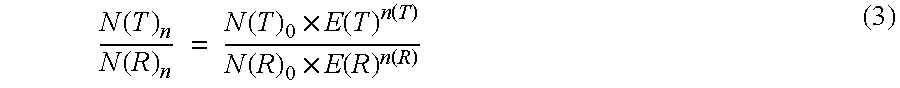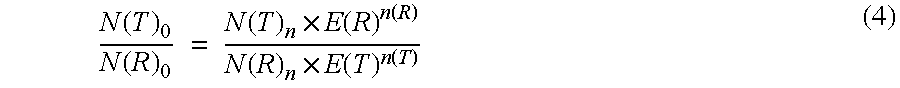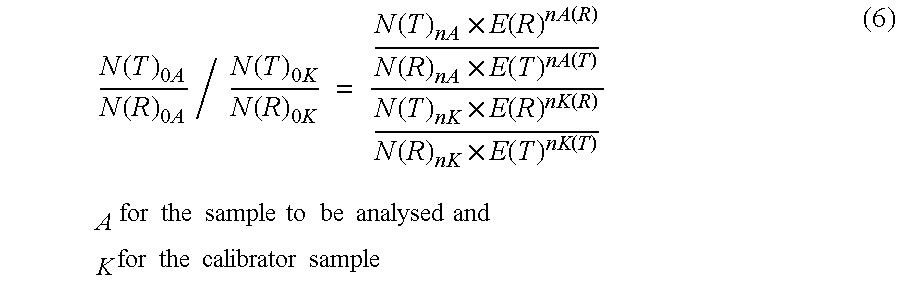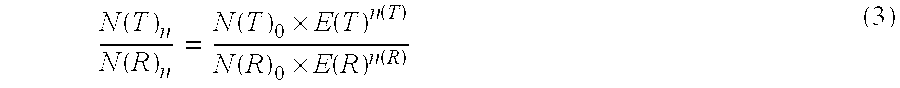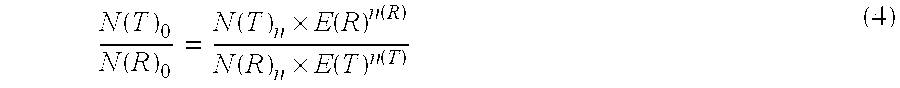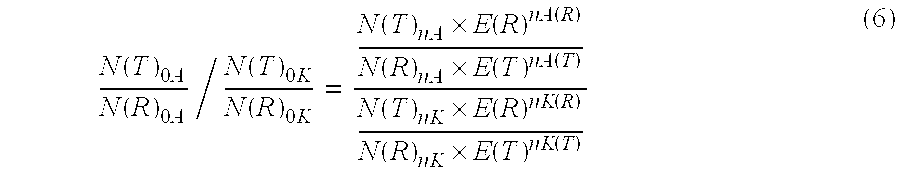Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Nucleic acid quantitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular biology, quantitation of nucleic acids is commonly performed to determine the average concentrations of DNA or RNA present in a mixture, as well as their purity. Reactions that use nucleic acids often require particular amounts and purity for optimum performance. To date, there are two main approaches used by scientists to quantitate, or establish the concentration, of nucleic acids (such as DNA or RNA) in a solution. These are spectrophotometric quantification and UV fluorescence tagging in presence of a DNA dye.
Method for the efficiency-corrected real-time quantification of nucleic acids
InactiveUS6691041B2Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHousekeeping geneInternal standard
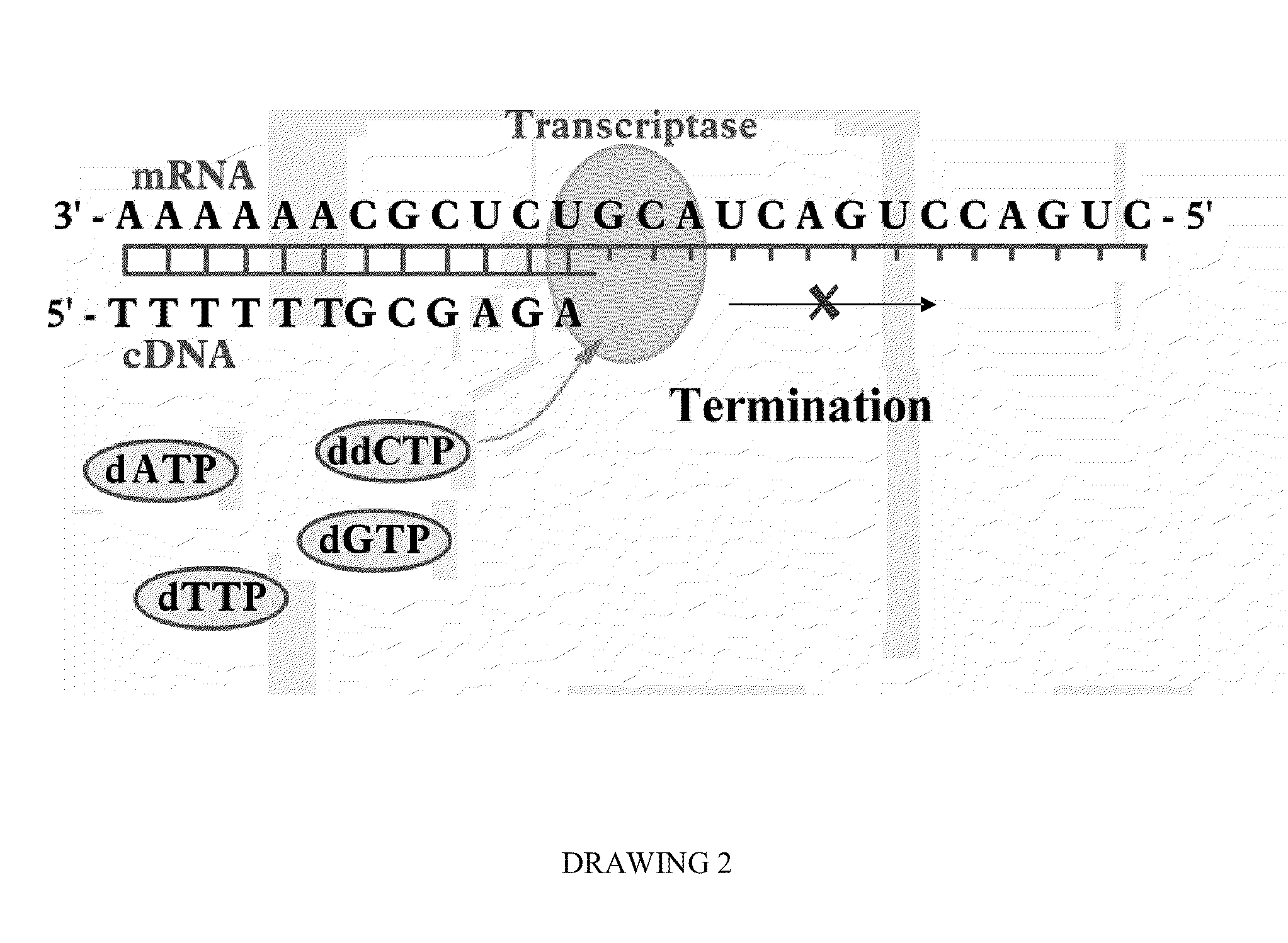
The present invention concerns a method for the quantification of a target nucleic acid in a sample comprising the following steps: (i) determination of the amplification efficiency of the target nucleic acid under defined amplification conditions, (ii) amplification of the target nucleic acid contained in the sample under the same defined reaction conditions, (iii) measuring the amplification in real-time, (iv) quantification of the original amount of target nucleic acid in the sample by correction of the original amount derived from step (iii) with the aid of the determined amplification efficiency. The efficiency correction of PCR reactions according to the invention for the quantification of nucleic acids can be used for absolute quantification with the aid of an external or internal standard as well as for relative quantification compared to the expression of housekeeping genes.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
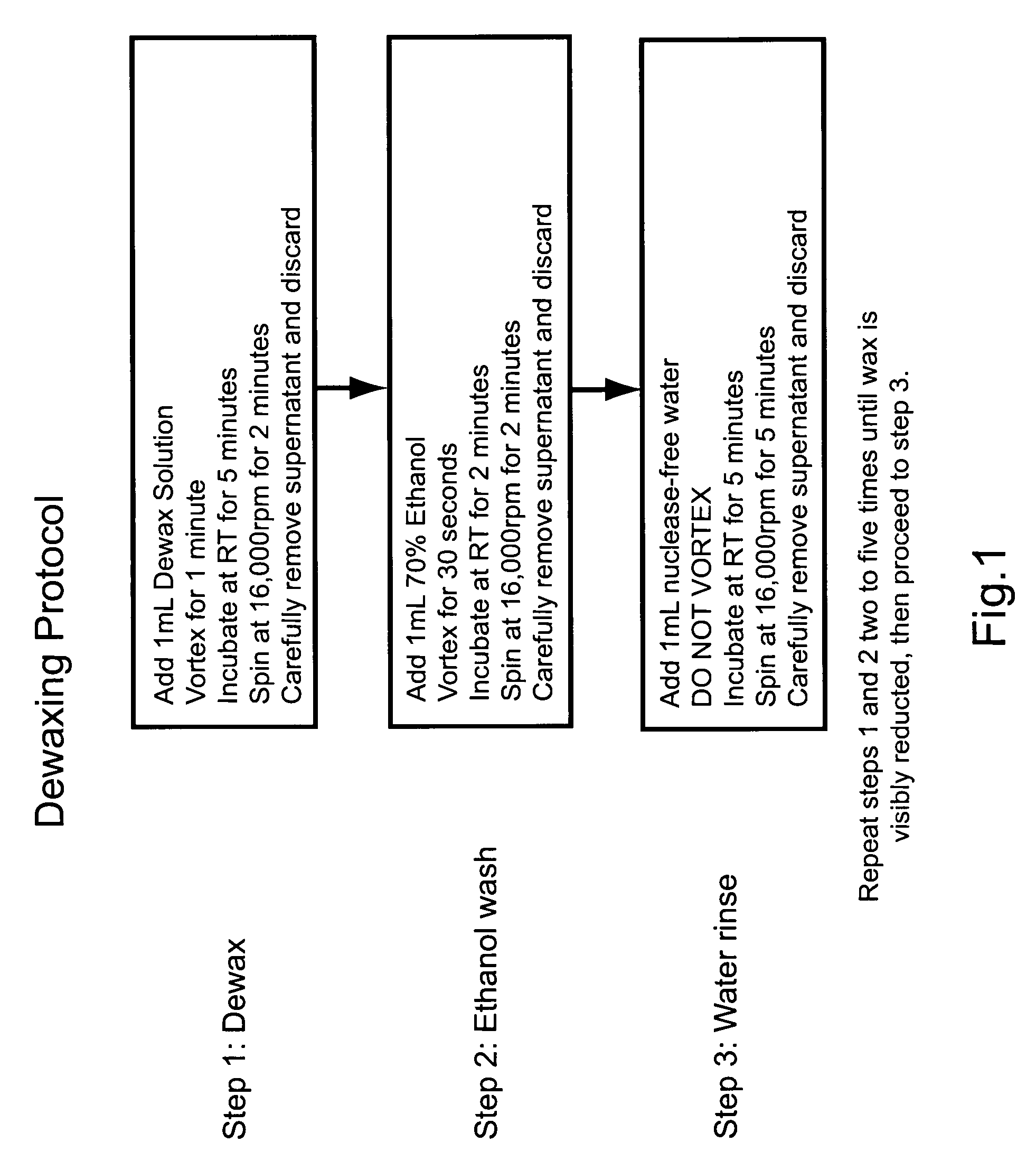
Nucleic acid quantitation from tissue slides
ActiveUS20080050746A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesParaffin embeddedAneuploid Cells
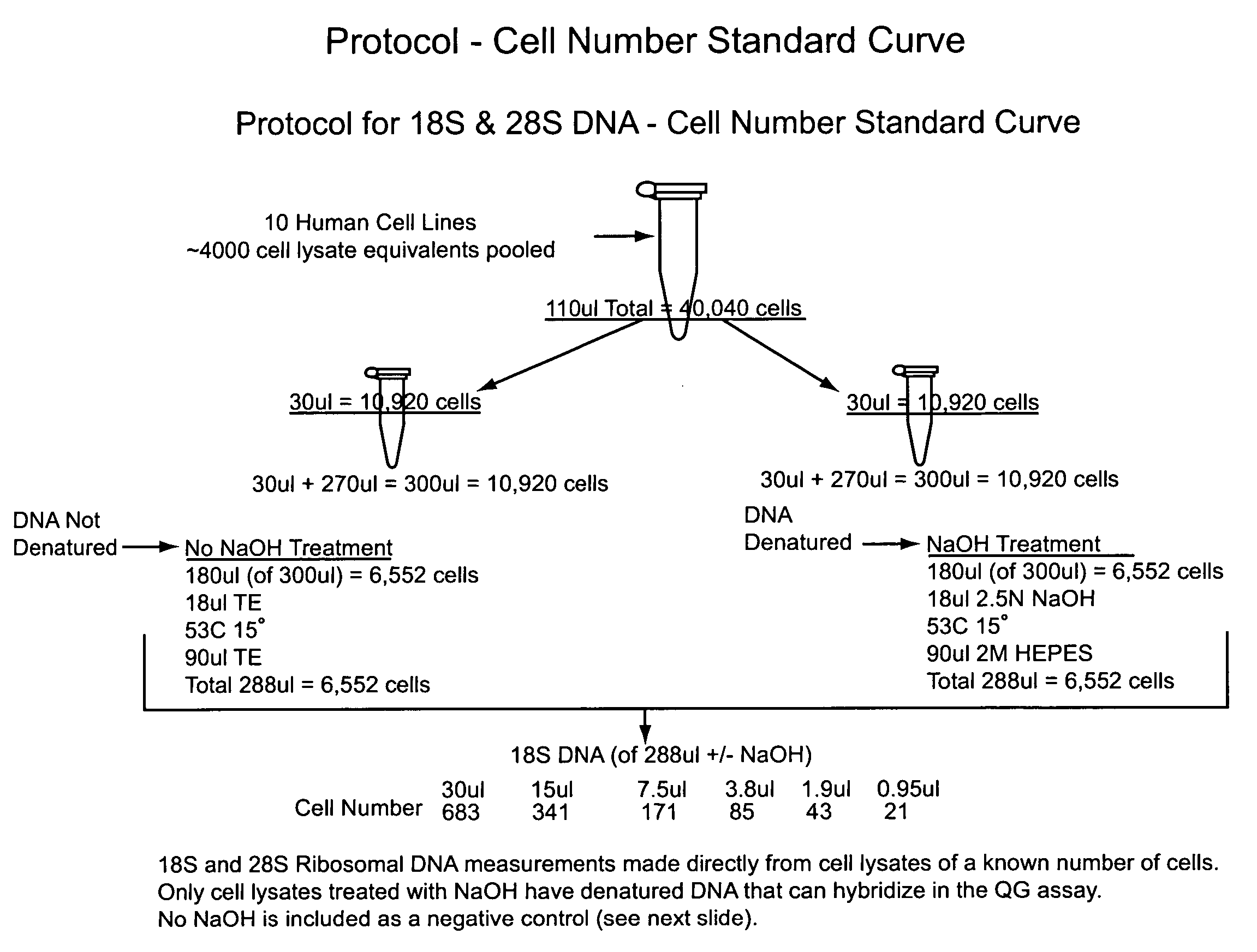
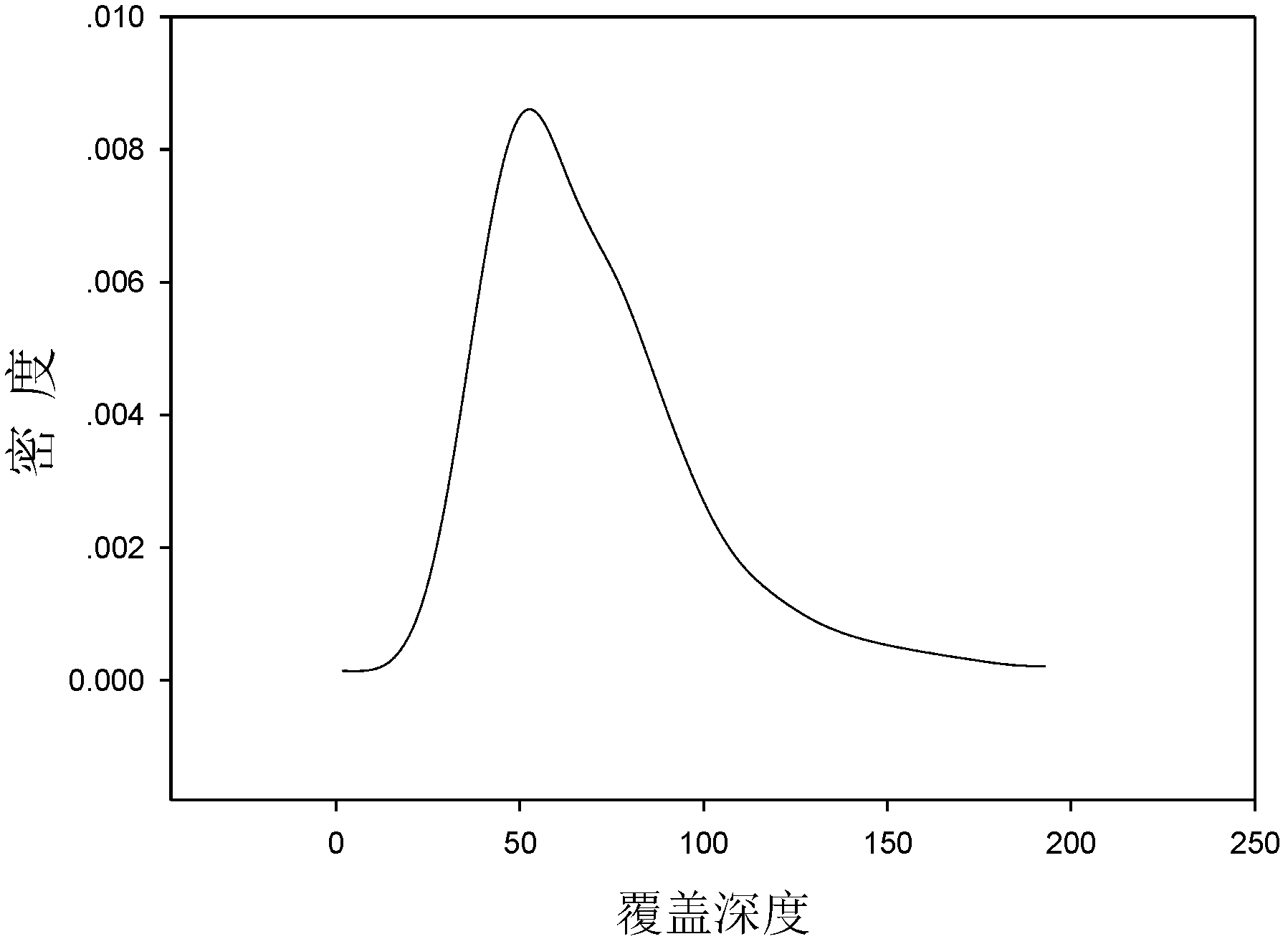
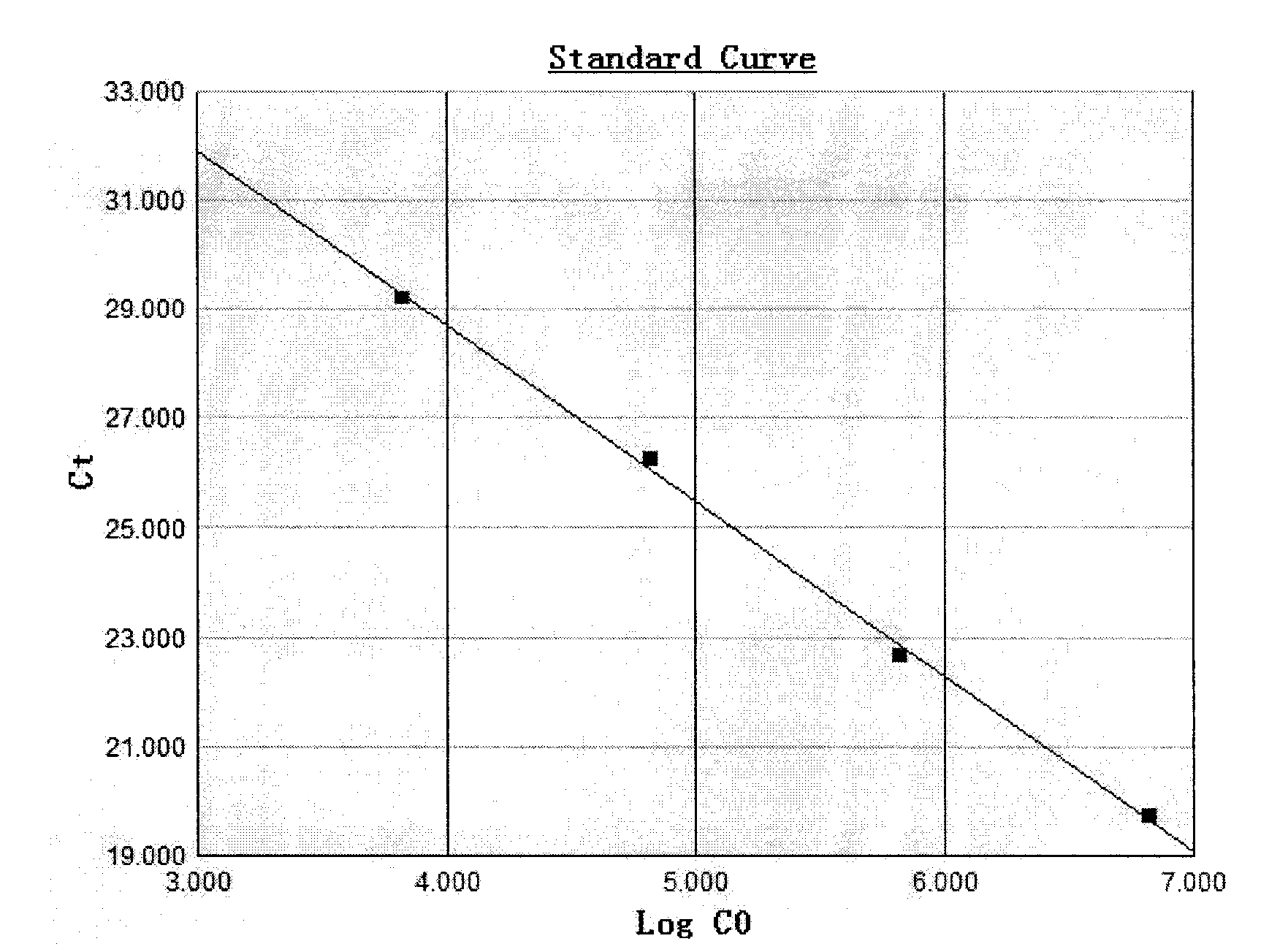
