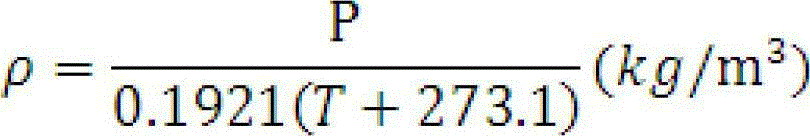Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Martian surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The study of surface characteristics (or surface properties and processes) is a broad category of Mars science that examines the nature of the materials making up the Martian surface. The study evolved from telescopic and remote-sensing techniques developed by astronomers to study planetary surfaces. However, it has increasingly become a subdiscipline of geology as automated spacecraft bring ever-improving resolution and instrument capabilities. By using characteristics such as color, albedo, and thermal inertia and analytical tools such as reflectance spectroscopy and radar, scientists are able to study the chemistry and physical makeup (e.g., grain sizes, surface roughness, and rock abundances) of the Martian surface. The resulting data help scientists understand the planet’s mineral composition and the nature of geological processes operating on the surface. Mars’ surface layer represents a tiny fraction of the total volume of the planet, yet plays a significant role in the planet’s geologic history. Understanding physical surface properties is also very important in determining safe landing sites for spacecraft.
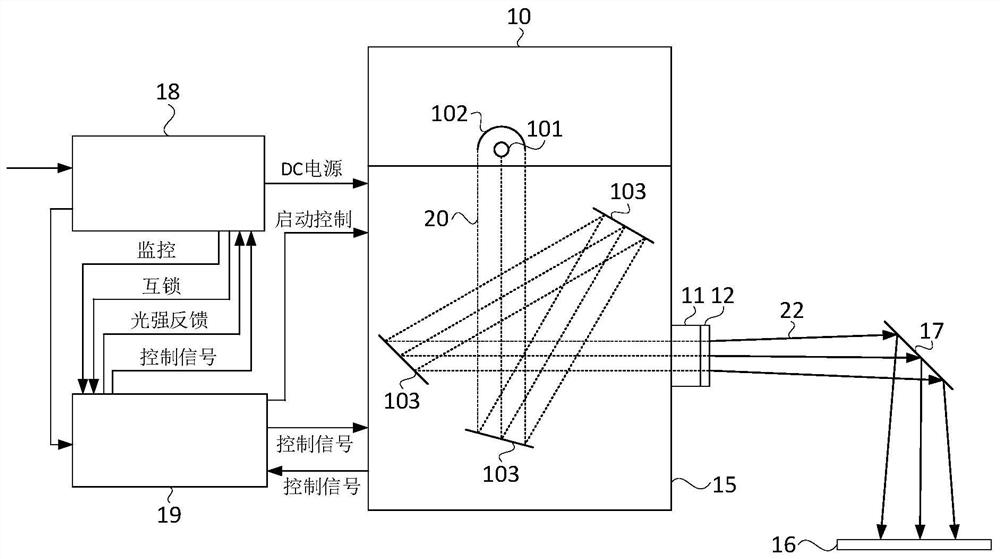
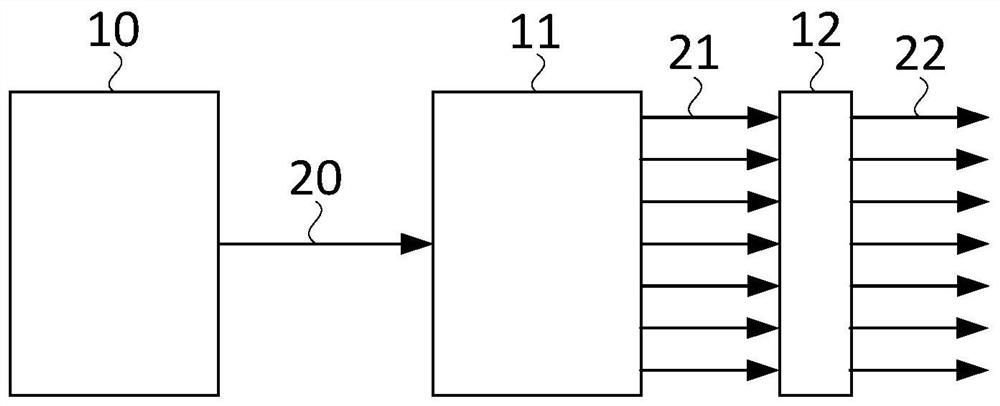
Obstacle avoidance method for soft landing of object outside earth under multi-obstacle constraint environment
ActiveCN105929844AVerify correctnessVerify feasibilityPosition/course control in three dimensionsThree-dimensional spaceMathematical model
The invention provides an obstacle avoidance method for soft landing of an object outside the earth under a multi-obstacle constraint environment, and belongs to the technical field of navigation, guidance and control. The invention provides an improved optimum soft landing guidance method based on convex optimization for the problem of optimum guidance under the multi-obstacle constraint environment on the basis of the previous achievements. The method is characterized by, to begin with, establishing an optimal second-order cone programming model without obstacle constraint, and standardizing the model; then, carrying out analysis modeling on bulge obstacles on the surface of the Mars, and carrying out linear conversion to enable nonconvex constraints to be converted into convex constraints; fusing an obtained bulge obstacle mathematical model into second-order cone programming problems, and establishing a complete optimal second-order cone programming model with the obstacle constraints being taken into consideration; and finally, verifying the correctness of the algorithm through simulation analysis of three different types of obstacle constraints. The method can be applied to the study of lunar soft landing; the simulation result shows that the new algorithm realizes effective avoidance of three-dimensional space obstacles; available space for flying above and surrounding the obstacles is utilized reasonably; and fuel minimization is met simultaneously.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
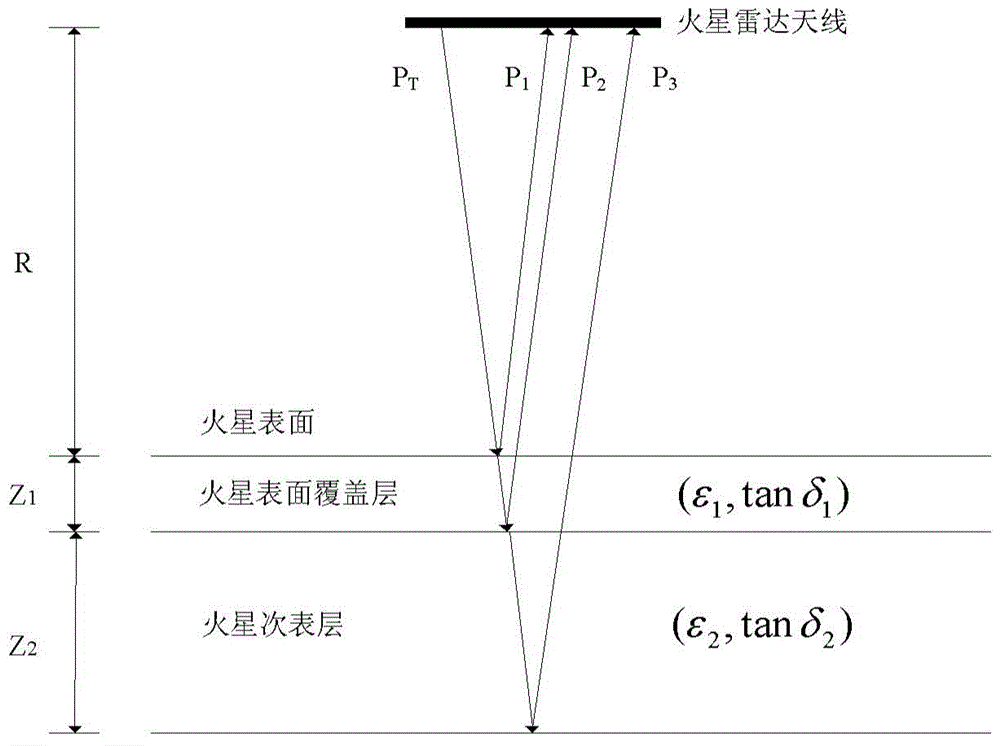
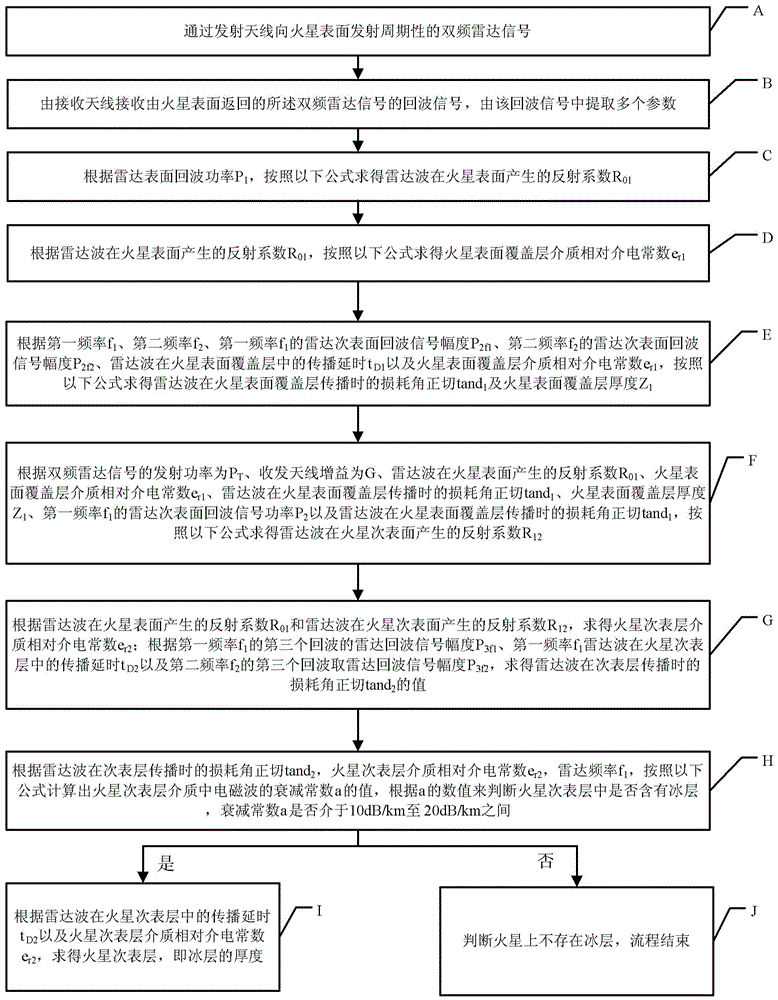
Method for detecting underground ice layer by use of double-frequency radar
ActiveCN103605166AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityUsing wave/particle radiation meansDetection using electromagnetic wavesTime delaysRadar
The invention provides a method for detecting a Mars underground ice layer by use of a double-frequency radar. According to the method, through analyzing characteristics including radar echo signal intensity and time-delay and the like, information such as the thickness of the cover layer on the surface of the Mars, whether the ice layer exists underground on the Mars, the thickness of the ice layer and the like can be obtained. Compared to a neutron measuring technology in the prior art, the accuracy and reliability are higher.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
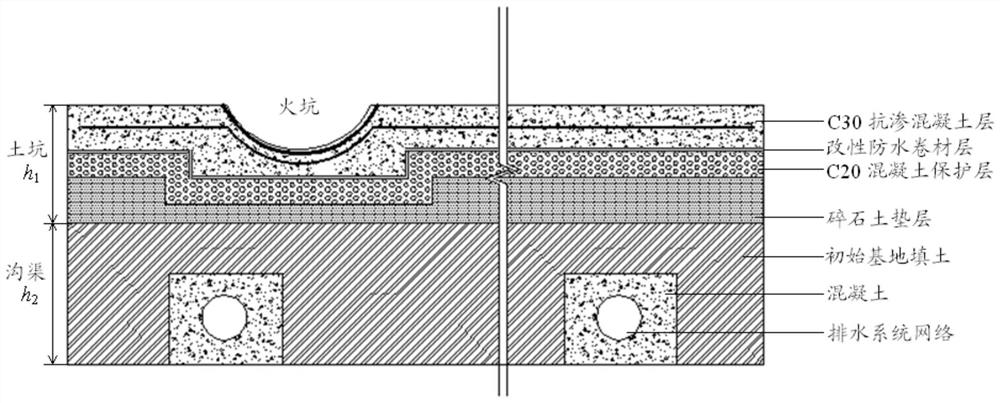
Comprehensive environment heat balance test system for Mars probe single-machine product
InactiveCN111458170AIncrease authenticityRealize fine controlCosmonautic condition simulationsStructural/machines measurementTemperature controlControl system
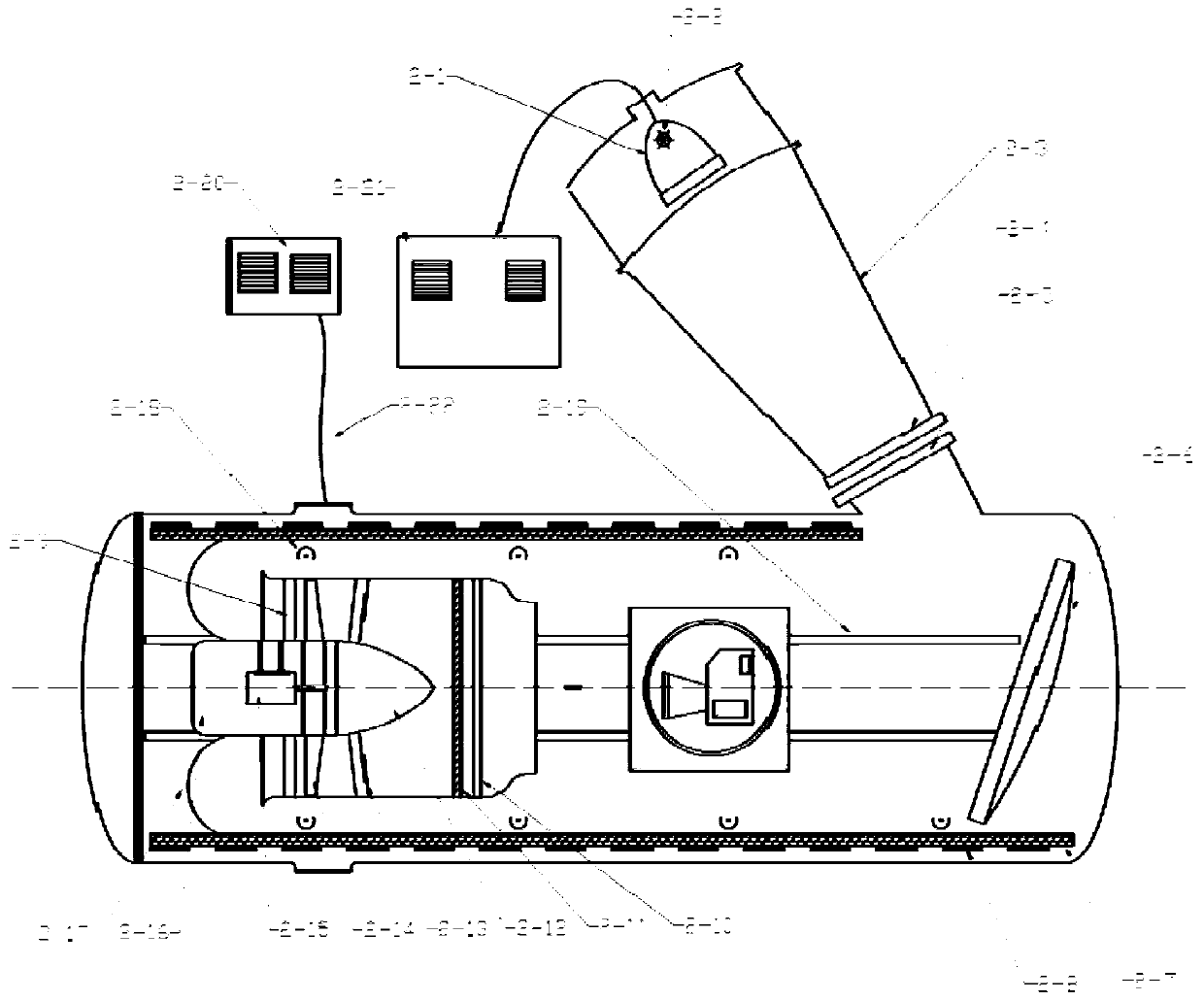
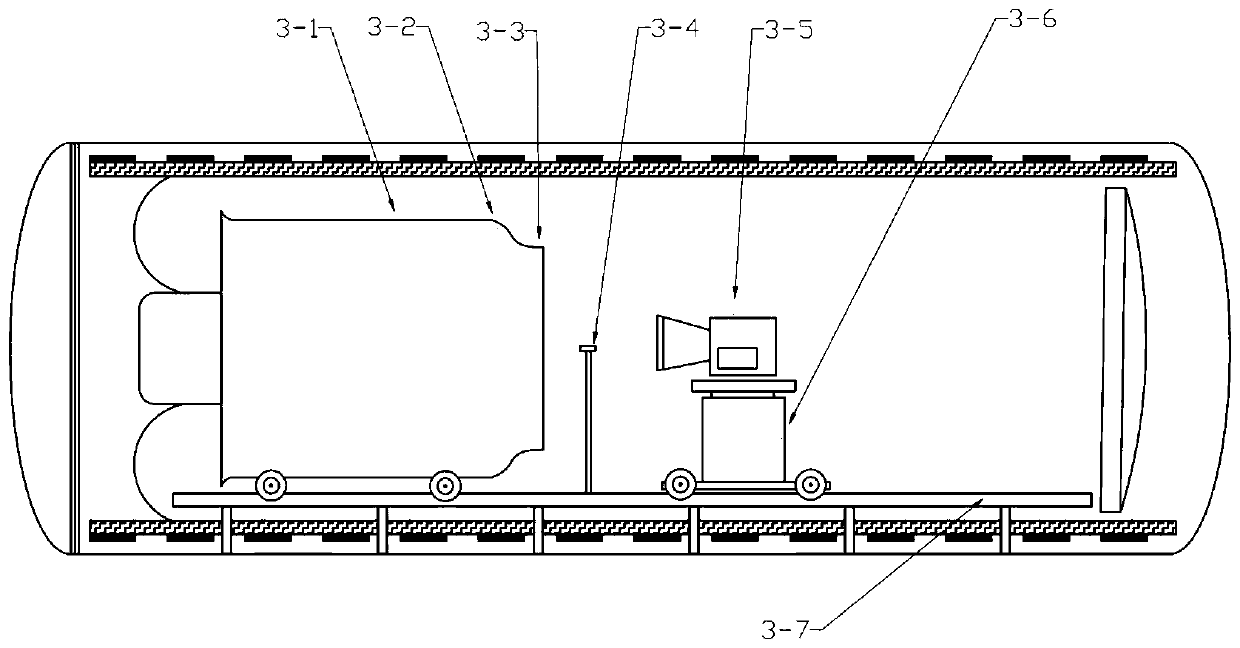
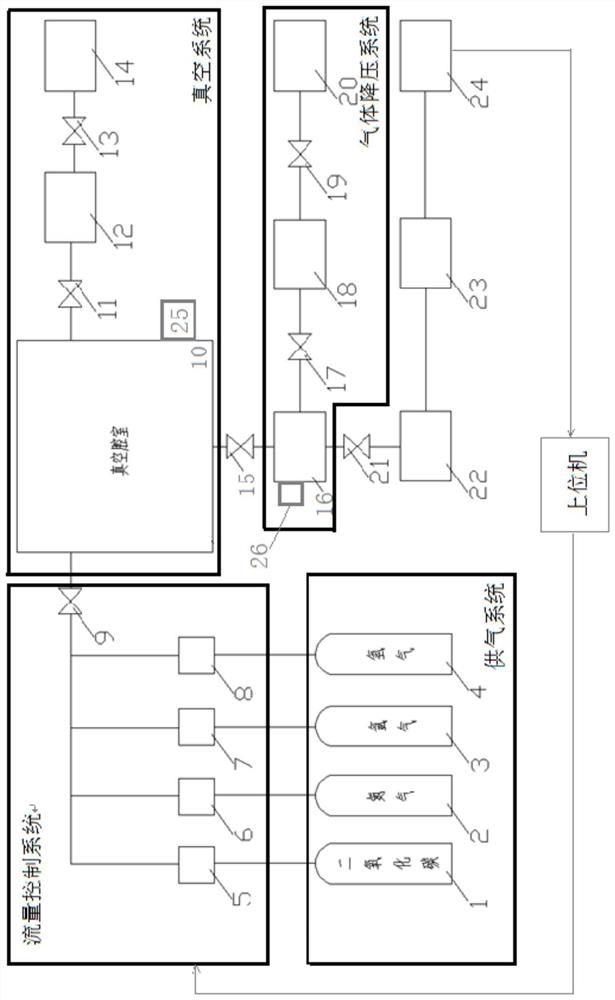
The invention discloses a comprehensive environment heat balance test system for a Mars detector single-machine product. The system comprises a Mars environment simulation chamber, a solar irradiationsimulation system, a Mars atmosphere simulation system, a Mars surface wind simulation system, a temperature control system and a test piece support system, wherein the Mars environment simulation chamber is a horizontal and capsule-shaped cabin body, container gates which can be opened are arranged at the two ends of the cabin body, and the Mars environment simulation chamber is mainly used forforming a closed space without obvious leakage and maintaining a special atmospheric environment in the cabin. The system can provide comprehensive stress environment tests of five parameters including gas atmosphere, wind speed, pressure, solar irradiation and environment temperature on the surface of Mars, and is easy to operate and good in generalizability.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Martian atmospheric dust aerosol optical thickness retrieval method
