Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "MRI diffusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for analyzing MRI diffusion data
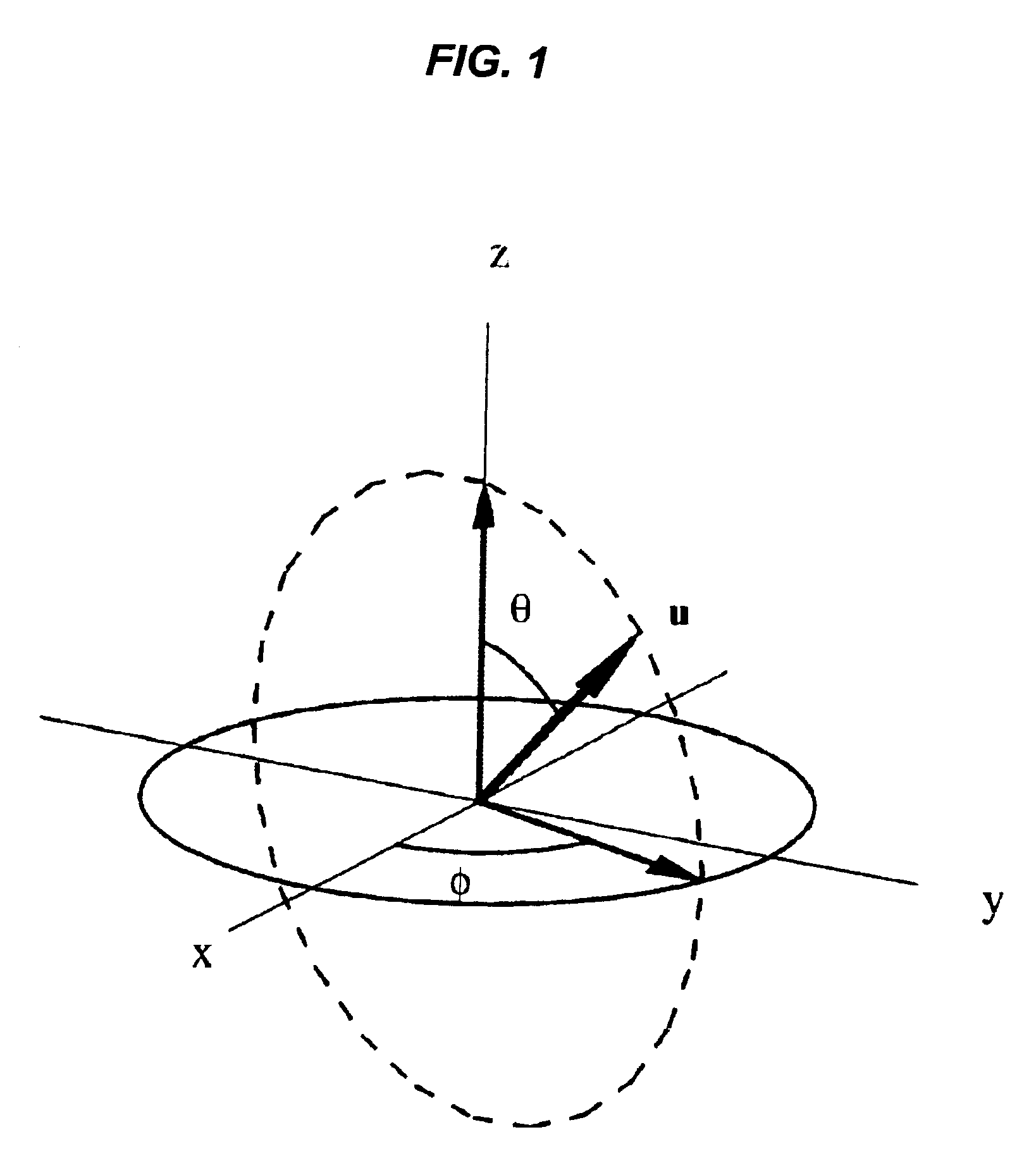
A new transform is disclosed, applying methods of group theory, with which the composition of a voxel of three channels comprising isotropic, single fiber and multiple fiber components can be determined, as well as the magnitude and orientation of the diffusion field. Asymmetries produced by experimental artifacts fall into channels distinct from the fiber channels, allowing their separation and a subsequent reduction in noise from the reconstructed fibers.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
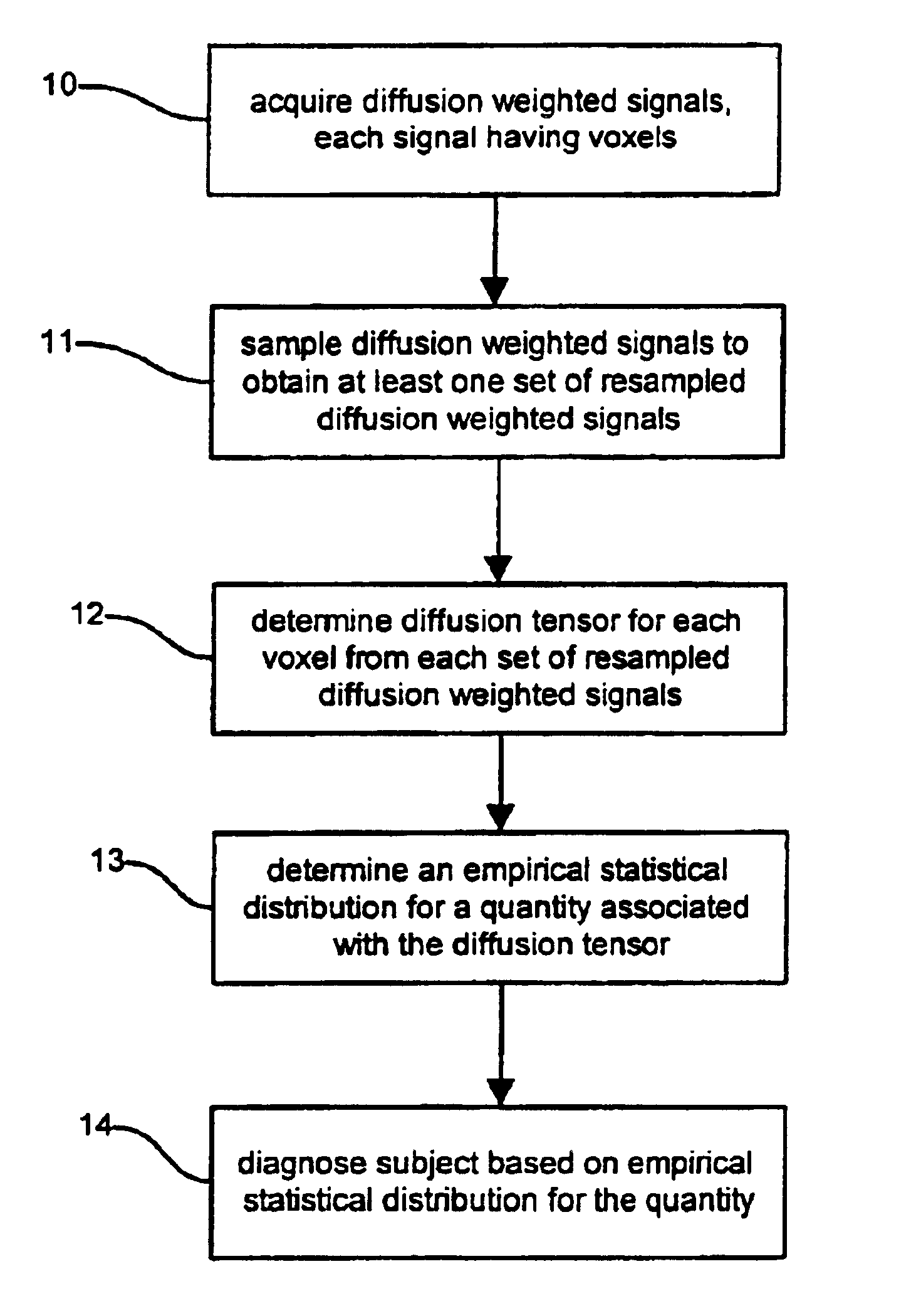
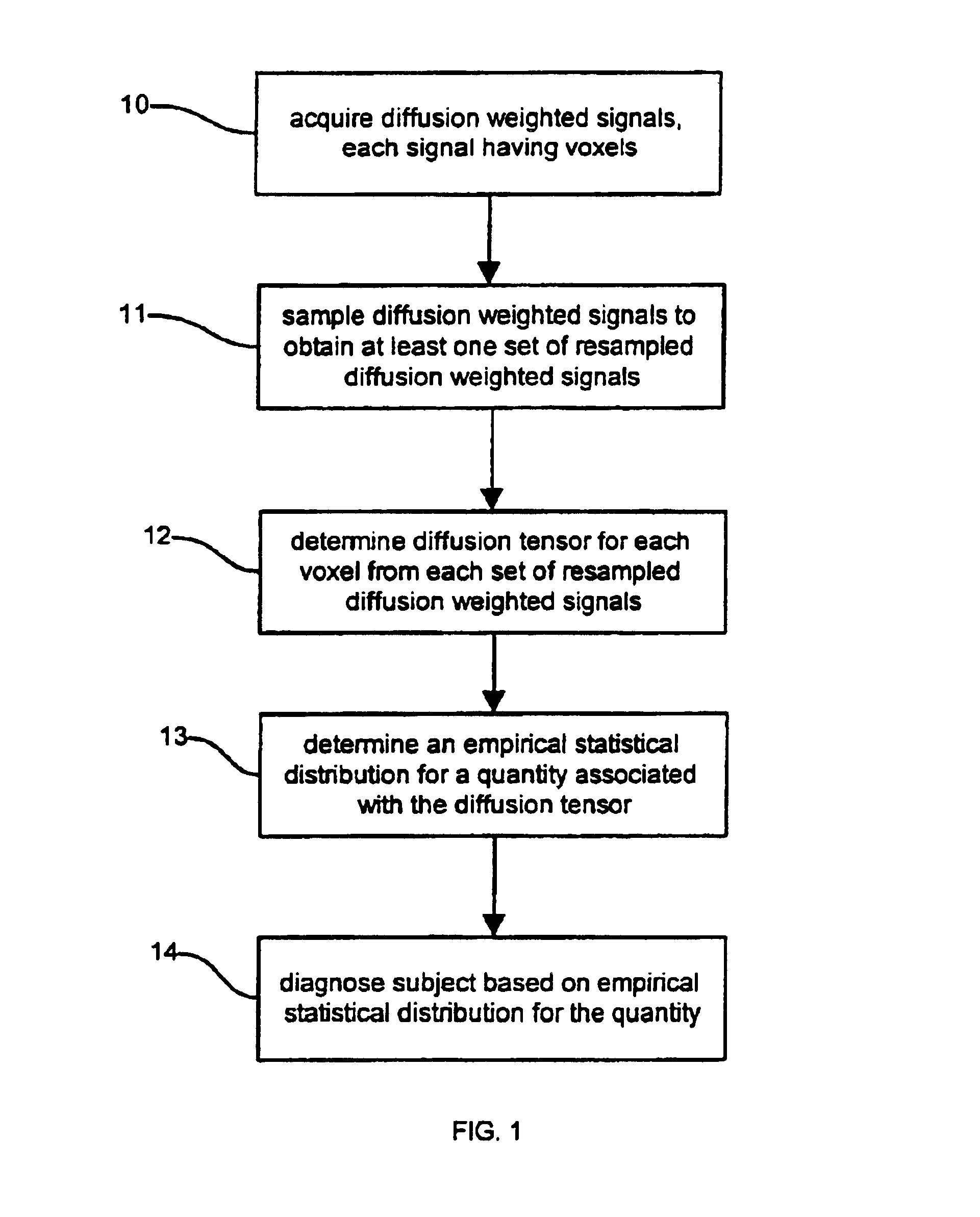
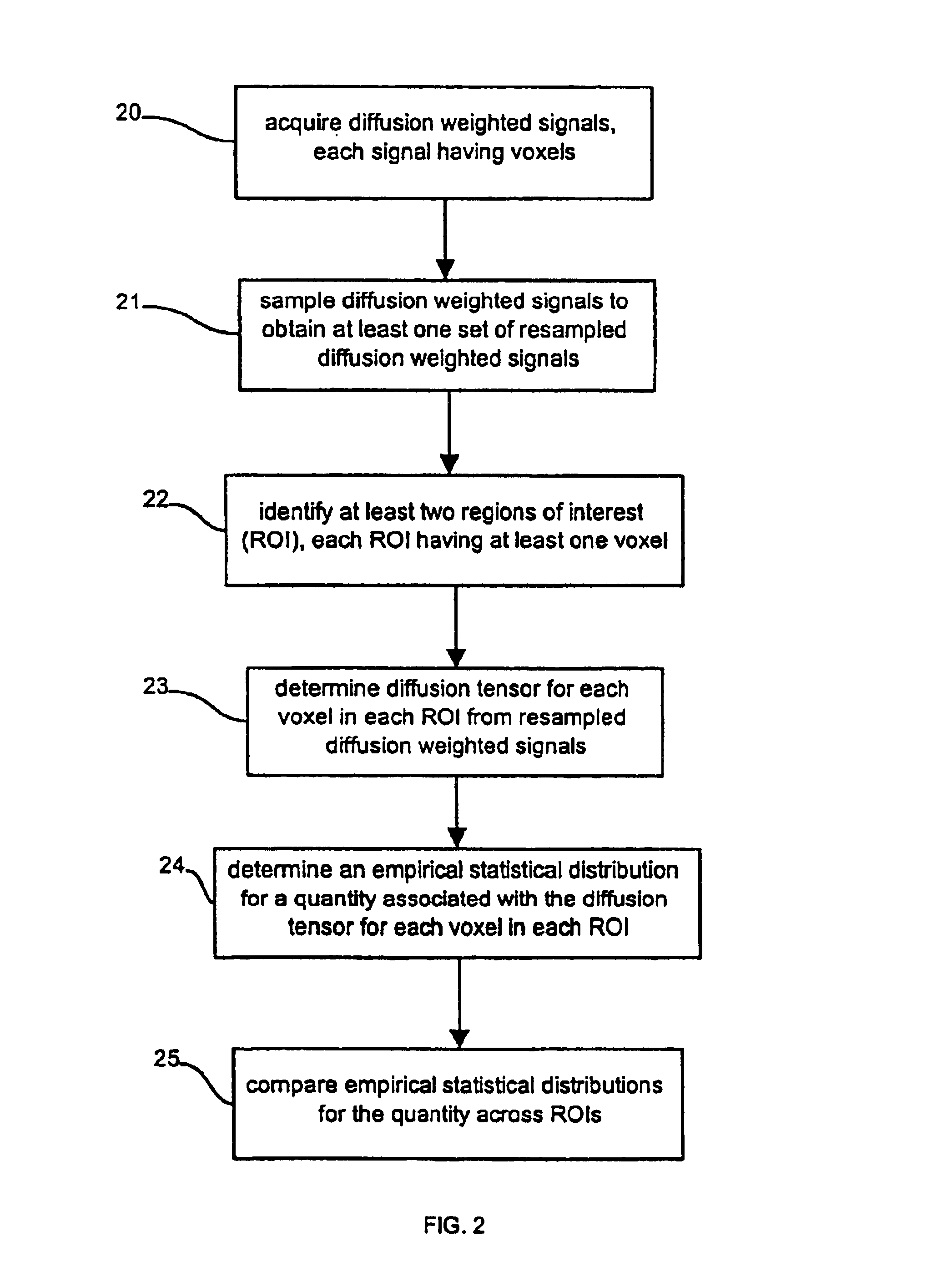
Determination of an empirical statistical distribution of the diffusion tensor in MRI
InactiveUS6845342B1Easy to learnLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear monitoringDiffusionVoxel
Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance signals are analyzed. Diffusion weighted, signals are acquired, each signal having a plurality of voxels (10). The diffusion weighted signals are sampled to obtain at least one set of resampled diffusion weighted signals (11). A diffusion tensor for each voxel is determined from each set of the resampled diffusion weighted signals (12). An empirical statistical distribution is determined for a quantity associated with the diffusion tensor from the diffusion tensors determined from the at least one set of the resampled diffusion weighted signals (13).
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF
Method of predicting stroke evolution utilising mri
InactiveUS20040106864A1Minimize impactLess-intensive therapyImage enhancementOrganic active ingredientsResonanceRisk stroke
A method predicting stroke evolution uses magnetic resonance diffusion and perfusion images obtained shortly after the onset of stroke symptoms to automatically estimate the eventual volume of dead cerebral tissue resulting from the stroke. The diffusion and perfusion images are processed to extract region(s) of interest presenting tissue at risk of infarction. A midplane algorithm is also used to calculate ratio and diffusion and perfusion measures for modelling infarct evolution. A parametric normal classifier algorithm is used to predict infarct growth using the calculated measures.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method for analyzing MRI diffusion data