This invention provides methods of quantitating nucleic acids from problematic samples, such as aged samples, formalin fixed samples, paraffin embedded samples, samples with aneuploid cells, and cells with fragmented nucleic acids. Methods include techniques to efficiently solublize the nucleic acids under non-denaturing conditions from preserved clinical samples without resort to organic extractions, to normalize cell counts regardless of aneuploidy, to access the fragmentation state of the nucleic acids, and to provide standard curves for degraded nucleic acid samples.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for the efficiency-corrected real-time quantification of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20030165832A1Minimize the differenceDifference in efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHousekeeping geneInternal standard
The present invention concerns a method for the quantification of a target nucleic acid in a sample comprising the following steps: (i) determination of the amplification efficiency of the target nucleic acid under defined amplification conditions, (ii) amplification of the target nucleic acid contained in the sample under the same defined reaction conditions, (iii) measuring the amplification in real-time, (iv) quantification of the original amount of target nucleic acid in the sample by correction of the original amount derived from step (iii) with the aid of the determined amplification efficiency. The efficiency correction of PCR reactions according to the invention for the quantification of nucleic acids can be used for absolute quantification with the aid of an external or internal standard as well as for relative quantification compared to the expression of housekeeping genes.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
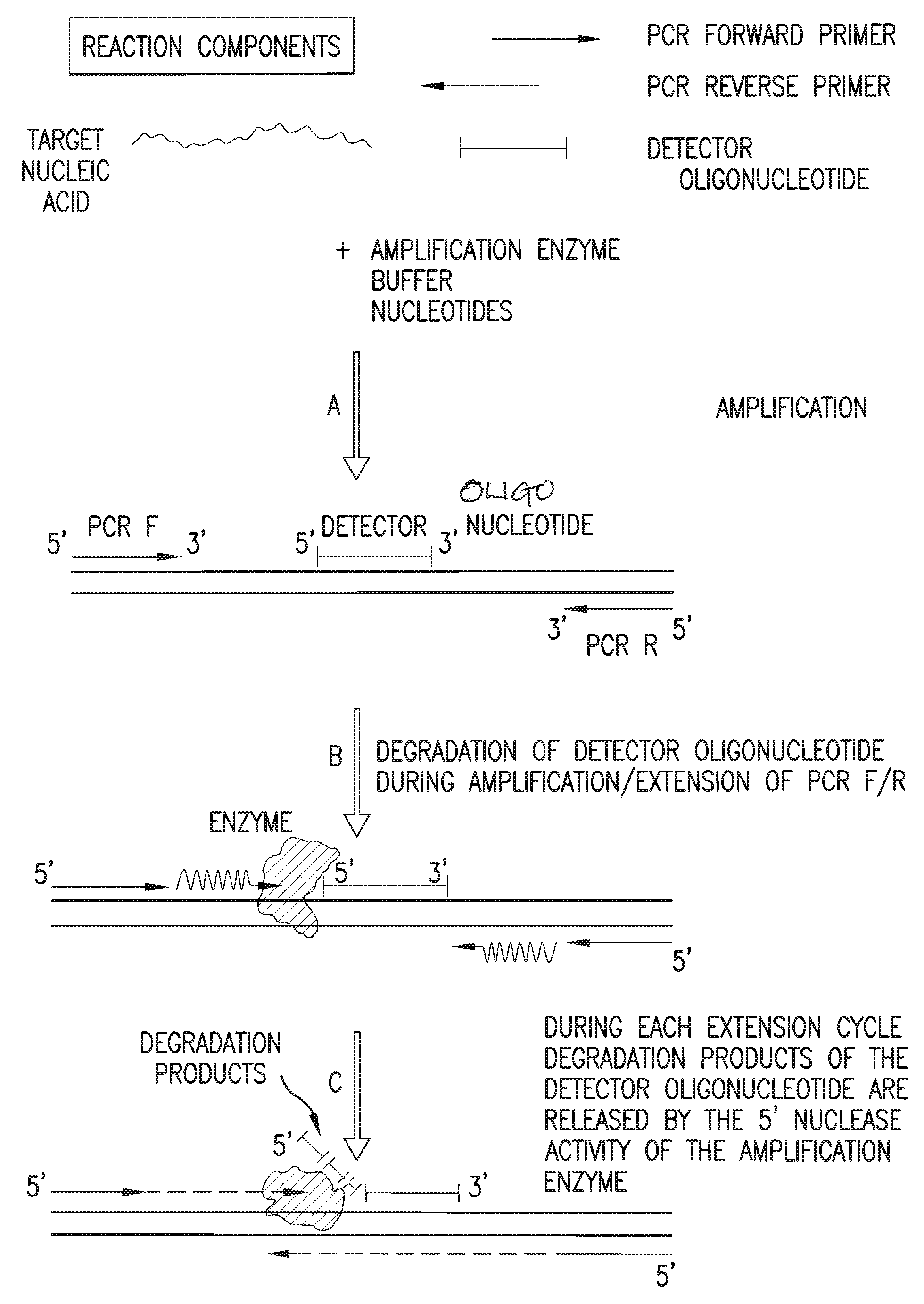
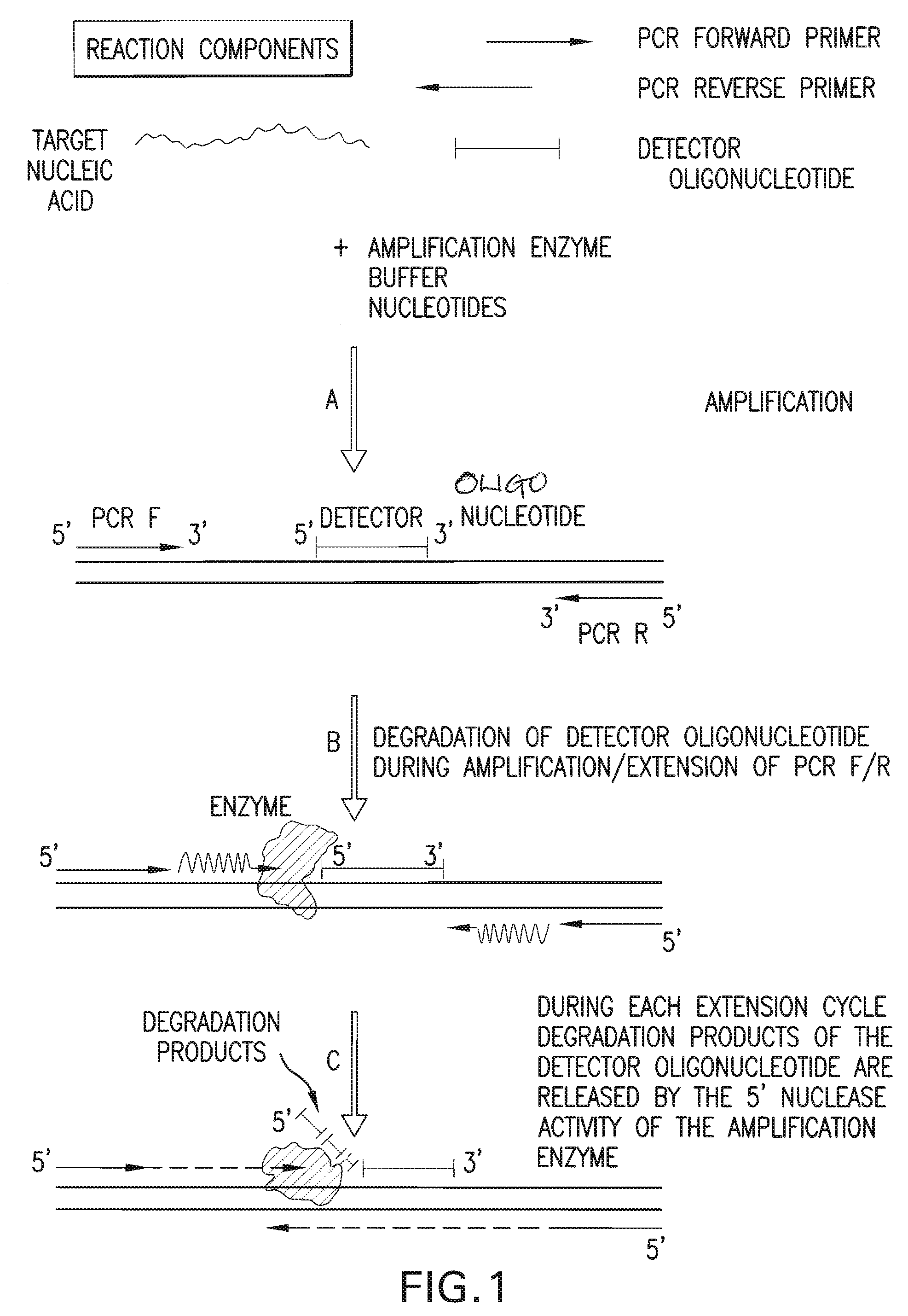
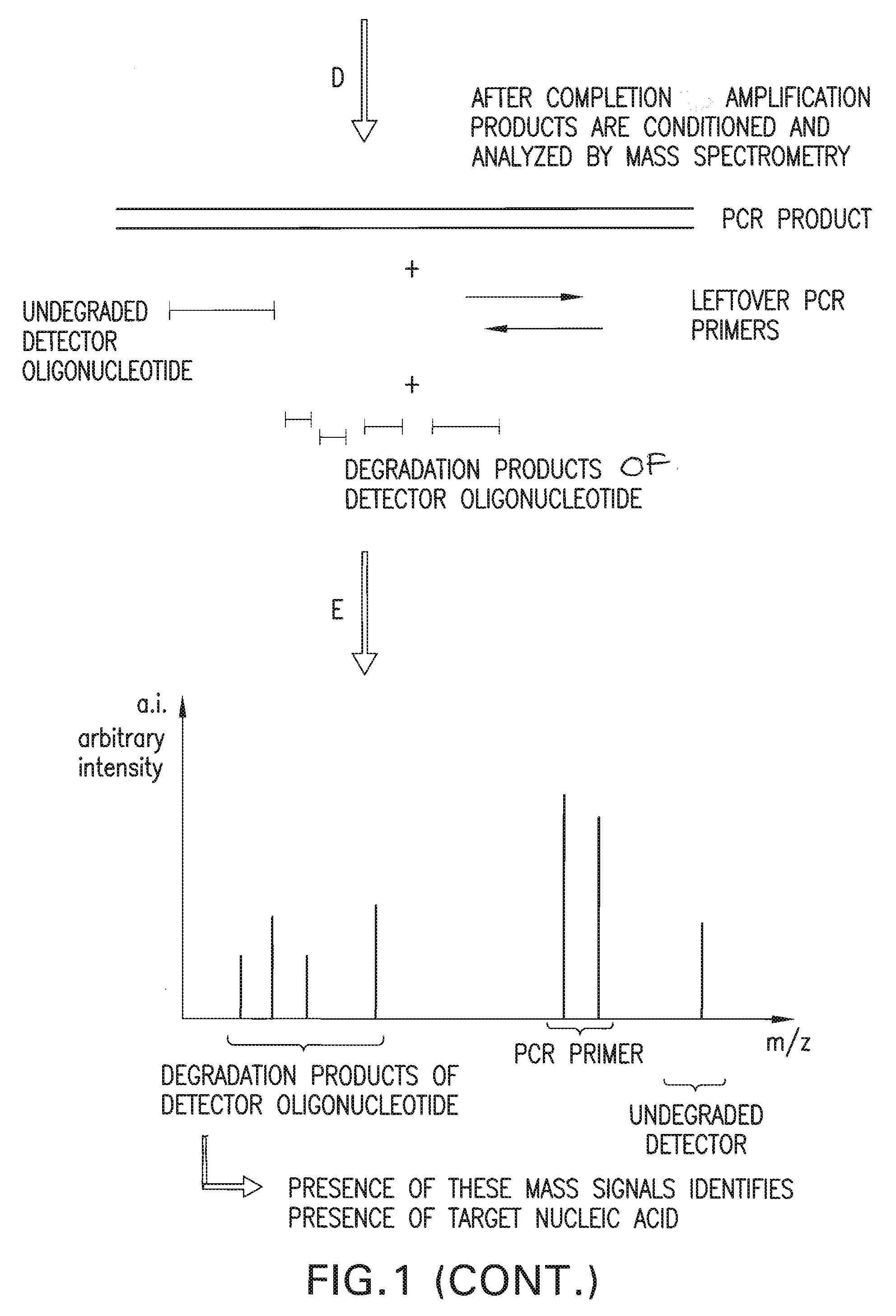
Detection and quantification of biomolecules using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20090111712A1Reduce processing stepsReduce rateSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesPolymerase LMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention is directed in part to a method for detecting a target nucleic acid using detector oligonucleotides detectable by mass spectrometry. This method takes advantage of the 5′ to 3′ nuclease activity of a nucleic acid polymerase to cleave annealed oligonucleotide probes from hybridized duplexes and releases labels for detection by mass spectrometry. This process is easily incorporated into a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification assay. The method also includes embodiments directed to quantitative analysis of target nucleic acids.