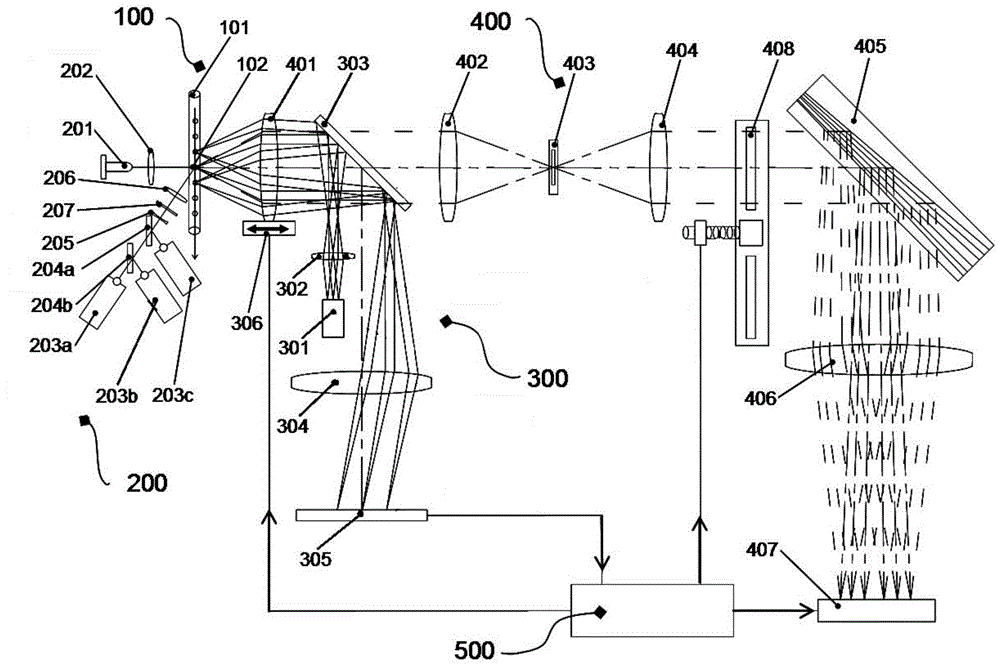
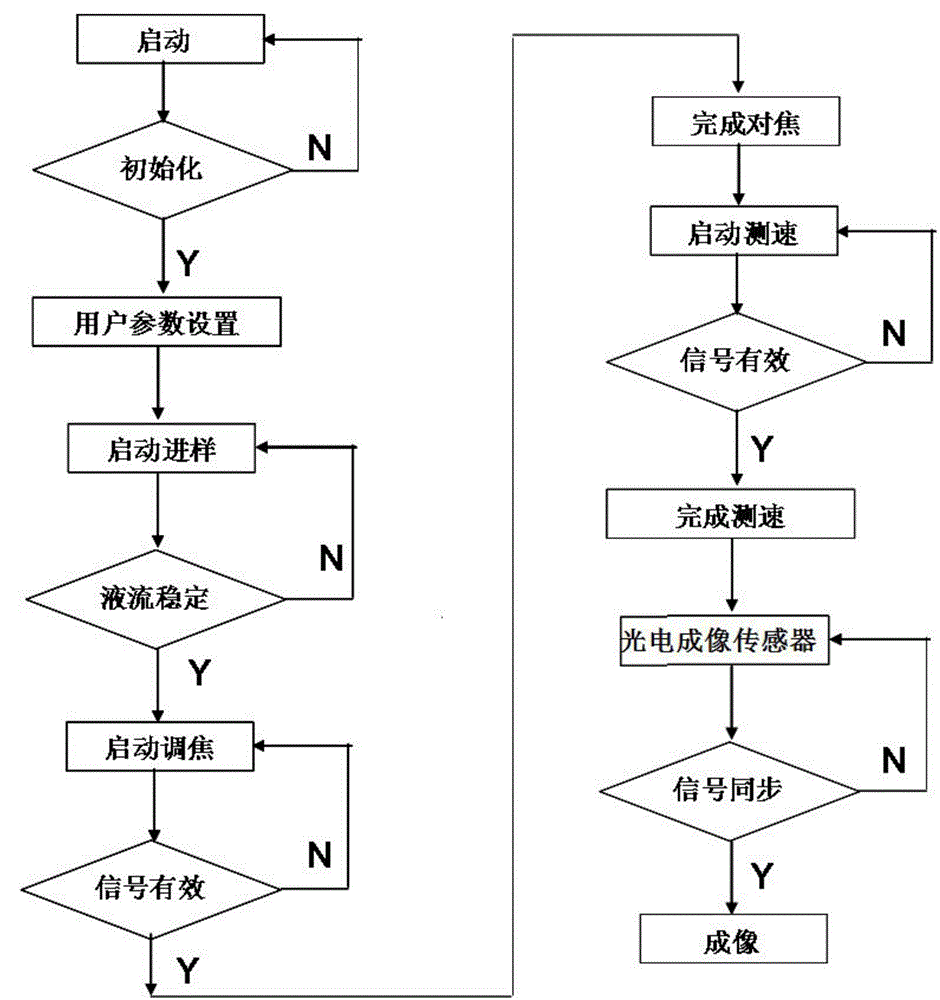
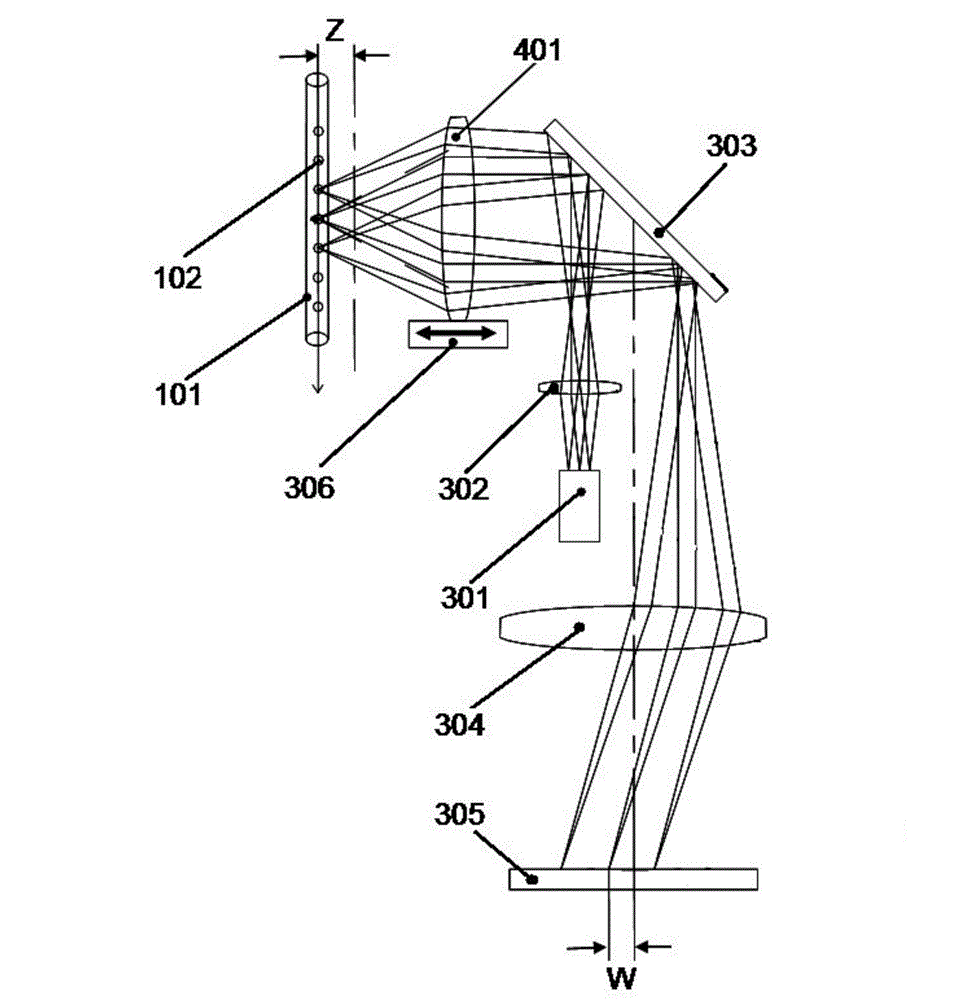
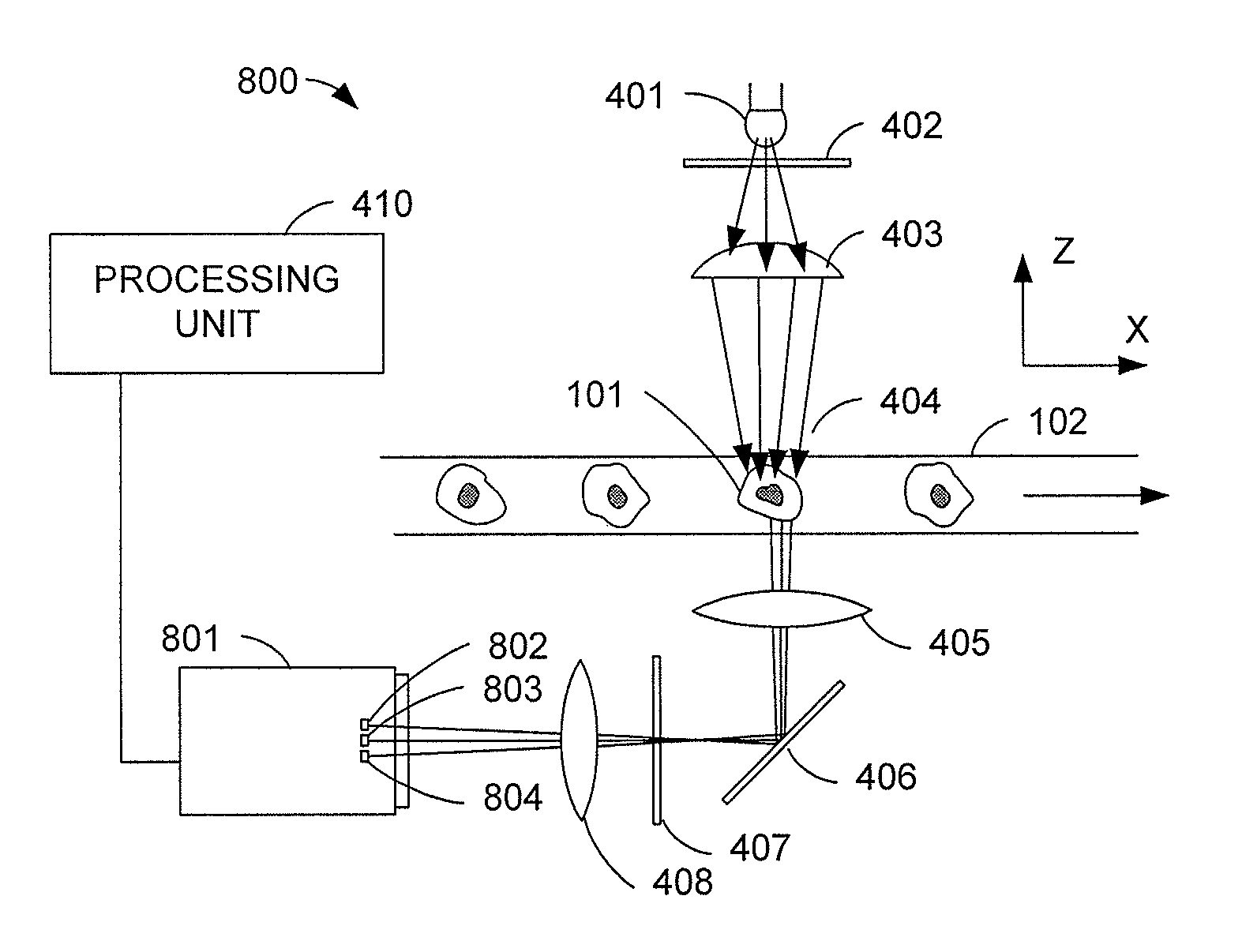
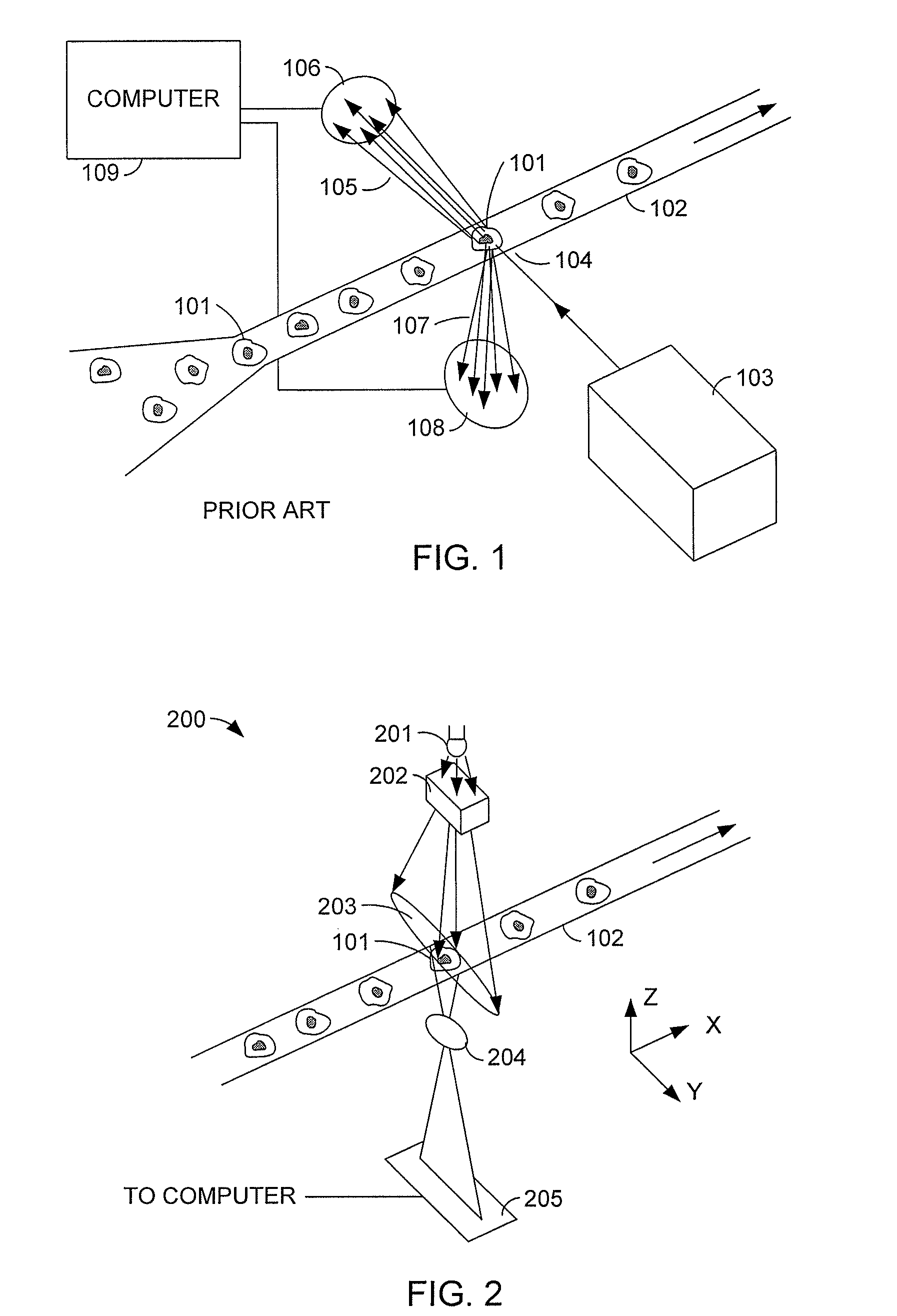
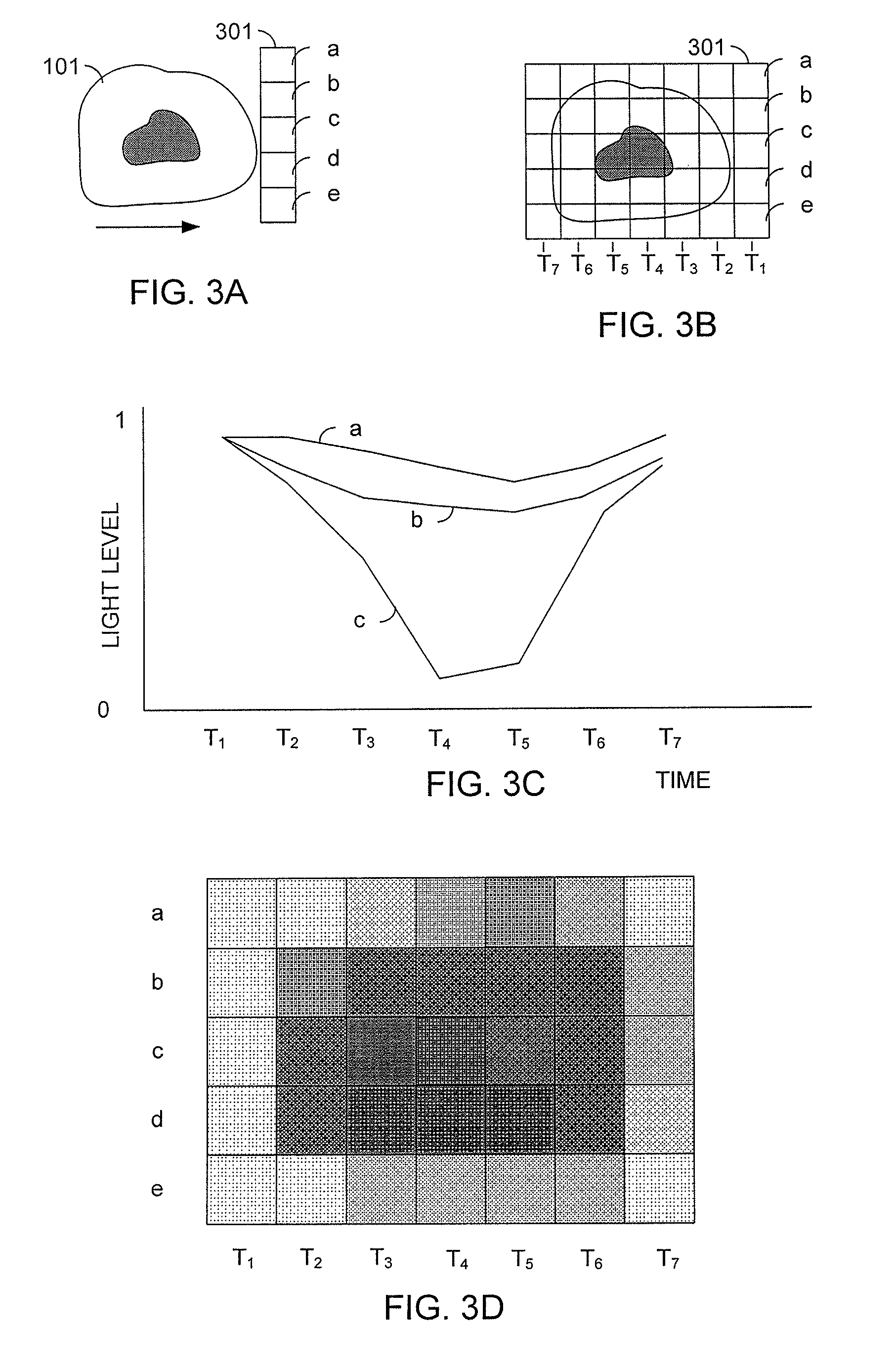
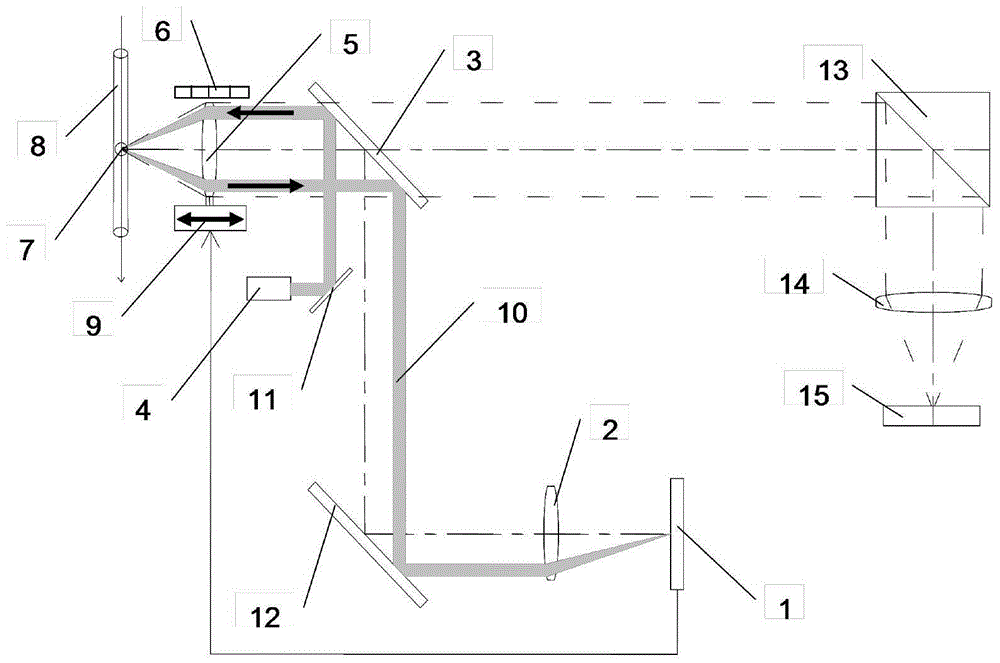
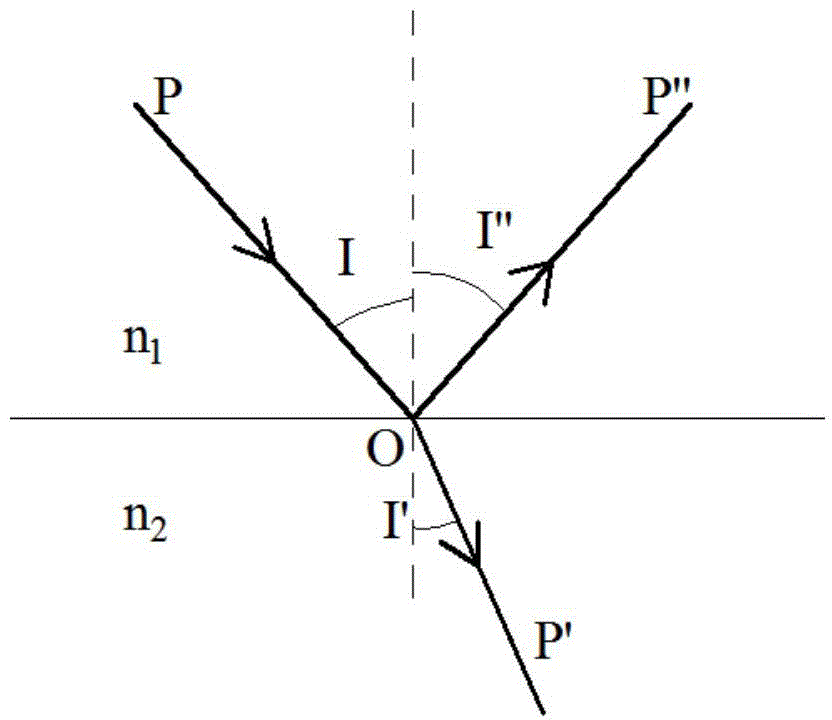
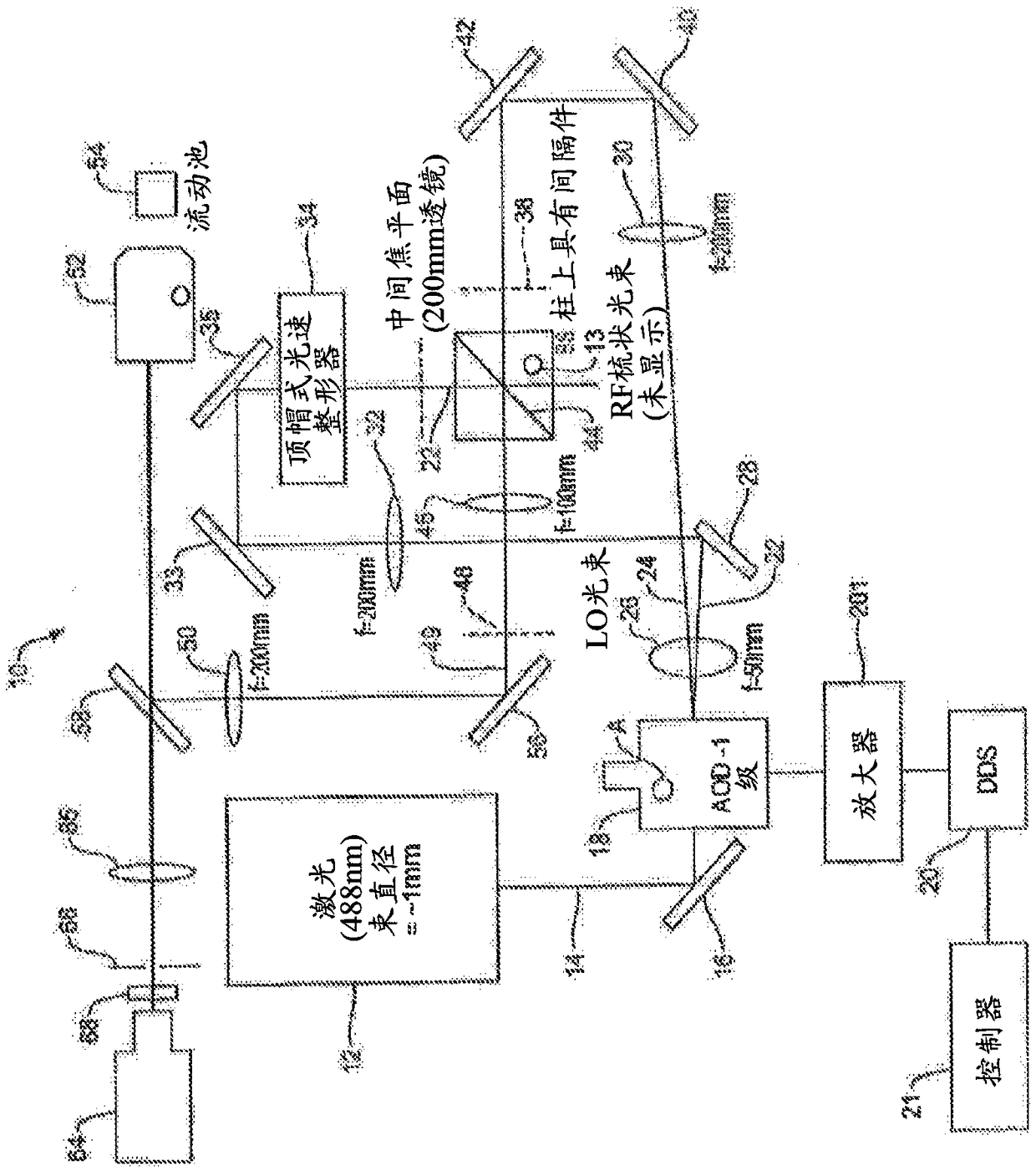
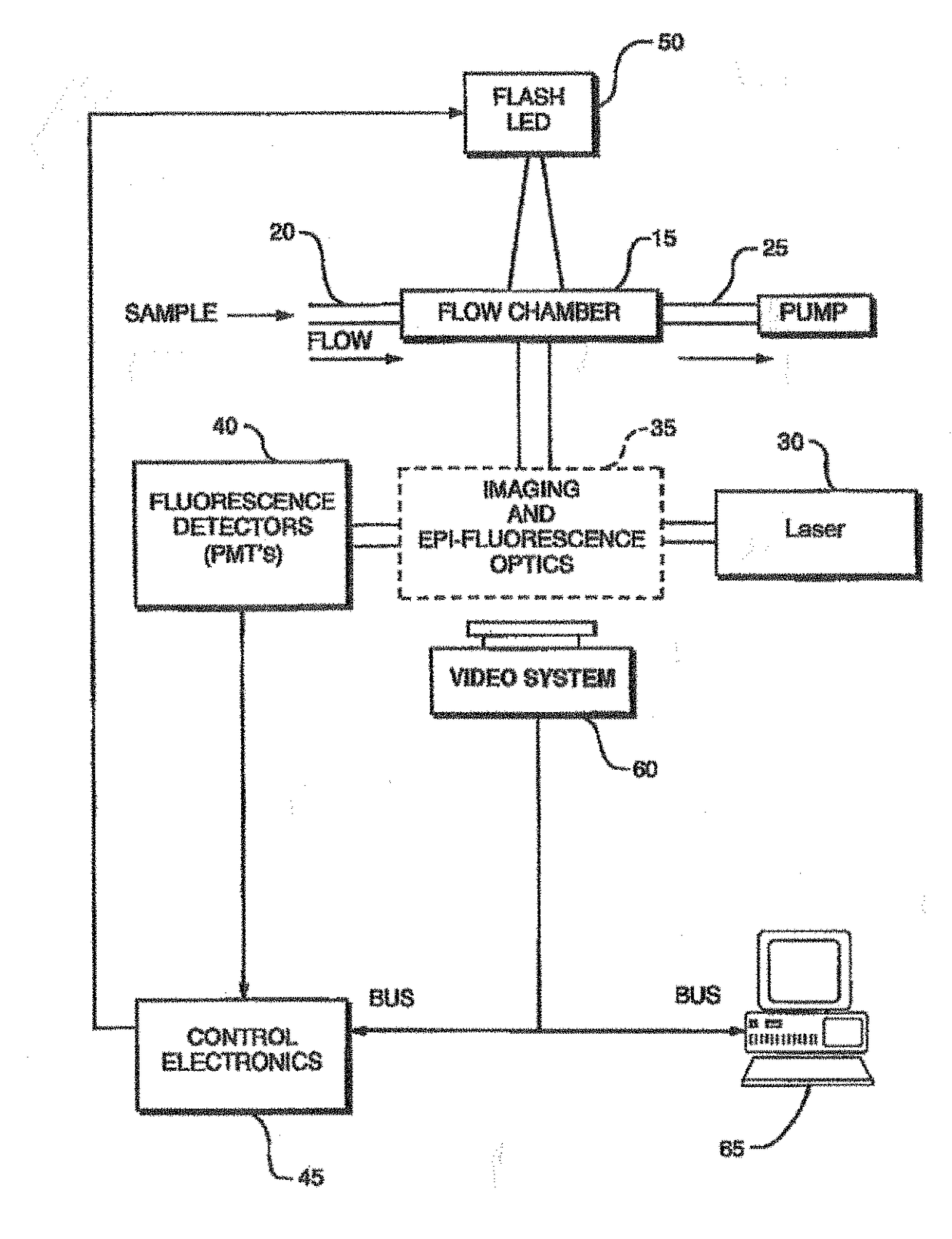
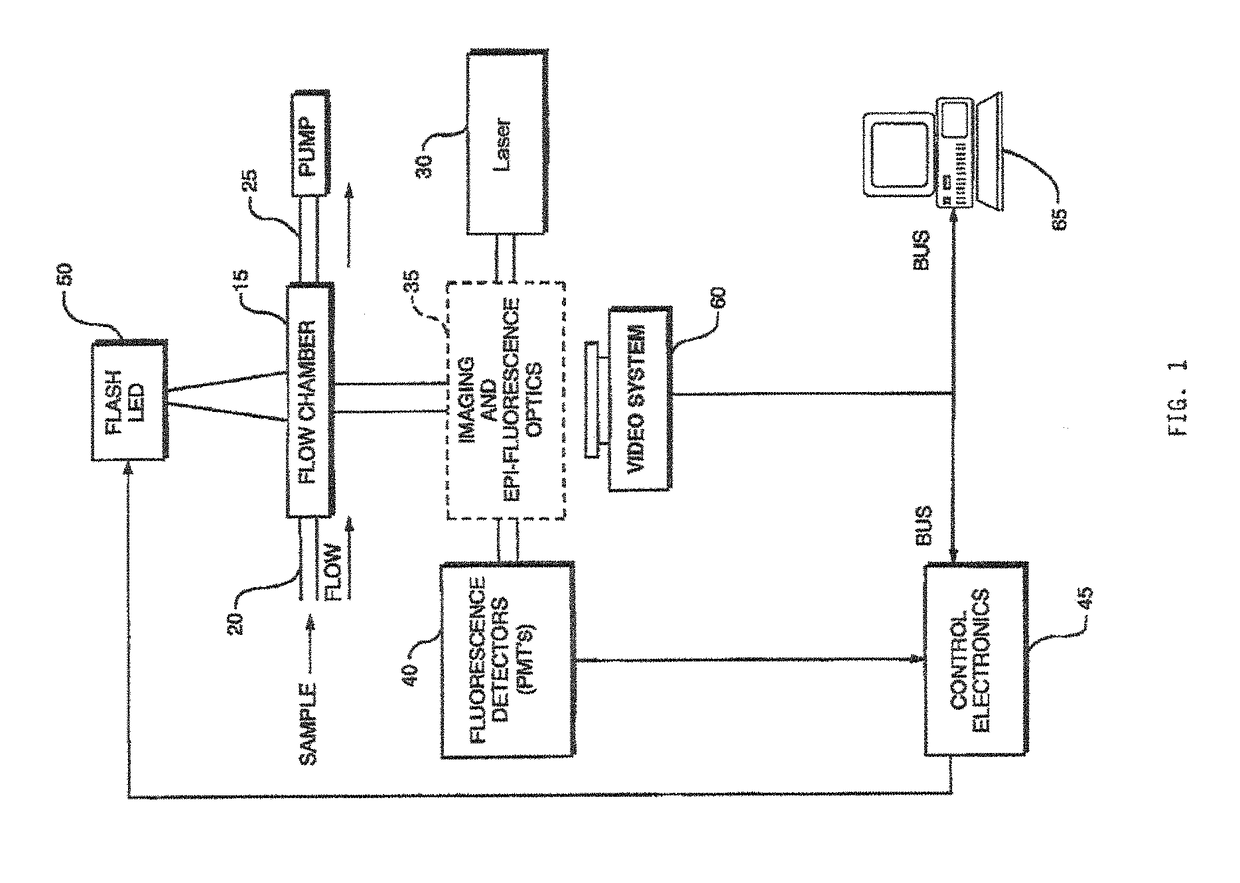
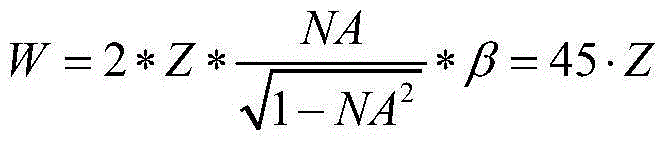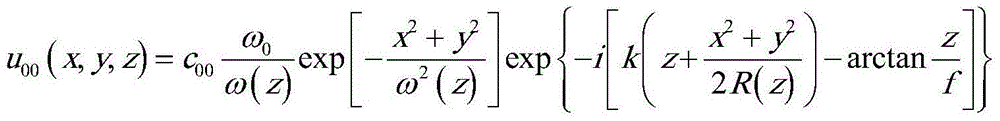Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Imaging flow cytometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
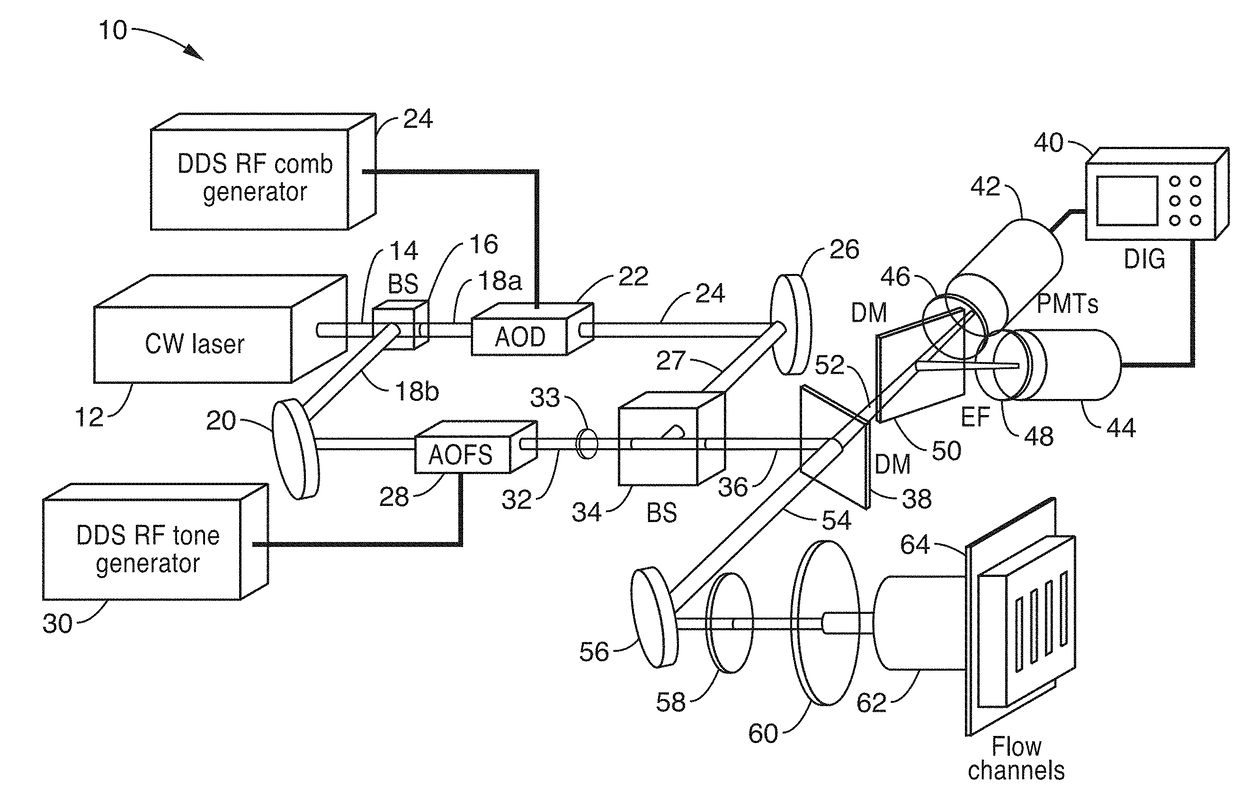
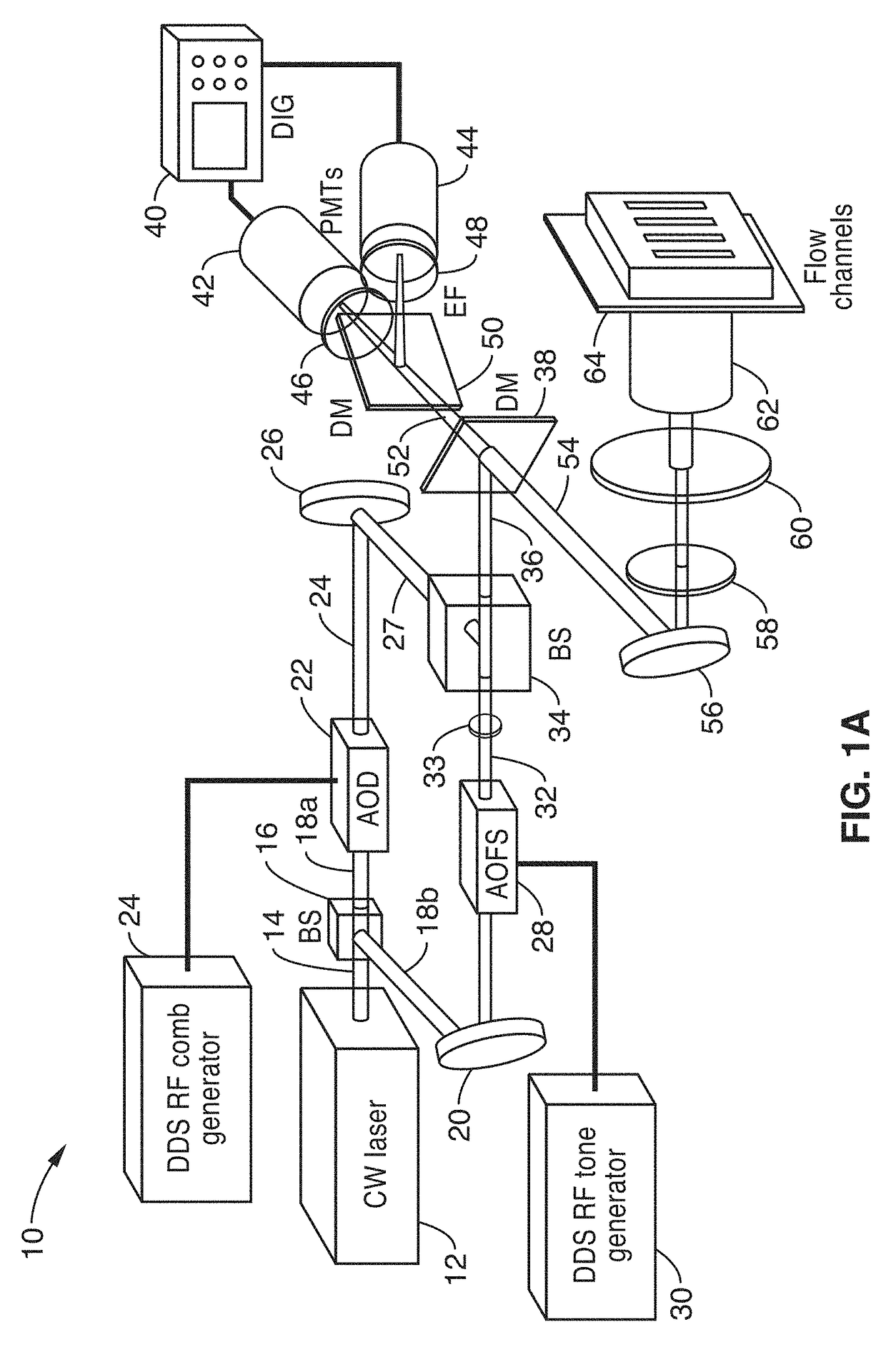
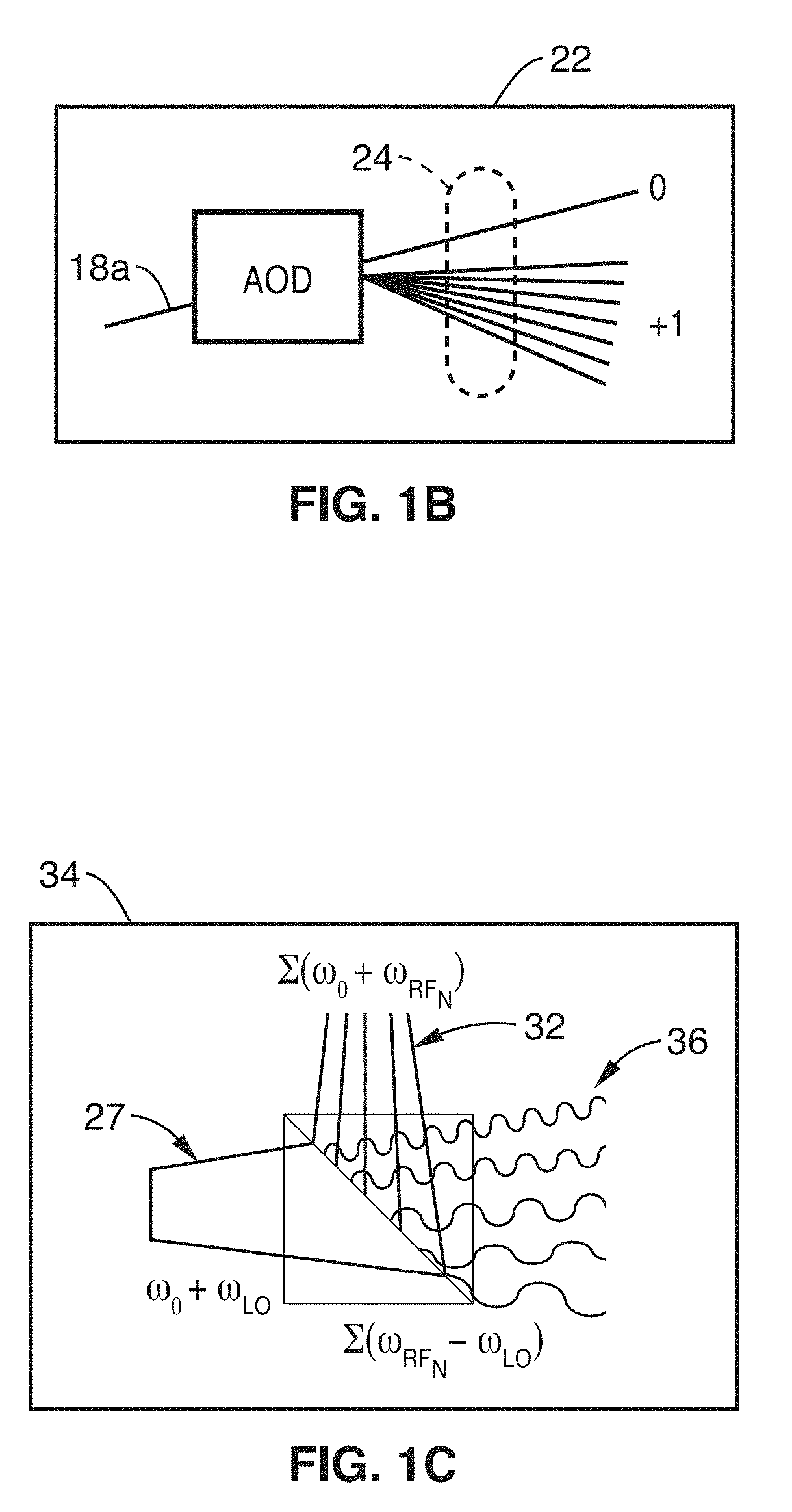
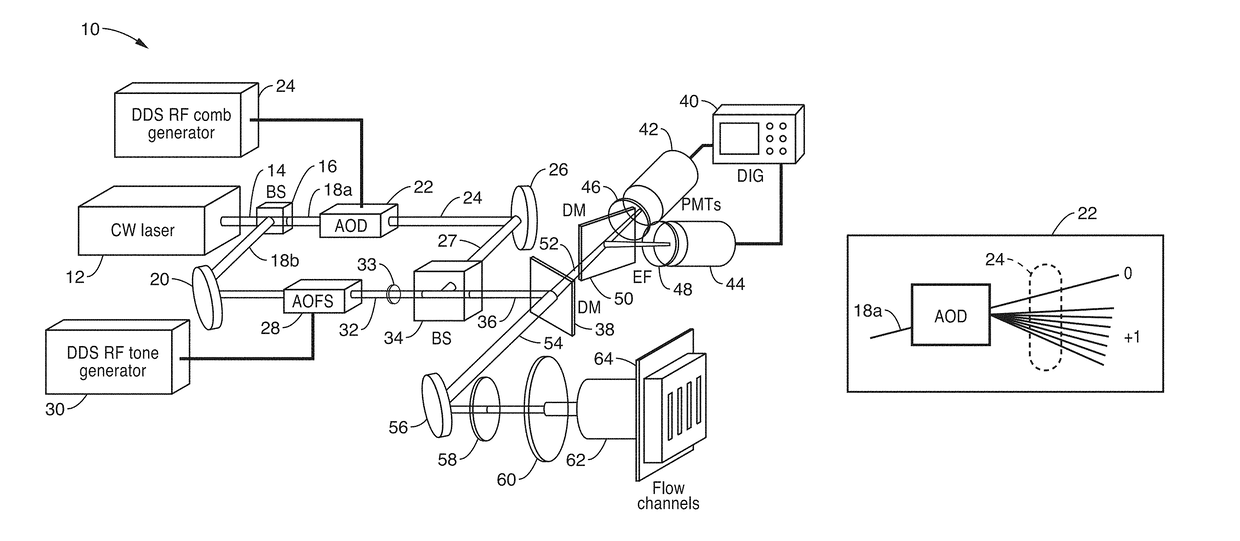
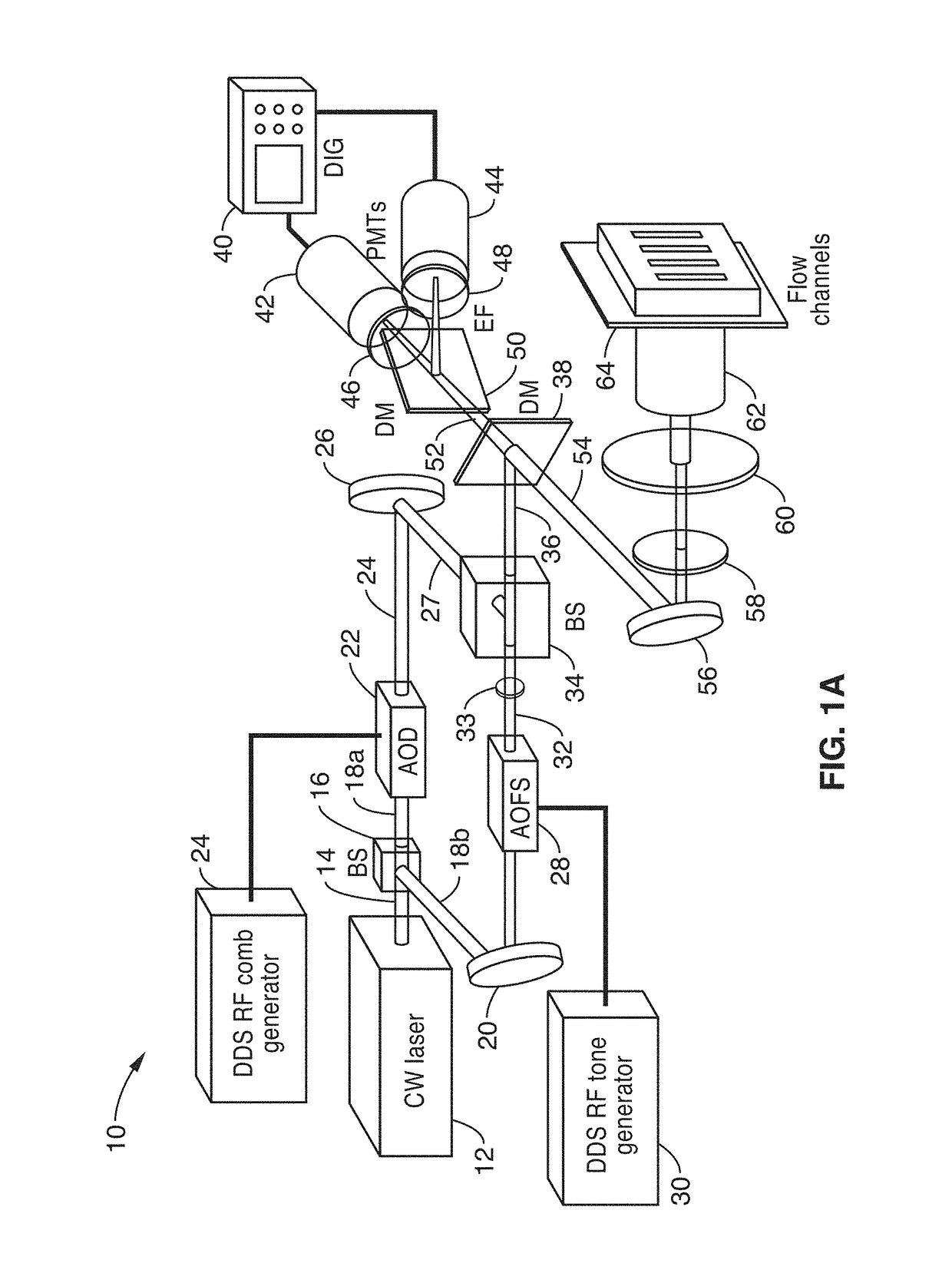
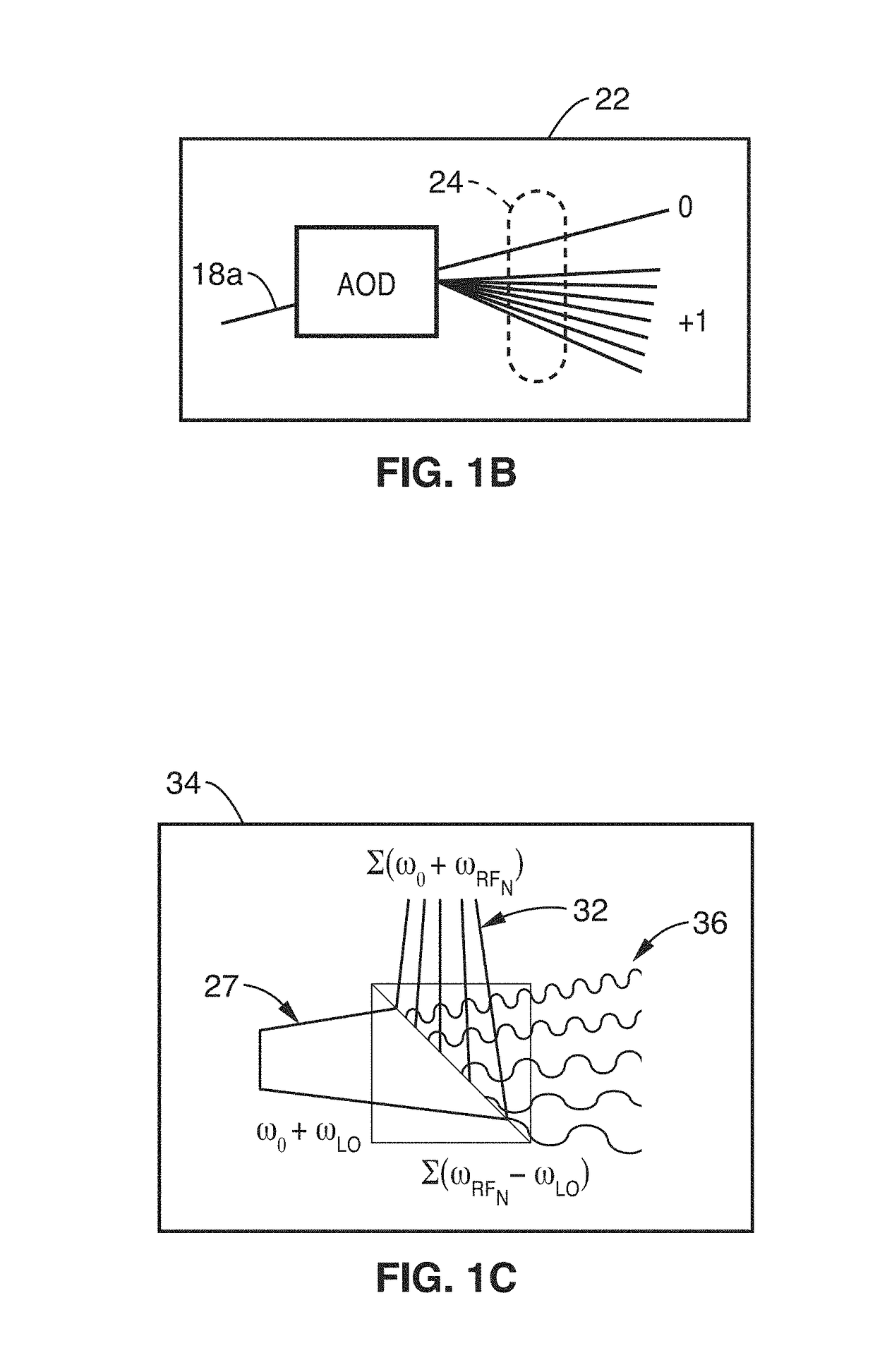
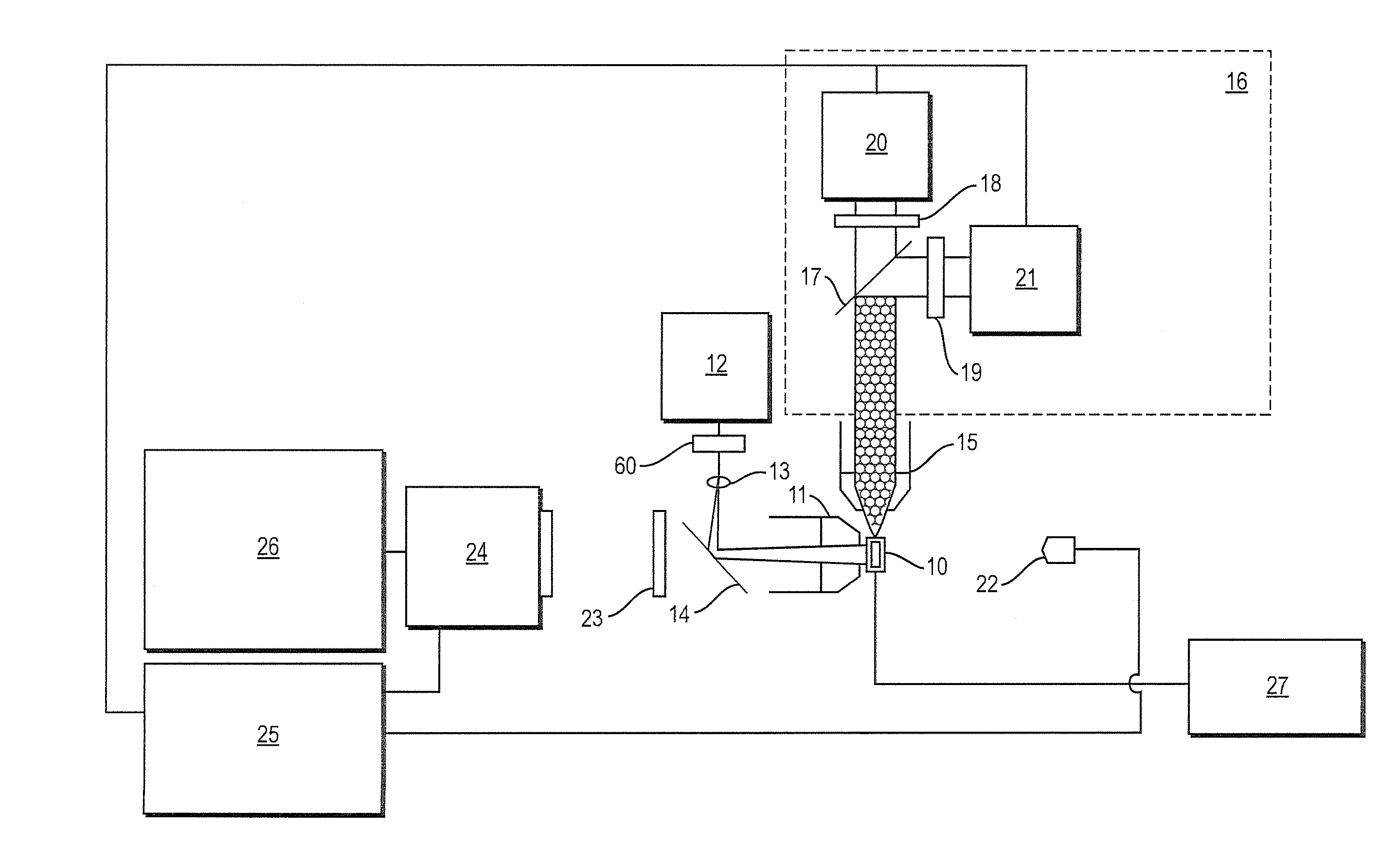
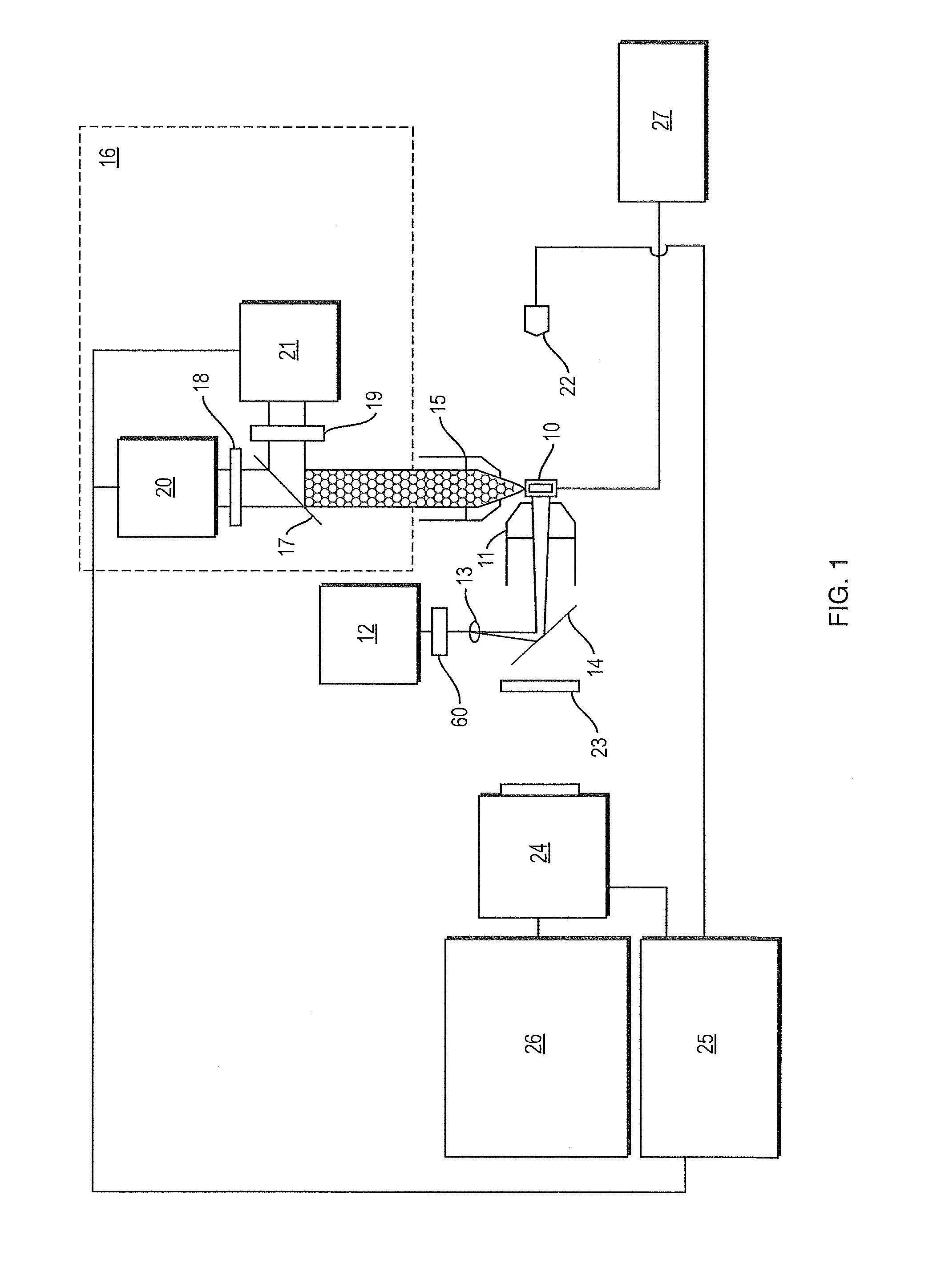
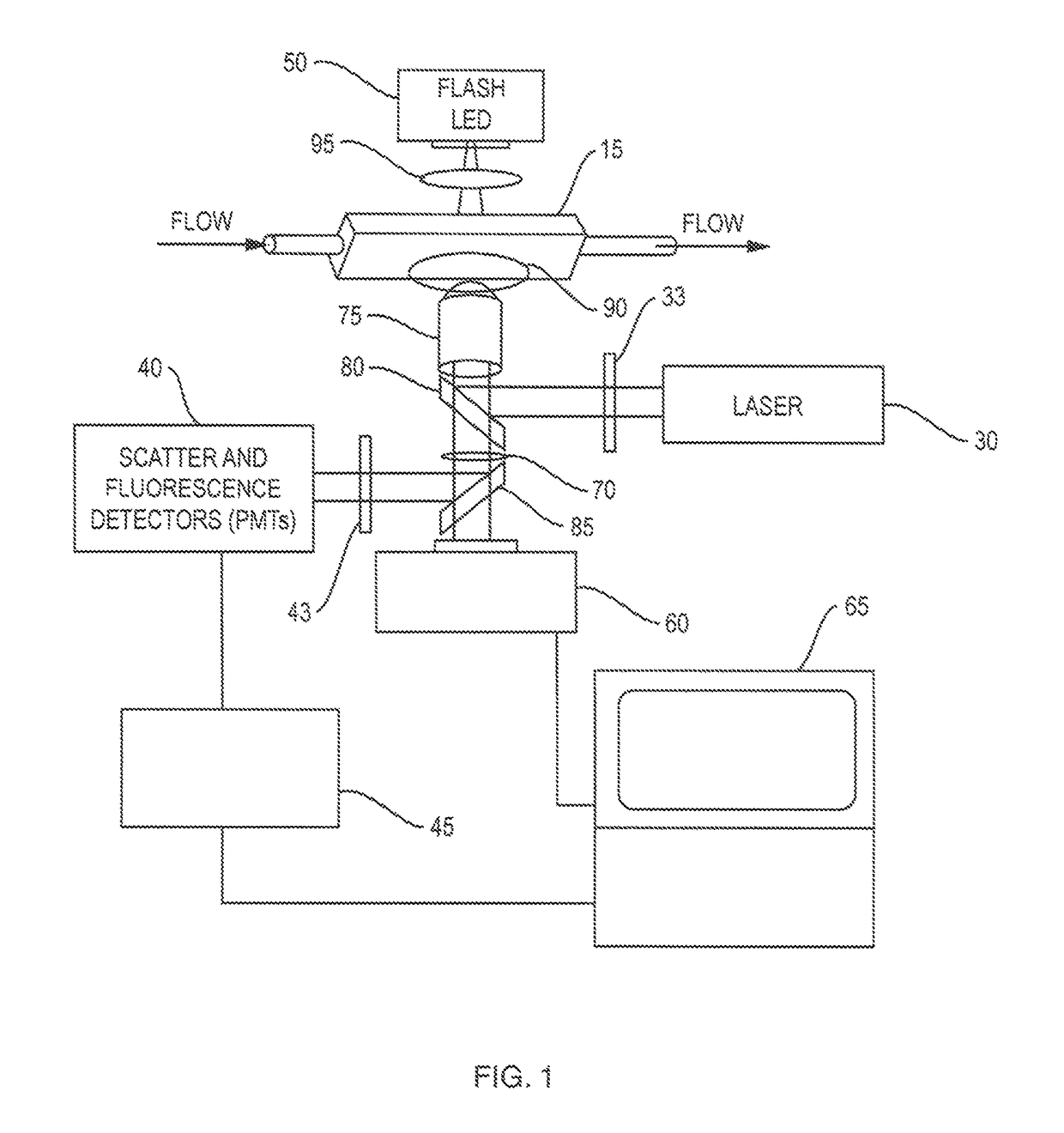
Parallel flow cytometer using radiofrequency multiplexing
ActiveUS20170350803A1Improve throughputLow costIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceMultiplexingFluorescence
An imaging flow cytometry apparatus and method which allows registering multiple locations across a cell, and / or across multiple flow channels, in parallel using radio-frequency-tagged emission (FIRE) coupled with a parallel optical detection scheme toward increasing analysis throughput. An optical source is modulated by multiple RF frequencies to produce an optical interrogation beam having a spatially distributed beat frequency. This beam is directed to one or more focused streams of cells whose responsive fluorescence, in different frequencies, is registered in parallel by an optical detector.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Parallel flow cytometer using radiofrequency multiplexing
