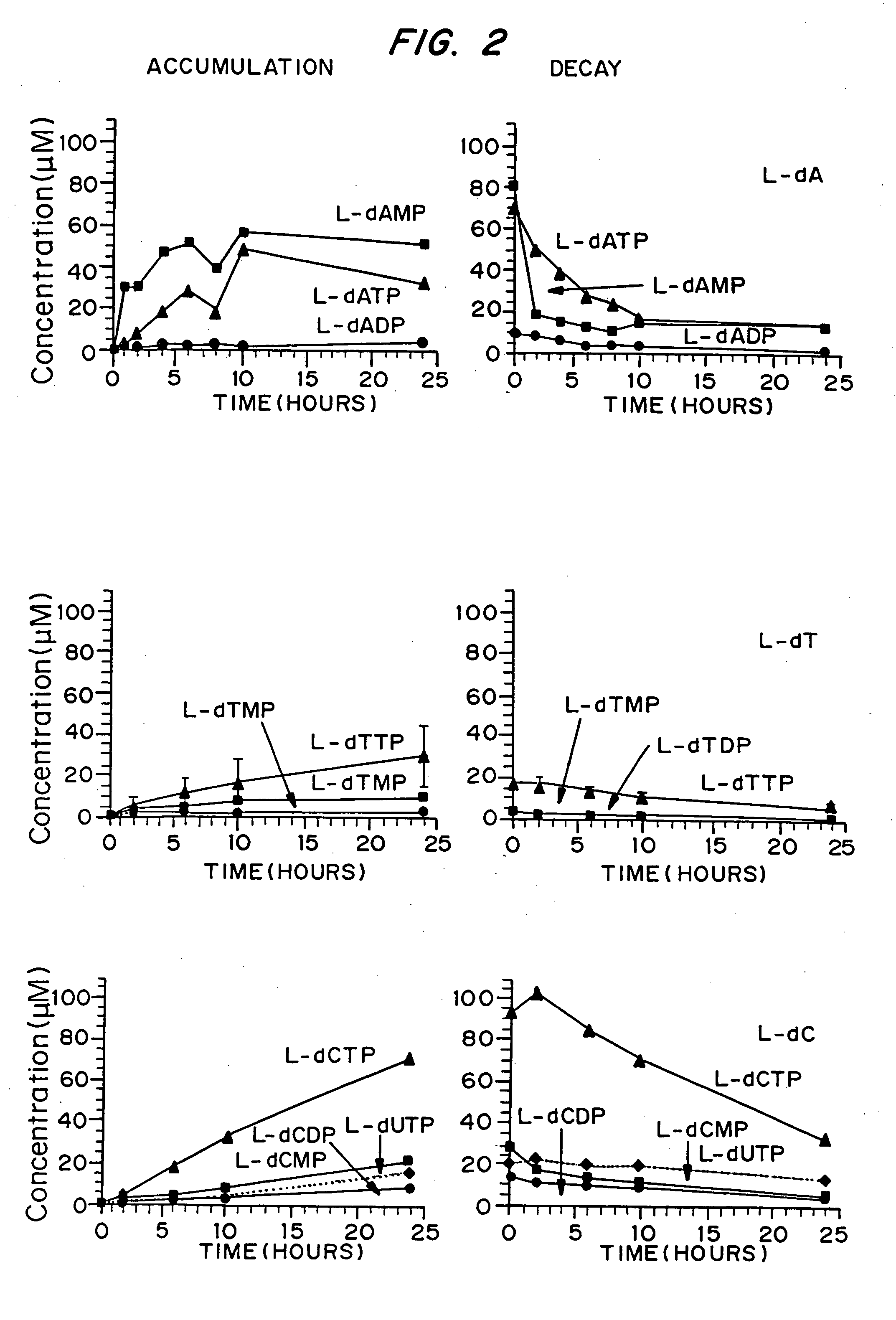
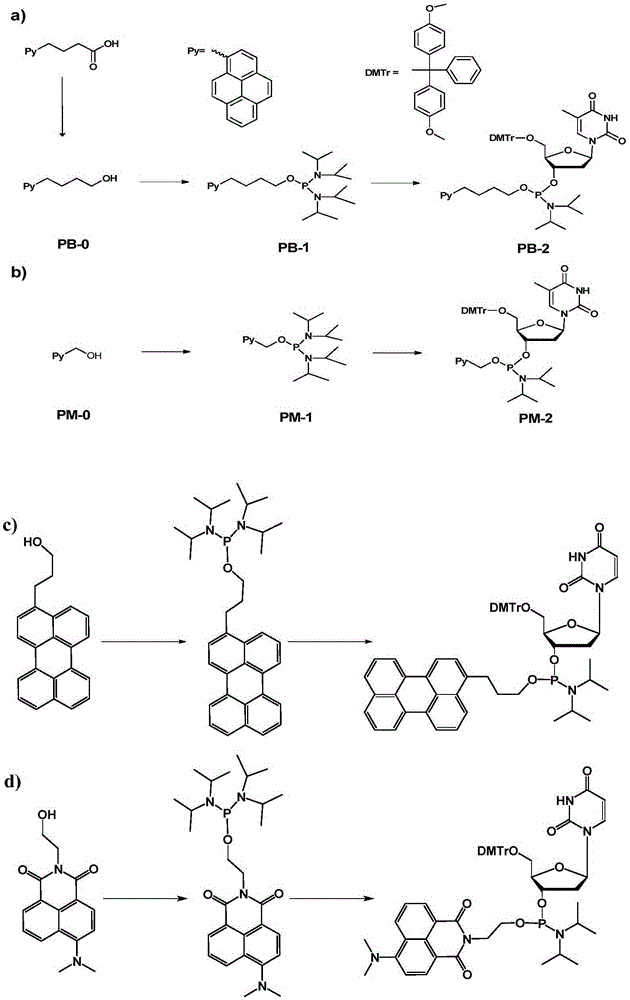
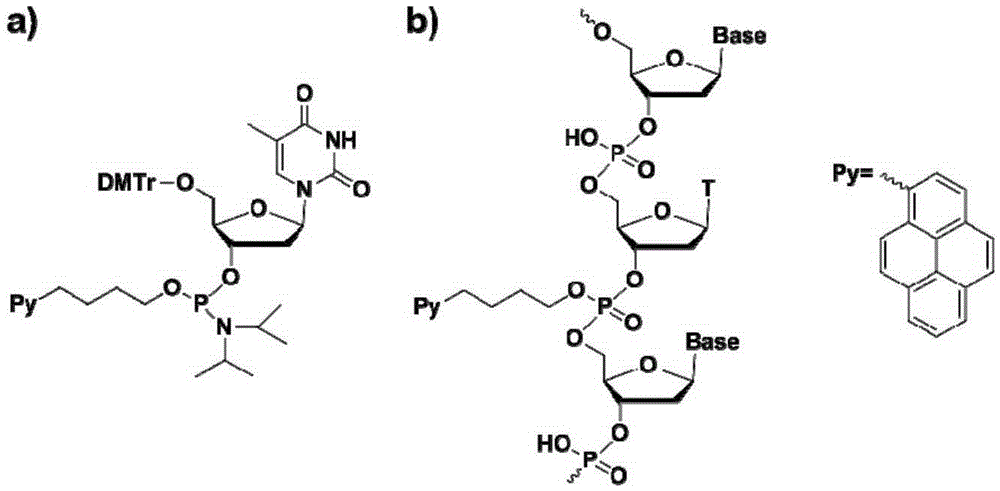
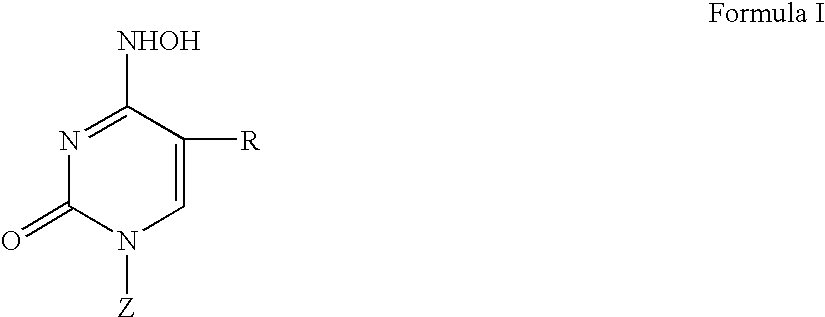Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
205 results about "Deoxynupharidine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
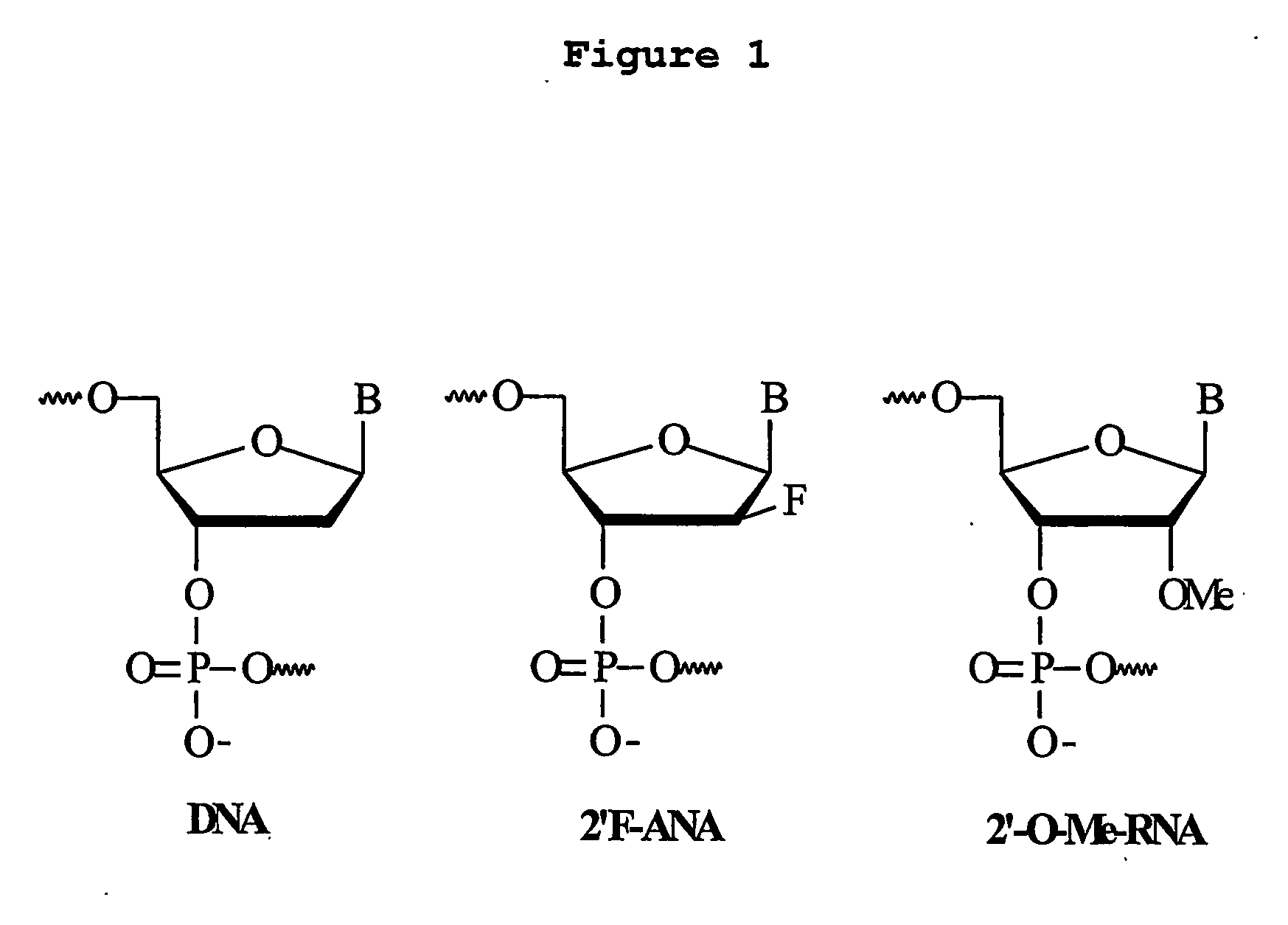
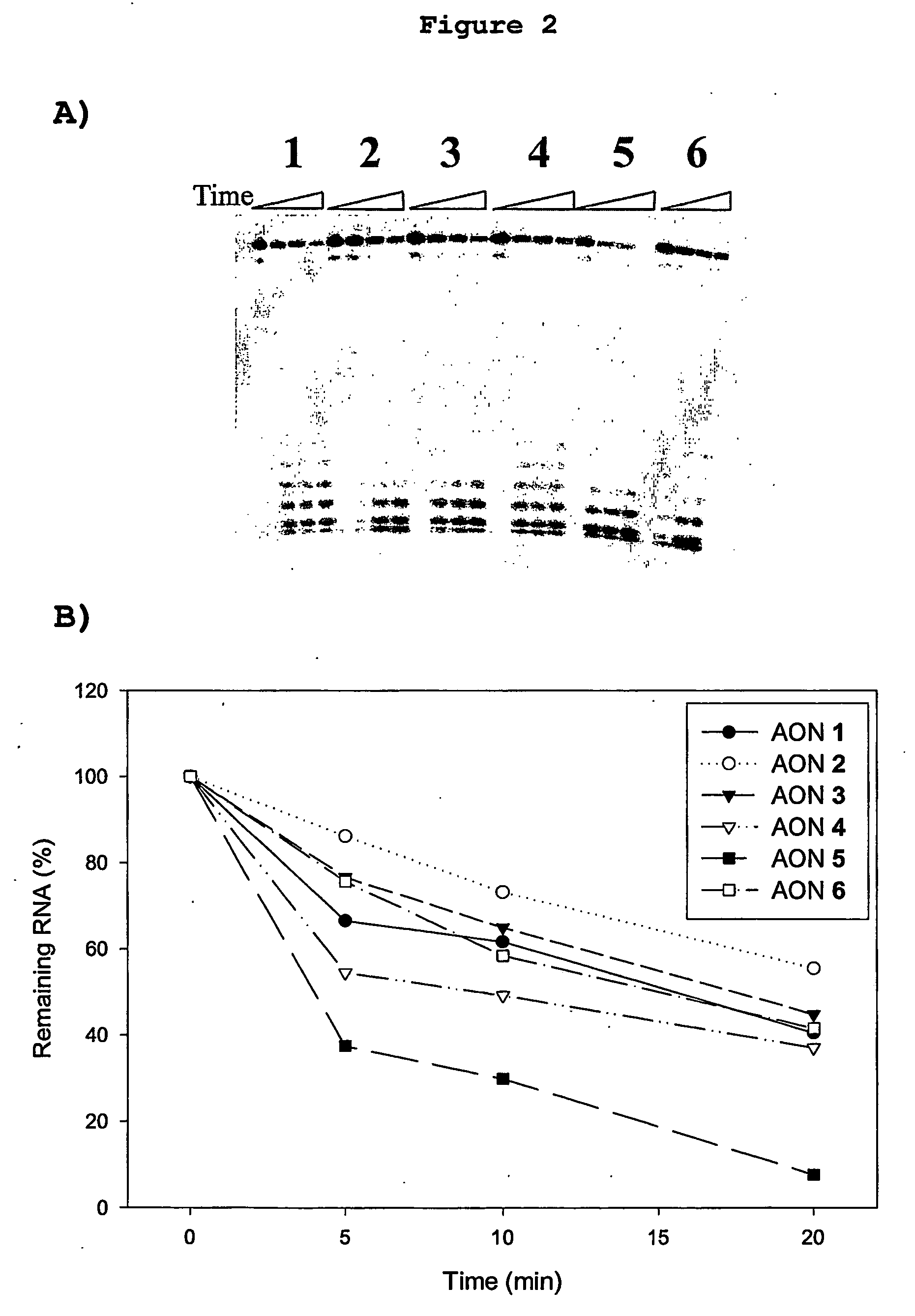
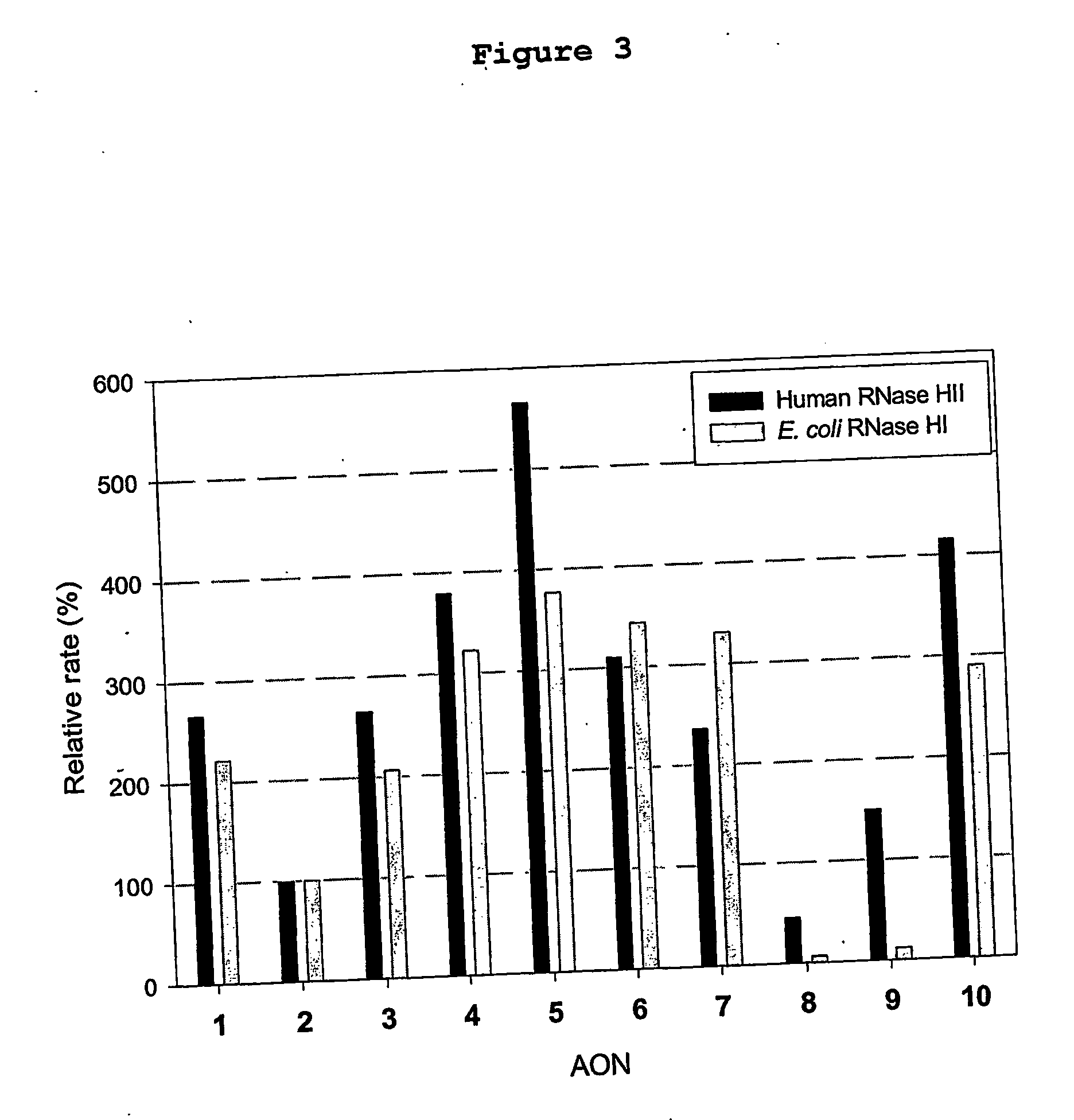
Modified nucleotide compounds
ActiveUS7495088B1Increased nuclease resistanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyModified nucleosides
Disclosed is a nuclease resistant nucleotide compound capable of hybridizing with a complementary RNA in a manner which inhibits the function thereof, which modified nucleotide compound includes at least one component selected from the group consisting of MN3M, B(N)xM and M(N)xB wherein N is a phosphodiester-linked modified 2′-deoxynucleoside moiety; M is a moiety that confers endonuclease resistance on said component and that contains at least one modified or unmodified nucleic acid base; B is a moiety that confers exonuclease resistance to the terminus to which it is attached; and x is an integer of at least 2.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Ogligonucleotides comprising alternating segments and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050142535A1Preventing and decreasing translationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSugarBiology
The invention relates to oligonucleosides having alternating segments of sugar-modified nucleosides and 2′-deoxynucleosides, and uses thereof. The invention further relates to oligonucleotides having alternating segments of sugar-modified nucleotides and 2′-deoxynucleotides, and uses thereof. Such uses include the preparation of antisense oligonucleotides and their use for the prevention or depletion of function of a target nucleic acid of interest, such as an RNA, in a system. Accordingly, an oligonucleotide of the invention is useful for therapeutic, analytical and diagnostic methods and uses, as well as a component of compositions and commercial packages corresponding to such methods and uses.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Anti-Ctla-4 Antibody and Cpg-Motif-Containing Synthetic Oligodeoxynucleotide Combination Therapy for Cancer Treatment
InactiveUS20090117132A1Improve immune activityReducing cytotoxic side effectAntibody ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsThird-line therapyPhases of clinical research
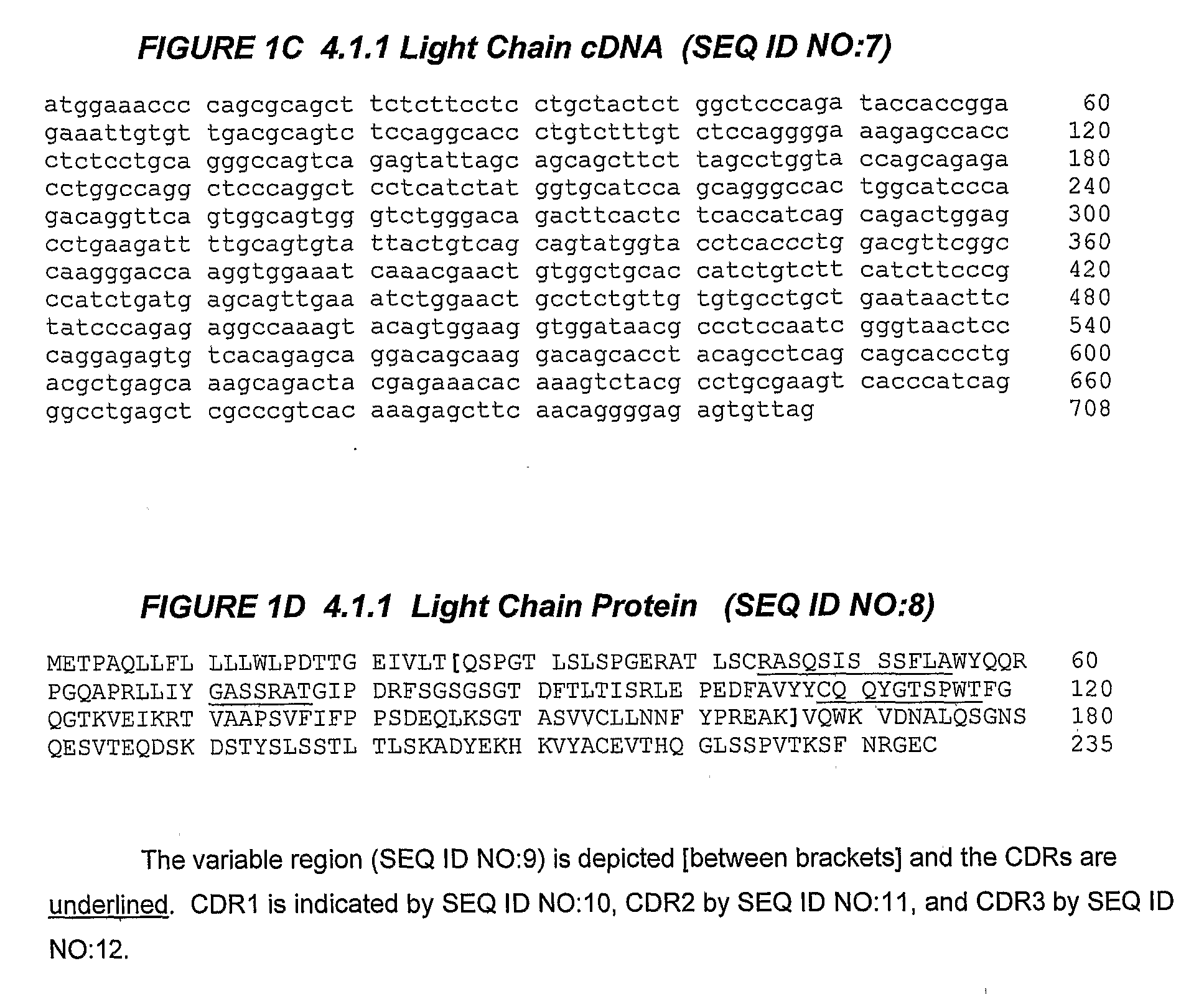
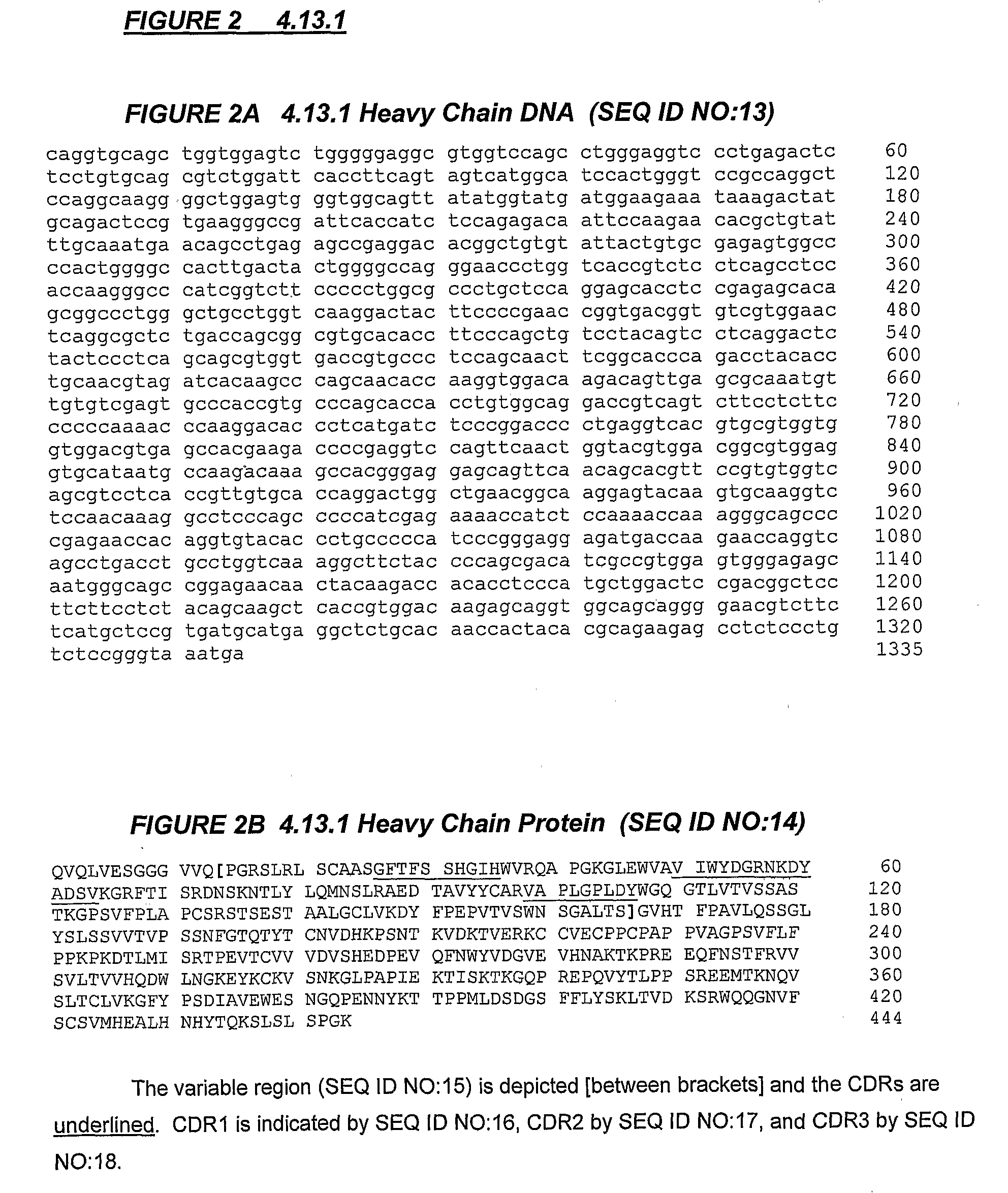
The invention relates to administration of an anti-CTLA-4 antibody, particularly human antibodies to human CTLA-4, such as those having amino acid sequences of antibodies 3.1.1, 4.1.1, 4.8.1, 4.10.2, 4.13.1, 4.14.3, 6.1.1, 11.2.1, 11.6.1, 11.7.1, 12.3.1.1, 12.9.1.1, and MDX-010, in combination with an immunostimulatory nucleotide, i.e, CpG ODN PF3512676, for treatment of cancer. The invention relates to administering a combination of an anti-CTLA-4 antibody and CpG ODN PF3512676 as neoadjuvant, adjuvant, first-line, second-line, and third-line therapy of cancer, whether localized or metastasized, and at any point(s) along the disease continuum (e.g, at any stage of the cancer).
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
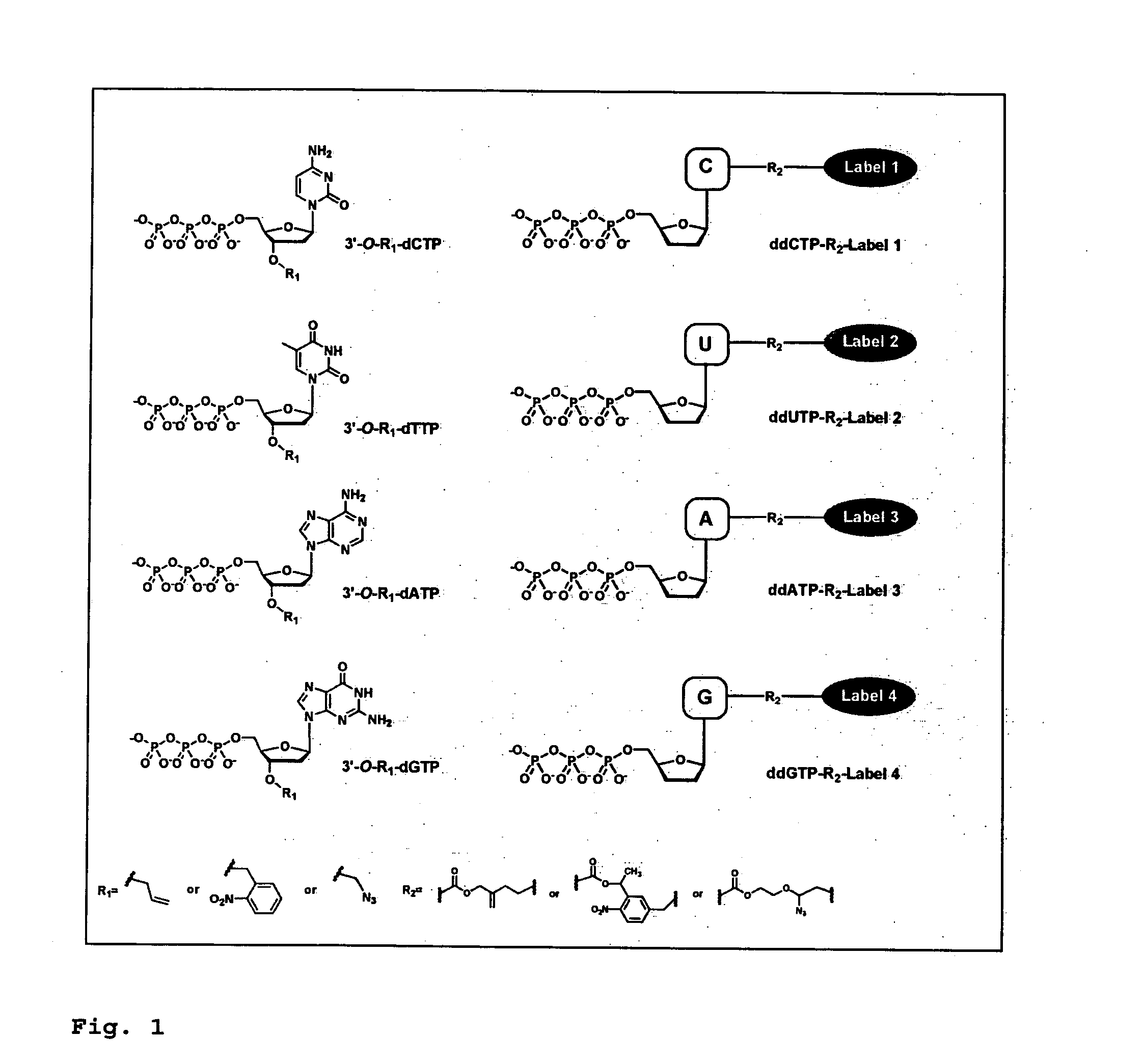
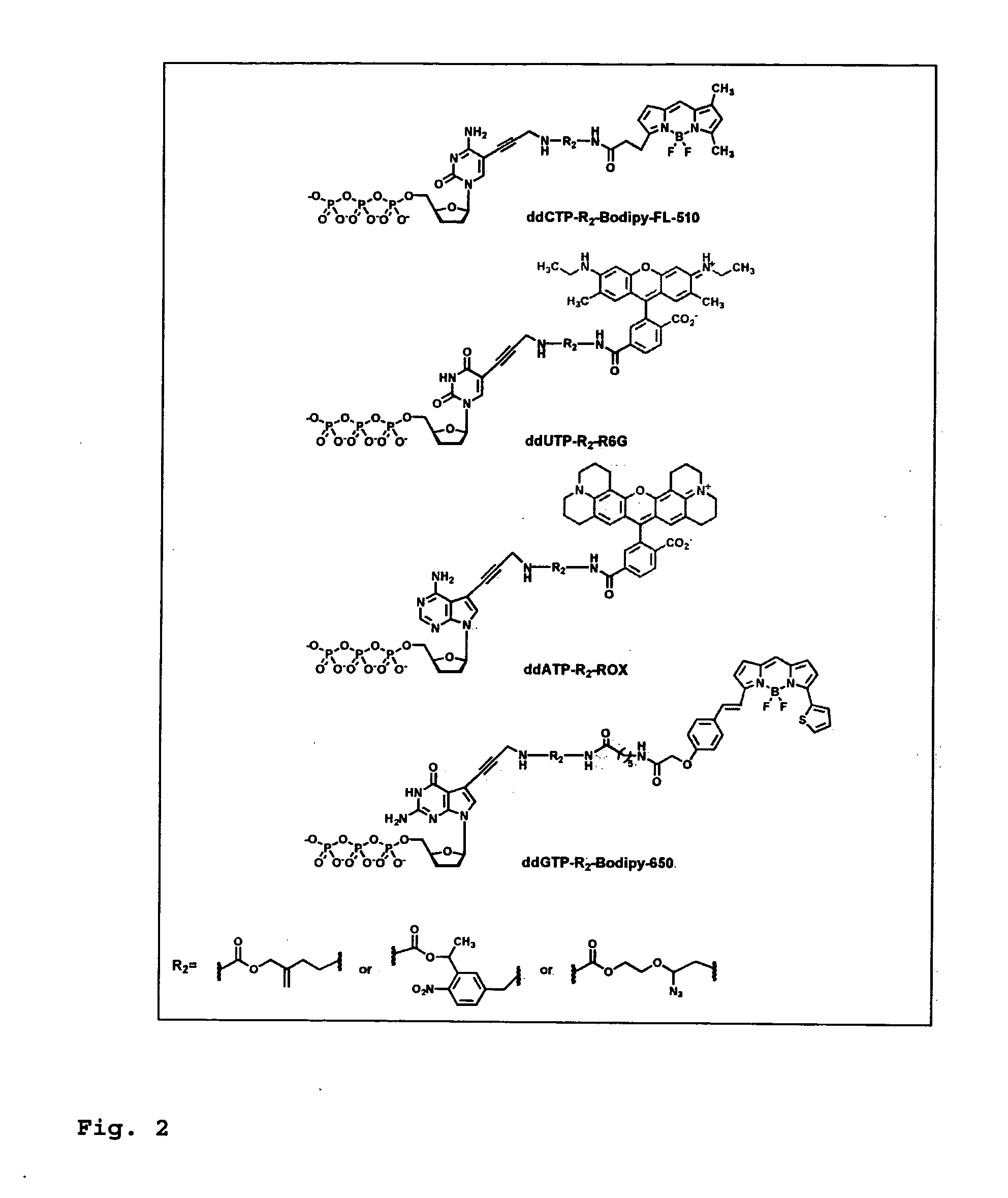