A new transform is disclosed, applying methods of group theory, with which the composition of a voxel of three channels comprising isotropic, single fiber and multiple fiber components can be determined, as well as the magnitude and orientation of the diffusion field. Asymmetries produced by experimental artifacts fall into channels distinct from the fiber channels, allowing their separation and a subsequent reduction in noise from the reconstructed fibers.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Method and apparatus for multi-frequency NMR diffusion measurements in the presence of internal magnetic field gradients
ActiveUS20050162162A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Pulse sequences are applied to a fluid in an earth formation in a static magnetic field having internal gradients. From the received signals, relaxation and diffusion characteristics of the fluid are determined. The determination takes into account the internal field gradients.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echoes
The invention provides a single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echo, and relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method. According to the method, two echoes with the same evolution time are generated through two small-angle excitation pulses with the same turning angle, so that the same transverse relaxation time is achieved; a displacement gradient is added after each excitation pulse to achieve central displacement of the two echo signals in a signal space, and a diffusion gradient is added after the first excitation pulse, so that diffusion reduction only exists in the first echo signal; accordingly, signals under different diffusion factors are obtained. The two echo signals are from one imaging slice, so that the two echo signals can be separated through priori knowledge of the two echo signals by matching sparse conversion with a corresponding separation algorithm. Finally, a quantitative ADC image is obtained by performing apparent diffusion coefficient calculation on two signals obtained through separation. Single-scanning quantitative ADC imaging is obtained through the method, and the quality of the obtained ADC image is good.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Image distortion correcting method and device based on image contour
InactiveCN102542534AEliminate artifactsDoes not increase scan timeImage enhancementResonanceImage contour
The embodiment of the invention discloses an image distortion correcting method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting an image contour of a source image; obtaining distortion information according to the image contour; and correcting the source image by using the distortion information so as to register the source image with a target image. By using the method and device, disclosed by the invention, the influences of the contrast, b value, direction variation and the like in a diffusion weighted magnetic resonance image on the correction are avoided; moreover, additional reference scanning is not needed so that convenient, fast and accurate image distortion correction is realized.
