Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Nonline of sight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and method for high rate uniform coating, including non-line of sight
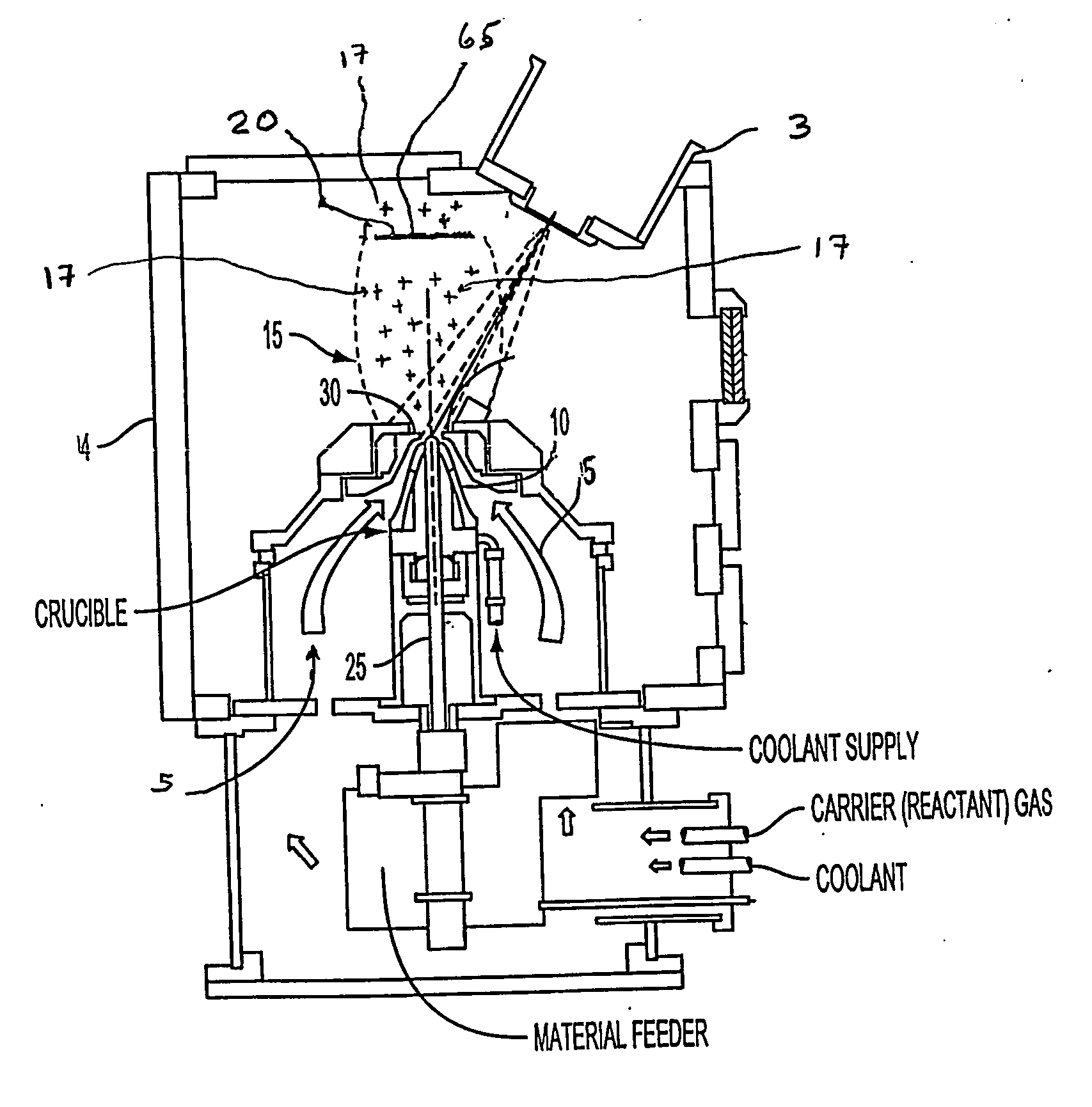
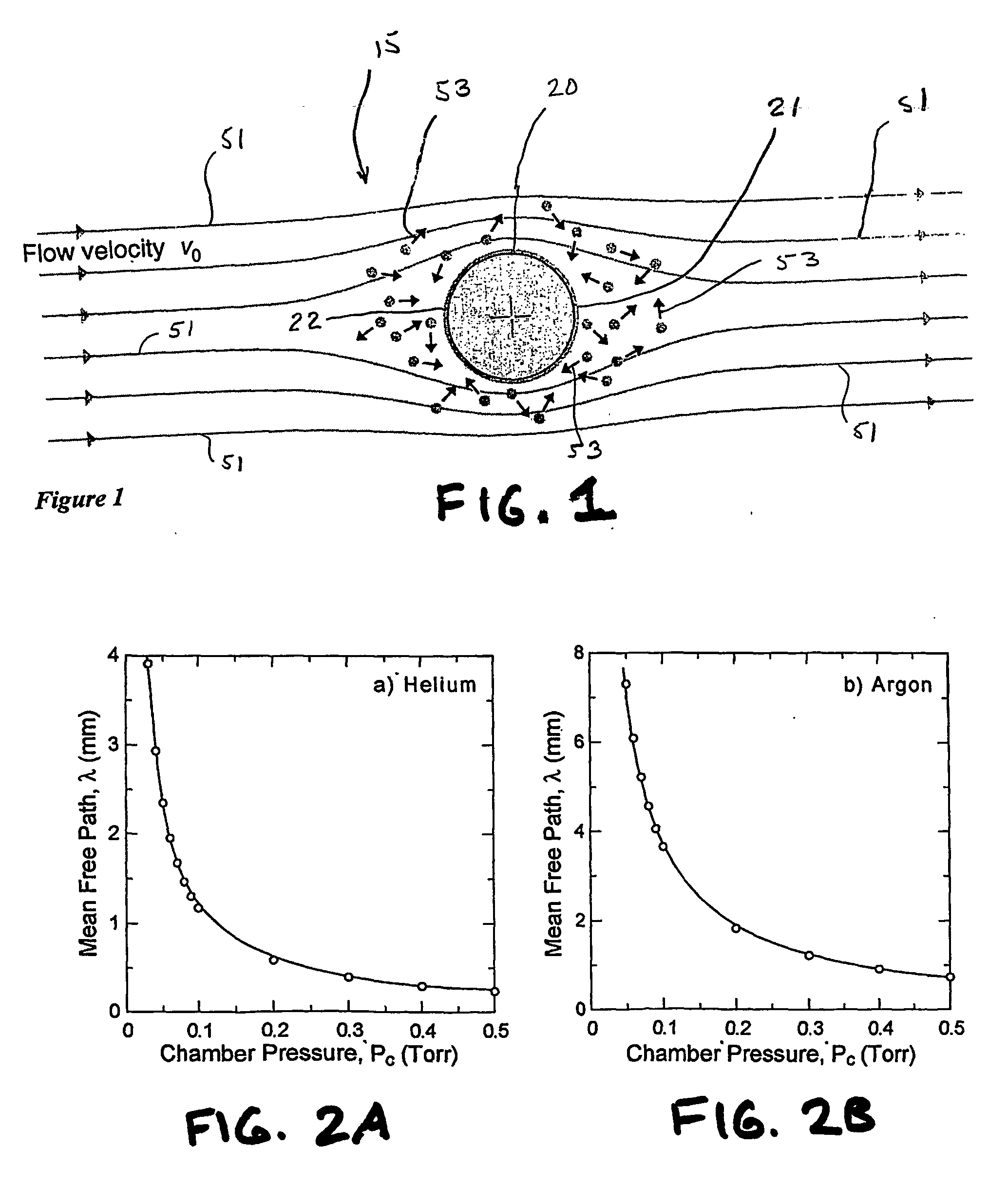
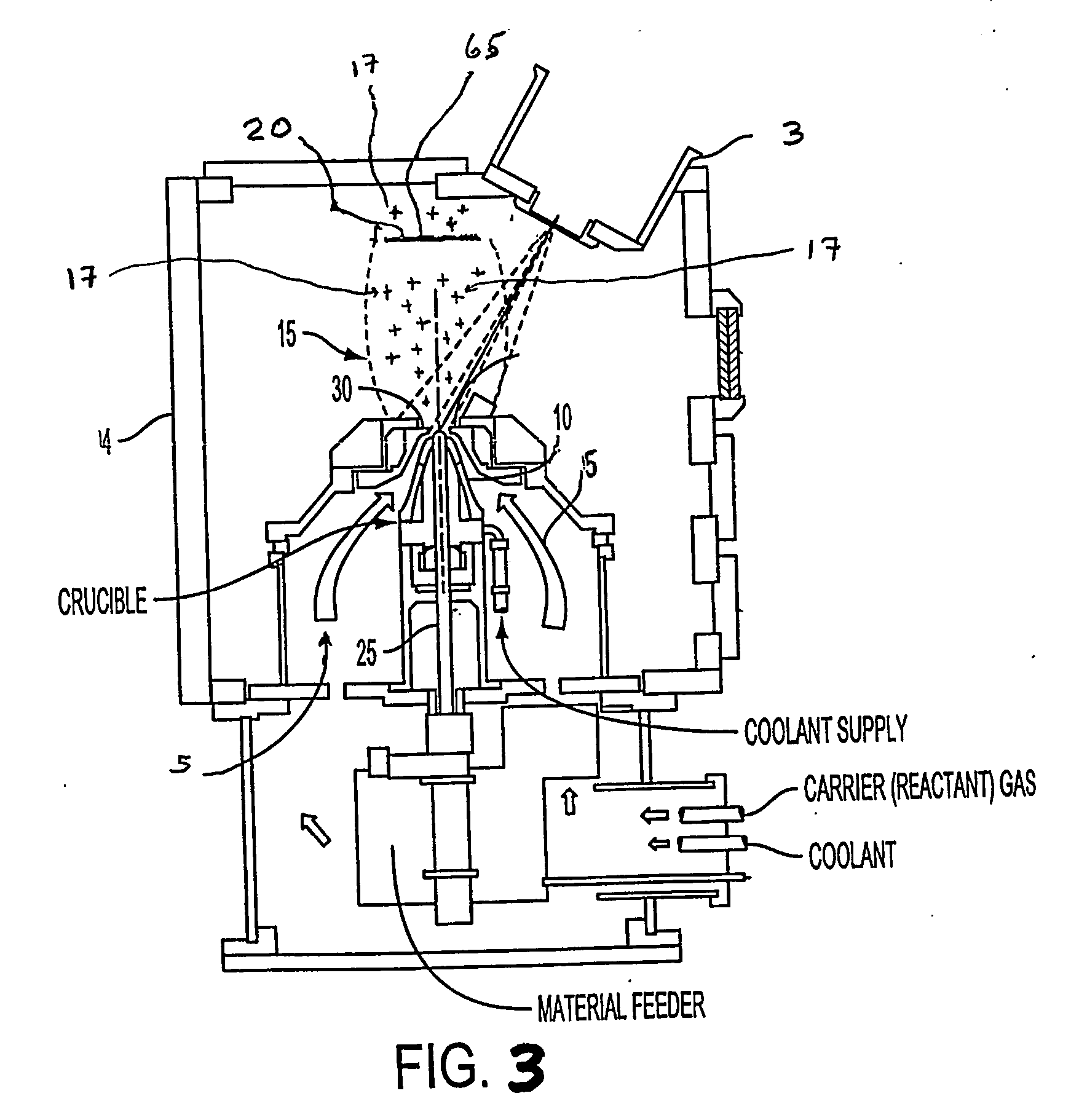
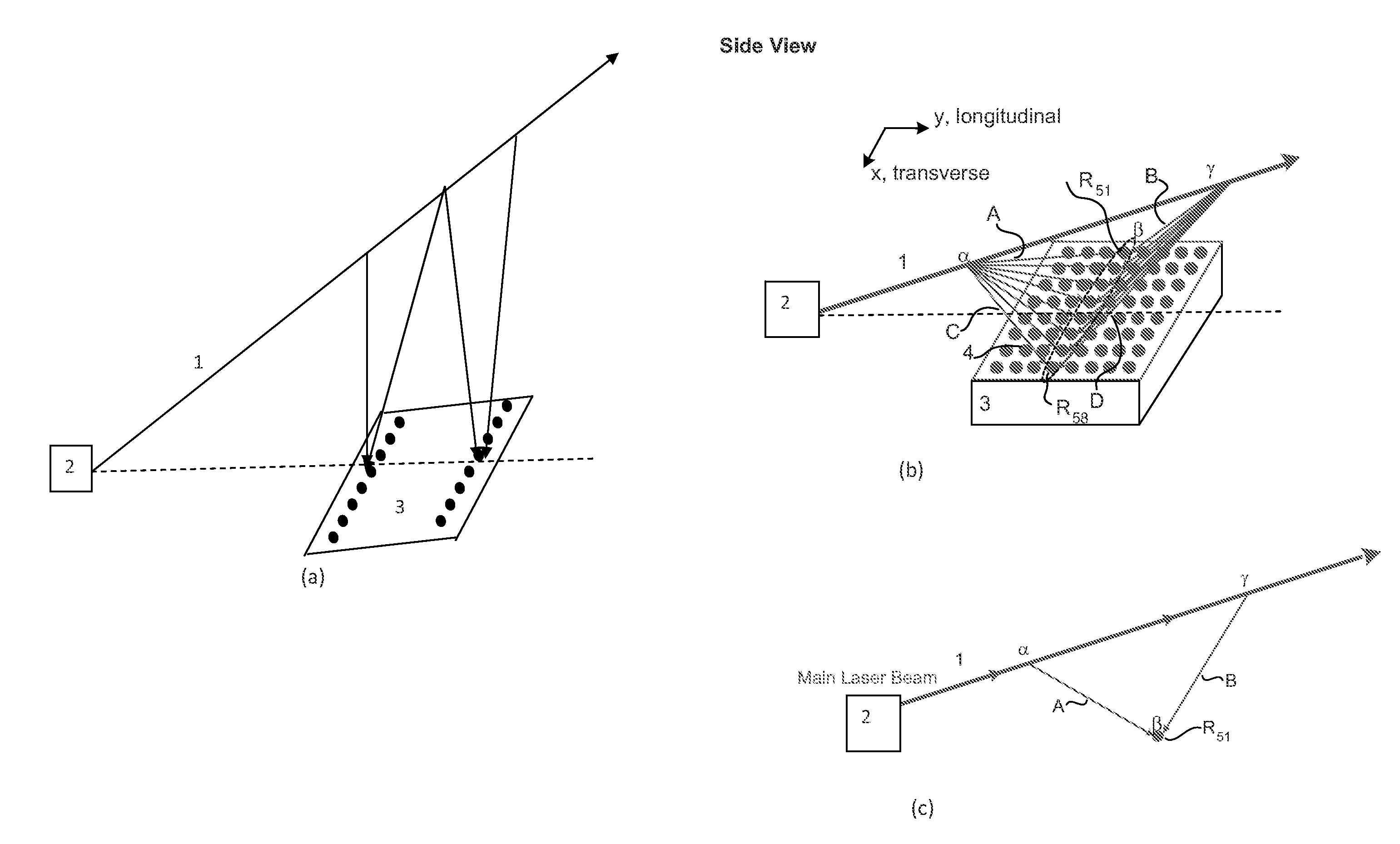
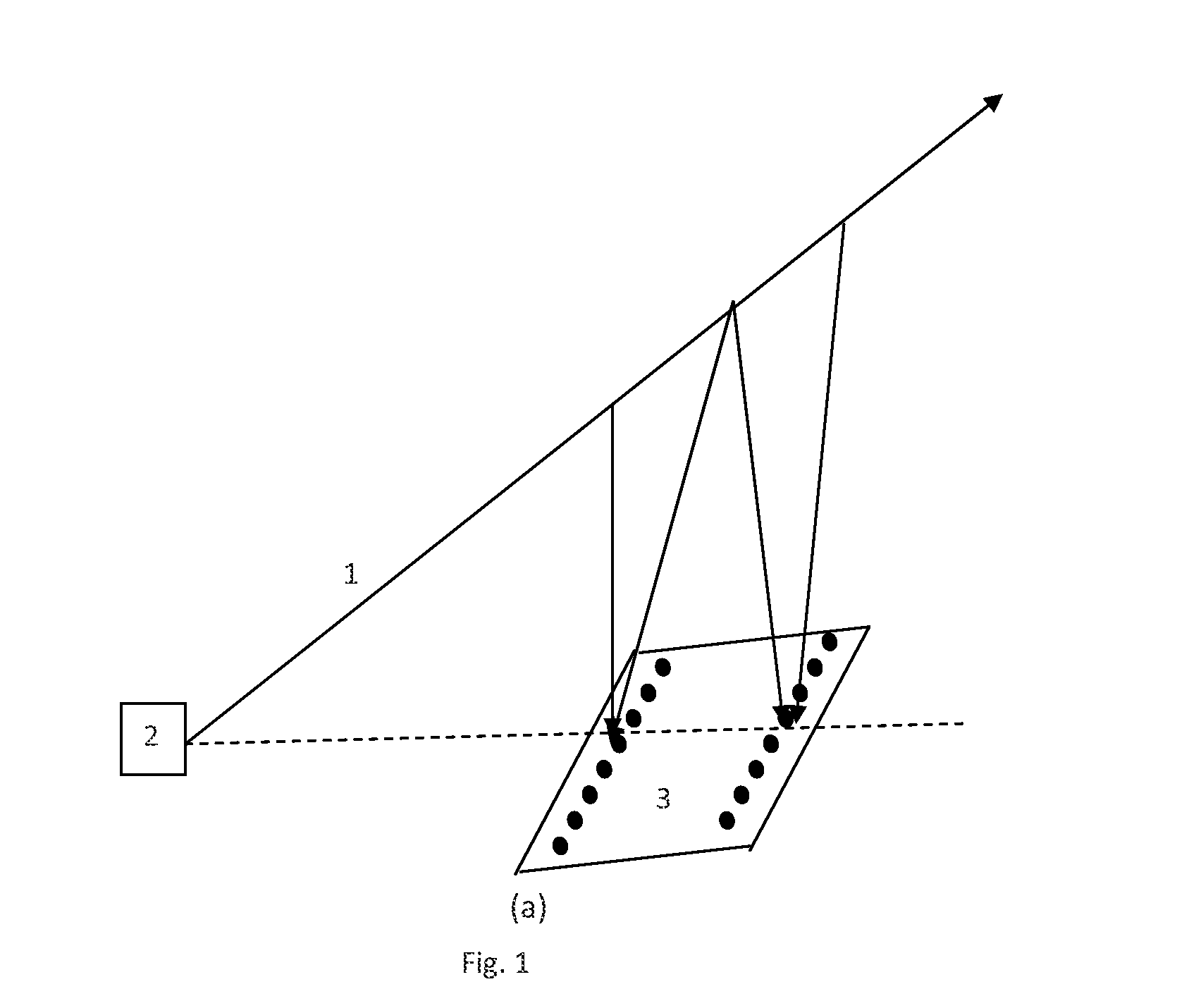
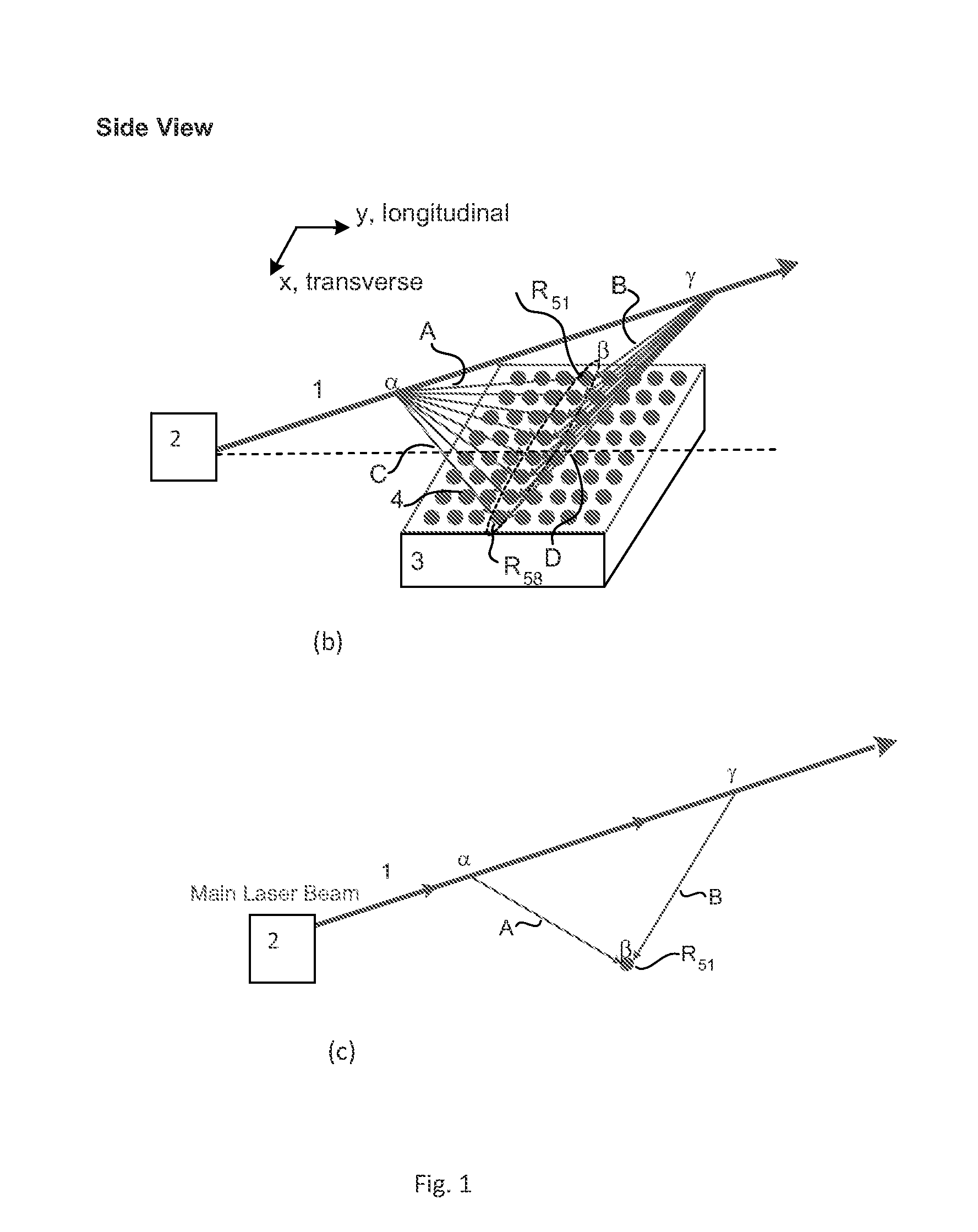
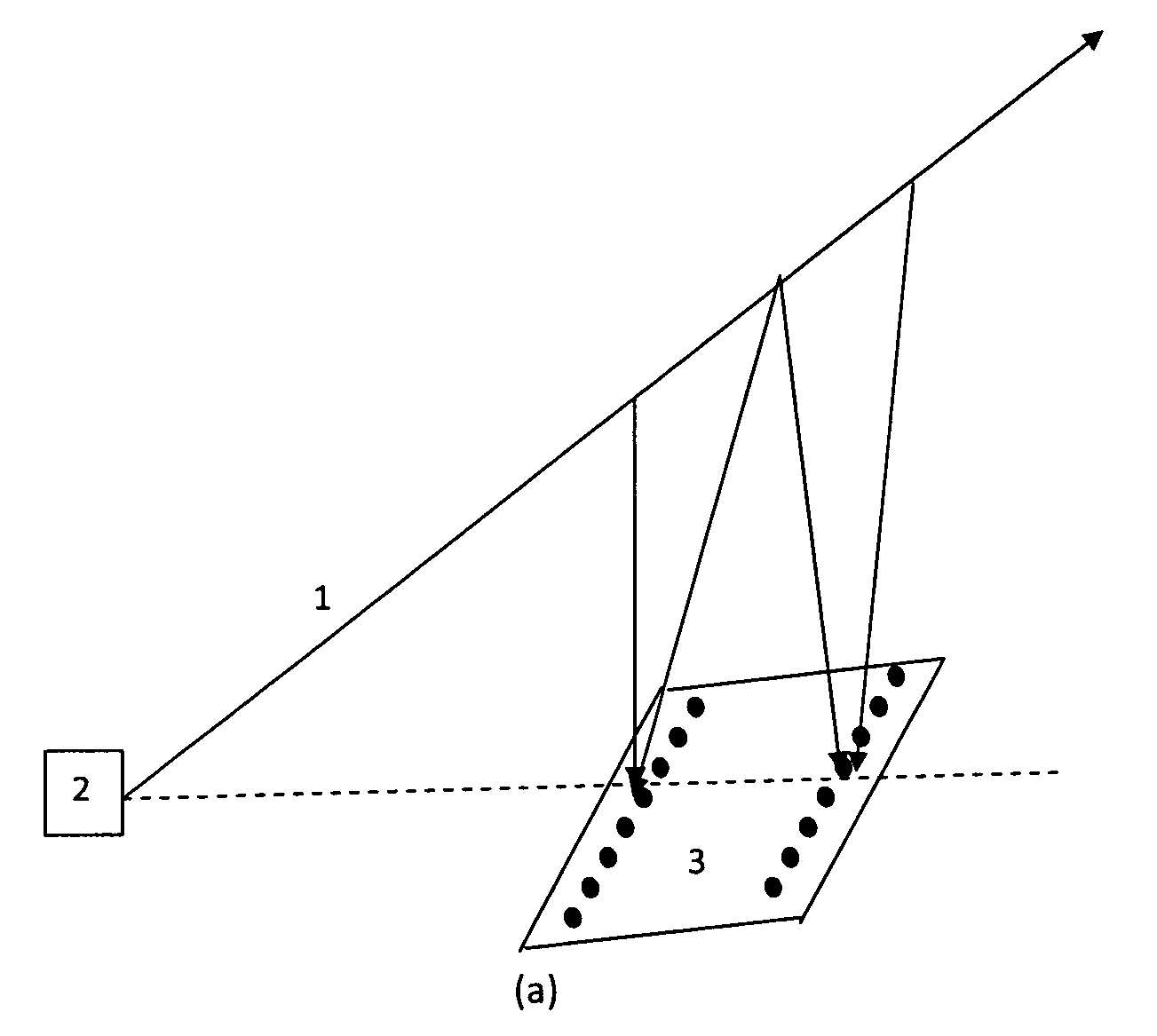
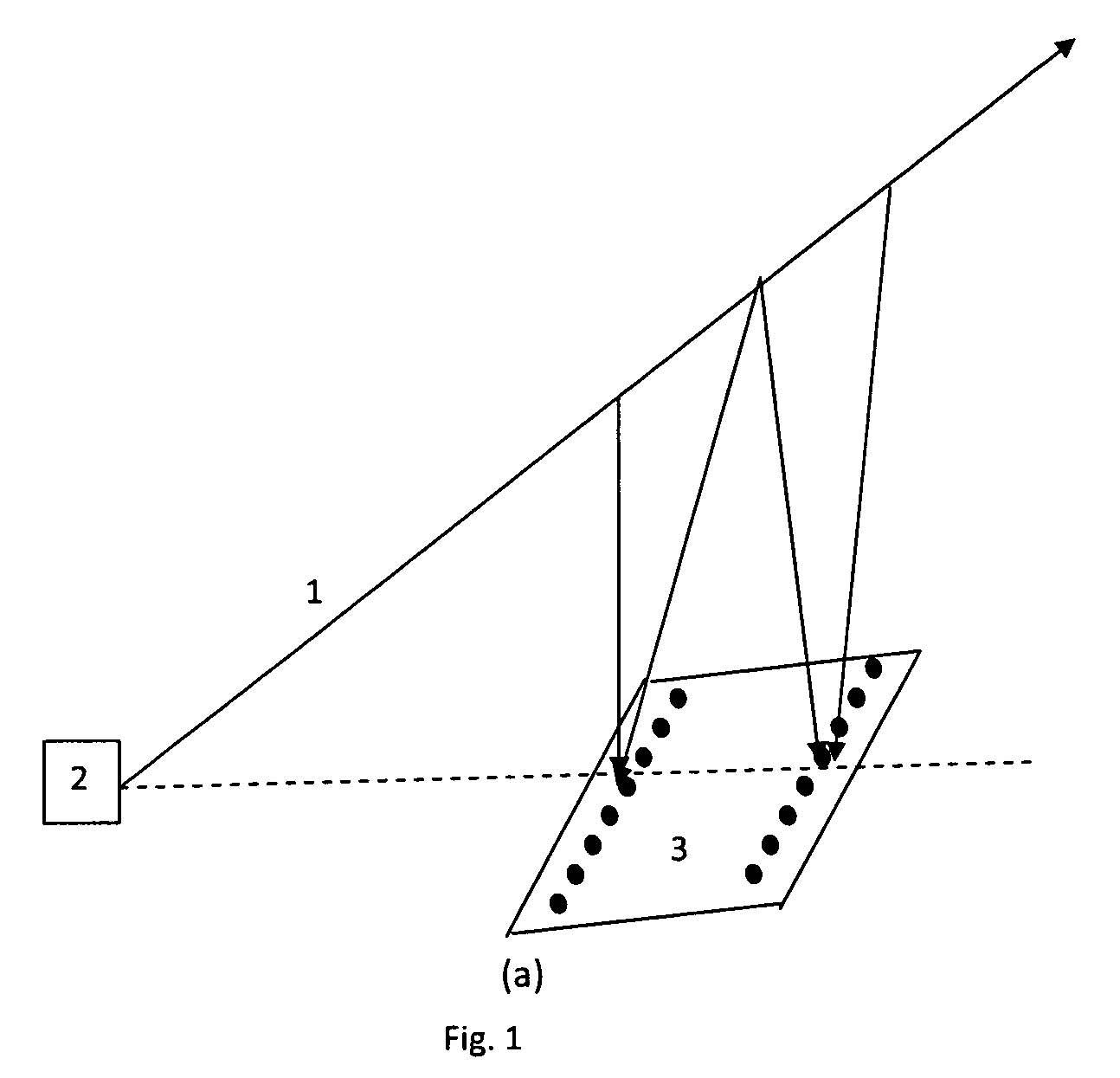
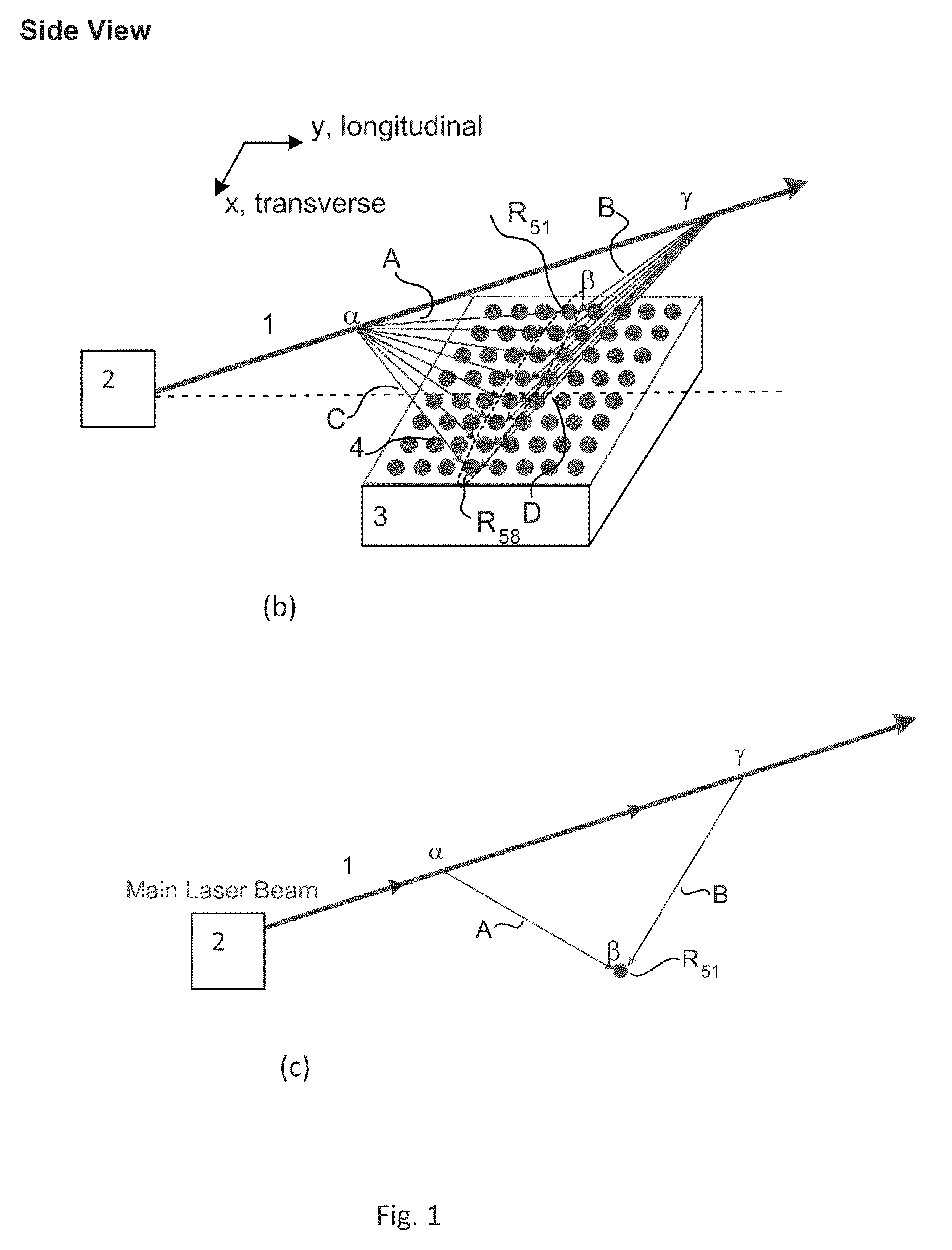
A direct vapor deposition (DVD) apparatus and method is taught, that provides a carrier gas flow entraining vapor atoms for the coating of regions on a substrate that are not in line-of-sight. The degree of non line-of-sight (NLOS) coating, hence thickness uniformity around the substrate is a sensitive function of the flow conditions. For a fixed background pressure in the region of deposition, an increase in the uniformity of the coating thickness is accomplished as the flow velocity is reduced. This improvement in uniformity is a result of an increase in the fraction of vapor atoms which deposit in NLOS positions on the substrate such as backside (21) of fiber (65) as indicated by vapor streamlines (51). Vapor impact width (VIW) is the width of the vapor flux impacting on some area of the fiber. Front side coating (FSC) width is the vapor width of atoms impacting on the substrate frontside (22).
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
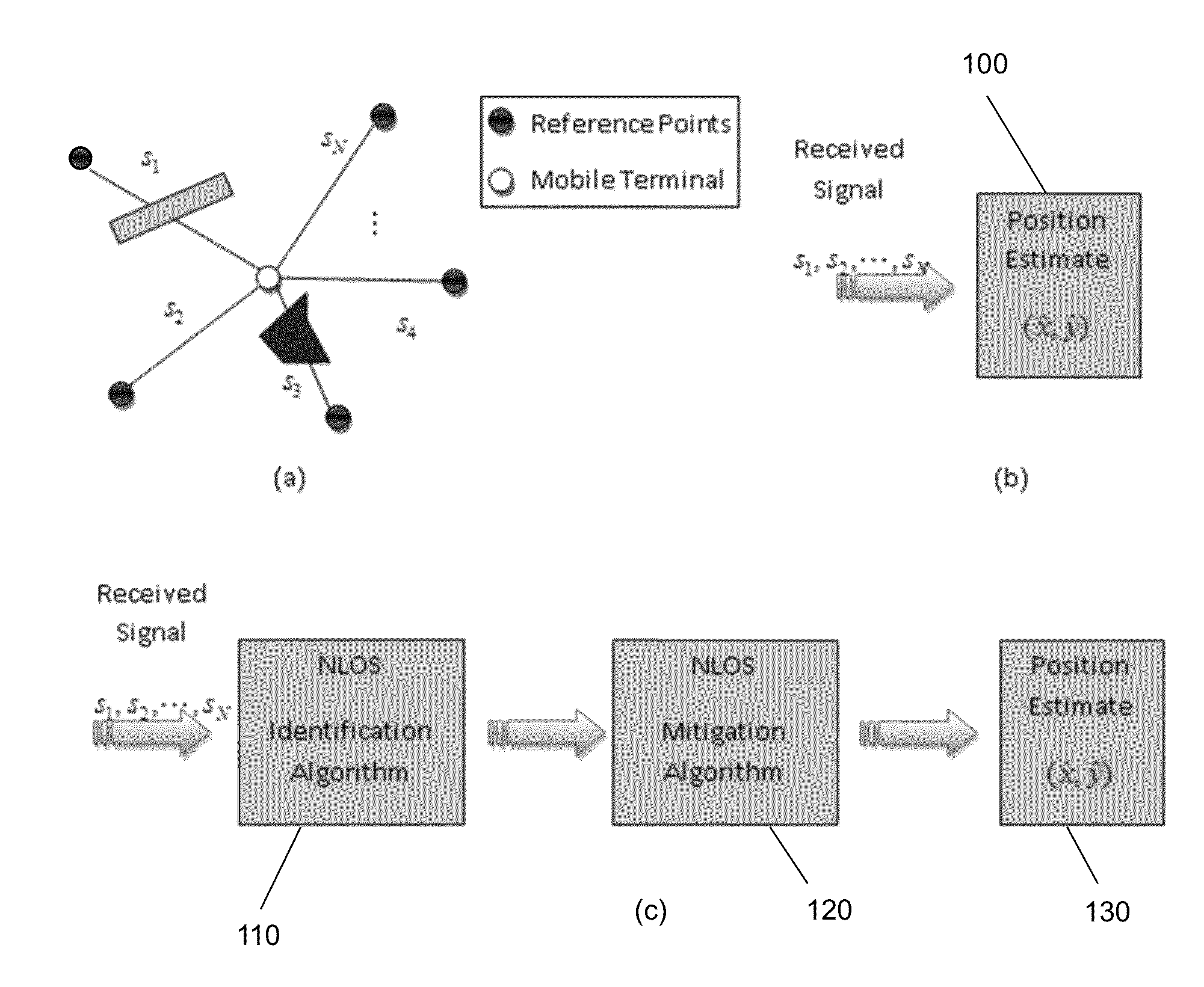
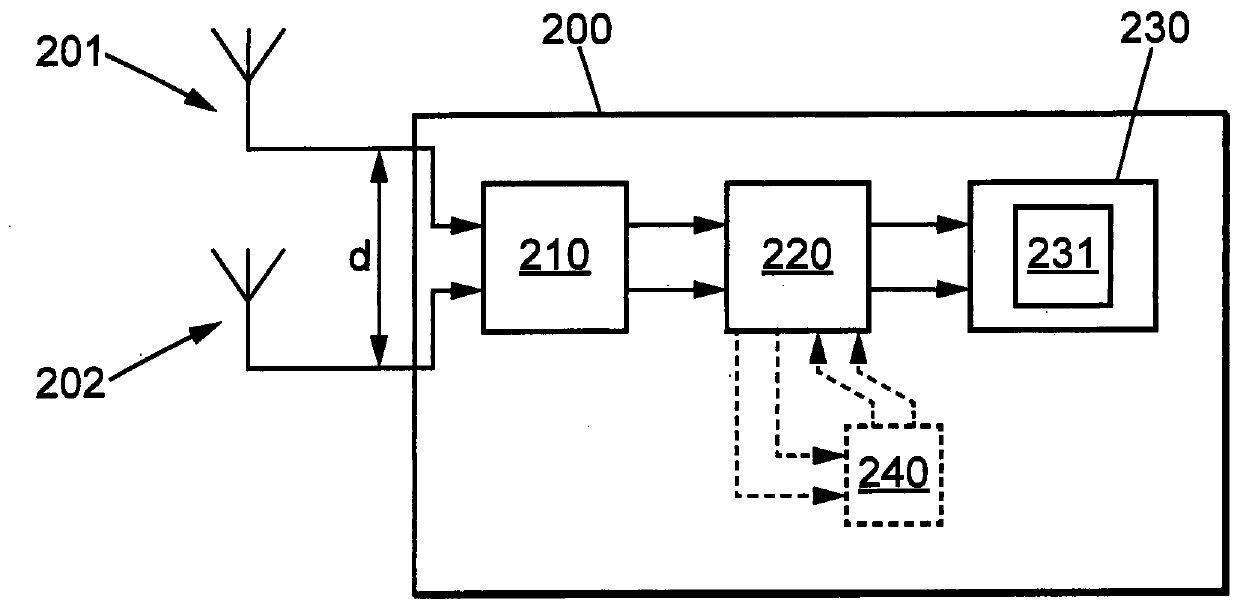
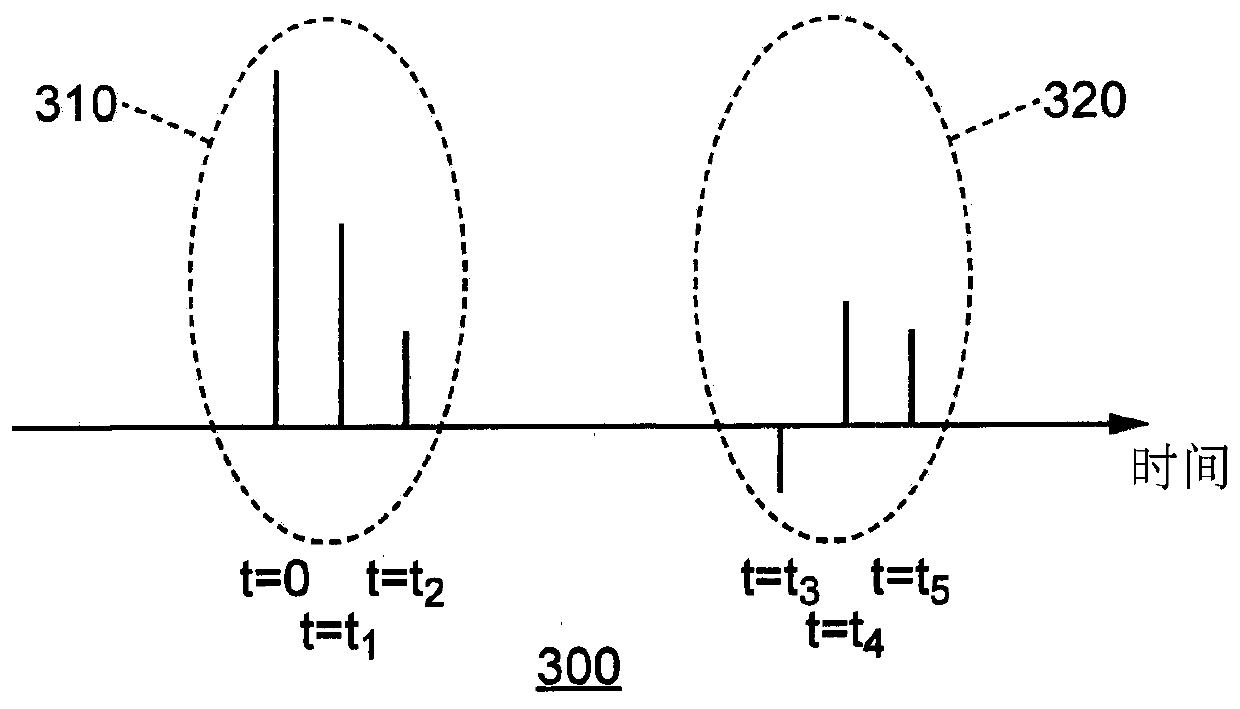
Methods and devices for channel identification
ActiveUS20140062793A1Receivers monitoringDirection finders using radio wavesChannel impulse responseGeolocation
