Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Forward looking infrared" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation. The sensors installed in forward-looking infrared cameras, as well as those of other thermal imaging cameras, use detection of infrared radiation, typically emitted from a heat source (thermal radiation), to create an image assembled for video output.
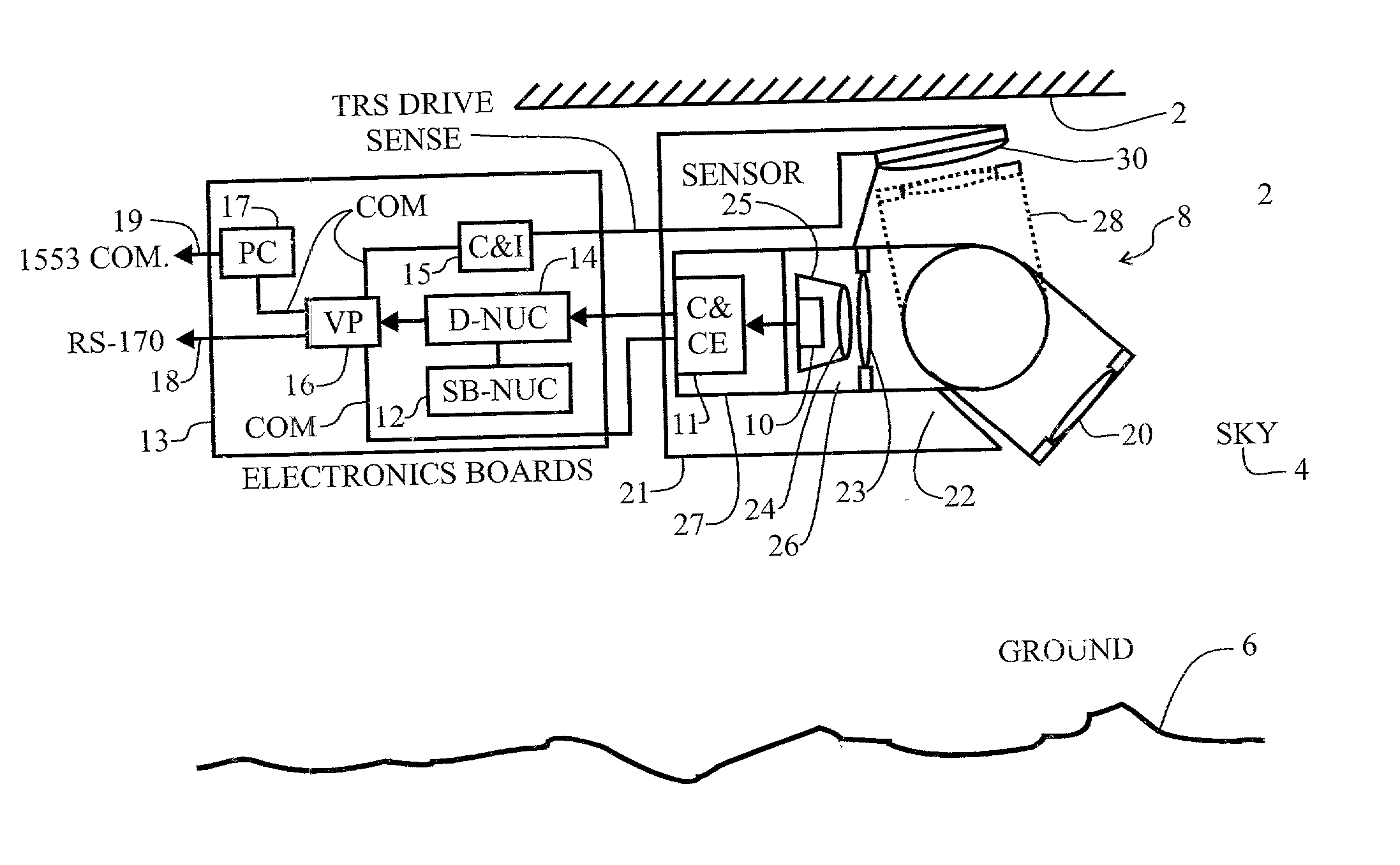
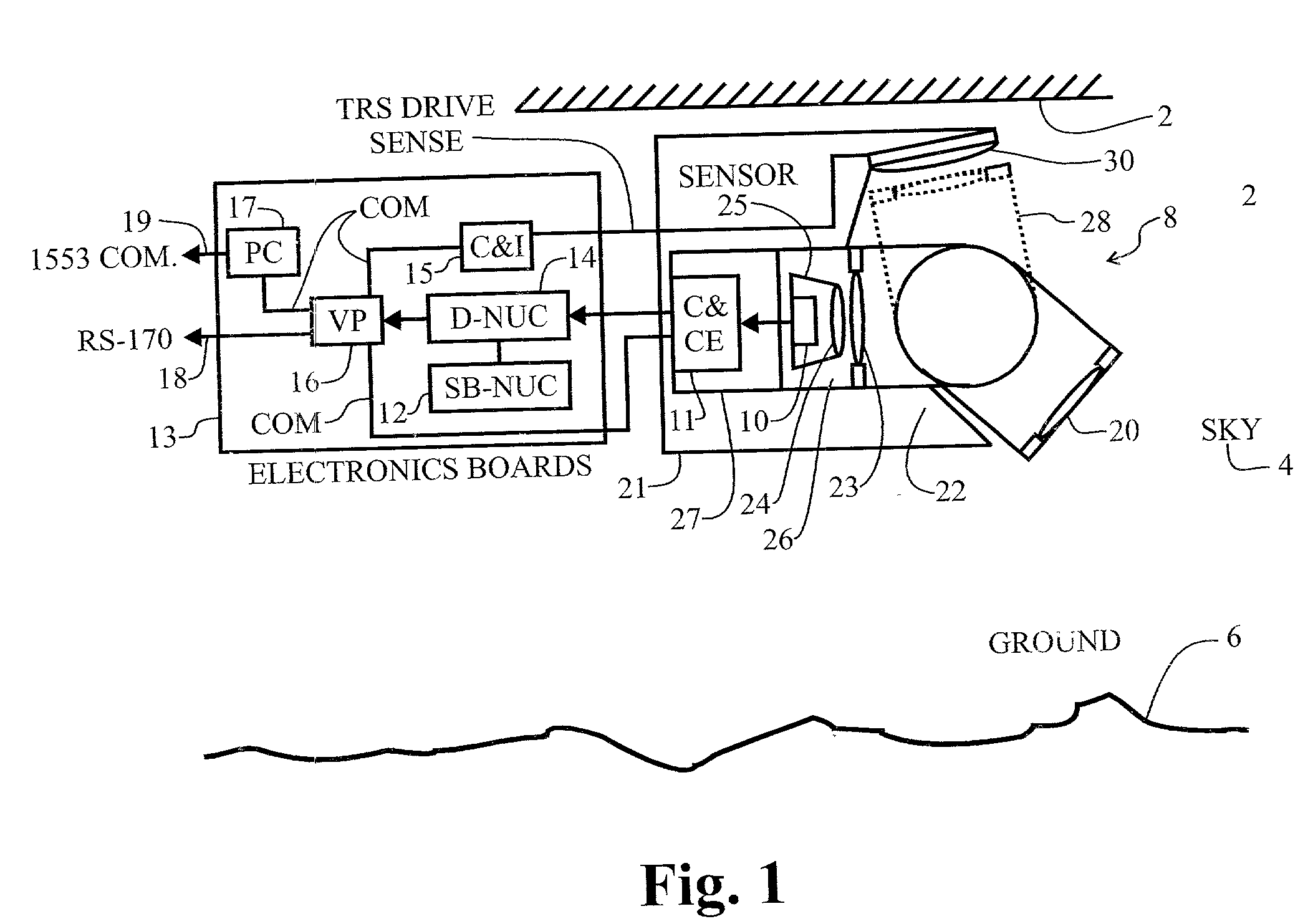
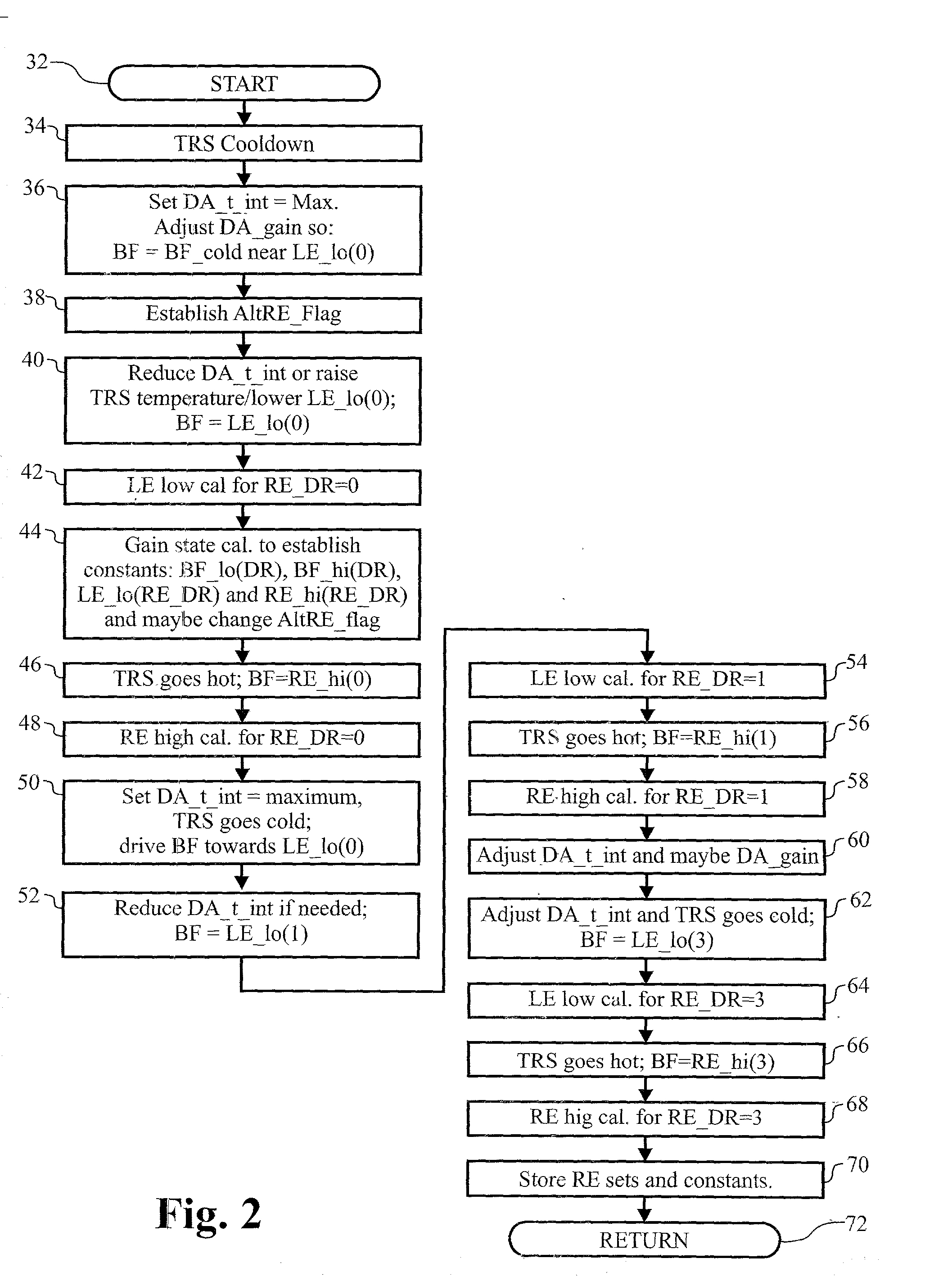
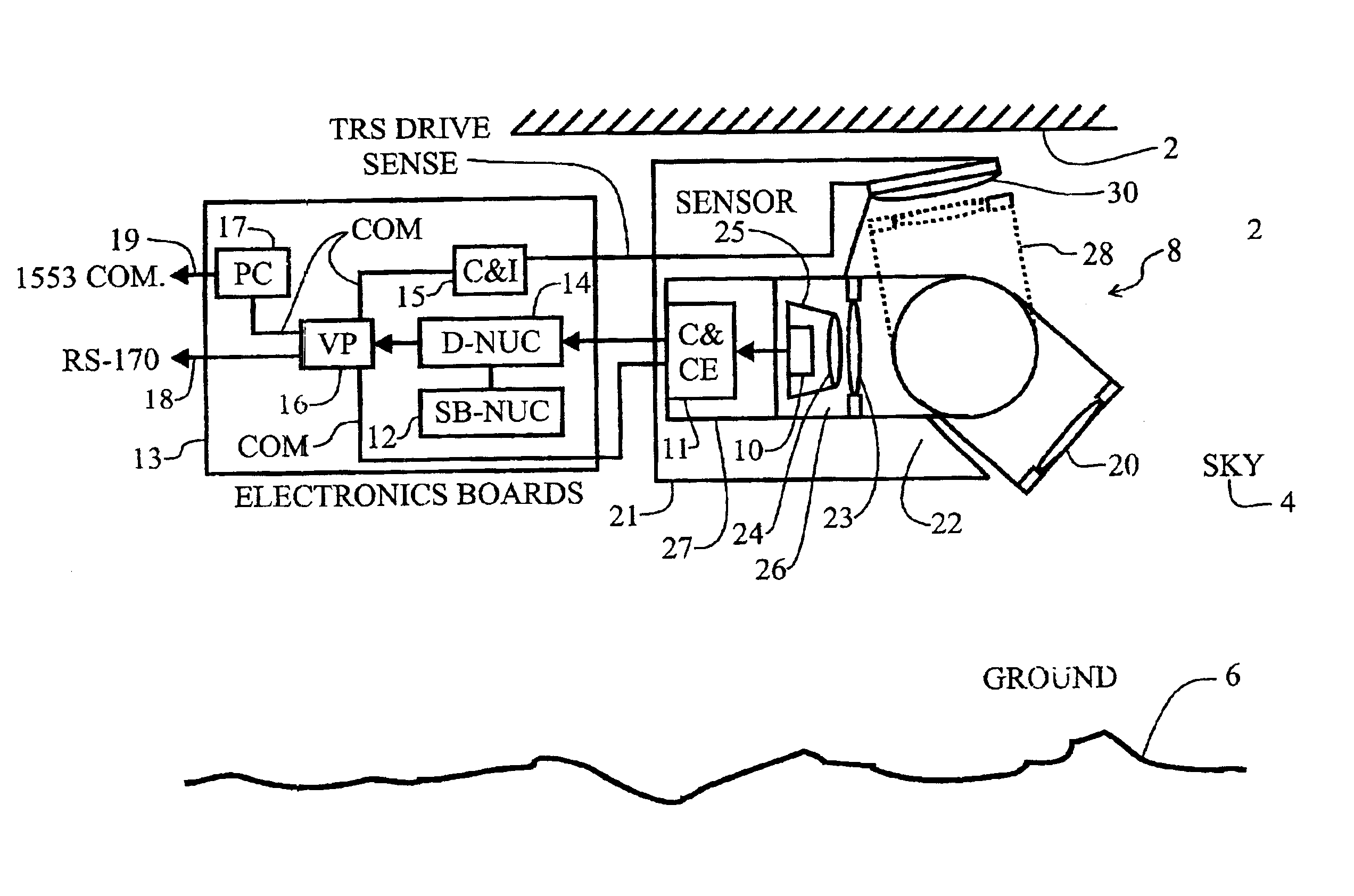
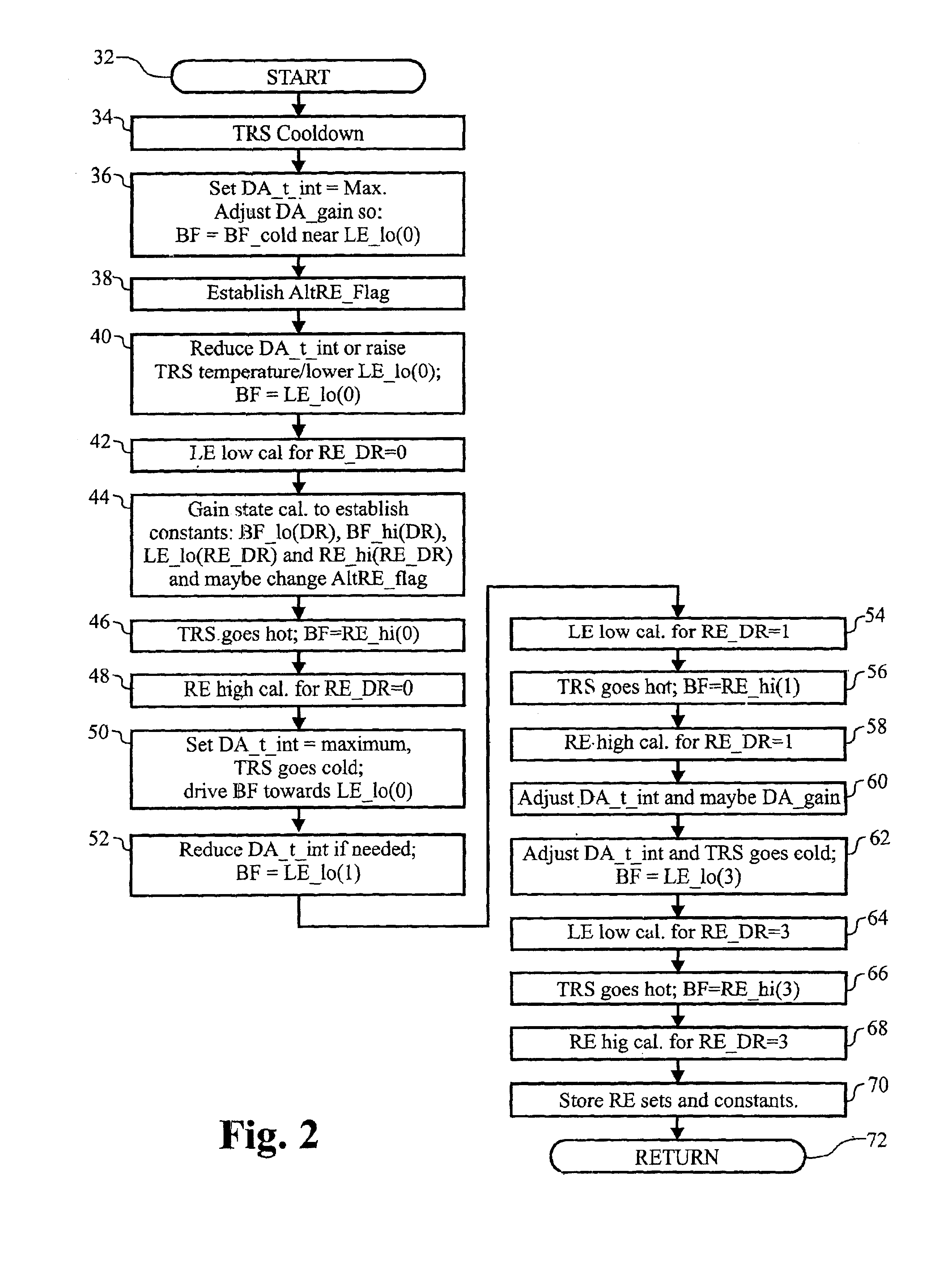
Display uniformity calibration system and method for a staring forward looking infrared sensor
InactiveUS20030183756A1Eliminate needHysteresis effectTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesHysteresisEngineering
A method and system for maintaining uniformity in a FLIR display. During a one-time initialization procedure, a plurality of dynamic ranges are defined by covering a specific range of bucket fill levels when in a certain gain. To cover all dynamic ranges possible, a plurality of pairs of responsivity equalization (RE) calibrations (each pair producing a RE set of pixel gain corrections) are also accomplished in the same one time initialization period. A plurality of corresponding level equalization (LE) calibrations (each using the appropriate calibrated RE set and producing a LE set of pixel level corrections) for each anticipated dynamic range are made at every power-up initialization. Each of the calibrations is done with respect to a thermal reference source to produce a uniform scene at the desired bucket fill level. An algorithm is employed which forces the two bucket fill points defined during the responsivity calibration to span as far as possible the dynamic range and forces the level equalization bucket fill point to fall within the two bucket fill points of the responsivity calibration. Then, during an operational time period, the scene and optics temperatures are monitored, and if the average bucket fill value exceeds the bucket fill range of the present dynamic range, the presently selected dynamic range is changed to a second dynamic range (gain is changed along with the RE set and LE set). The dynamic ranges are designed to overlap so that a hysteresis effect is achieved. The pre-calibrations and automatic dynamic range switching prevent saturation and create the best uniformity (lowest fix pattern noise) possible while allowing for continuous operation of the FLIR system, thus eliminating the interruption caused by the prior art touch-up calibration procedure.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Disaster condition acquisition system
InactiveCN101979961AImprove quick response abilityHigh speedTransmission systemsSatellite radio beaconingDisaster areaImaging analysis
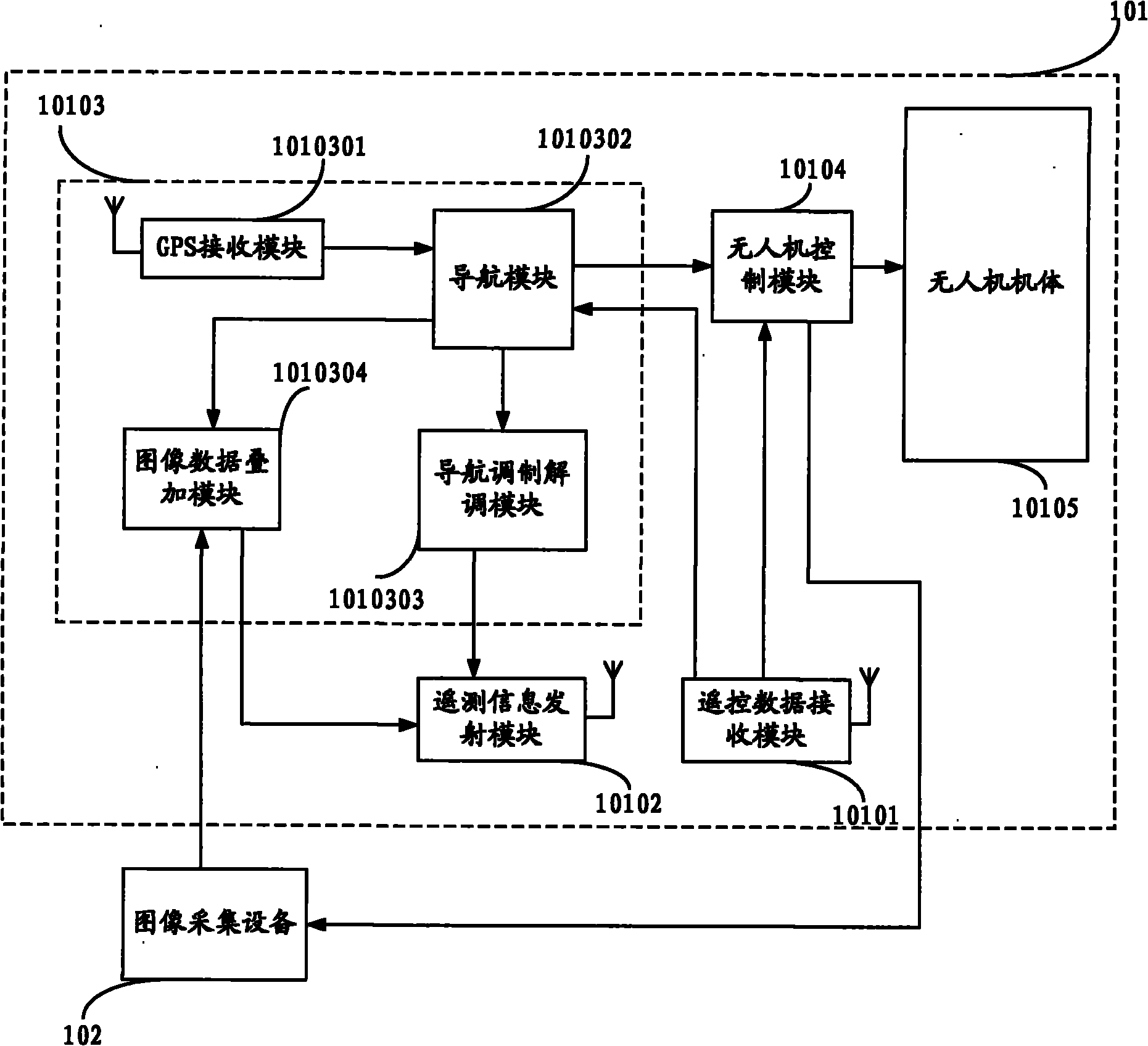
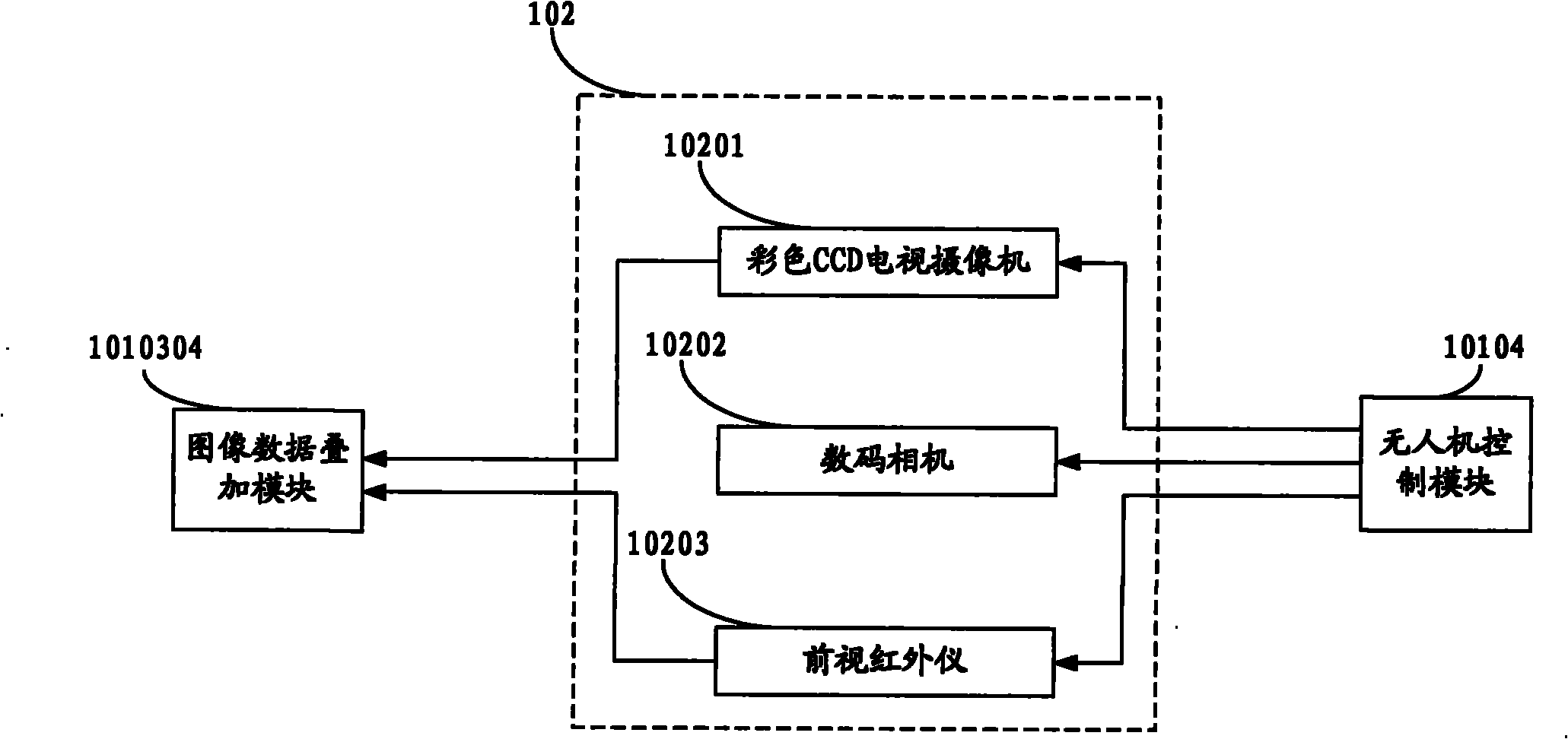
The invention relates to a disaster condition acquisition system capable of quickly acquiring disaster conditions after a disaster. Disaster condition images of a disaster area are acquired in real time by controlling an unmanned aerial vehicle to fly over the disaster area and using image acquisition equipment such as a video camera, a digital camera, a forward looking infrared unit and the like carried by the unmanned aerial vehicle, and the disaster condition images are transmitted to an image analysis device on the ground in real time; and the image analysis device processes the disaster condition images returned by the unmanned aerial vehicle in real time to acquire the disaster condition images of the disaster area in shortest time. The system breaks through the adverse situation that disaster relief is delayed because the communication of the disaster area is interrupted and the disaster conditions of the disaster area cannot be acquired in time after a catastrophe such as an earthquake and the like; and the system can provide first hand information for activities of quickly organizing rescue and relief work and reconstruction work after the disaster.
