Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Flow instability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
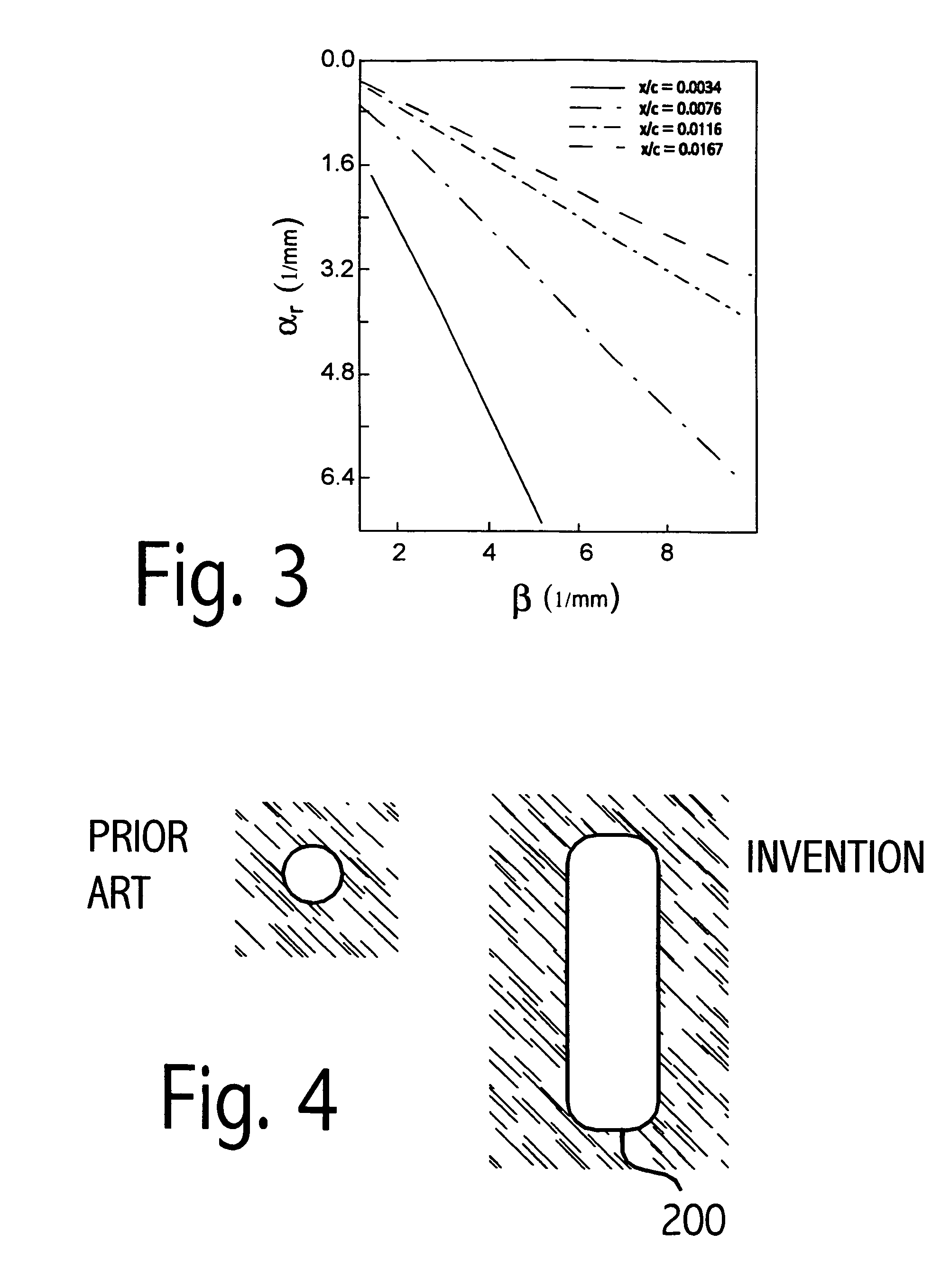
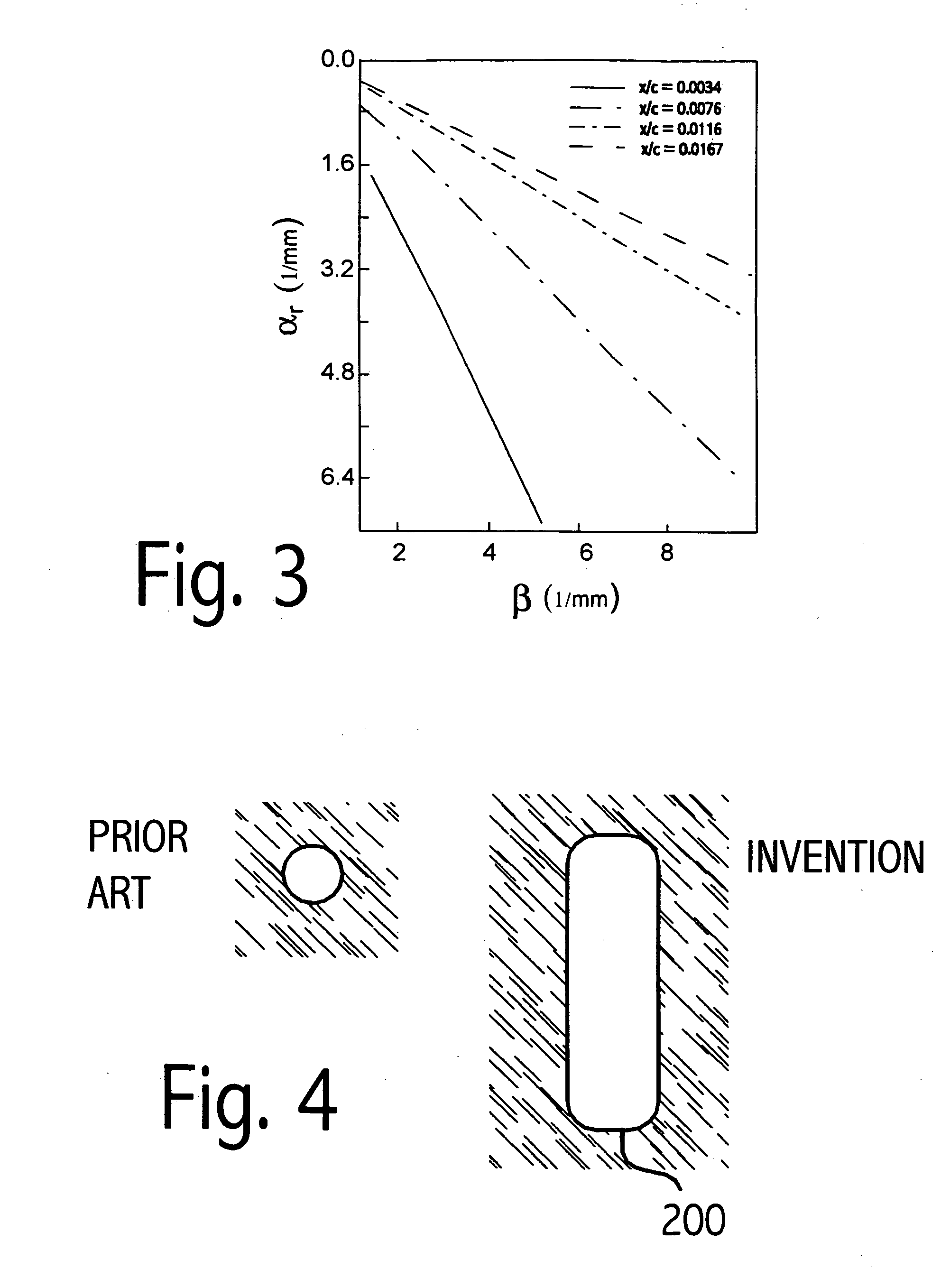
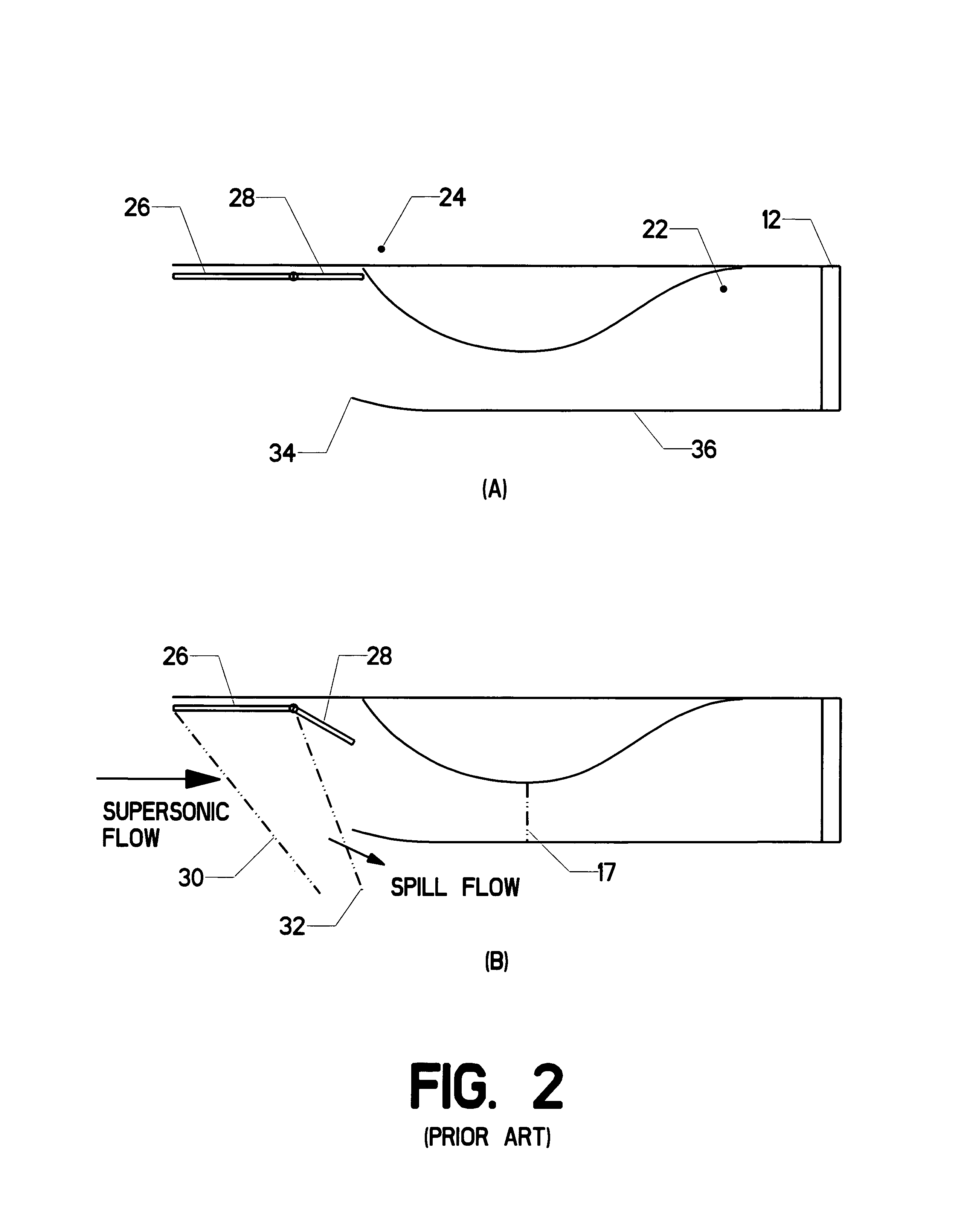
Applied Flow Instability. Flow instability is formally a linear concept, applicable only for infinitesimal perturbations to a steady or periodic solution to the governing equations. Nevertheless, it can be applied to turbulent flows with surprising success, yielding useful information about how to control such flows.
Cold-performance fluidic oscillator
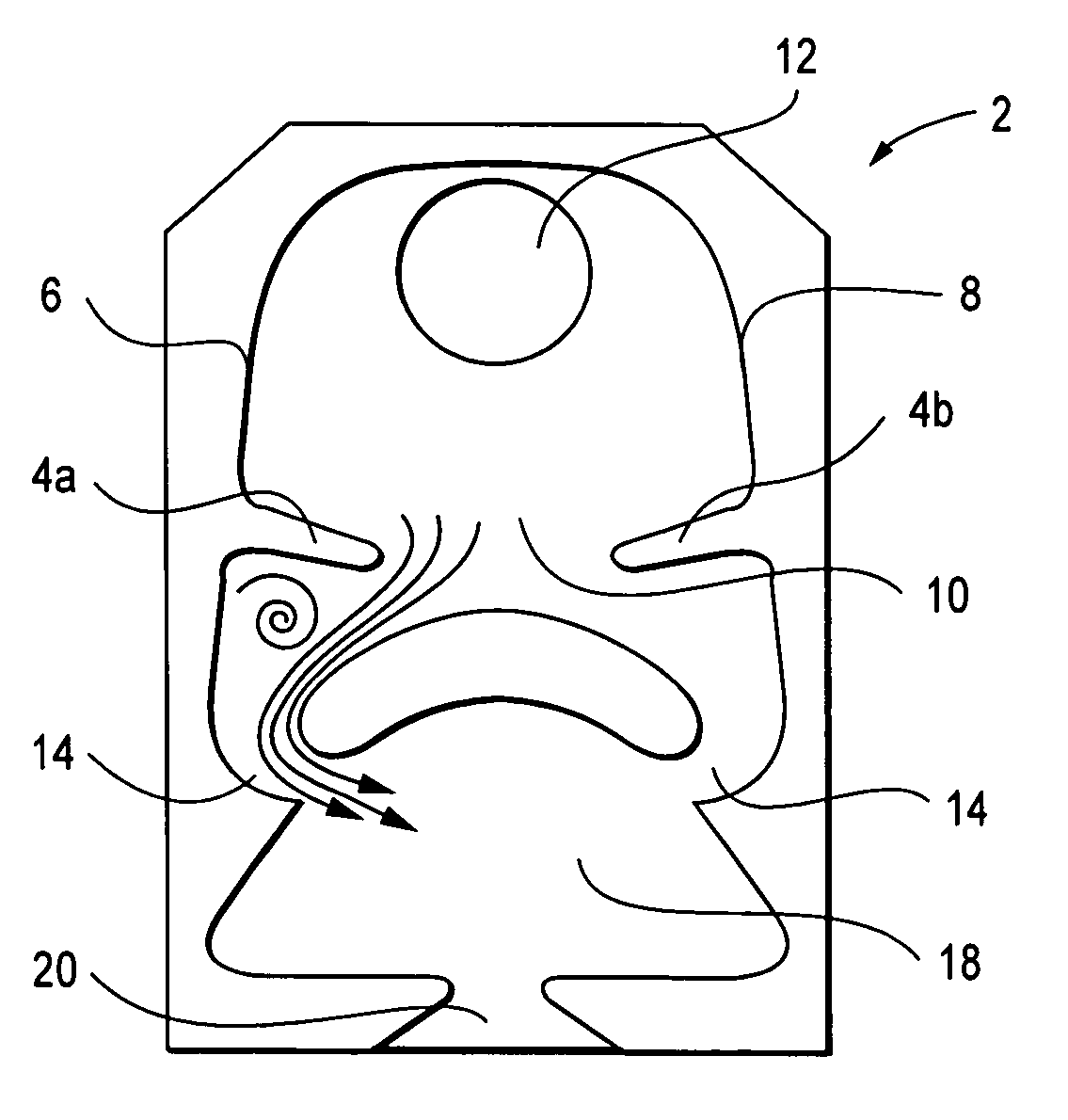
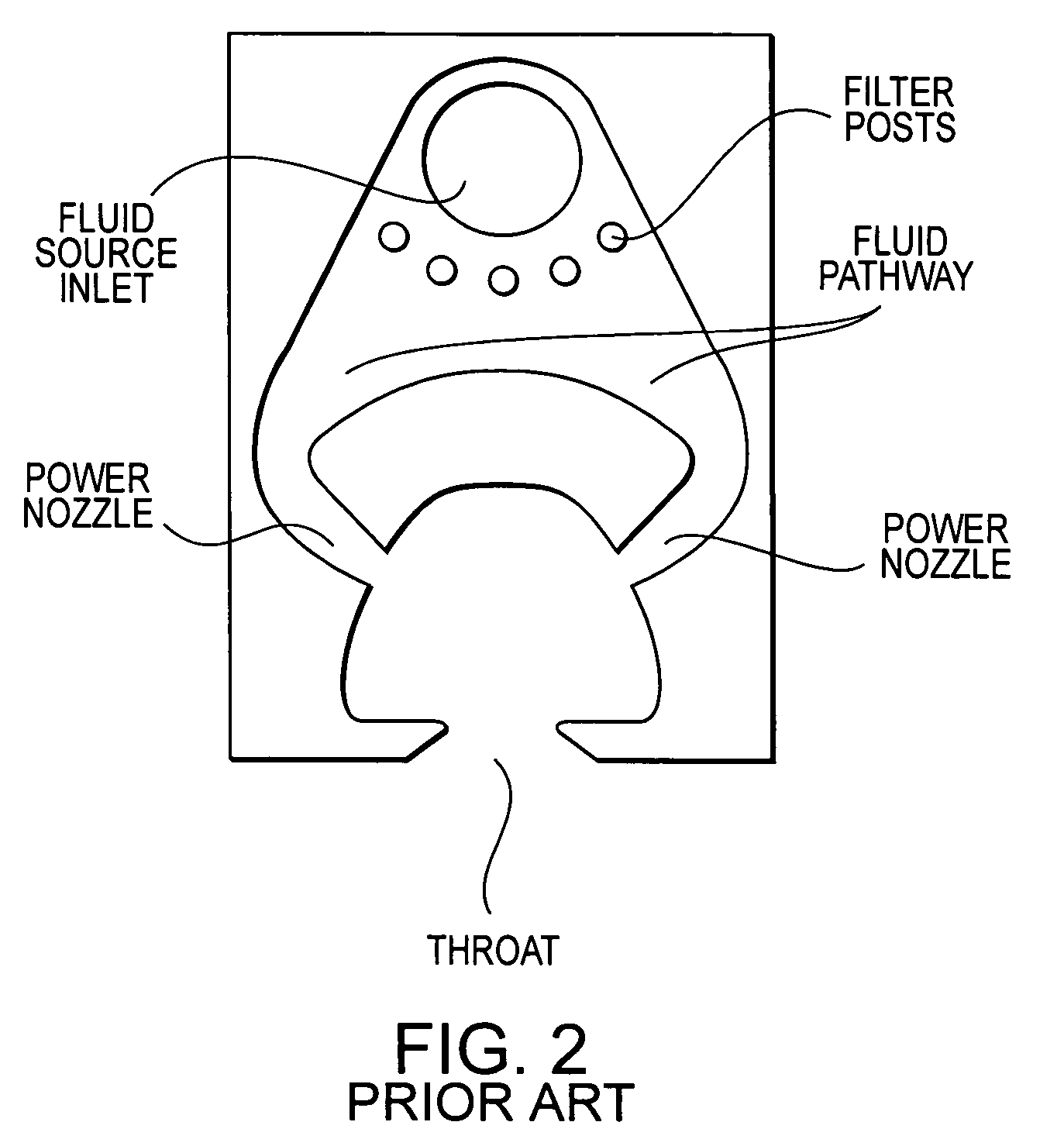
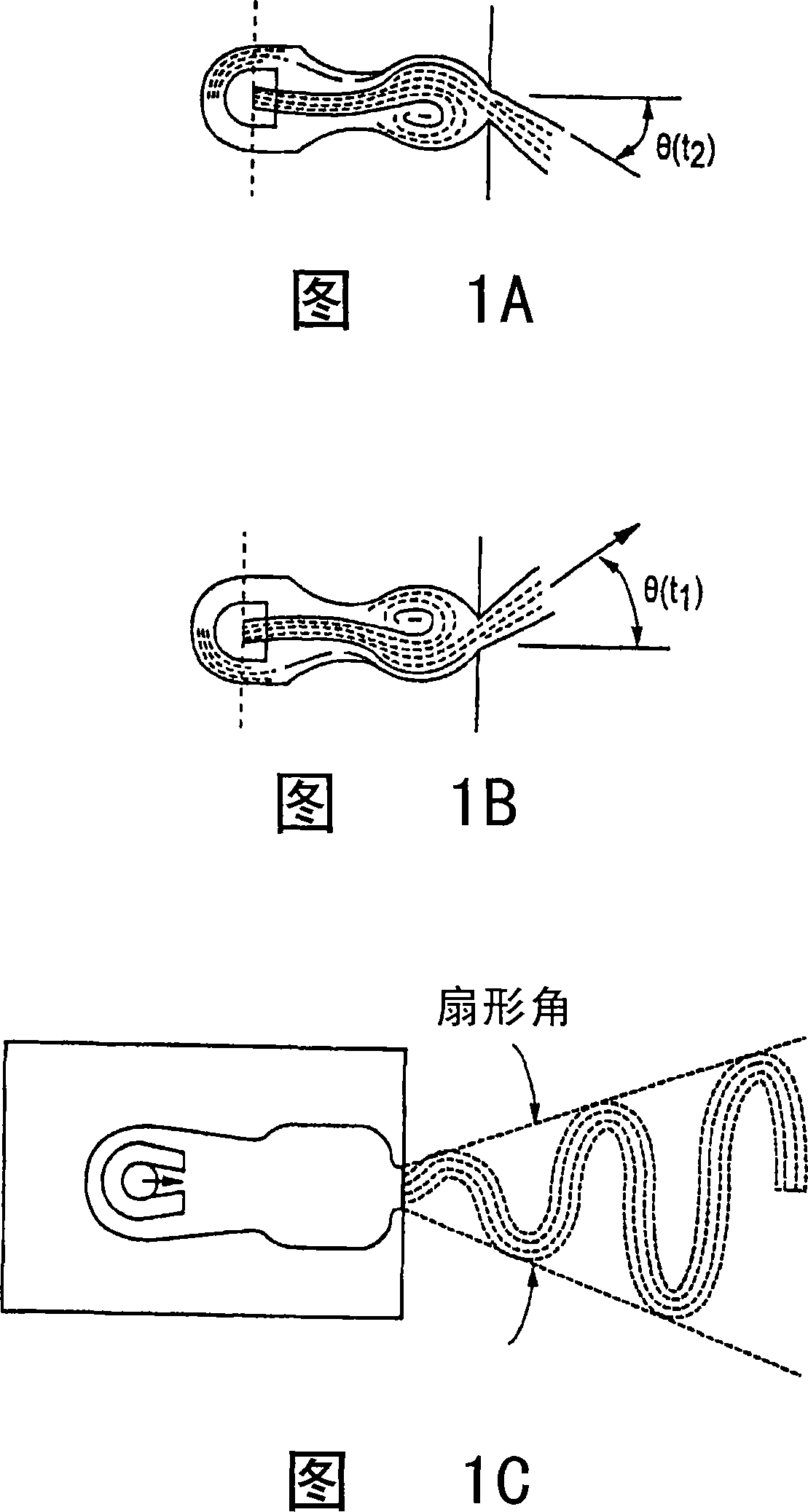
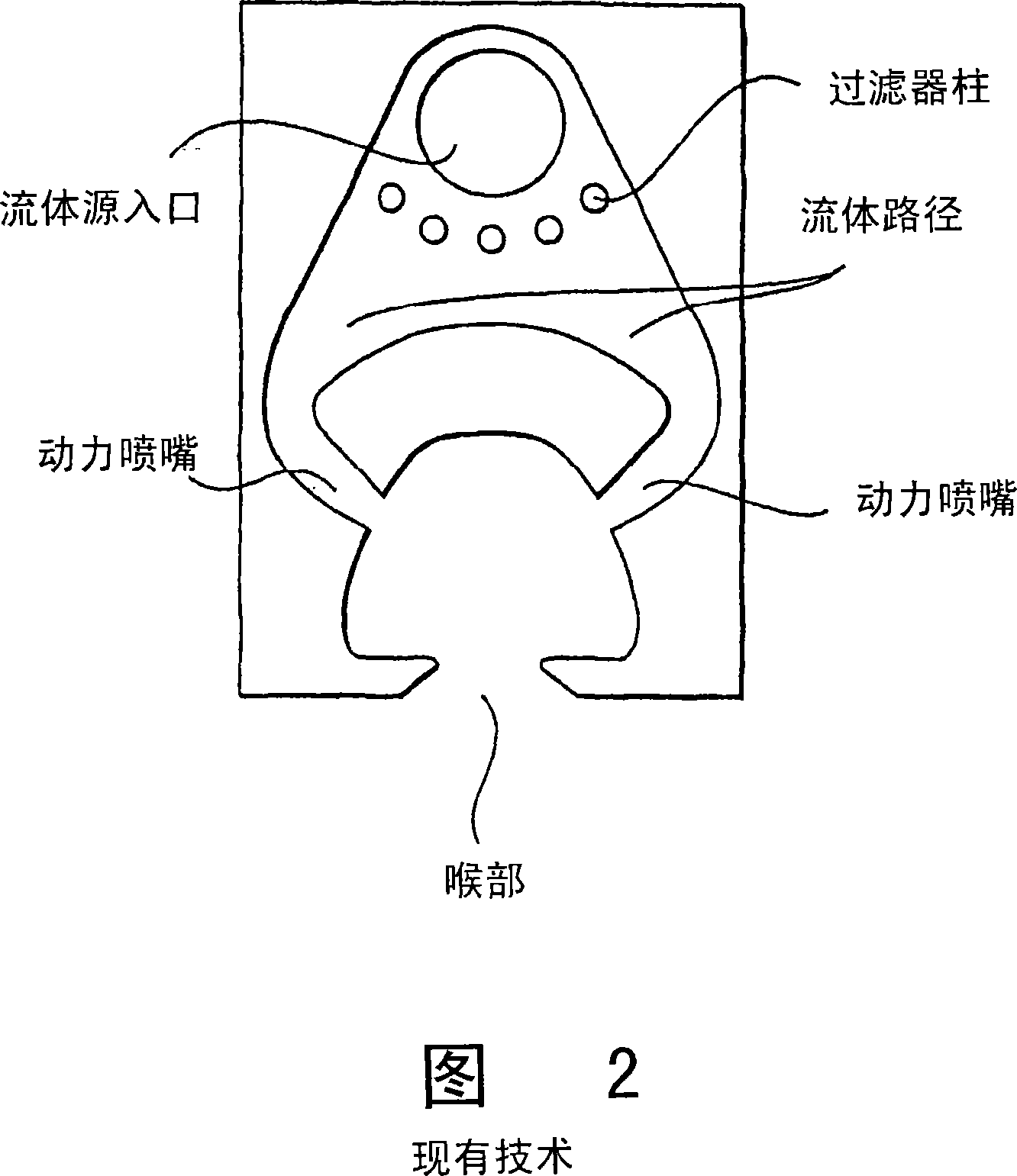
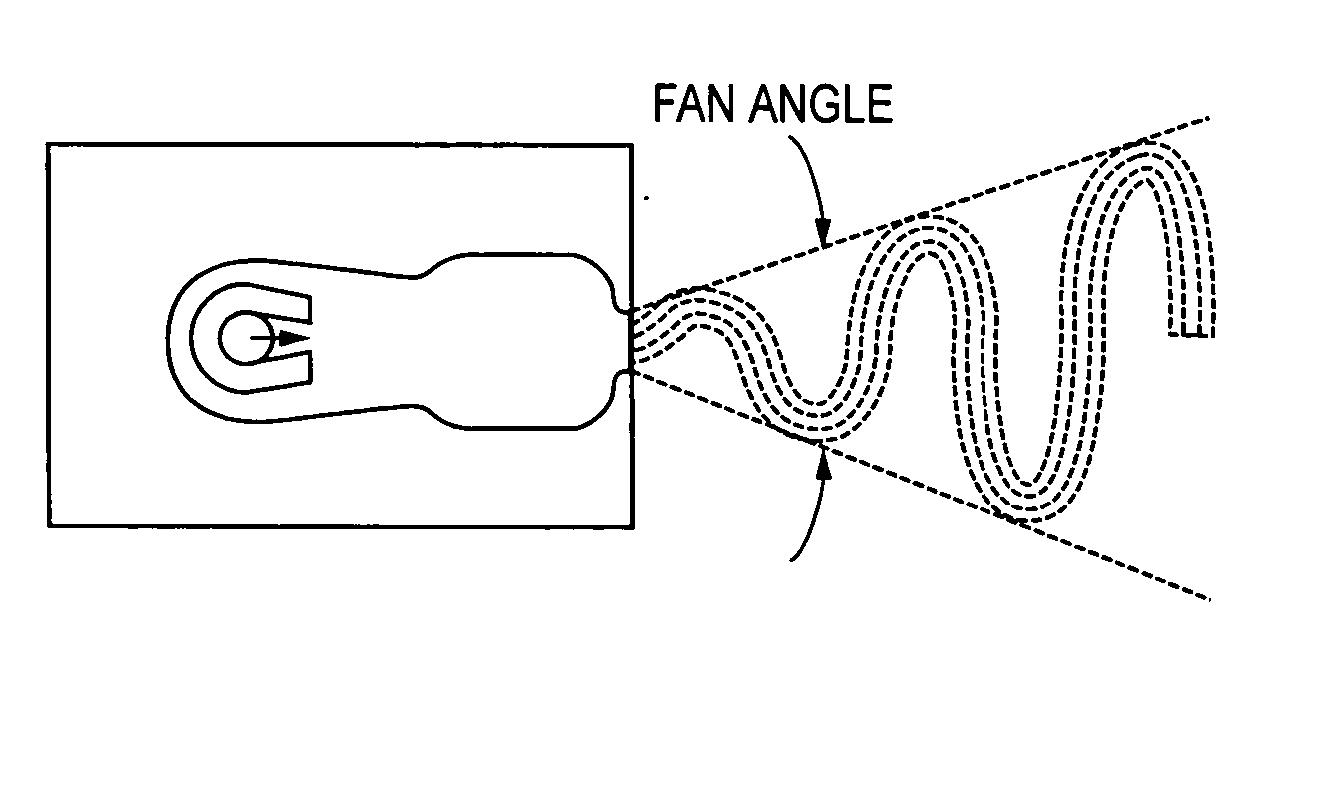
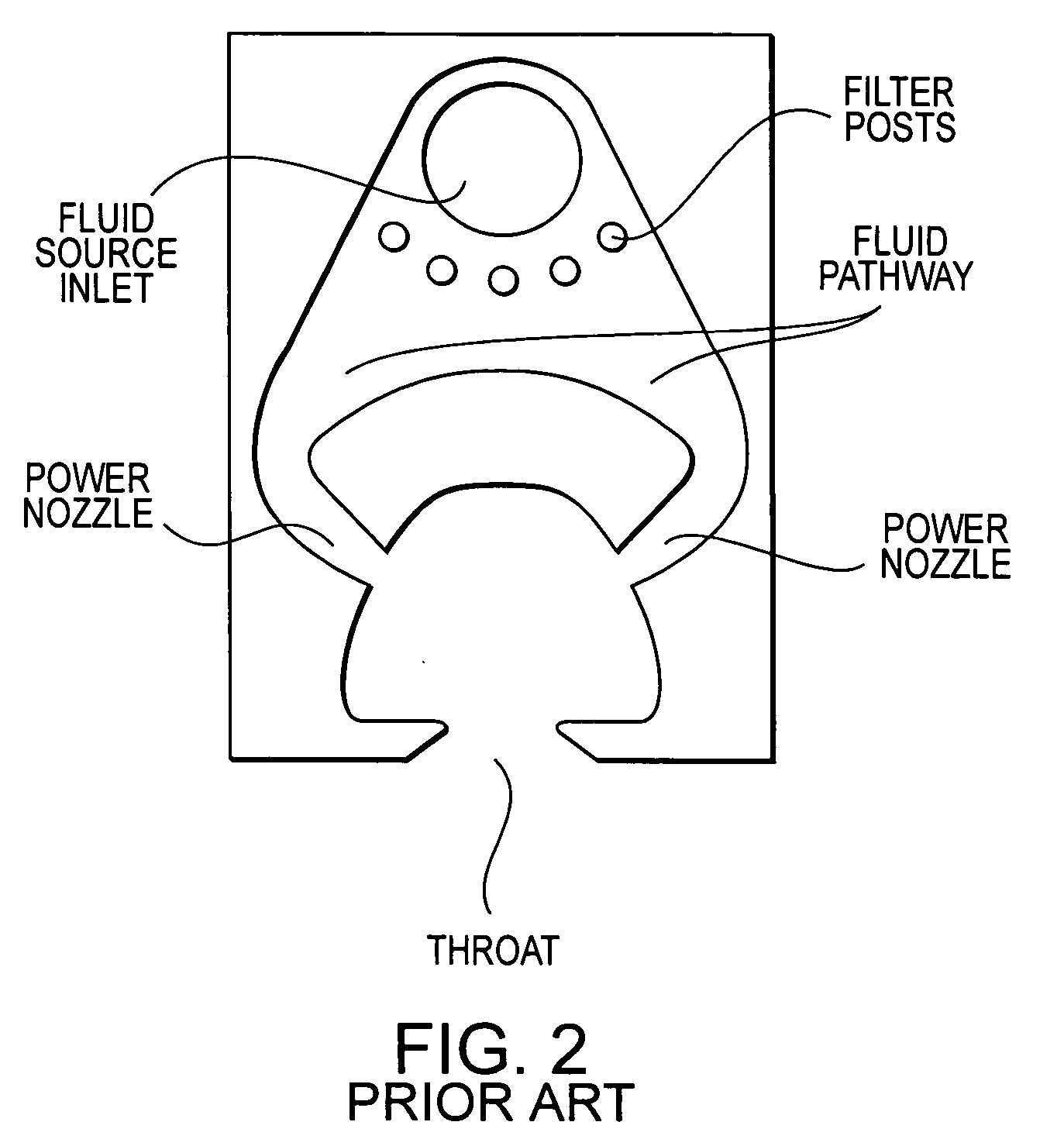
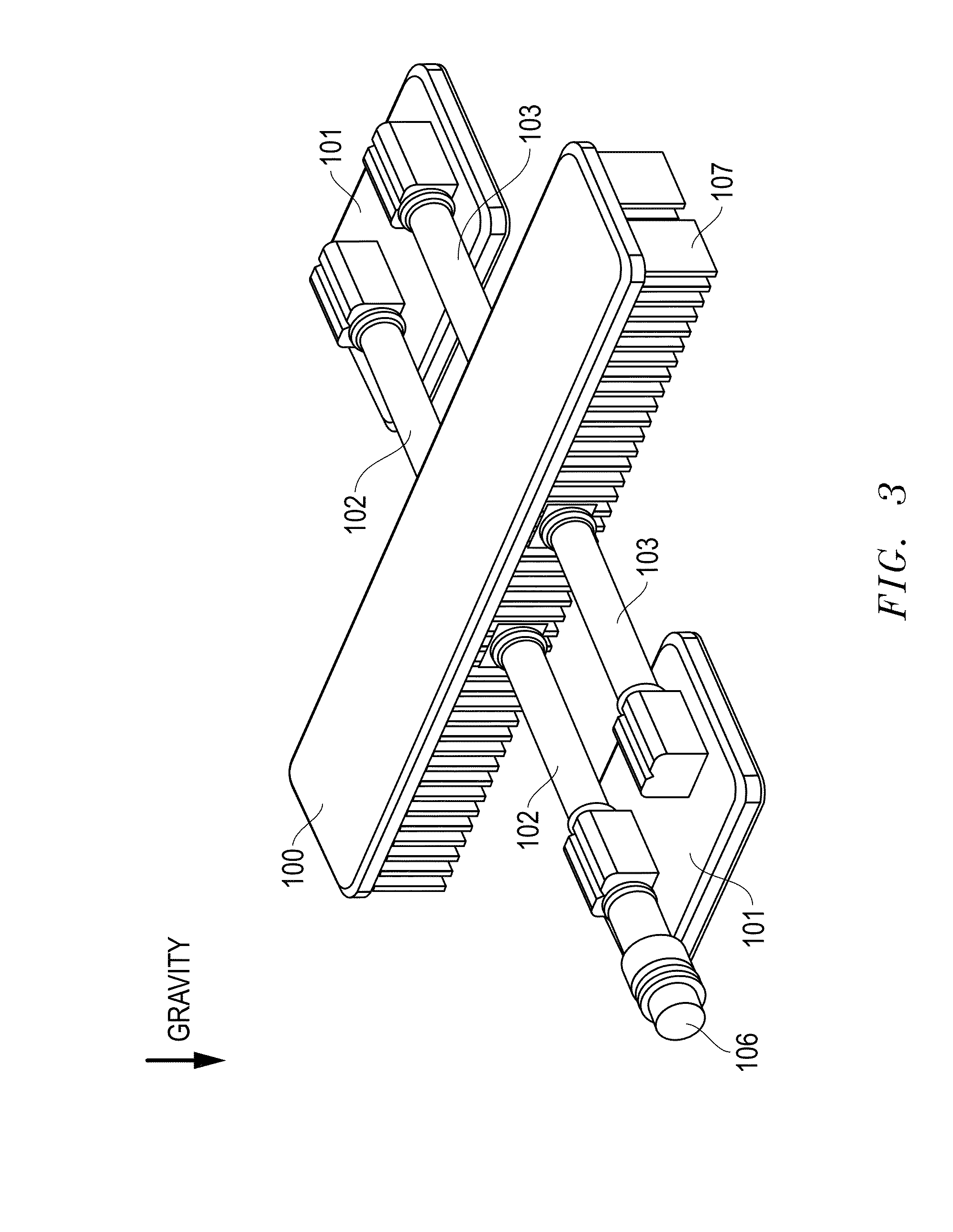
A fluidic oscillator suitable for use at colder temperatures for generating an exhaust flow in the form of an oscillating spray of fluid droplets has an inlet for pressurized fluid, a pair of power nozzles configured to accelerate the movement of the pressurized fluid, a fluid pathway that connects and allows for the flow of pressurized fluid between its inlet and the power nozzles, an interaction chamber which is attached to the nozzles and receives the flow from the nozzles, a fluid outlet from which the spray exhausts from the interaction chamber, and a means for increasing the instability of the flow from the power nozzles, with this means being situated in a location chosen from the group consisting of a location within the fluid pathway or proximate the power nozzles. In a first preferred embodiment, the flow instability generating means comprises a protrusion that extends inward from each side of the fluid pathway so as to cause a flow separation region downstream of the protrusions. In a second preferred embodiment, the flow instability generating means comprises a step in the height elevation of the floor of the power nozzles with respect to that of the interaction chamber.
