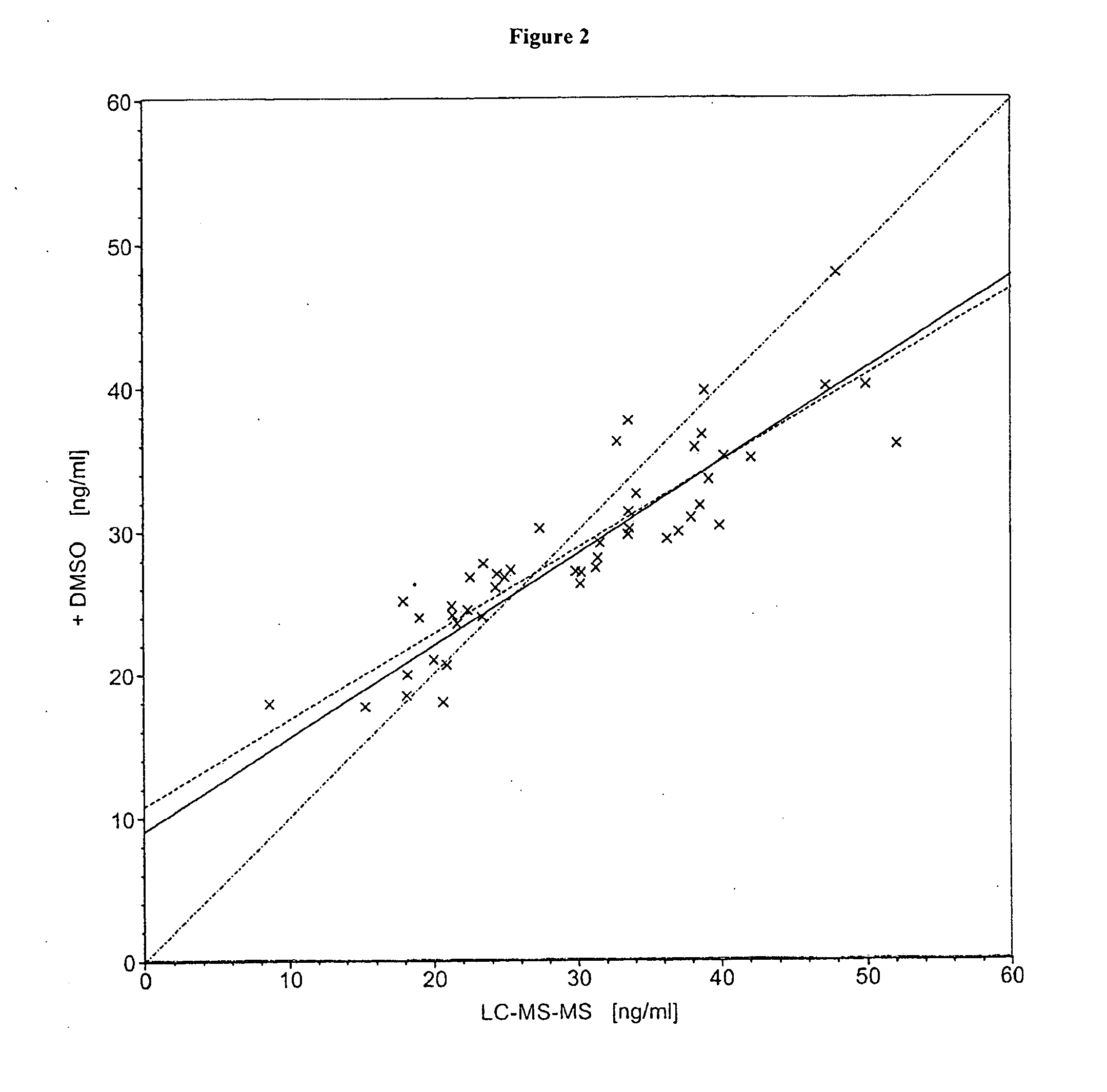
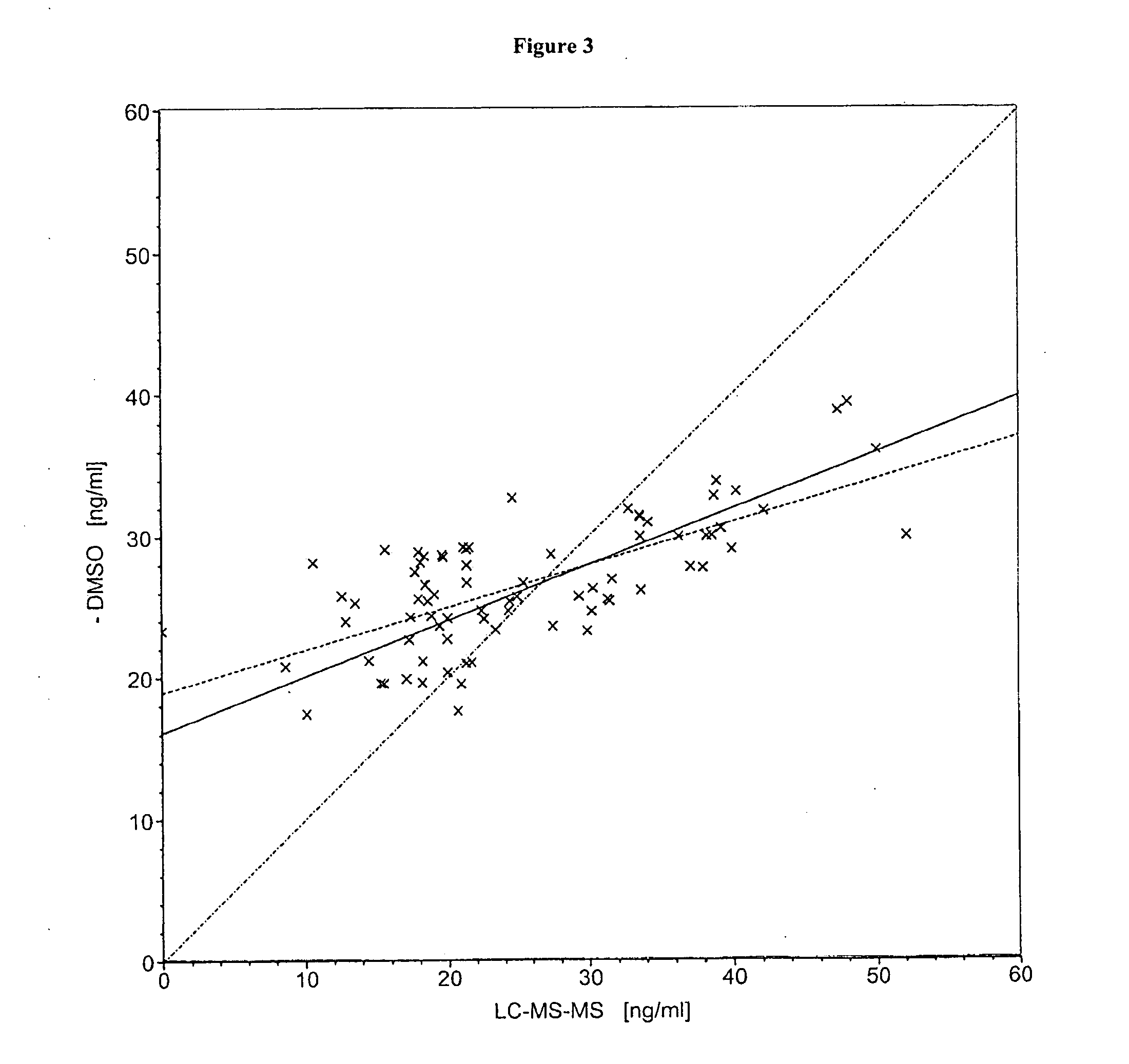
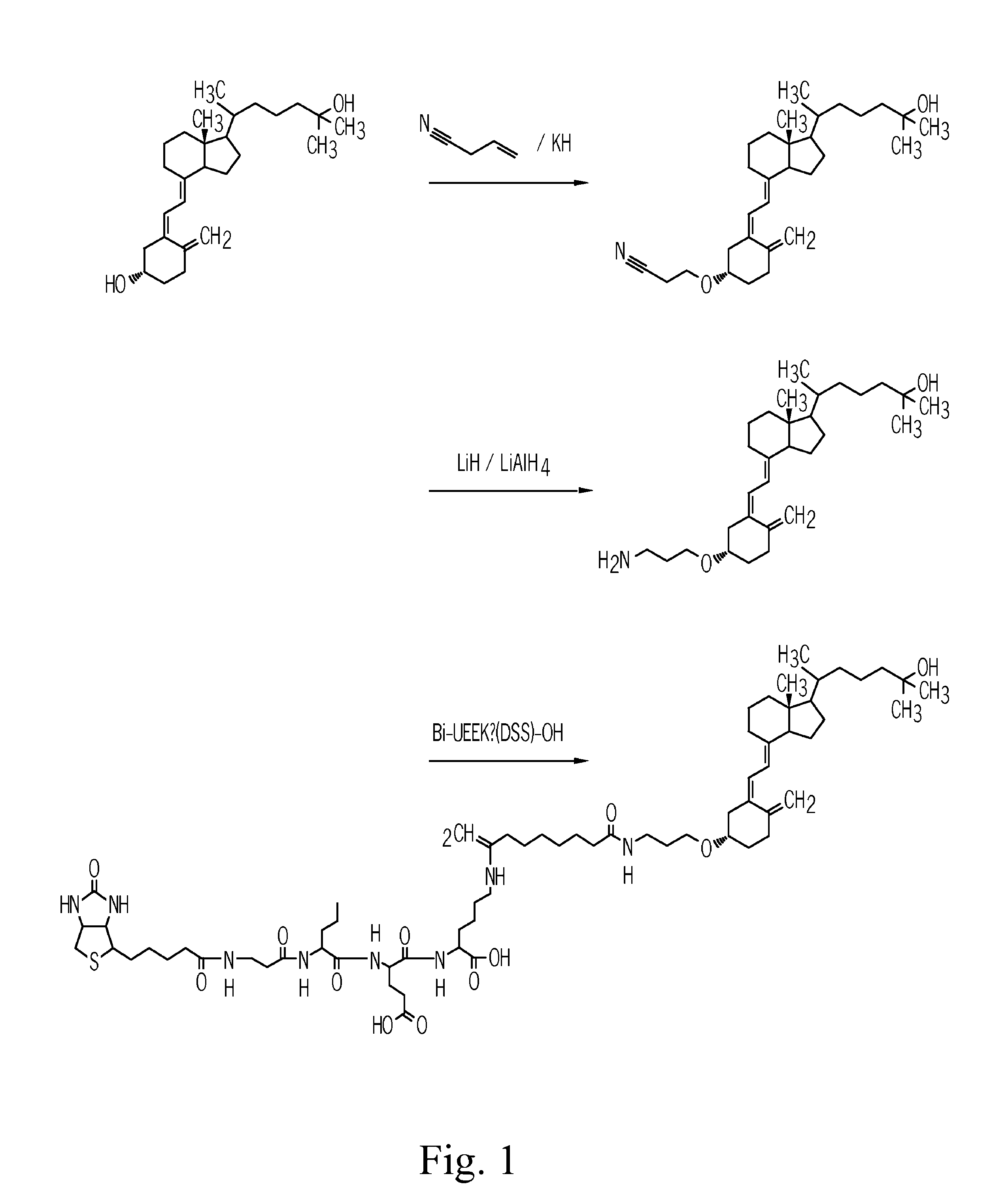
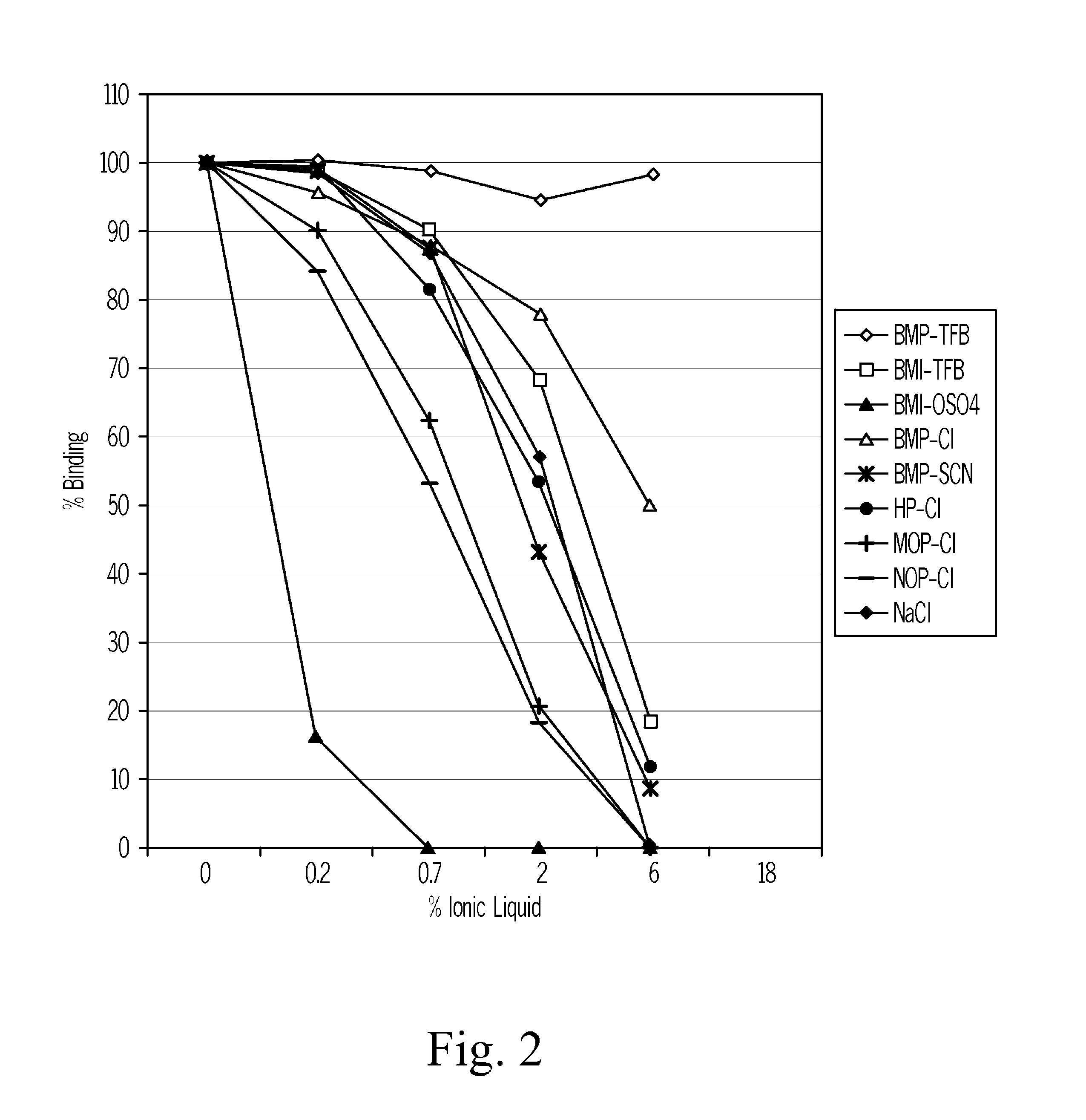
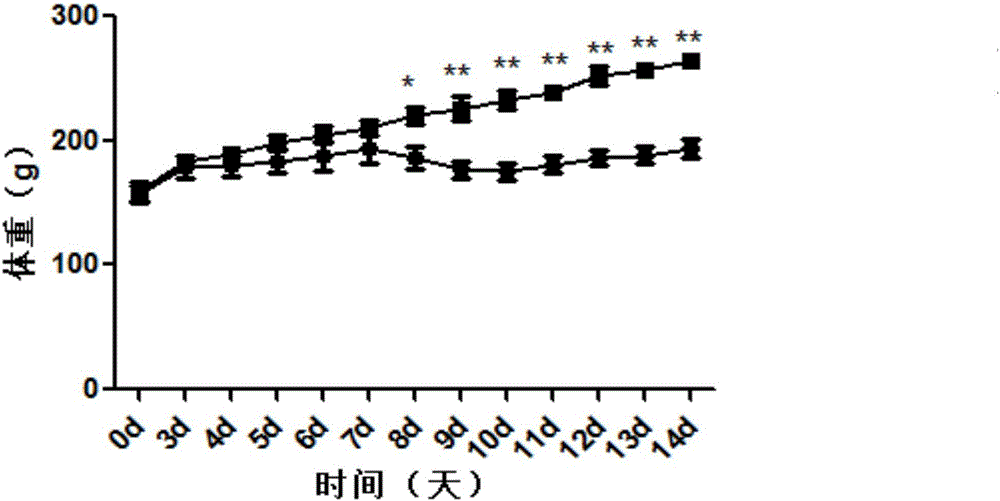
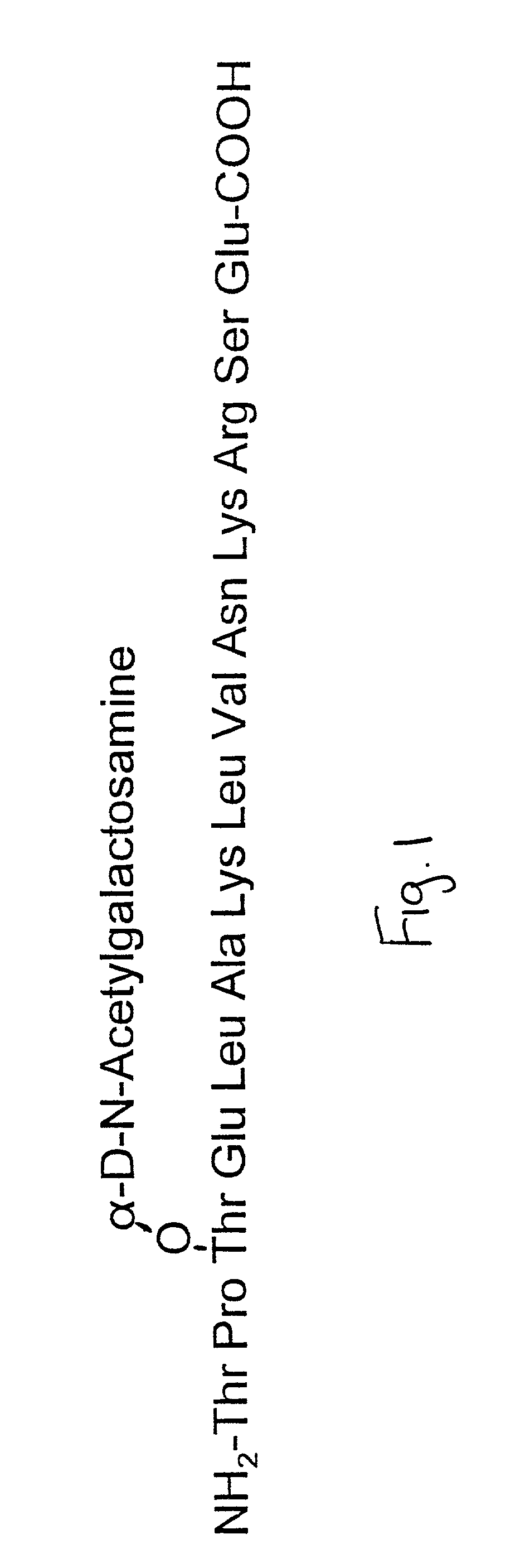Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "GC globulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
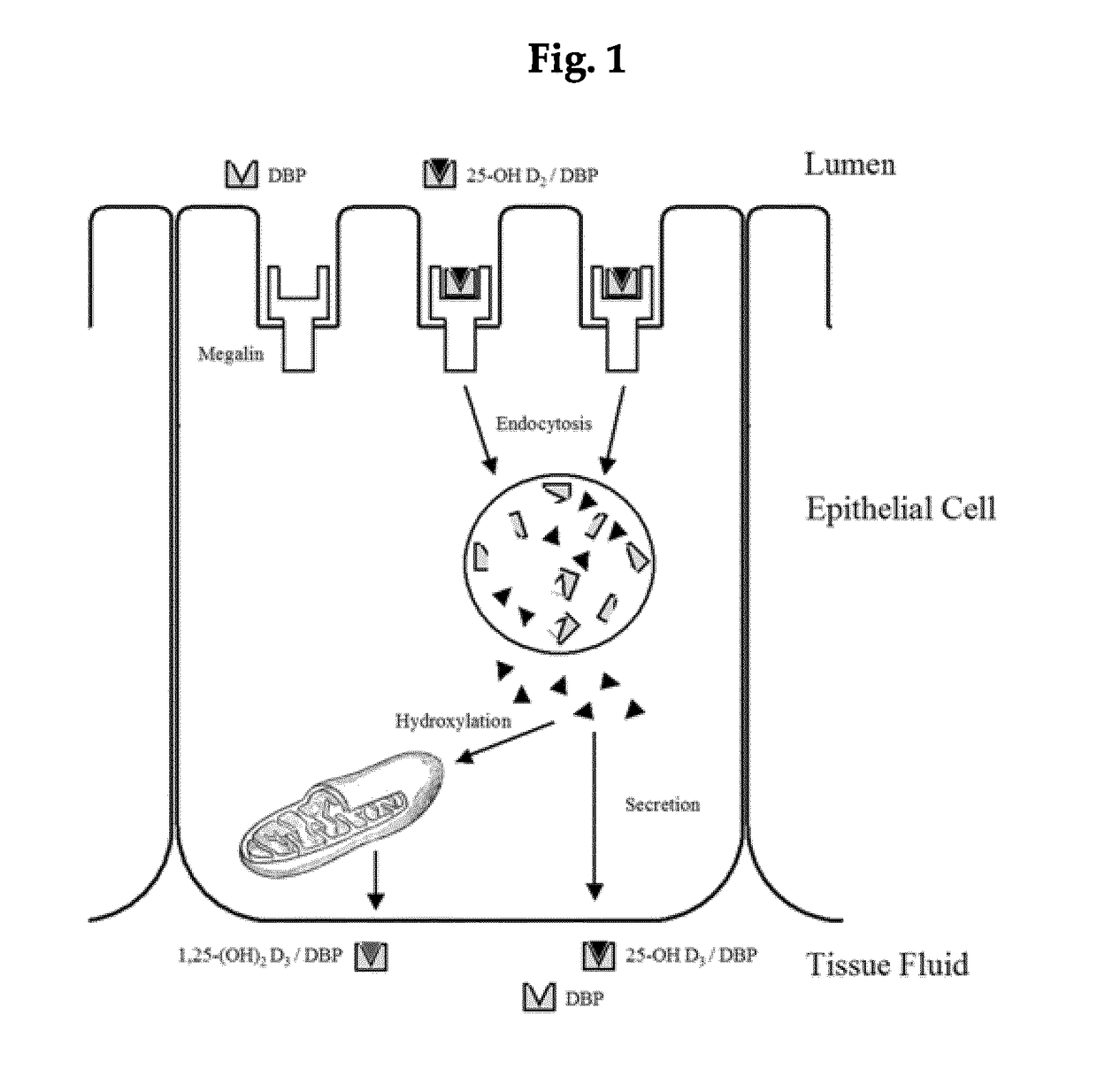
Vitamin D-binding protein (DBP), also/originally known as gc-globulin (group-specific component), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GC gene.
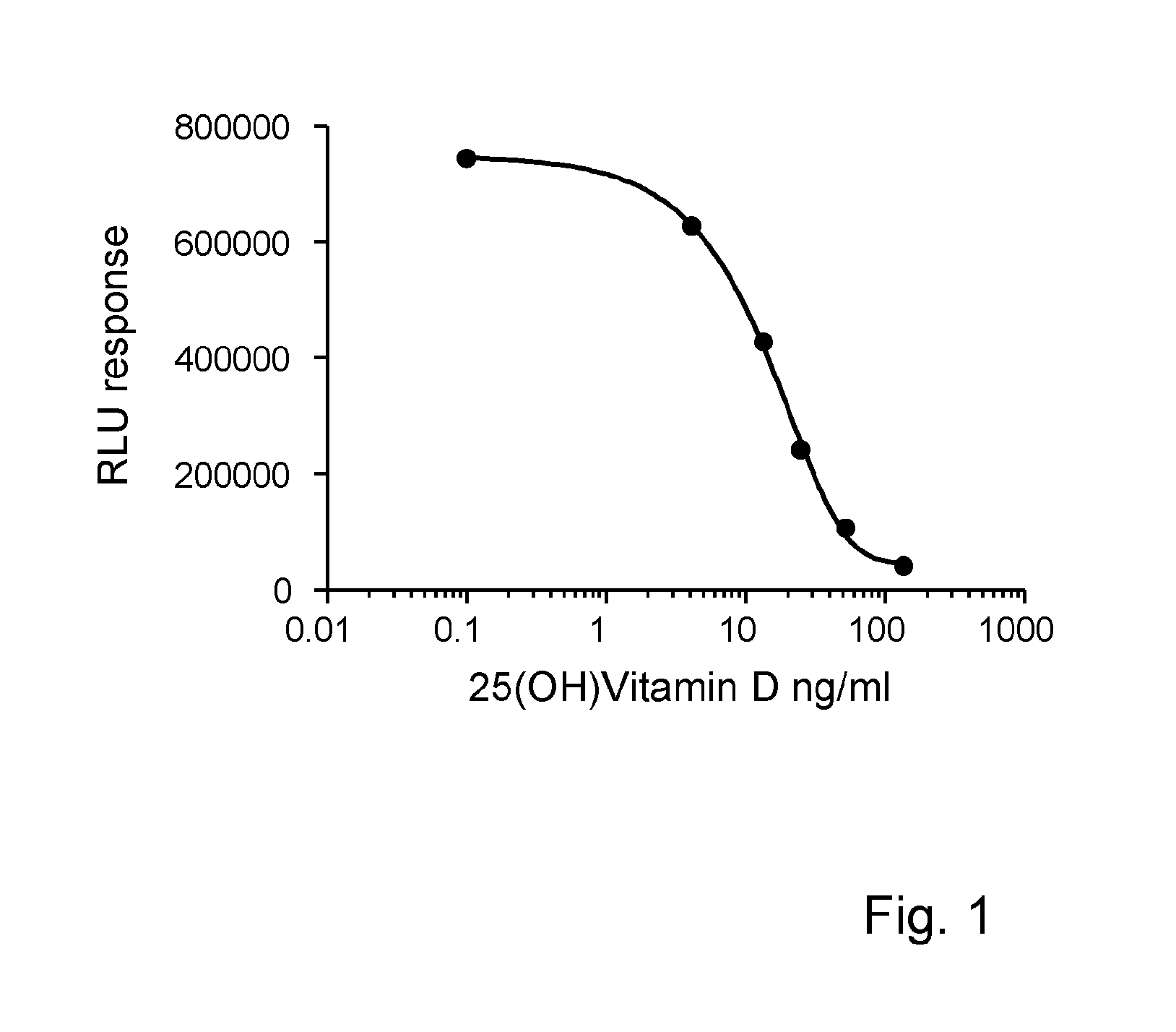
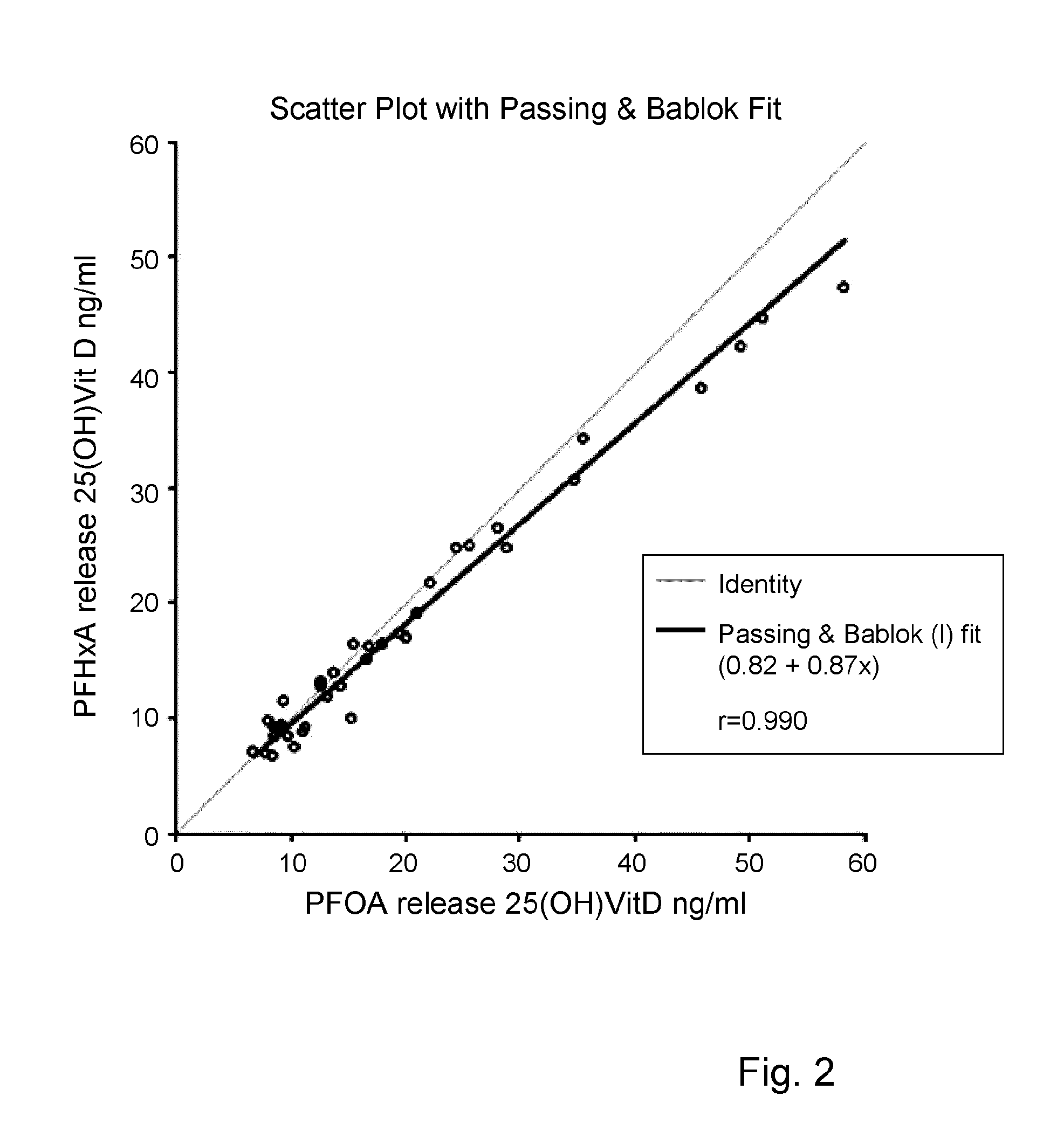
Measurement of vitamin d
ActiveUS20100285603A1Eliminate needAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementChromatographic separationVitamin D metabolism
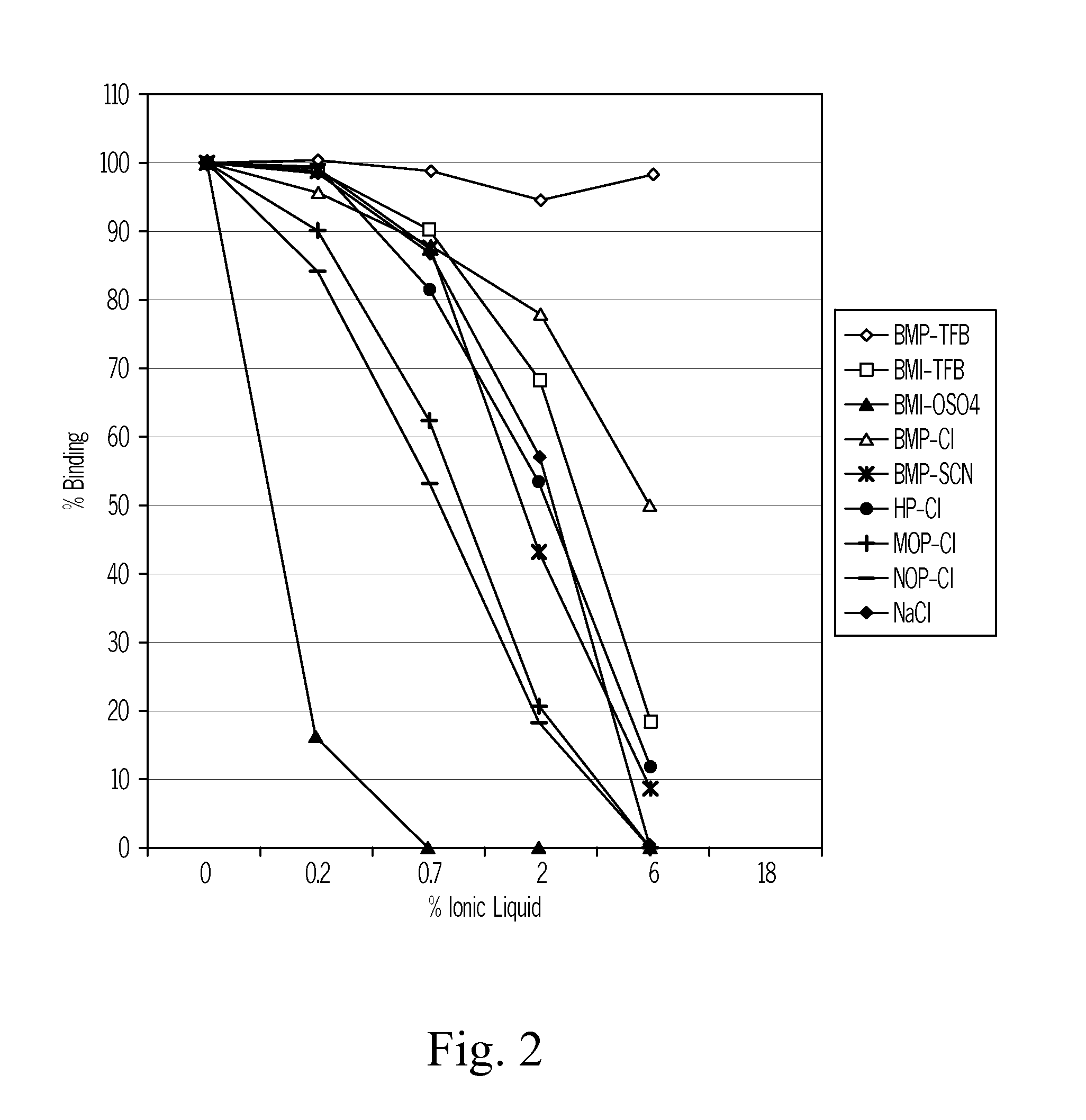
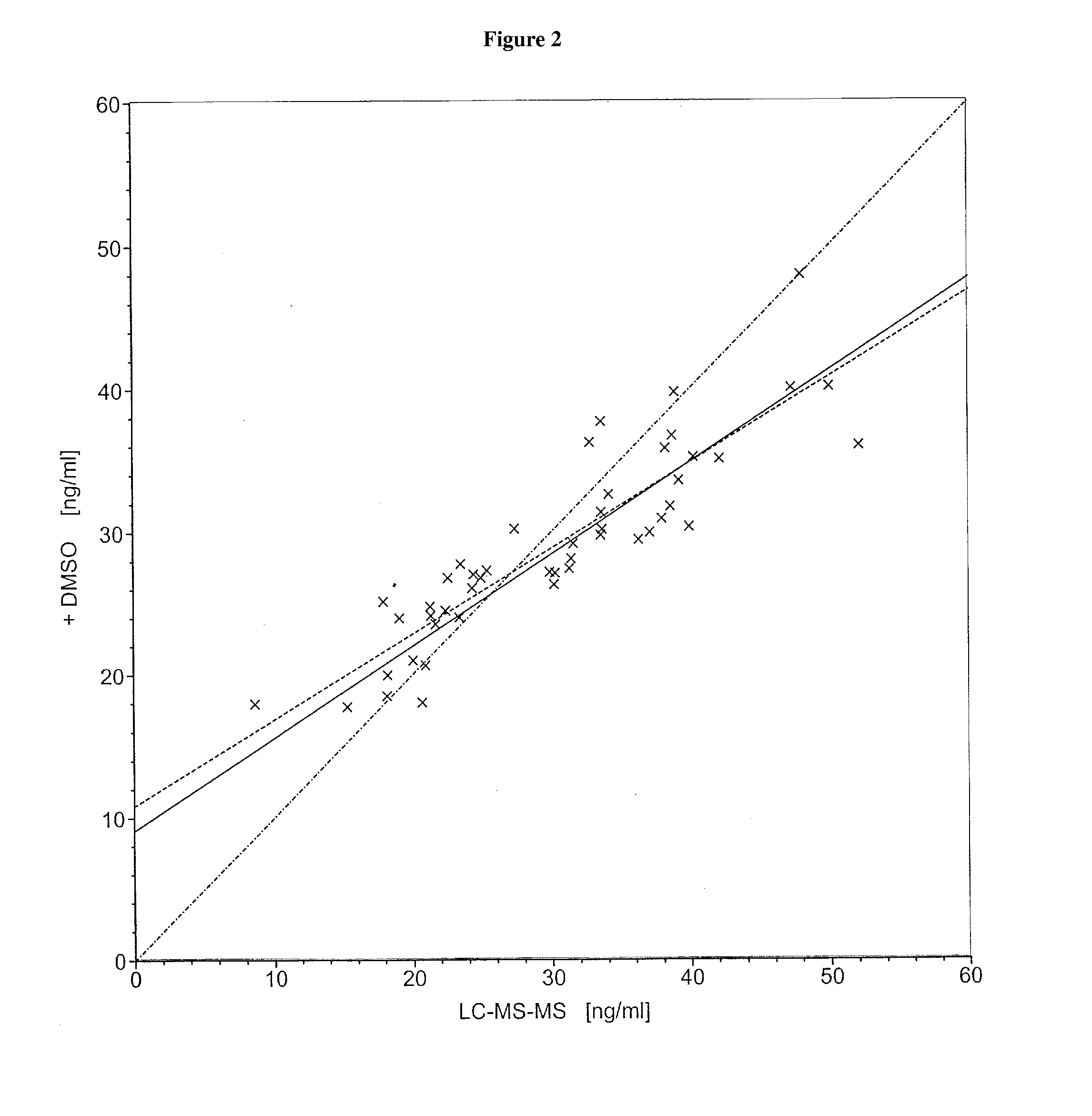
The present invention relates to a method of measuring a vitamin D metabolite in a sample, the method comprising the steps of (a) treating said sample with a vitamin D metabolite releasing