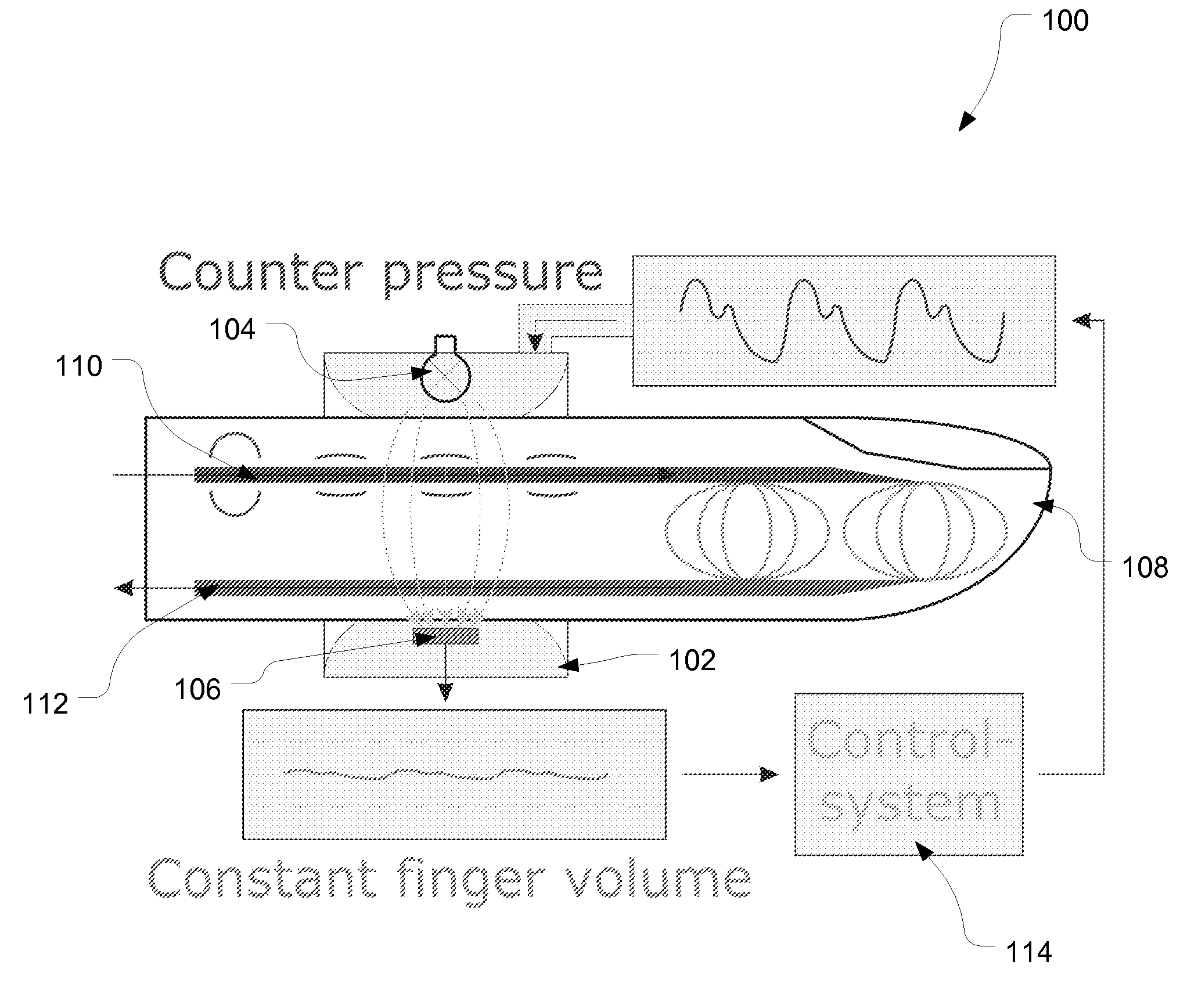
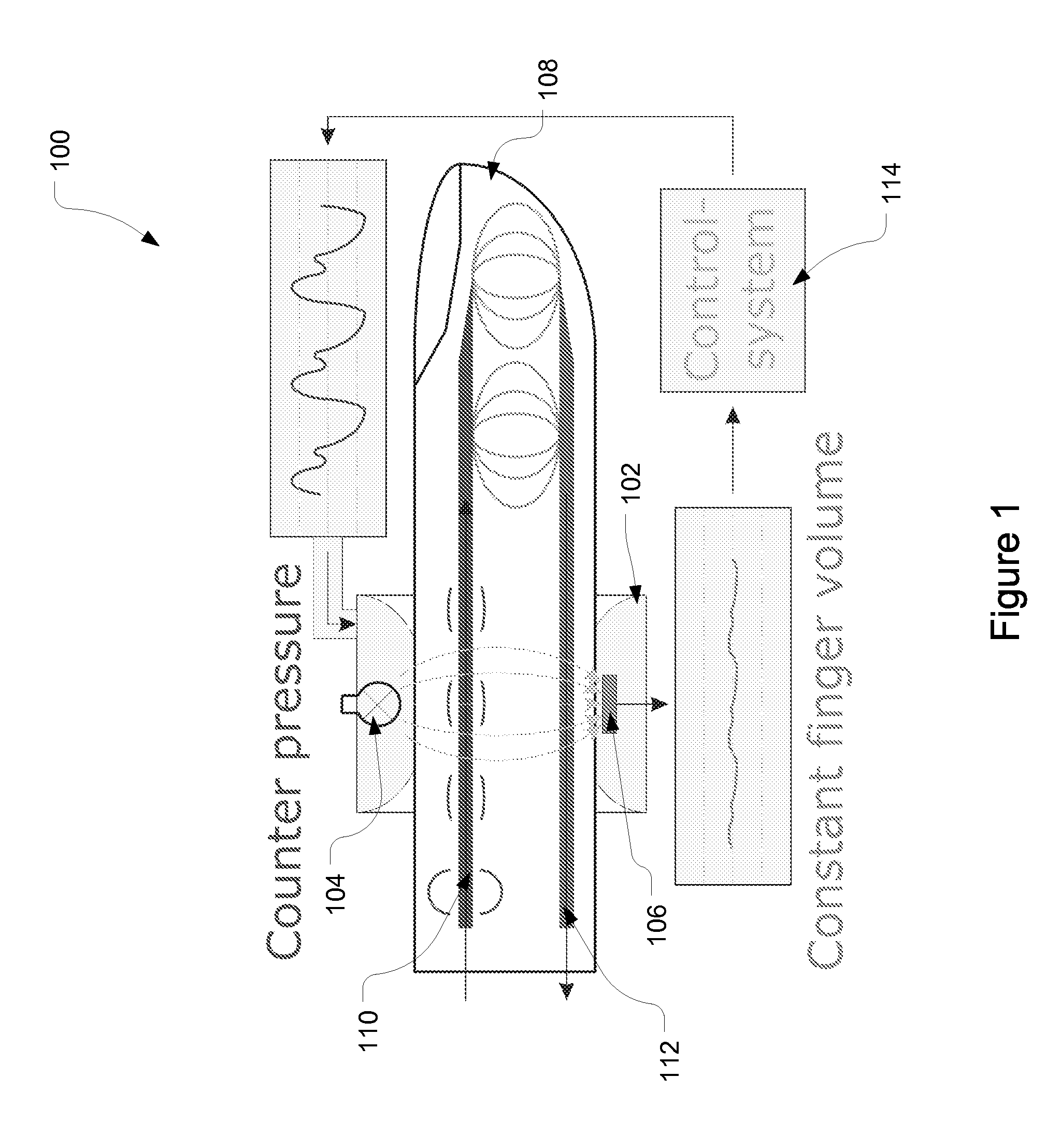
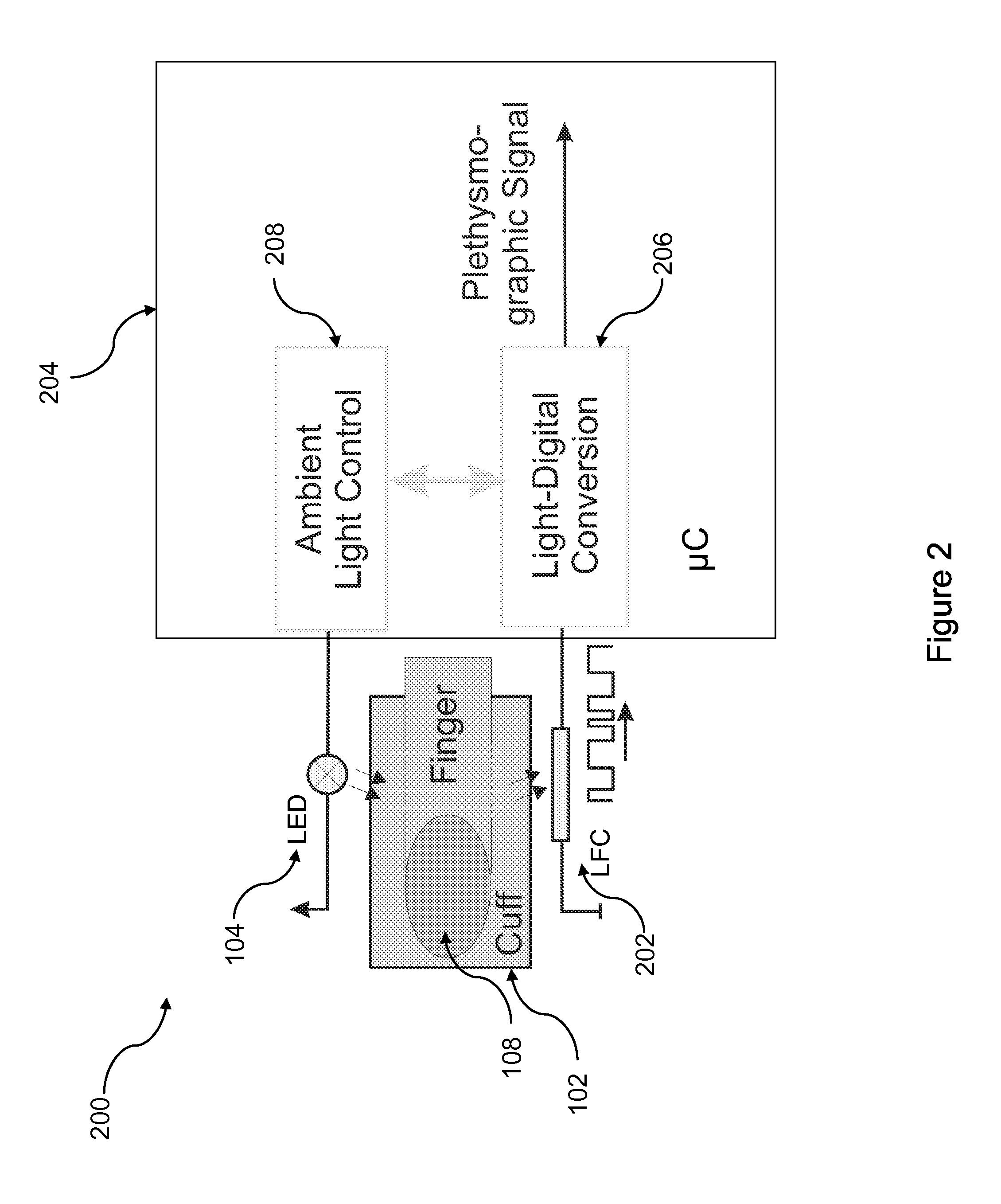
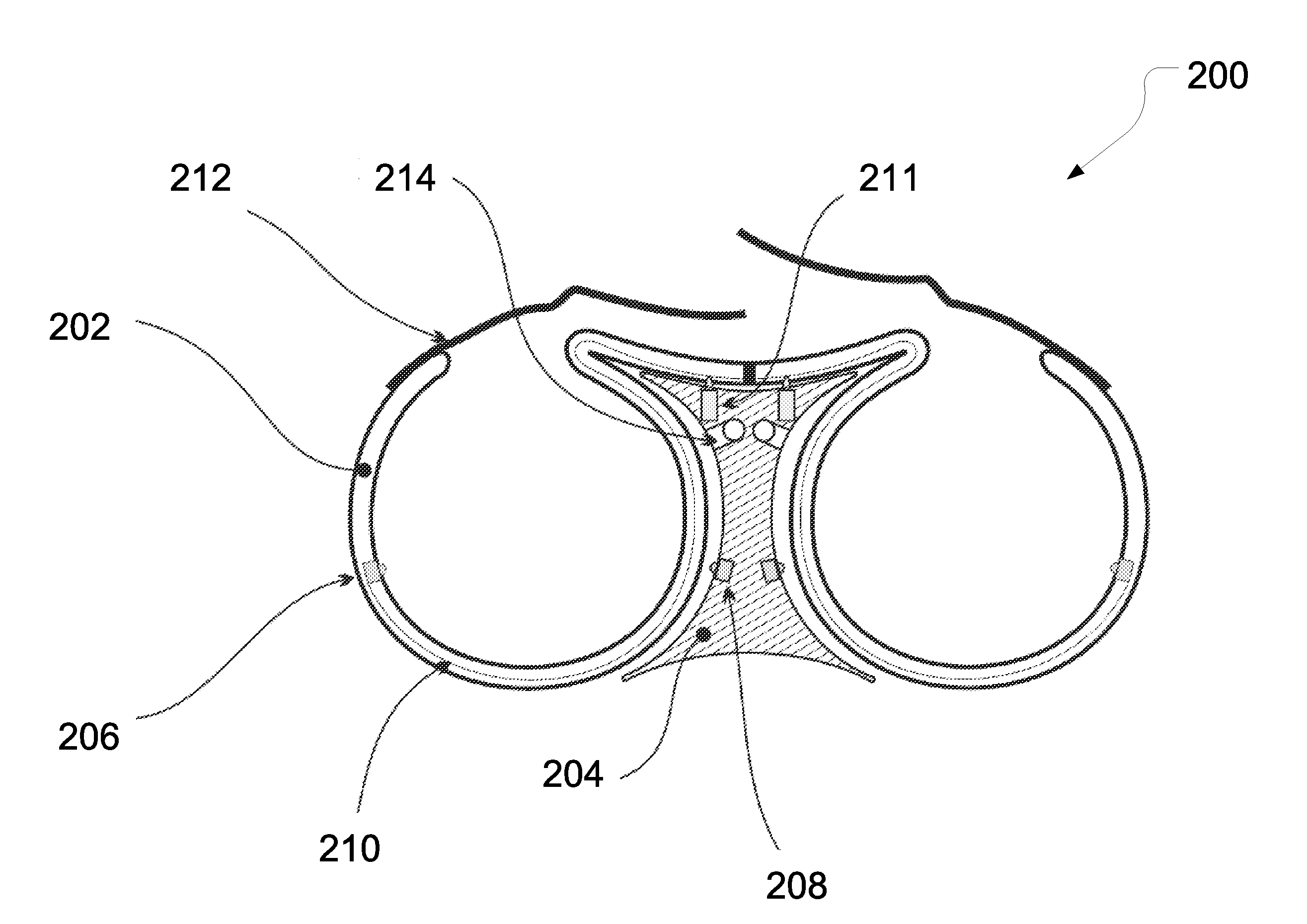
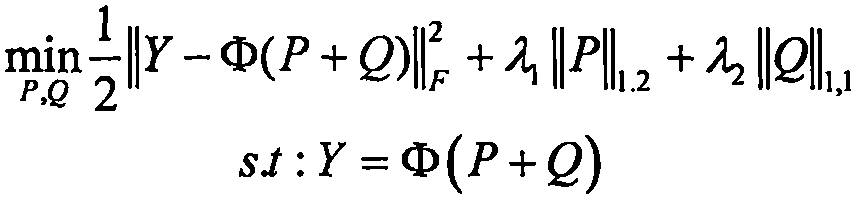Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Photoelectric plethysmography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
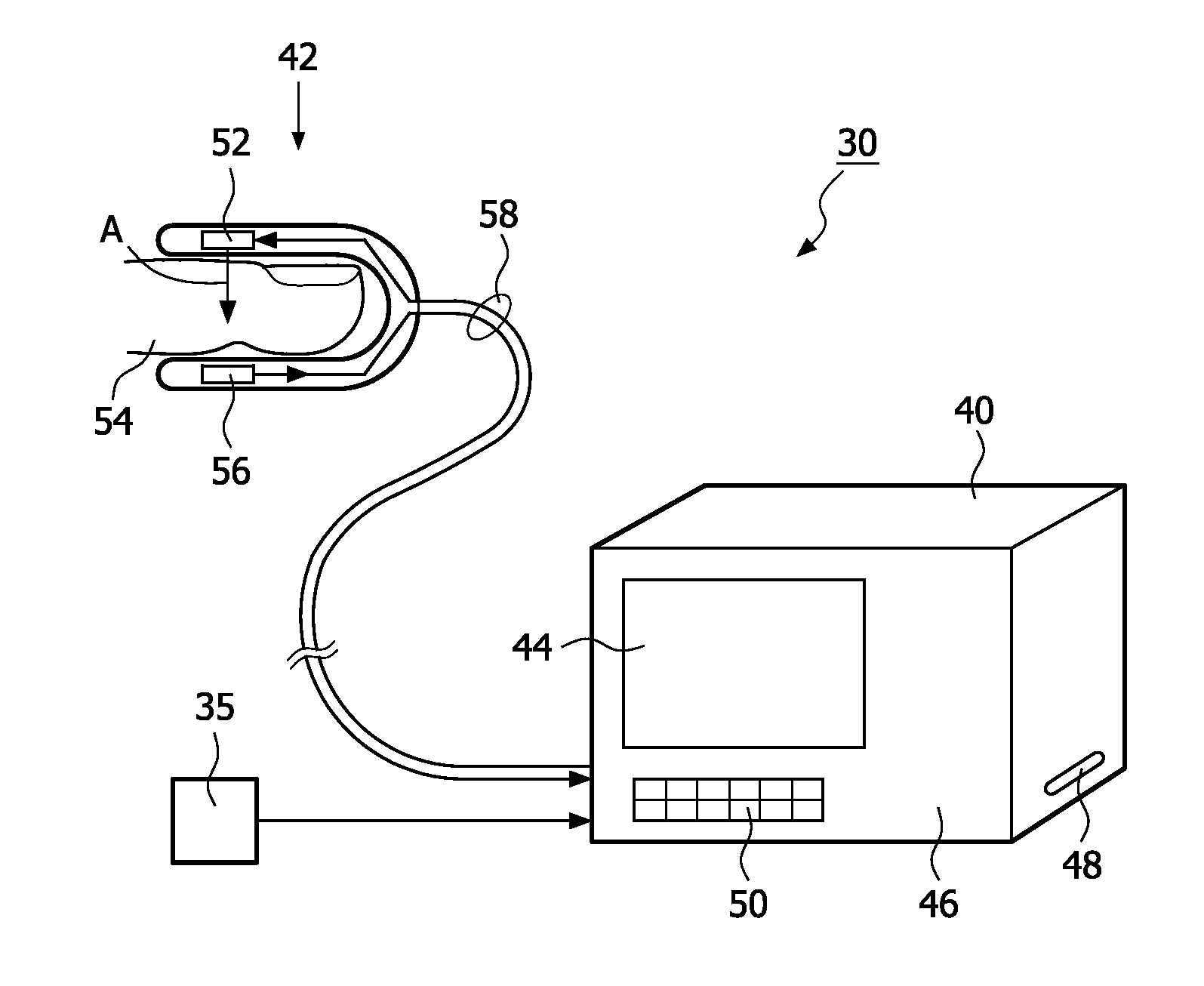
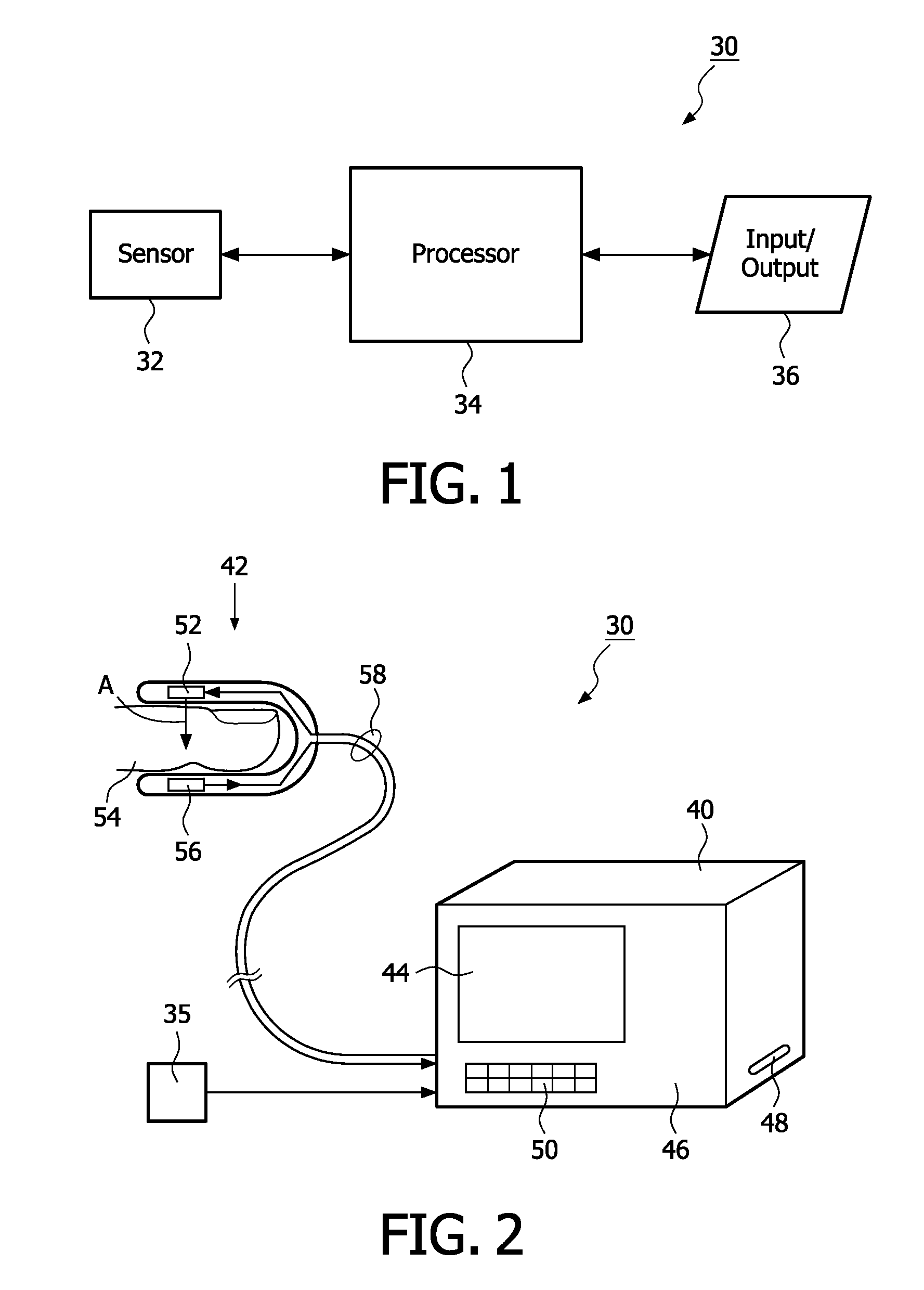
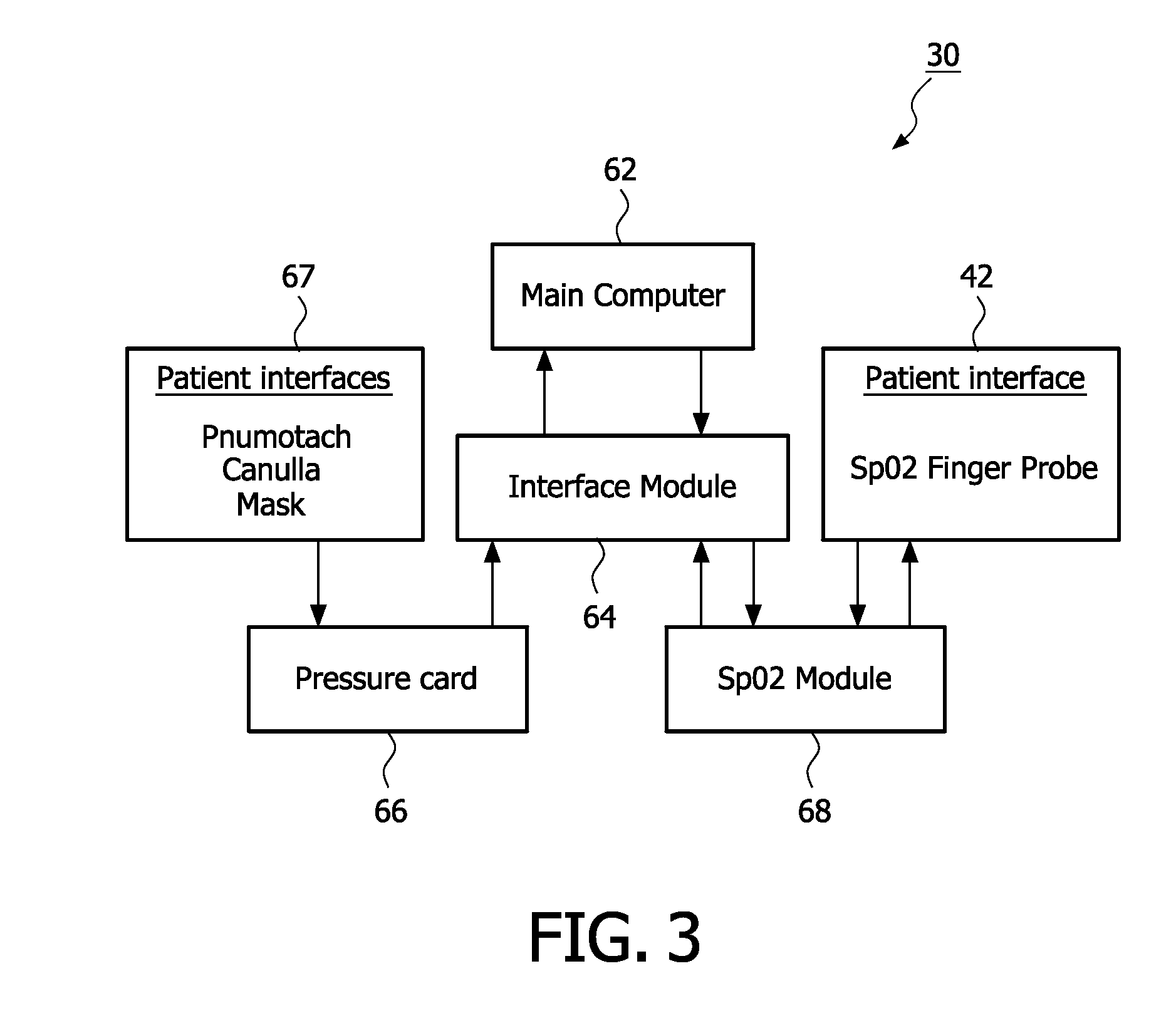
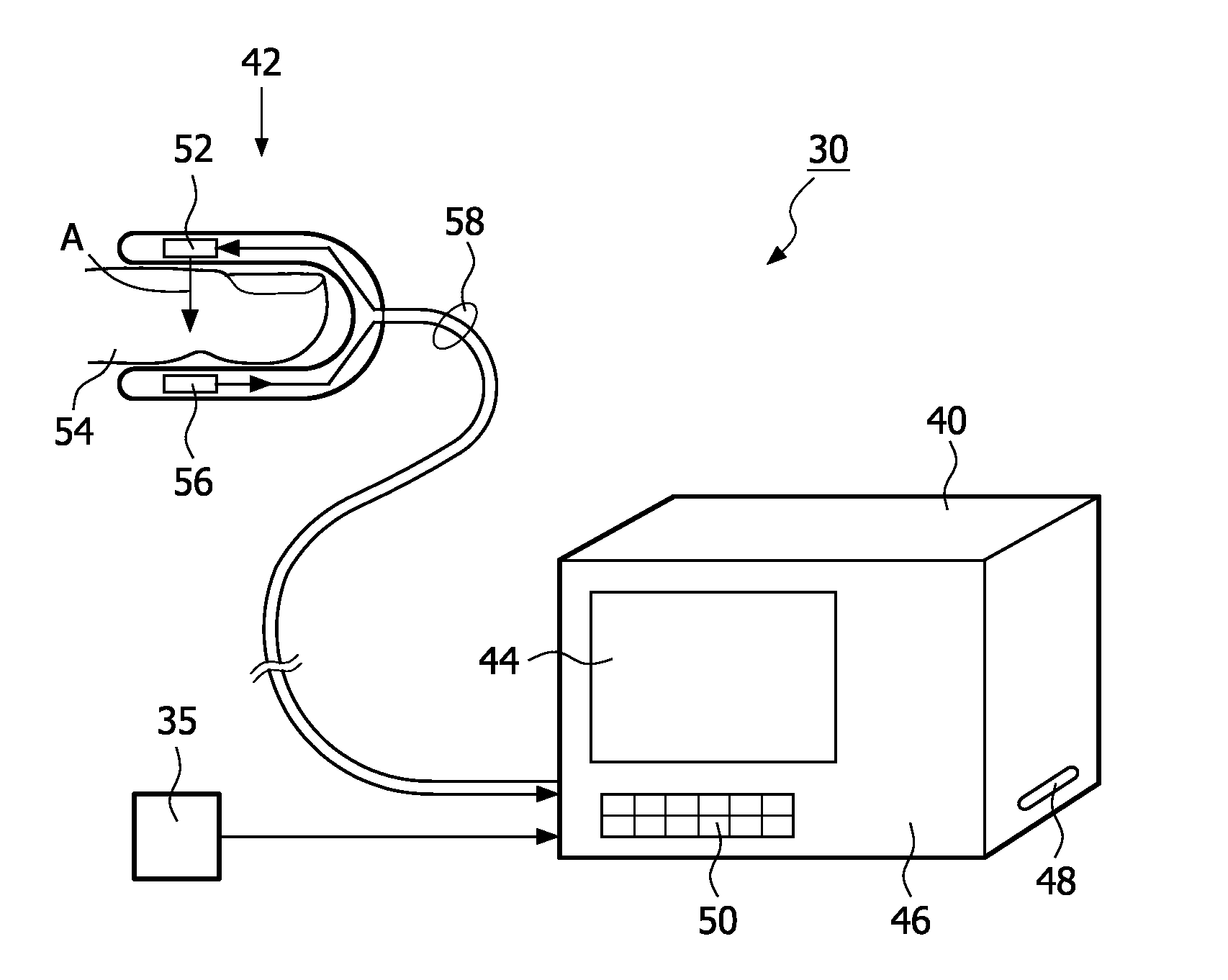
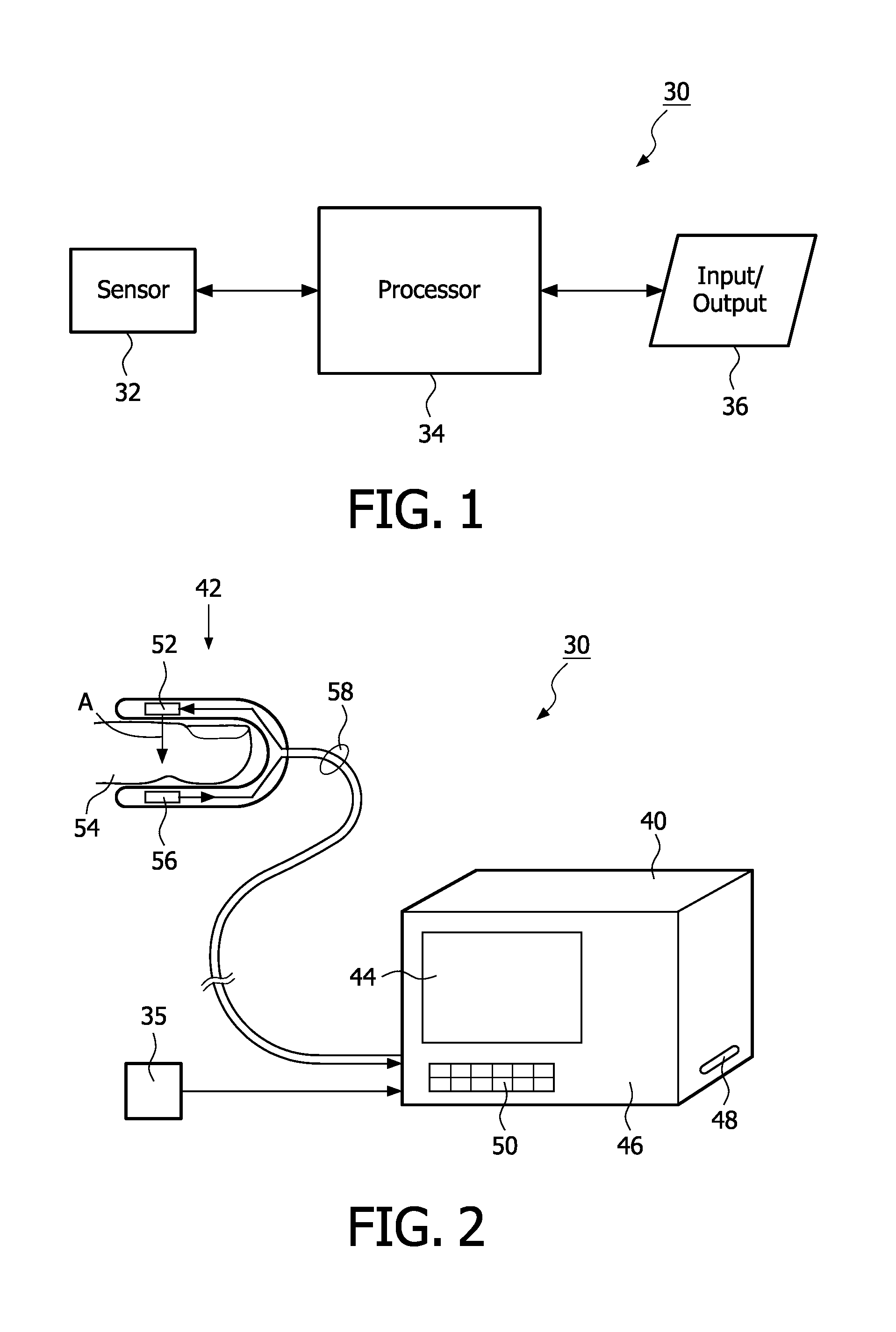
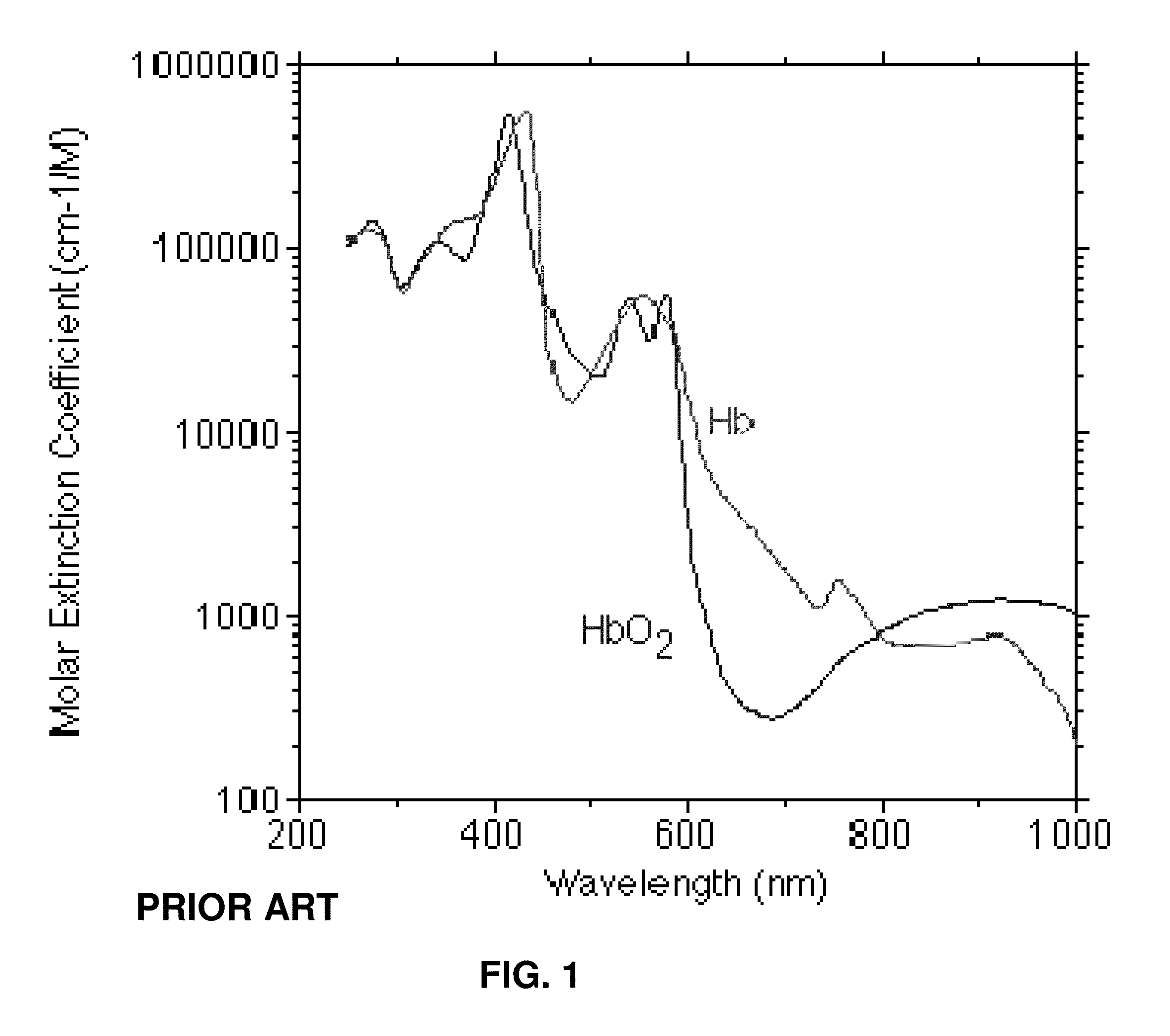
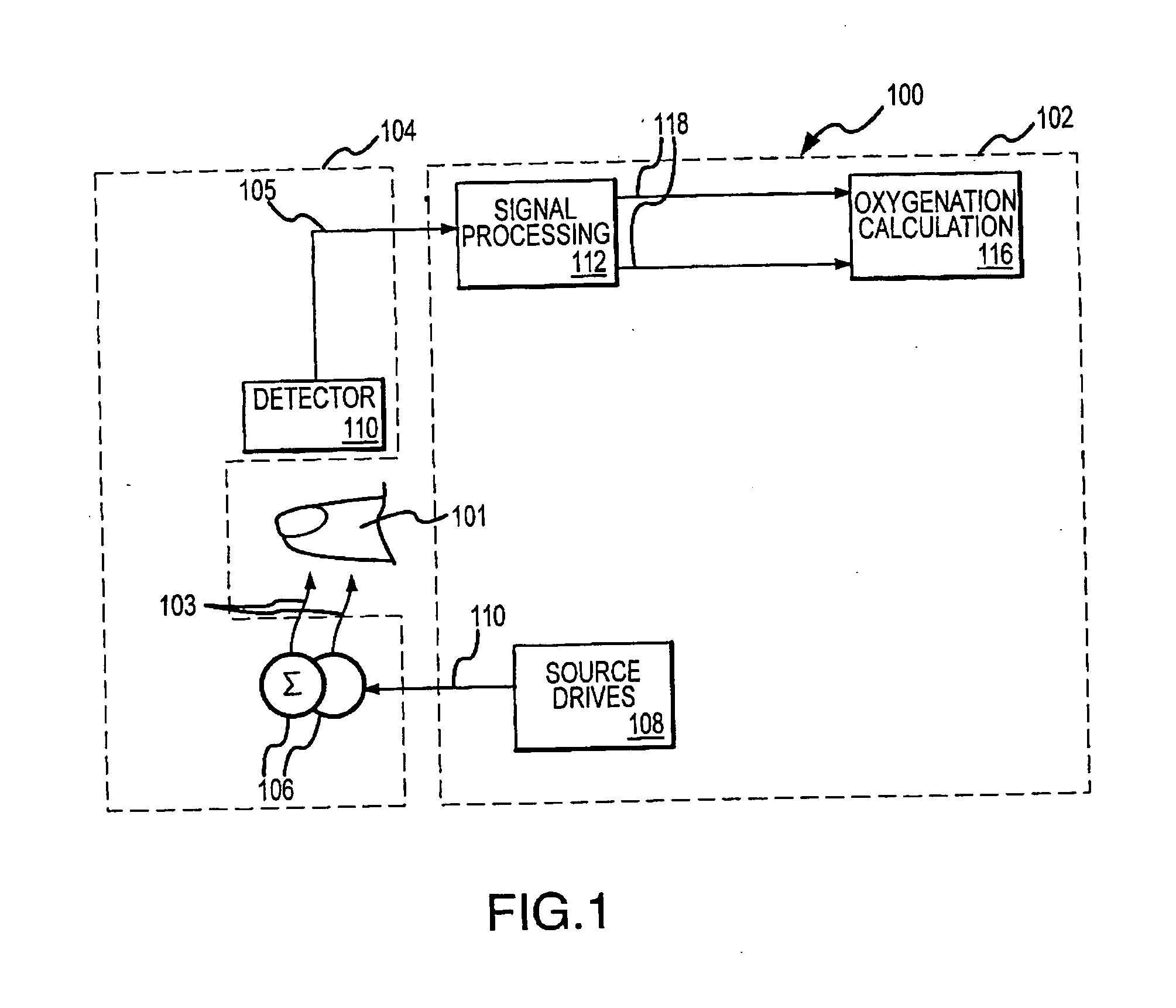
Measurement of the intensity of light reflected from the skin surface and the red cells below to determine the blood volume of the respective area.
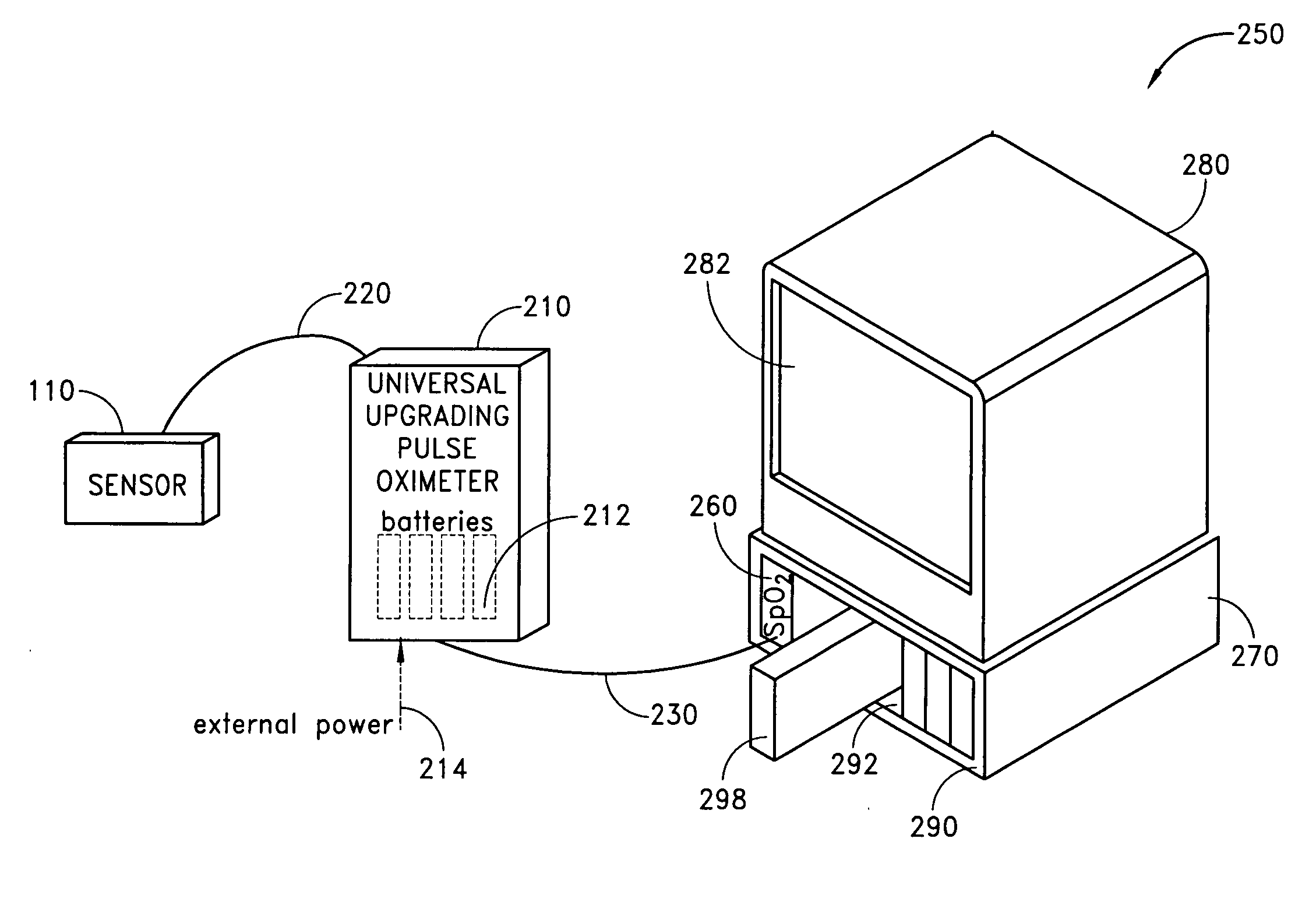
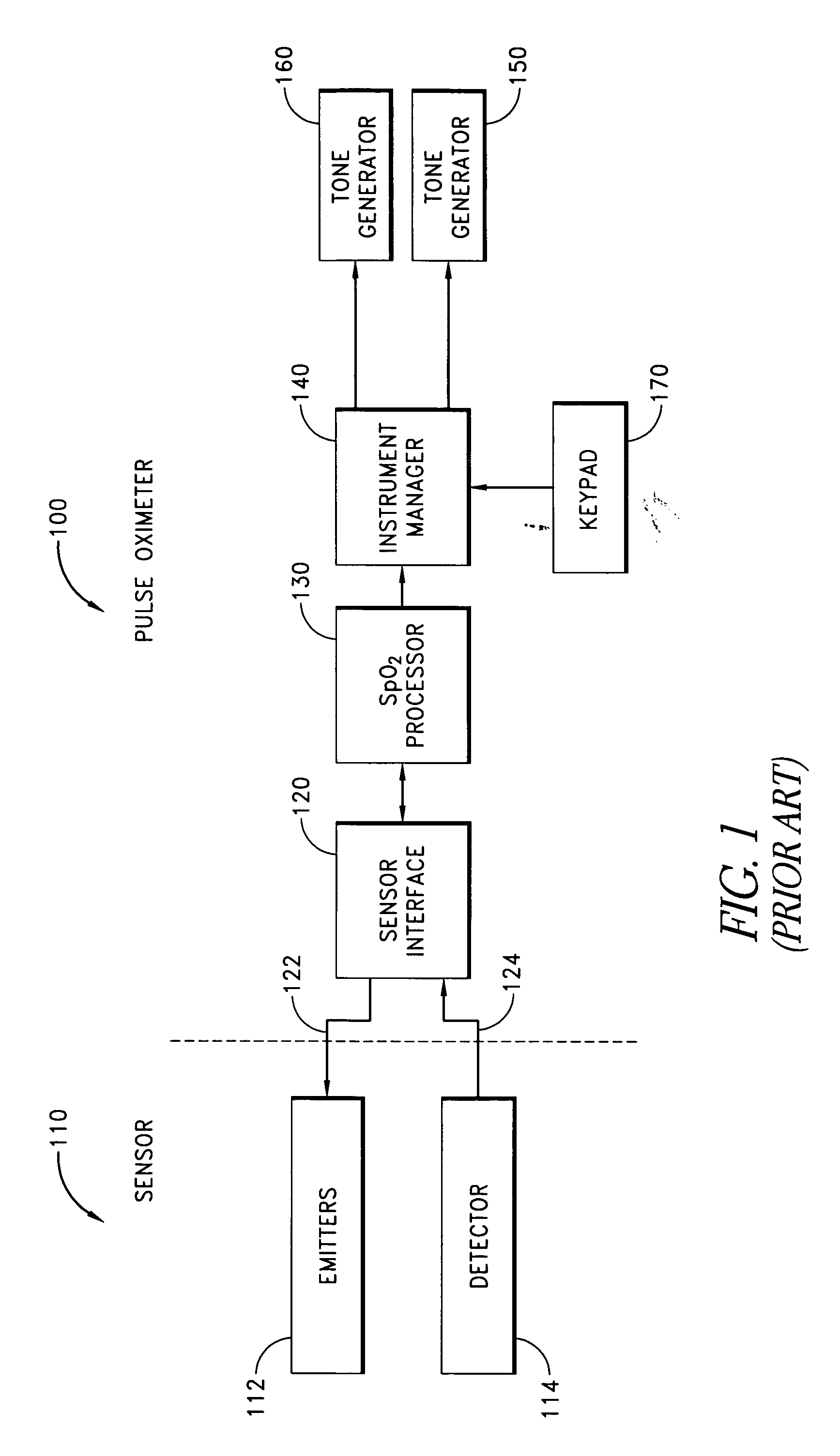
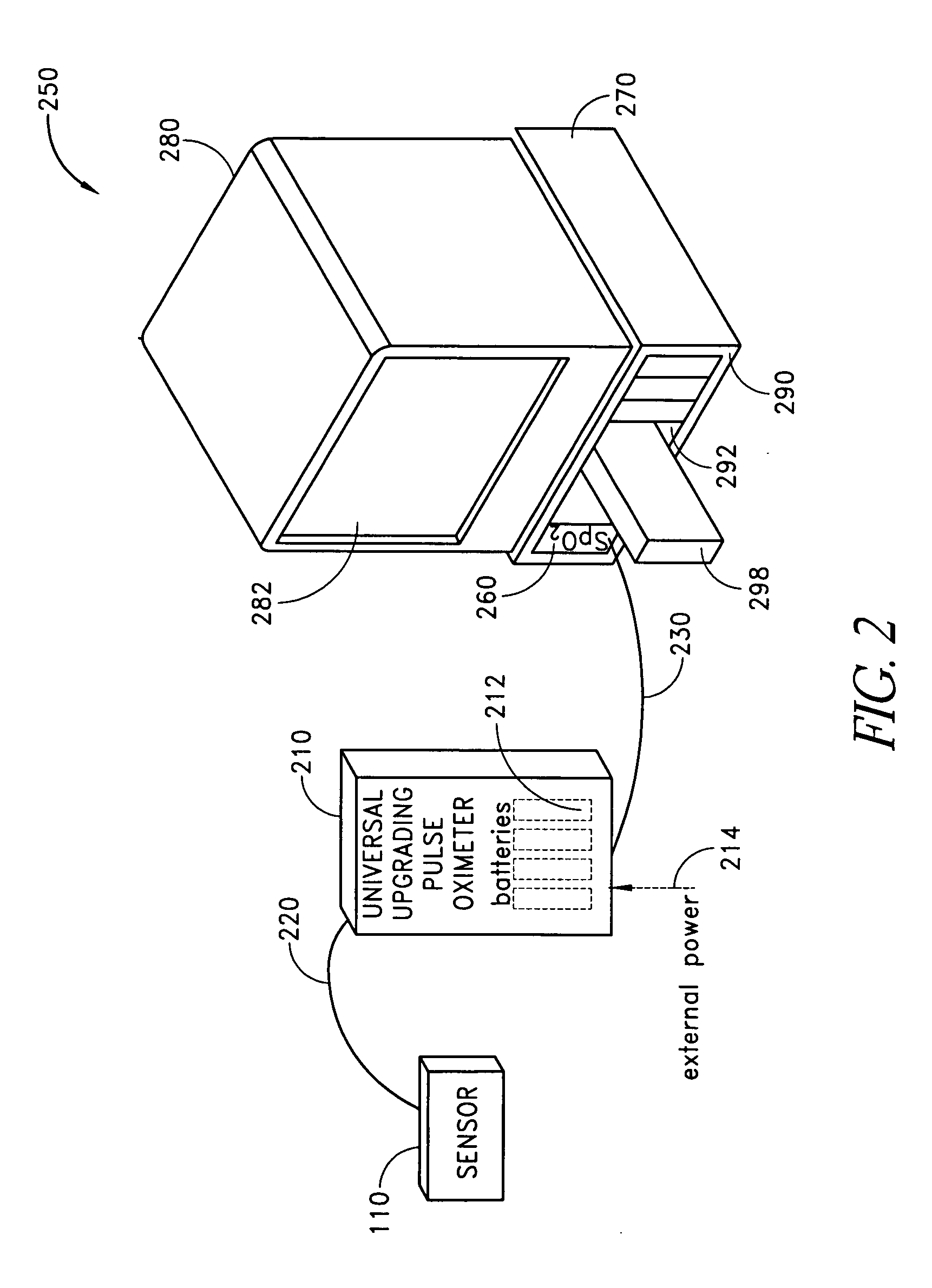
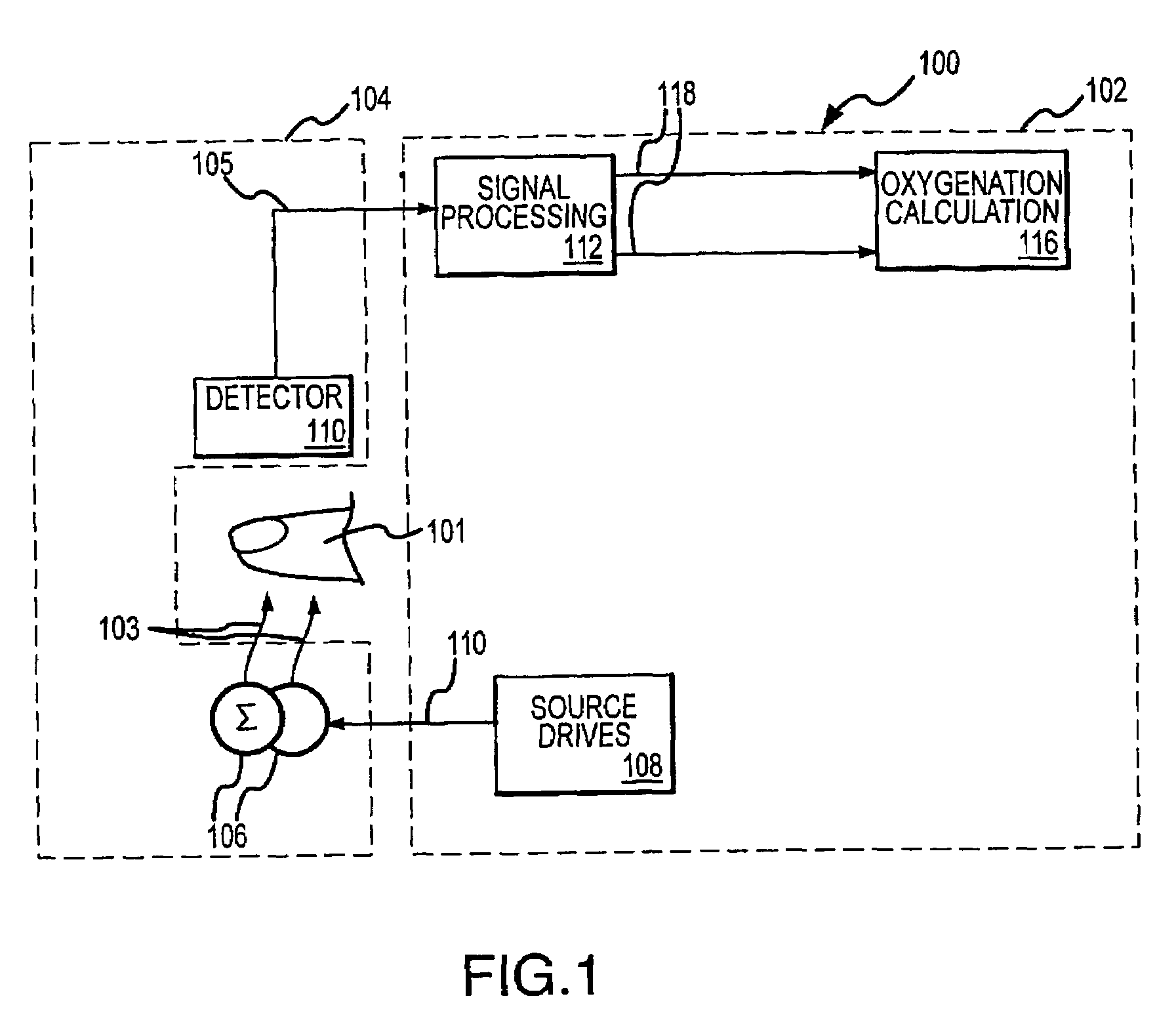
Dual-mode pulse oximeter
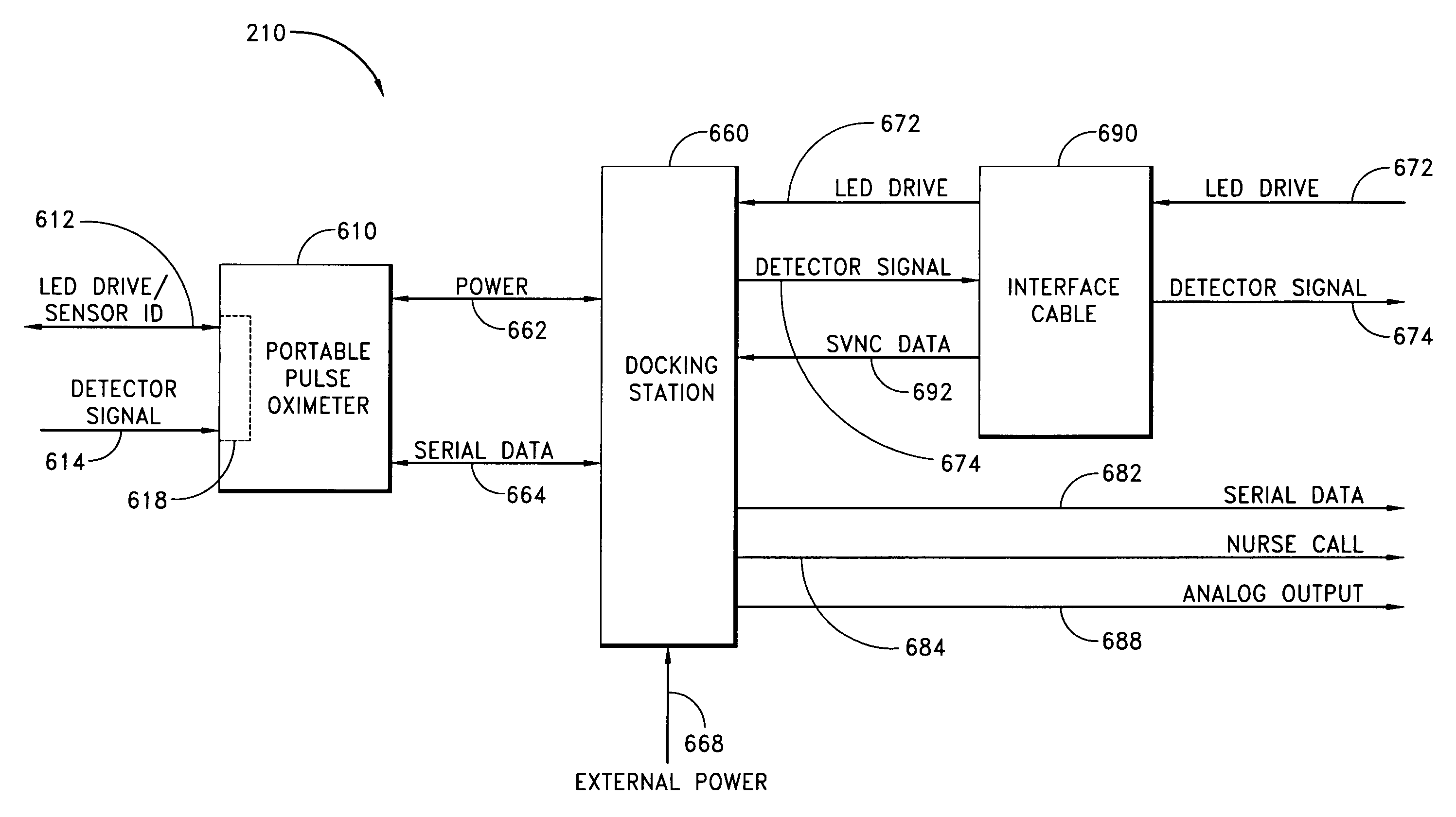
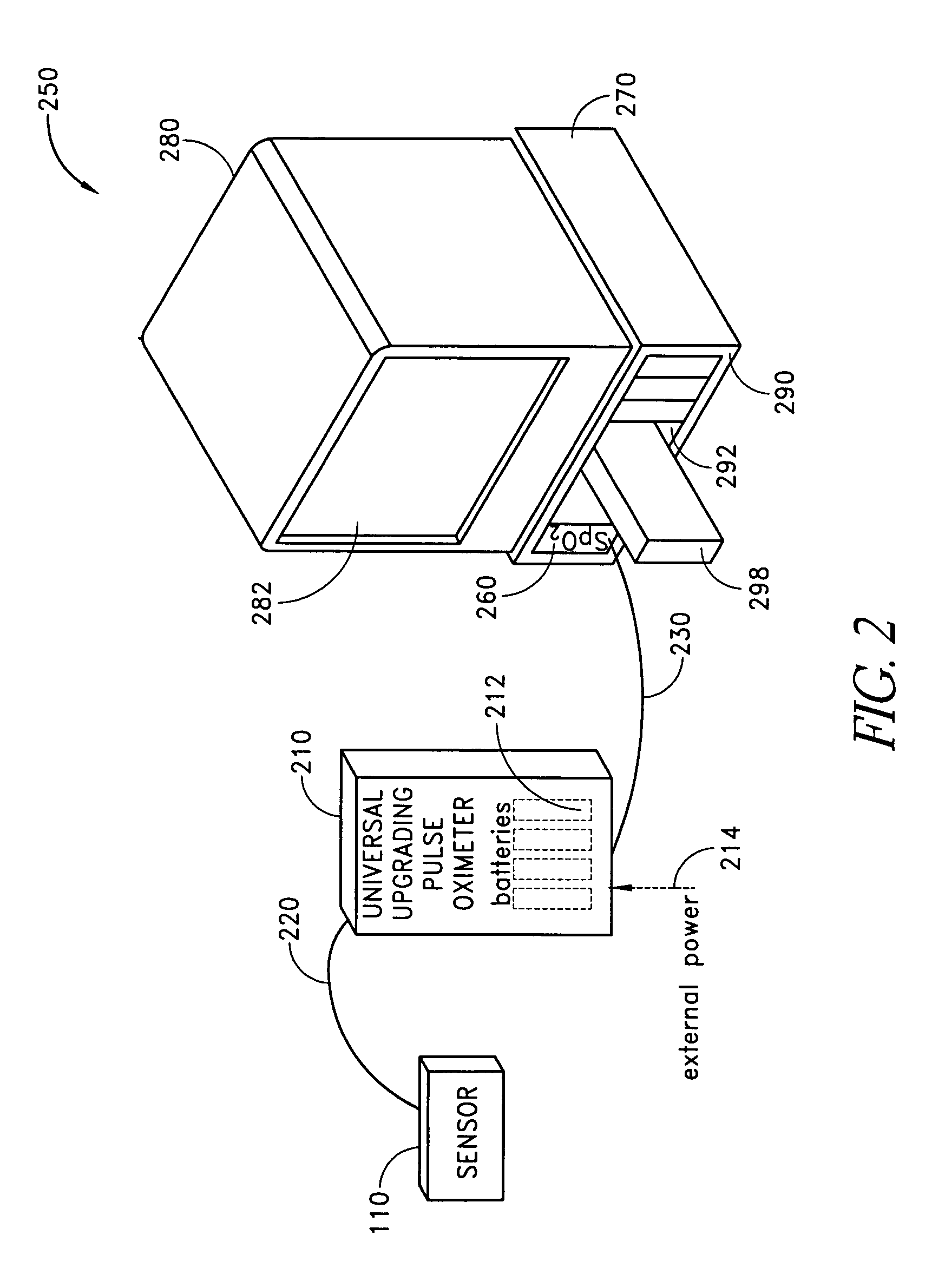
A pulse oximeter has an integrated mode in which it operates as a plug-in module for a multiparameter patient monitoring system (MPMS). The pulse oximeter also has a portable mode in which operates separately from the MPMS as a battery-powered handheld or standalone instrument. The pulse oximeter has a sensor port that receives a photo-plethysmographic signal as input to an internal processor. The pulse oximeter processes this sensor signal to derive oxygen saturation and pulse rate measurements. In the portable mode, this information is provided on its display, and stored in memory for trend capability. In the integrated mode, the pulse oximeter provides oxygen saturation and pulse rate measurements to the MPMS through a docking station to be displayed on a MPMS monitor. In the integrated mode, the portable pulse oximeter docks to the docking station, which in turn is inserted in one or more MPMS slots. The docking station can function as a simple electrical pass-through device between the docked portable pulse oximeter and the MPMS or it can provide a MPMS communications interface.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
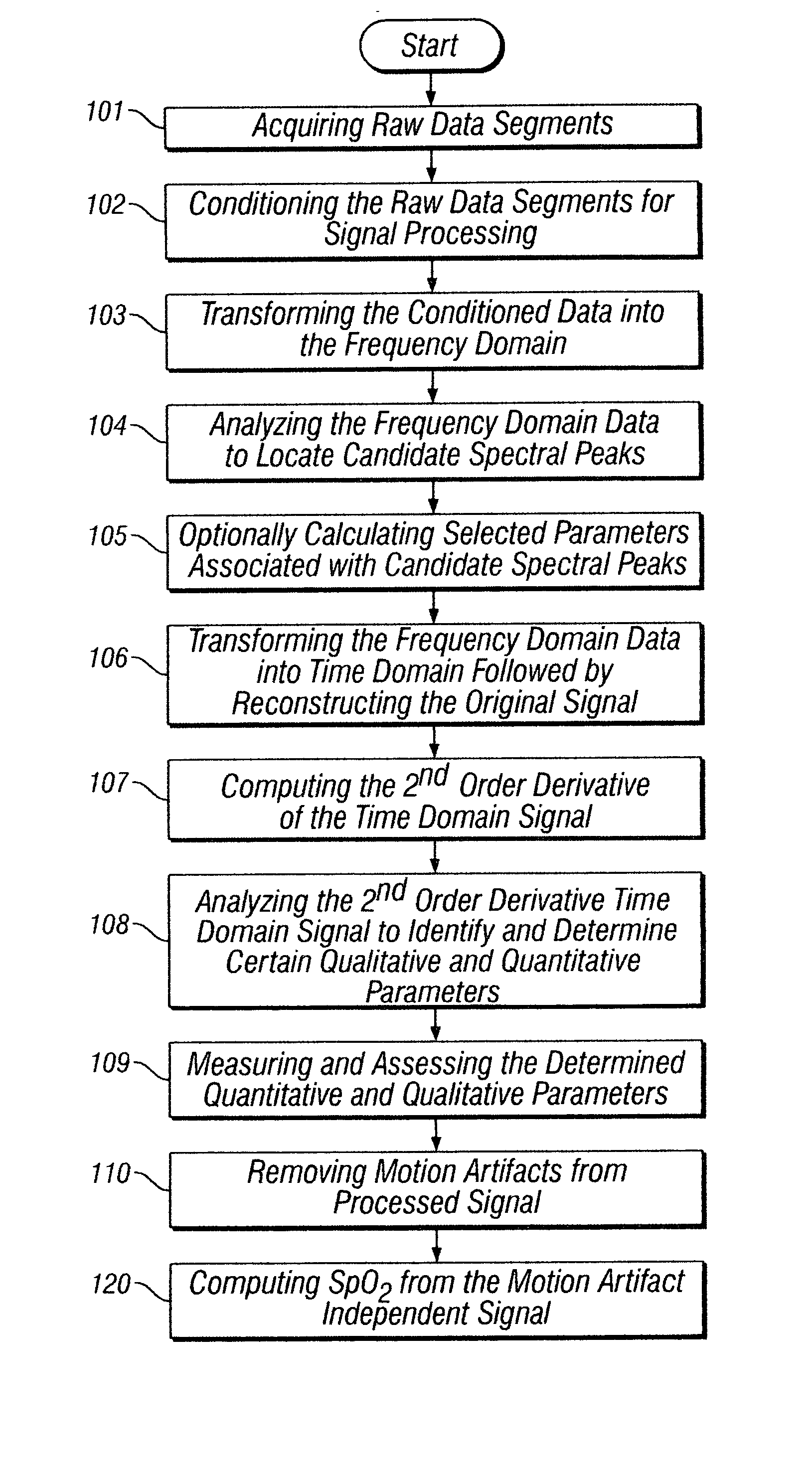
Separating motion from cardiac signals using second order derivative of the photo-plethysmogram and fast fourier transforms
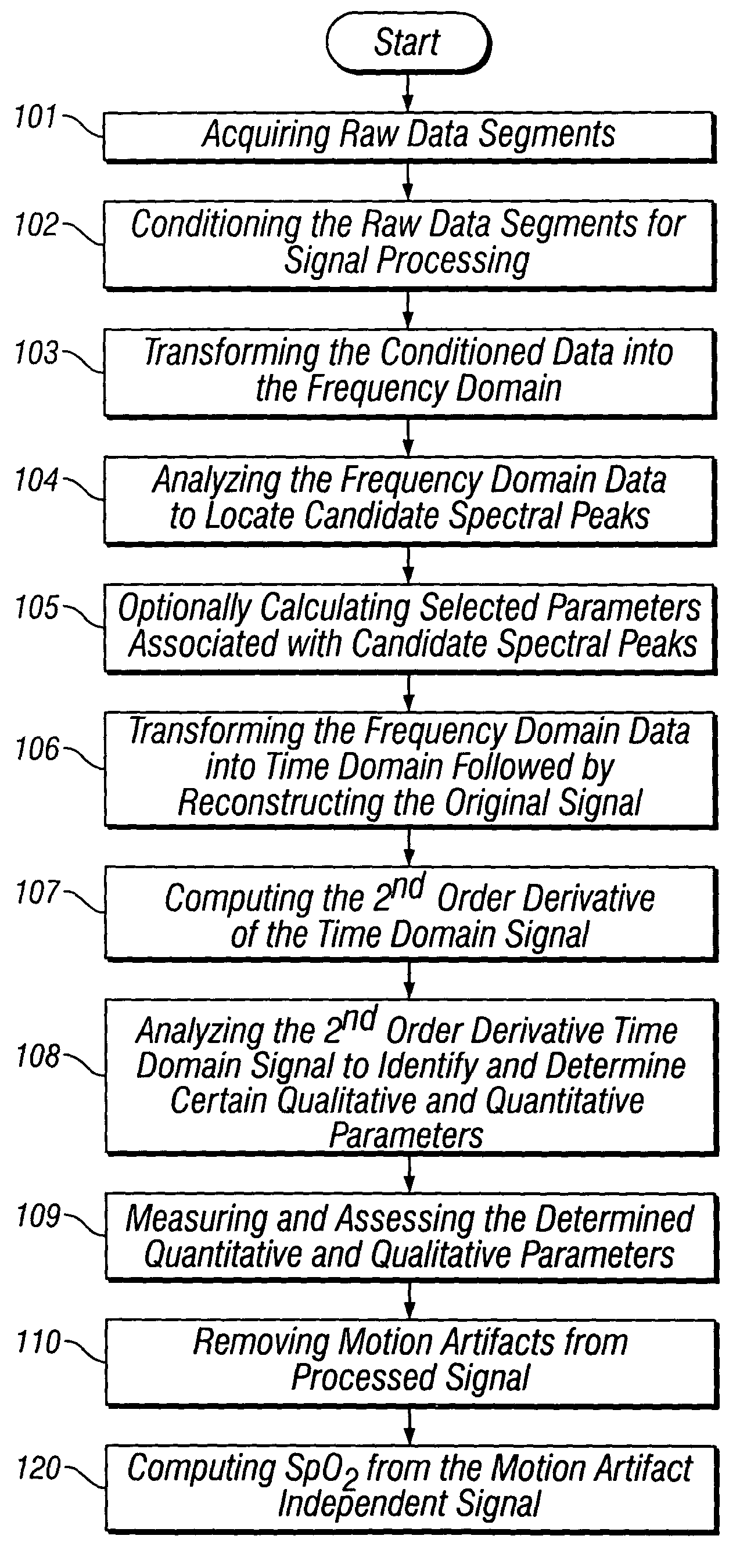
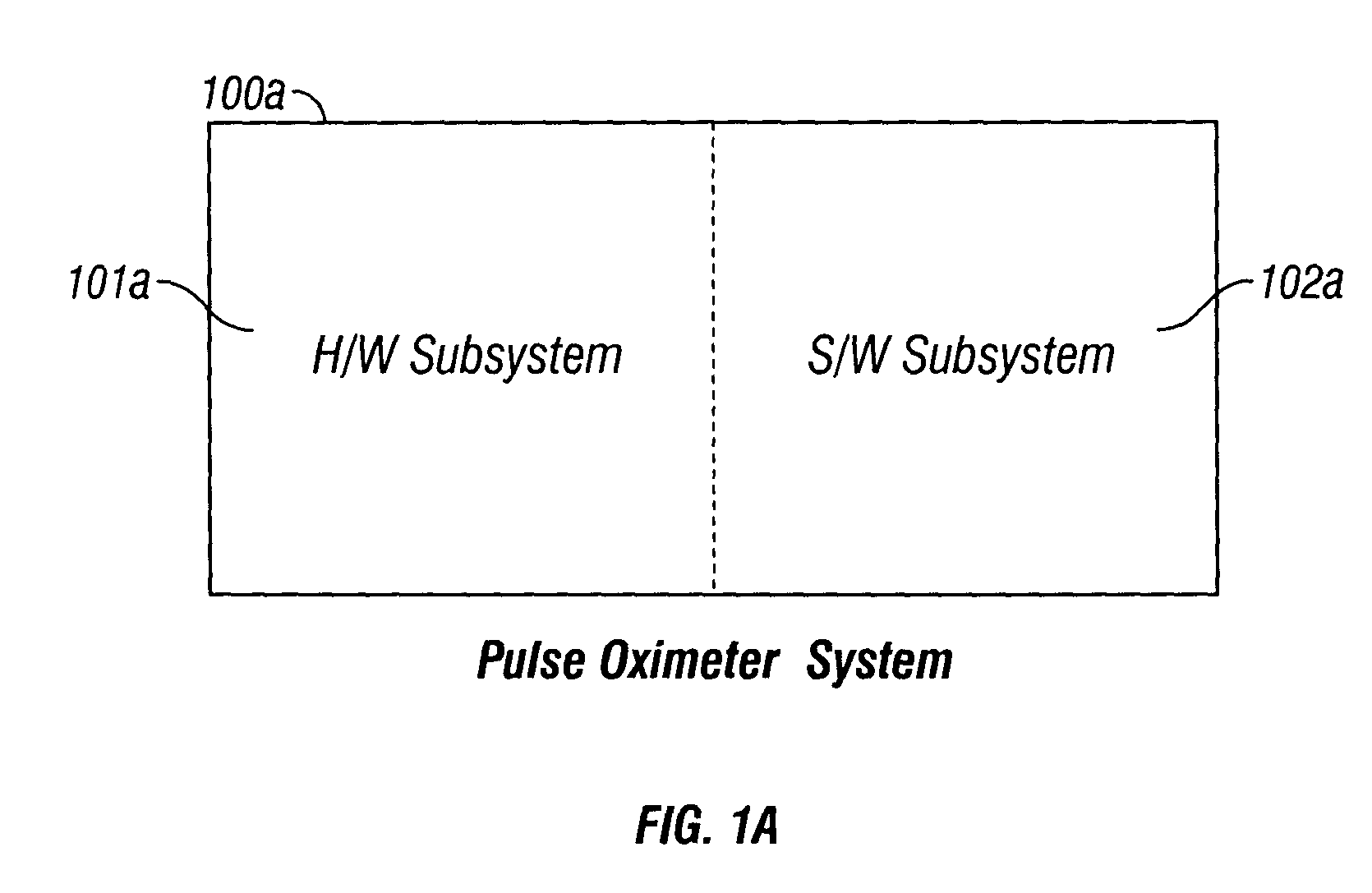
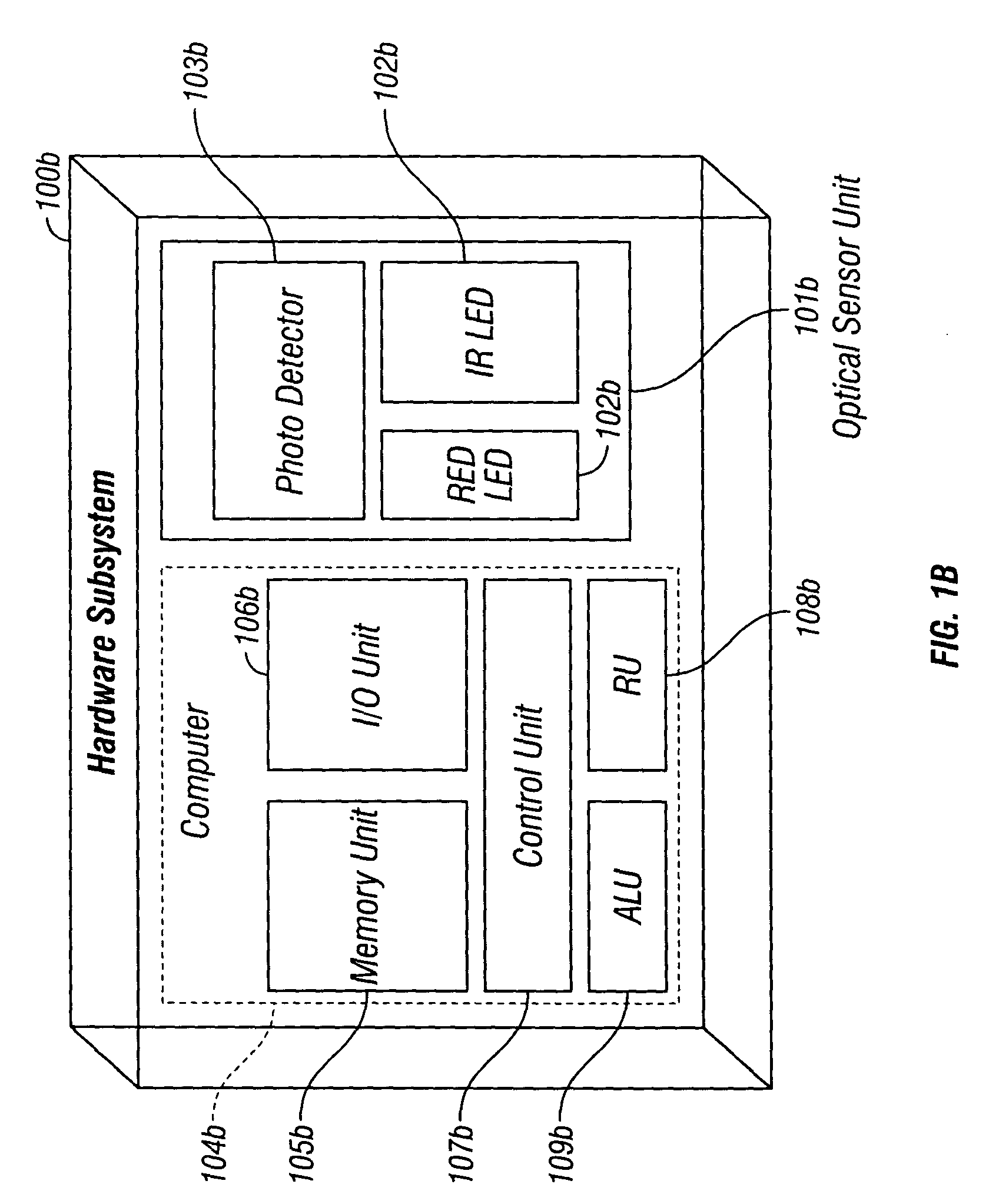
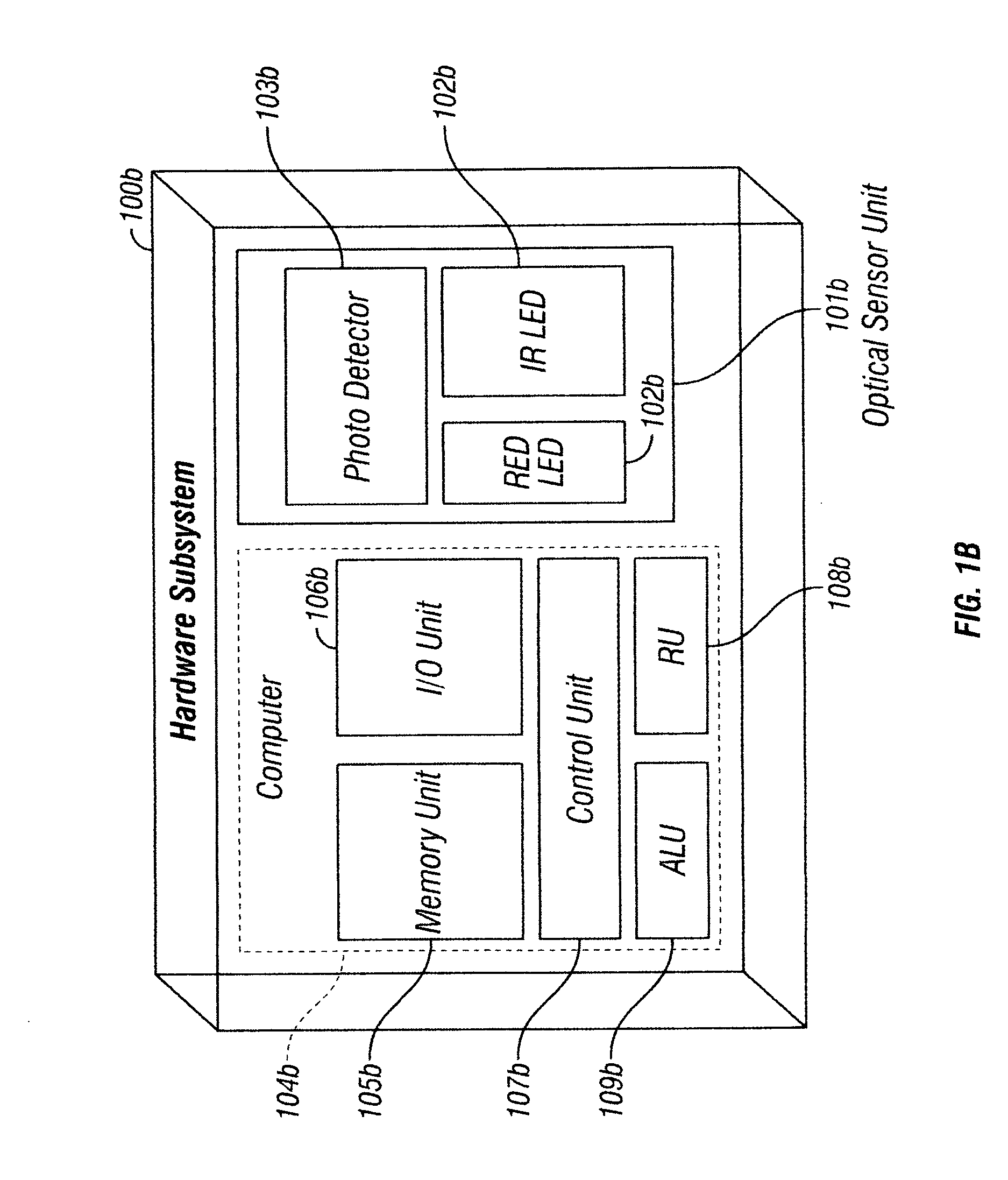
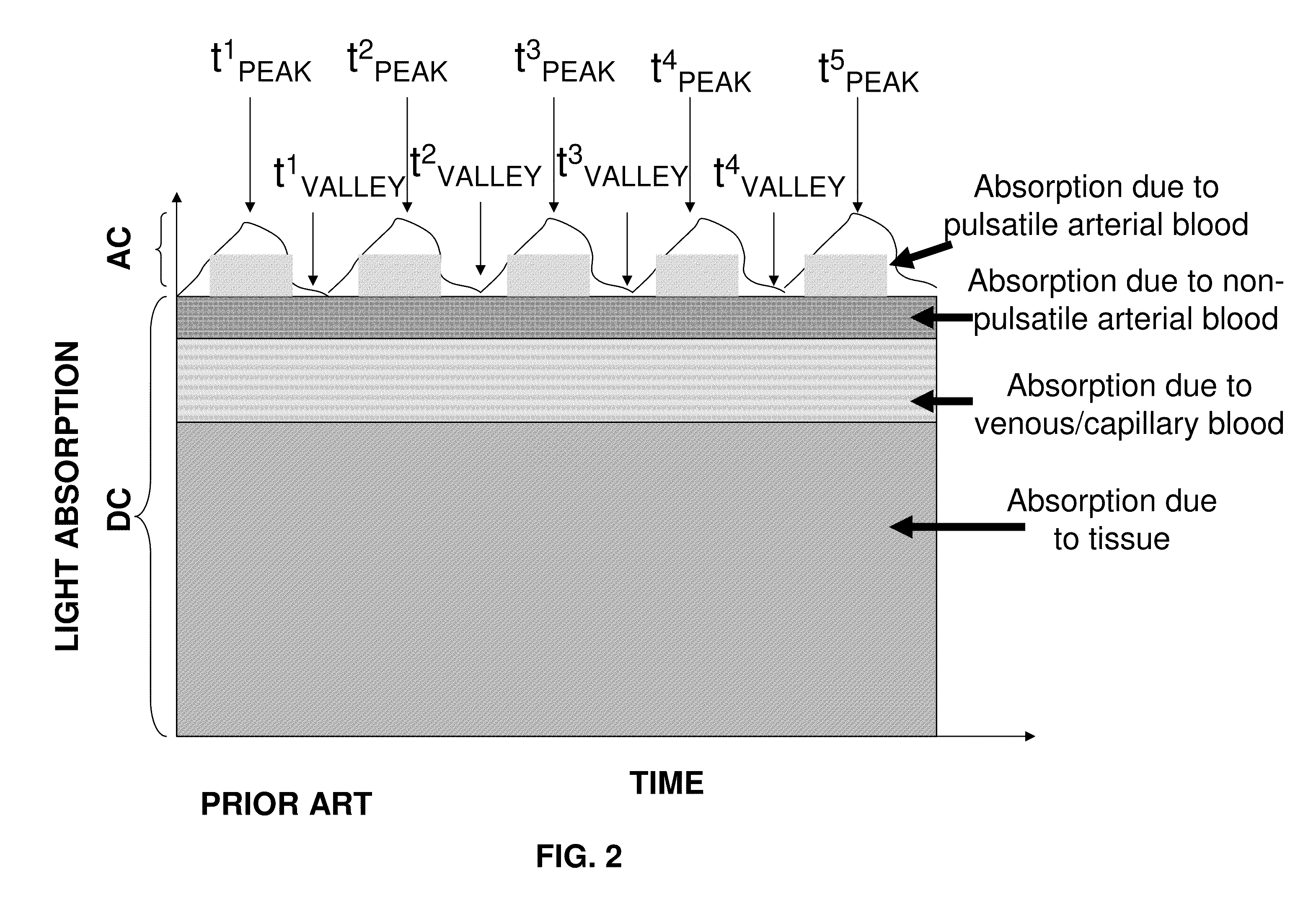
The present invention is directed toward a pulse oximetry system for the determination of a physiological parameter capable of removing motion artifacts from physiological signals comprises a hardware subsystem and a software subsystem. The software subsystem is used in conjunction with the hardware subsystem to perform a method for removing a plurality of motion artifacts from the photo-plethysmographic data and for obtaining a measure of at least one physiological parameter from the data. The method comprises