Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Magneto-optical drive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
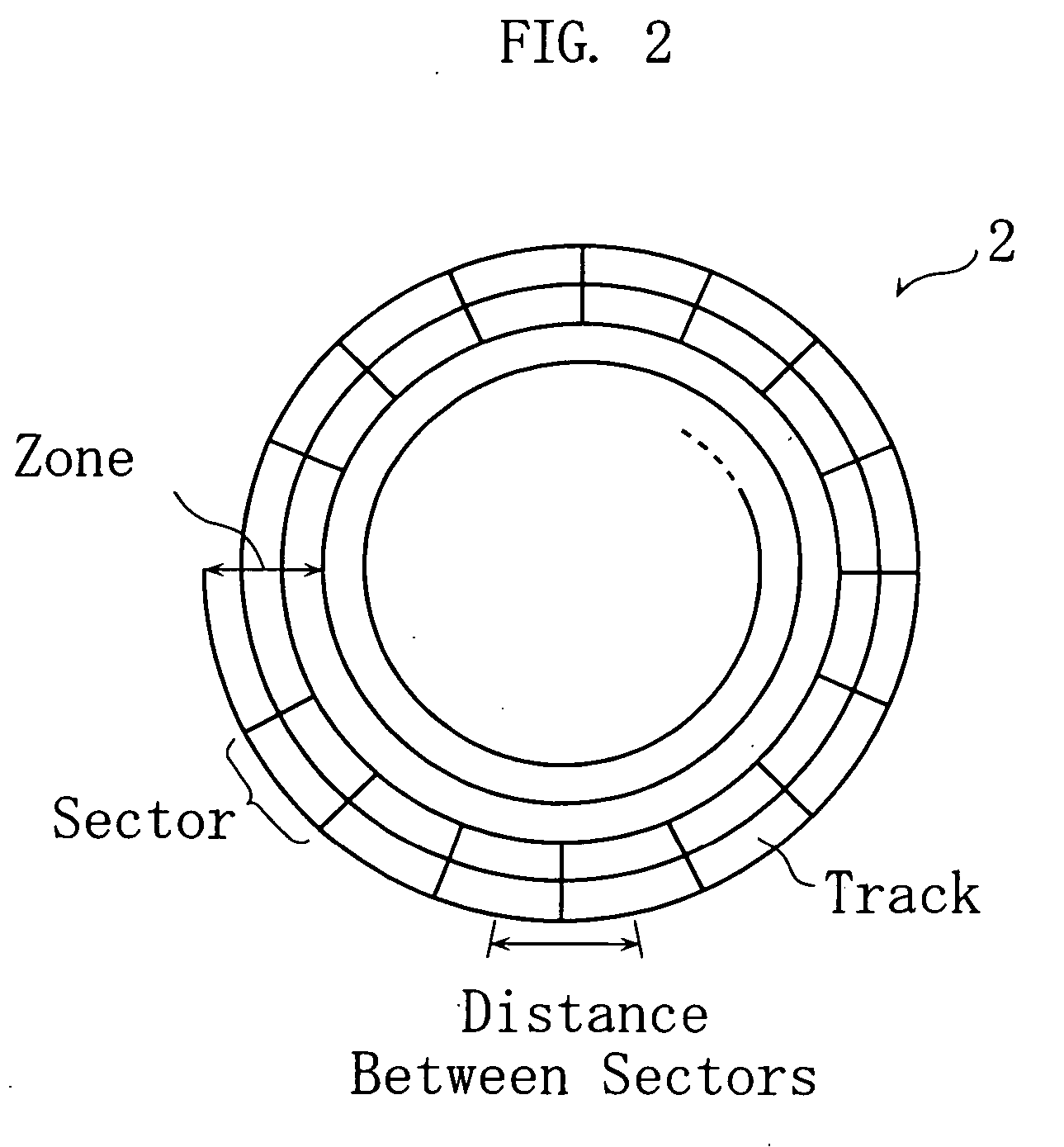
A magneto-optical drive is a kind of optical disc drive capable of writing and rewriting data upon a magneto-optical disc. Both 130 mm (5.25 in) and 90 mm (3.5 in) form factors exist. In 1983, just a year after the introduction of the Compact Disc, Kees Schouhamer Immink and Joseph Braat presented the first experiments with erasable magneto-optical Compact Discs during the 73rd AES Convention in Eindhoven. The technology was introduced commercially in 1985. Although optical, they appear as hard disk drives to the operating system and can be formatted with any file system. Magneto-optical drives were common in some countries, such as Japan, but have fallen into disuse.
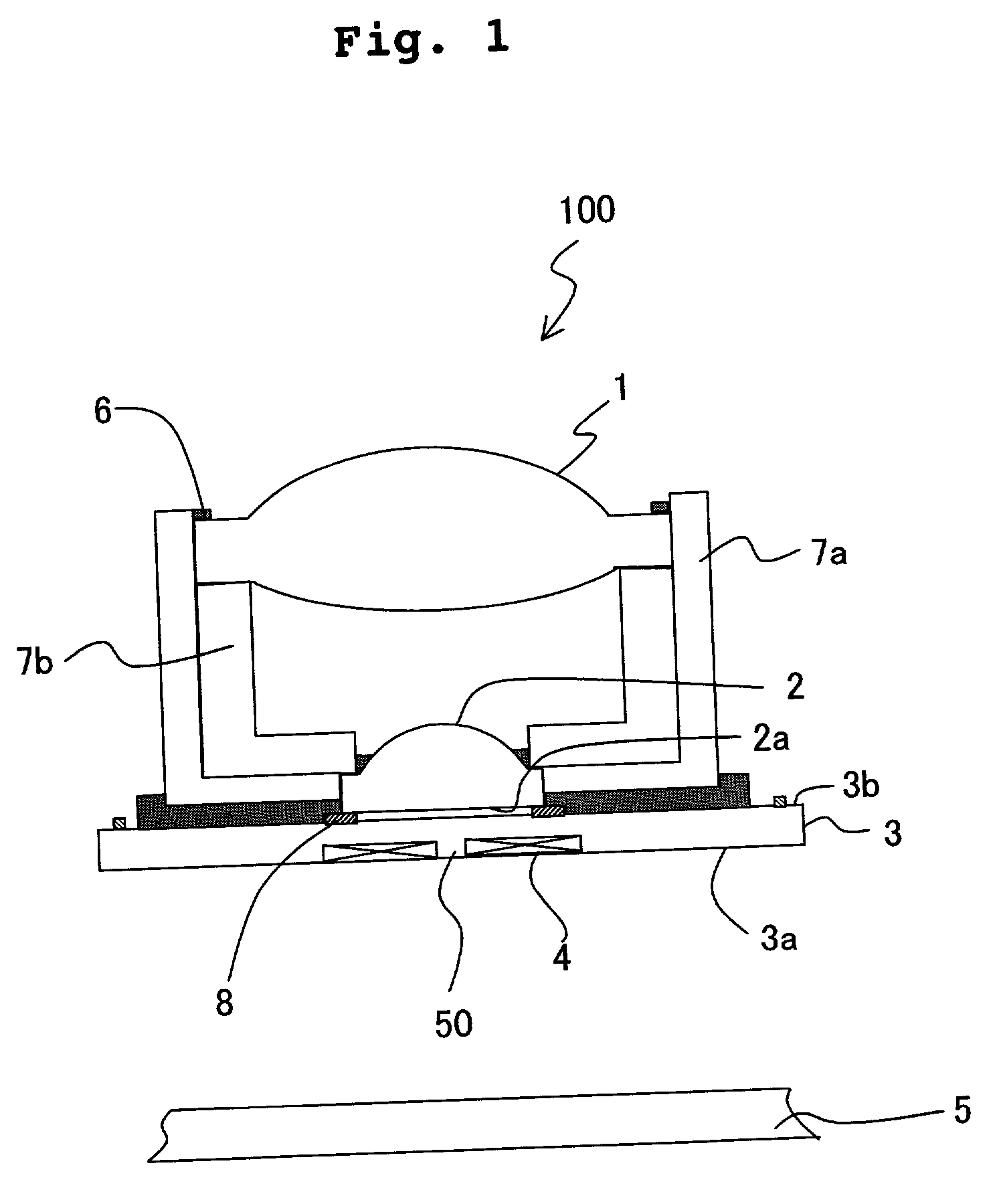
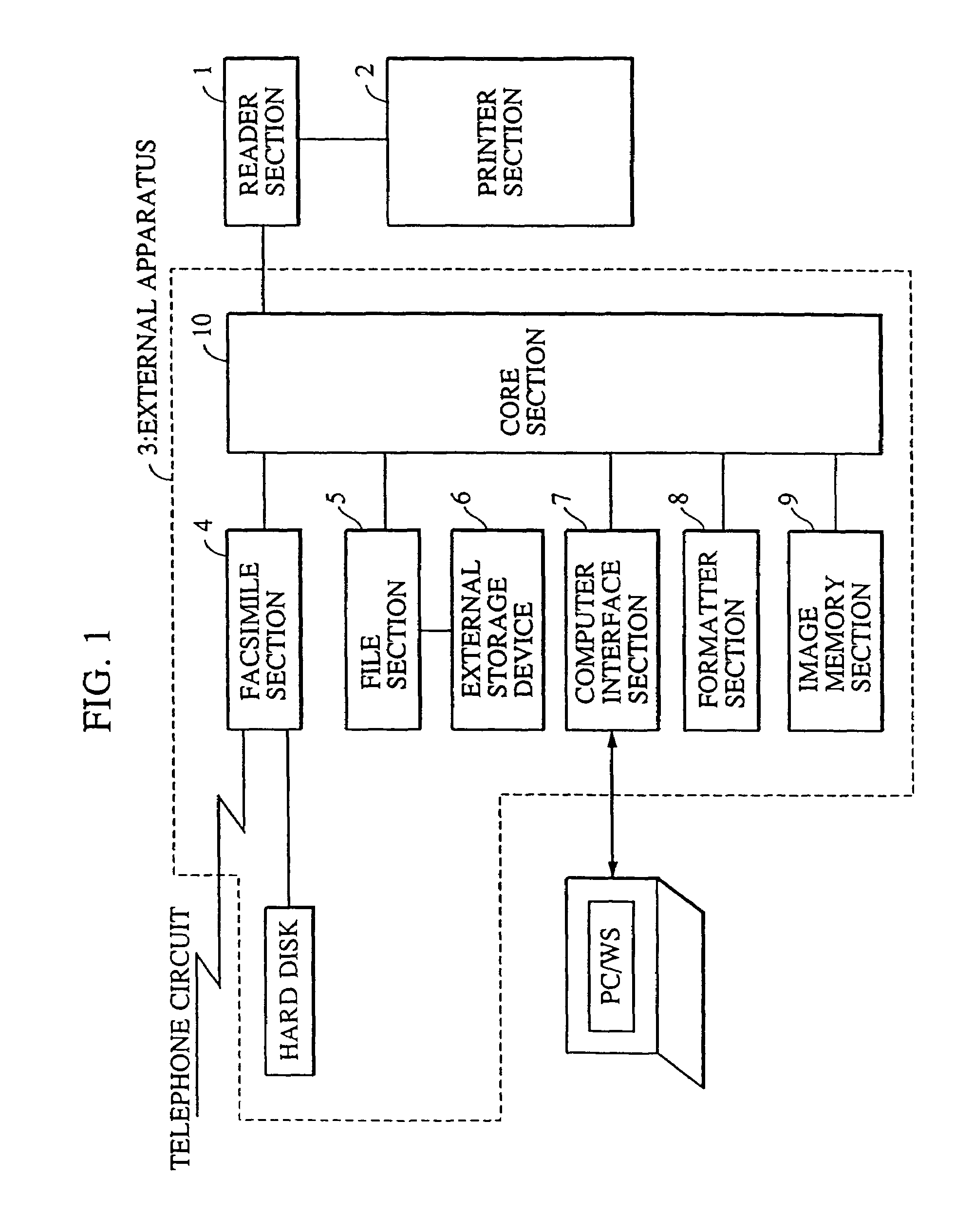
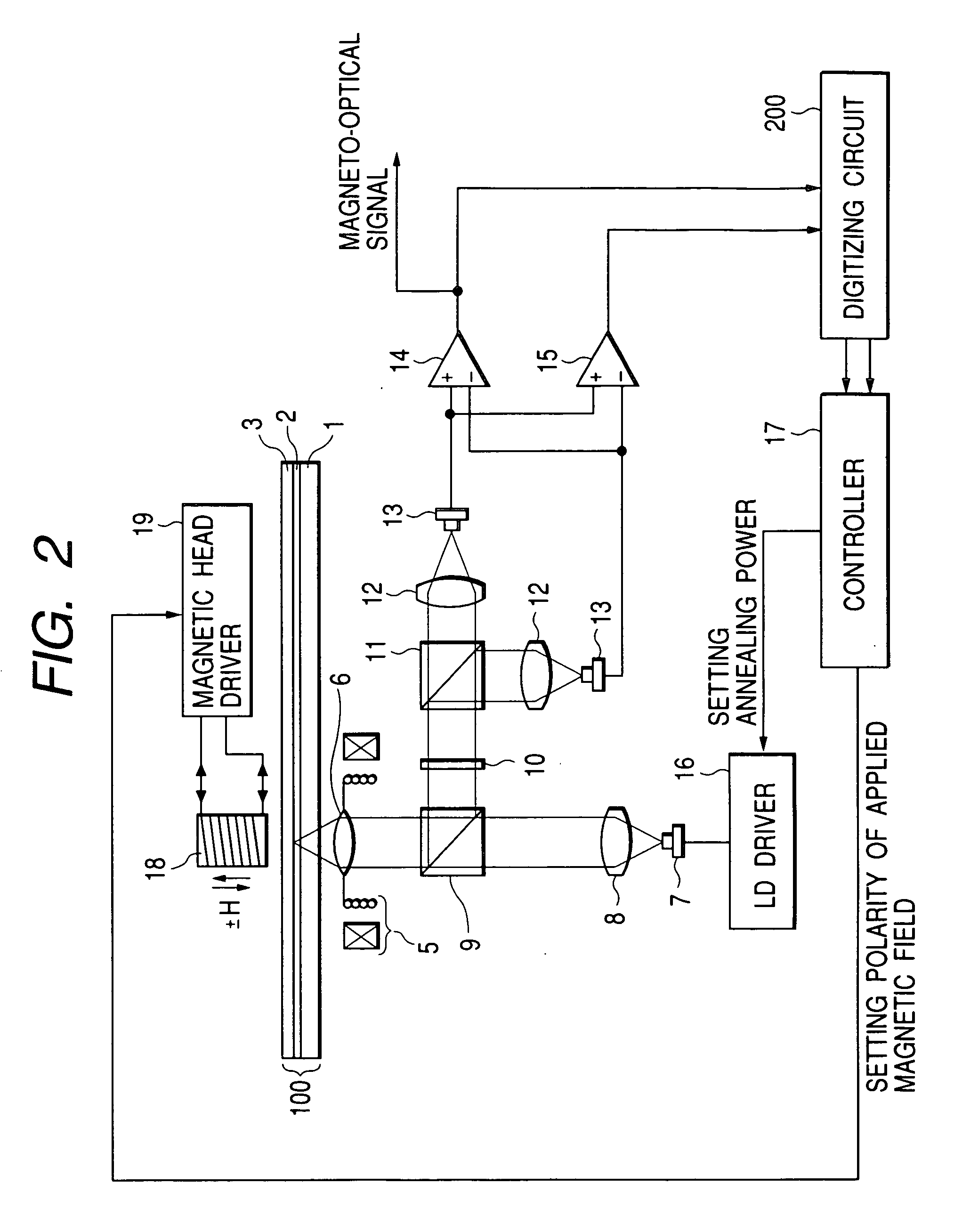
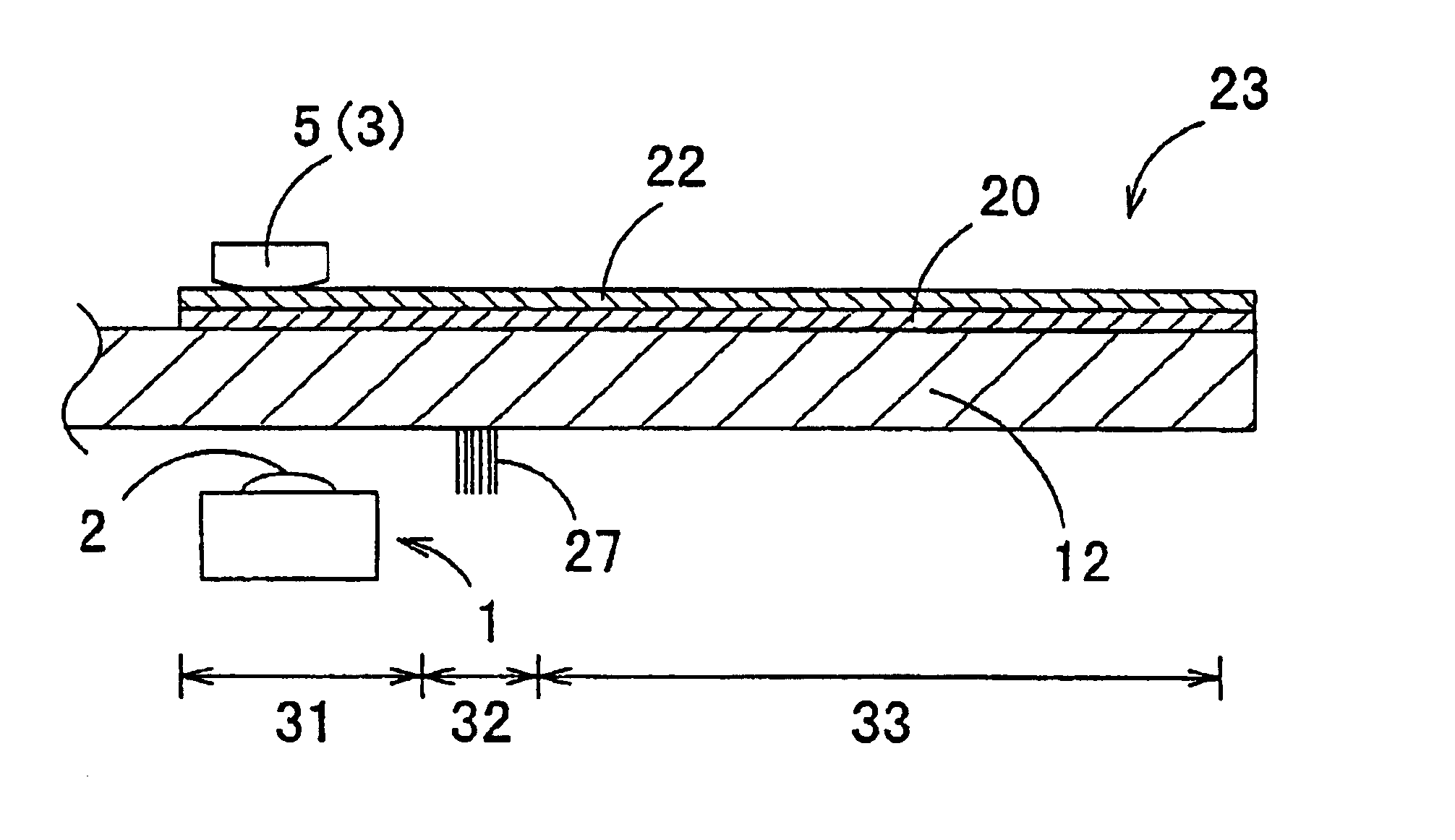
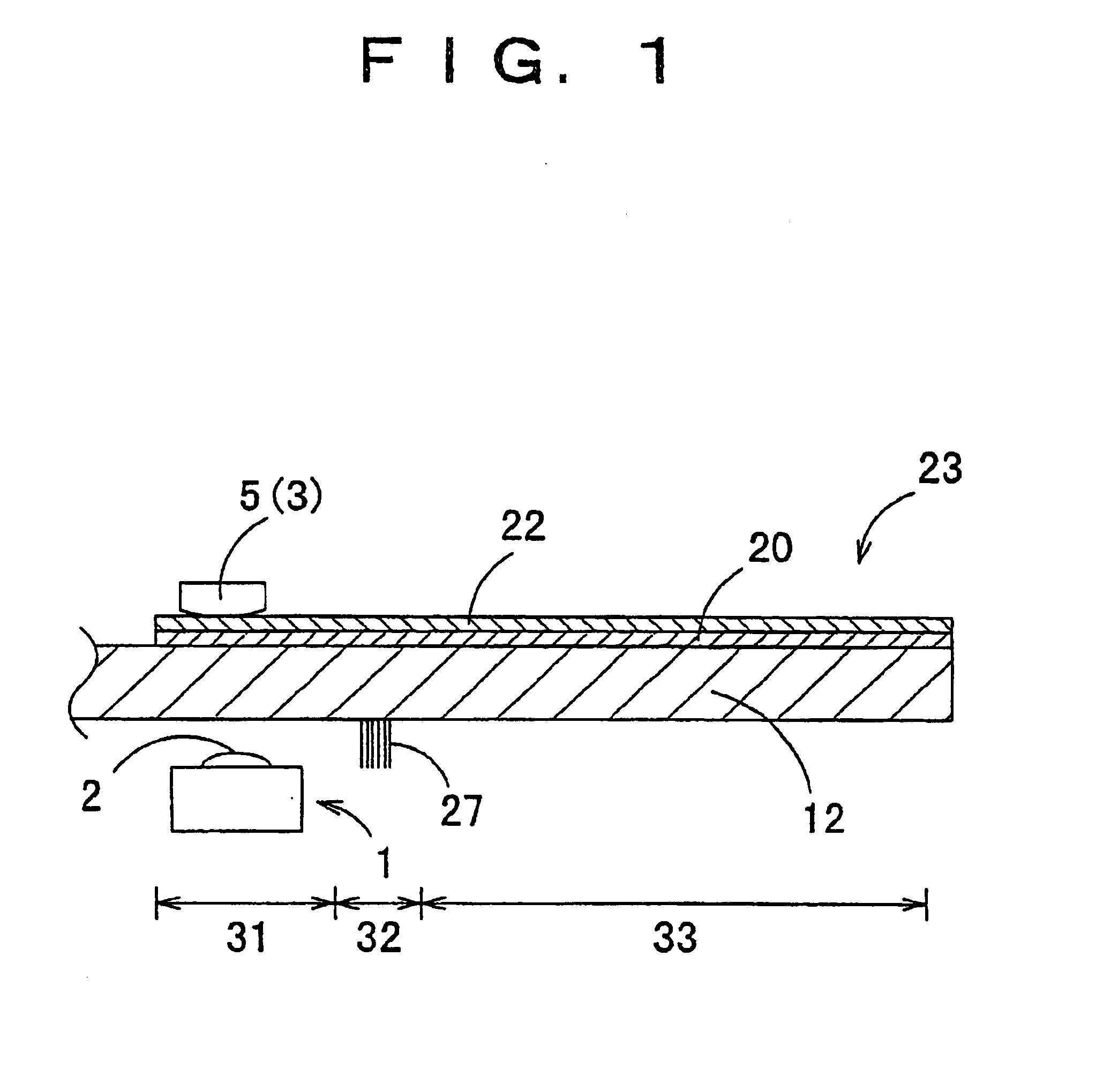
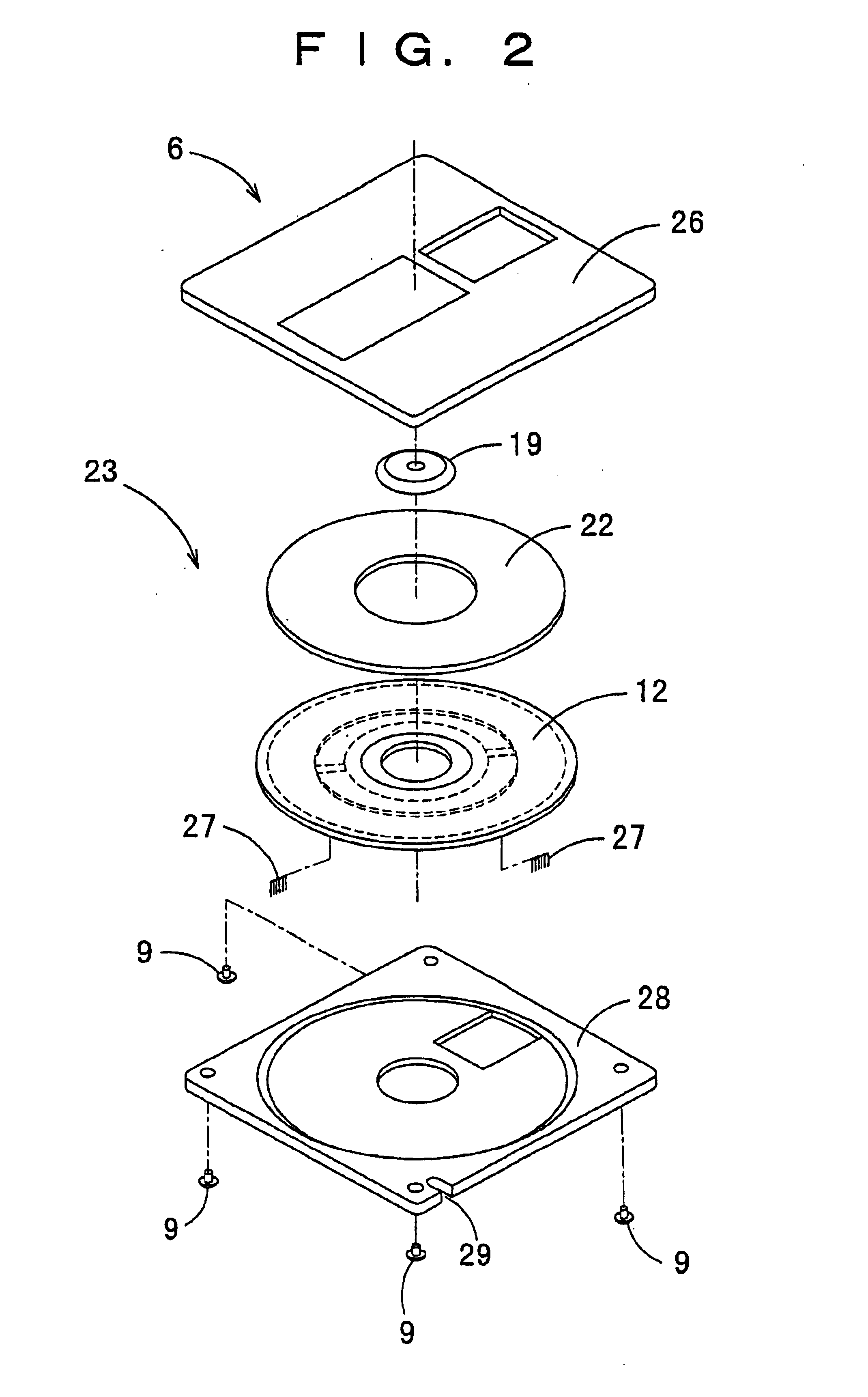
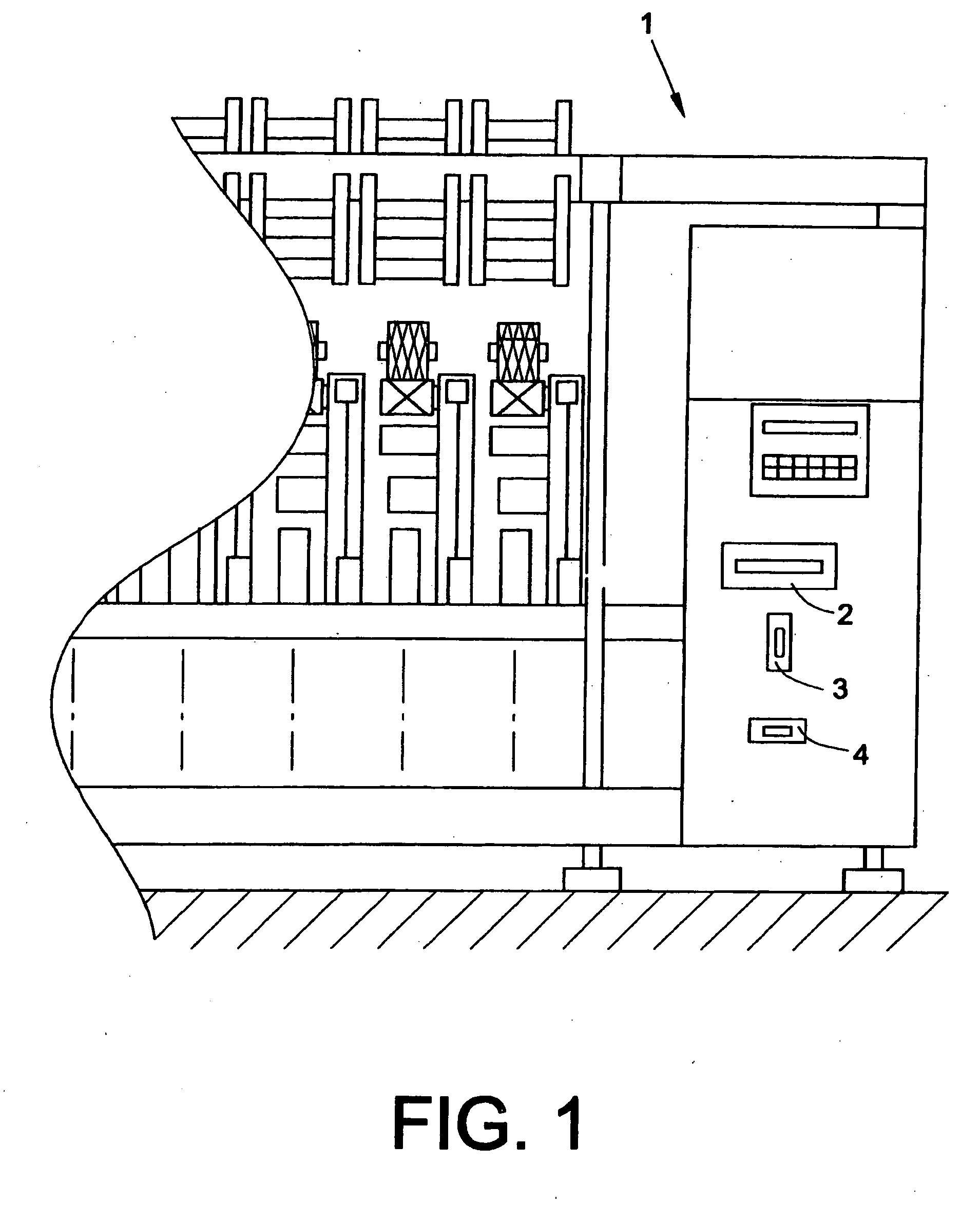
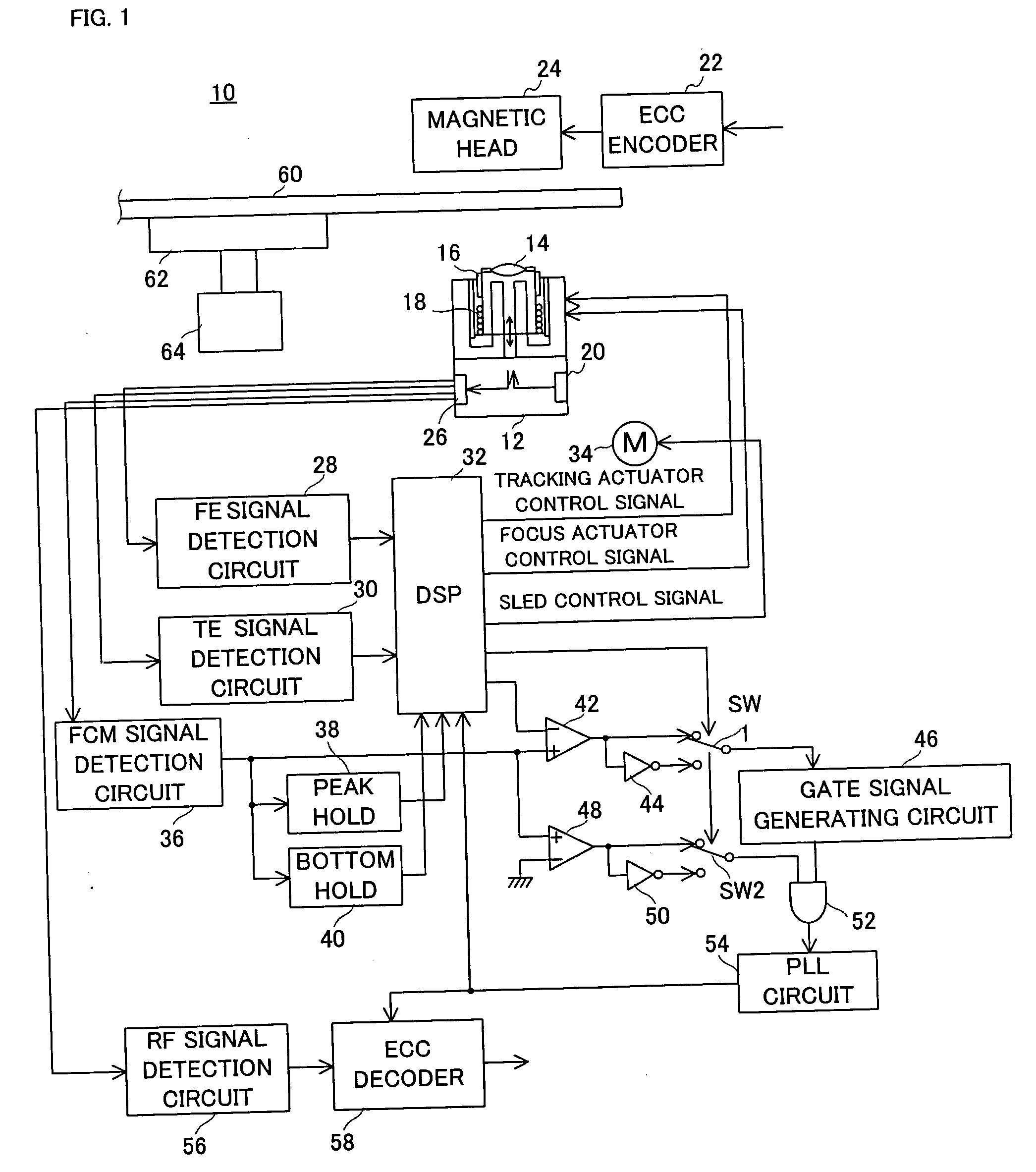
Magneto-optical head and magneto-optical recording apparatus including same
InactiveUS20020097639A1Avoid thermal expansionAppropriately maintain optical characteristicOptical head protectionOptical flying-type headsOptical propertyEngineering
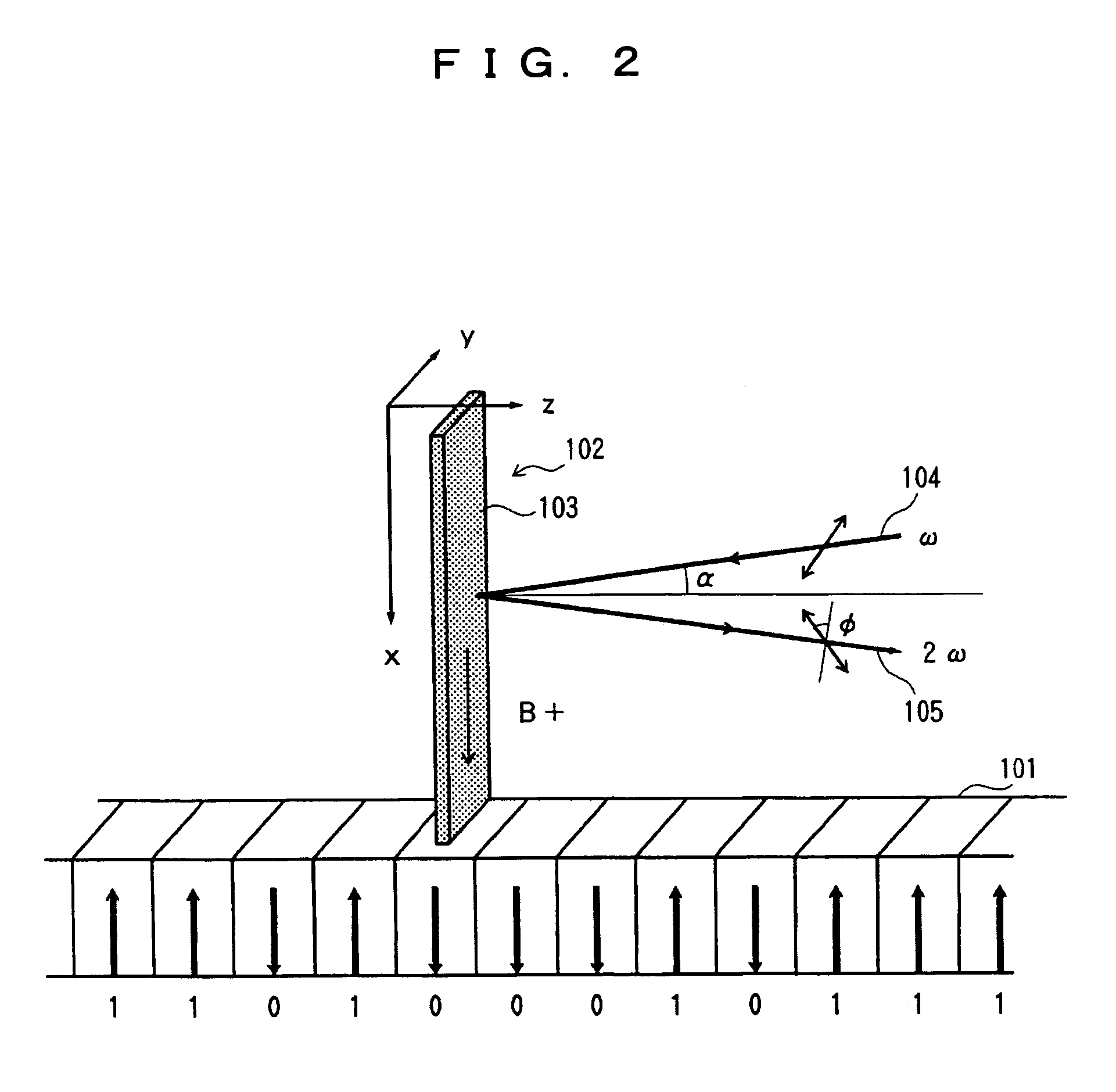
A magneto-optical recording head comprises a magnetic coil formed on a lower surface of a transparent substrate opposed to a magneto-optical disk. A heat sink layer is provided at the outside of the magnetic coil on the lower surface. An objective lens is supported on an upper surface of the transparent substrate. The heat, which is generated by the