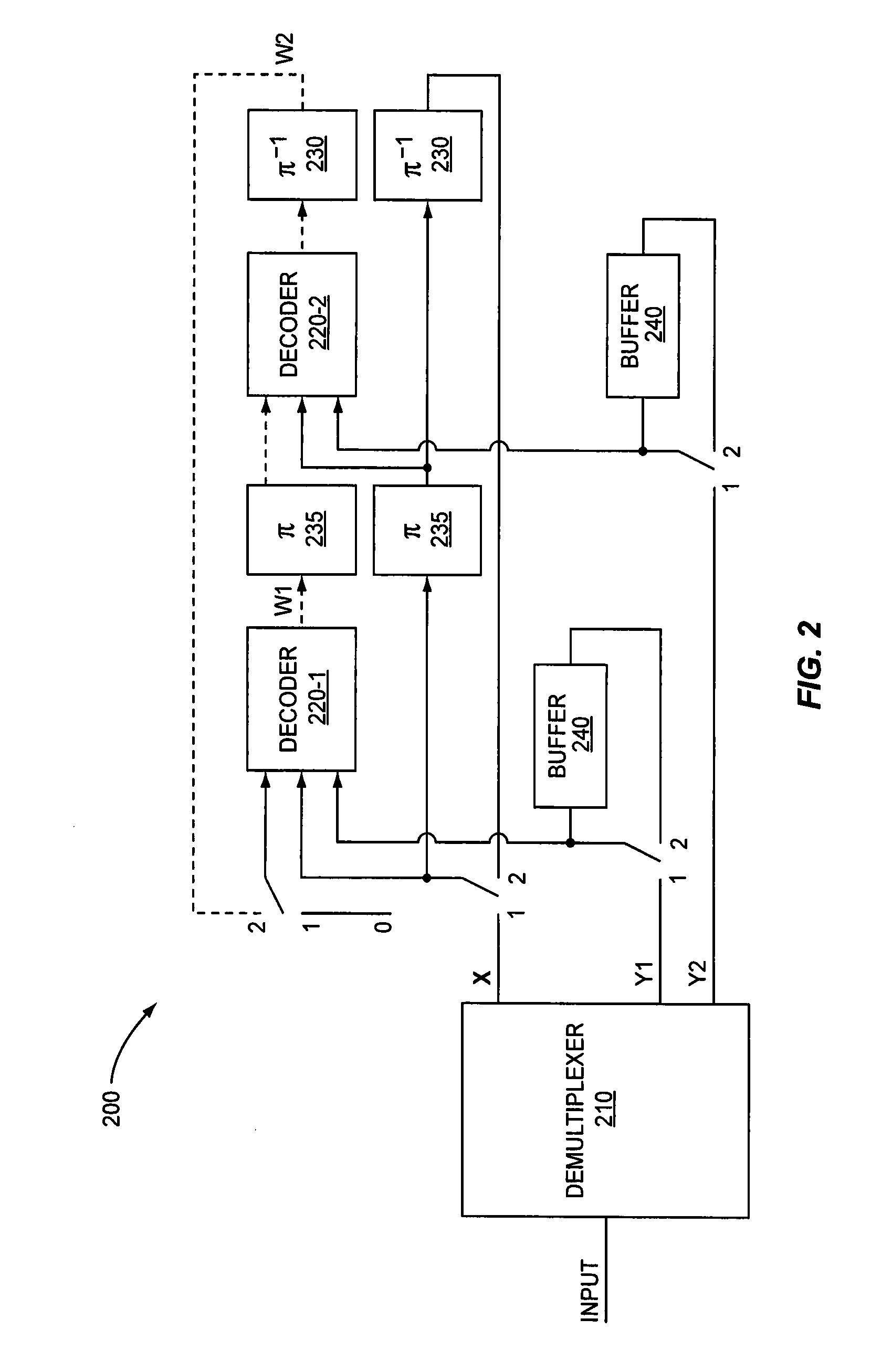
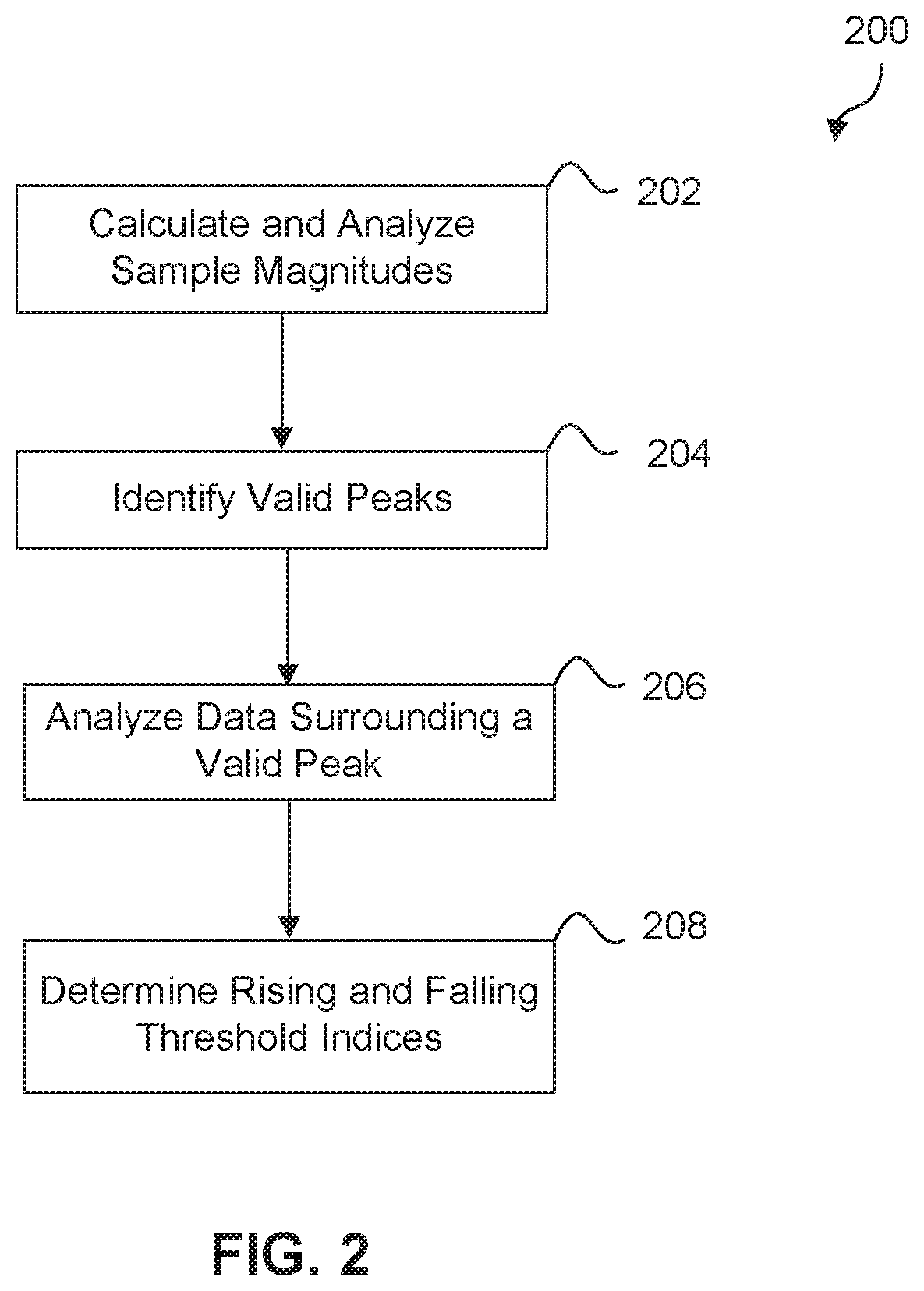
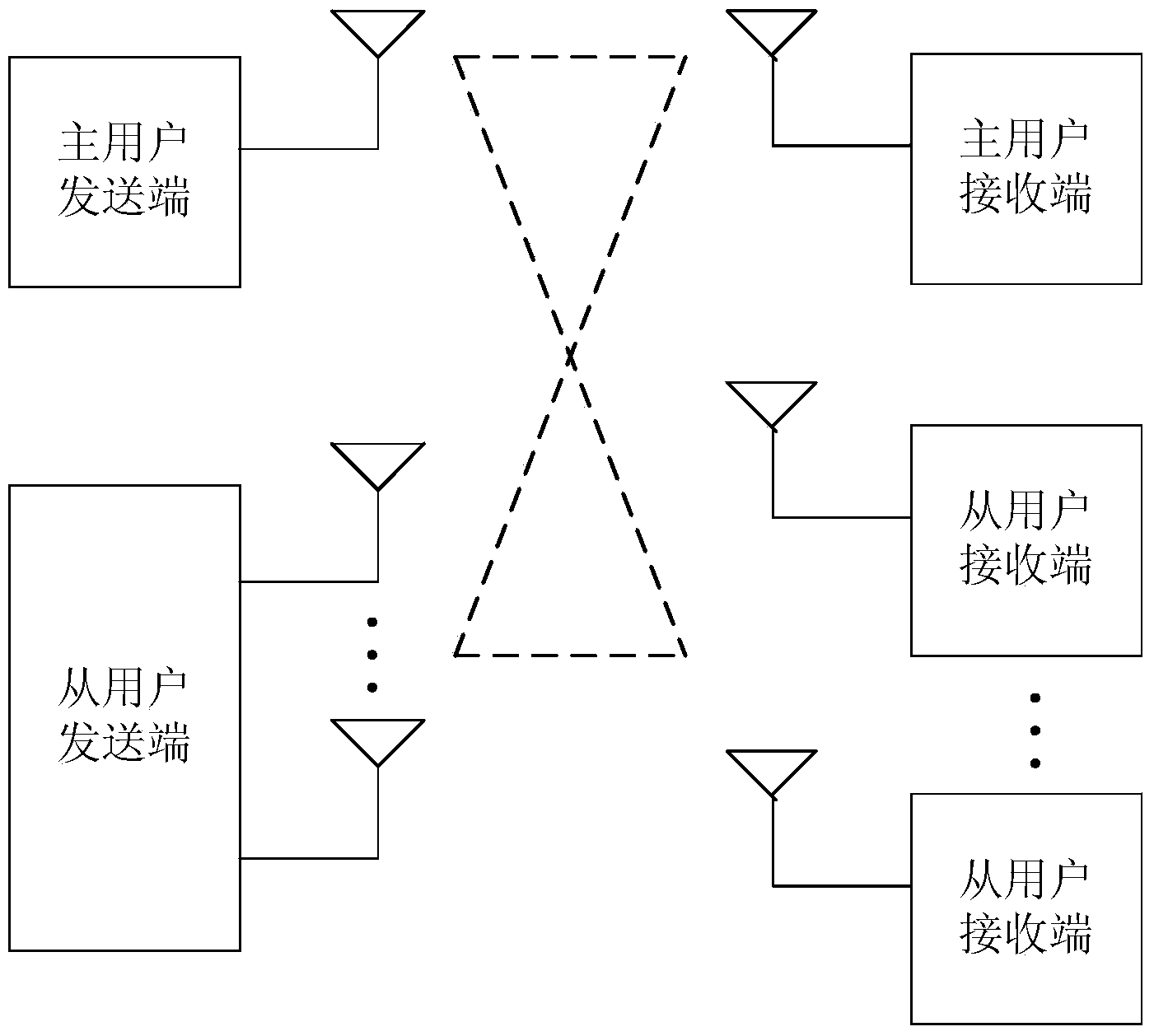Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Convolutional decoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
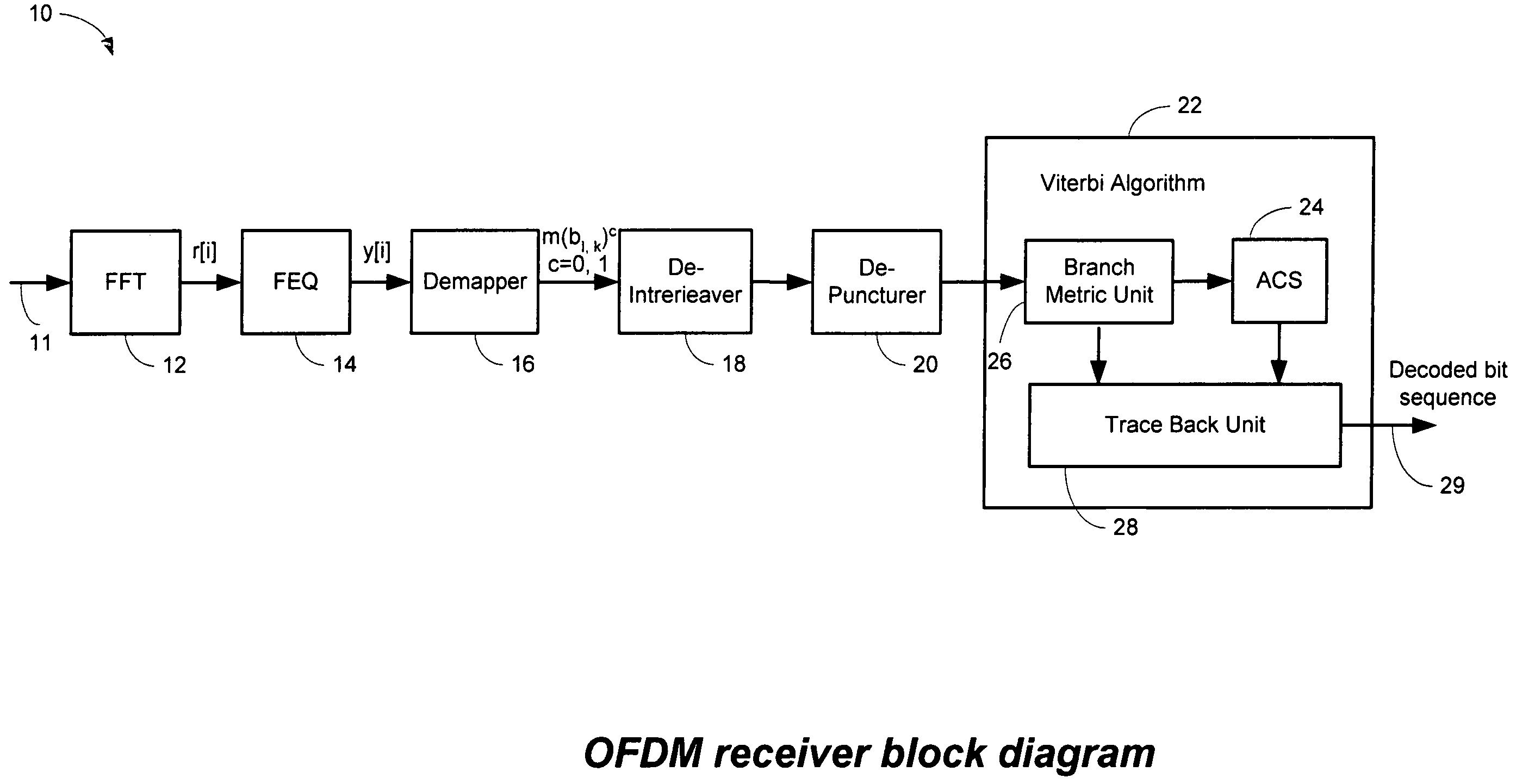
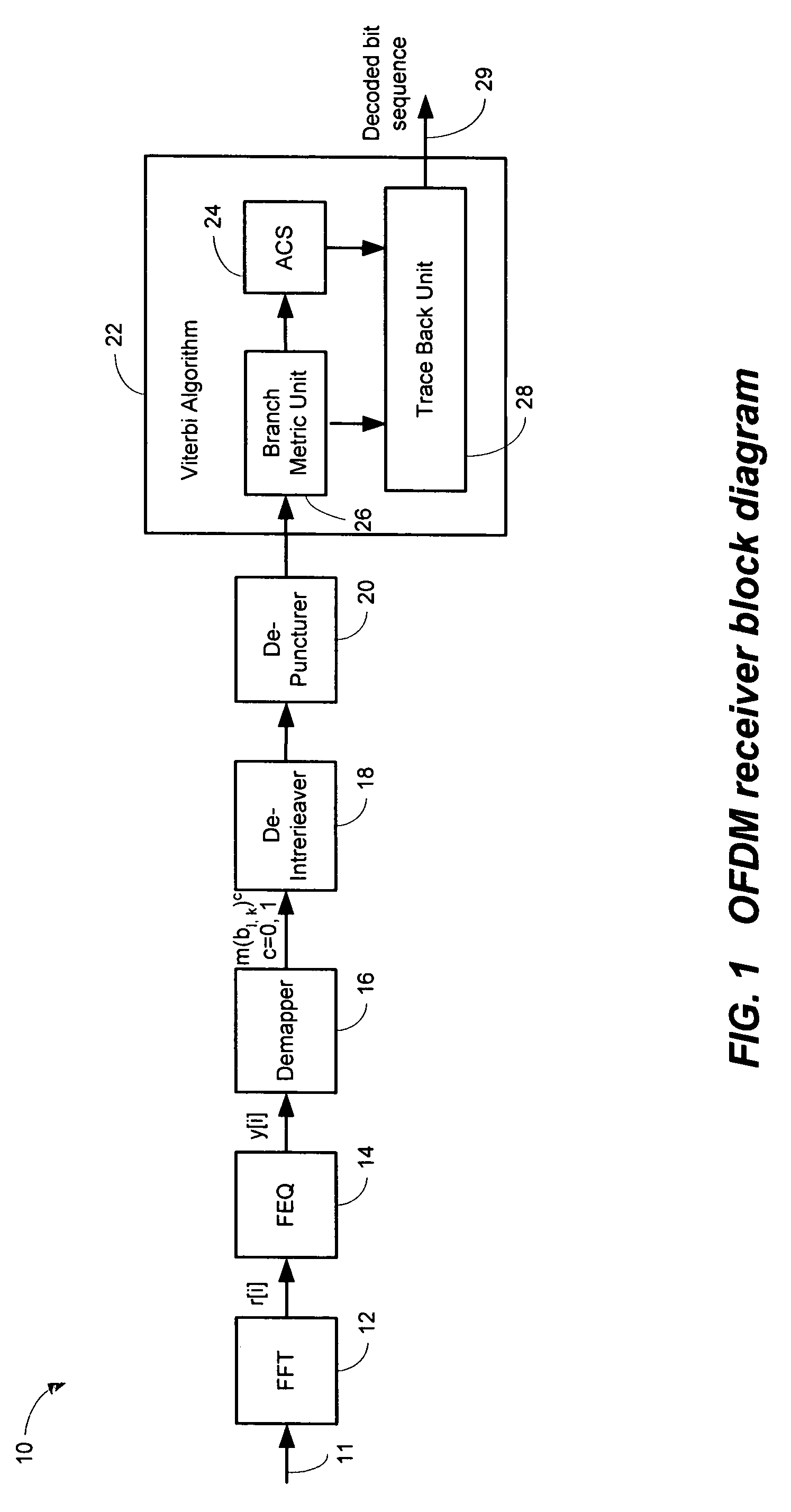
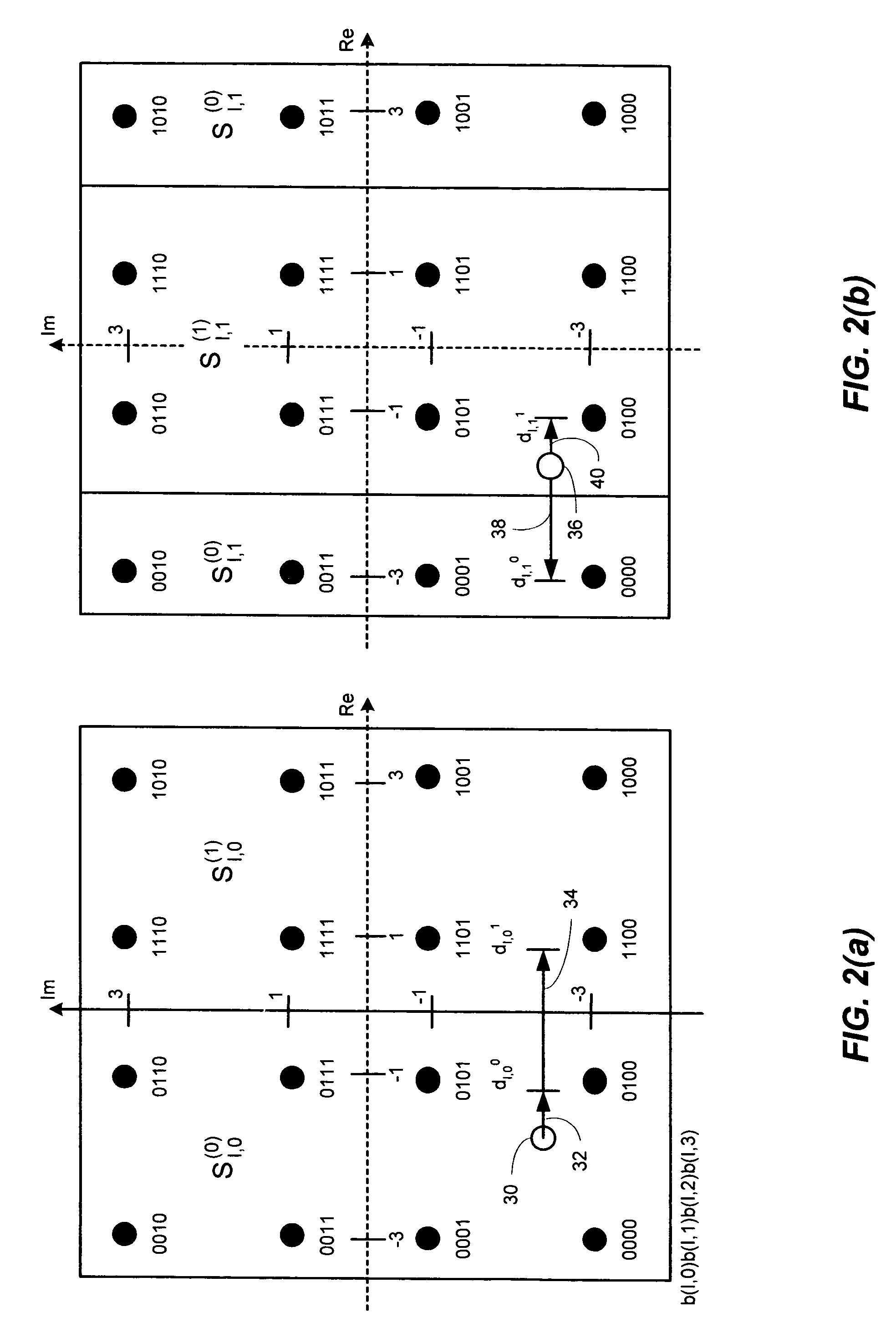
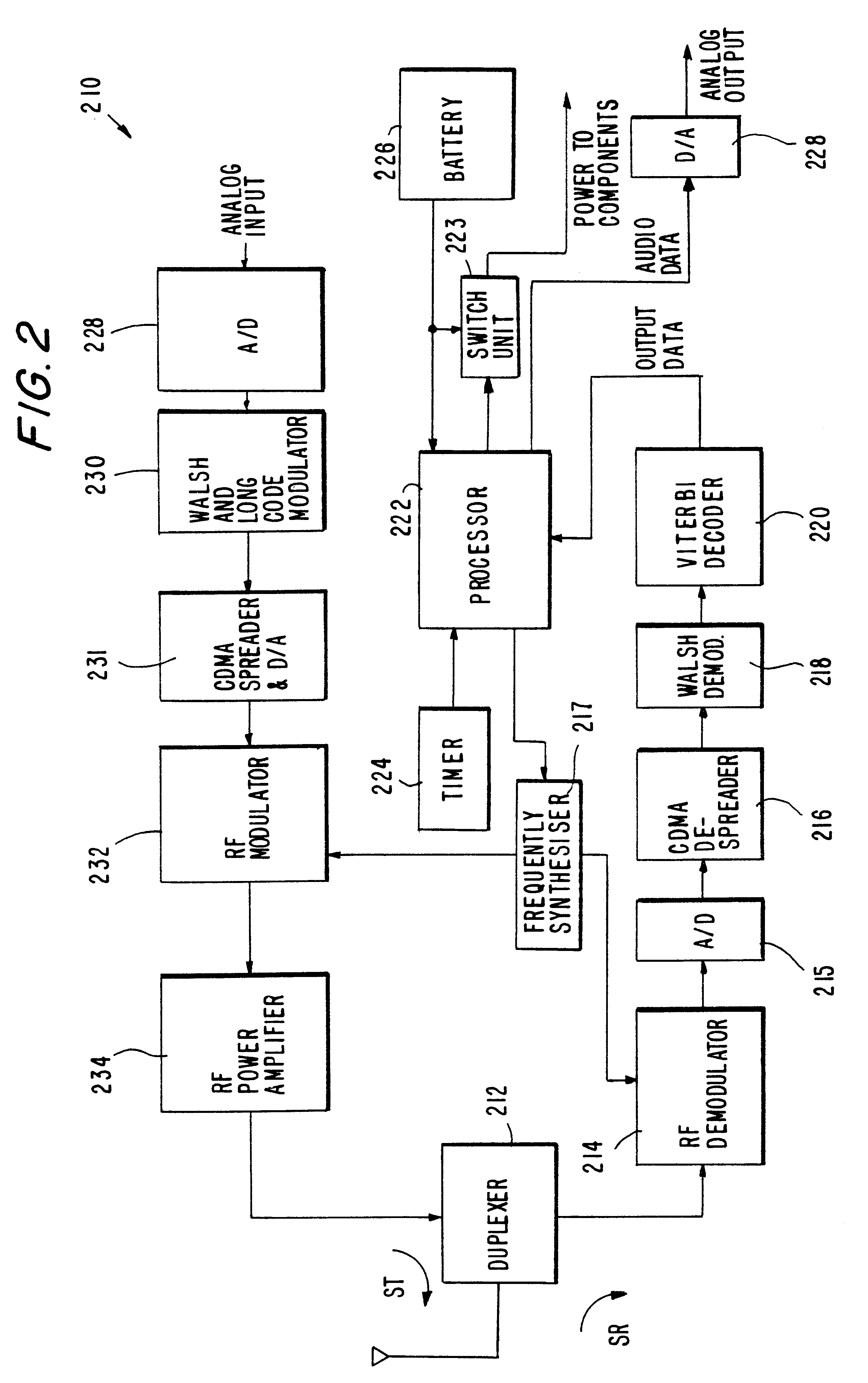
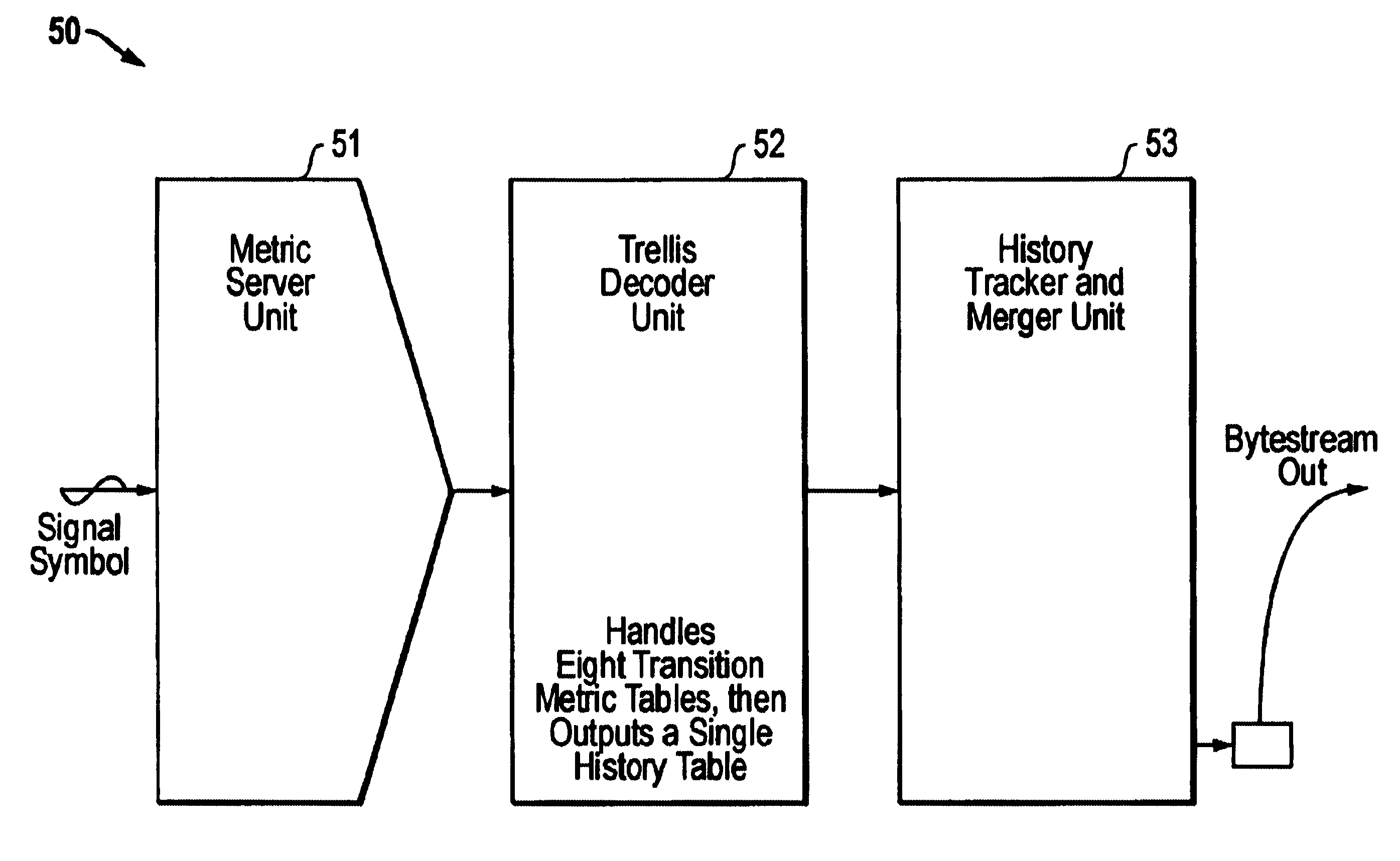
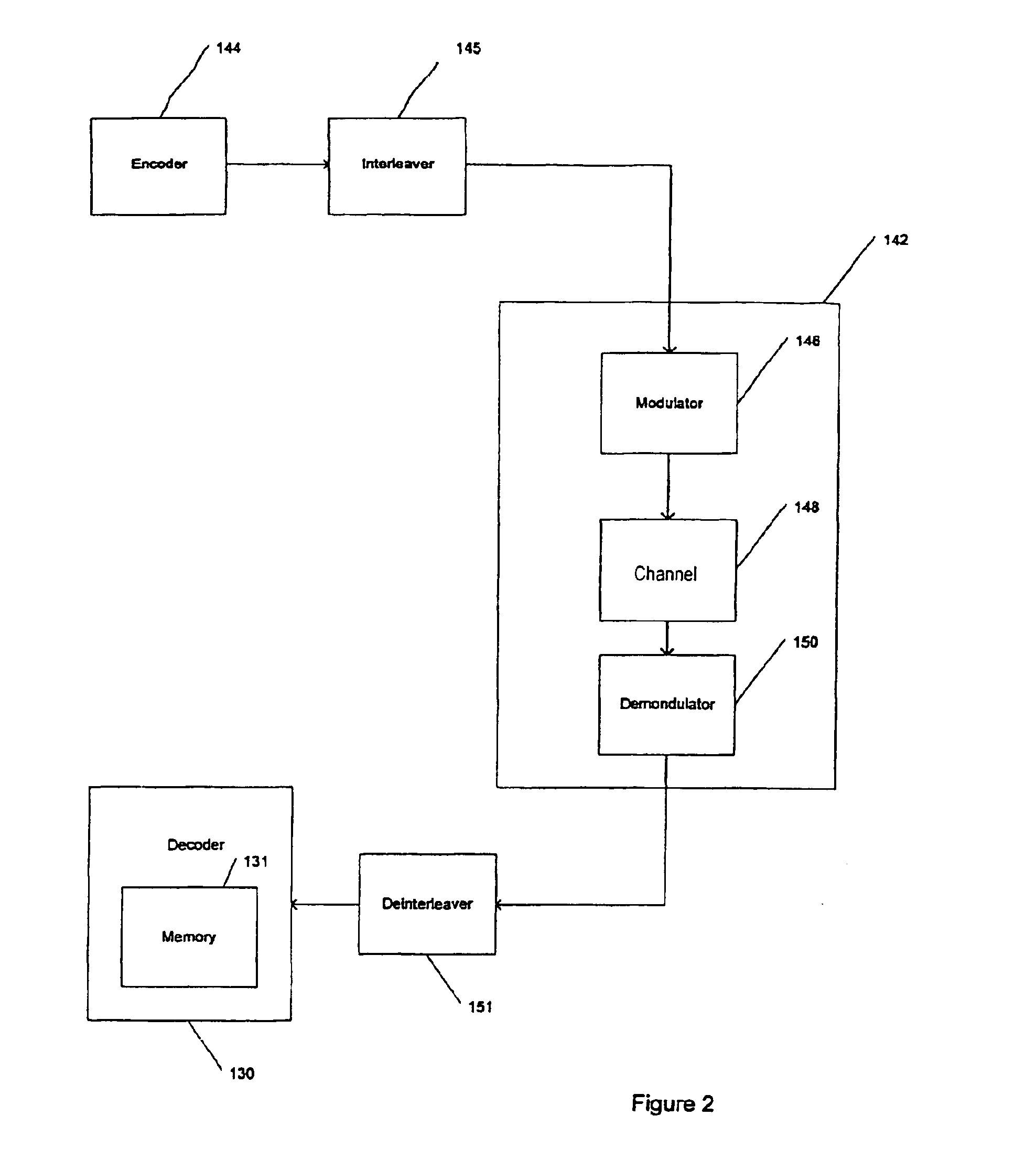
Efficient soft decision demapper to minimize viterbi decoder complexity
InactiveUS7313750B1Improve performanceSmall sizeData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderComputer science
A receiver system that receives signals and has a demapper device that is responsive to an equalizer output and generates a demapper output including one or more bit metrics. The receiver system also generates equalizer output, and the demapper uses distance measure to calculate bit metrics. The receiver system uses demapper output to generate a processed output. The receiver system further includes a convolutional decoder which is responsive to the processed output, and subsequently generates a decoded bit sequence, as well as uses the processed output to generate one or more path metrics. The convolutional decoder uses bit metrics and path