Owner:北京海思威科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for multi-frequency NMR diffusion measurements in the presence of internal magnetic field gradients
ActiveUS7049815B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method for integration and reconstruction based on Gaussian model acting as instance
ActiveCN106997034AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsParallel imagingSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
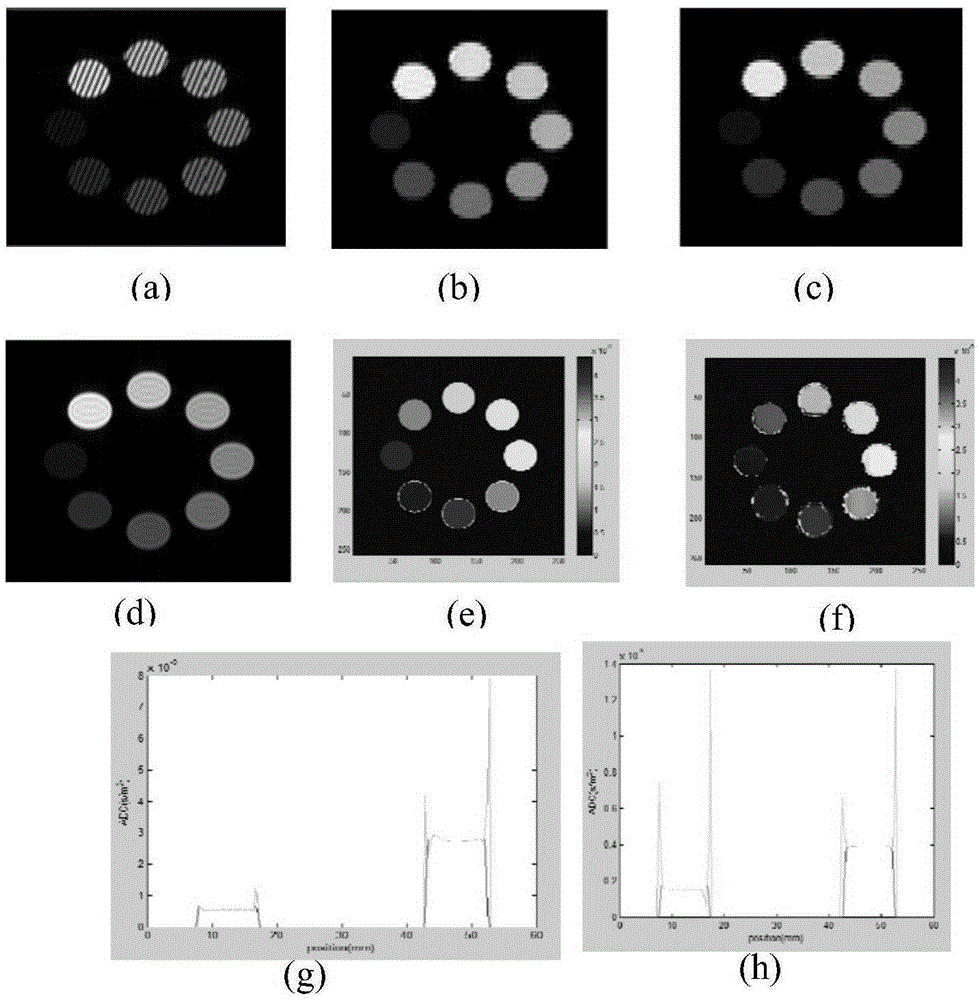
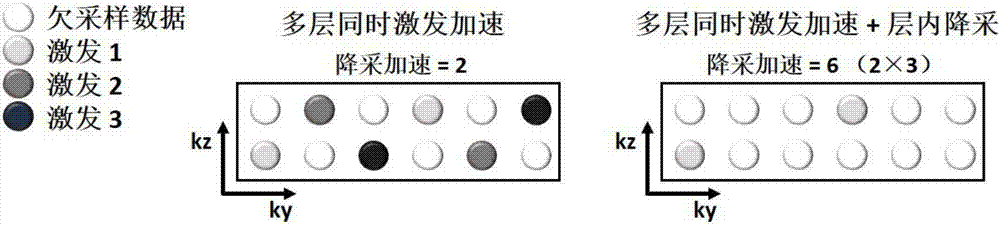
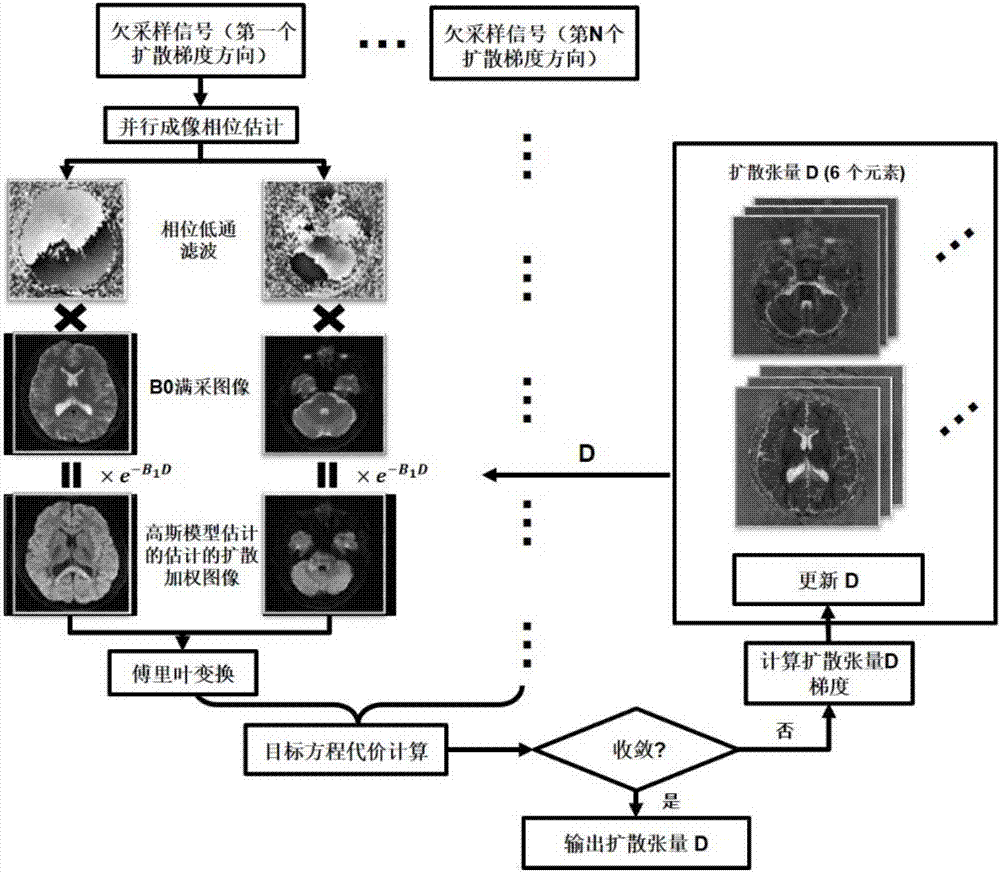
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method for integration and reconstruction based on a Gaussian diffusion model acting as an instance. The method comprises the steps that signal acquisition is performed on a tested target based on multilayer simultaneously excited preset sequences; phase estimation is performed on the acquired under-sampled signals through a parallel imaging technology; the Gaussian diffusion model is established through the estimated phase, the acquired under-sampled signals and a reference image without diffusion weight; the under-sampled signals of all the directions are integrated according to the Gaussian diffusion model, and a target equation is established; the target equation is iteratively solved by using a nonlinear conjugate gradient algorithm so as to obtain a diffusion tensor parameter; and a diffusion coefficient and a diffusion weight image are calculated according to the diffusion tensor parameter. Therefore, high acceleration acquisition of magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging can be realized so that the acquisition time can be effectively reduced, the diffusion tensor parameter can be accurately estimated to obtain the diffusion image of high signal-to-noise ratio and high resolution, and the requirement of clinical application can be met.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and system for reconstructing incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging parameters in voxels
ActiveCN110889897AOvercoming the problem of grainy reconstruction resultsImage smoothingImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelGraph generation
The invention discloses a method and system for reconstructing incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging parameters in voxels. The method comprises the following steps: setting a parameter D, a parameter f, a parameter D * and a parameter S (0) in a geometric figure generated in a simulation area, and judging whether the total area of all geometric figures covers the simulation area or not; ifso, generating a D parameter graph, an f parameter graph, a D * parameter graph and an S (0) parameter graph; generating a magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image corresponding to each b value, and training the neural network model to obtain a trained neural network model; and performing Fourier transform and normalization processing on the k-space data, and inputting the normalized magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image into the trained neural network model to obtain a reconstructed IVIM parameter image. By adopting the method and the system provided by the invention, the problem that the reconstruction result presents granular sensation due to point-by-point fitting is solved, the image is smoother, the influence of the small b value on the IVIM double-exponential model is considered, and the reconstruction effect is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
A Method for Extracting Tissue Fiber Bundle Structure Information Based on Adaptive Diffusion Basis Function Decomposition
InactiveCN102298128AHigh precisionFit closelyMagnetic property measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceVoxelWeight coefficient
A method for extracting tissue fiber bundle structure information based on adaptive diffusion basis function decomposition, which belongs to the field of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging data processing. The purpose of the present invention is to more accurately extract tissue fiber structure information from acquired magnetic resonance diffusion weighted data . Method: 1. Construct a set of tensor basis functions of adaptive eigenvalues; 2. Express the diffusion weighted signal by the linear combination of the constructed tensor basis functions, and then list the diffusion weighted signal represented by the linear combination of tensor basis functions and the actual measured The minimum objective function of the error between diffusion weighted signals; 3. Use an iterative method to solve the weighted coefficients and eigenvalues that minimize the value of the minimized objective function in step 2; 4. Perform the weighted coefficients and eigenvalues obtained in step 3 After post-processing, the running direction of the fiber bundle in the voxel is obtained, which is completed. The advantage of the present invention is that the accuracy of extracting tissue fiber structure information from acquired magnetic resonance diffusion weighted data is high.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Equal voxel magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method and equal voxel magnetic resonance diffusion imaging device based on multi-plate simultaneous excitation
