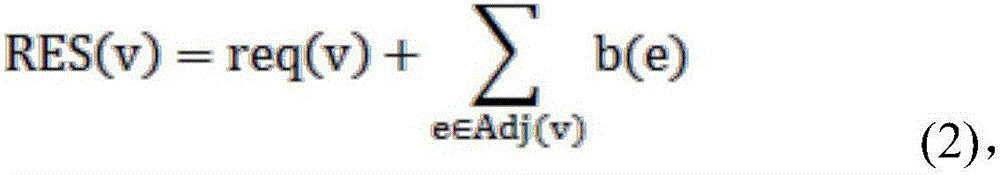Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
195 results about "Infrastructure network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
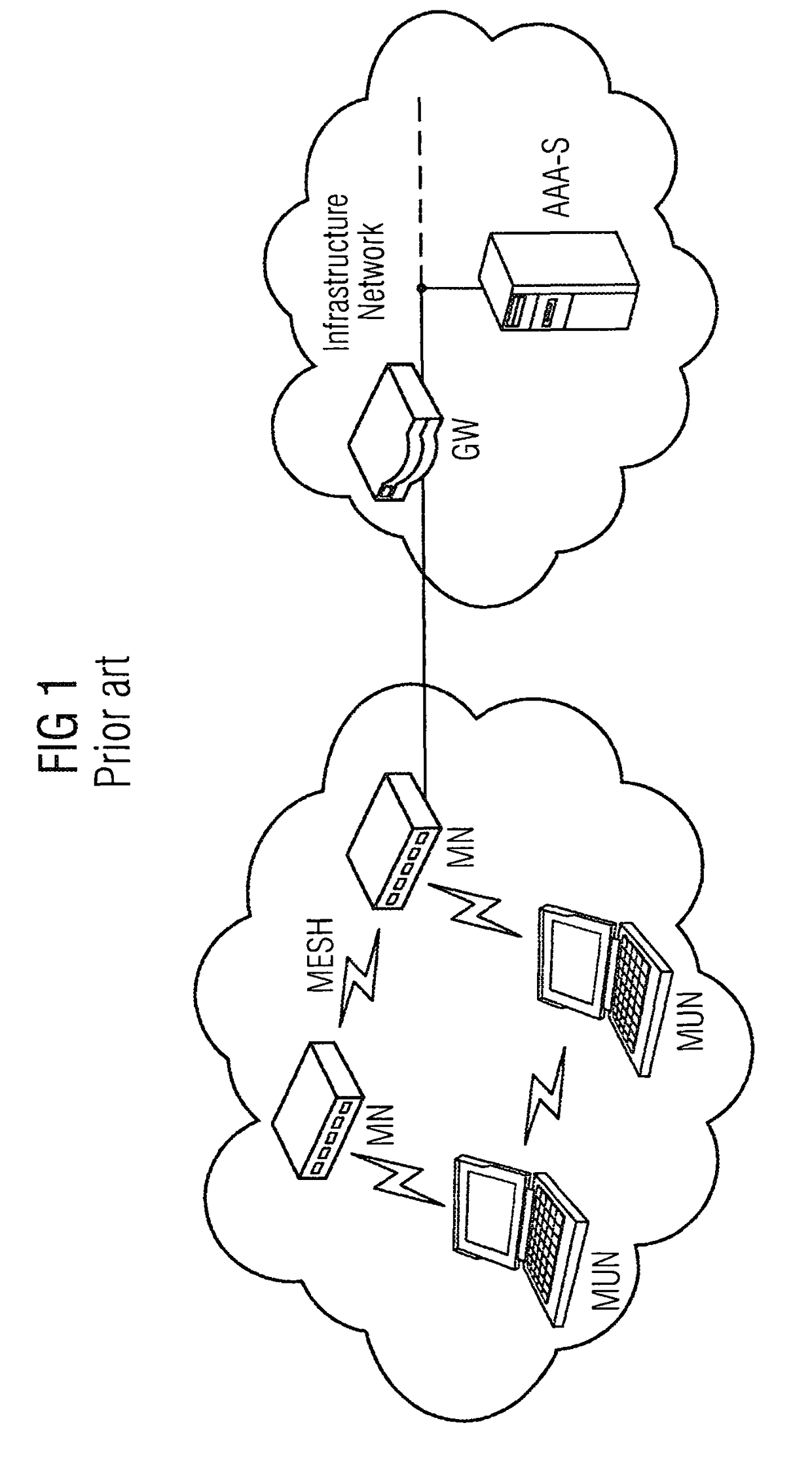
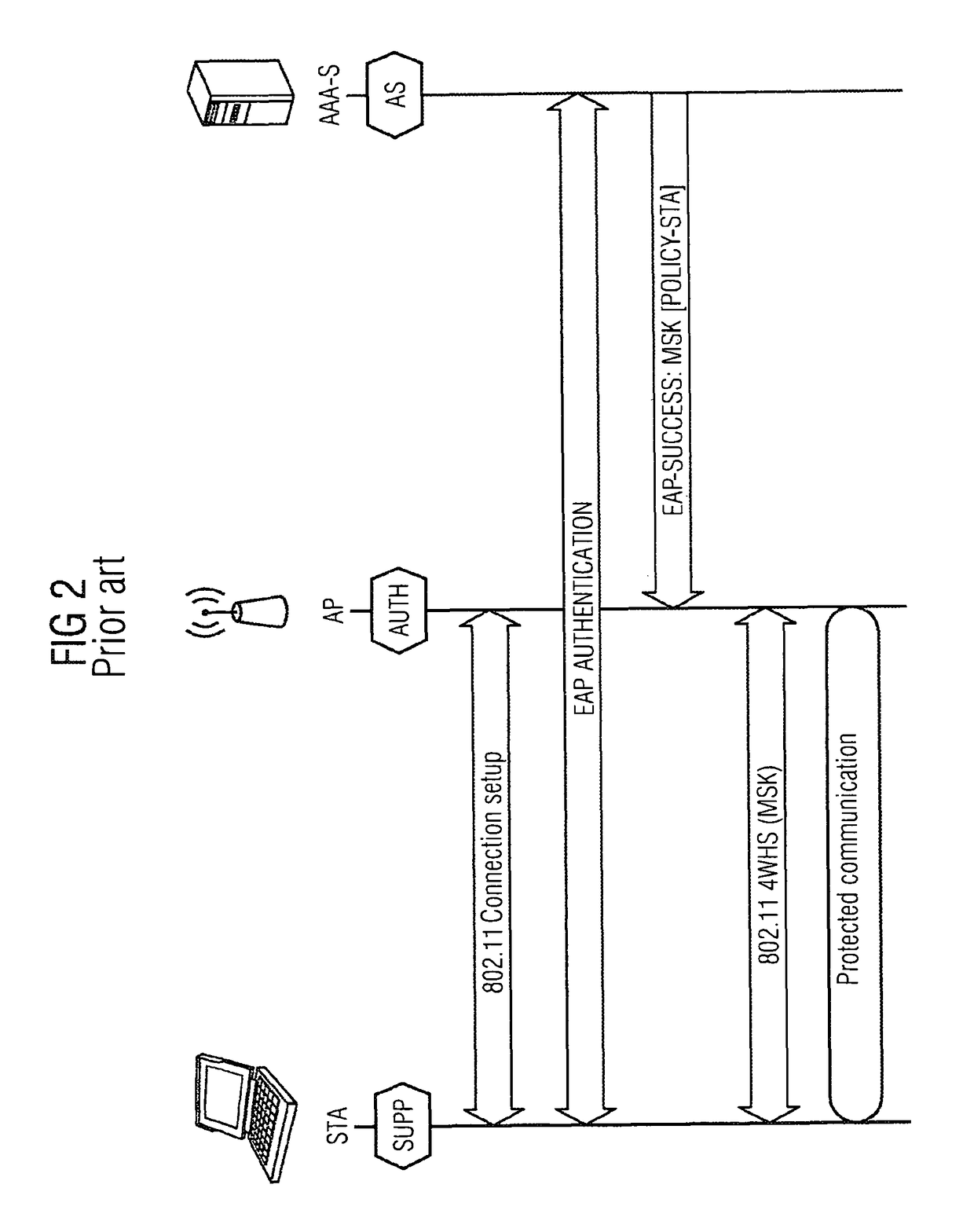
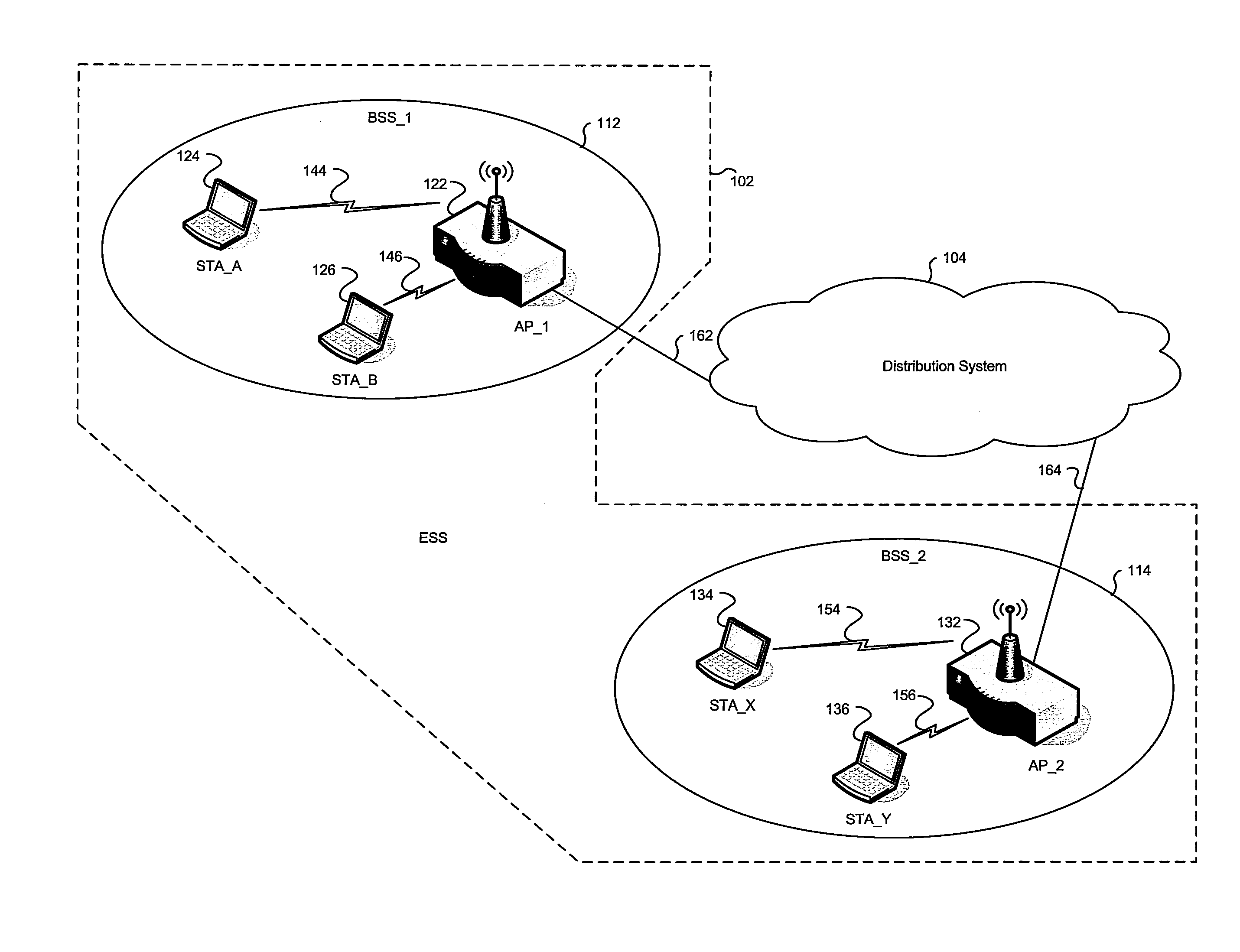
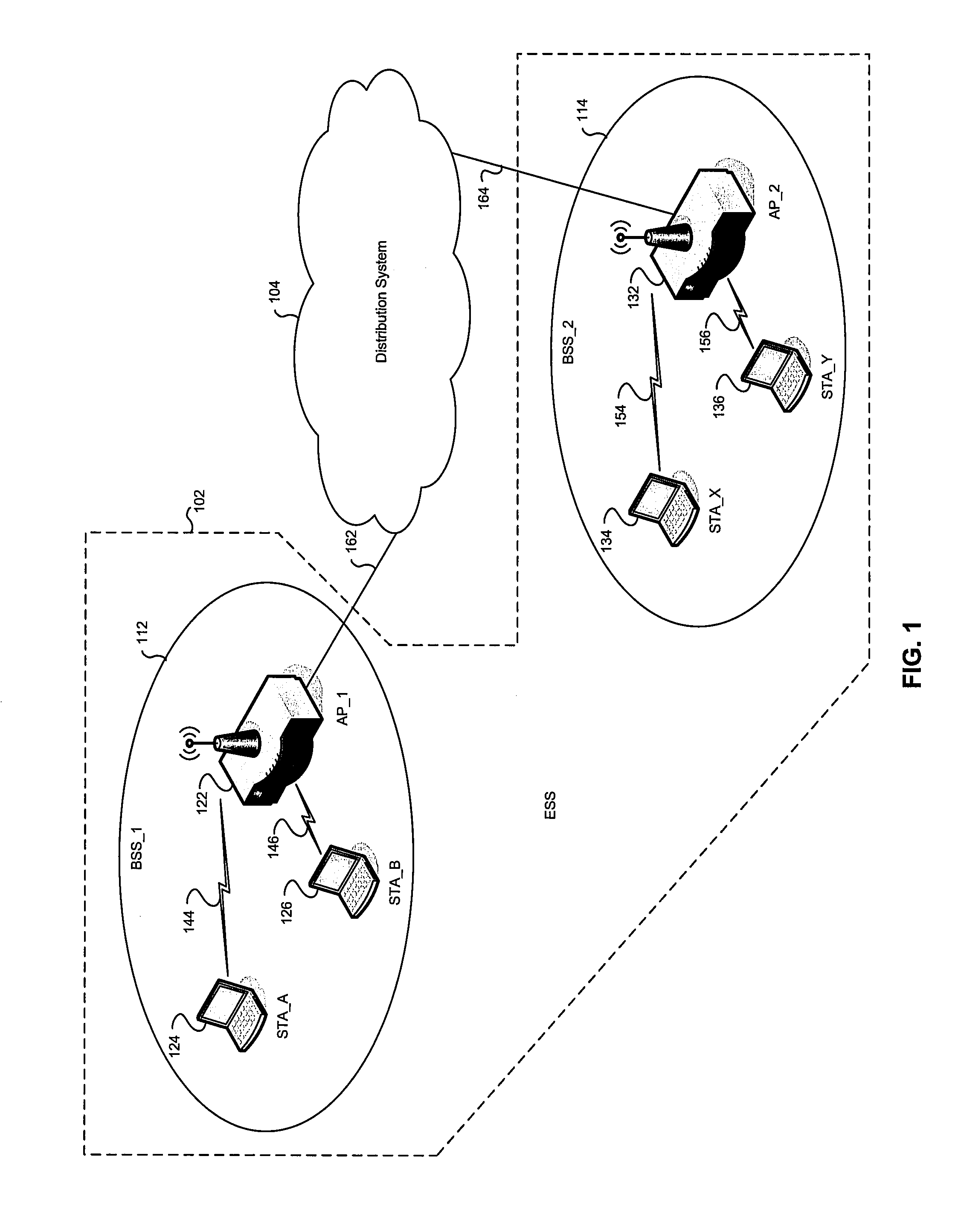
Network infrastructure is typically part of the IT infrastructure found in most enterprise IT environments. The entire network infrastructure is interconnected, and can be used for internal communications, external communications or both.
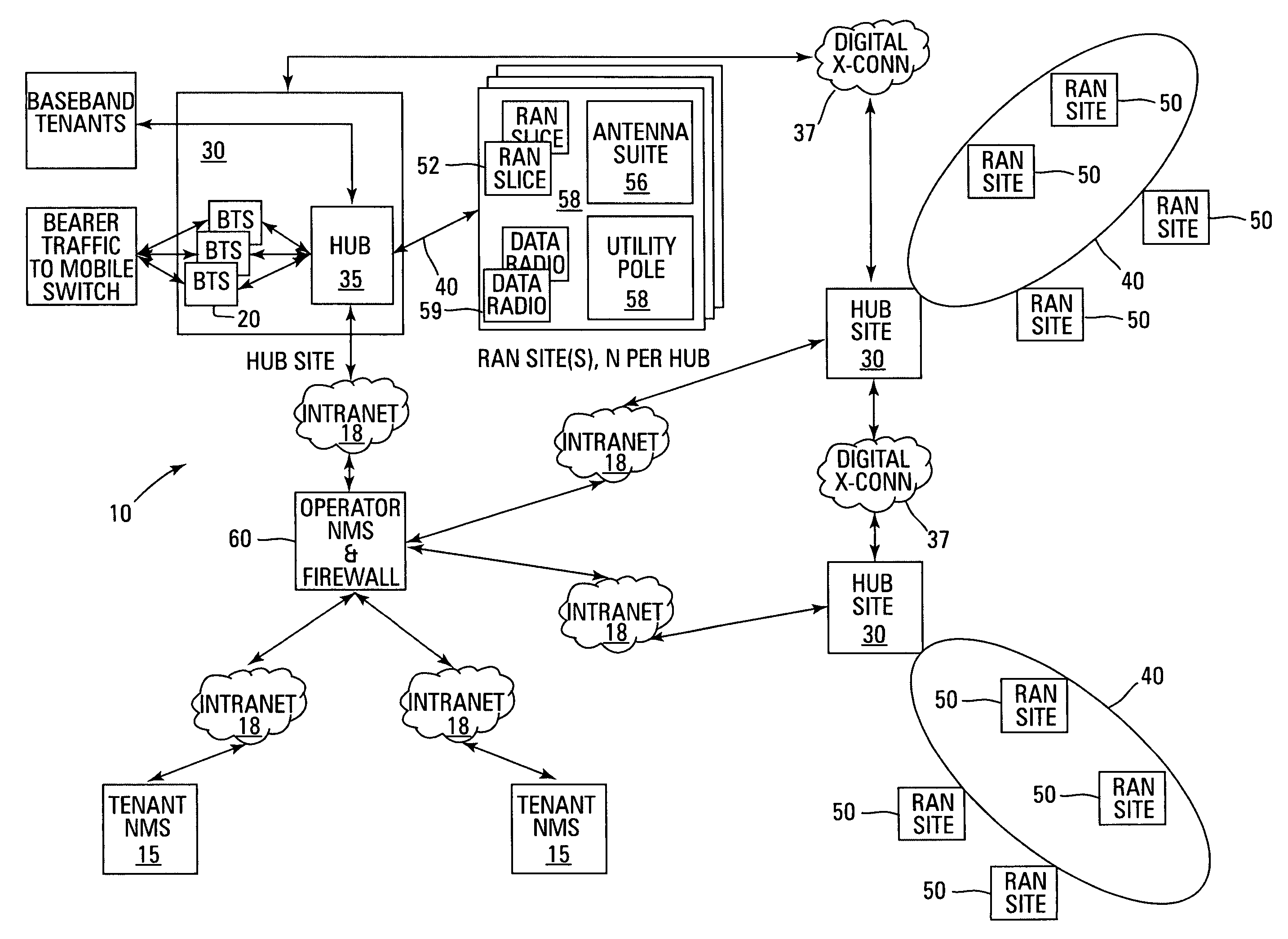
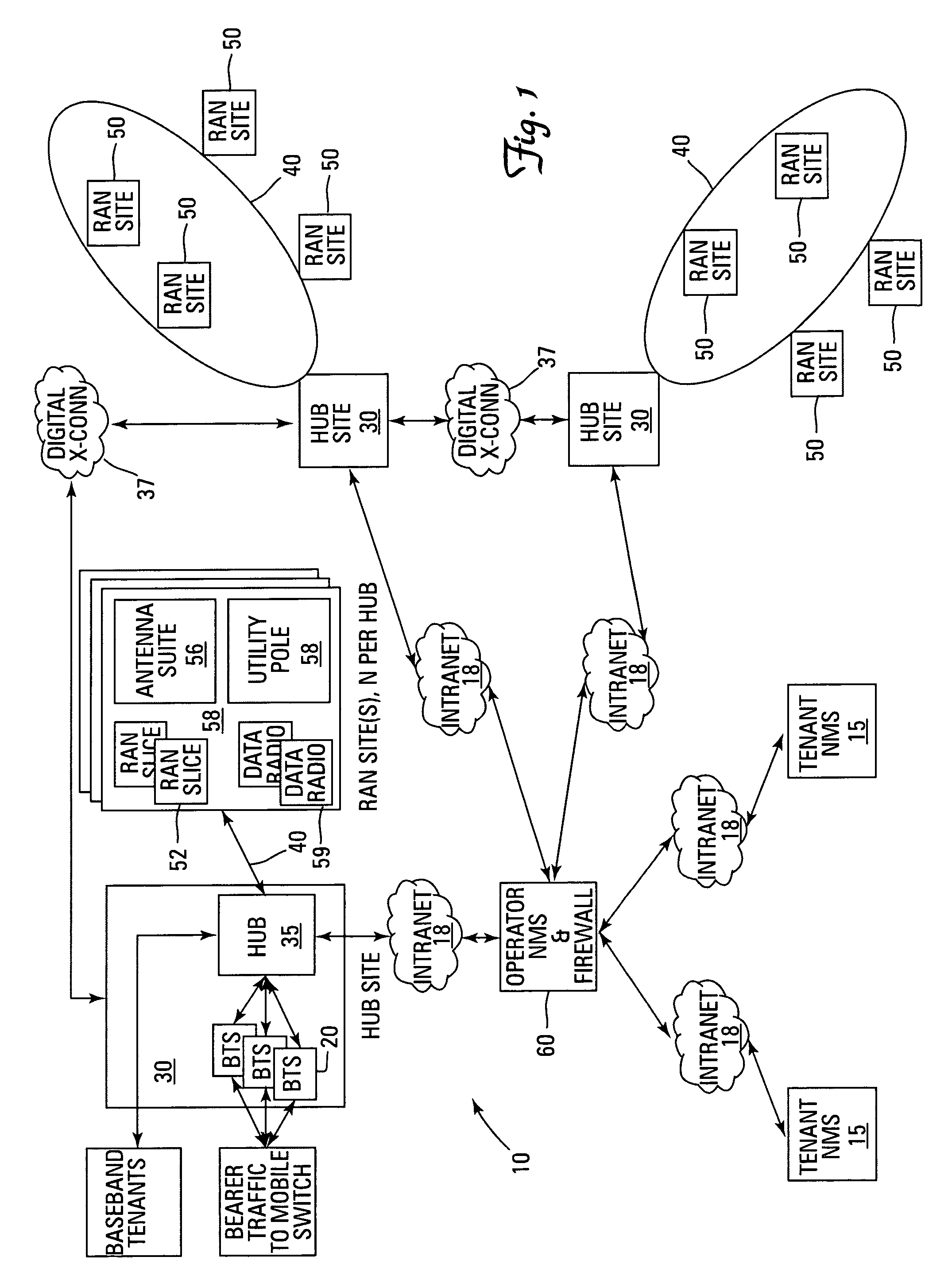
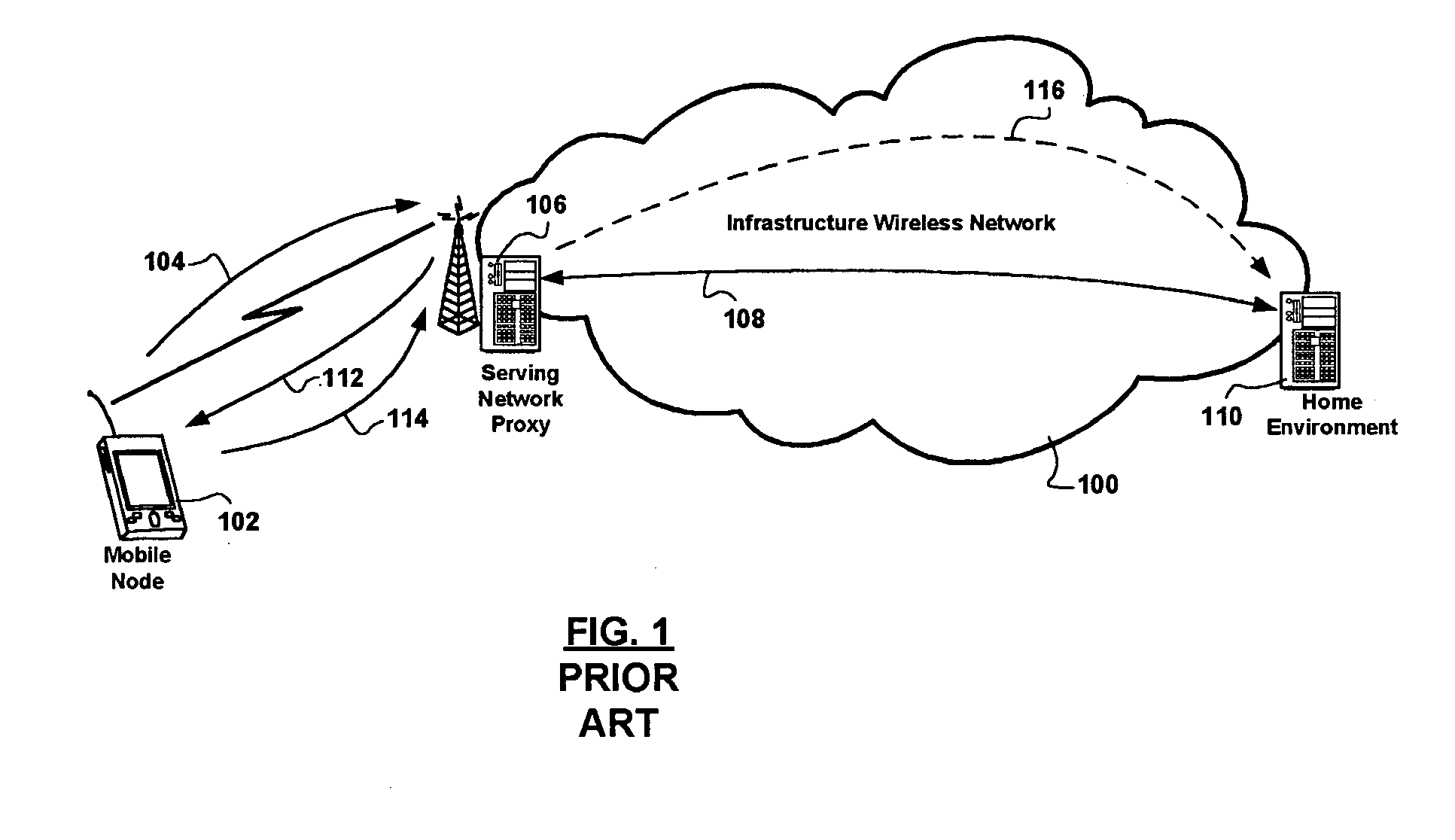
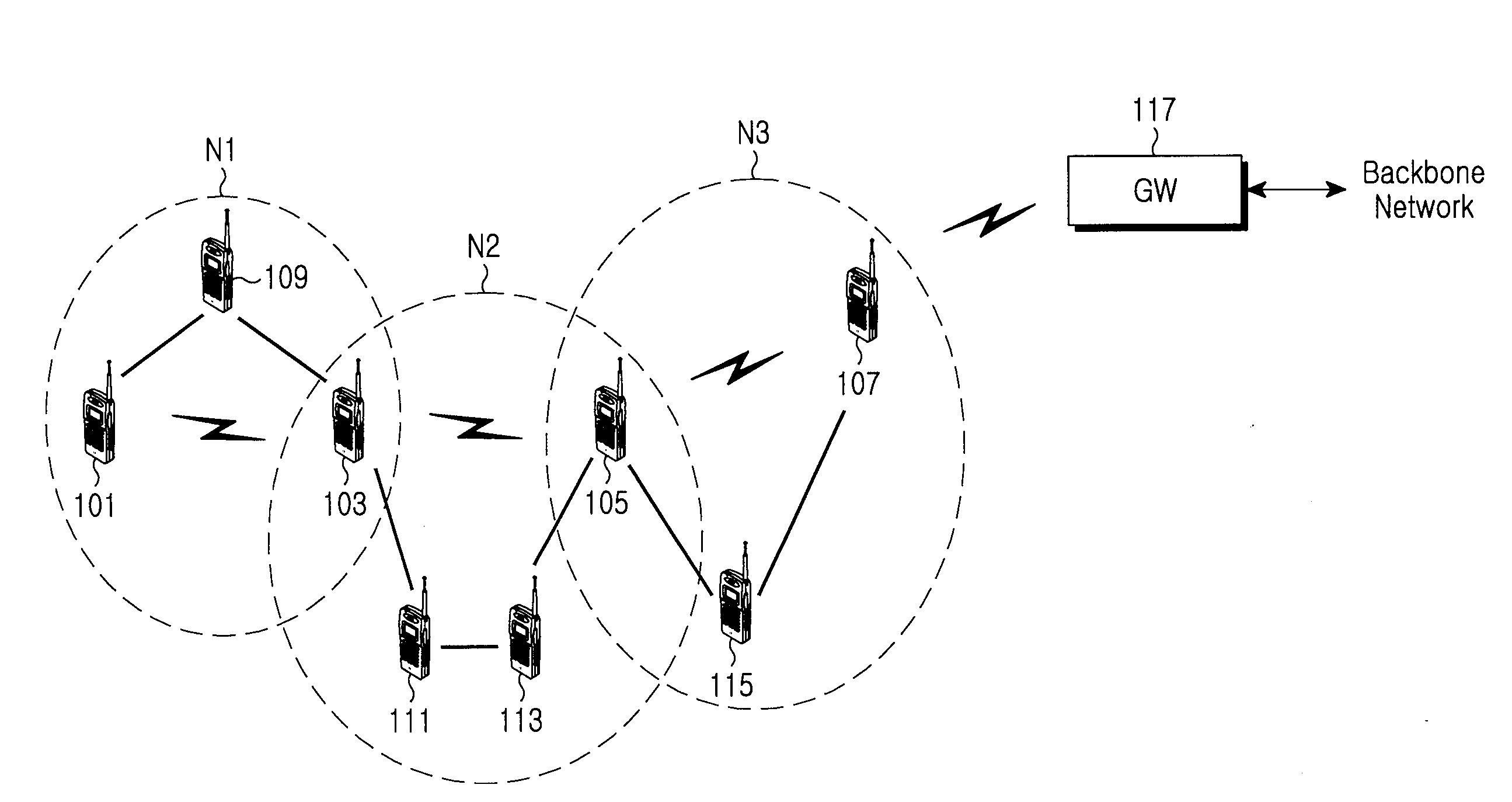
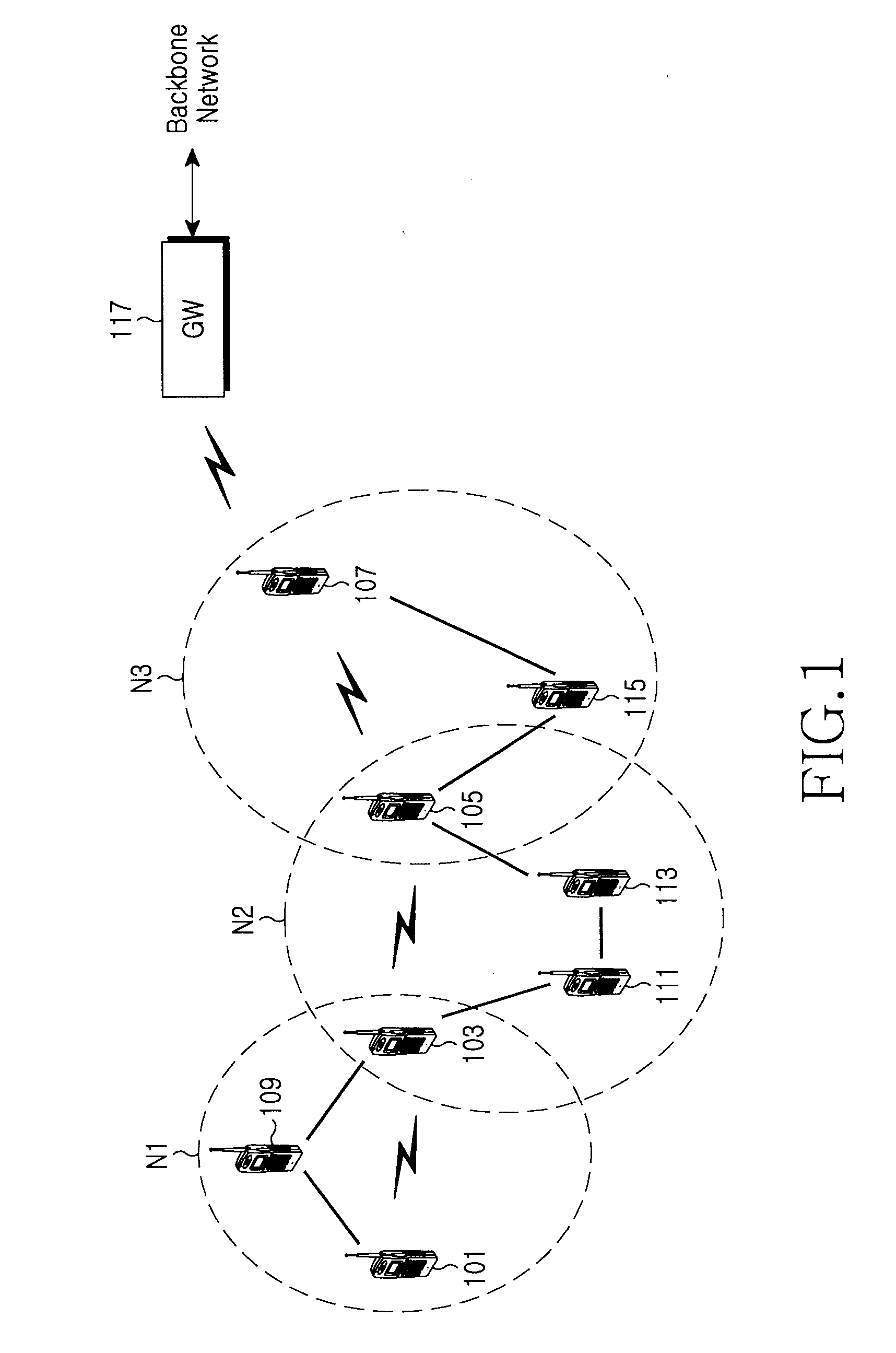
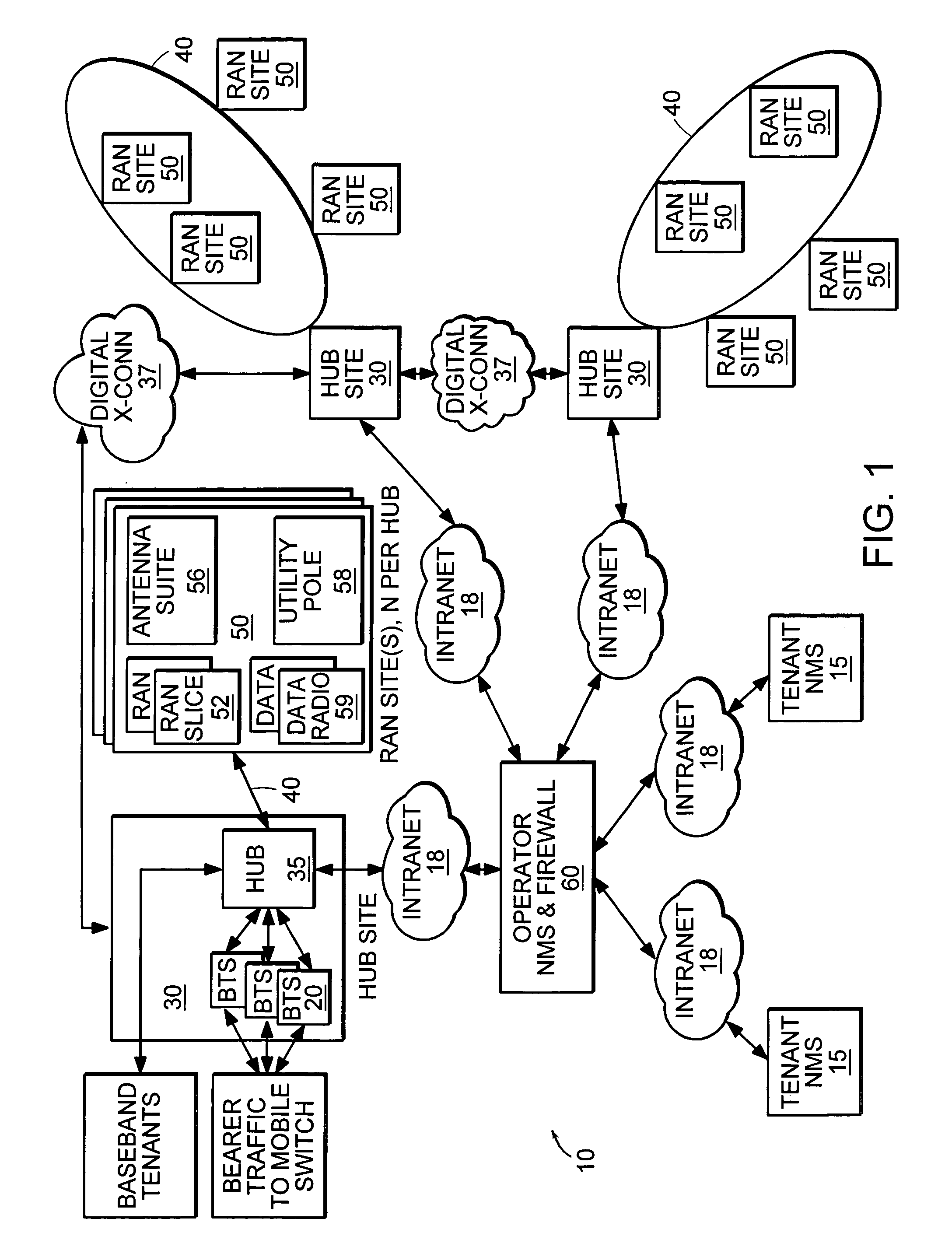
Multi-protocol distributed wireless system architecture
InactiveUS6963552B2Easy to shareRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAir interfaceDistribution system
An open access signal distribution system in which a variety of wireless voice, data and other services and applications are supported. The open access system makes use of a distributed Radio Frequency (RF) distribution network and associated network entities that enable the system operator to employ a wireless infrastructure network that may be easily shared among multiple wireless service providers in a given community. The open access system provides the ability for such operators and service providers to share the infrastructure regardless of the specific RF air interface or other signal formatting and / or managing messaging formats that such operators choose to deploy.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Routing method for mobile infrastructureless network
InactiveUS6940832B2Improve efficiencyImprove performanceError preventionTransmission systemsComputer scienceMobile wireless
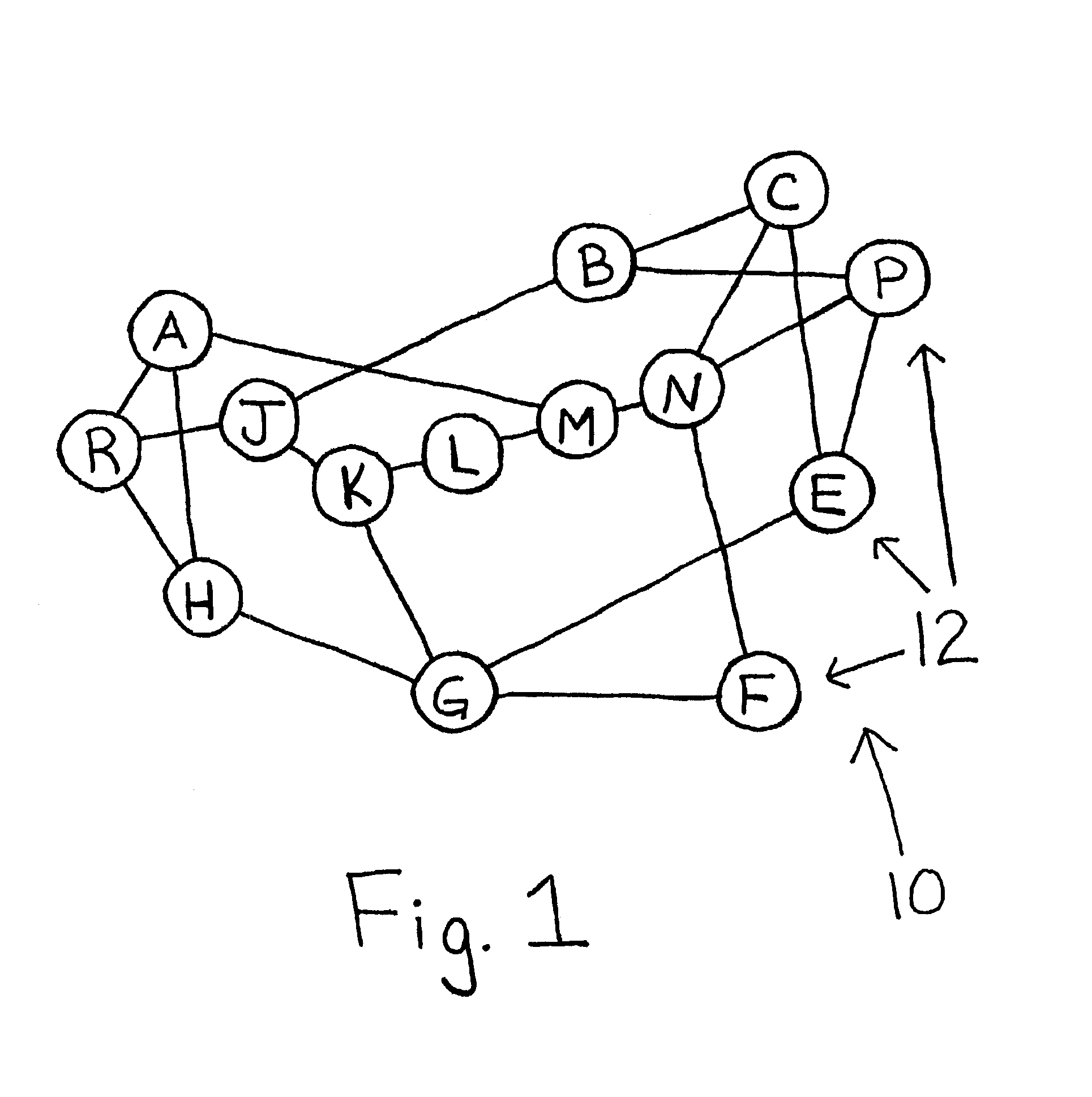
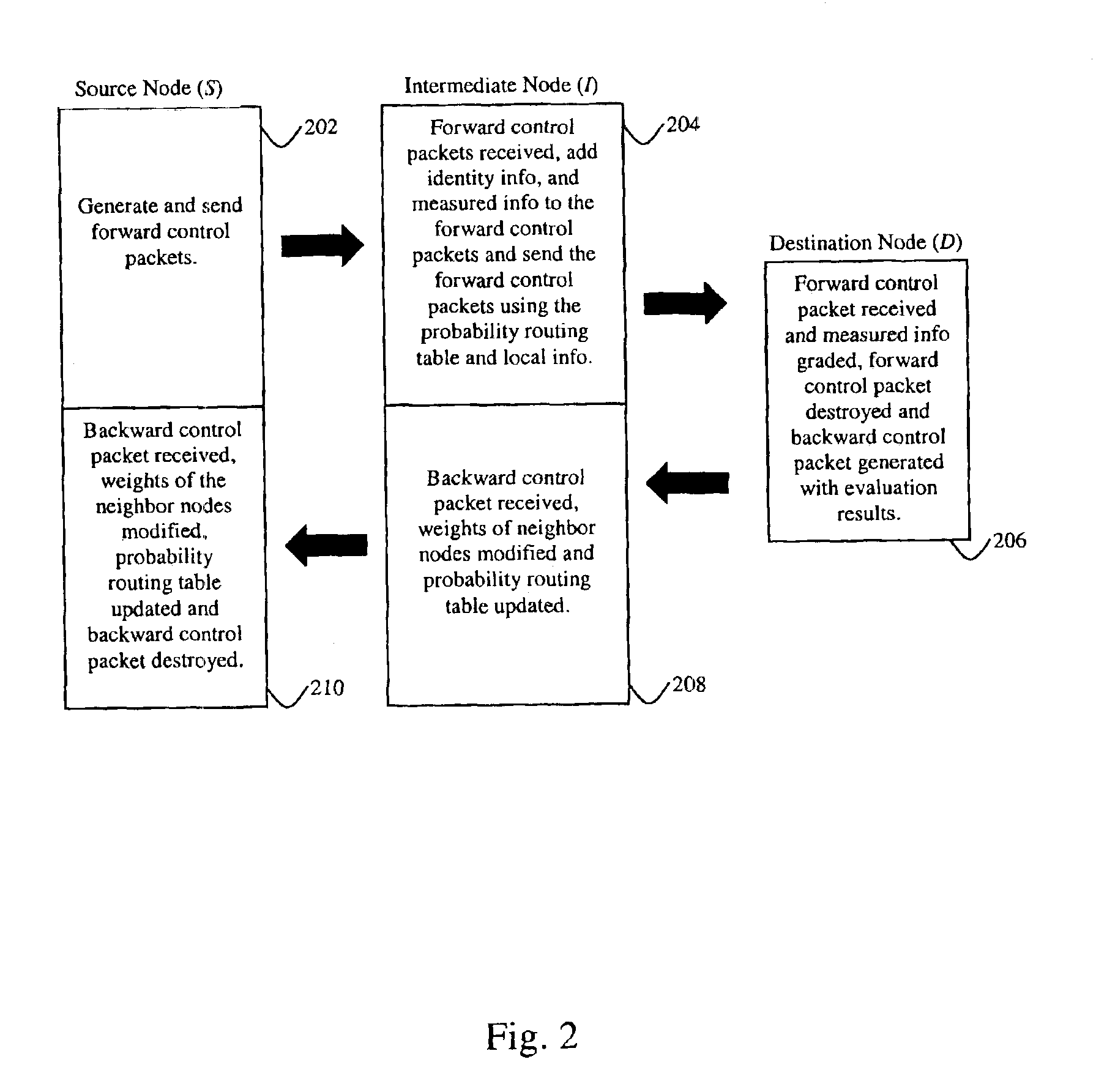
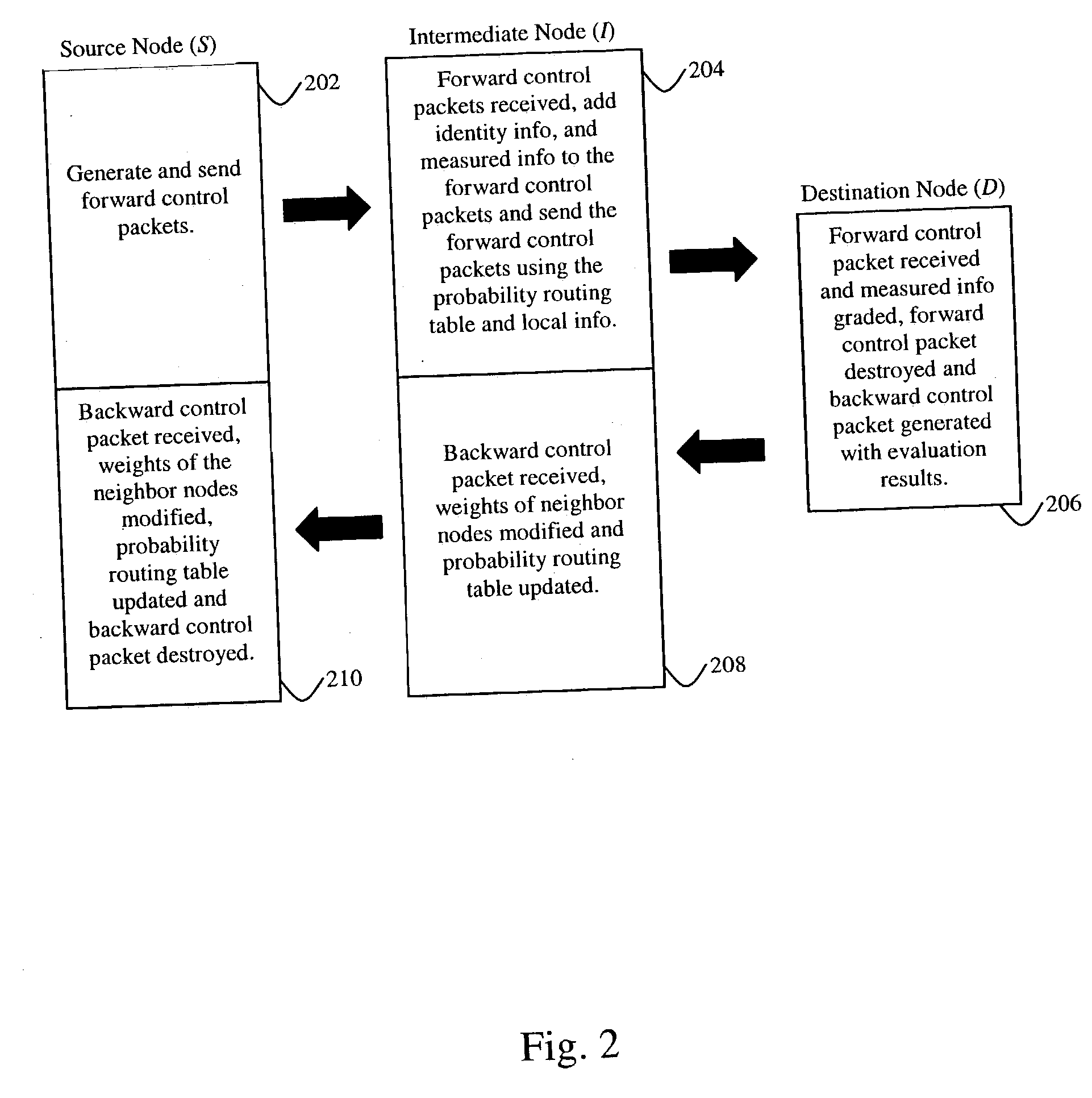