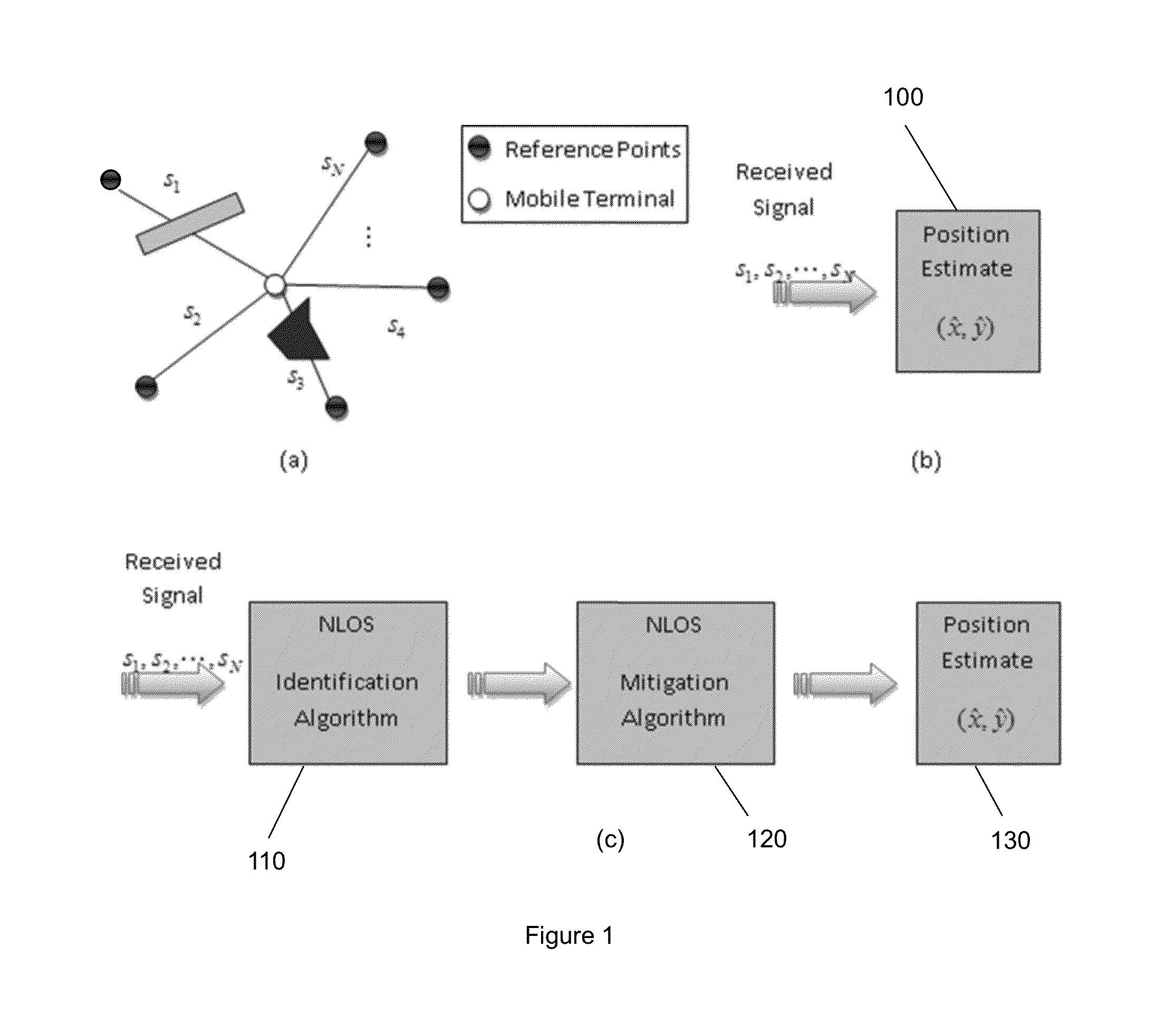
This invention relates to methods and devices for channel identification. The invention is particularly concerned with techniques for non-line of sight channel identification. In embodiments of the invention the methods and devices are used for channel identification in wireless geolocation systems. Embodiments of the invention make use of an entropy estimation of the channel to distinguish channel conditions and in particular to identify line-of-sight and non-line-of-sight channels and which can be used to solve the NLOS problem of determining relative distances between transmitter and receiver. In particular embodiments an entropy estimation of the channel impulse response (CIR) is used to construct a robust entropy-based channel identification technique. As a result, more accurate localization in indoor and other multipath environments may be possible.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Control forwarding techniques for wireless communications
ActiveUS20200236655A1Network traffic/resource managementParticular environment based servicesCommunications systemCommunication control
User equipment (UEs) within a sidelink communications system may employ control forwarding techniques. For example, a UE may piggyback resource reservation information received from other UEs when broadcasting its own resource reservation. A UE that may be in line of sight (LOS) with two other UEs that themselves are in a non-line of sight (NLOS) situation and may include resource reservation information associated with other UEs when broadcasting the control information. For example, when forwarding control information, a UE may identify additional resources available in a transmission interval, and may convey neighbor control information (e.g., known