magnetic coil, is released via the heat sink layer to the space between the magneto-optical disk and the substrate. The release of the heat is facilitated by the air stream which is generated by the rotation of the magneto-optical disk. The heat can be effectively released from the magnetic coil without inhibiting optical characteristics of the objective lens.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
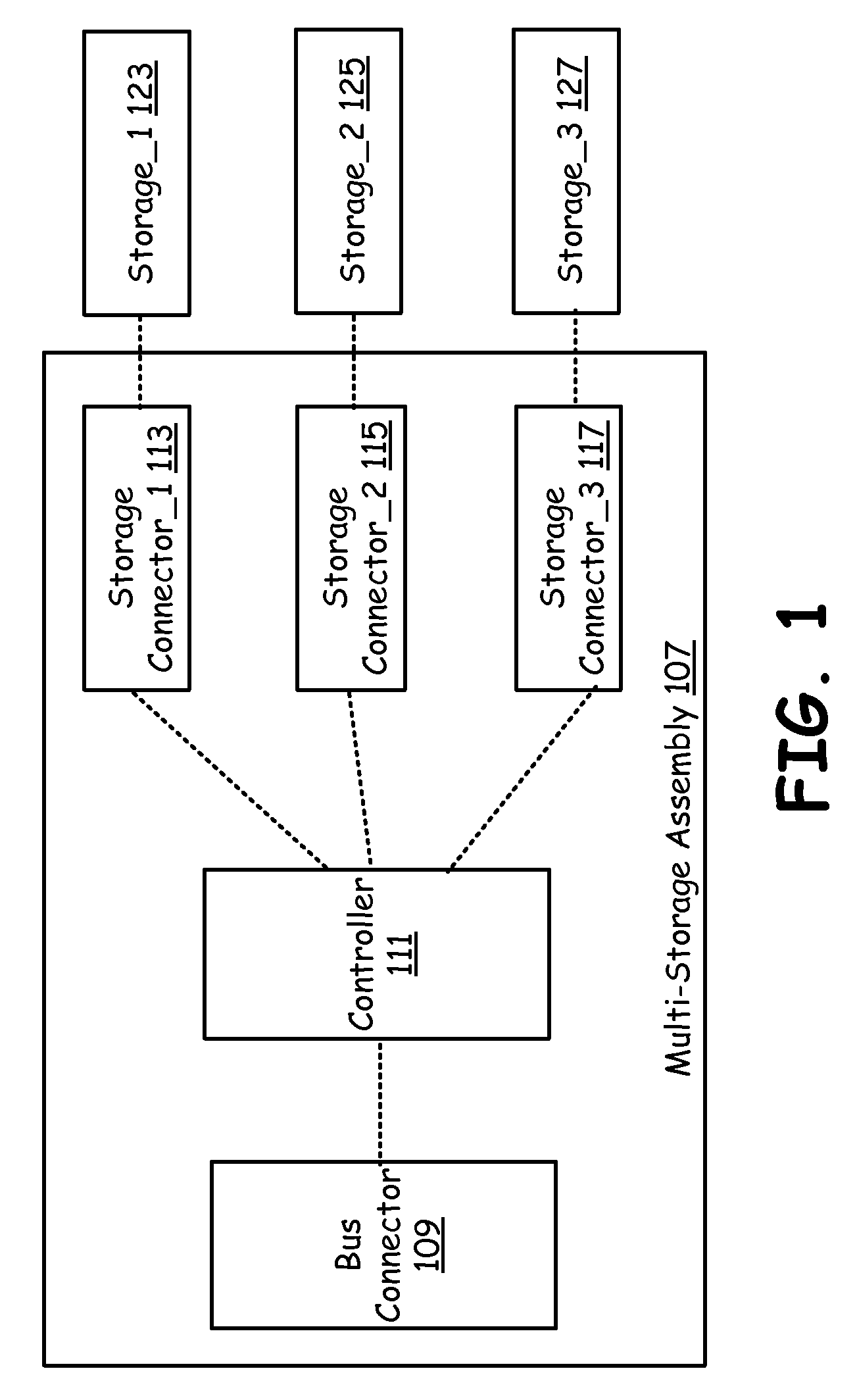
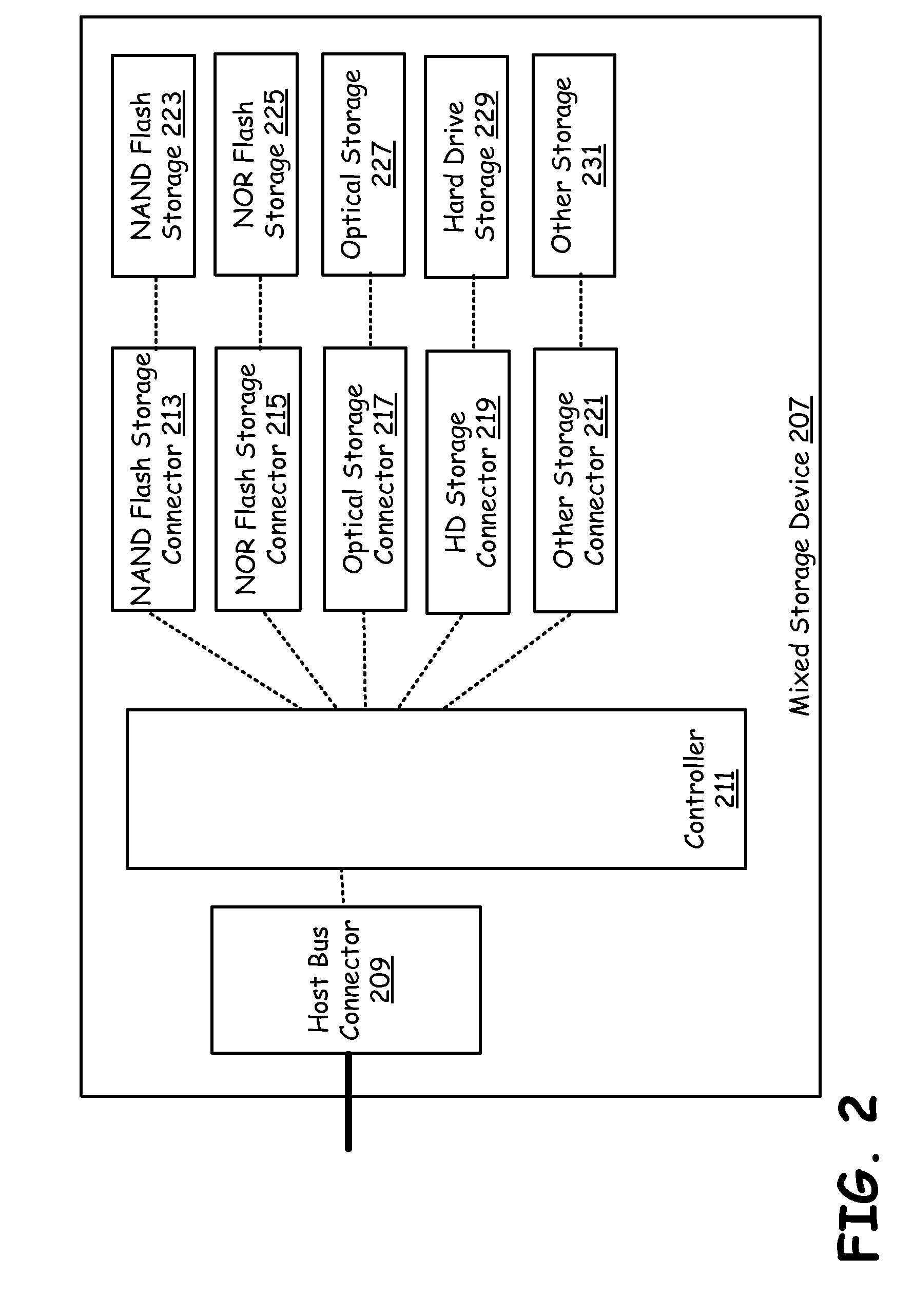
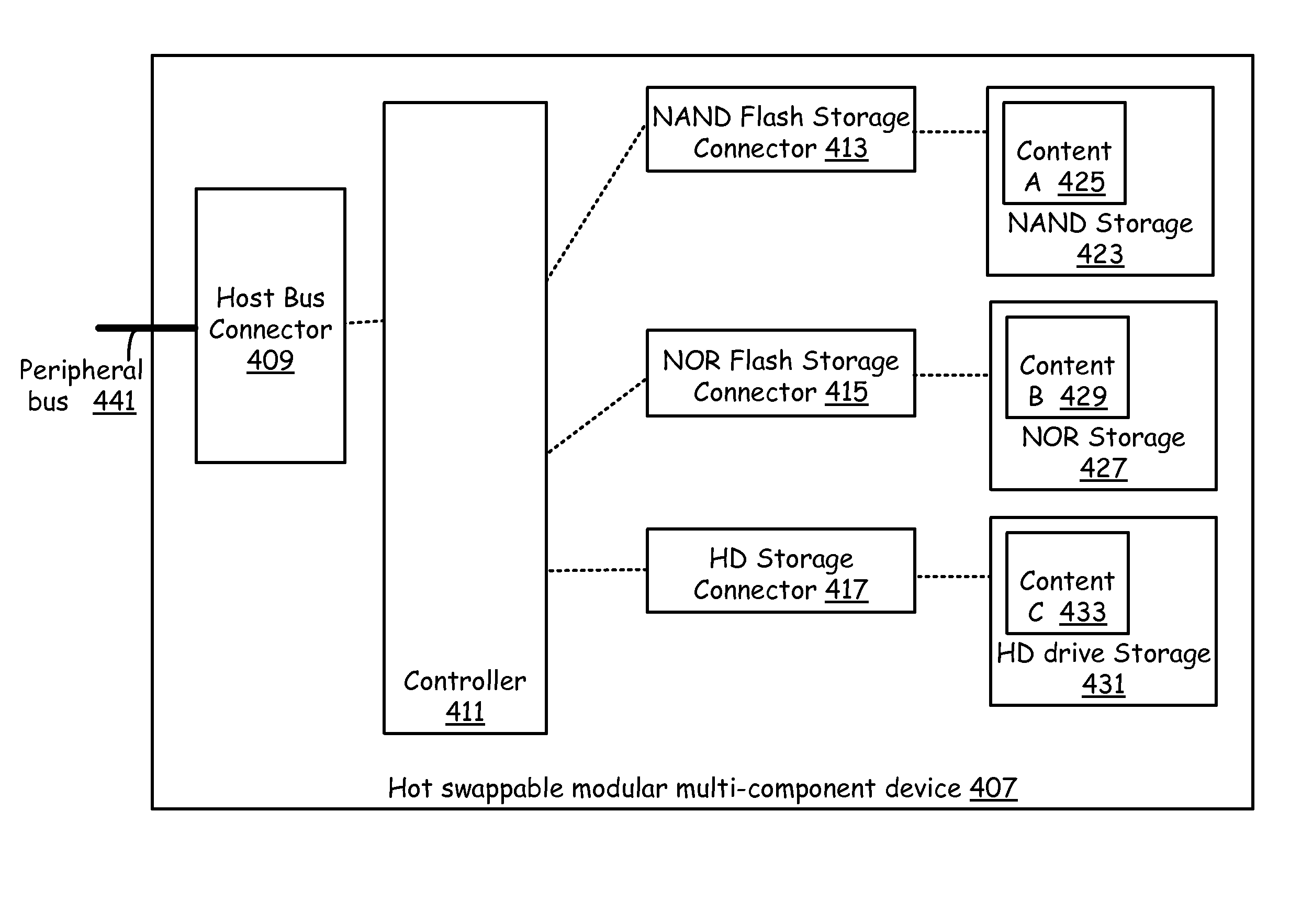
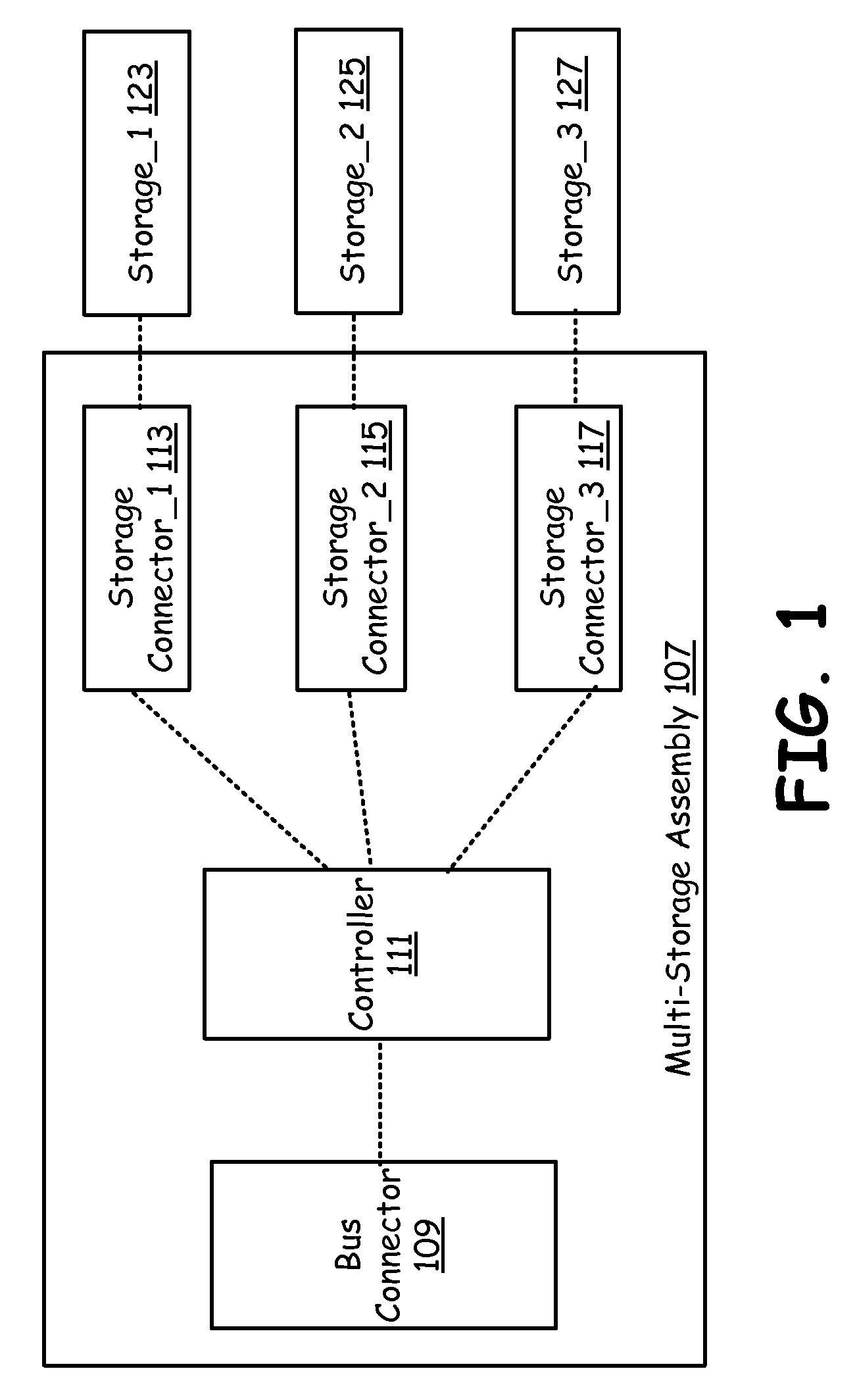
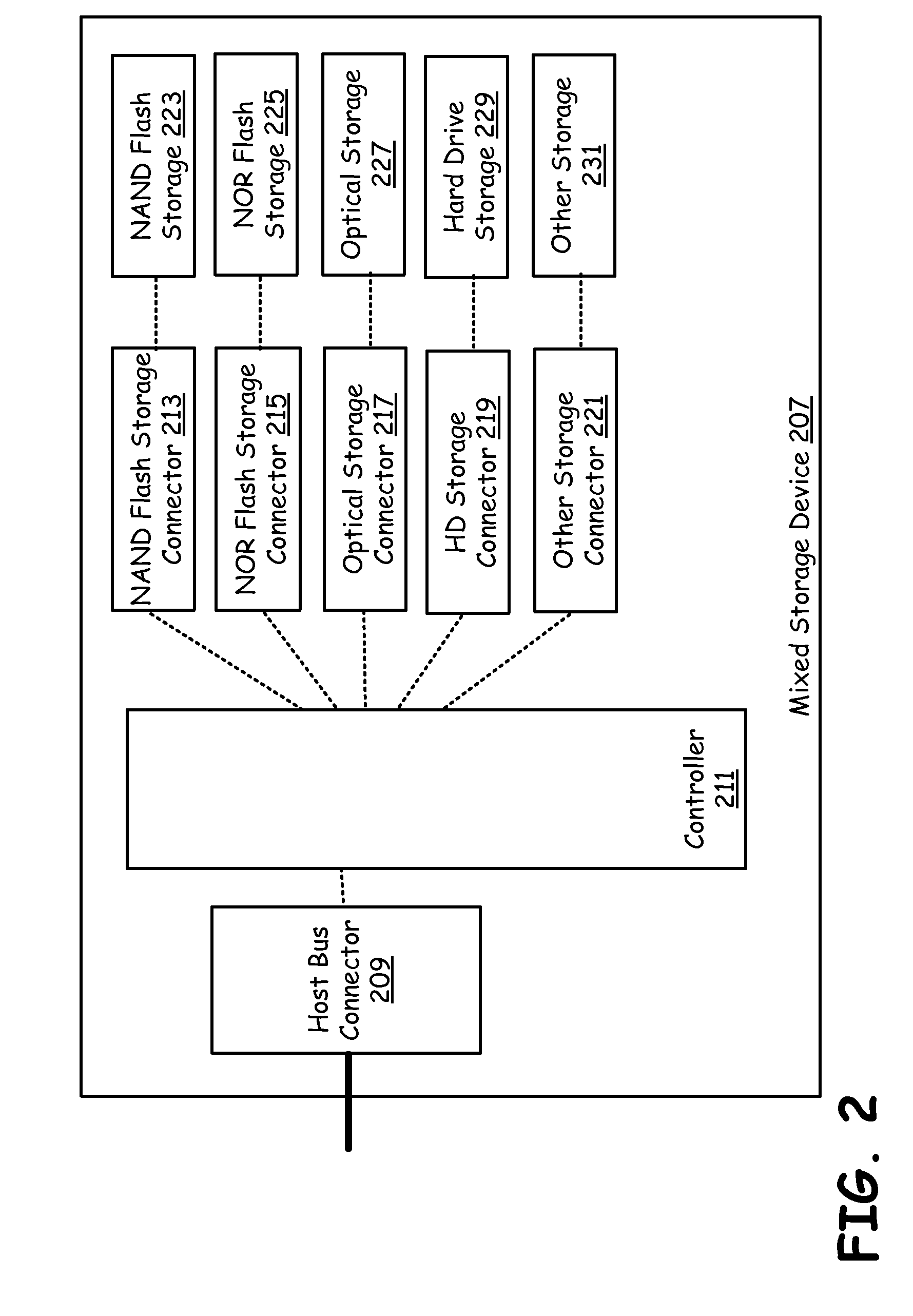
Mixed technology storage device
ActiveUS20100037002A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHard disc driveOptical storage
A mixed storage device includes a set of storage units, each potentially based on a different storage technology, such as NAND flash drive, NOR flash drive, magnetic hard drive, magneto-optical drives, optical drives, etc. The mixed storage device comprises a host bus connector that is used to connect to a peripheral bus that facilitates communication to a processor of a device (such as a PC) and a controller. The controller manages a NAND flash storage device, a NOR flash storage device, an optical storage device, a hard drive and other storage components plugged into or integrated with the mixed storage device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Magneto-optical disc device and method for writing data on magneto-optical disc
InactiveUS20060158976A1High reference valueData buffering arrangementsMagneto-optical discsComputer hardwareOriginal data
