Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
400 results about "Post surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Postoperative (post-op) [-op′ərətiv′] Etymology: L, post + operari, to work. pertaining to the period of time after surgery. It begins with the patient's emergence from anesthesia and continues through the time required for the acute effects of the anesthetic and surgical procedures to abate.
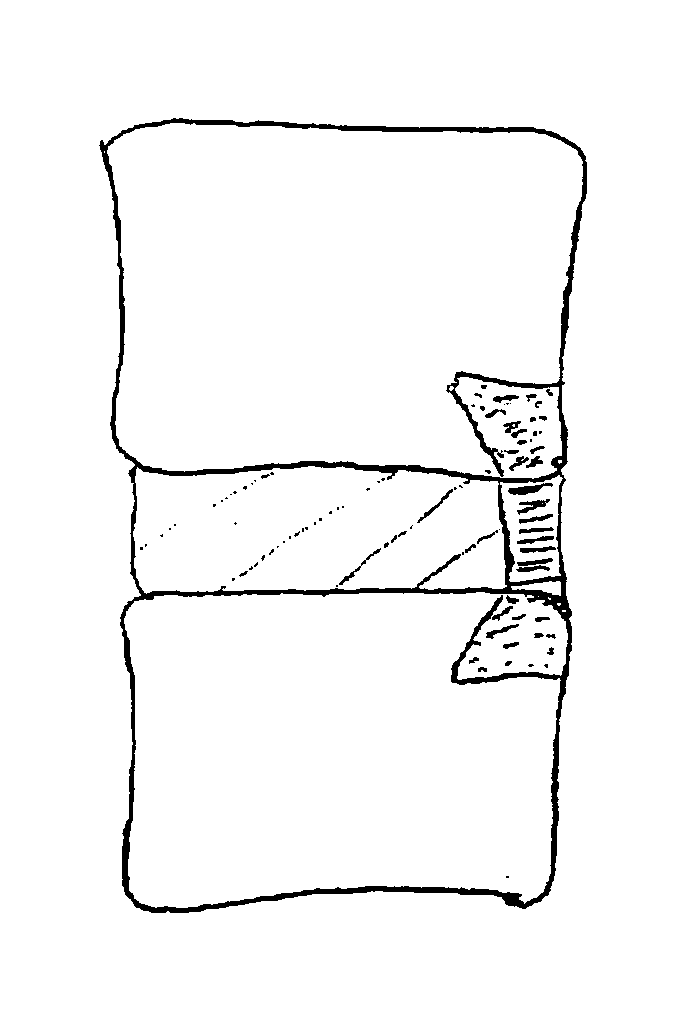
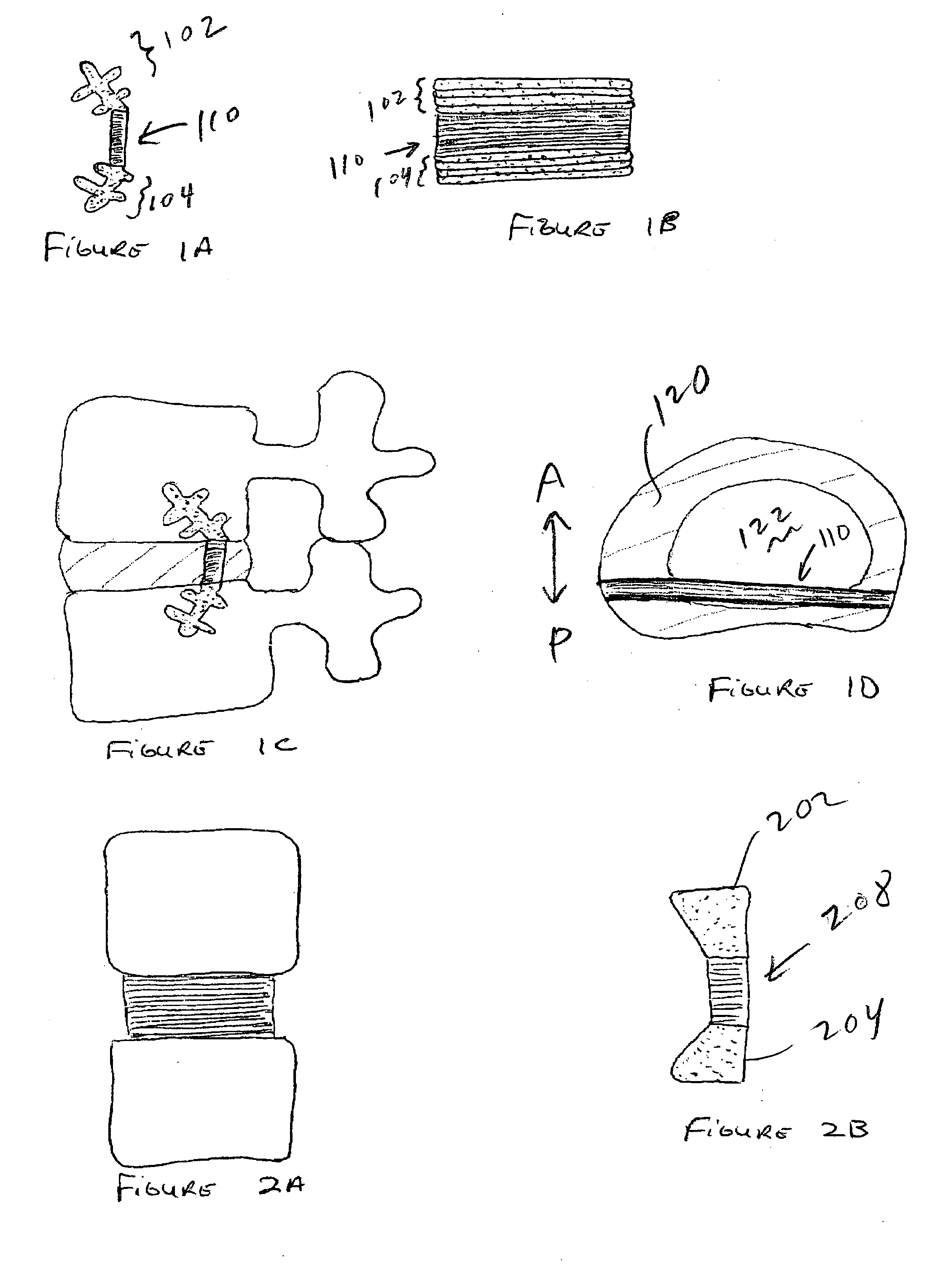
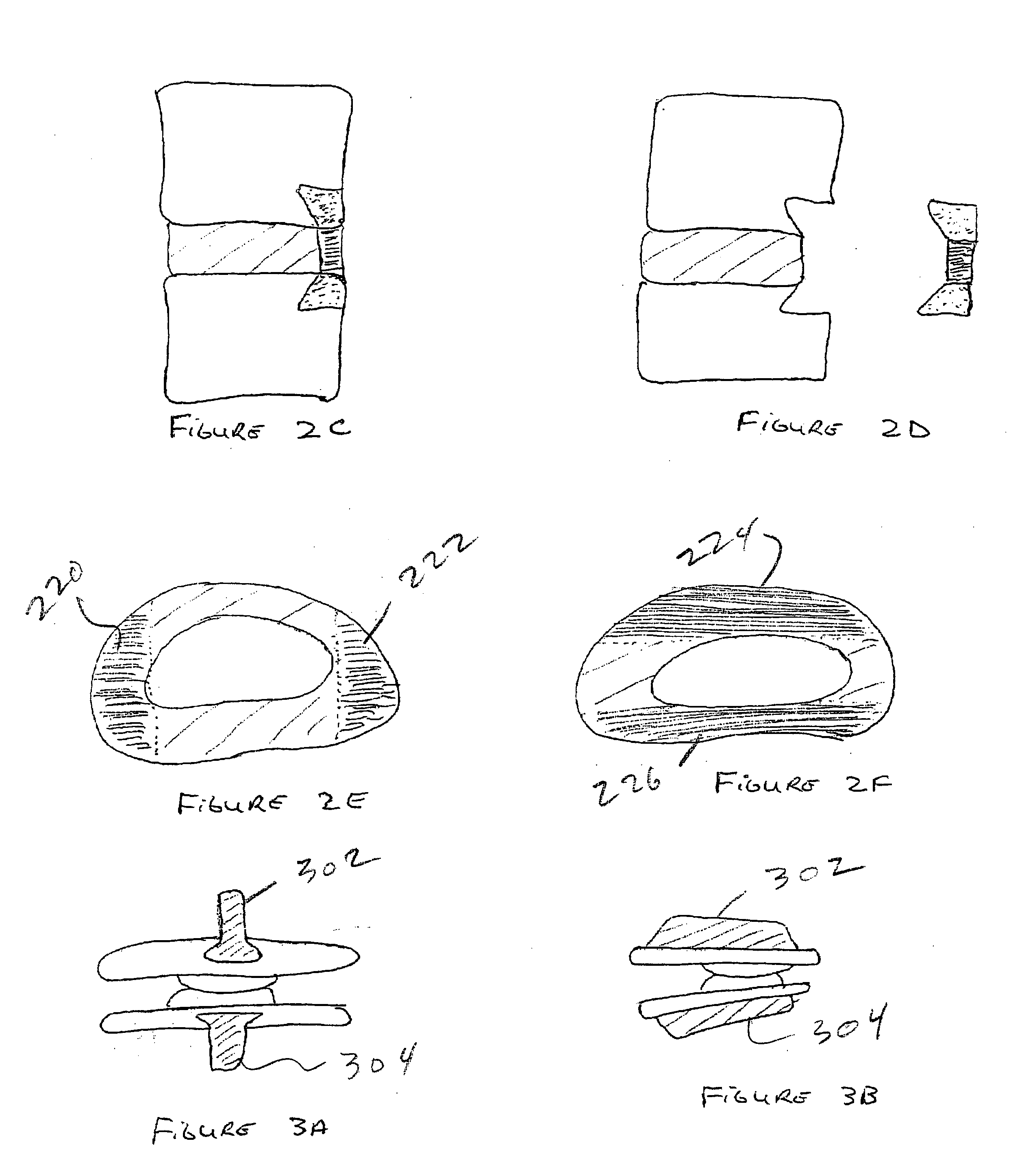
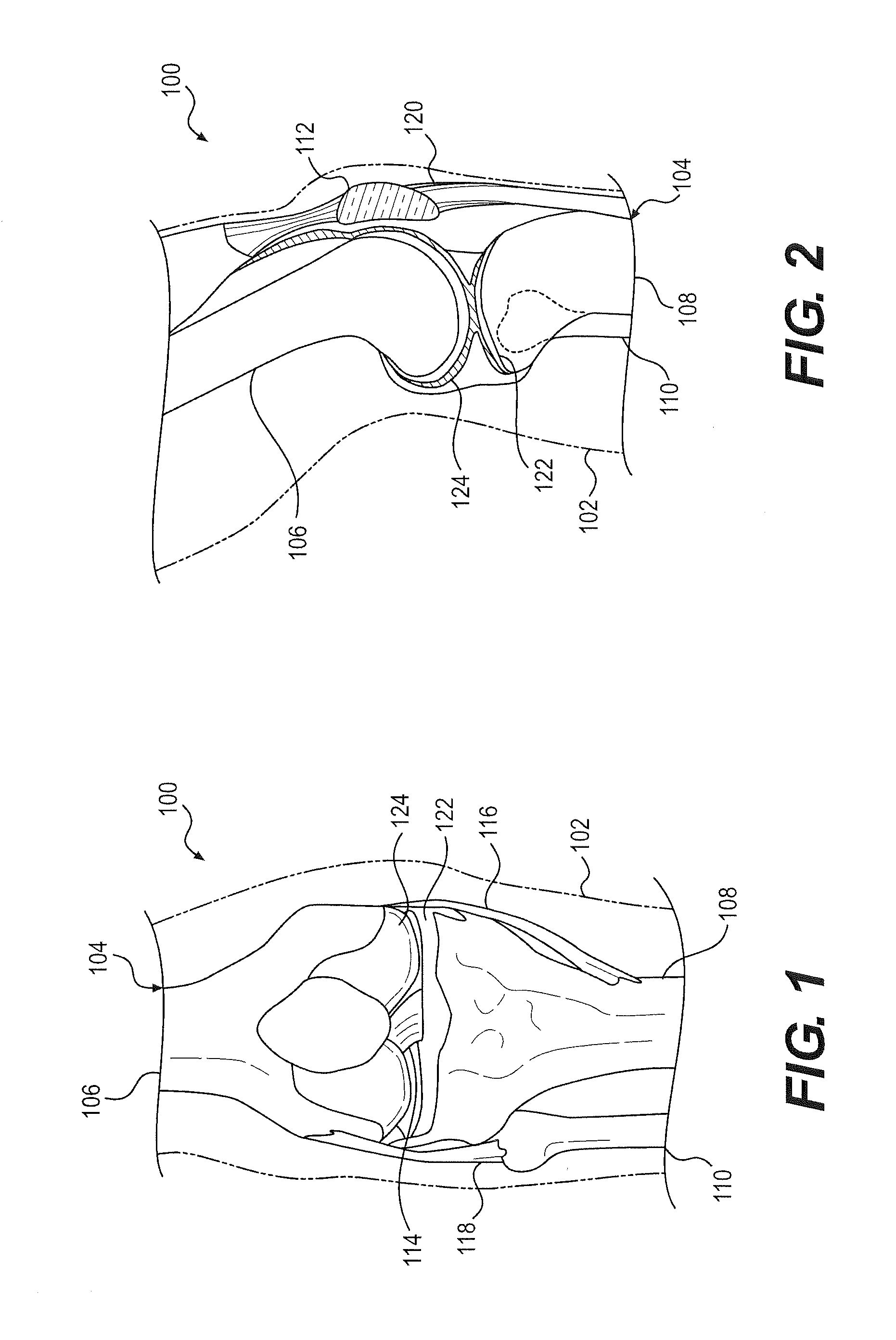
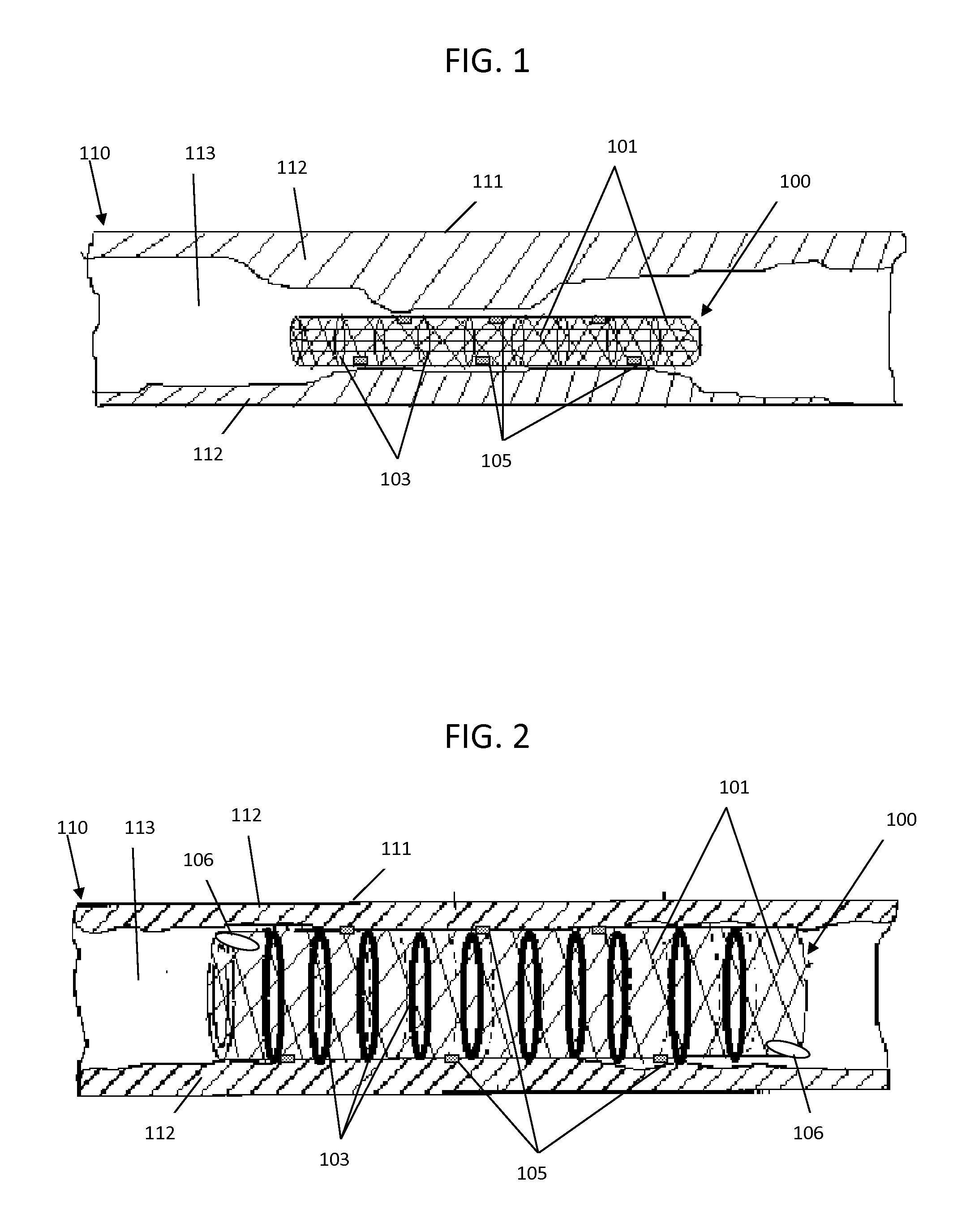
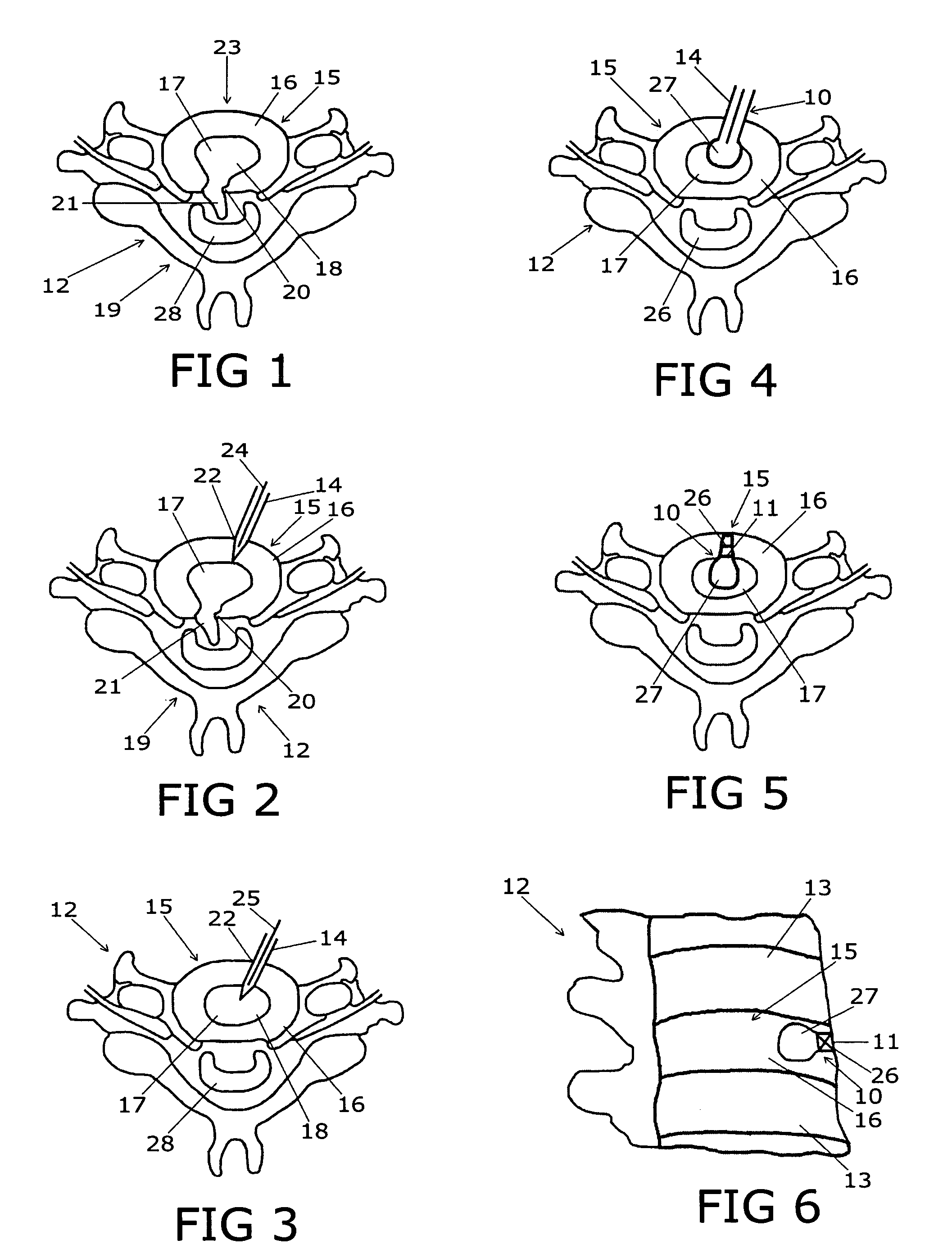
Spinal implants, including devices that reduce pressure on the annulus fibrosis
InactiveUS20050256582A1Promote reconstructionPrevents herniationInternal osteosythesisBone implantFibrosisDiscectomy
The invention broadly facilitates reconstruction of the Annulus Fibrosus (AF) or the AF and the Nucleus Pulposus (NP). Such Reconstruction prevents recurrent herniation following Microlumbar Discectomy (MLD) other procedures. The invention may also be used in the treatment of herniated discs, annular tears of the disc, or disc degeneration, while enabling surgeons to preserve the contained NP. The methods and apparatus may be used to treat discs throughout the spine including the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines of humans and animals. In the preferred embodiment, a spinal repair system according to the invention comprises a first end portion adapted for placement within an intervertebral body, a second end portion adapted for placement within an adjacent intervertebral body, and a bridge portion connecting the first and second end portions, the bridge portion being adapted to span a portion of an intervertebral disc space and prevent excessive outward bulging.
