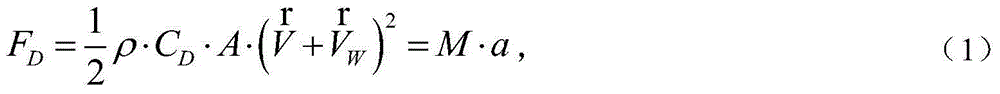Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Orbital speed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
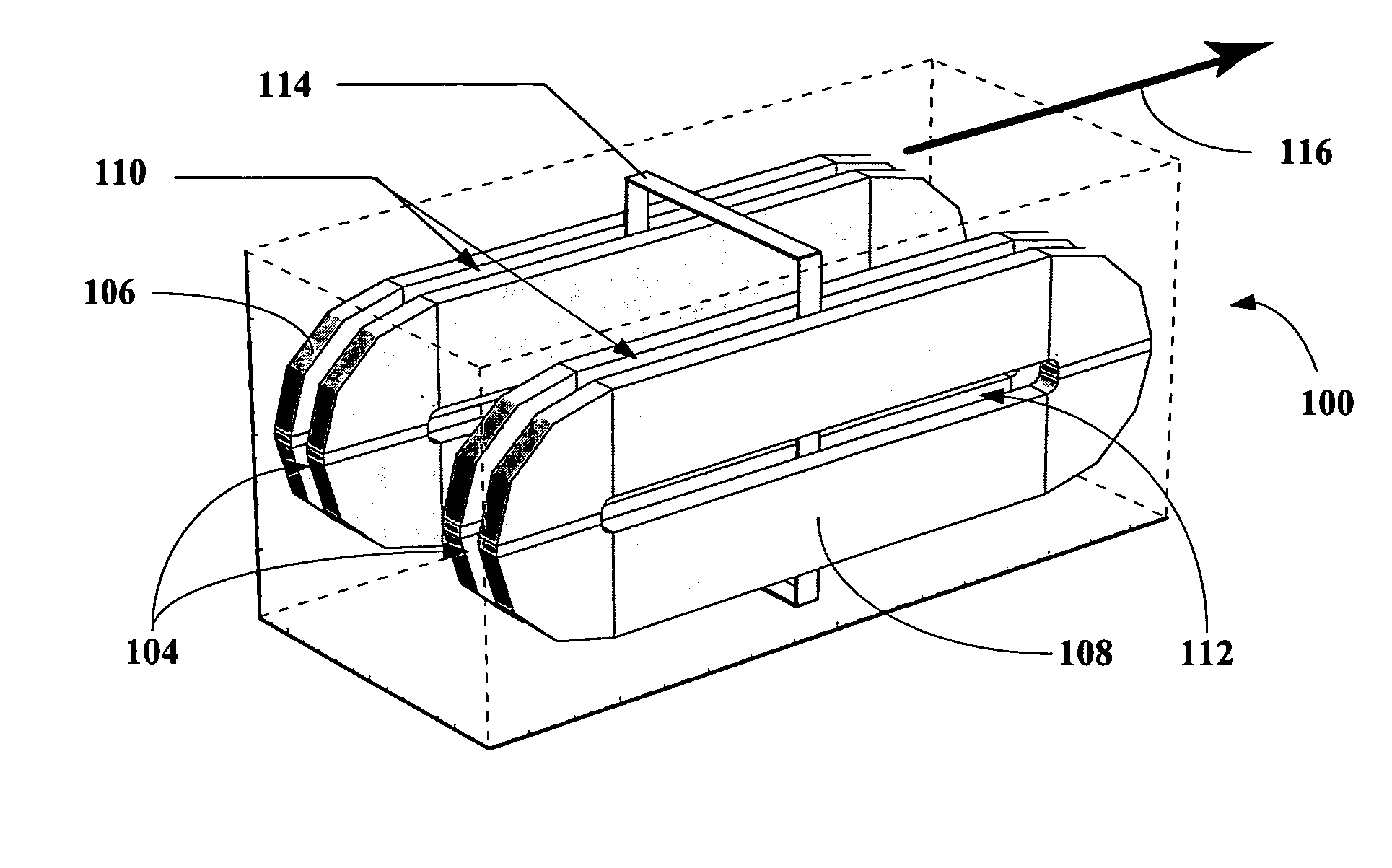
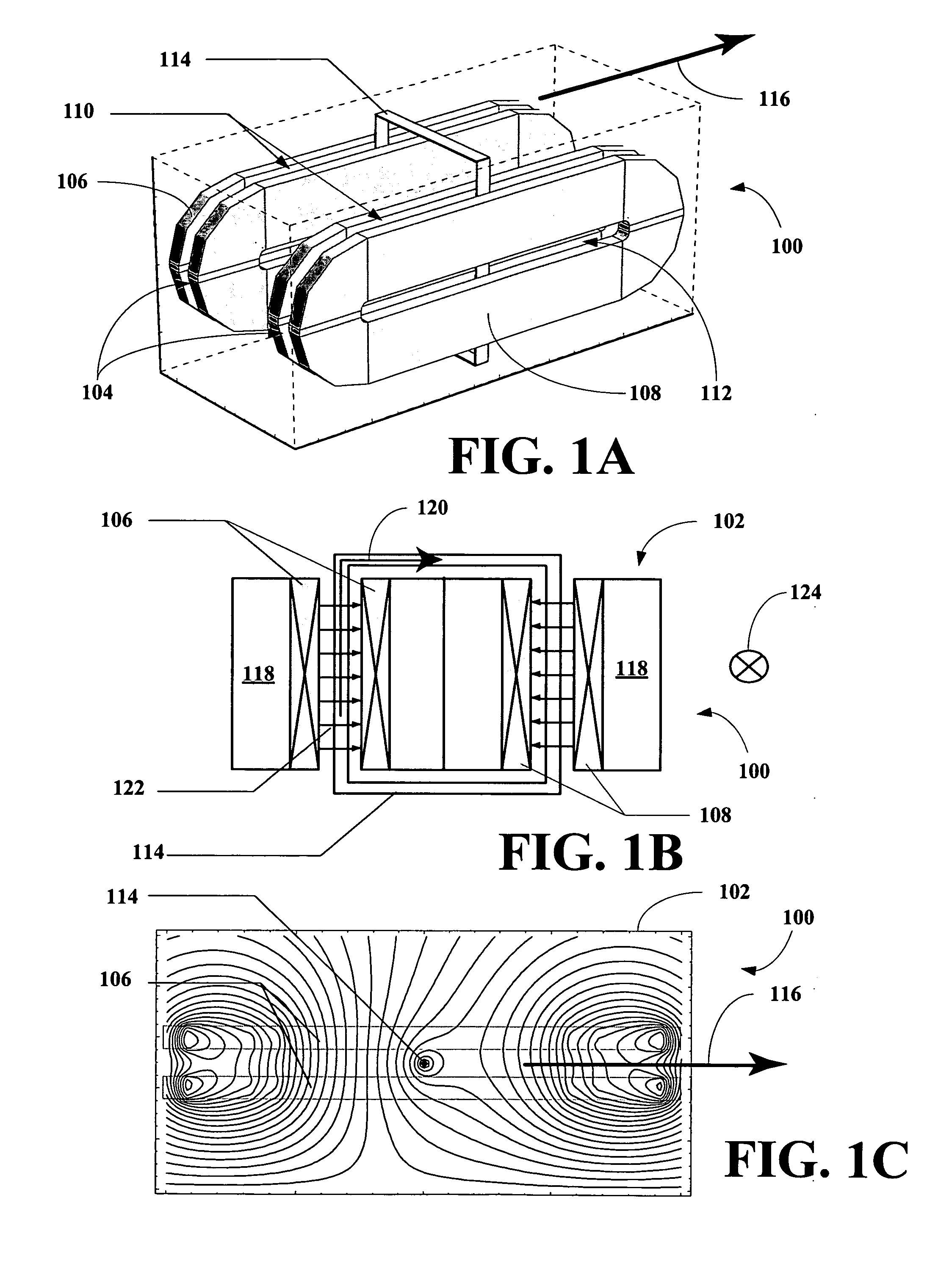
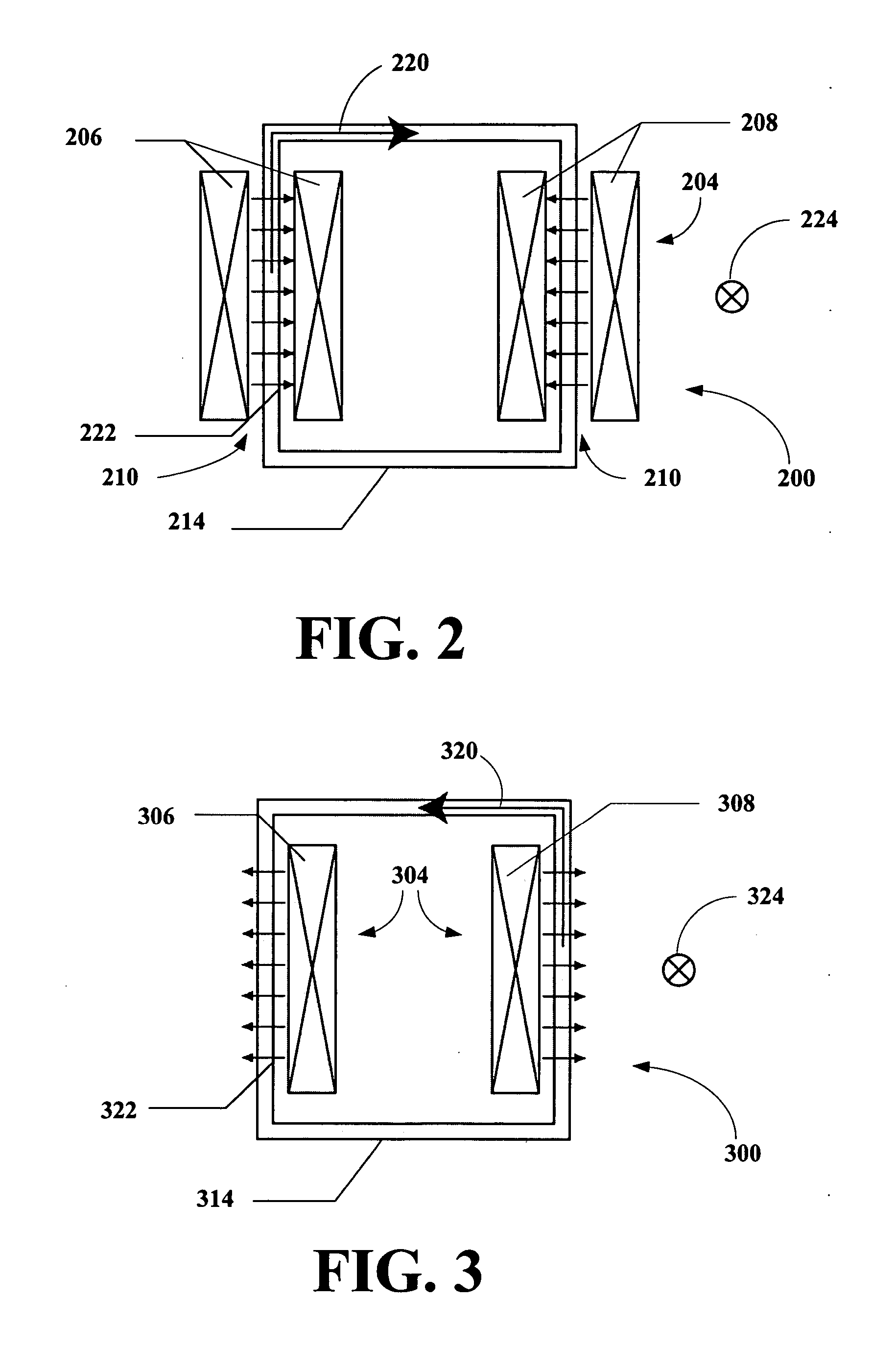
In gravitationally bound systems, the orbital speed of an astronomical body or object (e.g. planet, moon, artificial satellite, spacecraft, or star) is the speed at which it orbits around either the barycenter or, if the object is or relative to its center of mass.
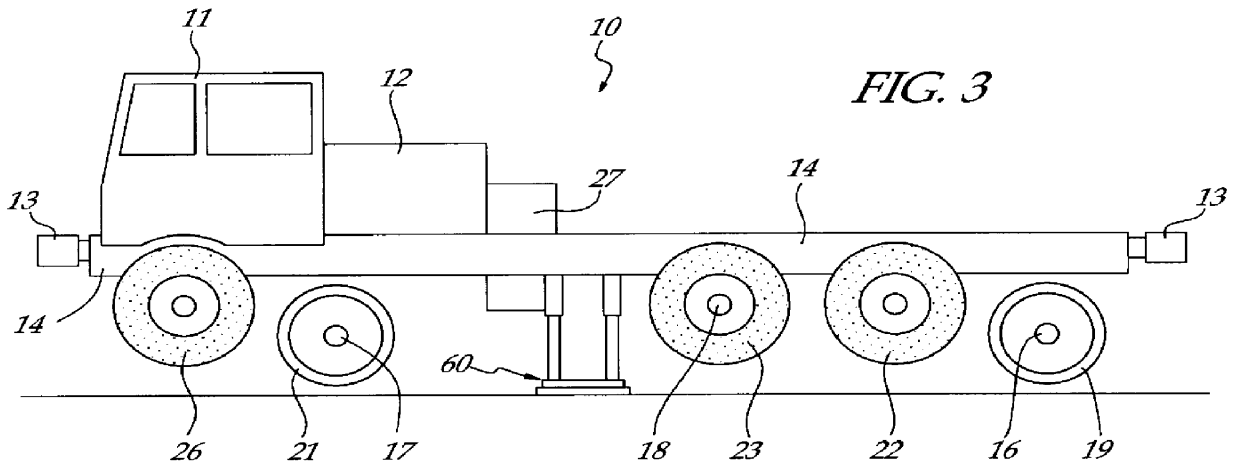
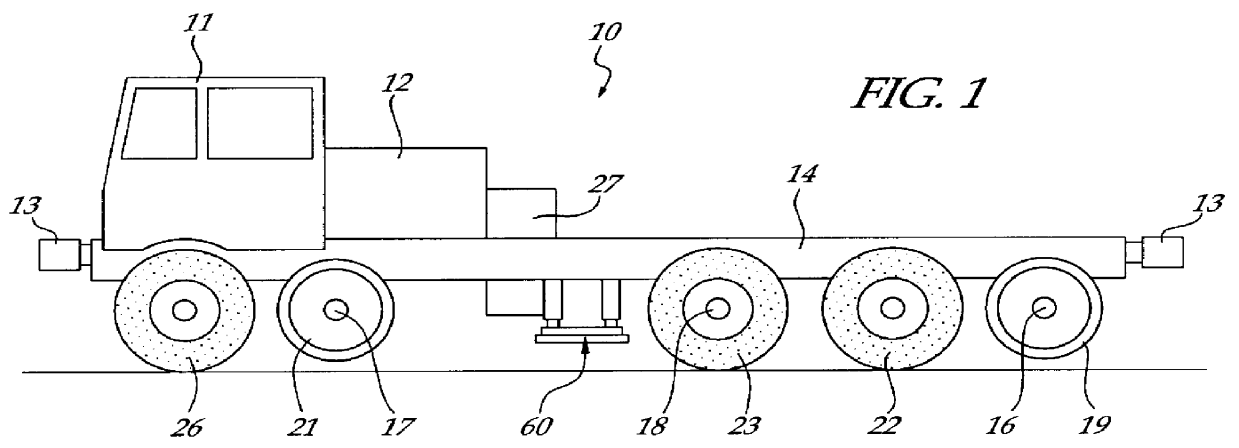
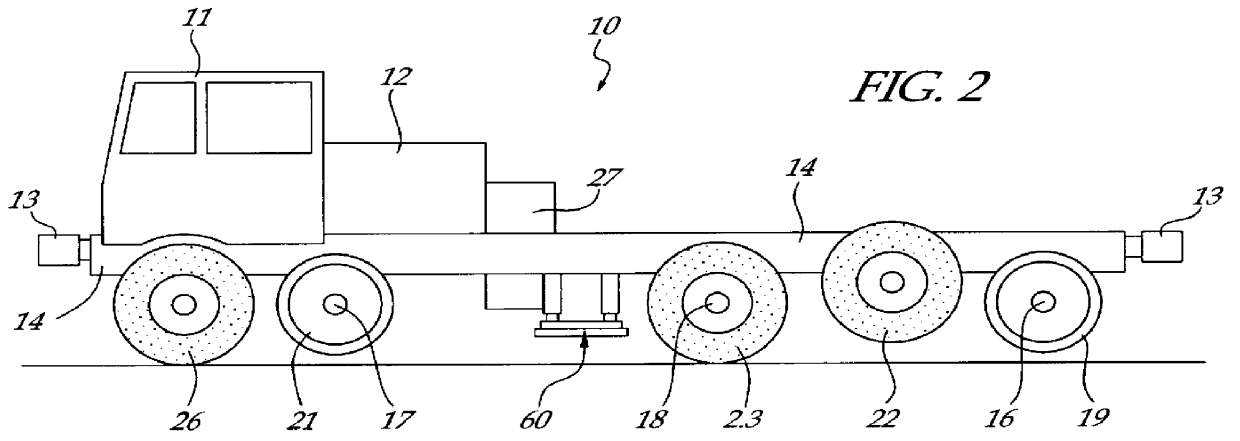
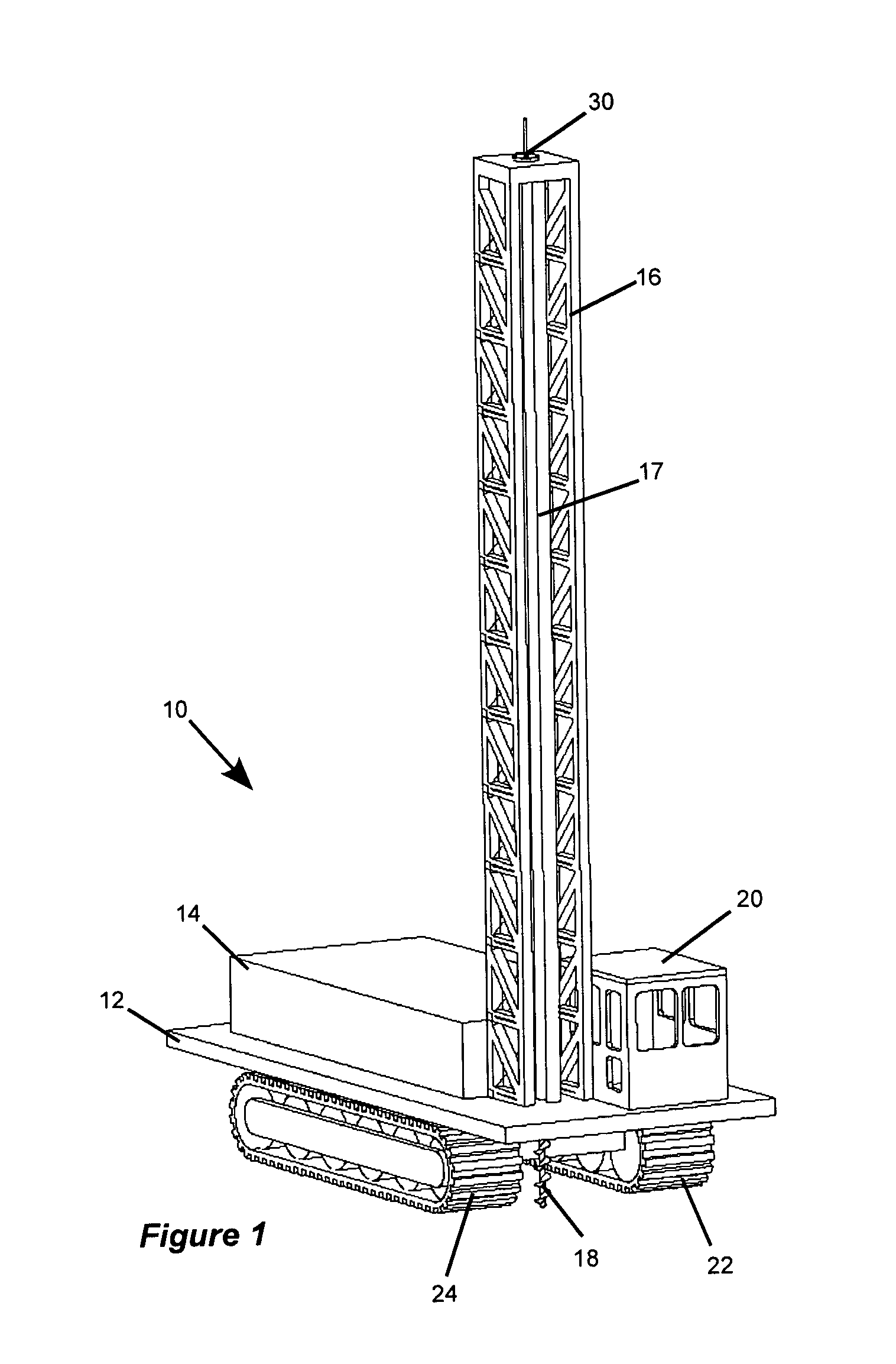
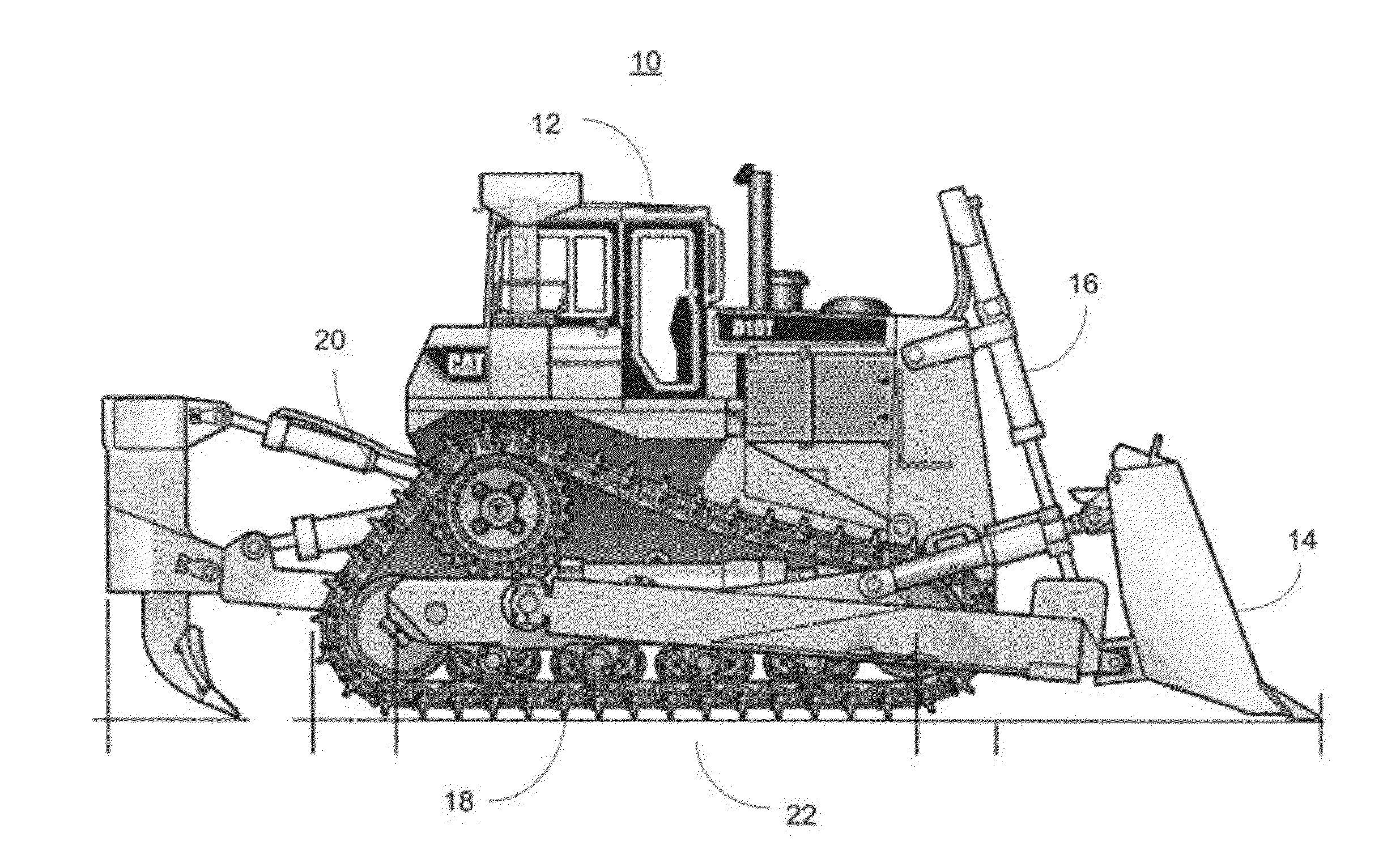
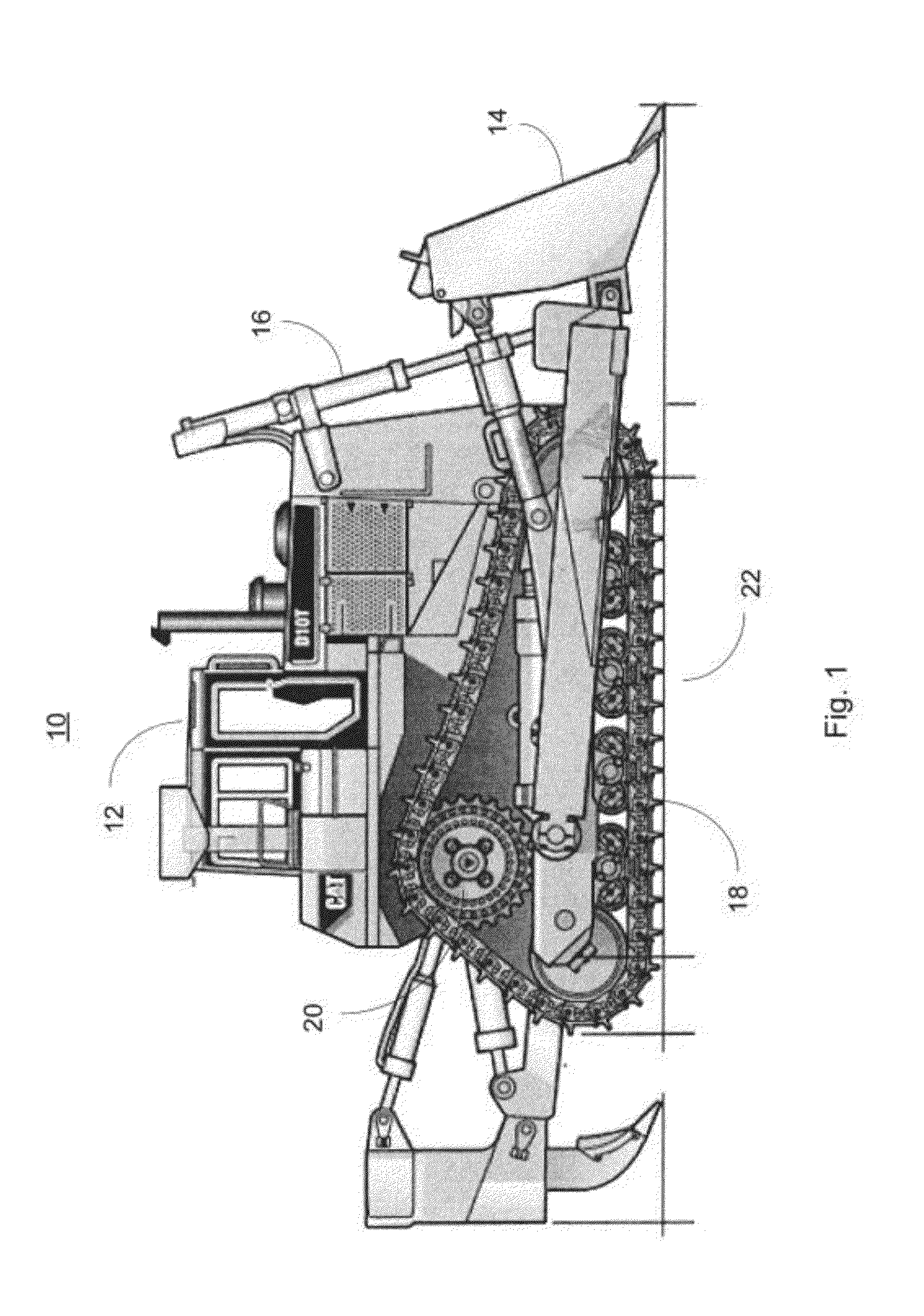
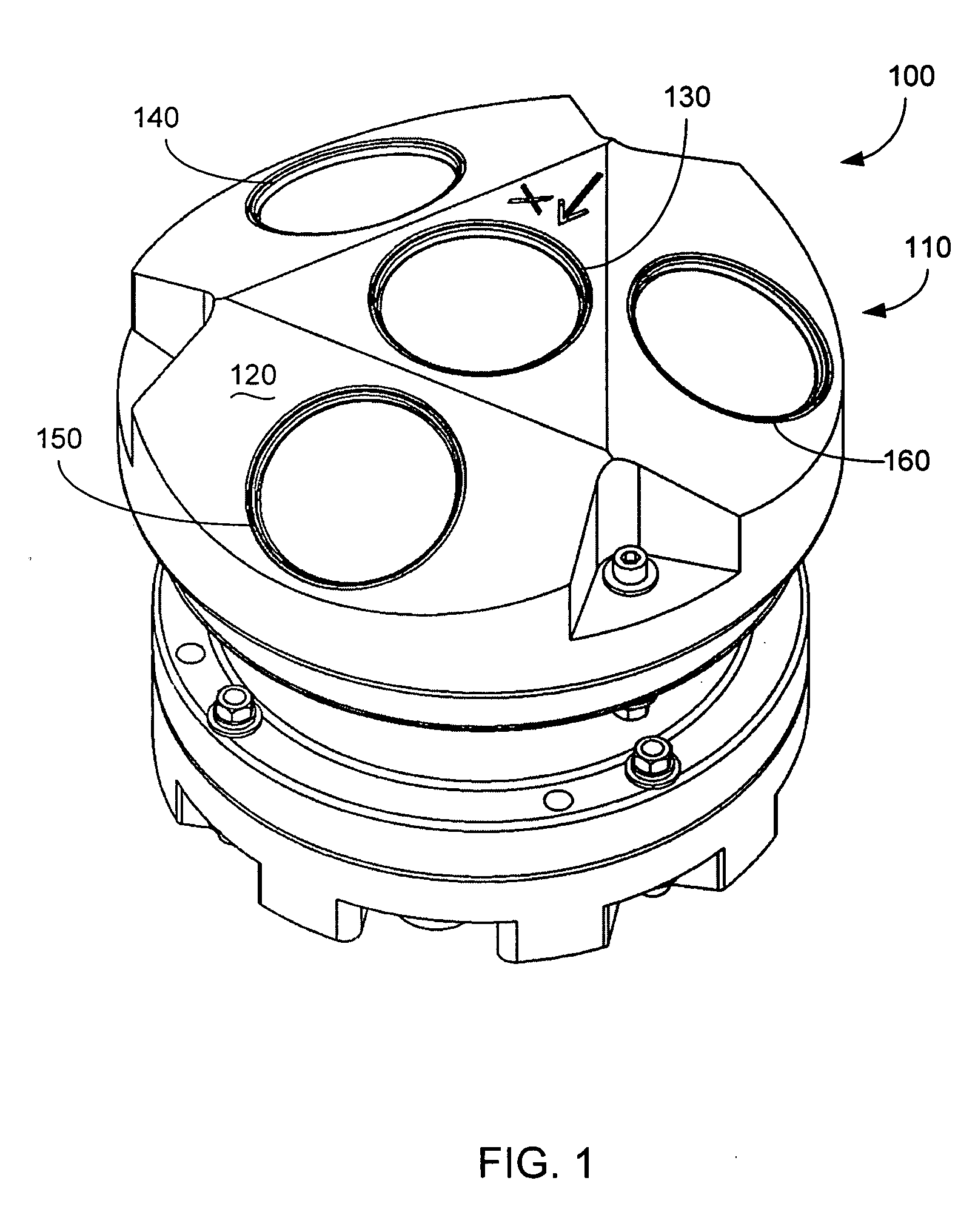
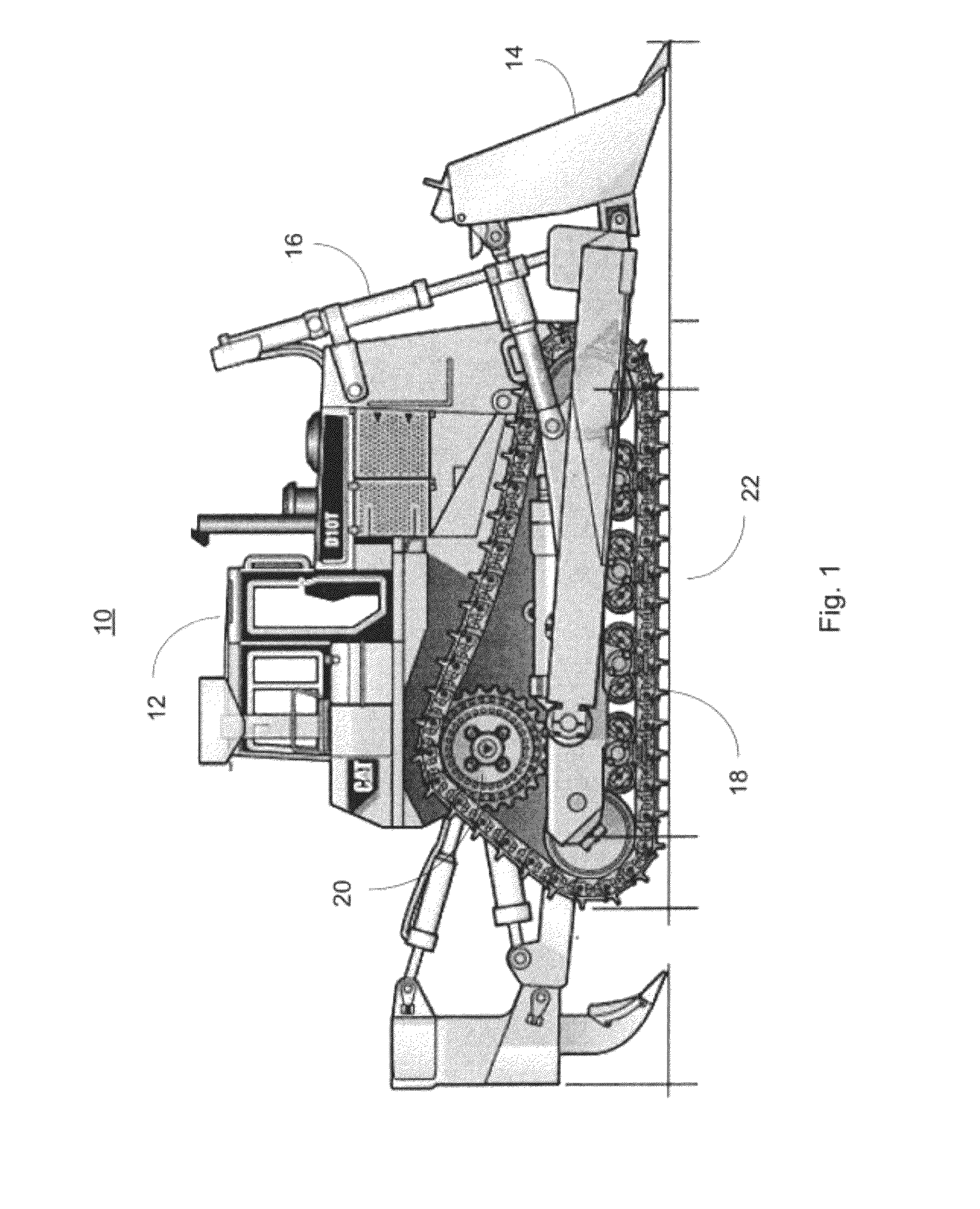
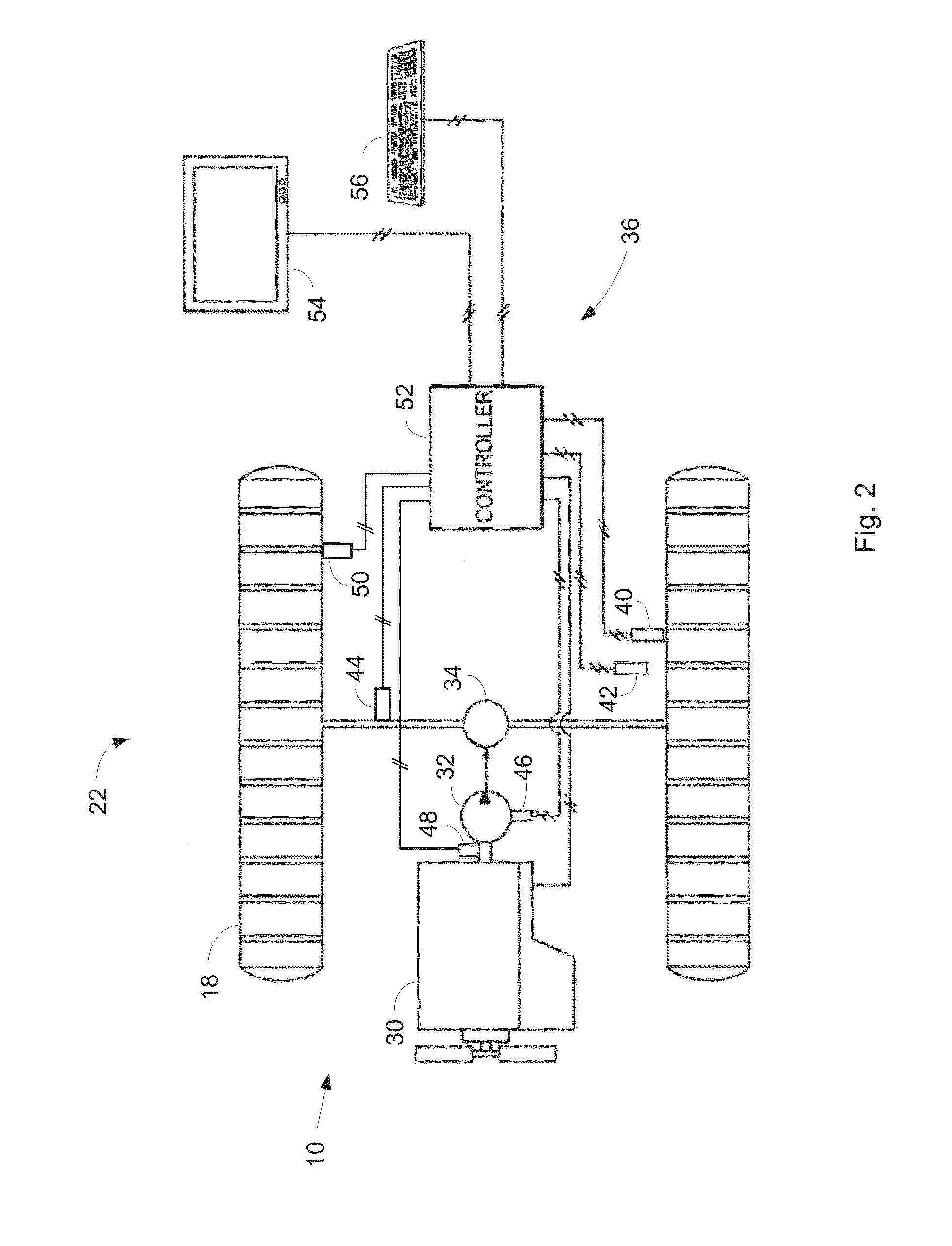
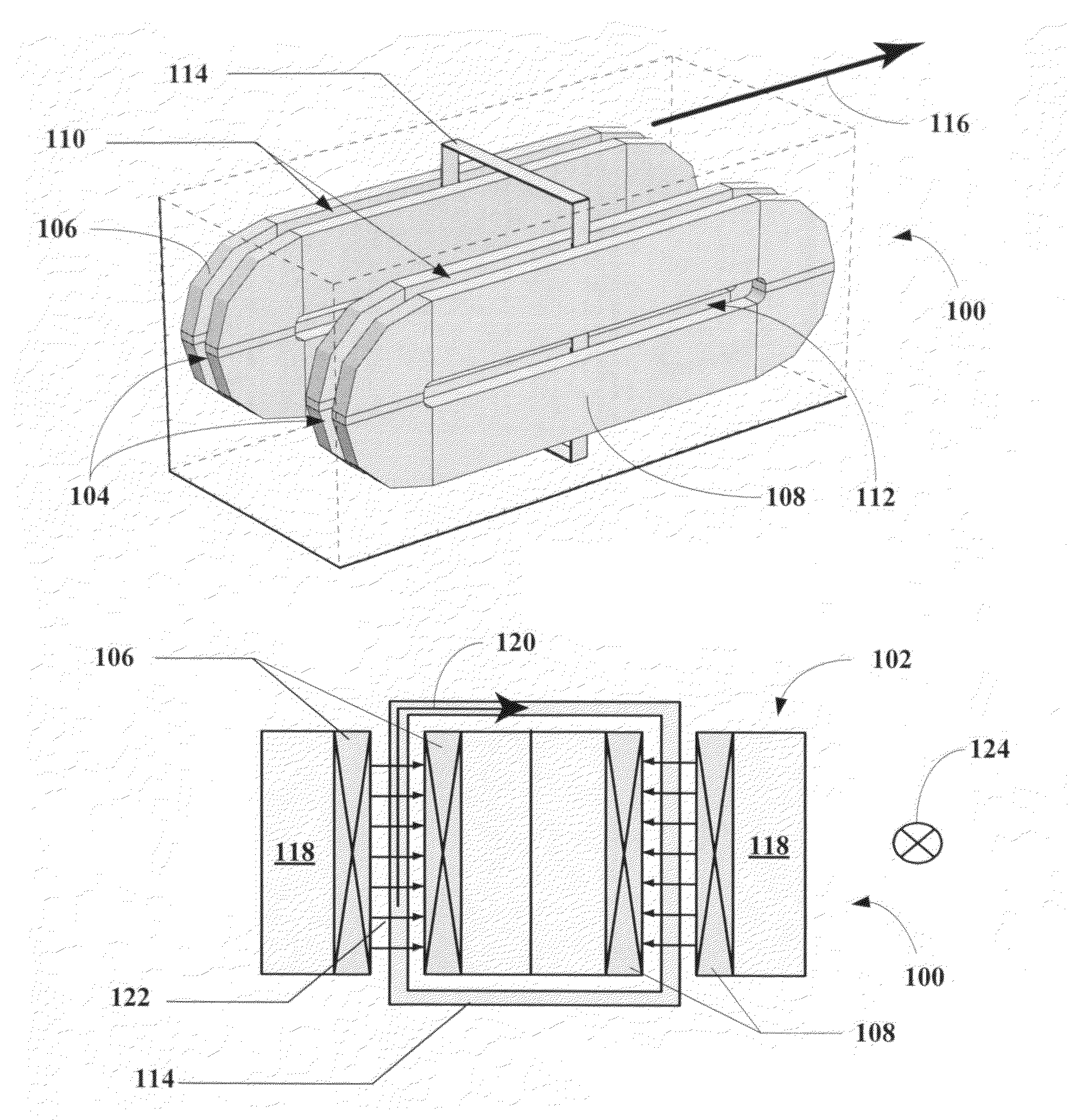
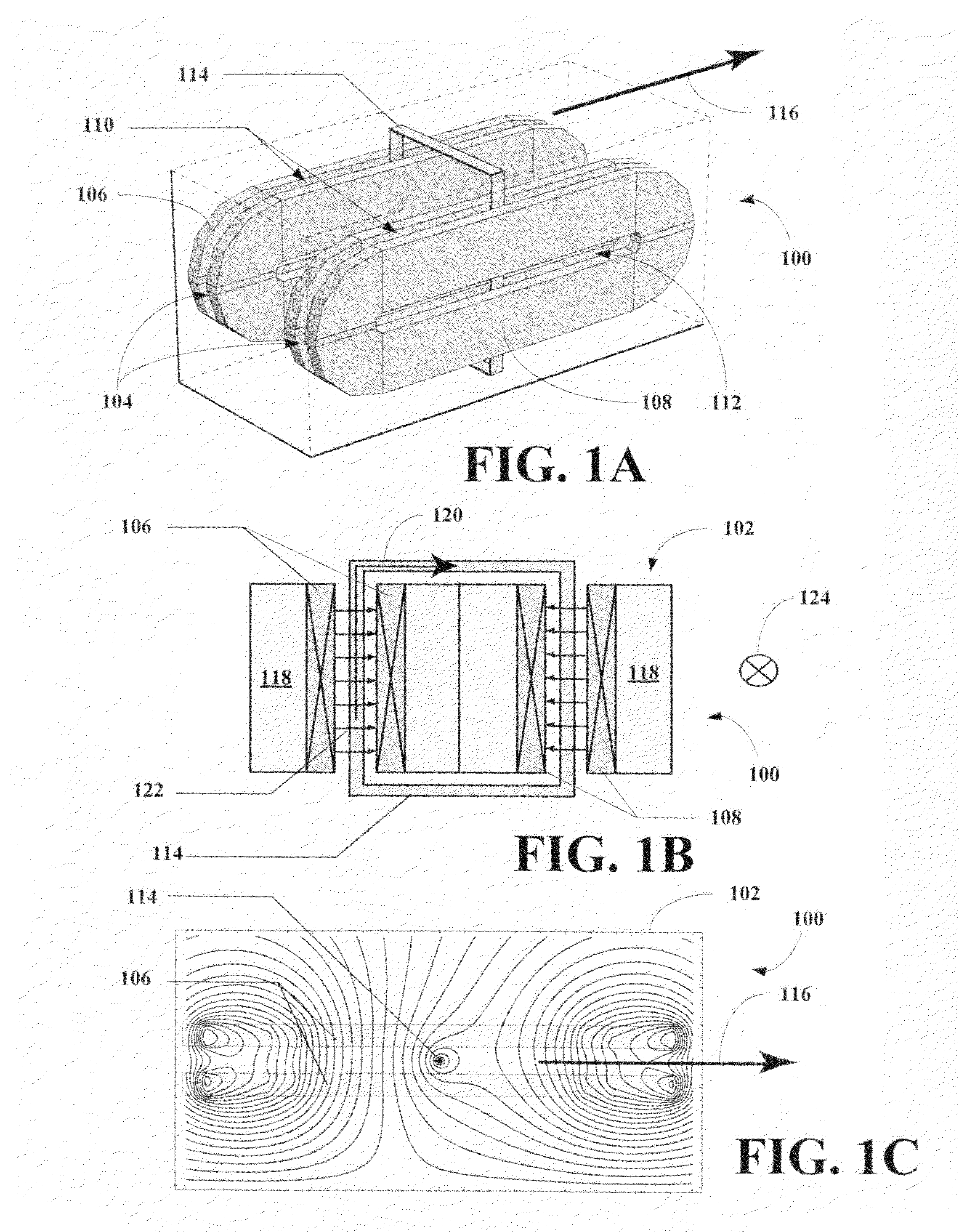
Mobile track vehicle
InactiveUS6021719AHigh and safe speedEasy to operateRail and road vehiclesCarriagesLevel crossingRoad crossing
An improved self-propelled mobile track vehicle (MTV) capable of traveling by road at normal highway speeds and traveling by rail after conversion at a narrow railroad crossing by producing a device for rotating the vehicle 90 degrees. The vehicle is powered by a diesel engine driving through a power shift transmission to the roadway and railway axles. A significant advantage over other types of road / rail vehicles is that 100 percent of the vehicle's weight is carried on the rail wheels, which are powered and braked, thereby allowing higher and safer rail speeds. One