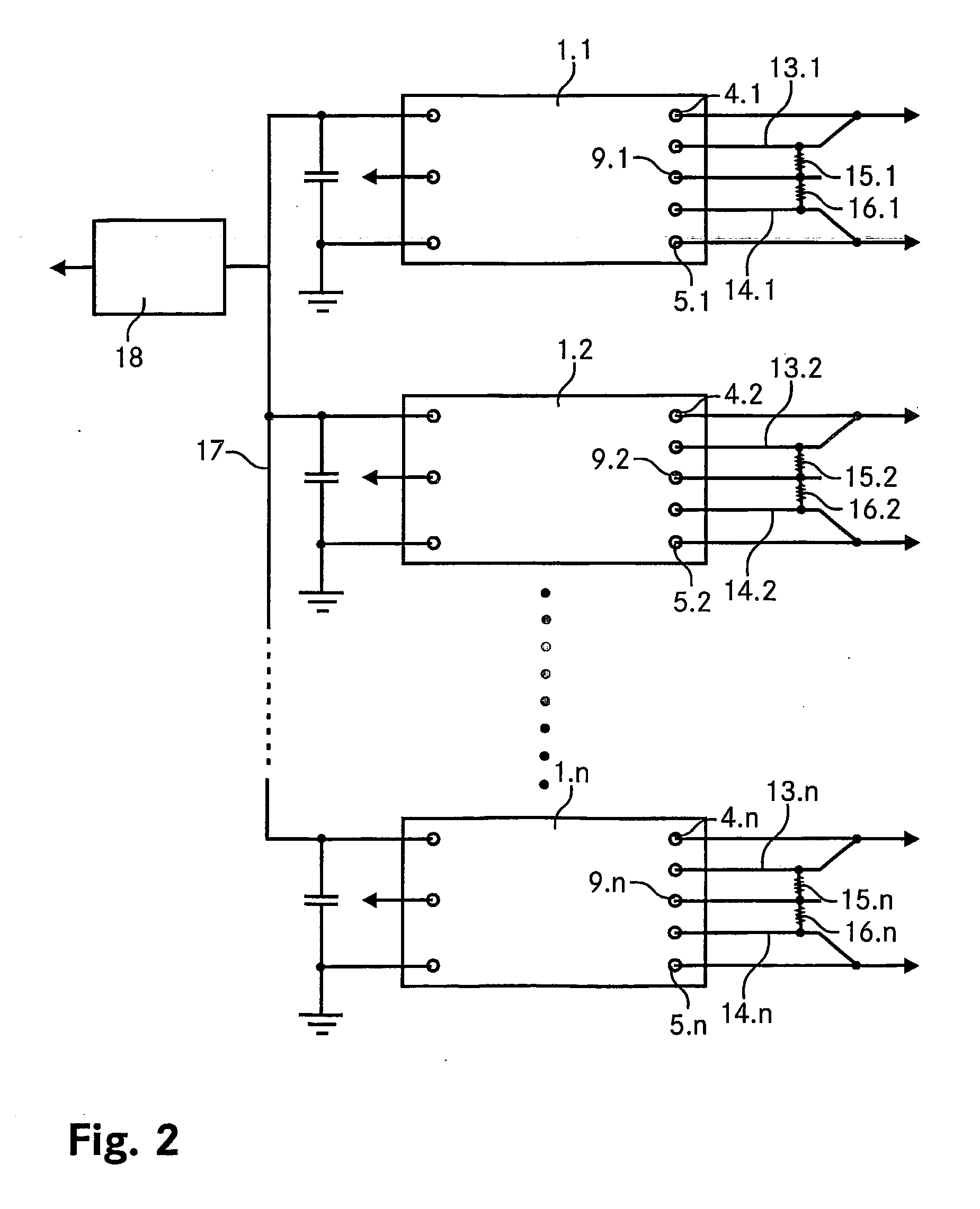
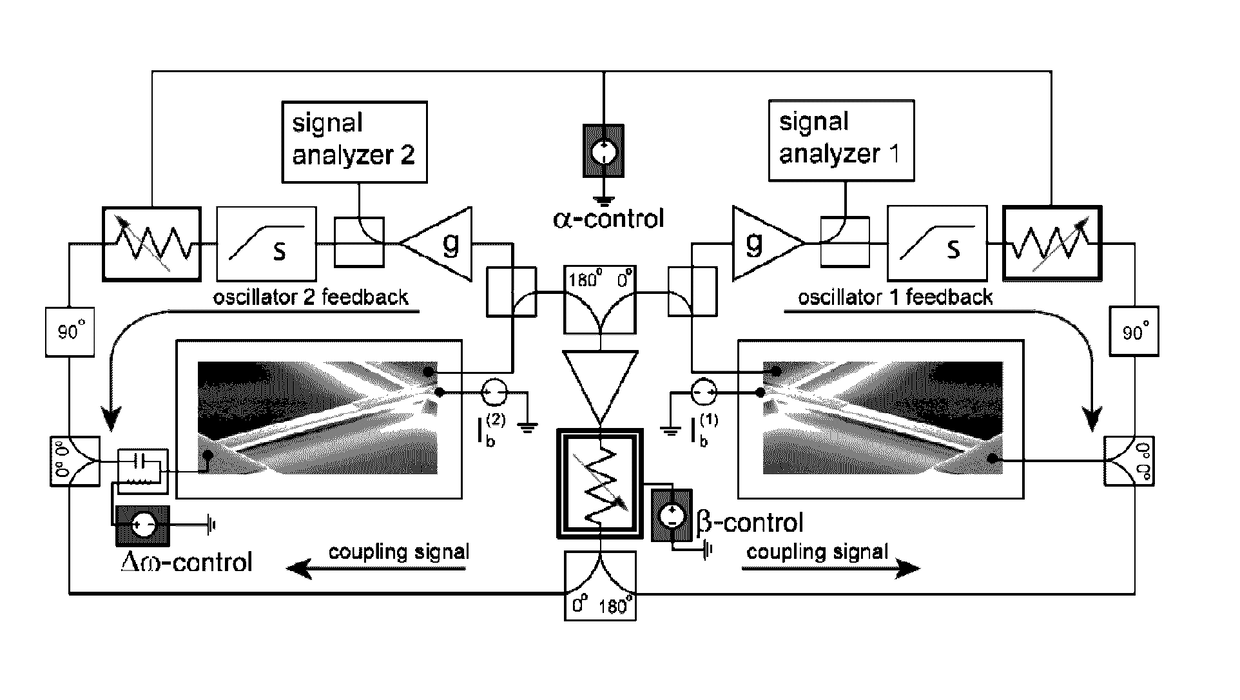
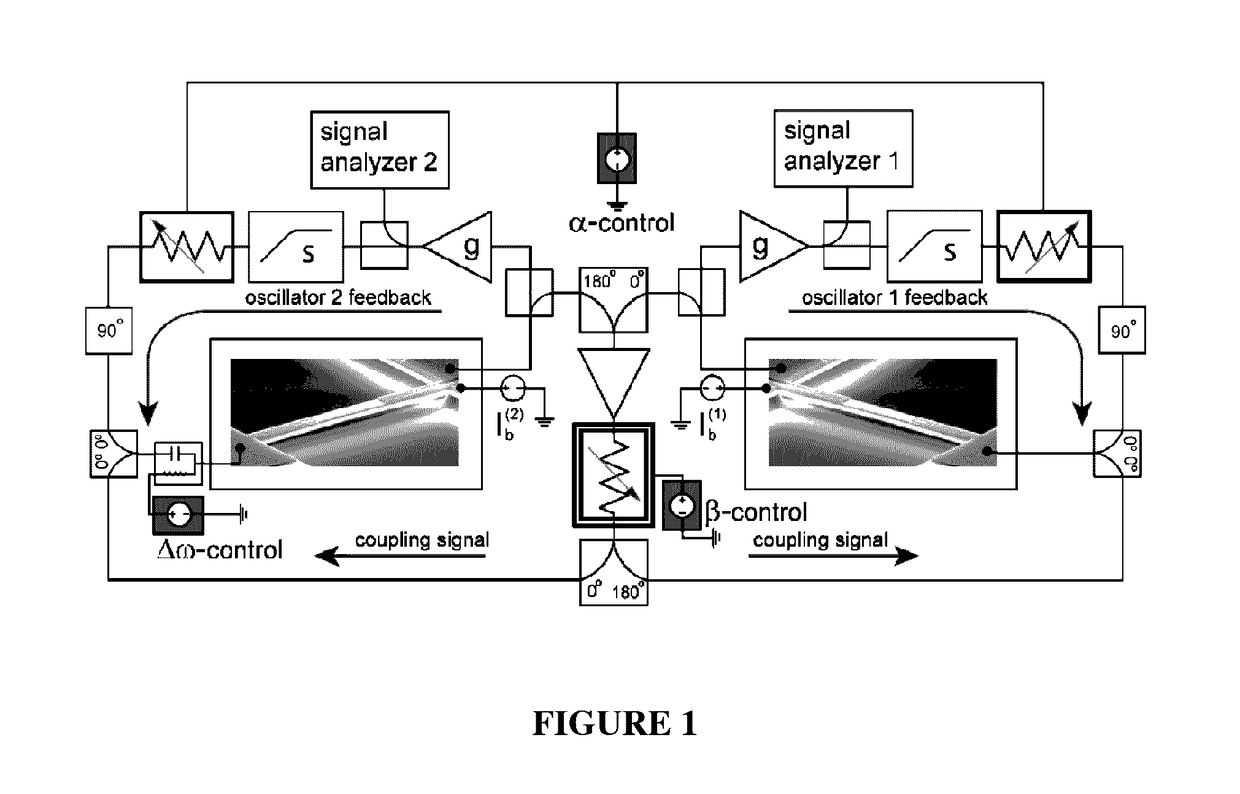
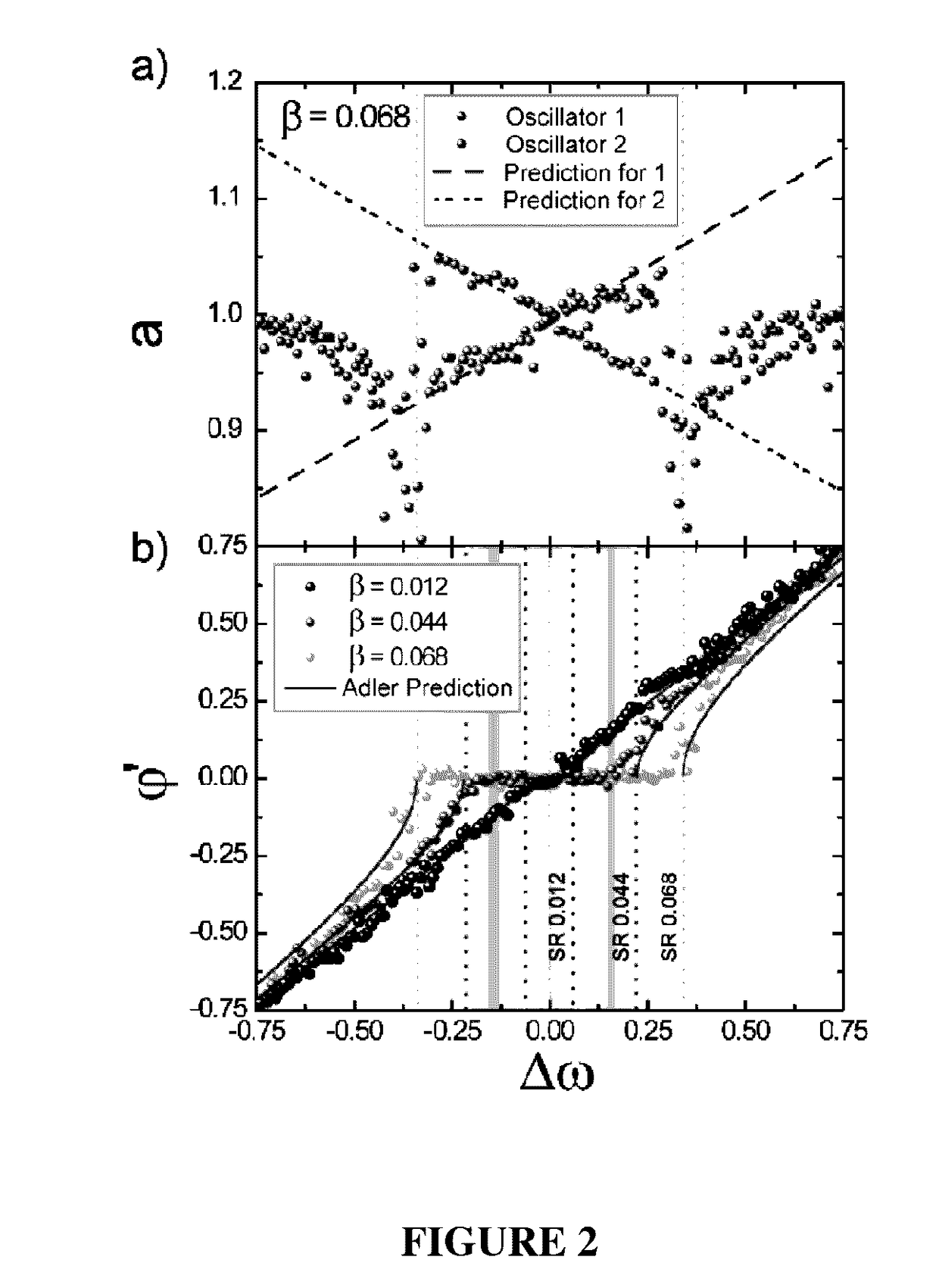
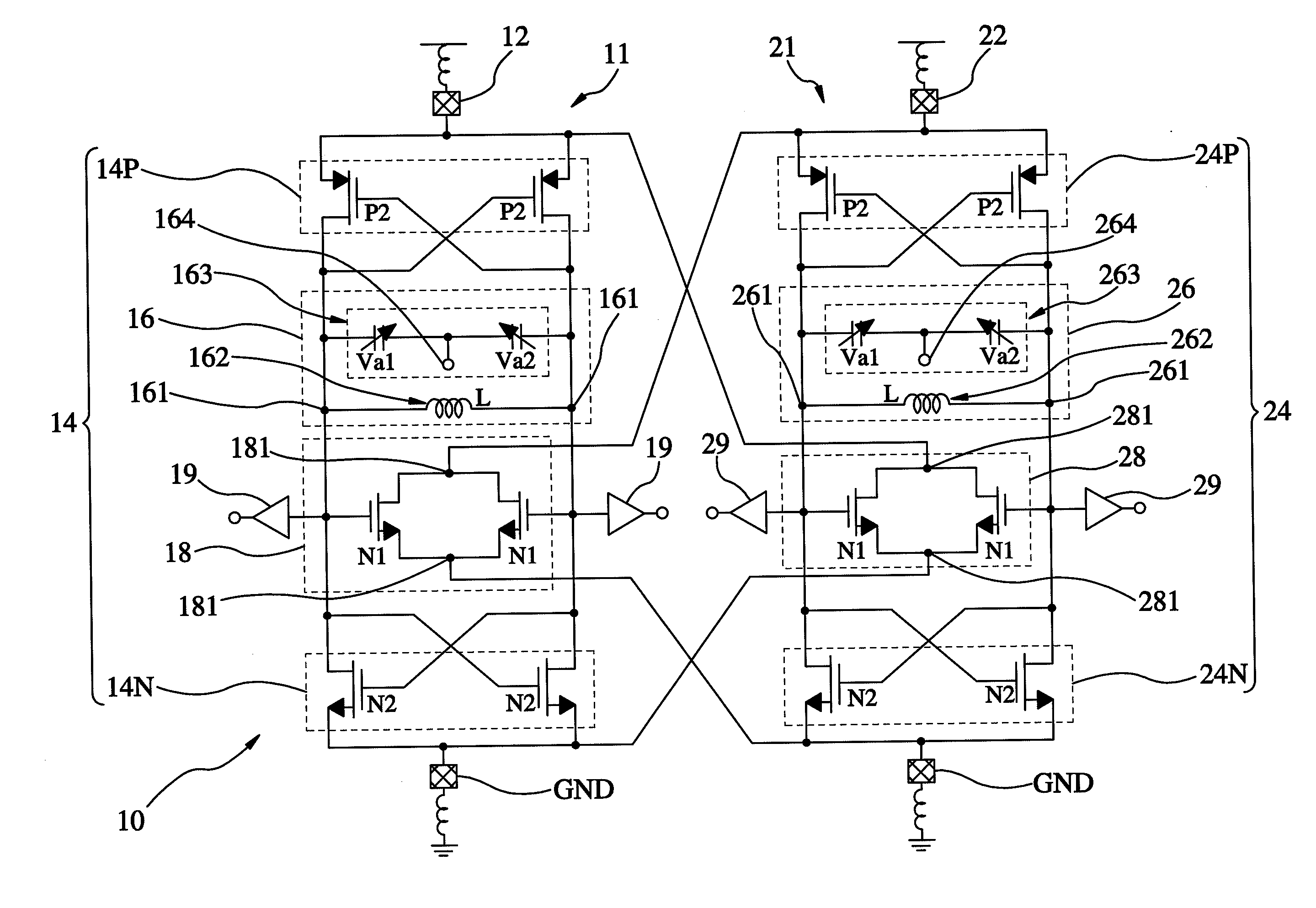
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Oscillator sync" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
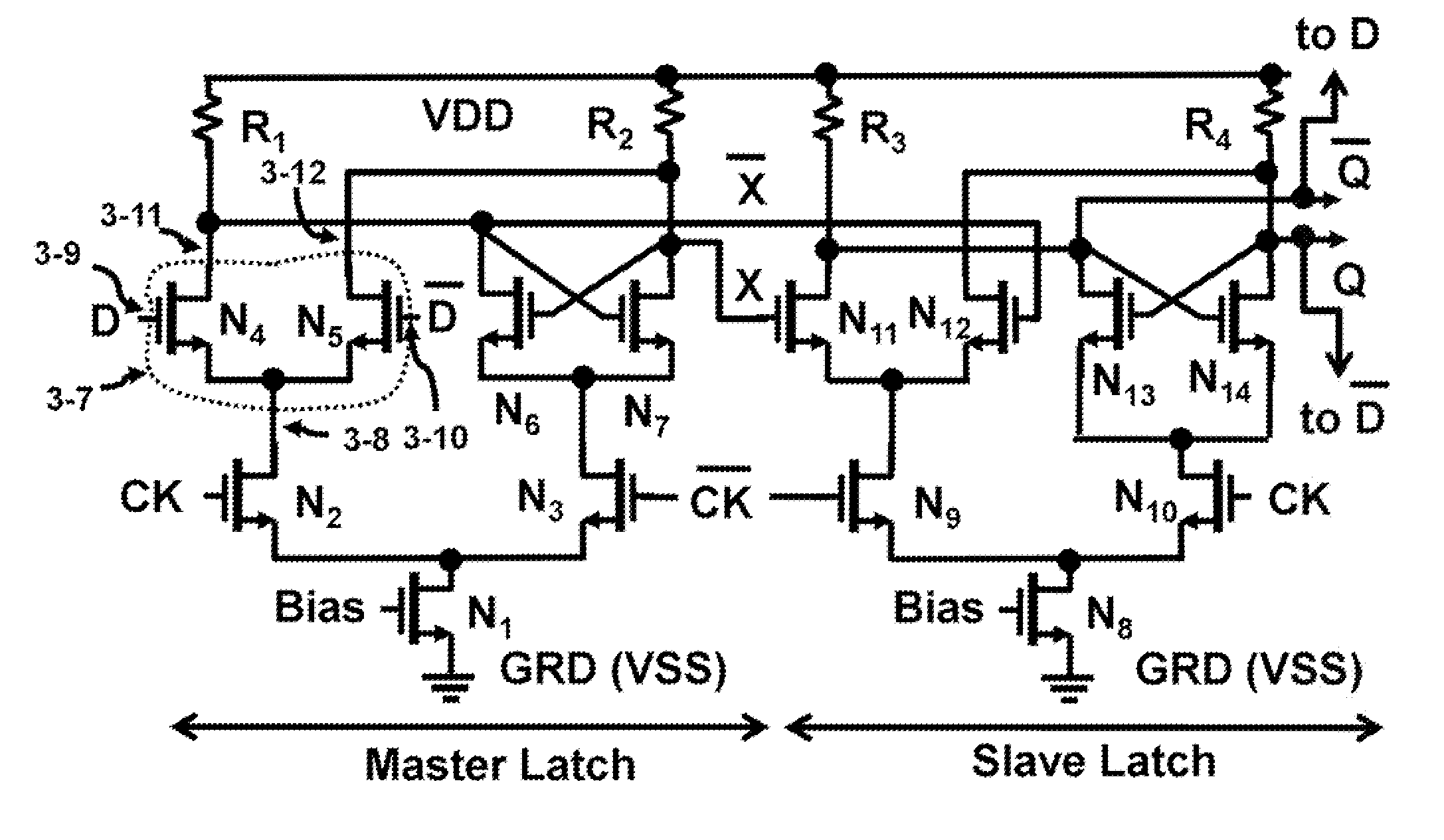
Oscillator sync is a feature in some synthesizers with two or more VCOs, DCOs, or "virtual" oscillators. As one oscillator finishes a cycle, it resets the period of another oscillator, forcing the latter to have the same base frequency. This can produce a harmonically rich sound, the timbre of which can be altered by varying the synced oscillator's frequency. A synced oscillator that resets other oscillator(s) is called the master; the oscillators which it resets are called slaves. There are two common forms of oscillator sync which appear on synthesizers: Hard Sync and Soft Sync. According to Sound on Sound journalist Gordon Reid, oscillator sync is the least understood feature for many users of a synthesizer.
