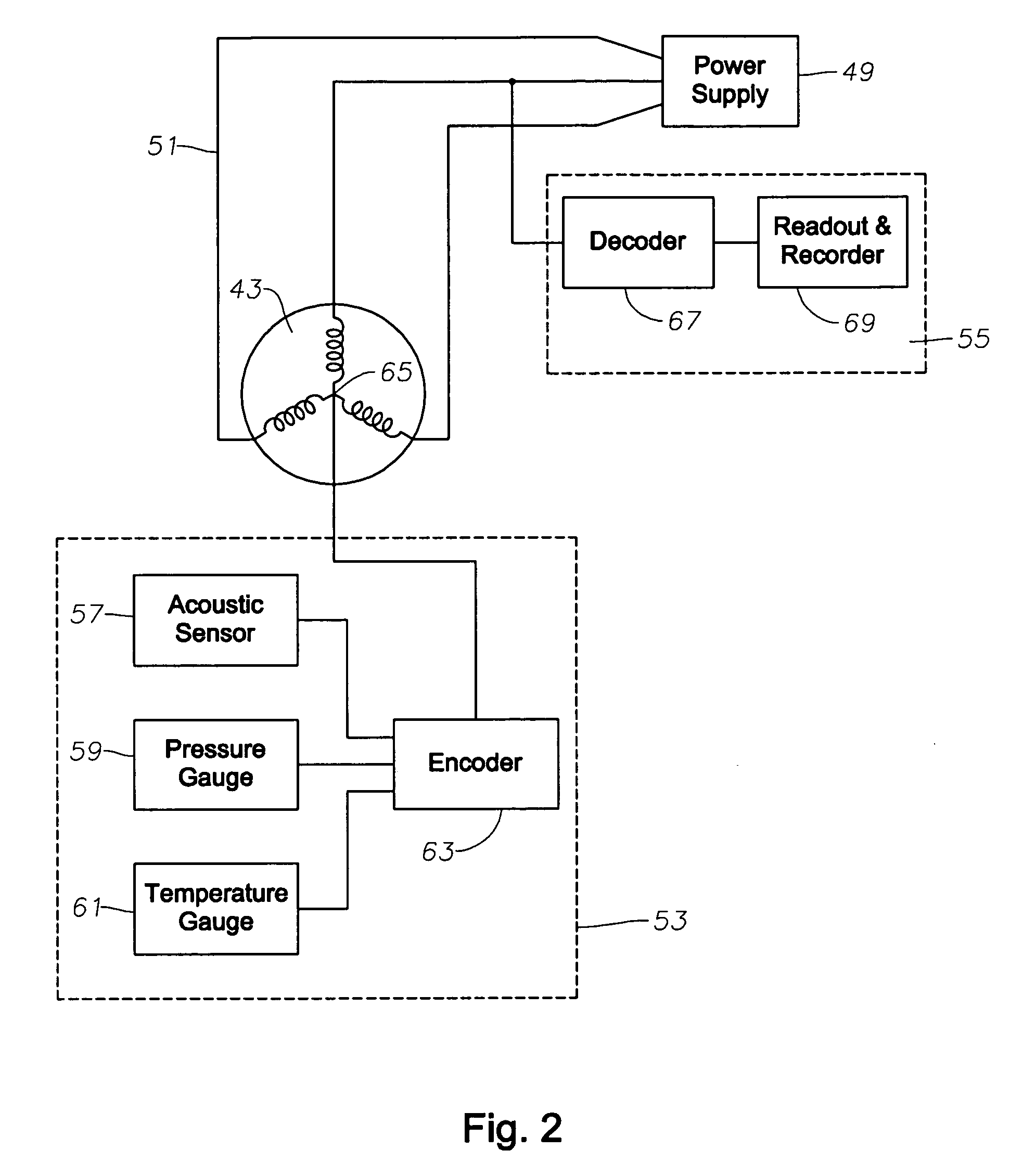
Transmission coefficient method for AVO seismic analysis
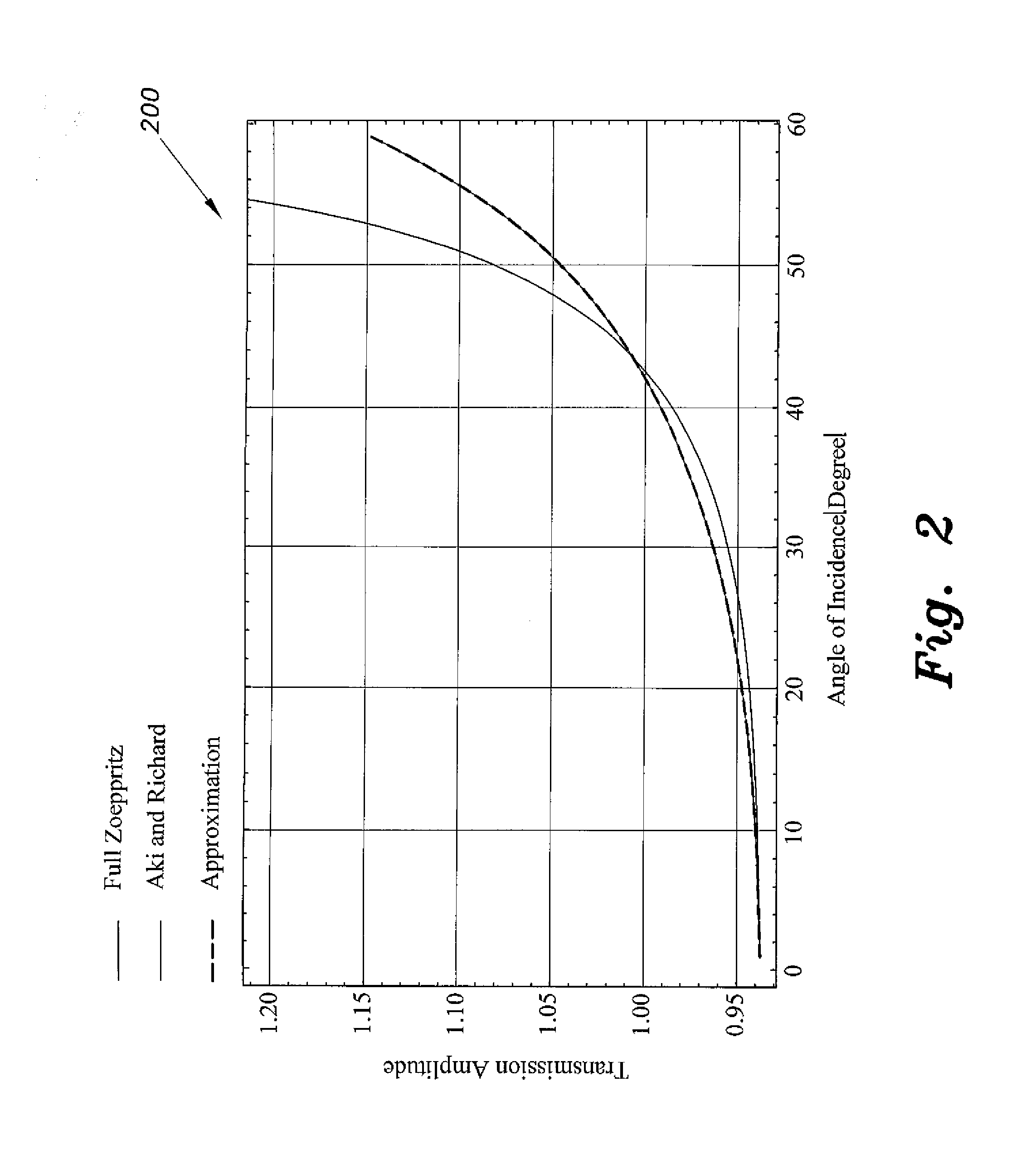
InactiveUS20140324354A1Simple calculationEasy to analyzeSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsPresent methodZoeppritz equations
The transmission coefficient method for AVO (amplitude variation with offset) seismic analysis computes incident-to-transmitted pressure wave and incident-to-transmitted shear wave data in a manner that is compatible with existing AVO applications for analysis on the transmission coefficients of VSP data. Amplitude variation with offset (AVO) computation techniques known in the art provide estimates of pressure wave, shear wave and pseudo-Poisson's reflectivity. Such estimates are based on the Aki-Richards approximation of Zoeppritz's formulation of reflection amplitude and polarity variation with respect to incidence angle. The Zoeppritz equations describe the amplitudes of body waves when incident on an interface, resulting in a scattering matrix in which all possible incident and generated modes are addressed. The present method further simplifies the Aki and Richards computations to facilitate further AVO analysis.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Crossplot analysis of A.V.O. anomolies in seismic surveying
ActiveUS7095677B2Increase the sectionEnhance the imageSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic attributeSurveyor
A method of seismic data analysis to provide clustering of A.V.O. data into A.V.O. anomaly types, the method comprising: obtaining successive values of a plurality of seismic attributes, each seismic attribute comprising a respective property of a seismic reflection event, grouping said values using a running