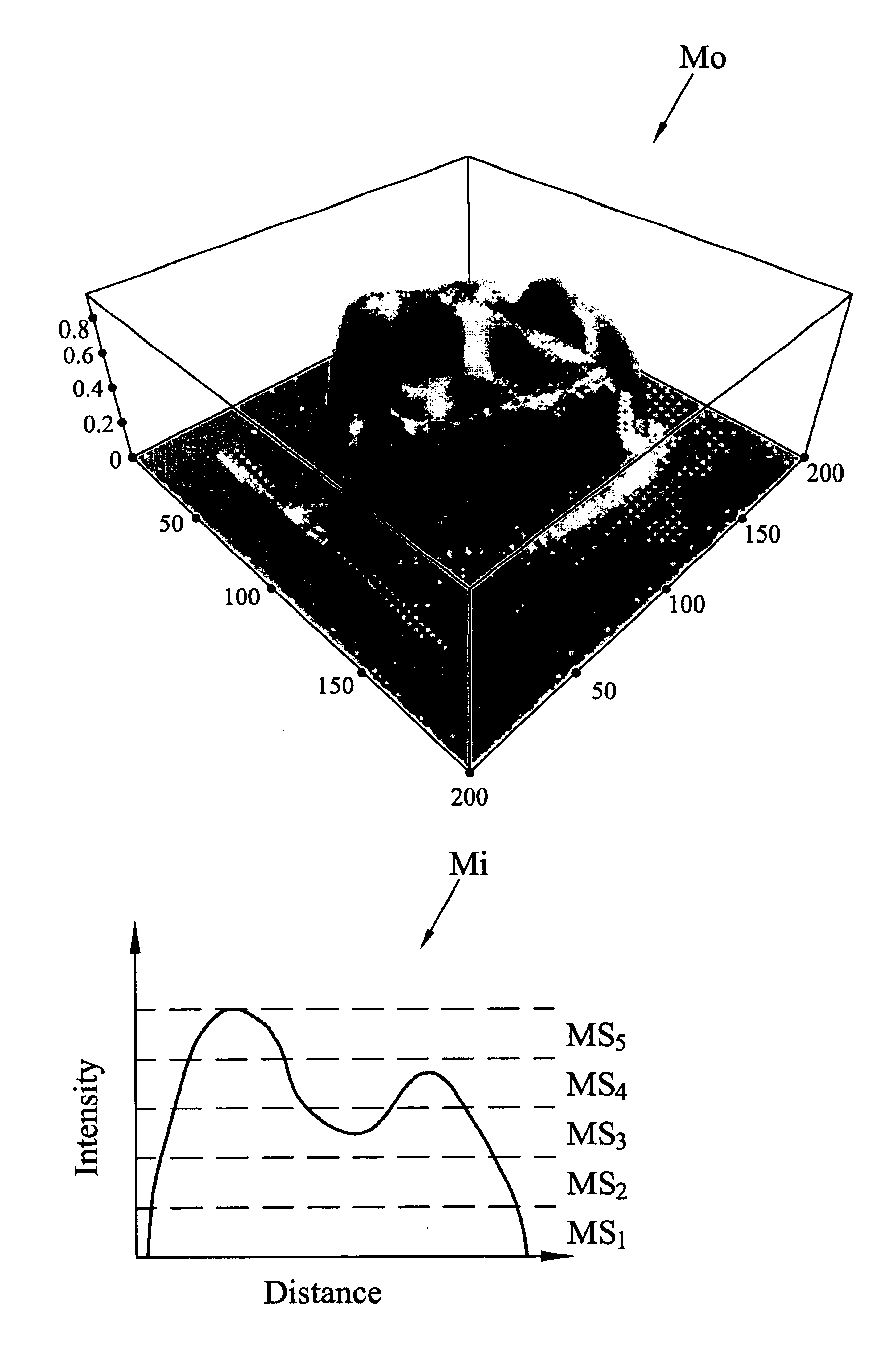
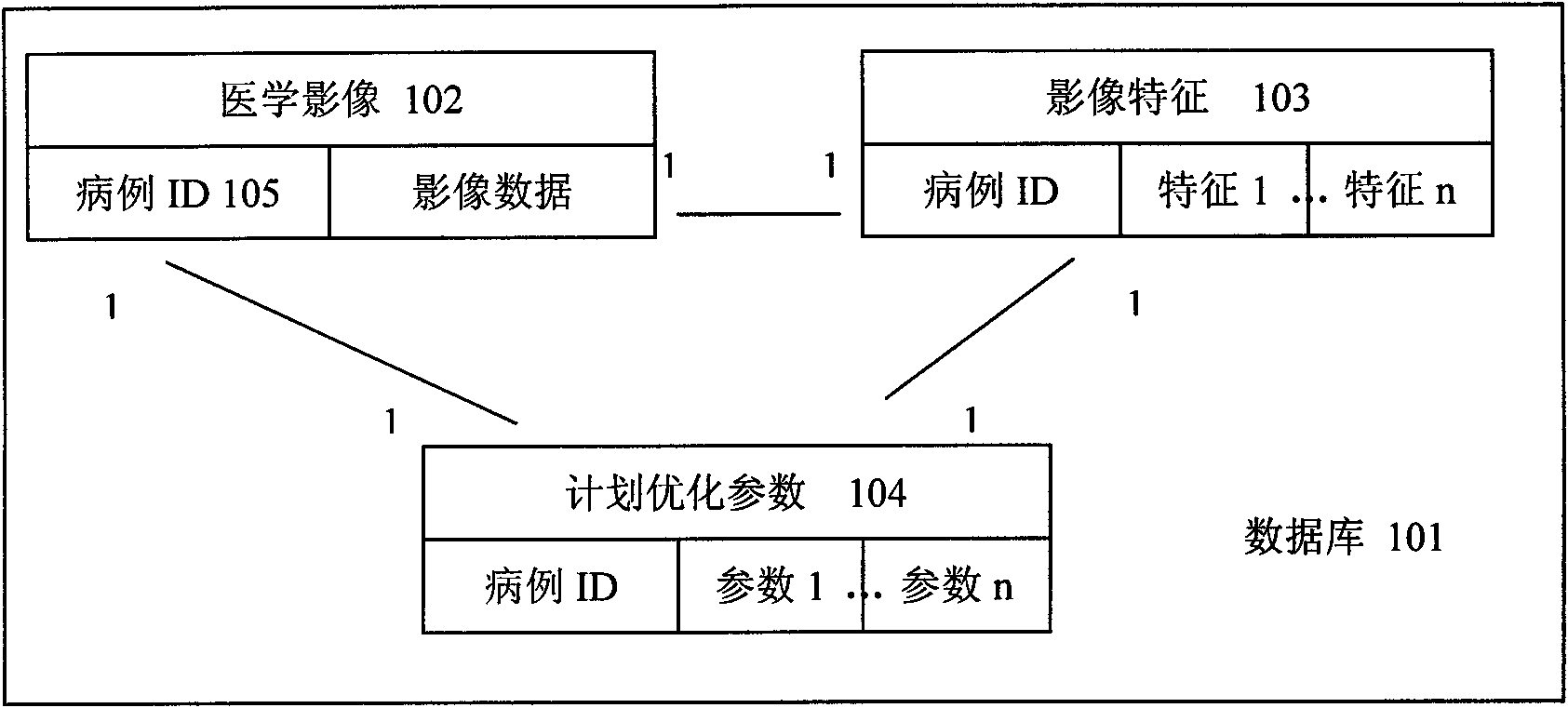
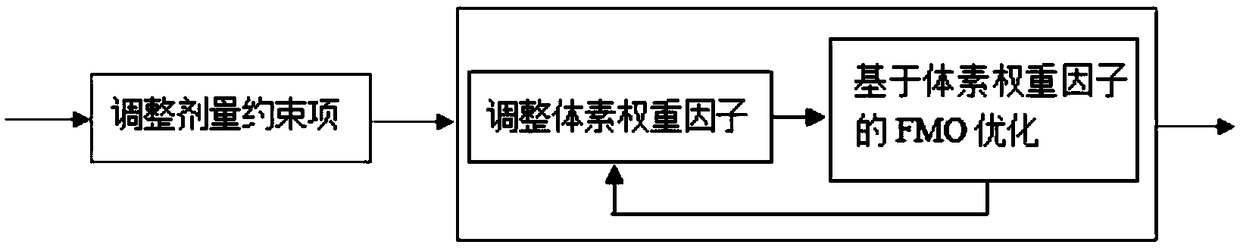
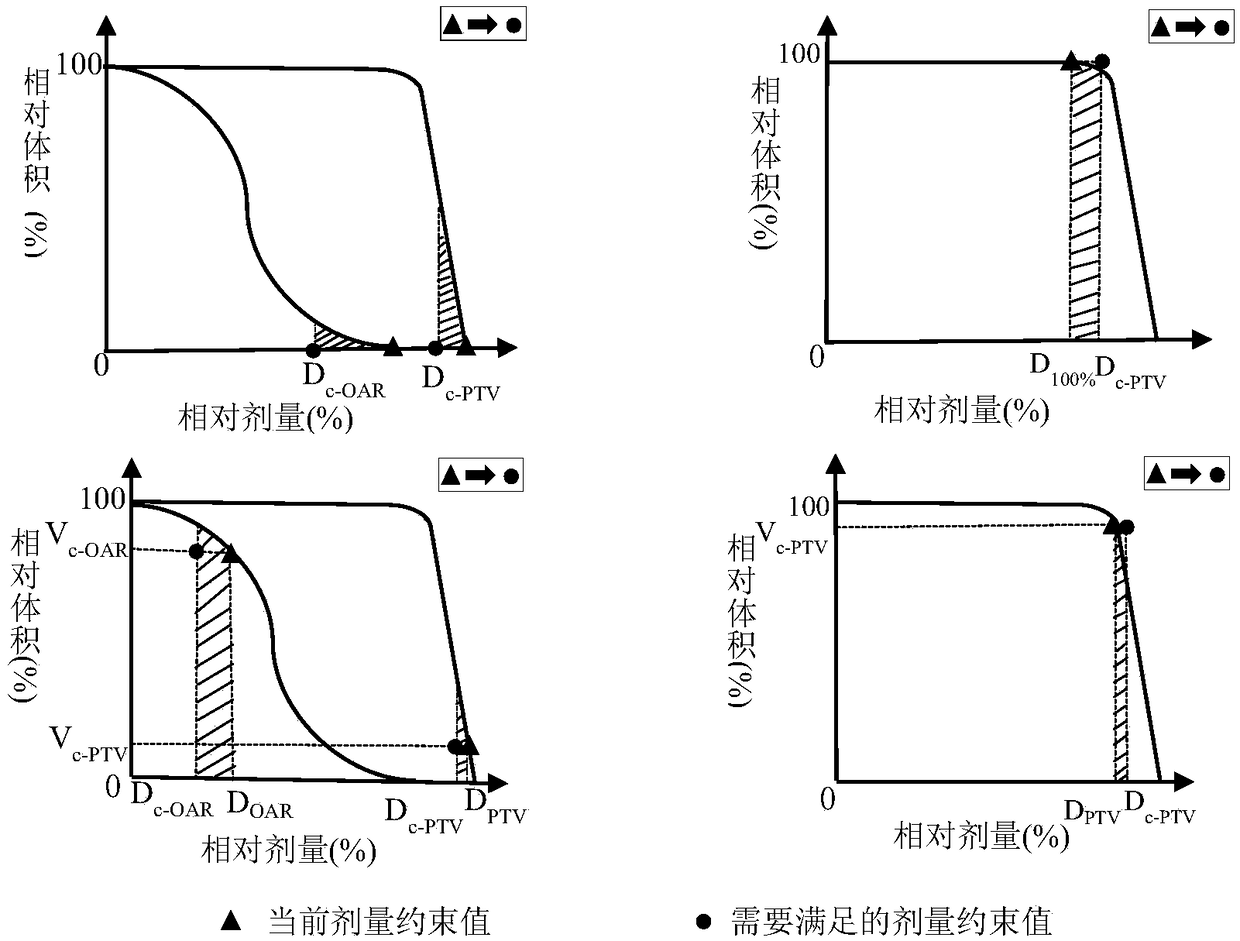
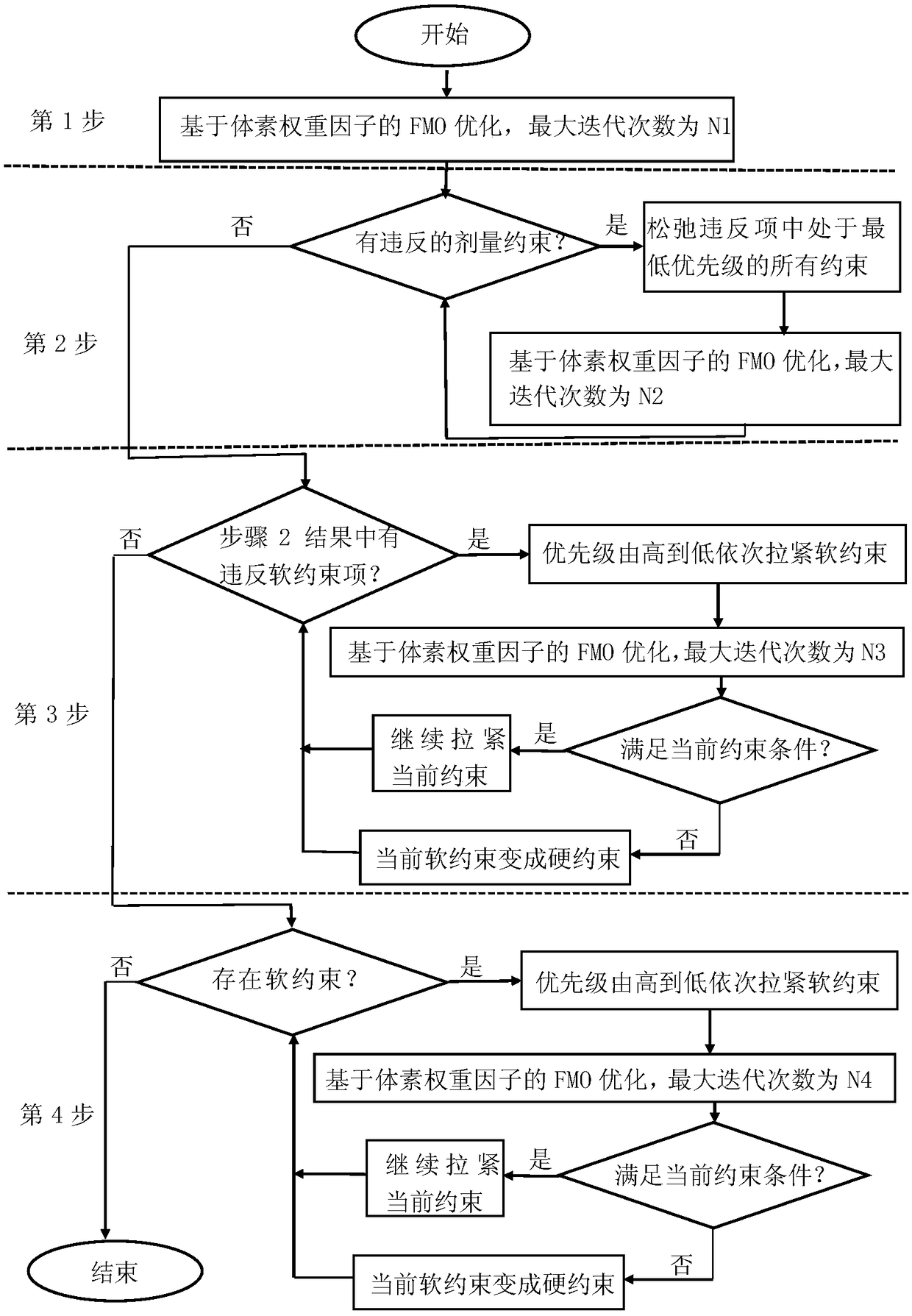
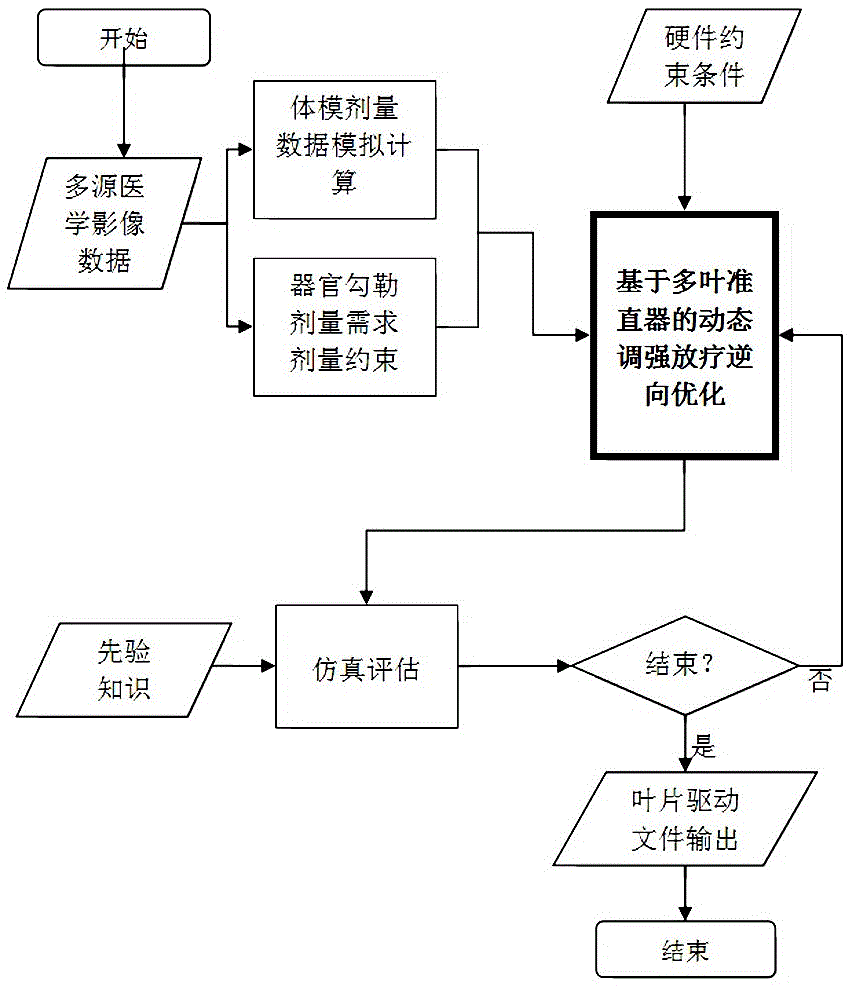
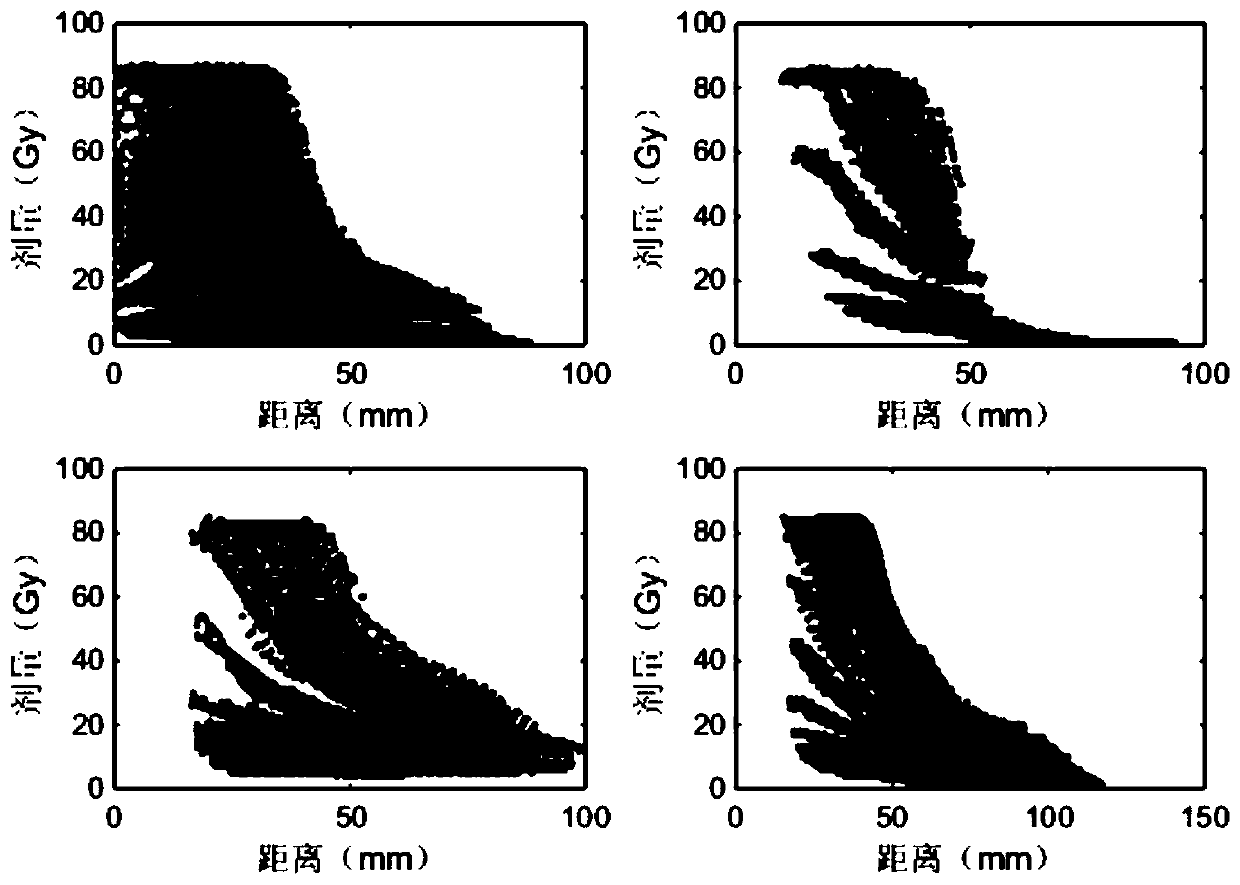
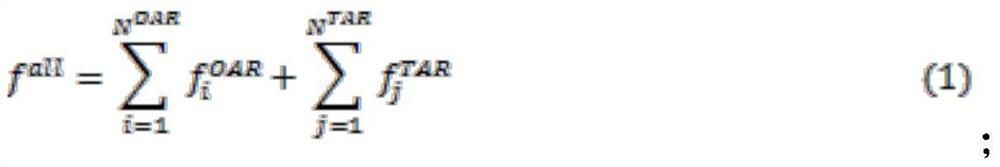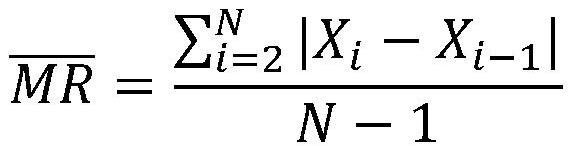Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Intensity modulate radiotherapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Residual map segmentation method for multi-leaf collimator-intensity modulated radiotherapy
InactiveUS6853705B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyMulti leaf collimator
In a method for sequentially generating segment fields for use in delivering intensity modulated radiotherapy an input continuous intensity map is generated. A segment field is generated directly from the input intensity map. A residual continuous intensity map is generated that is based on the respective photon fluence contributions from the input intensity map and a fractionally intensity map corresponding to the segment field. These steps are repeated for a number of iterations to generate a like number of additional segment fields and residual maps derived therefrom. In each iteration, the residual map generated in the previous iteration is used as the input intensity map.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
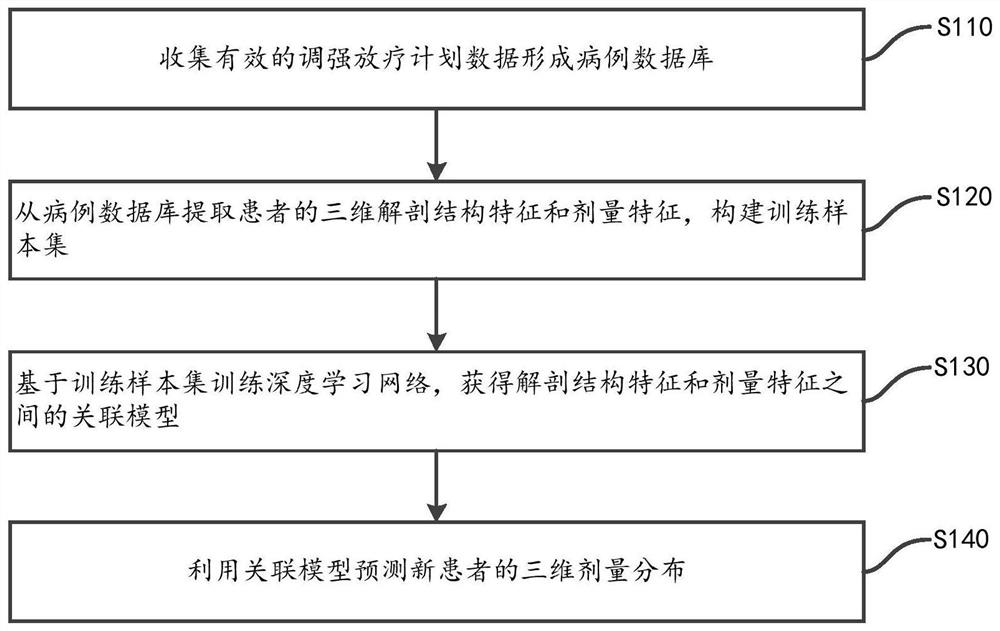
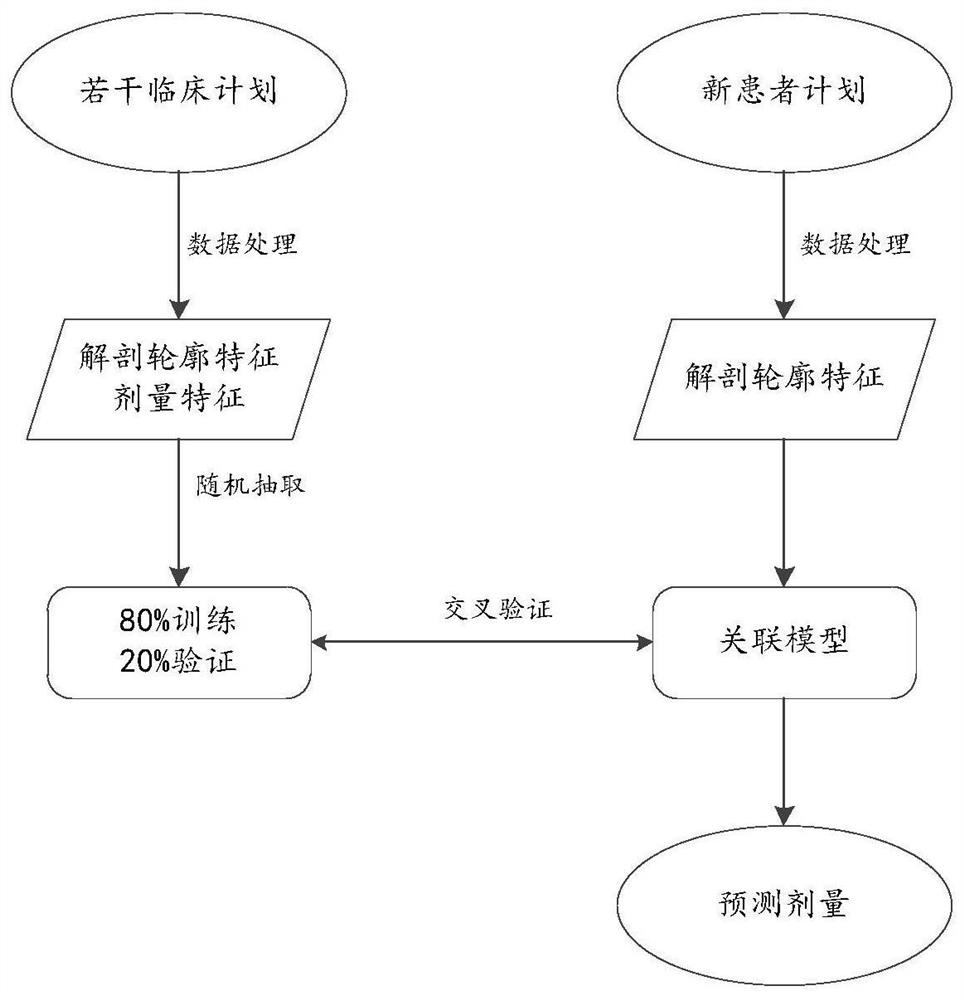
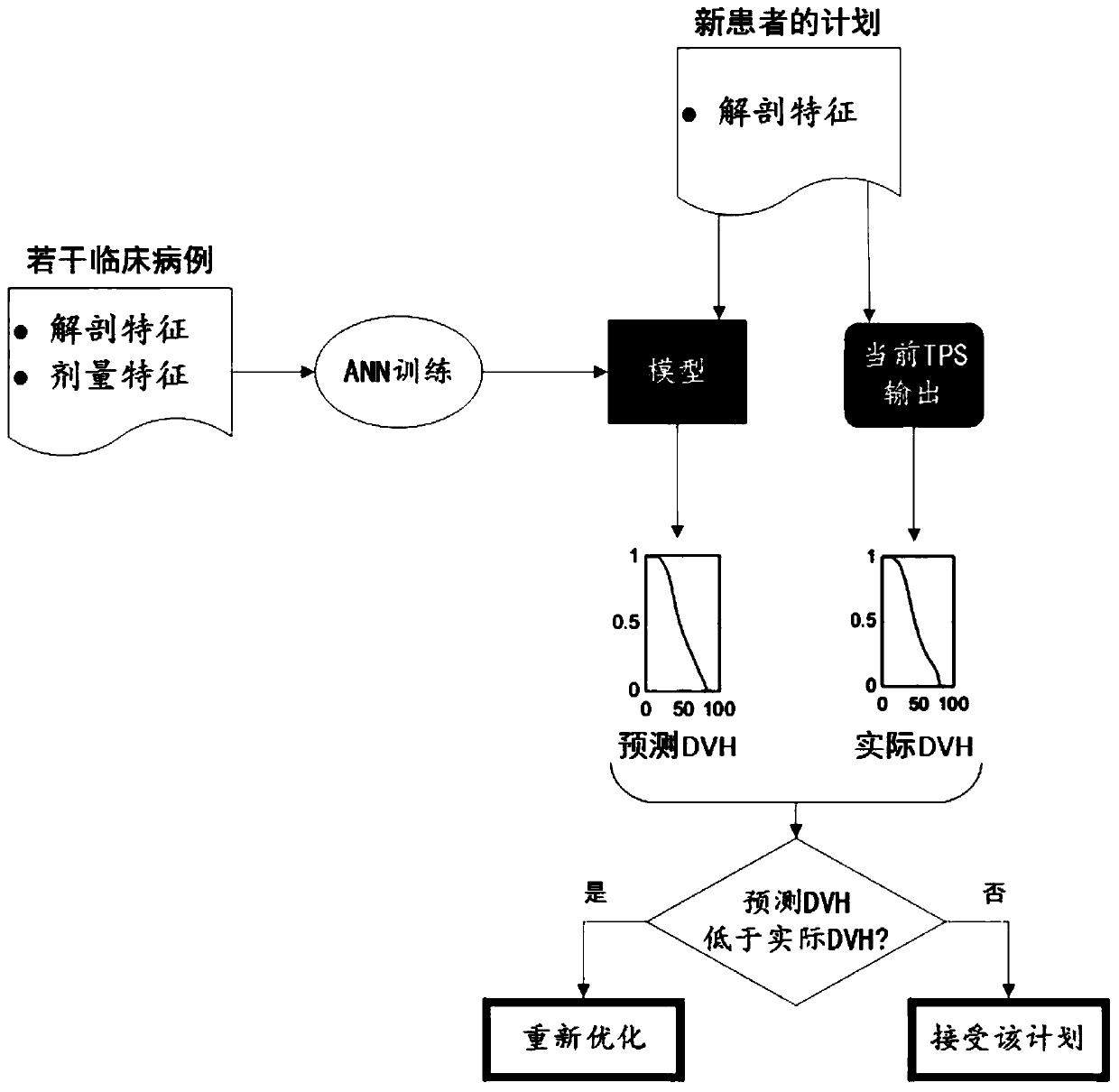
Predication method for three-dimensional dose distribution in intensity modulated radiation therapy plan and application of predication method
ActiveCN107441637AThoroughly describe anatomical featuresDescribe anatomical featuresX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVoxelImage resolution
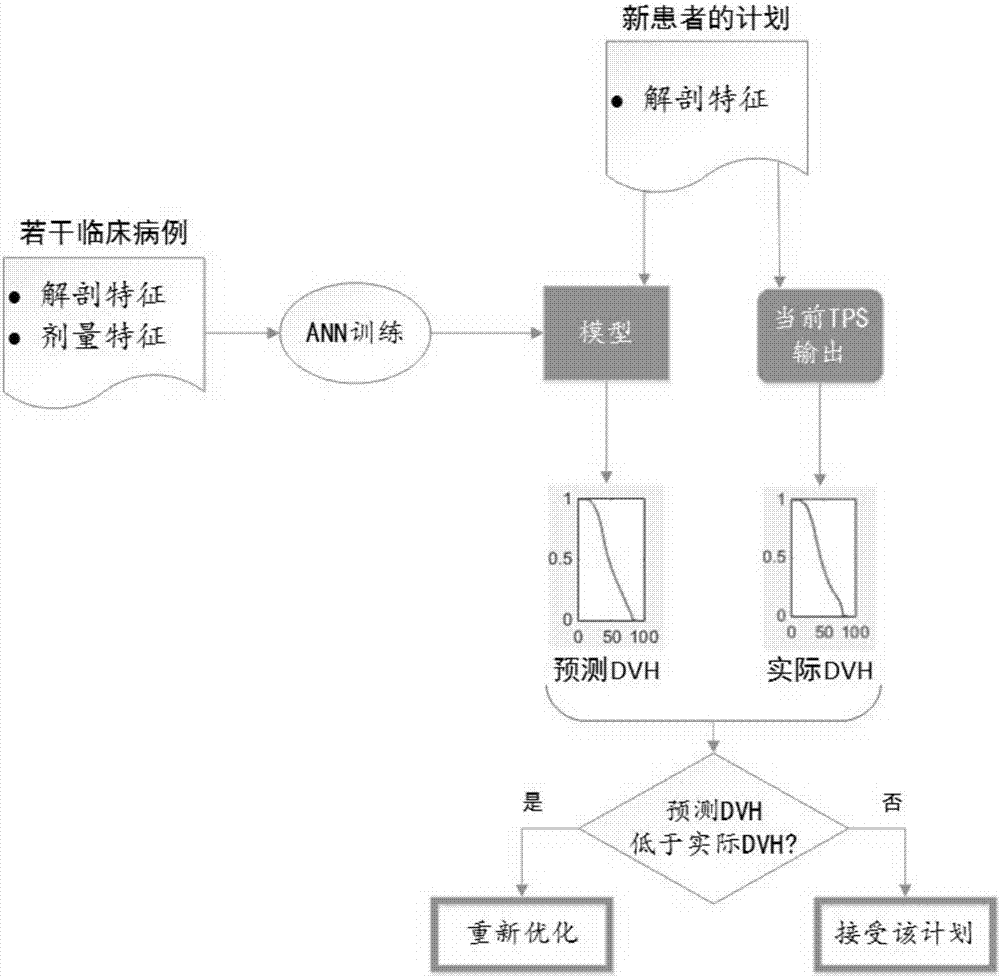
The invention discloses a predication method for three-dimensional dose distribution in intensity modulated radiation therapy plans. The method includes steps of (1) collecting valid intensity modulated radiation therapy plan data and forming a case database; (2) dividing a PTV and different to-be-endangered organs of patients into a plurality of voxels according to the resolution ratio of CT images; (3) extracting anatomical characteristics of each patient in the database; (4) extracting dose characteristics of each patient in the database; (5) constructing an artificial neural