ActiveUS9784661B2Improve throughputLow costIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceMultiplexingFluorescence
An imaging flow cytometry apparatus and method which allows registering multiple locations across a cell, and / or across multiple flow channels, in parallel using radio-frequency-tagged emission (FIRE) coupled with a parallel optical detection scheme toward increasing analysis throughput. An optical source is modulated by multiple RF frequencies to produce an optical interrogation beam having a spatially distributed beat frequency. This beam is directed to one or more focused streams of cells whose responsive fluorescence, in different frequencies, is registered in parallel by an optical detector.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Serial-line-scan-encoded multi-color fluorescence microscopy and imaging flow cytometry
InactiveUS20100238442A1Improved signal-to-noise ratioRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometryHigh resolution imagingSerial line
A system for performing high-speed, high-resolution imaging cytometry utilizes a line-scan sensor. A cell to be characterized is transported past a scan region. An optical system focuses an image of a portion of the scan region onto at least one linear light sensor, and repeated readings of light falling on the sensor are taken while a cell is transported though the scan region. The system may image cells directly, or may excite fluorescence in the cells and image the resulting light emitted from the cell by fluorescence. The system may provide a narrow band of illumination at the scan region. The system may include various filters and imaging optics that enable simultaneous multicolor fluorescence imaging cytometry. Multiple linear sensors may be provided, and images gathered by the individual sensors may be combined to construct an image having improved signal-to-noise characteristics.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Parallel flow cytometer using radiofrequency multiplexing