metrics to the decode processed output, to generate a decoded bit sequence. The receiver system uses the distance measure to reduce the size of the bit metrics and the size of the path metrics to improve the performance of said convolutional decoder.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
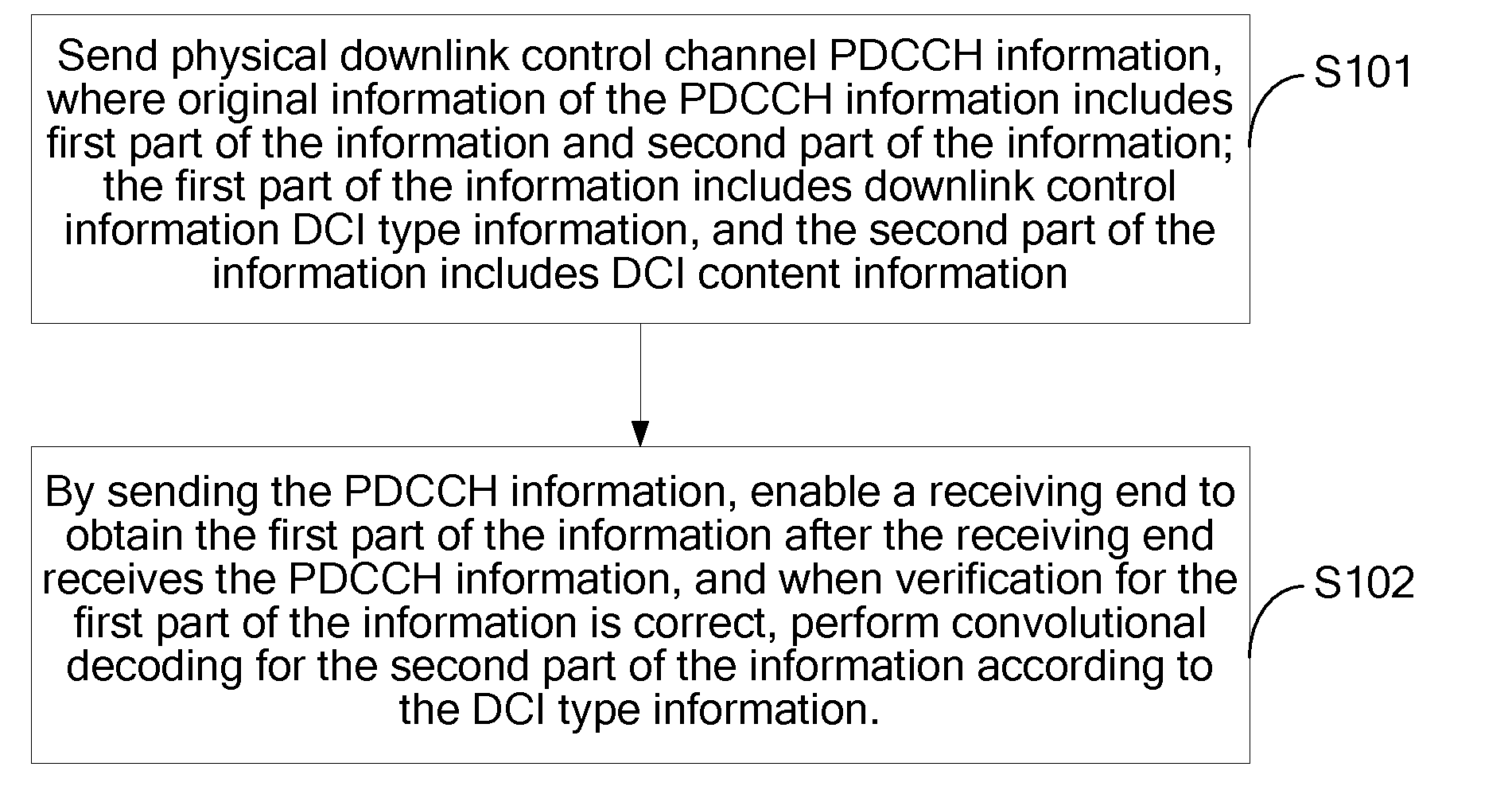
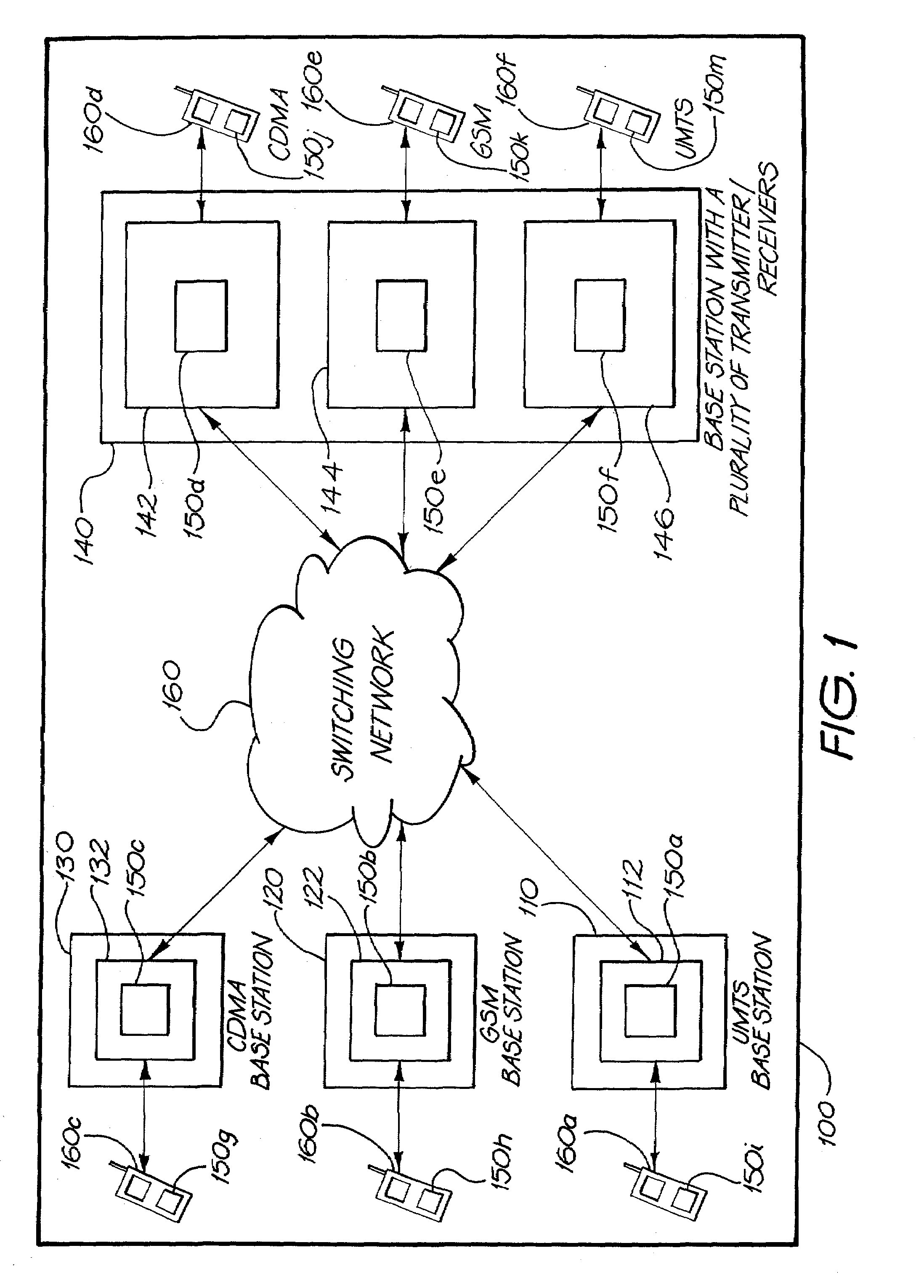
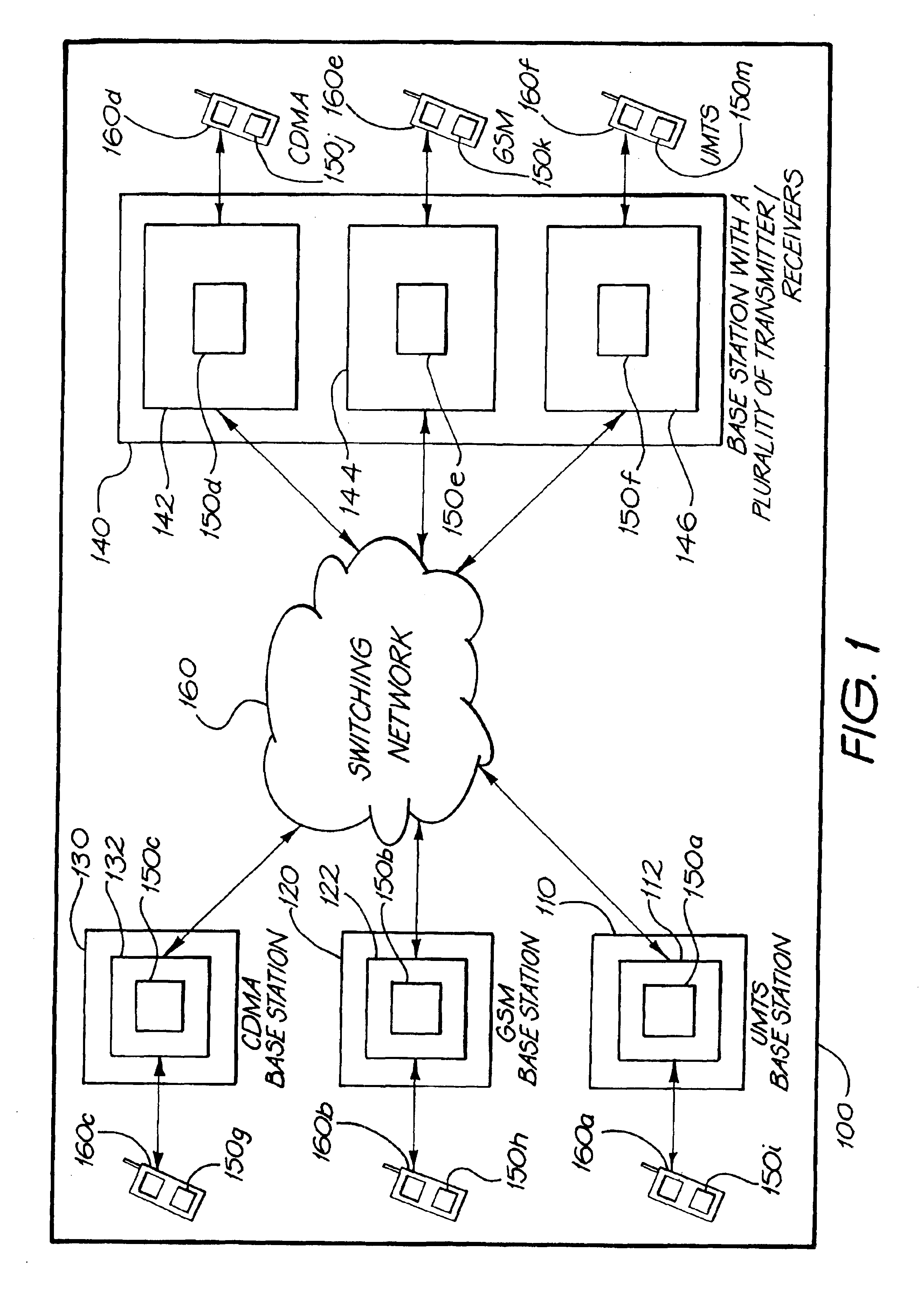
Method, apparatus and system for downlink channel transmission
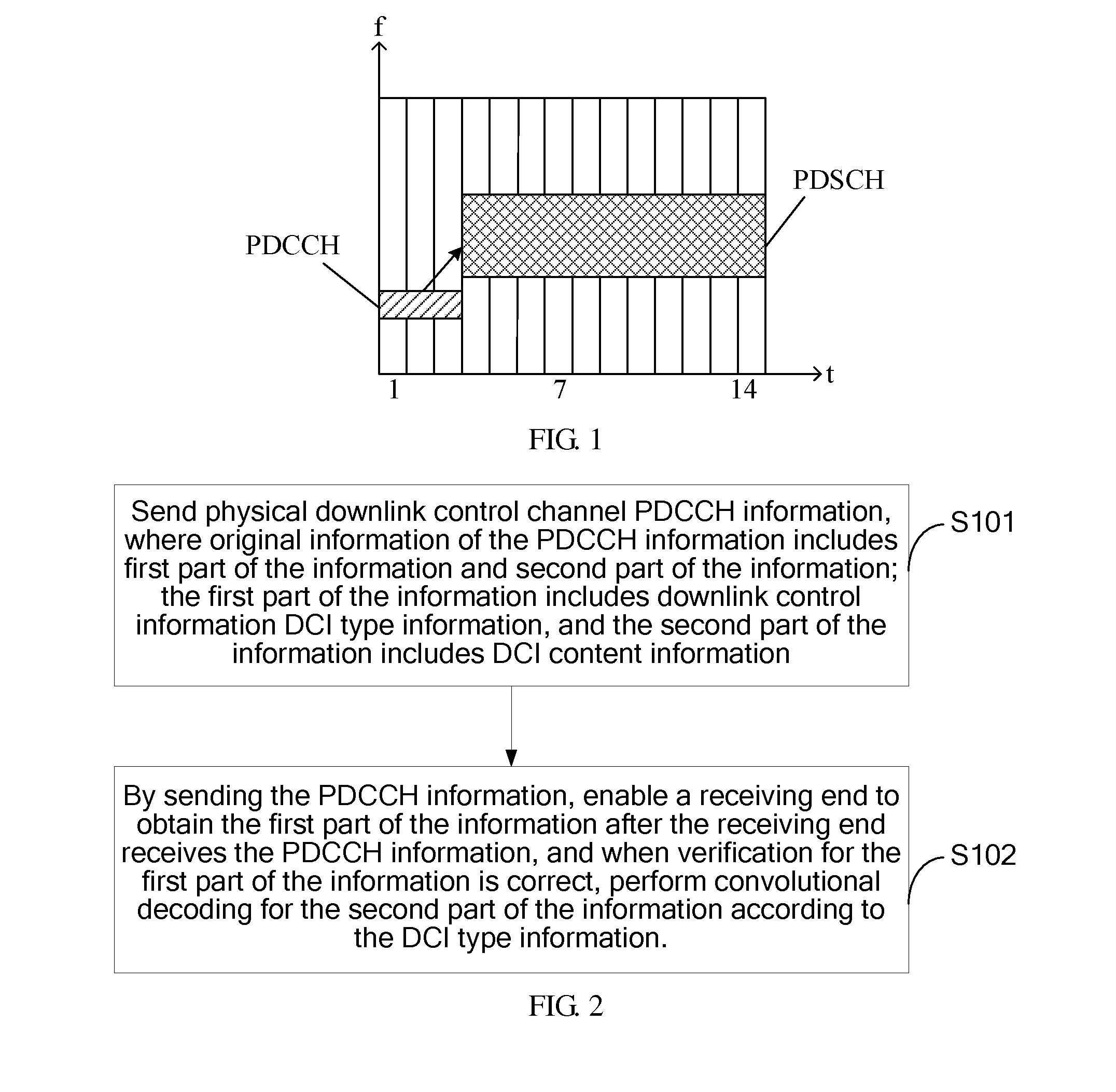
ActiveUS20120201216A1Reduce the number of timesReduce the amount of calculationNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionComputer scienceConvolutional decoding
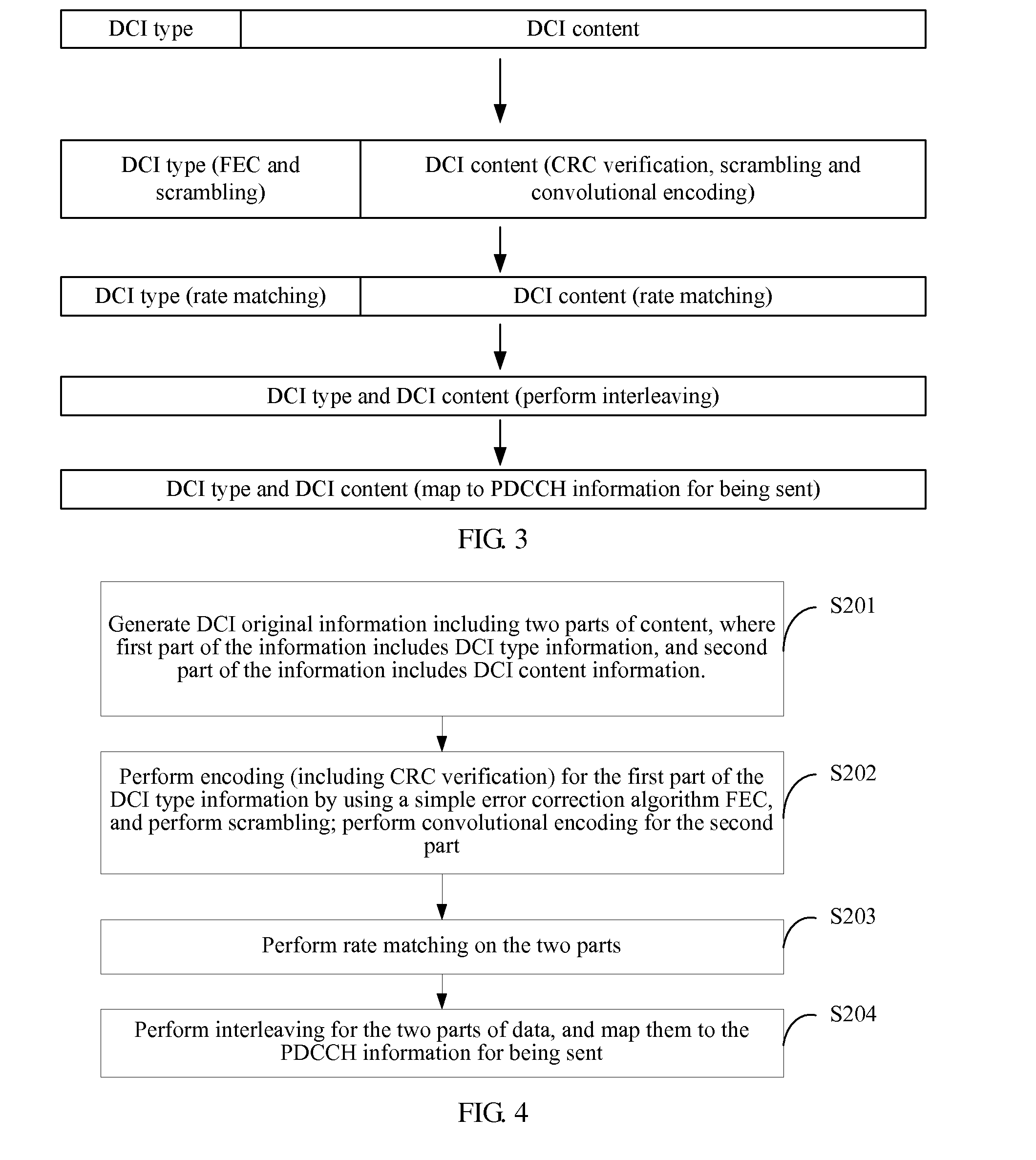
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a method, an apparatus and a system for downlink channel transmission. The method for downlink channel transmission includes: sending PDCCH information, where original information of the information includes a first part of the information and a second part of the information; the second part of the information includes downlink control information DCI content information, and the first part of the information includes indication information for indicating a related parameter of the DCI content information in the second part of the