reagent under conditions appropriate to release a vitamin D metabolite from vitamin D-binding protein and not to cause protein precipitation, (b) subjecting the treated sample obtained in step (a) to a chromatographic separation, and (c) measuring a vitamin D metabolite during or after said chromatographic separation. The present invention also relates to methods for determining the vitamin D status of a subject, for use in the diagnosis of disease, and to agents and kits for use in performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
25 hydroxyl vitamin d detection kit and preparation method thereof
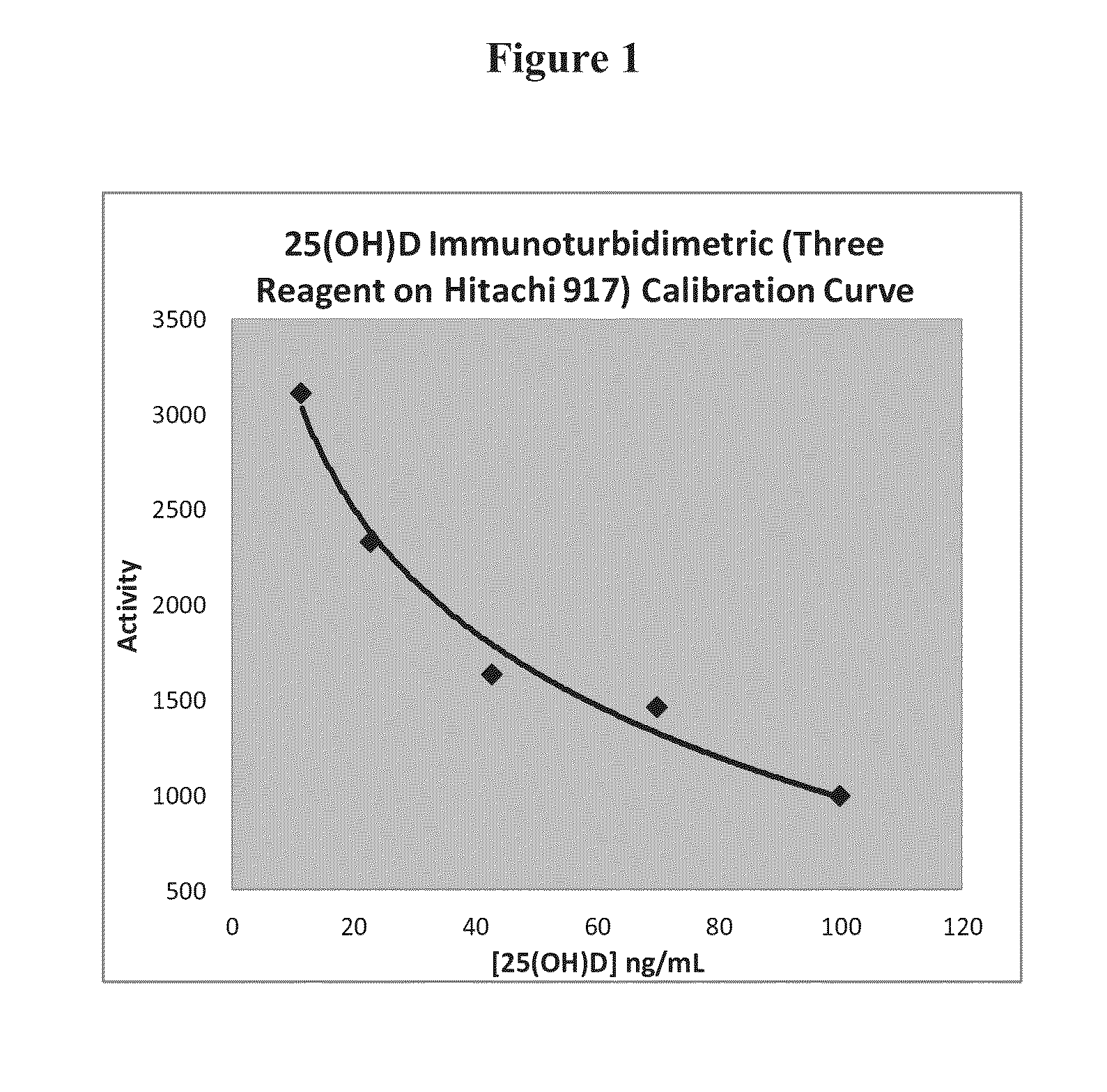
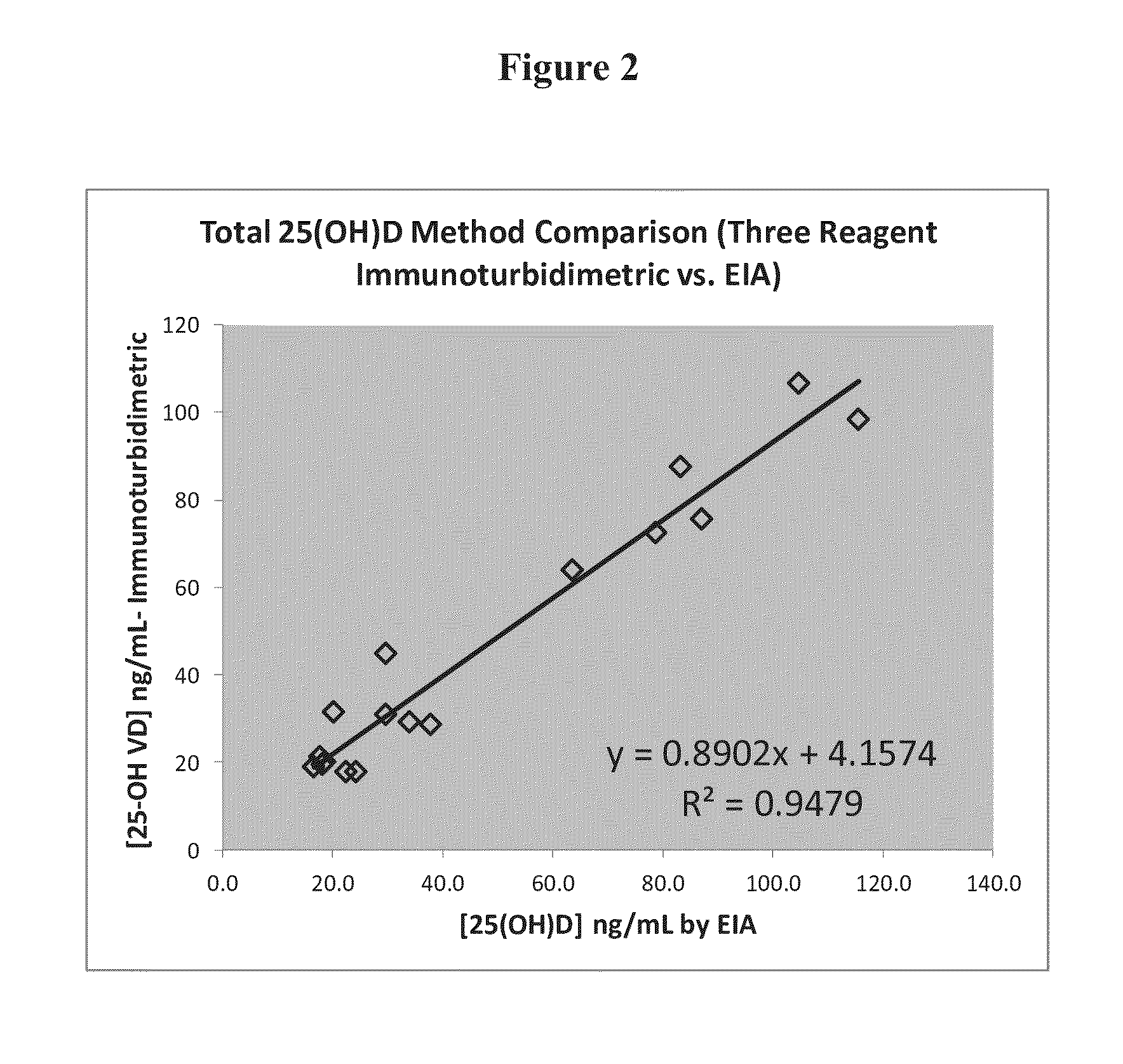
The invention relates to a 25 hydroxyl vitamin D detection kit and a preparation method thereof. A reagent comprises a first reagent and a second reagent and selectively further comprises a correction product. The first reagent comprises a 25 hydroxyl vitamin D antibody, a vitamin D binding protein antibody and buffer liquid. The second reagent comprises a micro-balloon combined with a 25 hydroxyl vitamin D antigen and the buffer liquid. The 25 hydroxyl vitamin D and the antigen on a surface of the micro-balloon are combined with the 25 hydroxyl vitamin D antibody in a competing mode so that turbidity generated by reaction of the micro-balloon combined with the 25 hydroxyl vitamin D and the 25 hydroxyl vitamin D antibody is reduced. Content of the 25 hydroxyl vitamin D in a sample can be calculated according to reducing degree of the turbidity.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Methods and compositions for assaying vitamin d
The present invention provides methods for assaying a vitamin D moiety in a sample, using a water miscible organic solvent, a specific binding partner that specifically binds to said vitamin D moiety, the binding partner being different from a natural vitamin D binding protein for the vitamin D moiety, and a water soluble polymer that facilitates binding between the specific binding partner and the vitamin D moiety. Kits and reaction mixtures for assaying a vitamin D moiety in a sample are also provided.
