Three-dimensional dose distribution prediction method for intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning based on deep network learning
An intensity-modulated radiotherapy and deep learning technology, applied in neural learning methods, radiotherapy, biological neural network models, etc., can solve problems such as incomplete description of anatomical information, inability to predict multiple regions of interest at the same time, and avoid manual extraction The effect of incomplete information and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] In order to make the objects, technical solutions, design methods, and advantages of the present invention more clearly, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are for explaining the present invention and is not intended to limit the invention.
[0053] In all examples shown in and discussed herein, any specific value should be construed as is merely exemplary, not a limitation. Therefore, other examples of exemplary embodiments may have different values.
[0054] For technical, methods, and equipment known to those of ordinary skill in the art may not be discussed in detail, in appropriate, the techniques, methods, and equipment should be considered part of the specification.
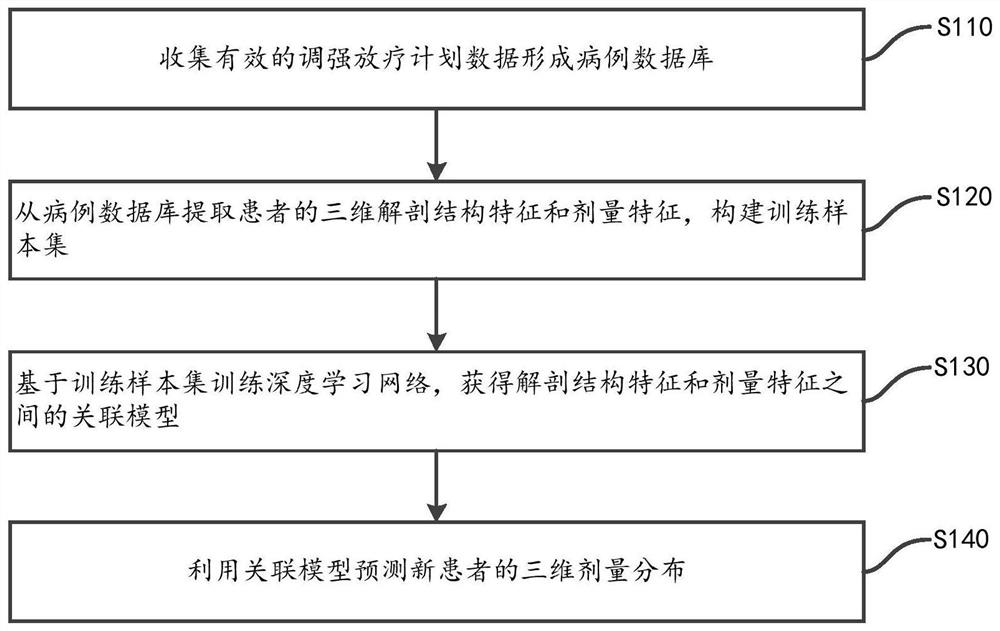
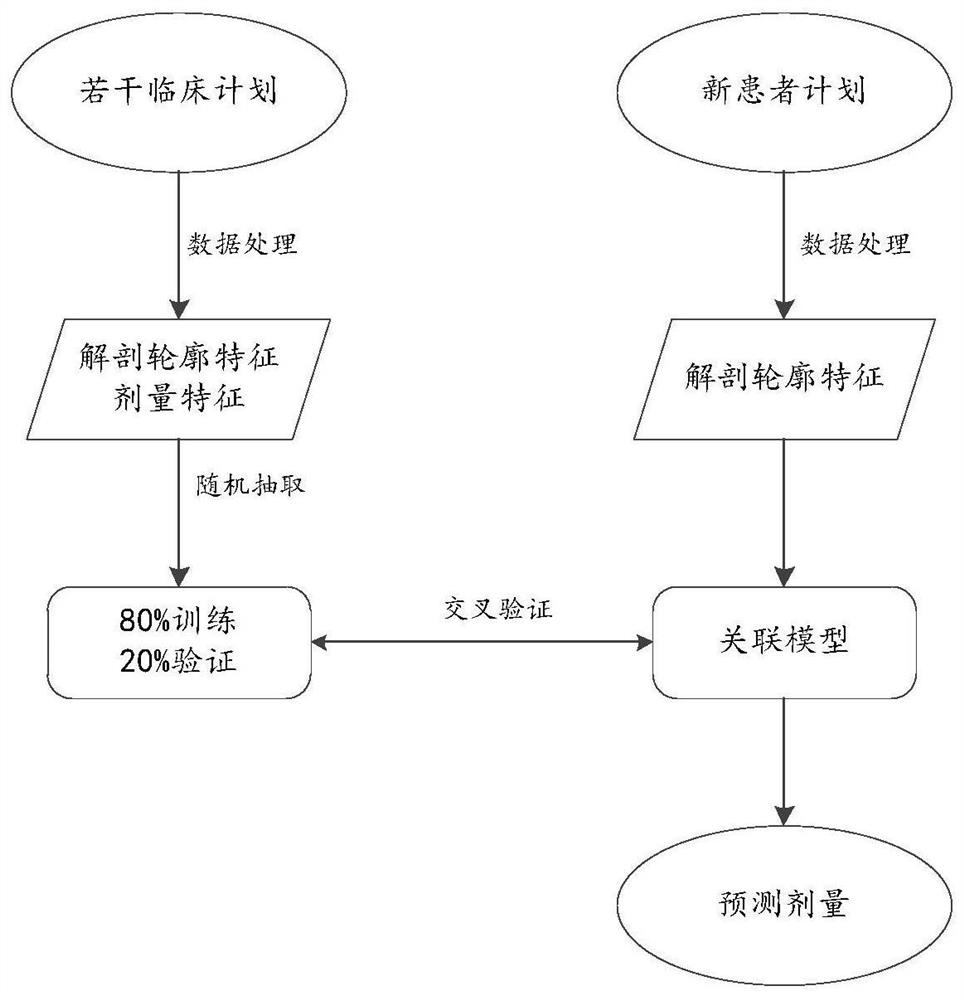
[0055] According to an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a three-dimensional distribution prediction method based on a depth network learn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com