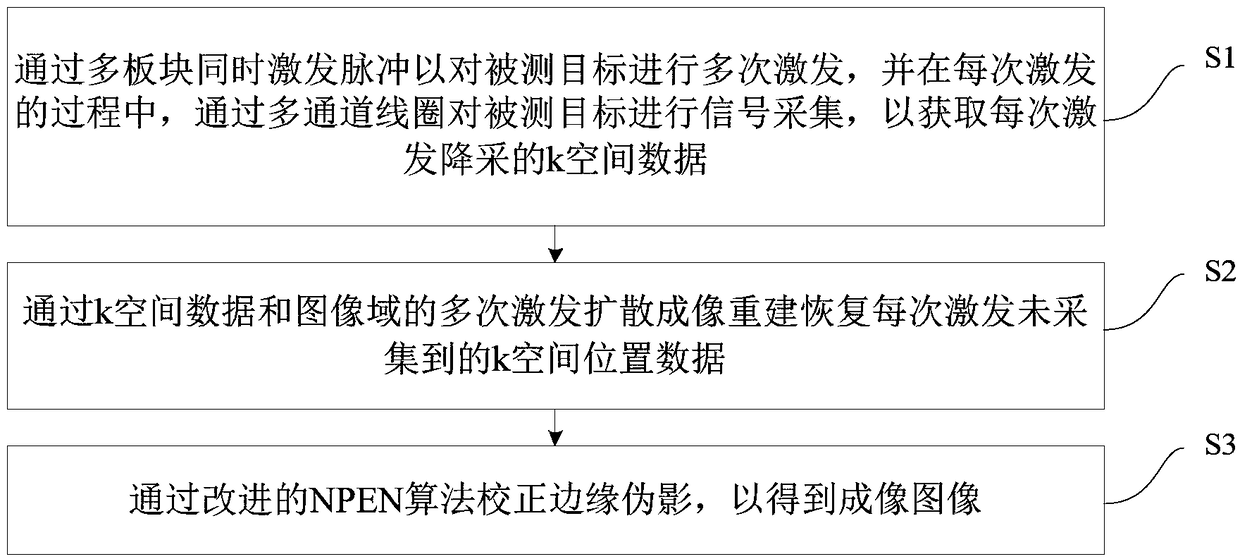
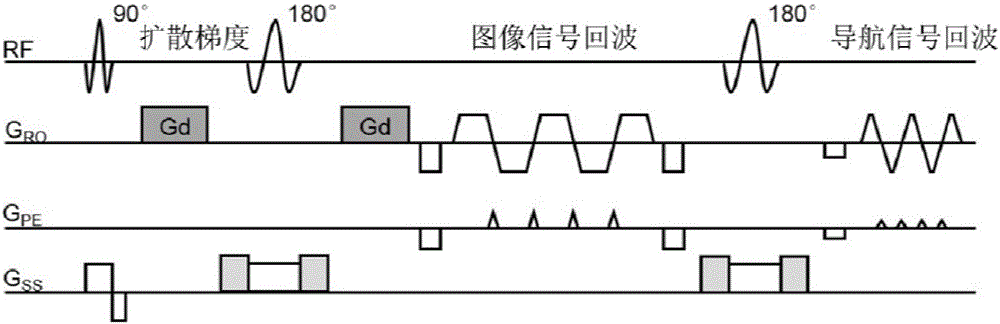
The invention discloses an equal voxel magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method and an equal voxel magnetic resonance diffusion imaging device based on multi-plate simultaneous excitation, whereinthe method comprises the following steps: S1, performing excitation for a tested target for many times through multi-plate simultaneous excitation pulse, and in a process of excitation each time, performing signal acquisition for the tested target through a multi-channel coil, and thereby obtaining k space data acquired through down sampling in excitation each time; S2, by a multi-excitation diffusion imaging reconstruction algorithm uniting the k space and an image domain, recovering k space position data which is not sampled in excitation each time; S3, correcting edge artifacts through an improved NPEN algorithm, thereby obtaining an imaged image. The method can obtain high-resolution images and also can keep relatively high signal-to-noise ratio at the same time, can reduce interference of three-dimensional navigation echo errors and improve quality and stability of reconstructed images, and can improve signal-to-noise ratio efficiency and scanning efficiency on the basis of guaranteeing the quality of the images.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Motion correction method for magnetic resonance multiple excitation diffusion imaging
ActiveCN106780643AHigh resolutionLess geometric distortionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionParallel imagingDiffusion gradient
The invention discloses a motion correction method for magnetic resonance multiple excitation diffusion imaging. The method comprises the steps of collecting a magnetic resonance multiple excitation sequence; obtaining an image echo signal and a two-dimensional navigation signal through a magnetic resonance scanning sequence; estimating motion parameters through the two-dimensional navigation signal; performing rotational and translational correction on the image echo signal and the two-dimensional navigation signal according to the motion parameters, and discarding tainted data, thereby obtaining corrected data; integrating the corrected data collected in multiple excitation to perform parallel imaging reconstruction; estimating rotational motion parameters through an image registration algorithm to perform diffusion gradient correction on a reconstructed image; and performing final calculation by utilizing corrected diffusion image and diffusion gradient to obtain diffusion tensor imaging parameters. According to the method, various motion errors in a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging scanning process can be effectively corrected, so that an artifact-free high-resolution diffusion tensor image is obtained, the errors are effectively reduced, and the accuracy of calculating magnetic resonance diffusion imaging tensor parameters is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus to correct distortions in magnetic resonance diffusion images
InactiveUS20150146999A1Rapid and robust correctionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiffusionResonance
In a method and apparatus to correct distortions in magnetic resonance diffusion images, a distortion model is provided to a computer, at least one reference image is acquired, multiple diffusion images are acquired and after the acquisition of one diffusion image of the multiple diffusion images the following steps are executed in the computer. The diffusion image is brought into registration with the at least one reference image, the distortion model is adapted using the result of the registration, and distortions of the diffusion image are corrected using the distortion model.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
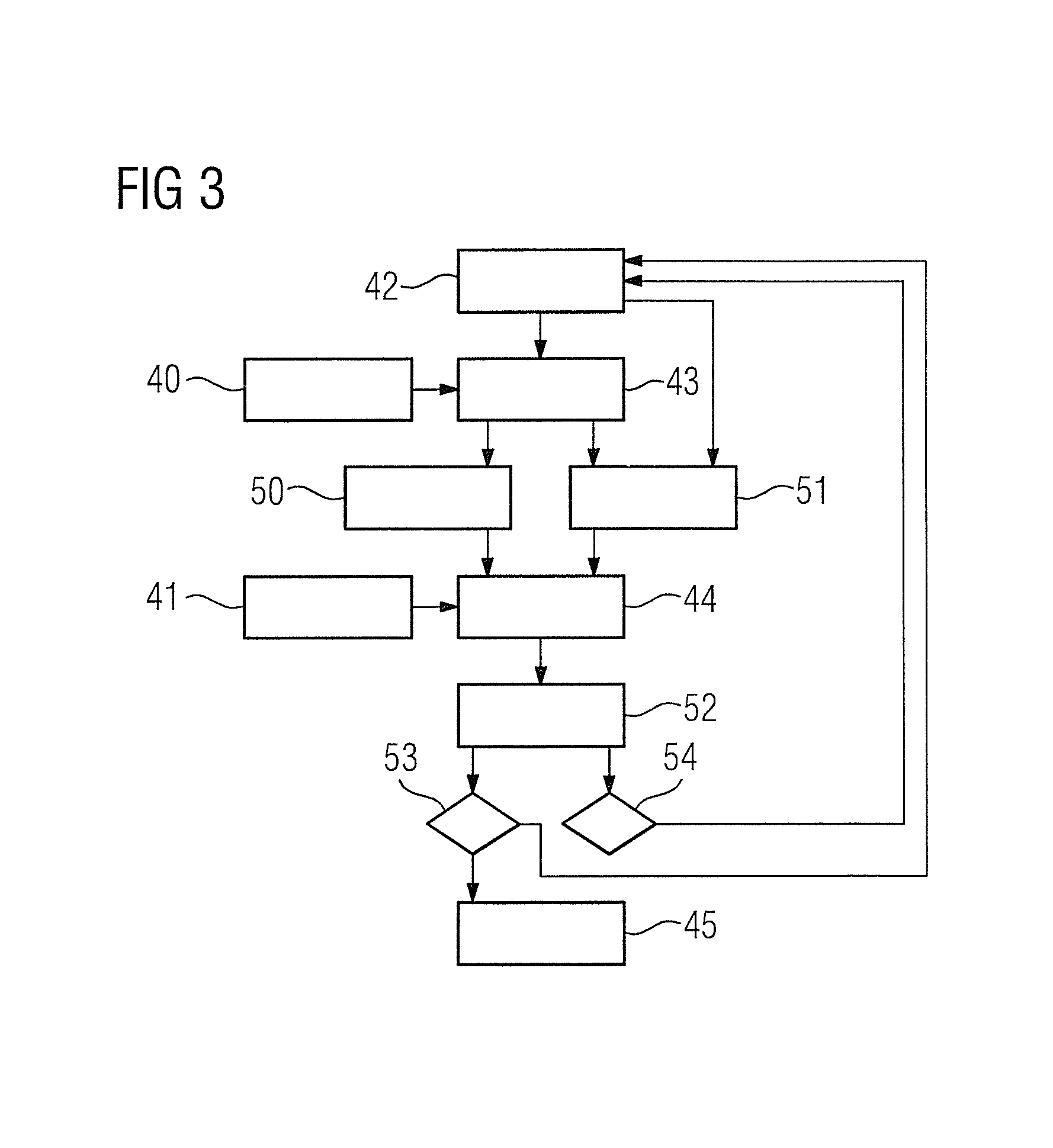
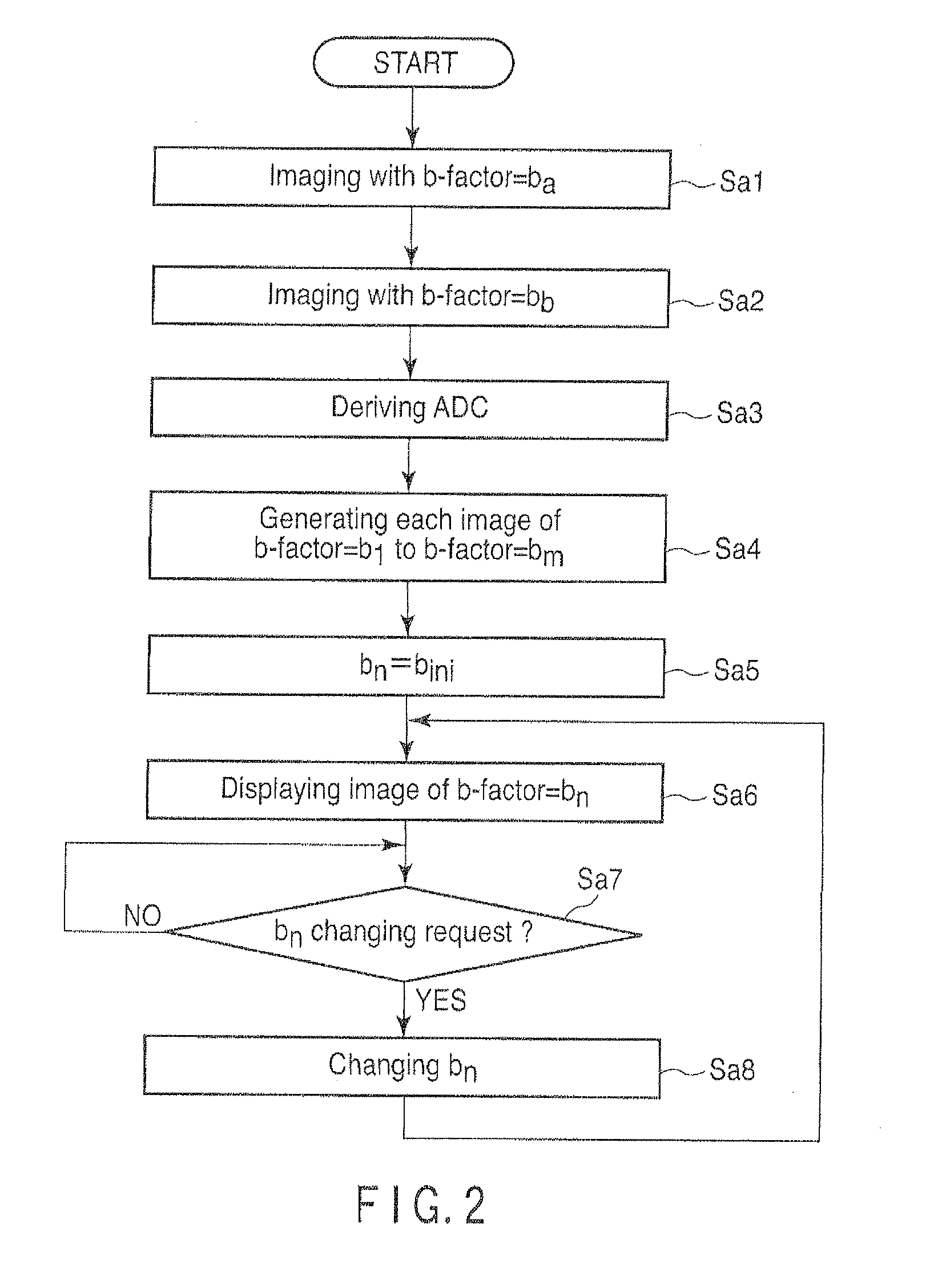
MRI DIFFUSION WEIGHTED IMAGING WITH ESTIMATED MOTION PROBING GRADIENT b-FACTORS BASED ON ACQUIRED APPARENT DIFFUSION COEFFICIENTS FOR EACH PIXEL
ActiveUS20140212017A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiffusionResonance
A magnetic resonance diagnostic apparatus includes a derivation unit to derive an apparent diffusion coefficient regarding a pixel position for each pixel position included in a region of interest in at least two original images obtained by imaging a same imaging region of a same subject using at least two b-factors that are different from each other, respectively, based on pixel values of each of at least two original images regarding the pixel positions, and a first estimation unit to estimate a pixel value obtained by using a b-factor that is different from the at least two b-factors, regarding each pixel position included in the region of interest, based on the apparent diffusion coefficient derived for each pixel position.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Multi-tensor-based magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image structure adaptive smoothing method