network, inputting the anatomical characteristics and the dose characteristics of the patients, and learning the mapping relation between the anatomical characteristics and the dose characteristics by the aid of the artificial neural network, and obtaining a correlation model of the anatomical characteristics and the dose characteristics; (6) using the correlation model to predicate the three-dimensional dose distribution of a new patient. The application of said method is using the dose distribution predication method for dose prediction for to-be-endangered organs of patients and quality control is achieved. By adopting the above method, predication of three-dimensional dose distribution in intensity modulated radiation therapy plans can be realized and the method can be applied to a quality control link.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Image feature and smart regressive model-based method for optimizing intensity modulated radiotherapy plan
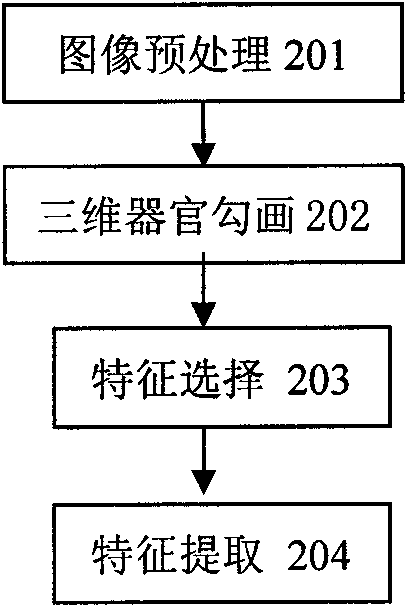
InactiveCN102184330AQuality improvementImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionProgram planning
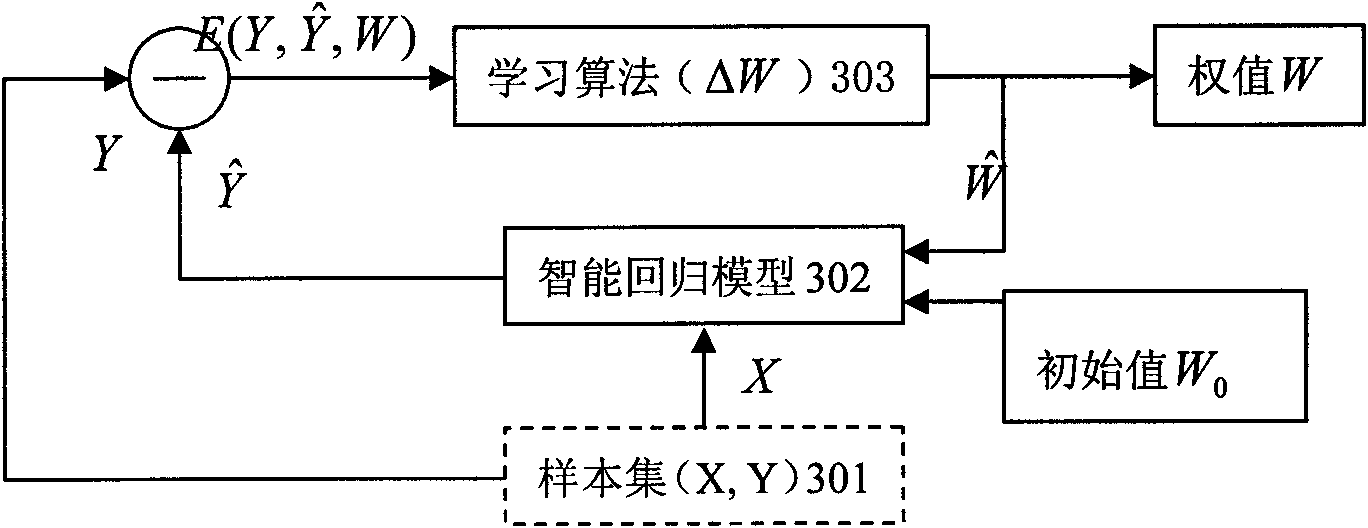
The invention discloses an image feature and smart regressive model-based method for optimizing an intensity modulated radiotherapy plan, which comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing a database of an expert-level intensity modulated radiotherapy plan, and storing a record of each intensity modulated radiotherapy case in the database; secondly, establishing a smart regressive model of medical image feature-based intensity modulated radiotherapy plan optimization parameters by supervised machine learning according to relevance information between the original medical image characteristics in the database of the expert-level intensity modulated radiotherapy plan and the intensity modulated radiotherapy plan optimization parameters; carrying out image analysis on a medical image of a specific intensity modulated radiotherapy object, and carrying out characteristic extraction; inputting the image characteristics into the smart regressive model, and outputting the intensity modulated radiotherapy plan optimization parameters; and setting the intensity modulated radiotherapy plan optimization parameters on a therapy plane system (TPS) according to the results, and operating a plan optimization function of the TPS to obtain an optimal therapy plane of intensity modulated radiotherapy.