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Detection and quantification of biomolecules using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS8133701B2Reduce processing stepsReduce rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention is directed in part to a method for detecting a target nucleic acid using detector oligonucleotides detectable by mass spectrometry. This method uses the 5′ to 3′ nuclease activity of a nucleic acid polymerase to cleave annealed oligonucleotide probes from hybridized duplexes and release labels for detection by mass spectrometry. This process is easily incorporated into a PCR amplification assay. The method also includes embodiments directed to quantitative analysis of target nucleic acids.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Quantitative detection kit of hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleic acid
ActiveCN103642941AAvoid PCR false negativesHighly conservativeMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic beadReference product
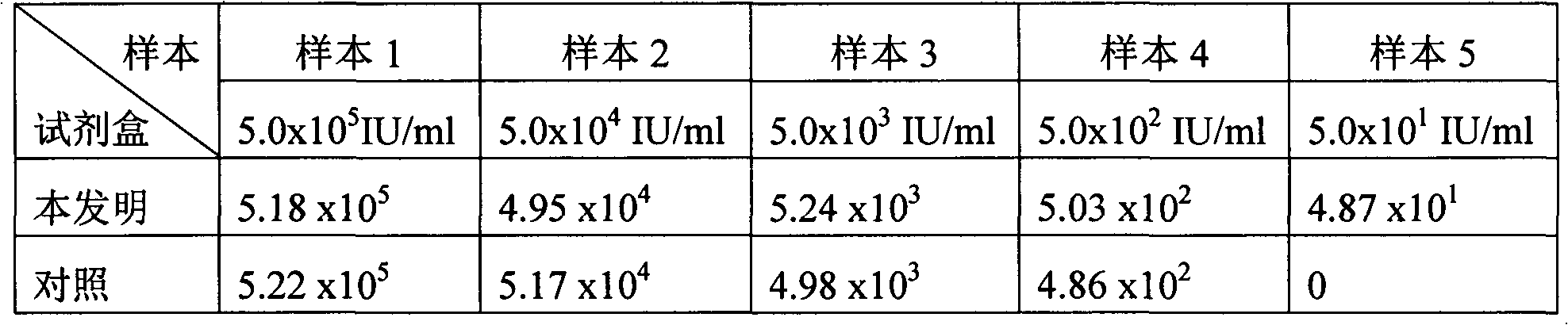
The invention discloses a quantitative detection kit of a hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleic acid applied to the field of biomedical clinic diagnosis. The kit comprises a paramagnetic particle method extraction kit and an HBV nucleic acid amplification kit, wherein the paramagnetic particle method extraction kit comprises a pyrolysis binding solution, a rinsing solution, an eluant and magnetic bead liquid; the HBV nucleic acid amplification kit comprises an HBV-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction solution, an enzyme mixed solution, an HBV-interior label, HBV quantitative reference products 1-4, a negative quality product, a clinical positive quality product and a strong positive quality product. The quantitative detection kit is simple, convenient and fast in operation, low in cost, high in detection sensitivity, good in repeatability, high in conservative property of primer and probe, and strong in specificity, and covers different subtypes or variants of the hepatitis B virus, improvement of the accuracy and the specificity of the hepatitis B detection is facilitated, an efficient interior label system is led in, the problems such as reciprocal inhibition, interference and the like caused by simultaneous amplification of a target gene and the interior label are solved, the overall PCR amplification process can be effectively monitored, and a false negative result is avoided.