The invention discloses a multi-tensor-based magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image structure adaptive smoothing method, relates to a magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image smoothing method, belongs to the field of medical image processing, and solves the problem that the accuracy of the fiber structure information of each obtained voxel is low because of poor noise suppression in the conventional method. The multi-tensor-based magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image structure adaptive smoothing method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting related parameters, and setting an initial neighborhood radius; secondly, calculating the initial fiber structure information of each voxel; thirdly, calculating the weights of all voxels in the neighborhood radius on the voxel according to the fiber structure information, performing weighted smoothing on a magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image, and recalculating the fiber structure information of each voxel after the magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image is smoothed; fourthly, judging whether a stopping criterion for iteration is met or not, if not, expanding the neighborhood radius and continuing to performing the third step, or else, ending the calculating. The multi-tensor-based magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image structure adaptive smoothing method is applicable to processing the information of the magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image.
Owner:严格集团股份有限公司
Method for determining ischemic status or assessing stroke onset time of a brain region
The invention relates to a method for determining ischemic status. The method comprises acquiring magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices and obtaining a relative decrease of diffusion magnitude due to the ischemic status from the magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices. The invention also relates to a method for assessing stroke onset time. The method comprises acquiring magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices and obtaining a relative decrease of pure anisotropy due to stroke from the magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
Under-sampling magnetic resonance diffusion spectrum reconstruction method in combination with sparse and low-rank characteristics
ActiveCN108828482AHigh precisionImprove reconstruction accuracyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDiffusionResonance
The invention discloses an under-sampling magnetic resonance diffusion spectrum reconstruction method in combination with sparse and low-rank characteristics, and relates to an under-sampling reconstruction method of magnetic resonance diffusion spectrum. The method comprises generating a Laplace-Fourier joint transformation matrix; establishing an under-sampling reconstruction model in combination with sparse and low-rank characteristics; solving an algorithm based on the under-sampling reconstruction model in combination with sparse and low-rank characteristics; obtaining a recovered diffusion spectrum vector s by the step 3, and obtaining [Rho]s by an operator [Rho] as the ultimately recovered diffusion spectrum. The method comprises generating a Laplace-Fourier joint transform matrix according to experimental parameters; then establishing an under-sampling reconstruction model in combination with sparse and low-rank characteristics; reconstructing the diffusion spectrum vector by an iterative algorithm; and finally transforming the diffusion spectrum vector into the diffusion spectrum. The method reconstructs a complete magnetic resonance diffusion spectrum with a small amountof data, has high reconstruction precision and a good anti-noise ability.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
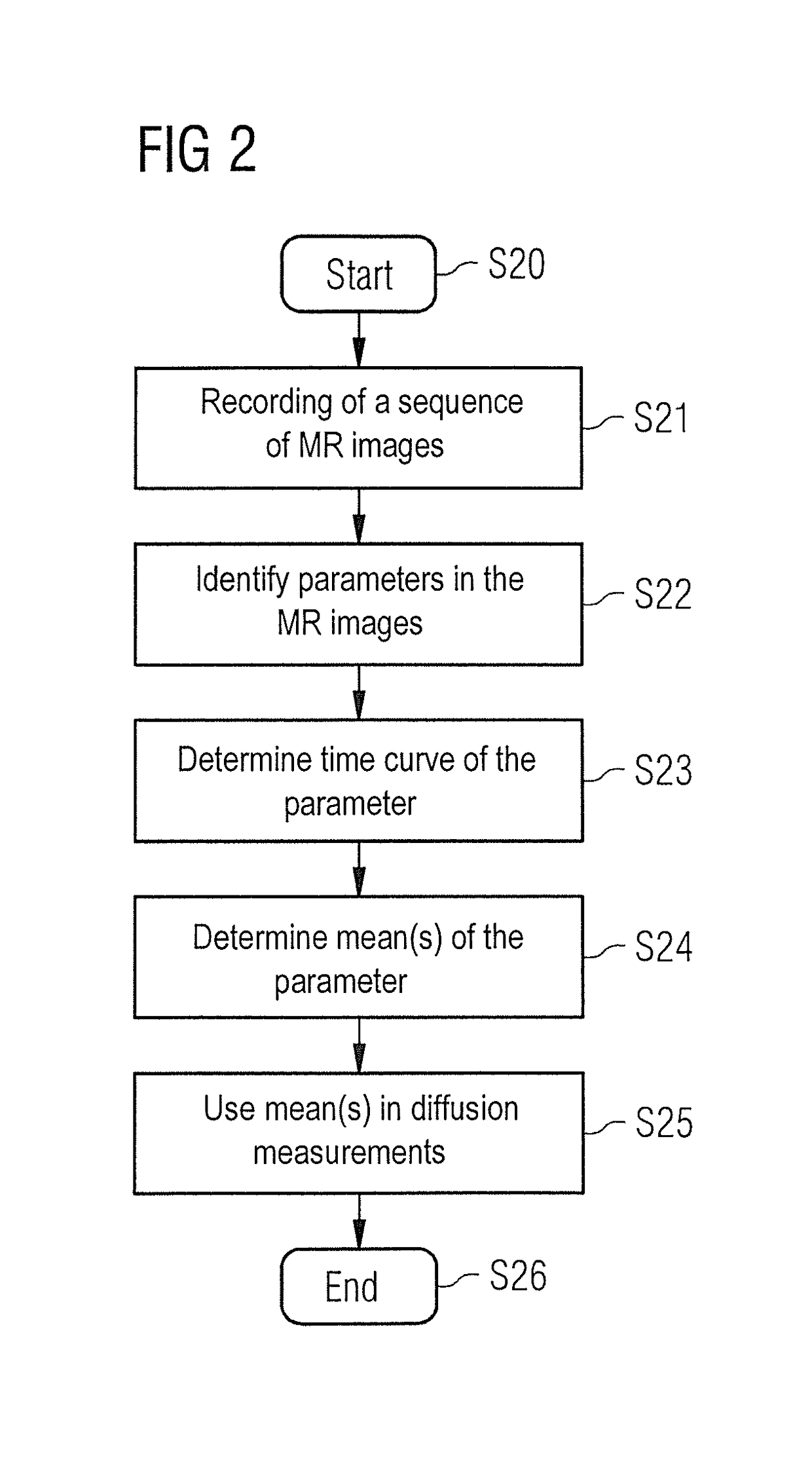
Determining a measuring point-in-time in a cardiac cycle for conducting magnetic resonance diffusion measurements
ActiveUS20150241526A1Sure easyEasy to measureCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringDiffusionResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) system for determining at least one measuring point-in-time in a cardiac cycle for conducting diffusion measurements of the myocardium of an examination object, a sequence of MR images of the heart is acquired and a time curve of a parameter of the cardiac geometry is determined in the sequence of MR images. At least one mean of the parameter of the cardiac geometry is determined from the time curve of the parameter. For the determined at least one mean of the parameter, the associated point-in-time in the time curve of the parameter is determined in which the determined mean occurs, wherein the determined point-in-time defines the at least one measuring point-in-time in a cardiac cycle during which the diffusion measurements of the myocardium are carried out.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