way to convert the vehicle from roadway travel to railway travel is to maneuver it into a position parallel to the track at a road crossing. The rail axles are then extended and road axles retracted. In addition, a turntable mounted at the vehicle's center of gravity also allows the vehicle to convert at a narrow road crossing. While at railway / roadway crossing the unit raises and rotates 90 to align with the desired roadway or railway. The vehicle can assist in starting a train by extending the powered road axle so that the inner rubber tires contact the rail and the high traction of rubber on rail assists in increasing starting traction of the vehicle thus allowing the vehicle to assist in starting a train.
Owner:KERSHAW JR ROYCE G
Configuration of a two-track tractor
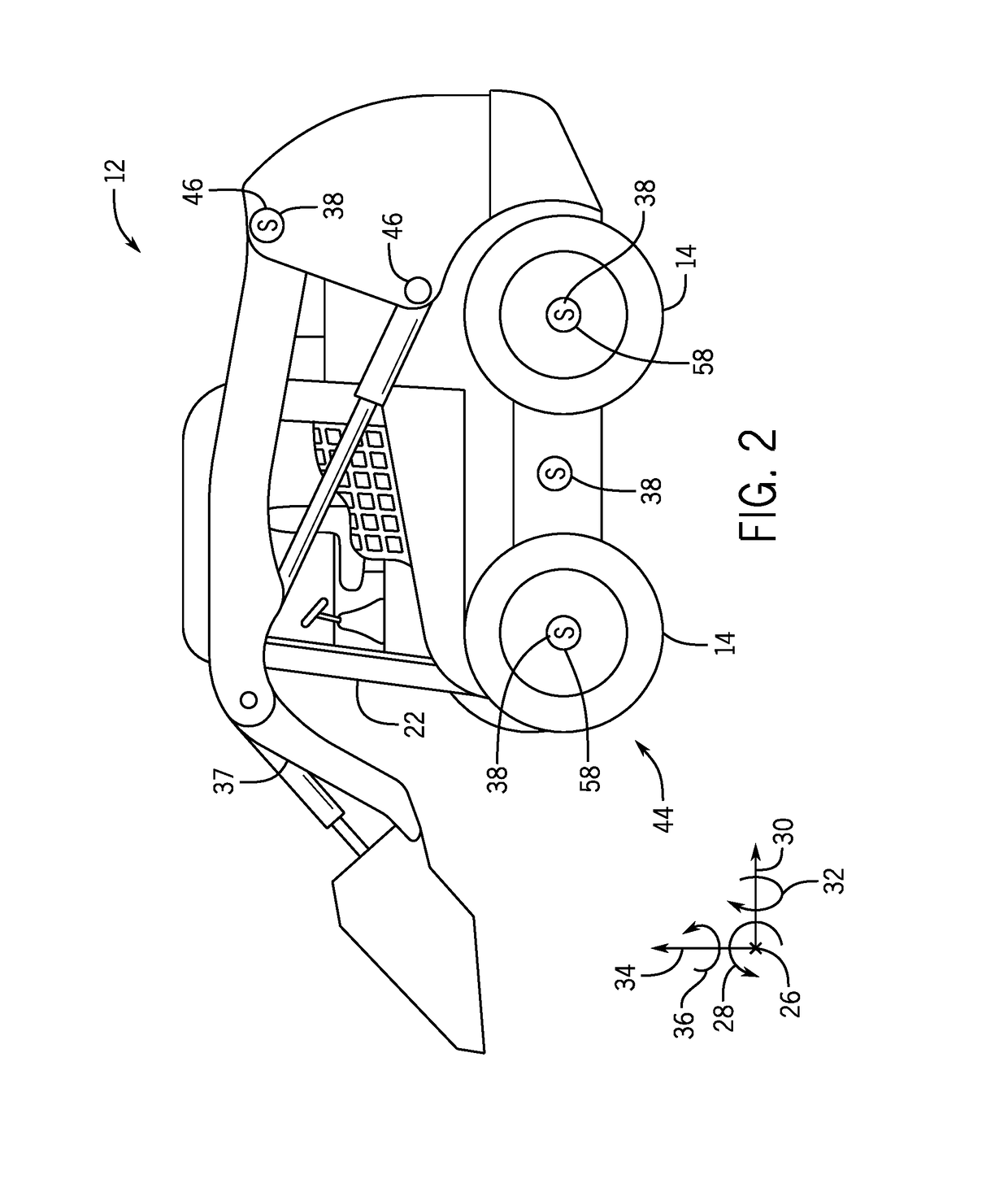
ActiveUS20130192905A1Minimize rubber tread wearMinimize tread wearVehicle body stabilisationTractorsVertical loadOrbital speed
A tractor configuration includes a mainframe structure, a control station having a means of controlling the tractor, an undercarriage system having one left side and one right side track assembly, a wheel mechanism containing one or more wheels located forward of the track assemblies, a power train for forcing both track assemblies to travel at the same or different speeds, a controller responsible for exerting force to transfer vertical load back and forth between the front portion of the track assemblies and the wheel mechanism and controlling the amount of weight carried by the wheel mechanism. The controller causes or allows the wheel or wheels of the wheel mechanism to follow the tractor's curved path caused by track speed difference.