Owner:东北制药集团辽宁生物医药有限公司
High-precision nucleic acid quantitative detection kit for hepatitis C virus (HCV)
ActiveCN103642942AAvoid PCR false negativesIncrease coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic beadGenotype
The invention relates to a high-precision nucleic acid quantitative detection kit for hepatitis C virus (HCV) applied to the field of biomedical clinical diagnosis. The kit comprises a nucleic acid extraction kit based on a paramagnetic particle method and an HCV nucleic acid amplification box, wherein the nucleic acid extraction kit based on the paramagnetic particle method comprises a splitting combining liquid, a rinsing liquid A, a rinsing liquid B, a rinsing liquid C, an eluting liquid and a magnetic bead liquid. The HCV nucleic acid amplification box comprises an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction liquid, enzyme mixed liquor, an HCV-interior label, an HCV quantitative reference 1-4, a negative quality control product, a critical positive quality control product and a positive quality control product. The splitting combining liquid in the nucleic acid extraction agent based on the paramagnetic particle method comprises 0.5-2.5% of lauryl sodium sulfate, 0.5-2.0ml / 100ml of TritonX-100, 2-6mol / L of guanidinium isothiocyanate and 1-10mM of EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) (PH 7.5). The kit provided by the invention is simple and fast to operate, low in cost, high in coverage of primer and probe genotype, high in conservative property, strong in specificity, high in detection sensitivity and good in repeatability, and can better simulate the extraction state of real viruses.
Owner:东北制药集团辽宁生物医药有限公司
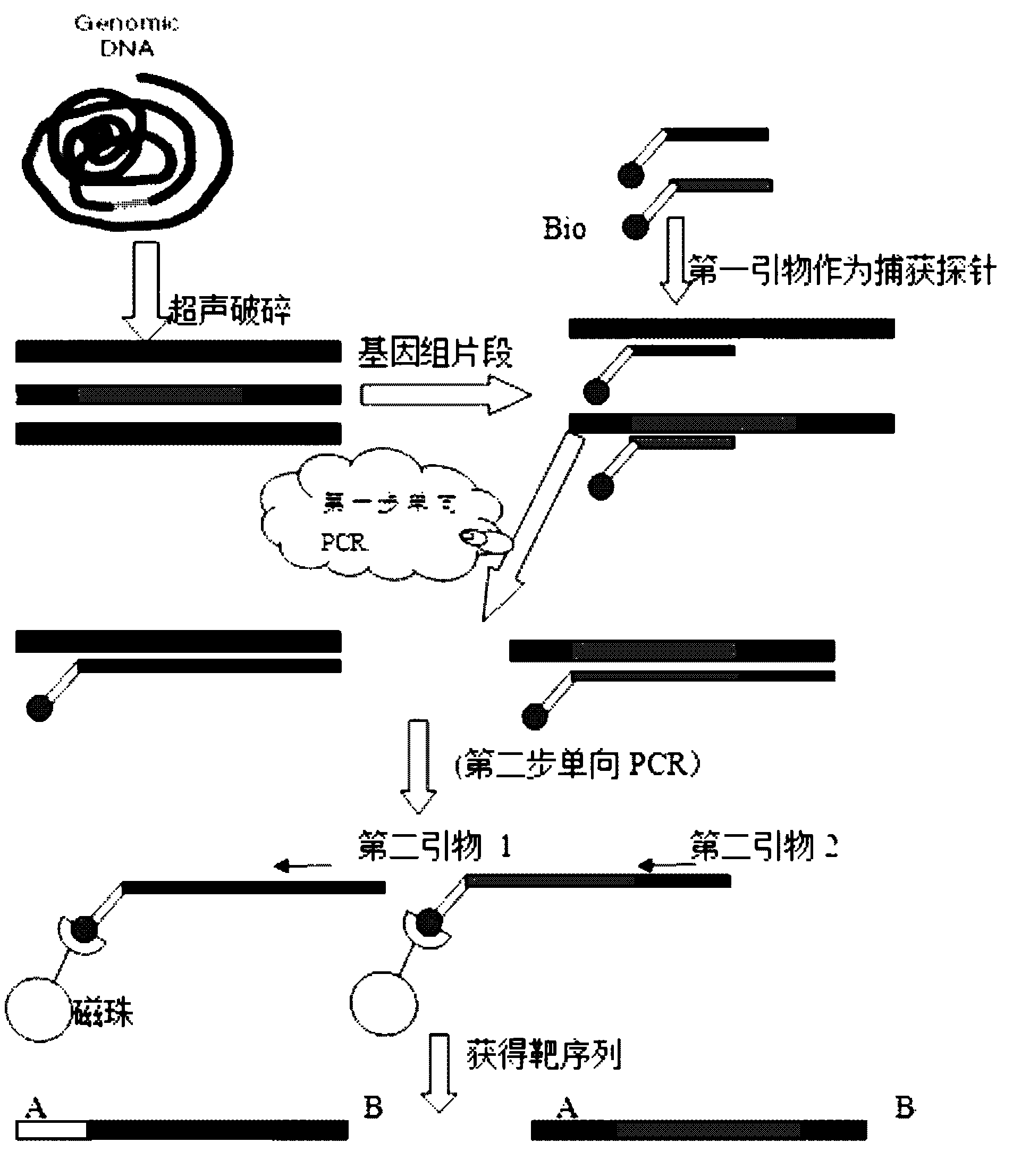
Method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting nucleic acid based on high-flux sequencing technology
ActiveCN102628082AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurement3-deoxyriboseHigh flux
The invention discloses a method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting nucleic acid based on a high-flux sequencing technology. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a single-chain DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) library with a method for capturing a specific nucleic acid target through multi-gene multi-region two-step and one-direction amplification; sequencing the obtained single-chain DNA library based on a high-flux sequencing technology; and qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing nucleic acid according to a sequencing result to obtain a qualitative and quantitative detection result of nucleic acid. Compared with an ordinary real-time Q-PCR (Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) quantifying method, the method has the advantages of lower cost, wider application, increase in the quantifying sample flux of nucleic acid and capability of accurately qualifying and quantifying the series of nucleic acids.