InactiveCN107798154AReduce the impact of inversionFast inversionSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsContent retrievalAtmospheric temperature
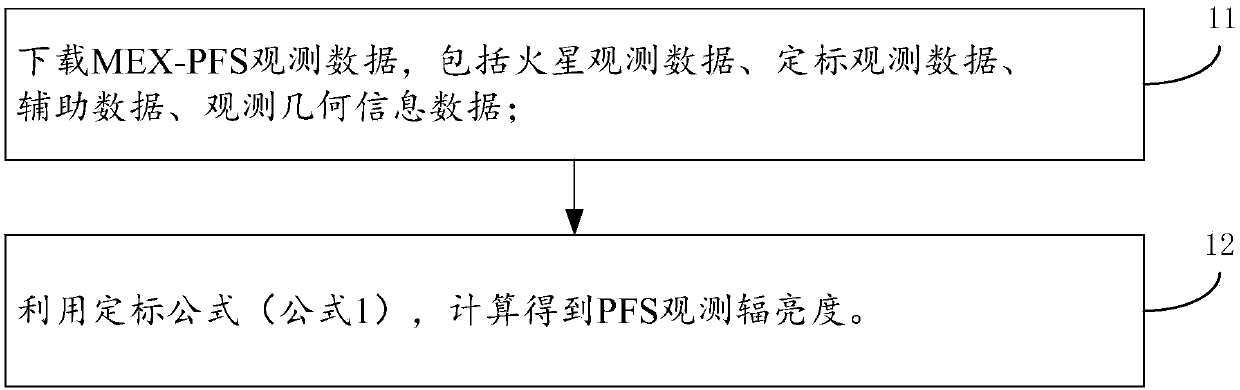
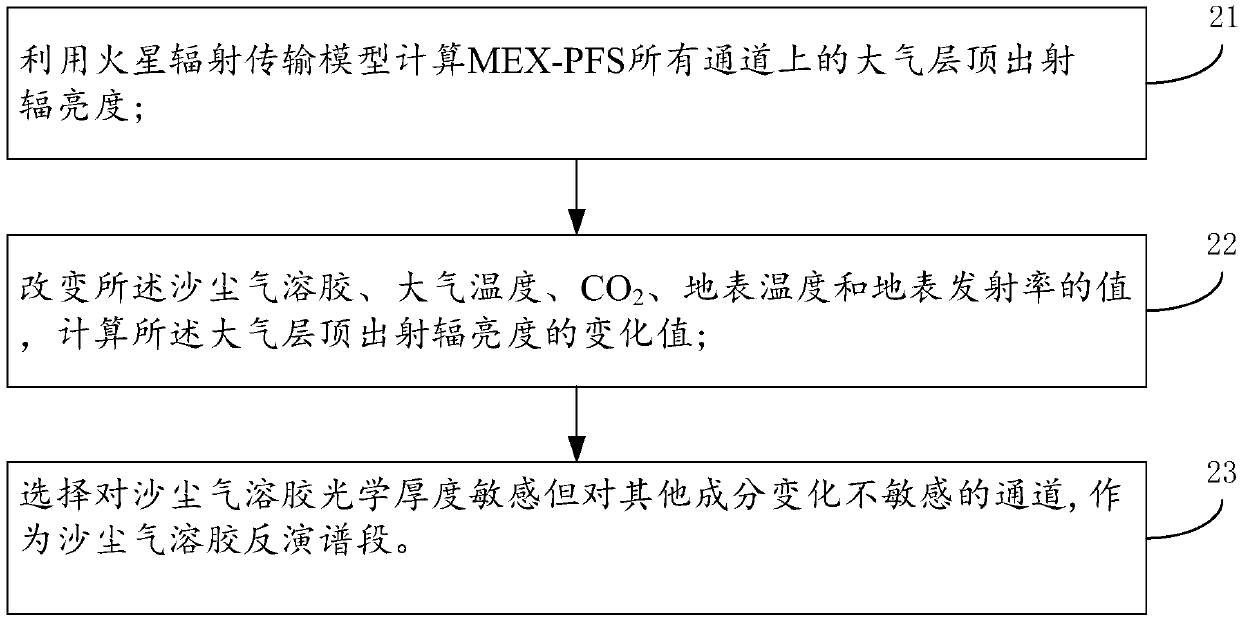
The invention discloses a Martian atmospheric dust aerosol optical depth retrieval method. The method comprises the steps of performing calibration on MEX-PFS data to obtain PFS observation radiance data and observation noises; performing sensitivity analysis on factors including dust aerosol, atmospheric temperature, carbon dioxide, surface temperature and surface emissivity, and selecting a dustaerosol retrieval spectrum section; by using a surface emissivity real value, an atmospheric background data initial value and a surface temperature initial value, generating a Martian atmospheric state vector initial value; at the dust aerosol retrieval spectrum section, calculating atmospheric layer top outgoing radiance under the atmospheric state vector initial value condition, and adding theobservation noises to obtain simulated PFS radiance; and retrieving an atmospheric state vector, and cyclically calculating the simulated PFS radiance to minimize a cost function. According to the method, the dust aerosol content retrieval can be stably, quickly and conveniently performed; and the influence of Martian surface contribution inaccuracy on atmospheric retrieval result precision is reduced.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
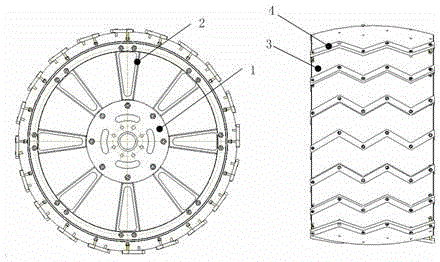
Wheel suitable for terrain environment of Mars
The invention discloses a wheel suitable for the terrain environment of the Mars. The wheel comprises a wheel body, a wheel driving joint, spokes, a driving mechanism, a hub, and pawls, wherein the wheel driving joint enables the wheel body and the driving mechanism to be connected, and connection joints connecting the spokes and connecting the driving mechanism are respectively designed; the wheel driving joint is connected with the spokes through screws and nuts; the spokes are rigid spokes and are mounted on one side of the wheel; the driving mechanism is arranged at the inner part of the hub; the spokes are connected with the hub through screws and nuts; the pawls are connected with the hub through screws and nuts. The wheel is beautiful in structural appearance, easy in machining, compact in structure, high in passability on the surface of the Mars and high in strength, can bear the weight of a Mars patrolling device, and can bear certain torque.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
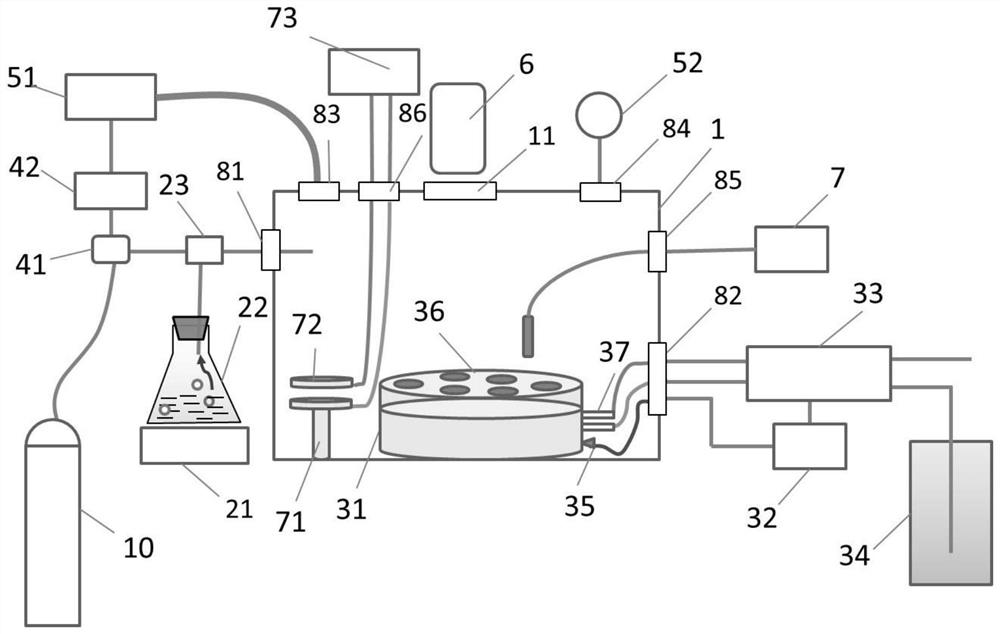
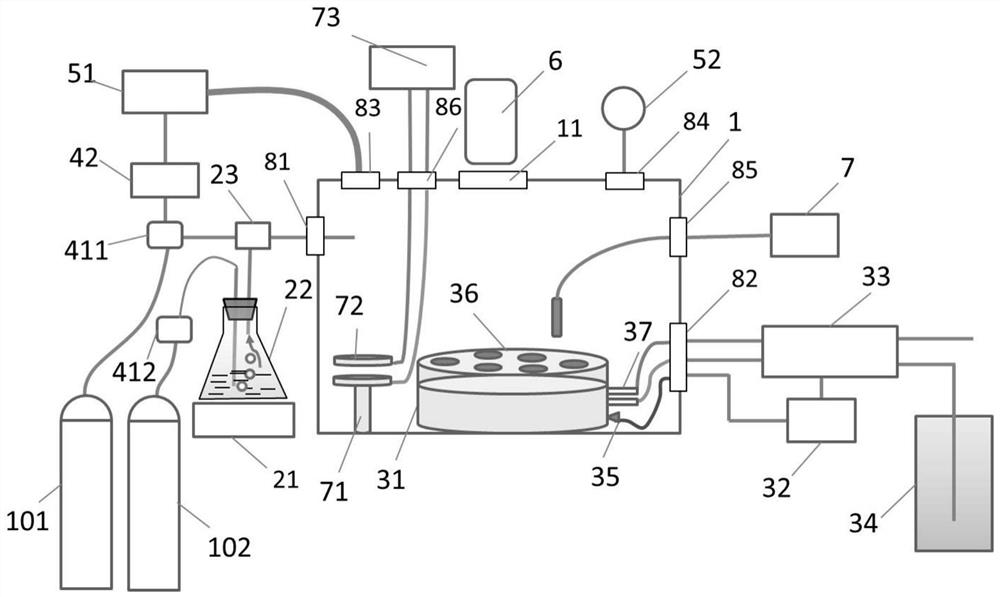
Spark surface gas component simulation device and method
ActiveCN111579261ASave materialEasy to controlContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsEngineeringAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a spark surface gas component simulation device and method. In order to solve technical problems that an existing ground simulation scheme has large simulation errors and cannot truly and accurately simulate the pressure environment of the surface of Mars, the invention provides a device and a method for simulating gas components on the surface of Mars. The gas componentson the surface of the Mars are considered to the maximum extent, an atmospheric state of the Mars can be simulated close to the actual atmospheric state, and technical support is provided for a real and accurate environment simulation test of a Mars detector on the ground.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
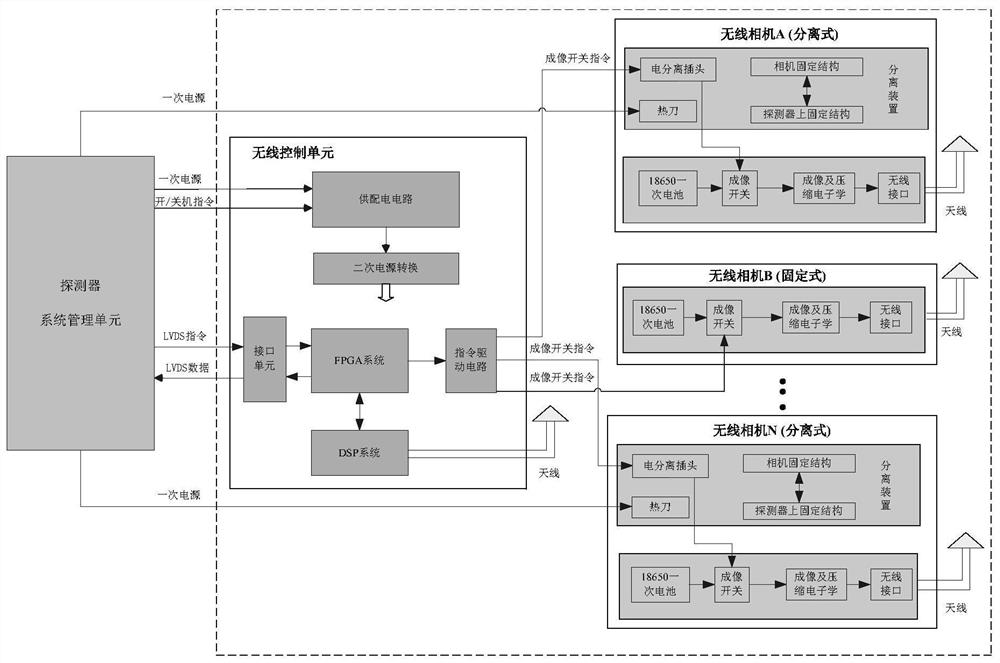
Separable wireless networking imaging system and method suitable for extraterrestrial celestial body detection
PendingCN114143444AAchieving shared designRealize light and small integrated designTelevision system detailsNetwork topologiesWireless controlMars rover
The invention discloses a separable wireless networking imaging system and an imaging method suitable for extraterrestrial celestial body detection. The imaging system comprises a wireless control unit and a plurality of wireless cameras, the wireless control unit and the wireless cameras adopt a wireless connection communication mode, and the wireless cameras are divided into a fixed type and a separated type, so that the problem of third-view-angle imaging of extraterrestrial celestial body detection is solved, independent imaging on the extraterrestrial celestial body is realized, and the imaging efficiency is improved. Image and video data with more unique visual angles are obtained, the visuality and the display degree of key link engineering state monitoring are better achieved, and the effect that human beings obtain process images of a Mars rover moving on the surface of Mars for the first time is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
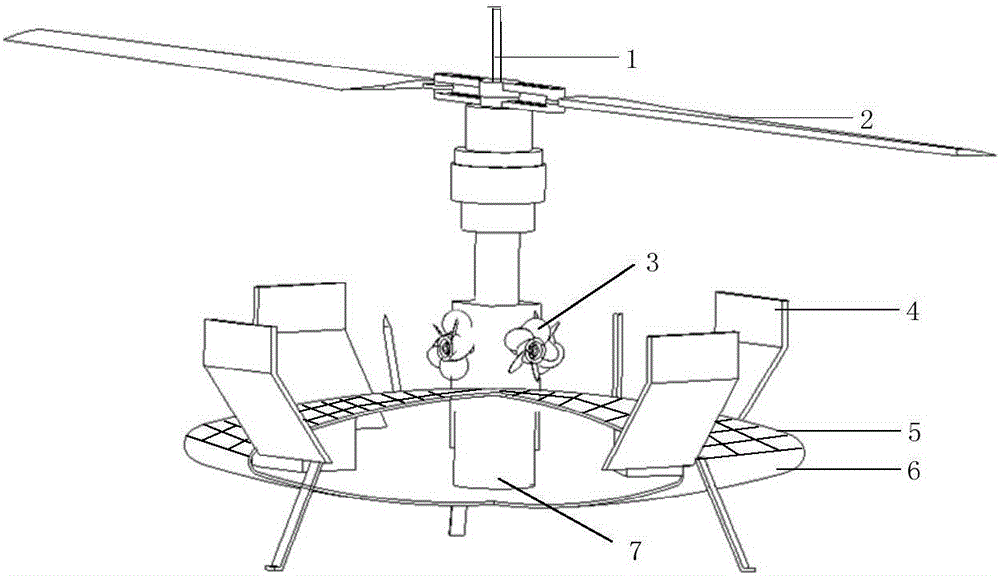
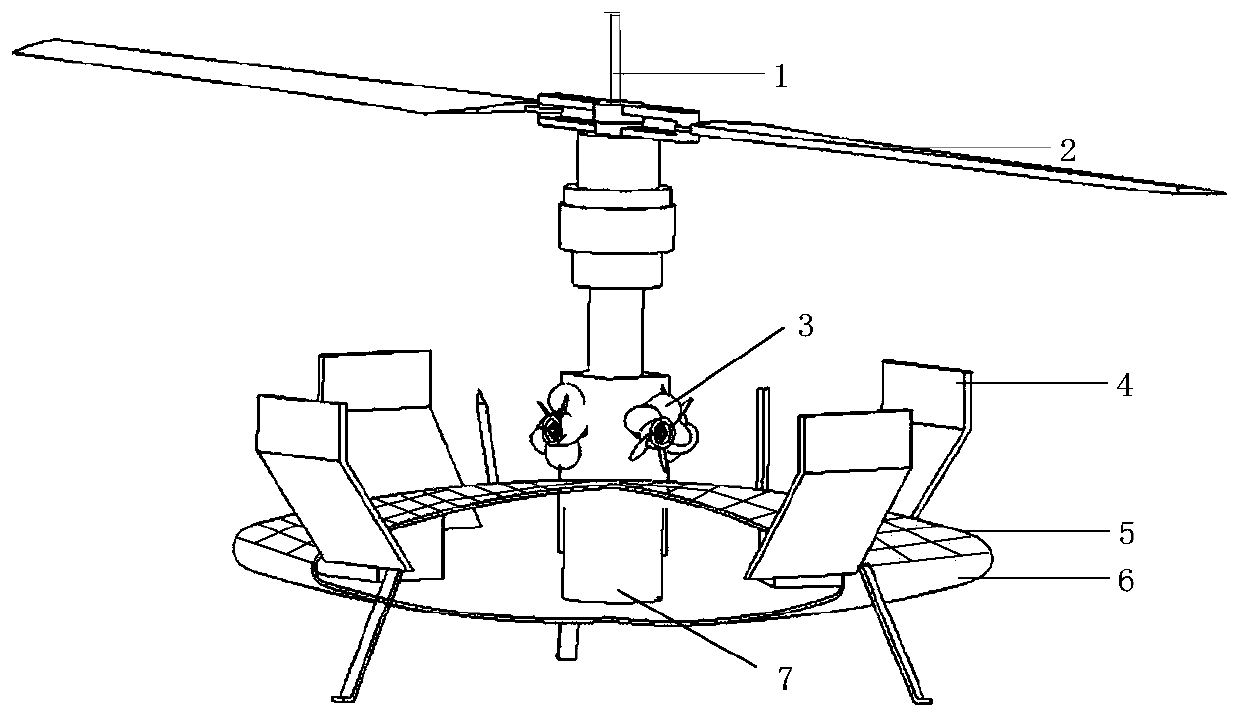
Gyroplane for random detection using Mars atmospheric circulation and application method thereof