Owner:ANOVA
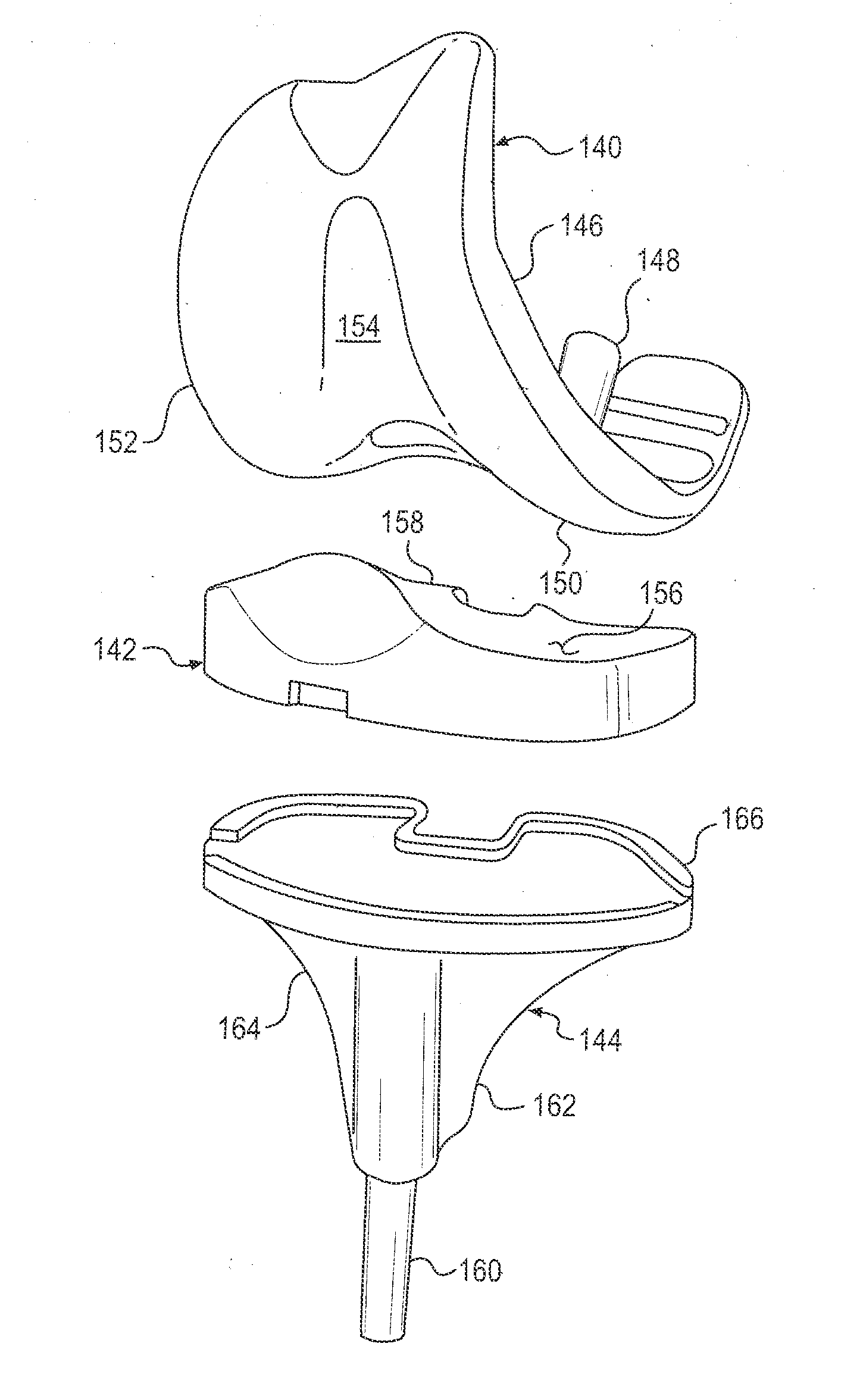
Customized process for facilitating successful total knee arthroplasty with outcomes analysis
InactiveUS20140013565A1Address bad outcomesMedical data miningMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBone morphologyTotal hip arthroplasty
A method for producing a custom resection jig for a current patient scheduled to receive total knee arthroplasty using outcomes analysis comprising the steps of maintaining a database on a computer system of (1) prior patient bone morphology, (2) along with anatomical and mechanical bone alignment data and (3) data defining a custom resection jig design with a generally transverse resection window operable to guide a surgeon's transverse bone cut for prior patients that have received total knee arthroplasty and a post-surgery medically recognized scoring register greater or equal to a predetermined highly successful score value for a total knee arthroplasty procedure using prior success data to guide production of a current patient custom jig resection windows.
Owner:MACDONALD M D JAMES
Surgical procedures
InactiveUS20080281190A1Efficient and reliable and identificationEfficient and reliable locationSurgeryDiagnostic markersSurgical operationScanner
A method of locating and identifying, during surgery, target regions within a body intended for excision of suspect tissue and / or removal of diseased organs or foreign objects, resides in implantation within the body proximate the suspect tissue or object prior to surgery of one or more passive integrated transponder tags and, at the time of and / or during surgery, scanning of the body with a radio frequency scanner or reader that activates the tag or tags and provides the surgeon with one or more signals indicative of the approximate location and unique identification of each of the tags, thereby to aid the surgeon in performance of the surgery. Verification of the success of the surgical procedure is obtained following surgery by scanning the site for absence of the tag or tags and / or by scanning the excised tissue for presence of the tag or tags.
Owner:HEALTH BEACONS
Pain reliever and method of use
InactiveUS6653352B2Does not burnGood effectSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideCapsicum extractHemorrhoids pain
A composition containing capsicium extract together with other ingredients to neutralize the discomfort resulting from the application of capsicium extract to the skin enabling treatment of many types of discomforts, including arthritis pain, neuropathy, post surgical scarring, hemorrhoid pain and itching, and pruritis without the discomfort normally associated with the topical application of capsicium extract.
Owner:MEDICAL MERCHANDISING
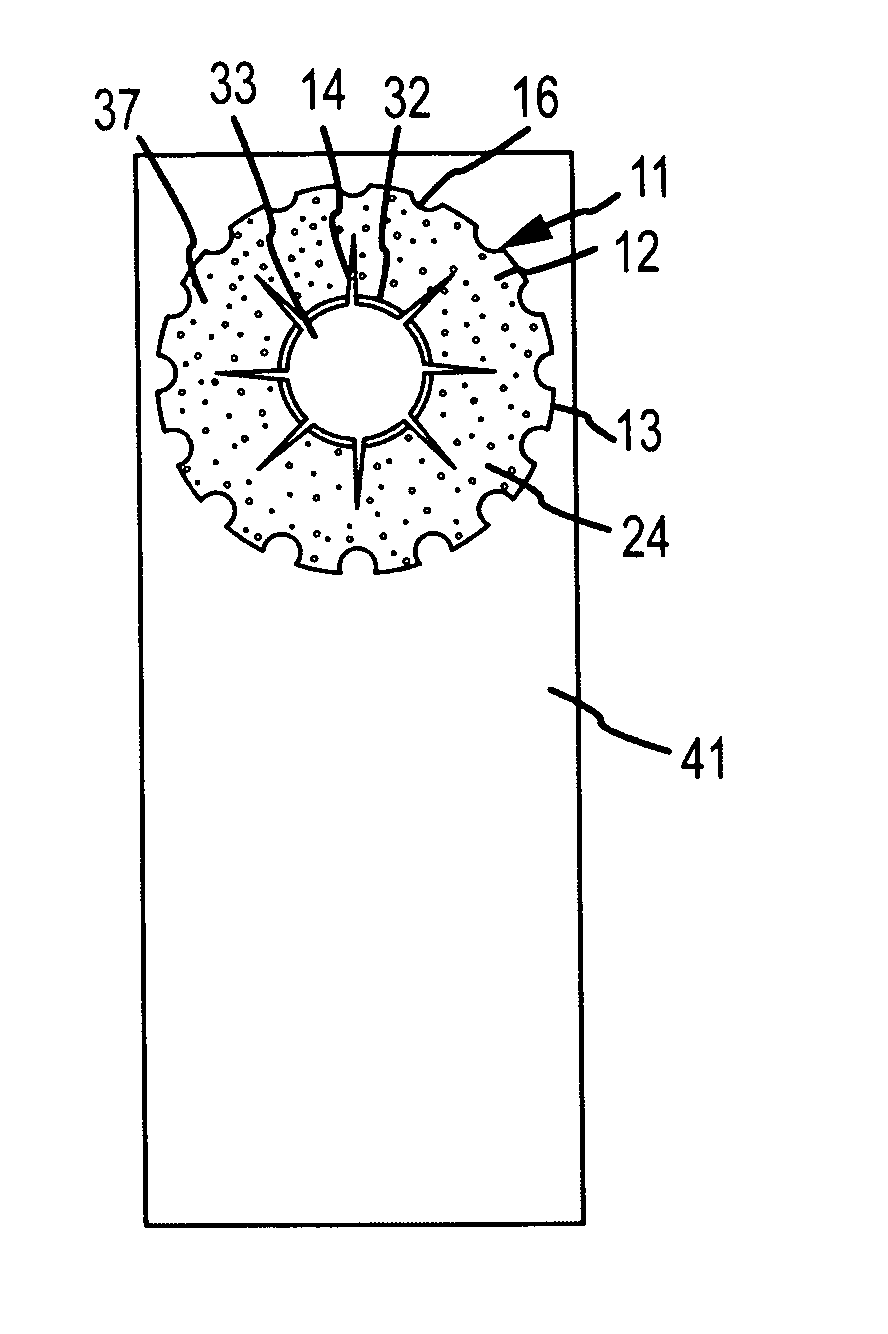
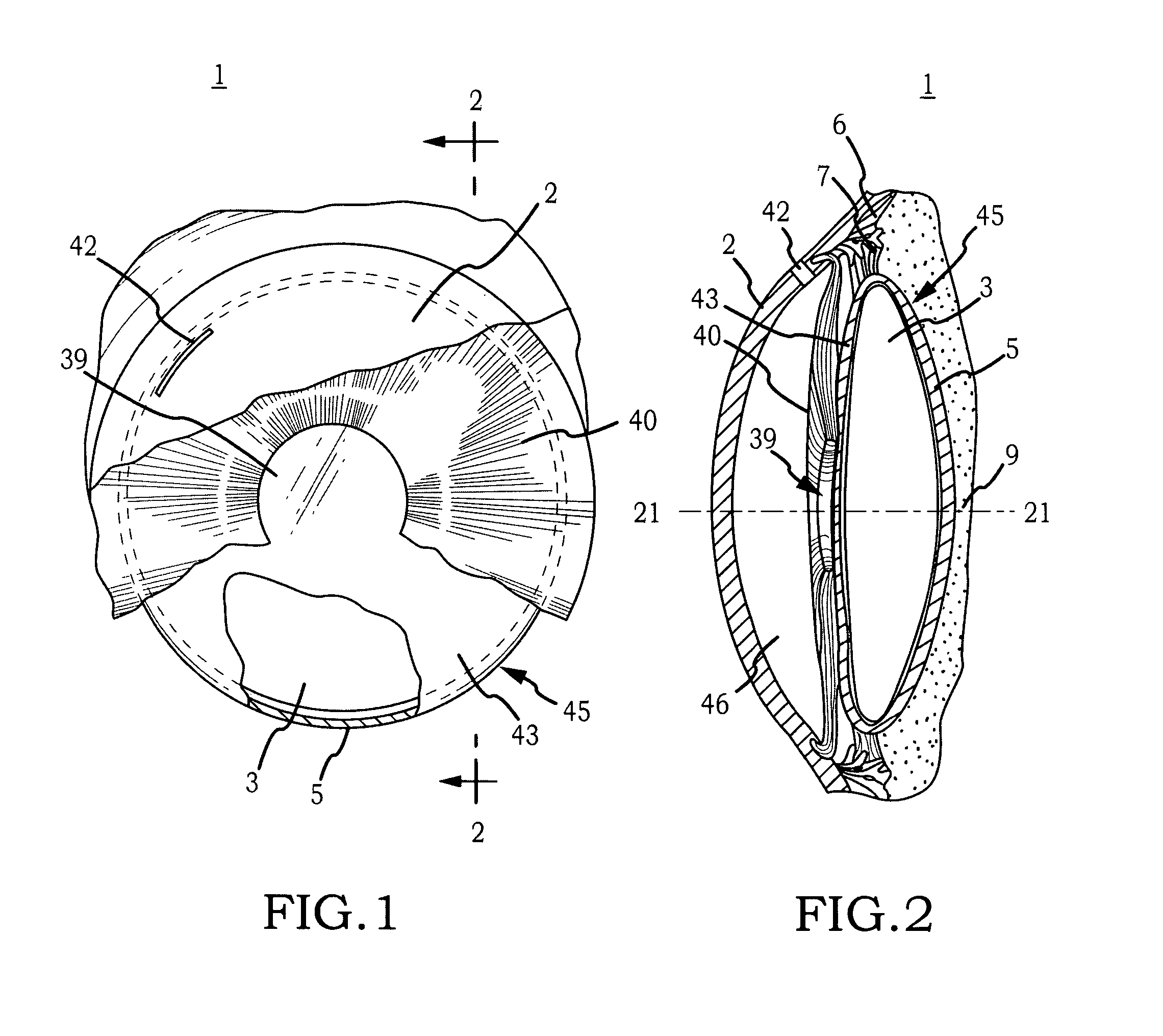
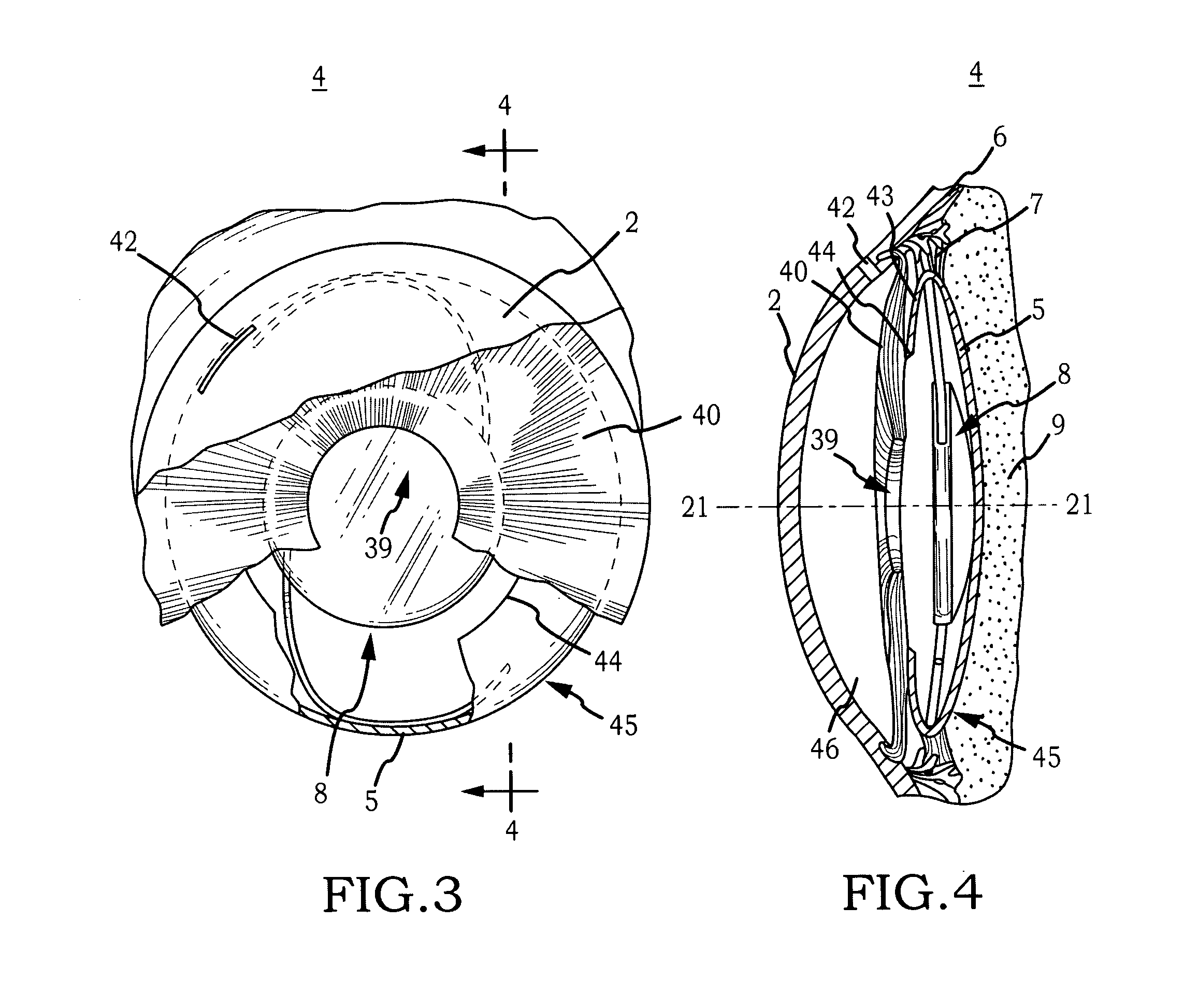
Biocompatible biodegradable intraocular implant system
InactiveUS20110230963A1Prevent proliferationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEye treatmentIntraocular lensActive agent
Generally, an intraocular implant and methods for treating an ocular condition. As to certain embodiments, an intraocular biocompatible biodegradable implant (11) which can provide a biocompatible biodegradable material in the form of a flexible membrane (12) containing an active agent (24) which implanted between an intraocular lens (8) and the surface of the posterior capsule (5) of the eye (1)(4) inhibits migration of residual lens epithelial cells after cataract surgery by providing structural or pharmaceutical barriers to reduce posterior capsule (5) opacification of the eye (1)(4).
