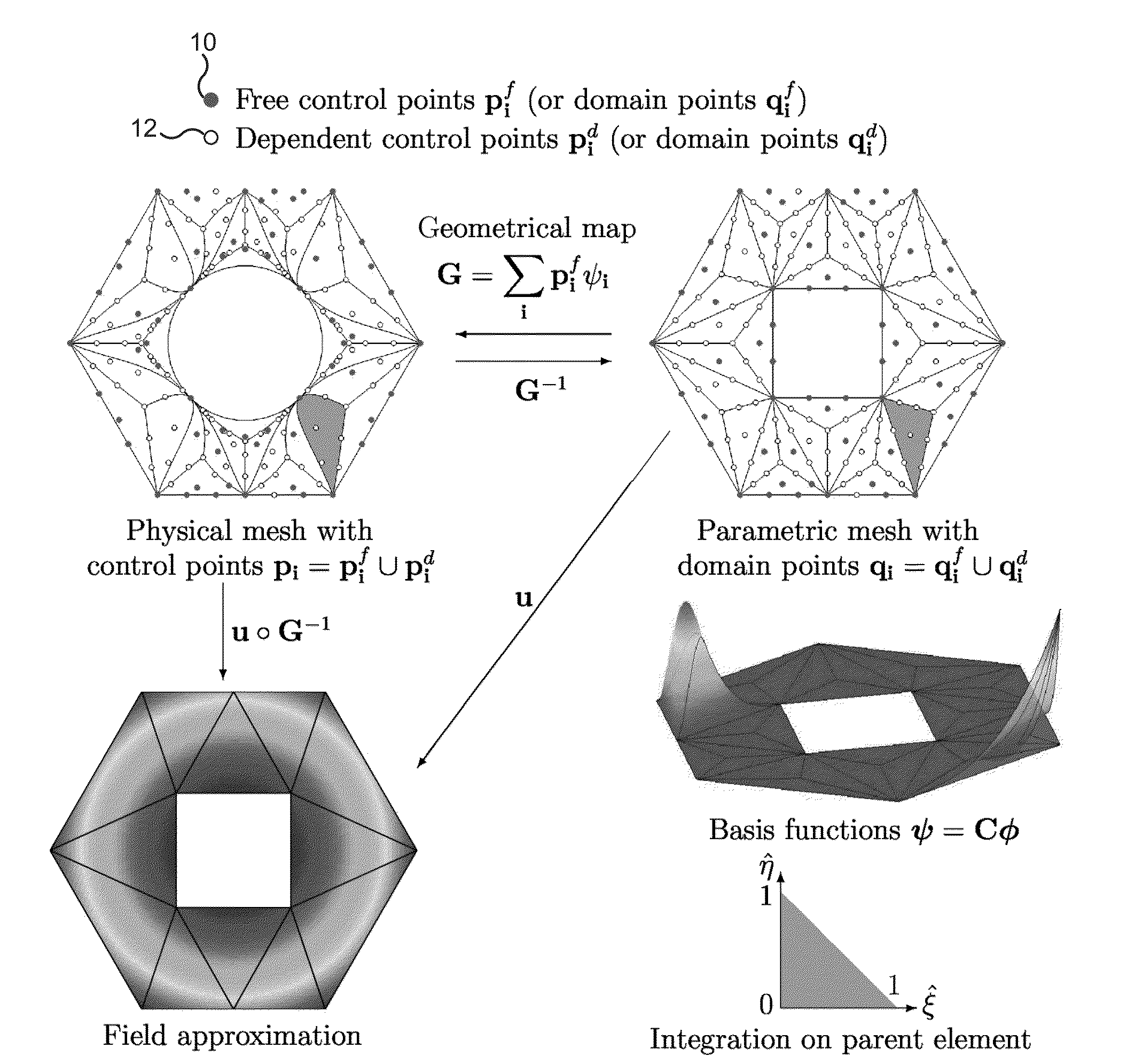
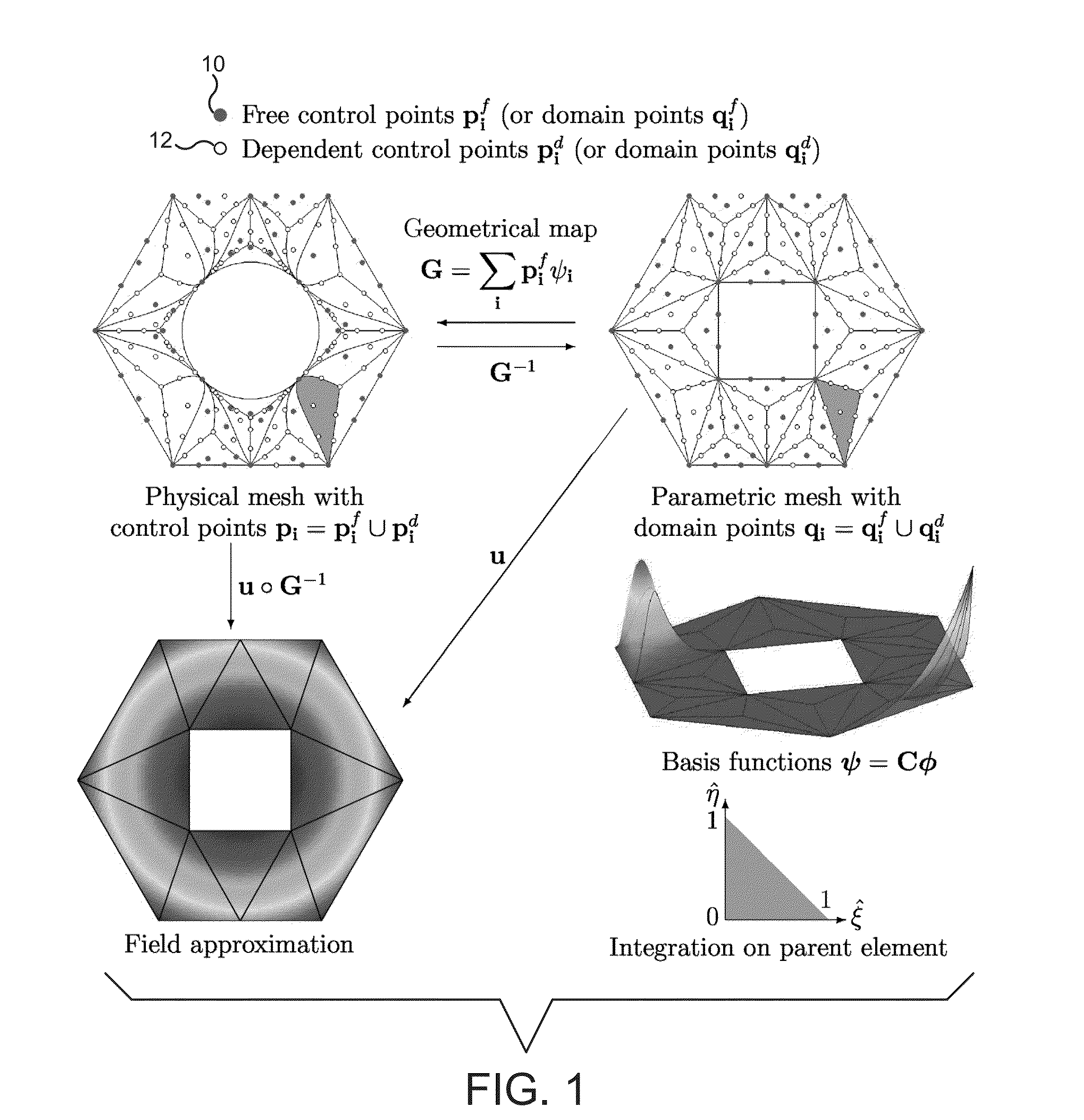
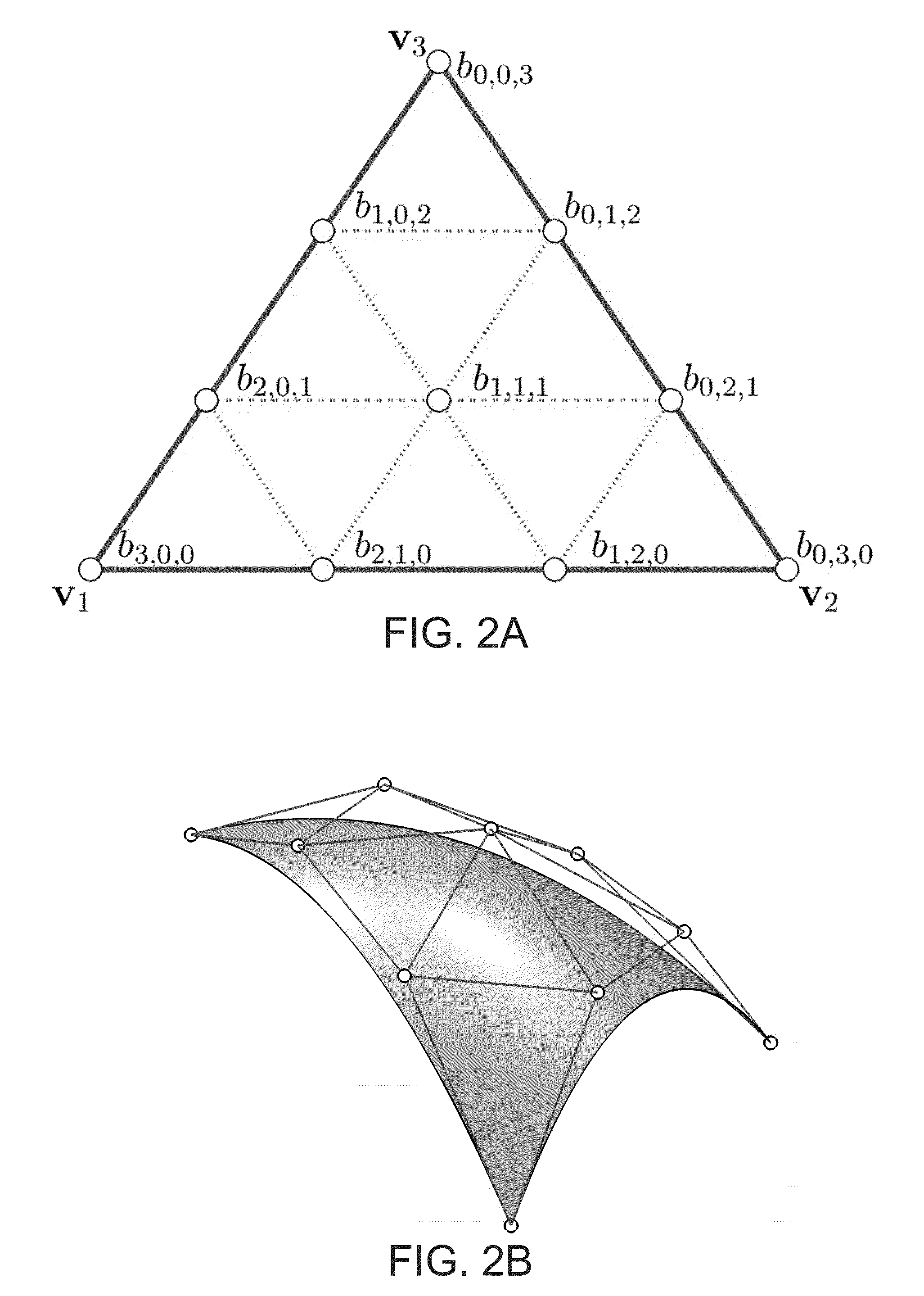
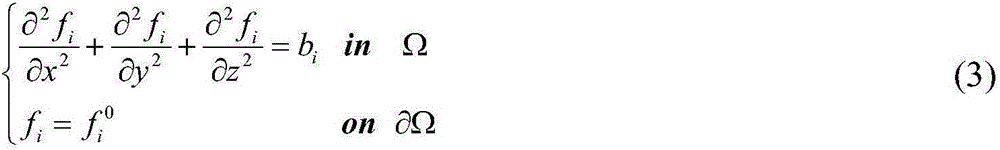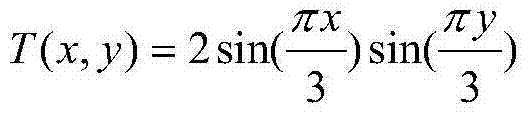Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Isogeometric analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
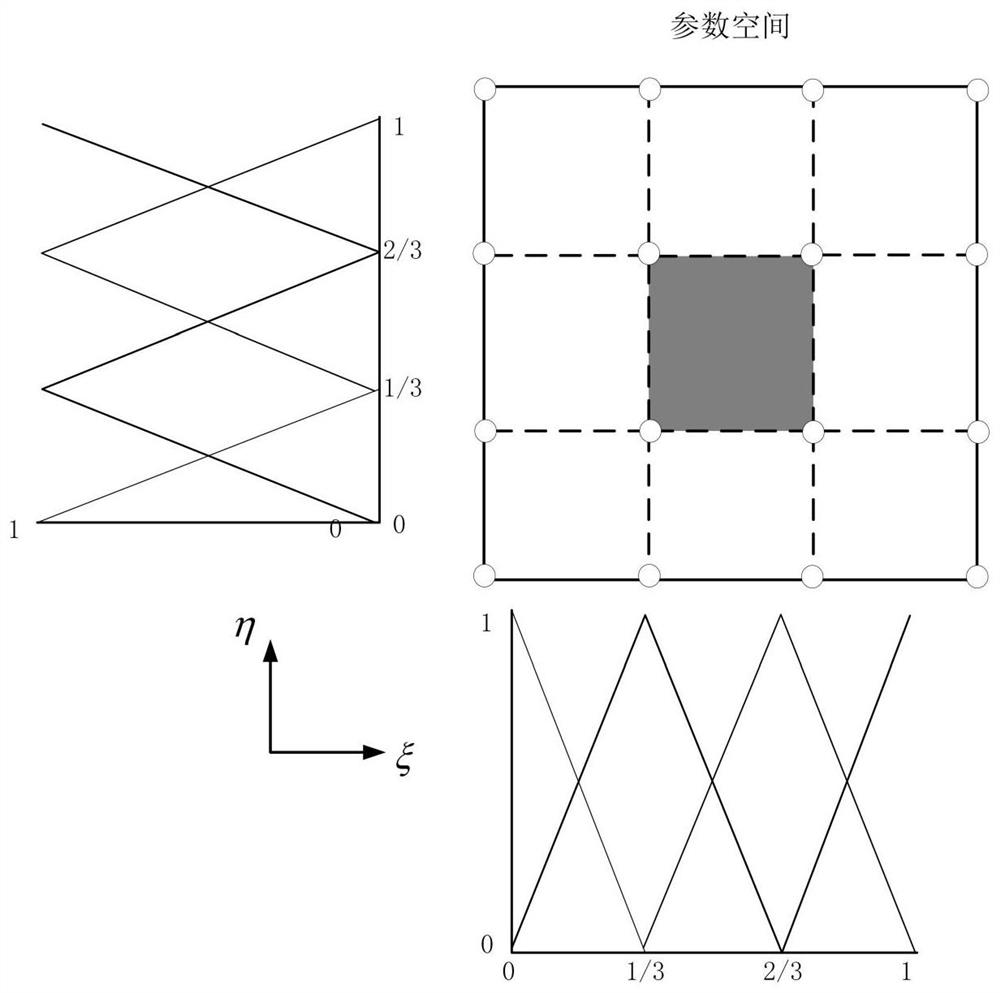
Isogeometric analysis is a computational approach that offers the possibility of integrating finite element analysis (FEA) into conventional NURBS-based CAD design tools. Currently, it is necessary to convert data between CAD and FEA packages to analyse new designs during development, a difficult task since the two computational geometric approaches are different. Isogeometric analysis employs complex NURBS geometry (the basis of most CAD packages) in the FEA application directly. This allows models to be designed, tested and adjusted in one go, using a common data set.