Owner:SUZHOU KELESI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Anti-collision control method for leaves of multileaf collimator
InactiveCN104240785AAvoid collisionPrevent failures such as mechanical damageHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyLower limitIntensity modulate radiotherapy
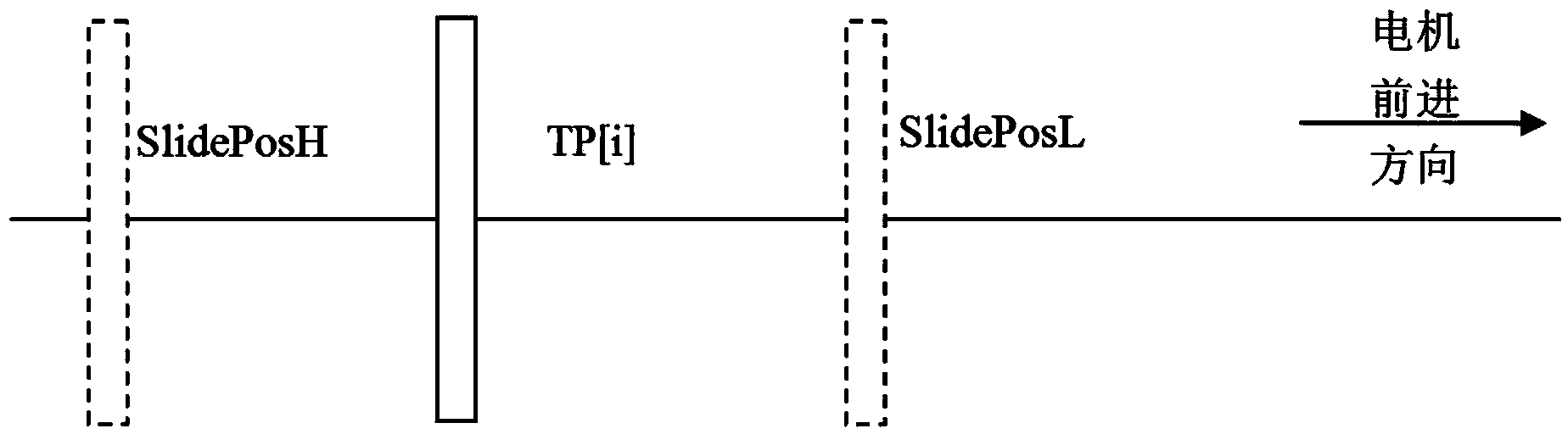
The invention relates to an anti-collision control method for leaves of a multileaf collimator. The anti-collision control method for the leaves of the multileaf collimator includes the following steps that in static intensity modulated radiotherapy, the difference between the real-time positions and the target positions to which the leaves move is compared with the difference between the initial positions of the leaves and the target positions to which the leaves move to keep adjusting the operating speed of a motor for driving the leaves to move; the closer the real-time positions of the leaves are to the target positions, the lower the operating speed of the motor is, and then collision between the leaves caused when the two sets of leaves are closed can be effectively prevented; in dynamic intensity modulated radiotherapy, when whether the motor moves forward or backward is judged, the number of pulses emitted by an actual motor position coder and measured by the i sub-field in real time is compared with the upper limit value SlidePosH and the lower limit value SlidePosL to judge whether the motor brakes or keeps sliding forward due to inertia or keeps running at a certain speed of Vo[i]. Thus, the position actually reached by the motor in the operating process is basically identical to the target position, it is guaranteed that the error of the position is within + / -e, faults such as mechanical damage caused by leaf collision are prevented, and the end faces of the leaves are prevented from leaking rays.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
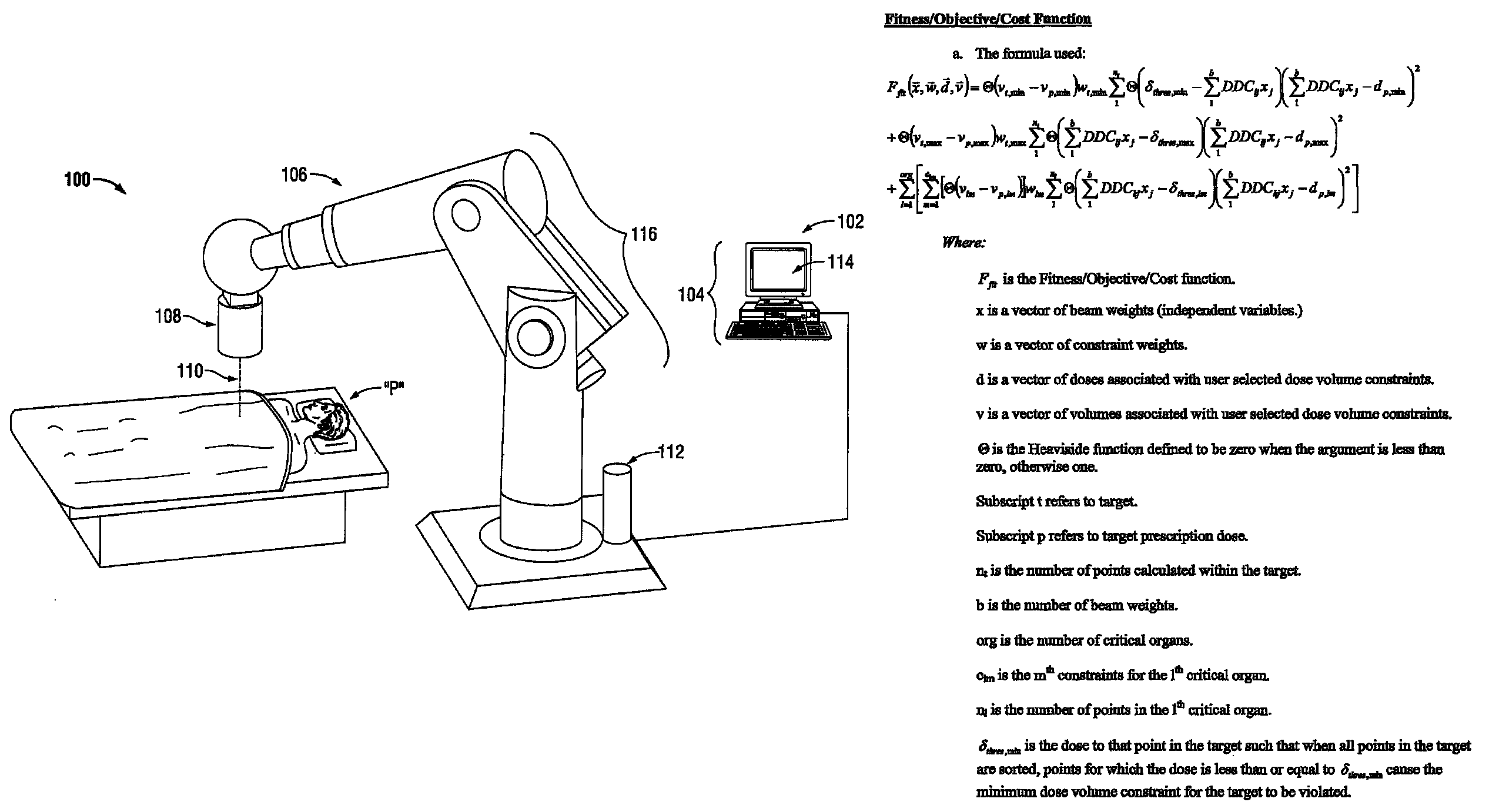
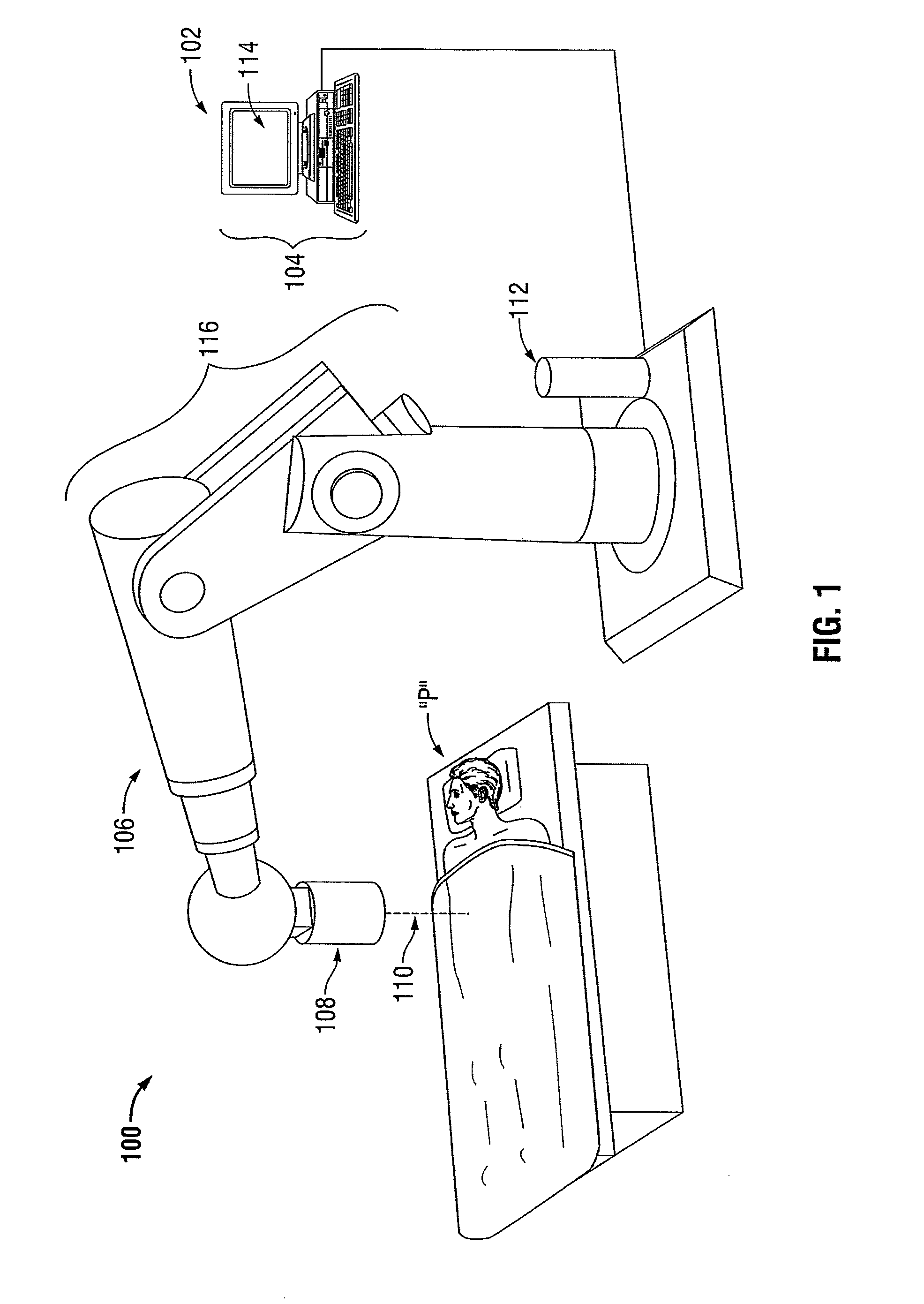
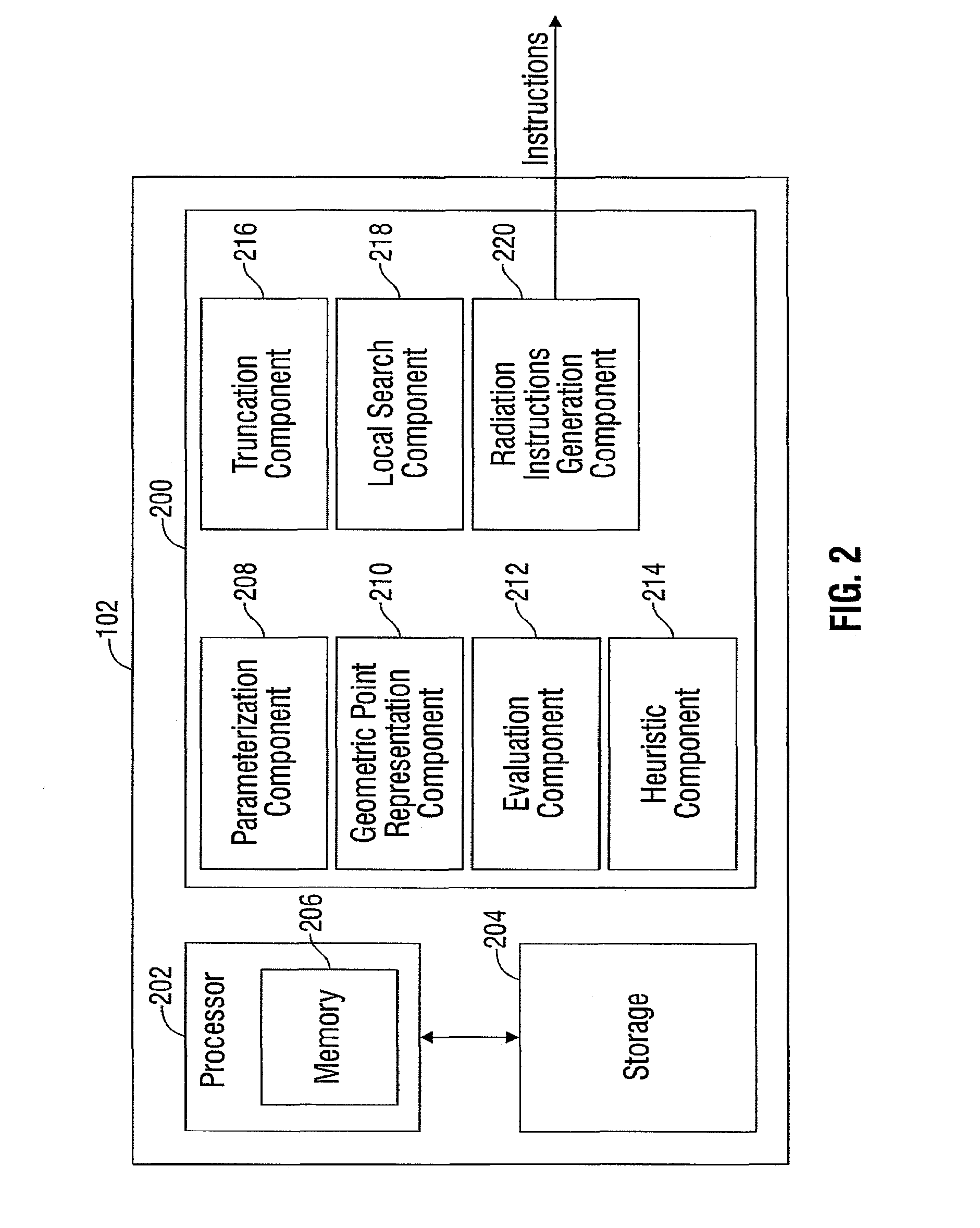
System and method for radiation therapy treatment planning using a memetic optimization algorithm
ActiveUS20120020460A1Antineoplastic agentsX-ray apparatusIntensity modulate radiotherapyVolumetric modulated arc therapy
A method for the optimization of radiation therapy treatment plans is disclosed. The disclosed method is equally-applicable to robotic radiosurgery as well as other types of radiosurgical delivery, intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT), and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT). A population-based heuristic approximation is used to perform a global search, and subsequently, a deterministic local trajectory search is employed to further refine the initial solution.
Owner:WITTEN MATTHEW R +1
Automatic intensity modulated multi-objective optimization method based on voxel weight factor and application thereof
ActiveCN108711447AReduce dependenceQuality assuranceMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDesign optimisation/simulationVoxelDose constraints
The clinical artificial trial and error method repetitively adjusts the dose constraint mode to optimize the plan because of the multi-objective performance of plan optimization and the unknown performance of dose constraint, which has the problems of low plan efficiency and quality uncertainty. The invention discloses an intensity modulated radiation therapy multi-objective optimization method based on voxel weight factor. The thinking mode in design of the plan designer is simulated and the constraint is automatically adjusted so as to guarantee the plan quality. According to the method, theconstraints are sorted and classified according to the clinical degree of importance for the area of interest dose constraints to form a constraint priority list, and then the dose constraints are adjusted according to the list. When the obtained solution does not meet the current constraint, the violation items are relaxed in turn according to the ascending order of priority; and when the obtained solution meets the current constraint, all the items are tightened (the violation dose constraints are tightened firstly) in turn according to the descending order of priority. The method is used for the cervical cancer patient and the result shows that the workload of the plan designer can be reduced and the plan quality can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
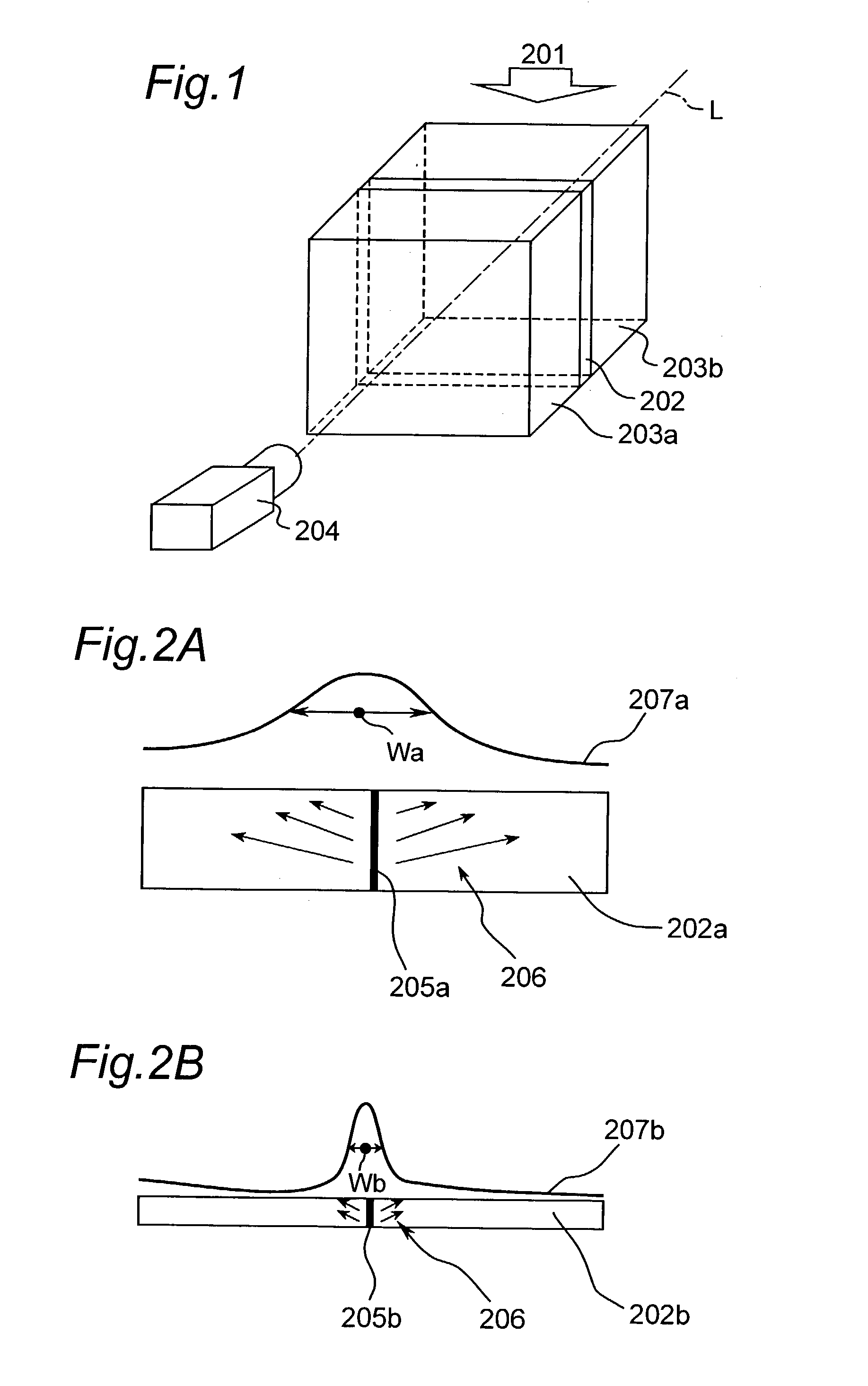
Apparatus for measuring absorption dose distribution
InactiveUS6998604B2Short timeHighly accurately and quickly measureDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiosurgeryDose profile
An apparatus for measuring absorption dose distribution may be used for radiotherapy, such as intensity modulated radiotherapy and radiosurgery. In the apparatus, measurement or evaluation of the distribution of the radiated dose within a phantom can be achieved accurately and in a relatively short length of time. The apparatus includes a phantom with a plastic plate scintillator having a thickness within the range of 0.15 to 1 mm and plastic blocks sandwiching the plastic scintillator, and an image analyzer. At least one of the plastic blocks is transparent and the image analyzer measures a pattern of intensity distribution of light emitted from the plastic scintillator when the phantom is irradiated.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
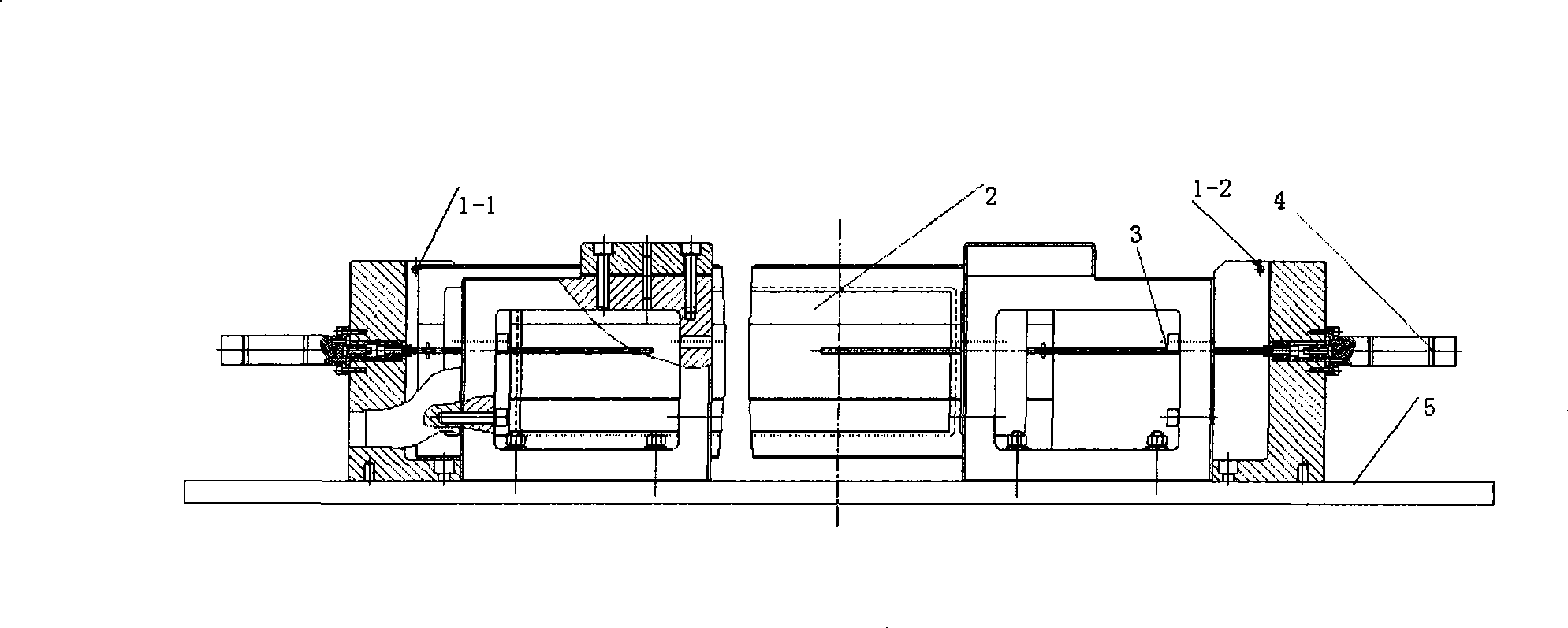
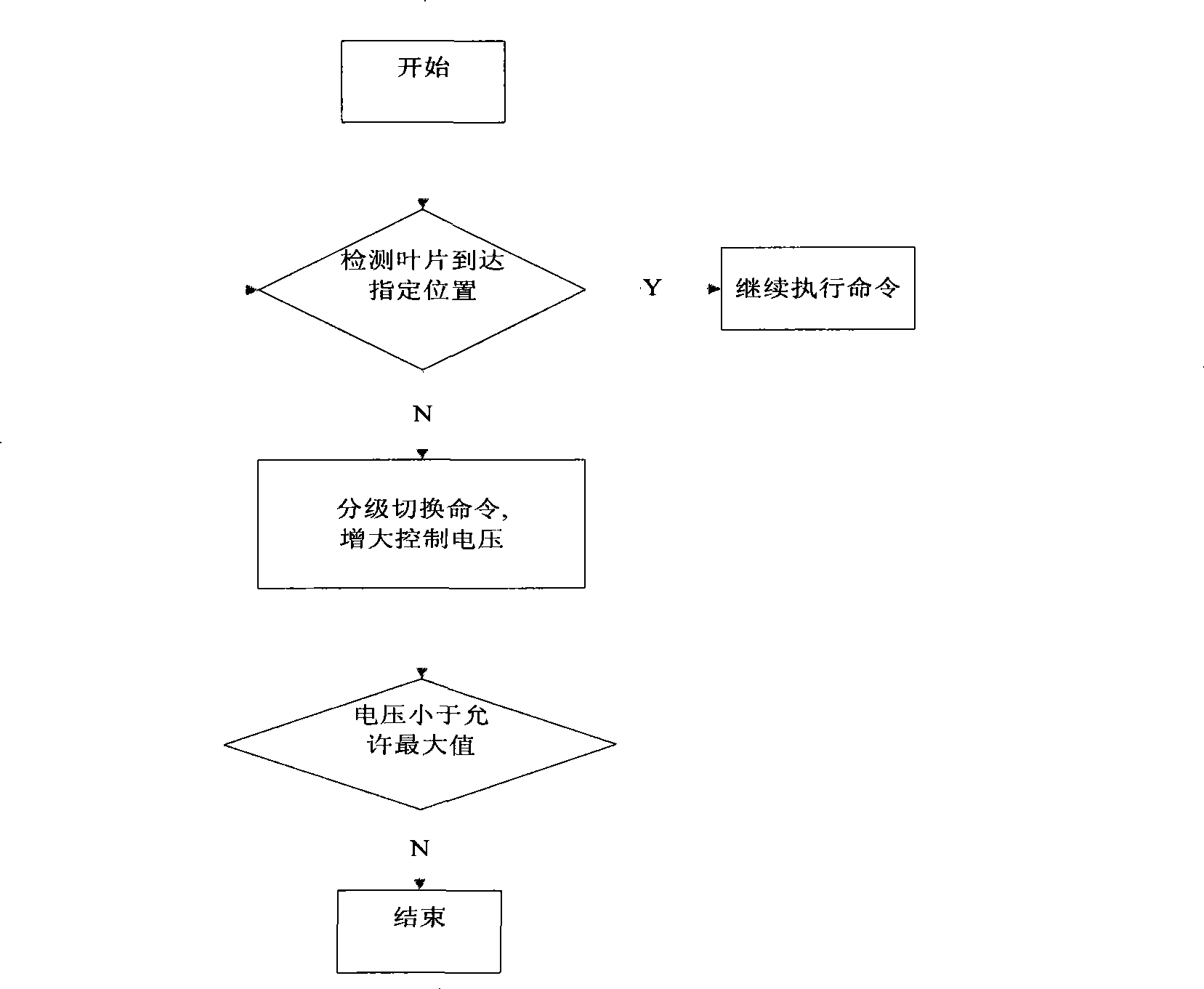
Zeroing calibration resetting and blade dead-lock solving method for electric multiblade optical grating
InactiveCN101364453AAvoid damageHigh positioning accuracyHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyInfraredGrating
The invention is applied to solve the deadlock fault of vanes and the zeroing position limit problems in intensity-modulated radiotherapy, while the prior art can only retune the vanes from the deadlock state and perform zeroing by dismantling. The invention realizes zeroing and position limit by adopting opposite type photoelectric detection; and adopts multistage switch to return the vanes from the deadlock state. The invention can return a system to the normal operation state under software control. In the opposite type photoelectric detection, a narrow far infrared ray beam is arranged at each end of a multi-vane grate. An infrared ray receiving terminal sets the tail end of each vane, which is positioned at the edge of the infrared ray, to be a zero point to limit the vane position, and codes the zero position of each vane corresponding to the encoder code of a motor at the same time. The multistage switch is realized through controlling a micro-motor with an encoder by an electric control element, and a system control unit detects the occurrence of deadlock according to the vane position information which is returned from the motor encoder. If the deadlock occurs, the system control unit sends a control signal to a motor driving unit to increase control voltage stage by stage, so as to gradually increase the driving force of a driving chip, and further allow the vanes to return from the deadlock state.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Prediction method for organs at risk average dosage in intensity modulated radiation therapy and application thereof
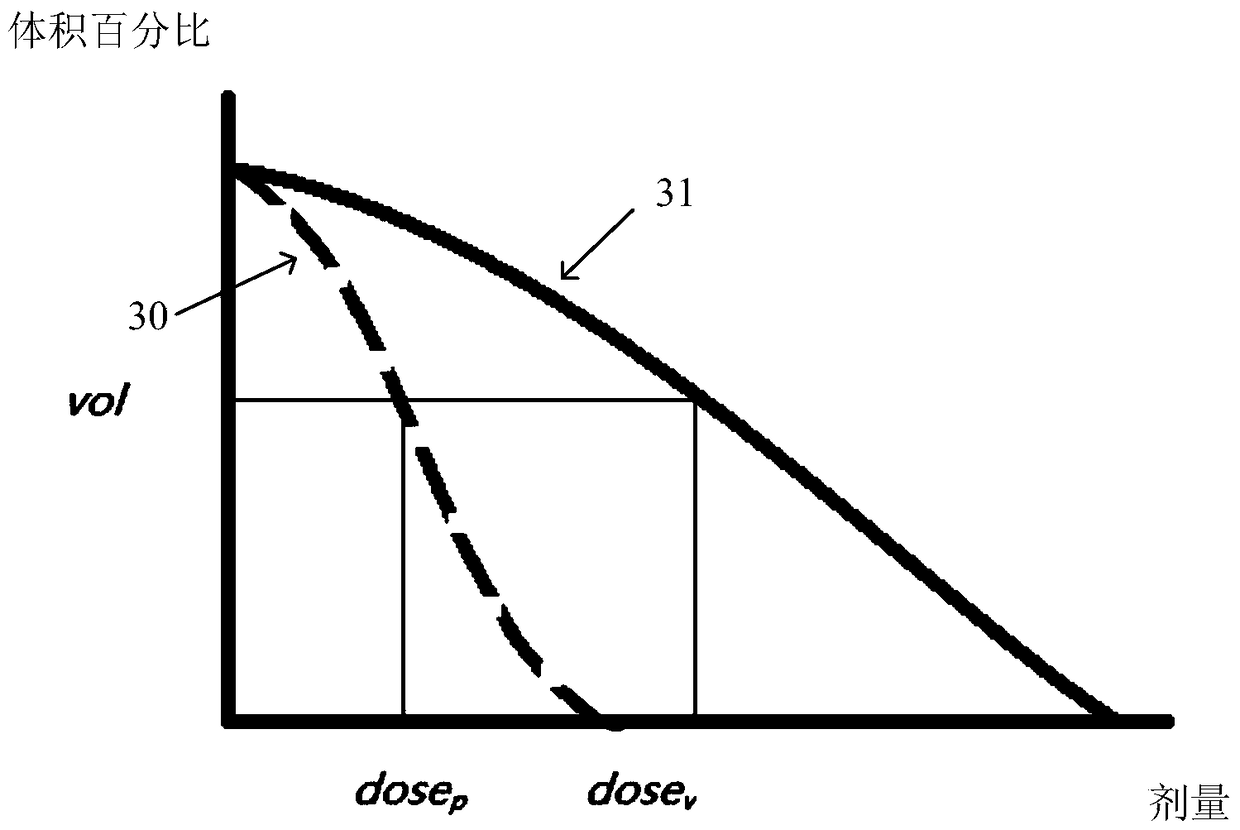
InactiveCN106039599AReduce the influence of subjective factorsEasy to collectX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMedicineData acquisition