Owner:INSIGHT INNOVATIONS
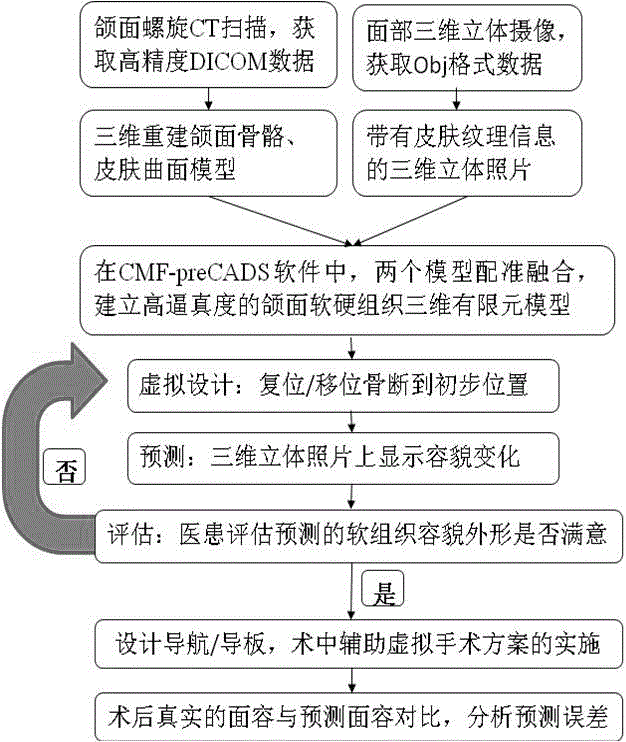
Computer simulation method for predicting soft tissue appearance change after maxillofacial bone plastic surgery
InactiveCN105608741ASymmetrical shapeShape coordinationImage generation3D modellingSurgical operationComputer-aided
The invention belongs to the computer aided surgical technique and maxillofacial plastic medical treatment equipment field and relates to a computer simulation method for predicting soft tissue appearance change after a maxillofacial bone plastic surgery. The method comprises the following steps that: spiral CT scanning is performed on the maxillofacial of a patient before the surgery; data are led into maxillofacial surgery design simulation software, namely, CMF-pre CADS, so that a three-dimensional maxilla and skin surface model is re-constructed; a bone segment is reset / shifted to a preliminary location; and the similarity of a pre-surgery prediction model and a post-surgery true appearance is judged through comparison through Geomagic software. With the method adopted, the post-surgery appearance and stomatognathic system functions can be recovered excellently; the appearance of soft tissues are symmetrical, harmonious and beautiful; the post-surgery satisfaction degree of the patient reaches 95%; the effects of the plastic surgery are stable; and long-term satisfaction is also very high.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
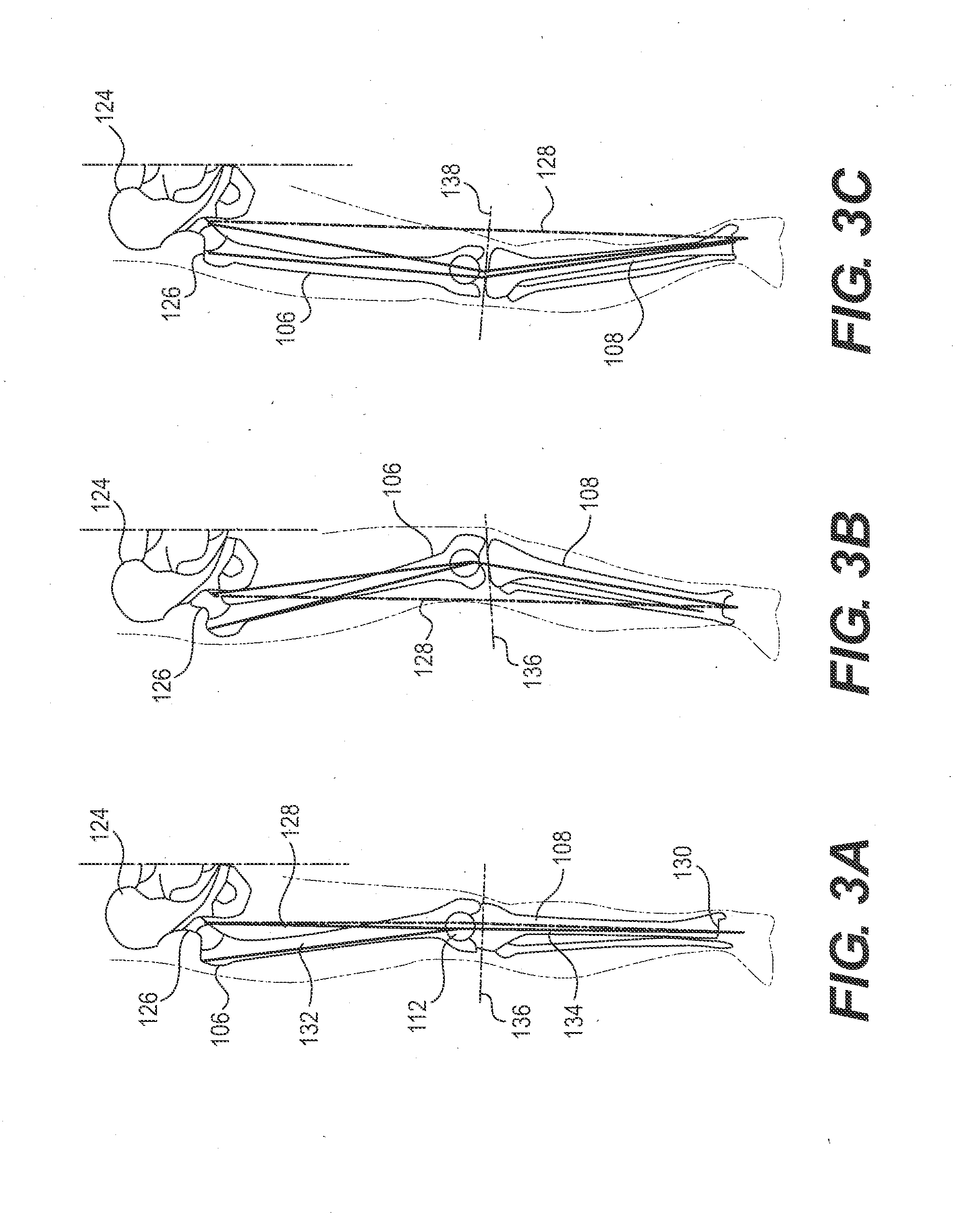
Device for correcting spinal deformities
InactiveCN1697630AConstant and controllable correction forceInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention relates generally to a device of and a method for correcting spinal deformities, such as scoliosis and kyphosis. The invention employs the superelasticity or pseudoelasticity, such as found in a nickel-titanium alloy, to provide a continuous, predictable, and controllable correction force and to achieve a gradual and full correction. The correction force can be exerted on the deformed spine either at the time of the spine surgery or after the surgery or both, to afford a full or substantially full correction. The continuous and controllable correction force of the present invention is safer than an instantaneous and large correction force applied only at the time of surgery. Additionally, the continuous and controllable correction force is capable of gradually and fully correcting the spinal deformities without any post-operative manipulation of the correction device or re-operation.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +1
Fracture fixation plate
Owner:SKELETAL HLDG LLC
Spinal rod and bone screw caps for spinal systems assemblies
InactiveUS20130079826A1Prevent slippage and disassemblyShorten the timeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPost operativeScrew thread
A threaded cap or c-clip that attaches to a spinal rod or bone screw. Such a threaded cap or c-clip prevents slippage of the spinal system assemblies along or off their rods or bone screws during intra- or post-operative periods.
Owner:SIMONSON PETER M
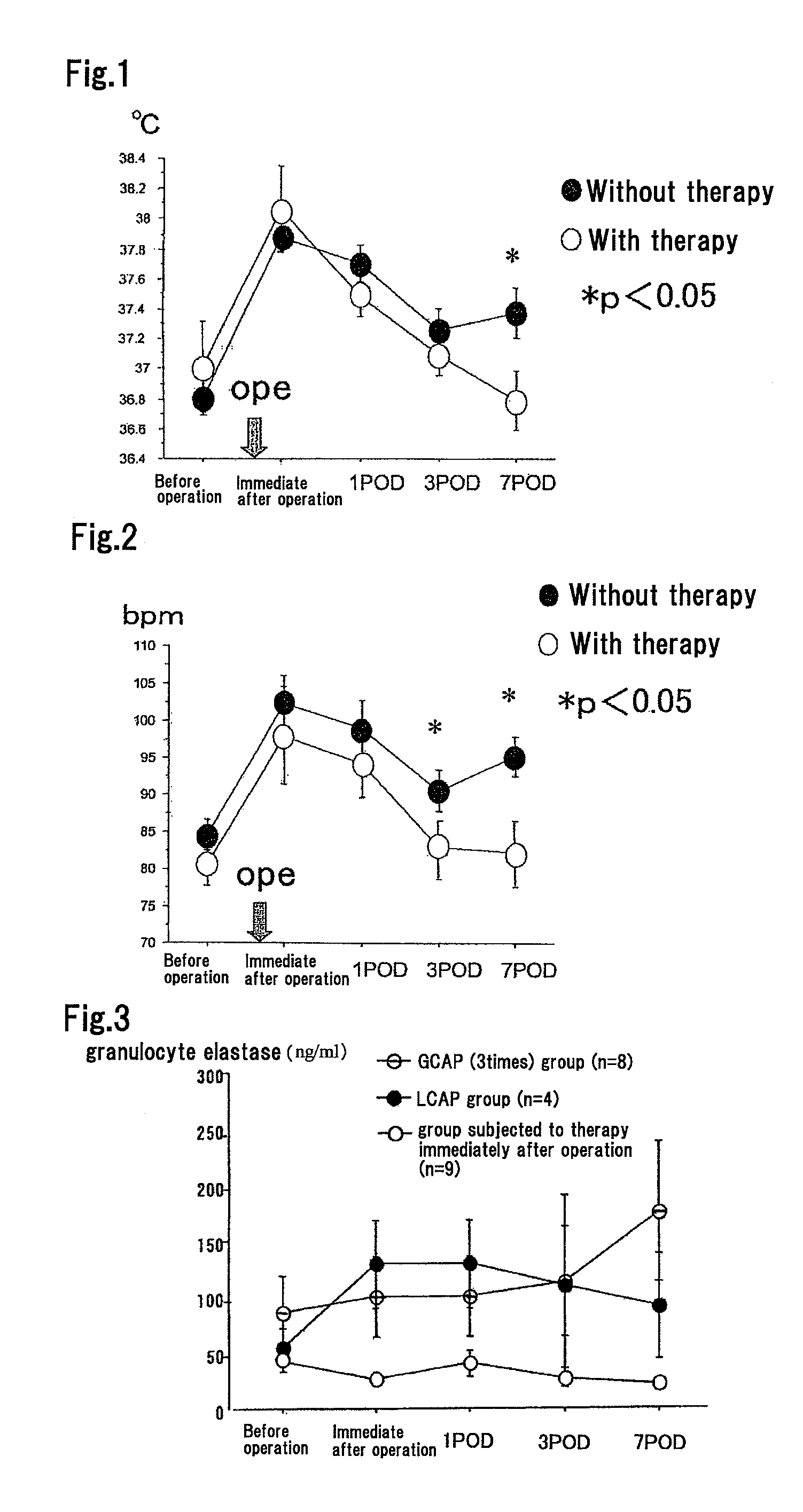
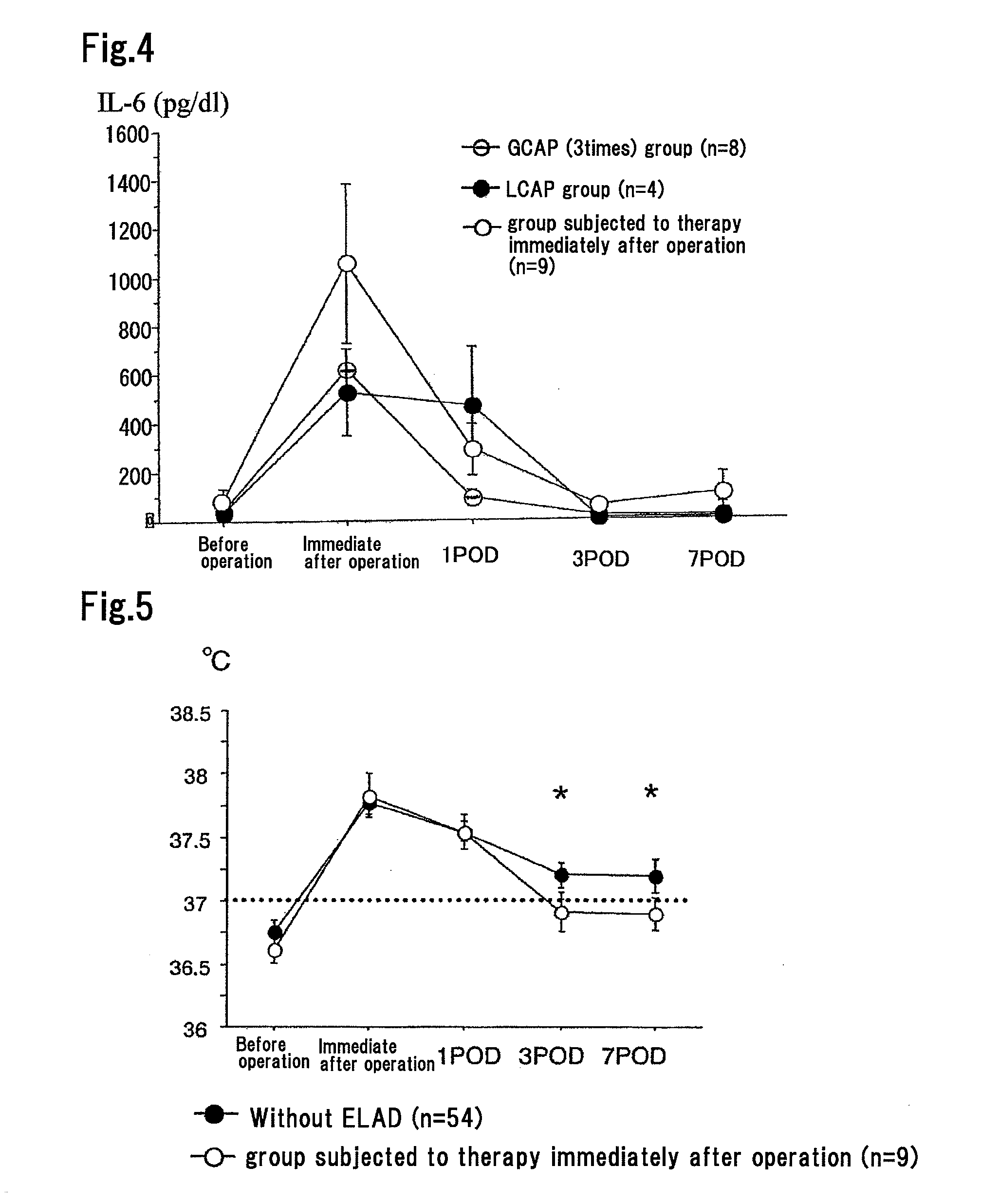
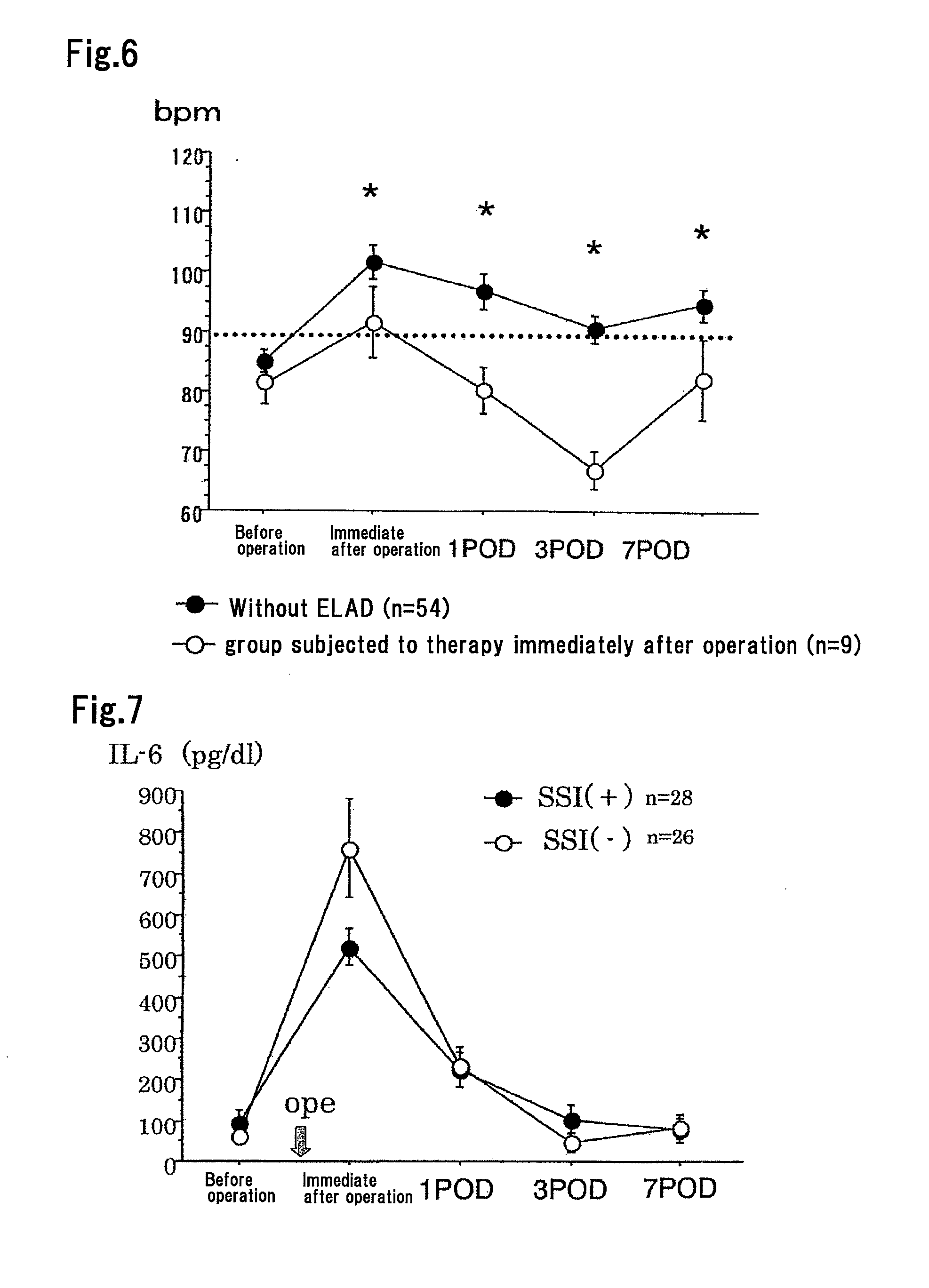
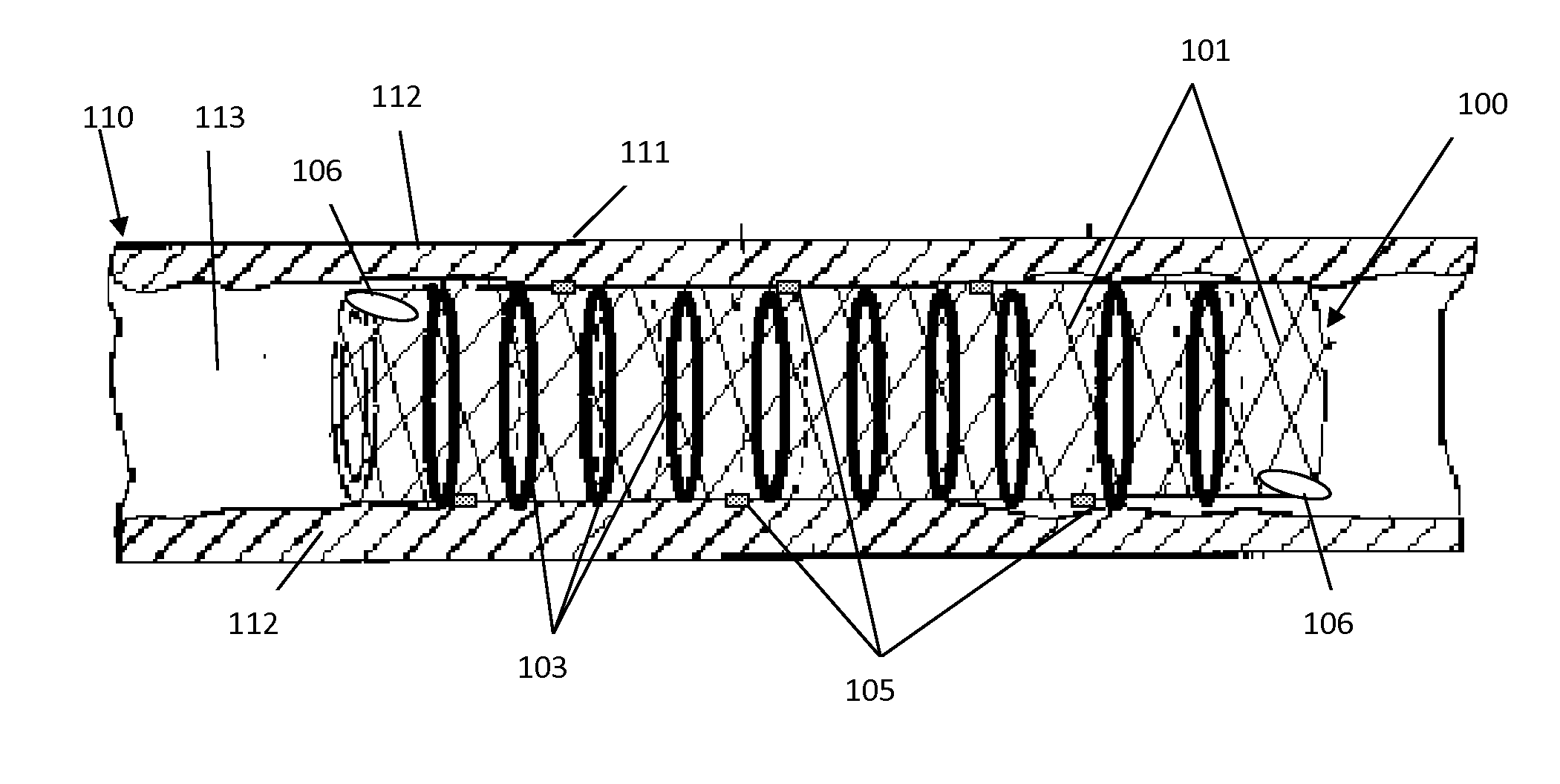
Method for Suppressing Surgical Site Infection and Column to be Used for the Method
ActiveUS20080260710A1Suppress complicationMore responsiveBiocideSurgical drugsSurgical operationSurgical site infection