acquiring the raw photo-plethysmographic data, transforming the data into the frequency domain, analyzing the transformed data to locate a series of candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), reconstructing a photo-plethysmographic signal in the time domain with only the candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), computing the second order derivative of the reconstructed photo-plethysmographic signal, analyzing the candidate second order derivative photo-plethysmographic signal to determine the absence or presence of cardiac physiologic signal characteristics, and finally selecting the best physiologic candidate from the series of potential cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics) based upon a second derivative scoring system. This scoring system is preferentially based upon second derivative processing analysis, but can be equally applied using the first, third, fourth or other similar derivative processing analysis.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
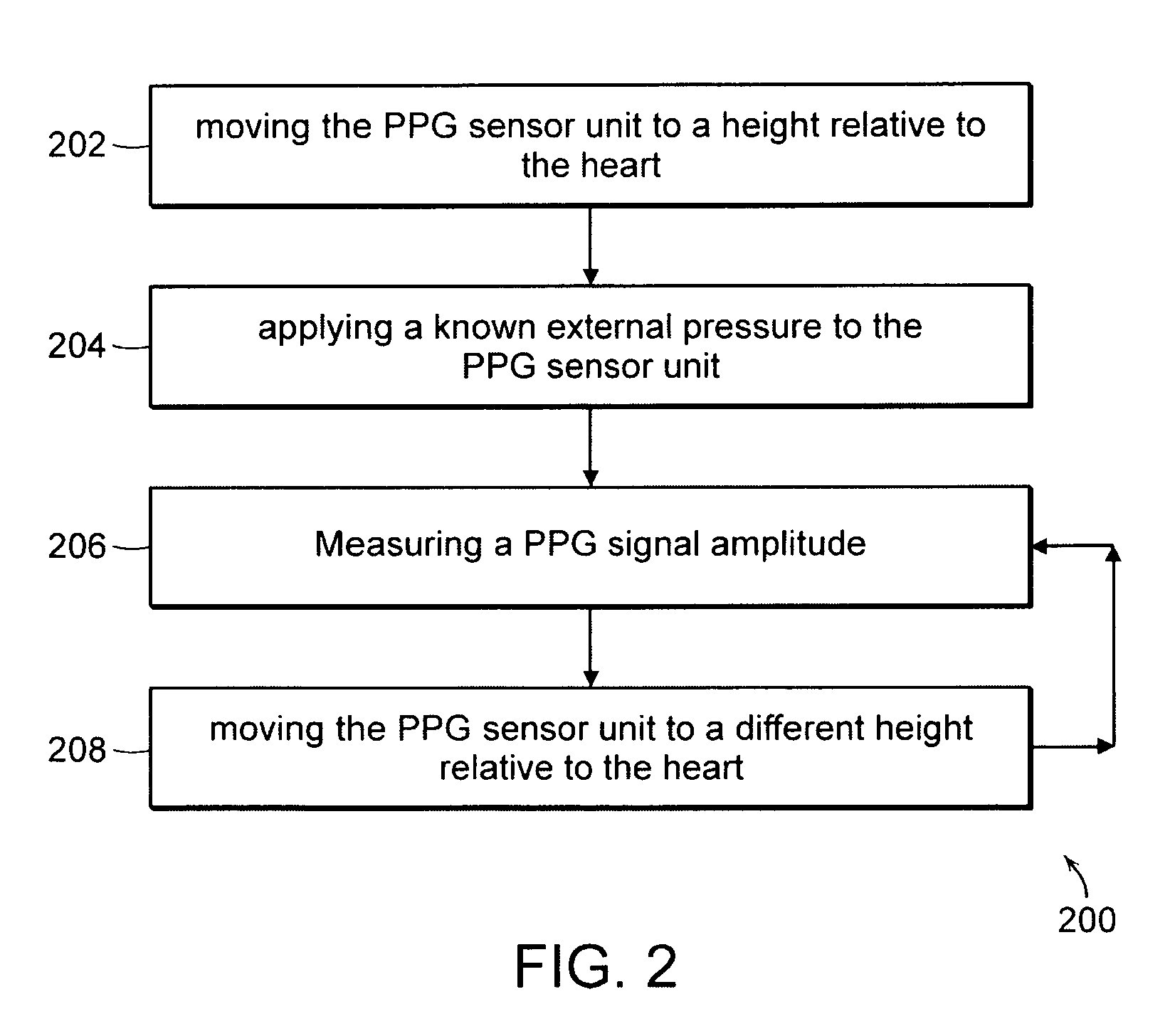
Wearable blood pressure sensor and method of calibration
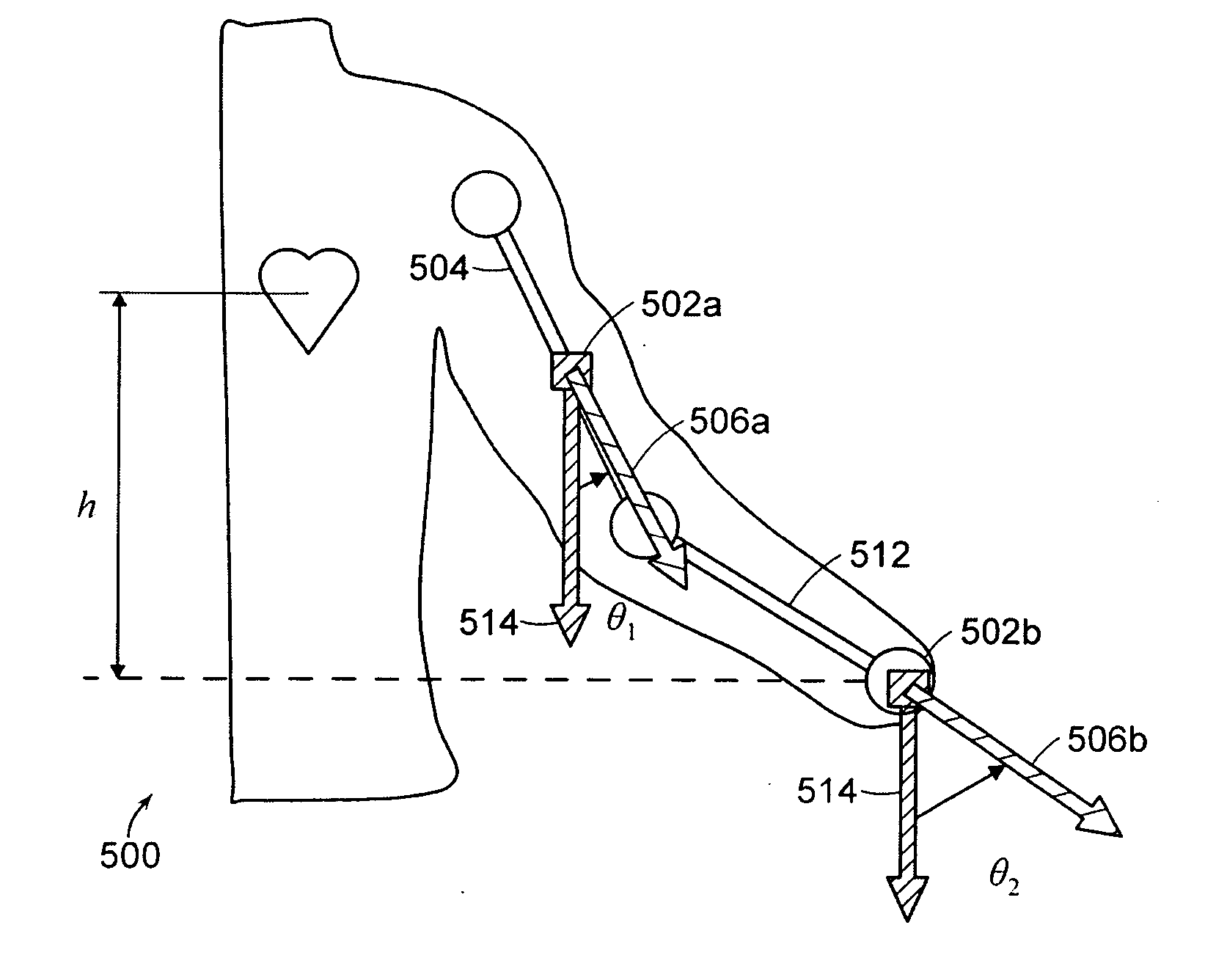
Methods and apparatus for measuring arterial blood pressure at an extremity of a subject. Arterial blood pressure is derived from a circulatory measurement performed on an extremity of a subject and the circulatory measurement is normalized to account for the instantaneous vertical displacement of the extremity. The vertical displacement of the extremity relative to the heart of the subject is obtained using the angular orientation of the subject's extremity. An improved photoplethysmograph can discriminate light traversing the extremity from ambient light on the basis of differential response. The apparatus may have a conducting polymer actuator for applying pressure to the extremity of the subject. A pulsatile waveform from the photoplethysmographic signal may be obtained at a plurality of externally applied pressures to calibrate the photoplethysmograph.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Dual-mode pulse oximeter
InactiveUS20050065417A1Easy to disassembleCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationDocking stationCommunication interface
A pulse oximeter has an integrated mode in which it operates as a plug-in module for a multiparameter patient monitoring system (MPMS). The pulse oximeter also has a portable mode in which operates separately from the MPMS as a battery-powered handheld or standalone instrument. The pulse oximeter has a sensor port that receives a photo-plethysmographic signal as input to an internal processor. The pulse oximeter processes this sensor signal to derive oxygen saturation and pulse rate measurements. In the portable mode, this information is provided on its display, and stored in memory for trend capability. In the integrated mode, the pulse oximeter provides oxygen saturation and pulse rate measurements to the MPMS through a docking station to be displayed on a MPMS monitor. In the integrated mode, the portable pulse oximeter docks to the docking station, which in turn is inserted in one or more MPMS slots. The docking station can function as a simple electrical pass-through device between the docked portable pulse oximeter and the MPMS or it can provide a MPMS communications interface.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Separating motion from cardiac signals using second order derivative of the photo-plethysmogram and fast fourier transforms