ActiveUS20170227444A1Increase costImprove simplicityIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceMultiplexingFluorescence
An imaging flow cytometry apparatus and method which allows registering multiple locations across a cell, and / or across multiple flow channels, in parallel using radio-frequency-tagged emission (FIRE) coupled with a parallel optical detection scheme toward increasing analysis throughput. An optical source is modulated by multiple RF frequencies to produce an optical interrogation beam having a spatially distributed beat frequency. This beam is directed to one or more focused streams of cells whose responsive fluorescence, in different frequencies, is registered in parallel by an optical detector.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
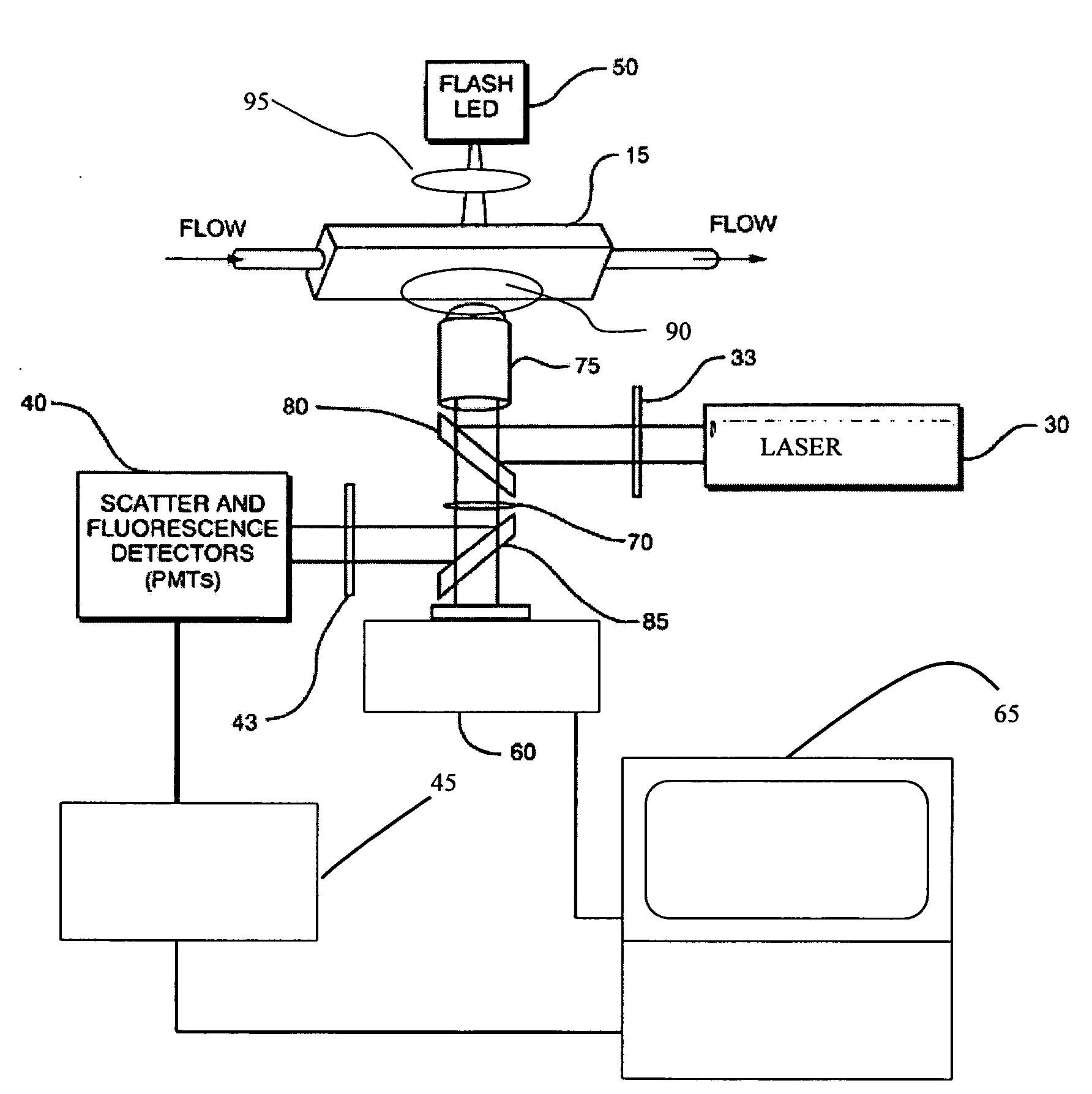
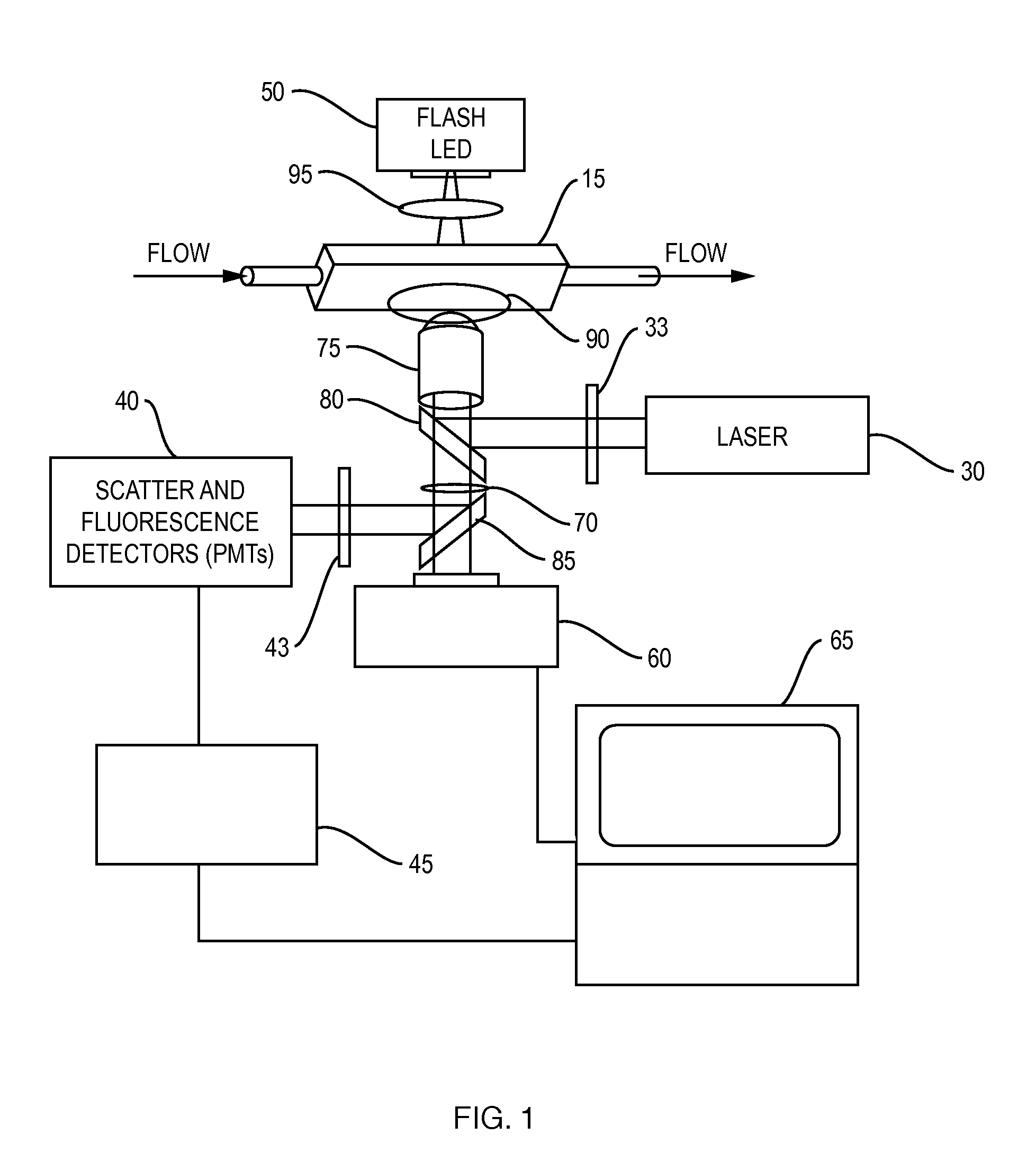
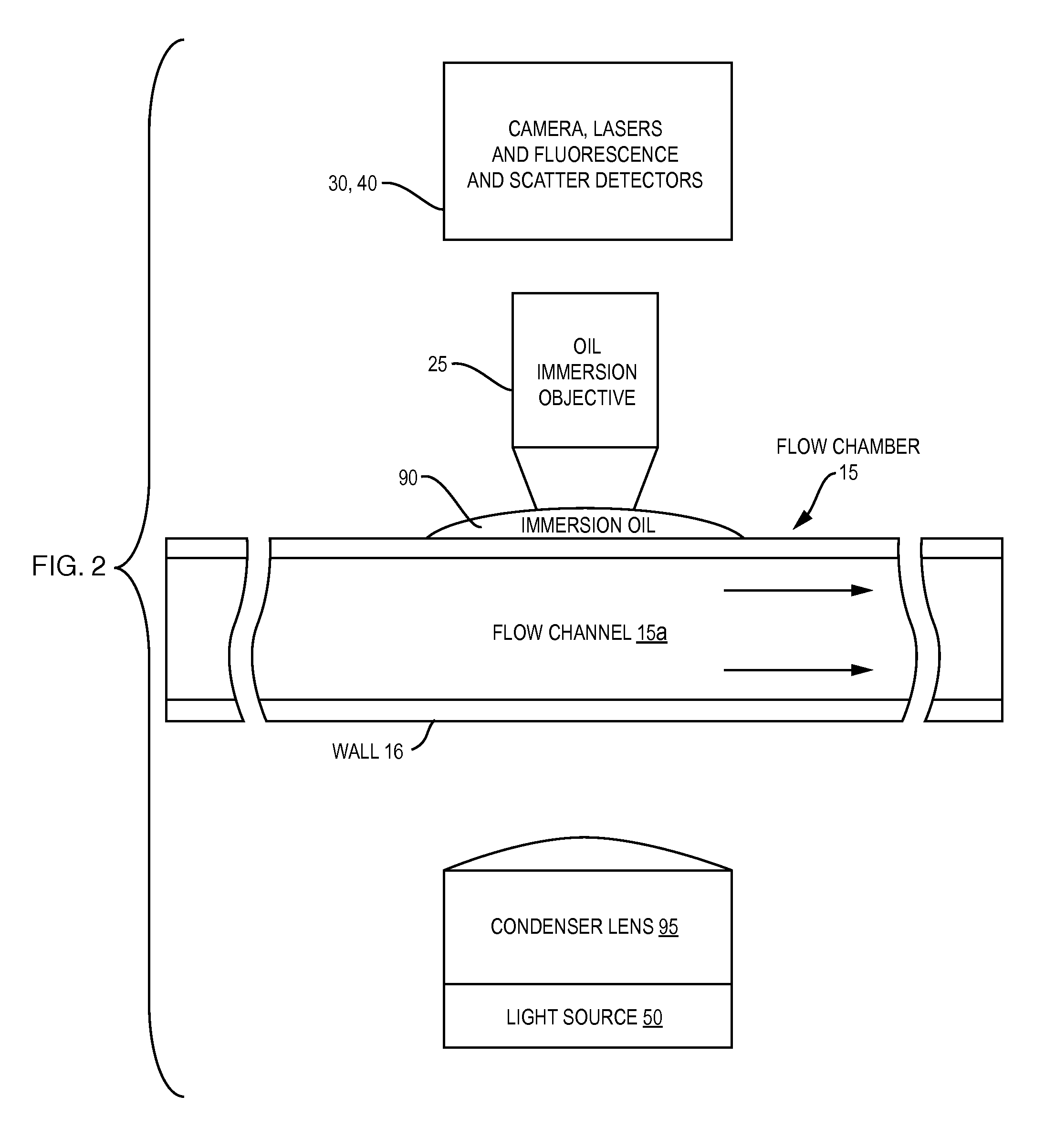
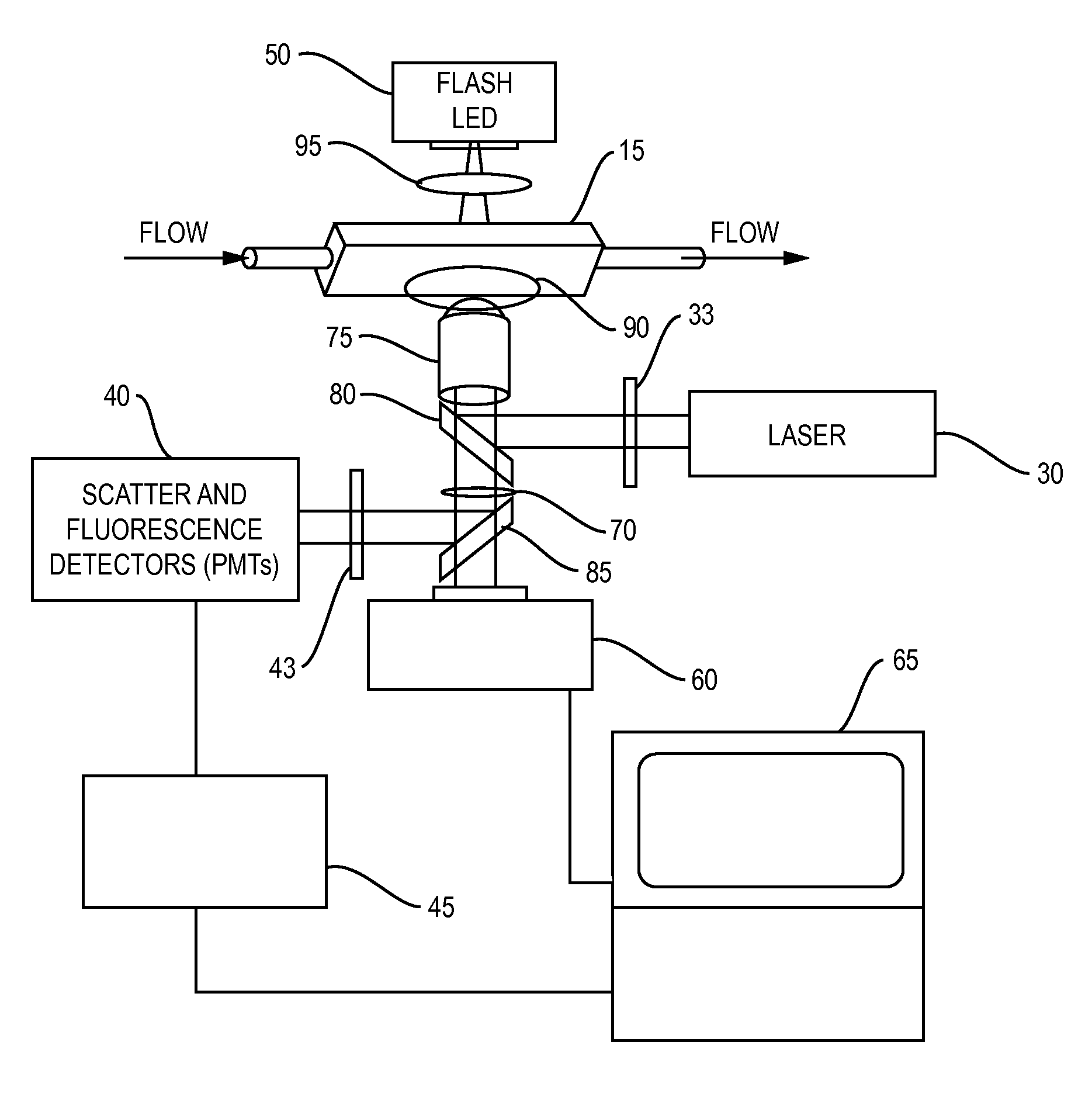
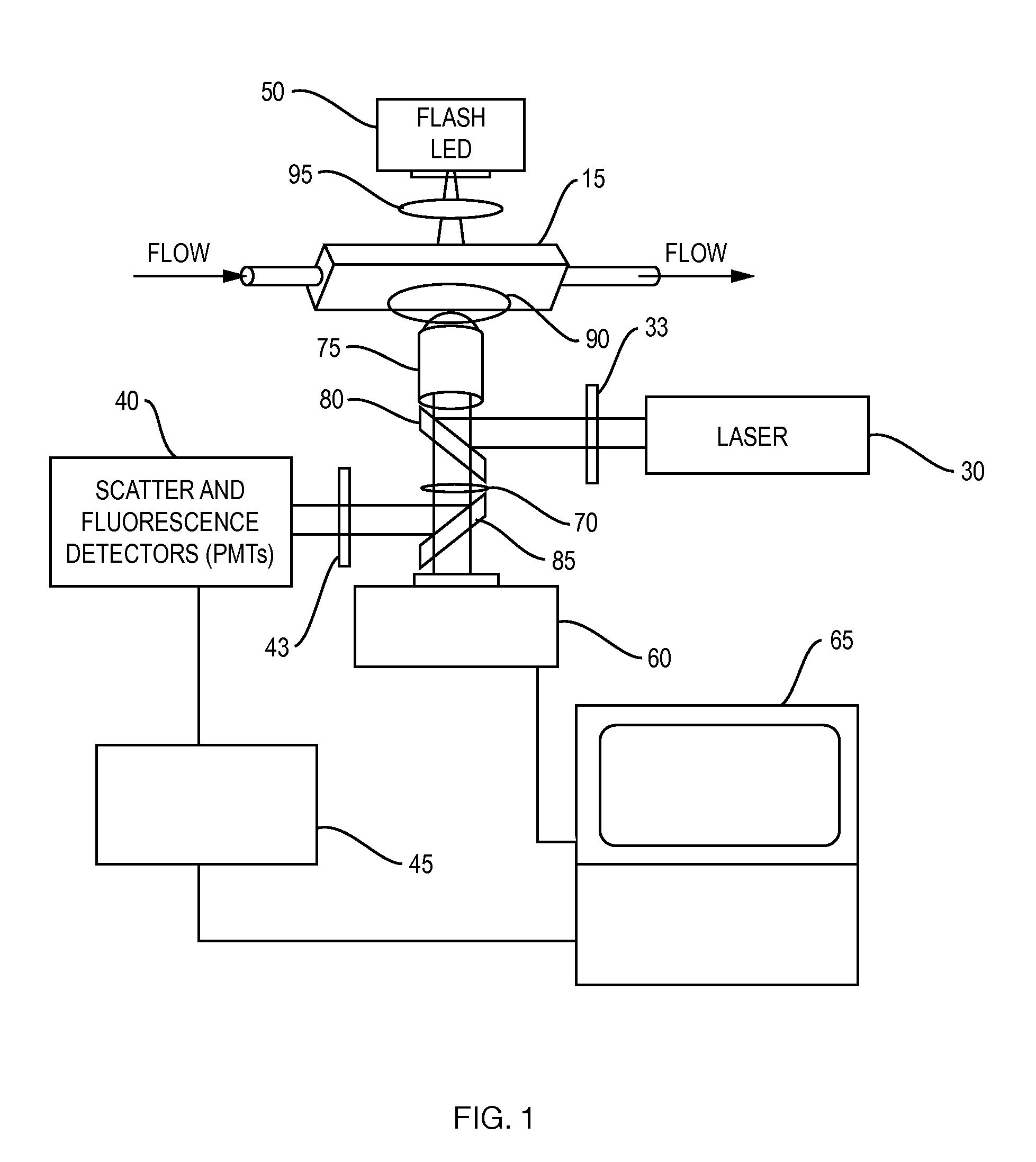
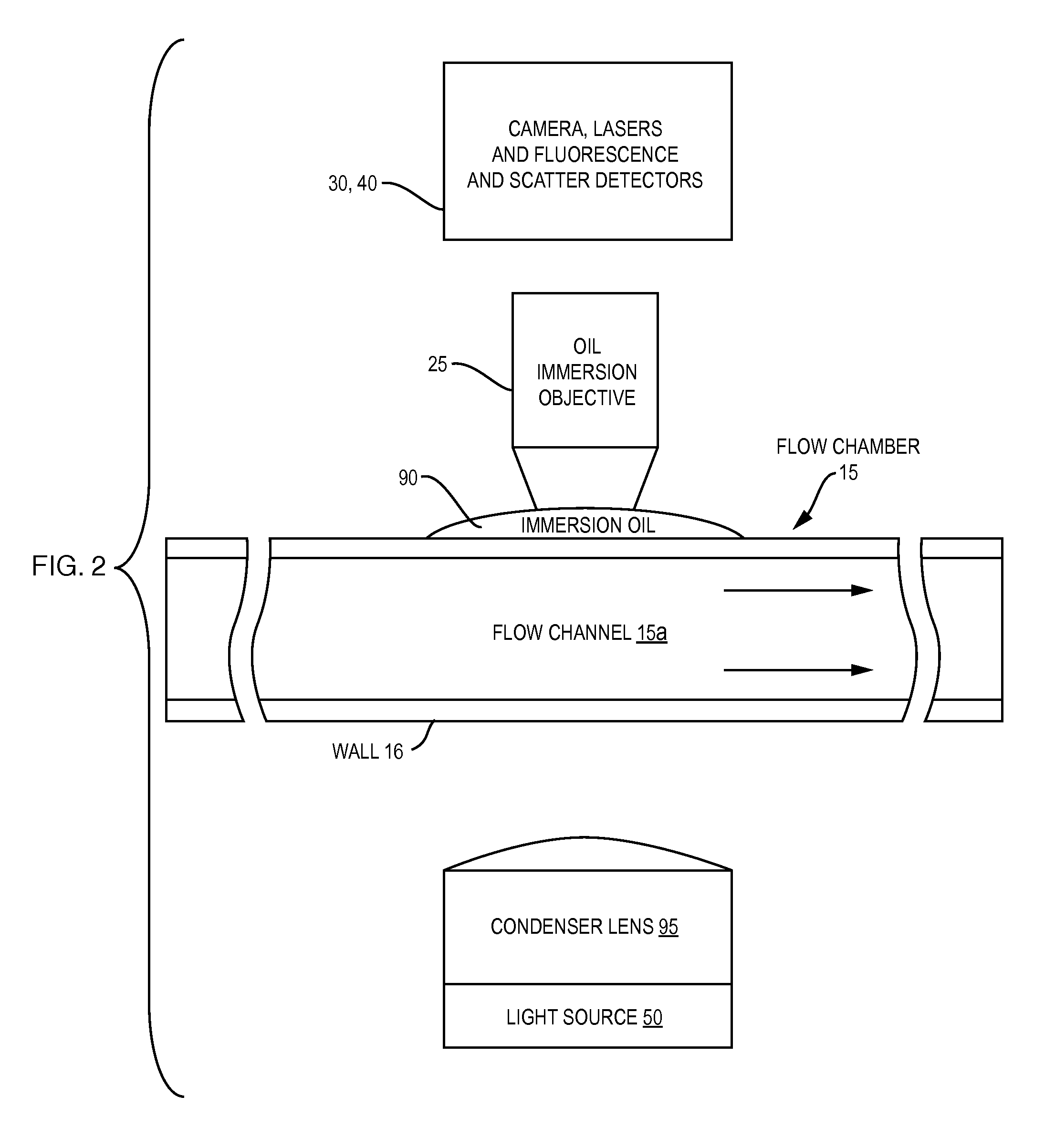
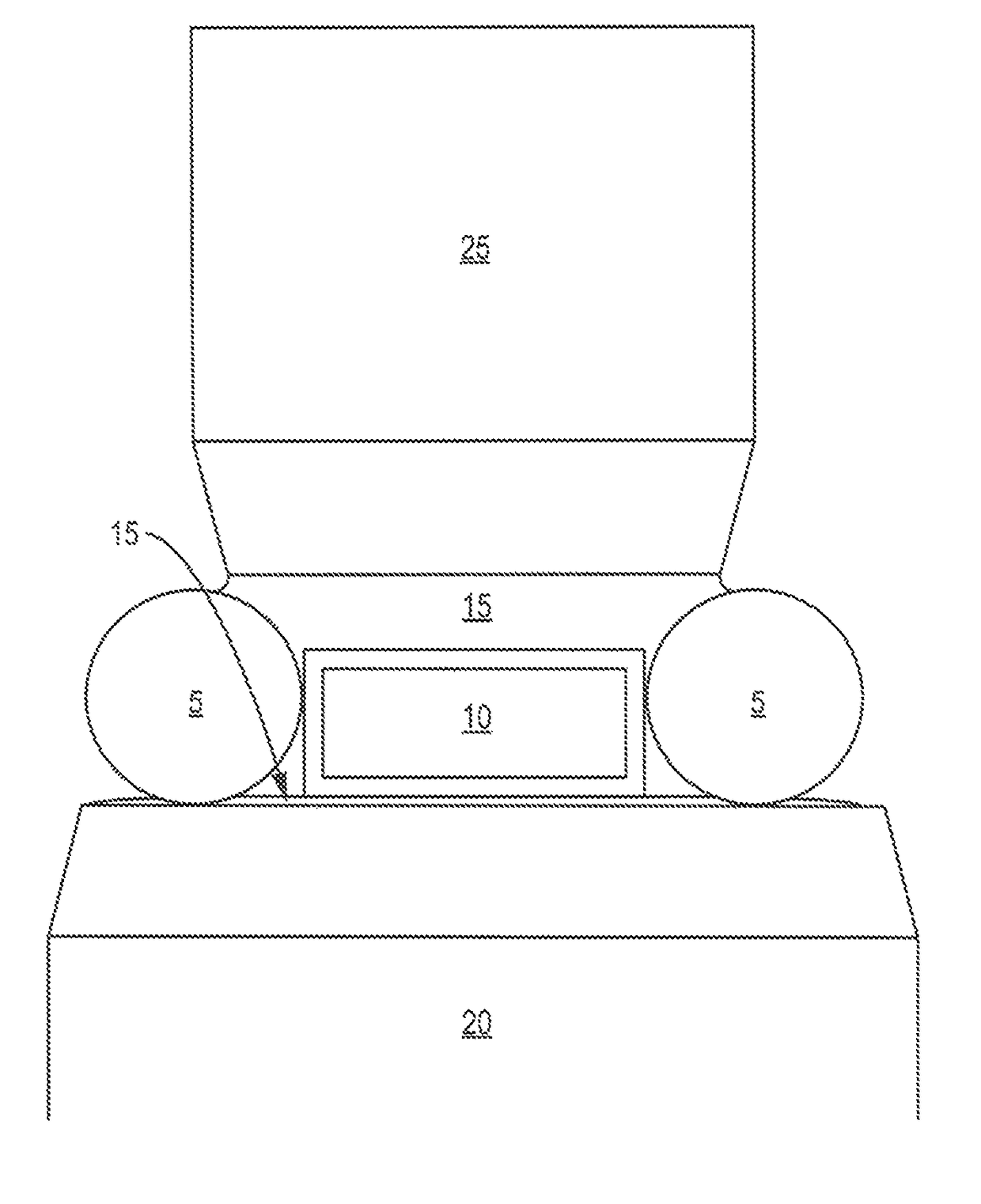
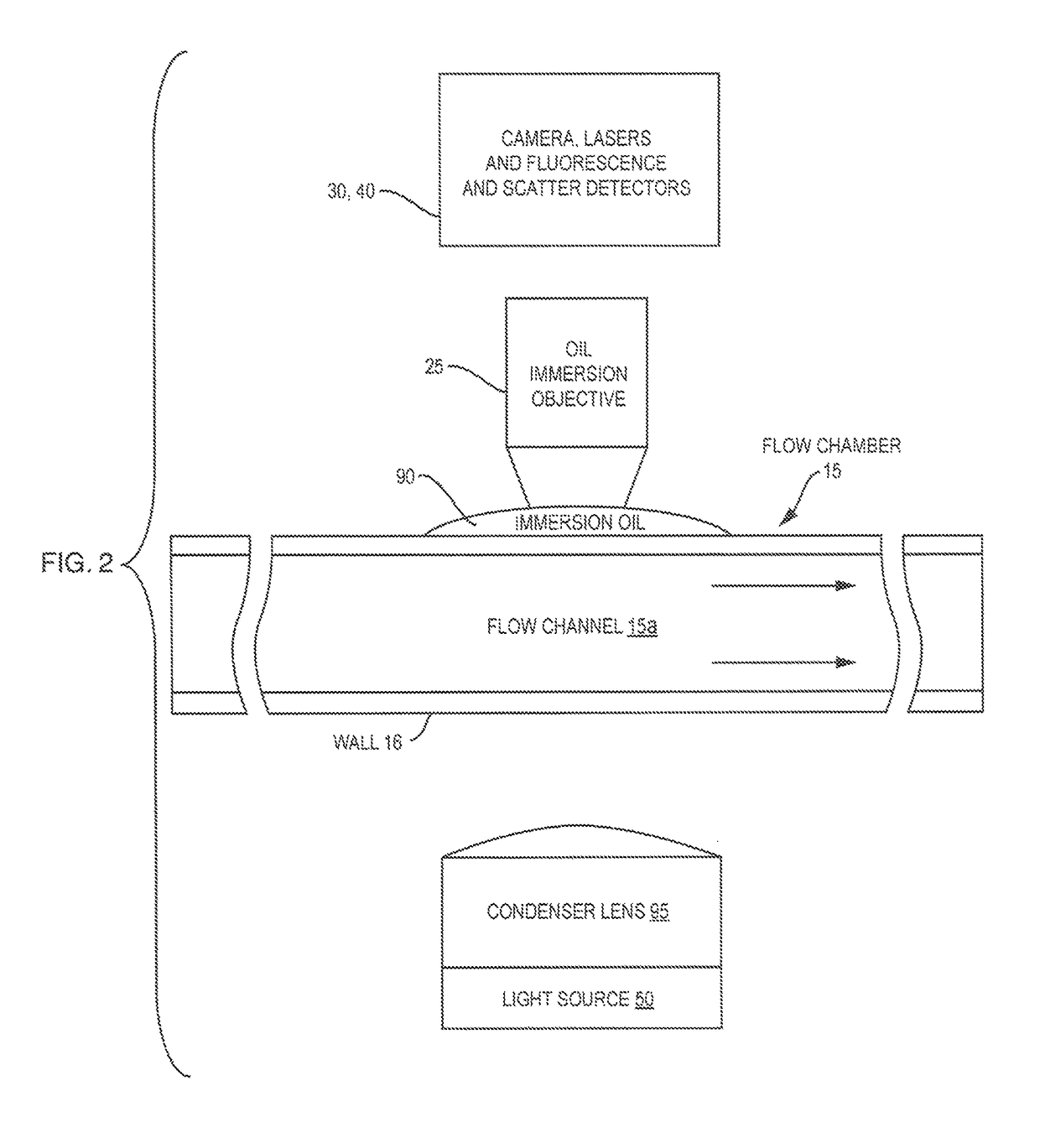
Oil-immersion enhanced imaging flow cytometer
ActiveUS20090273774A1High resolutionImprove analytical abilityRadiation pyrometryNanoparticle analysisFluorescenceHigh numerical aperture