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for suppressing surgical site infections (SSI) that have occurred at extremely high incidence rates at the time of surgical operations and particularly surgical operations on digestive system organs, and to provide a column to be used for the method. According to the present invention, a method is provided for suppressing surgical site infections, which comprises the steps of: (a) administering a chemotherapeutic drug for treating and / or preventing a surgical site infection; and (b) collecting blood from a surgical subject and removing leukocytes that comprise neutrophils from the blood during or within 24 hours after surgical operation, and then returning the blood from which the leukocytes have been removed to the surgical subject. The present invention also provides a column for blood circulation which is filled with a carrier having affinity for leukocytes comprising neutrophils, which is used for suppressing a surgical site infection during or within 24 hours after surgical operation on a digestive system organ.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Sensor Actuated Stent
InactiveUS20130041454A1Avoid complicationsSafety and efficacyStentsBlood vesselsVascular lumenRadial position
The invention is an implantable medical device to expand a vascular lumen into various positions, internally or from a remote location. The device is designed as a stent having a framework for radial or longitudinal expansion, including one or more integrated shape memory materials. The shape memory materials, or halos, radially expand to fix the framework into a first radial position. Sensors integrated with the framework mechanically or electro-mechanically monitor and control the positioning of the framework to a fixed second position, or gradually expand the framework to various radial positions. Visualization and communications devices assist in the monitoring and controlling mechanisms to position the implantable device during surgery or catherization, post-surgery, or at follow-up. The device is biocompatible, alleviating complications. The device can be utilized as a substitute, or in combination with another stent. Devices may be utilized in cardiovascular, neurovascular surgery or other intervention.
Owner:ITRACKEVERYTHING LLC
Adjustable drill guide assembly and method of use
An adjustable drill guide is provided that can be used to deliver a cross pin at a distance near the entrance to the femoral bone tunnel during ligament surgery. The cross pin positioned at the joint line, or tunnel opening, compresses and secures the graft within the bone tunnel, thereby preventing the graft from swaying back and forth post surgery when the joint is in motion. The adjustable drill guide assembly comprises a guide frame that includes an arm portion and a base portion that extends transversely to the arm portion. A rod member connects to the base portion for extending into the hone tunnel of the bone. Also included is a guide member configured for connection to the arm portion. The guide member is configured to be in moveable and lockable disposition along a length of the arm portion.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
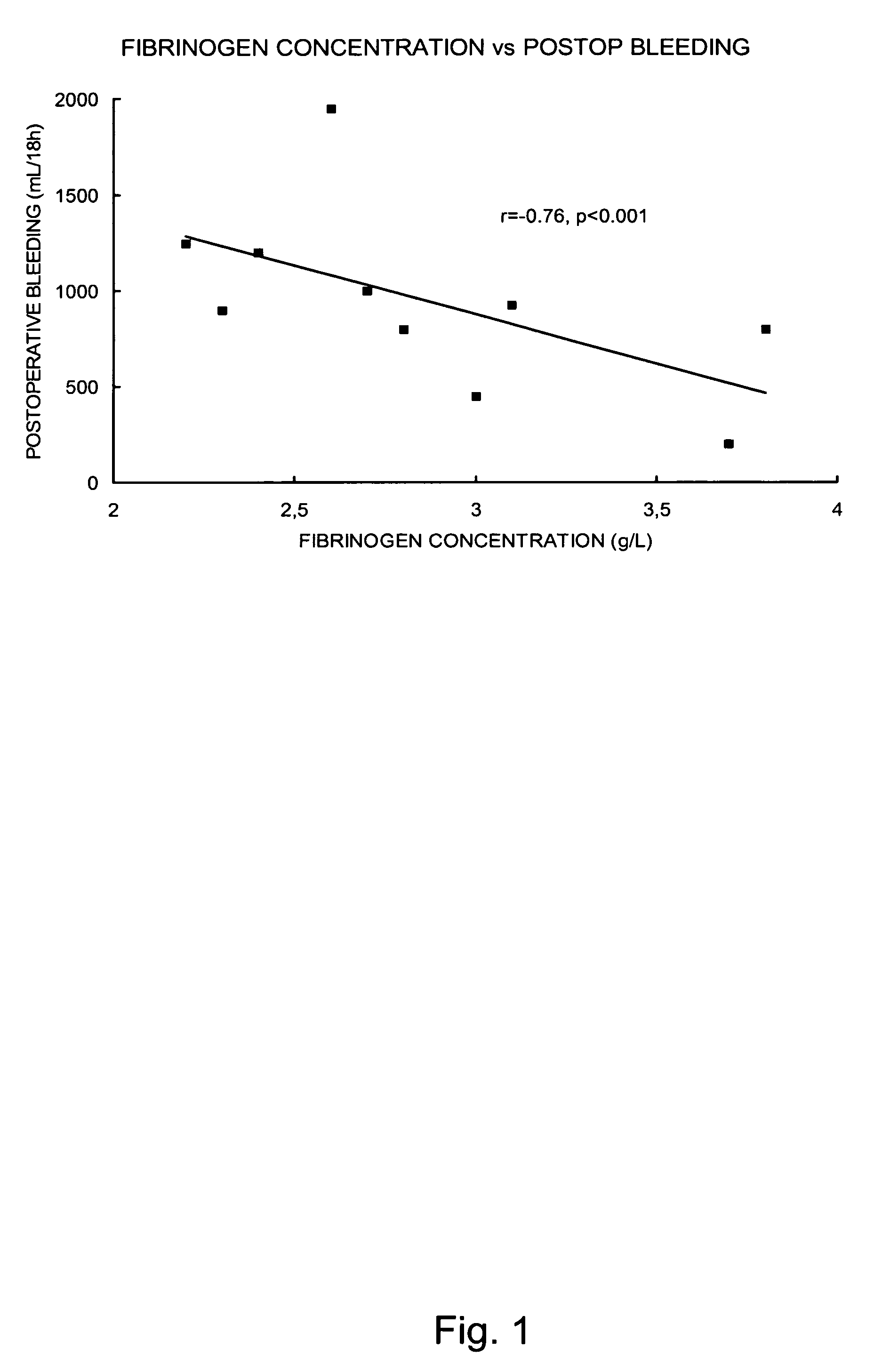
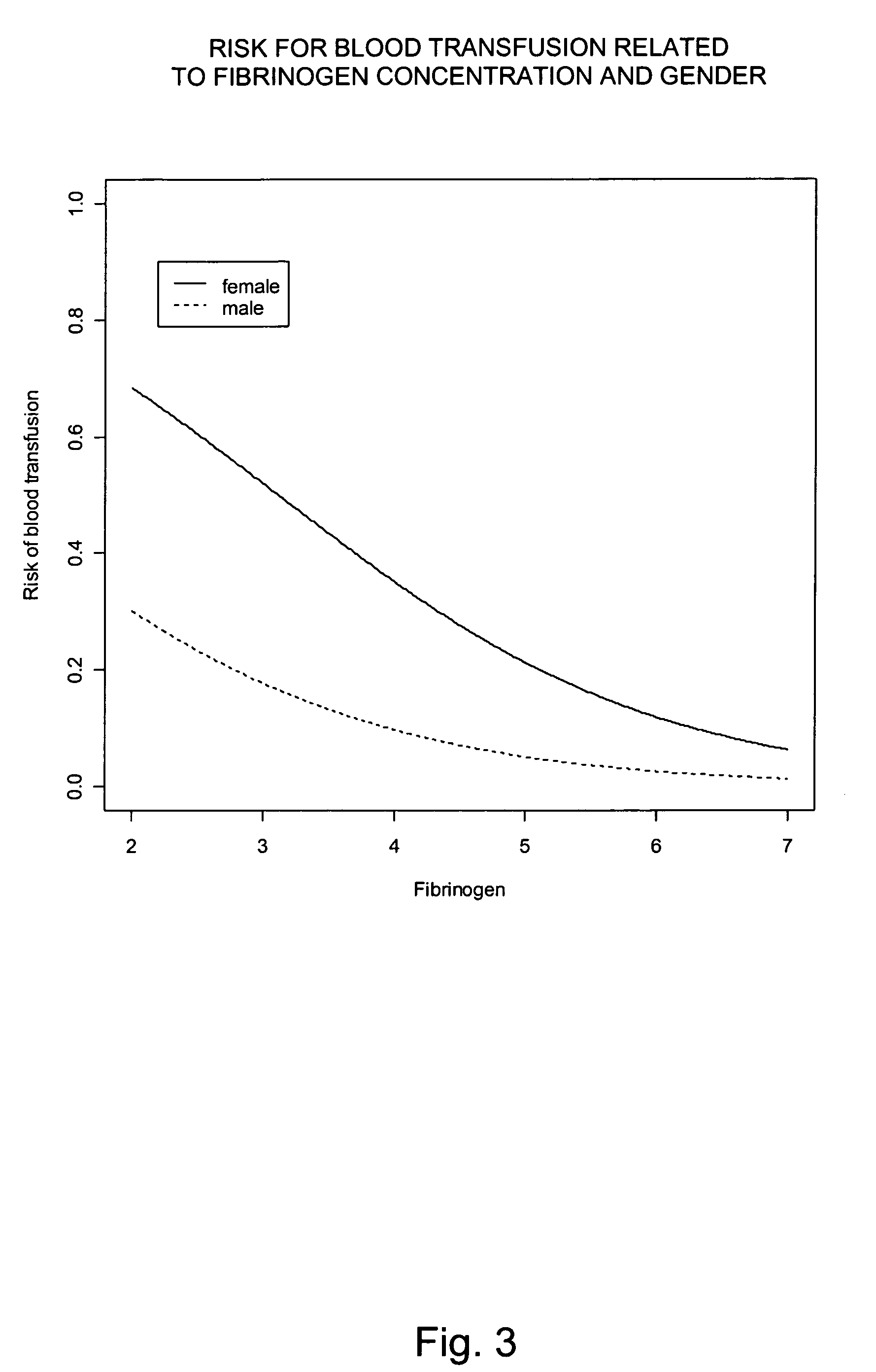
Use of fibrinogen as a prophylactic treatment to prevent bleeding during and after surgery and as a biomarker to identify patient with an increased risk for excessive bleeding and blood transfusion
InactiveUS20100062981A1Preventing perk and postoperative bleedingAvoid bleedingPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgical departmentIncreased risk
The present invention provides a method for preventing peri- and postoperative bleeding in subjects undergoing surgery, in particular subjects with a preoperative fibrinogen plasma level equal to or above the normal range. The method comprises administration of a substance with fibrinogen-like activity to the subject in an amount that result in a circulating fibrinogen plasma level of from about 1.0 g / L. The present invention also provides a method for determining the risk of subjects with a preoperative fibrinogen plasma level equal to or above the normal range to bleed postoperatively. Furthermore, the present invention provides means for predicting the necessity of blood or plasma transfusion after a subject with a preoperative fibrinogen plasma level equal to or above the normal range has been subject to a surgical procedure. The means involves measurement of the fibrinogen level of the subject before surgery and comparing the level with a risk curve.