The invention discloses a method for predicting the average dose of organs at risk in intensity-modulated radiotherapy, comprising the following steps: 1) Obtaining the functional relationship formula between Vox / Vx and Dmx / Dp, wherein, Vx is the volume of organs at risk, and Vox is The intersection volume of the organ at risk and the planned target area, Dp is the prescribed dose, and Dmx is the average dose of the organ at risk; 2) The average dose of the organ at risk is predicted by the functional relationship formula. The specific application of this prediction method includes the following steps: A) determine Dp; B) obtain the average dose Dmx1 of the relevant organs at risk according to the functional relationship formula between Vox / Vx and Dmx / Dp obtained by the prediction method; C) carry out simulation adjustment Strong optimization, get the average dose Dmx2; D) Compare Dmx1 and Dmx2; E) When Dmx2≤Dmx1, meet the standard; Dmx2>Dmx1, continue to optimize the intensity modulation. The invention is easy to collect data, conveniently establishes an organ-at-risk prediction model suitable for corresponding departments' treatment planning systems and equipment, and reduces the influence of subjective factors in the optimization process of radiotherapy plans.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
Dynamic intensity-modulated radiotherapy method based on quadratic programming model suppressing total beam-out time
InactiveCN105477789AEliminate the bump-and-groove effectOvercoming wear and tearRadiation therapyReciprocating motionIntensity modulate radiotherapy
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Rectal cancer radiotherapy plan automatic design method based on deep learning
PendingCN110349665AMedical data miningMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesIntensity modulate radiotherapyData mining
The invention provides a rectal cancer radiotherapy plan automatic design method based on deep learning. The method comprises the steps: establishing a U-Net neural network used for deep learning, andestablishing a case database, wherein the case database is clinical intensity modulated radiotherapy plan data of rectal cancer; performing deep learning on the case database to train the U-Net neural network; transmitting a img file of the CT positioning data to the trained U-Net neural network to obtain a prediction target area and prediction dose distribution output by the U-Net neural network; obtaining a dose objective function according to the prediction target area and the prediction dose distribution; and designing a radiotherapy plan by using a Pinnacle planning system according to the prediction target area and the dose objective function. Therefore, the rectal cancer radiotherapy plan automatic design method based on deep learning integrates the target area sketching technology, the dose prediction technology and the automatic planning technology, and the full-automatic design process of the individualized radiotherapy plan is realized in combination with the Pinnacle plansystem.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
System and method for radiation therapy treatment planning using a memetic optimization algorithm
ActiveUS8792614B2Antineoplastic agentsX-ray apparatusIntensity modulate radiotherapyVolumetric modulated arc therapy
Owner:WITTEN MATTHEW R +1
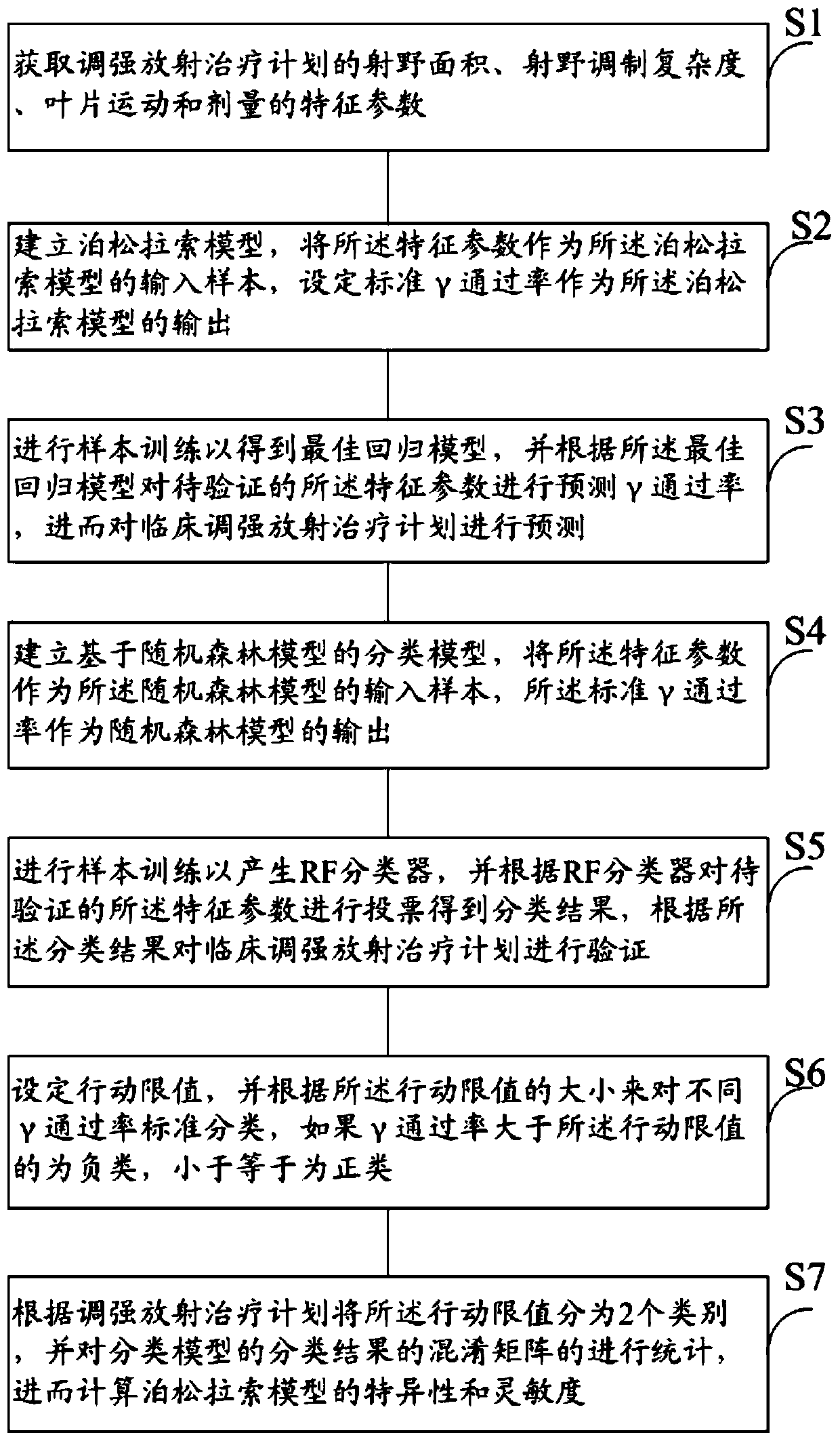
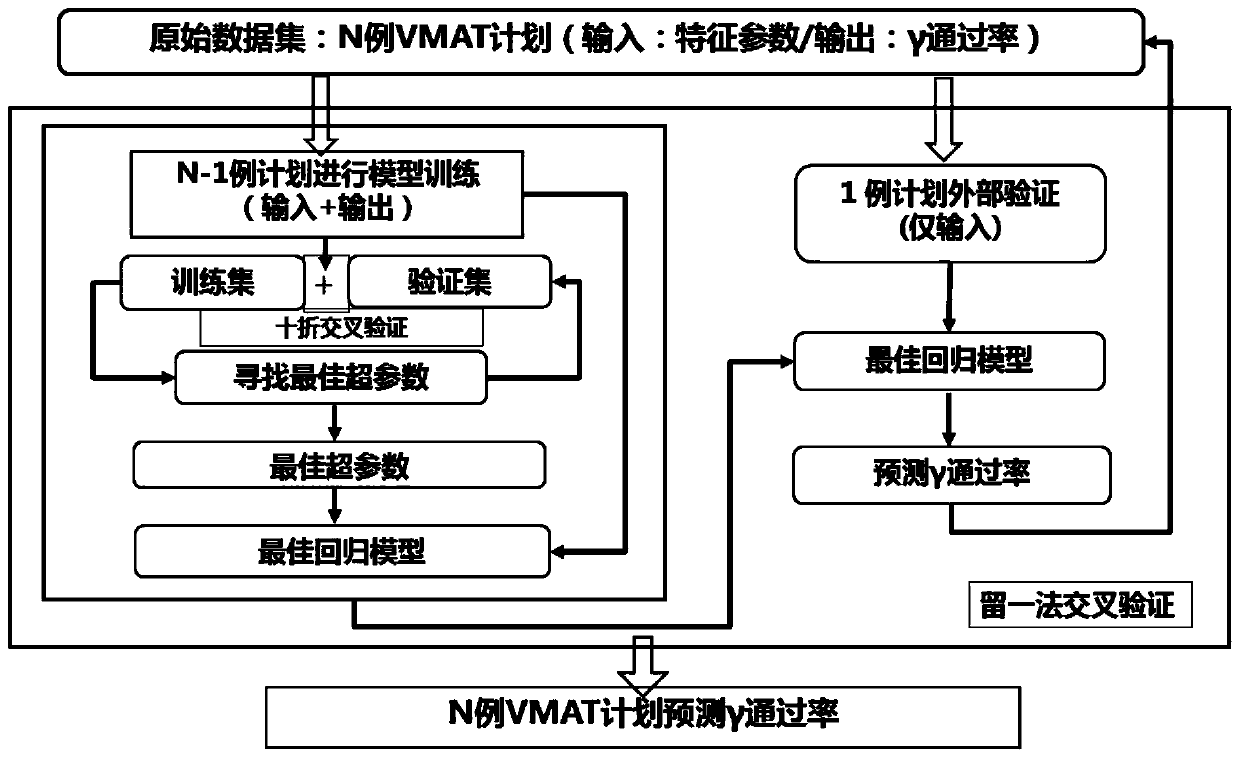
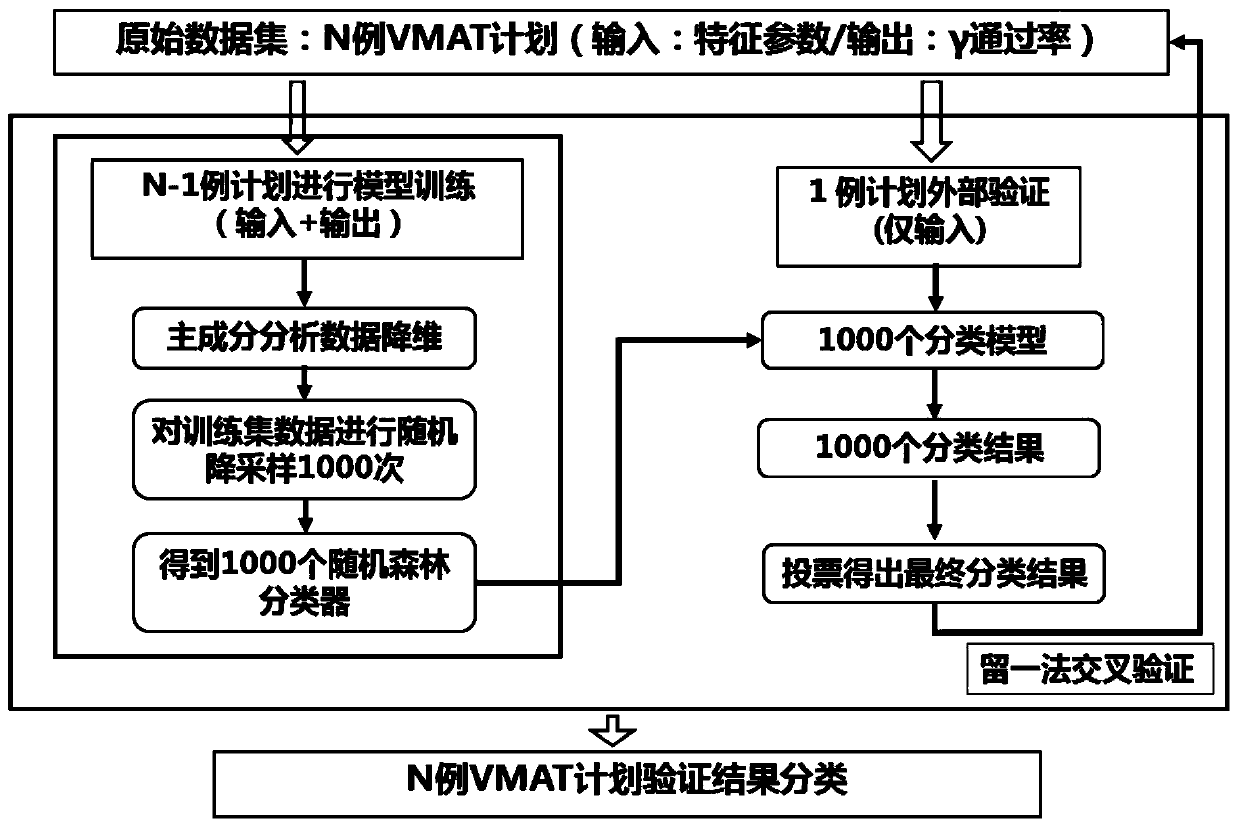
Dosage verification method and system based on artificial intelligence
ActiveCN111540437AImprove efficiencyQuality improvementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesCharacter and pattern recognitionDose verificationAlgorithm
The invention provides a dosage verification method and system based on artificial intelligence. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring the radiation field area, the radiation field modulation complexity and the blade motion and dosage characteristic parameters of an intensity modulated radiation therapy plan; establishing a regression model based on a machine learning model, taking the characteristic parameters as an input sample of the machine learning model, and setting a standard gamma passing rate as an output of the machine learning model; establishing a classification model basedon a machine learning model, taking feature parameters as an input sample of the machine learning model, and taking the standard gamma passing rate as an output of the machine learning model; performing sample training to obtain a regression model and a classification model for optimal prediction, predicting the gamma passing rate of the to-be-verified characteristic parameters according to the optimal prediction model, and predicting and classifying clinical intensity modulated radiation therapy plans. According to the invention, the problems of long consumed time and high labor cost of the existing radiotherapy dosage verification work can be solved, and the efficiency and the quality can be improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Body position fixing device for spiral tomography of patient with large breasts after breast-conserving surgery
PendingCN110575626AAvoid influenceNo swinging phenomenonX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLarge breastIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The invention provides a body position fixing device for spiral tomography of patient with large breasts after breast-conserving surgery of breast cancer. According to the body position fixing device,a prone design is adopted, and a 3D printed breast fixing cover and a breast tray are correspondingly and specially arranged for an affected side breast and a healthy side breast of the patient. According to the body position fixing device, the influence of respiratory movement on the breast position can be avoided, an arc holding claw is firstly used for gathering and locating the affected sidebreast, then the personalized breast fixing cover is installed to completely fix the whole affected side breast, when the spiral tomography is conducted, the phenomenon of breast swing can be avoided,it can be guaranteed that the affected side breast is consistent with positioning of a radiotherapy target area in height during each radiotherapy, thus the repeated positioning accuracy is high, andthe needs of intensity-modulated radiotherapy of a TomoTherapy system can be effectively met; the breast tray is directly installed on the healthy side breast, the healthy side breast is lifted and covered by the breast tray, and thus the healthy side breast can be prevented from entering the field of irradiation due to swing.
Owner:广西医大开元埌东医院有限责任公司
In-beam high-energy radiotherapy device with PET developing function
PendingCN106215335ARealize scanning imagingNo interferenceComputerised tomographsTomographyFixed bearingIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The invention discloses an in-beam high-energy radiotherapy device with a PET developing function. The in-beam high-energy radiotherapy device comprises radiotherapy equipment and open-loop PET developing equipment, wherein the radiotherapy equipment comprises a vertical fixed rack, an L-shaped rotary rack, a circular therapy head and an accelerator, a vertical portion of the L-shaped rotary rack is rotatably mounted to the vertical fixed rack through a fixed bearing, an open-loop portion of the open-loop PET developing equipment is opposite to the circular therapy head, and the accelerator is arranged in the rotary rack and is connected with the therapy head through a beam current pipeline; the open-loop PET developing equipment is mounted in the L-shaped rotary rack through a slide rail assembly and a support assembly. According to the device, accurate three-dimensional biological conformal intensity-modulated radiotherapy and verification are achieved really.