Owner:DLHBOWLES INC
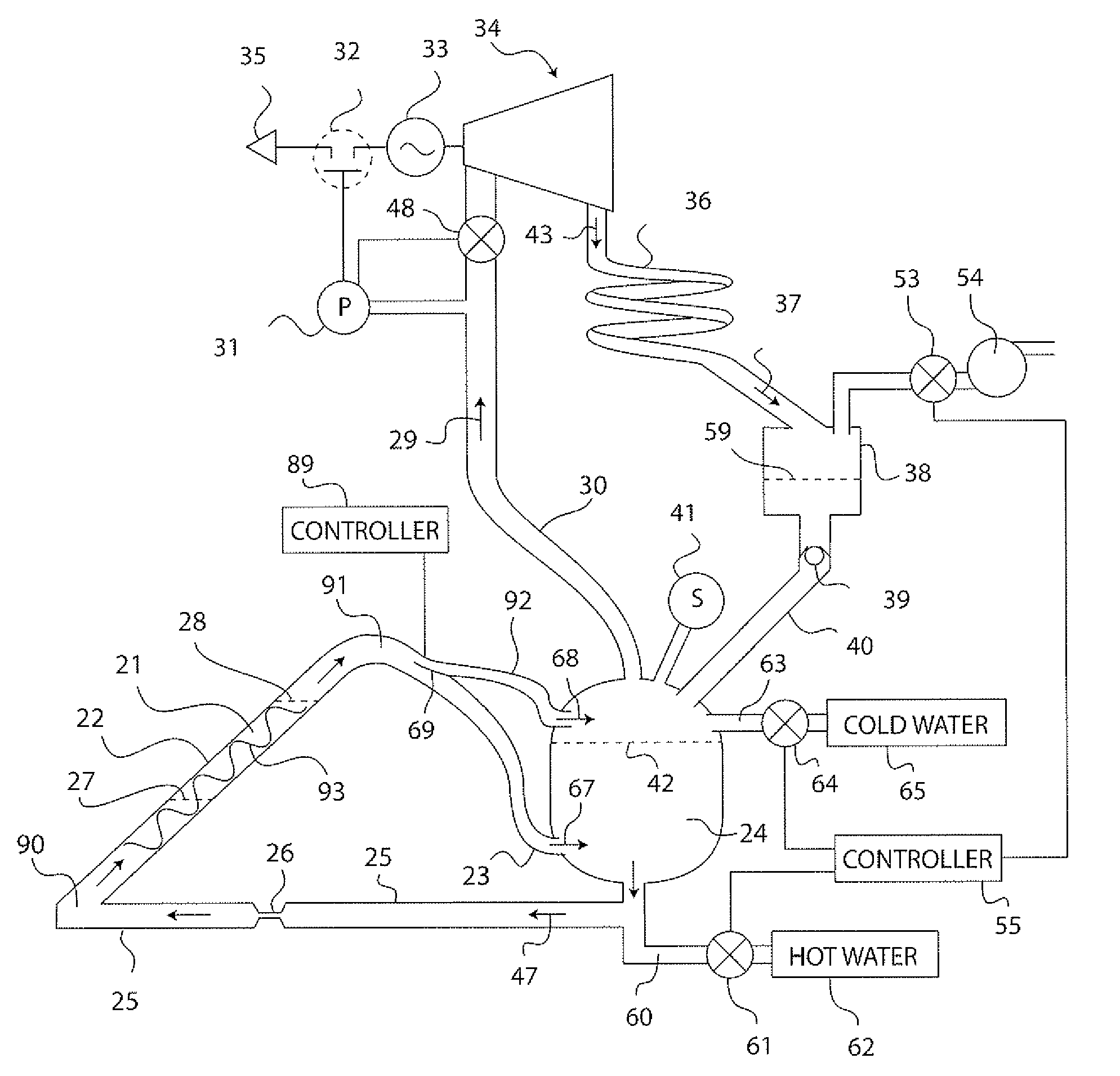
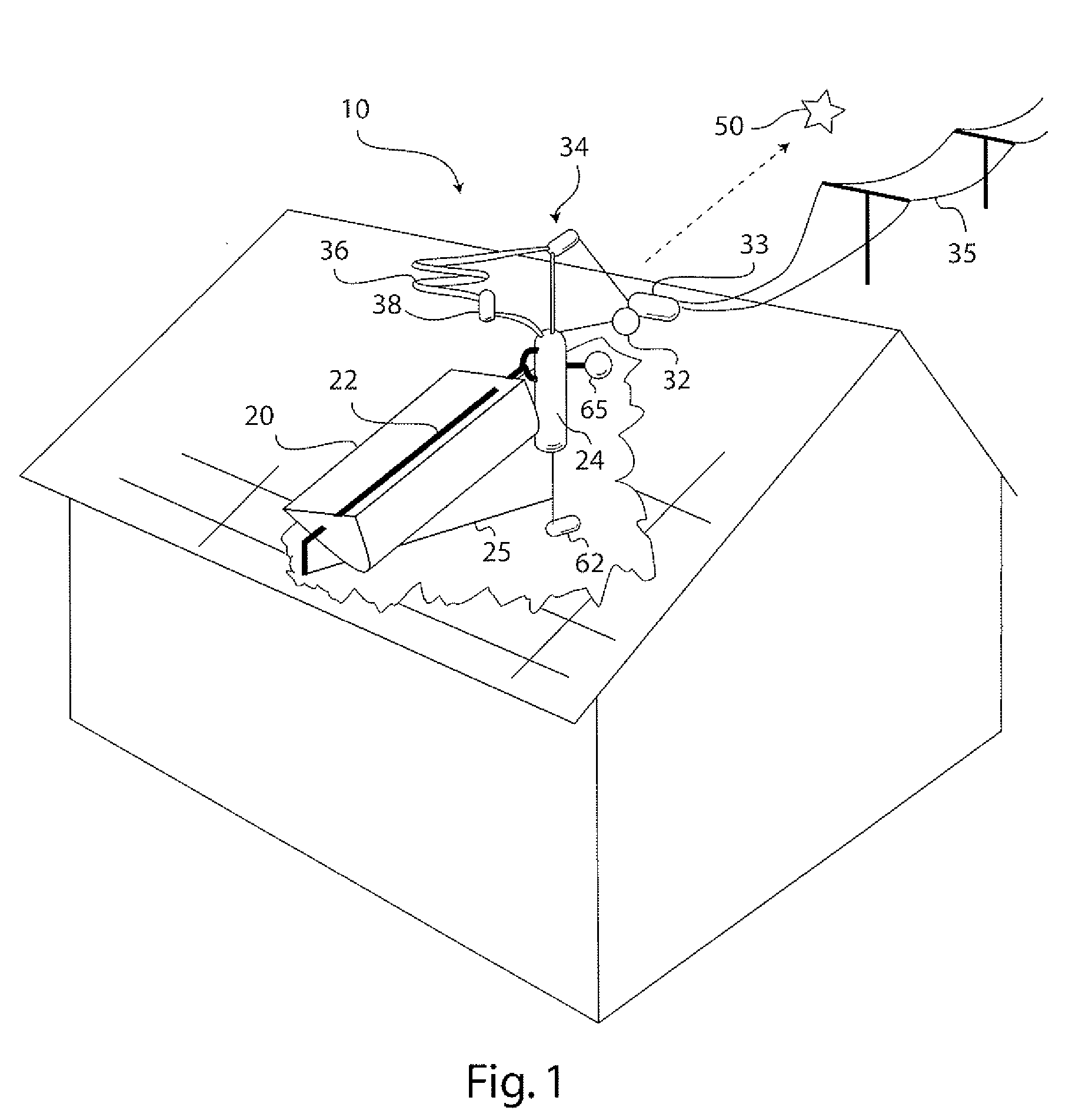
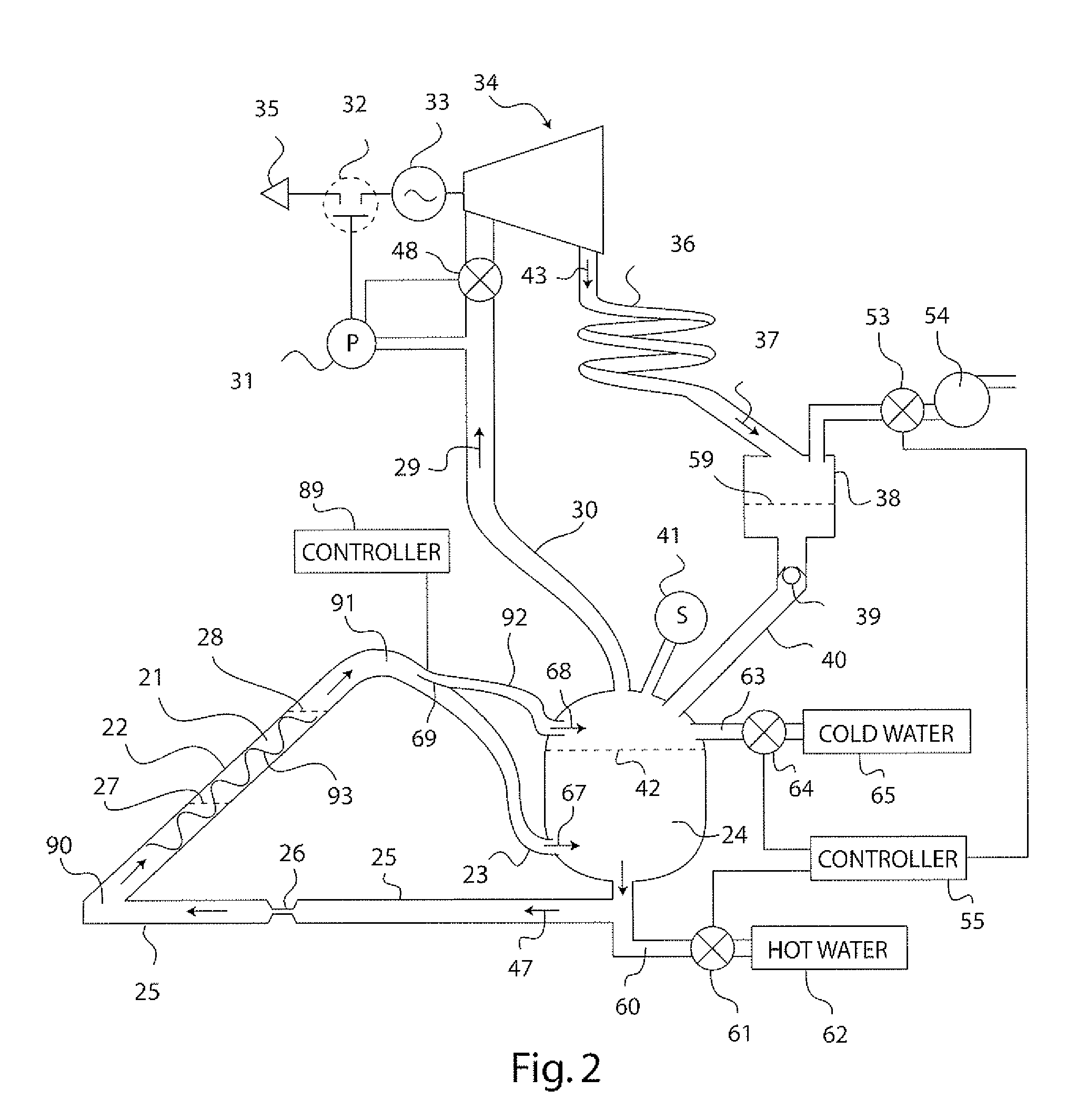
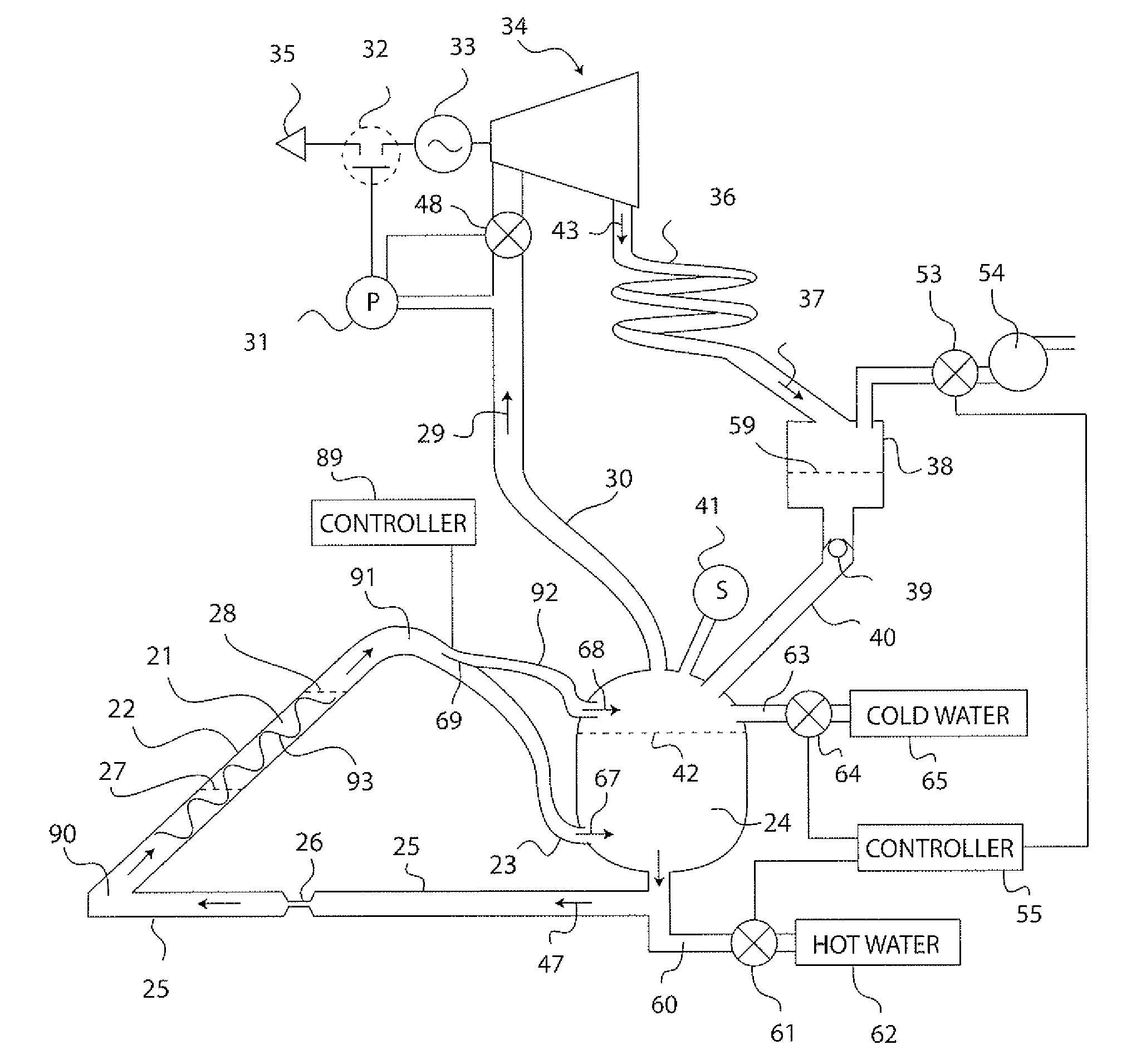
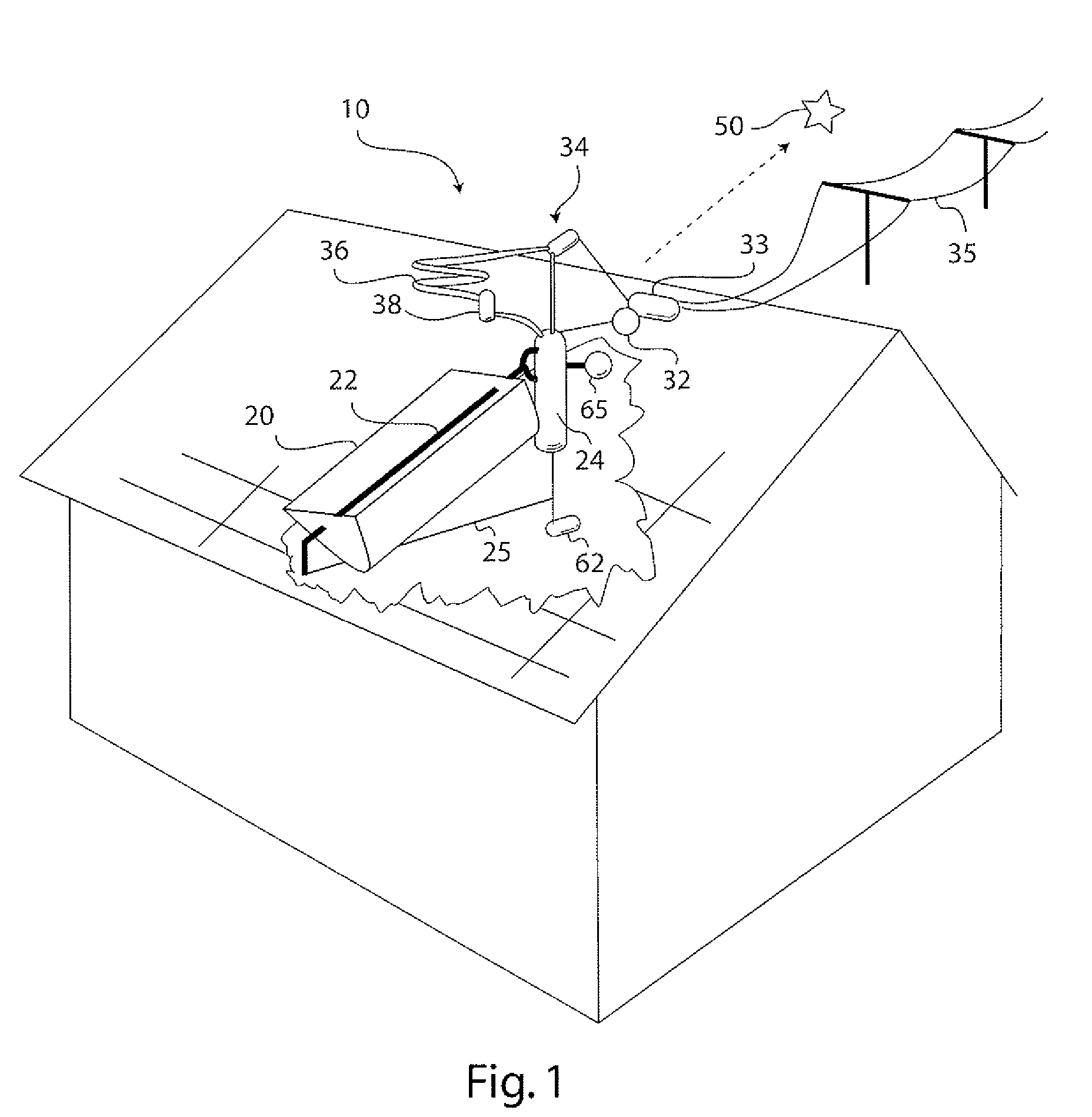
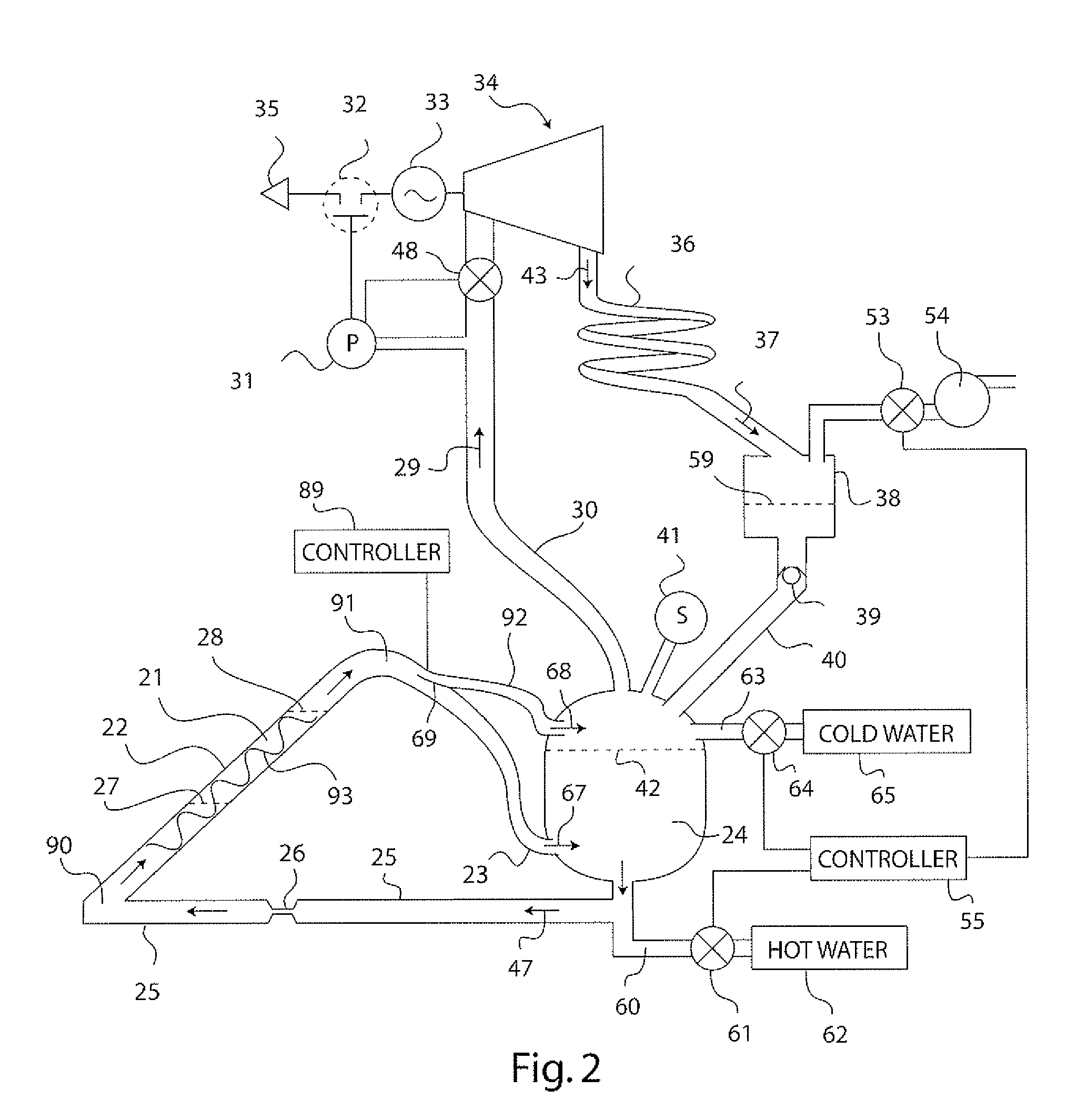
Solar Thermal Power System
InactiveUS20090199557A1Simple efficiencyTechnology being suitableAuxillary drivesSteam separation arrangementsThermal energy storageEngineering
A solar thermal power generator includes an inclined elongated boiler tube positioned in the focus of a solar concentrator for generating steam from water. The boiler tube is connected at one end to receive water from a pressure vessel as well as connected at an opposite end to return steam back to the vessel in a fluidic circuit arrangement that stores energy in the form of heated water in the pressure vessel. An expander, condenser, and reservoir are also connected in series to respectively produce work using the steam passed either directly (above a water line in the vessel) or indirectly (below a water line in the vessel) through the pressure vessel, condense the expanded steam, and collect the condensed water. The reservoir also supplies the collected water back to the pressure vessel at the end of a diurnal cycle when the vessel is sufficiently depressurized, so that the system is reset to repeat the cycle the following day. The circuital arrangement of the boiler tube and the pressure vessel operates to dampen flow instabilities in the boiler tube, damp out the effects of solar transients, and provide thermal energy storage which enables time shifting of power generation to better align with the higher demand for energy during peak energy usage periods.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
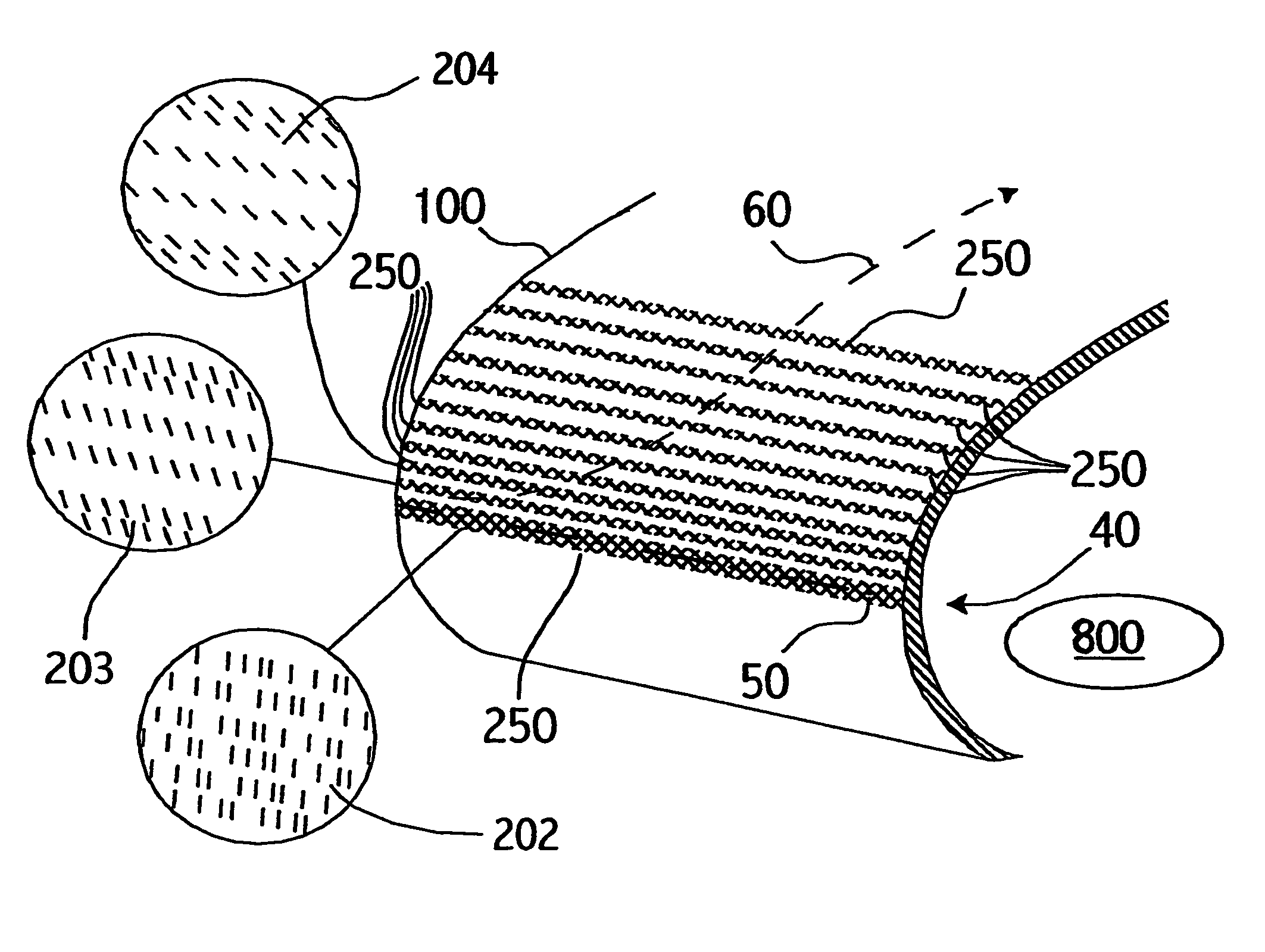
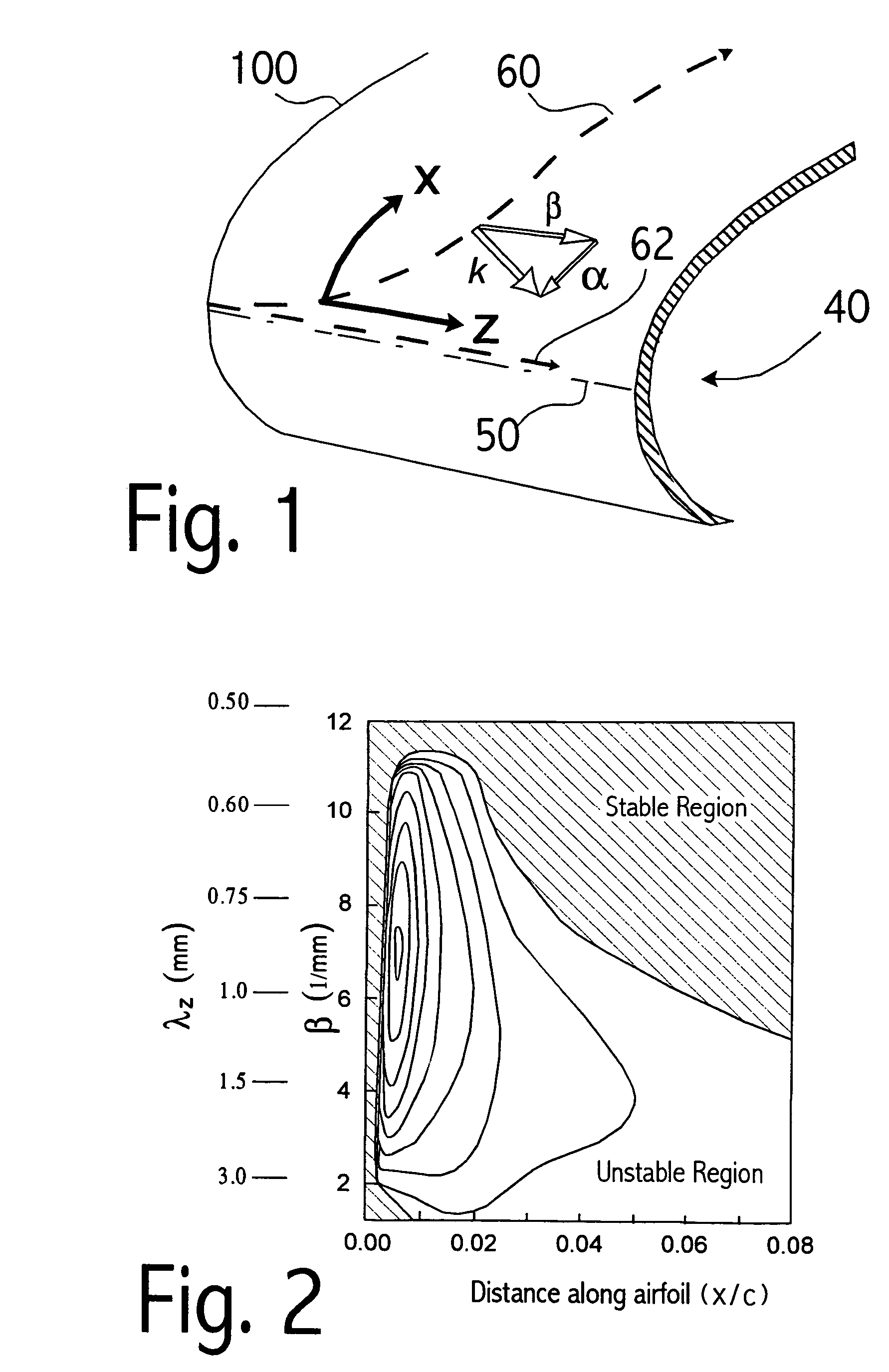
Perforated skin structure for laminar-flow systems
InactiveUS7152829B2Improve thermal conductivityBoundary layer controlsWingsThrottle controlStreaming instability
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Localized arc filament plasma actuators for noise mitigation and mixing enhancement
InactiveUS20060005545A1Increase amplitudeEnhance and weaken vorticityAircraft navigation controlEngine fuctionsPlasma actuatorStreaming instability
A device for controlling fluid flow. The device includes an arc generator coupled to electrodes. The electrodes are placed adjacent a fluid flowpath such that upon being energized by the arc generator, an arc filament plasma adjacent the electrodes is formed. In turn, this plasma forms a localized high temperature, high pressure perturbation in the adjacent fluid flowpath. The perturbations can be arranged to produce vortices, such as streamwise vortices, in the flowing fluid to control mixing and noise in such flows. The electrodes can further be arranged within a conduit configured to contain the flowing fluid such that when energized in a particular frequency and sequence, can excite flow instabilities in the flowing fluid. The placement of the electrodes is such that they are unobtrusive relative to the fluid flowpath being controlled.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Microfluidic electrophoresis chip having flow-retarding structure
InactiveUS20060042948A1Reducing electrokinetic flow instabilityHigh hydraulic resistanceSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
A capillary electrophoresis device and separation protocol uses a hydraulic resistance-providing structure (HRPS) in the main separation channel to separate the divide the main separate channel into an upstream portion and a downstream portion. The HRPS may take the form of a porous plug, or a solid plug provided with at least one shallow channel. A sample separates and migrates through the porous structure or the shallow channel, upon application of a voltage difference between the upstream and downstream sides. Among other things, the HRPS helps reduce electrokinetic flow in the presence of conductivity gradients and facilitates robust, high-gradient on-chip field amplified sample stacking. The HRPS also enables the use of a pressure-injection scheme for the introduction of a high conductivity gradient in a separation channel and thereby avoids flow instabilities associated with high conductivity gradient electrokinetics. The approach also allows for the suppression of electroosmotic flow (EOF) and benefits from the associated minimization of sample dispersion caused by non-uniform EOF mobilities. An injection procedure employing a single pressure-flow high-conductivity buffer injection step followed by standard high voltage control of electrophoretic fluxes of sample, may be employed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