window of a predetermined size into a plurality of groups, for each group identifying first and second parameters corresponding to said first and second attributes, and plotting each group as a single event based on said group parameters, said group parameters having been selected to cause clustering of said seismic reflection events on said plot according to the presence or absence of A.V.O. anomalies.
Owner:ASPEN PARADIGM HLDG LLC
Stretch free trace processing using block move sum and phase-based move out corrected data
InactiveUS20060227662A1Reduced and substantially eliminated stretchReduce distortion problemsSeismic signal processingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Image resolution
The present invention is directed to generating moveout data for a gather with reduced or substantially eliminated stretch and with improved resolution of potentially overlapping events. In one embodiment, a zero offset trace is obtained and a phase information for the zero offset trace is substituted into phase information for each of the offset traces to perform a phase-based moveout. The zero offset trace may be obtained by a block move sum process and that process may be enhanced for improved resolution of overlapping events. The phase moveout data may be used for analysis of offset dependent relationships such as AVO. Additionally, the phase offset data may be stacked to obtain high signal to noise ratio data for further seismic analysis.
Owner:TRICON GEOPHYSICS
Multi-segment natural ground motion synthesis method based on set response spectrum
PendingCN107589445ASeismic signal processingComplex mathematical operationsSynthesis methodsResponse spectrum