Owner:JEPPSSON ANDERS +4
Inflatable surgical retractor
An expandable surgical retractor for minimally invasive surgical applications is disclosed. The expandable retractor, preferably in the form of an inflatable balloon retractor, is inserted in a surgical corridor and expanded to the desired size and shape. The retractor of the present invention is amenable to many shapes including cylindrical, conical with the base at the depth of the corridor, hourglass, and crescent and are dictated by the surgeon's needs. Cooling of the retractor allows the retractor to maintain the expanded characteristic. The expanded relatively rigid retractor provides an ideal corridor for surgical applications. In a preferred embodiment, a second retractor, of the invention, can be placed at a greater depth through the first placed retractor; the “telescoping” effect rapidly provides greater exposure with minimal manipulation. Following surgery, such retractor(s) can be removed in a manner that minimizes bleeding and tissue damage. One such method is reheating to soften and restore the retractor to its unexpanded size. Or, laterally placed perforations allow for fracturing of the retractor by bovie cautery, facilitating removal by “unzipping” the retractor.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
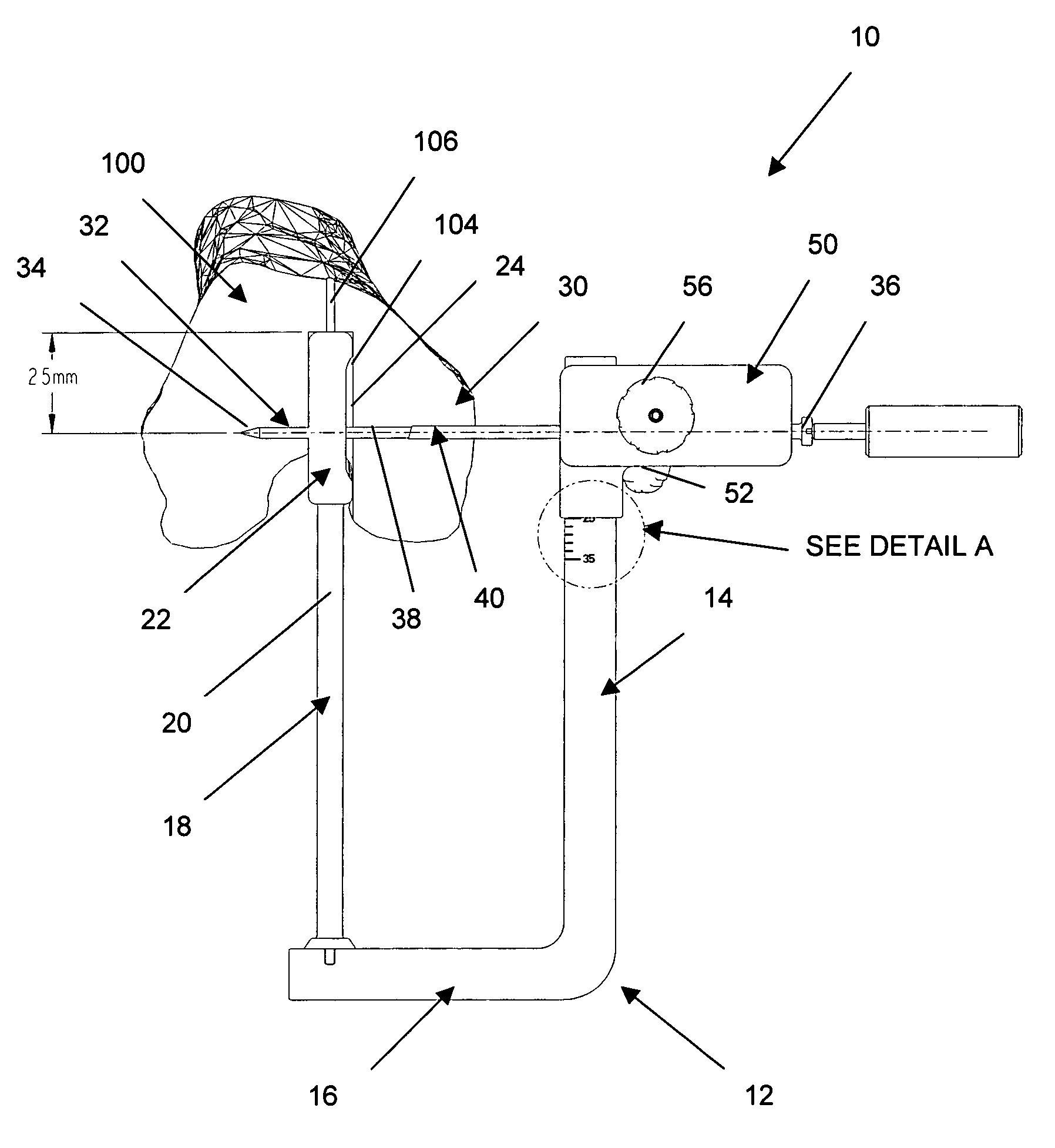
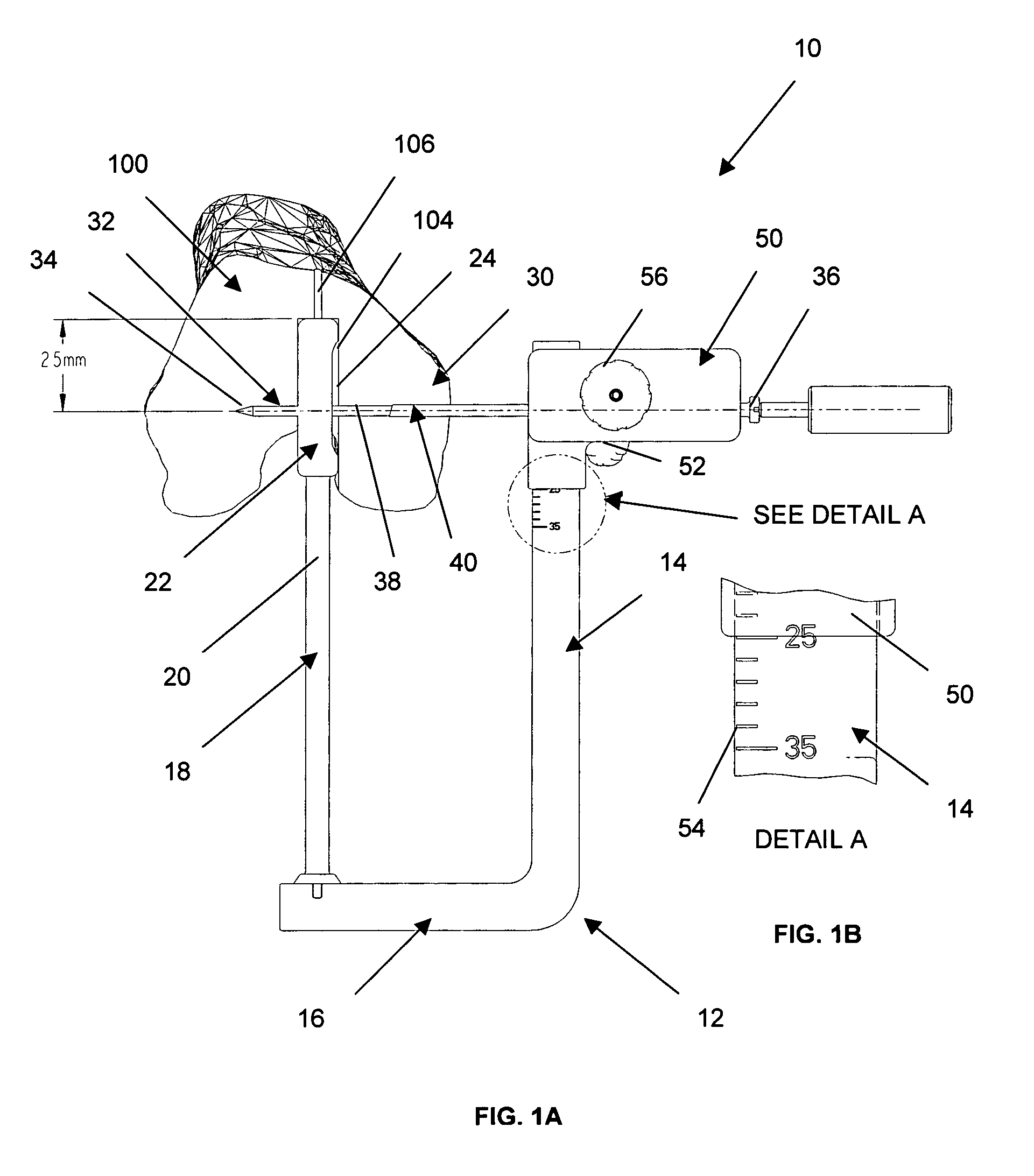
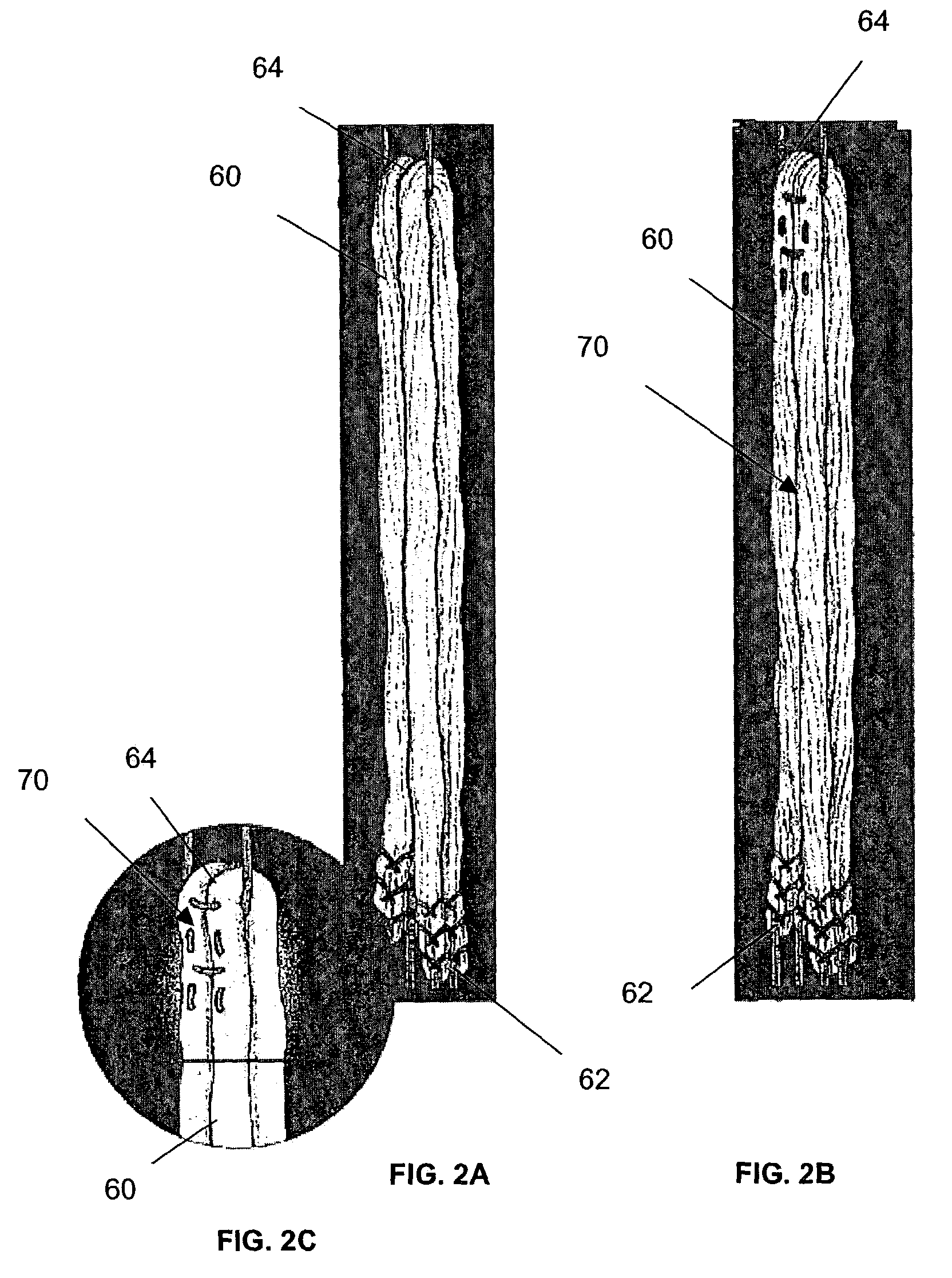
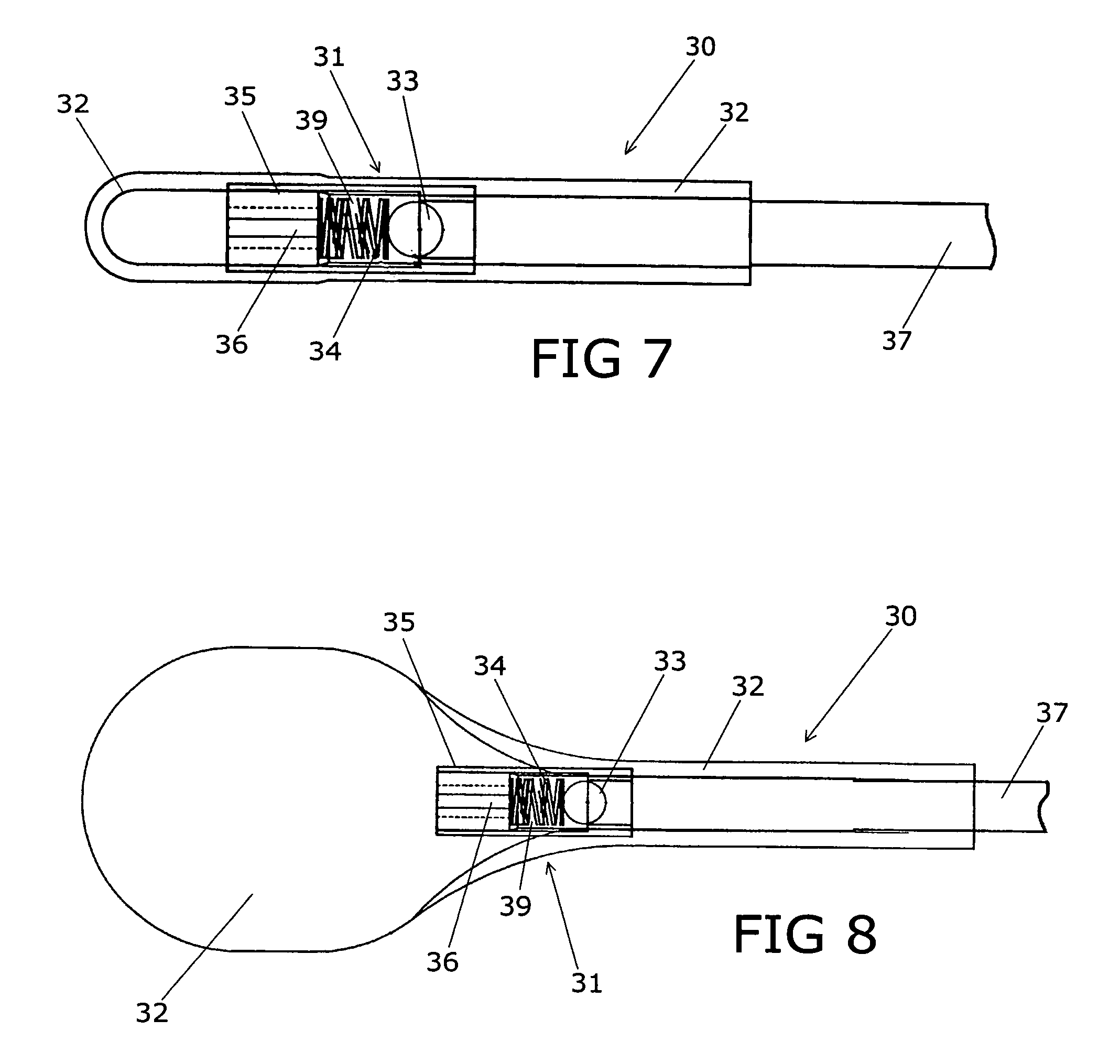
Device for treating intervertebral disc herniations
InactiveUS20050049604A1Minimize compressionMore processedJoint implantsSpinal implantsDistractionEndoscopic Procedure
A method and device for treating human intervertebral disc herniations using an endoscopic procedure. An access port is opened into and through the annulus of a disc to remove nucleus pulposus. Subsequent treatment, a balloon device having a valve structure is positioned via an endoscopic procedure into the disc space. The balloon device is filled with a physiological fluid to occupy the disc interspace or to maintain some degree of distraction of the created disc space. Post surgery, after fibrocollagenous tissue has grown into the disc space, a second endoscopic procedure is performed to remove the balloon device. Fluid is removed to collapse the balloon structure and then removed via the guide tube. The ingrowth of fibrocollagenous tissue will continue to fill the void formerly occupied by the balloon device. The balloon device has a rigid valve body and a flexible balloon member. The valve body has an end plug, a valve chamber holding a valve member and a cooperating biasing structure. The balloon member of the device is inserted into a vacated nucleus space of a herniated disc and then inflated with a physiological fluid using a fill tube. The balloon member, valve body, and fill tube or portions thereof may be constructed of a radiolucent material to provide visibility during implantation, surveillance and removal. The balloon device may be used in the cervical, lumbar or thoracic region of the spine.
Owner:PMT
Compositions and methods for treating pain
ActiveUS20060280718A1Reduce severityReduce thrombosisBiocideNervous disorderNervous systemPost injury
In the present invention, Applicants demonstrate the effect of a biomembrane sealing agent on the development of chronic pain following tissue injury as well as acute pain in a model of acute inflammation. Applicants demonstrate the ability of this class of agents referred to as “biomembrane sealing agents” to reduce the severity of hyperalgesia and allodynia following mechanical insult to the nervous system as well as their ability to reduce acute pain in a model of acute inflammation. Applicant describes the use of injectable or depot formulations of biomembrane sealing agent(s) for prophylactic treatment such as they could be administered after the insult (i.e. post-injury or post-surgery) but before the onset of acute or chronic pain. Alternatively, biomembrane sealing agents could be used to reduce the severity of acute or chronic pain after onset.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods of promoting enhanced healing of tissues after cardiac surgery
Resorbable polylactide polymer healing membranes and methods of their applications are disclosed. In a broad embodiment, the invention features methods for inducing proper tissue healing after an open heart surgery. In one embodiment, the methods includes a step of forming a patch with a healing membrane over the open pericardium to induce proper tissue healing and placement in other open heart surgery procedures to facilitate re-entry by the surgeon.