A flow chamber, imaging objective, condenser and imaging light source as part of an optical system includes an oil-immersion objective and high numerical aperture condenser matched to a rectangular flow chamber. The oil-immersion objective and flow chamber include a high index of refraction immersion oil so as to enhance the optical resolution and optical coupling therethrough. The imaging light source generates light which passes through the condenser, the flow chamber and then the objective before being focused onto an imaging camera. Fluorescence excitation passes through the objective to the flow chamber where the oil immersion configuration enhances the focus and collection of the light back through the objective.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
Flow type fluorescence microscopy imaging device and method
InactiveCN103308440ASolve tailingOvercoming the smearing problemIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceTrailing phenomenonMicroscopy
The invention discloses a flow type fluorescence microscopy imaging device, in order to solve the problems of small focal depth of an imaging flow cytometer as well as trailing which occurs when a moving object is imaged. The imaging device has the following beneficial effects that (1) auto-fluorescence or non-auto-fluorescence of cells is excited by a light sheet source with the thickness near a diffraction limit, so that the problem of small focal depth of fluorescence microscopy imaging can be solved; (2) only the cells positioned within the range of focal depth are excited to emit fluorescence and a background of a fluorescence image can be lowered effectively, so that the sensitivity of a system can be enhanced effectively; (3) the cells perpendicularly pass through an excitation light source and are subjected to fluorescence imaging in a way that the imaging direction is parallel to the flowing direction of a sample, so that the trailing phenomenon can be well inhibited; (4) multiple cells are allowed to be detected simultaneously, so that the detection speed of the system can be increased.