The invention relates to the technical field of civil and architectural engineering, in particular to a multi-segment natural ground motion synthesis method based on a set response spectrum. The method includes the following steps: collecting a large number of natural original ground motion records; screening out eligible seismic wave fragments through a specific method; and synthesizing the seismic wave fragments into a synthetic response spectrum closest to a target design response spectrum. The synthesis method follows the principle that the ground motion response spectrum is approximatelyconsistent with the target design response spectrum of the site. The ground motion synthesized can maintain the frequency-domain non-stationary property possessed by a natural ground motion record. The synthesis method is applicable to the anti-seismic analysis of all structure forms under the same fortification intensity and site conditions.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Fitting method for seabed near-fault seismic oscillation
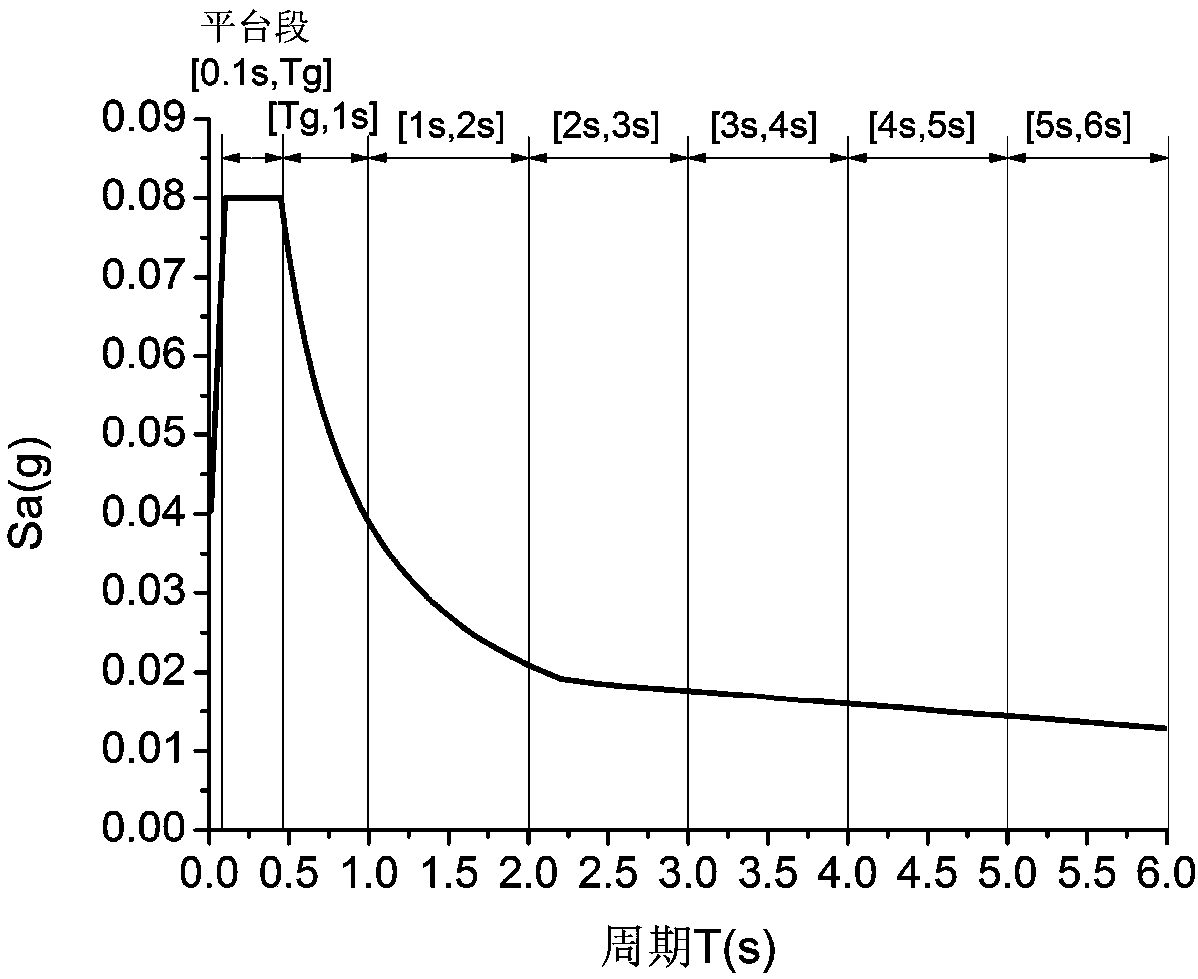
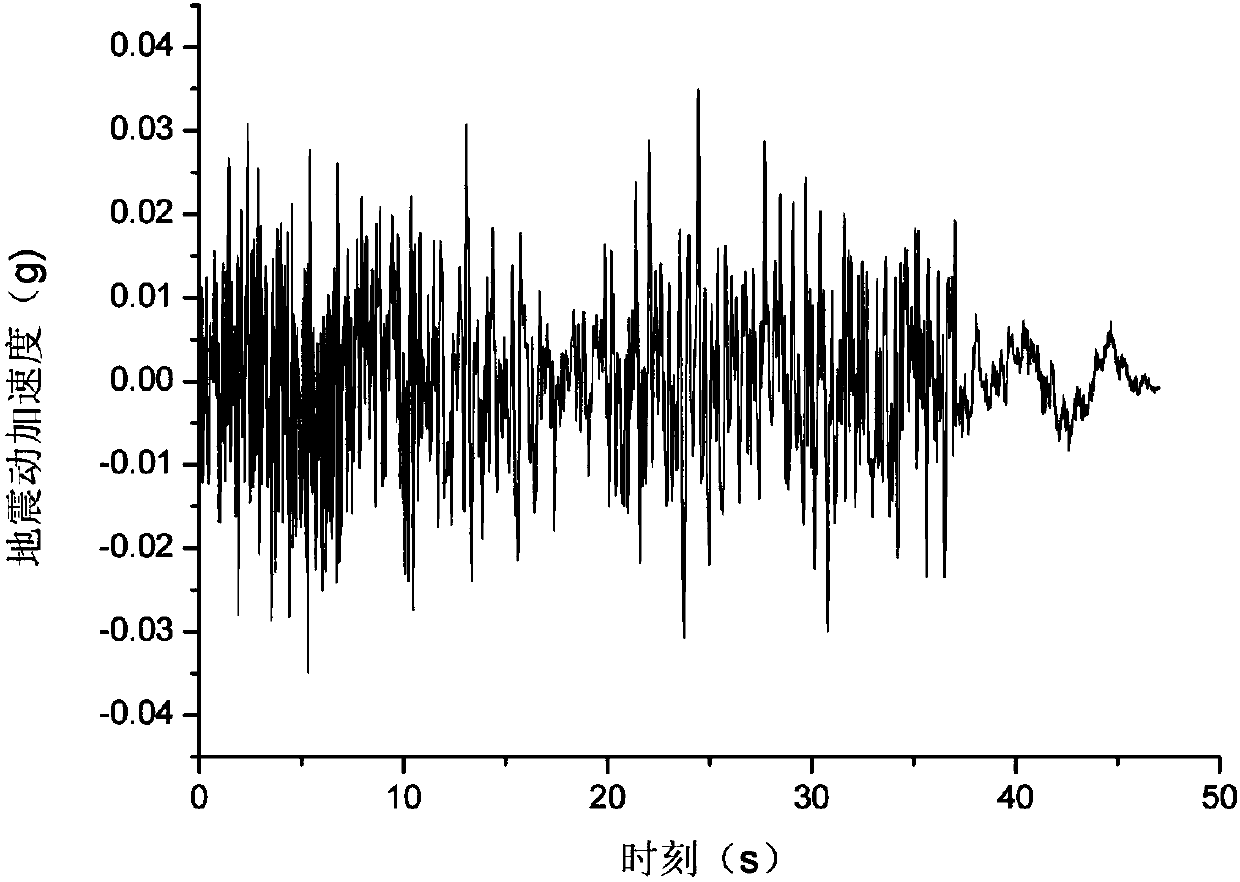
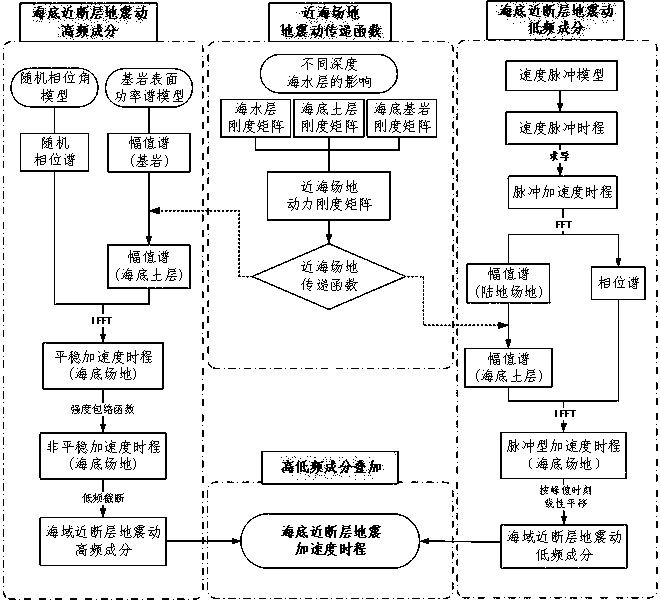
ActiveCN110794459ADriving and Improving Seismic Performance EvaluationSolve bottlenecksSeismic signal recordingSeismic signal processingSeismic resistanceSeismic analysis
The invention relates to a fitting method for seabed near-fault seismic oscillation. The fitting method comprises the following steps: S1, calculating a seismic oscillation transfer function of an offshore site; S2, fitting high-frequency components of seabed seismic oscillation to obtain high-frequency acceleration time-history components of near-sea area near-fault seismic oscillation; S3, fitting low-frequency pulse components of the seabed seismic oscillation to obtain a low-frequency pulse type acceleration