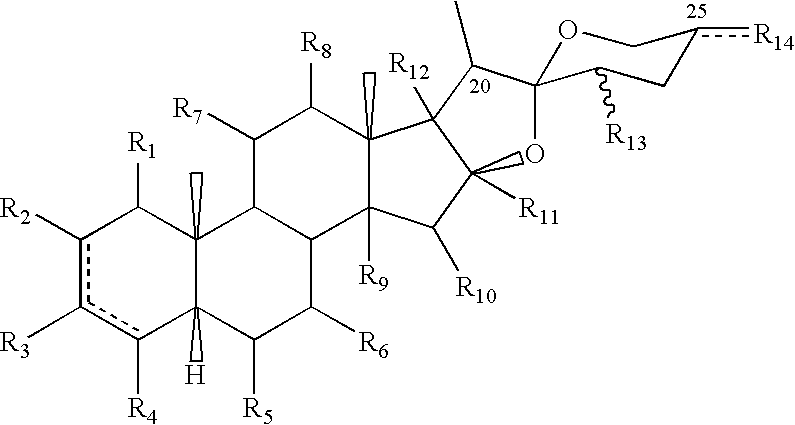
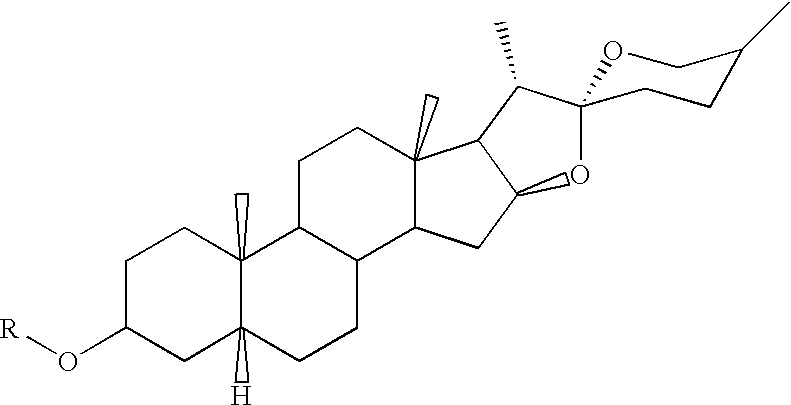
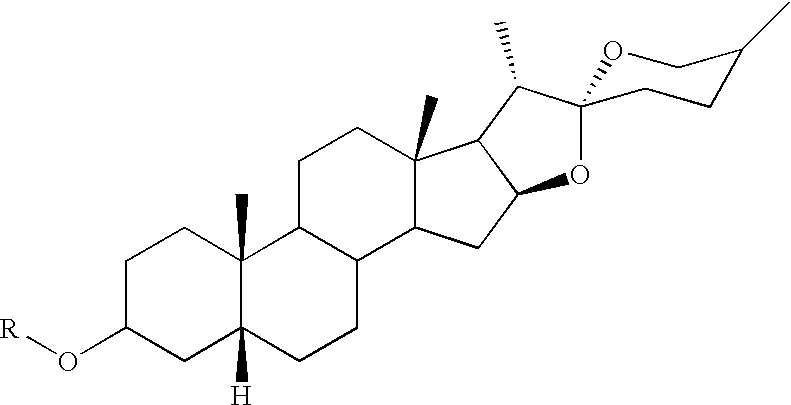
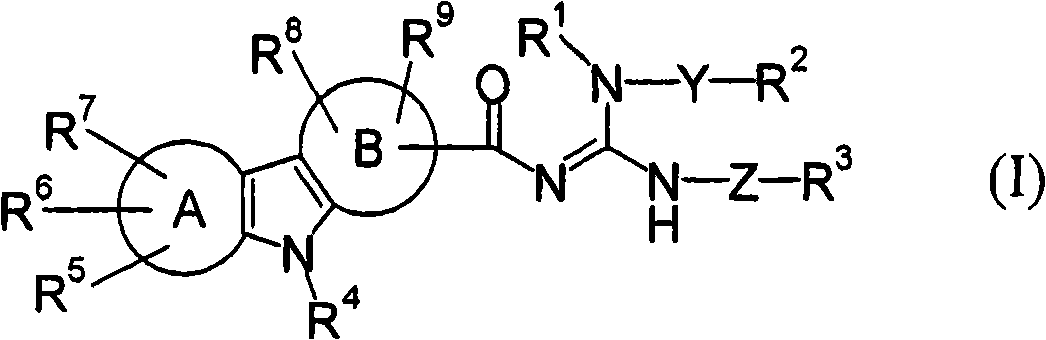
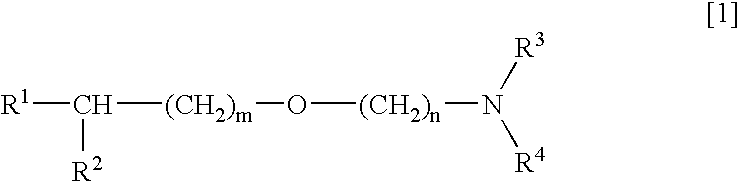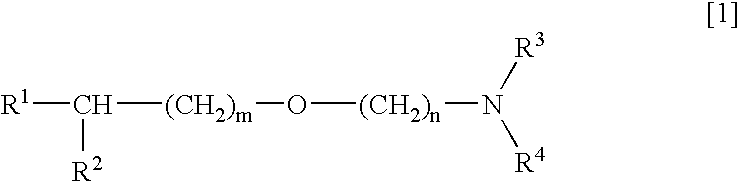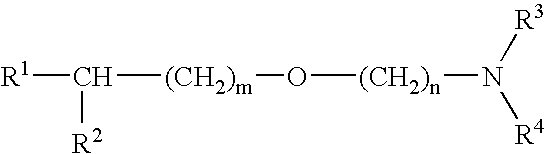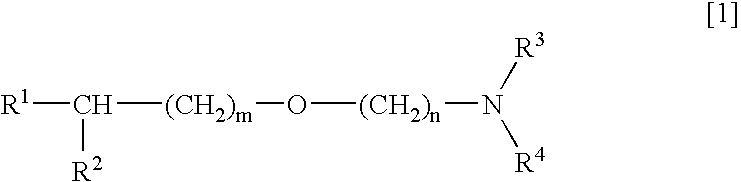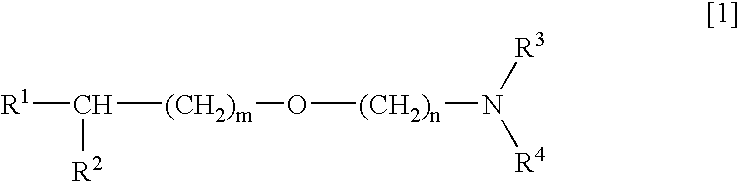Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Functional impairment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
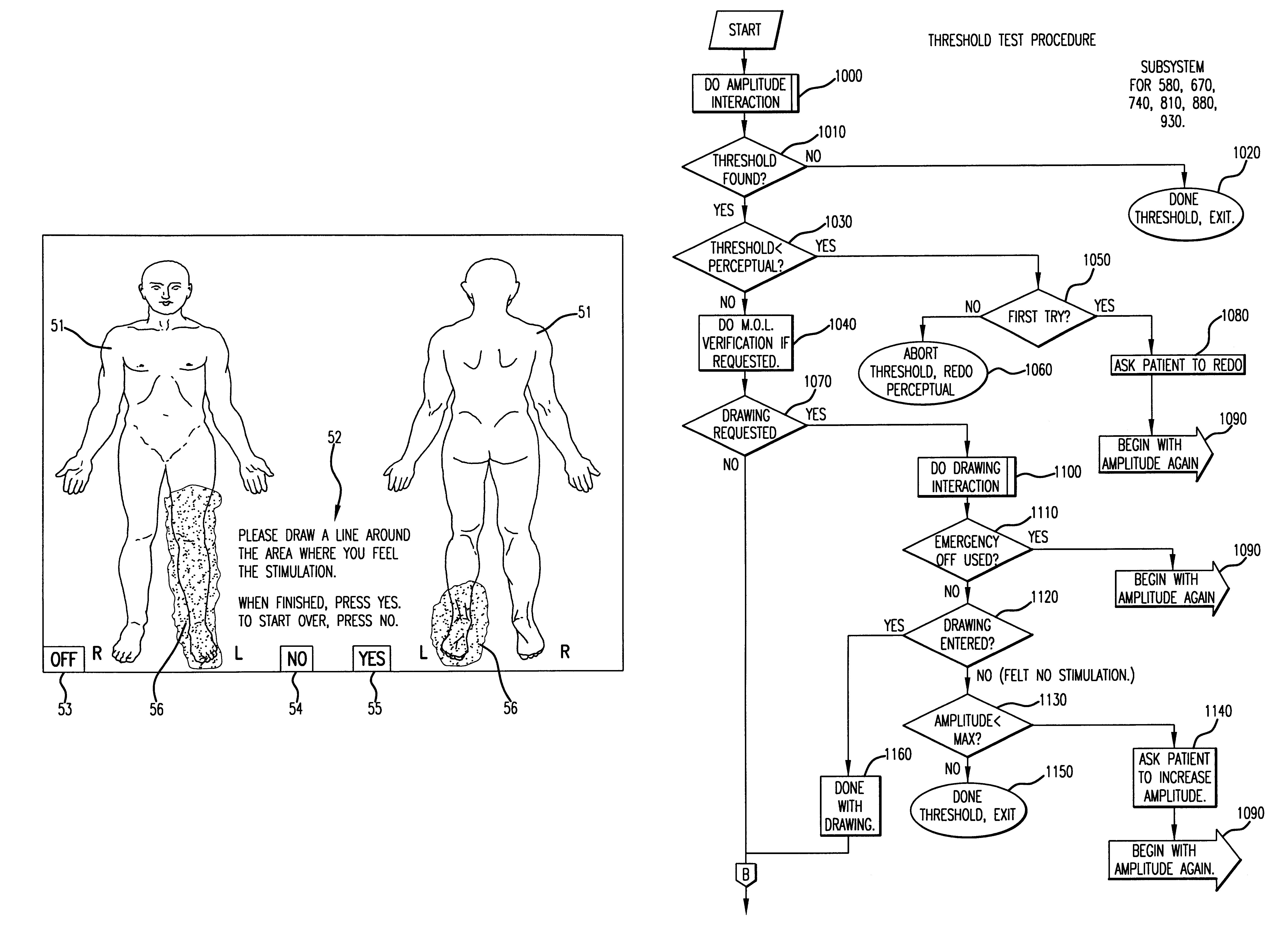
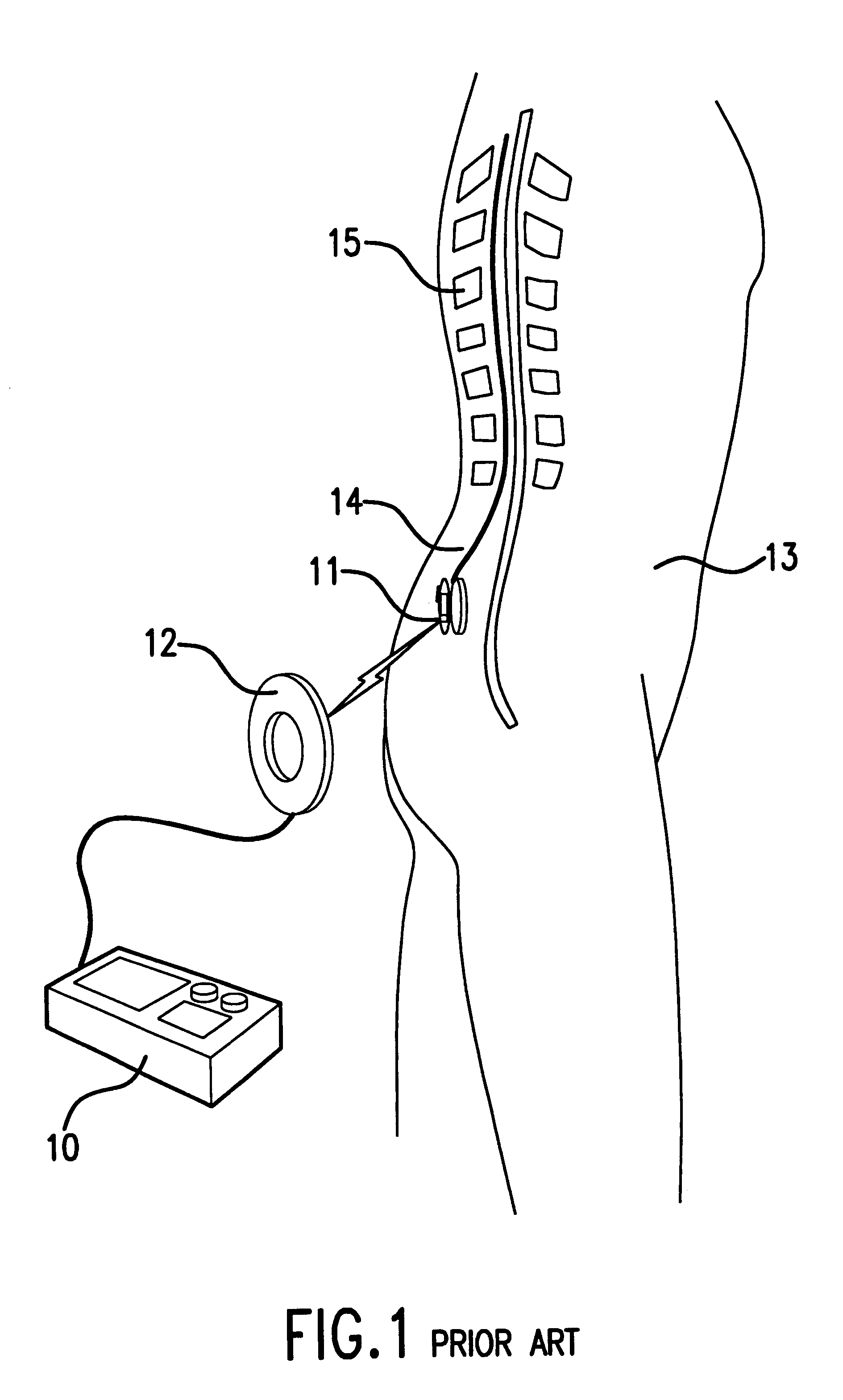
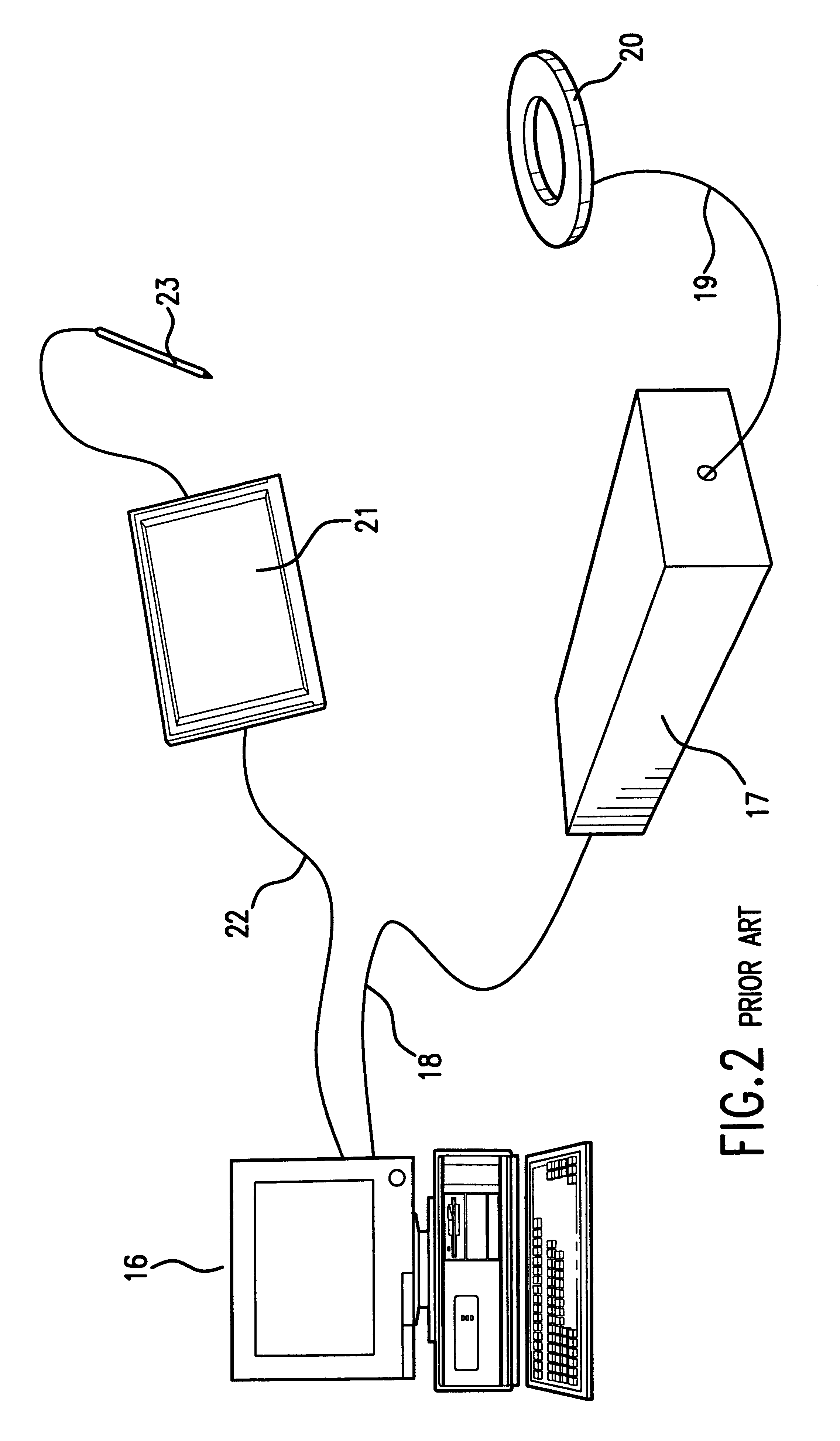
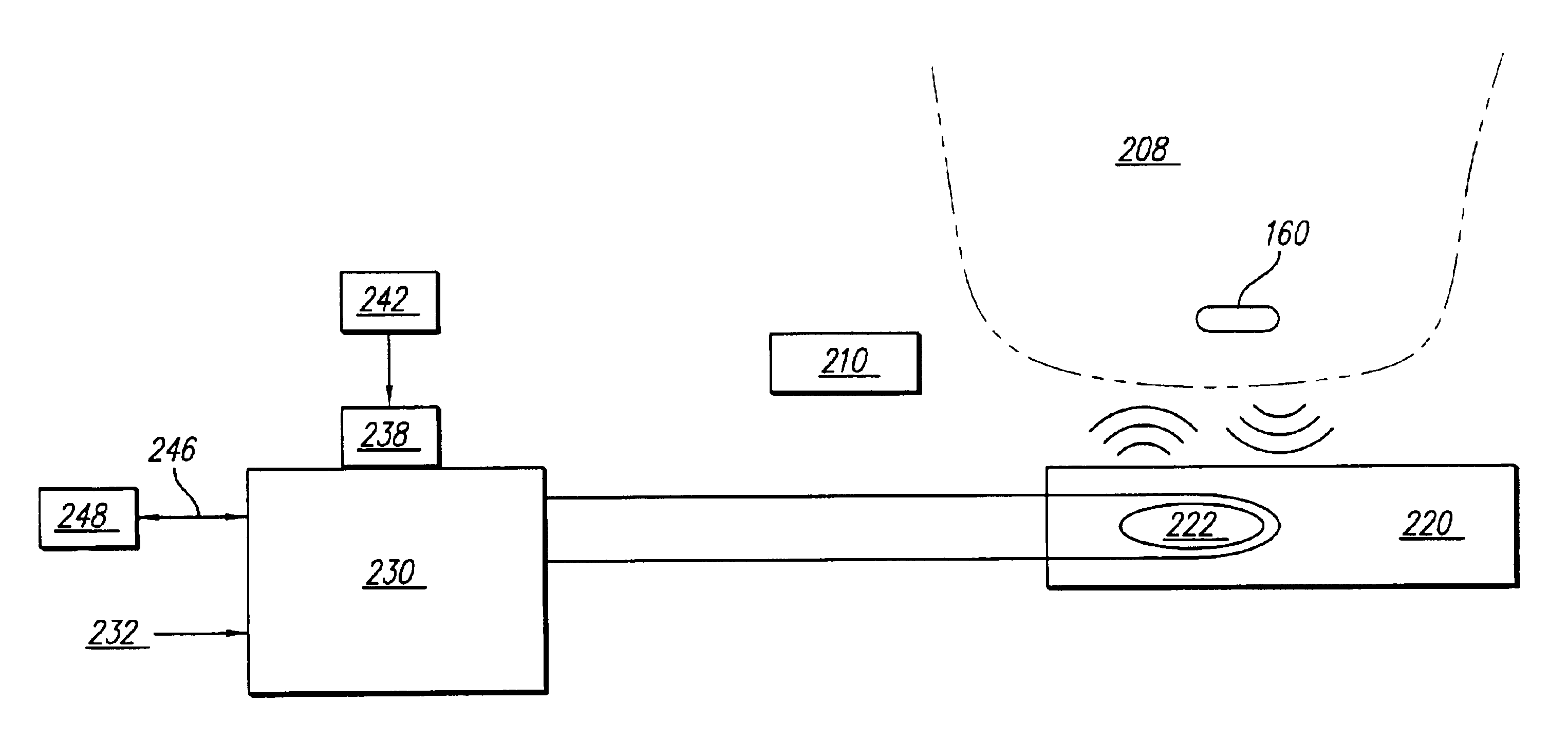
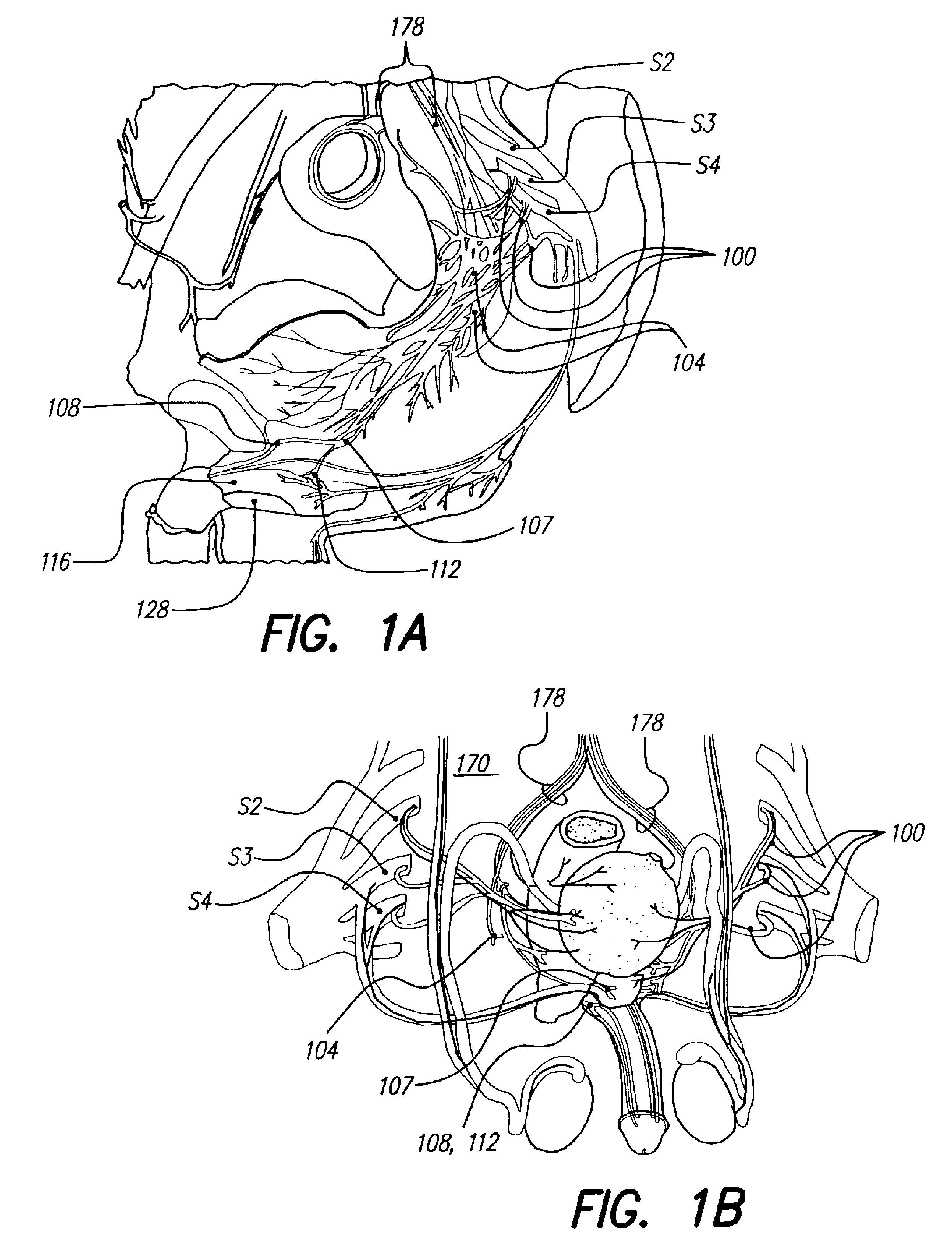
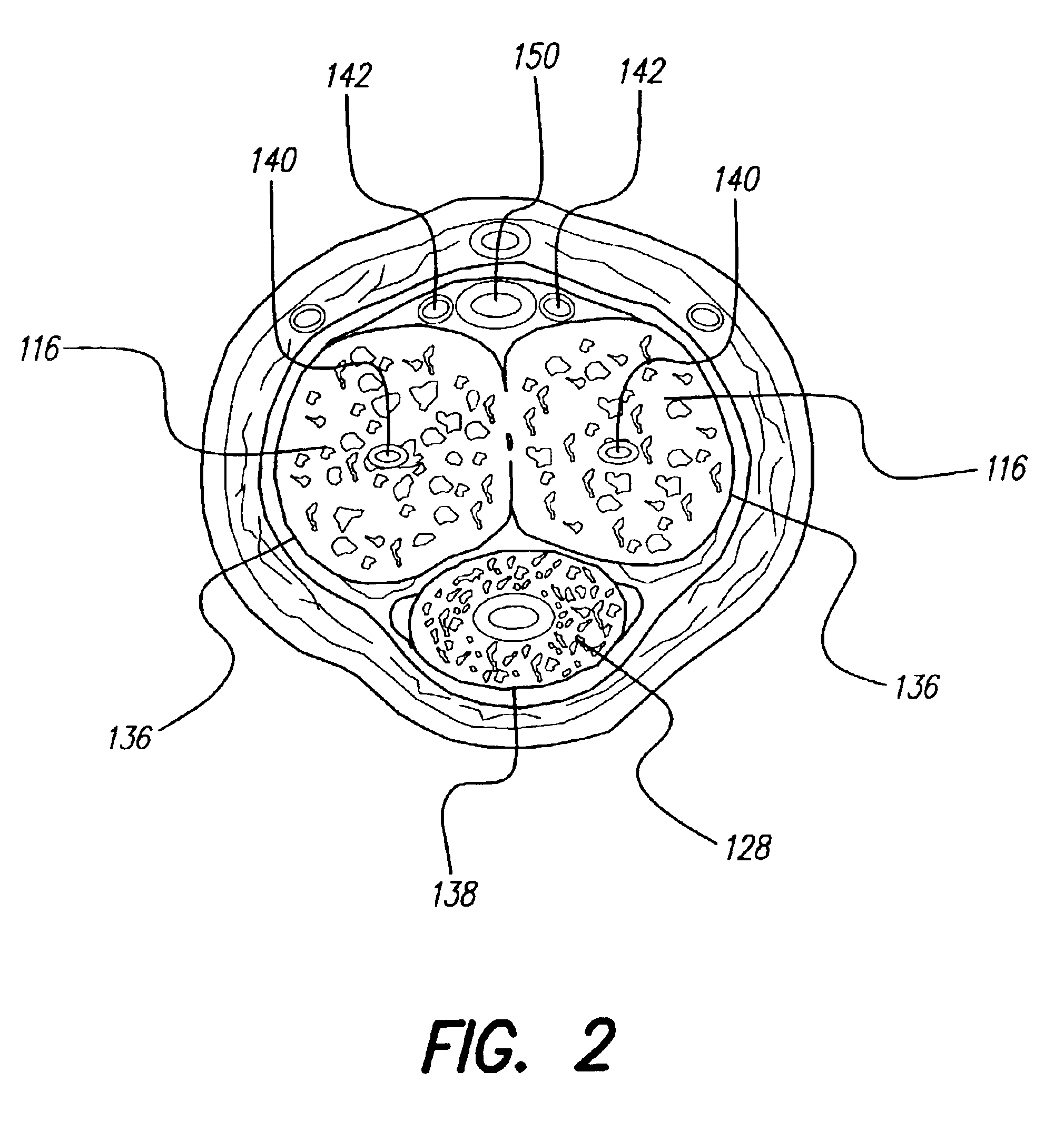
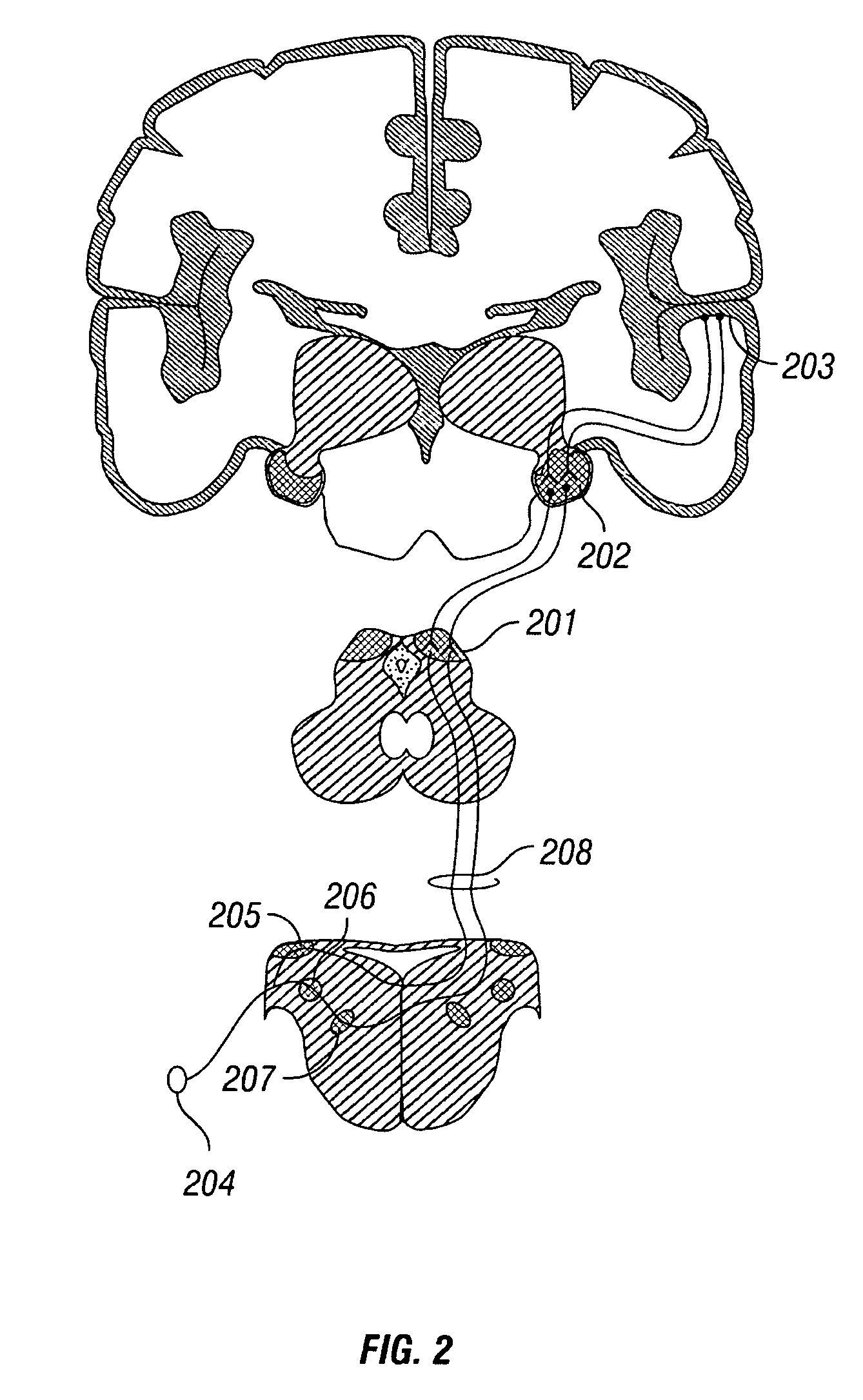
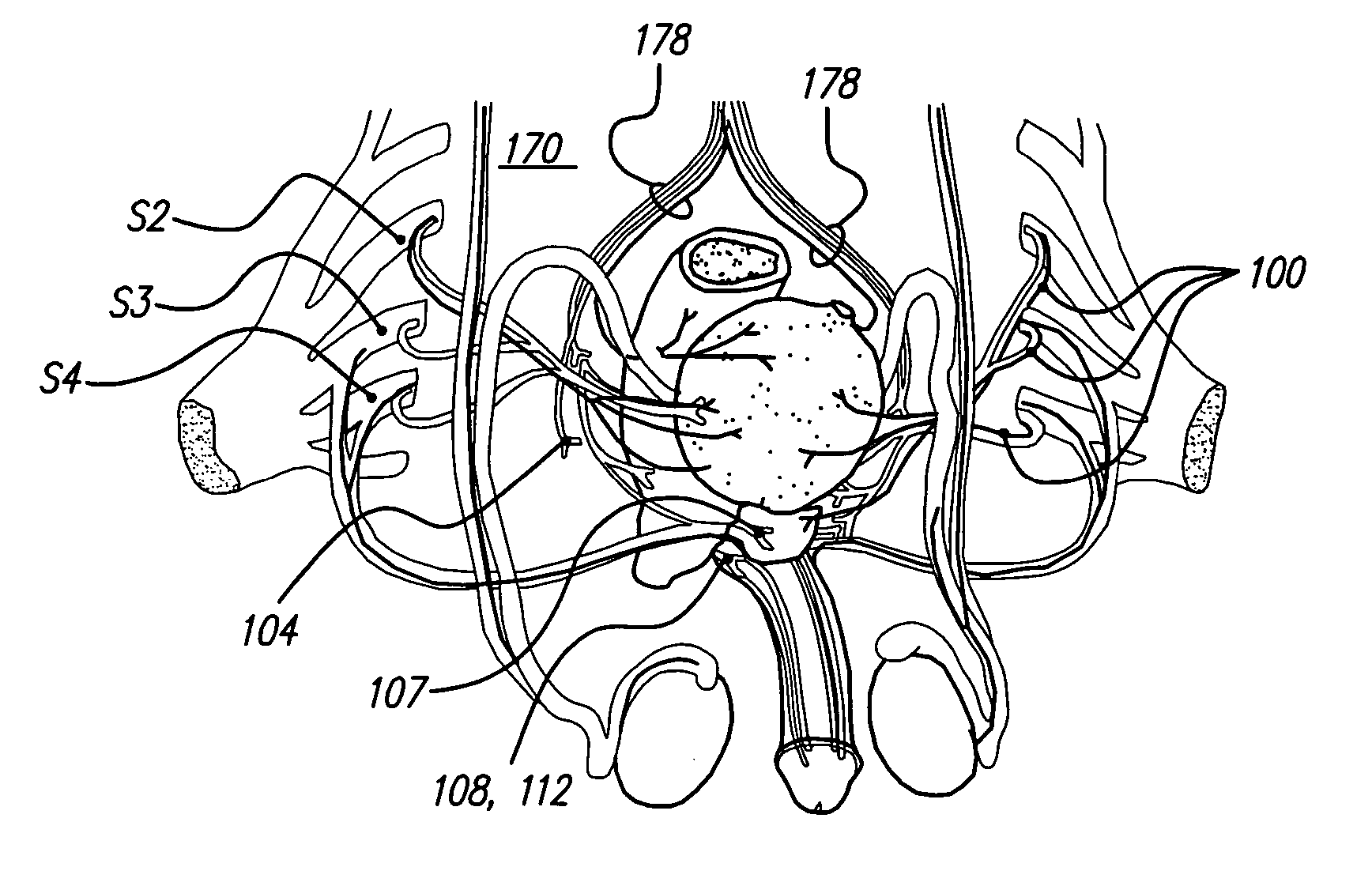
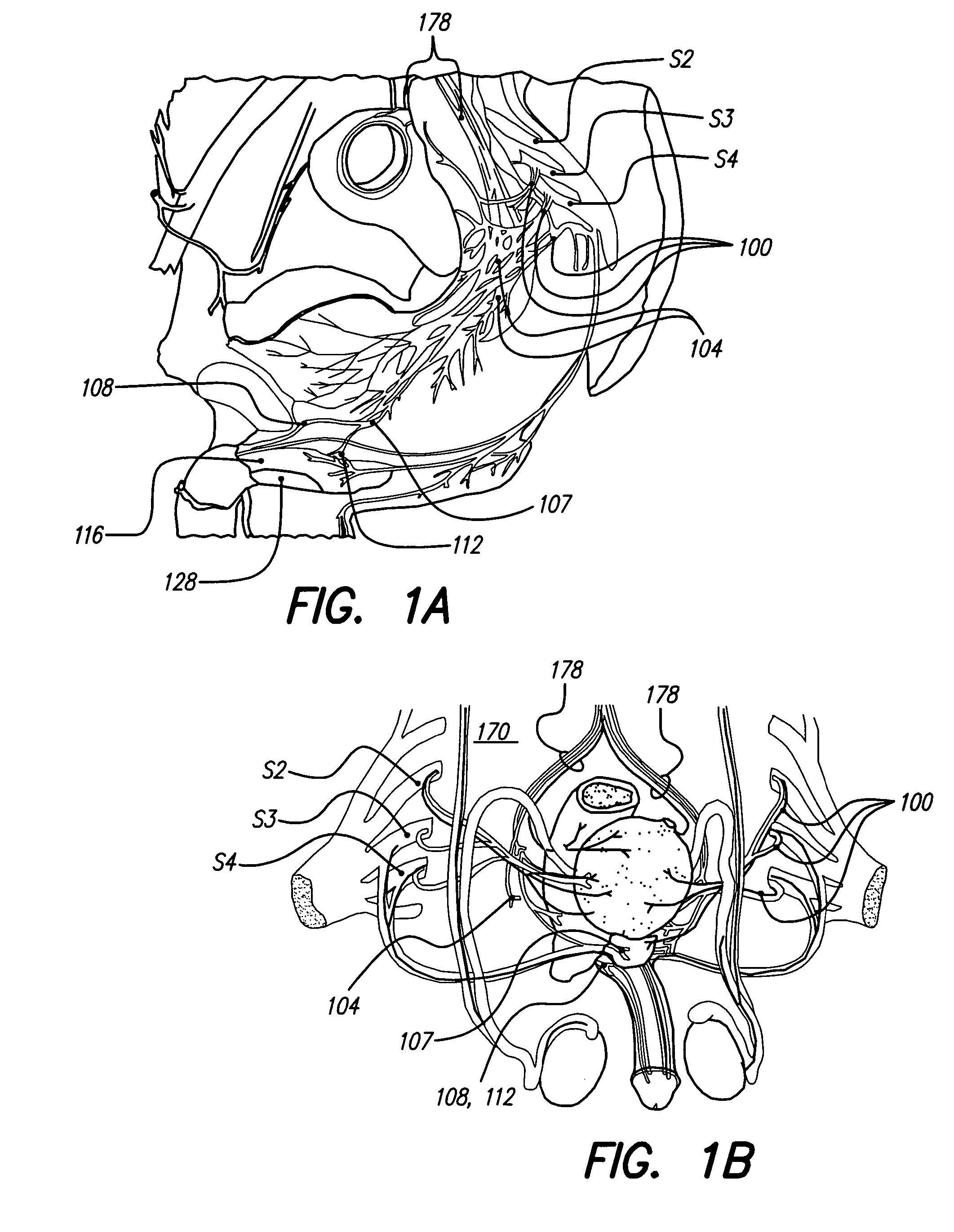
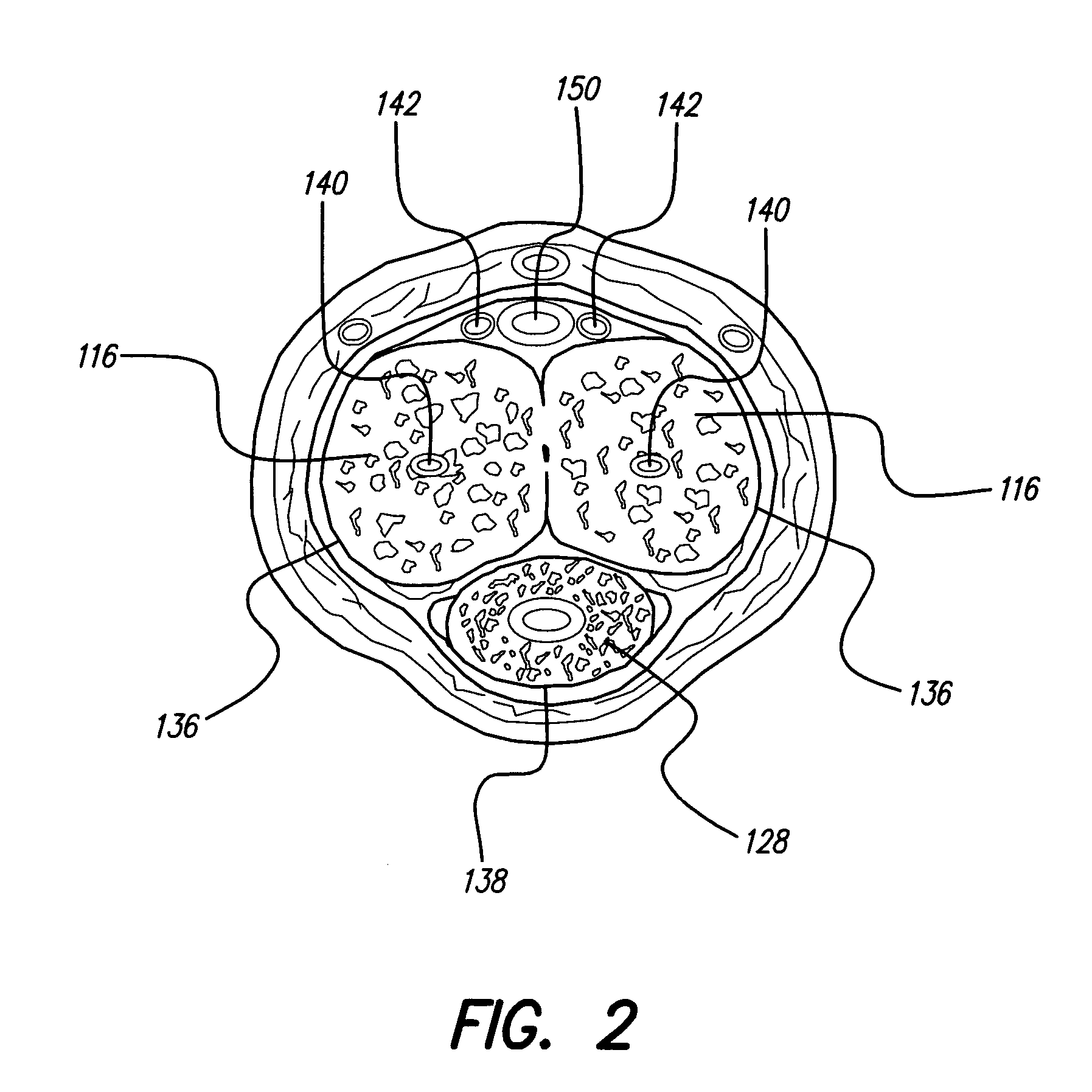
Patient interactive neurostimulation system and method
The present invention is a fully automated computer controlled system for adjustment of neurostimulation implants used in pain therapy and in treating neurological dysfunction which includes a patient interactive computer, and a universal transmitter interface integrally embedded in the patient interactive computer, or built into the antenna which is capable of stimulating any type of implanted neurostimulation devices by imitating any of the proprietary programming codes. The patient interacts with the system through the patient interactive computer (containing a unique software) which provides for consistency check of the data entered by the patient, deleting the entered data if the consistency check was not satisfactory, and requesting the patient to re-enter the data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Combination therapy for depression, prevention of suicide, and various medical and psychiatric conditions
InactiveUS7973043B2Preventing disease progression/modifyingDelaying/preventing relapseBiocideNervous disorderInitial treatmentTherapy resistant
The present invention relates to a new method of treatment for persons meeting diagnoses for major depressive disorder, or other unipolar (non-bipolar, non-psychotic and non-treatment resistant) depression. The method comprises administering a combination of two categories of drugs, antipsychotics or dopamine system stabilizers, in combination with a newer antidepressant such as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, as initial treatment or as soon as possible. The method targets the prevention of suicide, and provides other benefits including preventing disease progression development of tolerance toward the antidepressants. Another aspect of the invention relates to using the method for alleviating cognitive distortion and related functional impairment or health risks, and / or using the method for smoking cessation or nicotine withdrawal.