High-stability valve arrangement for a governor valve
InactiveUS7108244B2Improve stabilityCheck valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyStreaming instabilityEngineering
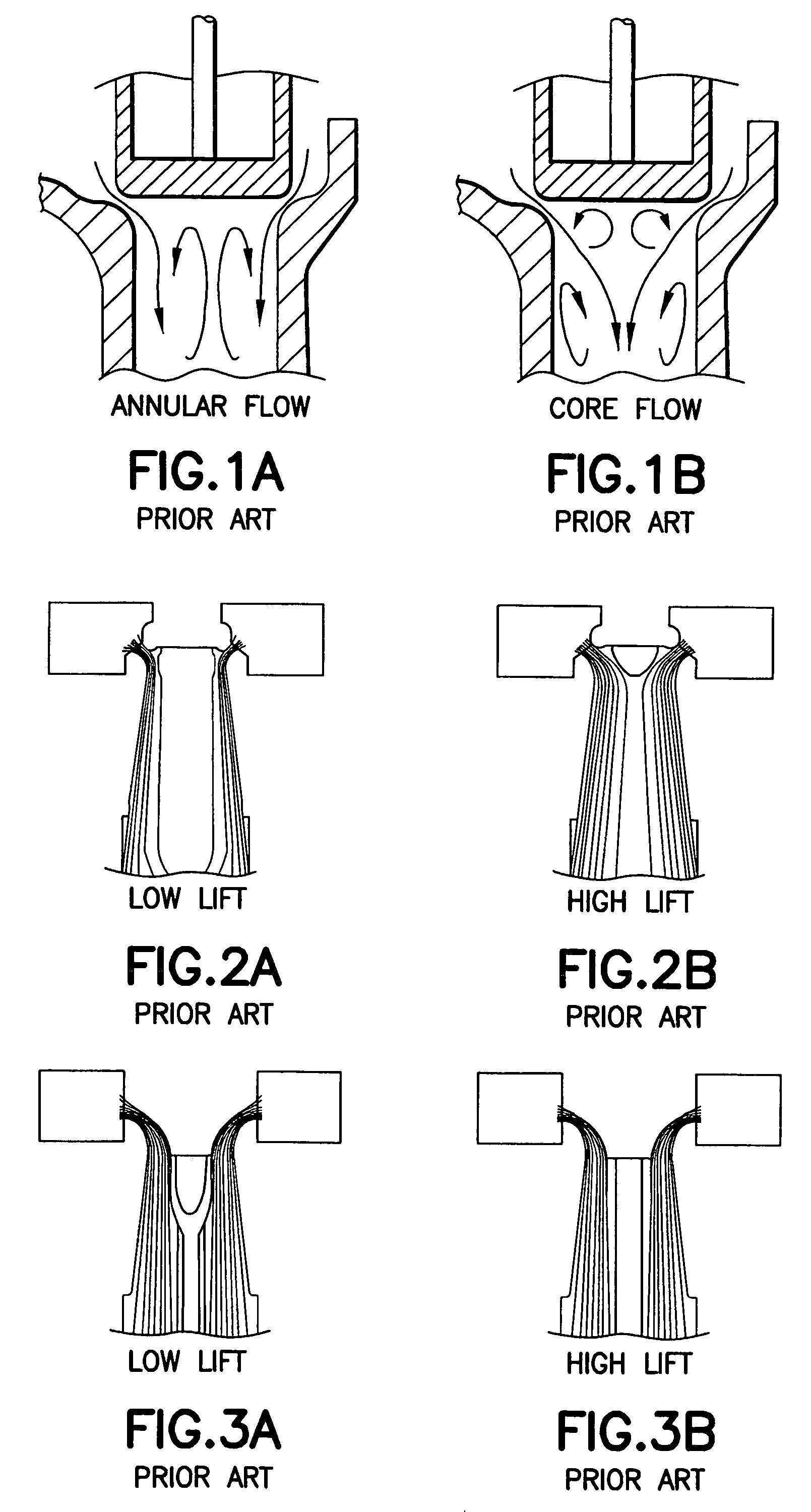
A valve arrangement (10) for reducing the instability of fluid flow in a compressible flow governor valve includes a cutoff plug (12) with a lateral concave surface (14) and an end portion (16) having a substantially circular cross section, and a seat (30) with a convex surface (32). The lateral concave surface (14) and the end portion (16) of the cutoff plug (12) define an abrupt cutoff corner (18). The radius (re) of the end portion (16) of the cutoff plug (12) is less than the radius (Rs) of the seat (30). The radius of curvature (R) of the seat (30) is less than the radius of curvature (rq) of the lateral concave surface (14) of the cutoff plug (12). The configuration of the cutoff plug (12) and seat (30) enhances the annular flow pattern beneath the cutoff plug (12) at all lift positions thus reducing flow instability.
Owner:ELLIOTT CO
Localized arc filament plasma actuators for noise mitigation and mixing enhancement
InactiveUS7334394B2Increase amplitudeHigh bandwidthAircraft navigation controlEngine fuctionsPlasma actuatorStreaming instability
A device for controlling fluid flow. The device includes an arc generator coupled to electrodes. The electrodes are placed adjacent a fluid flowpath such that upon being energized by the arc generator, an arc filament plasma adjacent the electrodes is formed. In turn, this plasma forms a localized high temperature, high pressure perturbation in the adjacent fluid flowpath. The perturbations can be arranged to produce vortices, such as streamwise vortices, in the flowing fluid to control mixing and noise in such flows. The electrodes can further be arranged within a conduit configured to contain the flowing fluid such that when energized in a particular frequency and sequence, can excite flow instabilities in the flowing fluid. The placement of the electrodes is such that they are unobtrusive relative to the fluid flowpath being controlled.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
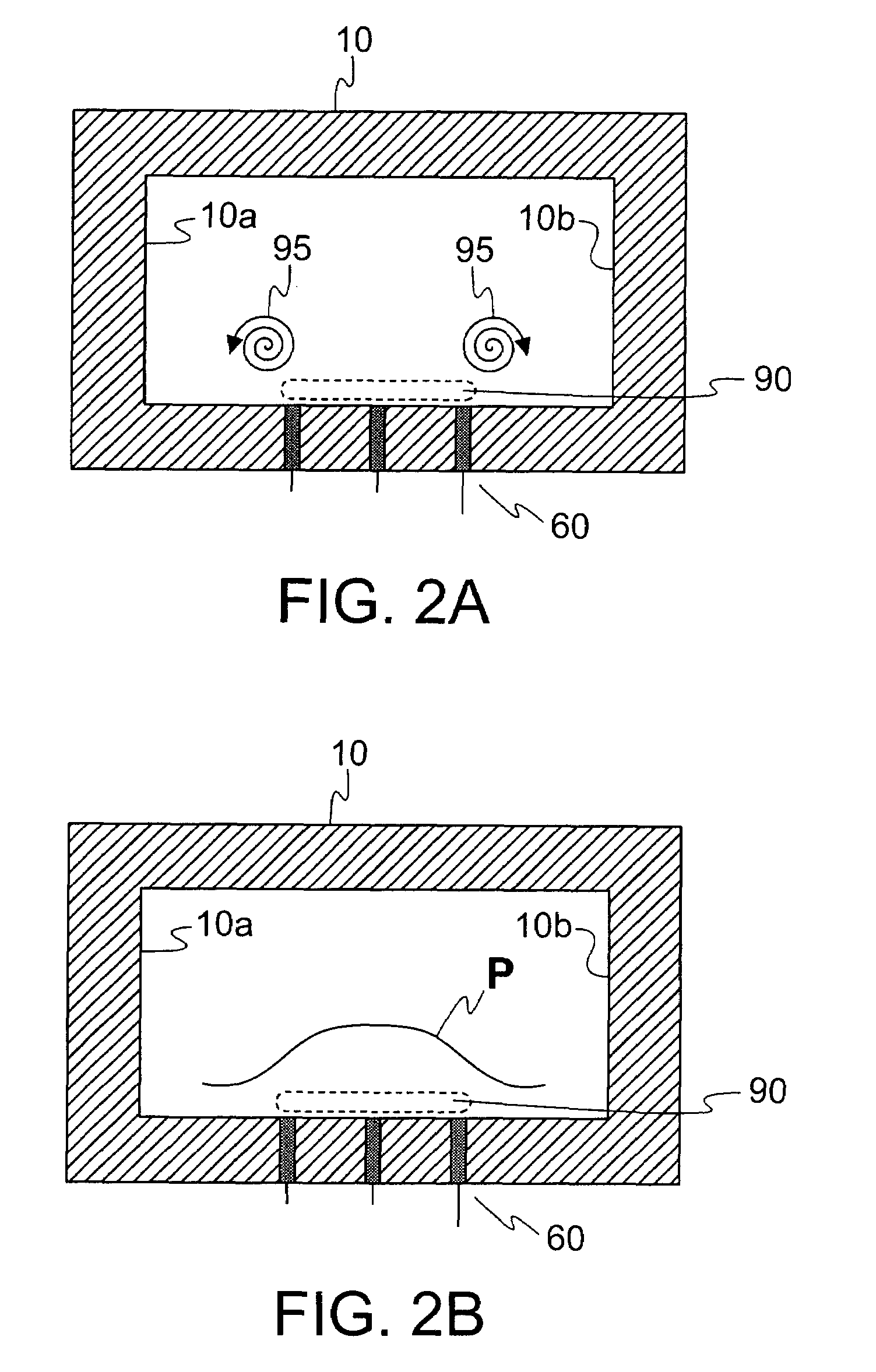
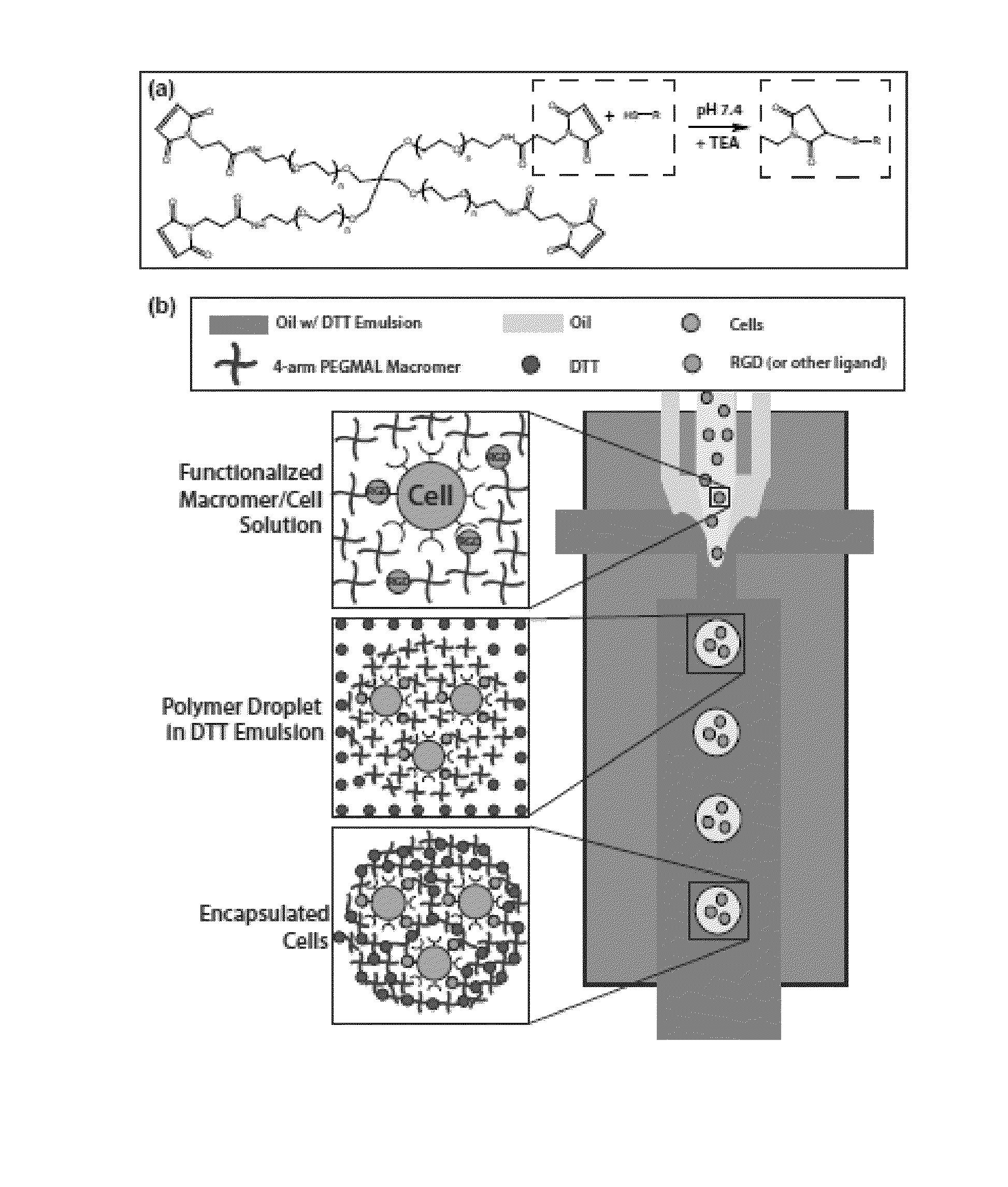
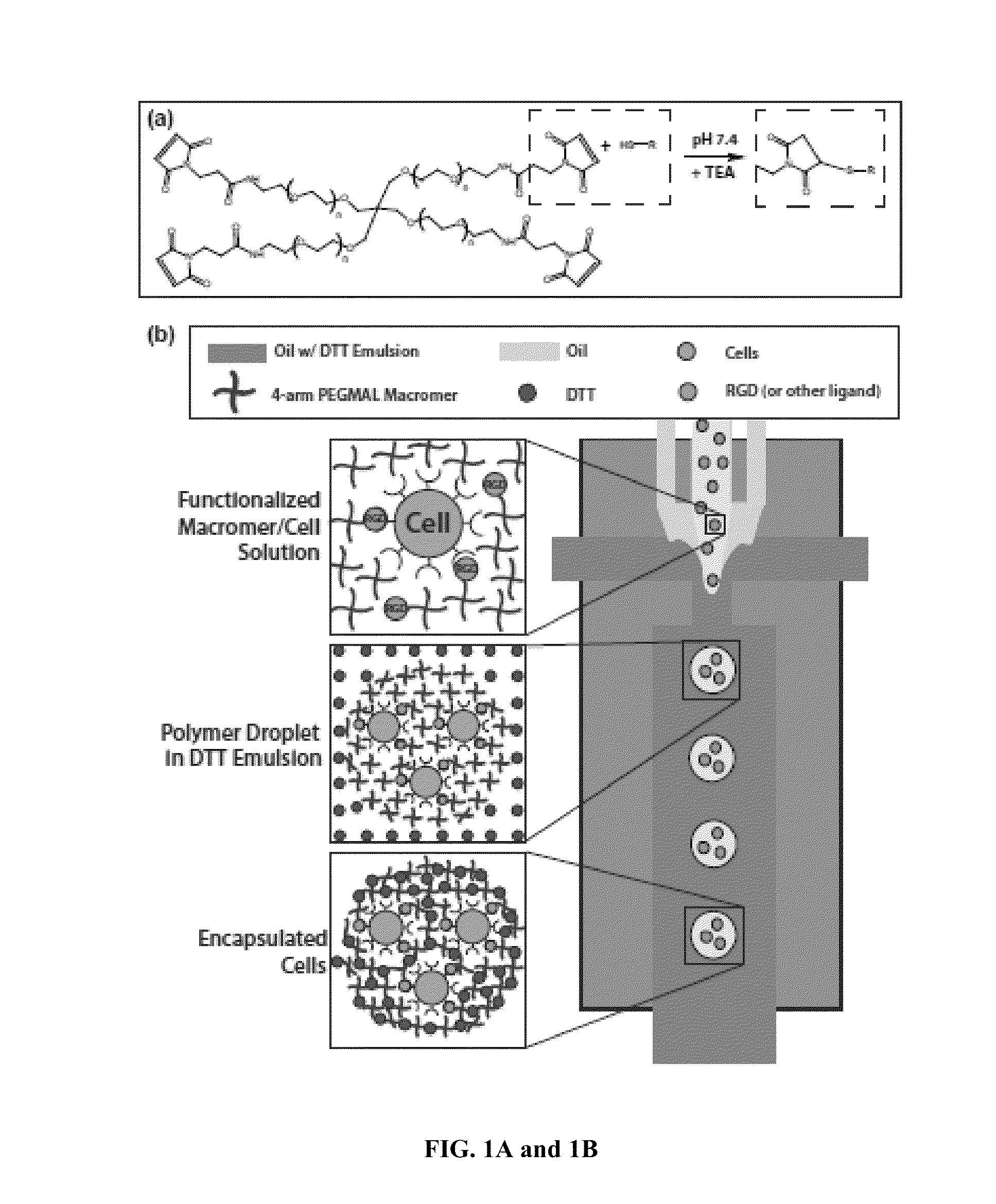
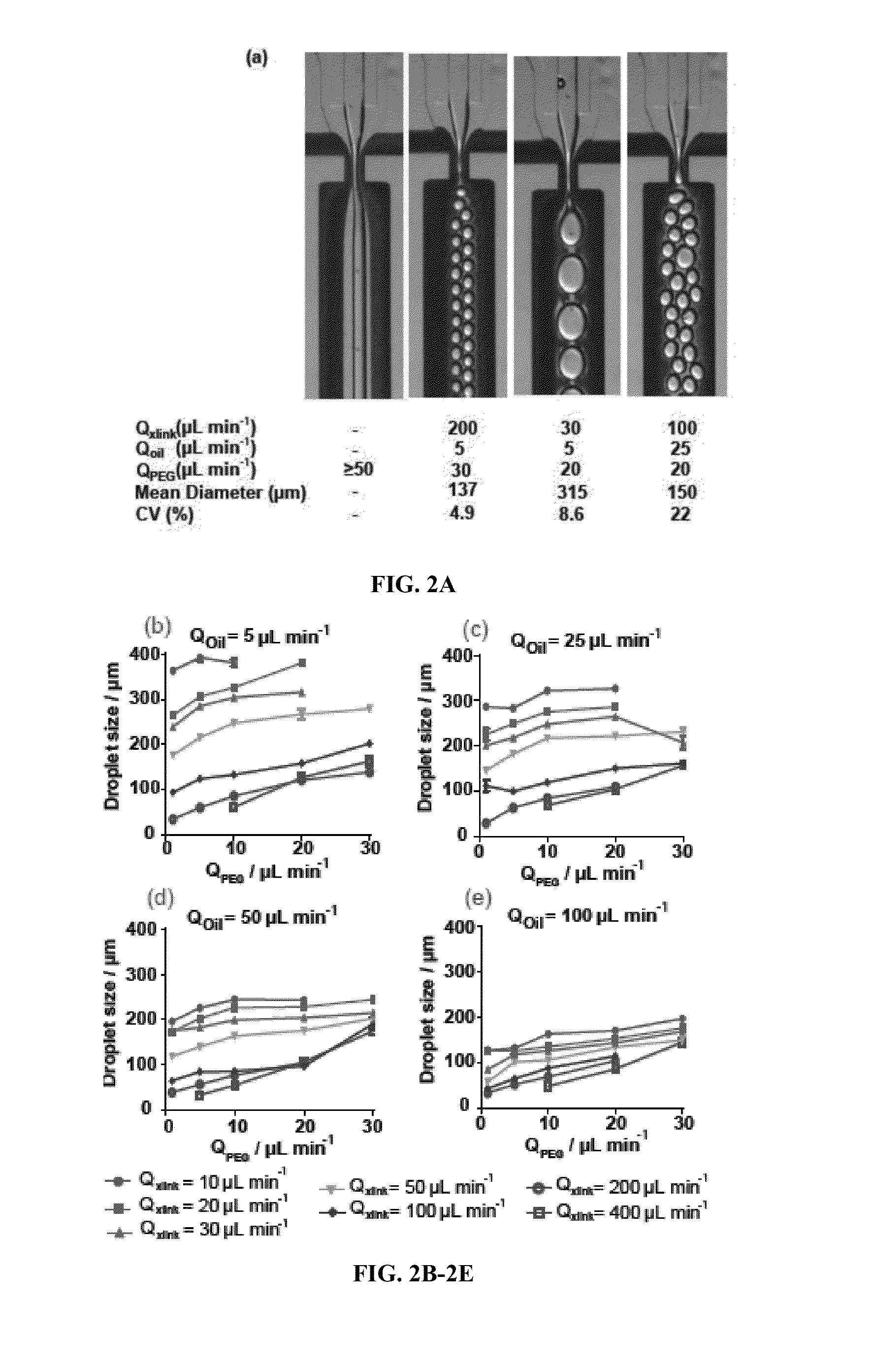
Microgels for Encapsulation of Cells and Other Biologic Agents
ActiveUS20150071997A1Increase cell adhesionConducive to survivalBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOil water emulsionOil phase
Methods of encapsulating cargo in a microgel droplet, microgel droplets prepared according the provided methods, and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The methods of preparing cargo-encapsulated microgels generally include flowing through a flow-focusing nozzle of a microfluidic device a macromer phase, an oil phase, and a crosslinker phase to form microgel droplets by oil-water emulsion. The phases are pumped, injected, or flowed through the microfluidic device such that as the macromer phase approaches the flow focusing nozzle, the co-flowing oil phase shields the macromer from contact with the crosslinker phase until flow instability occurs and macromer phase droplets form. After flow instability occurs, the crosslinker diffuses from the crosslinker phase into the droplets in an effective amount to covalently crosslink the macromer into a microgel network encapsulating the cargo in the crosslinked macromer. Microgels prepared according to the disclosed methods and methods of use thereof are also provided.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Perforated skin structure for laminar-flow systems
InactiveUS20050178924A1Improve thermal conductivityEnhanced advantageBoundary layer controlsWingsThrottle controlEngineering