information; after receiving the PDCCH, obtaining, by a receiving end, the first part of the information and verifies it, if correct, obtaining the related parameter of the DCI content information in the second part of the information according to the indication information, and performing convolutional decoding for specific DCI content information in the second part of the information according to the related parameter.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for decoding continuously coded convolutionally encoded messages
InactiveUS6356595B1Reduce power consumptionReduce error rateData representation error detection/correctionError preventionViterbi decoderCommunications system
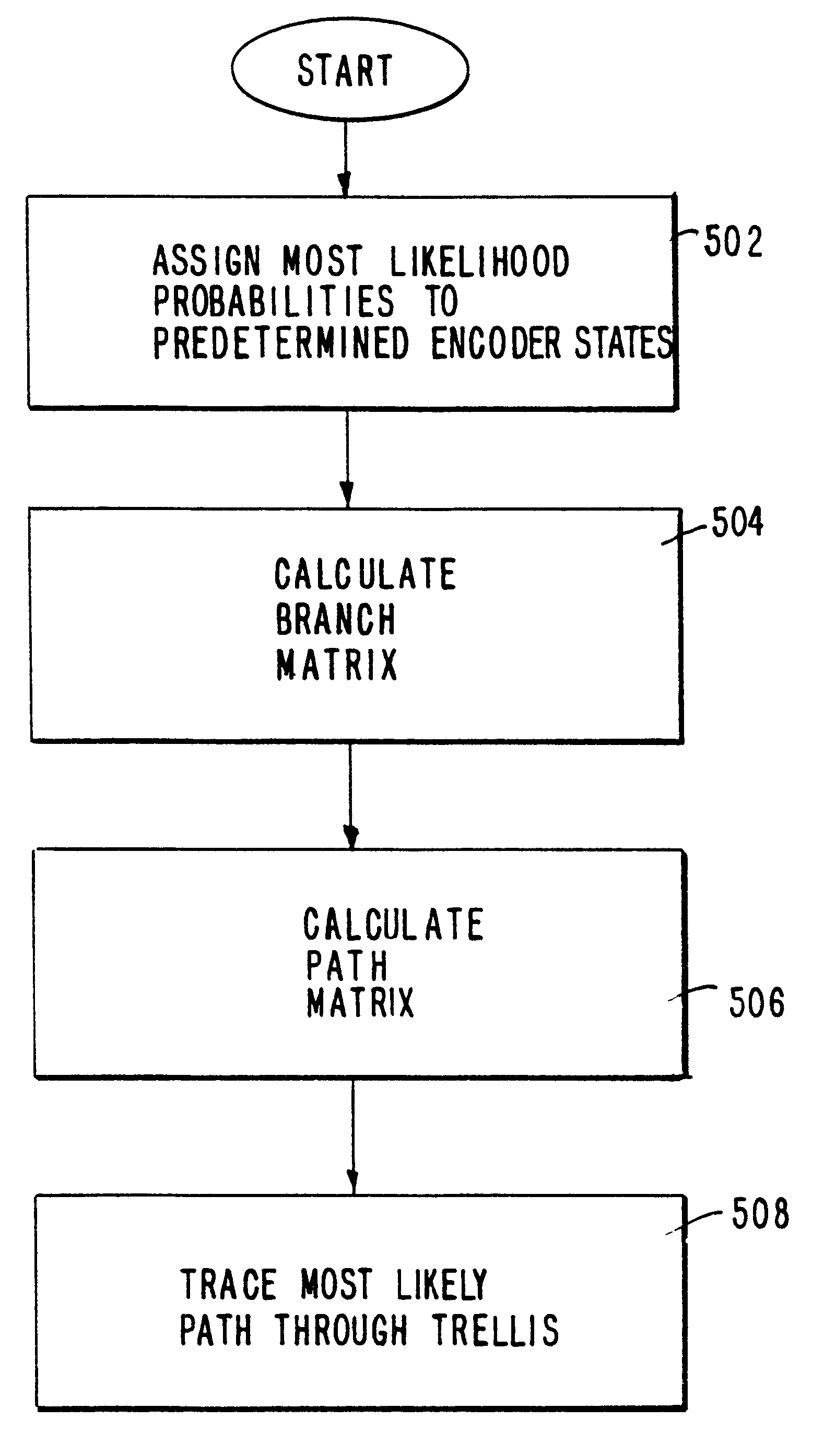
A decoding method for use in a communications system employing a communication channel in which a message is convolutionally encoded by a base station encoder and transmitted to a remote terminal during a time slot allocated to at least that remote terminal. The encoder is not completely reset immediately prior to the allocated time slot such the encoder state is unknown at the onset thereof. The decoding method includes assigning a most likelihood probability for an initial encoder state as being one of a number of predetermined encoder states; and, convolutionally decoding ensuing bits of