Owner:MAST BIOSURGERY
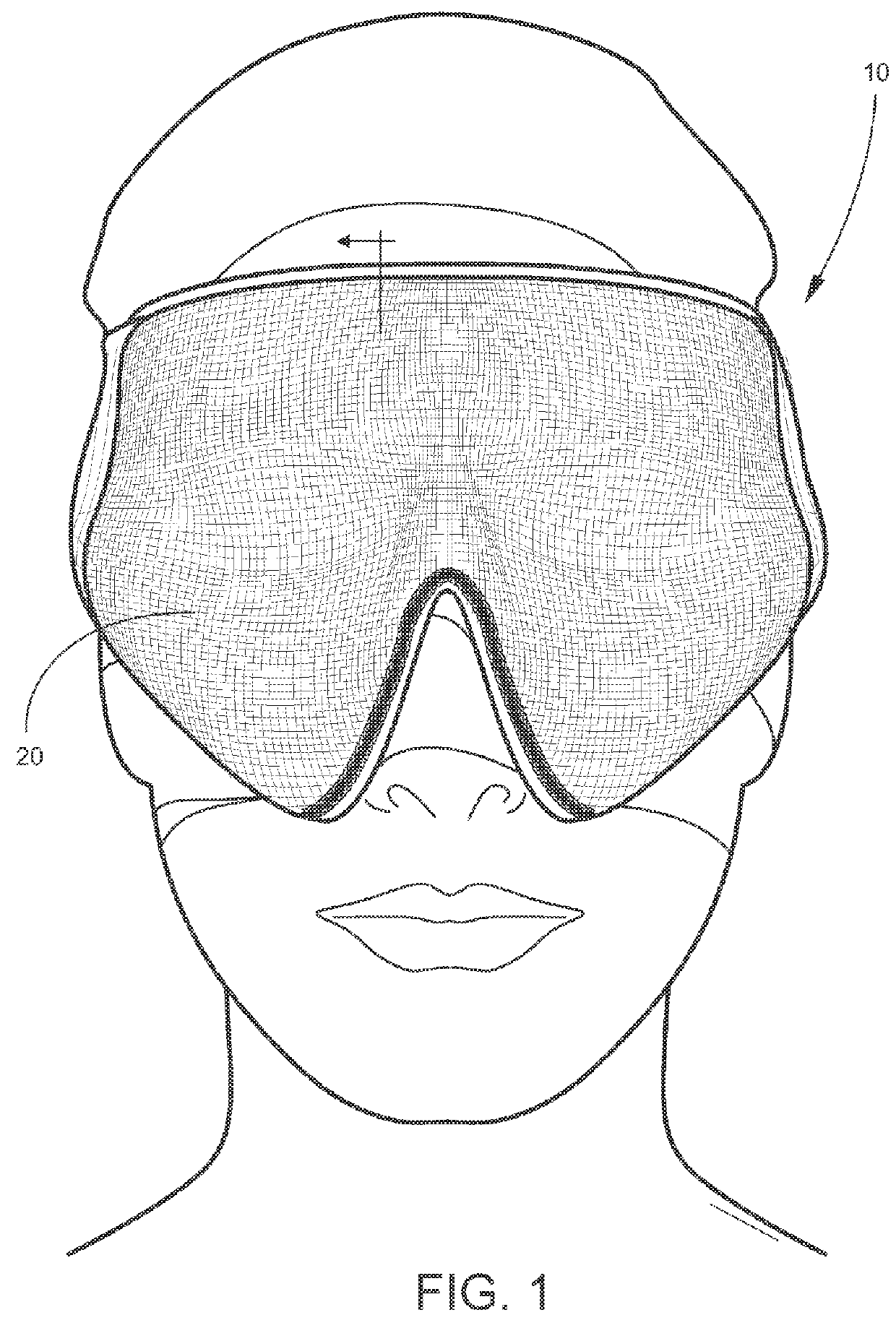
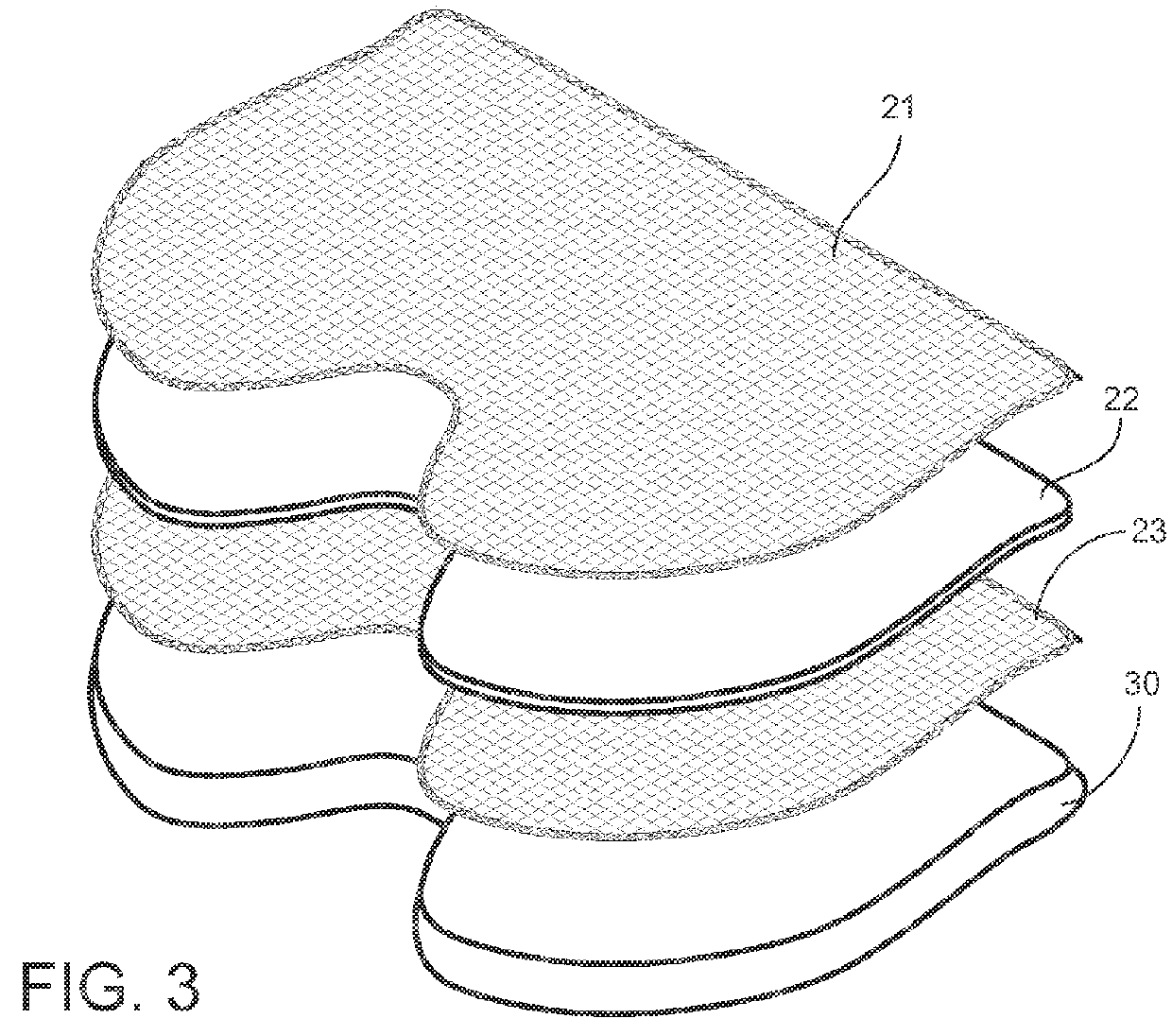
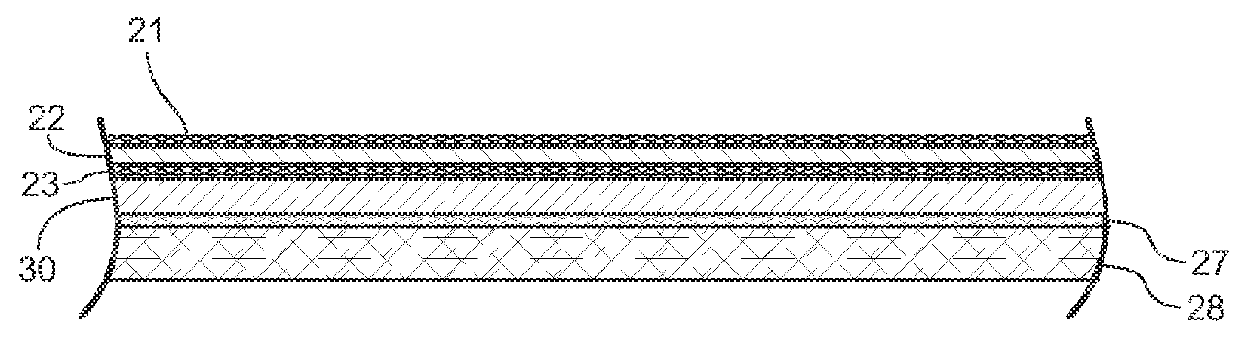
Post-surgical articles for reduction of swelling, edema, and bruising
InactiveUS20160051402A1Reduce heating capacityIncreased durabilityHead bandagesTherapeutic coolingPatient comfortGlass transition
Disclosed herein are garments having any combination of low thermal conductivity, high durability and resiliency, and with the optional ability to evenly distribute compressive forces. When compared to currently used compression garments, these compression garments advantageously result in better patient comfort and overall improved healing processes. In certain aspects, the disclosed compression garments include post-surgical treatment masks. For example, the post-surgical treatment mask may include a thermoformable assembly having a thermoformable resin arranged between inner and outer knitted fabric layers, the thermoformable assembly configured to be heated to a glass transition temperature of the thermoformable resin such that the thermoformable assembly can be shaped to conform to contours of a user's face, and a styrene-based polymeric gel layer arranged on the inner knitted fabric layer.
Owner:ALPS SOUTH EURO
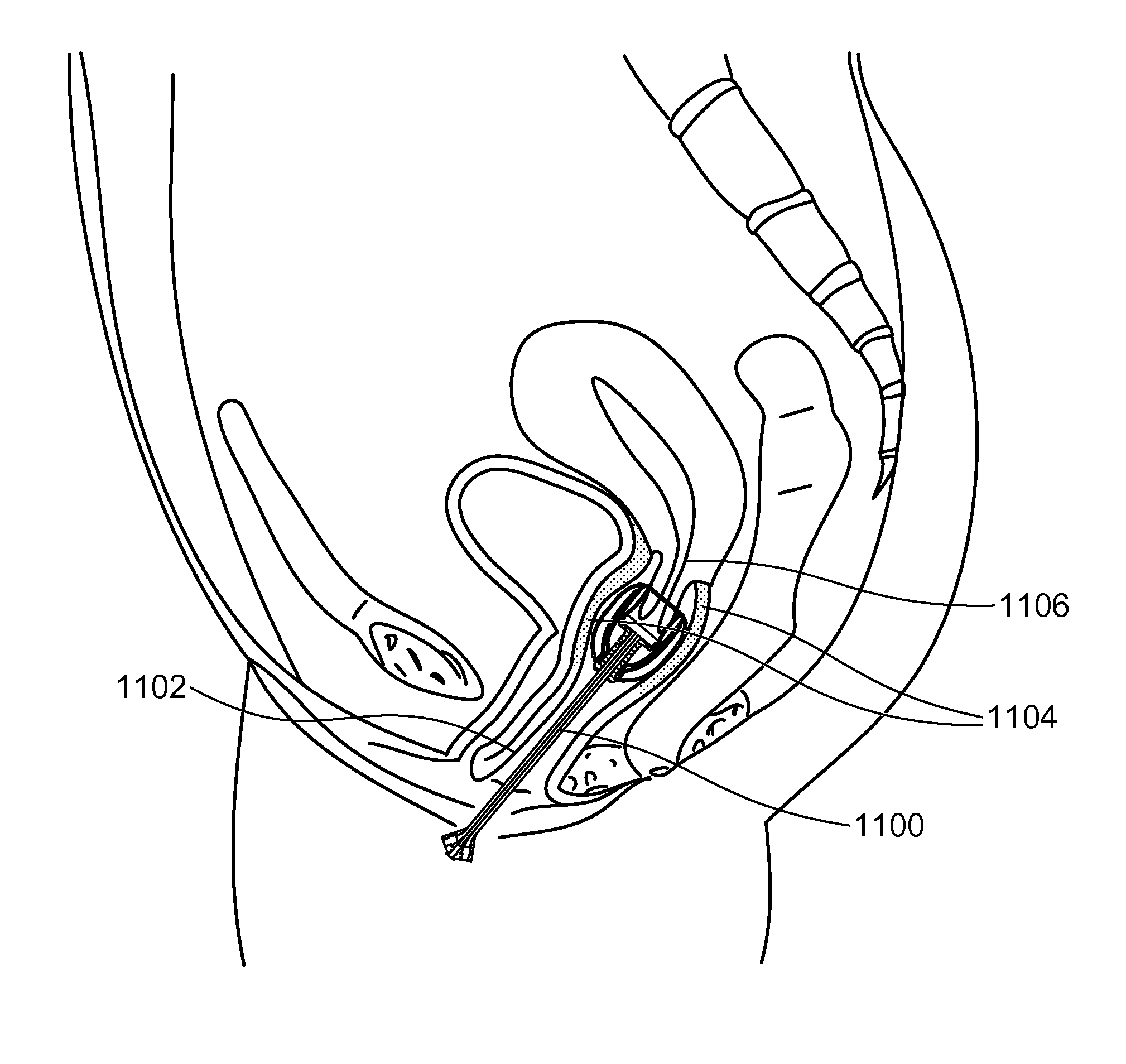
Stent devices for support, controlled drug delivery and pain management after vaginal surgery
InactiveUS20130138134A1Good supportControl drug deliveryStentsBalloon catheterVaginal epitheliumControl drugs
Stent devices comprising an inflatable inner balloon defined by an envelope and an outer balloon surrounding the inner balloon concentrically, the outer balloon serving as a therapeutic agent reservoir used for controlled therapeutic agent delivery. In some embodiments, the outer balloon has two separate walls which define its volume and is independently inflatable. In some embodiments, the two concentric balloons form a substantially cylindrical structure which has a proximal end and a distal end. A catheter carrying inflation and drainage lumens extends outward from the proximal end. In some embodiments, the distal end includes an embedded cervix accommodating tip or has a non-embedded cervix accommodating tip attached thereto. The stent devices can be used to maintain the integrity and placement of vaginally placed mesh or graft after reconstructive procedures, prevent vaginal hematoma formation and bleeding, provide pain control after surgery and deliver antibiotics or hormones to the vaginal epithelium.