The outer skin (100) of an aerodynamic body (40) has perforations (200) arranged in particular patterns in respective spanwise extending groups or bundles (250). Each perforation is preferably a micro-slot with a length of 100 to 3000 μm and a width of 50 to 250 μm. Air is sucked through the micro-slots from the boundary layer flowing over the outer skin, to achieve boundary layer control. In each bundle, the pattern, size, orientation, and other parameters of the micro-slots are designed to achieve mutual destructive interference of flow disturbances arising due to the suction, to minimize the excitation of flow instabilities in the boundary layer. Particularly, the spatial spectrum of the perforation pattern of a given bundle is essentially absent of significant energy at predetermined wavelengths of predetermined flow instabilities that otherwise appear in the boundary layer air flow. The aerodynamic body further includes supporting ribs (300) extending parallel to the perforation bundles (250) and a perforated inner plate (400) providing a throttling control of the suction flow through groups of the bundles.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Magnet-actuated seat valve hydraulic brake systems of motor vehicles
InactiveUS6322049B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsStreaming instabilityMotorized vehicle
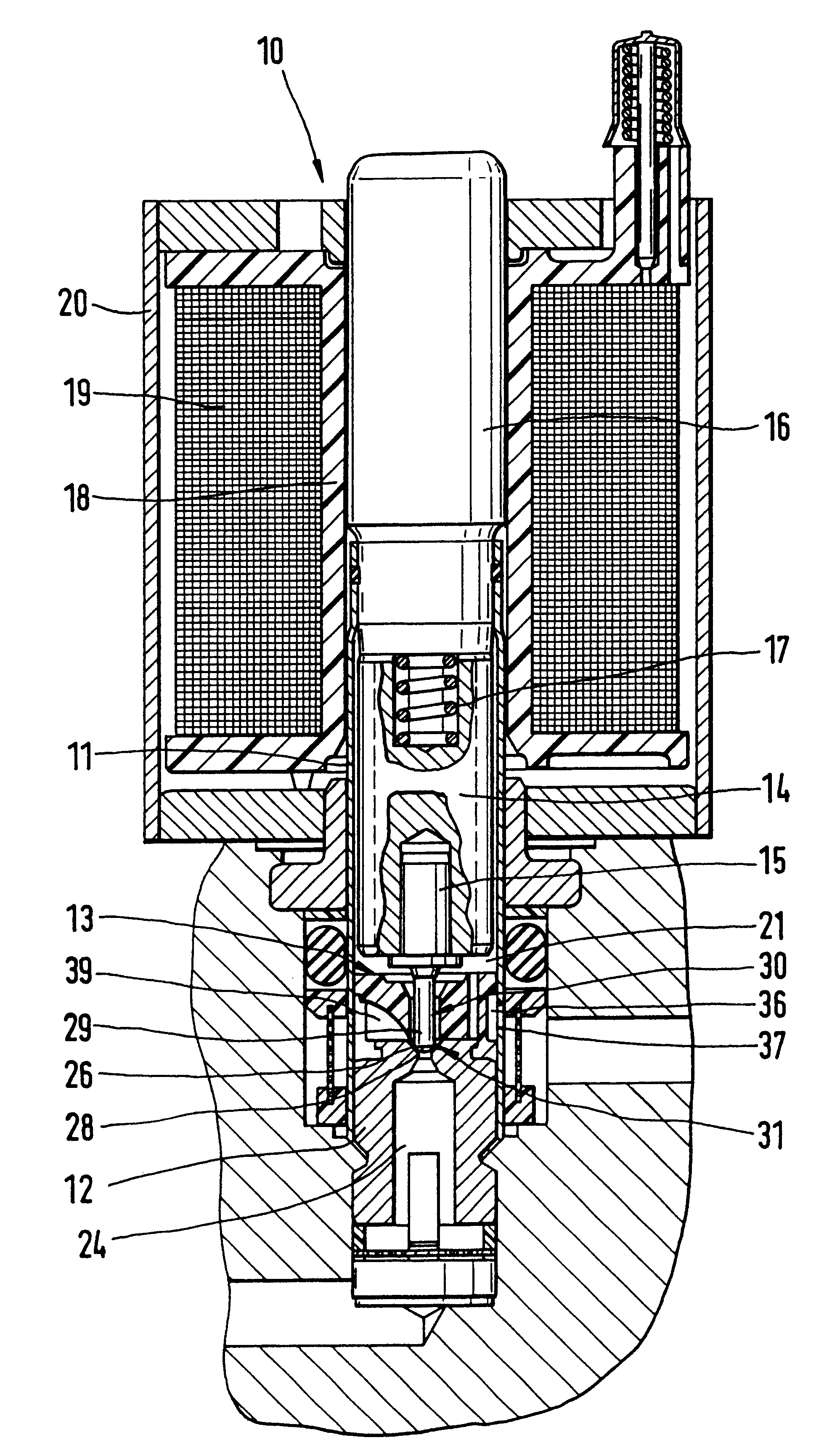
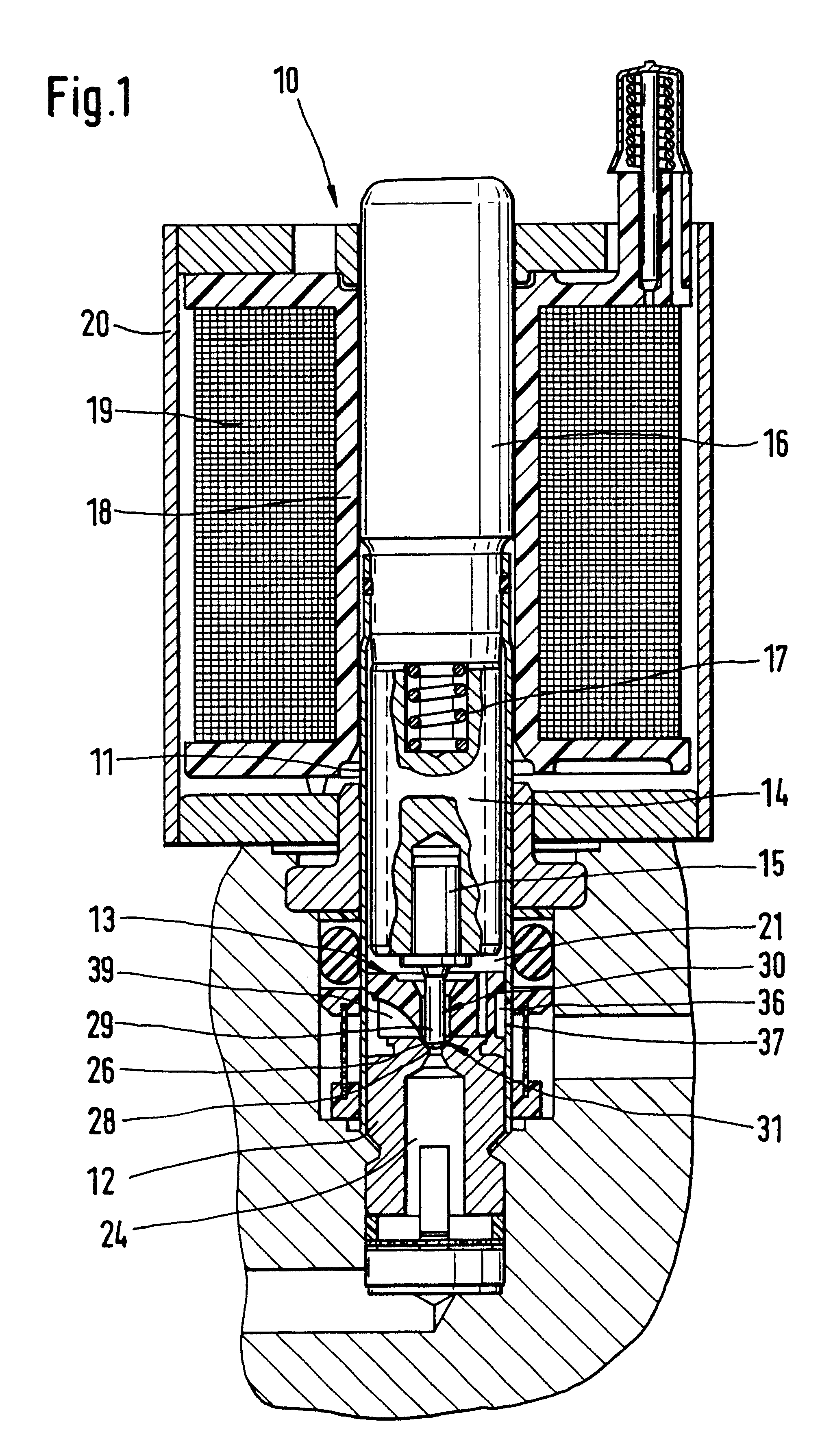
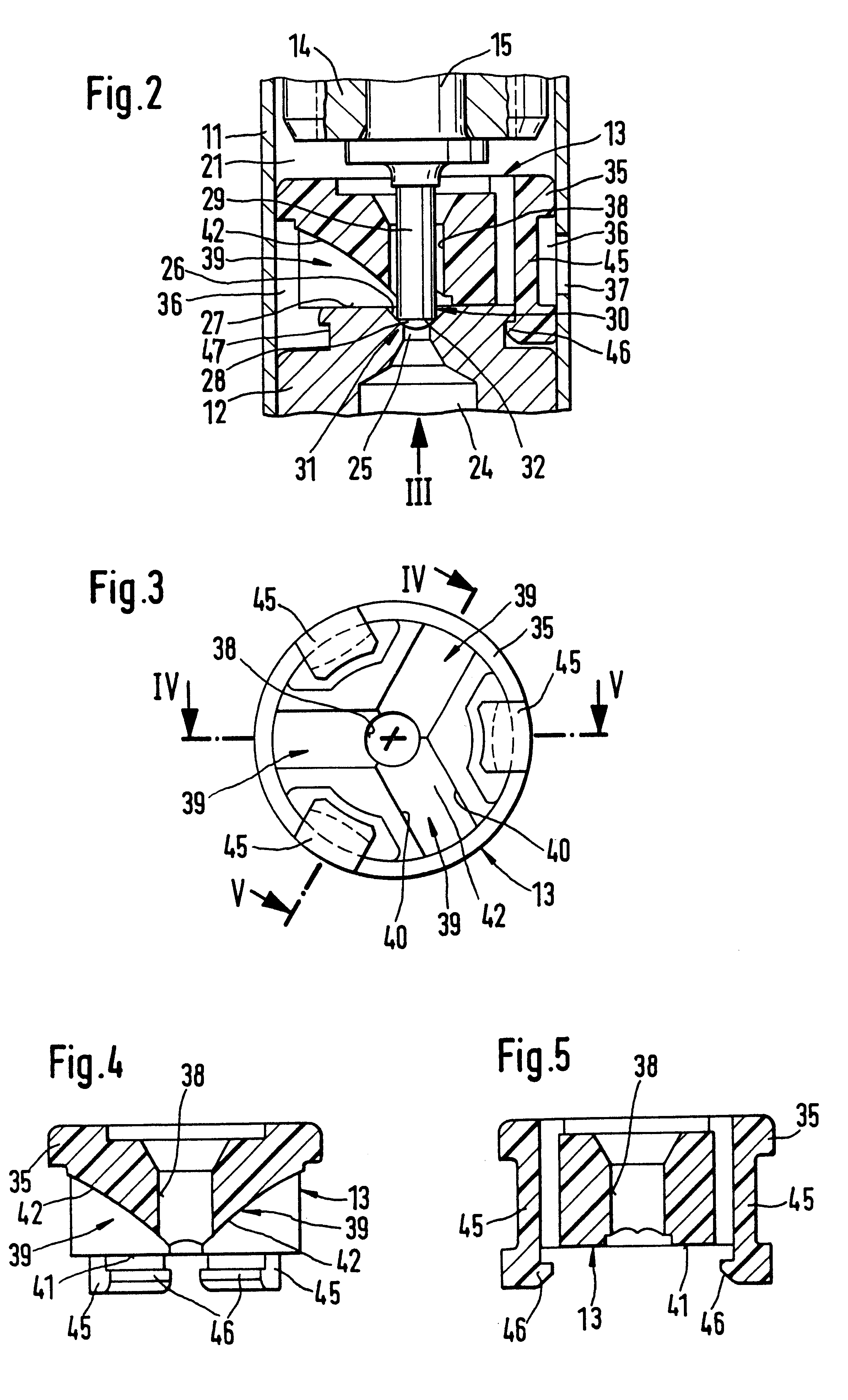
A tubular valve housing includes a guide body for pressure fluid that is disposed between a valve body having a hollow-conical valve seat and a chamber of the valve housing, in which actuating means of the valve are received in the chamber. The guide body is penetrated by a closing body of the valve which divides the chamber from an annular conduit. The annular conduit carries the pressure fluid and communicates with the valve seat and has circumferential outlet openings of the valve housing. The guide body is braced on the valve body, with a face end contacting the valve body, and has guide conduits, fitting over an outline of the valve seat, which on the outlet side discharge into the annular conduit. The face end of the closing body, which cooperates with the valve seat, is a spherical portion that makes a transition with sharp edges to the cylindrical shaft of the closing body. With the guide body, the stream of pressure fluid emerging from the valve seat is diverted into the annular conduit, so that flow instabilities are largely without any effect on the chamber of the valve. The valve can be used in brake systems of motor vehicles.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
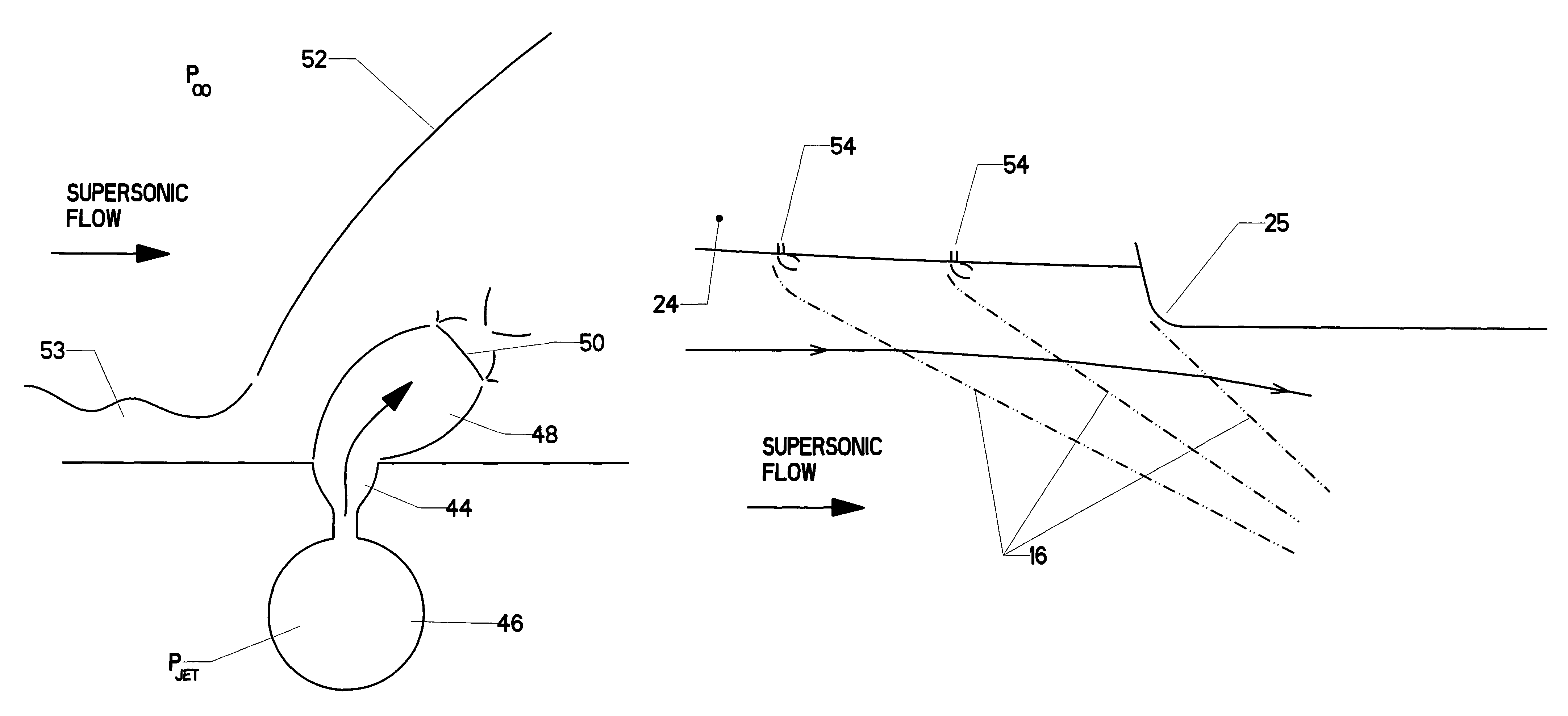
Microjet creation and control of shock waves
InactiveUS20090288711A1Increase flow rateCosmonautic vehiclesCombustion enginesShock waveEngine efficiency
A method of using one or more microjets to create and / or control oblique shock waves. The introduction of microjet flow into a supersonic stream creates an oblique shock wave. This wave can be strengthened—by increasing microjet flow rate or the use of many microjets in an array—in order to form an oblique shock. Such an oblique shock can be used to decelerate flow in a jet aircraft engine inlet in a controlled fashion, thus increasing pressure recovery and engine efficiency while reducing flow instability. Adjusting the pressure ratio across the microjet actually alters the angle of the oblique shock. Thus, the use of microjets allows decelerating shock waves in an inlet engine to be properly positioned and controlled. Microjet arrays can also be used to ameliorate shock waves created by external aircraft surfaces, such as sensor pods and weapons. Microjets placed forward of any external protuberance can convert a single substantial shock wave into a series of much milder waves which will not produce unwanted external effects, such as strong sonic booms.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Path detection method and device
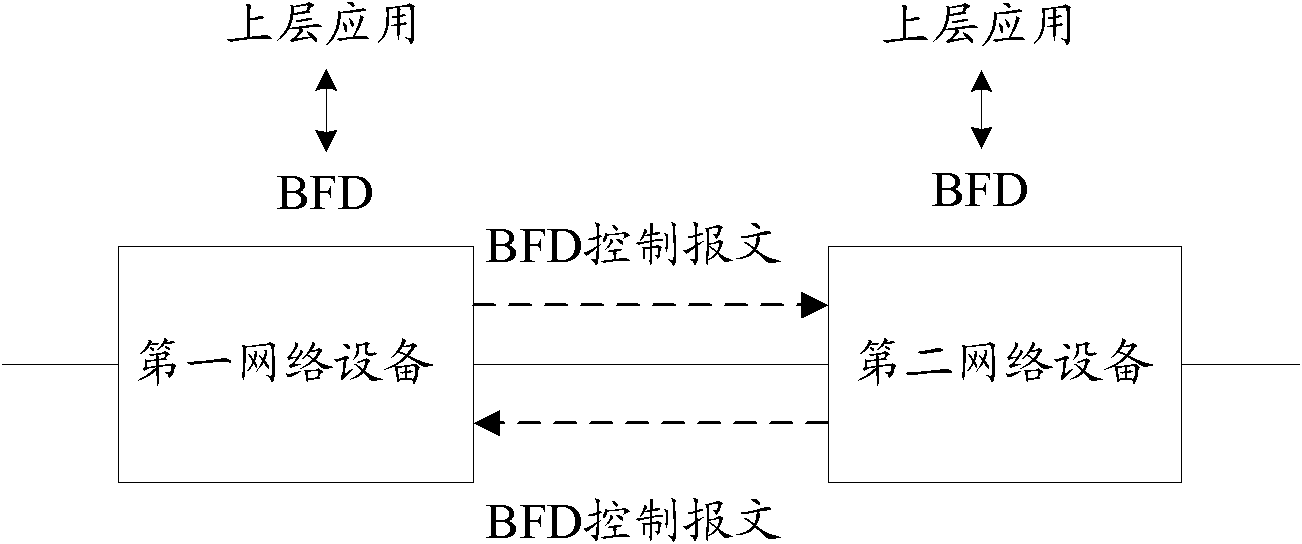
InactiveCN102025562ASolve the shockFix stability issuesData switching networksBidirectional Forwarding DetectionComputer science
The invention discloses a path detection method and a device, which can be used for solving the problems of link oscillation and unstable flow caused by bidirectional forwarding detection failure in the active / standby switchover process of a master control board on network equipment. The path detection method of the invention comprises the steps of: periodically sending bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) control message to opposite terminal network equipment by local network equipment, and performing BFD overtime detection; and when the local network equipment needs to perform active / standby switchover between the master board and the standby board of the master control board, stopping the BFD overtime detection of the local network equipment, and notifying the opposite terminal network equipment to stop the BFD overtime detection, wherein the BFD overtime detection means to detect whether the BFD message sent by the opposite terminal network equipment is received within the preset time.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Skimmer for Concentrating an Aerosol