the message based on the assumption of the initial encoder state as one of the predetermined states. The method affords low error rate decoding, and allows for improved power conservation by a mobile station, since the mobile station need not awaken significantly prior to its allocated time slot. Preferably, a Viterbi decoder is used to perform the convolutional decoding. The method has particular utility when used for decoding page messages indicative of call notifications in a paging channel of a code division multiple access (CDMA) wireless telecommunications system.
Owner:SONY ELECTRONICS INC +1
Reconfigurable architecture for decoding telecommunications signals
InactiveUS7127664B2Improve scalabilityEasy to handleError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionCDMA2000Computer hardware
The present invention discloses a single unified decoder for performing both convolutional decoding and turbo decoding in the one architecture. The unified decoder can be partitioned dynamically to perform required decoding operations on varying numbers of data streams at different throughput rates. It also supports simultaneous decoding of voice (convolutional decoding) and data (turbo decoding) streams. This invention forms the basis of a decoder that can decode all of the standards for TDMA, IS-95, GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS, and CDMA2000. Processors are stacked together and interconnected so that they can perform separately as separate decoders or in harmony as a single high speed decoder. The unified decoder architecture can support multiple data streams and multiple voice streams simultaneously. Furthermore, the decoder can be dynamically partitioned as required to decode voice streams for different standards.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Butterfly processor for telecommunications
InactiveUS6865710B2Reduction in hardwareError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionExternal dataComputer module
The present invention discloses a butterfly processor capable of performing convolutional decoding and LogMAP decoding in telecommunications systems. First and second add-compare-select modules are provided for receiving input path metrics. A branch metric calculator is also provided for receiving input data and extrinsic data. The branch metric calculator generates output branch metrics to each of the first and second add-compare-select modules. Each of the add-compare-select modules includes a log-sum correction means coupled to compare and select components. A controllable switch selectively couples outputs of the select components and the log-sum corrections means to enable either one of convolutional or LogMAP decoding.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Iterative Signal Receiving Method and Related Iterative Receiver