Owner:BEIJING TOP GRADE HEALTHCARE MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
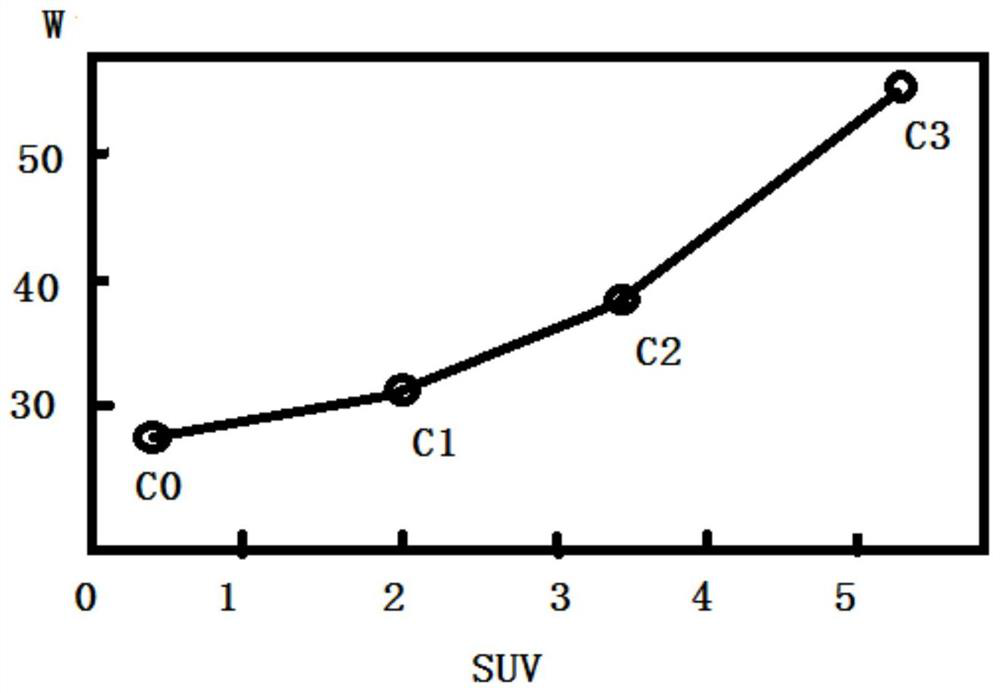
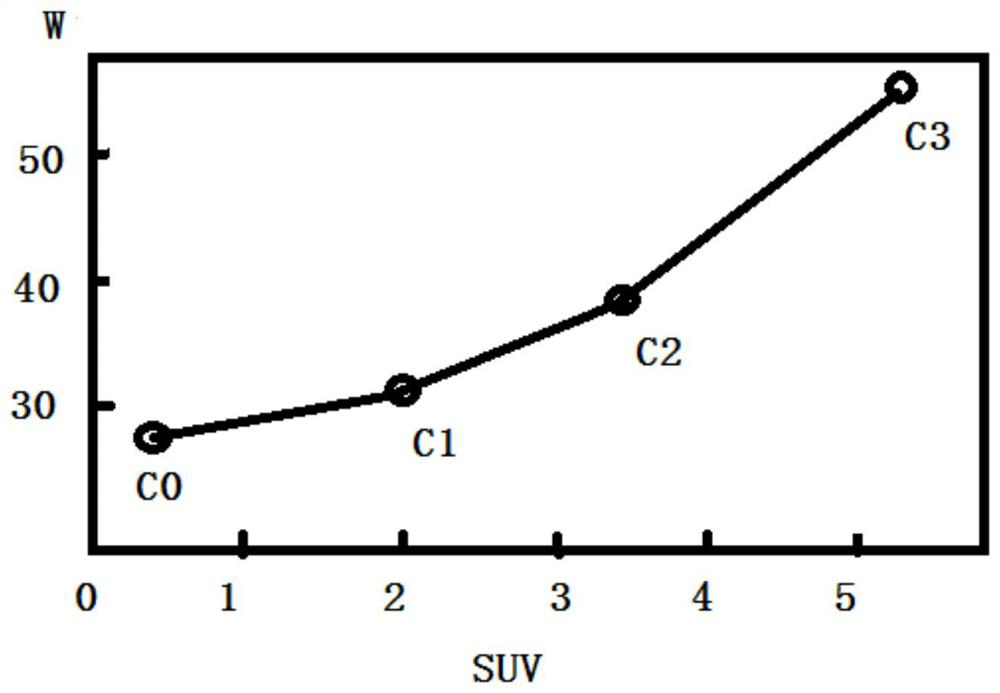
A monitoring system and method for intensity-modulated radiotherapy based on suv value
ActiveCN110368604BX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyImaging processingIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The invention provides a SUV (standard uptake value) based intensity modulated radiation therapy monitoring system and method. The system comprises image processing equipment, computer equipment and display equipment. The image processing equipment is used for acquiring a to-be-monitored PET-CT image and transmitting the acquired image to the computer equipment. The computer equipment is used fordetermining a target area and a critical organ on the PET-CT image, setting planned active marrow constraint conditions, generating an objective function according to the constraint conditions and a SUV of the image and optimizing the objective function according to an optimization algorithm, and an optimization result is an active marrow dose volume histogram obtained under the condition that active marrow dose is guaranteed against exceeding clinical dose limit. The display equipment displays the optimization result namely the active marrow dose volume histogram. The system has the advantagethat by embedding of the SUV into the objective function of intensity modulated radiation therapy, aimed protection of active marrow or killing of high-activity tumors can be realized.
Owner:SHANDONG RES INST OF TUMOUR PREVENTION TREATMENT
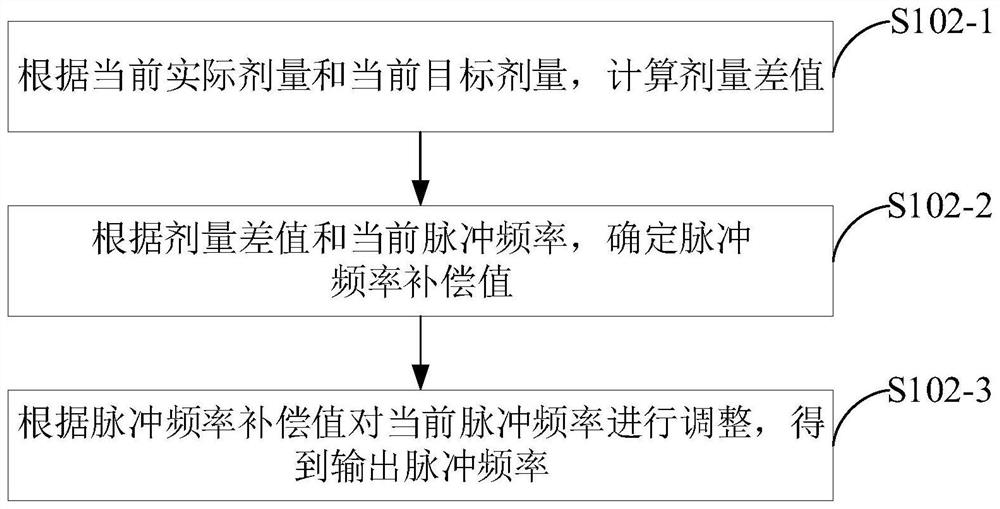
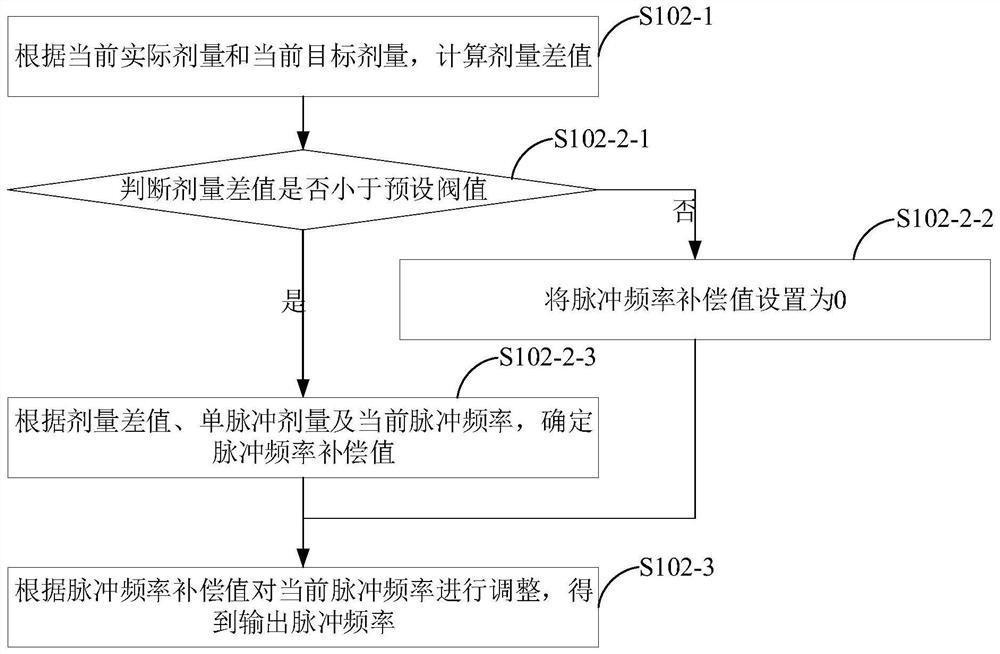
Dose rate intensity modulation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114367062AX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyDose rate
The embodiment of the invention provides a dose rate intensity modulation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and relates to the field of intensity modulated radiotherapy. In the embodiment of the invention, firstly, a current actual dose, a current target dose and a current pulse frequency are obtained, and the current pulse frequency is used for representing a dose rate of a radiation beam emitted by a radiation source device; then determining an output pulse frequency according to the current actual dose, the current target dose and the current pulse frequency; and finally, the dose rate of the radiation beam emitted by the radiation source equipment is updated according to the output pulse frequency. According to the embodiment of the invention, the output pulse frequency is determined based on the current actual dose, the current target dose and the current pulse frequency, and the dose rate of the radiation beam emitted by the radiation source equipment is updated so as to continue to irradiate the target region; the degree of deviation between the actual radiotherapy effect and the result specified by the treatment plan is within an acceptance range.
Owner:CYBERMED TECH XIAN +1
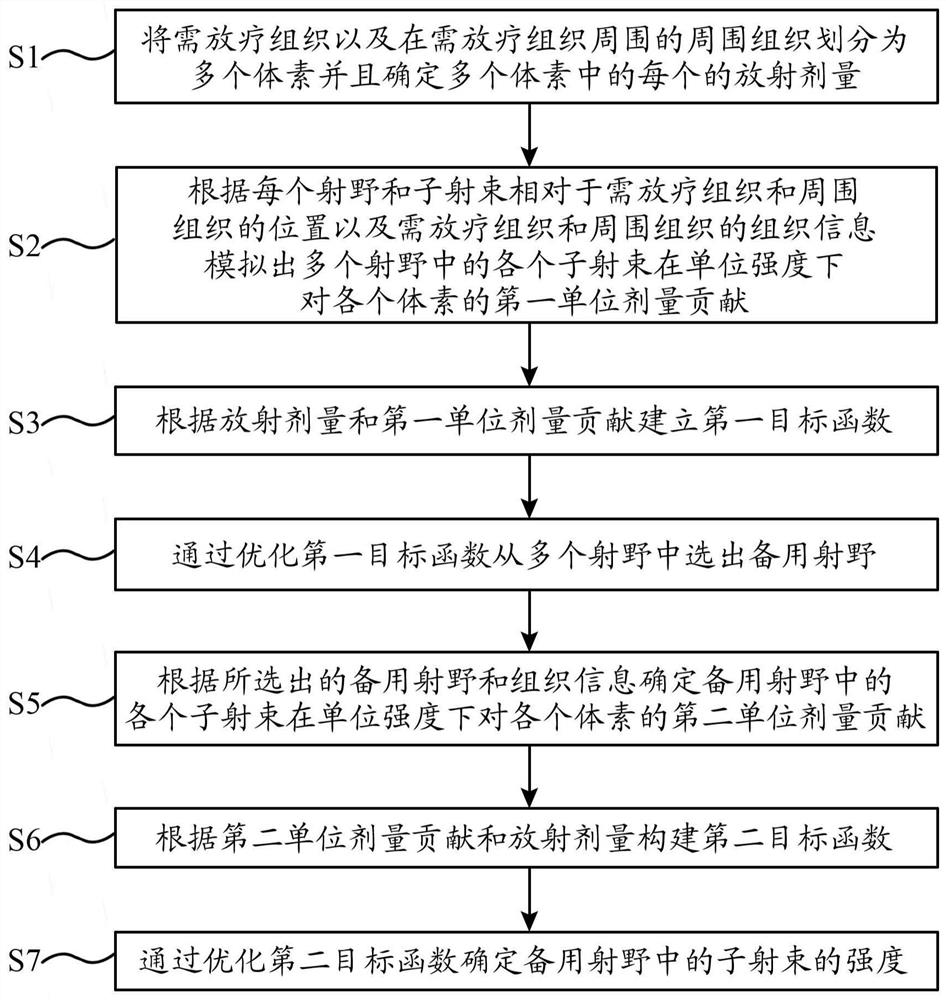
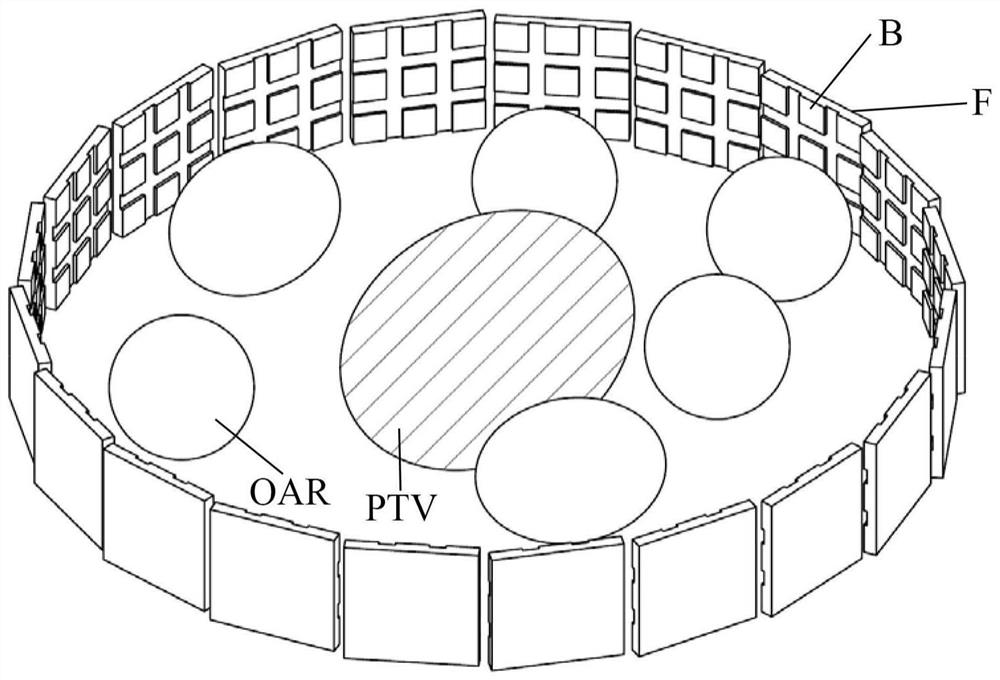
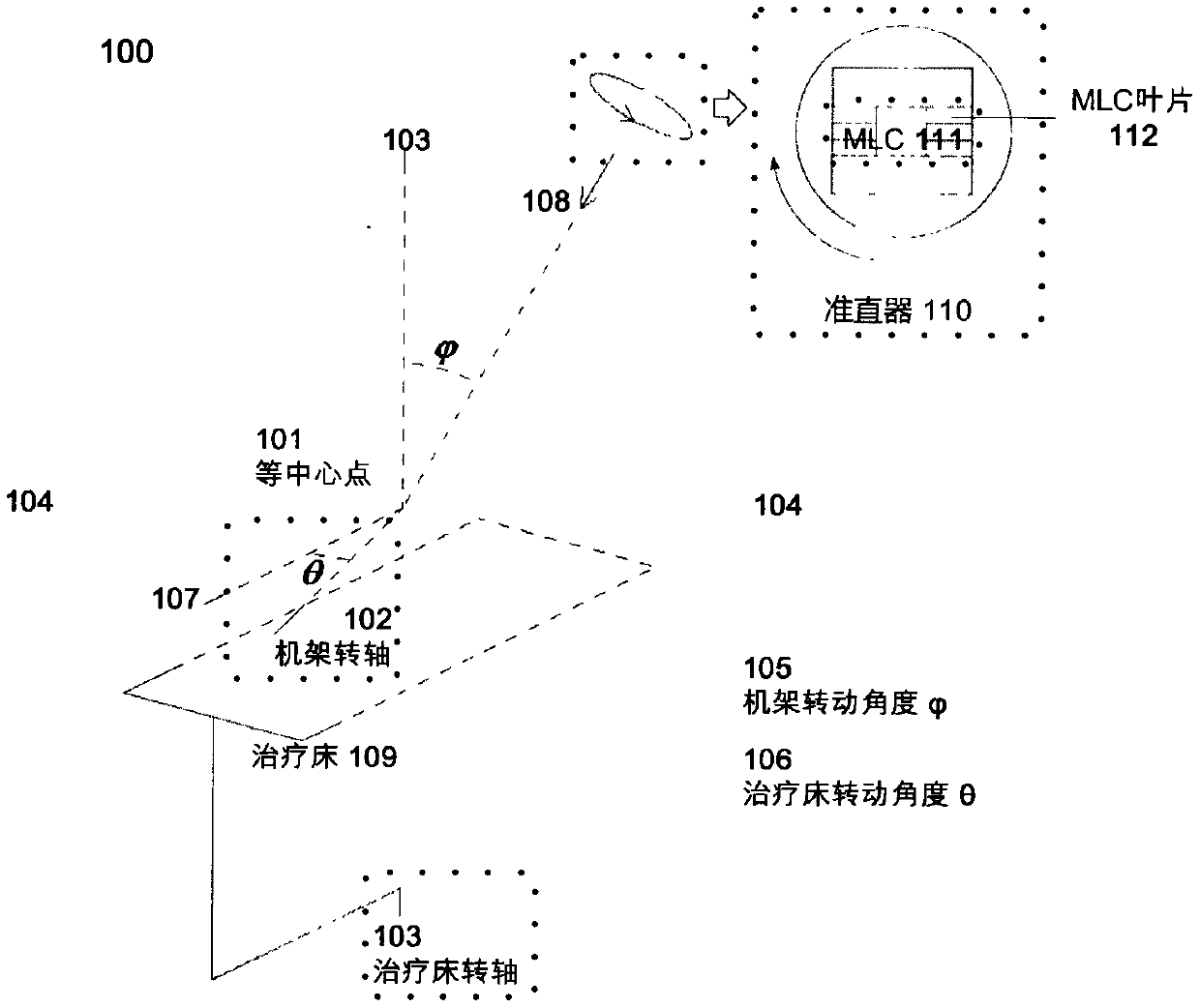
Method, apparatus and computer system for determining beamlet intensity in a radiotherapy system
The present application provides a method, device and computer system for determining beamlet intensity in a radiotherapy system. The method according to the present application is based on the compressive sensing theory by introducing the position of the radiation field and the sub-beam into the traditional objective function to obtain the objective function. Then the objective function is optimized to select a backup field from multiple fields. Based on the spare fields, the sub-beam intensity is obtained by optimizing the traditional intensity-modulated radiotherapy plan.
Owner:YOFO MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for designing noncoplanar volumetric rotational intensity modulated radiotherapy plan
InactiveCN110404186ASmall toxicityEffectively handle coupled relationshipsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyComputer Aided DesignIntensity modulate radiotherapy
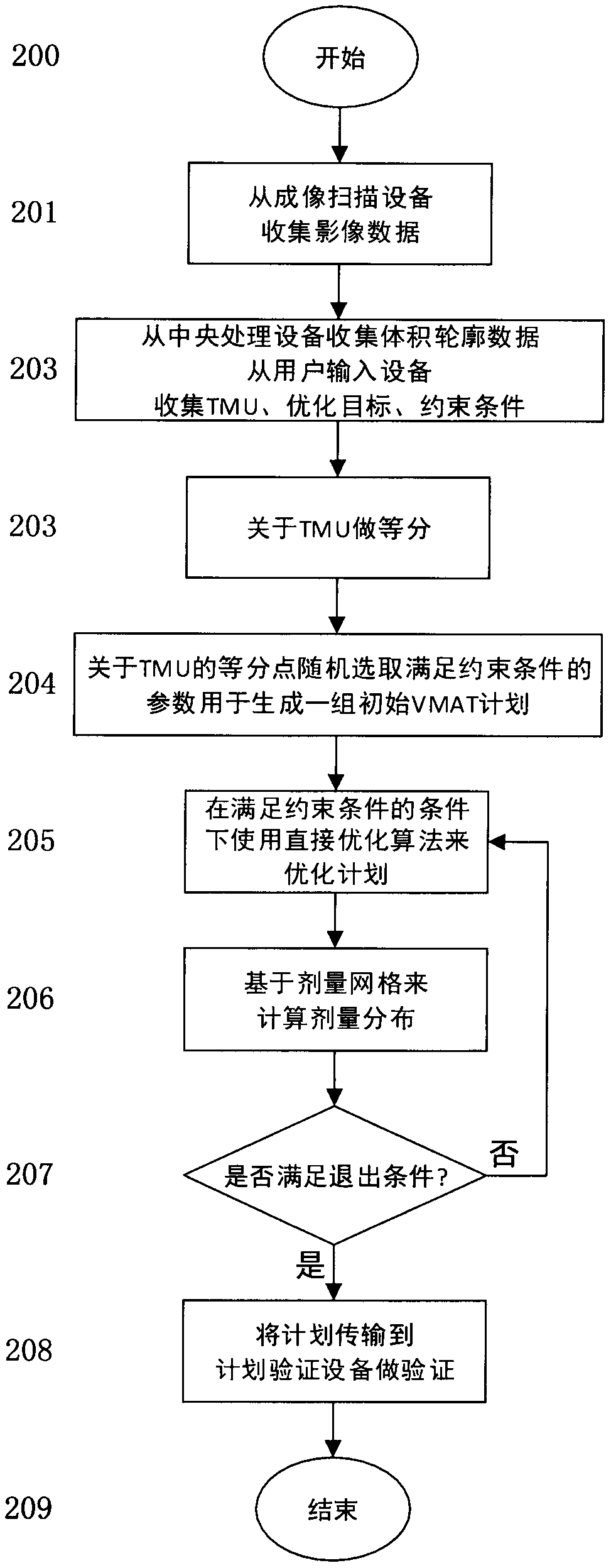
The invention discloses a method for computer-assisted designing noncoplanar volumetric rotational intensity modulated radiotherapy plan. The content of the method includes the steps that medical images of a diseased area and a peripheral human tissue of a patient are collected through an imaging device, three-dimensional contour data of a region of interest are collected through a software assembly, the total hop count is collected through a user input device, a target and a constraint condition are optimized, the hop count of a treating device is taken as a time unit, the total hop count isequally divided, a group of machine parameters are selected randomly for all equal diversion points, a group of machine parameters with the equal diversion points of any adjacent hop count meeting theconstraint condition are screened and retained, a group of initial VMAT plan is generated on the basis of the machine parameter, on the premise of the constraint condition is met, the plan is updatedby using a direct optimizing algorithm, dosage gridding is built according to patient data, dosage distribution is calculated based on the dosage gridding, an objective function value is calculated,the plan is updated by repeatedly using the direct optimizing algorithm until a suspensive condition is met, and an optimized plan is output.