resource reservations of other UEs in the sidelink communications system) using the additional resources. In some cases, the piggybacked resource reservation information associated with the other UEs may be selected based on the amount of additional resources in the transmission interval, a priority of known resource reservation information, etc.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Space diversity optical receiver and system and method using the same
InactiveUS20090185811A1Large optical powerMaximizes output optical powerPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling ratioWaveguide
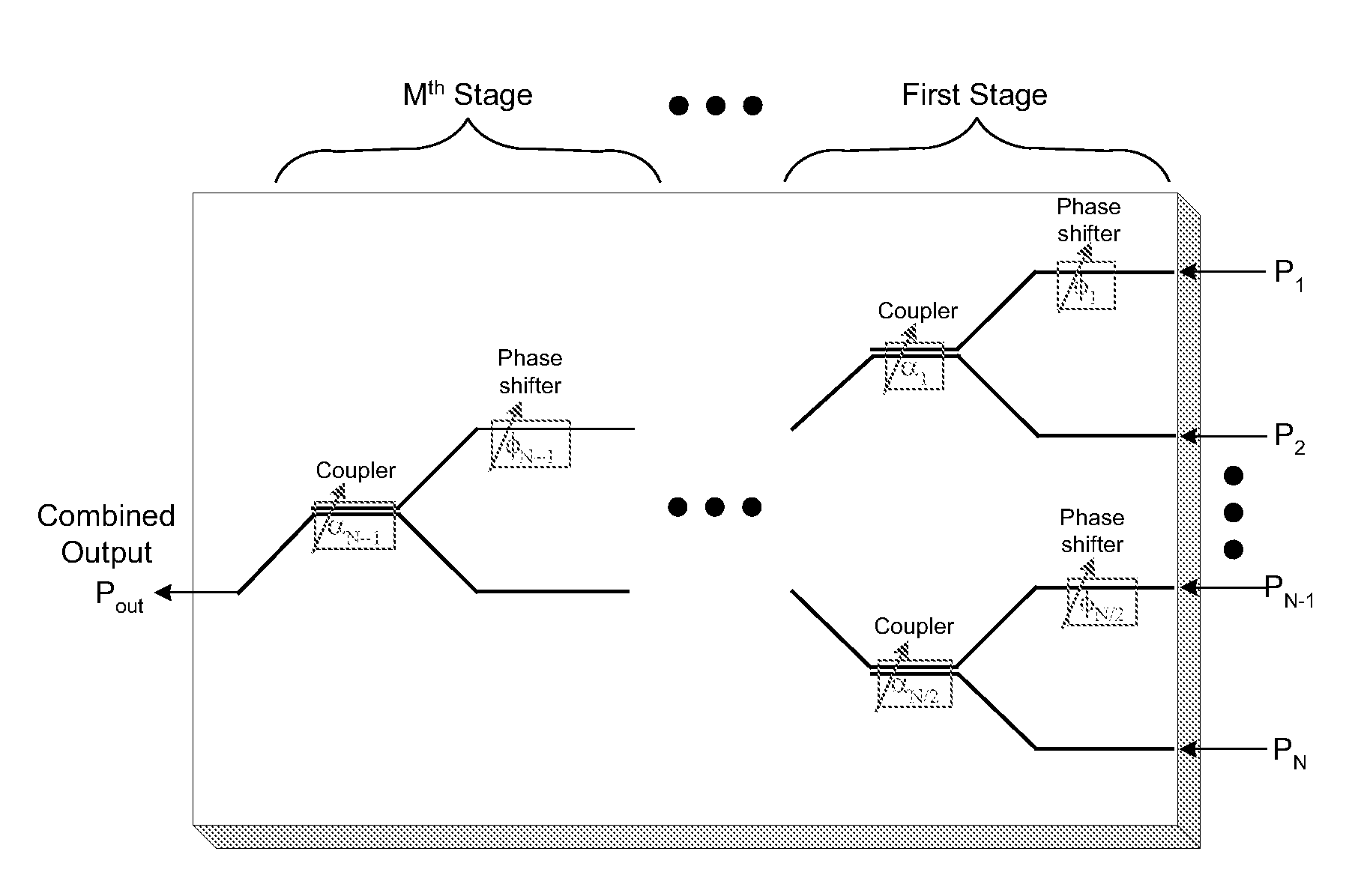
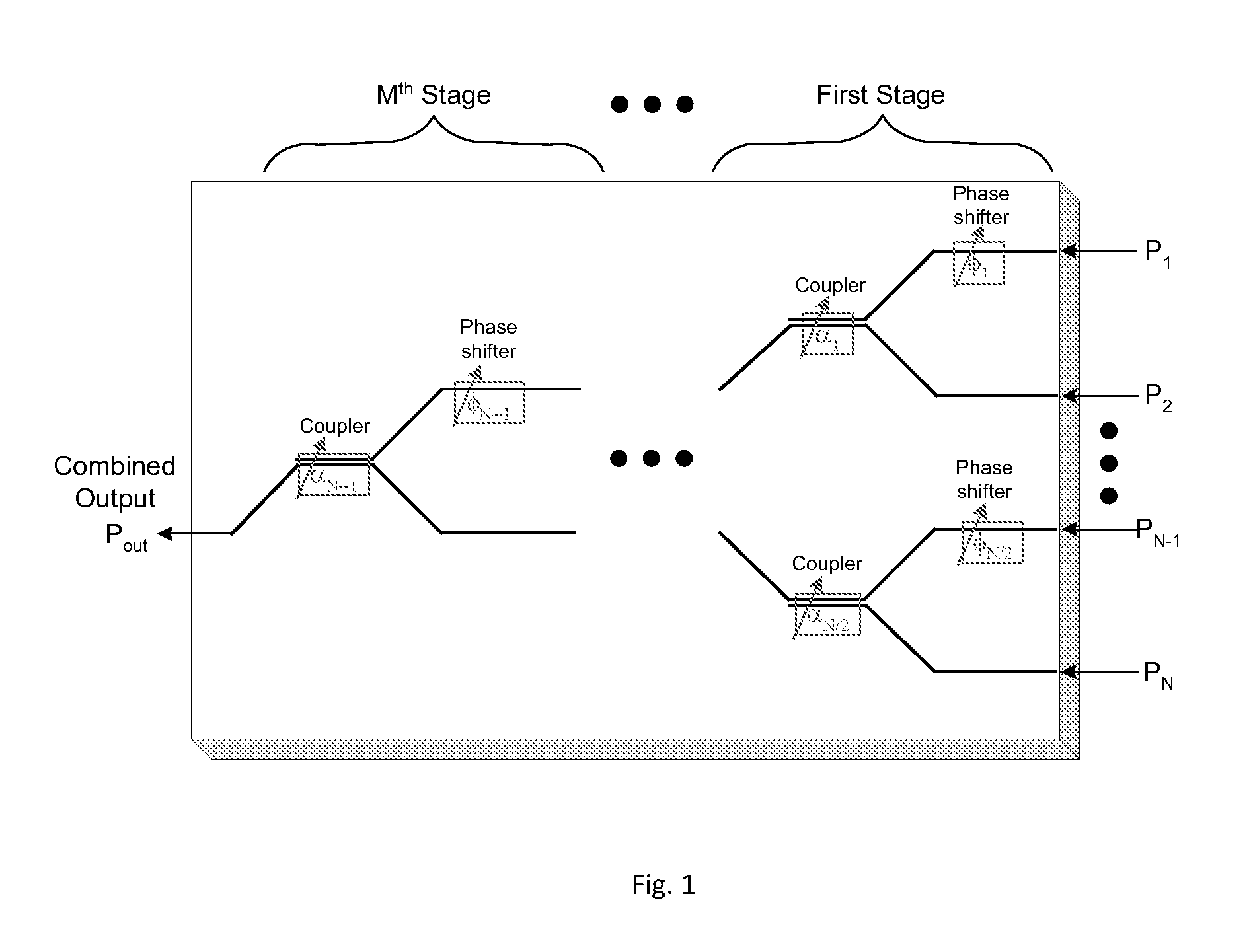
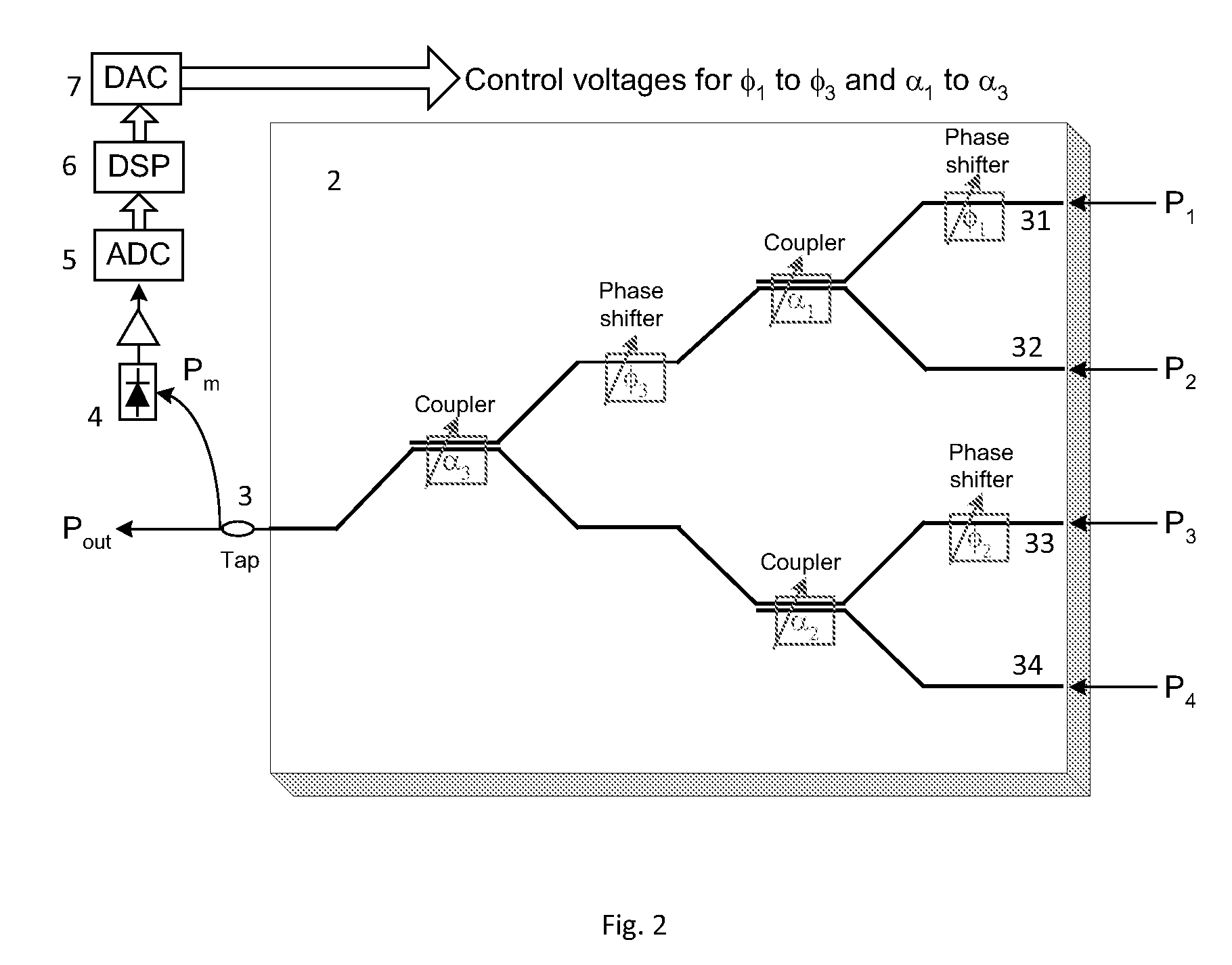
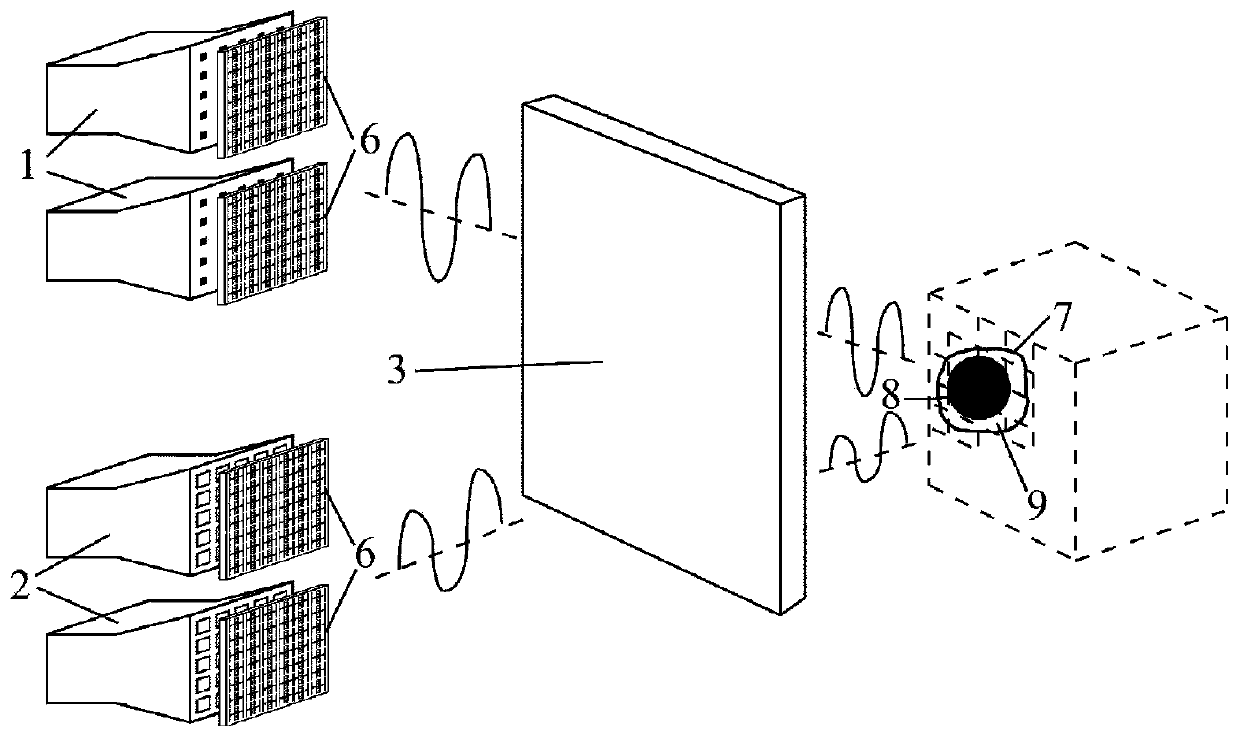
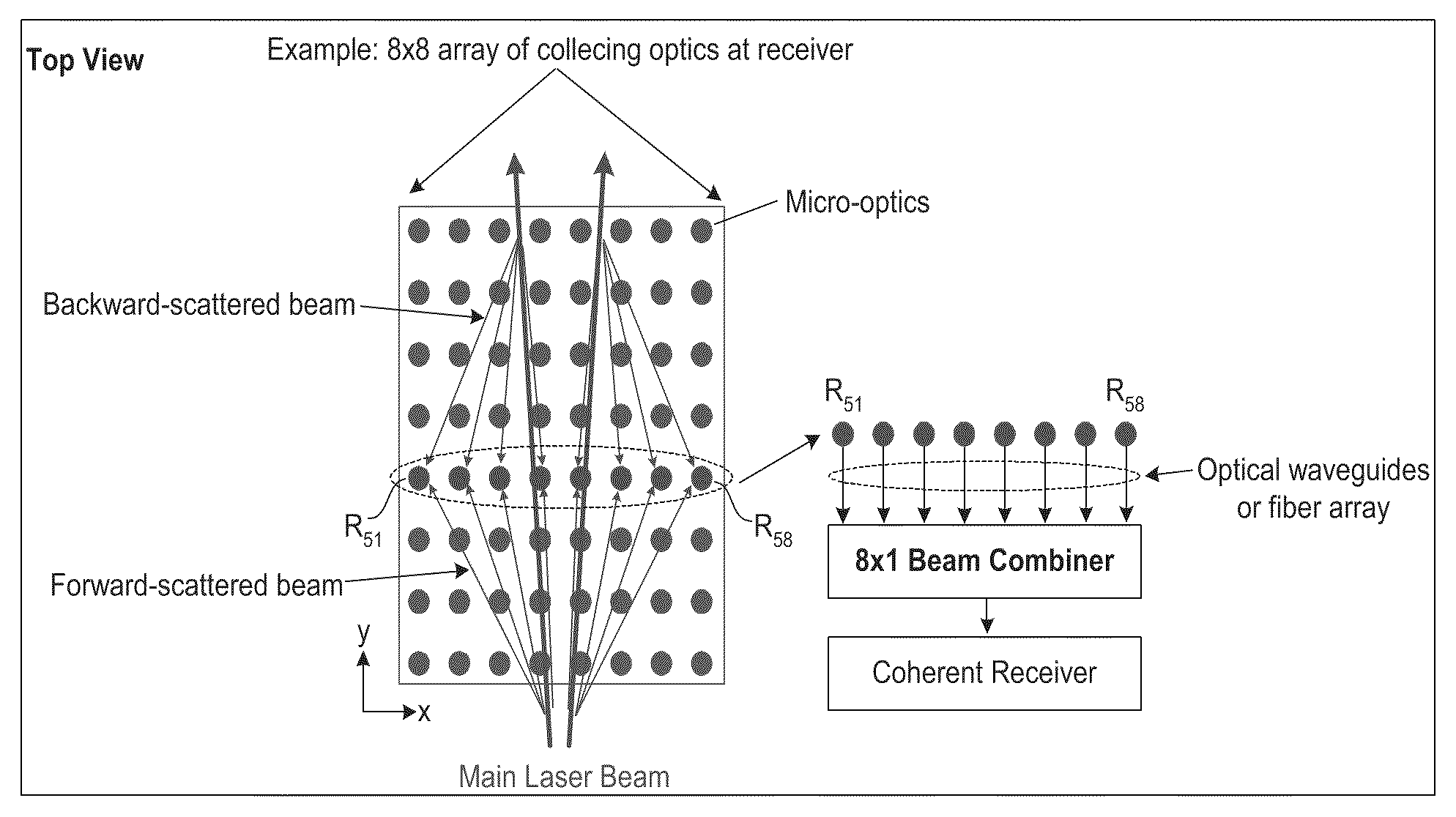
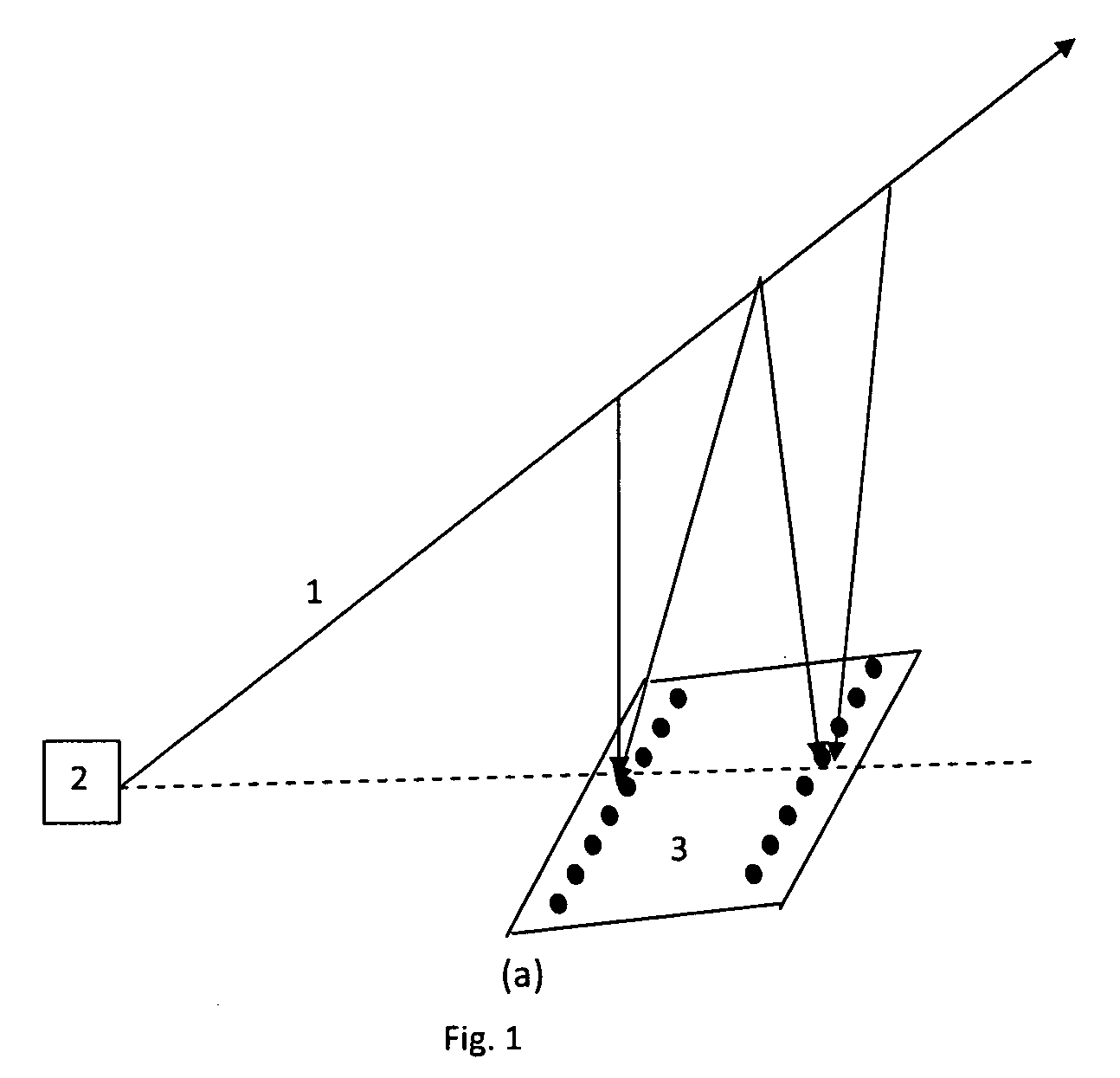
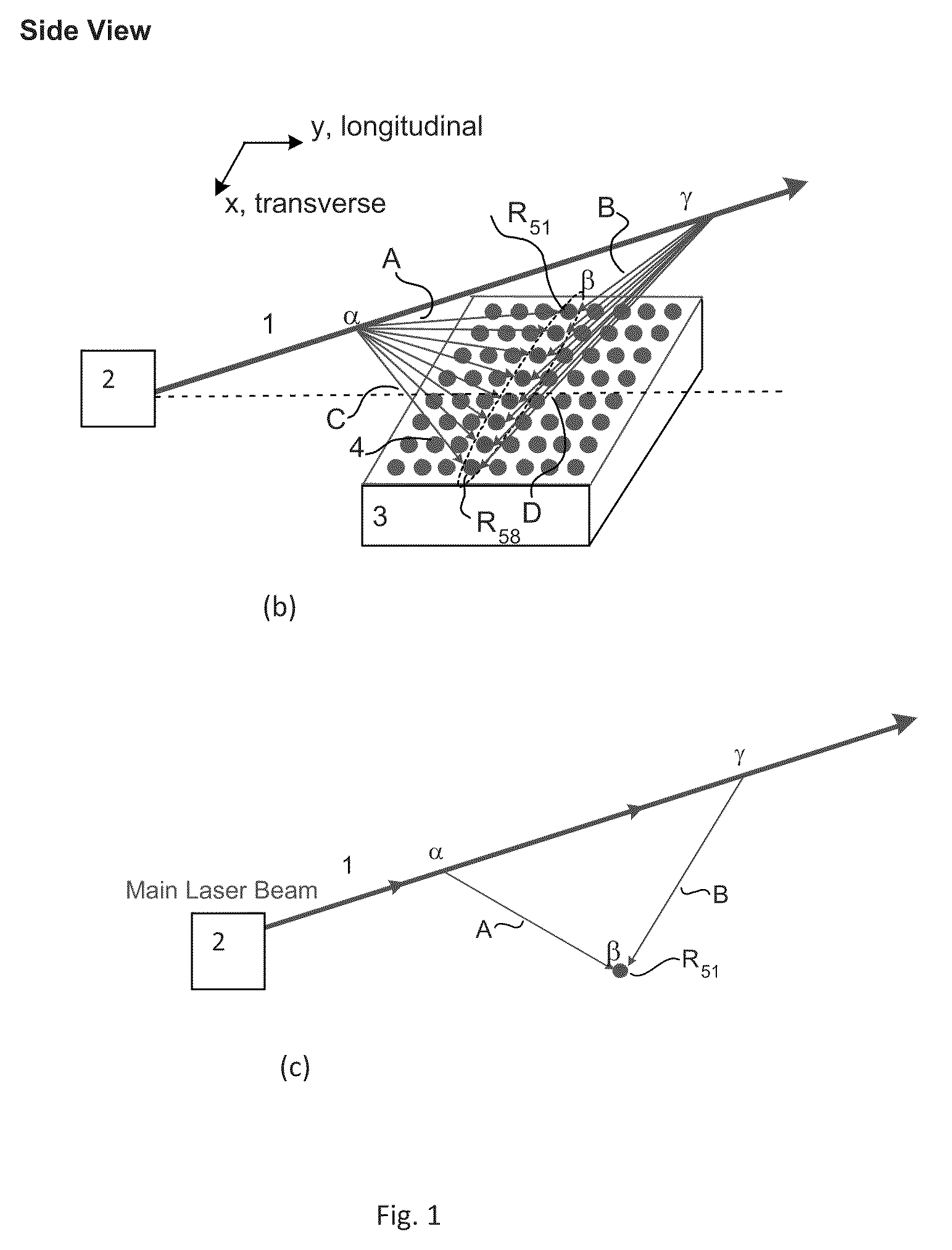
An optical beam combiner is provided, which allows efficient collection of light for various applications: non-line of sight and free space optical communications, remote sensing, optical imaging and others. A multitude of optical beam portions is captured by a space diversity receiver that includes an optical beam combiner, which has a tree-like topology with interconnected waveguides, electro-optic phase shifters, and directional couplers. For each of the beam portions the phase of the phase shifter and the coupling ratio of coupler in the optical beam combiner are tuned sequentially to maximize the final output power in the final optical waveguide. A portion of the final output beam is used for the power detection and forming a feedback signal for the phases and coupling ratios adjustment. The data or information is recovered from the received final optical beam using coherent detection.