Owner:ELMAN NOEL M +1
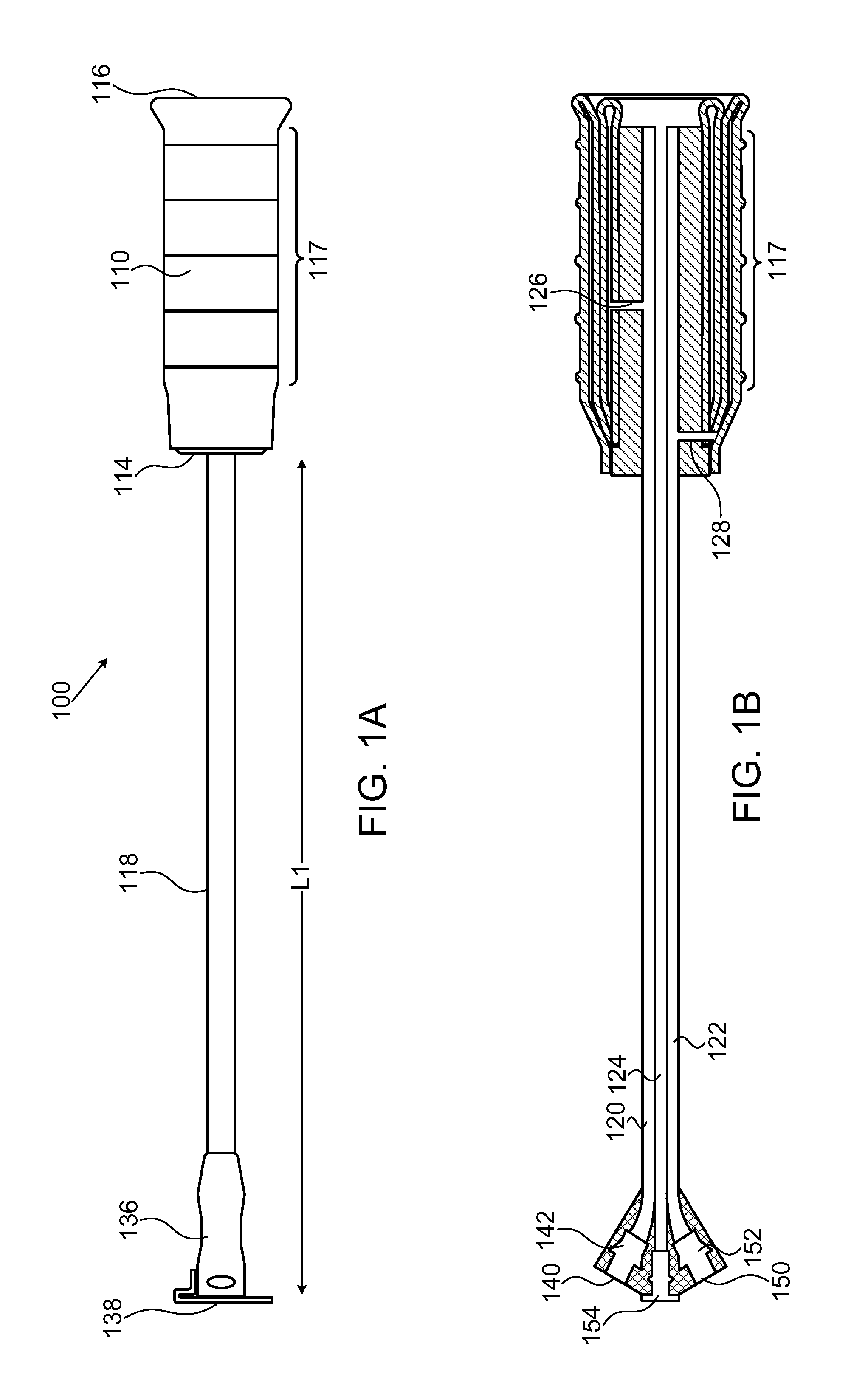
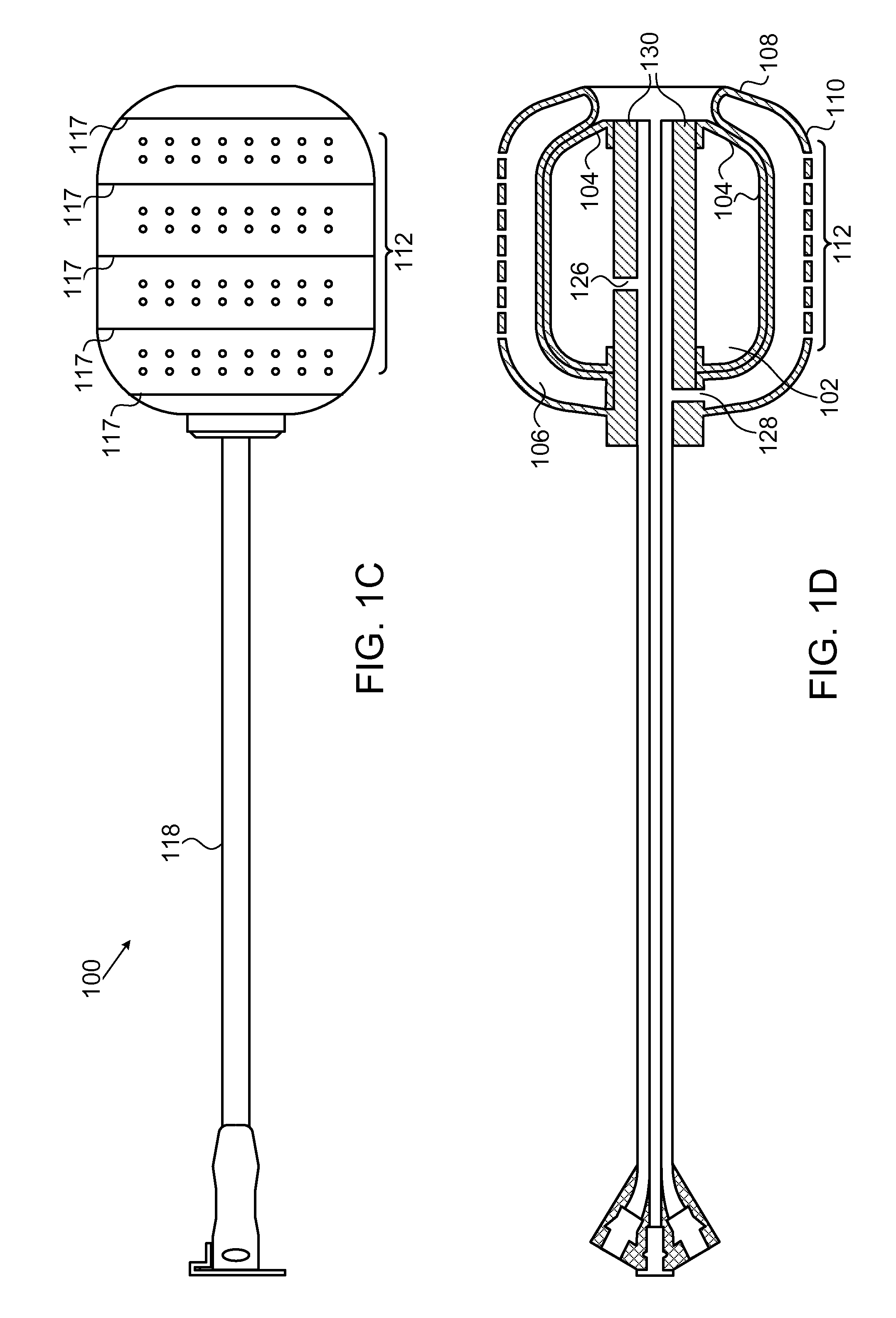
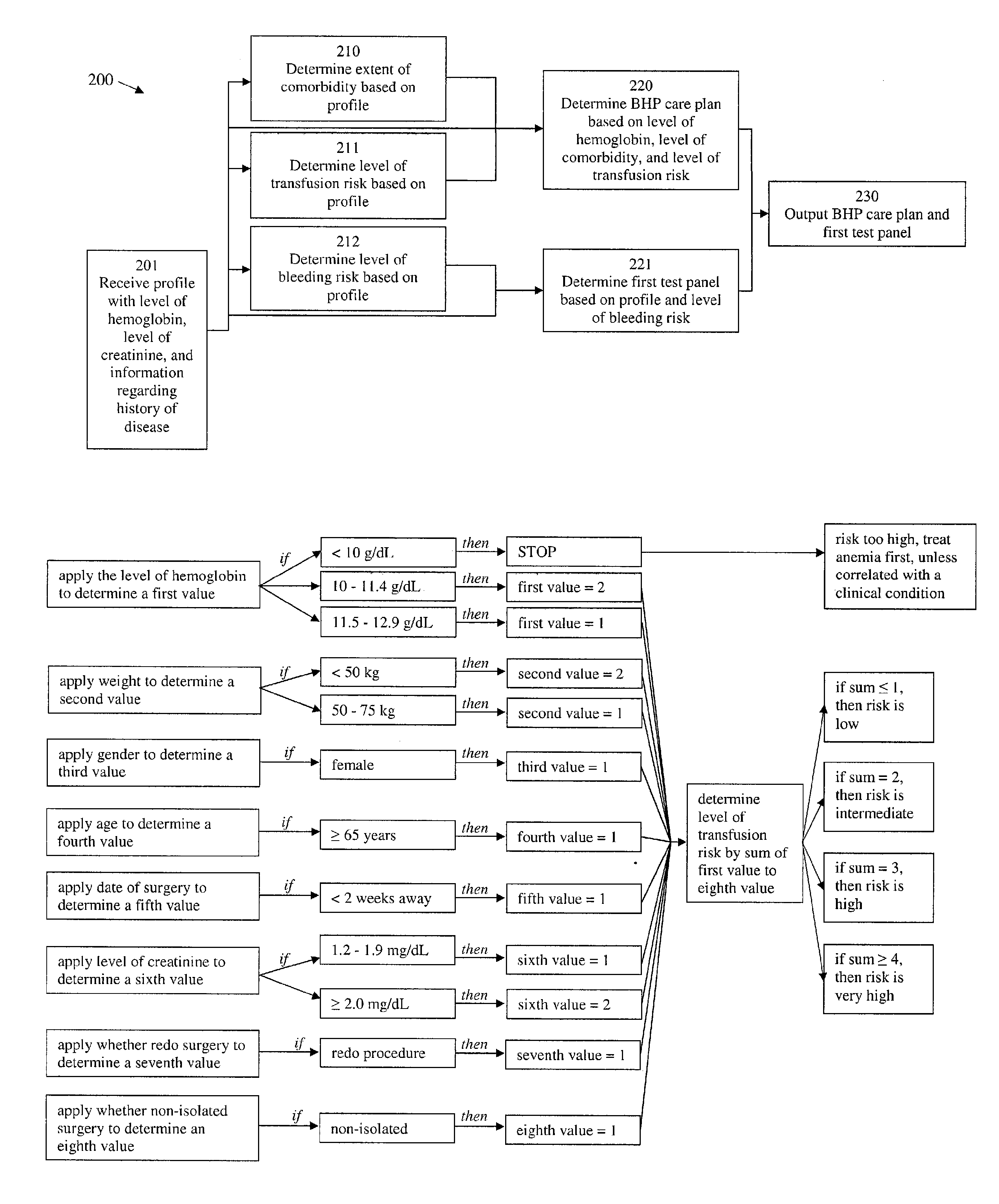
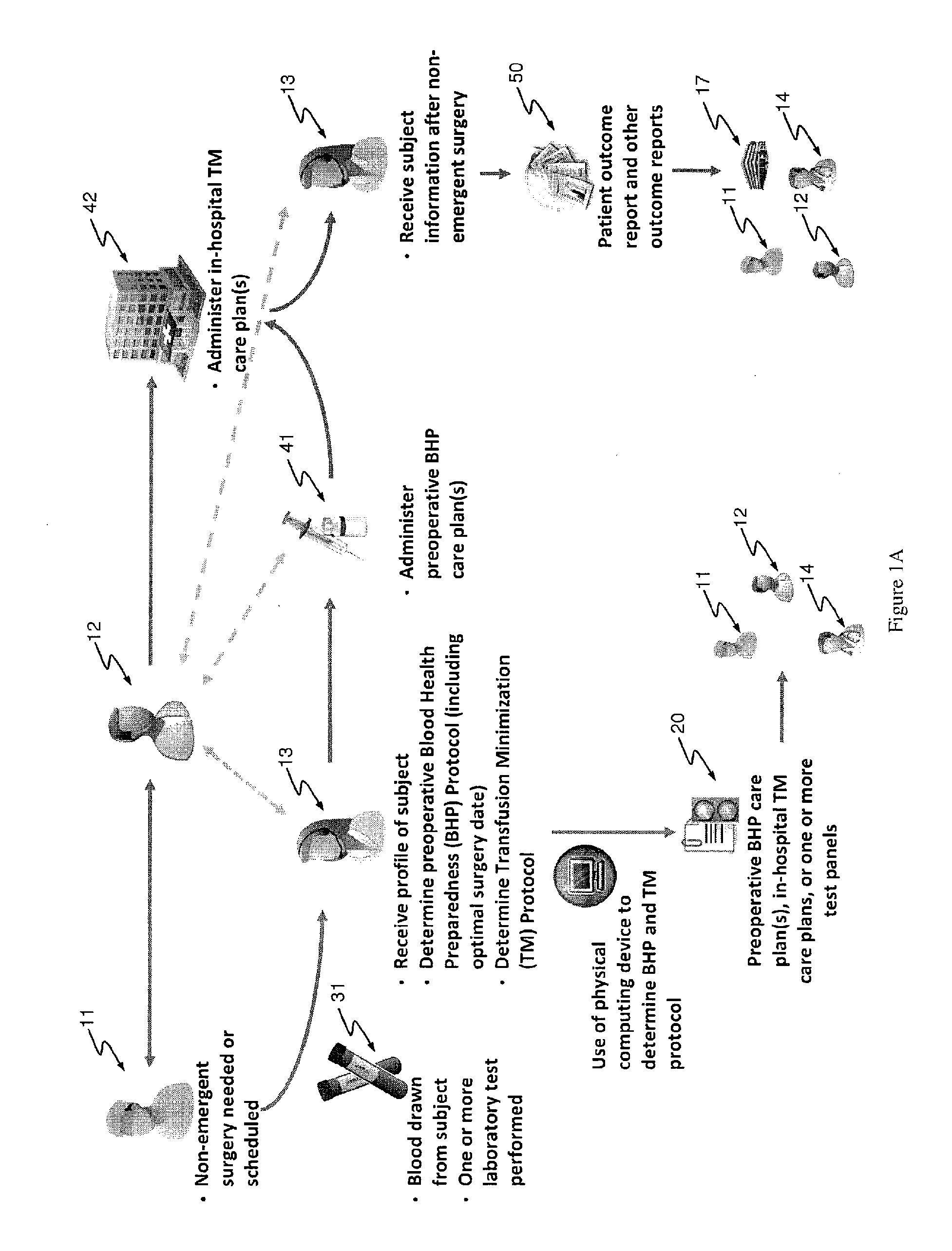
Methods and devices for reducing transfusions during or after surgery and for improving quality of life and function in chronic disease
ActiveUS20130035951A1Good health outcomeRisk minimizationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesFinanceCreatinine riseTransfusion risk
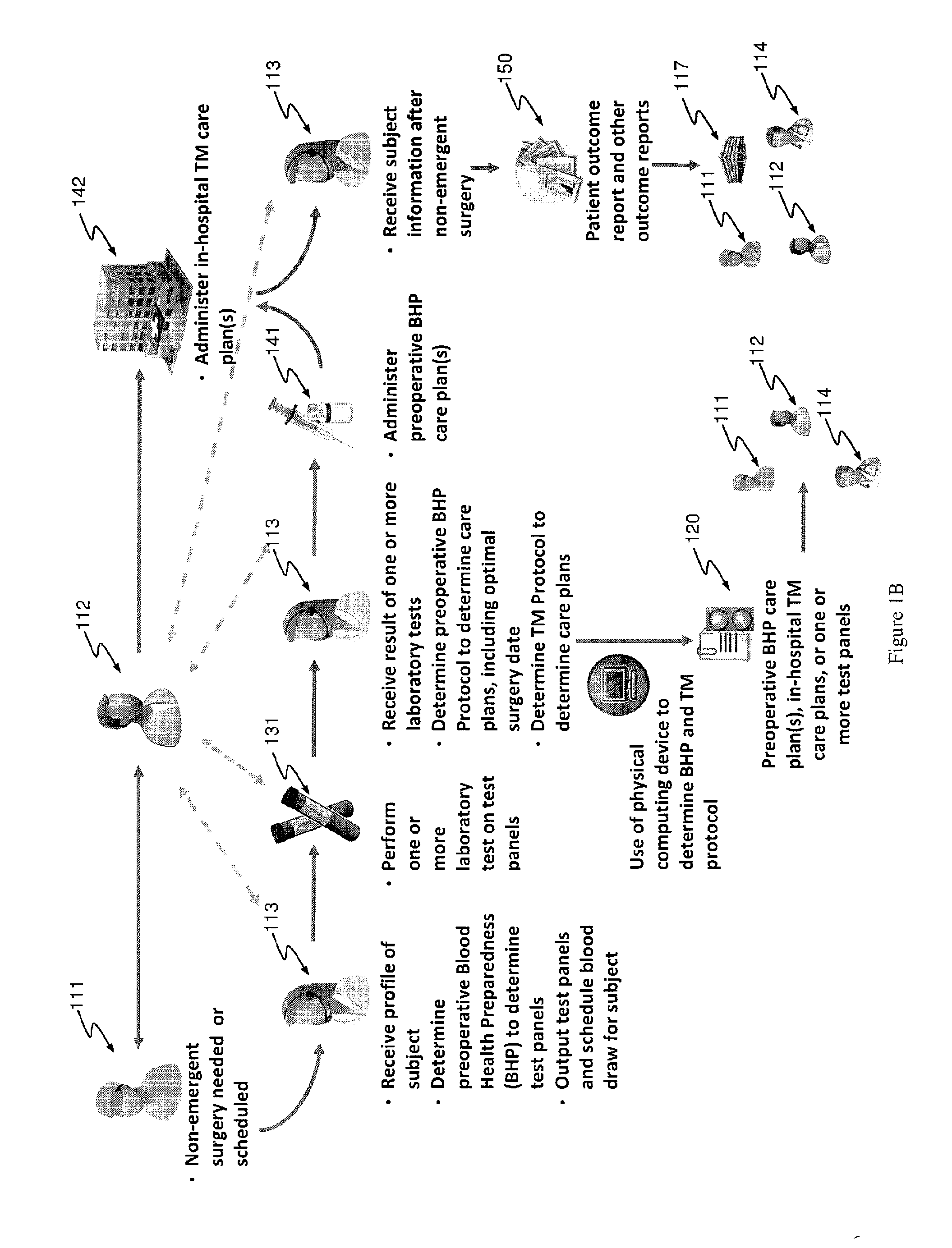
The present invention relates to methods of treating subjects preparing to undergo surgery or methods of treating chronic disease and methods for reducing transfusions and a computer readable storage medium and a physical computing device for carrying out these methods which include: a) receiving a profile of said subject, in a physical computing device, including a level of hemoglobin of said subject, level of creatinine of said subject, and information regarding current or past history of disease; b) applying said level of hemoglobin and said level of creatinine, in said physical computing device, to determine level of transfusion risk; c) applying said information regarding current or past history of disease of said subject, in said physical computing device, to determine level of comorbidity; d) applying said level of hemoglobin, said level of transfusion risk, and said level of comorbidity, in said physical computing device, to determine a patient care plan.