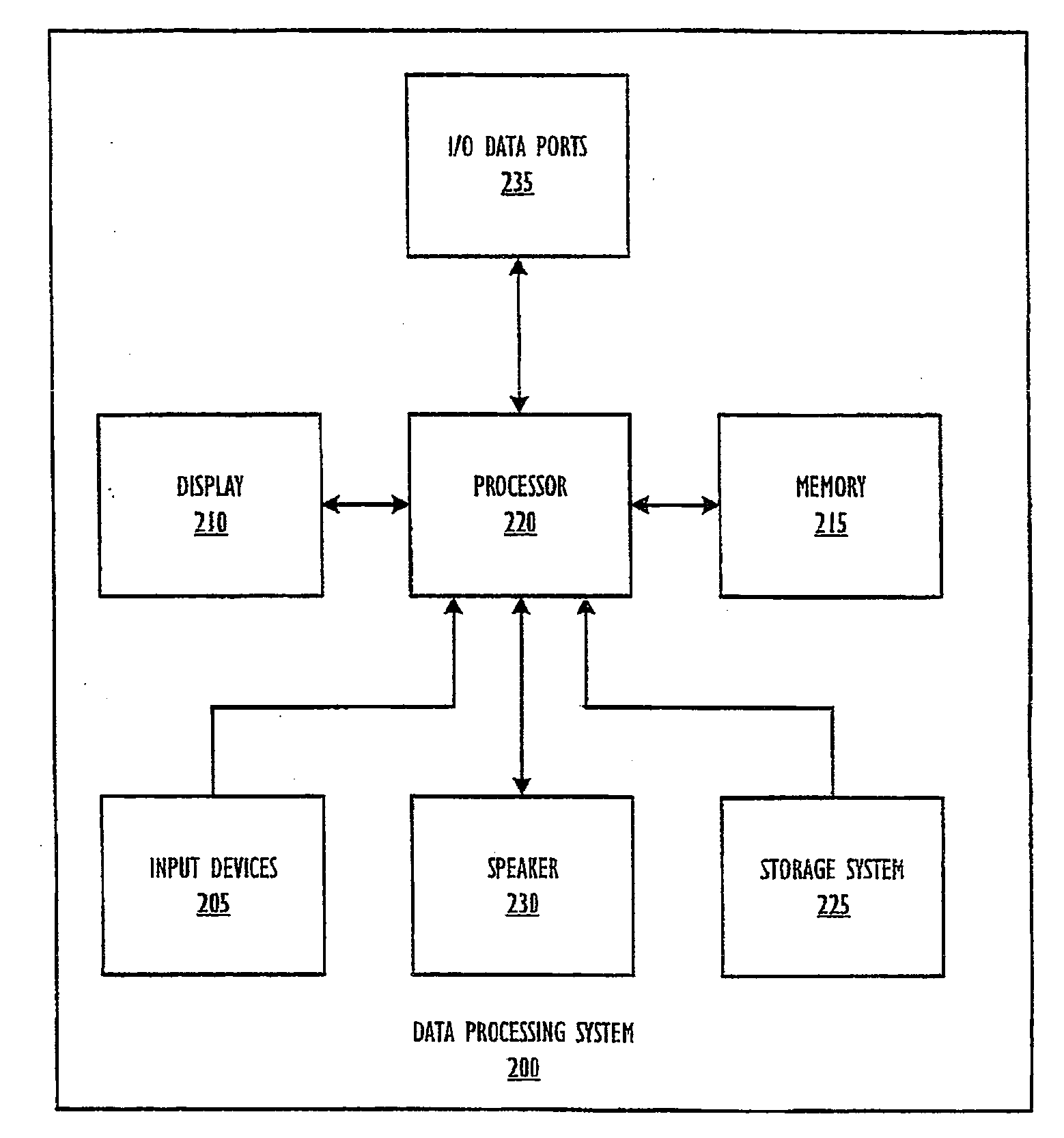
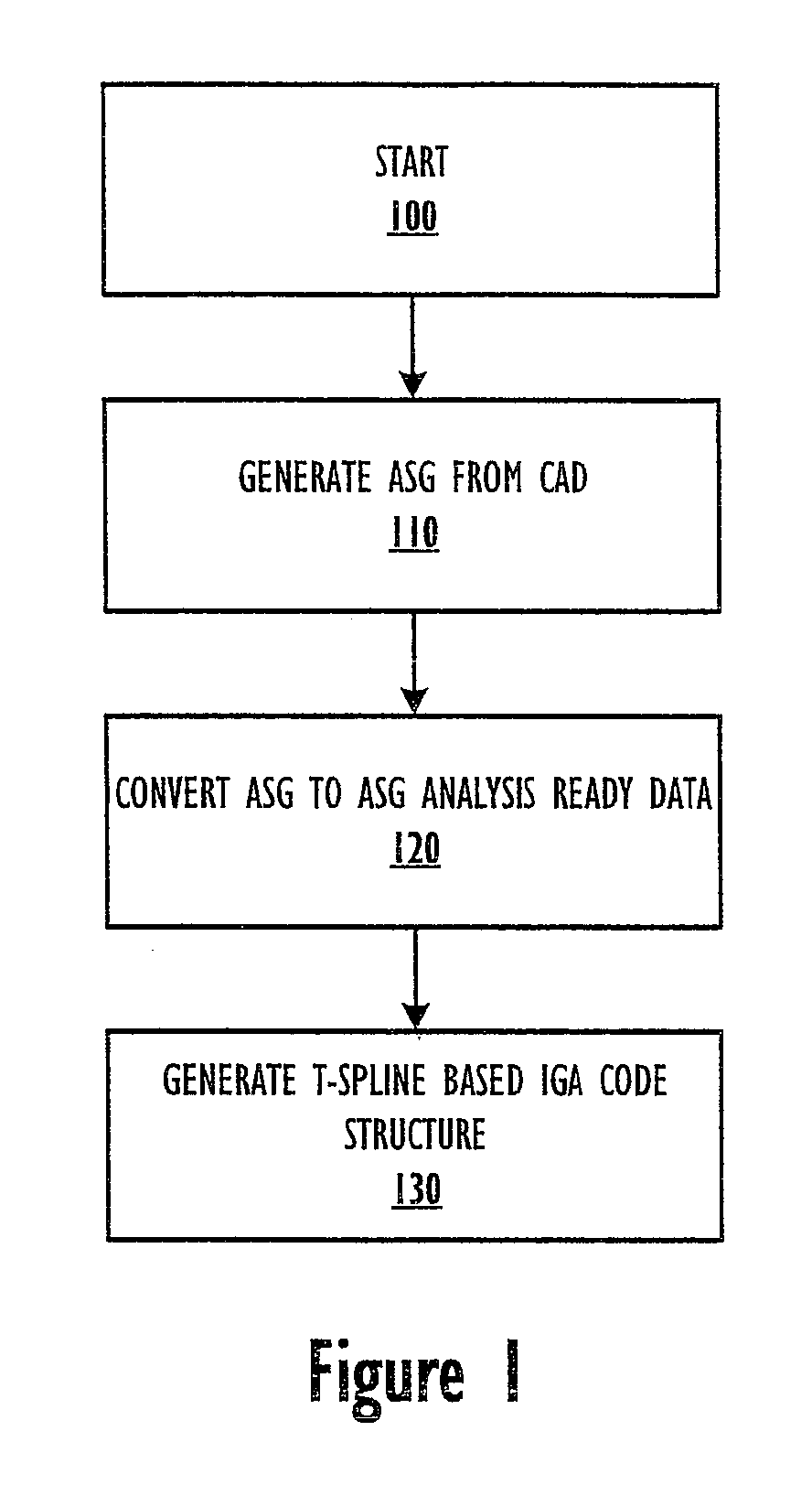
Method and System for Performing T-Spline Based Isogeometric Analysis
InactiveUS20090024370A1Easy to implementGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer Aided DesignProgramming language
A method for performing T-spline based isogeometric analysis is disclosed. An analysis suitable geometry (ASG) description is initially generated from a T-spline surface or volume computer-aid design (CAD) description. Subsequently, a T-spline based isogometric analysis (IGA) code structure that uses the ASG description having ASG analysis ready data is generated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Reconstruction of parameterization model of quadrilateral finite element grid model
InactiveCN105787226AHigh expressionReduce in quantityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALReconstruction algorithm
The invention provides a parameterization reconstruction algorithm of a quadrilateral finite element grid model. By taking a quadrilateral grid model obtained by finite element analysis software as the basis, a unit number and a node coordinate of the quadrilateral grid model are used as input information for reconstructing a topological relation between quadrilateral grid units; merging operation including unit grid standard merging, block domain self-adaptive merging and the like are carried out according to obtained topological information, so that the quantity of block domains is reduced and merged sub-domains are obtained; characteristic points on boundaries of the sub-domains obtained by merging are remained and are connected to form a certain quantity of quadrilateral final sub-domains; and finally, a body parameterization model is obtained by carrying out construction, adjustment and optimization of a body parameter model according to the boundaries of the obtained final sub-domains. The algorithm can be used for carrying out parameterization reconstruction on the quadrilateral grid model of structures including a porous plate and the like, and the obtained body parameterization model is applicable to isogeometric analysis; and the algorithm has the advantages of simplicity in expression, whole-domain smoothing and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
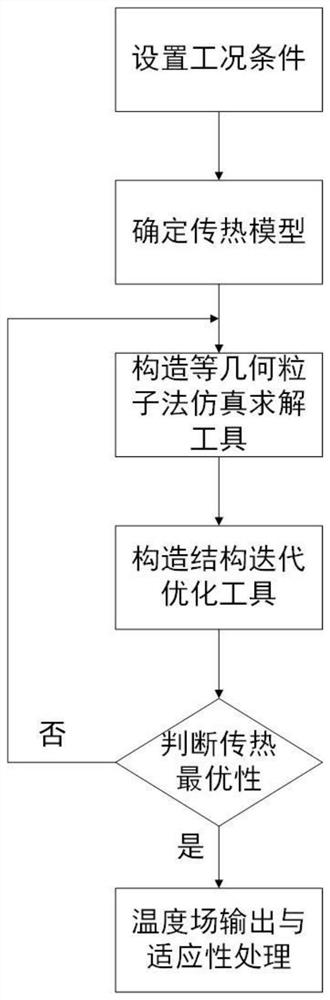
Isogeometric solution and heat dissipation topology generation method for heat flow strong coupling problem
ActiveCN111709171AAvoid complex processAvoid frequent interactionsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationHeat flowGeometric modeling
The invention discloses an isogeometric solution and heat dissipation topology generation method for a heat flow strong coupling problem. A physical field model is constructed through isogeometric analysis, the geometric model is accurately described by the analysis model, the precision of numerical solution of the heat flow strong coupling physical field is effectively improved, meanwhile, the isogeometric analysis grid is defined by a node vector corresponding to the isogeometric analysis grid for describing a geometric model parameter domain, a redundant grid division link in a classical finite element is avoided, and the calculation cost is saved; the method can solve the problems of low solving precision, large calculated amount, long consumed time and the like of the heat flow strongcoupling problem, and is suitable for optimal design of a heat flow structure.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
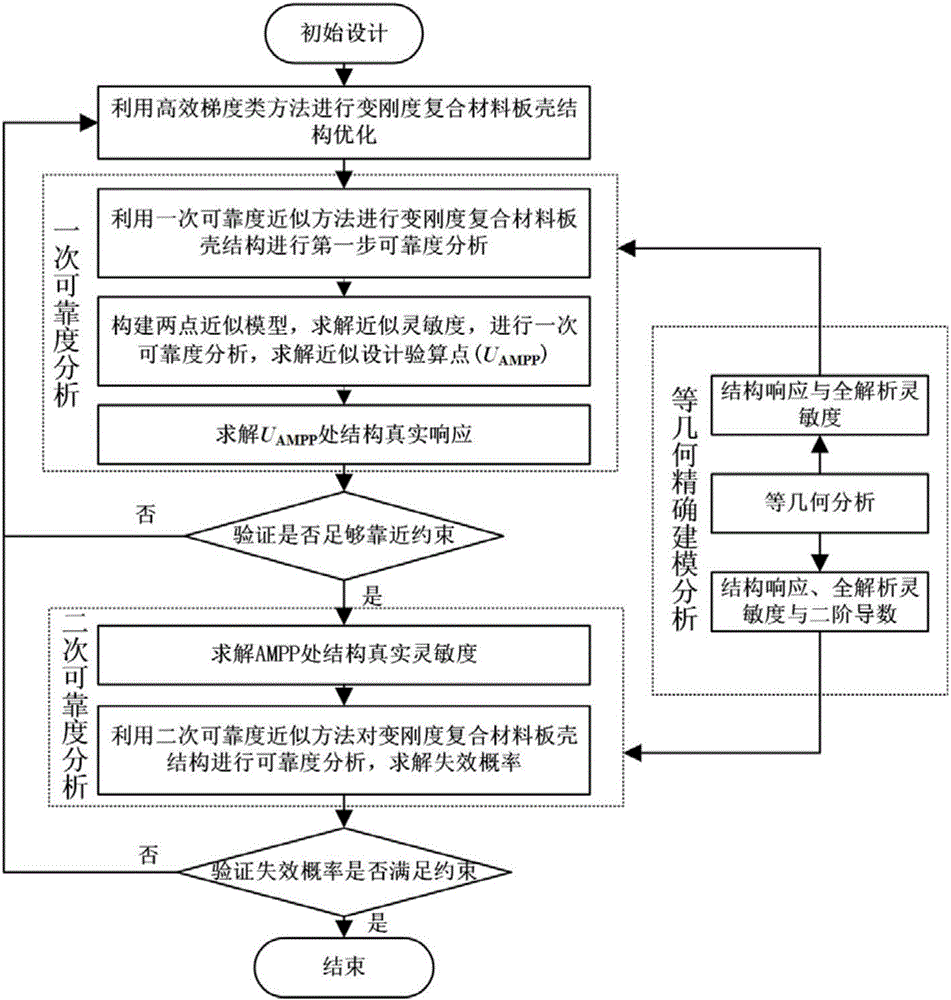
Integrated design method of accurate modeling analysis and reliability optimization for variable stiffness composite plate shell structure
ActiveCN107526898AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStructural reliabilityVariable stiffness
The present invention relates to the field of structural reliability optimization, and provides an integrated design method of accurate modeling analysis and reliability optimization for a variable stiffness composite plate shell structure. The method comprises: using a primary reliability approximation method, a non-linear approximate function and a secondary reliability approximation method to carry out high reliability optimization on the variable stiffness composite plate shell structure; using a non-uniform rational B-spline function to carry out accurate modeling on the fiber lay-up path of the variable stiffness composite plate shell; and carrying out equal geometric analysis on the variable stiffness composite plate shell structure, wherein the step comprises: carrying out linear buckling analysis on the variable stiffness composite plate shell structure based on the equal geometric method, and deriving full design sensitivity of the design variables and random variables on the response to the structure. According to the method provided by the present invention, seamless docking of modeling, analysis and reliability optimization for the variable stiffness composite plate shell structure can be realized, the reliability optimization efficiency and accuracy of the method can be obviously improved, and the development cycle can be significantly shortened.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Shape optimization algorithm for three-dimensional product model
ActiveCN106384384AEnhanced interactionMeet design needs3D modellingPattern recognitionFeature Dimension
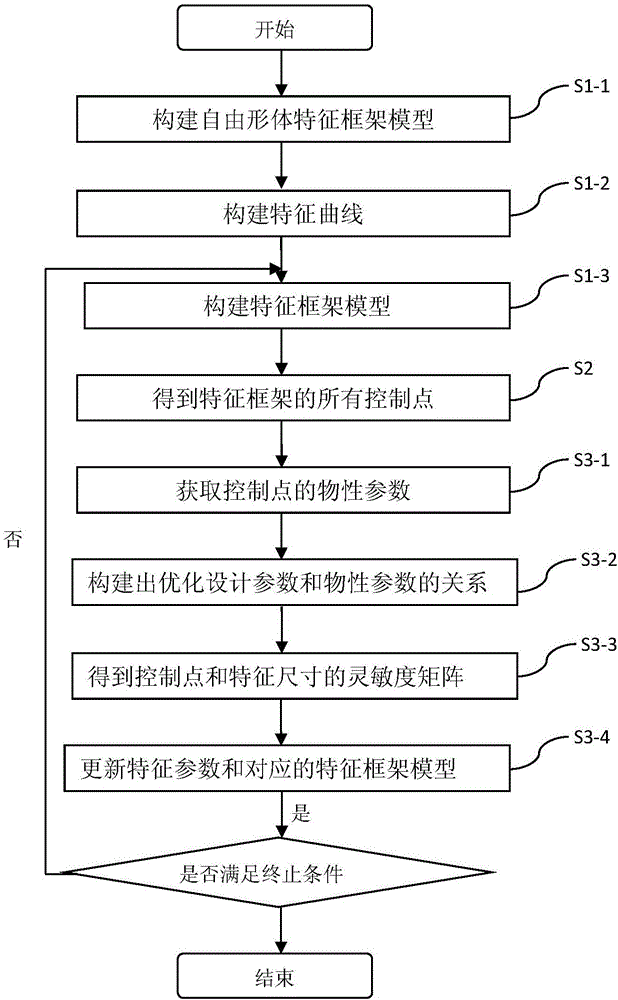
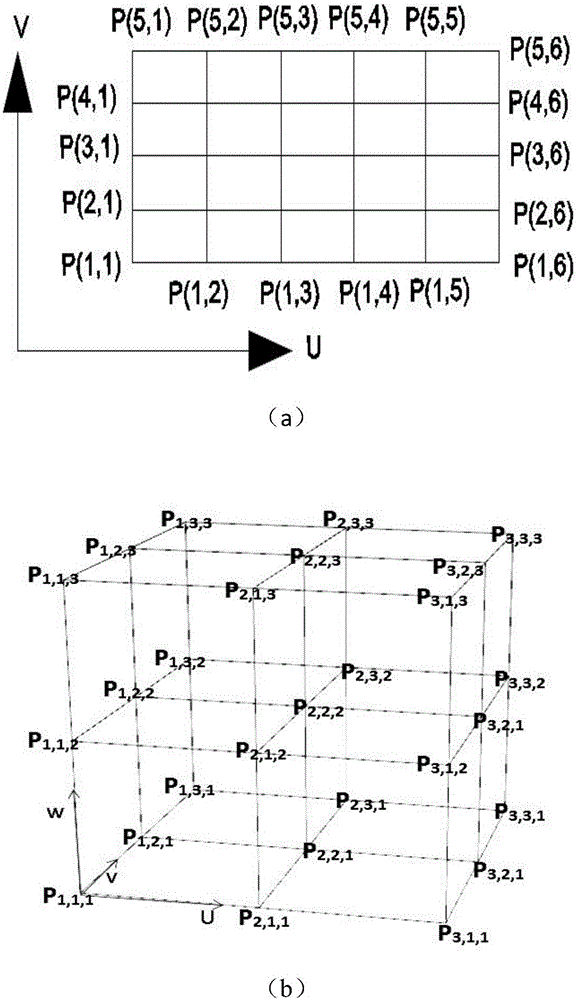
The invention provides a shape optimization algorithm for a three-dimensional product model, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly constructing a product model which is a feature frame model comprising point, line and surface features through employing a reverse solving method or a size measurement method; adding the constraint between the feature elements, and constructing a parameterized feature frame; employing a multi-drive mode, maintaining the constraint between the features, and achieving the modification of the feature frame model; employing a volume parameterization theory for the feature frame to obtain a volume parameterization model which can be used for geometrical analysis; enabling the feature size of the feature frame to serve as the product size or a shape optimization parameter, deducing the physical performances of a product and the sensitivity matrix of the design parameters, and optimizing the parameters, so as to achieve the optimized design of a product model.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for isogeometric analysis