InactiveUS20090254797A1Low costData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemMinimum mean square error
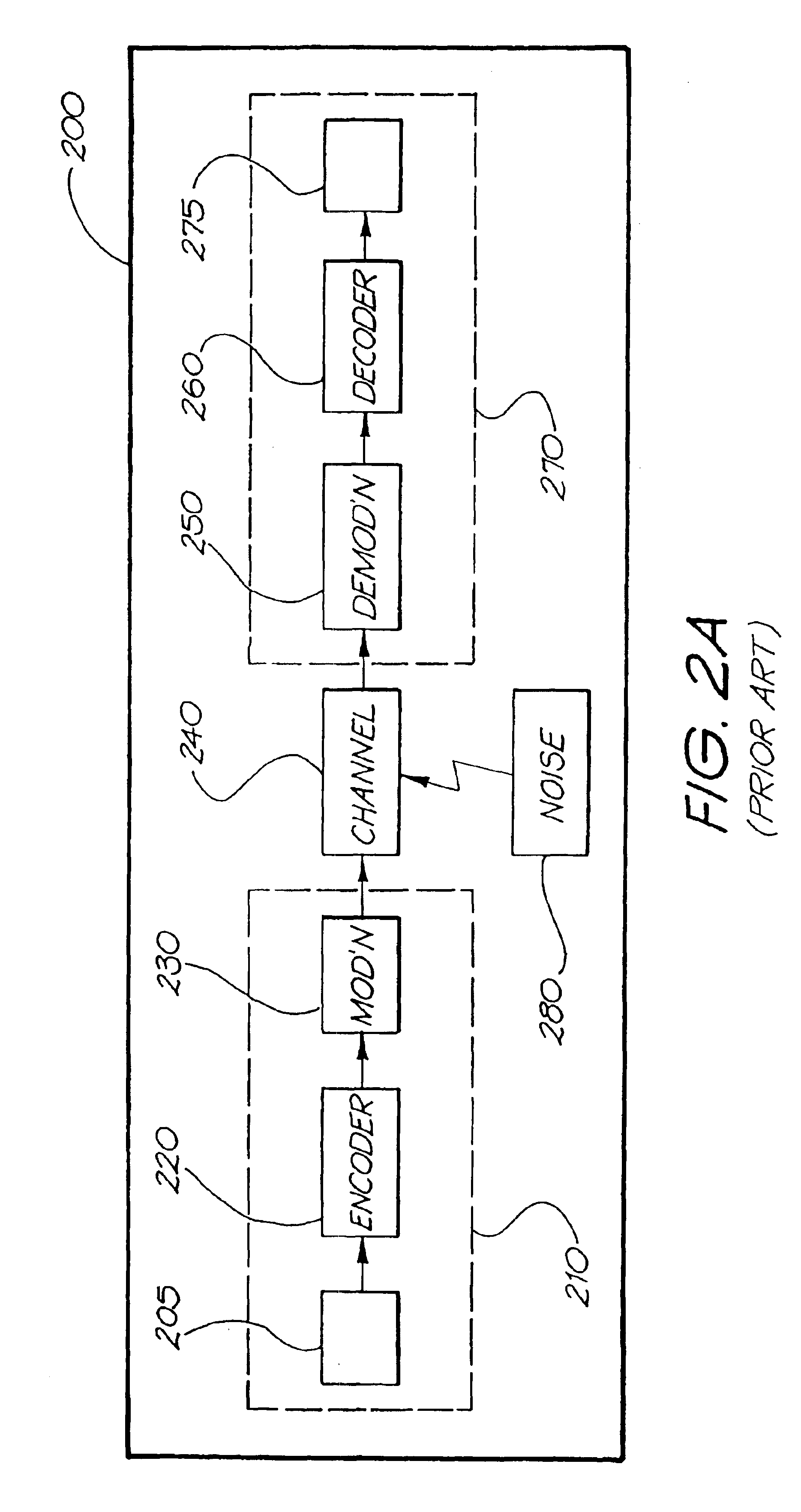
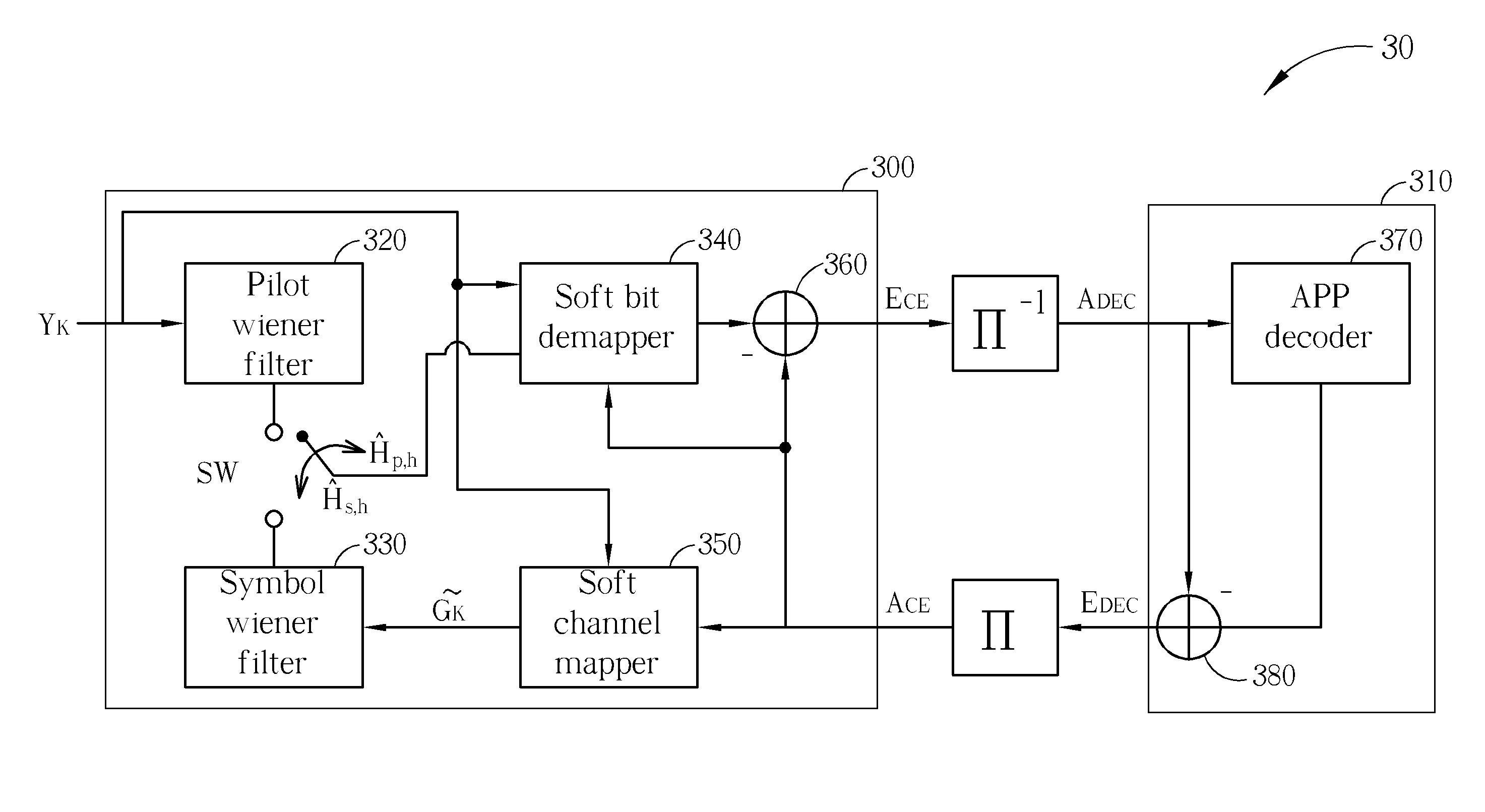
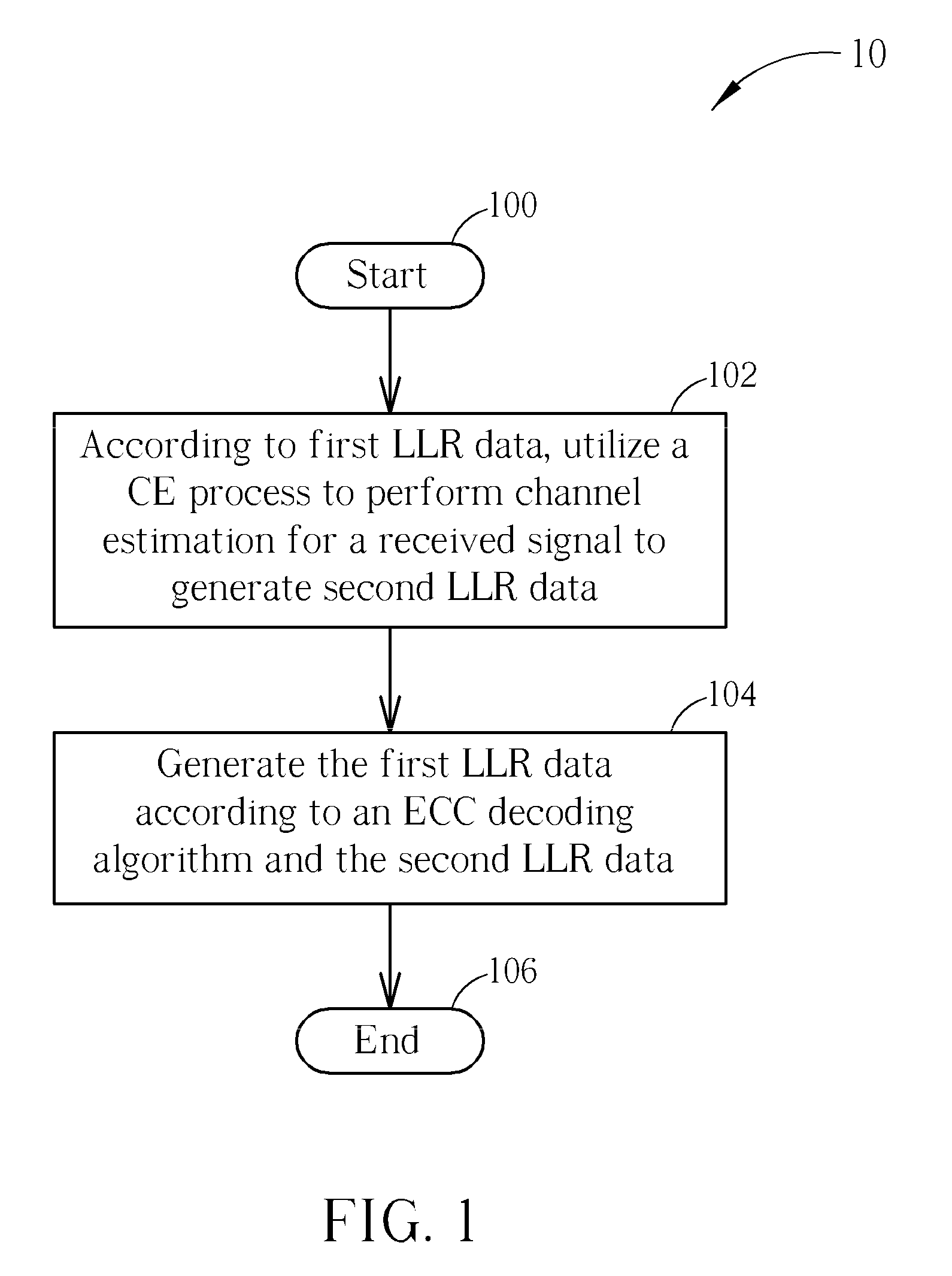
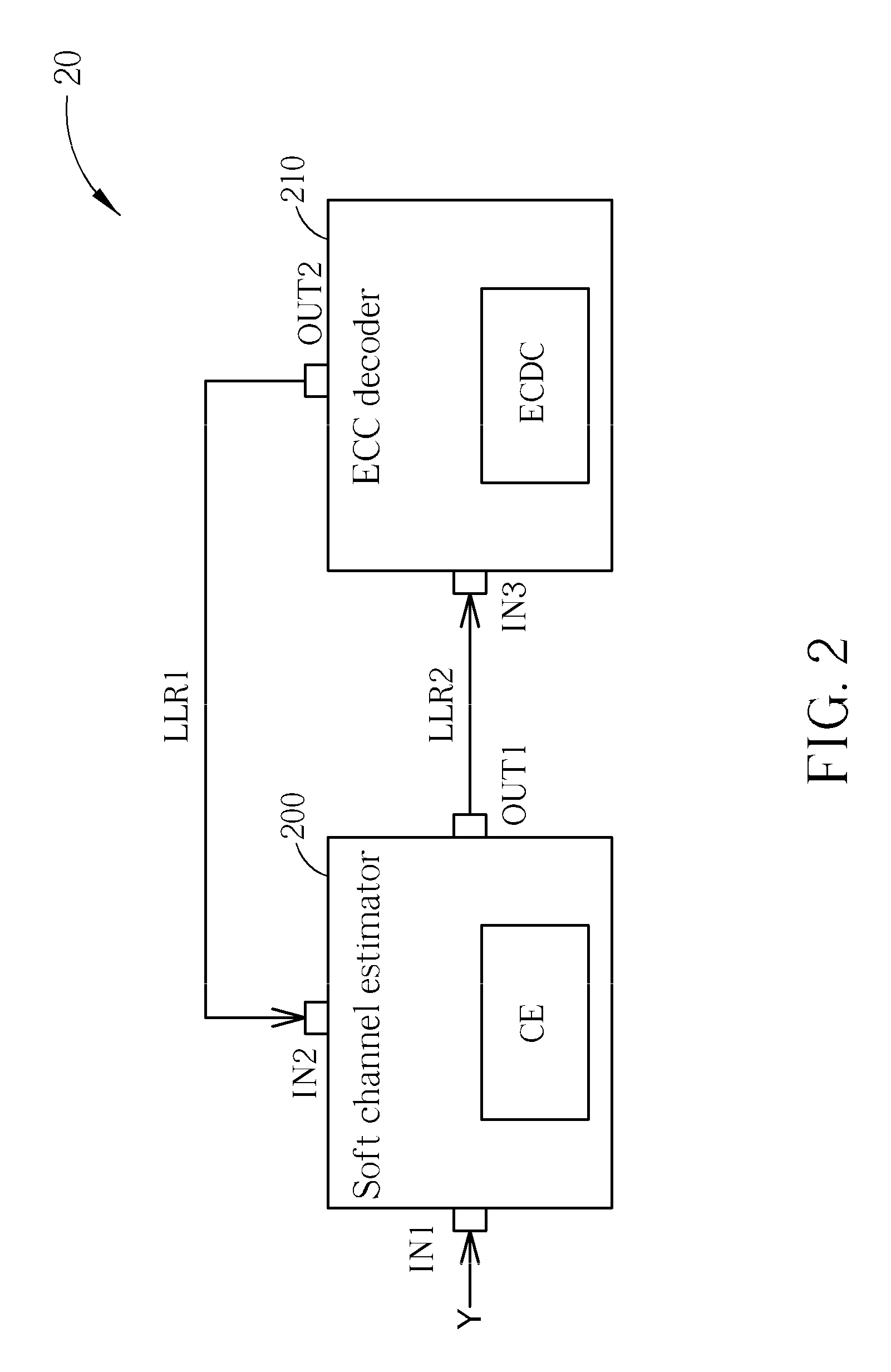
Considering both performance and cost of an iterative receiver, the present invention provides an iterative signal receiving method for a wireless communications system. The iterative signal receiving method includes utilizing a channel estimating (CE) process to perform channel estimation for a received signal according to first log-likelihood ratio (LLR) data to generate second LLR data, and then generating the first LLR data according to an error correction code (ECC) decoding process and the second LLR data. When the ECC decoding process is a convolutional decoding process, the CE process is a zero-forcing process, a minimum mean square error (MMSE) process or an interpolation-based process. When the ECC decoding process is a low density parity check code (LDPC) decoding process, the CE process is a maximum likelihood (ML) process or a maximum a posteriori (MAP) process.