The present invention provides a method for selecting and routing data in an ad-hoc mobile wireless network having a plurality of Nodes including multiple sources and destinations. The method includes sending a forward control packet from a source to the destination via at least one intermediate Node at intervals of time, where the intermediate Node is randomly selected. Each of the intermediate Nodes store weights of the neighbor Nodes. When the forward control packets reach the destination Node, they are evaluated in accordance with one or more given parameters and send back as backward control packets storing the evaluation results. As each of the intermediate Nodes receive the backward control packets, the weights of the corresponding neighbor Nodes are modified based on the stored evaluation results. Similarly, as the backward control packets are received at the source Nodes and the weights of the corresponding neighbor Nodes are modified based on the stored evaluation results. Finally, a group of routing routes to the destination are selected based on the modified weights of the neighbor Nodes and data packets are send from the source to the destination via the intermediate Nodes upon selection of the group.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
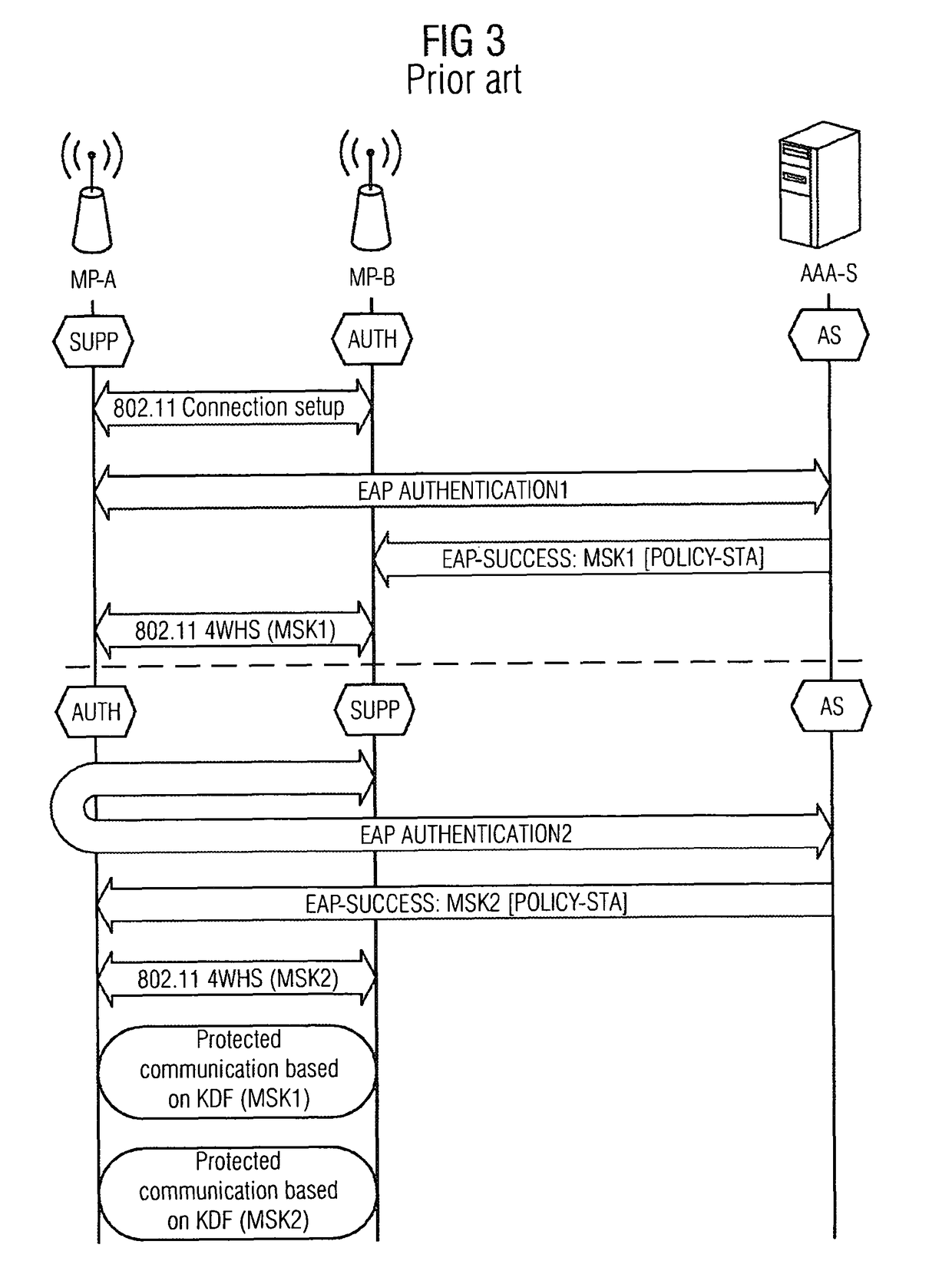
Method and arrangement for providing a wireless mesh network
ActiveUS8122249B2Small loadReduce signaling overheadUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesProxy serverMesh node
Provided are a method and an arrangement for creating a wireless mesh network in which a new node is provided that is connected between mesh nodes and an AAA server located in an infrastructure network. Based on basic encoding data that is available to the new node following successful initial authentication of a first mesh node, the new node performs the authentication similar to a proxy server instead of an AAA server, particularly for a limited time, during subsequent authentication attempts.