Owner:DIAZYME LAB INC
Multiplexed biomarkers for monitoring the alzheimer's disease state of a subject
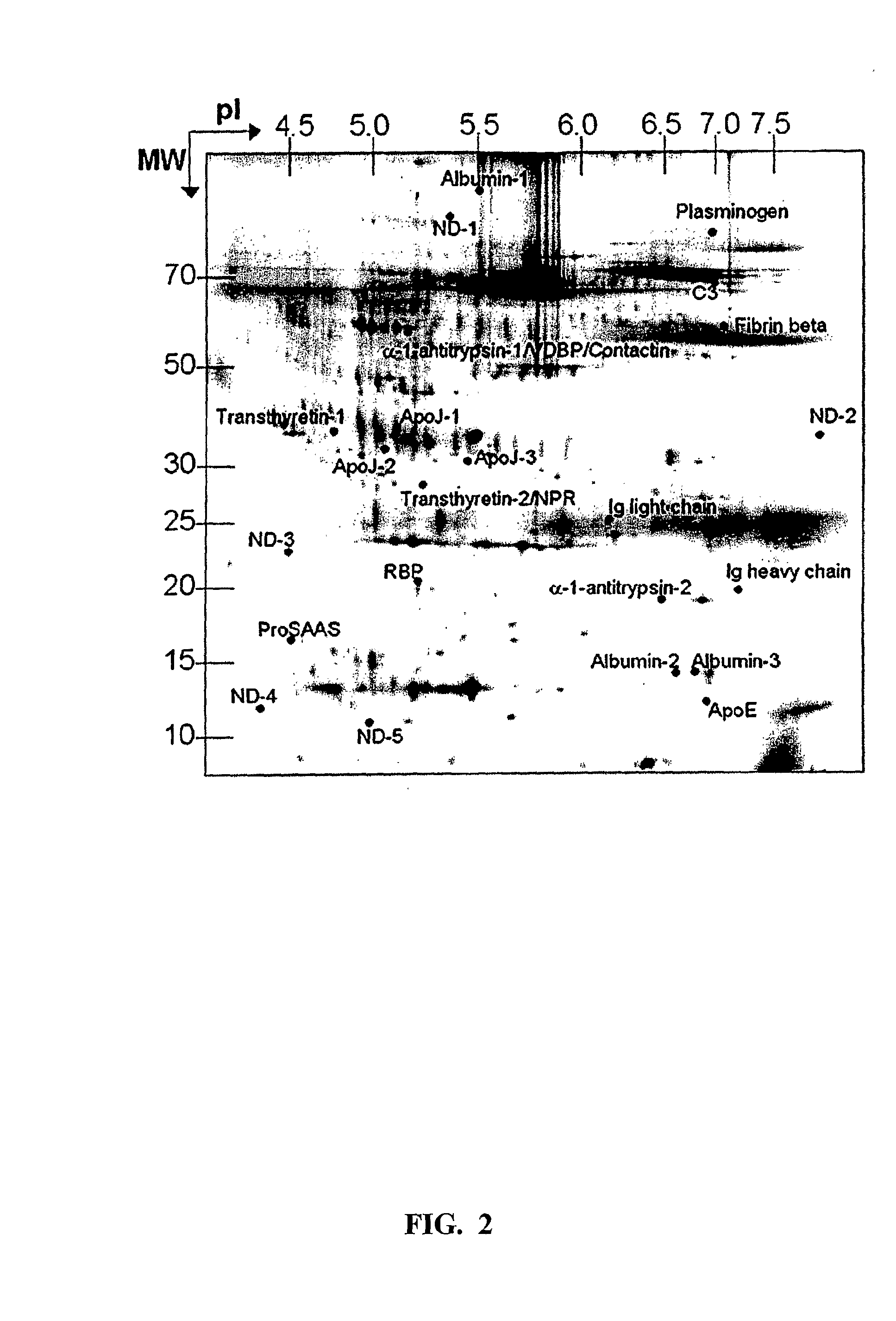
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing a subject's Alzheimer's disease state. The method involves providing a database containing information relating to protein expression levels associated and not associated with Alzheimer's disease. The database includes information relating to at least a majority of the following proteins: albumin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, apolipoprotin E, apolipoprotein J, complement component 3, contactin, fibrin beta, Ig heavy chain, Ig light chain, neuronal pentraxin receptor, plasminogen, proSAAS, retinol-binding protein, transthyretin, and vitamin D binding protein. Information relating to proteins found in one or more cerebrospinal fluid samples from a subject is also provided and a database is used to analyze the information from the subject to diagnose the subject's Alzheimer's disease state. Also disclosed is a computer readable medium and a system, both useful in carrying out the present invention.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Release reagent for vitamin d compounds
The present invention concerns a reagent composition for releasing vitamin D compounds bound to vitamin D-binding protein, a method for the detection of a 25-hydroxyvitamin D compound in which the 25-hydroxyvitamin D compound is released from vitamin D-binding protein using this reagent and the mixture obtained in this manner is analyzed, the use of the reagent to release vitamin D compounds as well as a kit for detecting 25-hydroxyvitamin D which contains the reagent for releasing vitamin D compounds in addition to the usual immunological reagents.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Method For Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis
The present invention relates to methods for diagnosing multiple sclerosis in a subject, the method, comprising determining the level of phosphorylation of a marker in a biological sample from the subject, wherein the marker is selected from α1-antitrypsin (a1AT) and vitamin D binding protein (VDBP); and comparing the level of phosphorylation of the marker in the sample to a reference value.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Measurement of vitamin D
ActiveUS8003400B2Eliminate needAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementChromatographic separationVitamin D metabolism
The present invention relates to a method of measuring a vitamin D metabolite in a sample, the method comprising the steps of (a) treating said sample with a vitamin D metabolite releasing reagent under conditions appropriate to release a vitamin D metabolite from vitamin D-binding protein and not to cause protein precipitation, (b) subjecting the treated sample obtained in step (a) to a chromatographic separation, and (c) measuring a vitamin D metabolite during or after said chromatographic separation. The present invention also relates to methods for determining the vitamin D status of a subject, for use in the diagnosis of disease, and to agents and kits for use in performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
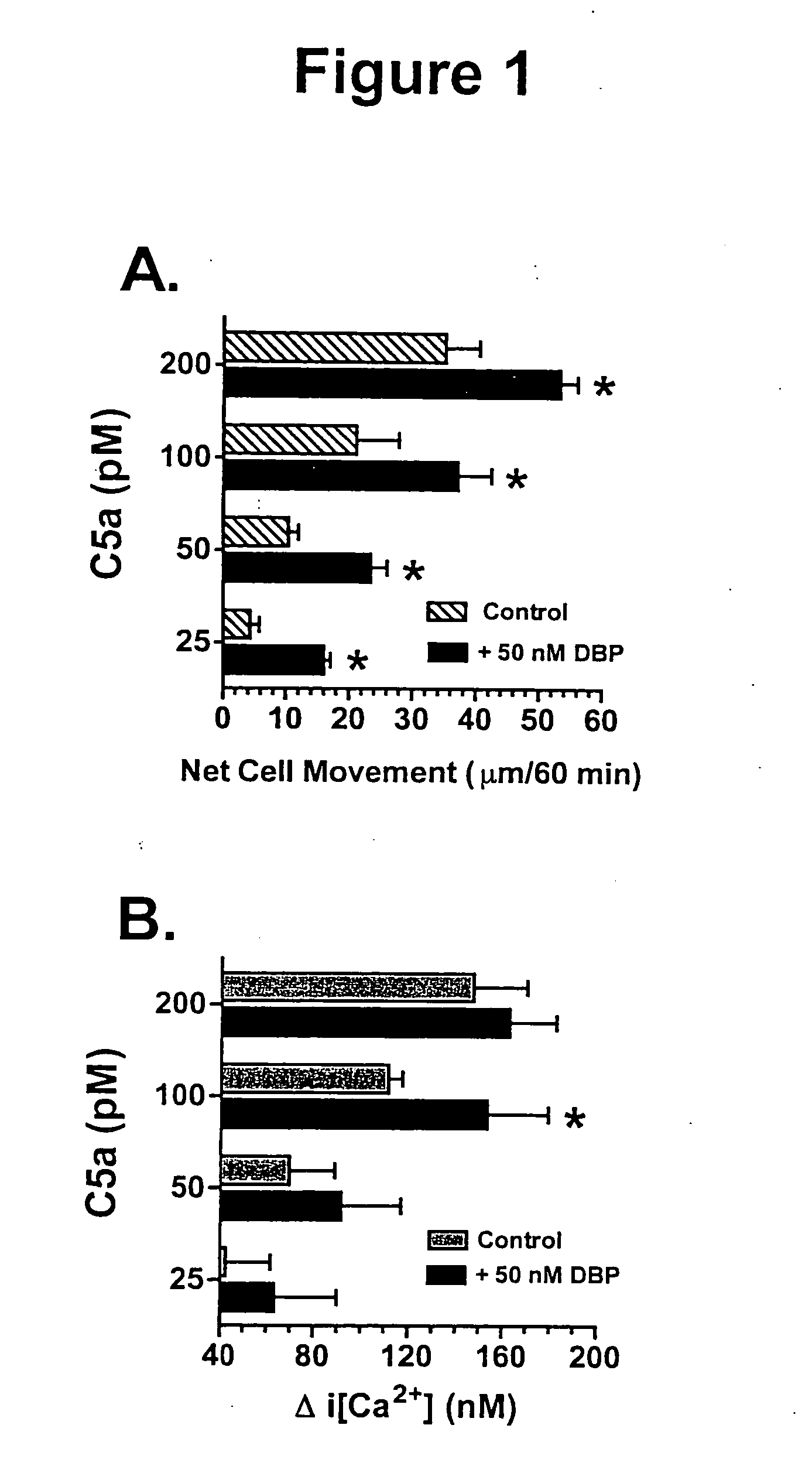
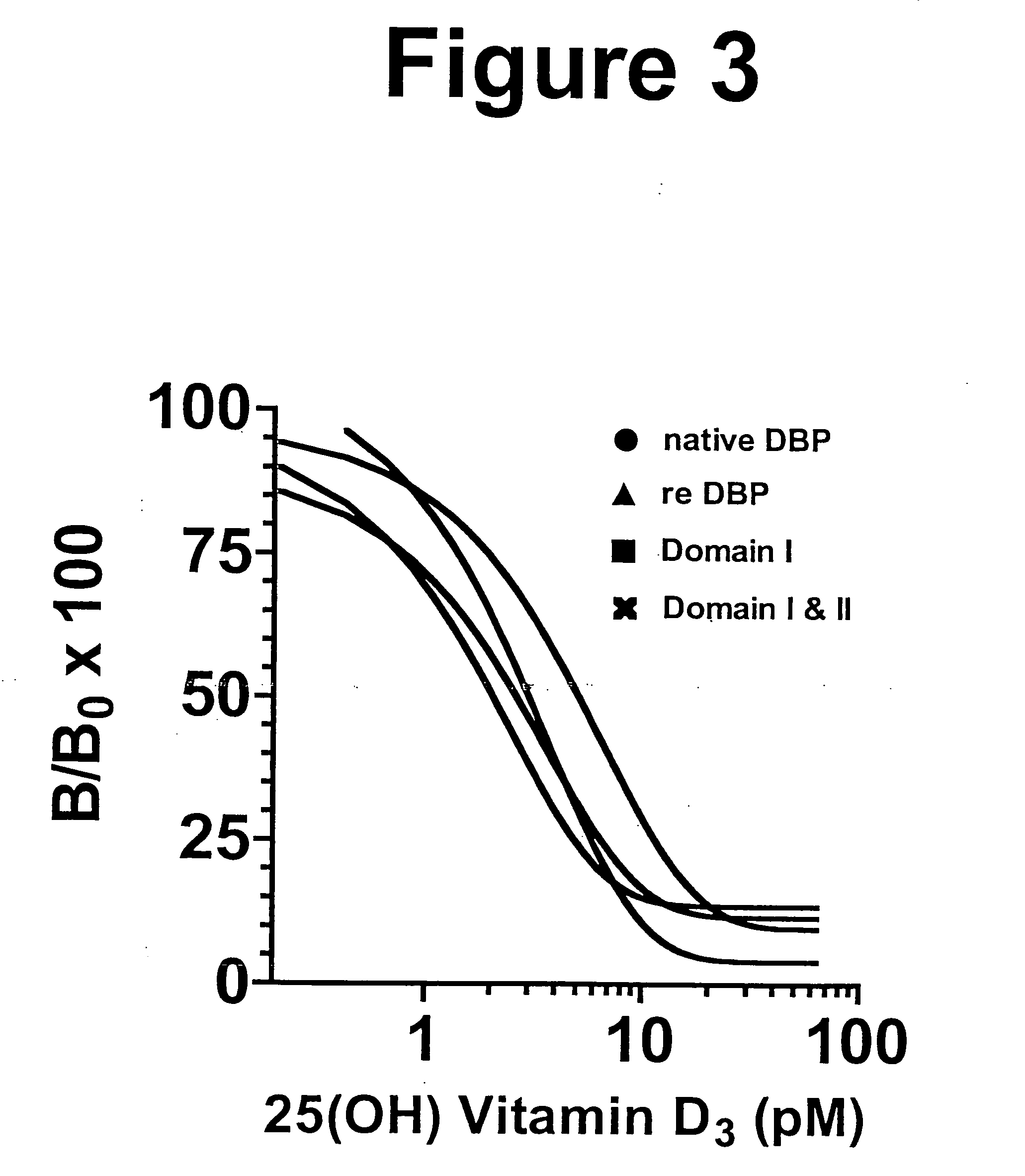
Purification process for large scale production of Gc-globulin, the Gc-globulin produced hereby, a use of Gc-globulin and a Gc-globulin medicinal product
InactiveUS20050020816A1High yieldHigh purityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPlasma derivedPurification methods
A purification process for large-scale production of Gc-globulin is described. The source of Gc-globulin is preferably a crude plasma fraction but can be any solution, suspension or supernatant containing Gc-globulin, e.g., a milk product, colostrum or a fermentation broth. The Gc-globulin can be plasma-derived or produced by a genetic modified organism. The process includes two key elements: purification by series of ion exchange chromatography steps, and performing at least two virus-reduction steps. A diagnostic method to measure the free Gc-globulin in a patient blood sample, a use of Gc-globulin in medicine and the preparation of a Gc-globulin medicinal product is also provided. The product can be used in therapy for patients with circulatory disorders and complications, i.e., where it is contemplated that patients would benefit from the administration of Gc-globulin.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Agents and methods for promoting bone growth
InactiveUS20050261172A1Assist in repairFacilitate depositionBone-inducing factorOsteogenic factorWhole bodyBone growth
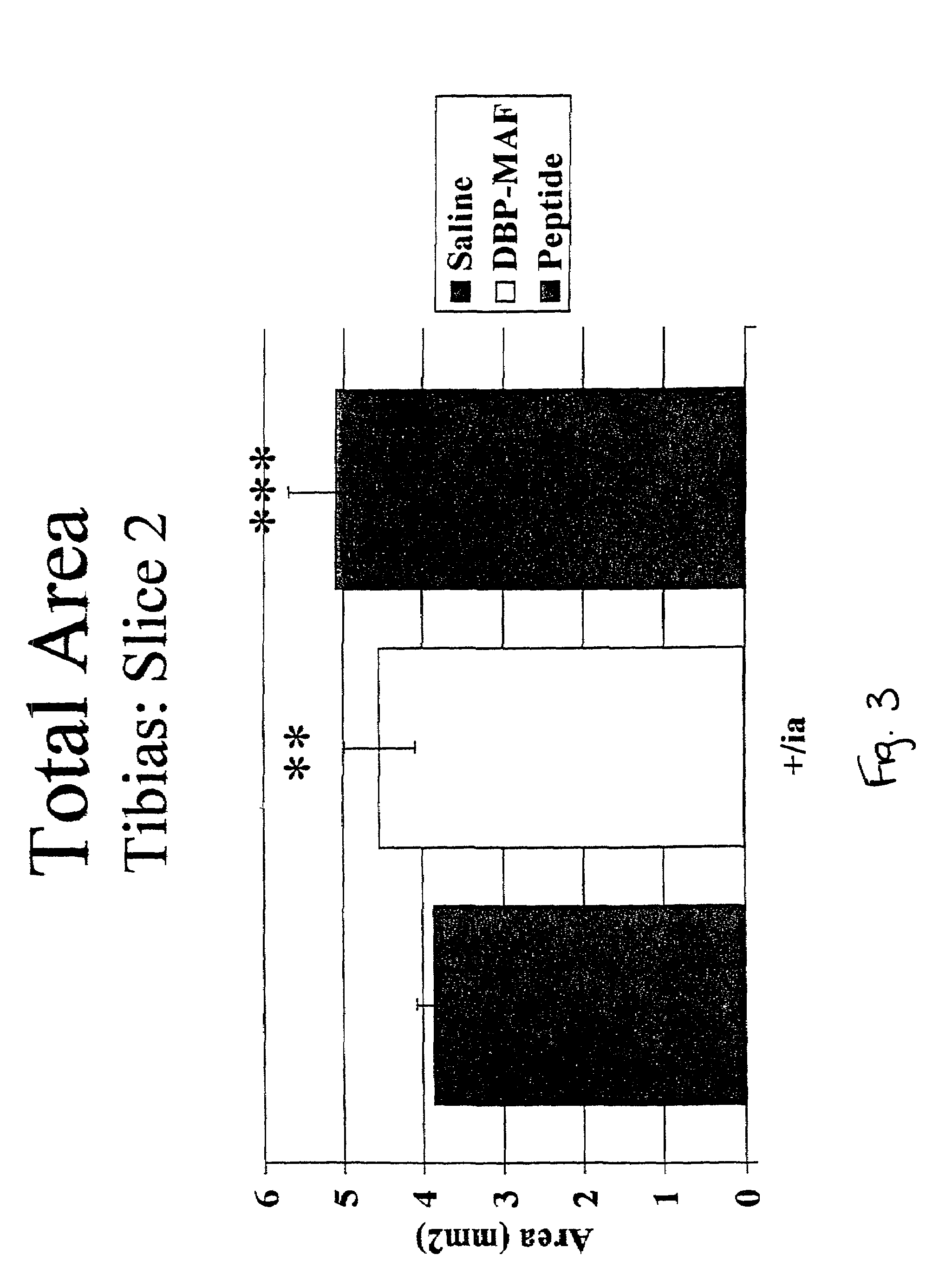
Agents for promoting bone deposition and growth in a mammalian subject. The agents are O-glycosylated and non-glycosylated peptides that are derived from vitamin D binding protein, collectively referred to hereinafter as “DBP” peptides. The DBP peptides are from 3 to 18, preferably from 4 to 14 amino acids in length and comprise a sequence which is at least 80% identical, preferably at least 90% identical to the amino acid sequence of a fragment contained within domain III of DBP. Methods for promoting bone deposition in a subject in need of the same are also provided. The methods comprise administering to the subject a therapeutically effective quantity of an agent selected from the group consisting of an activated form of vitamin D binding protein referred to hereinafter as “ADBP”, one or more DBP peptides, and combinations thereof. The agents may be administered locally or systemically.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN OHIO UNIVERSITIES COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Application of vitamin D binding protein as marker in diagnosis of mental disease depression
ActiveCN111351945AHigh clinical application valueHigh differential diagnostic accuracyDisease diagnosisBiological testingBipolar maniaDepressed - symptom
The invention discloses application of vitamin D binding protein as a marker in diagnosis of mental disease depression, and particularly relates to application of a reagent for detecting the content of the vitamin D binding protein in preparation of a reagent for diagnosing the mental disease depression. Differential expression of the vitamin D binding protein in plasma of schizophrenia, bipolar mania, depression and non-mental disease control persons is indicated, and the specificity of the vitamin D binding protein in plasma of depression patients is only improved; the protein is singly usedas a peripheral blood biomarker to detect the content of the protein and is used for diagnosing depression, so that the differential diagnosis accuracy of depression and healthy people or schizophrenia and bipolar mania of other mental diseases can be remarkably improved. Therefore, vitamin D binding protein content detection has high clinical application value in depression diagnosis, and a brand-new way is provided for rapid and effective diagnosis of mental disease depression.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Release reagent for vitamin d
Disclosed is an invention in the field of conducting an immunoassay of 25(OH) vitamin D in blood or blood components, notably serum or plasma. The invention employs a perfluoro alkyl acid, or a salt thereof, to release 25(OH) vitamin D from vitamin D binding protein. Thereafter the binding protein comprising the 25-OH vitamin D is subjected to a competitive binding assay with a labeled vitamin D compound.