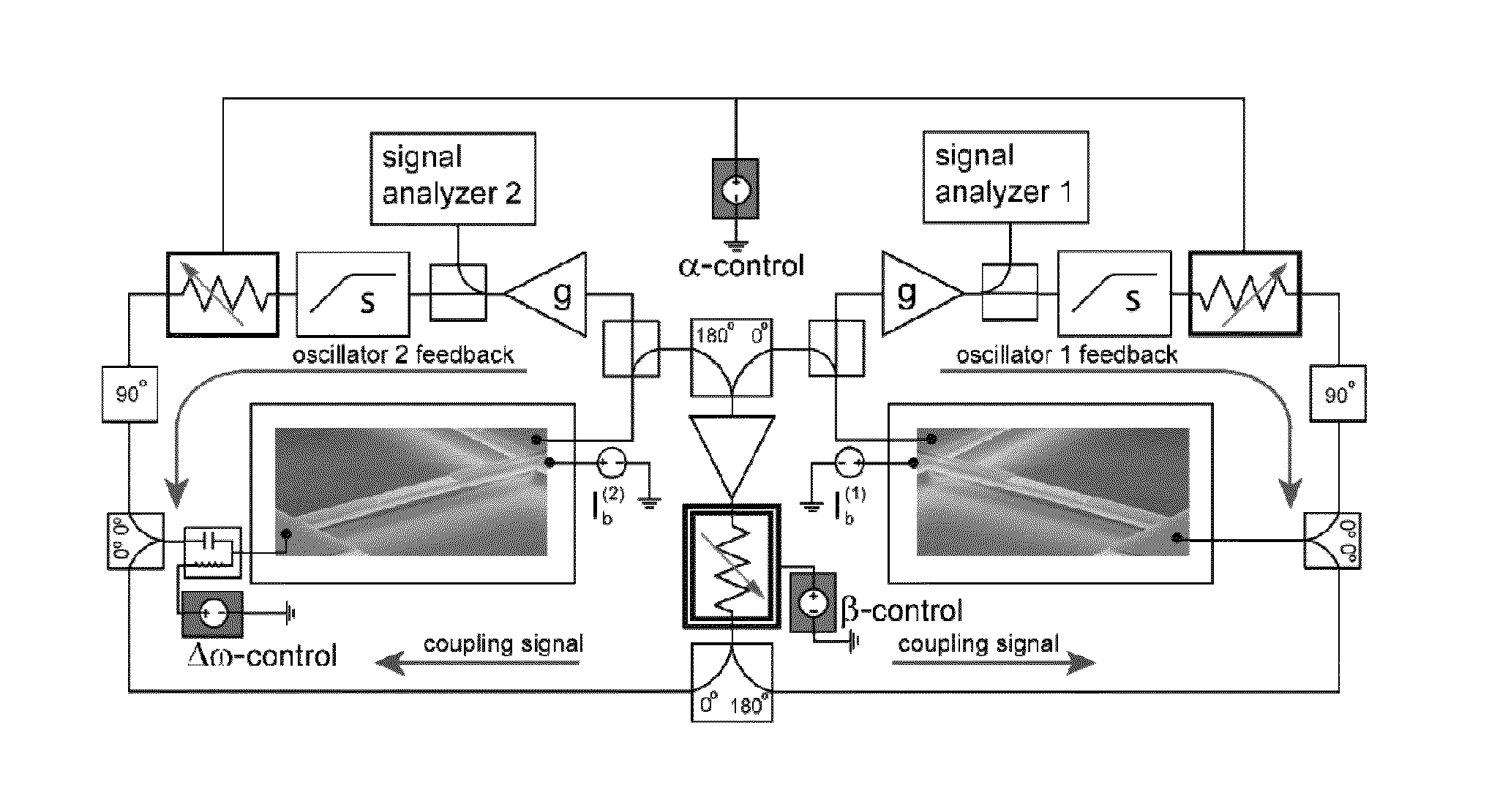
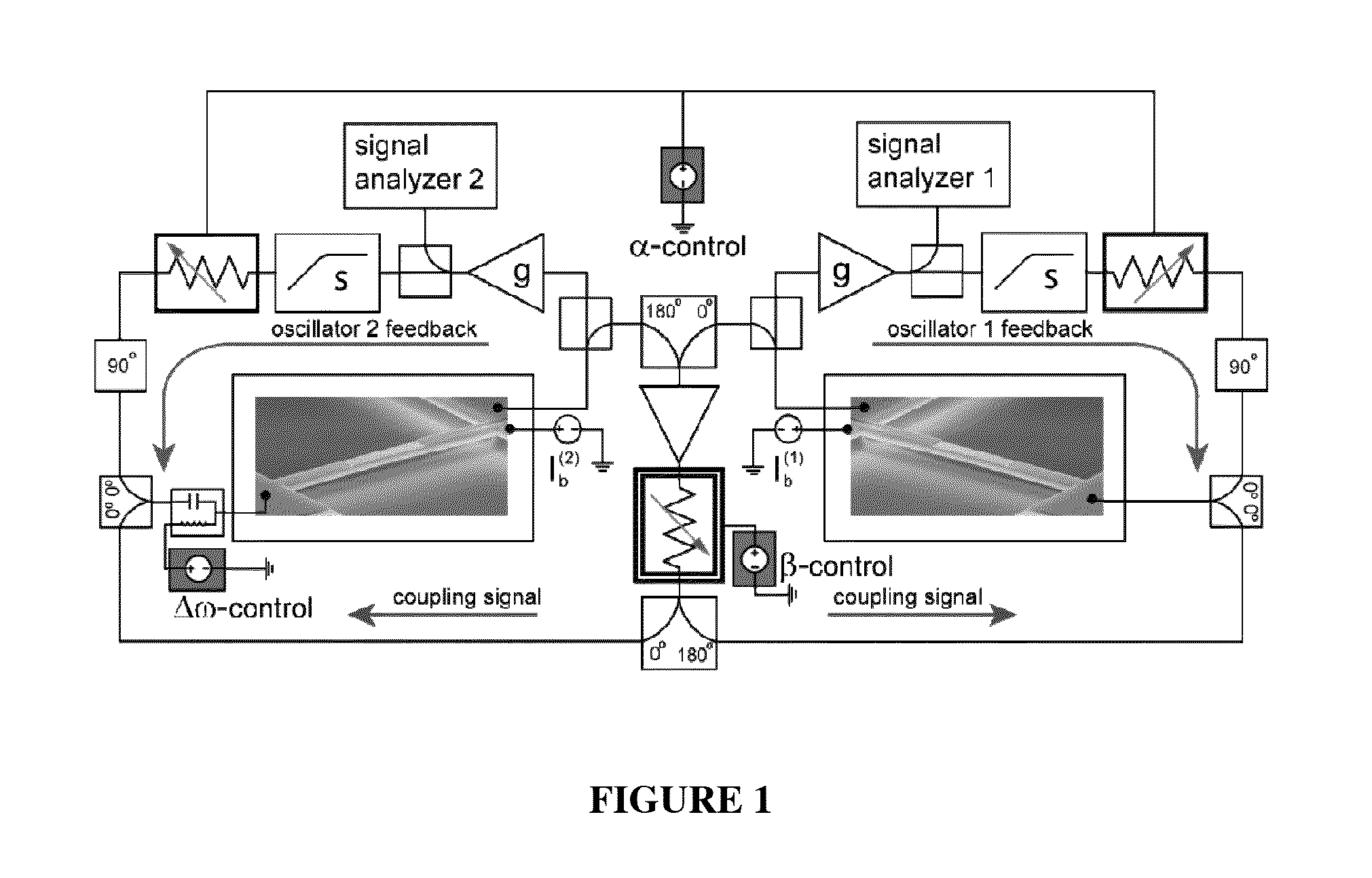
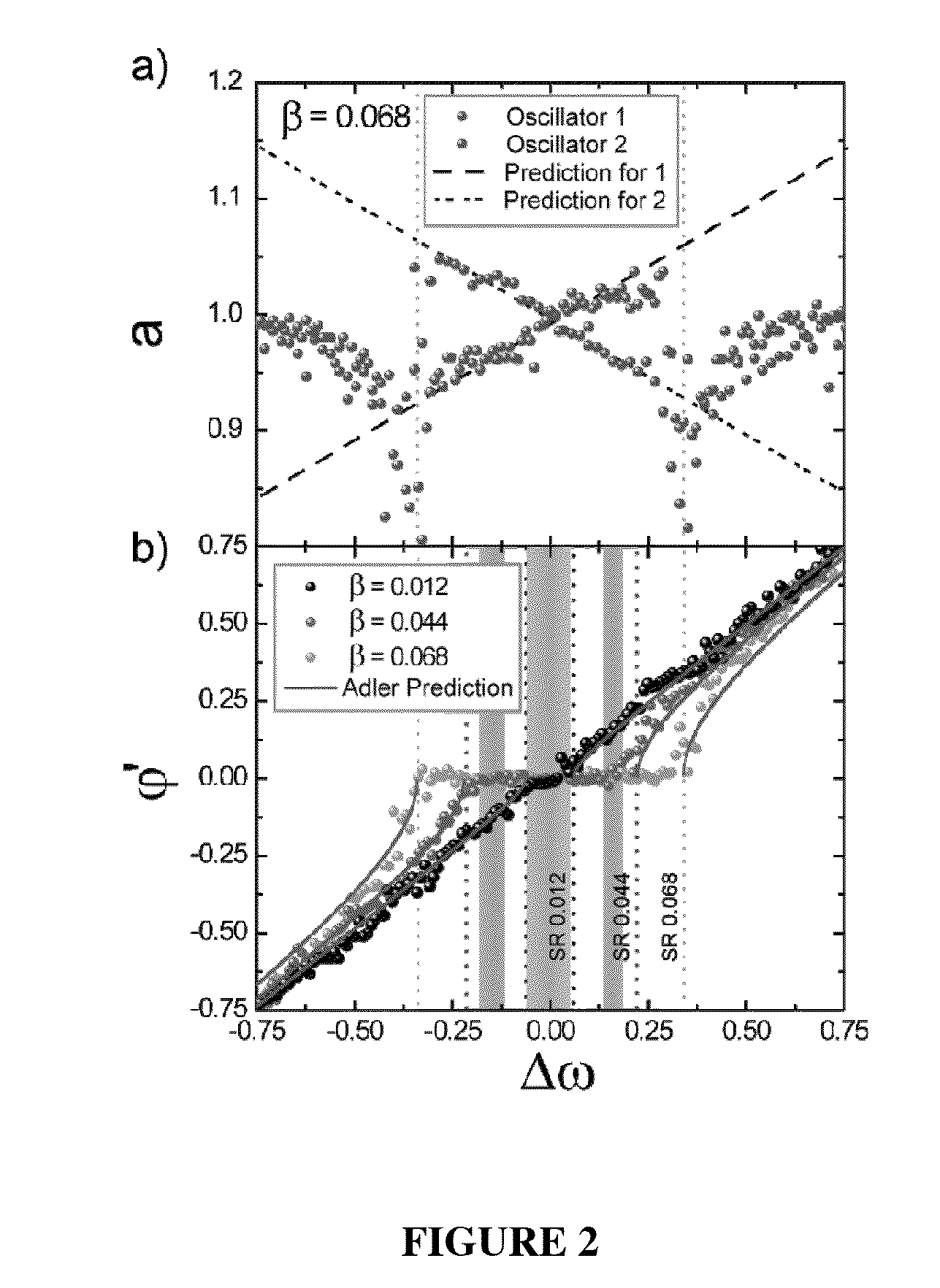
Synchronization of nanomechanical oscillators
ActiveUS20140176203A1Good for observationEasy to controlAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPulse automatic controlPhase noiseOscillator network
Synchronization of oscillators based on anharmonic nanoelectromechanical resonators. Experimental implimentation allows for unprecedented observation and control of parameters governing the dynamics of synchronization. Close quantitative agreement is found between experimental data and theory describing reactively coupled Duffing resonators with fully saturated feedback gain. In the synchonized state, a significant reduction in the phase noise of the oscillators is demonstrated, which is key for applications such as sensors and clocks. Oscillator networks constructed from nanomechanical resonators form an important laboratory to commercialize and study synchronization—given their high-quality factors, small footprint, and ease of co-integration with modern electronic signal processing technologies. Networks can be made including one-, two-, and three-dimensional networks. Triangular and square lattices can be made.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
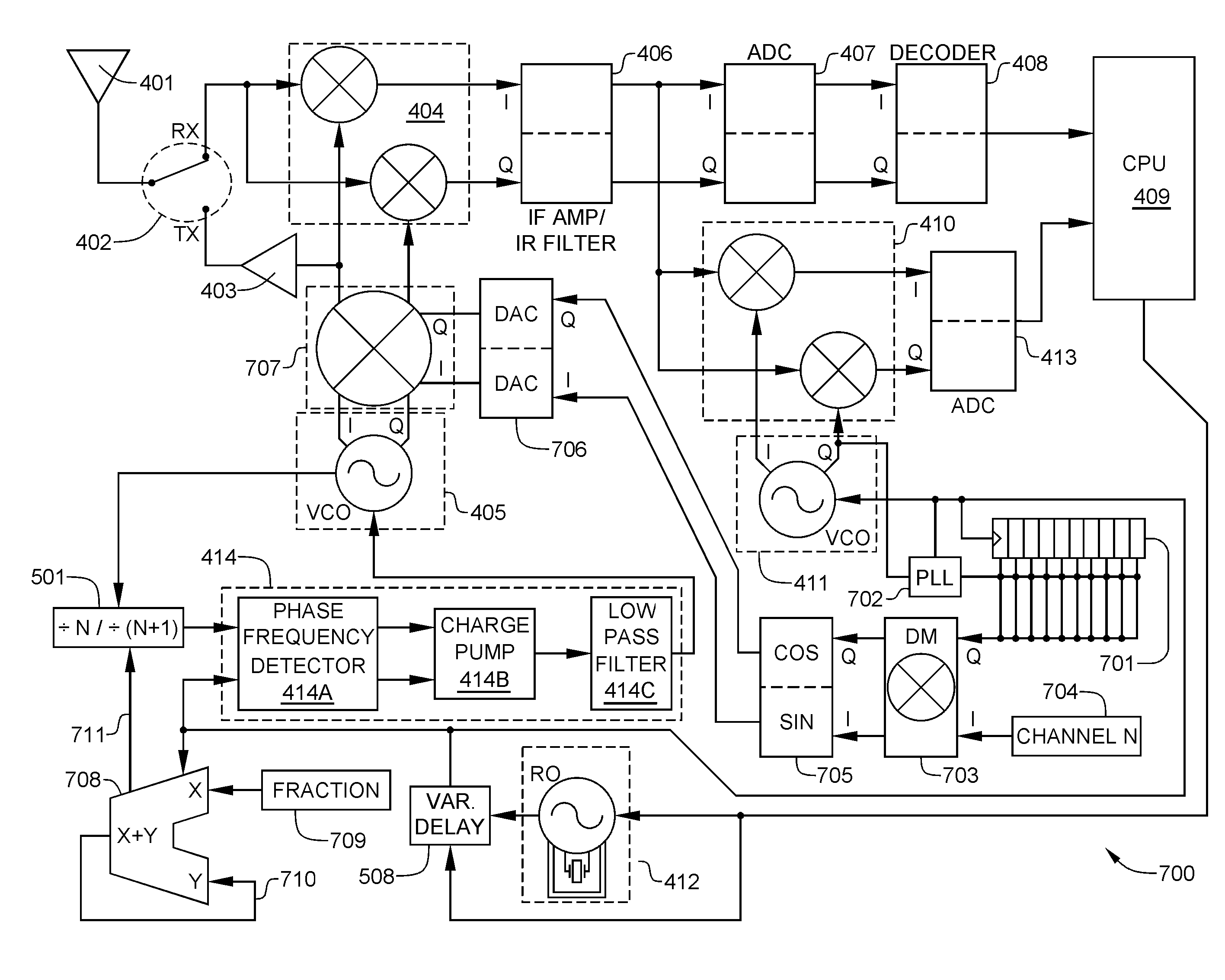
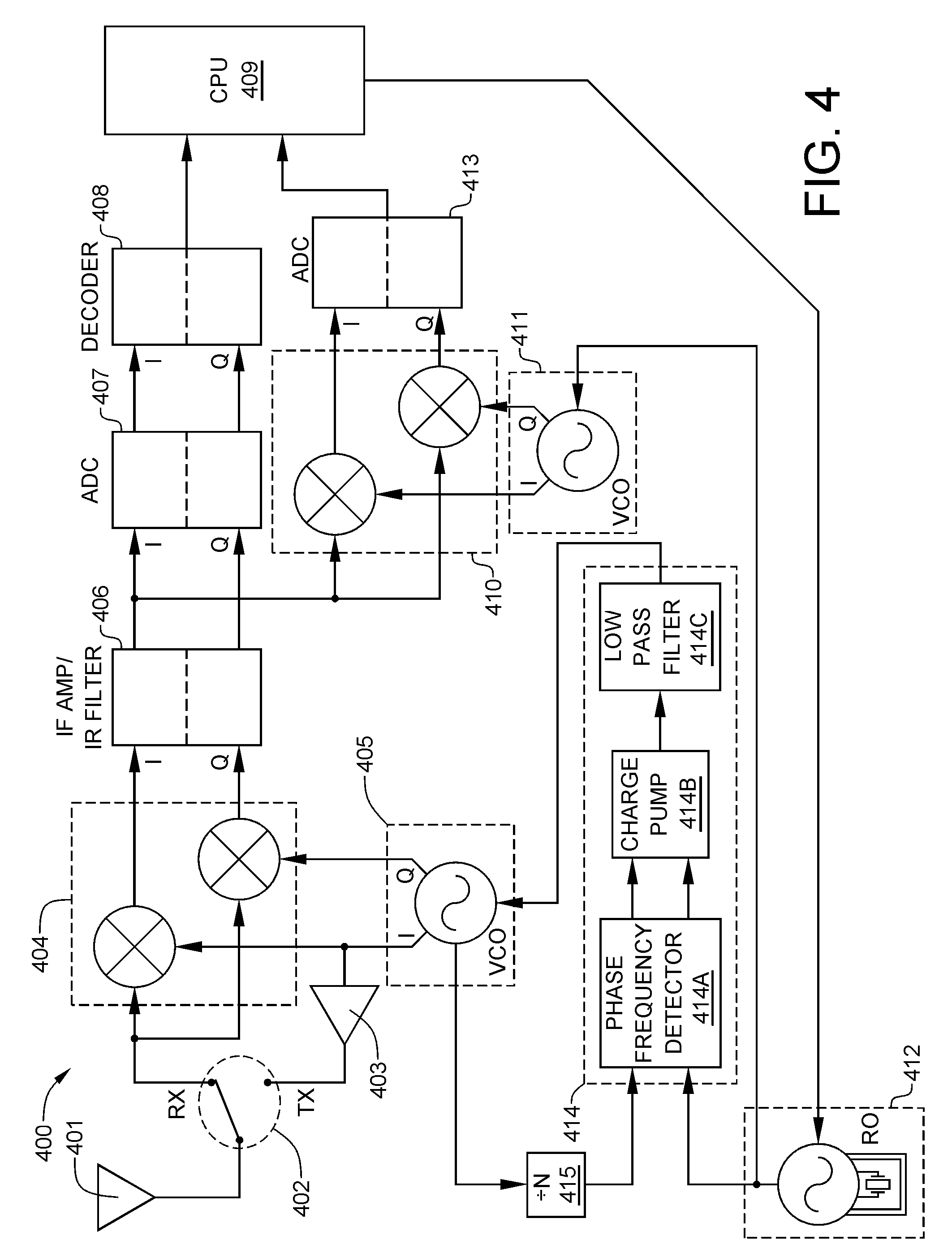
Synchronization of transmitter and receiver frequencies in multiaccess networks
InactiveUS7103374B2Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexFrequency spectrumRadio networks
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for integrating the operation of a plurality of radio networks. The plurality of radio networks may utilize a common frequency spectrum. The radio center frequencies are adjusted so that frequency drift in relation to each radio network is reduced. Also, system information about the plurality of radio networks may be sent on a radio channel that is associated with one of the radio networks. An oscillator synchronizer synchronizes a first reference oscillator that is associated with a first radio network and a second reference oscillator that is associated with a second radio network in order to adjust radio center frequencies. With a variation of the embodiment, a reference oscillator of one of the radio network adjusts center frequencies for radios that are associated with the other radio network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
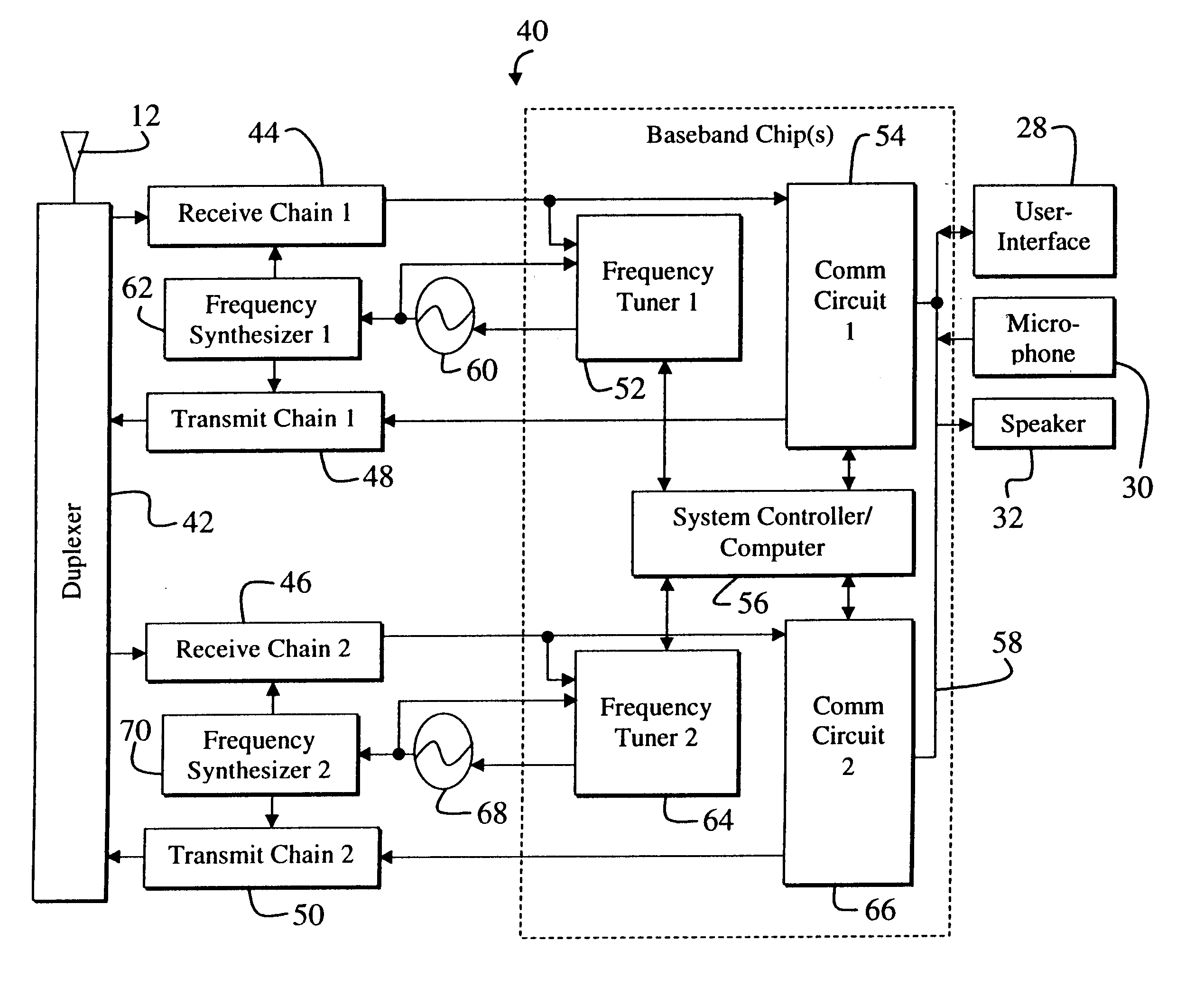
Multi-mode communications system with efficient oscillator synchronization
InactiveUS6466803B1Substation equipmentRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemFrequency synthesizer
A system for synchronizing a second receive chain relative to a first receive chain in a multi-mode communication system. The system includes a first circuit that measures a first frequency associated with the first receive chain. A second circuit adjusts a second frequency associated with the second receive chain based on the first frequency and provides a desired second frequency to the second receive chain in response thereto. In a specific embodiment, the first circuit includes a first counter that receives a signal associated with an output of a first oscillator and provides a measurement of the first frequency in response thereto. The second circuit includes a frequency synthesizer for providing the desired second frequency in response to a frequency control or reference signal. Another circuit generates the control or reference signal based on a difference between the second frequency and the first frequency. A second counter receives a signal characterized by the second frequency and provides the second frequency in response thereto.