time history of the seismic oscillation; and S4, superposing the high-frequency acceleration time-history components with the translated low-frequency pulse type acceleration time history to obtain seabed near-fault seismic oscillation. According to the method, the bottleneck of lack of seismic oscillation records in existing cross-sea structure seismic analysis can be practically solved; the accurate and reasonable seismic oscillation input is provided for seismic performanceanalysis of the seabed near-fault structure; and the anti-seismic performance evaluation of the ocean structure can be promoted and improved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
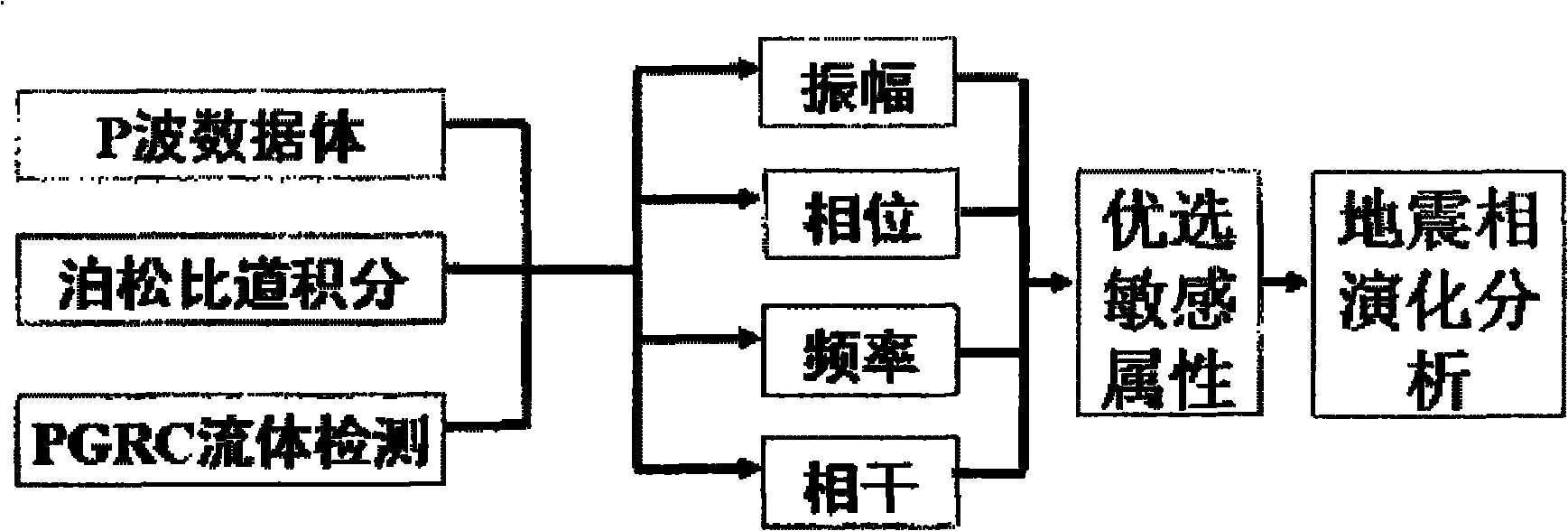
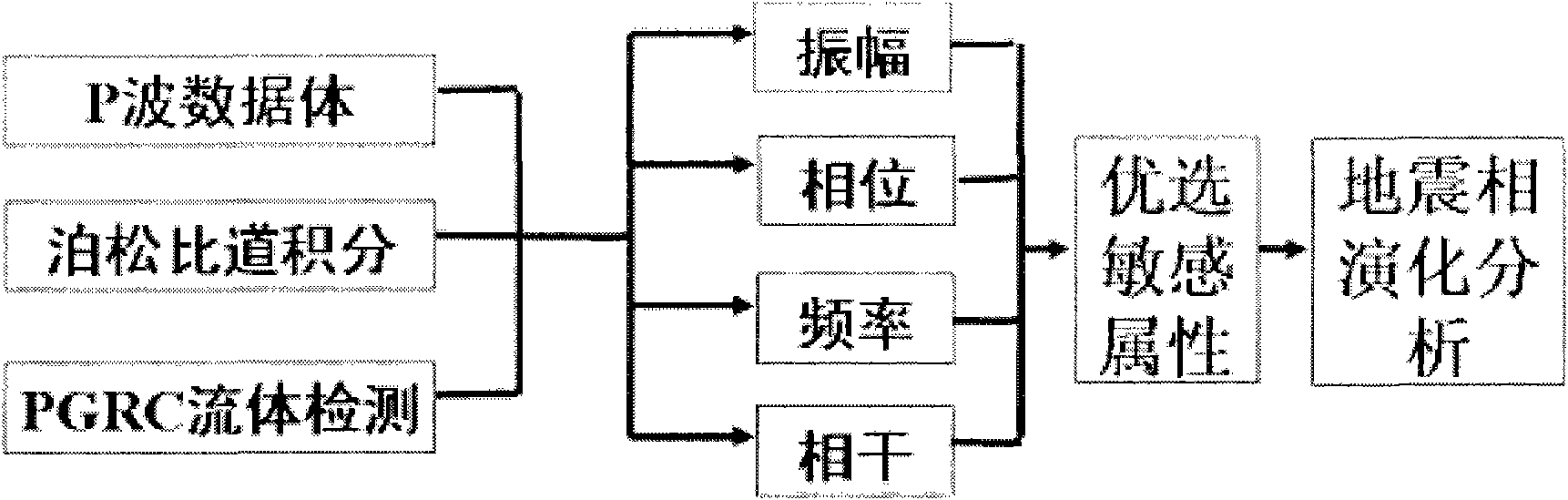
Seismic attribute extracting method
InactiveCN102096098AImprove accuracyThe operation steps are simplified and simpleSeismic signal processingSeismic attributeComputer science
The invention discloses a seismic attribute extracting method which belongs to a seismic analysis technical and mainly solves the problems of inaccurate seismic attribute extraction and low extraction efficiency. The seismic attribute extracting method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a P wave, a Poisson's ratio trace integration and PGRC fluid from seism and detecting the three data volumes; (2) carrying out base attribute analysis on each data volume; (3) selecting the sensitive attribute of each data volume; (4) carrying out seismic phase evolutional history analysis according to the sensitive attributes; and (5) acquiring the seismic attribute from the seismic phase evolutional history. The method has higher seismic attribute extraction accuracy and extraction efficiency and higher practical value.