Owner:FUTURE DIAGNOSTICS
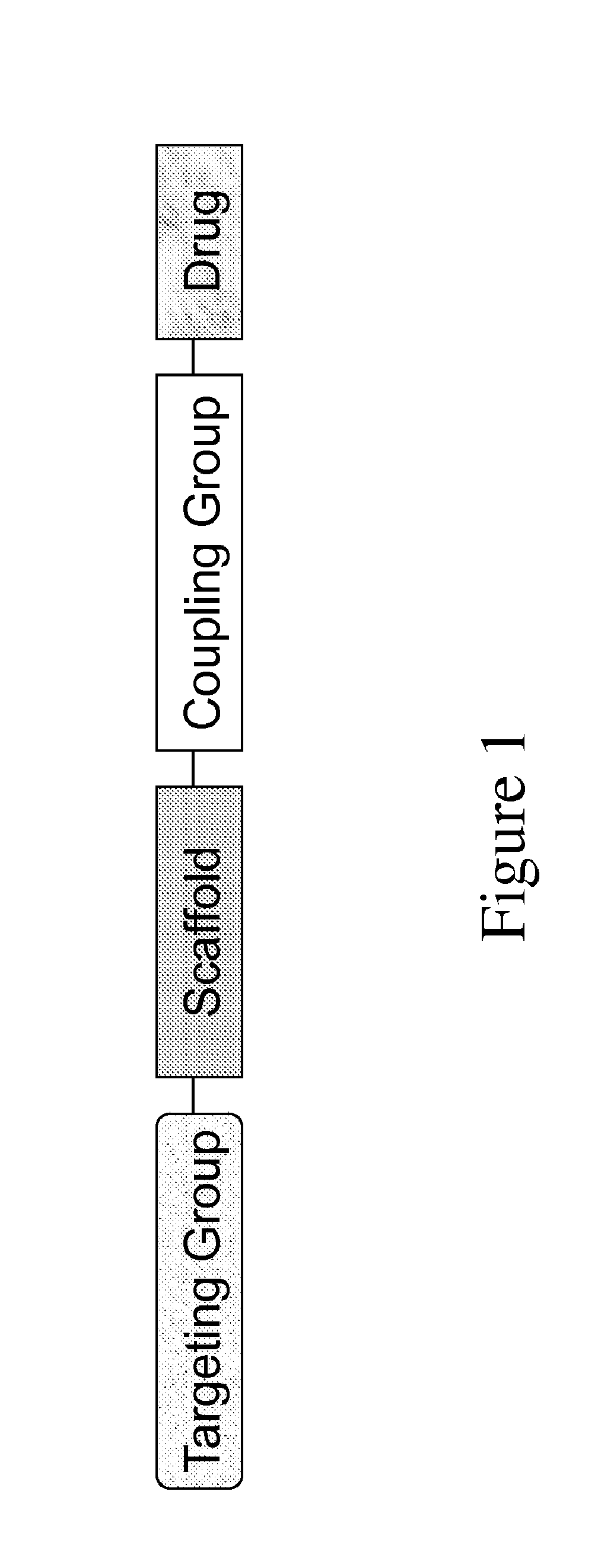
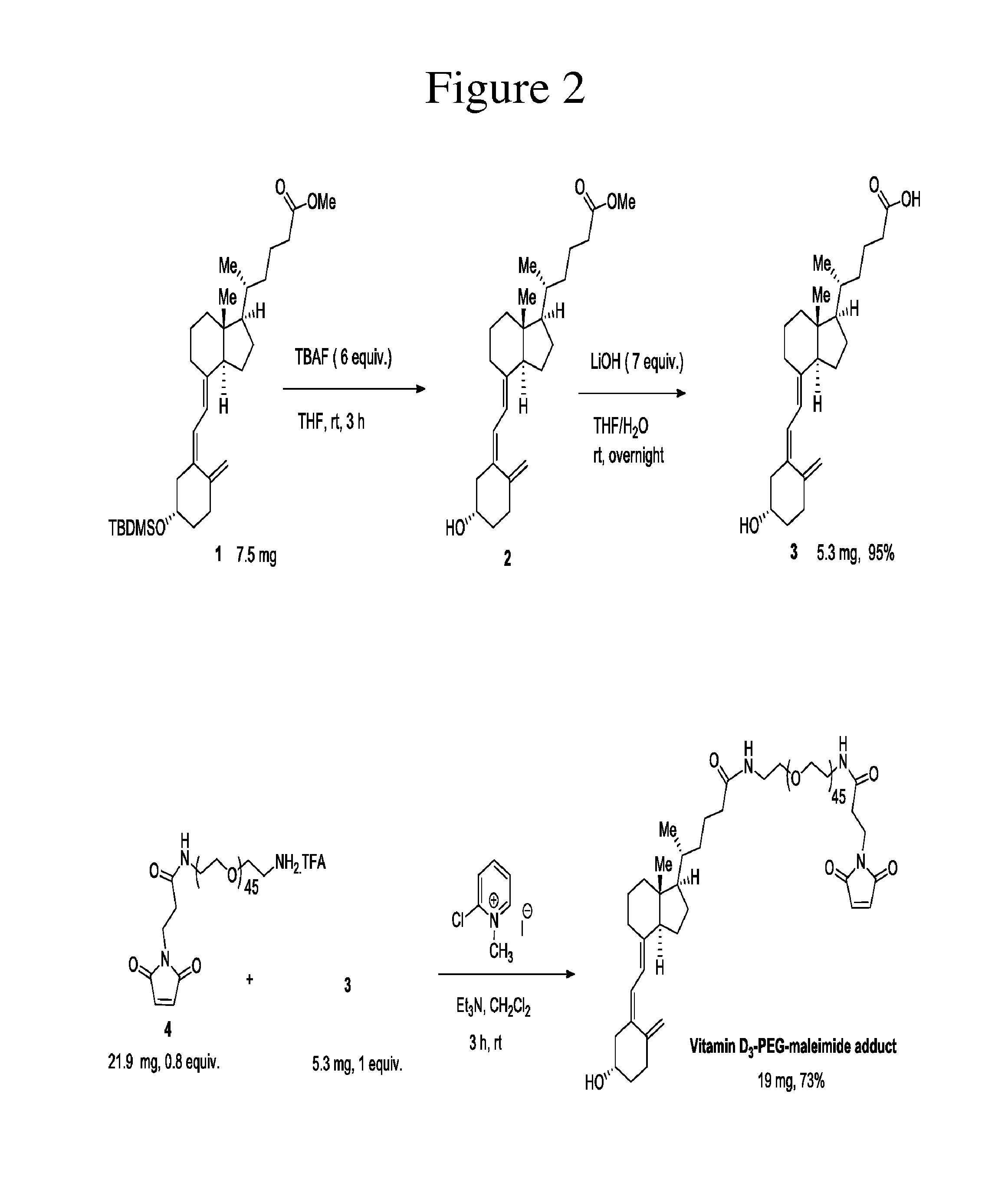
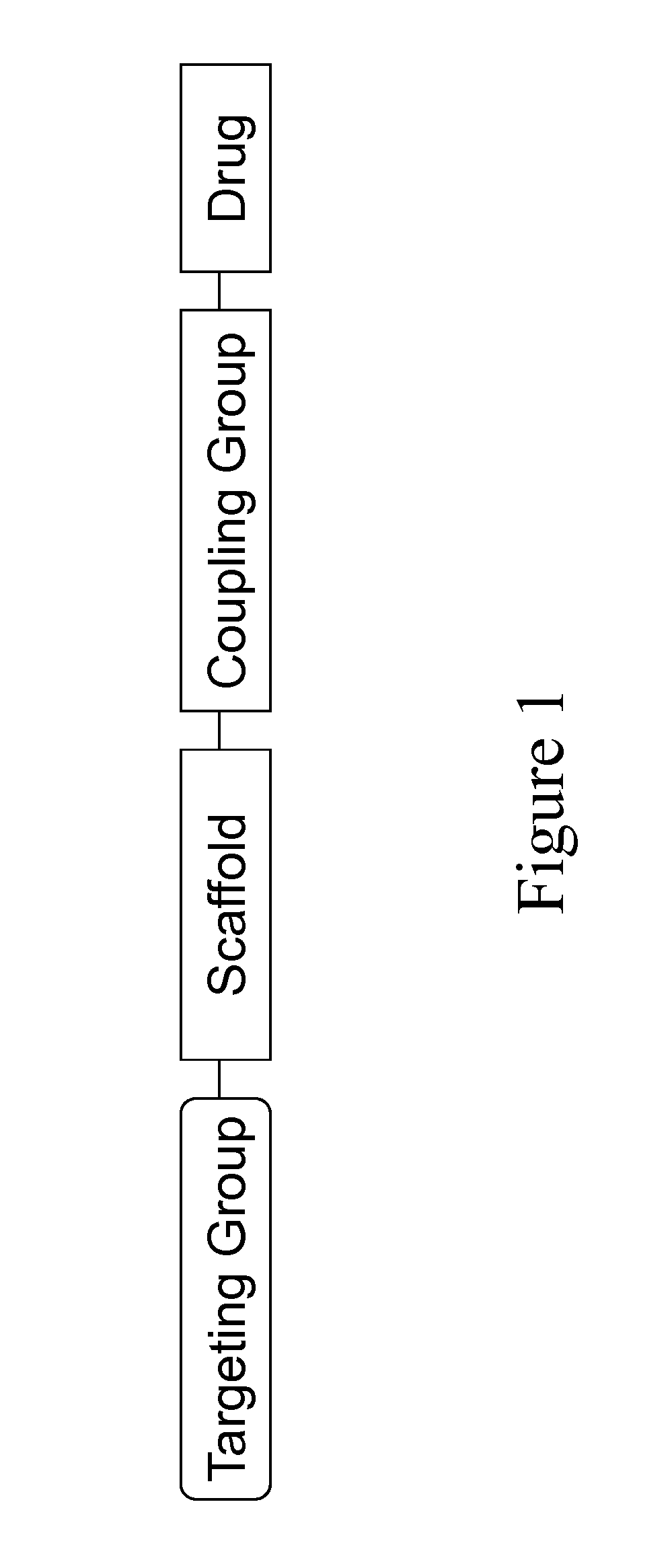
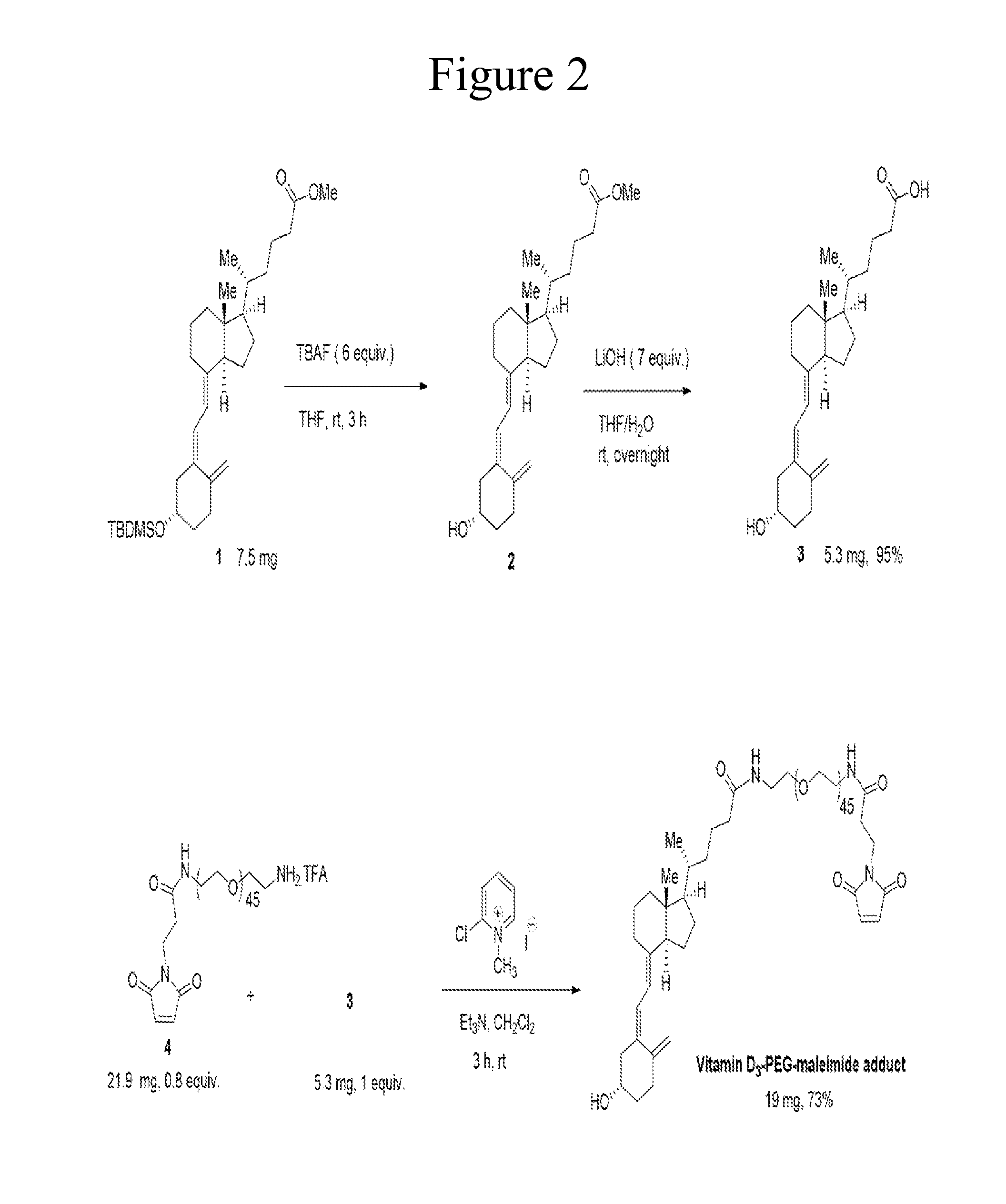
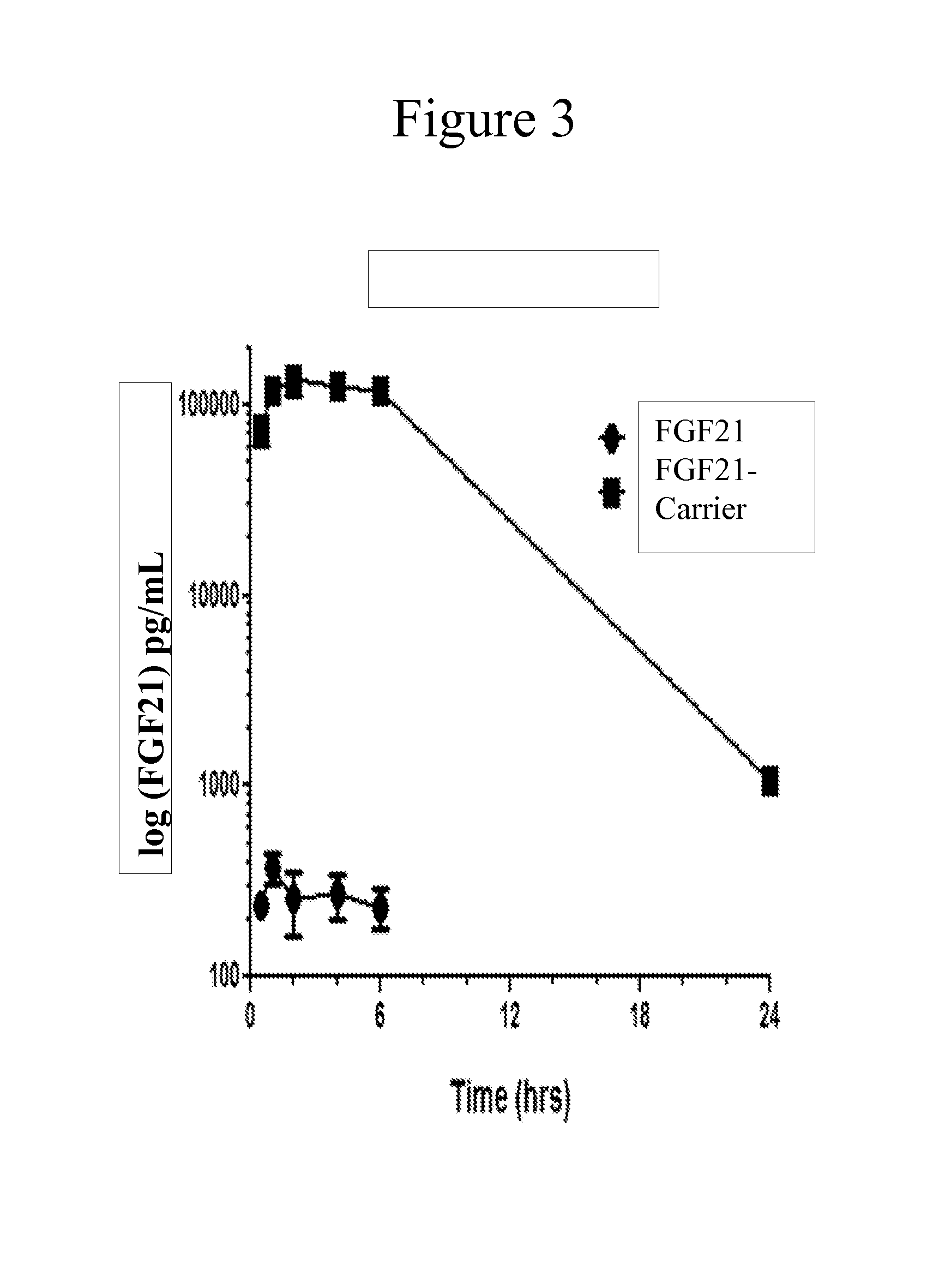
Carriers for improved drug delivery
ActiveUS20150104469A1Promote absorptionImprove bioavailabilityNervous disorderAntipyreticCrystallographyHalf-life
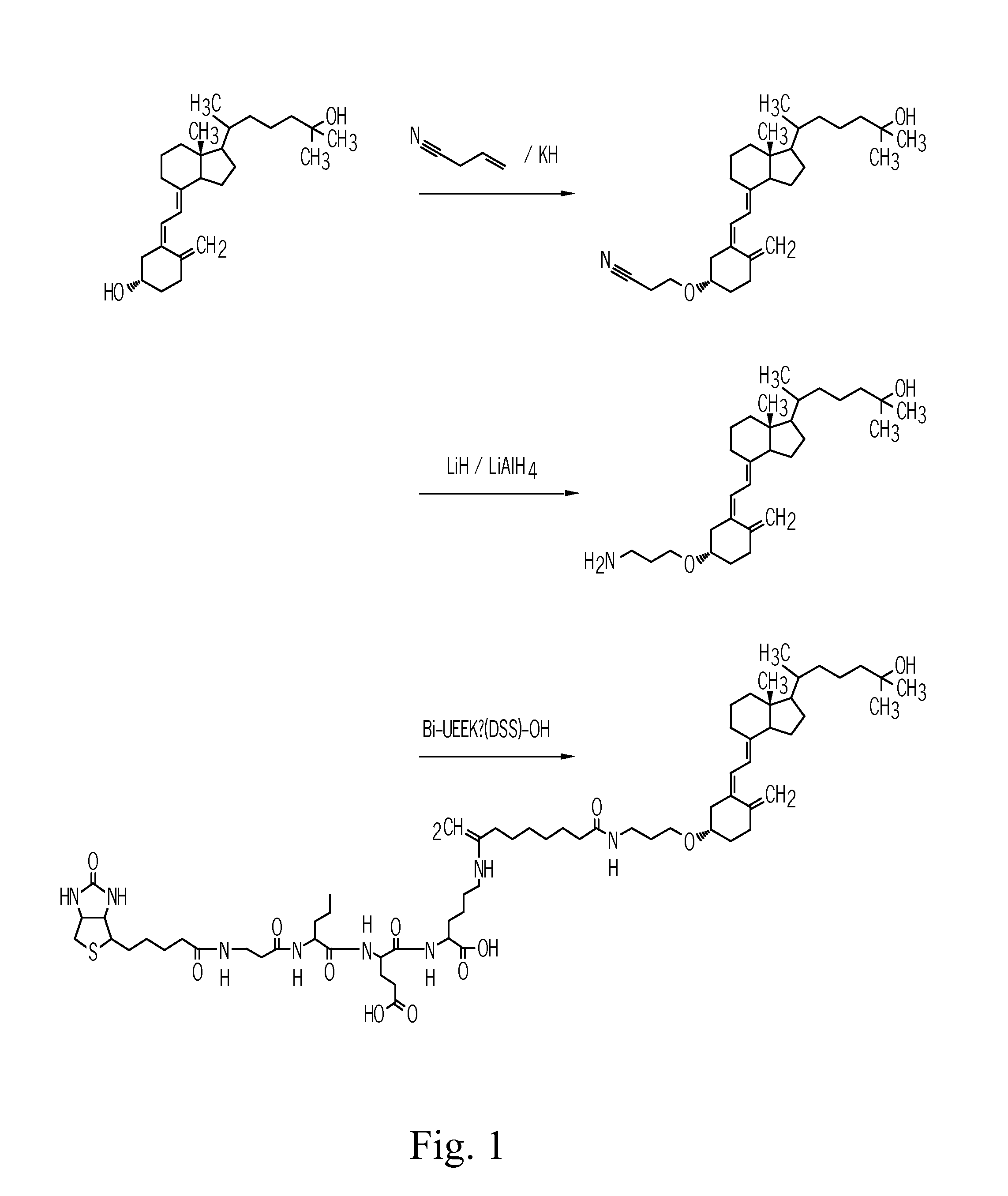
The invention provides carriers that enhance the absorption, half-life or bioavailability of therapeutic compounds. The carriers comprise targeting groups that bind the Vitamin D Binding protein (DBP), conjugation groups for coupling the targeting groups to the therapeutic compounds, and optionally scaffolding moieties.