Owner:UNIFY PATENTE GMBH & CO KG
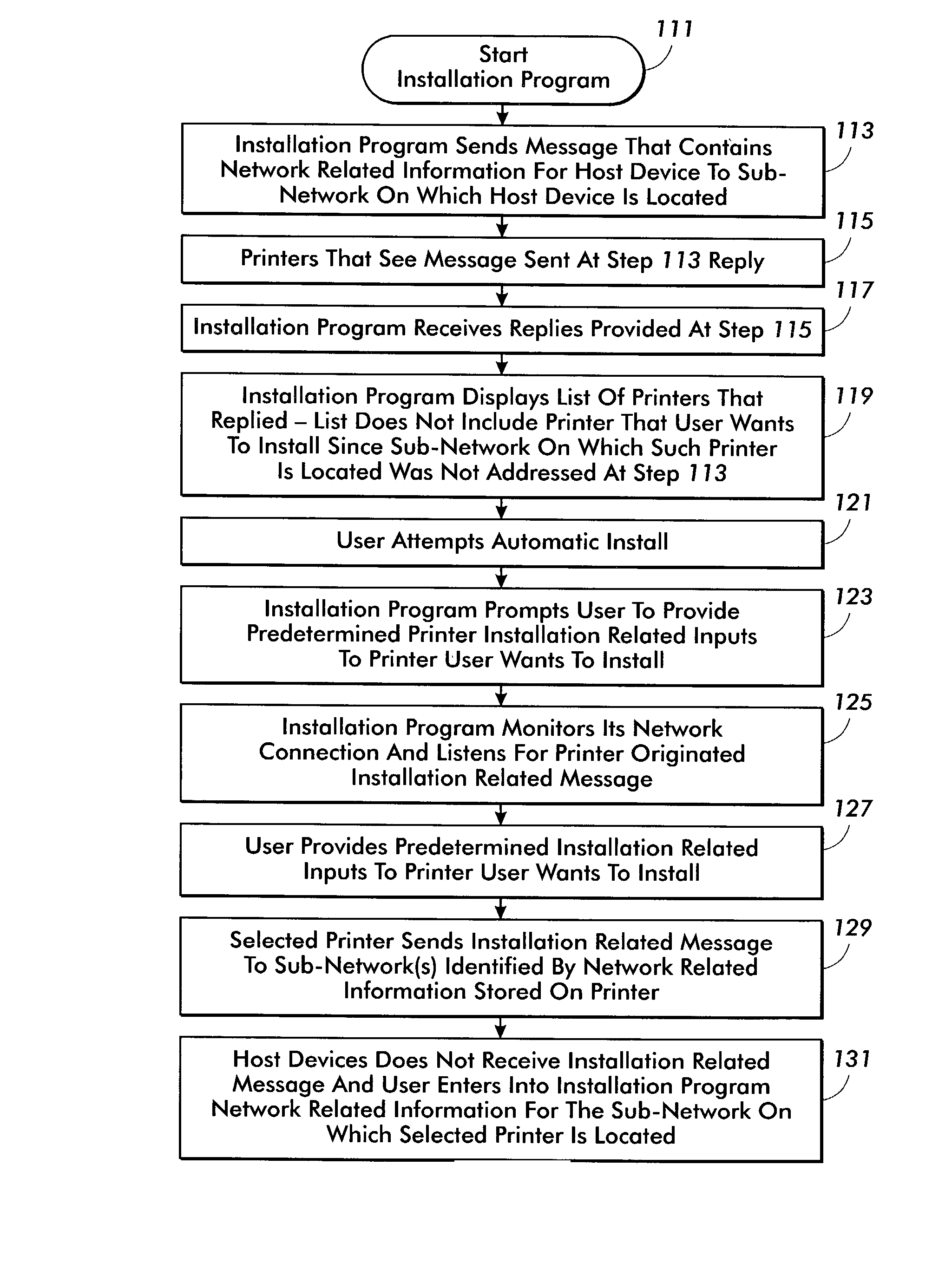
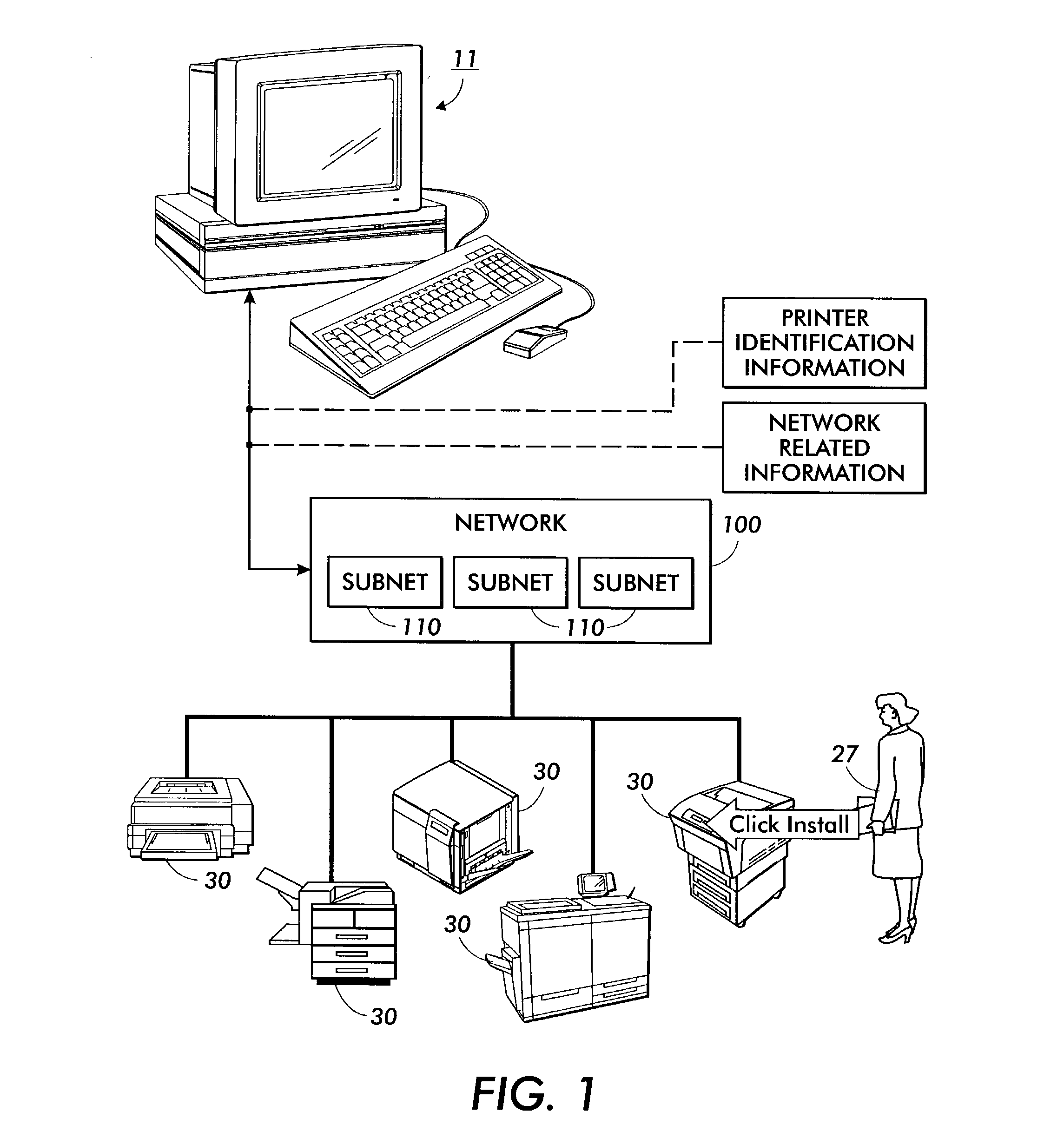
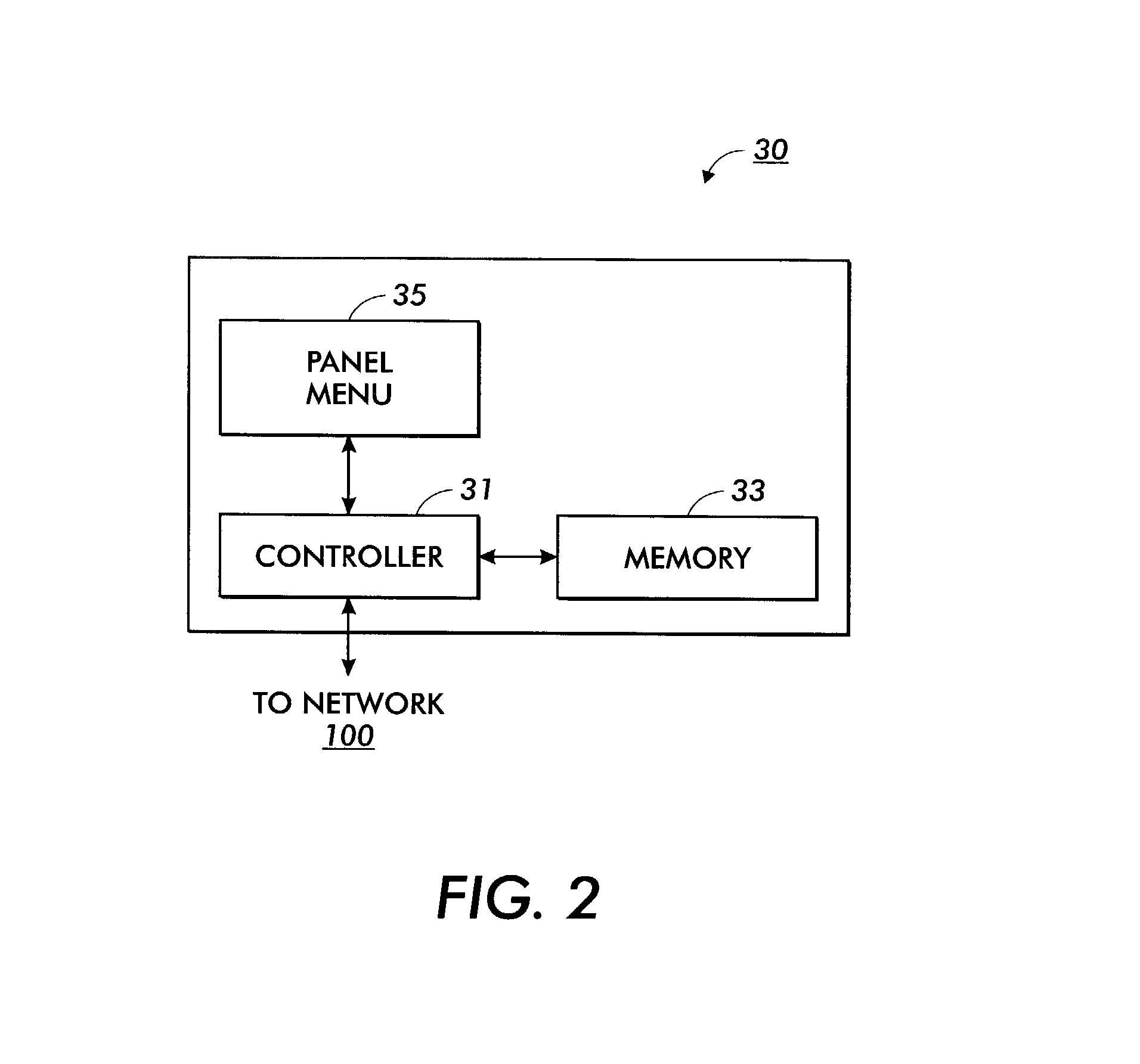
Network device installation
A system for installing a non-infrastructure network device including a device installation program located on a host device connected to a first sub-network, a device controller configured to be connected to a second sub-network for receiving network information for the first sub-network from the device installation program, and a device memory for storing the network information for the first sub-network.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Mobile ad hoc network system and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20050157661A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAccess technologyNetwork service
A mobile ad-hoc network system includes: a plurality of mobile terminals; and a central control means for setting an optimal route among terminals, performing connection with an infrastructure network and connecting networks using different wireless access technologies. By including the central control means, the ad-hoc network system can overcome the limitation of the related art ad-hoc network and provide a network service with high quality and stability to each terminal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
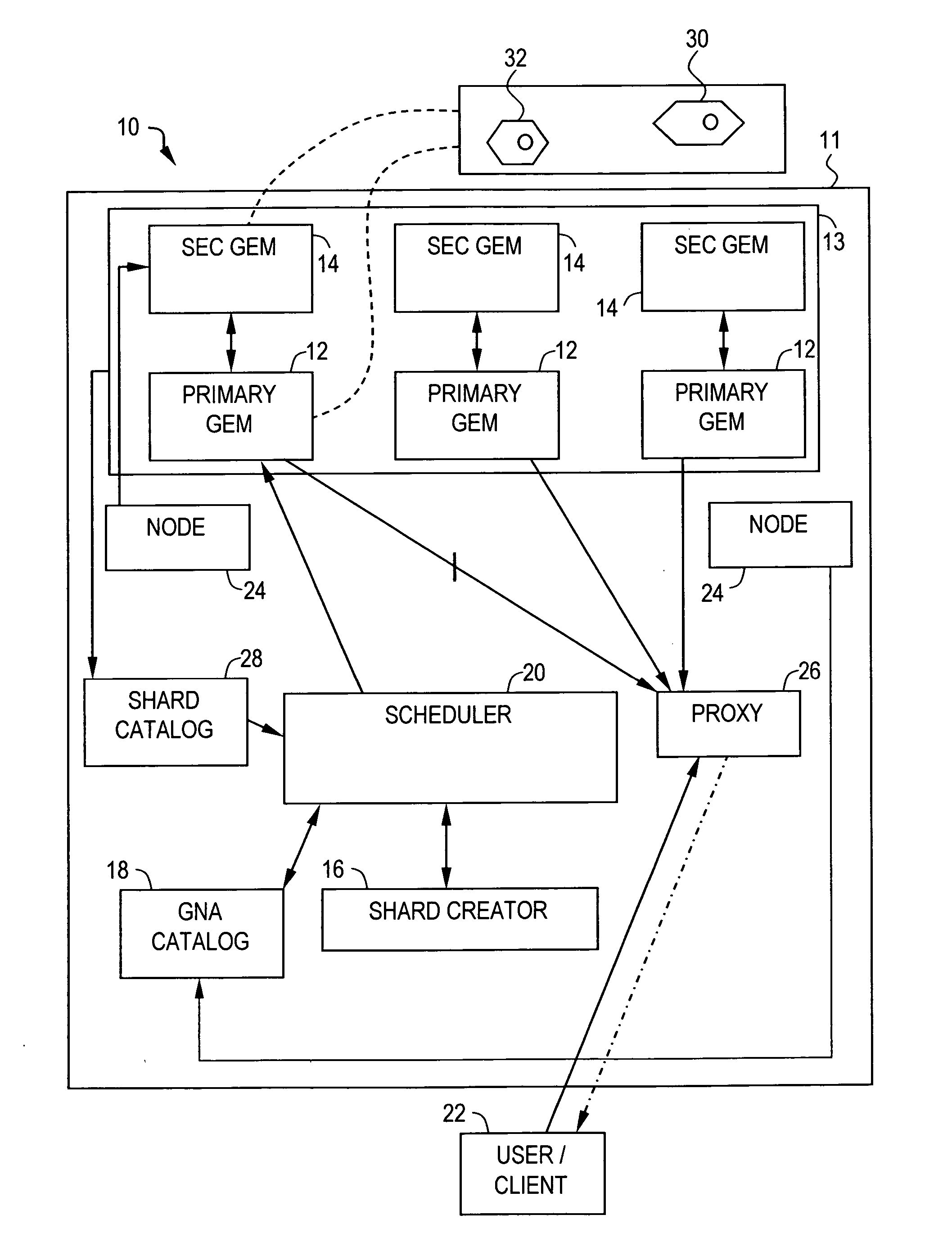
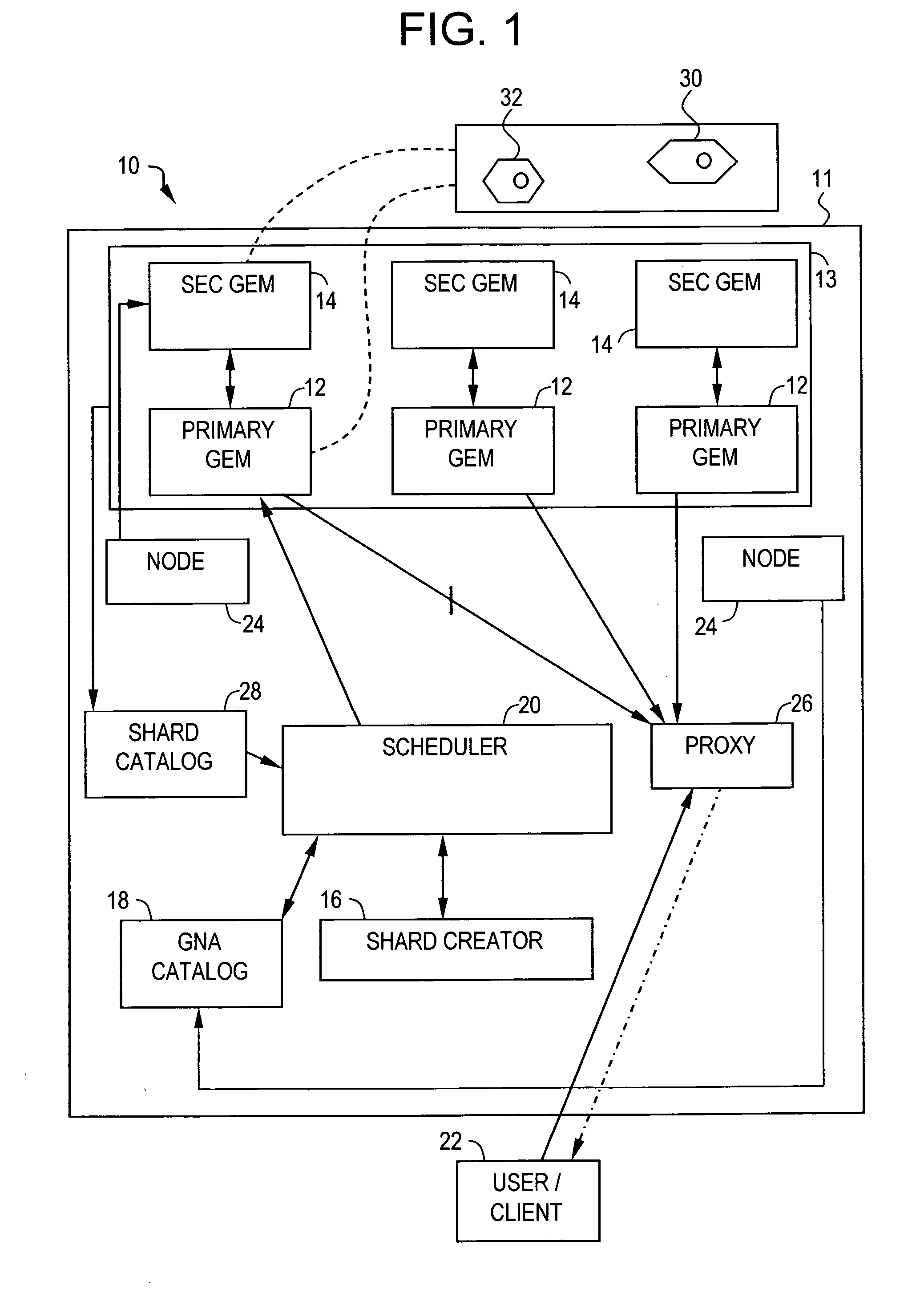
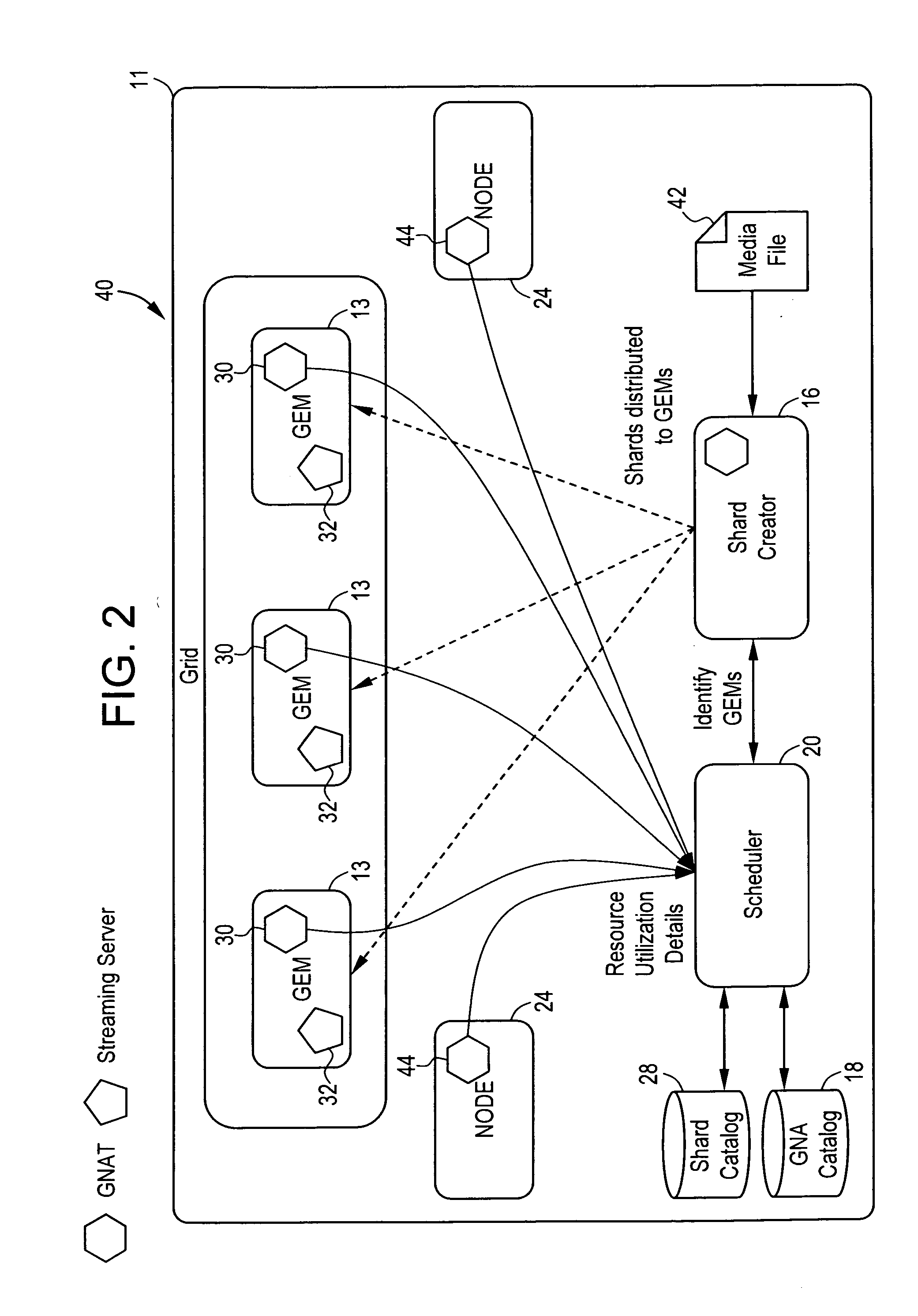
Video on demand system and methods thereof
ActiveUS20070083617A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsPower gridGrid network
A method for transmitting a video data over a grid infrastructure network is disclosed. The method includes receiving a request from at least one user for viewing the video data and identifying a plurality of attributes from a plurality primary grid enabled mini servers (GEMS), wherein the plurality of primary GEMS together form the grid network. The method further includes partitioning video data into a plurality of discrete fragments using a shard creator indicative of the plurality of attributes in each of the plurality of primary GEMS and allocating the plurality of discrete fragments among the plurality of primary GEMS based on the plurality of attributes of each of the plurality of primary GEMS. The method also includes decoding the plurality of discrete fragments of the video data using a streaming server for transmitting the video data to the at least one user.
Owner:INFOSYS TECH LTD (IN)
Routing method for mobile infrastructureless network
InactiveUS20040146007A1Improve performanceOvercomes drawbackError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMobile wirelessReal-time computing
The present invention provides a method for selecting and routing data in an ad-hoc mobile wireless network having a plurality of Nodes including multiple sources and destinations. The method includes sending a forward control packet from a source to the destination via at least one intermediate Node at intervals of time, where the intermediate Node is randomly selected. Each of the intermediate Nodes store weights of the neighbor Nodes. When the forward control packets reach the destination Node, they are evaluated in accordance with one or more given parameters and send back as backward control packets storing the evaluation results. As each of the intermediate Nodes receive the backward control packets, the weights of the corresponding neighbor Nodes are modified based on the stored evaluation results. Similarly, as the backward control packets are received at the source Nodes and the weights of the corresponding neighbor Nodes are modified based on the stored evaluation results. Finally, a group of routing routes to the destination are selected based on the modified weights of the neighbor Nodes and data packets are send from the source to the destination via the intermediate Nodes upon selection of the group.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
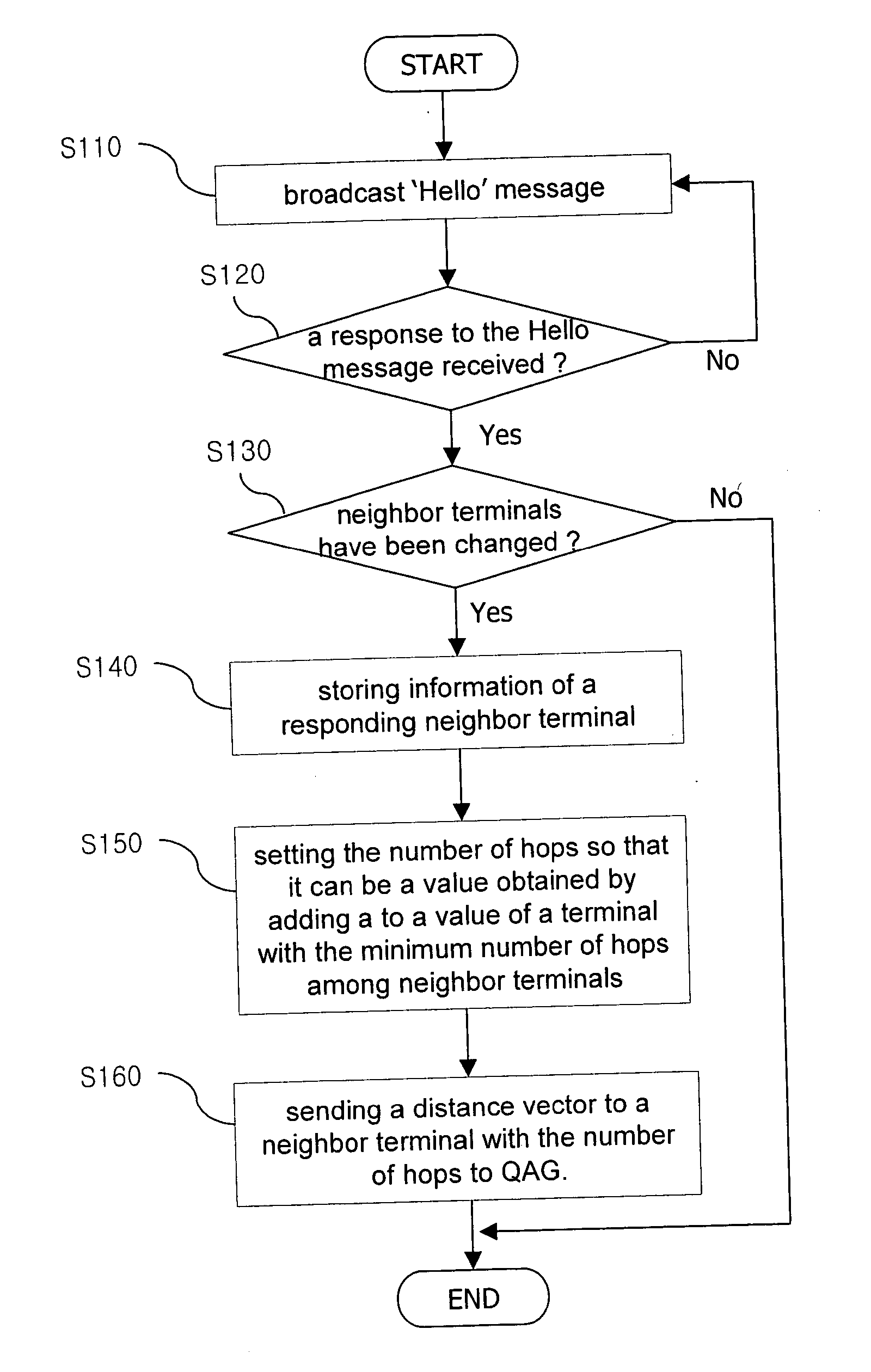
System clock synchronization in an ad hoc and infrastructure wireless networks
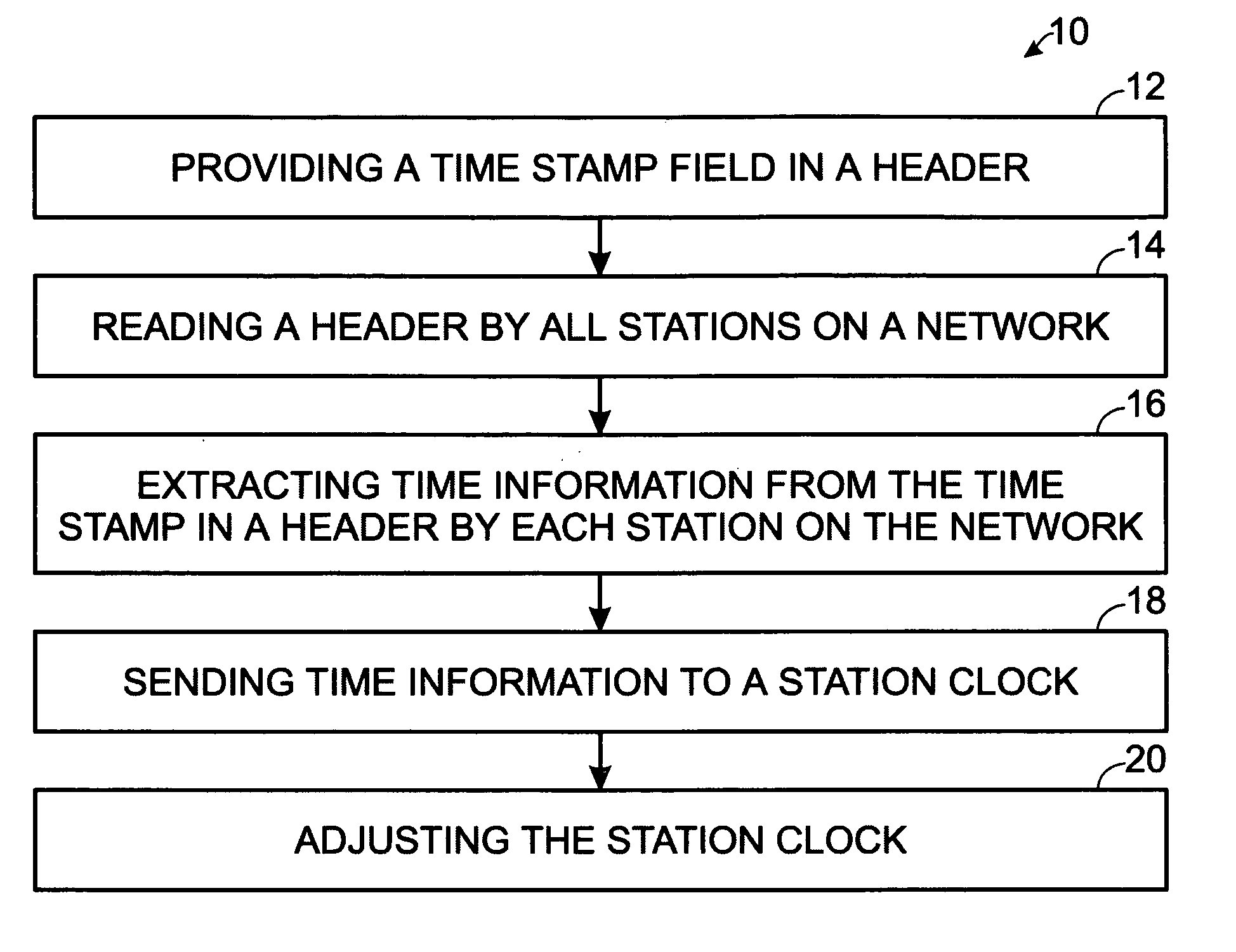
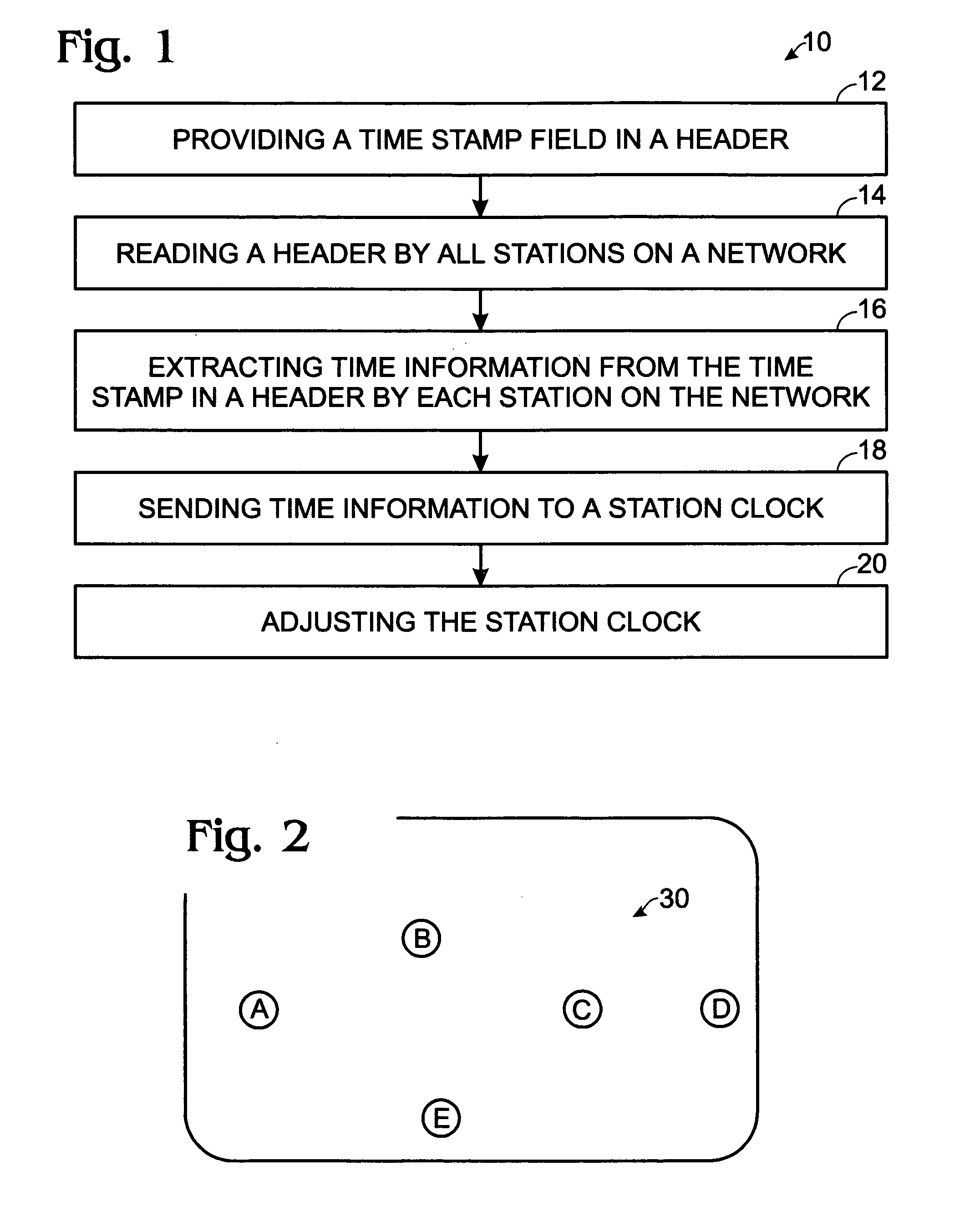
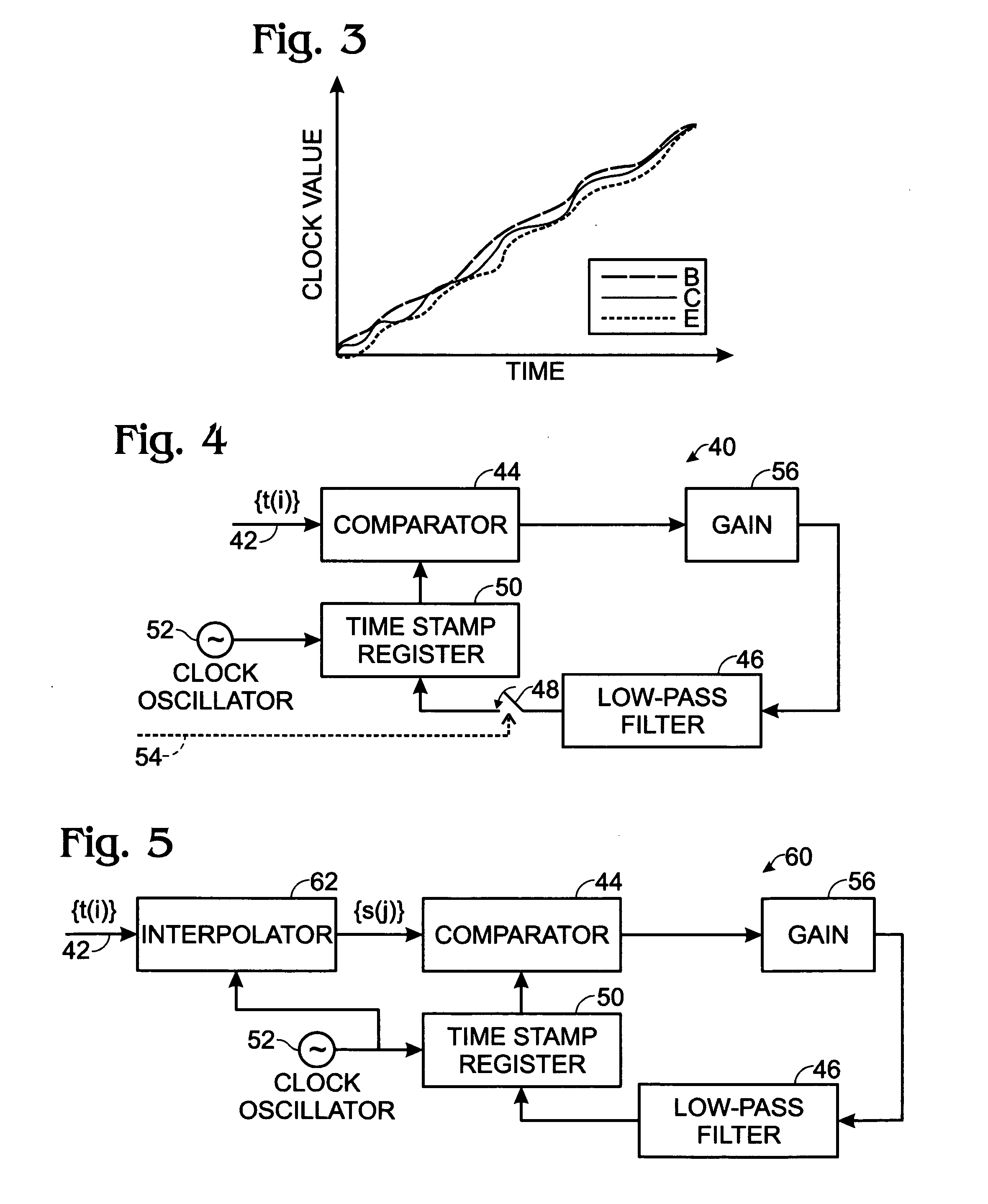
A method of synchronizing clocks in the stations of ad hoc and infrastructure networks includes providing a time stamp field in a header; reading the header by all stations in a network; extracting the time stamp information from the header by each station in the network as time information; sending extracted time information to a station clock; and adjusting the station clock as a function of the extracted time information. A system for synchronizing clocks in the stations of ad hoc and infrastructure networks includes a DLL having a comparator for receiving the time stamp information and a low-pass filter having a long time-constant for adjusting the station clock in a gradual manner; a time stamp field in a header; and time information extracted from the time stamp information of the header by each station in the network.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for realizing medical and healthy care system based on Internet of things
InactiveCN101695440AEasy to replaceOvercome limitationsNetwork topologiesDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyThe Internet
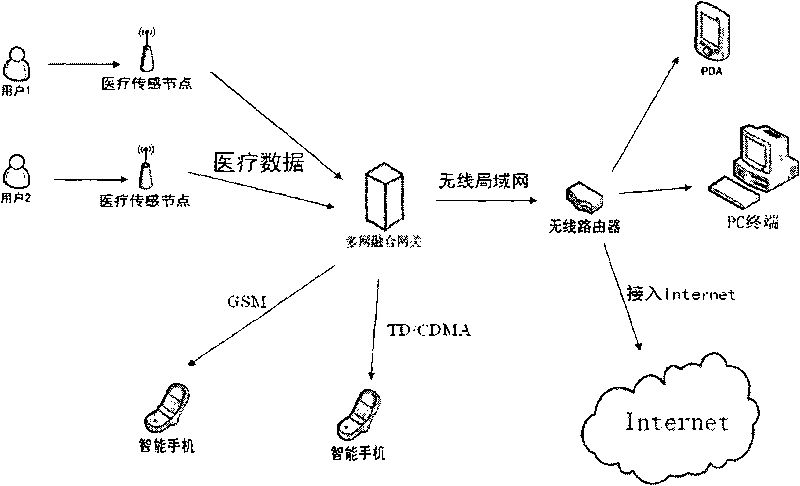
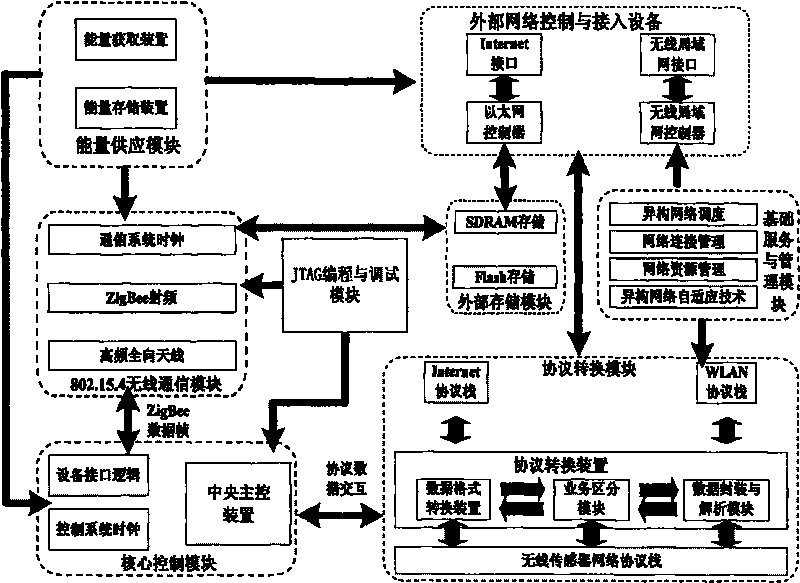
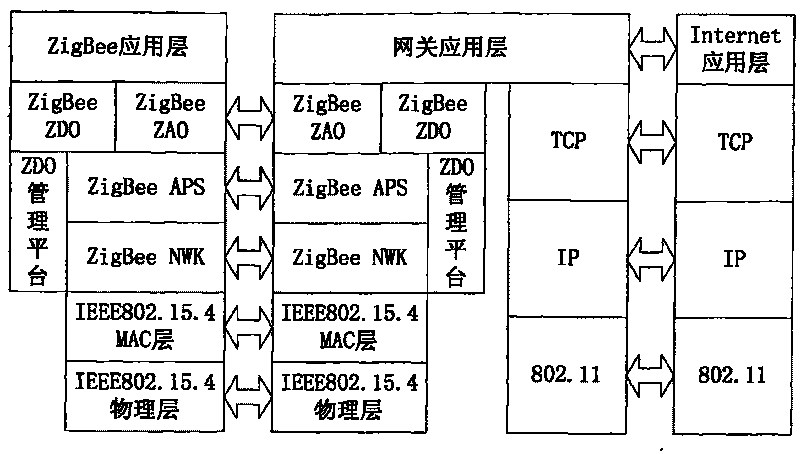
The invention discloses a method for realizing a medical and healthy care system based on the Internet of things, which consists of five parts, namely a medical sensing node, a wireless sensor network gateway, mobile terminal equipment, system software and terminal software. The medical sensing node acquires pathological information of a human body, such as blood oxygen, sphygmus, pulse and body temperature, by various probes, such as a blood oxygen probe, a pulse probe and a body temperature probe and then transmits data to wireless sensor network gateway equipment through a wireless sensing module; and the gateway equipment transmits pathological data to terminal equipment through an infrastructure network by implementing seamless switching among the wireless sensing network, an Ethernet and a wireless local area network to get rid of the restrict of wireline equipment and use related mobile equipment, such as a PDA and a smart phone, to monitor the pathological information of a patient conveniently and fast, in a hospital or a wireless network coverage. The system can be applied to daily life and work of people actually so that a medical personnel and a patient family member can conveniently and fast monitor the pathological information of the wirelessly and remotely.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