ActiveUS20160275207A1Design optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsComputer visionIsogeometric analysis
A system and method for carrying out an isogeometric analysis process includes accessing the CAD model of the object from the memory. The process also includes analyzing the CAD model to generate a pre-refinement geometric map of the CAD object that has a smoothness projected to maintain a consistency of a geometric map based on the pre-refinement geometric map during a refinement of the mesh. The process further includes refining the mesh based on the pre-refinement geometric map to converge toward a refinement criteria associated with the CAD model.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
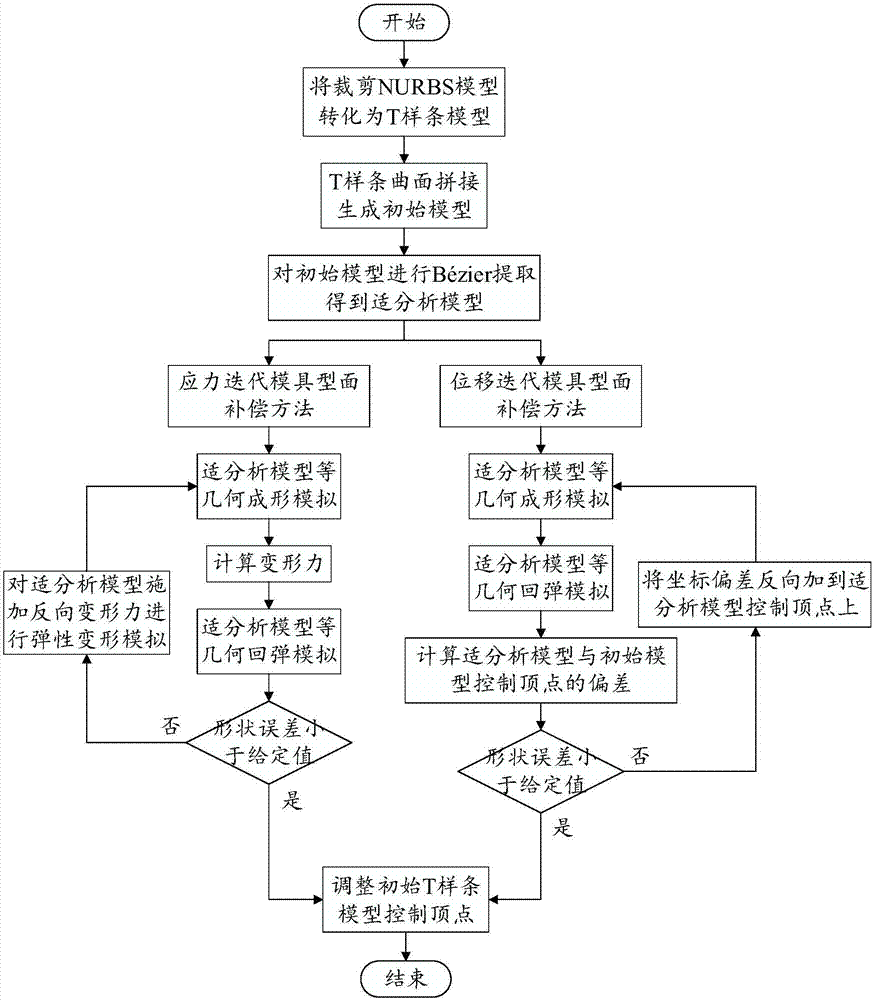
T-spline and isogeometric analysis-based die surface springback compensation method
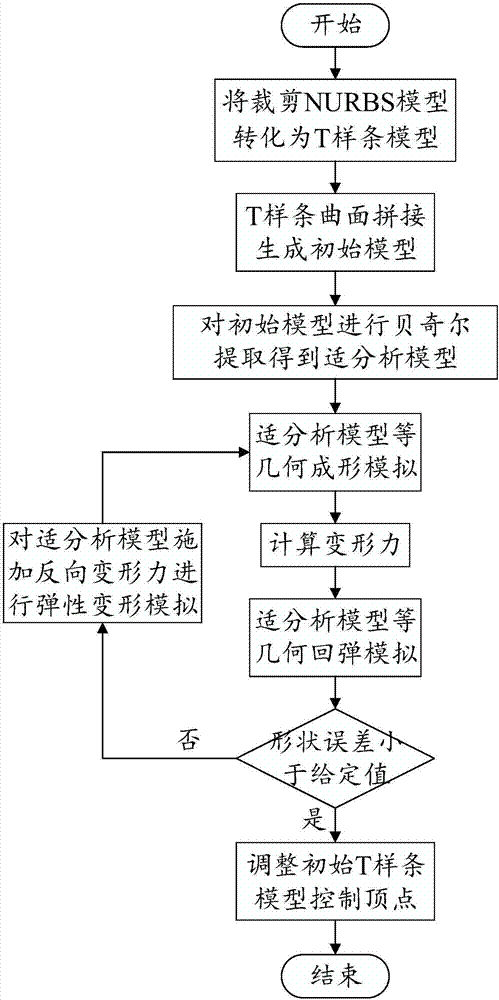
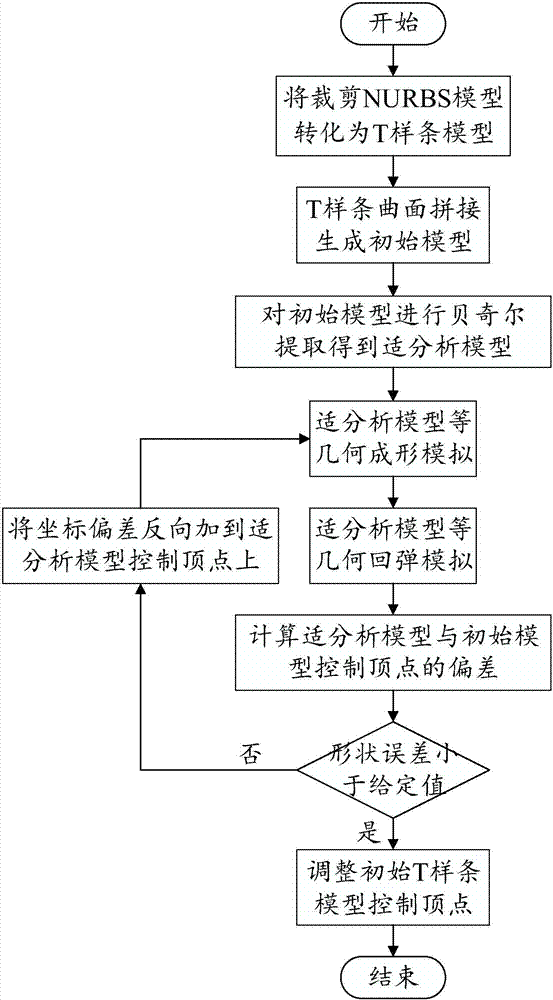
InactiveCN107122510AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed validityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringIsogeometric analysis
The invention discloses a T-spline and isogeometric analysis-based die surface springback compensation method. The method comprises (1) a stress iteration die surface compensation method and (2) a displacement iteration die surface compensation method. The stress iteration die surface compensation method comprises the steps of 1, converting a trimmed NURBS model into T-splines; 2, splicing the T-splines; 3, performing Bezier extraction to obtain an adaptive analysis model; 4, performing forming simulation; 5, calculating deformation force; 6, performing springback simulation; 7, calculating a shape error, and if a condition is met, going to the step 9, otherwise, going to the step 8; 8, reversely applying the deformation force to the adaptive analysis model to perform simulation, and going to the step 4; and 9, modifying an initial T-spline model. The displacement iteration die surface compensation method comprises the steps of 1, converting the trimmed NURBS model into the T-splines; 2, splicing the T-splines; 3, performing the Bezier extraction to obtain the adaptive analysis model; 4, performing the forming simulation; 5, calculating the deformation force; 6, calculating a deviation of a control vertex; 7, calculating the shape error, and if the condition is met, going to the step 9, otherwise, going to the step 8; 8, reversely applying the deviation of the control vertex to the adaptive analysis model to perform simulation, and going to the step 4; and 9, modifying the initial T-spline model. According to the method, numerical simulation of a plate forming springback process and compensation of a simulation result are realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Geometric reconstruction method based on finite element model
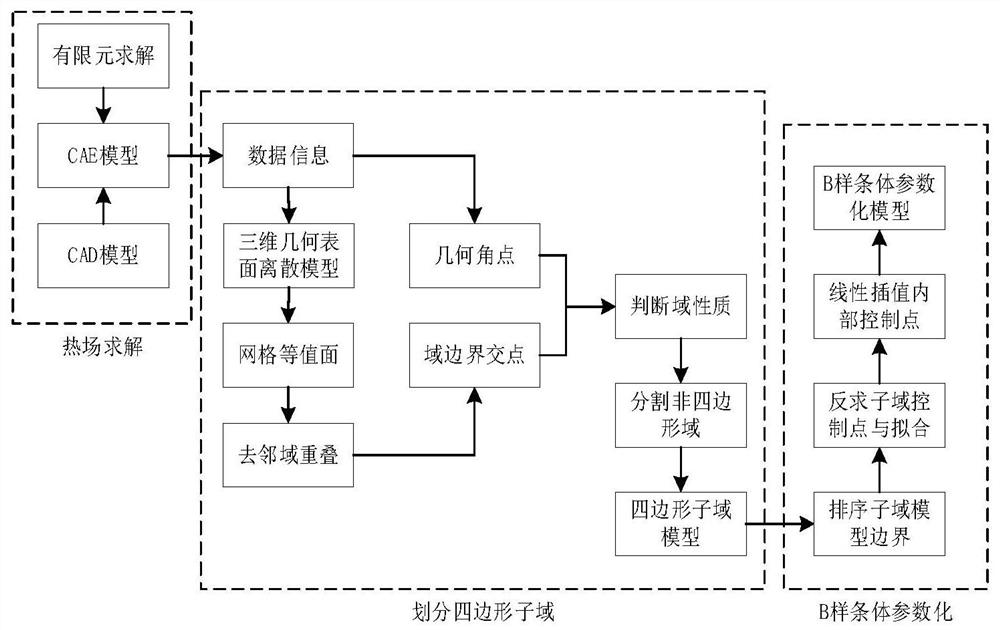
ActiveCN111797555AAchieve seamless integrationGuaranteed Continuity of ExpressionImage analysisDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelAlgorithm
The invention provides a reconstruction algorithm for a finite element discretized geometric model. The reconstruction algorithm comprises the following steps: firstly, inputting a finite element discrete grid to determine a grid topological relation, and adding a steady-state thermal field value to a grid node by solving a Laplace partial differential equation; secondly, extracting surface gridsand boundaries of a model, and setting a reasonable threshold value according to a geometric discrete boundary vector value to determine an isothermal surface; performing overlapping removal, extracting an isotherm and a domain boundary, setting an objective function to perform boundary intersection operation, judging the parity of sub-domains according to an intersection result, and setting an objective function for different sub-domains to perform reasonable quadrilateral sub-domain division; and finally, carrying out discrete boundary sorting and boundary fairing on the sub-domains, obtaining control points in the sub-domains through linear interpolation to realize B-spline parameterization, and verifying the accuracy of reconstructed geometry by utilizing isogeometric analysis. Exampleresults show that the algorithm provided by the invention well solves the geometric reconstruction problem of the finite element model.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Graphical method for generating heat dissipation topology by zero-depletion grid curved surface
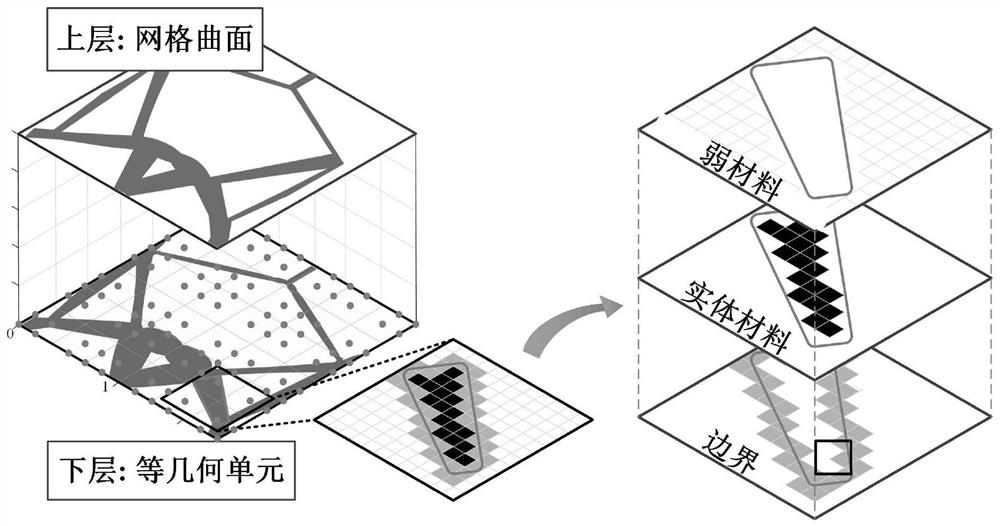
ActiveCN111832203AFull release of deformation abilityControl feature sizeDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADAnalytic modelHeat flow
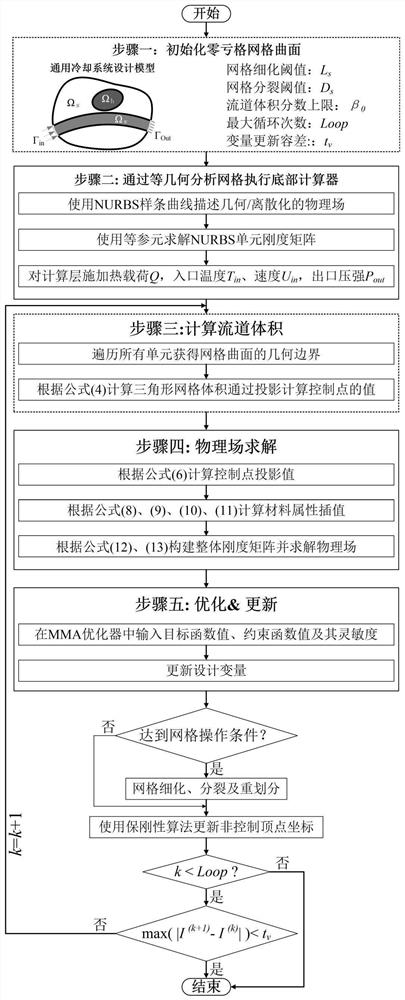
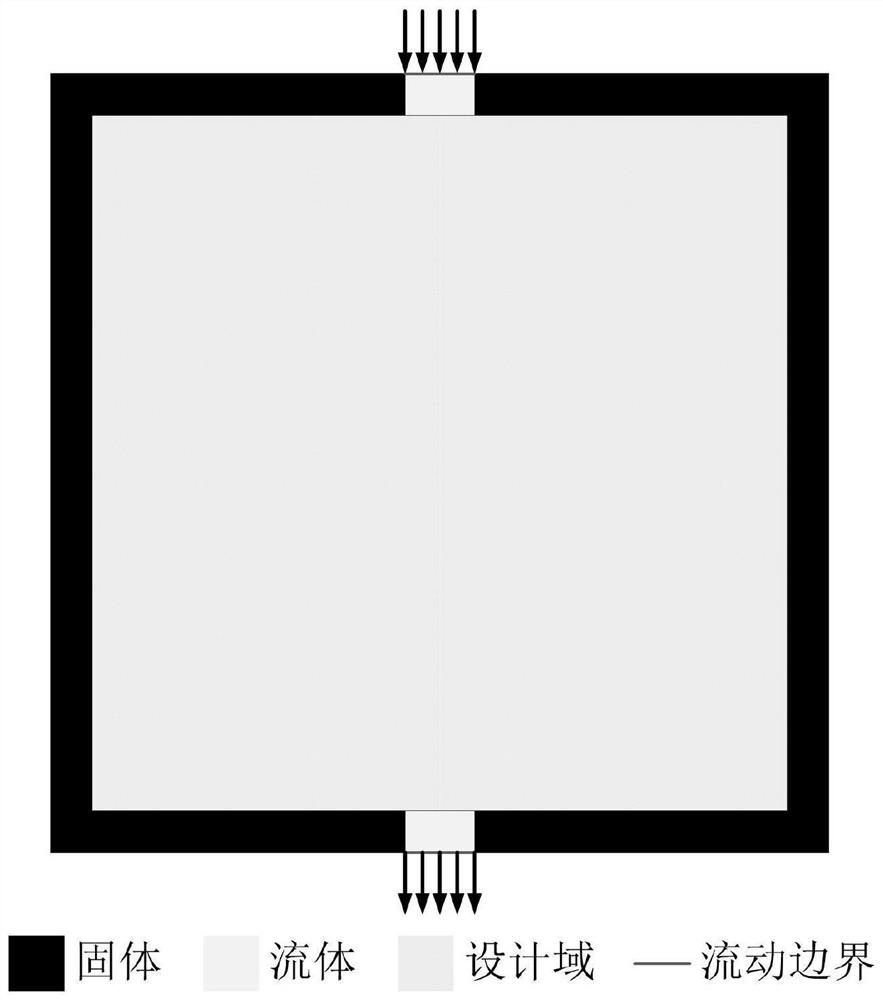
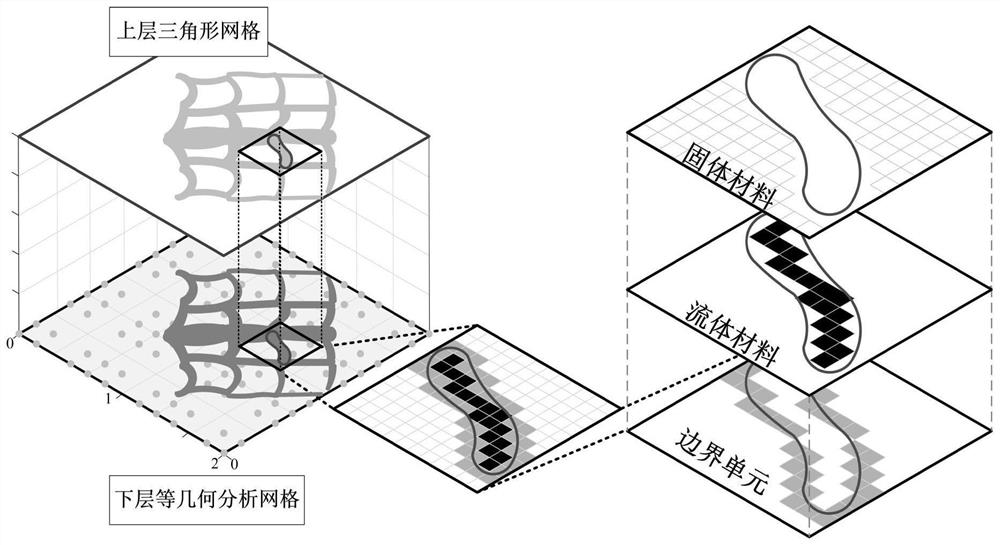
The invention discloses a graphical method for generating a heat dissipation topology by a zero-depletion grid curved surface. The method comprises the following steps: a heat dissipation structure isdesigned by utilizing a double-layer grid; the upper layer uses a zero-depletion deformable triangular mesh to describe a topological geometric model, and a heat dissipation topological structure canbe generated only through one component, so that the initial layout dependence is eliminated, a clear geometric boundary is obtained, design variables are reduced, and the calculation speed is increased; the lower layer uses an isogeometric unit to perform heat flow coupling steady-state heat conduction calculation and sensitivity analysis; the geometric model is accurately described by the analysis model, errors caused by the fact that a traditional finite element adopts a piecewise function to approach the geometric model are avoided, the solving precision of the fluid heat dissipation problem is improved, redundant grid division links in a classical finite element are avoided in the isogeometric analysis process, and the calculation cost is saved; a more reliable thought is provided for topological optimization of the heat dissipation structure.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