Owner:MIGALY PETER
Methods and systems for electrical and/or drug stimulation as a therapy for erectile dysfunction
InactiveUS6885895B1Restoring erectile functionEffective therapyElectrotherapyArtificial respirationPenisMedicine
Systems and methods for introducing one or more stimulating drugs and / or applying electrical stimulation to tissue affecting the penis to treat erectile dysfunction (for instance, following prostate surgery) uses at least one implantable system control unit (SCU) producing electrical pulses delivered via electrodes and / or producing drug infusion pulses, wherein the stimulating drug(s) are delivered via one or more pumps and infusion outlets.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
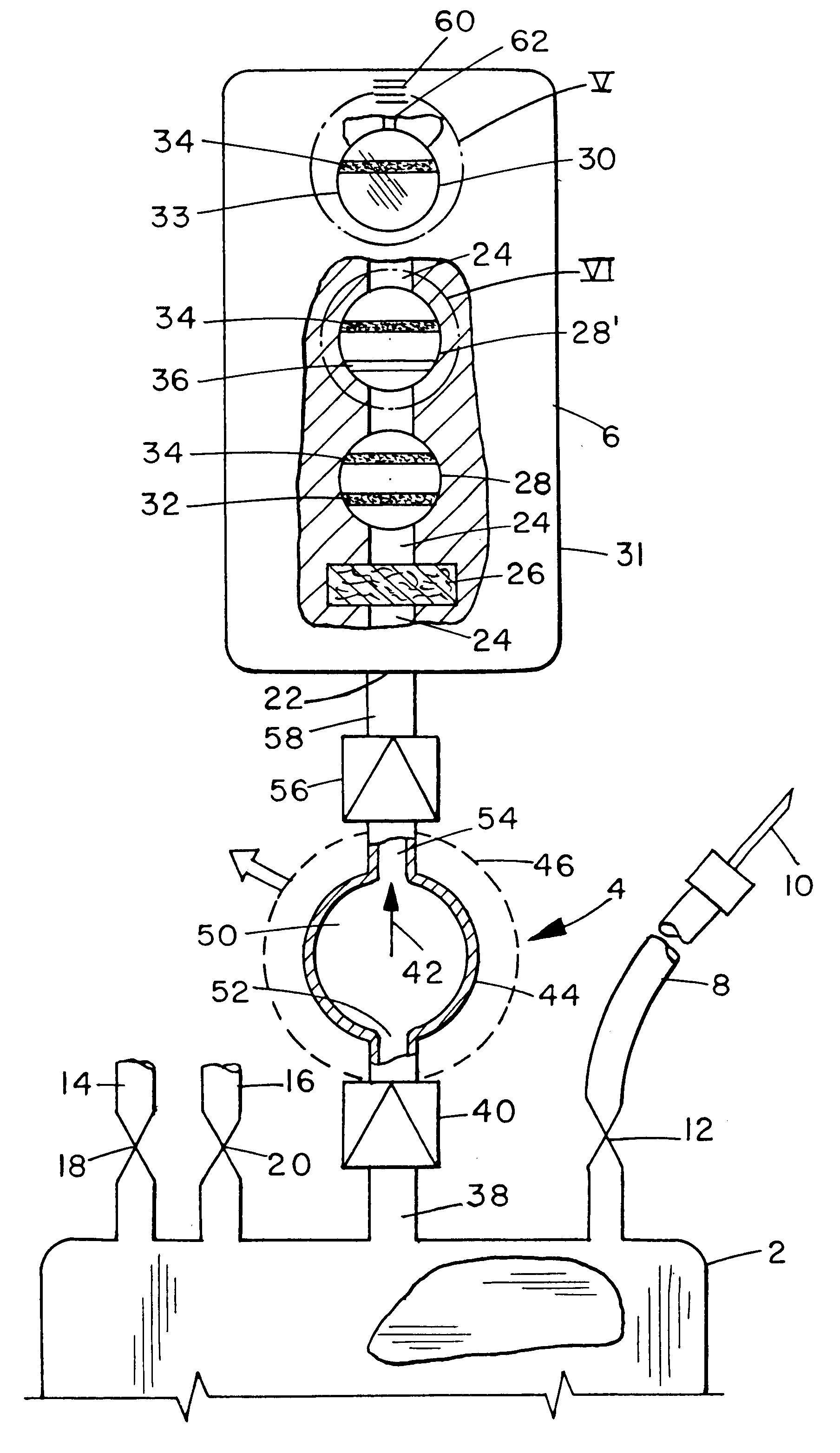
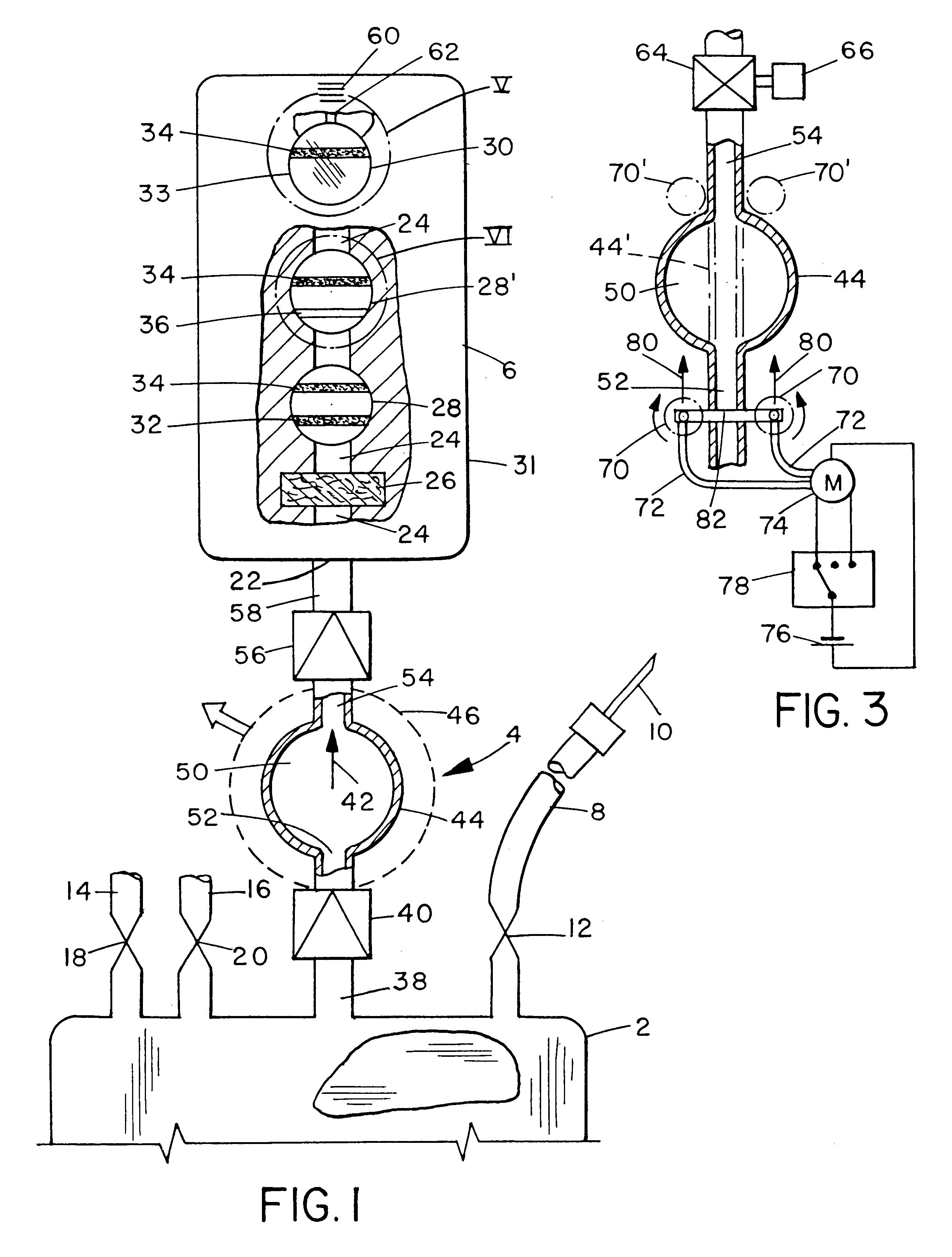
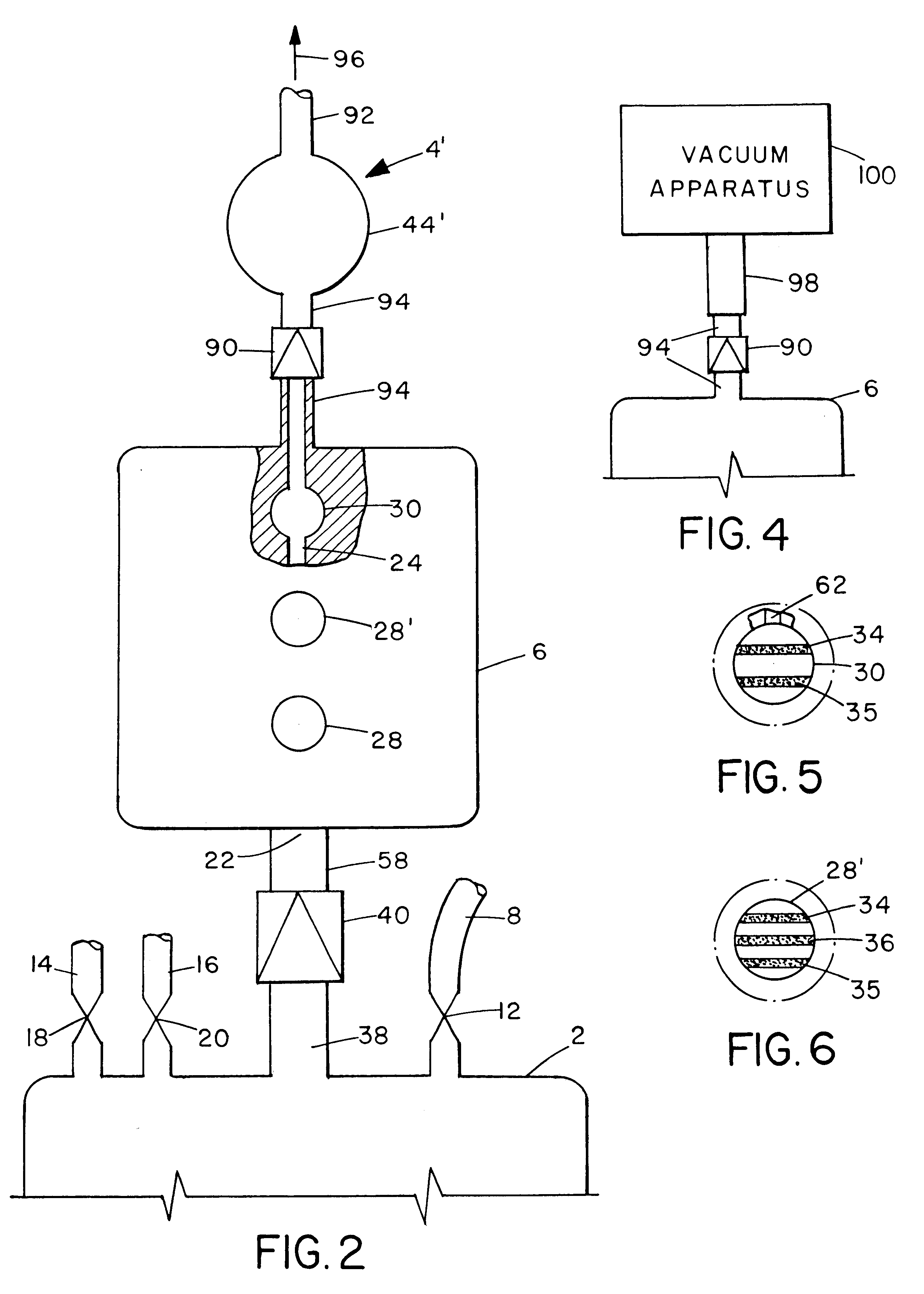
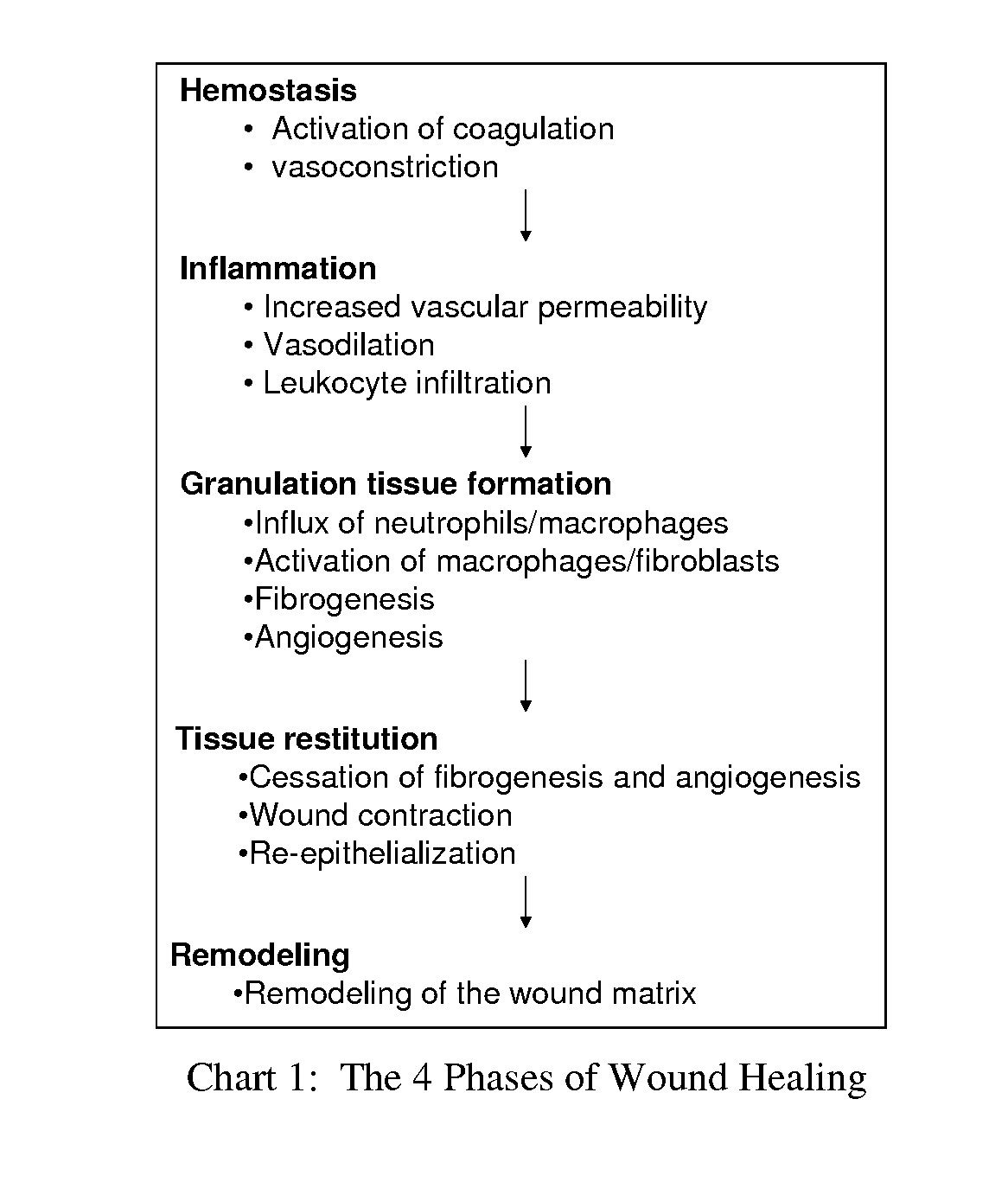
Integrated body fluid collection and analysis device with sample transfer component
A single, integrated device in which a body fluid (e.g., blood) of a human or animal can be both collected and analyzed easily and without risk of contamination is disclosed. The collection portion and analysis portion of the device are permanently joined to permit movement of small quantities of body fluid under controlled conditions, to minimize any waste of the body fluid, to ensure that no contamination reaches the main body fluid volume, and to create a permanent physical record of the results of the analysis in association with the fluid sample itself: A wide variety of different body fluid components which may be indicative of various diseases, dysfunctions and abnormalities of the human or animal or the body fluid itself can be tested for. The device includes a container for collecting human or animal body fluid, one or more testing chambers containing one or more analysis units activated by body fluid; a transfer pump or vacuum assembly to transfer one or more samples into the analysis units; and one-way valves or the equivalent to prevent any portion of the withdrawn sample from being returned to the collection container. The body fluid acted upon may be blood, blood plasma, urine, bile, pleural fluid, ascites fluid, stomach or intestine fluid, colostrom, milk or lymph.
Owner:AALTO SCI
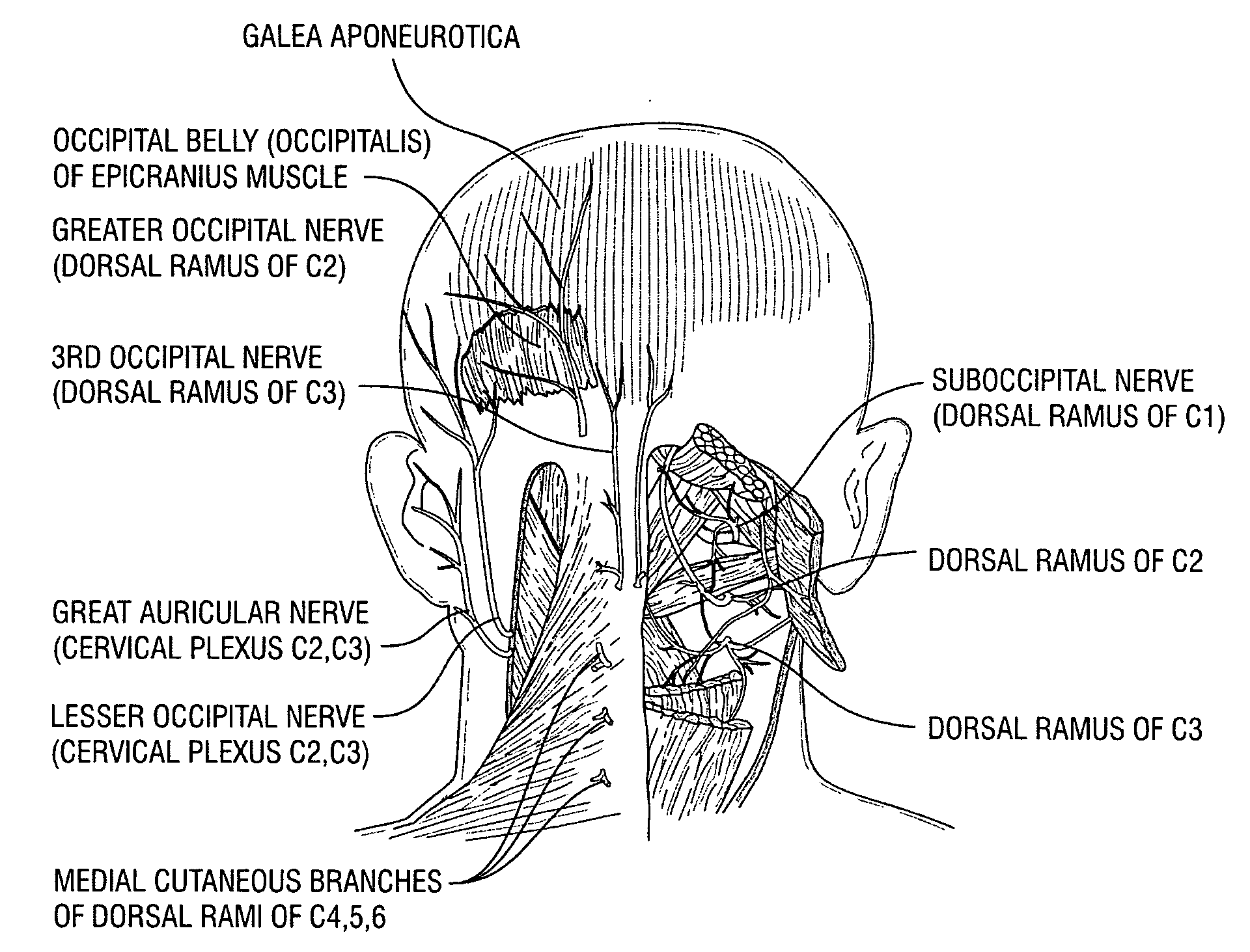
Peripheral nerve stimulation to treat auditory dysfunction
A system and / or method for treating auditory dysfunction by somatosensory system stimulation. The system and / or method comprises a probe and a device to stimulate the probe. The probe has a stimulation portion implanted in communication with a predetermined peripheral nerve site. The stimulation portion of the probe may be implanted in contact with a peripheral nerve dorsal root ganglia, cranial nerve or dermatome area, for example C2 dermatome area or a trigeminal dermatome area. The stimulation portion may be a laminotomy, paddle, surgical, or multiple electrode lead. The device to stimulate the probe may be implanted subcutaneously or transcutaneously.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Methods and systems for electrical and/or drug stimulation as a therapy for erectile dysfunction
InactiveUS20050209652A1Recovery functionEffective therapyElectrotherapyArtificial respirationPenisMedicine
Systems and methods for introducing one or more stimulating drugs and / or applying electrical stimulation to tissue affecting the penis to treat erectile dysfunction (for instance, following prostate surgery) uses at least one implantable system control unit (SCU) producing electrical pulses delivered via electrodes and / or producing drug infusion pulses, wherein the stimulating drug(s) are delivered via one or more pumps and infusion outlets.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
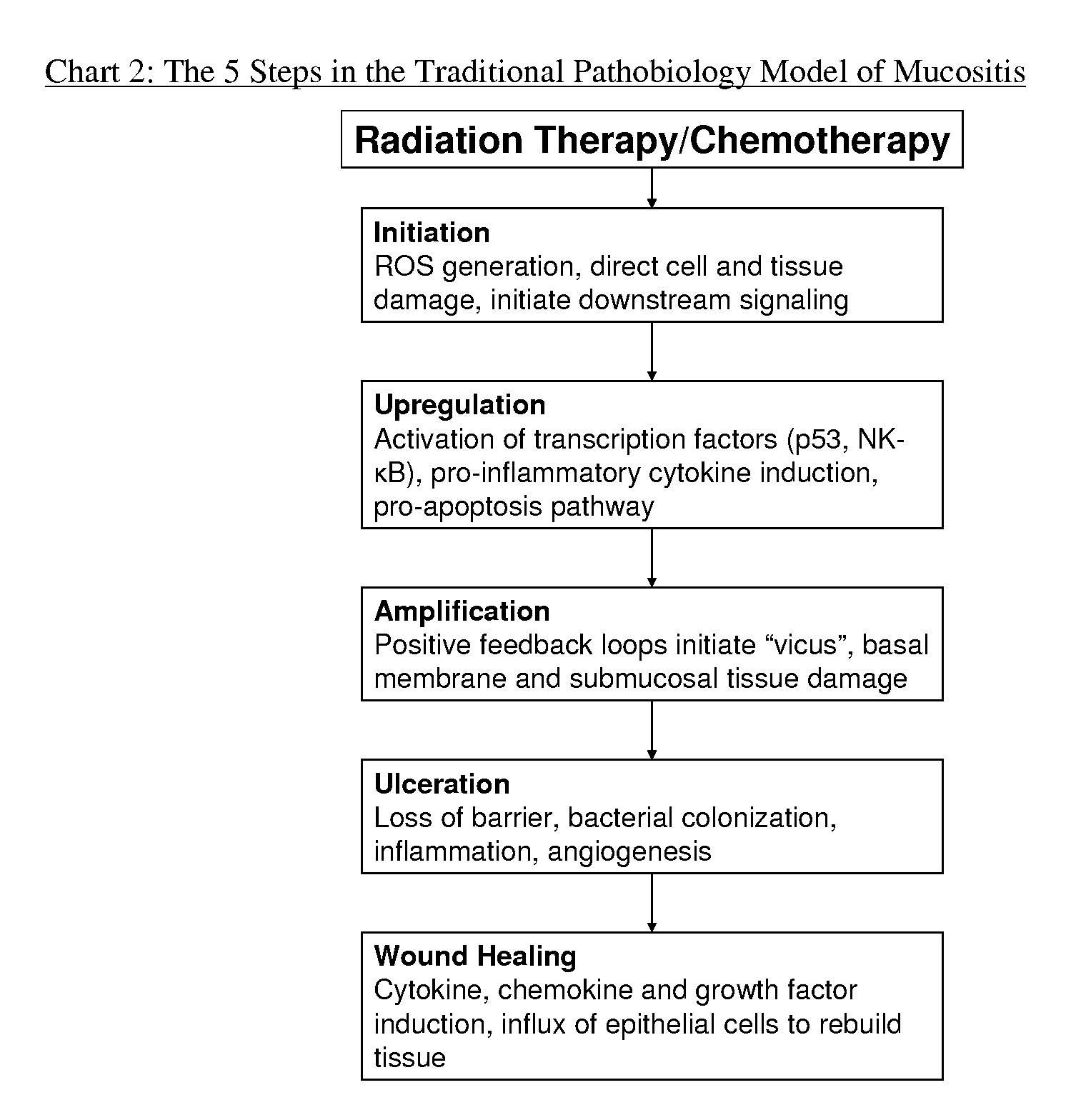
Compositions and methods for mucositis and oncology therapies
In alternative embodiments, this invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer or any condition caused by dysfunctional cells, side effects from treatments for cancer or any condition caused by dysfunctional cells, e.g., mucositis therapies (e.g., for oral mucositis; digestive mucositis; esophageal mucositis; intestinal mucositis). In alternative embodiments, the invention provides cytoprotection products that may be used either alone or in combination with other medical therapies such as cancer chemotherapies and radiation therapies.