Owner:CLAAS INDTECHN
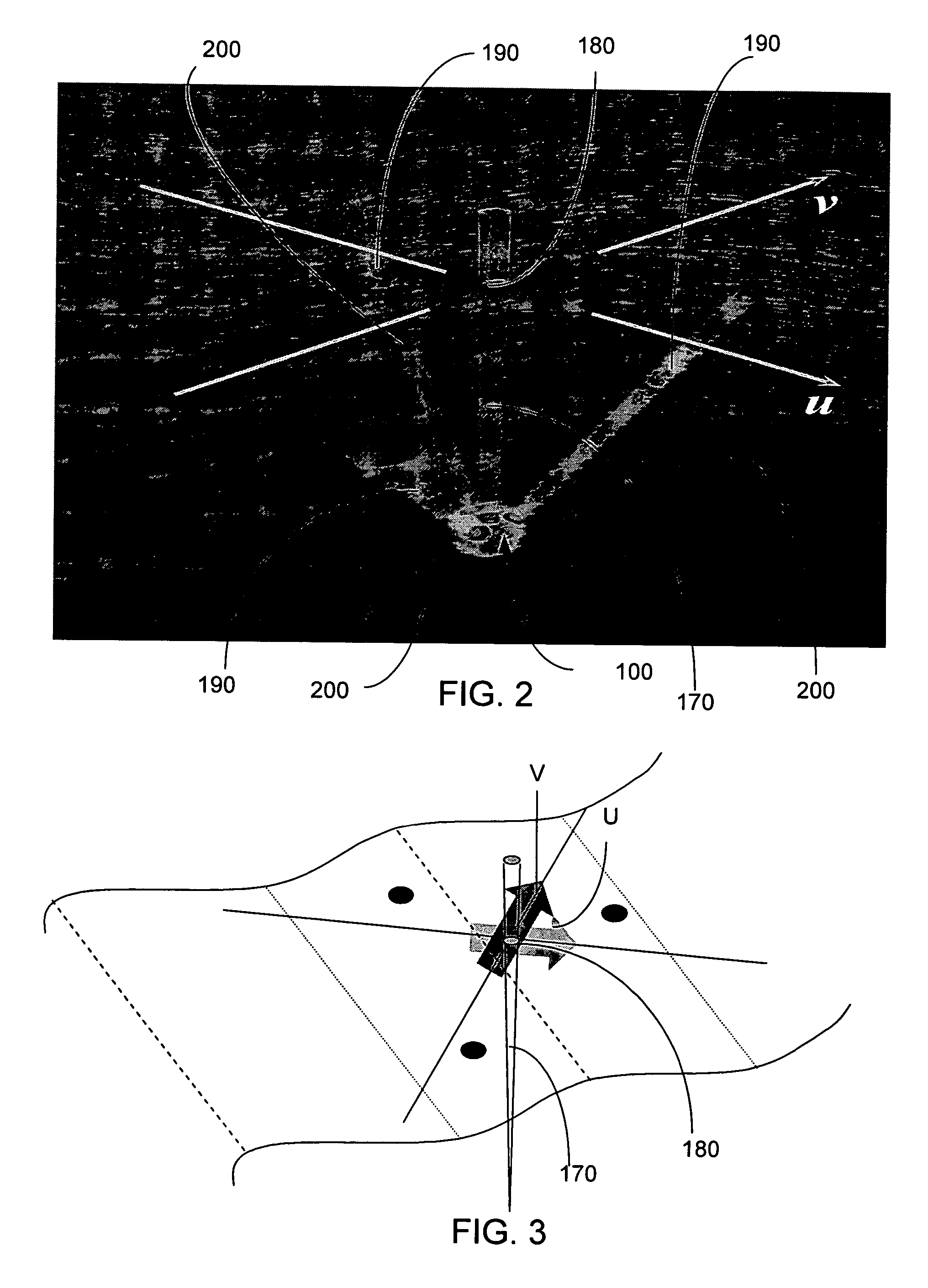
System and Method for Determining Directional and Non-directional Fluid Wave and Current Measurements
A system for determining the directional properties of surface waves or internal waves of a fluid medium includes a sonar system having a plurality of transducers for generating respective, separate acoustic beams and receiving echoes from one or more range cells located substantially within the beams; and a computer program for determining the directional properties associated with the surface waves or internal waves from the received echoes, wherein the computer program determines along-beam velocities along the separate acoustic beams and combines the along-beam velocities to form an equivalent orbital velocity vector. The system is mounted on or in a sub surface buoy that can move or rotate during measurement and includes a motion sensor measuring six degrees of freedom to account for horizontal velocity and vertical displacement in the subsurface buoy mounted sonar system.
Owner:NORTEK
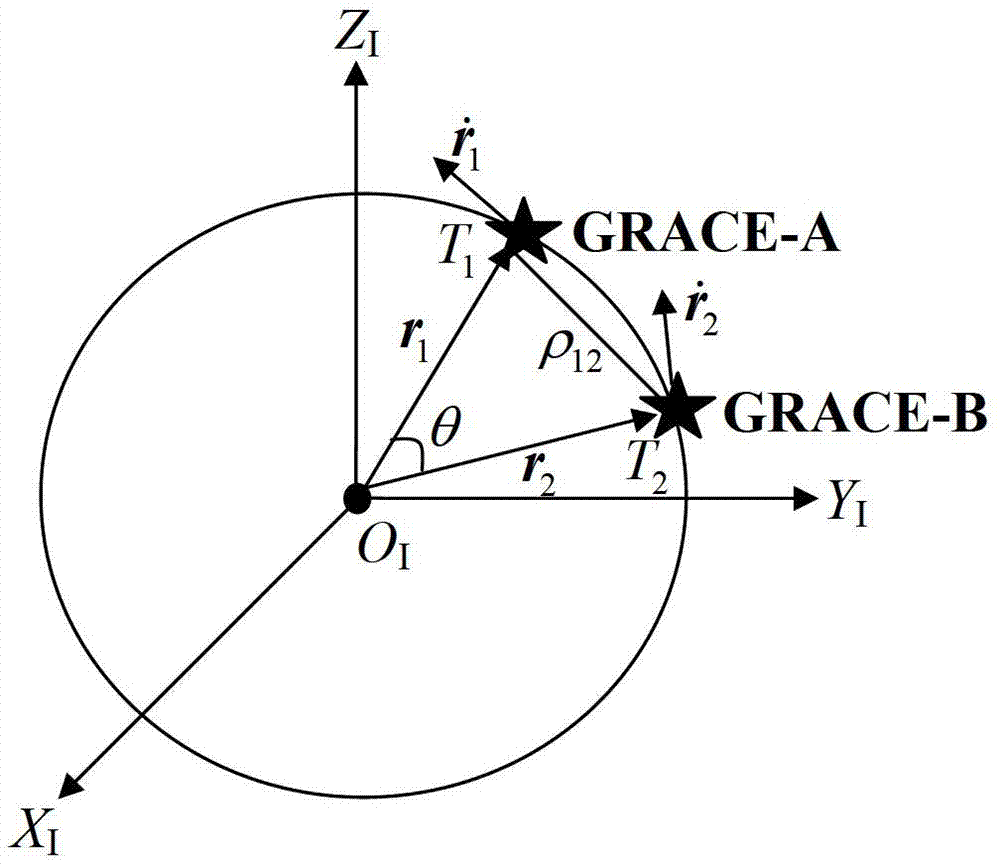
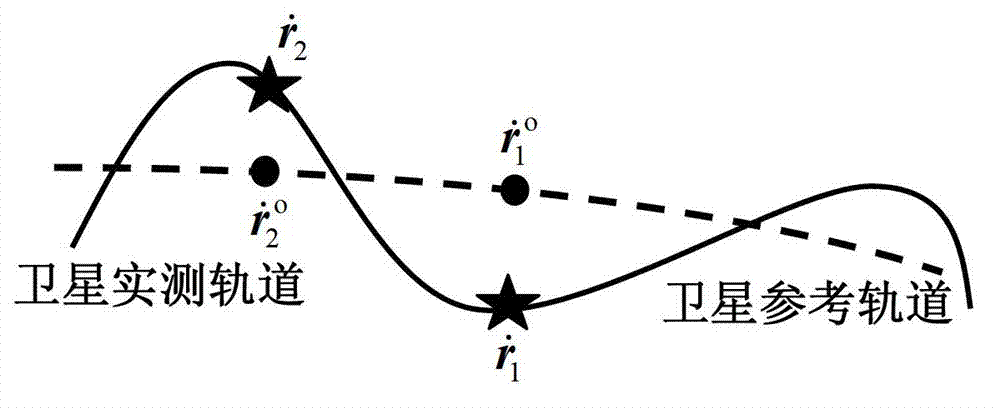
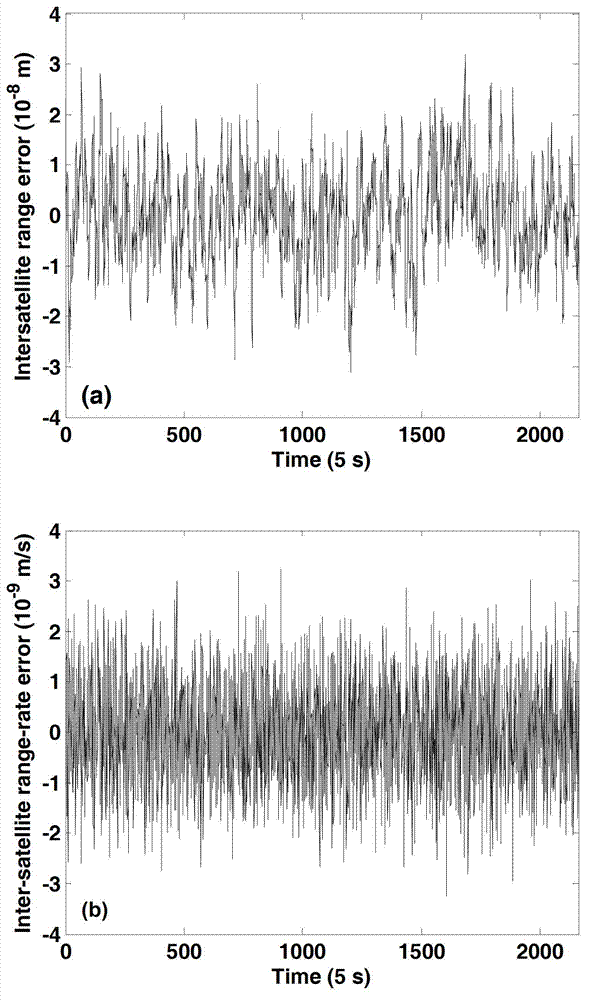
Satellite gravity inversion method based on inter-satellite velocity interpolation principle
InactiveCN102313905AGood senseHigh Gravity Inversion AccuracyGravitational wave measurementNatural satelliteComputer performance
The invention relates to a precise measuring method of an earth gravity field, in particular to a satellite gravity inversion method based on an inter-satellite velocity interpolation principle; an inter-satellite velocity interpolation observation equation is established by leading high-precision inter-satellite velocity into a satellite-satellite link component of the relative orbital velocity vector of double satellites, so as to precisely and quickly invert the earth gravity field; the method has high satellite gravity inversion precision, so that the physical meaning of the satellite observation equation is clear, the gravity satellite system sensitivity analysis is easy, the exploration of gravity field signals in medium and short wave is favorable, and the requirement on computer performance is low; and an inter-satellite velocity interpolation method is an effective method for resolving the earth gravity field with high precision and high spatial solution.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
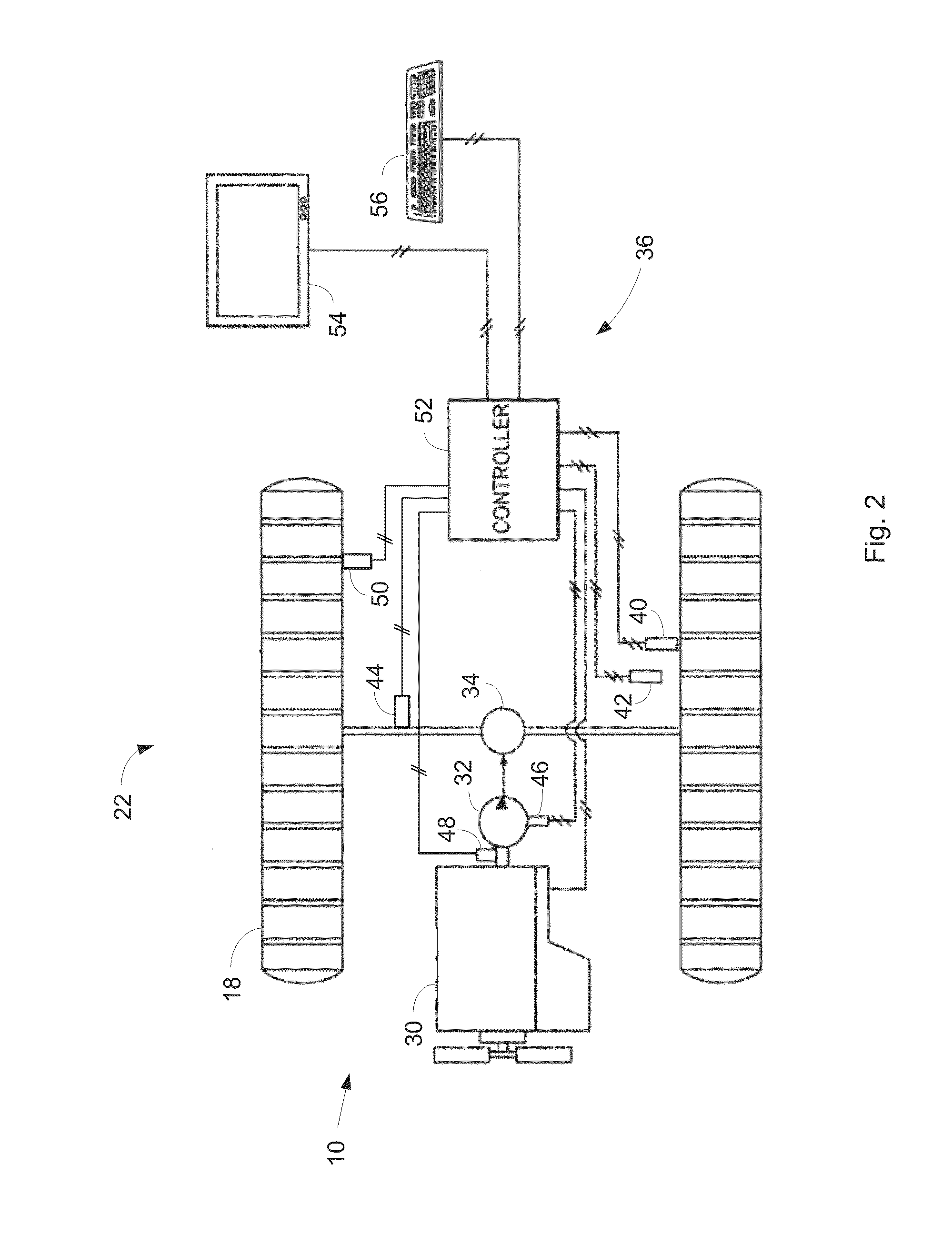
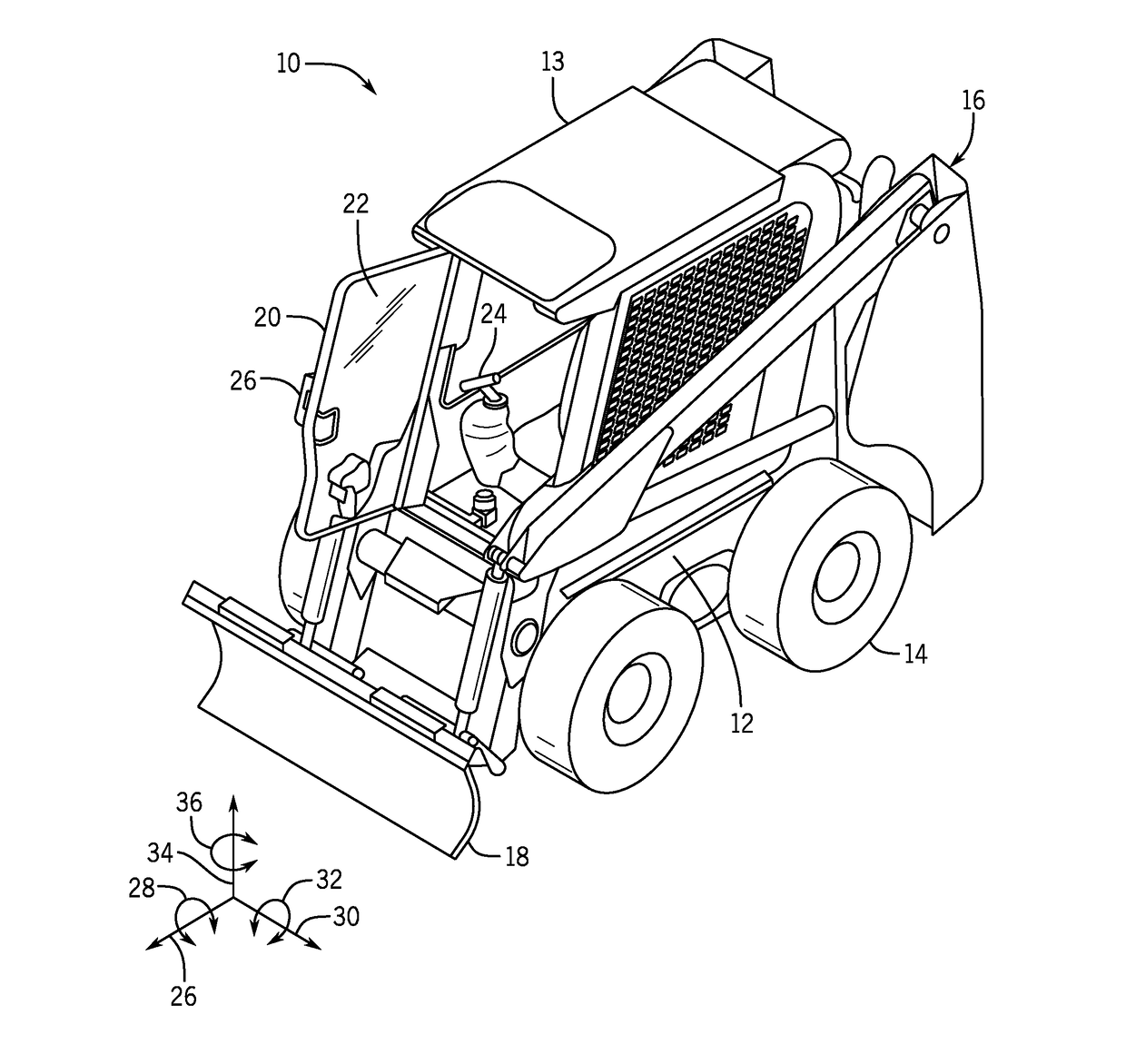
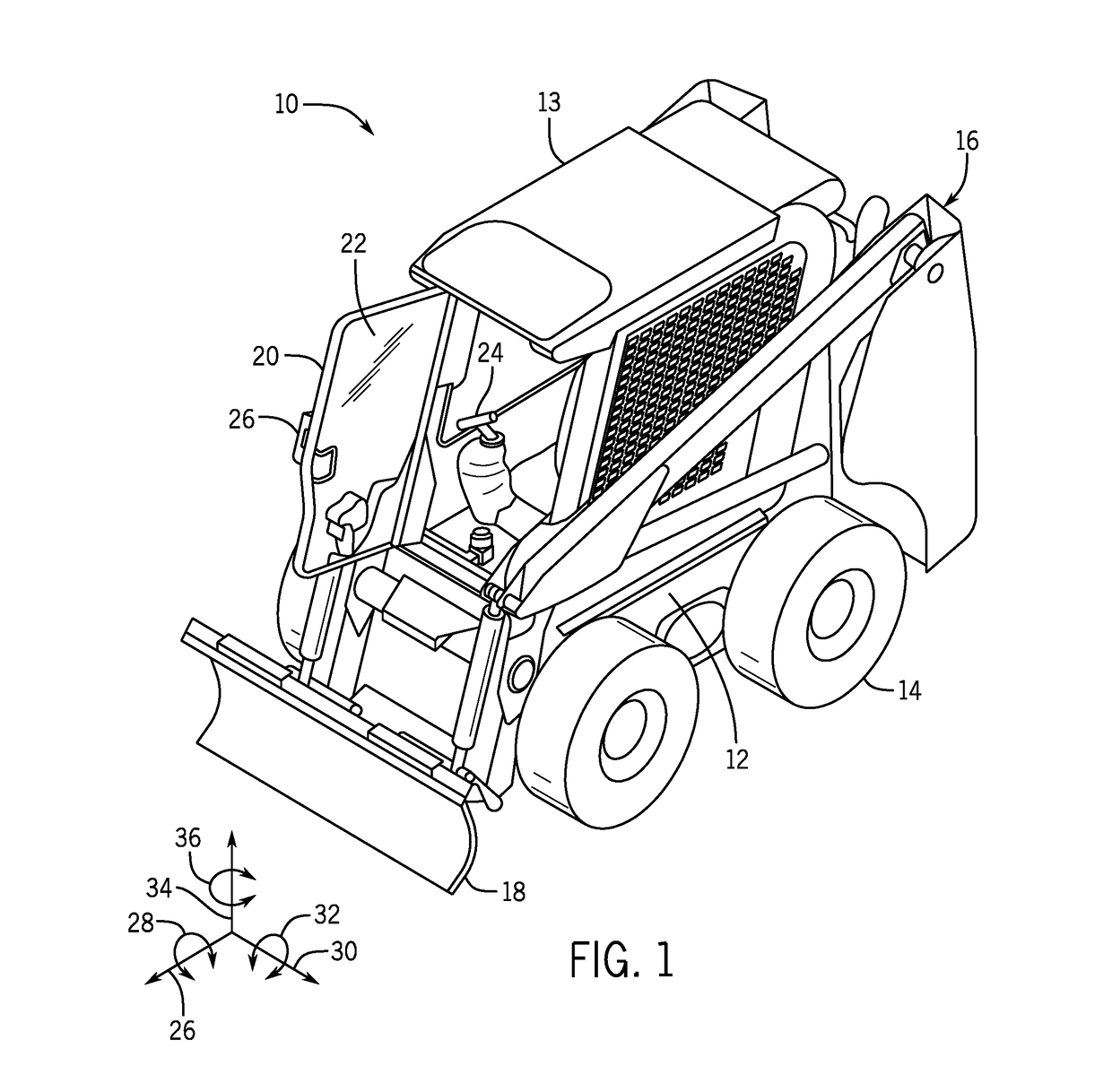
System and method for autonomous navigation of a tracked or skid-steer vehicle
ActiveUS8612084B2Programme-controlled manipulatorRoad vehicles traffic controlAutonomous Navigation SystemControl theory
An autonomous navigation system for a tracked or skid-steer vehicle is described. The system includes a path planner (54) that computes a series of waypoint locations specifying a path to follow and vehicle location sensors (82). A tramming controller (60) includes a waypoint controller (62) that computes vehicle speed and yaw rate setpoints based on vehicle location information from the vehicle location sensor and the locations of a plurality of neighboring waypoints, and a rate controller (64) that generates left and right track speed setpoints from the speed and yaw rate setpoints. A vehicle control interface actuates the vehicle controls in accordance with the left and right track speed setpoints.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
High altitude space launcher
InactiveUS20180134414A1Less velocityShooting angleRocket launchersLaunch systemsElectric forceRocket
Disclosed is a high altitude space launcher system for transferring payloads from surface to orbit at a significantly lower cost than conventional rockets. It comprises a aerostat lifted one stage light gas gun operating in stratosphere that shoots rocket assisted projectiles containing payload at near orbital velocities to a low angle trajectory. Alternatively, to launch acceleration sensitive payloads such as astronauts the light gas gun is replaced with a muzzle loaded conventional gun that shoots a single stage rocket at a much lower velocity. The system is mostly static structure, attached to a tether-elevator that moors it to land or a ship and provided it with electricity and lifts the projectiles to the gun.