A magneto-optical disc device (1) writes data, for each sector, onto a magneto-optical disc (2) using an optical head portion (21) which outputs light onto the magneto-optical disc, at which time the data on the magneto-optical disc (2) is erased and after data is erased, data is written onto the magneto-optical disc (2), and the original data is then verified against the written data for each sector. When verifying the original data against the written data, if a verification error is detected for a sector, position information for the sector on the magneto-optical disc (2) in which a verification error is detected is stored in memory (16). Data verification is continued even when a verification error is detected, and at the end of data verification, data verification is again performed for sectors in which verification errors are detected, based on the position information for sectors stored in memory (16).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
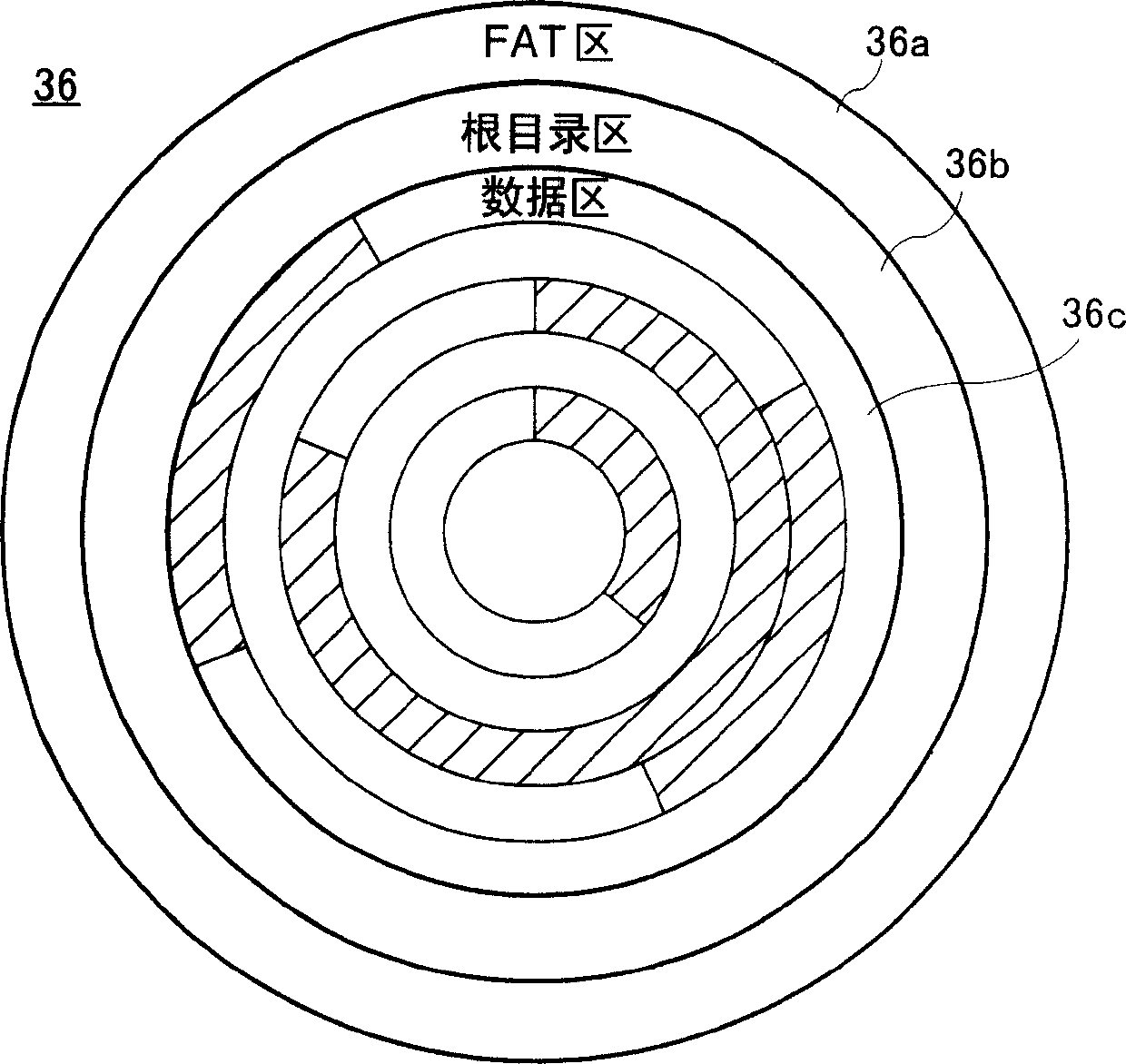
Data recording device
InactiveUS20040034617A1Easy to operateTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsWrite protectionData recording
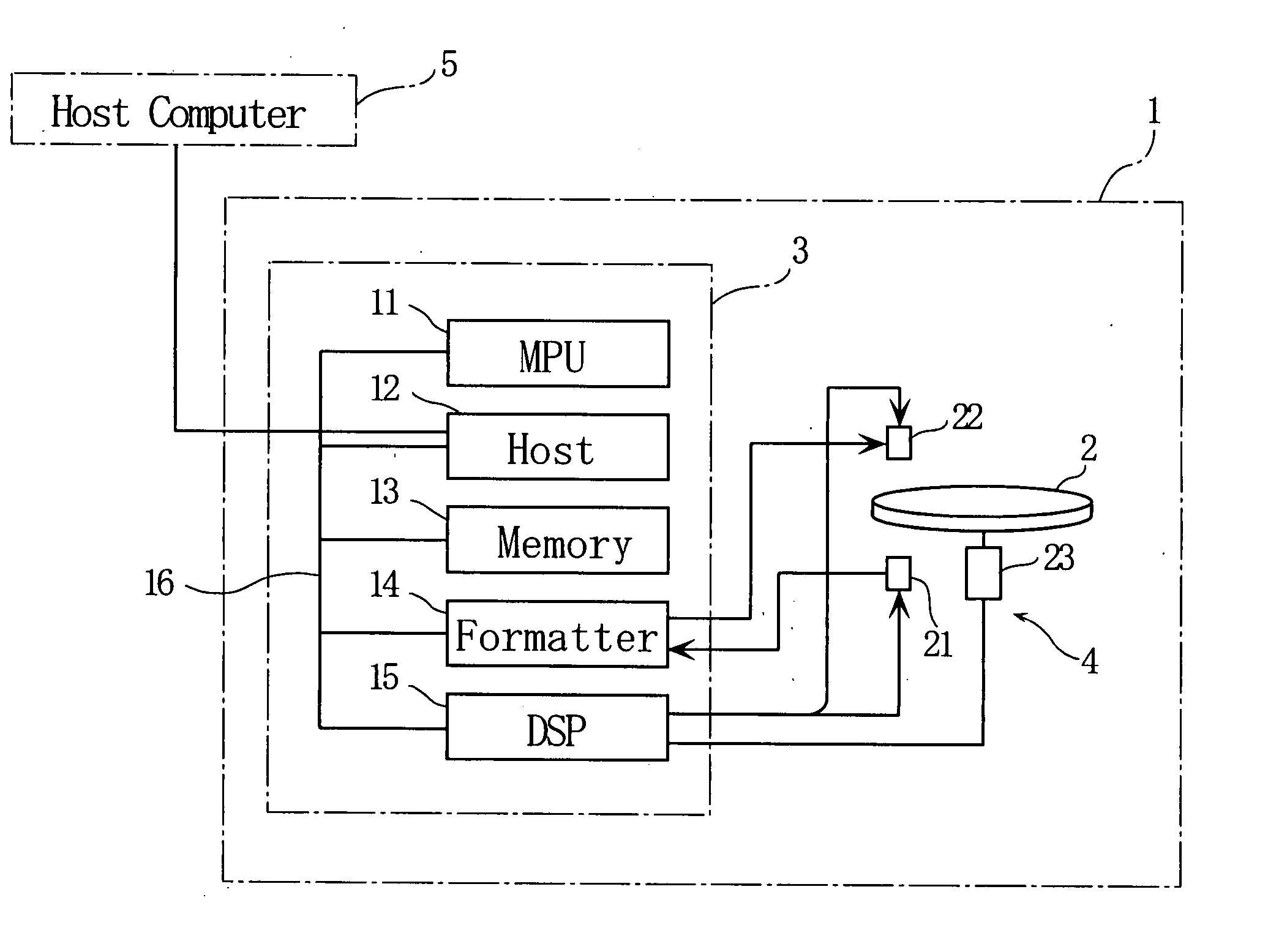
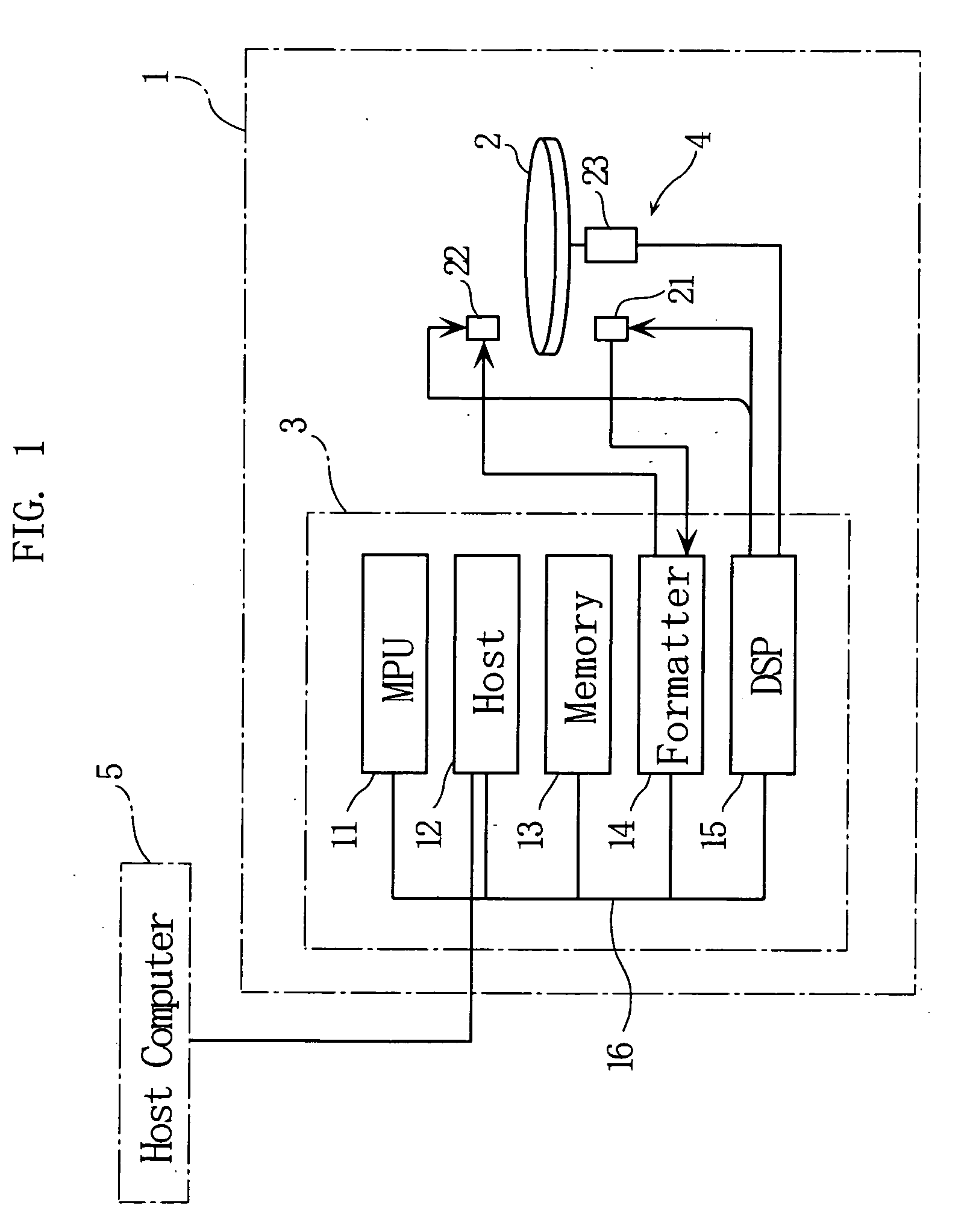
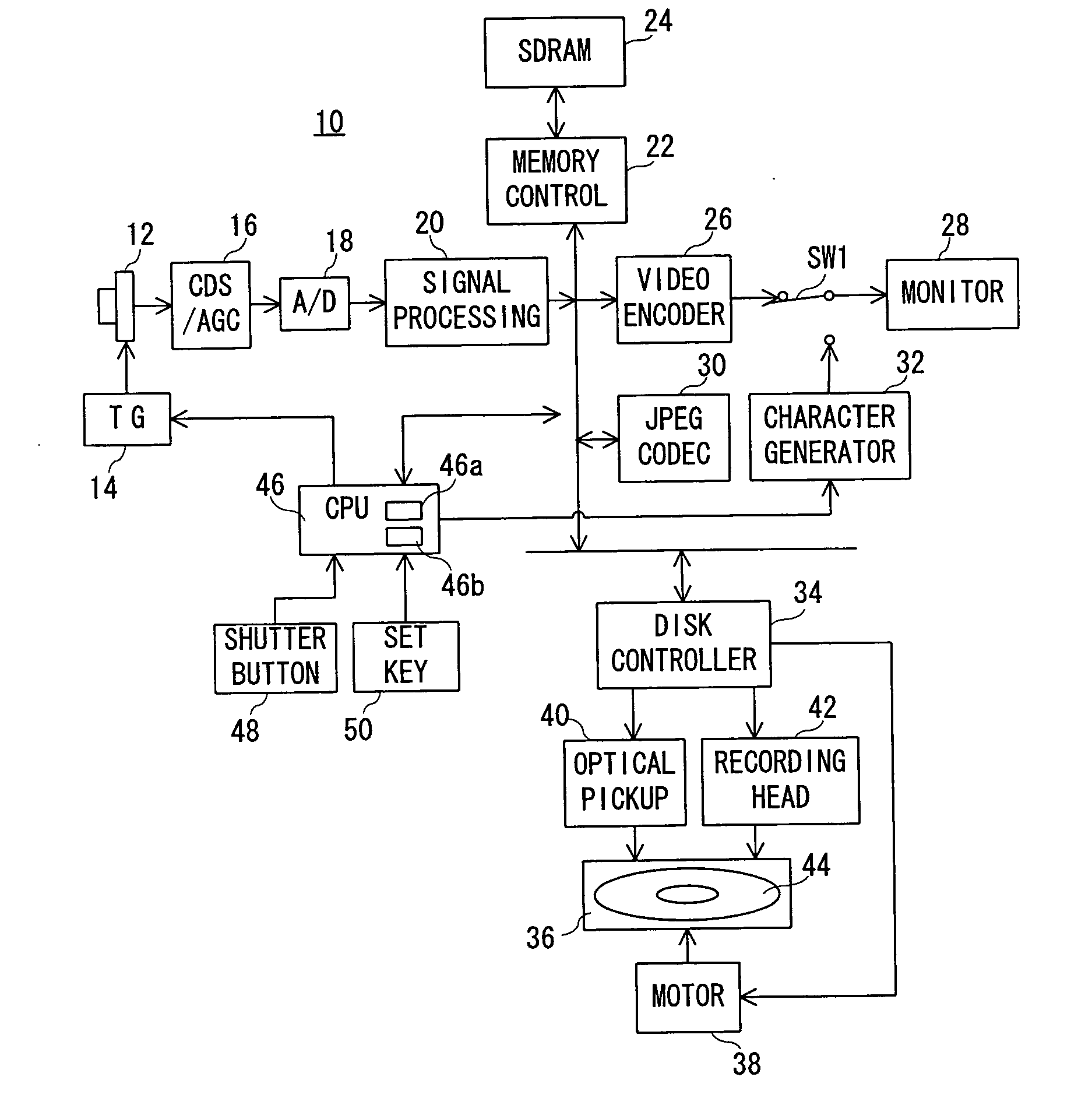
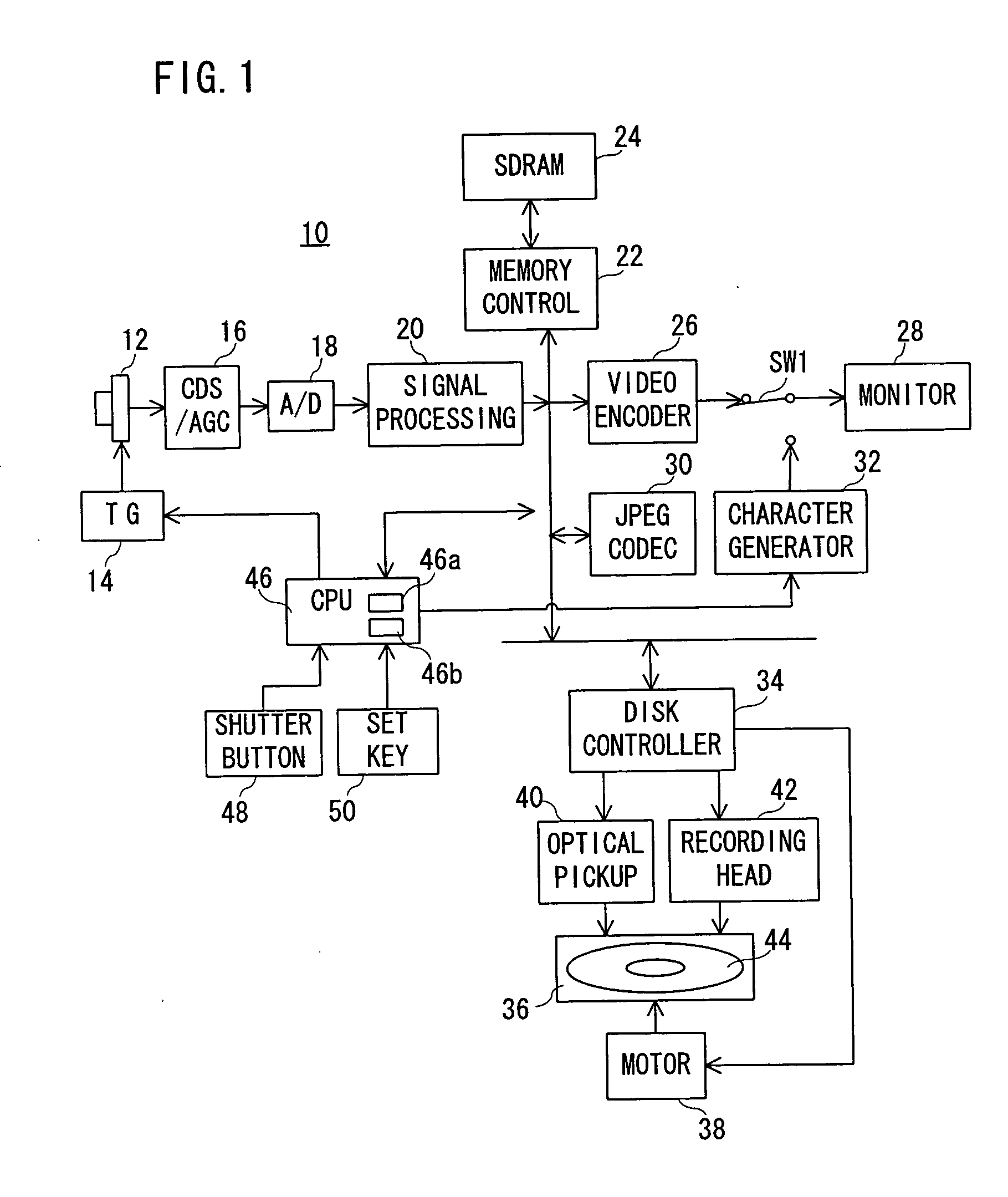
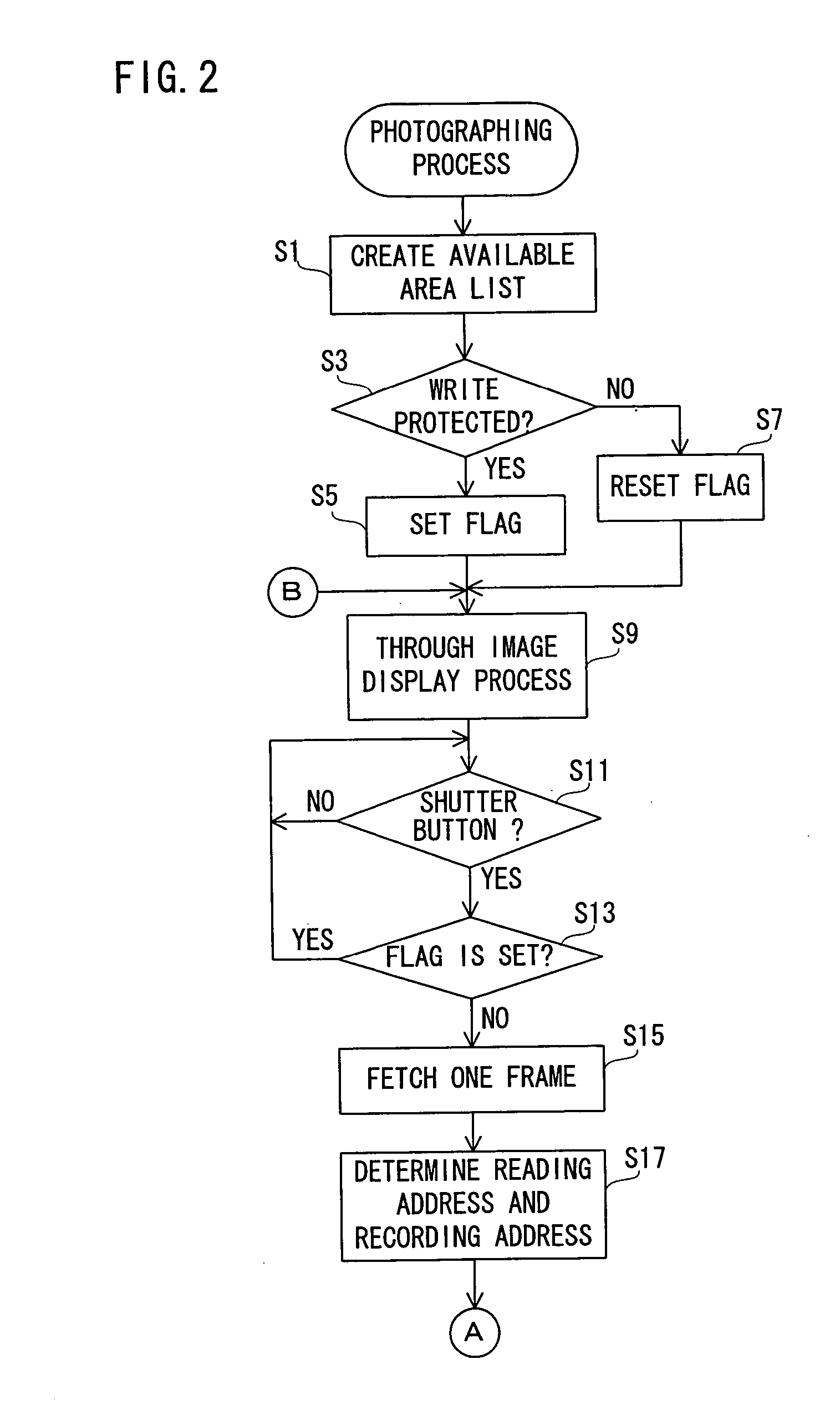
A digital camera (10) includes a CPU (46). When a power source is turned on, the CPU (46) determines an available area of a recording destination on the basis of an FAT recorded on a magneto-optical disk (44). Compressed image data created on the basis of an operation of a shutter button (48) is recorded on the determined available area. When succeeding in recording, the FAT is renewed. When failing in recording due to a defect of the magneto-optical disk (44), a message is displayed on a monitor (28). When a set key (50) is operated after displaying the message, a write protection is set on the magneto-optical disk (44).
