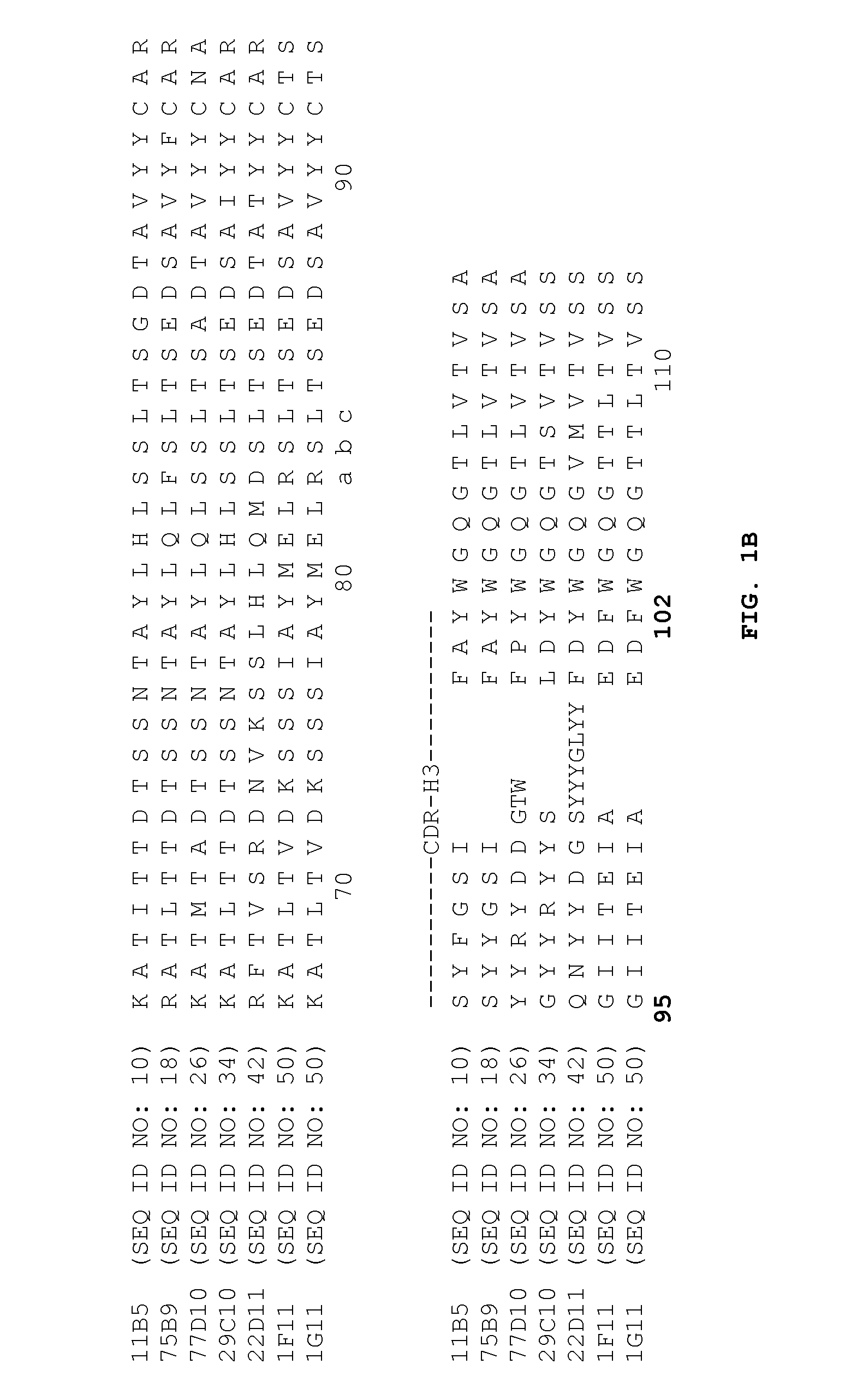
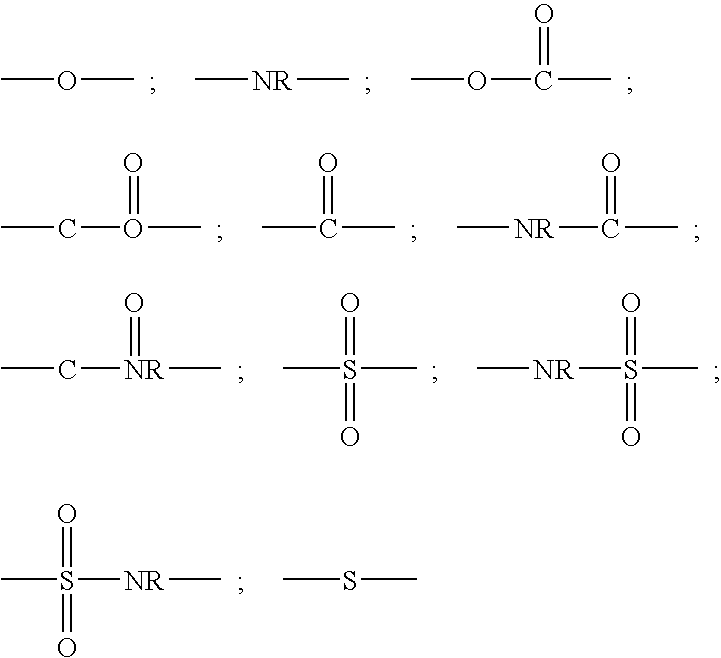
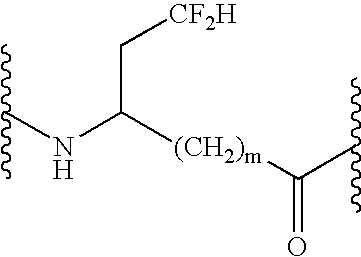
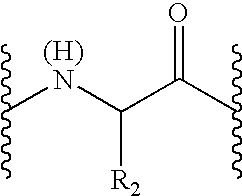
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
223 results about "Peptide inhibitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
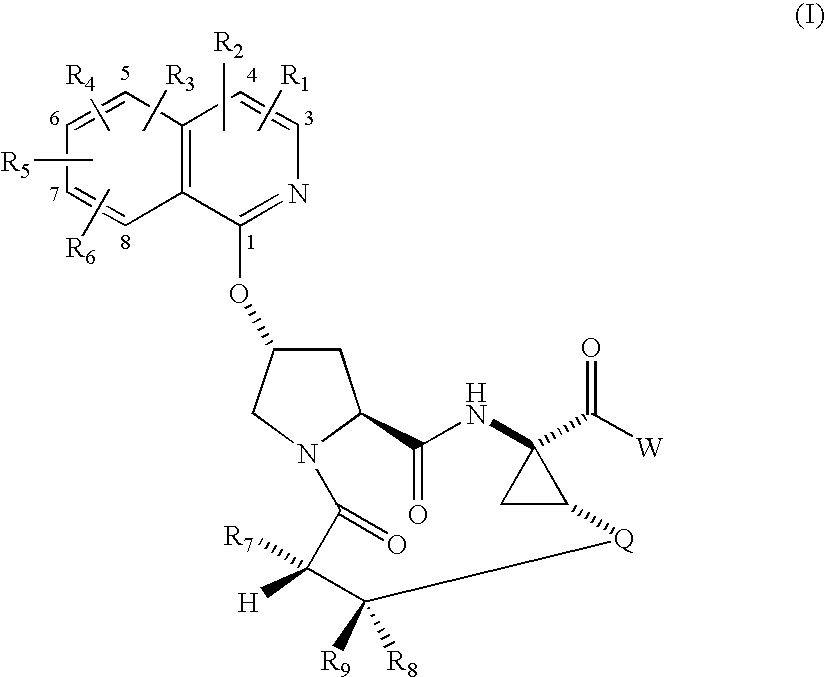
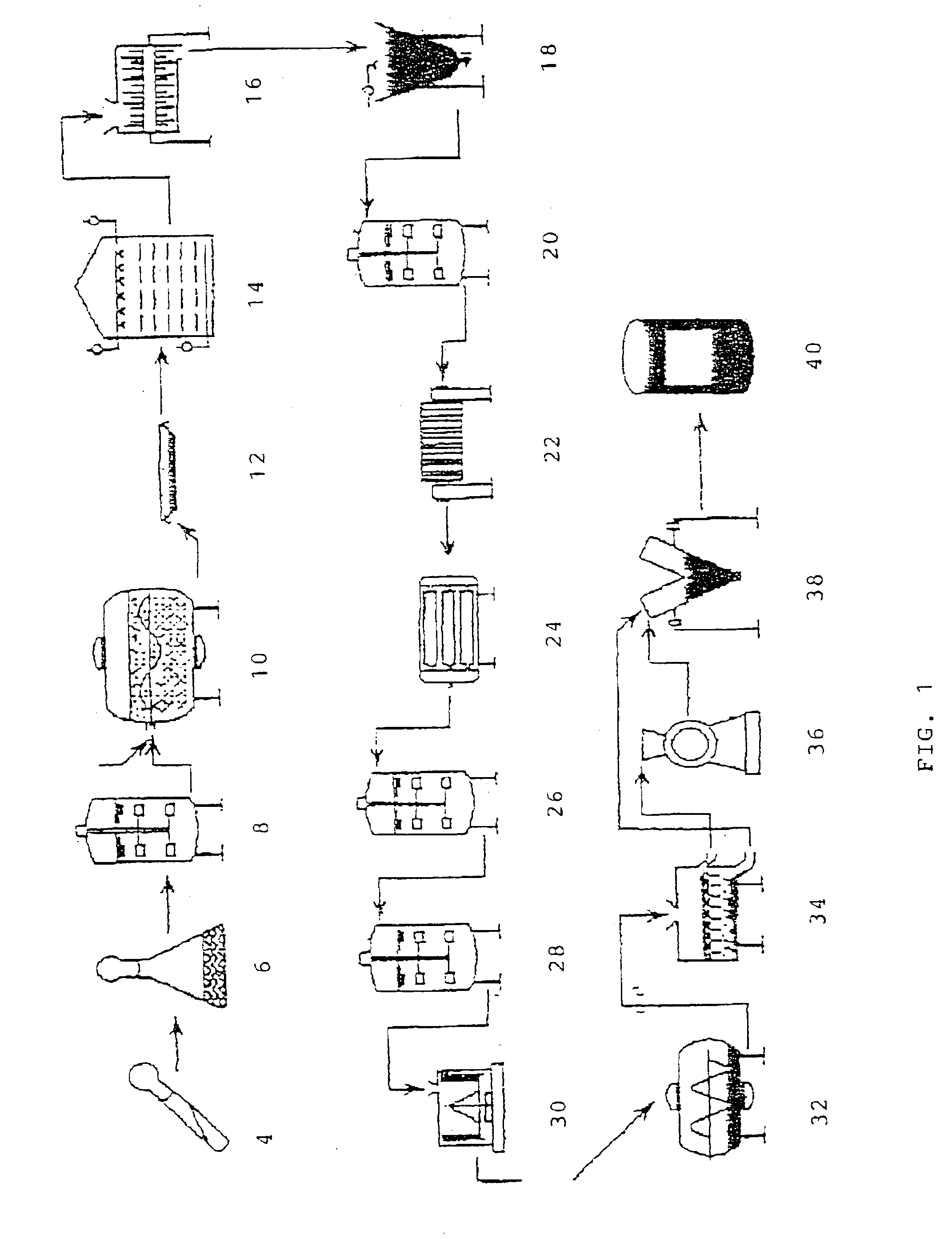
Macrocyclic isoquinoline peptide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus
InactiveUS20060257980A1Inhibit functioningEffective treatmentDigestive systemAntiviralsIsoquinolineCombinatorial chemistry
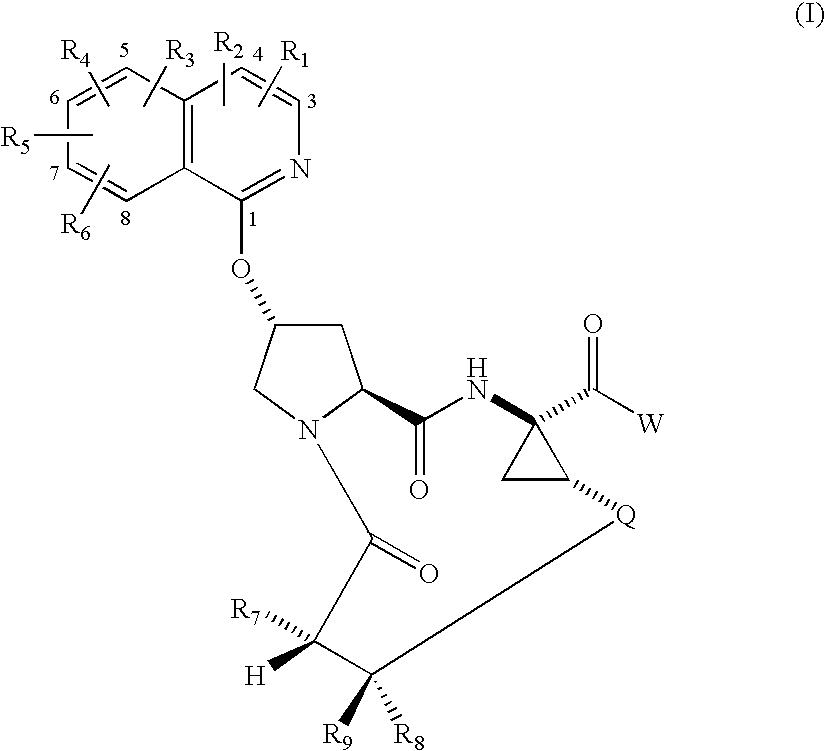
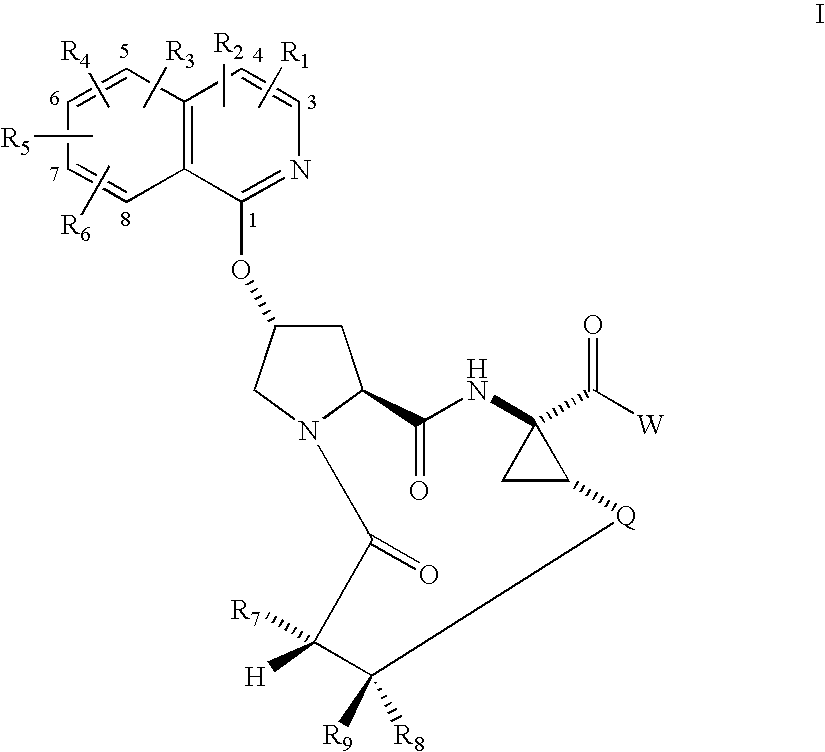
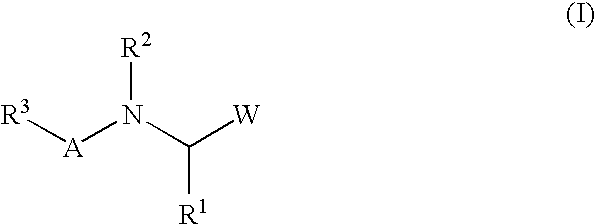
Macrocyclic isoquinoline peptides are disclosed having the general formula: A compound of formula I: wherein R1 to R9, Q and W are described in the description. Compositions comprising the compounds and methods for using the compounds to inhibit HCV are also disclosed.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Anti-pcsk9 and methods for treating lipid and cholesterol disorders
ActiveUS20110033465A1Overcome technical difficultiesOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticPeptide inhibitorPCSK9
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating disorders of cholesterol and lipid metabolism by administration of an anti-PCSK9 antibody or a peptide inhibitor of PCSK9.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Peptide inhibitors of Hepatitis C virus NS3 protease
InactiveUS6846806B2Peptide/protein ingredientsOrganic compound preparationSerine Protease InhibitorsProteinase activity
This invention relates to a novel class of peptides having the Formula (I): which are useful as serine protease inhibitors, and more particularly as Hepatitis C virus(HCV) NS3 protease inhibitors. This invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and methods of using the same in the treatment of HCV infection.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Compositions and methods relating to reduction of symptoms of autism
InactiveUS6899876B2Relieve symptomsMany symptomPeptide/protein ingredientsOxidoreductasesNormorphineMedicine
Methods and compositions that can reduce the symptoms of autism in a human patient comprising administering a physiologically effective amount of one or both of a purified casomorphin inhibitor selected from the group consisting of a casomorphinase and a casomorphin ligand, and a physiologically effective amount of a purified gluteomorphin inhibitor selected from the group consisting of a gluteomorphinase and a gluteomorphin ligand, to a human patient in sufficient quantities to reduce the effects of the autism. In some embodiments, the compositions and methods further comprise a physiologically effective amount of an enkephalin inhibitor, preferably an enkephalinase, and a physiologically effective amount of an endorphin inhibitor, preferably an endorphinase.