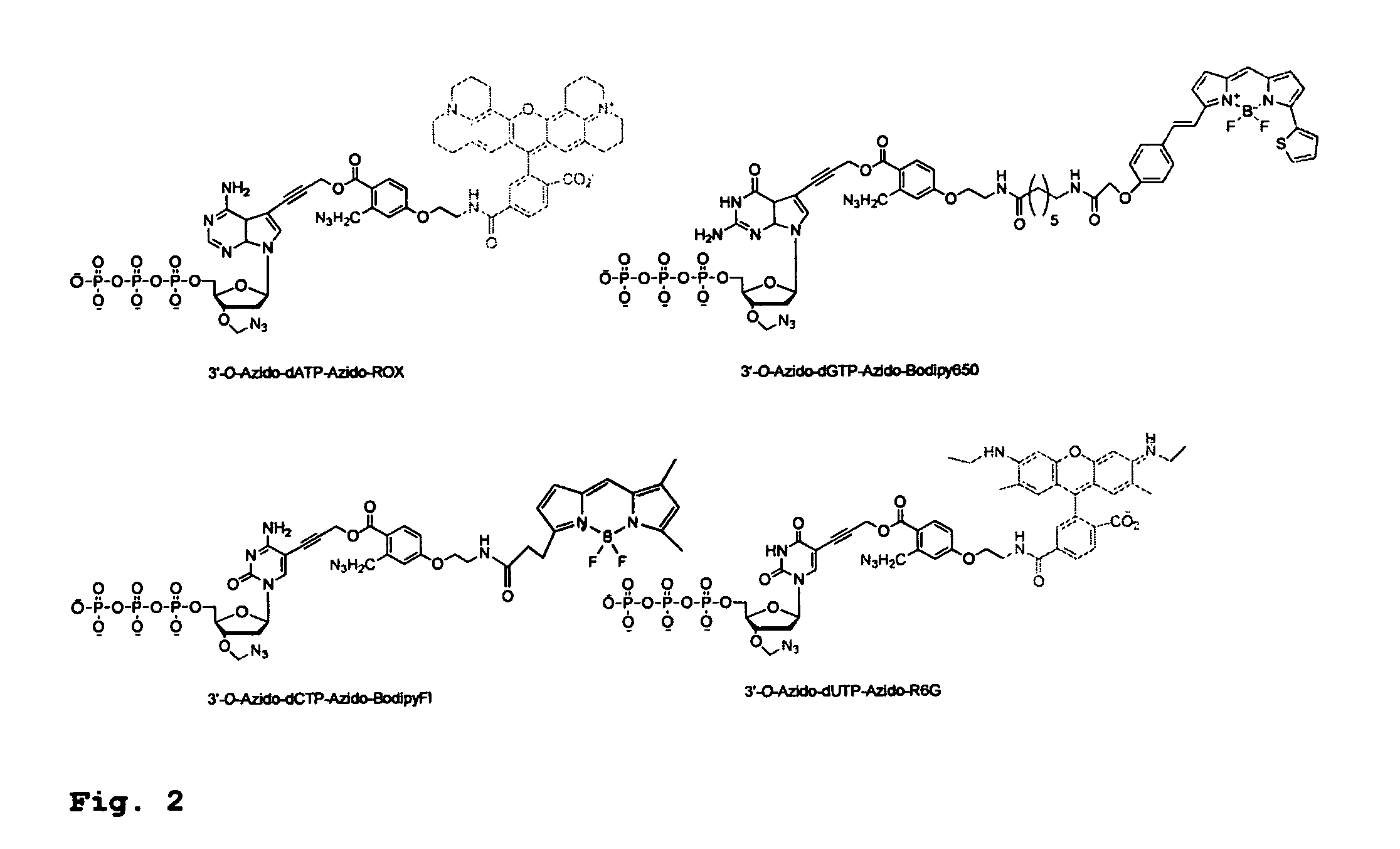
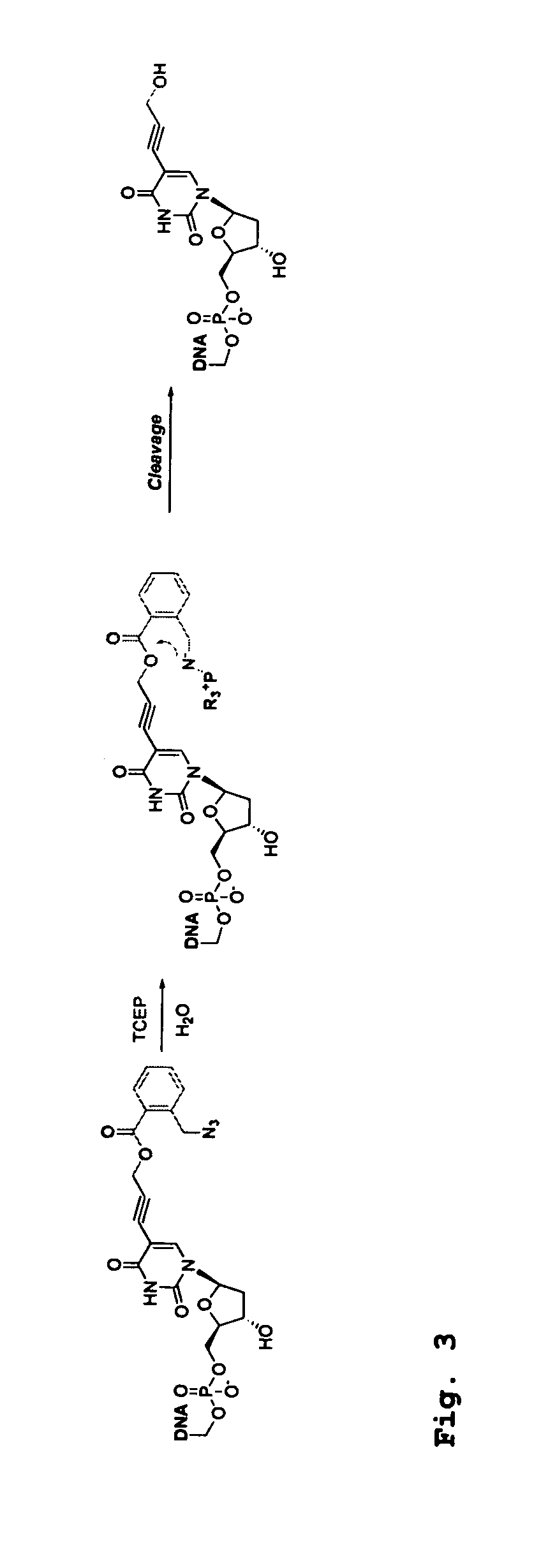
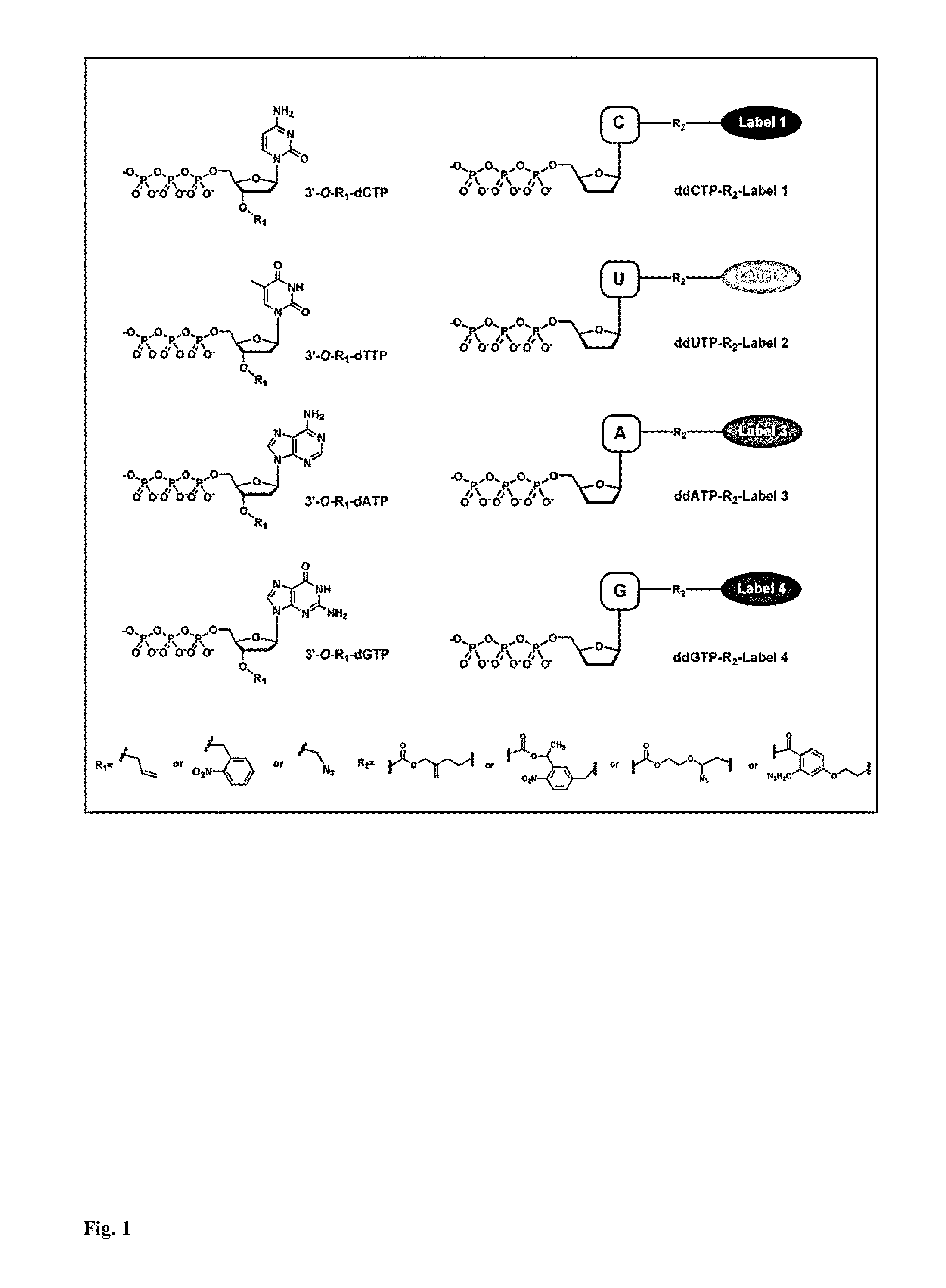
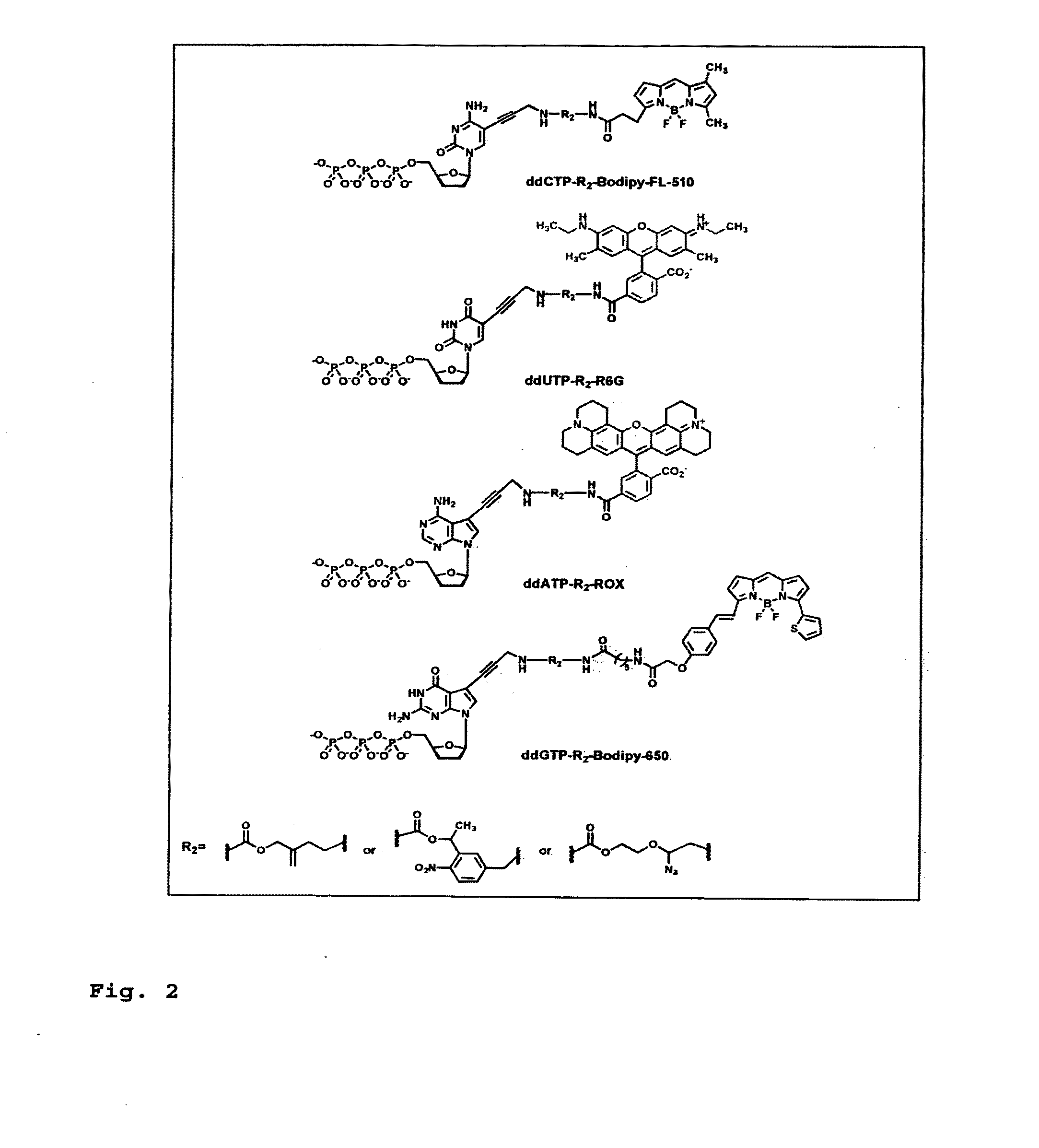
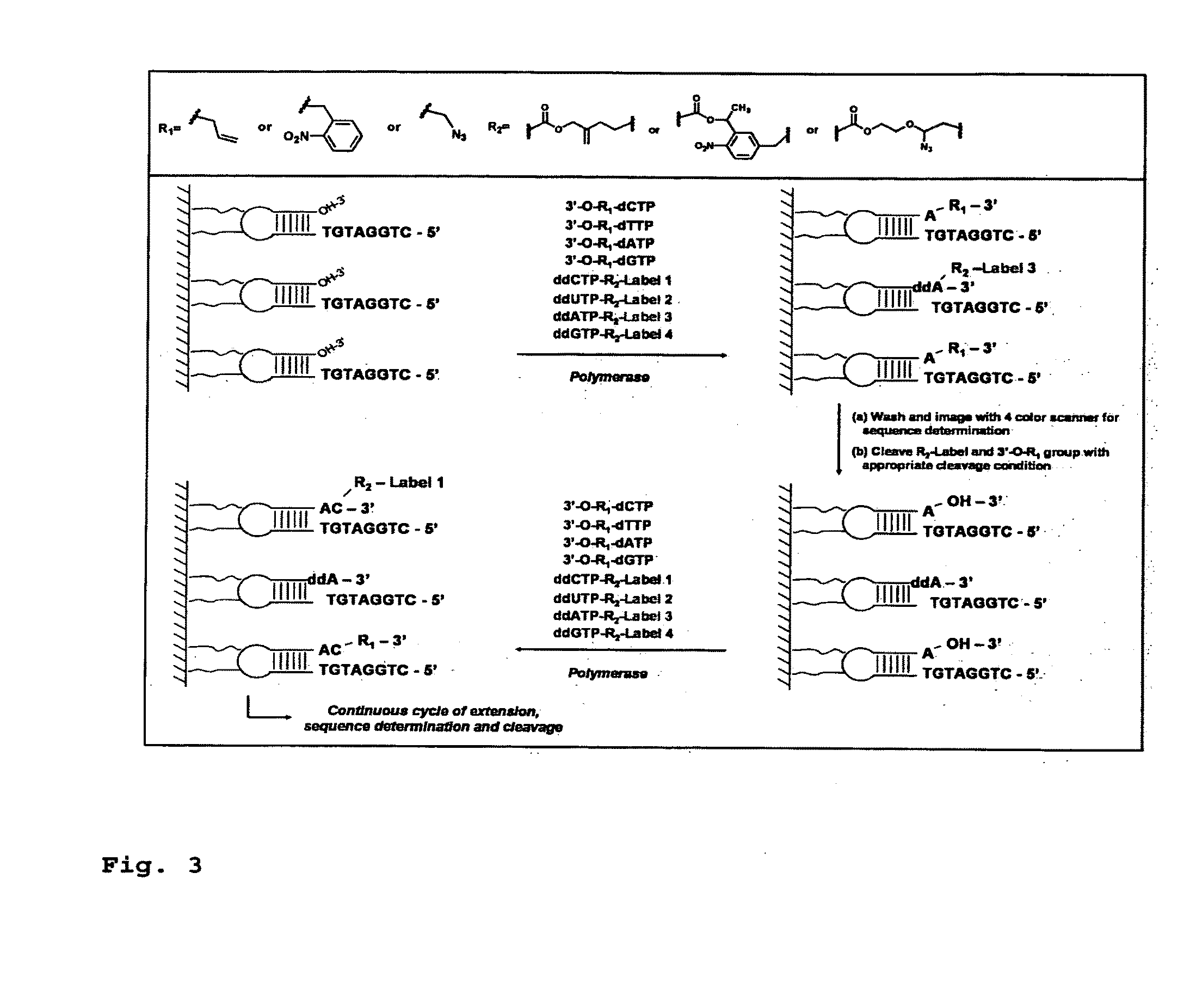
DNA sequence with non-fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators and cleavable label modified nucleotide terminators
ActiveUS20110039259A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDNA
This invention provides a process for sequencing nucleic acids using 3′ modified deoxynucleotide analogues or 3′ modified deoxyinosine triphosphate analogues, and 3′ modified dideoxynucleotide analogues having a detectable marker attached to a base thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
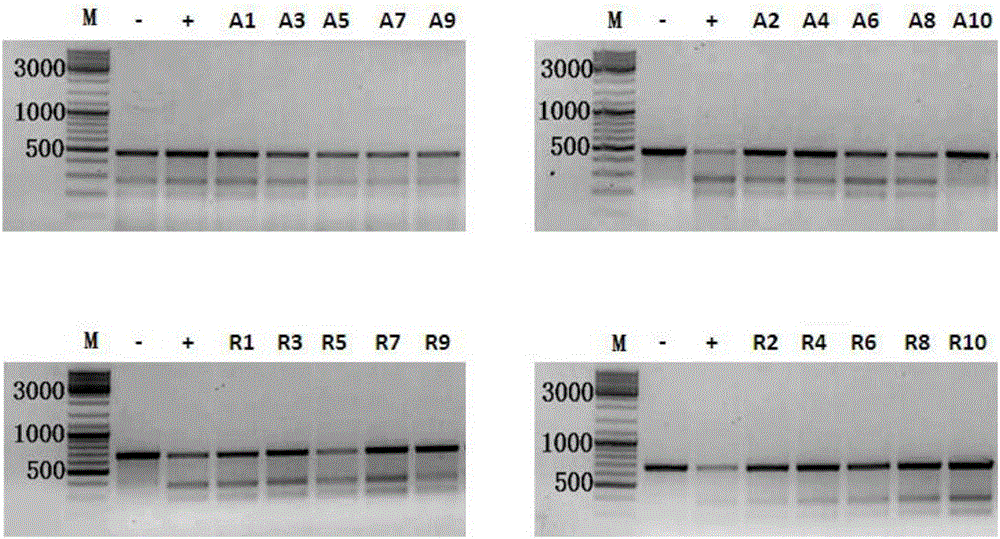
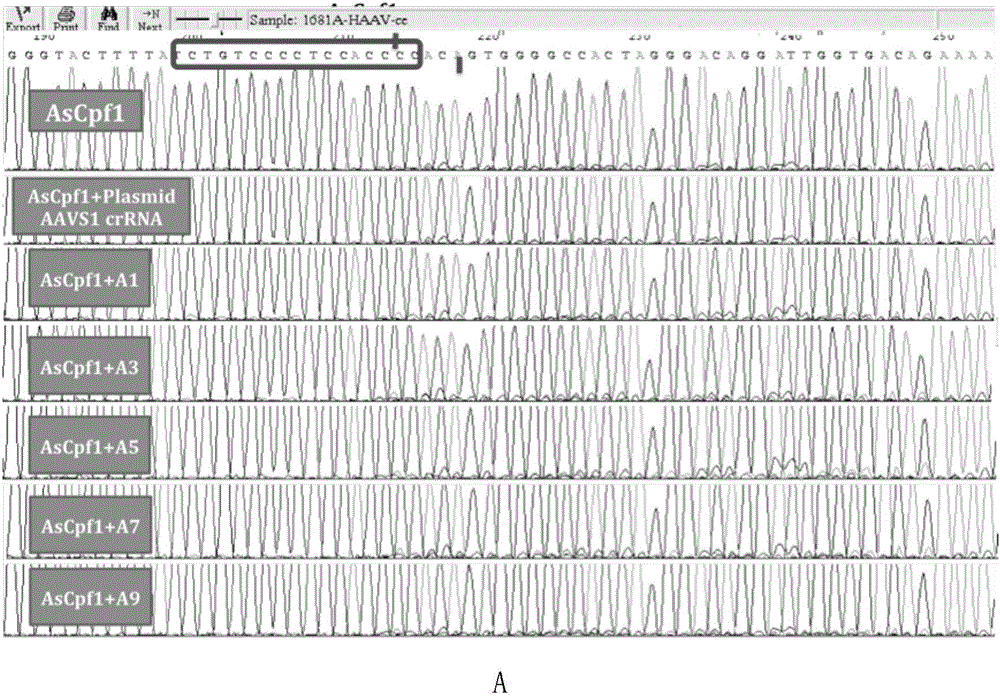
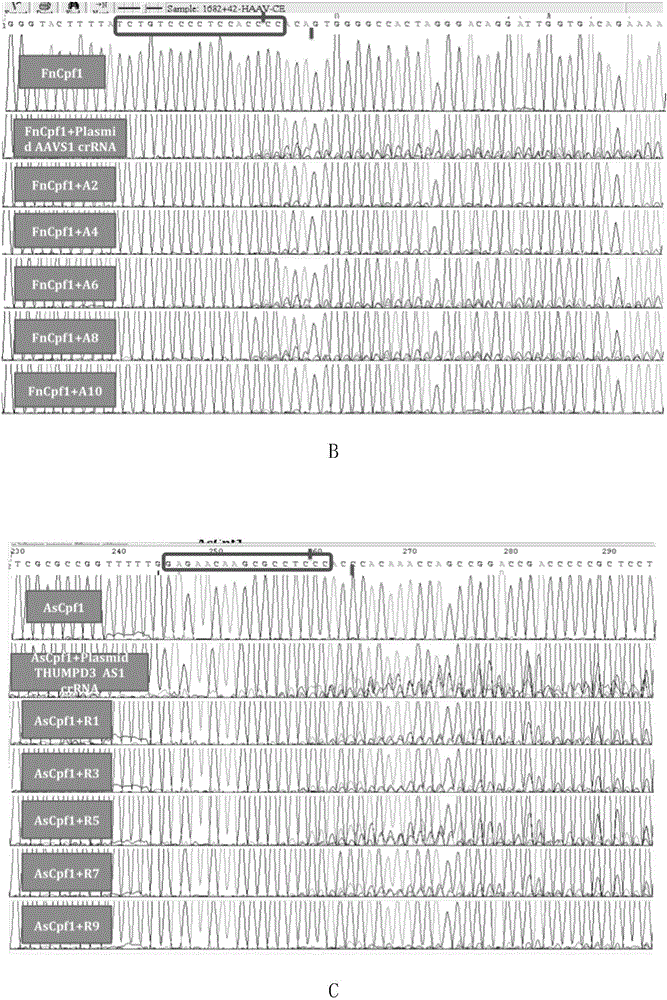
Applications of modified crRNA in CRISPR/Cpf1 gene editing system
InactiveCN106244591AStrong gene editing abilityNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionChemical synthesisThymine
The invention discloses applications of a CRISPR / Cpf1 system in gene editing. CrRNA in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system is modified crRNA; the modification manner is desoxyribonucleic acid modification; the desoxyribonucleic acid modification method comprises the step of increasing 1-3 desoxyribonucleic acid at the 5' terminal and / or increasing 1-3 desoxyribonucleic acid at the 3' terminal of crRNA; and the desoxyribonucleic acid is deoxythymidine acid. The experiment proves that the crRNA formed through chemical synthesis and having the modification can cause the mutation of an hAAVS1 gene and a THUMPD3-AS1 gene when used for the AsCRISPR / Cpf1 system or the FnCRISPR / Cpf1 system, namely, the modified crRNA has certain gene editing capacity when used for the AsCRISPR / Cpf1 system or the FnCRISPR / Cpf1 system, and therefore, the modified crRNA has a significant application value in gene editing utilizing the CRISPR / Cpf1 system.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA
Synthesis of cleavable fluorescent nucleotides as reversible terminators for DNA sequencing by synthesis
ActiveUS9175342B2Increase read lengthSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBiochemistry
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
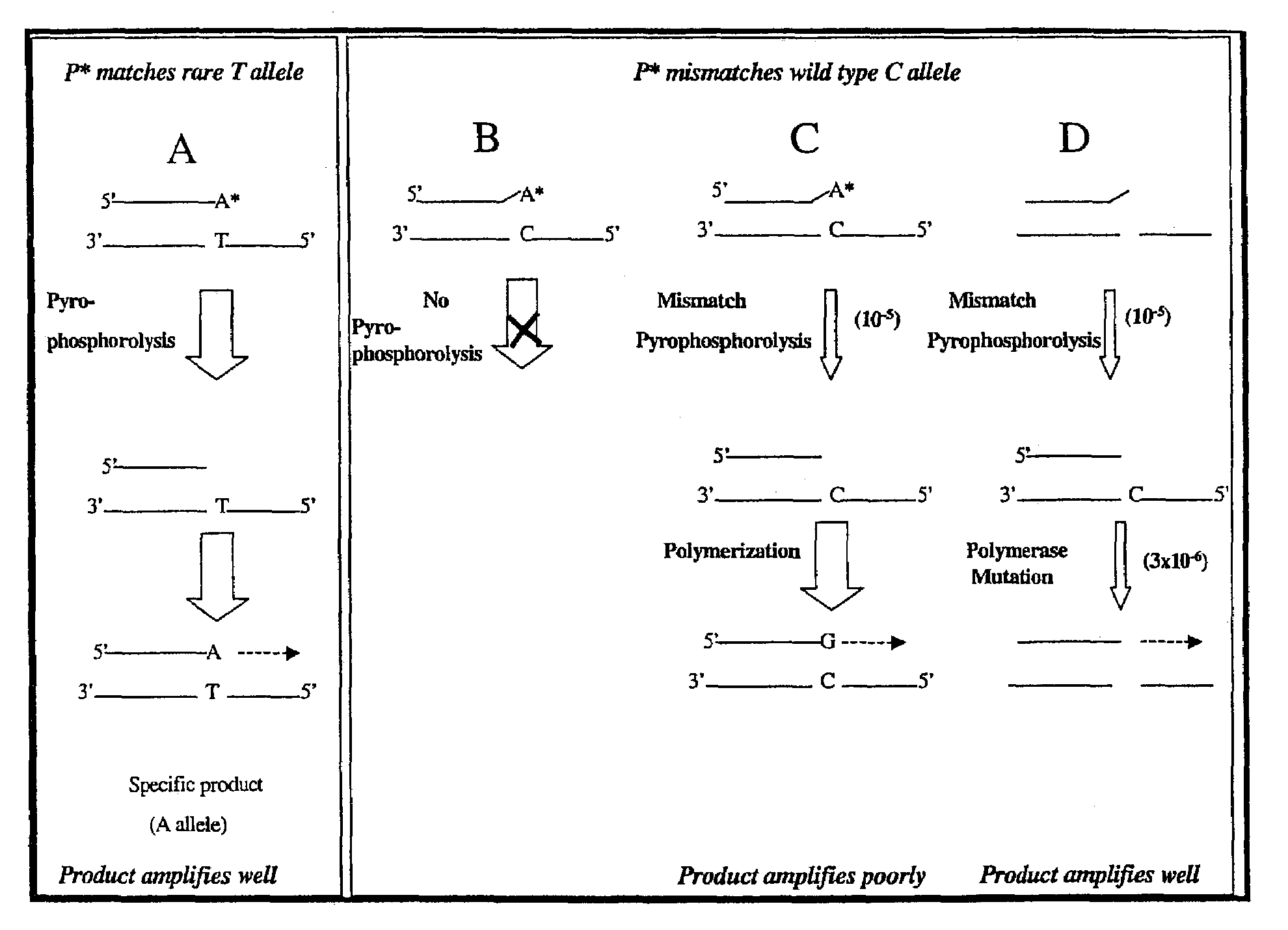
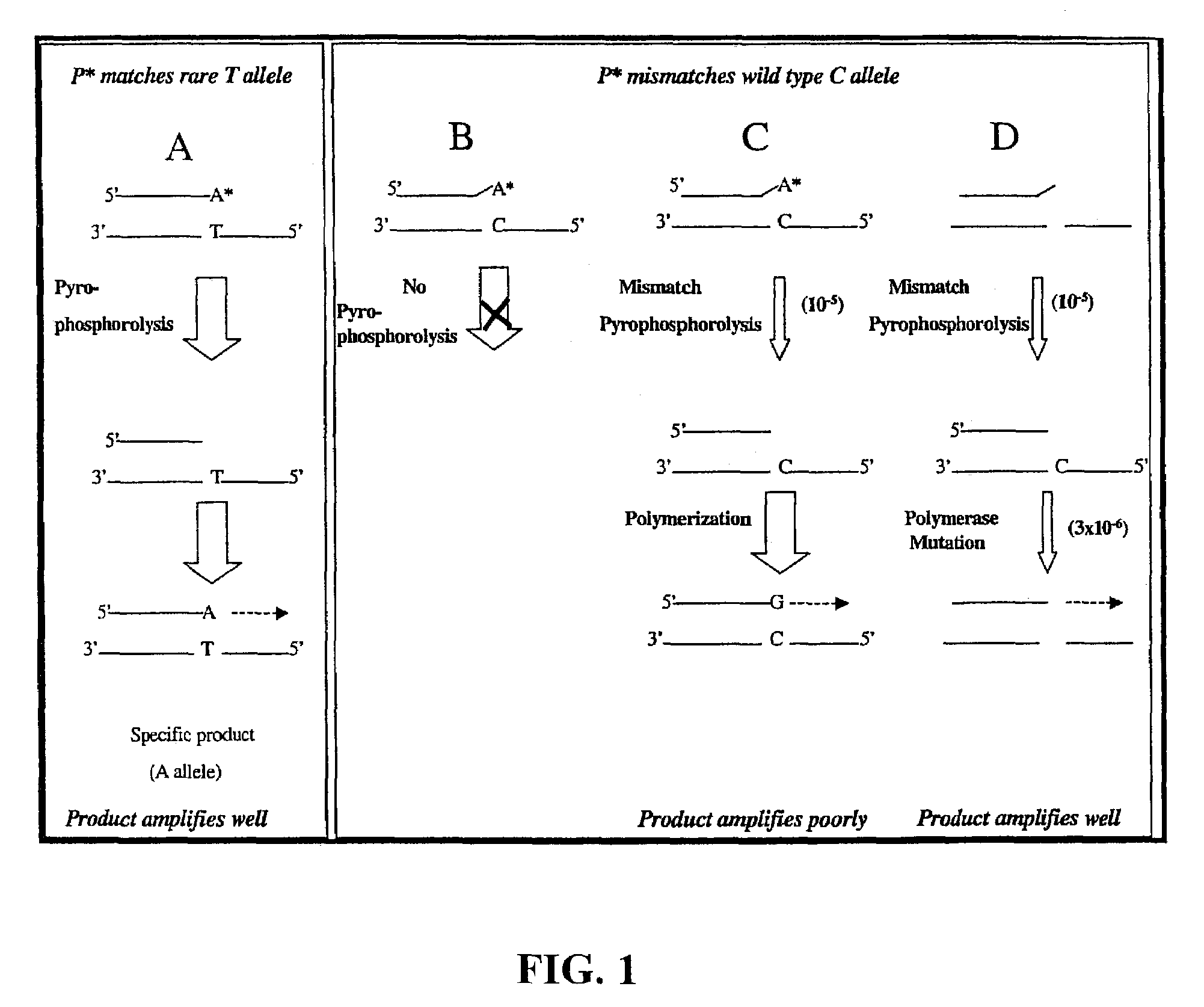
Pyrophosphorolysis activated polymerization (PAP)
InactiveUS7033763B2Eliminate errorsMost efficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
A novel method of pyrophosphorolysis activated polymerization (PAP) has been developed. In PAP, pyrophosphorolysis and polymerization by DNA polymerase are coupled serially for each amplification by using an activatable oligonucleotide P* that has a non-extendible 3′-deoxynucleotide at its 3′ terminus. PAP can be applied for exponential amplification or for linear amplification. PAP can be applied to amplification of a rare allele in admixture with one or more wild-type alleles by using an activatable oligonucleotide P* that is an exact match at its 3′ end for the rare allele but has a mismatch at or rear its 3′ terminus for the wild-type allele. PAP is inhibited by a mismatch in the 3′ specific sequence as far as 16 nucleotides away from the 3′ terminus. PAP can greatly increase the specificity of detection of an extremely rare mutant allele in the presence of the wild-type allele. Specificity results from both pyrophosphorolysis and polymerization since significant nonspecific amplification requires the combination of mismatch pyrophosphorolysis and misincorporation by the DNA polymerase, an extremely rare event. Using genetically engineered DNA polymerases greatly improves the efficiency of PAP.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Methods of copying the methylation pattern of DNA during isothermal amplification and microarrays