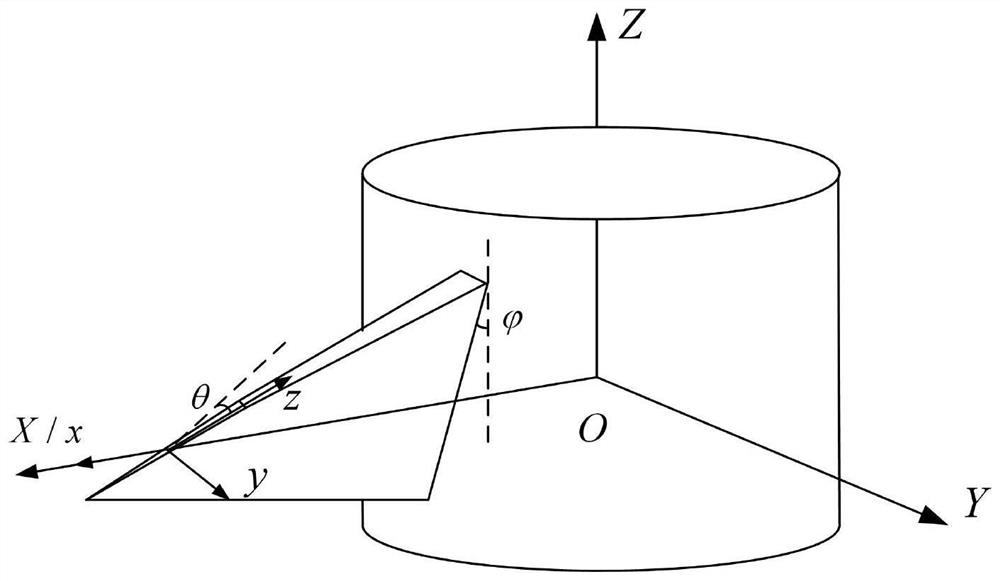
A blade high-rigidity design method based on random isogeometric analysis
ActiveCN109766604AIncrease stiffnessGuaranteed hydrodynamic performanceGeometric CADFinal product manufactureComputer scienceOptimal design
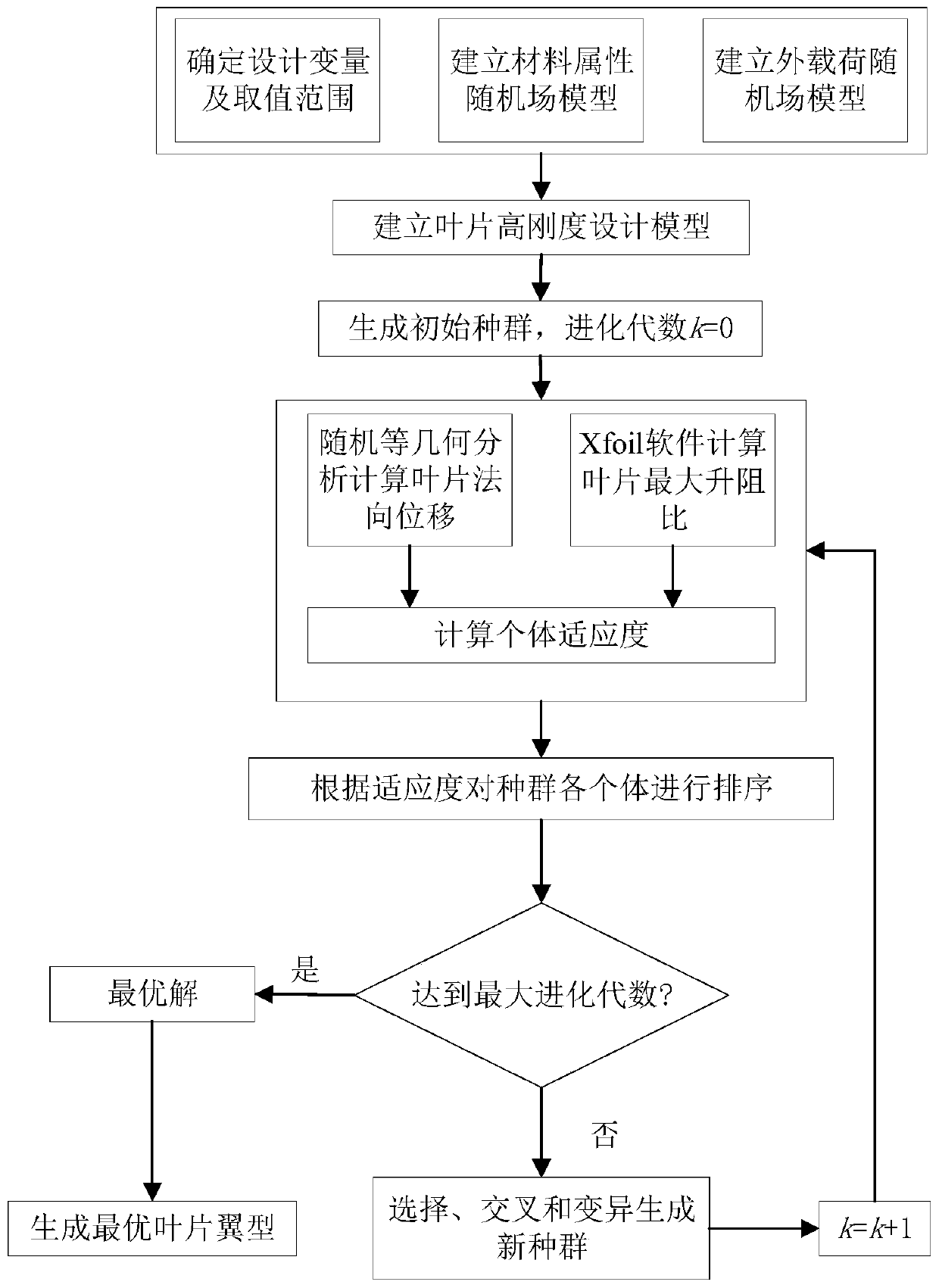
The invention discloses a blade high-rigidity design method based on random isogeometric analysis. According to the method, firstly, a random field model of the material attribute and the external load is established according to the manufacturing condition and the service environment of the blade, on the basis, an optimal design model is established according to the high-rigidity design requirement and the lift-drag ratio constraint condition of the blade, and the model is solved. During the solving process, a random isogeometric analysis method is adopted for calculating the random displacement of the blade under the influence of the material attribute and the external load randomness, meanwhile, the maximum lift-drag ratio of the blade wing section is calculated, then the fitness of theindividual of the current population is calculated, and therefore high-rigidity design of the blade on the premise that the lift-drag ratio is guaranteed is achieved. According to the blade high-rigidity design method, the randomness of blade material attributes and external loads is comprehensively considered, a random isogeometric analysis method based on a random Krylov subspace base vector discrete scheme is adopted for calculating the random displacement of the blade, and the high-precision blade random displacement can be efficiently obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Shape optimization method for I-beam two-dimensional model
ActiveCN110210130AAchieve seamless integrationHigh precisionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmGeometric modeling
The invention relates to a shape optimization method for an I-beam two-dimensional model, and the method comprises the steps: firstly, employing an NURBS spline to give a two-dimensional body parameterization model of an I-beam, and enabling parameters to comprise an NURBS coordinate point, a weight and the like; giving a shape optimization target equation and constraint conditions, deriving a sensitivity equation with control points and weights as design variables and achieving shape optimization design of the I-beam two-dimensional model by optimizing the two parameters. According to the method, the geometric model is constructed by adopting the NURBS spline, and the shape of the geometric model can be expressed more accurately. Seamless combination of the CAD system model and the CAE system model is realized by adopting an isogeometric analysis method. The advantages and characteristics of the spline model are integrated, the geometric analysis method is effectively applied to structural boundary shape optimization, the analysis process and the optimization process are integrated, the optimization accuracy and the calculation efficiency are improved, and a smooth model boundaryshape can be expressed more accurately.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Geometric analysis method based functionally gradient material part modeling method
ActiveCN106682286AAdaptableOmit node interpolationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALPartial differential equation
The invention discloses a geometric analysis method based functionally gradient material part modeling method and aims to solve the technical problem of low efficiency of an existing functionally gradient material part modeling method. According to the technical scheme, the method includes: adopting a Poisson equation for precisely describing part internal material distribution; adopting a tensor product NUPBS parameter entity for coupling expression of functionally gradient material part geometry and materials; adopting material information appointed by a designer as boundary conditions; solving the Poisson equation according to an isogeometric analysis algorithm to finally realize functionally gradient material modeling. Since the Poisson equation is a partial differential equation and a computational domain of the Poisson equation can be any complicated geometric spaces, high adaptability is realized; part geometric expression and material space calculation can be brought into a unified framework according to the isogeometric analysis algorithm, so that procedures of node interpolation, model conversion and the like are avoided, and material space calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Fast isogeometric analysis numerical simulation method based on multiple grids
InactiveCN103218493AImprove Simulation EfficiencyFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmDegrees of freedom
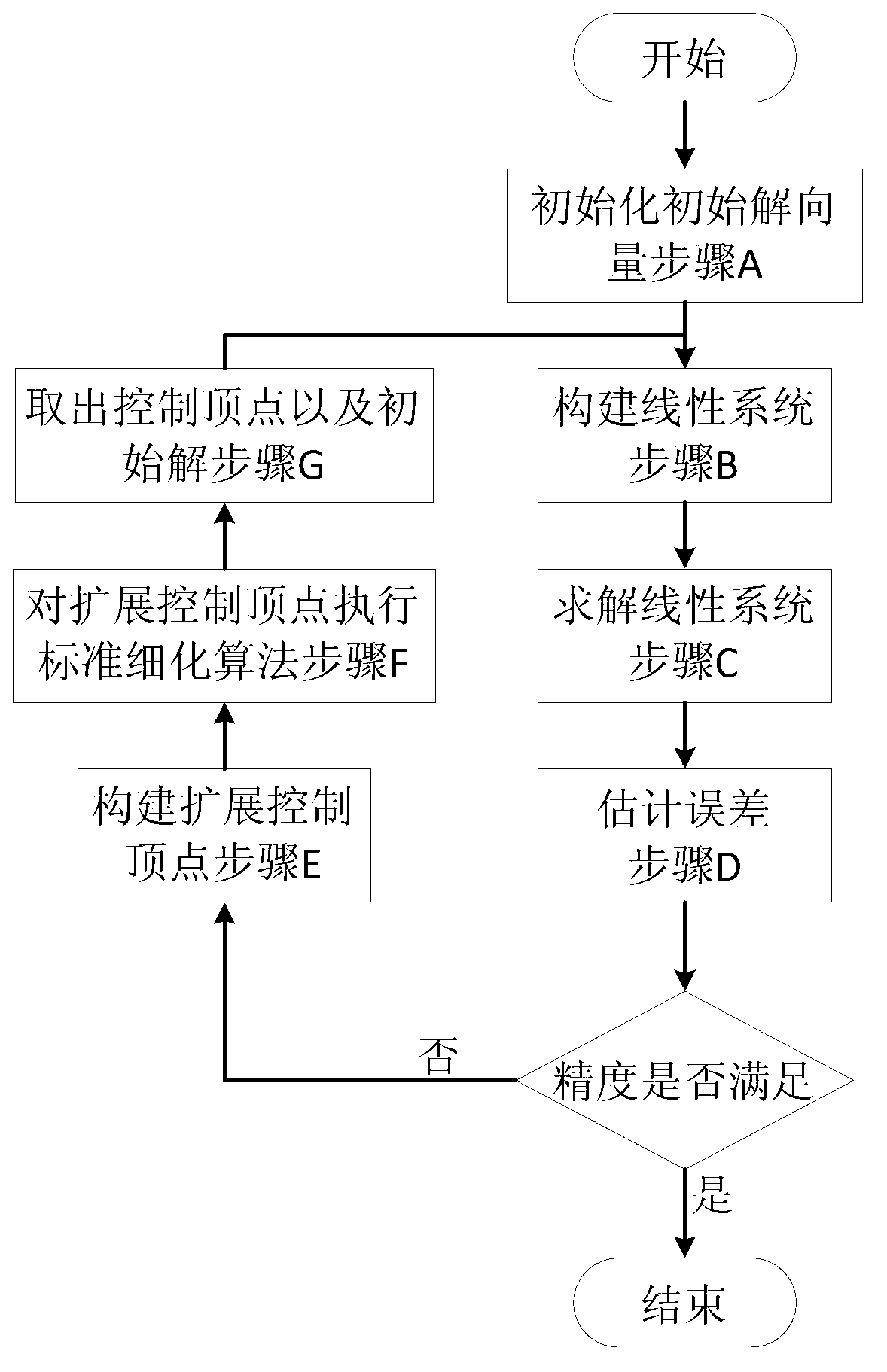
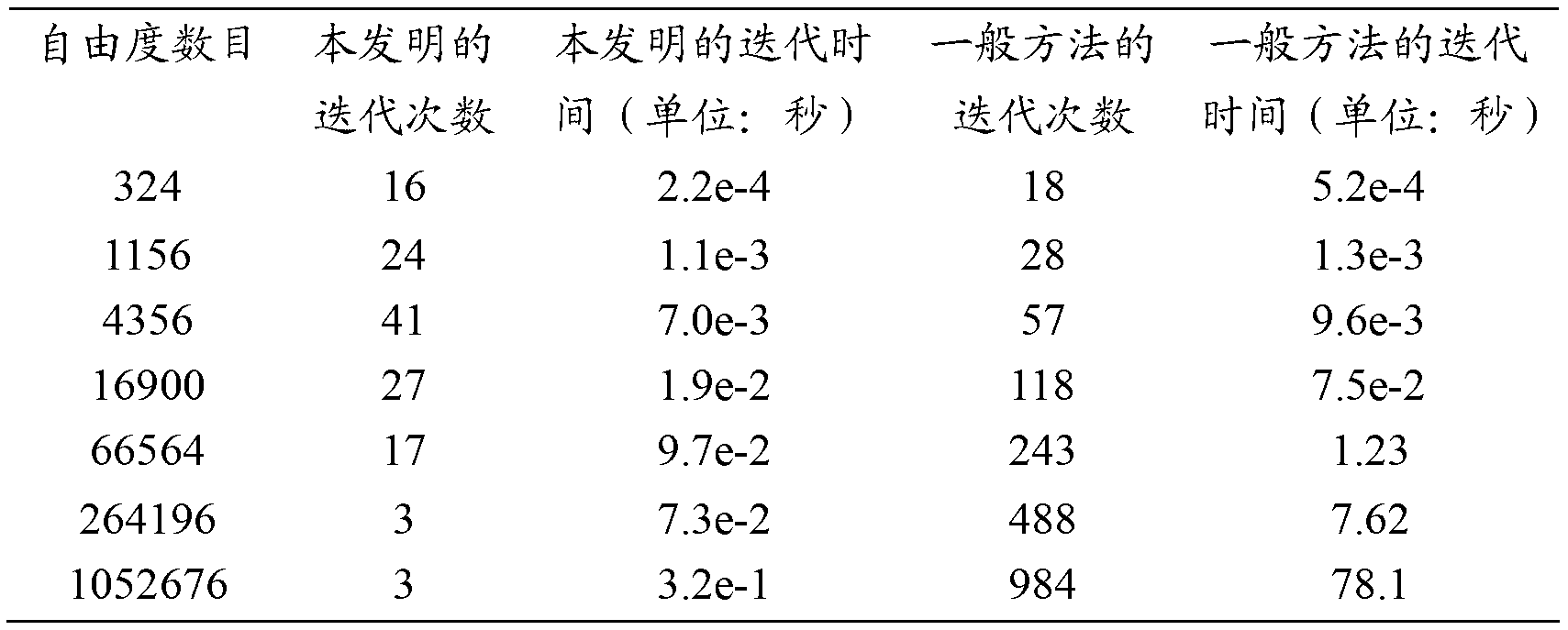