Owner:INST OF GEOPHYSICS CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
System and method for electronic stabilization for second generation forward looking infrared systems
InactiveUS6720994B1Television system detailsColor television detailsControl signalForward looking infrared
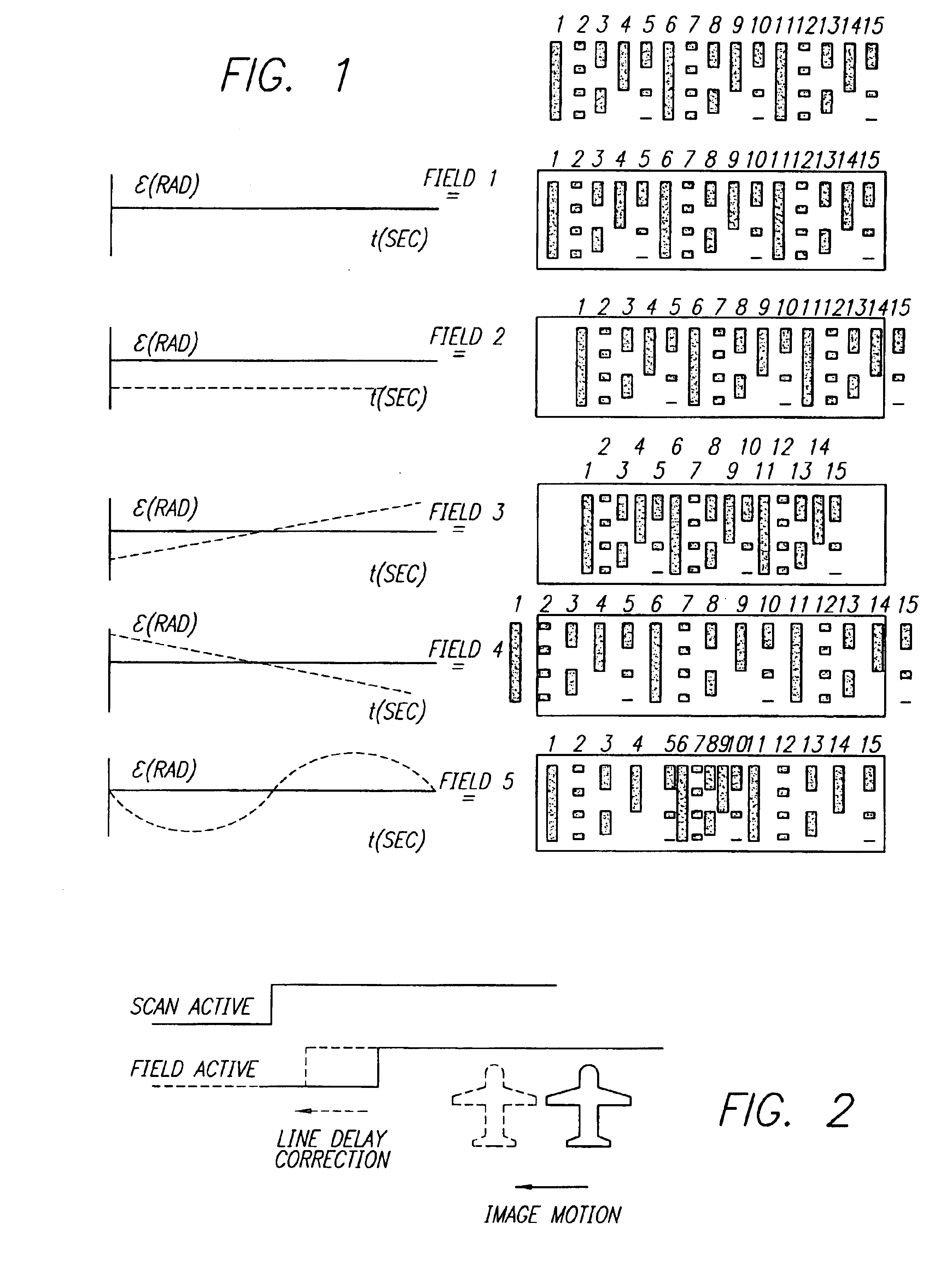
An image stabilization system and method. The inventive system (100) includes an image sampling circuit (230) mounted on a platform (400) for sampling an image in response to timing control signals and outputting a plurality of imaging signals in response thereto. An azimuth resolver (310) detects vibration of the platform and providing a signal in response thereto. A microprocessor (540) adjusts the timing control signals to cause the image sampling circuit (230) to sample the image and thereby compensate for an effect of vibration on the image. In the illustrative embodiment, the microprocessor (540) includes software for compensating for vibration that causes image offset, compressed images, expanded images, and compression and expansion within a single field. The invention provides image stabilization in a purely electronic manner without the need for any moving parts that would typically require control hardware and a significant amount of space. In addition, since LOS motion compensation takes place as the image is being sampled, this method eliminates the need for the large amounts of memory required to store a field of video as well as LOS information for post processing.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
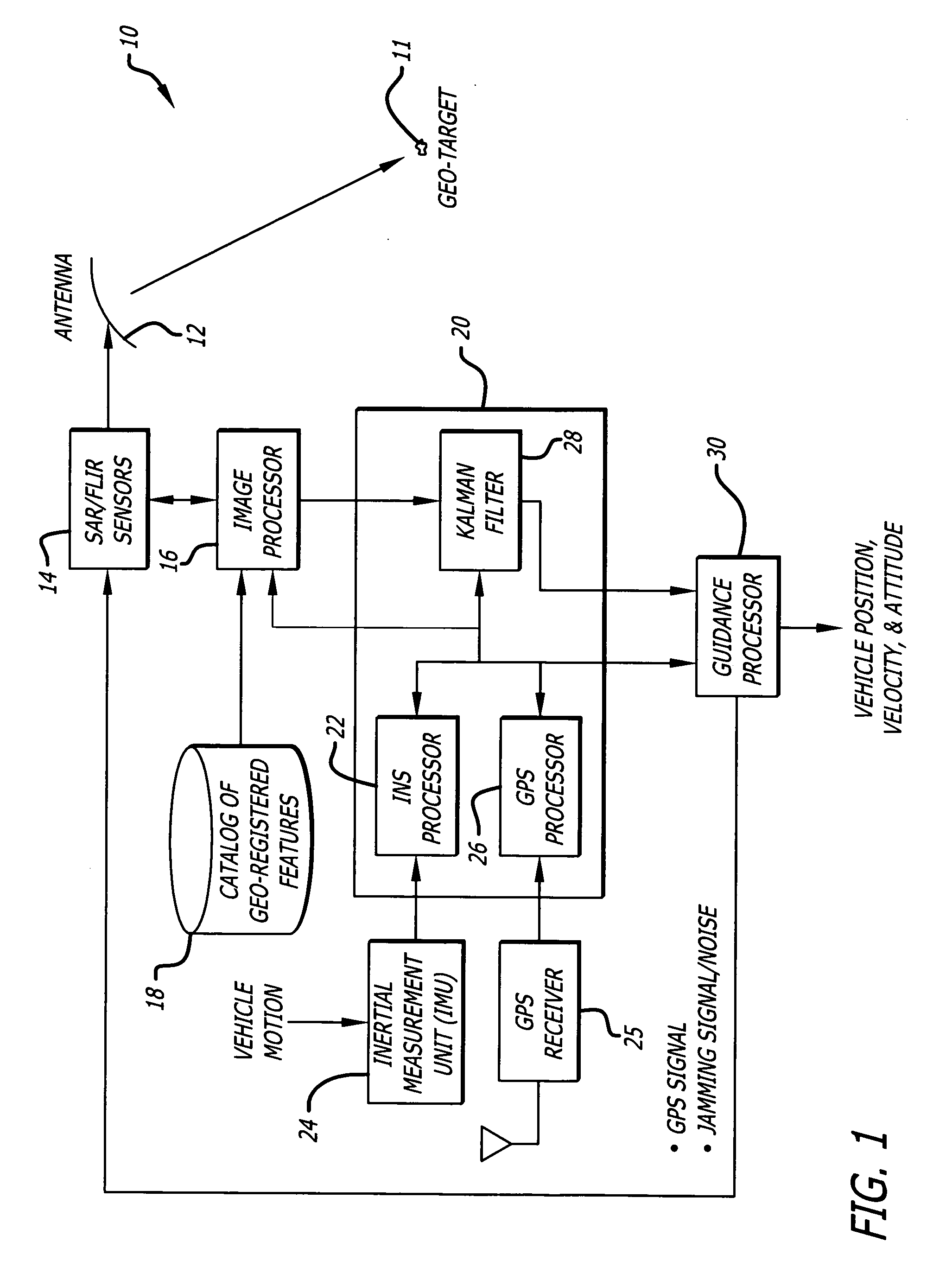
System and method for geo-registration with global positioning and inertial navigation
ActiveUS20060293854A1Improve navigation accuracyAnti-collision systemsPosition fixationSynthetic aperture radarForward looking
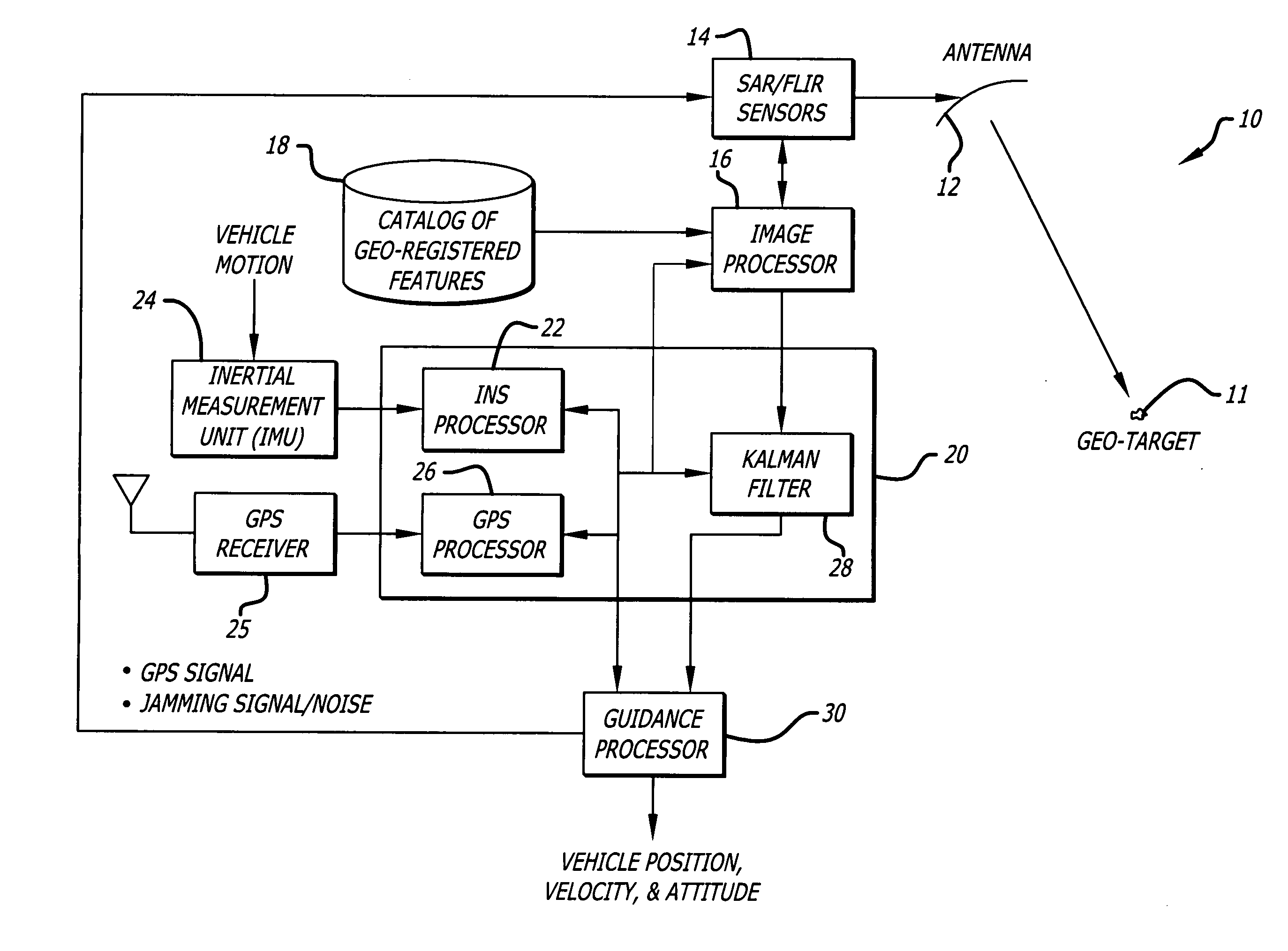
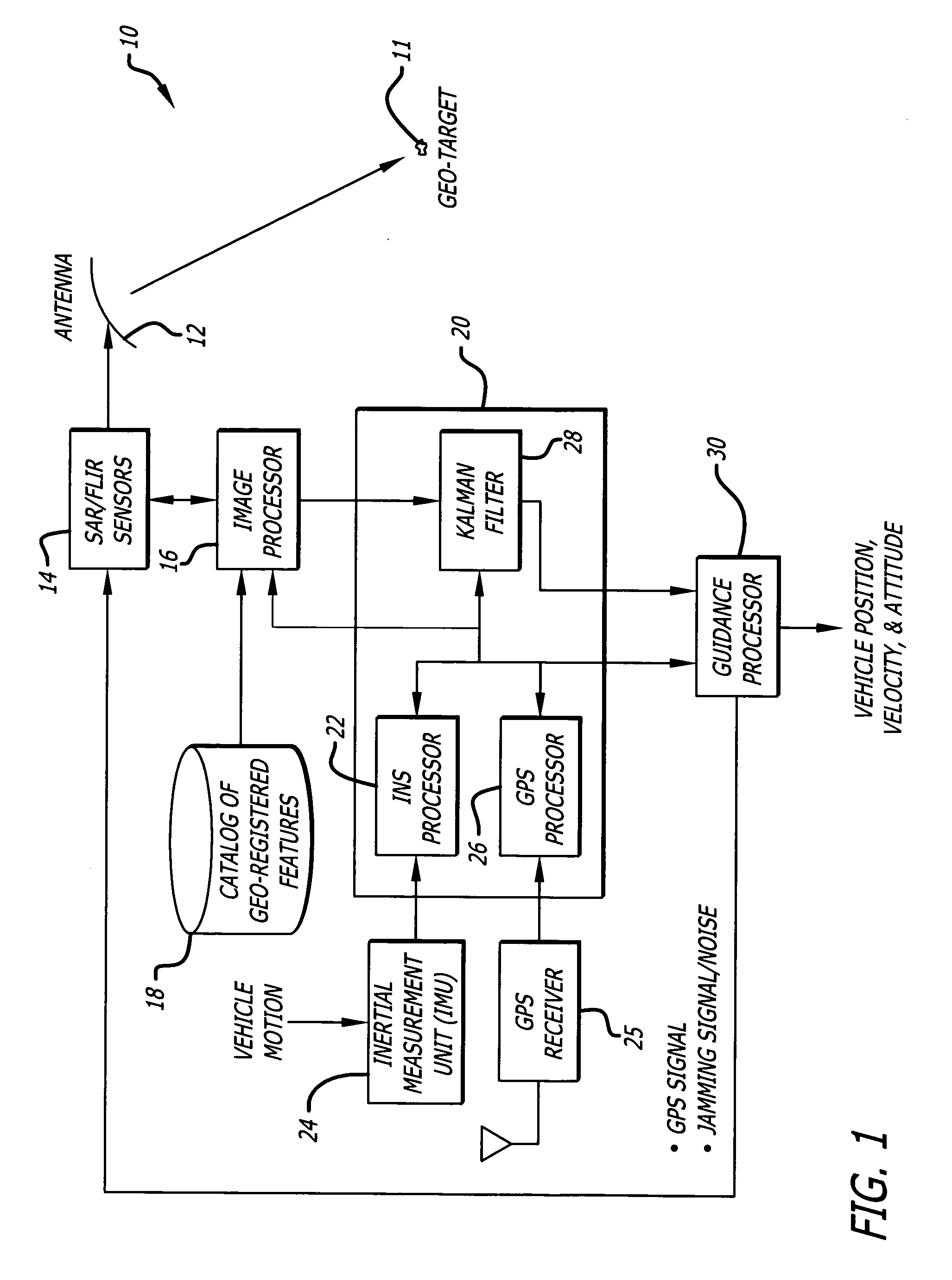
A position estimation system including a first arrangement for providing an image with a known target in a known reference frame. A second arrangement correlates the image with a stored image. The correlation is used to compute an error with respect to a position estimate. In a specific embodiment, the error is referenced with respect to first (x), second (y) and third (z) directions. A target location error is computed with respect to a stored image provided by a target image catalog. The target image catalog includes target geo-locations and digital terrain elevation data. In an illustrative application, the image data is provided by synthetic aperture radar and forward-looking infrared systems. An observation model and a measure noise matrix are Kalman filtered to ascertain a position error in navigation data generated by an integrated inertial navigation and Global Positioning system. In the illustrative application, geo-registered SAR / FLIR imagery is used to track targets and to determine a target location error (TLE). This TLE information is a set of error equations that describe the relationship between vehicle navigation information and target data. In accordance with the invention, this relationship is used to form an observation model for vehicle navigation with respect to target locations. Using Kalman filtering and the observation model, vehicle navigation errors can be bound and the navigation accuracy of the vehicle can be improved.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
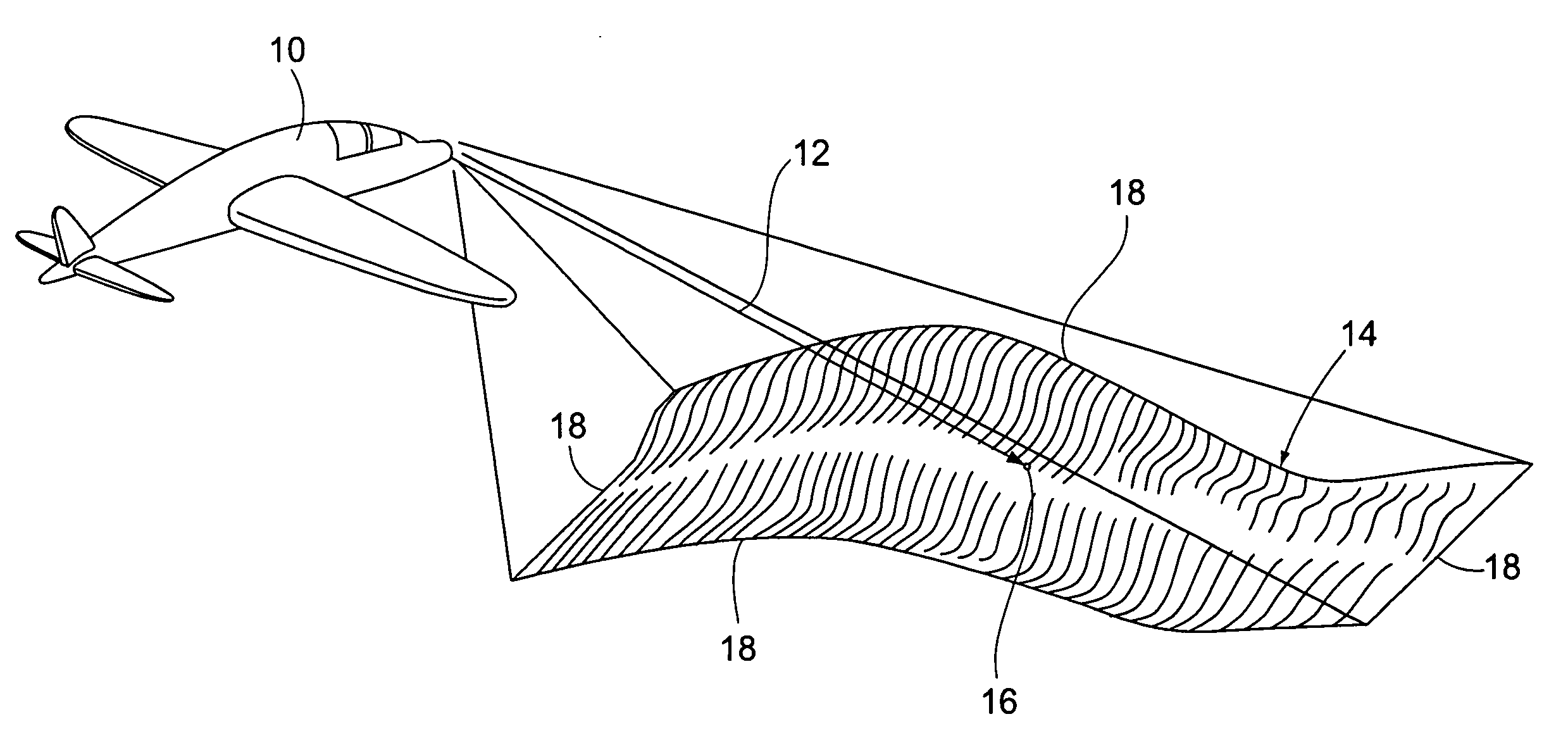
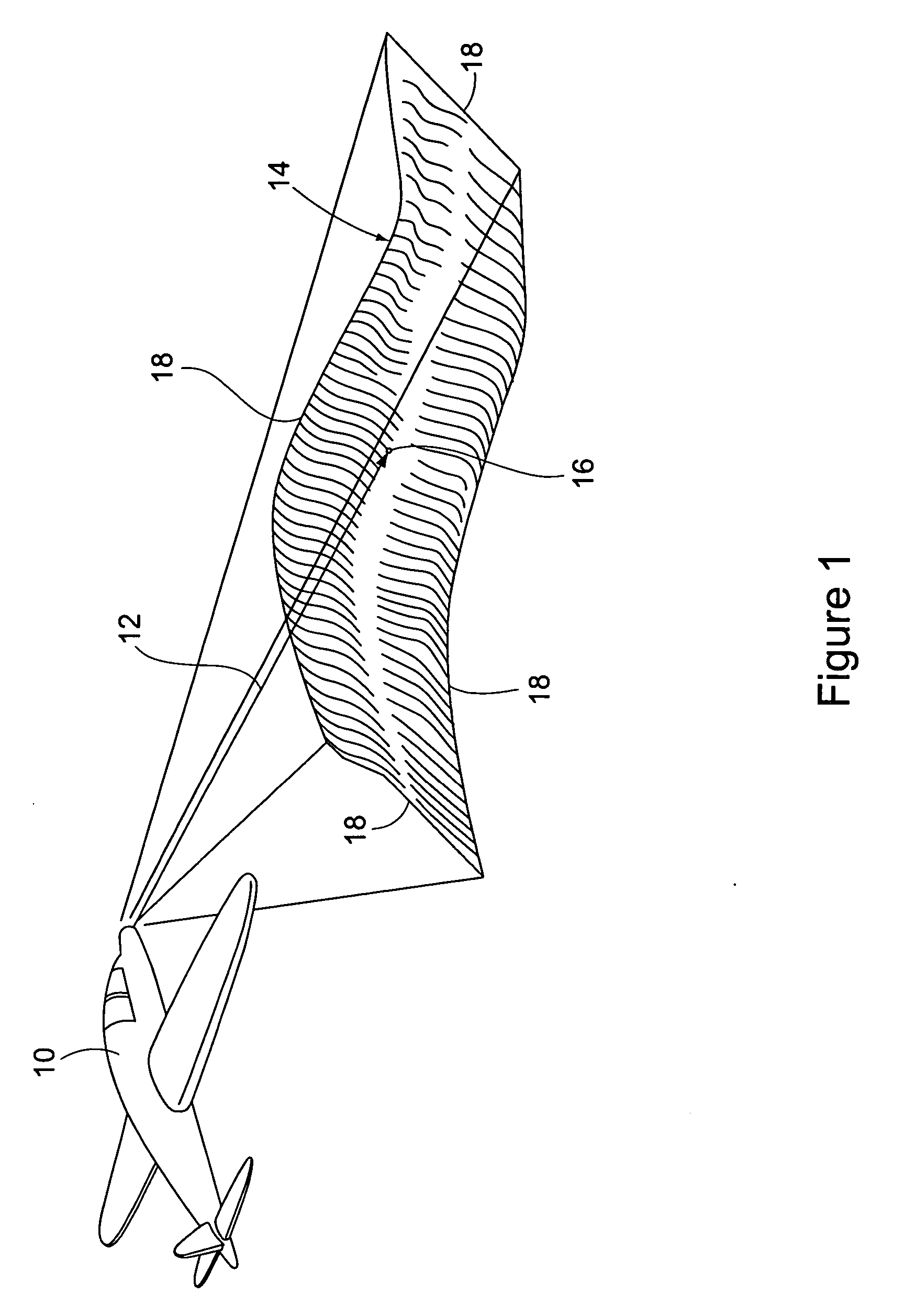
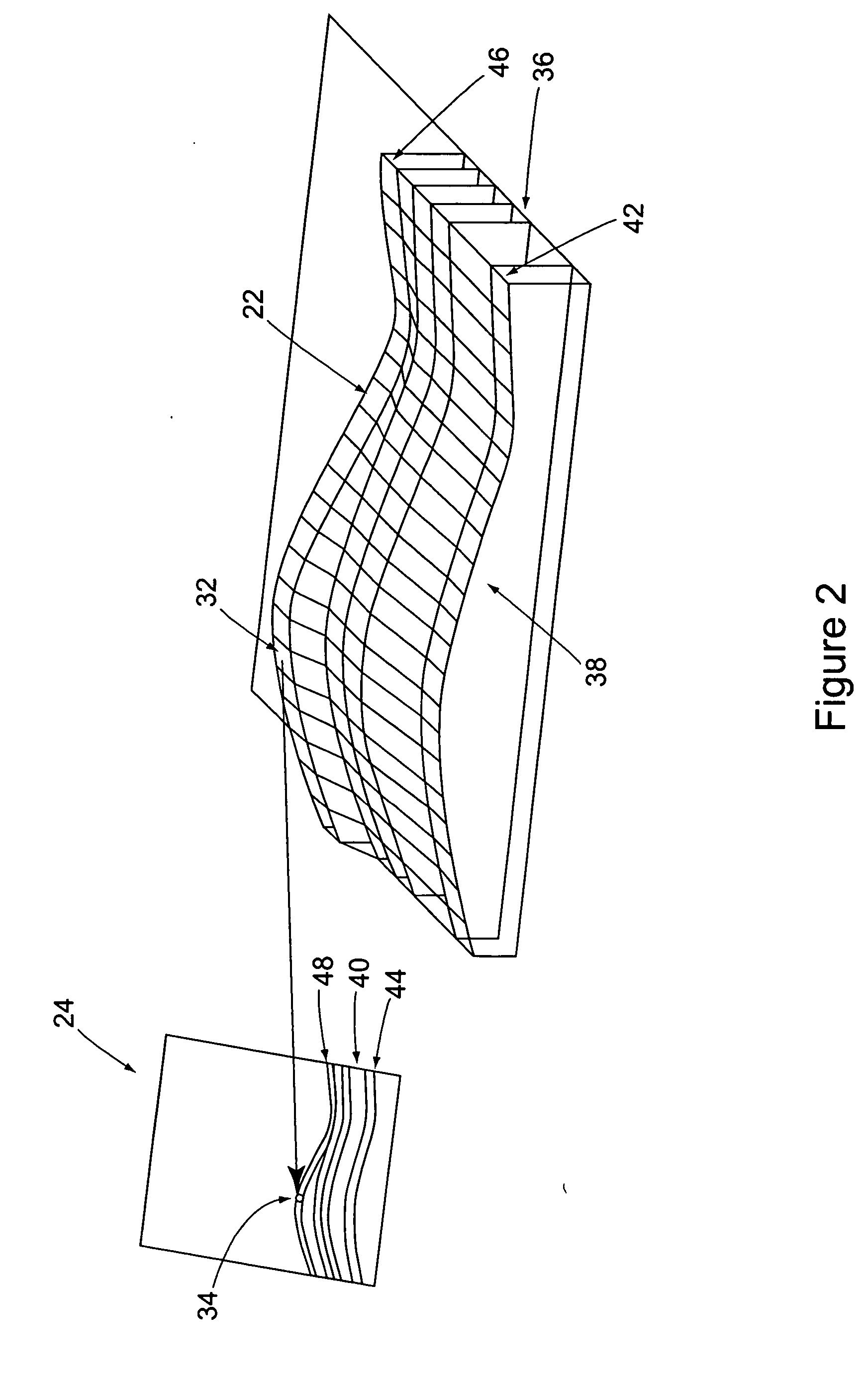
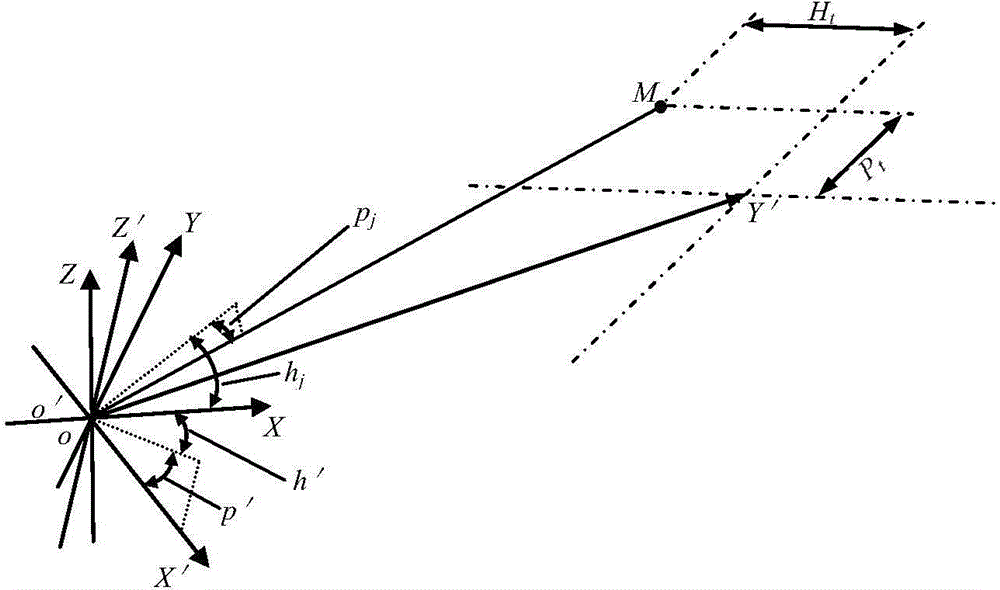
Method for generating a synthetic perspective image
ActiveUS20070002138A1Without computational difficultySufficient speedCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsSynthetic aperture radarReference image