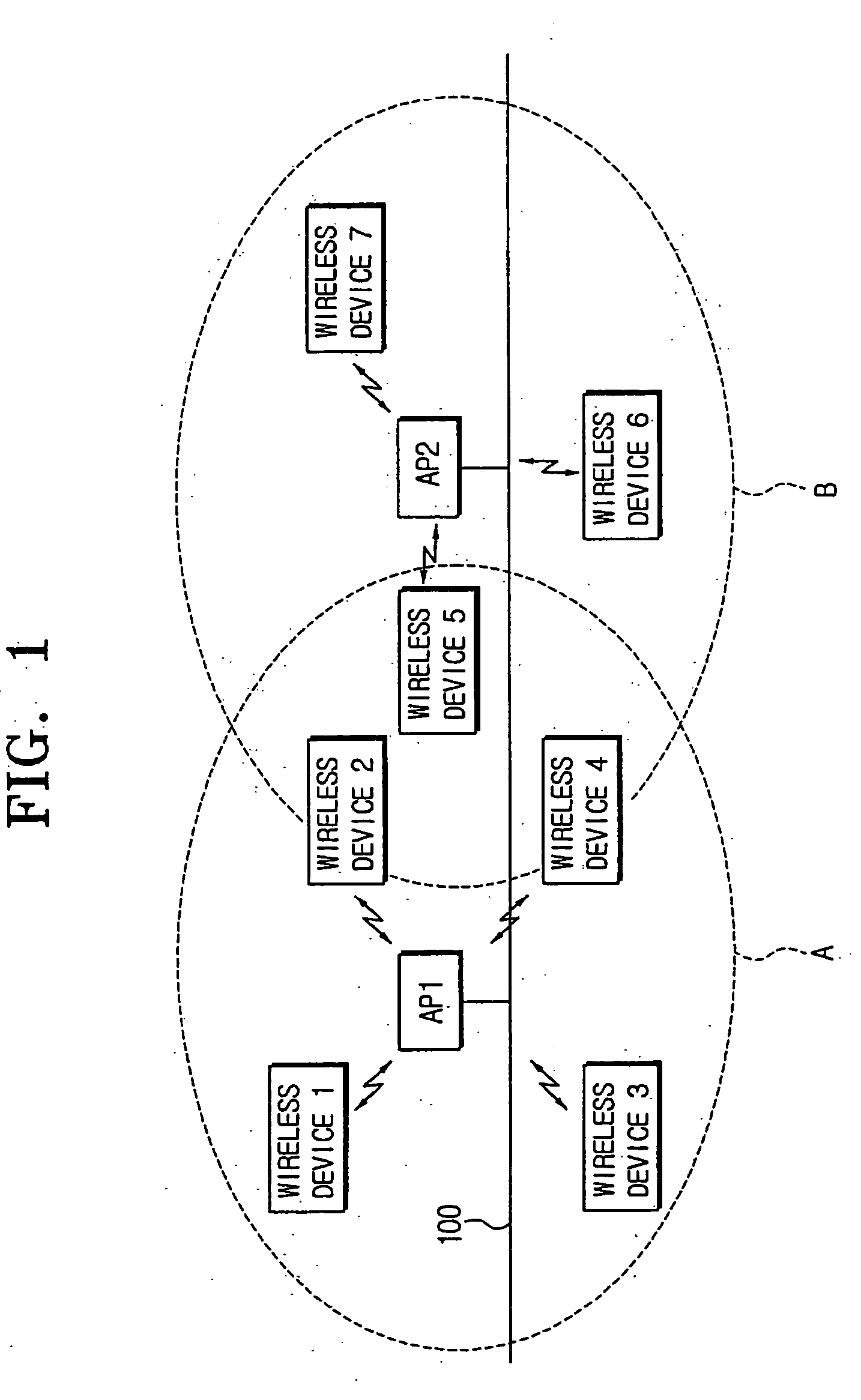
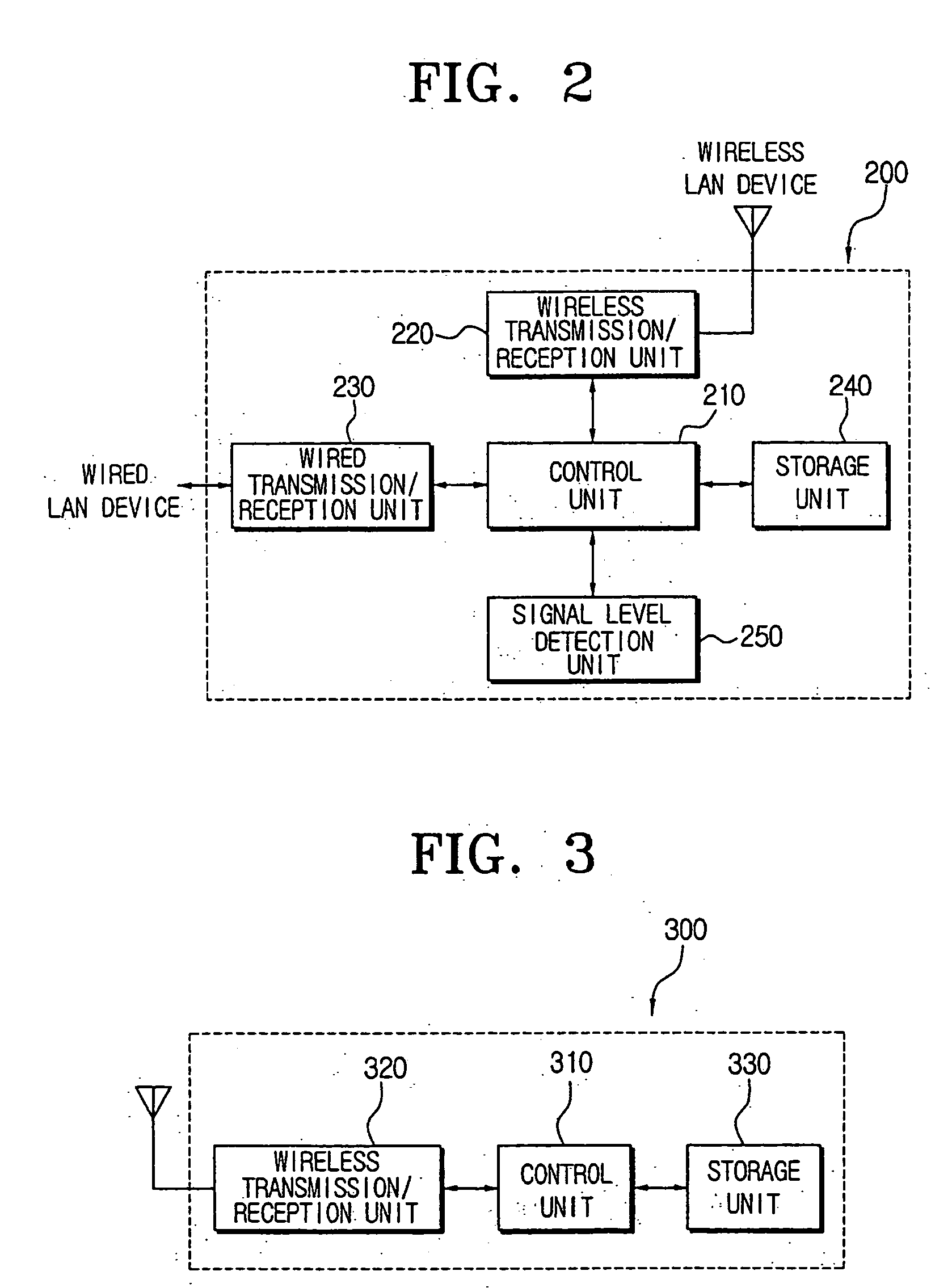
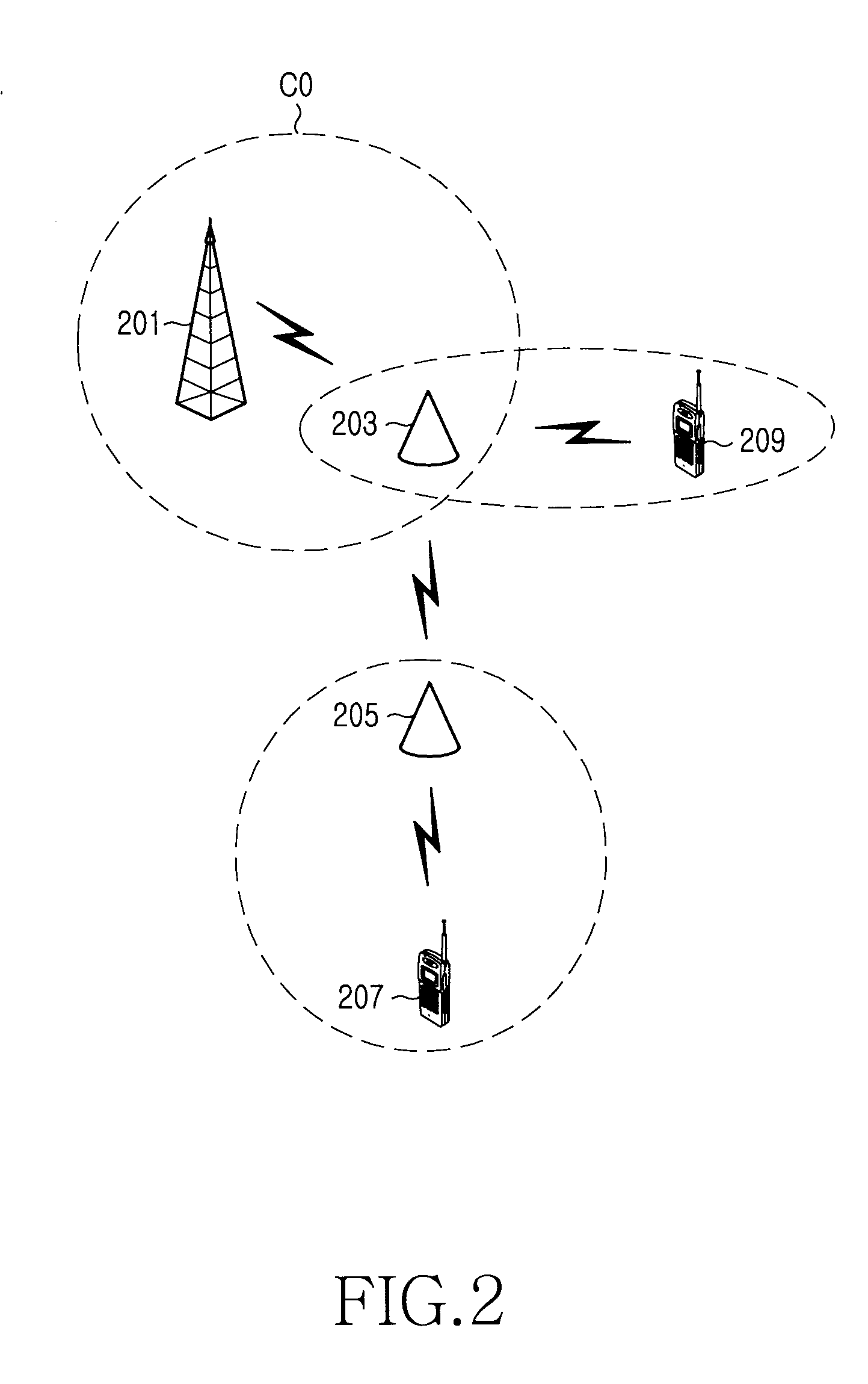
Communication system and method in wireless infrastructure network environments
ActiveUS20050020262A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexCommunications systemReal-time computing
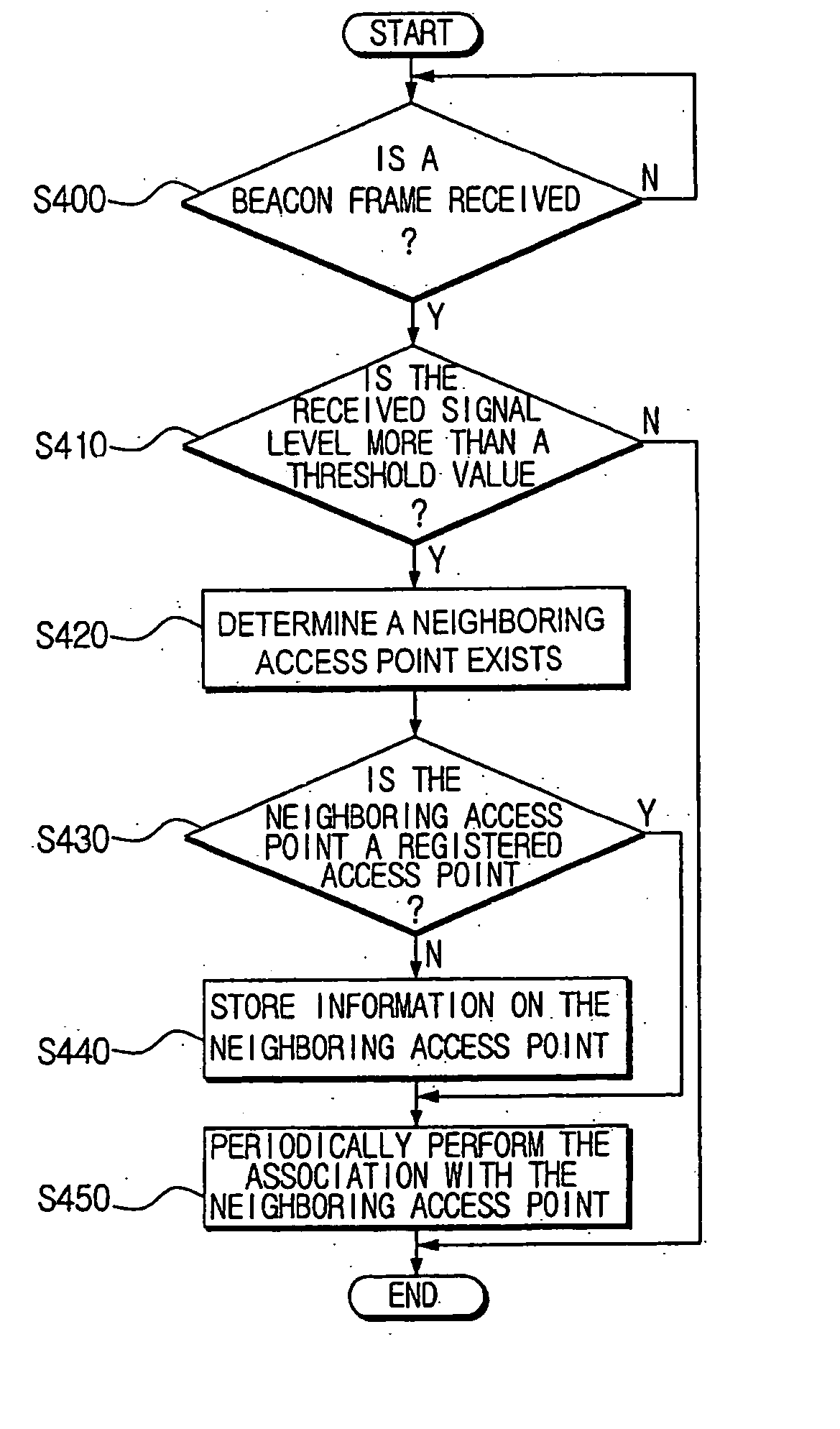
A wireless communication system including first and second wireless devices, and first and second access points to synchronize the first and second wireless devices, wherein the first access point determines whether the second access point exists in a neighboring area, periodically checks communication states of the second access point, sends an access point replacement command to the second wireless device linked to the second access point in response to determining the second access point is communication-disabled, and forms a new communication channel with the second wireless device according to an association request signal received from the second wireless device in response to the access point replacement command.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
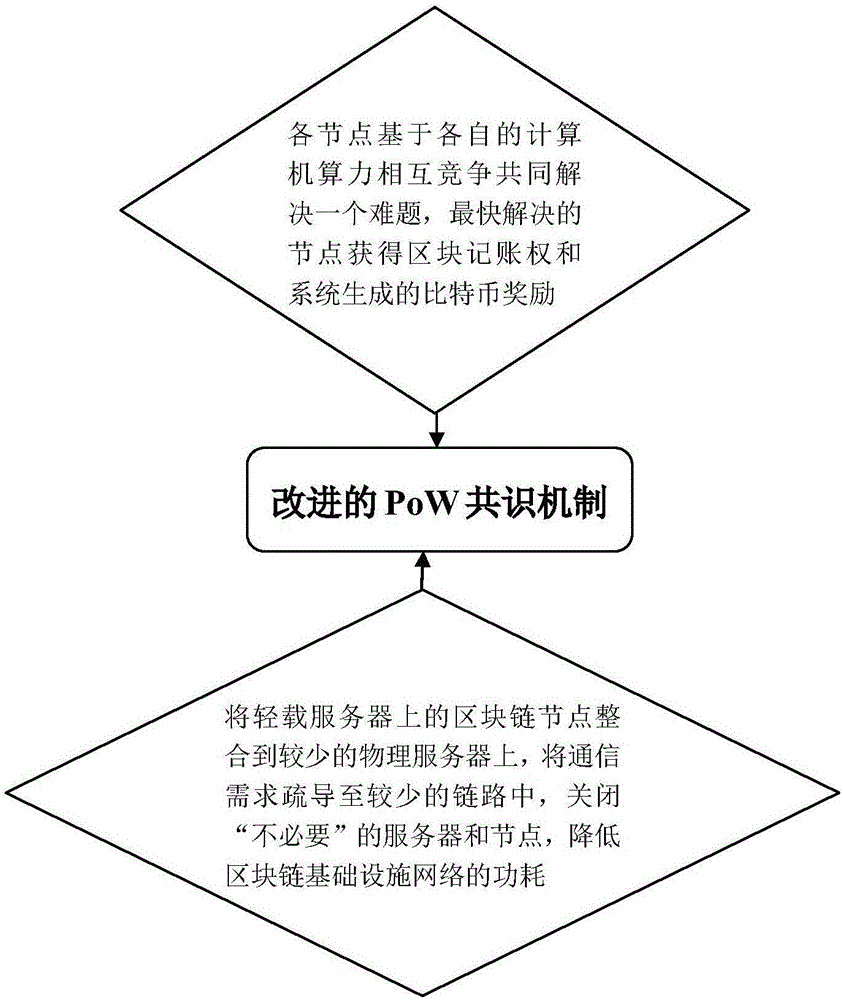
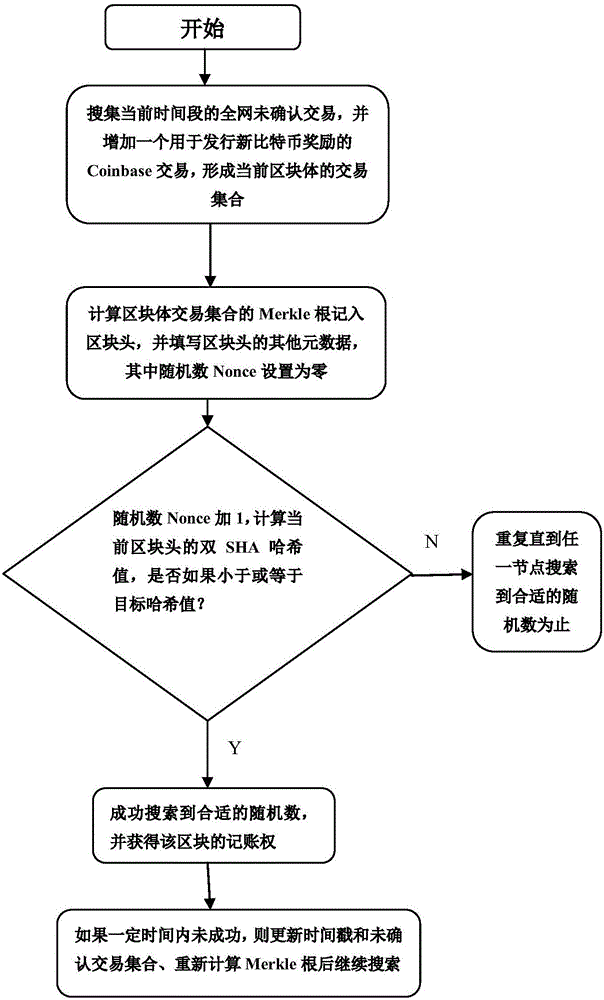
Block chain power consumption perception PoW consensus mechanism
InactiveCN106296191AImprove performanceEmission reductionResource allocationPayment protocolsGeolocationWdm mesh networks
The present invention provides a block chain power consumption perception PoW consensus mechanism. The mechanism comprises the following steps: (1) in a Bitcoin system, each node is subjected to mutual competition based on each computer power to commonly solve an SHA math problem with complex solution and easy verification, and the node which solves the problem at the fastest speed obtains a block account right and Bitcoin award automatically generated by the system; and (2) employing a WDM mesh network to interconnect physics servers located at different geographic positions to form a block chain basic facility network, respond to the block chain request generation power consumption and allow the block chain node on a light load server to integrate on few physics servers, and the communication requirement is dredged to few chains to close unnecessary servers and nodes. The power consumption perception PoW consensus mechanism is employed to further execute the resources potential of the basic facility network while improving the block chain performance, perform power consumption perception and reduce the carbon emission and the greenhouse effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN FANXI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of authenticating a mobile network node in establishing a peer-to-peer secure context between a pair of communicating mobile network nodes
ActiveUS20060087999A1Near-field transmissionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSecure communicationSecret code
Methods for authenticating peer mobile network nodes for establishing a secure peer-to-peer communications context in an ad-hoc network are presented. The methods include accessing wireless infrastructure network entities at low bandwidth and for a short time duration to obtain cryptographic information regarding a peer mobile network node for the purpose of establishing secure peer-to-peer communications therewith ad-hoc network. Having received cryptographic information regarding a peer mobile network node, the method further includes challenging the peer network node with a challenge phrase derived from the cryptographic information received, receiving a response, and establishing a secure communications context to the peer mobile network node based on the validity of the received response. Advantages are derived from addressing security threats encountered in provisioning ad-hoc networking, by leveraging wireless infrastructure network security architecture, exemplary deployed in UMTS / GSM infrastructure networks, enabling seamless mobile network node authentication through the existing UMTS and / or GSM authentication infrastructure, while pervasively communicating with peer mobile network nodes in an ad-hoc network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
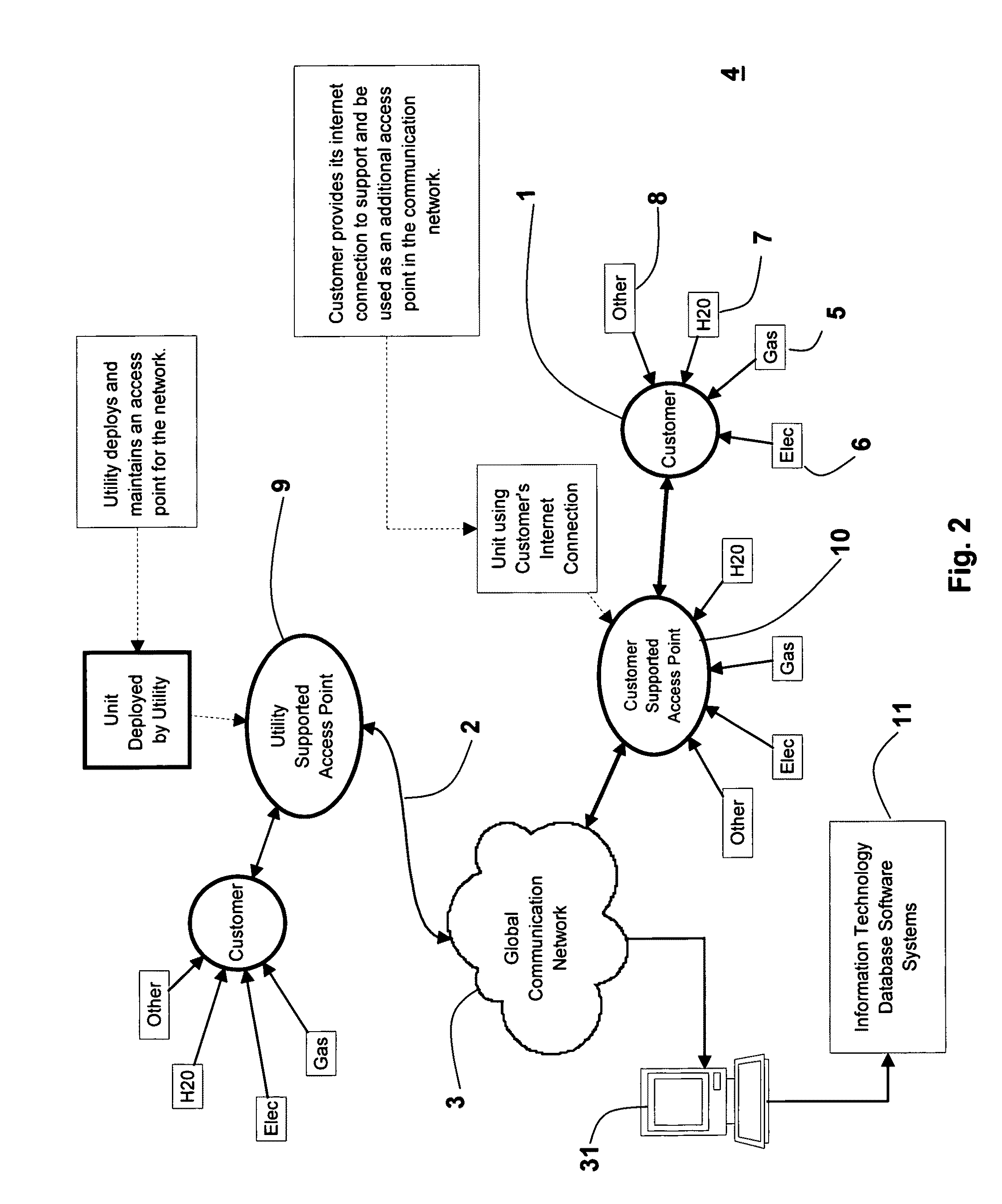
Customer supported automatic meter reading method
InactiveUS20090267792A1Reduce operating costsMuch-reduced capital costElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusUtility computingDistribution system
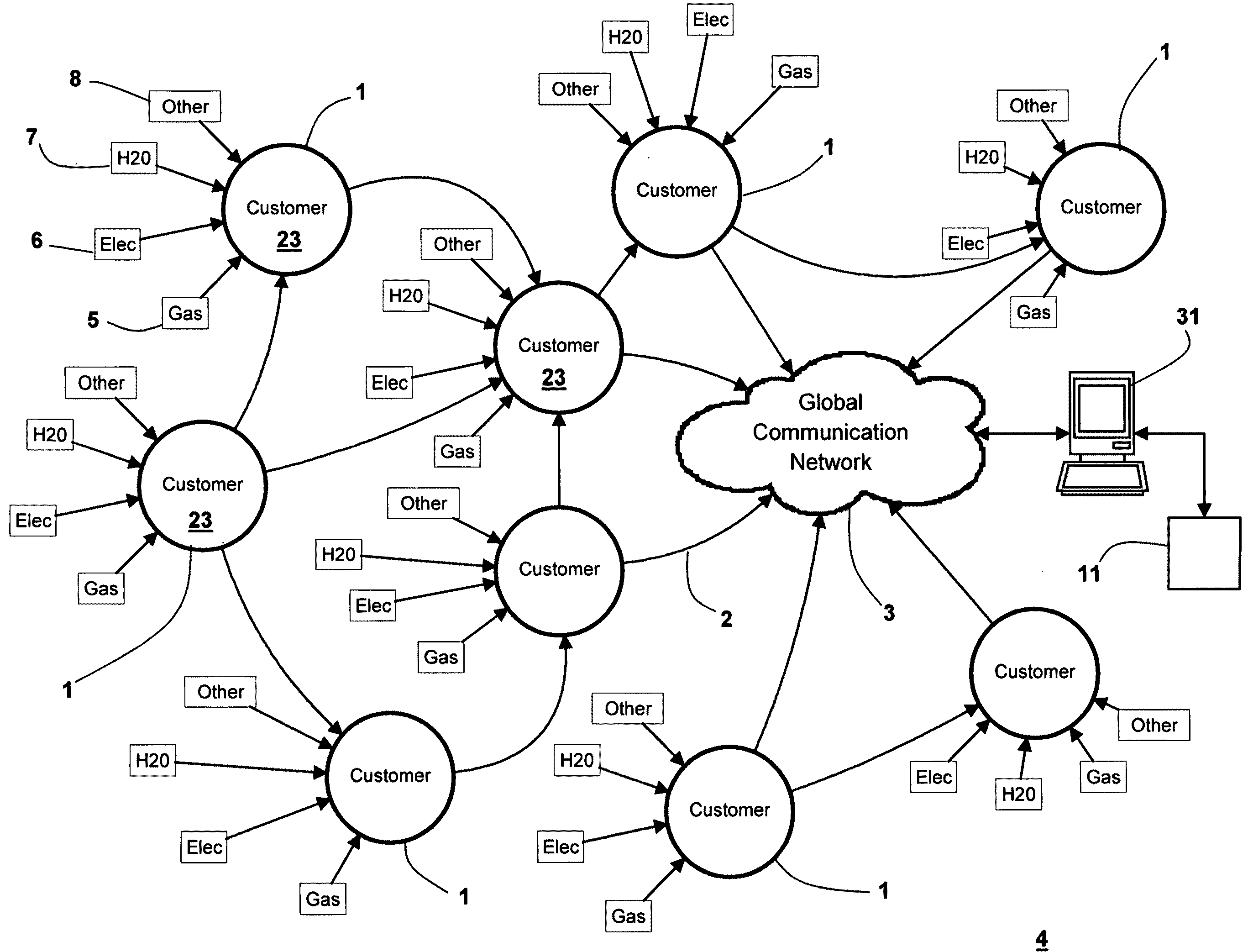
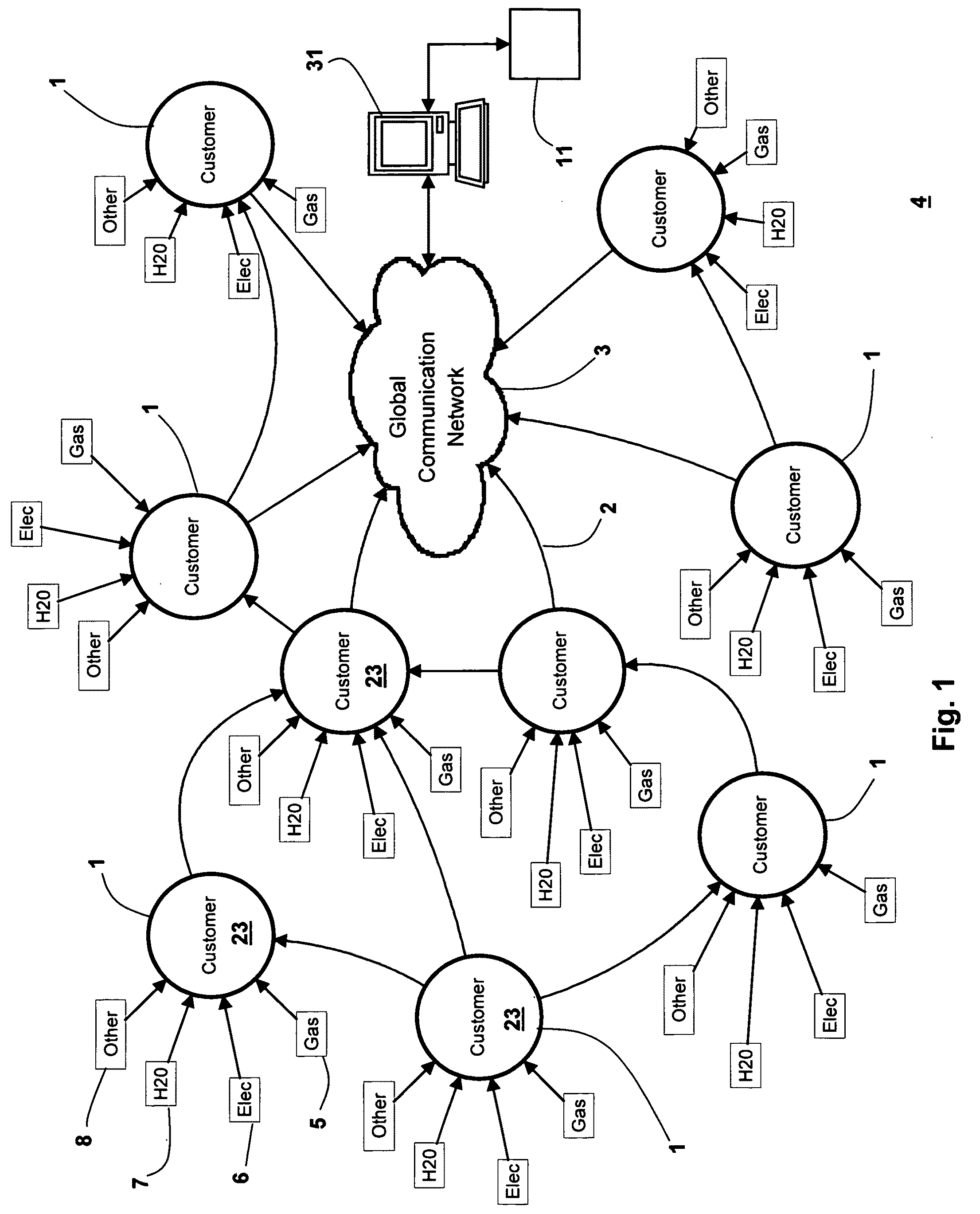
A method is described in which an automatic metering reading (AMR) method is implemented in the utility distribution system. The AMR method comprises a mesh network in which selected customers of the utility company support the network by providing collocated internet access points via the customer's existing internet connections; thus providing AMR data “backhaul”, thereby minimizing the need for the utility to build and deploy all the access points needed to populate the mesh infrastructure network. This customer access point for which the customer is remunerated, in whole or in part by the utility, allows the utility to develop and implement all the network elements to meet the utility AMR needs at a much lower cost. The customer-supported method can allow the utility to efficiently and effectively service its metering needs via the global communications network without a major investment in hardware, software and personnel.