The invention discloses a gyroplane for random detection using Mars atmospheric circulation and an application method thereof. The gyroplane comprises a rotor shaft, a rotor hub, a wind sensor, a foldable blade, propellers, a body and a control plane, wherein the wind sensor is arranged at the top of the rotor hub and used for monitoring the wind direction and wind speed on the Mars surface; the foldable blade is mounted at the top end of the rotor shaft through the rotor hub; the blade is in a folded state whenlaunched and is expanded after reaching the Mars surface; 4 propellers are arranged at the root of the rotor shaft in a cross shape; the control plane is symmetrically arranged on the upper surface of the body; a solar cell is also arranged on the upper surface of the body; and a storage battery connected with the solar cell is arranged in the body. Different from the scientific detection form of the current Mars surrounding devices and landing patrollers, in the invention, random on-site detection is carried out by use of the Mars atmospheric circulation; and the invention is applied to the 'Mars Green Home' project and has very broad application prospects in the field of deep space exploration.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
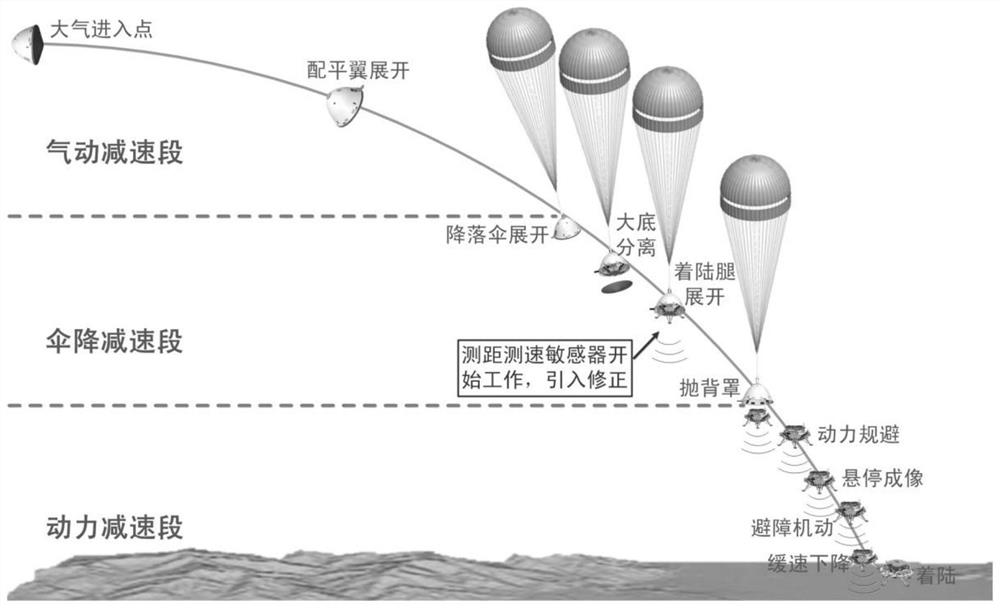
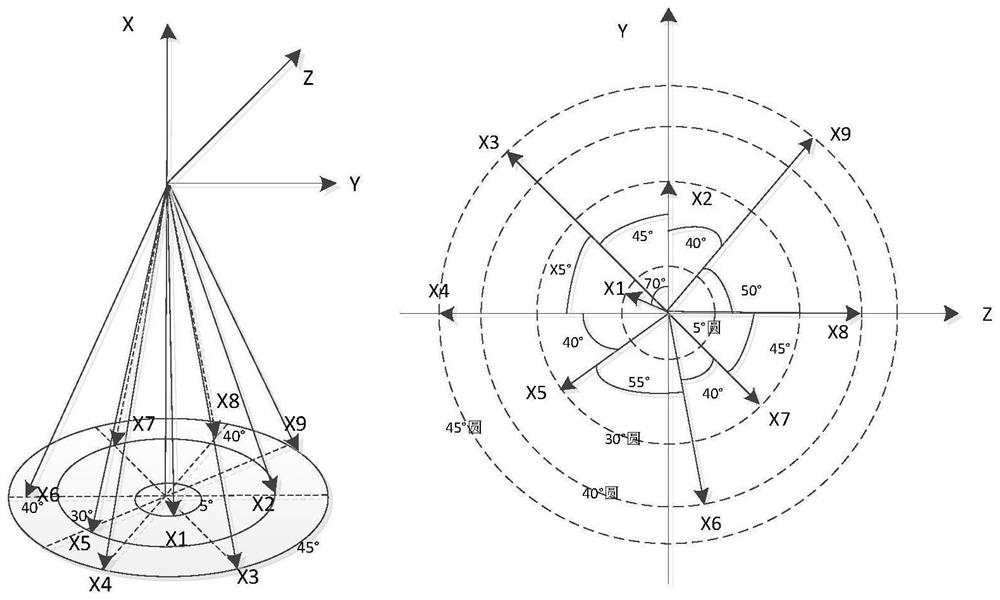
Distance and speed measurement sensor beam pointing determination method for Mars landing
ActiveCN113772134AWith rangingAbility to measure speedSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesMicrowaveBeam direction
The invention relates to a distance and speed measurement sensor beam pointing determination method for Mars landing, which comprehensively considers the configuration layout of a detector, and considers the measurement precision requirements of long and short distance sections and heterogeneous backup of two types of distance and speed measurement sensors. The pointing directions of four fixed pointing beams of the microwave distance and speed measuring sensor and nine fixed beam pointing directions of the phased array sensor are determined. In actual use, the phased array sensor calculates and appoints four wave beams through a spaceborne computer in each measurement period to provide distance measurement and speed measurement information. Multi-beam information fusion processing is carried out on relative distance and speed information obtained in eight beam directions of the microwave distance and speed measuring sensor and the phased array sensor, so that the relative distance, speed and other information of the detector relative to the surface of the Mars can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Device and method for simulating gas composition on the surface of Mars
ActiveCN111579261BSave materialEasy to controlContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsAtmospheric sciencesEnvironmental simulation
The invention relates to a spark surface gas component simulation device and method. In order to solve technical problems that an existing ground simulation scheme has large simulation errors and cannot truly and accurately simulate the pressure environment of the surface of Mars, the invention provides a device and a method for simulating gas components on the surface of Mars. The gas componentson the surface of the Mars are considered to the maximum extent, an atmospheric state of the Mars can be simulated close to the actual atmospheric state, and technical support is provided for a real and accurate environment simulation test of a Mars detector on the ground.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-case weak supervision Mars surface morphology detection method based on online learning
ActiveCN114415254AEasy to findImprove detection accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical detectionEngineeringNetwork model
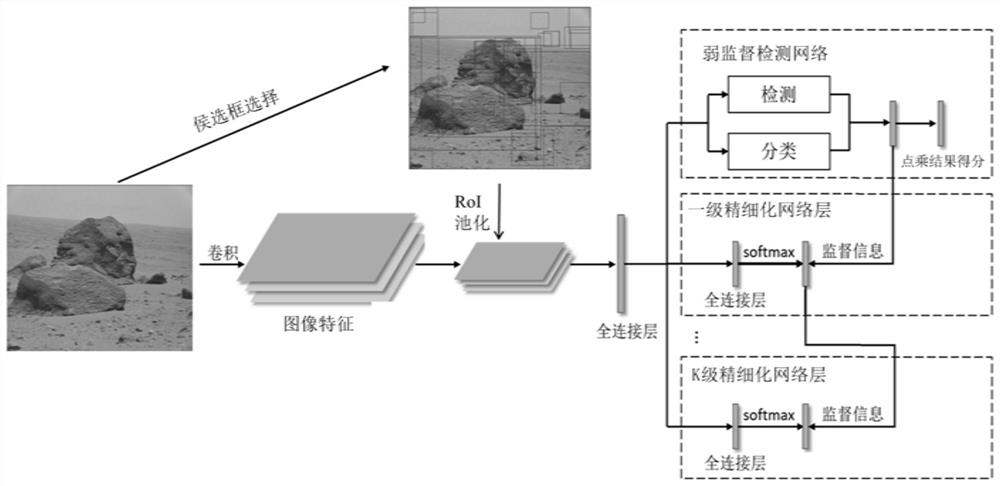
The invention discloses a multi-case weak supervision Mars surface morphology detection method based on online learning, and belongs to the field of machine vision object detection. The method aims at solving the problems that an existing weak supervision object detection method is low in detection precision and converges to a local optimal solution. Comprising the steps of generating a plurality of candidate boxes for a Mars long-range image by adopting a selective search algorithm; a VGG16 network model is adopted to carry out image feature extraction on the Mars long-range image; obtaining a full connection feature of each candidate box; in the weak supervision detection network, full connection features of candidate boxes are input, the category of each candidate box is judged through classification and detection branches, position information of the candidate boxes is scored, and finally scores of the candidate boxes are obtained by multiplying scores of the two branches and serve as case-level labels; and the K-level refined network layer takes the score of each candidate box of the multi-case learning network or the previous-level branch as supervision information, trains other optimized branches of the network, and carries out backward propagation calculation. The method is used for detecting the surface topography and the target of the Mars.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
An anti-jamming and fault-tolerant control method for a Mars lander
ActiveCN105629987BImprove anti-interference abilityImprove reliabilityAttitude controlKinematicsDynamic models