A method of generating a synthetic perspective image that matches the viewing perspective and internal geometry of a known image sensor, for example, a forward-looking infrared sensor or a synthetic aperture radar sensor, without using specialized hardware and without the computational difficulty inherent in standard image generating means is provided. The synthetic perspective image is generated in a forward mapping process, which solves the problems of complete mapping of the perspective image and of hidden surfaces, in a manner that provides sufficient speed and adequate quality or accuracy for standard reference images to be used in registering with the sensor images.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
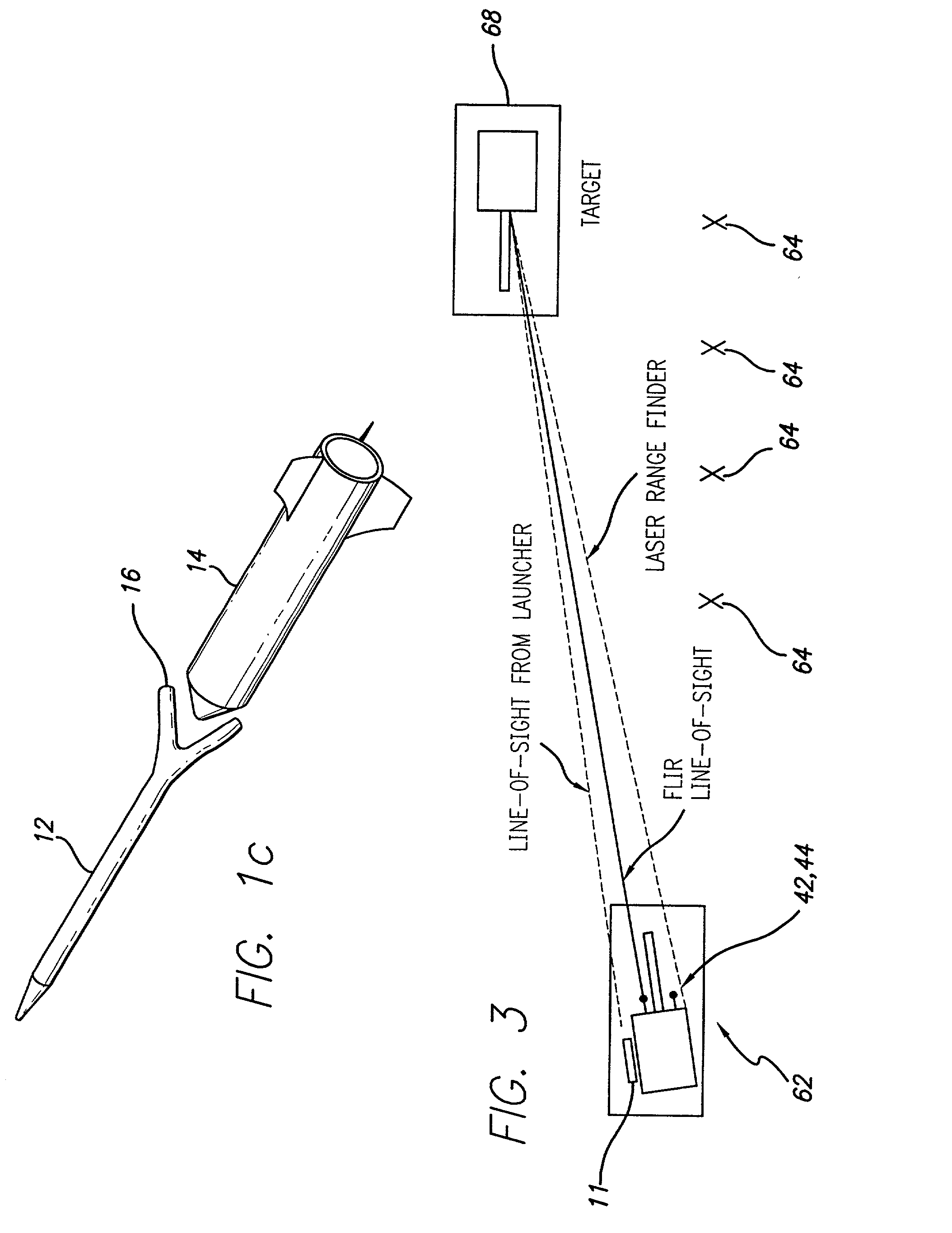
Precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system
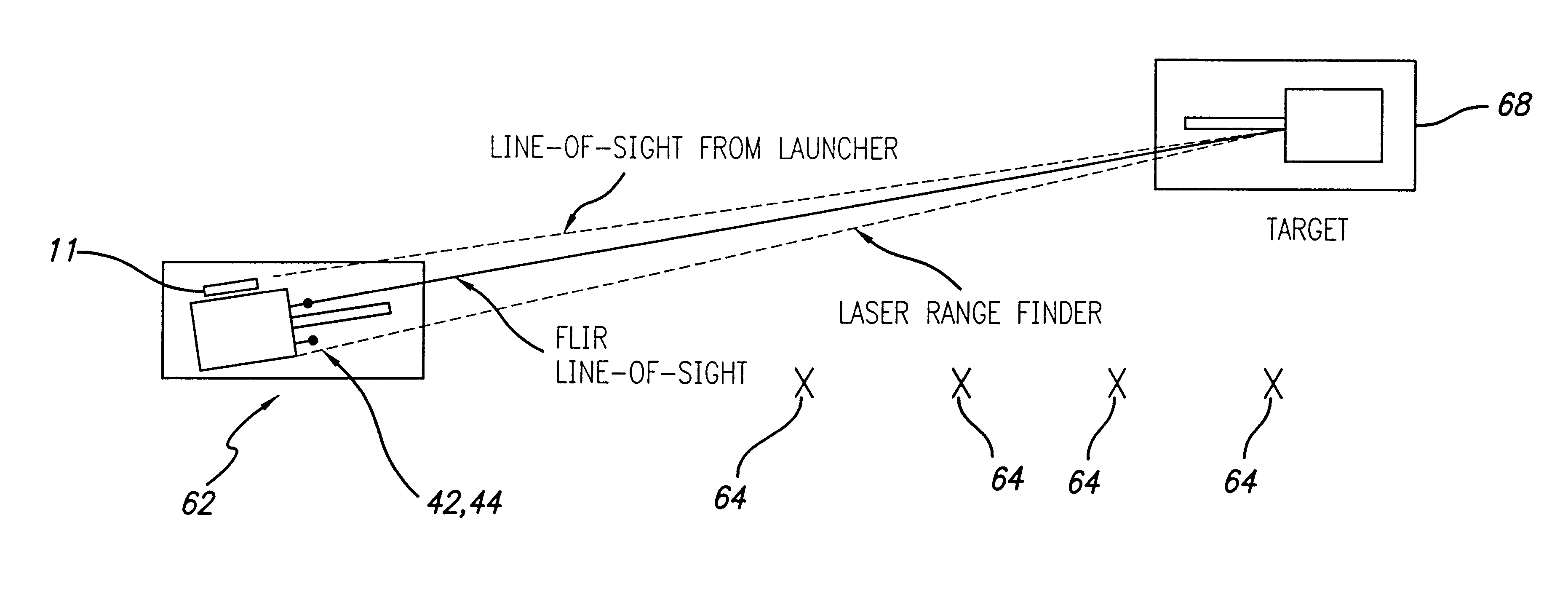
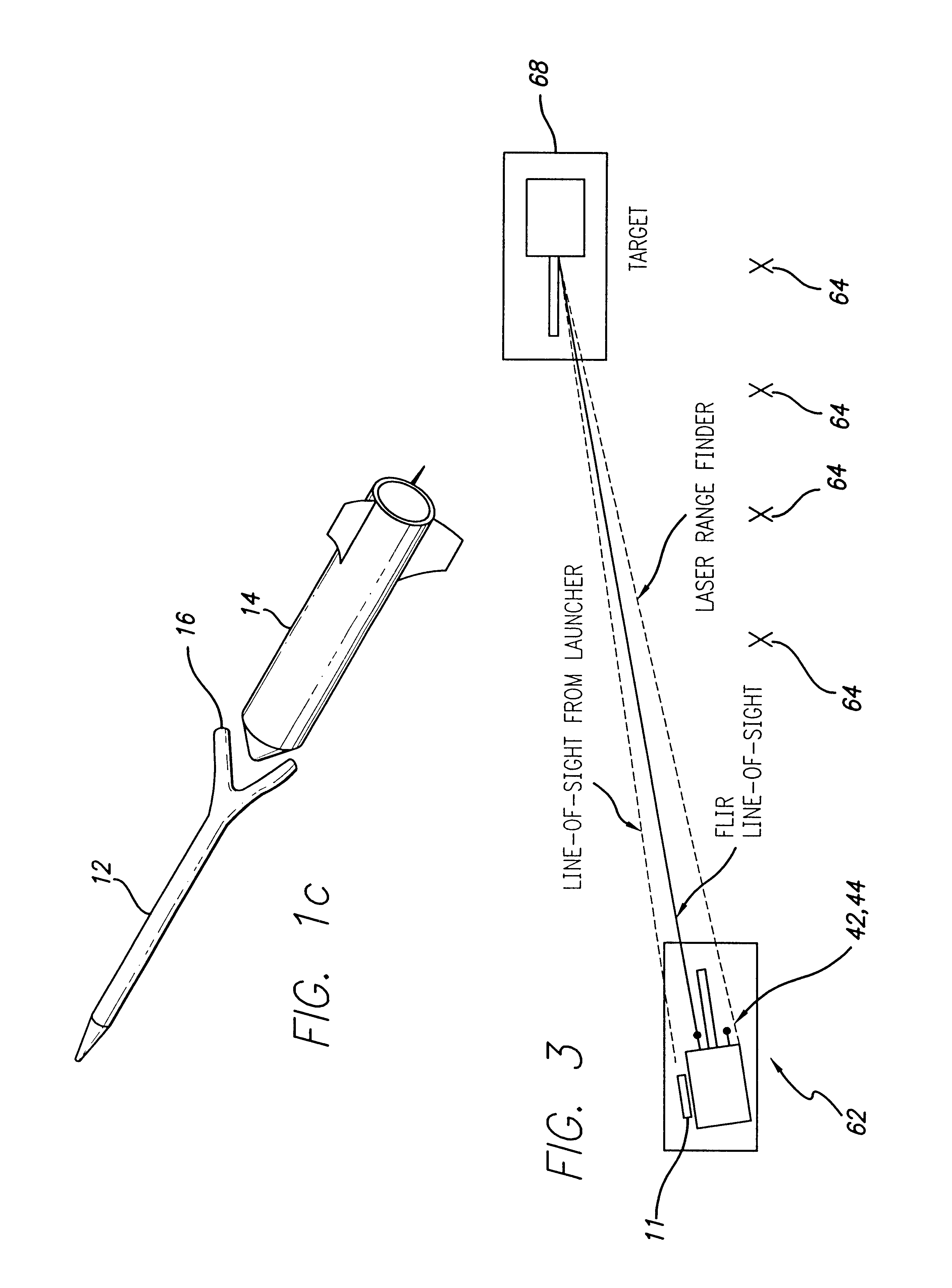
A precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system. The inventive system includes a first subsystem for determining a target location and providing data with respect thereto. A second subsystem calculates trajectory to the target based on the data. The projectile is then launched and guided in flight along the trajectory to the target. In the illustrative application, the projectile is a tungsten rod and the first subsystem includes a forward-looking infrared imaging system and a laser range finder. The second subsystem includes a fire control system. The fire control system includes an optional inertial measurement unit and predicts target location. The projectile is mounted in a missile launched from a platform such as a vehicle. After an initial burn, the missile launches the projectile while in flight to the target. The missile is implemented with a rocket with a guidance system and a propulsion system. In accordance with the present teachings, the guidance system includes a transceiver system mounted on the projectile. The transceiver system includes a low-power continuous wave, millimeter wavelength wave emitter. A system is included at the launch platform for communicating with the projectile. The platform system sends a blinking command to the projectile and measures the round trip delay thereof to ascertain the range of the projectile. Velocity is determined by conventional Doppler techniques or differentiation. Azimuth and elevation are then determined by a monopulse antenna on the launch platform. As a consequence, the platform ascertains the location of the projectile and the impact point thereof. The platform generates a command to the projectile which is received by the projectile and used to actuate control surfaces to adjust the trajectory and impact point thereof as necessary.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
System and method for geo-registration with global positioning and inertial navigation
ActiveUS7395156B2Improve navigation accuracyAnti-collision systemsPosition fixationSynthetic aperture radarForward looking
A position estimation system including a first arrangement for providing an image with a known target in a known reference frame. A second arrangement correlates the image with a stored image. The correlation is used to compute an error with respect to a position estimate. In a specific embodiment, the error is referenced with respect to first (x), second (y) and third (z) directions. A target location error is computed with respect to a stored image provided by a target image catalog. The target image catalog includes target geo-locations and digital terrain elevation data. In an illustrative application, the image data is provided by synthetic aperture radar and forward-looking infrared systems. An observation model and a measure noise matrix are Kalman filtered to ascertain a position error in navigation data generated by an integrated inertial navigation and Global Positioning system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
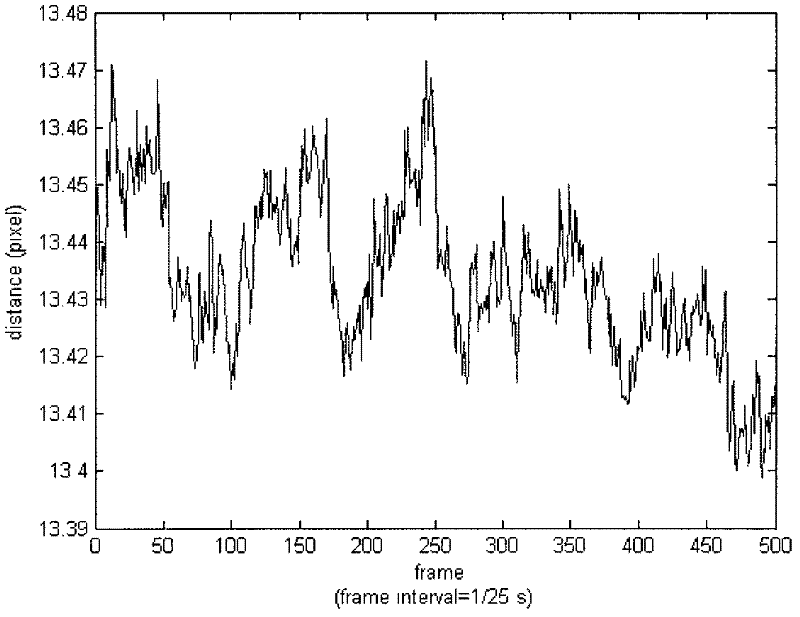
Method for detecting human body physiological parameters on basis of infrared sequence image
InactiveCN102309318AReliable reflectionFully documentedCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringPattern recognitionHuman body