The present invention is directed toward a pulse oximetry system for the determination of a physiological parameter capable of removing motion artifacts from physiological signals comprises a hardware subsystem and a software subsystem. The software subsystem is used in conjunction with the hardware subsystem to perform a method for removing a plurality of motion artifacts from the photo-plethysmographic data and for obtaining a measure of at least one physiological parameter from the data. The method comprises acquiring the raw photo-plethysmographic data, transforming the data into the frequency domain, analyzing the transformed data to locate a series of candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), reconstructing a photo-plethysmographic signal in the time domain with only the candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), computing the second order derivative of the reconstructed photo-plethysmographic signal, analyzing the candidate second order derivative photo-plethysmographic signal to determine the absence or presence of cardiac physiologic signal characteristics, and finally selecting the best physiologic candidate from the series of potential cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics) based upon a second derivative scoring system. This scoring system is preferentially based upon second derivative processing analysis, but can be equally applied using the first, third, fourth or other similar derivative processing analysis.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
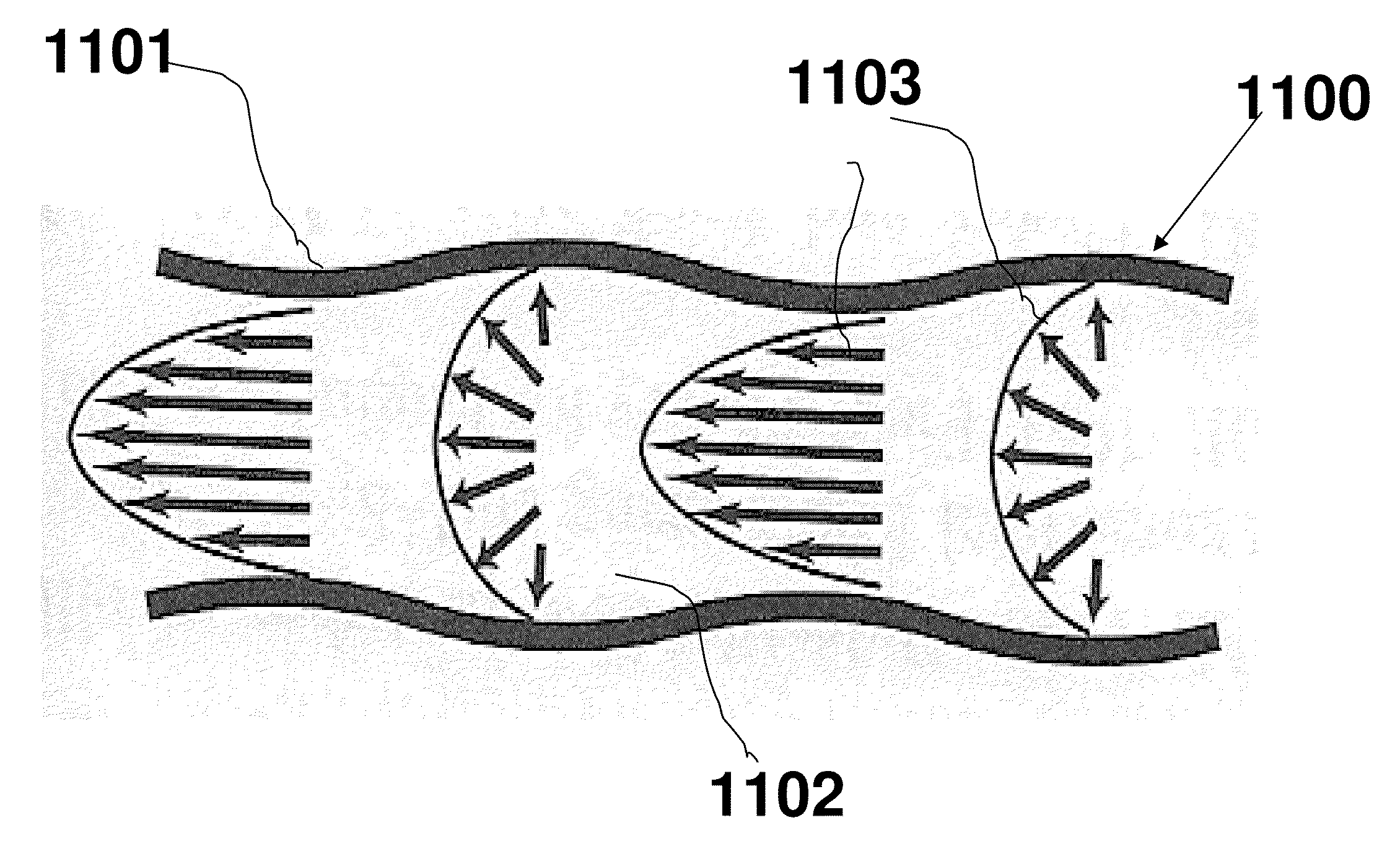
Method of assesing blood volume using photoelectric plethysmography
A method and system for assessing blood volume within a subject includes generating a cardiovascular waveform representing physiological characteristics of a subject and determining blood volume of the subject by analyzing the cardiovascular waveform. The step of analyzing includes generating a first trace of the per heart-beat maximums of the cardiovascular waveform, which is representative of the systolic pressure upon the cardiovascular signal, generating a second trace of the per heart-beat minimums of the cardiovascular waveform, which is representative of the diastolic pressure upon the cardiovascular signal, and comparing the respective first trace and the second trace to generate an estimate of relative blood volume within the subject. In accordance with an alternate method of analyzing harmonic analysis is applied to the cardiovascular waveform, extracting a frequency signal created by ventilation and applying the extracted frequency signal in determining blood volume of the subject.