Owner:ALIKOUHI ABBAS
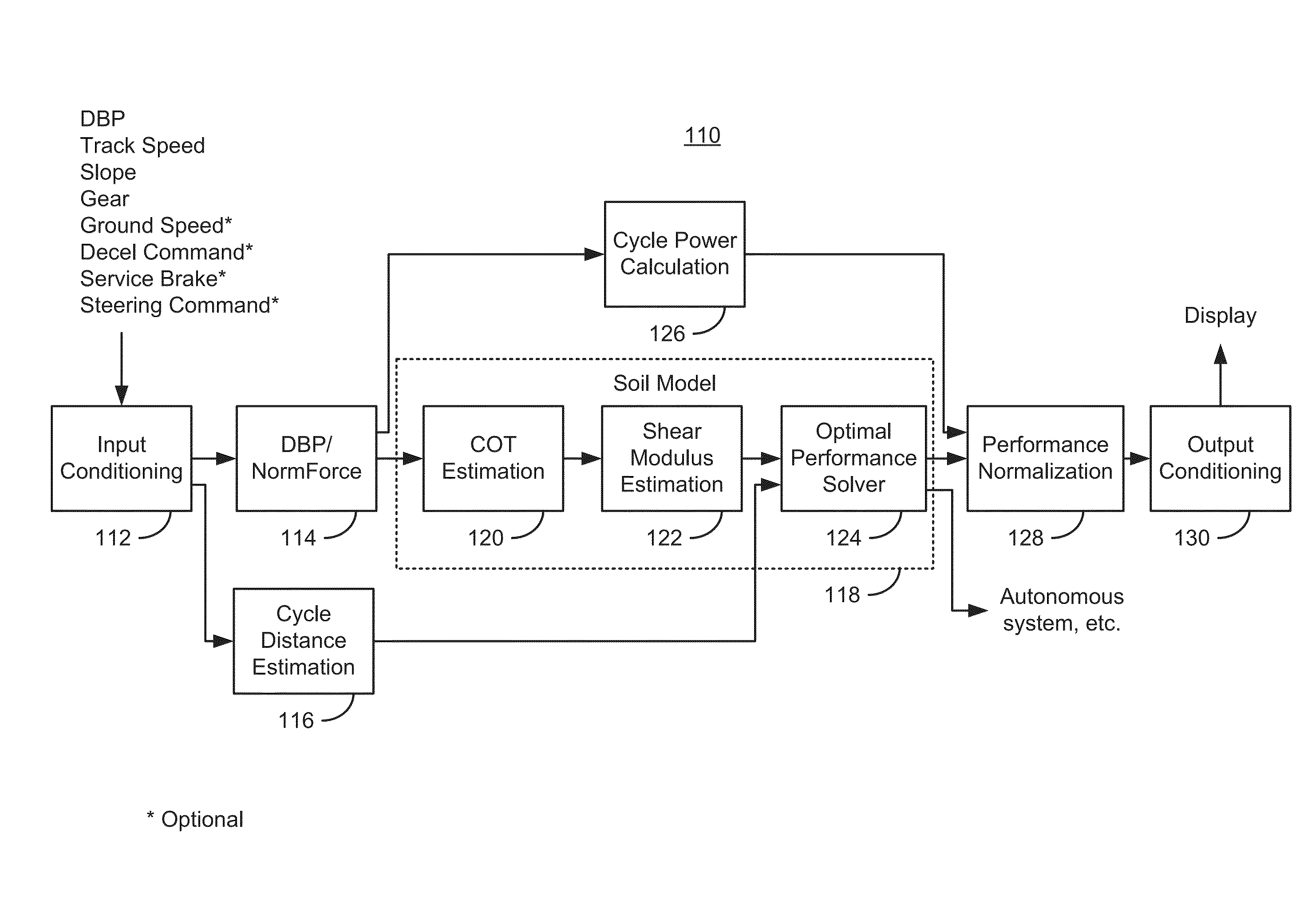
Measuring and Displaying Tractor Performance
ActiveUS20140156162A1Improve performanceDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsShear modulusOperating point
A method of measuring and displaying track-type tractor performance in real time calculates both a measure of work performance and a theoretical optimum work performance for a given input state, such as track speed. After estimating soil conditions, the theoretical optimum is estimated using an iterative technique. The optimum and current performance are normalized and displayed using a first bar representing a full range of work performance, a second bar depicting a range of optimum performance for current conditions is presented overlying the first bar, and an indicator line showing the current performance. This allows an operator to adjust speed or load accordingly. A coefficient of traction and a shear modulus adjustment, reflecting soil conditions, are calculated at the tractor during operation and used to offset a table of ideal condition operating points to produce the second bar.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
System and method for determining directional and non-directional fluid wave and current measurements
A system for determining the directional properties of surface waves or internal waves of a fluid medium includes a sonar system having a plurality of transducers for generating respective, separate acoustic beams and receiving echoes from one or more range cells located substantially within the beams; and a computer program executed by a processor for determining the directional properties associated with the surface waves or internal waves from the received echoes, wherein the computer program determines along-beam velocities along the separate acoustic beams and combines the along-beam velocities to form an equivalent orbital velocity vector.
Owner:NORTEK
Real time pull-slip curve modeling in large track-type tractors
ActiveUS8983739B2Registering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsShear modulusEngineering
A method of estimating soil conditions of a work surface during operation of a track-type tractor measures current operating conditions and current operating state to develop adjustments to a nominal pull-slip curve. The adjusted pull-slip curve is used to calculate optimum performance in terms of an input variable such as track speed. Two factors are developed to reflect soil conditions, coefficient of traction and a shear modulus adjustment that affect different portions of the nominal pull slip curve.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Satellite gravity inversion method based on load error analysis theory
InactiveCN103091722AImprove inversion accuracyGuaranteed calculation accuracyGravitational wave measurementAccelerometerSatellite orbit
The invention relates to a method for accurately detecting the earth gravity field, in particular to a method which includes: based on the load error analysis theory, accurately building the distance error between satellites of a K wave band distance meter, the satellite orbit position error and the orbital velocity error of a global positioning system (GPS) receiver and an error model in which accumulative geoid accuracy is affected by the nonconservative force error coalition of a satellite-bone accelerometer, and further accurately and rapidly inversing the earth gravity field. The method is high in inversion accuracy of the earth gravity field, simple in satellite gravity inversion process, low in performance requirements of a computer and definite in physical meanings of a satellite observation equation, and effectively improves inversion speed on the premise of ensuring calculation accuracy. The satellite gravity inversion method based on the load error analysis theory is an effective method for calculating the earth gravity field which is high in accuracy and spatial resolution.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Middle and high layer atmosphere density separation type detector
InactiveCN104391299AReduce measurement noiseHigh precisionICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAccelerometerSolar cell
A middle and high layer atmosphere density separation type detector comprises a universal module with a microsatellite platform, and is characterized by further comprising a spherical structural body shell used for simplifying an atmosphere resistance analysis model, an accelerometer, a GPS receiver and an attitude control system, the surface of the special structural body shell is covered with a solar cell, the accelerometer is arranged in the spherical structural body shell, the accelerometer is formed by distributing 4 to 6 static suspension type accelerometers around the axis, the accelerometer is used for measuring the atmosphere resistance, the GPS receiver is arranged in the spherical structural body shell and used for tracking and monitoring the track speed and the position of a microsatellite, the attribute control system is arranged in the spherical structural body shell and used for controlling the attribute of the microsatellite so as to keep the spinning of the satellite stable and ensure the correct directing of a GPS receiver antenna and a data transmission antenna.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Linear motor geometry for use with persistent current magnets
ActiveUS20050285452A1Electromagnetic launchersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsLinear motorPersistent current
Owner:HOUSTON SYST UNIV THE