Owner:CRICHLOW HENRY
Bearer control mode (nw-only or user-only) handling in intersystem handover
ActiveUS20110065435A1More flexibility in controlMaintain backward compatibilityConnection managementWireless network protocolsRadio access networkHandover
A method, a gateway node, a policy control node and a infrastructure network for handling a handover of a User Equipment communicating wirelessly with the infrastructure network. A first gateway node receives handover information indicative of a handover of the user equipment between two radio access networks the first gateway node determining a bearer control mode on the basis of the handover information the first gateway node transmitting control information determined on the basis of the bearer control mode to a policy control node the first gateway node controlling the bearer binding on the basis of the bearer control mode.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
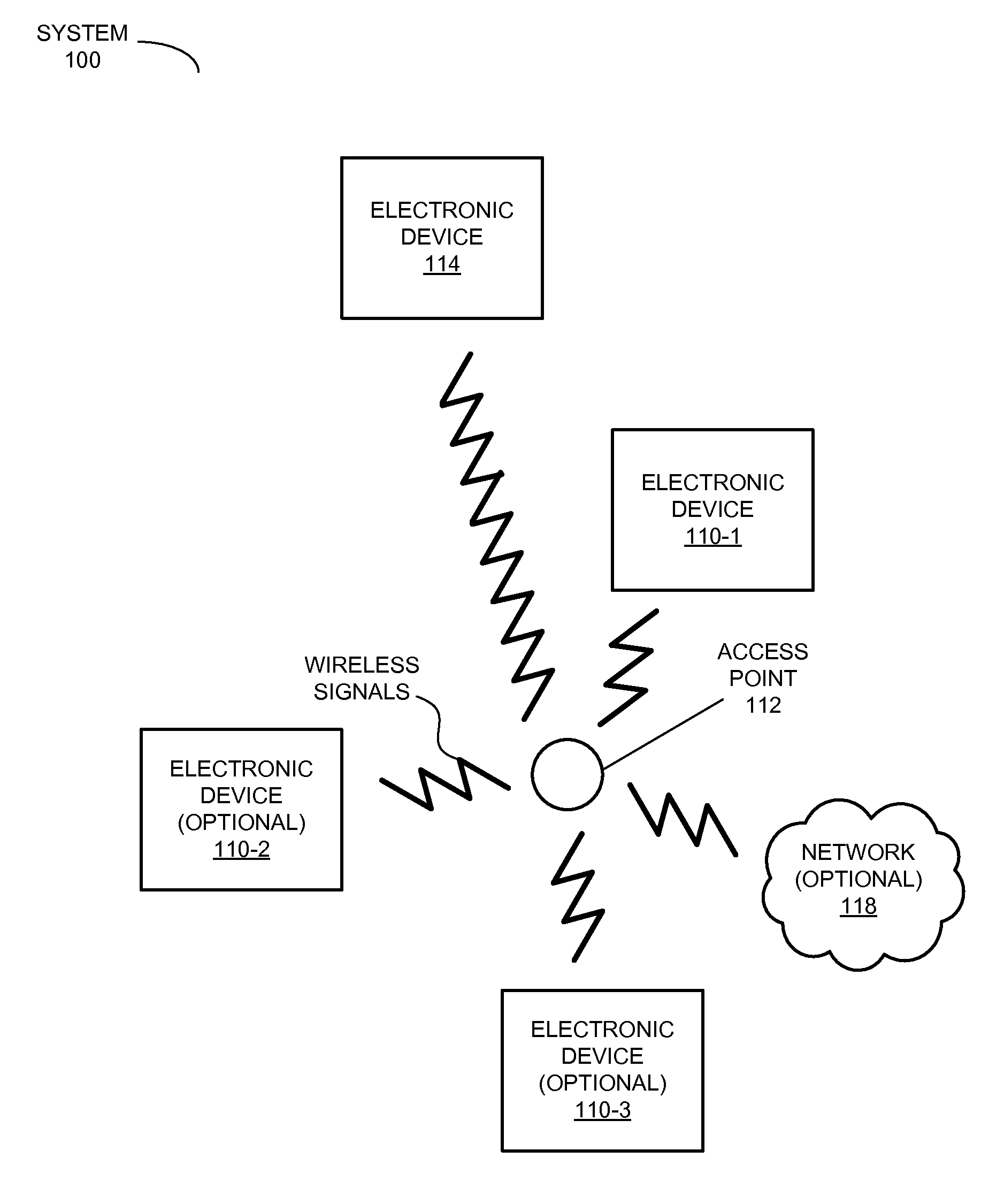
Infrastructure offload wake on wireless LAN (WOWL)
Aspects of an infrastructure offload wake on wireless LAN (WOWL) are described. An aspect of the system may include a networked device, or station, which may communicate one or more filters to an infrastructure networking device. The infrastructure networking device may utilize the filters to perform pattern matching operations on frames or packets received from the network for delivery to at least the station while the station is in an inactive, or low-power, state. When pattern matching operations performed at the infrastructure networking device indicate receipt of a frame or packet on behalf of the inactive station, which matches at least one of the filters, the infrastructure networking device may store an indication value. The indication value may denote receipt of at least one frame or packet that matched at least one of the filters, which were communicated to the infrastructure networking device by the station.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
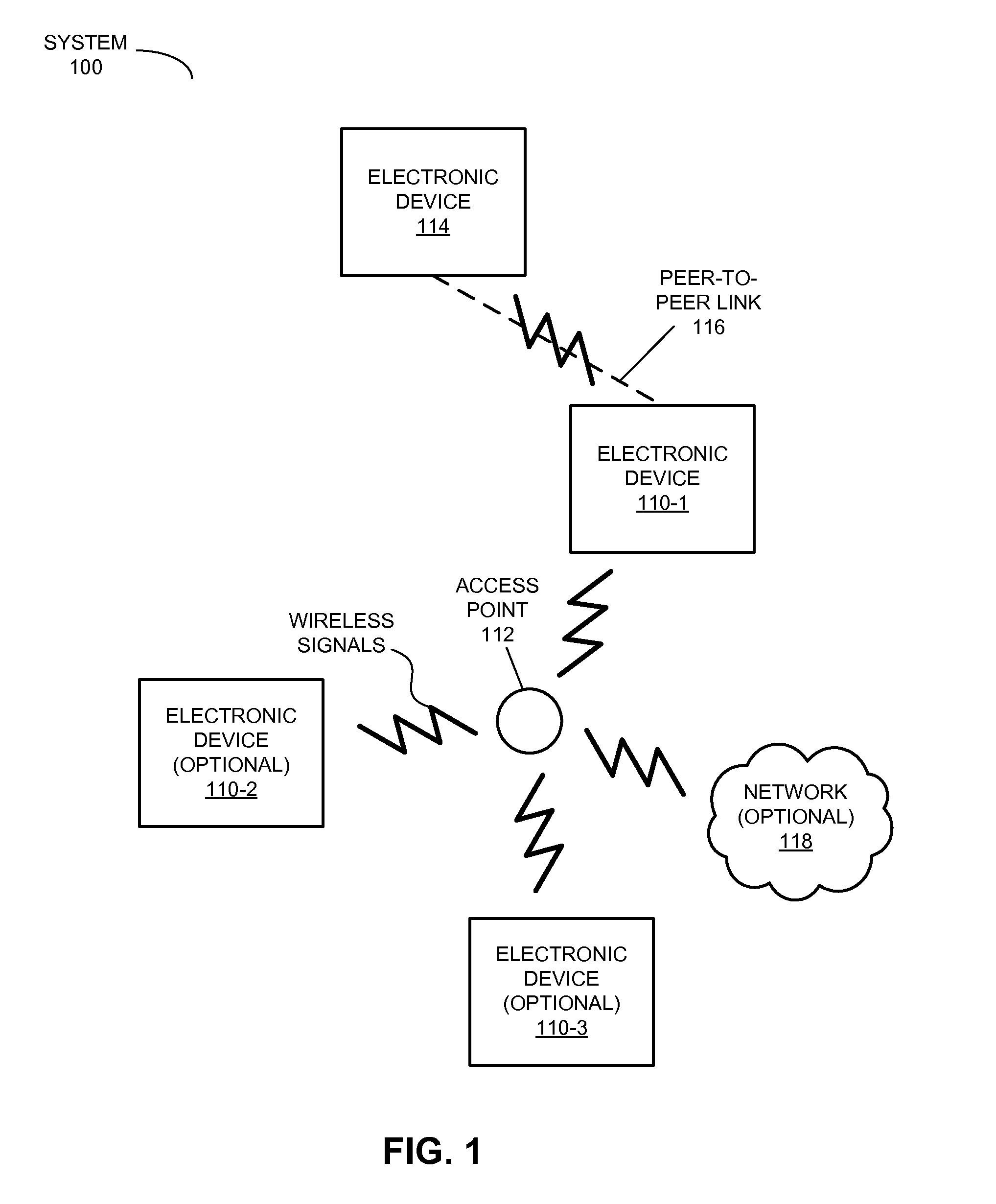
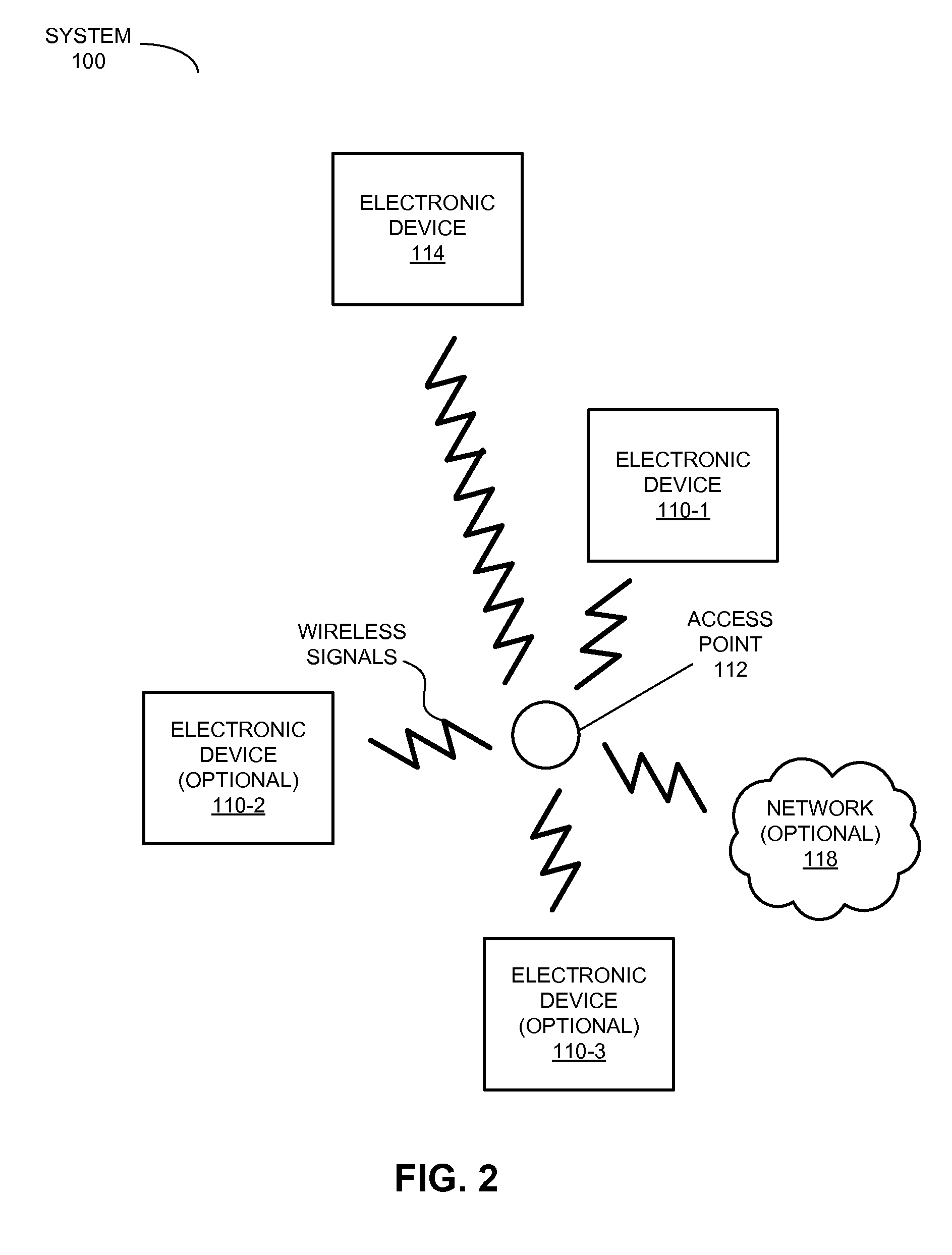
Shared network access via a peer-to-peer link
InactiveUS20130227647A1Easy accessCommunication securityDigital data processing detailsAssess restrictionSecure communicationPeer-to-peer
An electronic device receives a request for access to the infrastructure network (and, more generally, a ‘resource’) from the other electronic device via a peer-to-peer link. In response to the request, the electronic device determines that it has access to the infrastructure network, and provides a response to the other electronic device via the peer-to-peer link indicating that the electronic device has access to the infrastructure network. Then, the electronic device establishes secure communication with the other electronic device, and provides access information to the other electronic device via the peer-to-peer link using the secure communication. This access information facilitates access to the infrastructure network.
Owner:APPLE INC
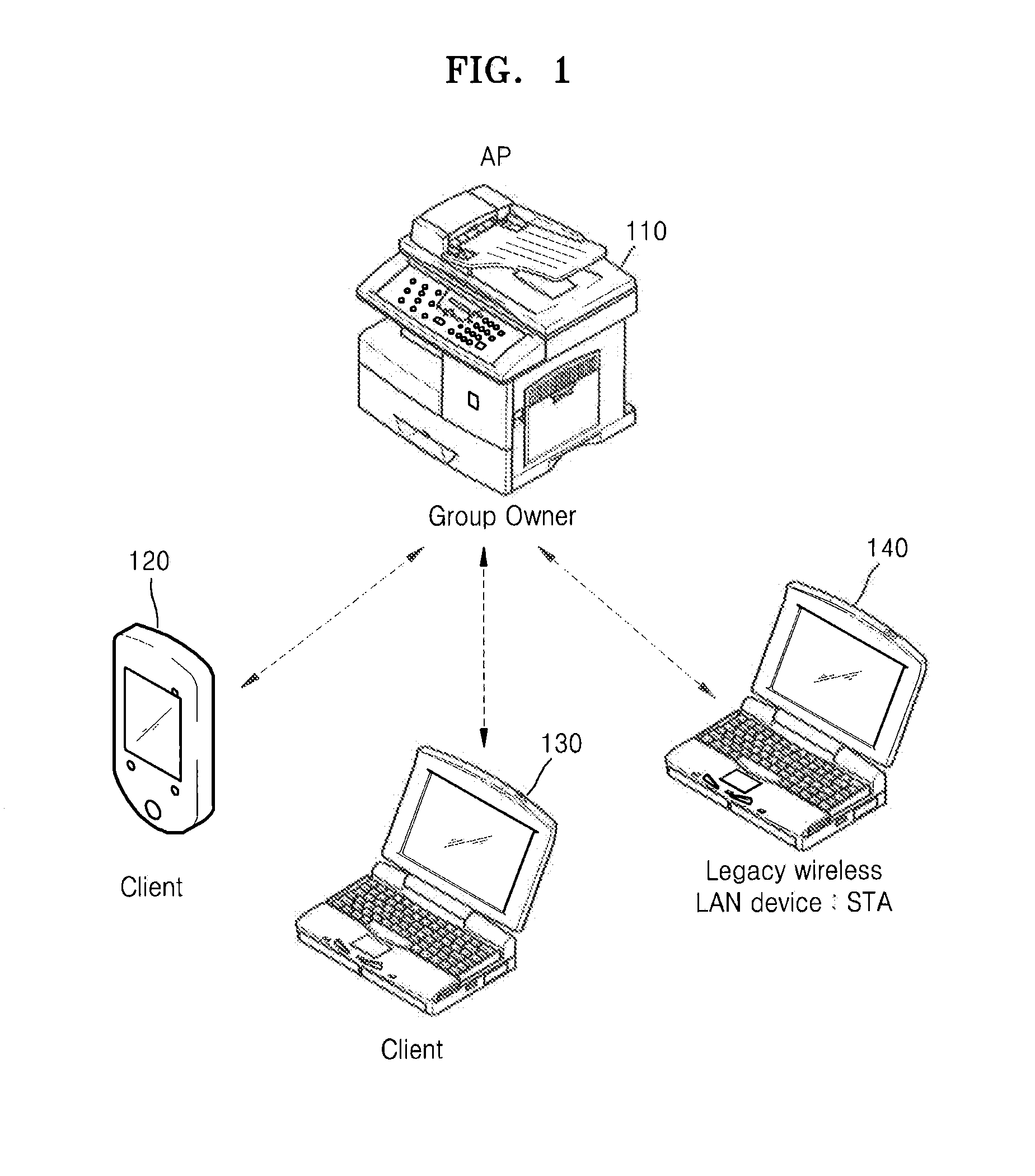
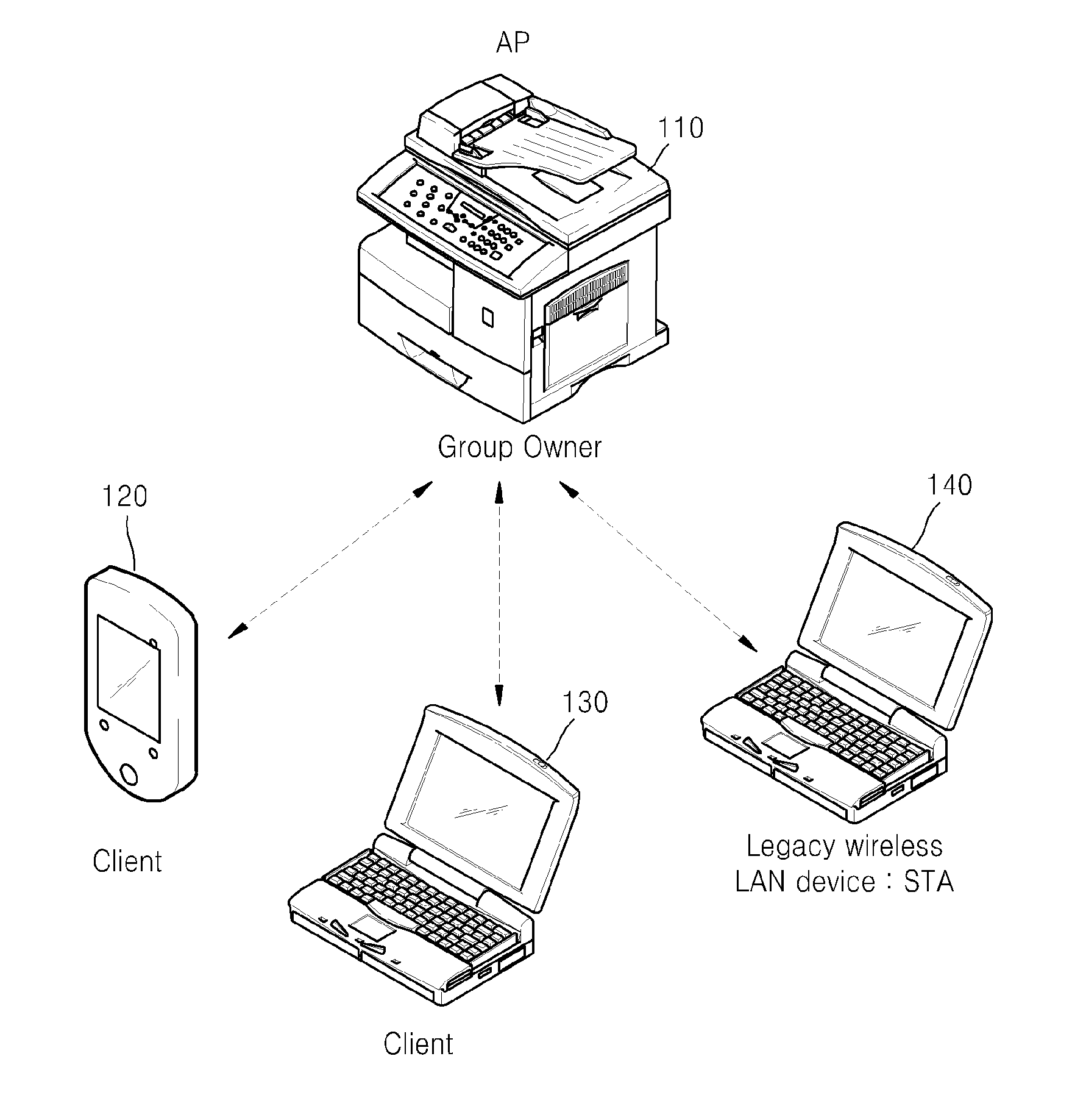
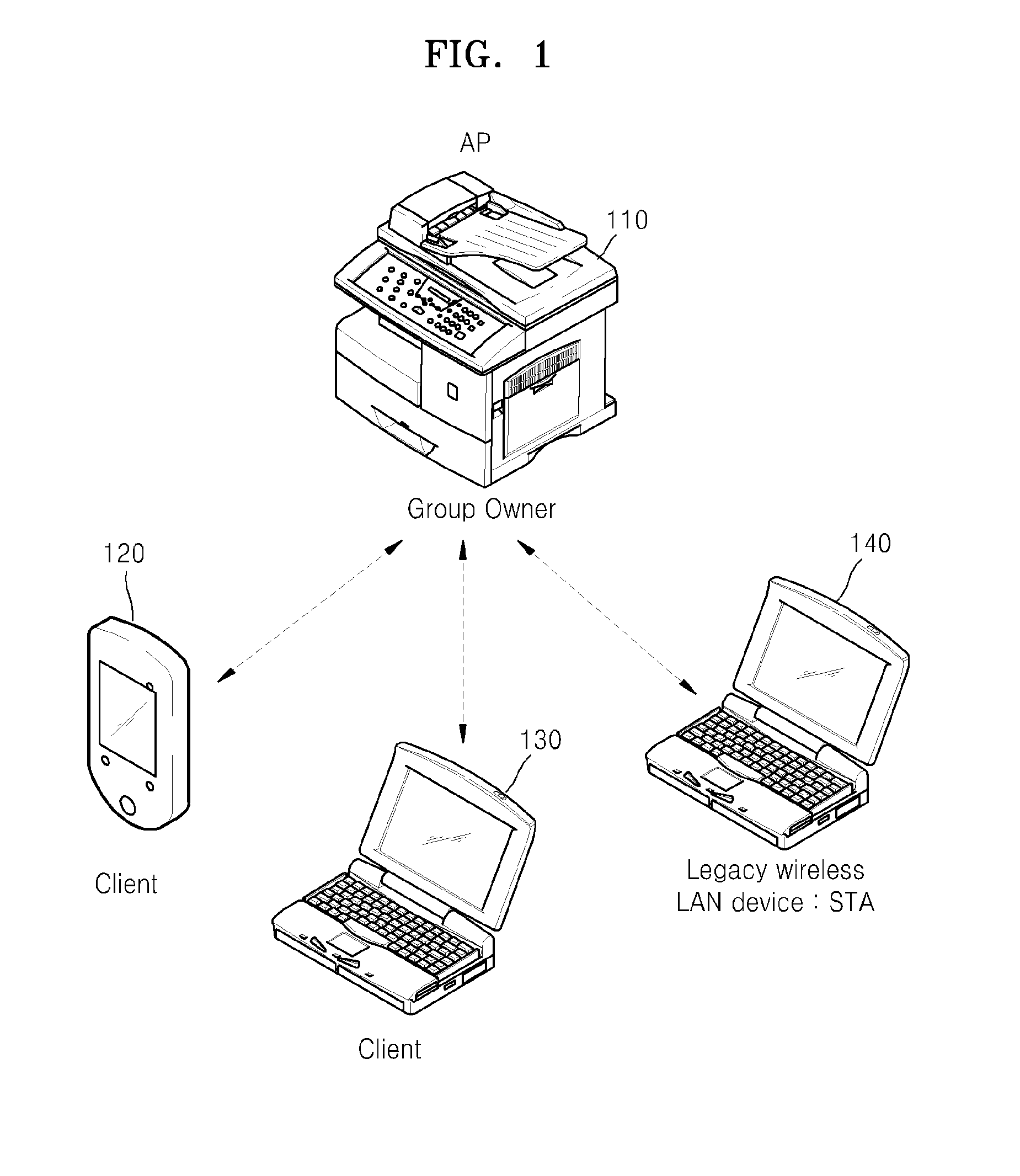
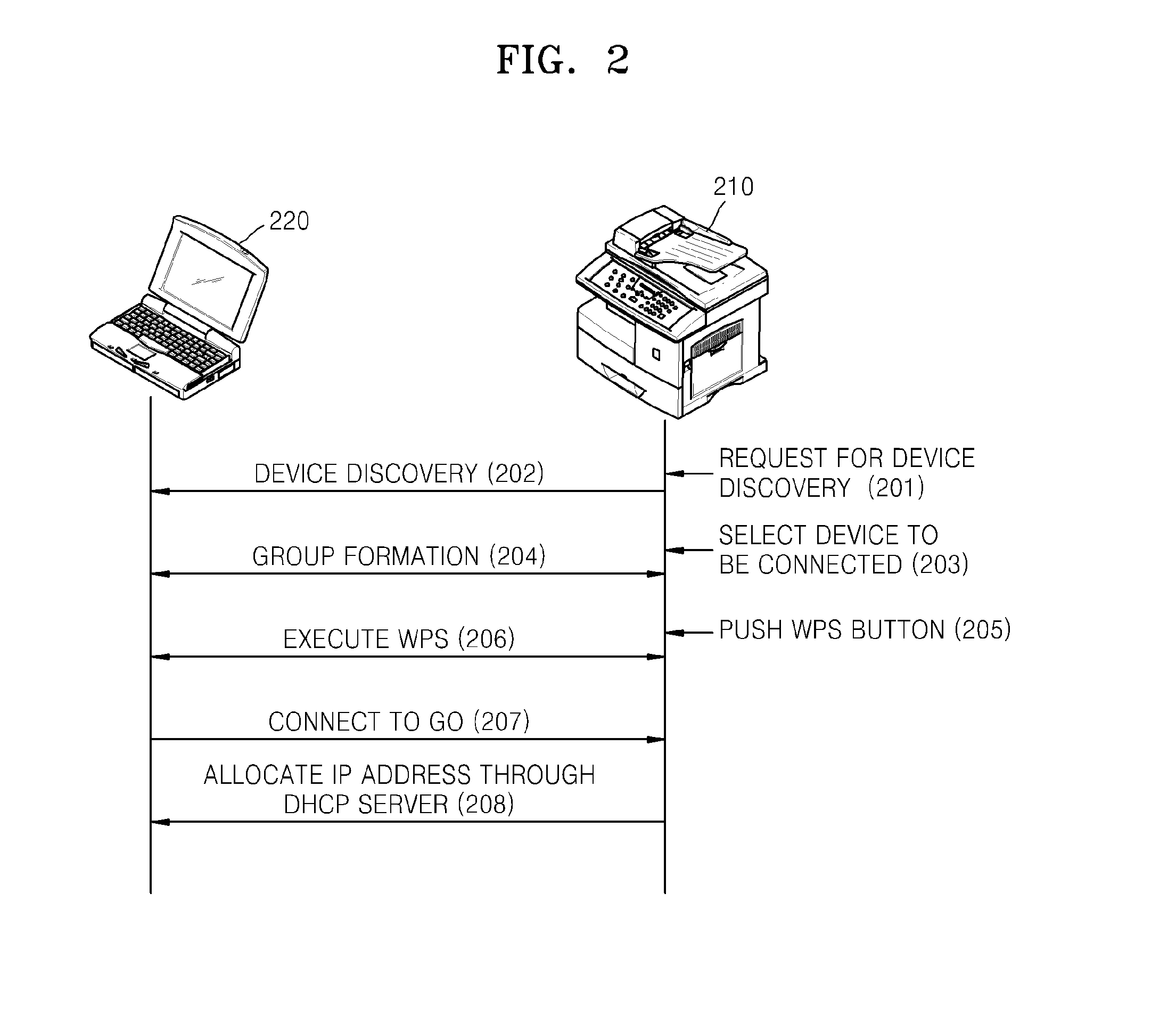
Image forming apparatus supporting peer-to-peer connection and method of managing channel thereof
ActiveUS20130148161A1Increase profitSafely and conveniently useEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesStructure of Management InformationImage formation
Provided is a multi-function printer (MFP) supporting Wi-Fi Direct. The MFP includes a print engine to perform a printing operation, a first wireless interface to connect the MFP to an access point (AP) of an infrastructured network, a second wireless interface to connect the MFP to an external wireless terminal in a Wi-Fi Direct, a soft AP to allow the MFP to perform as an AP when the MFP is Wi-Fi Direct connected, and a dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) server unit allocating an internet protocol (IP) address to the wireless device that is Wi-Fi Direct connected to the MFP, where the MFP is simultaneously connected to an AP of the infrastructured network and an external wireless terminal via the first wireless interface and the second wireless interface by using one channel.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Mobile ad hoc network system and operating method thereof
InactiveUS7450517B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork serviceAccess technology
A mobile ad-hoc network system includes: a plurality of mobile terminals; and a central control means for setting an optimal route among terminals, performing connection with an infrastructure network and connecting networks using different wireless access technologies. By including the central control means, the ad-hoc network system can overcome the limitation of the related art ad-hoc network and provide a network service with high quality and stability to each terminal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
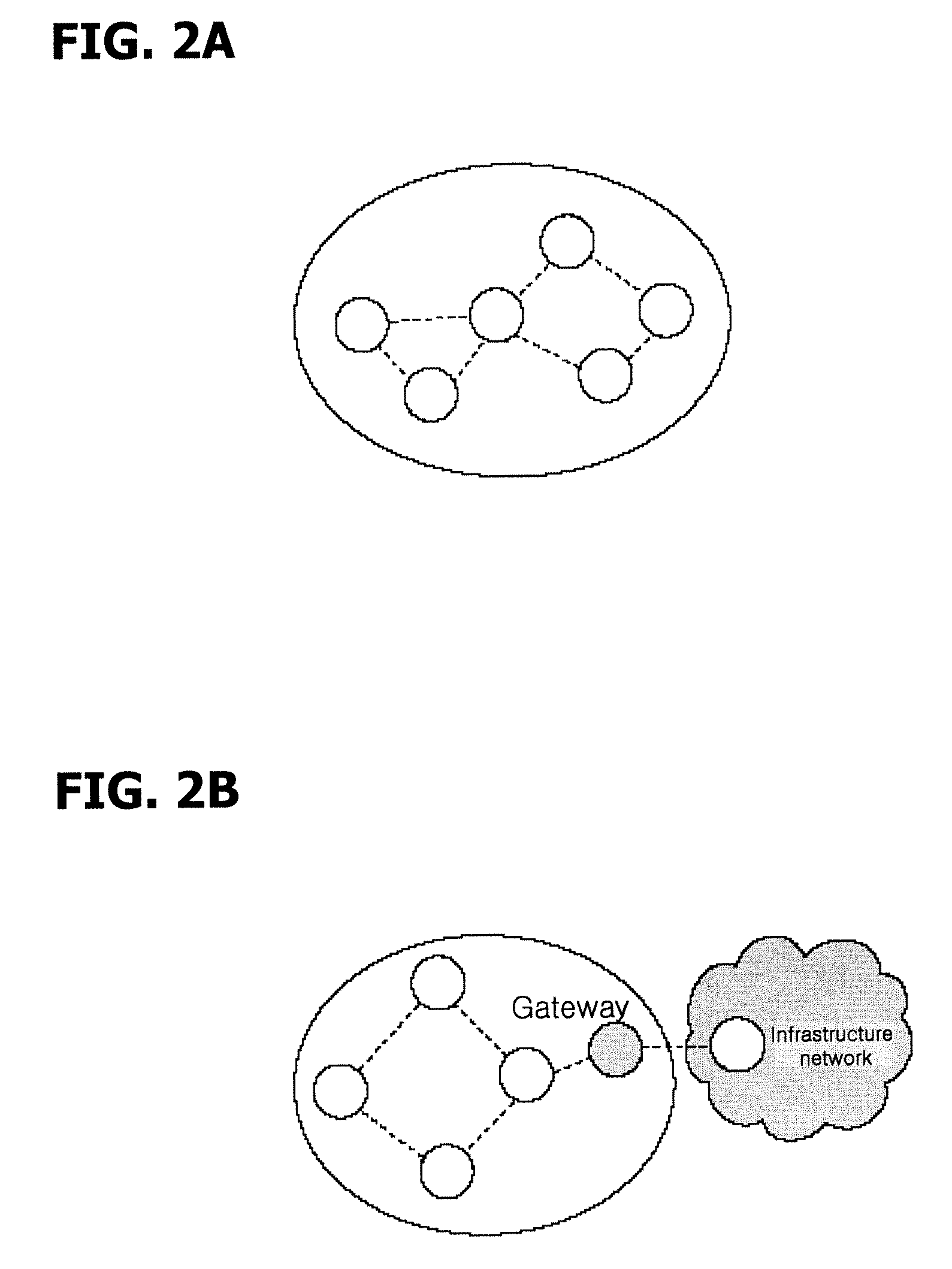
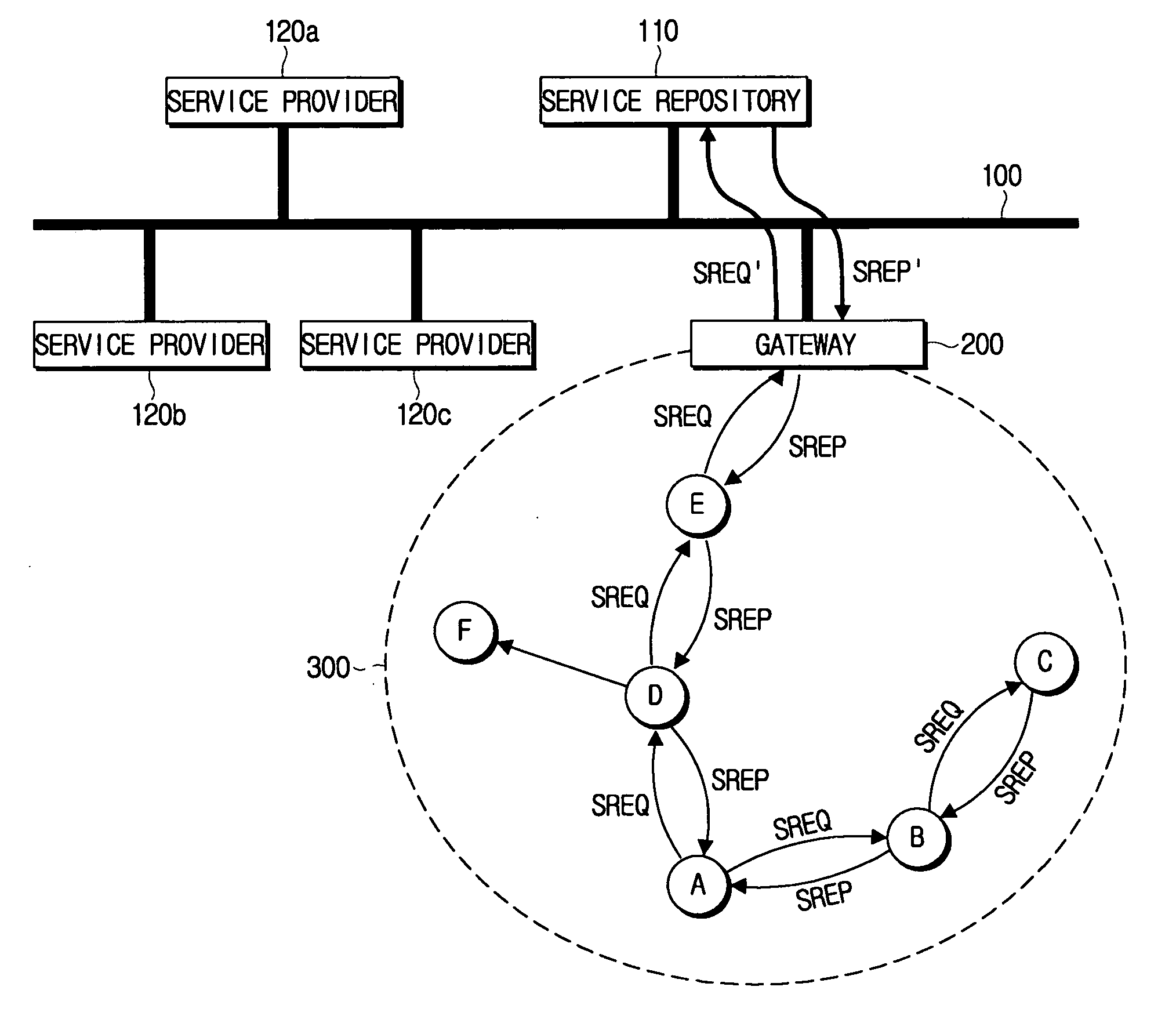