The invention provides a method for detecting human body physiological parameters on basis of an infrared sequence image. By the method, non-contact measurement on heart rate and breath is realized. The invention adopts the detailed technical scheme which comprises the following steps of: 1, building an infrared dynamic image acquisition system which consists of a forward looking infrared radar (FLIR) infrared long-wave sensor, a daheng image acquisition card and a video storage working station; 2, acquiring the infrared sequence image of a tested man by using the infrared dynamic image acquisition system, and filtering irregular movement of a head of the sequence image; 3, selecting temples as interesting areas, and extracting time sequence signals from the interesting areas by using a gravity method; 4, performing empirical mode decomposition on the extracted time sequence signals; and 5, performing spectral analysis on the result of the empirical mode decomposition, and identifying breath and heart rate signals. By the method, the non-contact measurement on heart rate and breath is realized by using the infrared sequence image. Therefore, the method has better application value in physiological feature monitoring in human face feature information identification and clinical surgery.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
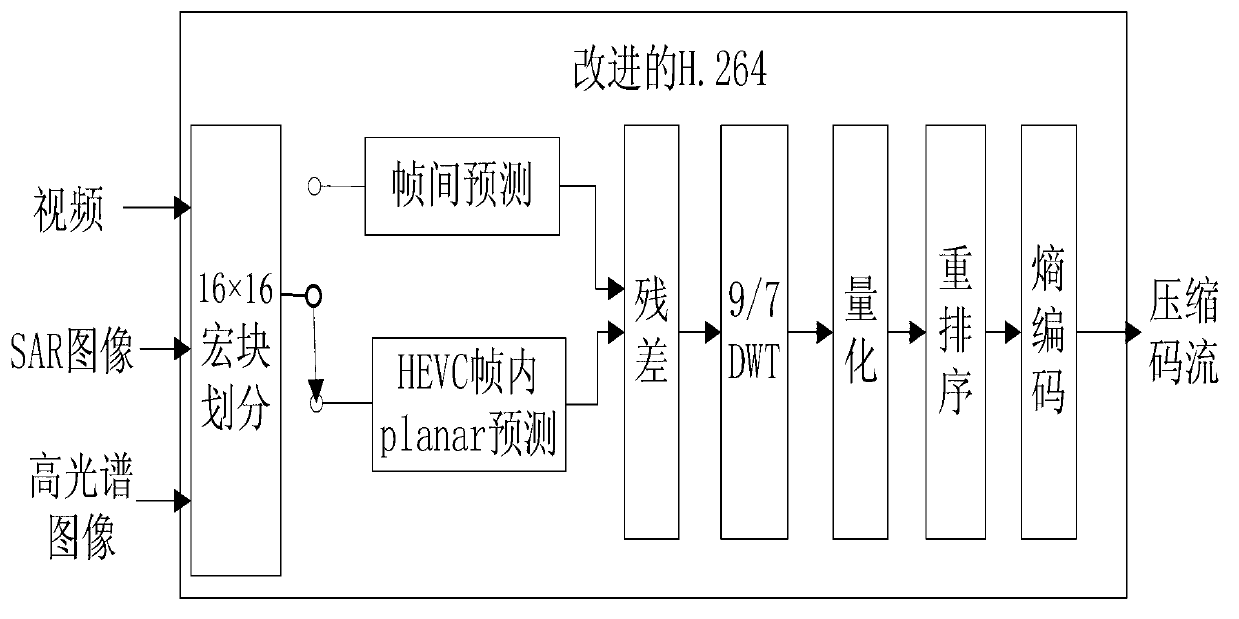
Multi-source special unmanned plane reconnoitered image general compression method
ActiveCN103108182AImprove fitStrong targetingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDigital videoImaging processing
The invention discloses a multi-source special unmanned plane reconnoitered image general compression method, and belongs to the technical field of digital video image processing. Firstly, image video information is read through a port of a compression system and converted to a uniform format, and then an improved H264 video coding standard is used for compression coding of the information to obtain a compressed code stream. Aiming at the characteristics of multi-task-load and multi-mode work of an unmanned plane, the method can be used for compression work of video information, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images and hyperspectral images collected by a forward looking infrared and other different devices, and after decompression, image source information is discernible, and the scheme is systematized.
Owner:北京北航天宇长鹰无人机科技有限公司
Foreign object damage protection device and system for aircraft
A foreign object damage protection system comprises a sensor for detecting a foreign object, a fluid in a reservoir, a means for dispensing the fluid, the means for dispensing the fluid in communication with the reservoir, and a control unit, whereby when the sensor detects a foreign object, the control unit causes fluid to be dispensed from the reservoir through the means for dispensing and towards the foreign object. The sensor is attachable to one or more locations on an aircraft, such as a wing, nose, windshield, fuselage or tail. The sensor can be a radar sensor, weather radar sensor, weather radar sensor modified to detect objects at short ranges, infra-red sensor, forward-looking infrared sensor, a light detection and ranging sensor, motion sensor, thermal sensor, or video sensor. The system provides a way to protect an aircraft from striking foreign objects, such as birds, in the path of the aircraft.
Owner:MARGALIT ZAMIR
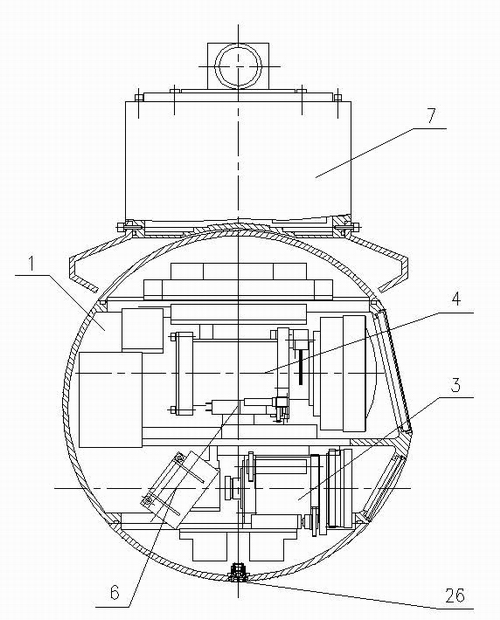
Airborne turret with in-built CCD camera and forward looking infrared device and control system thereof
InactiveCN101860684AImprove coaxial accuracyImprove imaging effectTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryControl systemOptical axis