Owner:PROTHERA
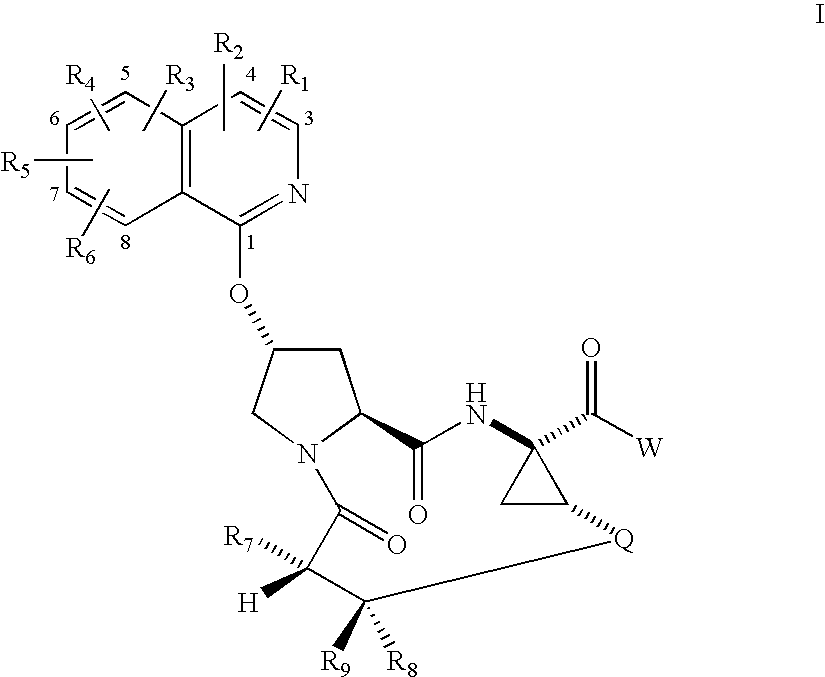
Macrocyclic isoquinoline peptide inhibitors of Hepatitis C virus
ActiveUS20050090432A1Inhibit functioningEffective treatmentBiocideAntiviralsIsoquinolineCombinatorial chemistry
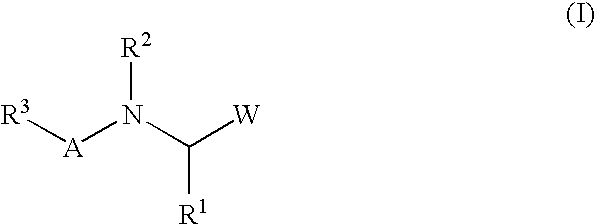
Macrocyclic isoquinoline peptides are disclosed having the general formula: A compound of formula I: [0001]wherein R1 to R9, Q and W are described in the description. Compositions comprising the compounds and methods for using the compounds to inhibit HCV are also disclosed.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Peptide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Synthetic peptide inhibitors of HIV transmission
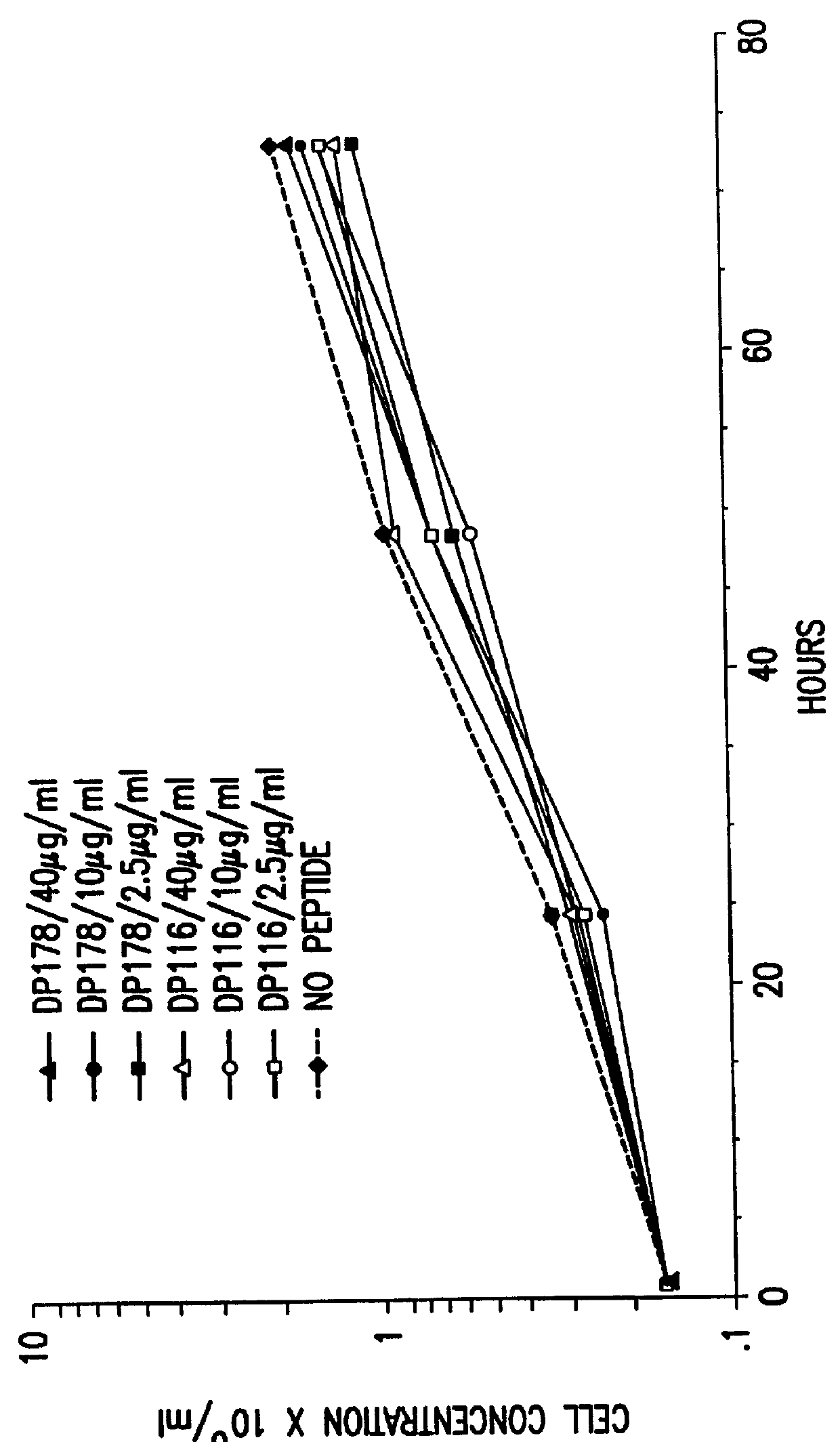
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit potent anti-retroviral activity. The peptides of the invention comprise DP-178 (SEQ ID:1) ptide corresponding to amino acids 638 to 673 of the HIV-1LAI gp41 protein, and fragments, analogs and homologs of DP-178. The invention further relates to the uses of such peptides as inhibitory of human and non-human retroviral, especially HIV, transmission to uninfected cells.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Anti-PCSK9 and methods for treating lipid and cholesterol disorders
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating disorders of cholesterol and lipid metabolism by administration of an anti-PCSK9 antibody or a peptide inhibitor of PCSK9.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Peptide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease
InactiveUS6867284B1Organic compound preparationTripeptide ingredientsProteinase activityHcv hepatitis
Fluorinated oligopeptides, especially those having 4,4-difluoro-2-amino butyric acid at the C terminus, may be effective inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease. Examples of hexapeptides of the invention, optimized for binding in the S1 specificity pocket of the enzyme, may display IC50s at the sub-micromolar level. Embodiments of tripeptides of the invention, having a keto-acid group at the C-terminus are, likewise, potent inhibitors of NS3 protease.
Owner:IST DI RICERCHE DI BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE P ANGELETTI
Long lasting fusion peptide inhibitors for hiv infection
InactiveUS20050065075A1Prolong half-life in vivoBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusHuman Parainfluenza Virus
The present invention relates to C34 peptide derivatives that are inhibitors of viral infection and / or exhibit antifusogenic properties. In particular, this invention relates to C34 derivatives having inhibiting activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human parainfluenza virus (HPV), measles virus (MeV), and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) with long duration of action for the treatment of the respective viral infections.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