Owner:CELIGHT
Space diversity receiver for optical communications
An optical beam combiner is provided, which allows efficient collection of light for various applications: non-line of sight and free-space optical communications, remote sensing, optical imaging and others. A multitude of transverse scattered optical beam portions is captured by the multi-aperture array positioned perpendicular to the beam projection direction. These beam portions are combined first into a single optical waveguide with modulating the beam portions phase and coupling ratio of directional couplers in the optical beam combiner tuned to maximize the final output power. A portion of the output beam is used for the power detection and forming a feedback signal for the phases and coupling ratios adjustment. The data is recovered from the received optical beam using coherent detection.
Owner:CELIGHT
Adhesive protective coatings, non-line of sight methods for their preparation, and coated articles
A method for depositing a protective coating upon a substrate includes the steps of dipping a substrate into a slurry composed of an aqueous solution, at least one refractory metal oxide, and at least one transient fluid additive present in an amount of about 0.1 percent to 10 percent by weight of the slurry; heat treating the substrate; and cooling the substrate to form a protective coating thereon.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Electromagnetic non-line-of-sight imaging method based on time reversal and compressed sensing
ActiveCN111239730AHigh strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioWaveguide hornsProtective material radiating elementsRadar imagingMedical imaging
The invention discloses an electromagnetic non-line-of-sight imaging method based on time reversal and compressed sensing. An electromagnetic signal passively scattered by a target behind a shieldingobject is received through an antenna, contour imaging of the target is achieved through compressed sensing, the signal-to-noise ratio of the target electromagnetic signal is increased through time reversal for a contour area, and the purpose of staring to detect a non-sight target is achieved. By transmitting a plurality of random radiation signals through active metasurface modulation, and carrying out compressed sensing calculation imaging after receiving, the number of targets in a shielding region and a contour region is judged; for the target contour area, the amplitudes and phase differences of signals obtained at different positions are further adjusted through the active metasurface, and focusing and scanning of electromagnetic signals at different positions behind the shielding object are achieved. According to the invention, a wall body where an electromagnetic signal cannot penetrate and a target in a non-closed scene behind a metal structure can be detected, the detectioncapability of traditional detection and imaging radars is expanded, and the method has a wide application prospect in civil and military fields such as unmanned driving, medical imaging and complex environment radar detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and method for localization for non-line of sight sound source
ActiveUS20200225344A1Accurate estimateMicrophonesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSound sourcesSource orientation
Disclosed is a method and system for diffraction-aware non-line of sight (NLOS) sound source localization (SSL) that may reconstruct an indoor space, may generate acoustic rays into the indoor space based on an audio signal collected from the indoor space, and may estimate a position of an NLOS sound source based on a point at which one of the acoustic rays is diffracted.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Optical receiver using beam combining and system using the same
InactiveUS20090169221A1Maximizing output signalNanoopticsCoupling light guidesCoupling ratioLight beam
An optical beam combiner is provided, which allows efficient collection of light for various applications: non-line of sight and free space optical communications, remote sensing, optical imaging and others. A multitude of transverse scattered optical beam portions is captured by the multi-aperture array positioned perpendicular to the beam projection direction. These beam portions are combined first into a single optical waveguide with minimal loss of power. This is achieved by modulating the beam portions phase and coupling ratio of couplers in the optical beam combiner tuned to maximize the final output power. The data is recovered from the received optical beam using coherent detection.
Owner:CELIGHT
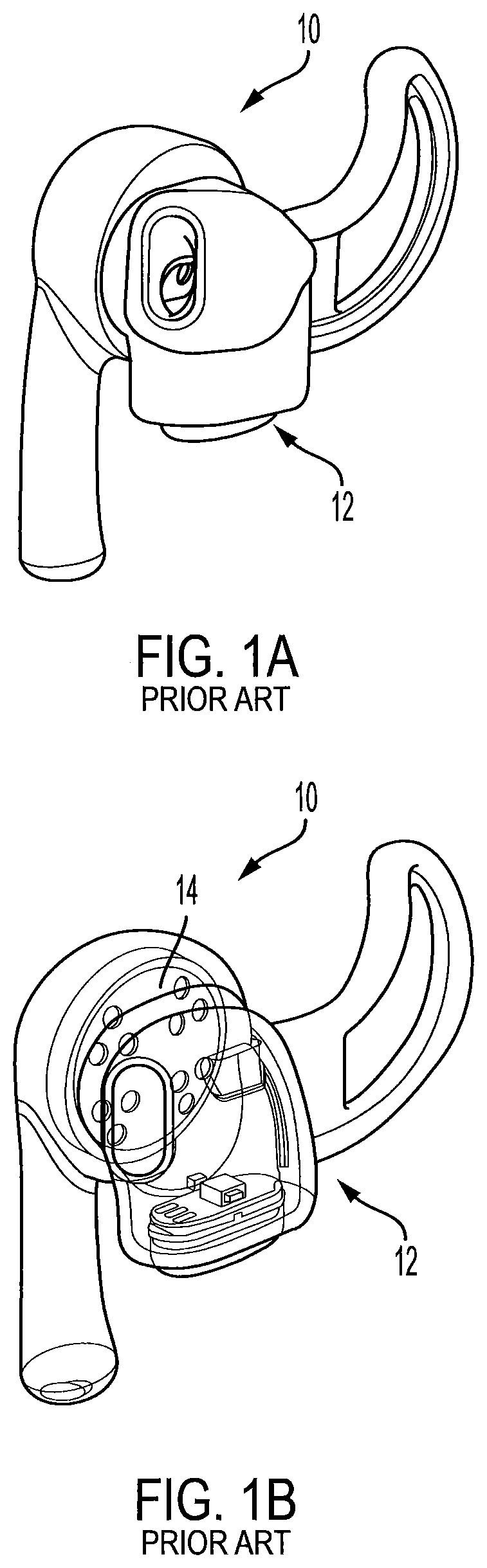
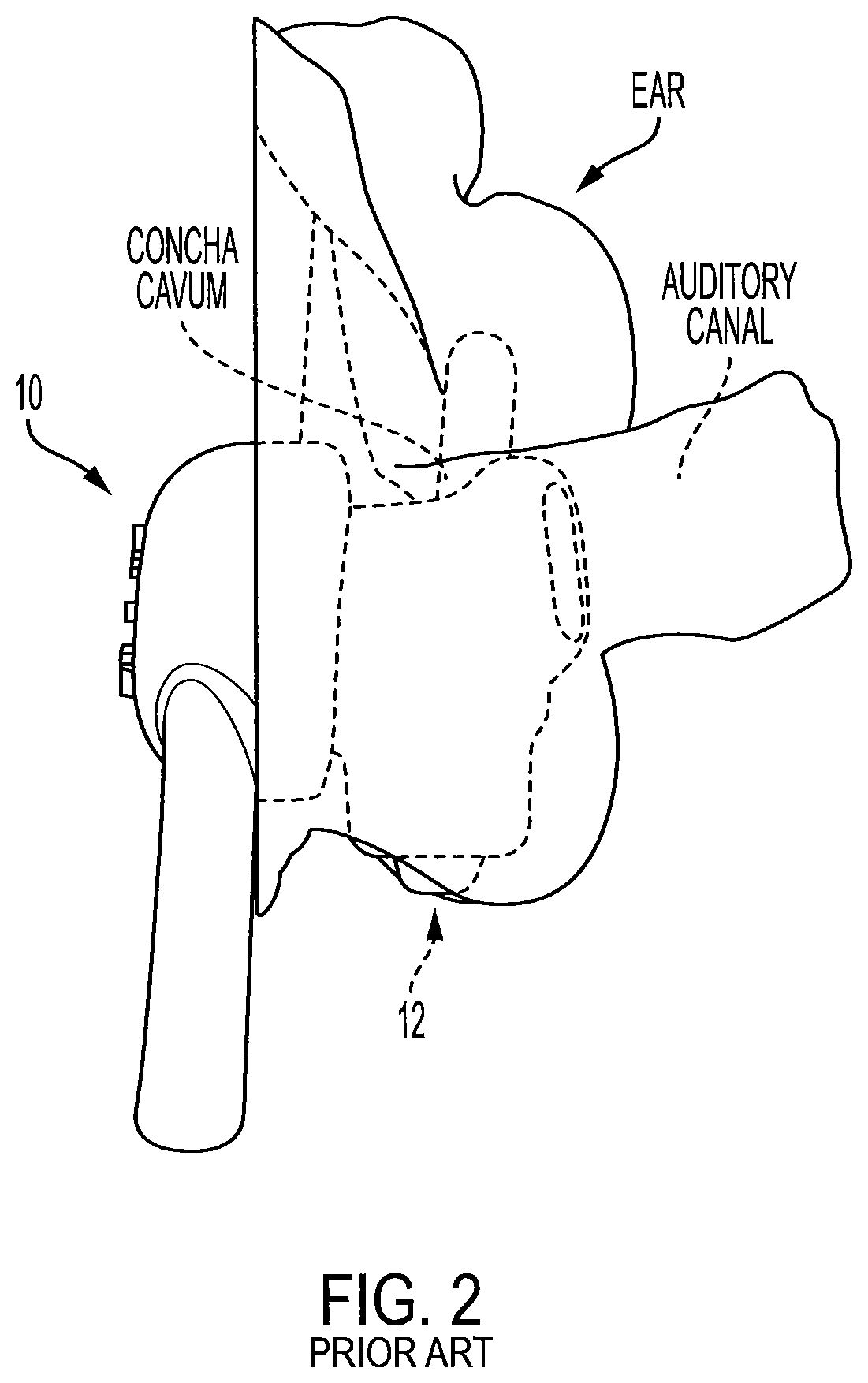
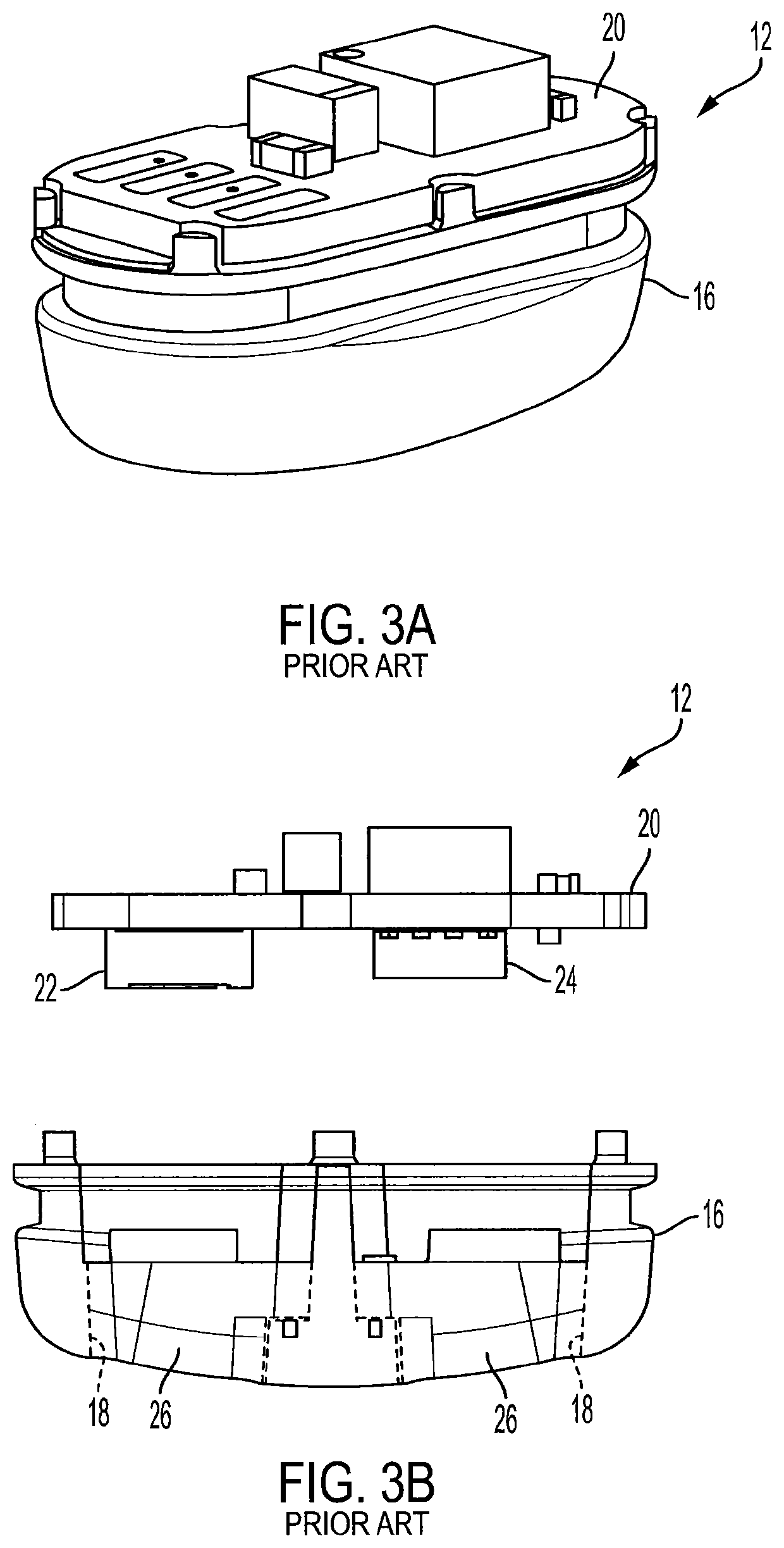
Hearing aid device with biometric sensor
PendingUS20210168539A1Avoid crosstalkDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical sensorsLight guideHearing aid
A hearing aid module includes an elongated housing, an optical sensor module within the housing, an audio driver positioned within the housing adjacent the optical sensor module, and first and second light guides positioned near the audio driver. The module has a rectangular configuration with opposite first and second sides, opposite third and fourth sides, and opposite first and second ends. The first and second sides each include an opening. An ear tip is coupled to the housing first end and is configured to retain the module within the auditory canal. The first light guide guides light from an optical emitter through the opening in the housing first side and into skin of the auditory canal in a non-line of sight manner. The second light guide collects light from the skin of the auditory canal and directs the collected light to an optical detector in a non-line of sight manner.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
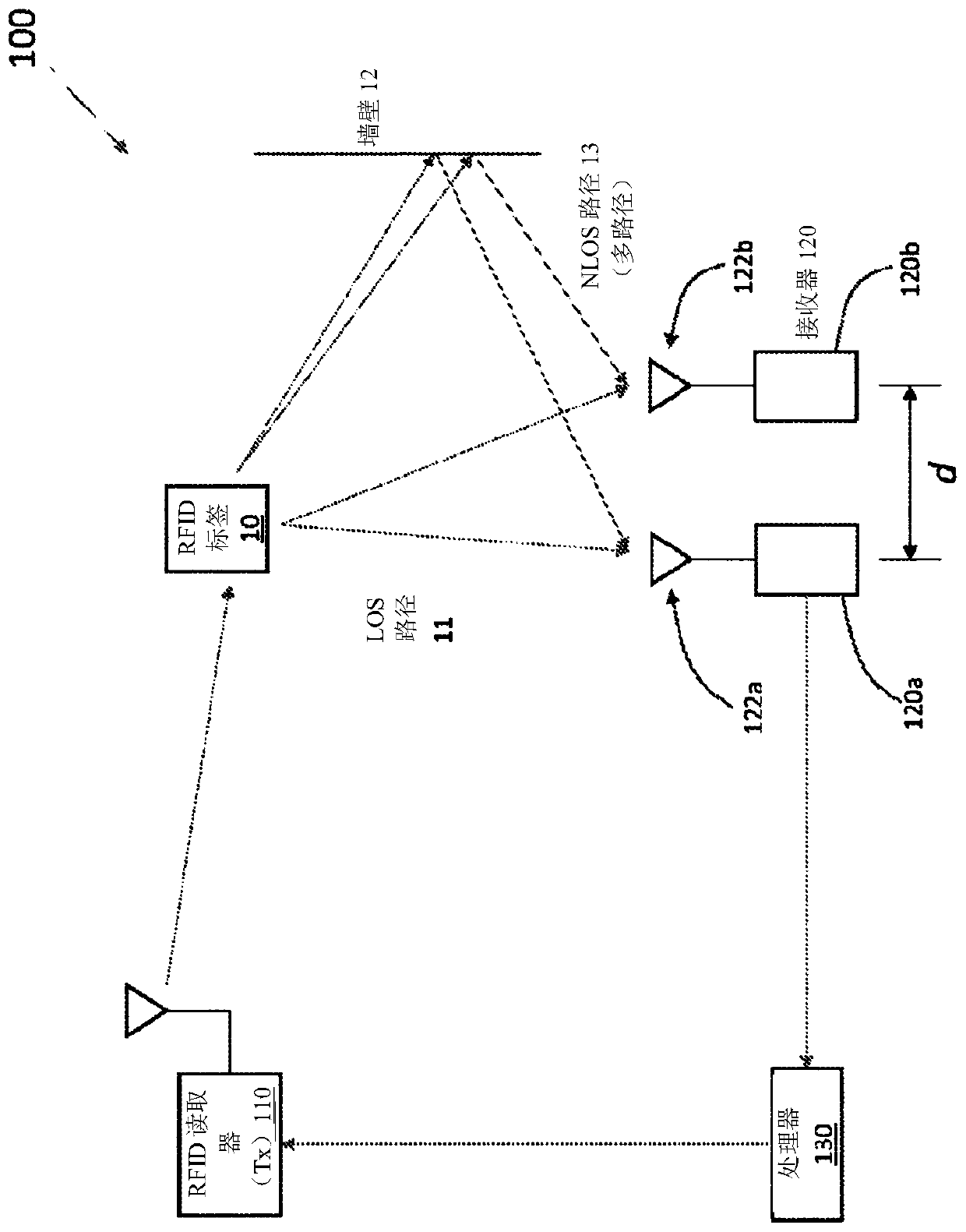
Methods and apparatus for locating RFID tags
PendingCN110691981ASub-station arrangementsWireless architecture usageRadio frequency signalRemote sensing
A radio frequency identification (RFID) system includes an array of antennas to distinguish line-of-sight (LOS) paths from non-line-of-sight (NLOS) paths. The distance between adjacent antennas in thearray of antennas is less than half the wavelength of the radio frequency (RF) signal of the system. Each antenna in the antenna array is also digitally controlled to change relative phase differenceamong the antennas, thereby allowing digital steering of the array of antennas across angles of arrival (AOAs) between 0 and pai. The digital steering generates a plot of signal amplitudes as a function of AOAs. LOS paths are distinguished from NLOS paths based on the shapes (e.g., depth, gradient, etc.) of local extremes (e.g., maxima or minima) in the plot.