Owner:戴建荣
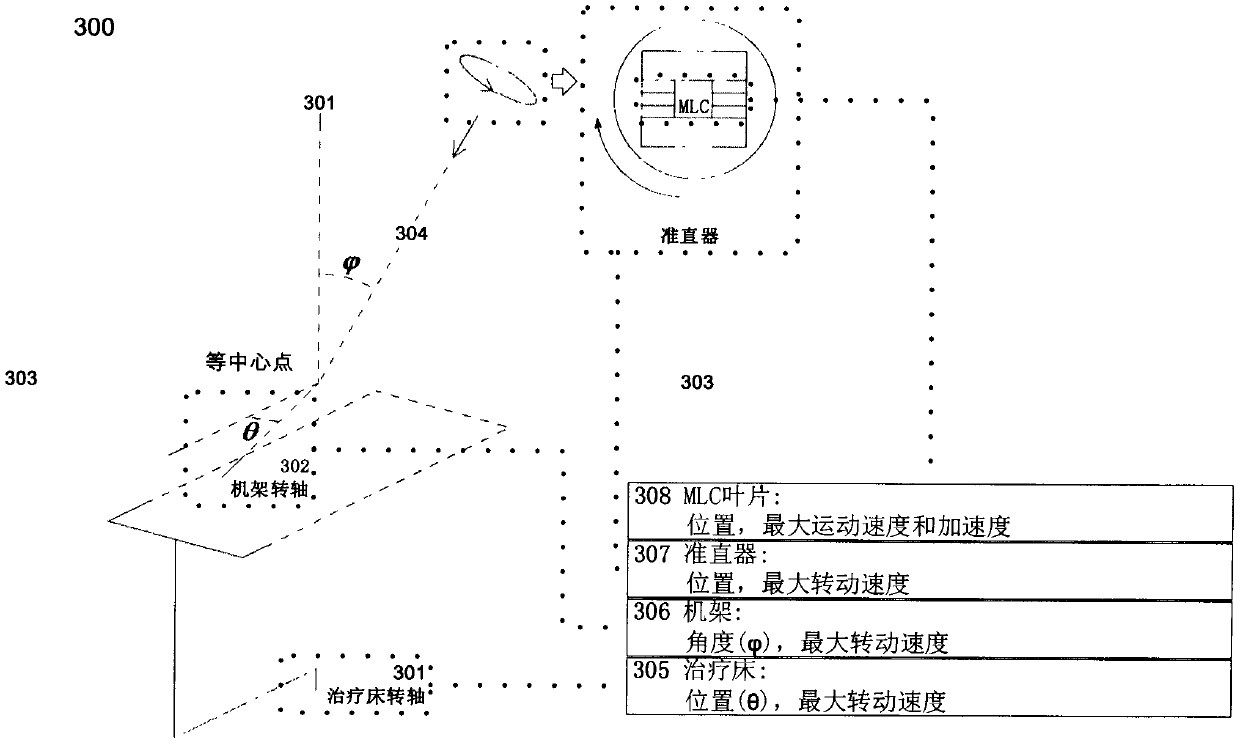
Non-isocentric rotary intensity-modulated radiotherapy device
PendingCN109771849AEliminate the risk of collisionReduce volumeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyMedicine
The invention overcomes defects in the prior art, provides a non-isocentric rotary intensity-modulated radiotherapy device, the volume of equipment is reduced, the central dose rate and the clinical treatment efficiency are improved, and the risk of collision between a frame and a treatment bed (or a patient) is eliminated; in order to solve the technical problems, the technical scheme adopted isas follows: the non-isocentric rotary intensity-modulated radiotherapy device comprises a base, a roller, a treatment head frame and a treatment head, wherein the roller is movably arranged on the base and can make circular motion on the base in the own central axis; the treatment head frame is fixedly arranged on the inner wall of the roller, the treatment head is movably arranged on the treatment head frame through a rotating shaft, and the treatment head can rotate with the rotation shaft, so that the beam emitted by the treatment head does not always shoot to an isocenter; the non-isocentric rotary intensity-modulated radiotherapy device can be widely applied to the technical field of radiation therapy.
Owner:上海伽玛星科技发展有限公司
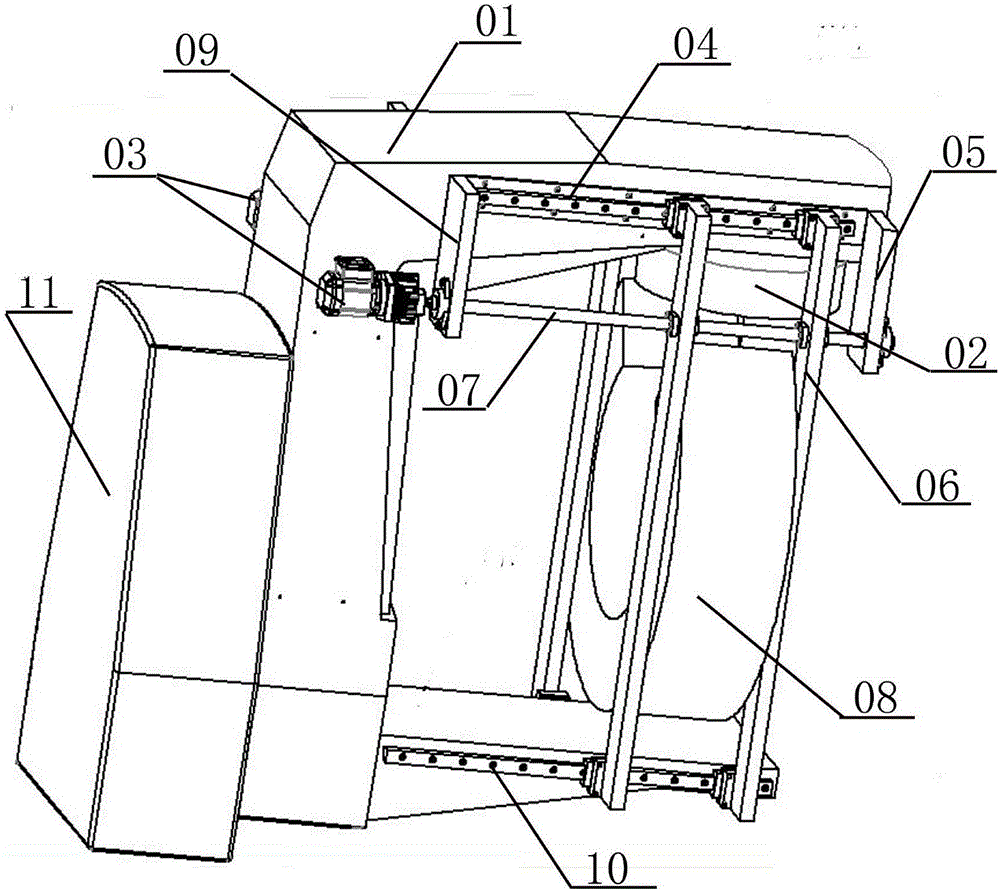
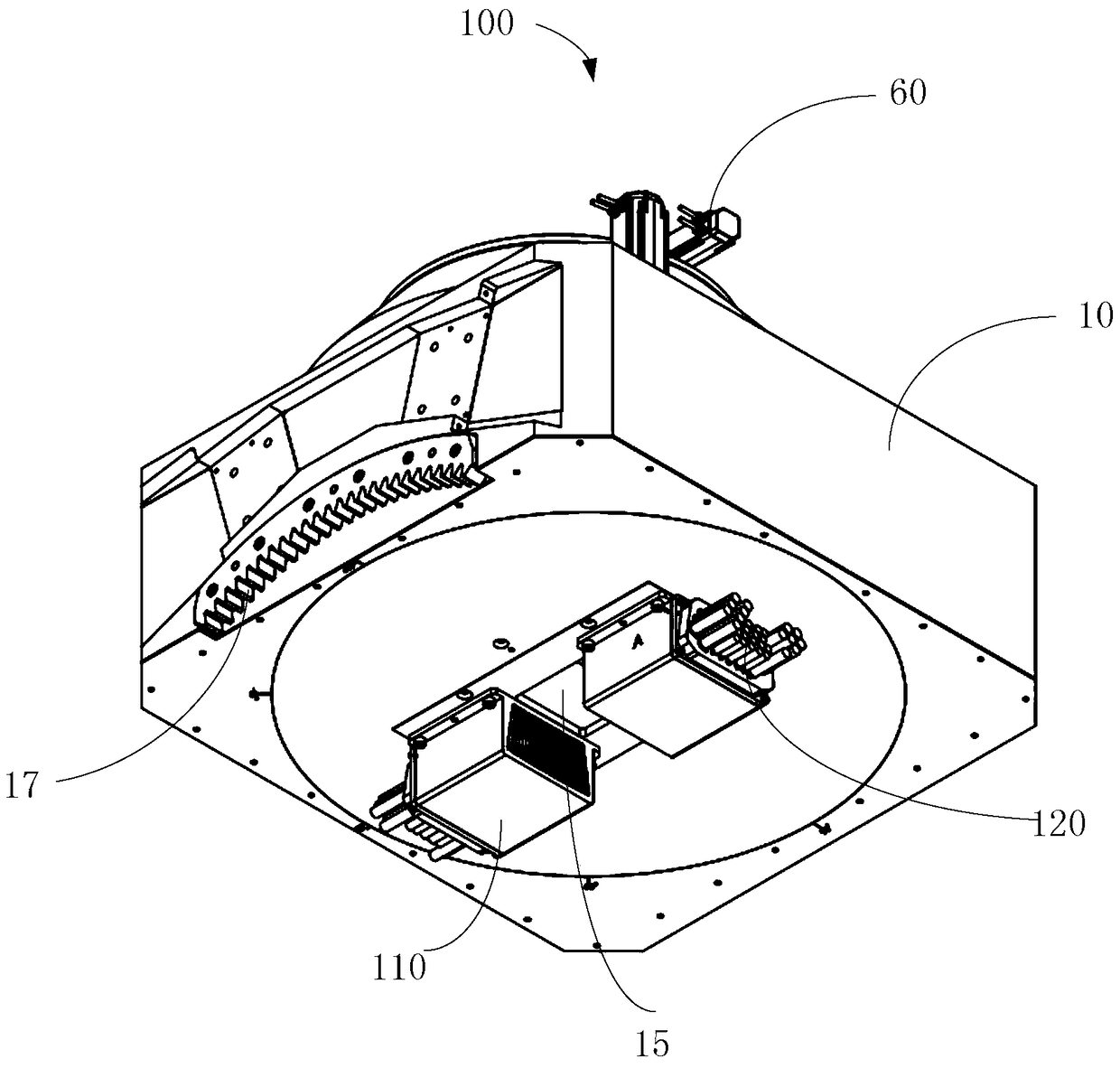
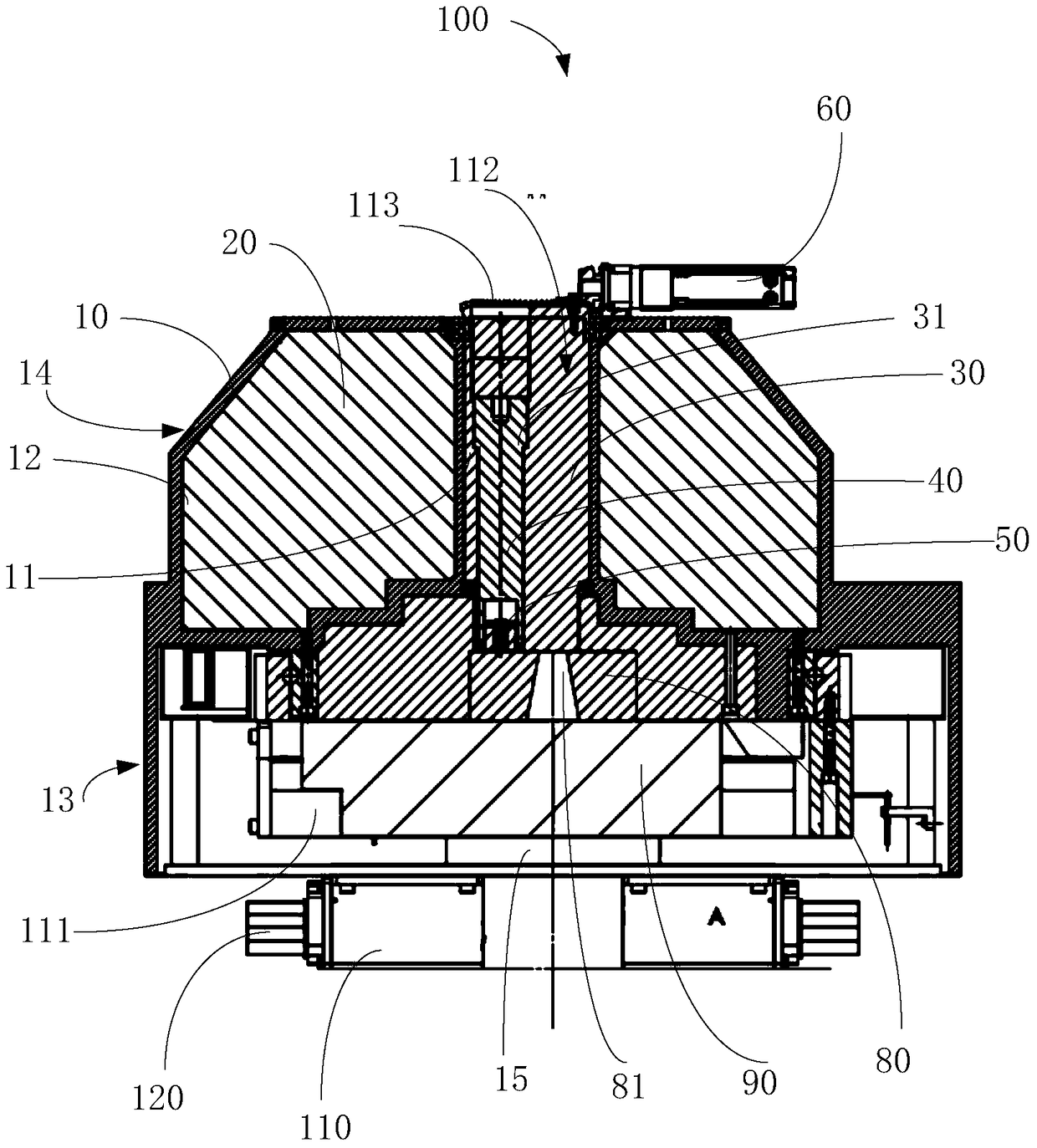
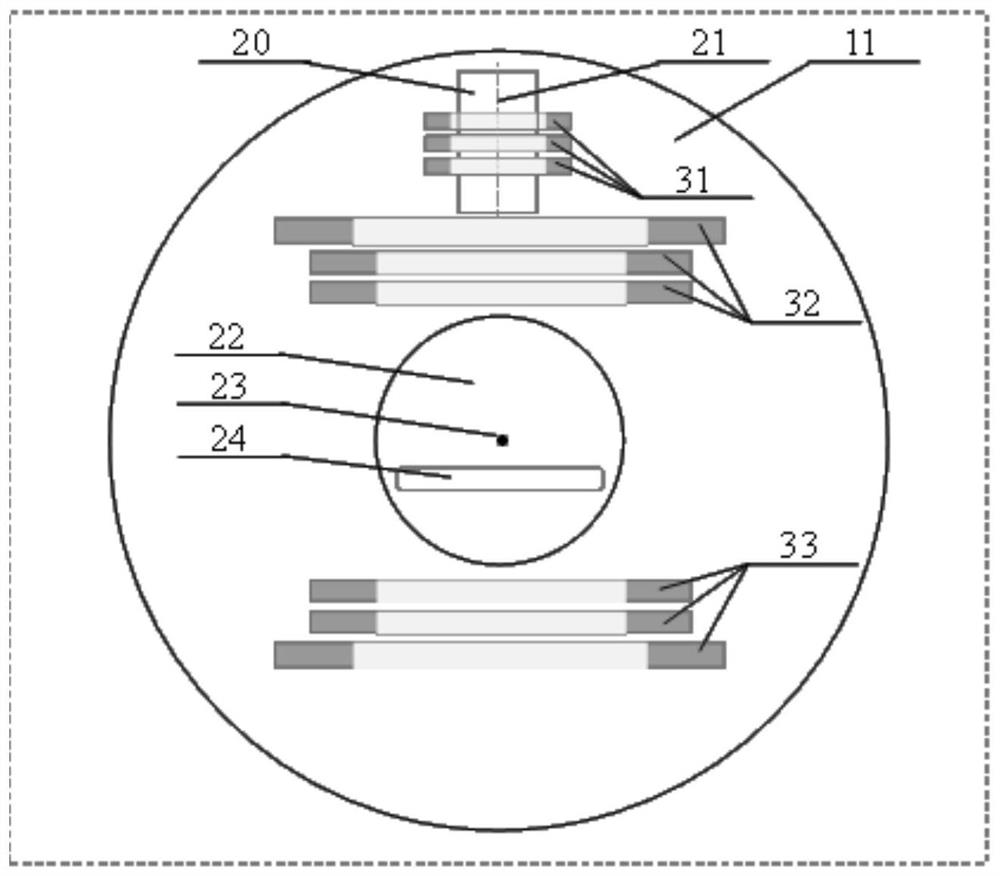
Conformal Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Device
ActiveCN105031832BCompact structureX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyMulti leaf collimator
Provided is a conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy device, comprising: a housing, formed with an accommodating space and a shielding cavity; shielding material, filled within the shielding cavity; a rotary source-carrying body, accommodated within the accommodating space; a shielding rod, accommodated within the rotary source-carrying body; a source body, accommodated at a bottom end of the shielding rod and used for carrying a radiation source; a first driving portion, arranged on the housing and driving the rotary source-carrying body to rotate around a rotary axis thereof so that the radiation source switches between an open source position and a closed source position; a pre-collimation body, arranged at an emission end of the radiation source and comprising a collimation hole, the collimation hole directly facing the radiation source when the radiation source is in the open source position; a shielding door, arranged at the side of the pre-collimation body away from the radiation source and directly facing the radiation source; a multi-leaf collimator, arranged outside the housing and directly facing the shielding door. Also provided is a conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy system.
