Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Destructive sampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Destructive sampling is one of the sampling techniques which the samples are destroyed so that the population is changed in the process of a random sampling. Examples: During the test for quality control of bulbs, the bulbs are destroyed.
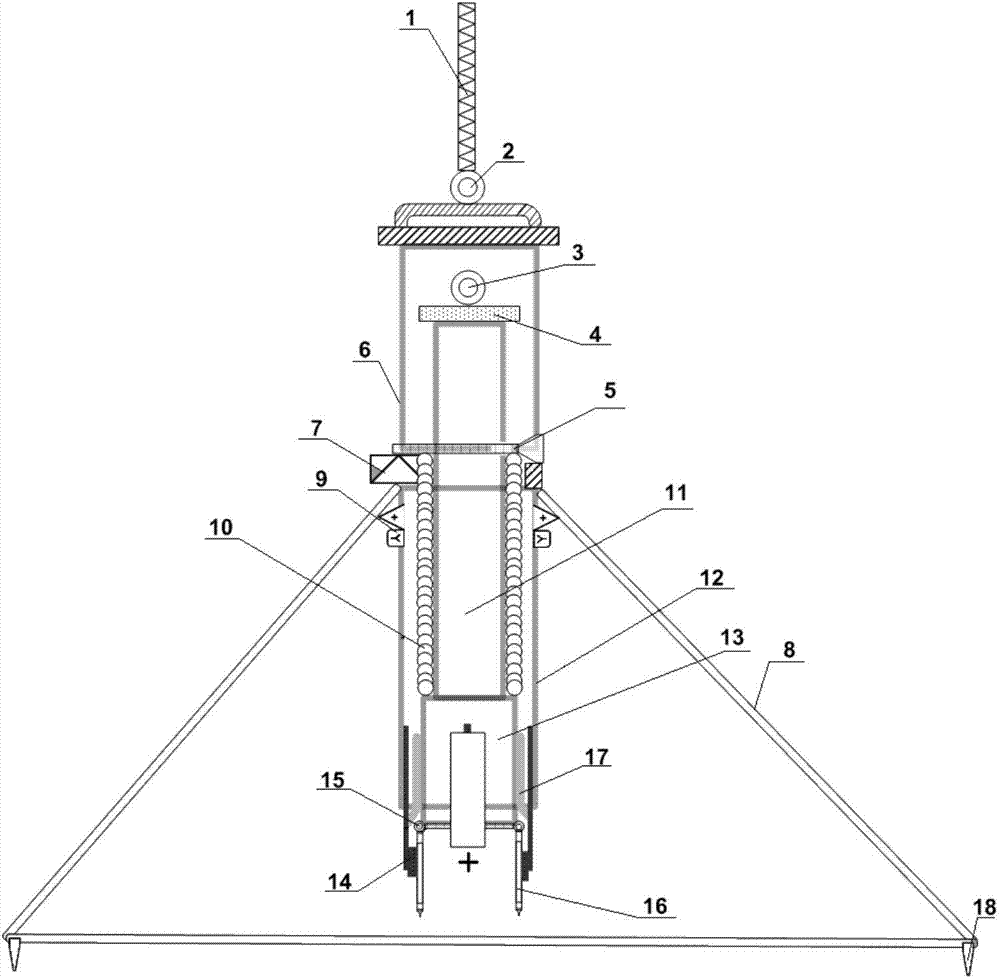
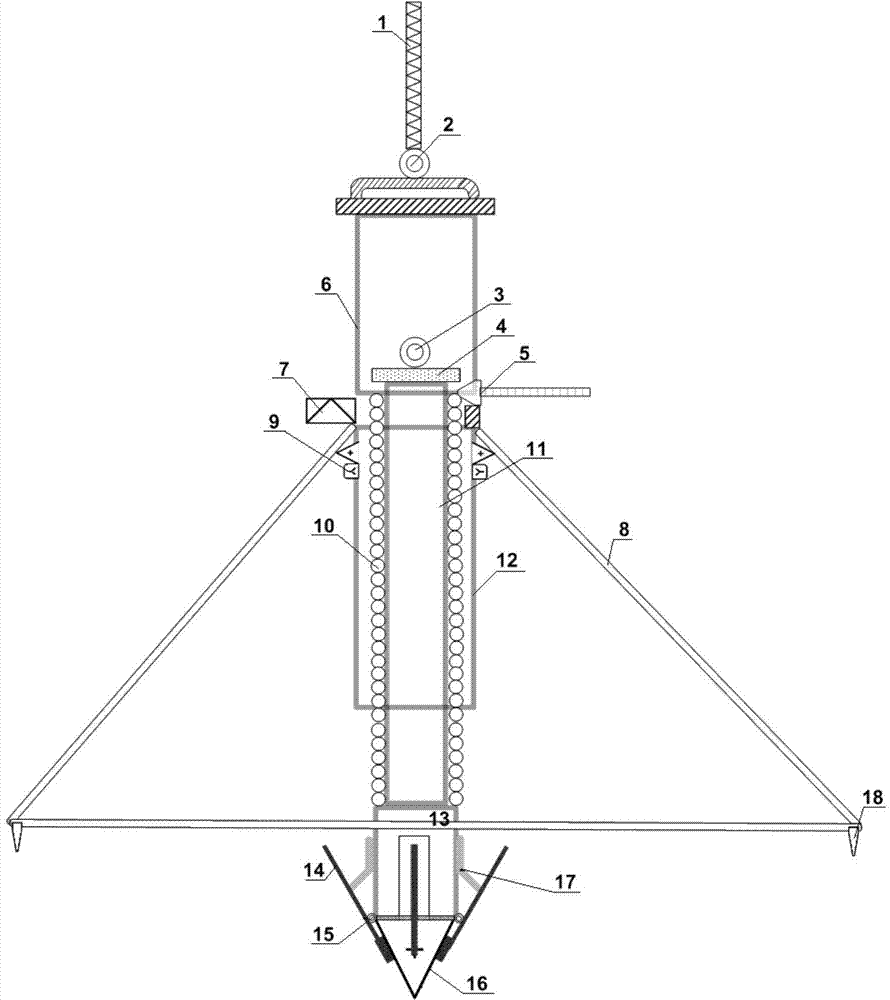
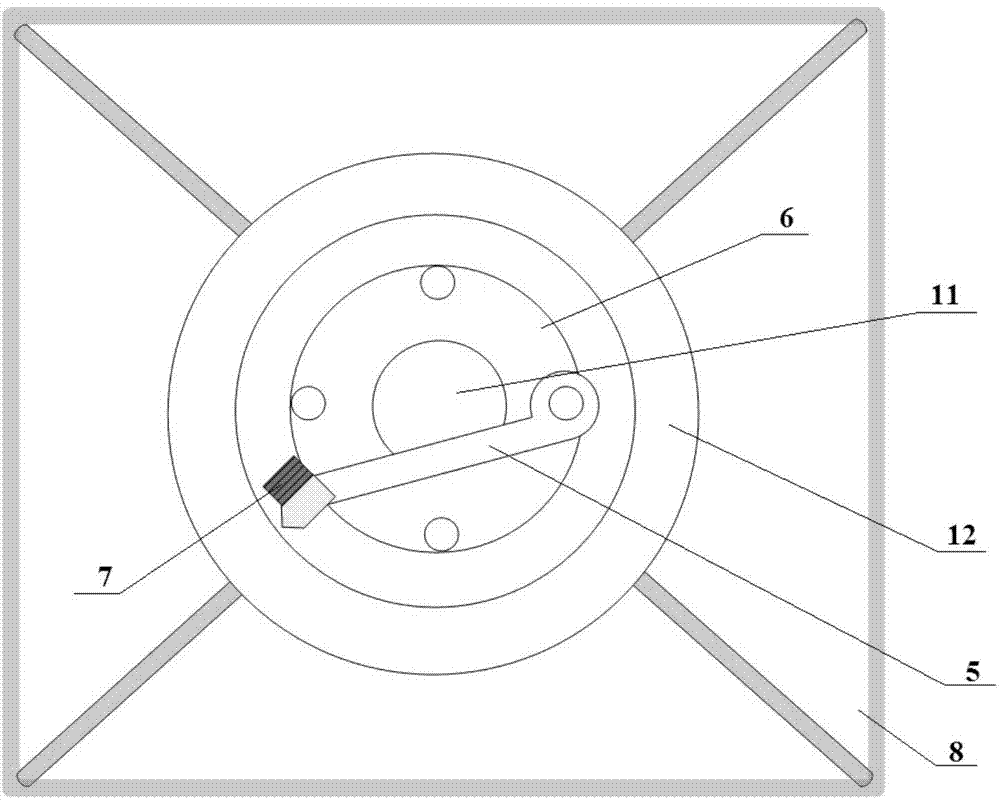
Inertial differential unlocking spring impact type collector of bottom sediment sample
ActiveCN104849095AStrong reliabilityEasy maintenanceWithdrawing sample devicesWater flowDestructive sampling
The invention relates to an inertial differential unlocking spring impact type collector of a bottom sediment sample. The inertial differential unlocking spring impact type collector comprises an outer frame device, a nozzle sampling device, a spring impact device and an inertial differential unlocking device. According to the inertial differential unlocking spring impact type collector, the structural design of a chained inertial differential unlocking-spring impact device is utilized, so as to realize the purpose of collecting the bottom sediment sample in the condition of no extraneous source power, and on the basis of an elastic principle, the bottom sediment sample can be instantaneously collected, so as to avoid water erosion. According to the inertial differential unlocking spring impact type collector, the problem that an existing underwater sampling device has difficulty in considering the sampling representativeness and the adaptability to different bottom sediment samples on the basis that destructive sampling is reduced as far as possible can be solved. The inertial differential unlocking spring impact type collector can adapt to different water depth and current conditions and has the advantages of strong reliability and simplicity and convenience in maintenance; if the inertial differential unlocking spring impact type collector can be made into an array and is integrated with automatic lifting machinery, the purpose of quickly collecting bottom sediment samples in different positions with high throughput can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND +1
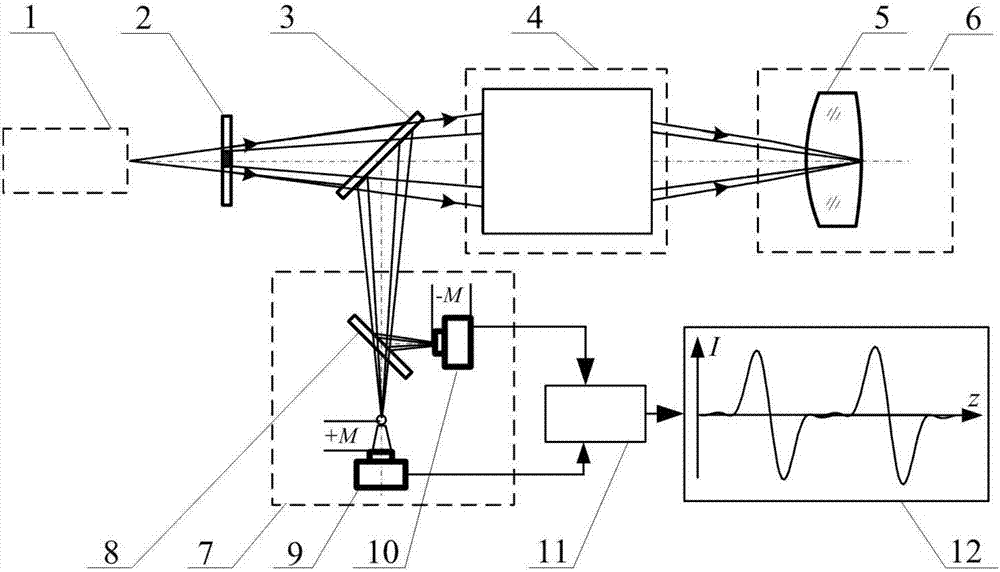
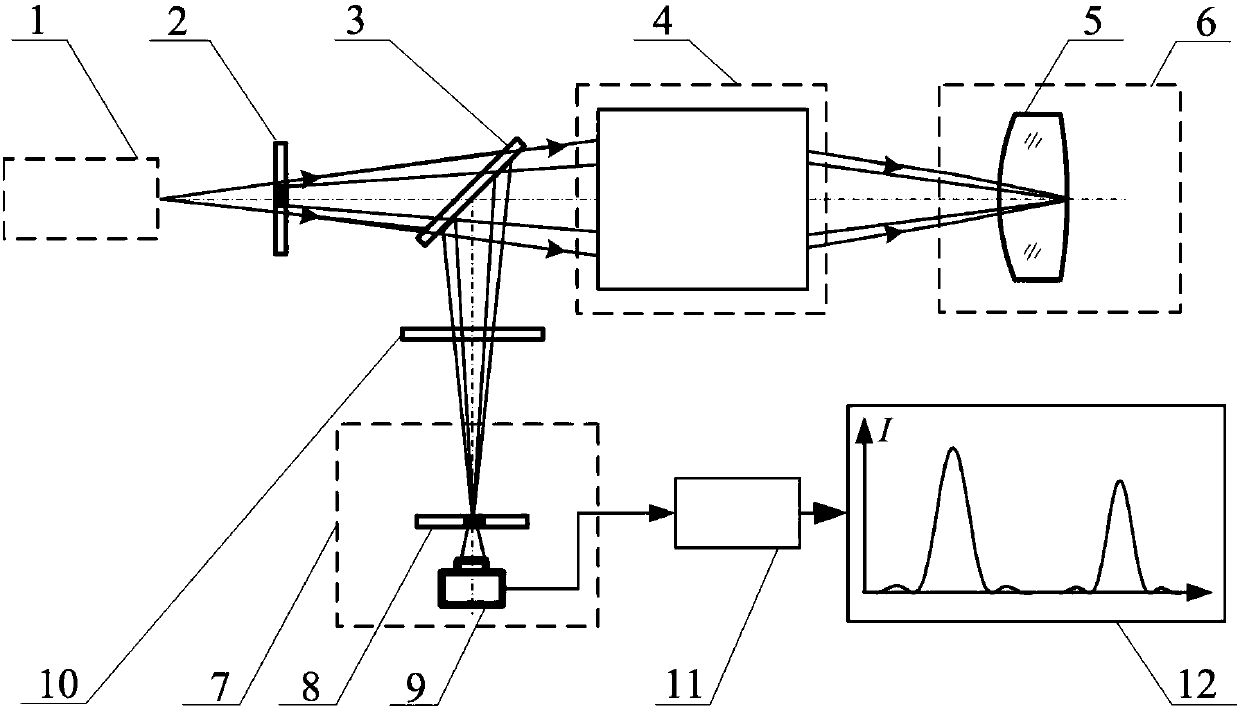
Method and device for measuring refractive index of broadband differential confocal infrared lens element
ActiveCN107462405ANo sampling requiredNo sample preparation requiredRefractive power measurementEffect lightRefractive index
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring a refractive index of a broadband differential confocal infrared lens element and belongs to the technical field of precise optical measurement. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: generating a specified wavelength lighting point light source through a wavelength gating system by adopting a blackbody source; performing tomographic focus fixing on vertexes of the front and rear surfaces of a measured lens by utilizing a differential confocal light path, and measuring to obtain the optical thickness of the measured lens; and calculating to obtain the refractive index of the lens element by a ray tracing algorithm, thereby realizing high-precision non-contact measurement of the refractive index of the infrared lens element in a visible-to-infrared broadband range under any wavelength condition. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the measured lens does not need to be subjected to destructive sampling, nondestructive direct measurement of the refractive index of the infrared lens element in the visible-to-infrared range under any wavelength condition is realized for the first time, and the method has the advantages of being convenient in measurement process, high in measurement accuracy and high in environmental disturbance resistance and can provide a brand new effective technical approach for detecting the refractive index of the lens element.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
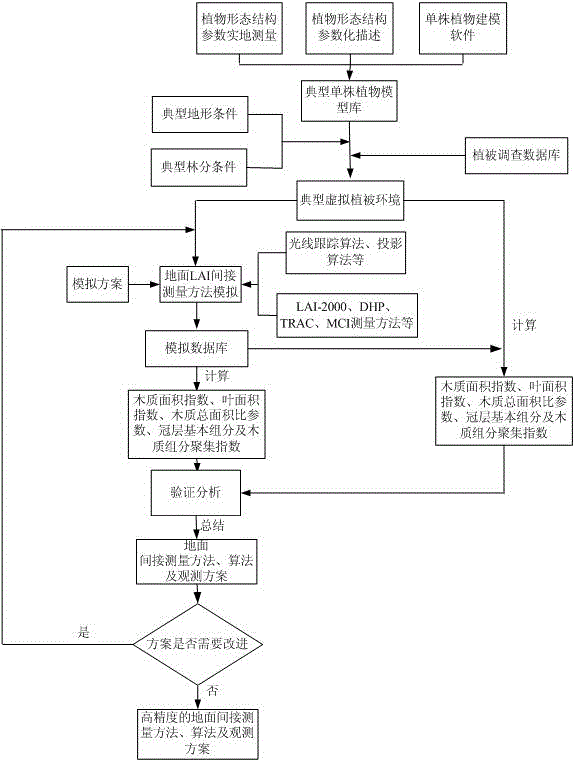
Verification method for indirect measurement of ground leaf area index