Owner:香港浸会大学深圳研究院
System and method for monitoring blue-green algae in a fluid
InactiveUS20090283697A1Accurate detectionHigh resolutionPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceChlorophyll b
A particle detection system with a detection mechanism that includes detectors positioned to detect two different ranges of fluorescence produced by particles in the fluid in a flow chamber. Each of the detectors is arranged to generating a trigger signal whenever fluorescence is detected. The system and related method enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of blue-green algae monitoring by utilizing imaging flow cytometry combined with particle analysis and the measurement of the ratio of each particle's phycocyanin to chlorophyll b detected by using the two detectors configured for detection of two different fluorescence ranges, one associated with the phycocyanin and the other associated with the chlorophyll b. Optionally, captured images may be used in comparison to known images of a library of images.
Owner:FLUID IMAGING TECH
Oil-immersion enhanced imaging flow cytometer
ActiveUS7796256B2Easy to collectEnhance excitationRadiation pyrometryNanoparticle analysisHigh numerical apertureFluorescence
A flow chamber, imaging objective, condenser and imaging light source as part of an optical system includes an oil-immersion objective and high numerical aperture condenser matched to a rectangular flow chamber. The oil-immersion objective and flow chamber include a high index of refraction immersion oil so as to enhance the optical resolution and optical coupling therethrough. The imaging light source generates light which passes through the condenser, the flow chamber and then the objective before being focused onto an imaging camera. Fluorescence excitation passes through the objective to the flow chamber where the oil immersion configuration enhances the focus and collection of the light back through the objective.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
Three-dimensional imaging flow cytometer device
InactiveCN104502255ADescribe wellMultiple biomedical informationIndividual particle analysisLow speedFluorescence
The invention relates to a three-dimensional imaging flow cytometer device, relating to the field of biological and medical optical apparatuses and aiming at solving the problems that the flow testing efficiency is influenced by low speed of a liquid flow when cells are scanned by an existing imaging flow cytometer device and a micro-objective is easily polluted by a sample flow and the service life of the micro-objective is influenced since the sample flow needs to directly contact the micro-objective, etc. A moving cell is synchronously imaged in two directions through two vertical imaging flow systems; the relative position distribution of the internal structure of the cell is extracted; and therefore, the three-dimensional structural image of the cell is obtained. A lateral scattering and fluorescence exciting laser light source illuminates at 45 DEG and is shared by a speed-measuring and focusing unit and an imaging unit. By means of three-dimensional cell imaging, the original position information of the internal structure of the cell is kept; the morphological description authenticity is better; and thus, the imaging flow cytometer is capable of obtaining more meaningful biomedical information.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Imaging flow cytometer
InactiveCN104535481ASimple detection structureImprove energy utilizationIndividual particle analysisSequence signalLaser source
The invention provides an imaging flow cytometer and relates to the field of optical instruments in biology and medical science. The problems that an existing imaging flow cytometer system is low in energy use rate in defocusing distance and speed measurement, complex in structure and high in cost are solved. A polarization optical system is introduced, richer biological information relative to samples to be measured can be acquired, and the imaging flow cytometer is mainly composed of a sample injection unit, a laser source, a speed measurement-focusing unit, an imaging unit and a central control unit. Meanwhile, based on the laser back scattering light spot imaging principle, the speed detection function of the samples to be measured and the automatic focusing function of the cytometer are finished. Through analysis of sequence signals of light signal intensity of the samples to be measured in different sensing positions of an array optical sensor and analysis of distribution of light signal intensity of the detection face of the sensor, the cell movement speed and the defocusing distance can be acquired at the same time, measurement is more accurate and visual, the energy use rate and the signal to noise ratio are higher by the adoption of a laser back scattering mode, and a single optical path detection structure is simpler.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Serial-line-scan-encoded multi-color fluorescence microscopy and imaging flow cytometry
InactiveUS8639012B2Improved signal-to-noise ratioRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometrySerial lineHigh resolution imaging
A system for performing high-speed, high-resolution imaging cytometry utilizes a line-scan sensor. A cell to be characterized is transported past a scan region. An optical system focuses an image of a portion of the scan region onto at least one linear light sensor, and repeated readings of light falling on the sensor are taken while a cell is transported though the scan region. The system may image cells directly, or may excite fluorescence in the cells and image the resulting light emitted from the cell by fluorescence. The system may provide a narrow band of illumination at the scan region. The system may include various filters and imaging optics that enable simultaneous multicolor fluorescence imaging cytometry. Multiple linear sensors may be provided, and images gathered by the individual sensors may be combined to construct an image having improved signal-to-noise characteristics.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Automatic focusing device for imaging flow cytometer
InactiveCN104568711AIntuitive amount of defocusAccurate amount of defocusIndividual particle analysisInstrumentationScattered light
The invention provides an automatic focusing device for an imaging flow cytometer, and belongs to the field of optical instruments in biology and medicine. The device comprises a focusing detector, a focusing lens, a light splitting plate, a laser, a microscope objective, a position sensor and a micro displacement mechanism, wherein the laser is used for emitting collimation laser with field angles, the collimation laser is reflected by the light splitting plate to be focused through the microscope objective on cells to be measured in a liquid flow chamber, the back scattered light of the cells to be measured passes through the microscope objective to penetrate through the light splitting plate and is converged into the position sensor through the focusing lens, the position sensor is used for calculating the defocusing amount, and the defocusing amount is fed back to the position sensor and the micro displacement mechanism which are arranged on the microscope objective; the focusing function is realized through the movement of the micro displacement mechanism and the measurement of the position sensor. The device adopts a laser spot imaging method, and the defocusing amount of the cells can be directly and accurately obtained; the defocusing amount of the cells is tested through the back scattering of the cells, the usage ratio of the energy is higher, and the signal to noise ratio of the whole system is better; the volume of the system is more compact and simpler.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-wash image flow fluorescence detection method and system thereof
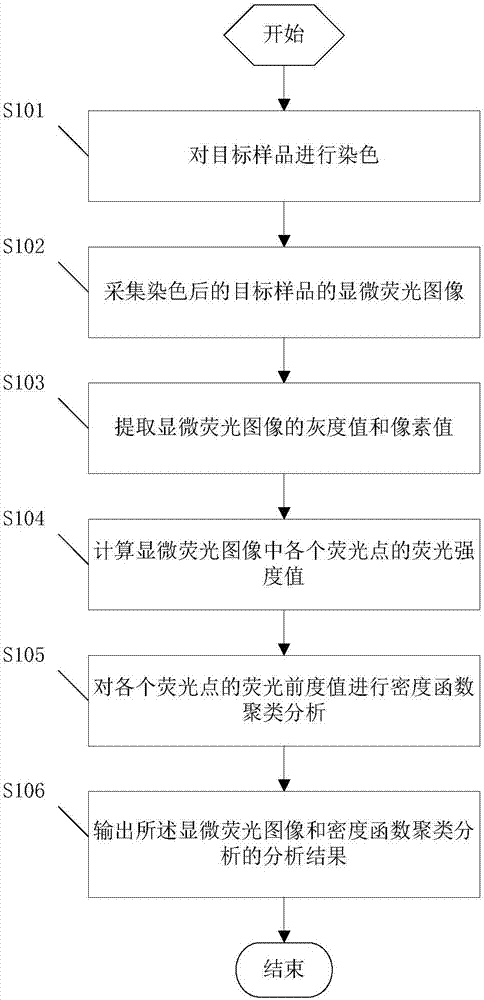
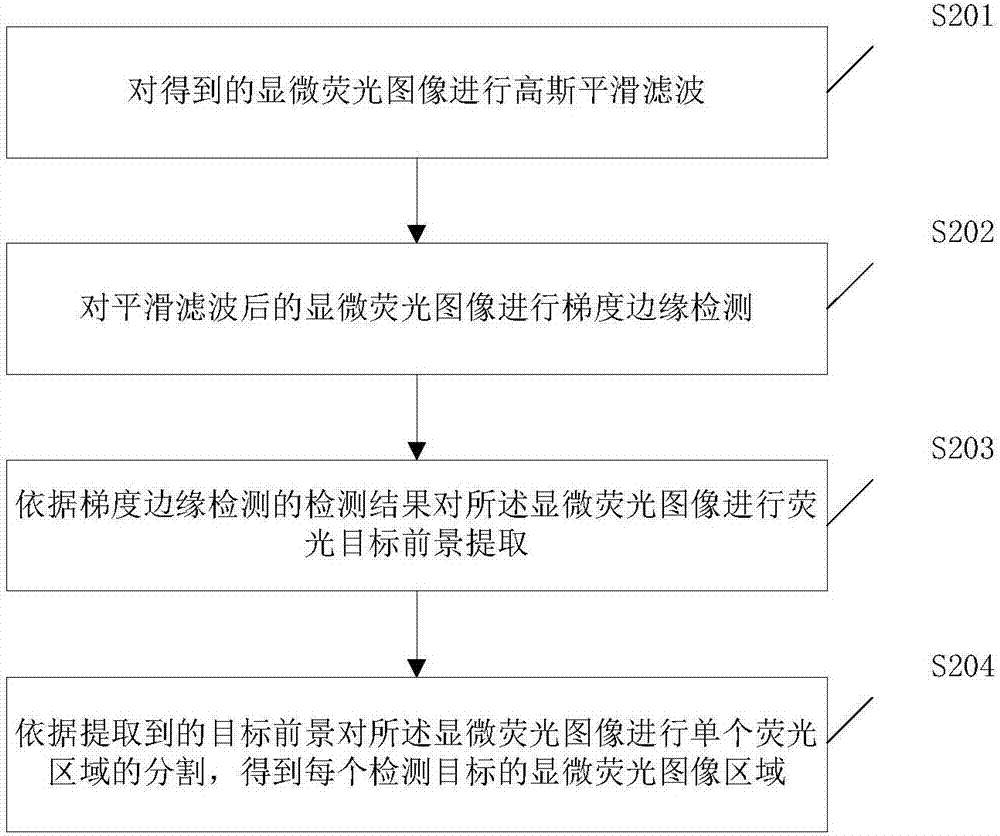
ActiveCN107367456APreventing Fluorescence Intensity CliffsIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceComputer imageImage flow
The invention provides a non-wash image flow cytometry fluorescence detection method and a system thereof. The method includes the following steps: dyeing a target sample with a preset target fluorescent dye through a dyeing technology, and ensuring the formation of a certain free fluorescent dye after dyeing and incubation to make all cells in the target sample acquire the fluorescence intensity value used for density function clustering resolution analysis under the non-wash flow fluorescence detection system; acquiring the microscopic fluorescence image of the dyed target sample based on a microscopic imaging system; extracting the gray value and the pixel value of the target sample by adopting a computer image recognition technology; and calculating the fluorescence intensity value of the target sample based on the gray value and the pixel value of the target sample, and outputting the microscopic fluorescence image of the target sample and the density function clustering analysis result. A problem that the detected fluorescence intensity value of undyed or dyed negative cells is zero or obviously sharps declines under the image flow fluorescence detection system after common dyeing washing is solved in the invention.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUIYU BIOTECH
Cell detection method and cell detection system
InactiveCN109752308AAccessible and well detectedShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisBiological bodyCell based
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
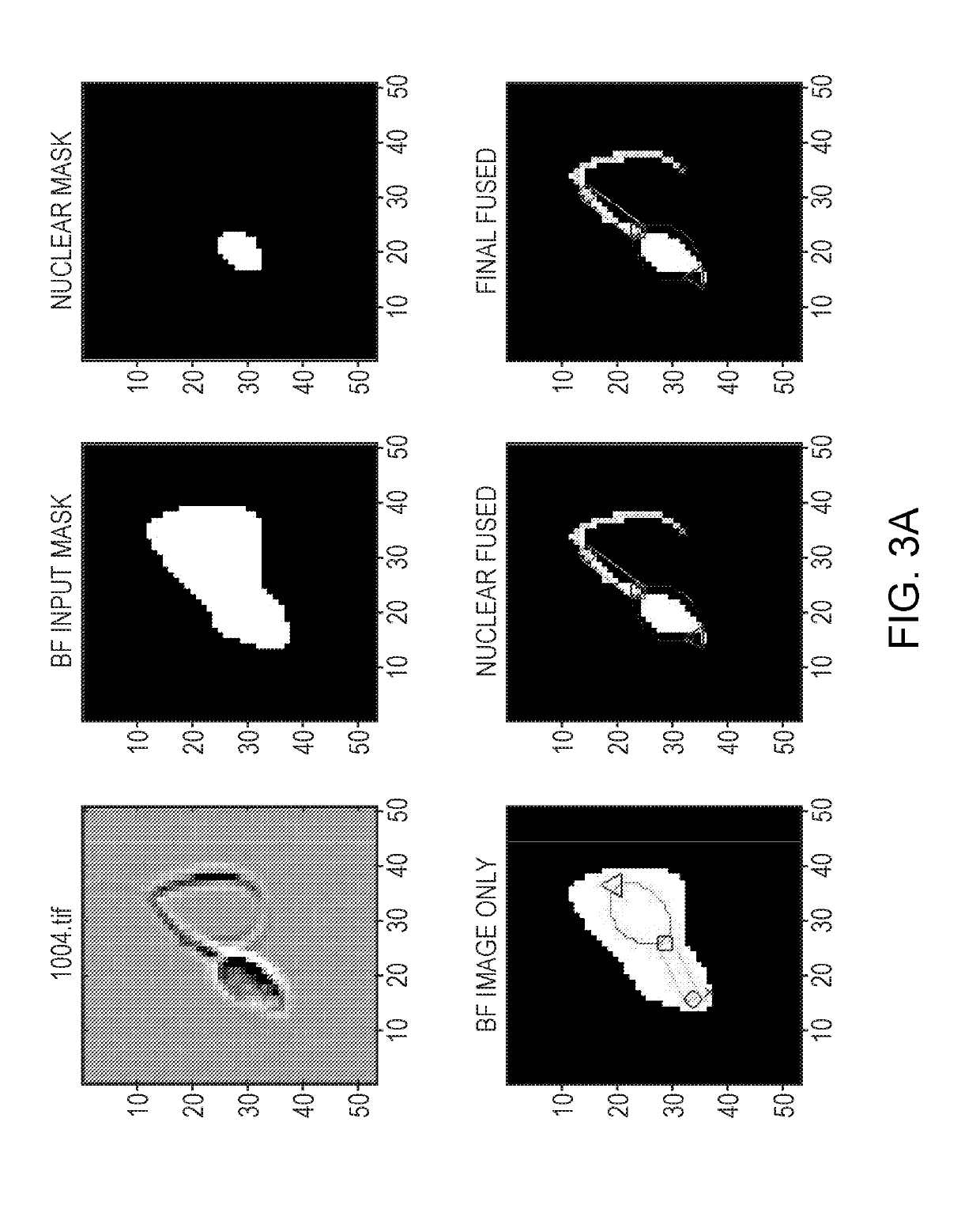
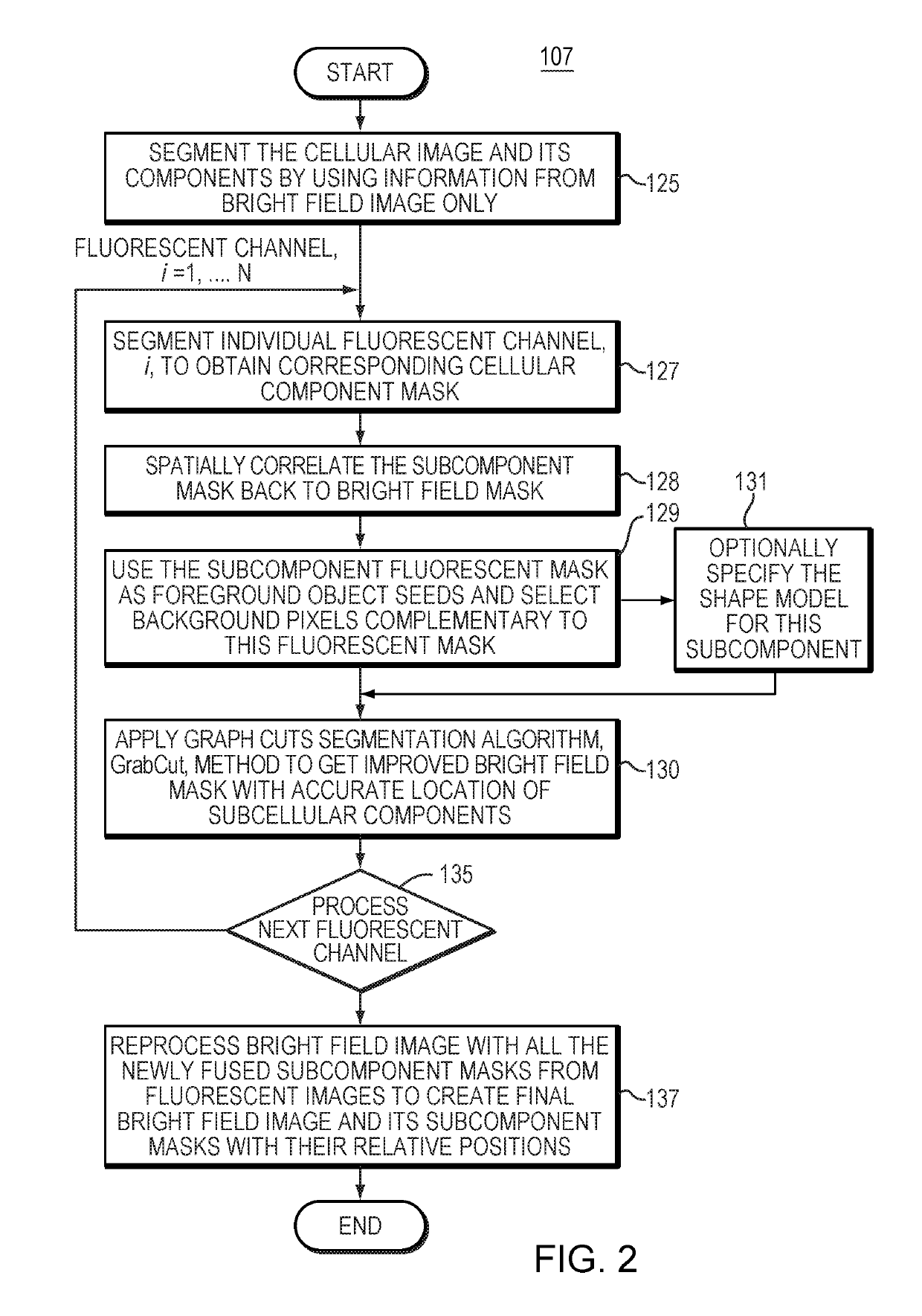
A Method To Combine Brightfield And Fluorescent Channels For Cell Image Segmentation And Morphological Analysis Using Images Obtained From Imaging Flow Cytometer (IFC)
ActiveUS20190163956A1High resolutionIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionFluorescence
A classifier engine provides cell morphology identification and cell classification in computer-automated systems, methods and diagnostic tools. The classifier engine performs multispectral segmentation of thousands of cellular images acquired by a multispectral imaging flow cytometer. As a function of imaging mode, different ones of the images provide different segmentation masks for cells and subcellular parts. Using the segmentation masks, the classifier engine iteratively optimizes model fitting of different cellular parts. The resulting improved image data has increased accuracy of location of cell parts in an image and enables detection of complex cell morphologies in the image. The classifier engine provides automated ranking and selection of most discriminative shape based features for classifying cell types.