The present invention relates to an anti-interference fault-tolerant control method of a Mars lander. Firstly, building the attitude kinematics and the dynamics model of the Mars lander; secondly, designing a wind interference estimator to estimate the gust influence on the Mars lander aiming at the influence of the gust at the powered lowering stage at the surface of the Mars so as to perform compensation through a feedforward channel; thirdly, designing an execution mechanism partial failure observer to estimate and compensate the partial failure value of the Mars lander execution mechanism; and finally, recombining the gust interference estimator, the execution mechanism partial failure observer and a PD attitude controller, and constructing a fault tolerance controller of partial failure of the Mars lander execution mechanism. The anti-interference fault-tolerant control method of Mars lander has high anti-interference ability and high reliability, and has a higher practical engineering value compared with a traditional Mars lander control method.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Flying method on Mars, and Mars flying device
PendingCN111516905AExtended detectionExpansion inspectionCosmonautic power supply systemsArtificial satellitesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a flying method on Mars, and a Mars flying device. According to the method, a medium on the surface of Mars and a medium acceleration unit are adopted; under the action of electric power, the medium acceleration unit works, the medium is conveyed to the medium acceleration unit, and is separated from the medium acceleration unit after being accelerated by the medium acceleration unit, and reactive force is generated due to momentum conservation and overcomes Mars attraction to drive a load to take off. The method is novel and unique, is suitable for the Mars environmentwhich does not have atmosphere and cannot fly by means of atmospheric buoyancy, breaks through the obstacle of Mars morphology to scientific investigation, and can expand the detection, investigationand development capacity of human beings to Mars.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A deep space landing geometric orbit determination method, system and deep space lander
ActiveCN109000665BImprove robustnessImprove fault toleranceInstruments for comonautical navigationAutonomous Navigation SystemClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a geometrical orbit and gesture determining method and system for deep space landing and a deep space lander. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining adirection vector of the lander relative to the Mars and the distance from the lander to the center of the Mars; solving the height from the lander to the surface of the Mars according to the distancefrom the lander to the center of the Mars and the radius of the Mars; establishing an inertial coordinate system xIyIzI to obtain a gesture matrix from the inertial coordinate system to a body coordinate system; further solving the inertial position and the inertial speed of the lander. According to the method and system, geometrical orbit and gesture determination is carried out by using a distance and speed measuring sensor automatically. Under the circumstance that IMU in a power falling section fails, orbit and gesture determination can be carried out by means of the distance and speed measuring sensor so as to achieve initial standard capturing of autonomous navigation, the dependent degree of the inertial navigation system to the initial standard is alleviated, and the robustness andthe failure tolerant capability of the autonomous navigation system of soft landing are improved. The algorithm is an analytical algorithm which is convenient for on-star algorithm, thereby laying afoundation for implementing a soft landing task successfully.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
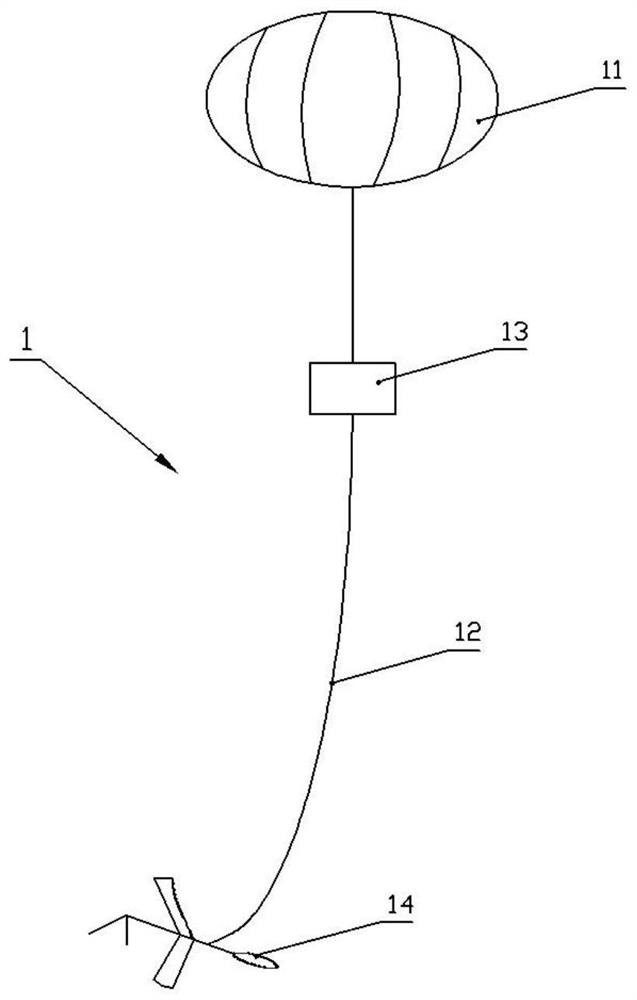
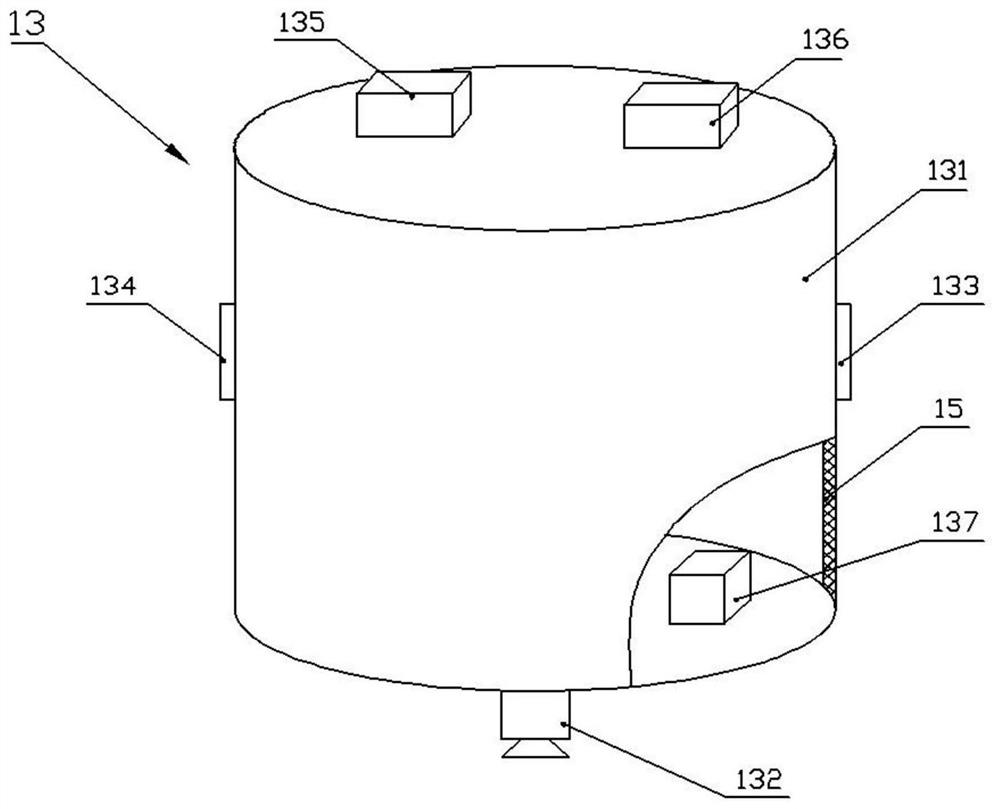
Mars floating detection system
ActiveCN111605728AWide detection rangeArtificial satellitesSystems for re-entry to earthMarine engineeringEngineering
The invention discloses a Mars floating detection system. The system comprises a floating system, an inflation system and a landing cabin, wherein the floating system comprises an overpressure balloon, a tying rope, an instrument cabin and a track controller, the track controller comprises a main rod, a main wing, an empennage and a balance weight, the main wing is connected to the middle of the main rod, the empennage and the balance weight are arranged at the two ends of the main rod respectively, the instrument cabin is tied below the overpressure balloon through the tying rope, and the track controller is tied below the instrument cabin; the inflation system is arranged in the landing cabin and used for inflating the overpressure balloon. The system is carried by a lander to reach thesurface of the Mars, and when the meteorological condition of the surface of the Mars is good, the inflation system inflates the overpressure balloon until the floating system lifts off and is separated from the landing cabin; then the floating system is separated from the inflation system, and the inflation system is left in the landing cabin; and after the floating system reaches a preset height, detection work is started, and different areas are detected through Mars atmospheric motion. Movement is not limited by Mars topography and geomorphism, and the detection range is wider.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A posture correcting device for a Mars landing module