The invention provides a fast isogeometric analysis numerical simulation method based on multiple grids. The fast isogeometric analysis numerical simulation method based on the multiple grids is characterized in that an expanded control vertex is used for transforming an exact solution corresponding to a current geometric representation into a space formed by a primary function of the next geometric representation in an expansion mode; the exact solution is used as an initial solution of a system of linear equations, wherein the system of linear equations corresponds to the next geometric representation; an iterative algorithm is used for carrying out iteration on the basis of the initial solution, so that the convergence rate of the iterative algorithm is greatly increased, time consumed for solving the system of linear equations is shortened, and efficiency of numerical simulation of isogeometric analysis is improved. Through the fast isogeometric analysis numerical simulation method based on the multiple grids, the result of the solution at each time is fully utilized, and under the situation that the figure of degree of freedom is very large (more than 60,000), the solution of a linear system can be carried out quickly; and experimental results show that in the face of a large-scale linear system, time which is consumed for solving the large-scale linear system when the fast isogeometric analysis numerical simulation method based on the multiple grids is used can be reduced by more than 90% compared with time which is consumed for solving the large-scale linear system when an existing basic numerical simulation method is used.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Compliant mechanism generation method based on zero-depletion grid curved surface continuous deformation
ActiveCN111709097ASolve the problem that the initial layout has a heavy dependencyImprove continuityGeometric CADConstraint-based CADTopology mappingAlgorithm
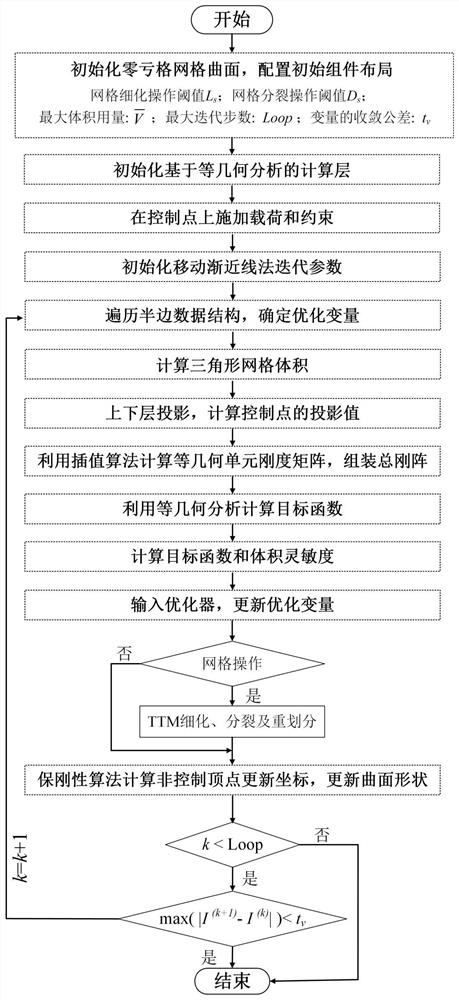
The invention discloses a compliant mechanism generation method based on zero depletion grid surface continuous deformation. The compliant mechanism generation method comprises the following steps: firstly, configuring initial component layout, initializing a calculation layer based on isogeometric analysis, applying load and constraint on isogeometric unit control points of the calculation layer,initializing iterative parameters of a moving asymptotic method, and optimizing iteration; calculating the volume of the triangular mesh, mapping the topology described by the upper triangular mesh to a lower calculation layer, calculating the projection value of a control point, and assembling an overall rigidity matrix; calculating a target function value of the structure response, solving thesensitivity of the volume, and inputting the sensitivity into an optimizer to obtain an updated coordinate value; judging triggering conditions of grid refinement, grid splitting and grid re-divisionoperation according to the updated vertex coordinate value, completing grid re-update, calculating non-control vertex update coordinates, updating the triangular grid curved surface shape, and completing one iteration; repeating iteration until convergence conditions are met. According to the method, structural response calculation and sensitivity analysis in the topological optimization process are reliably realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Half-edge data structure-based T-mesh local refinement realizing method
InactiveCN106296824ANo redundant dataLower control vertices3D modellingComputer Aided DesignComputer-aided
The invention provides a half-edge data structure-based T-mesh local refinement realizing method, which comprises the following steps: 1, establishing half-edge data structure-based T-mesh of the current T-splines; 2, determining all the surface patches, which need to be subjected to local refinement, in the current T-mesh; 3, increasing new edge points in the surface patches which need local refinement, and marking points related to segmentation of the surface patches; 4, determining peaks which the segmented surface patches and the non-segmented surface patches contain; and 5, reestablishing the half-edge data structure-based T-mesh which is subjected to local refinement. The half-edge data structure-based T-mesh local refinement realizing method realizes self-adaptive local refinement of the T-mesh of the T-splines, is absolutely necessary in actual application of triangular mesh curved surface fitting, T-splines based isogeometric analysis and the like, and is conducive to pushing further application of the T-splines in the fields of computer aided design, computer aided analysis and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
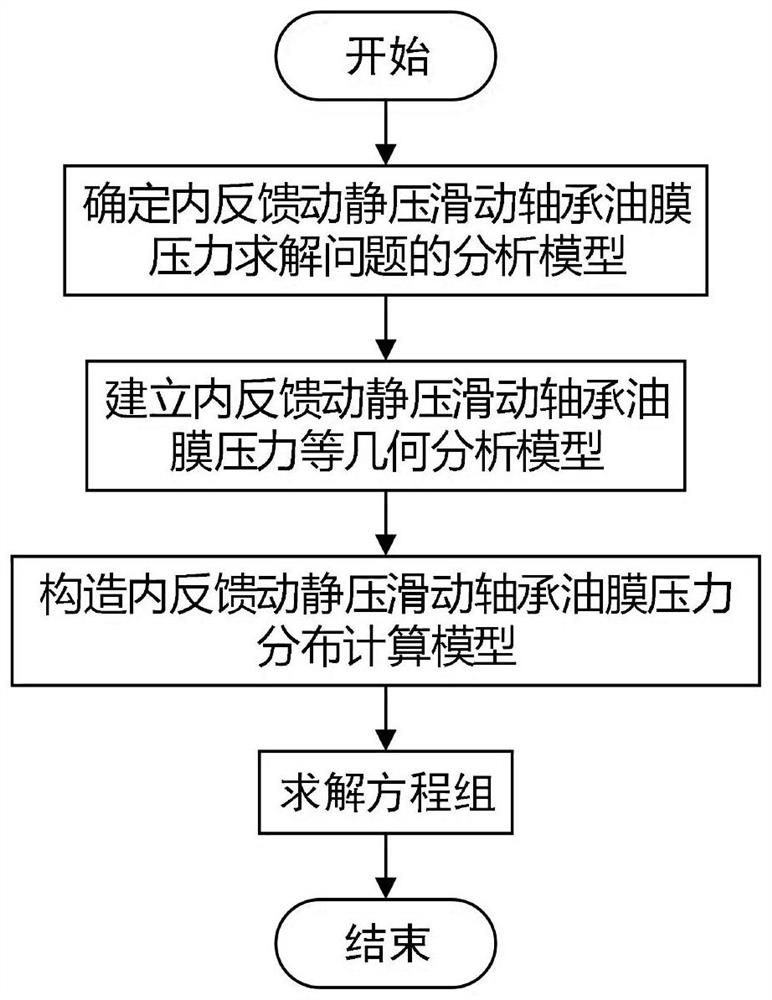
NURBS isogeometric solving method for internal feedback dynamic and static pressure sliding bearing oil film pressure field
ActiveCN111967107AEliminate introduced errorsImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADLiquid cushion bearingsSlider bearingEngineering
The invention discloses an NURBS isogeometric solving method for an internal feedback dynamic and static pressure sliding bearing oil film pressure field. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining an analysis model of a bearing oil film pressure solving problem, defining a shape control point representing a solving region, establishing a complete isogeometric analysis node vector and a shape interpolation basis function based on an NURBS theory under a parameter coordinate system, generating a numerical analysis grid, and obtaining an accurate analysis model according to calculation precision and capability; establishing a geometric analysis model of bearing oil film pressure and the like; based on an equal parameter conversion idea, carrying out isogeometric method discretization on the analysis domain to construct an inner bearing oil film static pressure distribution field; constructing a bearing oil film pressure distribution calculation model; deriving an equivalent integral weak form of a steady incompressible oil film Reynolds equation; integrating and deriving an equivalent integral weak form of a steady incompressible oil film Reynolds equation on a solving domain, applying a boundary condition, deriving an oil film pressure calculation equation based on an isogeometric analysis theory to obtain a linear equation set, and solving to obtain bearingoil film thickness and static pressure distribution.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
NURBS isogeometric analysis method for analyzing energy density field of medium-high frequency vibration structure