Owner:XACTI CORP
Method and apparatus of converting a series of data words into a modulated signal
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Opto-magnetic recording medium with a garnet ferrite recording layer, and opto-magnetic information recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS6759137B1Raise the ratioReduce the required powerRecord information storageMagnetic materialsFerrite layerRecording layer
This invention relates to magneto-optical recording media such as magneto-optical disks and cards, manufacturing methods of the medium and a magneto-optical recording and playback device to record and play back data using the magneto-optical recording media. The magneto-optical recording medium of the present invention has a recording layer and a reflective layer on a substrate, and the recording layer has a layered structure in which at least one spinel ferrite (or rutile-type oxide or hematite) layer and at least one garnet ferrite layer are piled together. It is preferable that the layered structure is formed on tracks where data are recorded. The manufacturing method of the present invention comprises the steps of heat treatment in the range of 500-700° C., preferably 600-630° C., after the formation of the recording layer. In the magneto-optical recording and playback device to record and play back data of the present invention, the wavelength of light for recording data is different from that for reading data, which is preferable for a magneto-optical recording medium comprising a garnet ferrite layer.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
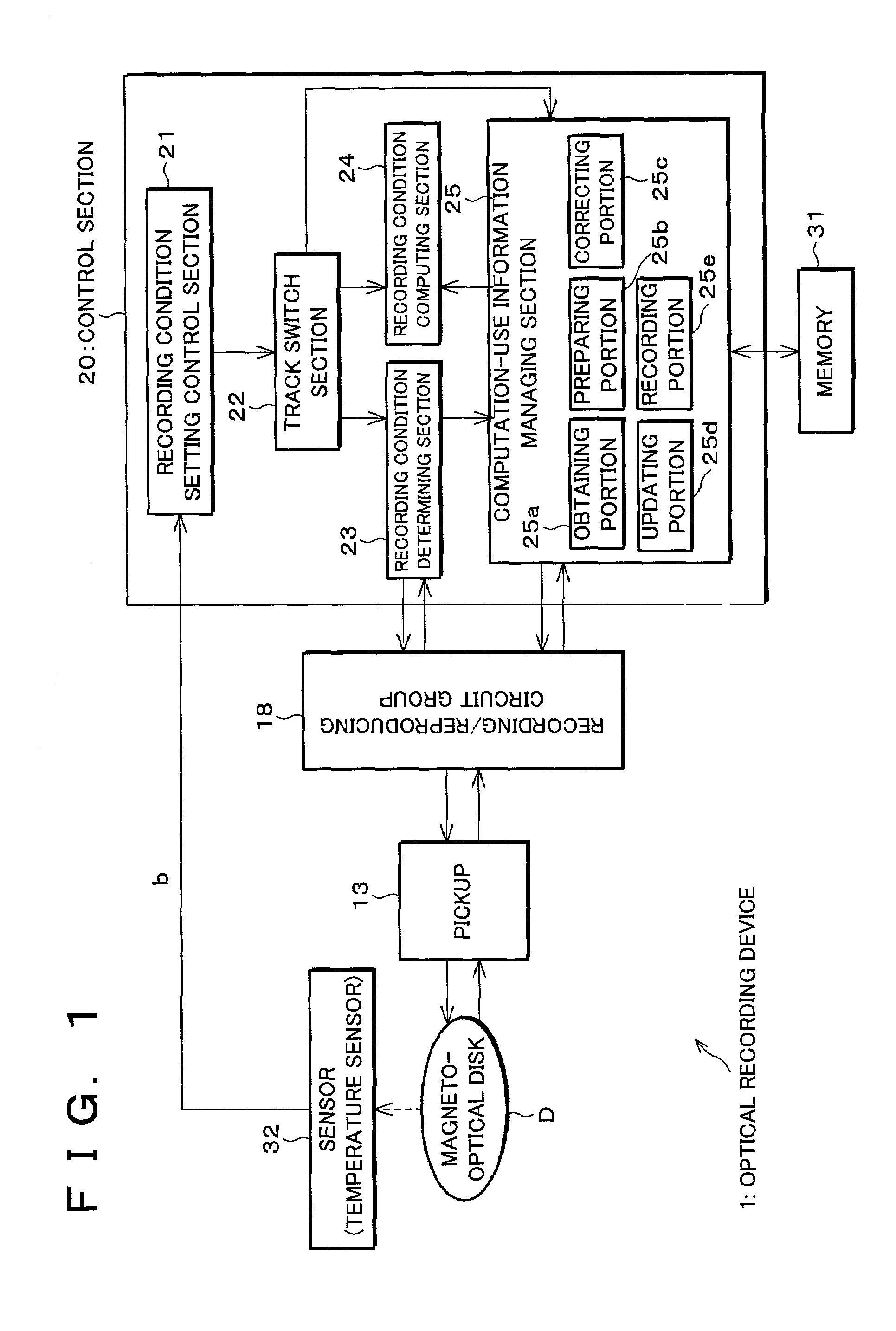
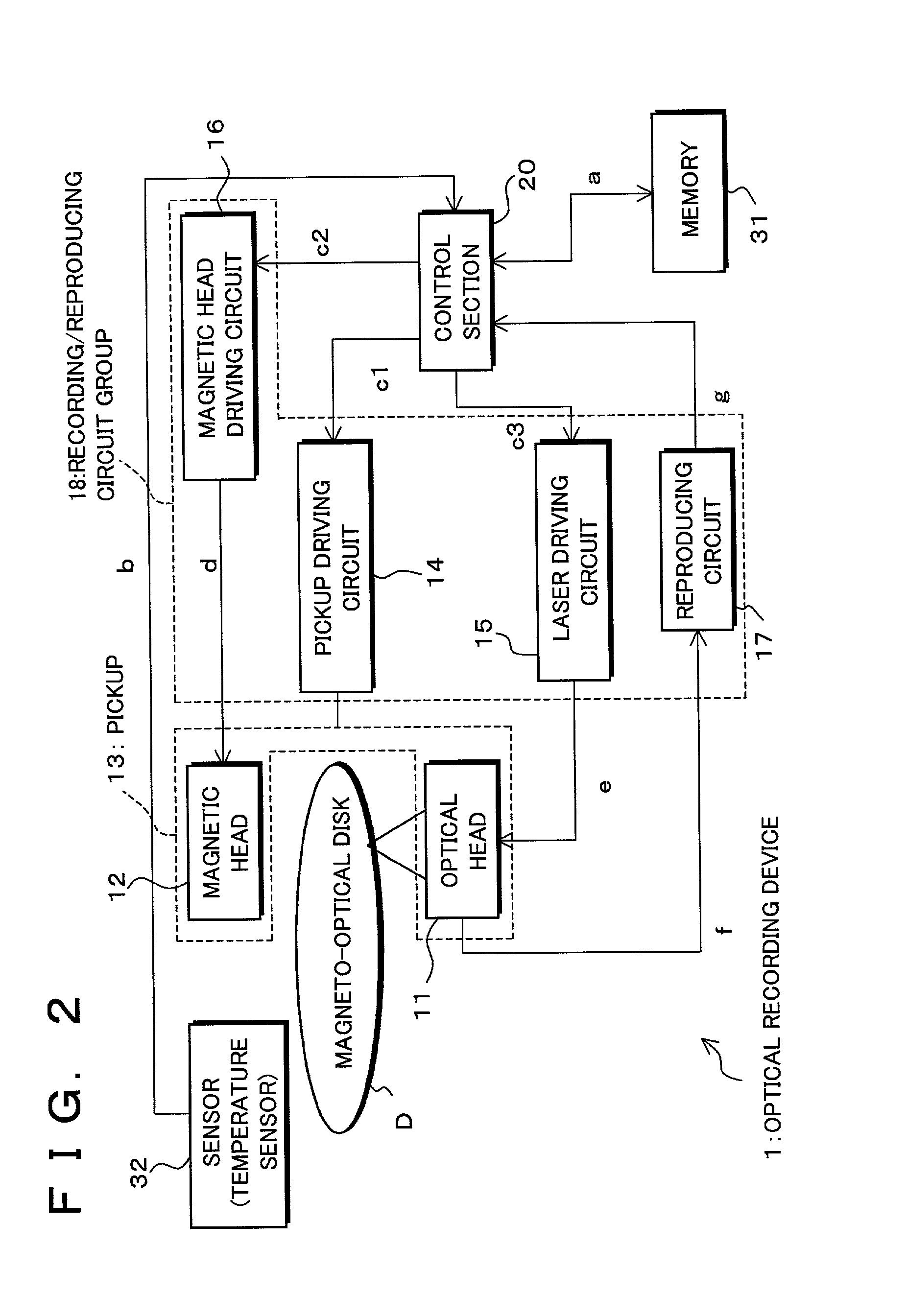
Optical recording device and optical recording method, control program for the optical recording device, and computer-readable recording medium recording the control program
InactiveUS7027370B2Short timeImprove accuracyFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesComputer hardwareEngineering
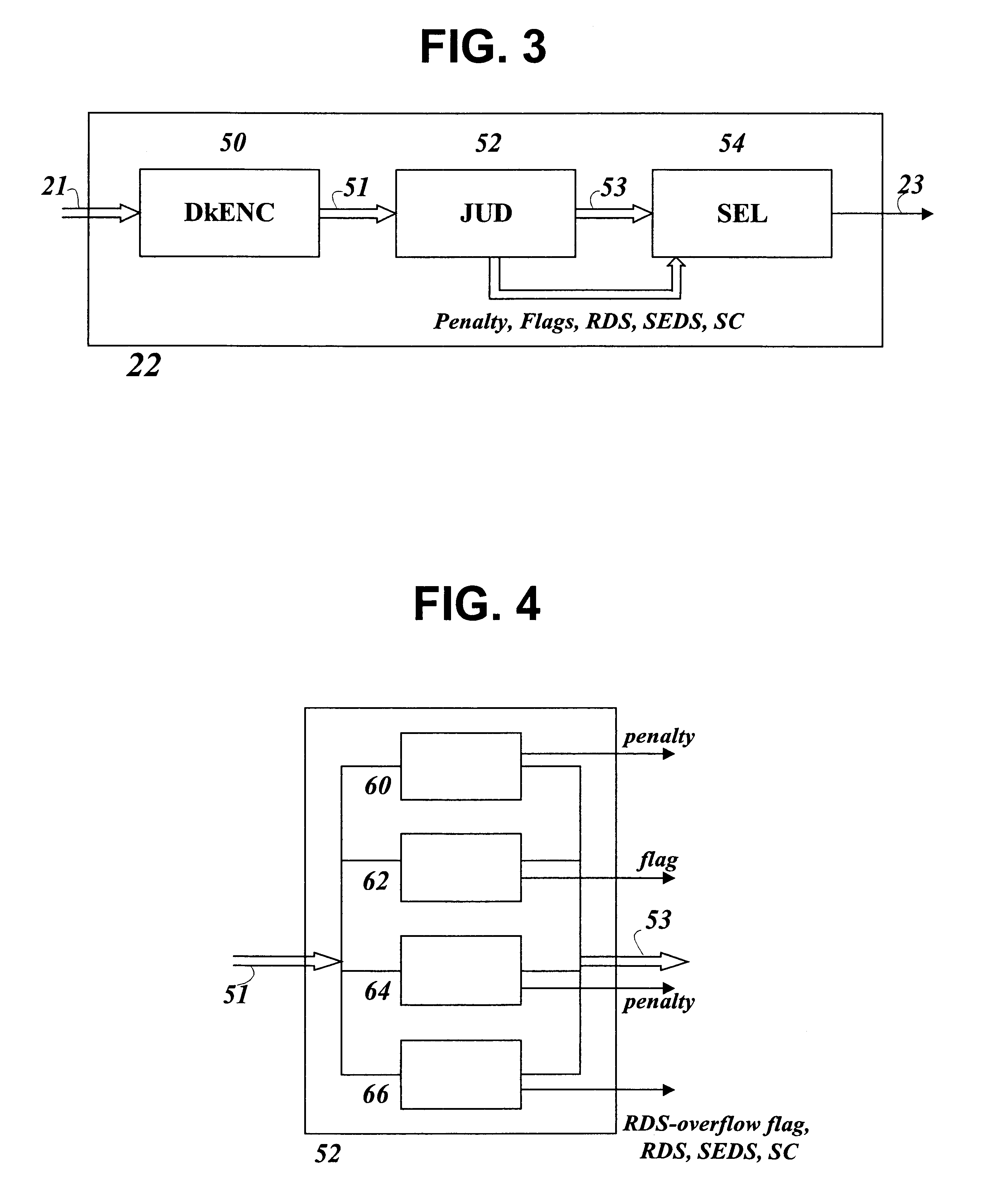
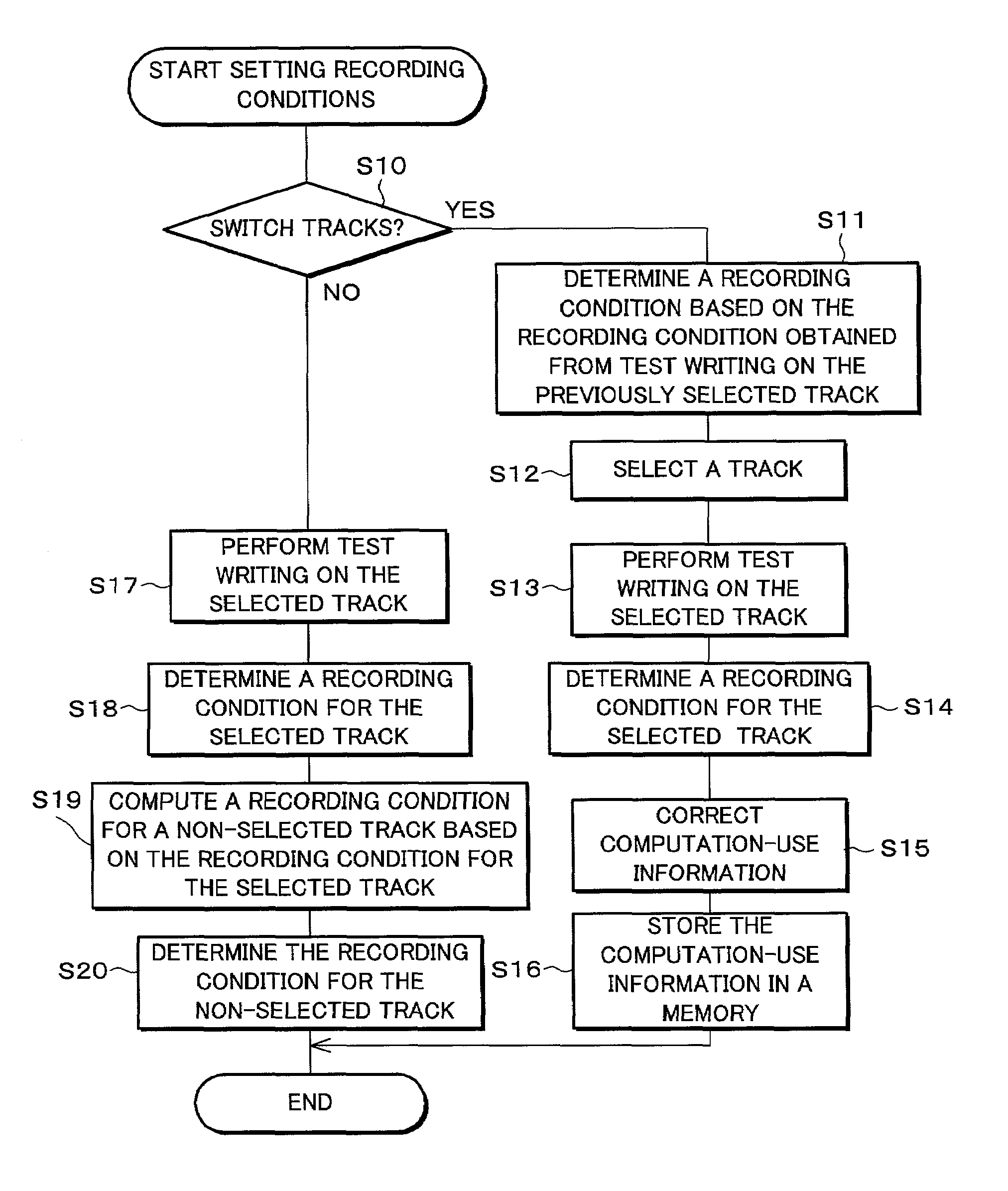
An optical recording device includes a recording condition determining section for determining recording conditions for a track by performing test writing with respect to the track which is, for example, either a land or a groove of a magneto-optical disk, a recording condition computing section for performing computation in accordance with computation-use information based on the recording conditions for the track so as to determine recording conditions for the other track, a track switch section for switching tracks to be used for test writing, and a computation-use information managing section for correcting the computation-use information based on respective results of test writing before and after the switch, thereby determining recording conditions for one of the tracks in short time by computation, while, because the computation-use information is corrected based on the results of test writing, improving accuracy in recording conditions obtained by computation.
Owner:SHARP KK
Magnetic sensor
InactiveUS7084624B2Increase memory capacityRecord information storageDigital storageHarmonicMagnetization
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Magnetooptical recording apparatus having retreatable magnetic head
InactiveUS7016267B2Small sizeRecord information storageMaintaining head carrier alignmentOptical pickupLight beam
A magnetooptical recording apparatus that records information by applying a magnetic field from a magnetic head while irradiating a light beam onto a magnetooptical disk from an optical pickup. The apparatus includes an optical pickup, a magnetic head having a slider that moves in a radial direction of the magnetooptical disk together with the optical pickup and is abutted against a recording surface of the magnetooptical disk and first and second elastic members that support the magnetic head.