Owner:武侯区巅峰机电科技研发中心
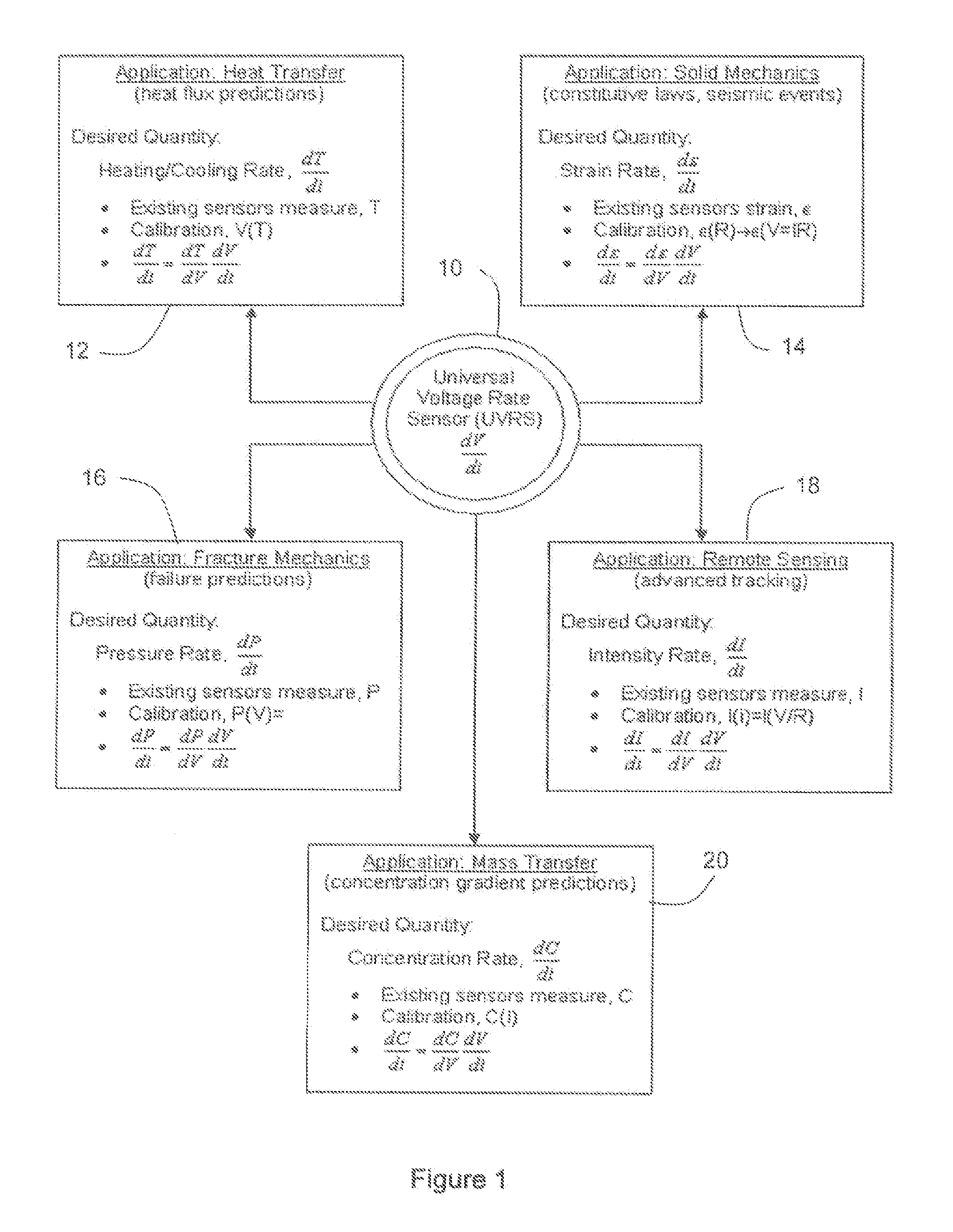
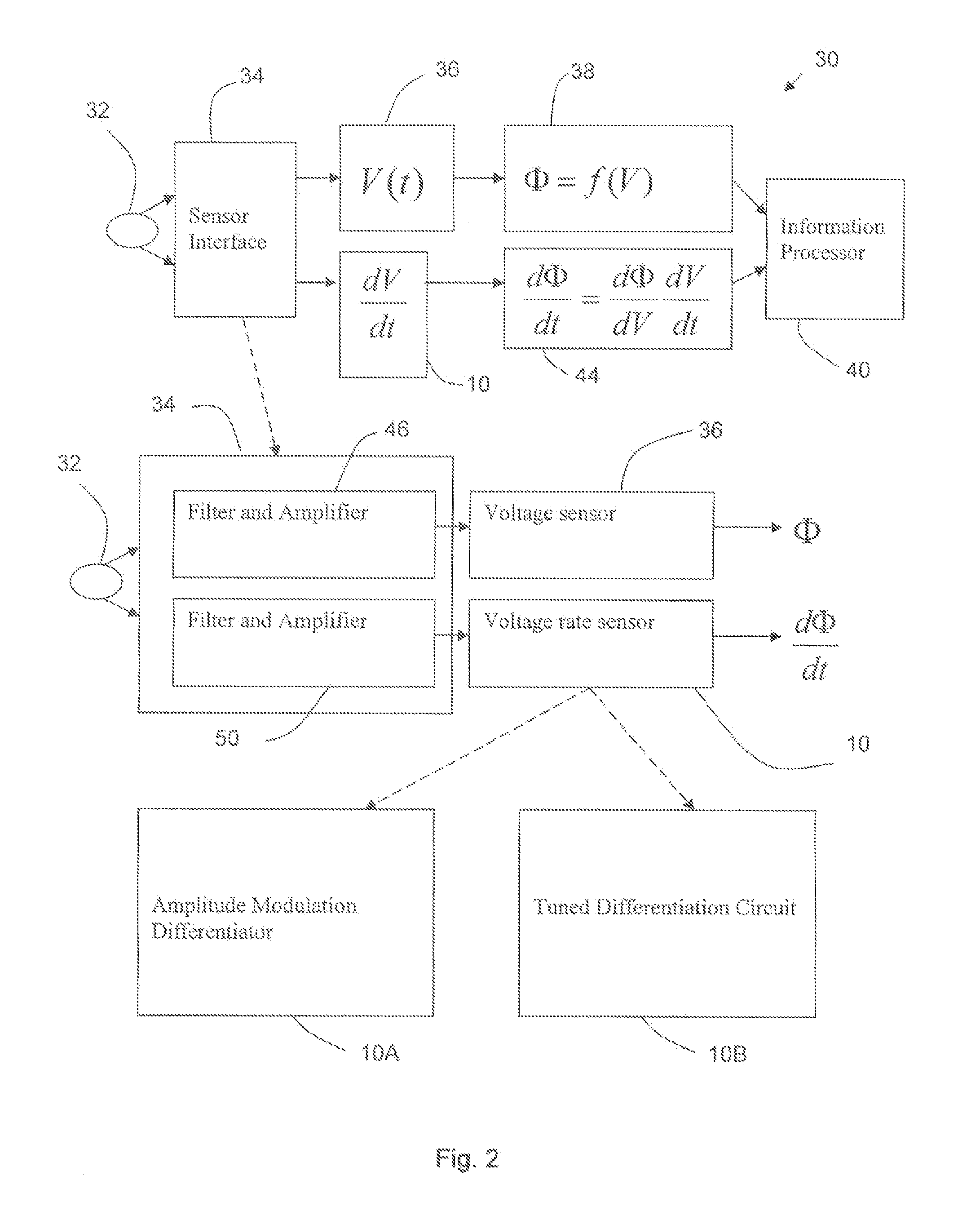
Rate-based sensors for advanced real-time analysis and diagnostics
InactiveUS20070252633A1Digital data processing detailsMeasurement arrangements for variableAviationMetrology
The invention provides a universal rate-based transducer for advancing diagnostic and predictive analyses of low frequency physical phenomena, such as associated with heat and mass transfer, solid and fluid mechanics, pressure and seismic analysis. In many applications, such as in the fire metrology, aerospace, security and defense sectors, rate information is crucial for reaching fast and reliable diagnosis and prediction. In one preferred embodiment, the invention comprises a universal voltage rate sensor interface that accurately recovers the instantaneous heating / cooling rate, dT / dt. Upon appropriate calibration, this sensor interface allows real-time extraction of rates associated with many physical quantities of interest (e.g., temperature, heat flux, concentration, strain, stress, pressure, intensity, etc.).