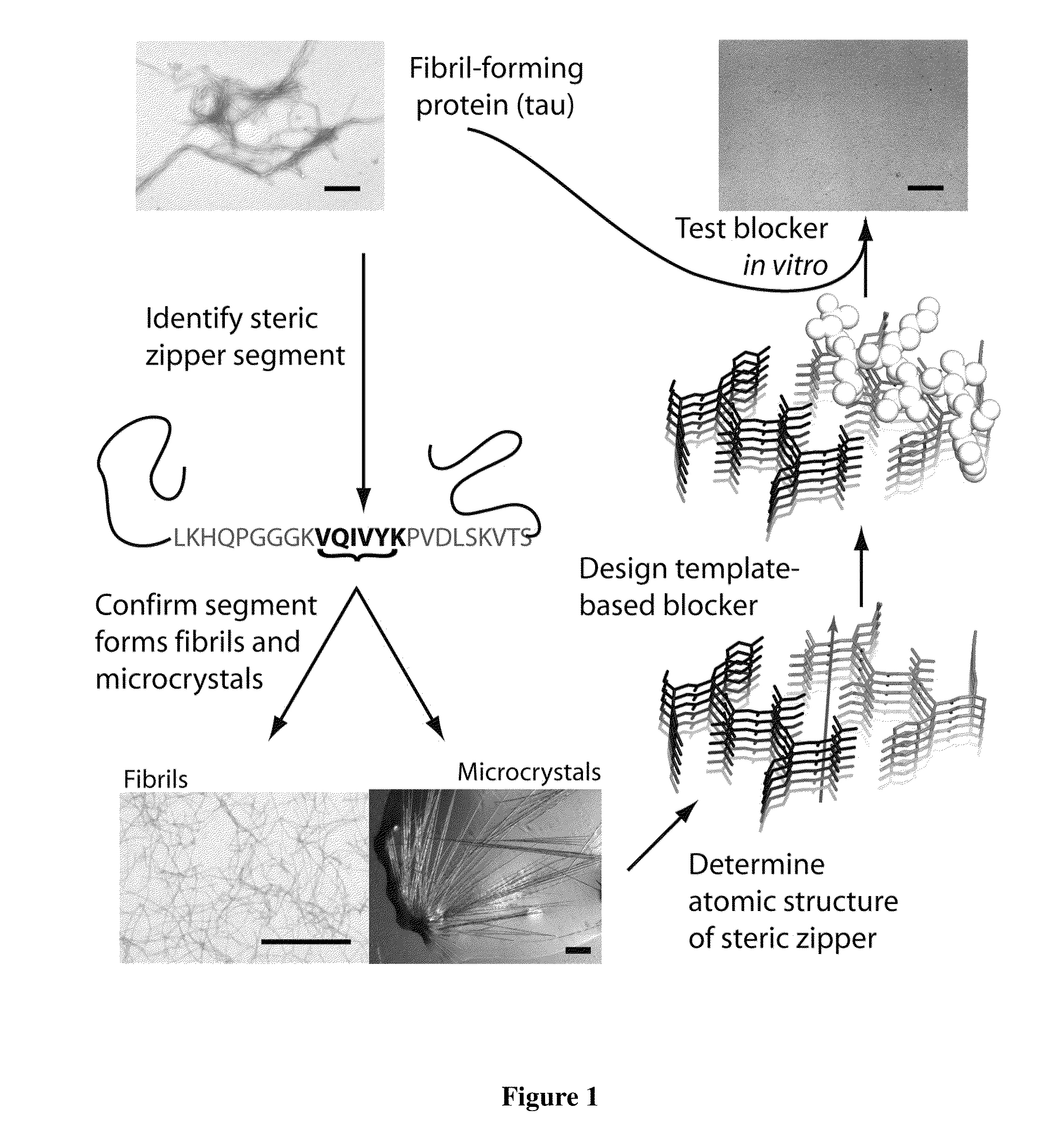
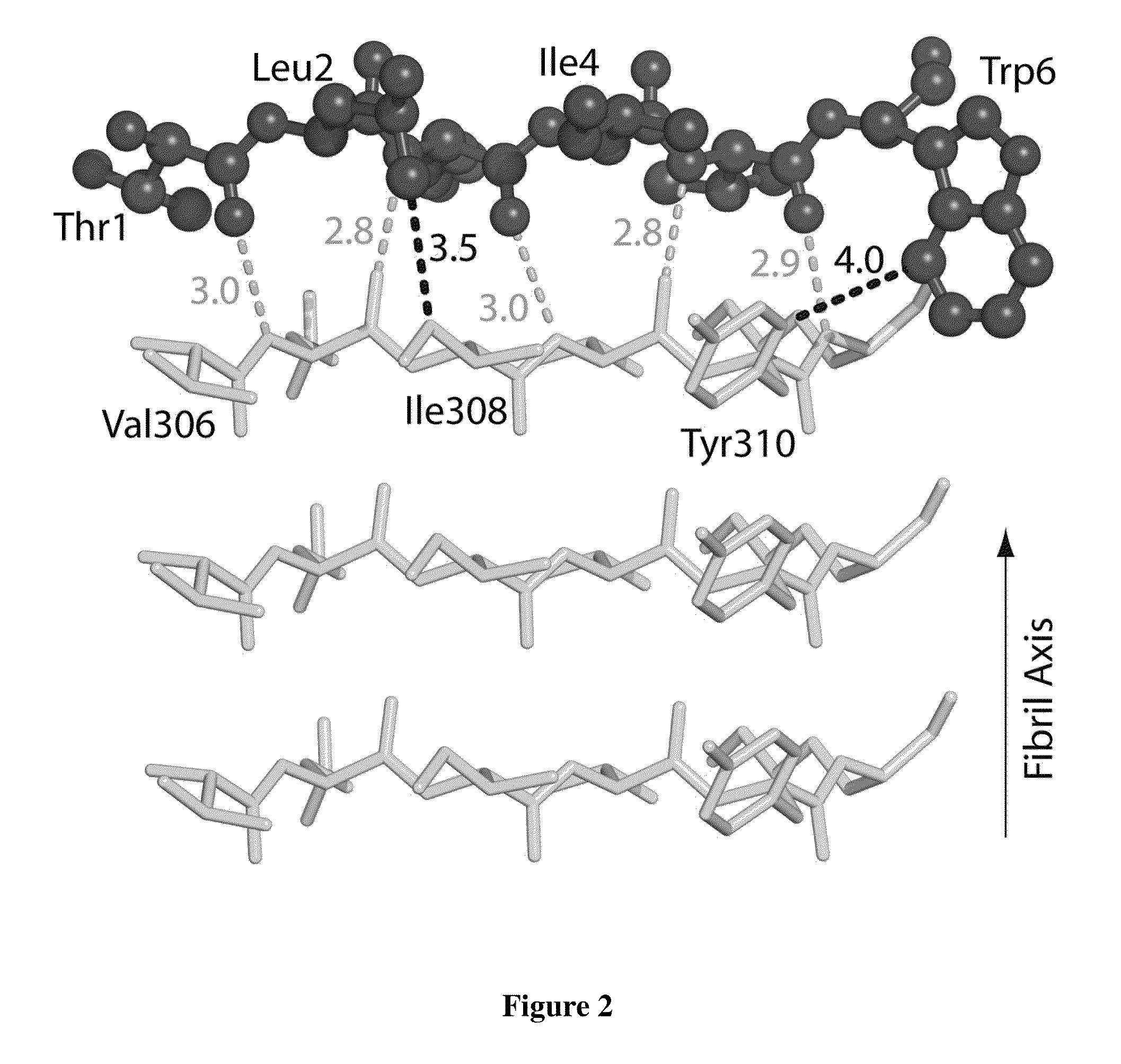
Structure-based design of peptide inhibitors of amyloid fibrillation
The invention provides methods for designing peptides that inhibit aggregation in target polypeptides. The candidate inhibitory peptidic compounds have an oligomeric sequence that forms energetically-favorable interactions with the amino acid sequence of the steric zipper region of the target protein, and also possess a zipper-disrupting feature that disrupt the peptide stacking at the steric zipper region. This method can be used to obtain inhibitory peptides to disrupt fibril formation involving any protein for which a steric zipper sequence can be identified. The invention also provides inhibitory peptidic compounds, which can be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating polypeptide aggregation-associated diseases or conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
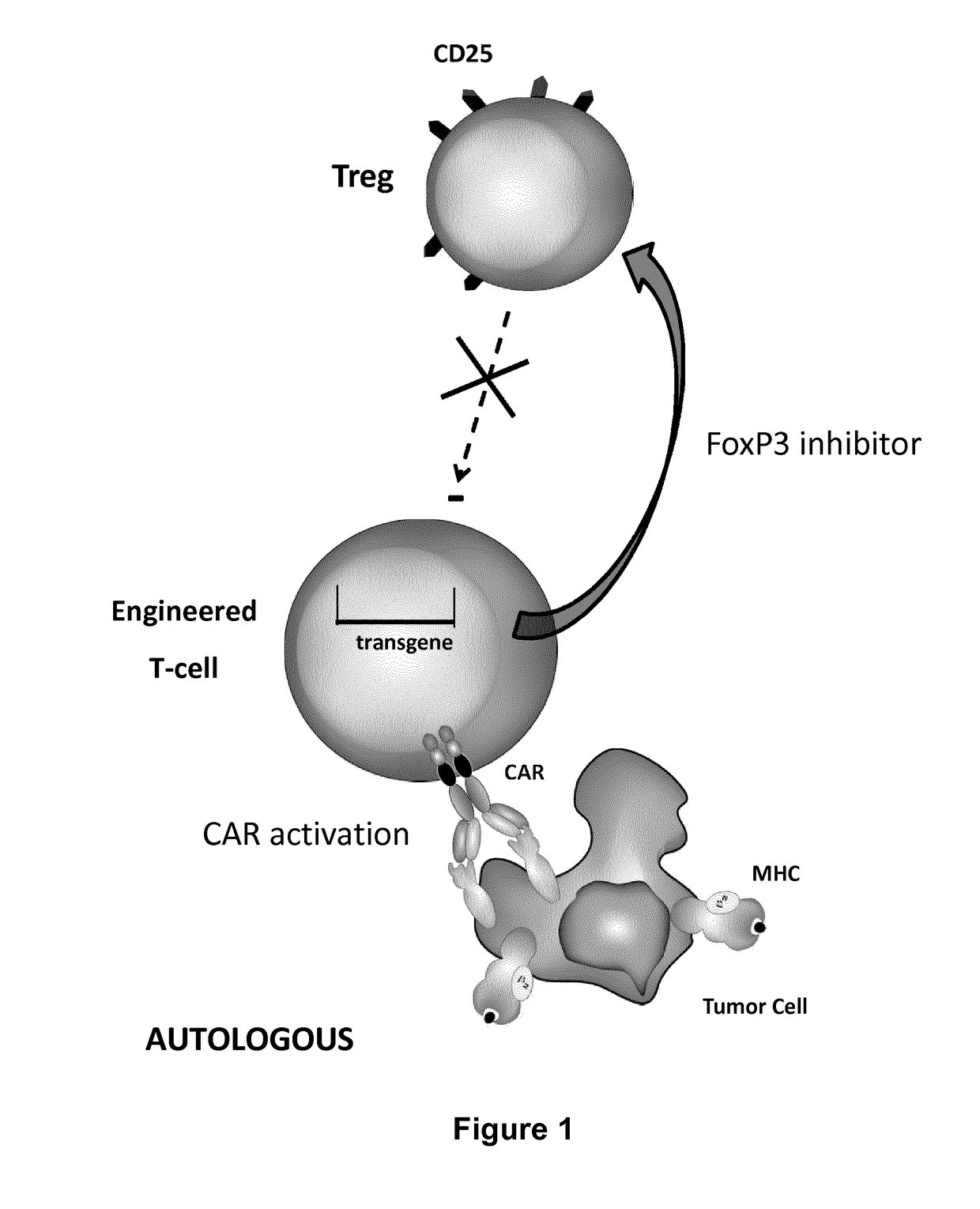
Method for in situ inhibition of regulatory t cells
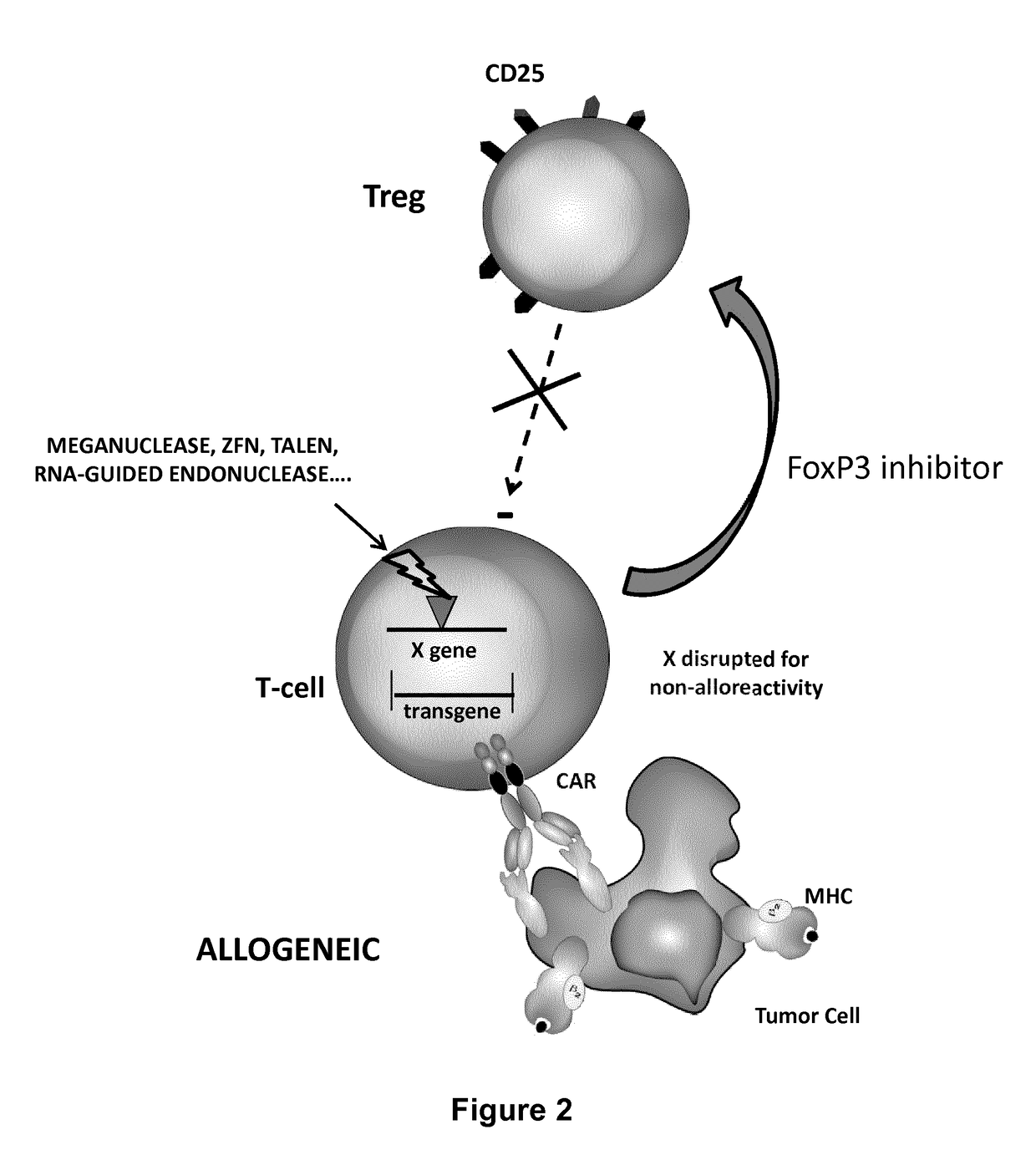
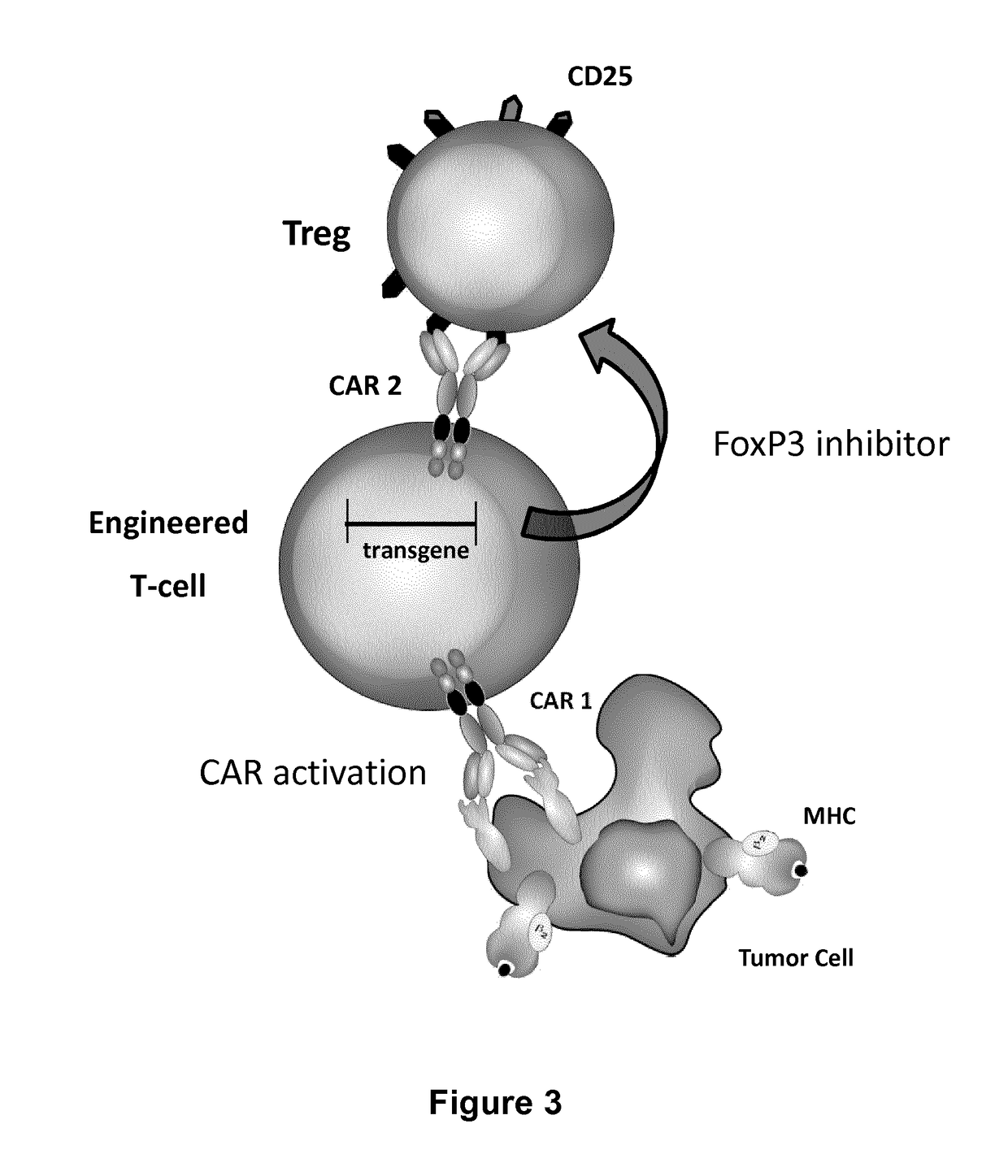
ActiveUS20170067022A1Reducing FoxP transcriptional activityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenInfected cell
The present invention pertains to engineered T-cells, method for their preparation and their use as medicament, particularly for immunotherapy. The engineered T-cells of the invention are designed to express both a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) directed against at least one antigen expressed at the surface of a malignant or infected cell, and a secreted inhibitor of regulatory T-cells (Treg). Preferably, such secreted inhibitor is a peptide inhibitor of forkhead / winged helix transcription factor 3 (FoxP3), a specific factor involved into the differentiation of T-cells into regulatory T-cells. The engineered T-cells of the invention direct their immune activity towards specific malignant or infected cells, while at the same time will prevent neighbouring regulatory T-cells from modulating the immune response. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies, especially for treating or preventing cancer, and bacterial or viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
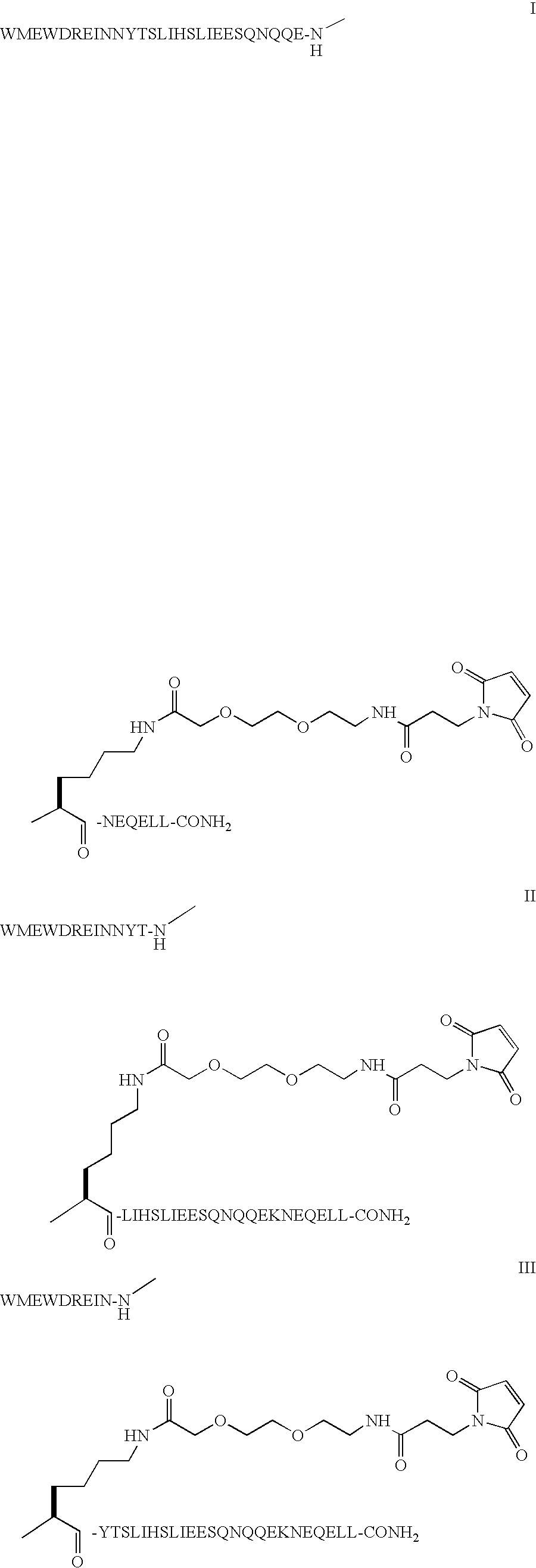
Peptide inhibitors of protein kinase C gamma for pain management
Peptide sequences derived from the V5 domain of isozymes of protein kinase C for use in pain management are described. Also described are compositions comprising the peptides for treating pain and / or inducing analgesia. Methods of pain treatment and methods of identifying compounds that mimic the activity of the peptides are also described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Inhibitors of receptor activator of NF-κB and uses thereof