ActiveCN112001004ANon-negativitySmoothGeometric CADSustainable transportationEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an NURBS isogeometric analysis method for analyzing an energy density field of a medium-high frequency vibration structure. Firstly, an isogeometric analysis model of a designdomain is established; a design domain is described by utilizing an NURBS curve, an NURBS curved surface and an NURBS body; an energy density control equation in a steady state is constructed; a unitenergy density control equation matrix form is constructed; and then an energy density control equation based on an NURBS primary function is calculated, adaptive processing is finally performed, theenergy density control equation obtained by transformation under an isogeometric analysis framework is substituted into kinetic analysis calculation of the structure, and an energy density response atany position in the structure under high-frequency excitation is obtained through solution calculation. Based on an isogeometric analysis framework, starting from an energy density control equation in a steady state, the energy density subjected to time and space averaging is used as a research object, and an energy finite element method is adopted to carry out dynamic analysis on a mechanical structure, so that the shackle of vibration wavelength is eliminated in grid division during analysis, and the precision is greatly improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A two-dimensional structure internal acoustic performance analysis method
ActiveCN109684723AHigh precisionAvoid reprogramming processingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALAcoustic area
The invention belongs to the field of computer acoustic aided design, and particularly relates to a two-dimensional structure internal acoustic performance analysis method, which comprises the following steps of: extracting NURBS geometric parameters representing a two-dimensional acoustic area, including a node vector, a polynomial order and a control point network; Converting the NURBS parameterto obtain a new interpolation point and an interpolation basis function; Describing an internal sound field and a partial derivative of the internal sound field in the two-dimensional area by adopting the interpolation primary function; Applying the Gauss-Lobatto integral rule to calculate the numerical integral of sound pressure in the unit parameter space [0,1]*[0,1]; Compared with a traditional finite element, isogeometric analysis does not need conventional grid division, and the acoustic performance of the structure can be analyzed under the condition that the accuracy of a geometric model is reserved, so that the analysis precision is improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
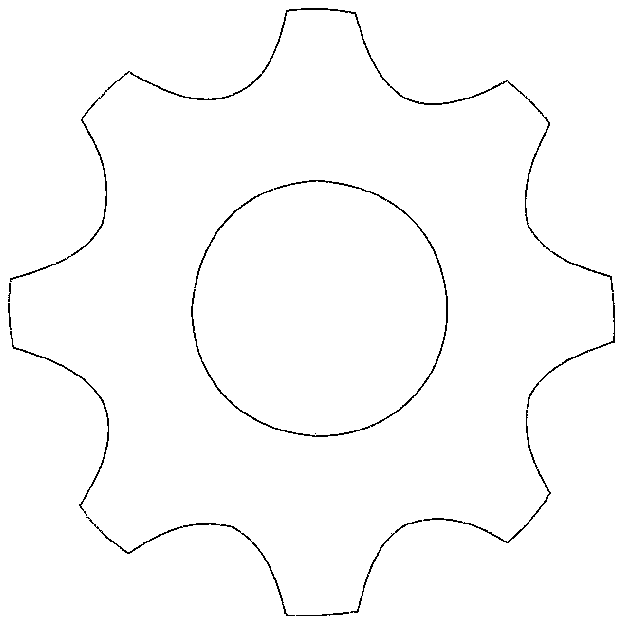
Gear model region parameterization method based on subdivision technology and boundary replacement
ActiveCN108763668AReduce bumpinessIncrease spawn rateGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsGeneration rateSubdivision method
The invention discloses a gear model region parameterization method based on subdivision technology and boundary replacement. A graph model with a complex region is difficultly subjected to high-quality parameterization. According to the method, the concave-convex degree of each section of a curve is reduced through a curve segmentation method, and a turnover quadrilateral mesh model is ensured not to be generated, so that the parameterization quality of a gear model is optimized, and the effectiveness requirement of the gear model on isogeometric analysis in engineering application is met; then by modifying a mean distance value of polygonal boundaries of the gear model and uniformizing the distances between the vertexes of the boundaries, the generation rate of quadrilateral meshes is improved; and a boundary replacement method is used to ensure that the shape of the gear model is not changed, and a smoothing method and a C-C subdivision method are used to optimize the gear model insmoothness and continuity, so that the smoothness and the robustness requirements of the engineering application on the isogeometric analysis are met.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
An isogeometric analysis-based porous plate mechanical property analysis method
InactiveCN105868452ASimplify the scaleAccurately establishedComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsExtended finite element methodMixed finite element method
The invention provides an isogeometric analysis-based porous plate mechanical property analysis method. The method comprises the steps of converting a porous plate computation domain into a simply-connected computation domain with complex borders; dividing the simply-connected computation domain into a plurality of sub-segment domains through a segmentation method; incorporating the problem of physical domains to a linear equation system via a finite element method for solving the problem; finally obtaining the analysis results of all the physical domains through the solution of the linear equation system. Through comparison validation with analysis results of the conventional finite element method, it is proved that the method is practical and effective for the computation of porous plates. The method can establish a porous plate model more accurately and greatly increase the problem solving efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Phononic crystal material structure design method based on extended isogeometric analysis method
ActiveCN112765884AAccurate descriptionReduce computing timeGeometric CADArtificial lifePhotonic crystalComputational physics
The invention discloses a photonic crystal material structure design method based on an extended isogeometric analysis method. By changing the shape of the scatterer, the phononic crystal material with wide sound insulation frequency band and low sound insulation frequency is designed. The computational grid of the extended isogeometric analysis method is independent of the geometry inside the structure, so that the computational grid does not need to be reconstructed when the shape of the scatterer changes; when the energy band structural characteristics of the phononic crystal material are analyzed by adopting an extended geometric analysis method based on LR-NURBS, small-scale grids are adopted near a scatterer interface, and large-scale grids are adopted in other areas, so that the precision can be improved, and the time can be saved. The shape of the scatterer is described by adopting an NURBS spline function, so that the scatterer in any complex shape can be constructed. The scatterer obtained by the method is smooth in shape and can be directly used for design; the method can accurately describe phononic crystal periodic cell elements with complex shapes, and realizes the design of the structure of the phononic crystal material by seamless combination of CAD and CAE.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Complex lattice structural body parametric modeling method