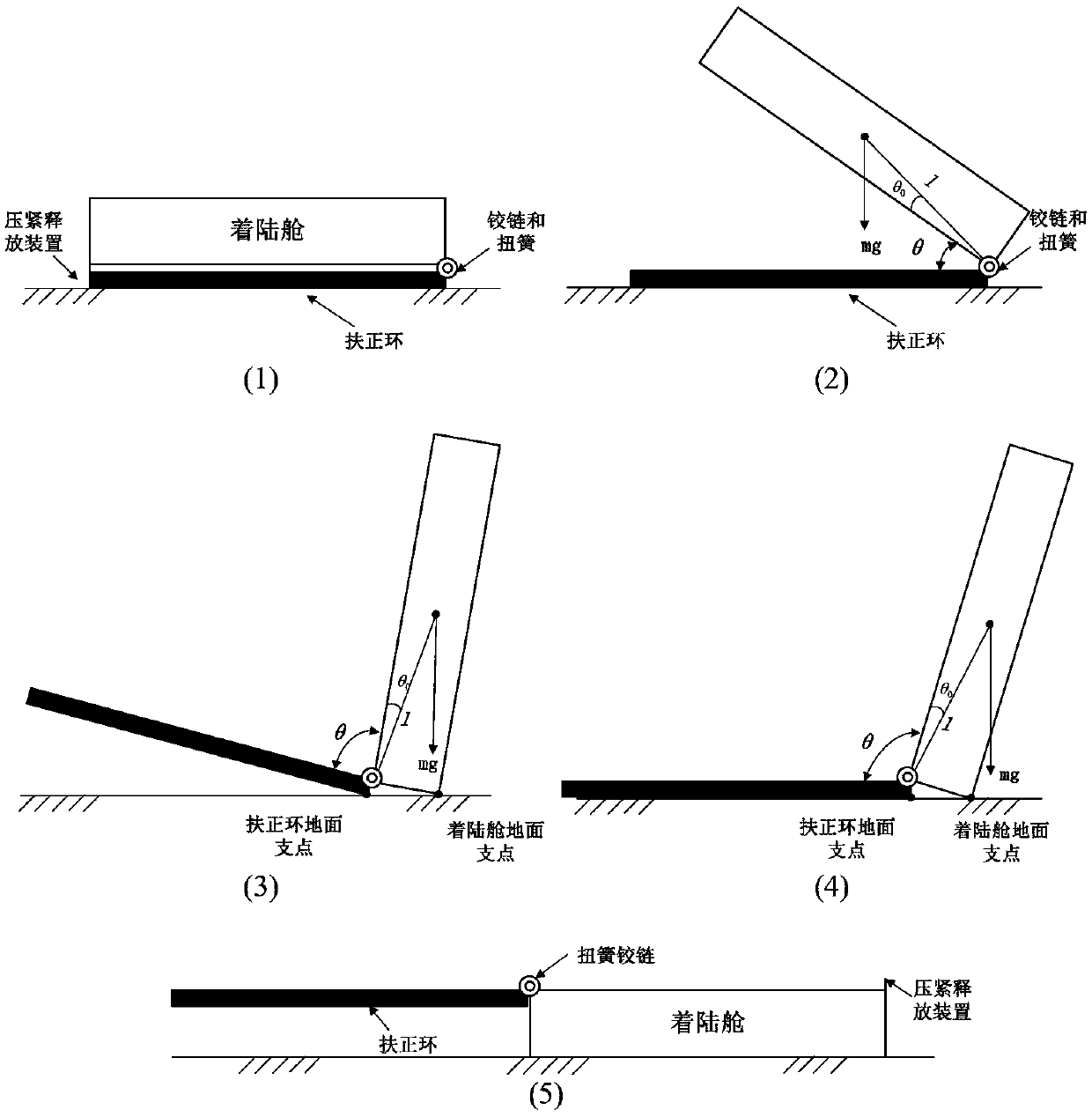
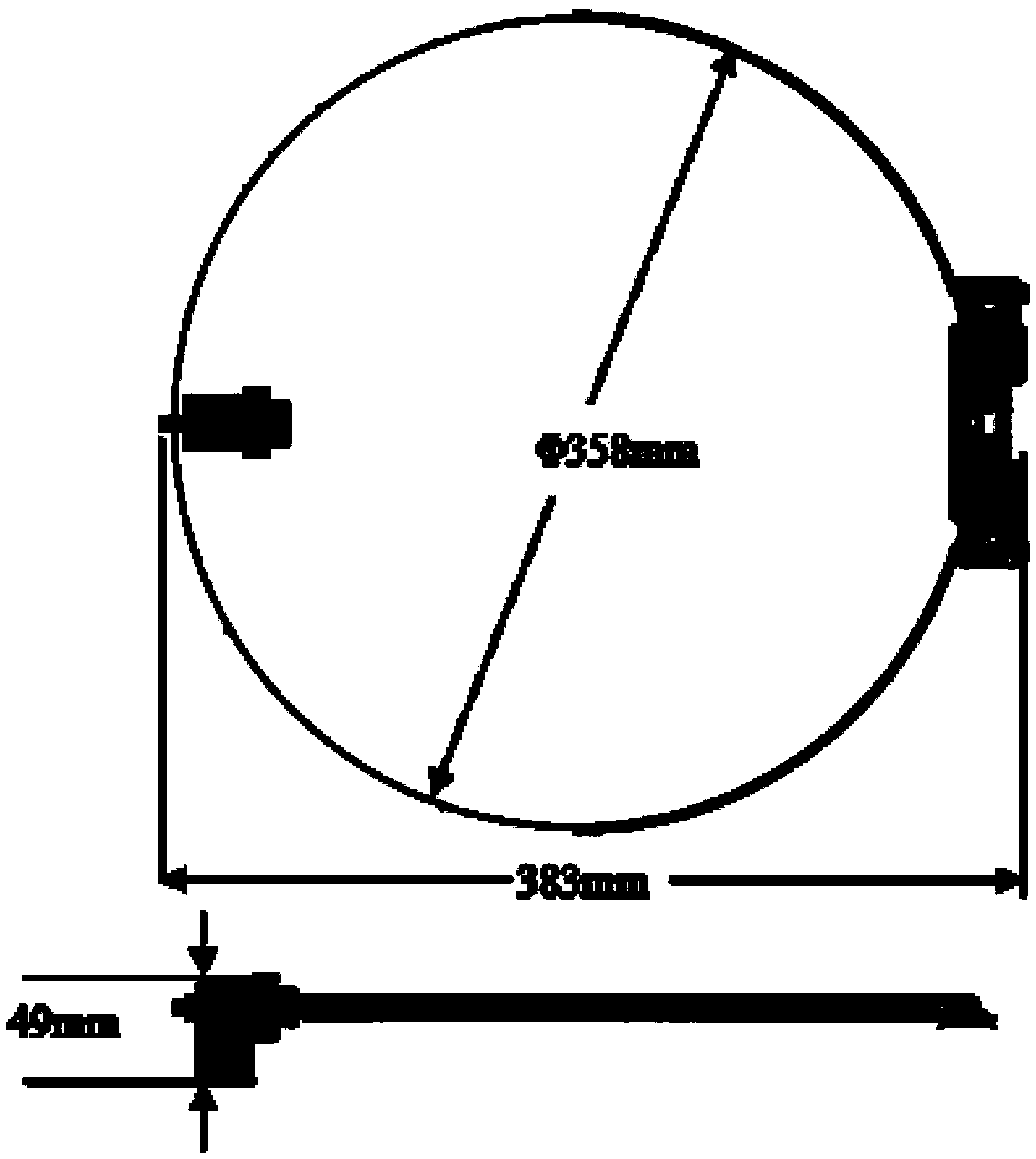
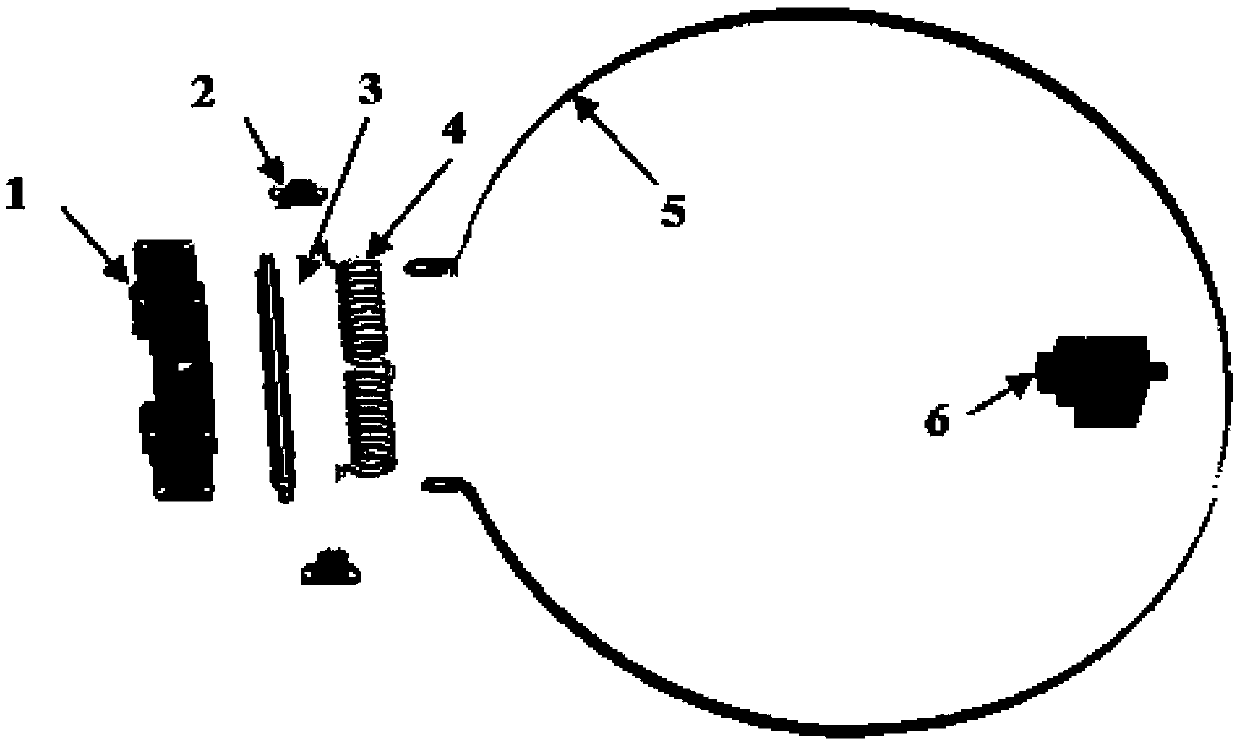
ActiveCN103274062BSimple structureReduce volumeSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesEnergy supplyEngineering
The invention provides a device for centering postures of a Mars landing capsule. The device comprises a base plate (1), a support (2), a connecting shaft (3), a torsional spring (4), a centering ring (5) and a compressing and releasing device (6). Under the conditions that the size, the weight and the energy supply of the device are limited strictly, an initiating explosive device acts to release the compacted torsional spring, and therefore the centering ring is driven to center the postures of the Mars landing capsule. The device for centering the postures of the Mars landing capsule has the advantages of being simple in structure, safe, reliable, small in size and light in weight. As the effective means for guaranteeing the correct postures of the landing capsule on the Mars, the device for centering the postures of the Mars landing capsule can be directly applied to development for a landing capsule in the first Chinese Mars landing detecting task, and can also provide reference for design of Chinese follow-up small-scale planet landing capsules.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Method for simulating surface morphology of Mars in earth environment
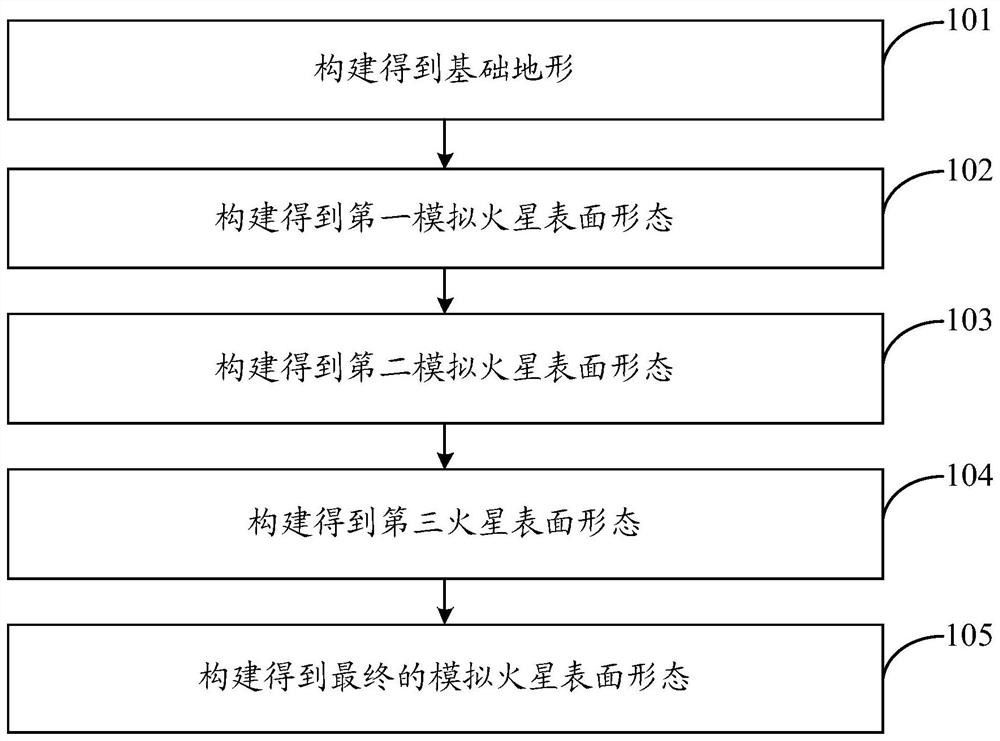
ActiveCN113247317AMeet the requirements of backscattering characteristicsEasy to cleanCosmonautic condition simulationsTerrainEngineering
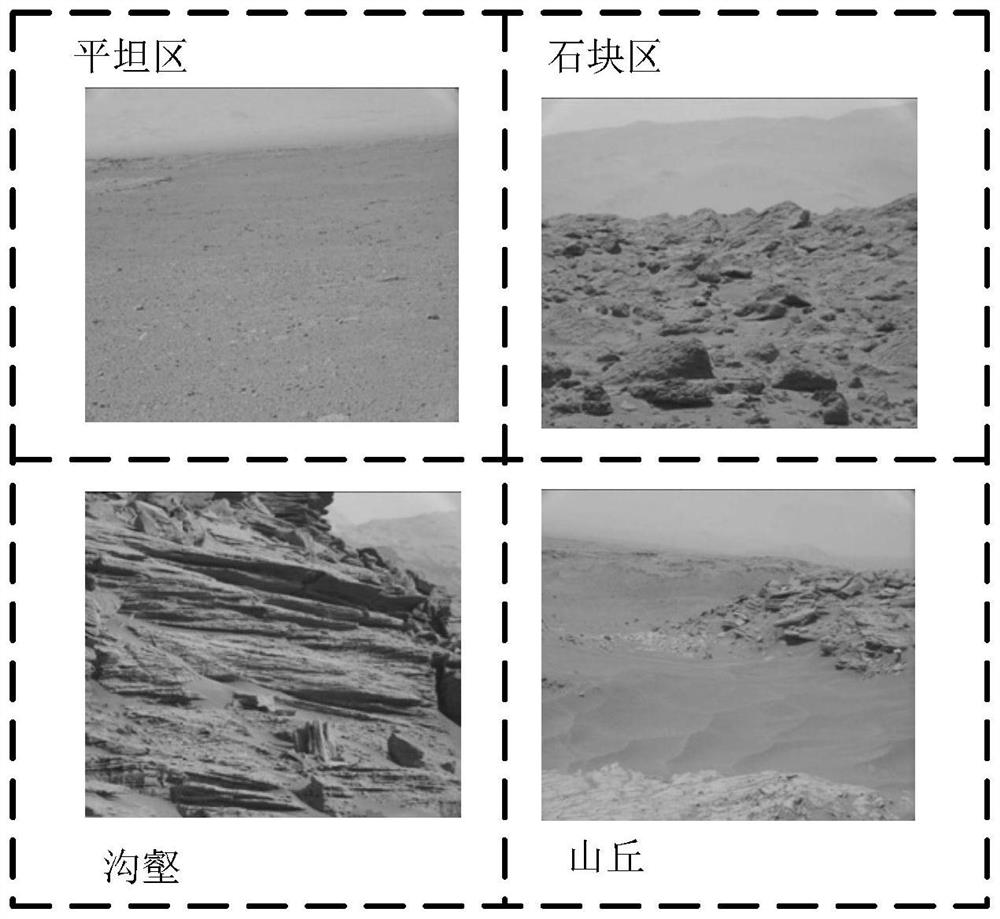
The invention discloses a method for simulating the surface morphology of Mars in an earth environment. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a basic terrain for simulating the surface morphology of Mars; based on the basic terrain, constructing a first simulated Mars surface morphology with different Mars pit distribution characteristics; based on the first simulated Mars surface morphology, constructing a second simulated Mars surface morphology with different Mars pit distribution characteristics and Mars rock distribution characteristics; based on the second simulated Mars surface morphology, constructing a third Mars surface morphology with different Mars pit distribution characteristics, Mars rock distribution characteristics and fire slope distribution characteristics; and based on the third Mars surface morphology, constructing a simulated Mars surface morphology which has different Mars pit distribution characteristics, Mars rock distribution characteristics and fire slope distribution characteristics and can reflect Mars surface microwave and aurora reflection characteristics. The invention aims to realize the real representation of the Mars surface topography and landform, and ensures that the Mars lander can identify the Mars surface morphology (Mars pit, Mars rock, Mars slope and the like) with high precision in the Mars surface landing process.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
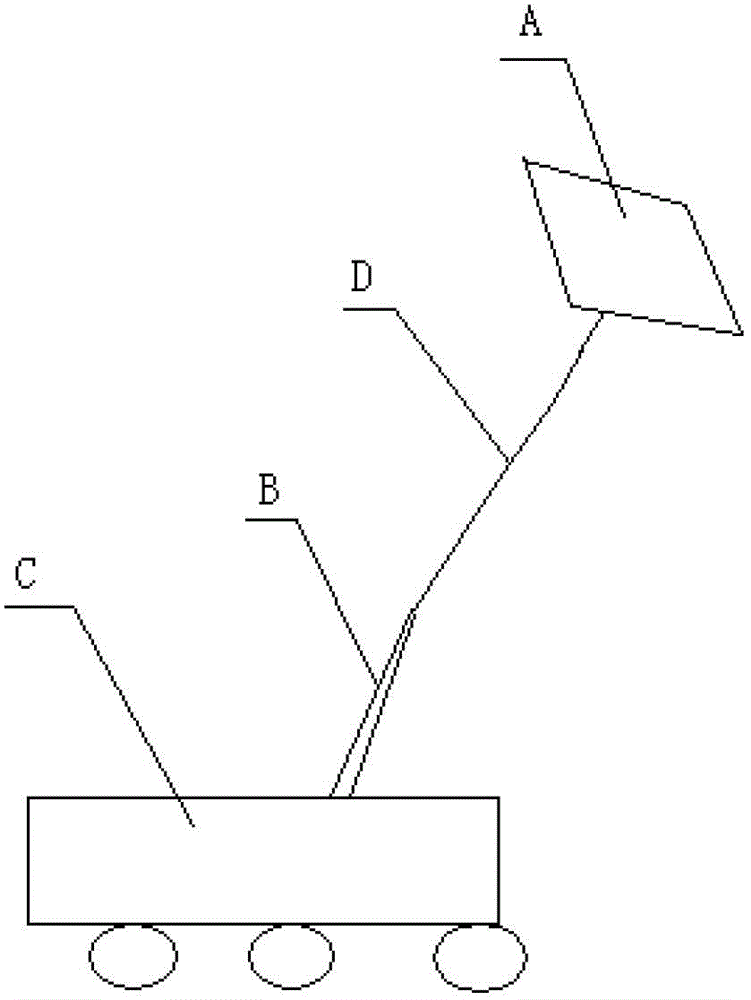
Design method for repeatedly using floating detector system on Martian surface
ActiveCN102998717BLoad Weight AdjustmentRealize the collectionGeological measurementsFlying heightEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of spaceflight test control and relates to a design method of aerospace instruments, in particular to a design method for repeatedly using a floating detector system on the Martian surface. The floating detector system is composed of a floating detector, a mooring rope, a mechanical arm and a movable floating detector base. The design method comprises six steps and has the advantages that the floating detector system can be used repeatedly, survey with unlimited times on one area of the same Martian target location can be achieved in theory, and different three-dimensional weather resource collection of flying height of the flying detector can be achieved in different time periods of the same area.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
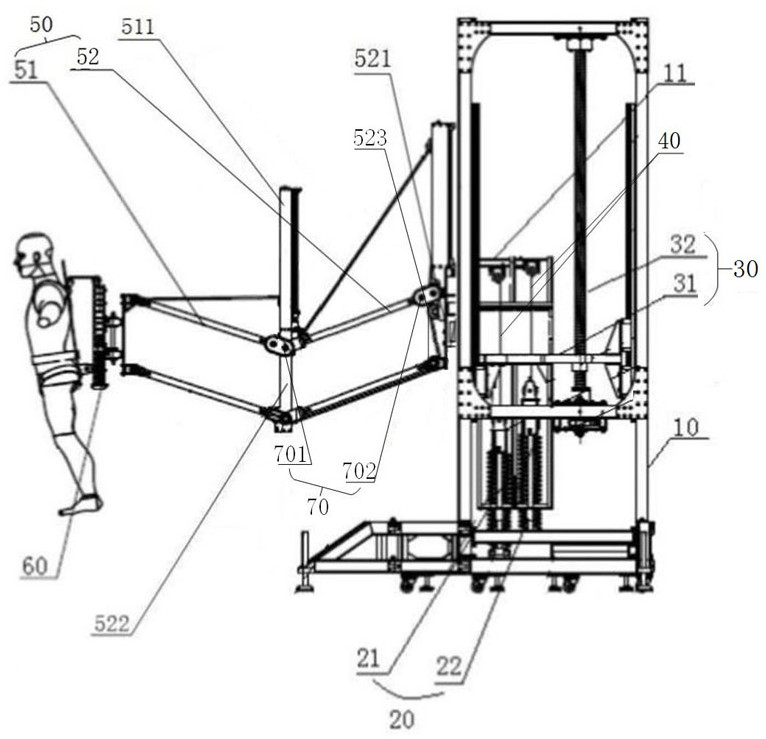
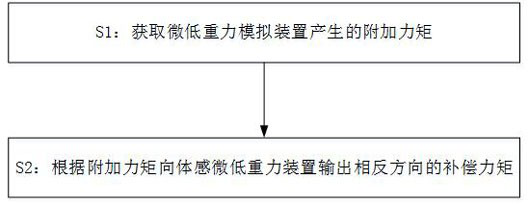
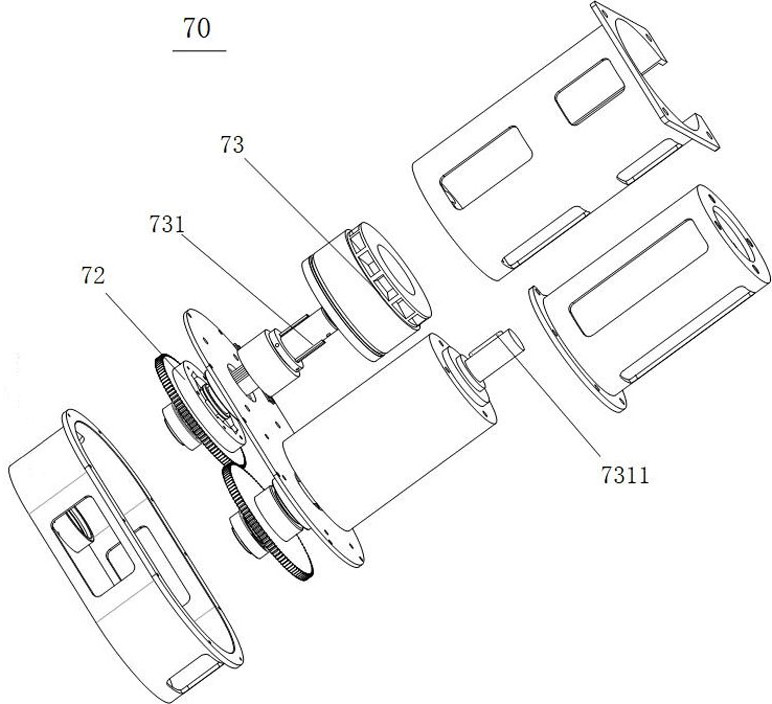
Active compensation method for somatosensory micro-low gravity simulation device
ActiveCN114162359AImprove the efficiency of active compensationHigh precisionCosmonautic condition simulationsSustainable transportationEngineeringMicro gravity
The invention discloses an active compensation method for a somatosensory micro-low gravity simulation device, and the somatosensory micro-low gravity simulation device comprises a gravity balance assembly, and a buffer assembly which provides buffer potential energy for the gravity balance assembly to at least partially balance the gravity of a human body. The active compensation method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring an additional torque generated by a micro-low gravity simulation device; and S2, outputting compensation torque in the opposite direction to the somatosensory micro-low gravity device according to the additional torque. The reverse compensation torque is output according to the obtained additional torque, so that the walking effect of the astronaut in the training system is consistent with or close to the actual walking effect on the moon surface and the Mars surface, the active compensation efficiency is improved, and the simulation precision of the device is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Simulated Mars soil preparation method and test bed construction method