InactiveUS20060257905A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationGenomic DNA
A method for copying the methylation patterns of molecules of genomic DNA (MGD) during isothermal amplification of the MGD comprising obtaining MGD, copying the methylation patterns of the MGD using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the MGD using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a method for copying the methylation patterns in double-stranded DNA molecules during isothermal amplification of the DNA molecules comprising obtaining DNA molecules, contacting the DNA molecules with transposable elements and an enzyme, which can randomly insert the transposable elements into the DNA molecules, copying the methylation patterns of the DNA molecules using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the DNA molecules using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a buffer comprising a divalent ion, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), primers, and S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM); and a composition comprising a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, and the buffer.
Owner:EUCLID DIAGNOSTICS
DNA sequencing with non-fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators and cleavable label modified nucleotide terminators
This invention provides a process for sequencing nucleic acids using 3′ modified deoxynucleotide analogues or 3′ modified deoxyinosine triphosphate analogues, and 3′ modified dideoxynucleotide analogues having a detectable marker attached to a base thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
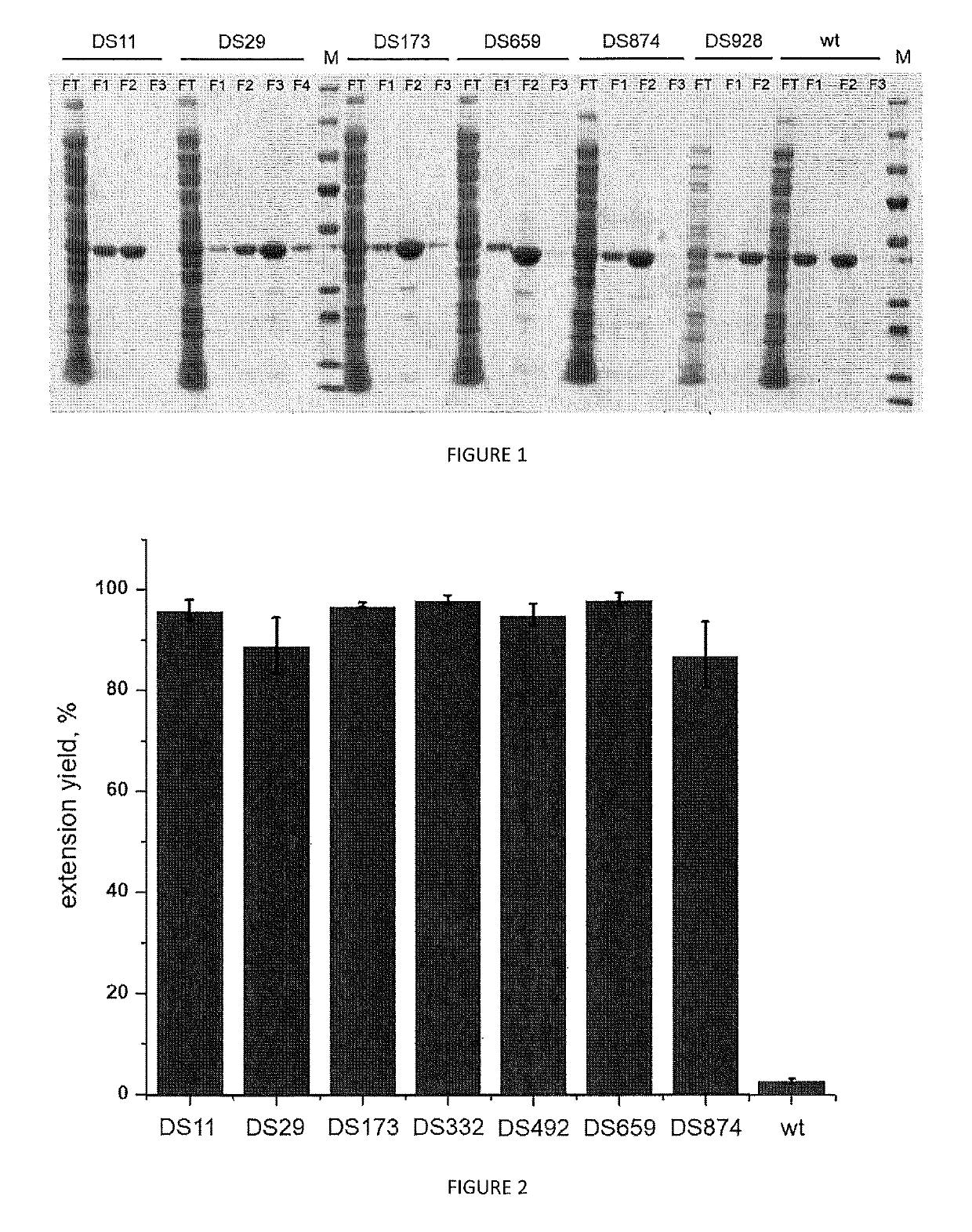
Variants of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and uses thereof
ActiveUS10435676B2Improve abilitiesLow costImmobilised enzymesTransferasesNucleotideAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to a variant of Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) which (i) comprises the amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID Nº 2 or a functionally equivalent sequence, with at least an amino acid substitution at position corresponding to residue C302 or functionally equivalent residue, wherein the position is numbered by reference to the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID Nº 1, (ii) is able to synthesize a nucleic acid fragment without template and (iii) is able to incorporate a modified nucleotide into the nucleic fragment.
Owner:DNA SCRIPT SAS +2
Method for treating non-small cell lung cancer
InactiveUS20130310440A1Organic active ingredientsRespiratory disorder5-MethylcytosineBorderline resectable