Method for inverting earth gravity field of residual inter-star velocity
InactiveCN103076639AFast inversionImprove calculation accuracyGravitational wave measurementComputer performanceGlobal Positioning System
The invention relates to a method for inverting an earth gravity field of a residual inter-star velocity, and the method is characterized in that high-precision residual inter-star velocity observation quantity of a satellite-borne laser interference range finder is introduced into a sight component of a residual track velocity differential vector of a global positioning system (GPS) receiving machine to establish a novel residual inter-star velocity observation equation so as to precisely and rapidly invert the earth gravity field; the precision for calculating the earth gravity field is high, the satellite gravity inversion velocity is fast, requirement on the computer performance is low, the method is sensitive to high-frequency signals in the gravity field, and easiness for analyzing the satellite gravity inversion error is realized; and the residual inter-star velocity method is a key technology for establishing a high-precision and high spatial-resolution global gravity field model.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
System and method for autonomous steering control of work vehicles
ActiveUS20170191244A1Good and more predictable controlSteering linkagesSoil-shifting machines/dredgersElectronic control systemControl system
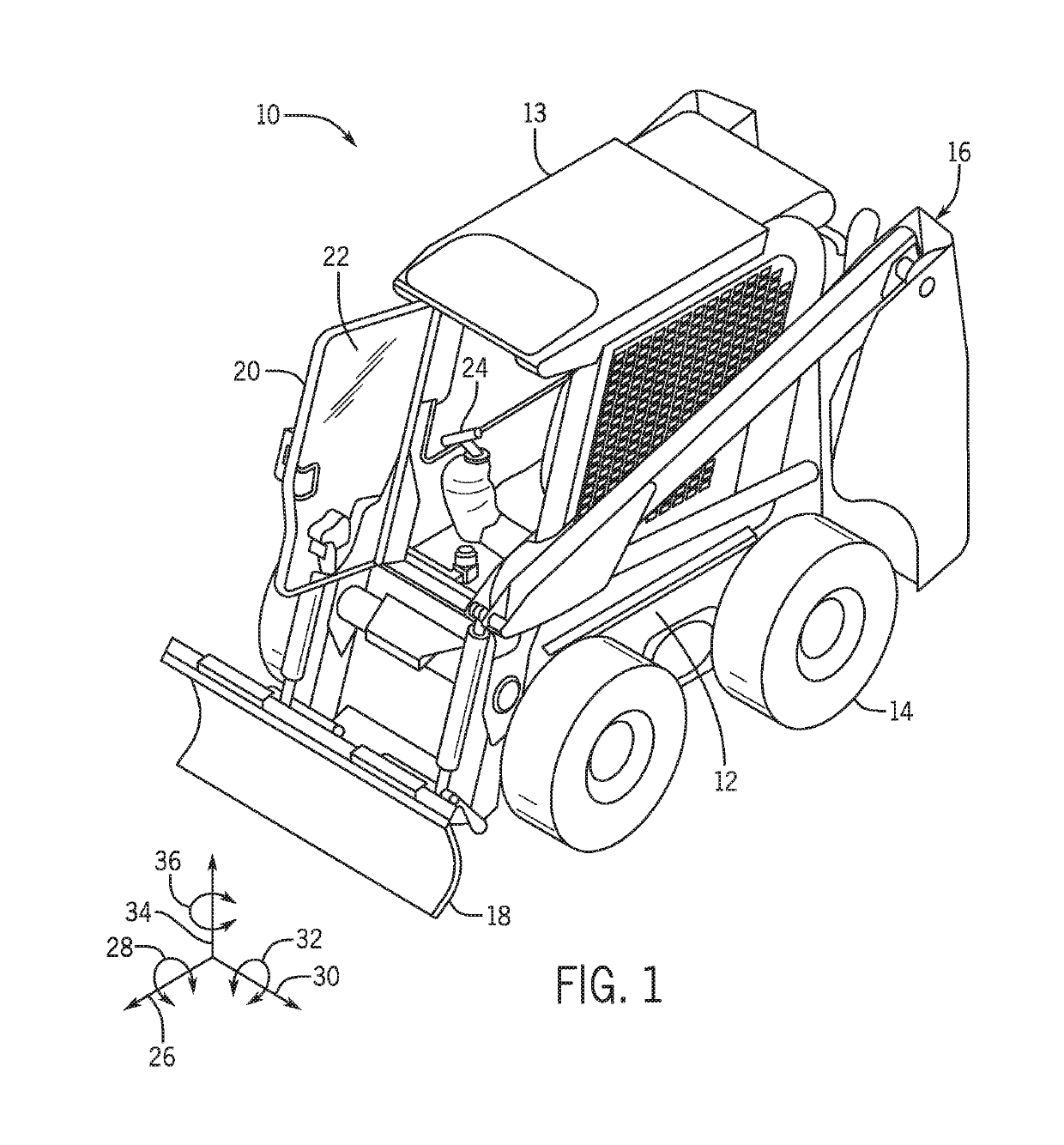
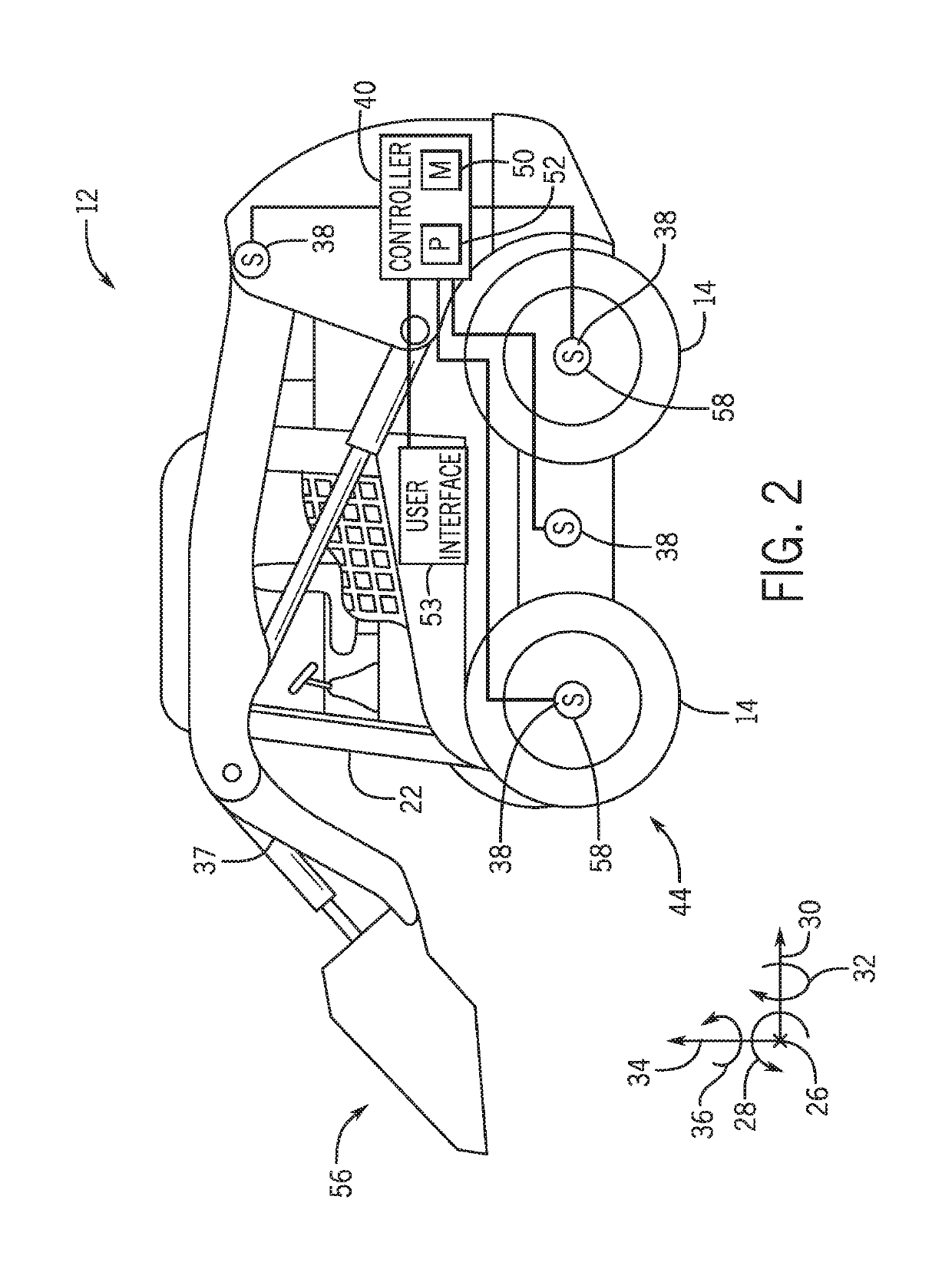
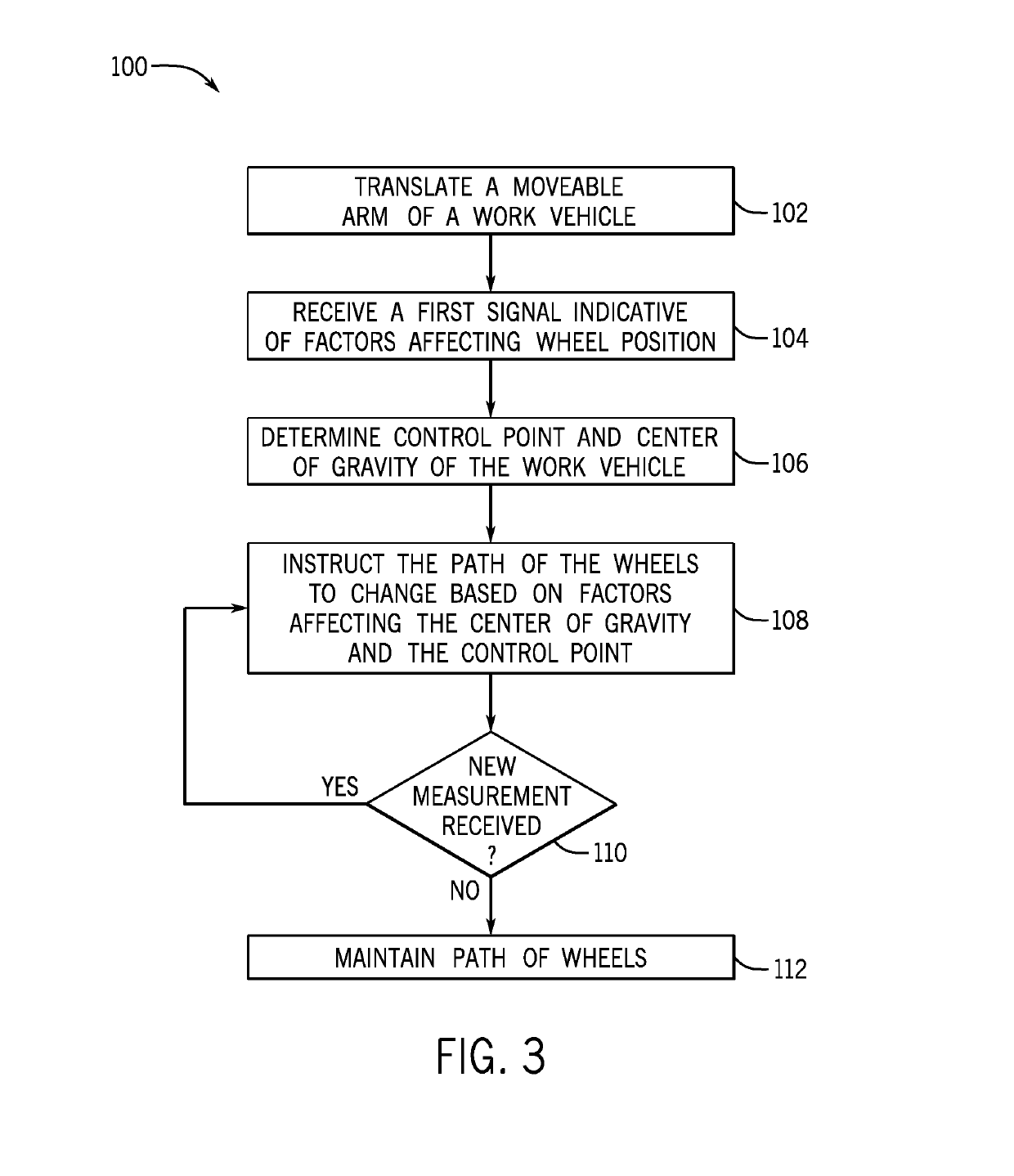
An electronic control system for a work allows for control of steering despite movement of an implement that may support a load. Control may be based on vehicle position, velocity, acceleration, center of gravity, and heading. A control point is determined despite movement of the load, and may be based upon one or more of roll, yaw, and pitch of the vehicle. The vehicle may be of the type that allows for control only of wheel or track speed and rotational direction. A desired center of gravity is maintained while controlling an error between a desired vehicle trajectory and a determined trajectory in a closed loop manner.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS SOLUTIONS +1
Position calculation method and apparatus with GPS
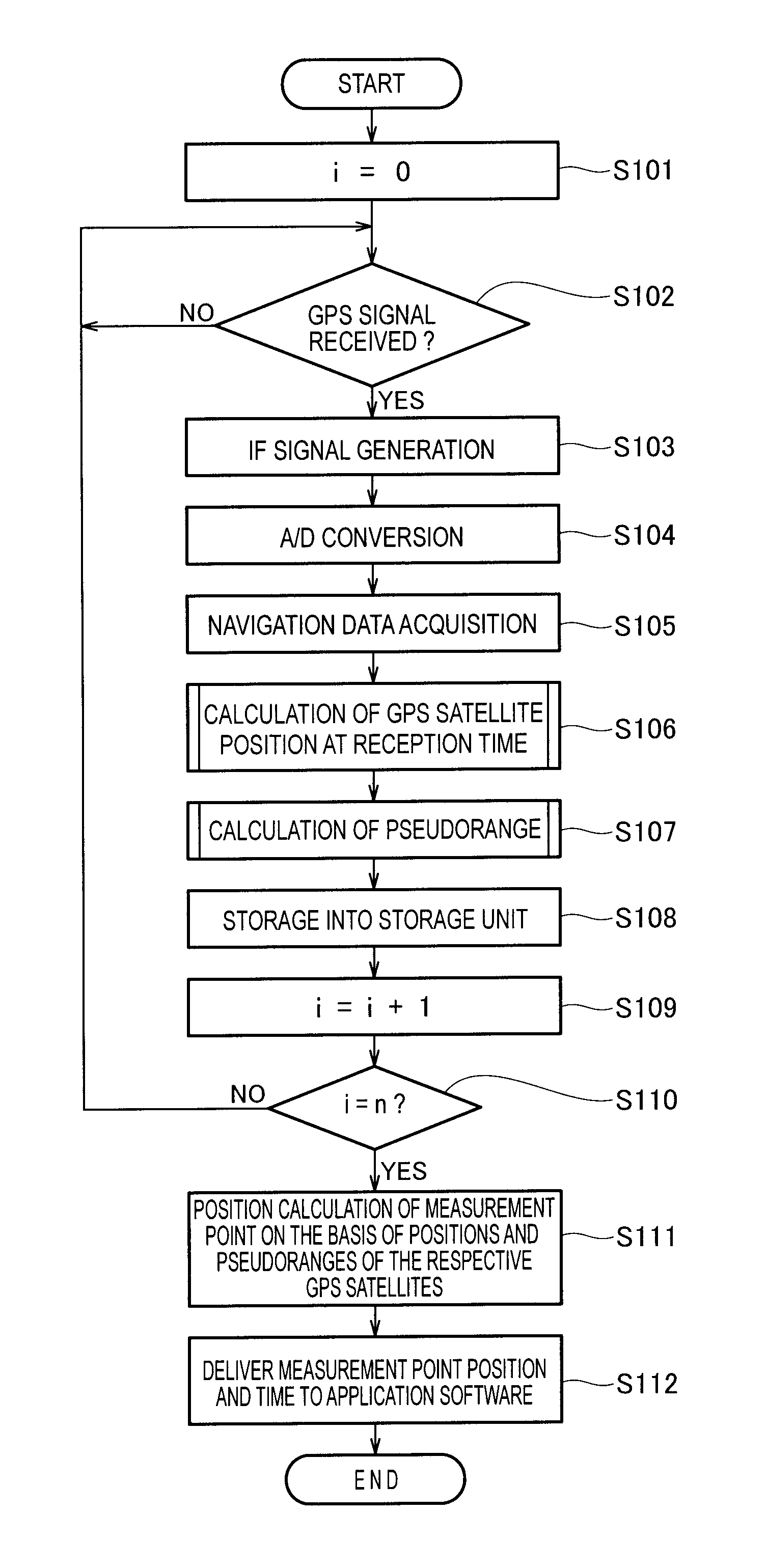
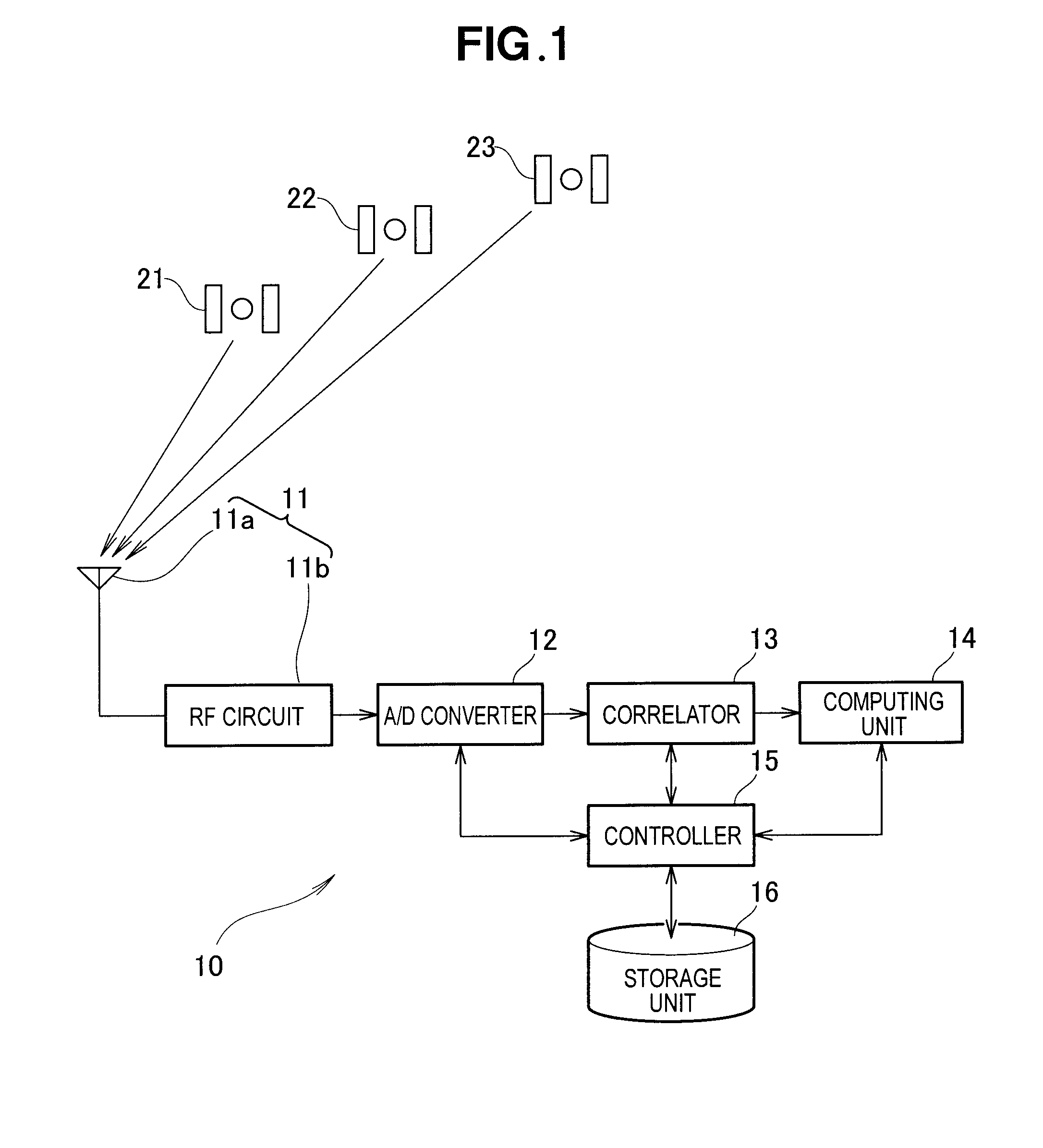
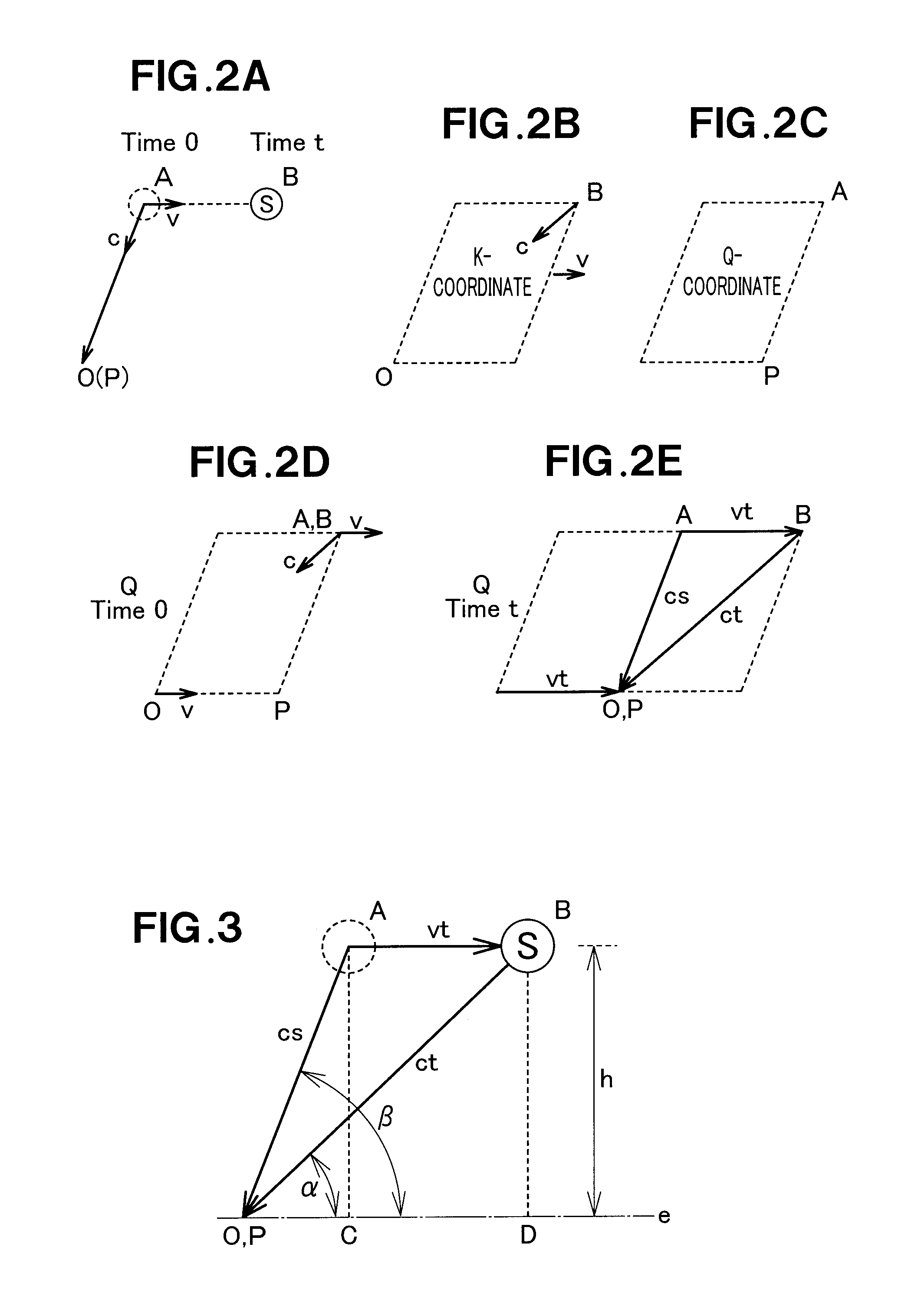
InactiveUS20120026034A1Calculation method is simpleSimple procedureSatellite radio beaconingHorizonMeasurement point
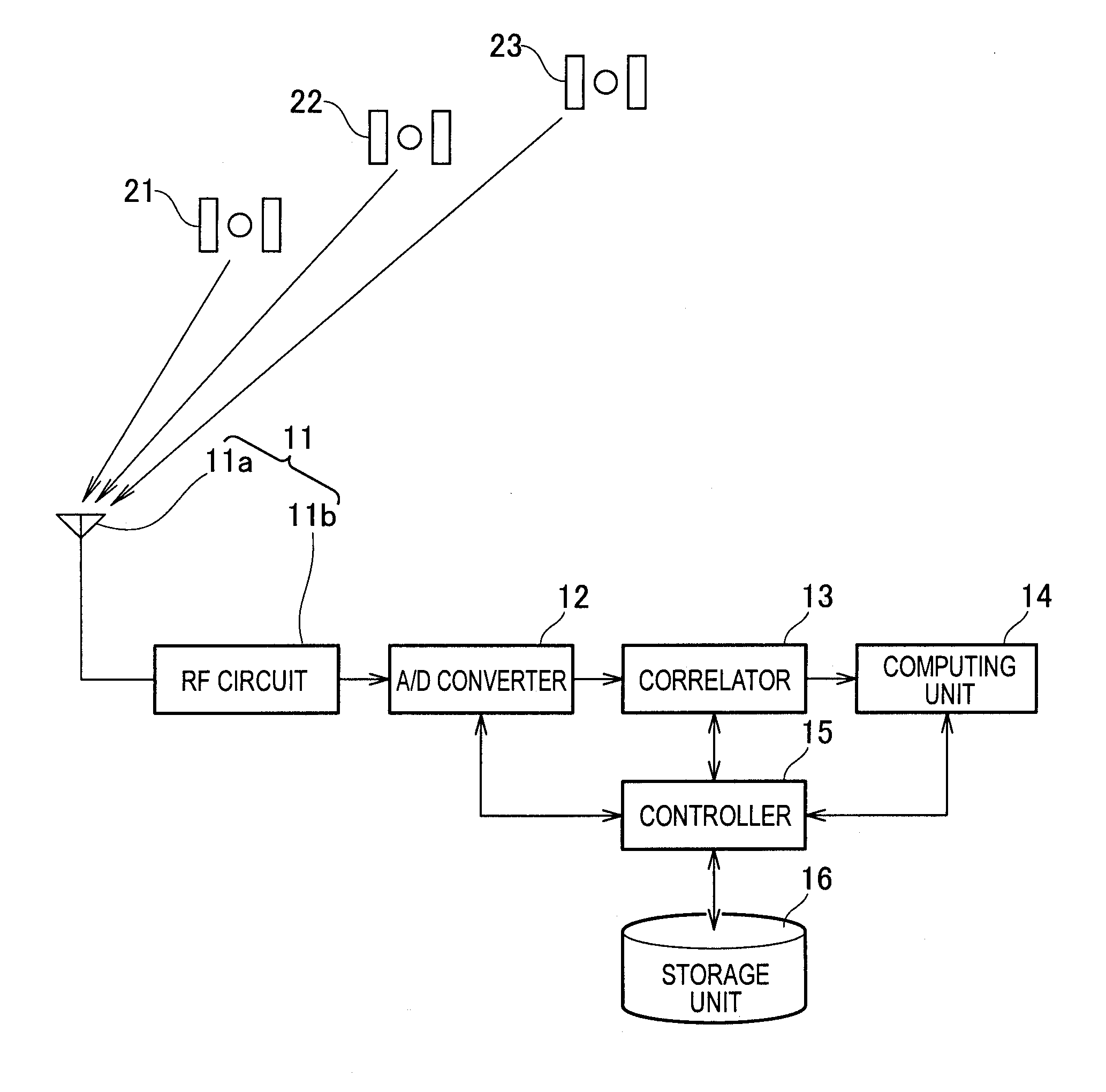
A GPS position calculating apparatus is configured to acquire from navigation data contained in signals transmitted from GPS satellites, orbit information including a position, clock time, orbital speed and altitude of each GPS satellite at a transmission time of each signal from a respective one of the GPS satellites, then calculate a position of each GPS satellite at a reception time of the same signal at a measurement point on the basis of the acquired orbital speed and a time difference between the reception time and the transmission time, further calculate a first angle of the horizon relative to a first line segment connecting the second position of each GPS satellite with a position of the measurement point on the basis of a range of the first line segment and the acquired altitude, subsequently calculate a range of a second line segment connecting the first position of each GPS satellite with the position of the measurement point on the basis of the range of the first line segment, the first angle, and the orbital speed, and finally perform calculation of the position of the measurement point. A GPS position calculating method carried out by the apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for determining directional and non-directional fluid wave and current measurements
A system for determining the directional properties of surface waves or internal waves of a fluid medium includes a sonar system having a plurality of transducers for generating respective, separate acoustic beams and receiving echoes from one or more range cells located substantially within the beams; and a computer program for determining the directional properties associated with the surface waves or internal waves from the received echoes, wherein the computer program determines along-beam velocities along the separate acoustic beams and combines the along-beam velocities to form an equivalent orbital velocity vector. The system is mounted on or in a sub surface buoy that can move or rotate during measurement and includes a motion sensor measuring six degrees of freedom to account for horizontal velocity and vertical displacement in the subsurface buoy mounted sonar system.
Owner:NORTEK
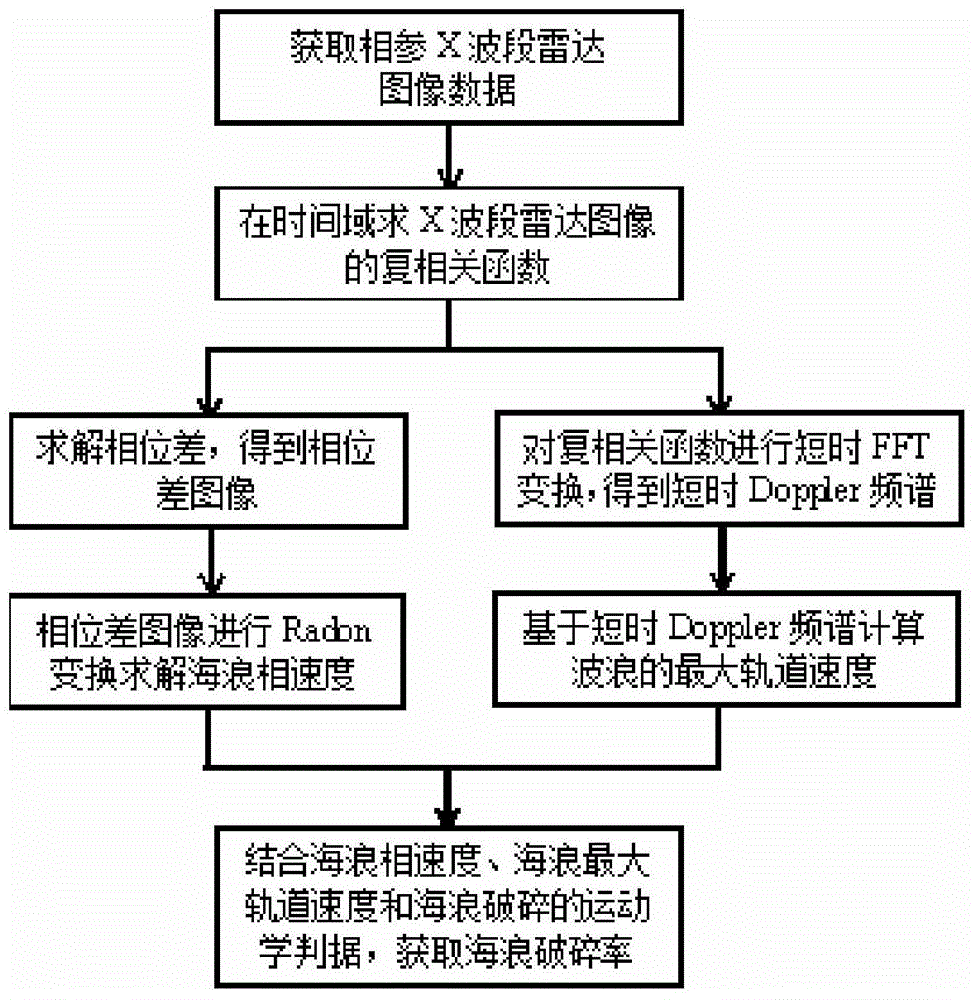
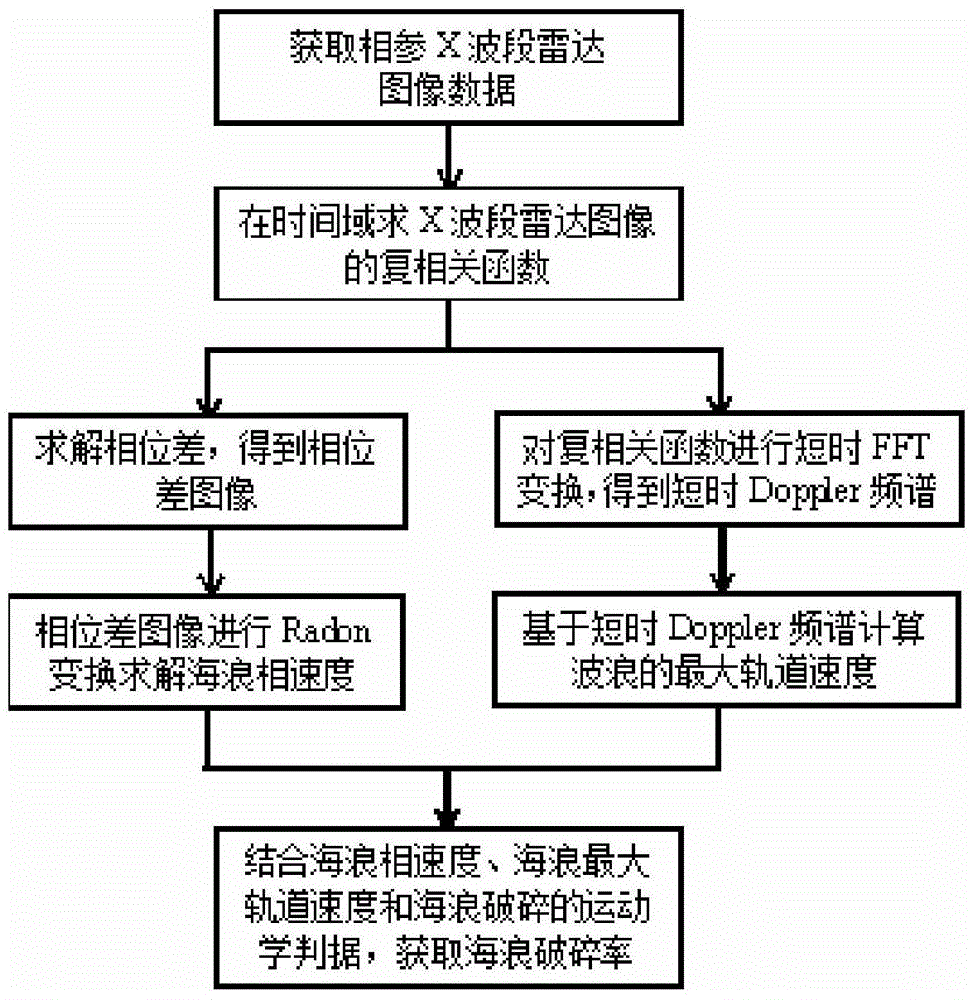
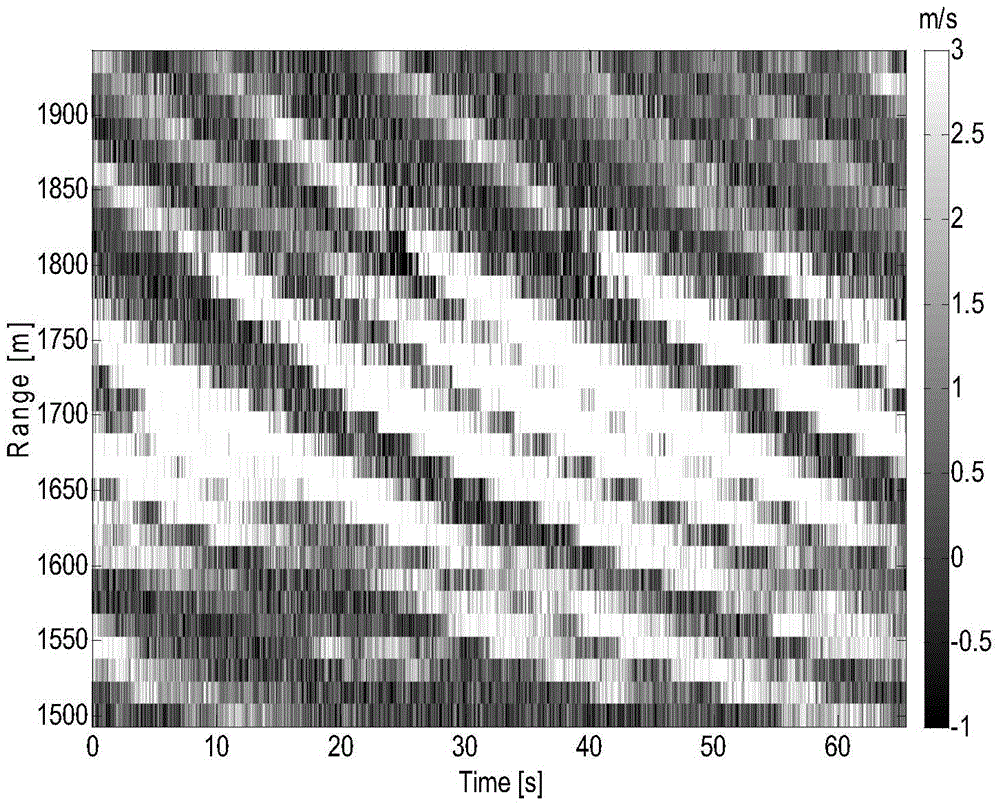
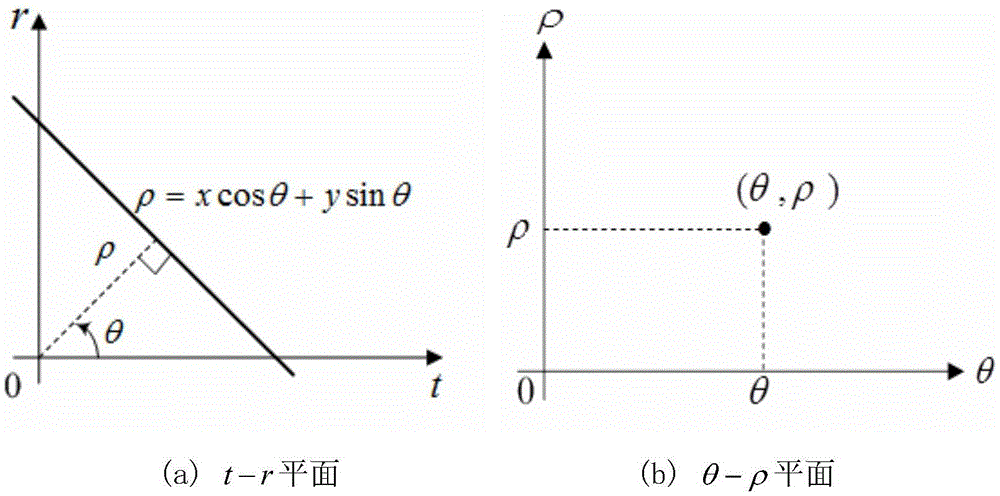
Ocean-wave broken-rate extraction method based on coherent X-waveband radar images
InactiveCN104133208ASmall amount of calculationHigh speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainFrequency spectrum
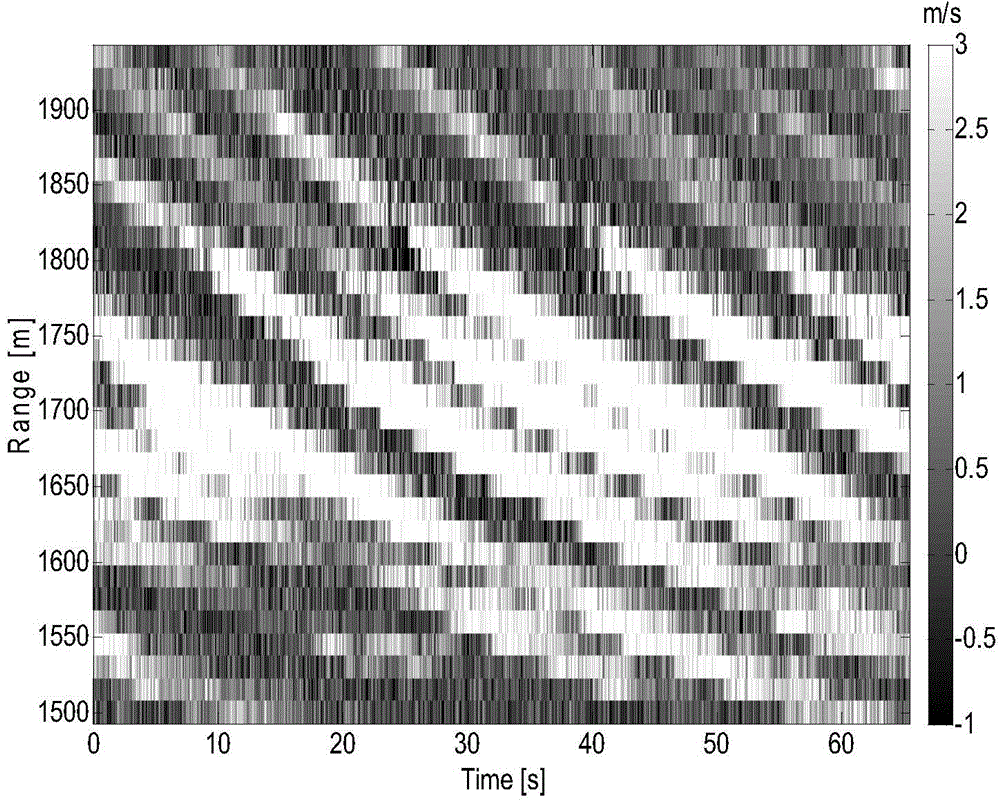