Owner:CANON KK
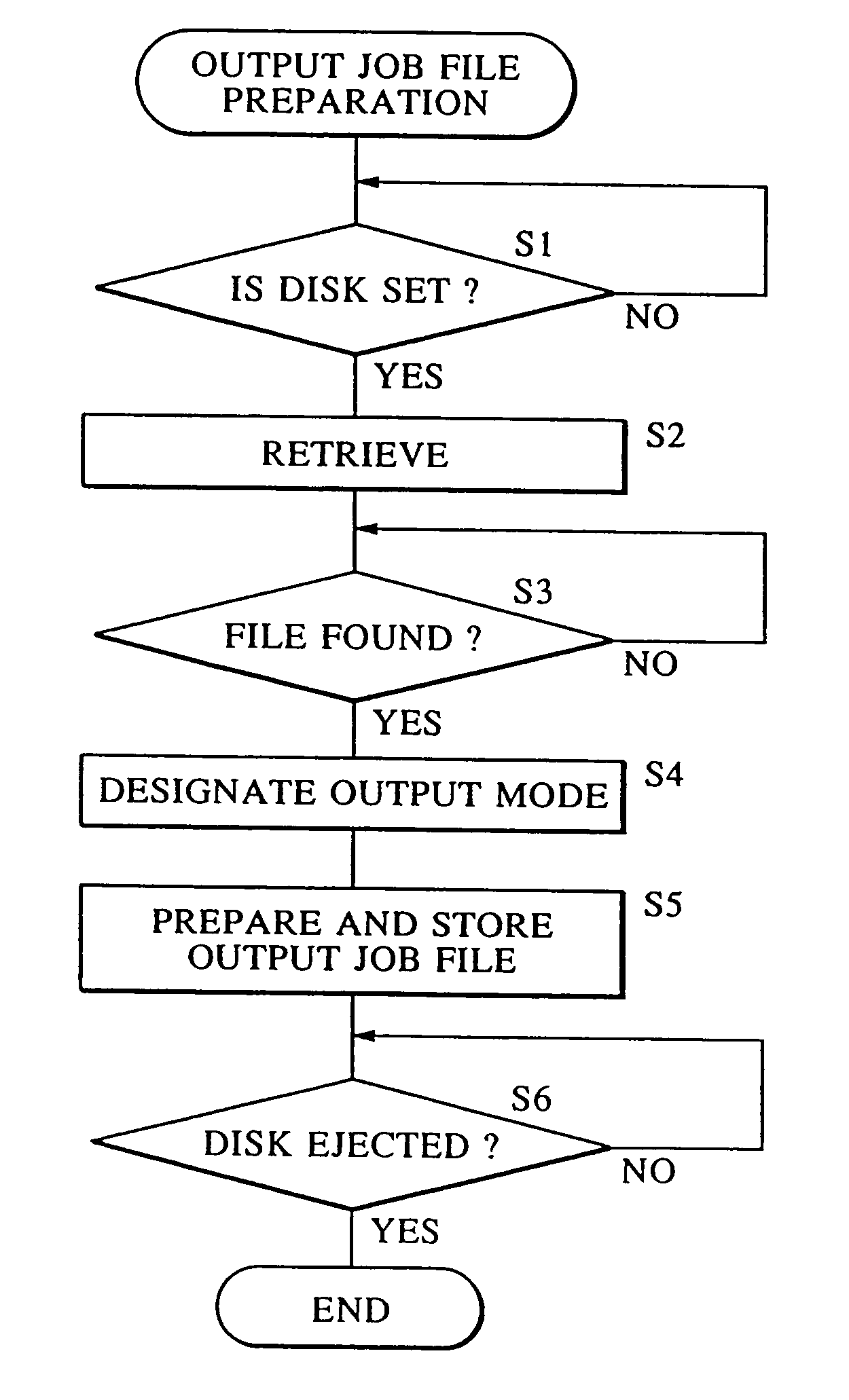
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
InactiveUS7095525B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingImage manipulation
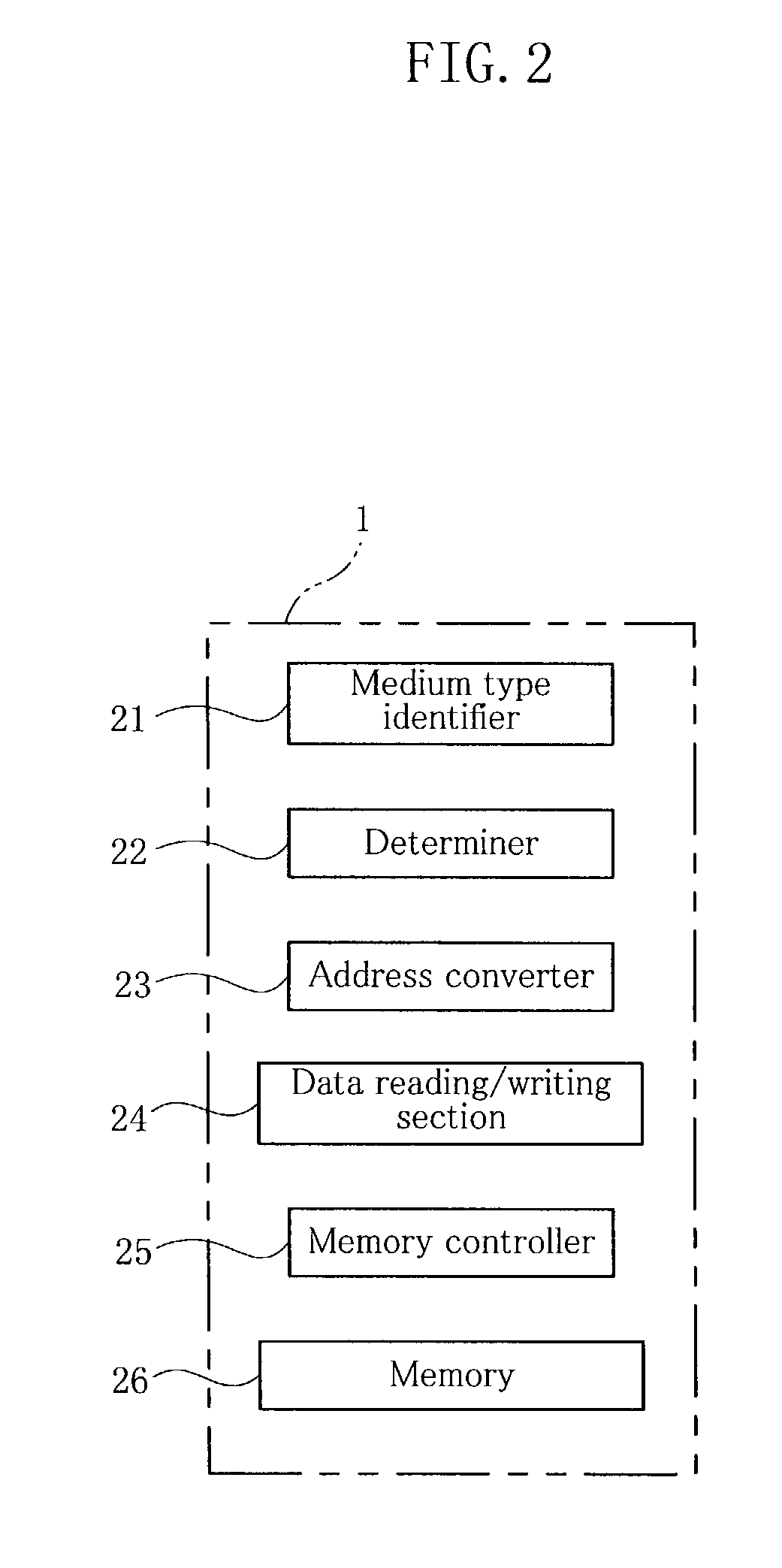
When reading image data stored on a detachable storage medium such as a magneto-optical disk and outputting the data using an image outputting device, data regarding modes in which the image data is to be output is stored in advance on a storage medium by an apparatus such as a personal computer, for example, which is different from the image outputting device. By loading the storage medium in the image outputting apparatus, the image data is read out and output in accordance with the stored output mode data, whereby it is possible to prevent the image outputting apparatus from being monopolized for a long period of time and to output data easily in a desired output mode.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic optical disk, recording and/or reproduction method and appts. using same
InactiveCN1540650AIncrease recording capacityRecord information storageLight beam reproducingMagnetizationRecording layer
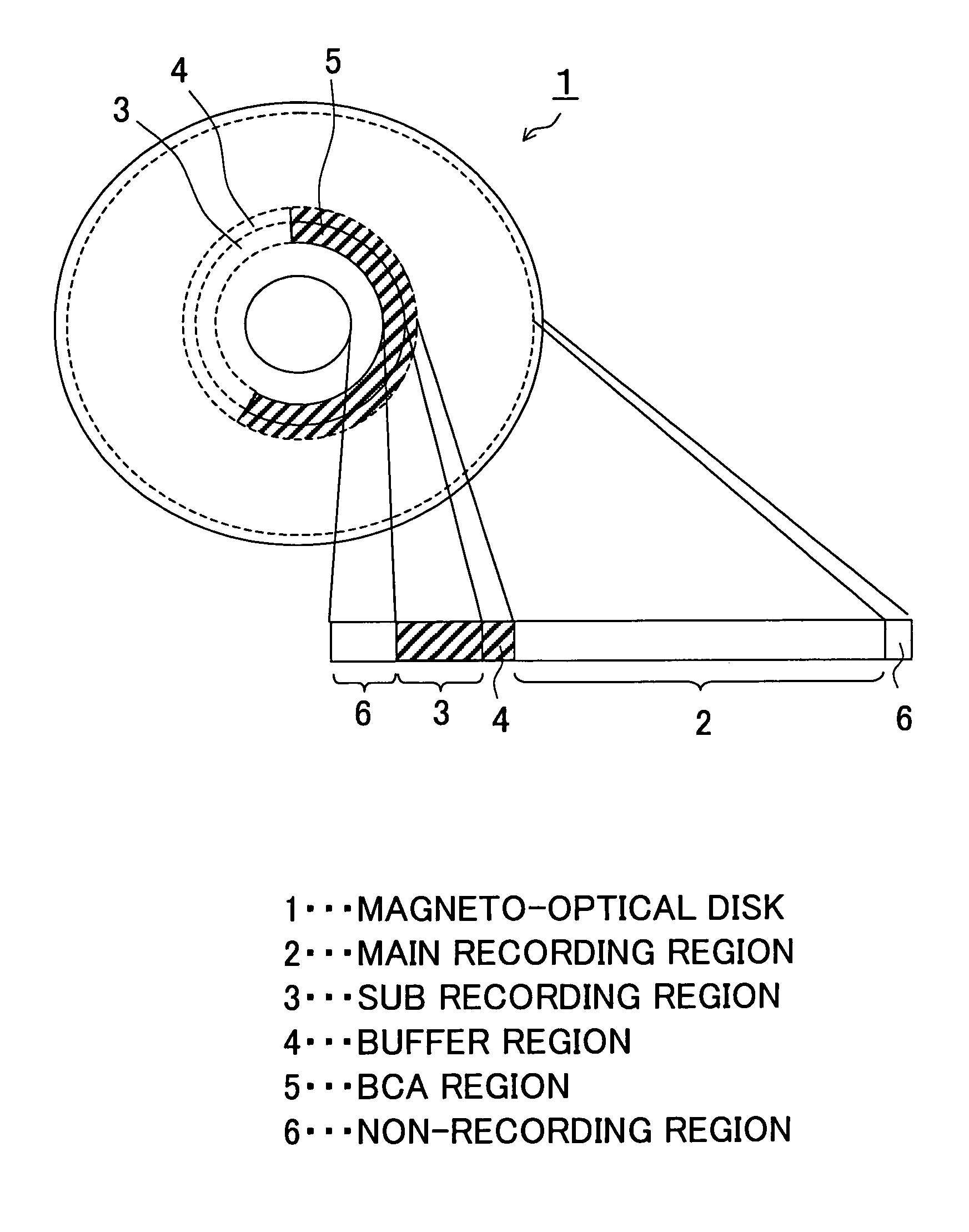
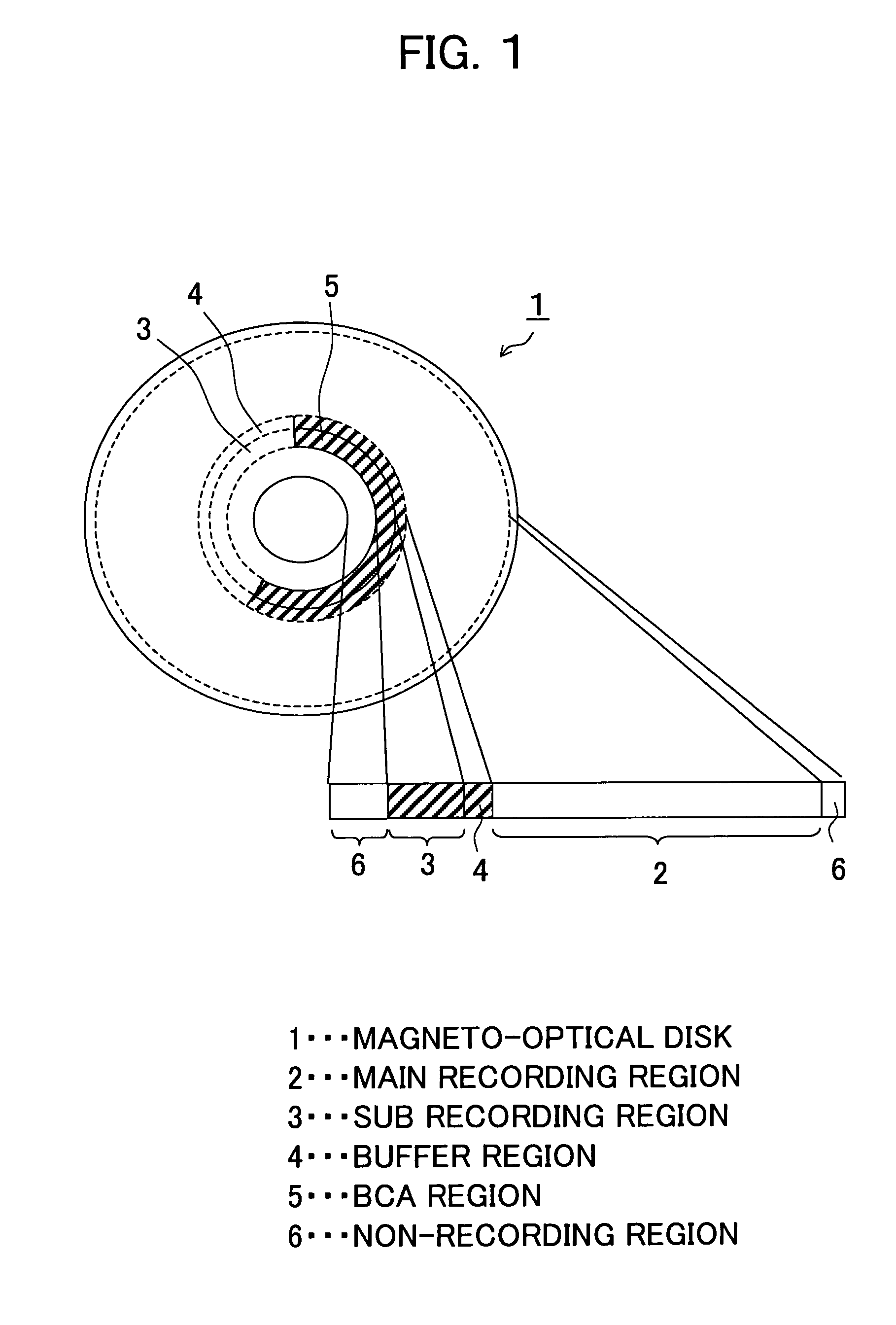
A magneto-optical disk having a small-sized diameter and a large capacity and able to record and reproduce disk discrimination information, and a recording method and a reproducing method of the same, wherein a recording layer including a main recording region in which a first information is recorded, a sub recording region in which a second information including the disk discrimination information is recorded, and a buffer region formed between the main recording region and the sub recording region and in which a third information is recorded is provided on a substrate, the second information is recorded by a mark array formed in stripe shapes in the sub recording region and the buffer region, a plurality of marks constituting the mark array are obtained by changing the magnetization state of the recording layer, and the third information is reproduced by a modulation signal of a reflection ratio along a circumferential direction of the disk.
Owner:SONY CORP
Disc-shaped recording medium, manufacturing method thereof, and disc drive device
InactiveUS7233547B2Good detrack characteristicComponent with highRecord information storageLight beam reproducingOptical pickupMagneto optical
A magneto-optical disk which reproduces information with an optical pickup head which uses an electromagnetic force as the driving force is provided. Other areas than at least the recording track are magnetized uniformly in a direction of canceling the influence of external magnetic field applied by the optical pickup head or a recording pattern having a frequency higher than modulation transfer function (MTF) of the optical pickup head is recorded to the other areas than at least the recording track. Read signals SP12 and SP14 from the magneto-optical disk are low in bit error rate.
Owner:SONY CORP
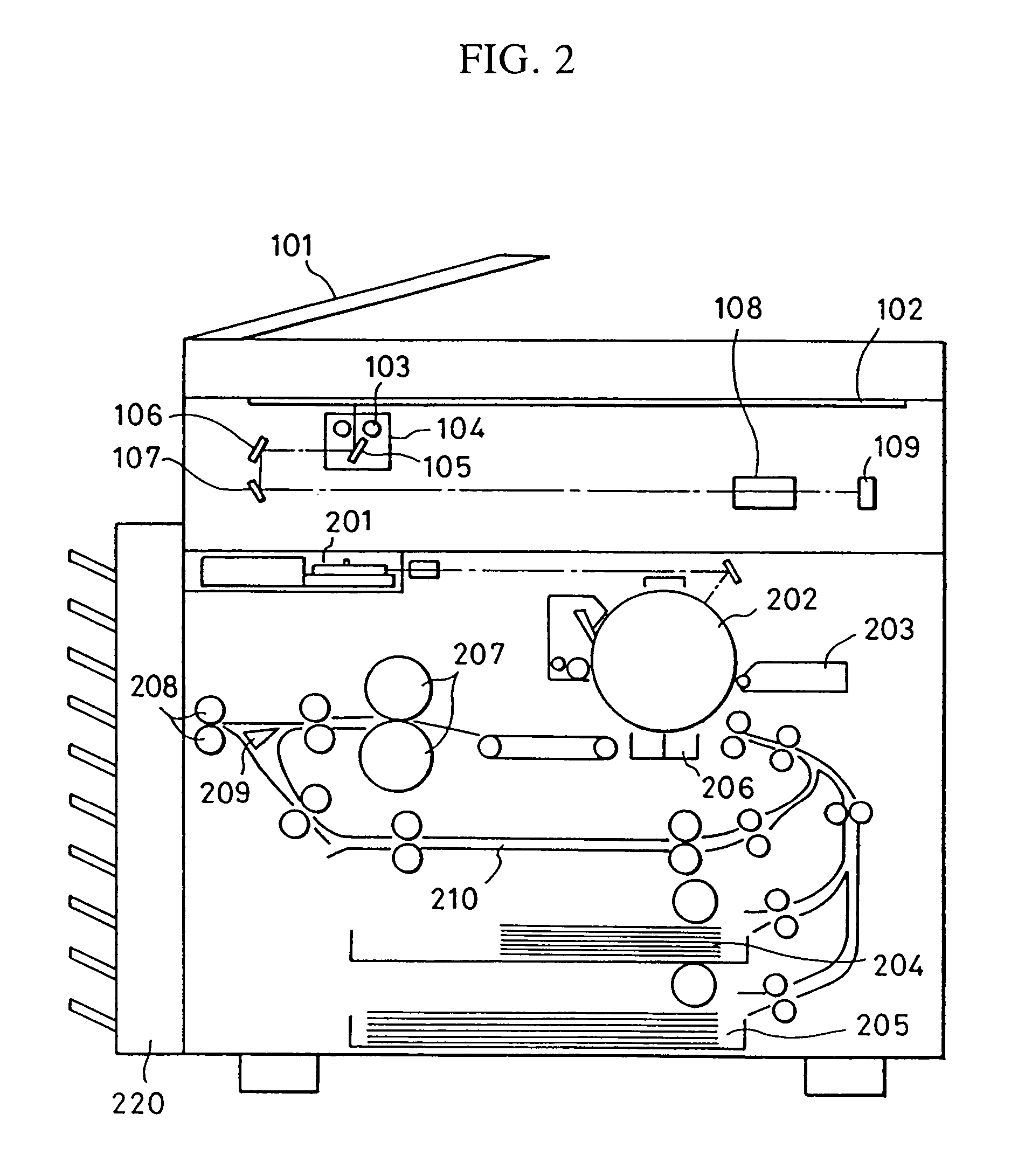
Magneto-optical disc recording and/or reproducing device
InactiveUS20050018548A1Easy to useAvoid damageMagneto-optical discsRecord information storageOptical pickupMiniaturization
A recording / reproducing device using a magneto-optical disc as a recording medium having a holder for holding a magneto-optical disc and moving the magneto-optical disc between a disc unloading position and a disc loading position, a turntable for rotating the magneto-optical disc, an optical pickup for casting a light beam onto a signal recording surface of the magneto-optical disc, a magnetic head arranged to face the optical pickup on the opposite sides side of the magneto-optical disc and moving toward and away from the magneto-optical disc, and a rotating ejection lever positioned on a base for ejecting the magneto-optical disc held by the holder. Since the ejection lever is arranged on the side of the base where the optical pickup is arranged, the space within the device body is effectively used, thus realizing miniaturization.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magneto-optical disk and recording and/or reproducing method and recording and/or reproducing apparatus using the magneto-optical disk
InactiveUS7355929B2Inhibition of informationHigh densityRecord information storageLight beam reproducingMagnetizationRecording layer
A magneto-optical disk having a small-sized diameter and a large capacity and able to record and reproduce disk discrimination information, and a recording method and a reproducing method of the same, wherein a recording layer including a main recording region in which a first information is recorded, a sub recording region in which a second information including the disk discrimination information is recorded, and a buffer region formed between the main recording region and the sub recording region and in which a third information is recorded is provided on a substrate, the second information is recorded by a mark array formed in stripe shapes in the sub recording region and the buffer region, a plurality of marks constituting the mark array are obtained by changing the magnetization state of the recording layer, and the third information is reproduced by a modulation signal of a reflection ratio along a circumferential direction of the disk.