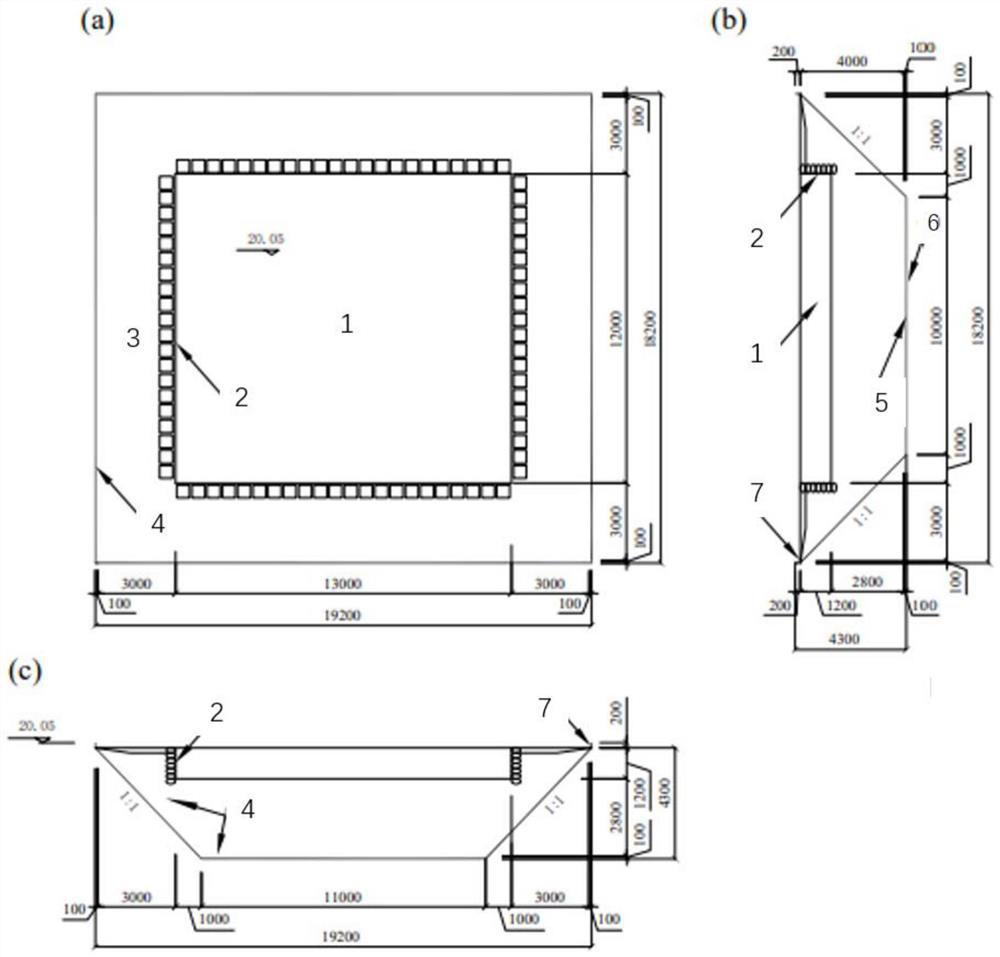
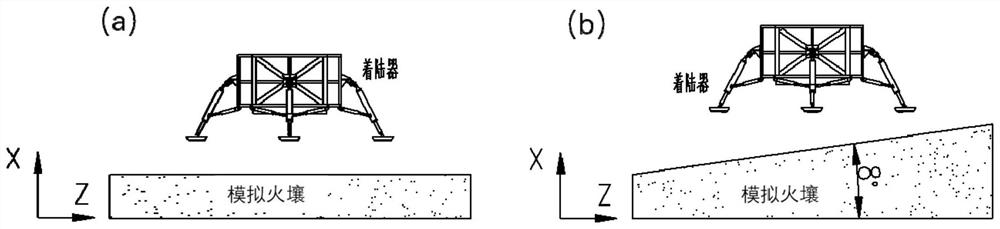
PendingCN114495677AThe physical and mechanical properties remain stableWide range of usesEducational modelsMartian soilSoil science
The invention discloses a simulated Mars soil preparation method which comprises the following steps: sequentially drying, removing impurities and crushing volcanic ash to obtain volcanic ash particle aggregates with different particle size ranges, and obtaining corresponding simulated Mars soil standard gradation according to a preset soil mechanical property target value range. The simulated Mars soil can be produced in batches according to the standard grading; the invention further discloses a construction method of the simulated Mars soil test bed, the simulated Mars soil laying area is arranged in the foundation pit, layered filling of the simulated Mars soil is carried out to obtain the test bed, and after filling of each layer is completed, the physical and mechanical parameters of the test bed are controlled according to the physical and mechanical property requirements; a severe landing environment is built on the surface of the test bed. The Mars surface fire soil landform and physical and mechanical properties can be truly reproduced, it is ensured that the Mars lander can recognize the severe environment of the Mars surface with high precision in the Mars surface soft landing process, and meanwhile accidents such as foot pad subsidence are avoided.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Multi-hole injection device for generating multi-type spark rotational flow
PendingCN114789802AConducive to long-term continuous researchImprove ejection effectCosmonautic condition simulationsEngineeringAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a porous injection device, in particular to a porous injection device for generating multi-type spark rotational flow. The invention aims to solve the problems that the authenticity of a high-speed dust storm environment effect on the surface of the Mars simulated by an existing Mars environment simulation device is poor, only a single rotational flow type can be generated, and people cannot conveniently research the real Mars dust storm environment. The device comprises a base, four pose adjusting mechanisms and four ejectors. The four pose adjusting mechanisms are evenly distributed and installed on the upper surface of the base, and each pose adjusting mechanism is provided with one ejector. The invention belongs to the field of aerospace.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
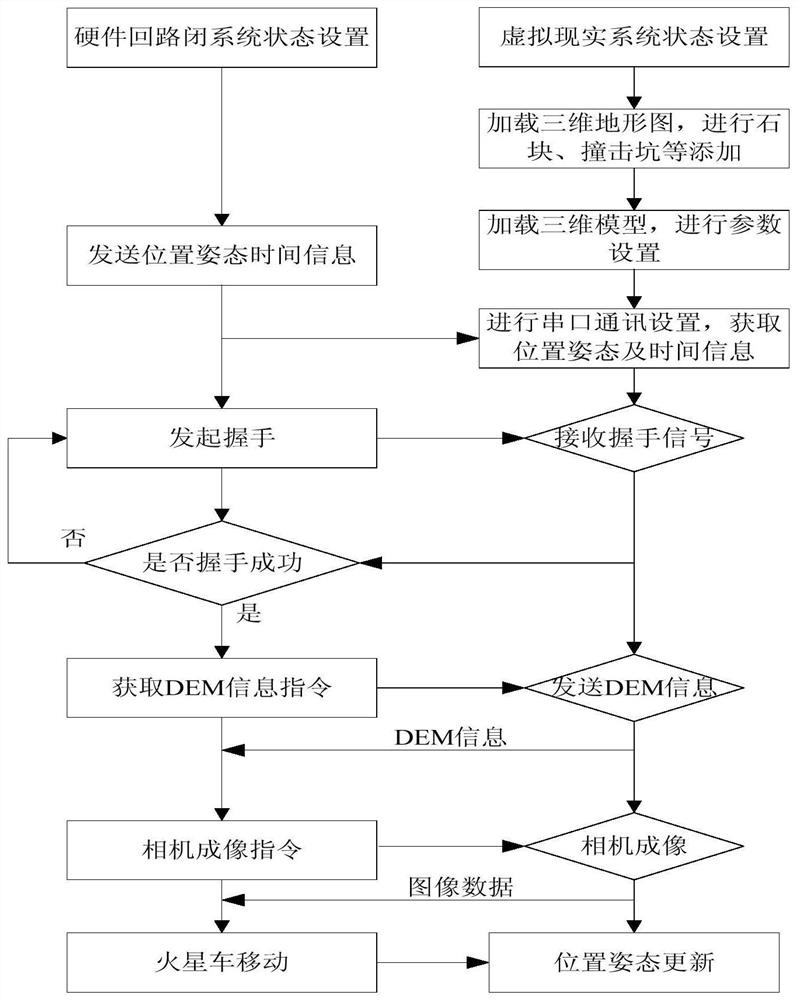
Kinematics closed-loop test system and method based on virtual reality and DEM information interaction
The invention discloses a kinematics closed-loop test system and method based on virtual reality and DEM information interaction, and belongs to the technical field of deep space probe ground system experimental testing. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a Mars surface three-dimensional topographic map by using a virtual reality system, loading a Mars rover real three-dimensional model into the three-dimensional topographic map, performing interaction of a DEM, an attitude position and time information by the virtual reality system and a kinematics module, and completing real-time transmission of camera images with a spaceborne computer at the same time. The test system effectively simulates the working environment of a Mars rover on the surface of the Mars.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
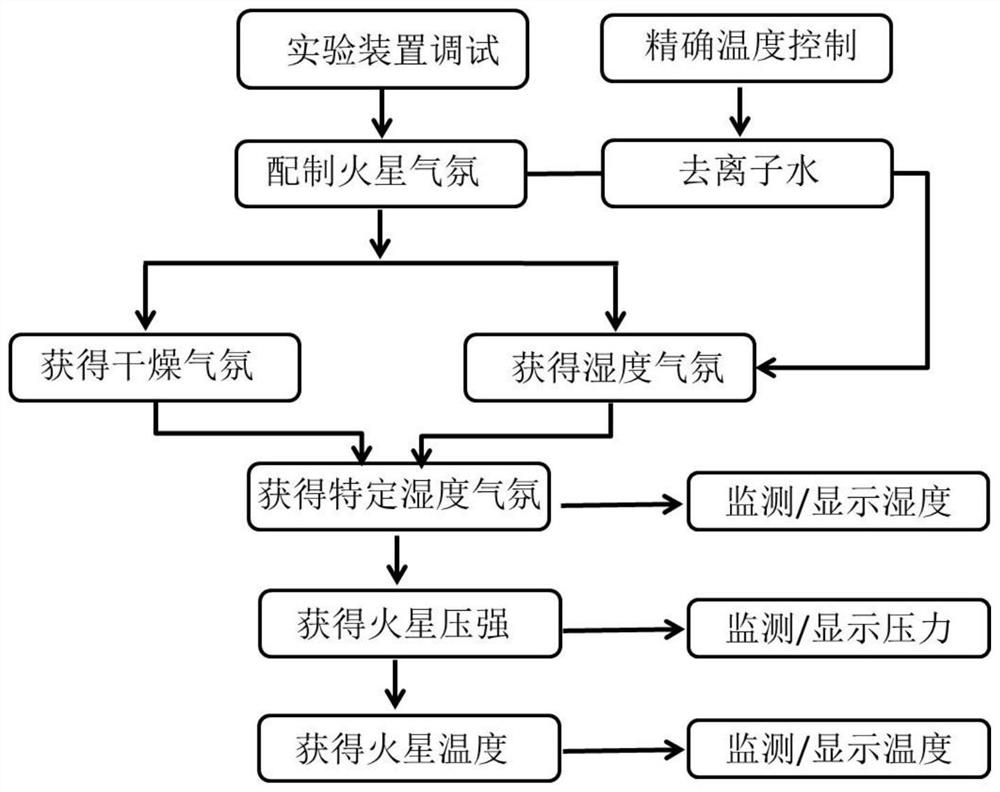
Mars environment simulation experiment device and experiment method
ActiveCN107290296BPrecise Humidity ControlPrecise regulationColor/spectral properties measurementsControl cellEngineering
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
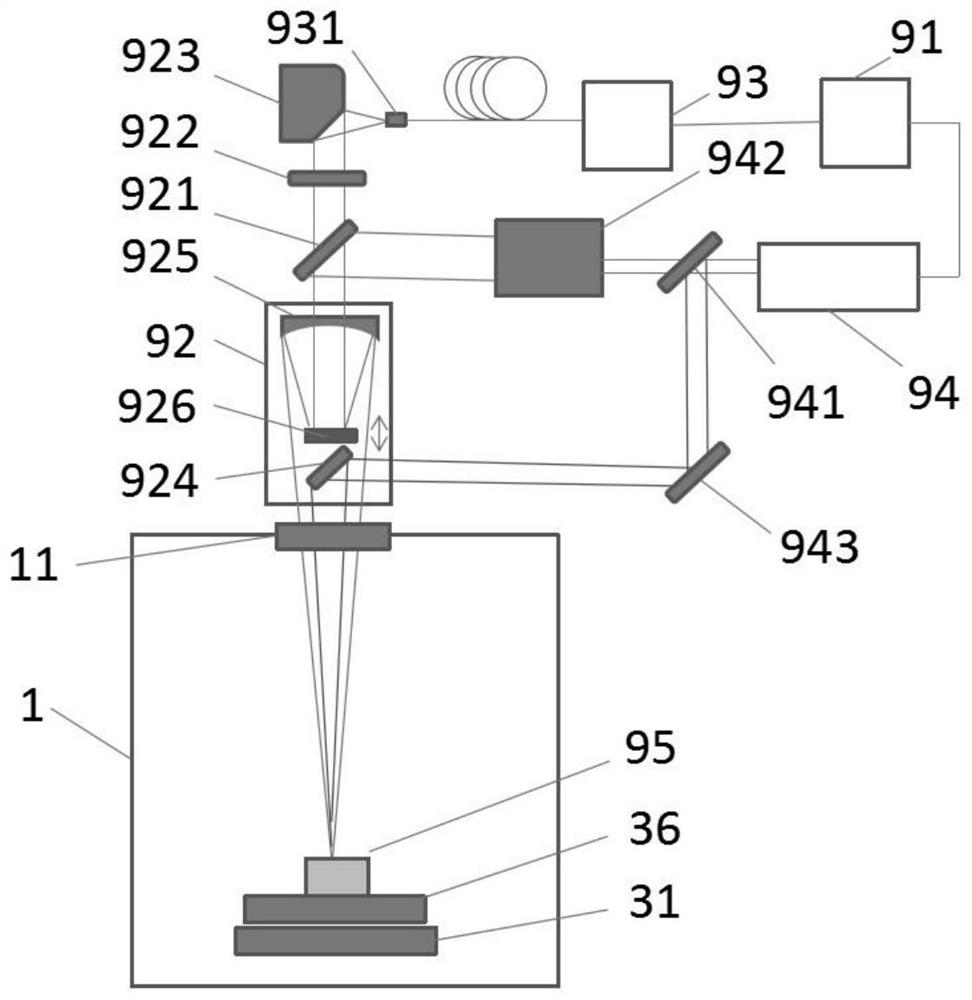
Mars surface spectrum simulator
PendingCN113054909AImprove test accuracyPhotovoltaic monitoringOptical filtersLight beamLight filter
The invention discloses a Mars surface spectrum simulator, which comprises a light source assembly, a dodging device and an optical filter group, the light source assembly is used for emitting a light beam, the light homogenizer and the optical filter group are sequentially located on a propagation path of the light beam, the light homogenizer comprises a plurality of discrete lens groups and is used for segmenting the light beam and emitting a uniform light beam, and the optical filter group is used for adjusting the spectrum of the uniform light beam and emitting a Mars surface simulation light beam. According to the Mars surface spectrum simulator provided by the embodiment of the invention, the light homogenizer comprises a plurality of discrete lens groups, a Gaussian distribution light beam is divided into a plurality of light beams, the plurality of light beams are superposed to form a uniform light beam with high uniformity distribution, and the light filter group is used for adjusting the spectrum of the uniform light beam, so that the spectrum of the uniform light beam is close to the spectrum of the Mars surface, so that the Mars surface simulation light beam with high uniformity distribution is realized.