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Centralized synchronization for wireless networks
InactiveUS7324559B2Undo distortion effectAccurate samplingSynchronisation arrangementFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio networksDigital radio
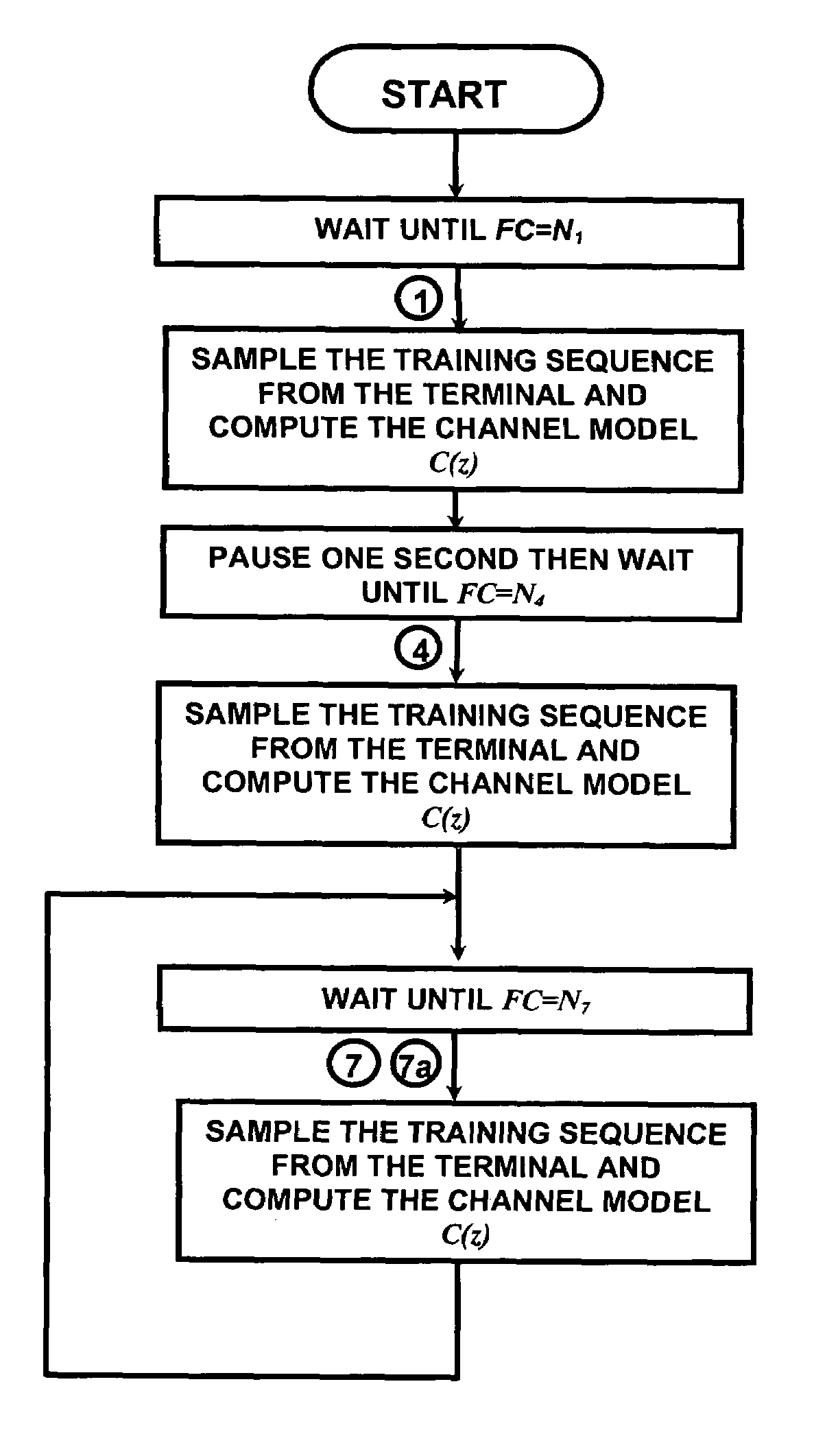
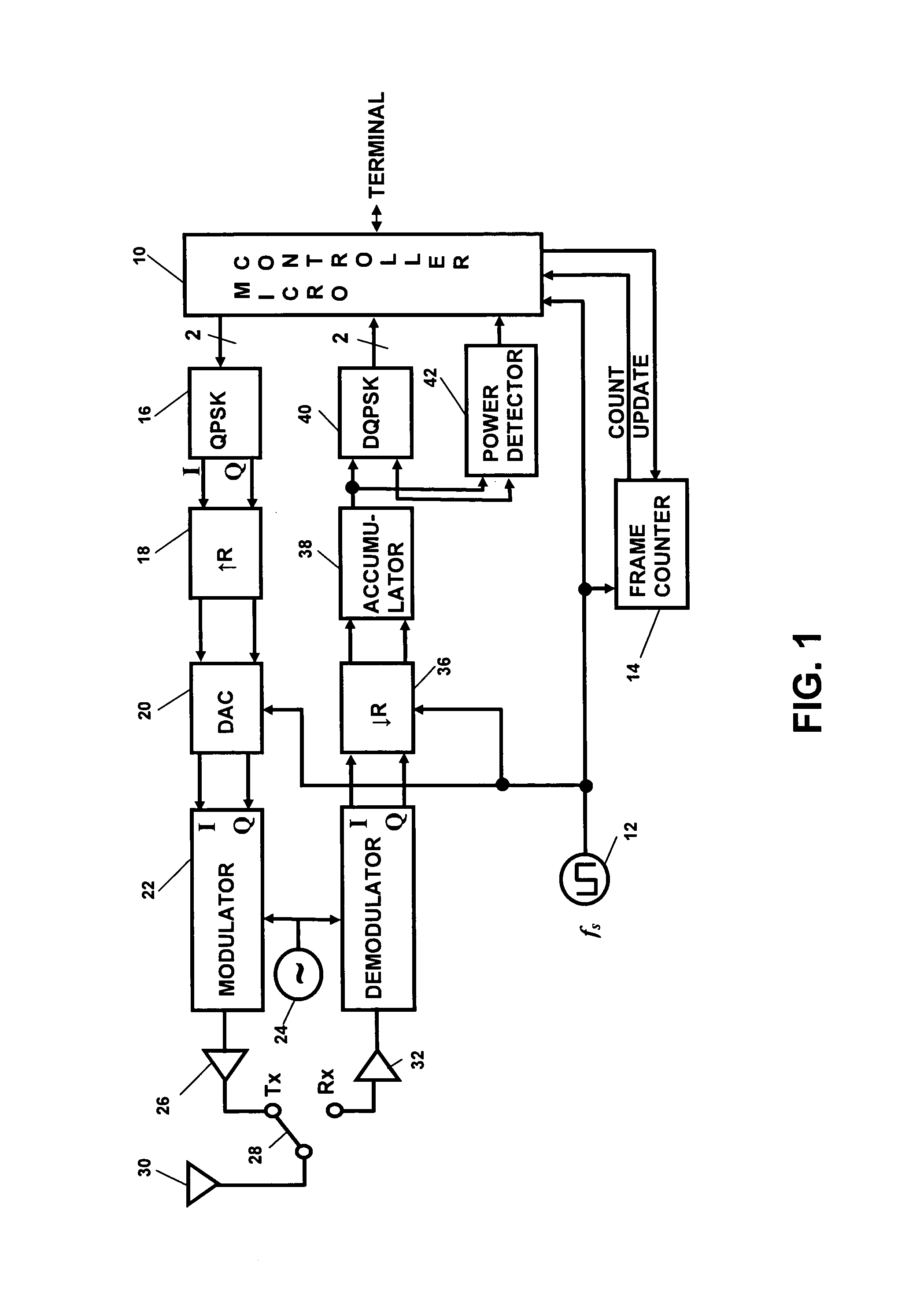
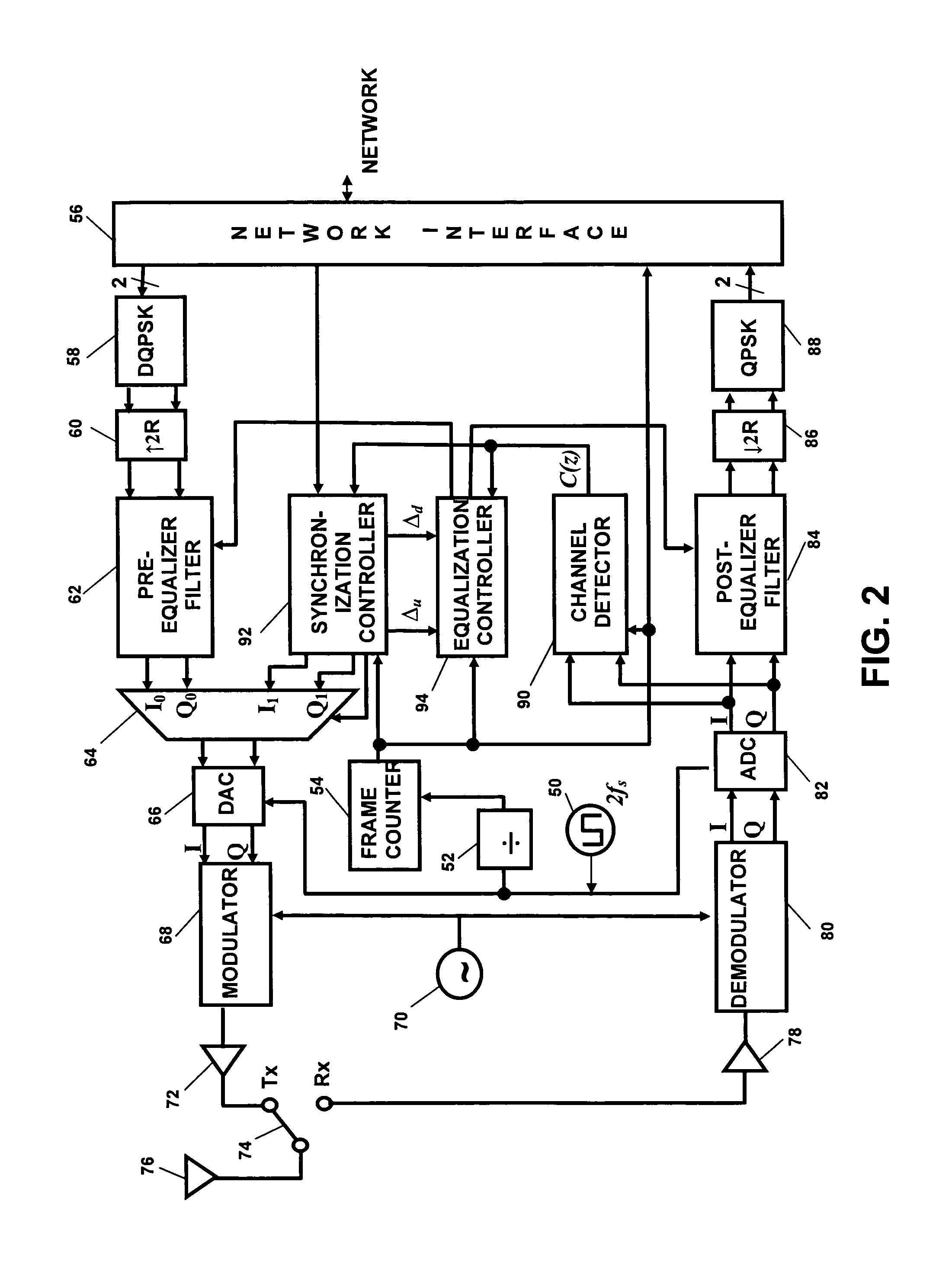
This invention synchronizes the sample clocks of an entire wireless network from a single central base station. Unlike a conventional digital radio network where every terminal must have a synchronization circuit in its receiver to adjust the sample clock, each of the radio terminals in this network is clocked from an independent free-running oscillator. For each terminal, the base station learns the frequency and phase of the oscillator by exchanging a special set of signals: first a vernier signal to determine the initial time and frequency offset, and then an early-late signal to track changes in the oscillator. Once the base station is synchronized to the terminal's oscillator, it can determine the absolute path delay between itself and the terminal and correct for the delay using an equalizer. Signals received from the terminal are corrected after the signal arrives at the base station. Signals sent to the terminal are corrected within the base station before they are transmitted so they arrive at the terminal at the precise time that the terminal's free running oscillator takes a sample.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
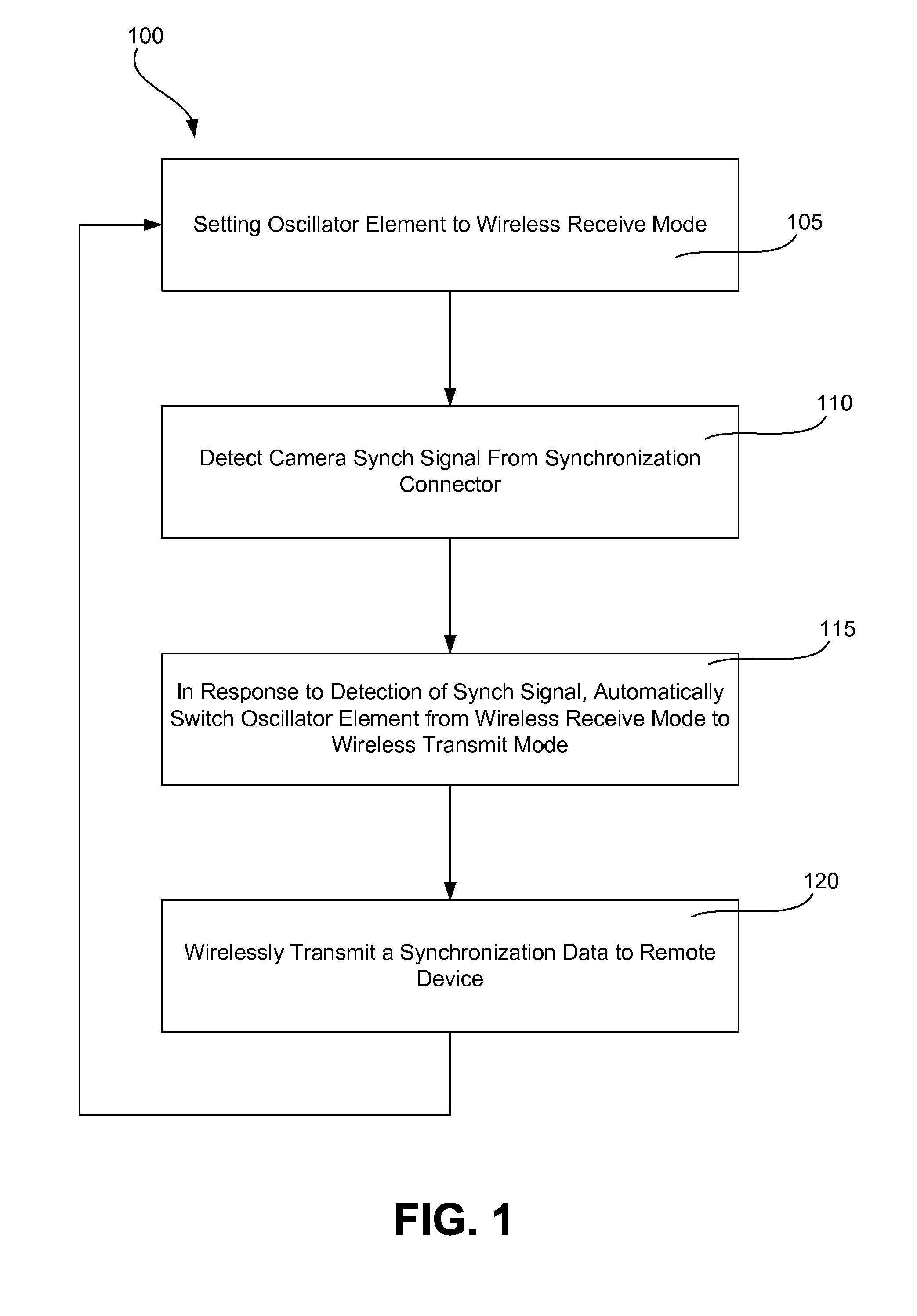
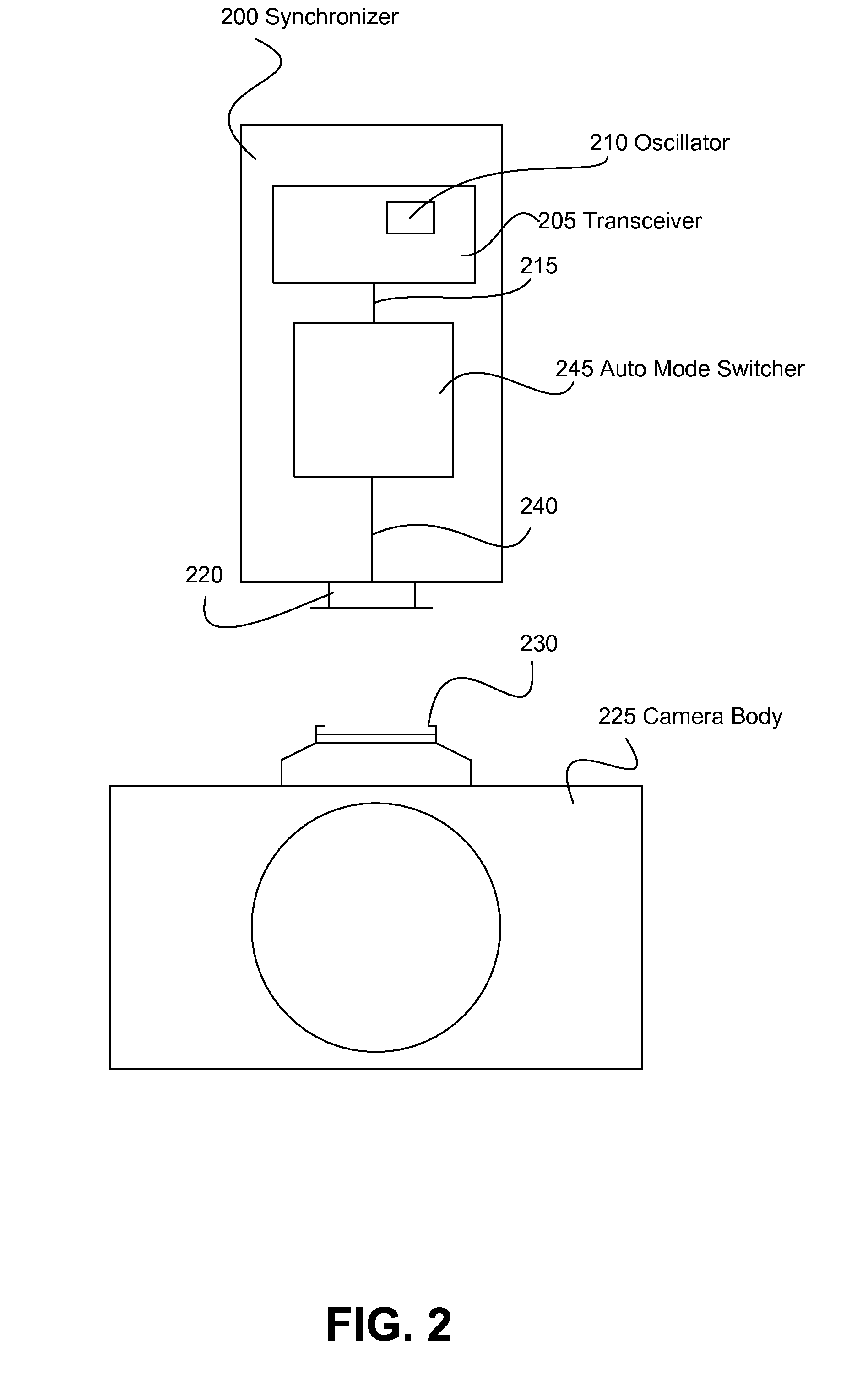
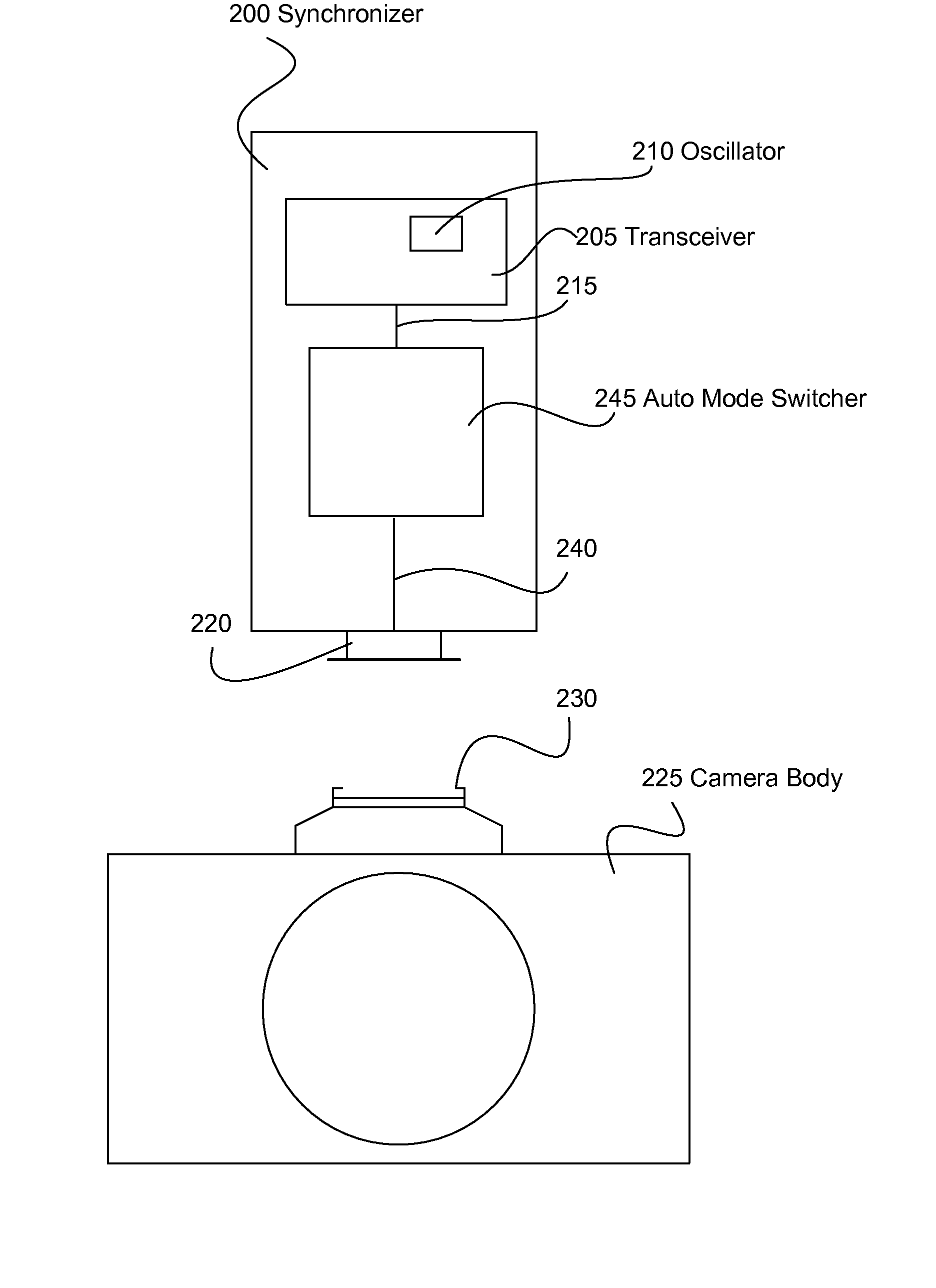
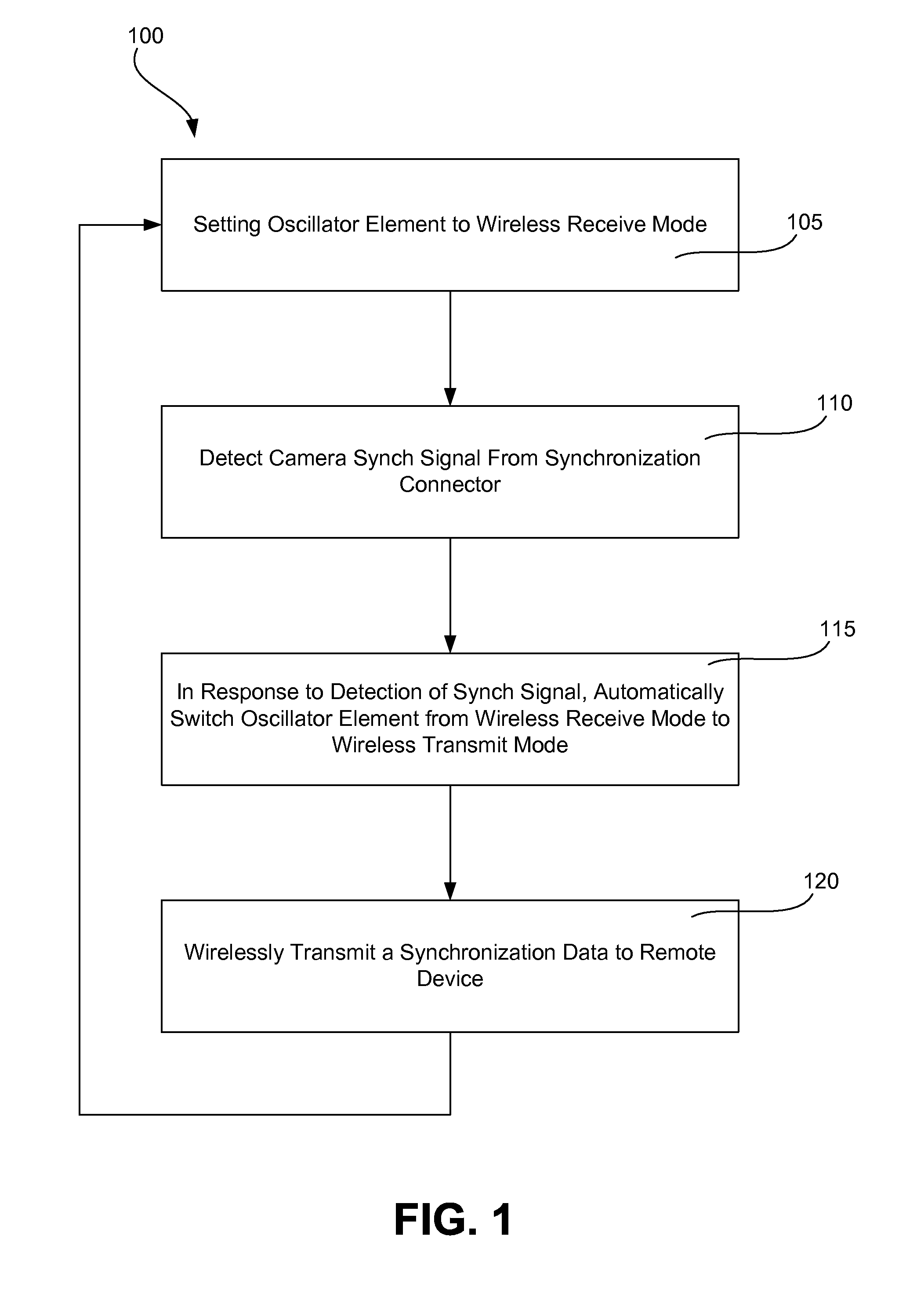
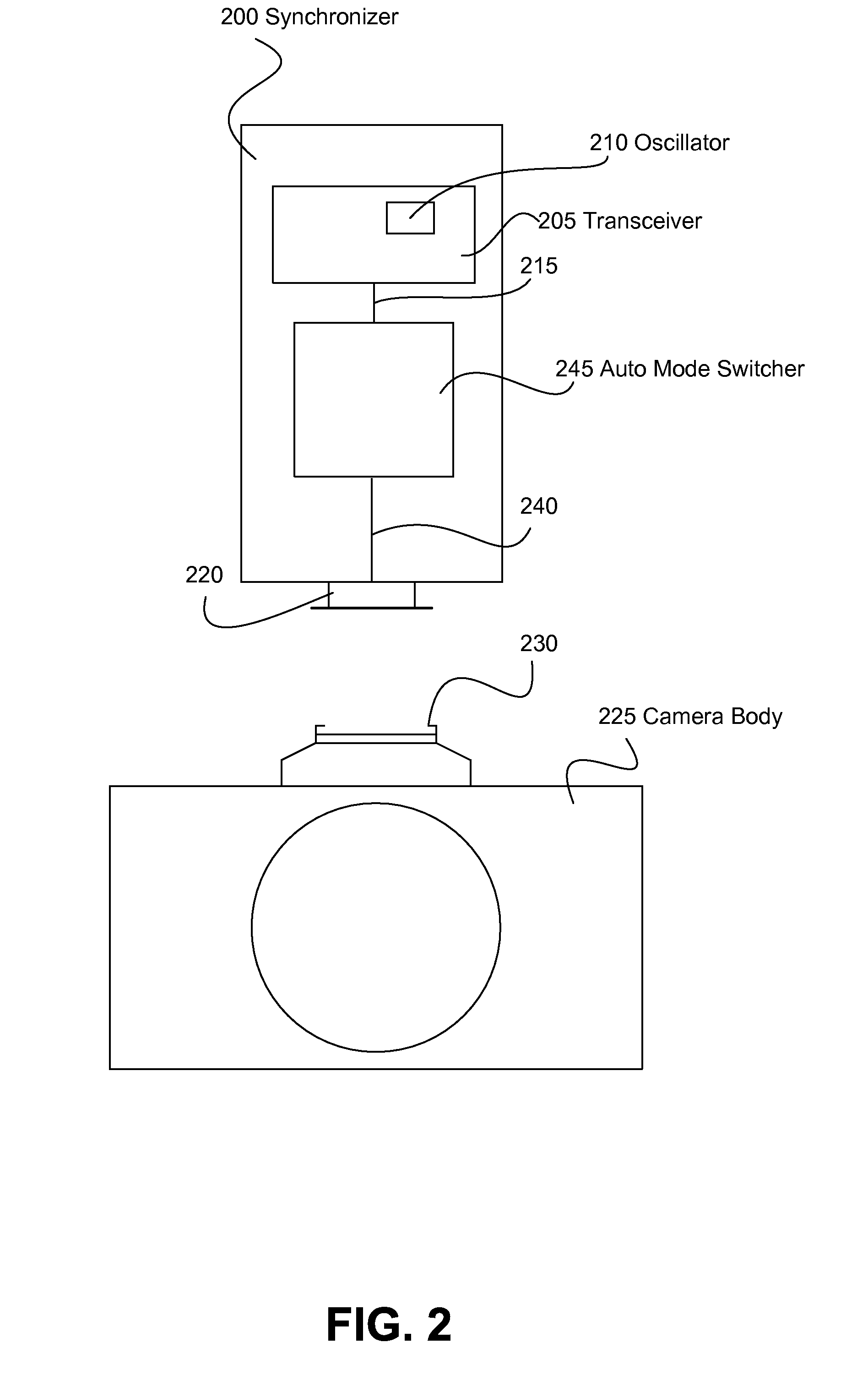
Wireless Camera Flash Synchronizer System and Method
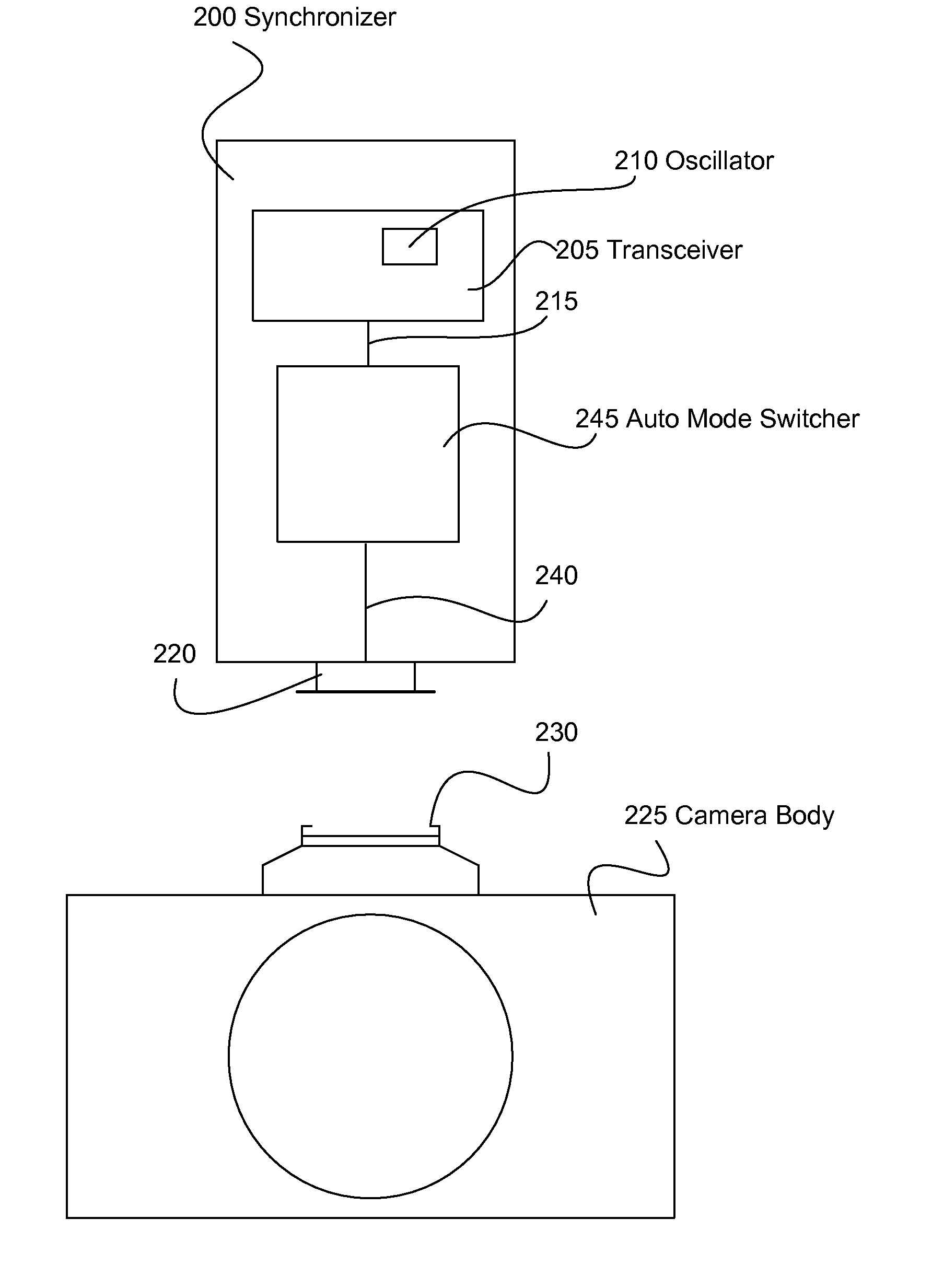
A single oscillator synchronizer system and method that automatically switches from a wireless receive mode of the oscillator to a wireless transmit mode of the oscillator upon the detection of a synchronization (synch) signal of a camera body. In one example, a method of wirelessly communicating a camera synchronization from a camera body to a remote device with a wireless camera flash synchronizer connected to a synchronization connector of the camera body, the wireless camera flash synchronizer including a transceiver having an oscillator element with a wireless receive mode and a wireless transmit mode, the oscillator element configured to be in only one of the wireless receive mode and wireless transmit mode at a time is provided. In another example, a wireless camera flash synchronizer that automatically switches from a wireless receive mode to a wireless transmit mode upon detection of a synch signal of a camera body is provided.