The present invention provides methods for treating a human patient afflicted with unresectable, advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer comprising periodically administering to the human patient chemotherapy comprising an amount of docetaxel; and 640 mg of an anti-clusterin oligonucleotide having the sequence CAGCAGCAGAGTCTTCATCAT (Seq. ID No.: 1), wherein the anti-clusterin oligonucleotide has a phosphorothioate backbone throughout, has sugar moieties of nucleotides 1-4 and 18-21 bearing 2′-O-methoxyethyl modifications, has nucleotides 5-17 which are 2′deoxynucleotides, and has 5-methylcytosines at nucleotides 1, 4, and 19, thereby treating the human patient afflicted with unresectable, advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. The present invention also provides compositions and combinations, packages, and uses thereof for treating a human patient afflicted with unresectable, advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
Methods of copying the methylation pattern of DNA during isothermal amplification and microarrays
InactiveUS7449297B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
A method for copying the methylation patterns of molecules of genomic DNA (MGD) during isothermal amplification of the MGD comprising obtaining MGD, copying the methylation patterns of the MGD using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the MGD using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a method for copying the methylation patterns in double-stranded DNA molecules during isothermal amplification of the DNA molecules comprising obtaining DNA molecules, contacting the DNA molecules with transposable elements and an enzyme, which can randomly insert the transposable elements into the DNA molecules, copying the methylation patterns of the DNA molecules using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the DNA molecules using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a buffer comprising a divalent ion, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), primers, and S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM); and a composition comprising a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, and the buffer.
Owner:EUCLID DIAGNOSTICS
Plants flower pesticide specificity promoter and uses thereof
InactiveCN101182523AAvoid pollutionEnhanced insemination capacityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a plant anther-specific promoter and application thereof. The promoter is 179 to 1174 bp in length at least containing the 996-1174th nucleotide sequence at the 5' end of sequence 1 in the sequence listing at the 3' end and extending to the 5' end according to the nucleotide arrangement of sequence 1 deoxynucleotide fragments. The anther-specific promoter of the present invention has great application prospects in the functional analysis and identification of plant anther growth and development genes, the establishment of artificial male sterile lines, the prevention of plant transgene drift or escape, and the extension of shelf life of flowers.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
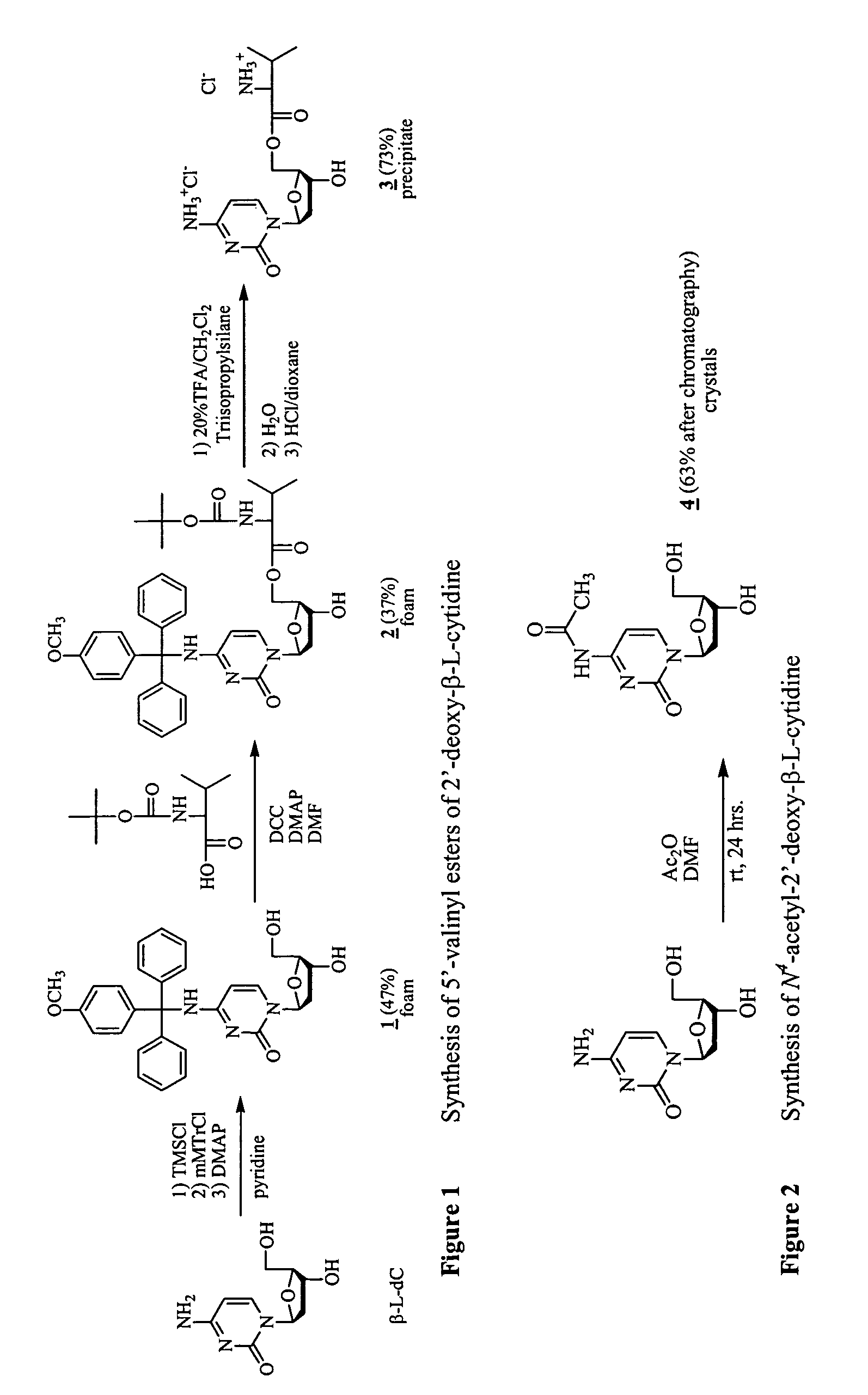
Beta-L-N4-Hydroxycytosine Deoxynucleosides and their use as Pharmaceutical Agents in the Prophylaxis or Therapy of Viral Diseases
The invention relates to β-L-N4-hydroxycytosine nucleo-sides, pharmaceutical agents comprising same, and to the use of said β-L-N4-hydroxycytosine nucleosides and pharmaceutical agents in the prophylaxis or therapy of an infection caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The invention also relates to a method for the preparation of said β-L-nucleoside analogs.