Owner:EXTEND BIOSCI
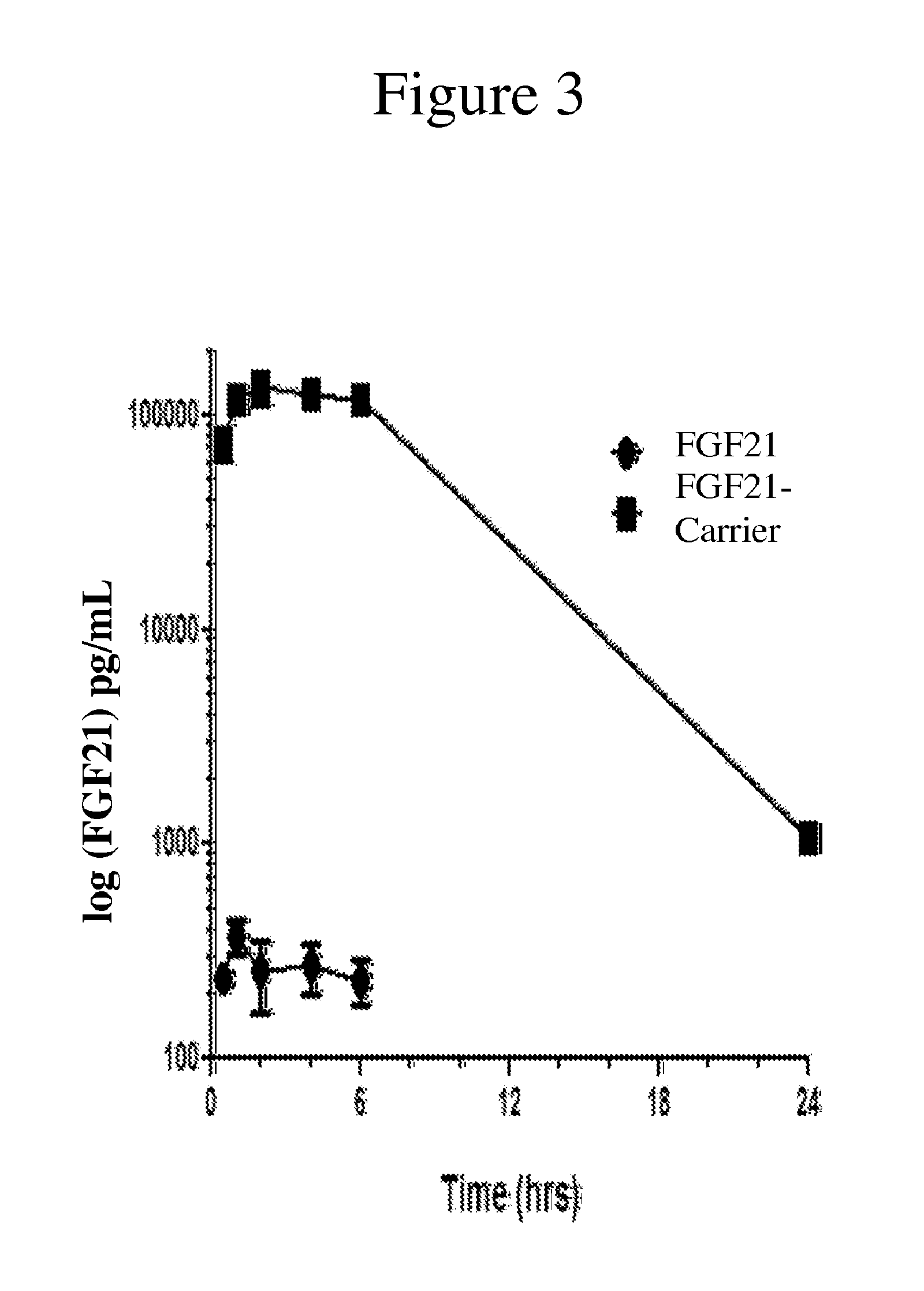
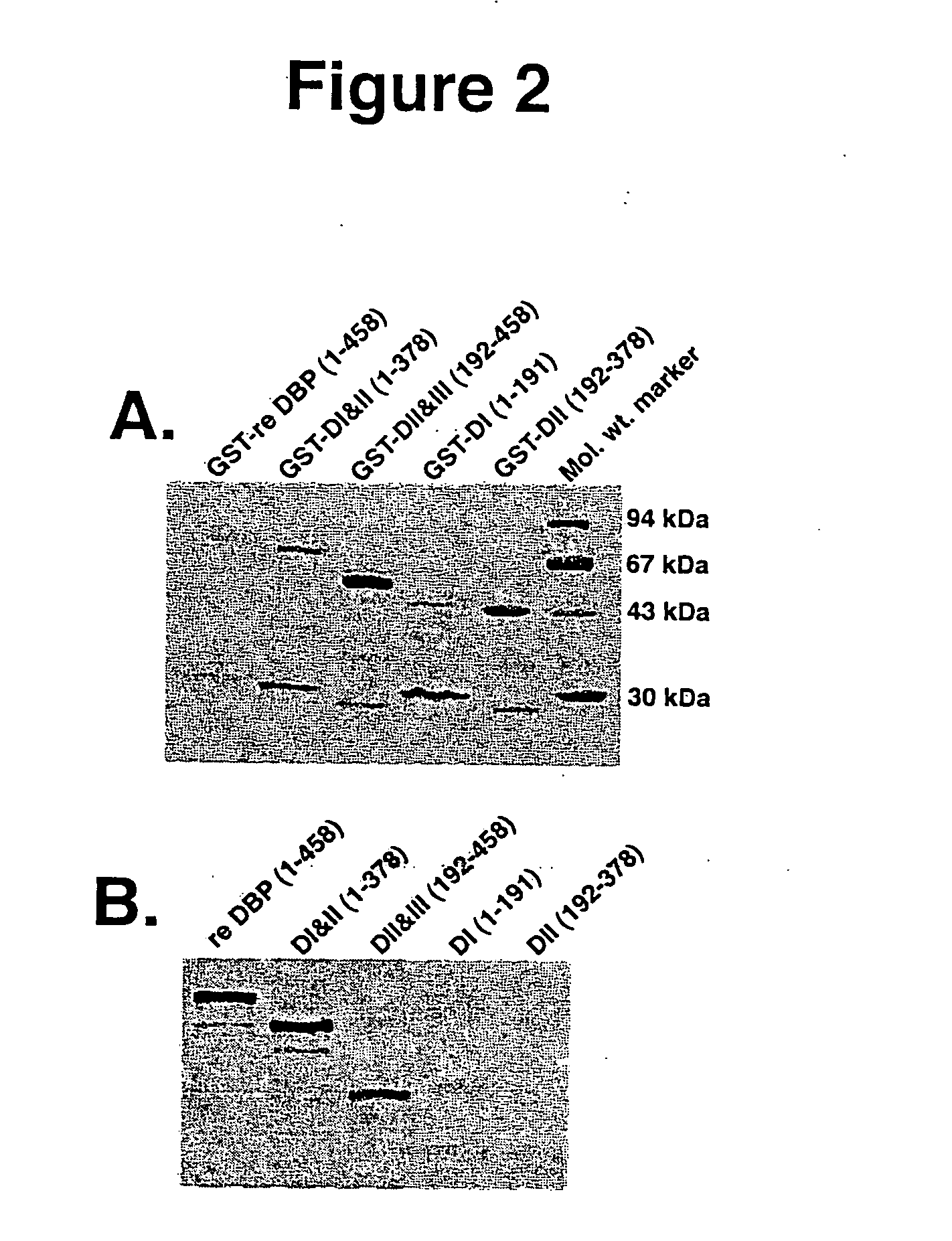
Antagonist peptides to the C5A chemotactic function of vitamin D binding protein
It has been demonstrated that one of Vitamin D Binding Protein (DBP) biological functions is to enhance the chemotactic activity of C5a and C5a des Arg. The present invention has found that peptides having sequences that substantially correspond to a specific region in the N-terminal domain I of DBP can block the DBP enhancement of C5a or C5a des Arg chemotactic activity. Based in this discovery the present invention provides DBP antagonist peptides and the use thereof for the treatment C5a or C5a des Arg-mediated disorders.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
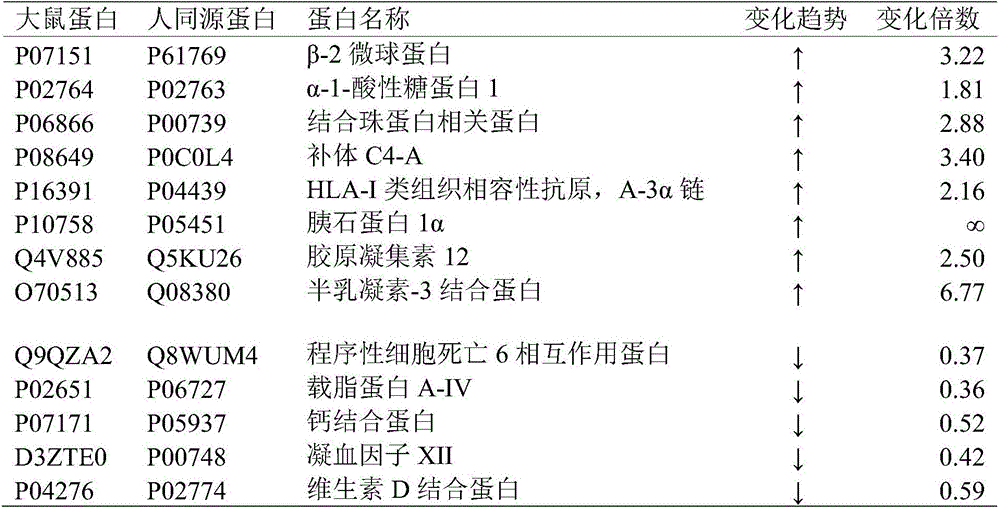
Urine protein marker of breast cancer and applications thereof in diagnosis and prognosis
The invention relates to a urine protein marker of breast cancer and applications thereof in diagnosis and prognosis. Specifically, the invention relates to applications of the urine protein marker of breast cancer in early diagnosis and disease monitoring of human breast cancer. The urine protein marker comprises beta-2 microglobulin, alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1, programmed cell death 6 interacting protein, haptoglobin related protein, addiment C4-A, apolipoprotein A-IV, calcium binding protein, HLA-I histocompatibility antigen, A-3 alpha chain, pancreatic stone protein 1 alpha, blood coagulation factor XII, collectin 12, galectin-3 binding protein, vitamin D binding protein, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Serum Biomarkers for Diagnosing Liver Fibrosis and Method for Measuring the Same
InactiveUS20100323374A1Measured safely and accuratelyDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsDiseaseMulti analyte
Disclosed are serum biomarkers for diagnosing liver fibrosis and methods for measuring the same. The serum biomarkers obtained from human serum include alpha2-macroglobulin (“A2M”), vitamin D binding protein (“VDBP”), apolipoprotein AI (“ApoAI”). The methods involve with immunoassay using specific antibodies to detect the biomarkers, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (“ELISA”), radio immune assay (“RIA”) and flexible multi-analyte profiling (“xMAP”). ELISA, RIA or xMAP is used to measure changes of protein concentration for the specific protein biomarkers in serum for diagnosing liver fibrosis with suffering hepatitis B or C or other liver diseases. The measurement is safe and accurate. The method can be used before and after treatment of liver fibrosis. Thus, it is possible to achieve early diagnosis and treatment advocated in the preventive medicine.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Vitamin d-ghrelin conjugates
ActiveUS20150065420A1Promote absorptionImprove bioavailabilityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderCrystallographyHalf-life
The invention provides carriers that enhance the absorption, half-life or bioavailability of Ghrelin peptides. The carriers comprise targeting groups that bind the Vitamin D Binding protein (DBP), conjugation groups for coupling the targeting groups to the therapeutic compounds, and optionally scaffolding moieties.