Owner:SHELLEY KIRK H +2
Wavelet transform of a plethysmographic signal
ActiveUS7515949B2Enhanced identification and isolationEfficient separationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsAnalyteEngineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for monitoring pressure related changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system
ActiveUS20100222655A1Overcome disadvantagesEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterFrequency spectrumCardiac functioning
A method and apparatus for monitoring changes in the intra-thoracic pressure of a patient due to the patient's respiratory activity or volumetric changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system due to cardiac function based on the changes in pressure in the patient's extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system as measured by a plethysmography sensor, such as an photoplethysmograph. A frequency spectrum is generated for the plethysmograph signal and the frequencies of interest is isolated from the frequency spectrum by setting appropriate cutoff frequencies for the frequency spectrum. This isolated frequency is used to filter the plethysmograph signal to provide a signal indicative of the patient's respiratory activity or cardiac function.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Apparatus and method for monitoring pressure related changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system
ActiveUS7740591B1Overcomes shortcomingOvercome disadvantagesEvaluation of blood vesselsRespiratory organ evaluationRespiratory rateIntensive care medicine
A method and apparatus for monitoring changes in the intra-thoracic pressure of a patient due to the patient's respiratory activity or volumetric changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system due to cardiac function based on the changes in pressure in the patient's extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system as measured by a plethysmography sensor, such as an photoplethysmograph. A frequency spectrum is generated for the plethysmograph signal and the frequencies of interest is isolated from the frequency spectrum by setting appropriate cutoff frequencies for the frequency spectrum. This isolated frequency is used to filter the plethysmograph signal to provide a signal indicative of the patient's respiratory activity or cardiac function. For corrections for breathing frequency roll-off and deviations of the I:E ratio from 1:1.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
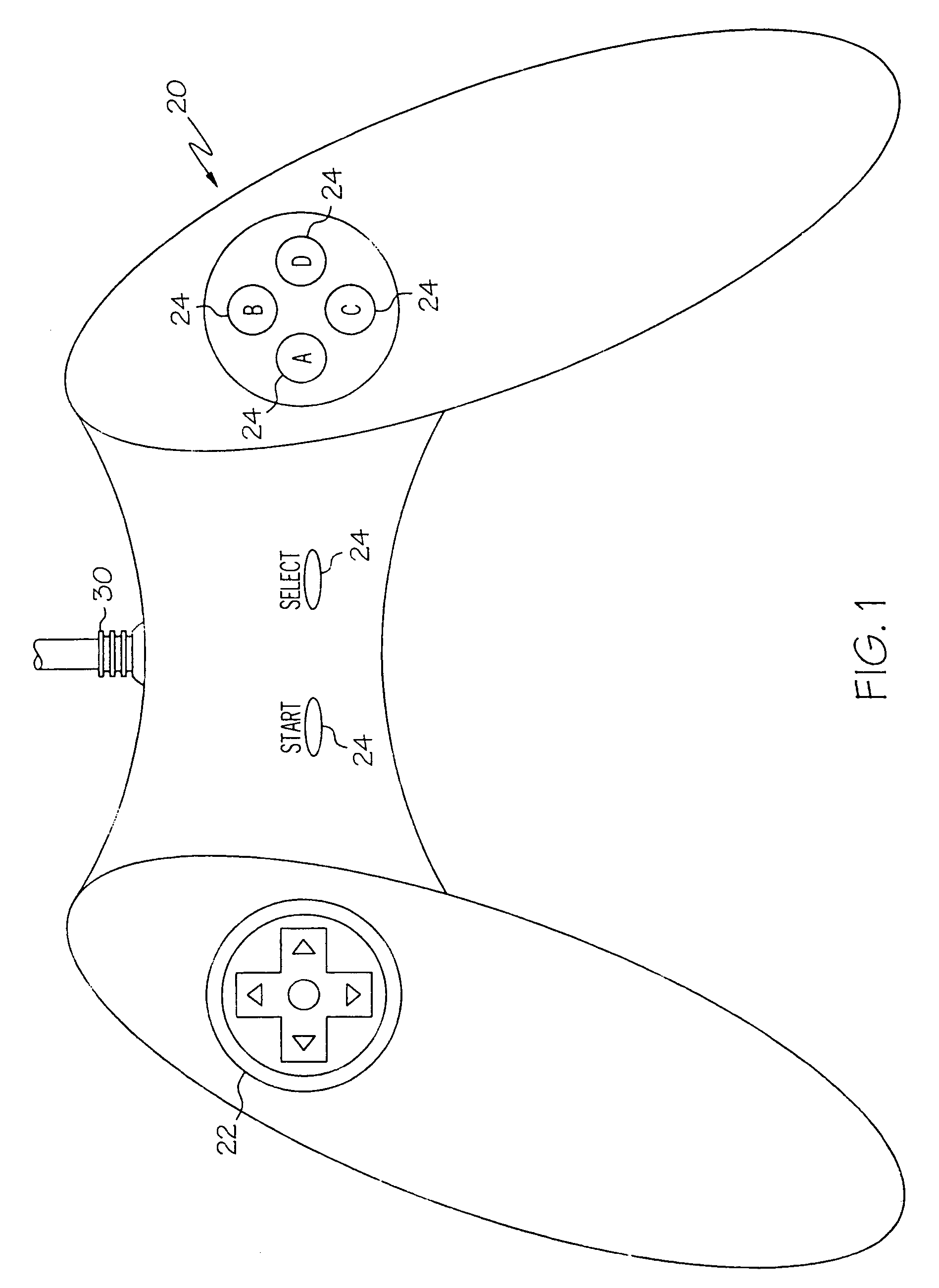
Video game system and game controller
InactiveUS7625285B2Overcome disadvantagesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGalvanometerCommunication link
Game controllers having a communication link to a game systems, a processor, and a photoelectric plethysmography, a galvanometer, or a thermocouple. Video game systems having a video game processor, a computer readable medium containing executable instructions for providing a video game and the game controller.