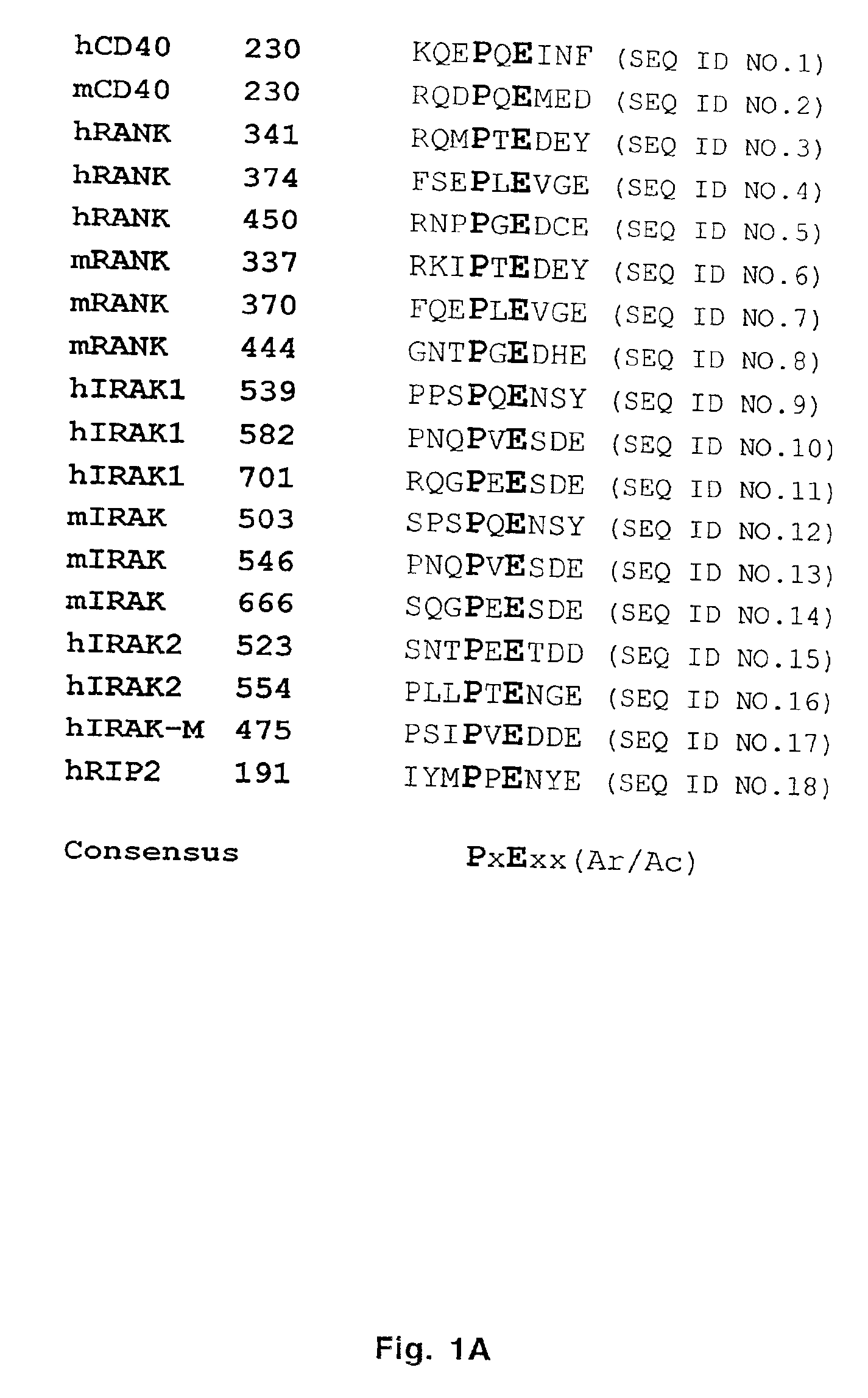
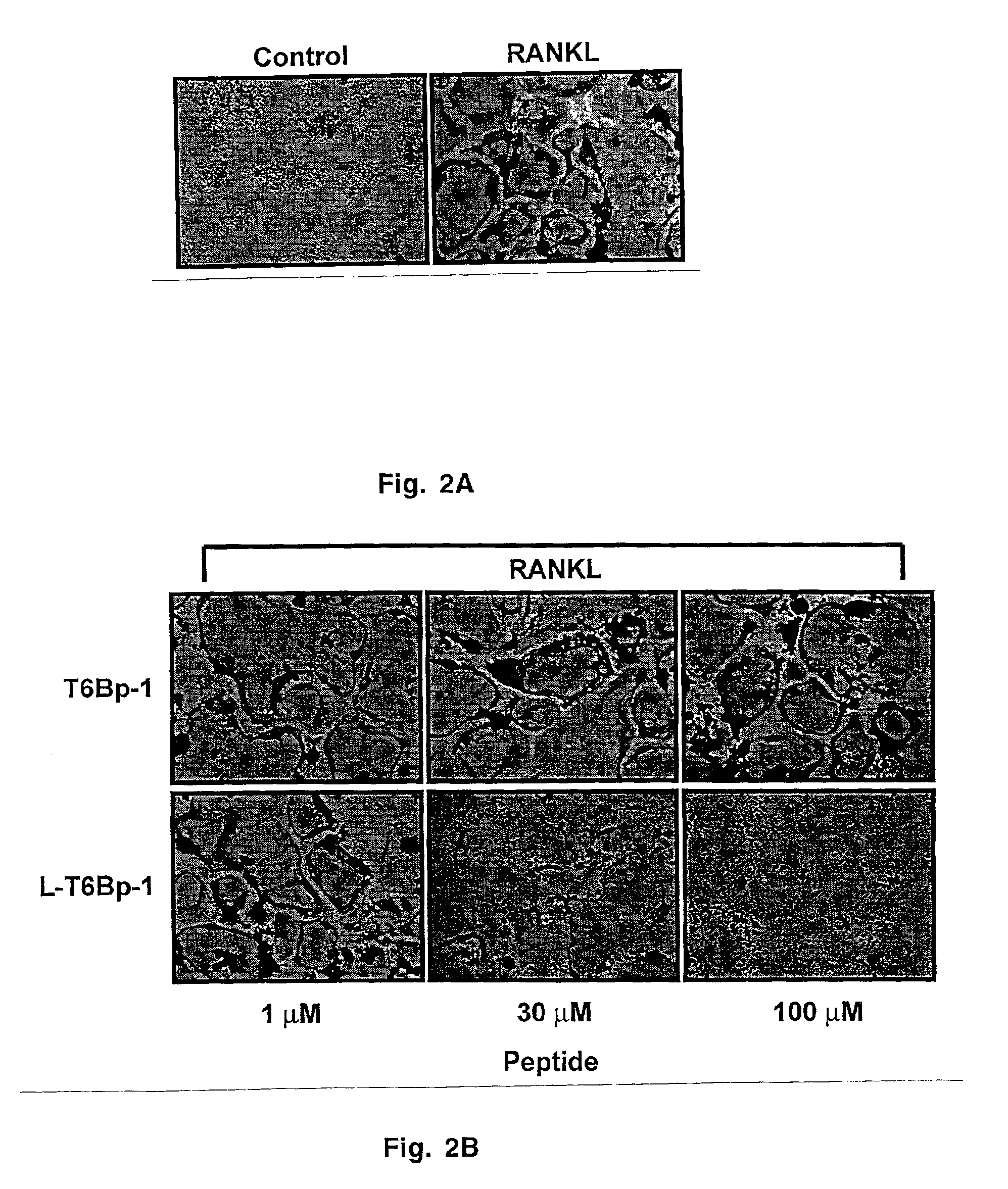
The present invention provides a RANK (receptor activator of NF-κB) inhibitor consisted of a TRAF-6 (TNF receptor-associated factor-6) binding domain attached to a leader sequence. The peptide inhibitor inhibits RANKL (RANK ligand)-mediated osteoclast differentiation, thus indicating that targeted disruption of interaction between RANK and TRAF6 may prove useful as a therapeutic for metabolic bone disorders, leukemia, arthritis, and metastatic cancer of the bone.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
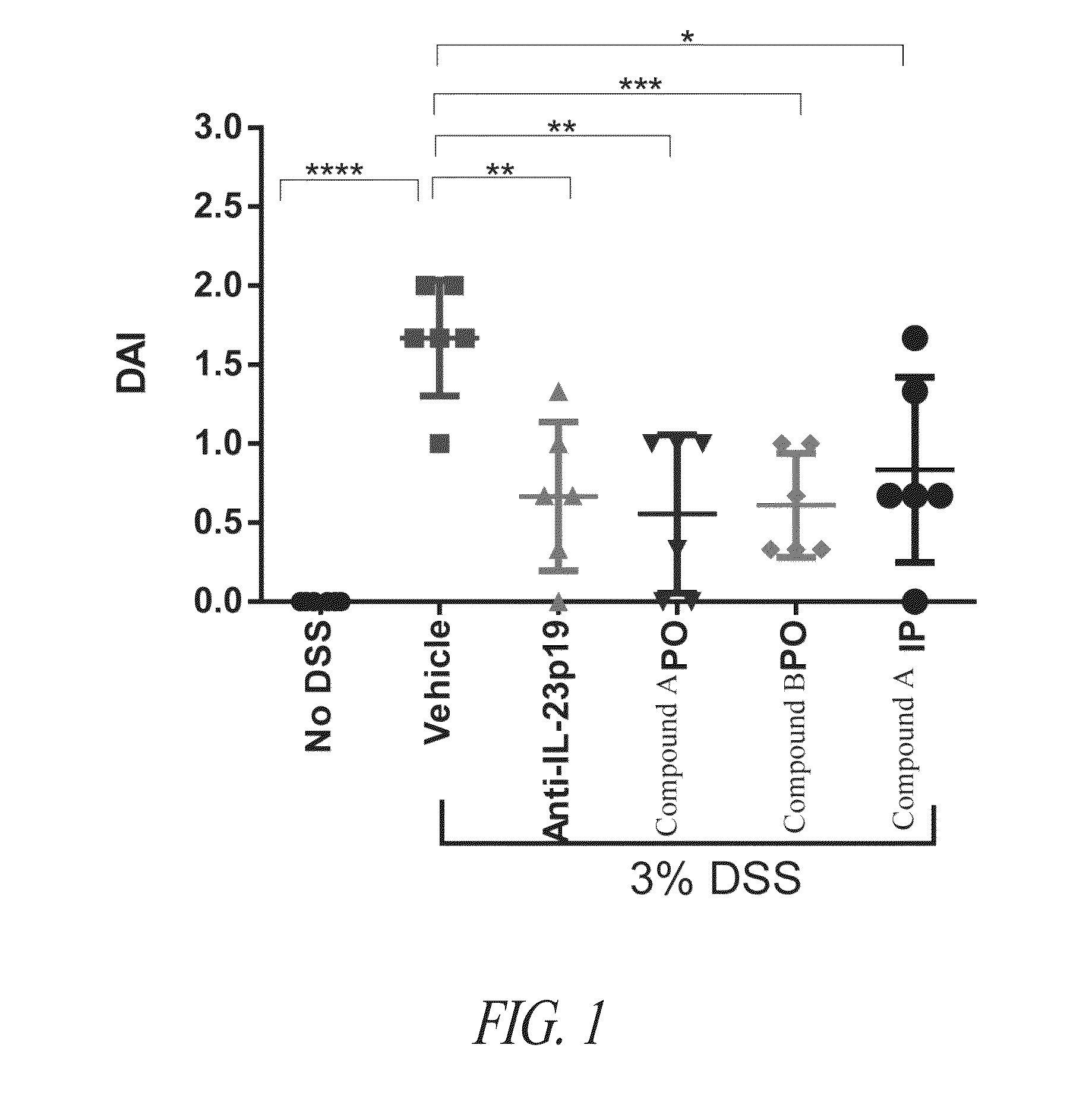
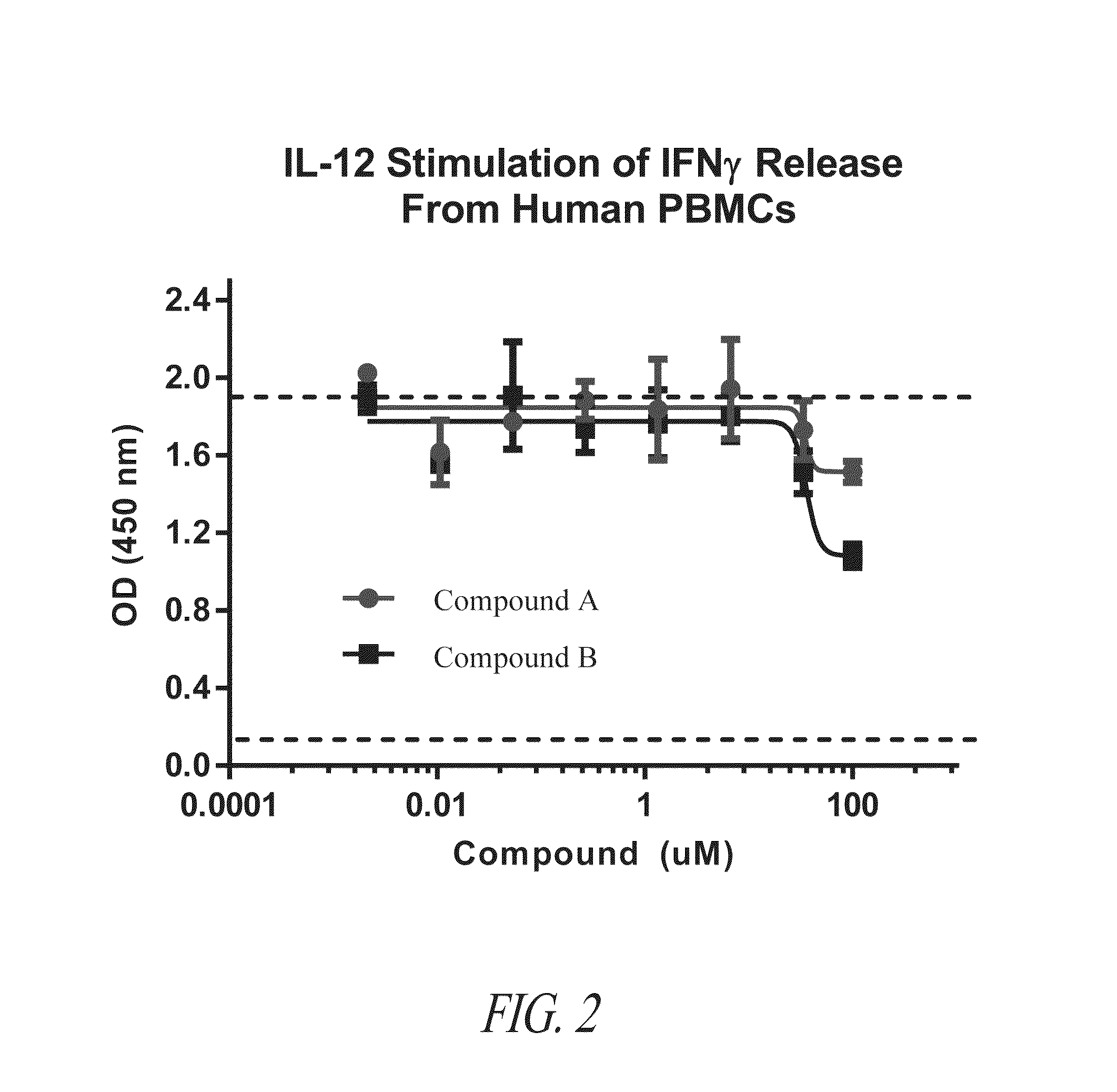
Oral peptide inhibitors of interleukin-23 receptor and their use to treat inflammatory bowel diseases
The present invention provides novel peptide inhibitors of the interleukin-23 receptor, and related compositions and methods of using these peptide inhibitors to treat or prevent a variety of diseases and disorders, including inflammatory bowel disease.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors
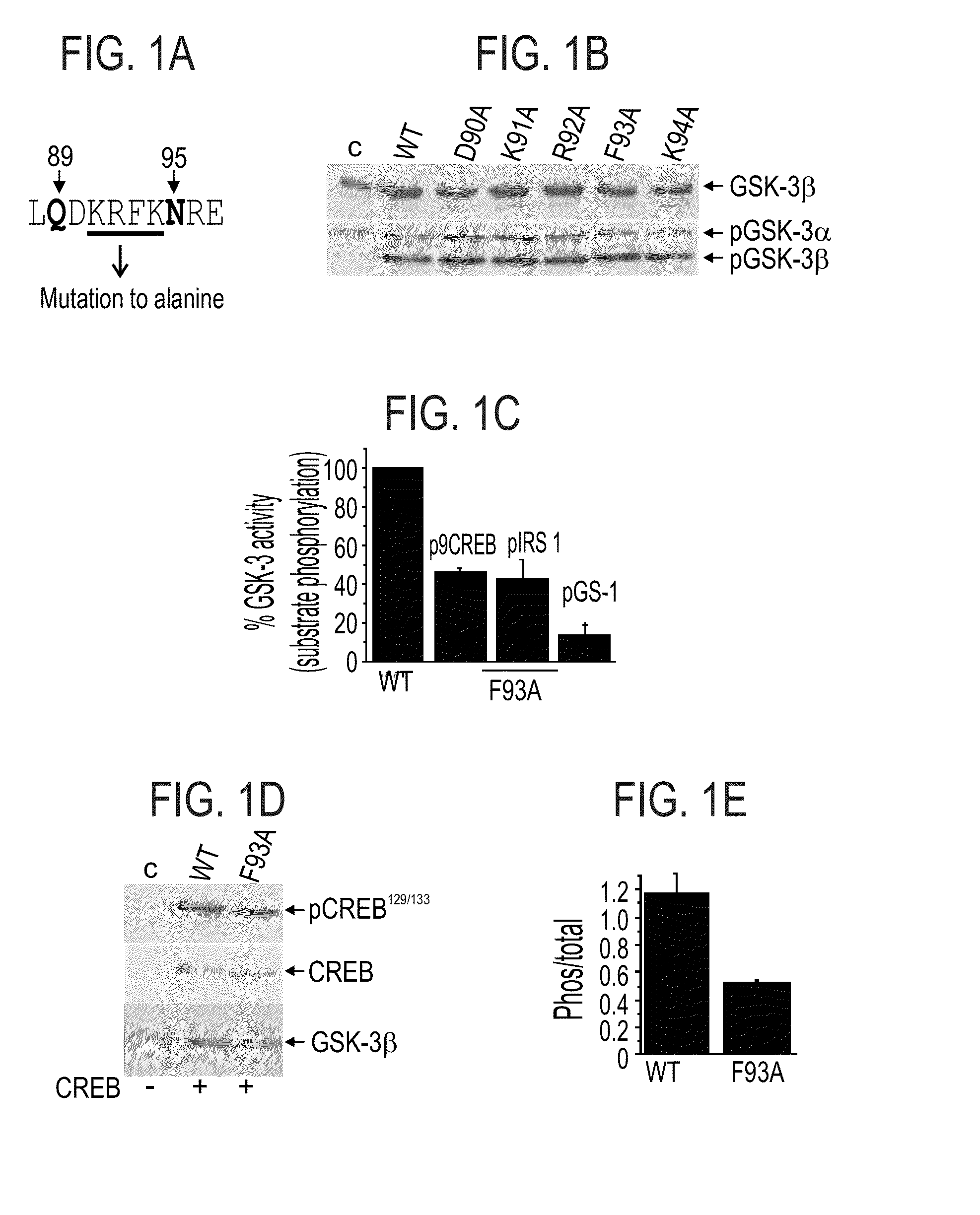
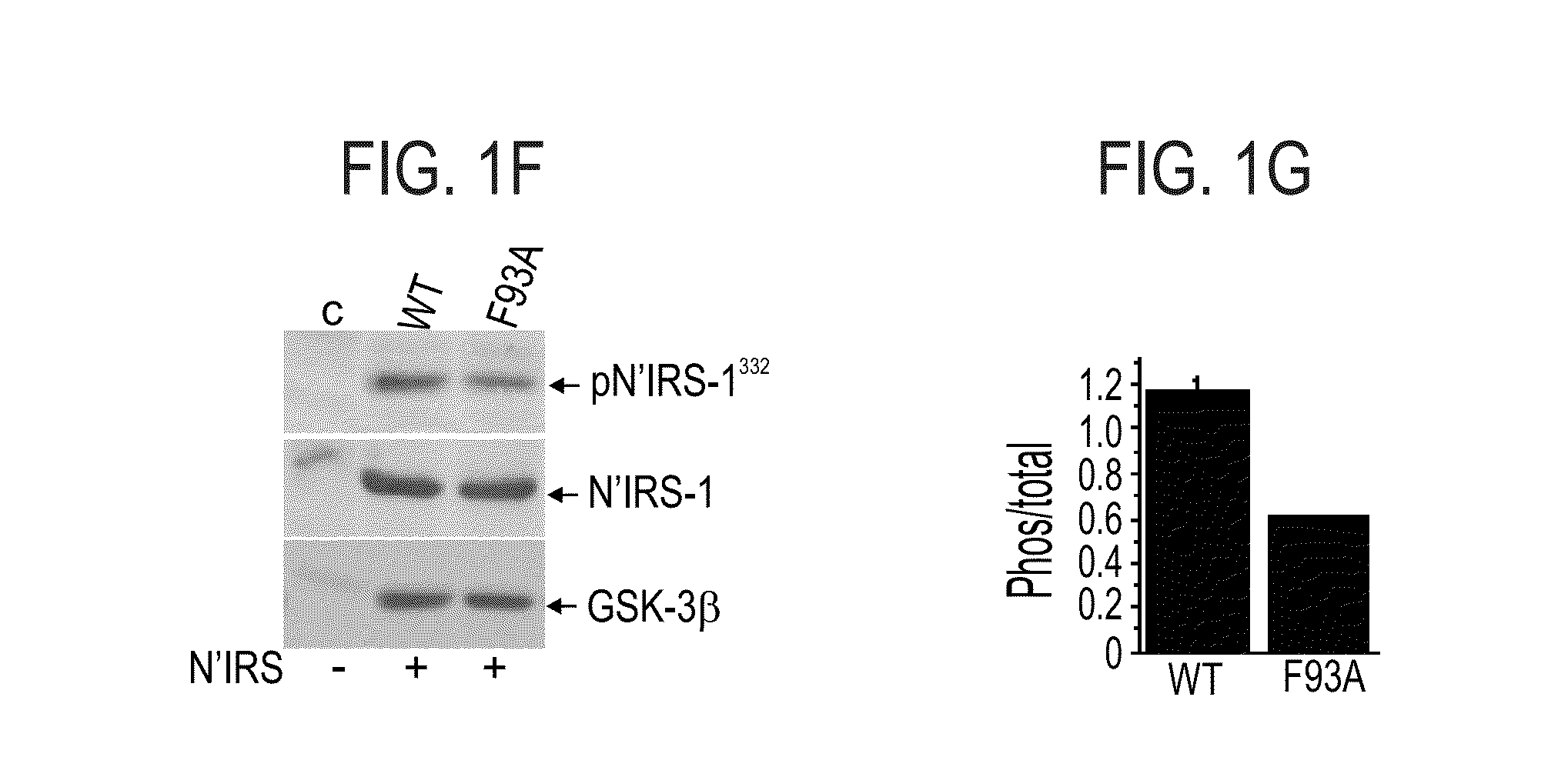
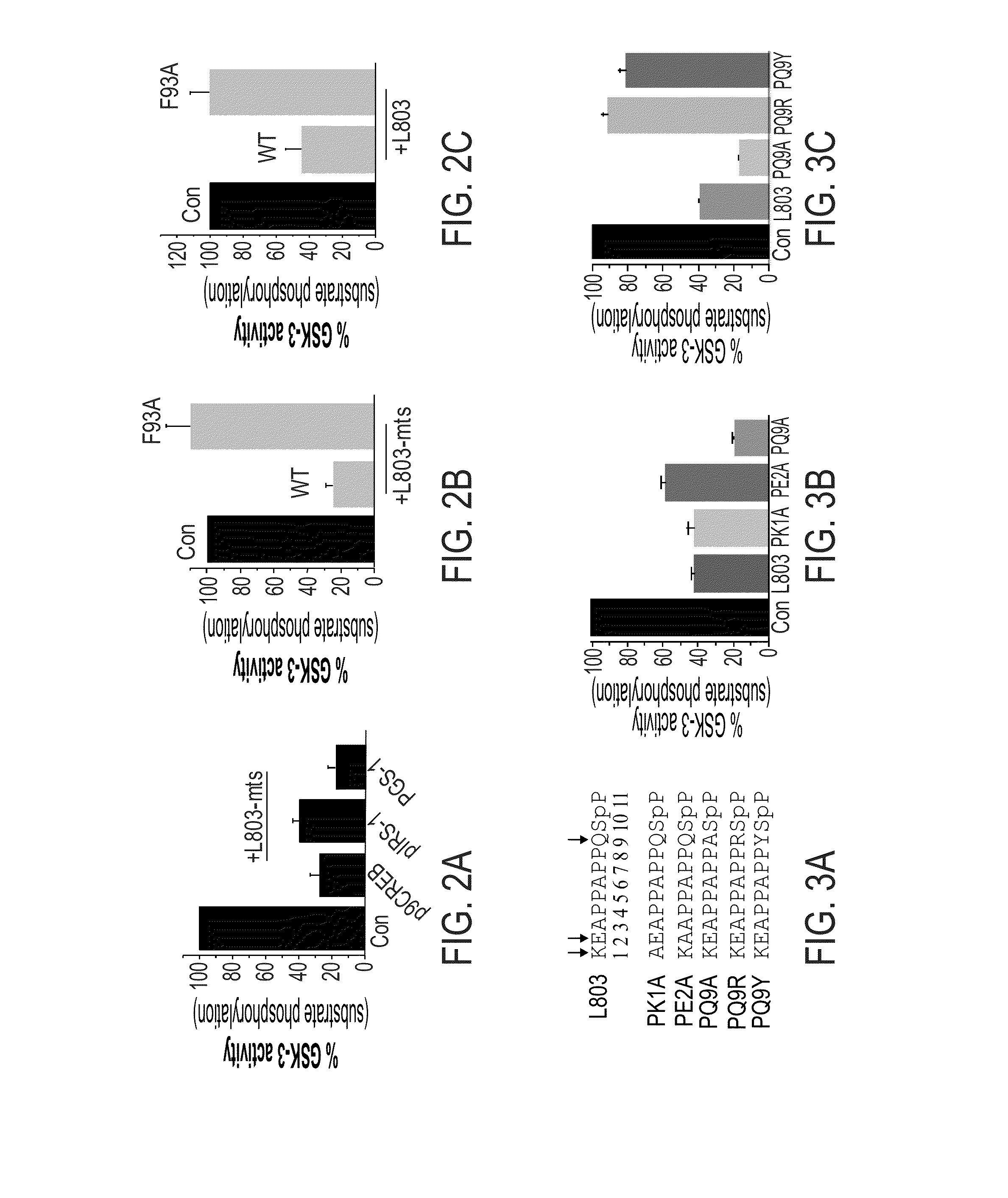
Novel peptide inhibitors of GSK-3, compositions containing same and uses thereof are disclosed. The novel peptide inhibitors are substrate-competitive inhibitors and have an amino acid sequence designed so as to bind to a defined binding site subunit in GSK-3. Also disclosed are GSK-3 substrate competitive inhibitors which bind to the defined binding site subunit in the enzyme. Also disclosed are mutants of GSK-3 and uses thereof for identifying a putative GSK-3 substrate competitive inhibitor.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Peptide inhibitors of c-jun dimerization and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100029552A1Enhances structural considerationRaise the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsProtein targetExpression Library
The present invention provides a method for the screening of nucleic acid fragment expression libraries and selecting encoded peptides based upon their ability to modulate the activity of a target protein or nucleic acid and assume conserved conformations compatible with albeit not reiterative of the target protein or nucleic acid. The present invention also provides methods for the diagnosis and treatment of ischemia. The present invention also provides c-Jun dimerization inhibitory peptides and analogues thereof that are useful for treatment of ischemia.