Owner:CYBERMED TECH XIAN
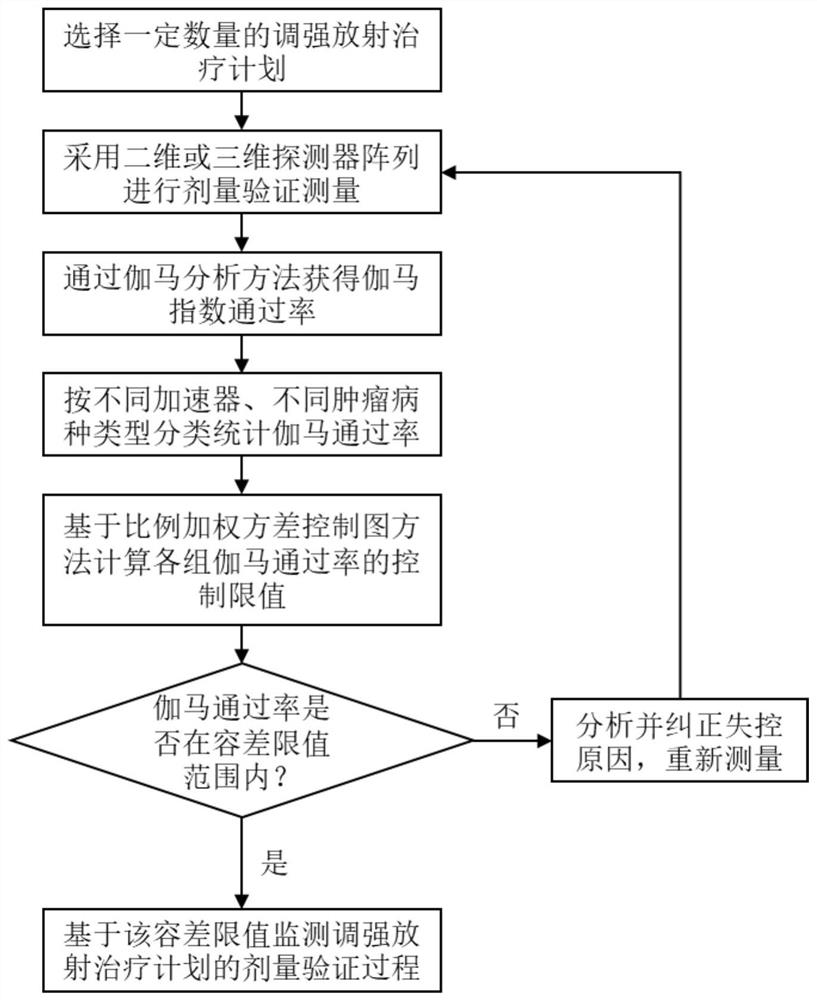
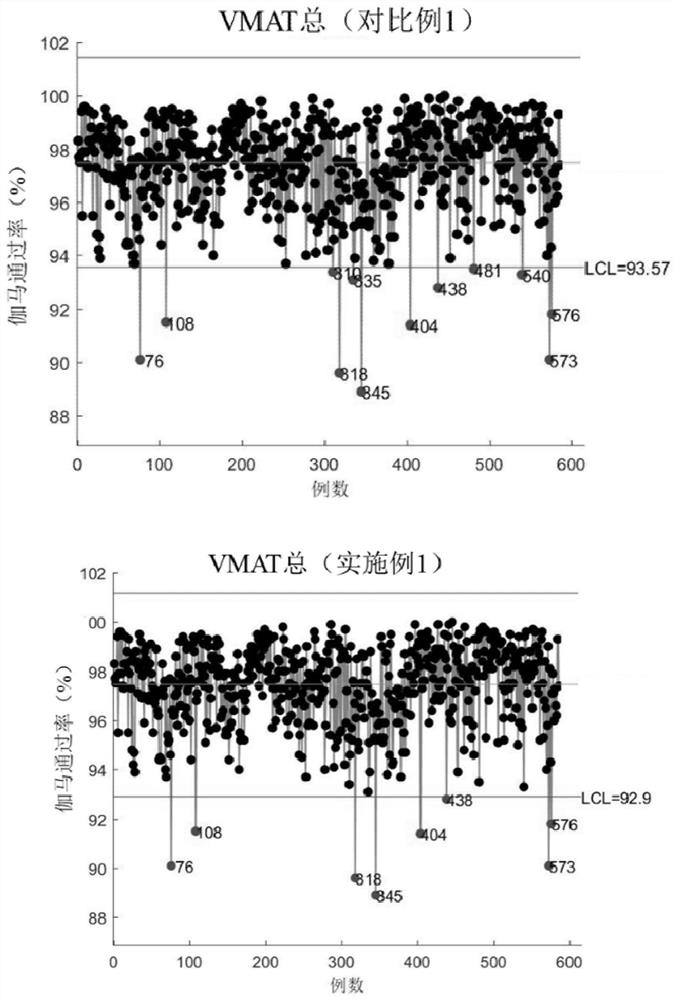
Method for setting tolerance limit value for monitoring intensity modulated radiation therapy dose verification process
ActiveCN113633897AReduce workloadReduce the impact of control limit calculationsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose verificationIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The invention provides a method for setting a tolerance limit value for monitoring an intensity modulated radiation therapy dose verification process, and belongs to the field of intensity modulated radiation therapy dose verification. The method is insensitive to the distribution of the gamma passing rate in the intensity modulated radiation therapy dose verification process, so that the influence of non-normality on control limit value calculation is reduced. Therefore, the tolerance limit value obtained through the method is more stable and reliable. The tolerance limit value obtained based on the method has good performance in monitoring the intensity modulated radiation therapy dose verification process; an intensity modulated radiation therapy plan with the out-of-control problem can be effectively detected, and in addition, the workload of a radiation therapy physicist for investigating the "problem" plan is reduced.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Three-dimensional dose distribution prediction method for intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning based on deep network learning
ActiveCN110085298BAvoid the disadvantages of manual extraction of incomplete informationHigh precisionMedical simulationMedical data miningAnatomical structuresIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The invention provides a method for predicting the three-dimensional dose distribution of an intensity-modulated radiotherapy plan based on deep learning. The method includes: collecting effective intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning data to form a case database; extracting the three-dimensional anatomical structure contour features of each patient's region of interest from the case database; dividing the three-dimensional anatomical structure contour of the patient's region of interest into several binary Two-dimensional contour slice map; extract the dose characteristics of each patient from the case database, and divide it into several two-dimensional dose slice distribution maps; build a deep convolutional network, input the patient's two-dimensional contour slice map and the corresponding two-dimensional dose slice distribution Figure, the association model between anatomical structure contour features and dose features is obtained through model training; the three-dimensional dose distribution of new patients is predicted using the trained association model. By using the method of the present invention, the correlation between anatomical structure features and dose features can be effectively obtained, and the accuracy of dose prediction can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
High-energy electron line multi-degree-of-freedom intensity modulated radiotherapy system based on longitudinal magnetic confinement
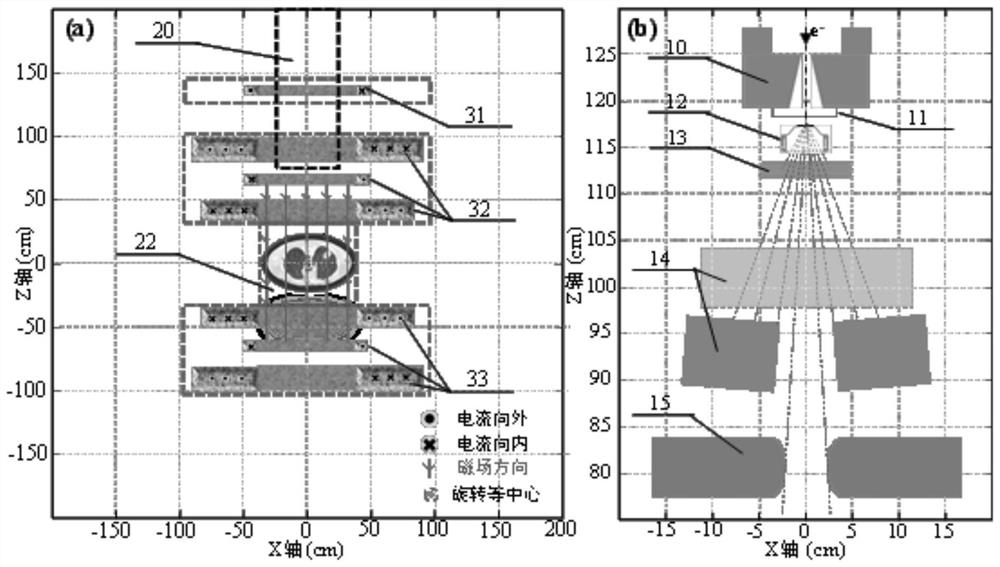
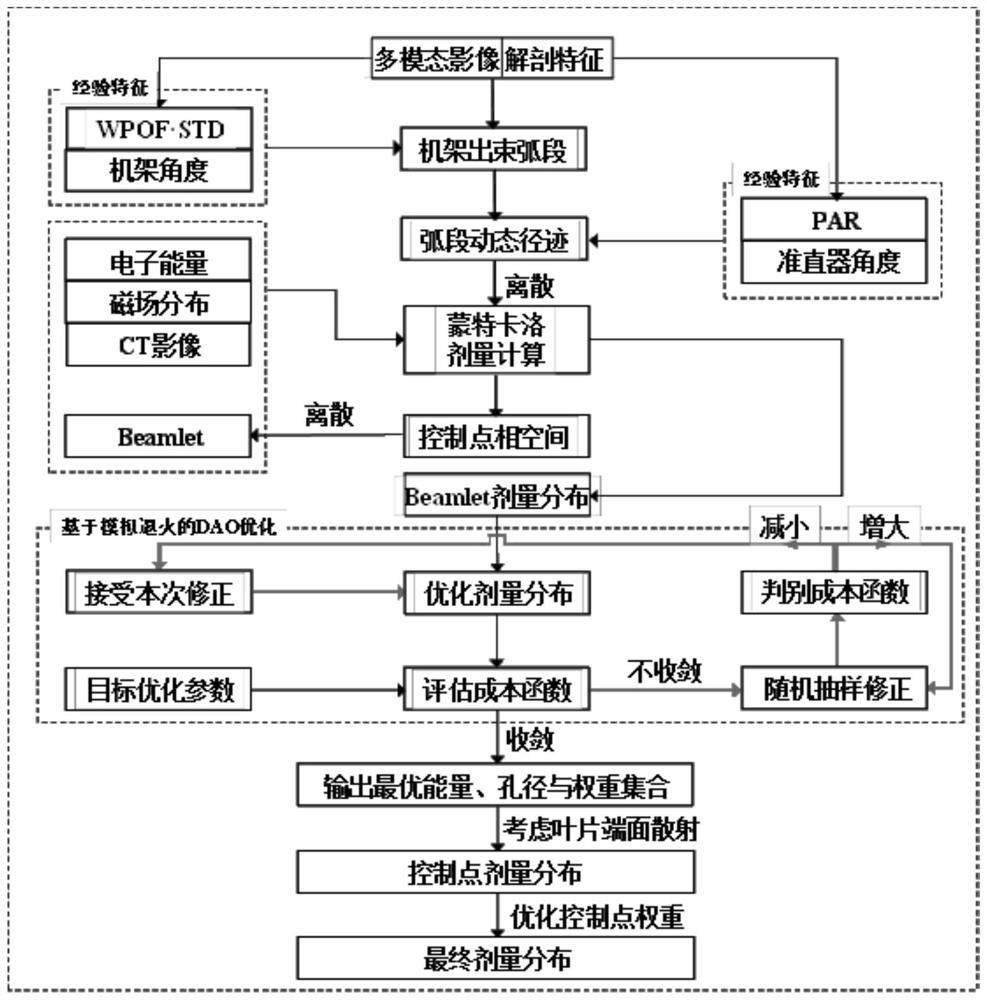
ActiveCN113181565AReduce side scatterRealize multi-degree-of-freedom intensity-modulated radiotherapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyParticle physics
The invention relates to a high-energy electron line multi-degree-of-freedom intensity modulated radiation therapy system based on longitudinal magnetic confinement. The system comprises longitudinal magnetic confinement high-energy electron line radiation therapy equipment and a multi-degree-of-freedom integrated optimization method for high-energy electron line intensity modulated radiation therapy. The equipment comprises a radiotherapy machine and a magnetic confinement device. The radiotherapy machine comprises a linear accelerator or a cyclotron for accelerating electrons and a multi-stage electron beam collimator, the magnetic confinement device comprises a three-stage split perforated coil, and the central axis of the coil coincides with the central axis of a high-energy electron beam. The optimization method comprises the following steps: 1, optimizing the head angle of the radiotherapy machine, and determining a beam arc section; 2, optimizing the angle of a collimator, and determining a beam dynamic track; and 3, synchronously optimizing the electron line energy and the beam intensity, and determining an optimal electron line multi-degree-of-freedom intensity modulated radiotherapy plan. Lateral scattering of high-energy electron rays in the air and in the body of a patient can be effectively reduced, multi-degree-of-freedom intensity modulated radiotherapy of the magnetic confinement high-energy electron rays is realized, and the curative effect of the patient is improved.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Prediction method and application of three-dimensional dose distribution in intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning
ActiveCN107441637BThoroughly describe anatomical featuresDescribe anatomical featuresX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentRadiation therapyVoxelImage resolution
The invention discloses a predication method for three-dimensional dose distribution in intensity modulated radiation therapy plans. The method includes steps of (1) collecting valid intensity modulated radiation therapy plan data and forming a case database; (2) dividing a PTV and different to-be-endangered organs of patients into a plurality of voxels according to the resolution ratio of CT images; (3) extracting anatomical characteristics of each patient in the database; (4) extracting dose characteristics of each patient in the database; (5) constructing an artificial neural network, inputting the anatomical characteristics and the dose characteristics of the patients, and learning the mapping relation between the anatomical characteristics and the dose characteristics by the aid of the artificial neural network, and obtaining a correlation model of the anatomical characteristics and the dose characteristics; (6) using the correlation model to predicate the three-dimensional dose distribution of a new patient. The application of said method is using the dose distribution predication method for dose prediction for to-be-endangered organs of patients and quality control is achieved. By adopting the above method, predication of three-dimensional dose distribution in intensity modulated radiation therapy plans can be realized and the method can be applied to a quality control link.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Shooting and Verification Method of Intensity Modulated Radiation Field Confirmation Film
ActiveCN107754097BRelieve painPrecise positioningX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyNormal tissue