Owner:EXTEND BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
InactiveUS20130316370A1Eliminate needEasy to adaptDisease diagnosisBiological testingWhite blood cellPancreatic hormone
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of Beta-nerve growth factor, Interleukin-17A, Follitropin subunit beta, Collagenase 3, Follistatin, Vitamin D Binding Protein, Islet amyloid polypeptide, Insulin C-peptide, Complement Factor H, Gastric inhibitory polypeptide, Glucagon-like peptide 1, Glucagon, Involucrin, Type II cytoskeletal Keratin-1 / Keratin-10, Type II cytoskeletal Keratin-6A / 6B / 6C, Osteocalcin, Lipopolysaccharide, Pancreatic prohormone, Peptide YY, Agouti-related protein, Ciliary neurotrophic factor, Appetite-regulating hormone, Transthyretin, Insulin receptor substrate 1, and NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker assays in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Purification process for large scale production of Gc-globulin, the Gc-globulin produced hereby, a use of Gc-globulin and a Gc-globulin medicinal product
InactiveUS6921808B2High yieldHigh purityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPurification methodsPlasma derived
A purification process for large-scale production of Gc-globulin is described. The source of Gc-globulin is preferably a crude plasma fraction but can be any solution, suspension or supernatant containing Gc-globulin, e.g., a milk product, colostrum or a fermentation broth. The Gc-globulin can be plasma-derived or produced by a genetic modified organism. The process includes two key elements: purification by series of ion exchange chromatography steps, and performing at least two virus-reduction steps. A diagnostic method to measure the free Gc-globulin in a patient blood sample, a use of Gc-globulin in medicine and the preparation of a Gc-globulin medicinal product is also provided. The product can be used in therapy for patients with circulatory disorders and complications, i.e., where it is contemplated that patients would benefit from the administration of Gc-globulin.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Release reagent for vitamin d compounds
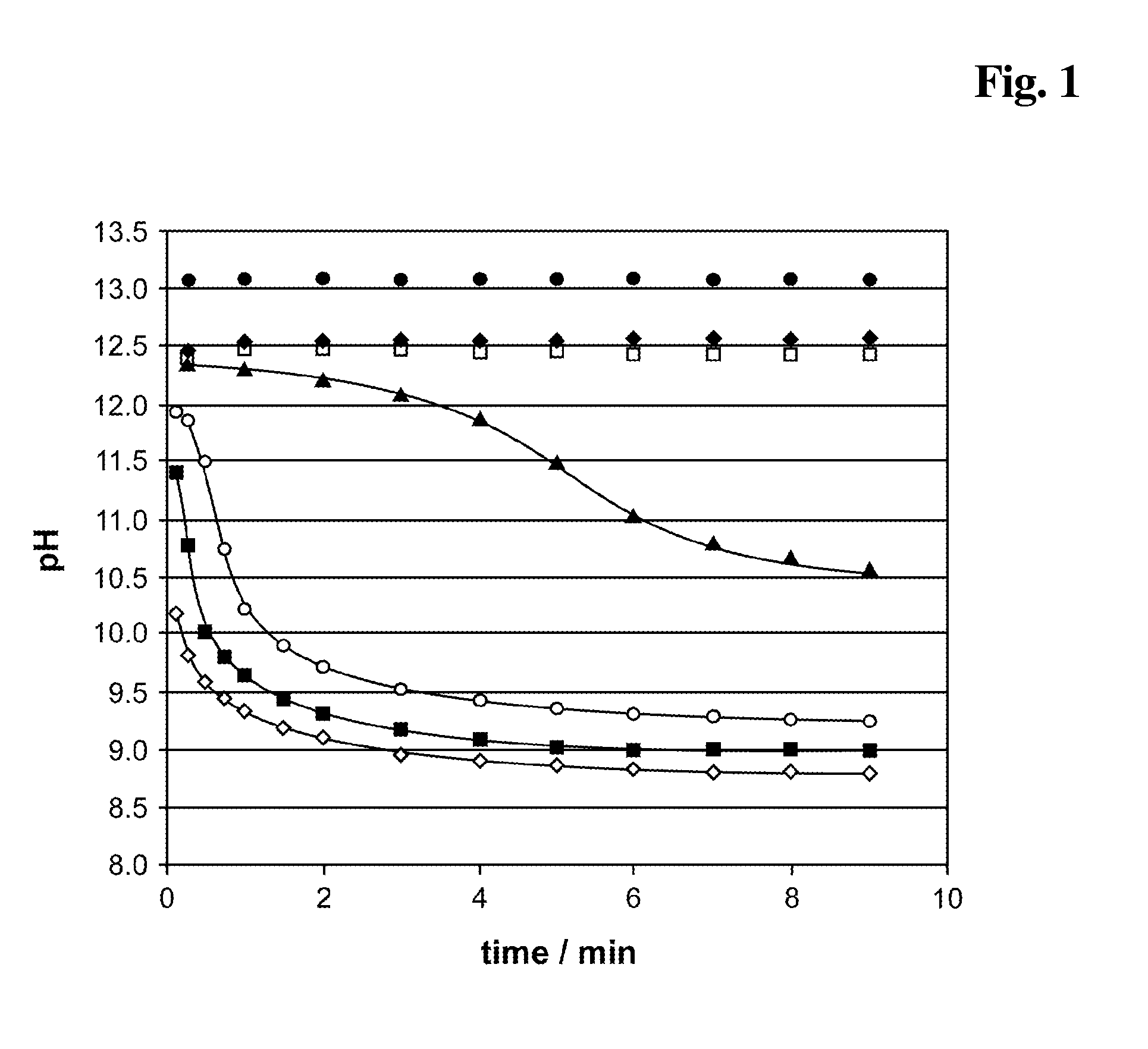
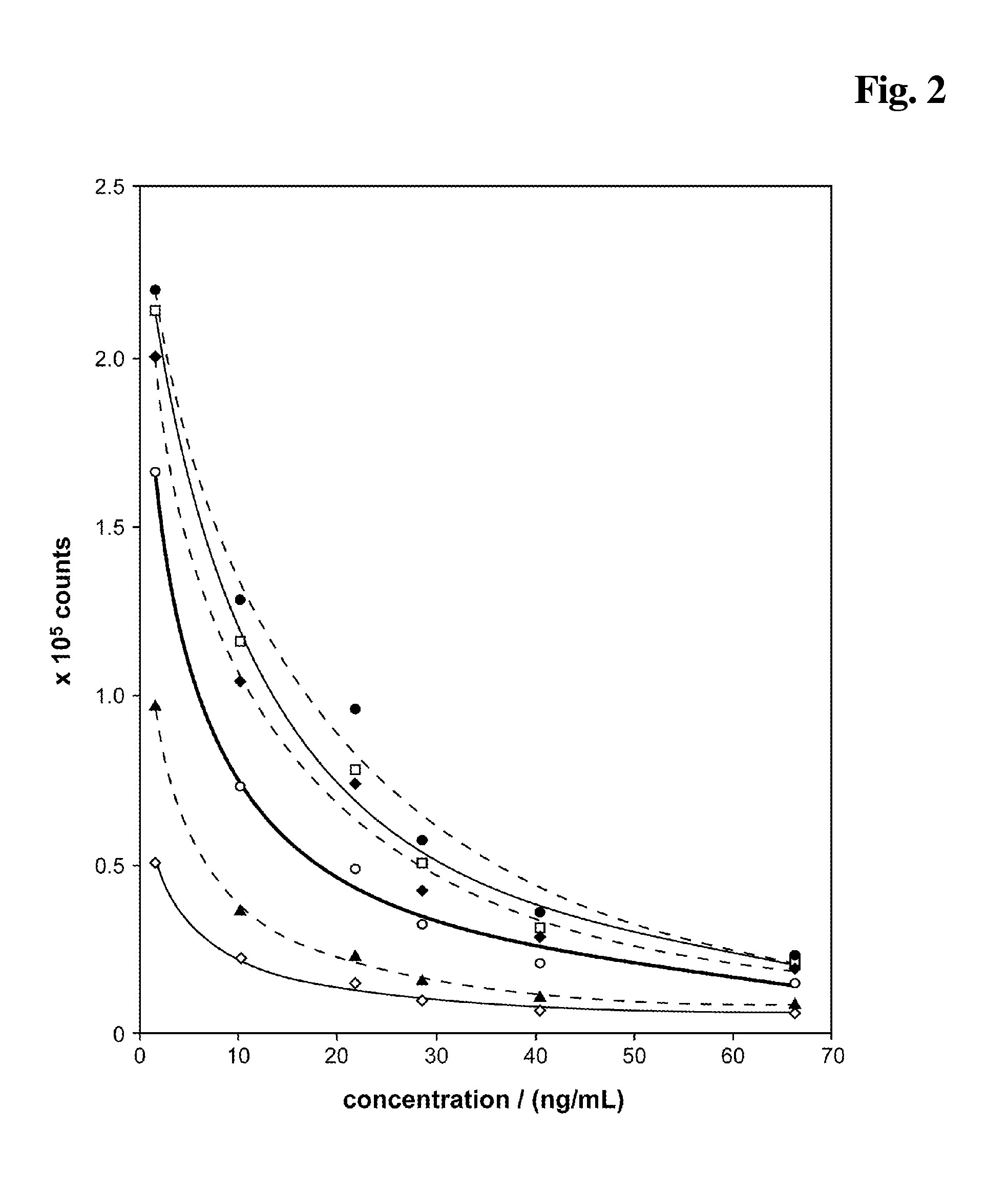
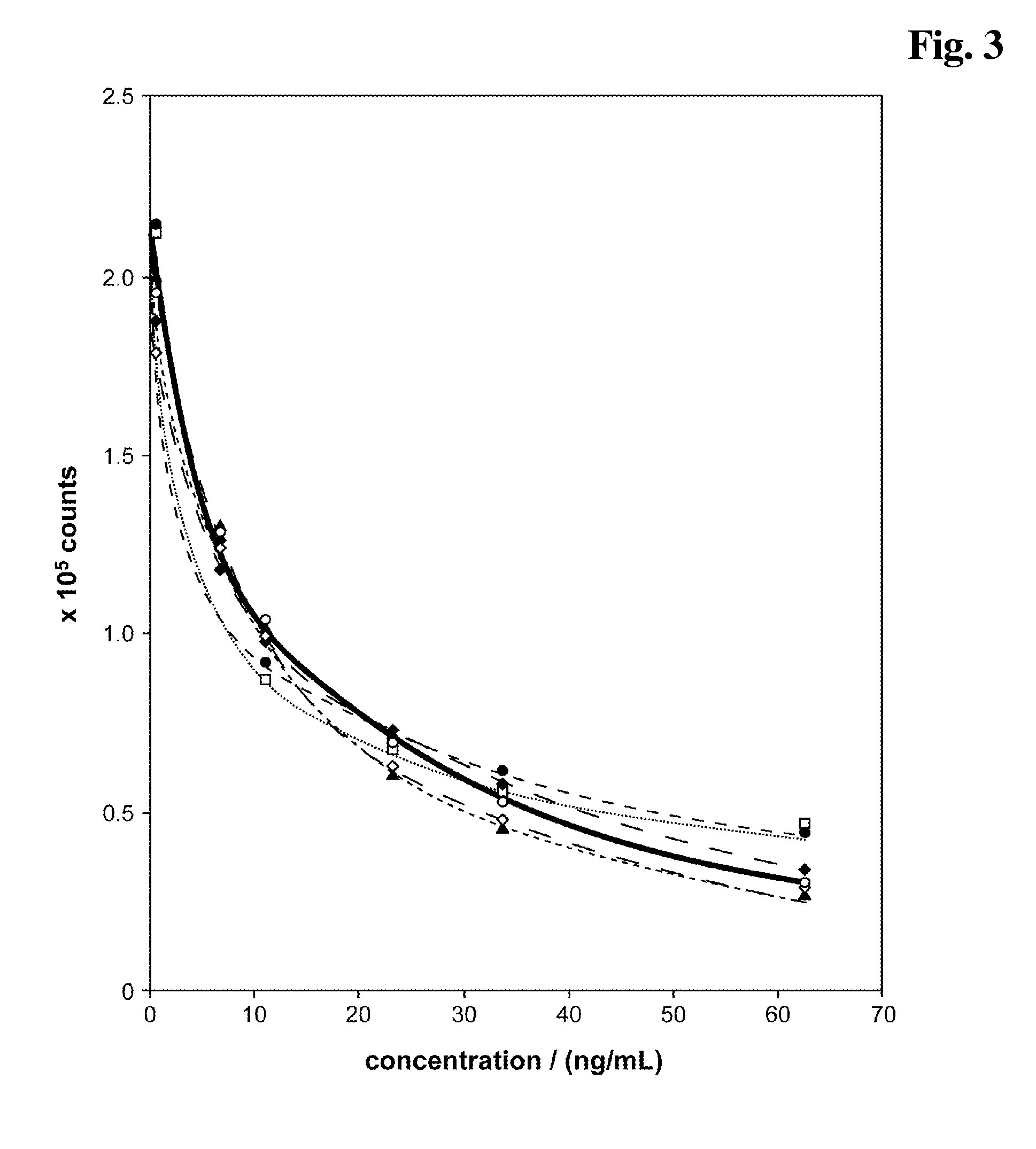
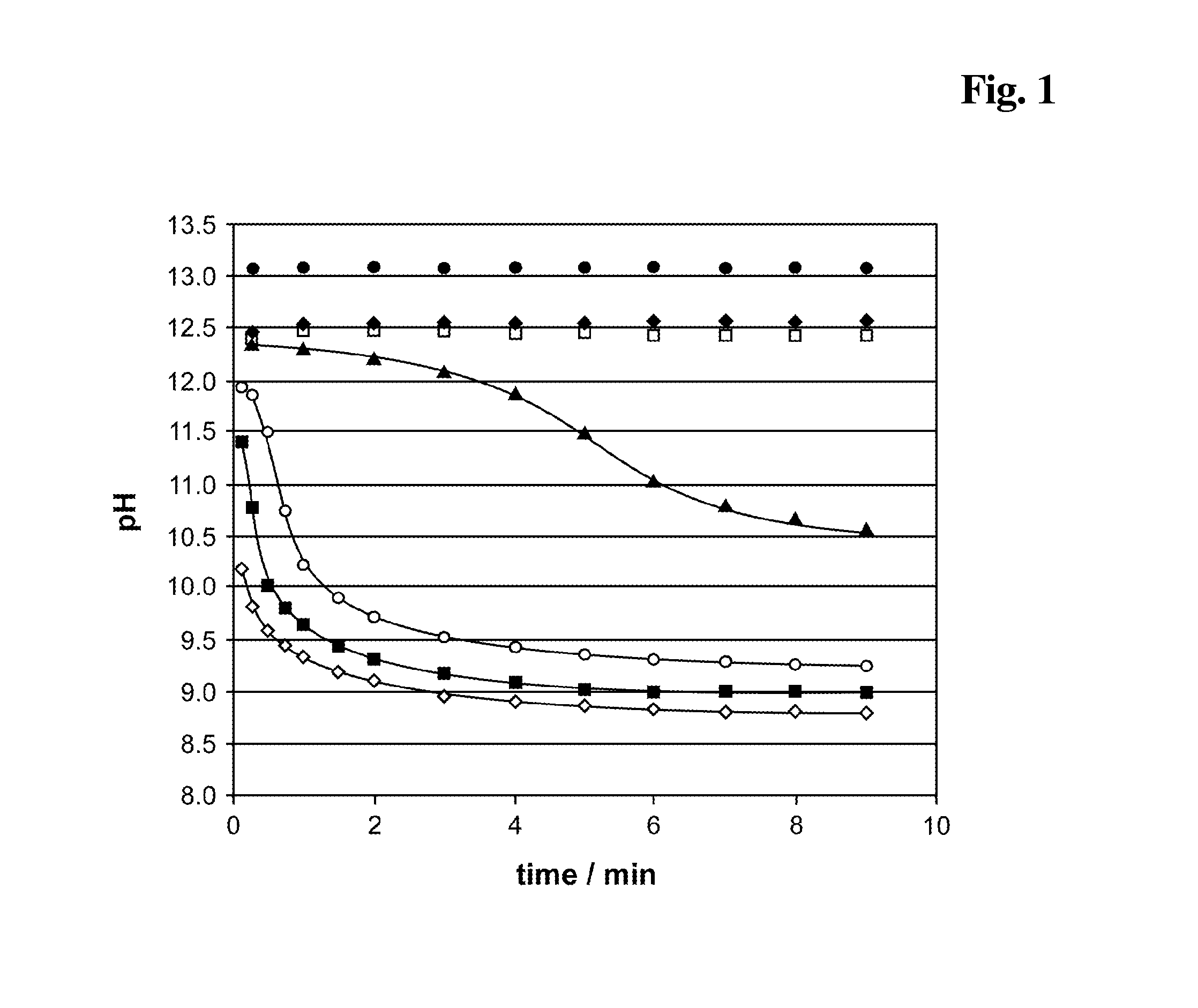
InactiveUS20140248707A1Slower pH reduction of the reagent mixtureFaster pH reduction of the reagent mixtureOrganic chemistryBiological testingGC globulinReagent
A reagent composition for releasing vitamin D compounds bound to vitamin D-binding protein and an in vitro method for the detection of a vitamin D compound in which the vitamin D compound is released from vitamin D-binding protein by the use of this reagent composition as well as the reagent mixture obtained in this manner. Also disclosed is the use of the reagent compositions to release vitamin D compounds as well as a kit for detecting a vitamin D compound.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Vitamin D binding peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN106220710ARealize quantitative detectionImmunoglobulinsBiological testingAntigenBinding peptide
The invention discloses a vitamin D binding peptide and application thereof. Sequence motif of the vitamin D binding peptide is LFLLLF. The vitamin D binding peptide and the application have the advantages that the vitamin D binding peptide can be used as an antigen for effectively inducing antibodies for vitamin D binding proteins, accordingly, the vitamin D binding proteins can be accurately quantified, and the in-vivo vitamin D contents can be quantitatively detected.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MILITARY COMMAND
Method for diagnosing multiple sclerosis
The present invention relates to methods for diagnosing multiple sclerosis in a subject, the method, comprising determining the level of phosphorylation of a marker in a biological sample from the subject, wherein the marker is selected from a1-antitrypsin (a1AT) and vitamin D binding protein (VDBP); and comparing the level of phosphorylation of the marker in the sample to a reference value.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Determination of alpha-N-acetamino galactosidase activity
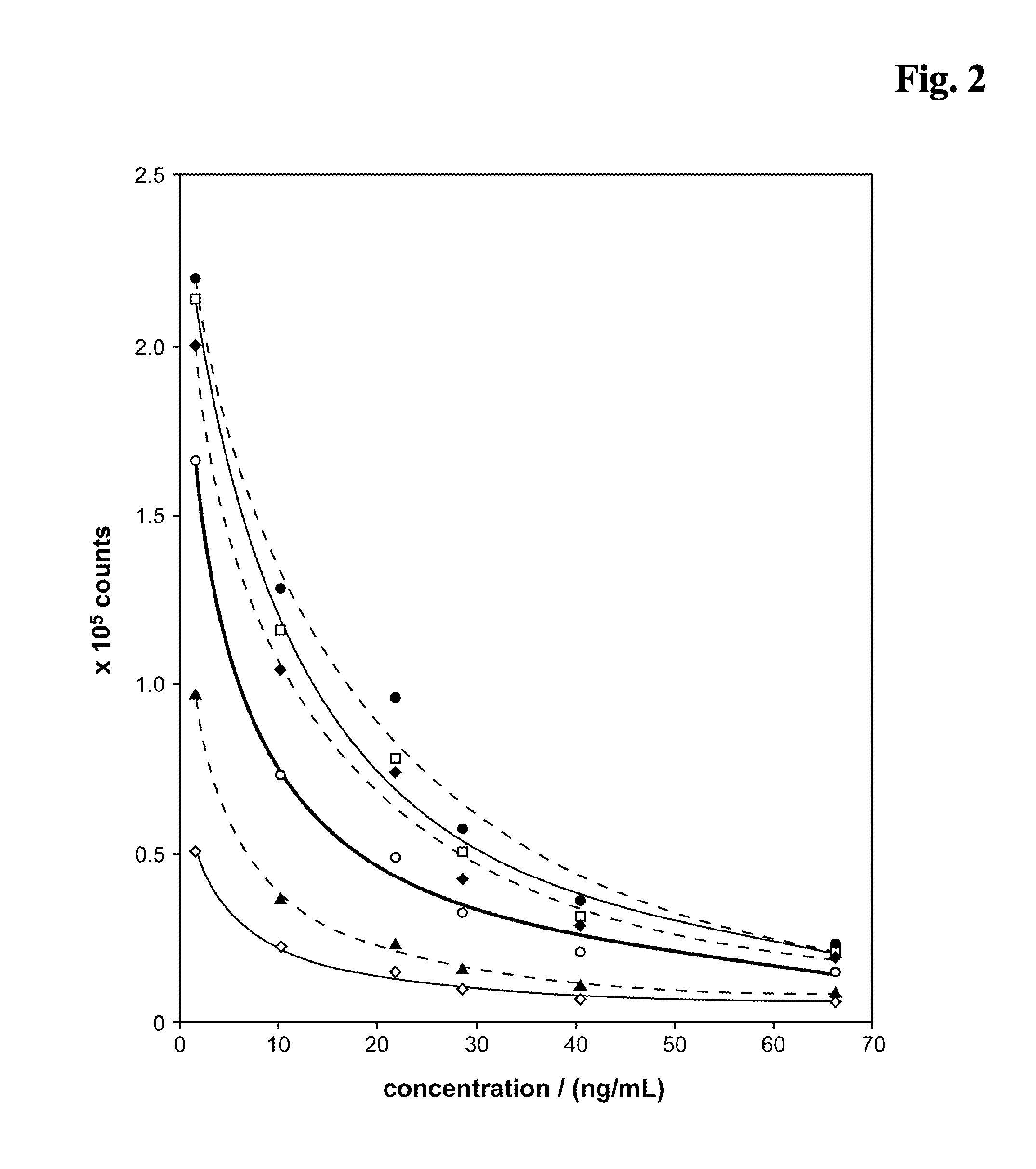
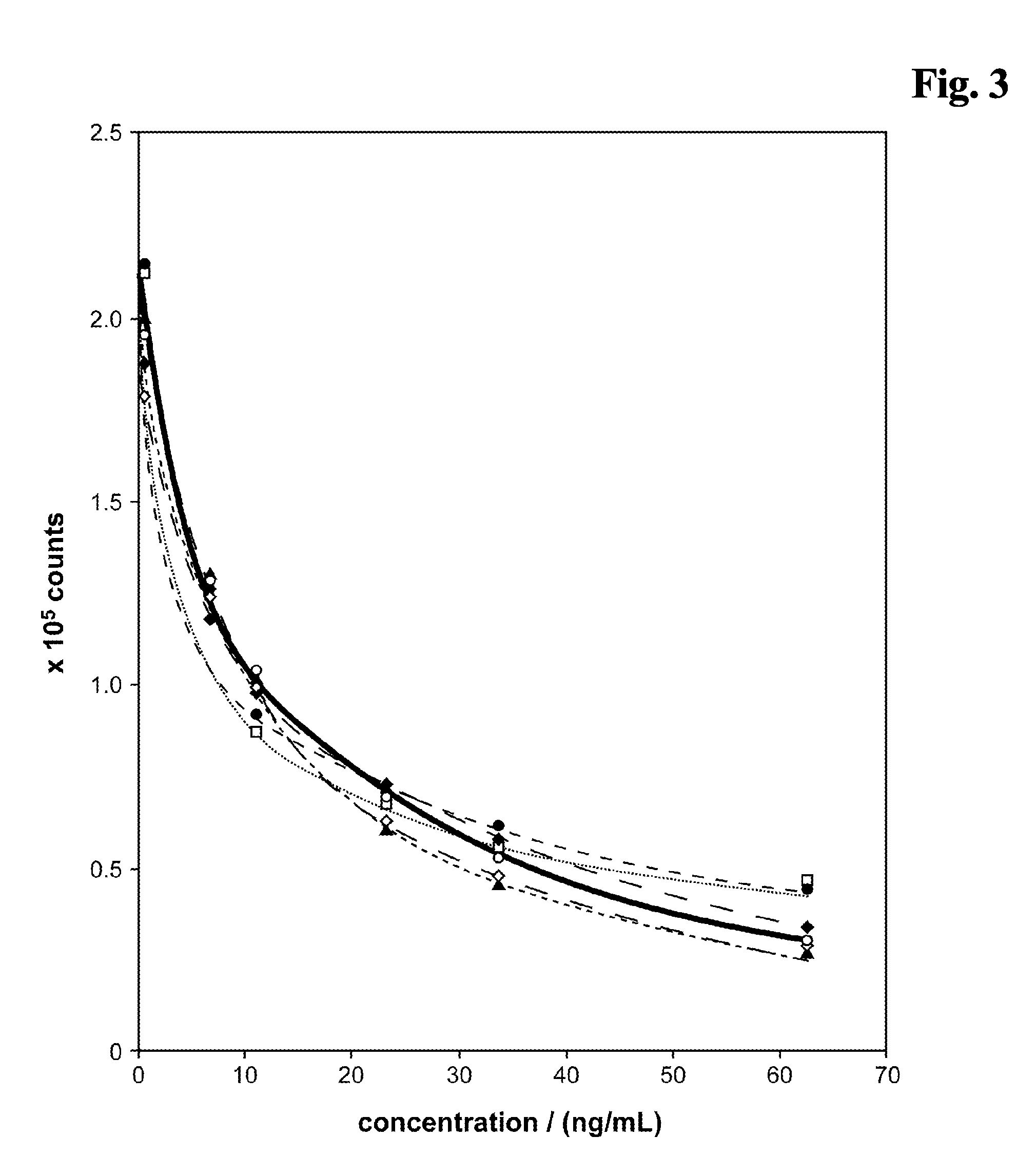
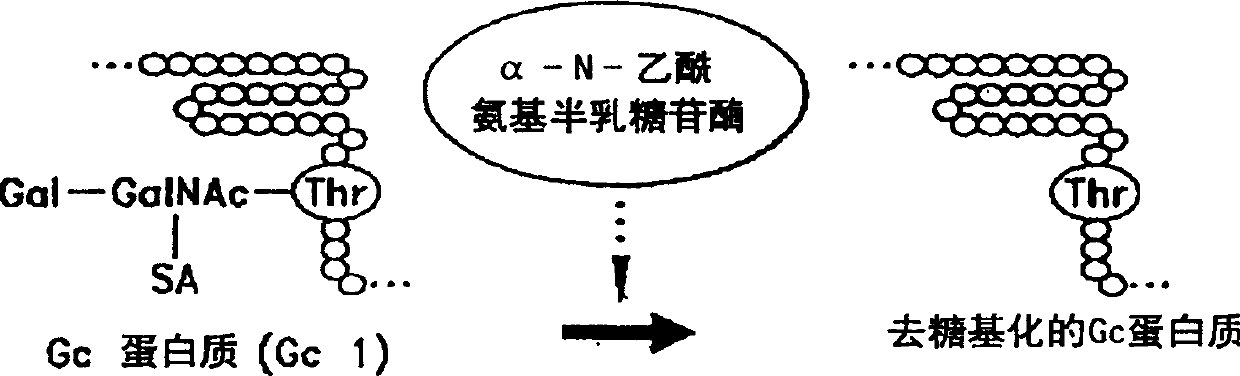
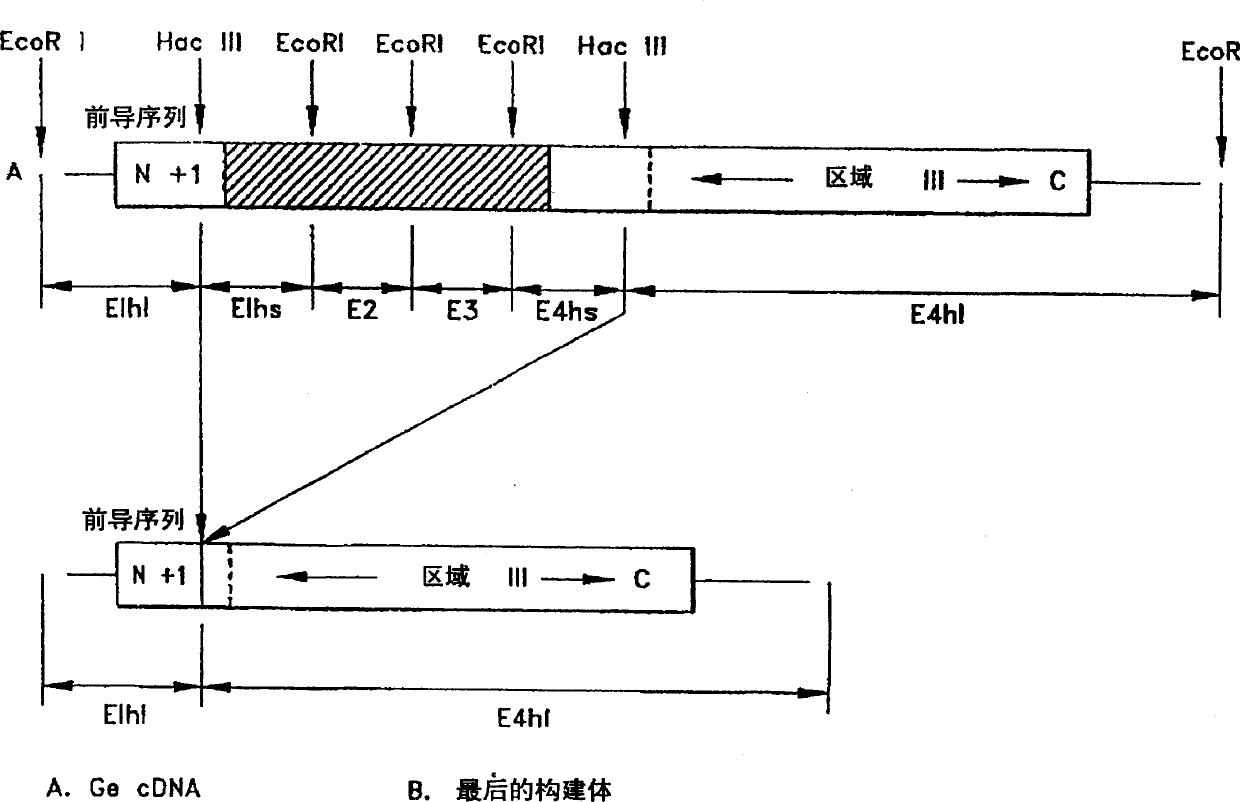
The vitamin D binding protein (Gc protein) and its small region (approximately 1 / 5 of the Gc peptide, known as region III) were cloned with the aid of baculovirus vectors. The cloned Gc protein and cloned domain (Cd) peptide were treated with immobilized β-galactosidase and sialidase to produce macrophage activating factors GcMAFc and CdMAF, respectively. These cloned macrophage activating factors and GcMAFs can be used to treat cancer, HIV infection, and osteoporosis, as well as as adjuvants for immunization and vaccination. Methods and antibody-sandwich ELISA kits for detecting serum or plasma α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity in patients with cancer and HIV infection were developed.
Owner:山本信人
Biomarkers for gastric cancer and uses thereof
The present invention provides biological markers associated with gastric cancer. In particular, the present invention provides a method of diagnosing gastric cancer (GC) in a subject, the method including: measuring an expression level of one or more proteins in the subject, wherein the one or more proteins are selected from the group consisting of vitamin D binding protein (VDBP), clusterin, insulin like growth factor binding protein complex acid labile subunit (IGFALS), and afamin; comparing the expression level of the or each protein in the subject to a reference expression level for the or each protein; and diagnosing GC in the subject on the basis of the comparison. On the basis of the identification of biological markers associated with gastric cancer, the present invention also provides a method of determining if a subject is susceptible to developing gastric cancer, a method of assessing progression of gastric cancer in a subject, a method for screening a candidate therapeutic agent useful for treating gastric cancer in a subject, and a kit for diagnosing gastric cancer in a subject.