Owner:AUTOMATION INC
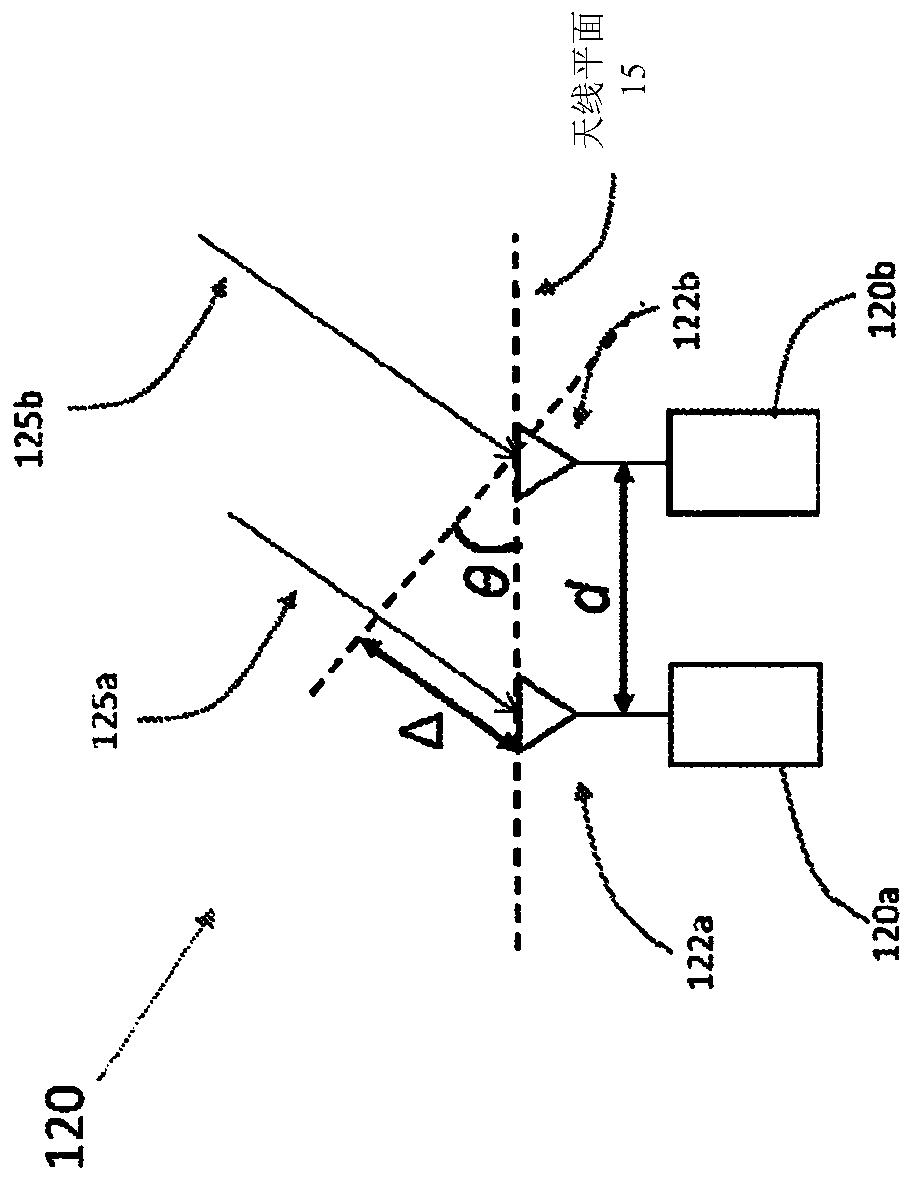
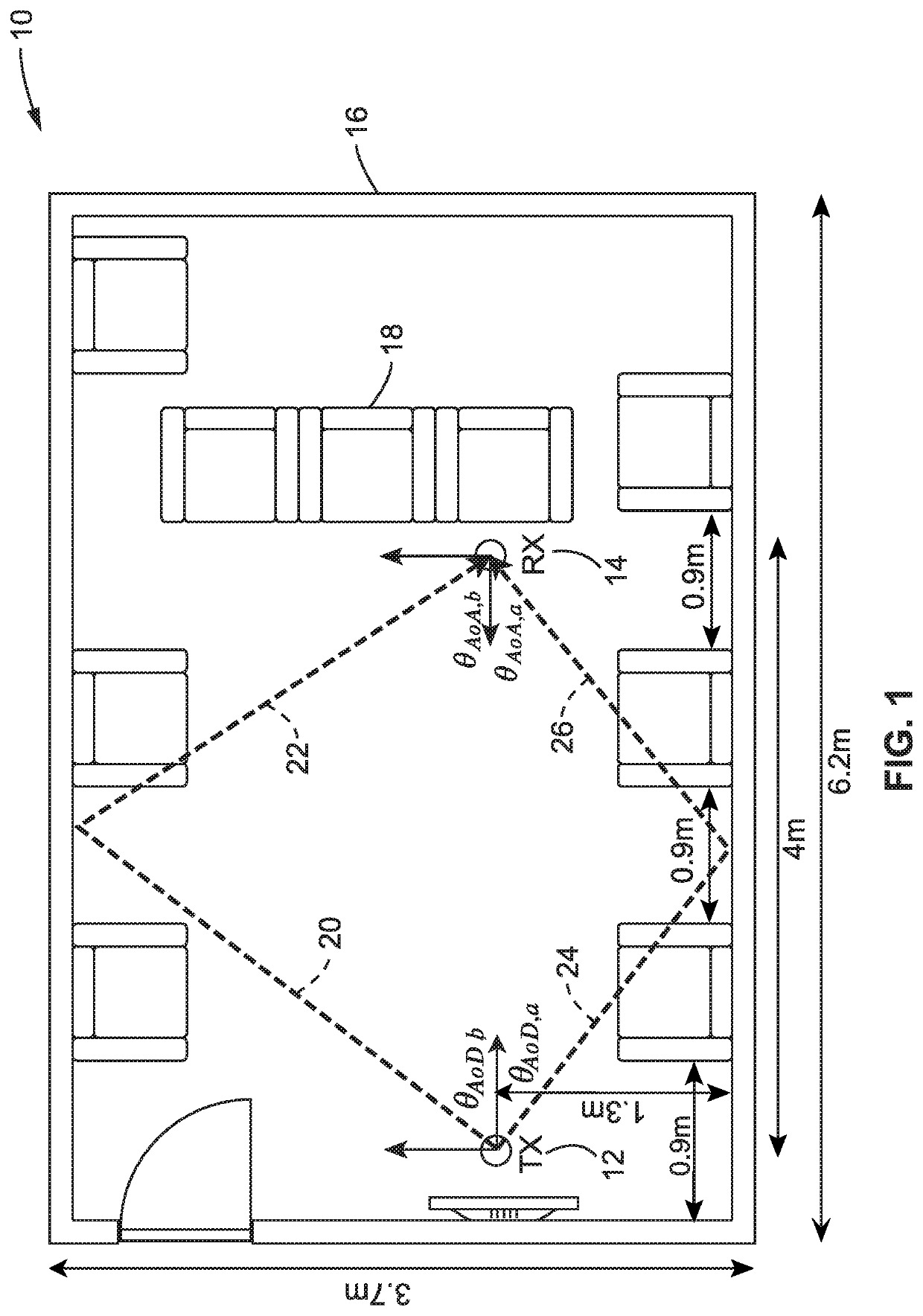
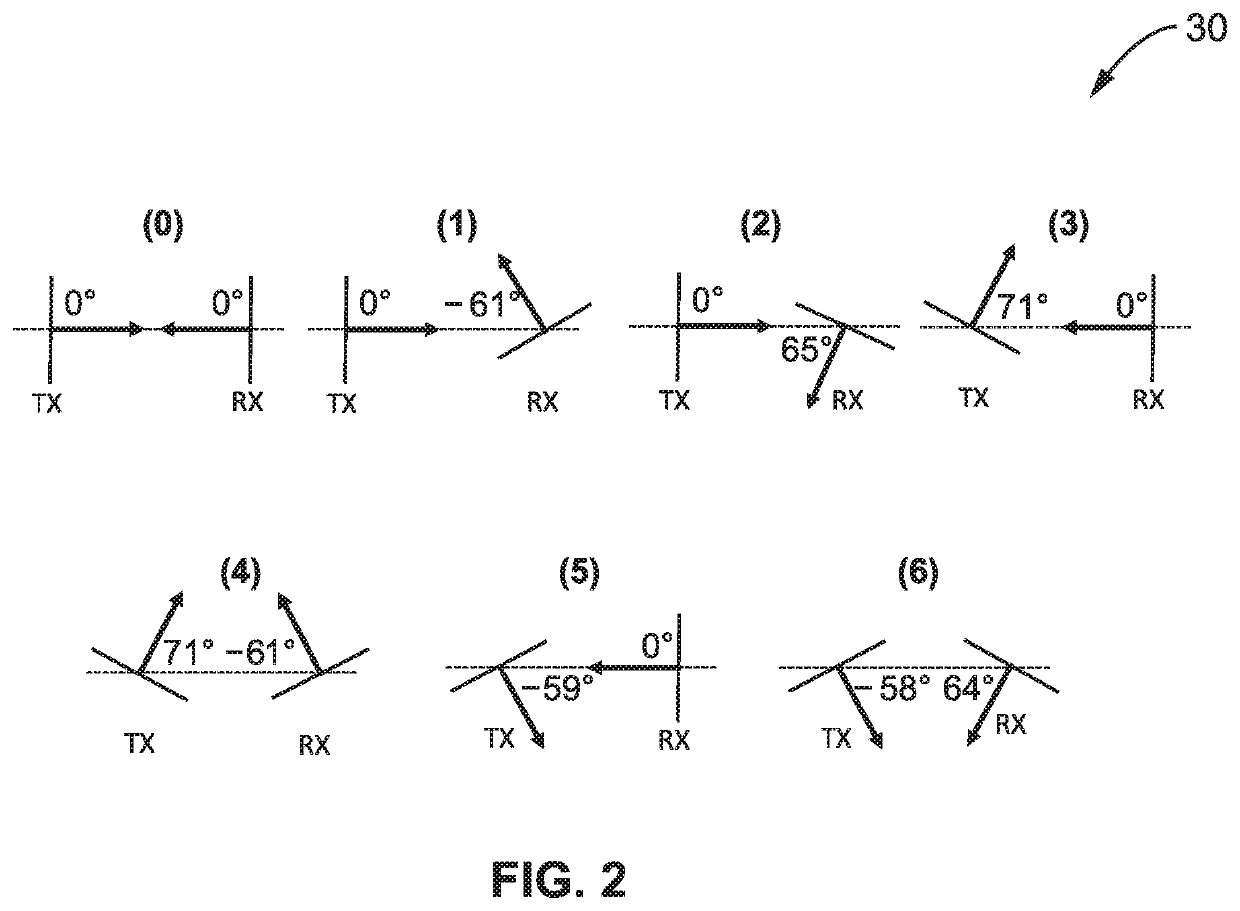
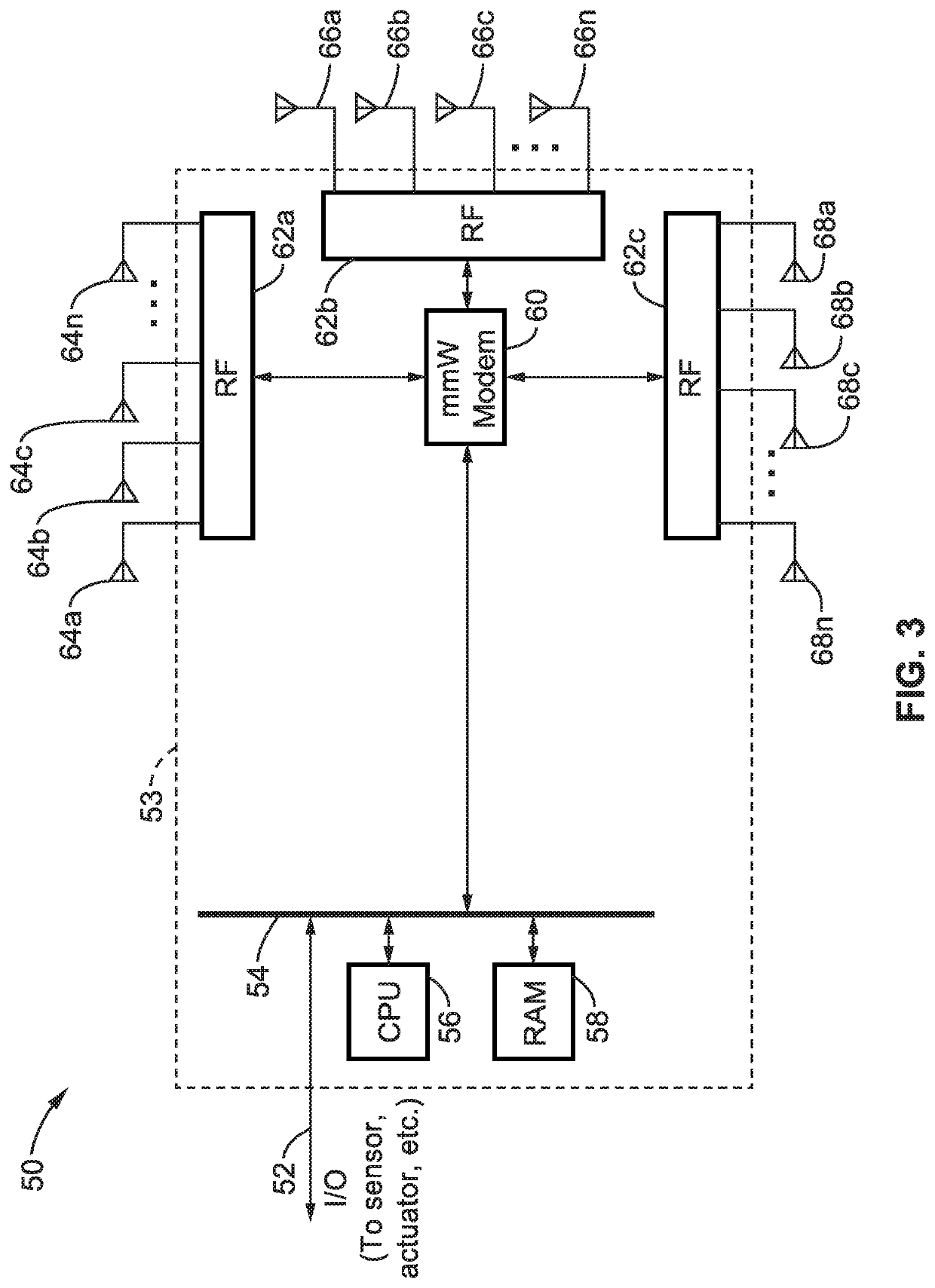
Millimeter-wave non-line of sight analysis
ActiveUS20210126695A1Transmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityDirectional antennaMillimetre wave
Reducing the effects of path loss in millimeter wave (mmWave) directional communications by performing channel measurements estimating non-line of sight (NLOS) blockages, to determine angle-of-departure (AoD) and angle-of-arrival (AoA) and gain of identified paths so that directional antennas can be reconfigured to overcome unfavorable propagation conditions and reduce path losses.
Owner:SONY CORP
Matching for GNSS signals
PendingUS20210325548A1Minimize polarization based distortionReduce decreasePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingPattern matchingComputer science
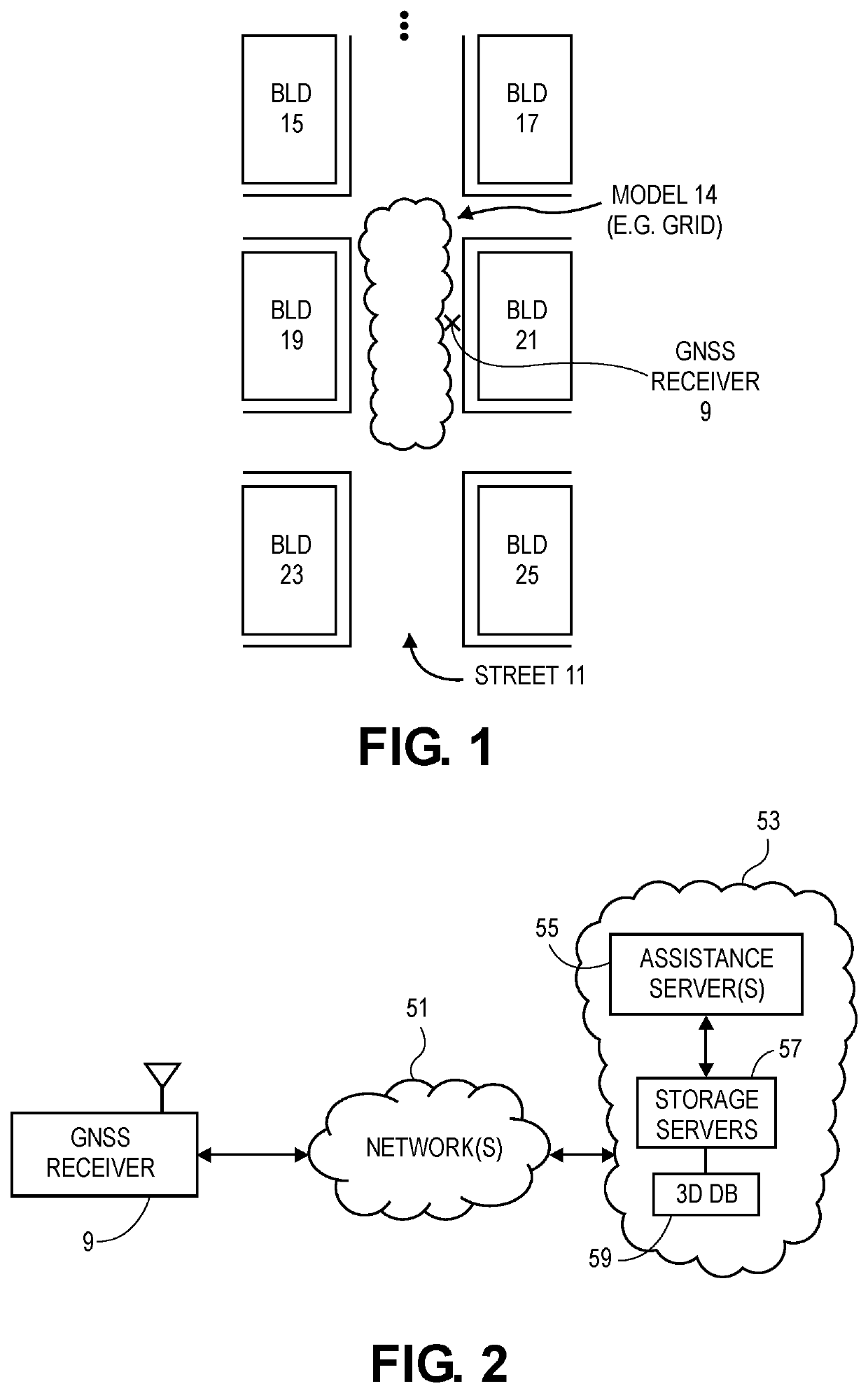
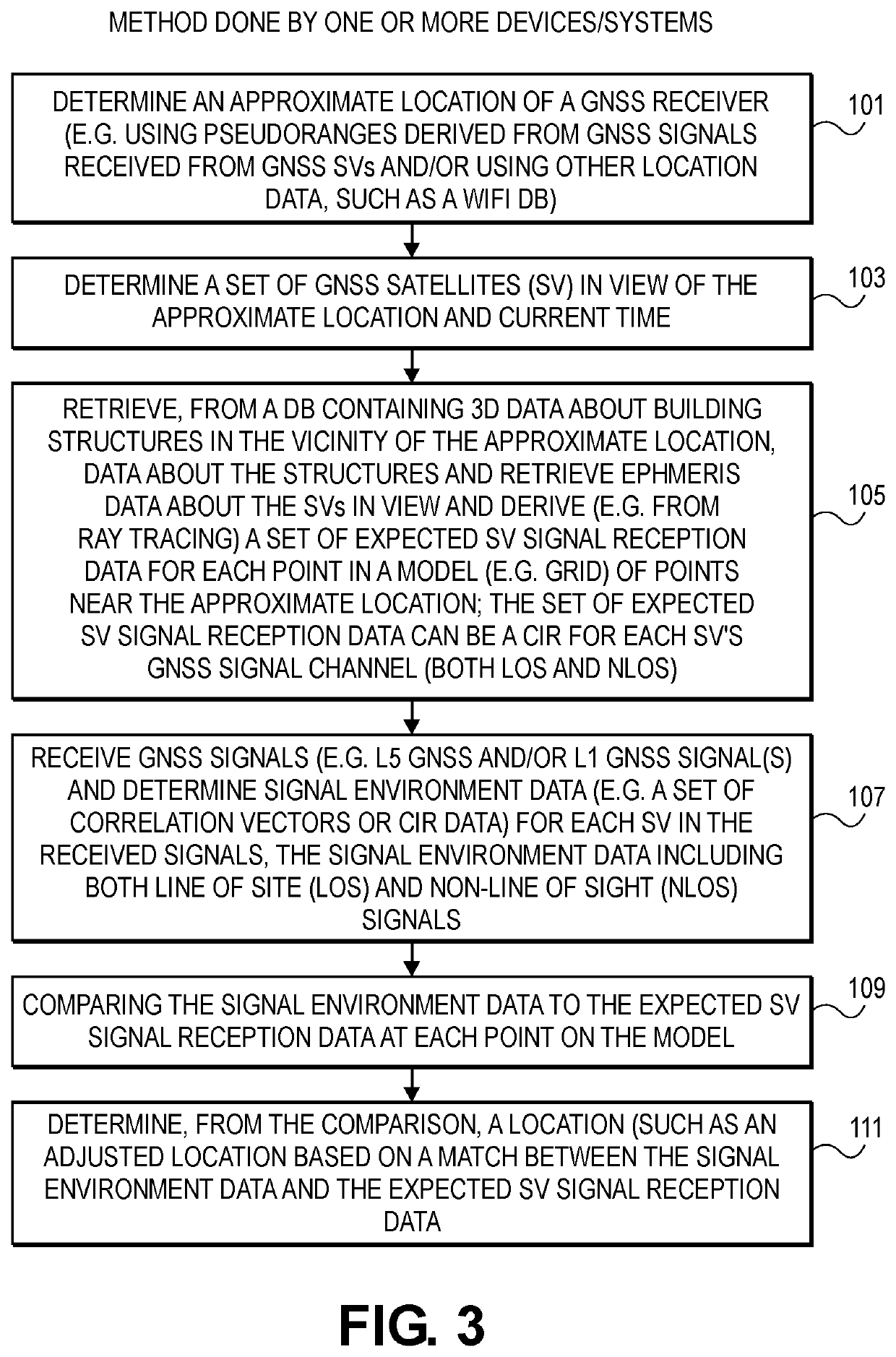
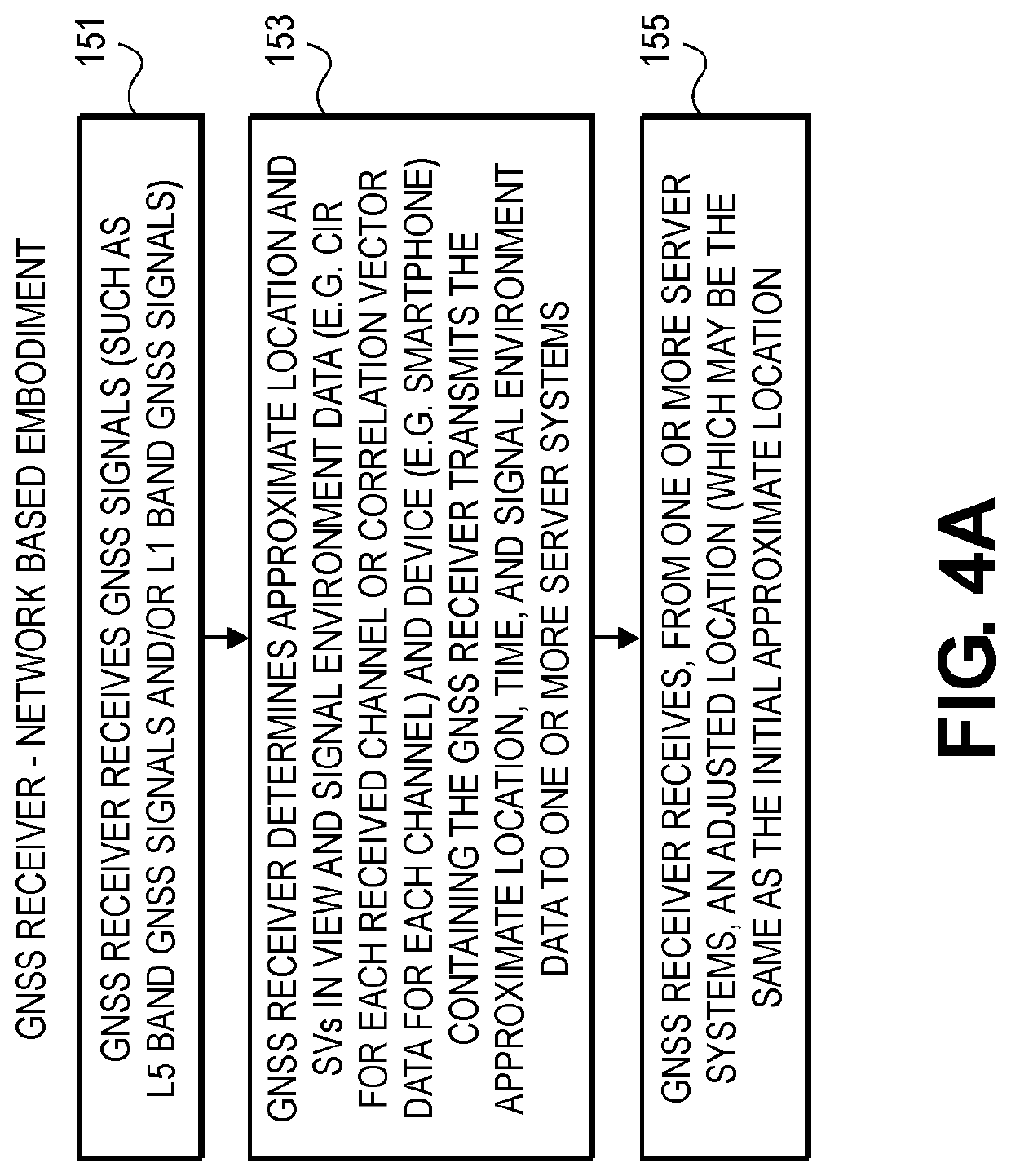
This disclosure describes methods, systems and machine readable media that can provide position solutions using, for example, pattern matching with GNSS signals in urban canyons. In one method, based upon an approximate location in an urban canyon and a set of 3D data about building structures in the urban canyon, an expected signal reception data can be generated for both line of sight and non-line of sight GNSS signals from GNSS satellites, or other sources of GNSS signals, at each point in a set of points in a grid (or other model) in the vicinity of the approximate location). This expected signal reception data can be matched to a received set of GNSS signals that have been received by a GNSS receiver, and the result of the matching can produce an adjustment to the approximate location that is used in the position solution of the GNSS receiver.