Owner:BREVING JOEL S
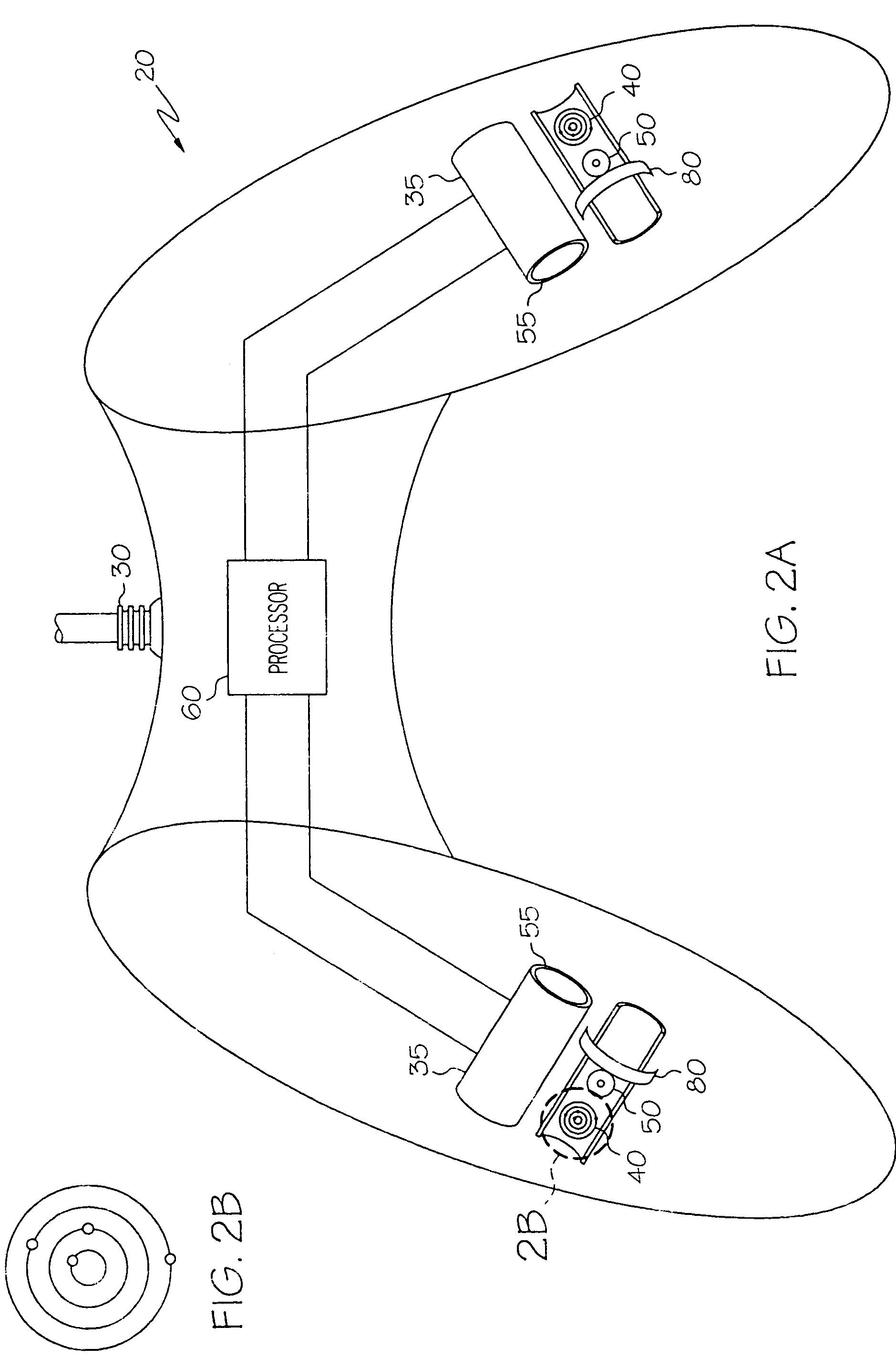
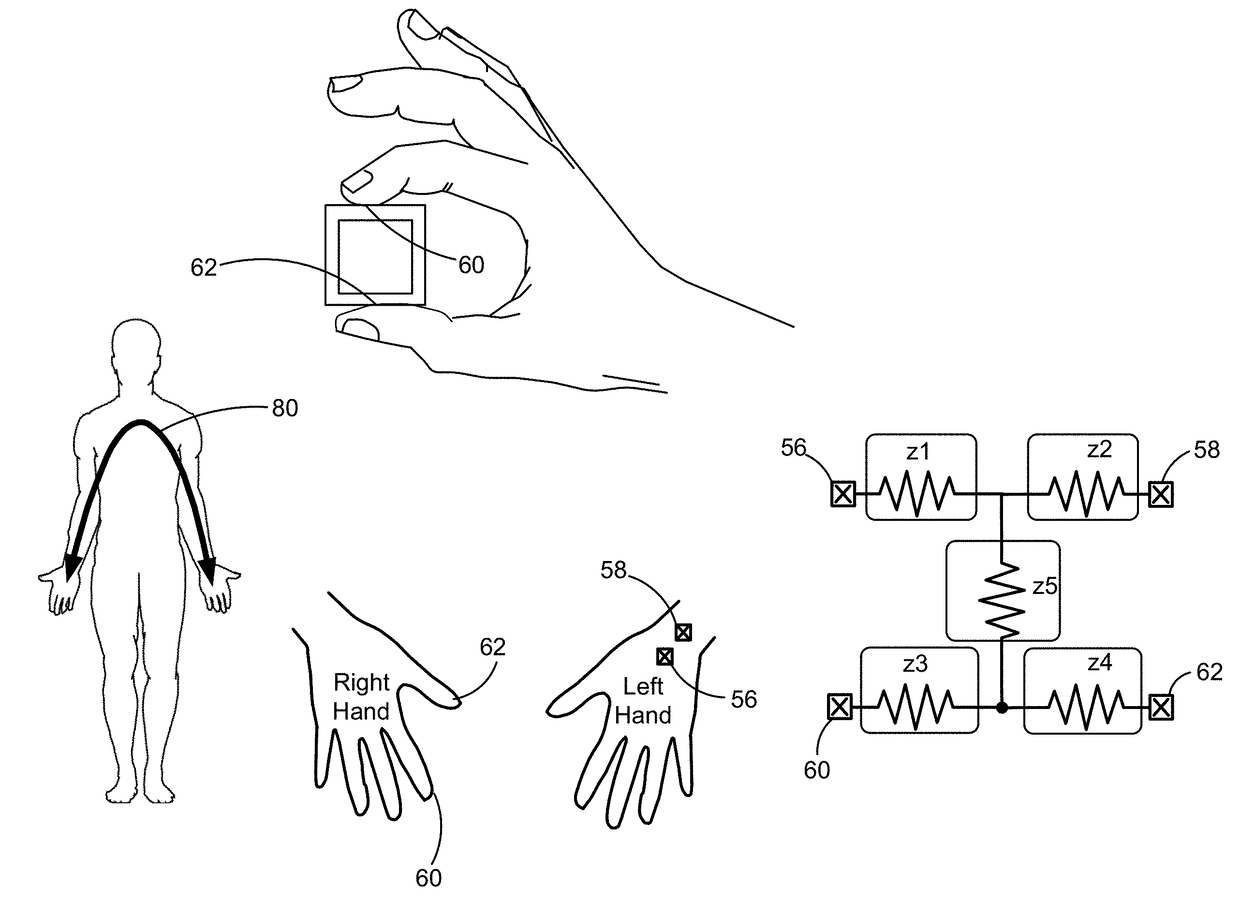
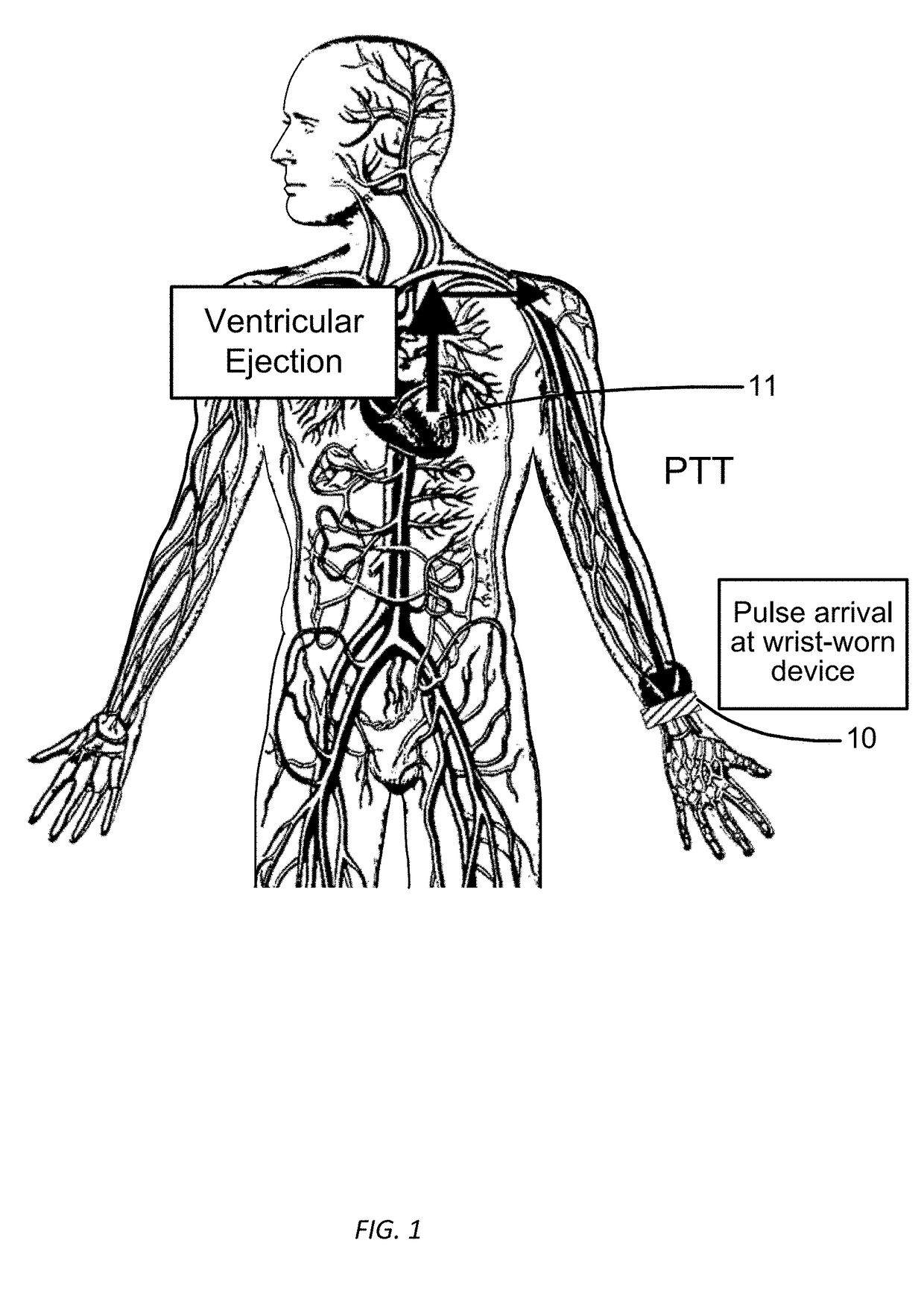
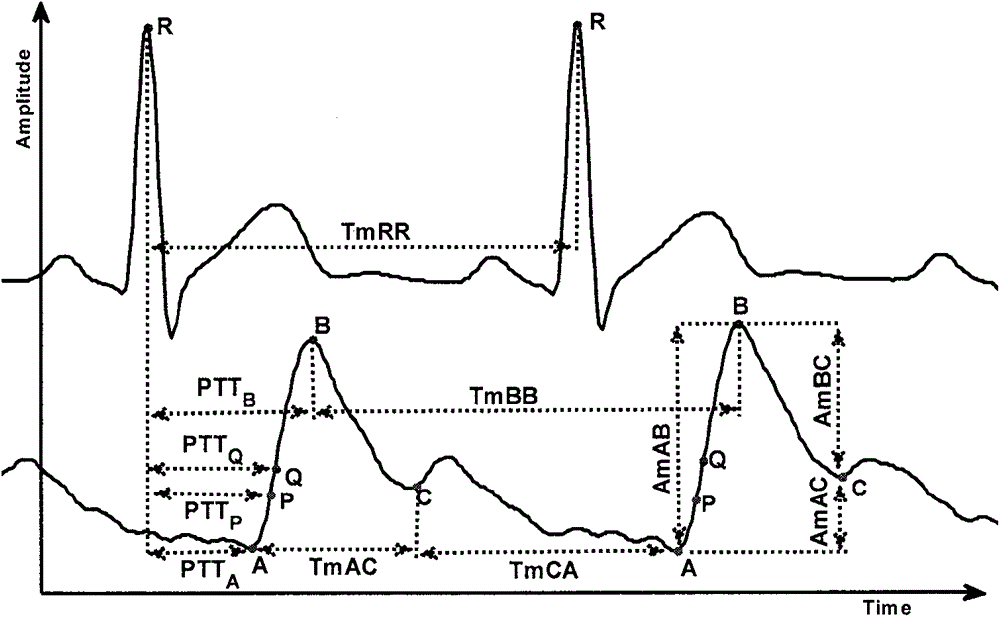
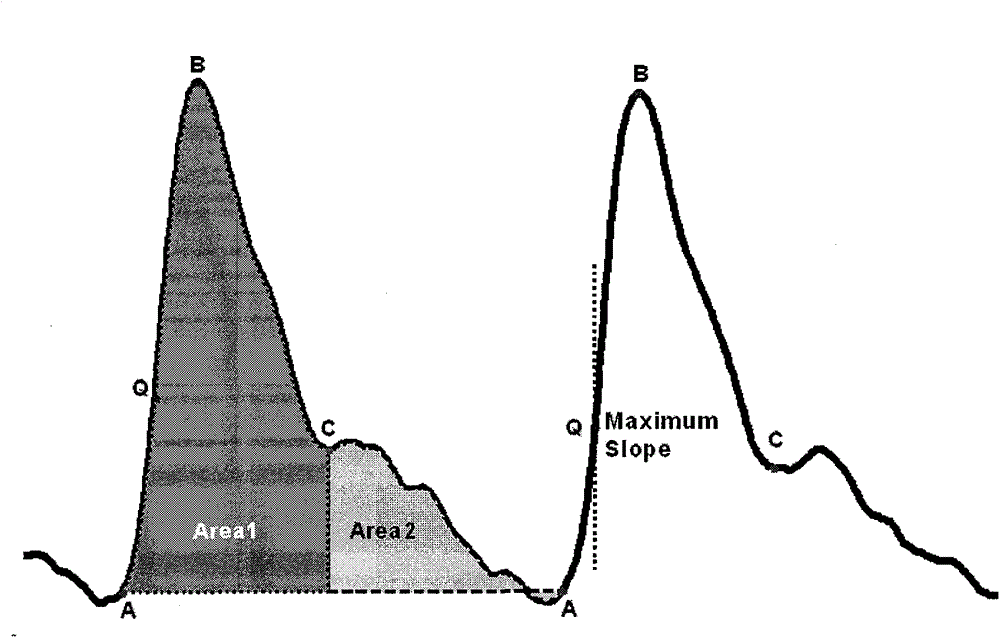
Wrist worn accelerometer for pulse transit time (PTT) measurements of blood pressure
ActiveUS20170281024A1Cancel noiseEasy to detectEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsAccelerometerPulse pressure
Wrist-worn devices and related methods measure a pulse transit time non-invasively and calculate a blood pressure value using the pulse transit time. A wrist-worn device includes an accelerometer, a photo-plethysmogram (PPG) or a pulse pressure sensor, and a controller. The PPG or the pulse pressure sensor coupled to the wrist-worn device for detecting an arrival of a blood pressure pulse at the user's wrist. The controller is configured to process output signals from the accelerometer to detect when the blood pressure pulse is propagated from the left ventricle of the user's heart, process a signal from the PPG or the pulse pressure sensor to detect when the blood pressure pulse arrives at the wrist, calculate a pulse transit time (PTT) for propagation of the blood pressure pulse from the left ventricle to the wrist, and generate one or more blood pressure values for the user based on the PTT.
Owner:APPLE INC
Photoplethysmography device and method
InactiveUS20110082355A1Accurate descriptionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalytePulse parameter
A system and method for measuring one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameters of a mammalian subject, is disclosed. In some embodiments, the system comprises: a) a photoplethysmography (PPG) device configured to effect a PPG measurement by illuminating skin of the subject with at least two distinct wavelengths of light and determining relative absorbance at each of the wavelengths; b) a dynamic light scattering measurement (DLS) device configured to effect a DLS measurement of the subject to rheologically measure a pulse parameter of the subject; and c) electronic circuitry configured to: i) temporally correlating the results of the PPG and DLS measurements; and ii) accordance with the temporal correlation between the PPG and DLS measurements, assessing value(s) of the one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameter(s).
Owner:OXITONE MEDICAL
Techniques for accurately deriving physiologic parameters of a subject from photoplethysmographic measurements
ActiveUS20080167564A1Good for scrollingUndesirable frequency content eliminated and reducedCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationData setPulse oximeters
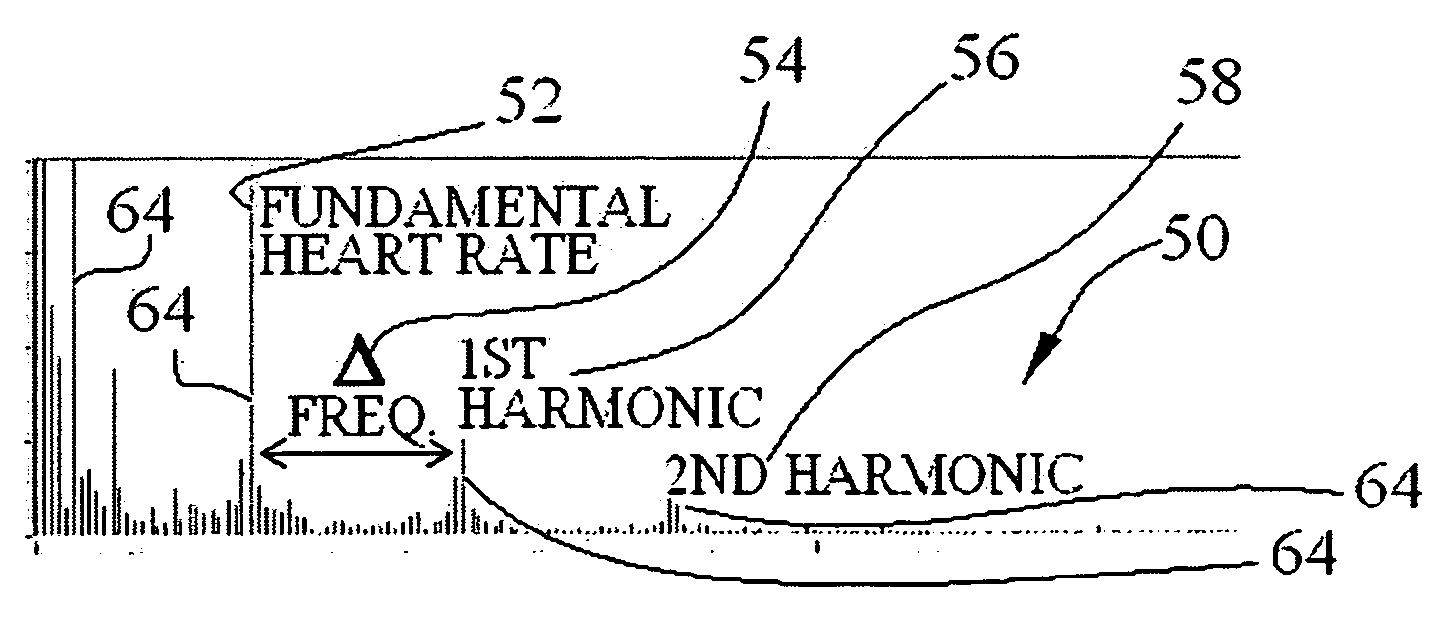
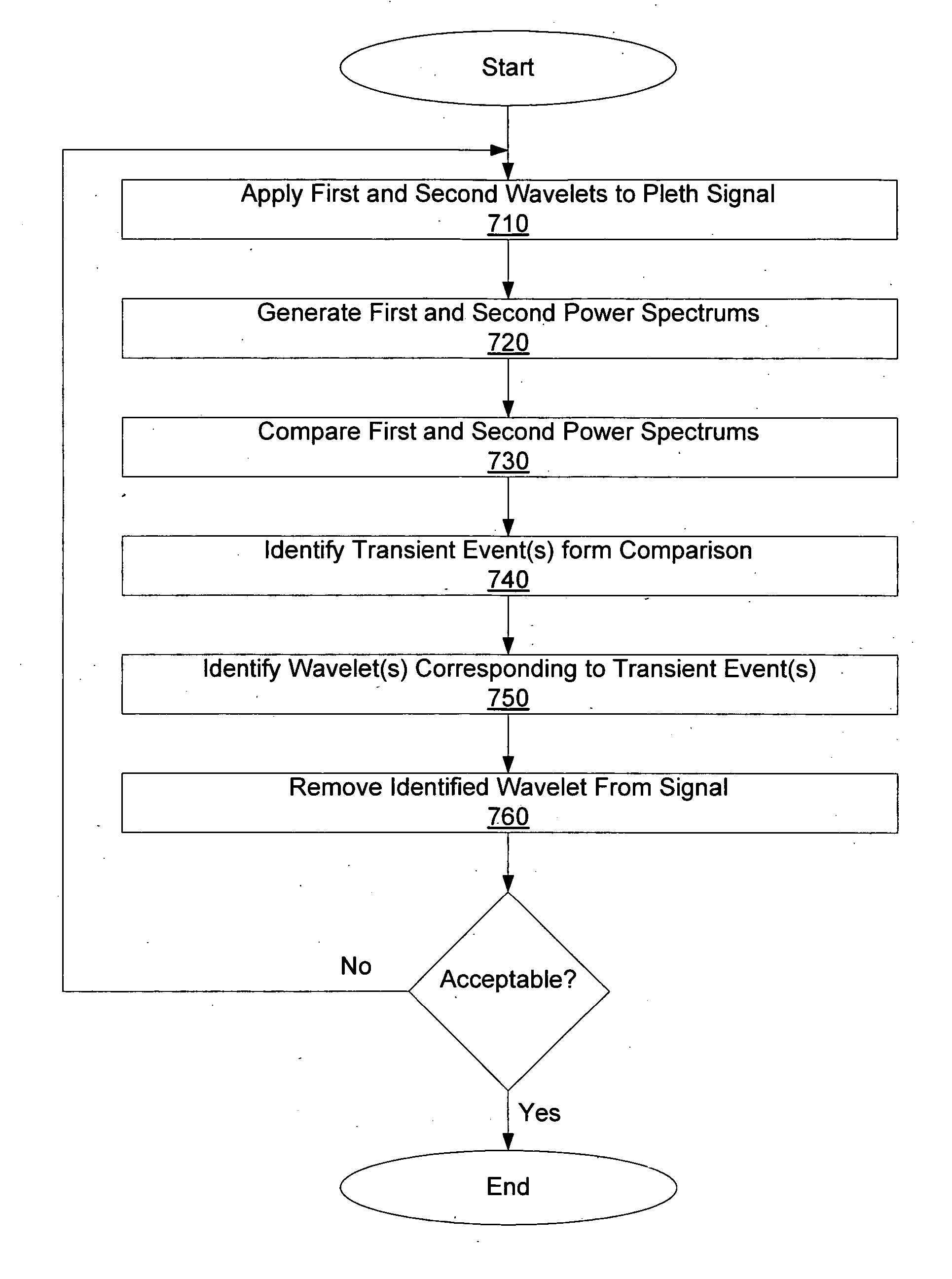
Several techniques are disclosed for isolating either heart or breath rate data from a photoplethysmograph, which is a time domain signal such as from a pulse oximeter. The techniques involve the use of filtering in the frequency domain, after a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) has been conducted on a given photoplethysmograph also references as a given set of discrete time-domain data. The filtering may be applied to an identified fundamental frequency and one or more harmonics for heart related parameters. The filter may be truncated to the frequency data set and further applied multiple times to improve roll off. After filtering, an Inverse FFT (IFFT) is used to reconstruct the time-domain signal, except with undesirable frequency content eliminated or reduced. Calculation or measurement of parameters is then conducted on this reconstructed time-domain signal.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
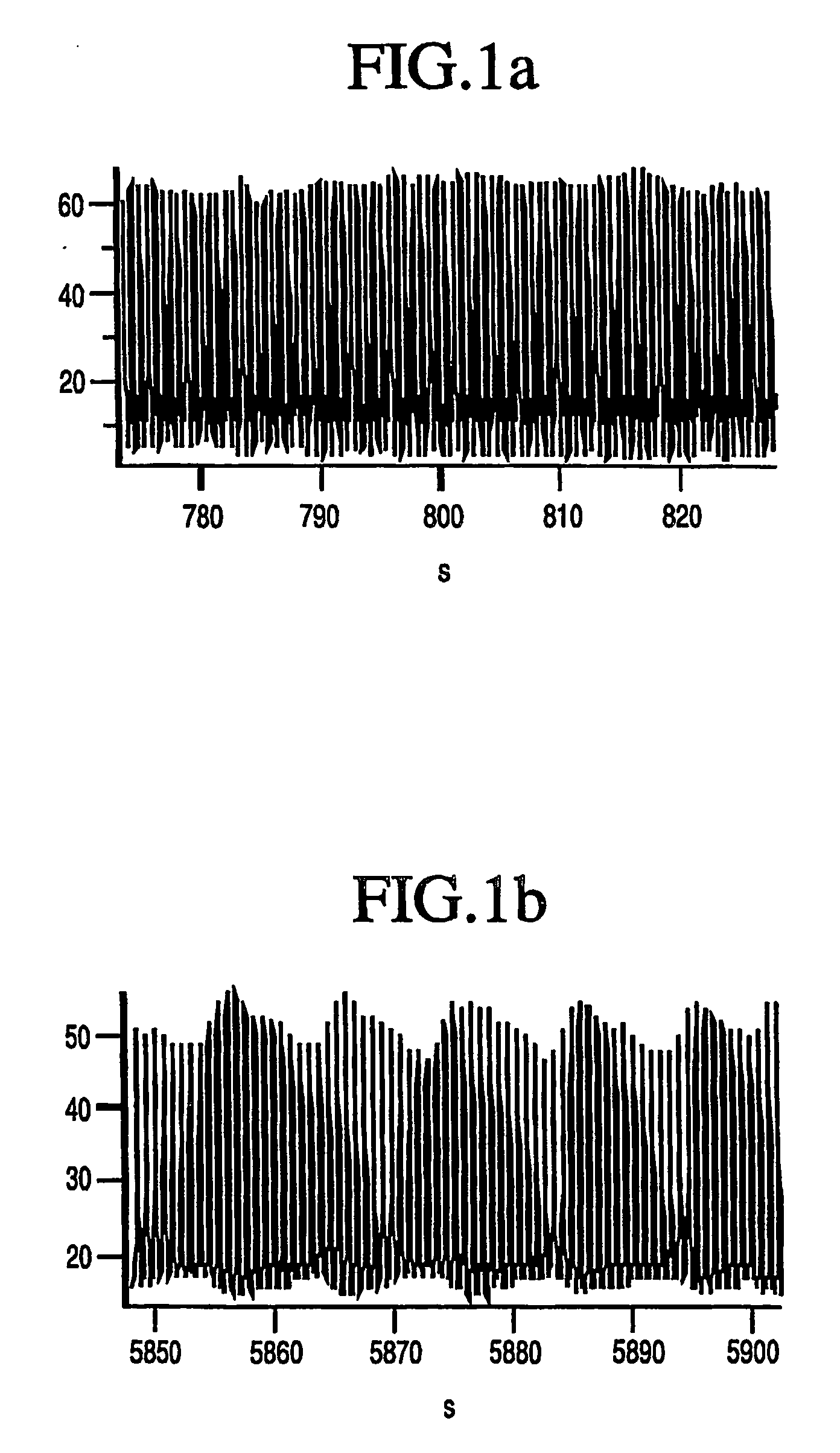
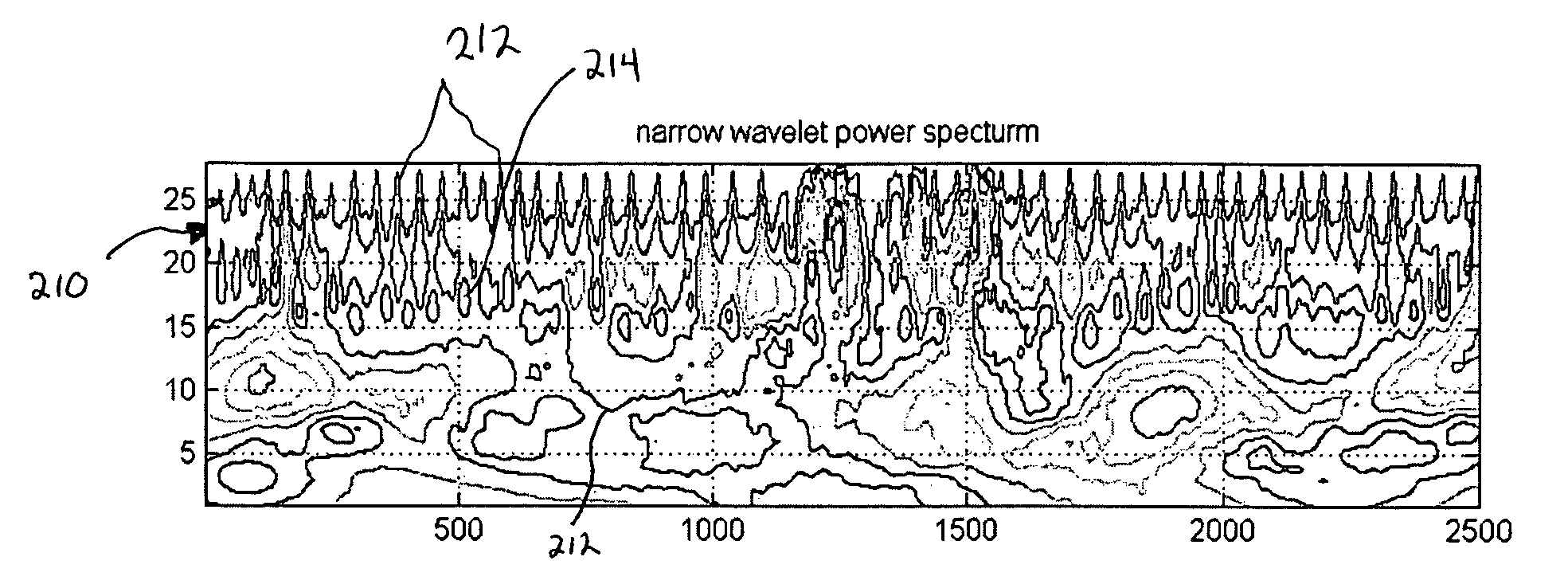
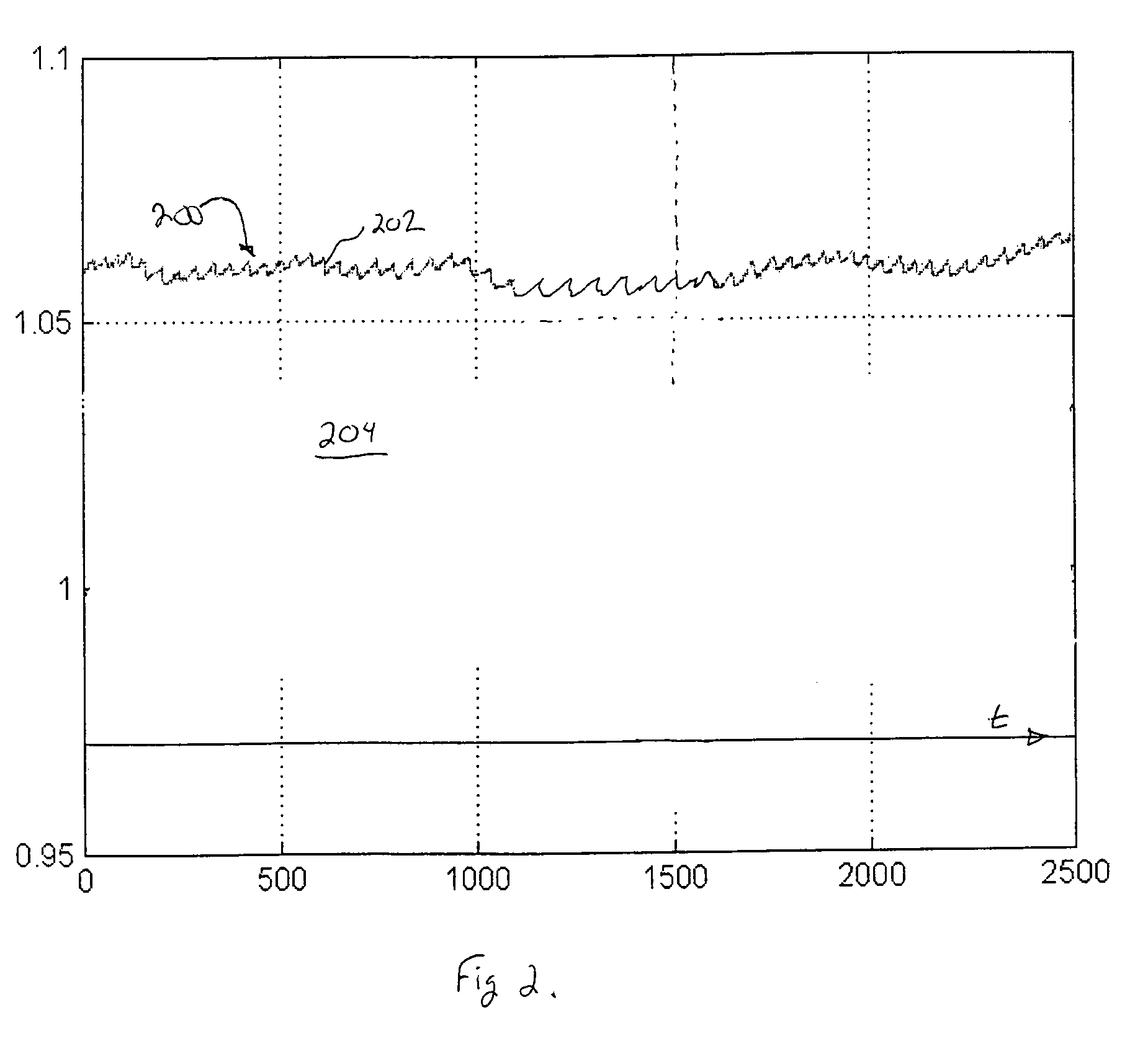
Wavelet transform of a plethysmographic signal
ActiveUS20070004977A1Easy to identifyEnhanced identification and isolationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsAnalyteEngineering
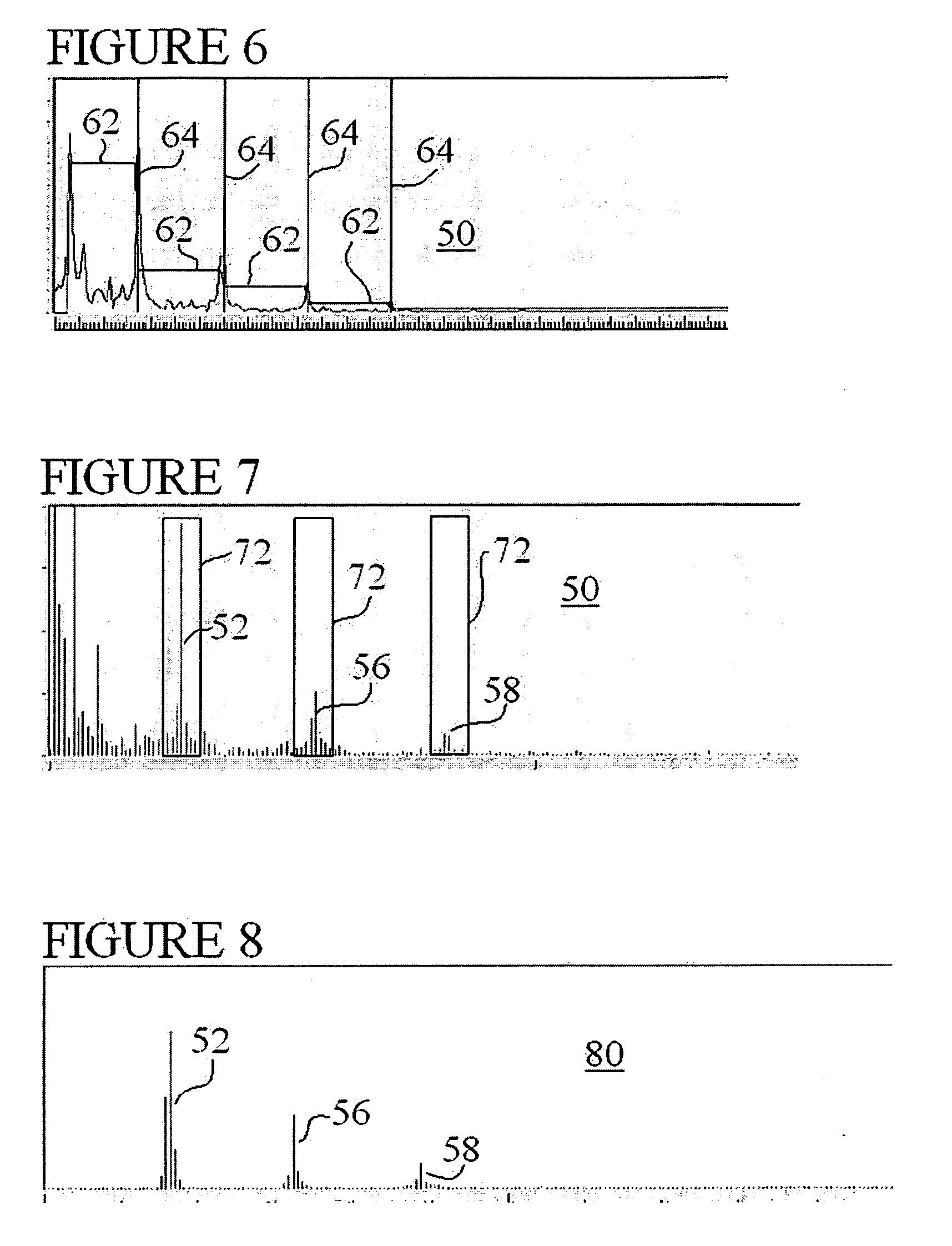
A photoplethysmographic system and method is provided for filtering a photoplethysmographic (pleth) signal to reduce the effects of noise in the signal. The system and method utilize a combination of frequency, time and / or magnitude information, to identify and separate transient signal components within a pleth signal from repeating signal components within the pleth signal. Typically, signal components of interest repeat over a period that corresponds with a patient's heartbeat. Such periodically repeating signals may be identified as stationary signals / objects within a frequency and time-based analysis. In contrast, motion artifacts or other sources of noise are often isolated (i.e., non-repeating) transient events and may be identified as non-stationary objects in a frequency and time-based analysis. Data associated with identified transient events may be filtered from or otherwise removed from a given signal. In this regard, a pleth signal may be cleansed prior to its use for, e.g., blood analyte determinations.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
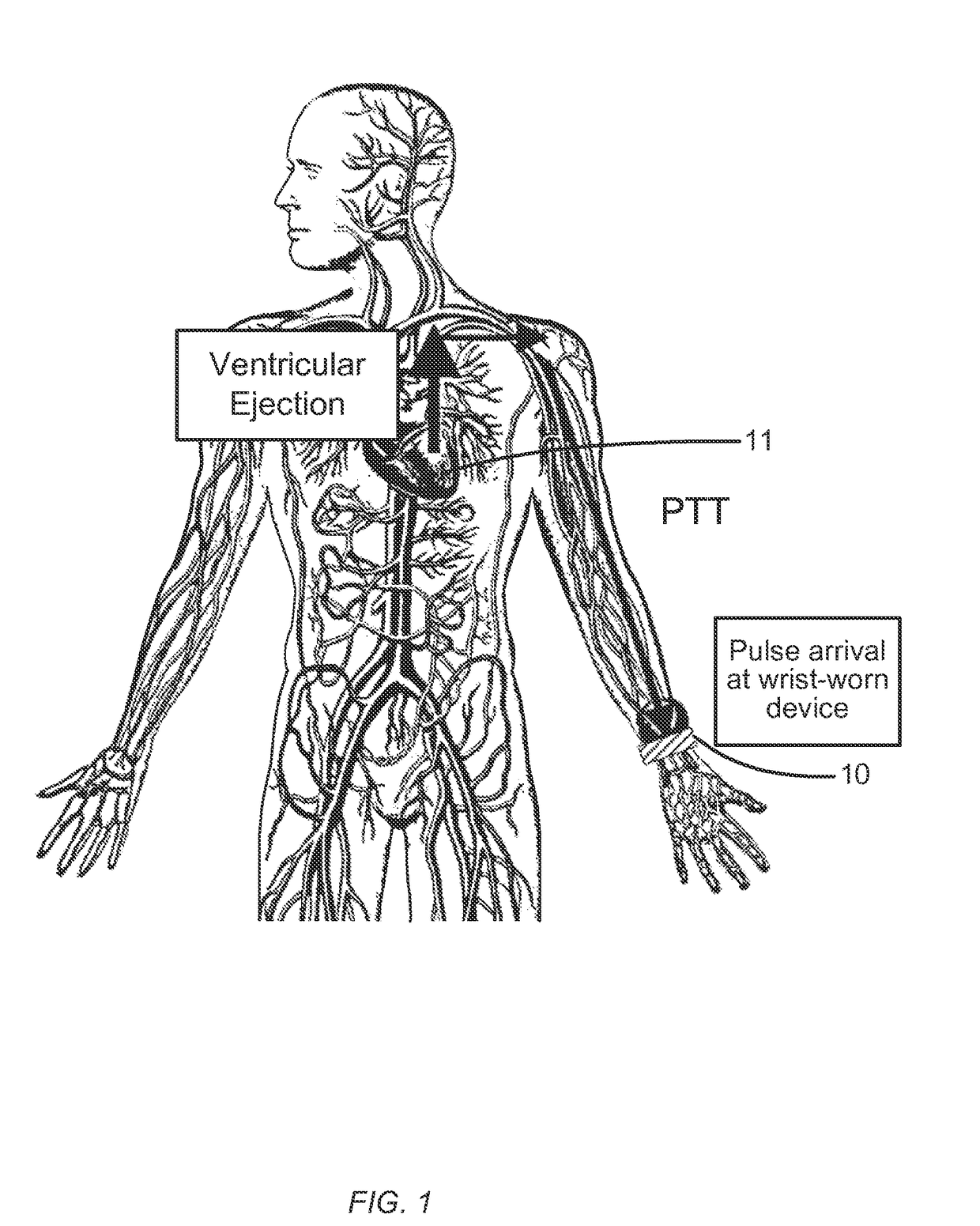
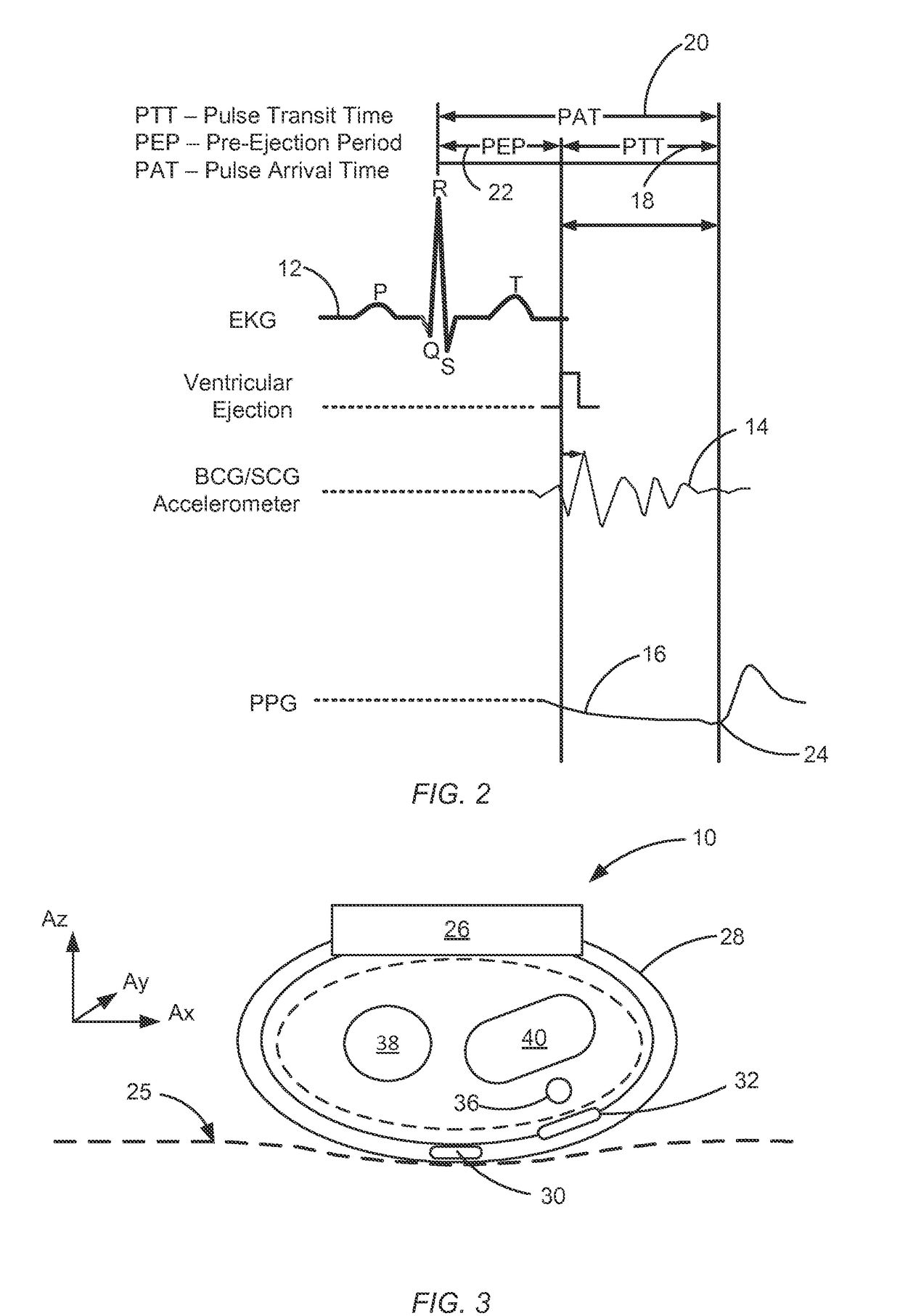
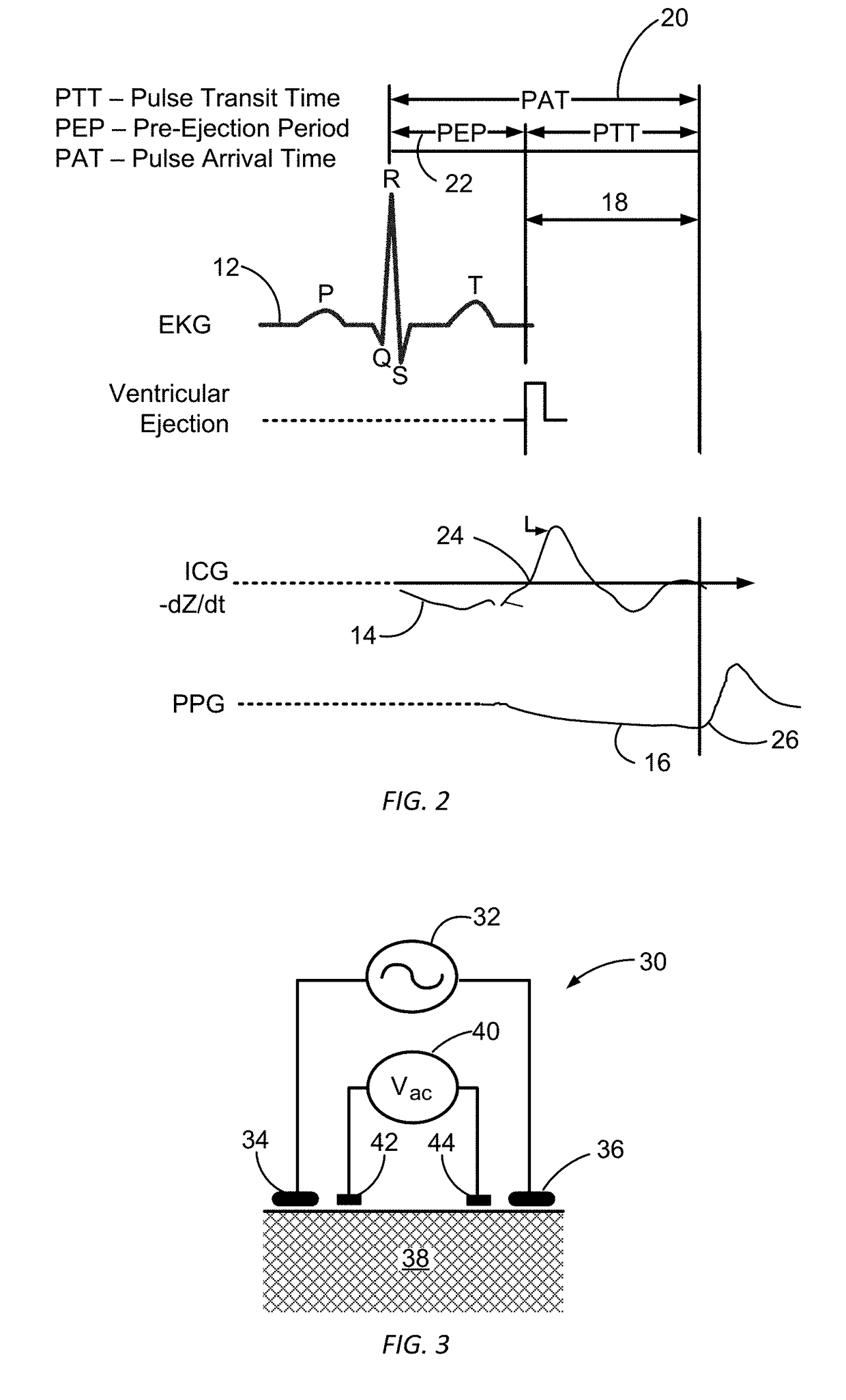
Electrical coupling of pulse transit time (PTT) measurement system to heart for blood pressure measurment
ActiveUS20170340219A1Reduce usageElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsCouplingMean transit time