Owner:ACCUMEN INC
Computer-Implemented Multi-Factor Patient Education Method
InactiveUS20180286509A1Increase opportunitiesLow costPhysical therapies and activitiesMedical data miningEducational dataPhysical therapy
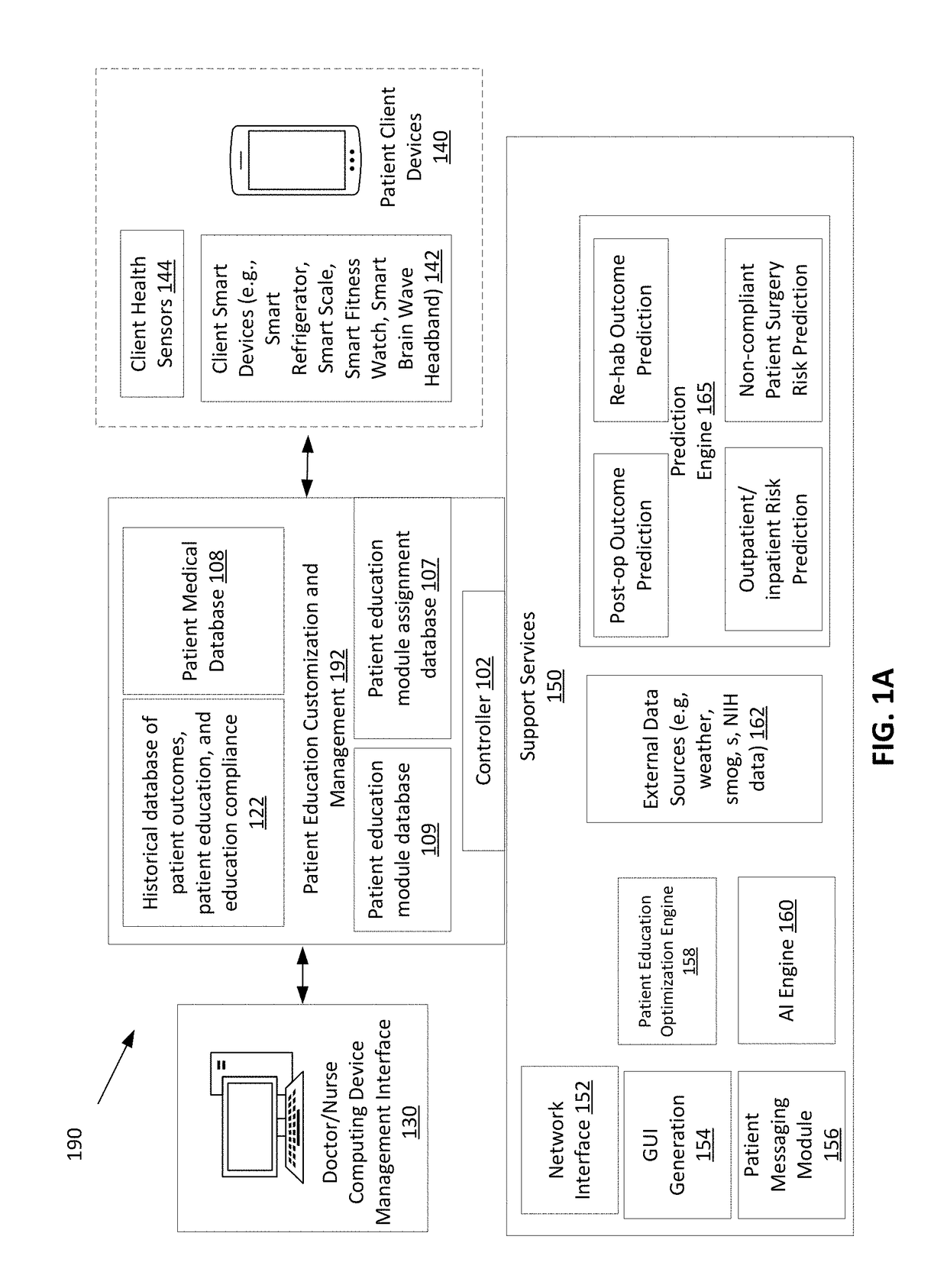
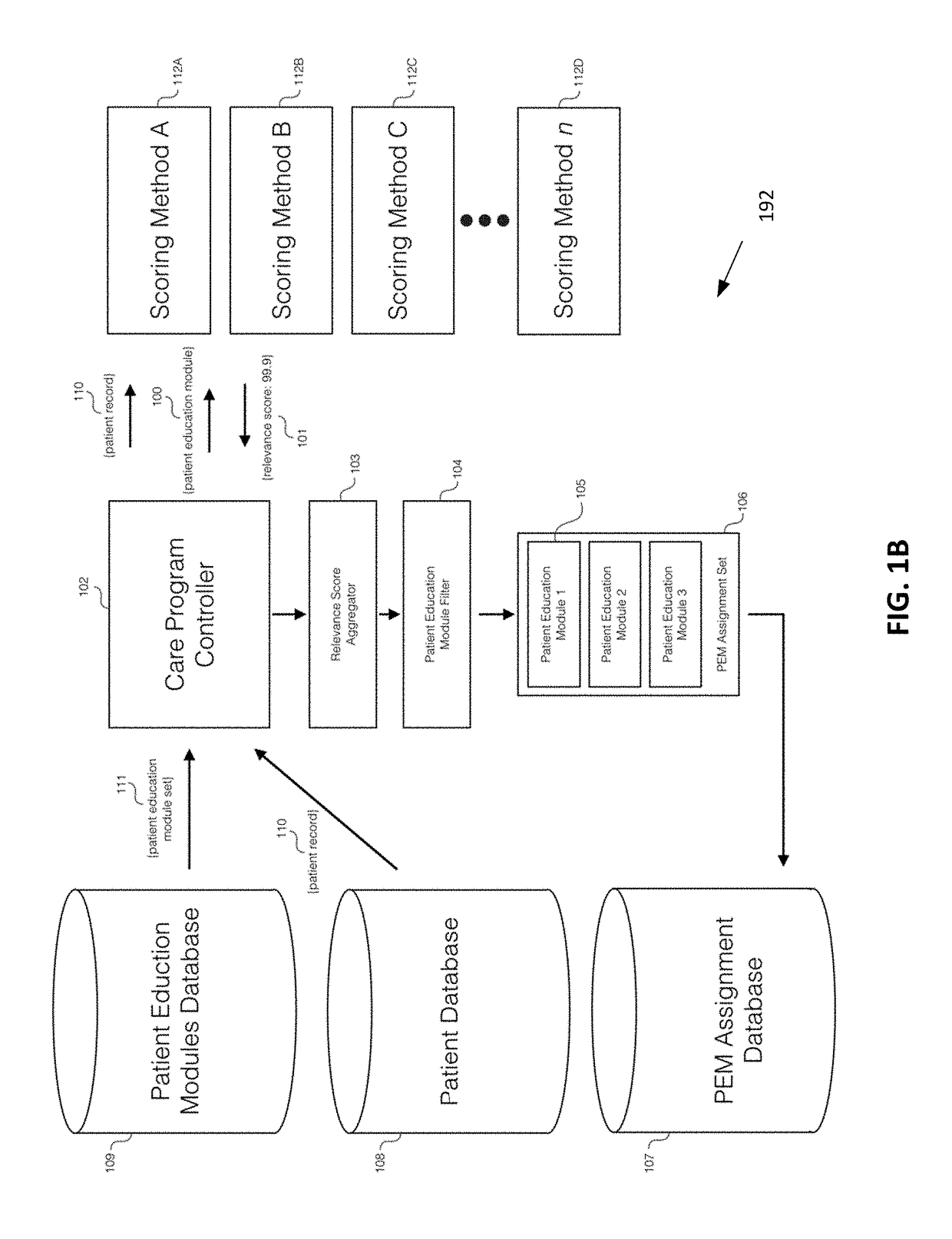
A system and method to provide patient education prior to surgery or post-surgery is disclosed. The patient education can be customized based on different factors and provided in a progressive sequence. Patients may be required to complete patient educational lessons and also provide feedback to assess how they are doing. Due to a variety of patient circumstances and the potential for abrupt changes in patient health status prior to, during, or following a health procedure, it is necessary for patient education to adapt to a patient's changing needs. The disclosure describes a technique to assign patient education materials in an adaptive and responsive manner.
Owner:PEERWELL INC
Device for treating intervertebral disc herniations
InactiveUS7128746B2Minimize compressionMore processedJoint implantsSpinal implantsDistractionEndoscopic Procedure
Owner:PMT
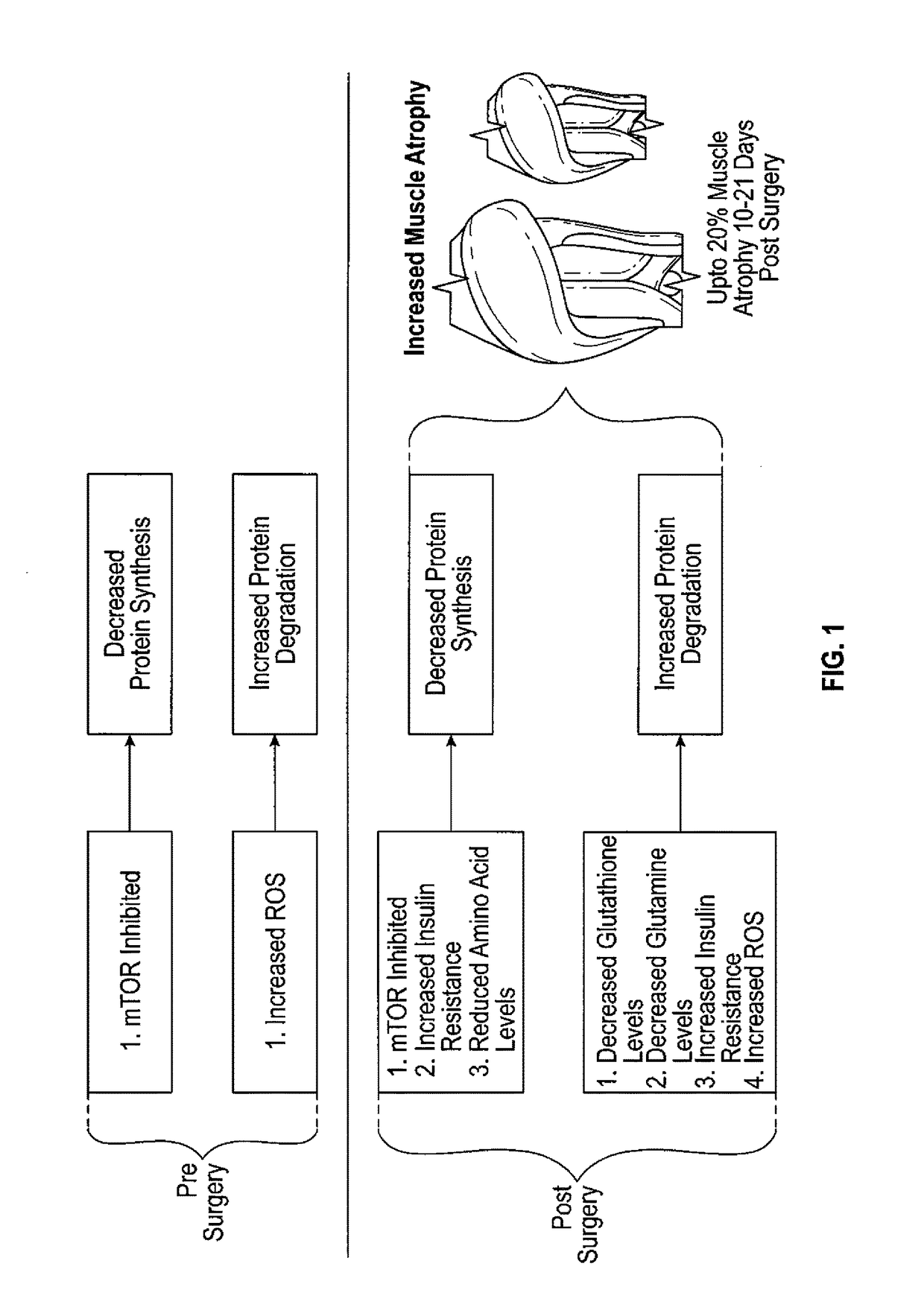
Method to reduce muscle atrophy following orthopedic surgery
InactiveUS20170196944A1Reduce rateIncreasing protein synthesisOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryArginineTert-leucine
A method for reducing muscle atrophy in an individual undergoing orthopedic surgery, the method comprising administering to said individual a mixture of protein and non-protein nutrients for 4-7 days pre-surgery and for 10-21 days post-surgery. The protein dosage is 15-30 g, of which 17-25% is leucine, 23-35% is 1-glutamine, 10-15% is 1-arginine and 1-2% is cysteine. The protein nutrients are derived from a combination of commercially available proteins and the appropriate free amino acid. The non-protein nutrients are a mono or disaccharide in the amount of 15-30%, N-acetyl-cysteine in the amount of 1-15% and the antioxidant Vitamin C.
Owner:PORTMAN ROBERT
Method and System for Diagnosing Post-Surgical Pulmonary Vascular Occlusions
InactiveUS20070078357A1Non-invasively diagnosingNon-invasively diagnosing postoperative pulmonary vascular occlusionsRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsSurgical departmentIntensive care medicine
A method of determining the presence of pulmonary embolism is a postoperative patient using the carbox ratio of the patient prior to the surgical procedure and the carbox ratio of the patient after to the surgical procedure. The characteristics of the breath of the patient are obtained prior to a surgical procedure for a baseline and then afterwards if the patient has difficult breathing. The mean carbox ratios from the baseline and post-surgical data collections are then compared to non-invasively predict the likelihood that the patient has developed pulmonary embolism. A decrease in the carbox ratio of more than twenty-five percent (25%) represents an abnormal test and is consistent with possible pulmonary embolism. No change or an increase in the carbox ratio suggests the absence of pulmonary embolism.
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
Post surgery brassiere
ActiveUS9545124B1Relieve painPrevent rotationBrassieresProtective garmentEngineeringReoperative surgery
A post-surgery bra includes an aperture appropriately sited to so that tubes from a boost-treatment device or drain implanted in a wearer of the bra protrude therethrough. The post-surgery bra includes a fixation element for immobilizing the tubes of the boost-treatment device that protrude through the aperture. In some embodiments, the post-surgery bra also includes a retaining ring, which is coupled to the bra below the breast cup nearest to the aperture and which is openable and closeable for engaging and securing a loop of material that extends from the collection bulb of the drain.
Owner:THOMPSON ELIZABETH CHABNER
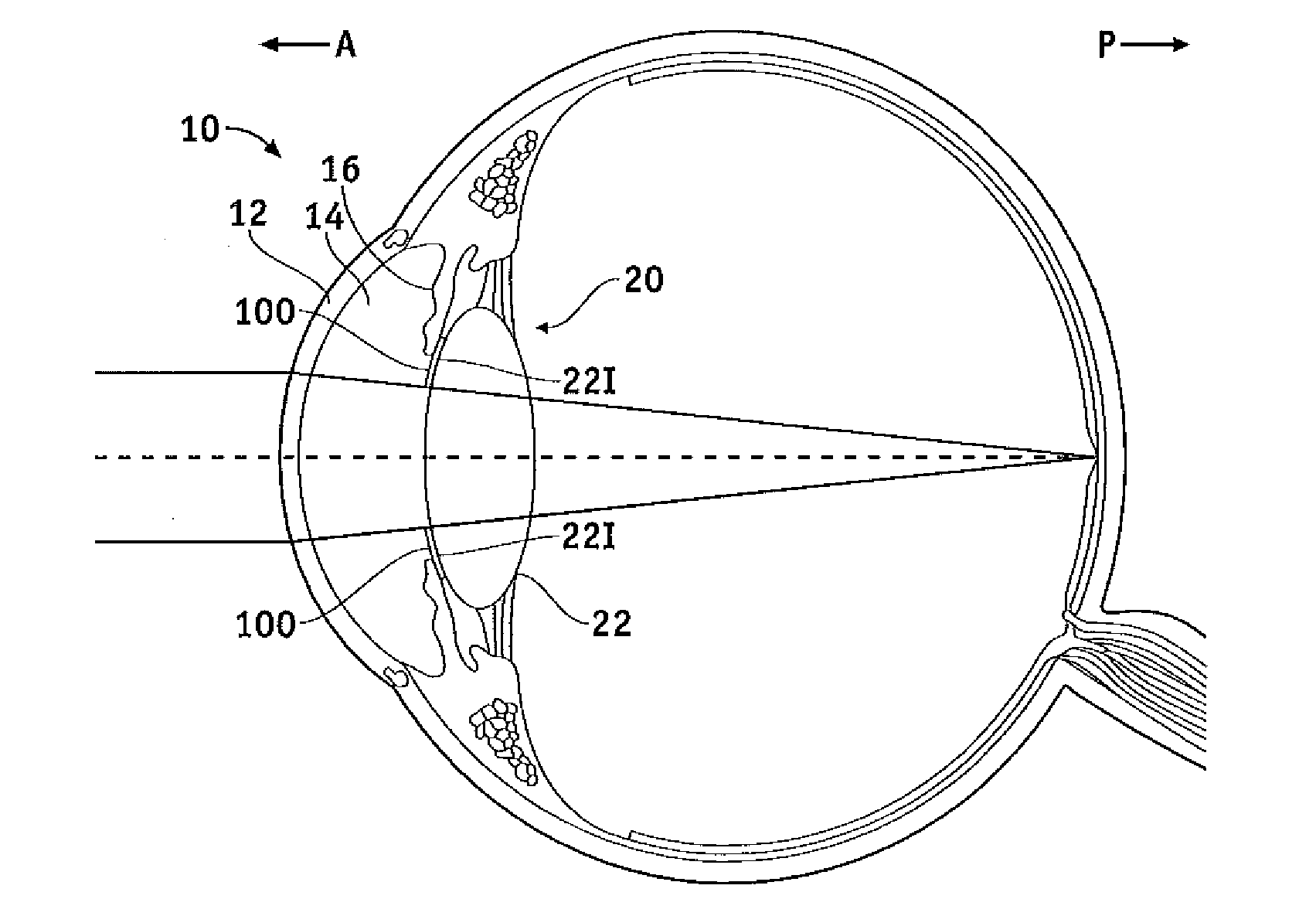
Capsular membrane implants to increase accommodative amplitude
ActiveUS20120059465A1Reduce radial movementCoupling stabilityLaser surgeryMachines/enginesCouplingLens placode
A support is coupled to the lens capsule to increase accommodation. The support may be adjustable, such that patient refraction and accommodation can be adjusted following surgery. The support may comprise rigidity sufficient to decrease radial movement of the intermediate portion of the lens capsule. The support can be placed on the intermediate portion to decrease radial movement of the intermediate portion of the lens capsule and increase radial stretching of an outer portion of the lens capsule extending between the zonules and the intermediate portion coupled to the support, such that the amount of accommodation of the eye is increased. The support may comprise a biocompatible material capable of stable coupling to the lens capsule following implantation, such that the far vision refraction and accommodation of the eye can be stable following surgery.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Anatomy reconstruction skull patch and quick manufacturing method for same
ActiveCN106923935AEasy to destroy and take outPrecise positioningTomographySkullCouplingBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses an anatomy reconstruction skull patch filling a skull defect opening part. An edge shape of the patch is identical to an edge shape of the skull defect opening; a patch stereoscopic structure is identical to a skull defect stereoscopic structure; and the patch is made of degradable biological hard material. The invention further discloses an anatomy reconstruction skull patch quick manufacturing method. The patch manufacturing method can produce patches with high accuracy, great coupling property, great repairing exactness, firmness and safety as well as reliability; great patch structure and biocompatibility can be achieved; surgery cost can be reduced and time can be shortened; and post-surgery complications can be reduced.
Owner:马驰原
Urinary incontinence sling apparatus and method
A sling apparatus and method of treatment for stress urinary incontinence, prolapse, and the like. The apparatus and method may comprise a support material of any construction known within the art which is temporarily held in position by at least one tension member. A tension member may be attached to an end of the support material and the remaining free end of the tension member may then be releasably fastened to a fixation device at or above the level of the skin. Both the tension member and the fixation device may have incremental and / or measurable indicia disposed thereon to provide for either incremental increases or decreases in support material tension post-surgery. Upon support material natural fixation, the tension member may be cut at or below the level of the patient's skin. The tension member may comprise either permanent or bio-absorbable material.
Owner:ZIPPER RALPH
Thyroid post-surgery neck care device
ActiveCN110123556AImprove securityImprove comfortNursing bedsSuction-kneading massageMassagePediatrics
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, and particularly relates to a thyroid post-surgery neck care device which comprises a sickbed. The sickbed comprises a bed plate support, a bed plate is arranged on the bed plate support, a supporting massage device is arranged on the bed plate and comprises a neck supporting plate, massage columns are uniformly distributed on the neck supporting plate and comprise upper massage columns and lower massage columns, a massage driving structure enabling the lower massage columns to slide along the neck supporting plate is arranged on the bed plate, sliding structures enabling the upper massage columns to vertically slide along the neck supporting plate are arranged on the lower massage columns and connected with swing structures enabling the upper massage columns to swing along the neck supporting plate, and a protective mechanism corresponding to the supporting massage device is further arranged on the bed plate supportand comprises a left protective device and a right protective device connected with the left protective device. The thyroid post-surgery neck care device effectively solves the problems that the neckof a patient in the care recovery process is easily fatigued and uncomfortable, and the patient is easily secondarily injured in the care process.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Kit For Treating or Relieving Pain at Incision Site Following Surgical Procedure
PendingUS20200086049A1Effective treatmentRelieve painInfusion syringesInorganic non-active ingredientsIncision SitePharmaceutical drug
The present in relates to a kit for treating or relieving incision site pain. According to the present invention, there is provided a kit for treating or relieving postoperative incision site pain, which makes effective treatment possible by injecting a pain relief drug or a treatment drug into a surgical site in situ after incisional surgery during an incisional surgical procedure, and stably and slowly releasing the drug.
Owner:GENEWEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com