Disclosed is an ocean-wave broken-rate extraction method based on coherent X-waveband radar images. The method includes the following steps: obtaining the coherent X-waveband radar complex images; solving a multiple correlation function of the complex image in a time domain; solving a phase difference of the radar complex images based on the multiple correlation function and obtaining a phase difference image; carrying out Radon transformation on the phase difference image so that an ocean-wave phase speed is obtained; carrying out short-time FFT transformation on the multiple correlation function so that a short-time Doppler frequency spectrum of the multiple correlation function is obtained; calculating an orbital speed of ocean waves based on the short-time Doppler frequency spectrum; and obtaining the ocean-wave broken rate of the whole measured sea area. The method significantly reduces a calculation quantity in an ocean-wave broken-rate extraction process and improves the speed; a coherent X-waveband radar is free from restriction of complex ocean environment conditions; and the effective action distance of the coherent X-waveband radar is far larger than a camera and the obtained ocean-wave broken rate can better reflect a true statistical characteristic.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method and device for guiding the movement of a moving machine element on a numerically controlled machine
ActiveUS8294405B2Simple methodEasy to produceComputer controlSimulator controlRight-SidedControl theory
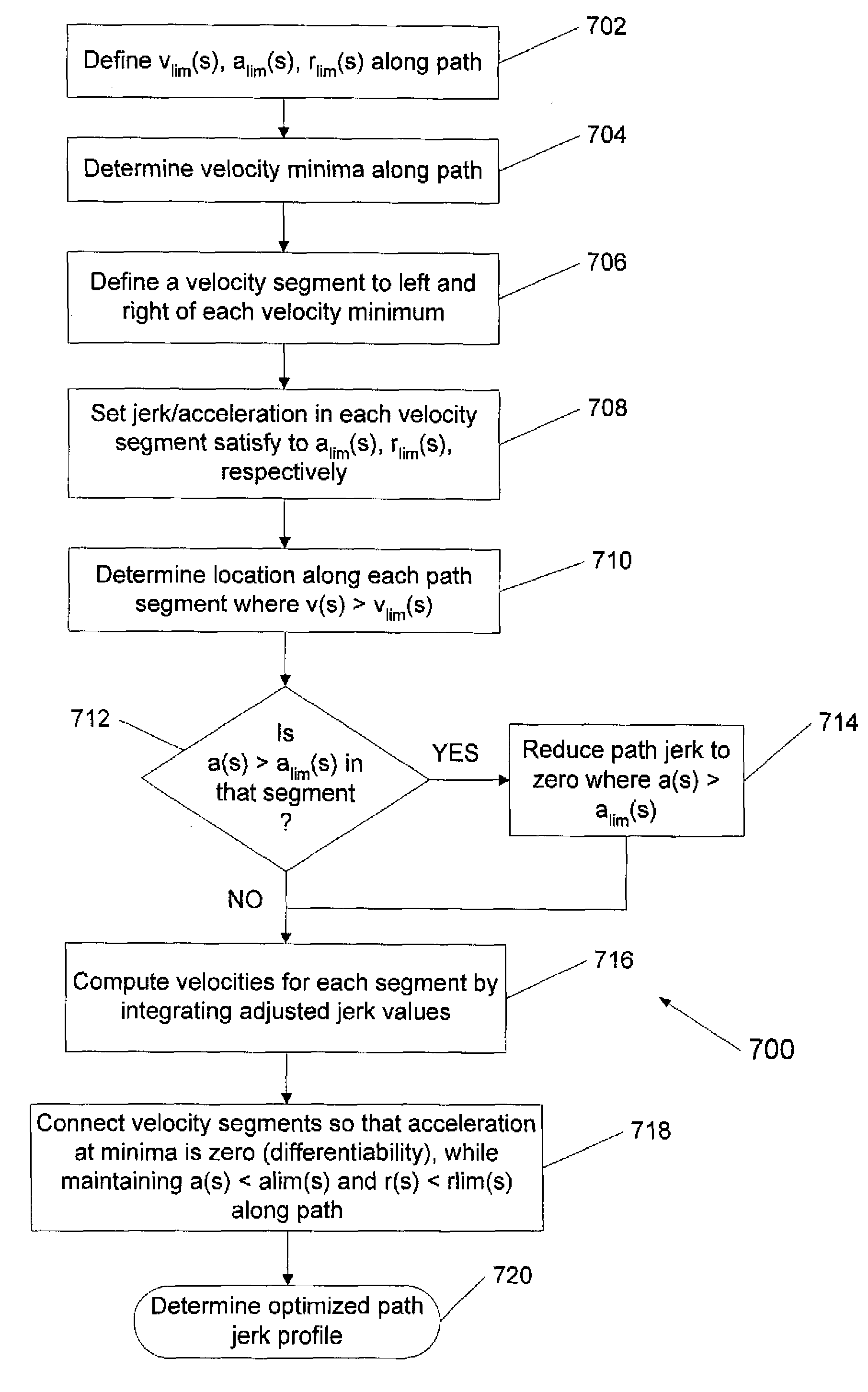
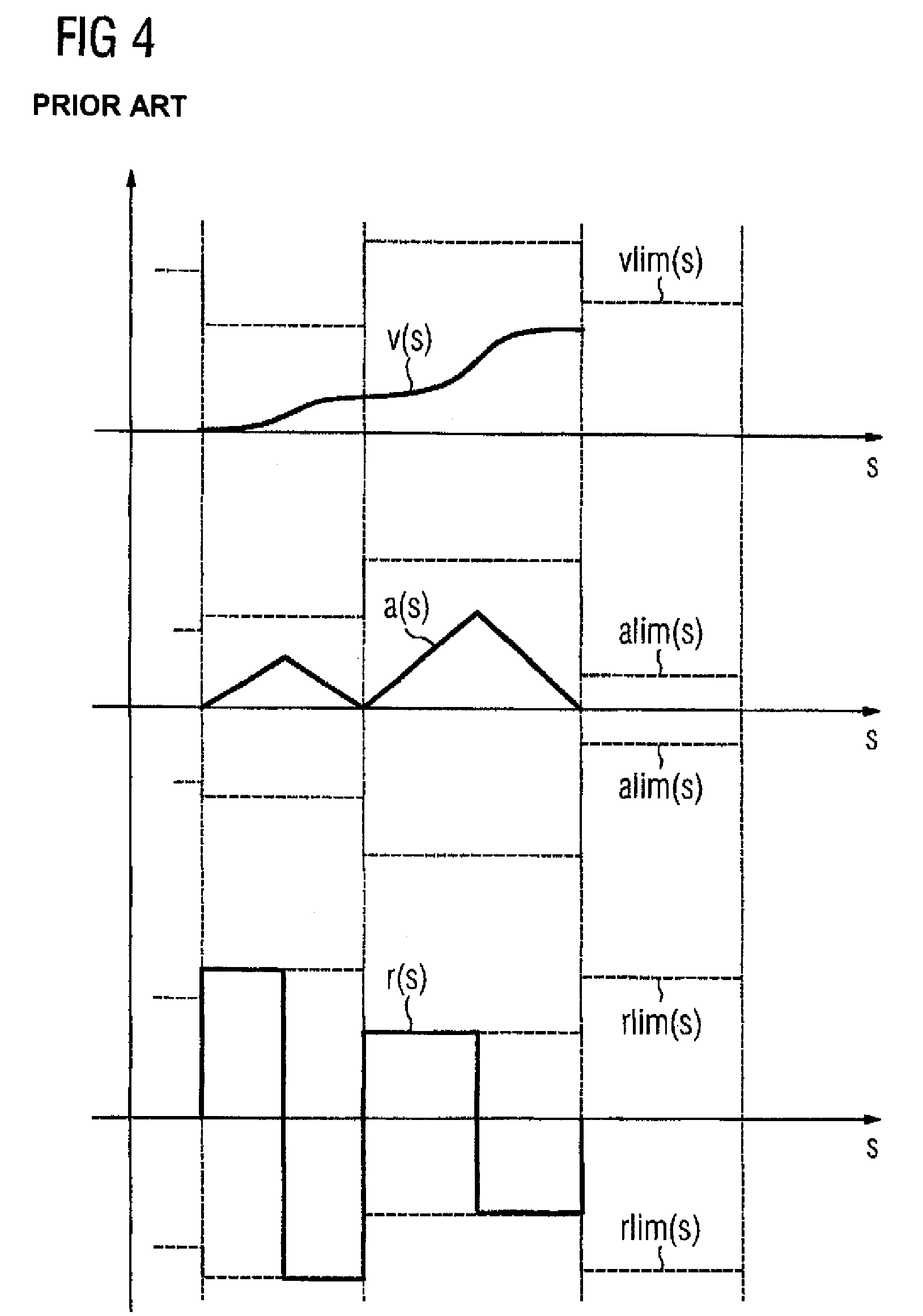
The invention relates to a method and a device for guiding the movement of a moving machine element on a numerically controlled machine, whereby maximum possible track speed, maximum possible track acceleration, and maximum possible track jerk are defined by means of given restrictions on track axes. The local minima for the maximum possible track speed are determined, whereby for each local minimum a corresponding left-sided and right-sided track speed segment is determined, whereby, for track values for the displacement track to the left and right of a given minimum, the resulting track speed is determined by using the maximum possible track jerk and the maximum possible track acceleration until the track speed exceeds the maximum possible track speed to the left and right of the minimum, a track jerk curve for the movement guidance is hence determined. According to the invention, a simple method and a simple device for movement guidance of a moving machine element on a numerically controlled machine are achieved, with as good as possible a usage of the restrictions on machine axes of the machine.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Position calculation method and apparatus with GPS
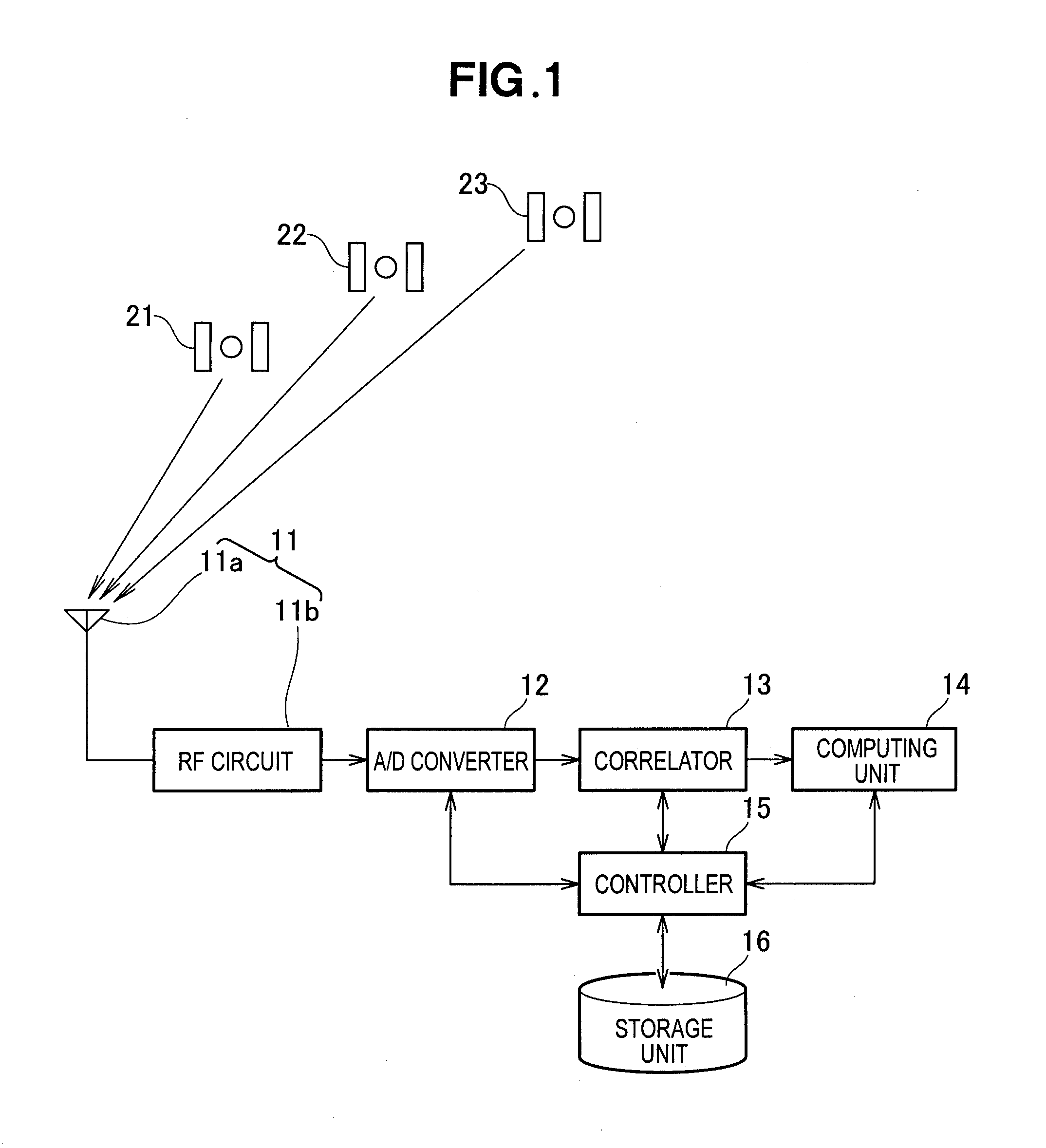
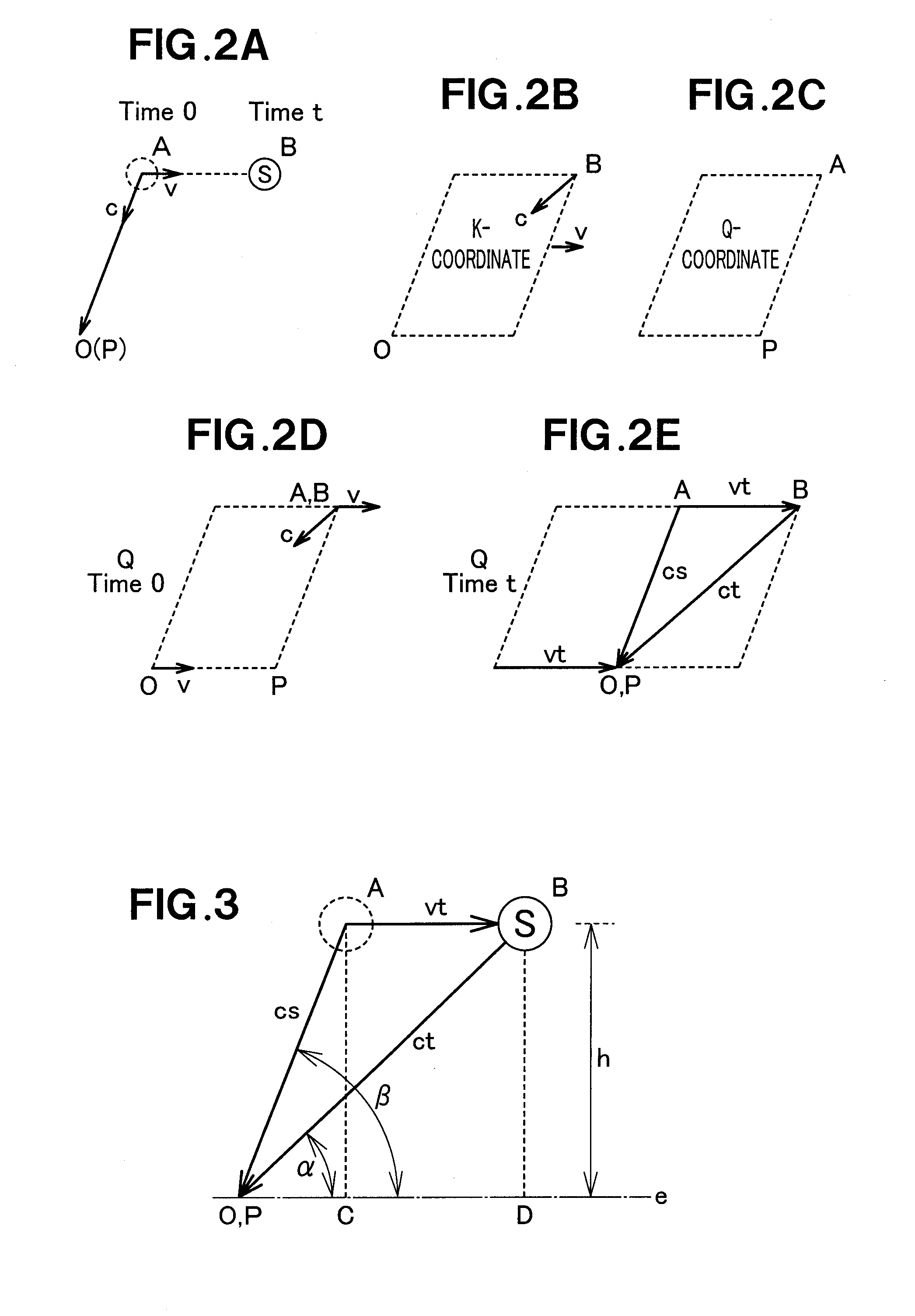
InactiveUS20120026033A1Simple and accurate mannerEasy to detectSatellite radio beaconingClock timeMeasurement point
A GPS position calculating apparatus is configured to acquire orbit information from navigation data contained in signals transmitted from GPS satellites, the orbit information including a position, clock time and orbital speed of each GPS satellite at a transmission time of each signal, to calculate a position of each GPS satellite at a reception time of the same signal at a measurement point, from the acquired orbital speed and clock time, to calculate a range of a line segment connecting the calculated position of each GPS satellite with a position of the measurement point using a time difference between the transmission time and the reception time, and to calculate the position of the measurement point using the calculated range of the line segment as a pseudorange. A GPS position calculating method carried out by the apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for displacably guiding a displaceable machine element of a numerically controlled tool machine or production machine
ActiveCN1791846AConvenient timeAccurately determineProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorNumerical controlPresent method
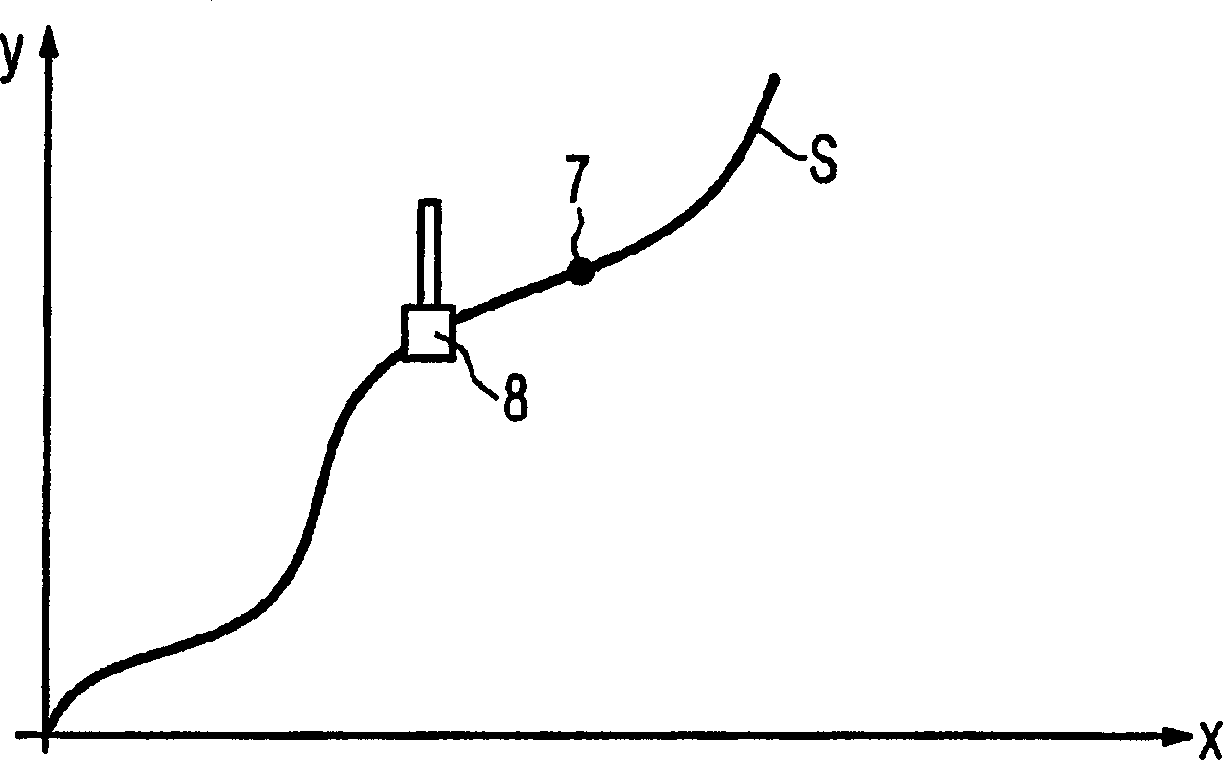
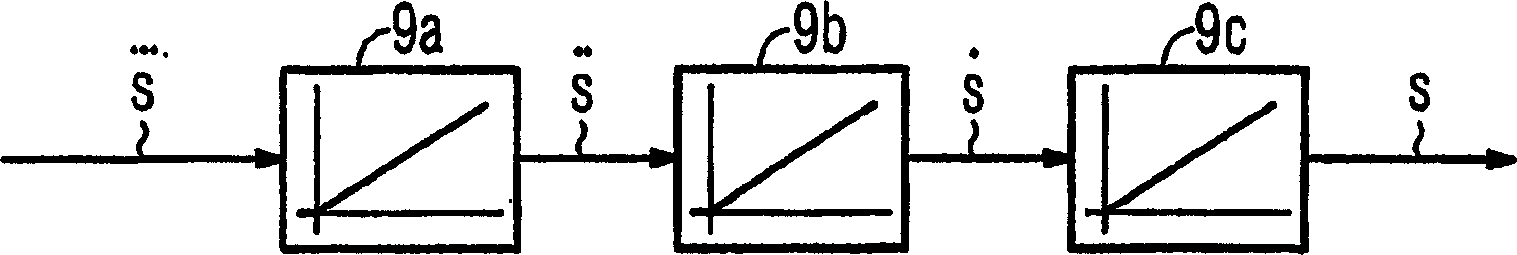
The invention relates to a method for guiding the motion of a movable machine part (8) of a numerically controlled or special machine tool on a predetermined trajectory (S) of the machine part (8), wherein the workspace (31) of the machine tool is defined The support points (32) within, wherein the maximum possible orbital impulse () and / or the maximum possible orbital acceleration () and / or the maximum possible orbital velocity (), and the movement of the machine part (8) on the moving orbital (S) at the maximum possible orbital impulse () and / or maximum possible orbital acceleration () and / or maximum possible orbital velocity ( )conduct. Thus, the method provides a simple and inexpensive method of optimal motion guidance of a movable machine part (8) of the numerically controlled machine tool on a predetermined trajectory (S) of motion of the machine part (8).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Mitigation of orbiting space debris by momentum exchange with drag-inducing particles
InactiveUS20130181061A1Shorten the timeLower relative altitudeAircraft componentsCosmonautic vehiclesMomentumEngineering
A cloud of small to medium-sized space debris is mitigated by releasing drag-reducing particles into the cloud from a dispenser vehicle, causing the particles to collide or otherwise interact with, and thereby exchange momentum with, the debris particles, reducing the orbiting velocity of the debris to a degree sufficient to cause the debris to de-orbit, or to accelerate the de-orbiting of the debris, to Earth. Certain embodiments also include a shepherd vehicle containing systems for identifying and tracking the debris cloud and for coalescing the debris cloud to increase the particles density in the cloud.