Wrist-worn devices and related methods measure a pulse transit time non-invasively and calculate a blood pressure value using the pulse transit time. A wrist-worn device include a wrist-worn elongate band, at least four EKG or ICG electrodes coupled to the wrist-worn device for detecting a ventricular ejection of a heart, a photo-plethysmogram (PPG) sensor coupled to the wrist-worn device for detecting arrival of a blood pressure pulse at the user's wrist, and a controller configured to calculate a pulse transit time (PTT) for the blood pressure pulse. The controller calculates one or more blood pressure values for the user based on the PTT.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of Assessing Blood Volume Using Photoelectric Plethysmography
InactiveUS20100016739A1Diagnostics using lightLocal control/monitoringHarmonic analysisNormal blood volume
Owner:YALE UNIV
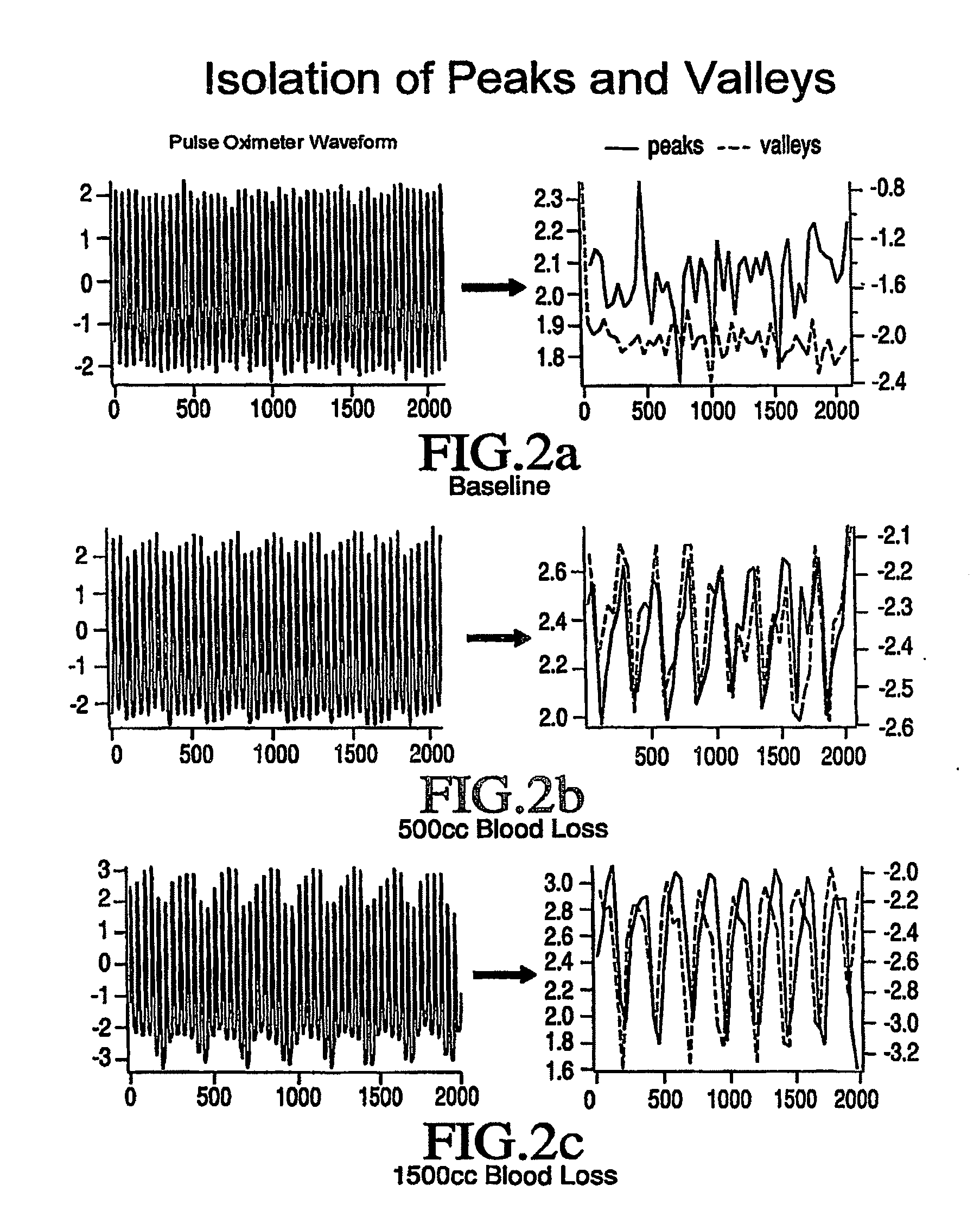
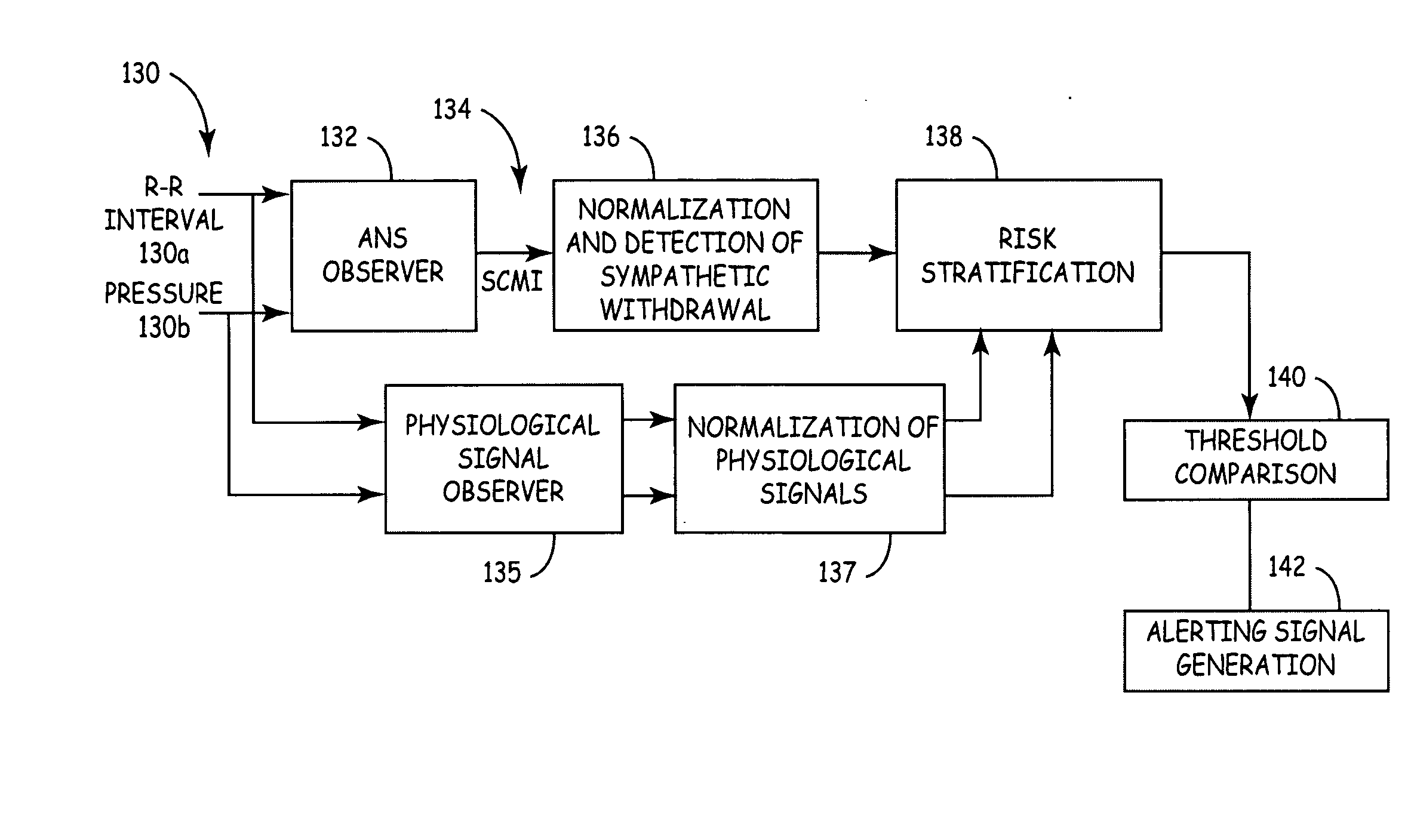
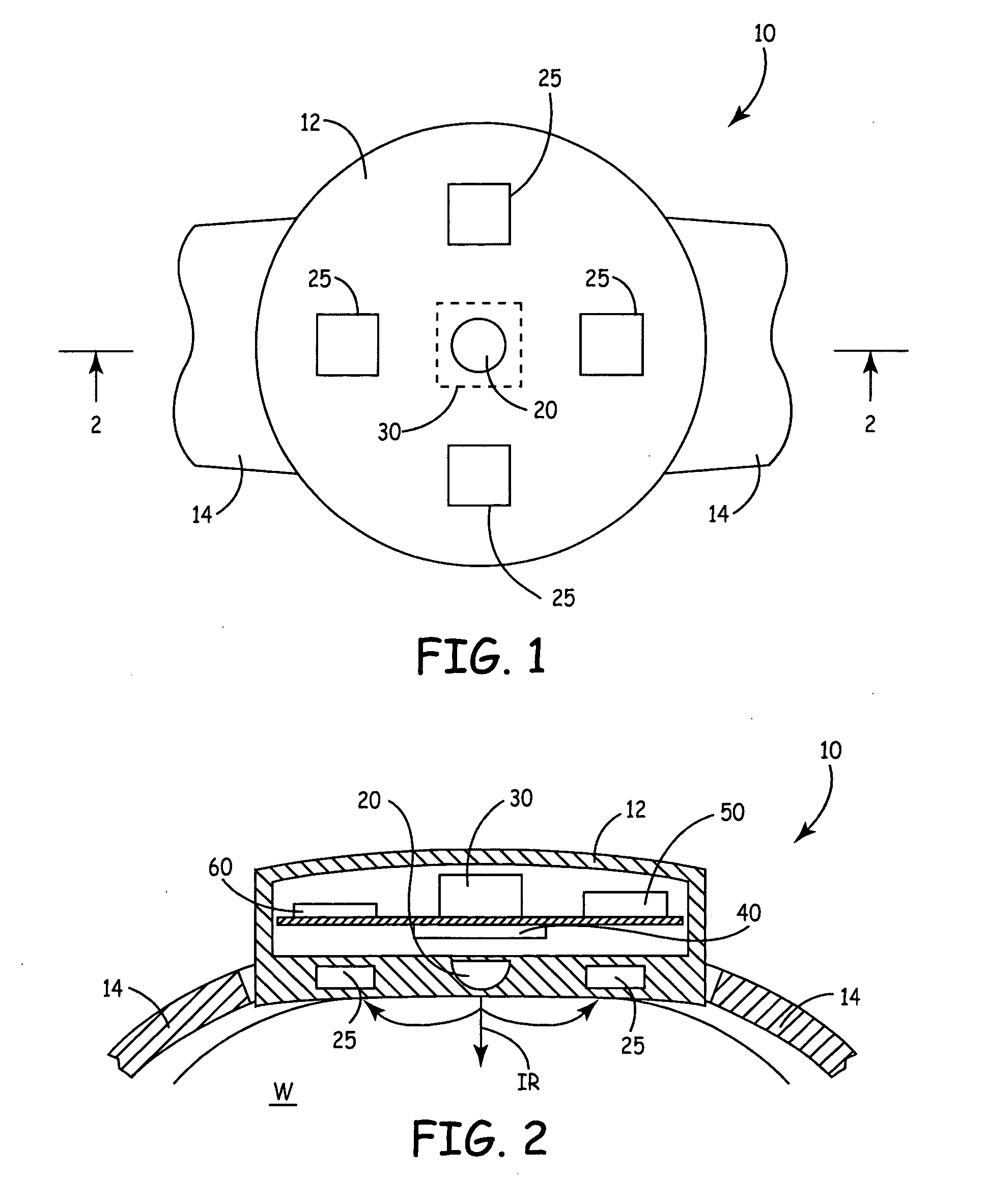
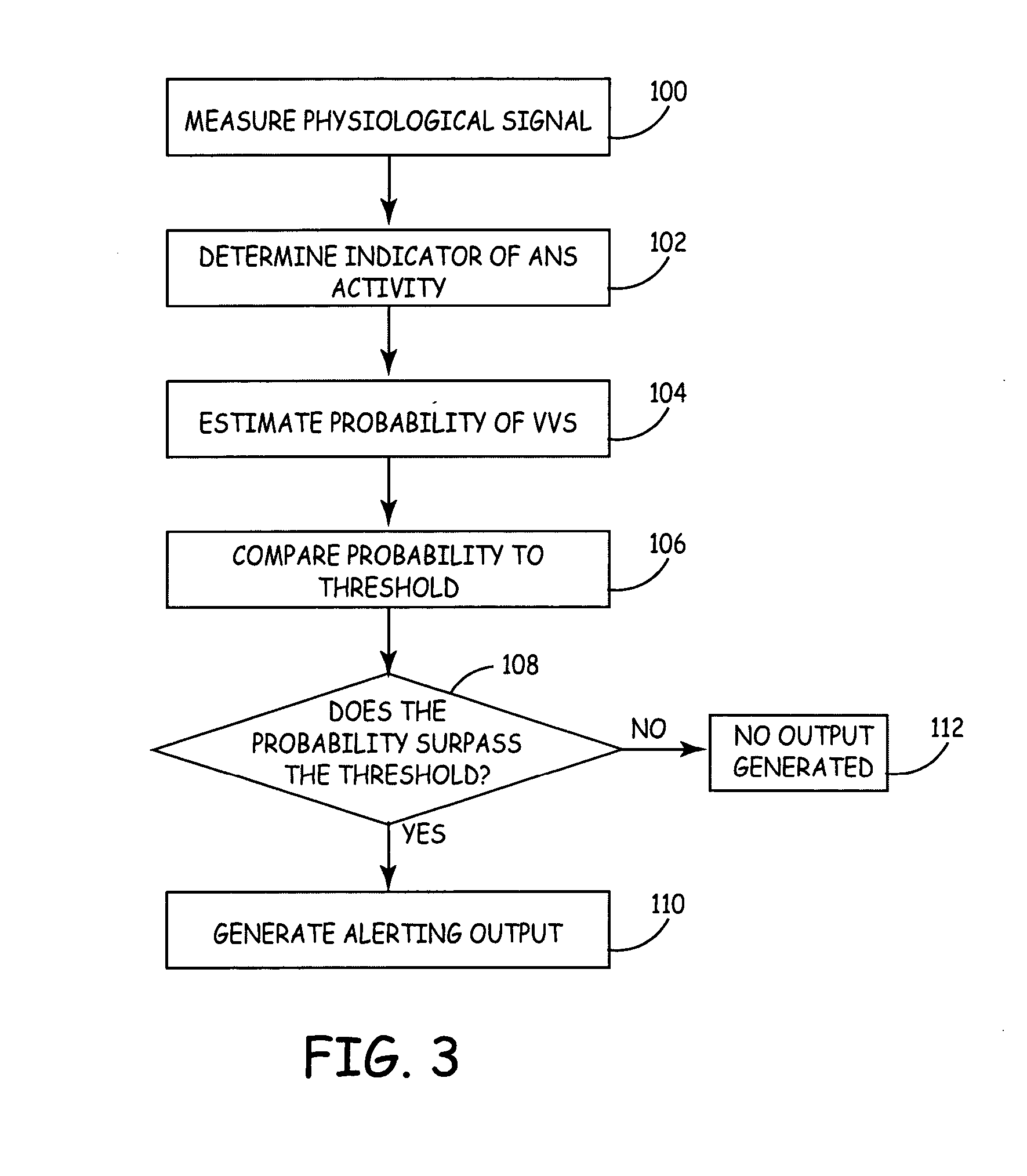
Externally worn vasovagal syncope detection device
A device is worn adjacent to tissue of a patient to detect vasovagal syncope (VVS). The device includes a photoplethysmographic sensor that measures a plethysmographic signal through tissue, and a processor that derives an indicator of an autonomous nervous system (ANS) activity from the plethysmographic signal and estimates a probability that the patient will experience VVS as a function of the indicator.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
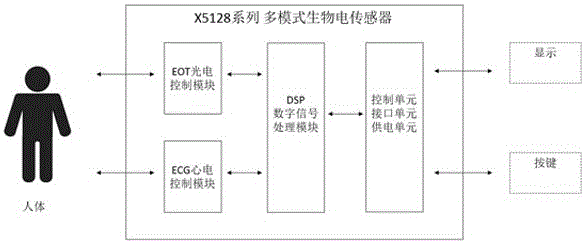
Non-invasive blood pressure detection method based on mixing of photoelectric green-light pulses and electrocardiogram
ActiveCN105943005AAvoid the defect problem of low measurement accuracyHigh hardware fitEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterMedicineMiniaturization
The invention relates to the technical field of non-invasive blood pressure detection, in particular to a non-invasive blood pressure detection method based on mixing of photoelectric green-light pulses and an electrocardiogram. A multi-mode bioelectricity sensor is adopted in the non-invasive blood pressure detection method. The non-invasive blood pressure detection method includes the following steps that a conventional method based on photoelectric plethysmography (PPG) is adopted, the characteristic parameters in PPG signals are extracted, a measurement model of the blood pressure of the human body is built, blood pressure calibration is carried out, the calibration parameters closely related to the blood pressure value of the human body are obtained, and then the calibration parameters are used to carry out blood pressure measurement of pulse waves based on PPG waveform and ECG waveform; a multi-parameter blood-pressure estimation model is built with the wave velocity measurement method of the pulse waves based on the PPG waveform and the ECG waveform, and the final measured data is compared, analyzed and corrected. According to the non-invasive blood pressure detection method, as the mixing mode of the PPG waveform and the ECG waveform is used for detection, the detection accuracy is effectively increased; the non-invasive blood pressure detection method and the multi-mode bioelectricity sensor have the extremely-high hardware integrating degree, and good conditions are created for convenience and miniaturization of products.
Owner:XINFOO SENSOR TECH CO LTD
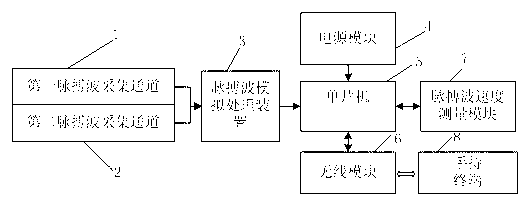
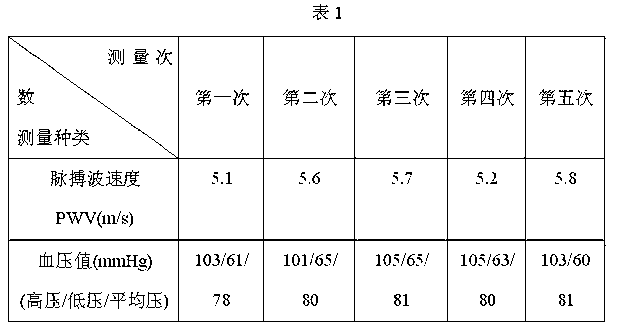
Measurement device and method for pulse wave velocity physiological parameters based on photoelectric plethysmography
The invention provides a measurement device and a measurement method for pulse wave velocity physiological parameters based on photoelectric plethysmography. The measurement device comprises a first pulse wave collecting channel and a second pulse wave collecting channel which are connected with a pulse wave analog processing device; the pulse wave analog processing device is also connected with a single chip microcomputer through a signal; the single chip microcomputer is electrically connected with a power module and is connected with a handheld terminal through a wireless module by utilizing the signal; the single chip microcomputer is also connected with a pulse wave velocity measurement module in a communication way; the single chip microcomputer is a central control processing unit and internally comprises a clock circuit, a storage, a timer, an A / D (Analog / Digital) converter and an I / O (Input / Output) interface which are controlled to connect through a single chip microcomputer processor; and the delay error can be effectively reduced by adopting the measurement device together with the measurement method.
Owner:BEIJING ANYI TECH CO LTD
Non-Reflective Optical Connections in Laser-Based Photoplethysmography
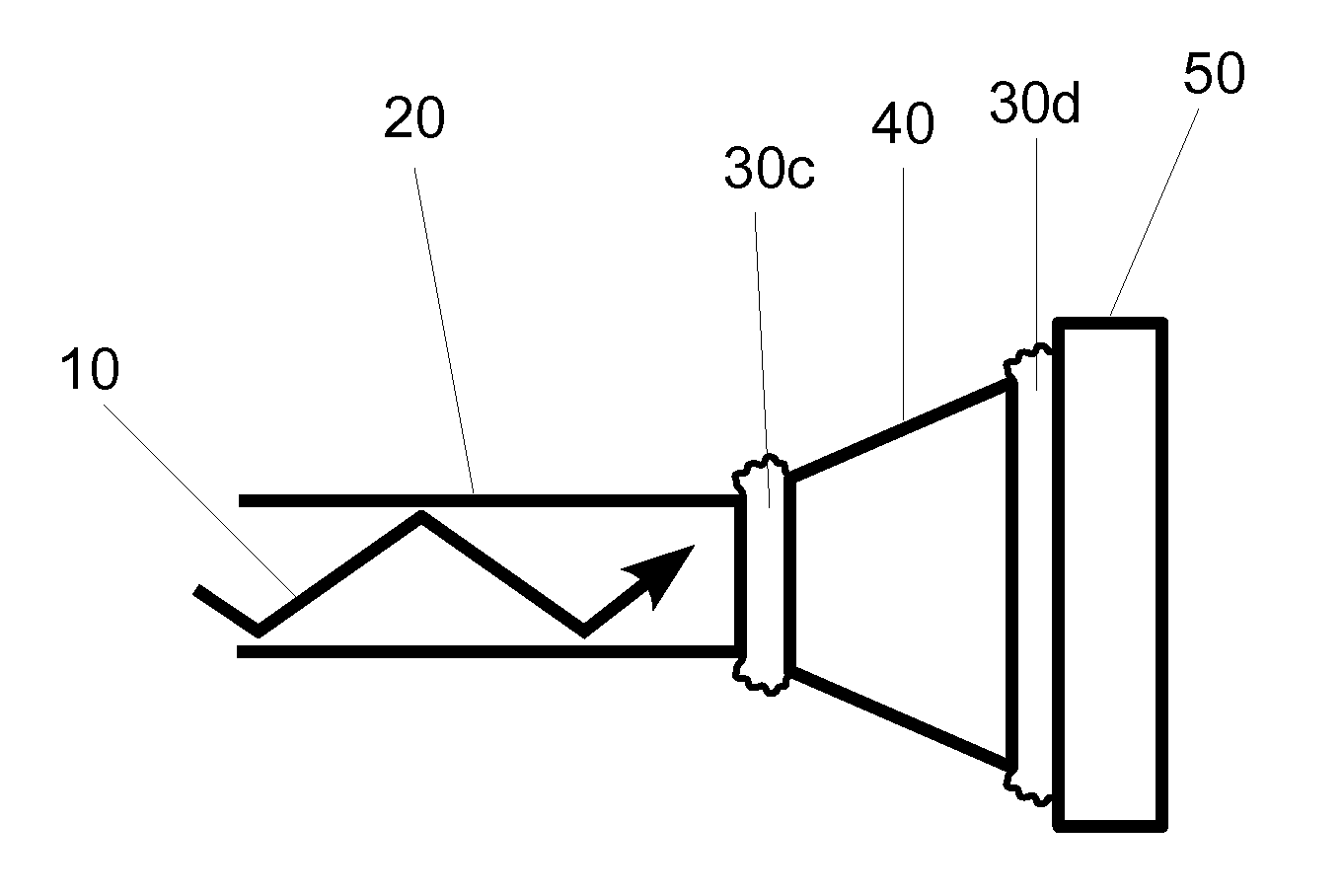
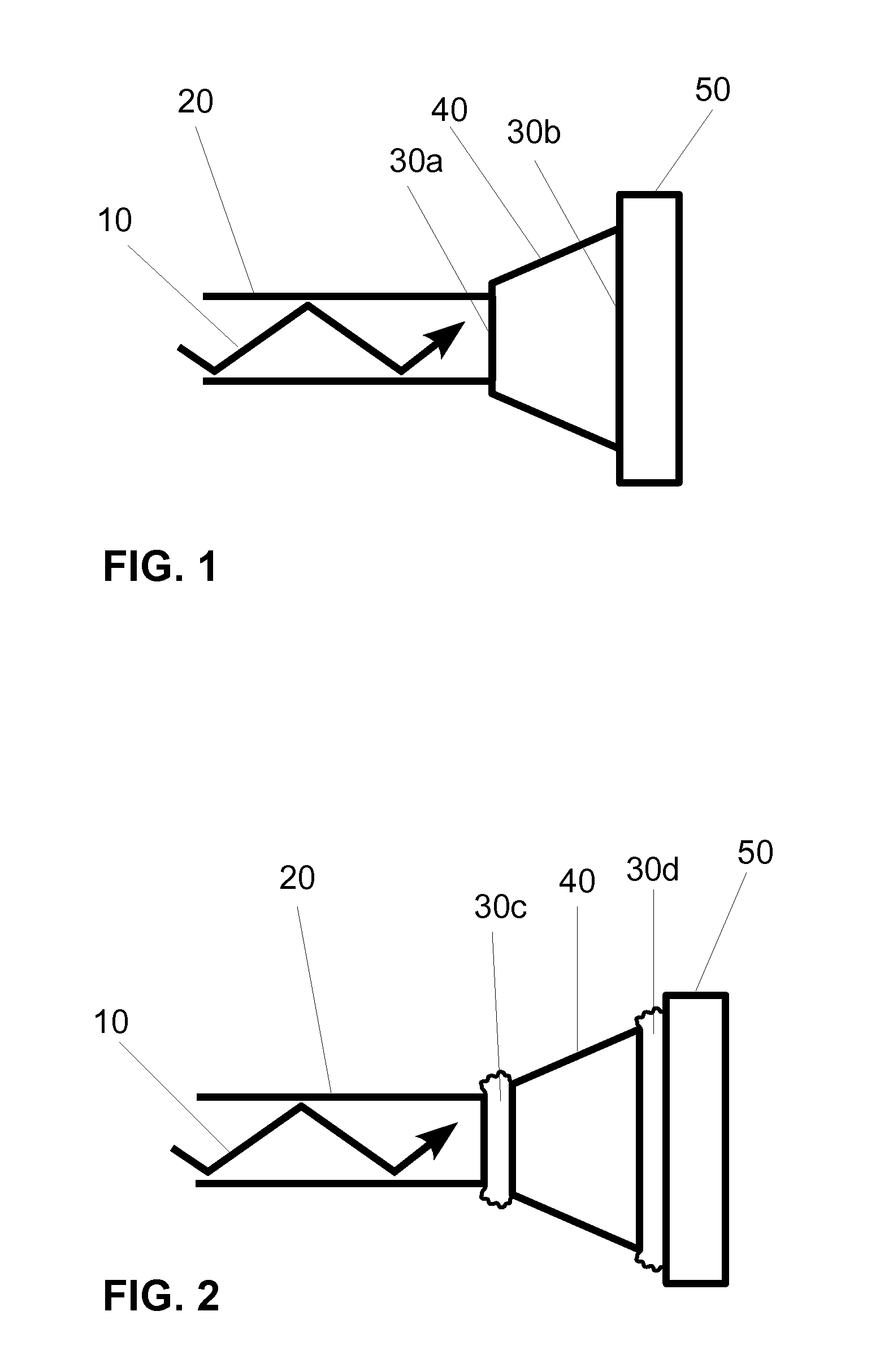
InactiveUS20120288230A1Minimize stabilityMaximize light availableMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesCatoptricsLight delivery
An embodiment of a light delivery portion of a photoplethysmographic device having a series of two or more optical elements. The series of two or more optical elements (20, 40, 50) are arranged to conduct light (10) from a laser and at least two consecutive elements of the series of two or more optical elements are coupled together by a non-reflective coupling (30a, 30b). This minimizes the extent to which back reflected light can re-enter the laser and adversely alter the optical output properties of the laser and additionally minimizes the light loss associated with back reflection thus helping to maximize the optical throughput. Other embodiments are described and shown.