The invention relates to an airborne turret with an in-built CCD camera and a forward looking infrared device and a control system thereof, wherein, the airborne turret comprises a turret main body. The invention is characterized in that the main body is internally provided with a pitching control cabinet; the middle of the pitching control cabinet is provided with a fixed clapboard; a visible light CCD camera system and a forward looking infrared system are respectively arranged at two sides of the fixed clapboard of the pitching control cabinet; the optical axes of the visible light CCD camera system and the forward looking infrared system are coaxial; a rotating direction control cabinet is internally provided with a pitching control shafting parallel with the optical axes; the side of a pitching control main shaft is provided with a pitching top image stabilization control system; the upper side part of the main body is provided with the rotating direction control cabinet which is internally provided with a direction control shafting along a longitudinal direction; and the side of a direction control main shaft is provided with a direction top image stabilization control system. The airborne turret has stable operation, clear image and precise positioning, can cruise all day long, and can output a visible-light video image and a medium-wave infrared thermal image, thereby achieving all-weather and all-day detection and tracking of a remote target.
Owner:FUJIAN FORECAM OPTICS CO LTD
Precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system
A precision-guided hypersonic projectile weapon system. The inventive system includes a first subsystem for determining a target location and providing data with respect thereto. A second subsystem calculates trajectory to the target based on the data. The projectile is then launched and guided in flight along the trajectory to the target. In the illustrative application, the projectile is a tungsten rod and the first subsystem includes a forward-looking infrared imaging system and a laser range finder. The second subsystem includes a fire control system. The fire control system includes an optional inertial measurement unit and predicts target location. The projectile is mounted in a missile launched from a platform such as a vehicle. After an initial burn, the missile launches the projectile while in flight to the target. The missile is implemented with a rocket with a guidance system and a propulsion system. In accordance with the present teachings, the guidance system includes a transceiver system mounted on the projectile. The transceiver system includes a low-power continuous wave, millimeter wavelength wave emitter. A system is included at the launch platform for communicating with the projectile. The platform system sends a blinking command to the projectile and measures the round trip delay thereof to ascertain the range of the projectile. Velocity is determined by conventional Doppler techniques or differentiation. Azimuth and elevation are then determined by a monopulse antenna on the launch platform. As a consequence, the platform ascertains the location of the projectile and the impact point thereof. The platform generates a command to the projectile which is received by the projectile and used to actuate control surfaces to adjust the trajectory and impact point thereof as necessary.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
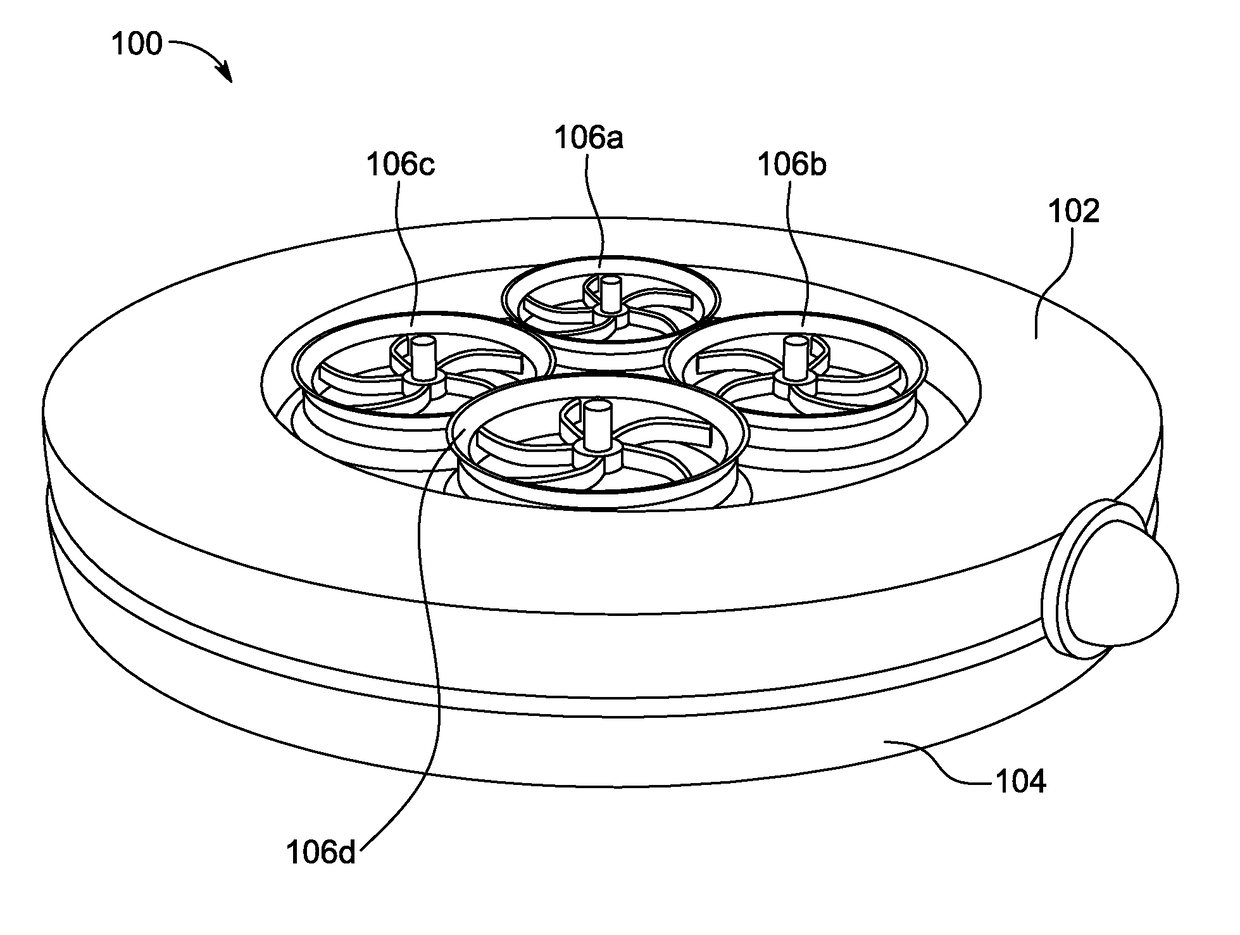
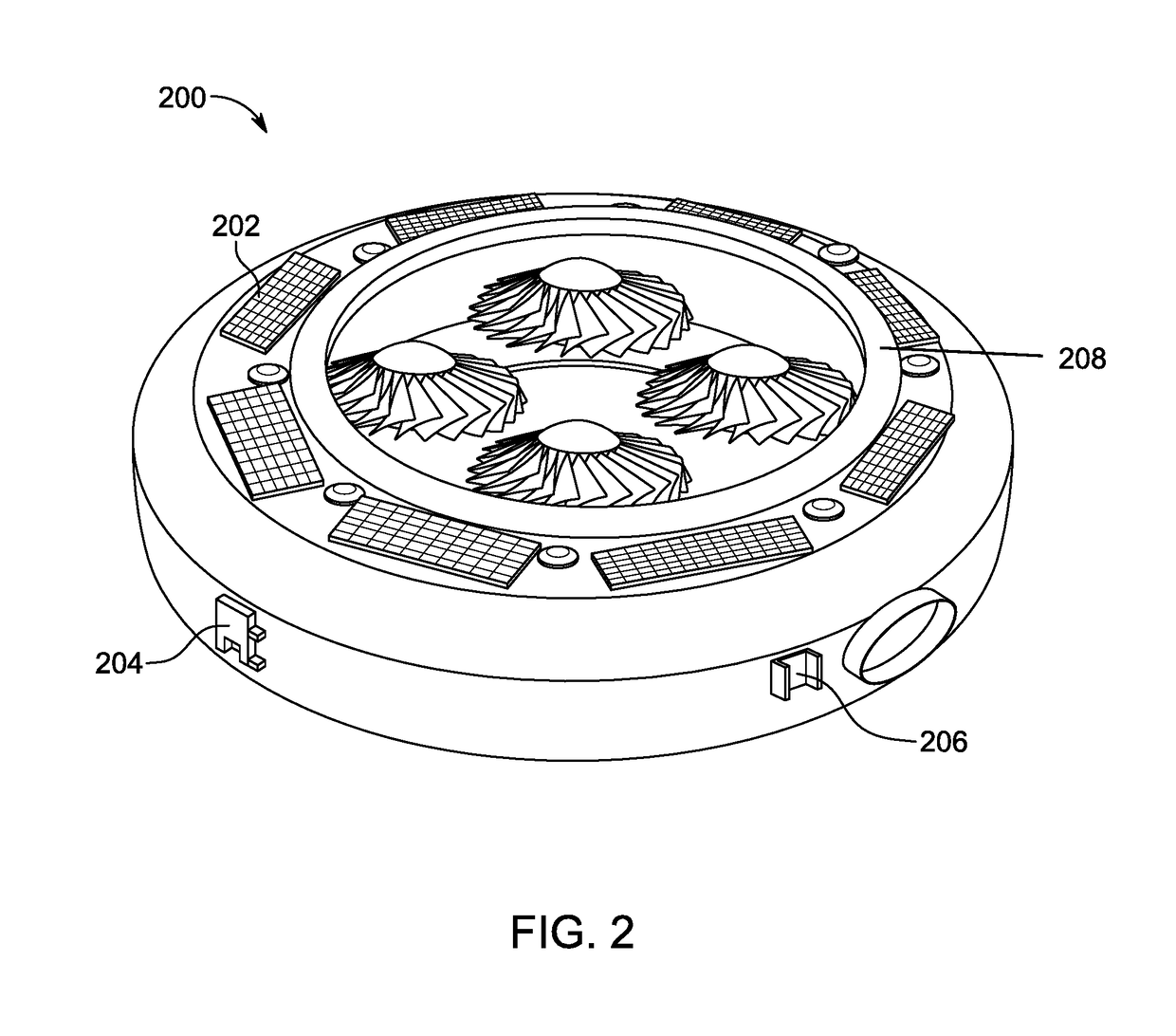
Drone with ring assembly
ActiveUS10099785B1Wide viewEnsure accelerated performanceUnmanned aerial vehiclesMilitary adjustmentGyroscopeEngineering
Disclosed is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) with a pre-defined shape to deploy one or more items. The unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) includes an upper housing, a lower housing, and a power unit. The upper housing includes plurality of rotors to lift and propel the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Further the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) includes various electronic components such as plurality of electronic cards, a processing unit, a Global Positioning System (GPS), a communication unit, an electronic gyroscope, a barometer, engines and flight control system, video camera, a forward looking infrared (FLIR) device, a microphone, and a laser telemeter / designator / range finder. The power unit powers the aforementioned electronic components. The lower housing includes plurality of storage units to stores one or more items. The lower housing is removably attached with the upper housing in a way to deploy the items at a predetermined location through plurality of openings.