Owner:苏州馥昶空间技术有限公司
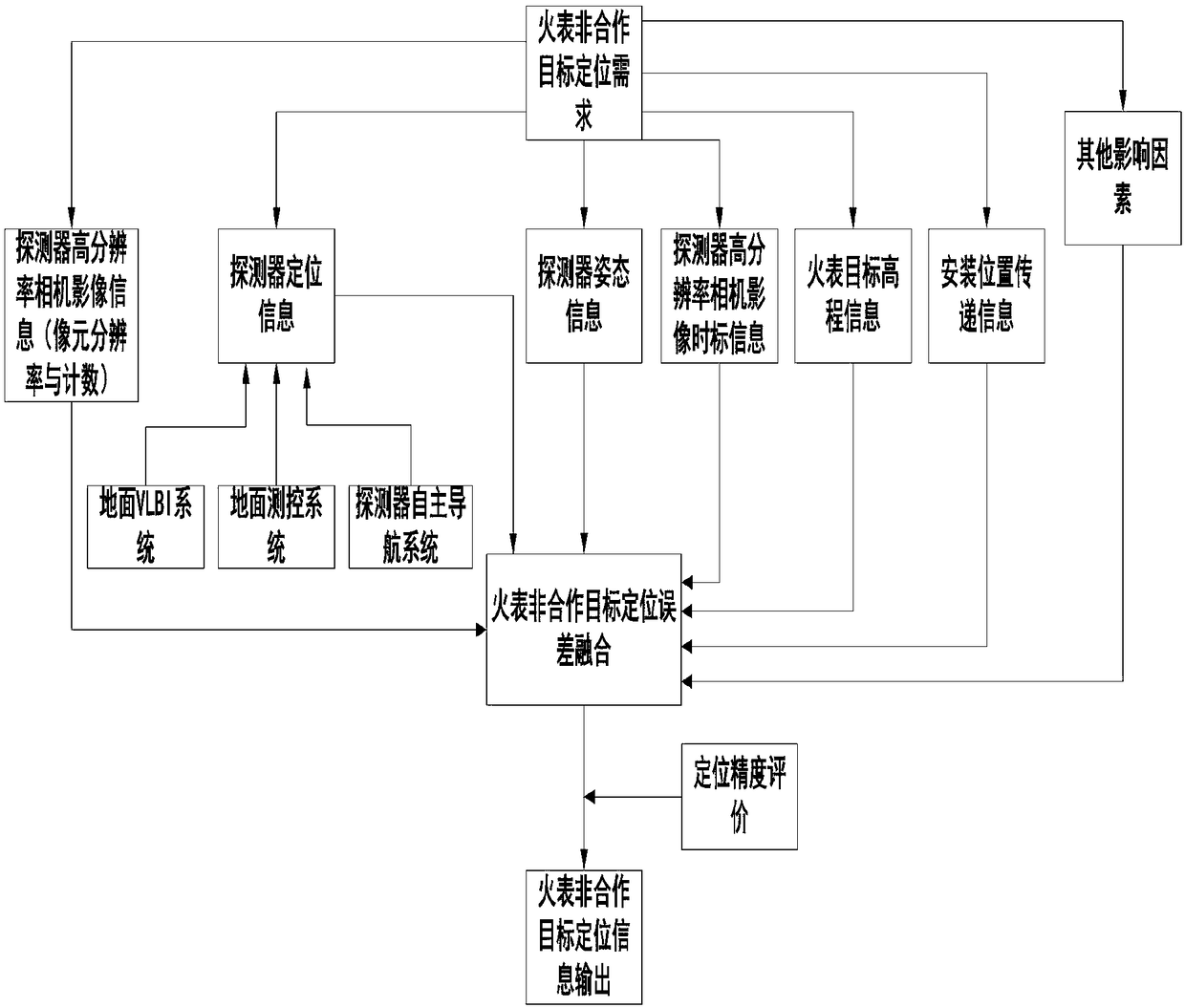
Locating method for non-cooperative targets in images of Martian surface
InactiveCN109084769AHigh positioning accuracyFacilitate and expand accessNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationData acquisitionCorrelation analysis
The invention provides a locating method for non-cooperative targets in images of the Martian surface. The locating method comprises the following steps that step 1, a Mars exploration mission groundapplication system is responsible for proposing the acquisition task, aiming to the targets on the Martian surface, of location locating information of the images on the Martian surface; step 2, the factors of device-ground time delay and device-ground timing system are considered, a ground observation and control system, a VLBI orbit measurement system and a detector autonomous navigation systemuse the images of the targets on the Martian surface in the step 1 as input to complete the extrapolation data acquisition of the orbit information of a detector and carry out the correlation analysisof positioning errors. The locating method further improves the locating information accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
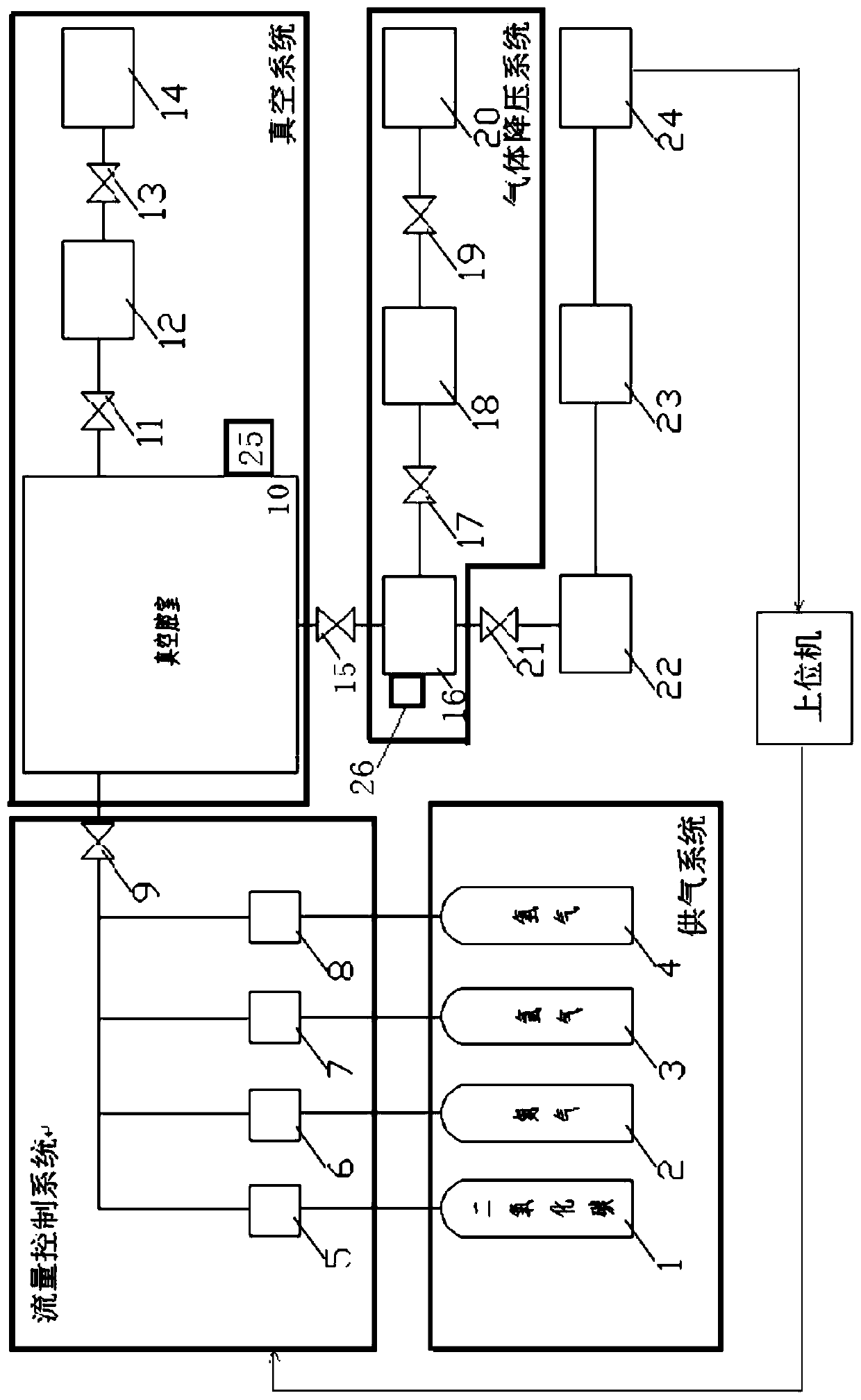
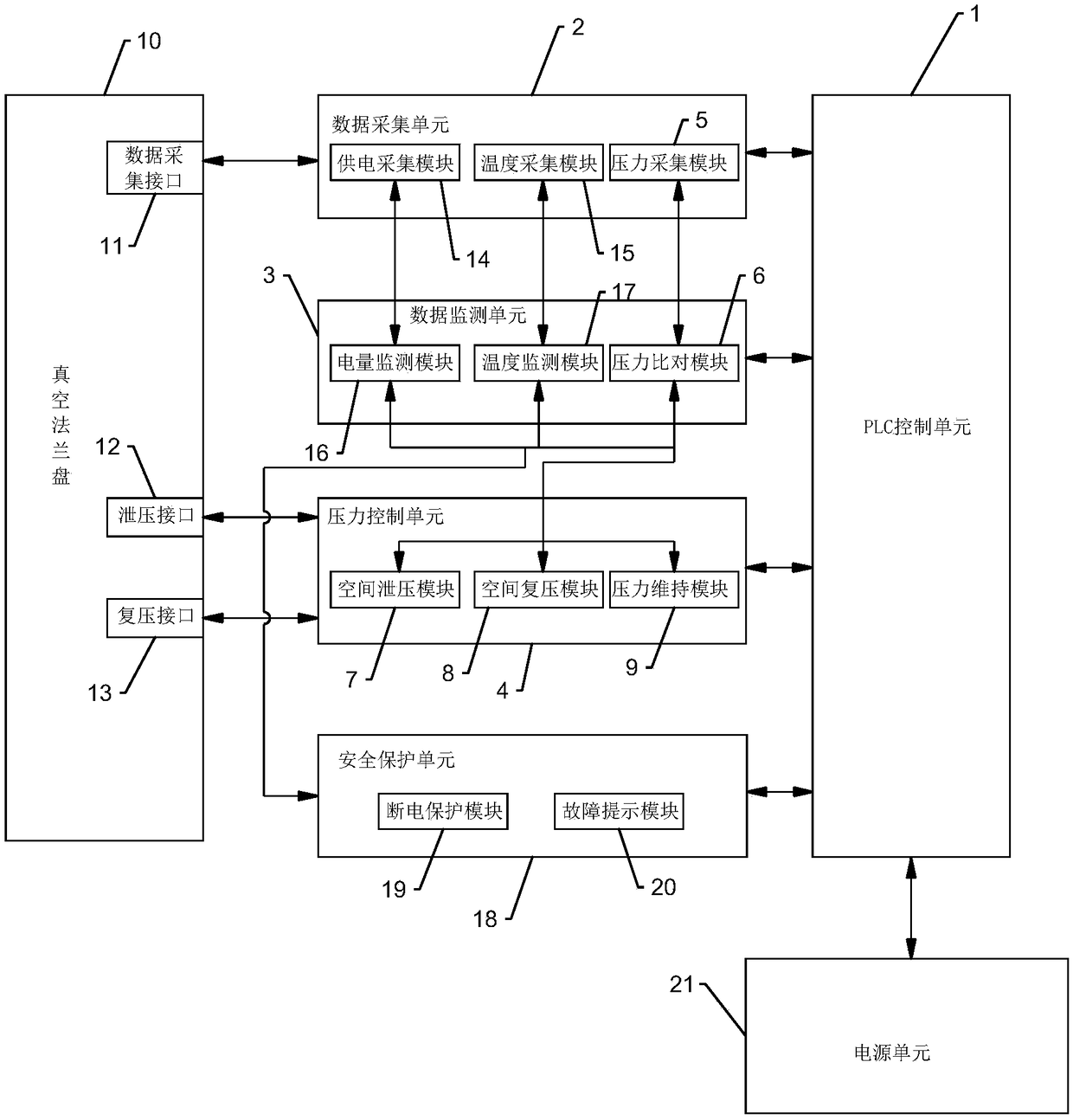
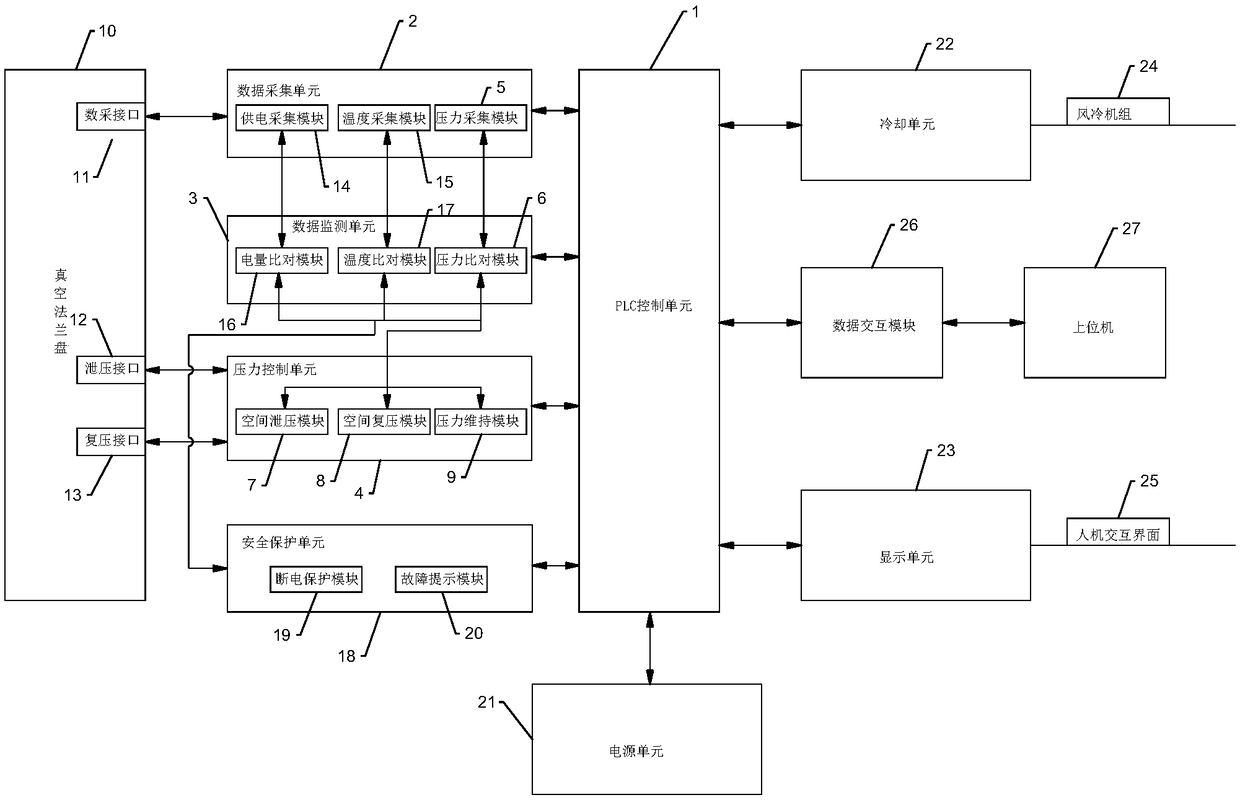
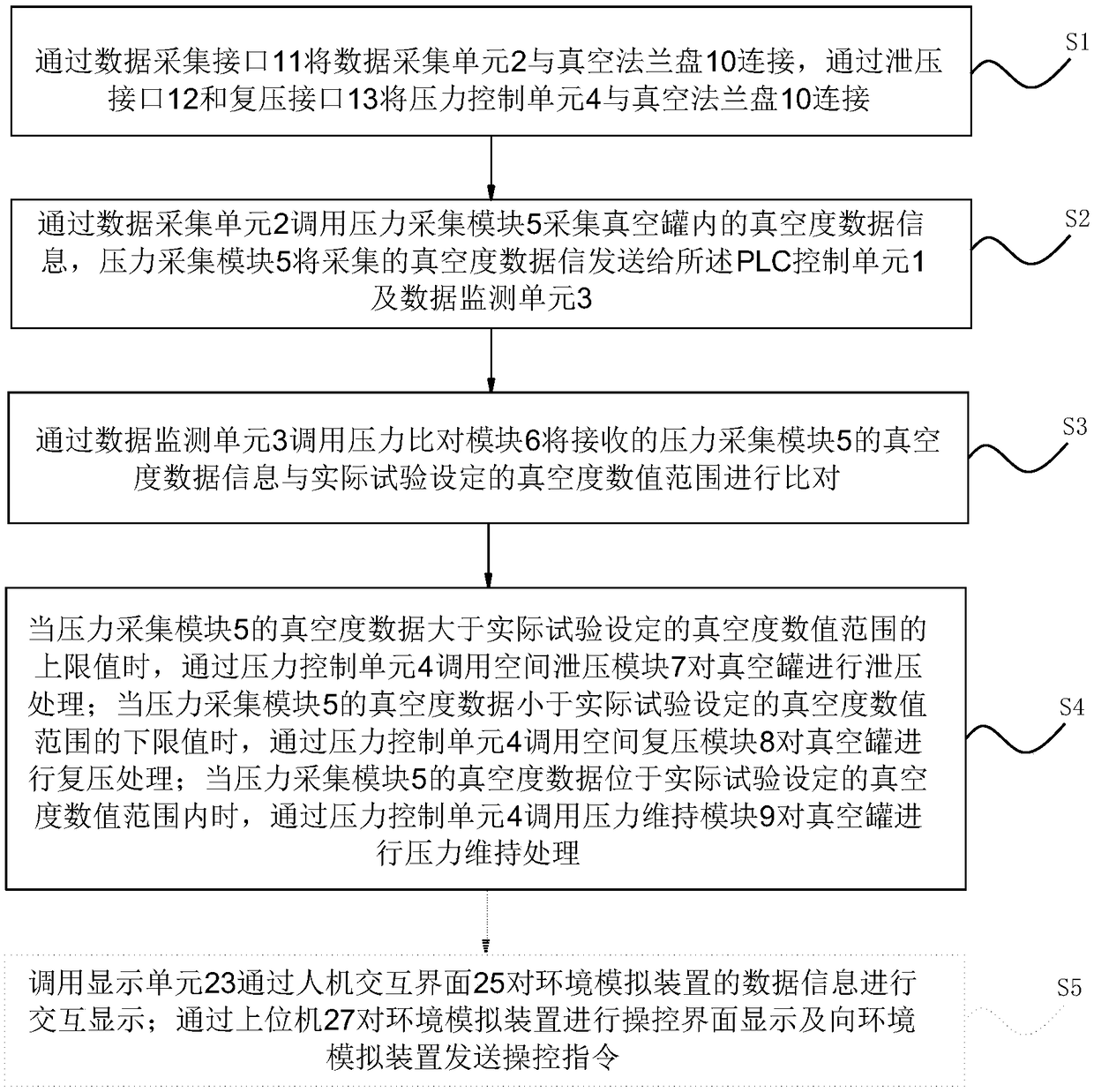
Environment simulation device, system and method for low air pressure discharge test on Mars surface
InactiveCN109212396AWith storageAnalyticalCosmonautic condition simulationsTesting dielectric strengthAutomatic controlData information
The invention discloses an environment simulation device, system and method for a low air pressure discharge test on Mars surface. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting the pressurecontrol unit with the vacuum flange through the pressure relief interface and the re-pressing interface; acquiring the vacuum degree data information in the vacuum tank, and comparing the received vacuum degree data information with the vacuum degree numerical range set by the actual test; when the vacuum degree data is larger than the upper limit value of the vacuum degree numerical range set bythe actual test, carrying out the pressure relief treatment on the vacuum tank; when the vacuum degree data of the pressure acquisition module is smaller than the lower limit value of the vacuum degree numerical range set by the actual test, carrying out the re-pressing treatment on the vacuum tank; and when the vacuum degree data of the pressure acquisition module is in the vacuum degree value range set by the actual test, carrying out the pressure maintenance treatment on the vacuum tank. According to the environment simulation device, system and method, the interference of a vacuum controlsystem is avoided, the function of pressure automatic control is provided, the pressure relief rate is controllable, the acquired data can be stored and analyzed, the power supply system is safe and reliable, and the stable operation time is long.