Owner:MAX DELBRUECK CENT FUER MOLEKULARE MEDIZIN
β-L-2′-deoxynucleosides for the treatment of resistant HBV strains and combination therapies
ActiveUS7186700B2Preventing and suppressing emergenceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineLamivudine resistance
It has been discovered that β-L-2′-deoxynucleosides are active against drug-resistant hepatitis B virus with mutations. A method for treating lamivudine resistant HBV (M552V) in a host is provided that includes administering a β-L-2′-deoxynucleoside or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or prodrug. In addition, a method for preventing lamivudine resistant HBV (M552V) mutation from occurring in a naïve host is provided that includes administering a β-L-2′-deoxynucleoside or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or prodrug. A method for preventing and / or suppressing the emergence of the HBV double mutant (L528M / M552V) in a host is also provided that includes administering a β-L-2′-deoxynucleoside or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or prodrug.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
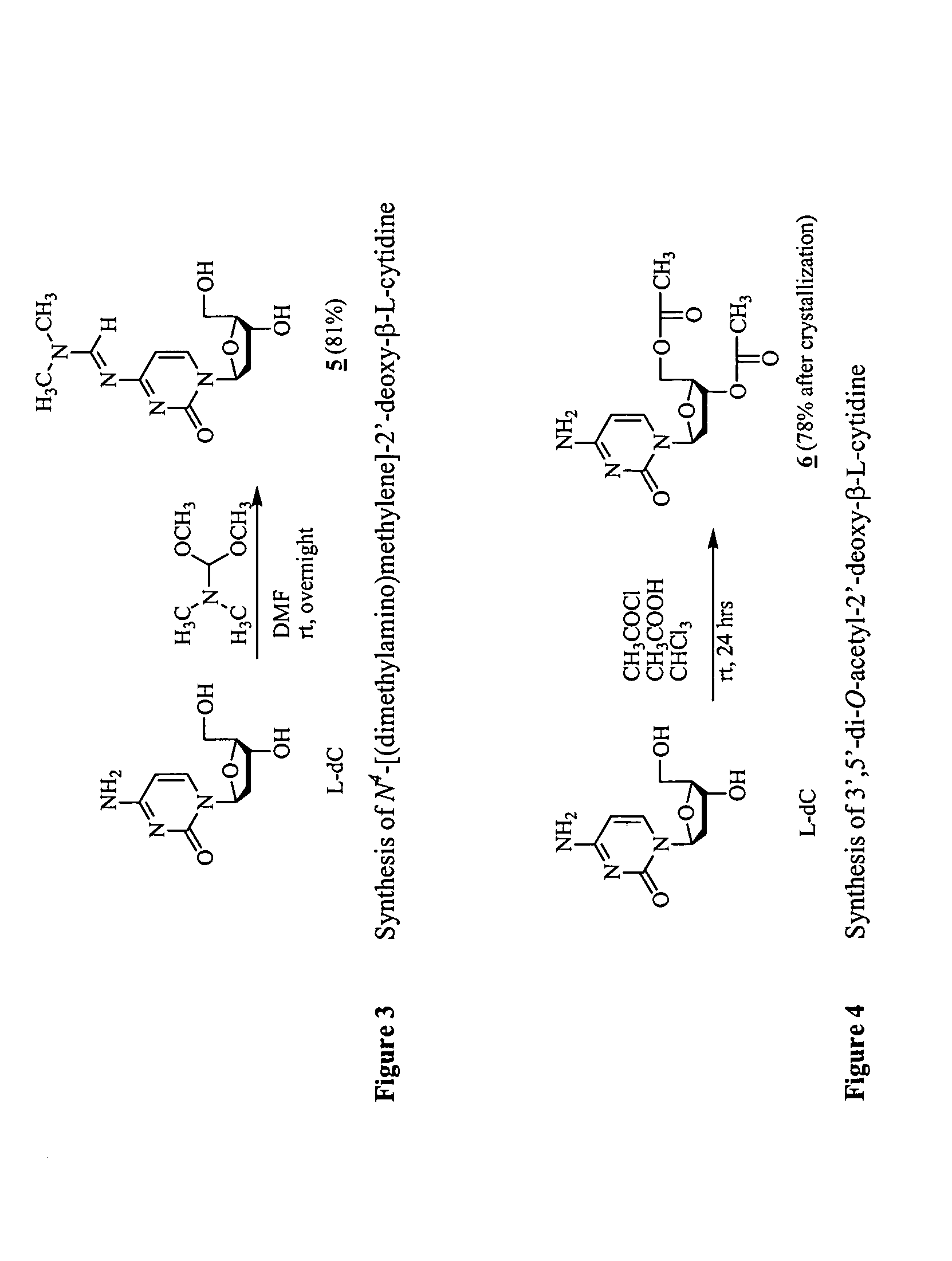
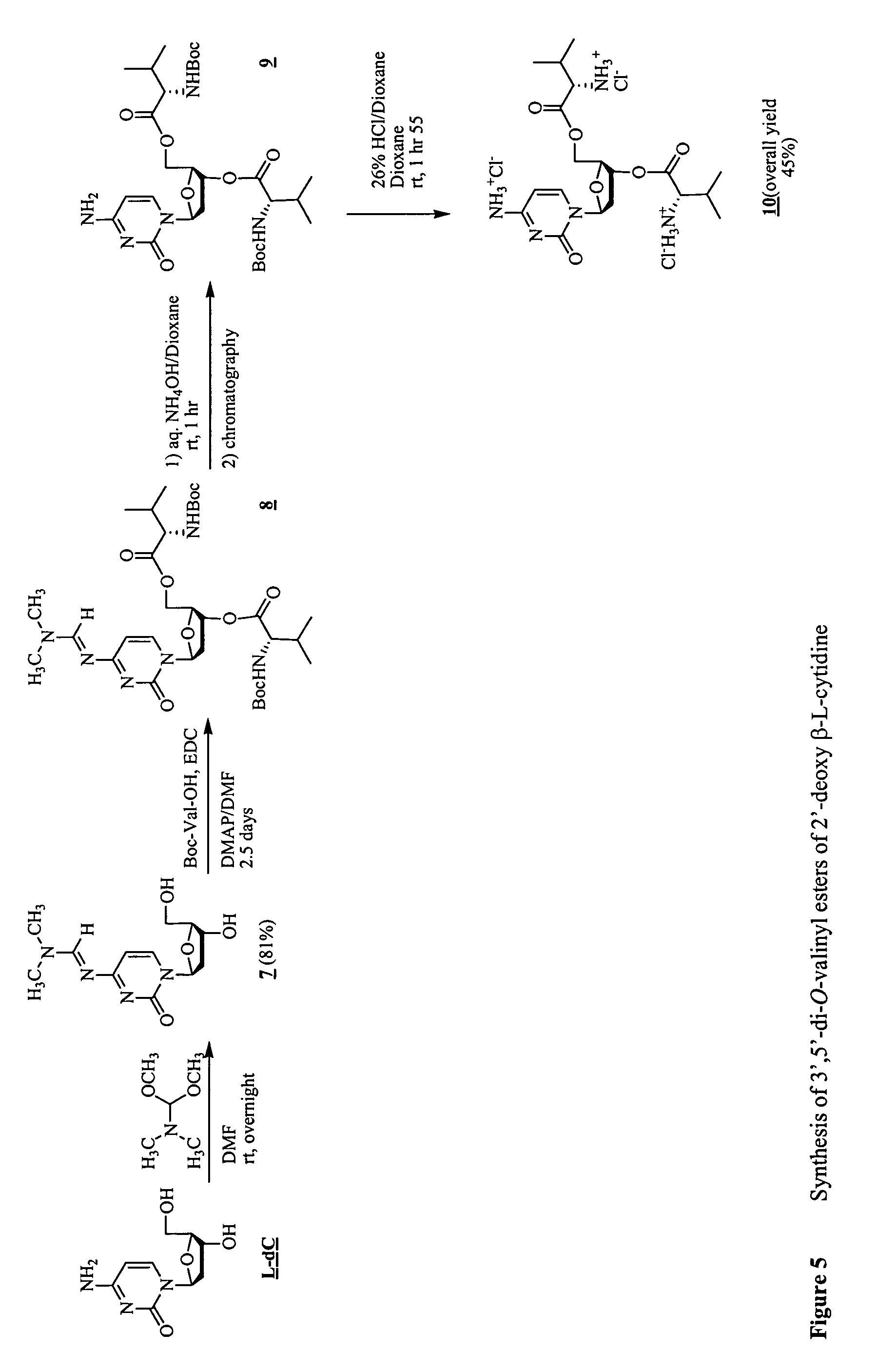
Synthesis of beta-L-2'-deoxy nucleosides
InactiveUS20050059632A1High percent product yieldPercent product yieldEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideDisplacement reactionsAlternative methods
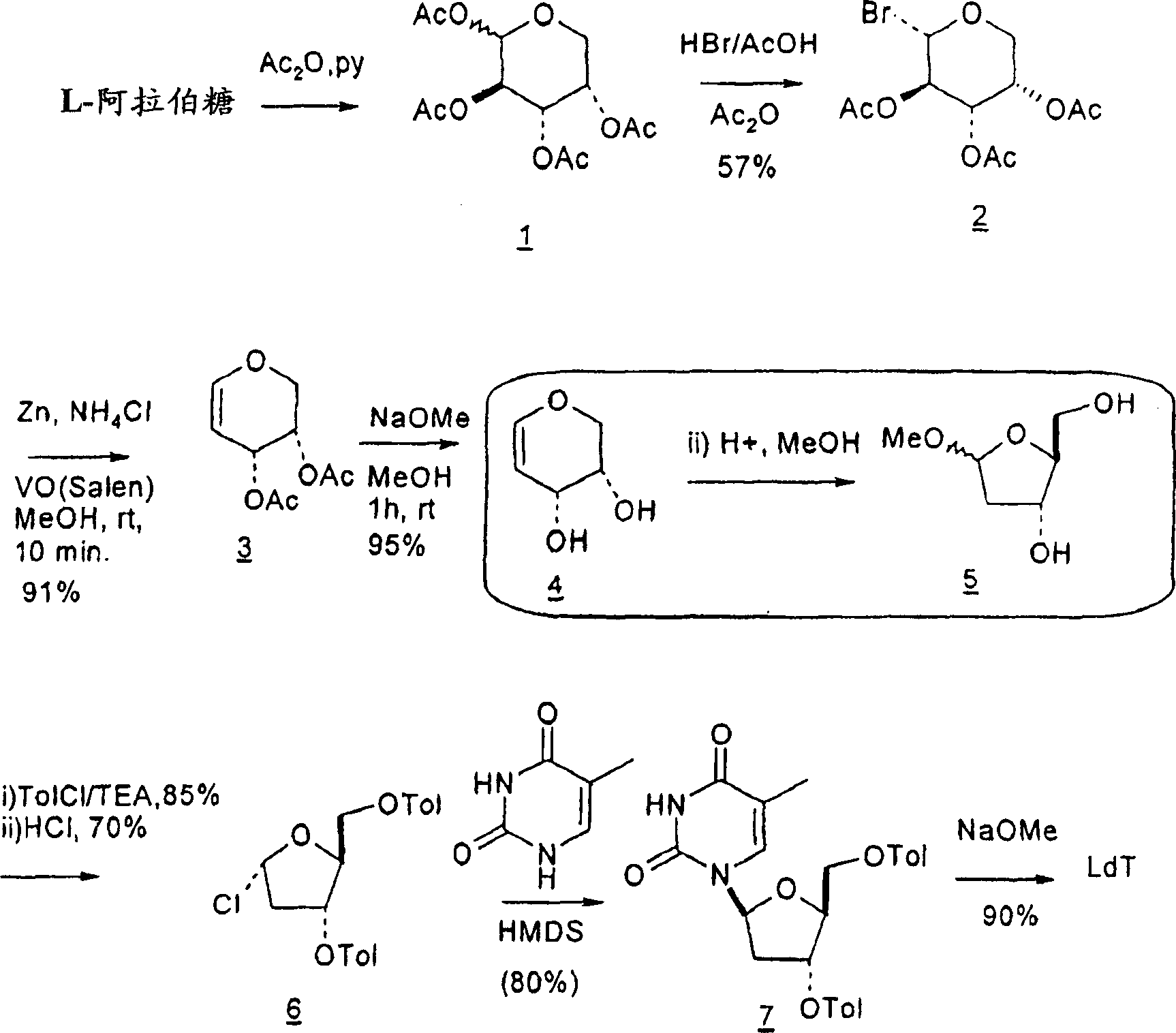
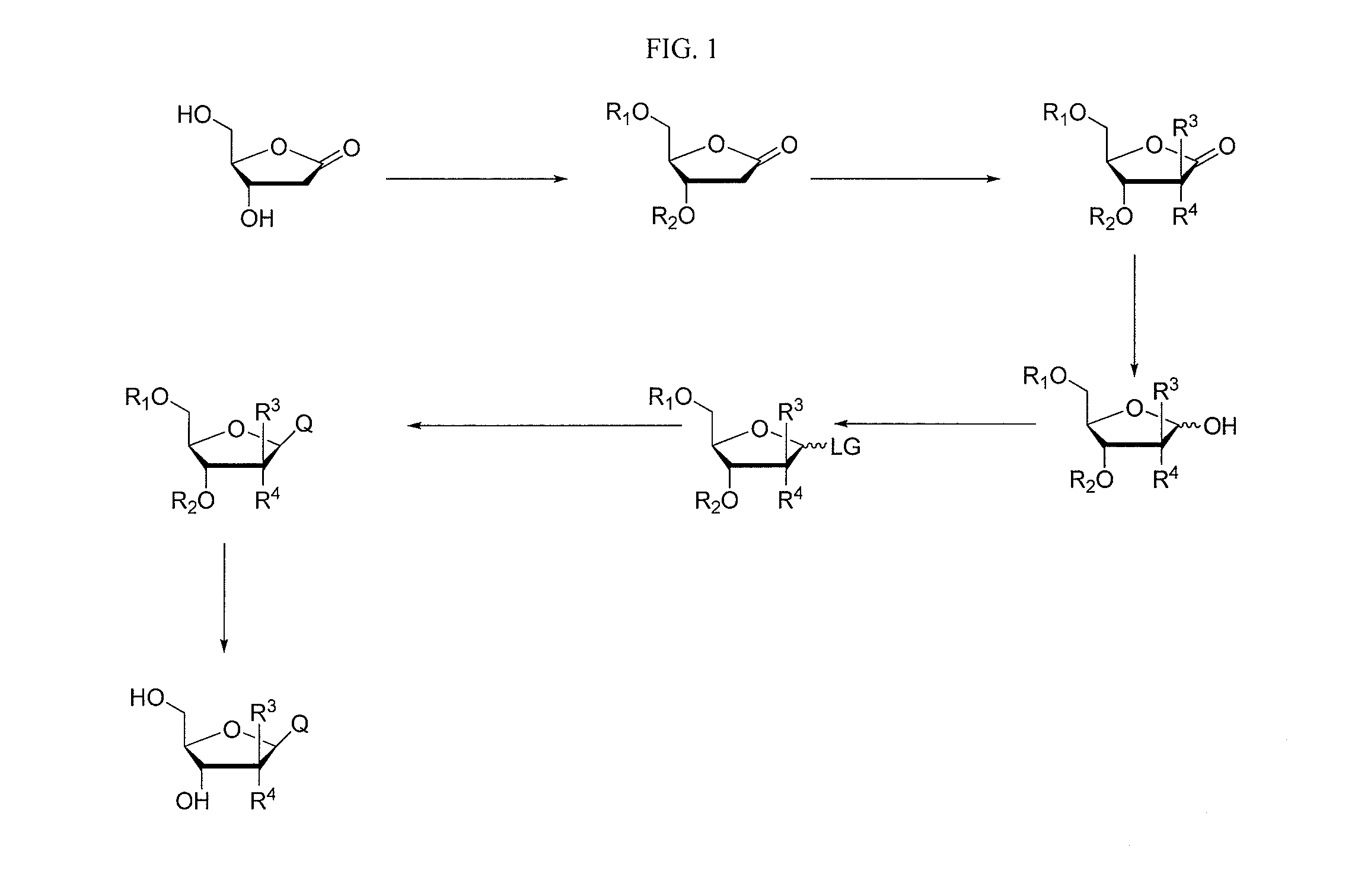
An improved process for the preparation of 2′-modified nucleosides and 2′-deoxy-nucleosides, such as, β-L-2′-deoxy-thymidine (LdT), is provided. In particular, the improved process is directed to the synthesis of a 2′-deoxynucleoside that may utilize different starting materials but that proceeds via a chloro-sugar intermediate or via a 2,2′-anhydro-1-furanosyl-nucleobase intermediate. Where an 2,2′-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate is utilized, a reducing agent, such as Red-Al, and a sequestering agent, such as 15-crown-5 ether, that cause an intramolecular displacement reaction and formation of the desired nucleoside product in good yields are employed. An alternative process of the present invention utilizes a 2,2′-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate without a sequestering agent to afford 2′-deoxynucleosides in good yields. The compounds made according to the present invention may be used as intermediates in the preparation of other nucleoside analogues, or may be used directly as antiviral and / or antineoplastic agents.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Novel use
ActiveUS20180023108A1Microbiological testing/measurementTransferasesEnzymeTerminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