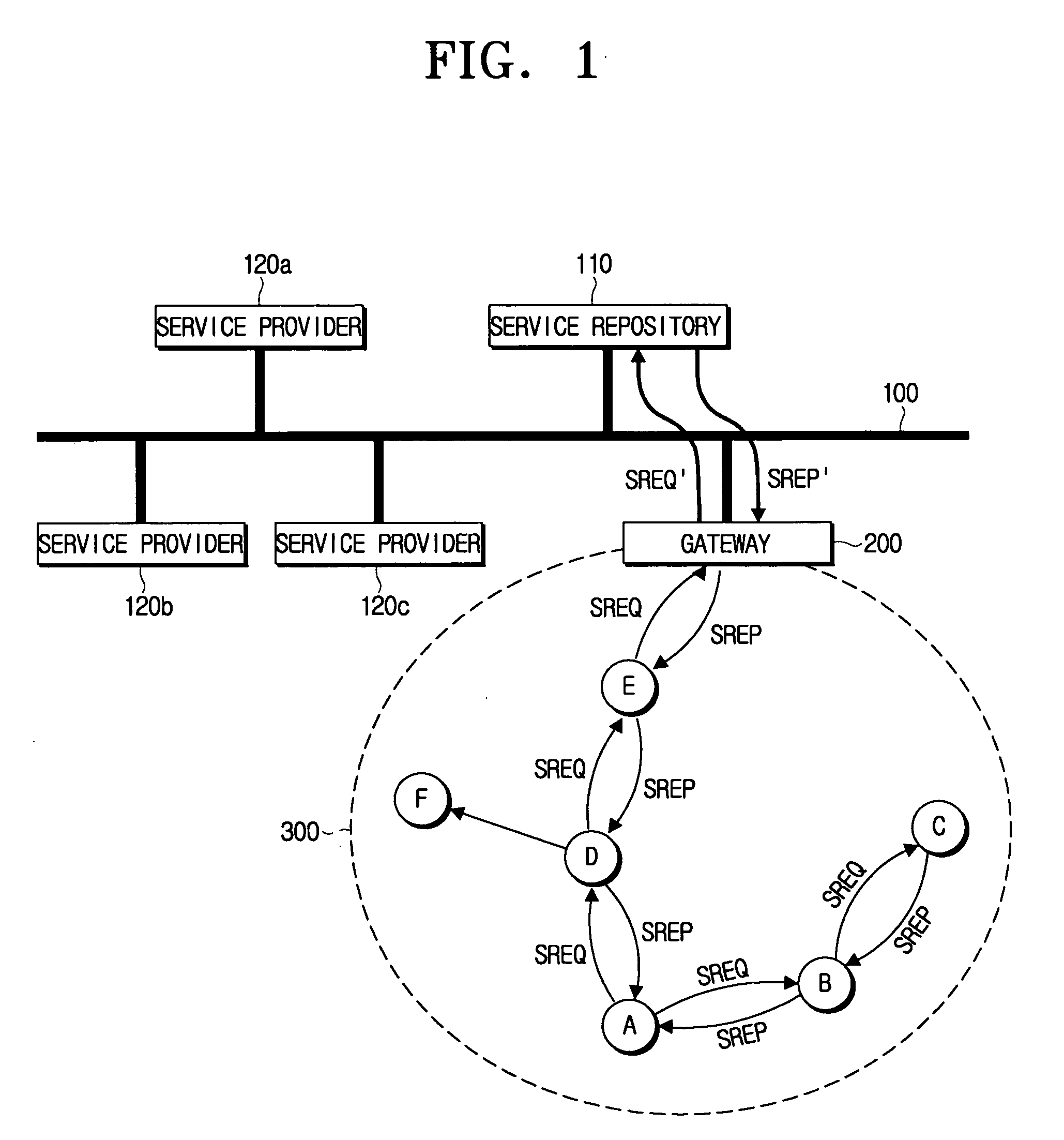
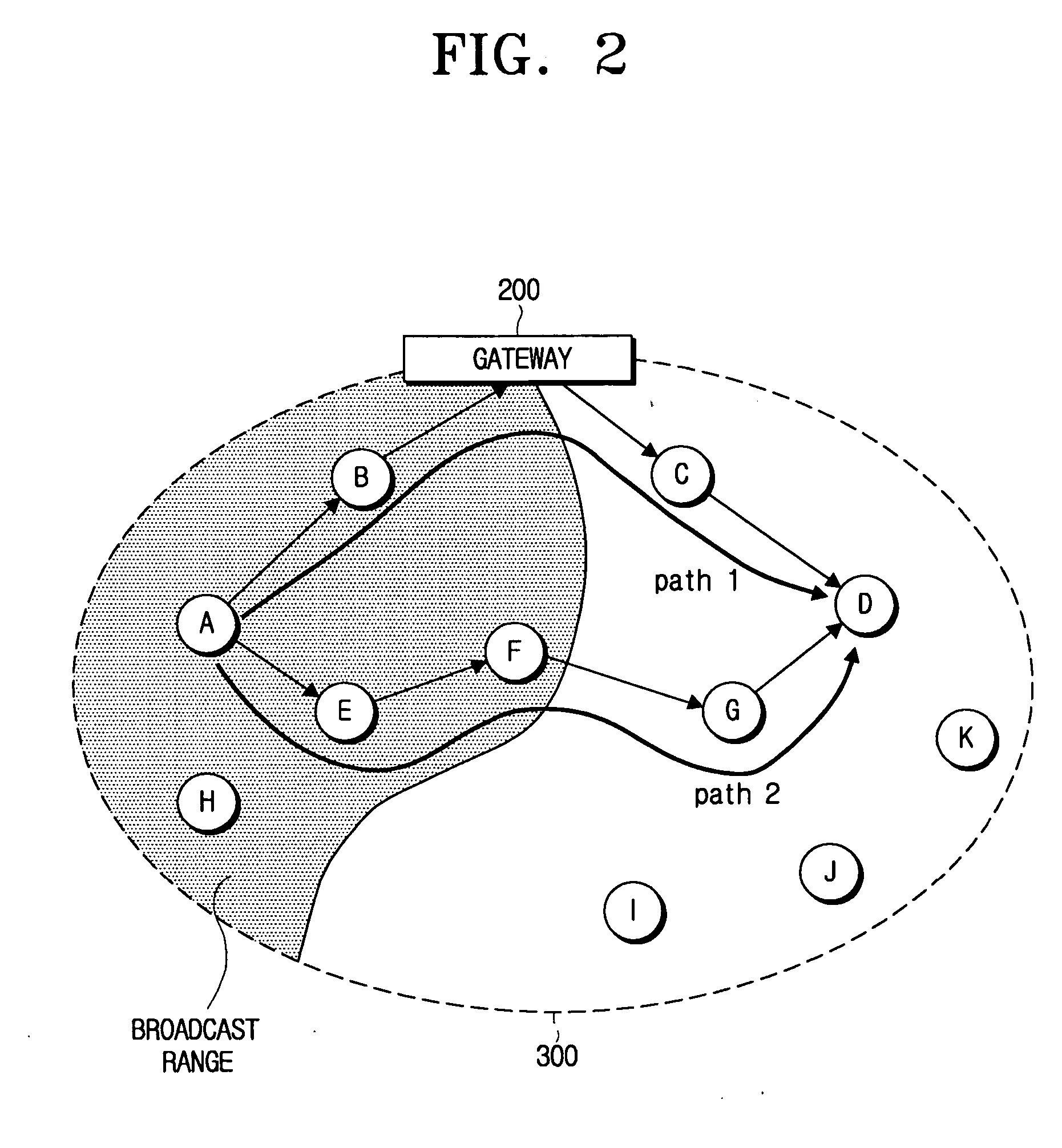
Gateway for interconnecting ad-hoc network and infrastructure network, and methods for discovering and registering service provider using gateway
ActiveUS20060171403A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsAssess restrictionService provisionSelf-organizing network
A service provider discovery method in a wireless network environment, includes receiving, by the gateway, a service request (SREQ) packet which is broadcast from a first mobile node in the ad-hoc network; updating and transmitting, by the gateway, the SREQ packet to a service repository which stores at least one service provider information, in the infrastructure network; transmitting, by the service repository, a service reply (SREP) packet containing information relating to a service provider which provides a service requested by the SREQ packet to the gateway, and updating and transmitting, by the gateway, the SREP packet to the first mobile node. Accordingly, the service can be used in association with the ad-hoc network and the infrastructure network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wireless communication system for interconnecting ad-hoc network and infrastructure network, and wireless terminal and communication method therefor
A wireless communication system for interconnecting an ad-hoc network and an IS network, and a wireless terminal and communication method therefor are disclosed. The communication method includes transmitting a discovery signal including terminal information of the wireless terminal to a radio network, receiving a response signal including information for network access from a base station or another wireless terminal, which has received the discovery signal, selecting an operation mode for access to a network through the base station or the other wireless terminal, based on the response signal, communicating with the base station and accessing the IS network when the selected operation mode corresponds to a first mode and accessing a network, to which the other wireless terminal belongs, through a licensed frequency band of the IS network when the selected operation mode corresponds to a second mode. Accordingly, it is possible to support communication through an existing infrastructure and support communication of an ad-hoc network scheme, through use of a licensed frequency band assigned to the provider of an existing IS network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-protocol distributed wireless system architecture
ActiveUS20050243785A1Easy to shareTime-division multiplexSubstation equipmentAir interfaceService provision
A open access signal distribution system in which a variety of wireless voice, data and other services and applications are supported. The open access systems makes use of a distributed Radio Frequency (RF) distribution network and associated network entities that enable the system operator to employ a wireless infrastructure network that may be easily shared among multiple wireless service providers in a given community. The open access system provides the ability for such operators and service providers to share the infrastructure regardless of the specific RF air interface or other signal formatting and / or managing messaging formats that such operators choose to deploy.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Image forming apparatus supporting peer to peer connection and method of performing image forming operation thereof
ActiveUS20130148162A1Control performanceEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesIp addressImage formation
A method of performing an image forming operation in an image forming apparatus supporting peer to peer (P2P) connection includes P2P connecting the image forming apparatus to an external wireless device while the image forming apparatus is wirelessly connected to an access point (AP) of an infrastructured network, receiving a discovery packet from the wireless device via a P2P interface, transmitting to the wireless device a response packet including an Internet protocol (IP) address of the P2P interface, receiving from the wireless device an image forming operation performing request having the IP address of the P2P interface as a destination, and performing the requested image forming operation.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Ggsn proxy for one tunnel solution
ActiveUS20100246500A1Connection managementWireless network protocolsProcessor registerPublic land mobile network
A method for roaming of a wireless mobile communication unit, a service support node and a proxy gateway support node for roaming between Public Land Mobile Networks, as well as a mobile communication infrastructure network arranged to handle roaming between different PLMN areas, where the support node is located in a current PLMN and arranged to send a context request to a first service support node in another PLMN for a user equipment, receive a context response from the first service support node, send a context acknowledgement to the first service support node, send an update location message to a home location register of the user equipment, receive a relocate PDP context response from the second proxy gateway support node and send a relocate PDP context request to a second proxy gateway support node in the current PLMN.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