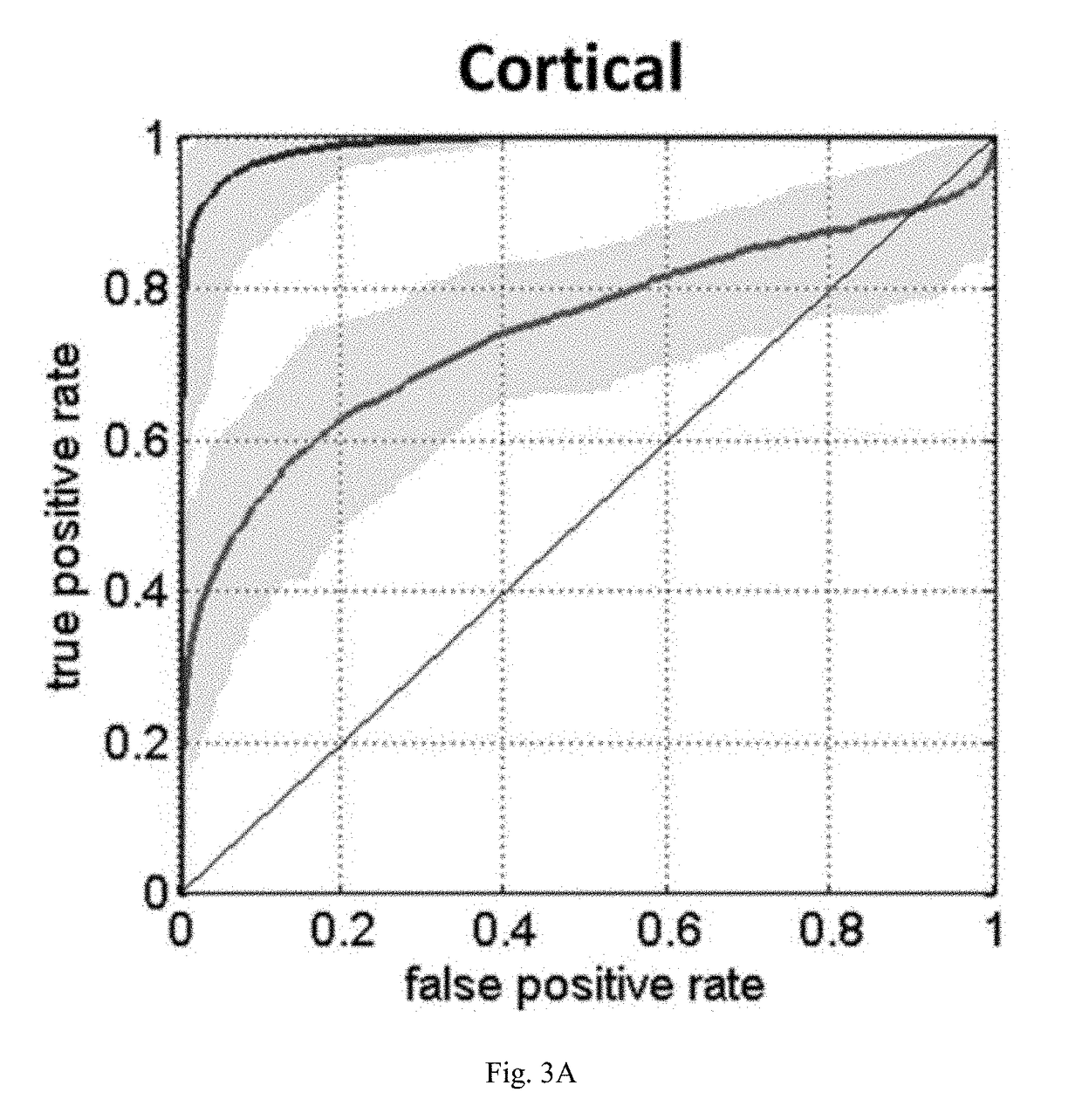
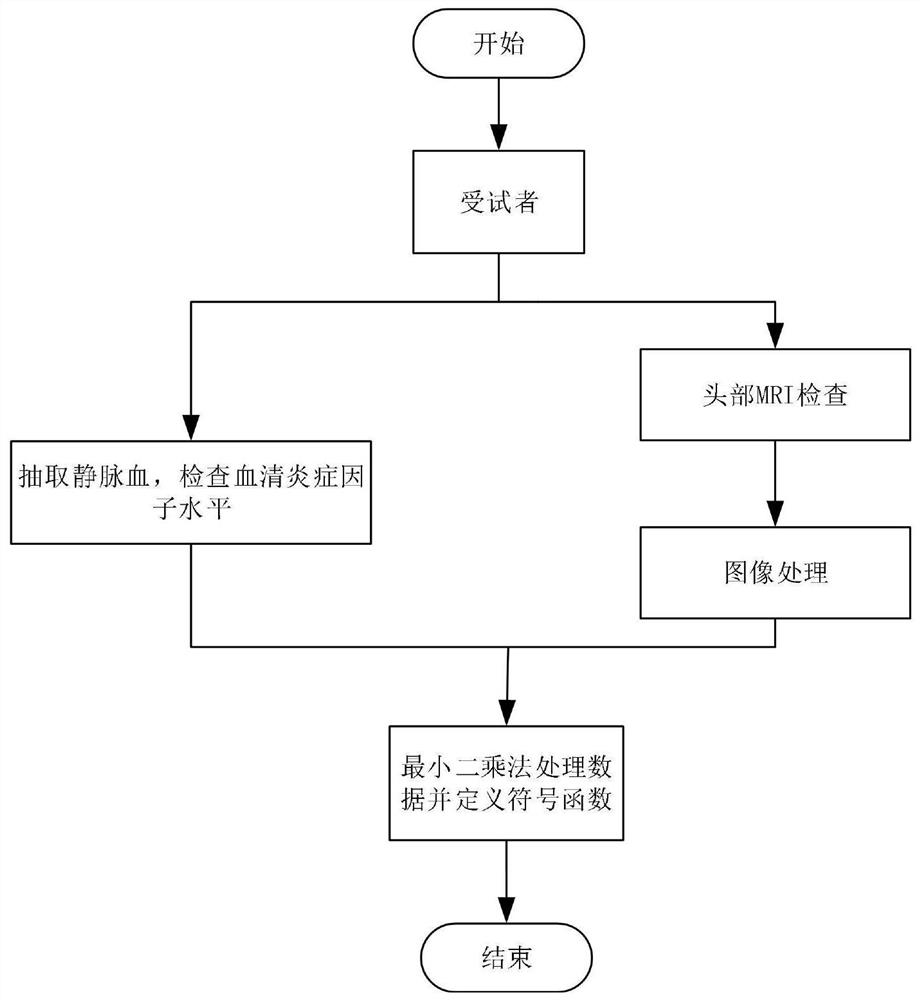
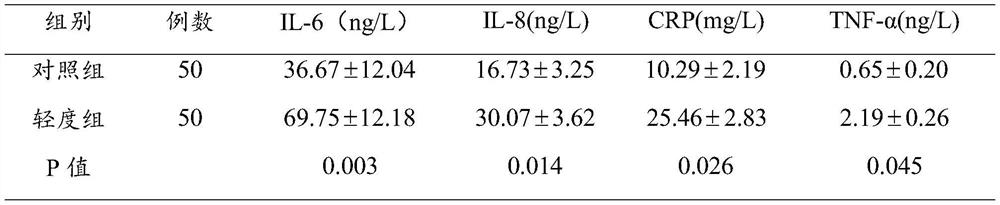
Brain injury marker analysis system based on DTI and serum factors
The invention relates to a brain injury marker analysis system based on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and a serum factor, the system comprises a DTI scanning module, a serum detection module and a data processing module, and the system is controlled according to the following modes: firstly, detecting the serum inflammatory factor level of venous blood extracted from an empty stomach by adopting an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; then, carrying out DTI scanning, carrying out image processing and data analysis on the collected images, and obtaining change data of the FA and the ADC; normalizing a serum inflammatory factor level parameter and an FA value and an ADC value obtained by magnetic resonance diffusion imaging by using a least square method, then defining a sign function, and taking a result of the sign function as a reference for a doctor to analyze and formulate a next detection scheme.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance detection methods for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis water compositions
InactiveCN109991258ARealize detectionWon't breakAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention belongs to the field of analysis chemistry of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis water composition detection and specifically relates to nuclear magnetic resonance detection methods for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis water compositions. According to a method, on the basis of a three-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance diffusion sorting spectrum -<1>H-<1>H homonuclear chemical shift correlationspectrum, through utilization of difference of a diffusion rate and a coupling signal of each composition of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis water in a solvent, obtained diffusion rate and coupling signal data is represented in a three-dimensional map form; horizontal and longitudinal coordinates of a map are chemical shift; vertical coordinates are diffusion coefficients; chemical shift planes with different diffusion coefficients are obtained on the vertical coordinates according to the difference of the diffusion coefficient of each composition in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis water; compounds with the same diffusion coefficient value are identified in sequence according to the coupling signals of the -<1>H-<1>H homonuclear chemical shift correlation spectrum; and each composition in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis water is detected. According to the method, an obtained analysis result is visual and clear, detection resolution is high, operation is simple, the result is accurate and precision is high. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis water sample compositions can be detected qualitatively and quantitatively. The method is applicable to qualitative detection of various low carbon small molecular compound compositions.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Brain structure network connection optimization method based on random partitioning model
ActiveCN106251379AImplement the buildIncrease credibilityReconstruction from projectionDiffusionFiber bundle
The invention relates to an image processing technology, and specifically relates to a brain structure network connection optimization method based on a random partitioning model. The problem that a brain structure network built using the existing brain structure network building method is of low credibility is solved. The brain structure network connection optimization method based on a random partitioning model is implemented according to the following steps: S1, preprocessing a magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image, and partitioning the preprocessed magnetic resonance diffusion weighted image; S2, calculating the number of fiber bundles of every two brain intervals; S3, binarizing a fiber bundle number matrix of the brain intervals according to a threshold; S4, building a brain structure central network model based on multiple brain structure network model samples; S5, calculating the credibility of connection in the brain structure central network model; and S6, rebuilding and optimizing the brain structure central network model. The method is suitable for brain structure network building.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for determining ischemic status or assessing stroke onset time of a brain region