Owner:SONY CORP
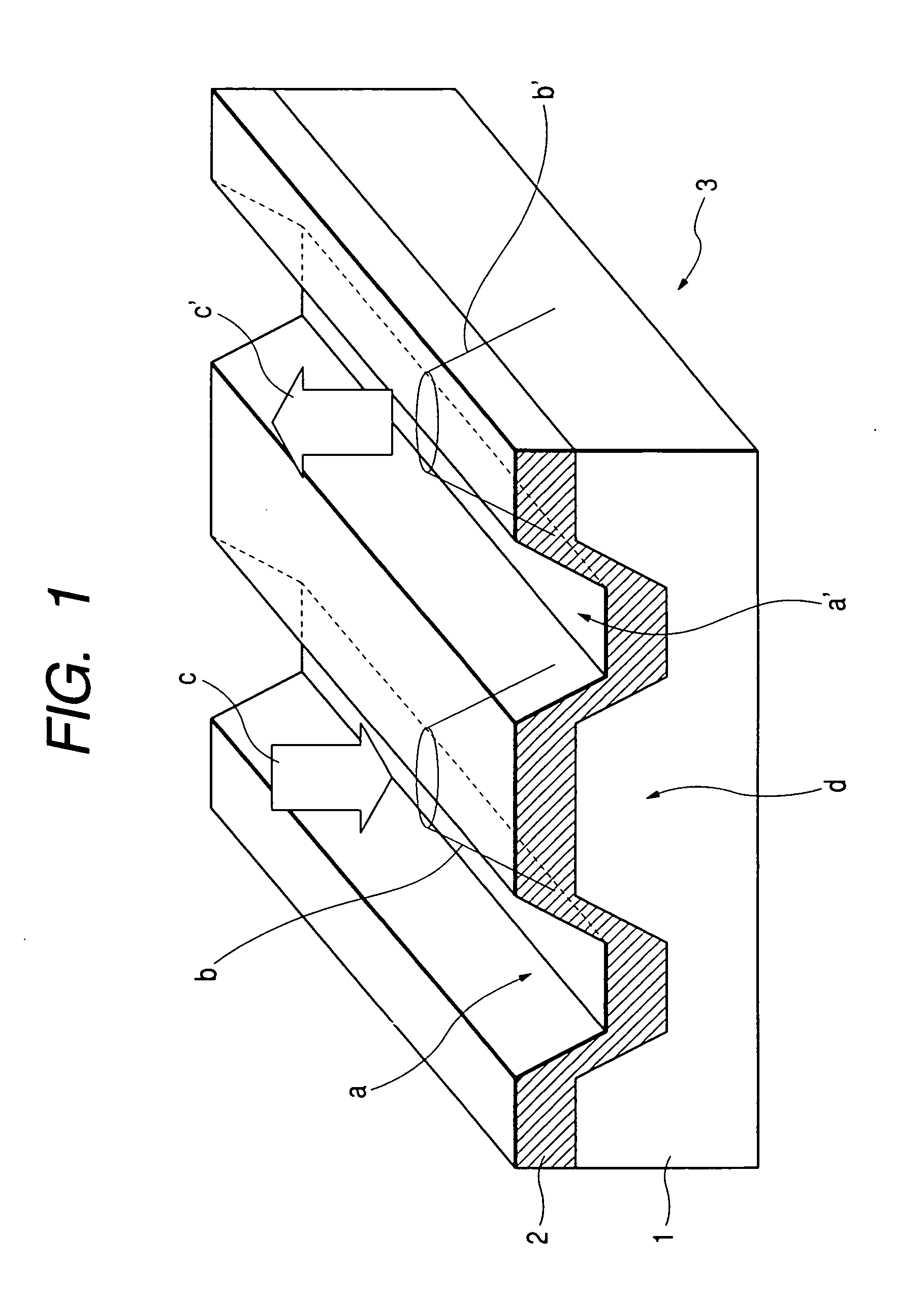
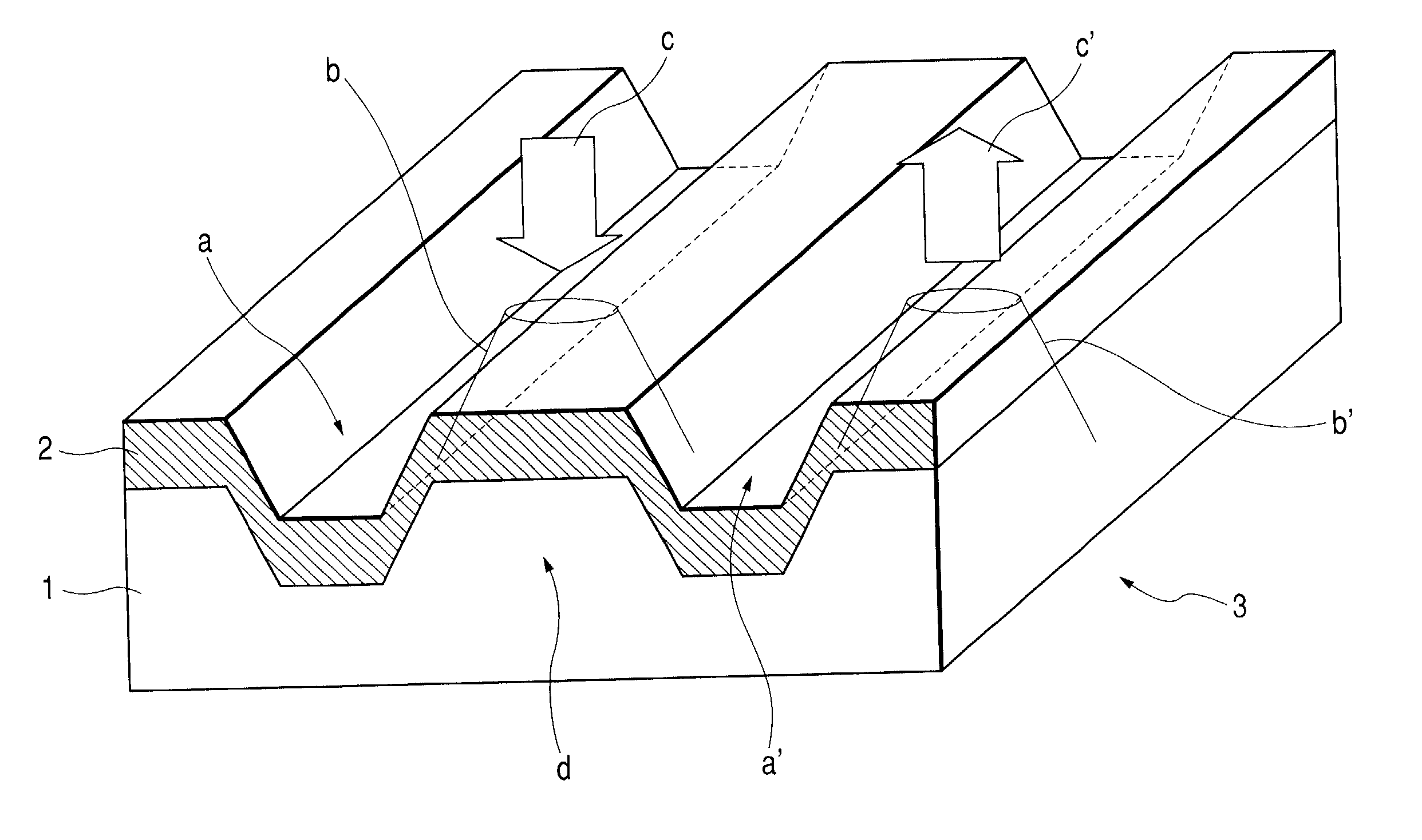
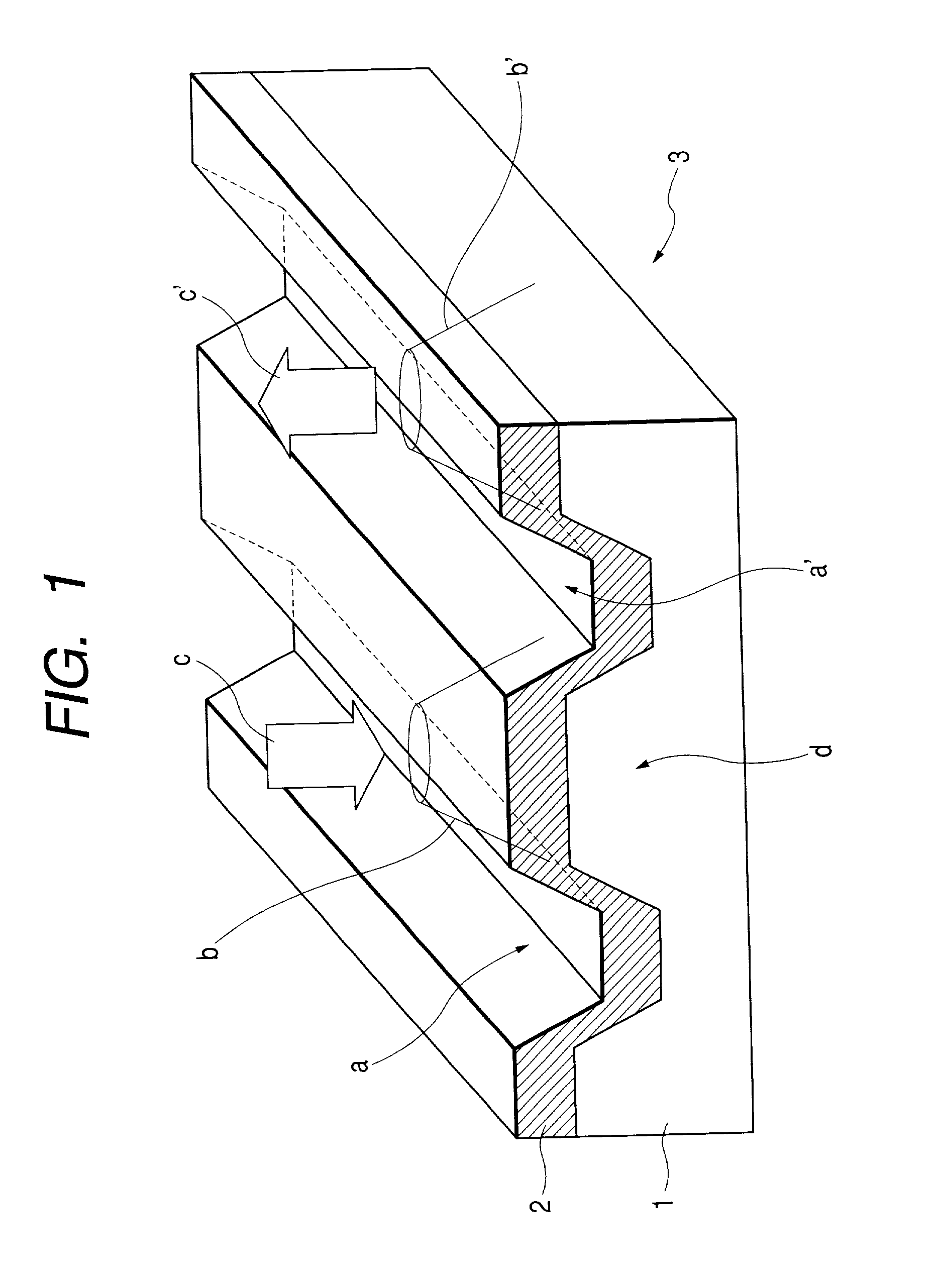
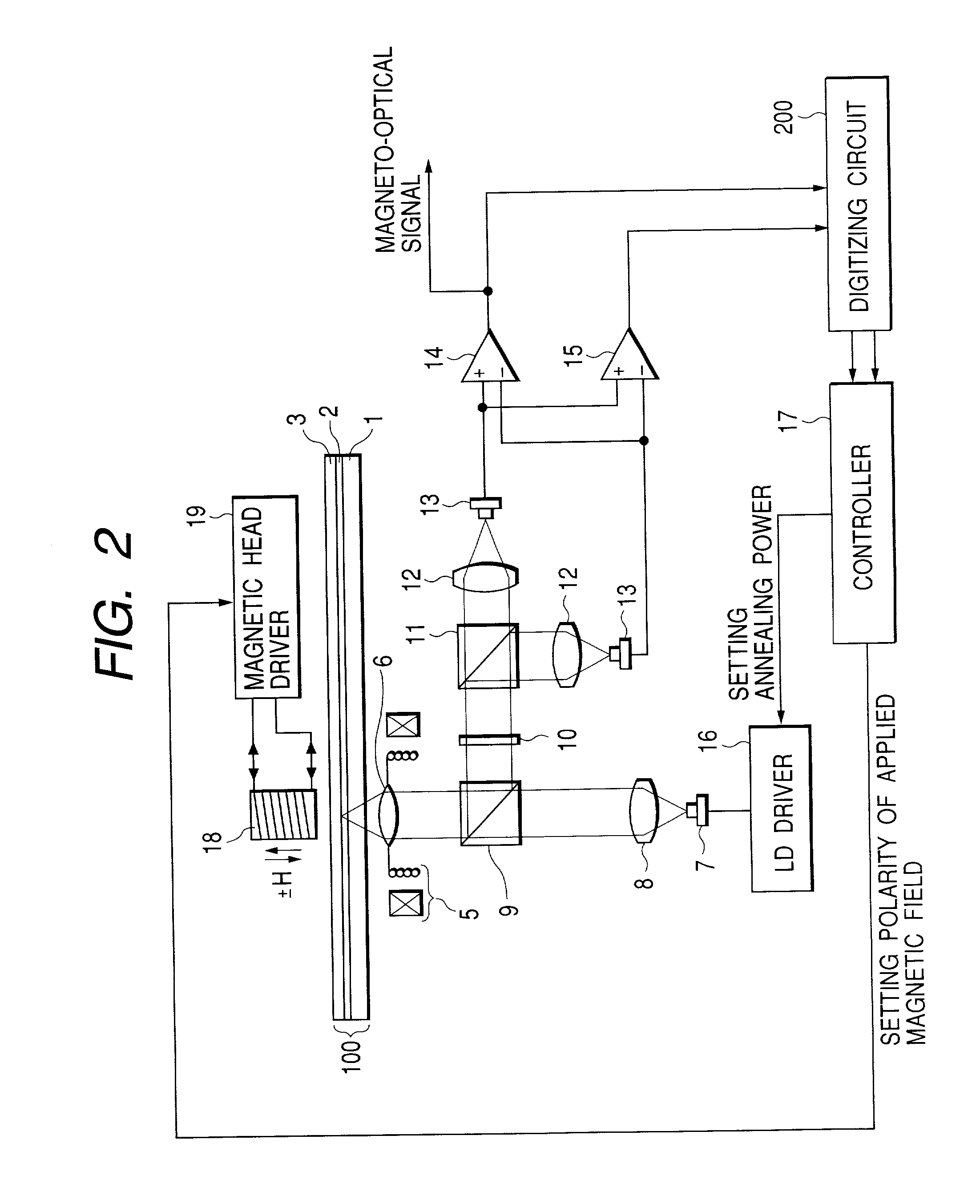
Method for annealing domain wall displacement type magneto-optical disc and magneto-optical disc
InactiveUS20040158849A1Record information storageFlat record carrier containersLight beamCurie temperature
A manufacturing method of a domain wall displacement type magneto-optical recording medium comprises the steps of depositing a magnetic layer on a substrate to prepare a disc, and irradiating the magnetic layer with a converged light beam while applying a magnetic field and annealing the magnetic layer a converged light beam between information tracks. A domain wall displacement type magneto-optical disc comprises a domain wall displacement layer in which a domain wall displaces, a memory layer that holds a recording magnetic domain according to information, a switching layer that is provided between the domain wall displacement layer and the memory layer and has a Curie temperature lower than that of those layers, and a disconnecting area that is provided in the domain wall displacement layer and disconnects a switching connection between information tracks, wherein the polarity of a residual magnetization at a boundary between the information track and the disconnection area is oriented in a certain direction.
Owner:CANON KK
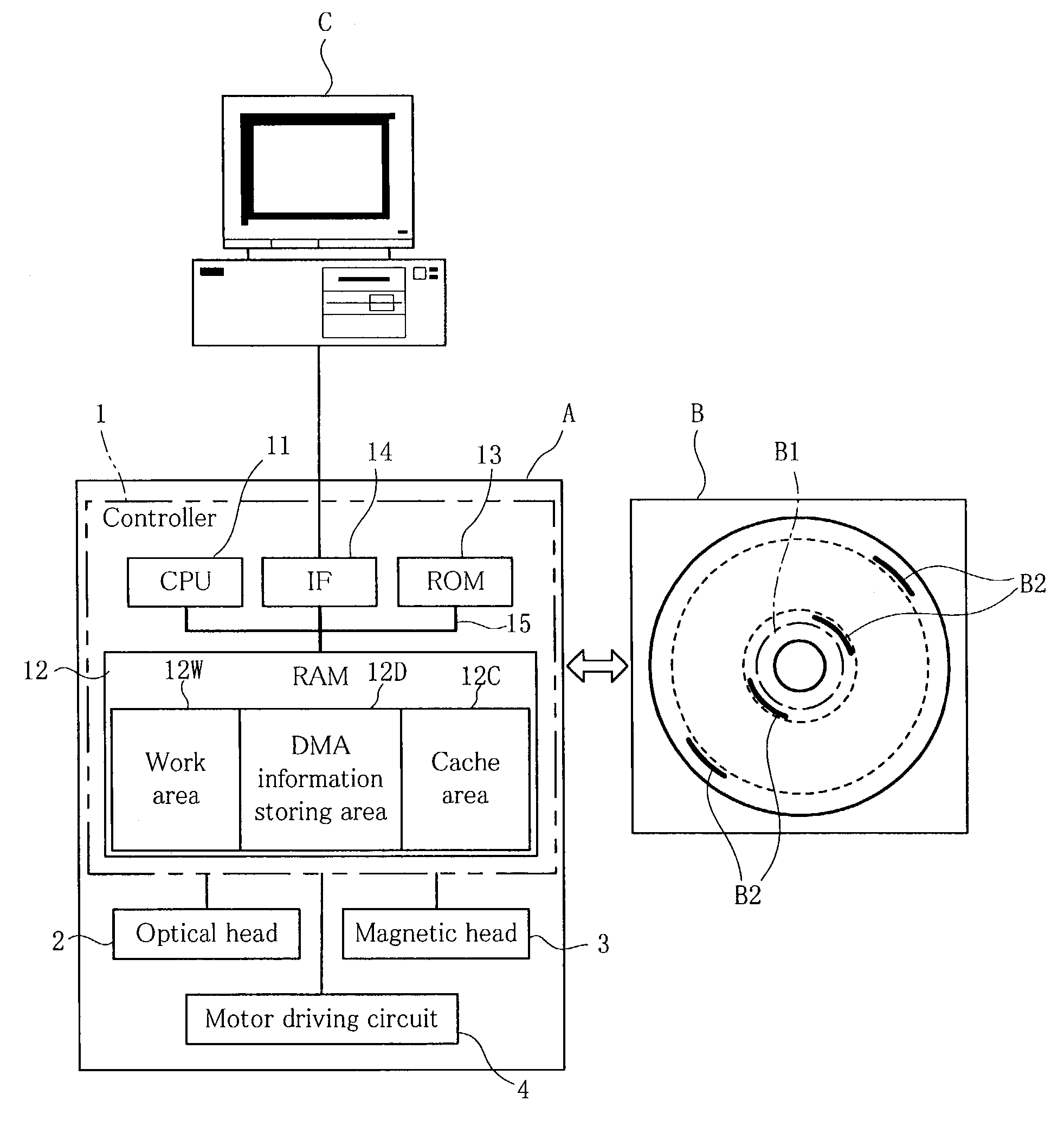
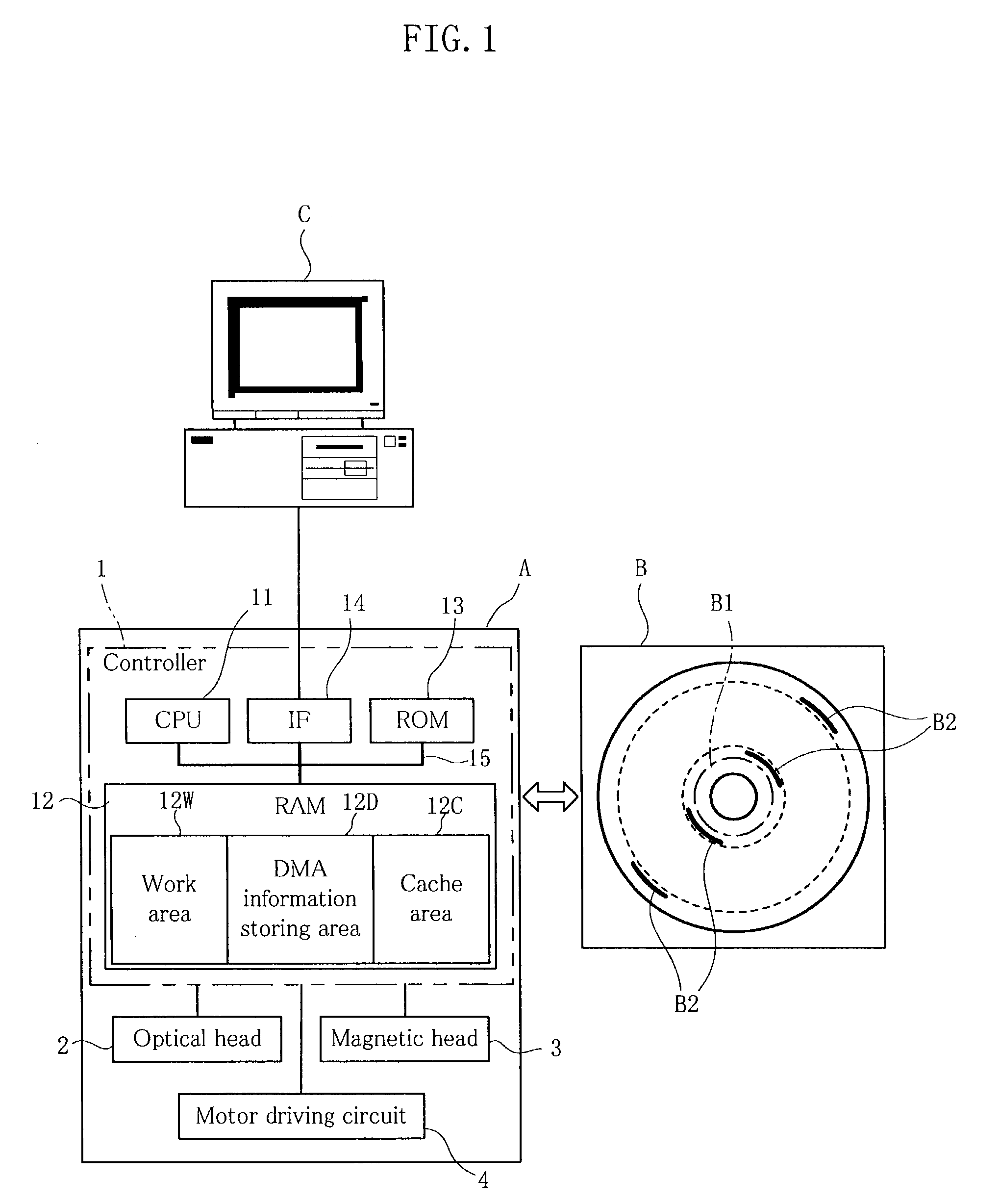
Disc drive and recording-disc loading control method
InactiveUS7076693B2Short response timeShort timeMagneto-optical discsError detection/correctionTerm memoryData transmission
A disc drive (A) for data transfer between a magneto-optical disc (B) and a host (C) is provided. The disc drive reads and stores in a RAM (12) medium identification information unique to the magneto-optical disc (B) and DMA information (B2) including a list of addresses indicating defective areas upon loading, and performs address conversion with reference to the DMA information (B2) for the data transfer. A CPU (11) checks if the medium identification information obtained when loading the magneto-optical disc (B) is identical with or different from medium identification information obtained in the previous loading. The CPU (11) allows the reading of DMA information (B2) and replacing of the previous DMA information remaining in a DMA information storage area (12D) of the RAM (12) with the newly obtained DMA information only when the newly obtained medium identification information is different from the previous medium identification information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Printer with controller responsive to stored image files and processing information, related method, and recording media having related executable code
InactiveUS6963410B2Visual presentation using printersSpecial data processing applicationsComputer printingEngineering
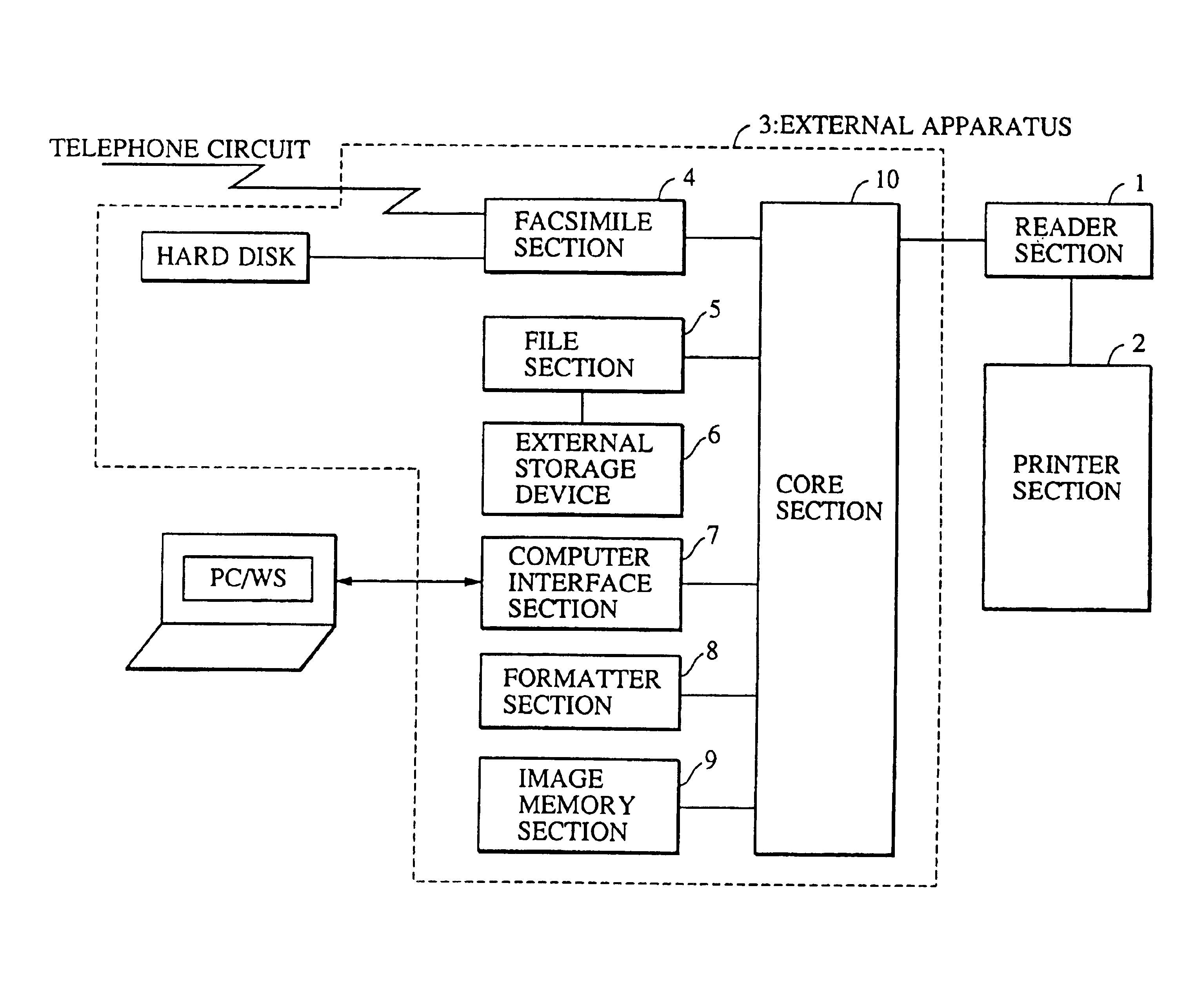
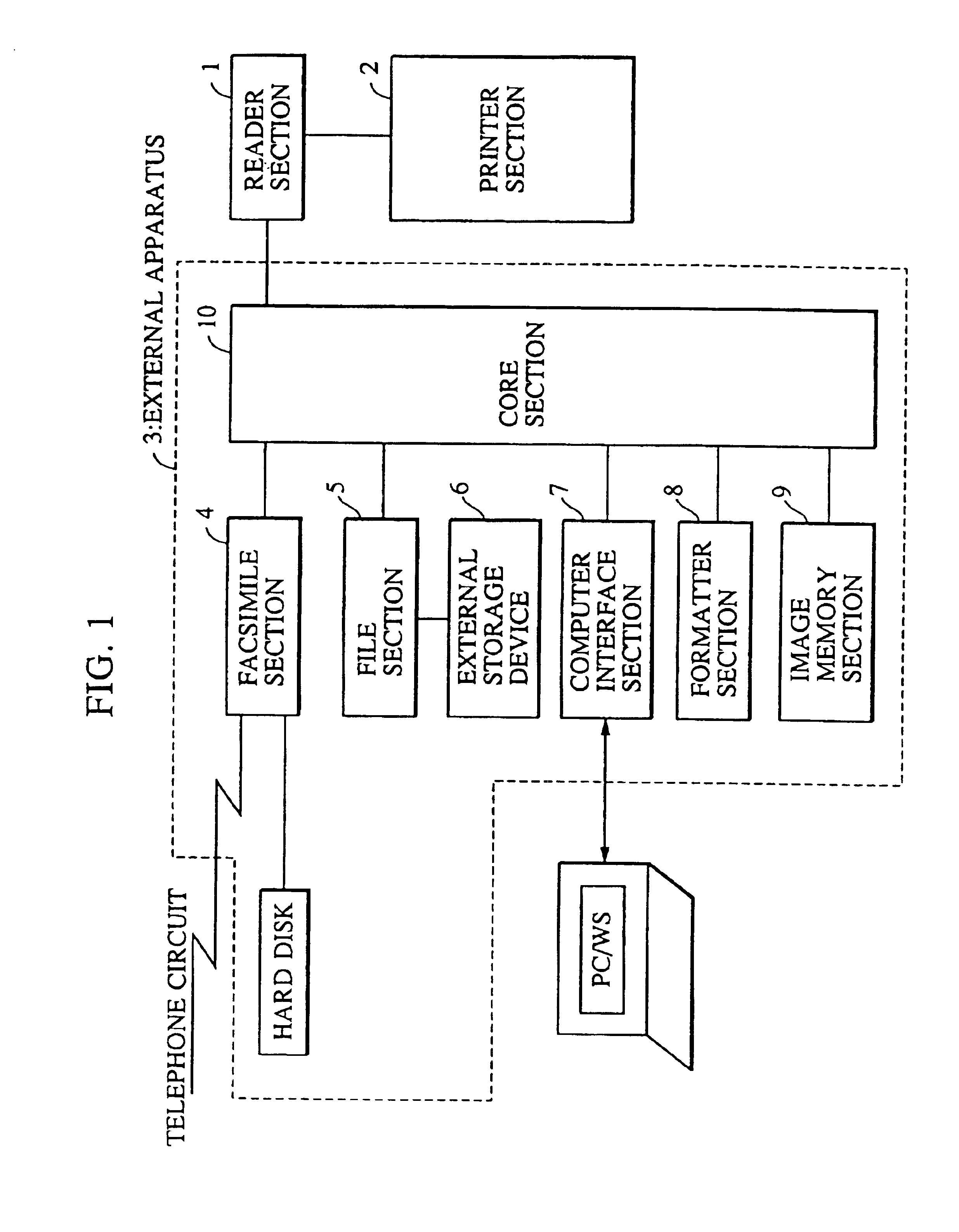
When reading image data stored on a detachable storage medium such as a magneto-optical disk and outputting the data using an image outputting device, data regarding modes in which the image data is to be output is stored in advance on a storage medium by an apparatus such as a personal computer, for example, which is different from the image outputting device. By loading the storage medium in the image outputting apparatus, the image data is read out and output in accordance with the stored output mode data, whereby it is possible to prevent the image outputting apparatus from being monopolized for a long period of time and to output data easily in a desired output mode.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic head cleaning disk for use in magneto-optical recording and reproducing device
InactiveUS6973011B2Simple structureReduce power consumptionOptical head protectionRecord information storageInformation layerEngineering
The present invention provides a cleaning disk and a magneto-optical disk drive apparatus being simple in structure, adaptable to cleaning disks having various specifications, low in power consumption, low in electromagnetic noise, and preventing damage to the magnetic head and the optical head; the cleaning disk comprises a magneto-optical disk having an information layer, and a head-cleaning member, provided on the magneto-optical disk, for cleaning the magnetic head of the magneto-optical disk drive apparatus, wherein information regarding a magnetic head cleaning condition for setting the operation condition of the magneto-optical disk drive apparatus during cleaning of the magnetic head has been recorded in advance on the information layer of the magneto-optical disk. The magneto-optical disk drive apparatus reads the information regarding the magnetic head cleaning condition so as to set the operation condition properly.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for the Bidirectional Transmission of Data Between One or More Textile Machines
InactiveUS20090225634A1High degreeEasy to operateCombination recordingSafety devices for fibre treatmentBobbinComputer handheld
Method for the bidirectional transmission of data between one or more textile machines (1) producing cross-wound bobbins and / or one or more same-level and / or higher level control systems with a device (2) for transmitting data to a transport medium, which is used for the transporting of data located on the transport medium, the transport medium being in operative connection with the textile machine (1) producing cross-wound bobbins to transmit data via the device (2). According to the invention, a a memory, a hard disc, a magnetic tape, a writable contact disc (CD), a writable digital versatile disc (DVD), a magneto-optical disc (MO disc), a minidisc (MD) or a digital memory card provided in a mobile telephone or a palm-top computer (personal digital assistant) are used as the transporting medium and the device (2) is integrated in an exchangeable manner in the textile machine (1).