Owner:VICUS THERAPEUTICS
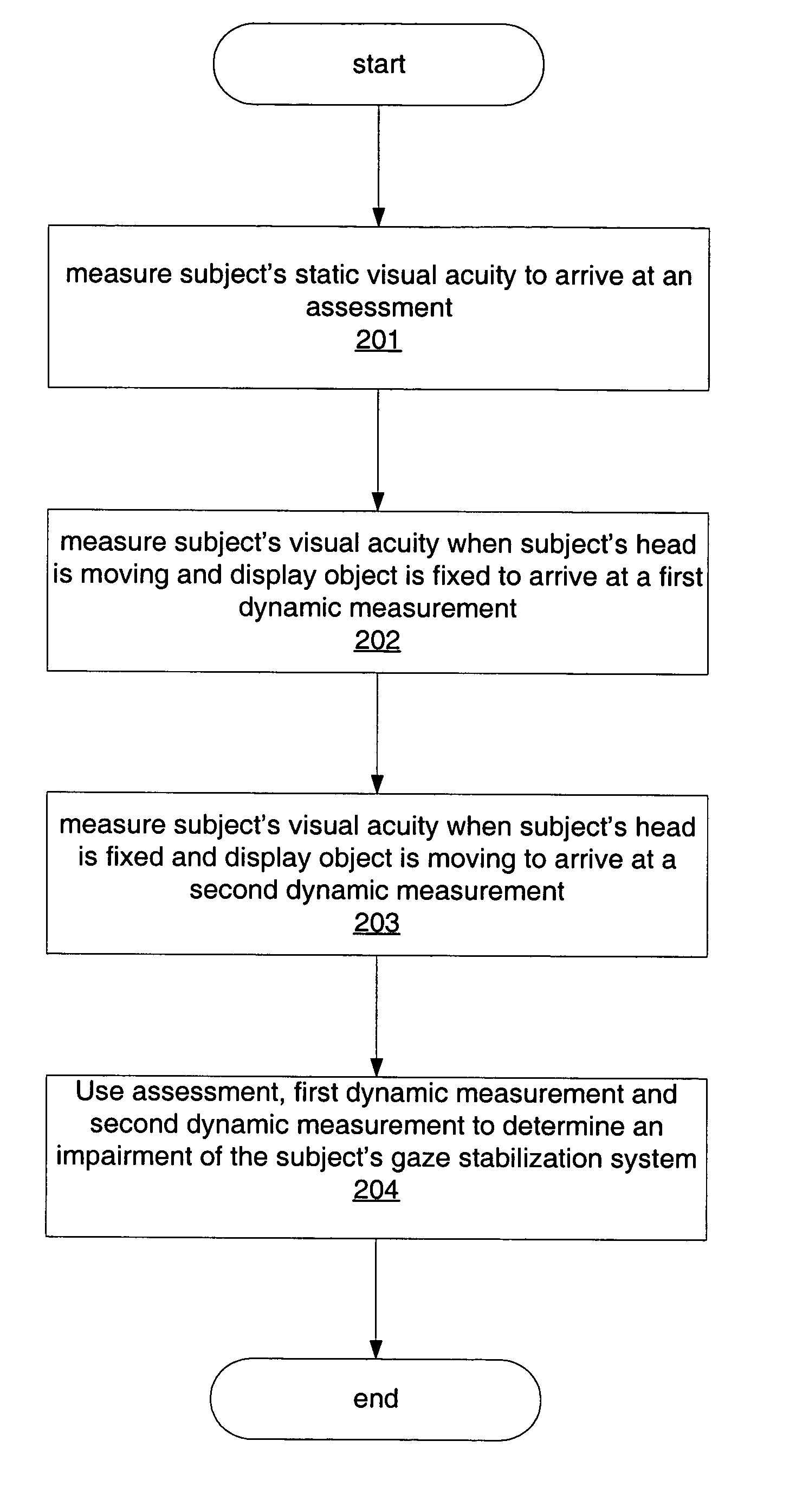
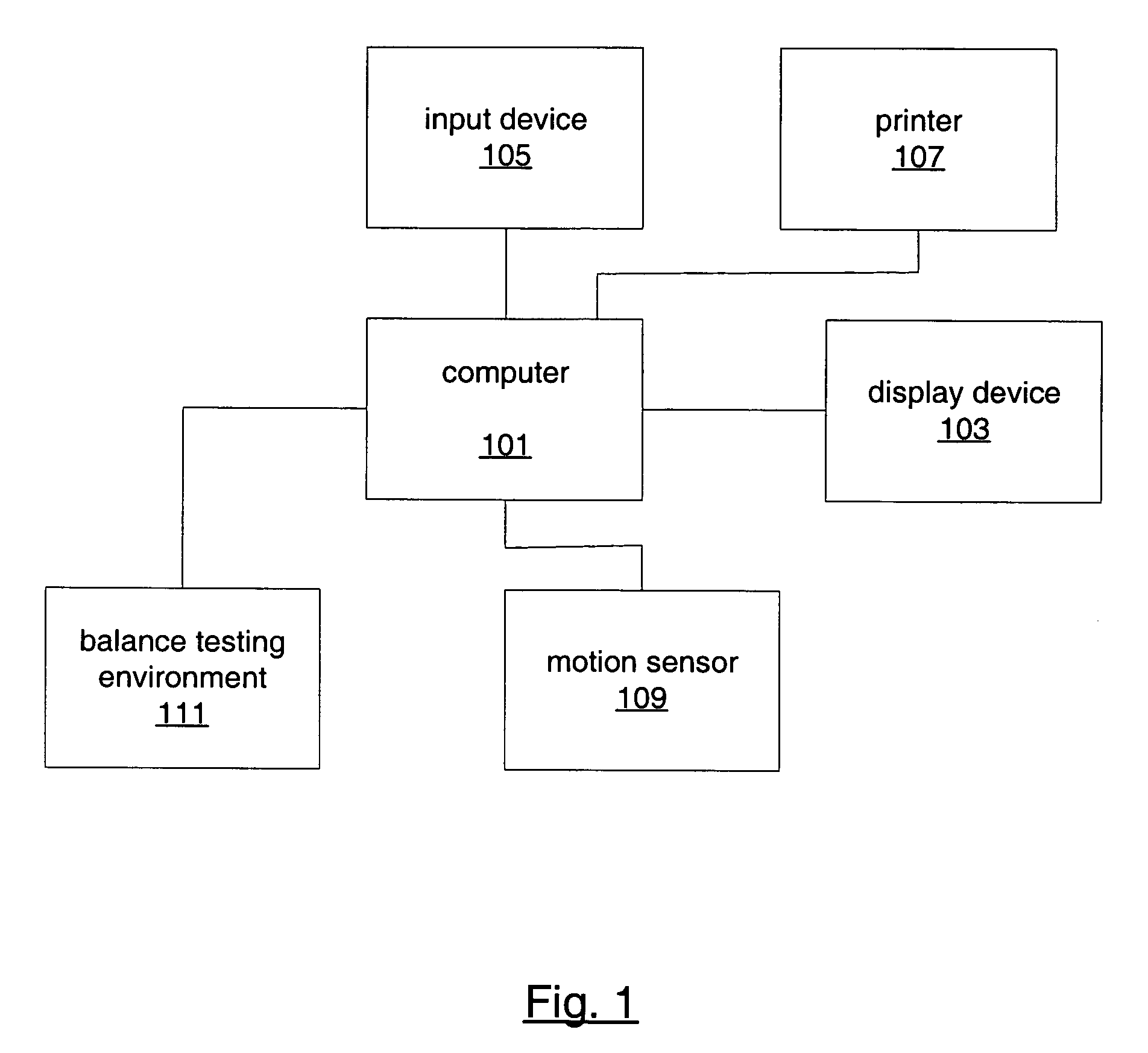
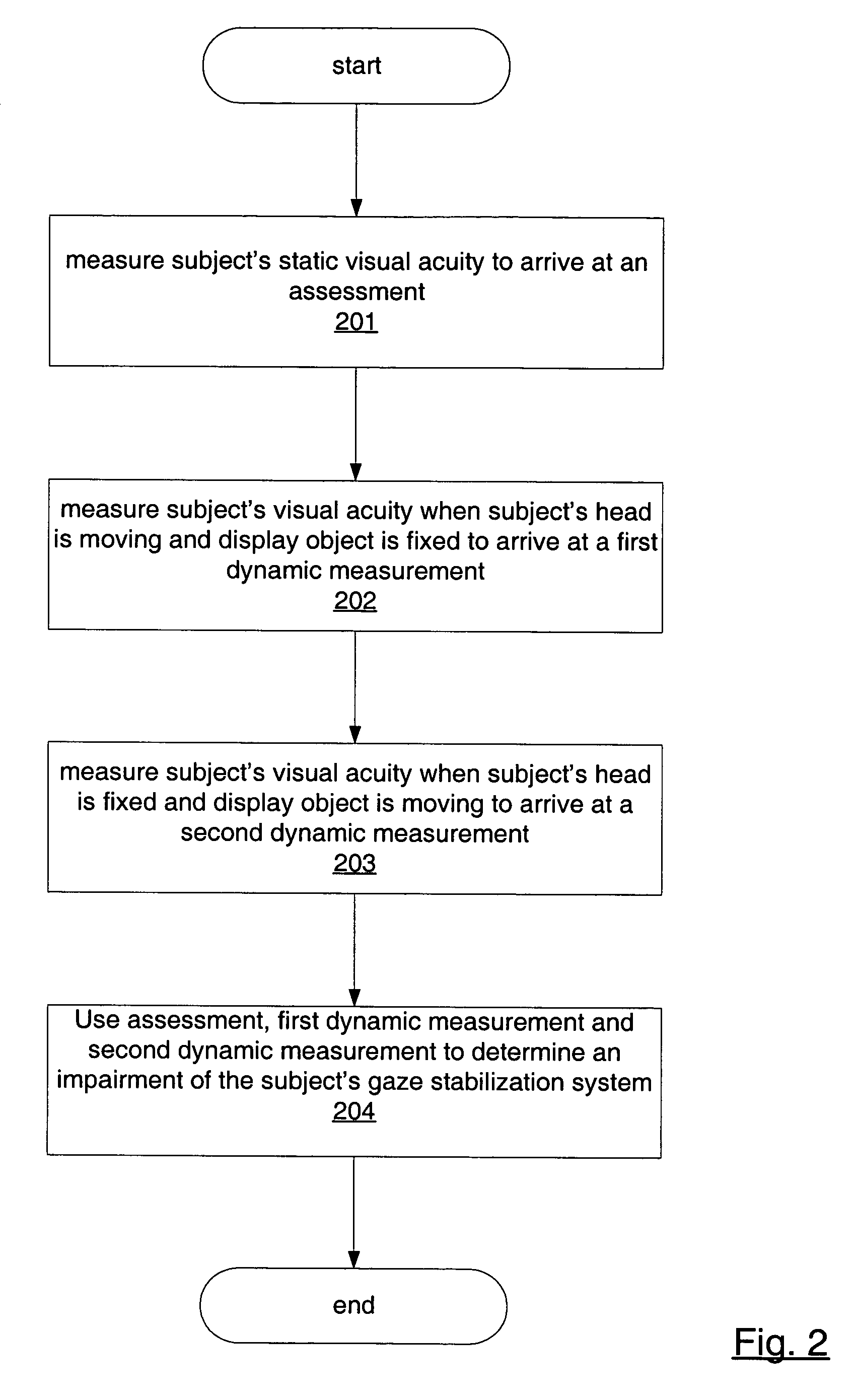
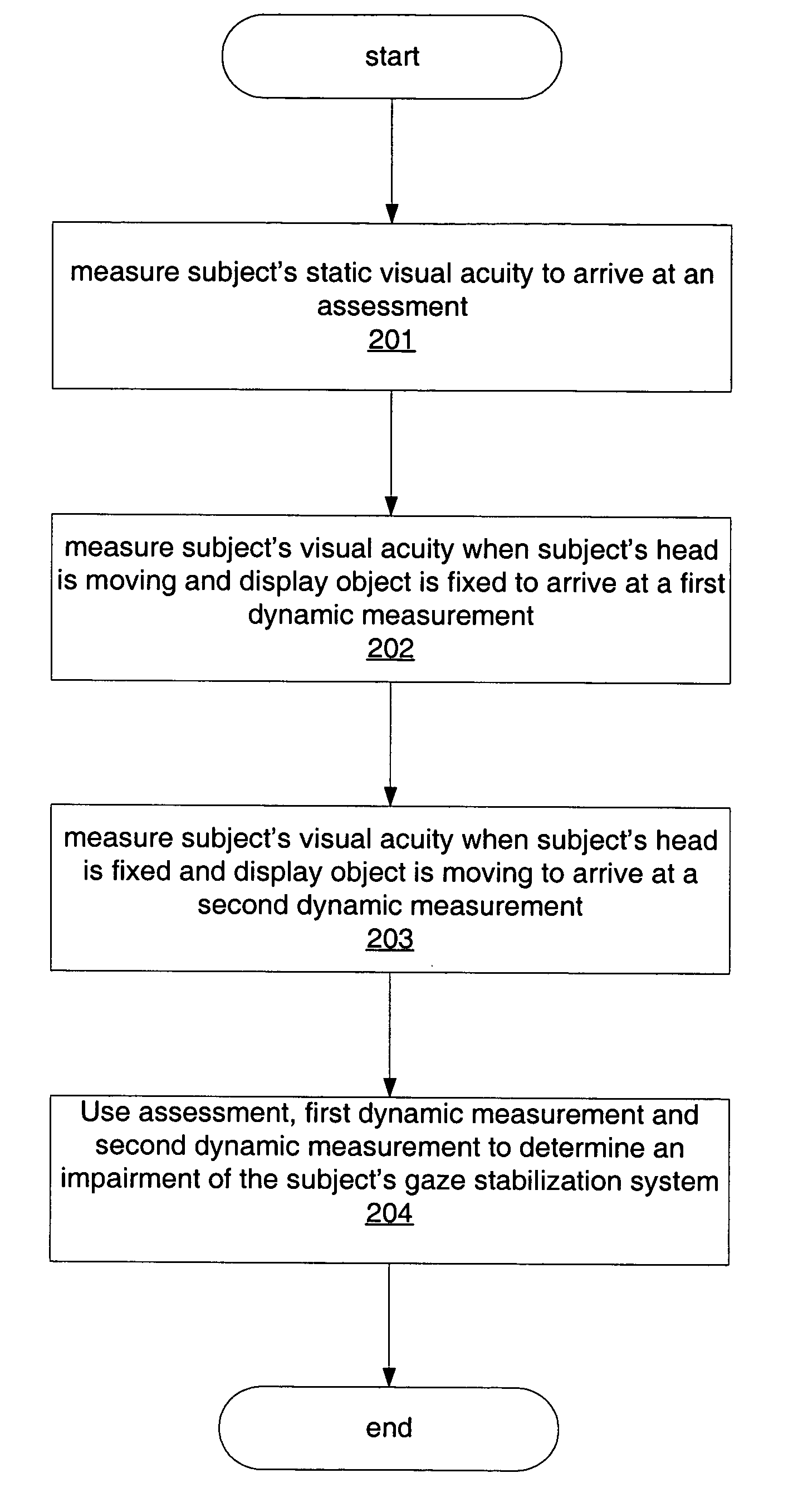
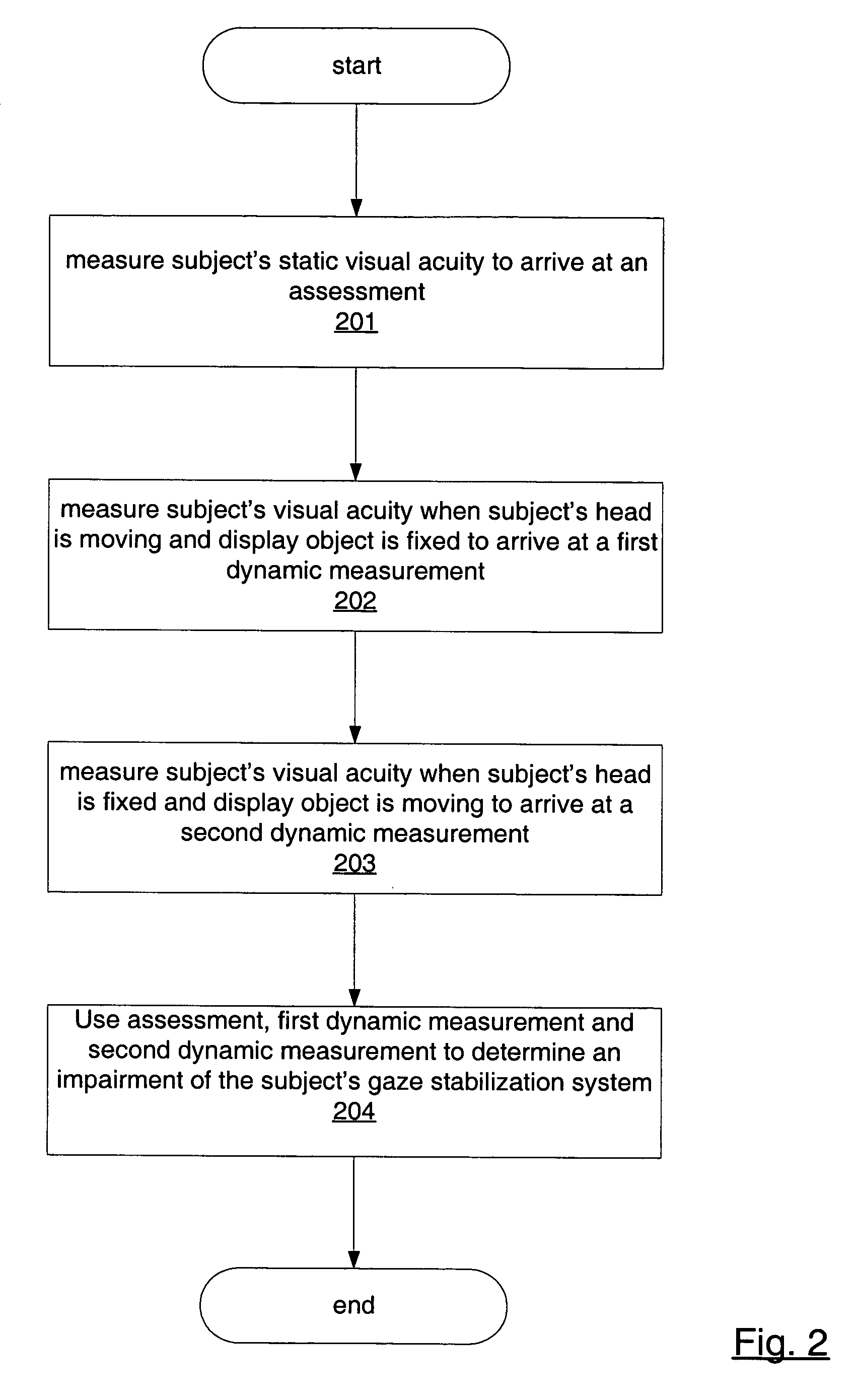
Isolating and quantifying functional impairments of the gaze stabilization system
A method for isolating and quantifying impairments of a subject's gaze stabilization system is provided. A subject's static visual acuity is measured to arrive at an assessment. The subject's visual acuity is then measured when the subject's head is moving and a display object is fixed to arrive at a first dynamic measurement. The subject's visual acuity is also measured when the subject's head is fixed and the display object is moving to arrive at a second dynamic measurement. The assessment and the first and second dynamic measurements are then used to determine an impairment of the subject's gaze stabilization system.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
Isolating and quantifying functional impairments of the gaze stabilization system
A method for isolating and quantifying impairments of a subject's gaze stabilization system is provided. A subject's static visual acuity is measured to arrive at an assessment. The subject's visual acuity is then measured when the subject's head is moving and a display object is fixed to arrive at a first dynamic measurement. The subject's visual acuity is also measured when the subject's head is fixed and the display object is moving to arrive at a second dynamic measurement. The assessment and the first and second dynamic measurements are then used to determine an impairment of the subject's gaze stabilization system.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
Novel compounds
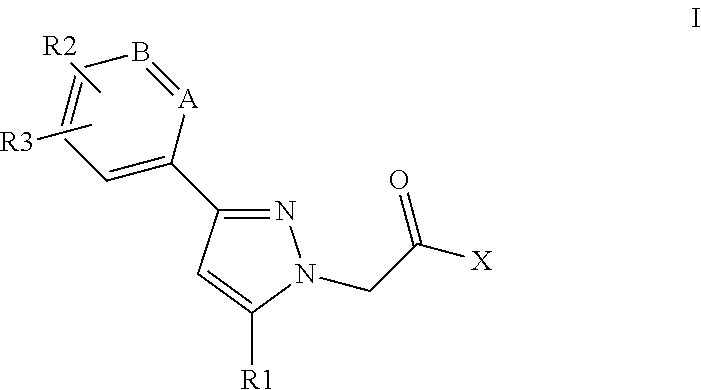
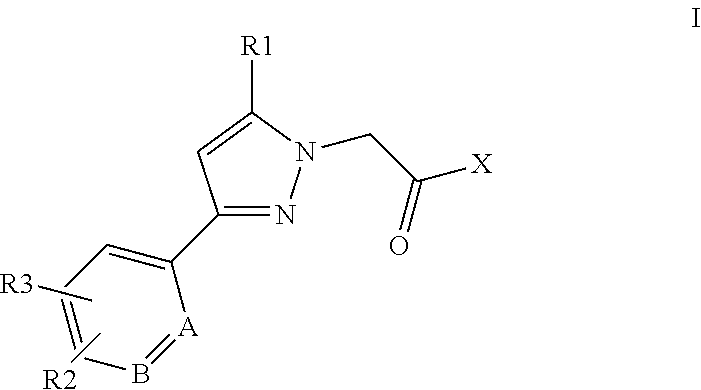
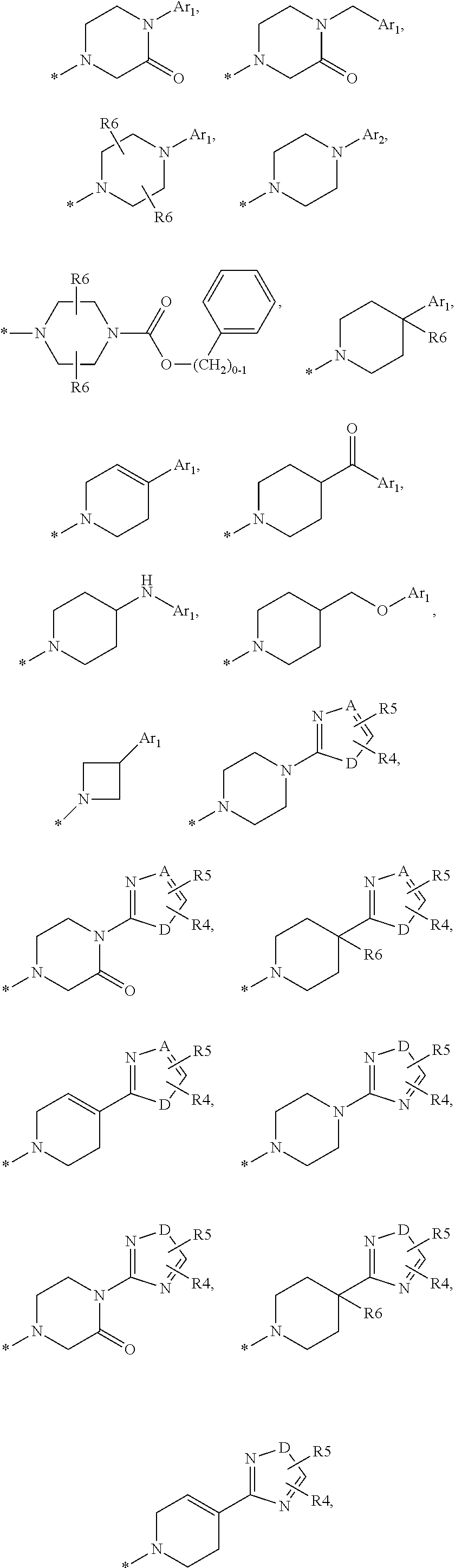
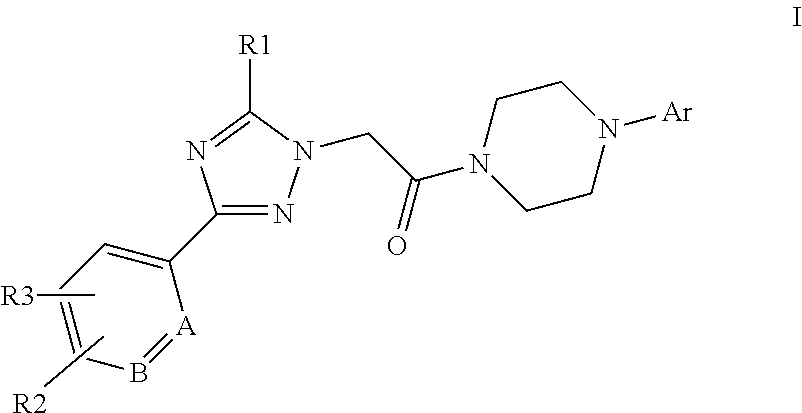
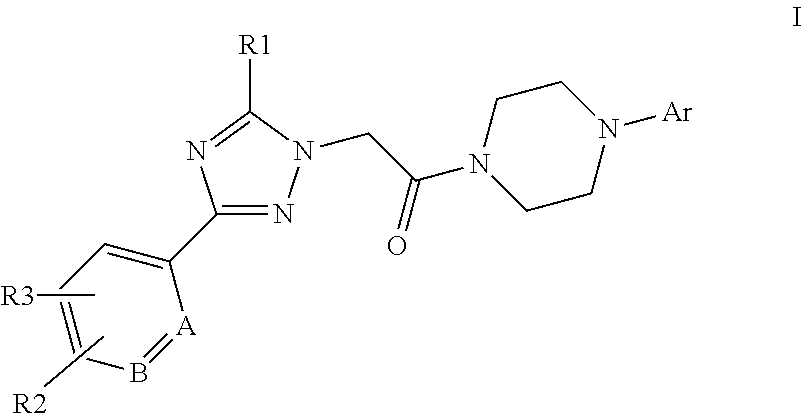
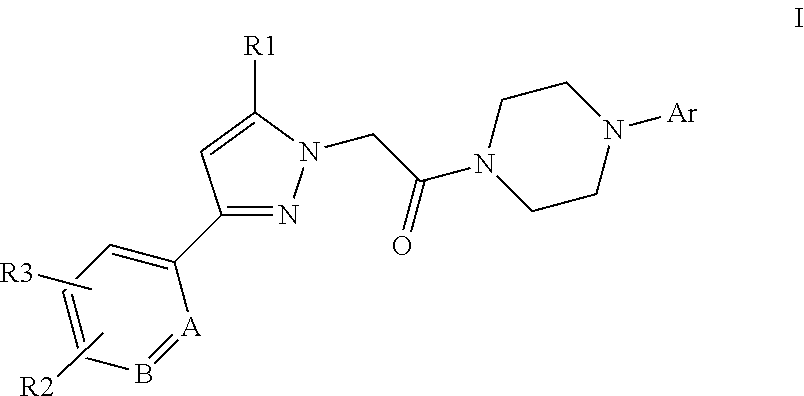
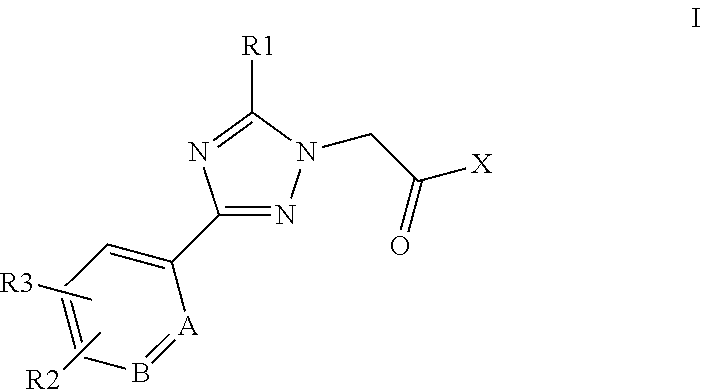
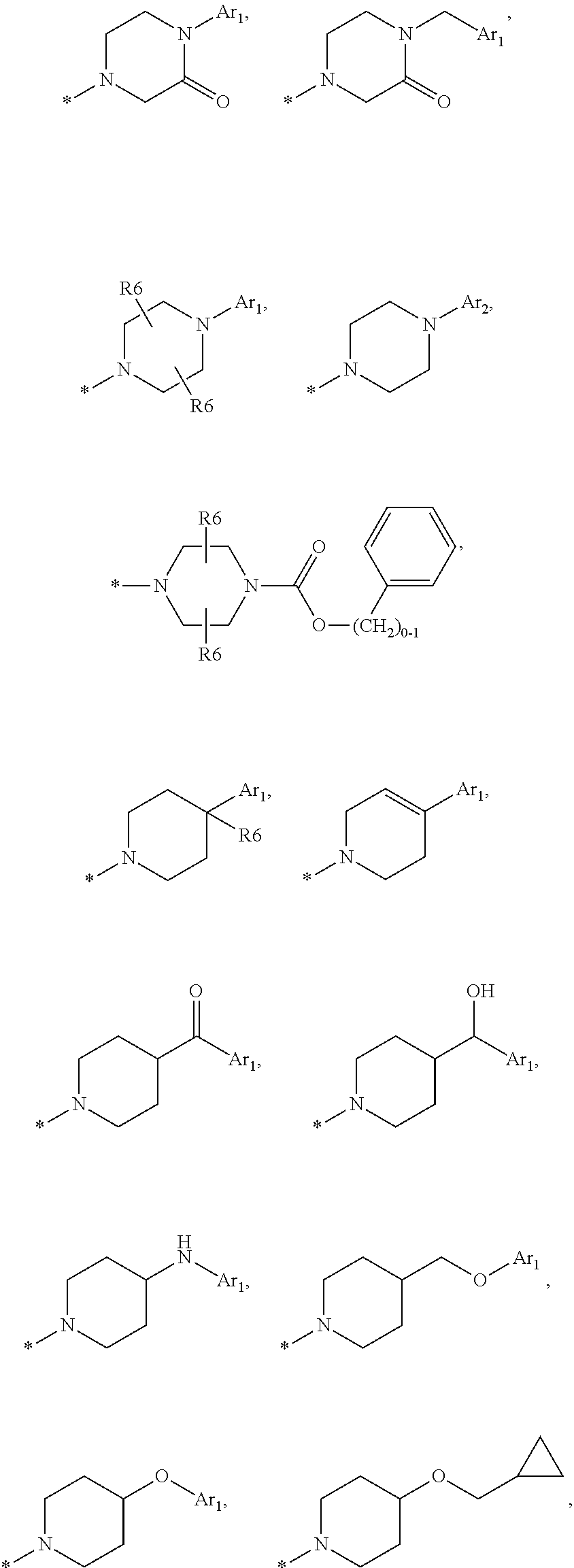
This invention relates to compounds of formula Itheir use as positive allosteric modulators of mGlu5 receptor activity, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods of using the same as agents for treatment and / or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders associated with glutamate dysfunction such as schizophrenia or cognitive decline such as dementia or cognitive impairment. A, B, X, R1, R2, R3 have meanings given in the description.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
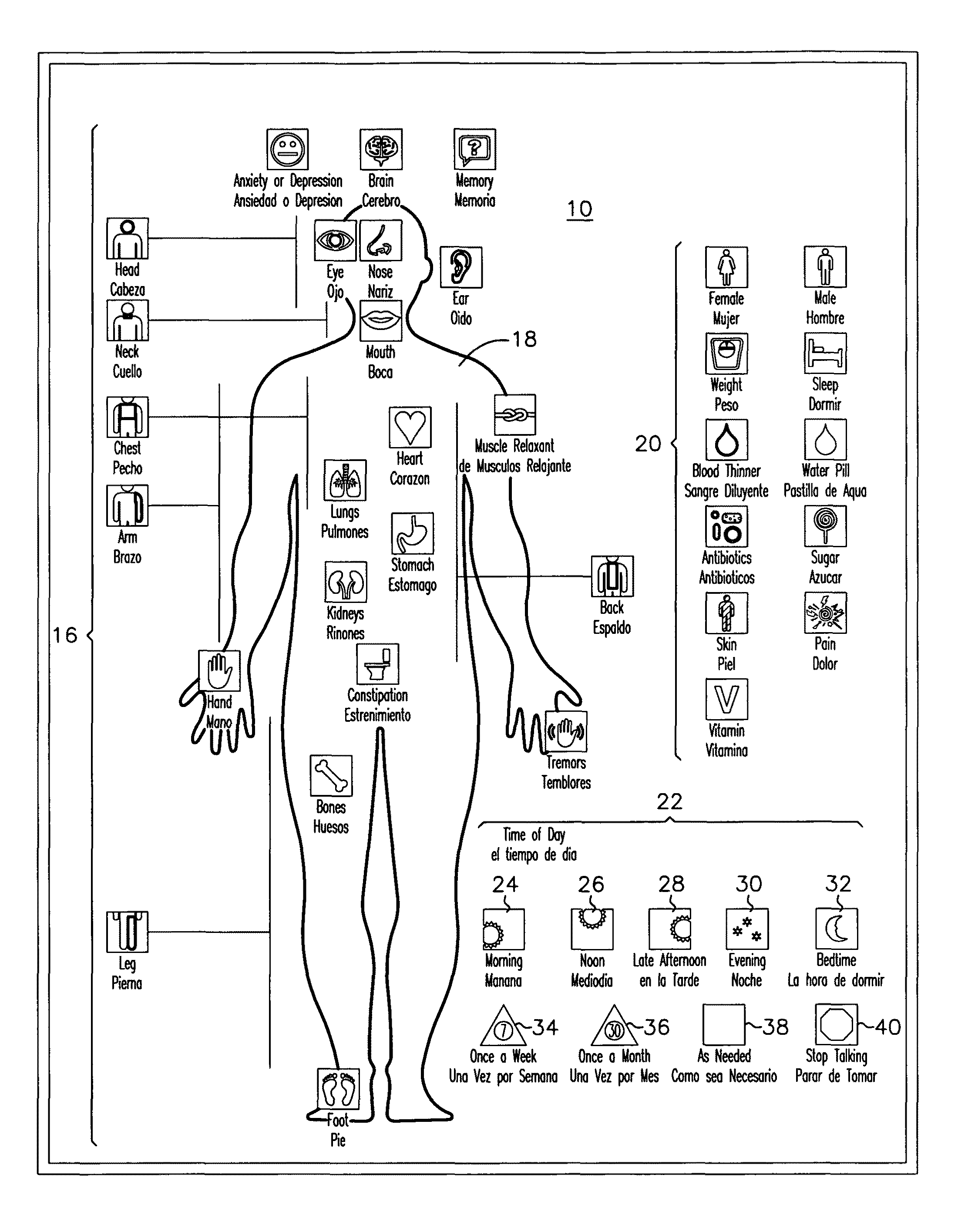
Color coded anatomical and non-anatomical sticker labels to be used on medication bottles to identify what medication is used for and when medication is due to be administered
Current medication labels are very difficult for people with disabilities, language barriers, functional impairments, or illiteracy to read, potentially increasing the risk for accidental medication overdoses and / or poor compliance with medication administration and adherence. By having a color coded sticker system with an enclosed full body guide in the form of a poster, and a home health medication record card, these stickers are placed on each medication bottle as a symbol for what the medication is used for. The stickers are color coded in order to distinguish the time the medication is to be administered. Home health agencies may use the poster and stickers as they educate their patients about the medications they take.