Owner:山东研讯智能科技有限公司
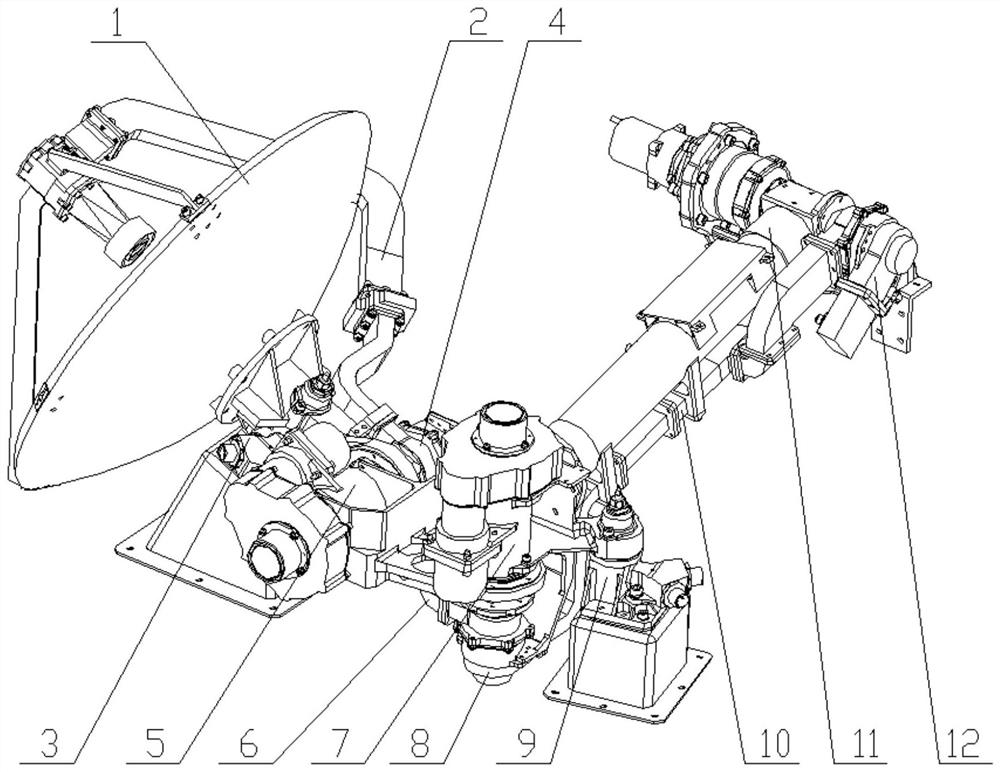
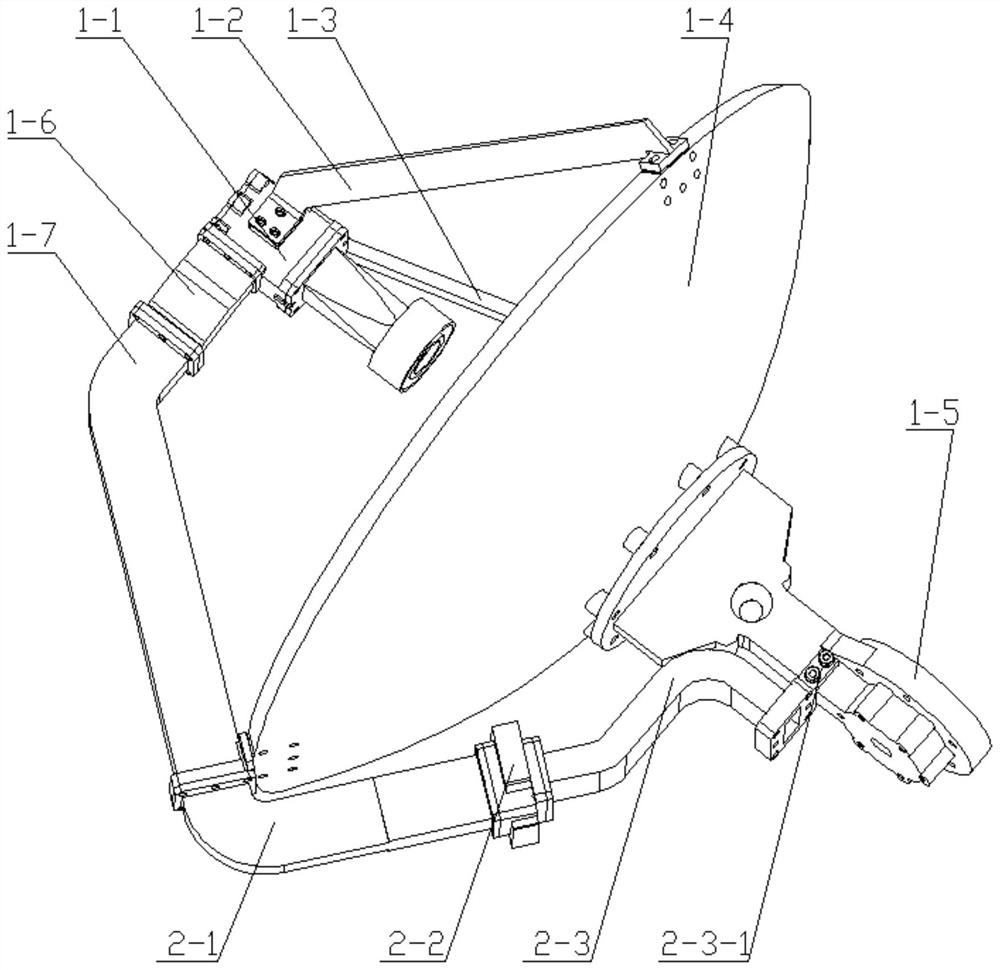
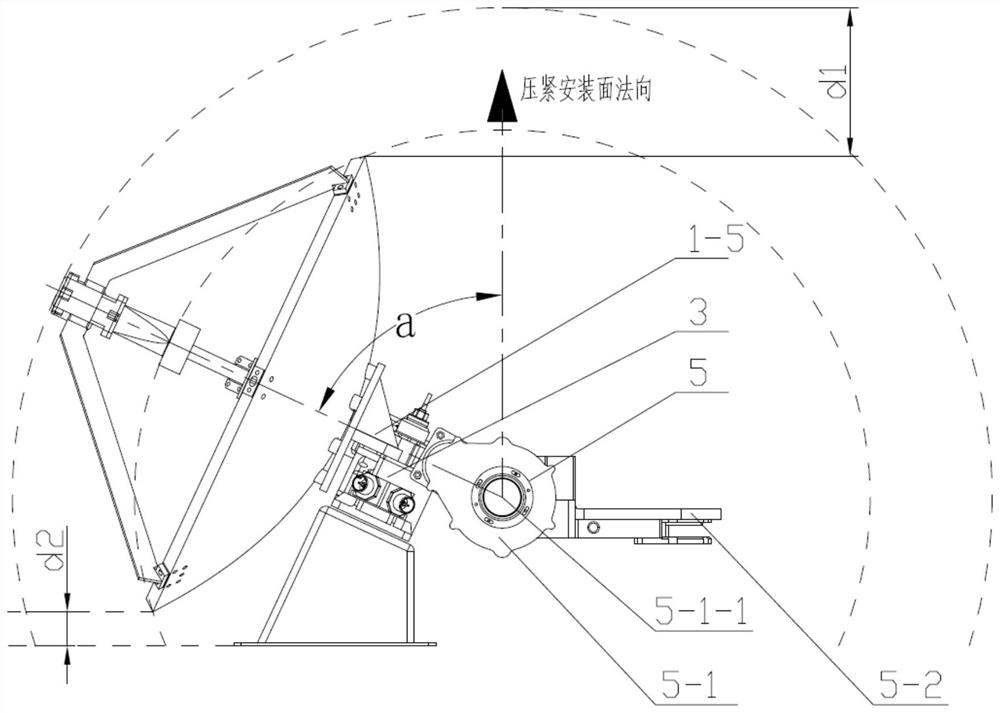
Movable spot beam antenna suitable for Mars surface landing and patrol detection
PendingCN114079139ALittle effect of occlusionDecrease increaseCollapsable antennas meansAntenna supports/mountingsMars roverMiniaturization
The invention discloses a high-gain movable spot beam antenna suitable for Mars landing and patrol detection. According to the invention, a feed source is supported by a waveguide D-waveguide E and other two supporting members in a three-point manner and is suspended in the center of a reflecting surface, so that the influence of the supporting structure on the antenna performance is effectively reduced; and meanwhile, the waveguide calibers of the waveguide D, the waveguide E and the feed source are changed, so that the miniaturization of the feed source is effectively realized, and the shielding influence of the feed source is reduced; meanwhile, a non-compact antenna assembly pressing structure is adopted, and a pressing mounting surface with a height difference and a mounting surface provided by an unfolding supporting structure are adopted, so that the working requirement after the antenna is unfolded is met, and meanwhile, the maximum additional envelope after the antenna is installed can reach the maximum height size of an unfolding driving shaft assembly part to the minimum, so the additional envelope is greatly reduced, and the application envelope requirement of the Mars rover is met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
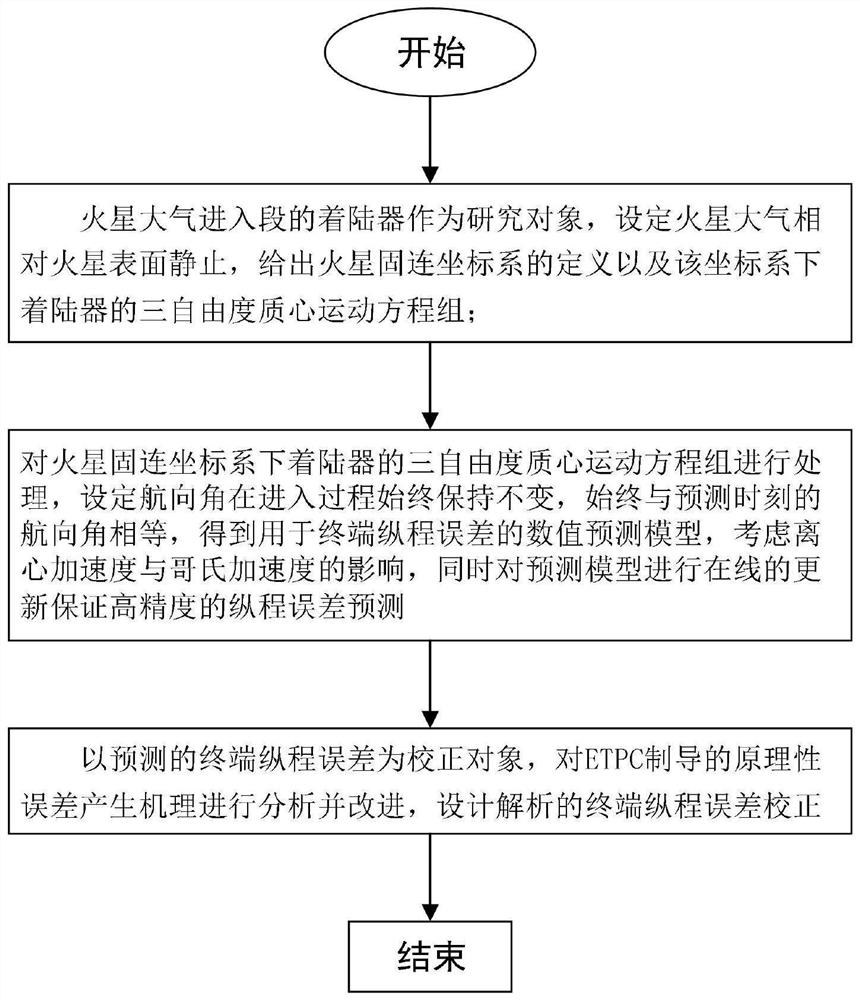
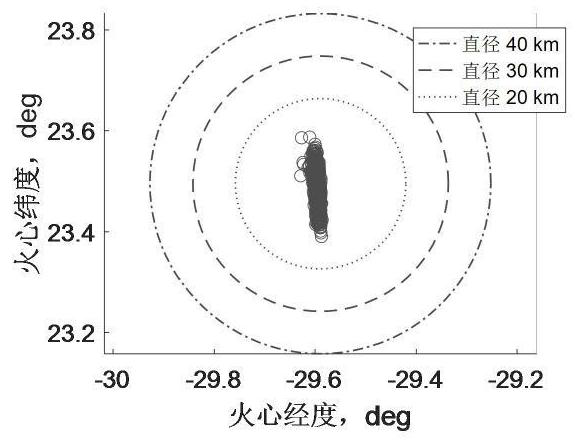
A Semi-Analytic Mars Entry Guidance Method
ActiveCN110015446BImprove robustnessImprove Guidance AccuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention discloses a semi-analytic Mars entry guidance method, comprising the following steps: taking the lander of the Mars atmosphere entry section as the research object, setting the Mars atmosphere to be stationary relative to the Mars surface, and giving the definition of the Mars fixed coordinate system and the coordinates The three-degree-of-freedom center-of-mass motion equations of the lander under the system; the three-degree-of-freedom center-of-mass motion equations of the lander under the fixed coordinate system of Mars are processed to obtain a numerical prediction model for the terminal longitudinal error, considering centrifugal acceleration and At the same time, the prediction model is updated online to ensure high-precision longitudinal error prediction; taking the predicted terminal longitudinal error as the correction object, the principle error generation mechanism of ETPC guidance is analyzed and improved, and the analysis method is designed. Terminal pitch error correction. The invention obviously improves the landing precision, and the obtained parachute opening point spread is very close to the calculation result obtained by the high-precision NPC guidance, which shows the validity of the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
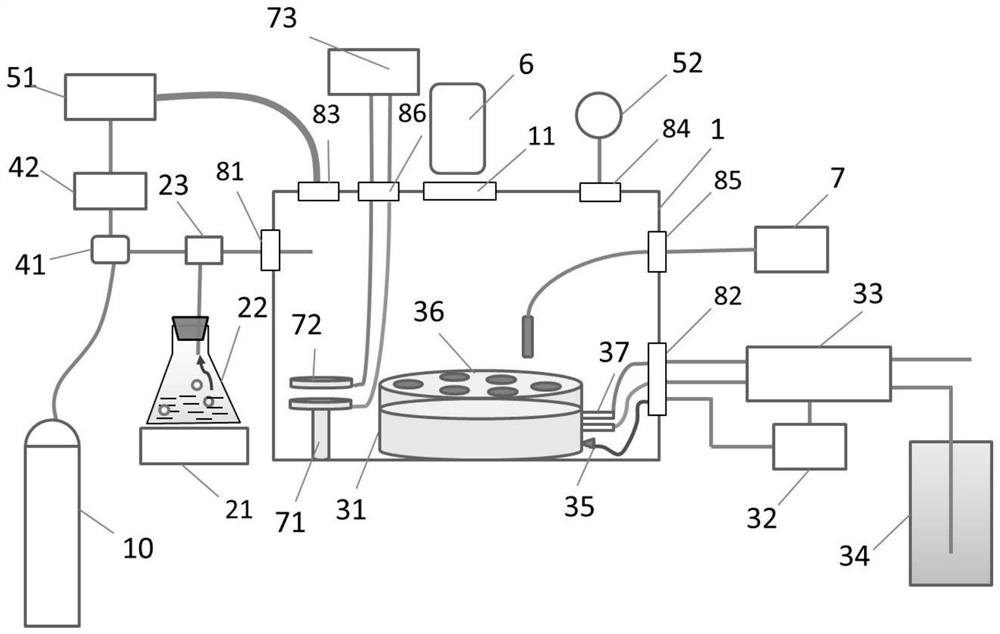
Experimental device and method for Mars in situ spectroscopic coupling
ActiveCN107300549BSimulate the realRealize regulationRaman scatteringAnalysis by thermal excitationSpectroscopyControl cell
The invention relates to a Mars in-situ spectroscopic combination experiment device and an experimental method. The experimental device includes a Mars environment simulation experiment device for simulating the Martian surface environment and an in-situ spectroscopic combination for in-situ spectrum testing in a Martian environment The experimental device, wherein the Mars environment simulation experiment device includes a vacuum cabin, a vacuum control unit connected to the vacuum cabin, a humidity control unit connected to the vacuum cabin, a first air supply unit connected to the humidity control unit, and a vacuum control unit connected to the vacuum cabin. The temperature control unit connected with the body; the in-situ spectrum test simulation experiment device is arranged outside the vacuum chamber, and is used for the joint test of the remote Raman spectrum and the remote LIBS spectrum. The present invention can truly simulate the Martian environment including temperature, humidity and atmosphere, and can also conduct in-situ testing on the spectrum of mineral samples in the Martian environment, to study the influence of environmental parameters on the spectrum of mineral samples, and at the same time perform single and multi-dimensional analysis of mineral content Quantitative analysis of variables.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Autogyro using Mars Atmospheric Circulation Random Detection and Its Application Method
The invention discloses a self-rotating rotorcraft using the random detection of Martian atmospheric circulation and its use method, which includes a rotor shaft and a rotor hub, and also includes a wind sensor, a foldable blade, a propeller, a fuselage and a rudder surface, the The wind sensor is set on the top of the rotor hub to monitor the wind direction and wind speed on the surface of Mars. The foldable blade is installed on the top of the rotor shaft through the rotor hub. It is in a folded state when launching, and the blade unfolds after reaching the surface of Mars. The number of the propellers is 4, which are arranged in the shape of a "ten" at the root of the rotor shaft; the rudder surface is symmetrically arranged on the upper surface of the fuselage, and the upper surface of the fuselage is also provided with solar cells; the inside of the fuselage A storage battery connected to the solar cells is provided. The present invention is different from the current scientific detection forms of Mars orbiter and landing patrol device, and utilizes Martian atmospheric circulation to carry out random on-site detection, which can be applied to the "Mars Green Home" project, and has a broad application prospect in the field of deep space detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com