The invention discloses a parameterization modeling method for a complex lattice structure body. The parameterization modeling method comprises the steps that firstly, a framework model of a lattice structure is given; dividing the node into three node types, namely a branch node, a connection node and a tail end node; and the branch nodes are comprehensively constructed by using an inner hexahedron group generation mechanism based on skeleton perception and an outer hexahedron group mapping mechanism based on transition curved surface sampling fitting interpolation. And connecting nodes are constructed by using a lofting body model of a multi-section group. And a tail end node is constructed by using a stretching body or swept body model of a single section group. And the node model is matched with the skeleton topological information, and a lattice structural body parameterized model is obtained through splicing and periodic array. According to the method, the parametric modeling problem of the complex lattice structure body is well solved, and the model can be directly applied to isogeometric analysis, so that a good model support is provided for realizing modeling and simulation integration of the complex lattice structure.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method for improving geometric analysis contact search efficiency
InactiveCN109918825AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsElement modelShortest distance
The invention relates to a method for improving geometric analysis contact search efficiency and stability of clearance revolute pair dynamic characteristics and the like. The method comprises the following steps: as for a clearance revolute pair finite element model, performing NURBS curve modeling and using a parameterization method on the contact boundary; setting a numerical integration pointat the bearing contact boundary; for any integral point on the bearing contact boundary, calculating the distance between the integral point and each end point on the rotating shaft contact boundary,comparing the sum of the distances between the two end points of each curve section and the integral points, locating the arc section with the minimum distance sum is the contact arc section where theprojection point so that contact search amount can be reduced to one fourth of that of a conventional algorithm. Parameter values corresponding to two end points of an arc section where a projectionpoint is located and a shorter distance from an integral point are selected as initial values of nonlinear iteration, so that the stability of iterative search is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Structure isogeometric topological optimization method considering meso-nano scale effect
ActiveCN113434921ASatisfy high-order continuity requirementsAvoid frequent interactionsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmGeometric modeling
The invention relates to a structure isogeometric topological optimization method considering a meso-nano scale effect. The method is based on a strain gradient mechanical theory, adopts an isogeometric analysis method, constructs a geometric model and an analysis model by using a non-uniform rational B spline (NURBS), and constructs a geometric analysis calculation tool by nesting a strain gradient theory by using an NURBS primary function with a preset order; and a topological optimization method based on variable density method structure description is adopted, and topological optimization design is carried out with the unit density as a design variable. According to the method, the mechanical behaviors of the meso-nano micro-component are accurately described, structural response calculation and sensitivity analysis are reliably realized, an accurate topological optimization structure is obtained, and meanwhile, the problems of low solving precision, large calculation amount, long consumed time and the like of micro-component topological optimization design can be solved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Local error driving isogeometric analysis computational domain self-adaptive optimization method
ActiveCN104331534AImprove application breadthImprove Simulation EfficiencySpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmAdaptive optimization
The invention discloses a local error driving isogeometric analysis computational domain self-adaptive optimization method. An isogeometric analysis method requires the optimization on all internal control top points, so the isogeometric analysis method is only applicable to a condition that a computational domain is in a simple shape. According to the method, firstly, a residual method is utilized for obtaining a local error indicator on a computational domain sub chip; then, a control top point set to be optimized is determined according to a local marking strategy; the optimum distribution of the marked internal control top points is obtained through marking the error indicator on a curve chip; a self-adaptive (h-r) type refinement algorithm is provided on the basis of a self-adaptive r type refinement algorithm; and the optimum parameterization of the computational domain is obtained. The method has the advantages that the simulation emulation efficiency and the isogeometric analysis solving precision are improved; the r type refinement algorithm can be applied to CAD models with complicated geometrical shapes; and the application range of the isogeometric analysis method is widened.