Owner:DOIRON WHITNEY
Methods and compositions for gene delivery to on bipolar cells
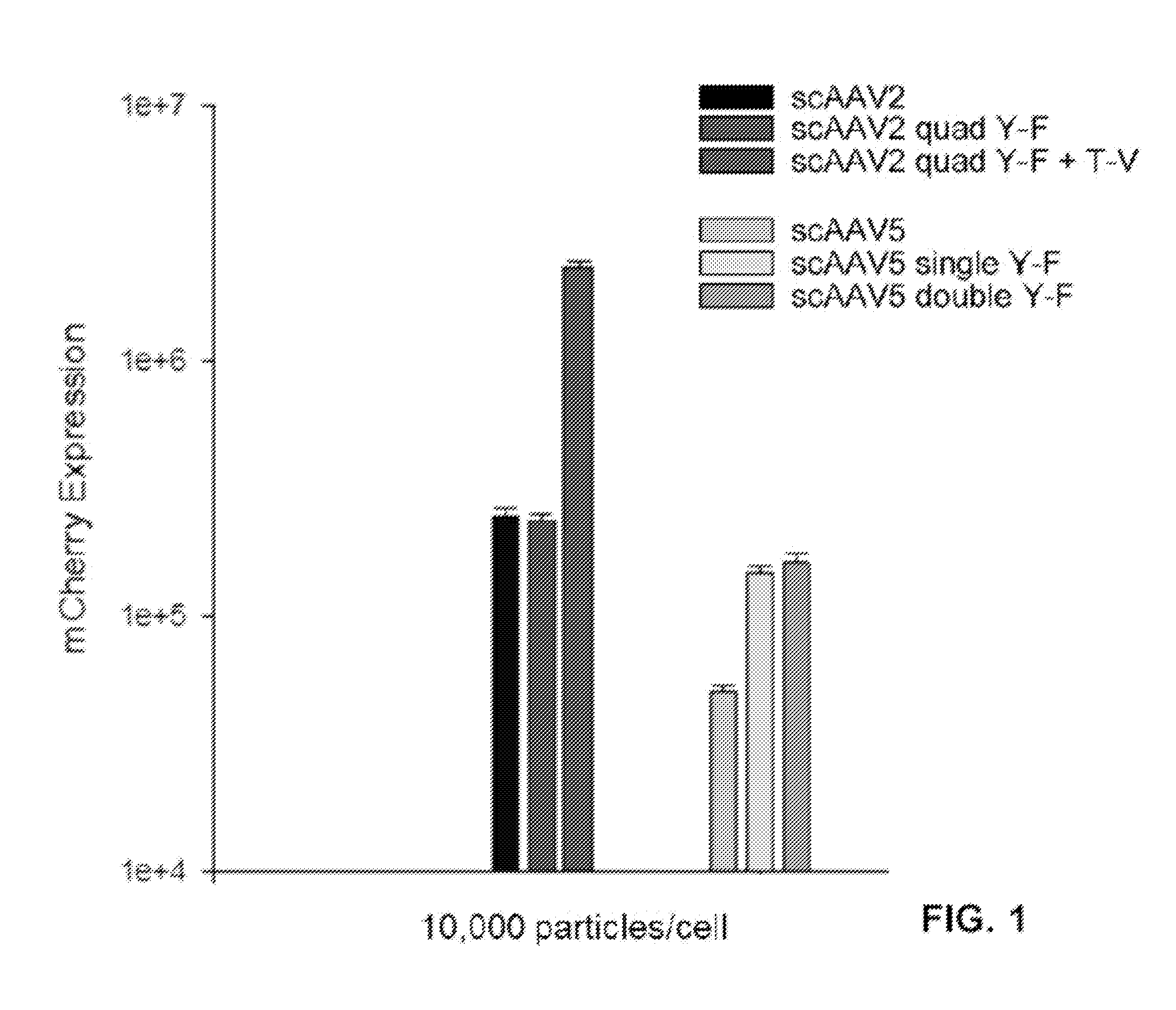
InactiveUS20170007720A1Overcome limitationsImprove efficiencyVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryRetinitis pigmentosa
Disclosed are capsid-modified rAAV expression vectors, as well as infectious virions, compositions, and pharmaceutical formulations that include them. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and using novel capsid-protein-mutated rAAV vector constructs in a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic applications including, inter alia, as delivery agents for diagnosis, treatment, or amelioration of one or more diseases, disorders, or dysfunctions of the mammalian eye. Also disclosed are methods for intravitreal delivery of therapeutic gene constructs to retinal neuron cells, and specifically to ON bipolar cells, of the mammalian eye, as well as use of the disclosed compositions in the manufacture of medicaments for a variety of in vitro and / or in vivo applications including the treatment of retinitis pigmentosa, melanoma-associated retinopathy, and congenital stationary night blindness.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Novel compounds
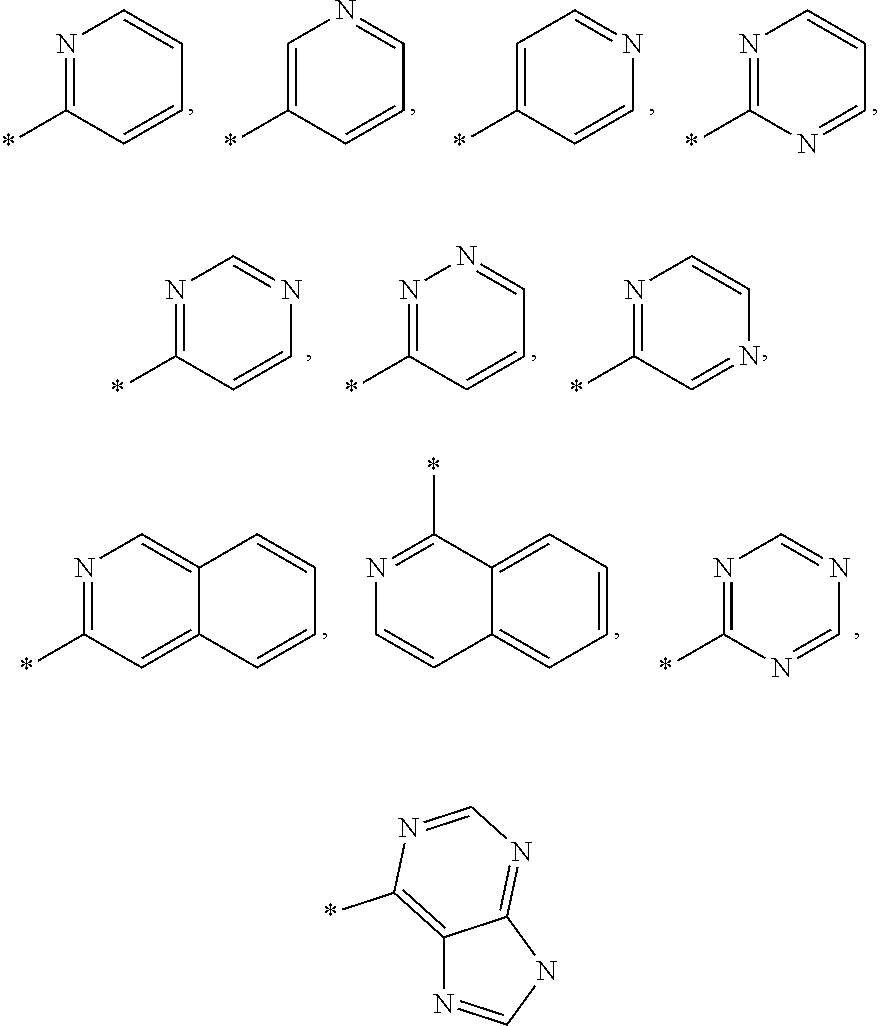
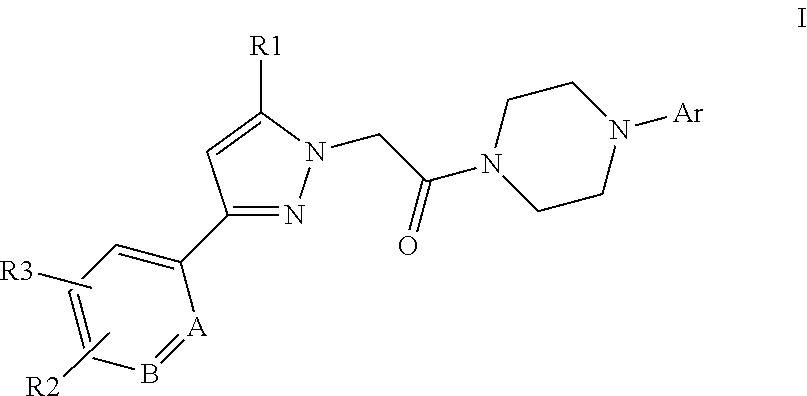
This invention relates to compounds of formula Itheir use as positive allosteric modulators of mGlu5 receptor activity, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods of using the same as agents for treatment and / or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders associated with glutamate dysfunction such as schizophrenia or cognitive decline such as dementia or cognitive impairment. A, B, Ar, R1, R2, R3 have meanings given in the description.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Novel compounds
This invention relates to compounds of formula Itheir use as positive allosteric modulators of mGlu5 receptor activity, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods of using the same as agents for treatment and / or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders associated with glutamate dysfunction such as schizophrenia or cognitive decline such as dementia or cognitive impairment. A, B, Ar, R1, R2, R3 have meanings given in the description.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Novel compounds
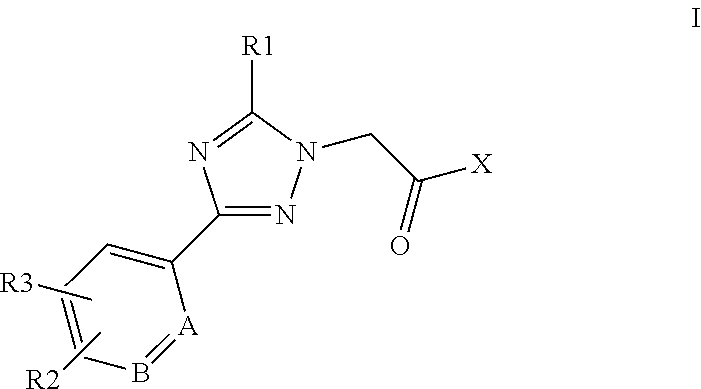
This invention relates to compounds of formula Itheir use as positive allosteric modulators of mGlu5 receptor activity, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods of using the same as agents for treatment and / or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders associated with glutamate dysfunction such as schizophrenia or cognitive decline such as dementia or cognitive impairment. A, B, X, R1, R2, R3 have meanings given in the description.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
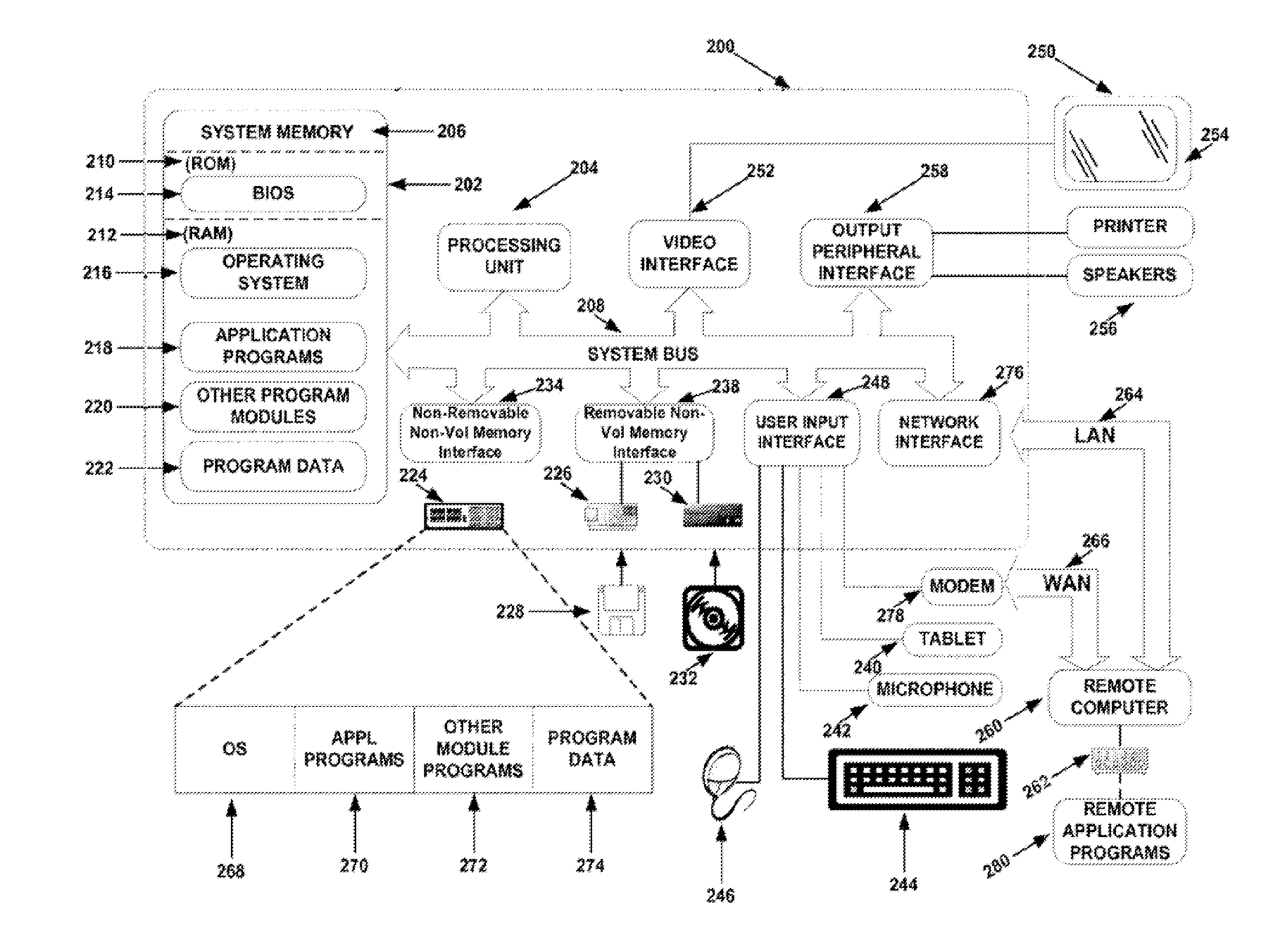
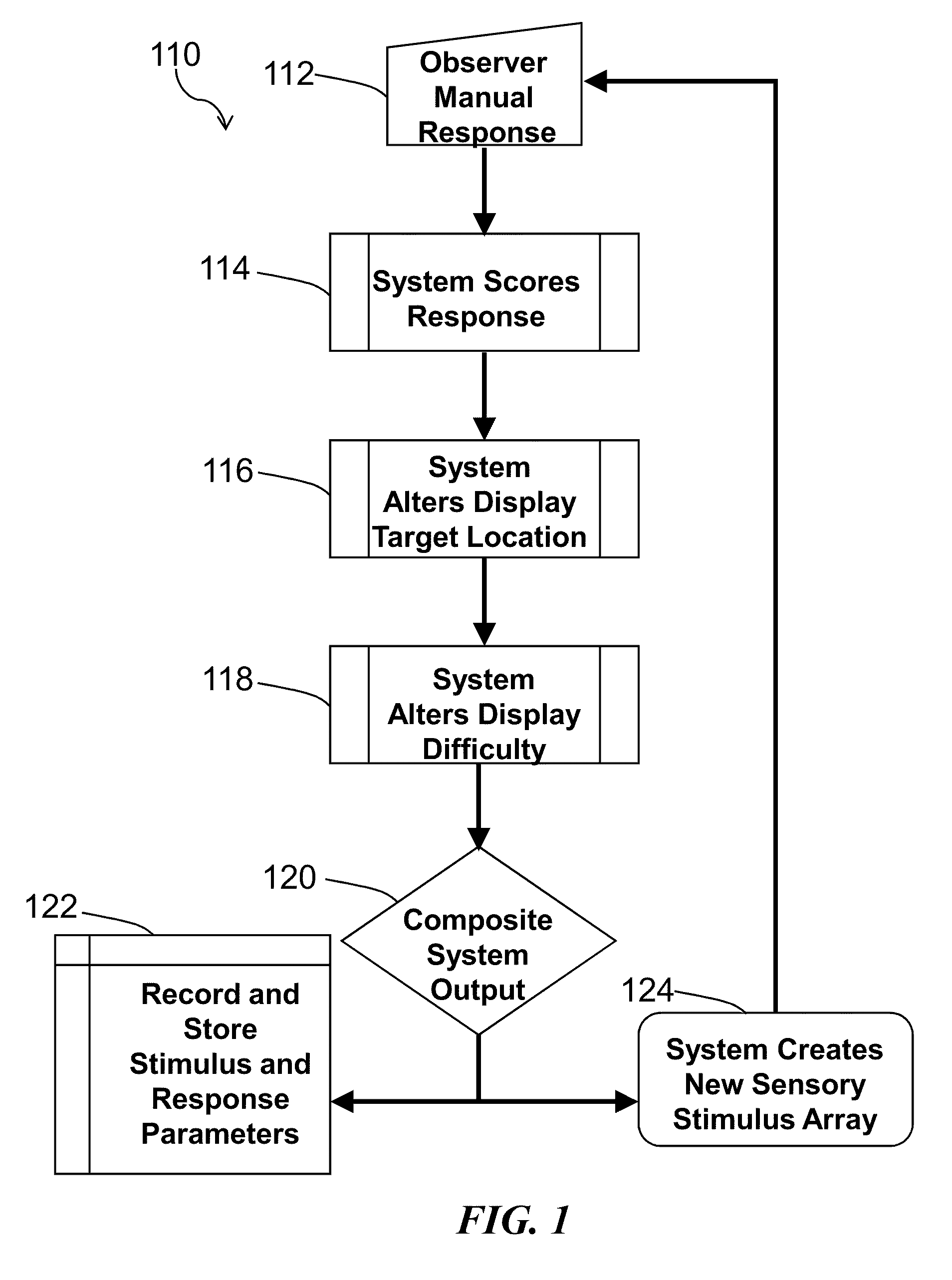
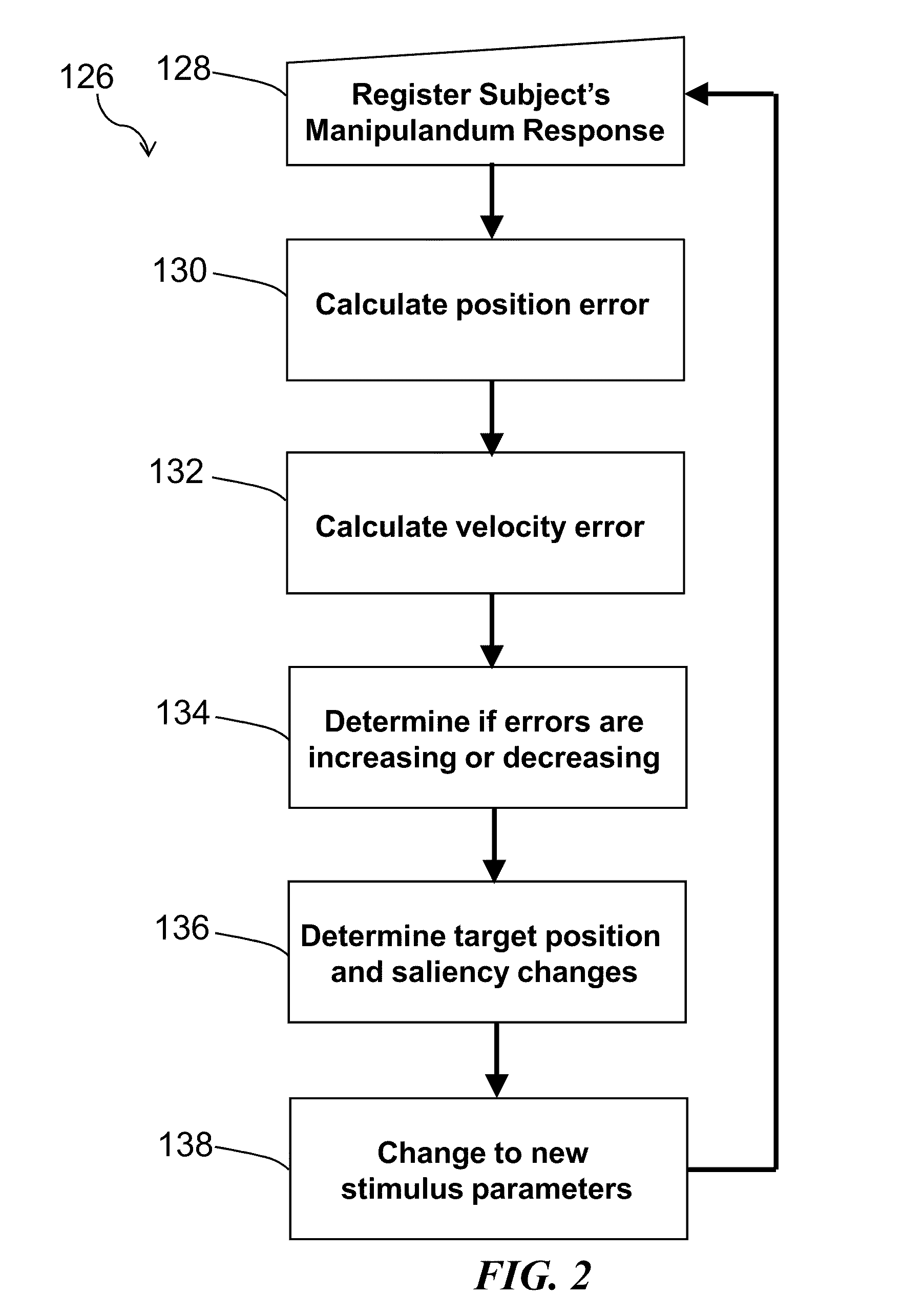
Method and system for quantitative assessment of functional impairment
InactiveUS20110066068A1Improves and simplifies complex experimental paradigmImproved and simplifiedLocal control/monitoringMedical automated diagnosisDisplay deviceFunctional impairment