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE INC
Aircraft orbit injection control method using space vector matching
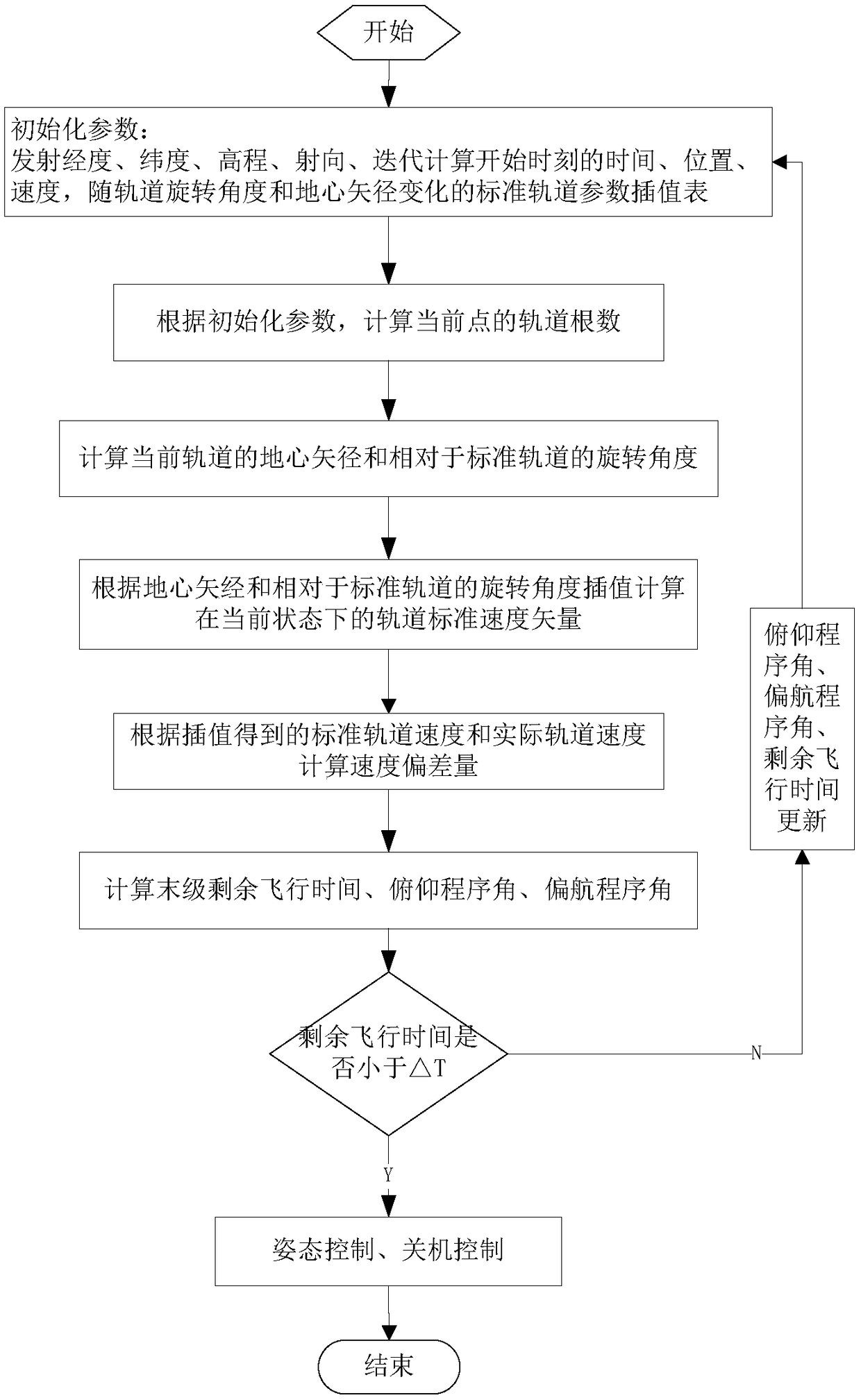
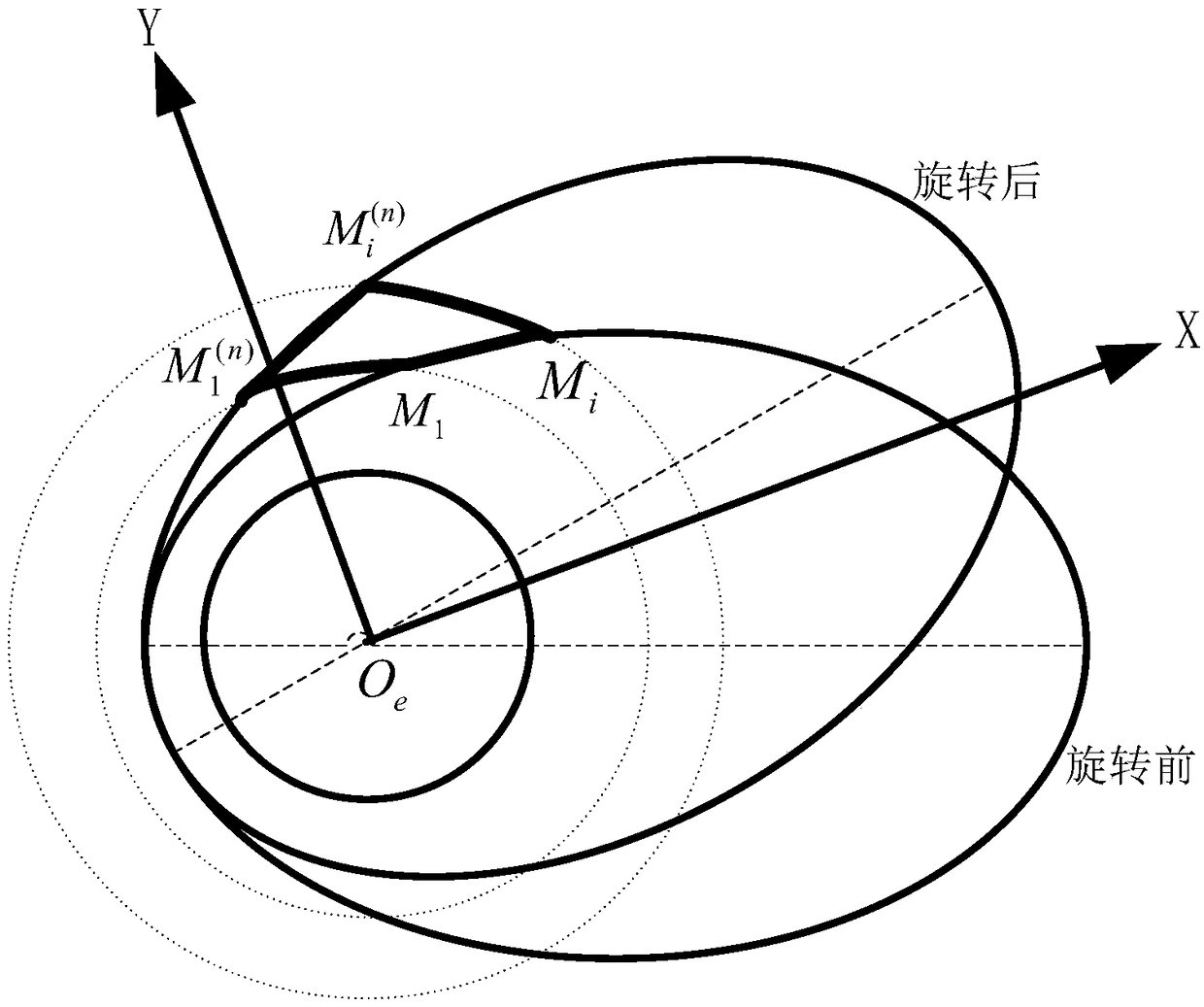
ActiveCN109484675AEasy to adjustPreparing Computational Work Requirements LowCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusAttitude controlState parameter
The invention discloses an aircraft orbit injection control method using space vector matching. The method includes the following steps of initiating state parameters of an aircraft, calculating the root and geocentric radius vector of a current orbit of the aircraft and the rotating angle of the current orbit relative to a standard orbit, obtaining a standard orbit speed vector which a current orbit state should have according to the geocentric radius vector and the rotating angle of the current orbit relative to the standard orbit, calculating the deviation value of the speed vector, the residual flight time DT, the pitching program angel and the yaw program angle according to the standard orbit speed vector and a current actual orbit speed vector, and conducting posture control and shutdown control through the calculated residual flight time DT, pitching program angel and yaw program angle. The invention relates to the technical field of orbit control. The method is high in real-time performance, high in guidance precision and high in orbit adjusting capacity, flight software on the aircraft is simple, and the work requirements for preparing and calculating various elements on the ground are low.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
Linear motor geometry for use with persistent current magnets
ActiveUS7459807B2Electromagnetic launchersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsLinear motorPersistent current
Owner:HOUSTON SYST UNIV THE
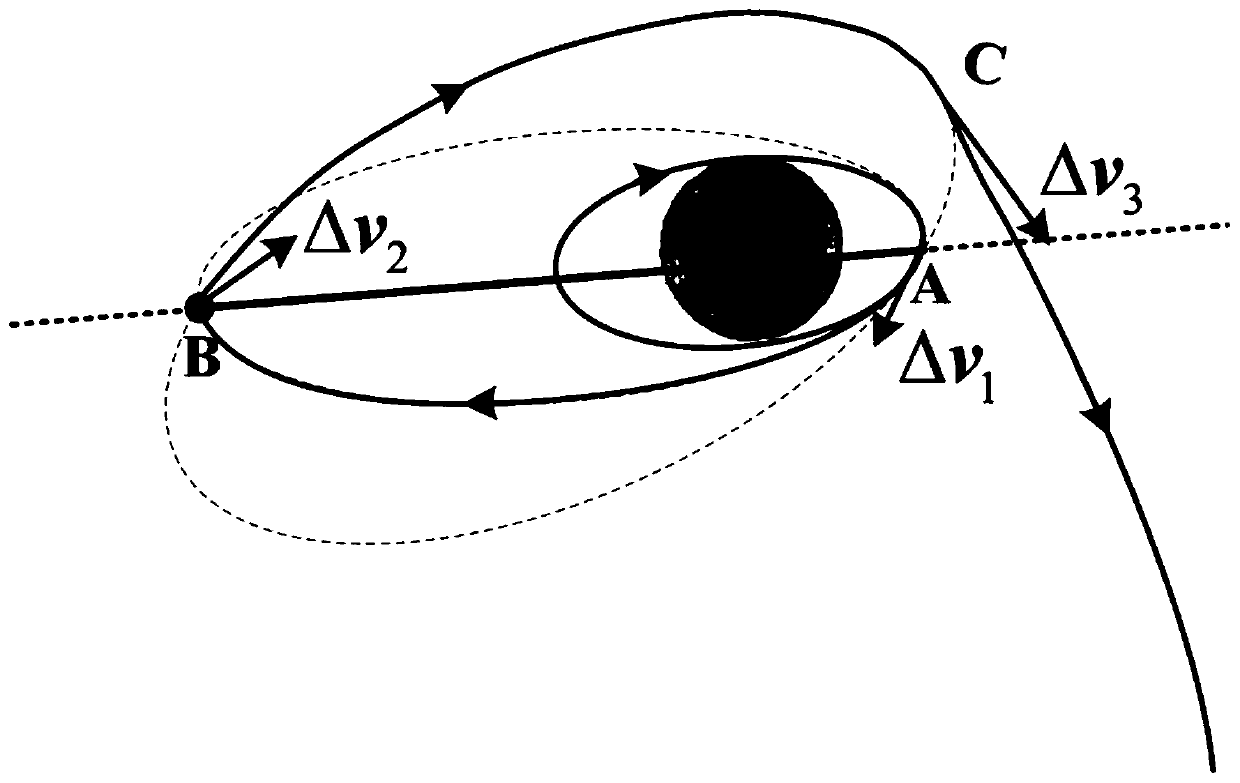
Month-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method
ActiveCN110704952AFast and efficient preliminary approximation analysisIntuitive and concise preliminary approximate analysisGeometric CADDelta-vEngineering
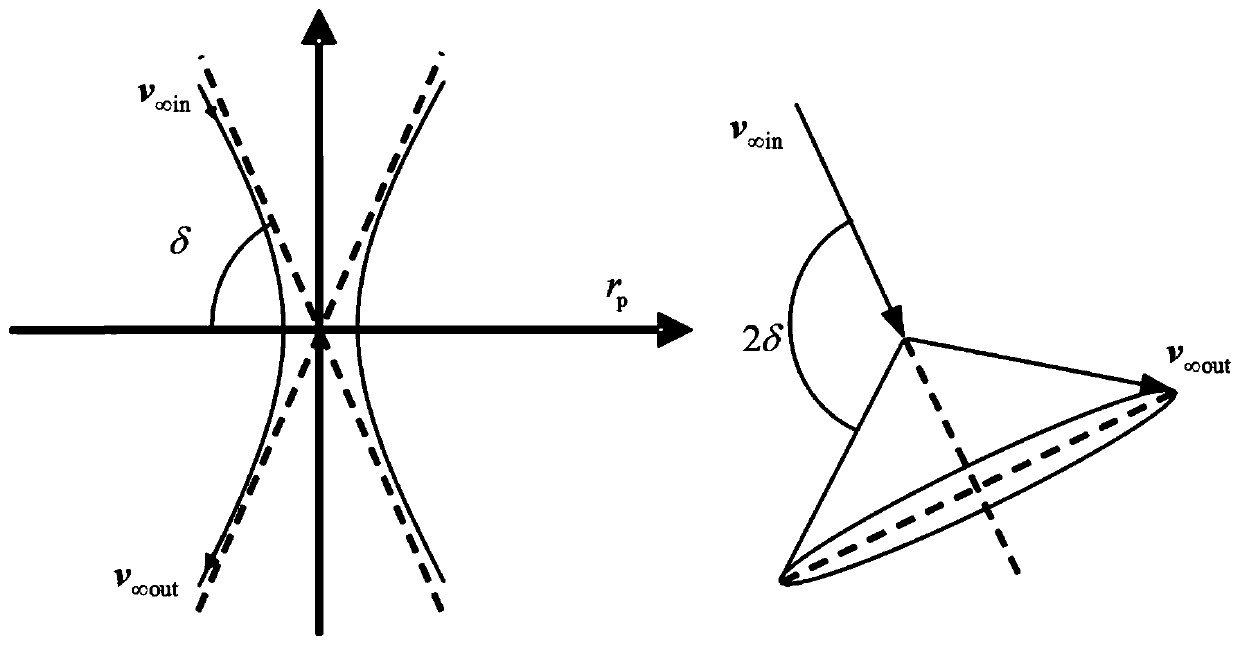
The invention discloses a moon-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method, which comprises the following steps: A, obtaining a normal unit vector h1 of a lunar orbit plane, a normal unit vector h2 of a lunar escape orbit plane and positions rA, rB and rC for applying three pulses by taking a moon center as an original point; B, obtaining a conical surface S1 with the lunar escape orbit aiming v infinity out as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S1 is eta; C, enabling the plane where v infinity out and h1 are located to serve as the datum plane, setting the rotating angle sigma of rC around the straight line where v infinity out is located, and determining rC and a lunar escape orbit plane; D, obtaining a conical surface S2 with the straight line where rC is located as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S2 is alpha; E, obtaining the included angle beta between h1 and v infinity out and the different-plane differencexi between the lunar orbit and the lunar escape orbit; F, solving the sizes delta v1, delta v2 and delta v3 of the three pulses; G, solving a total speed increment delta v; and H, changing the independent variable influencing the delta v to obtain a change rule of the delta v. According to the method, the spatial geometrical relationship is utilized, and preliminary approximate analysis can be rapidly, effectively, visually and simply carried out on the speed increment required by the three-pulse maneuvering process.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
System and method for autonomous steering control of work vehicles
ActiveUS10494789B2Mechanical machines/dredgersEndless track vehiclesAutomatic steeringControl system
An electronic control system for a work allows for control of steering despite movement of an implement that may support a load. Control may be based on vehicle position, velocity, acceleration, center of gravity, and heading. A control point is determined despite movement of the load, and may be based upon one or more of roll, yaw, and pitch of the vehicle. The vehicle may be of the type that allows for control only of wheel or track speed and rotational direction. A desired center of gravity is maintained while controlling an error between a desired vehicle trajectory and a determined trajectory in a closed loop manner.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS SOLUTIONS +1
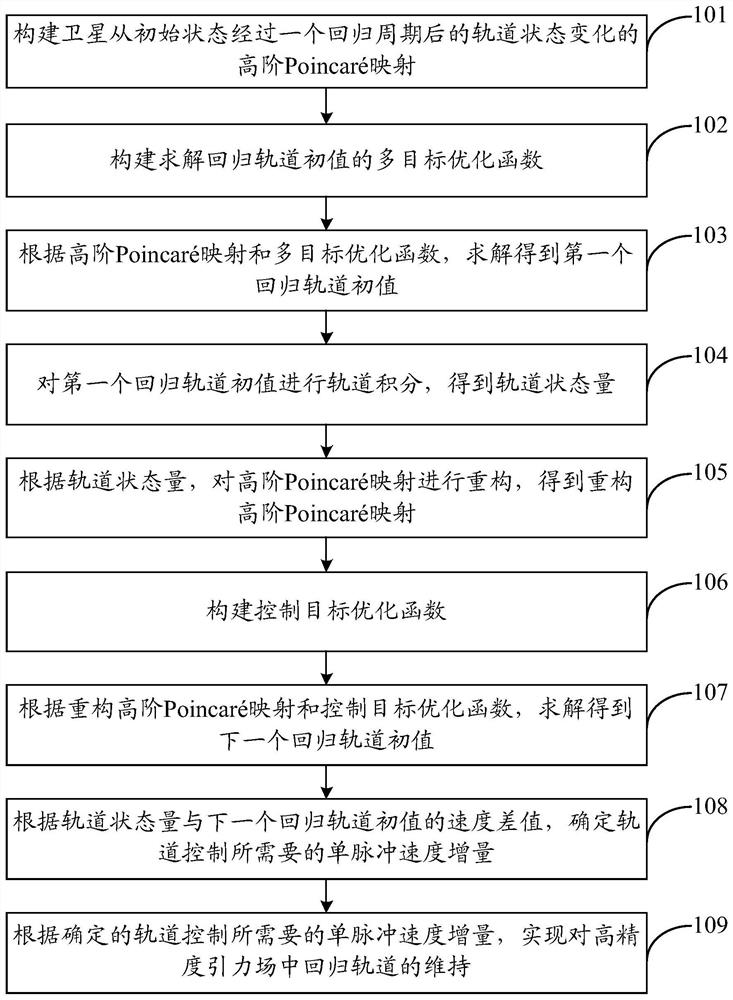
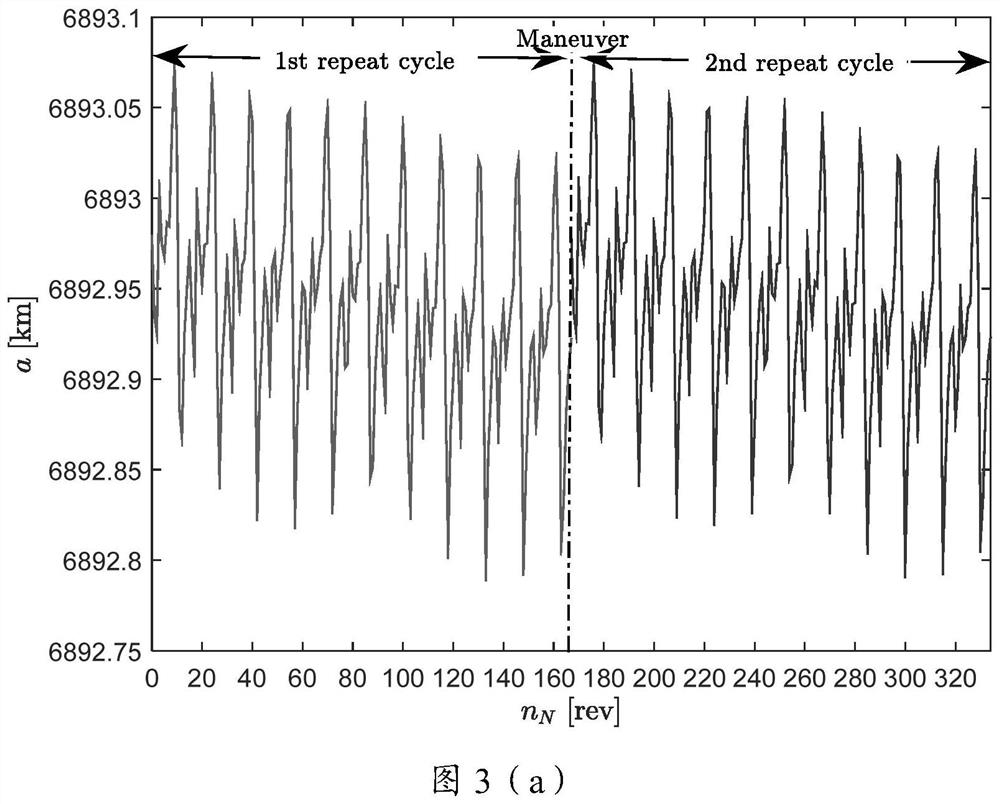
Method for maintaining regression orbit in high-precision gravitational field based on monopulse orbit control
ActiveCN111731513ANon-conservative gravitational increaseIncreased non-conservative gravitational perturbationAttitude controlSpacecraft guiding apparatusComputational physicsPoincare mapping
The invention discloses a method for maintaining a regression orbit in a high-precision gravitational field based on monopulse orbit control. The method comprises the steps of constructing high-orderPoincare mapping, solving a multi-objective optimization function of an initial value of the regression orbit, and solving to obtain a first initial value of the regression orbit,performing orbit integration on the first regression orbit initial value to obtain an orbit state quantity,reconstructing the high-order Poincare mapping according to the orbit state quantity, and solving to obtain a nextregression orbit initial value,and determining a monopulse speed increment required by track control according to the speed difference between the track state quantity and the initial value of the next regression track, thereby realizing maintenance of the regression track in the high-precision gravitational field. According to the method, on the basis that the orbit design is used as a nominal value, the orbit speed states in the adjacent regression periods are connected by applying the speed pulse at the ascending node of the equator, so that high-precision orbit control is realized, and the actual sub-satellite point orbit of the satellite deviates from the nominal position by a distance within a threshold range set by a user.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Orbital speed reducer by belt
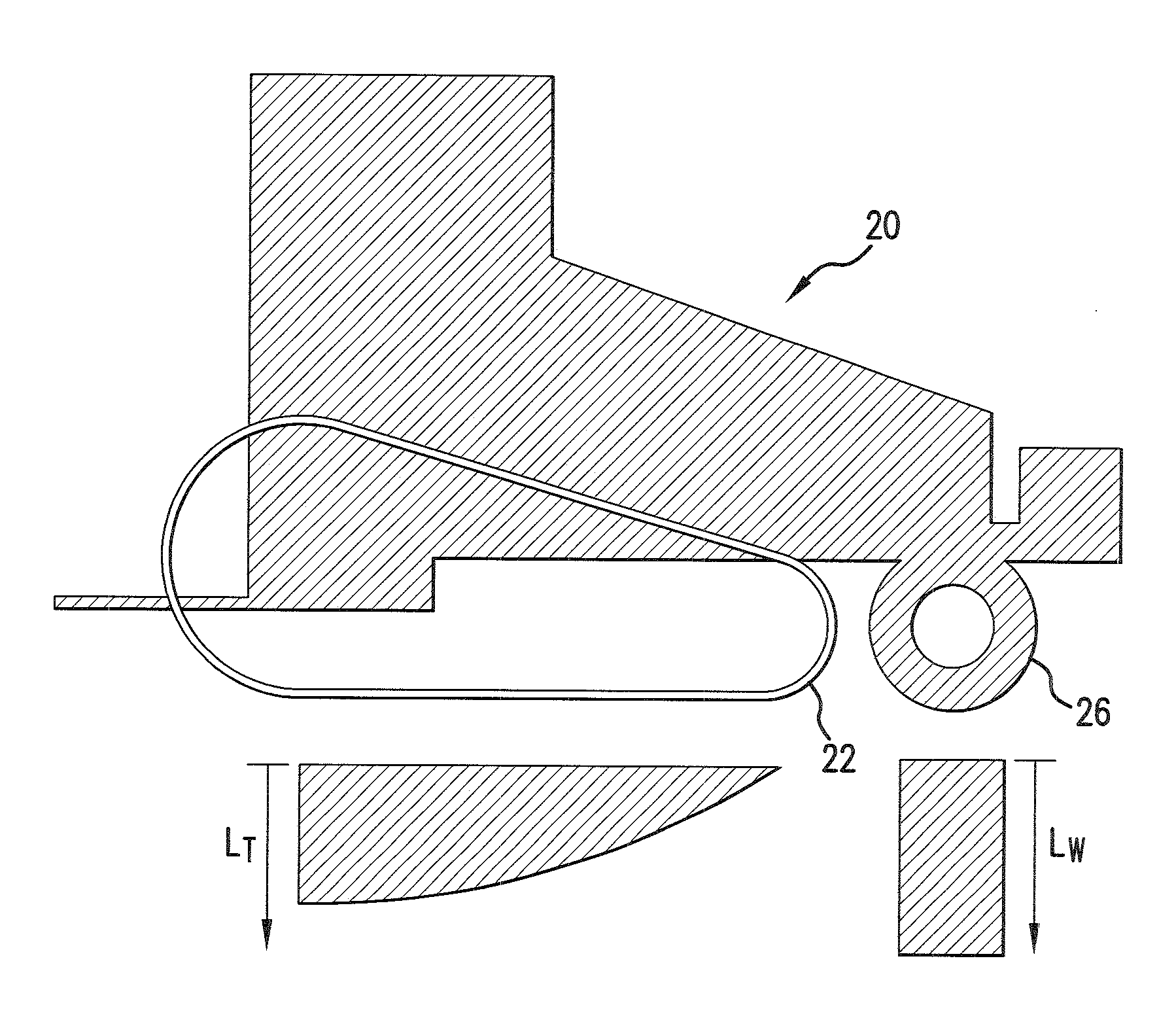
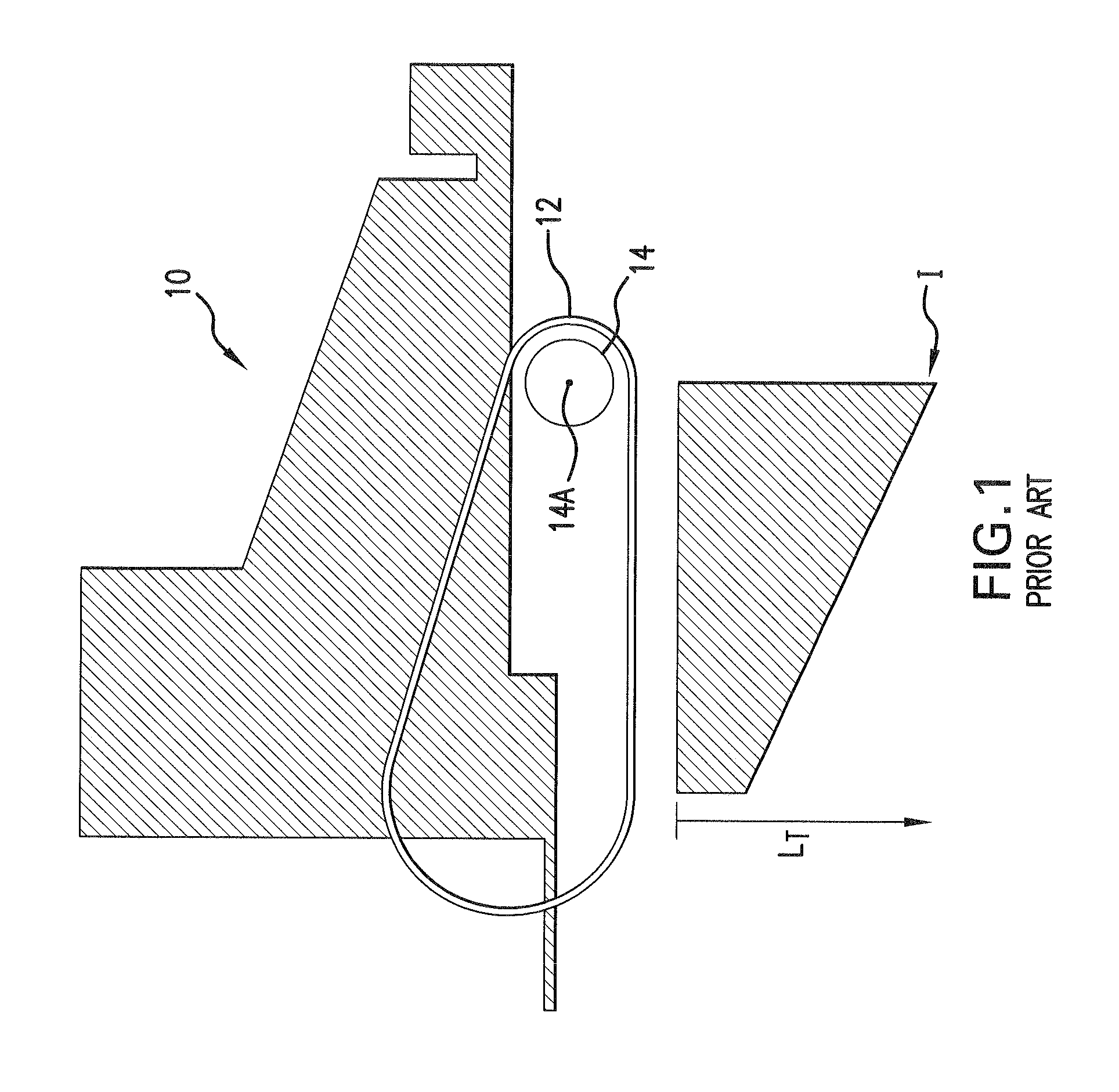
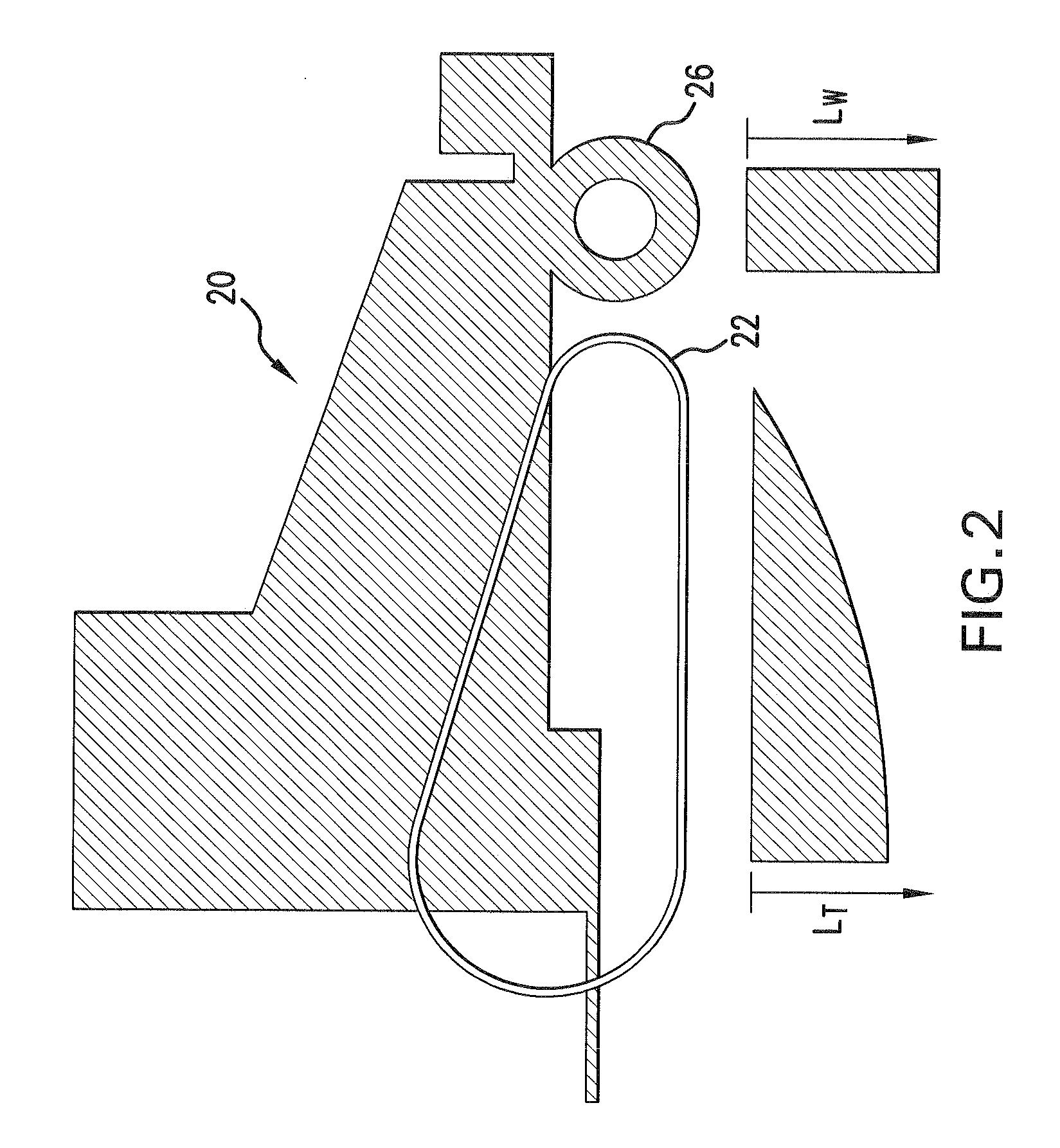
InactiveUS20080161143A1Simple structureLow production costFriction gearingsReduction driveGear wheel
It is an epicyclic gear system for use in speed reducer or overdrive, however using an inner pulley, an external ring and a driving belt or a tire instead of using toothed gears. The system particularity is an inner pulley drivingly coupled to an external ring and the torque transmission between the inner pulley and the external ring is done through a belt or a tire, as either the inner pulley or the external ring has orbital motion.