The invention discloses a shooting method and validation for a validation film of intensity modulated radiation therapy. The method is characterized in that a therapeutic machine MV level image validation device is utilized, a shooting function is used, and a double-exposure, triple-exposure and multi-exposure imaging technology, a therapy interruption field joint technology and a single-frame continuous collection mode are adopted; first, through common confirmation of a physician and a doctor, a therapy plan of a patient is transmitted to an image guide system; points are marked on surface of skin according to three-dimensional coordinate values given by a system in first-time body position arrangement and then triple- or multi-exposure imaging technology is adopted; then a sub field shape is formed by adopting the therapy interruption field joint technology and validation film image information is stored. According to the invention, a problem of a conventional method that a validation film in the actual treatment angle in intensity modulated radiation therapy cannot be acquired is solved, the neighboring relation between the field shape and the exposure range and normal tissuesis confirmed, and the invention has advantages of being accurate in positioning and causing less pain of patients.
Owner:新乡市中心医院 +1
A method and system for direct field optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy
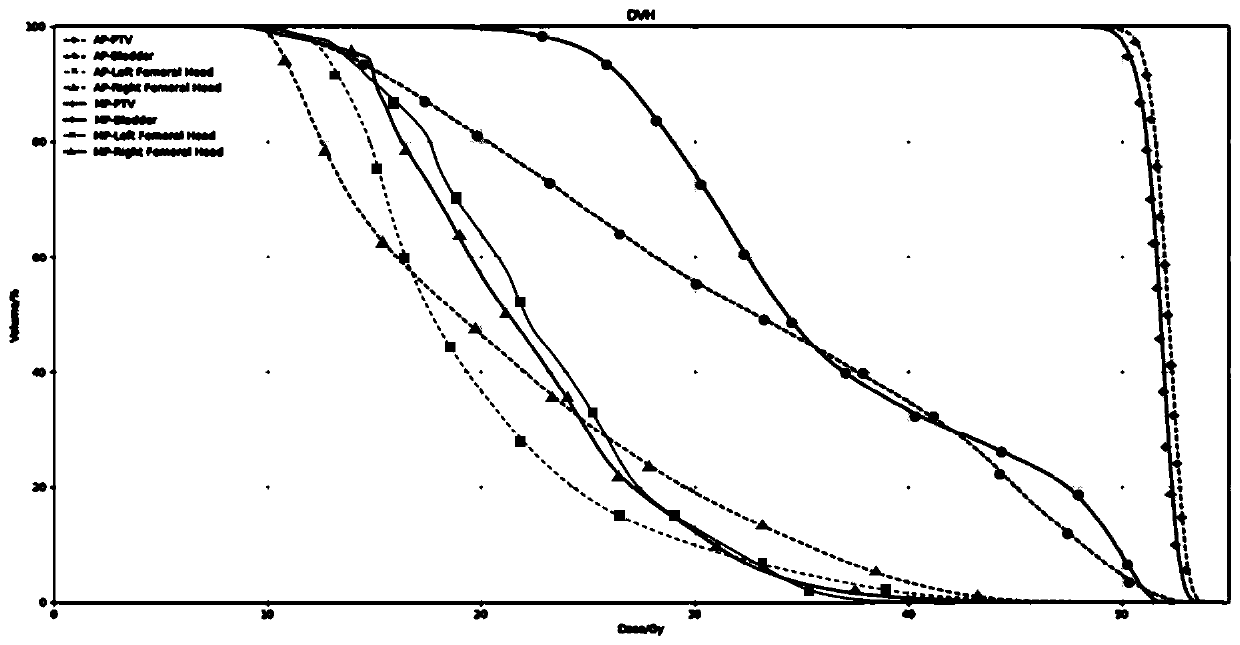
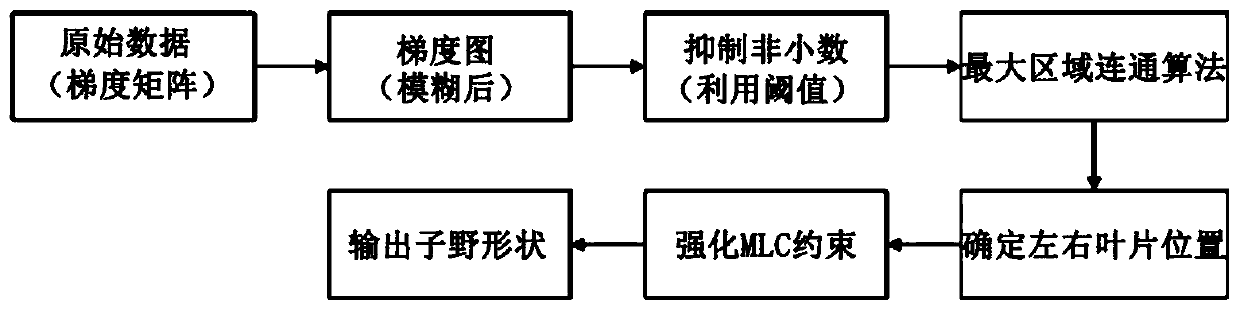
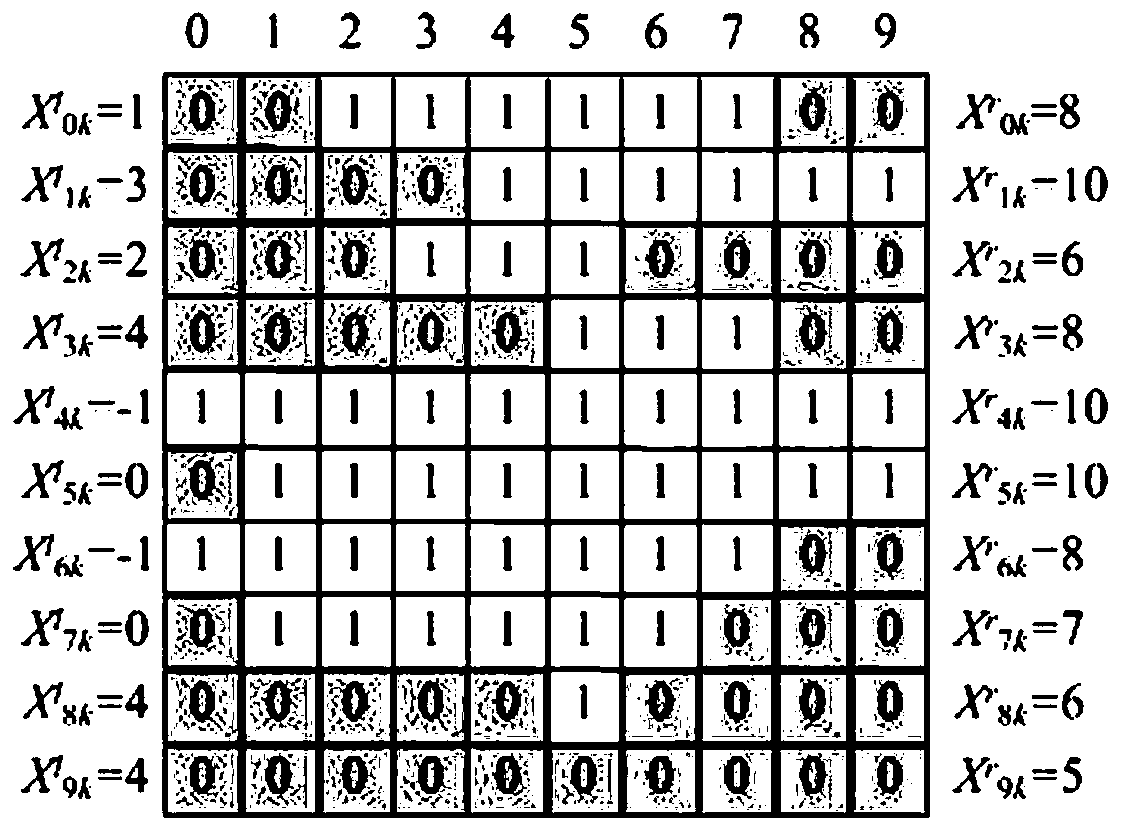
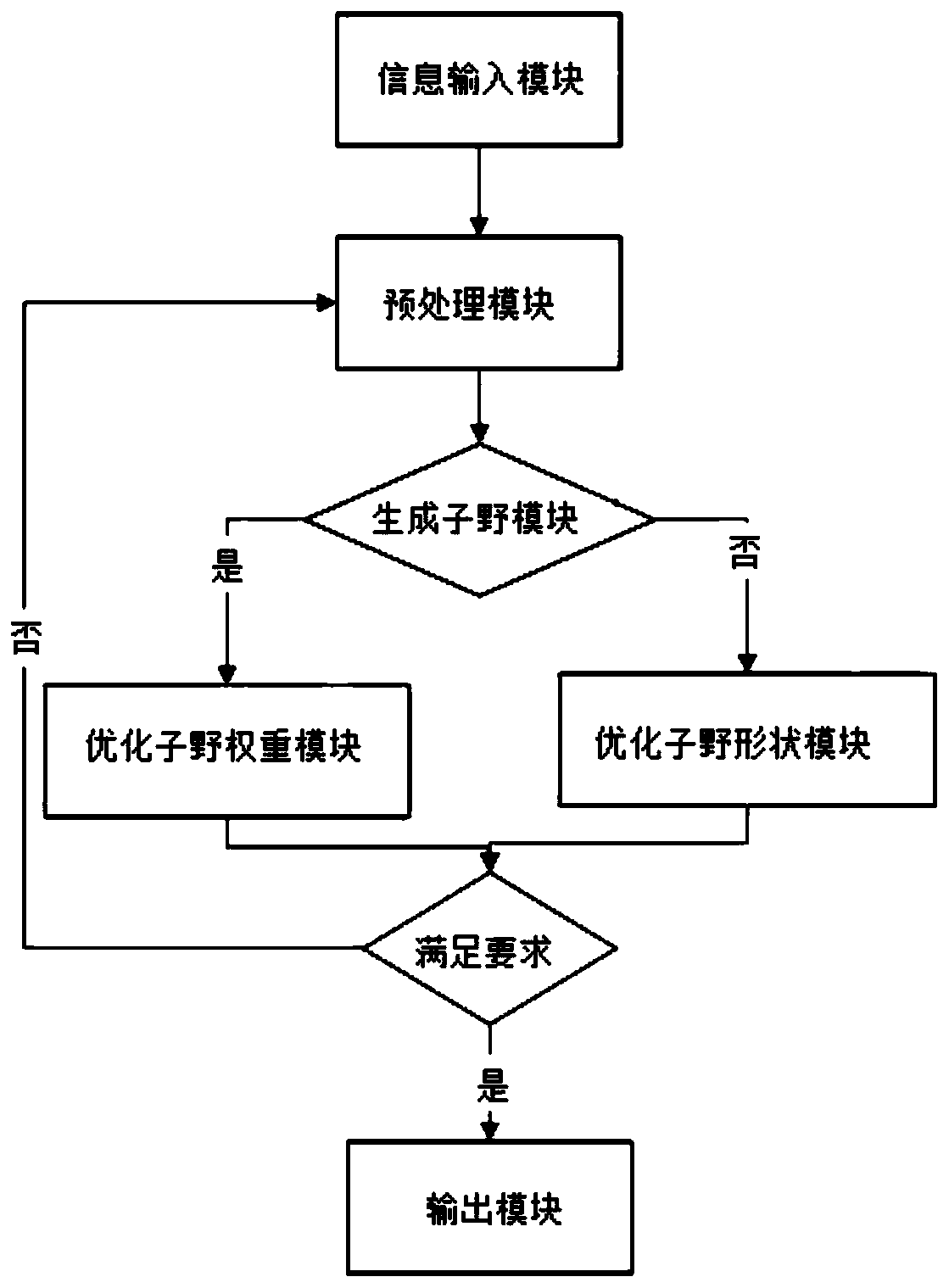
InactiveCN107823806BSmall doseIncrease coverageX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyIntensity-modulated radiation therapy
The invention discloses a method used for direct segment optimization in intensity-modulated radiotherapy. The method comprises steps of acquiring basic information of a patient; calculating a targetfunction gradient matrix, and using a fuzzifier to eliminate noise; using an adaptive threshold segmentation principle to generate a new segment shape; optimizing the segment weight and optimizing allexisting segment weights; optimizing the segment shape and optimizing all existing segment shapes; and outputting information of three-dimensional dosage distribution, DVH curves, the number of the segments, the segment shapes and the segment weights. The invention also discloses a system including the method used for direct segment optimization in intensity-modulated radiotherapy. The system comprises an information acquisition module, a preprocessing module, a segment generation module, a segment weight optimization module, a segment shape optimization module and an information outputting module. According to the invention, problems of low accuracy and low optimization efficiency of segment shapes in the current optimization methods and optimization systems are solved.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
An optimization system for intensity modulated radiotherapy
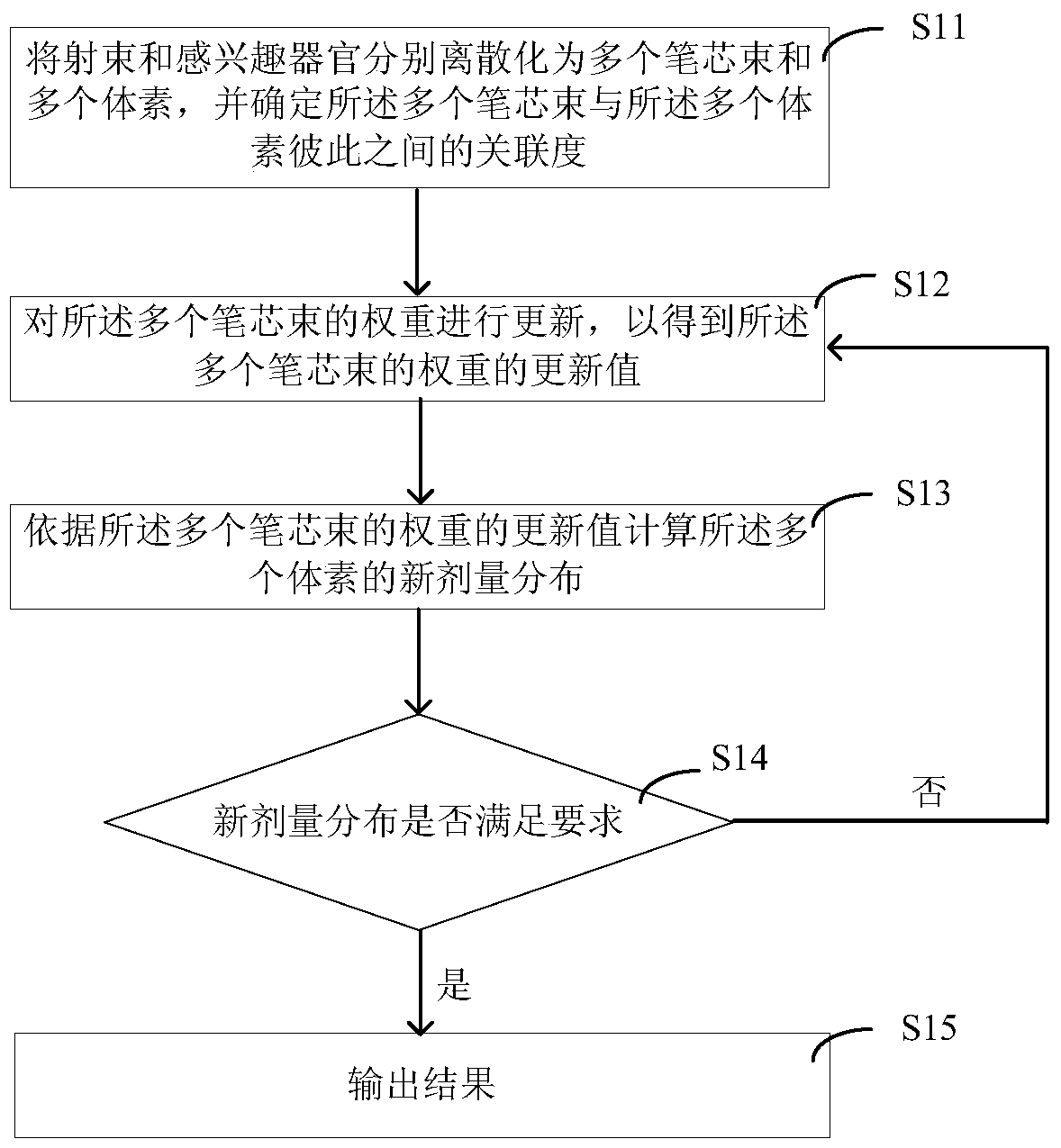
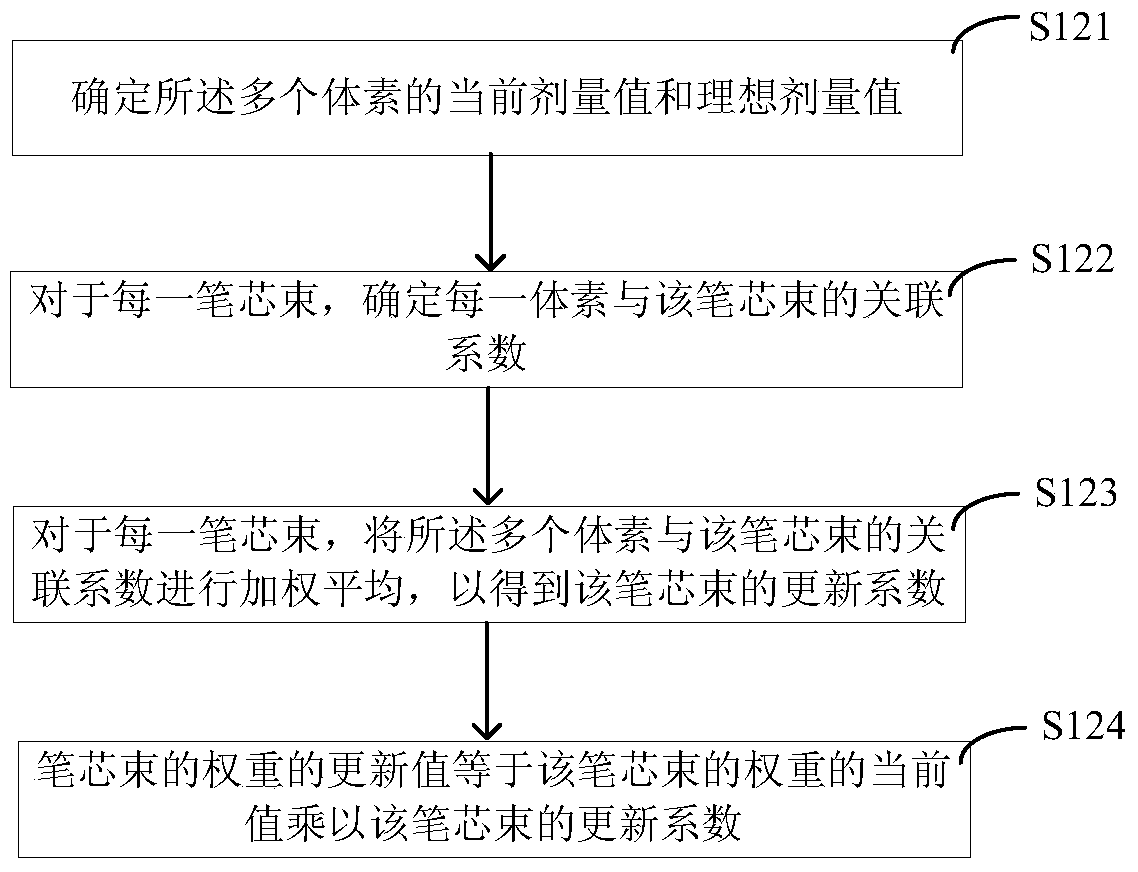
ActiveCN104645500BFast optimizationSmall footprintRadiation therapyVoxelIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The present invention provides a method and system for optimizing intensity-modulated radiotherapy. The method includes: discretizing the radiation beam and the organ of interest into multiple core beams and multiple voxels respectively, and determining the relationship between multiple core beams and multiple voxels The degree of correlation between multiple pen core bundles and multiple voxels, the current dose distribution and ideal dose distribution of multiple voxels, and the weights of multiple voxels, the weights of multiple pen core bundles are updated to Get the update value of the weight of multiple pen core bundles; calculate the new dose distribution of the planned target area according to the update value of the weight of multiple pen core bundles, if the new dose distribution does not meet the requirements, then re-weight the weight of multiple pen core bundles Updates are made until the new dose distribution for multiple voxels meets the requirements. The present invention can avoid pre-calculating and storing the dosage distribution matrix of the pen core beam, and can also avoid the process of solving equations, and at least has the advantages of fast optimization speed and small memory occupation.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
A method for optimizing collimator angle in volume rotation and intensity modulated radiotherapy planning
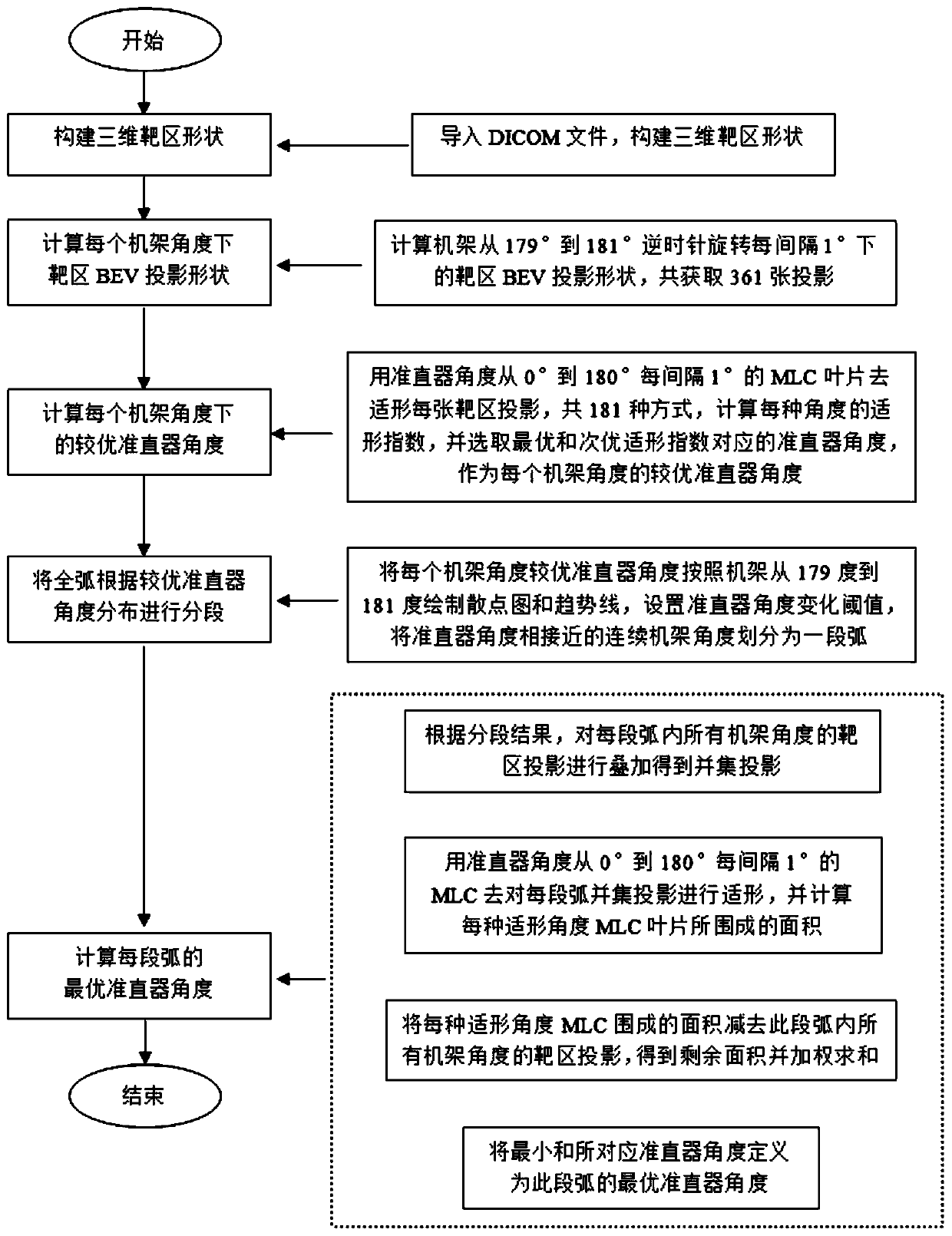
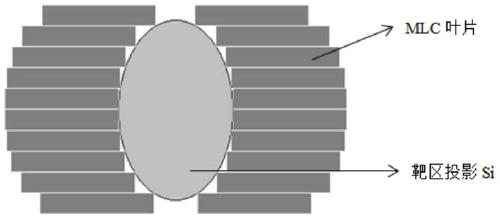
ActiveCN109513119BHigh benefit from radiotherapyAvoid damageX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyProjection image
The invention discloses a collimator angle optimization method for a volumetric-modulated arc therapy plan. Patient-specific target region structure information is used to perform three-dimensional reconstruction on a target region in order to obtain the projection images of the target region at different frame angles, and segmented optimization of the complete arc according to the conformal indexes of the different collimator angles to the target region and pertinent optimization of the collimator angle of each arc segment are carried out to achieve the personalized dynamic collimator angleoptimization method for the volumetric-modulated arc therapy plan. The method can dynamically optimize the collimator angle according to the patient-specific target region information, so the manual participation degree and the degree of dependence of the plan quality on the artificial experience are reduced, the increase of the efficiency and the consistency of the plan design is facilitated, a specific optimal plan is designed for every patient, and the resulting dosimetric improvement can avoid unnecessary tumor control rate decline and normal tissue damages and improve the efficacy of clinical radiotherapy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy plan optimization method and application based on predicted dose distribution guidance
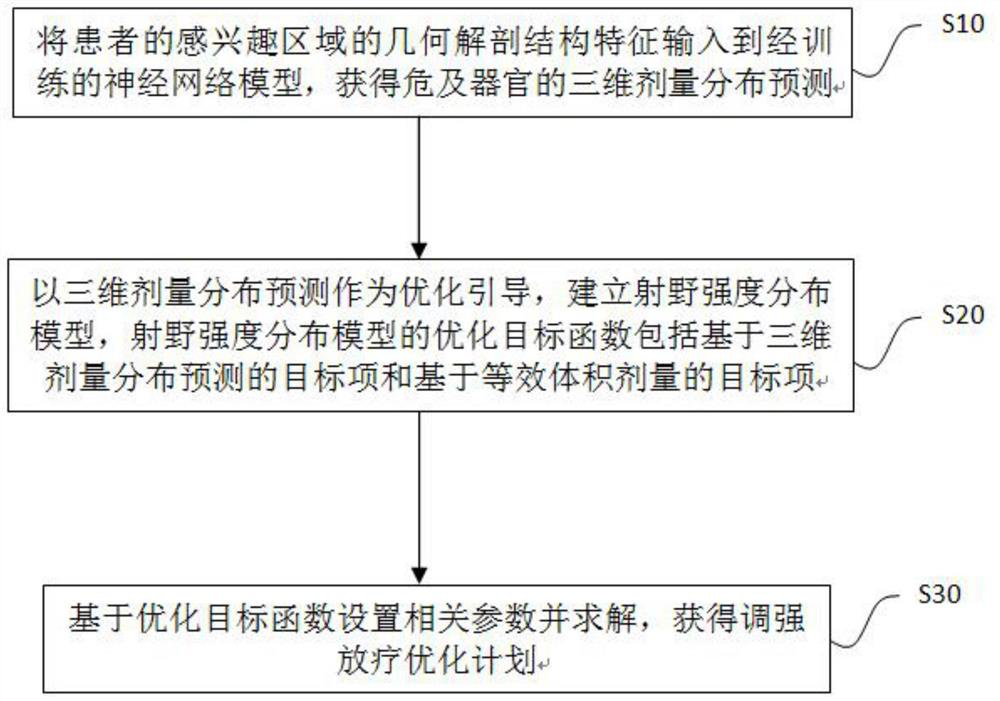
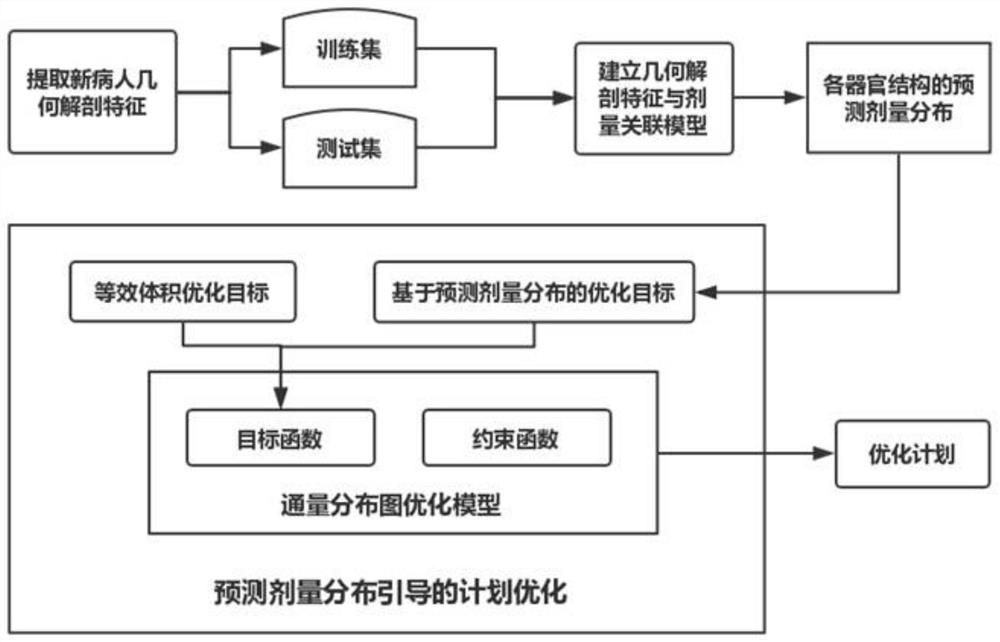
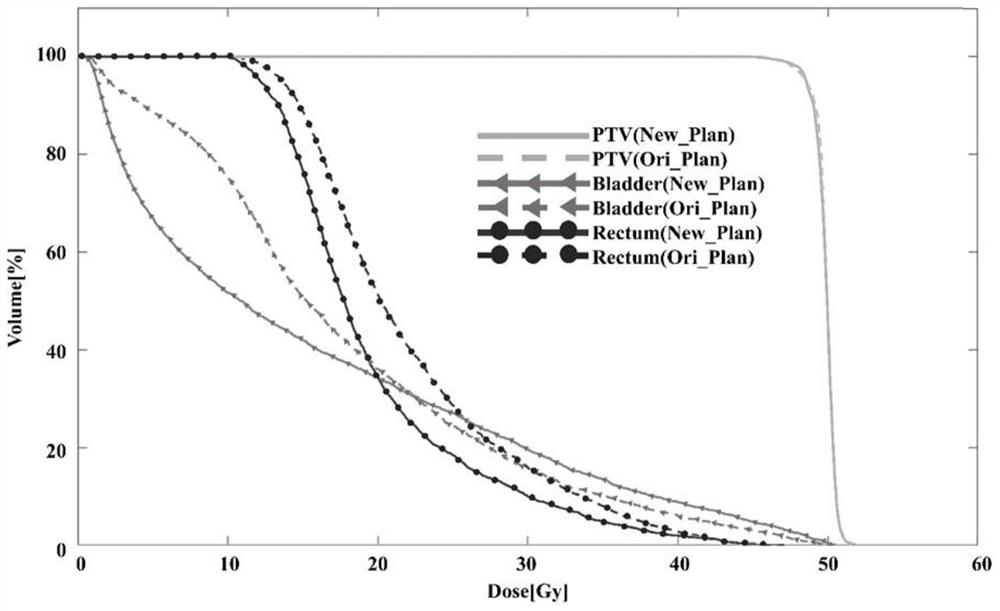
ActiveCN110327554BRealize individual optimizationWide solution spaceMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The invention discloses an intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan optimization method based on predictive dose distribution guidance and application thereof. The method includes the steps of: inputting geometric anatomical structural features of a region of interest of a patient into a trained neural network model so as to obtain three-dimensional dose distribution prediction that endangers anorgan; establishing a field intensity distribution model by taking the three-dimensional dose distribution prediction as optimization guide, wherein an optimization objective function of the field intensity distribution model comprises a target item based on the three-dimensional dose distribution prediction and a target item based on equivalent volume dose; and setting relevant parameters basedon the optimization objective function and performing solution to obtain an intensity-modulated radiation therapy optimization plan. According to the invention, the predicted three-dimensional dose distribution is utilized to guide the optimization of the intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan, so that the individual optimization and the voxel-level precise dose optimization can be realized. According to the invention, the equivalent volume target is constructed to compensate the influence of a loose prediction error on a guidance optimization result, a wider solution space is provided atthe same time, and the advancing direction of plan optimization is ensured.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com