A method is presented to address quantitative assessment of functional impairment in a subject, where the method comprises the steps of: (1) presenting a plurality of tests to a subject on a display, the plurality of tests comprising a series of scenes, the scene comprising at least one stimulus, wherein the scene may be associated with visual, auditory, and tactile stimulus arrays; (2) modulating at least one spatial characteristic of at least one stimulus; (3) receiving feedback from the subject via at least one input device; (4) quantitatively refining the scene relative to the received feedback; (5) calculating the relationship between at least one of the scene, the stimulus, and the quantitatively refined scene; (6) adjusting the scene relative to the calculated relationship; (7) determining equilibrated scene parameter of the subject; (8) recording the equilibrated scene parameter onto a tangible computer readable medium; (9) generating at least one diagnosis to the functional impairment associated with the equilibrated scene parameter; (10) recommending at least one treatment to the subject. An apparatus for quantitative assessment of functional impairment in a subject comprising an input device, a display device, a control device, and a tangible computer readable medium. A quantitative assessment profile of functional impairment by continuous modulation of specific perceptual domains on a stimulus and generating psychophysical responses on a tangible computer readable medium.
Owner:CEREBRAL ASSESSMENT SYST
Medicinal compositions improving brain function and method for improving brain function
An alkyl ether derivative represented by the formula: wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, m and n are as defined in the specification, or salts thereof exhibits synergistically improved anti-hypoxic activity when combined with a compound having an acetylcholine esterase inhibitory activity. Therefore, the combination according to the present invention is useful as a method for improving cerebral function. Further, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound relating to the combination according to the present invention is useful for treatment and prevention of dysfunction of cerebral acetylcholine neurons in the sequelae of cerebrovascular dementia, senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease and ischemic cerebral lesion and in the cerebral apoplexy or the memory impairment caused by selective neuronal death.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
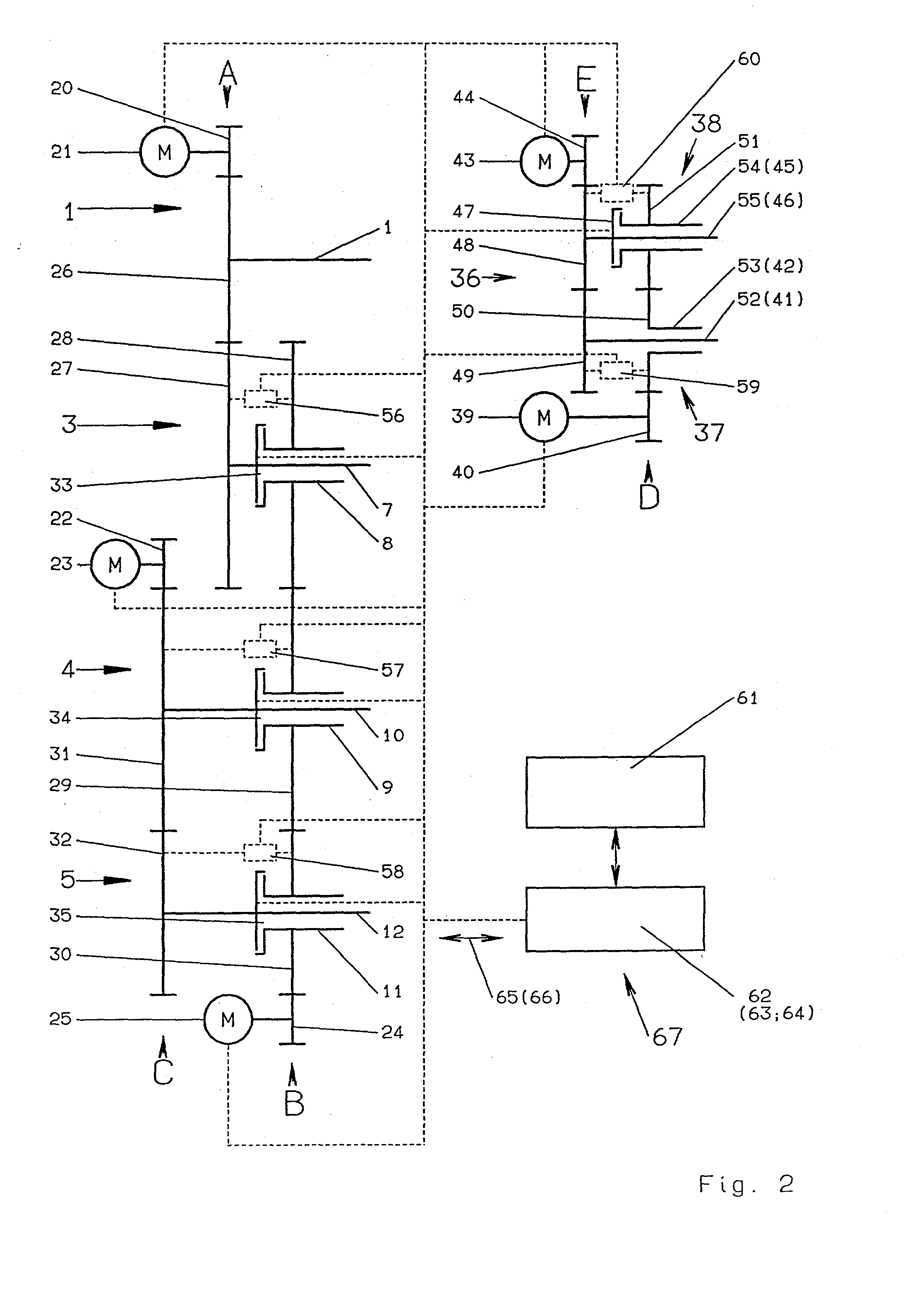
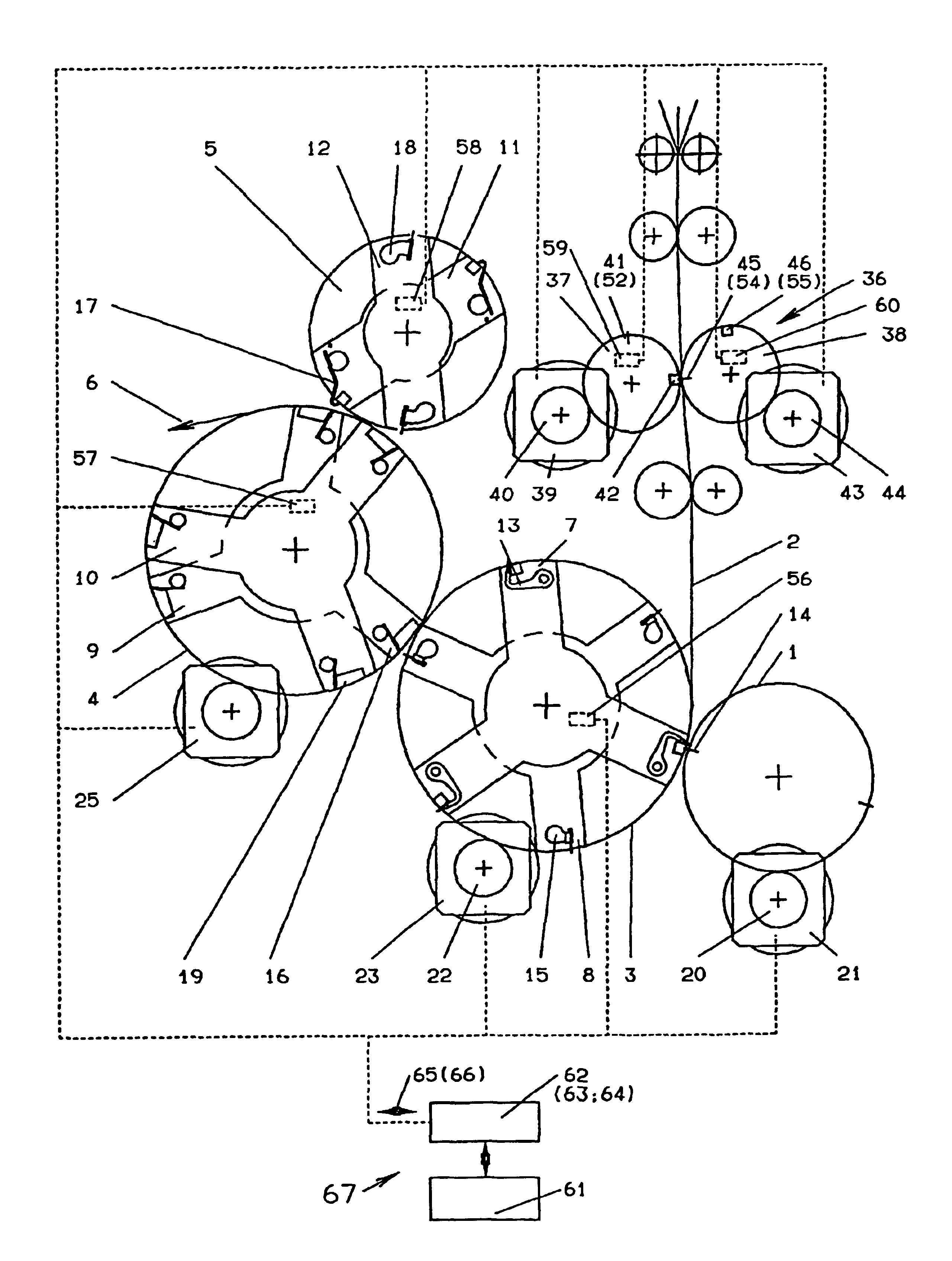
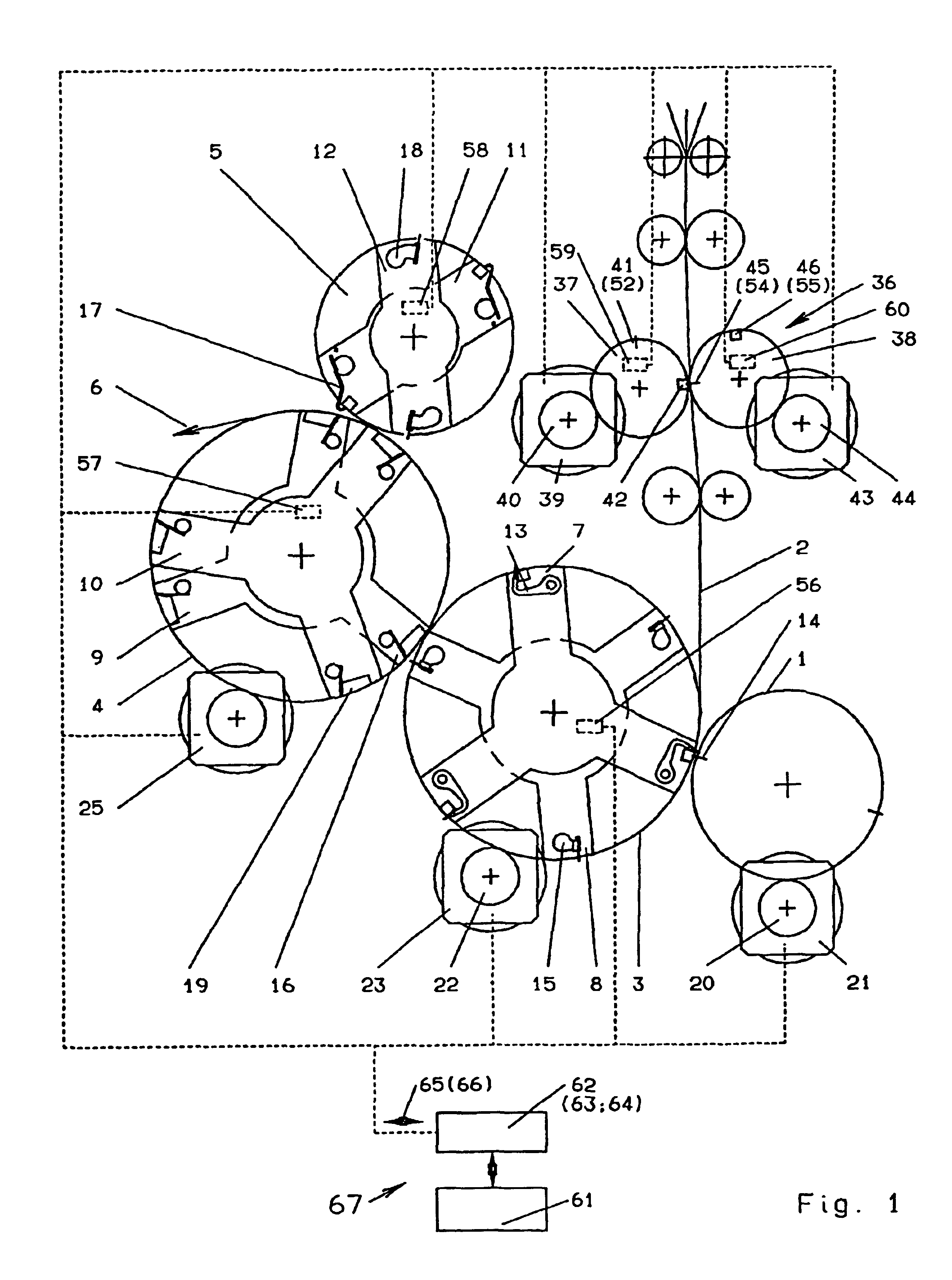
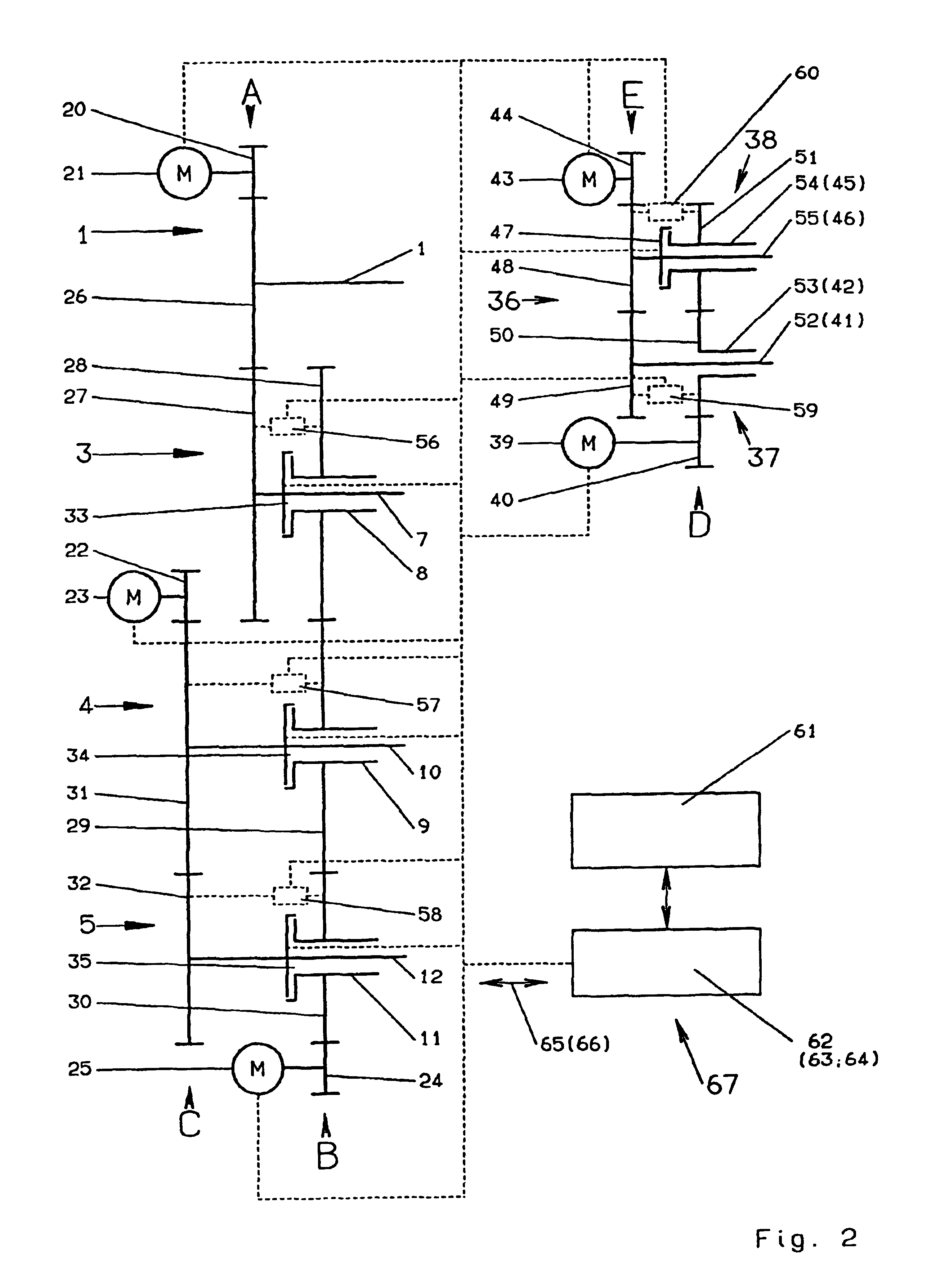
Drive for a folder
InactiveUS20020185022A1Transmission of oscillations between the subsystems is minimizedMinimize transmissionMechanical working/deformationFolding thin materialsDrive motorKnife blades
A low-oscillation and space-saving drive for a changeable format folder of a rotary printing is provided, the rotary printing machine having rotating subassemblies that can be driven, in particular a cutting cylinder, a pin folding blade cylinder, a folding jaw cylinder, a gripper folding blade cylinder, and perforating cylinders belonging to a perforating device. The drive is split up into individual subsystems, and each subsystem is assigned a controlled-position drive motor. In the event of failure of a drive motor, the drive continues to operate without functional impairment.