Owner:ONENAV INC
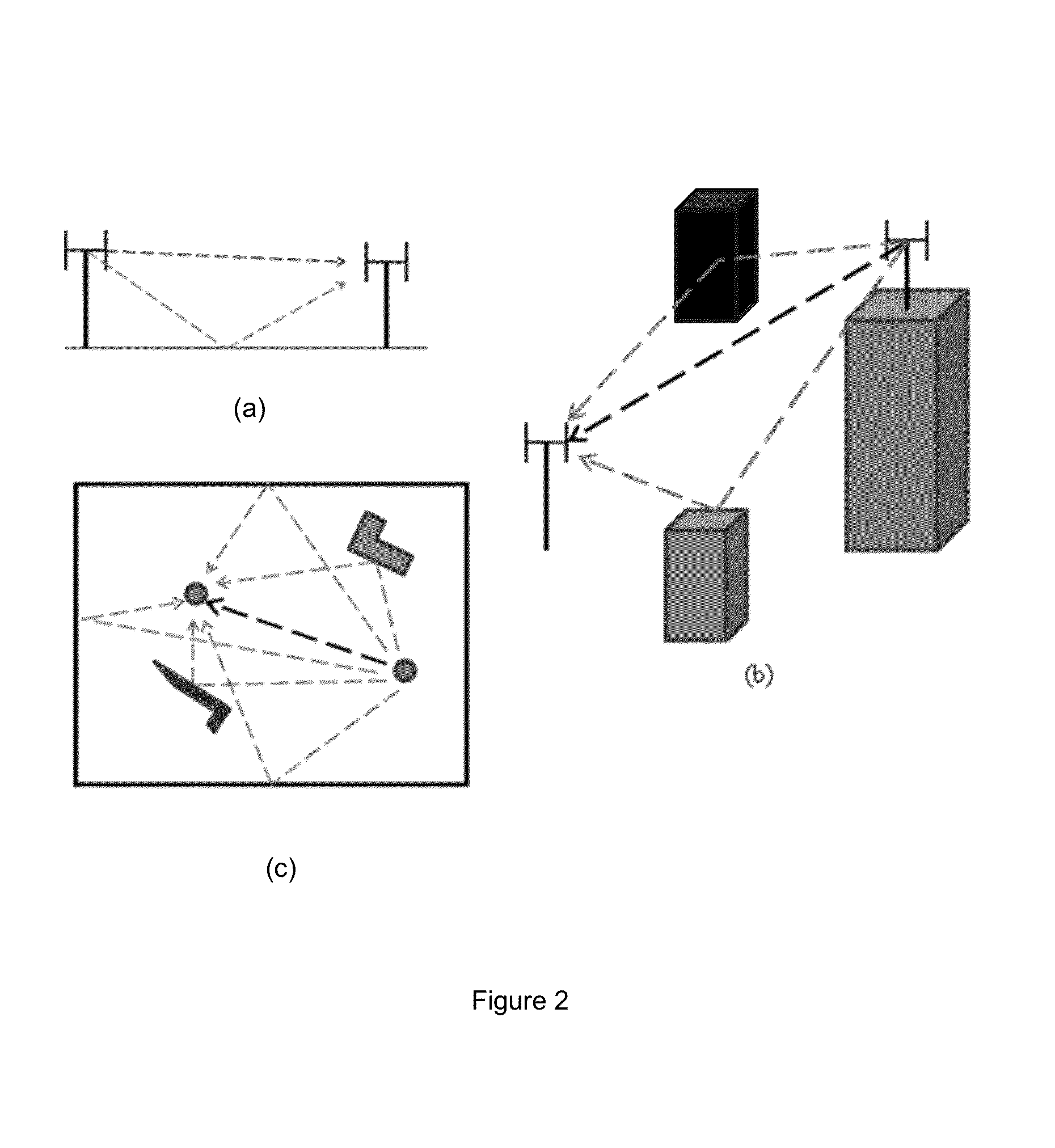
Method and apparatus for distinguishing line of sight from non line of sight in vehicular communication systems
InactiveCN110869791AParticular environment based servicesPosition fixationTelecommunicationsMultipath component
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
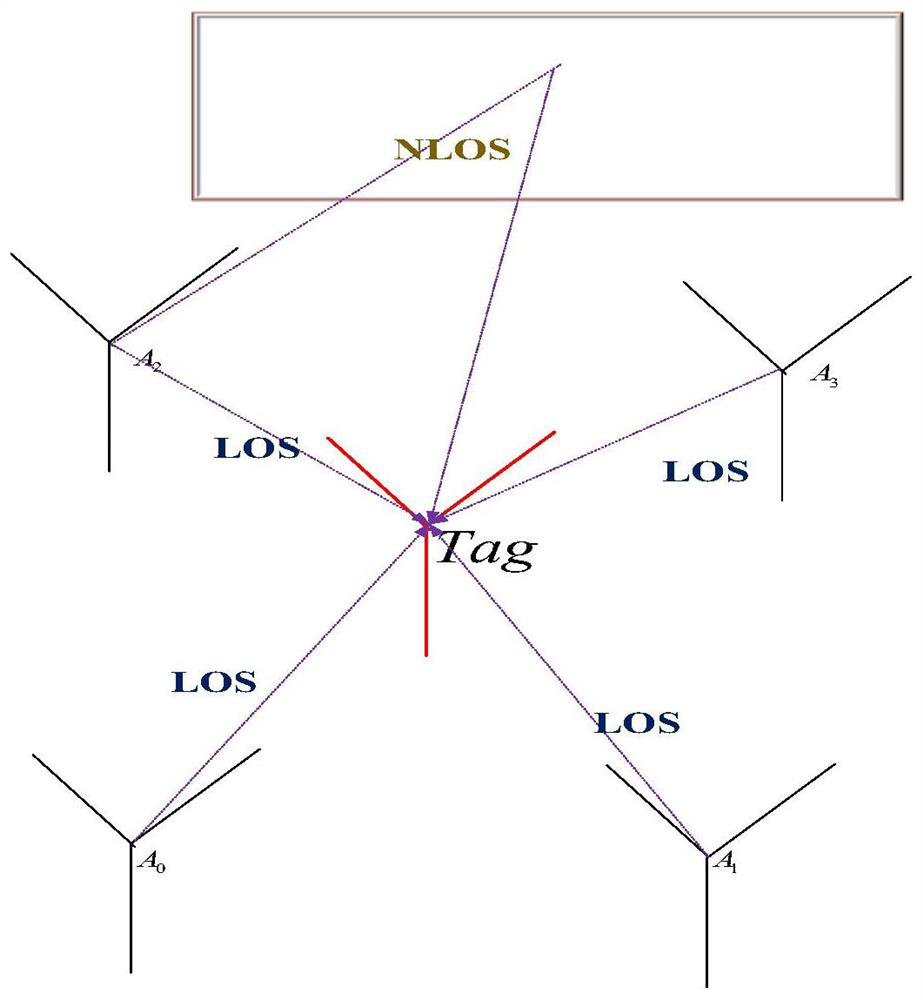
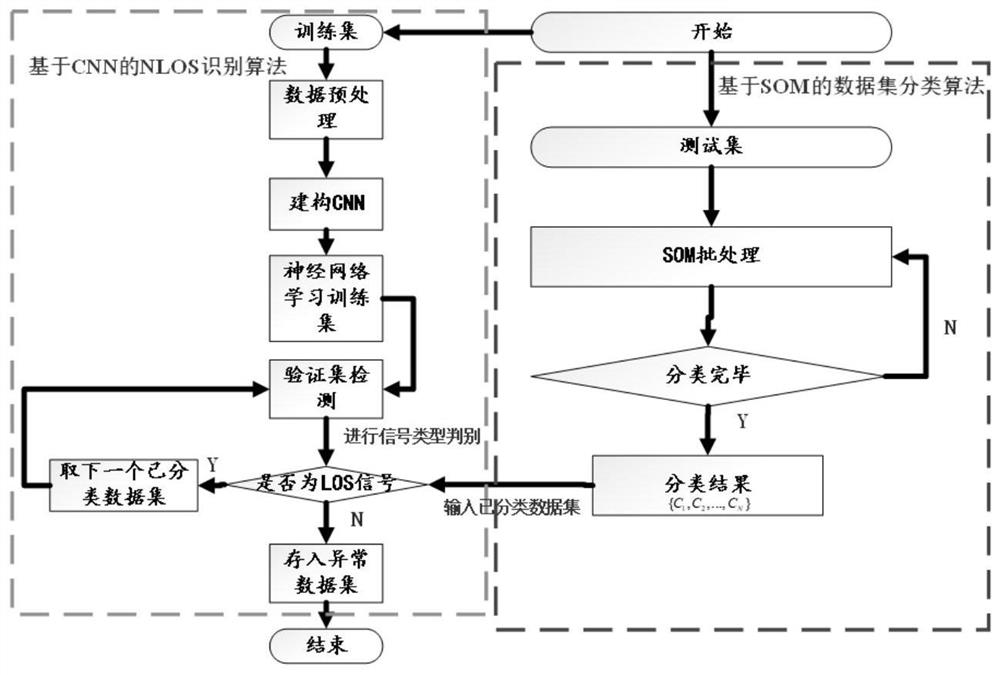
NLOS signal identification method and system
ActiveCN114742102AImprove accuracyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setAlgorithm
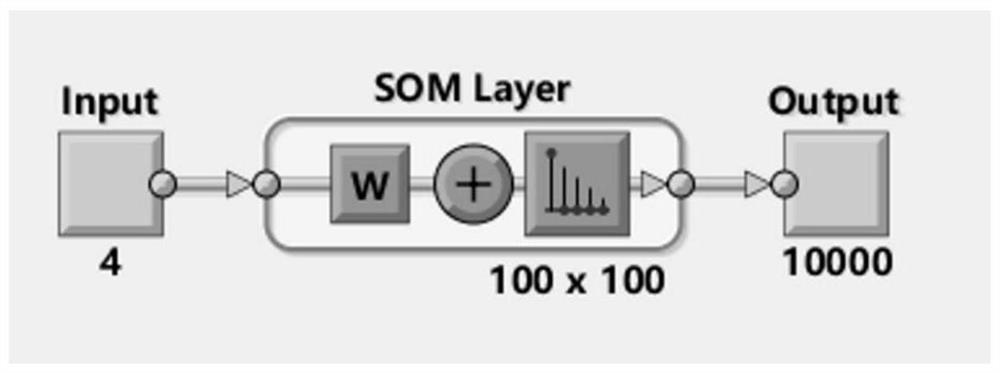
The invention discloses an NLOS signal identification method and system, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the classification of a large amount of data sets through a self-organizing mapping algorithm SOM, and carrying out the recognition training and signal identification through a CNN, thereby accurately completing the identification of an NLOS signal. Wherein the data set for neural network training of the SOM comprises a non-line-of-sight transmission signal NLOS data set, a line-of-sight transmission signal LOS data set and an NLOS-LOS data set, and the NLOS-LOS data set comprises NLOS-LOS data subsets with different initial values and sample numbers, so that the classification precision of neural network training of the SOM can be higher.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Estimation and improvement for reliability and accuracy of position hunting method by means of radio chaining les factor
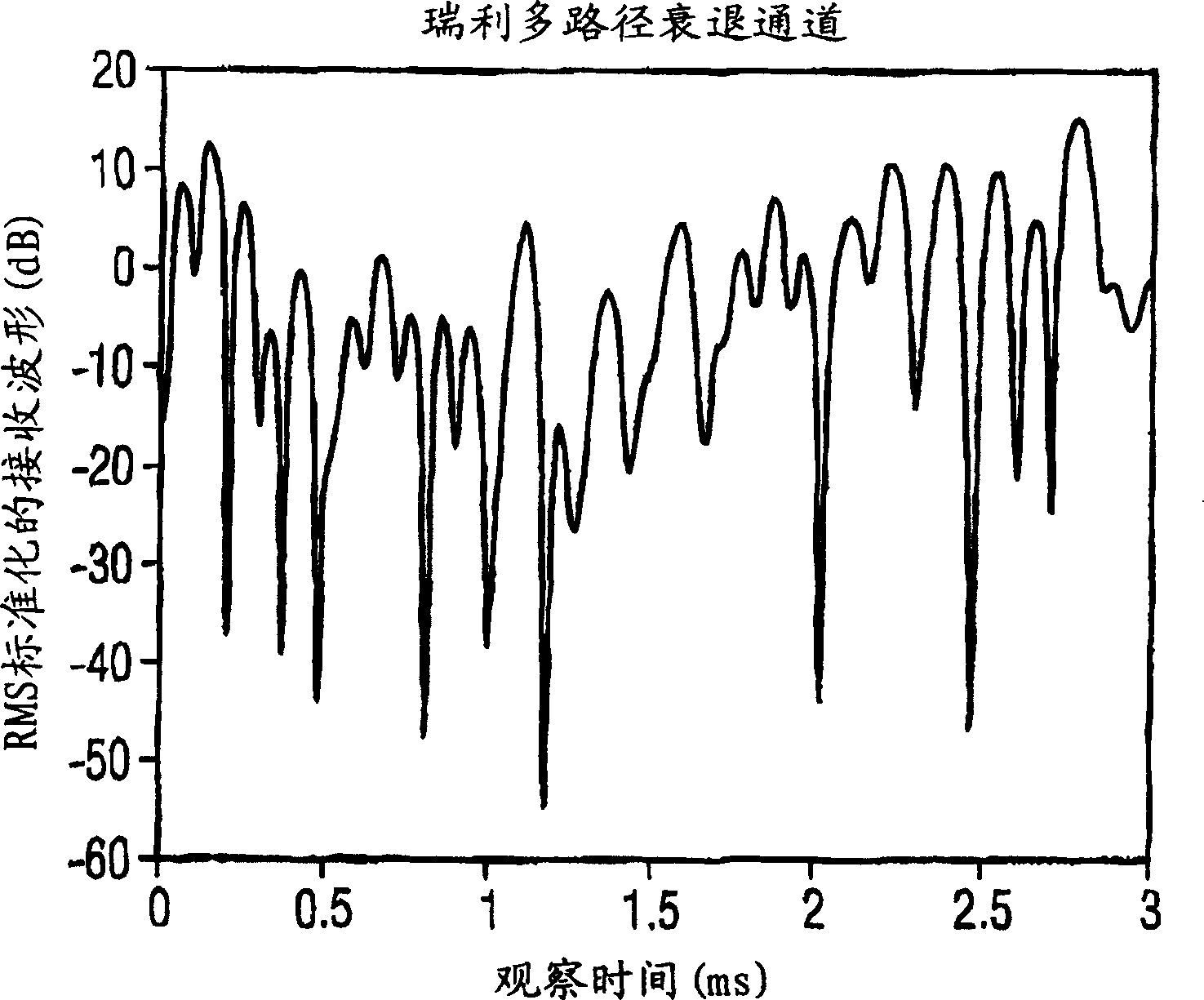
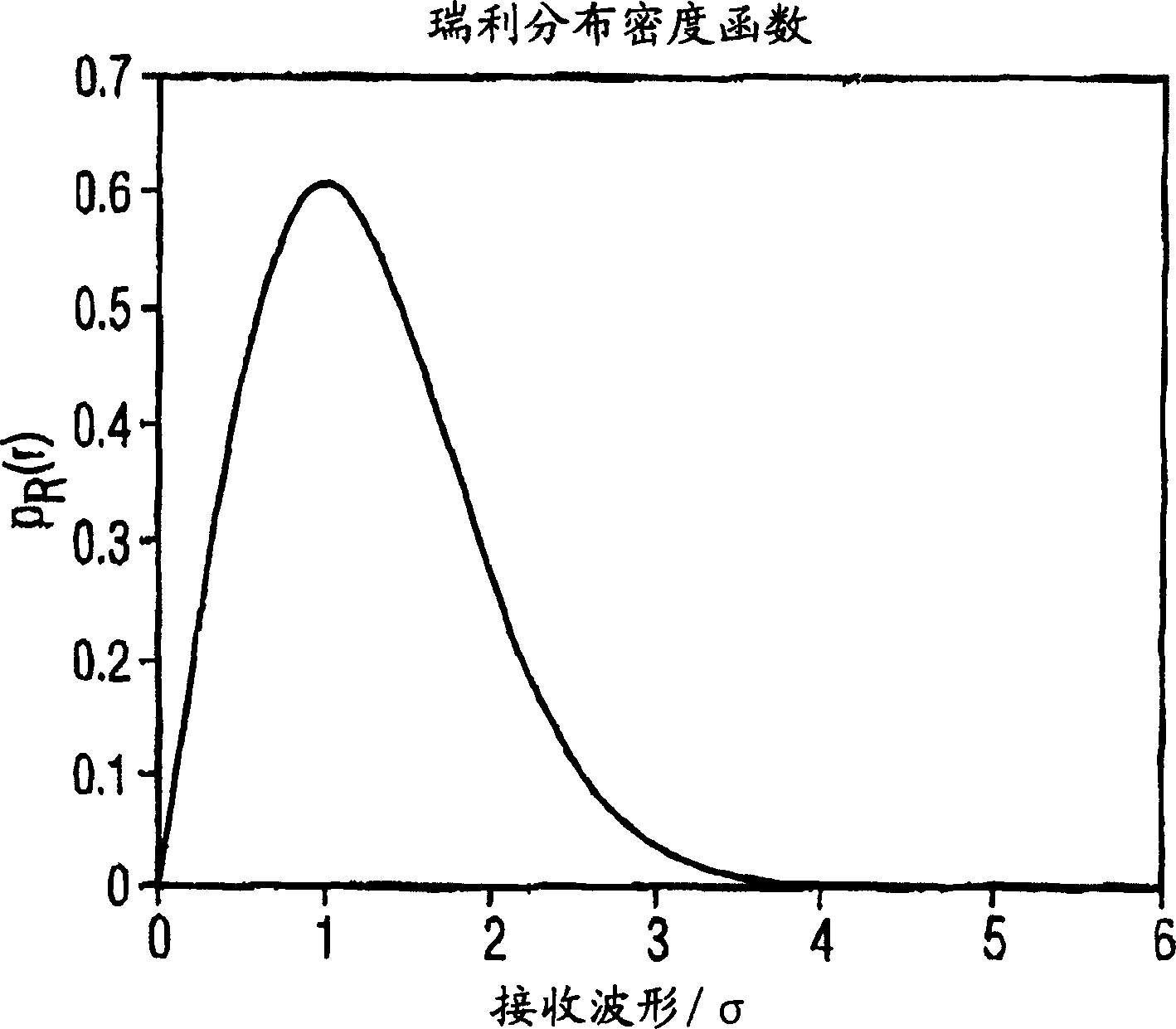
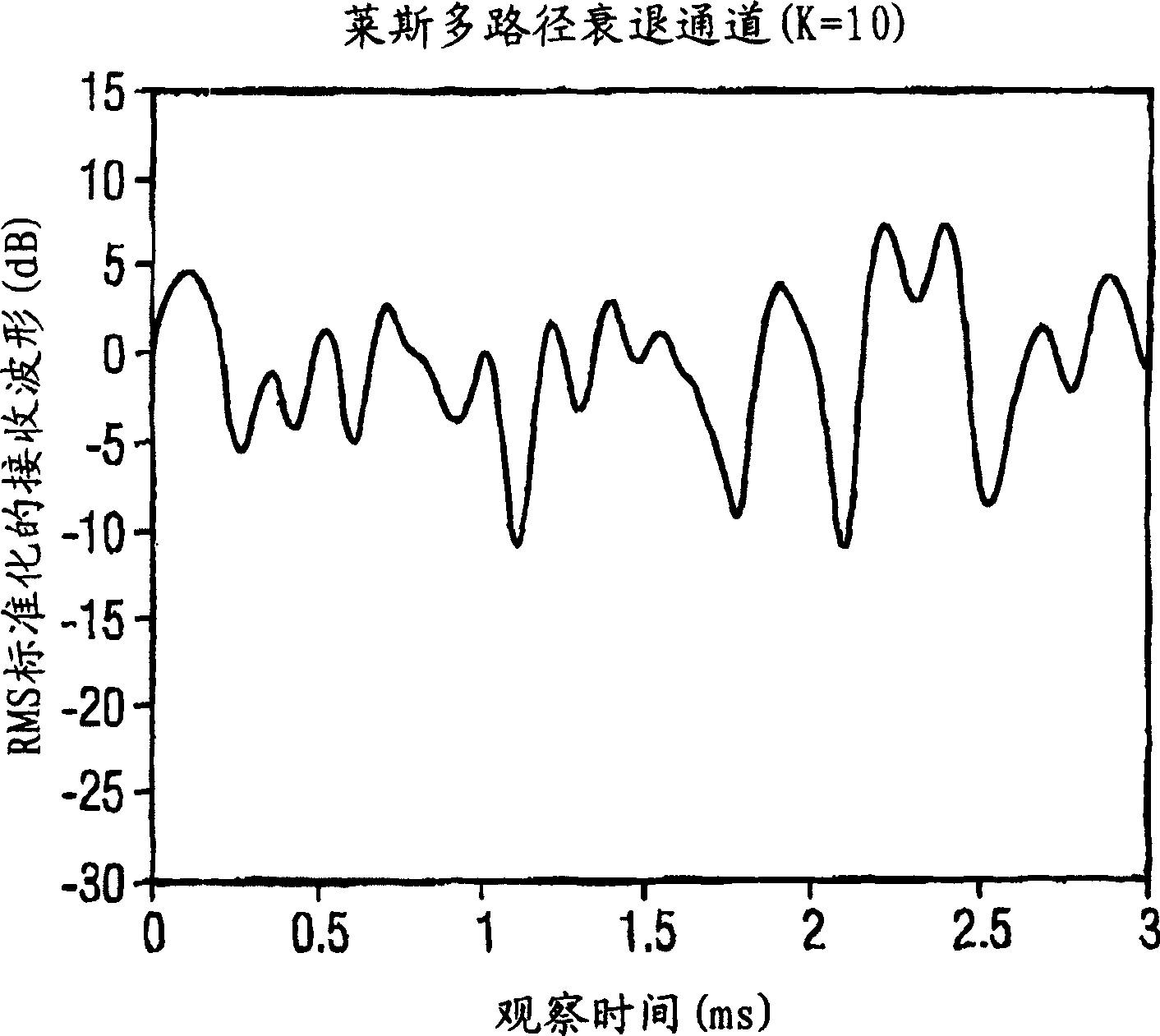
In order to improve the reliability and accuracy of a position finding method of a GPS method, the quality of a wireless link for the position finding method is determined by evaluating a parameter, in particular the Rice factor of the amplitude distribution density, which is represented by The ratio of the signal strength transmitted over a line-of-sight path to the signal strength transmitted over a non-line-of-sight path.