Owner:ANHUI ANKE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GRP) CO LTD
Nucleic acid quantitation from tissue slides
ActiveUS7968327B2Improve accuracyHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesParaffin embeddedAneuploid Cells
This invention provides methods of quantitating nucleic acids from problematic samples, such as aged samples, formalin fixed samples, paraffin embedded samples, samples with aneuploid cells, and cells with fragmented nucleic acids. Methods include techniques to efficiently solublize the nucleic acids under non-denaturing conditions from preserved clinical samples without resort to organic extractions, to normalize cell counts regardless of aneuploidy, to access the fragmentation state of the nucleic acids, and to provide standard curves for degraded nucleic acid samples.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
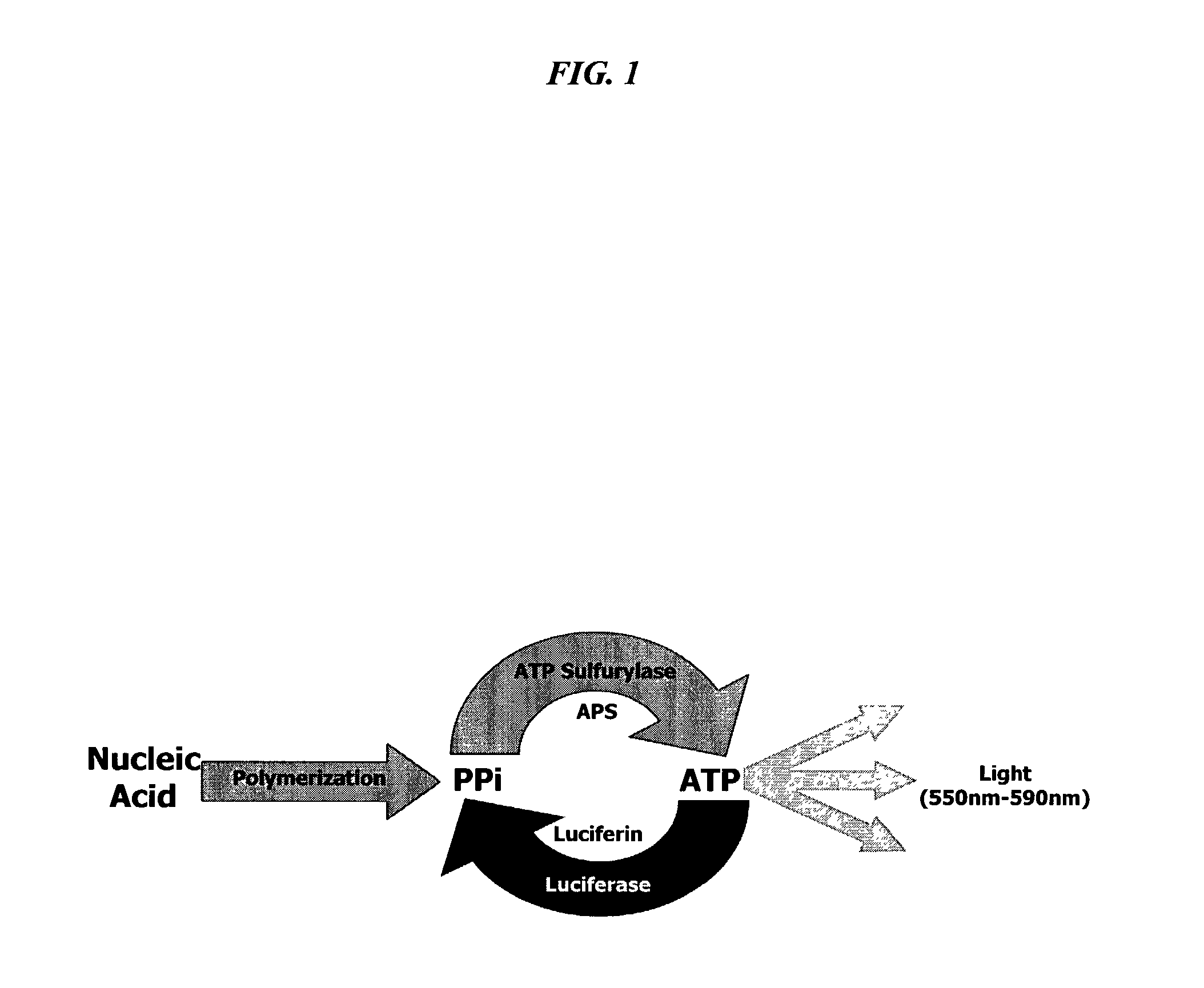
Bioluminescence regenerative cycle (BRC) for nucleic acid quantification
InactiveUS7141370B2High sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGeneration ratePyrophosphate
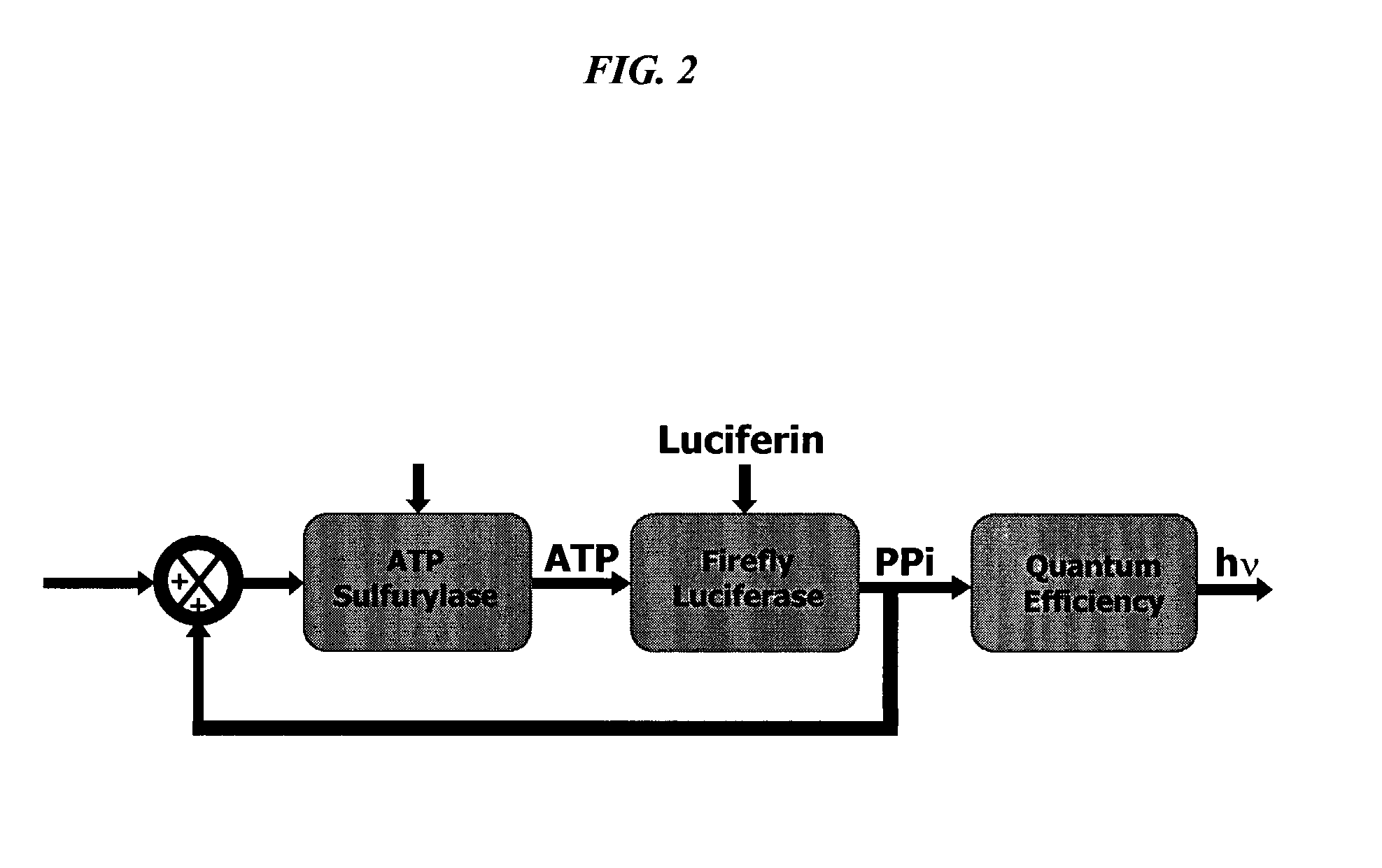
The present invention concerns methods of quantifying nucleic acids using a bioluminescence regenerative cycle (BRC). In BRC, steady state levels of bioluminescence result from processes that produce pyrophosphate. Pyrophosphate reacts with APS in the presence of ATP sulfurylase to produce ATP. The ATP reacts with luciferin in a luciferase-catalyzed reaction, producing light and regenerating pyrophosphate. The pyrophosphate is recycled to produce ATP and the regenerative cycle continues. Because the kinetic properties of ATP sulfurylase are much faster than luciferase, a steady state results wherein concentrations of ATP and pyrophosphate and the rate of light production remain relatively constant. Photons are counted over a time interval to determine the number of target molecules present in the initial sample. The BRC process has a controllable dynamic range up to seven orders of magnitude and is sensitive enough to detect a few thousand molecules of target nucleic acid.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Preparation and detection method for electrochemical quantitative polymerase chain reaction detecting chip
InactiveCN1605861AThere will be no mutual contamination problemReduce testing costsMaterial electrochemical variablesActive matterElectrical wiring
The present invention is the electrochemical preparation process of quantitative PCR detection chip, and relates to the electrochemical detection technology for quantitative nucleic acid PCR chip. The preparation process includes preparing a micro electrode array on the surface of solid carrier; fixing nucleic acid capturing molecular probes on the electrodes of the micro electrode array; preparing closed micro cavity for carrying liquid in the electrode area of molecular probes; and connecting wires to the electrodes on the solid carrier. The detection process includes adding nucleic acid, enzyme, deoxyribonucleotide, electrochemically active matter and other reaction components into the micro cavity; setting the chip in large cavity for controlling temperature; detecting the current and voltage variance caused by reaction of the captured DNA probe molecule with constant potential instrument; and detecting the variance rule of PGR circulating process in different electrodes for PCR detection of genes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Digital PCR-based novel coronavirus nucleic acid quantitative detection kit and application
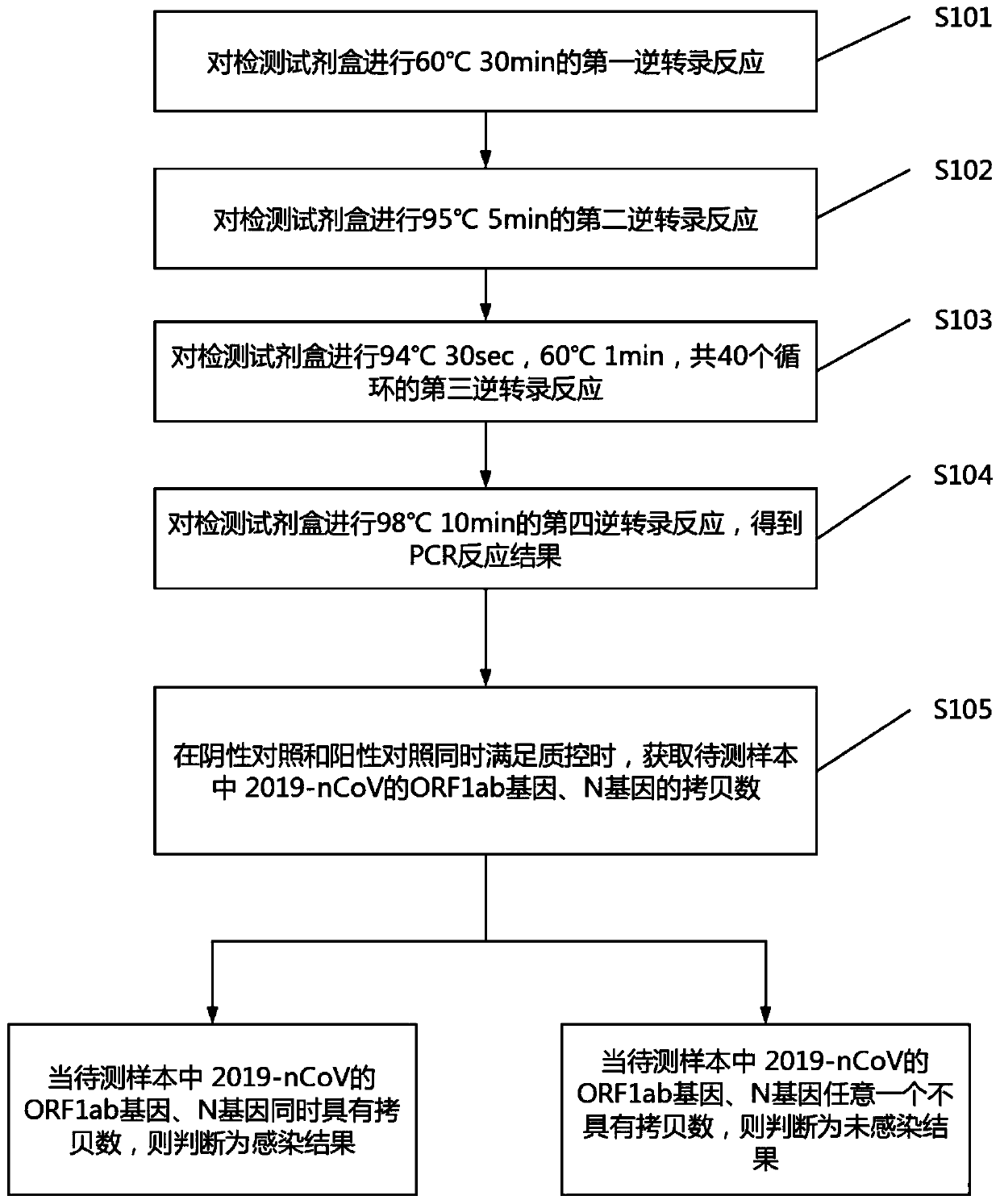
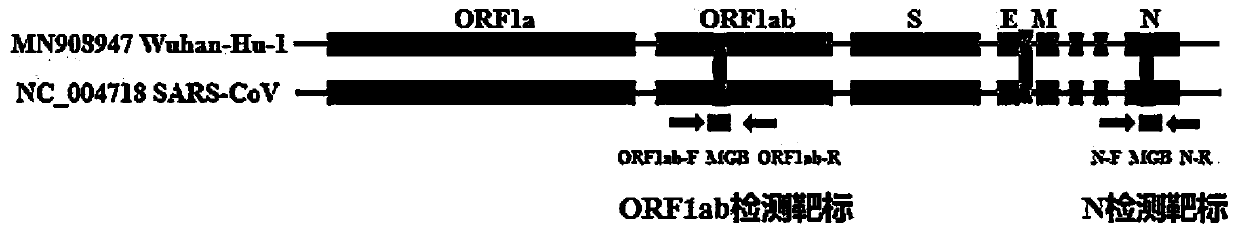
ActiveCN111394519AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesRNA extractionAbsolute quantification
The invention discloses a digital PCR-based novel coronavirus nucleic acid quantitative detection kit and an application. The reaction total system of the digital PCR-based novel coronavirus nucleic acid quantitative detection kit has 20 ul, comprising 10ul of 2x One-Step RT-ddPCR Supermix, 0.8ul of 25mM manganese acetate solution, 5ul of to-be-detected sample RNA, 1ul of ORFlab gene primer probeworking solution, 1ul of N gene primer probe working solution, 1ul of RPP30 gene primer probe working solution and 1.2ul of Nuclease-Free Water, wherein 5ul of negative control RNA extraction solutionand 5ul of positive control RNA extraction solution are adopted to replace the to-be-detected sample RNA in a negative control reaction system and a positive control reaction system respectively. Based on the innovative RNA one-step reverse transcription microdroplet type digital PCR technology, nucleic acid absolute quantification is carried out specific to highly conservative ORFlab gene and Ngene in the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) genome, so that the detection accuracy is improved, and the kit can be used for clinical assisted diagnosis and viral load analysis of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infection, and has a wide clinical application value.