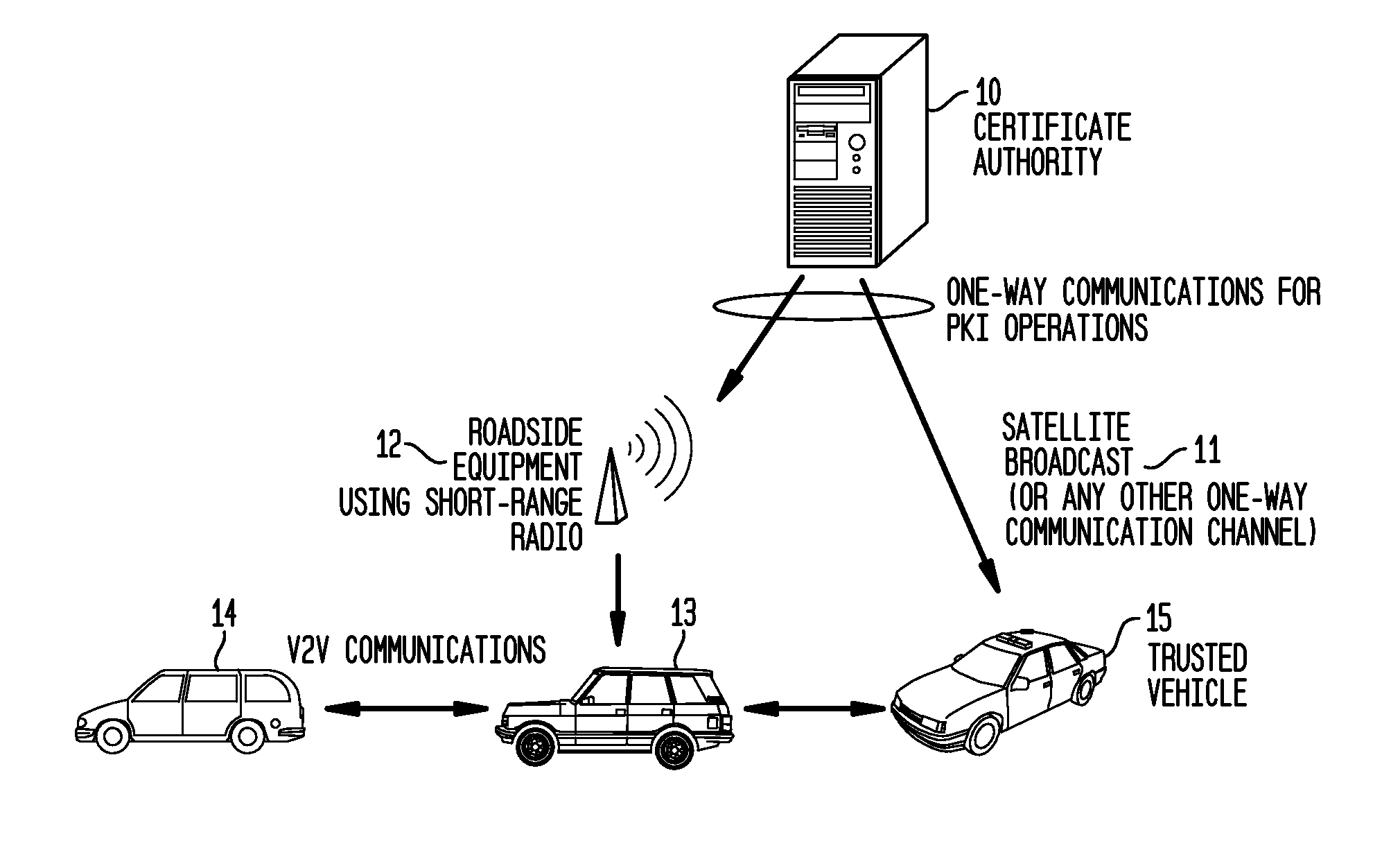
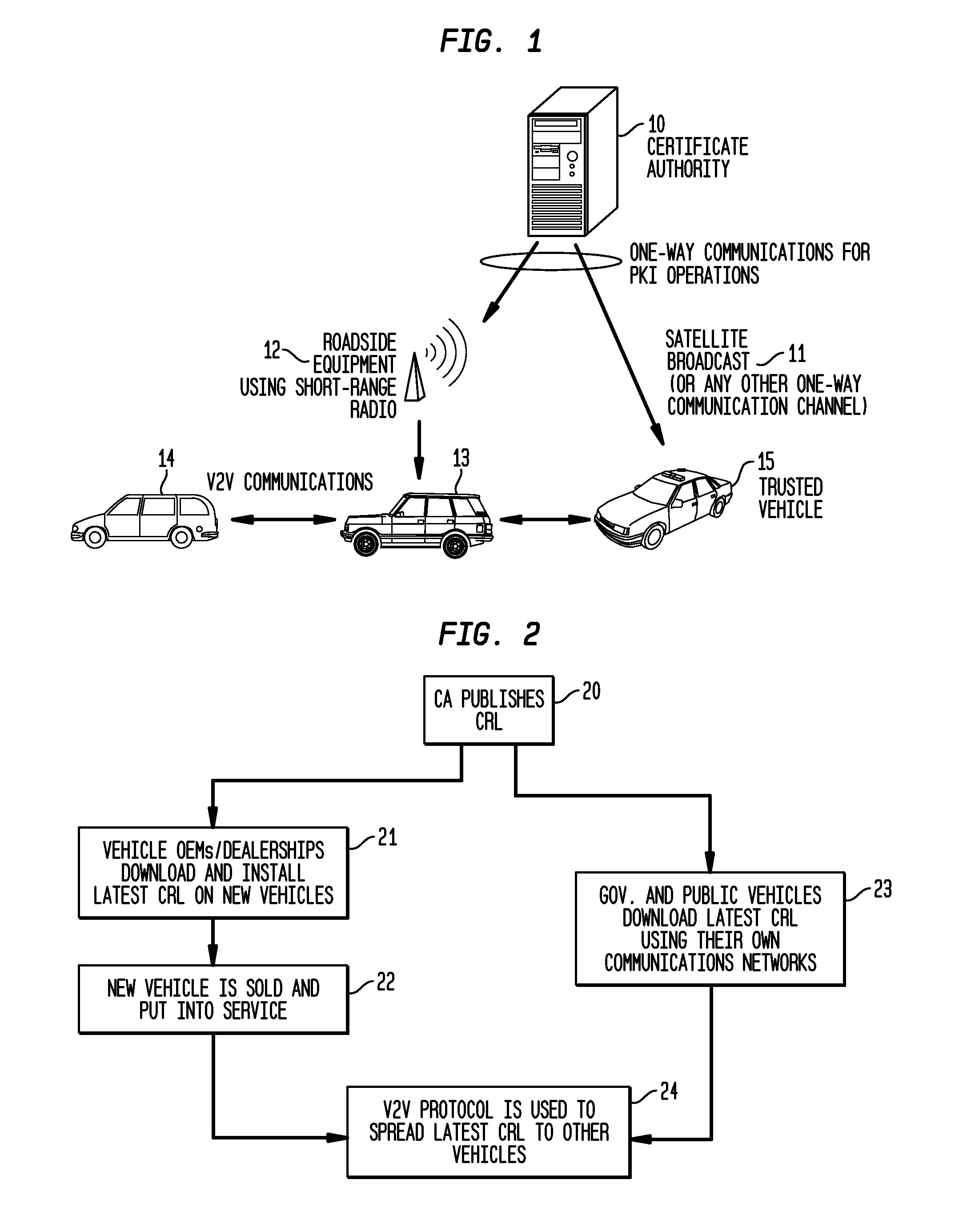
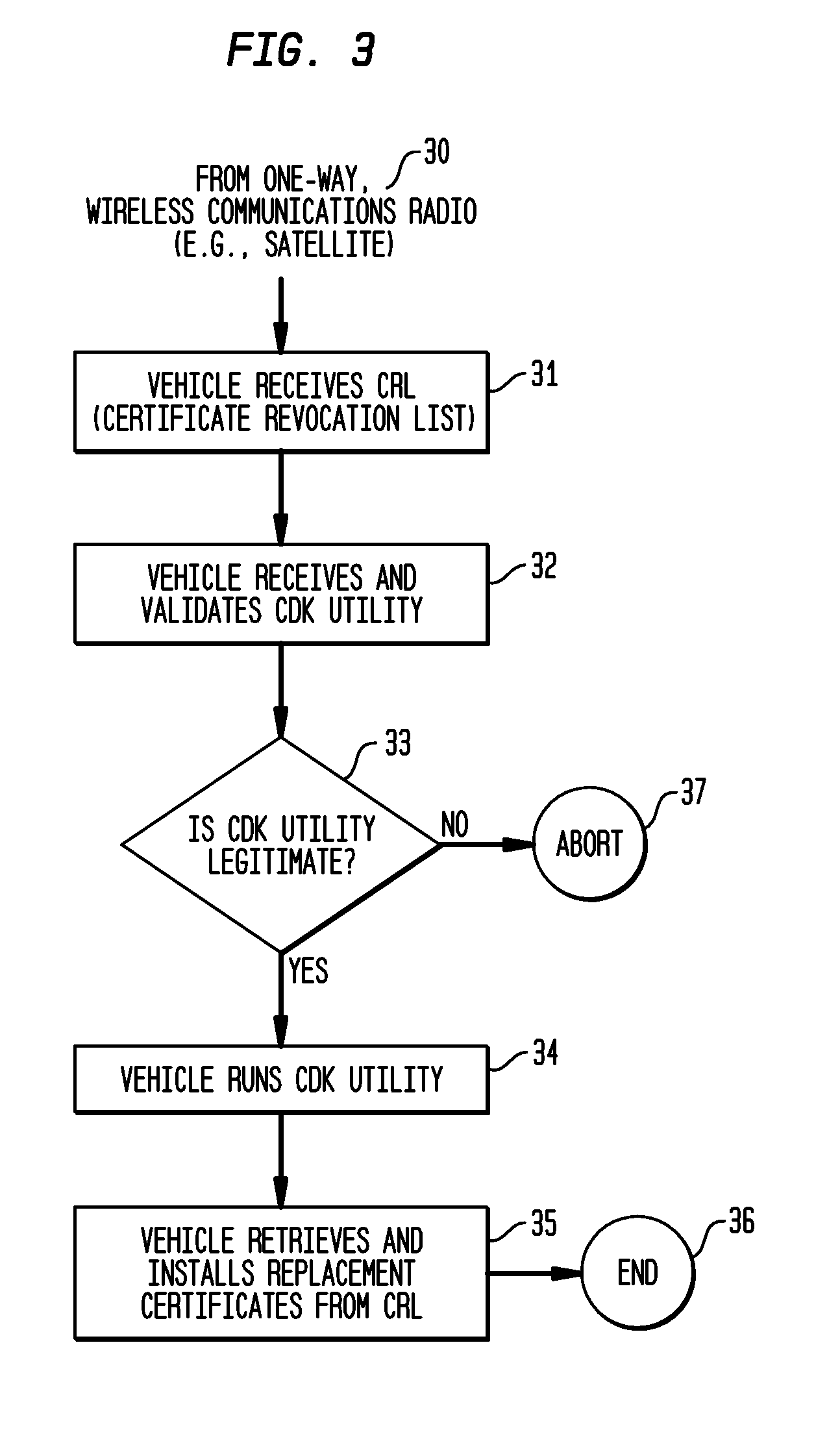
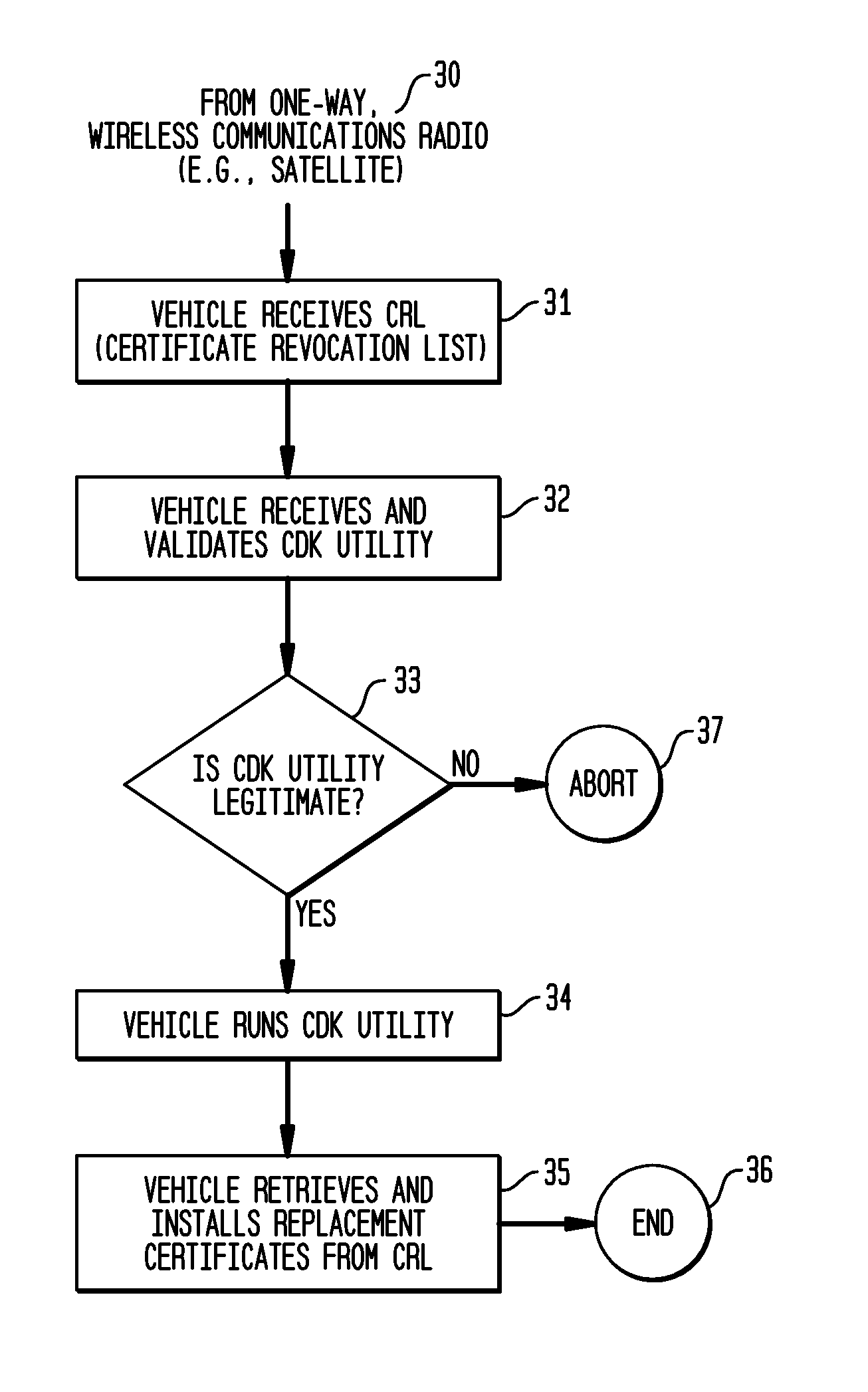
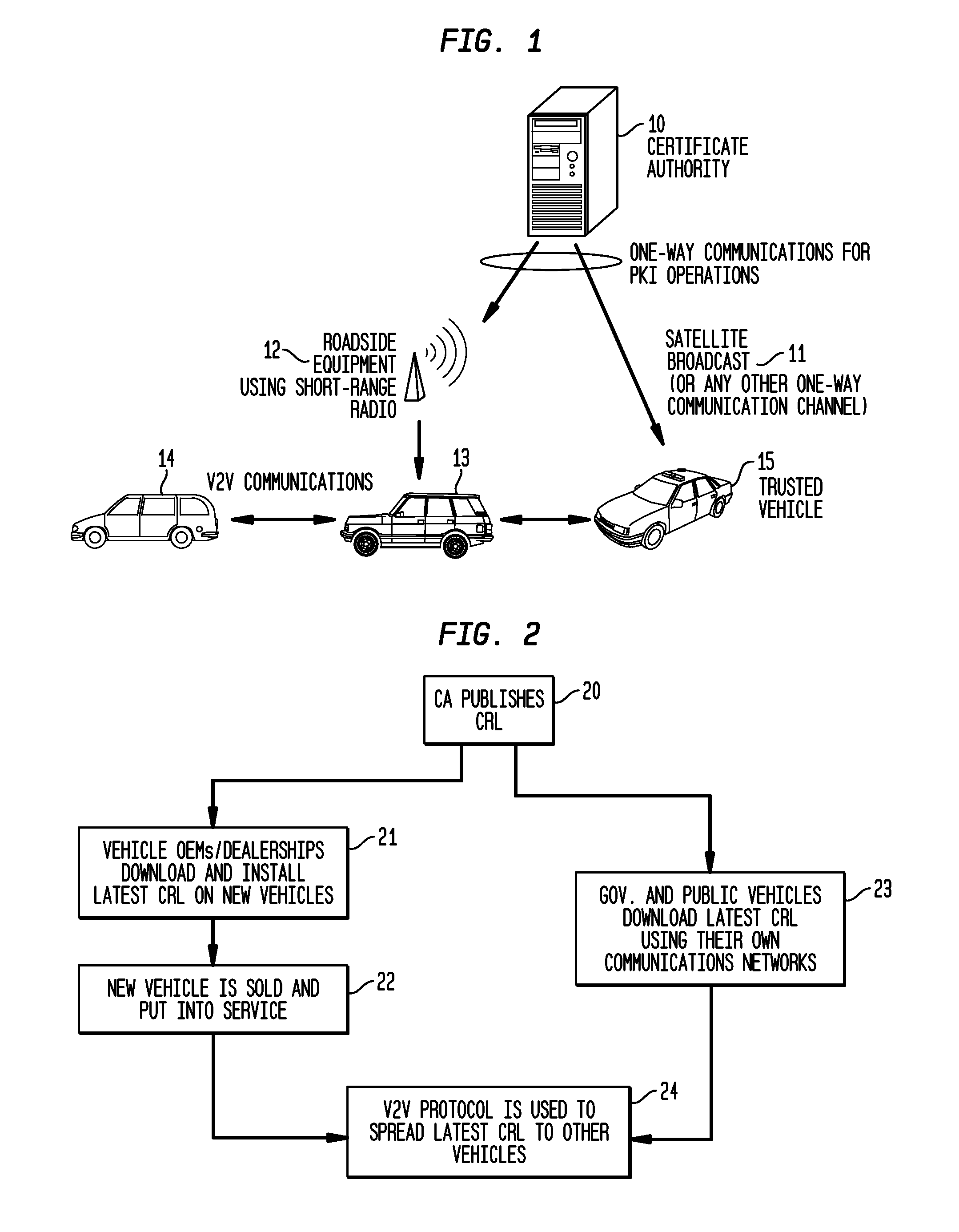
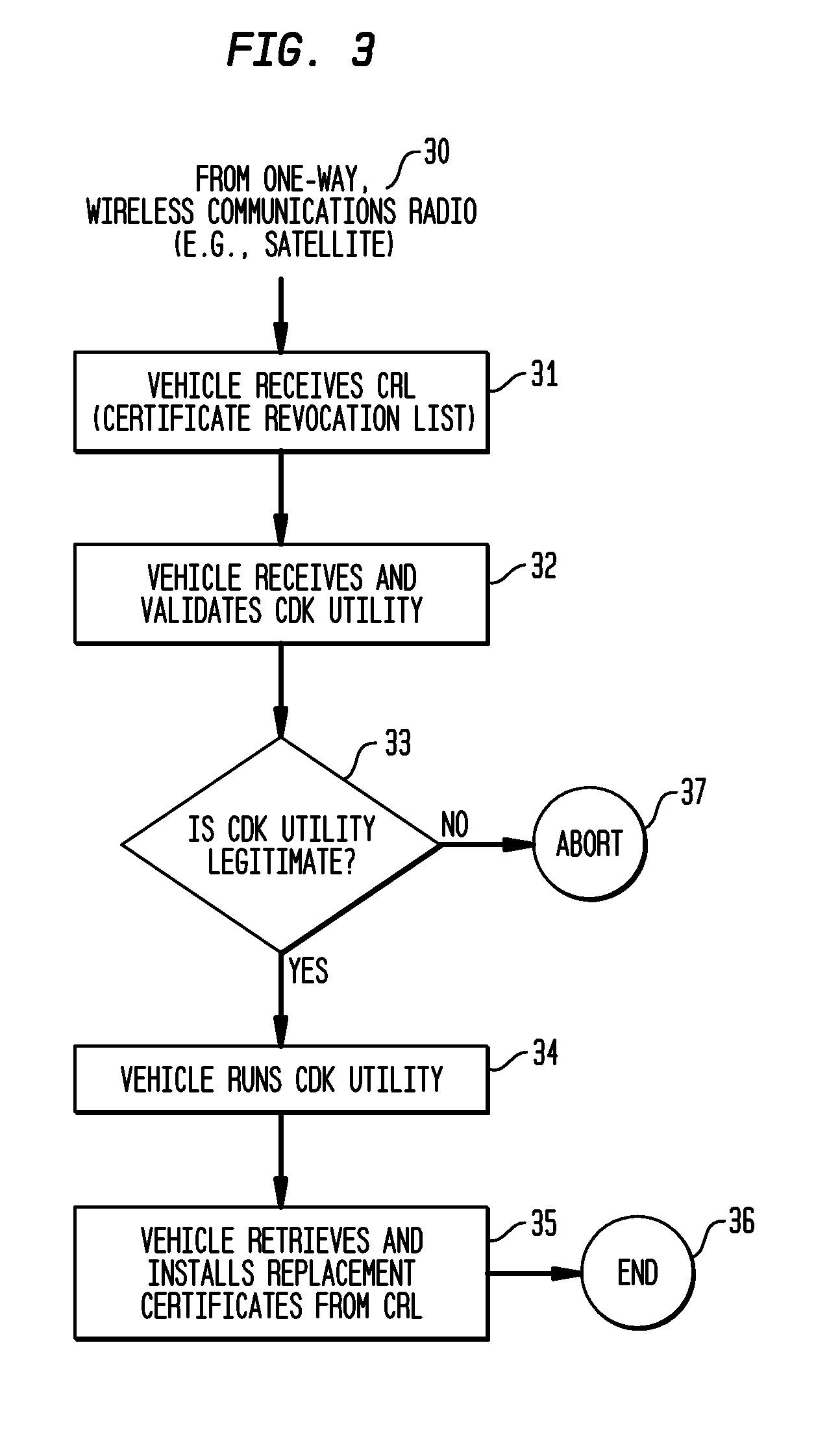
System and Methods to Perform Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Operations in Vehicle Networks using One-Way Communications Infrastructure
ActiveUS20110213968A1Reduces and eliminates relianceParticular environment based servicesUser identity/authority verificationIn vehicleRevocation list
A set of certificate management methods designed to significantly reduce or eliminate reliance on infrastructure network connectivity after vehicles are sold uses techniques to support certificate management operations in order to reduce the frequency which vehicles need to communicate with the Certificate Authorities (CAs) and the amount of data that needs to be exchanged between vehicles and the CA. These methods include, for example, approaches to use one-way communications and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications to replace expired certificates, approaches to use one-way communications and V2V communications to replace revoked certificates, and use of a small subset of vehicles as proxies to help retrieve and distribute Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) and replacement certificates. The combination of these techniques leads to solutions that can eliminate the need for roadside infrastructure networks completely.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
System and methods to perform public key infrastructure (PKI) operations in vehicle networks using one-way communications infrastructure
ActiveUS8522013B2Reduces and eliminates relianceParticular environment based servicesServices signallingIn vehicleRevocation list
A set of certificate management methods designed to significantly reduce or eliminate reliance on infrastructure network connectivity after vehicles are sold uses techniques to support certificate management operations in order to reduce the frequency which vehicles need to communicate with the Certificate Authorities (CAs) and the amount of data that needs to be exchanged between vehicles and the CA. These methods include, for example, approaches to use one-way communications and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications to replace expired certificates, approaches to use one-way communications and V2V communications to replace revoked certificates, and use of a small subset of vehicles as proxies to help retrieve and distribute Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) and replacement certificates. The combination of these techniques leads to solutions that can eliminate the need for roadside infrastructure networks completely.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
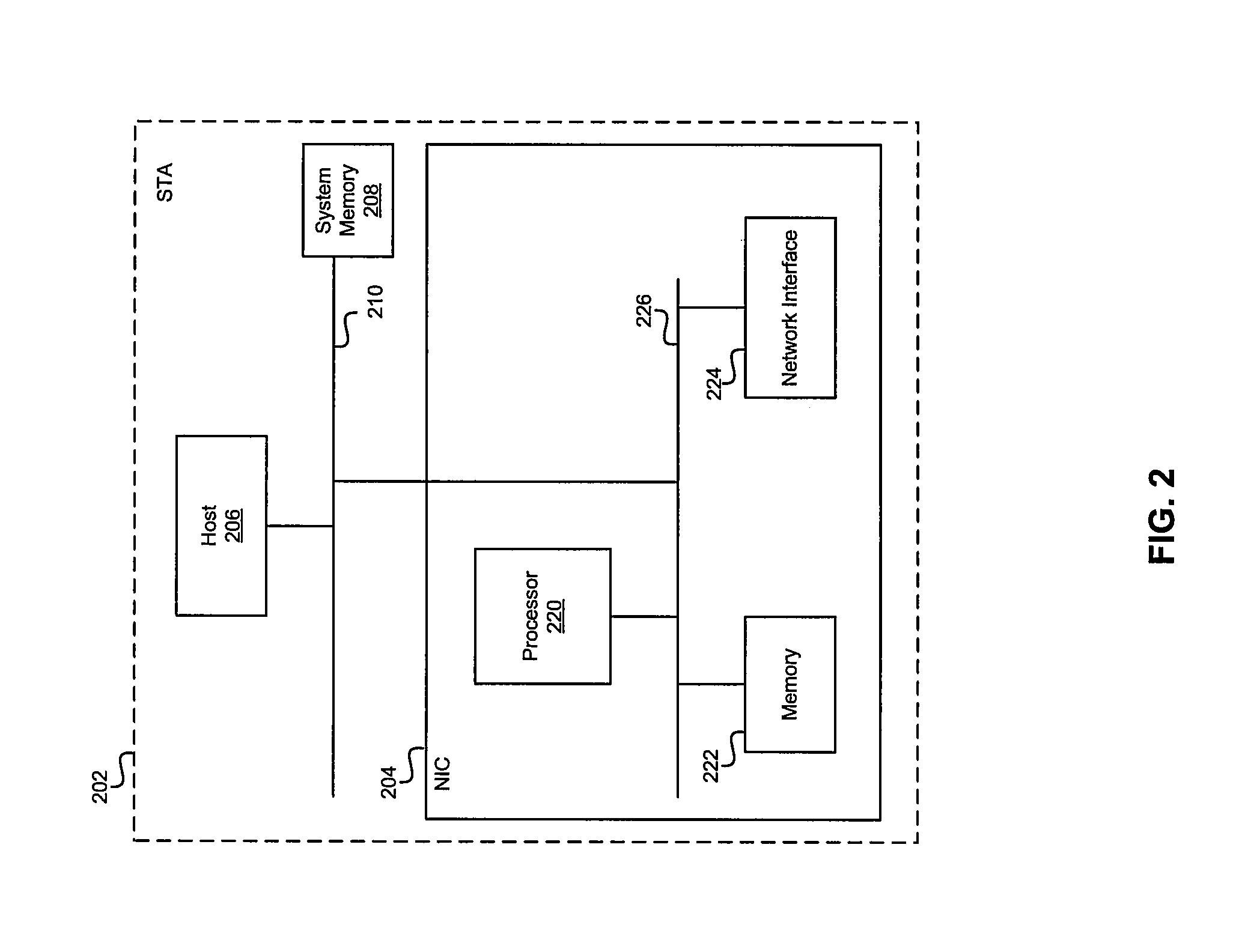
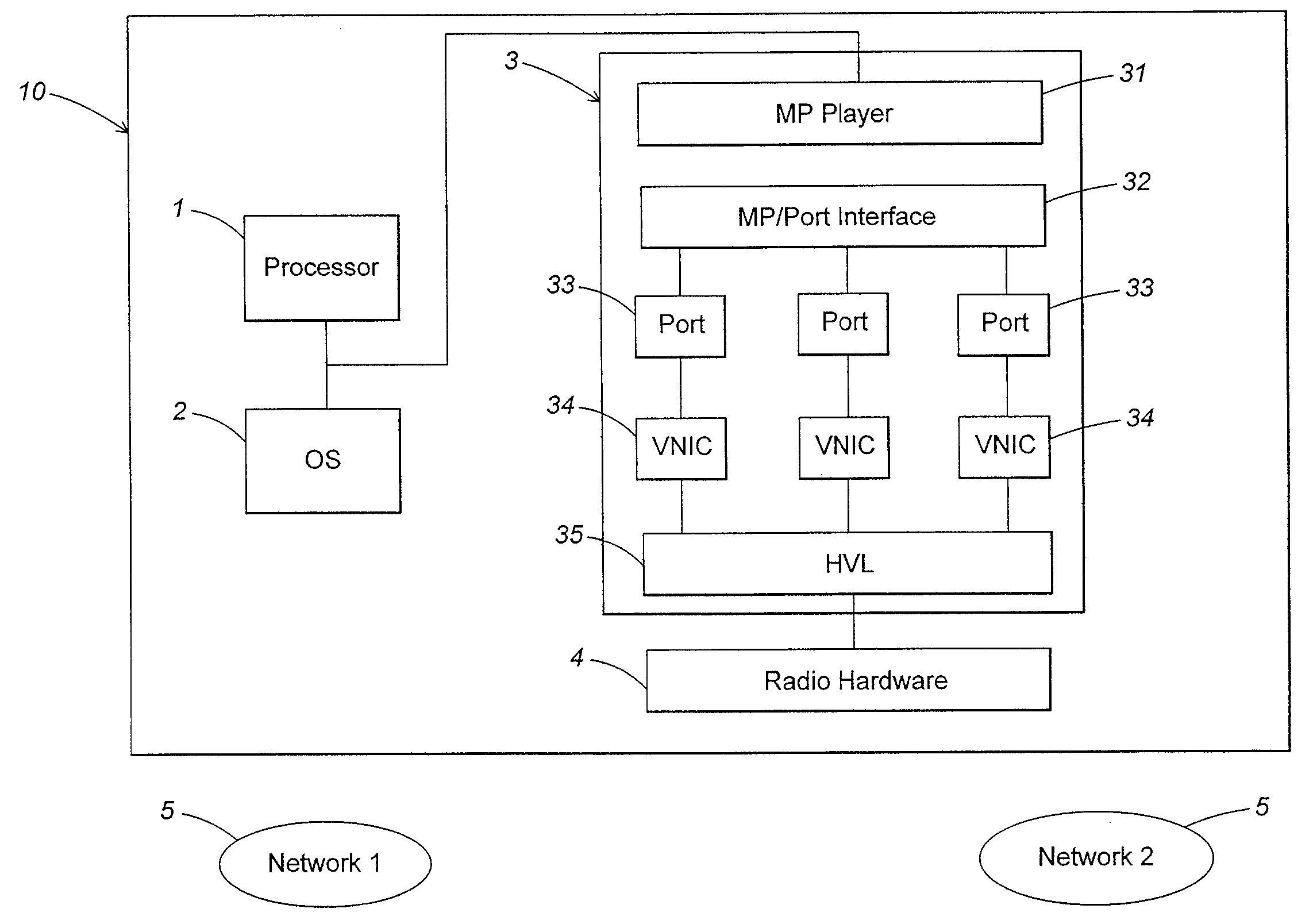
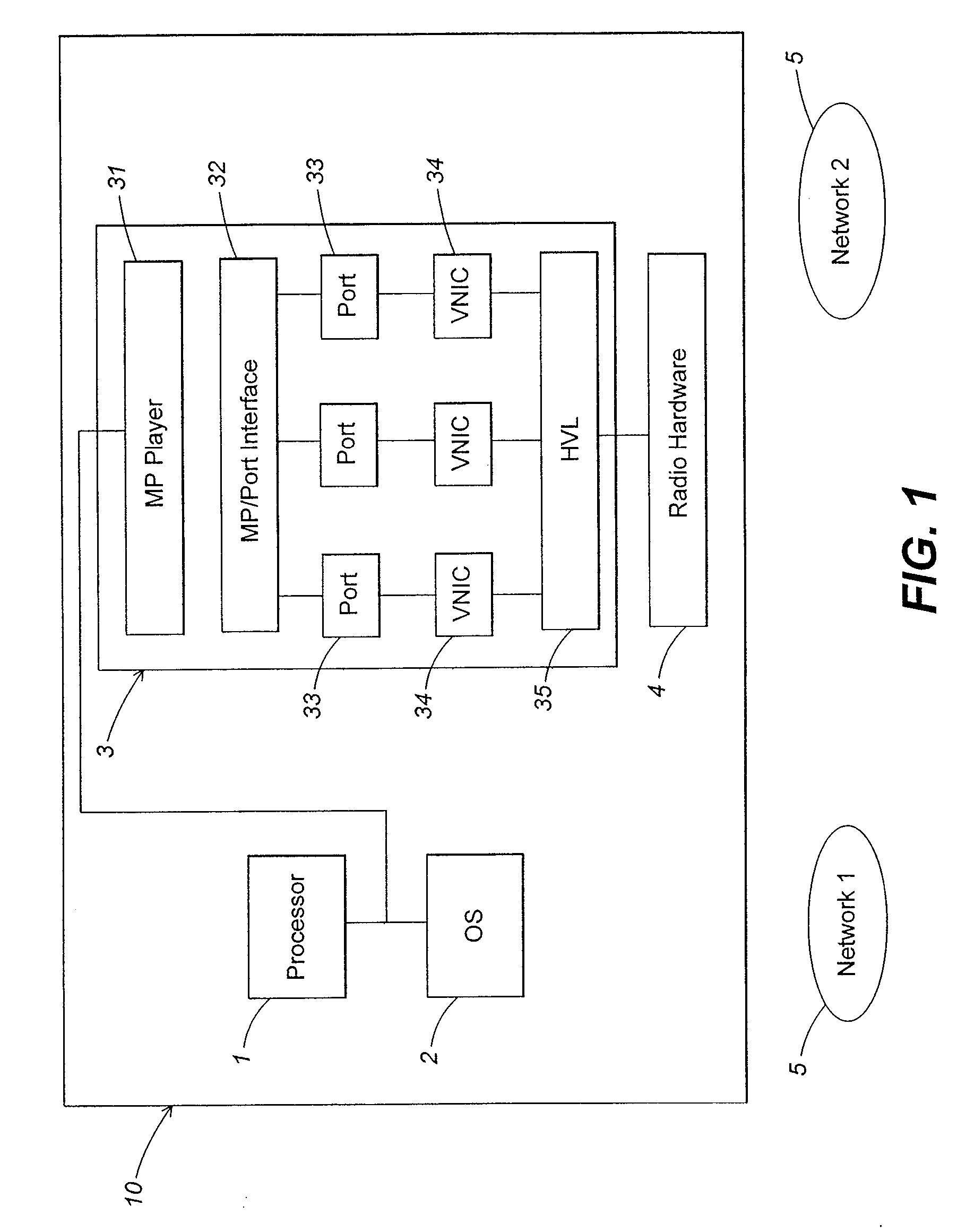
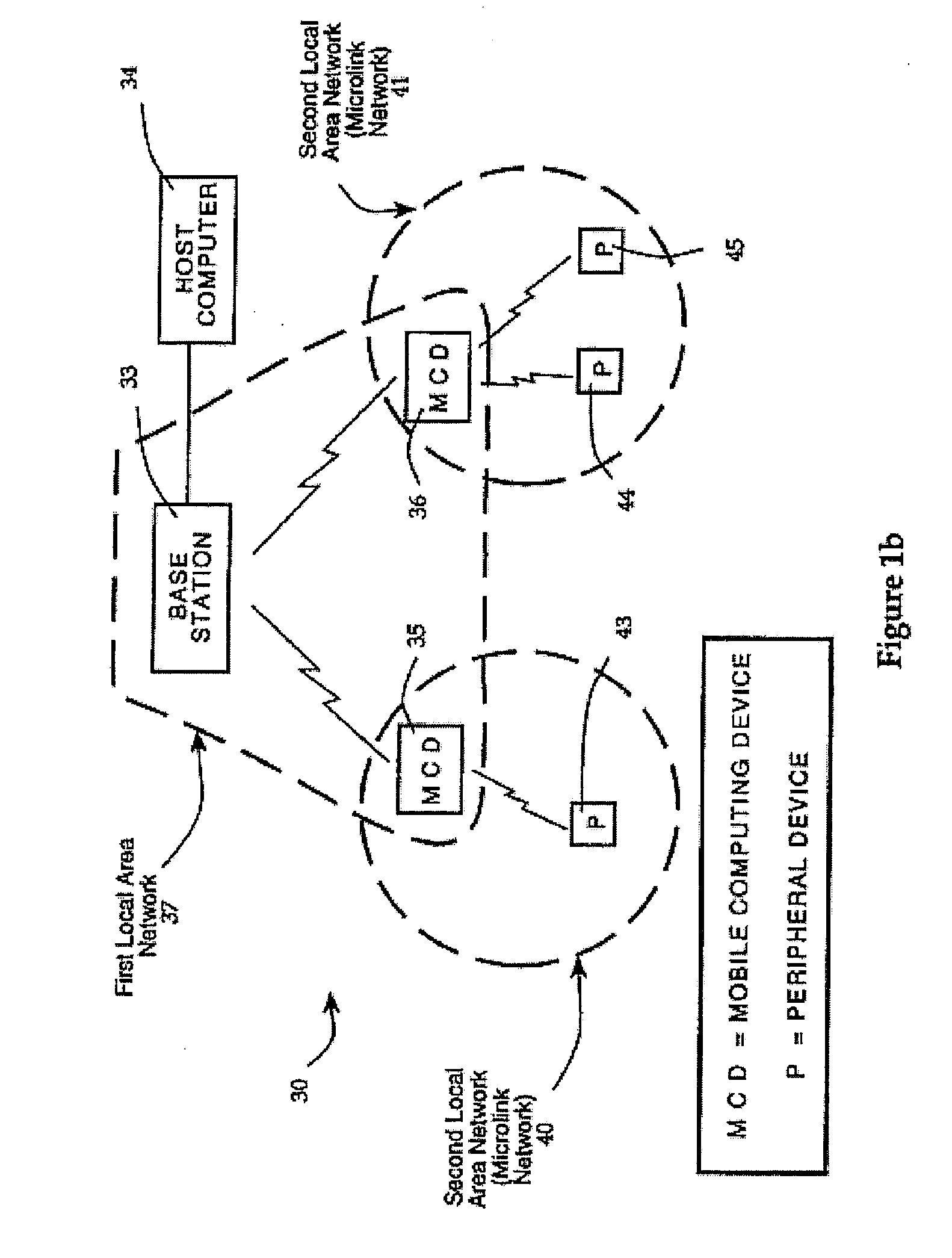
Maintaining multiple, simultaneous wireless network connections using a single radio
ActiveUS20090103481A1Keep in touchTransmission control/equalisingData switching by path configurationVirtualizationNetwork connection
A method and apparatus for managing simultaneous virtual connections with multiple wireless networks. A plurality of ports in a hardware driver may be each associated with a corresponding wireless network and maintain a unique MAC state relative to other ports. Each port may have a corresponding virtual NIC that communicates directly with the radio hardware via a hardware virtualization layer that multiplexes communication between the virtual NICs and the radio hardware. Simultaneous virtual connections may be made with one or more infrastructure networks or adhoc networks, and / or the computer may function as an access point for one or more of the networks.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
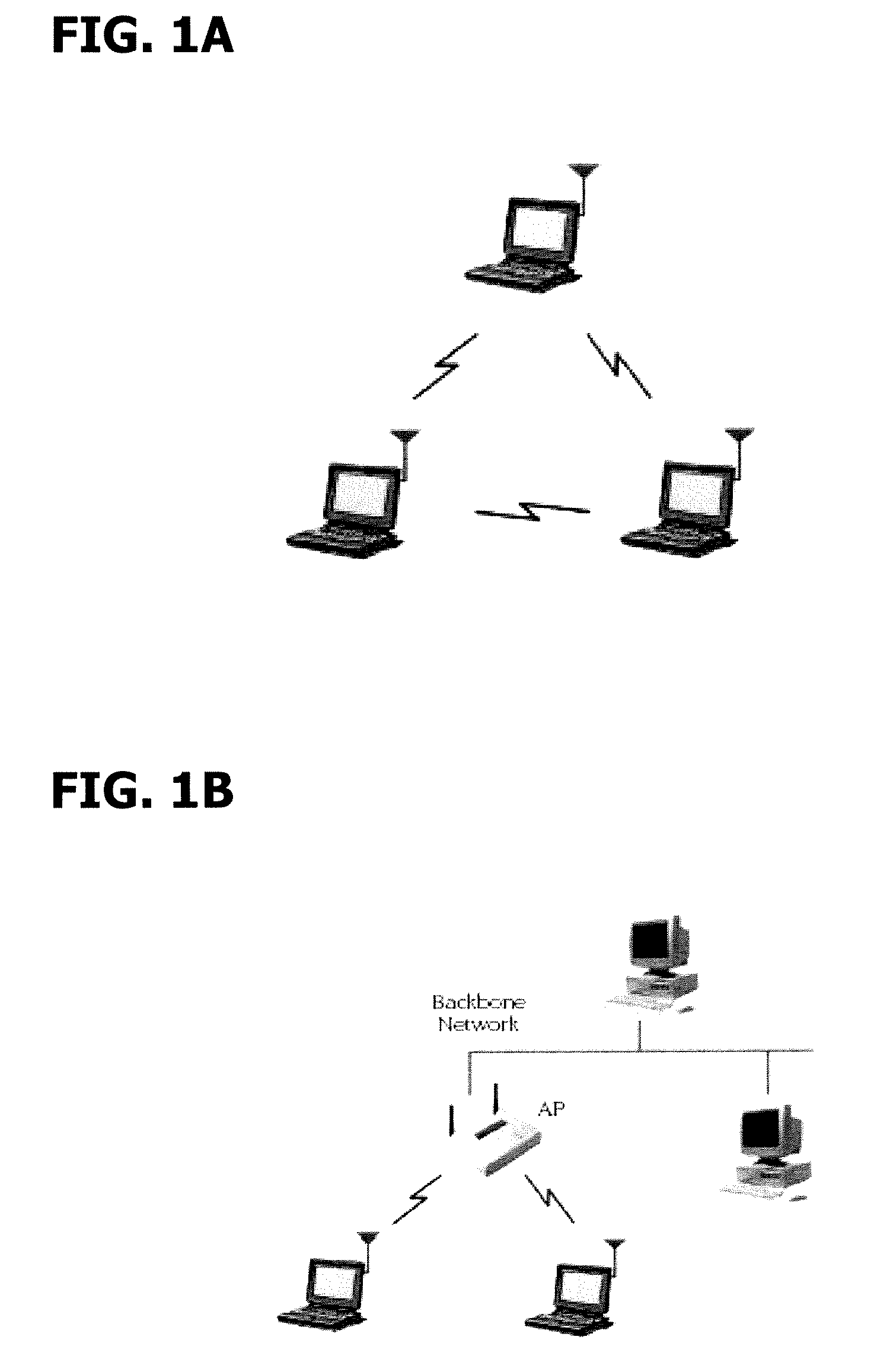
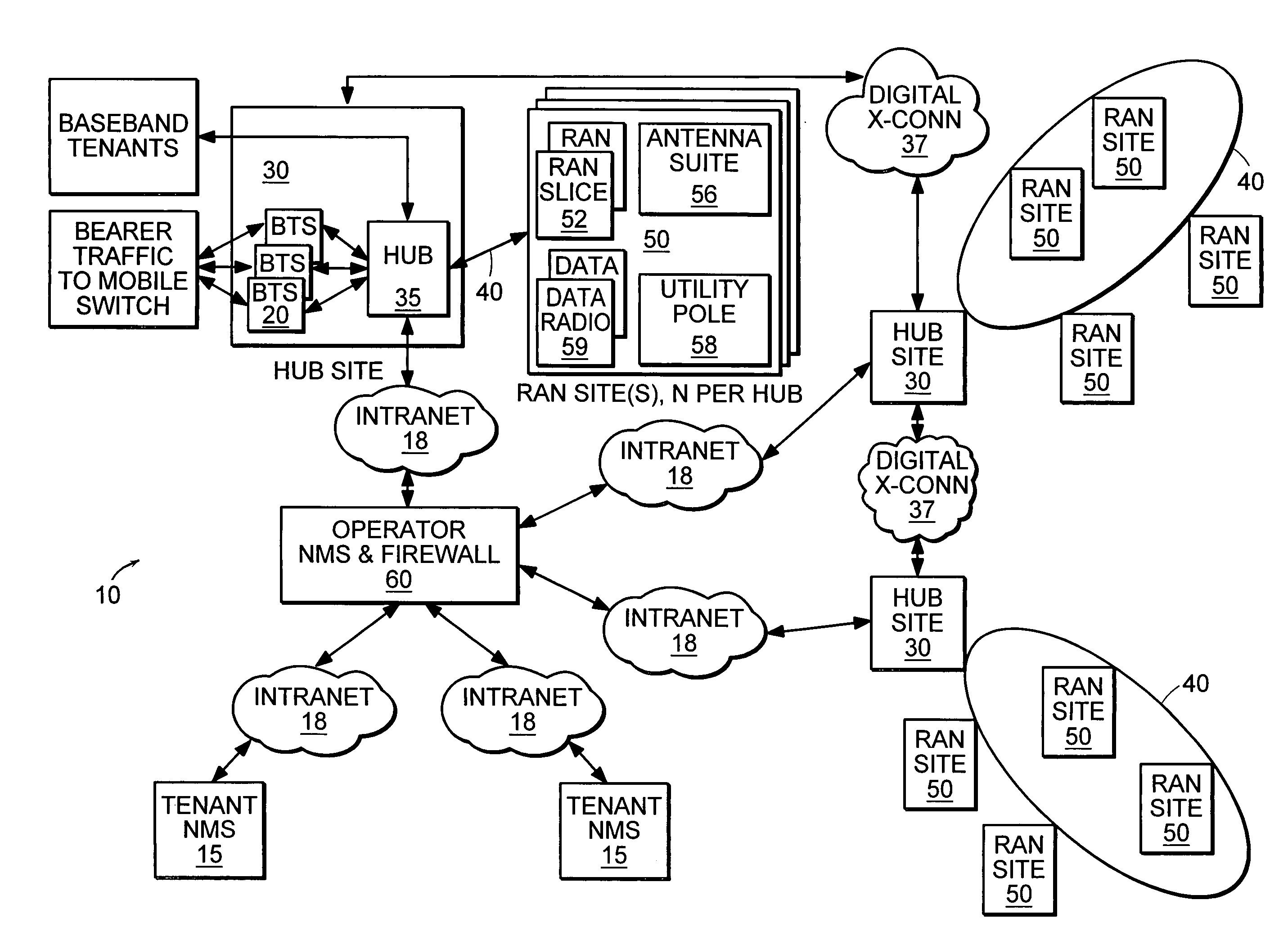
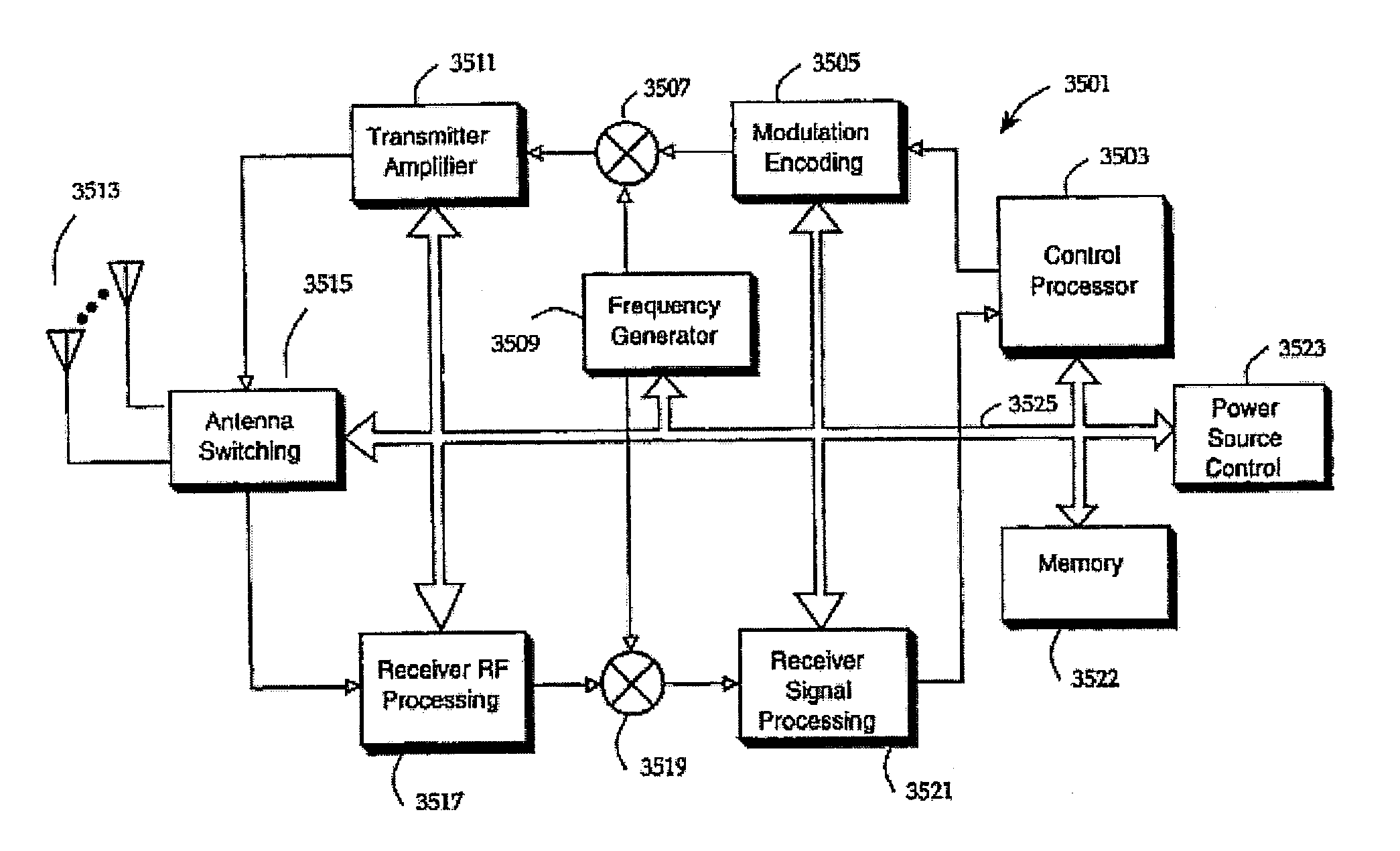
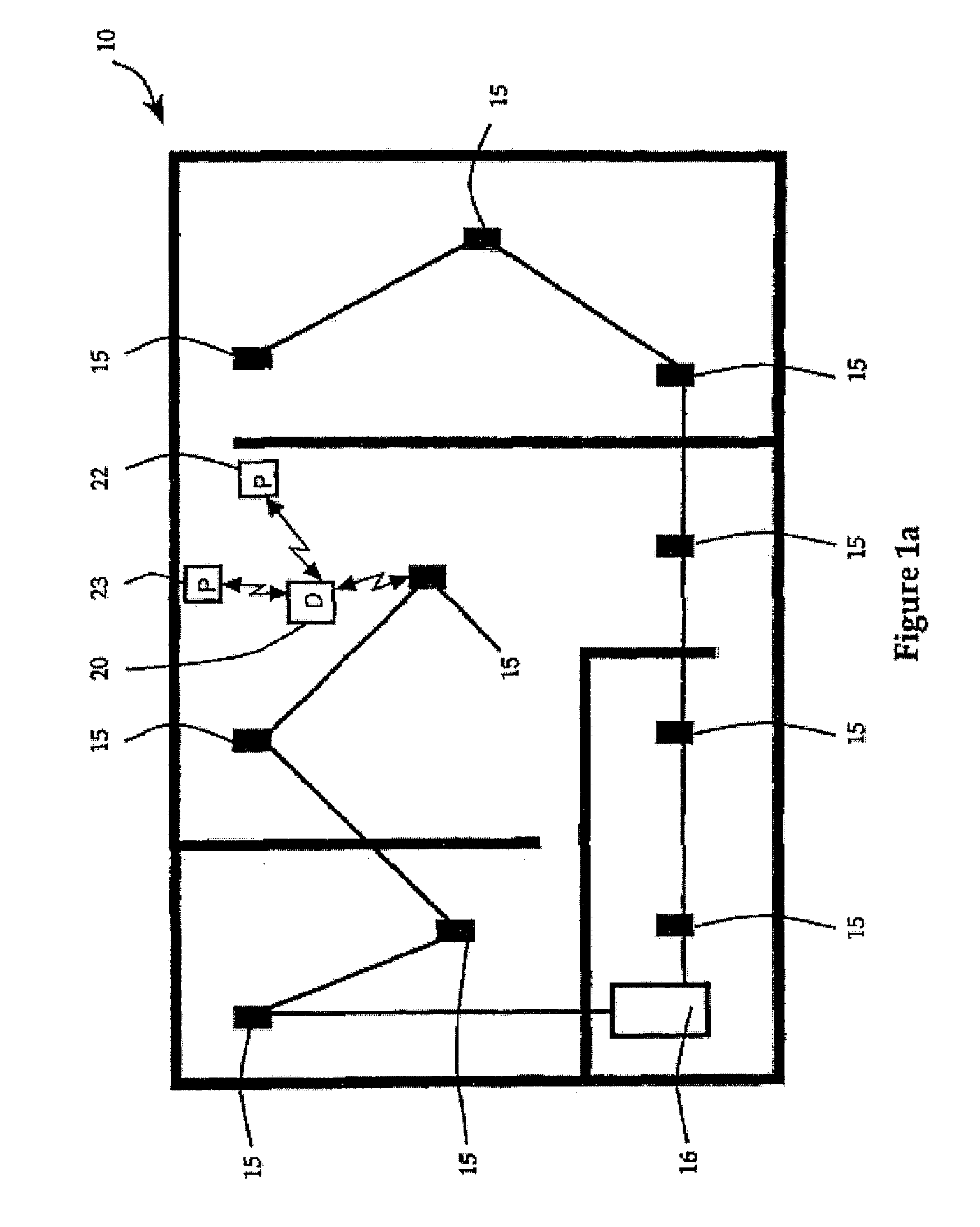
System and method for determining data rate
InactiveUS20080025378A1Efficient communication pathwayReduce traffic problemsError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementTransceiverRadio unit