InactiveUS20090288475A1Improved particle recoveryMore compactWithdrawing sample devicesDispersed particle separationStreaming instabilityLong axis
A skimmer device for concentrating an aerosol from a flowing gas stream, having an inlet with inlet aperture and inlet raceway, an outlet with virtual impact void and collector channel, and bulk flow divertors symmetrically disposed on either side of the long axis of flow, further characterized in that the downstream walls of the bulk flow divertors are concavedly curved and reverse the direction of bulk flow. In section, the four channels or passages of the “skimmer” thus form a “crossed tee” with concavedly contoured lateral arms curving back around. The lateral flow channels are for diverting the bulk flow into exhaust chimney spaces, and the chimney spaces are positioned proximate to the inlet element and anterior to the collection channel. In operation, the bulk flow streamlines are thereby folded more than 90 degrees away from the long axis of flow on the laterally disposed concave walls of the bulk flow channels. While counterintuitive, this was found using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and experimentation to dramatically reduce wall separation and related instabilities and to improve particle recoveries. Large two-dimensional arrays of closely stacked inlet and skimmer elements are thus achieved by fitting the chimneys into spaces between parallel inlet elements. The interlinked problems of flow instability, manufacturability of arrays, and scale-up of chimney cross-sectional area to equalize pressure differentials in the bulk flow diverter exhaust ducts, particularly in two-dimensional arrays at high throughput, are uniquely solved with this geometry.
Owner:ENERTECHNIX
Localized arc filament plasma actuators for noise mitigation and mixing enhancement
InactiveUS20080115477A1Increase amplitudeEnhance and weaken vorticityCosmonautic vehiclesEngine fuctionsPlasma actuatorStreaming instability
A device for controlling fluid flow. The device includes an arc generator coupled to electrodes. The electrodes are placed adjacent a fluid flowpath such that upon being energized by the arc generator, an arc filament plasma adjacent the electrodes is formed. In turn, this plasma forms a localized high temperature, high pressure perturbation in the adjacent fluid flowpath. The perturbations can be arranged to produce vortices, such as streamwise vortices, in the flowing fluid to control mixing and noise in such flows. The electrodes can further be arranged within a conduit configured to contain the flowing fluid such that when energized in a particular frequency and sequence, can excite flow instabilities in the flowing fluid. The placement of the electrodes is such that they are unobtrusive relative to the fluid flowpath being controlled.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Improved cold-performance fluidic oscillator
An ejecting flowing fluid oscillator (2) suitable for generating a fluid drop oscillating ejecting form has: an entrance (12) for pressing fluid, a dynamic nozzle (14) for constructing accelerate pressurization fluid motion, a fluid path (10) allow pressed fluid flowing between the entrance (12) and the dynamic nozzle (14), an interaction chamber (18) attached to the dynamic nozzle (14) and receiving the flowing from the nozzle, an outlet (20) ejecting fluid discharged during through the interaction chamber (18), and a device for increasing flowing instability flowing from the dynamic nozzle (14). In one first optimization embody, the device comprises a projection (4) internal extending from each side of the fluid path (10). In a second optimization embody, the device comprises a step (24), its height is the height of the dynamic nozzle (14) hoisting relative to bottom plate of the interaction chamber (18).
Owner:BOWLES FLUIDICS
Solar thermal power system
InactiveUS7735323B2Dampening flow instabilitySimple efficiencyAuxillary drivesSteam separation arrangementsThermal energy storageEngineering