Owner:南京实践医学检验有限公司
Kits and methods for direct nucleic acid amplification from whole blood samples
The invention discloses a reaction kit for nucleic acid amplification using whole blood as a starting template, which is characterized in that the nucleic acid reaction system of the kit includes several primer pairs for amplifying target sequences of target genes; And the concentration of tris in the system is between 25-100mmol / L, the concentration of magnesium ions is between 1.5-3.0mmol / L, and the concentration of glycerol is between 10%-14%. The kit can efficiently amplify the target nucleic acid from the whole blood sample containing a large amount of substances that inhibit nucleic acid amplification without going through the nucleic acid separation and purification process, and without any pretreatment of the whole blood sample.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Nucleic Acid Purification
ActiveUS20140051844A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPurification methodsSolvent
Methods and composition for nucleic acid isolation are provided. In one embodiment, a method is provided for nucleic acid purification from biological samples, such as whole blood samples, extracted with phenol-based denaturing solvents, which does not require phase separation or nucleic acid precipitation. Methods according to the invention may also be used for of small RNAs (e.g., siRNAs or miRNAs) purification and are amenable to automation.
Owner:ZYMO RES CORP
Nucleic acid purification
ActiveUS9206469B2Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionPurification methodsSolvent
Methods and composition for nucleic acid isolation are provided. In one embodiment, a method is provided for nucleic acid purification from biological samples, such as whole blood samples, extracted with phenol-based denaturing solvents, which does not require phase separation or nucleic acid precipitation. Methods according to the invention may also be used for of small RNAs (e.g., siRNAs or miRNAs) purification and are amenable to automation.
Owner:ZYMO RES CORP
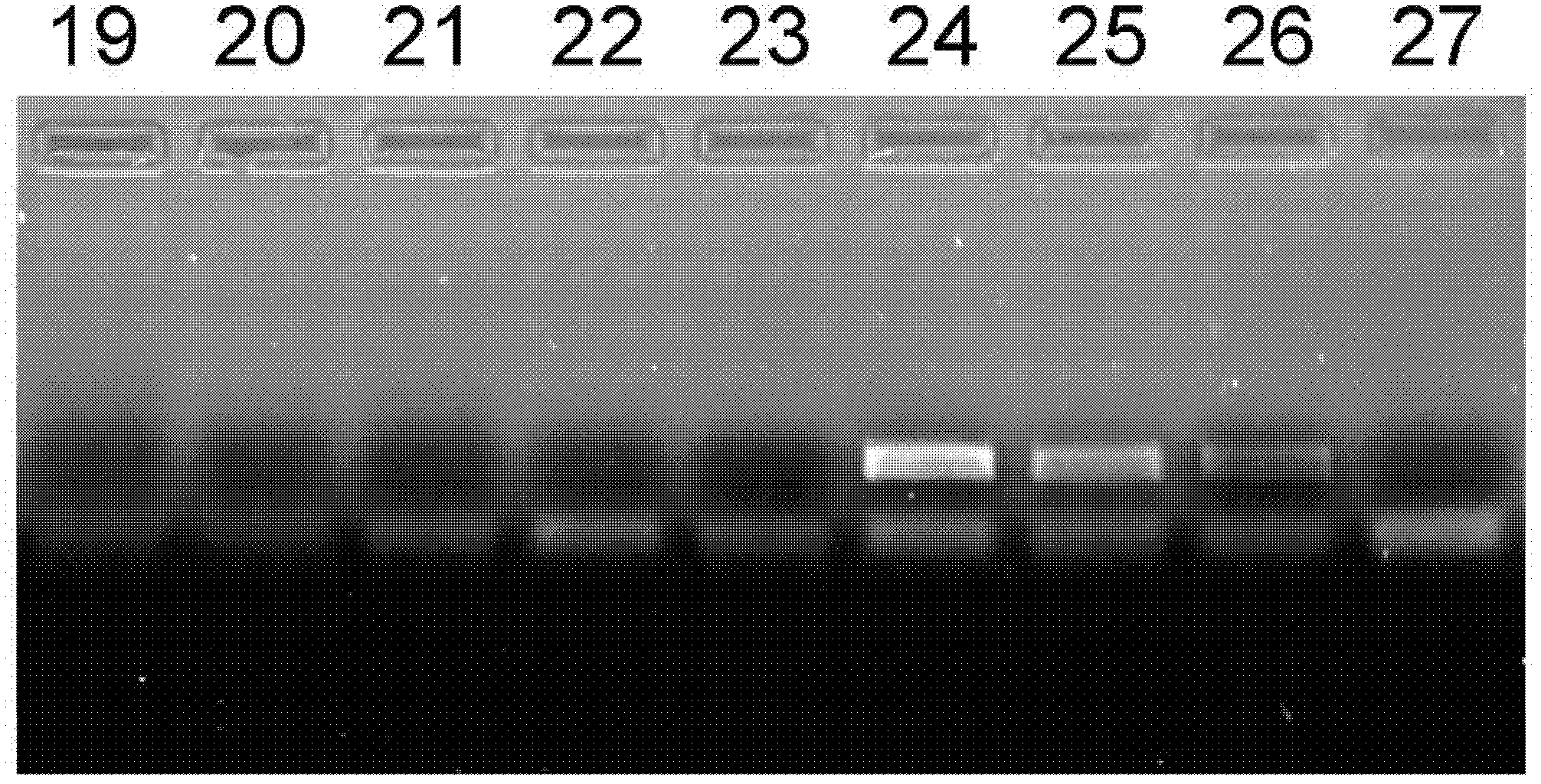
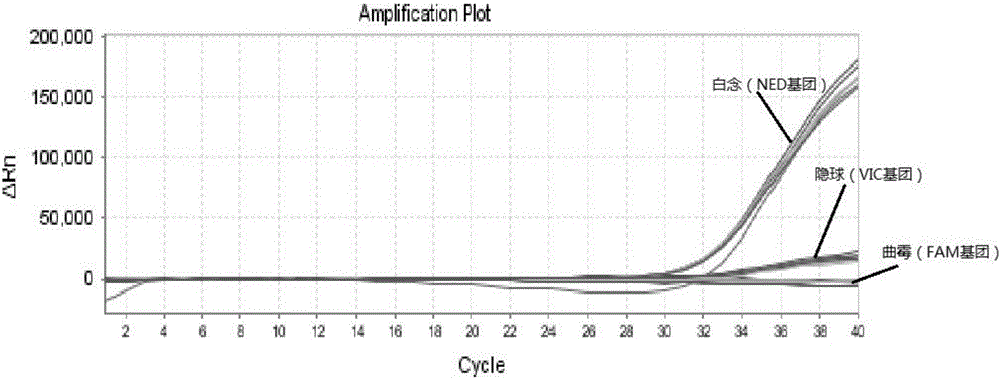
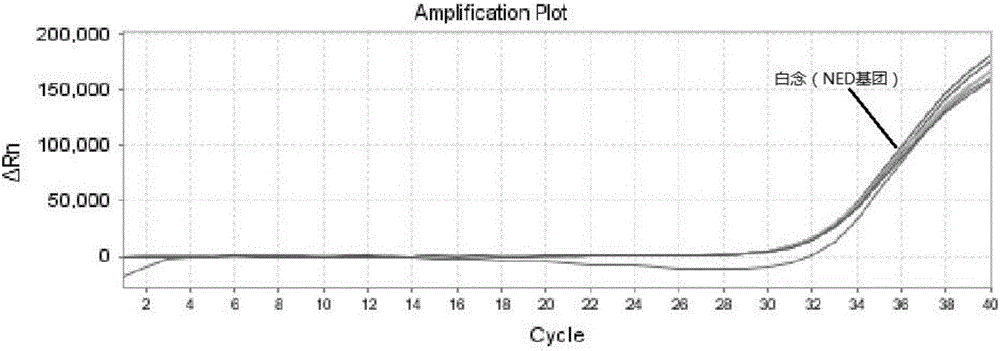
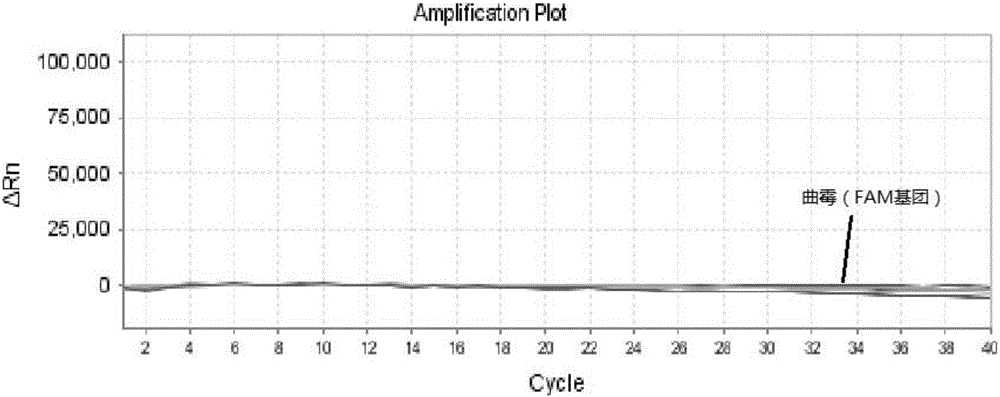
Triple nucleic acid test kit
ActiveCN106319055AHigh similarityPrimer design is difficultMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid testCandida famata
The invention relates to a triple nucleic acid test kit. The kit comprises a thallus lysate, a positive quantitative reaction liquid, a negative control reaction liquid and a thallus test reaction liquid, wherein the thallus test reaction liquid contains specific primers, specific probes and doping fluorescent dye for aspergillus, Cryptococcus neoformans and candida albicans, the three specific oprimers are designed according to areas of ITS sequences of aspergillus, Cryptococcus neoformans and candida albicans, FAM, VIC and CY-5 are selected for mark report groups of the three specific probes, MGB serves as a quenching group, the excitation wavelength of the FAM group is 492 nm, and the emission wavelength is 517 nm; the excitation wavelength of the VIC group is 557 nm and the emission wavelength is 574 nm; the excitation wavelength of the CY-5 group is 646 nm and the emission wavelength is 664 nm. The triple nucleic acid test kit for aspergillus, Cryptococcus neoformans and candida albicans can assist in diagnosing infection caused by aspergillus, Cryptococcus neoformans and candida albicans.
