Methods and apparatus for locating RFID tags
A technology of RFID tags and tags, applied in the directions of positioning, utilizing re-radiation, substation devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
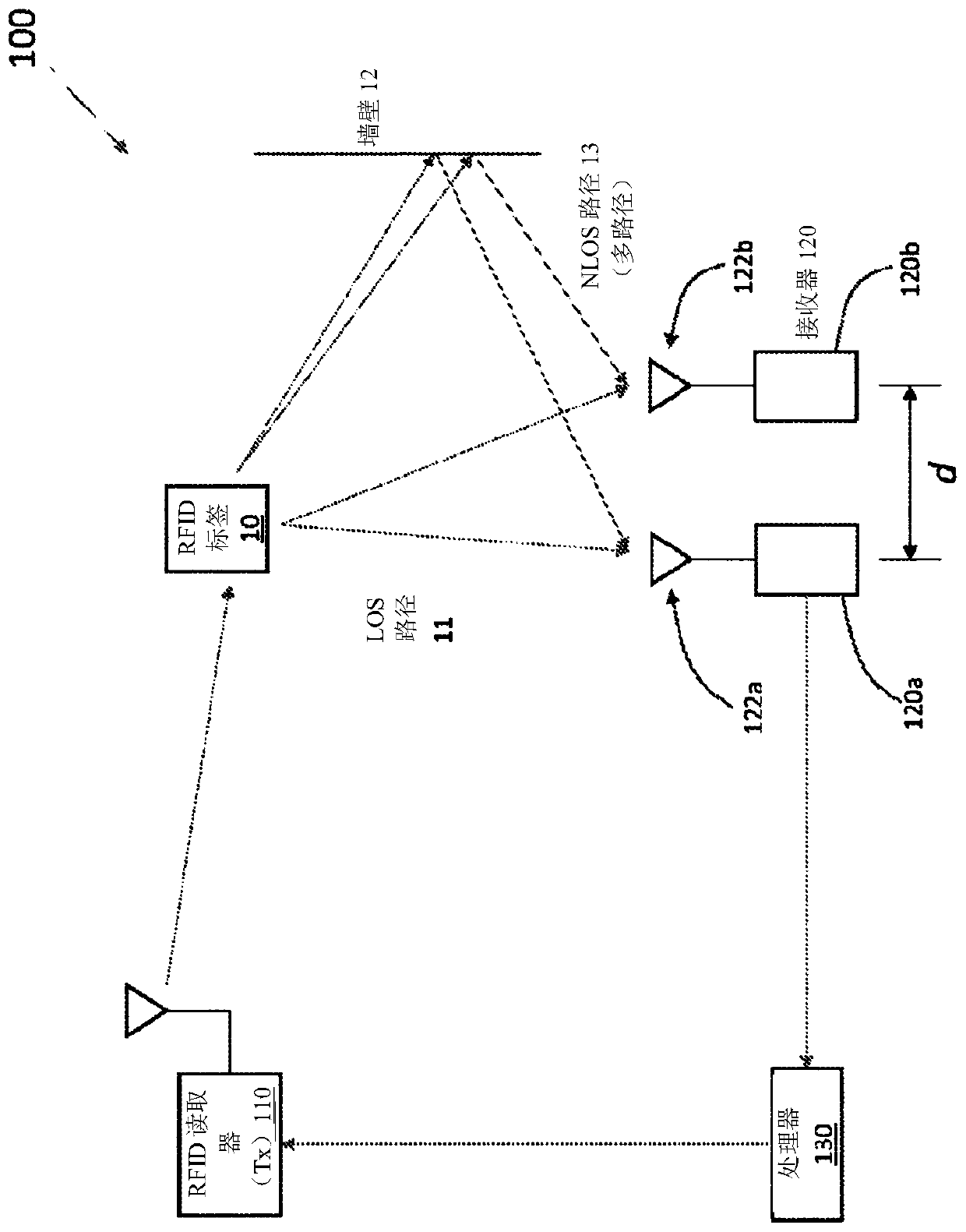
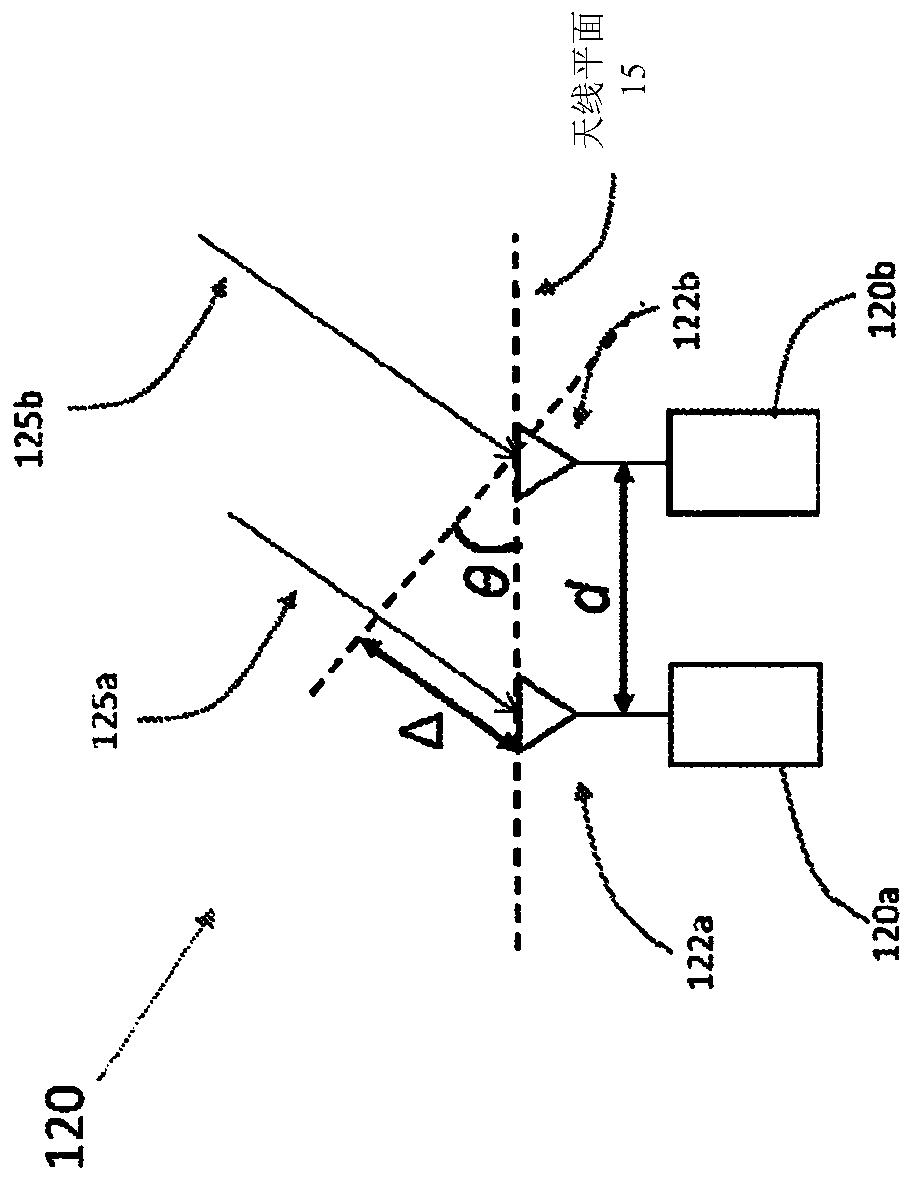
[0036] So far, RFID positioning technology has not lived up to expectations. Combined with computer vision technology, the RFID location technology of the present invention provides unprecedented speed and accuracy. In fact, it can be as much as 300 times more accurate than traditional RFID positioning technology. For example, the systems and methods disclosed below may be used to position an RFID tag within 50 cm, 40 cm, 30 cm, 25 cm, 20 cm, 15 cm, 10 cm, 5 cm, or 2.5 cm of its actual location. With this speed and accuracy, it can be used to track even the slightest movement of RFID-tagged items in real time. This level of speed and precision enables items to be found and restocked almost instantly, and to track interactions between RFID tags. For RFID tags on products in stores, this generates item-by-item data about customer interactions with products and enables autonomous checkout.
[0037] Unless physically incompatible, all techniques disclosed herein can be used wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com