Eyeball tracking calibration method and device
A calibration method and eye tracking technology, applied in the fields of instruments, electrical digital data processing, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve problems such as user inconvenience, improve user experience and save calibration time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
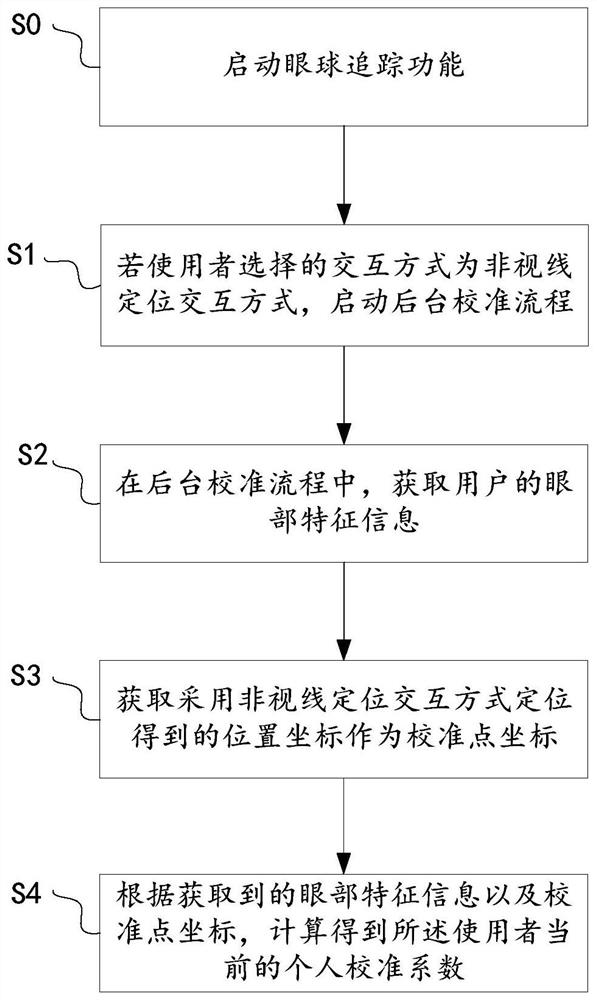
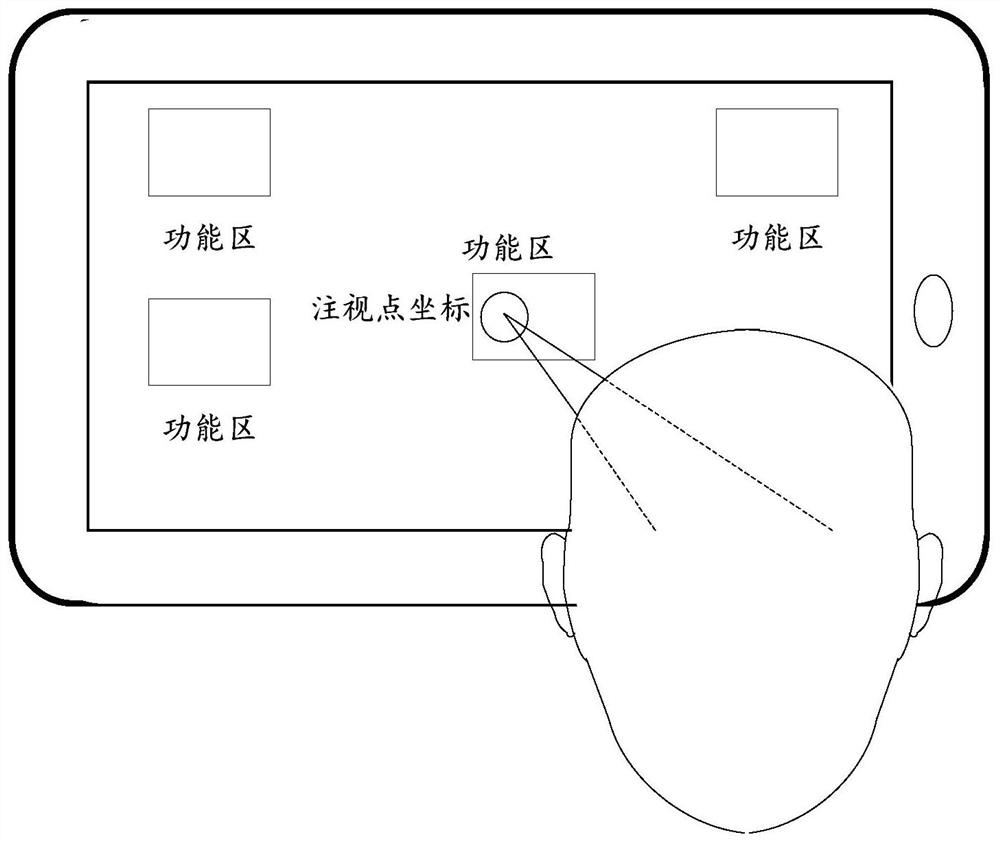
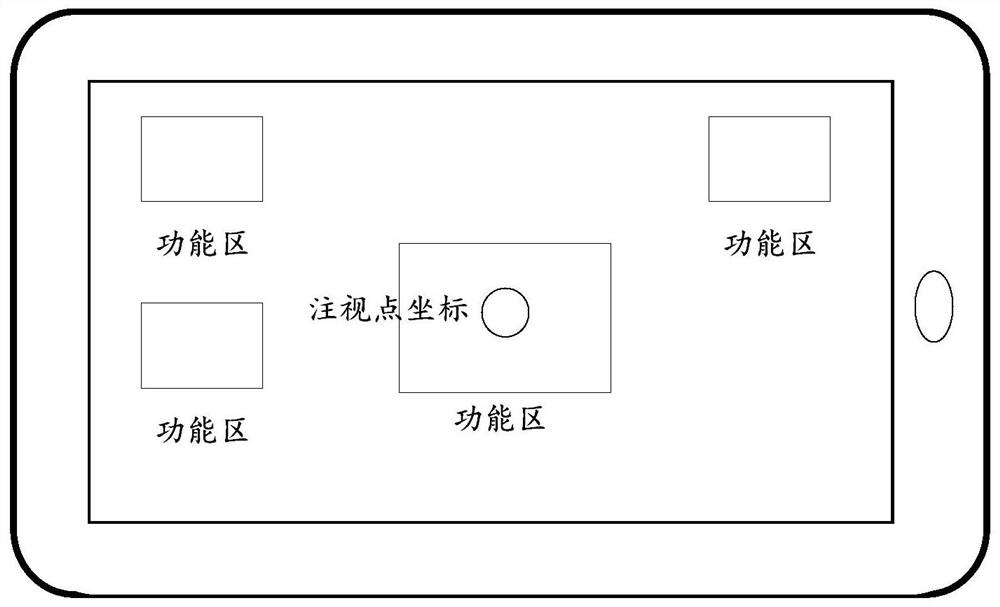
[0049] In order to solve the problems existing in the existing calibration method: if the user finds that the sight positioning is inaccurate in the scene where the sight positioning interaction is applied, or the relative position of the head-mounted display and the eyes changes due to adjustment of the position of the head-mounted display, etc., it is necessary to Exit scene recalibration issue.
[0050] In Embodiment 1 of the present application, an eye tracking calibration method is provided to complete calibration in a scene where gaze positioning interaction is applied, without requiring a separate calibration link.
[0051] See figure 1 , the eye tracking calibration method includes:
[0052] S0: Activate the eye tracking function.
[0053] In one example, the eye-tracking function of the gaze-locating device is turned on by default.
[0054] Of course, the eye tracking function can also be activated according to the user's operation.
[0055] S1: In an interactive ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] In general, eye tracking technologies have default calibration coefficients. The default calibration factor is the one most people use with higher accuracy.