Owner:INTEL MOBILE COMM GMBH
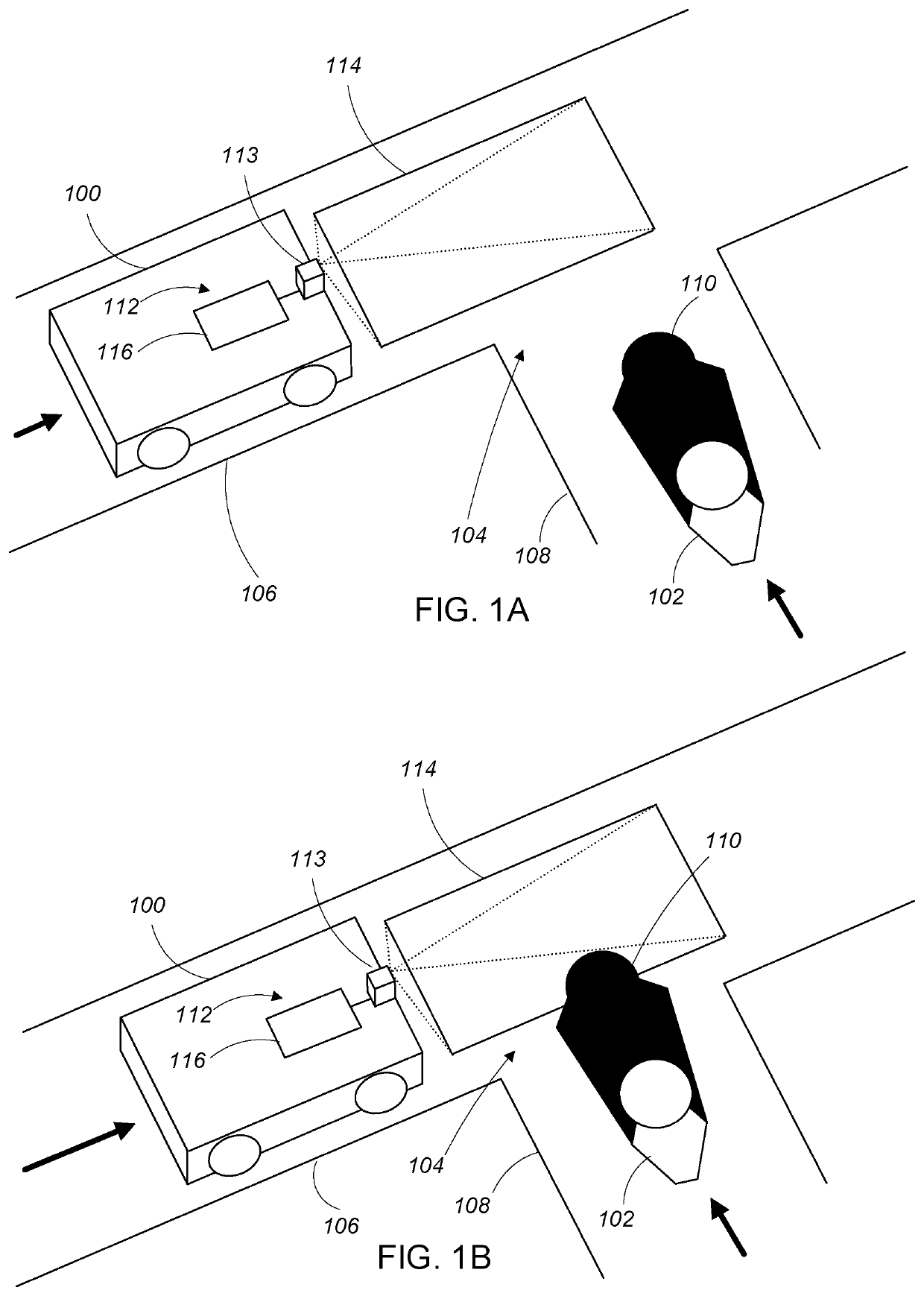
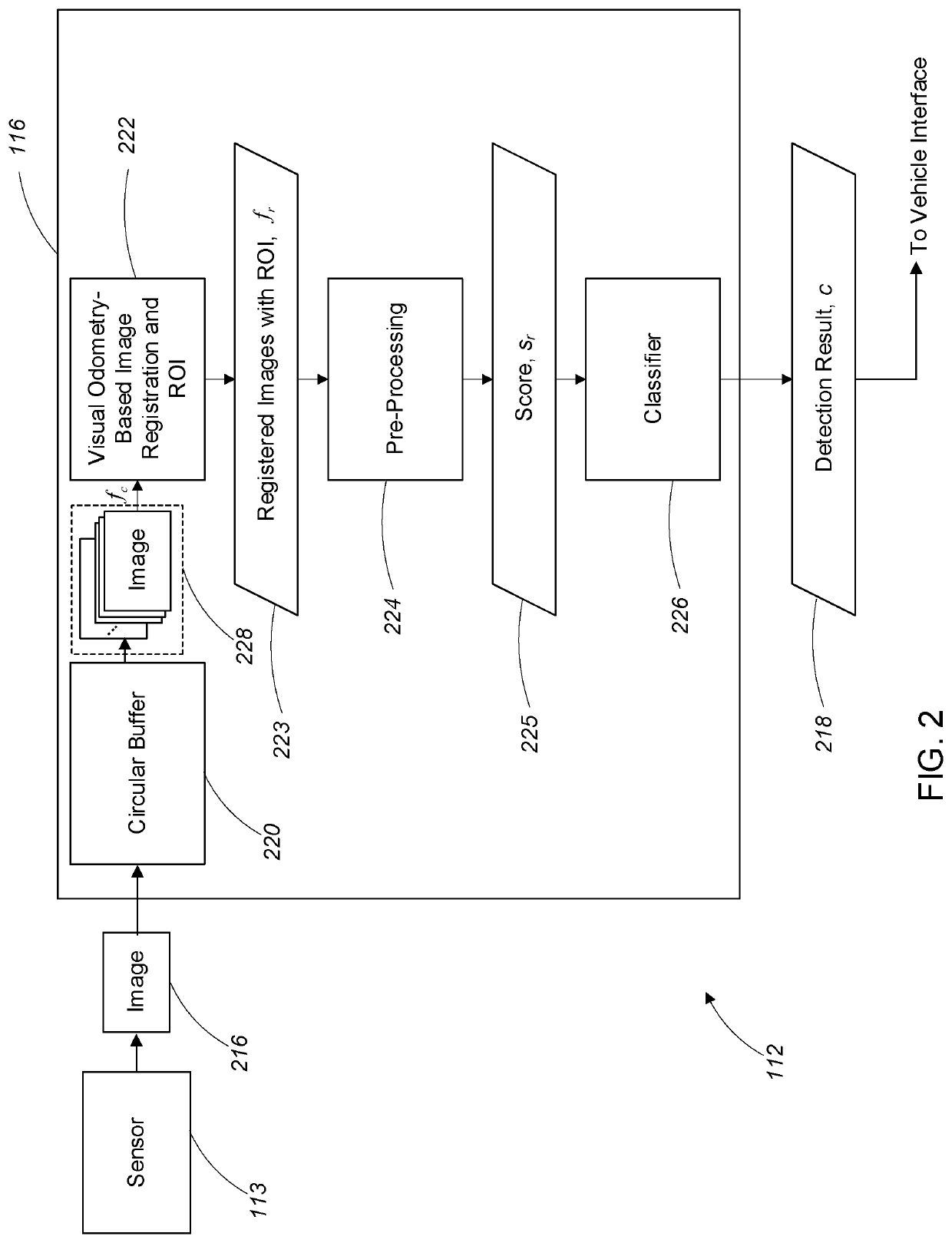
Non-line of sight obstacle detection
PendingUS20210049382A1Improve securityEnhanced Situational AwarenessImage enhancementImage analysisIlluminanceComputer graphics (images)
An object detection method includes receiving sensor data including a number of images associated with a sensor region as the actor traverses an environment, the plurality of images characterizing changes of illumination in the sensor region over time, the sensor region including a region to be traversed by the actor in the future, processing the plurality of images determine a change of illumination in sensor the region over time. The processing includes registering the plurality of images to a common coordinate system based at least in part on odometry data characterizing the actor's traversal of the environment, determining the change of illumination in the sensor region over time based on the registered plurality of images. The method further includes determining an object detection result based at least in part on the change of illumination in the sensor region over time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
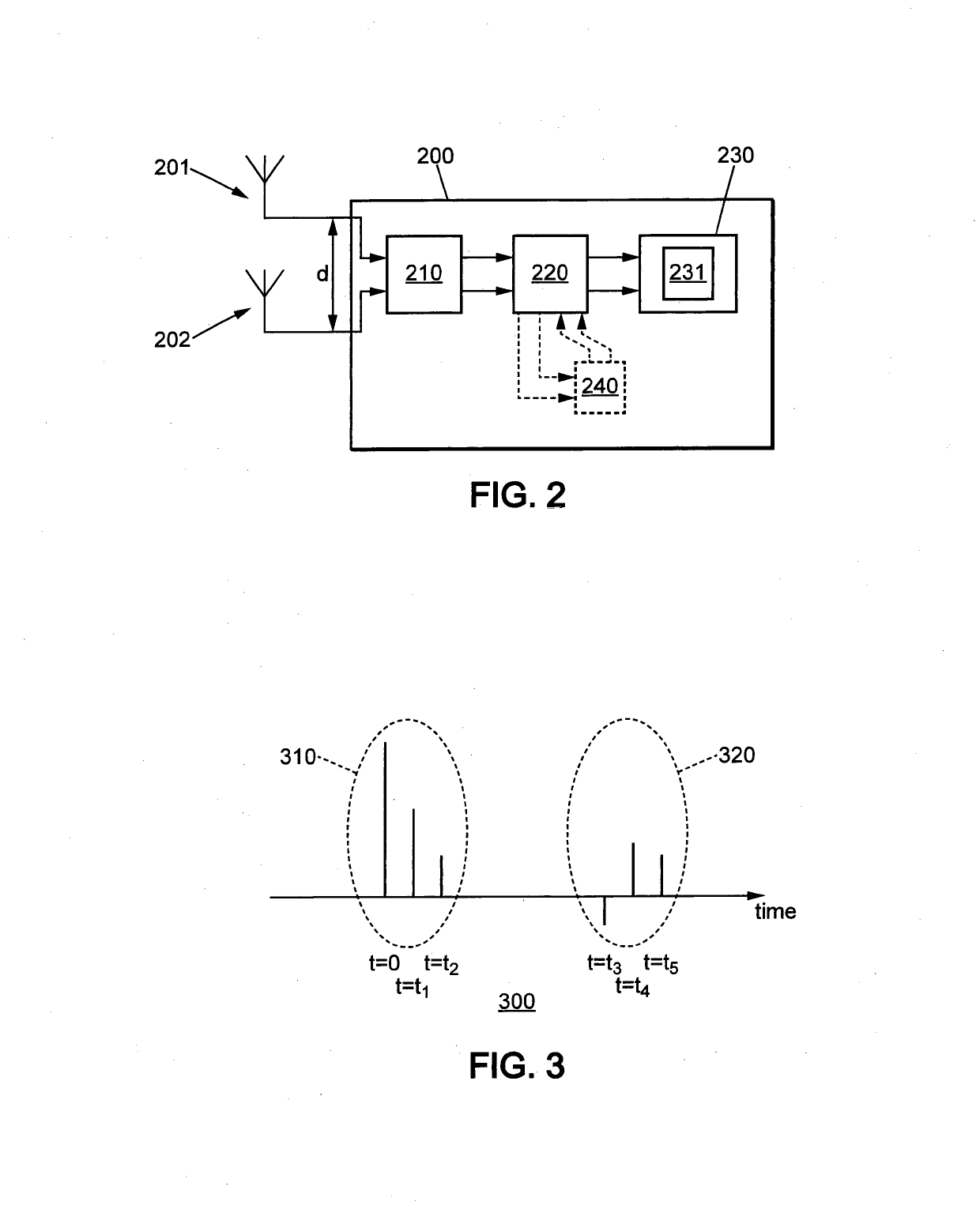
Apparatus for identifying line of sight and non-line of sight
InactiveUS20210409132A1Particular environment based servicesPosition fixationTelecommunicationsMultipath component
Embodiments include apparatuses and methods of identifying line of sight, LOS, and non-line of sight, NLOS, conditions in a multipath channel of a vehicular communication system. It is proposed to equip the receiving node with a dual antenna receiver. Then the proposed solution uses the first cluster of multipath components of channel estimates measured on the two antennas to derive the LOS / NLOS channel conditions based on hypothesis testing.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and system for navigating a mobile platform in an environment
ActiveUS20220097730A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsEngineeringInformation processor
Methods and systems are provided for navigating a mobile platform in an environment. A processor obtains information about an object in the environment, obtains information about a first satellite, and estimates a probability indicator for a non-line of sight signal transmission between a current satellite location of the first satellite and a current location of the mobile platform using the information about the first satellite and the information about the object. The processor further determines a discrepancy indicator using a movement information of the mobile platform and a movement information of the first satellite such that a weighting indicator can be determined using the estimated probability indicator and the determined discrepancy indicator. The processor then assigns a weighting indicator to a satellite signal transmitted from the first satellite in order to provide a first weighted signal for navigating the mobile platform.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
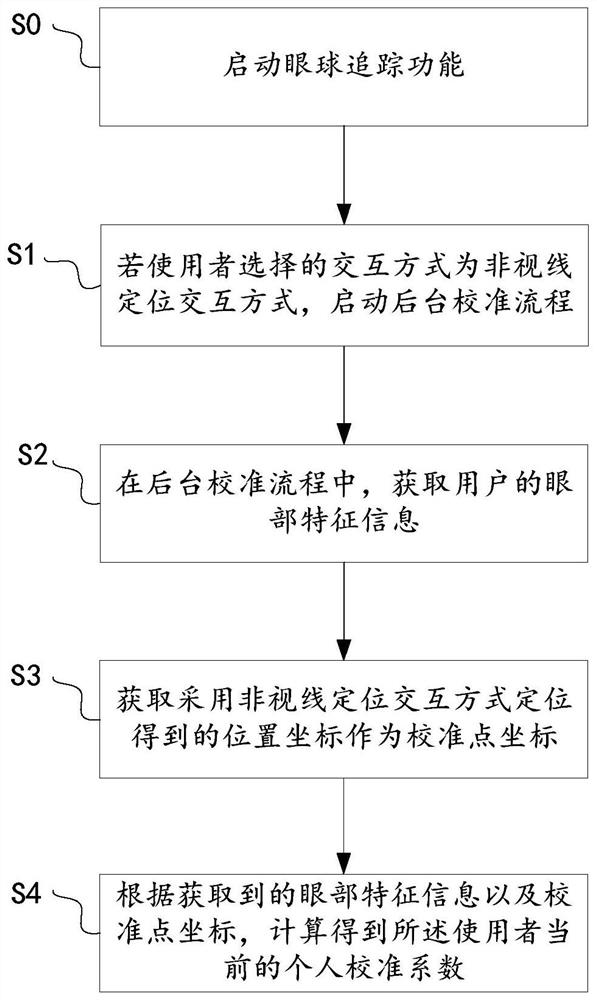
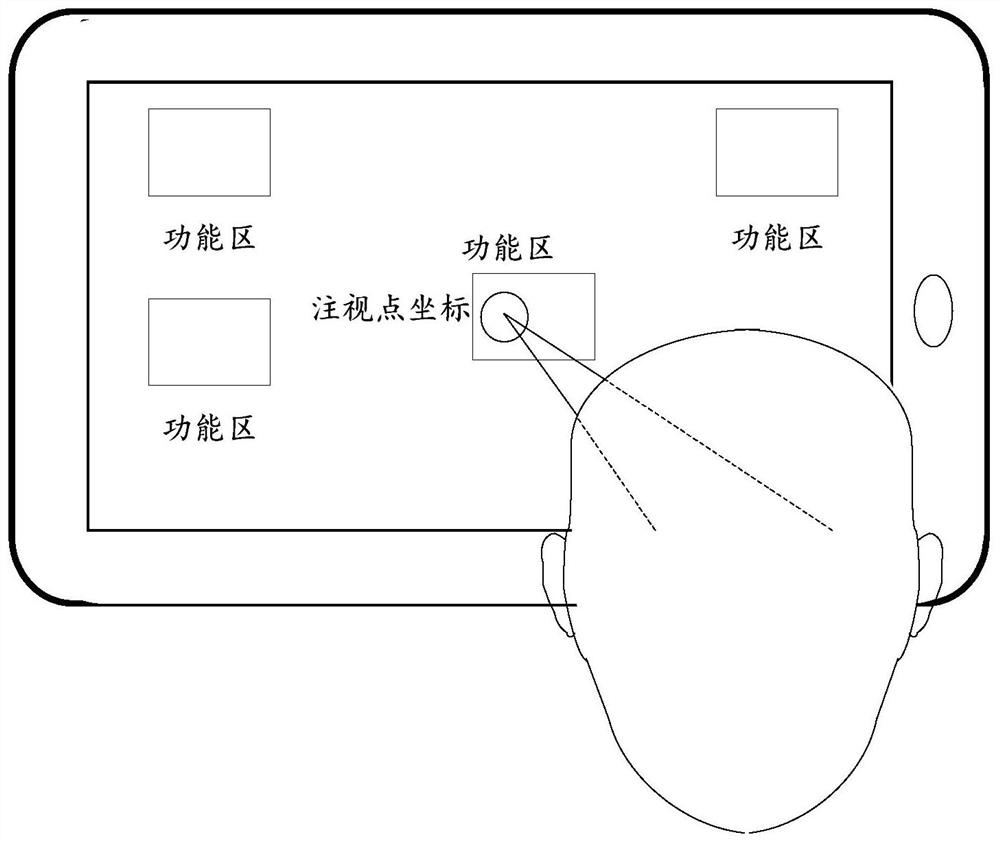
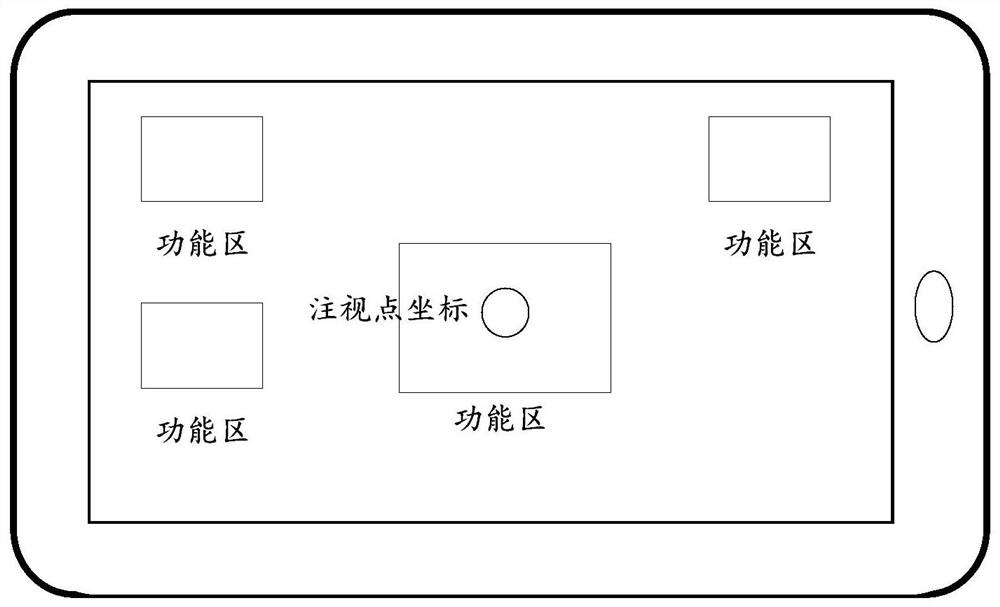
Eyeball tracking calibration method and device
PendingCN113495613AImprove user experienceReduce calibration timeInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an eyeball tracking calibration method and an eyeball tracking calibration device, which are used for completing calibration in a scene applying sight line positioning interaction and do not need an independent calibration link. The method comprises the steps: in one-time interaction operation, if a user selects a non-sight-line positioning interaction mode, starting a background calibration process; in the background calibration process, acquiring eye feature information of a user; acquiring a position coordinate obtained by positioning in a non-line-of-sight positioning interaction mode as a calibration point coordinate; according to the obtained eye feature information and the calibration point coordinates, obtaining the current personal calibration coefficient of the user through calculation. Therefore, in the embodiment of the invention, if the user selects the non-line-of-sight positioning interaction mode for positioning, the background calibration process is started at the same time, and the position coordinates obtained by positioning in the non-line-of-sight positioning interaction mode are used as the calibration point coordinates in the background calibration process to calculate the personal calibration coefficient. According to the embodiment of the invention, the background calibration process is hidden for the user, and the user does not need to exit from the current scene.
Owner:BEIJING 7INVENSUN TECH
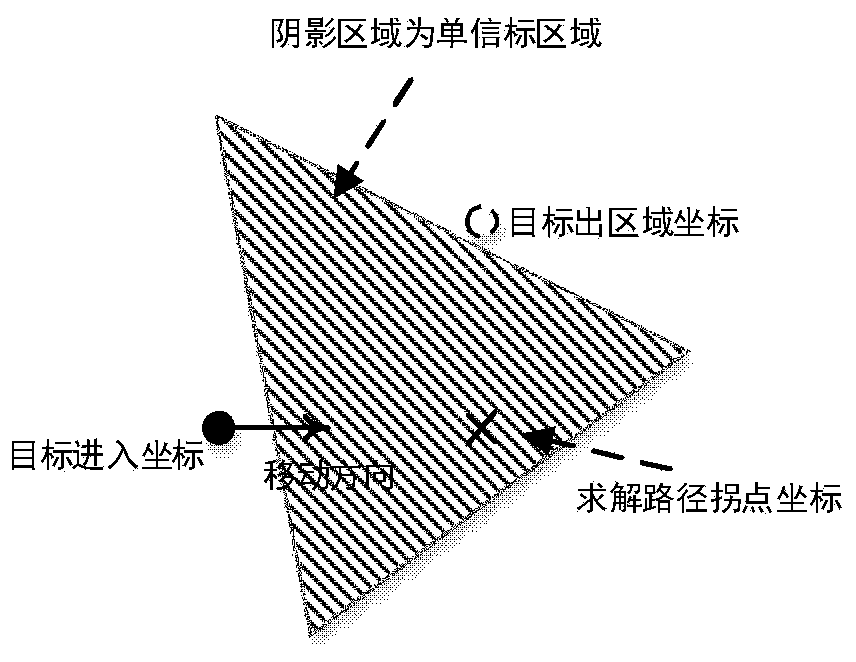
High-precision positioning method for ultra-wideband non-line-of-sight transmission in complex environment
ActiveCN111190139AImprove robustnessLow costPosition fixationWireless communicationUltra-widebandPositioning system
The invention discloses a high-precision positioning method for ultra-wideband non-line-of-sight transmission in a complex environment. The method comprises the steps of: calculating the speed and direction of a target by utilizing a high-precision positioning result of an ultra-wideband algorithm under a line-of-sight transmission condition and employing an ultra-wideband-based indoor positioningsystem using a signal flight time algorithm for distance measurement; when the target enters an area which cannot be positioned by the ultra-wideband for the first time, calculating an entering coordinate, a walking-out coordinate and a path of the target in the area; when the target enters the same area which cannot be positioned by ultra-wideband for the second time and later, calculating an entering coordinate, a walking-out coordinate and a path in the area, and calculating an mean value so as to improve the accuracy; and completing the positioning of the target according to the obtainedspeed and direction of the target and the walking path in the area that cannot be positioned by ultra-wideband. By applying the method provided by the invention, the number of the beacon nodes capableof communicating with a label can be possibly less than 3 under the condition of non-line-of-sight transmission, and the positioning can still be completed by applying the method provided by the invention, so that the positioning robustness is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method and device for selecting sensor of wireless sensor network based on TDOA (time difference of arrival) positioning under non-line-of-sight condition
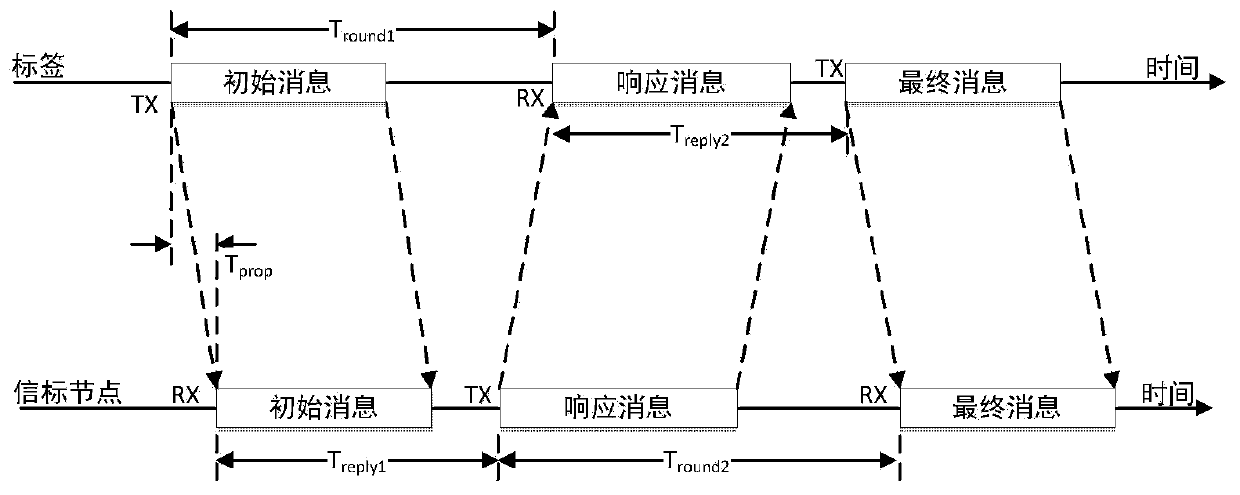
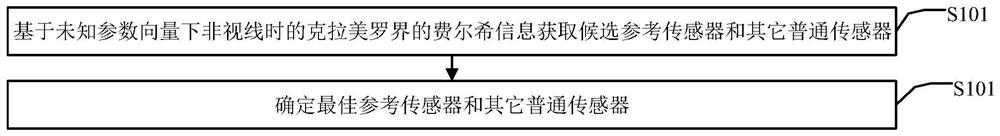
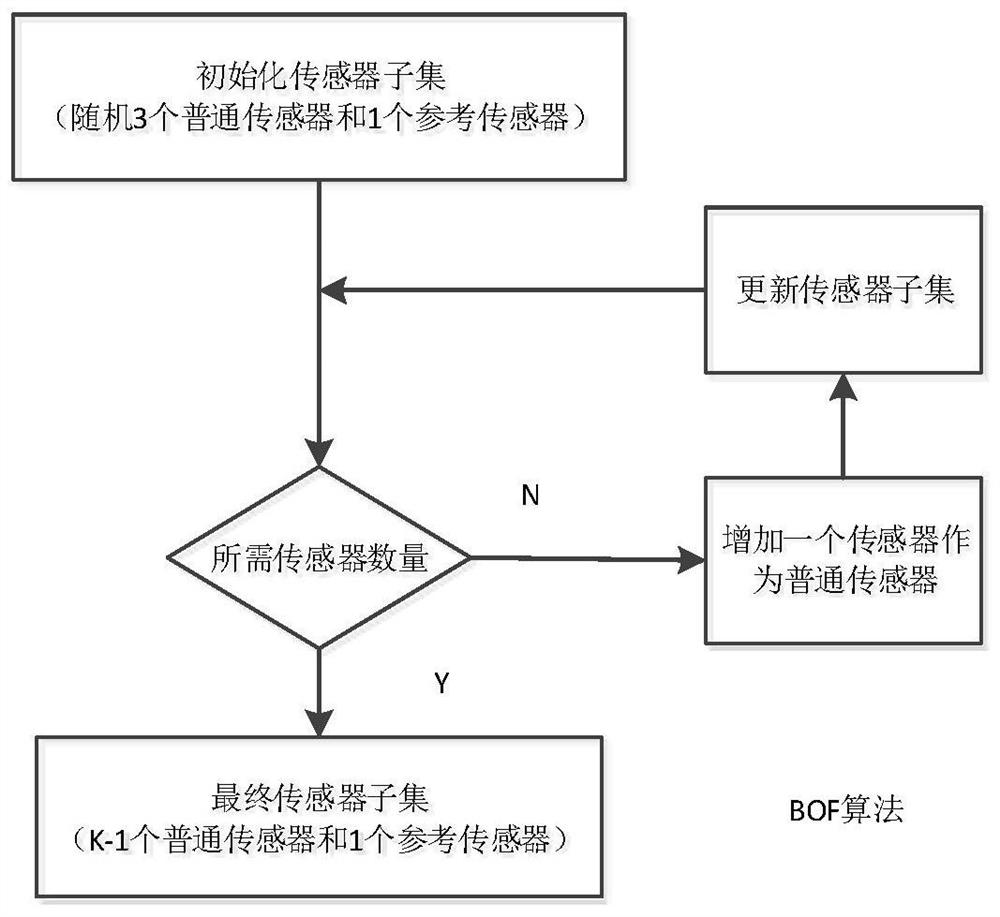
InactiveCN113010837AHigh positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesComplex mathematical operationsLine sensorEngineering
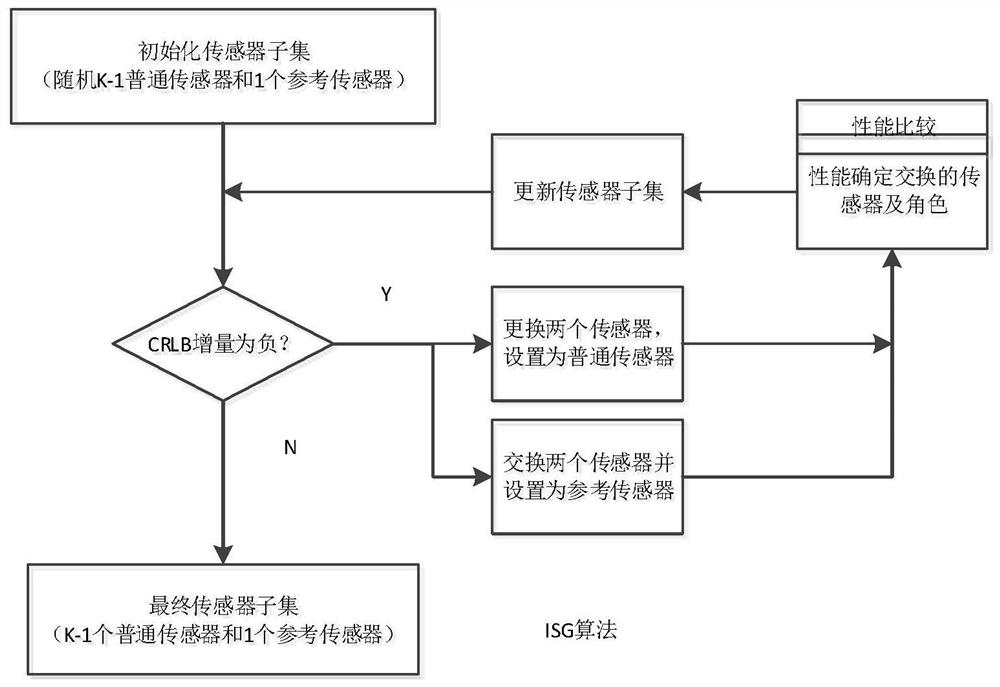
The invention discloses a method and a device for selecting a wireless sensor under a non-line-of-sight condition based on TDOA (Time Difference of Arrival) positioning. The method comprises the steps: selecting two independent Boolean vectors, and determining a reference sensor and other sensors at the same time; and a Cramer-Rao bound (CRLB) of TDOA positioning under a non-line-of-sight (NLOS) condition with an unknown prior statistical probability and a non-line-of-sight (NLOS) condition with a known prior statistical probability is provided respectively. After two independent Boolean vectors are selected, an analysis reference algorithm based on a convex relaxation technology is provided for selection of a wireless sensor, so that the Cramer-Rao bound (CRLB) is minimum; and a best choice fill (BOF) algorithm and an iterative exchange greedy (ISG) algorithm are combined. Compared with an existing sensor selection method, positioning errors and algorithm complexity are reduced.