Owner:LUMINEX
System and method for total internal reflection enhanced imaging flow cytometry
ActiveUS8879797B2Improve integrityHigh strengthInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsTotal internal reflectionFluorometric Analysis
An imaging flow cytometry system and method which includes a flow chamber, fluorescence analysis and imaging optics, image capturing system, device to regulate fluid flow through the chamber, and backlighting generator. The flow cell is configured so as to enhance the fluorescence signal collection by the system with total internal reflections. The fluorescence collection optics are configured to enhance the collection of the fluorescence from the side of the flow cell and concentrate it on light detectors.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
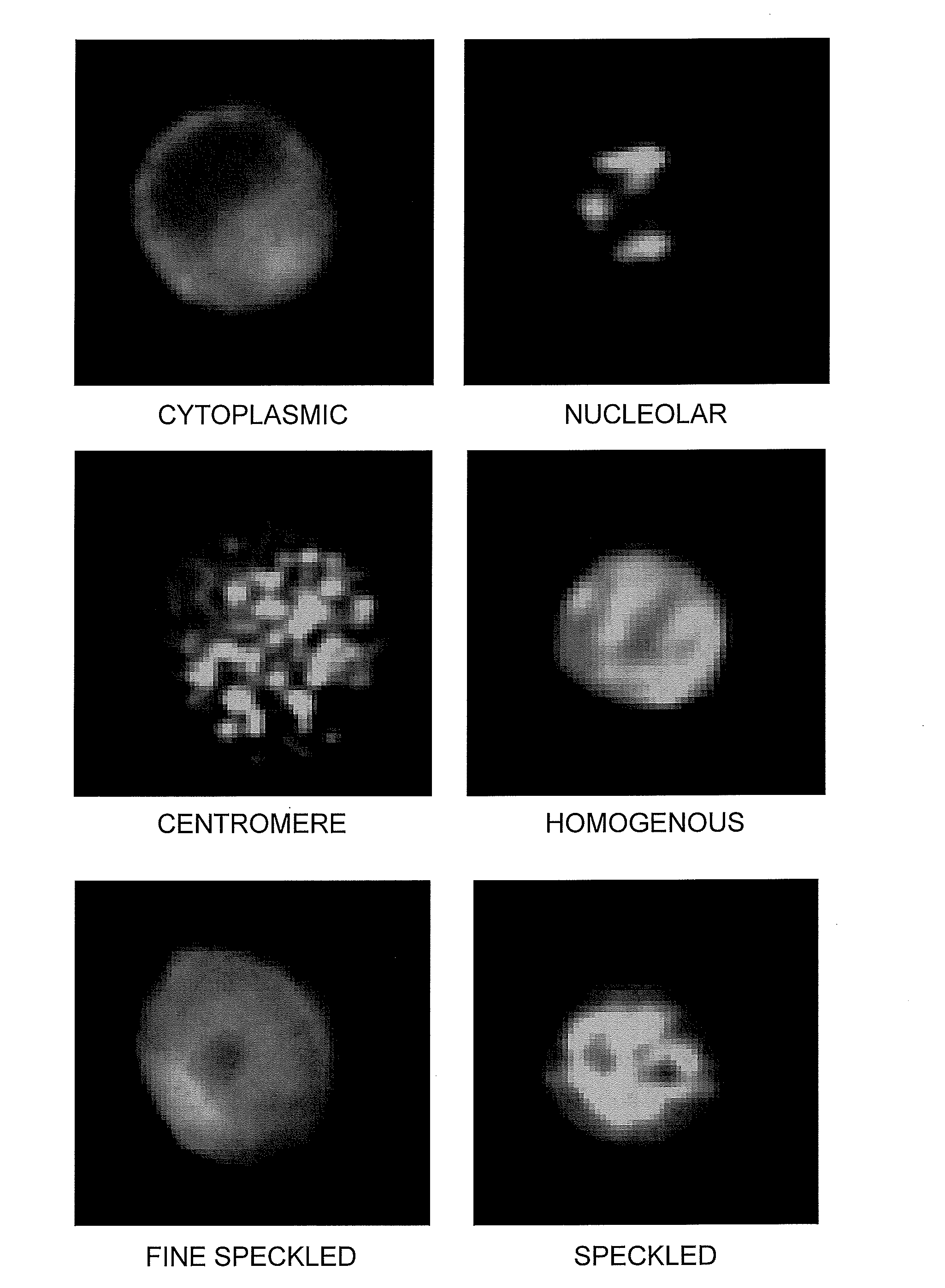
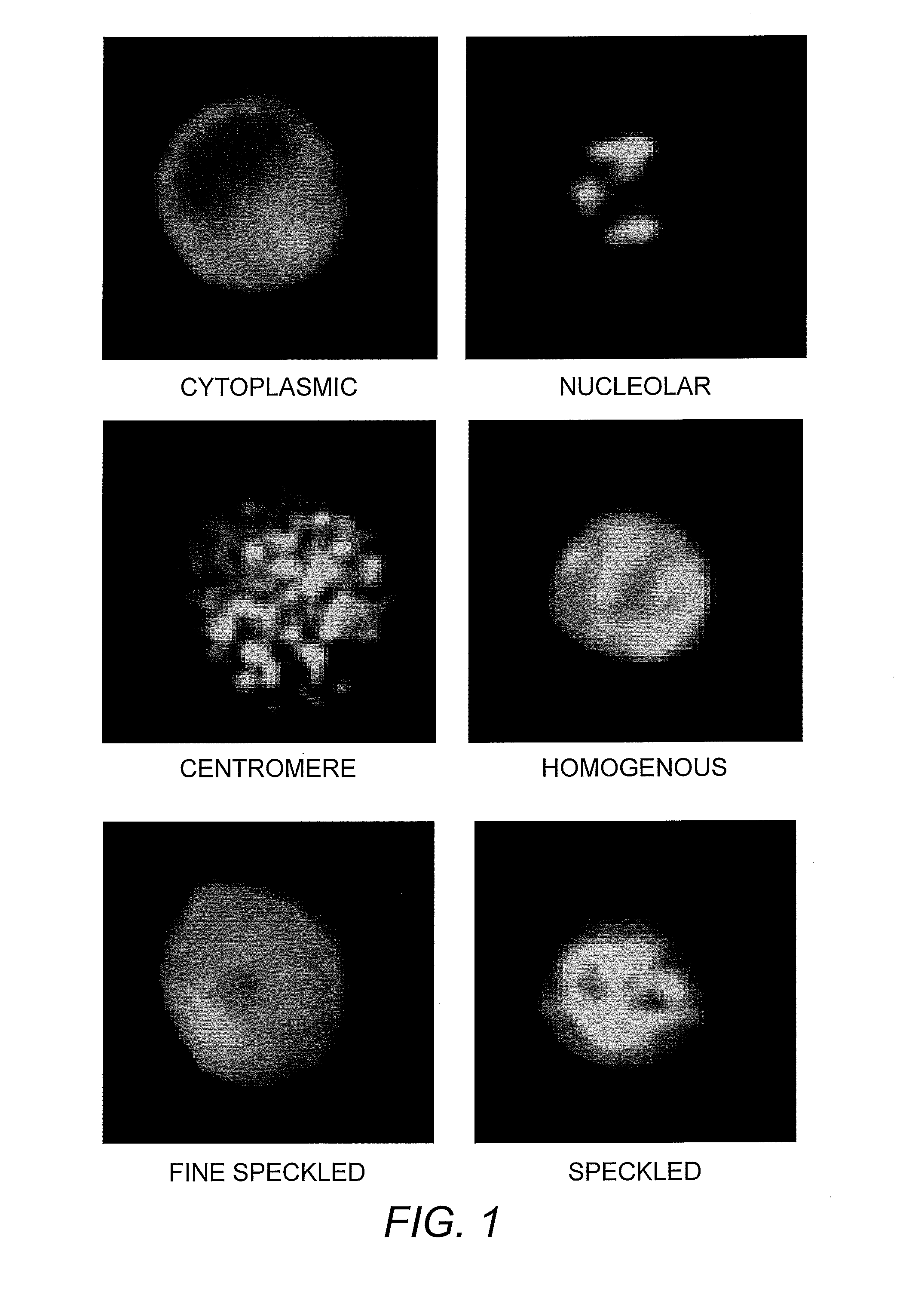
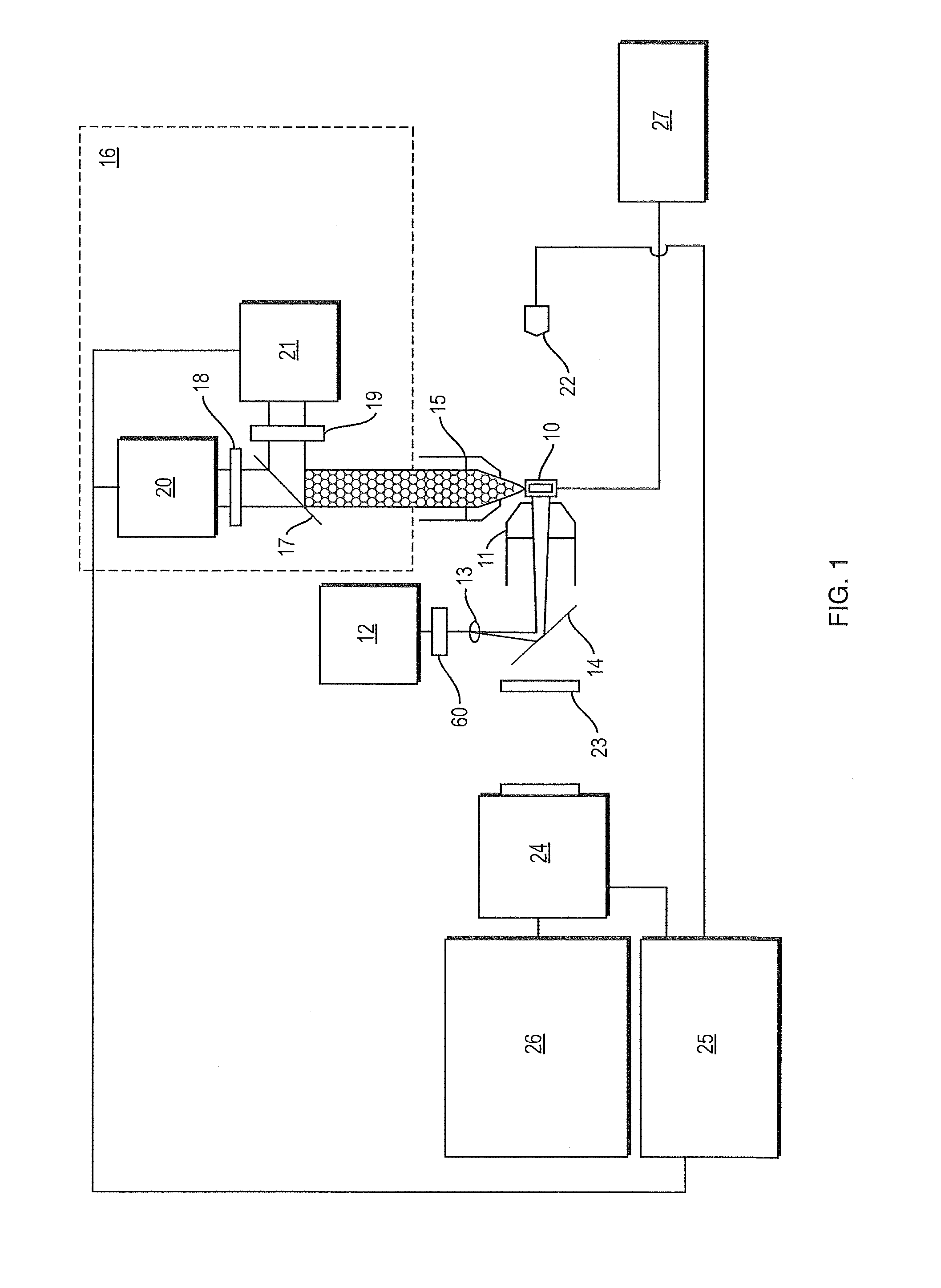
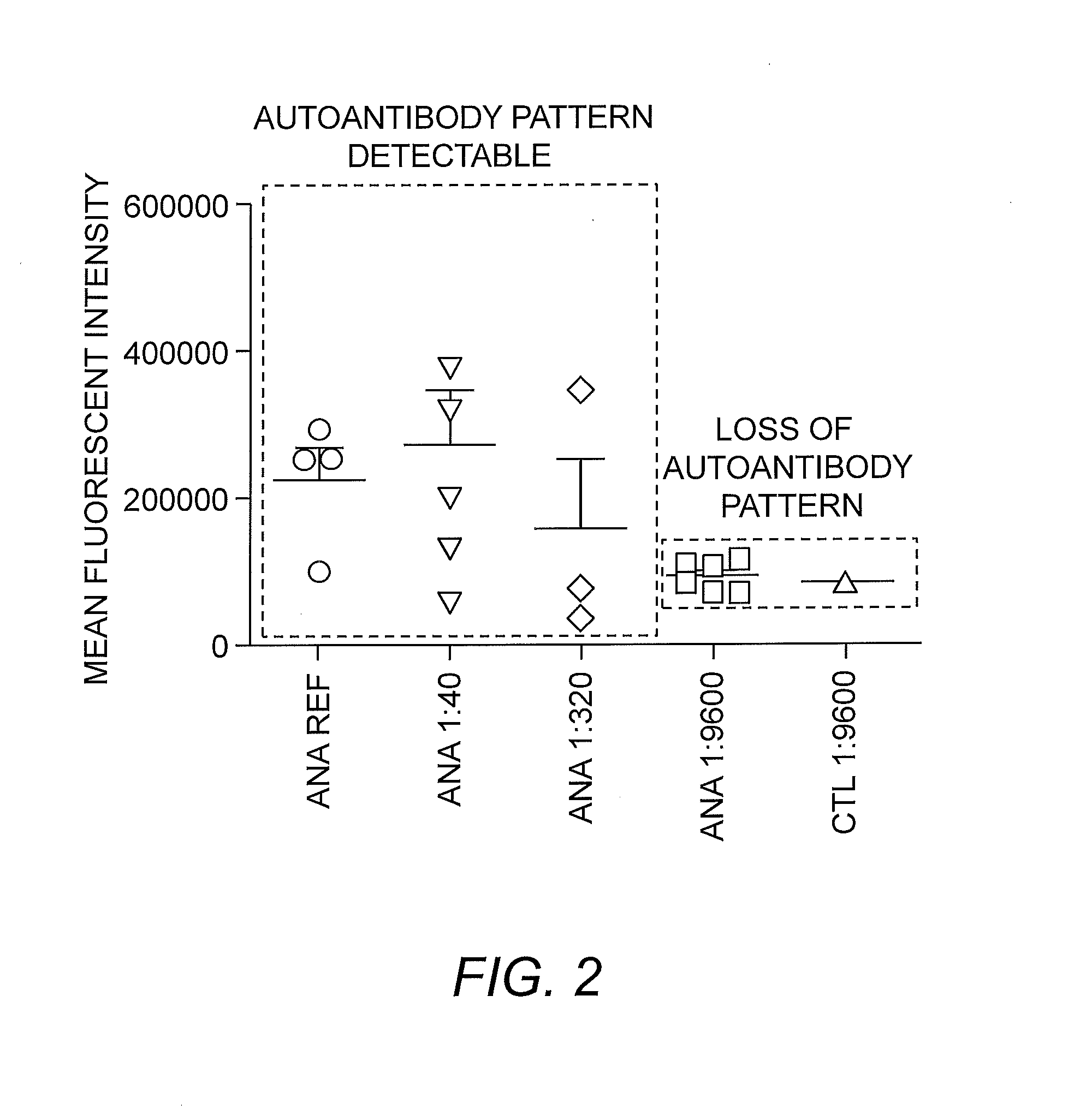
Method for Automated Autoantibody Detection and Identification
InactiveUS20130052662A1Biological testingFluorescence/phosphorescencePattern recognitionAutoantibody
The present invention is a kit and method for detecting and identifying autoantibodies. The invention employs the use of indirect immunofluorescence, imaging flow cytometry and pattern recognition software to automatically identify autoantibodies associated with autoimmune disorders.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Imaging flow cytometry adhesion counting and activity detection method and device based on bidirectional background difference process
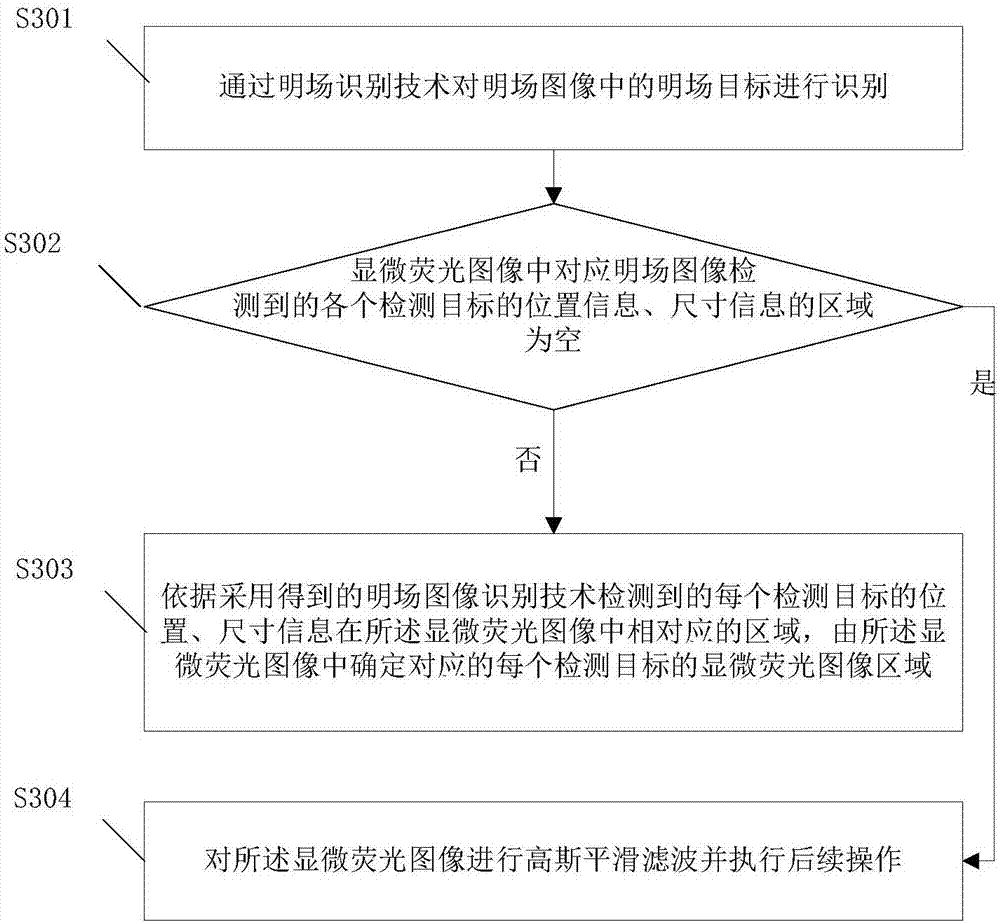
PendingCN113222969AIdentification indicators are stableAddressing the effects of countingImage enhancementImage analysisLymphocytic cellRadiology
The invention provides an imaging flow cytometry adhesion counting and activity detection method and device based on a bidirectional background difference process. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bright field image and a cell fluorescence image of a to-be-detected sample and a background image during empty detection, and carrying out binarization processing on the cell fluorescence image; extracting a target contour difference image and a target center bright spot difference image by using a bidirectional background difference method, and carrying out fusion and binarization processing on the two difference images to determine the position of a moving target; performing morphological closed operation on the binarized image, and then performing morphological open operation; and traversing the binary image matrix to realize quantity calculation of the cells to be detected and identification and classification of types of the cells to be detected. According to the technical scheme, the problems of time and labor consumption, incomplete functions, low flux, high price and the like in the prior art are solved. Counting and activity judgment of multiple cells such as microalgae cells, 293T lymphocytes and mouse cells can be achieved, the application range is wide, and identification indexes are stable.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
System and method for total internal reflection enhanced imaging flow cytometry
ActiveUS20130315447A1Good fluorescence measurementEffective imagingInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsTotal internal reflectionFluorometric Analysis
An imaging flow cytometry system and method which includes a flow chamber, fluorescence analysis and imaging optics, image capturing system, device to regulate fluid flow through the chamber, and backlighting generator. The flow cell is configured so as to enhance the fluorescence signal collection by the system with total internal reflections. The fluorescence collection optics are configured to enhance the collection of the fluorescence from the side of the flow cell and concentrate it on light detectors.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
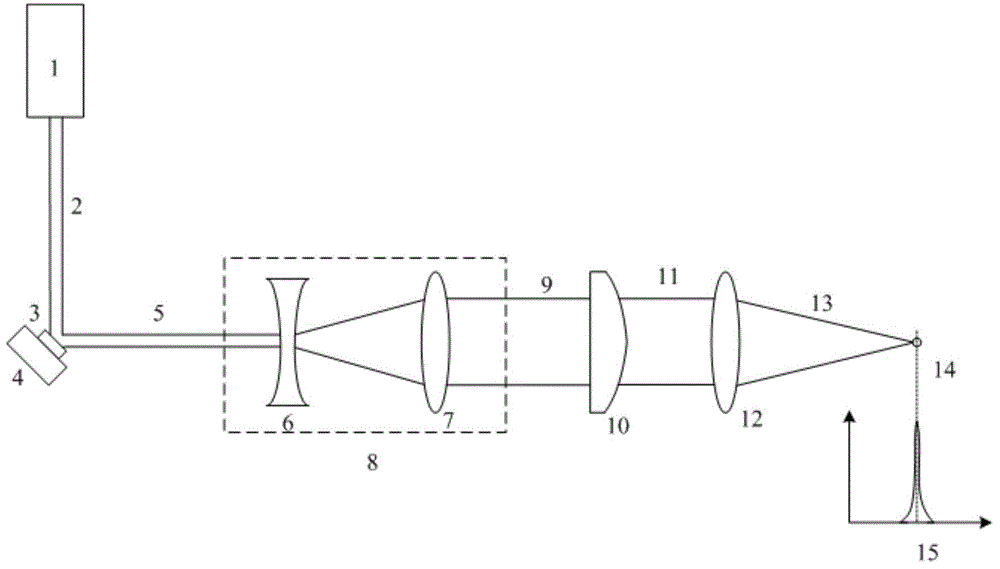
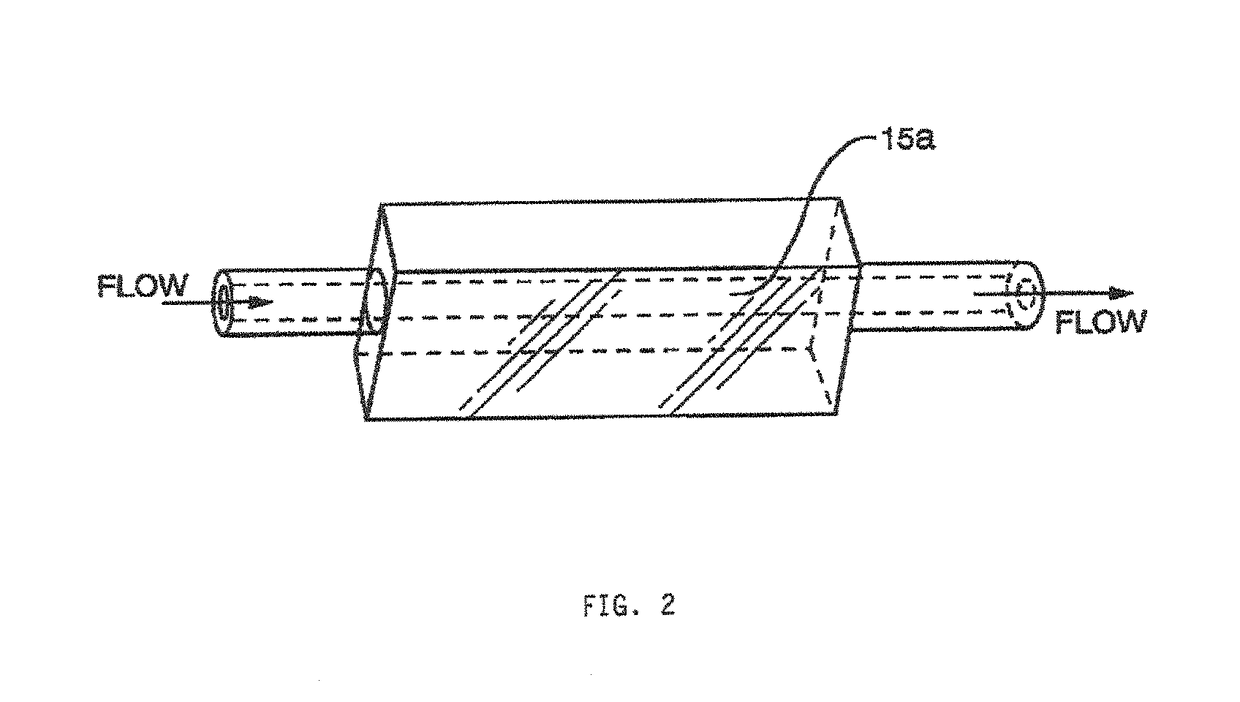
Illuminating system of imaging flow cytometry
The invention discloses an illuminating system of an imaging flow cytometry and belongs to the technical field of optical design. The system aims to solve the problems of the prior art that optical energy loss is high, utilization rate is low, researching and manufacturing cost is high, stability is poor, and the design of a beam-focusing machine is limited to a certain extent. The system comprises a laser light source, a digital micro mirror array, a piezoelectric ceramics tilt platform, a laser expanding system, a cylindrical mirror and a focusing lens, wherein basic mode light rays output by the laser light source become reflection light rays through the digital micro mirror array, the reflection light rays are expanded through the laser expanding system to form round spot expanded light rays, the expanded light rays are imaged to be oval light spots through the cylindrical mirror, the oval light spots become focused light rays through the focusing lens, the focused light rays are focused into a uniform linear light spot at the position of a target surface, and the digital micro mirror array is arranged on the piezoelectric ceramics tilt platform and achieves high-speed scanning under the control of the piezoelectric ceramics tilt platform.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Oil-immersion enhanced imaging flow cytometer
ActiveUS9891160B1Flow cell durability and immersion oil retentionSpeed up the flowMicroscopesIndividual particle analysisHigh numerical apertureRefractive index