InactiveCN103983230AOvercoming Destructive SamplingOvercome the large consumption of manpower and material resourcesMeasurement devicesVegetationValidation methods
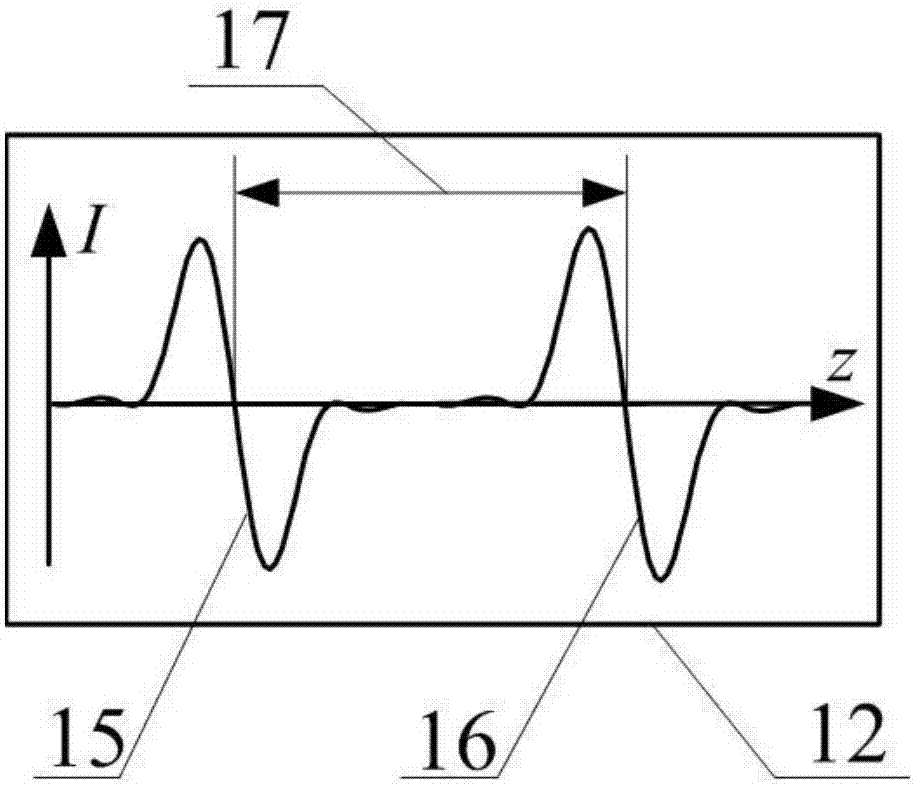
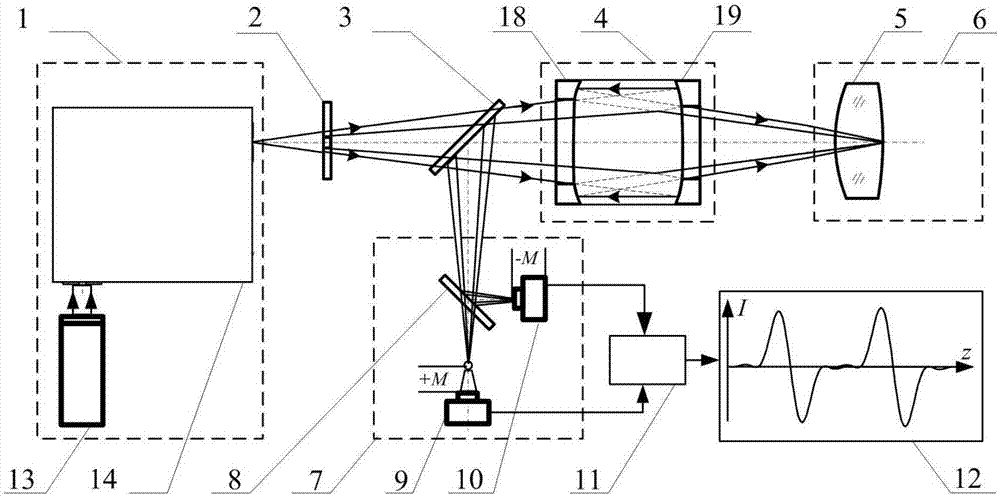
The invention relates to a verification method for indirect measurement of a ground leaf area index (LAI). The method includes the steps that a virtual plant geometric model base and a virtual vegetation scene base are set up; an observation scheme is designed, simulation implementation is carried out in a virtual vegetation scene according to the principles of all indirect measurement methods of the ground LAI and the observation scheme to form a simulation database; the sum total of the area of xylon parts and the area of triangular patches of leaves in the scene is counted to obtain true values of the LAI, the WAI, the PAI, the parameter of the xylon total area ratio, base components of canopies and the xylon component aggregation index; simulation results of all the measurement methods of the LAT are calculated, the true values of the scene are taken as the simulation calculation results to verify reference values, and the existing indirect measurement methods of the ground LAI are improved, realized in the virtual vegetation scene base and repeatedly circulated to obtain the final existing indirect measurement method of the ground LAI. The verification method does not need to destructively sample vegetation, manpower and material resource investments are small, and verification efficiency, precision and expandability are improved substantially.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
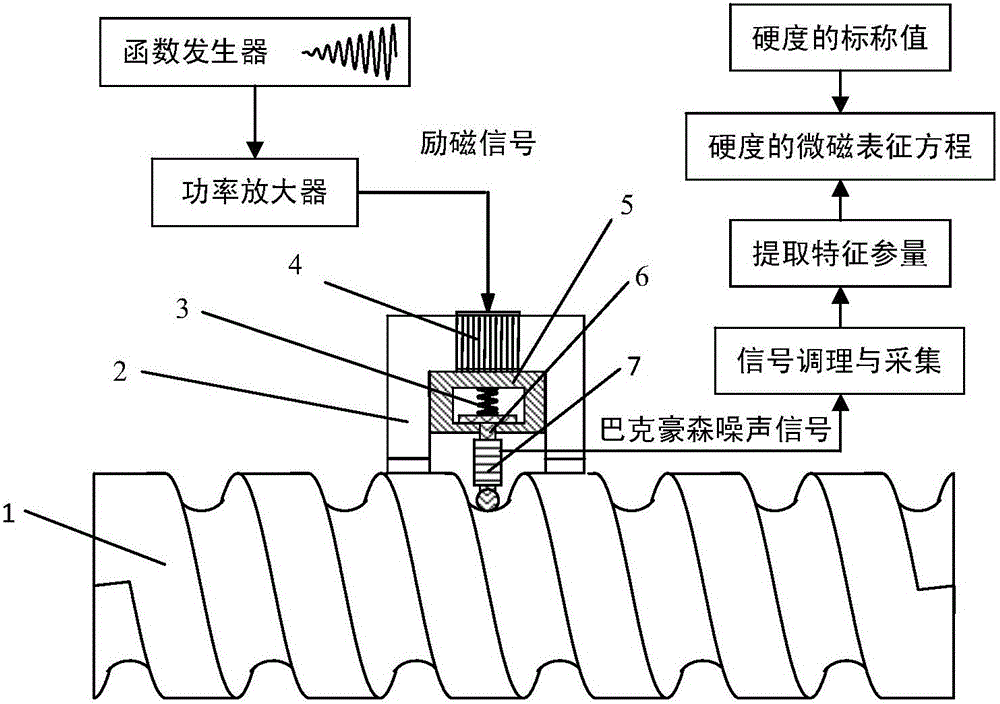
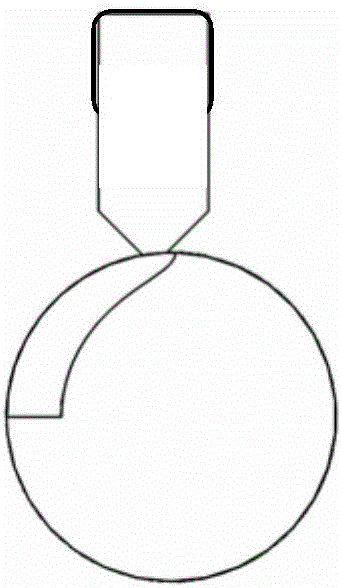
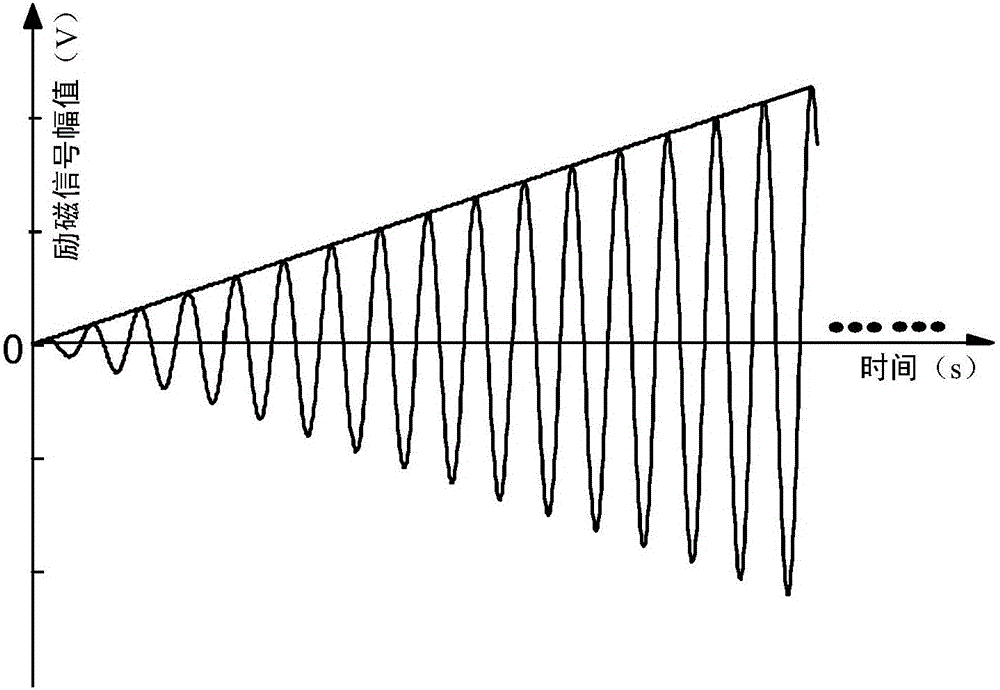
Lead screw thread bottom hardness micro-magnetic nondestructive detection method
The invention discloses a micromagnetic nondestructive testing method for the hardness of the bottom of a screw tooth, belonging to the field of nondestructive testing. The two pole pieces of the electromagnet using the micro-magnetic probe are attached to the two adjacent tooth tops of the lead screw to form an excitation circuit. The electromagnet is driven by a sine wave signal with a gradually increasing amplitude and a different frequency to gradually control the tooth bottom. Strong periodic magnetization, the detection coil in contact with the surface of the tooth bottom receives the Barkhausen noise signal during the periodic magnetization. Extract the characteristic parameters (including peak value, half-height width, and root mean square), and obtain the curve of the characteristic parameters changing with the amplitude of the scanning sine wave, and finally use the characteristic parameters of the Barkhausen noise signal at different frequencies and the amplitude of the scanning sine wave and The slope of its change curve characterizes the hardness. During continuous testing, the micro-magnetic probe travels with the rotating screw to complete the hardness testing of the tooth bottom of the entire screw. The method realizes the rapid non-destructive testing of the hardness of the tooth bottom of the ball screw, and overcomes the deficiency that the traditional hardness testing method can only perform the testing of the destructive sampling pattern.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Broadband confocal method and device to measure refractive index of infrared lens element
ActiveCN107782697ANo sampling requiredNo sample preparation requiredPhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexBroadband
The invention relates to a broadband confocal method and device to measure refractive index of an infrared lens element and belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement. A black light source is used herein to generate a lighting point source of specific wavelength through a wavelength gating system, a confocal light path is used to perform chromatographic focus fixation on apexes of front and rear surfaces of a lens under measurement, optical thickness of the lens under measurement is acquired by measuring, element refractive index of the lens is acquired by calculating through a ray tracking algorithm, and high-precision noncontact measurement of element refractive index of an infrared lens under any wavelength in a wide band range of from visible light to infrared is achieved. The method and device of the invention have the advantages that destructive sampling on a lens under measurement is not required, nondestructive direct measurement of element refractive indexof the lens under any wavelength from visible light to infrared is achieved, the measuring process is convenient, measurement precision is high, the ability to resist ambient interferences is great,and a brand-new effective technical means to detect the element refractive index of the lens is provided.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
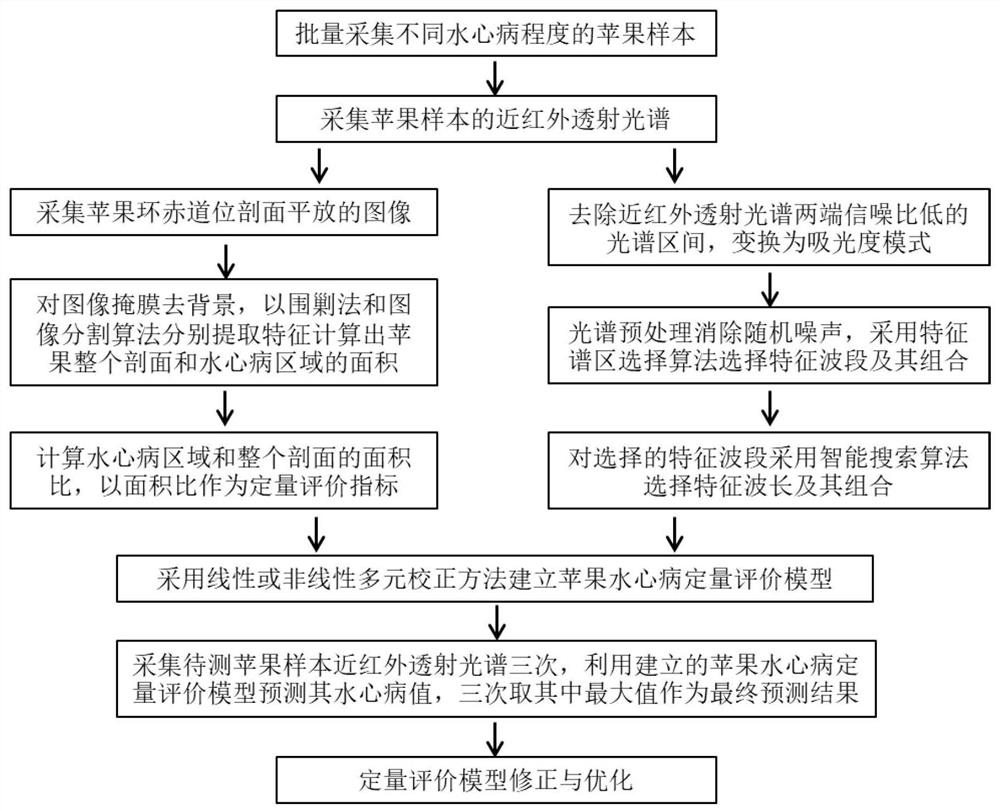
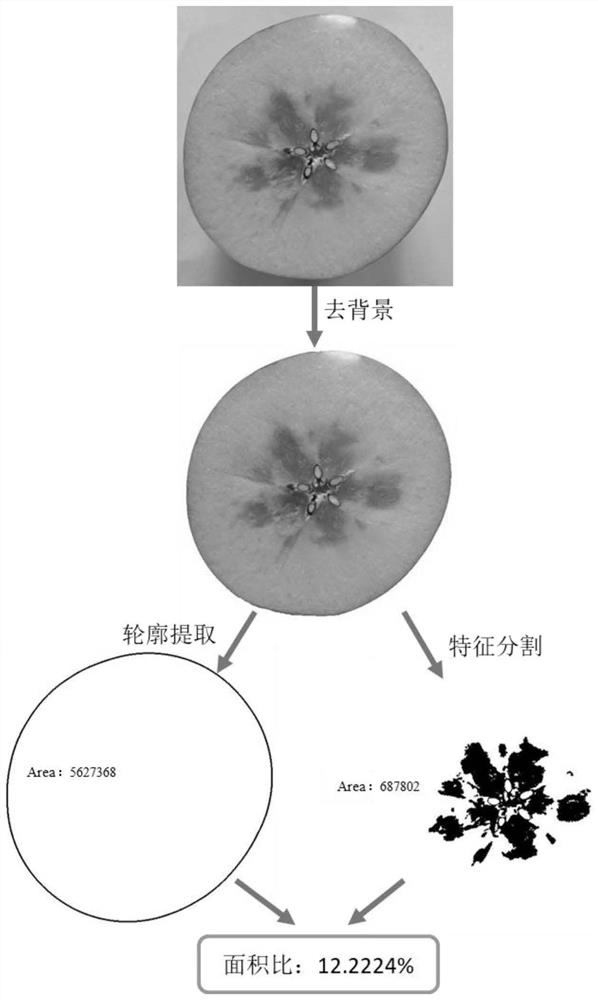
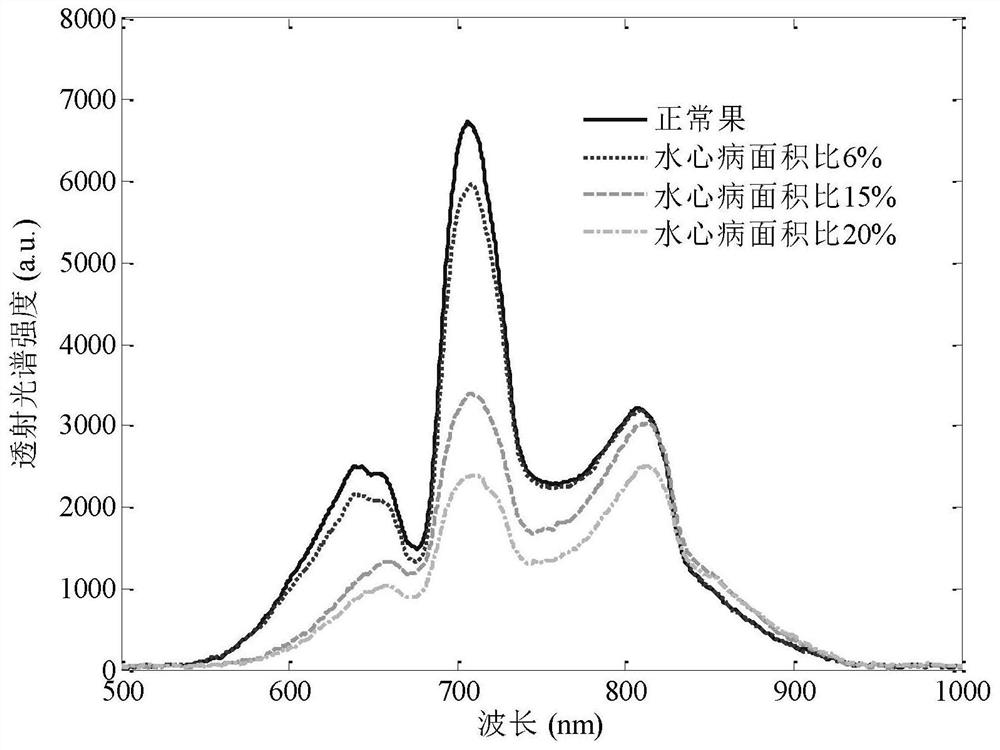
Transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation method of apple watercore
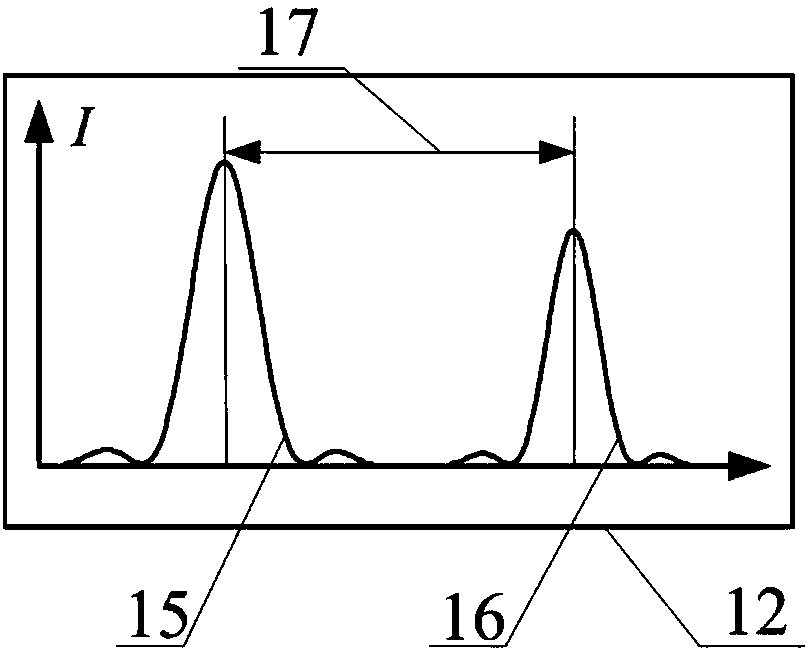
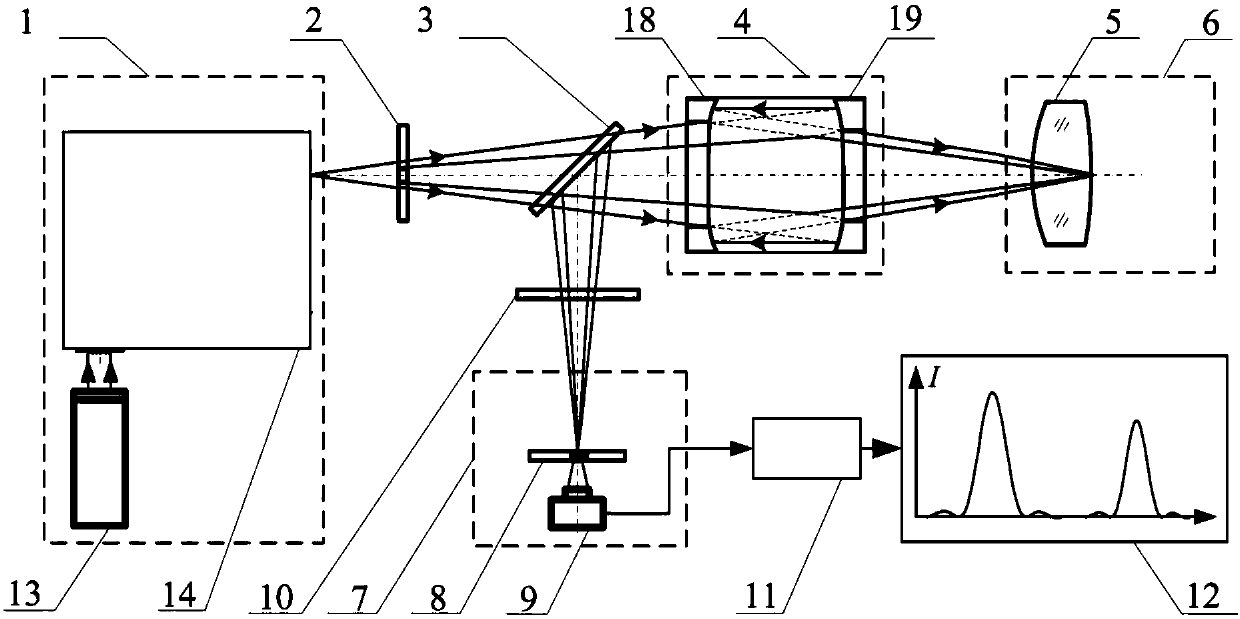
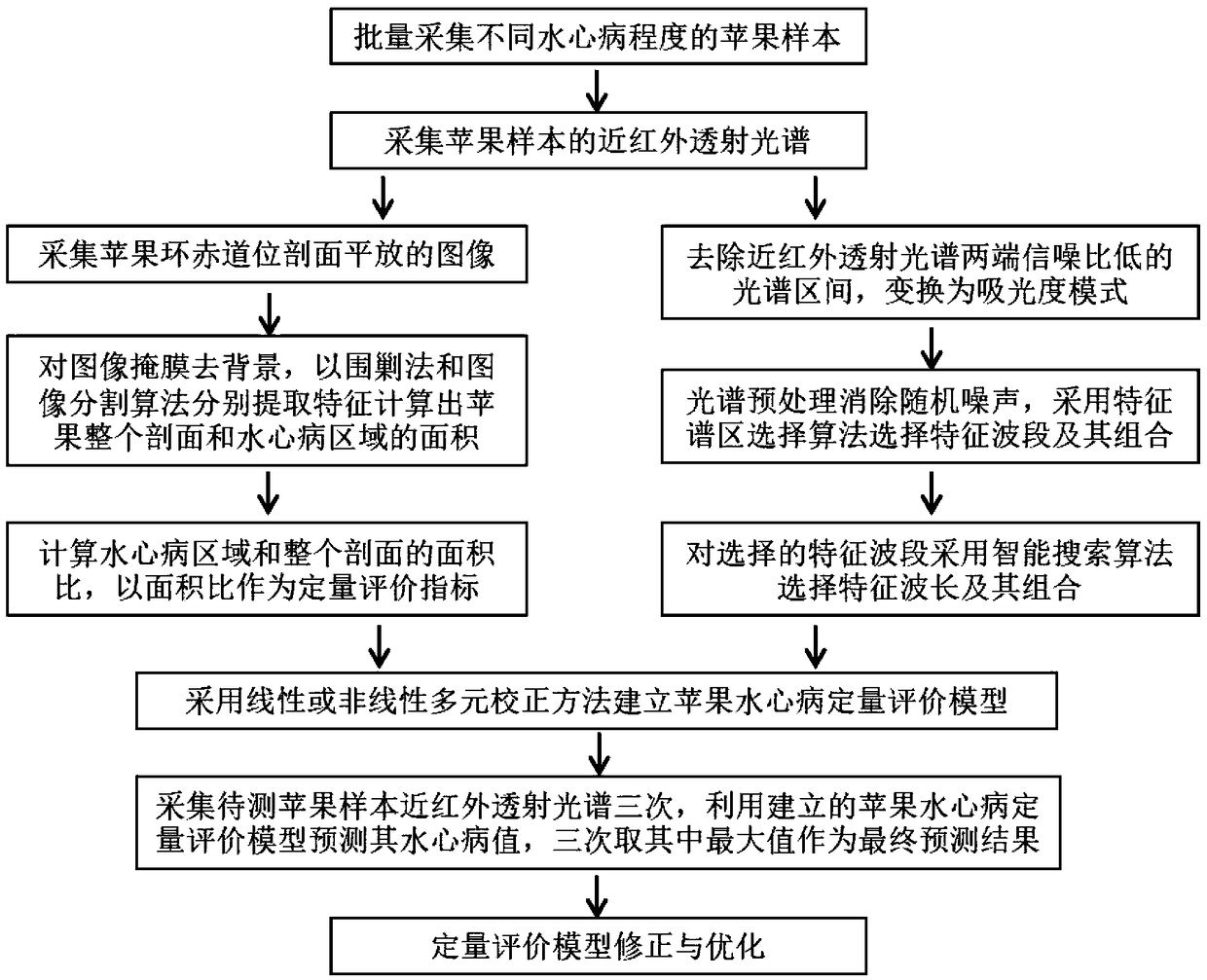
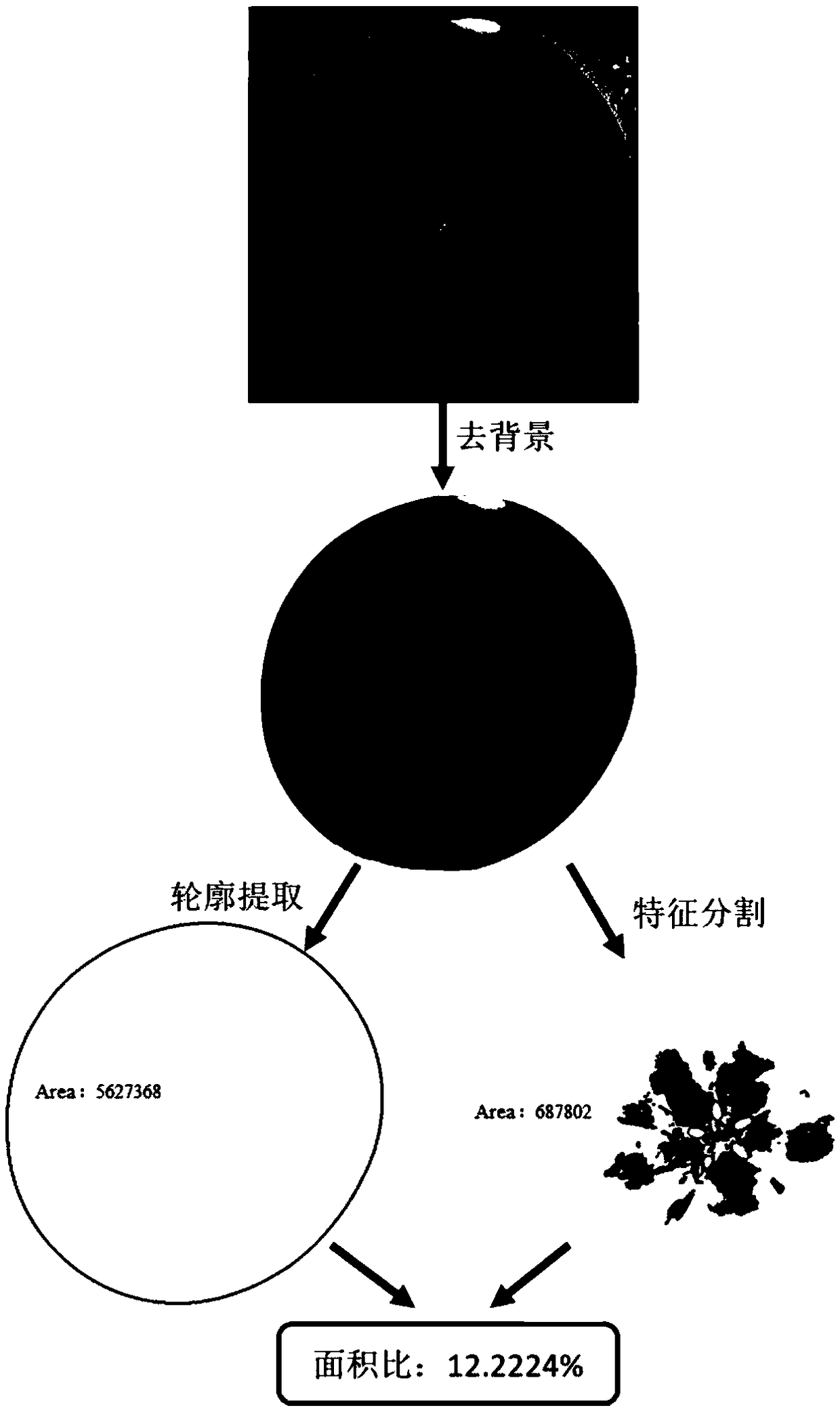
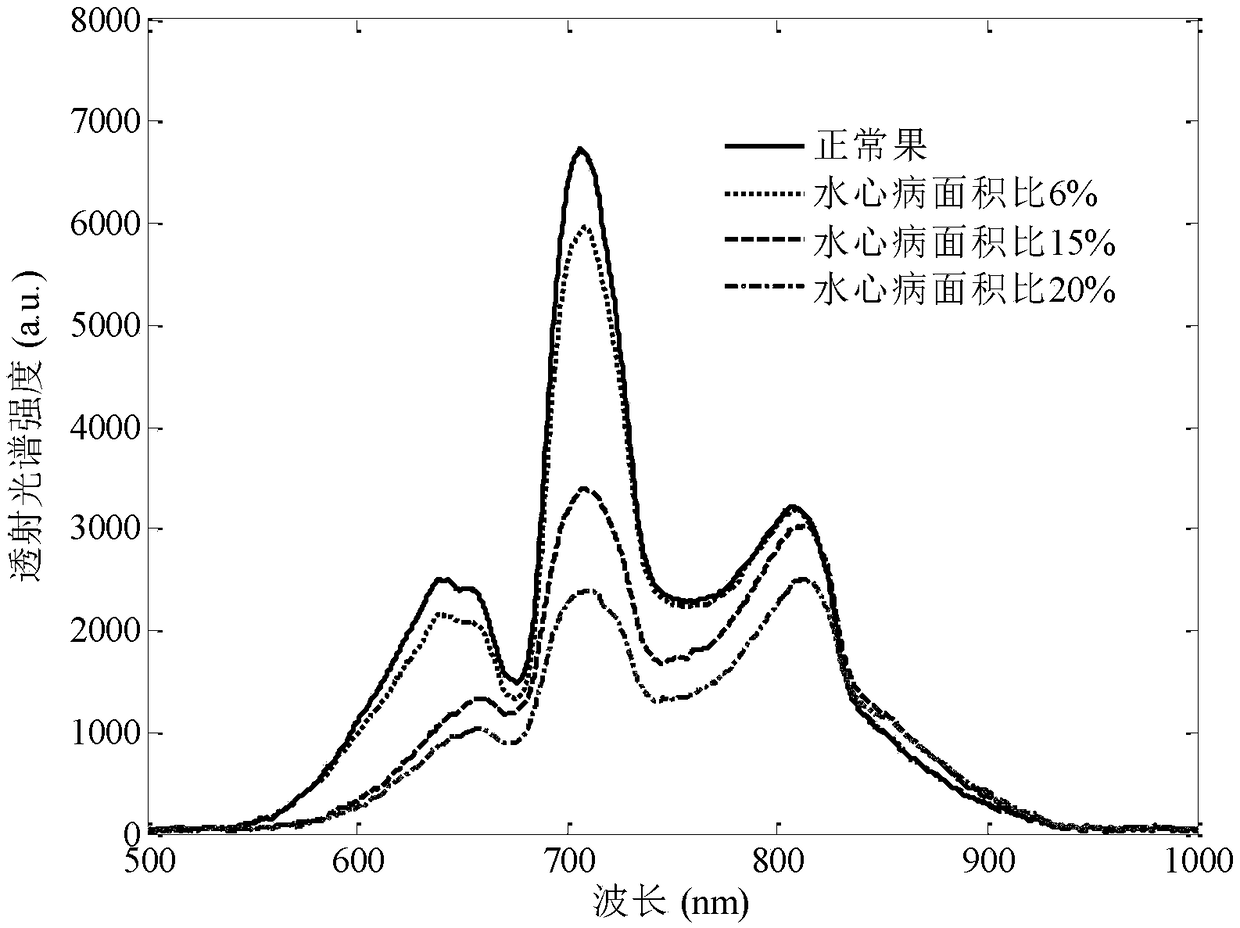
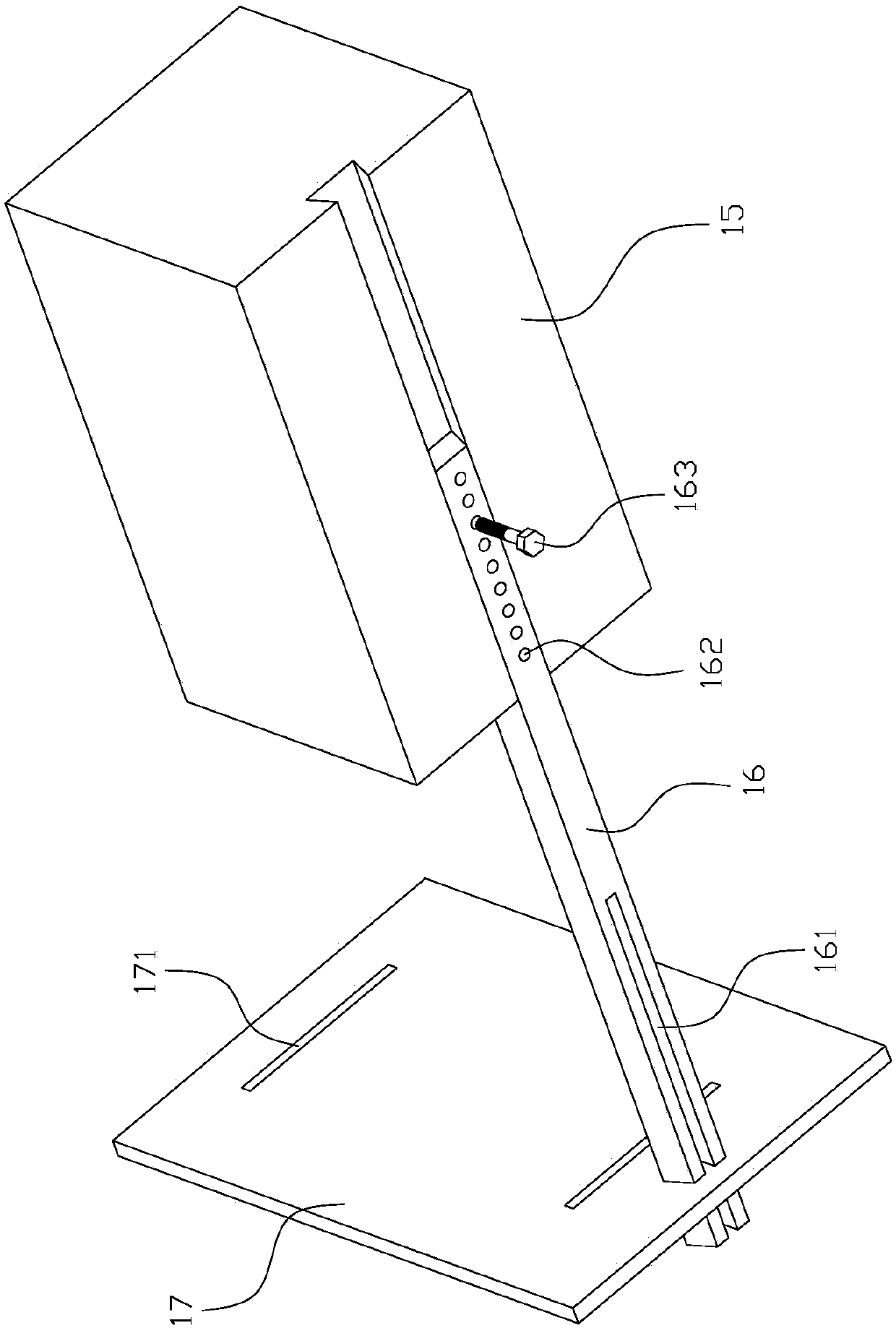
ActiveCN109100323AResolve identifiabilitySolve the problem of difficult boundary demarcationColor/spectral properties measurementsNon destructiveCollection system
The invention discloses a transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation method of apple watercore, and belongs to the technical field of rapid evaluation of food quality. The transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: non-destructively obtaining entire optical information in an apple by using an near-infrared transmission spectrum collection system, collecting an image of a equatorial profile of the apple by using a camera, dividing the image by using an encirclement and suppression algorithm, calculating a watercore area and a sectional area of the apple, using the ratio of the area of a watercore section on a cross section to the area of the entire section as a quantitative prediction index, establishing a transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation model of the apple watercore by using a multielement correction method after preprocessing an obtained near-infrared transmission spectrum, so as to achieve the non-destructive quantitative prediction of the apple watercore. According to the transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation method disclosedby the invention, the degree of the apple watercore is quantitatively predicted by using the transmission spectrum technology, thereby avoiding the disadvantages of destructive sampling of a sectionvisualization method, and solving the technical problems of low recognition rate and blurred boundary of the watercore.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for grading wheat scab disease
ActiveCN109544538AImprove Segmentation AccuracyThe segmentation result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseLab color space
The invention particularly relates to a method for grade wheat scab disease, which comprises that follow steps: (A) acquiring an original image; B) carrying out grayscale processing, binarization processing, and opening and closing operation on that original image in turn, and obtaining a binary image; (c) combining that original image and the binary image; (D) Convertting to Lab color space, using IABC-K-PCNN method to process the a-channel gray scale image to obtain binary single-spike scab lesion pattern. (e) calculating a single ear area S1 and a lesion area S2, and then calculating a ratio R of that single ear area S1 and the lesion area S2; (F) according to the national standard, the ratio R, grading the disease of the single ear and outputting the disease grade; A grading device isalso disclosed. The disease grade grading method provided by the invention is tested by a large number of samples and is not destructive in sampling in field investigation of wheat scab, and has the advantages of reliable grading accuracy and high popularization value.