Owner:SAURER GERMANY GMBH & CO KG
Method for annealing domain wall displacement type magneto-optical disc and magneto-optical disc
InactiveUS20020132138A1Magnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingLight beamCurie temperature
A manufacturing method of a domain wall displacement type magneto-optical recording medium comprises the steps of depositing a magnetic layer on a substrate to prepare a disc, and irradiating the magnetic layer with a converged light beam while applying a magnetic field and annealing the magnetic layer a converged light beam between information tracks. A domain wall displacement type magneto-optical disc comprises a domain wall displacement layer in which a domain wall displaces, a memory layer that holds a recording magnetic domain according to information, a switching layer that is provided between the domain wall displacement layer and the memory layer and has a Curie temperature lower than that of those layers, and a disconnecting area that is provided in the domain wall displacement layer and disconnects a switching connection between information tracks, wherein the polarity of a residual magnetization at a boundary between the information track and the disconnection area is oriented in a certain direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical recording medium, master for optical recording medium manufacture, recording and reproducing apparatus, and recording and reproducing method
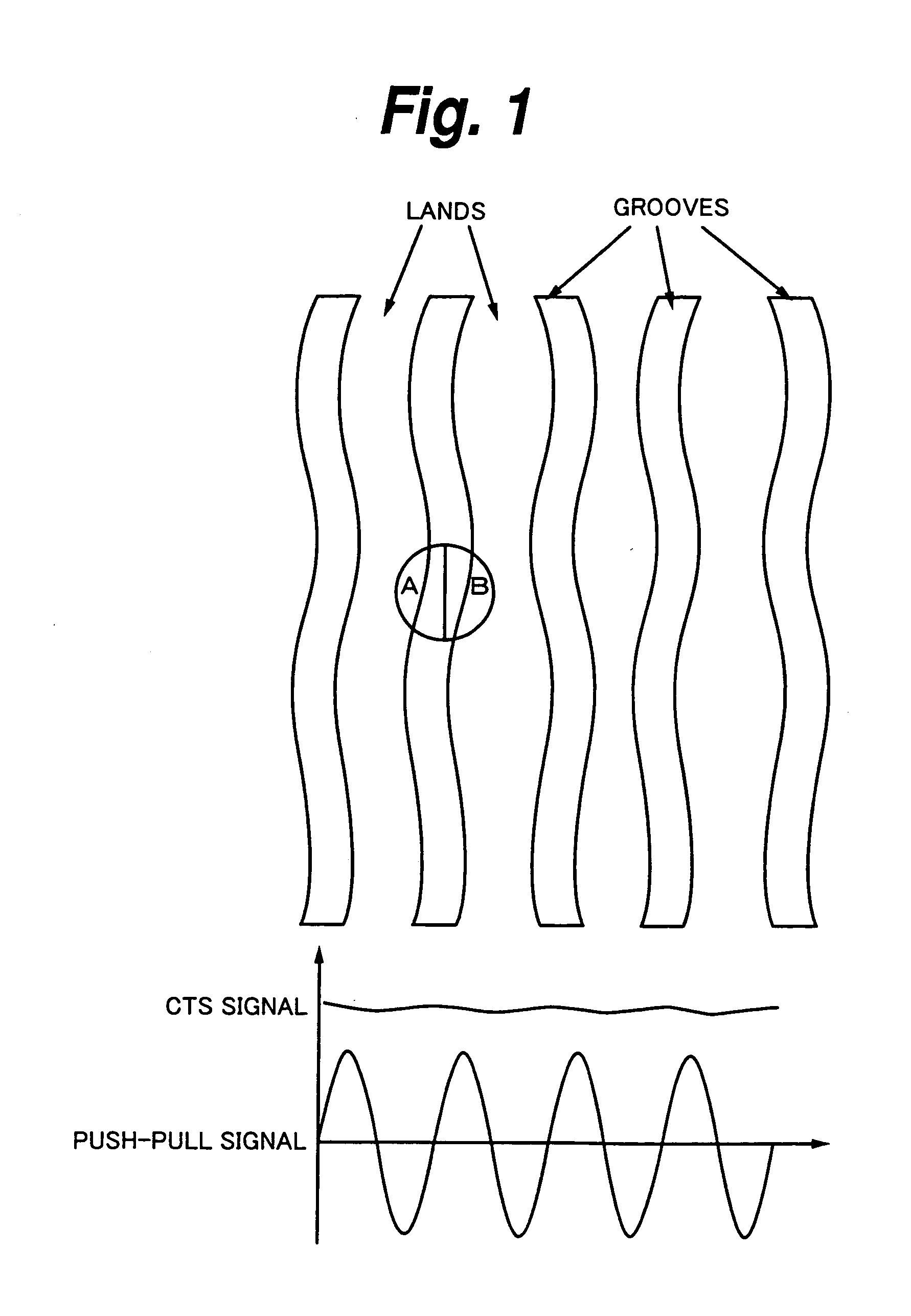
InactiveUS20050007940A1Stable tracking servoGood recording and reproduction characteristicMechanical record carriersSaving energy measuresTrack densityPush pull
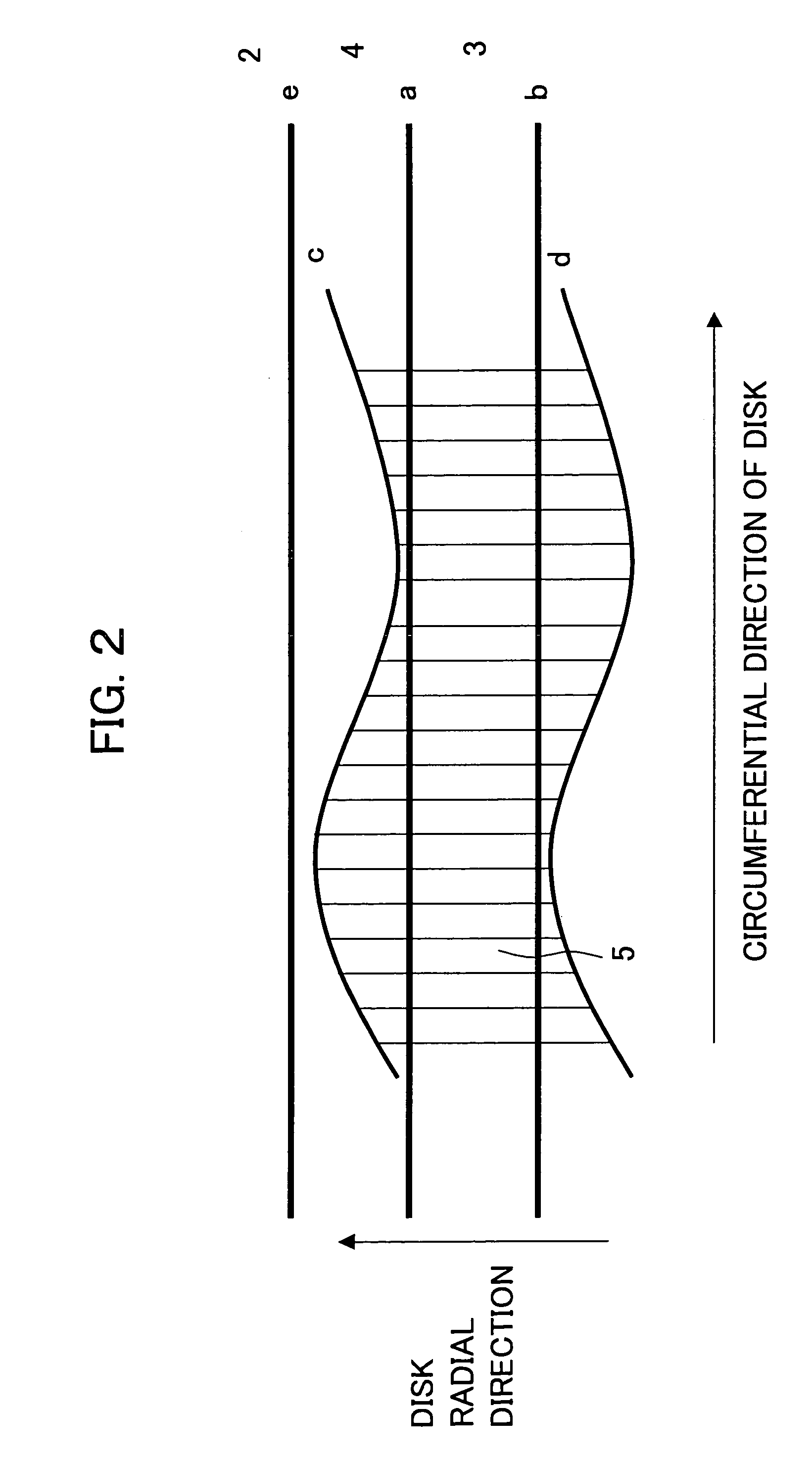
To make a magneto-optical disk to have higher track density and enable stable tracking servo to be performed thereon. On an magneto-optical disk, a first groove Gv1, a second groove Gv2, and a third groove Gv3 are formed so as to be adjacently arranged. The first groove Gv1 and the second groove Gv2 are deep grooves, and the third groove Gv3 is a shallow groove. Data is recorded on six recording tracks of these three grooves and three lands between respective grooves. A CTS signal is obtained by a sum signal (A+B+C+D) of a photo-detector 6, and a push-pull signal is obtained by a difference signal (A+D)−(B+C) of a photo-detector 8.
Owner:SONY CORP
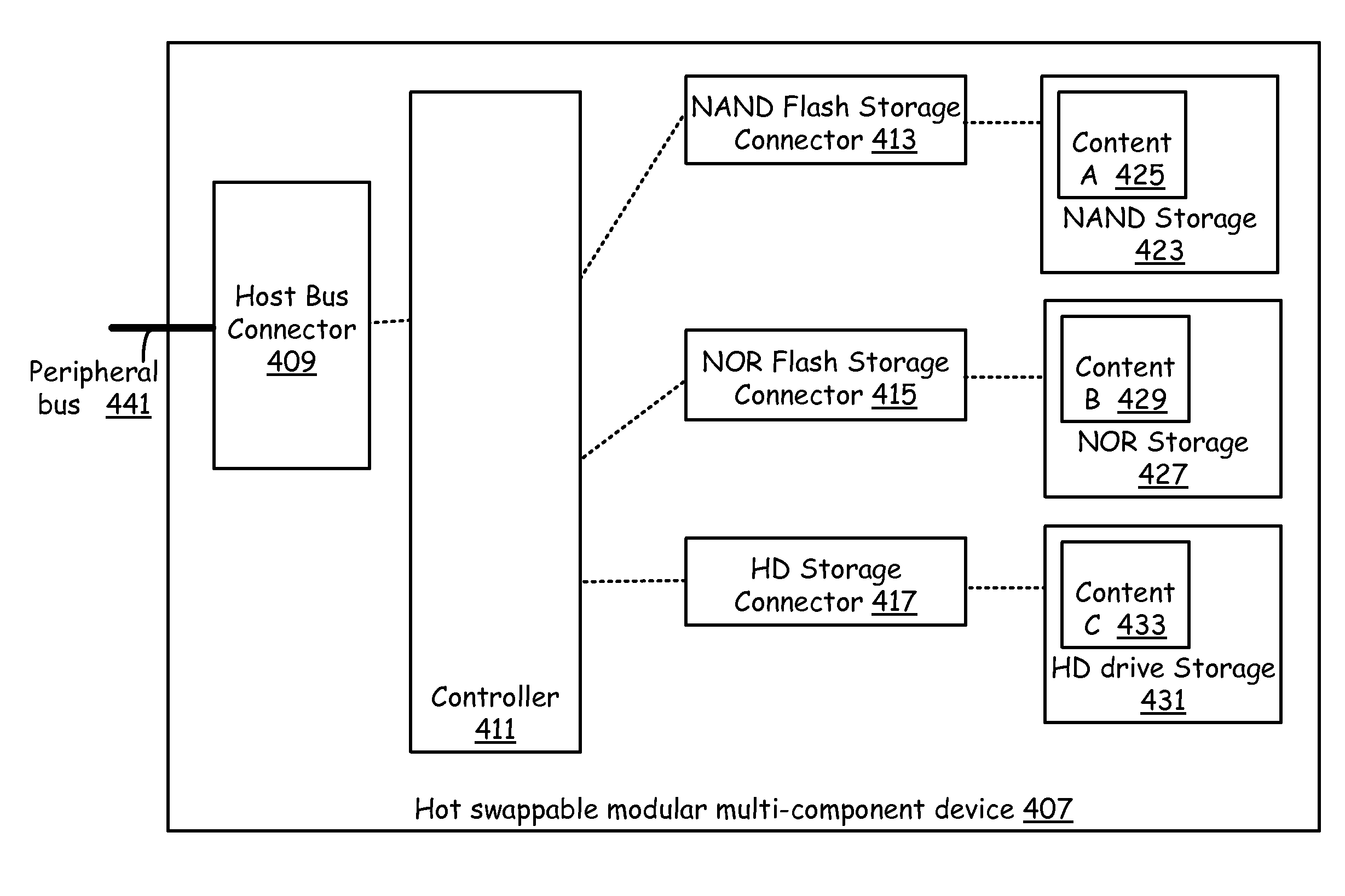
Mixed technology storage device that supports a plurality of storage technologies
ActiveUS8812805B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersHard disc driveOptical storage
A mixed storage device includes a set of storage units, each potentially based on a different storage technology, such as NAND flash drive, NOR flash drive, magnetic hard drive, magneto-optical drives, optical drives, etc. The mixed storage device comprises a host bus connector that is used to connect to a peripheral bus that facilitates communication to a processor of a device (such as a PC) and a controller. The controller manages a NAND flash storage device, a NOR flash storage device, an optical storage device, a hard drive and other storage components plugged into or integrated with the mixed storage device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
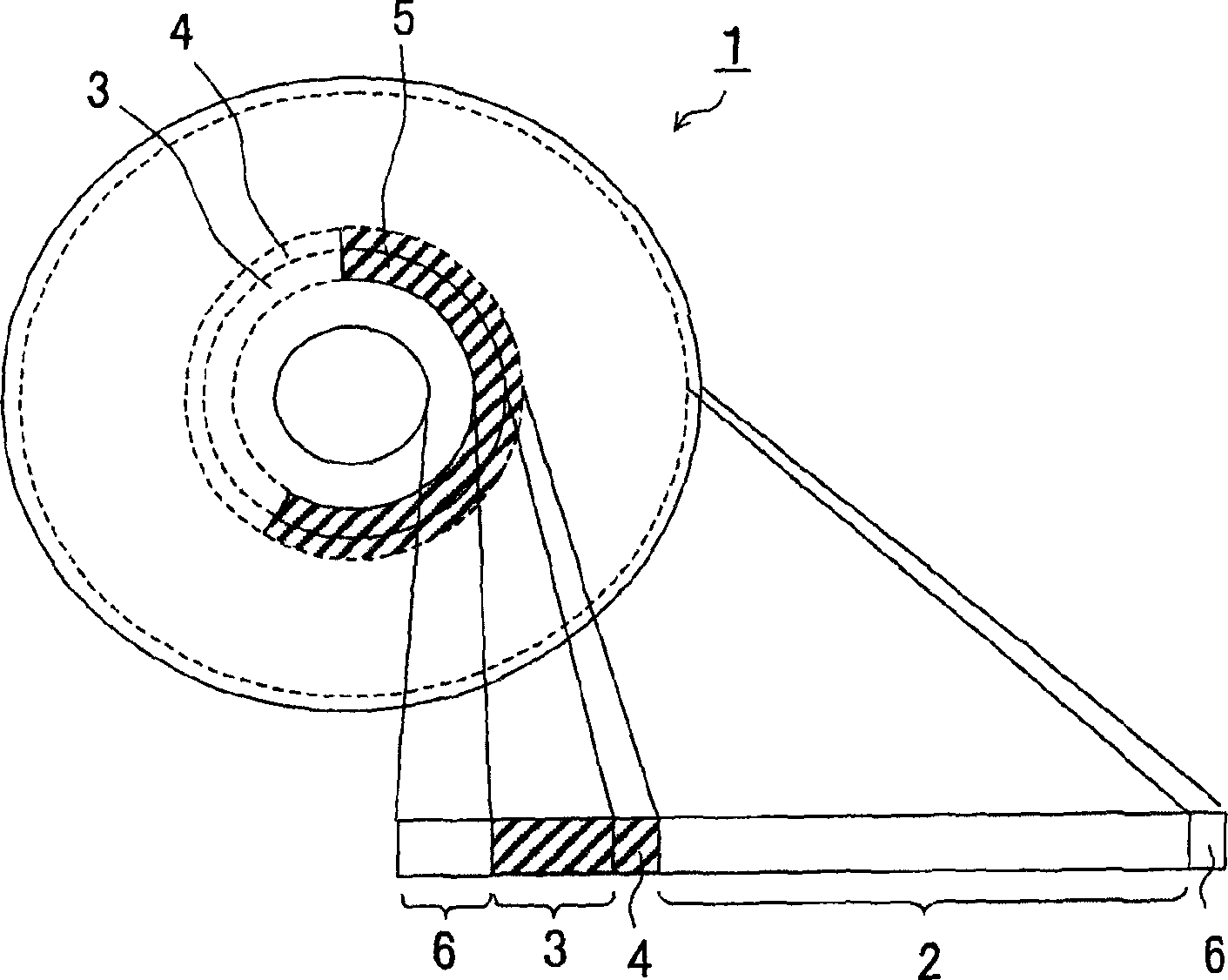
Magnet-optical disk
InactiveCN1547744ASolve processing problemsLarge off-track toleranceMultilayered discsInformation arrangementImage resolutionA domain
A disk reproducing device for reproducing a domain-wall-displacement type, super-resolution reproducing magnetooptic disk, wherein when the wavelength of a laser beam for reproducing signals recorded on an MO disk by being applied to the MO disk is lambda and its numerical aperture NA, the width Tw of a track provided on the MO disk satisfies Tw <= 0.046 x (lambda / NA), whereby a detrack allowance of at least 160 nmpp is ensured and designing of tracking of a disk drive is made easy.
Owner:SONY CORP
A blue magnetic optical disk
InactiveCN1963927AIncreased readout threshold powerImprove signal-to-noise ratioRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHeat transmissionRecording layer
This invention discloses one blue light magnetic disc, which comprises underlay, first SiN media layer, TbFeCo record layer, second SiN media layer and A1 reflection layer. The invention is characterized by the following: the said record layer and second SiN media layer set with one layer of thermal control film. This invention coats one layer of metal film tightly to record layer as heat transmission layer to control over high temperature of record layer to improve the read valve efficiency and to improve signal to noise proportion.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Optical recording medium
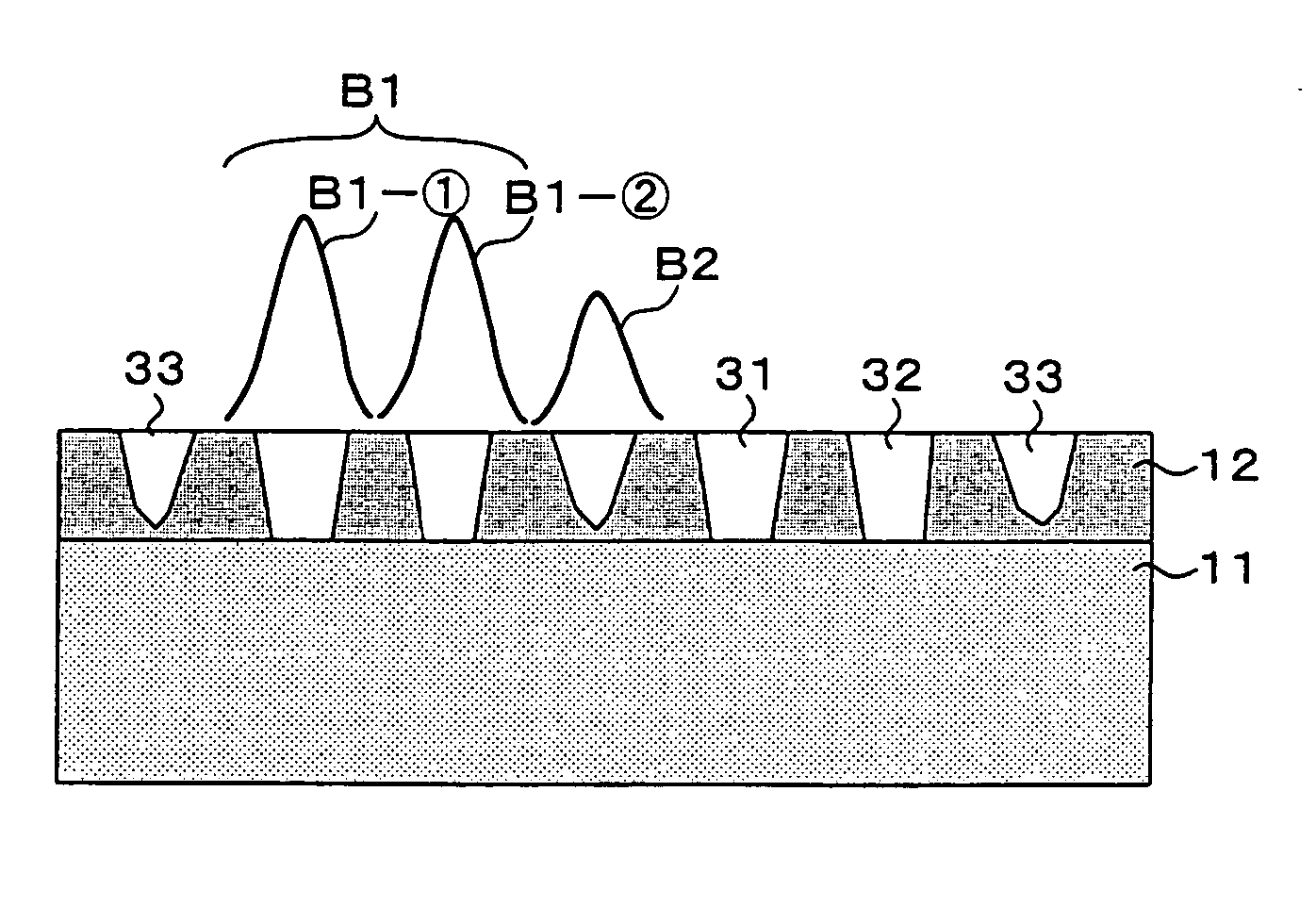
InactiveUS20020127365A1High-speed accessFormed with easeLayered productsMagneto-optical discsPit patternEngineering
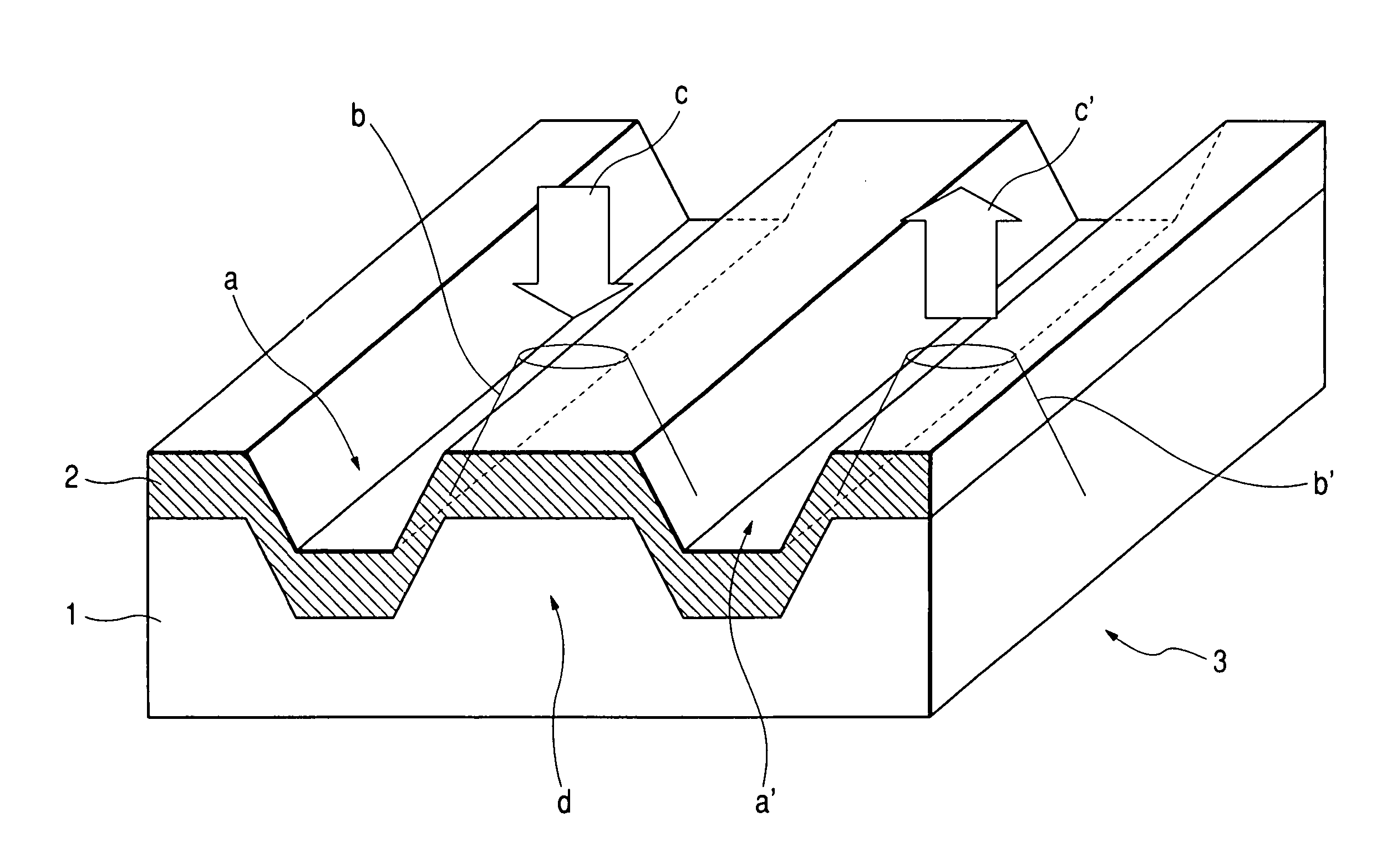
A magneto-optical disk 10 having recording tracks 11 are formed along concentric grooves 12 or a spiral groove 12. A non-groove region where no grooves 12 are made is provided in a middle part of each recording track 11. In the non-groove region there is formed a pit pattern representing information about the recording track 11. A track-counting U-groove 14 is formed in the non-groove region, for detecting that the light spot of a reading laser beam has moved across the recording track 11. With the disk thus structured, it is possible to record information at high density and to access a desired recording track at high speed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Photomagnetic memory structure
ActiveCN113223562ASolve space problemsSolve difficultyRecord information storageInterchangable mountingsOptical disk storageMagnetic storage
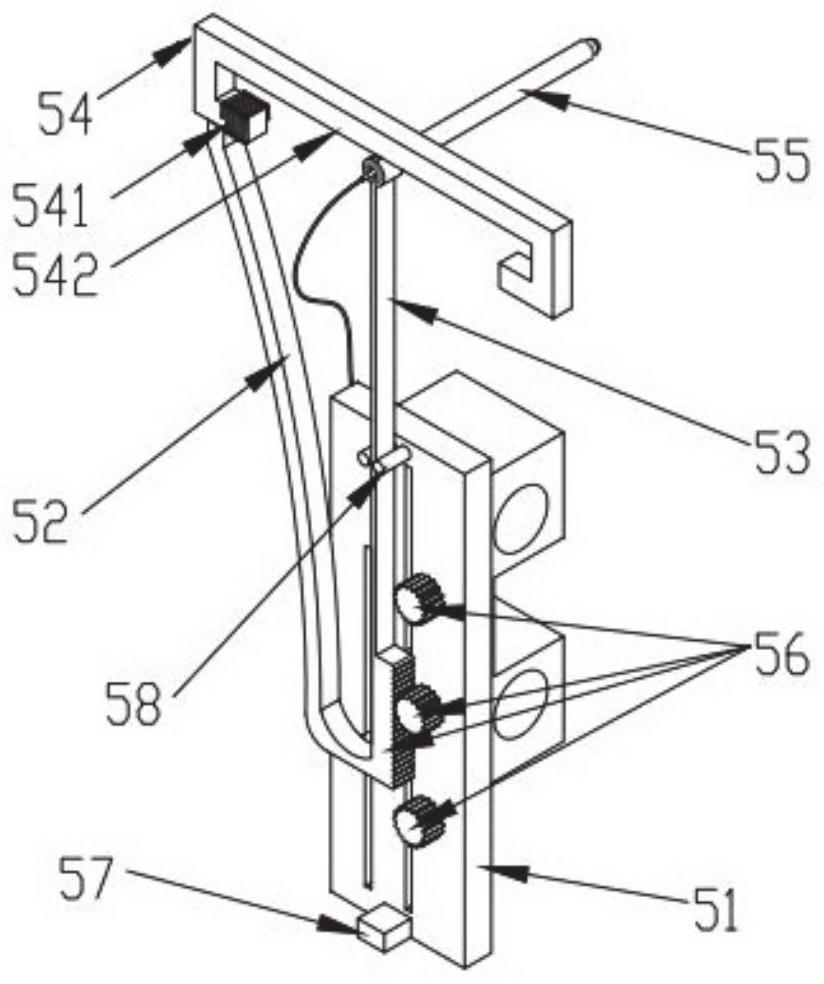
The invention provides a photomagnetic memory structure. According to the technical scheme, the photomagnetic memory structure comprises a main frame provided with a memory disk array, first sliding rails are symmetrically installed on the two transverse sides of the main frame, one or more second sliding rails are connected between the first sliding rails located on the same side of the main frame, and the second sliding rails are slidably connected with a read-write assembly; the read-write assembly comprises a read-write head connected to one end of the vibration arm and an electromagnet arranged on the side face of the vibration arm, and the electromagnet and the other end of the vibration arm are connected into a whole through a connecting rod. The electromagnet generates a magnetic field in a set period to attract the vibrating arm to drive the read-write head to perform simple harmonic vibration, so that the read-write head forms a set data read-write track on the surface of the memory disk. No high-speed rotating assembly is arranged, the number of storage disks and read-write assemblies is easy to expand, and storage capacity expansion and read-write speed improvement of a single magnetic / optical disk storage product are facilitated.