A solar thermal power generator includes an inclined elongated boiler tube positioned in the focus of a solar concentrator for generating steam from water. The boiler tube is connected at one end to receive water from a pressure vessel as well as connected at an opposite end to return steam back to the vessel in a fluidic circuit arrangement that stores energy in the form of heated water in the pressure vessel. An expander, condenser, and reservoir are also connected in series to respectively produce work using the steam passed either directly (above a water line in the vessel) or indirectly (below a water line in the vessel) through the pressure vessel, condense the expanded steam, and collect the condensed water. The reservoir also supplies the collected water back to the pressure vessel at the end of a diurnal cycle when the vessel is sufficiently depressurized, so that the system is reset to repeat the cycle the following day. The circuital arrangement of the boiler tube and the pressure vessel operates to dampen flow instabilities in the boiler tube, damp out the effects of solar transients, and provide thermal energy storage which enables time shifting of power generation to better align with the higher demand for energy during peak energy usage periods.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Microjet creation and control of shock waves
InactiveUS8359825B2Increase flow rateAmeliorate shock waveCosmonautic vehiclesCombustion enginesShock waveEngine efficiency
A method of using one or more microjets to create and / or control oblique shock waves. The introduction of microjet flow into a supersonic stream creates an oblique shock wave. This wave can be strengthened—by increasing microjet flow rate or the use of many microjets in an array—in order to form an oblique shock. Such an oblique shock can be used to decelerate flow in a jet aircraft engine inlet in a controlled fashion, thus increasing pressure recovery and engine efficiency while reducing flow instability. Adjusting the pressure ratio across the microjet actually alters the angle of the oblique shock. Thus, the use of microjets allows decelerating shock waves in an inlet engine to be properly positioned and controlled. Microjet arrays can also be used to ameliorate shock waves created by external aircraft surfaces, such as sensor pods and weapons. Microjets placed forward of any external protuberance can convert a single substantial shock wave into a series of much milder waves which will not produce unwanted external effects, such as strong sonic booms.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
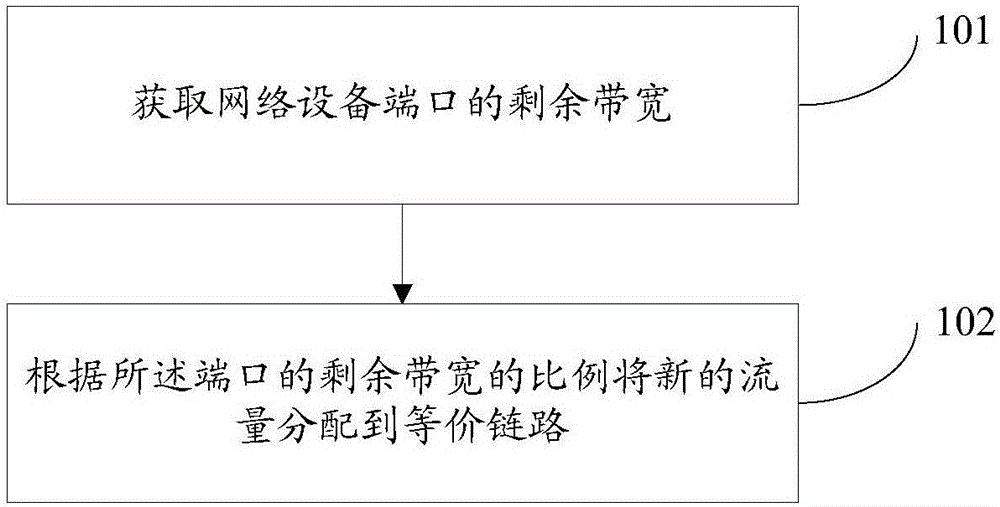
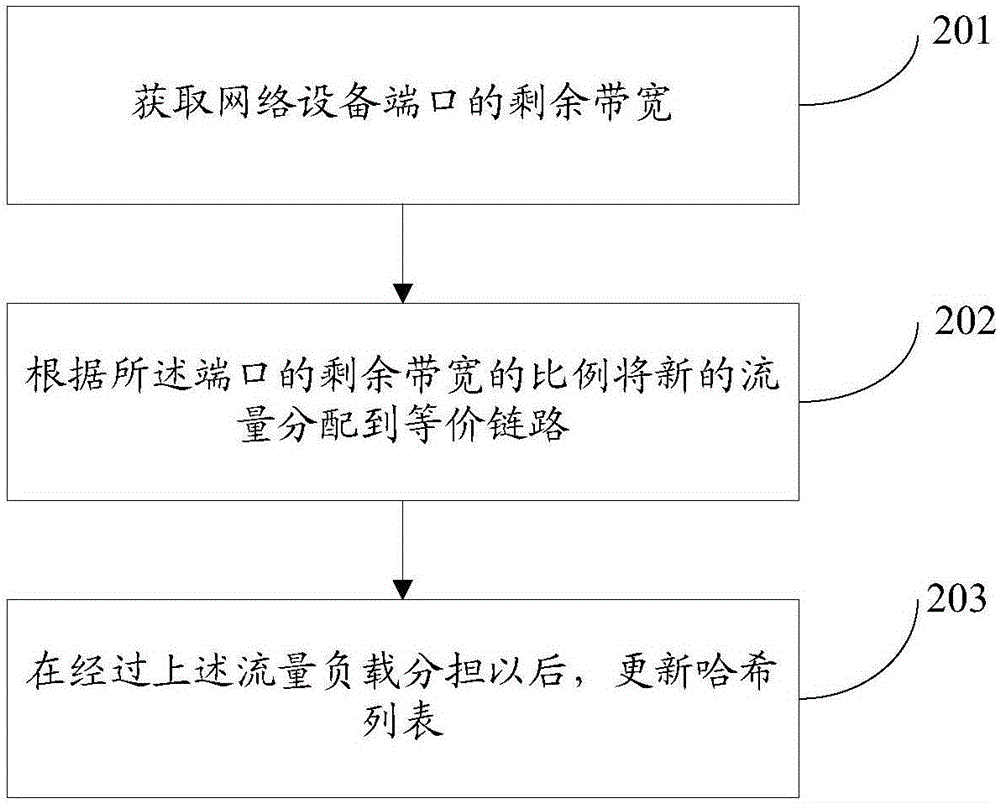
Flow load sharing method and flow load sharing device
InactiveCN106332141ATraffic will not affectNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed computingTraffic volume
The invention provides a flow load sharing method and a flow load sharing device. The flow load sharing method is used for a system having two or more than two equivalence links disposed among network devices, and comprises steps that residual bandwidths of network device ports are acquired; and new flow is allocated to the equivalence links according to the proportion of the residual bandwidths of the ports, and therefore a problem of instable link flow is solved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Cold-performance fluidic oscillator
ActiveUS20060091242A1High viscosityReadily apparentCircuit elementsSpray nozzlesFluidic oscillatorStreaming instability
A fluidic oscillator suitable for use at colder temperatures for generating an exhaust flow in the form of an oscillating spray of fluid droplets has an inlet for pressurized fluid, a pair of power nozzles configured to accelerate the movement of the pressurized fluid, a fluid pathway that connects and allows for the flow of pressurized fluid between its inlet and the power nozzles, an interaction chamber which is attached to the nozzles and receives the flow from the nozzles, a fluid outlet from which the spray exhausts from the interaction chamber, and a means for increasing the instability of the flow from the power nozzles, with this means being situated in a location chosen from the group consisting of a location within the fluid pathway or proximate the power nozzles. In a first preferred embodiment, the flow instability generating means comprises a protrusion that extends inward from each side of the fluid pathway so as to cause a flow separation region downstream of the protrusions. In a second preferred embodiment, the flow instability generating means comprises a step in the height elevation of the floor of the power nozzles with respect to that of the interaction chamber.