Owner:BEIHAI SINLON BIOTECH CO LTD
Detection and quantification of biomolecules using mass spectrometry
InactiveCN101605909AEnhanced Multiplex Analysis CapabilitiesEase of analysis is shortMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention is directed in part to a method for detecting a target nucleic acid using detector oligonucleotides detectable by mass spectrometry. This method uses the 5' to 3' nuclease activity of a nucleic acid polymerase to cleave annealed oligonucleotide probes from hybridized duplexes and release labels for detection by mass spectrometry. This process is easily incorporated into a PCR amplification assay. The method also includes embodiments directed to quantitative analysis of target nucleic acids.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Method for the quantitative detection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7029843B1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleasePolymerase
Provided herein is a method for the quantitative detection of nucleic acids based on the use of a calibrator, suitable primers and probes, and a nucleic acid polymerase with 5′-3′ nuclease activity.
Owner:SCARLATTI GABRIELLA +2
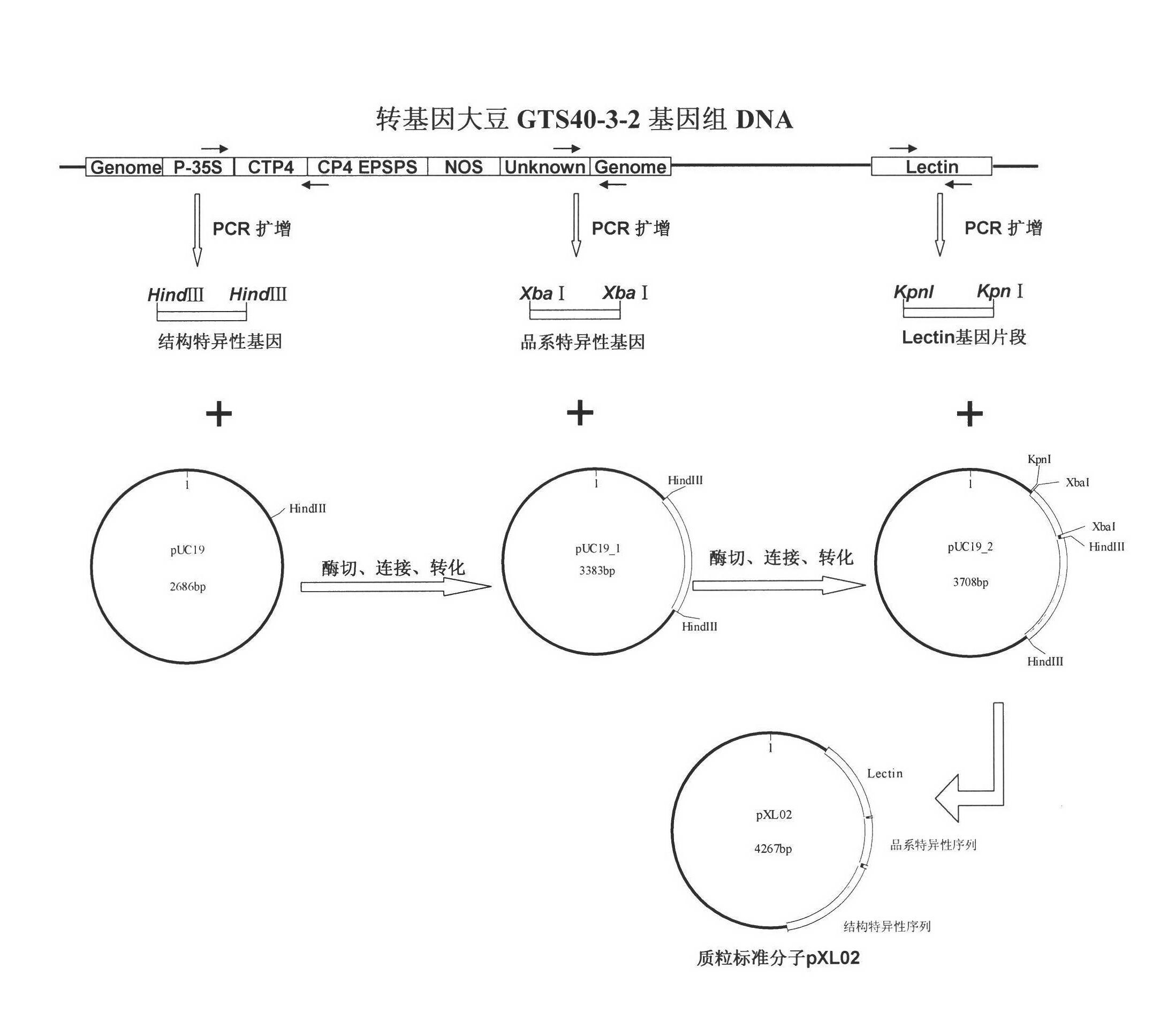
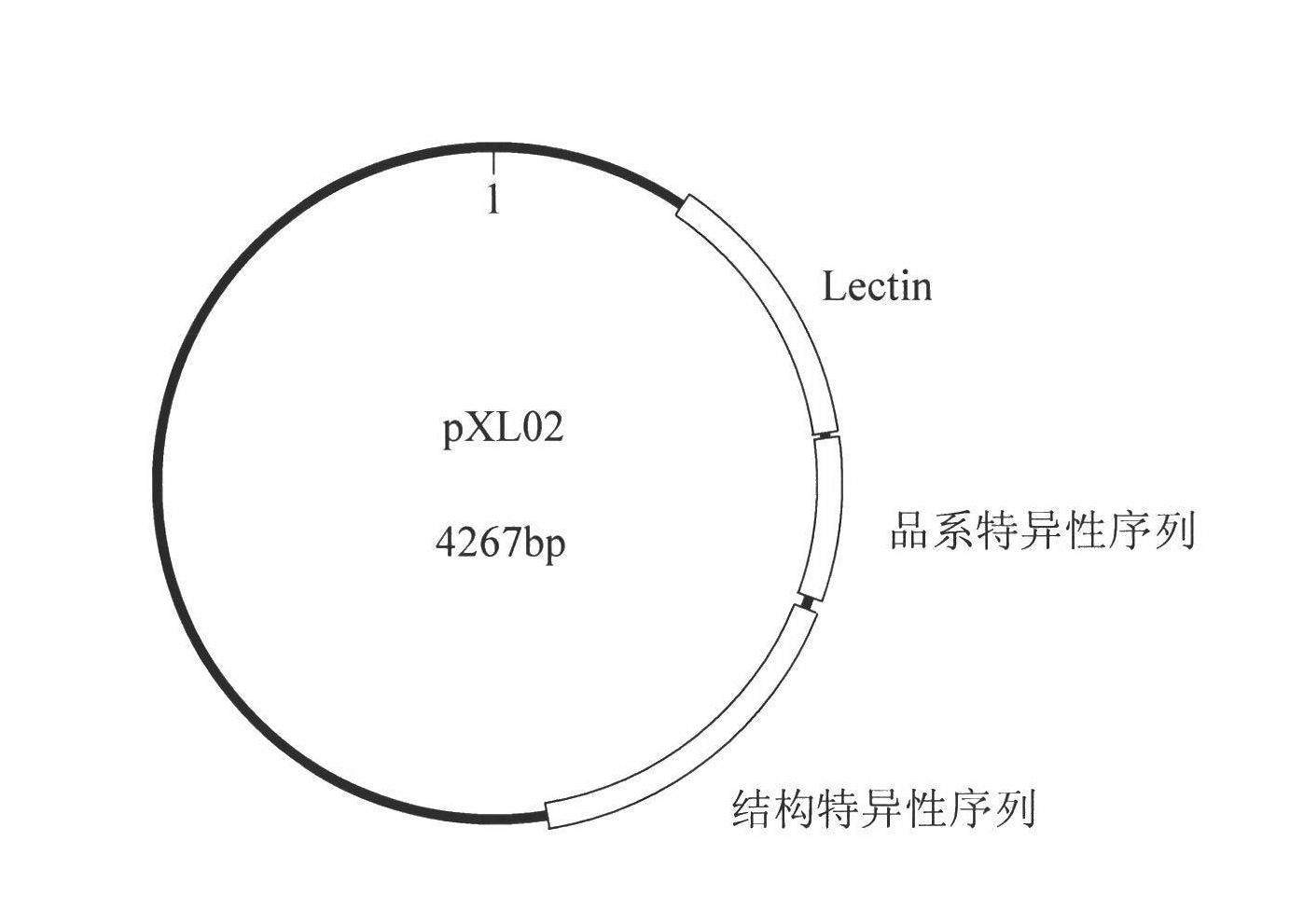
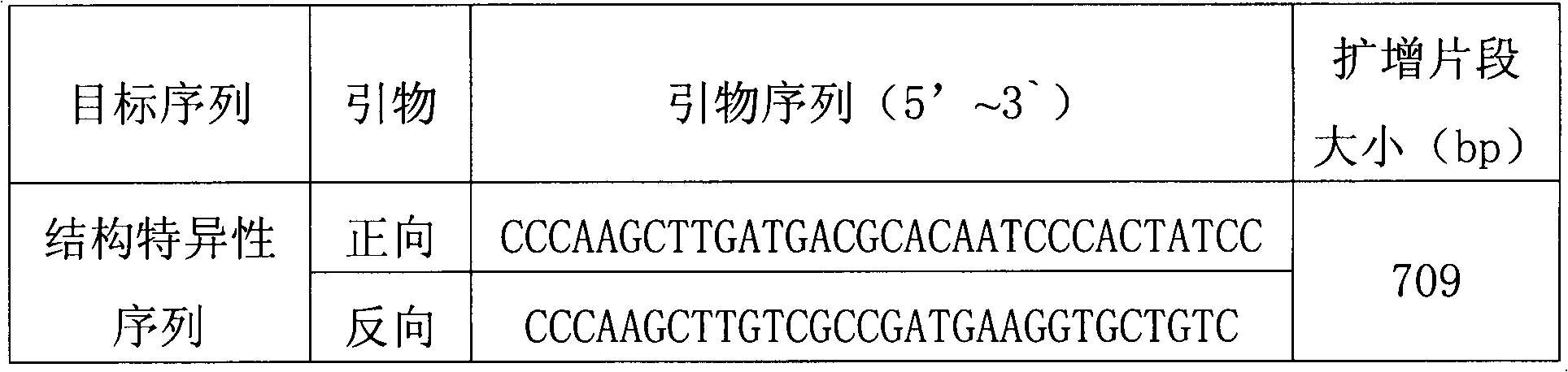
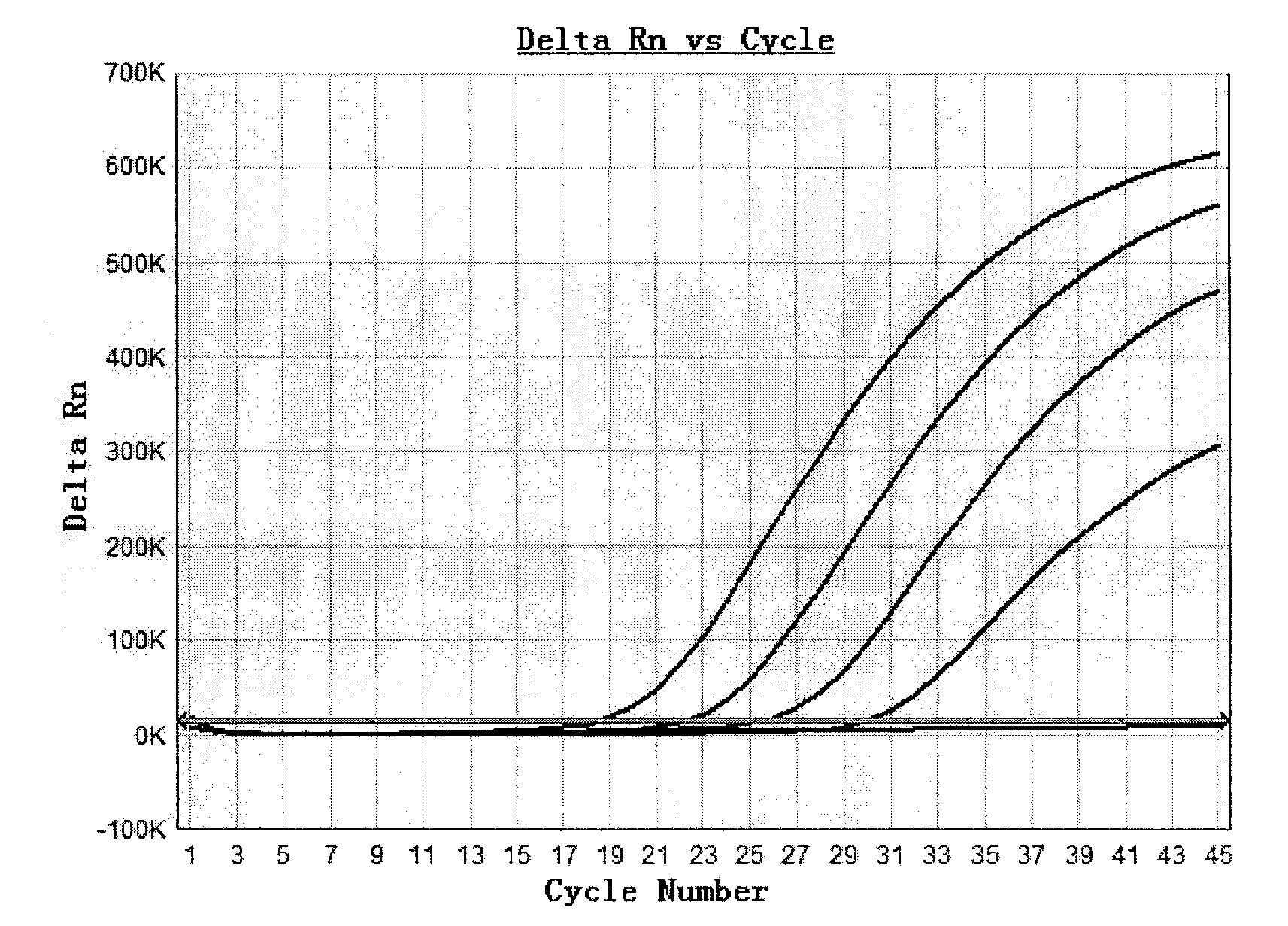
Plasmid reference molecule of quantitative determination of nucleic acids from transgenic soybean GTS40-3-2
InactiveCN102517393AAchieve traceabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionInductively coupled plasmaMass spectrometric
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
Hepatitis B virus nucleic acid quantitative detection method and kit
ActiveCN103184295AAvoid lossAvoid false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMagnetic beadEnzyme system
The invention relates to a hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleic acid quantitative detection method and a kit. The method includes: employing a magnetic bead technique to extract HBV and internal reference nucleic acid from a sample to serve as a template, and finishing HBV nucleic acid quantitative detection based on a fluorescent PCR technology. The introduced internal reference can be used for monitoring the loss and misoperation of the nucleic acid template or existent PCR inhibitors during operation, thus avoiding a false-negative result. An adopted dUTP-UNG enzyme system can reduce cross contamination of amplification products and prevents a false-positive result. The kit includes a nucleic acid extraction reagent, an amplification reagent, quantitative calibration substances, reference substances and the internal reference. The method and the kit solve the shortcomings of poor detection accuracy and low sensitivity in the prior art, and are suitable for application in clinical HBV nucleic acid quantitative detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGYAO MED TECH DEV CO LTD +1
Nucleic acid quantitative detection reagent kit of multiple digital PCR based on dual-fluorescence probe
PendingCN111218501AReduce dosageSave materialMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFluoProbesFluorophore
The invention provides a nucleic acid quantitative detection reagent kit of multiple digital PCR based on a dual-fluorescence probe. The reagent kit comprises a first probe for detecting a first target, a second probe for detecting a second target and a third probe for detecting a third target, wherein the first probe is labelled with a first fluorophore, the second probe is labelled with a secondfluorophore, one part of the third probe is labelled with the first fluorophore, the other part of the third probe is labelled with the second fluorophore, and the first fluorophore and the second fluorophore are two different fluorophores; and the nucleic acid quantitative detection reagent kit comprises a two-dimensional result figure obtained based on multiple digital PCR of three targets to realize respective quantitation of the three targets to be tested. Based on a conventional dual-fluorescence passage detecting system, development of a dual-fluorescence probe multiple digital PCR method is great in significance, so that a digital PCR technique conforms to clinical requirements, and is wide to apply.
Owner:TARGETINGONE TECH (BEIJING) CORP +1
High-accuracy quantitative detection method and kit for HIV-1 nucleic acid
ActiveCN103667534AAvoid false negativesAvoid PCR false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid quantitationQuality control
The invention provides a high-accuracy quantitative detection kit for HIV-1 nucleic acid. The kit is applied to the field of biomedical clinical diagnosis. The gene amplification locus of the kit is positioned in the 5'LTR conserved region of an HIV genome; the kit comprises a nucleic acid extraction kit based on a magnetic bead method and an HIV nucleic acid amplification kit, wherein the nucleic acid extraction kit based on the magnetic bead method comprises a lysed combined liquid, a rinsing liquid A, a rinsing liquid B, a rinsing liquid C, eluant and a magnetic bead liquid; the HIV nucleic acid amplification kit comprises an RT-PCR reaction liquid, an enzyme mixed liquid, an HIV-interior standard, an HIV quantitative reference product 1-4, a negative quality control product, a critical positive quality control product and a strong positive quality control product. The kit provided by the invention is simple and quick to operate, low in cost, high in detection sensitivity, good in repeatability, high in primer and probe gene type coverage rate, high in conservative property and strong in specificity, an efficient internal standard system is introduced, and the problems of mutual inhibition and interference due to the simultaneous amplification of a target gene and the internal standard are solved.
Owner:东北制药集团辽宁生物医药有限公司
Methods for nucleic acid isolation and instruments for nucleic acid isolation
ActiveUS8048681B2Efficiently isolate long nucleic acids and short nucleic acidsSimple and safe operationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSilicon dioxideBiology
The present invention relates to a technique for efficient isolation of long nucleic acids and short nucleic acids from a sample containing long nucleic acids and short nucleic acids via safe and convenient operations. Specifically, long nucleic acids and short nucleic acids are isolated from a sample containing nucleic acids by mixing a chaotropic agent with the sample containing nucleic acids, allowing the mixed solution to pass at least twice through a first solid phase containing silica that has passage pores having predetermined pore sizes, allowing the mixed solution to pass at least twice through a second solid phase containing silica that has passage pores having pore sizes smaller than those of the first solid phase containing silica, and separately recovering nucleic acids that have bound to the first solid phase containing silica and those that have bound to the second solid phases containing silica.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Assay for Detecting Circulating Free Nucleic Acids
This invention is directed, inter alia, to methods and kits for rapid, easy and cost-effective methods of all free nucleic acid quantification in inter alia, biological fluid samples.
Owner:MOR RES APPL LTD
Aggregation-induced emission/surface plasma chroma analysis dual mode nucleic acid detection method
ActiveCN108949919AChemical label freeFree of purificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDual modeColor changes