Owner:LAB PARTNERS ASSOC INC
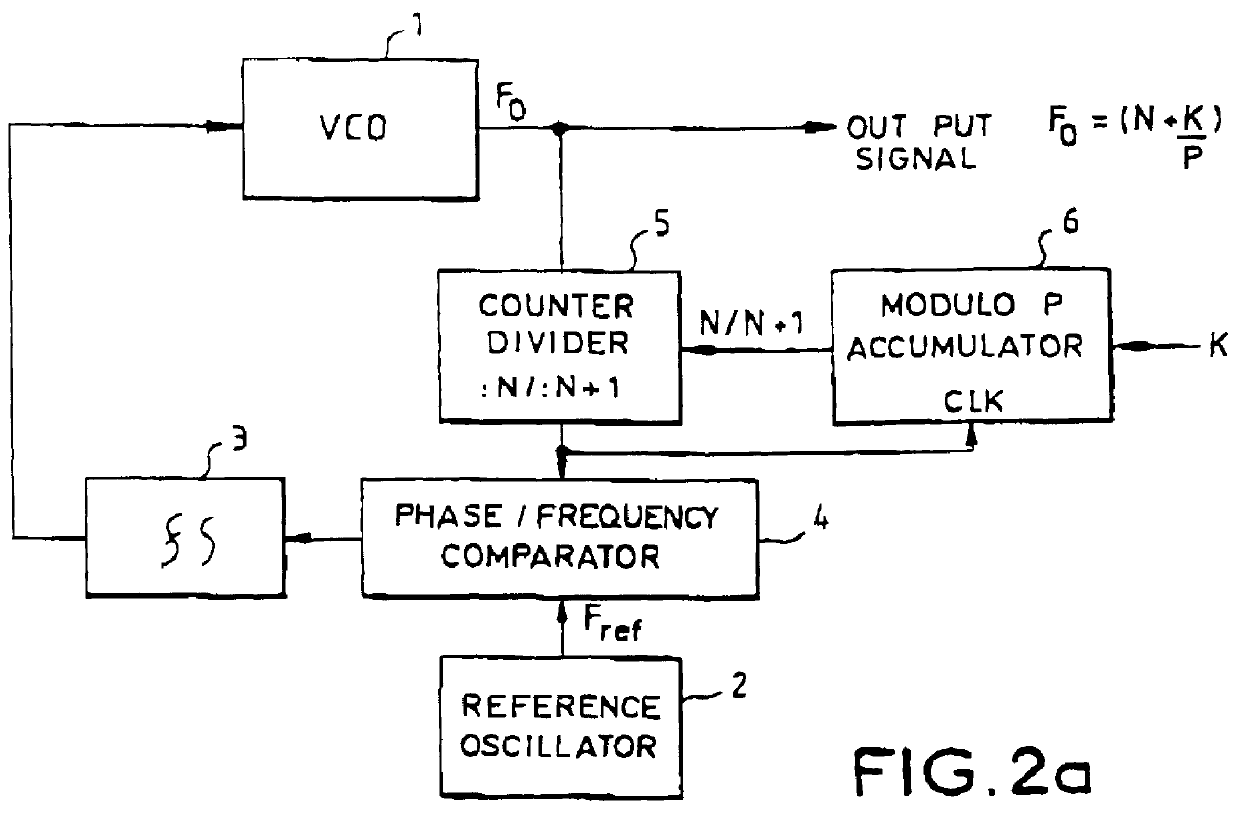
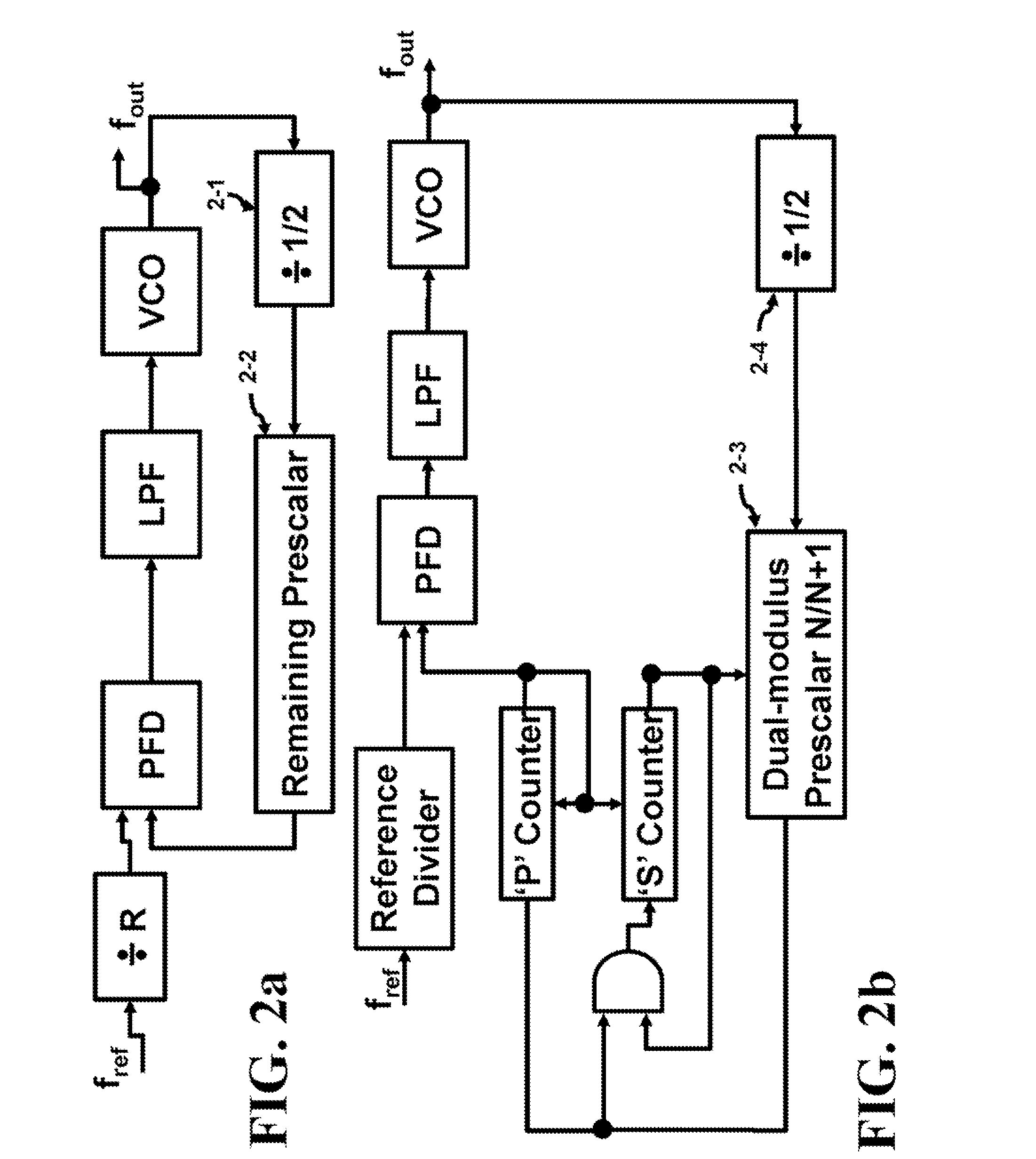
Fractional phase-locked loop coherent frequency synthesizer
InactiveUS6107843APulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersPresent dayFrequency synthesizer
Present-day single or multiple fractional phase-locked loop frequency synthesizers are not phase coherent for they use a digital accumulator modulo a number P with a variable increment K, whose state is a function of the history of the change in values that have been imposed on the increment. This lack of phase coherence rules out the use of these synthesizers in certain fields such as that of Doppler radars. A novel type of single or multiple fractional phase-locked loop frequency synthesizer that is coherent in phase is proposed herein. This type of synthesizer comprises one or more counters with an increment of one, having their rate set by the reference oscillator of the synthesizer and being used in phase memories to enable changes in the increment or increments following a change in the fractional division ratio at instants that are synchronous with the reference oscillator.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
Wireless camera flash synchronizer system and method
A single oscillator synchronizer system and method that automatically switches from a wireless receive mode of the oscillator to a wireless transmit mode of the oscillator upon the detection of a synchronization (synch) signal of a camera body. In one example, a method of wirelessly communicating a camera synchronization from a camera body to a remote device with a wireless camera flash synchronizer connected to a synchronization connector of the camera body, the wireless camera flash synchronizer including a transceiver having an oscillator element with a wireless receive mode and a wireless transmit mode, the oscillator element configured to be in only one of the wireless receive mode and wireless transmit mode at a time is provided. In another example, a wireless camera flash synchronizer that automatically switches from a wireless receive mode to a wireless transmit mode upon detection of a synch signal of a camera body is provided.
Owner:LAB PARTNERS ASSOC INC
Long Range Radio Frequency Identification System
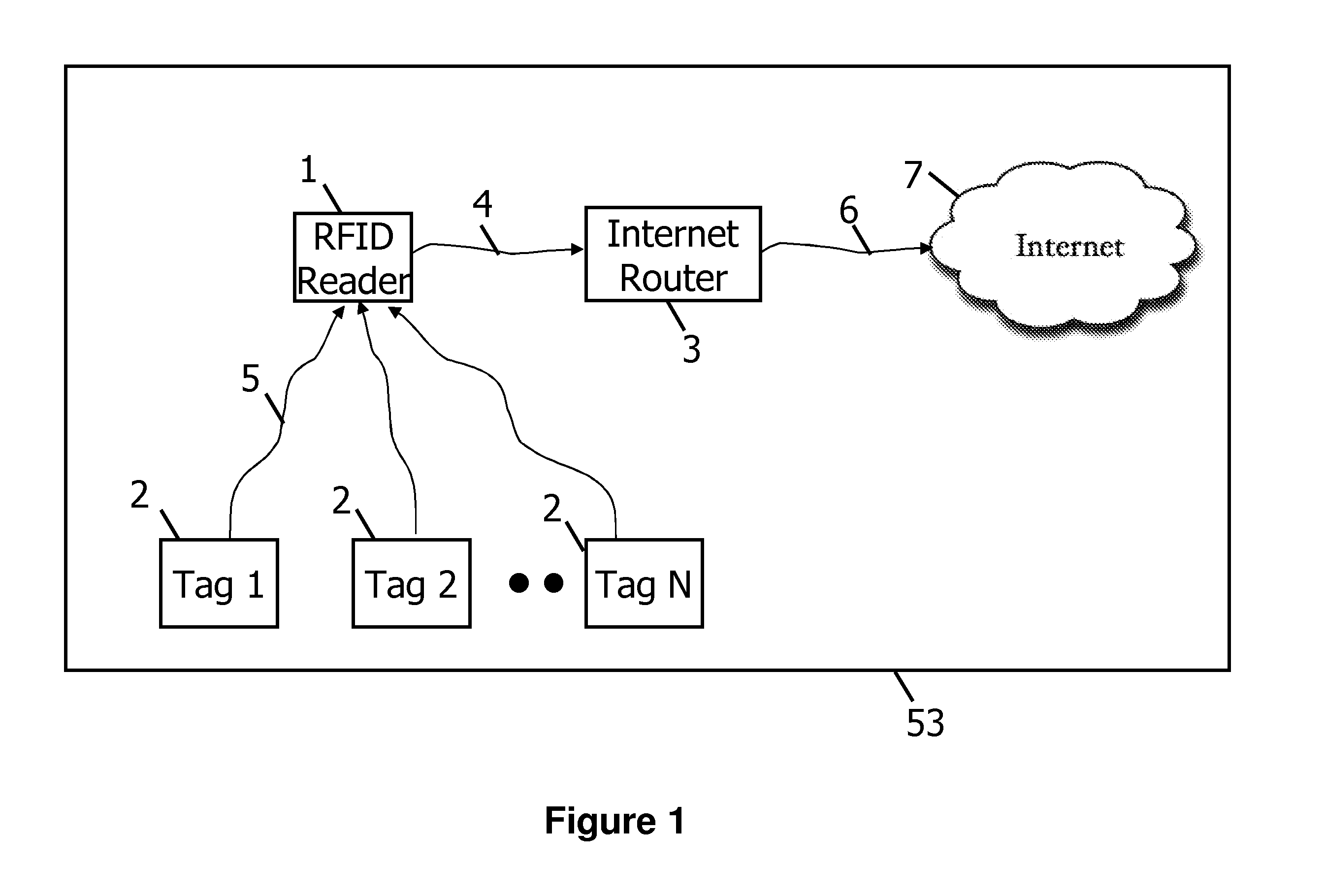
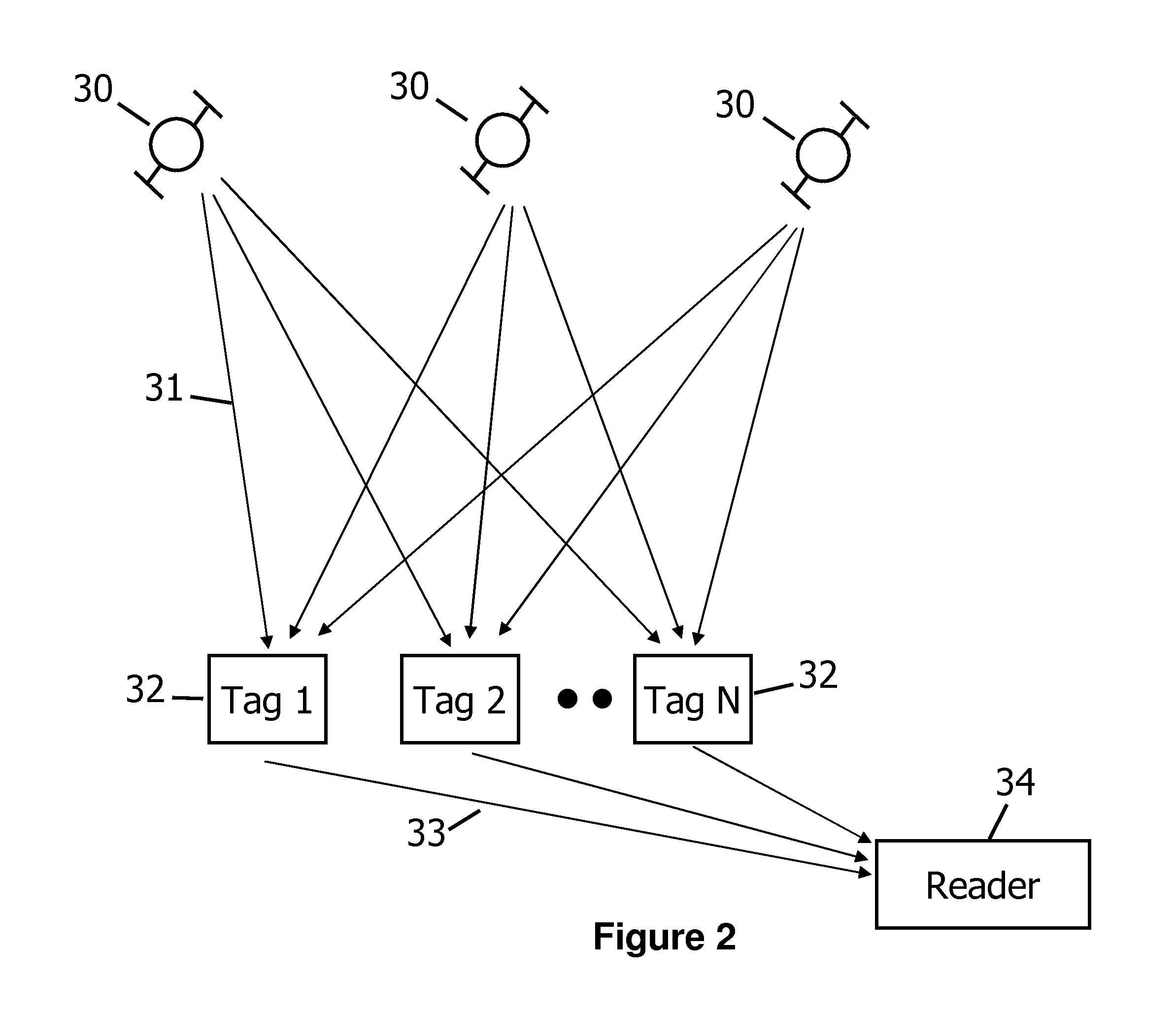
ActiveUS20110032081A1Large coherent processing gainMaximizing wireless rangeMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsOn boardGps receiver
A method and apparatus for building a long range RFID system is disclosed. A new signaling structure called Block Pseudo Noise is described that allows for more computationally efficient decoding. A novel approach to synchronize the RFID reader local oscillator with the RFID tag oscillator using an on board GPS receiver on the RFID tags and RFID reader is also disclosed. A novel positioning technique called Asynchronous Time Difference of Arrival used to located RFID tags is also disclosed.