Owner:DLHBOWLES INC
MEMS mass flow sensor assembly and method of making the same
ActiveUS20140190252A1Minimum footprintMinimizes instabilityVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFlow transducerWire rod
A silicon mass flow sensor manufacture process that enables the backside contacts and eliminates the conventional front side wire binding process, and the assembly of such a mass flow sensor is disclosed in the present invention. The achieved assembly enhances the reliability by eliminating the binding wire exposure to the flow medium that may lead to detrimental failure due to the wire shortage or breakage while the miniature footprint could be maintained. The assembly further reduces flow instability from the flow sensor package including the bump of wire sealing. The invented mass flow sensor assembly can be a flow sensor module if the supporting sensor carrier is pre-designed with the control electronics. Without the control electronics, the said mass flow sensor assembly is easy to install into desired flow channels and connect to the external control electronics.
Owner:M TECH INSTR HLDG
Process and apparatus for expanding multi-stage axial flow gas compressor stable operation zone
InactiveCN1464179ABroaden the stable operating regionIncrease pressure ratioMachines/enginesEngine componentsLow-pass filterGas compressor
The present invention is the method of expanding the stable operation region of multi-stage axial-flow air compressor based on the feedback control principle. During the running of the multi-stage axial-flow air compressor, the dynamic pressure signal is collected, amplified, low-pass filtered and A / D converted and treated in a DSP for the synchronous analysis of varying characteristic of the first order harmonic wave in premonitory flow instability signal. According to the set threshold, premonitory flow instability signal inside the system is collected and control signal is output and transmitted via D / A converter to several mini electromagnetic control valves and one HF pneumatic conveyance controlling valve to control the mini nozzles to jet high pressure airflow altering the non-stationary characteristic of the airflow inside the movable blade channel. The said process can postpone stalling and expand stable operation region.
Owner:江苏中国科学院能源动力研究中心 +1
Method for exciting and controlling gas flow of stator blade end wall of axial-flow compressor by aid of plasmas
InactiveCN102606502AInhibition of flow separationImprove stabilityPump controlNon-positive displacement fluid enginesControl signalEngineering
The invention relates to a method for exciting and controlling gas flow of the stator blade end wall of an axial-flow compressor by the aid of plasmas, which is characterized by including the steps: laying a plasma pneumatic exciter on the stator blade passage end wall of the axial-flow compressor, wherein the front edge and the tail edge of an electrode of the plasma pneumatic exciter are level to the front edge and the tail edge of a stator blade respectively, and the direction of the electrode is parallel to a mean camber line of the stator blade; when an engine controller detects flow instability indication, loading electric signals to the electrode of the plasma pneumatic exciter by employing a pulse plasma power source; and when the engine controller detects disappearance of flow instability indication, sending out control signals, and closing the plasma pneumatic exciter. The control method is capable of effectively suppressing stator blade angle area flow separation of the axial-flow compressor, short in exciting response time and wide in bandwidth, and has an important role in reduction of stator blade wake pitot loss and improvement on stability and efficiency of the compressor.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Intermittent Thermosyphon
ActiveUS20160245593A1High heat transfer rateEnhanced solid/liquid/vaporIndirect heat exchangersHeat transfer modificationEvaporation heat transferStreaming instability
The device and methods described herein relate to the isothermal heat transport through an intermittent liquid supply to an evaporator device, thereby enabling high evaporative heat transfer coefficients. A liquid and vapor mixture flows through miniature and micro-channels in an evaporator and addresses flow instabilities encountered in these channels as bubbles rapidly expand. Additionally, a high percentage of the fins are exposed to vapor and limit the required charge of refrigerant within the system due to effective condensate removal in the condenser.
Owner:J R THERMAL LLC
Manifold insert having distribution guides and fuel cell stack comprising the same
ActiveUS20120122008A1Reduces output voltage deviationPrevents local flow instabilityElectric devicesFuel cells groupingFuel cellsHydrogen
The present invention provides a manifold insert having a plurality of distribution guides which reduce output voltage deviation due to flow instability between unit cells and prevent local flow instability of electrodes by stably distributing the flow of fluid (such as air, hydrogen, and coolant) supplied to a fuel cell stack, thereby maintaining a stable performance of the unit cells, and a fuel cell stack comprising the same. In particular, manifold insert having distribution guides is provided, the manifold insert being configured to form a flow field from an inlet port of fluid to an outlet port connected to a fuel cell stack, the manifold insert including: a plurality of distribution guides for dividing the flow field from the inlet port to the outlet port such that the fuel cell stack is divided into a plurality of regions according to the distance from the inlet port, wherein the distribution guides have surfaces that are at least partially curved such that the flow of the fluid from the inlet port to the outlet port is changed by the curved surfaces and form a plurality of guide flow fields for guiding the fluid to the divided regions of the fuel cell stack such that the fluid is supplied to the divided regions of the fuel cell stack along the plurality of guide flow fields at different flow rates.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Device for detecting clearance flow instability phenomenon in nuclear reactor
InactiveCN103219055ASuitable for engineering applicationsIn line with the experimental resultsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention provides a device for detecting a clearance flow instability phenomenon in a nuclear reactor. The device comprises a heat source, a cooling source, an ascending section, a flow source and a data collection device, wherein the heat source is providing energy input and located at the lower part, the cooling source is located at the upper part, the ascending section is connected between the cooling source and the heat source and is used for simulating the clearance flow instability phenomenon, the flow source connected with the other end of the heat source, a first switching valve is arranged between the heat source and the flow source and is used for cutting off an enforced circulated flow. The device disclosed by the invention is used for elaborating the clearance flow instability phenomenon initiated under a low-pressure condition, explaining the characteristics of clearance flow instability, and qualitatively and quantitatively establishing a mutual relation of characteristic parameters and clearance flow instability characteristics of the system, and finding out key parameters and influence factors.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Laser-based flow modification to remotely control air vehicle flight path
Owner:KREMEYER KEVIN
Preprocessing system for near-infrared online detection and application thereof
InactiveCN102200507ARealize automatic positive and negative flushingEasy to cleanPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredSolid particle
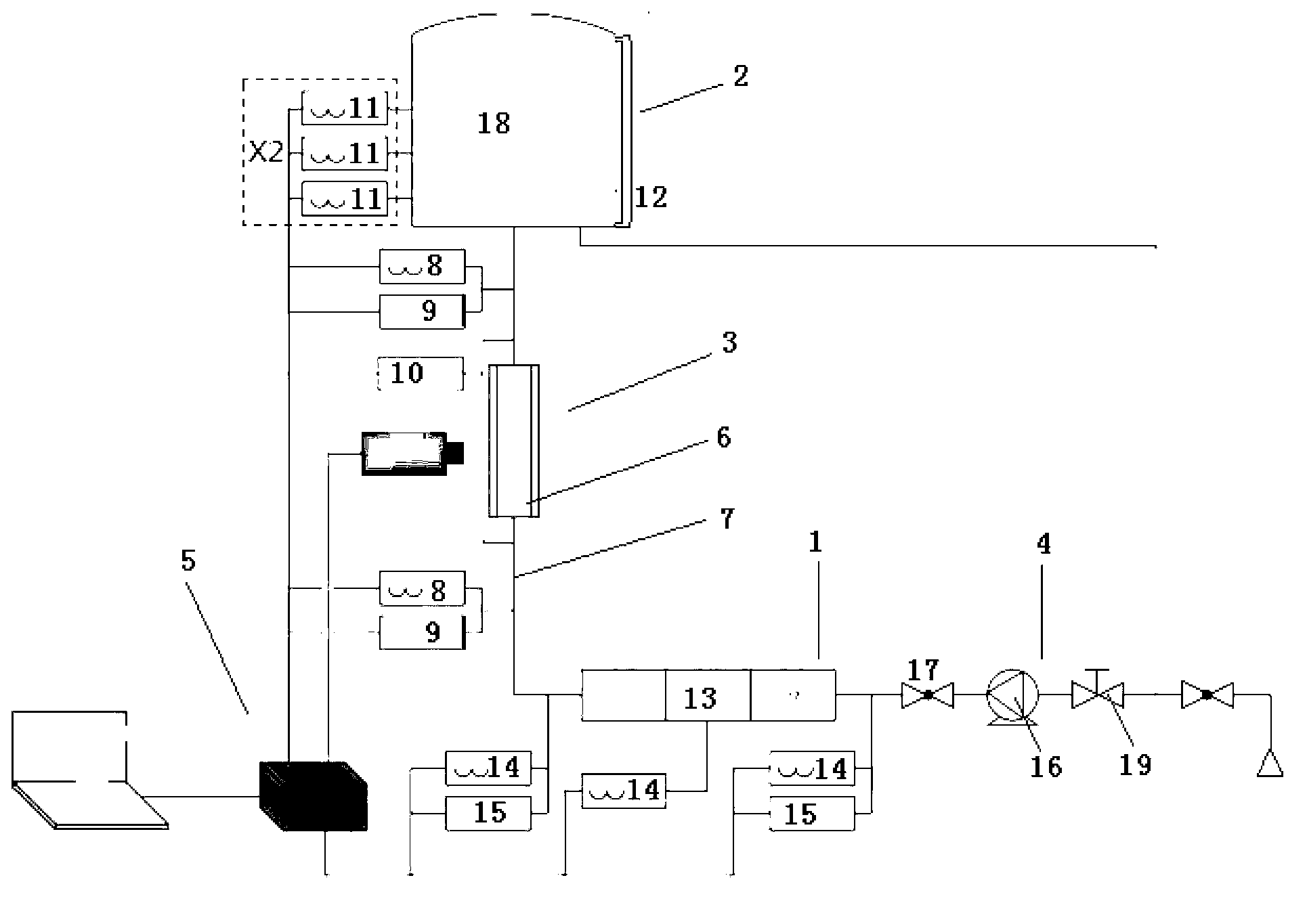
The invention provides a preprocessing system for near-infrared online detection, which is composed of a filter, a back-up filter, a variable-frequency centrifugal pump, a temperature control device, a buffering device, a flowmeter, a near-infrared spectrum acquisition device, an automatic sampling device, a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet. The preprocessing system provided by the invention can run automatically, continuously and reliably, and can be switched for use under the condition of not affecting the function of the whole system, therefore, the automatic positive and negative washing can be realized simultaneously, the samples of acquired spectrums can be acquired in a targeted mode, and the cleaning and beauty of the whole system can be maintained. By using the preprocessing system provided by the invention, the problem of difficulty in detection caused by more insoluble solid particles, unstable flow, easily-produced bubbles and large temperature fluctuation in the process of near-infrared online detection is solved, so that the acquired near-infrared spectrum is stable, reliable, and good in repeatability, thereby improving the accuracy of results of near-infrared on-line detection, promoting the development and application of the near-infrared spectral analysis technology in pharmaceutical production processes, and then truly realizing on-line quality control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Localized arc filament plasma actuators for noise mitigation and mixing enhancement
InactiveUS7669404B2Increase amplitudeHigh bandwidthCosmonautic vehiclesEngine fuctionsPlasma actuatorStreaming instability
A device for controlling fluid flow. The device includes an arc generator coupled to electrodes. The electrodes are placed adjacent a fluid flowpath such that upon being energized by the arc generator, an arc filament plasma adjacent the electrodes is formed. In turn, this plasma forms a localized high temperature, high pressure perturbation in the adjacent fluid flowpath. The perturbations can be arranged to produce vortices, such as streamwise vortices, in the flowing fluid to control mixing and noise in such flows. The electrodes can further be arranged within a conduit configured to contain the flowing fluid such that when energized in a particular frequency and sequence, can excite flow instabilities in the flowing fluid. The placement of the electrodes is such that they are unobtrusive relative to the fluid flowpath being controlled.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Vapor phase epitaxy device and vapor phase epitaxy method
ActiveCN102181923ASolving Thickness Control ProblemsQuality improvementFrom chemically reactive gasesVapour phase epitaxyQuantum well
The invention discloses a vapor phase epitaxy device and a vapor phase epitaxy method. The disclosed vapor phase epitaxy device comprises a reaction chamber, a plurality of reaction gas spraying heads arranged in the reaction chamber, a plurality of trays corresponding to the plurality of reaction gas spraying heads, and a power shaft driving the trays, wherein the power shaft comprises revolution shafts and a plurality of rotation shafts, the rotation shafts correspond to the trays one by one; and the trays are respectively connected with the corresponding rotation shafts, or connected with the revolution shafts and the corresponding rotation shafts alternatively. By utilizing the vapor phase epitaxy device and the vapor phase epitaxy method, the flow instability in the chemical vapor phase epitaxy can be reduced effectively, the spurious response times can be decreased, also the problem of the thickness of a quantum well can be solved effectively, different selections can be provided for the growing process of different heterogenous junctions, and the quality of semiconductor elements can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YUNFENG NEW ENERGY TECH
Two-phase separation micro-channel heat sink
ActiveCN108461460ASolve the excessive pressure dropFix stability issuesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransmission channelEngineering
The invention discloses a two-phase separation micro-channel heat sink. The heat sink comprises a microchannel array, a bottom plate and a cover plate. The bottom plate and the cover plate are connected through a boding mode to form a main body structure of the heat sink. The microchannel array is etched on the bottom plate. The microchannel array is formed by gas channels and liquid channels, wherein the gas channels and the liquid channels are arranged alternately, and the side walls of the gas channels and the liquid channels are respectively in a multi-through-hole structure. The heat sinkadopts the two-phase separation transmission channels, which are formed by the gas channels and the liquid channels; and the gas channels and the liquid channels realize separate transmission to allow working liquid and gas to be transmitted separately, thereby enhancing phase change process of fluid in the micro-channel heat sink, solving the problems of too large fluid pressure drop and flow instability in the liquid channels and enhancing heat exchange capability.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG COMP TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com