Owner:MANROLANAD AG
Medicinal compositions improving brain function and method for improving brain function
An alkyl ether derivative represented by the formula:wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, m and n are as defined in the specification, or salts thereof exhibits synergistically improved anti-hypoxic activity when combined with a compound having an acetylcholine esterase inhibitory activity. Therefore, the combination according to the present invention is useful as a method for improving cerebral function. Further, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound relating to the combination according to the present invention is useful for treatment and prevention of dysfunction of cerebral acetylcholine neurons in the sequelae of cerebrovascular dementia, senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease and ischemic cerebral lesion and in the cerebral apoplexy or the memory impairment caused by selective neuronal death.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
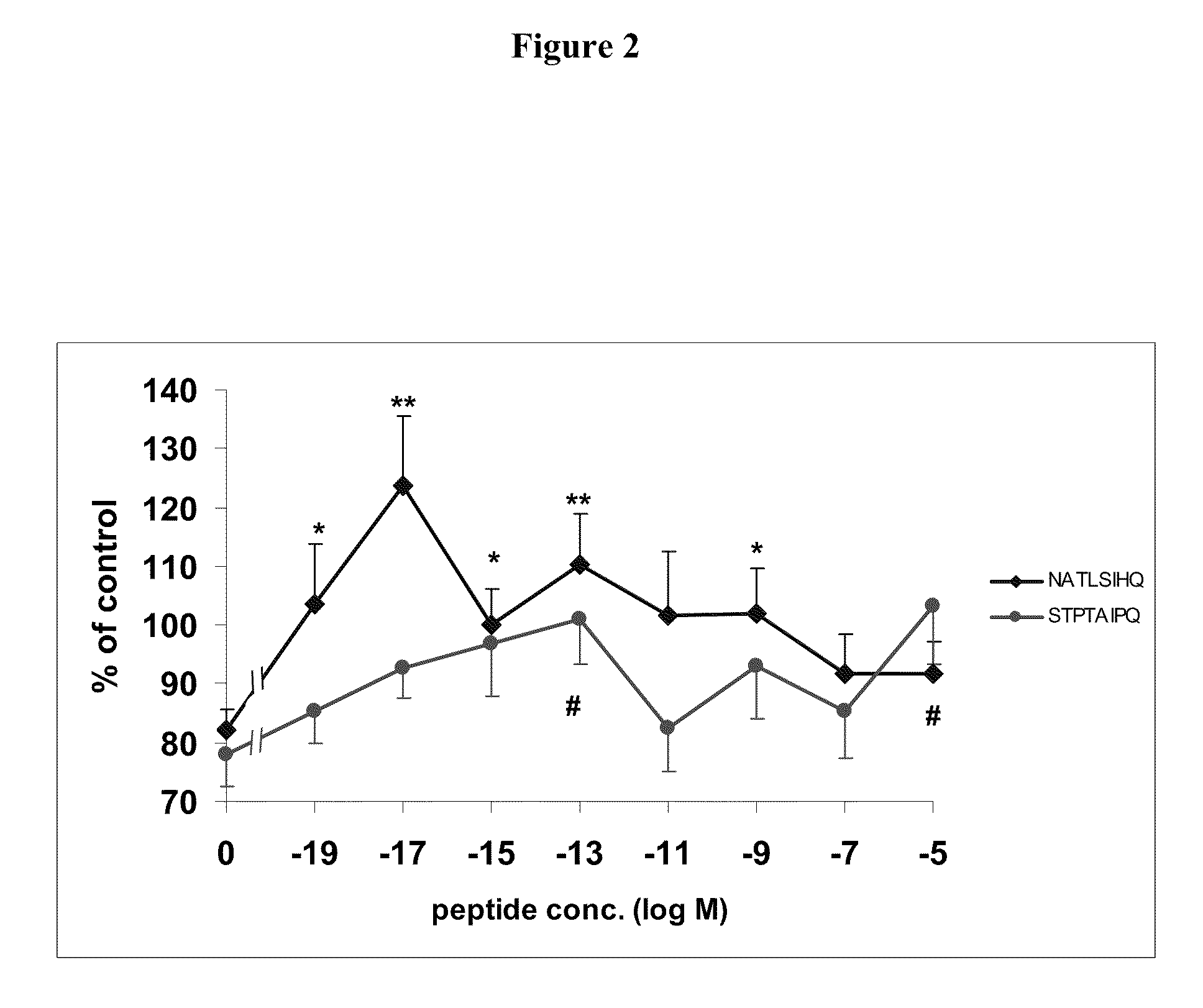
Neuroprotection using NAP-like and SAL-like peptide mimetics
This invention relates to NAP-like and SAL-like peptide mimetics, polypeptides, or small molecules derived from them, and their use in the treatment of neuronal dysfunction, neurodegenerative disorders cognitive deficits, neuropsychiatric disorders, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Drug compositions and methods for preventing and treating thrombosis or embolism
InactiveUS20090281074A1Potent FXa-inhibiting effectExhibit some effectBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseExtracorporeal circulation
Drug compositions containing a substituted diamine compound represented by formula (1):Q1-Q2-r-N(R1)-Q3-N(R2) (1)wherein Q3 represents the following groupwherein Q5 represents an alkylene group having 4 carbon atoms, R3 represents a hydrogen atom, and R4 represents a 3-6 membered heterocyclic group which may be substituted; are useful for preventing and / or treating cerebral infarction, cerebral embolism, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, pulmonary infarction, pulmonary embolism, Buerger's disease, deep venous thrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, thrombus formation after artificial valve or joint replacement, thrombus formation and reocclusion after angioplasty, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), thrombus formation during extracorporeal circulation, or blood clotting upon blood drawing.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Choline esters useful for the treatment of cognitive dysfunctions and enhancement of memory, learning and cognition
InactiveUS20060205815A1Improve behaviorEasy to learnBiocideOrganic chemistryMammalFunctional impairment
The present invention provides compounds of formula I described herein. The present invention also provides a method of treating a cognitive dysfunction in a mammal. The method includes administering to the mammal an effective amount of a compound of formula I described herein (e.g., stearyl choline chloride).
Owner:PATEL HASS
Sapogenin derivatives, their synthesis and use, and methods based upon their use
InactiveUS20040147495A1Facilitate transmissionIncreased activationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicineSynthesis methods
The invention discloses certain steroidal sapogenins and derivatives thereof, and their use in the treatment of cognitive dysfunction, non-cognitive neurodegeneration, non-cognitive neuromuscular degeneration, and receptor loss in the absence of cognitive, neural and neuromuscular impairment. Methods of synthesis, treatment and pharmaceutical compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYTOPHARM LTD
Acylguanidine derivative
InactiveCN101627013AEnhance pharmacological effectsPrevent dementiaOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmacologic actionReceptor
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel and excellent agent for treating or preventing dementia, schizophrenia and the like, based on the 5-HT 5A receptor modulating action. It was confirmed that a compound characterized by a structure that a tricyclic hetero ring having a pyrrole ring at the center and guanidine are bonded via a carbonyl group has a potent 5-HT 5A receptor modulating action and an excellent pharmacological action based thereon, and thus, it was found that the compound can be an excellent agent for treating or preventing dementia, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, particularly for memory-related functional disorders such as cognitive impairments including dementia and schizophrenia, thereby completing the present invention.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
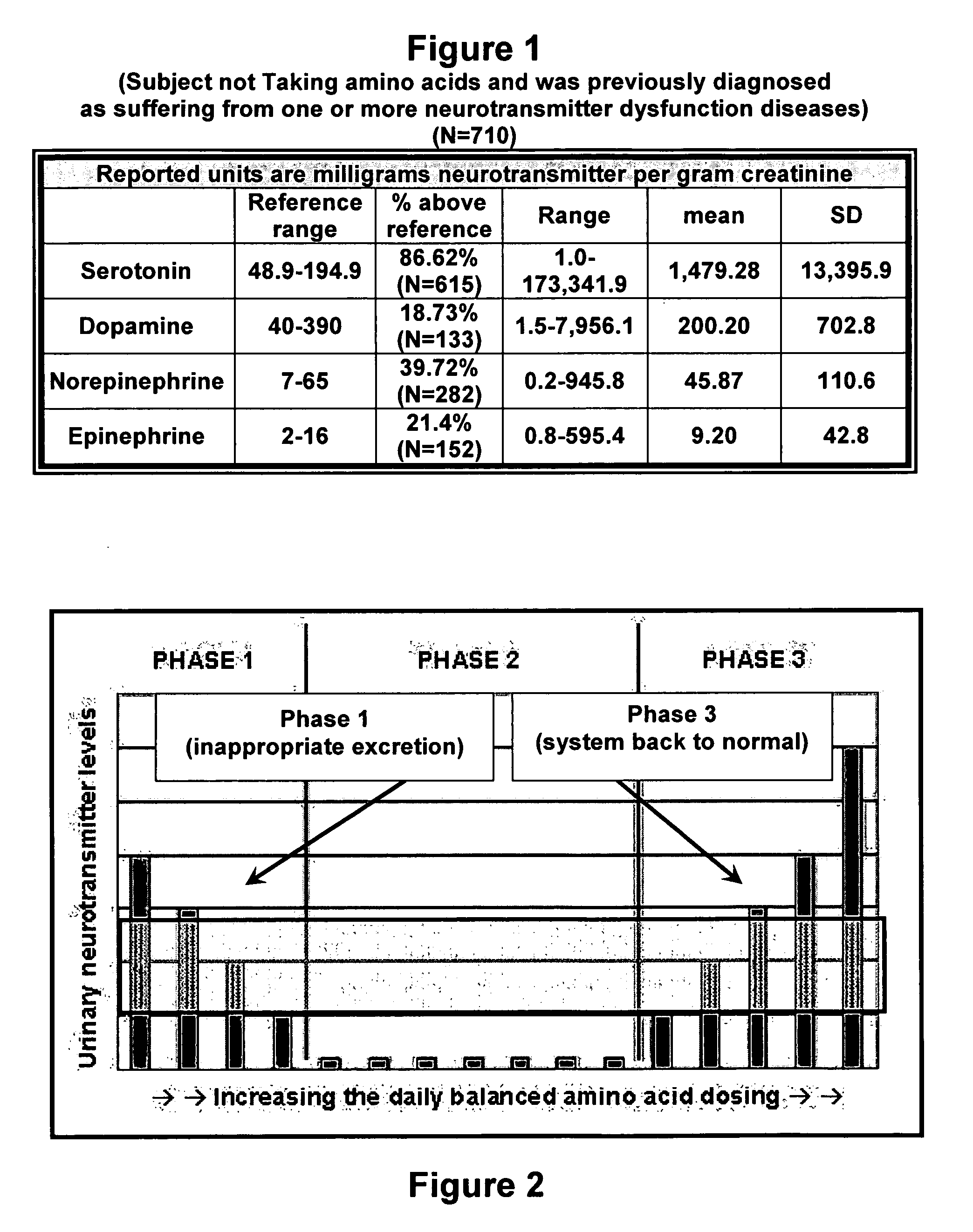
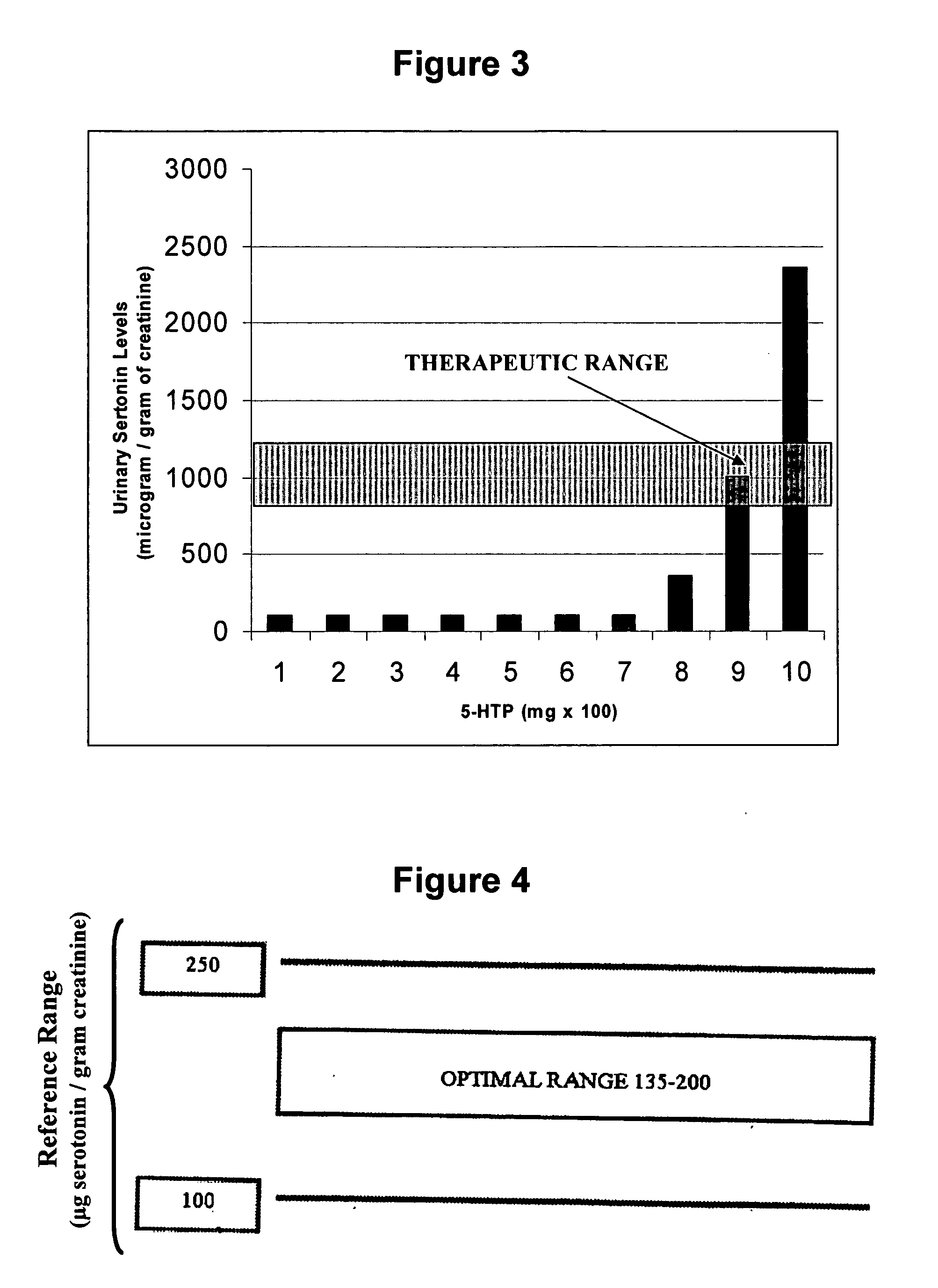
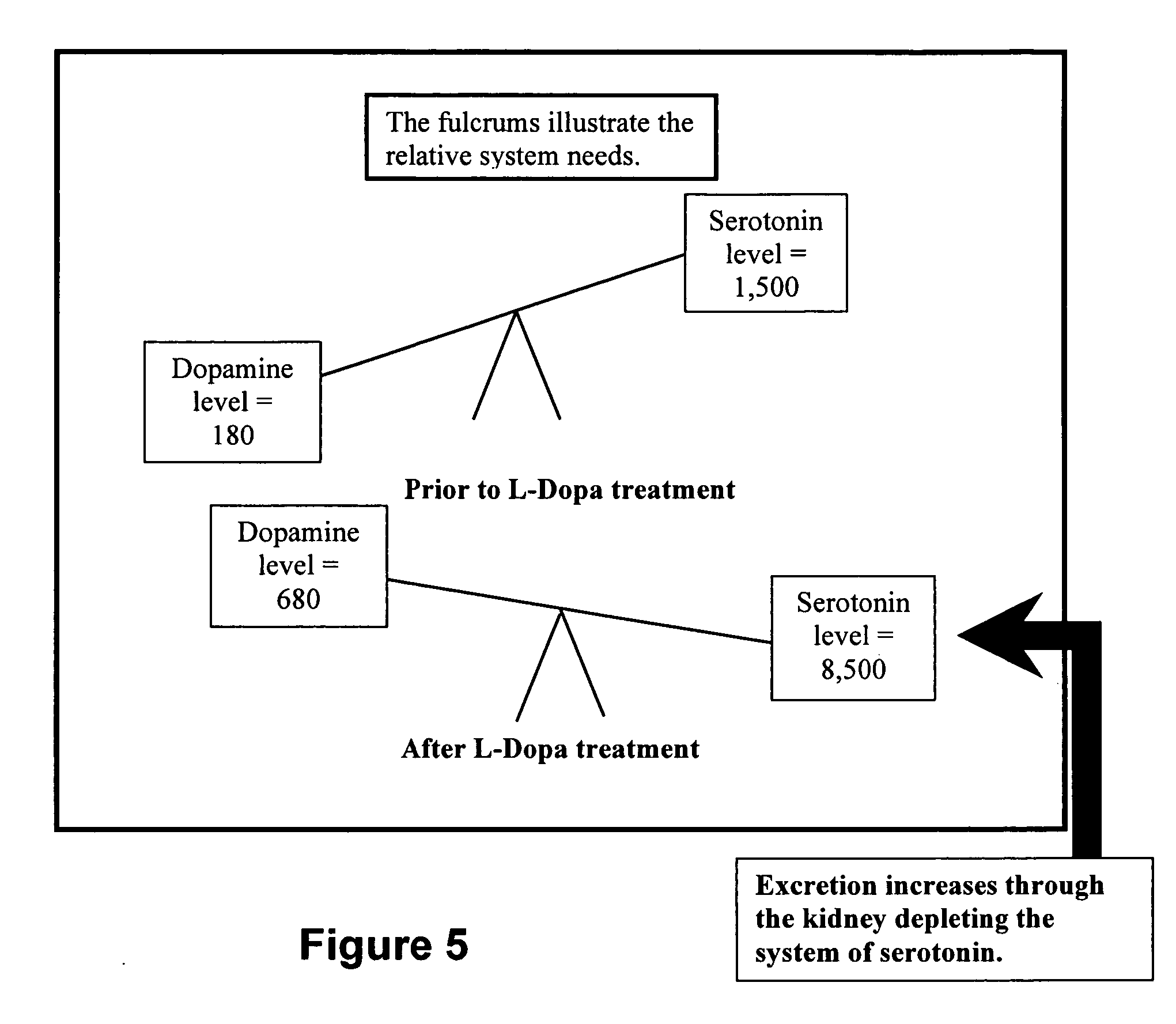
Serotonin and catecholamine segment optimization technology
InactiveUS20060110325A1Risk minimizationLeveling precisionBiocideBiological testingSerotoninCatecholamine
Methods of using amino acid precursors of the serotonin and catecholamine neurotransmitter systems and laboratory urinary assay of serotonin and catecholamine neurotransmitter levels for optimal treatment of neurotransmitter dysfunction and dysfunction of systems regulated or controlled by the serotonin and / or catecholamine neurotransmitter systems. The methods may also include determining a urinary neurotransmitter phase response to a change in dosing of supplemental amino acid precursors of the serotonin and catecholamine neurotransmitters to optimally treat neurotransmitter dysfunction and dysfunction of systems regulated or controlled by the serotonin and / or catecholamine neurotransmitter systems.
Owner:FEDERAL LAW ENFORCEMENT DEV SERVICES
Drive for a folder
InactiveUS6776750B2Transmission of oscillations between the subsystems is minimizedMinimize transmissionMechanical working/deformationFolding thin materialsEngineeringDrive motor
A low-oscillation and space-saving drive for a changeable format folder of a rotary printing is provided, the rotary printing machine having rotating subassemblies that can be driven, in particular a cutting cylinder, a pin folding blade cylinder, a folding jaw cylinder, a gripper folding blade cylinder, and perforating cylinders belonging to a perforating device. The drive is split up into individual subsystems, and each subsystem is assigned a controlled-position drive motor. In the event of failure of a drive motor, the drive continues to operate without functional impairment.