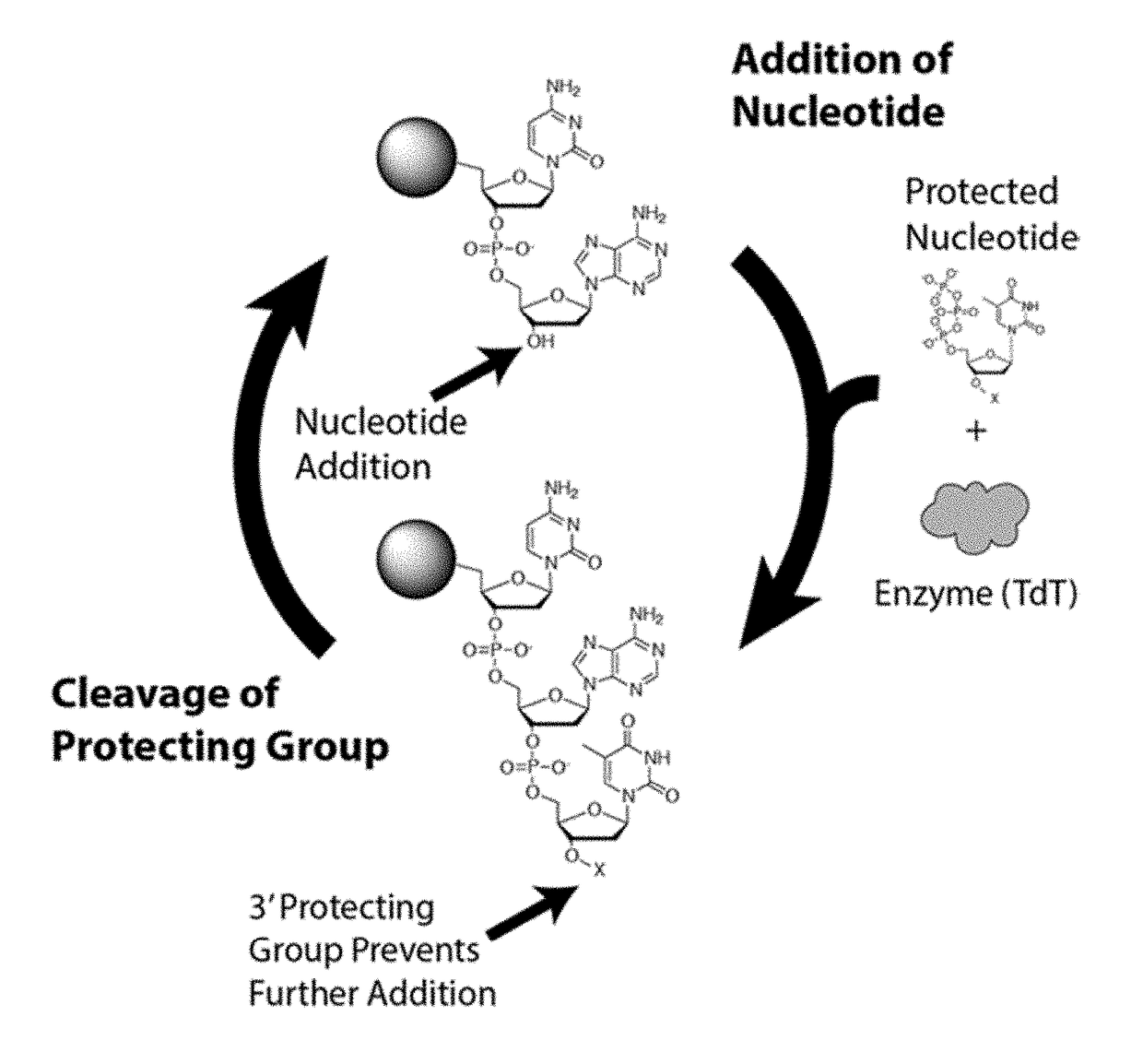
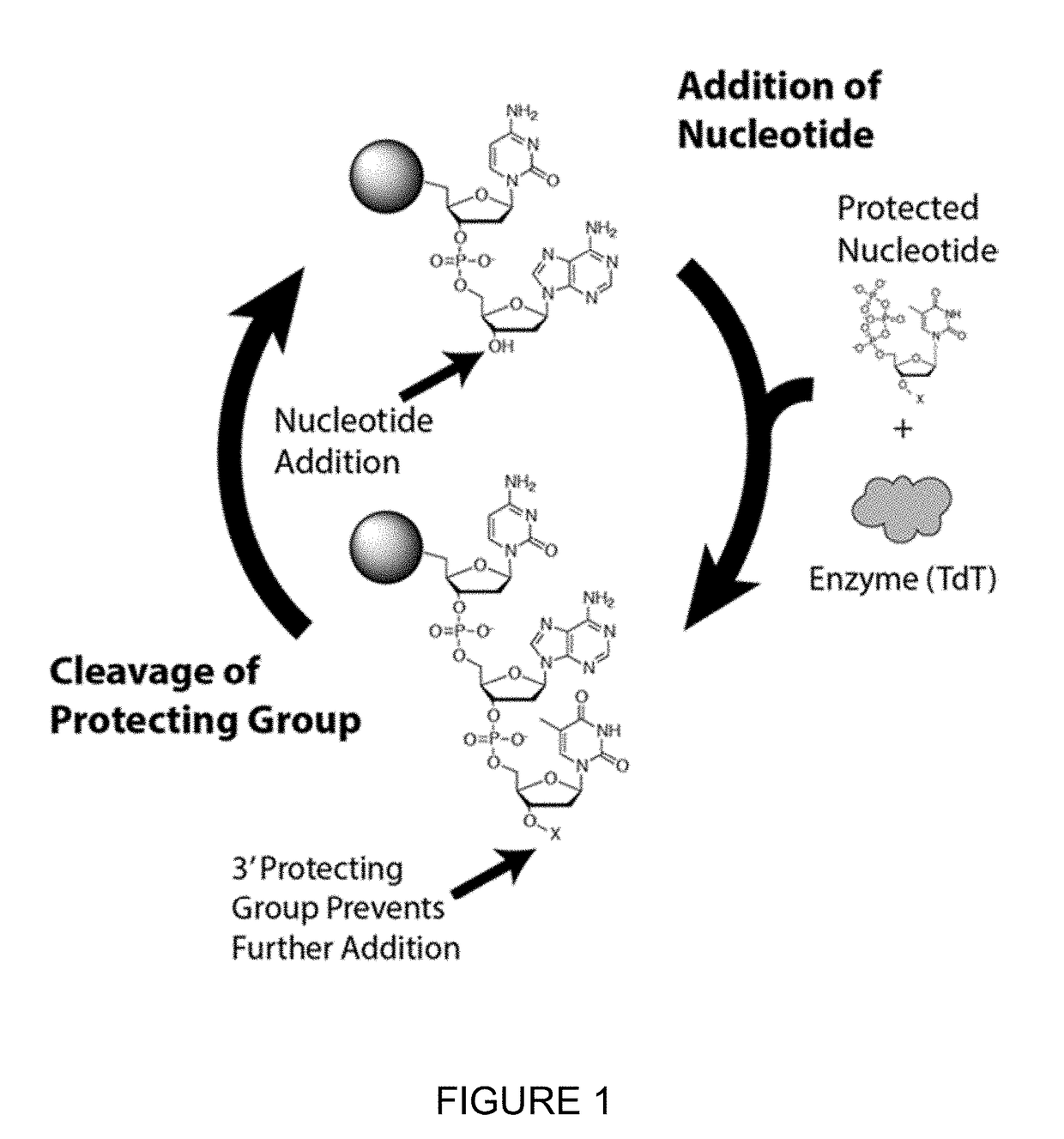
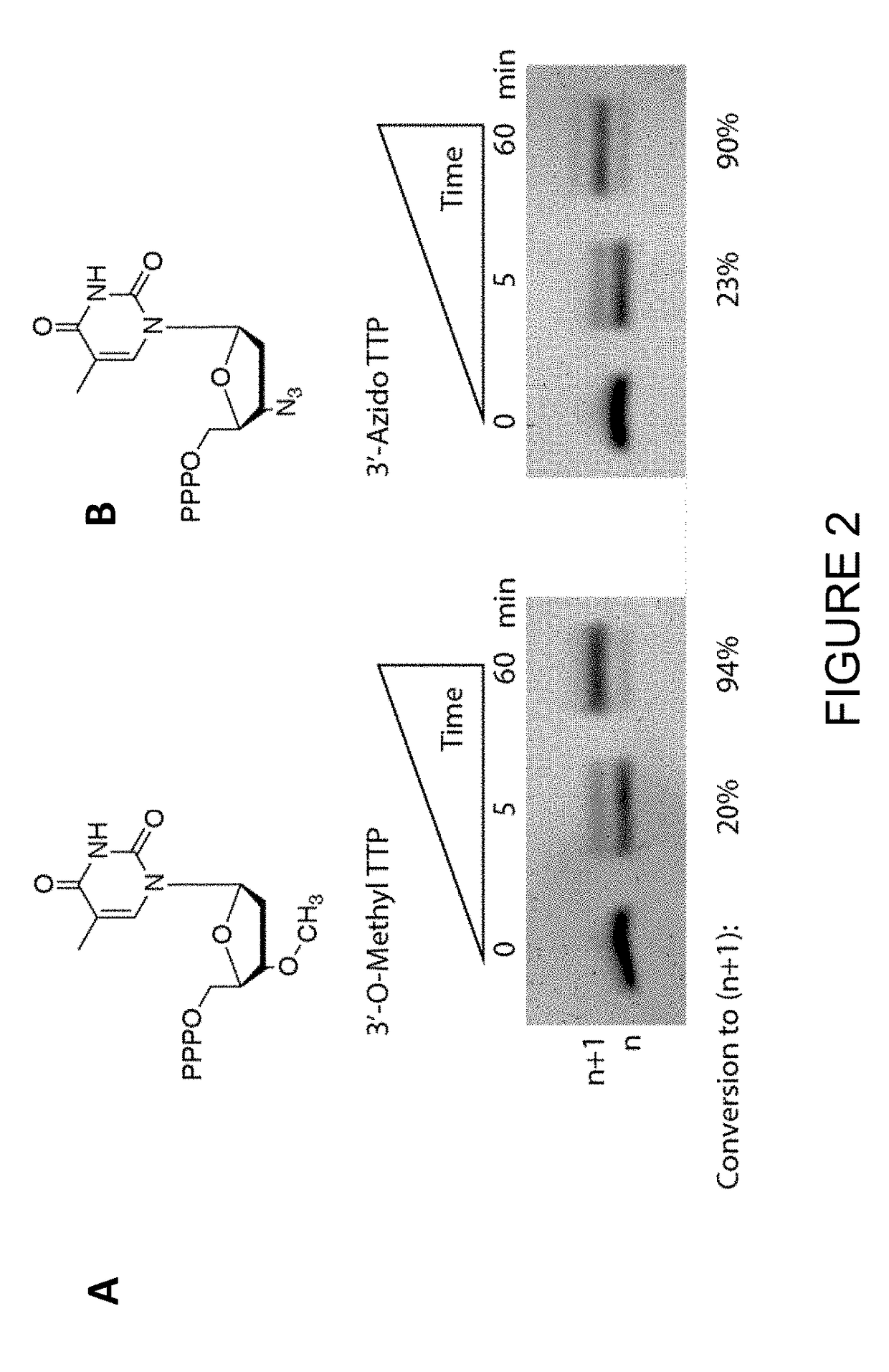
The invention relates to the use of specific terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) enzymes in a method of nucleic acid synthesis, to methods of synthesizing nucleic acids, and to the use of kits comprising said enzymes in a method of nucleic acid synthesis. The invention also relates to the use of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferases and 3′-blocked nucleotide triphosphates in a method of template independent nucleic acid synthesis.
Owner:NUCLERA NUCLEICS LTD
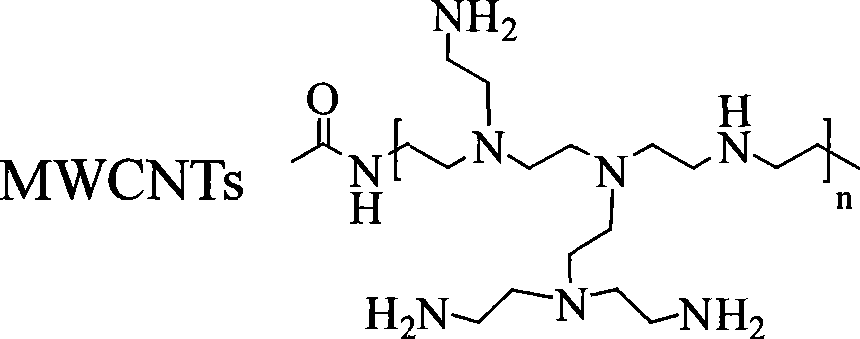
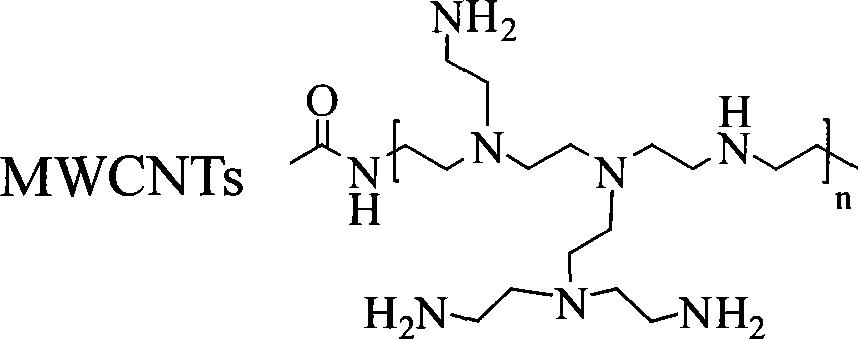
Polyethylene imine modified carbon nano-tube, its complexes, production method and uses thereof
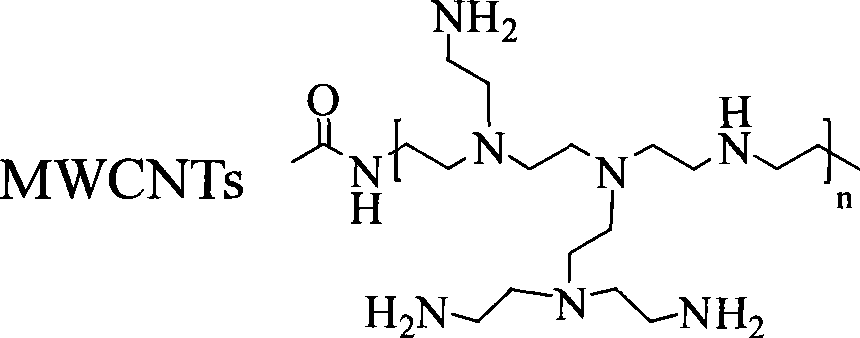
The invention discloses a carbon nanometer tube decorated by polyethyleneimine and a compound of plasmid DNA thereof. The plasmid DNA adopted in the invention comprises P53DNA, green fluorescent protein expression (JPC) and unmethylated oligomerization deoxynucleotide plasmid DNA. The carbon nanometer tube decorated by the polyethyleneimine and the compound of the plasmid DNA have the advantages of high transfection efficiency and less toxicity to cells; in particular, when the concentration is 30 g / ml, the transfection efficiency is larger than 90 percent, and the validity of the cells is larger than 80 percent. The carbon nanometer tube decorated by the polyethyleneimine and the compound of the plasmid DNA have wide application prospect during the process of preparing medicaments for remedying genes outside transfecting osteosarcoma cell bodies and in animal bodies; and the carbon nanometer tube decorated by the polyethylene imine / the plasmid DNA / an adriacin nanometer compound also have wide application during the process of preparing medicaments for restraining the growth of tumor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
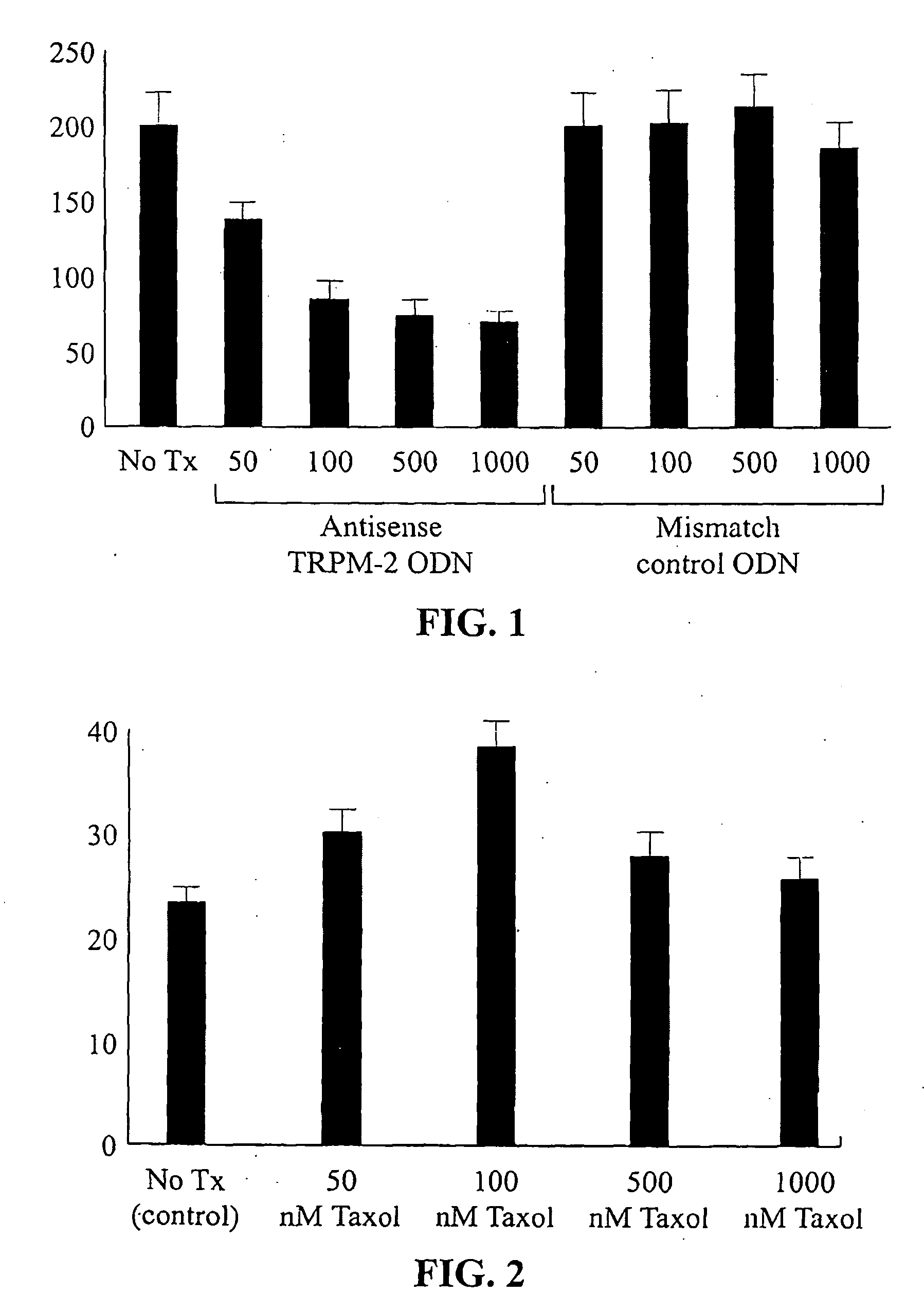
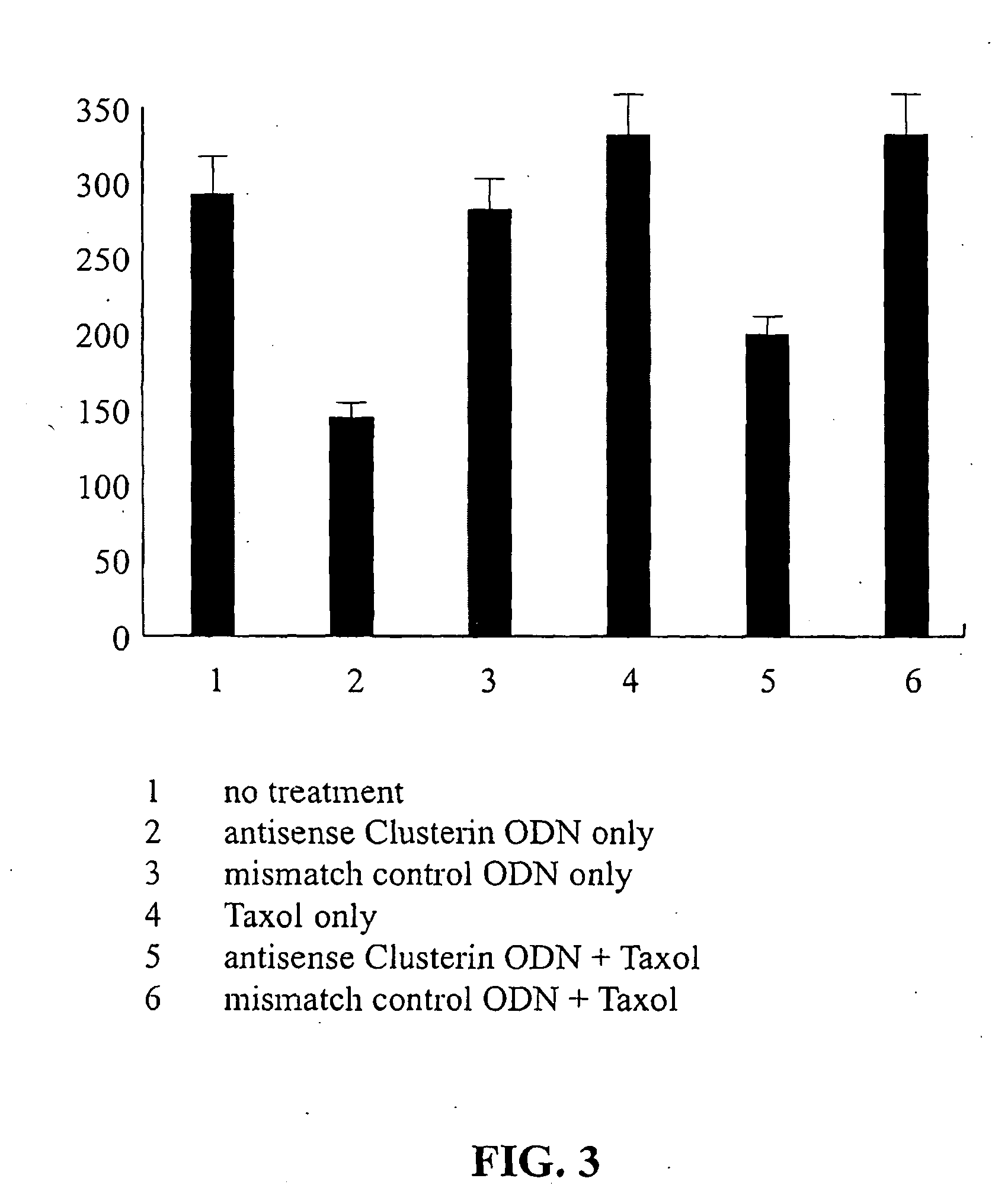
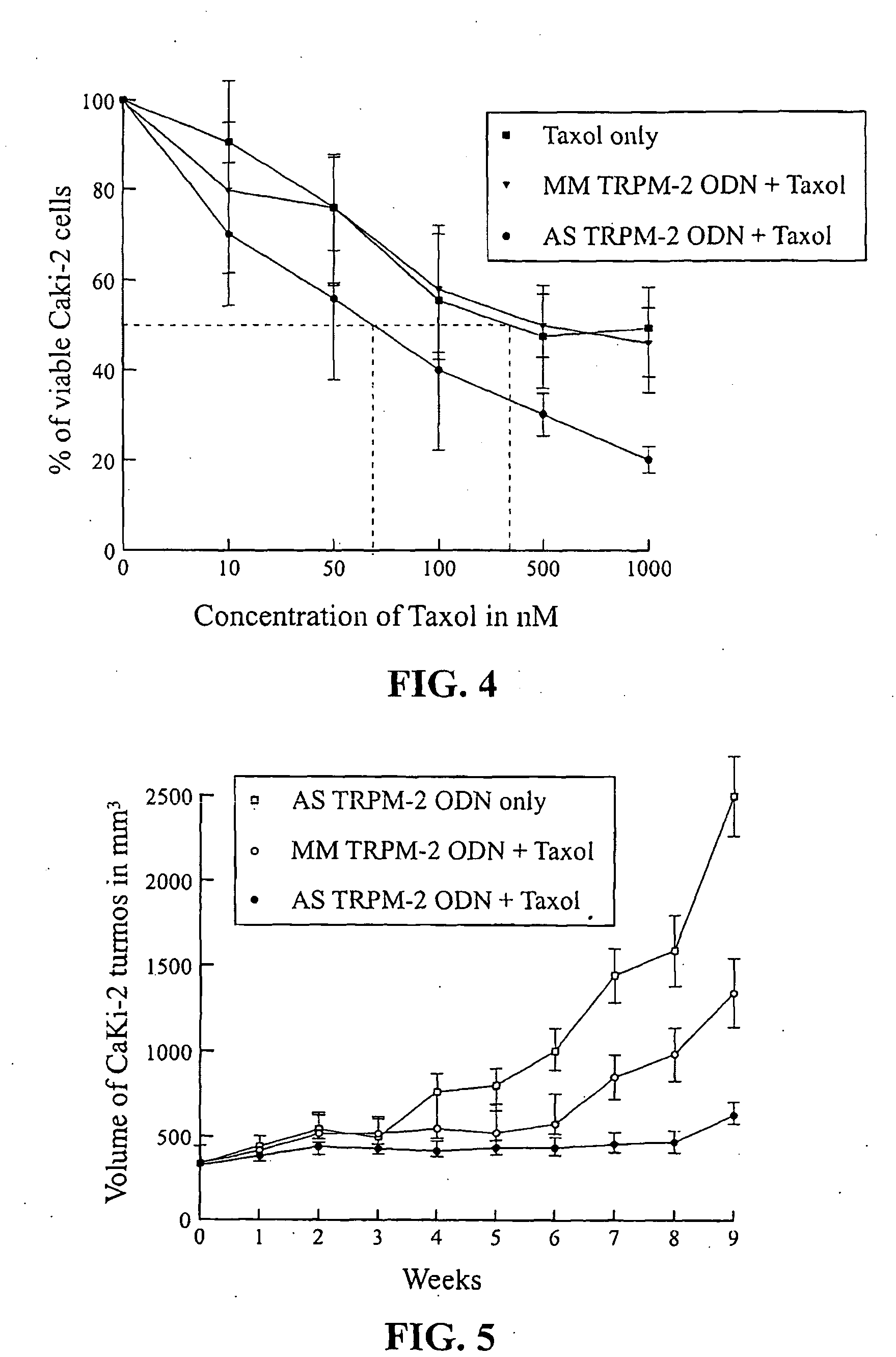
Chemo- and Radiation-sensitization of Cancer by Antisense TRPM-2 Oligodeoxynucleotides
InactiveUS20090258089A1Reduce expressionHigh sensitivityHeavy metal active ingredientsApolipeptidesCancer cellAntisense oligodeoxynucleotides
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
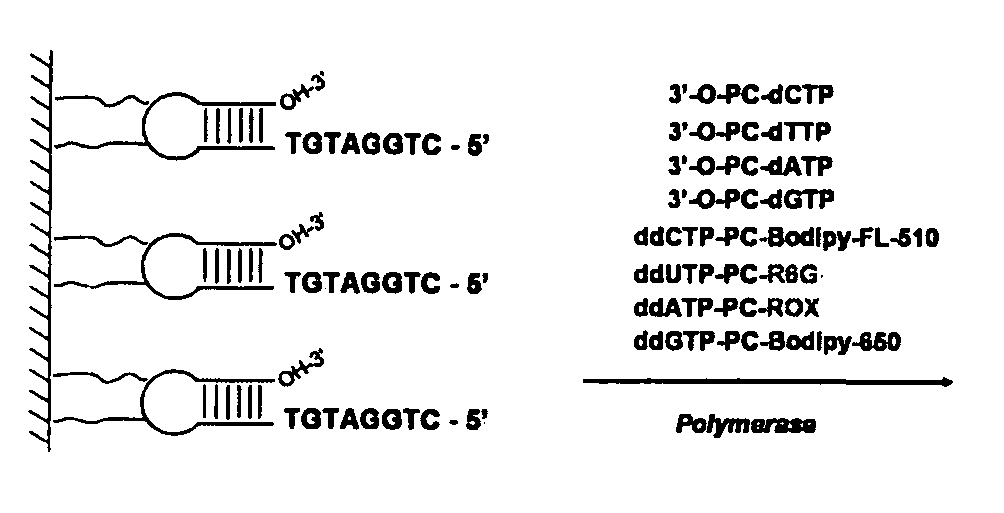
Reagents for reversibly terminating primer extension