Owner:GONZALEZ OSWALDO
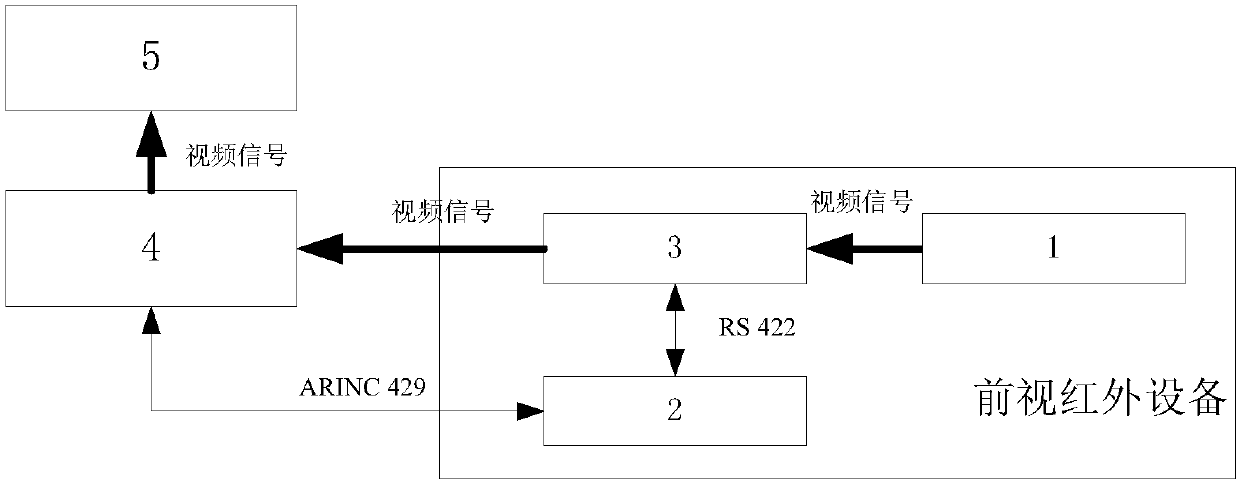
Method for carrying out closed-loop test on airborne forward-looking infrared search equipment by using simulation system
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
Continuous variable aperture for forward looking infrared cameras based on adjustable blades
A continuous variable non-circular aperture for an infra-red camera is formed by a plurality of positionable metal blades arranged to define there between an aperture of non-circular shape. A rotatable actuator plate positions the blades. Actuator rotation in one direction moves the metal blades to increase the size of the non-circular aperture without changing the non-circular shape of the aperture and vice-versa when the actuator plate is rotated in the opposite direction also maintaining the non-circular aperture shape. A preferred non-circular shape for a continuous variable aperture now possible is a rectangle; another is configured as a racetrack.
Owner:OPTO KNOWLEDGE SYST
Method for generating a synthetic perspective image
ActiveUS7580591B2Without computational difficultySufficient speedCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsSynthetic aperture radarReference image
A method of generating a synthetic perspective image that matches the viewing perspective and internal geometry of a known image sensor, for example, a forward-looking infrared sensor or a synthetic aperture radar sensor, without using specialized hardware and without the computational difficulty inherent in standard image generating means is provided. The synthetic perspective image is generated in a forward mapping process, which solves the problems of complete mapping of the perspective image and of hidden surfaces, in a manner that provides sufficient speed and adequate quality or accuracy for standard reference images to be used in registering with the sensor images.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
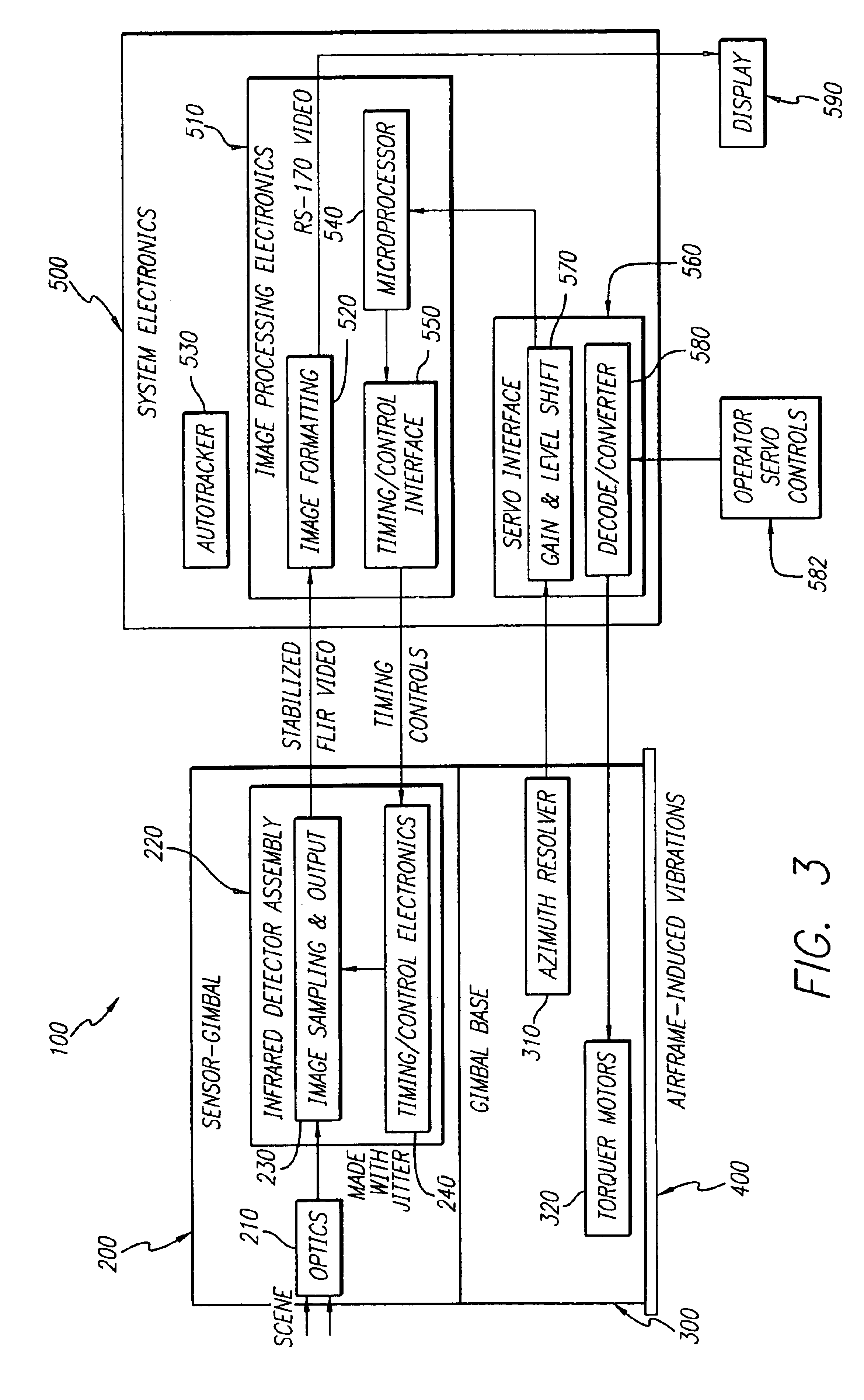
Infrared imaging system
ActiveUS20140002665A1Easy to detectEasy to identifyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical ModuleForward looking infrared
An infrared imaging sensor compatible with 2nd Generation Forward Looking Infrared (FLIR) Horizontal Technology Integration (HTI) B-Kit based sensors. In one example, the infrared imaging sensor includes a set of refractive opto-mechanical modules, including an afocal optical module, a receiver assembly, and backward- and forward-compatible electronics modules. The afocal optical module is configured to provide a plurality of different fields of view for the infrared imaging sensor. In one example, the sensor is configured for MWIR and LWIR imagery.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Foreign object damage protection device and system for aircraft
A foreign object damage protection system comprises a sensor for detecting a foreign object, a fluid in a reservoir, a means for dispensing the fluid, the means for dispensing the fluid in communication with the reservoir, and a control unit, whereby when the sensor detects a foreign object, the control unit causes fluid to be dispensed from the reservoir through the means for dispensing and towards the foreign object. The sensor is attachable to one or more locations on an aircraft, such as a wing, nose, windshield, fuselage or tail. The sensor can be a radar sensor, weather radar sensor, weather radar sensor modified to detect objects at short ranges, infra-red sensor, forward-looking infrared sensor, a light detection and ranging sensor, motion sensor, thermal sensor, or video sensor. The system provides a way to protect an aircraft from striking foreign objects, such as birds, in the path of the aircraft.
Owner:MARGALIT ZAMIR
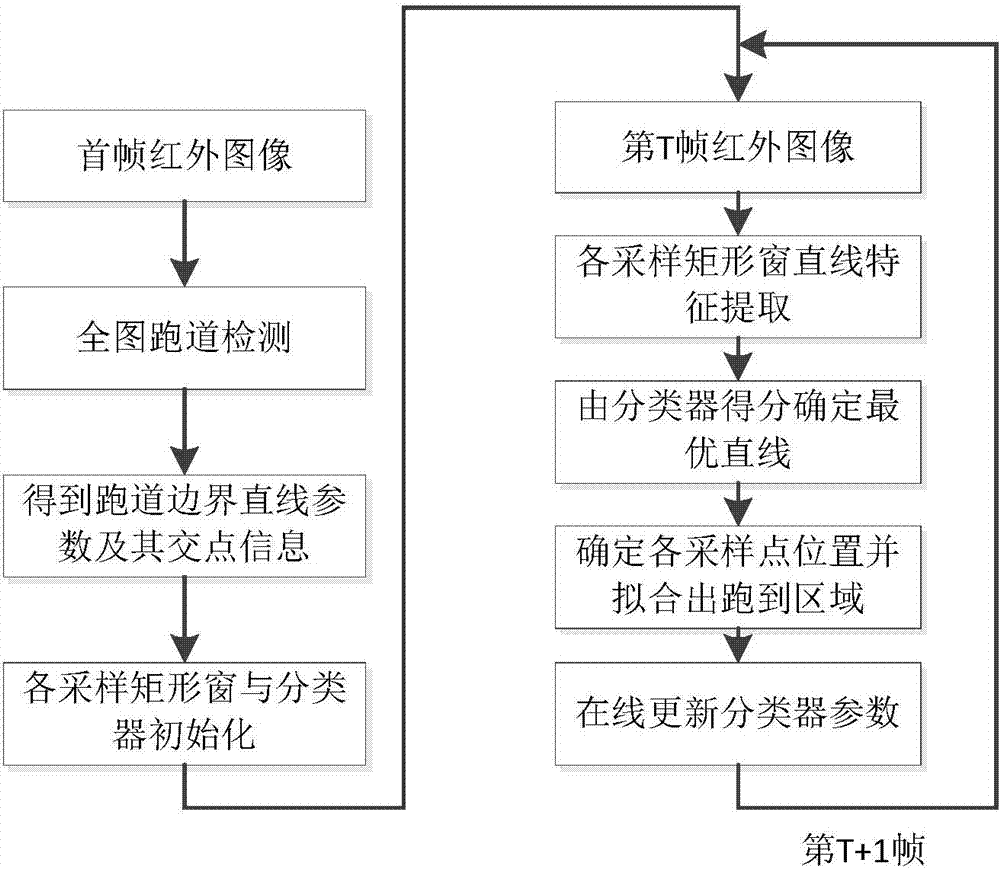
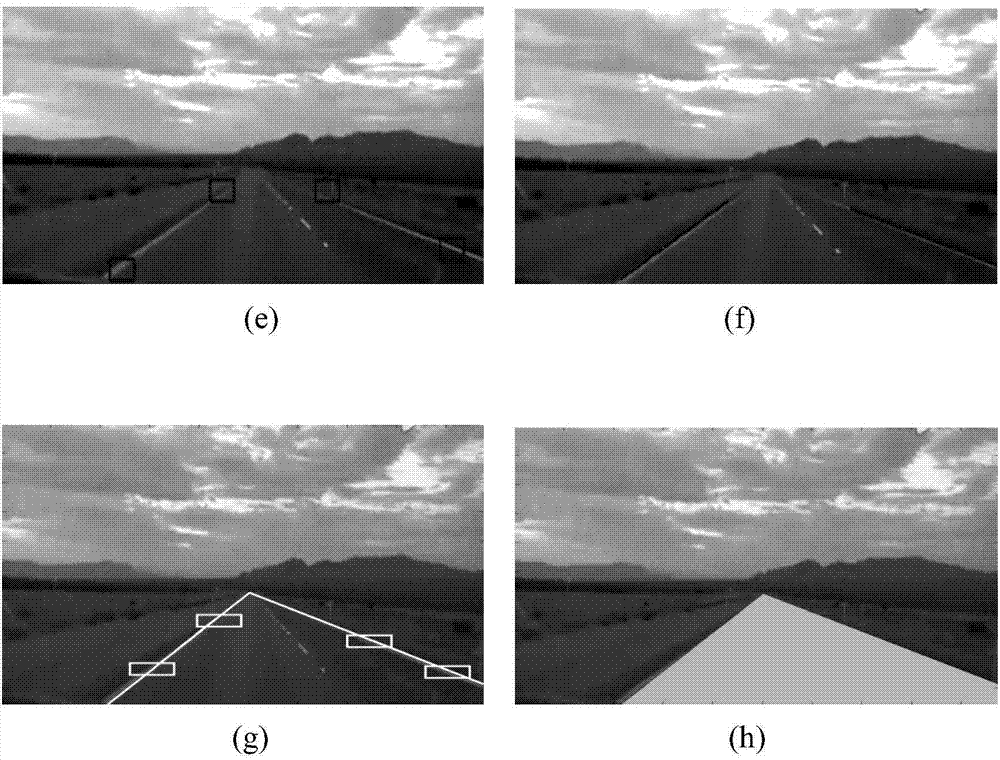
Aircraft landing vision enhancement method based on runway boundary enhancement
ActiveCN104766337AReal-time trackingEffective trackingImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringAircraft landing
The invention relates to an aircraft landing vision enhancement method based on runway boundary enhancement. The method comprises the steps that straight line features in a first-frame image of a forward looking infrared video are extracted through the line segment detection (LSD) algorithm, and line segments of runway boundaries are screened according to the intrinsic constraint conditions of the runway boundaries; two points are selected randomly from each of the line segments on the two runway boundaries, and rectangular sampling windows are selected with the points as the centers; the graded distribution features of the sampling windows are extracted, and parameters of a target classifier are initialized; all sampling points are tracked and positioned in following video frames, the runway boundaries are fitted according to the tracking results of all the sampling points, and finally a runway area and the runway boundaries are determined; finally, the runway boundaries are enhanced so as to improve the vision sensory ability of a pilot. By means of the method, inter-frame information of aircraft forward looking landing infrared video images can be fully utilized, the runway boundaries of an airport are tracked and recognized through the target tracking method, and the time performance of the vision enhancement algorithm is greatly improved while the recognition accuracy of the runway boundaries is guaranteed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
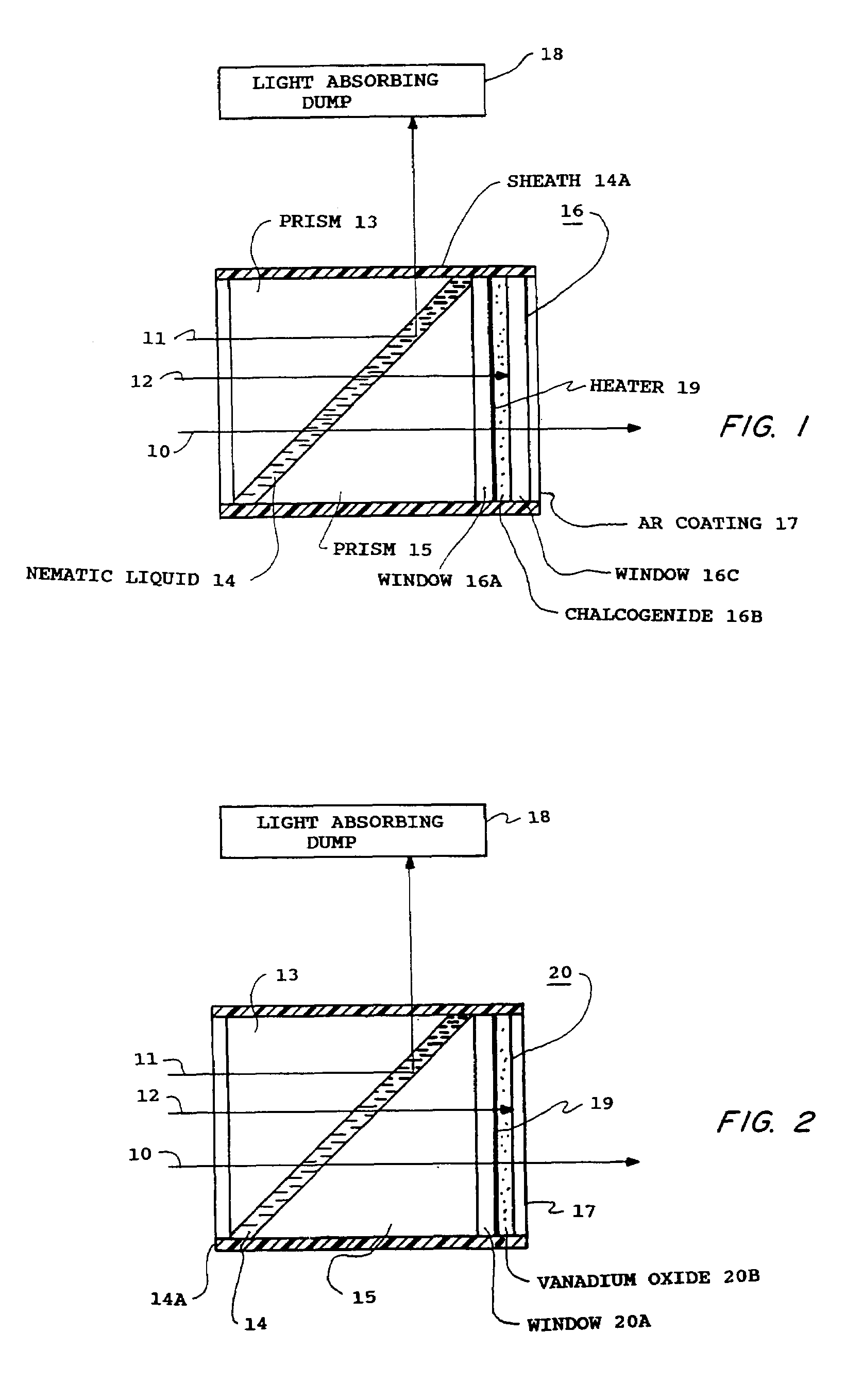
Optical power switch
InactiveUS7259925B1Small attenuationLow switching thresholdMountingsNon-linear opticsVanadium dioxideHigh power lasers