Owner:MANROLANAD AG
Optimized cardiac contraction through differential phosphorylation of myosin
InactiveUS20040126860A1Reduce the amplitudeReduce impactVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDifferential effectsCardiac dysfunction
The present disclosure provides a cDNA, protein sequence, and genomic structure of the human cardiac isoform of myosin light chain kinase (cMLCK), and describes mutations in the cMLCK gene that are associated with cardiac dysfunction. Methods are provided for identifying individuals who can harbor mutations in the cMLCK gene, or carry alleles that can predisposed them to cardiac dysfunction. Disclosed also is a significant role for cMLCK in modulating cardiac contractility. The cMLCK protein is shown herein to reduce the amplitude of stretch activation and increase the tension production, a property of muscle which has heretofore had an unknown role in cardiac contraction. Moreover, the cMLCK protein is shown to be regionally distributed in the heart, thereby having differential effects on contractility and stretch activation. Methods herein are provided to exploit this effect of cMLCK, to treat individuals who have or are prone to cardiac dysfunction. In addition, methods are provided to identify agents that modulate cMLCK activity, thereby having potential therapeutic importance in the treatment of cardiac dysfunction.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
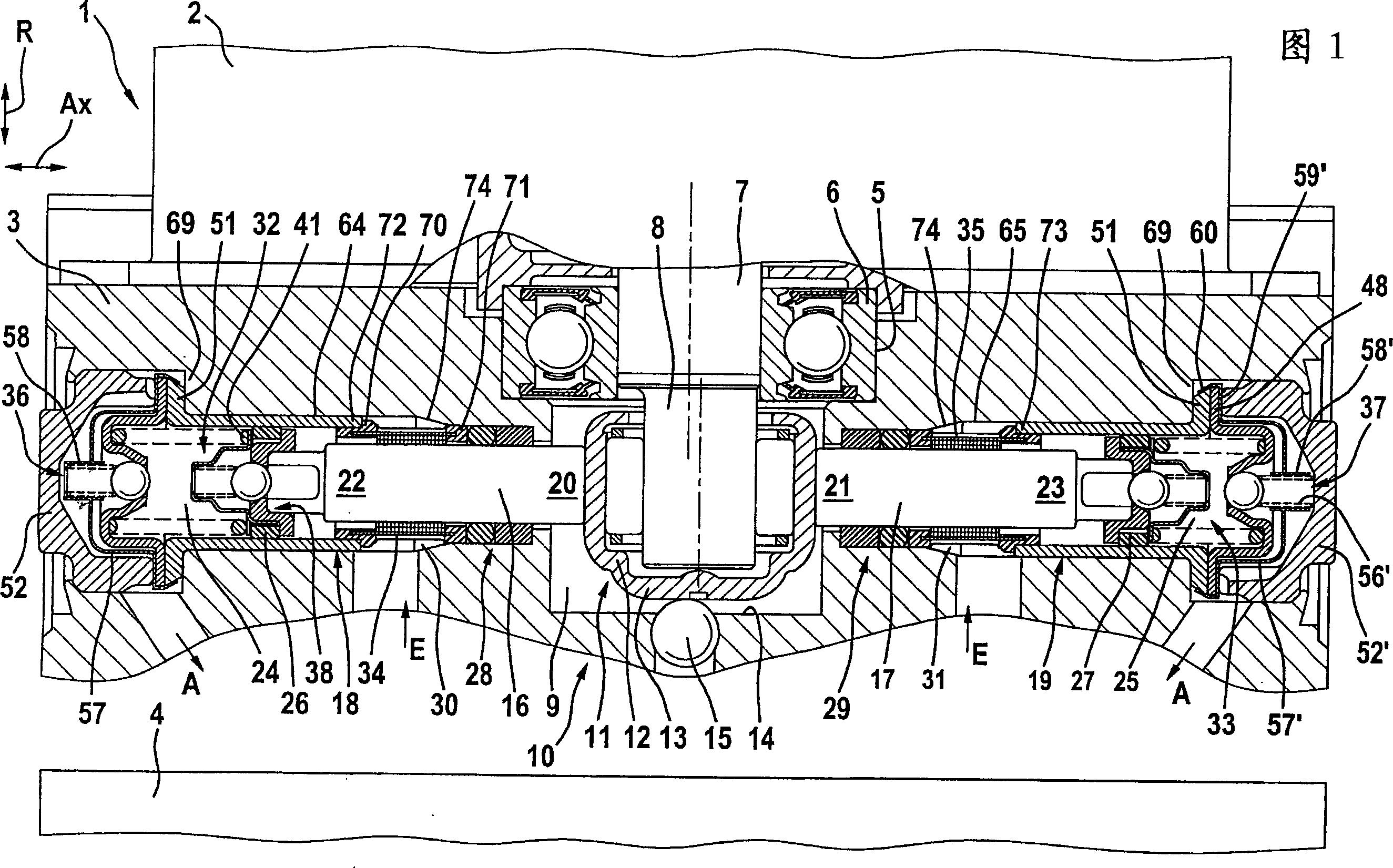
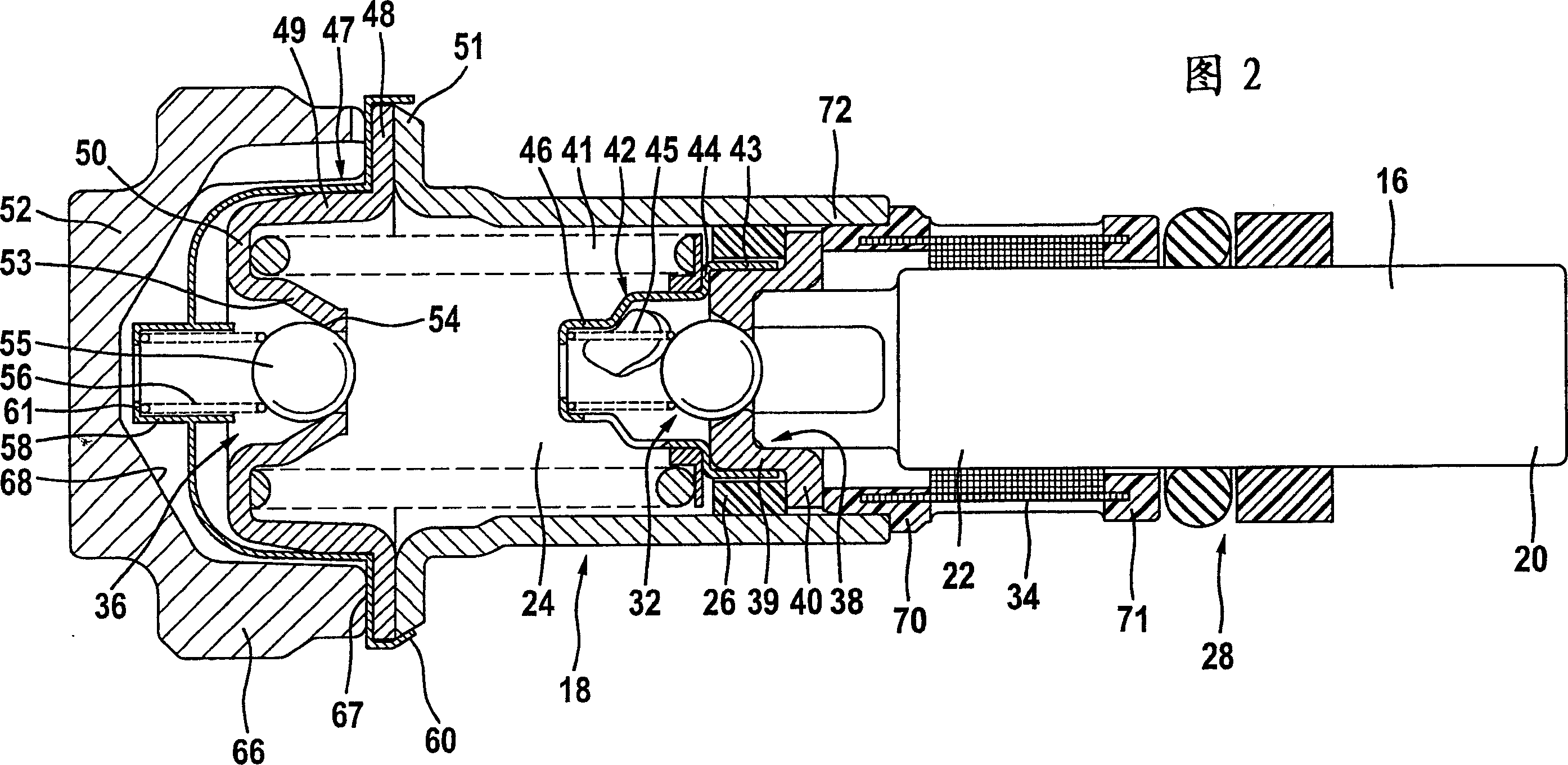
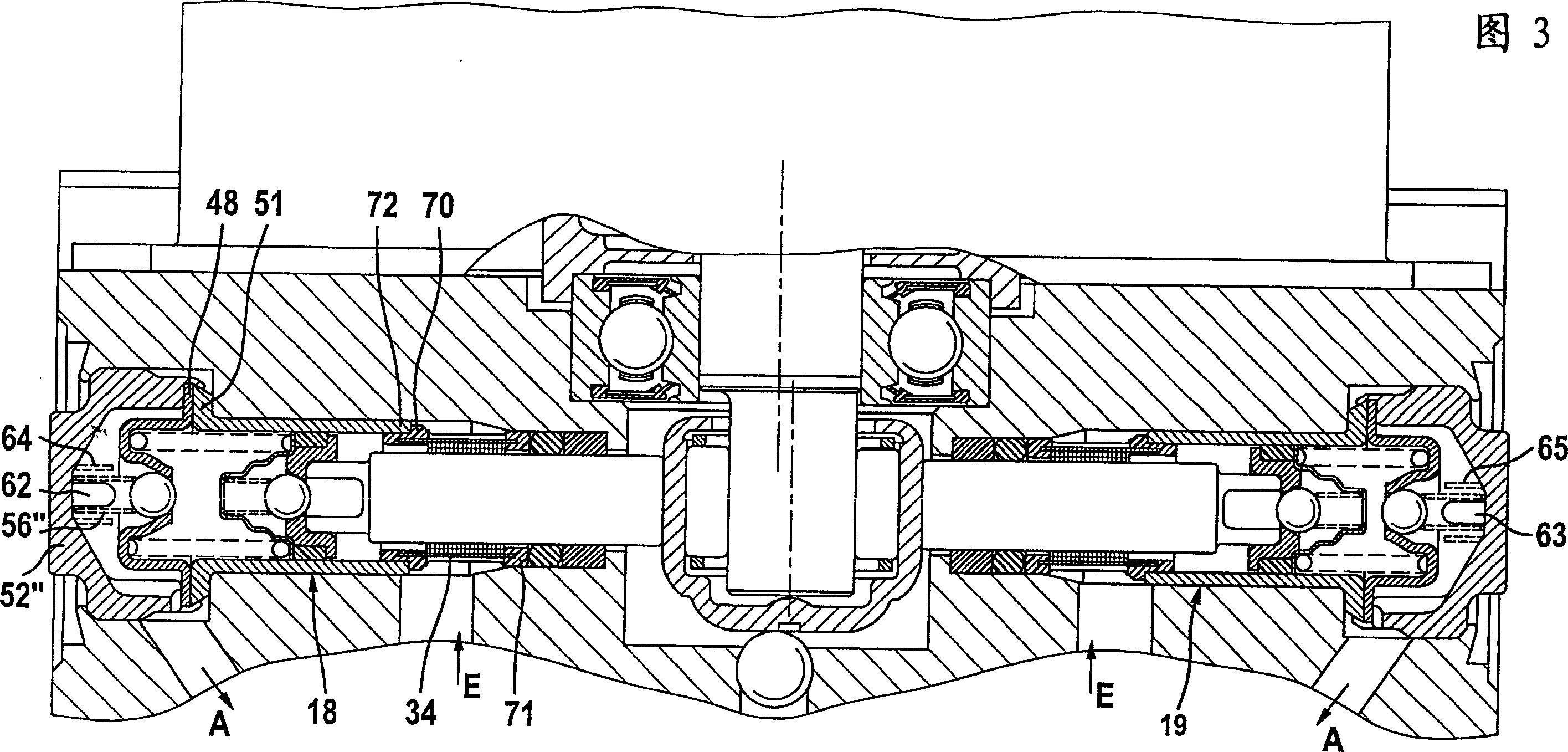
Piston pump
ActiveCN1748084AAvoid deformationLayout size shortPositive displacement pump componentsPump/compressor arrangementsEngineeringFunctional impairment
The invention relates to a piston pump (10) for supplying a pressure medium to at least one vehicle brake, a main cylinder, a pressure medium container, or a pressure medium store, of a regulated vehicle brake installation. The aim of the invention is to enable a piston pump (10) joined to a structural unit to be integrated into a receiving body (3) in a simple manner and in such a way that the construction space is reduced. The invention also aims to keep valve seats (38, 54) of check valves (32,33,36,37) as free as possible from pressing or fixing forces, in order to prevent the deformation or functional impairment thereof. To this end, a sleeve (18,19) has a radial flange for fixing between the closing element (52) and the receiving body (3).
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE TECH GMBH
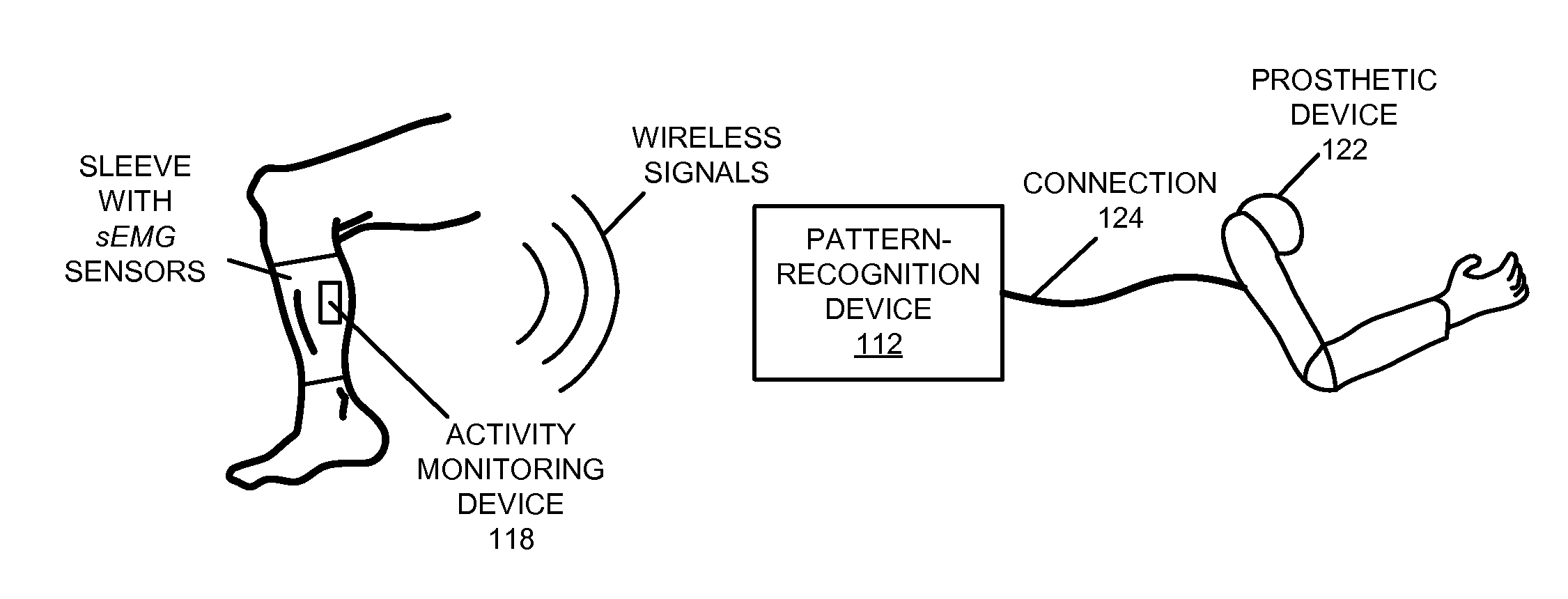
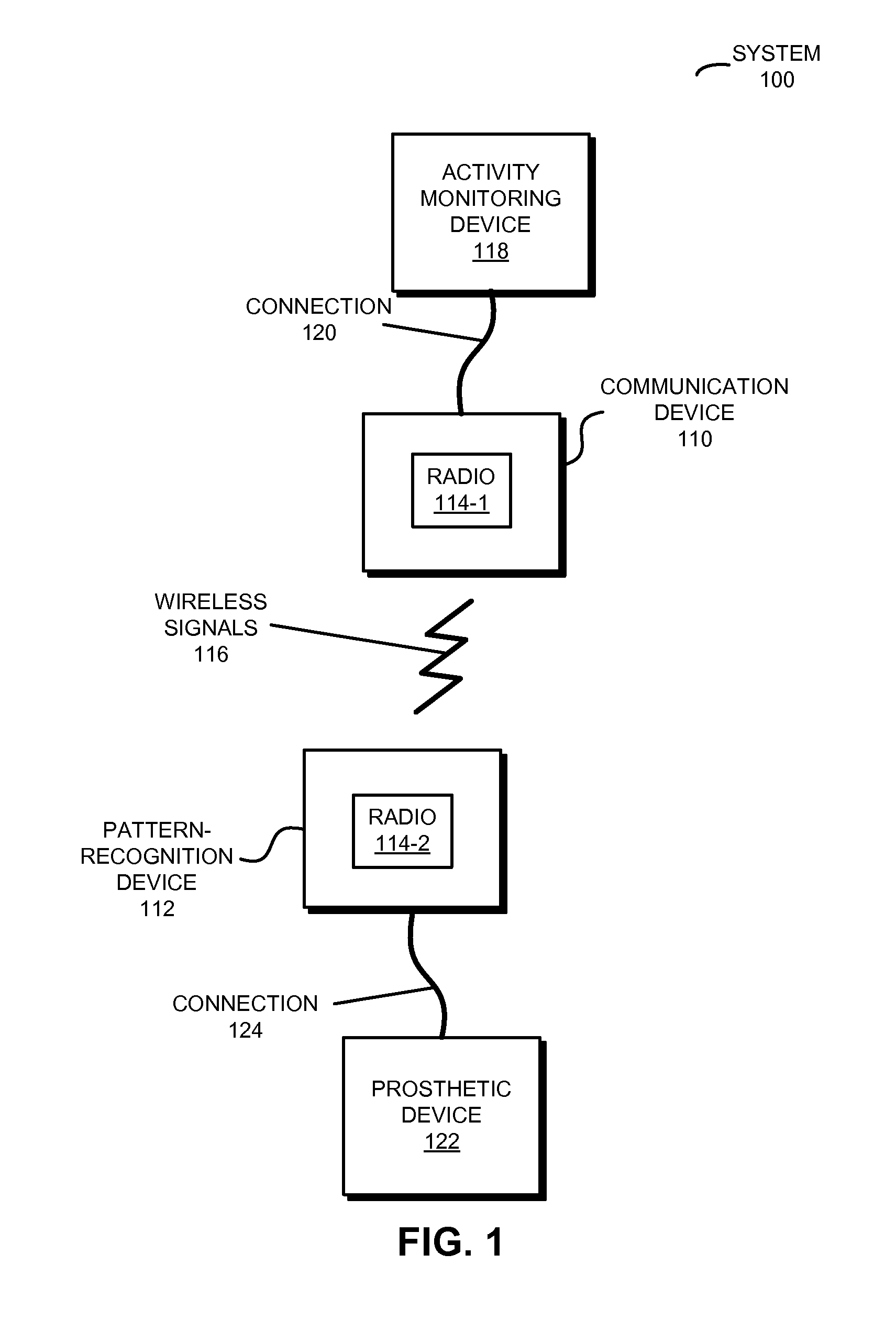
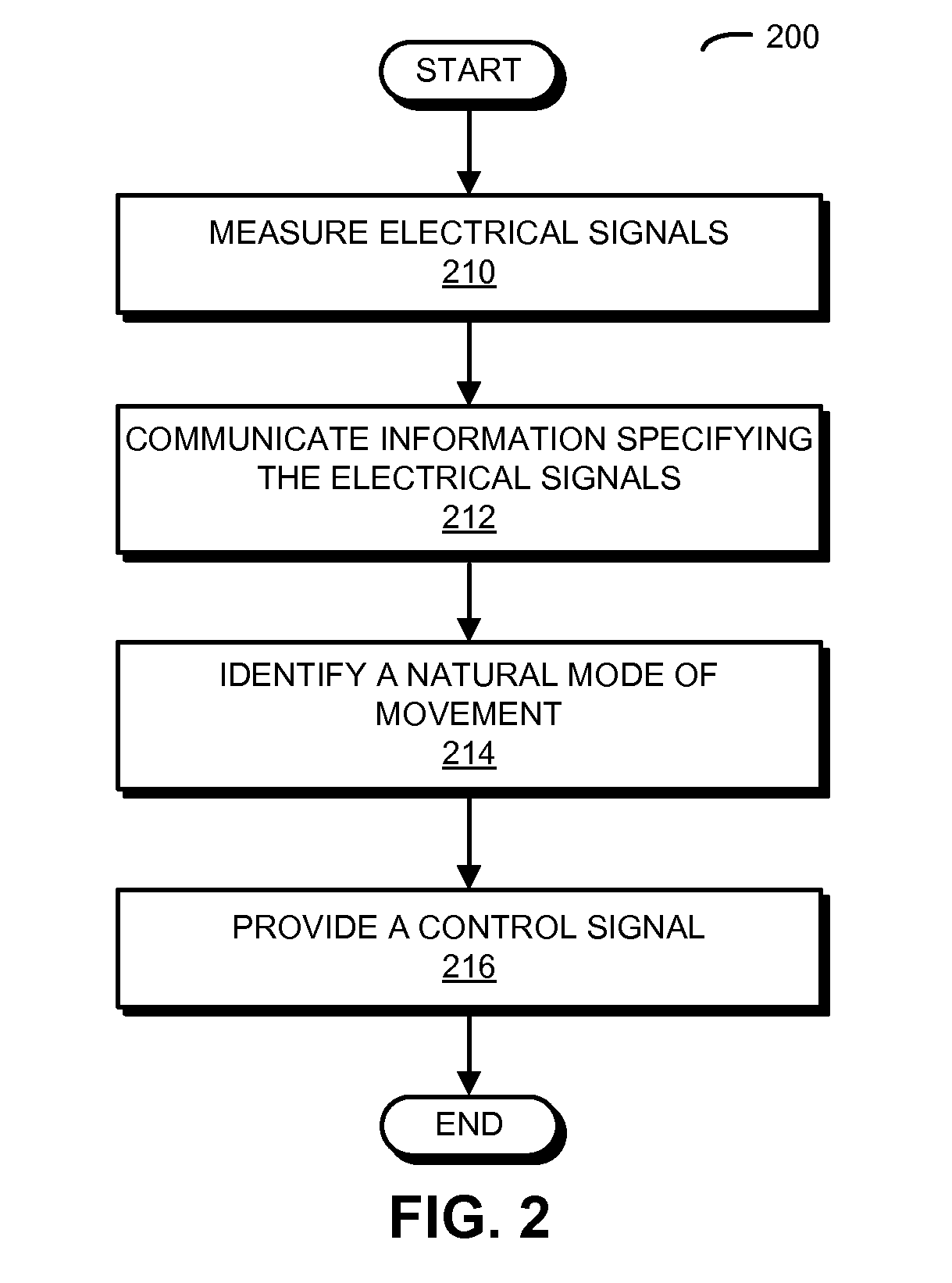
Intuitive prosthetic interface
A prosthetic device is controlled based on measured electrical signals corresponding to muscle activity in a lower-extremity anatomical analog to a dysfunctional or absent portion of an upper extremity of an individual. In particular, an activity monitoring device measures electrical signals corresponding to muscle activity in the lower-extremity anatomical analog. Then, a communication device communicates information specifying the electrical signals to a pattern-recognition device. The pattern-recognition device identifies a natural mode of movement of the lower-extremity anatomical analog based on the information. For example, the natural mode of movement may be identified using a pattern-recognition technique. Next, the pattern-recognition device provides a control signal to a prosthetic device associated with the dysfunctional or absent portion of the upper extremity, where the control signal specifies a natural mode of movement of the prosthetic device that is an analog to the natural mode of movement of the lower-extremity anatomical analog.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Color coded anatomical and non-anatomical sticker labels to be used on medication bottles to identify what medication is used for and when medication is due to be administered
Current medication labels are very difficult for people with disabilities, language barriers, functional impairments, or illiteracy to read, potentially increasing the risk for accidental medication overdoses and / or poor compliance with medication administration and adherence. By having a color coded sticker system with an enclosed full body guide in the form of a poster, and a home health medication record card, these stickers are placed on each medication bottle as a symbol for what the medication is used for. The stickers are color coded in order to distinguish the time the medication is to be administered. Home health agencies may use the poster and stickers as they educate their patients about the medications they take.
Owner:DOIRON WHITNEY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com