Owner:RING LLC
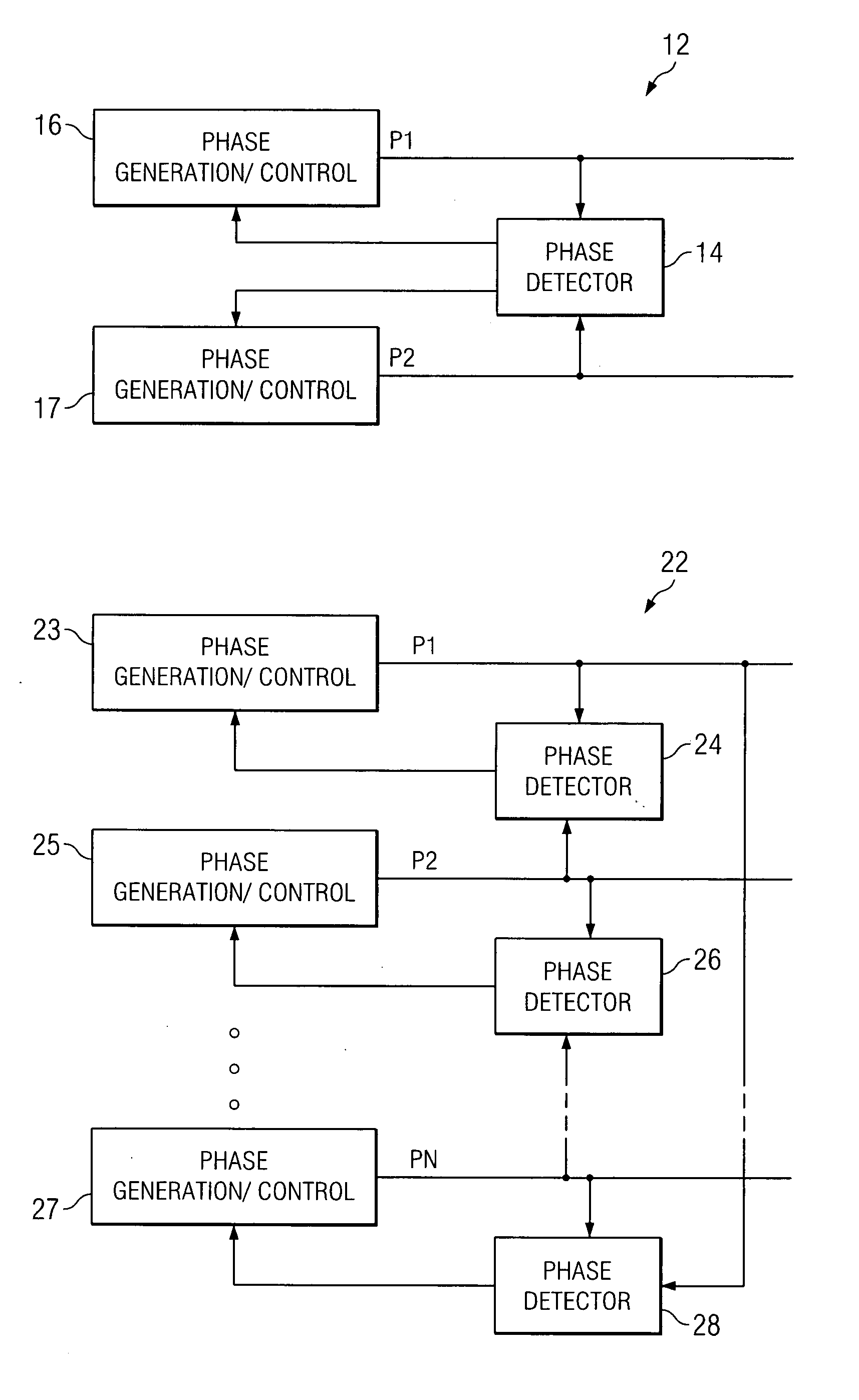
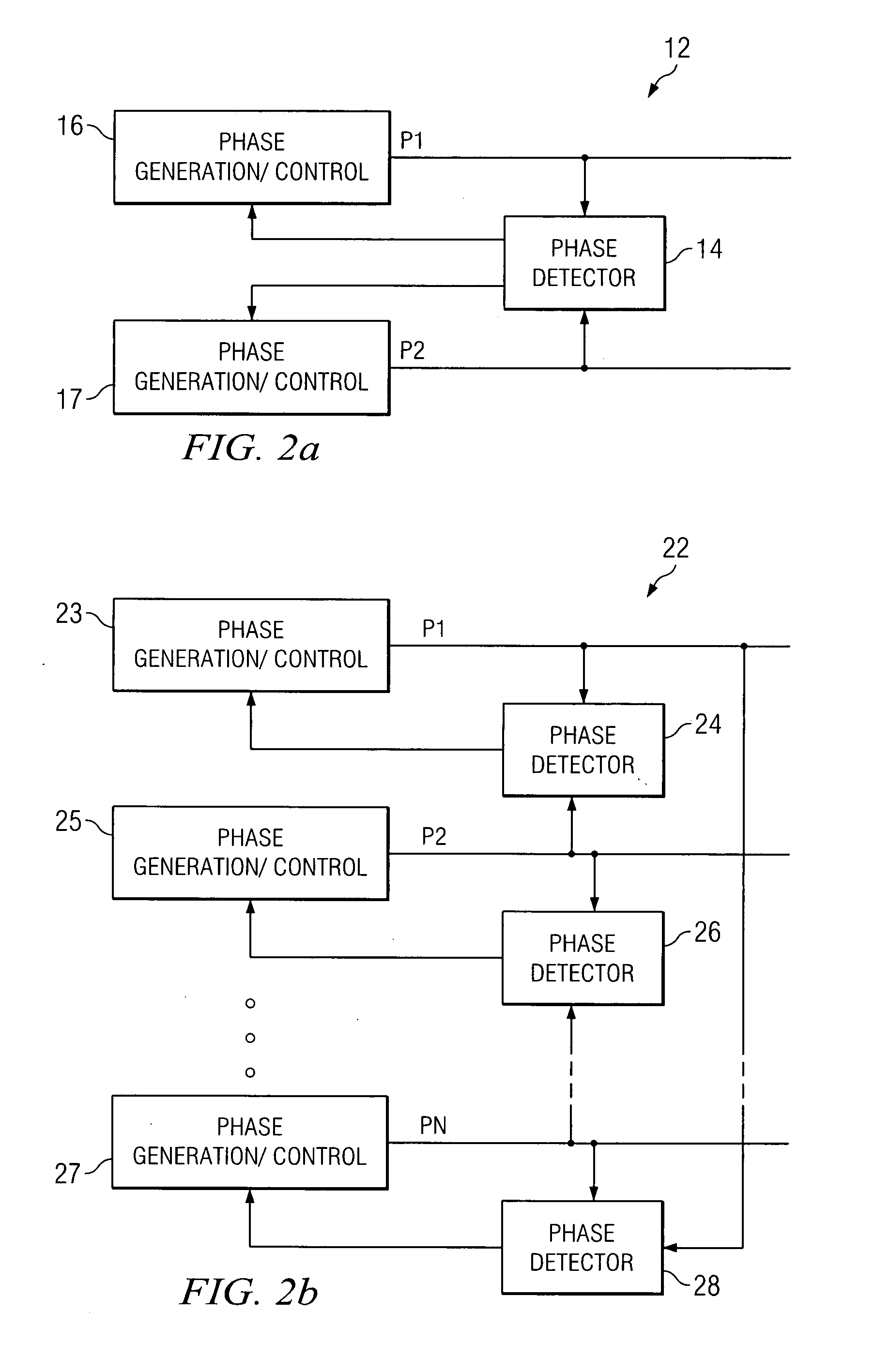
System and method for synchronizing multiple oscillators
ActiveUS20070262823A1Tempo syncReduce complexityPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase angle differencePhysics
A system and method for synchronizing an oscillator with multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that are synchronized to a common frequency such as an average of the different frequencies.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High-resolution, active reflector radio frequency ranging system
ActiveUS8274426B2Reduce the amount of solutionReduce bandwidth utilizationPosition fixationTransmissionLocal oscillatorEngineering
A radio frequency ranging system is grounded in establishing and maintaining phase and frequency coherency of signals received by a slave unit from a master unit and retransmitted to the master unit by the slave unit. For a preferred embodiment of the invention, coherency is established through the use of a delta-sigma phase-lock loop, and maintained through the use, on both master and slave units, of thermally-insulated reference oscillators, which are highly stable over the short periods of time during which communications occur. A phase relationship counter is employed to keep track of the fractional time frames of the phase-lock loop as a function of the reference oscillator, thereby providing absolute phase information for an incoming burst on any channel, thereby enabling the system to almost instantaneously establish or reestablish the phase relationship of the local oscillator so that it synchronized with the reference oscillator.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Crystal reference clock and radio localization receiver
InactiveUS7728684B2Easy to handleRadiation pyrometryPulse automatic controlEngineeringCrystal oscillator
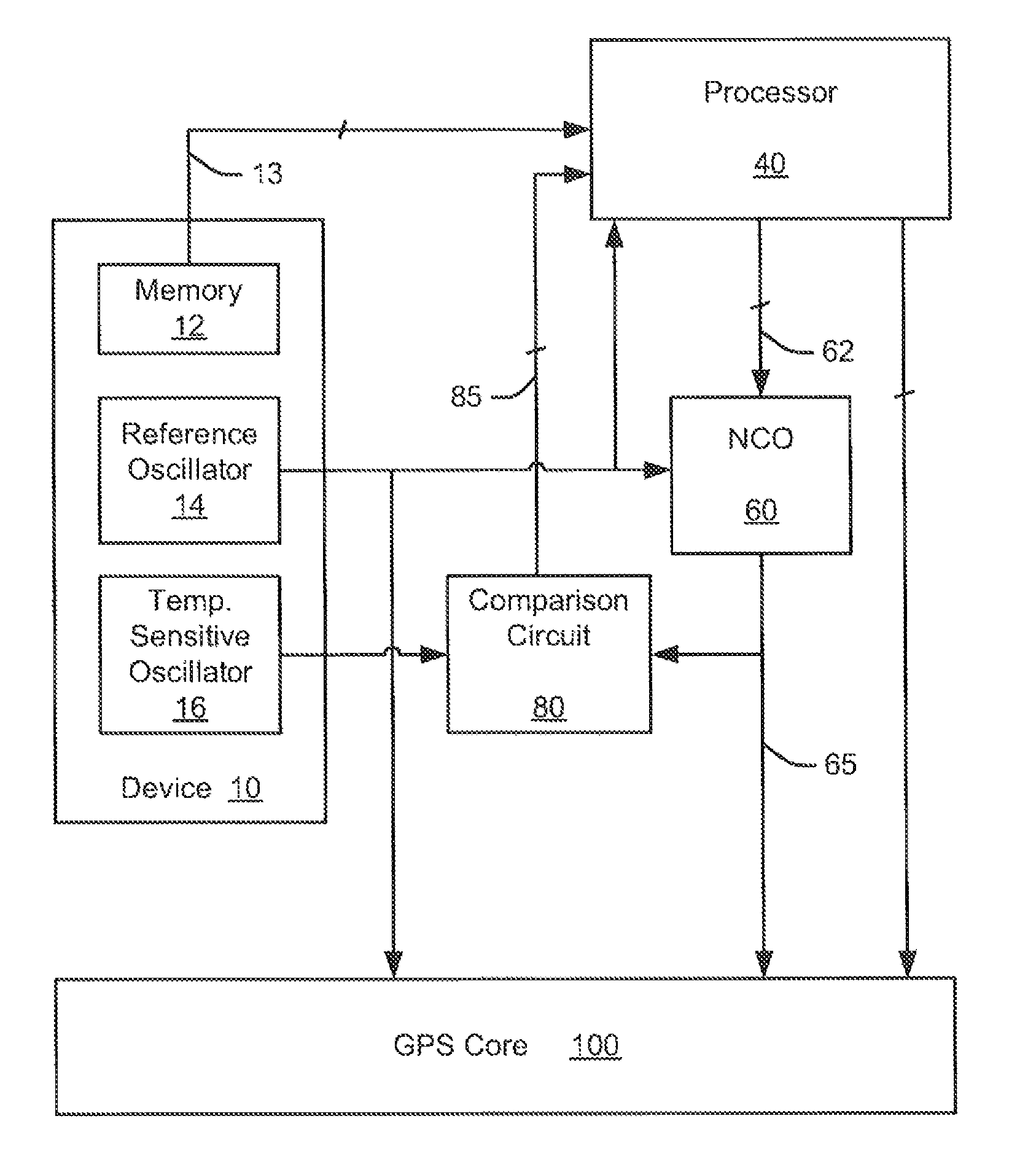
Device and method for temperature compensation in a clock oscillator using quartz crystals, which integrates dual crystal oscillators. The minimal power consumption is achieved through an efficient use of a processor in charge of the synchronization of the two oscillators. The invention is particularly adapted for the provision of a precise reference clock in portable radiolocalization devices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
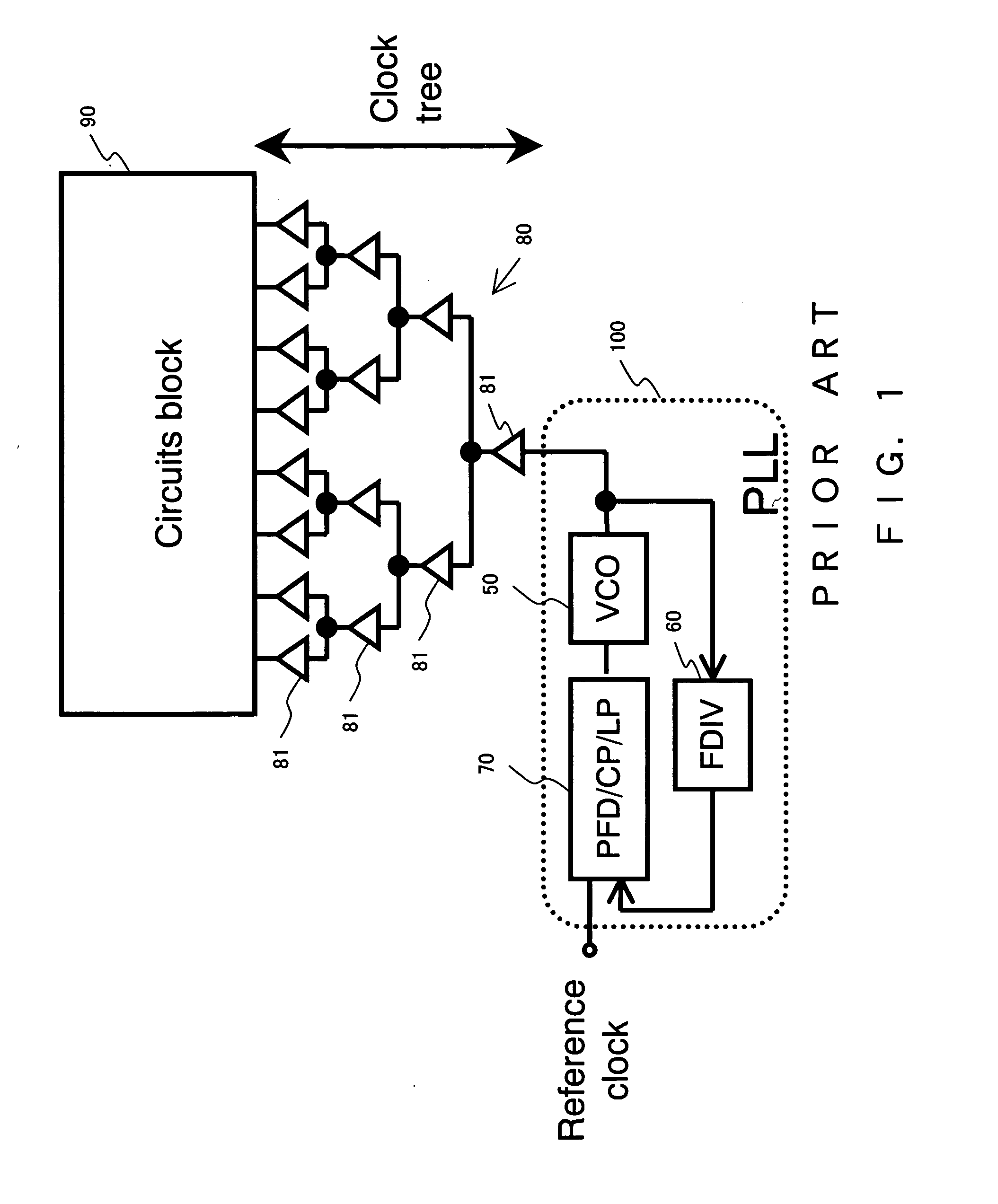
Clock signal generating and distributing apparatus
InactiveUS7863987B2Improve accuracyMore stablyPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsInjection lockedEngineering
LC resonant voltage control oscillators are adopted as voltage control oscillators for the purpose of providing a clock generating and distributing apparatus that can generate and distribute a clock signal of high precision even in a high-frequency region of several giga hertz or higher, and of providing a distributive VCO-type clock generating and distributing apparatus in which voltage control oscillators oscillate in the same phase, and which can generate a clock signal of a desired frequency and distributes a high-frequency clock signal to each part within a chip more stably even in a high-frequency region reaching 20 GHz. Furthermore, an inductor component of a wire connecting the oscillation nodes of the oscillators is made relatively small, or the LC resonant oscillators are oscillated in synchronization by using injection locking, whereby the LC resonant voltage control oscillators stably oscillate in the same phase.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Clock signal generating and distributing apparatus
InactiveUS20070063779A1Improve accuracyMore stablyPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsInjection lockedEngineering
LC resonant voltage control oscillators are adopted as voltage control oscillators for the purpose of providing a clock generating and distributing apparatus that can generate and distribute a clock signal of high precision even in a high-frequency region of several giga hertz or higher, and of providing a distributive VCO-type clock generating and distributing apparatus in which voltage control oscillators oscillate in the same phase, and which can generate a clock signal of a desired frequency and distributes a high-frequency clock signal to each part within a chip more stably even in a high-frequency region reaching 20 GHz. Furthermore, an inductor component of a wire connecting the oscillation nodes of the oscillators is made relatively small, or the LC resonant oscillators are oscillated in synchronization by using injection locking, whereby the LC resonant voltage control oscillators stably oscillate in the same phase.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Small Cell Network Self-Synchronization
ActiveUS20130281080A1Synchronisation arrangementCarrier regulationSynchronization networksHeterogeneous network
A system, method, and apparatus to facilitate the synchronization of oscillators between members of a Heterogeneous Network (HetNet) to form a self-synchronizing network (SSN). The network members are configured to broadcast information indicative of the reliability of their oscillator. Network members attempt to look for reliable sources such as those originating from a macrocell base station or GPS. If such a source is found, the member cell updates it clock accuracy confidence level number (CACL) to indicate this. Network members also share information regarding the frequency offsets between one another. Every cell member then applies a weighted average function to determine how to update its own oscillator and CACL value accordingly. Cell members can also update their functionality, such as RF power level, in response to varying degrees of CACL values. This operation results in a convergence of all cell members to the most accurate oscillator offset value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tunable ultrashort pulse fiber optic parametric oscillator
PendingCN106654829AWide working bandHigh pulse qualityActive medium shape and constructionOptical fiber couplerFiber gratings
The invention discloses a tunable ultrashort pulse fiber optic parametric oscillator and relates to the fields of parametric oscillators and lasers. The oscillator comprises a tunable laser, an isolator, an intensity modulator, a first amplifier, a filter, a phase modulator, a second amplifier, a first polarization controller, a circulator, a chirped fiber grating, a wavelength division multiplexer, a high-nonlinearity optical fiber, an optical fiber coupler and a second polarization controller. The oscillator adopts a time lens system to compress optical pulse to realize an ultrashort pulse source with tunable repetition frequency and operating wavelength, the repetition frequency is decided by a radio frequency signal applied to a time lens and is very easy to be synchronous to the parametric oscillator. Through utilization of the tunable characteristics of the repetition frequency and the wavelength of the light source of the time lens and combination of time dispersion tuning and pump wavelength tuning mechanism, the fiber optic parametric oscillator can realize the ultrashort pulse laser output at tunable wide working waveband and high pulse quality.
Owner:苏州龙格库塔光电科技有限公司
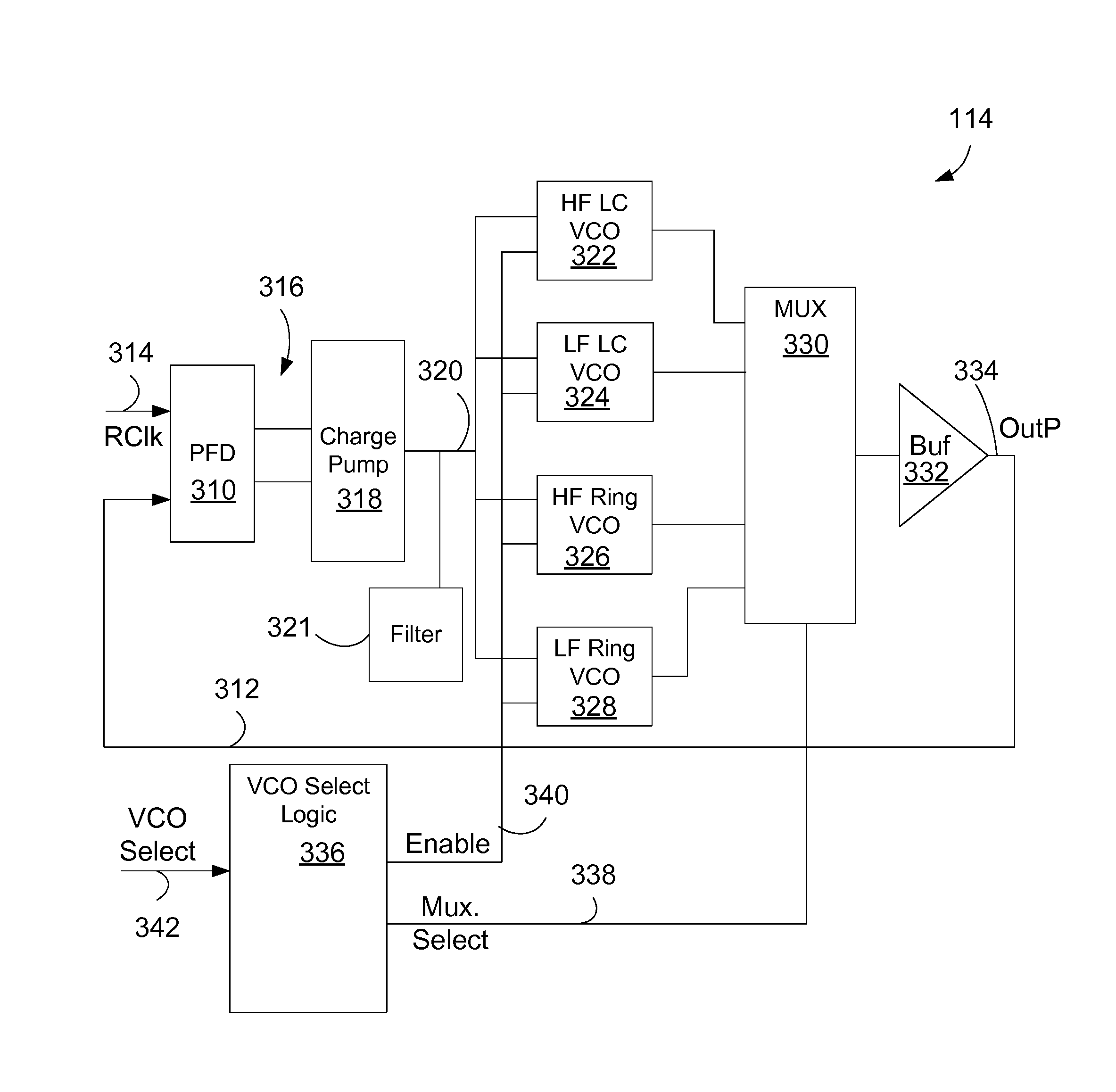
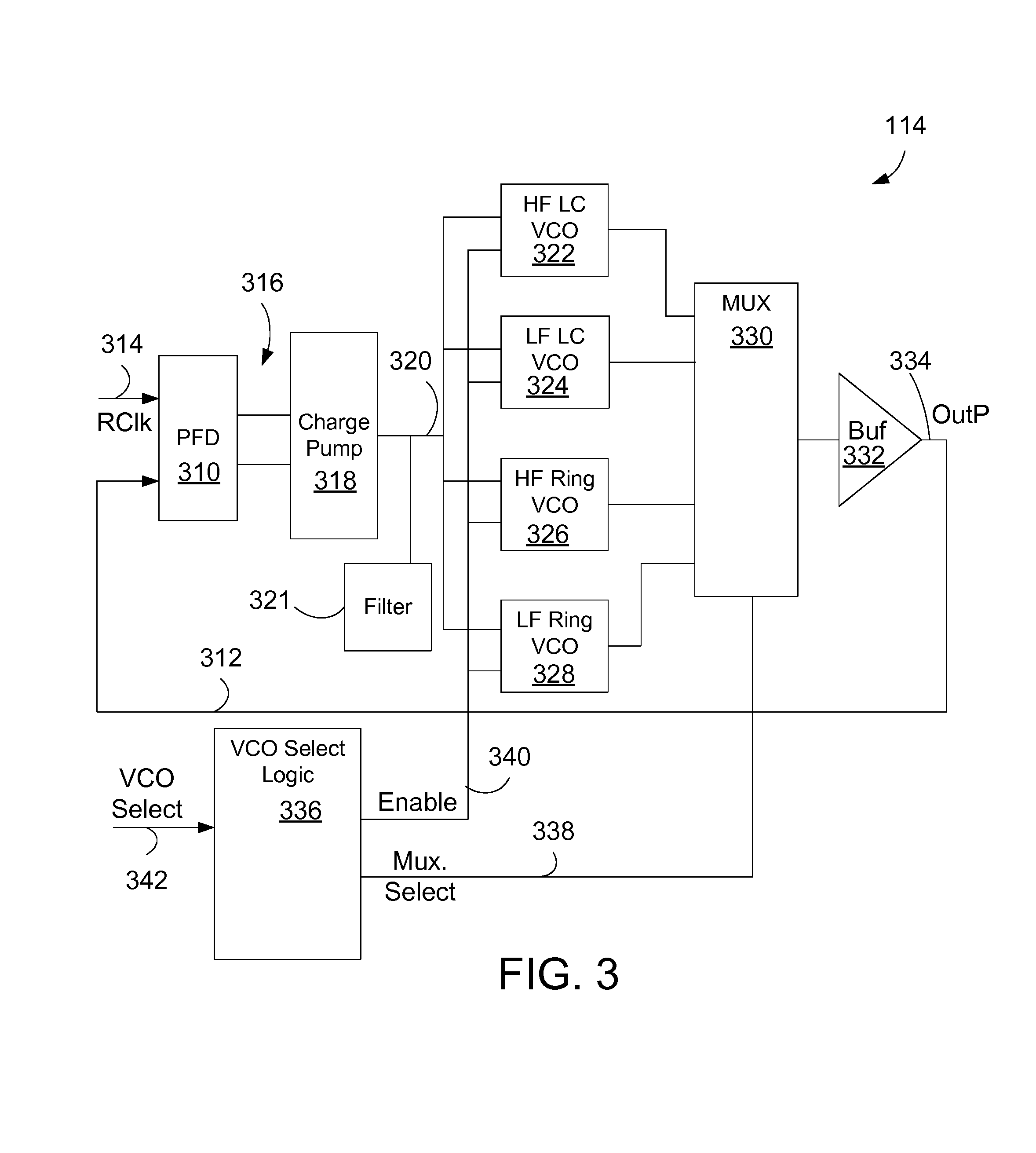
Phased locked loop with multiple voltage controlled oscillators
InactiveUS9467092B1Increase the areaCostPulse automatic controlVolume/mass flow measurementPhase-locked loopRing oscillator
A phased locked loop (PLL) incorporates multiple voltage controlled oscillators including one that operates in a lower frequency range than an operational VCO used by the PLL. A VCO selection circuit allows the system to select from one or more alternate VCOs. A ring oscillator VCO may be used as the alternate VCO for a PLL that uses a LC VCO for the operational VCO. While the ring oscillator VCO provides lower performance, the ring oscillator VCO allows the system with the PLL to be run at a lower speed for testing, debugging or characterization.
Owner:IBM CORP
High Performance Divider Using Feed Forward, Clock Amplification and Series Peaking Inductors
ActiveUS20130076408A1Reduced voltage headroomReduce power supply voltagePulse automatic controlDifferential amplifiersInjection lockedSoi cmos technology
A phase lock loop (PLL) is an important component in wireless systems. CMOS technology offers voltage controlled oscillator designs operating at 60 GHz. One of the difficulties is dividing the high frequency clock down to a manageable clock frequency using conventional CMOS. Although injection locked dividers can divide down this clock frequency, these dividers have limitations. A divide by 2 is presented that uses several techniques; feed forward, clock amplification and series peaked inductors to overcome these limitations.