The invention belongs to the technical field of biodetection and discloses an aggregation-induced emission / surface plasma chroma analysis dual mode nucleic acid detection method. The method comprisesthe following steps: carrying out a hybrid chain reaction to amplify a signal of a target nucleotide sequence to obtain an HCR reaction product; mixing water soluble aggregation-induced emission molecules with HCR reactants of different concentrations, and drawing a standard curve of concentration of nucleic acids by measuring the fluorescence intensity to analyze the nucleic acids quantitatively;and adding gold nanoparticles modified by sulfydryl DNA into the HCR reactants adsorbing the aggregation-induced emission molecules, and observing color change of the solution to analyze the nucleicacids qualitatively, wherein the water soluble aggregation-induced emission molecules have the structural formula as shown in a formula (I). The detection method combining aggregation-induced emissioneffect and surface plasma chroma analysis has the advantages of being simple, real-time, free of purifying treatment and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Enzymatic time-resolved luminescent assay for nucleic acids quantitation
InactiveUS20090317803A1Fast and highly sensitive identificationFast and highly sensitive and measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayMicroRNA
The objects of the present invention are to provide a new technology platform for quantitation number of copies of nucleic acid molecules of interest by lumonogenic (i.e., enzymatic luminescence) detection. The detection approach of the method of present invention is essentially employing time-resolved approach, e.g., based on detection transient parameters of luminescent signal. The various disclosed embodiments allow DNA and RNA quantification in a broad dynamic range; can be used for detection of DNA, as well as long (mRNA) and short (microRNA) RNA targets. The present invention provides methods, instruments, and kits for fast and highly sensitive identification and measurements of nucleic acids in various life science and biomedical applications.
Owner:GOLOVLEV VALERI +1
Precise quantification method of HBV (hepatitis B virus) cccDNA (covalent closed circular DNA)
InactiveCN106636466ASolve the problem of false positive interferenceRealize closed tube operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlMicroparticle
The invention relates to a precise quantification method of HBV (hepatitis B virus) cccDNA (covalent closed circular DNA). The precise quantification method of the HBV cccDNA comprises steps as follows: the copy number of a sample is quantitatively controlled within 10,000 copes through nucleic acid; primers and probes of cccDNA and rcDNA are designed and detected with a double-gap method; digital PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed; analysis parameters are adjusted in digital PCR instrument analysis software, 1 / 2-1 / 3 of the average fluorescence intensity of positive particles in positive control holes is set as a positive threshold, the to-be-detected sample is analyzed and the copy number of cccDNA in the sample is calculated using software of the digital PCR instrument, and false positive caused by non-specific amplification is eliminated. The method solves the false positive interference problem of double-gap method and the PCR method for rcDNA; compared with other digital PCR detection methods for cccDNA, the method has the advantages that specific DNA enzyme is not required to treat the sample, closed pipe operation is realized, the cross-pollution risk is reduced, and the operation process is simplified.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Primers, probe, kit and detection method for type II nucleic acid quantitative detection of herpes simplex virus
InactiveCN103805714AEfficient removalHas the effect of nucleic acid extraction and enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceSignal-to-noise ratio
The invention provides primers, a probe, a kit and a detection method for type II nucleic acid quantitative detection of herpes simplex virusherpes simplex virus. The primers are as shown in the sequences of SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2; the probe is as shown in the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 4, and a reporter fluorescent group and a non-quenching fluorescent group are marked at the two ends of the probe, respectively; the kit comprises the primers and the probe. The primers, the probe and the kit thereof are low in fluorescent background value, high in signal-to-noise ratio and high in detection sensitivity when used for detecting type II nucleic acid quantitation of the herpes simplex virus.
Owner:厦门安普利生物工程有限公司
Method for the efficiency-corrected real-time quantification of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20100021923A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHousekeeping geneInternal standard
The present invention concerns a method for the quantification of a target nucleic acid in a sample comprising the following steps: (i) determination of the amplification efficiency of the target nucleic acid under defined amplification conditions, (ii) amplification of the target nucleic acid contained in the sample under the same defined reaction conditions, (iii) measuring the amplification in real-time, (iv) quantification of the original amount of target nucleic acid in the sample by correction of the original amount derived from step (iii) with the aid of the determined amplification efficiency. The efficiency correction of PCR reactions according to the invention for the quantification of nucleic acids can be used for absolute quantification with the aid of an external or internal standard as well as for relative quantification compared to the expression of housekeeping genes.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Uses of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin in preparation of nucleic acid freeze-drying protection agent
ActiveCN108070583AImprove visibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationUltra Low Temperature FreezerFluorescence
The invention discloses uses of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin in preparation of a nucleic acid freeze-drying protection agent. According to the present invention, DNA can be well protected by usinghydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin or a hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin aqueous solution as a DNA freeze-drying protection agent, RNA can be well protected by using a composition H and a solution H as RNA freeze-drying protection agents, and nucleic acid quantitative analysis, subsequent DNA digestion, PCR / RT-PCR amplification, fluorescence quantitative PCR / RT-PCR amplification and other operations are not affected; and RNA, hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin and DEPC are mixed, and the mixture is freeze-dried, wherein the RNA stored within 6 months at the room temperature has the variation coefficient of 5.90%, and is significantly superior to the RNA stored in a -70 DEG C liquid state (the variation coefficient is 13.33%), and the storing condition does not require the arrangement of -70 DEG Cultra-low temperature refrigerator and other complex equipment so as to easily achieve the long-distance transportation and storage of RNA samples.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL DISEASE CONTROL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com