Owner:安徽黄鹄电子信息技术有限公司
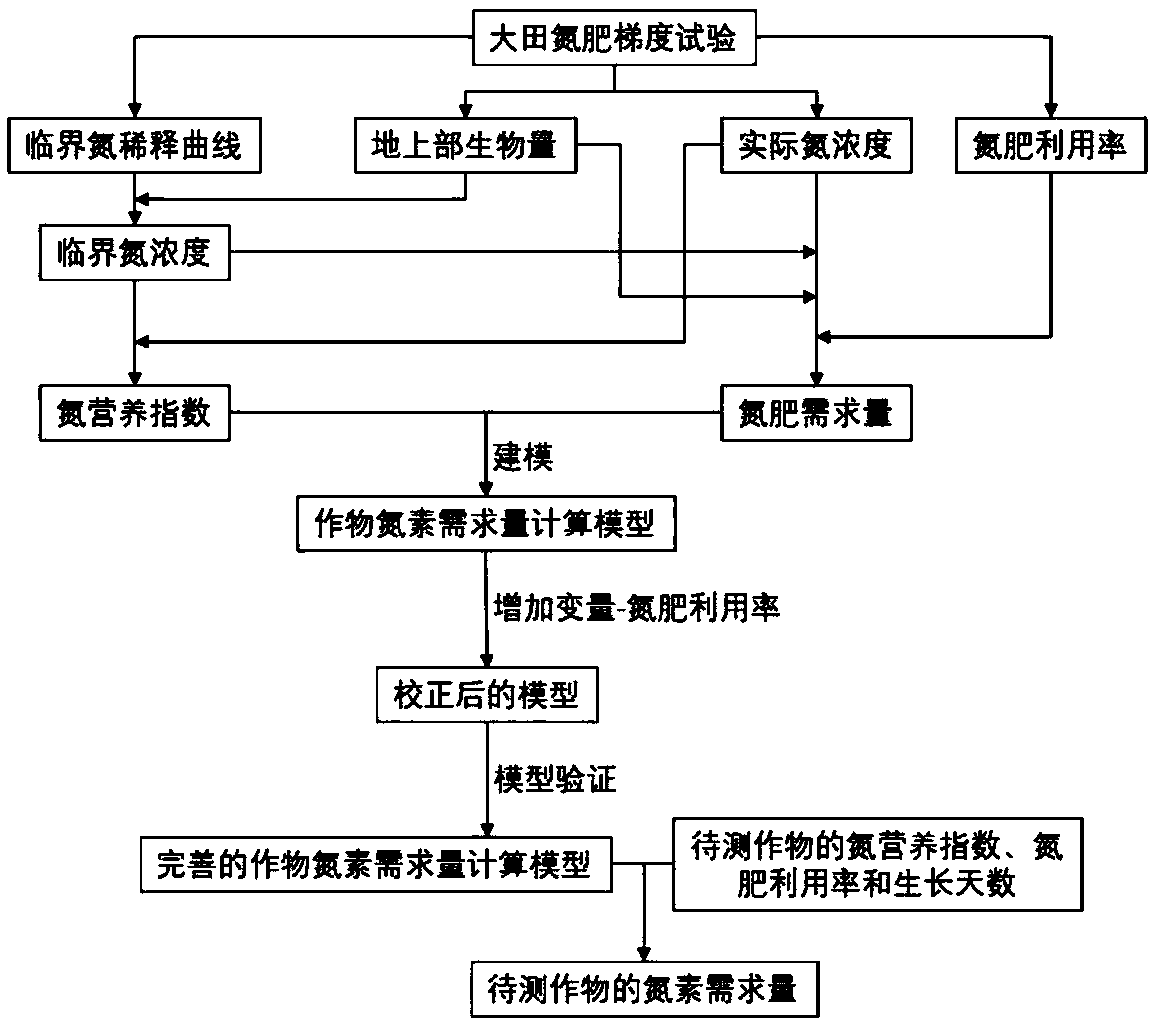
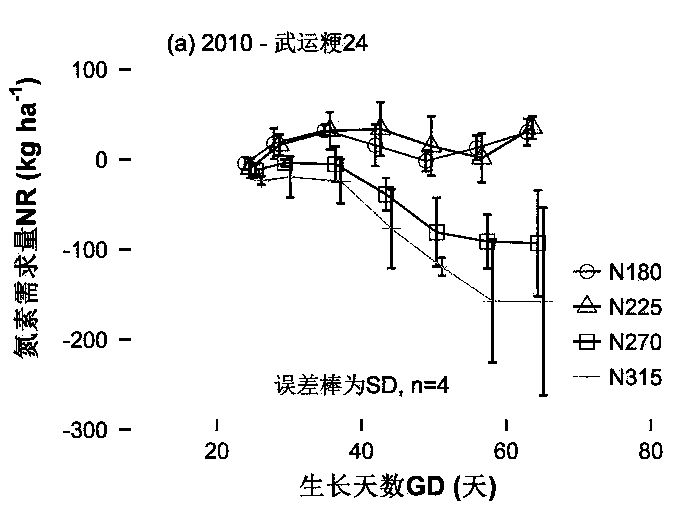
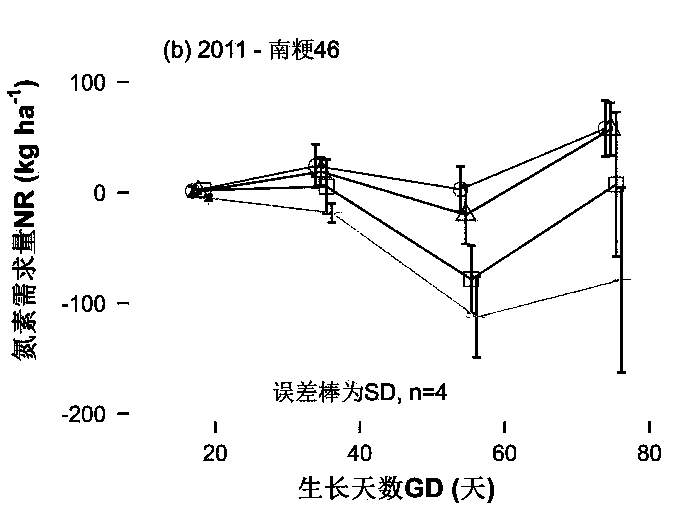
Crop nitrogen demand real-time acquisition method
ActiveCN109211801AImprove timelinessHigh precisionInvestigation of vegetal materialColor/spectral properties measurementsNutrition IndexesAgricultural science
The invention relates to a crop nitrogen demand real-time acquisition method. For the problems of large workload and relatively poor timeliness due to the fact that crops need to be subjected to destructive sampling analysis in a traditional crop nitrogen demand calculation method, a model between a crop nitrogen demand and a crop nitrogen nutrition index is built, and the complex crop nitrogen demand calculation is converted into the crop nitrogen nutrition index acquisition, so that the timeliness of crop nitrogen nutrition diagnosis is greatly improved; the design model not only has relatively high precision but also considers the growth period difference of the crops and the utilization ratio difference of nitrogen fertilizers in different planting regions, thereby having relatively high universality; and the building of the model can provide guidance for precise nitrogen fertilizer management of the crops, and has important practical significance for nitrogen fertilizer reductionand agricultural sustainable development.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
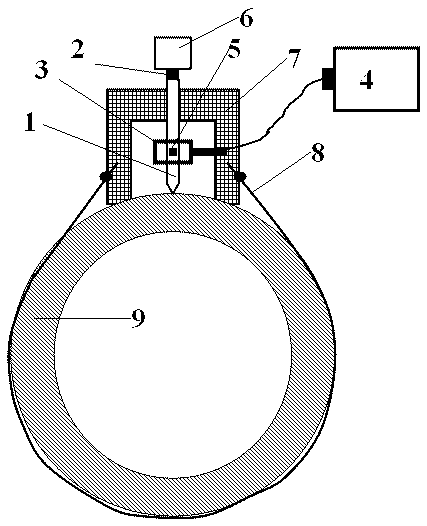
In-situ material detection device and method of in-service equipment
ActiveCN105547824AImprove detection efficiencyInvestigating material hardnessEngineeringDestructive sampling
The invention discloses an in-situ material detection device and method of in-service equipment. Based on a vortex induction principle, a uniquely-designed material rigidity in-situ detection device of the in-service equipment comprises a probe, a pressure sensor, a vortex detection probe, a vortex detector, a metal induction block, a driving and pressurizing device, a bracket and a fixed chain. For the in-service equipment, the equipment is subjected to in-situ and micro-loss material rigidity detection without the need of destructive sampling, and the detection efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:EDDYSUN (XIAMEN) ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for detecting quantity of nitrogen fixed by soybean root nodules
InactiveCN102007846ANodule nitrogen fixation data is accurateImprove detection efficiencySeed and root treatmentHorticulturePlant noduleTotal nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for detecting the quantity of nitrogen fixed by soybean root nodules, which relates to a method for detecting the quantity of the nitrogen fixed by root nodules and solves the problem of low accuracy of the conventional method for detecting the nitrogen fixed by the soybean root nodules. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the variety of detected soybeans and the variety of homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans; soaking seeds of the detected soybeans and the homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans in aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and then sowing the seeds in culture pots respectively, wherein three strains are planted in each pot and cultured under the same growth condition; performing destructive sampling on the strains at the maturation stage; detecting the total nitrogen quantity of the detected soybeans and the homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans respectively; and subtracting the total nitrogen quantity of the homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans from that of the detected soybeans to obtain the quantity of the nitrogen fixed by root nodules of the detected soybeans. The method has the detection accuracy of over 90 percent and can be used for detecting the quantity of the nitrogen fixed by the root nodules of leguminous crops.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
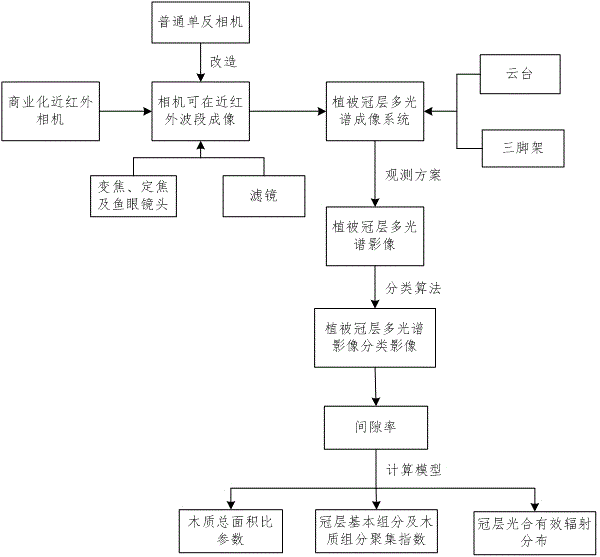
Implementation method of vegetation canopy multi-spectral imaging system
The invention relates to an implementation method of a vegetation canopy multi-spectral imaging system. Firstly, a single lens reflex camera is enabled to have a near infrared band imaging capability by reconstruction, the camera is placed on a holder and a tripod, the holder is rotated to a direction of setting a zenith angle and an azimuth angle, a fish-eye lens or telephoto and prime lens is installed, a filter is installed on the lens, the camera is enable to form an image within a single near infrared band or two or more visible light and near infrared bands, and canopy multi-spectral imaging in multiple zenith angle and azimuth angle directions is completed according to a set scheme. Collected vegetation canopy multi-spectral images are classified, and based on classified images, a vegetation canopy woody total area ratio parameter, an aggregation index and photosynthetically active radiation distribution can be calculated The invention prevents vegetation canopy destroyed sampling, is low in manpower and material resource investment, solves problems of a traditional optical measurement method that the error is large, the efficiency is low and the like, and can be applied to measurement of the vegetation canopy wood-total area ratio parameter, the aggregation index and the photosynthetically active radiation distribution.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
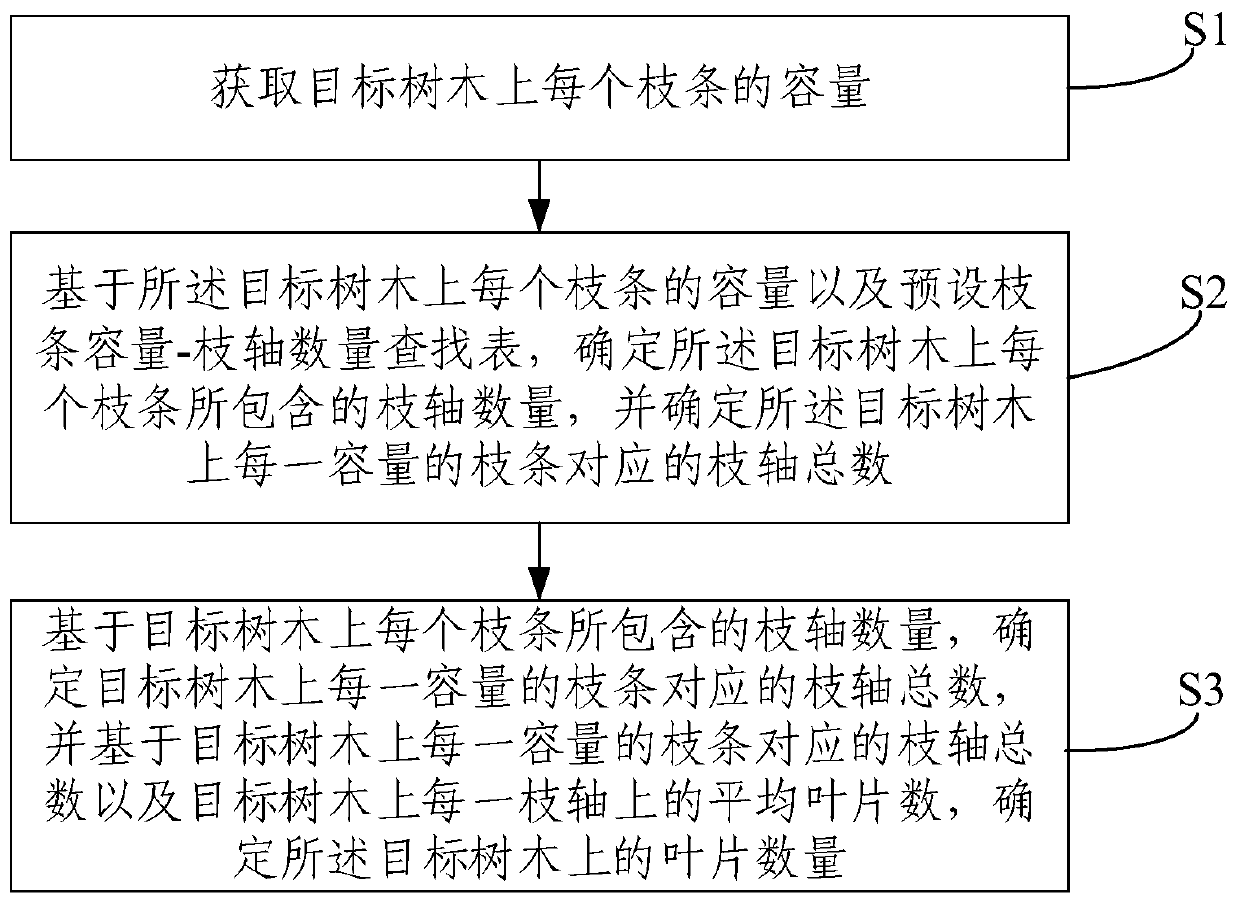
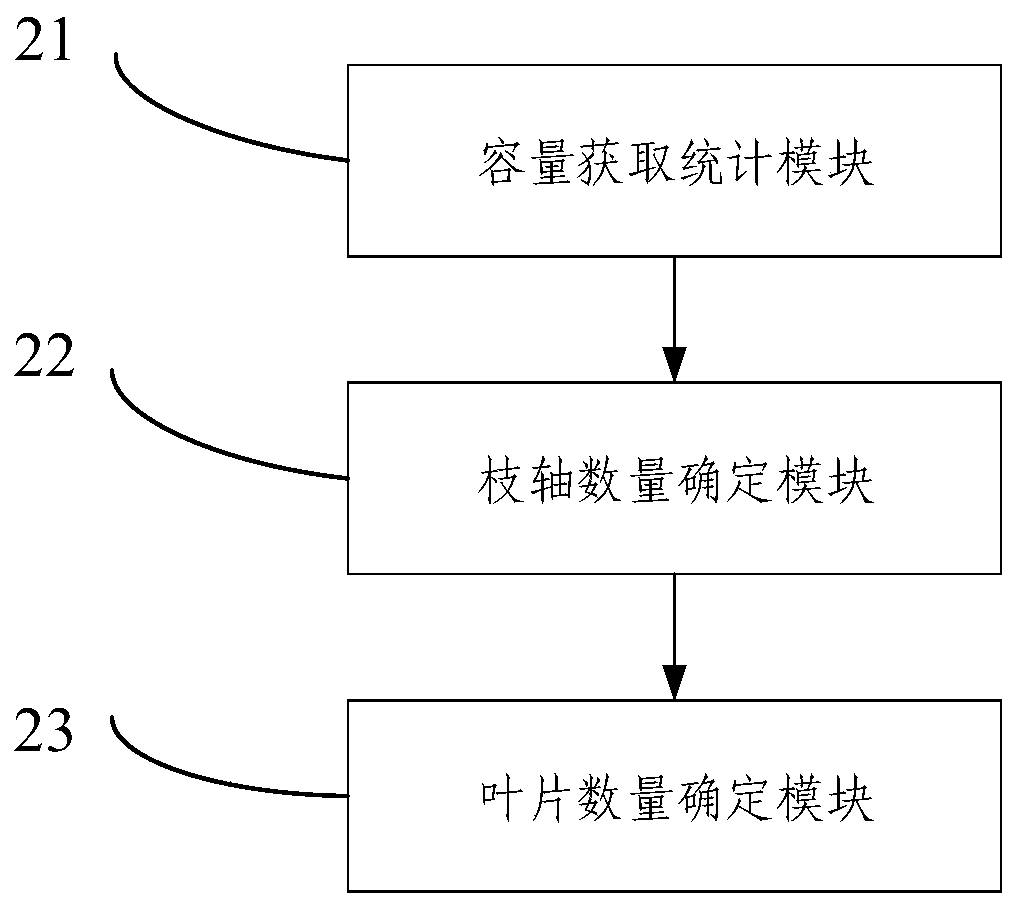
Method and system for estimating number of tree leaves
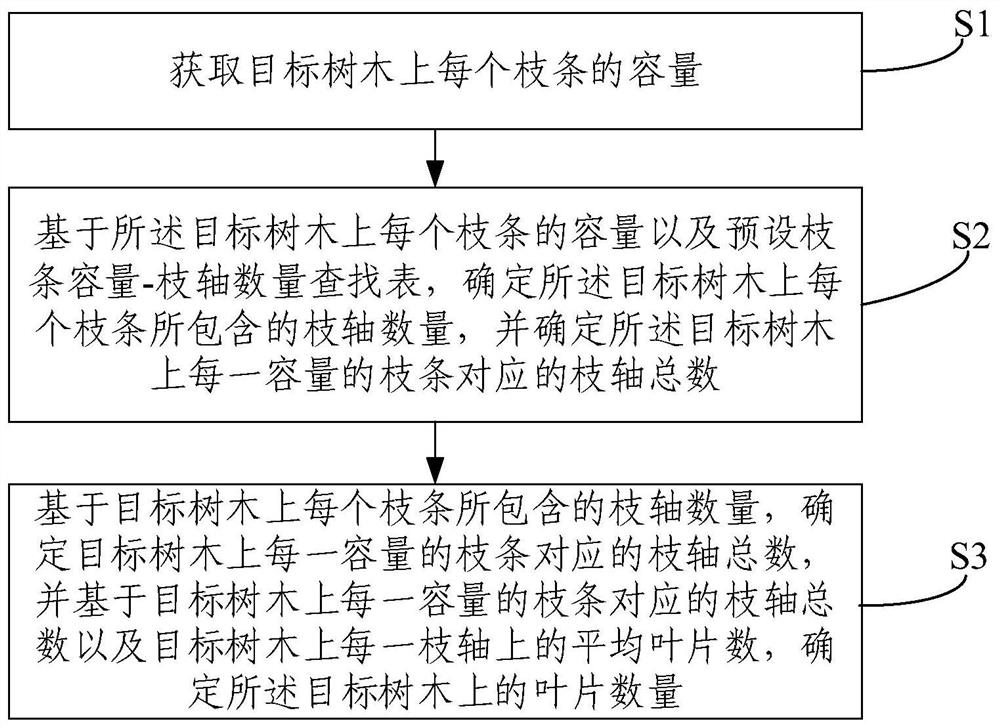
InactiveCN109856139AImprove efficiencyVarious methodsMaterial analysis by optical meansPlant communityDestructive sampling