Owner:PHYLOGICA
Signal-1/signal-2 bifunctional peptide inhibitors
InactiveUS20050107585A1Decreased LFA-1 : ICAM- signalingPreventing translocation stepCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsMajor histocompatibilityPeptide sequence
A novel peptide sequence having the general formula AB wherein each of A and B represent a chain of amino acid residues and wherein said A chain is capable of binding with a major histocompatibility complex on an antigen presenting cell, and wherein said B chain is capable of binding with a Signal-2 receptor on an antigen presenting cell. Preferred forms of the peptide sequence further include an X chain positioned intermediate the A chain and the B chain. Moreover, preferred forms include an A chain which has at least about 10% sequence homology with a Signal-1 moiety, or is a peptidomimetic of a Signal-1 moiety, said B chain has at least 10% sequence homology with a Signal-2 receptor moiety, or is a peptidomimetic of a Signal-2 receptor moiety, and wherein the X chain has at least one amino acid residue, or is a peptidomimetic of that amino acid residue. Advantageously, the novel peptide sequence is capable of shifting a type-1 immune response to a type-2 immune response or from a type-2 immune response to a type-1 immune response.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF
Preparation method of cannabis sativa protein ACE (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) peptide inhibitor
InactiveCN104480177AImprove the level of deep processing utilizationAntioxidantPeptide preparation methodsFermentationCannabisWater baths
The invention provides a preparation method of a cannabis sativa protein ACE (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) peptide inhibitor. The preparation method comprises the steps of A, weighing kernel meal of degreased cannabis sativa; drying; crushing; sieving to remove impurities; feeding water until reaching fixed material-liquid ratio; homogenizing through a colloid mill; sieving; regulating the pH value; ultrasonically assisting to extract; extracting protein with alkali under a constant temperature; performing isoelectric precipitation; centrifuging to remove supernate; extracting protein from precipitate with alkali for the second time; feeding water to reach the fixed material-liquid ratio; homogenizing through a homogenizing machine; sieving; regulating the pH value; performing isoelectric precipitation again; centrifuging to remove supernate; neutralizing; drying to obtain separated-out protein of kernel meal of cannabis sativa; B, feeding deionized water to separated-out protein of kernel meal of cannabis satival; regulating pH; feeding mixed protease for enzymolysis under the constant temperature; deactivating enzyme by boiling water bath; centrifuging to obtain supernate; C, separating and purifying protease enzymolysis solution of kernel meal of cannabis satival; collecting to obtain the ACE peptide inhibitor of protein of kernel meal of cannabis satival; freezing and drying to obtain the cannabis sativa protein ACE peptide inhibitor. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the product yield is increased, and the ACE inhibition effect is excellent.
Owner:AGRI PROD PROCESSING INST GUANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
VEGF-D/VEGF-C/VEGF peptidomimetic inhibitor
InactiveUS7045133B2Long half-lifeHigh activityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsPeptide inhibitorChemistry
Monomeric monocyclic peptide inhibitors and dimeric bicyclic peptide inhibitors based on exposed loop fragments of a growth factor protein, such as loop 1, 2 or 3 of VEGF-D, and methods of making them are described as well as pharmaceutical compositions containing them and methods utilizing them.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
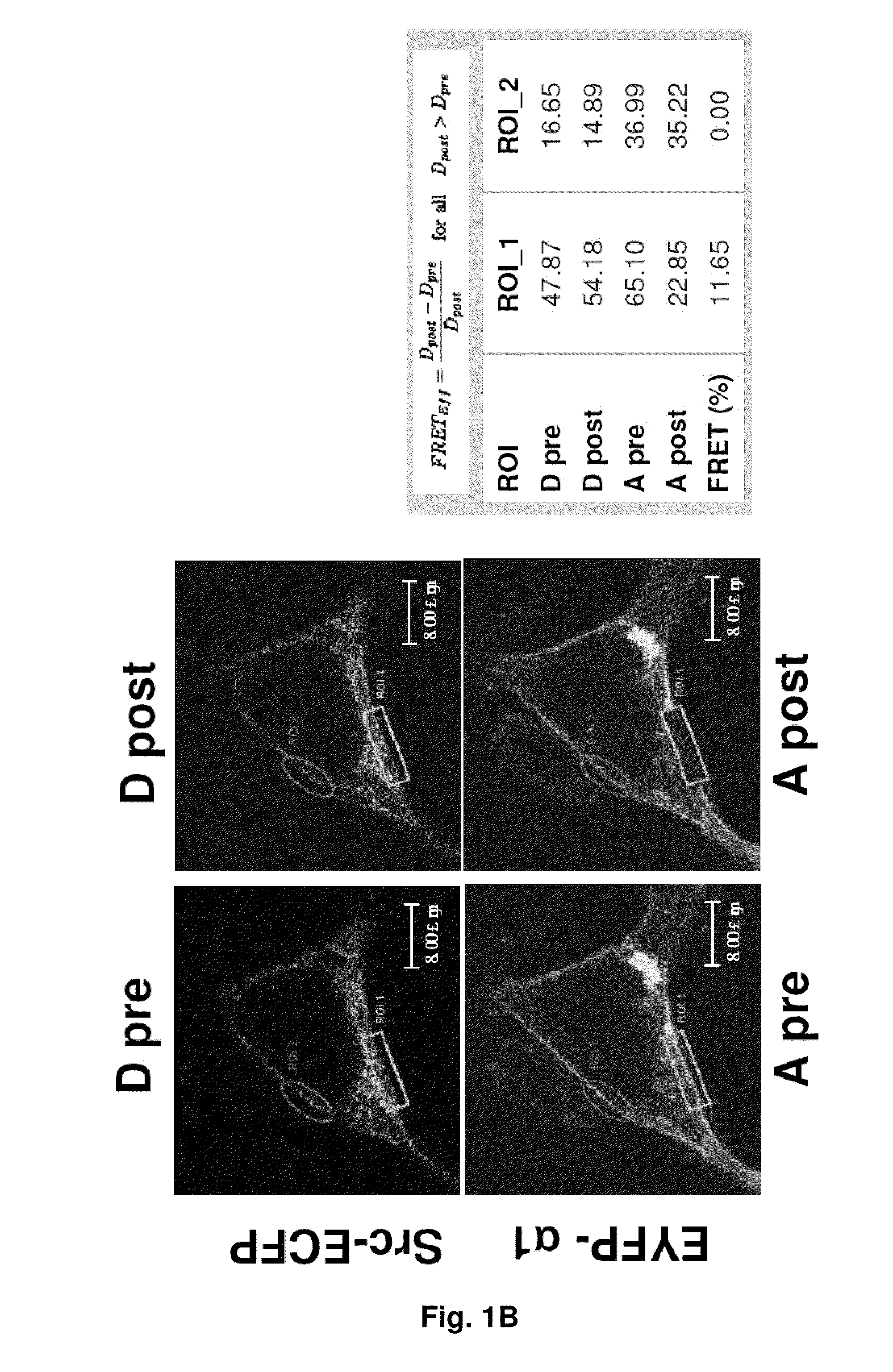
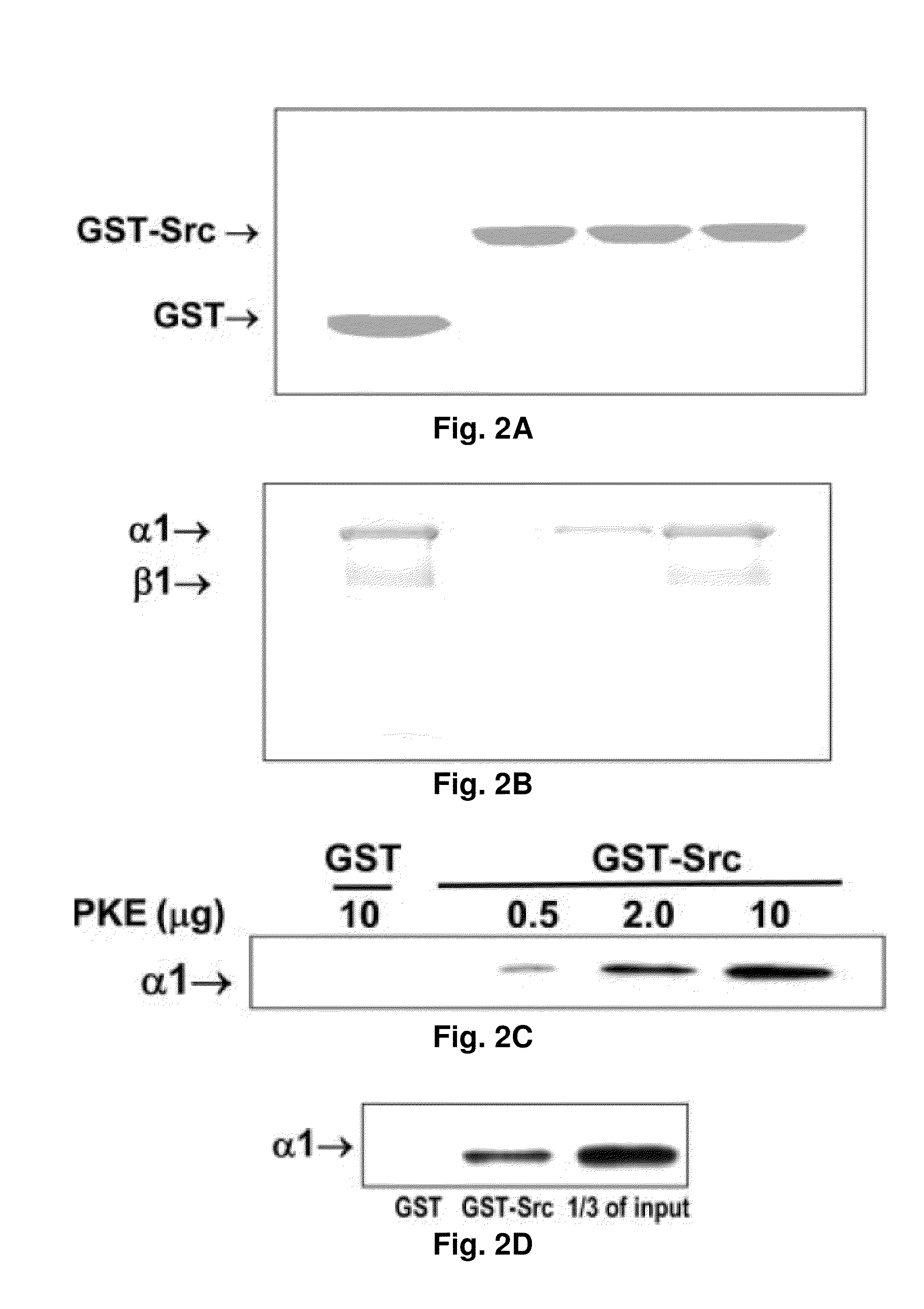
NA+K+-ATPase-Specific Peptide Inhibitors/Activators of SRC and SRC Family Kinases
ActiveUS20100056446A1Reduce expressionSilencing expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesATPaseCardiotonic steroid
A method for regulating Src and its downstream signaling pathway which includes binding between Src and Na+ / K+-ATPase is disclosed. The Na+ / K+-ATPase / Src complex is a functional receptor for cardiotonic steroids such as ouabain. Also disclosed are Src inhibitors or activators which include either Na+ / K+-ATPase or Src that interfere with the interaction between the Na / K-ATPase and Src, act via a different mechanism from ATP analogues, and is pathway (Na+ / K+-ATPase) specific.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Long lasting fusion peptide inhibitors for HIV infection
InactiveUS7741453B2Prolong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunodeficiency virusHuman Parainfluenza Virus
The present invention relates to C34 peptide derivatives that are inhibitors of viral infection and / or exhibit antifusogenic properties. In particular, this invention relates to C34 derivatives having inhibiting activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human parainfluenza virus (HPV), measles virus (MeV), and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) with long duration of action for the treatment of the respective viral infections.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Method for detecting proteinaceous inhibitors of protein-protein or DNA-protein interactions
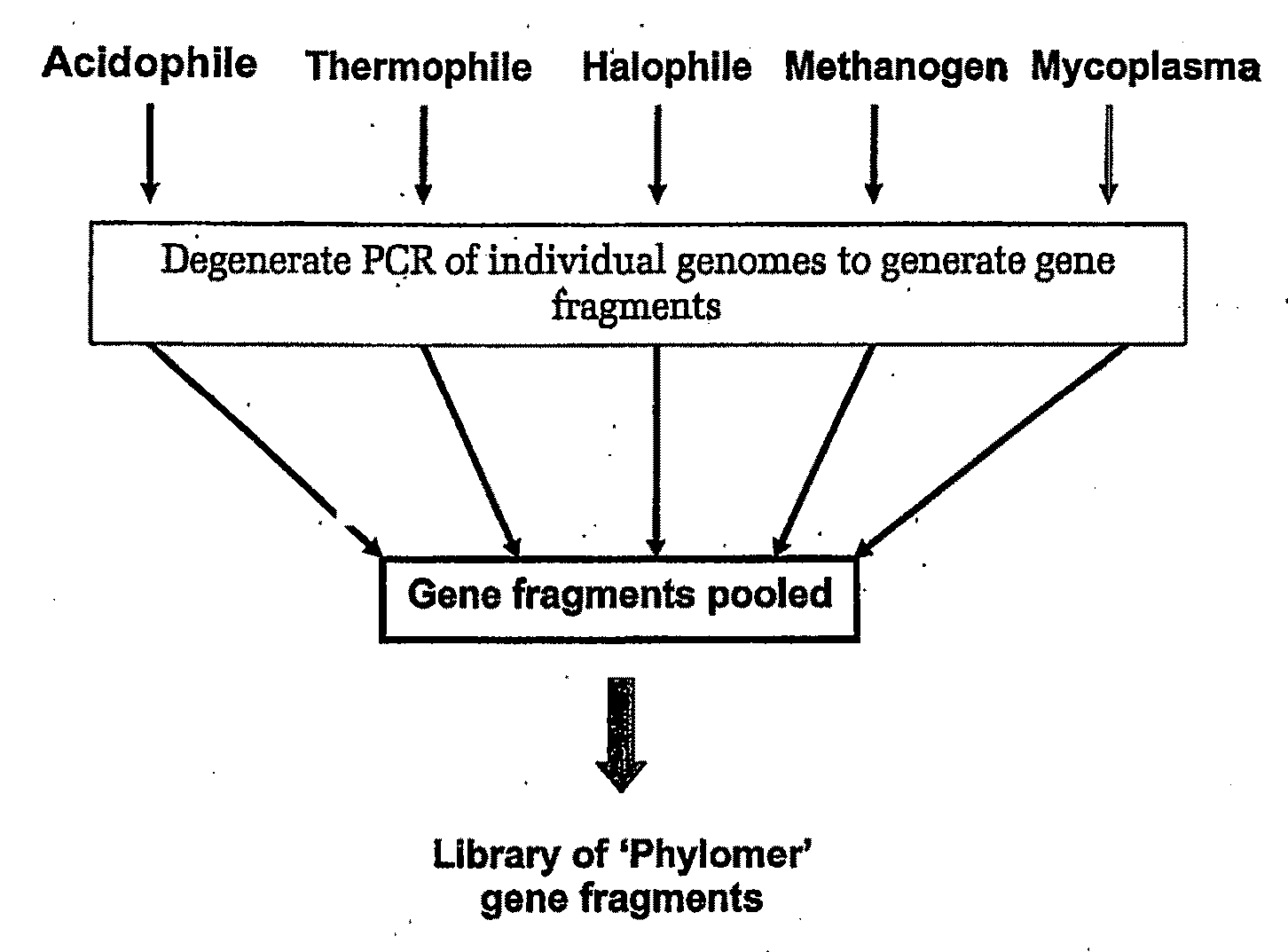
The present invention relates generally to a method of identifying modulators of biological interactions and agents useful for same. More particularly, the present invention contemplates a method of detecting inhibitors of biological interactions involving proteinaceous and / or nucleic acid molecules and more particularly a method of identifying peptide inhibitors of biological interactions having adverse effects on living cells, tissue or organisms. The present invention provides the means by which a wide range of peptide-based therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic reagents may be developed.