Owner:王旭
A blue magnetic optical disk
InactiveCN1963927BIncreased readout threshold powerImprove signal-to-noise ratioRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHeat transmissionRecording layer
This invention discloses one blue light magnetic disc, which comprises underlay, first SiN media layer, TbFeCo record layer, second SiN media layer and A1 reflection layer. The invention is characterized by the following: the said record layer and second SiN media layer set with one layer of thermal control film. This invention coats one layer of metal film tightly to record layer as heat transmission layer to control over high temperature of record layer to improve the read valve efficiency and to improve signal to noise proportion.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
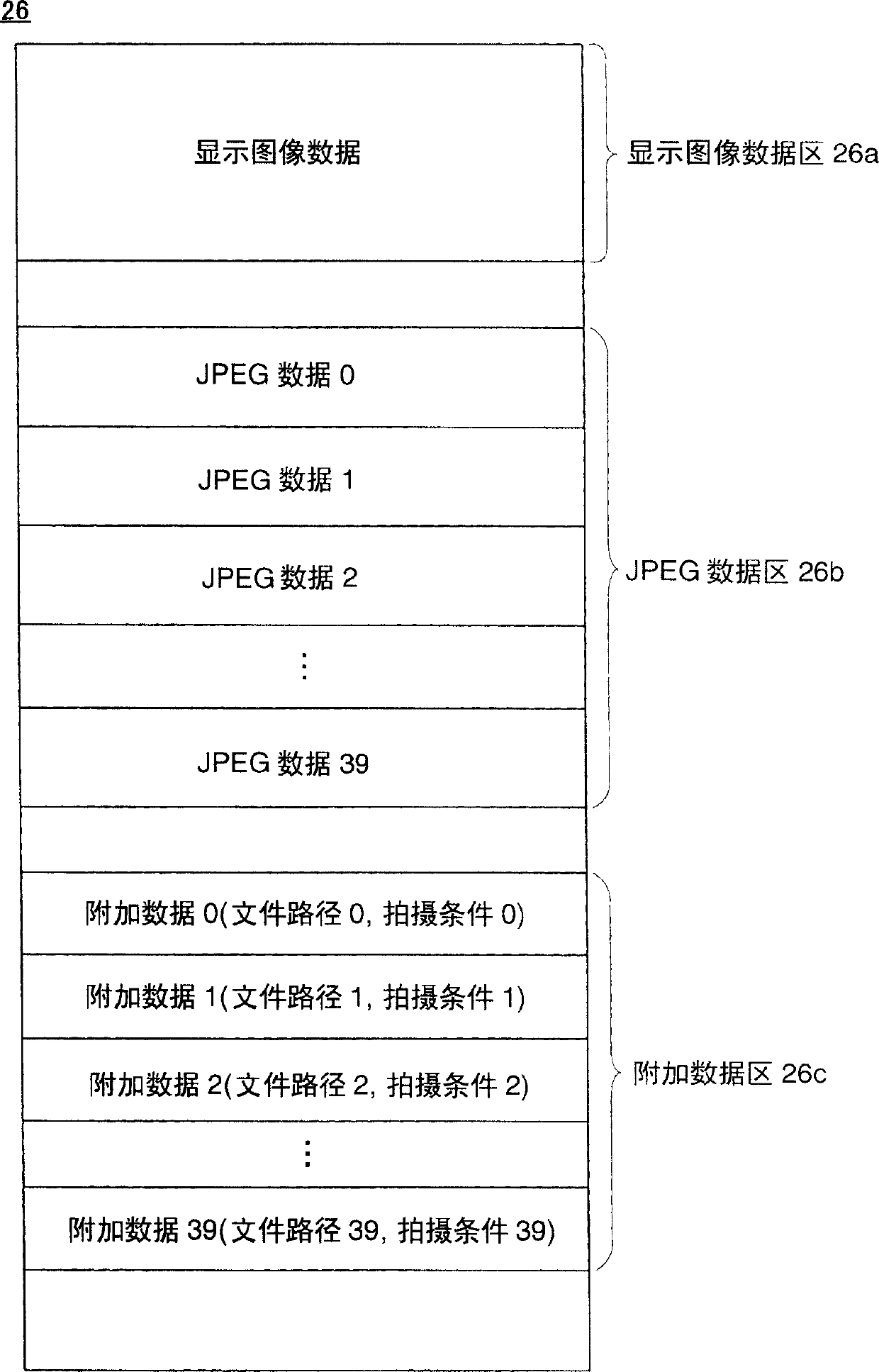
Image recording equipment
InactiveCN1256844CIncrease flexibilityImprove responsivenessTelevision system detailsMagneto-optical discsComputer hardwareImage recording
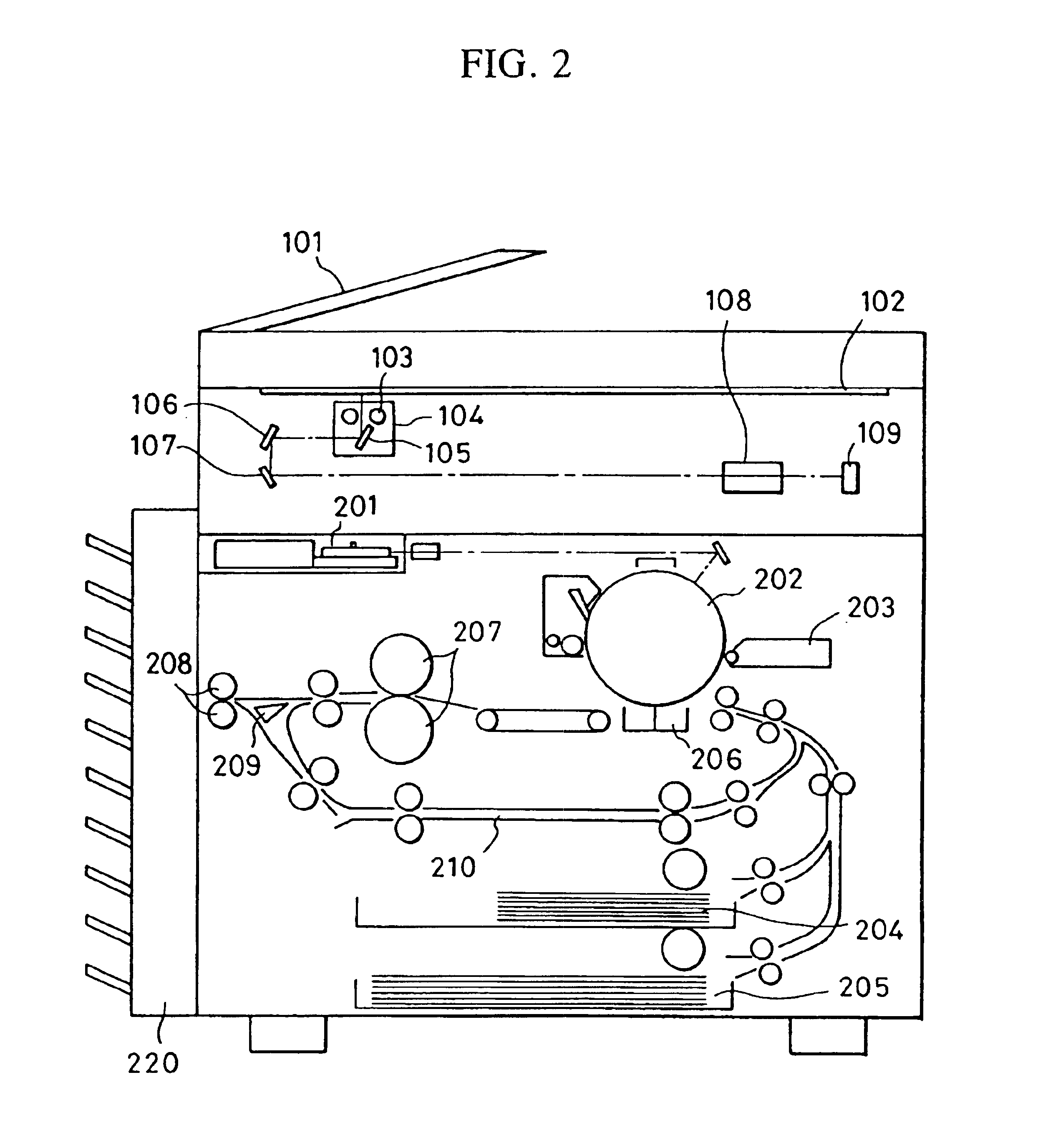
The digital camera (10) includes an SDRAM (26). When 40 frames of image signals were gathered in SDRAM (26), in the data area of magneto-optical disc (36), create the combination file that comprises 40 frames of image signals, and the FAT information of combination file is written into the FAT of magneto-optical disc (36) in the district. When meeting the predetermined condition, the image data of the combined file is read out by each frame, and an image file comprising the read image data is created in the data area of the magneto-optical disk (36), and the FAT information of the image file is written into The FAT area of the magneto-optical disk (36). Repeat this process 40 times, after which the combined file is deleted.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
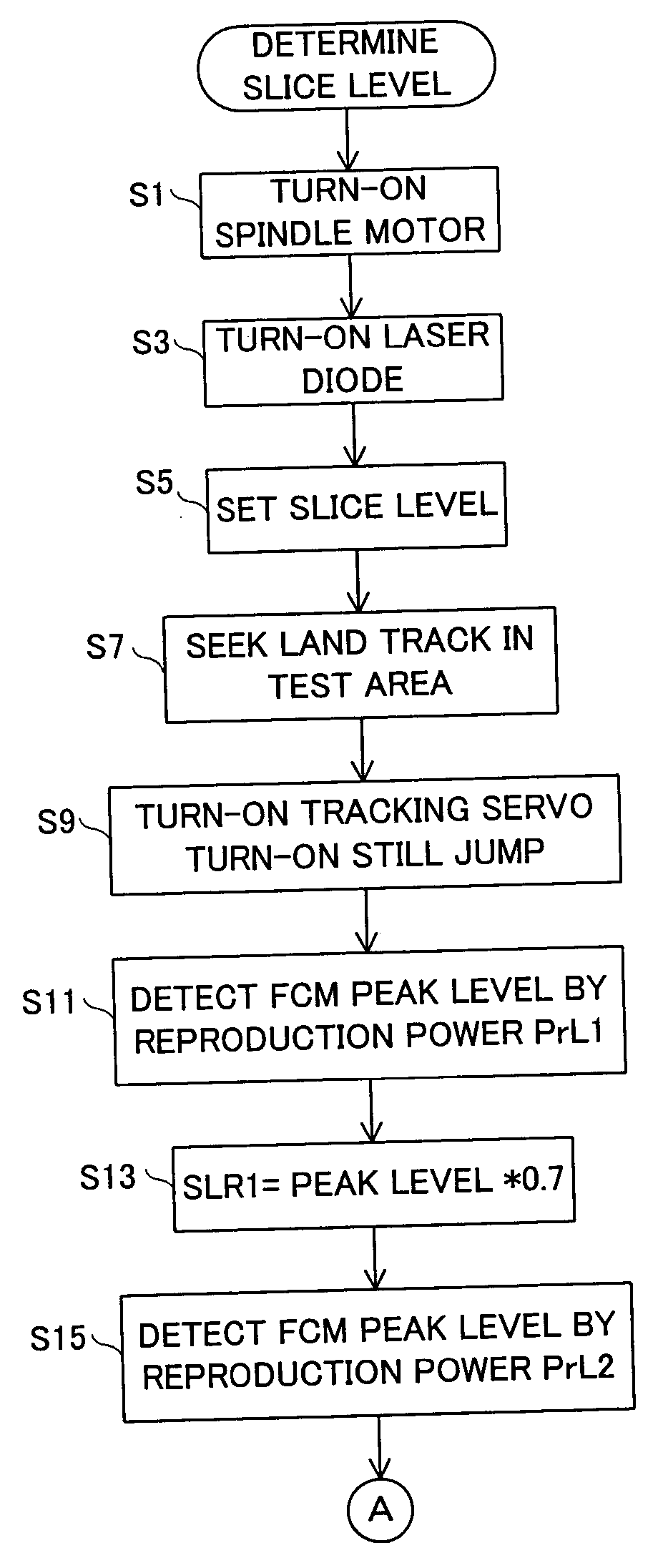
Disk device and method for controlling threshold value of disc device
InactiveUS20040032810A1Generate accuratelyTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersPeak valueLaser beams
A disk apparatus (10) includes a spindle (62) to which a magnetooptical disk (60) is attached. An FCM is formed on the magnetooptical disk (60) along a track at intervals of a predetermined period, a laser beam having a different light amount depending on a time of an execution and an interruption of a recording process is incident upon the track. The FCM signal detection circuit (36) detects an FCM signal based on the laser beam reflected from the track, a comparator (42) compares a level of the FCM signal and a slice level, and a PLL circuit (54) generates a clock signal based on a comparison result by the comparator (42). When a change request between an execution / interruption of the recording process is applied, a predetermined first slice level is set to the comparator (42) until 200 mili seconds passes since a reception of the change request. When 200 mili seconds passes, a second slice level calculated based on a peak level of the FCM signal is set to the comparator (42).
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
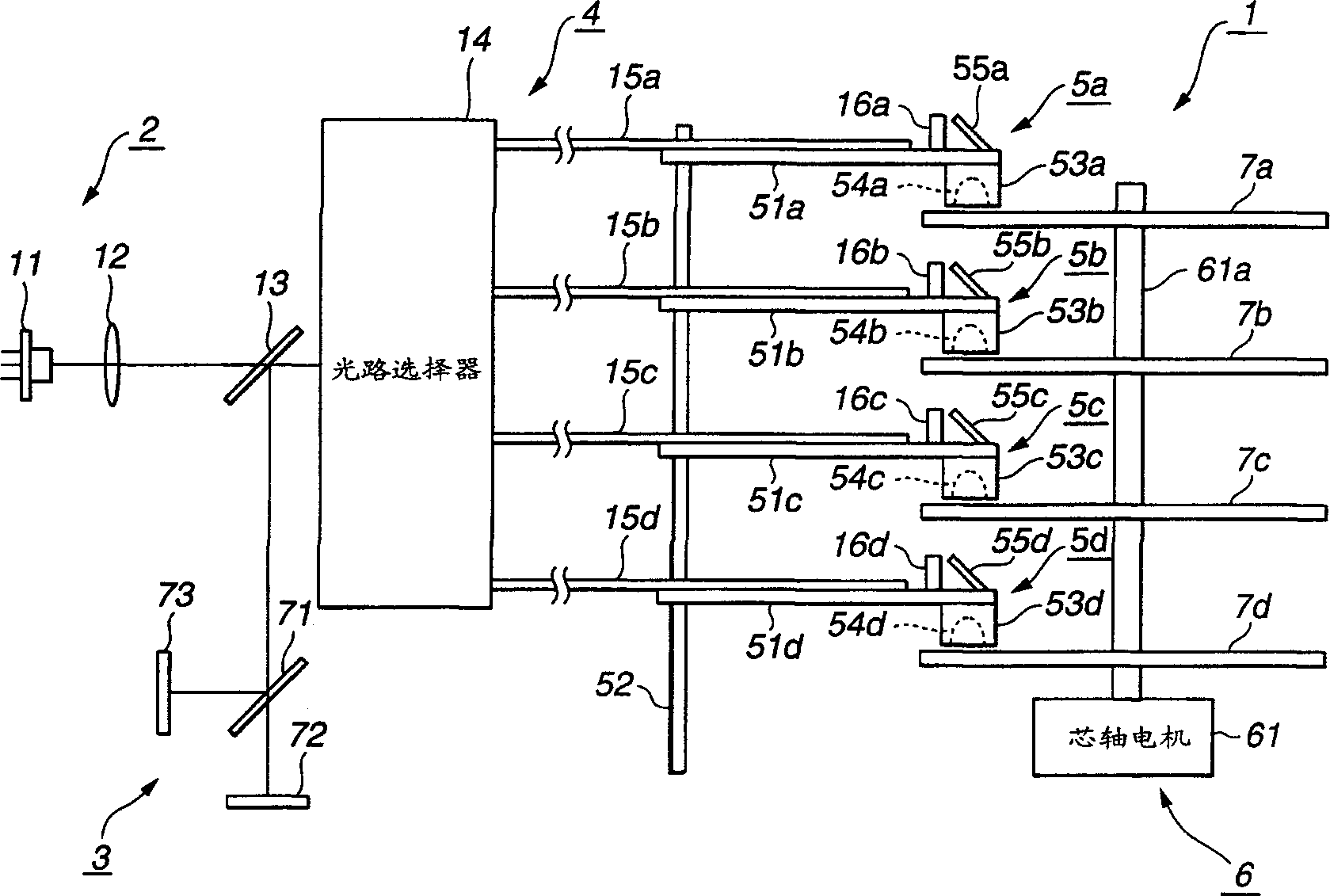
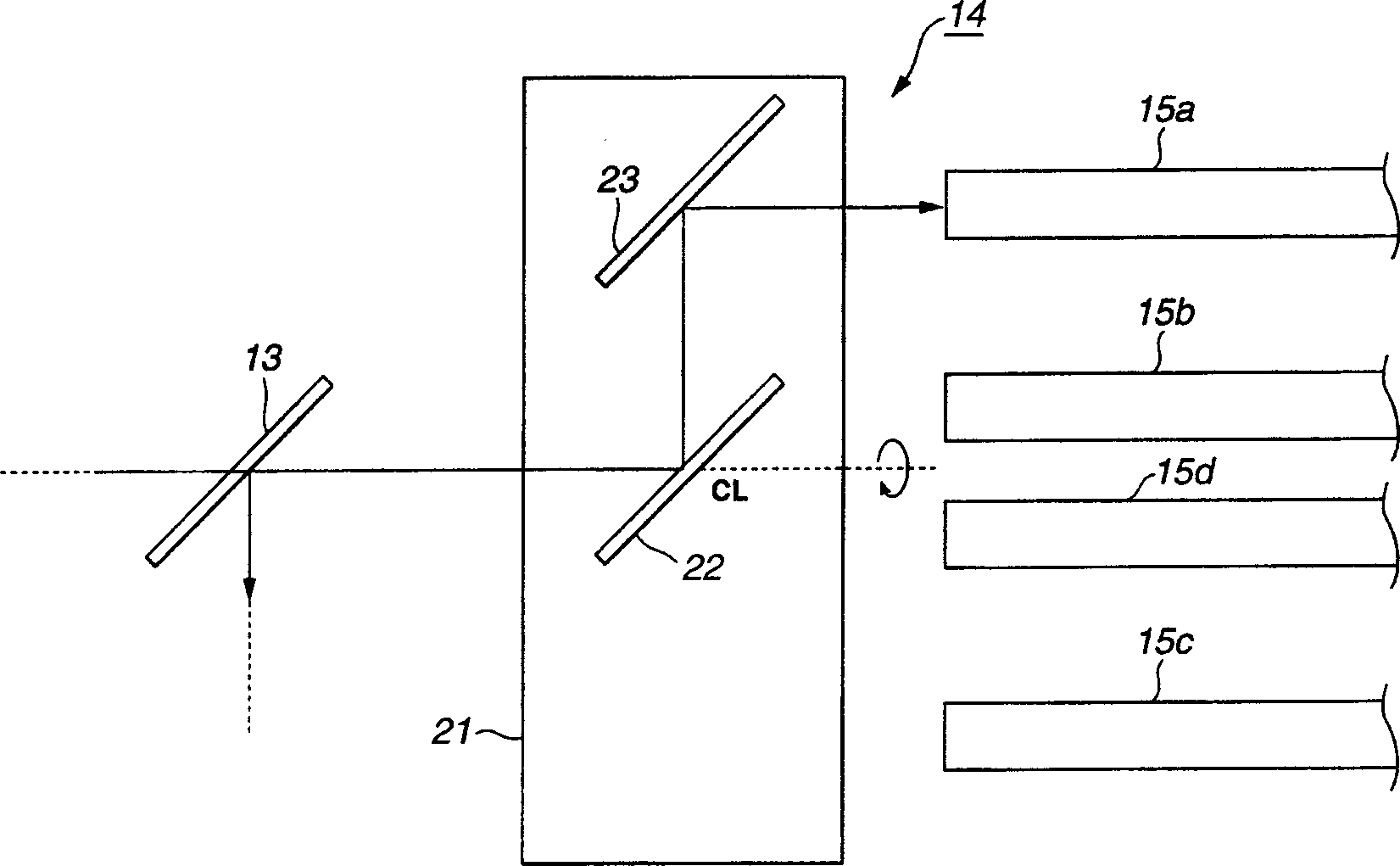
Optical disk driver
Light beams emitted from a light source (11) and returned light beams reflected off magneto-optical disks (7a), (7b), (7c), (7d) are transmitted by using polarization preserving optical fibers (15a), (15b), (15c), (15d). Phase difference generating means (16a), (16b), (16c), (16d) are disposed in the optical paths of the light beams, and the phase differences of electric field vibration components occurring in the light beams due to double refraction of polarization preserving optical fibers (15a), (15b), (15c). (15d) are offset by phase differences produced by phase difference producing means (16a), (16b), (16b), (16c), (16d), or the phase differences are adjusted to be multiples of pi .
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com