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and system for estimating the number of tree leaves. The method comprises the steps of determining the capacity of each branch on a tree directly through visual measurement, and then determining the number of branch shafts contained by each branch on the target tree through a preset branch capacity-branch shaft number lookup table; determining thetotal branch shaft number corresponding to the branch of each capacity on the target tree based on the capacity of each branch on the target tree and the number of branch shafts contained by each branch, and determining the number of leaves on the target tree according to the total branch shaft number corresponding to the branch of each capacity on the target tree and the average number of leaveson each branch shaft of the target tree. The whole estimation process does not need to cut down the target tree and can be implemented without damage. The method is not only high in efficiency, but also suitable for the case of limited destructive sampling, and enriches the forest measurement and plant community carbon accounting method.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for detecting plant nitrogen content and electronic device
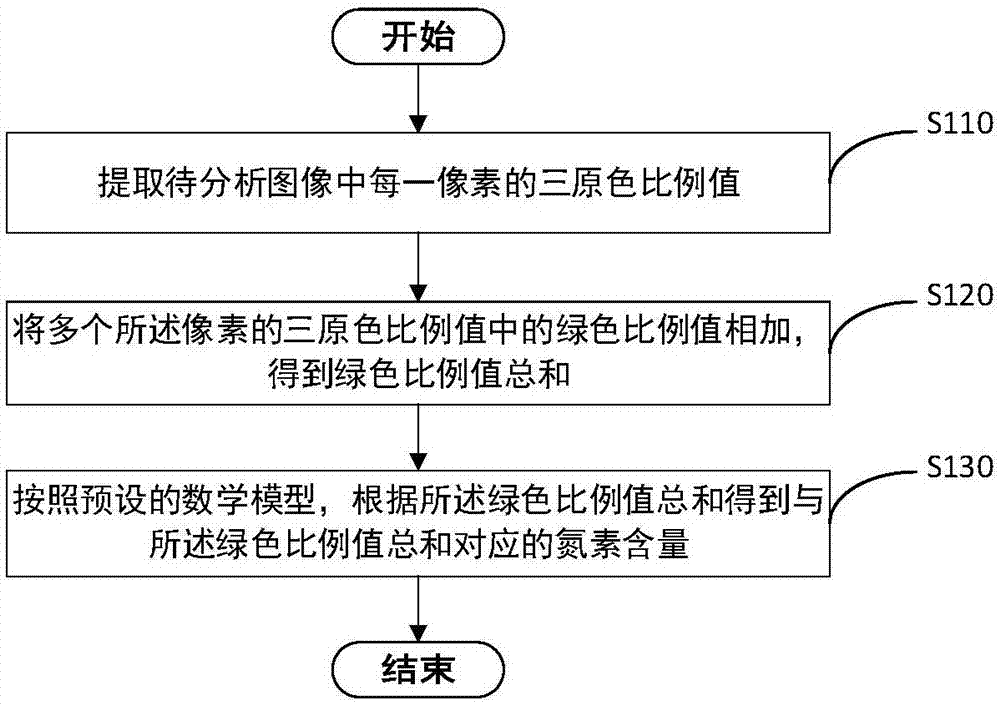
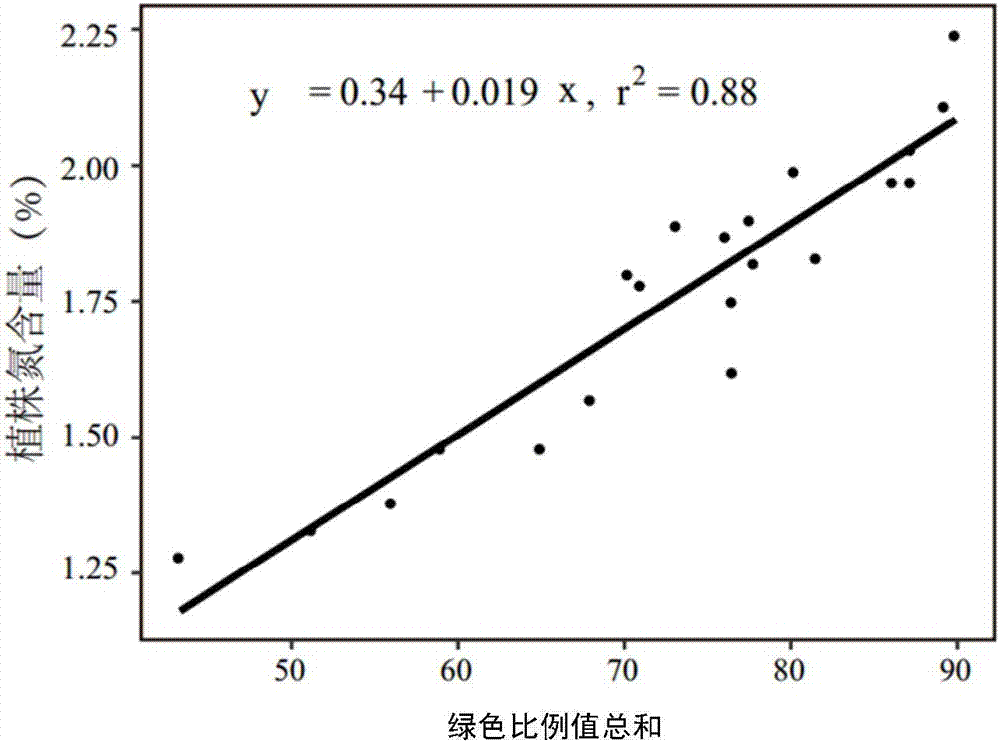
InactiveCN106919740AAvoid Destructive SamplingImage analysisData processing applicationsMathematical modelComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to the technical field of plants and concretely relates to method and apparatus for detecting plant nitrogen content and an electronic device. The method detecting plant nitrogen content comprises steps of extracting a three-primary color proportion value of each pixel in a to-be-analyzed image, adding green proportion values of the three-primary color proportion values of a plurality of pixels to achieve a green proportion value total, and achieving a corresponding nitrogen content corresponding to the green proportion value total according to the green proportion value total through a preset mathematic model, and further analyzing the plant image to achieve a nitrogen content condition of the plant. Destructive sampling to the plant can be achieved; and the method is high efficient and quick.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
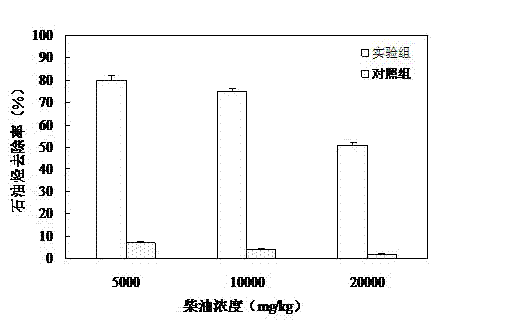
Method for repairing diesel oil polluted soil by fringed iris herbs
InactiveCN103240265AImprove the environmentAdaptableContaminated soil reclamationEnvironment of AlbaniaDestructive sampling
The invention relates to a method for repairing diesel oil polluted soil by fringed iris herbs. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the fringed iris herbs are planted into the diesel oil polluted soil to grow for about 104 days, one time of destructive sampling is carried out on the fringed iris herbs in a mature period, and the fringed iris herbs are properly treated, so that the degradation rate of total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) in the soil can be determined. When the fringed iris herbs are compared with a blank control, the degradation rate increases by 11-25 times, so that the fringed iris herbs have an excellent capability of removing diesel oil pollutants. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of no damage to physical and chemical properties of the soil, no secondary pollution, simple technology, convenience in operation, low cost, high tolerance to the diesel oil polluted soil, high TPH degradation rate and the like; more importantly, the fringed iris herbs are flowers which are beautiful and have high ornamental values, so that not only the environment can be beautified, but also the fringed iris herbs have economic and ecological benefits; and therefore, the method is applicable to repair of the large-area diesel oil polluted soil and environment beautifying.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method and device for measuring refractive index of broadband differential confocal infrared lens element
ActiveCN107462405BEasy to measureReduce sources of errorRefractive power measurementEffect lightRefractive index
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring a refractive index of a broadband differential confocal infrared lens element and belongs to the technical field of precise optical measurement. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: generating a specified wavelength lighting point light source through a wavelength gating system by adopting a blackbody source; performing tomographic focus fixing on vertexes of the front and rear surfaces of a measured lens by utilizing a differential confocal light path, and measuring to obtain the optical thickness of the measured lens; and calculating to obtain the refractive index of the lens element by a ray tracing algorithm, thereby realizing high-precision non-contact measurement of the refractive index of the infrared lens element in a visible-to-infrared broadband range under any wavelength condition. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the measured lens does not need to be subjected to destructive sampling, nondestructive direct measurement of the refractive index of the infrared lens element in the visible-to-infrared range under any wavelength condition is realized for the first time, and the method has the advantages of being convenient in measurement process, high in measurement accuracy and high in environmental disturbance resistance and can provide a brand new effective technical approach for detecting the refractive index of the lens element.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
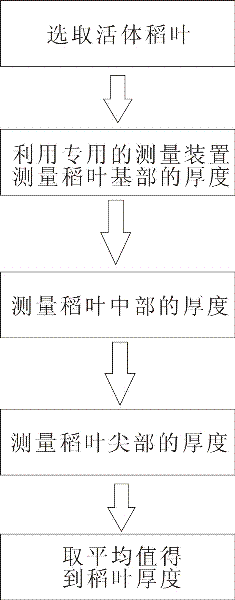
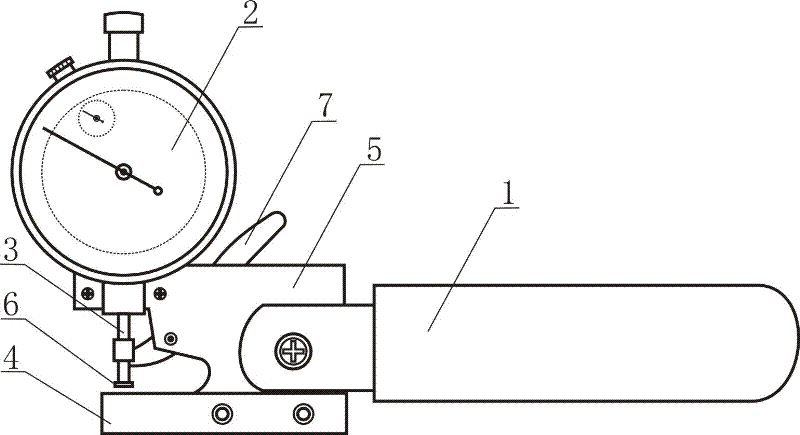
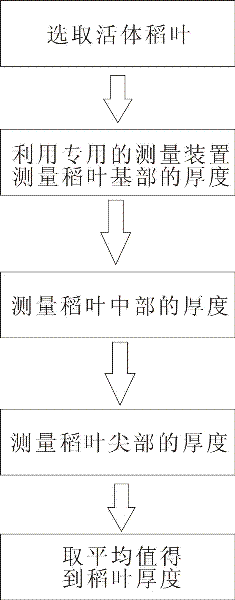
Living body measurement method and device of thickness of rice leaf
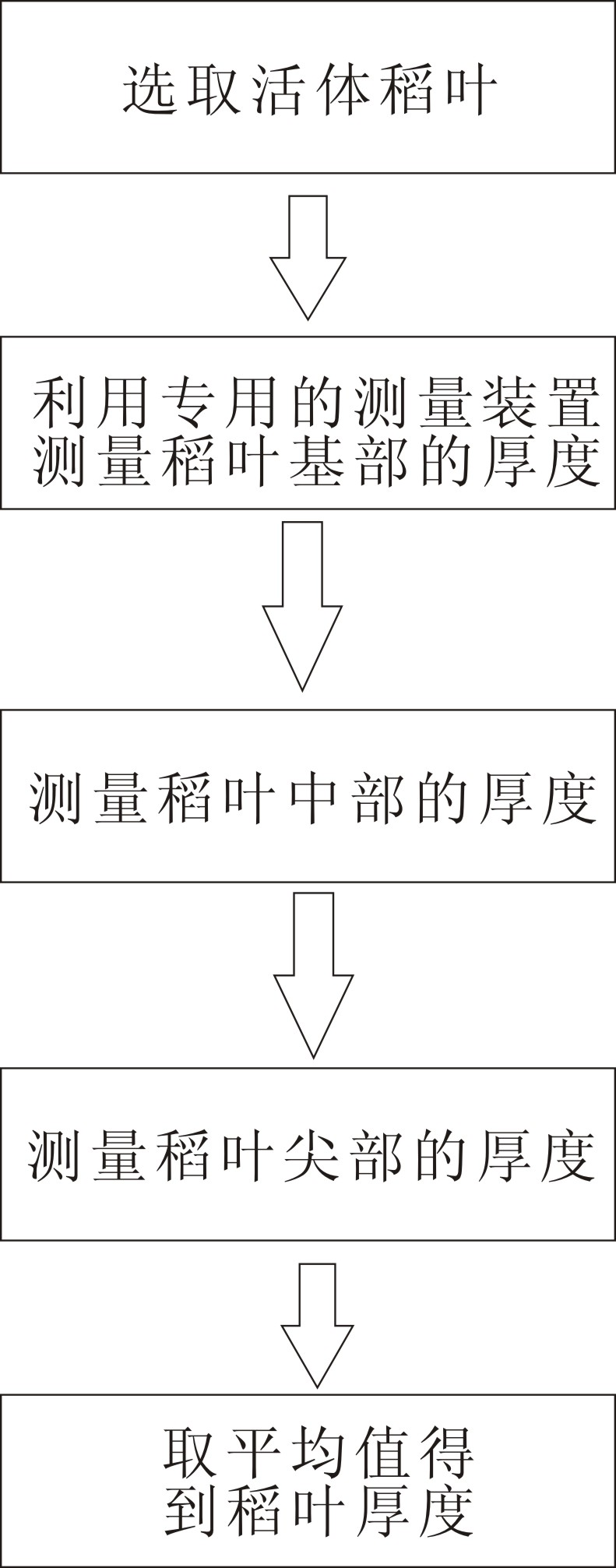
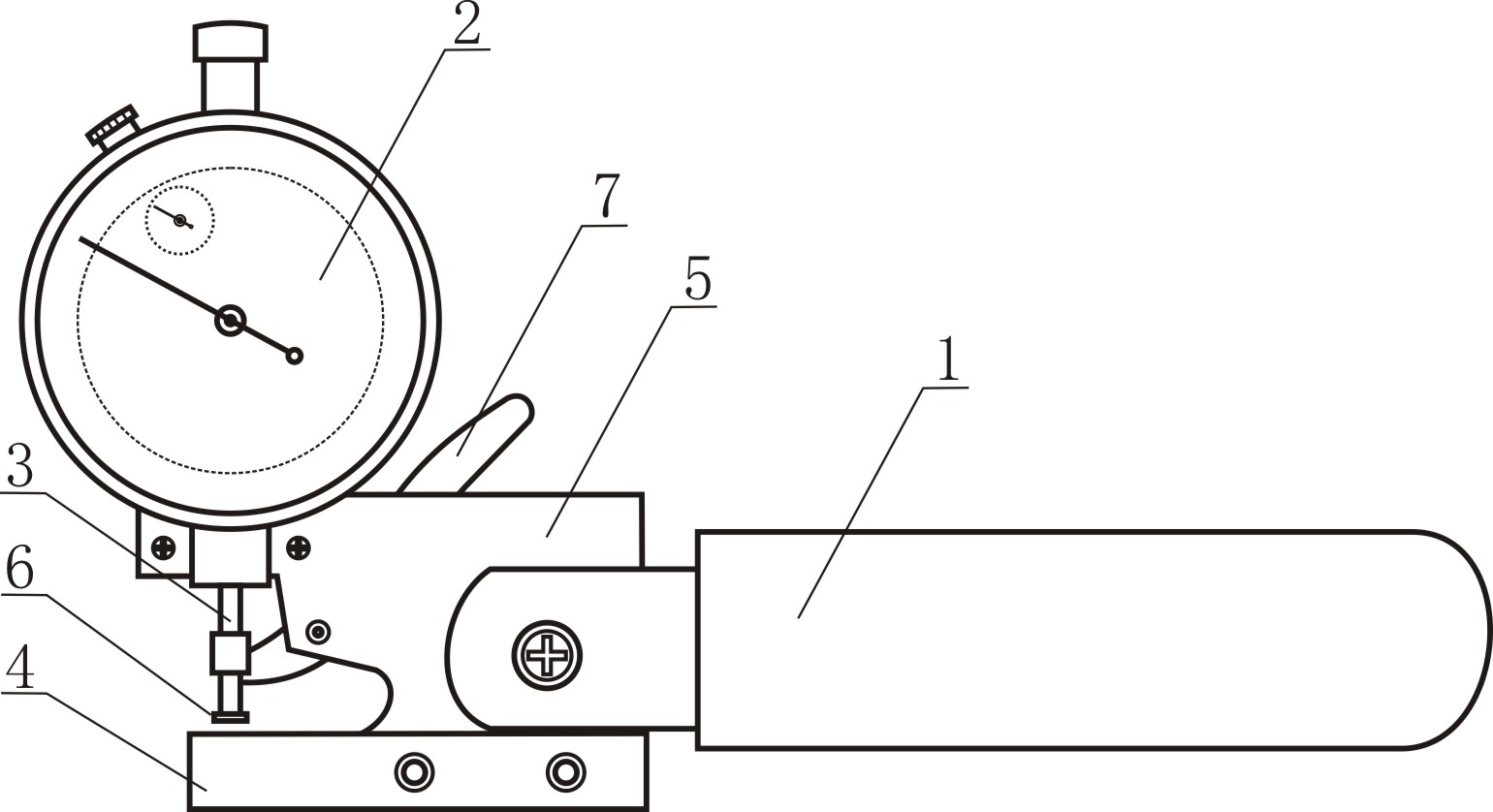
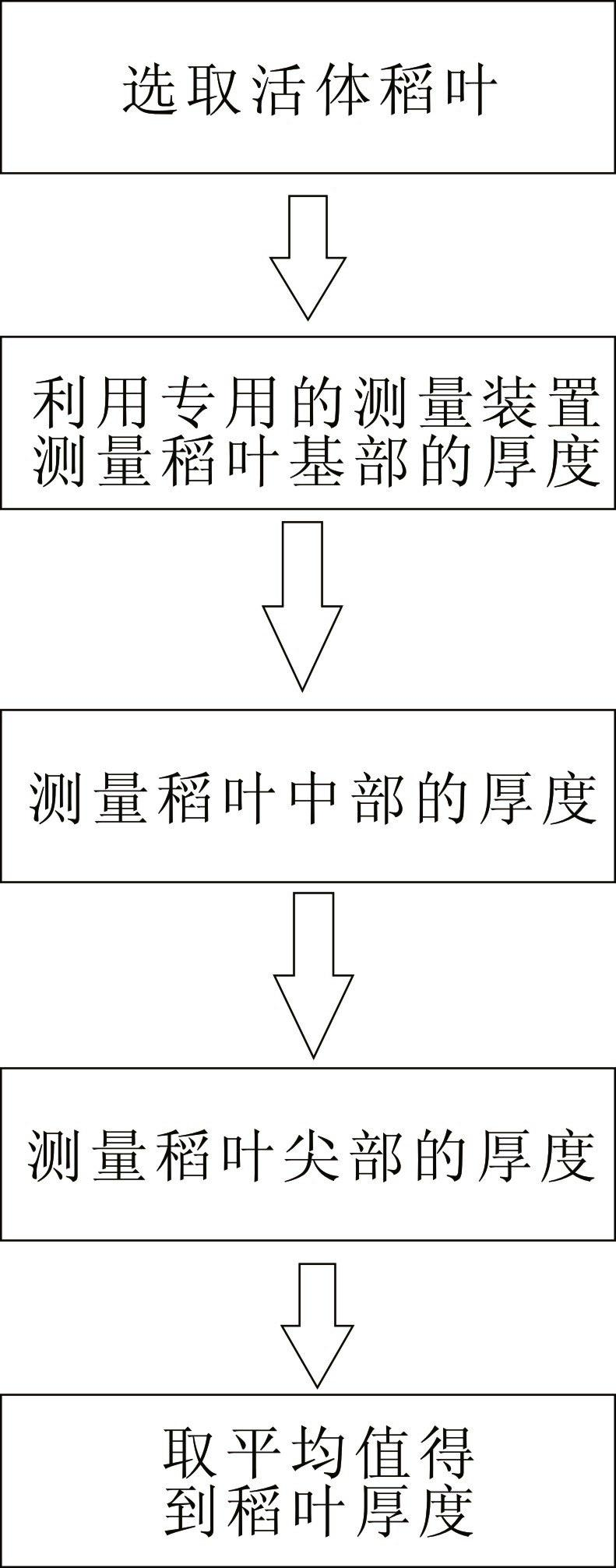
InactiveCN102175115AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionMechanical thickness measurementsVeinDestructive sampling
The invention discloses a living body measurement method and device of thickness of a rice leaf. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting the growing rice leaf as a measuring object; measuring the fixed position of the rice leaf by using a special leaf thickness measuring device; placing the fixed position of the leaf between a rice leaf contact plate and a base of the leaf thickness measuring device and keeping the fixed position away from the main vein of the leaf rice; when the full-leaf thickness of the fully spread rice leave is measured, measuring leaf tip, middle and base, wherein the base measuring point of the rice leaf is at 2 / 3 of the full leaf length; and averaging the measured leaf thickness data of three points, wherein the obtained average value is the thickness value of the full leaf. The method can directly measure the thickness of the living body rice leaf so as to improve the efficiency, simplify the operation, reduce the cost and improve the accuracy; and the method can perform living body measurement to the rice leaf thickness in the field so as to eliminate the sampling steps, implement the continuous tracking to the sample and eliminate the complex process of the data statistic analysis of the destructive sampling experimental data.