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
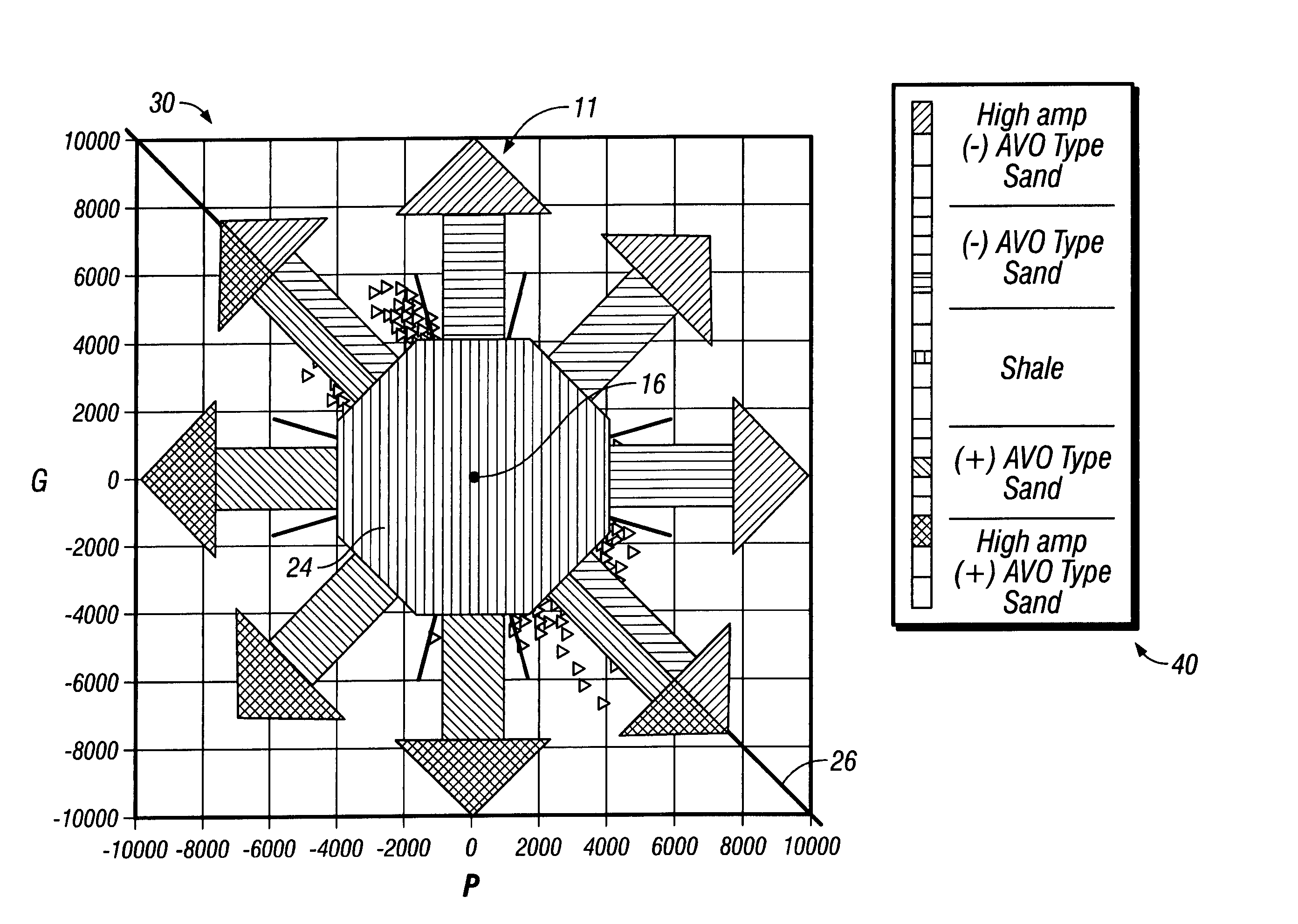
Method of processing seismic data to extract and portray AVO information
InactiveUS20060282220A1Change shapeSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsPorosityLithology
A method of seismic analysis is disclosed for extracting information relating to lithology, porosity, fluids, and AVO types and / or displaying the extracted information. In one possible embodiment, AVO points are plotted and a distance and / or angle is utilized for extracting this information. Various portrayals of the extracted information displays may be produced including displays wherein the extracted information is then displayed in terms of colors for respective x, y, z locations. The AVO points may or may not be normalized based on a shape of a cluster of the AVO points prior to extraction of the information.