Owner:PHYLOGICA
Perfusion and/or preservation solution for organs
InactiveUS20060160062A1Decreased blood flowFacilitated releaseVertebrate cellsDead animal preservationSuperoxide releaseNitric oxide
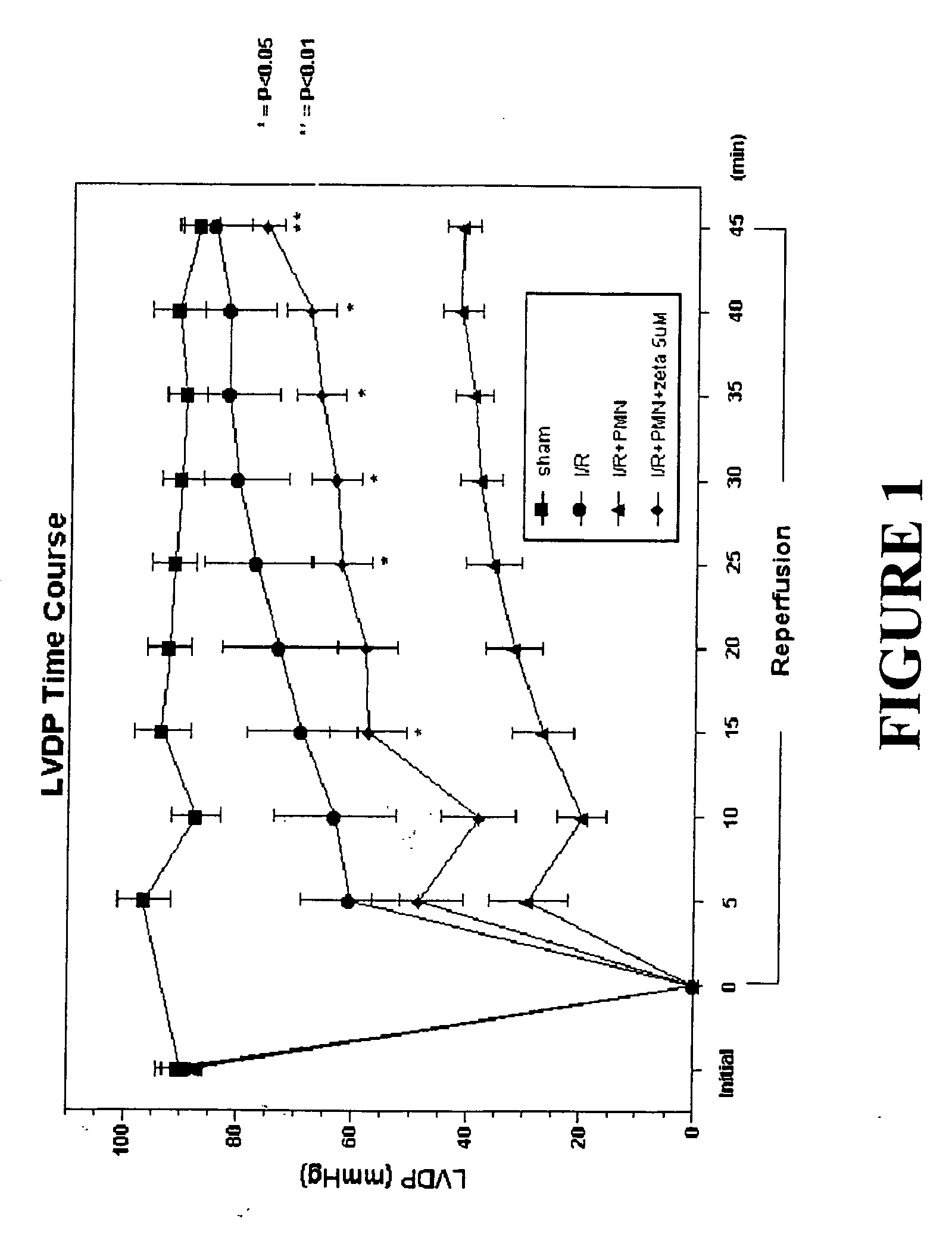
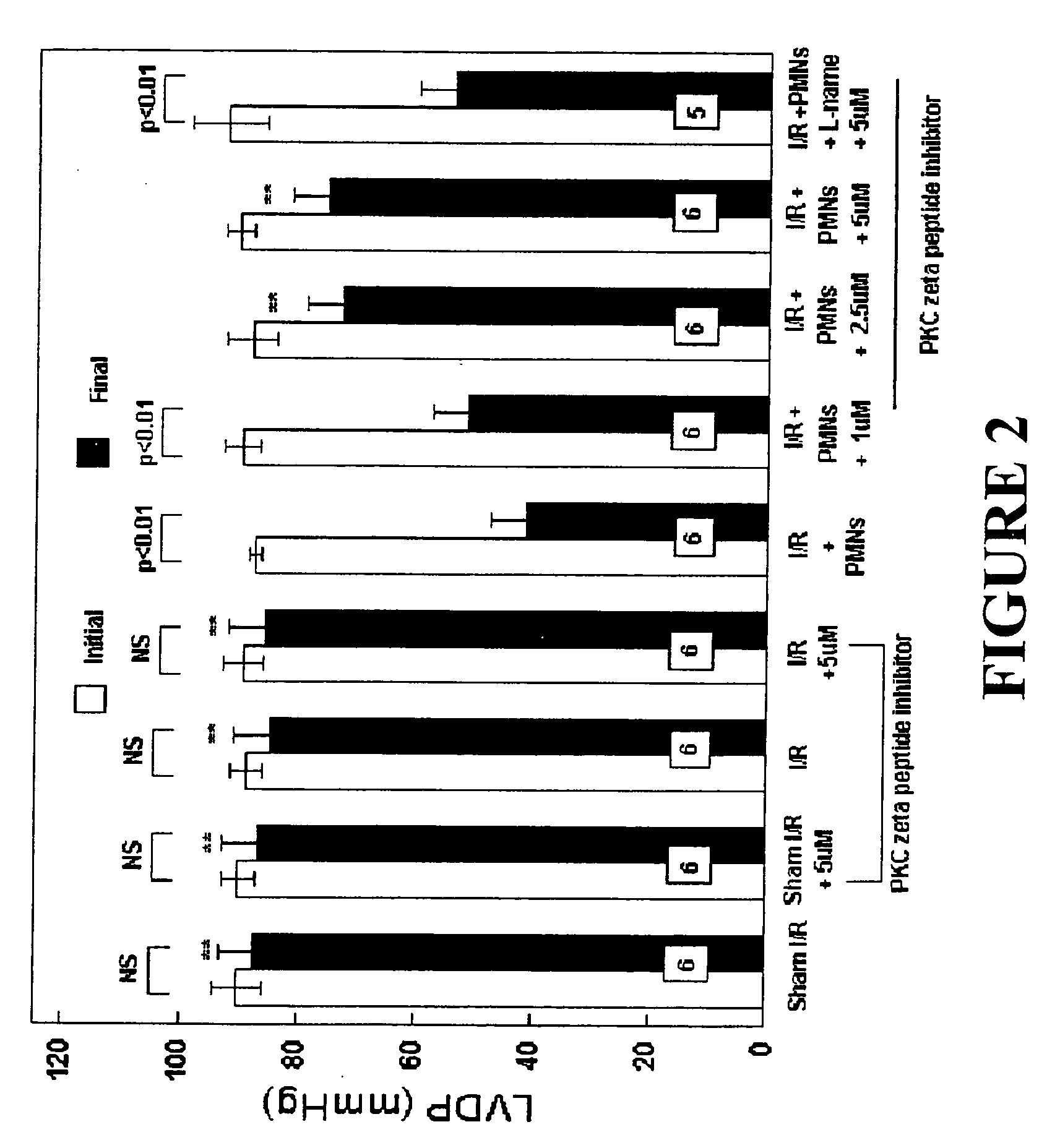
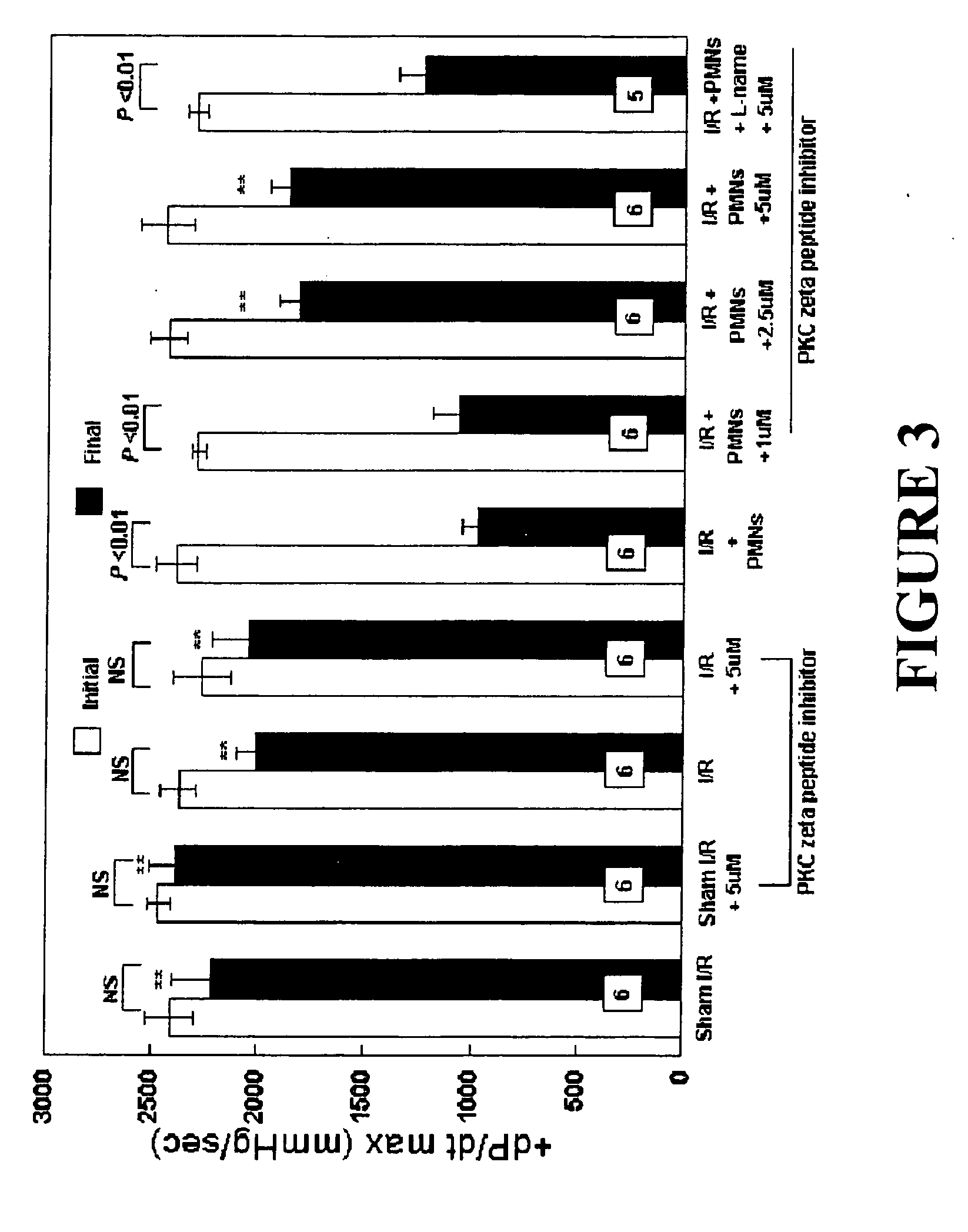
The present invention relates to a solution for preservation, perfusion, and / or reperfusion of an organ, especially the heart, for transplantation. The solution contains peptide inhibitor(s) of protein kinase C βII (PKC βII) and / or of protein kinase C ζ (PKC ζ) and / or peptide activator(s) of protein kinase C δ (PKCδ). Methods for using the inventive solution are also disclosed, including methods for preserving an organ for transplantation, for protecting an ischemic organ from damage, for attenuating organ dysfunction after ischemia, for maintaining nitric oxide release and / or inhibiting superoxide release in an ischemic organ, and for protecting an organ from damage when isolated from the circulatory system.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA COLLEGE OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE
Na+K+-ATPase-specific peptide inhibitors/activators of SRC and SRC family kinases
ActiveUS8283441B2Reduce expressionSilencing expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesATPaseSrc inhibitor
A method for regulating Src and its downstream signaling pathway which includes binding between Src and Na+ / K+-ATPase is disclosed. The Na+ / K+-ATPase / Src complex is a functional receptor for cardiotonic steroids such as ouabain. Also disclosed are Src inhibitors or activators which include either Na+ / K+-ATPase or Src that interfere with the interaction between the Na / K-ATPase and Src, act via a different mechanism from ATP analogues, and is pathway (Na+ / K+-ATPase) specific.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
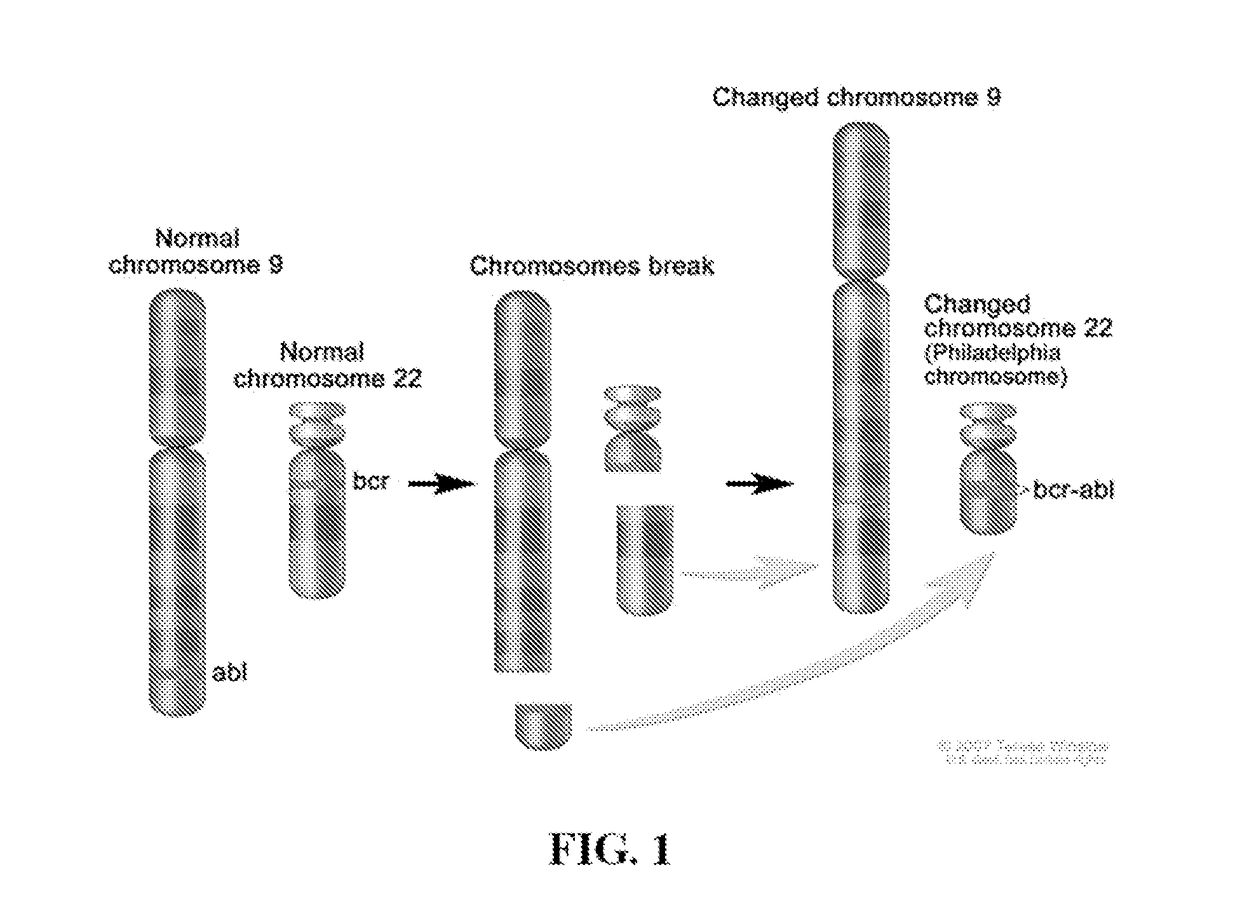
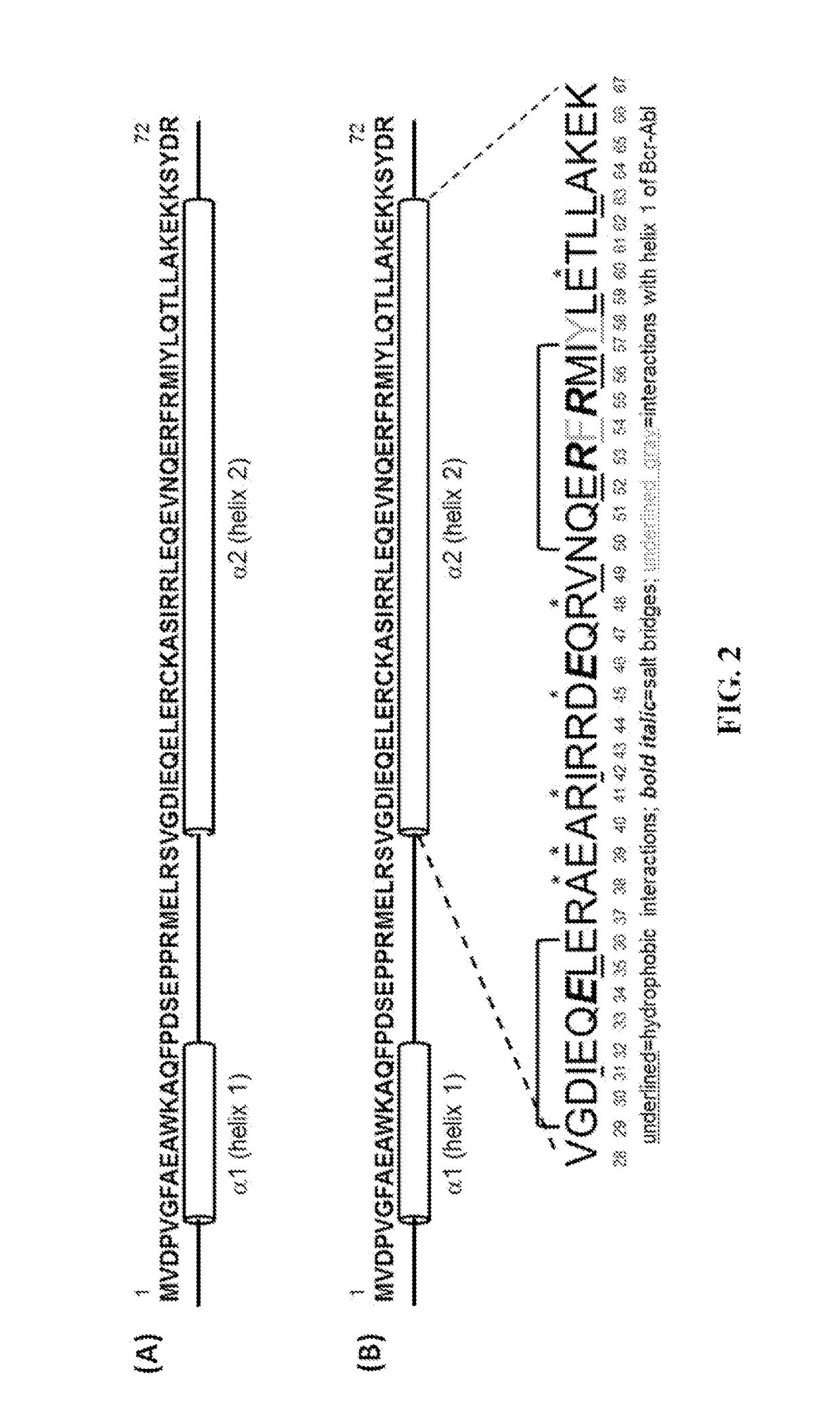
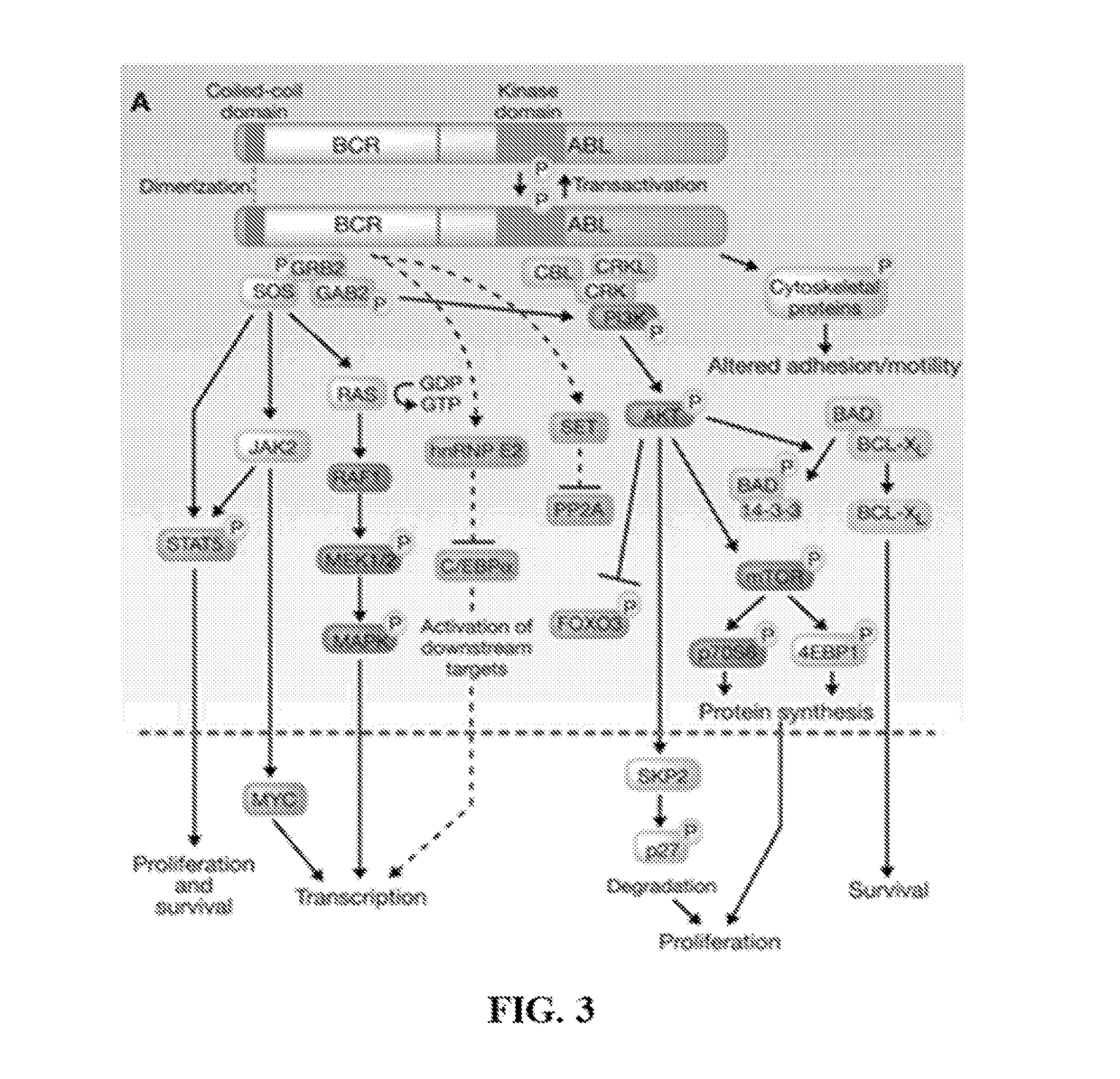