Owner:KESTREL LABS
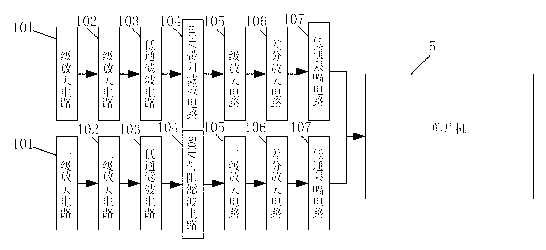
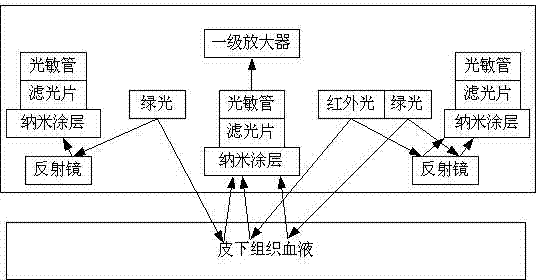
Photoelectric plethysmography photoelectric detection sensor
ActiveCN104224144AEffective filteringHigh measurement sensitivityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAudio power amplifierGreen-light
The invention discloses a photoelectric plethysmography photoelectric detection sensor. The photoelectric plethysmography photoelectric detection sensor comprises a first photoelectric detection assembly, a second photoelectric detection assembly and a third photoelectric detection assembly, wherein the first photoelectric detection assembly comprises a first light emitting module, a first reflecting mirror which is matched with the first light emitting module, a first light filter and a first photosensitive pipe, a light signal transmitted by the first light emitting module is reflected by the first reflecting mirror to run through the first light filter to be received by the photosensitive pipe, and the first light emitting module comprises a green-light LED lamp. According to the photoelectric plethysmography photoelectric detection sensor, green light and infrared light are adopted as light sources, the reflecting rate of the green light is high, the reflected light intensity is high, the measuring perceiving degree of the photosensitive pipe is high, the signal detected by the photosensitive pipe is processed through an amplifier, so that the precision of the sensor is high, and the sensitivity is good; the light filter which is coated with a nanometer coating is arranged in front of the photosensitive pipe, so that the light of a non-test light source and the light beyond the wavelength range of the photosensitive pipe can be effectively filtered.
Owner:CHENGDU VCARE QINYUAN HEALTH TECH
Digital control method for measuring blood pressure
A system and method of digital control for a blood pressure measurement system is provided. According to at least one embodiment, a photo-plethysmographic (PPG) system produces a frequency signal that corresponds to the measured light in the PPG system. Such light may be indicative of blood volume in a vein or artery. The frequency signal may be used to control one or more pressure valves of the system in order to measure blood pressure and hold the frequency signal constant.
Owner:CNSYST MEDIZINTECHN
Digital Control Method for Measuring Blood Pressure
ActiveUS20110105917A1Continuous measurementDiagnostics using lightEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood pressure kitMedicine
A system and method of digital control for a blood pressure measurement system is provided. According to at least one embodiment, a photo-plethysmographic (PPG) system produces a frequency signal that corresponds to the measured light in the PPG system. Such light may be indicative of blood volume in a vein or artery. The frequency signal may be used to control one or more pressure valves of the system in order to measure blood pressure and hold the frequency signal constant.
Owner:CNSYST MEDIZINTECHN
Method and system for detecting obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
ActiveCN103690168AAchieve initial screeningLow costRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsMedicineRespiration rate
The invention relates to a method for detecting obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. The method includes the following steps: using a photoelectric plethysmography (PPG) sensor for oxygen saturation information collection, using a snore sensor for snore information collection, and using a respiration signal sensor for respiration information collection; processing collected respiration information to acquire an average respiration rate and average respiration strength; processing collected snore information to acquire average snore strength within a time period before current moment; performing high-pass filtering on collected PPG signals; according to an artificial intelligent decision-making theory, building a fuzzy element set by the respiration information, the snore information and the oxygen saturation information after being processes, establishing a subordinate function, creating a fuzzy grade list and a fuzzy function set, building a multi-factor evaluation matrix and judging whether a person has the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome or not according to a maximum subordinate principe. The invention further relates to a system for detecting the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Disposable and detachable sensor for continuous non-invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring
A sensor system for continuous non-invasive arterial blood pressure (CNAP) is provided. The CNAP-sensor comprises of a base portion and a detachable and disposable portion. The base portion is connected to a control system. The disposable portion is for attachment to a human body part. The CNAP-sensor system includes a photo-plethysmographic (PPG) system having at least one light source, at least one light detector, electrical supplies, light coupling systems, one or more connectors, and a cuff including air supplies.
