Intensity-modulated radiotherapy plan optimization method and application based on predicted dose distribution guidance
A technology of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and dose distribution, applied in radiotherapy, neural learning methods, X-ray/γ-ray/particle irradiation therapy, etc., can solve problems such as prediction uncertainty, limitation, optimization guidance influence, etc. Impact of results, reduction of workload, effect of ensuring the direction of progress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
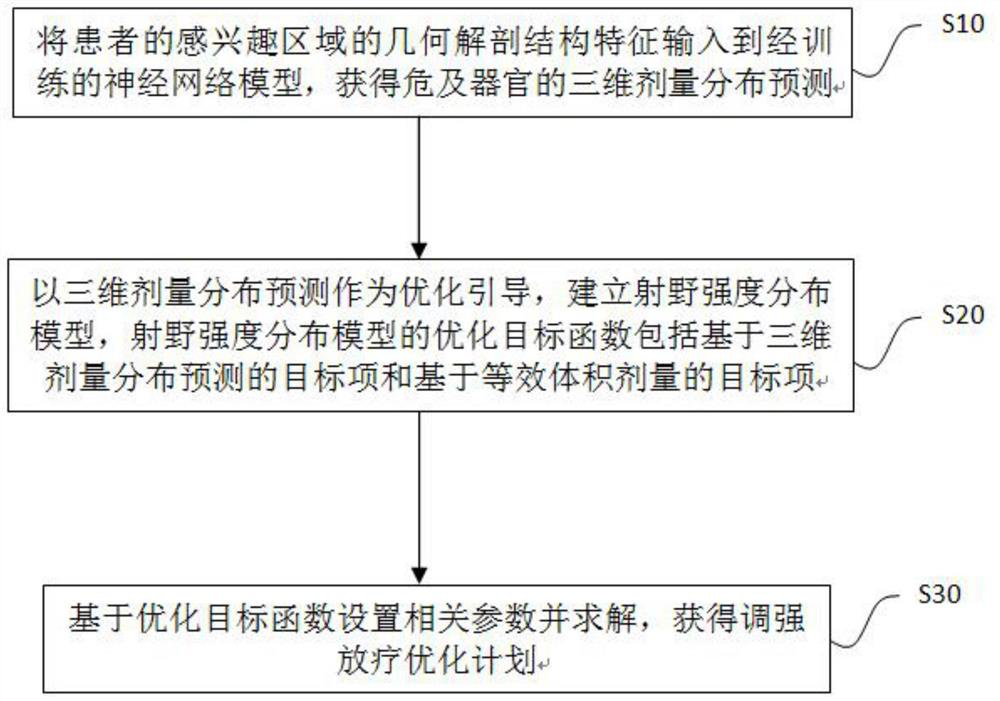
[0055] As an embodiment of the present invention, an intensity-modulated radiotherapy plan optimization method based on the predicted dose reconstruction equivalent volume minimization method is provided, by using the predicted three-dimensional dose distribution of organs at risk as the optimized initialization target to quickly guide individualized and Feasible plan, in addition to constructing an equivalent volume optimization target to compensate for the optimization difference guided by prediction errors, and at the same time ensure the optimization space of the plan quality, including the following steps, such as figure 1 Shown:
[0056] S10: Input the geometric anatomical structure characteristics of the patient's region of interest into the trained neural network model to obtain the three-dimensional dose distribution prediction of organs at risk: use the artificial neural network method to construct a correlation model between the patient's geometric anatomical structu...