Owner:广东省金稻种业有限公司
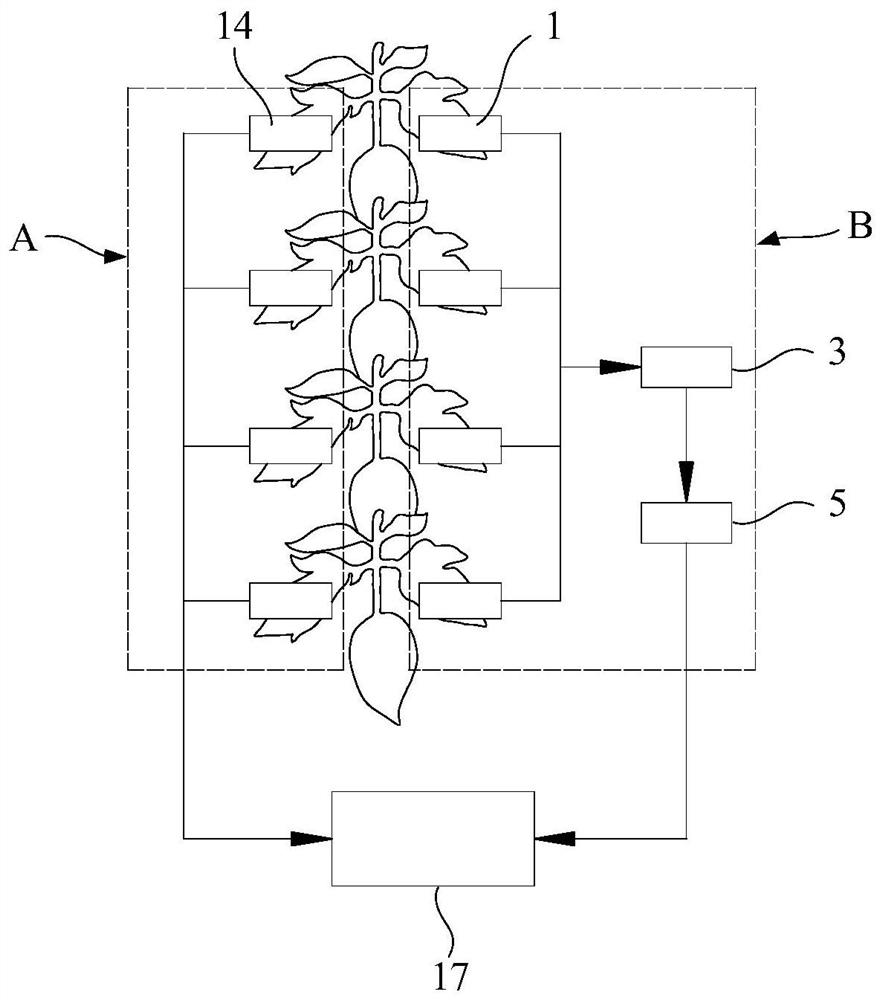
Crop leaf embolism vulnerability measurement system and method
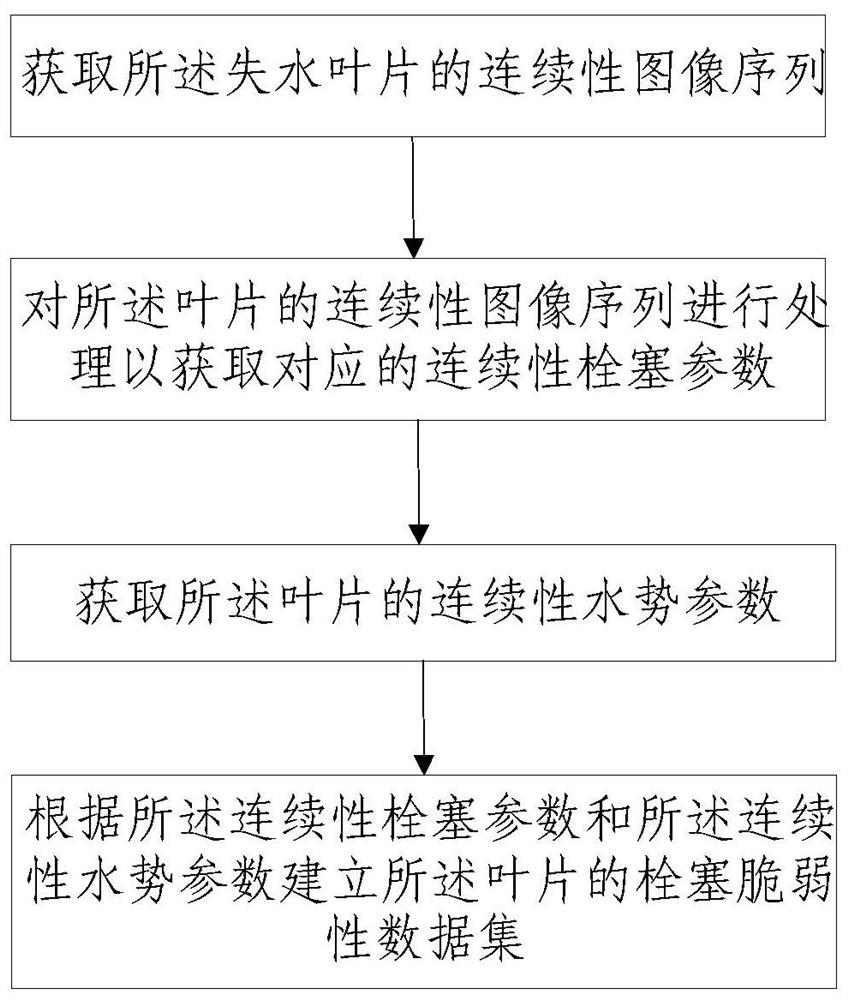
ActiveCN113466289AAutomatically createImage enhancementTelevision system detailsData setDestructive sampling
The invention provides a crop leaf embolism vulnerability measurement system and method. The system comprises an image collection device which is used photographing a water loss leaf continuously, so as to obtain a continuous image sequence of the leaf; a water potential monitoring device which is used for continuously monitoring the water potential of the leaf so as to obtain continuous water potential parameters of the leaf; and a data processing device which is used for processing a continuous image sequence of the lead to obtain a corresponding continuous embolism parameter and establishing an embolism vulnerability data set of the leaf. According to the method, the embolism area of the leaf is calculated through the data processing device, fitting of a water potential time sequence is combined, a leaf embolism vulnerability curve is constructed through the percentage of leaf embolism pixels in the dehydration process and the obtained water potential sequence, corresponding leaf hydraulic conductivity and water potential information can be obtained through the leaf embolism vulnerability curve, the irrigation strategy of the crops is adjusted, and the drought resistance characteristics of the plants are automatically, continuously and accurately determined on the basis that large-scale destructive sampling is not needed.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
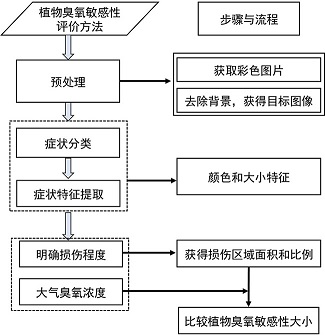
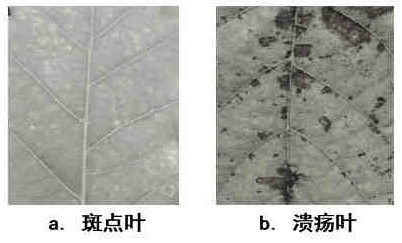
Method for losslessly evaluating ozone sensitivity of plant through leaves
The invention relates to a method for losslessly evaluating ozone sensitivity of a plant through leaves, belongs to the field of atmospheric pollution biological monitoring, and the method can be applied to lossless and continuous determination of injury symptoms of ozone sensitive plants such as soybeans, poplar trees, silver birches, tilia amurensis and quercus liaotungensis. The method comprises the following steps: classifying damage types according to a leaf surface image, then segmenting the leaf surface image, extracting and analyzing characteristics such as symptom shape and area size, establishing an extraction method based on an ISODATA algorithm in a Lab color mode, obtaining a spot rate, and then performing damage degree grading (figure 1). The method has the advantages that compared with an existing naked eye observation or destructive sampling method, the method can analyze the damaged area and proportion of the leaf surface without damage, continuous monitoring and accurate grading are achieved, the problem that the damage degree cannot be quantitatively compared due to the fact that ozone damage symptoms of different plants are different can be solved, the plant ozone damage can be simply and directly judged, and the method has the advantages of rapidness, no damage, continuous observation and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
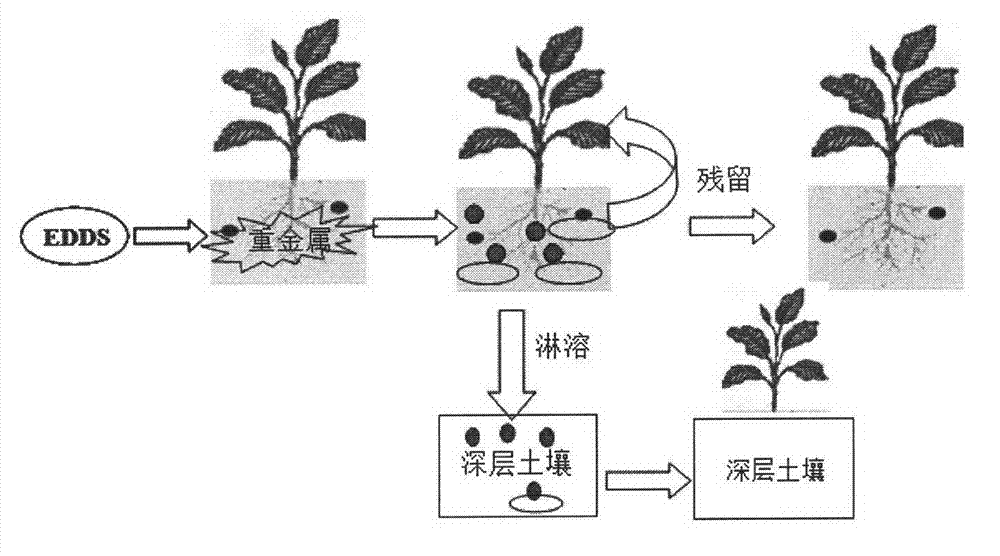
Residual and leaching risk evaluation technology of chelate-induced phytoremediation in heavy-metal contaminated soil
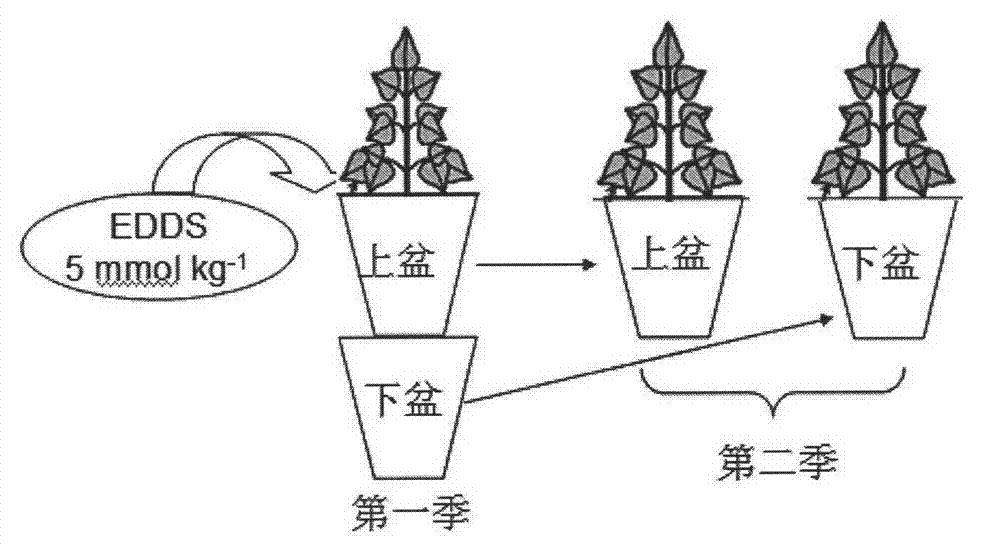
InactiveCN102921716AEasy plantingAccurate risk assessmentContaminated soil reclamationDestructive samplingMetal contamination
The invention belongs to the field of an evaluation technology of environmental pollution treatment, and relates to a leaching and residual risk evaluation technology of chelate-induced phytoremediation in heavy-metal contaminated soil. The technology provided by the invention is characterized by overlapping two pots up and down to simulate the soil at different depths, planting plants and analyzing the soil sample to precisely and conveniently evaluate a residual effect caused by using a chelating agent and the leaching risk on the soil on the lower layer. The design provided by the invention is capable of overcoming shortcomings of destructive sampling of traditional soil column experiments, conveniently simulating the soil on the deep layer to plant the plants and perform sample analysis. The invention provides a direct and reliable evaluation method for evaluating the residual effect of the chelating agent and the leaching risk in the chelate-induced phytoremediation process.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for simultaneous in-situ determination of enzymatic activity between straw and rhizosphere
PendingCN114058674AEliminates destructive samplingSeed and root treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant rootsFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous in-situ determination of enzymatic activity between straw and rhizosphere. The method comprises the following steps of: loading soil and straw into a root box, wherein the root box is wrapped with a light-proof material and obliquely placed on a support; transplanting plant seeds into the root box after germination, and after plants grow, exposing the plants out of soil surfaces and plant roots; meanwhile, taking a microporous filter membrane soaked in a substrate solution marked by fluorescent pigment, covering the surface of the microporous filter membrane, wrapping the root box with the light-proof material, and carrying out light-proof culture; after the culture is finished, taking down the microporous filter membrane, transferring the microporous filter membrane into an ultraviolet lamp box, and performing imaging under a 355nm reflection ultraviolet lamp; and processing and analyzing the obtained image, and comparing the image with a standard curve to obtain two-dimensional distribution of the enzymatic activity between the straw and the rhizosphere on the surface of the soil, namely simultaneously obtaining the enzymatic activity between the straw and the rhizosphere. According to the method, the in-situ enzyme activity determination between straw and rhizosphere under the control condition can be realized, destructive sampling of soil and plants is avoided, and the method is convenient and quick.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A rapid nondestructive testing method for the preservation state of water-saturated wooden cultural relics