Owner:浙江毅星科技有限公司
Control forwarding techniques for wireless communications
PendingCN113302973ANetwork traffic/resource managementParticular environment based servicesCommunications systemUser equipment
User equipment (UEs) within a sidelink communications system may employ control forwarding techniques. For example, a UE may piggyback resource reservation information received from other UEs when broadcasting its own resource reservation. A UE that may be in line of sight (LOS) with two other UEs that themselves are in a non-line of sight (NLOS) situation and may include resource reservation information associated with other UEs when broadcasting the control information. For example, when forwarding control information, a UE may identify additional resources available in a transmission interval, and may convey neighbor control information (e.g., known resource reservations of other UEs in the sidelink communications system) using the additional resources. In some cases, the piggybacked resource reservation information associated with the other UEs may be selected based on the amount of additional resources in the transmission interval, a priority of known resource reservation information, etc.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
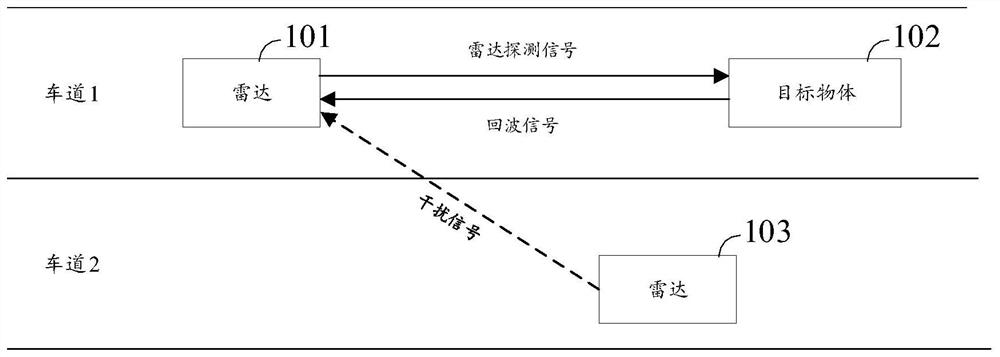
Detection method, detection device, detection system and radar
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and system for navigating mobile platform in environment
PendingCN114279454AInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsEngineeringComputer science
Methods and systems are provided for navigating a mobile platform in an environment. The processor obtains information about an object in the environment, obtains information about the first satellite, and estimates a probability indicator of non-line-of-sight signal transmission between a current satellite position of the first satellite and a current position of the mobile platform using the information about the first satellite and the information about the object. The processor also determines a difference indicator using the movement information of the mobile platform and the movement information of the first satellite such that a weighted indicator can be determined using the estimated probability indicator and the determined difference indicator. The processor then assigns the weighting indicator to a satellite signal transmitted from the first satellite to provide a first weighted signal for navigating the mobile platform.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
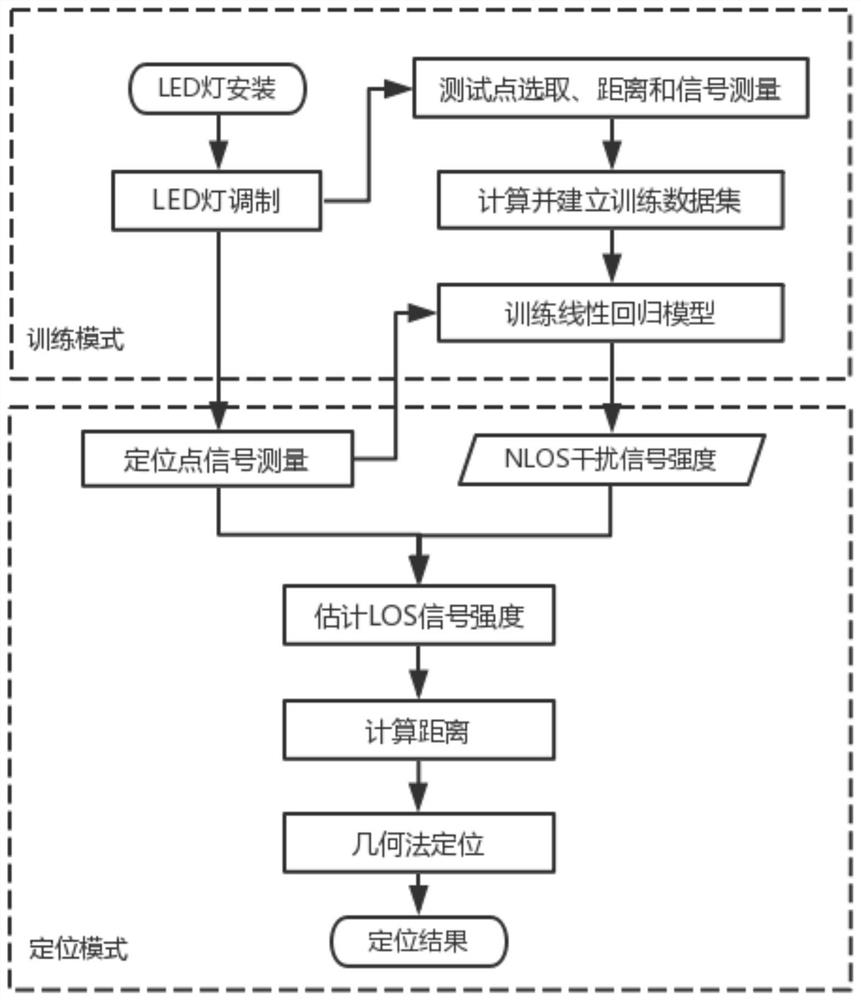
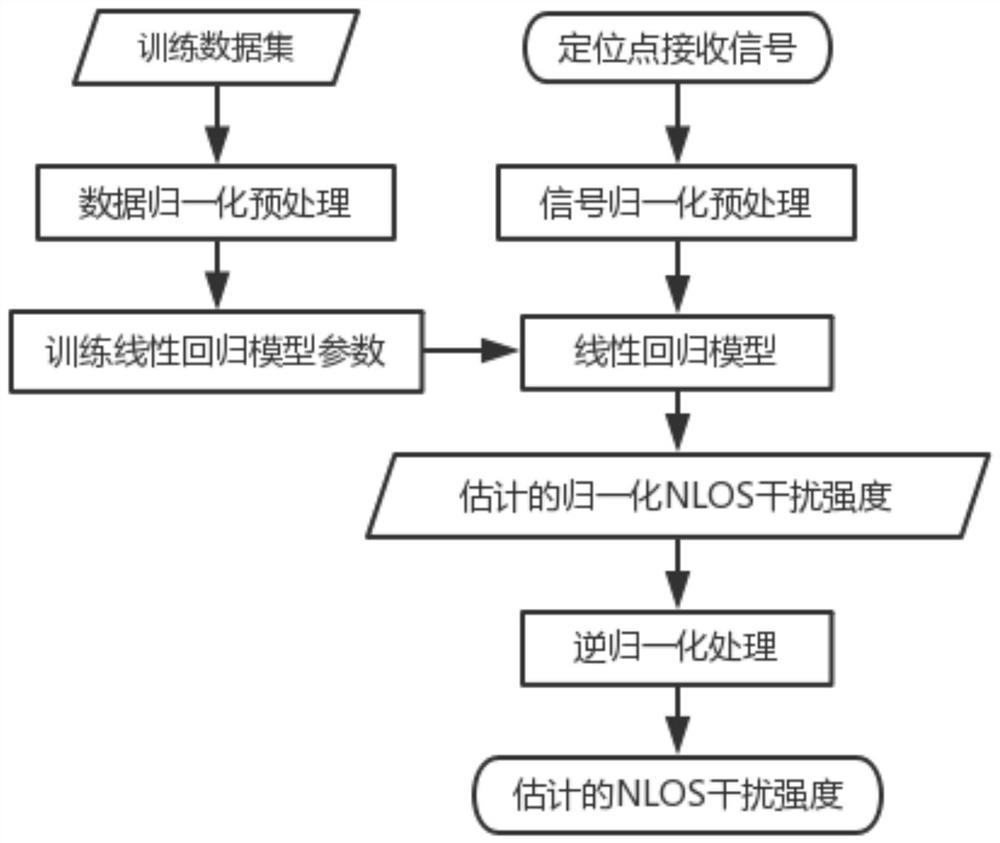
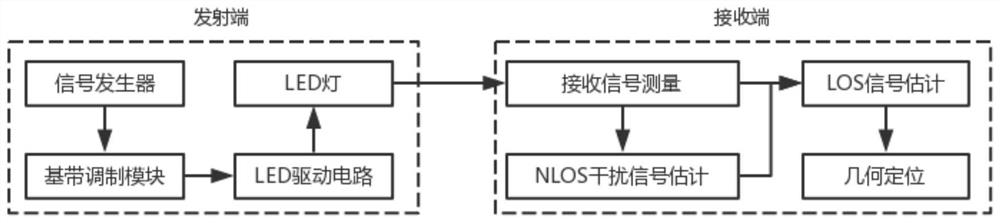
Anti-NLOS interference visible light positioning method and system based on linear regression model
ActiveCN111664853ALower requirementEliminate positioning effectsNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationEngineeringLinear regression
The invention discloses an anti-NLOS interference visible light positioning method and system based on a linear regression model. The anti-NLOS interference visible light positioning system comprisesa transmitting module, a receiving module, a training module and a positioning module. The transmitting module comprises a plurality of LED lamps, a signal generator, a baseband modulation module anda driving circuit; each LED lamp is provided with an ID; the receiving module comprises an optical filter, a photoelectric detector, an amplifier, an analog-to-digital converter and a microprocessor,and is used for receiving signals of different LED lamps in different time slices in one period and extracting the intensity of the received signals. According to the method, non-line-of-sight transmission (NLOS) interference is removed by adopting a machine learning method, and then, positioning is realized by adopting a geometric positioning method, so that the influence of the NLOS interferenceon positioning can be eliminated, the positioning precision is improved, and the requirement of an existing fingerprint positioning method based on machine learning on positioning data is also reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Method for estimating location of terminal in wireless communication system and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS11346931B2Accurate estimateElectromagnetic wave reradiationNeural learning methodsTelecommunicationsCommunications system
A method of estimating, by a user equipment (UE), a location of the UE in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The method includes measuring distances between a plurality of anchor nodes and the UE; creating a first matrix using values of the measured distances; creating a third matrix based on the first matrix and a second matrix, the second matrix being a centering matrix; and estimating the location of the UE based on a result of comparing a first value generated based on eigenvalues of the third matrix with a second value that is a pre-defined reference value, wherein when the first value is greater than the second value, all the measured distances are distances measured through a line of sight (LOS) path, wherein when the first value is less than the second value, some of the measured distances are distances measured through a non-line of sight (NLOS) path.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
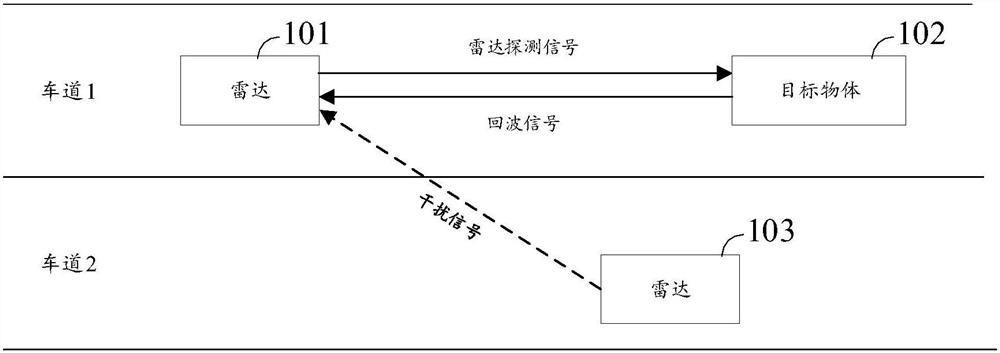
Detection method, detection device, detection system and radar
The embodiment of the invention provides a detection method, a detection device, a detection system and a radar, and the method comprises the steps: monitoring at least one signal from at least one direction, wherein the at least one signal comprises a first signal corresponding to a first direction; transmitting a second signal to a second direction, wherein the second signal is used for indicating the predicted interference time-frequency range; wherein the time-frequency range of the first signal and the time-frequency range of the second signal meet at least one of the following conditions: the frequency domain range of the first signal is a subset of the frequency domain range of the second signal; alternatively, the time domain range of the first signal is a subset of the time domain range of the second signal. The interference time-frequency range can be indicated to the second direction in the form of transmitting the second signal, so that the second detection device obtains the interference time-frequency range of a non-line-of-sight area, and the target detection accuracy of the second detection device is improved. The scheme can be further applied to the field of automatic driving, intelligent driving or unmanned driving, the interference avoidance capability of the vehicle is improved, and the driving safety of the vehicle is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
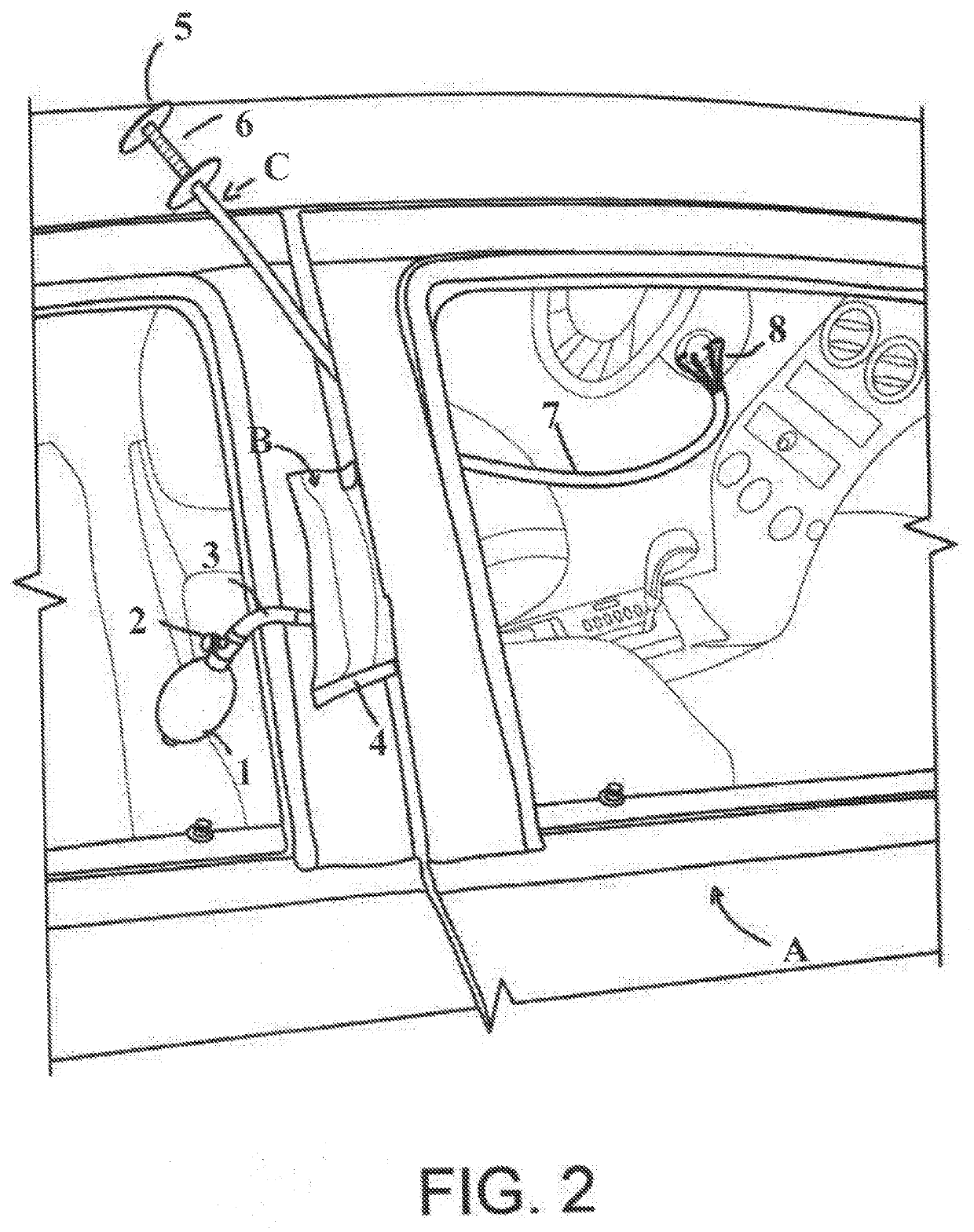
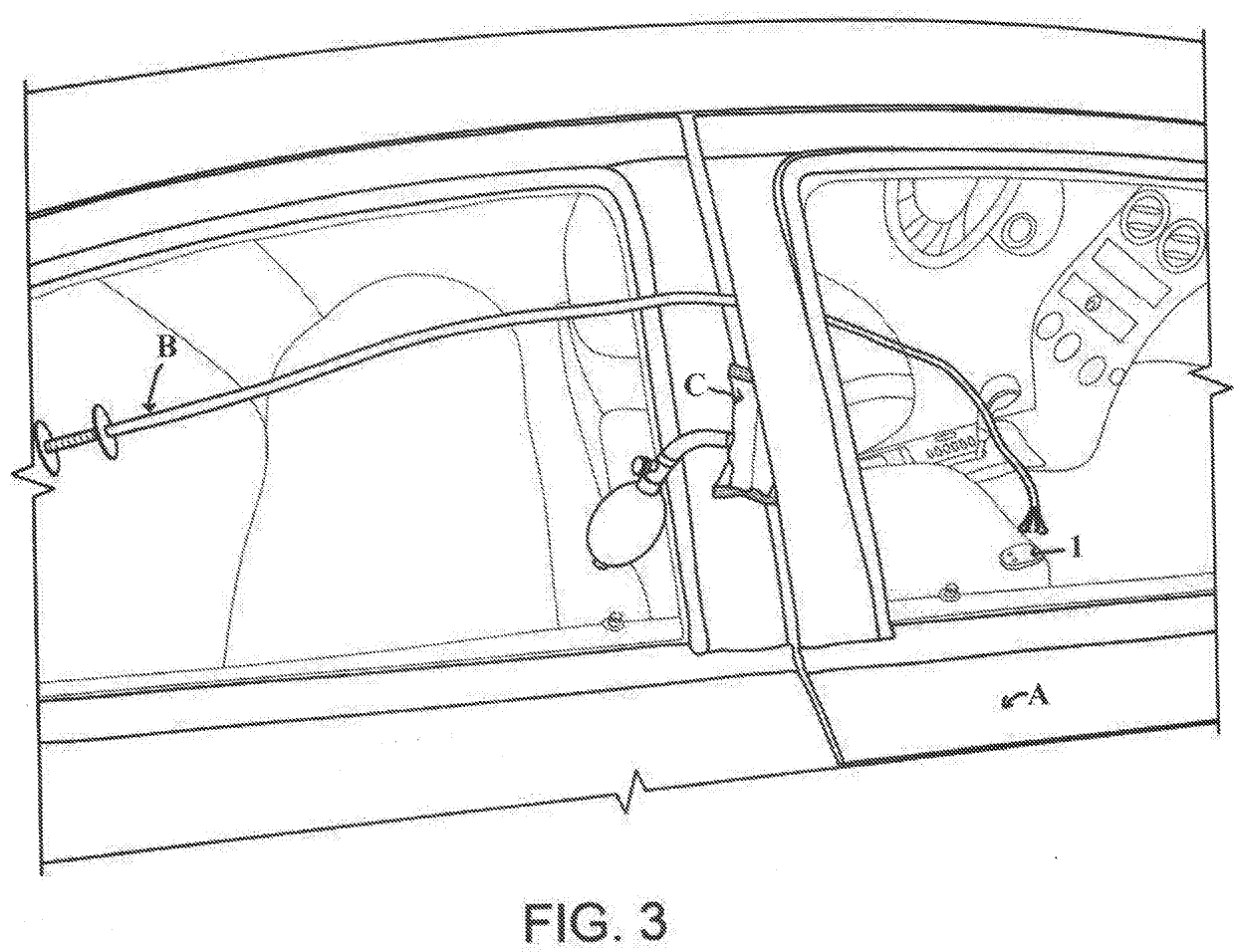
Form-able remote manipulation device
A form-able remote manipulation device comprised of an elongated form-able sheath and grasping distal end used in conjunction with an air wedge as a method for unlocking an automobile without causing damage to said automobile. The method of using an air wedge in conjunction with a form-able remote manipulation device which is infinitely position-able allows the end user to efficiently unlock a modern automobile that current tools will not allow. The grasping portion of this device may be forced outward or inward in order to grapple or release an object that the user wants to manipulate in order to unlock said automobile. Rotation of the device will cause the object in which it is grappled with to become rotated along with the device if rotated. This remote manipulation device may also include, but not limit to, a wired or wireless camera attachment, wired or wireless light attachment, permanent magnet attachment, or electric-magnet attachment, that may be used in a non line of sight or an obscured view application.
Owner:MORGAN NICHOLAS DUANE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com