A flow chamber, imaging objective, condenser and imaging light source as part of an optical system includes an oil-immersion objective and high numerical aperture condenser matched to a rectangular flow chamber. The oil-immersion objective and flow chamber include a high index of refraction immersion oil so as to enhance the optical resolution and optical coupling therethrough. The flow chamber is reinforced with stiffening wires that are arranged to extend above a surface of the sidewalls of the flow chamber so as to function as a barrier to leakage of the immersion oil away from the surface of the flow chamber.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
High-flux shooting method used for flow cytometry imaging
InactiveCN104486549AIncrease flow rateImprove shooting efficiencyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh fluxShooting method
The invention belongs to the field of imaging technologies and provides a high-flux shooting method used for flow cytometry imaging. The high-flux shooting method used for flow cytometry imaging aims to solve the problems in the prior art that shooting efficiency is low, luminous flux is low and shooting missing exists. The method includes the following steps that cells move from top to bottom from a micro-pipeline; when the first cell at an even number enters a view field of a camera A, the camera A is driven by a transmission device to perform tracking shooting on the first even number; the camera A resets to an initial position through the transmission device after completing shooting, then shoots the cell at the next even number and transmits a collected image to a computer; when the first cell at an odd number enters a view field of a camera B, the camera B is driven by a transmission device to perform tracking shooting on the first odd number; the camera B resets to an initial position through the transmission device after completing shooting, then shoots the cell at the next odd number and transmits a collected image to the computer; the steps are repeated until all the cells are shot.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
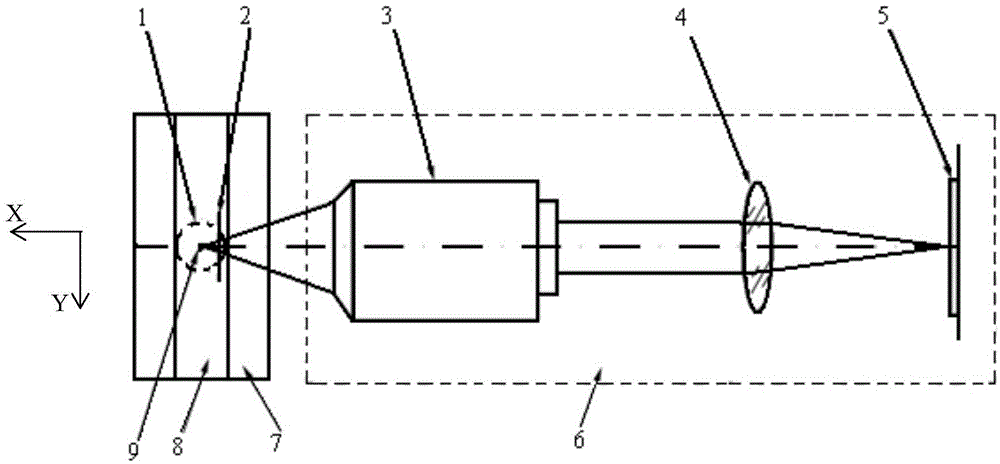
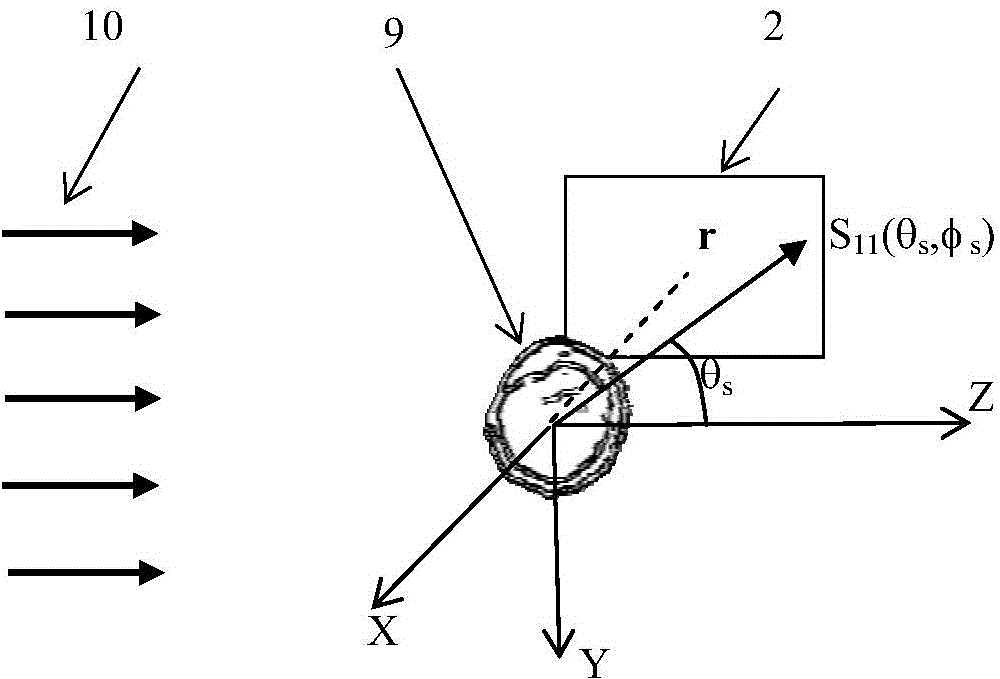
Particle diffraction diagram simulating method through geometrical optics ray tracing
ActiveCN104463961AAvoiding Coherent Diffractive Light Field ComputationsReduce computing costDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLaws of thermodynamicsMicroparticle
Disclosed is a particle diffraction diagram simulating method through geometrical optics ray tracing. The method comprises the steps that (1) light of a light source is generated through a far scattered light field, specifically, the far scattered light field is obtained, a matrix element S11 is projected to a microscope system incident plane x=x0, a light intensity distribution diagram of the scattered light field is obtained, a ray tracing light source is formed, and rays are built for all points (y, z) for imaging through a diffraction imaging flow cytometry microimaging system; (2) tracing calculation is carried out on each generated ray according to the Fresnel diffraction law; (3) after tracing calculation of all the rays is completed, cross points of the rays and an imaging plane are obtained, and the distribution density diagram of the cross points is the simulated diffraction diagram. The particle far scattered field is processed into the light source needed by geometrical optics, micrographic optical system diffraction imaging is calculated through ray tracing, a coherent diffraction optical field of the micrographic optical system of a complex structure can be prevented from being calculated, diffraction diagram calculation on various complex micrographic optical systems can be achieved, and graphical display interfaces are very convenient to operate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
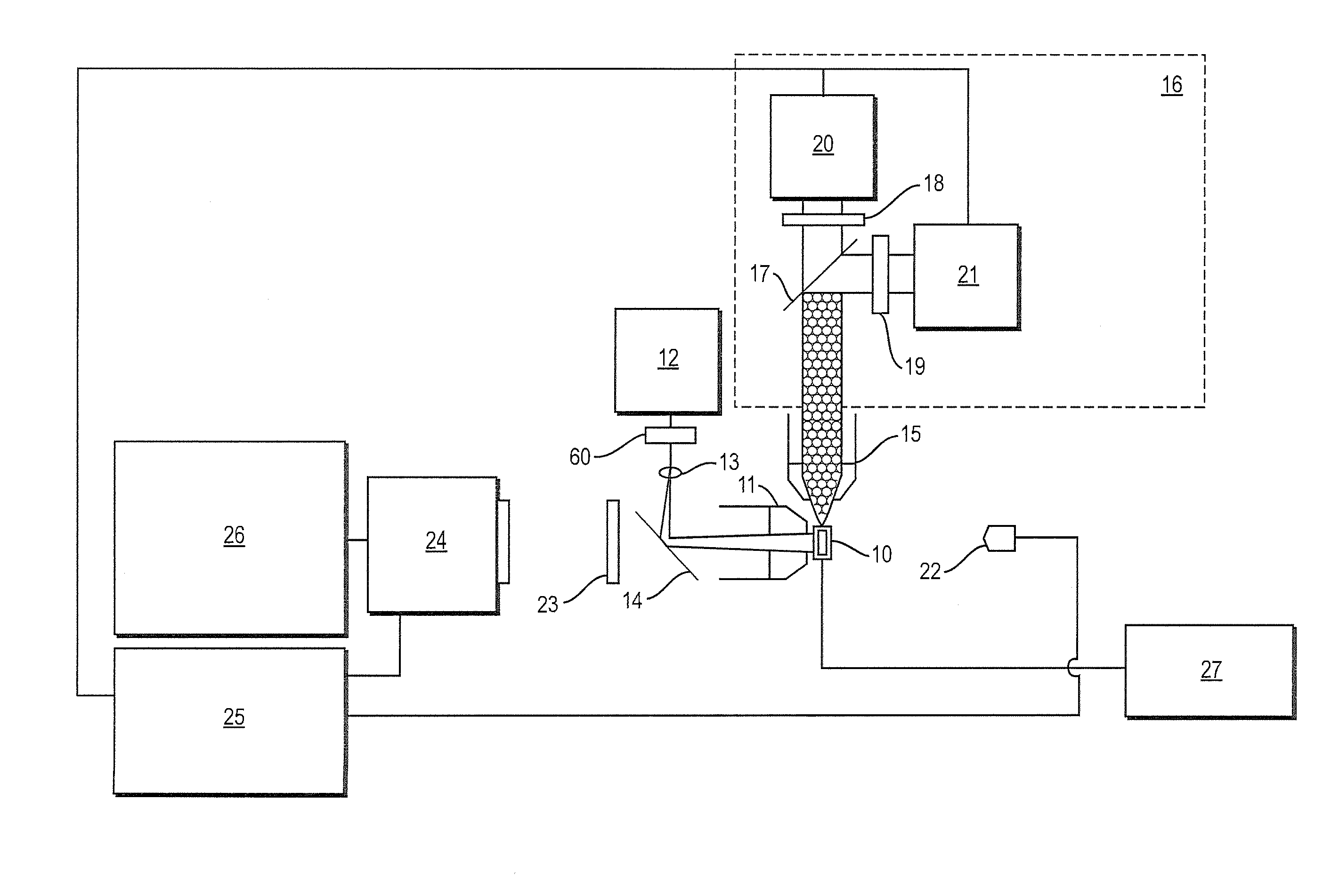
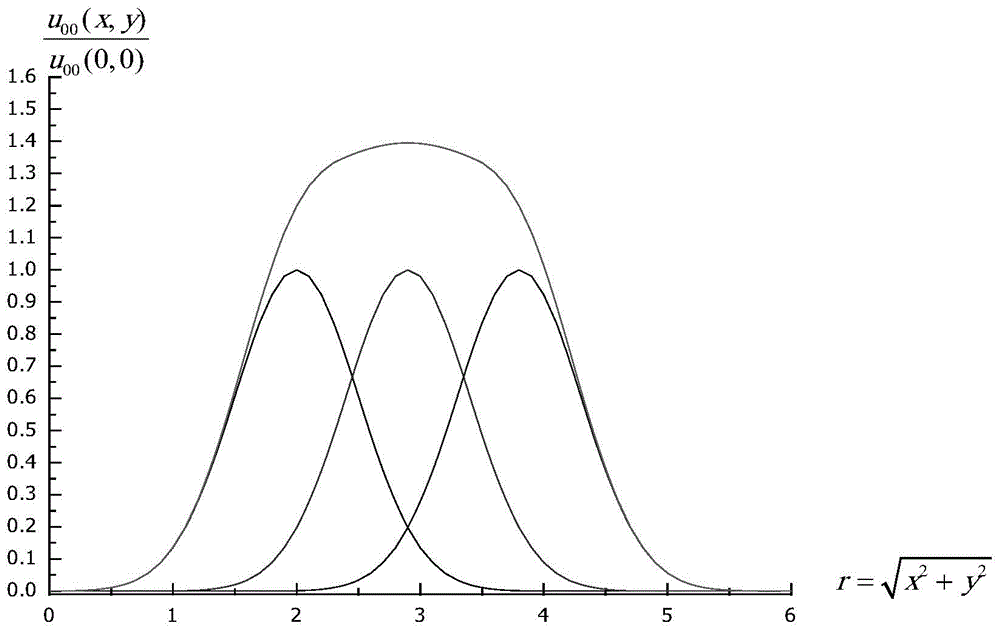
Fluorescence imaging flow cytometry with enhanced image resolution
In one aspect, a system for performing flow cytometry is disclosed, which comprises a laser for generating laser radiation for illuminating a sample, at least one detector for detecting at least a portion of a radiation emanating from the sample in response to said illumination so as to generate a temporal signal corresponding to said detected radiation, and an analysis module for receiving said temporal signal and performing a statistical analysis of said signal based on a forward model to reconstruct an image of said sample.
Owner:BD BIOSCI
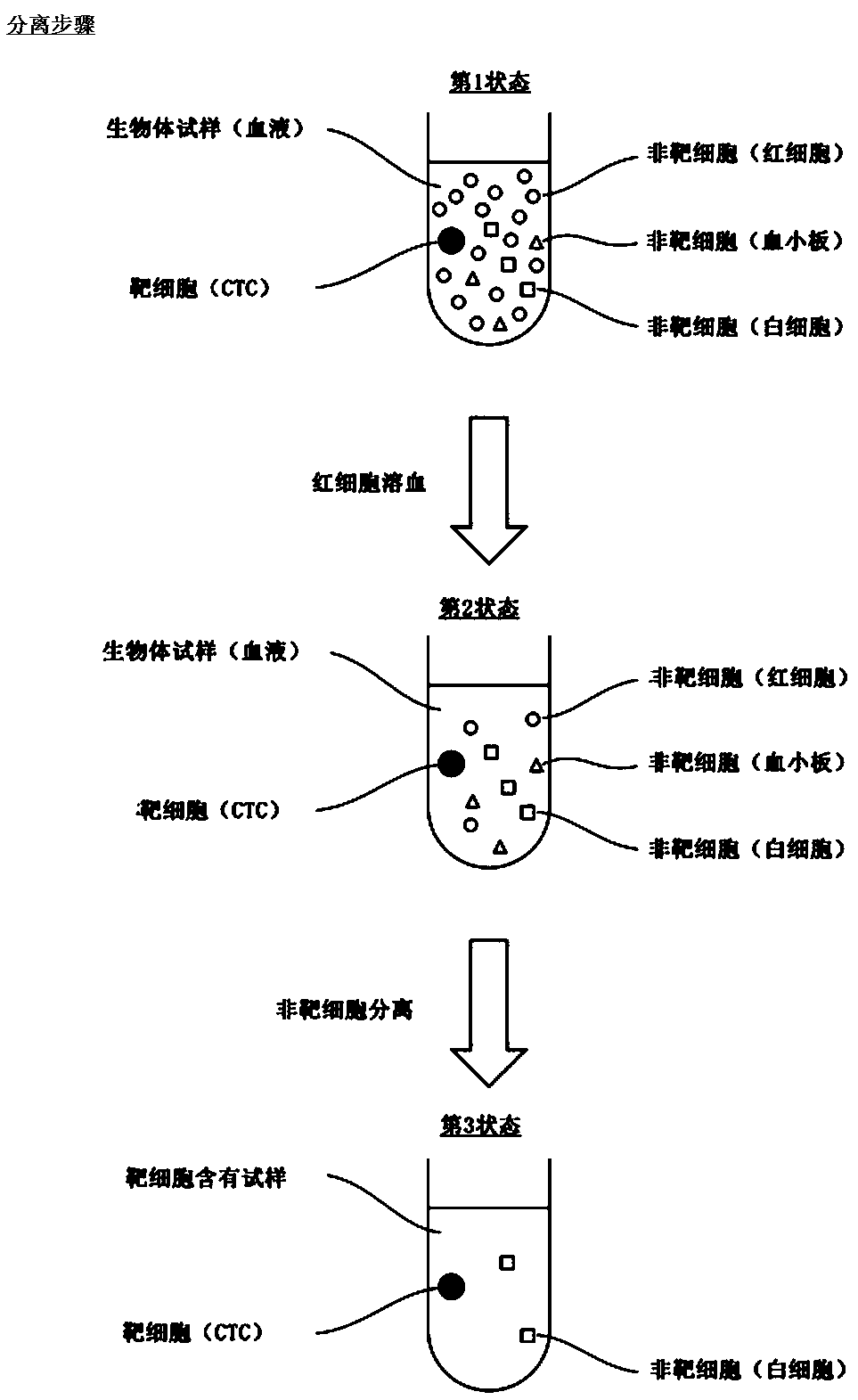
Improvements in or relating to cell analysis
PendingUS20200232019A1High sensitivityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationAntigenCell marker
The present invention provides a method for cell analysis, comprising: preparing a blood sample comprising nucleated cells having surface, cytoplasmic or nuclear antigens (markers); antibody staining the cell markers; fixing and permeabilising the cells; FISH probe hybridising to chromosomes in the cells; performing imaging flow cytometry on the cells; analysing data obtained from performing imaging flow cytometry; and diagnosing, prognosing or monitoring a medical condition based on the data analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
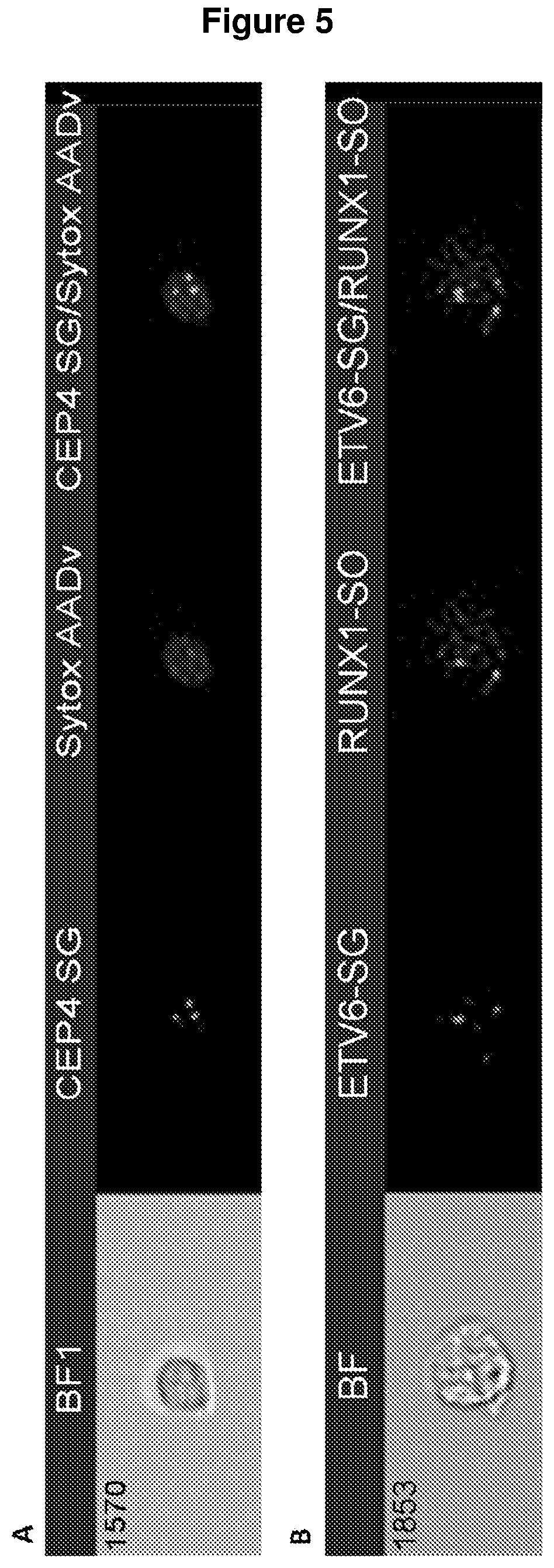
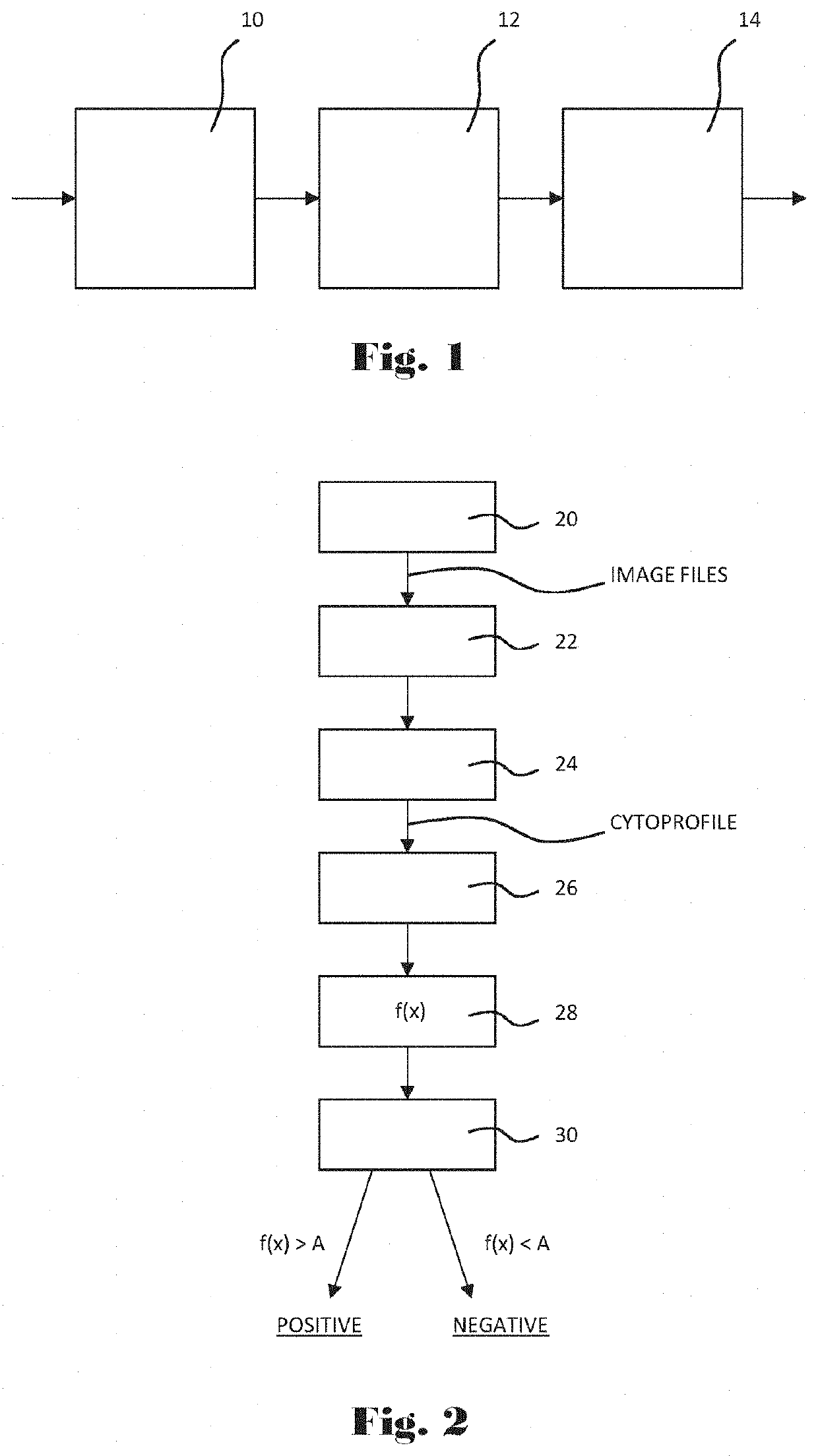
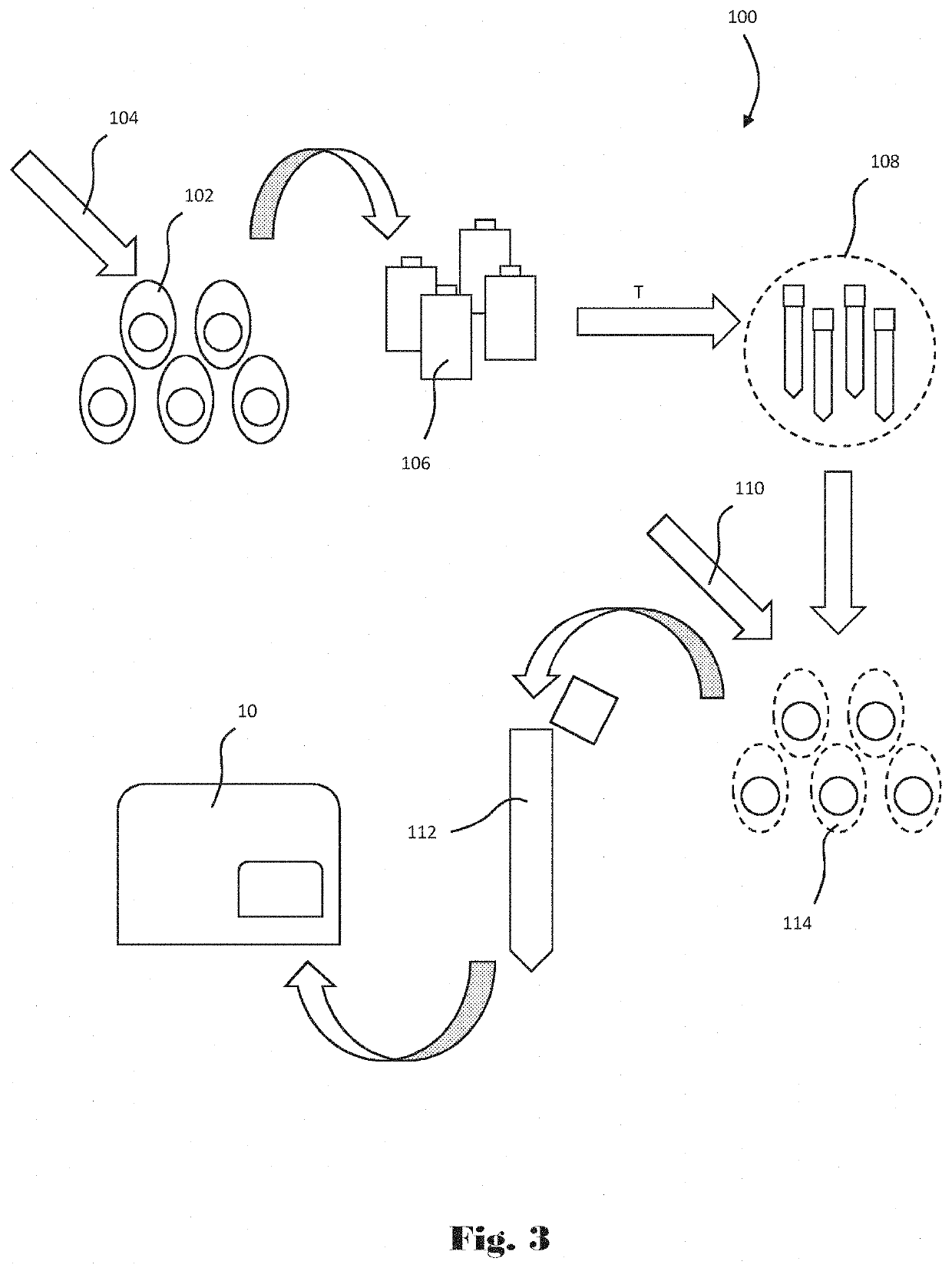
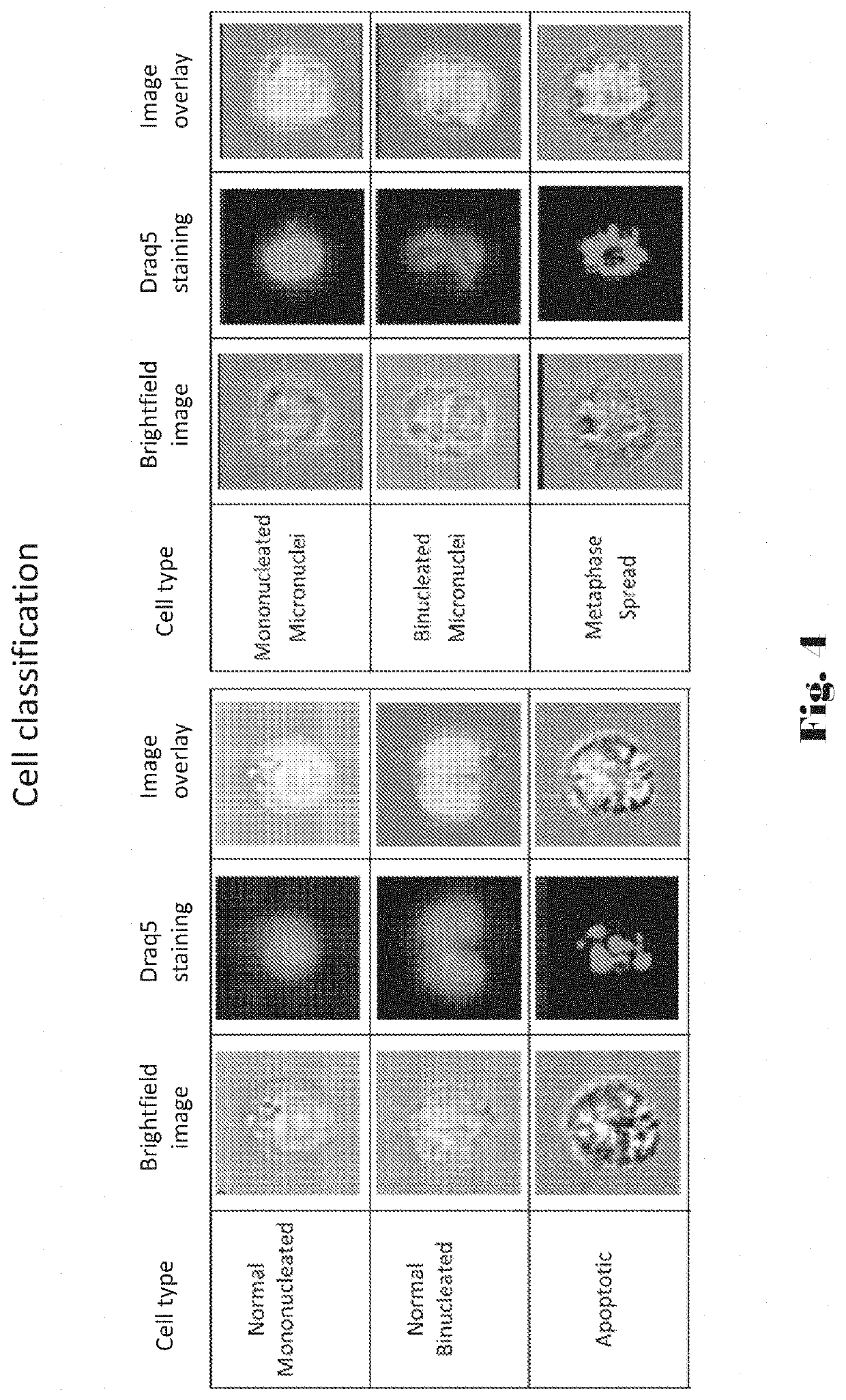
Computer-implemented apparatus and method for performing a genetic toxicity assay