ActiveCN112730011BDetermination of precisionNo lossy sampling corruptionPreparing sample for investigationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSoil scienceOptical spectrometer
The invention relates to the technical field of a method for determining the preservation state of water-saturated wooden cultural relics, and provides a rapid non-destructive testing method for the preservation state of water-saturated wooden cultural relics. The water-saturated wooden cultural relics are tested; the data acquisition step is to obtain the spectral data after the spectrometer test, and the spectral data is processed; the establishment of a calibration model step is used to establish a calibration model for the preservation state of the water-saturated wooden cultural relics; the preservation state step is determined, It is used to test the spectral data and clustering behavior of water-saturated wooden artifacts through the aforementioned steps, and determine their preservation status. With this technical solution, after the testing step and the data acquisition step, the steps of establishing a calibration model and determining the preservation state can be used to accurately determine the preservation state of the water-saturated wooden cultural relics, and it has the advantages of no destructive sampling damage and fast test speed. The advantages.
Owner:INST OF WOOD INDUDTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
A Non-destructive Quantitative Evaluation Method of Apple Water Core by Transmission Spectrum
ActiveCN109100323BReduce the recognition rateImprove calculation accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsCollection systemDestructive sampling
The invention discloses a transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation method of apple watercore, and belongs to the technical field of rapid evaluation of food quality. The transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: non-destructively obtaining entire optical information in an apple by using an near-infrared transmission spectrum collection system, collecting an image of a equatorial profile of the apple by using a camera, dividing the image by using an encirclement and suppression algorithm, calculating a watercore area and a sectional area of the apple, using the ratio of the area of a watercore section on a cross section to the area of the entire section as a quantitative prediction index, establishing a transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation model of the apple watercore by using a multielement correction method after preprocessing an obtained near-infrared transmission spectrum, so as to achieve the non-destructive quantitative prediction of the apple watercore. According to the transmission spectrum non-destructive quantitative evaluation method disclosedby the invention, the degree of the apple watercore is quantitatively predicted by using the transmission spectrum technology, thereby avoiding the disadvantages of destructive sampling of a sectionvisualization method, and solving the technical problems of low recognition rate and blurred boundary of the watercore.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for detecting quantity of nitrogen fixed by soybean root nodules
InactiveCN102007846BNodule nitrogen fixation data is accurateImprove detection efficiencySeed and root treatmentHorticulturePlant noduleTotal nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for detecting the quantity of nitrogen fixed by soybean root nodules, which relates to a method for detecting the quantity of the nitrogen fixed by root nodules and solves the problem of low accuracy of the conventional method for detecting the nitrogen fixed by the soybean root nodules. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the variety of detected soybeans and the variety of homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans; soaking seeds of the detected soybeans and the homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans in aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and then sowing the seeds in culture pots respectively, wherein three strains are planted in each pot and cultured under the same growth condition; performing destructive sampling on the strains at the maturation stage; detecting the total nitrogen quantity of the detected soybeans and the homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans respectively; and subtracting the totalnitrogen quantity of the homologous near-allele non-nodulating soybeans from that of the detected soybeans to obtain the quantity of the nitrogen fixed by root nodules of the detected soybeans. The method has the detection accuracy of over 90 percent and can be used for detecting the quantity of the nitrogen fixed by the root nodules of leguminous crops.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
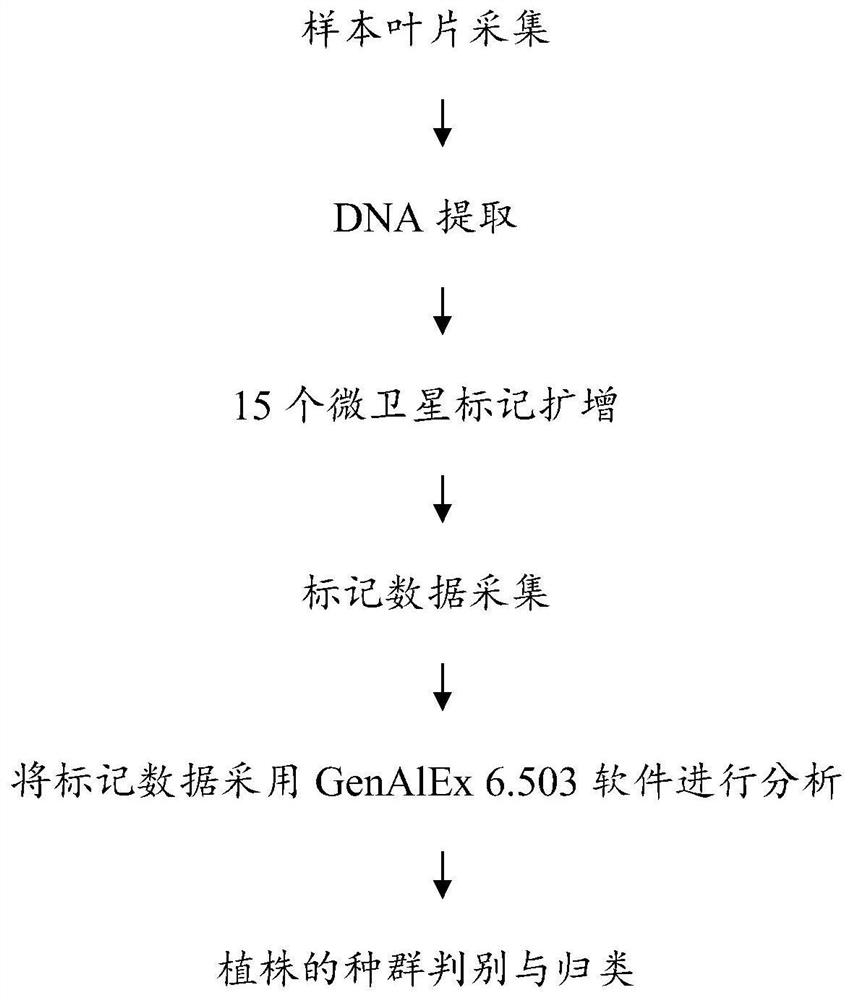
Molecular assays for rapid identification of eucalyptus populations
ActiveCN106967793BReduce workloadImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrosatelliteRapid identification
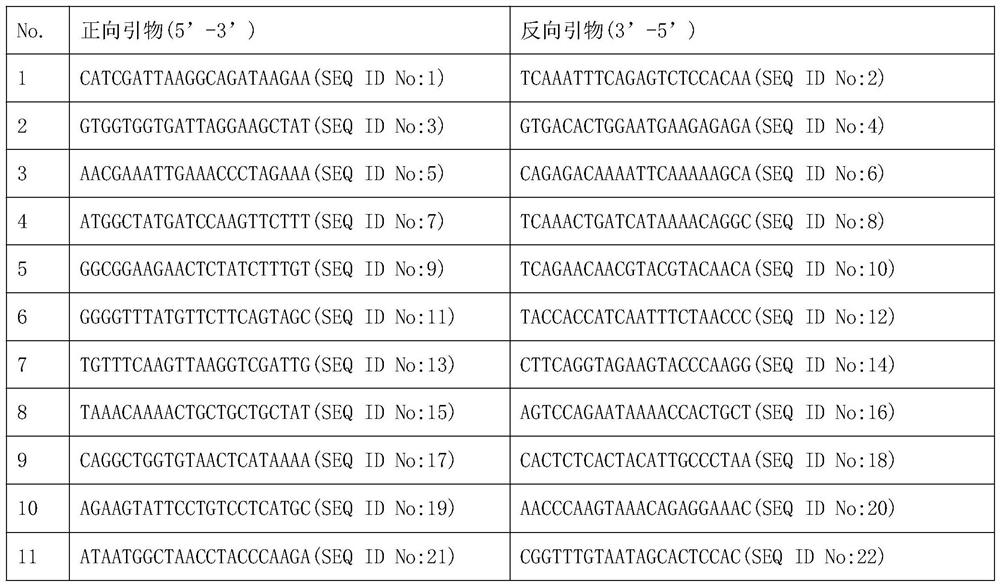
The invention discloses a molecular detection method for rapidly identifying cornus wilsoniana population. The method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out PCR amplification by using DNA of cornus wilsoniana as a template and taking SEQ ID No: 1-30 as primer pairs to obtain microsatellite molecular marker data; and carrying out statistic analysis on the microsatellite molecular marker data to identify and classify the cornus wilsoniana population. According to the molecular detection method for rapidly identifying cornus wilsoniana population, genome information can be rapidly obtained on the premise of non-destructive sampling, the work load is small, the efficiency is high, meanwhile, discrimination accuracy reaches up to 95%, and the method has the advantages of accuracy, time saving and labor saving. The method has important value and application prospect on rapid molecular detection of species population.