The invention relates to a method for determining ischemic status. The method comprises acquiring magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices and obtaining a relative decrease of diffusion magnitude due to the ischemic status from the magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices. The invention also relates to a method for assessing stroke onset time. The method comprises acquiring magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices and obtaining a relative decrease of pure anisotropy due to stroke from the magnetic resonance diffusion tensor matrices.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
Noninvasive measuring method of microstructure of biological tissue
InactiveCN105078456AEasy to analyzeImproved Diffusion PropertiesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsThree vesselsBiological tissue
Disclosed is a noninvasive measuring method of microstructure of biological tissue. The noninvasive measuring method includes: performing magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging on the biological tissue; measuring actual image signal strength of each pixel point in each magnetic resonance image; according to the actual image signal strength and calculated image signal strength, solving to acquire extracellular clearance volume ratio, cell volume ratio, blood vessel volume ratio, intracellular diffusion vector in a diffusion-weighted vector direction, blood diffusion vector in the diffusion-weighted vector direction and extracellular clearance diffusion vector in the diffusion-weighted vector direction of each pixel point in the magnetic resonance images; restructuring magnetic resonance images. By the noninvasive measuring method, structural information of different tissue components can be provided, and anisotropic diffusion characteristics of water molecules in the tissue can be analyzed well.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
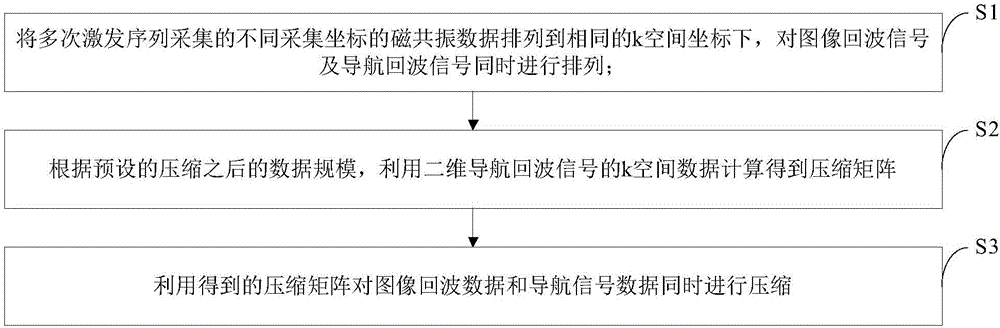
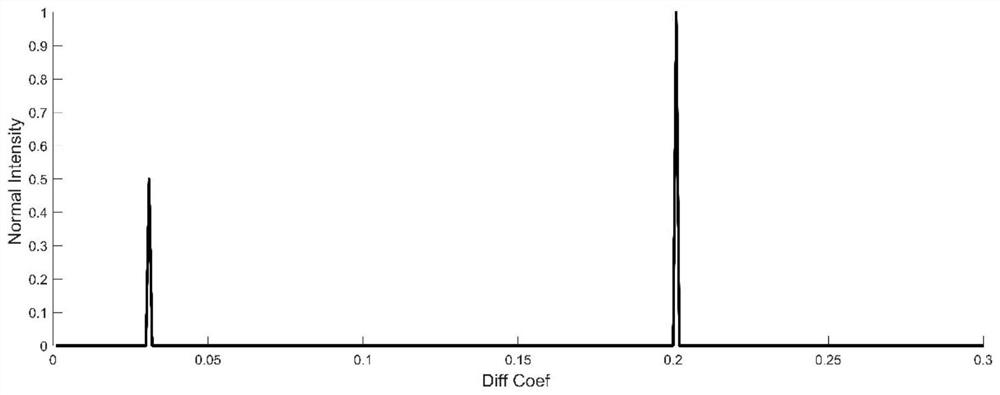
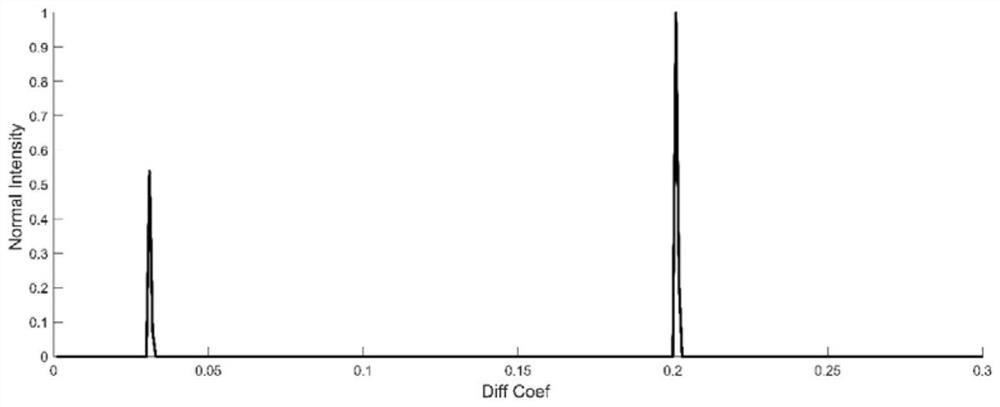
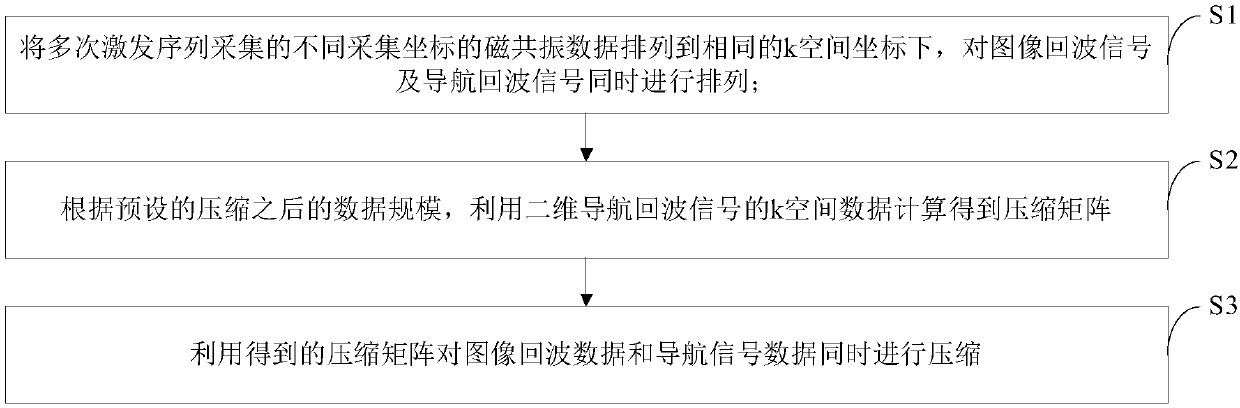
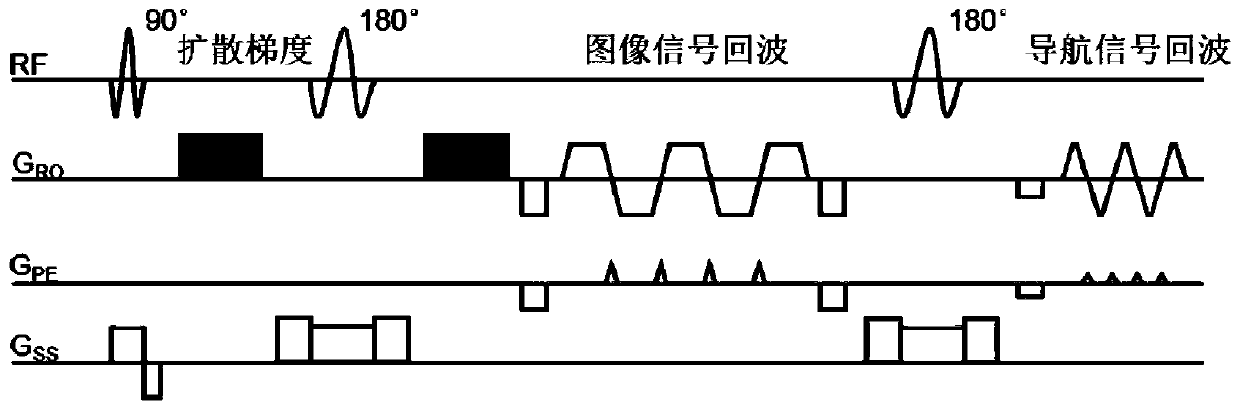
Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging data compression and accelerated reconstruction method
ActiveCN106526514ASmall scaleReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData compressionImaging quality
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging data compression and accelerated reconstruction method, which comprises the steps of arranging magnetic resonance data, which is acquired by exciting a sequence for multiple times, of different acquisition coordinates to the same k space coordinates, and simultaneously performing arrangement on image echo signals and navigation echo signals which are acquired by exciting the sequence for multiple times; calculating a compression matrix by using k space data of two-dimensional navigation echo signals according to a preset data scale after compression; and simultaneously performing compression on the image echo data and the navigation signal data by using the acquired compression matrix. The method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages: a rearrangement operation is performed on diffusion imaging data, which is acquired by exciting the sequence for multiple times, of magnetic resonance, data acquired by multiple times of excitation and data acquired by a multi-channel coil are integrated, an excitation-coil dimension of data is constructed so as to perform compression, and the data scale is effectively reduced; effective acceleration is provided for a follow-up magnetic resonance reconstruction algorithm, and memory occupation is reduced at the same time; and image noises are reduced while efficient accelerated calculation is performed, and the image quality is guaranteed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Determining a measuring point-in-time in a cardiac cycle for conducting magnetic resonance diffusion measurements
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
A High Resolution Reconstruction Method of Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Sorting Spectrum
ActiveCN109636725BAchieving High Resolution ReconstructionHigh resolutionGeometric image transformationDescent directionReconstruction method
A method for high-resolution reconstruction of magnetic resonance diffusion sorting spectra, relating to magnetic resonance diffusion sorting spectra. Construct the sparse reconstruction model of magnetic resonance diffusion sorting spectrum; transform the constrained model into an unconstrained model; initialize parameters t and x; perform the following sub-steps in a loop: ①Use the PCG algorithm to calculate the solution of Newton’s linear equations as the descending direction Δx; ②Use backtracking Calculate the descending step s with the straight-line method; ③ update the iteration value x=x+sΔx; ④ construct a dual feasible point v; ⑤ judge whether η / G(v) is less than the preset precision value ε=10 ‑8 , if satisfied, exit the loop. ⑥Update t, and jump back to step ①; output the reconstructed spectrum x.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