Owner:CNSYST MEDIZINTECHN
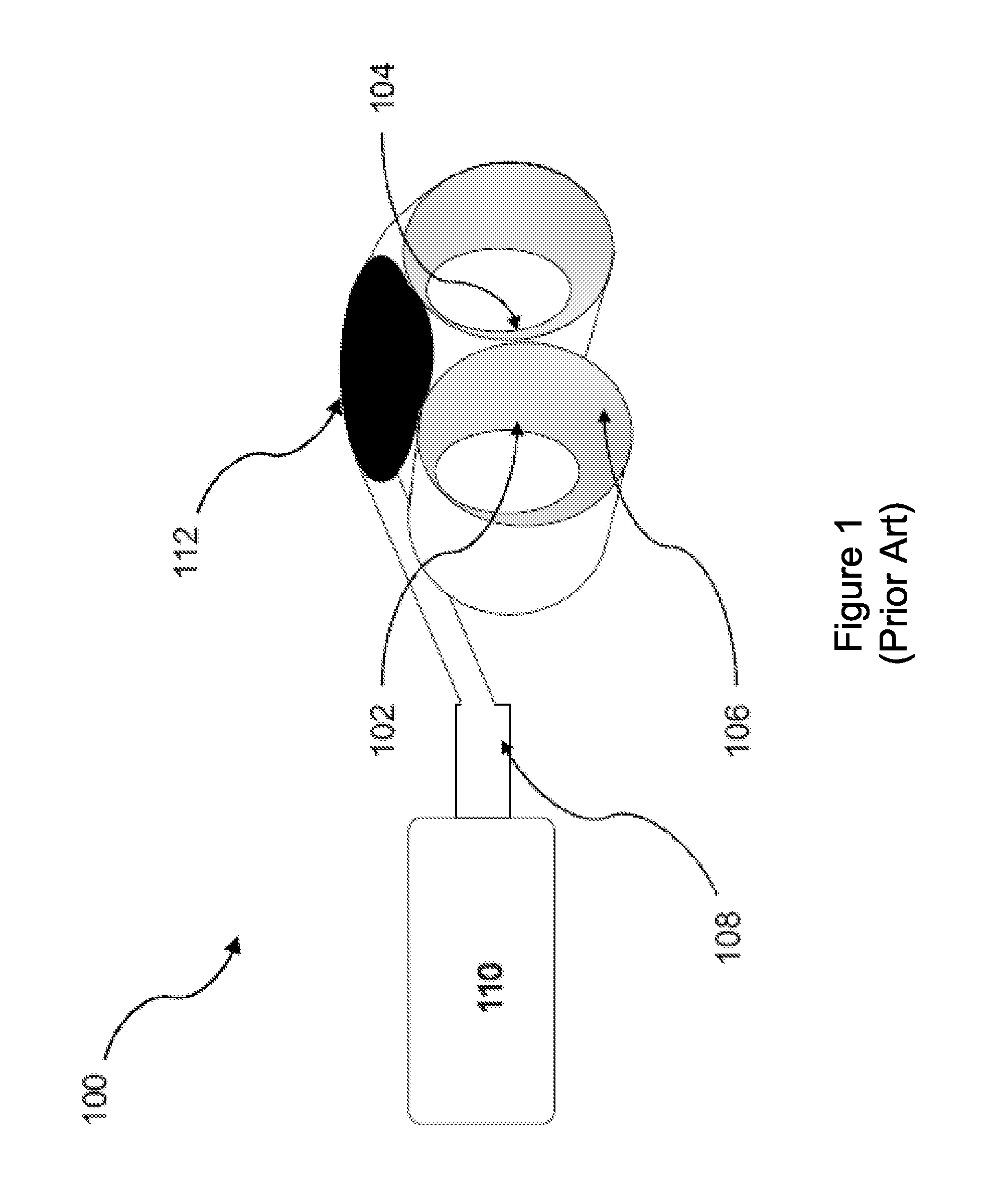
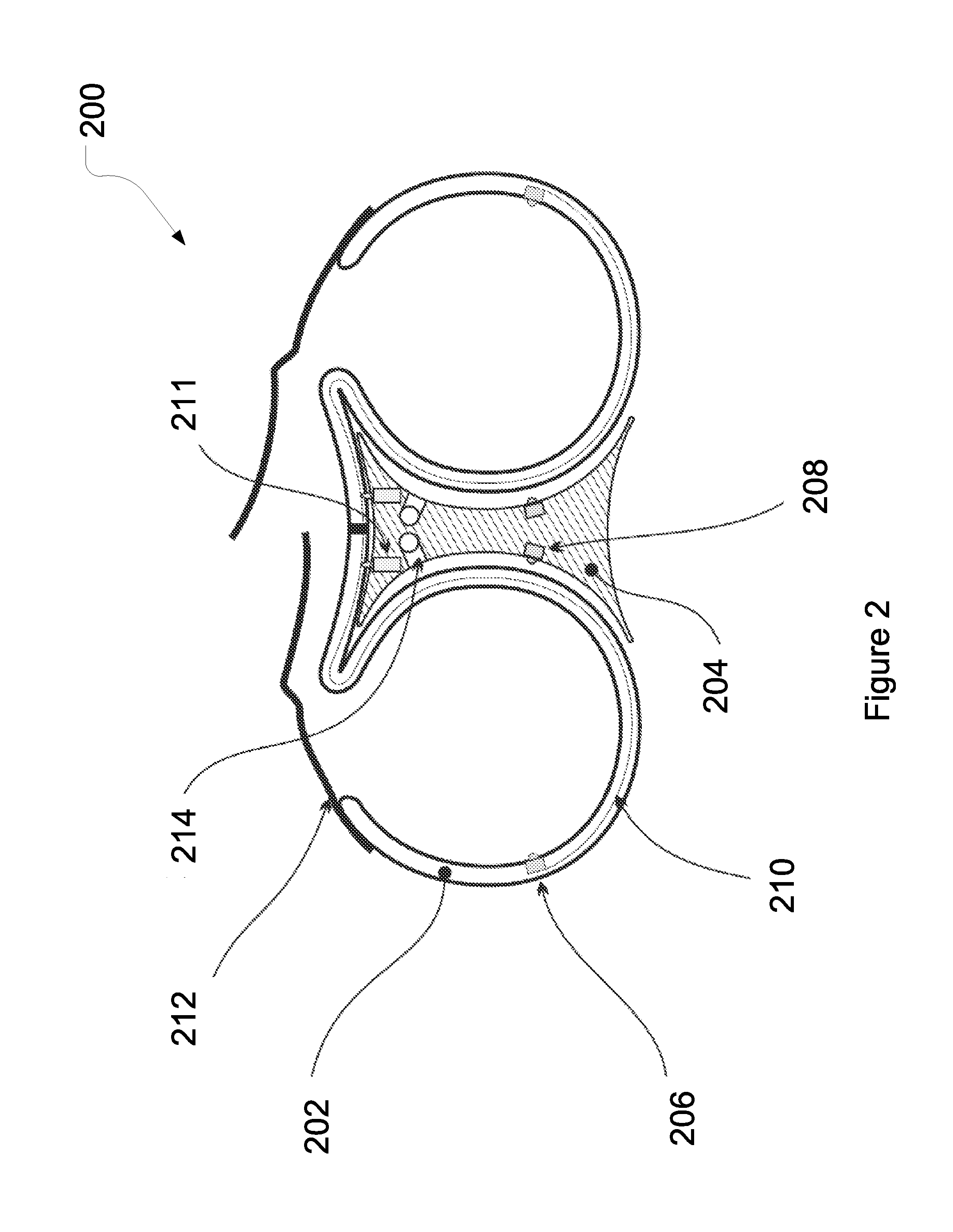
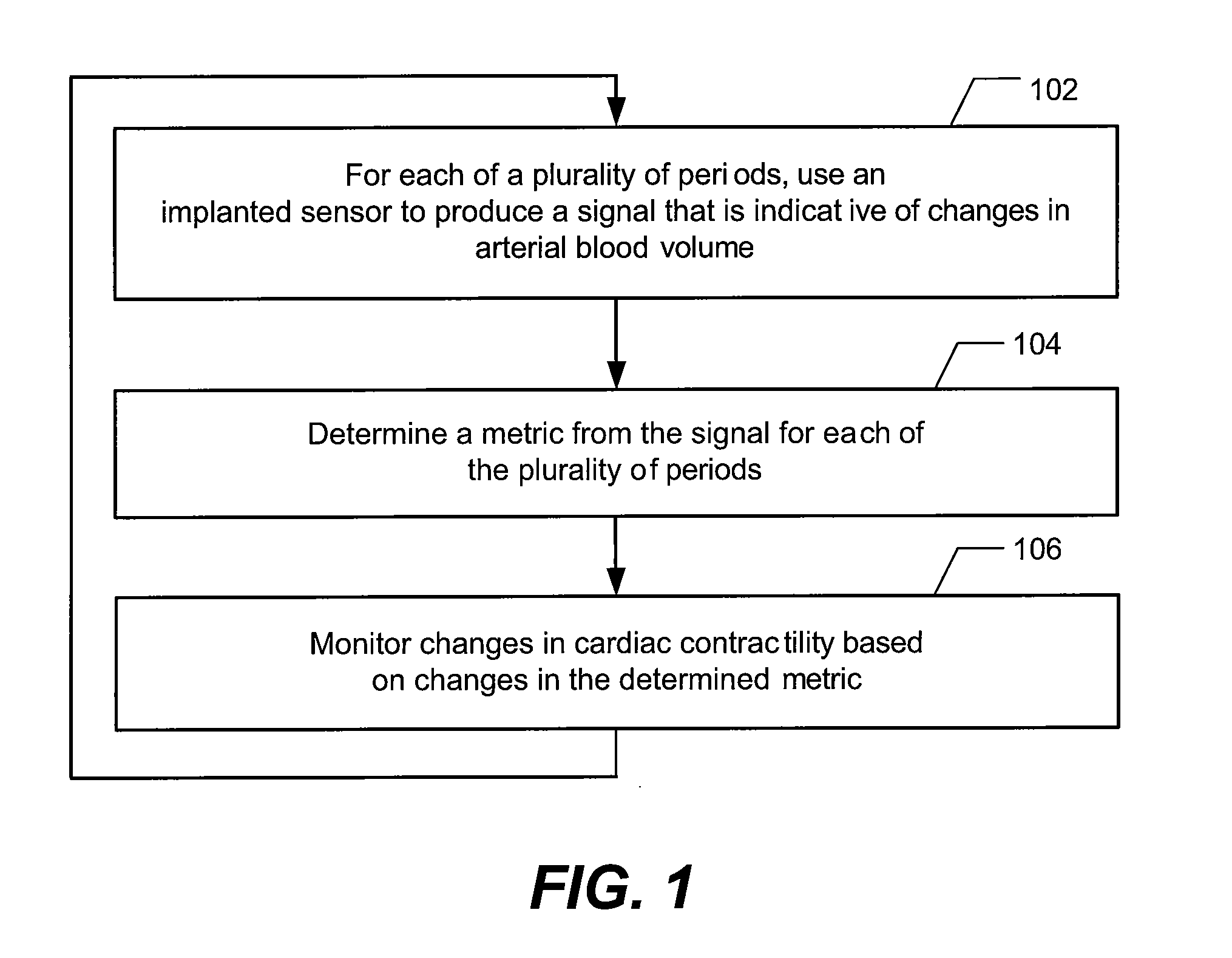
Methods and systems to monitor cardiac contractility
InactiveUS20110125208A1Increase cardiac contractilityDecrease cardiac contractilityCatheterHeart stimulatorsArteryContractility
An implanted sensor produces a signal that is indicative of changes in arterial blood volume, such as a photoplethysmography signal or an impedance plethysmography signal. A metric is determined from the signal for each of the plurality of periods. Changes in cardiac contractility are monitored based on changes in the determined metric.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method for estimating exercise load level based on cardiogenic signals
InactiveCN104055496AOvercome limitationsAccurate estimateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSensitive indexBlood pressure
The invention discloses a method for estimating an exercise load level based on cardiogenic signals. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting a great number of characteristics from electrocardiogram, beat-to-beat blood pressure and photoelectric plethysmography in a resting-exercise experiment; secondly, screening individual exercise load sensitive indexes from the characteristics to form an individual exercise load sensitive index vector; thirdly, estimating coefficients of an exercise load estimation equation through a numerical computation method according to the individual exercise load sensitive index vector; finally, in an actual exercise state or a non-exercise state, substituting the individual exercise load sensitive index vector screened from the characteristic parameters, obtained by real-time detection and computation, of the electrocardiogram, the beat-to-beat blood pressure and the photoelectric plethysmography into the load estimation equation to estimate an actual exercise load level. According to the technical scheme, the limitation on estimation of the exercise load level through a single independent index is avoided, and the exercise load level is accurately and comprehensively estimated through various cardiogenic signals.
Owner:SCI RES TRAINING CENT FOR CHINESE ASTRONAUTS
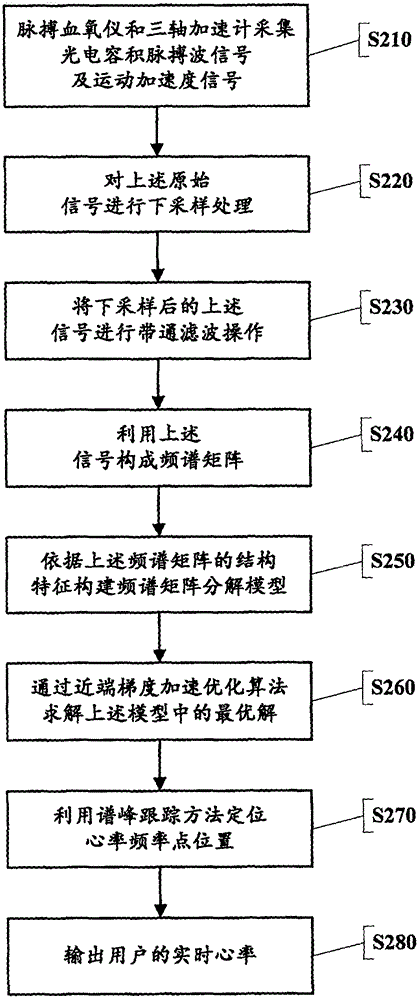
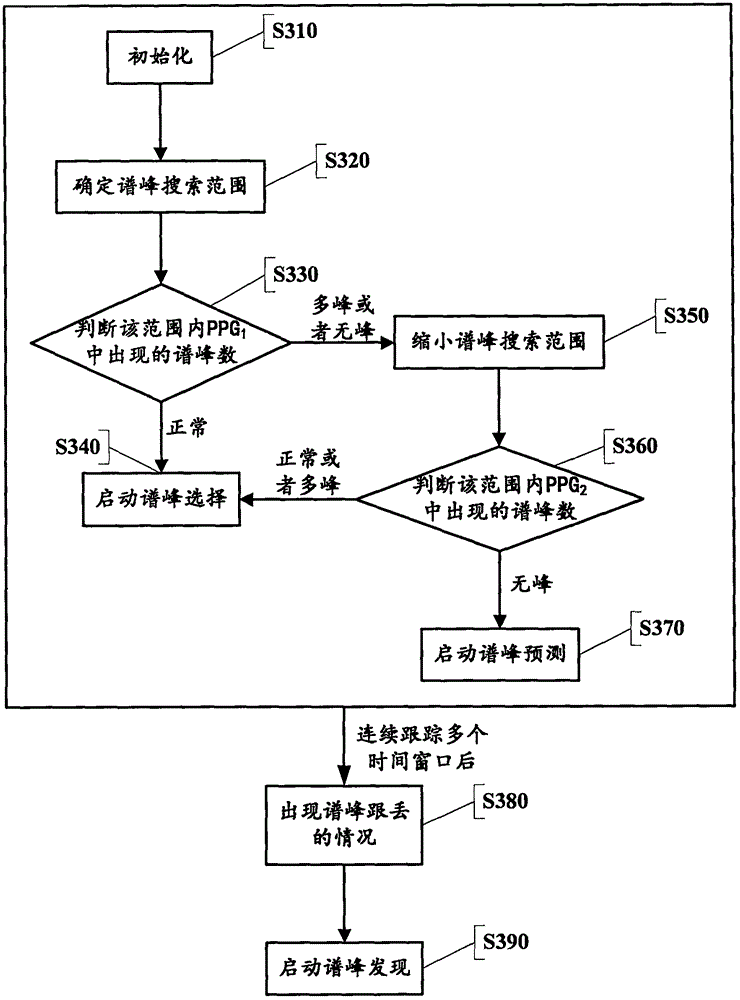
Heart rate measurement method capable of removing motion noise in photoelectric plethysmography signals
ActiveCN105943012ACancel motion noiseAccurate trackingCatheterSensorsMatrix decompositionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a heart rate measurement method capable of removing motion noise in photoelectric plethysmography signals; and the method is capable of effectively reducing influence of the motion noise in heart rate measurement. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a plurality of photoelectric plethysmography signals and motion acceleration signals of a user within a same time period by virtue of a pulse oximeter and a triaxial accelerometer; constituting a frequency spectrum matrix by virtue of the plurality of the photoelectric plethysmography signals and motion acceleration signals; then, constructing a frequency spectrum matrix decomposition model in accordance with the structural characteristics of overall sparsity and line sparsity of the frequency spectrum matrix, and solving an optimal solution of the frequency spectrum matrix decomposition model by virtue of a proximal gradient acceleration optimization algorithm; and finally, accurately positioning the location of a heart rate frequency point by virtue of a spectrum peak tracking method. With the application of the method disclosed by the invention, the motion noise in the photoelectric plethysmography signals can be effectively eliminated, and the accurate heart rate measurement based on a wearable device can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
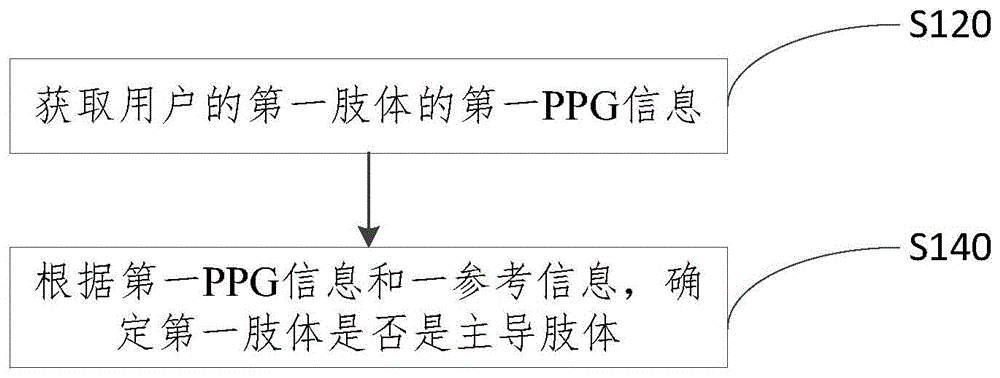
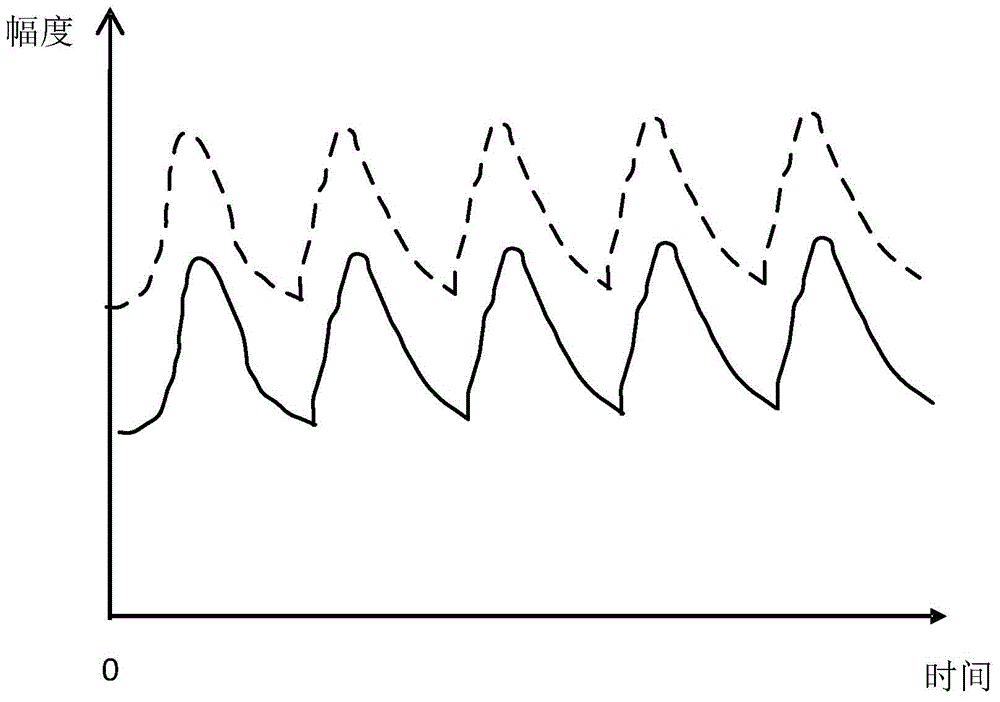
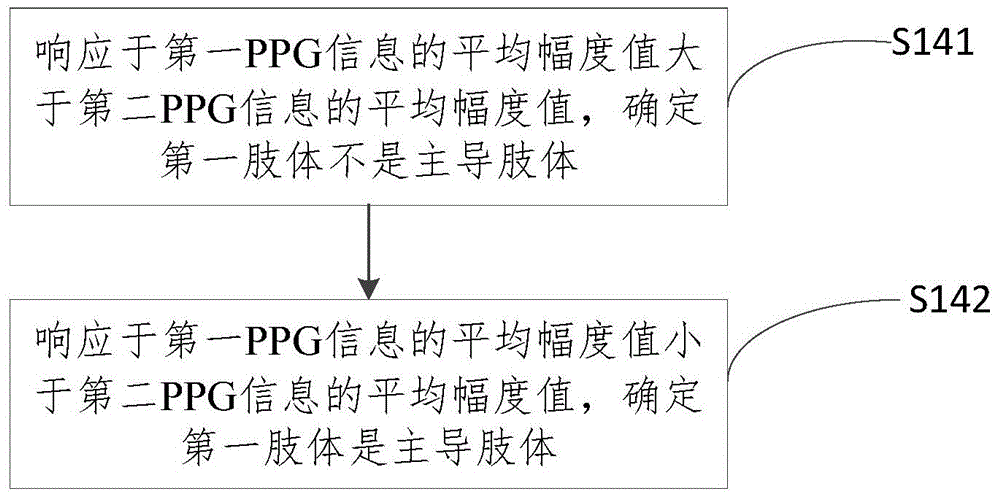
Dominant limb determination method and apparatus
InactiveCN104407703AImprove experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionCatheterComputer sciencePhotoelectric plethysmography
The application provides a dominant limb determination method and apparatus, and relates to the field of wearable devices. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the first photoelectric plethysmography PPG information of the first limb of a user; and determining whether the first limb is the dominant limb based on the first PPG information and reference information. The method and apparatus are beneficial to automatically configuring the device worn by the user based on the determination result, and enhancing the user experience.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIGU RUI TUO TECH
Method to quantify photoplethysmogram (PPG) signal quality
ActiveCN108289615AEvaluation of blood vesselsMedical automated diagnosisTemplate matchingSignal quality
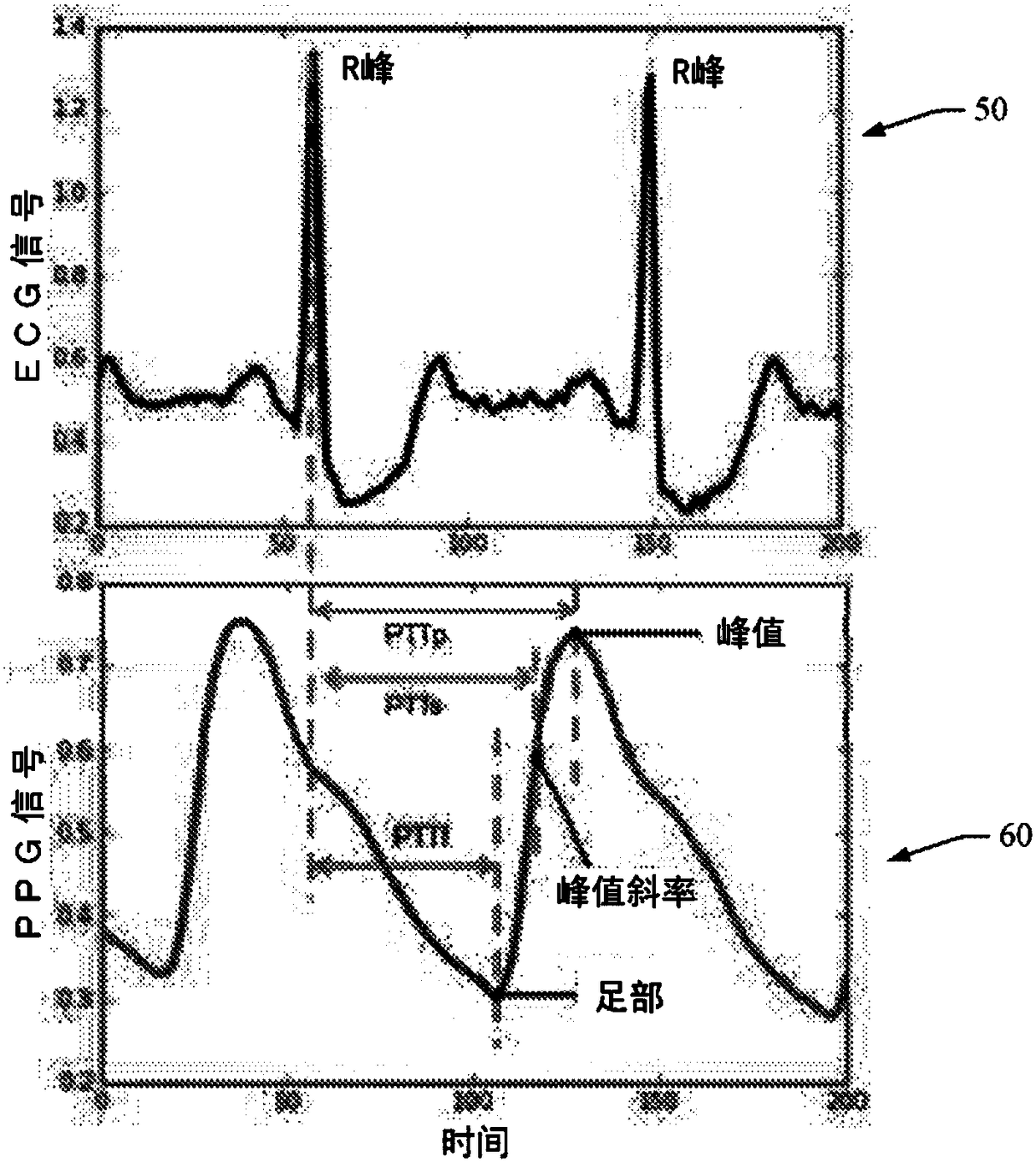
When evaluating the quality of photoplethysmography (PPG) signal (52) measured from a patient monitor (e.g., a finger sensor or the like), multiple features of the PPG signal are extracted and analyzed to facilitate assigning a score to the PPG signal or portions (e.g., heartbeats) thereof. Heartbeats in the PPG signal are segmented out using concurrently captured electrocardiograph (ECG) signal (50), and for each heartbeat, a plurality of extracted features are analyzed. If all extracted features satisfy one or more predetermined criteria for each feature, then the heartbeat waveform is compared to a predefined heartbeat template. If the waveform matches the template (e.g., within a predetermined match percentage or the like), then the heartbeat is classified as 'clean'. If the heartbeatdoes not patch the template, or if one or more of the extracted features fails to satisfy its one or more predetermined criteria, the heartbeat is classified as 'noisy'.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com