Owner:RALINK TECHNOLOGY CORP
Architecture for a communications device
InactiveUS20020129317A1Easy to handleReduce hardware costsError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionCDMA2000Computer hardware
The present invention discloses a single unified decoder for performing both convolutional decoding and turbo decoding in the one architecture. The unified decoder can be partitioned dynamically to perform required decoding operations on varying numbers of data streams at different throughput rates. It also supports simultaneous decoding of voice (convolutional decoding) and data (turbo decoding) streams. This invention forms the basis of a decoder that can decode all of the standards for TDMA, IS-95, GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS, and CDMA2000. Processors are stacked together and interconnected so that they can perform separately as separate decoders or in harmony as a single high speed decoder. The unified decoder architecture can support multiple data streams and multiple voice streams simultaneously. Furthermore, the decoder can be dynamically partitioned as required to decode voice streams for different standards.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Parallel VLSI architectures for constrained turbo block convolutional decoding
InactiveUS20150236723A1Reduce measurement errorCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresBlock codeMemory bank
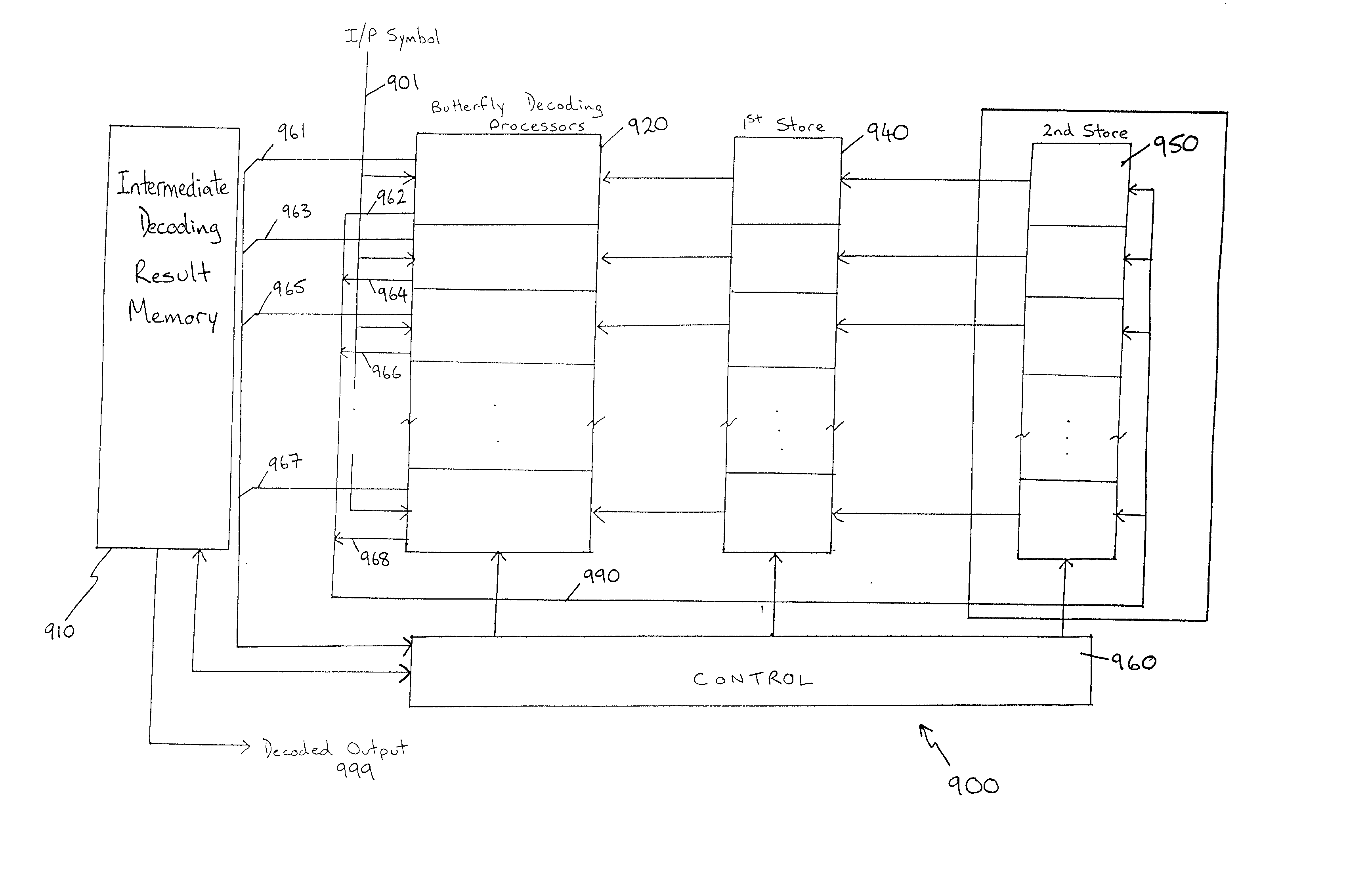
A constrained turbo block convolutional code (CTBC) involves a serial concatenation of a outer block code B with an inner recursive convolutional code, joined together by a constrained interleaver type 2 (CI-2). The CI-2 interleaver is designed off line, and prior to VLSI design time. The present invention provides massively parallel systems, methods, and apparatus for use in CTBC encoding and decoding. For example, a massively parallel CTBC decoder is be implemented using N processors, each with local private memory, and each with local access to a one or more respective memory locations (e.g., registers) in one or more respective multiported memory banks that each hold extrinsic or related information used in CTBC code iterative SISO decoding. Both the arithmetic decoding operations and the CI-2 interleaving and deinterleaving functions are performed in parallel using the systems, methods, and apparatus of the present invention.
Owner:DOWLING ERIC MORGAN
Underwater Acoustic Ofdm Decision Quadratic Channel Equalization Method
InactiveCN102299872AImprove interpolation accuracyReduce interpolation errorMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksOriginal dataCarrier signal
The purpose of the invention is to provide a method for decision of secondary channel equalization of underwater acoustic OFDM. According to the method, a CombMMSE channel estimation is carried out; once equalization is carried out on received data by utilizing a frequency response to obtain post-once equalization data; de-mapping processing is carried out on subcarriers of the post-once equalization data and then estimation of original data is obtained by convolutional decoding or Turbo decoding; coding is again carried out on the decoded data according to an original encoding rule to obtain post-secondary coding data; estimation on block pilot frequency is obtained by taking the estimated data subcarriers as a training sequence and by combining comb pilot frequency subcarriers, so that all subchannels have training data; and then secondary channel estimation is again carried out by utilizing a BlockMMSE algorithm. According to the invention, comb pilot frequency interpolation errors can be substantially reduced; moreover, a good balancing effect can be achieved on the condition that an interval between pilot frequencies is big.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Coding method and use of a receiver with a convolutional decoder
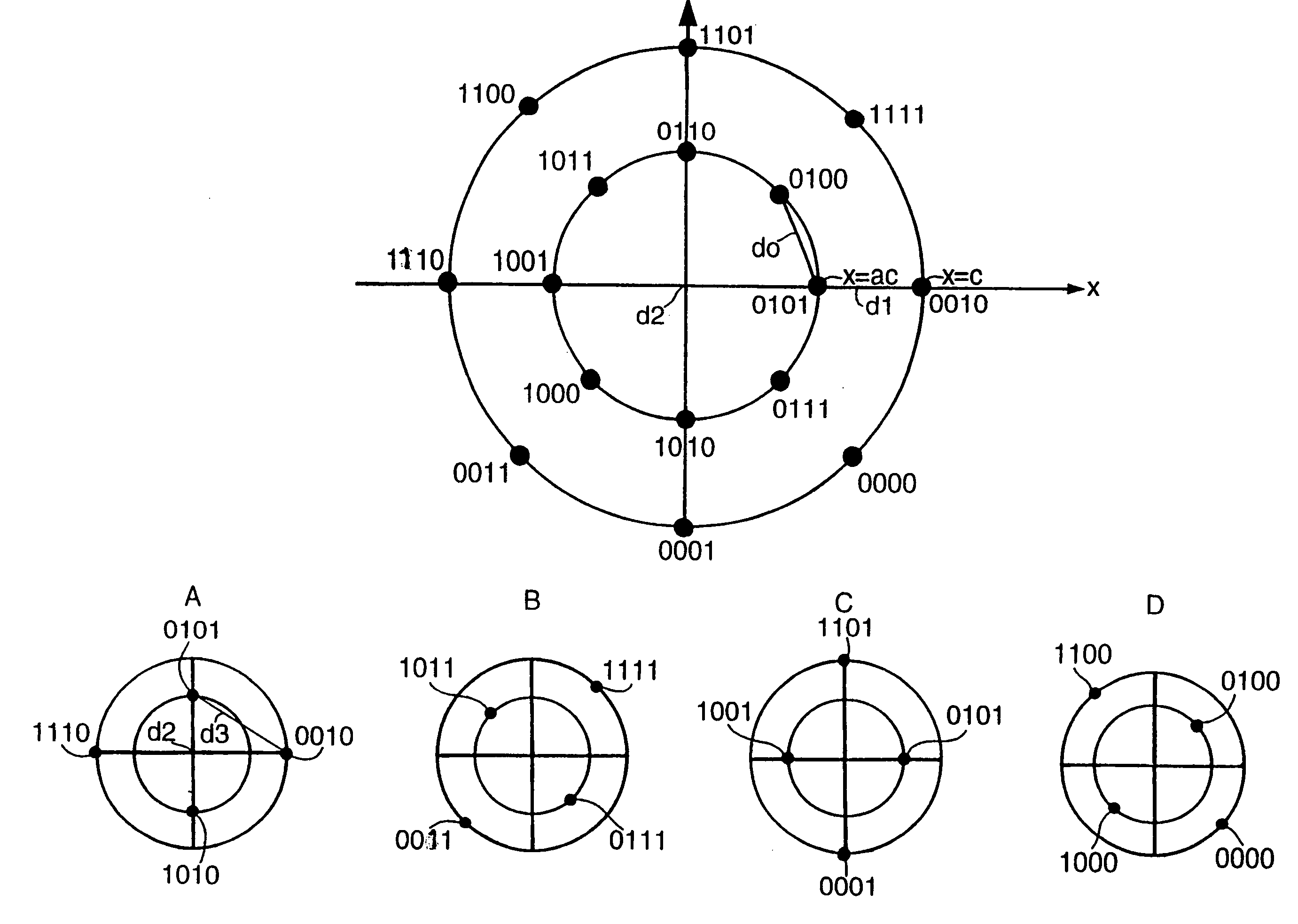
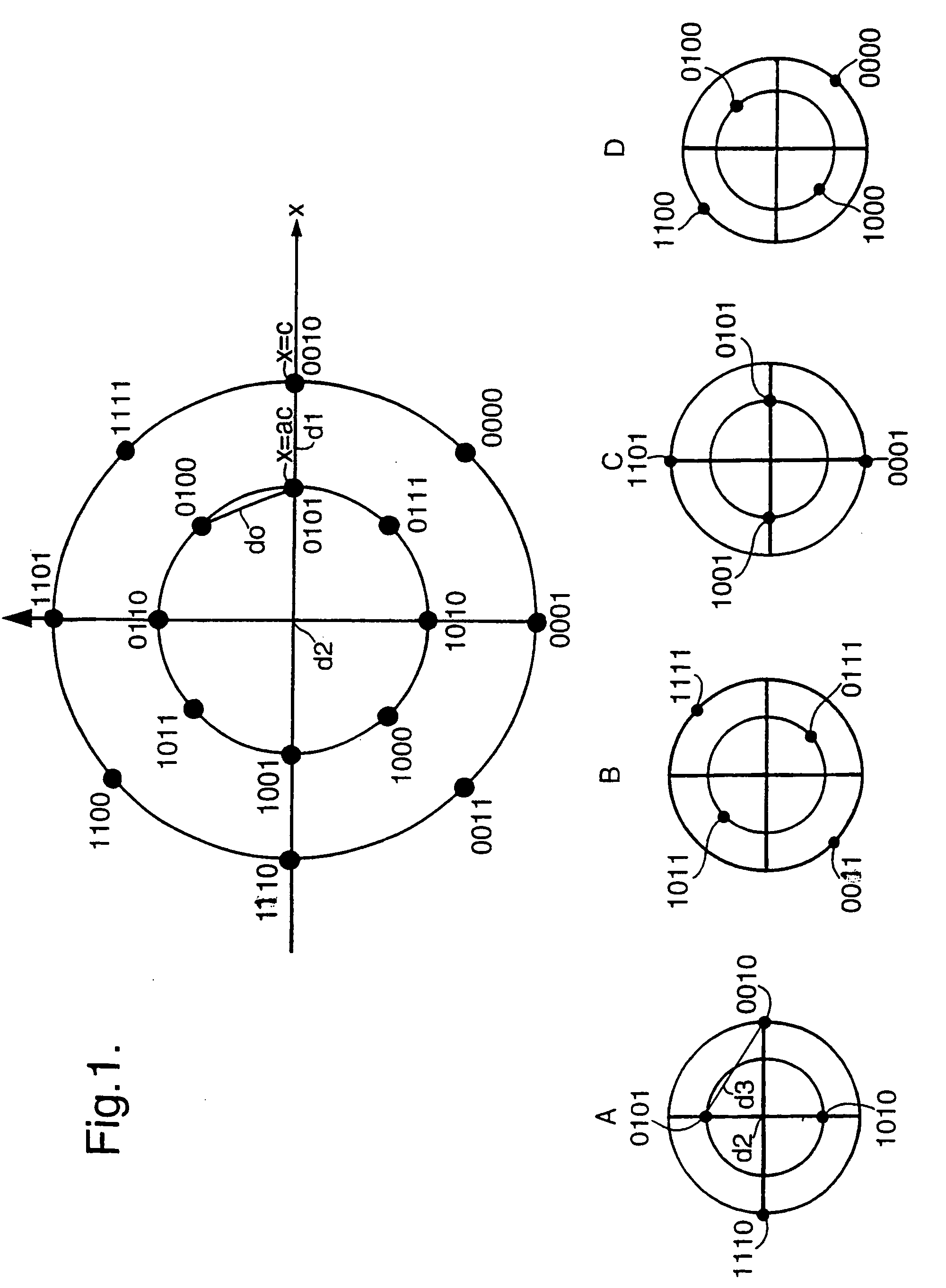
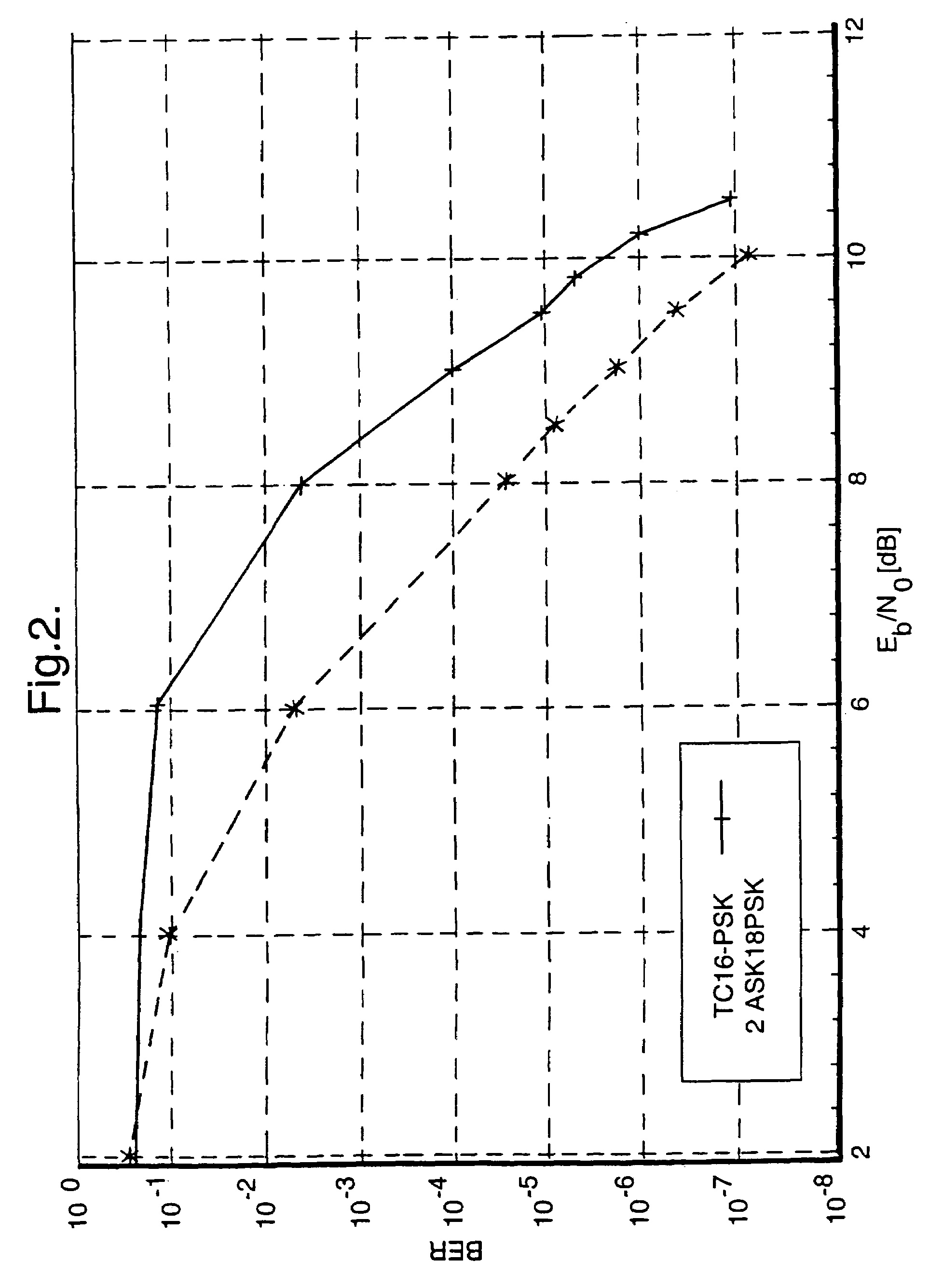
A coding method for modulating carrier signals with 16 different digital states (4 bit signals) possesses a high synchronicity robustness and an at least partially improved coding gain. The coding parameters are obtained by the following steps: a) using a 2 ASK / 8 PSK coding; b) choosing a convolutional code and determining all possible code word sequences with the free distance of the convolutional code; c) producing possible mappings by allocating a partial quantity of the 2 ASK / 8 PSK channel bits to subsets; d) choosing the mapping at which, after determination of the optimum radii of the two amplitudes for every possible mapping, the resulting minimum Euclidean distance takes a maximum value between two possible subset sequences code word sequence.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Digital signal processor decoding of convolutionally encoded symbols