This invention relates to the field of nucleic acid chemistry, more specifically to the field of compositions of matter that comprise triphosphates of modified 2'-deoxynucleosides and oligonucleotides that are formed when these are appended to the 3'-end of a primer, wherein said modifications comprise NH2 moiety attached to their 3'-hydroxyl group and a fluorescent species in a form of a tag affixed to the nucleobase via a linker that can be cleaved. Such compositions and their associated processes enable and improve the sequencing of oligonucleotides using a strategy of cyclic reversible termination, as outlined in US Patent 6,664,079. Most specifically, the invention concerns compositions of matter that are 5'-triphosphates of ribo- and 2'- deoxyribonucleosides carrying detectable tags and oligonucleotides that might be derived from them. The invention also concerns processes wherein a DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase, or reverse transcriptase synthesizes said oligonucleotides via addition of said triphosphates to a primer.
Owner:动态组合化学技术有限责任公司
Nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveUS8420323B2Simple and rapid methodShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotidePolymerase L
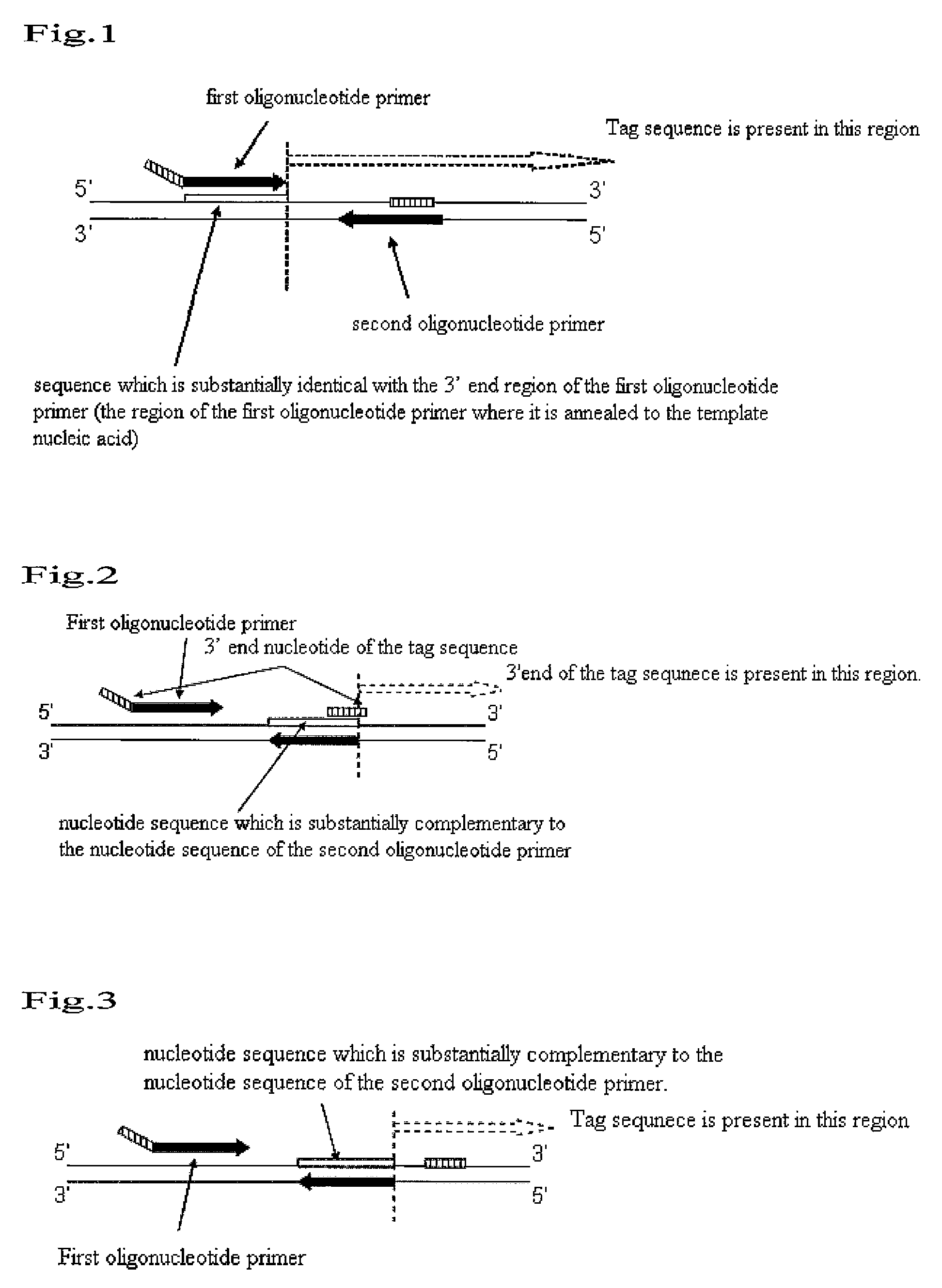
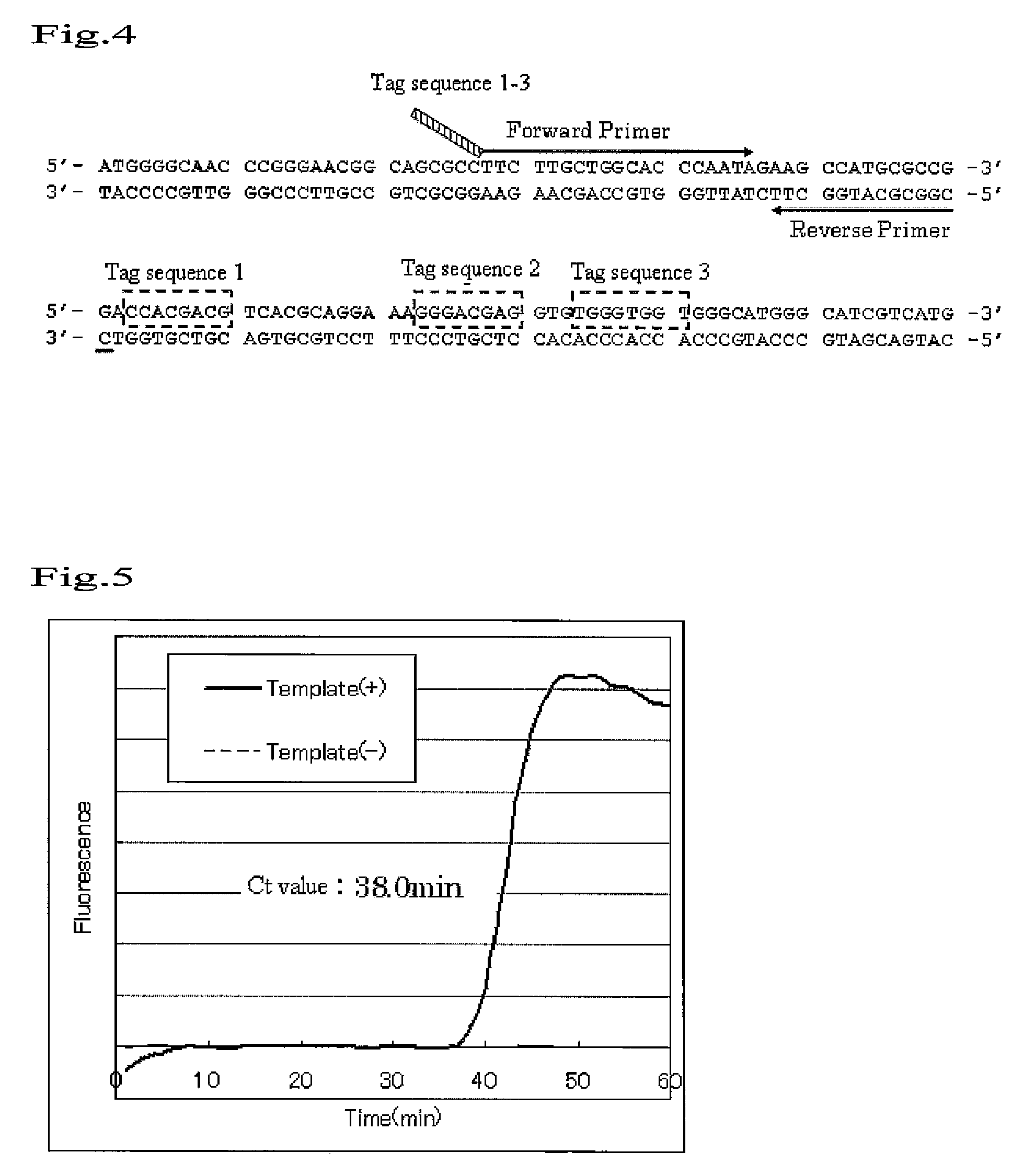
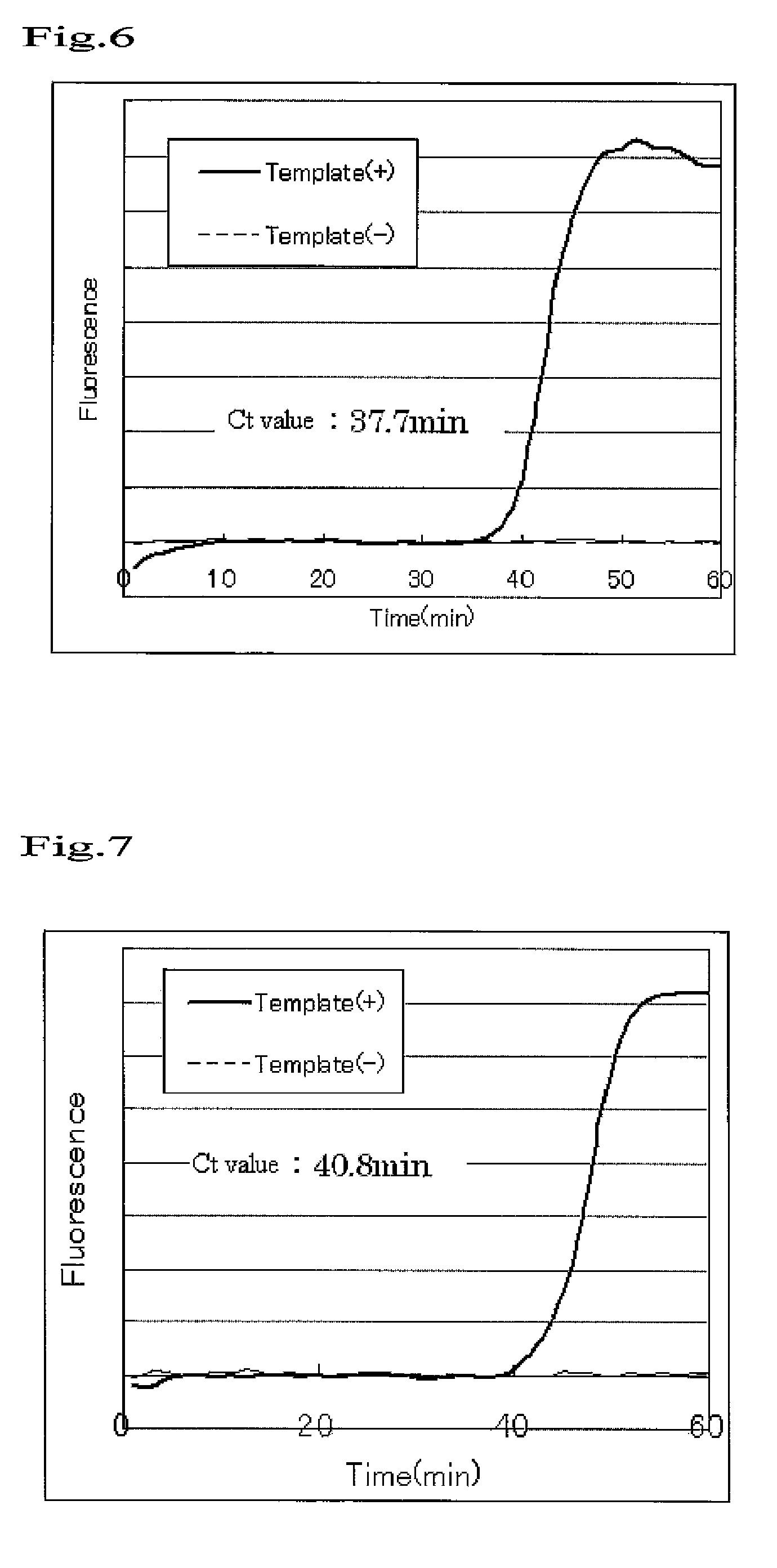
An object to be achieved by the present invention is to provide a nucleic acid amplification method by which a nucleic acid can be amplified using oligonucleotide primers and DNA polymerase. The present invention provides a nucleic acid amplification method which comprises performing incubation of a reaction solution containing at least one type of deoxynucleotide triphosphate, at least one type of DNA polymerase, at least two types of oligonucleotide primer, and the nucleic acid fragment as a template so as to perform a polymerase reaction that initiates from the 3′ end of the primer and thus amplifying the nucleic acid fragment, wherein a tag sequence is added at the 5′ end of the first oligonucleotide primer, and the tag sequence is a nucleotide sequence on the template nucleic acid fragment which is present downstream of the sequence which is substantially complementary with the 3′ end region of the first oligonucleotide primer (a region where the first oligonucleotide is annealed to the template nucleic acid).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for preparing auxin
InactiveCN102145998AReduce manufacturing costEasy to scale production and promotionOrganic fertilisersNucleotideAuxin
The invention discloses a method for preparing auxin, which comprises the following steps of: preparing nucleic acid from byproduct mycelia of a fermentation plant, hydrolyzing with the nucleic acid to prepare a nucleotide salt and a deoxynucleotide salt, and then mixing the nucleotide salt, the deoxynucleotide salt and an auxiliary agent uniformly. The raw materials are extensive, and the method is simple and convenient.