Owner:ESEIS
Method for identifying weak reflection reservoir
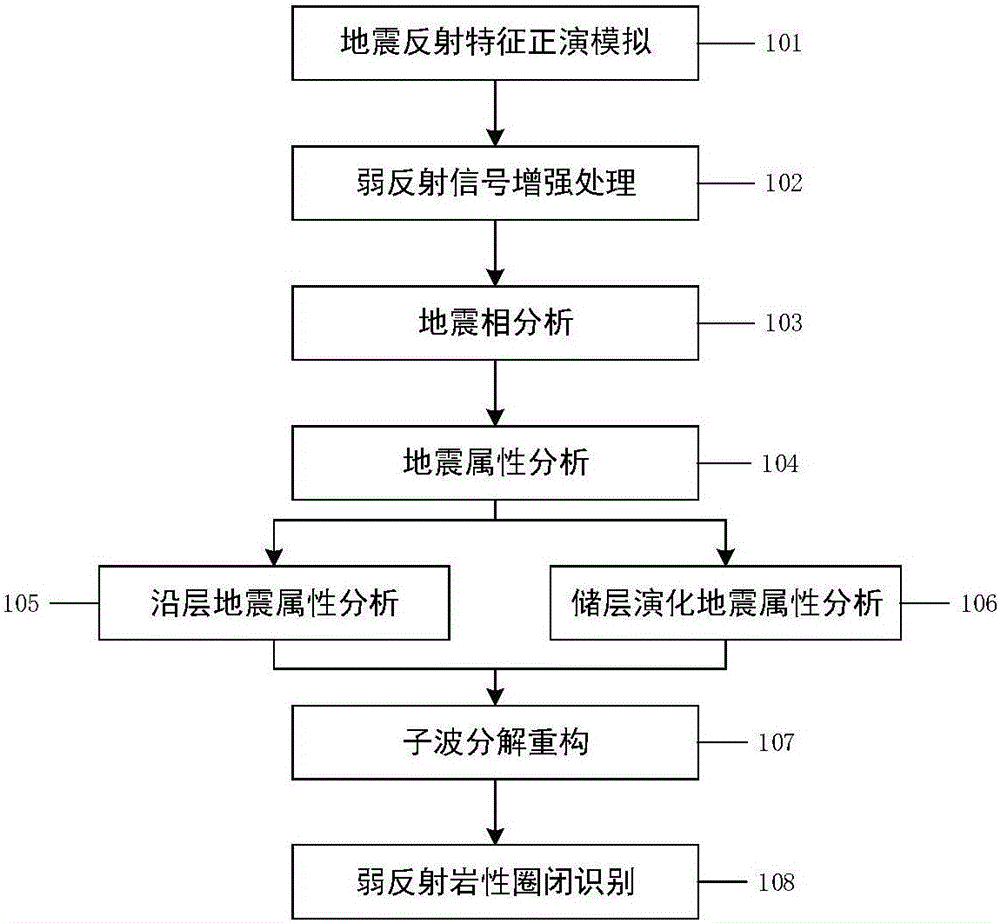
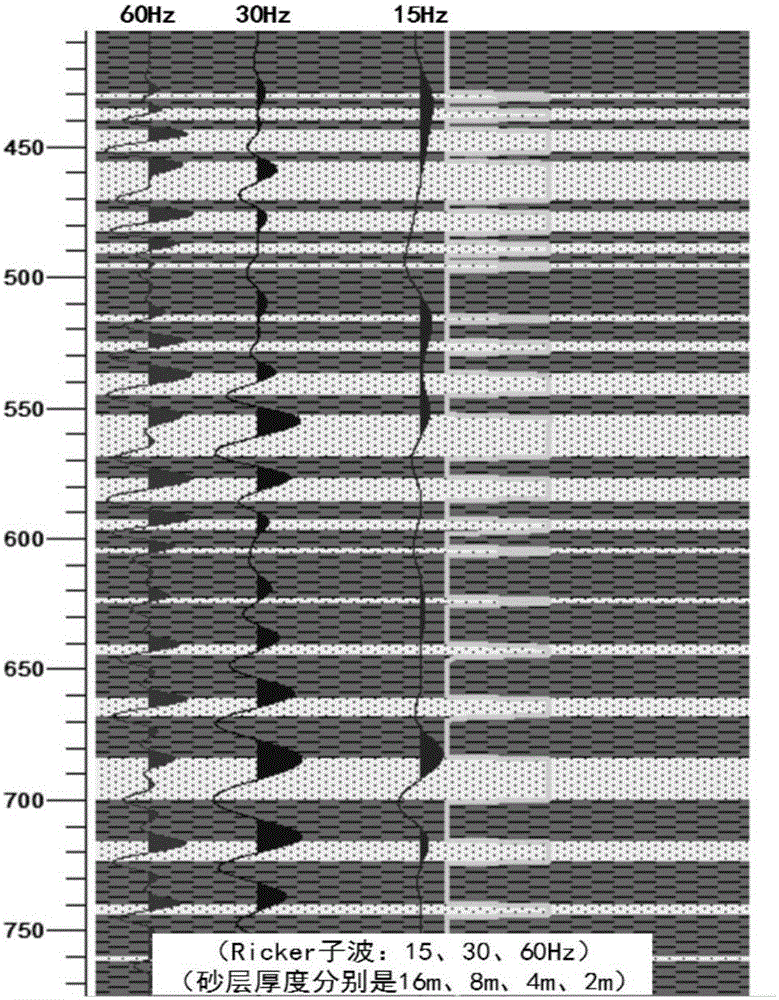
ActiveCN105116449AEasy to identifyHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingLithologyWavelet decomposition
The present invention relates to a method for identifying a weak reflection reservoir. Firstly, according to a formation lithology structural characteristic, the geological factors of seismic weak reflection lithology oil reservoir formation is determined through forward modeling, then seismic data is subjected to frequency extraction and filtering process so as to improve the identification ability of a weak reflection small size target by earthquake, then the seismic facies analysis is carried out, a seismic weak reflection development zone is determined, seismic attribute analysis is carried out, the distribution characteristics of the weak reflection reservoir is finely described, and the weak reflection reservoir is identified through the seismic weak reflection development zone and the reservoir distribution characteristics obtained according to the seismic facies and the seismic attribute. The identification and hydrocarbon potential detection are carried out through wavelet decomposition and reconstruction, the precision of reservoir prediction and trap identification are improved, and the purpose of improving the success rate of drilling is achieved. According to the method, the precision of weak reflection geological target identification and fine description are effectively raised, the method is systematic, effective, economical and practical, and the method is widely applied to the oil and gas exploration under the same geological conditions and has good social and economic values.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Concrete damage accumulation analysis method under cyclic load
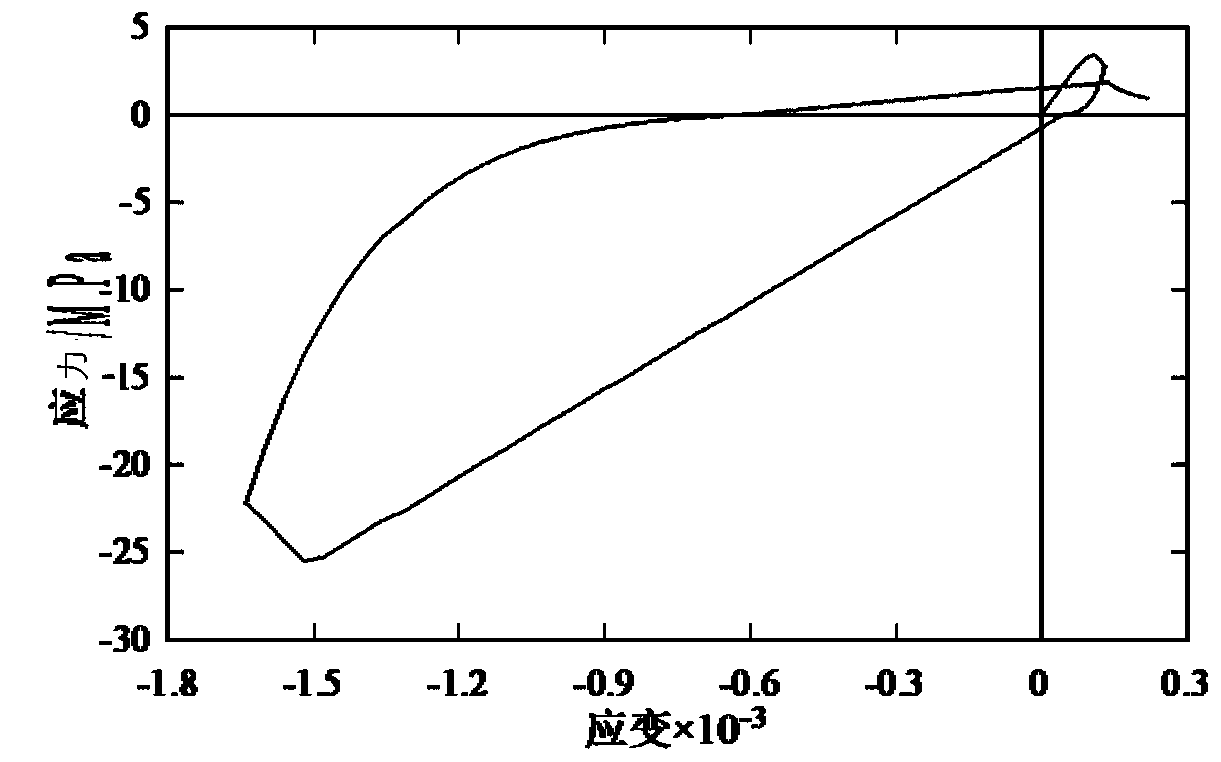
ActiveCN110926973AThe analysis result is accurateMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesArchitectural engineeringSeismic analysis