[0076] Of course, due to individual differences such as the radius of the user's eyeball, using the default calibration coefficient may result in inaccurate positioning, which is also the reason for obtaining the personal calibration coefficient after calibration.
[0077] The definable target calibration coefficients include: system default calibration coefficients, or personal calibration coefficients associated with the user ID of the user.
[0078] At the very beginning, the target calibration coefficient is the system default calibration coefficient. After at least one background calibration, the target calibration coefficient is updated to the latest personal calibration coefficient.
[0079] This embodiment will introduce an exemplary flow of eye tracking calibration based on target calibration coefficient...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Embodiment 3 will introduce how to perform eye tracking calibration when the initial target user ID is not associated with a personal calibration coefficient, please refer to Figure 4 , which may include, for example:
[0119] S41: The target user identifier is not associated with a personal calibration coefficient, and the system default calibration coefficient is determined as the target calibration coefficient.
[0120] S42-S45 are similar to the aforementioned S31-S34, and will not be repeated here.
[0121] S46: Associating the calculated current personal calibration coefficient with the target user identifier.
[0122] S47: Use the calculated personal calibration coefficient to update the target calibration coefficient, and return to S41.
[0123] After using the non-line-of-sight positioning interaction device to locate, it will return to the line-of-sight positioning interaction mode again.
[0124] This embodiment can realize: when the user has not associat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com