A computer-implemented apparatus for performing a genotoxicity assessment in respect of a population of labelled cells pre-treated with, or exposed to, one or more specified substances, conditions and / or environments. The apparatus comprises a imaging flow cytometry system for capturing image files representative of said cell population, wherein each image file is representative of a single cell of said population, a cell-image analysis module configured to receive said image files and generate, in respect of each one thereof, respective cytological profiles; and a machine learning module configured to receive said cytological profiles and, in respect of each of a plurality thereof obtain therefrom one or more characteristics and insert their respective value(s) into a predetermined algorithm to generate a classifier and compare said generated classifier with a predetermined rule to output a score for the respective cell.
Owner:SWANSEA UNIV
Specific probe for detecting hemocyanin gene expression of eriocheir sinensis and application of specific probe
The invention discloses a specific probe for detecting hemocyanin gene expression of Eriocheir sinensis and application of the specific probe. Based on the principle that a probe sequence is specifically combined with mRNA of a target gene in proportion, a fluorescence in-situ hybridization technology is combined with image flow cytometry, different groups are distinguished according to whether fluorescence signals exist in cells or not, functional differences are analyzed according to signal strength, and the target gene can be identified according to the functional differences. And whether different genes are expressed in the same cell or not can be known by using multicolor fluorescence co-localization. Cell classification serves for diagnosis, function research and other requirements. Conventional methods mostly adopt antibody recognition to classify cells, but the current situation that aquatic animals lack commercially available antibodies limits the application. The method does not need an antibody, starts from a gene sequence, prepares a fluorescently-labeled short probe, is mild in hybridization condition, can carry out quantitative analysis at a complete single cell level, and has a good application prospect in cell classification and other aspects.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
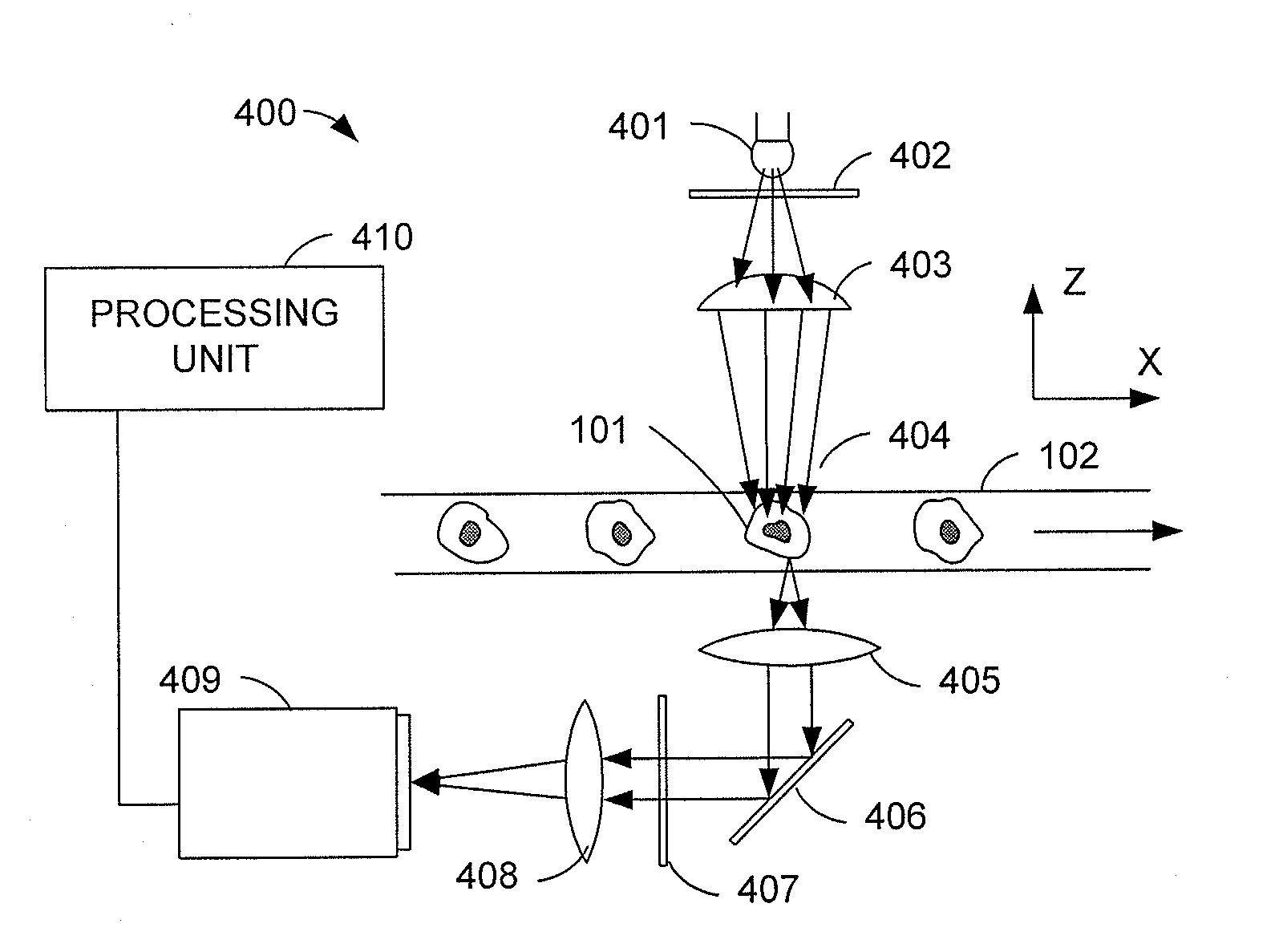
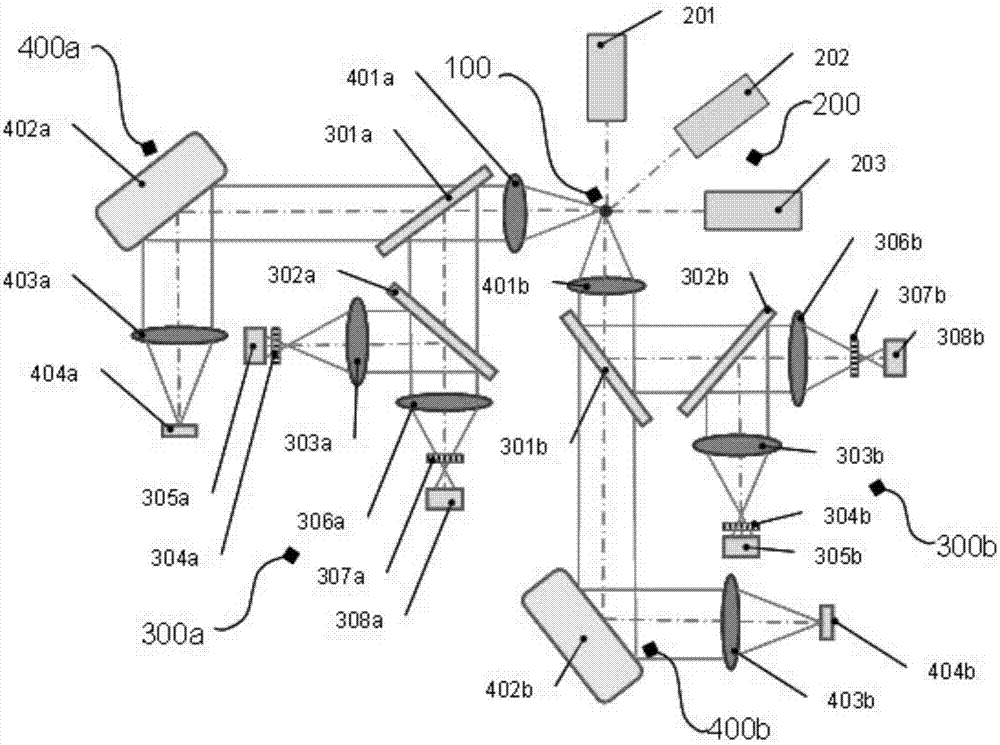
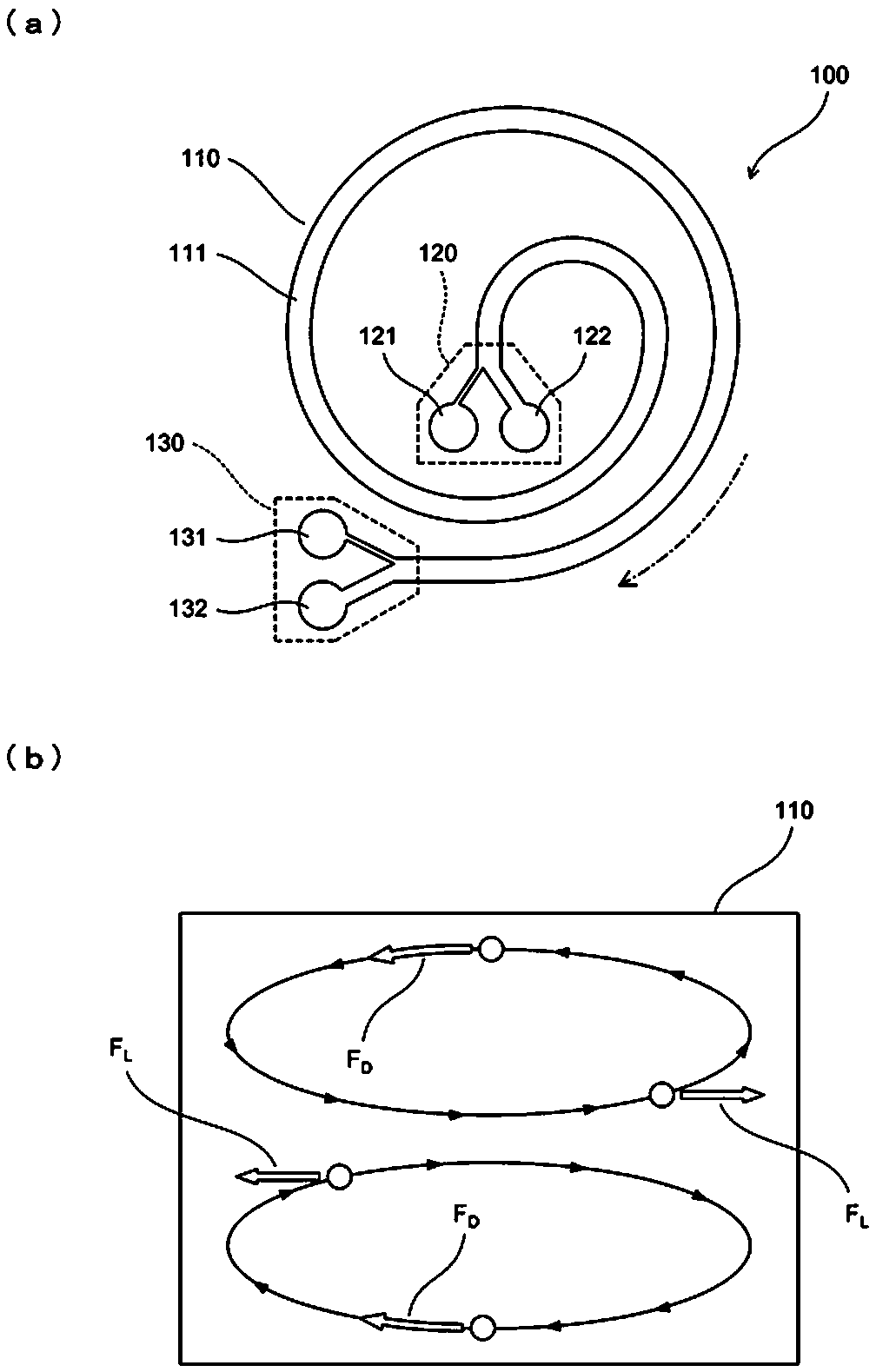
Imaging flow cytometer
An imaging flow cytometer includes at least one flow channel through which an observation target flows, a light source which irradiates the flow channel with sheet-like excitation light, an imaging unit which images a specific cross-section of the observation target by imaging fluorescence from the observation target having passed through a position irradiated with the excitation light, and a three-dimensional image generation unit which generates a three-dimensional image of the observation target as a captured image on the basis of a plurality of captured images obtained by cross-sectional imaging by the imaging unit.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
System and method for monitoring particles in a fluid using ratiometric cytometry
ActiveUS9983115B2High resolutionAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceChlorophyll b
A particle detection system with a detection mechanism that includes detectors positioned to detect two different ranges of fluorescence produced by particles in the fluid in a flow chamber. Each of the detectors is arranged to generating a trigger signal whenever fluorescence is detected. The system and related method enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of blue-green algae monitoring by utilizing imaging flow cytometry combined with particle analysis and the measurement of the ratio of each particle's phycocyanin to chlorophyll b detected by using the two detectors configured for detection of two different fluorescence ranges, one associated with the phycocyanin and the other associated with the chlorophyll b. Captured images are be used in comparison to known images of a library of images using a support vector machine classifier.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
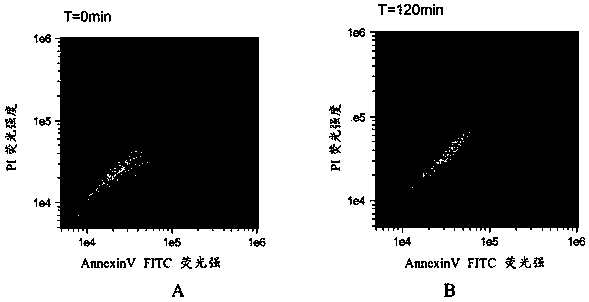
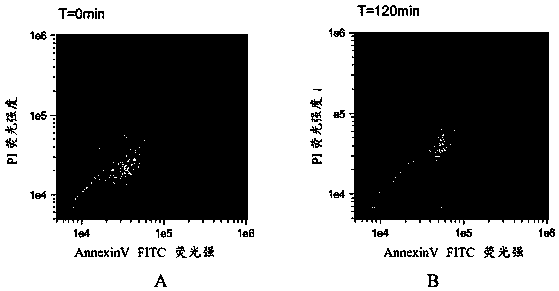
Method for detecting apoptosis of dinoflagellate cells
ActiveCN110018143AQuantitatively accurate and reliableAccurate analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceIodideImaging flow cytometry
The invention discloses a method for detecting apoptosis of dinoflagellate cells. The method for detecting the apoptosis of the dinoflagellate cells comprises the following steps: carrying out apoptosis processing on the dinoflagellate cells; carrying out concentration processing on the dinoflagellate cells subjected to the apoptosis processing; carrying out AnnexinV and propidine iodide (PI) dyeing processing on a concentrated dinoflagellate cell solution; carrying out imaging flow detection processing on a dyed dinoflagellate cell solution; and calculating an apoptosis rate of the dinoflagellate cells according to an AnnexinV / PI scatter diagram. The method for detecting the apoptosis of the dinoflagellate cells disclosed by the invention has the advantages that AnnexinV fluorescence, PIfluorescence and chlorophyll autofluorescence can be effectively distinguished through an imaging flow cytometer, so that the number of the dinoflagellate cells experiencing the apoptosis, which are among the dinoflagellate cells to be detected, can be directly and quantitatively measured, and an early cell apoptosis rate can be further obtained; and the quantification is reliable, the analysis isaccurate, and high-precision results can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com