Owner:TENSORCOM
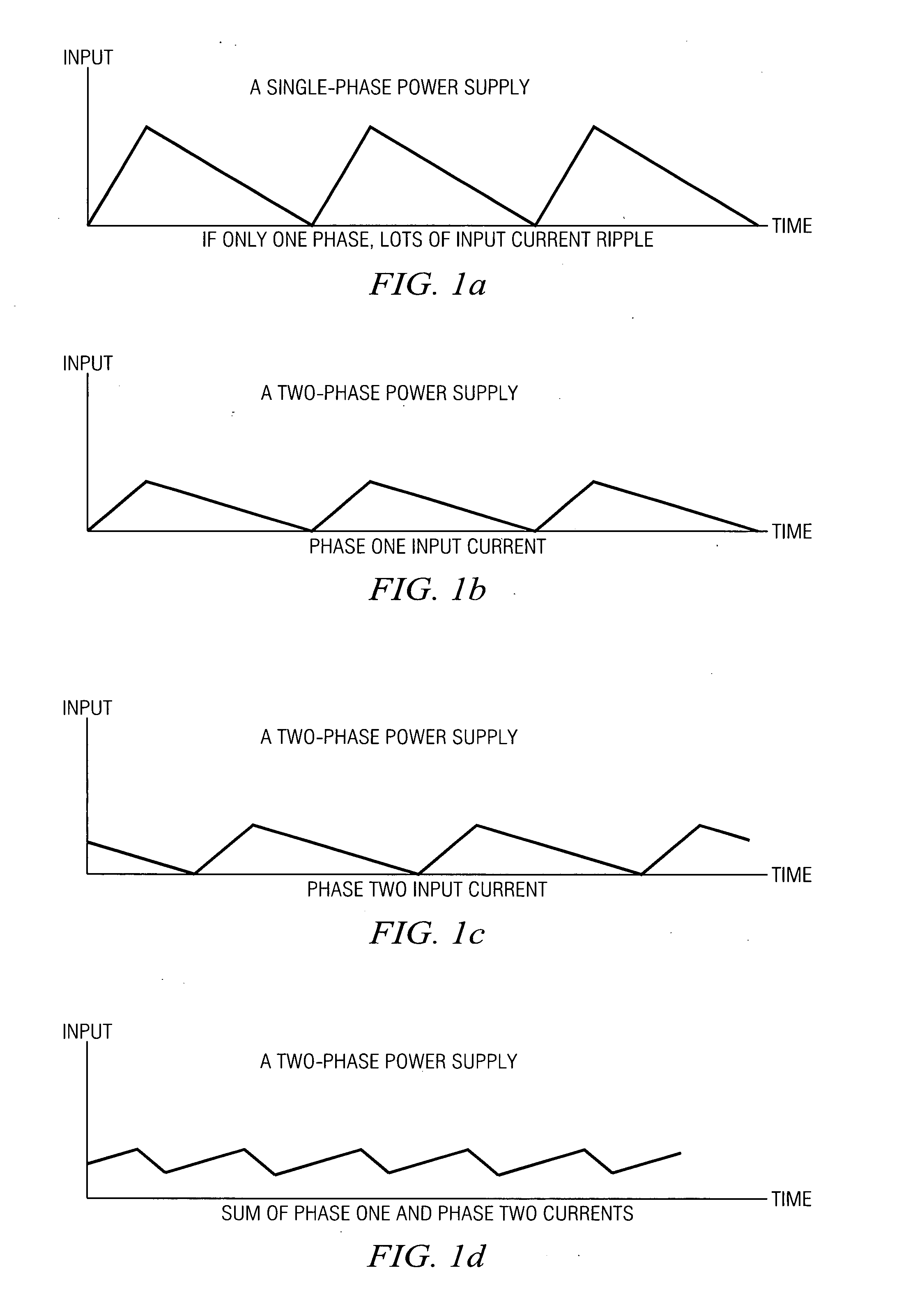
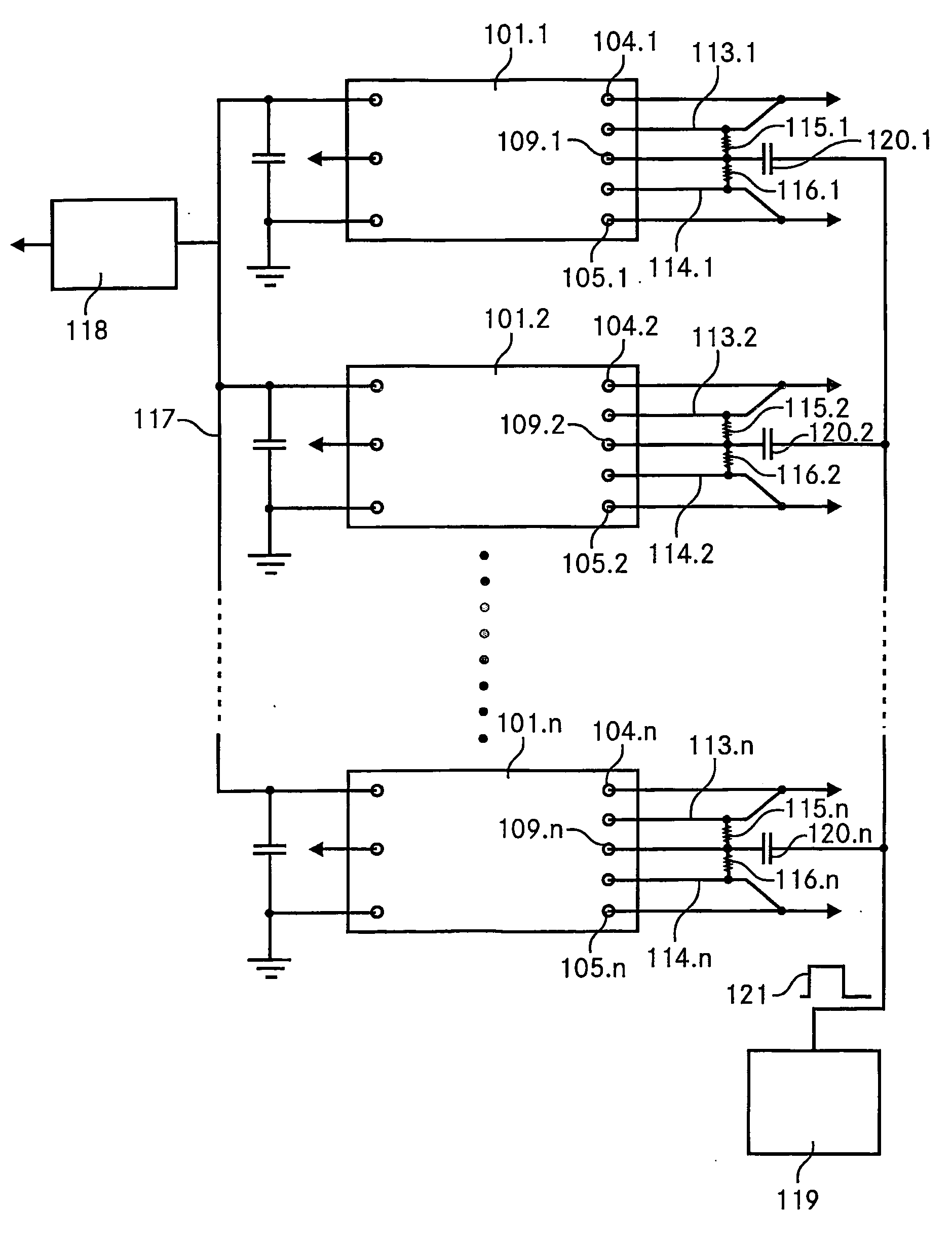
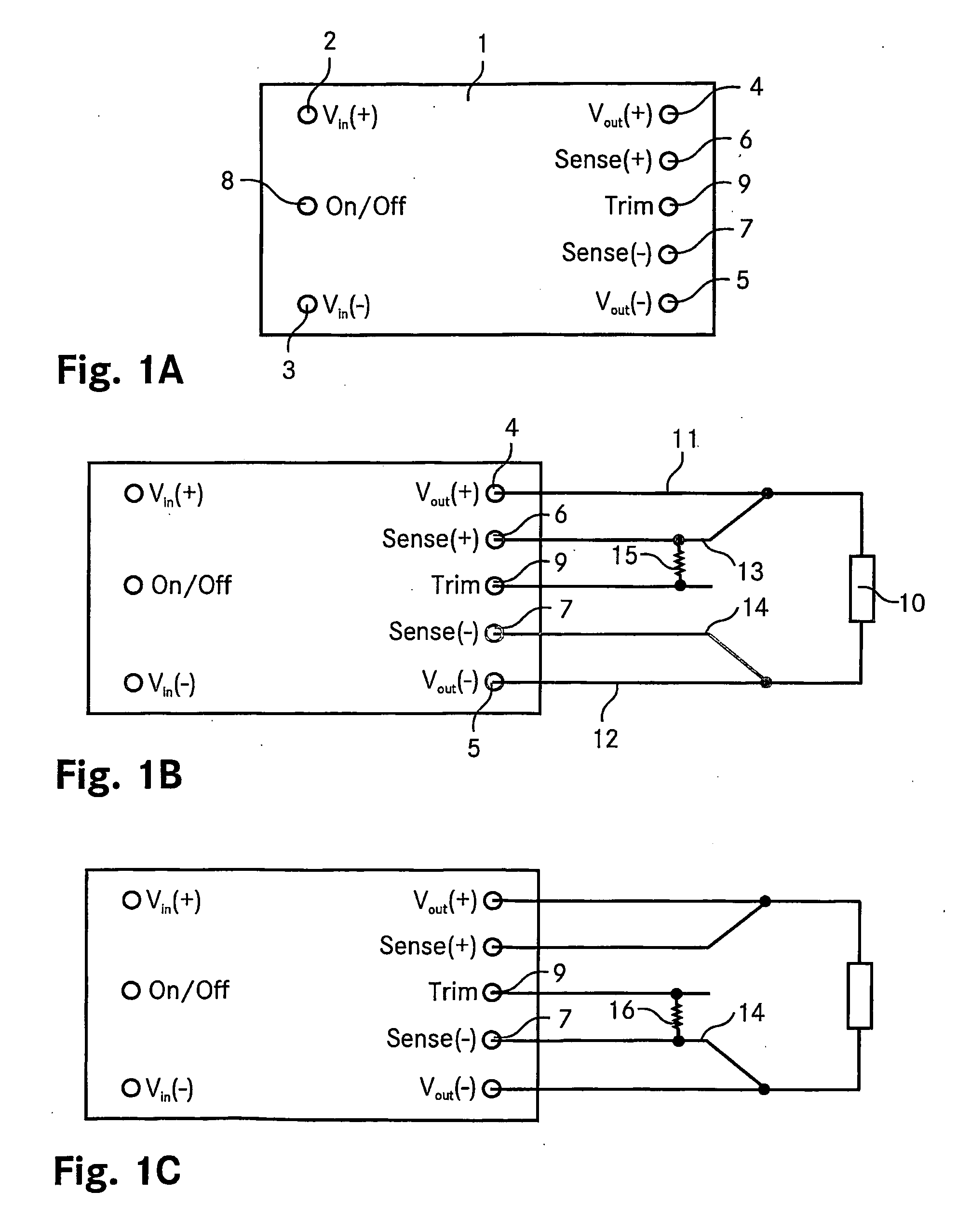
Dc dc switching converter device
ActiveUS20060197384A1Reduce noiseEasy to implementDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesAc network voltage adjustmentElectromagnetic interferenceTransfer switch
A DC-DC switching converter device (101), in particular a quarter-brick or eighth-brick device having an industry standard pin out, comprises a pulse-width modulation circuit (132) for driving a power converting switch, a trim connector (109) for adjusting an output voltage of the device, where the device (101) is designed such that the pulse-width modulation circuit (132) is synchronizable to an external oscillator by an external synchronization signal applied to the trim connector. A DC-DC converting circuit comprises a plurality of DC-DC switching converters (101) featuring trim connectors (109) for adjusting output voltages of the converters (101), whereby the converters (101) are connected such that they share a common input bus. It further features a system EMI (electromagnetic interference) filter common to all the DC-DC switching converters (101) and an external oscillator delivering an external synchronization signal to the plurality of DC-DC switching converters (101). The external oscillator is designed such that a frequency of the external synchronization signal is higher than a free running frequency of each of the plurality of DC-DC switching converters (101). The external oscillator is connected to the trim connectors (109) of the DC-DC switching converters (101).
Owner:DET INT HLDG LTD
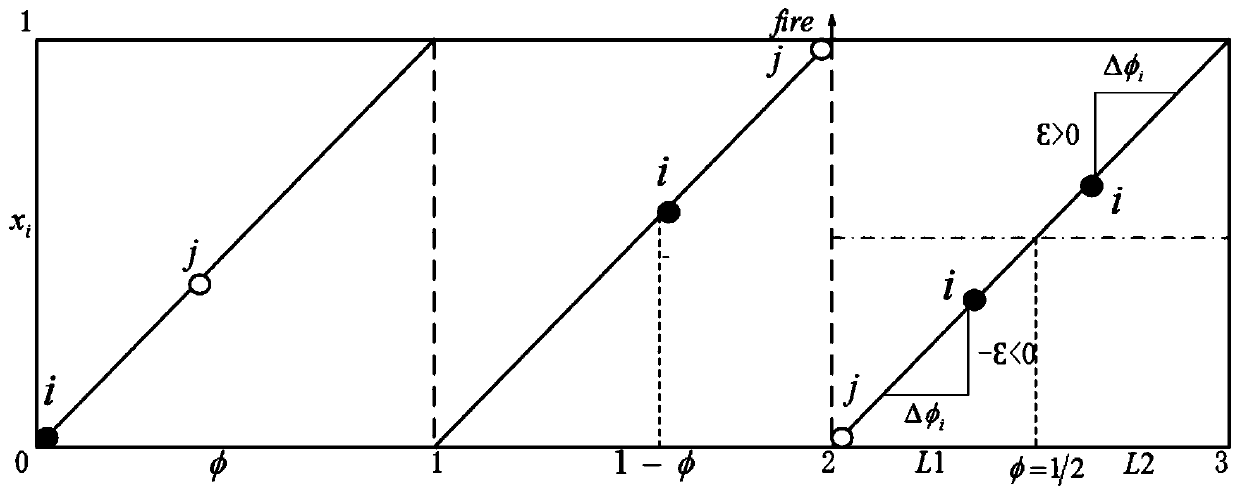
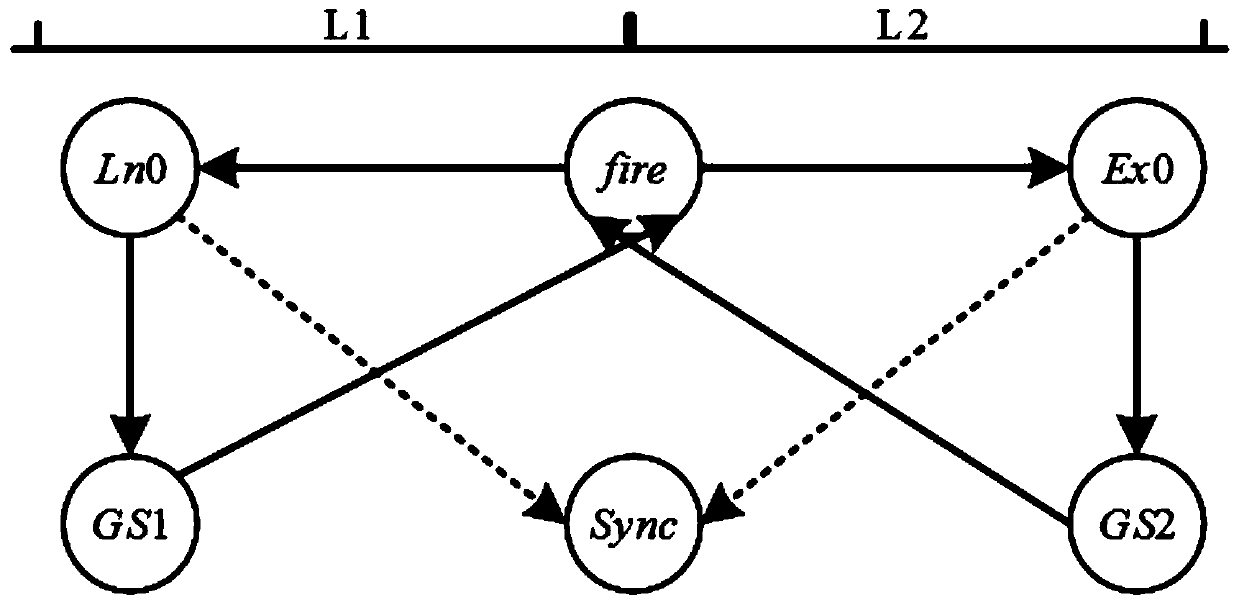
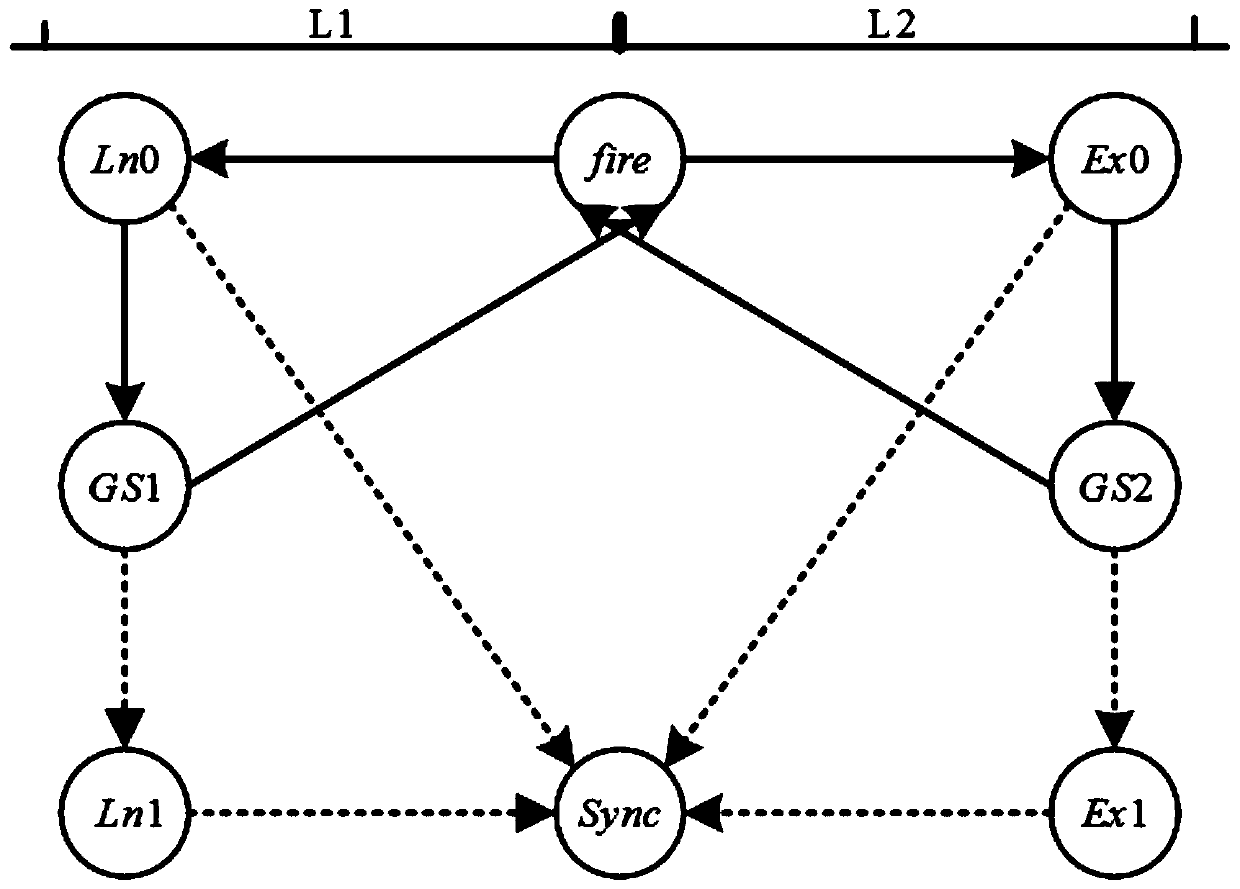
Pulse coupled oscillator time synchronization model and method based on firefly synchronization
ActiveCN110267295AReduce sync cycleSynchronization speed is fastSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesPulse coupled oscillatorPhase coupling
The invention discloses a pulse coupled oscillator time synchronization model and method based on firefly synchronization, and belongs to the technical field of wireless network communication. A model introduces a negative coupling factor in a phase coupling mode only with positive coupling, unifies a coupling strength reference, constructs positive and negative different coupling strengths, and divides the phase coupling mode into excitation coupling and inhibition coupling; the variation interval of the oscillator phase is divided in a halving mode, and synchronous tracking is carried out on the oscillator in different initial states. The method comprises the synchronization of two oscillators and the synchronization of two oscillators in the multi-oscillator system, and finally the synchronization of the multi-oscillator system is mapped. According to the model and the method, the phase coupling mode is optimized, the synchronization speed of the system is improved, and certain theoretical guiding significance and application value are achieved for actual production.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power supply and dc-dc-conversion
ActiveUS20110050315A1Increase the switching frequencyReduce power consumptionPulse generatorPulse automatic controlTransverterSwitching signal
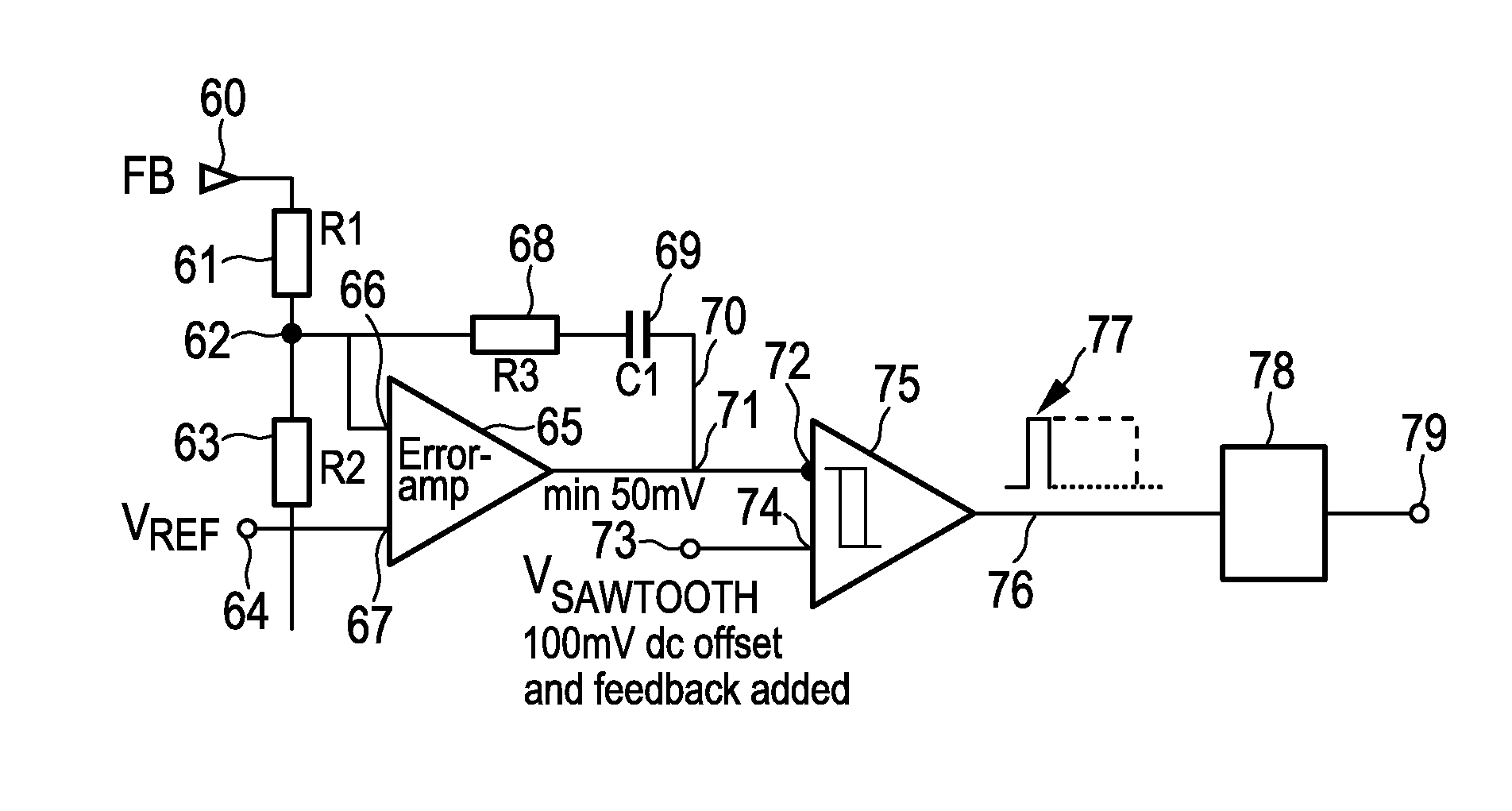
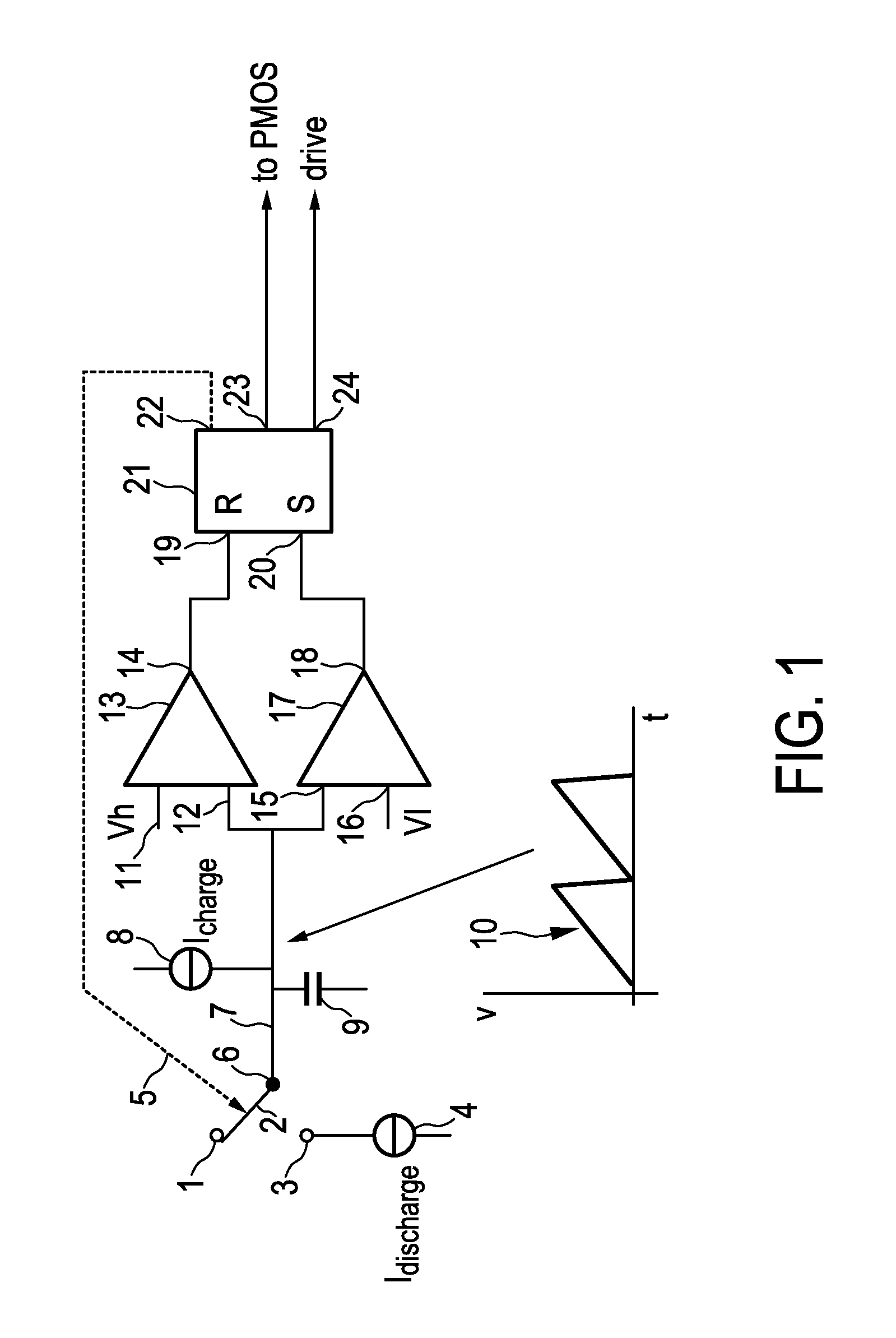
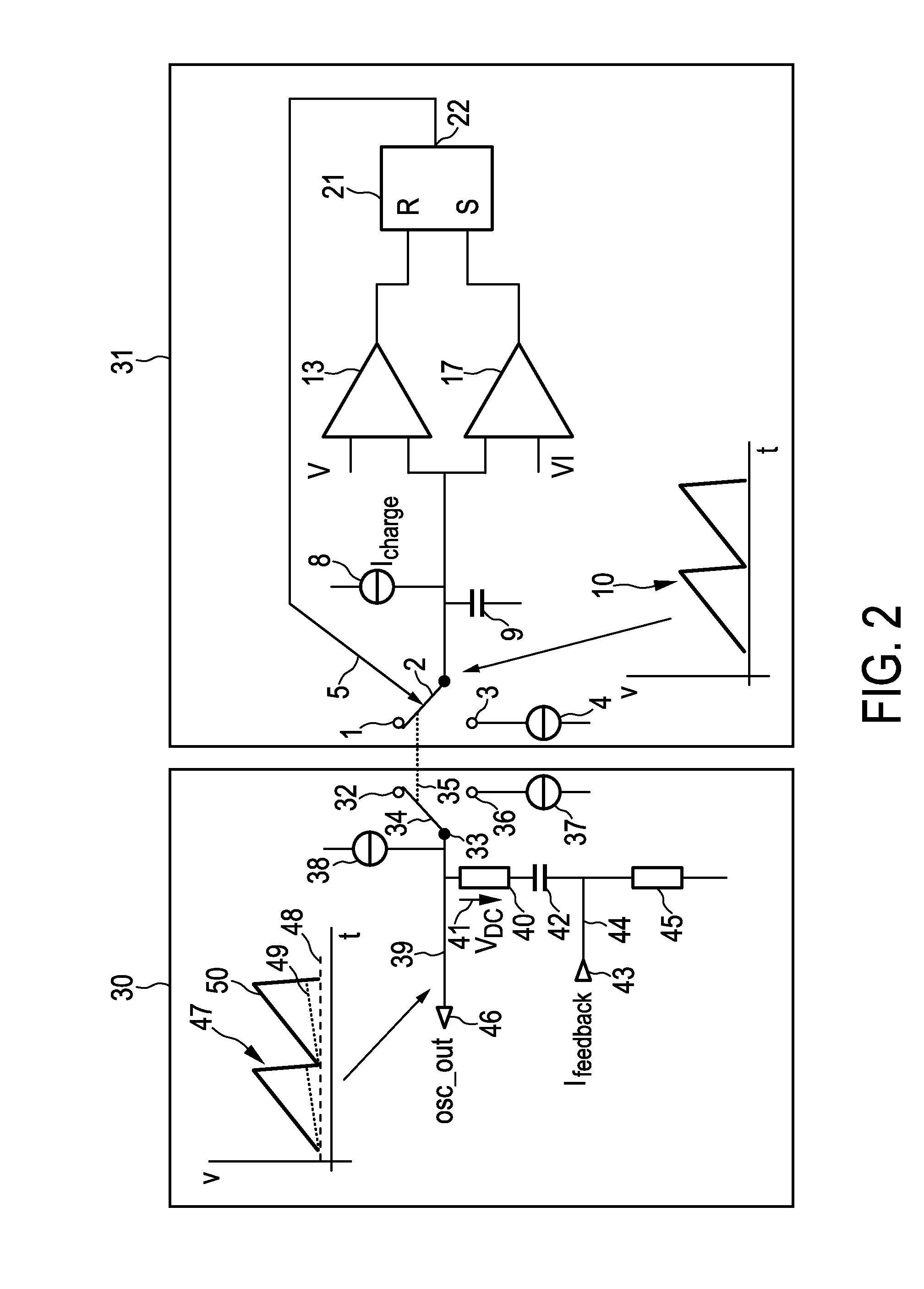
In an embodiment of a converter, a first oscillator provides switching signals for switching between charging and discharging of a capacitor, and a second oscillator is configured to add an offset voltage or a feedback-current-dependent voltage to a sawtooth waveform generated by the second oscillator switched in synchronism with the first oscillator.