The invention discloses a concrete damage accumulation analysis method under cyclic load. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a three-dimensional isoparametric unit finiteelement model representing a concrete material; selecting a model, applying a normal grading load on a single side, giving a boundary condition, and determining a calculation time step; converting themulti-axis strain into unit single-axis equivalent strain through a four-parameter equivalent strain calculation method, and judging the tension and compression state of the unit; judging the loadingand unloading state of the current time step unit, and calculating the residual plastic strain and equivalent stress of the current time step unit; and calculating a unit damage variable based on a strain equivalence principle. According to the method, the influence of the hysteretic effect of the softening section of the concrete stress-strain curve under cyclic load is considered; the loading and unloading path of the hysteretic effect is defined, the damage accumulation process of the concrete material under the cyclic load can be accurately simulated, the method can be used for researching the dynamic performance of the concrete material, and actual guiding significance is provided for actual concrete structure anti-seismic analysis.
Owner:江西省水利科学研究院
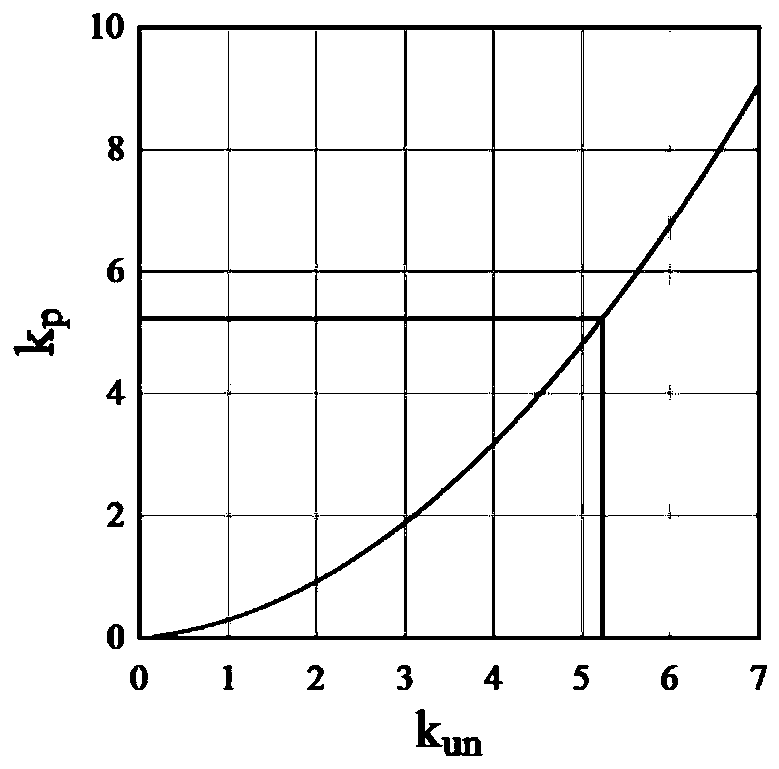
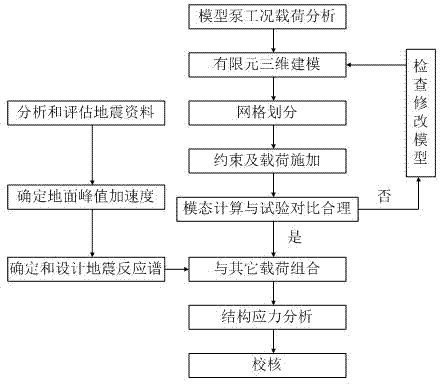
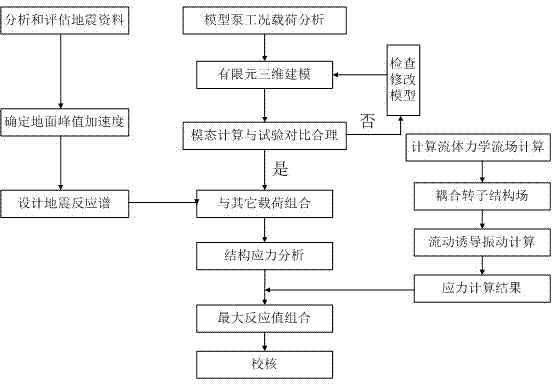
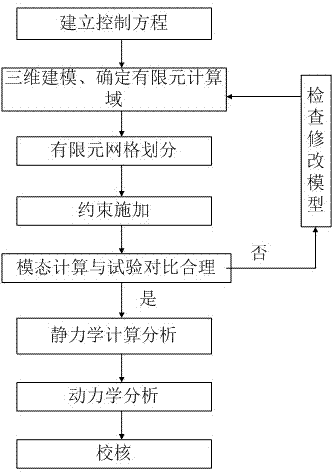
Anti-seismic analysis method for residual heat removal pump
ActiveCN103927416AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsResponse spectrumMechanical equipment
The invention discloses an anti-seismic analysis method for a residual heat removal pump. The anti-seismic analysis method includes: firstly, designing a seismic response spectrum by analyzing operating conditions and load of a pump model and analyzing seismic data; secondly, adopting a finite element calculation procedure for calculation to obtain stress variation conditions of equipment in a stationary state under seismic force; thirdly, adopting a fluid structure interaction based method for flow induction vibration calculation of a rotor system to obtain maximum stress generated by rotating fluid in the equipment to the structure; fourthly, combining maximum reaction values of modes of vibration; finally, checking according to material attributes and a minimum clearance between a static part and a rotor part. Acting force of the rotating fluid on equipment is calculated, stress calculation of rotary mechanical equipment for nuclear power under the most extreme condition is taken into account, and accuracy in anti-seismic analysis and calculation is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com