MRI data compression and accelerated reconstruction method
ActiveCN106526514BSmall scaleReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData compressionImaging quality
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging data compression and accelerated reconstruction method, which comprises the steps of arranging magnetic resonance data, which is acquired by exciting a sequence for multiple times, of different acquisition coordinates to the same k space coordinates, and simultaneously performing arrangement on image echo signals and navigation echo signals which are acquired by exciting the sequence for multiple times; calculating a compression matrix by using k space data of two-dimensional navigation echo signals according to a preset data scale after compression; and simultaneously performing compression on the image echo data and the navigation signal data by using the acquired compression matrix. The method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages: a rearrangement operation is performed on diffusion imaging data, which is acquired by exciting the sequence for multiple times, of magnetic resonance, data acquired by multiple times of excitation and data acquired by a multi-channel coil are integrated, an excitation-coil dimension of data is constructed so as to perform compression, and the data scale is effectively reduced; effective acceleration is provided for a follow-up magnetic resonance reconstruction algorithm, and memory occupation is reduced at the same time; and image noises are reduced while efficient accelerated calculation is performed, and the image quality is guaranteed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
MRI Multiple Excitation Diffusion Imaging Motion Correction Method
ActiveCN106780643BReduce calculation errorsImprove accuracyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionParallel imagingDiffusion gradient
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance multiple excitation diffusion imaging motion correction method, which includes: collecting multiple excitation magnetic resonance sequences; obtaining image echo signals and two-dimensional navigation signals through the magnetic resonance scanning sequence; and estimating motion through the two-dimensional navigation signals. Parameters; perform rotation and translation correction on the image echo signal and two-dimensional navigation signal according to the motion parameters, while discarding contaminated data to obtain correction data; integrate the corrected multiple excitation acquisition data for parallel imaging reconstruction; estimate through image registration algorithm The rotation motion parameters are used to correct the diffusion gradient of the reconstructed image; the corrected diffusion image and diffusion gradient are used for final calculation to obtain the diffusion tensor imaging parameters. This method can effectively correct various motion errors that occur during the magnetic resonance diffusion imaging scanning process, thereby obtaining high-resolution diffusion tensor images that eliminate artifacts, effectively reducing errors, and improving the accuracy of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging tensor parameter calculations. Spend.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method
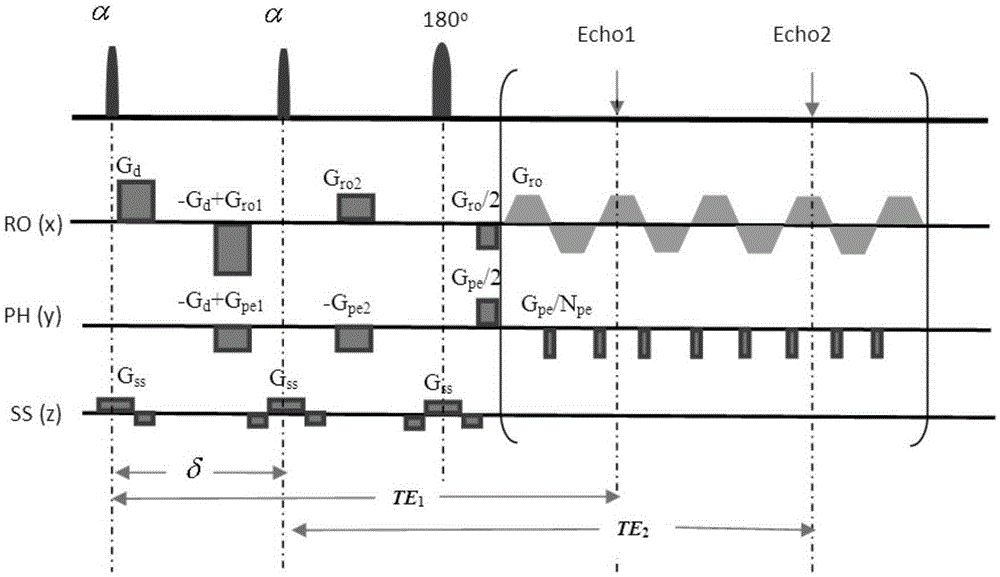
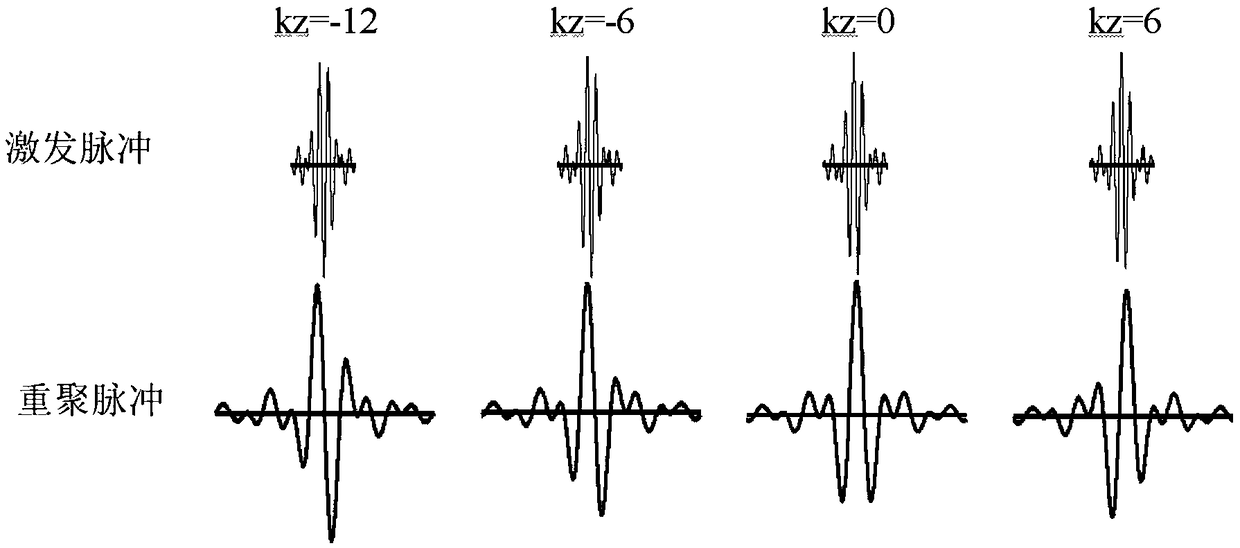
ActiveCN101143093BEliminate artifactsStable equilibriumDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonancePhase Code
The invention provides a magnetic resonance diffuse imaging method. At least two reunion phase radio frequency pulses are added at the back of an excitation radio frequency pulse of a magnetic resonance diffuse imaging pulse sequence, and two sides of each reunion phase radio frequency pulse are symmetrically provided with a diffuse sensitive gradient, wherein two sides of each reunion phase radio frequency pulse are symmetrically provided with a destroying gradient which is placed between the reunion phase radio frequency pulse and the diffuse sensitive gradients at two sides of the reunion phase radio frequency pulse and is used for completely dispelling the phase of the transverse magnetized vector to eliminate the artifact. At least one of a lamella selecting gradient, a phase coding gradient and a numerating gradient direction is provided with the destroying gradient to completely dispelling the phase of the transverse magnetized vector to achieve the steady and balanced state and eliminate the artifact of the diffuse imaging, and at the same time the characteristic of high b value is retained.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com