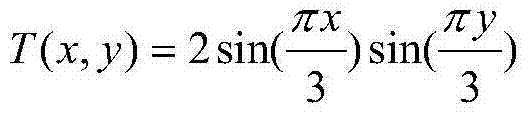Local error driving isogeometric analysis computational domain self-adaptive optimization method
An isogeometric analysis and error-driven technology, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of broadening the application range and improving the efficiency of simulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The local error-driven isogeometric analysis computational domain adaptive optimization method, the specific steps are as follows:
[0026] Step 1. Initially parameterize the plane B-spline in the two-dimensional computational domain Ω σ(u,v)={(u,v)|0≤u≤15,0≤v≤15};
[0027] Step 2. Calculate the two-dimensional Poisson equation by using the isogeometric analysis method
[0028] ΔT ( x , y ) = g ( x , y ) in Ω T ( x , y ) ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The local error-driven isogeometric analysis computational domain adaptive optimization method, the specific steps are as follows:
[0040] Step 1. Initially parameterize the plane B-spline in the two-dimensional computational domain Ω σ(u,v)={(u,v)|0≤u≤6,0≤v≤6};
[0041] Step 2. Calculate the two-dimensional Poisson equation by using the isogeometric analysis method
[0042] ΔT ( x , y ) = g ( x , y ) in Ω T ( x , y ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com