Owner:NXP BV
Auto trimming oscillator
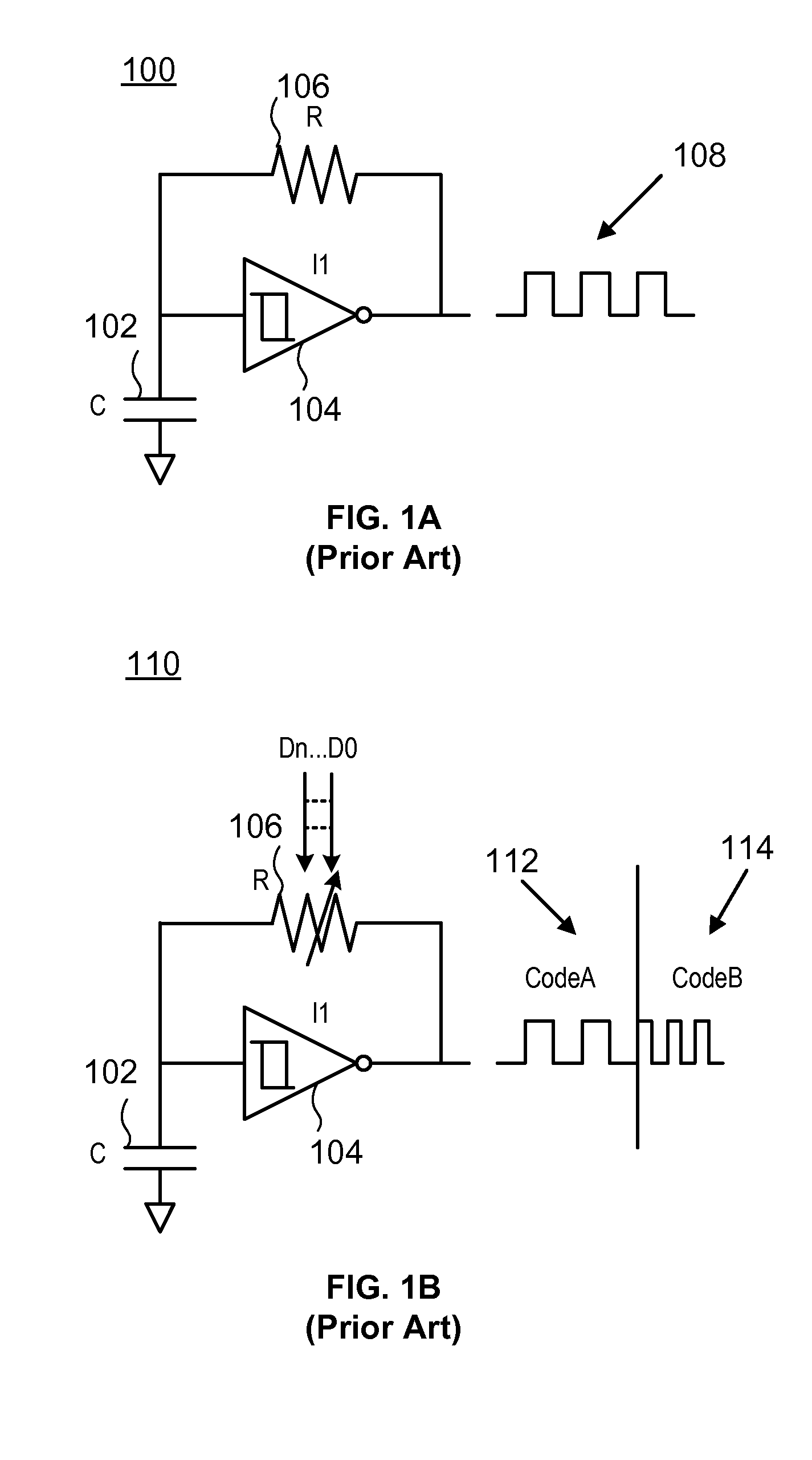
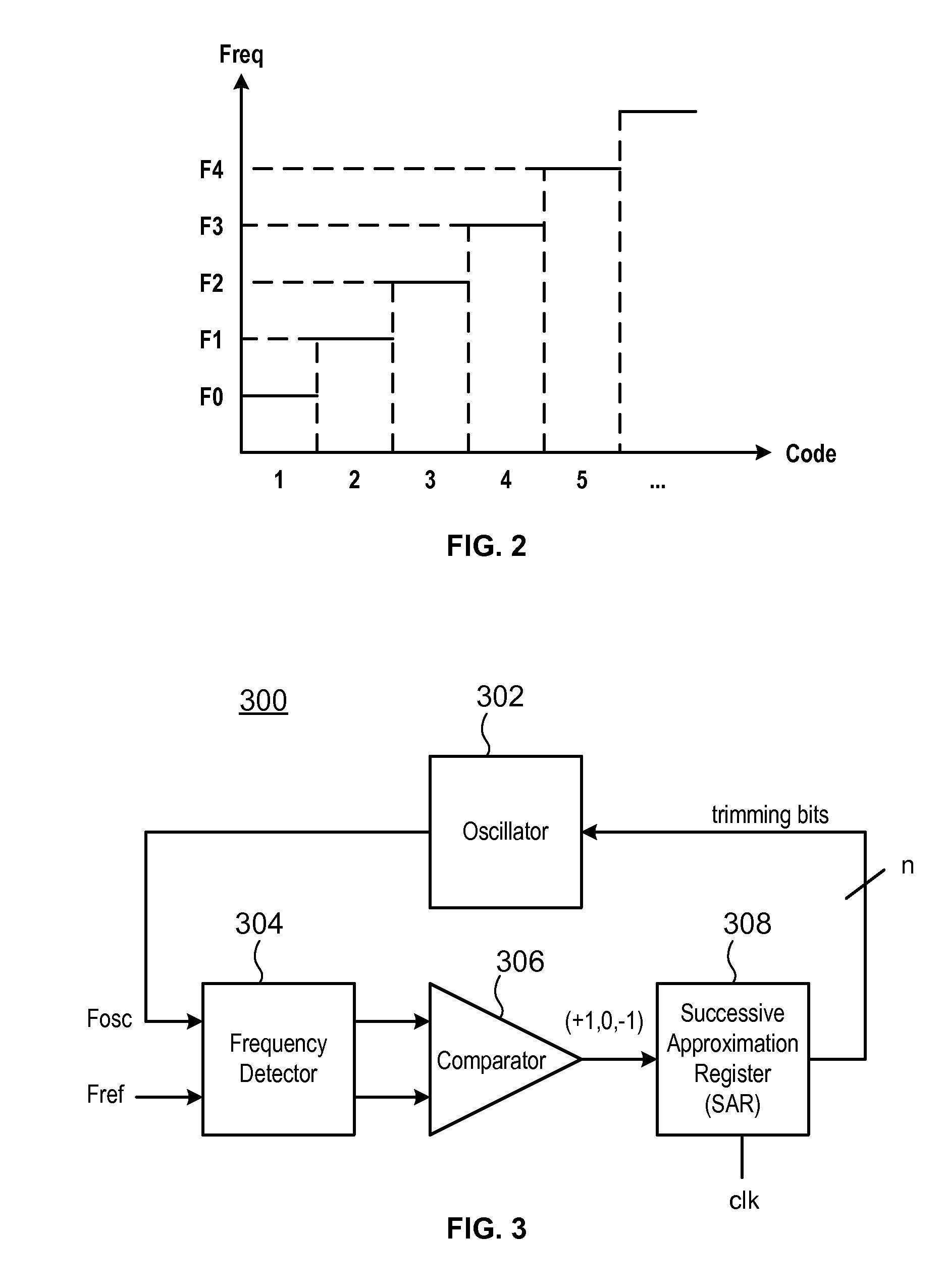
InactiveUS7994866B2Fast and accurate determinationLow cost manufacturingPulse automatic controlClock rateRC oscillator
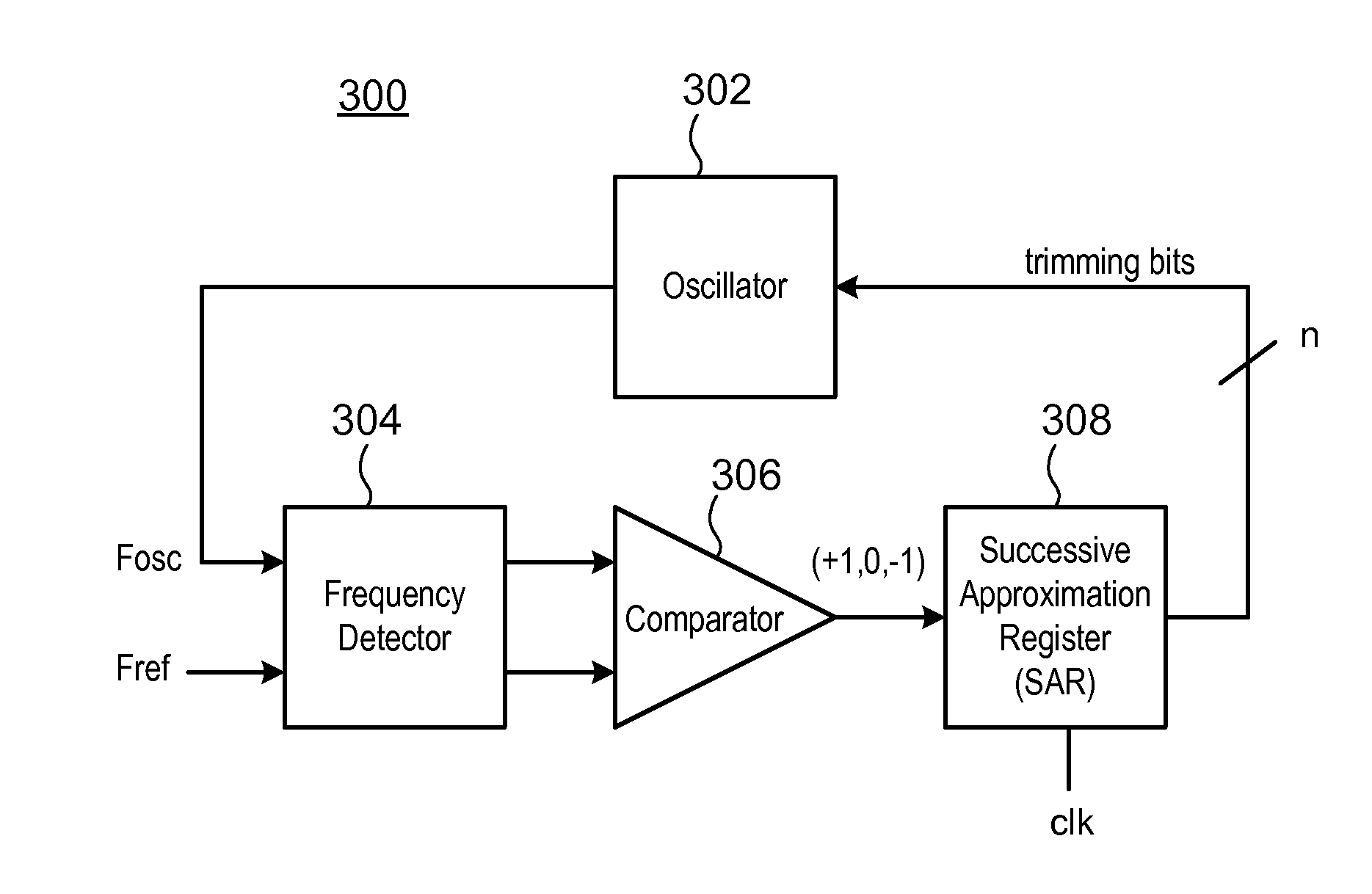
An auto trimming oscillator includes a Successive Approximation Register (SAR), a frequency detector and an n-bit comparator. The SAR is used to iteratively trim the oscillator output clock frequency based on a difference between a reference clock frequency and the oscillator output clock frequency. The oscillator is trimmed to deliver a clock frequency which is a closest match to the reference clock frequency.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
DC-DC switching converter device
ActiveUS7719137B2Easy to implementReduce noiseDc network circuit arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentElectromagnetic interferenceIndustry standard
A DC-DC switching converter device (101), in particular a quarter-brick or eighth-brick device having an industry standard pin out, comprises a pulse-width modulation circuit (132) for driving a power converting switch, a trim connector (109) for adjusting an output voltage of the device, where the device (101) is designed such that the pulse-width modulation circuit (132) is synchronizable to an external oscillator by an external synchronization signal applied to the trim connector. A DC-DC converting circuit comprises a plurality of DC-DC switching converters (101) featuring trim connectors (109) for adjusting output voltages of the converters (101), whereby the converters (101) are connected such that they share a common input bus. It further features a system EMI (electromagnetic interference) filter common to all the DC-DC switching converters (101) and an external oscillator delivering an external synchronization signal to the plurality of DC-DC switching converters (101). The external oscillator is designed such that a frequency of the external synchronization signal is higher than a free running frequency of each of the plurality of DC-DC switching converters (101). The external oscillator is connected to the trim connectors (109) of the DC-DC switching converters (101).
Owner:DET INT HLDG LTD
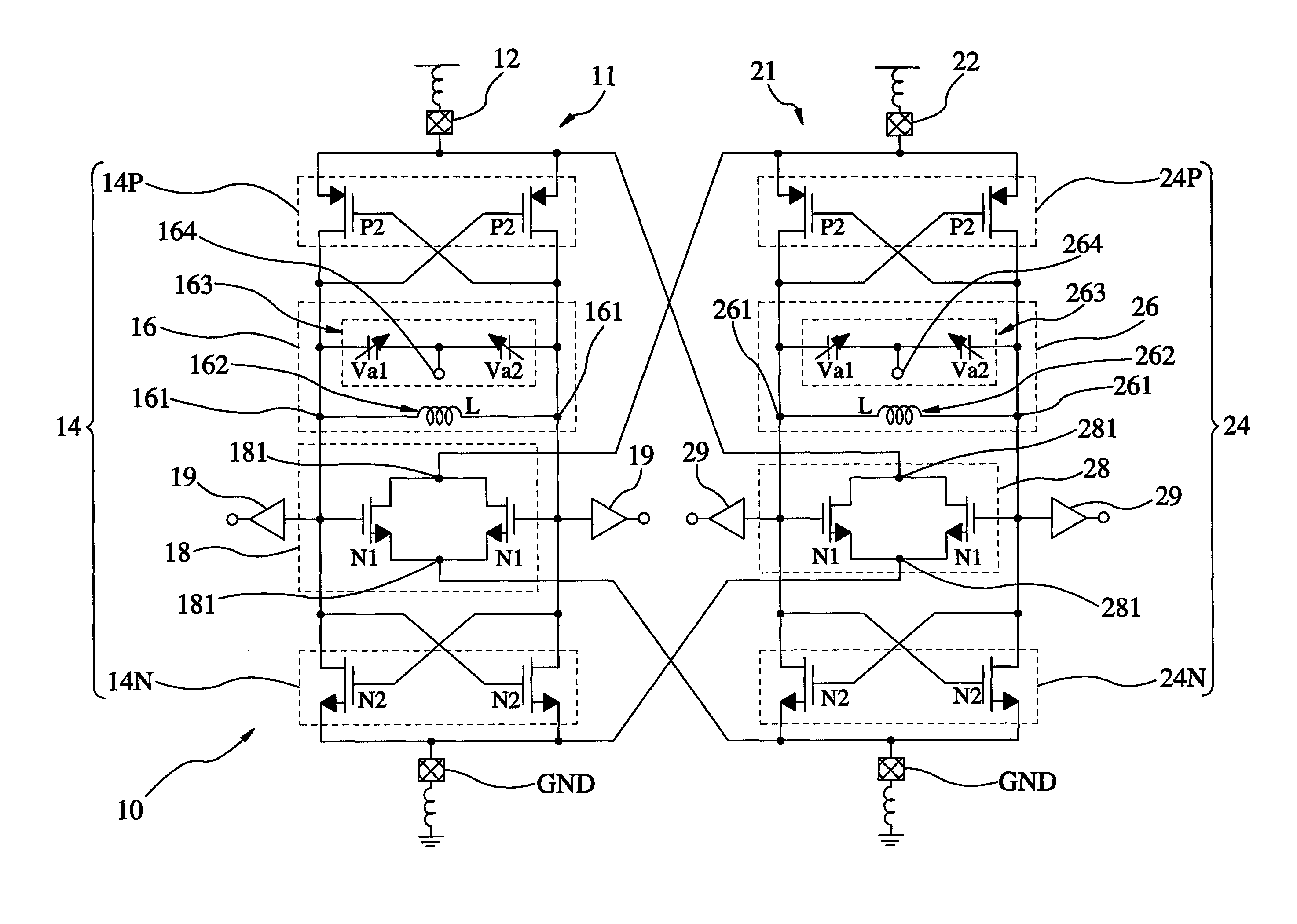
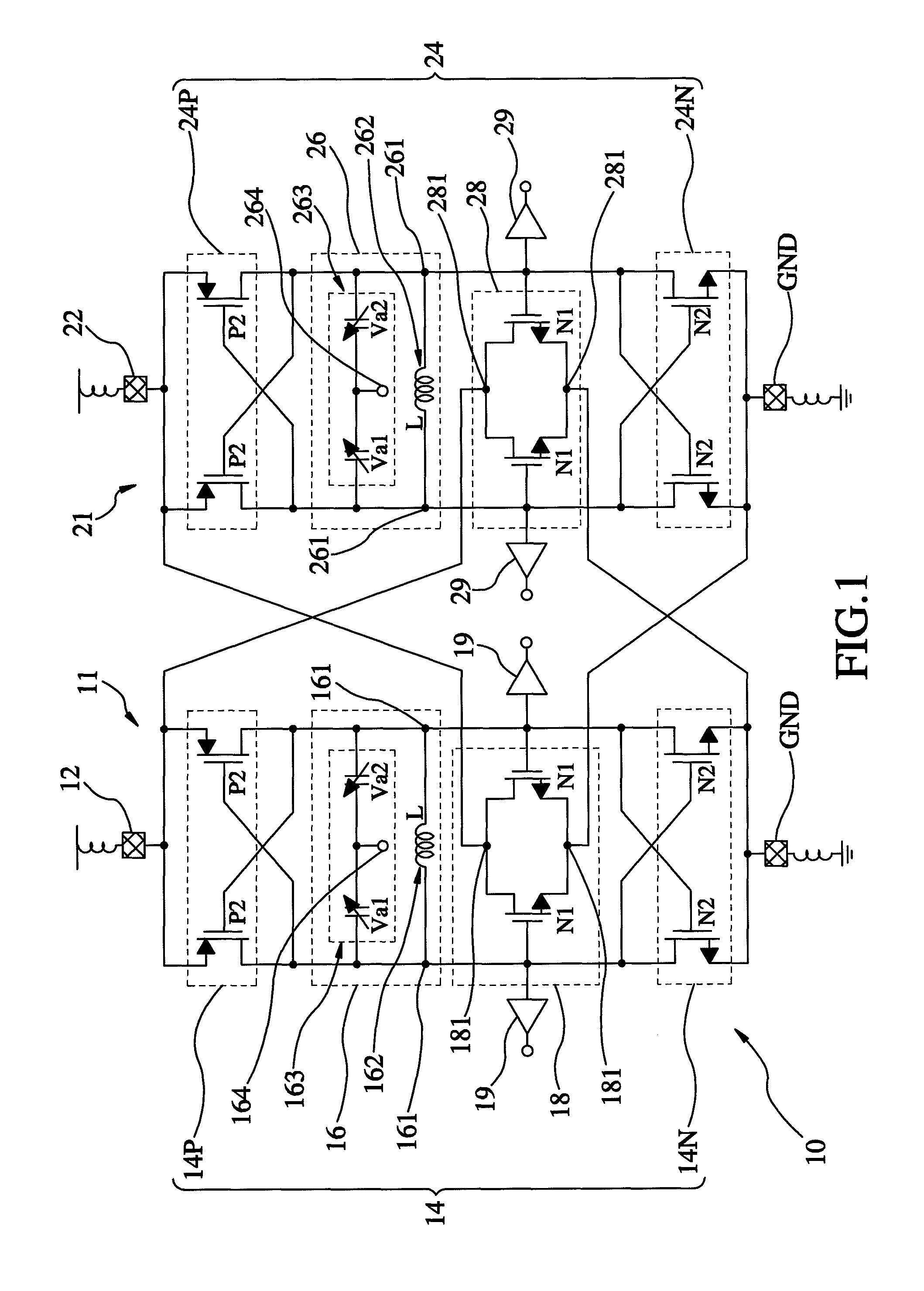
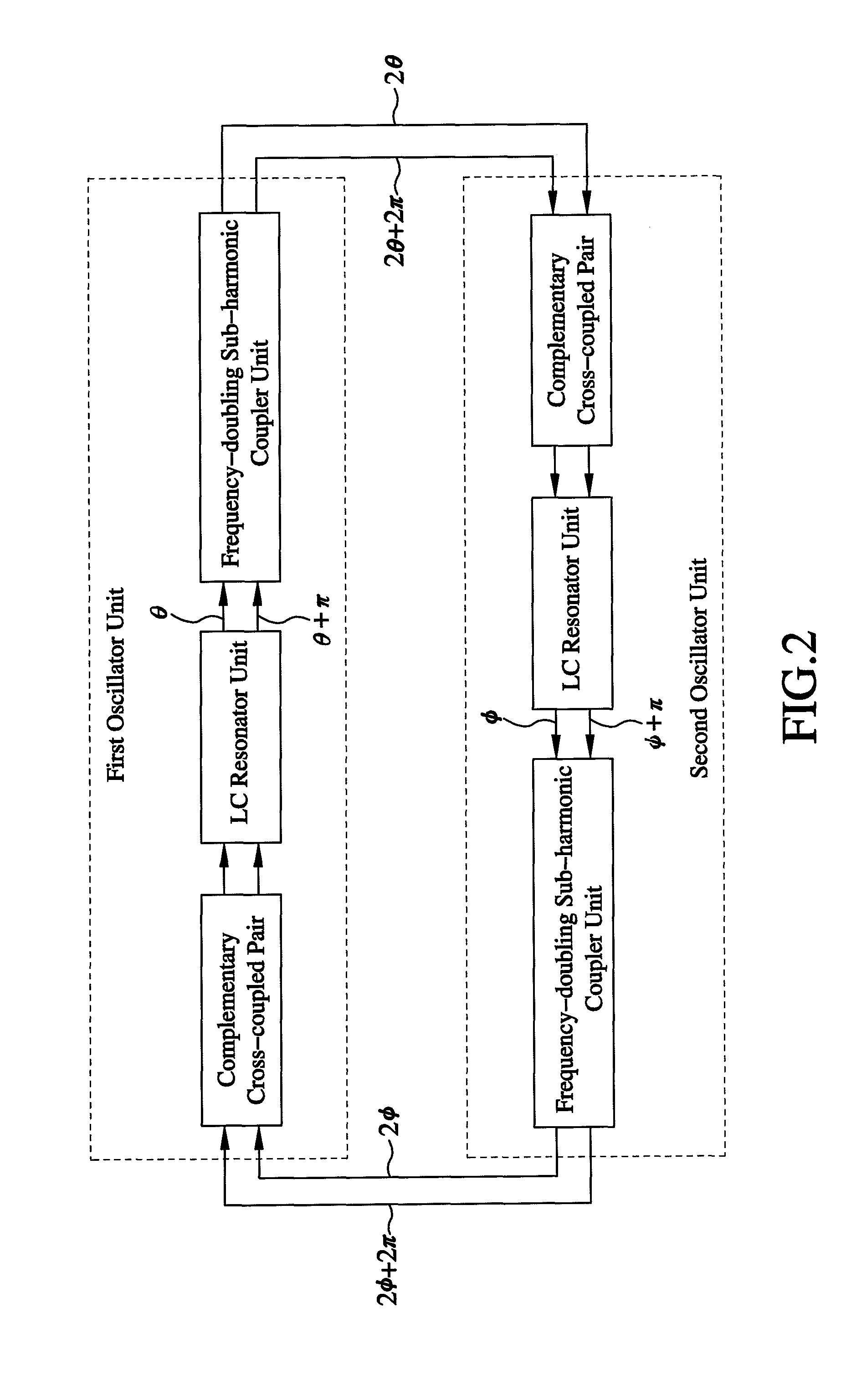
Quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator and method of providing four-phase output signals
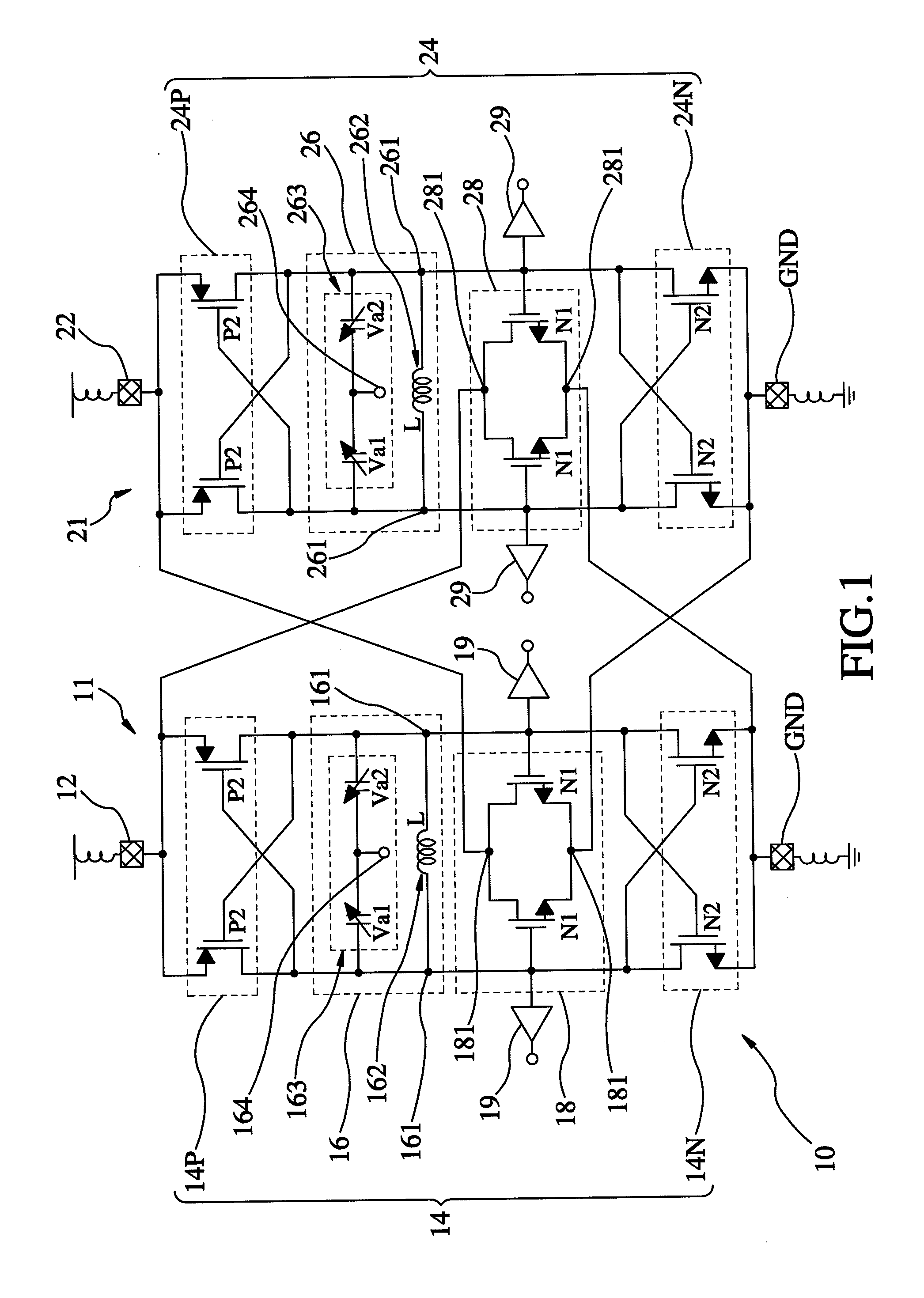
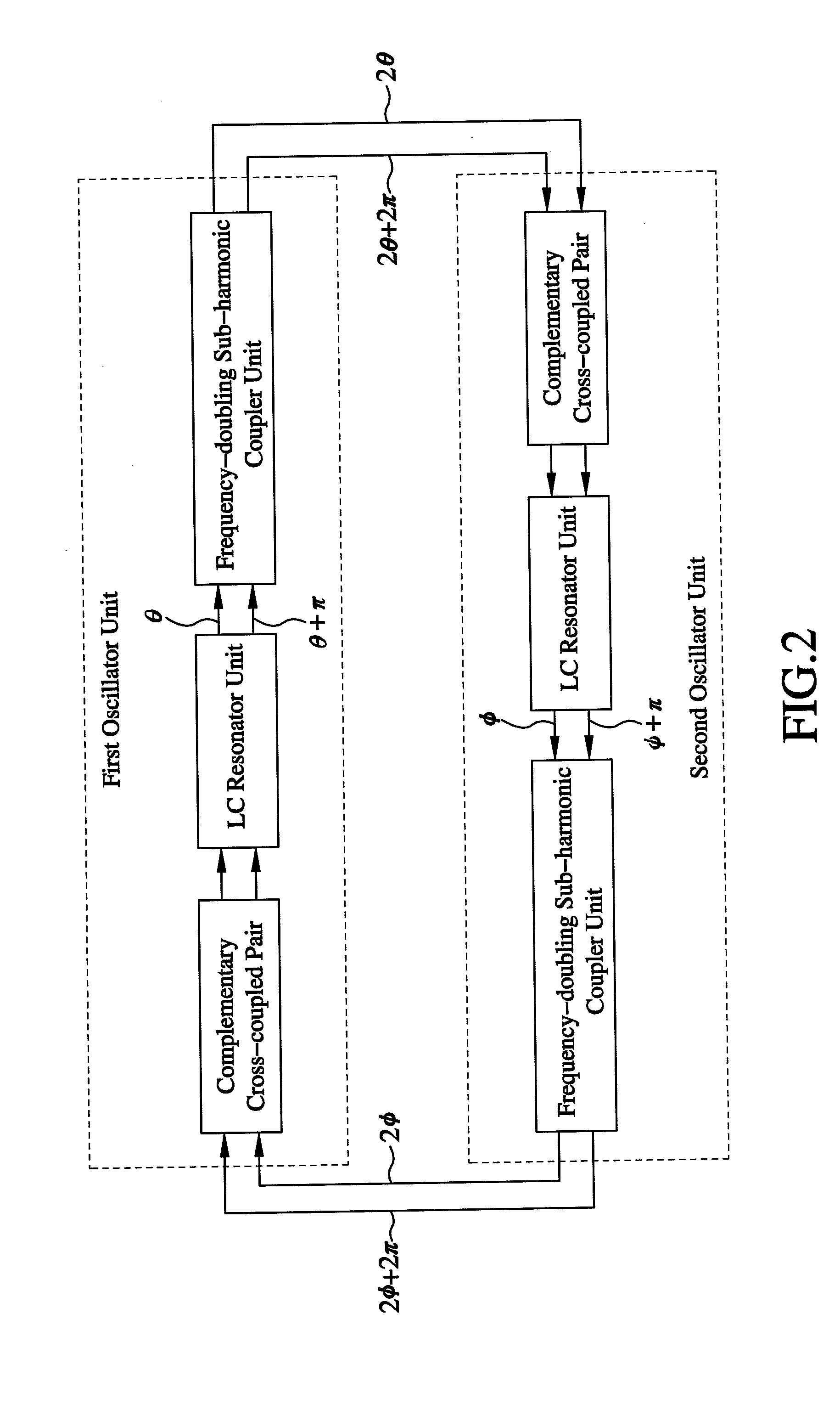
InactiveUS8456246B2Reduce impactAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlLc resonatorPhase difference
A quadrature VCO includes a first oscillator unit and a second oscillator unit. Each of the first and second oscillator unit is composed of a DC bias source, a complementary cross-coupled pair, an LC resonator unit, a frequency-doubling sub-harmonic coupler unit, and a ground terminal. When the LC resonator units of the first and second oscillator units are operated, four signals of different phases can be outputted via the output terminals. In this way, the output phase difference of the two oscillator units can keep 180 degrees and allow the two oscillator units to mutually inject signals to generate quadrature output signals.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Synchronization of nanomechanical oscillators
ActiveUS9660654B2Simple interfaceNanomechanical systems can be improvedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPulse automatic controlPhase noiseOscillator network
Synchronization of oscillators based on anharmonic nanoelectromechanical resonators. Experimental implimentation allows for unprecedented observation and control of parameters governing the dynamics of synchronization. Close quantitative agreement is found between experimental data and theory describing reactively coupled Duffing resonators with fully saturated feedback gain. In the synchonized state, a significant reduction in the phase noise of the oscillators is demonstrated, which is key for applications such as sensors and clocks. Oscillator networks constructed from nanomechanical resonators form an important laboratory to commercialize and study synchronization—given their high-quality factors, small footprint, and ease of co-integration with modern electronic signal processing technologies. Networks can be made including one-, two-, and three-dimensional networks. Triangular and square lattices can be made.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator and method of providing four-phase output signals