Peptide Inhibitors of BCR-ABL Oligomerization
In one aspect, the invention relates to peptides comprising the Bcr-Abl coiled-coil oligomerization domain and an alpha helix stabilizing moiety, mutant forms thereof, truncated forms thereof, derivatives thereof, and related peptides, which are useful as inhibitors of the Bcr-Abl chimeric protein; pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds; and methods of treating hyperproliferative disorders associated with Bcr-Abl using the compounds and compositions. This abstract is intended as a scanning tool for purposes of searching in the particular art and is not intended to be limiting of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
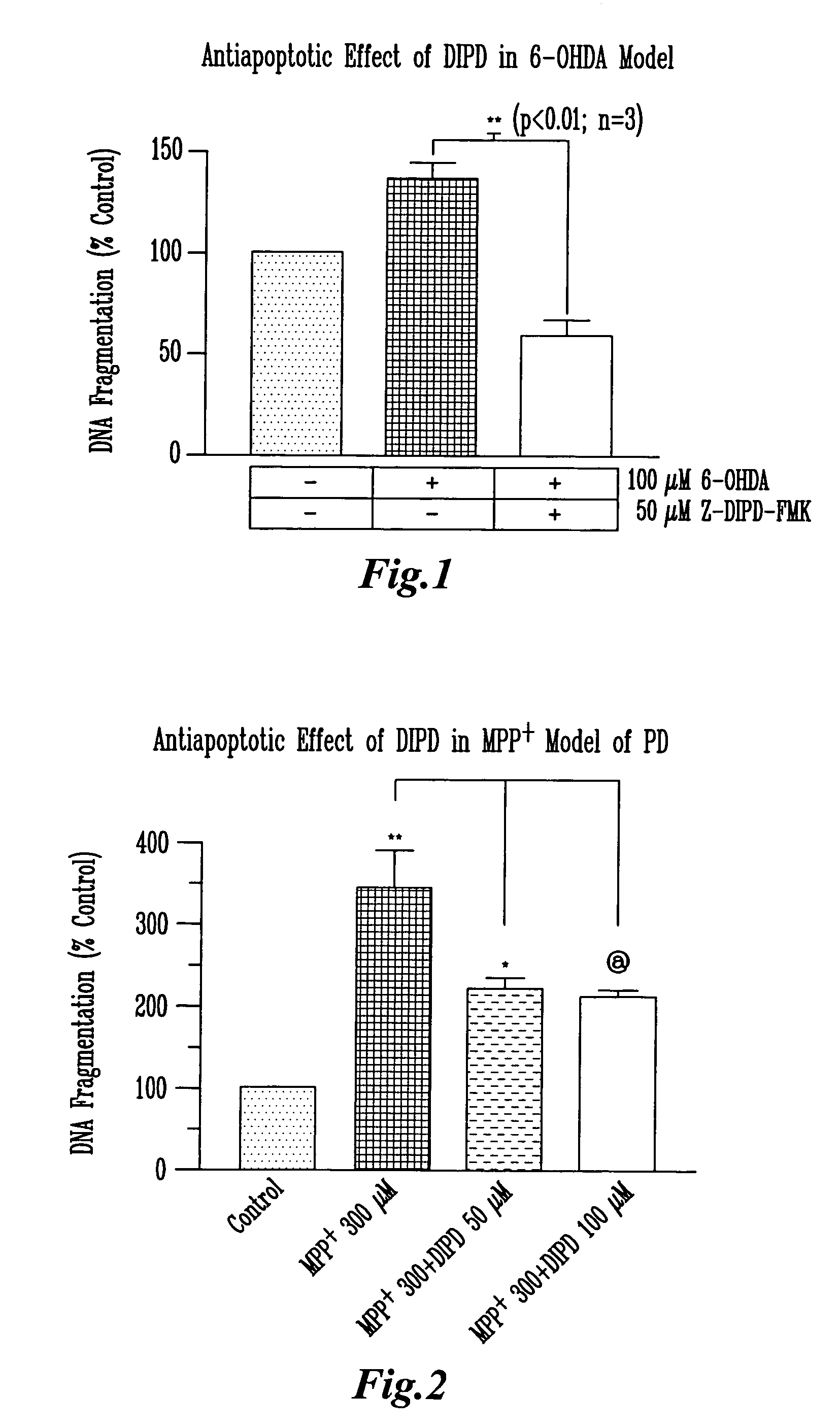
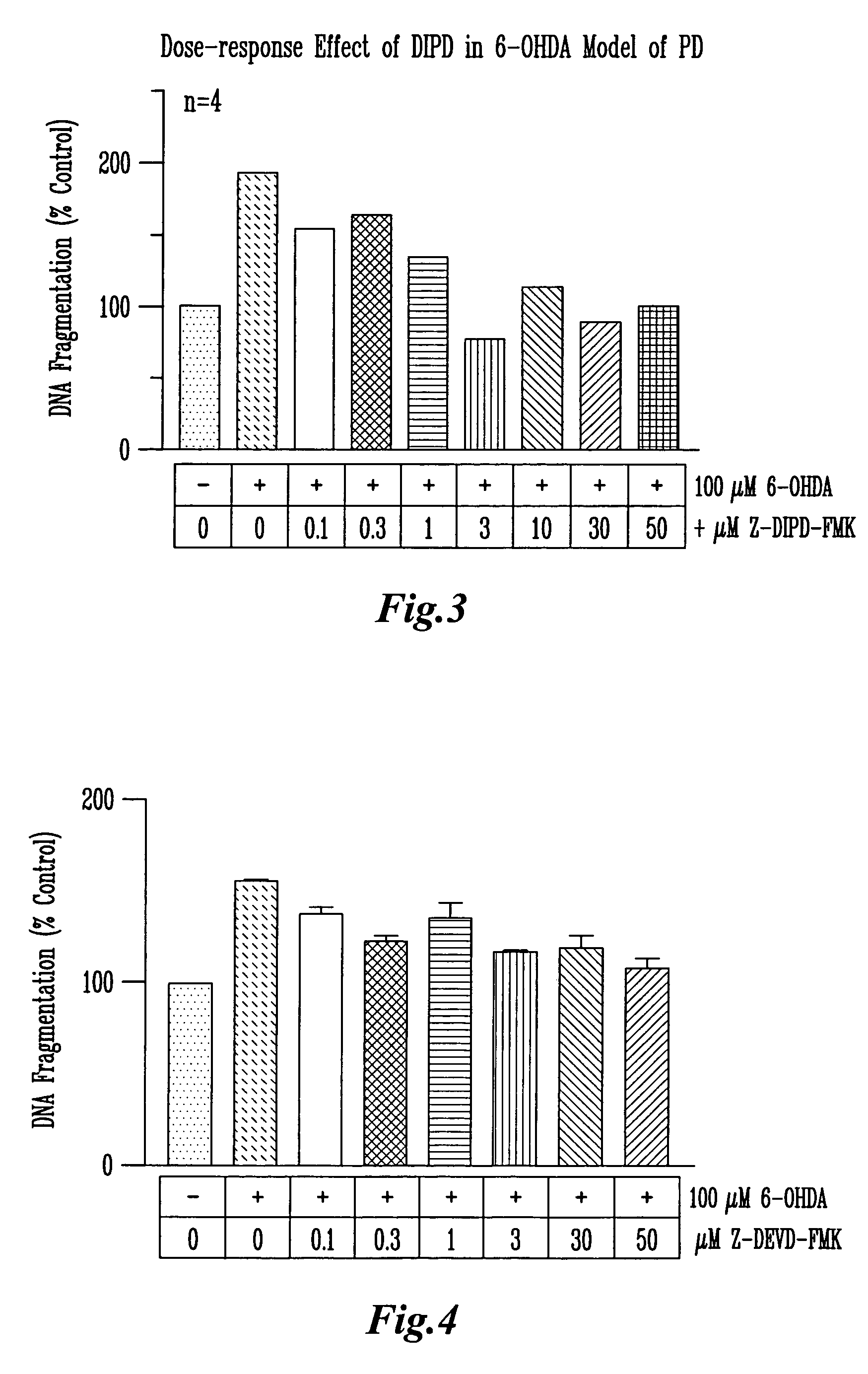
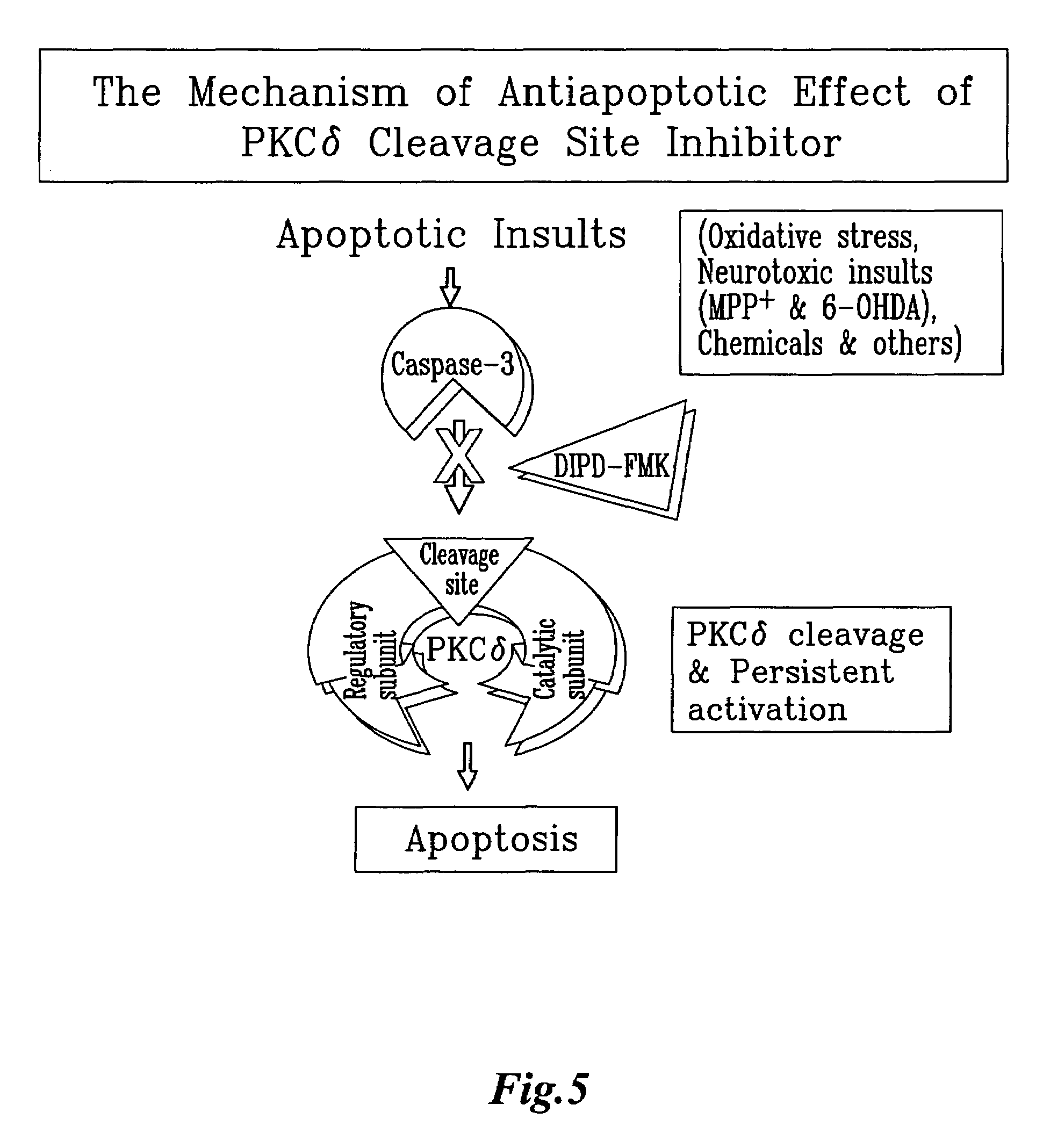
Methods and compositions for inhibiting PKC delta cleavage for treatment and prevention of neurodegeneration and apoptosis
Methods and compositions are provided which inhibit the apoptotic activity associated with oxidative stress in many disease states. According to the invention, inhibition of chemical cleavage of PKCδ by caspase-3 results in reduction of apoptosis. Novel peptide inhibitors with the amino acid motif Asp Ile Pro Asp (SEQ ID NO:5) are also disclosed. The peptides are useful as inhibitors of PKCδ-mediated apoptosis and oxidative stress, and other diseases regulated by a catalytically active PKCδ.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
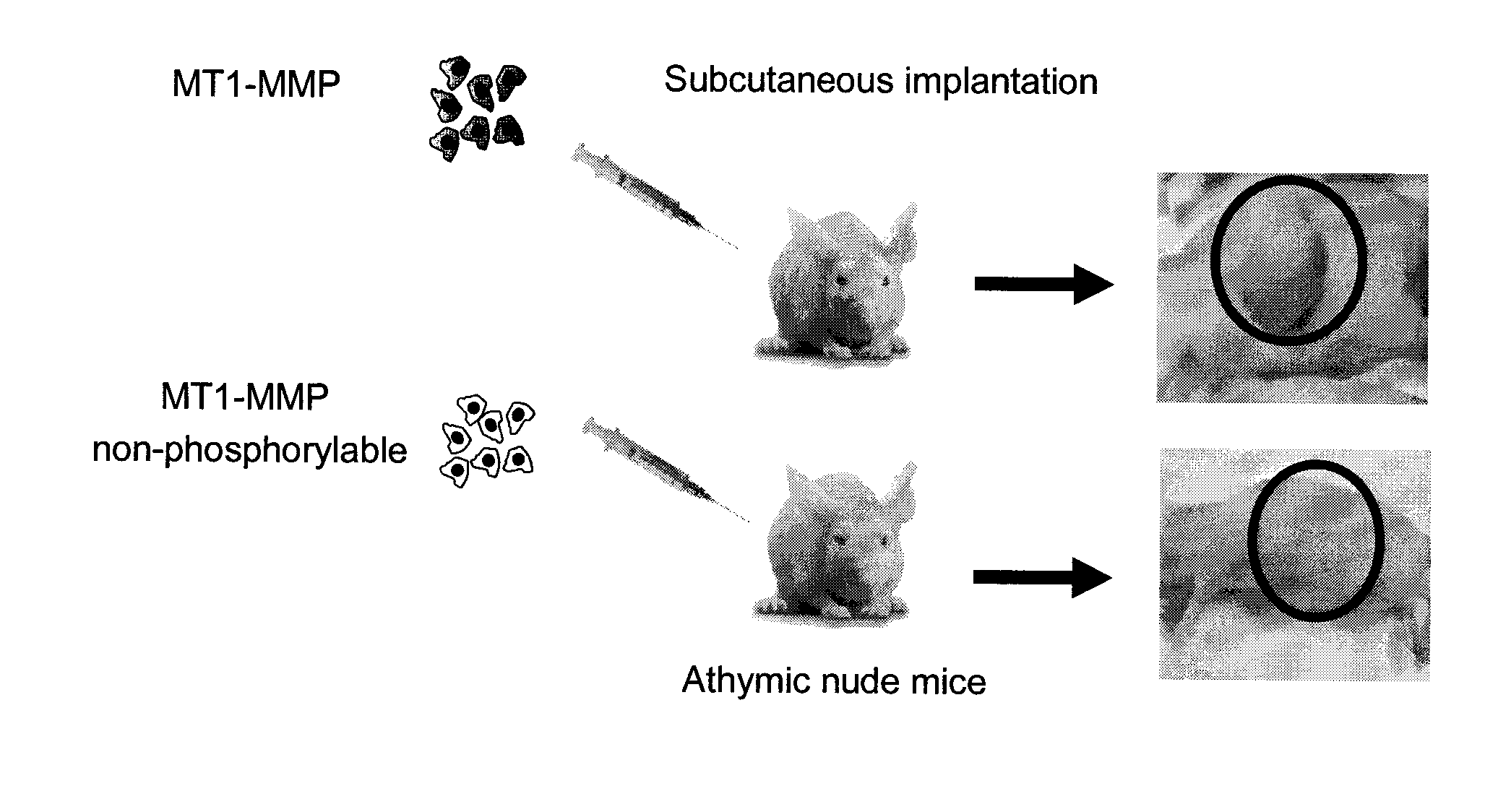
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloprotein inhibitors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110305750A1Reduce the frequency of occurrenceReduce severityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseasePhosphorylation
Based on the discovery that a soluble polypeptide including a nonphosphorylatable form of the cytoplasmic domain is capable of inhibiting in a dominant negative manner, the present invention provides compositions including MT1-MMP inhibitors such as peptide inhibitors, and methods for treating diseases associated with MT1-MMP activity. Such diseases include cancer, arthritis, and heart disease, and vascular disease.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
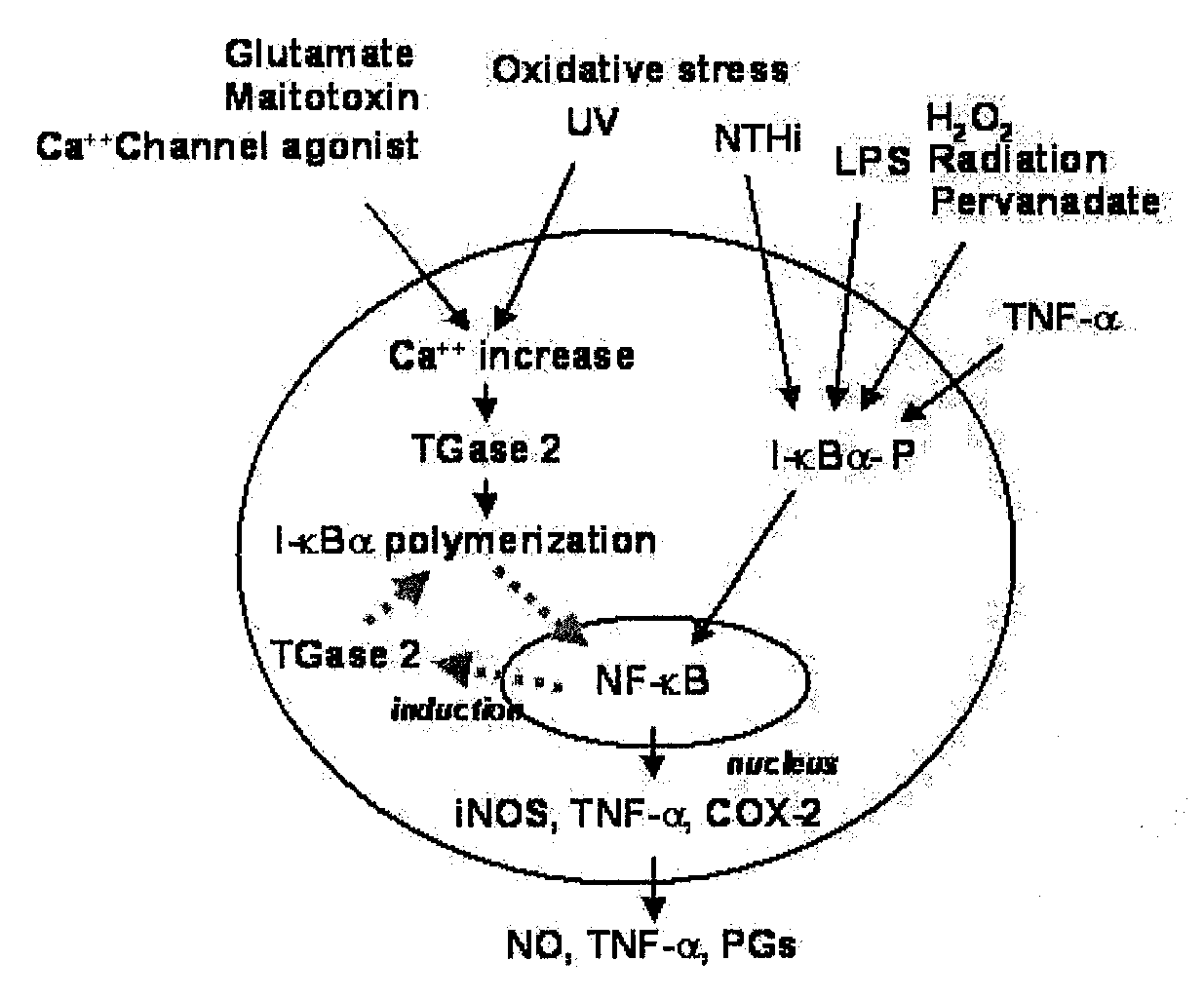
Peptides for Inhibiting Transglutaminase
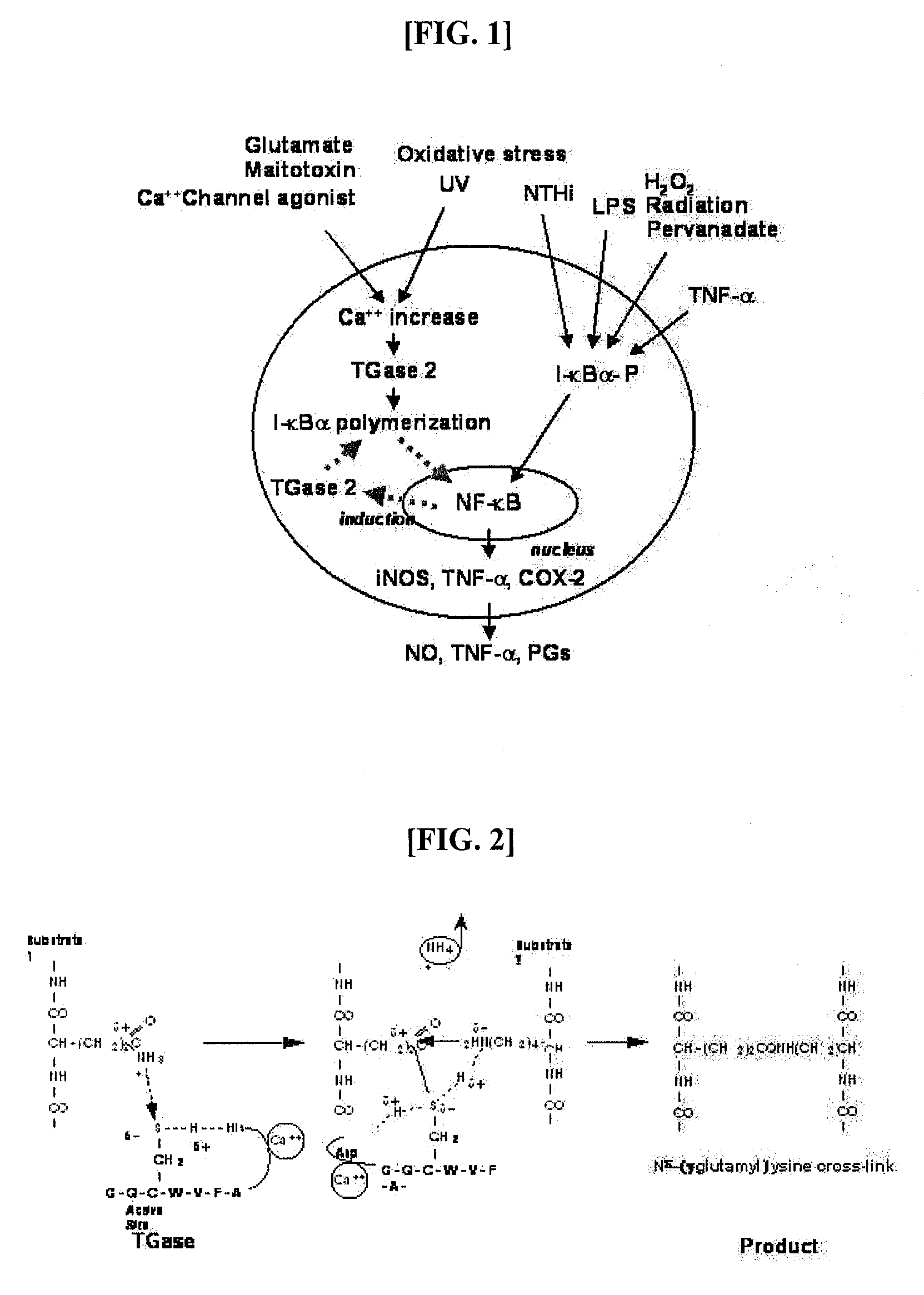
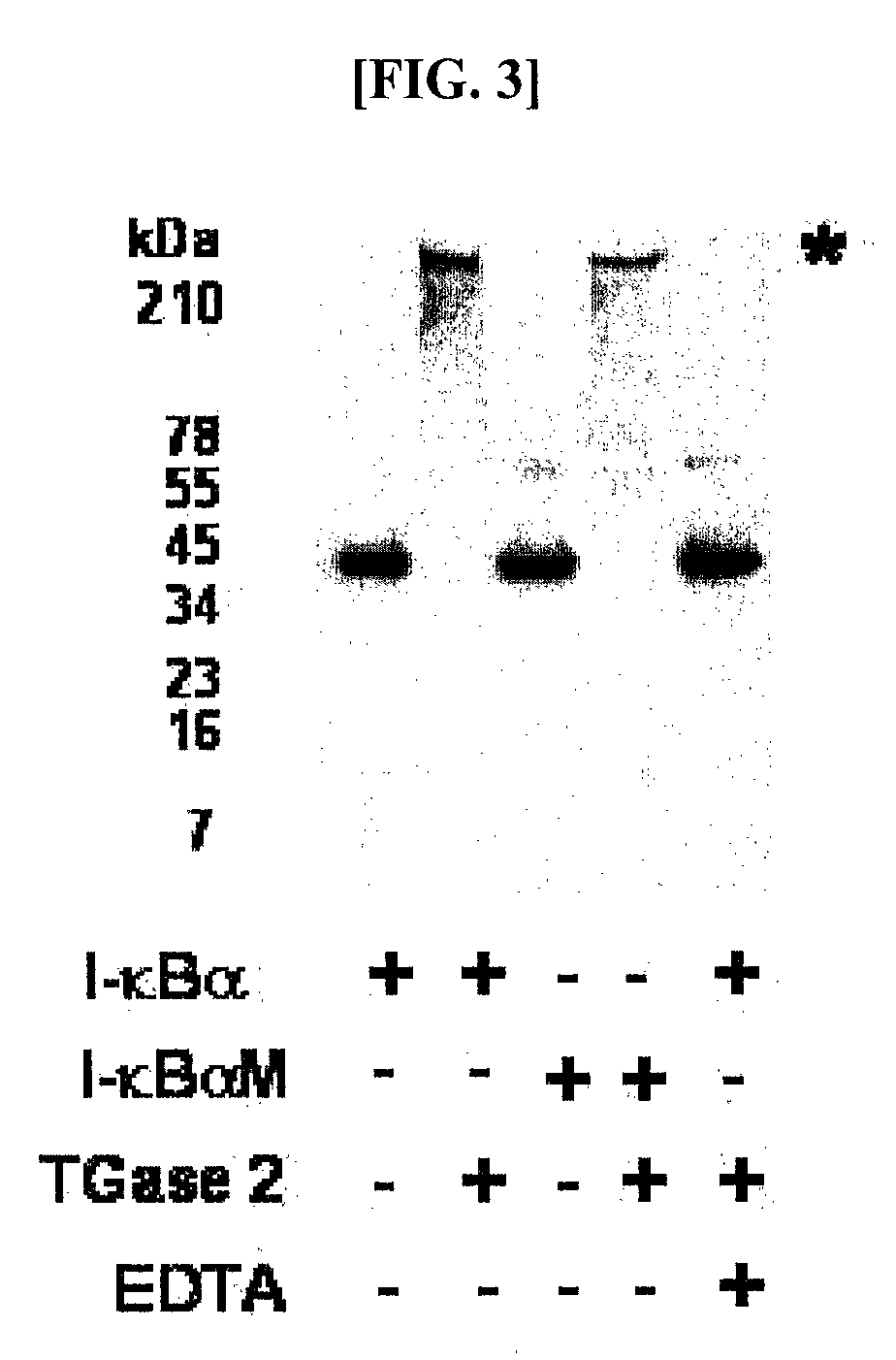
Disclosed herein are transglutaminase peptide inhibitors which have inhibitory activity against transglutaminase, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising one of them as an active ingredient. The inhibitors or the composition is useful in the prevention and treatment of various diseases caused by aberrant transglutaminase activation, including inflammatory diseases and cancers. Also, methods for treating various inflammatory diseases and cancers and for preparing mutant peptides capable of inhibiting transglutaminase are also disclosed.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT
Method to design therapeutically important compounds
InactiveUS6947847B2Long duration of actionMinimize the numberMolecular designAnalogue computers for chemical processesChemical structureBinding site
Disclosed is are methods of generating chemical structures of putative non-peptide inhibitors of biologically-active receptors. The method includes constructing a model of a receptor-ligand complex using empirical three-dimensional data of the receptor-ligand complex. The conformation of the binding site between the receptor and the ligand is then altered to yield novel conformations not exhibited in either the native receptor or the bound receptor. These conformations are then used to generate models of non-peptide chemical structures that are complementary in structure to the altered conformations of the binding site. In this fashion, chemical structures of putative non-peptide inhibitors of the altered conformation are revealed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com