Owner:ADELAIDE RES & INNOVATION PTY LTD
Release reagent for vitamin d compounds
InactiveUS20130078729A1Biological testingDetection of post translational modificationsGC globulinReagent
A reagent composition for releasing vitamin D compounds bound to vitamin D-binding protein, an in vitro method for the detection of a vitamin D compound in which the vitamin D compound is released from vitamin D-binding protein by the use of this reagent composition and the reagent mixture obtained in this manner. The use of the disclosed reagent composition to release vitamin D compounds as well as a kit for detecting a vitamin D compound which contains the reagent composition for releasing vitamin D compounds in addition to common detecting reagents.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Release reagent for vitamin d compounds
ActiveUS20150104876A1Preparing sample for investigationImmunoglobulinsGC globulinVitamin D+Metabolites
The present invention concerns a reagent composition for releasing vitamin D compounds bound to vitamin D-binding protein, a method for the detection of a 25-hydroxyvitamin D compound in which the 25-hydroxyvitamin D compound is released from vitamin D-binding protein using this reagent and the mixture obtained in this manner is analyzed, the use of the reagent to release vitamin D compounds as well as a kit for detecting 25-hydroxyvitamin D which contains the reagent for releasing vitamin D compounds in addition to the usual immunological reagents.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Release reagent for vitamin d compounds
InactiveUS20150024506A1Biological testingDetection of post translational modificationsGC globulinReagent
A reagent composition for releasing vitamin D compounds bound to vitamin D-binding protein, an in vitro method for the detection of a vitamin D compound in which the vitamin D compound is released from vitamin D-binding protein by the use of this reagent composition and the reagent mixture obtained in this manner. The use of the disclosed reagent composition to release vitamin D compounds as well as a kit for detecting a vitamin D compound which contains the reagent composition for releasing vitamin D compounds in addition to common detecting reagents.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Multiplexed biomarkers for monitoring the Alzheimer's disease state of a subject
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing a subject's Alzheimer's disease state. The method involves providing a database containing information relating to protein expression levels associated and not associated with Alzheimer's disease. The database includes information relating to at least a majority of the following proteins: albumin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, apolipoprotin E, apolipoprotein J, complement component 3, contactin, fibrin beta, Ig heavy chain, Ig light chain, neuronal pentraxin receptor, plasminogen, proSAAS, retinol-binding protein, transthyretin, and vitamin D binding protein. Information relating to proteins found in one or more cerebrospinal fluid samples from a subject is also provided and a database is used to analyze the information from the subject to diagnose the subject's Alzheimer's disease state. Also disclosed is a computer readable medium and a system, both useful in carrying out the present invention.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
25-hydroxyvitamin D content measurement method
ActiveCN110441537AEasy to operateShort timeBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceGC globulinProtein C
The invention relates to the technical field of analysis and detection, and in particular relates to a 25-hydroxyvitamin D content measurement method. According to the method, 25-hydroxyvitamin D is dissociated from vitamin D binding protein in a biological sample through a dissociation liquid; the dissociation liquid is mild in components and free of damage to an antibody; therefore the biological sample, the dissociation liquid and a fluorescent microsphere working solution can be jointly incubated, so that an anti-25-hydroxyvitamin D antibody in the fluorescent microsphere working solutionis fully combined with the 25-hydroxyvitamin D dissociated from the biological sample, the sensitivity can be effectively improved, and the linear range is 3-100 ng / mL.
Owner:BEIJING DIAGREAT BIOTECH CO LTD
In vitro diagnostic and prognosis of major adverse events in patients undergoing coronary angiography
Method of diagnosis and prognosis of contrast media induced nephropathy (CIN) including the steps of i) taking a urine sample from a patient exposed to the application of contrast media, notably patients subjected to coronary angiography; ii) assessing the level of vitamin D binding protein (VDBP) in the urine sample obtained in step (i); iii) relating the urinary vitamin D binding protein level determined in step (ii) to a pre-selected threshold level. A urinary vitamin D binding protein level higher than the pre-selected threshold level indicates that the patient is at risk of renal failure and in need of a dialysis treatment.
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK
Agents and methods for promoting bone growth
InactiveUS7038010B2Assist in repairFacilitate depositionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWhole bodyBone growth
Agents for promoting bone deposition and growth in a mammalian subject. The agents are O-glycosylated and non-glycosylated peptides that are derived from vitamin D binding protein, collectively referred to hereinafter as “DBP” peptides. The DBP peptides are from 3 to 18, preferably from 4 to 14 amino acids in length and comprise a sequence which is at least 80% identical, preferably at least 90% identical to the amino acid sequence of a fragment contained within domain III of DBP. Methods for promoting bone deposition in a subject in need of the same are also provided. The methods comprise administering to the subject a therapeutically effective quantity of an agent selected from the group consisting of an activated form of vitamin D binding protein referred to hereinafter as “ADBP”, one or more DBP peptides, and combinations thereof. The agents may be administered locally or systemically.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com