The present invention provides a protective device for sensitive infrared sensors as Forward Looking Infrared imagers (FLIRs). A prior device using materials with higher order susceptibilities to electric polarization, which provides protection against extremely intense radiation from high-power lasers is combined with a low energy optical power limiters such as the chalcogenide glass and the vanadium dioxide which respond reversibly to infrared radiation.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Multi-view-field medium-wave infrared optical system and view field switching method thereof
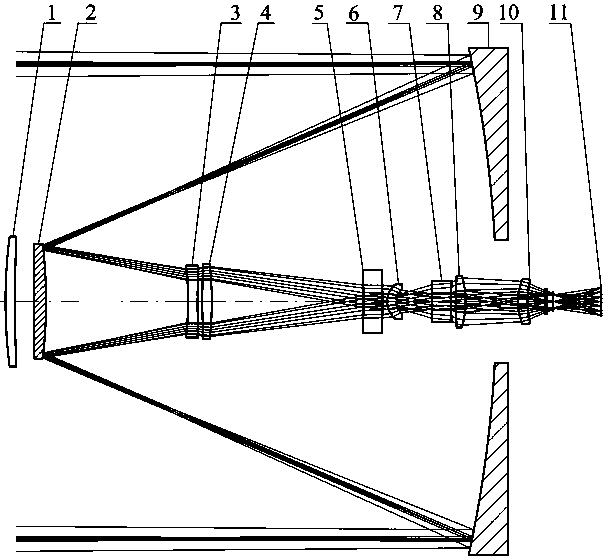
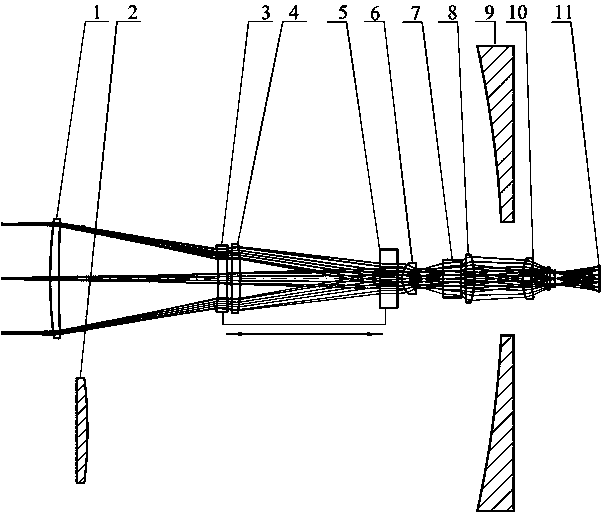
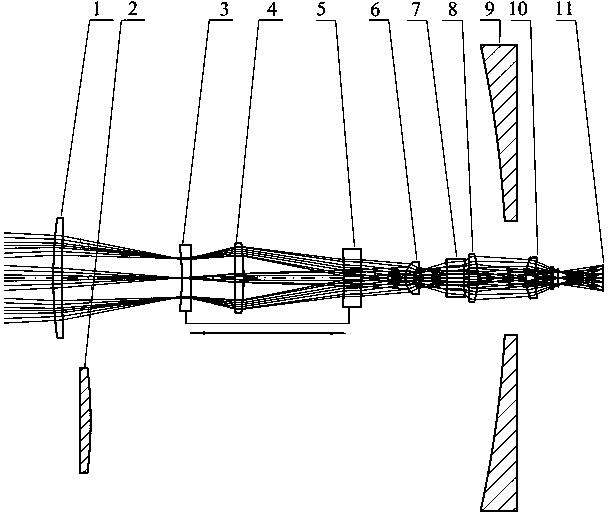
The invention relates to the field of forward-looking infrared imaging systems, in particular to a multi-view-field medium-wave infrared optical system and a view field switching method thereof. The system is composed of a first meniscus positive lens, a secondary reflecting mirror, a first double-concave negative lens, a first double-convex positive lens, a first meniscus negative lens, a secondmeniscus negative lens, a second double-concave positive lens, a second double-convex negative lens, a main reflecting mirror, a second meniscus positive lens, and an imaging plane that are distributed at the optical axis successively and coaxially from an object side to an image side. The system has a simple structure; the view field switching time is short and is controlled to be within 1s; theimaging quality is high; the optical axis consistency during the view field switching process can reach one pixel; and compared with the existing single-view-field and continuous zoom infrared opticalsystems, the multi-view-field medium-wave infrared optical system is simple and practical.
Owner:凯迈(洛阳)测控有限公司
Display uniformity calibration system and method for a staring forward looking infrared sensor
InactiveUS6737639B2Eliminate needHysteresis effectTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesHysteresisEngineering
A method and system for maintaining uniformity in a FLIR display. During a one-time initialization procedure, a plurality of dynamic ranges are defined by covering a specific range of bucket fill levels when in a certain gain. To cover all dynamic ranges possible, a plurality of pairs of responsivity equalization (RE) calibrations (each pair producing a RE set of pixel gain corrections) are also accomplished in the same one time initialization period. A plurality of corresponding level equalization (LE) calibrations (each using the appropriate calibrated RE set and producing a LE set of pixel level corrections) for each anticipated dynamic range are made at every power-up initialization. Each of the calibrations is done with respect to a thermal reference source to produce a uniform scene at the desired bucket fill level. An algorithm is employed which forces the two bucket fill points defined during the responsivity calibration to span as far as possible the dynamic range and forces the level equalization bucket fill point to fall within the two bucket fill points of the responsivity calibration. Then, during an operational time period, the scene and optics temperatures are monitored, and if the average bucket fill value exceeds the bucket fill range of the present dynamic range, the presently selected dynamic range is changed to a second dynamic range (gain is changed along with the RE set and LE set). The dynamic ranges are designed to overlap so that a hysteresis effect is achieved. The pre-calibrations and automatic dynamic range switching prevent saturation and create the best uniformity (lowest fix pattern noise) possible while allowing for continuous operation of the FLIR system, thus eliminating the interruption caused by the prior art touch-up calibration procedure.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
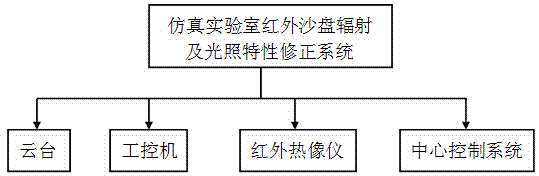
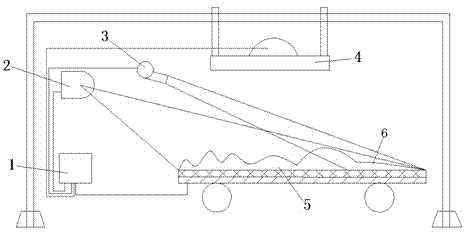
System for correcting radiation and illumination characteristics of infrared sand table of simulation lab
The invention discloses a system for correcting radiation and illumination characteristics of an infrared sand table of a simulation lab and belongs to the field of optical simulation tests. For solving the problem that an operator difficultly obtains timely feedback because of deficiency of a monitoring and correcting system during a foresight infrared seeker semi-physical simulation test, the invention provides the system for correcting the radiation and illumination characteristics of the infrared sand table of the simulation lab, and the system consists of a cloud deck, an industrial personal computer, an infrared thermal imager and a central control system. The system can be used for monitoring view characteristics of a sand table system and an illumination system in real time, reading the surface temperature, the illumination characteristics and the infrared radiation characteristics of the sand table, displaying the characteristics on a screen by a software system and correcting each index of the overall sand table and the overall illumination system in time according to actual simulation demands, so that the system can be used as corollary equipment of an infrared scene sand table and the illumination system of the infrared scene sand table.
Owner:韩平
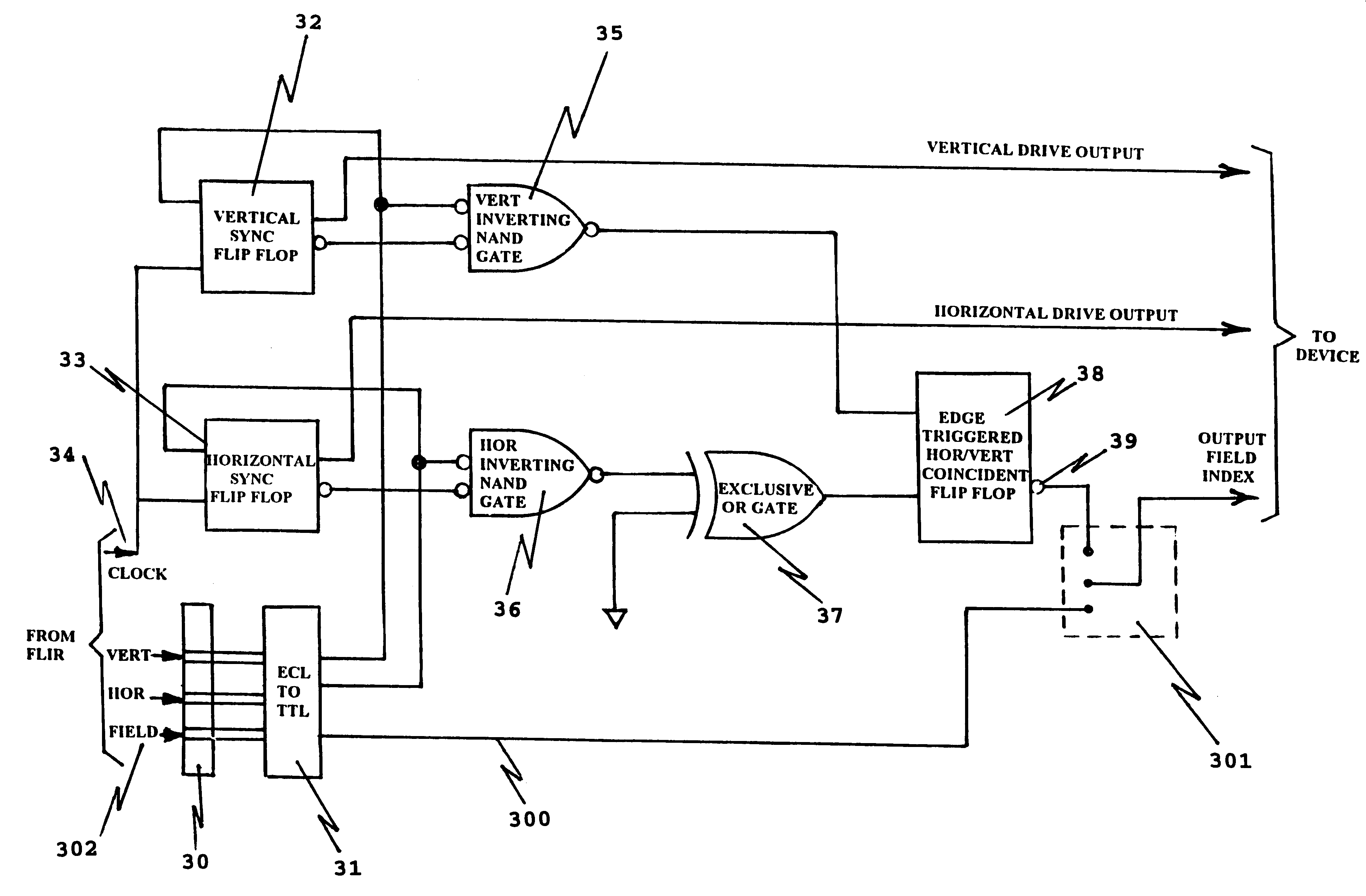
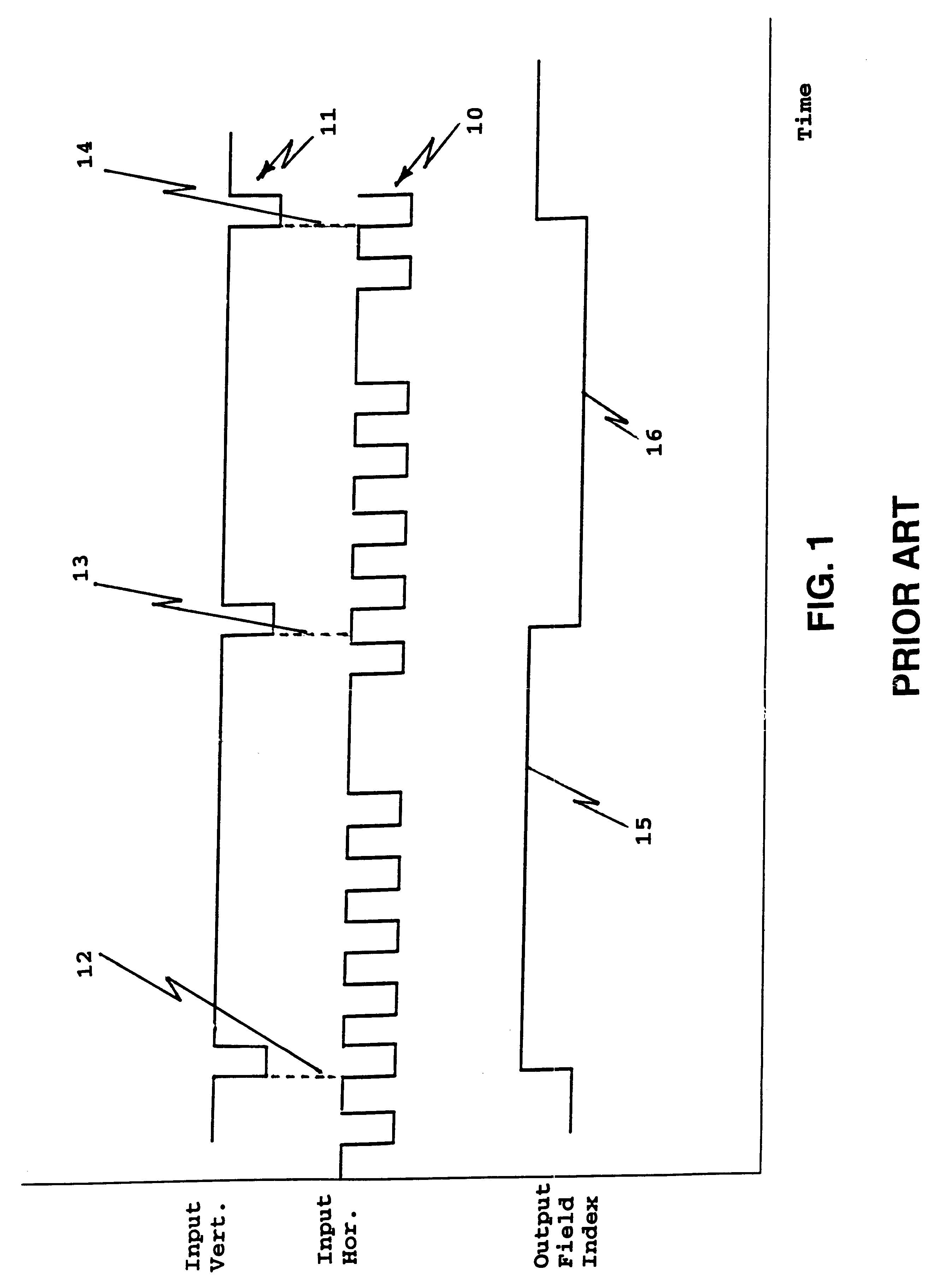
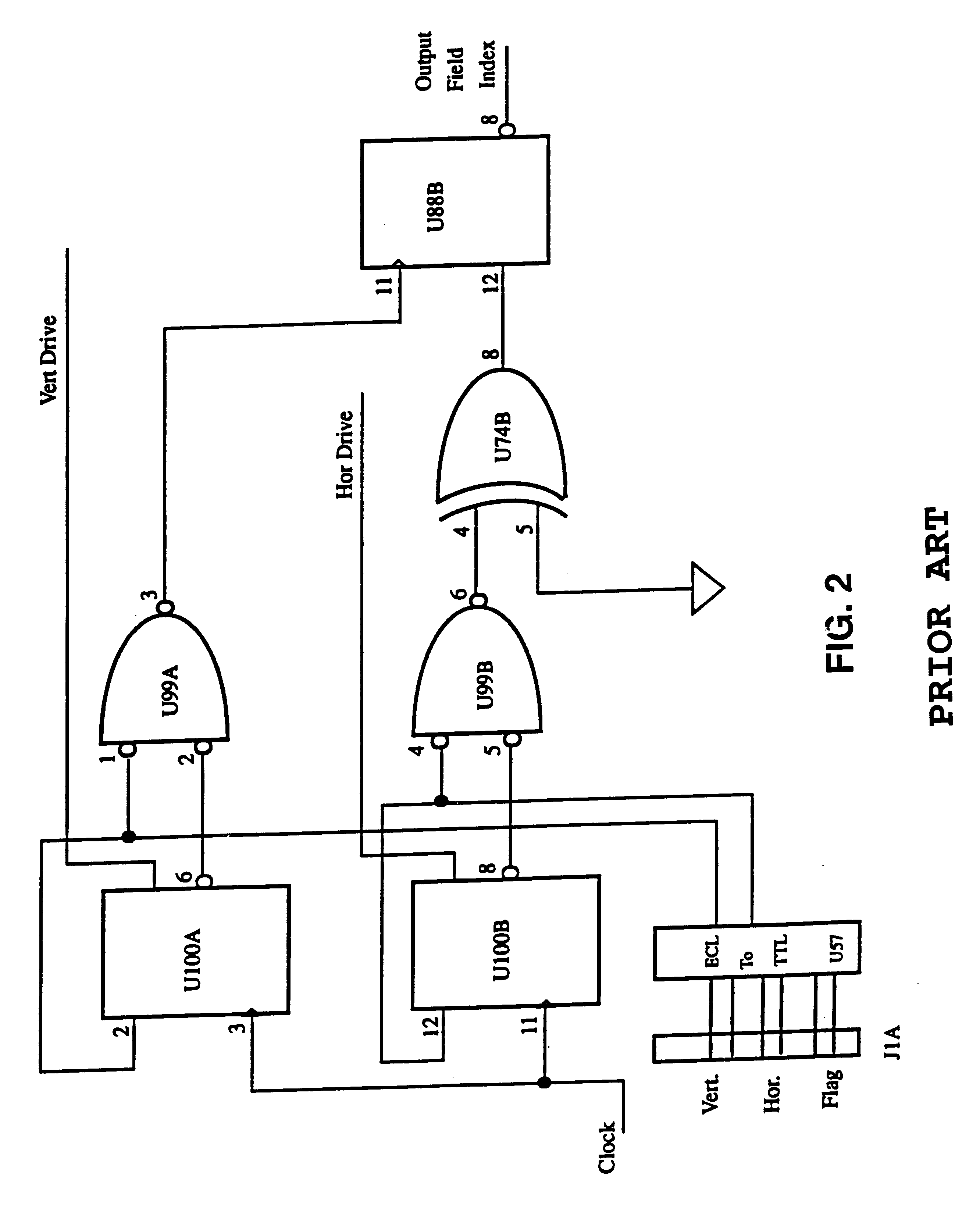
Field synchronization system and technique
A field synchronization system of a field detect circuit adaptable for use with non-standard output digital data of forward looking infrared (FLIR) sensors. Timing signals and digital data from a FLIR sensor are utilized and there is outputted a vertical and horizontal signal output. A bypass circuit allows for the optional bypass of frame grabber generated field index circuitry so that an external field index signal is utilized.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Infrared imaging system