Owner:GRAVIO VALMOR CUNHA
Calculation Method of Image Motion Compensation Based on Elliptical Orbit
ActiveCN107479565BReasonable analysisGuaranteed image motion compensation accuracyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsInertial coordinate systemImage motion
Based on the calculation method of image motion compensation of elliptical orbit, involving the field of aerospace, it solves the problem that the existing image motion compensation model cannot realize the compensation of image motion of elliptical orbit, and establishes an ellipse with the calculation model of image motion velocity vector of circular orbit and the parameters of elliptical orbit The image movement velocity vector model of the orbit, and calculate the spacecraft elliptical orbital velocity, perigee orbital velocity and apogee orbital velocity; calculate the angle between the orbital velocity and the centrifugal velocity, and obtain the orbital velocity and centrifugal velocity according to the calculated angle, Calculate the height of the elliptical orbit; convert the orbiting speed of the spacecraft to the image movement speed of the image plane through the horizontal coordinate system of the star vertical line, the planetary coordinate system, the planetary inertial coordinate system, the orbital coordinate system, the camera coordinate system and the image plane coordinate system respectively ; Obtain the image motion velocity of the scenic spot on the camera image plane, and compensate the image motion of the ellipse orbit according to the obtained image motion velocity of the image plane.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
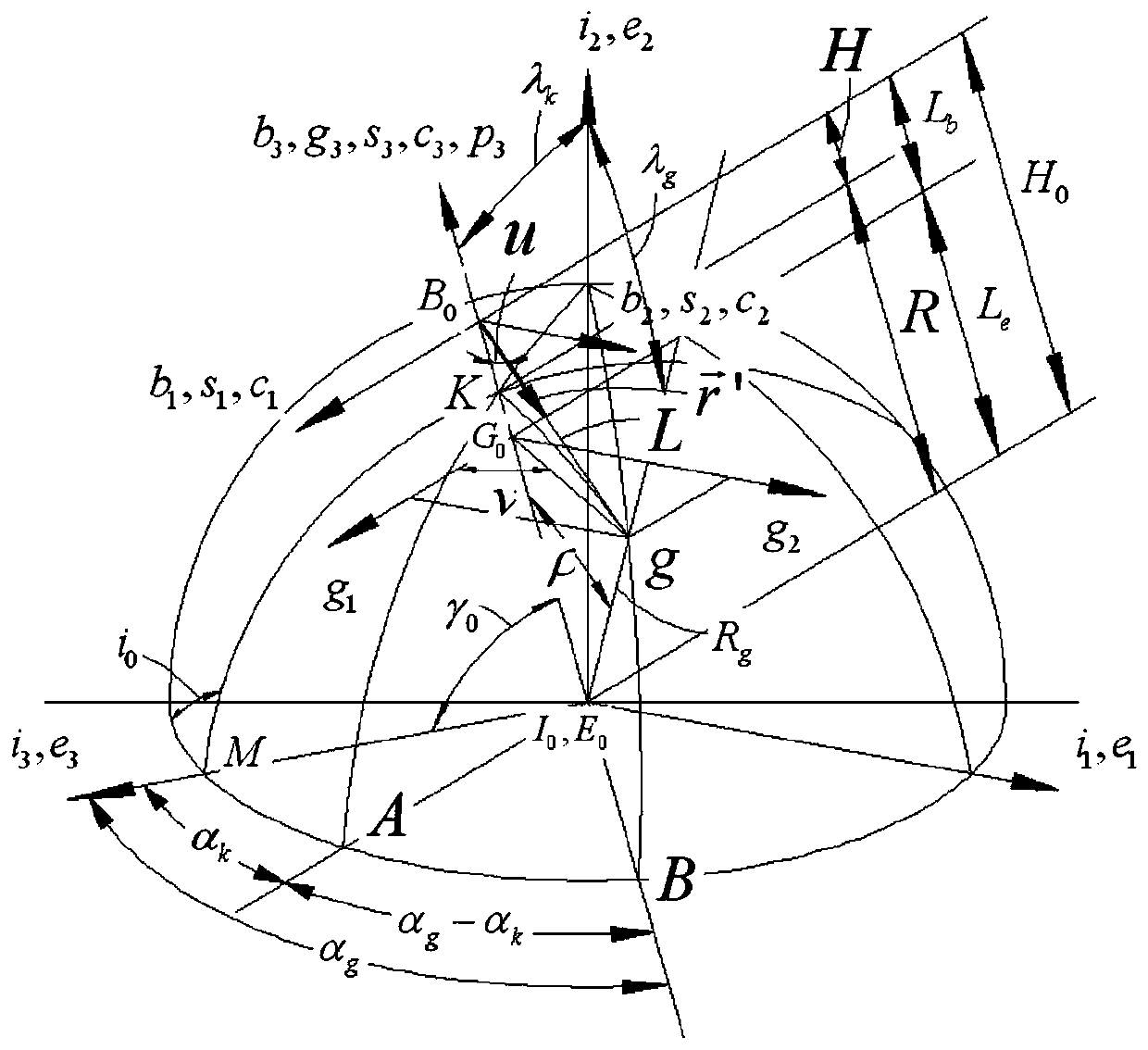
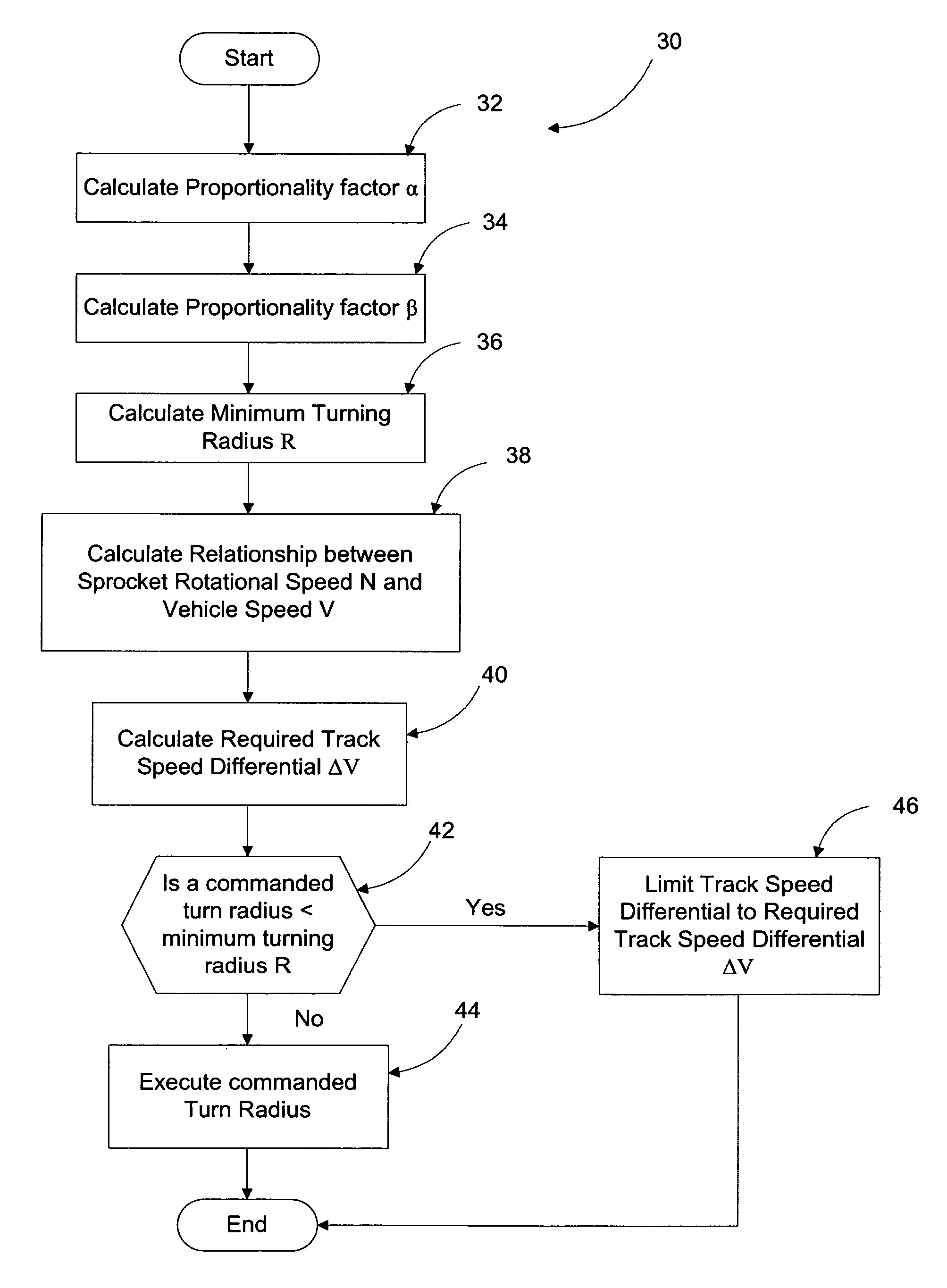
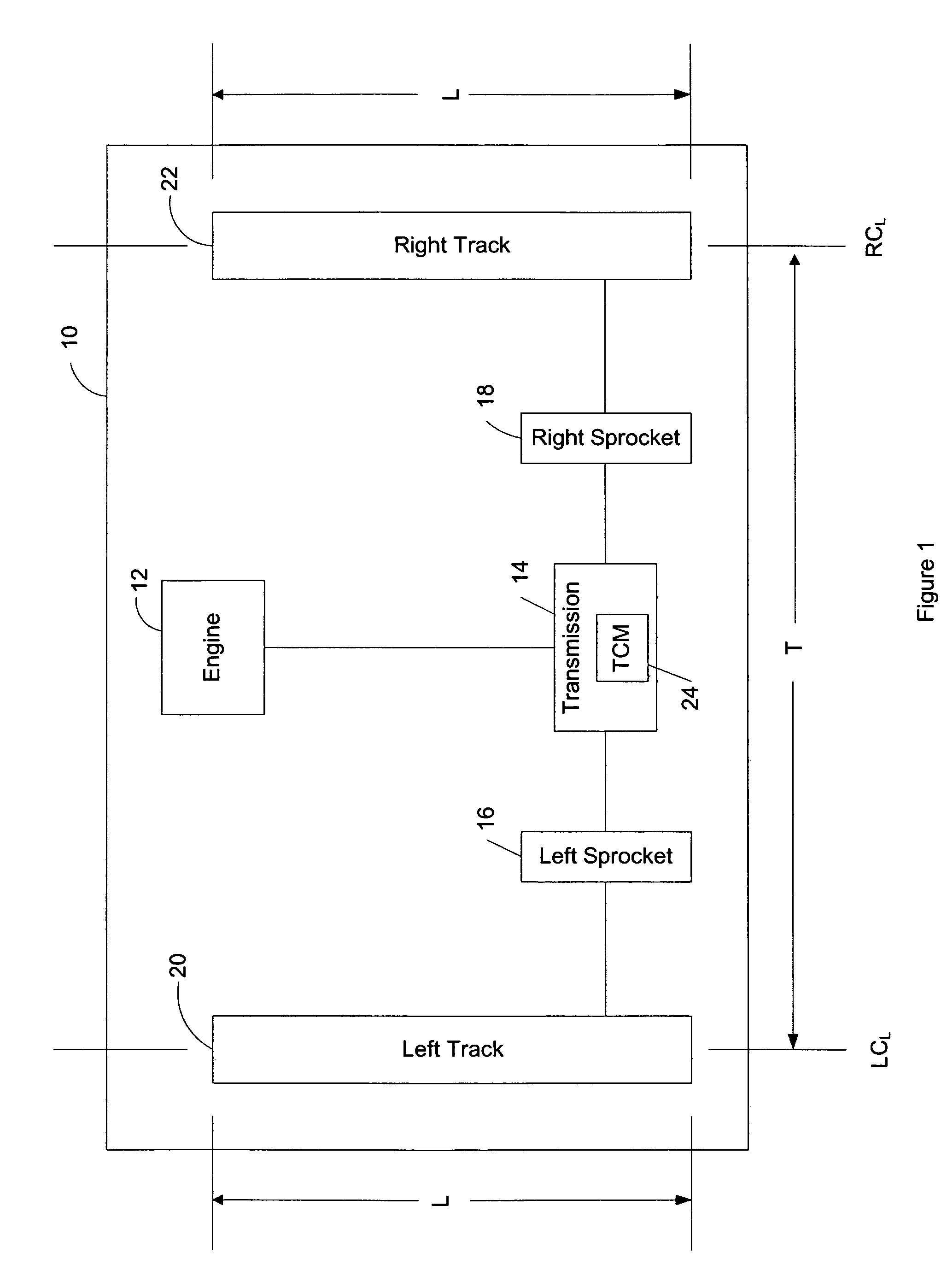
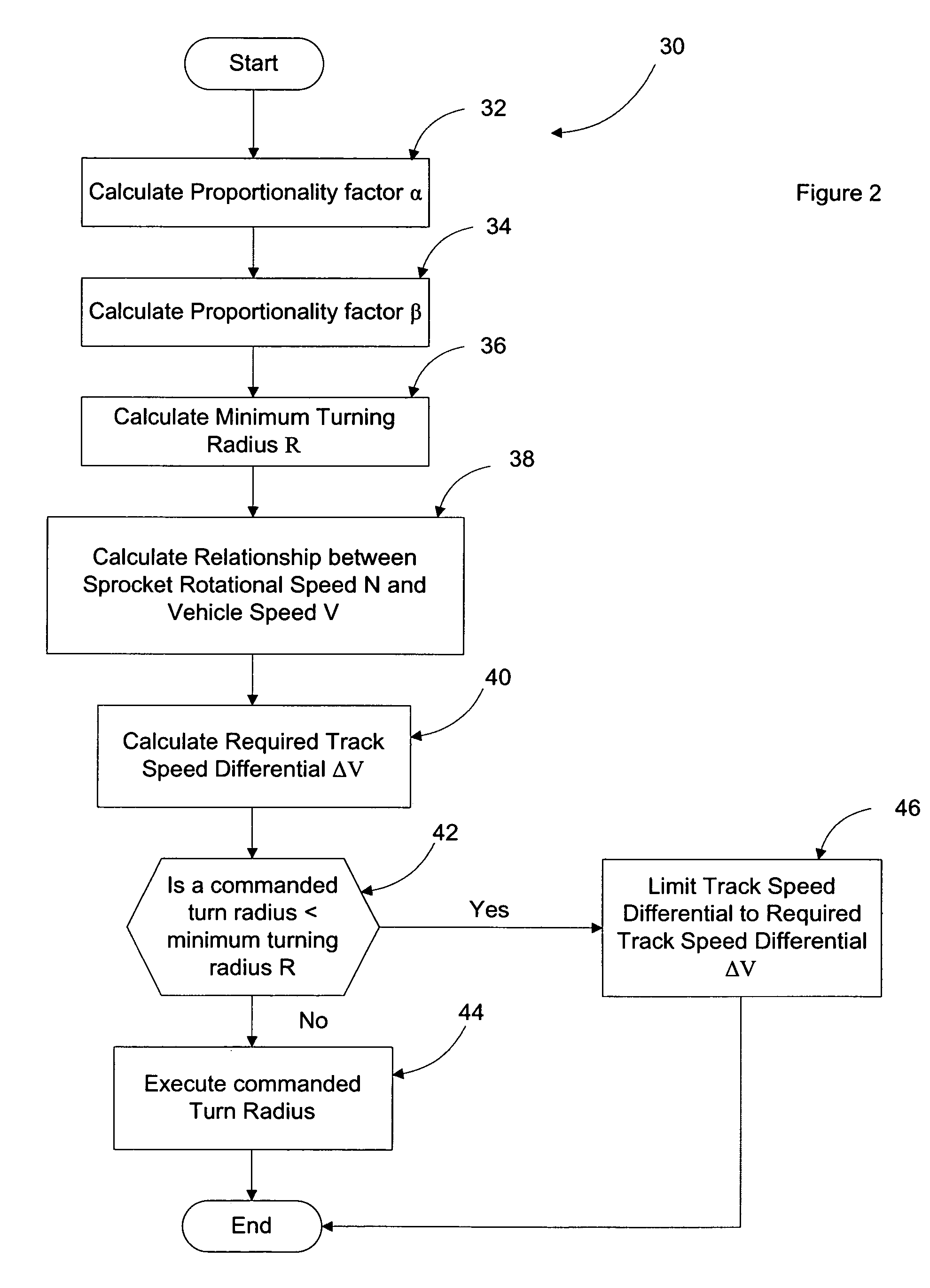
Traction control method for a tracked vehicle
The present invention provides a traction control method for a tracked vehicle such as a military tank. The method includes calculating a track proportionality factor and a vehicle proportionality factor based on predefined attributes of the tracked vehicle. A minimum turn radius of the tracked vehicle is calculated based on the velocity of the tracked vehicle, the maximum coefficient of friction between the tracks of the tracked vehicle and the ground (0.7), and gravitational acceleration (9.80665 m / s2). A sprocket rotational speed is calculated based on the pitch diameter of the tracked vehicle sprockets and the velocity of the tracked vehicle. Based on the preceding calculations, the method of the present invention calculates a required track speed differential configured to turn the tracked vehicle at the minimum turn radius. If a commanded turn radius is less than the minimum turn radius, the track speed differential of the tracked vehicle is limited to the required track speed differential to prevent the tracked vehicle from slipping.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
A Method for Extracting Wave Breaking Rate Based on Coherent X-band Radar Image
InactiveCN104133208BSmall amount of calculationHigh speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainFrequency spectrum
Disclosed is an ocean-wave broken-rate extraction method based on coherent X-waveband radar images. The method includes the following steps: obtaining the coherent X-waveband radar complex images; solving a multiple correlation function of the complex image in a time domain; solving a phase difference of the radar complex images based on the multiple correlation function and obtaining a phase difference image; carrying out Radon transformation on the phase difference image so that an ocean-wave phase speed is obtained; carrying out short-time FFT transformation on the multiple correlation function so that a short-time Doppler frequency spectrum of the multiple correlation function is obtained; calculating an orbital speed of ocean waves based on the short-time Doppler frequency spectrum; and obtaining the ocean-wave broken rate of the whole measured sea area. The method significantly reduces a calculation quantity in an ocean-wave broken-rate extraction process and improves the speed; a coherent X-waveband radar is free from restriction of complex ocean environment conditions; and the effective action distance of the coherent X-waveband radar is far larger than a camera and the obtained ocean-wave broken rate can better reflect a true statistical characteristic.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com