Owner:高旌
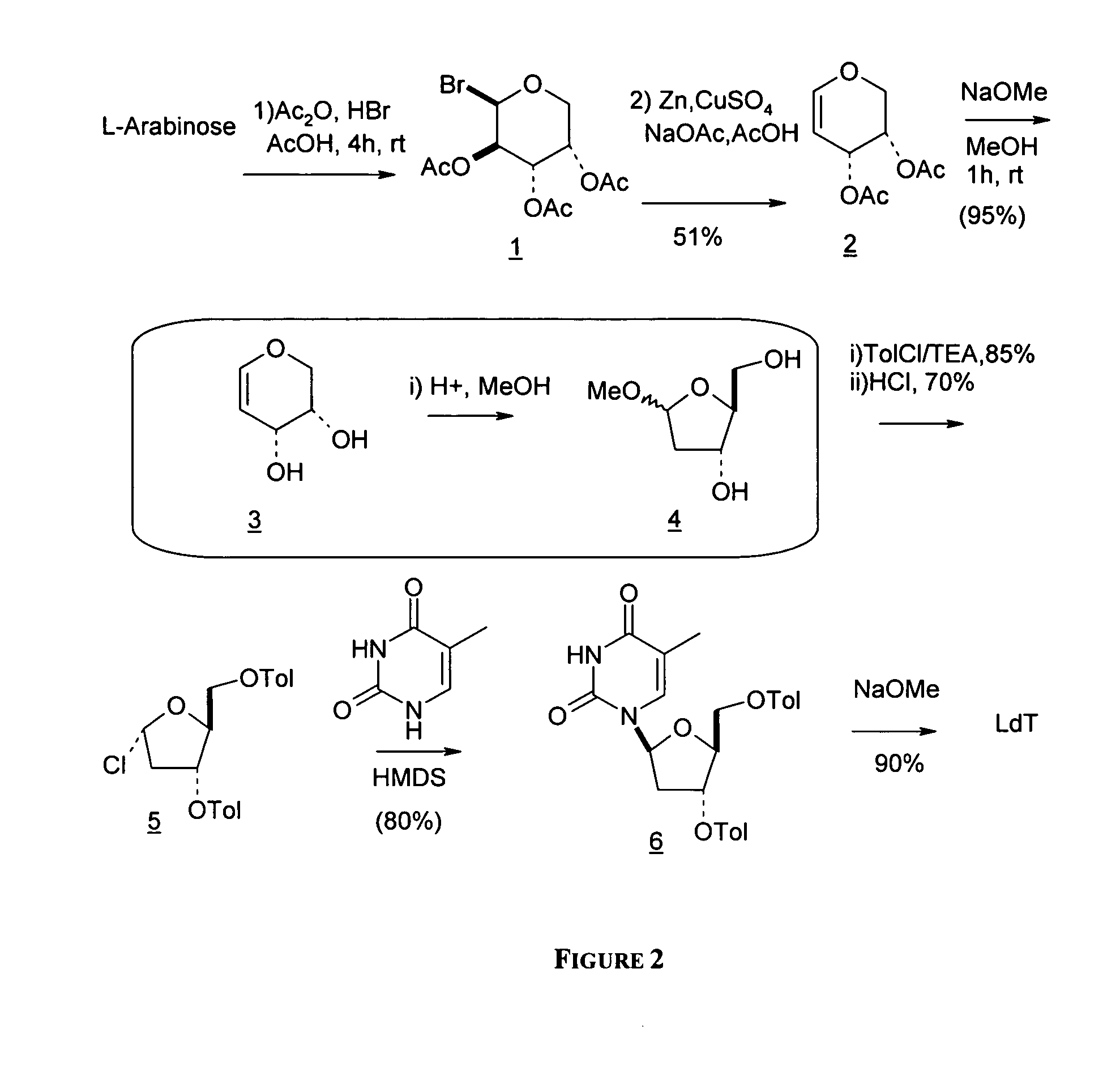
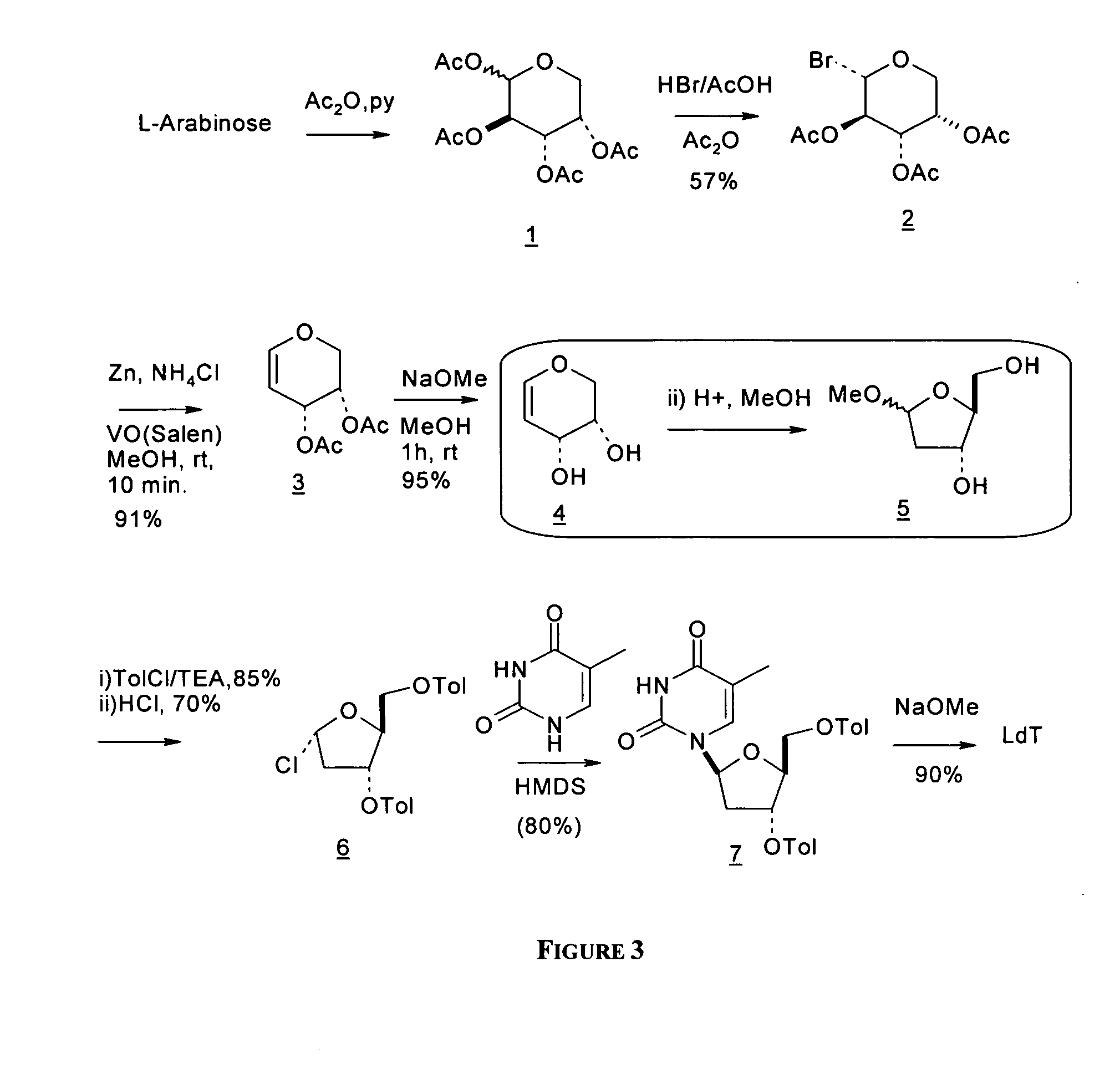
Synthesis of beta-l-2'-deoxy nucleosides
An improved process for the preparation of 2'-modified nucleosides and 2'-deoxy-nucleosides, such as, beta-L-2'-deoxy-thymidine (LdT), is provided. In particular, the improved process is directed to the synthesis of a 2'-deoxynucleoside that may utilize different starting materials but that proceeds via a chloro-sugar intermediate or via a 2,2' anhydro-1-furanosyl-nucleobase intermediate. Where an 2,2'-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate is utilized, a reducing agent, such as Red-Al, and a sequestering agent, such as 15-crown-5 ether, that cause an intramolecular displacement reaction and formation of the desired nucleoside product in good yields are employed. An alternative process of the present invention utilizes a 2,2'-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate without a sequestering agent to afford 2'-deoxynucleosides in good yields. The compounds made according to the present invention may be used as intermediates in the preparation of other nucleoside analogues, or may be used directly as antiviral and / or antineoplastic agents.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
2-fluorinated riboses and arabinoses and methods of use and synthesis
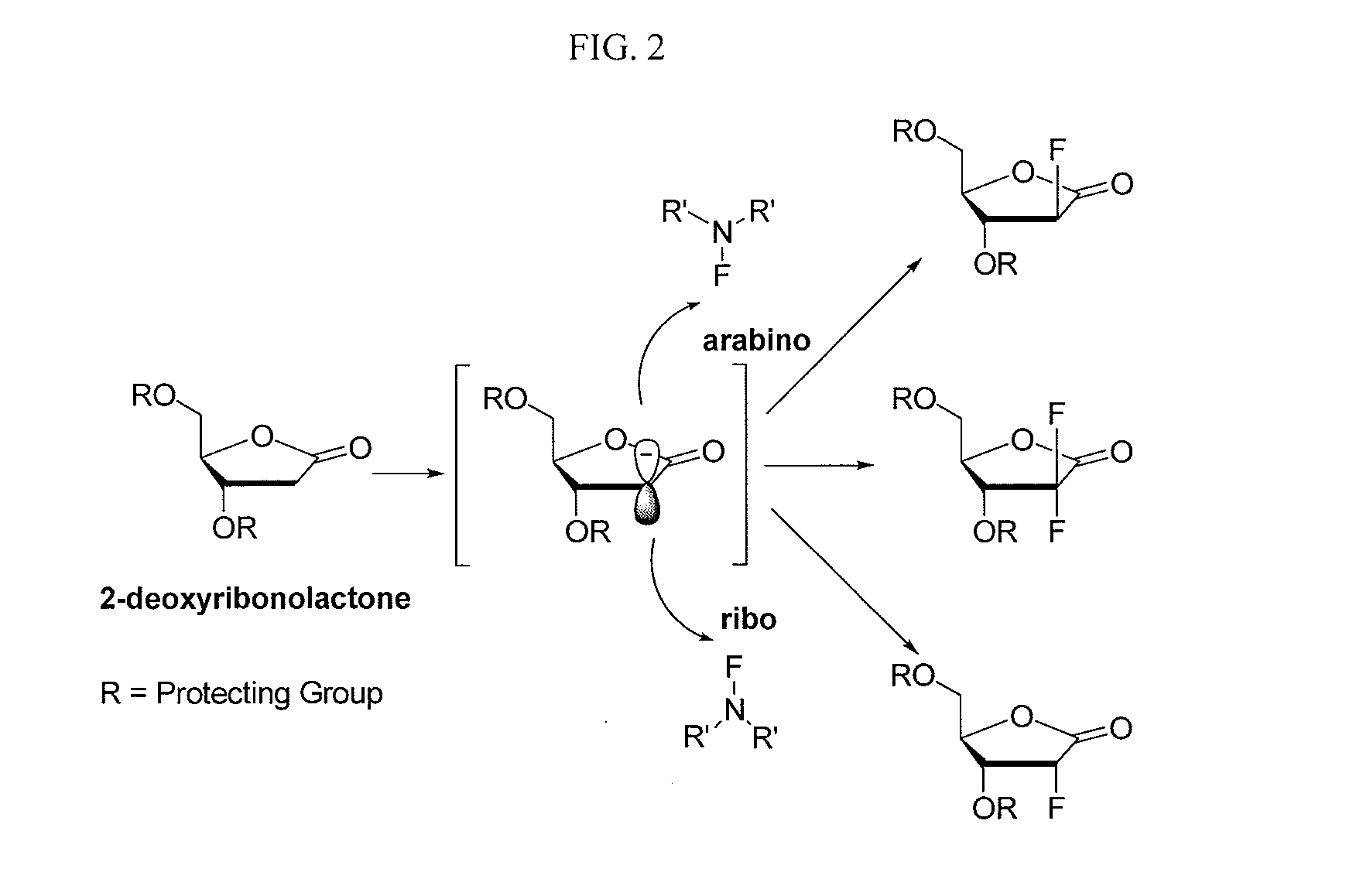
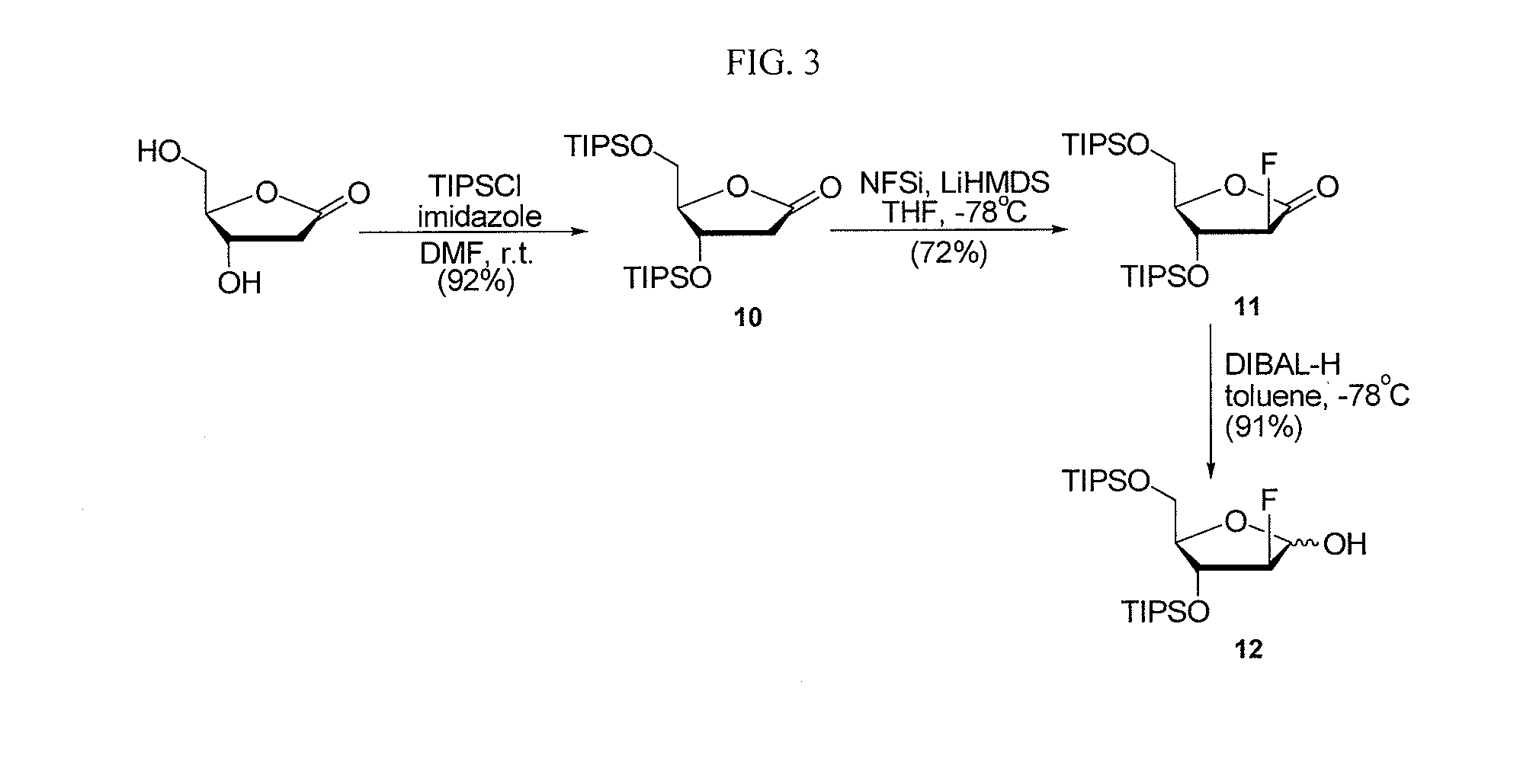
Disclosed are halogenated 2-deoxy-lactone, 2′-deoxy-nucleosides, and derivatives thereof, for example, a compound of formula (I). Also disclosed are a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and at least one compound or salt of the invention, and a method of treating a disorder is selected from the group consisting of an abnormal cellular proliferation, a viral infection, and an autoimmune disorder.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Variants of Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20190211315A1Improve abilitiesLow costTransferasesFermentationNucleotideAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to a variant of Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) which (i) comprises the amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID No 2 or a functionally equivalent sequence, with at least an amino acid substitution at position corresponding to residue C302 or functionally equivalent residue, wherein the position is numbered by reference to the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID No 1, (ii) is able to synthesize a nucleic acid fragment without template and (iii) is able to incorporate a modified nucleotide into the nucleic fragment.
Owner:DNA SCRIPT SAS +2
Beta-L-2'-deoxy-nucleosides for the treatment of hepatitis B
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
Kit for isothermal DNA amplification starting from an RNA template
A method of amplifying RNA template is provided. The method comprises reverse-transcribing a ribonucleic acid (RNA) template to form a cDNA using a first reaction mixture comprising RNA template, at least one primer capable of hybridizing to the RNA template, a reverse transcriptase and deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs); and amplifying the cDNA to form an amplified product using a second reaction mixture comprising at least one strand displacement DNA polymerase, at least one inosine-containing primer and a nuclease that is capable of nicking DNA 3' to an inosine residue of the primer. The method is accomplished under an isothermal condition without denaturing the cDNA template. A method of quantifying RNA template in a sample and a method of detecting RNA template in a sample are also provided. Kits for amplifying deoxynucleic acid (DNA) from ribonucleic acid (RNA) template are also provided.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Chromophore-modified deoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer compound, preparation method therefor and application thereof
InactiveCN105348343AStability is not affectedDoes not affect the structureSugar derivativesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFluorescenceDouble strand
The invention discloses a chromophore-modified deoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer compound, a preparation method therefor and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: connecting chromophores such as pyrene, perylene or naphthalene carboxamide with bis(diisopropylamino) chlorophosphine to obtain a phosphorous intermediate; and reacting the phosphorous intermediate with DMT-protected deoxynucleoside to obtain a chromophore-modified deoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer compound. By virtue of solid-phase synthesis of DNA, the compound is inserted into oligonucleotide at a fixed point to obtain a chromophore-modified fluorescent oligonucleotide probe with a stable double-chain structure. The fluorescent oligonucleotide probe is free of fluorescence-emission, and only being combined with a perfectly matching target chain, the fluorescence can be enhanced by 23.5 times, and the response speed is fast. Mismatched bases are obviously identified with nearly no fluorescence-emission, so that single base mismatch can be obviously identified. The compound can be applied to single base mutation analysis of a gene and detection of a PCR reaction process and the like, and is wide in application prospect in aspects of single base polymorphism detection and nucleic acid detection in a biochemical sample and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Identification of white leghorns red plumage mutagenic mutant genotype and cultivation method for supporting system of red plumage pink shell layer chickens
PendingUS20210007334A1Broad prospect for promotionShorten the generation intervalHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
The present invention discloses a method for breeding the commercial strains of red feather pink-shell laying hens. It provides a primer pair for identifying the red feather causative mutation homozygous genotype of white leghorn chickens, which is composed of the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 2 of the Sequence List and the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 3 of the list. After the primer was designed according to the upstream and downstream nucleotide sequences of the 18,288,303rd deoxynucleotide in the positive-sense strand of the 11th chromosome as shown in the sequence information of the chicken reference genome Gallus_gallus-4.0 version published in NCBI, the genotype (SNP) at this site is tested through the restriction fragment length polymorphism, the genotype of the site (SNP) was tested through the restriction fragment length polymorphism; the offspring hens obtained by cross breeding the homogenous female parent (the homogenous female parent was obtained through expanded propagation of the white leghorn chickens with the red feather causative mutation homozygous genotype) and the Rhode Island Red rooster as a male parent are all of red feather phenotype, meeting the market demands and enjoying a broad prospect for promotion.
Owner:BEIJING HUADU YUKOU POULTRY
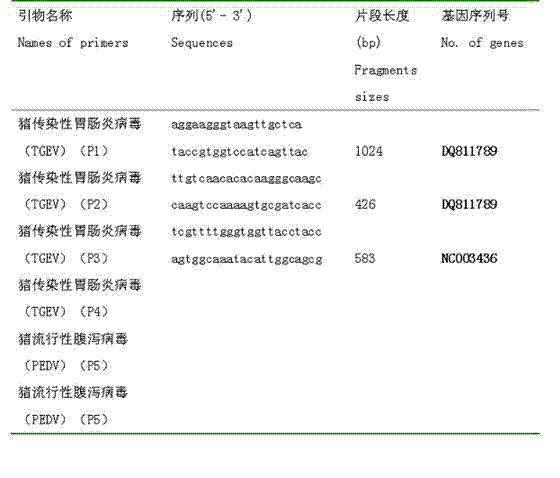
Multiple reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction detection method for swine transmissible gastroenteritis
InactiveCN102586409AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementSwine Transmissible GastroenteritisPorcine epidemic diarrhoea virus
The invention relates to a multiple reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction detection method for swine transmissible gastroenteritis. An antibody is needed to be prepared by an euzymelinked immunosorbent assay, so that the period is longer, and external factors have larger interference on the diagnostic method of the euzymelinked immunosorbent assay. The method comprises the following steps of: designing and synthesizing a transmissible swine gastroenteritis virus gene primer; establishing a multiple reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction diagnostic method of the transmissible swine gastroenteritis viruses and porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses; optimizing concentration of the primer of a bigeminy reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; optimizing the concentration of magnesium oxide of the bigeminy reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; optimizing the concentration of triphosphoric acid base deoxynucleotide of the bigeminy reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; determining the optimal annealing temperature of the bigeminy reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; testing the sensitivity of the bigeminy reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; and testing the specificity of the bigeminy reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. The multiple reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction detection method for swine transmissible gastroenteritis is suitable for detecting swine transmissible gastroenteritis.
Owner:郑世民
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com