ActiveUS9225914B2Easy to detectEasy to identifyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical ModuleForward looking infrared
An infrared imaging sensor compatible with 2nd Generation Forward Looking Infrared (FLIR) Horizontal Technology Integration (HTI) B-Kit based sensors. In one example, the infrared imaging sensor includes a set of refractive opto-mechanical modules, including an afocal optical module, a receiver assembly, and backward- and forward-compatible electronics modules. The afocal optical module is configured to provide a plurality of different fields of view for the infrared imaging sensor. In one example, the sensor is configured for MWIR and LWIR imagery.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Design method for active brake pedestrian collision prevention
InactiveCN108609001AAvoid false activation of anti-collision active brakingAvoid phenomena such as failure to startAutomatic initiationsEngineeringActuator
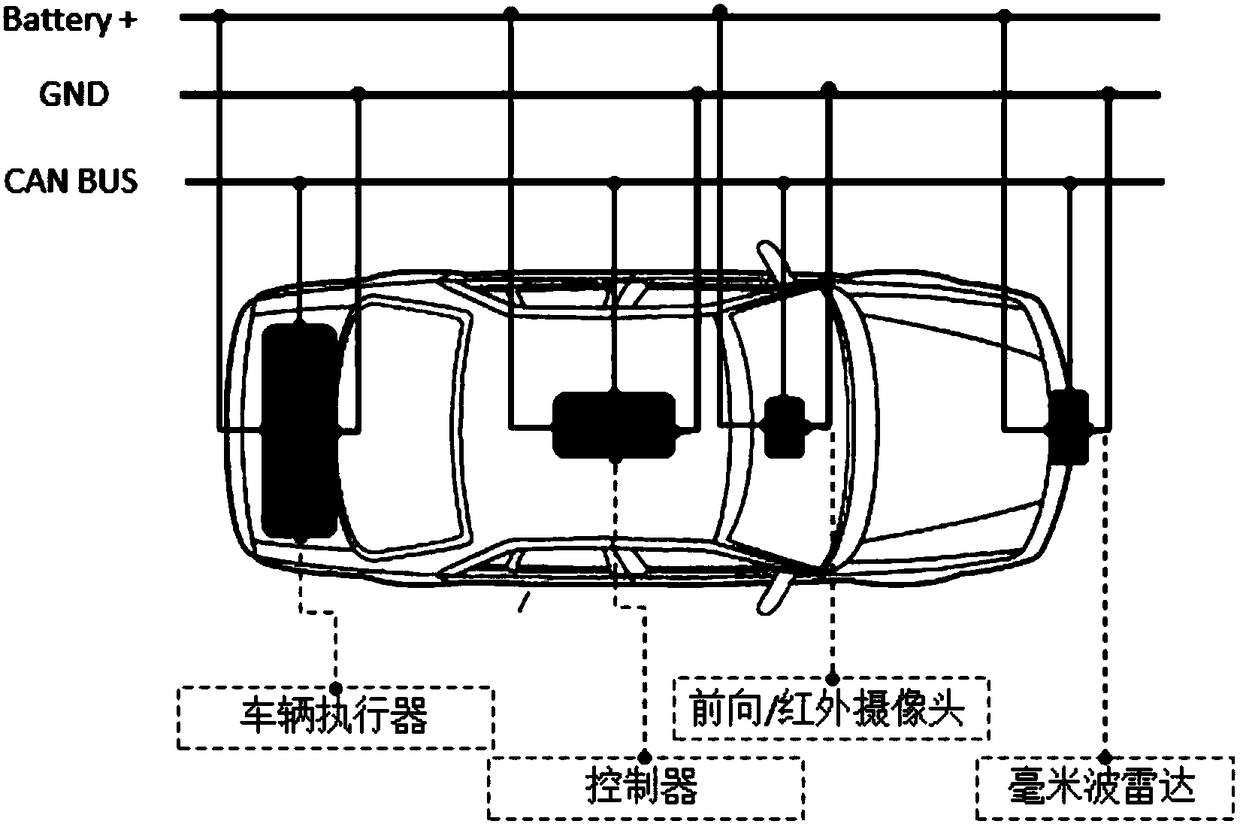
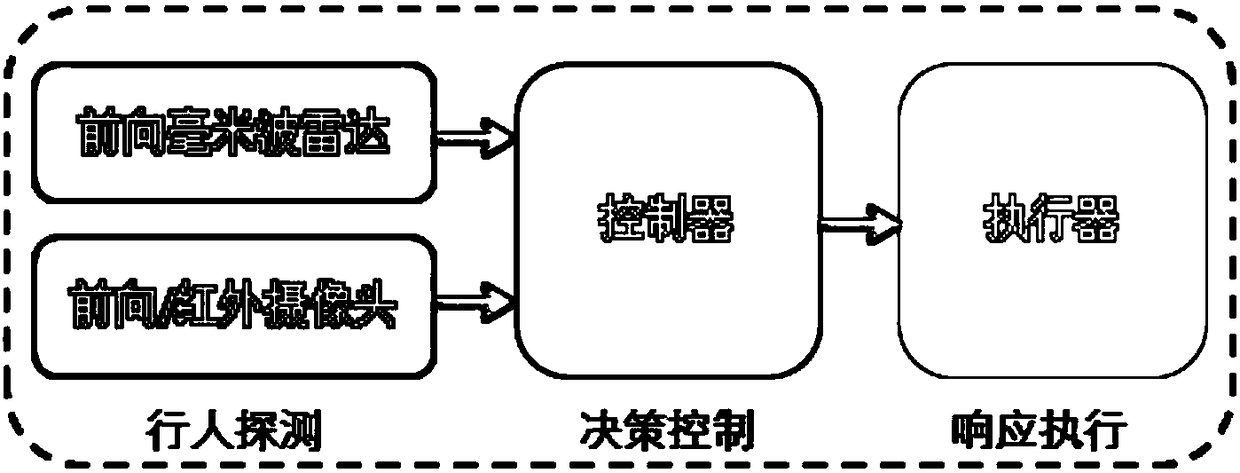
The invention discloses a design method for active brake pedestrian collision prevention. A forward millimeter wave radar, a forward looking infrared camera, a control module and an actuator are included. The millimeter wave radar is used for probing the longitudinal distance and the relative speed of a forward target object and a vehicle. The forward looking infrared camera is used for classifying the target object, conducting final confirmation on pedestrians, and meanwhile probing the transverse distance and the relative speed of the pedestrians and the vehicle. The control module is used for logical calculation and algorithmic processing. The actuator mainly executes the active brake function of the vehicle. According to the design method for active brake pedestrian collision prevention, through fusion processing of the forward looking infrared camera and the millimeter wave radar, the relative distance and orientation of the pedestrians and the vehicle are judged by a system moreprecisely, so that the phenomena such as mistaken starting and non-starting of pedestrian collision prevention active brake of the vehicle are avoided, and meanwhile, the user experience and feeling are also improved.
Owner:EASTONE AUTOMOTIVE TECH
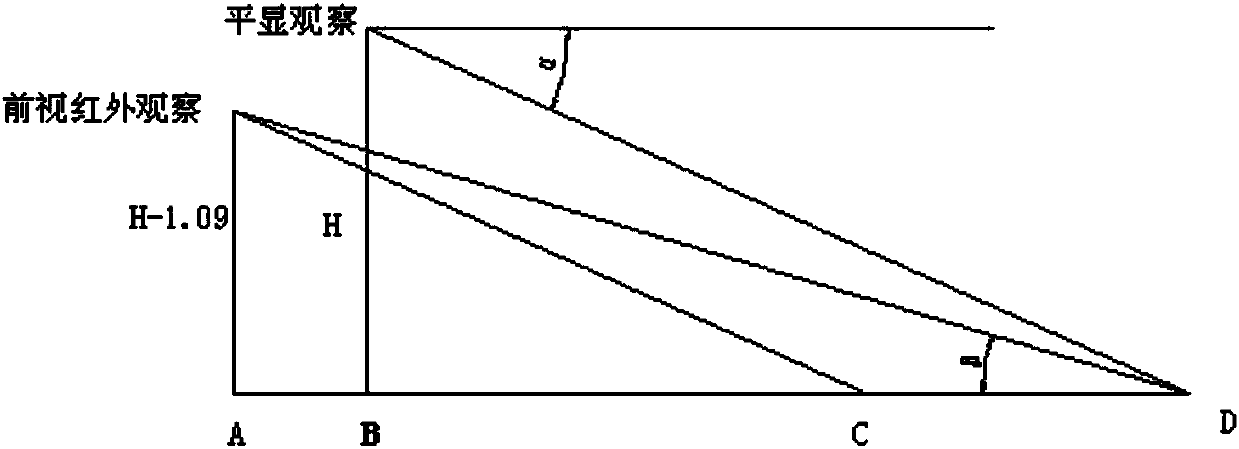
Method for eliminating visual error between forward-looking infrared device and head-up display
ActiveCN108055476AEliminate visual errorsAvoid visual errorsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHead-up displayDriver/operator
The invention relates to a method for eliminating a visual error between a forward-looking infrared device and a head-up display. By calculating a deviation of a visual axis of the forward-looking infrared device relative to a visual axis of the head-up display according to attitude data of a carrier aircraft, performing translation and shear processing on an infrared image output by the forward-looking infrared device and sending a processed infrared image to the head-up display to display, the visual error caused by mounting positions of the forward-looking infrared device and the head-up display can be solved, and an image displayed by the forward-looking infrared device on the head-up display is guaranteed to be consistent with an outside scene image seen by a driver via the head-up display.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Airsoft marking round
A spherical pellet marking round for gas propelled guns, such as airsoft electric guns and gas blow back guns, allows a user or military / law enforcement trainees to actually when they hit their opponent. The marking round is heavier than conventional gas propelled gun rounds, allowing for more reliable breaking on target. The marking round has a hard, brittle shell and is sized for the gun or rifle type. The marking round can include colored marking material, ultraviolet, infrared, forward looking infrared (FLIR) and luminous “glow-in-the-dark” shells for tracer versions. An oversized wedge can be used in production that allows for heavier weighted fill material to be used.
Owner:BOWDEN KERRY THADDEUS
Pulsed optical threat detection
InactiveUS6069358ARadiation pyrometryWave based measurement systemsPulse patternForward looking infrared
A technique for internal forward looking infrared (FLIR) system detection of laser pulses. For scanning systems image pixel output of each frame is sampled as image data which is used to determine a pattern of saturated image pixels. The pattern of saturated image pixels is compared to predetermined laser pulse patterns and is then analyzed to determine if a laser pulse was detected. For staring systems, the patterns are compared to previous and following frames to determine if short lived large changes occur to determine if a laser pulse was detected.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Airsoft marking round
A spherical pellet marking round for gas propelled guns, such as airsoft electric guns and gas blow back guns, allows a user or military / law enforcement trainees to actually when they hit their opponent. The marking round is heavier than conventional gas propelled gun rounds, allowing for more reliable breaking on target. The marking round has a hard, brittle shell and is sized for the gun or rifle type. The marking round can include colored marking material, ultraviolet, infrared, forward looking infrared (FLIR) and luminous “glow-in-the-dark” shells for tracer versions. An oversized wedge can be used in production that allows for heavier weighted fill material to be used.
Owner:BOWDEN KERRY THADDEUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com