Embodiment 2
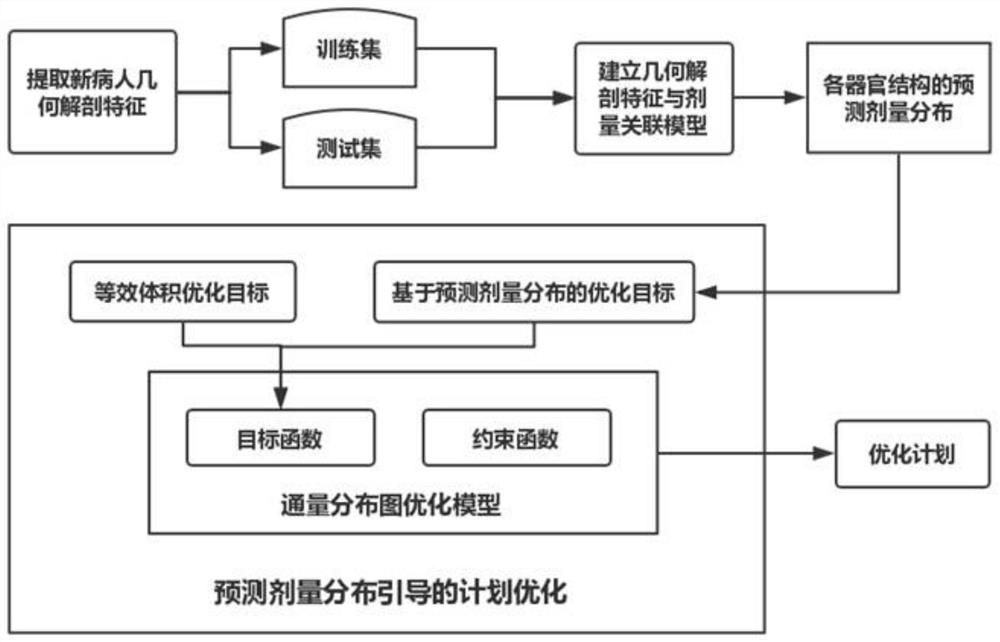
[0071] In an application example, the intensity-modulated radiotherapy plan optimization method based on predicted dose distribution guidance provided by the present invention includes the following processes, such as figure 1 and figure 2 Shown:
[0072] (1) Prediction of three-dimensional dose distribution of organs at risk in patients
[0073] Select the IMRT planning data to build a correlation model between the patient's voxel dose and its combined anatomical structure. The model takes the voxel of the organ at risk as the research object, extracts its dose as the output dosimetry feature, and the input features are voxel to PTV edge, PTV The distance of the geometric center and the edge of other organs at risk and the three-dimensional angle of the voxel to the geometric center of the PTV and the volume of the PTV. Randomly select 80% of the planned data from the experimental data as the training set for model building, and the rest as the test set. And the method of...
Embodiment 3
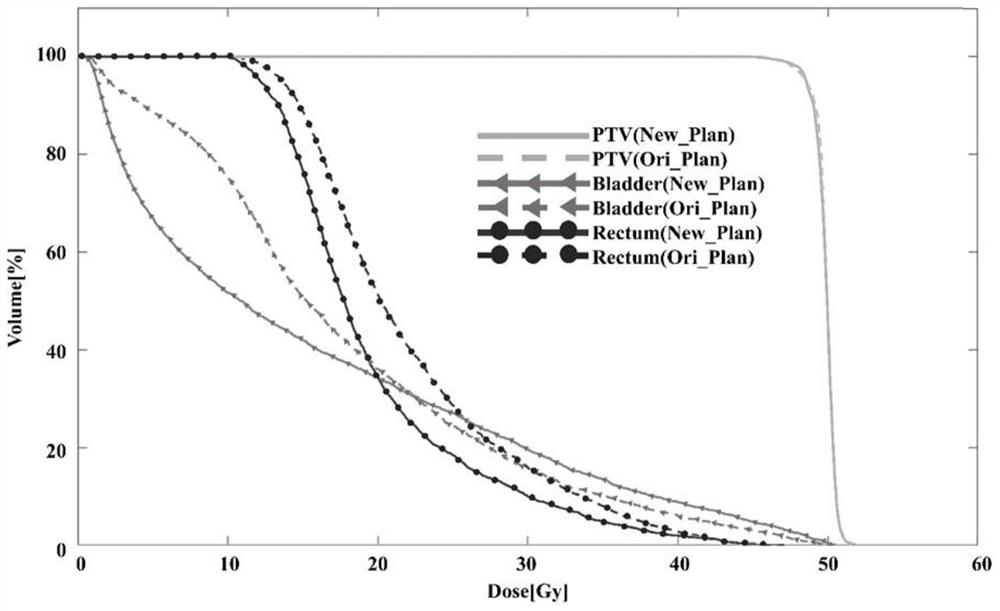
[0094] In order to further verify the technical effect, the IMRT plan of 2 prostate cancer patients was re-optimized by using the intensity-modulated radiotherapy plan optimization method guided by the prediction three-dimensional dose distribution of the present invention, and compared with the original clinical plan. The DVH curve comparison between the optimized plan and the original clinical plan is shown in Figure 3(a) and Figure 3(b), the abscissa is the dose value, and the ordinate is the volume percentage. It can be observed from the DVH diagram that, compared with the original plan, for the observation organ bladder in this experiment, the new plan curve has a downward trend in the entire dose range, especially in the low dose area below 30Gy. The results are in line with the optimization expectations of the new method.
[0095] The comparison results of the dose distribution at the isocenter level of different plans for a patient with prostate cancer are as follows: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com