Owner:广西鸿运设计有限公司
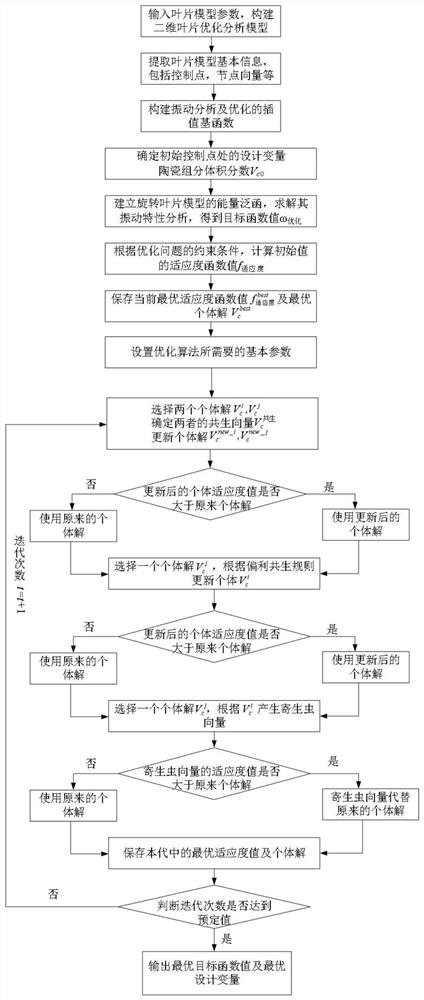
Material distribution optimization method for blade model
PendingCN114676529AShorten the design cycleImprove optimization efficiencyGeometric CADArtificial lifeAlgorithmMaterial distribution
The invention discloses a material distribution optimization method for a blade model, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a blade model, and extracting the basic information of the blade model; constructing a non-uniform rational B-spline basis function based on basic information of a blade model and an isogeometric analysis method refinement strategy; performing interpolation calculation by using a non-uniform rational B-spline basis function to obtain material attributes of the blade model; based on material attributes of the blade model, analyzing vibration characteristics of the blade model to obtain a target function value; based on the objective function value and constraint conditions of material distribution optimization, obtaining a blade model fitness function value; iterative solution is carried out by utilizing an optimization algorithm program, fitness function values of the blade model are calculated and compared, an optimal design variable individual solution and an optimal material distribution optimization blade model are obtained, and material distribution optimization of the blade model is completed. By means of the method, the continuously-changing optimized material distribution interface can be obtained, further smoothing treatment is not needed, the optimization efficiency is greatly improved, and the design period of whole blade material optimization is shortened.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
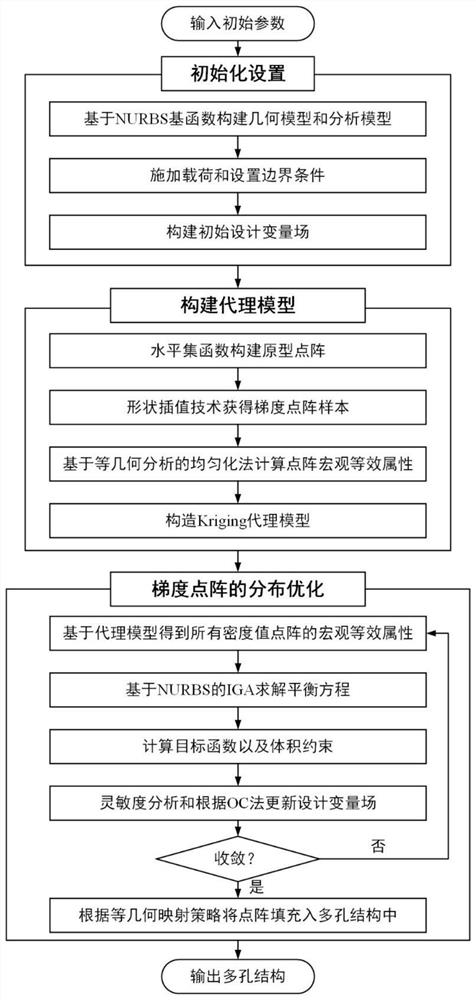
Gradient dot matrix isogeometric topology optimization method based on proxy model
PendingCN114254408AGuaranteed unityAvoid geometric approximation errorsGeometric CADMacroscopic scaleDot matrix
The invention belongs to the related technical field of structure optimization, and discloses a gradient dot matrix isogeometric topology optimization method based on an agent model, which comprises the following steps of: (1) calculating a macroscopic equivalent attribute of each gradient dot matrix sample of a porous structure to be optimized through an isogeometric analysis-based homogenization method; (2) constructing an agent model, and predicting the macroscopic equivalent attribute of any relative density dot matrix of the porous structure to be optimized through the agent model; (3) dispersing the macroscopic design domain of the to-be-optimized porous structure into a plurality of units through an isogeometric method, and further constructing an isogeometric topological optimization model taking the maximum fundamental frequency as a target so as to optimize the density value of a gradient dot matrix in each unit in the macroscopic design domain; and (4) calculating to obtain a specific gradient lattice configuration in each unit, and filling the obtained gradient lattice configuration into the corresponding unit through an isogeometric mapping strategy to obtain the three-dimensional porous structure with the required geometric shape. According to the method, the calculation precision and the applicability are improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
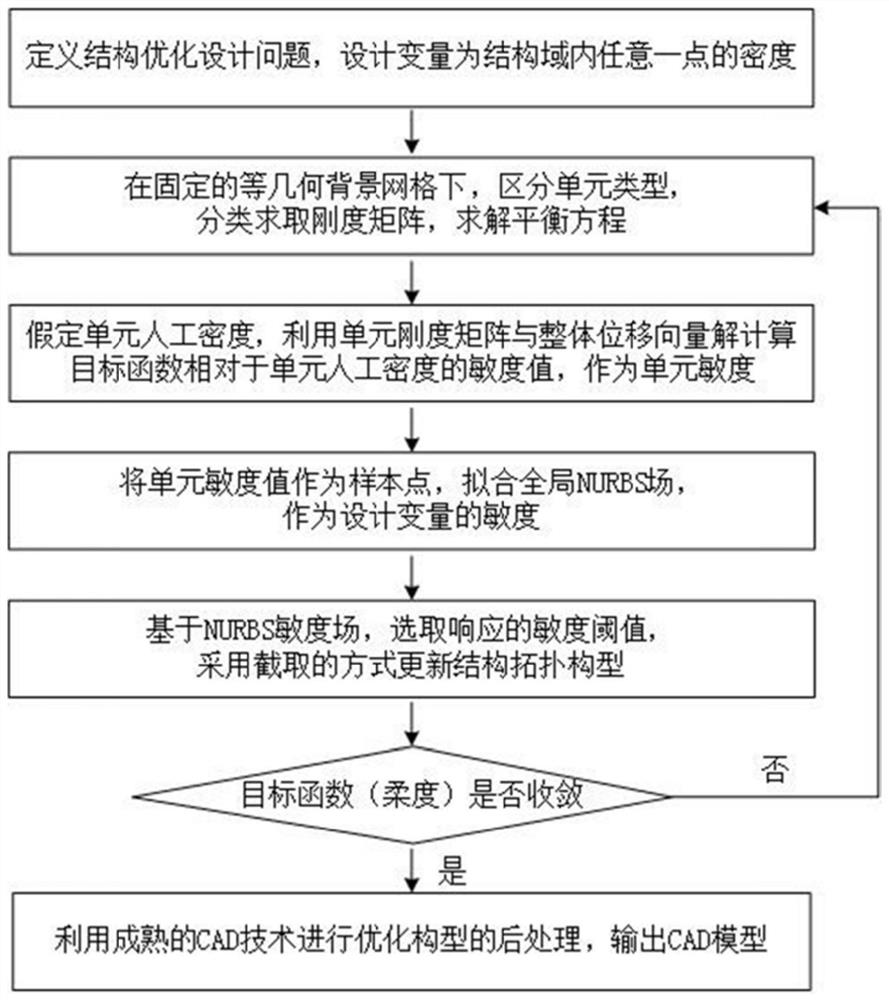
Progressive structure topological optimization method based on isogeometric analysis
PendingCN113887095AImprove convenienceAvoid duplicationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmEngineering
The invention belongs to the related technical field of structure optimization design, and discloses a progressive structure topology optimization method based on isogeometric analysis, which comprises the following steps of: (1) setting a design variable as a density value of any point in a design domain, constructing an optimization model, and dividing the design domain to obtain an isogeometric background grid; (2) respectively solving the element stiffness of each type of element by adopting a calculation rule of an extended finite element so as to obtain an overall displacement vector of the structure; (3) calculating to obtain a unit sensitivity value in combination with the set unit artificial density and the overall displacement vector; (4) fitting an NURBS sensitivity field by taking the unit sensitivity value as the unit center point sensitivity and as a sample point; (5) selecting a density threshold to intercept a current NURBS sensitivity field so as to update a design variable; and (6) judging whether the target function converges or not, and if yes, ending topological optimization; otherwise, turning to the step (2). The method is stable, effective and good in applicability.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Generative design method for special-shaped fuel structure of fast neutron reactor core
PendingCN114662375AAvoid distortionAvoid partitioning processGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAdaptive mesh refinementNuclear engineering
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
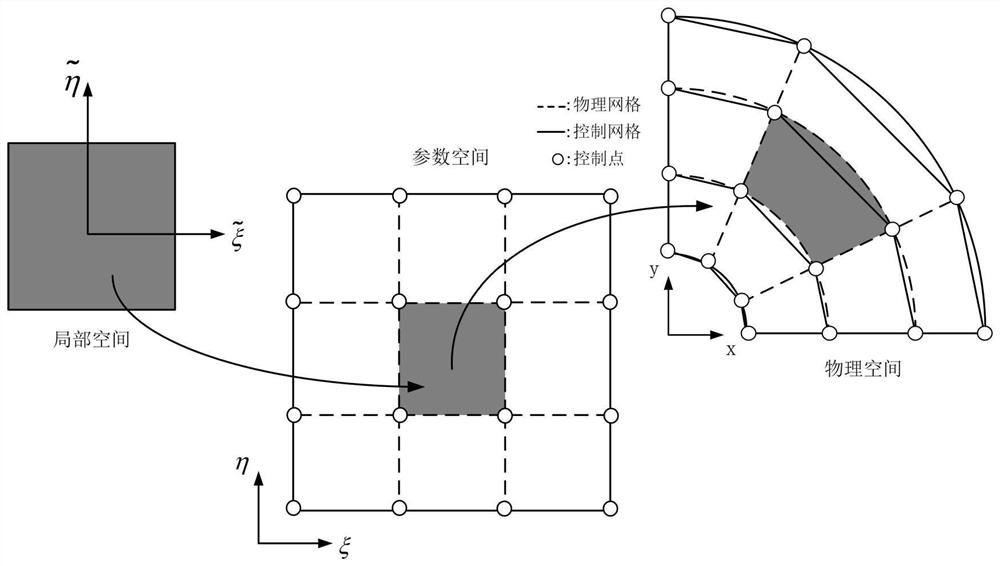
Inside and outside boundary treatment method of isogeometric analysis
InactiveCN104504223AImprove efficiencyEasy to implementSpecial data processing applicationsNODALDiscrete functions
The invention provides an inside and outside boundary treatment method of isogeometric analysis. The method includes the steps of establishing parameter space of the same topological structure with a part or a region, expressing the parameter space of the part or the region with open node vectors through a node insertion method, representing the surfaces of every three-dimensional body with normal and normal coordinates of the parameter space, generating open node vector expression of the surfaces of every three-dimensional body, calculating basis functions of the surfaces of every three-dimensional body in accordance with the obtained open node vector expression, and projecting inside and outside the boundary conditions of unknown field quantity in discrete function space through isogeometric analysis to complete boundary condition treatment. When the inside and outside boundary treatment method of isogeometric analysis is used for completing the boundary condition treatment of engineering problems, a numerical calculation problem can be converted into a logical judgment problem, and the logical judgment is more efficient than the numerical calculation and easier to achieve, so that the topological relationship judgment of isogeometric analysis is solved at higher efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com