Owner:GUANGDONG ACAD OF FORESTRY
Research method of soil microbial diversity and plant stress interaction
ActiveCN114375712AShort timeSimple and fast operationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
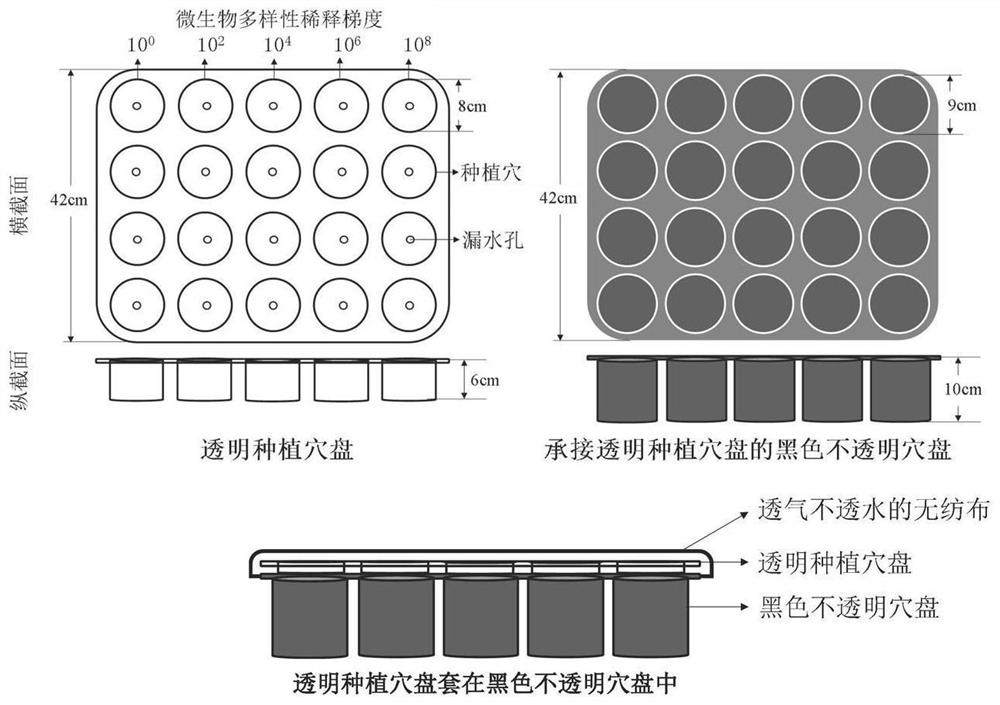
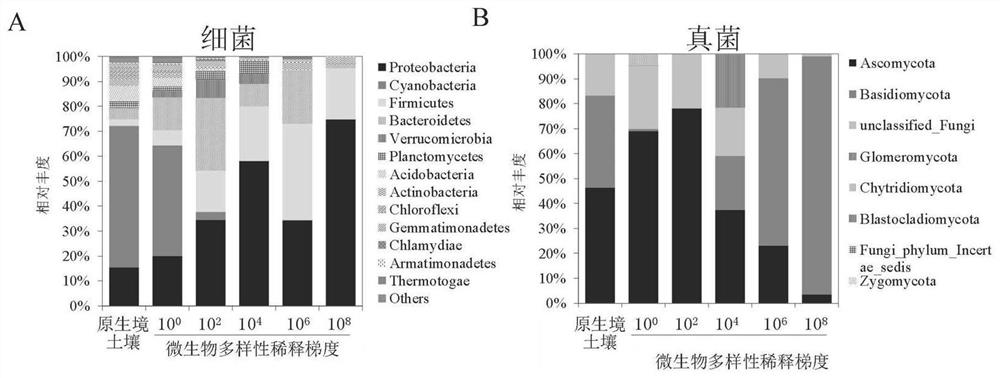
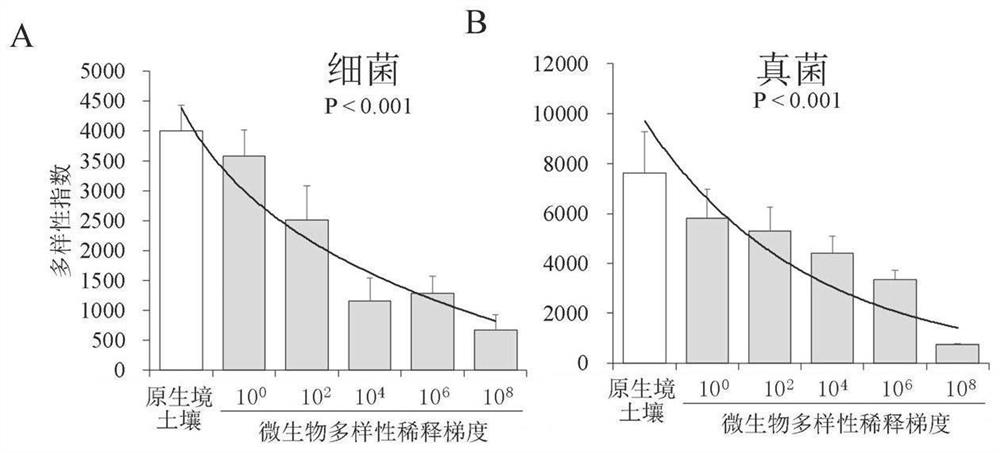
The invention provides a visual research method for interaction of soil microbial diversity and plant stress, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, the method comprises the following steps: sterilizing original habitat soil, respectively mixing original habitat soil gradient diluents with sterile soil, and culturing in darkness to obtain a microbial diversity gradient soil planting plate; through the modes of direct sowing, stress treatment after direct sowing and the like, the function of soil microbial diversity in plant stress is determined under the condition of the same microbial quantity, and regulation and control of the microbial diversity on plant growth under the stress are accurately reflected. The research method disclosed by the invention is short in time consumption, only needs 45-60 days, can be used for visually observing the response of the root system to the microbial diversity under the adverse situation in situ, does not need destructive sampling observation, and is simpler, more convenient and quicker to operate.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A kind of non-destructive sampling method and application of live crayfish
ActiveCN108184736BNo damageSimple and Feasible Nondestructive Sampling MethodMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBroodstockProcambarus
The invention discloses a live non-destructive sampling method of Procambarus clarkii and its application. The fertilized eggs of the ovipositing parents of the Procambarus clarkii are sampled to obtain sampling samples. Through the detection of molecular markers linked to specific economic traits, screen the brood parents containing the molecular markers linked to the target traits, carry out isolation and breeding, and artificially reproduce to obtain the first-generation population of Prochela Klinefelter, and continue to screen the population for the next generation of linkage markers. A breeding population in which the frequency of genes linked to markers for target traits can reach 100%. The present invention solves the problem of non-destructive sampling in the molecular linkage marker-assisted breeding of Procambarus clarkii, provides a scientific and feasible way for the molecular marker-assisted breeding of Procambarus clarkii, and is expected to breed Procambarus clarkii with excellent characteristics. A new variety of shrimp can improve the economic benefits of Procambarus clarkii farming.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Non-destructive sampling system and method for quality assessment of blood products, and sampling systems therefor
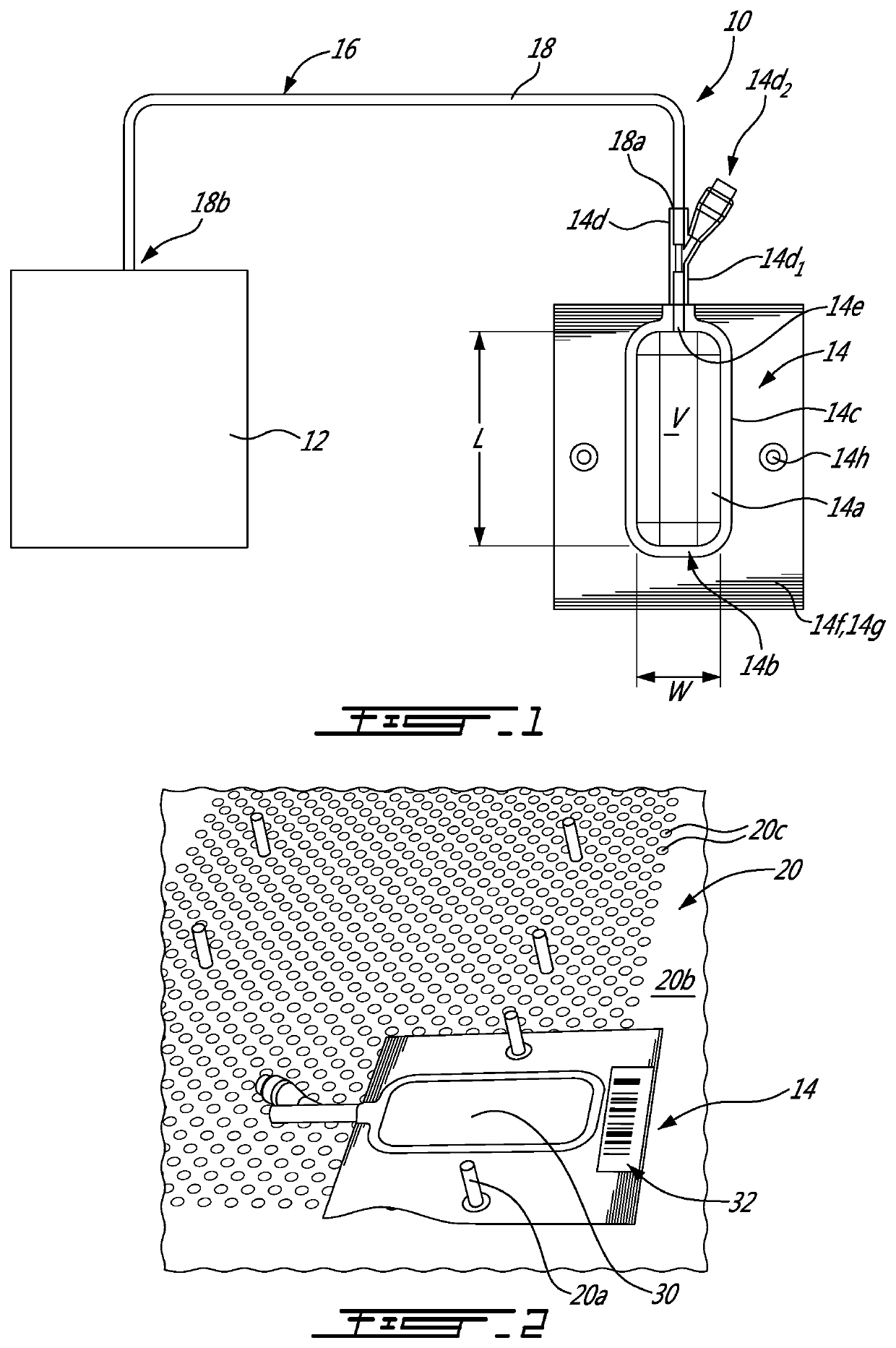
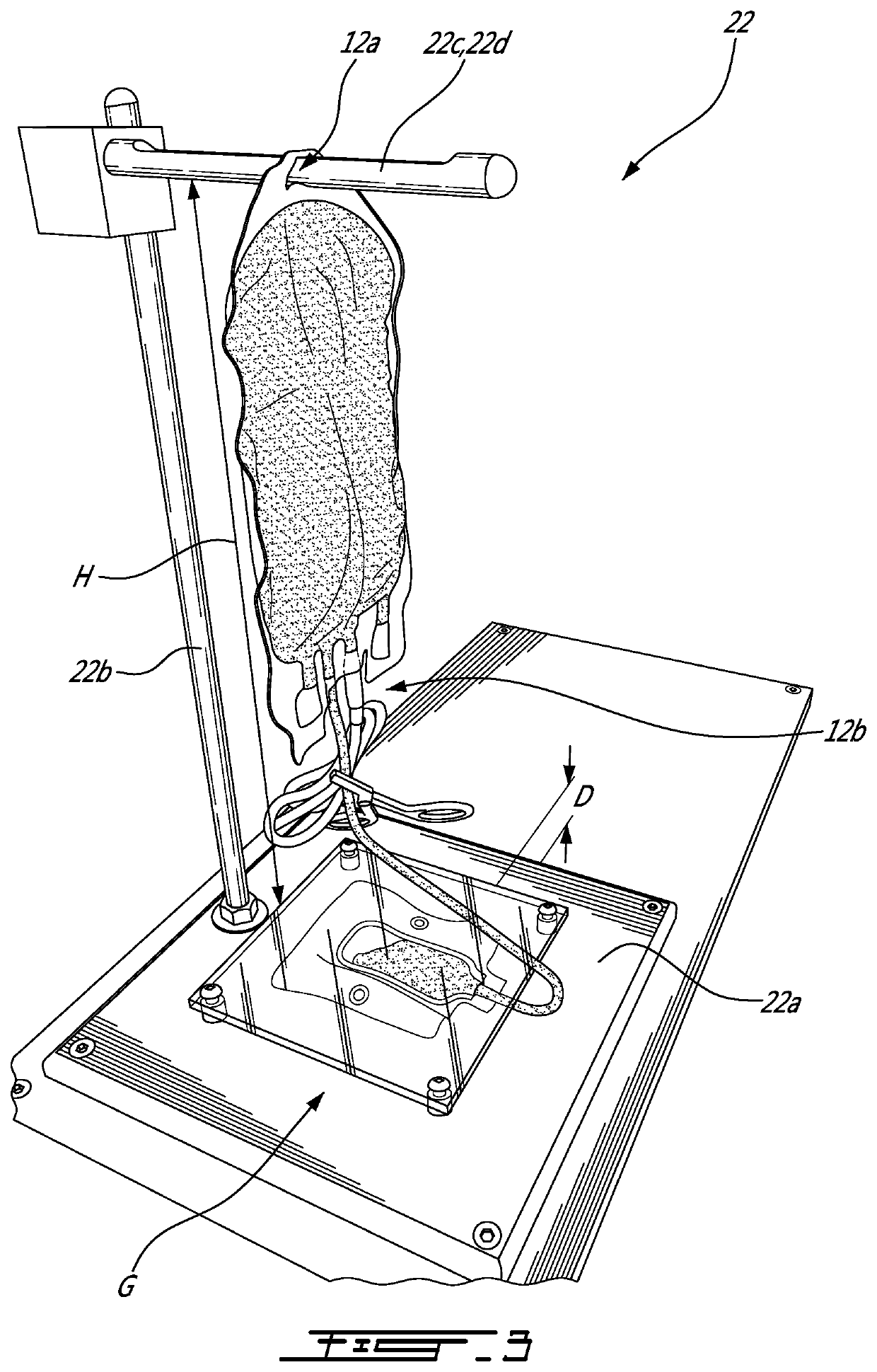
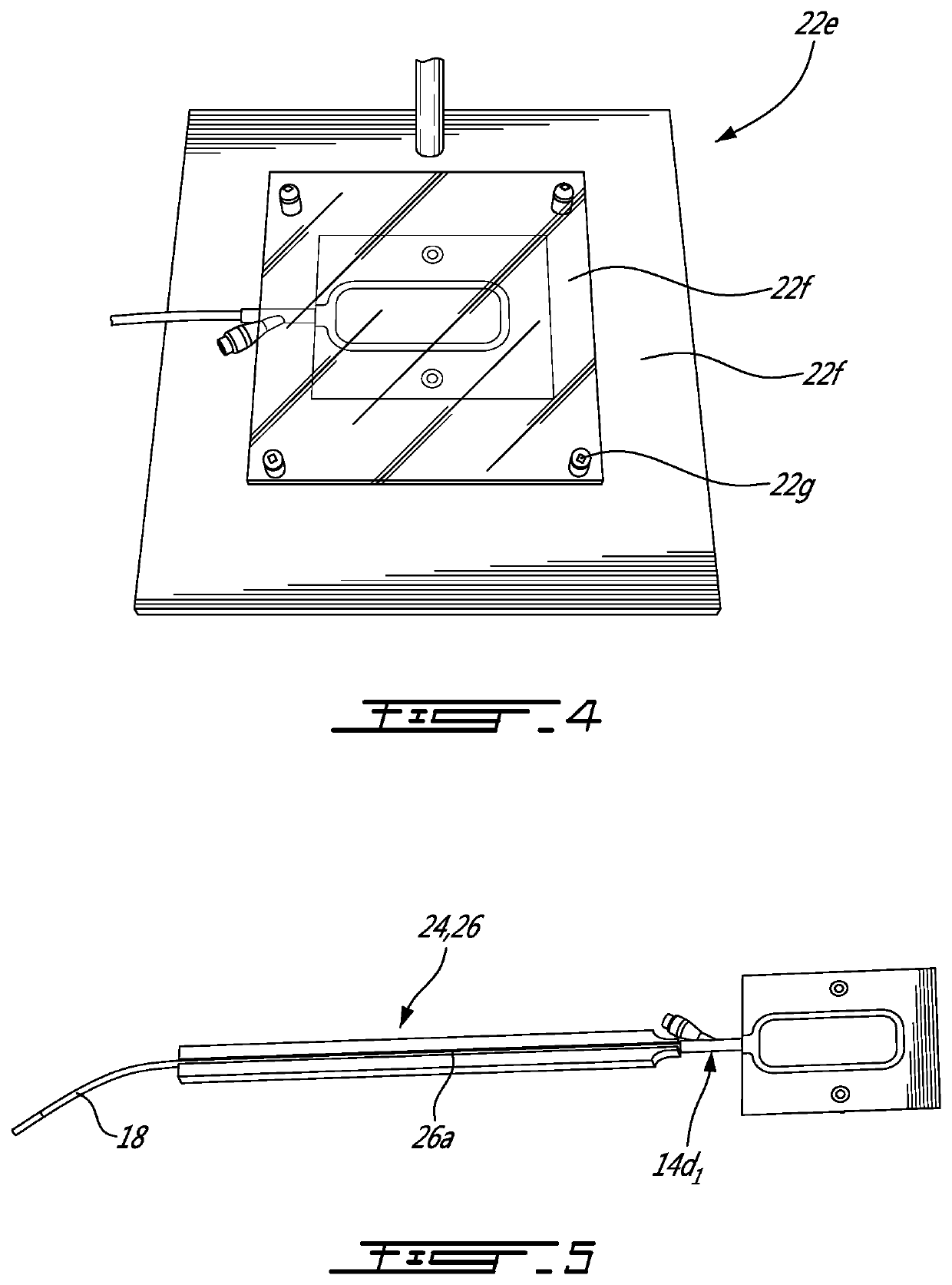
PendingUS20210262903A1Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationWhole blood productProcess engineering
There is provided a method of sampling an aliquot of blood products from a main container containing the blood products to be sampled. The method includes providing a sample container that is rectangular-shaped and has a length-over−width (L / W) ratio of at least that of the main container, and fluidly connecting the a sample container to the main container, transferring the aliquot of the blood products from the main container to the sample container, and forming an air bubble in the sample container by introducing a volume of air into the sample container with the aliquot of the blood products. The volume of air forming the air bubble corresponds to at least about 5% of a volume of the aliquot of the blood products. A sampling bag and a sampling system are disclosed.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
Method and system for estimating the number of tree leaves
InactiveCN109856139BImprove efficiencyVarious methodsMaterial analysis by optical meansDendrometryAlgorithm
The embodiment of the present invention provides a method and system for estimating the number of tree leaves, which can directly determine the capacity of each branch on the target tree by visual inspection, and then determine the target tree through the preset branch capacity-branch number lookup table The number of branches contained in each branch on the target tree; based on the capacity of each branch on the target tree and the number of branches contained in it, determine the total number of branches corresponding to each capacity branch on the target tree, and according to the capacity of each branch on the target tree The total number of branches corresponding to each capacity branch and the average number of leaves on each branch on the target tree determine the number of leaves on the target tree. The entire estimation process does not need to cut down the target trees, and can be achieved without damage. It is not only efficient, but also more suitable for situations where destructive sampling is limited. It enriches dendrology and plant community carbon measurement methods .
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A Verification Method for Indirect Measurement of Ground Leaf Area Index
InactiveCN103983230BReduce human and material resources inputDestructive Sampling OvercomesMeasurement devicesVegetationValidation methods
The invention relates to a verification method for indirect measurement of a ground leaf area index (LAI). The method includes the steps that a virtual plant geometric model base and a virtual vegetation scene base are set up; an observation scheme is designed, simulation implementation is carried out in a virtual vegetation scene according to the principles of all indirect measurement methods of the ground LAI and the observation scheme to form a simulation database; the sum total of the area of xylon parts and the area of triangular patches of leaves in the scene is counted to obtain true values of the LAI, the WAI, the PAI, the parameter of the xylon total area ratio, base components of canopies and the xylon component aggregation index; simulation results of all the measurement methods of the LAT are calculated, the true values of the scene are taken as the simulation calculation results to verify reference values, and the existing indirect measurement methods of the ground LAI are improved, realized in the virtual vegetation scene base and repeatedly circulated to obtain the final existing indirect measurement method of the ground LAI. The verification method does not need to destructively sample vegetation, manpower and material resource investments are small, and verification efficiency, precision and expandability are improved substantially.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Living body measurement method and device of thickness of rice leaf
InactiveCN102175115BImprove efficiencyHigh precisionMechanical thickness measurementsMeasurement deviceDestructive sampling
The invention discloses a living body measurement method and device of thickness of a rice leaf. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting the growing rice leaf as a measuring object; measuring the fixed position of the rice leaf by using a special leaf thickness measuring device; placing the fixed position of the leaf between a rice leaf contact plate and a base of the leaf thickness measuring device and keeping the fixed position away from the main vein of the leaf rice; when the full-leaf thickness of the fully spread rice leave is measured, measuring leaf tip, middle and base, wherein the base measuring point of the rice leaf is at 2 / 3 of the full leaf length; and averaging the measured leaf thickness data of three points, wherein the obtained average value is the thickness value of the full leaf. The method can directly measure the thickness of the living body rice leaf so as to improve the efficiency, simplify the operation, reduce the cost and improve the accuracy;and the method can perform living body measurement to the rice leaf thickness in the field so as to eliminate the sampling steps, implement the continuous tracking to the sample and eliminate the complex process of the data statistic analysis of the destructive sampling experimental data.
Owner:广东省金稻种业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com