A hierarchical communication system is described in which two wireless local area networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed to link inherently portable or mobile computer devices. A series of radio base stations make up a infrastructure network. The infrastructure network and at least one portable computer device make up the first local area network. The communication on the first local area network is accomplished by spread spectrum frequency hopping communication A second local area network allows for radio communication between a portable computer device and peripheral devices with built-in transceivers utilized by the portable computer device. The communication in each local area network is controlled by a reservation access communication protocol. The communication protocol facilitates frequency hopping synchronization and supports adaptive data rate selection based upon the quality of communication on the communication channel. The communication protocol prevents interference between communication on the first local area network and communication on the second local area network. In a premises LAN, a series of radio base stations and a backbone LAN make up an infrastructure network. The infrastructure network and at least one mobile computing device make up a higher-power LAN, utilizing a frequency hopping protocol. A lower-power LAN allows for radio communication between a mobile computing device and -peripheral devices, utilizing a single-frequency spread spectrum protocol. A vehicular LAN provides for short-range communication between a vehicle terminal and a portable terminal. When out of direct RF range of the premises LAN, the vehicle terminal maintains indirect communication when necessary with the premises LAN via one of several alternate RF channels. A microprocessor, located inside radio units which participate in multiple LAN's, selects the appropriate protocol, frequency band and power level for communicating through the network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
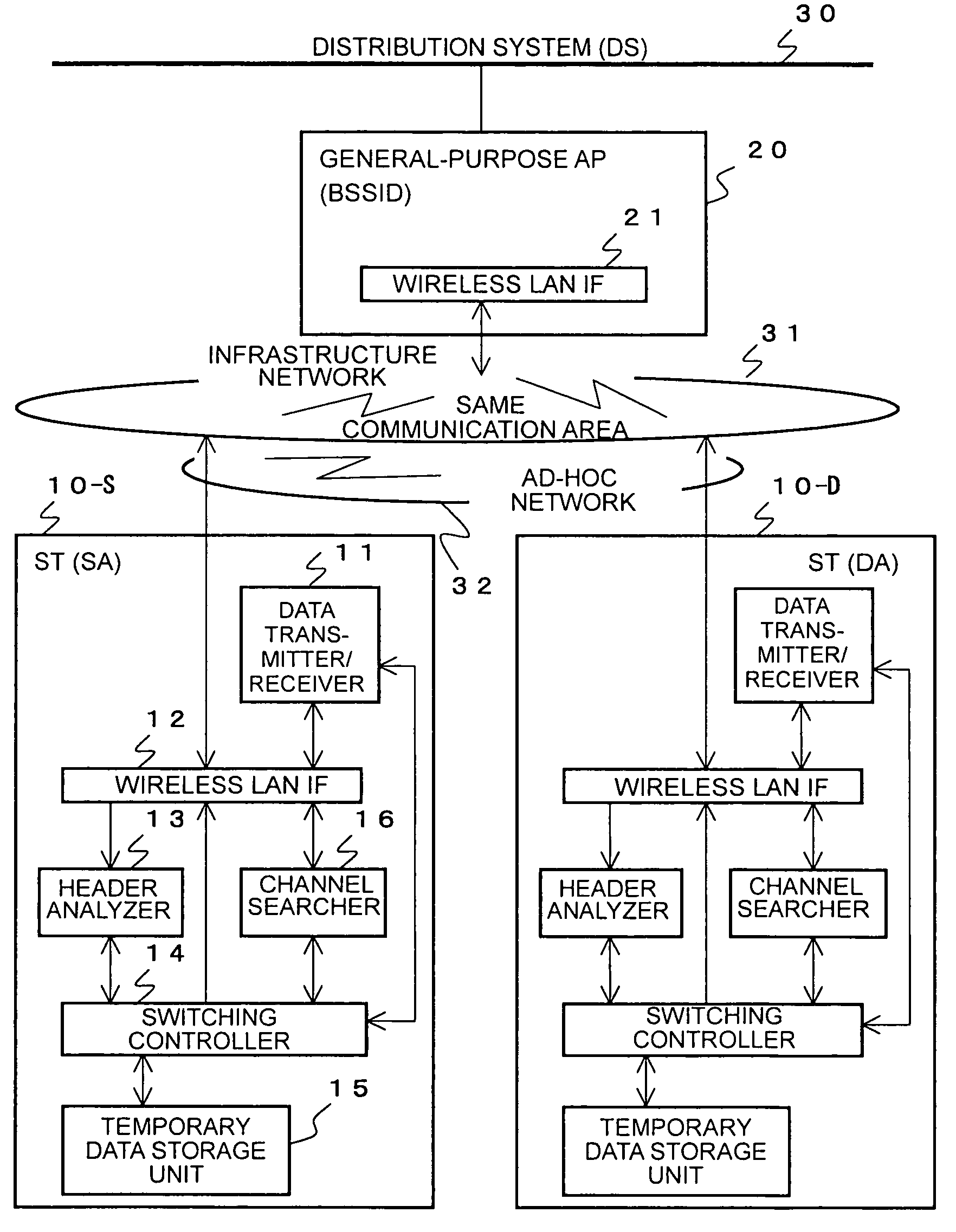
Wireless LAN communication system
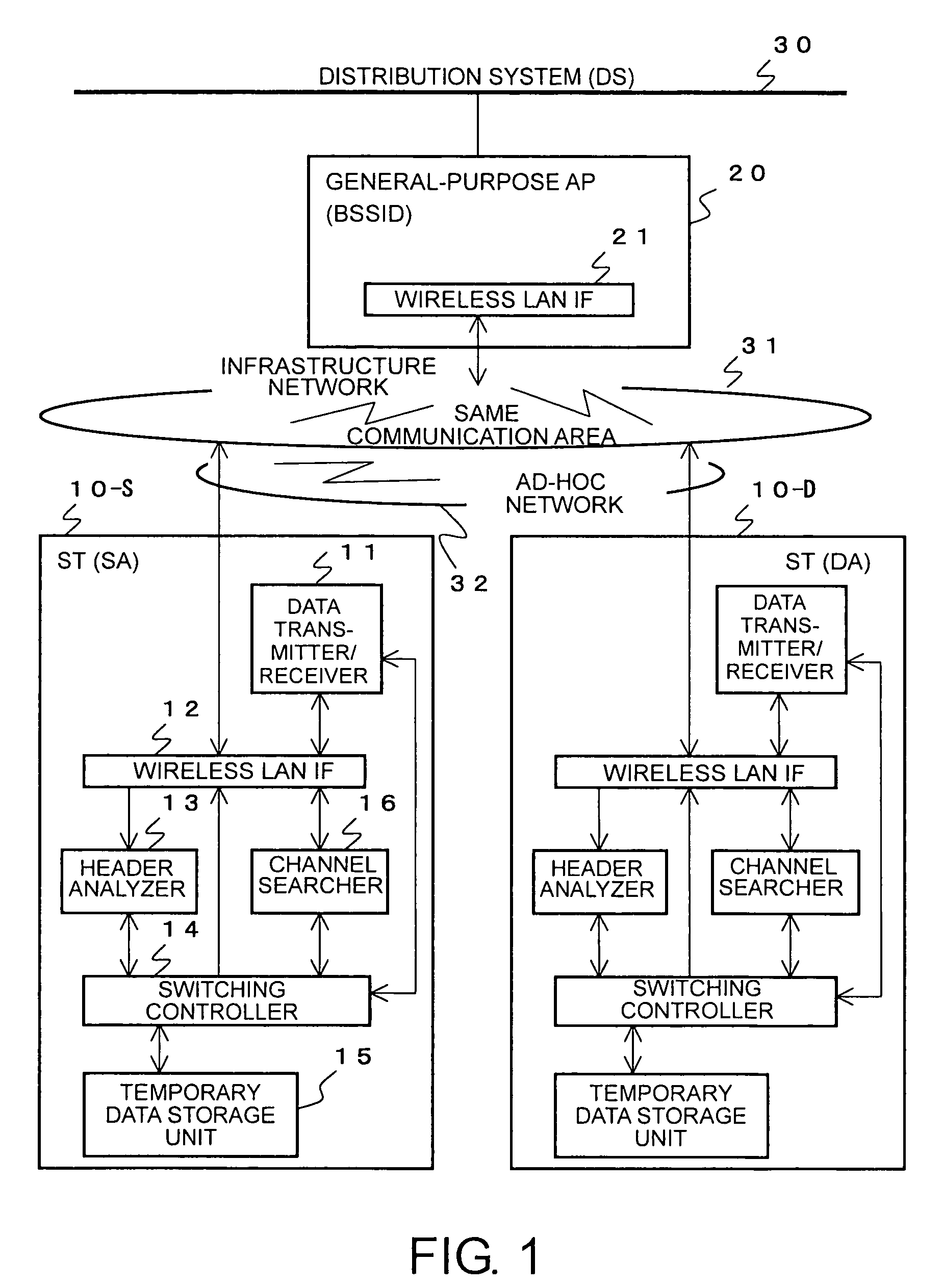
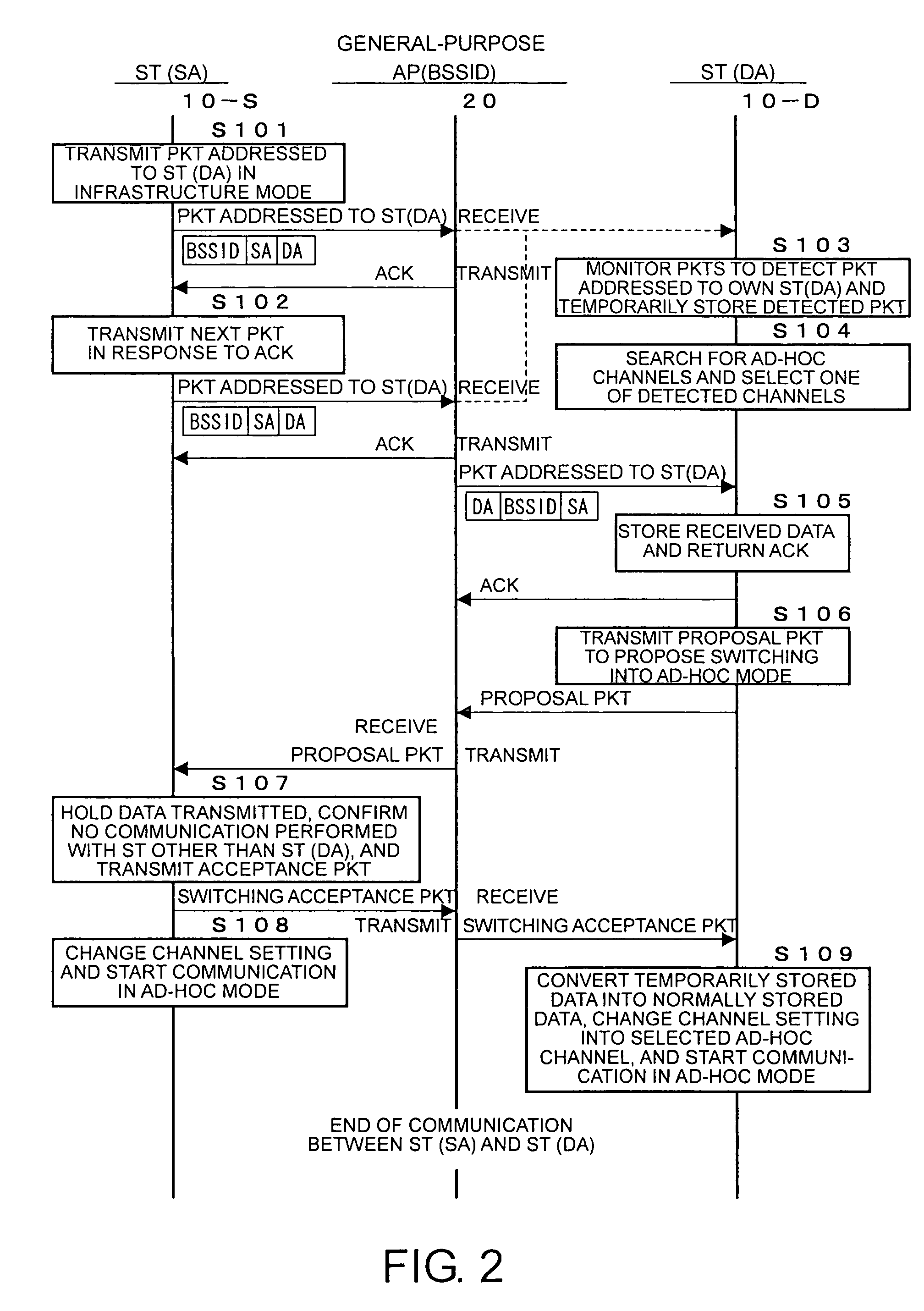
In a wireless LAN communication system, a communication mode is automatically switched between an infrastructure mode and an ad-hoc mode. Communication between two stations is started in the infrastructure mode. Packets transmitted in an infrastructure network are monitors to detect a packet transmitted to an access point and addressed, as a final destination, to one's own station or a destination station. If such a packet is detected, it is determined that a transmitting or source station is in a state that allows an ad-hoc communication. A channel searcher of the access point searches for available channels of an ad-hoc network. A switching controller selects one of the available channels and transmits information indicating the selected channel to the source and destination stations. In response to receiving the information indicating the selected channel, the source and destination stations starts direct communication using the selected channel of the ad-hoc network. The selection of the channel may be performed by a station. Associated data may be stored in a temporary data storage unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Wireless Network System and Wireless Communicaton Method
ActiveUS20100115262A1Easy to set network informationNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionUser deviceWireless mesh network
A wireless network system includes a user device, a client and an access point. In the wireless network system, a wireless network mode of the client is started in an AdHoc mode in response to specific operation, a wireless network mode of the user device is switched to an AdHoc mode when it is detected that the wireless network mode of the client is started in the AdHoc mode. Then, infrastructure network information including a network name and an encryption key for setting the wireless network communication in the infrastructure mode is transmitted from the user device to the client, and the wireless network mode of the client is switched to the infrastructure mode on the basis of the infrastructure network information.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
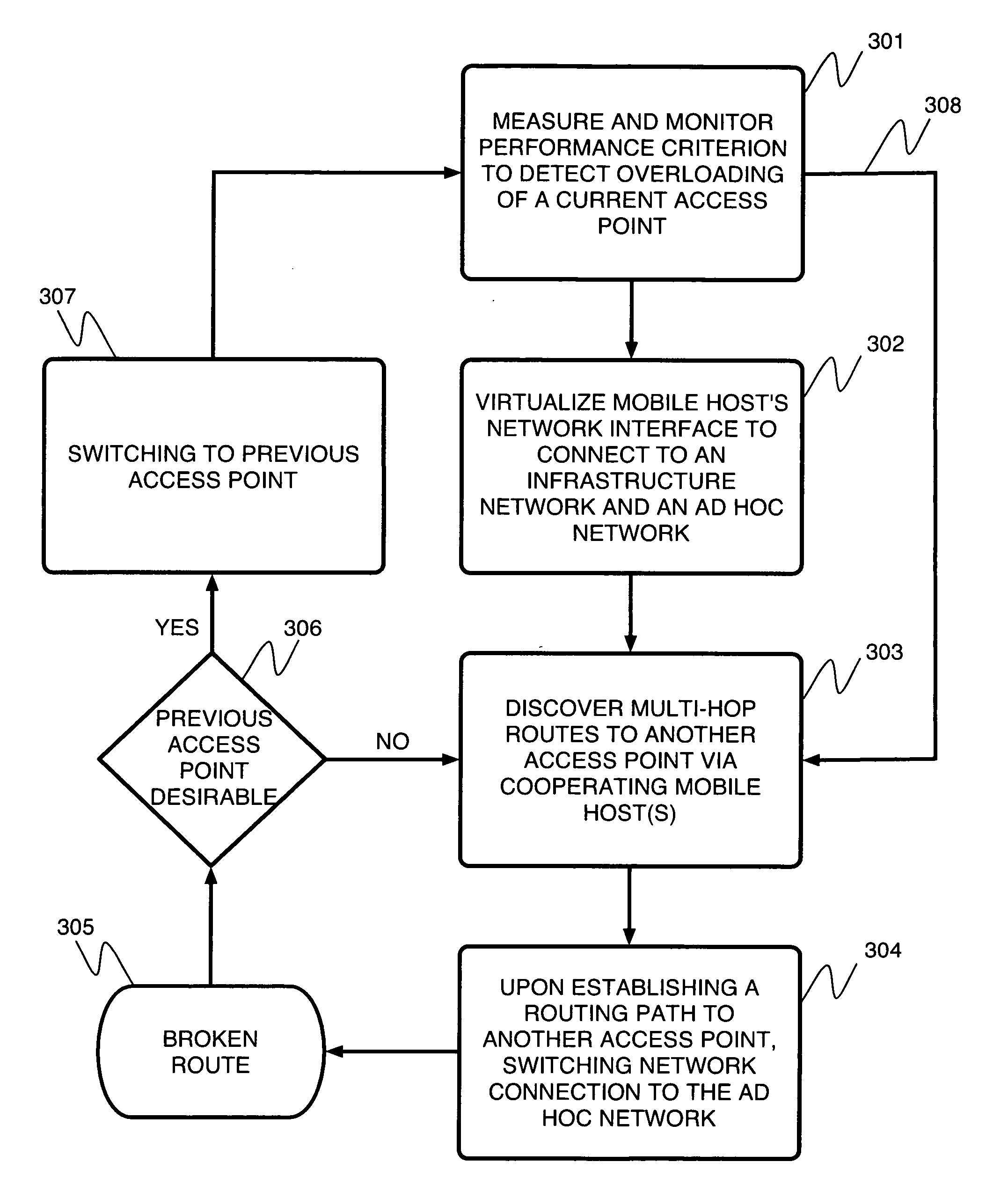
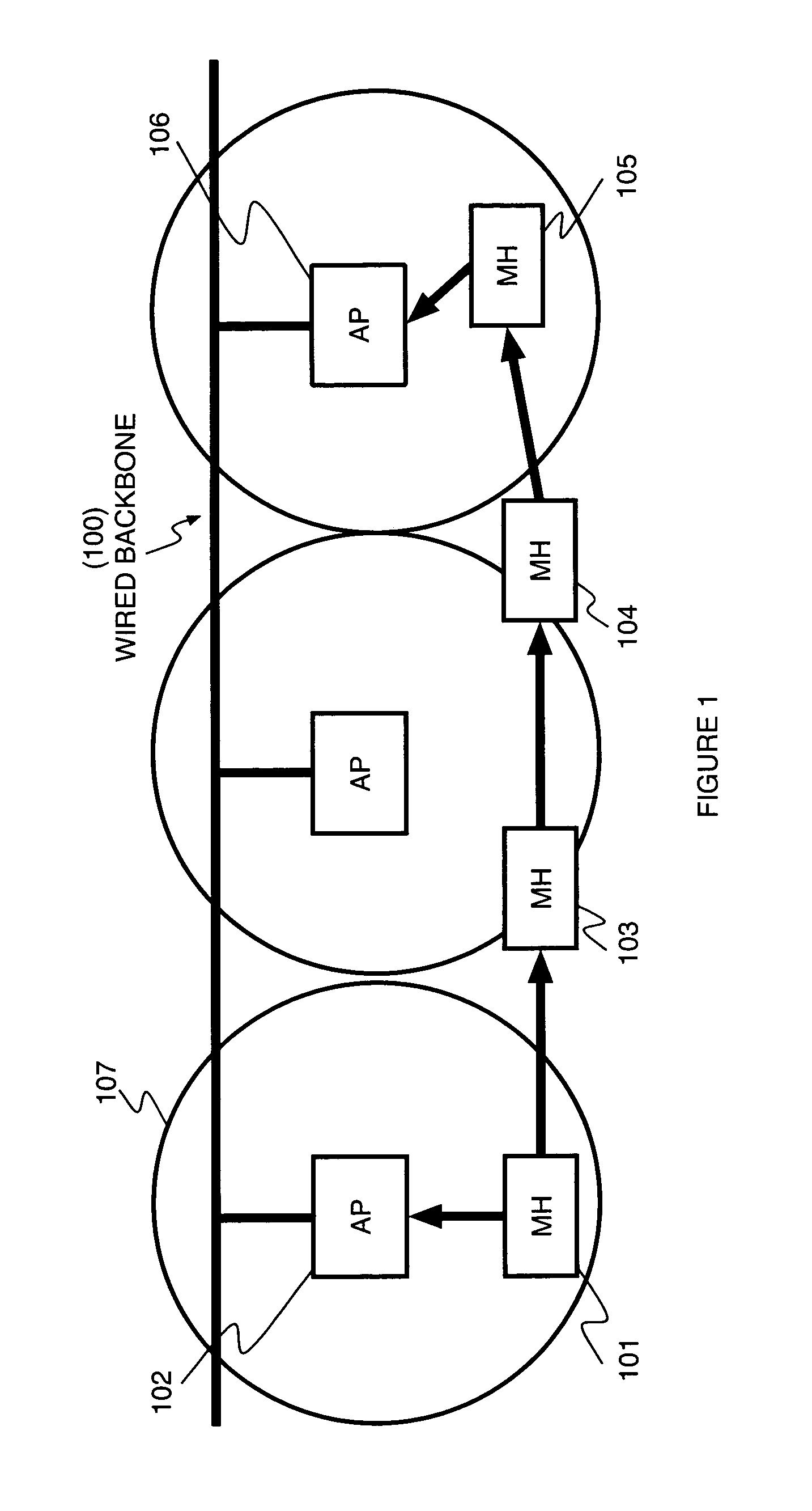
Ad hoc network routing for hotspot mitigation and load balancing in wireless LANs
InactiveUS20050100029A1Undesirable performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesVirtualizationBalancing network
A method for balancing network load among mobile hosts includes determining and monitoring a performance of a first access point connected to a mobile host by an infrastructure network, determining that the performance of the first access point is undesirable, and virtualizing a network interface of the mobile host connected to the first access point, wherein an ad hoc network are established in addition to the infrastructure network. The method further including determining a route to a second access point through at least one cooperating mobile host, and switching a connection of the mobile host to the second access point via the route to the second access point, wherein the connection is established via the ad hoc network.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com