InactiveUS20120182078A1Reduce the impactReduce impactPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsLc resonatorHarmonic
A quadrature VCO includes a first oscillator unit and a second oscillator unit. Each of the first and second oscillator unit is composed of a DC bias source, a complementary cross-coupled pair, an LC resonator unit, a frequency-doubling sub-harmonic coupler unit, and a ground terminal. When the LC resonator units of the first and second oscillator units are operated, four signals of different phases can be outputted via the output terminals. In this way, the output phase difference of the two oscillator units can keep 180 degrees and allow the two oscillator units to mutually inject signals to generate quadrature output signals.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Synchronization of transmitter and receiver frequencies in multiaccess networks
InactiveCN1663298ASynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio equipmentFrequency spectrum
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for integrating the operation of a plurality of radio networks. The plurality of radio networks may utilize a common frequency spectrum. The radio center frequencies are adjusted so that frequency drift in relation to each radio network is reduced. Also, system information about the plurality of radio networks may be sent on a radio channel that is associated with one of the radio networks. An oscillator synchronizer synchronizes a first reference oscillator that is associated with a first radio network and a second reference oscillator that is associated with a second radio network in order to adjust radio center frequencies. With a variation of the embodiment, a reference oscillator of one of the radio network adjusts center frequencies for radios that are associated with the other radio network.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Power supply and DC-DC-conversion
ActiveUS8686801B2Pulse generation by bipolar transistorsPulse automatic controlTransverterSwitching signal
In an embodiment of a converter, a first oscillator provides switching signals for switching between charging and discharging of a capacitor, and a second oscillator is configured to add an offset voltage or a feedback-current-dependent voltage to a sawtooth waveform generated by the second oscillator switched in synchronism with the first oscillator.
Owner:NXP BV
Crystal reference clock and radio localization receiver
InactiveUS20080174374A1Easy to handleRadiation pyrometryPulse automatic controlOscillator syncPower consumption
Device and method for temperature compensation in a clock oscillator using quartz crystals, which integrates dual crystal oscillators. The minimal power consumption is achieved through an efficient use of a processor in charge of the synchronisation of the two oscillators. The invention is particularly adapted for the provision of a precise reference clock in portable radiolocalization devices
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Voltage-controlled ring oscillator with delay line
InactiveUS20160173069A1Pulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase shiftedPhase oscillator
The invention relates to a multi-phase oscillator for generating multiple phase-shifted oscillator signals including: a ring oscillator having a number of concatenated oscillator delay cells which are interconnected to generate an oscillator signal, wherein phase-shifted oscillator signals are generated between the oscillator delay cells; a phase-blending unit configured to receive two phase-shifted oscillator signals and to generate a mid-phase oscillator signal whose phase shift is between the shifts of the two phase-shifted oscillator signals; and an interpolator delay line having a number of concatenated interpolator delay cells to generate further phase-shifted oscillator signals.
Owner:IBM CORP
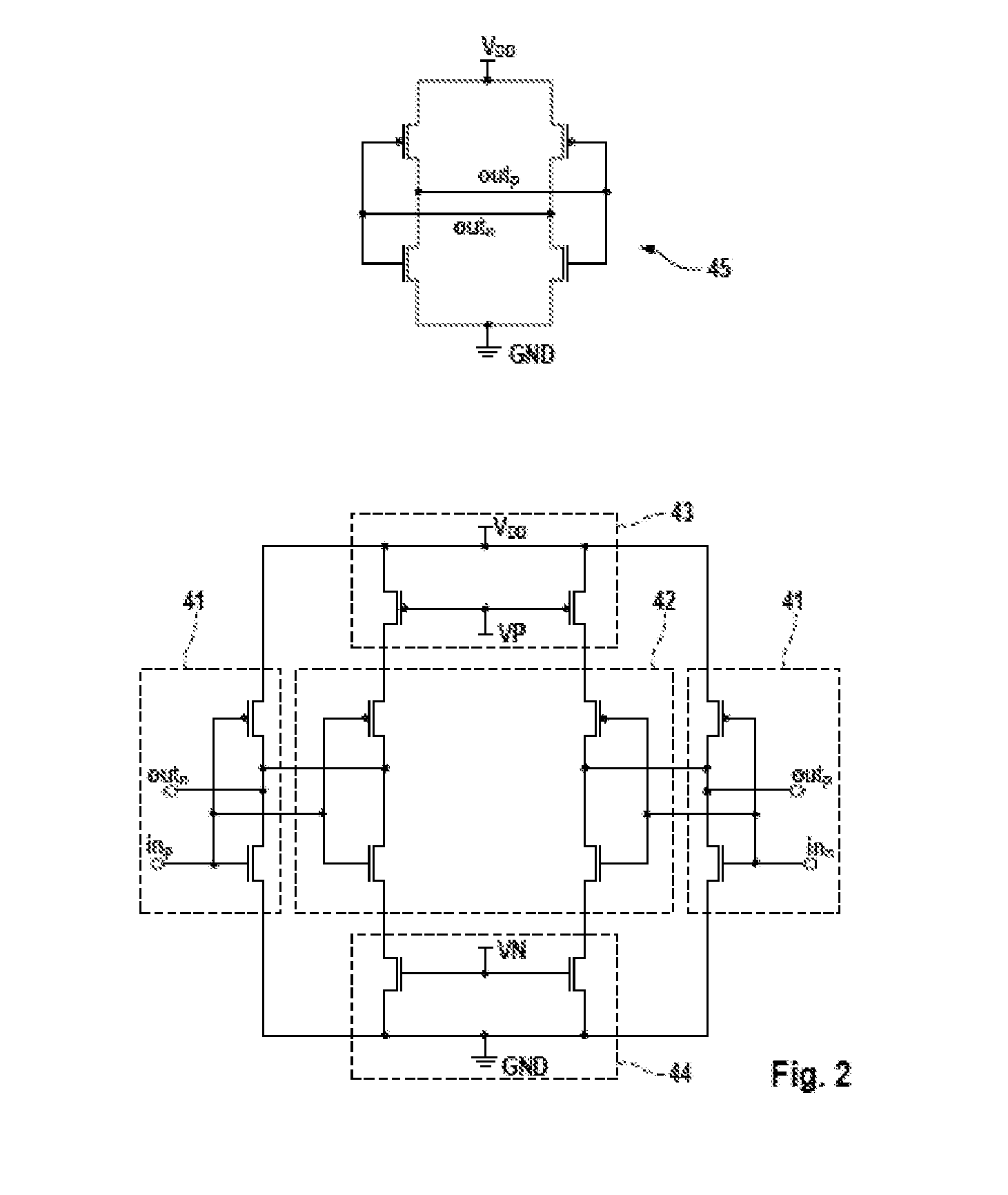
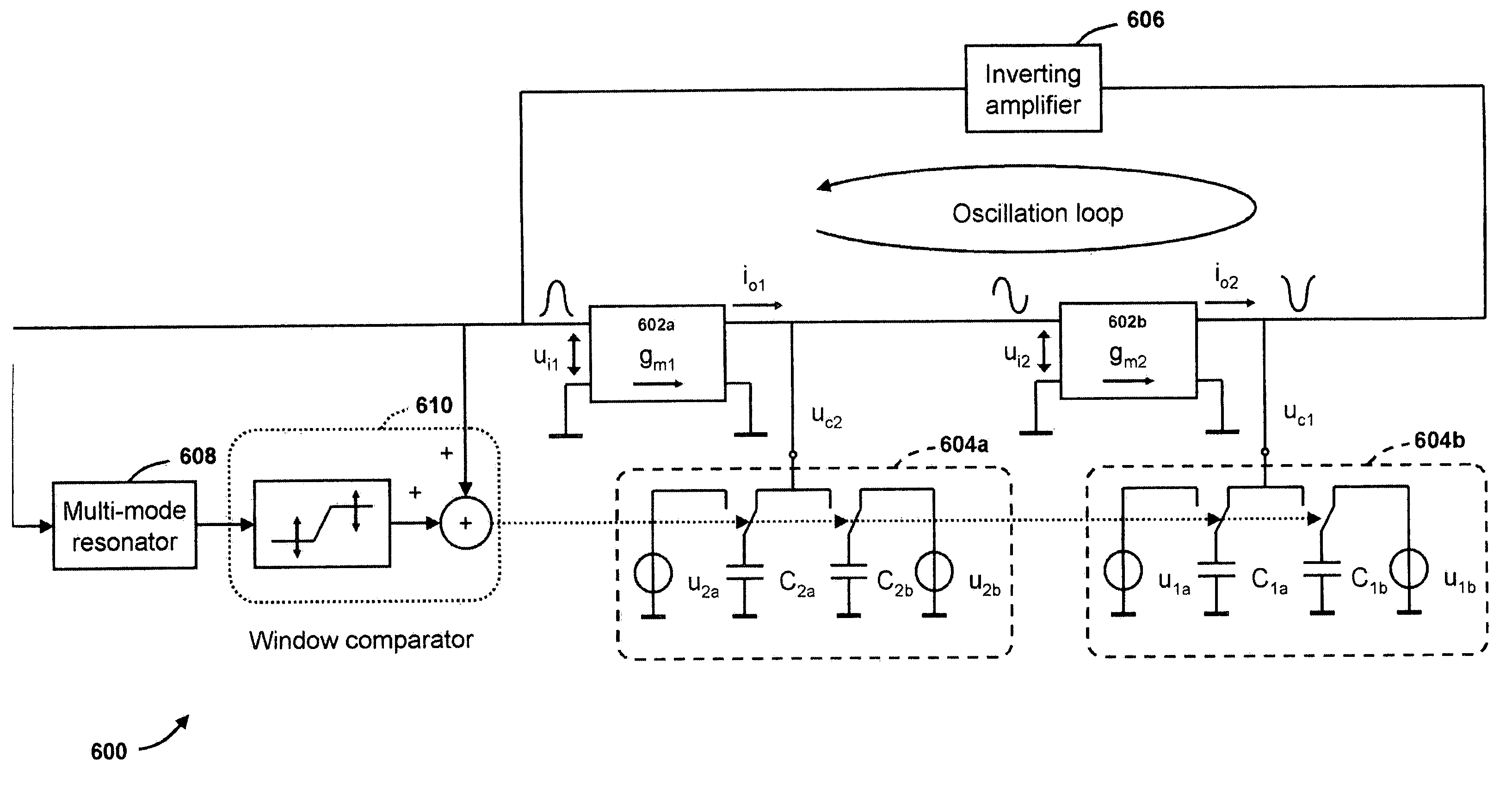
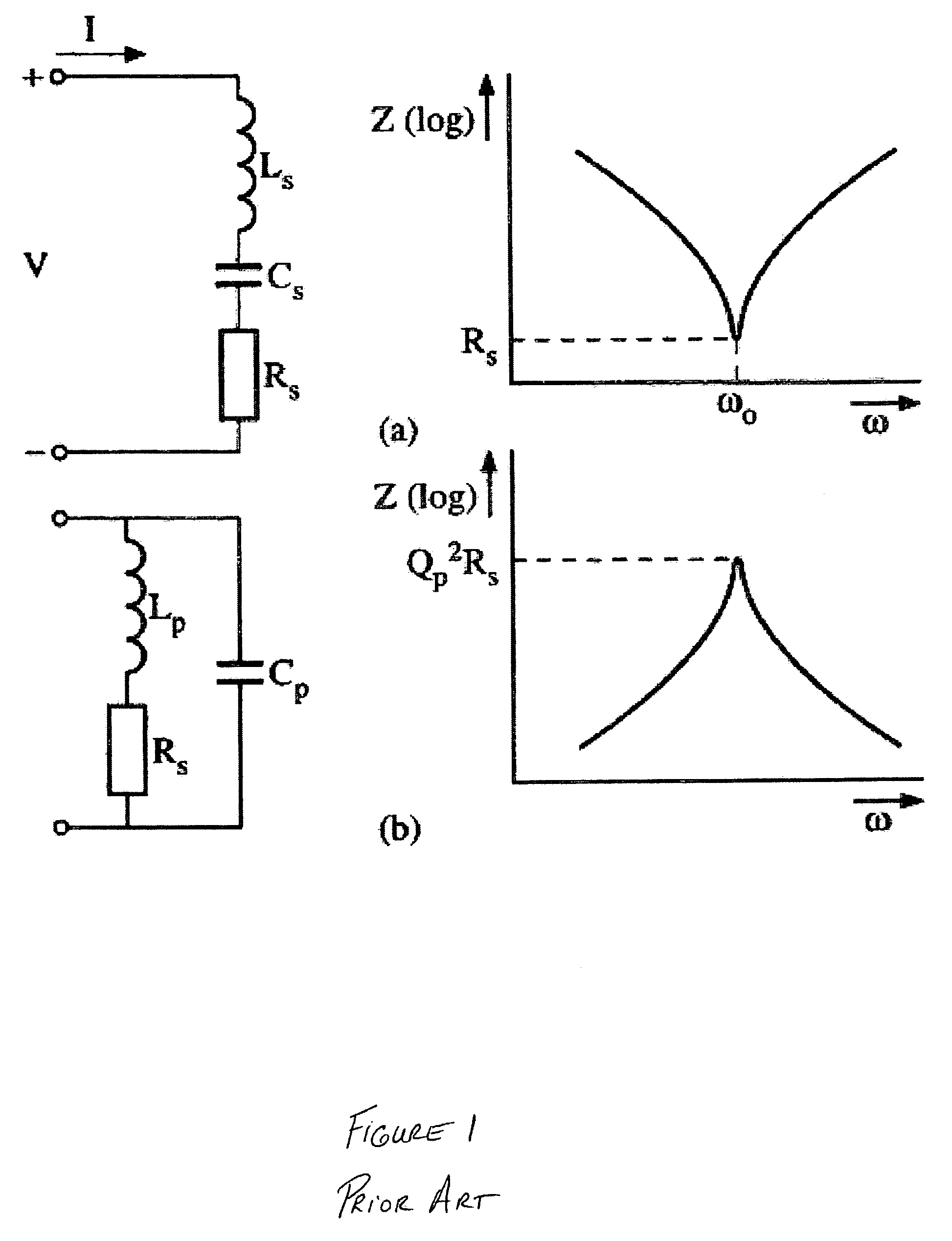
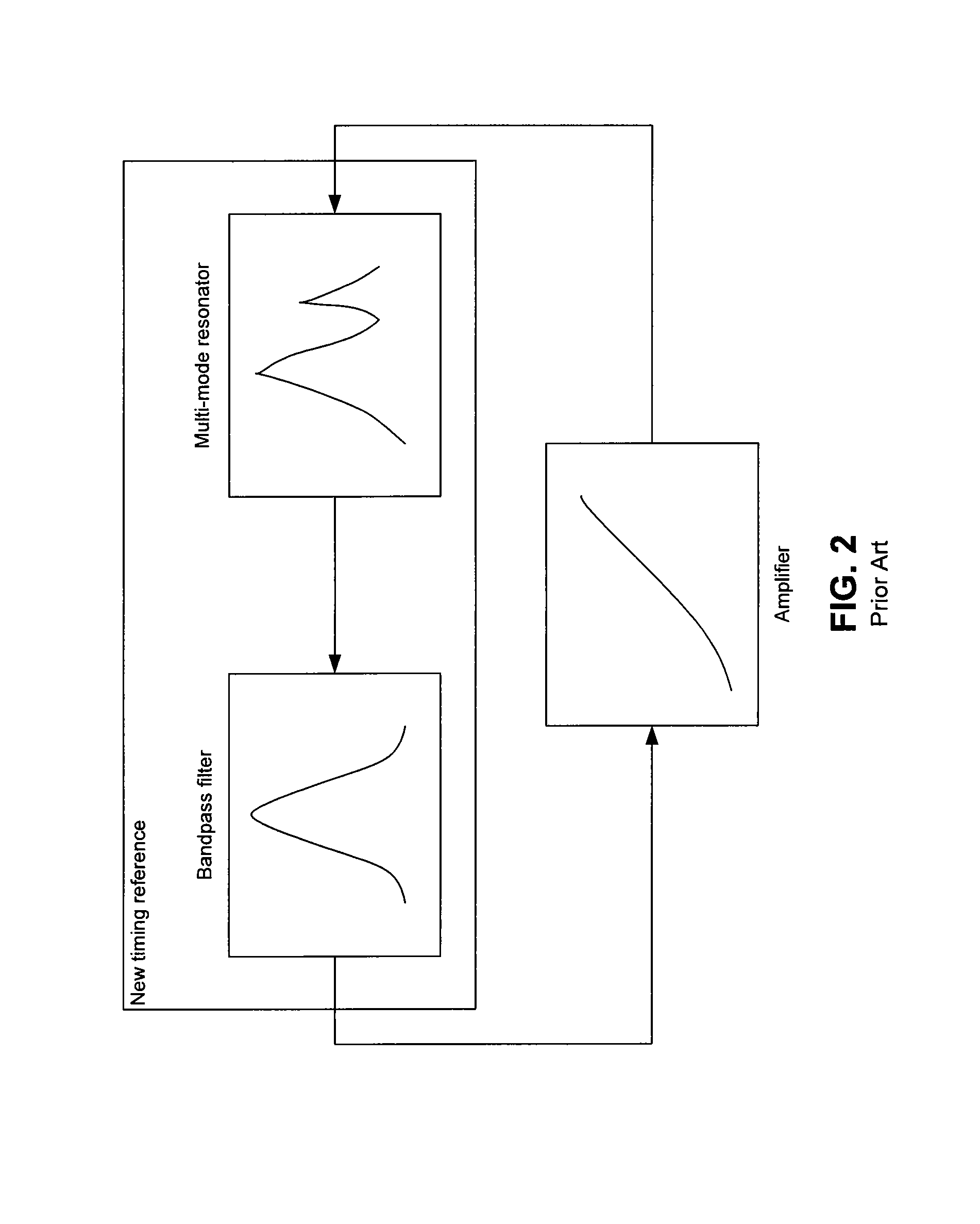
Resonance mode selection using a resonator-synchronized second-order oscillator
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com