InactiveUS6622283B1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionDigital signal processingState dependent
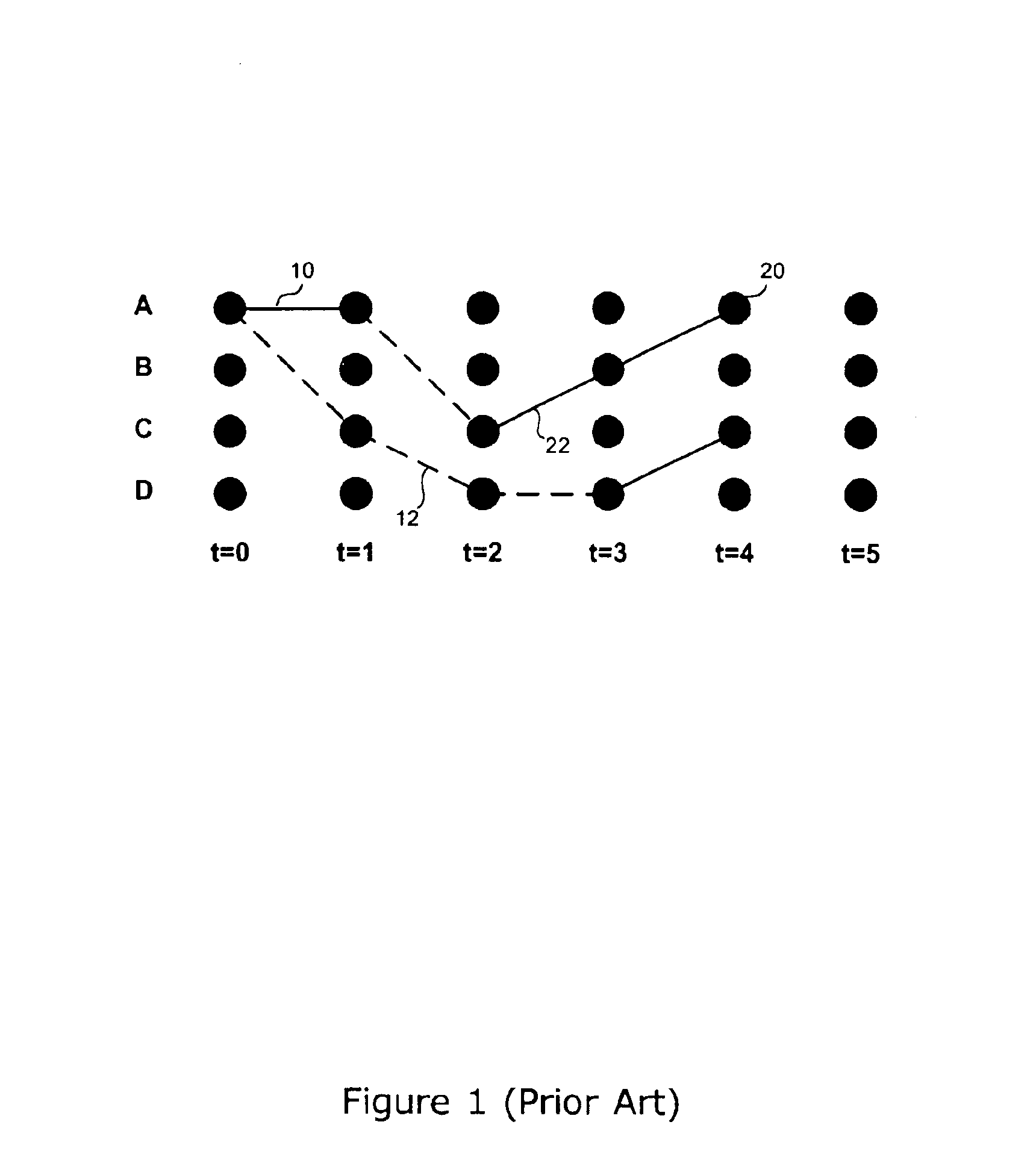
In one embodiment, a file of all the initial states (or their equivalents) and the nth surviving states associated with the initial states is stored along with the path metric. The initial states (or their equivalents) are an index to a previous file. A.new file or files are then generated. An appropriate criterion is utilized to select a final surviving state. The path can be traced back through a plurality of files and the "most likely" path determined. The identifying binary numbers of the final states of each file and the binary numbers of an original initial state determine the "most likely" sequence of convolutionally-encoded symbols received by the decoder. The convolutional decoding can be implemented with a digital signal processor and a dedicated peripheral unit. This apparatus can provide an efficient use of memory for the possible decoding paths.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS AMERICA
Parallel multicode-rate convolutional code decoding method and realization device thereof
InactiveCN101764622AMeet the requirements of high-speed information transmission communication systemImprove decoding throughputError correction/detection using convolutional codesControl signalAmbiguity
The invention discloses a parallel multicode-rate convolutional code decoding method and a realization device thereof. The parallel multicode-rate convolutional code decoding method comprises the following steps of: S1. receiving Nin paths of parallel input signals, and shifting the input signals under the effect of a shifting control signal and outputting the input signals, wherein output signals are also Nin paths of parallel signals, and the Nin is positive integers; S2. partially eliminating the phase ambiguity of the output signals; S3. taking the signals processed in the S2 as effectivedata, adding guard intervals for the effective data to assemble into a data frame, and taking the data frame as the input of a parallel convolutional code; S4. carrying out the convolutional decodingon the assembled data frame after being processed in the step S3; and S5. merging multipath outputs of the parallel convolutional decoding into one path and outputting in parallel. The invention provides the parallel multicode-rate convolutional code decoding method aiming at the defect that the throughput rate of the traditional convolutional decoding can not satisfy high-speed communication, improves the decoding throughput rate and the effective payload velocity by adopting a parallel partitioning processing technology, and can satisfy requirements of high-velocity information transmissioncommunication systems, such as satellite communication, and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
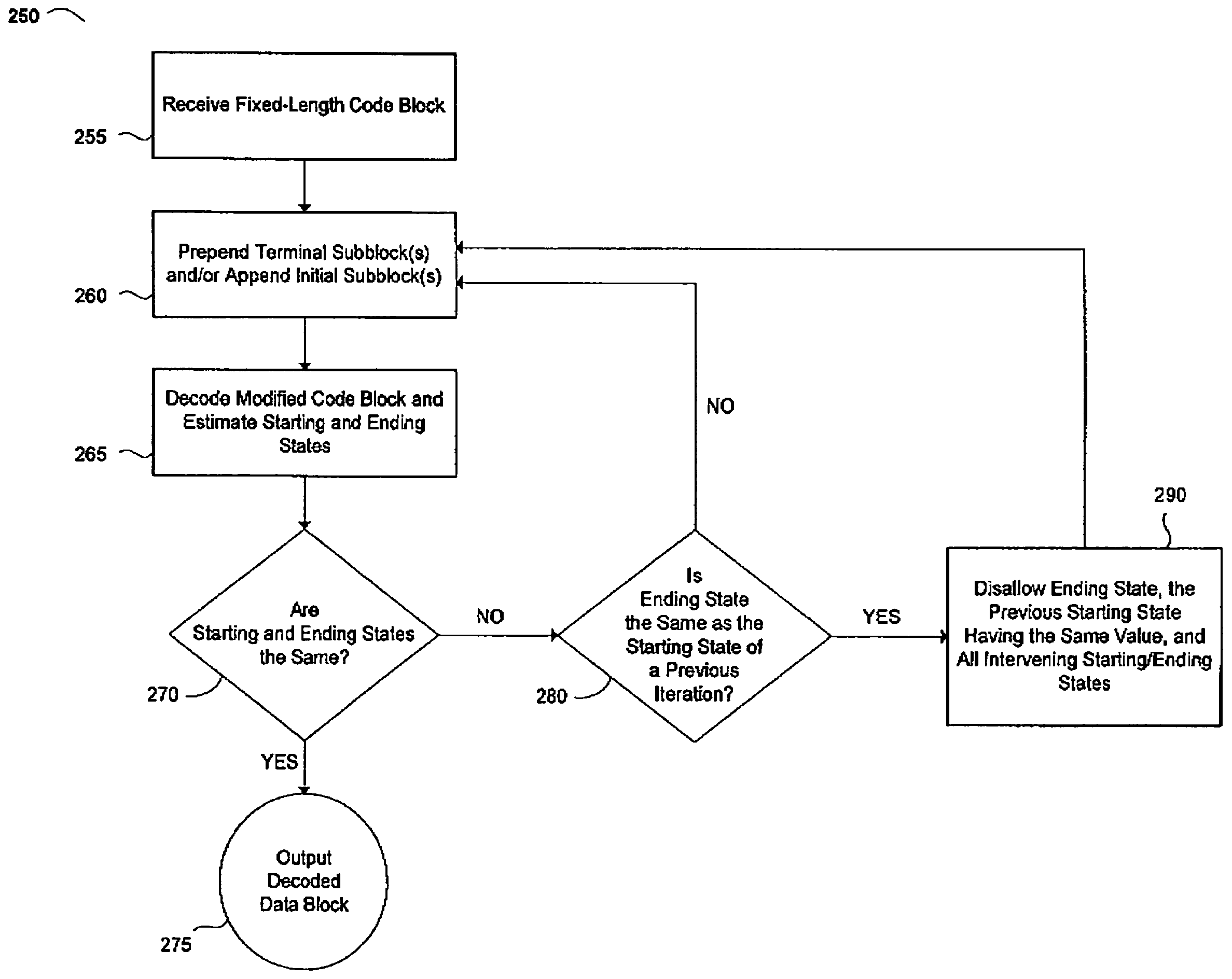
Methods, algorithms, software, circuits, receivers and systems for iteratively decoding a tailbiting convolutional code
ActiveUS7607073B1Reduce complexityImprove reliabilityData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionRound complexityTheoretical computer science
Methods, software, circuits and systems involving a low complexity, tailbiting decoder. The method relates to appending and / or prepending data subblocks to a serial data block, decoding and estimating starting and ending states for the serial data block, and when the starting and ending states are not identical, iterating the decoding and estimating step(s) and (eventually) disallowing at least one starting and / or ending state. The circuitry generally includes a buffer, tailbiting logic configured to append and / or prepend a subblock to the serial data block, a decoder configured to (i) decode the serial data block and (ii) estimate starting and ending states for the serial data block, and iteration logic configured to instruct the decoder to repeat the decoding and starting / ending state estimating functions when the starting and ending states are not identical. The invention advantageously reduces the complexity of a suboptimal convolutional decoder, increases the reliability of the starting and ending states, and may ensure smooth transitions at the data block ends during decoding, without adding any overhead to the transmitted data block.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
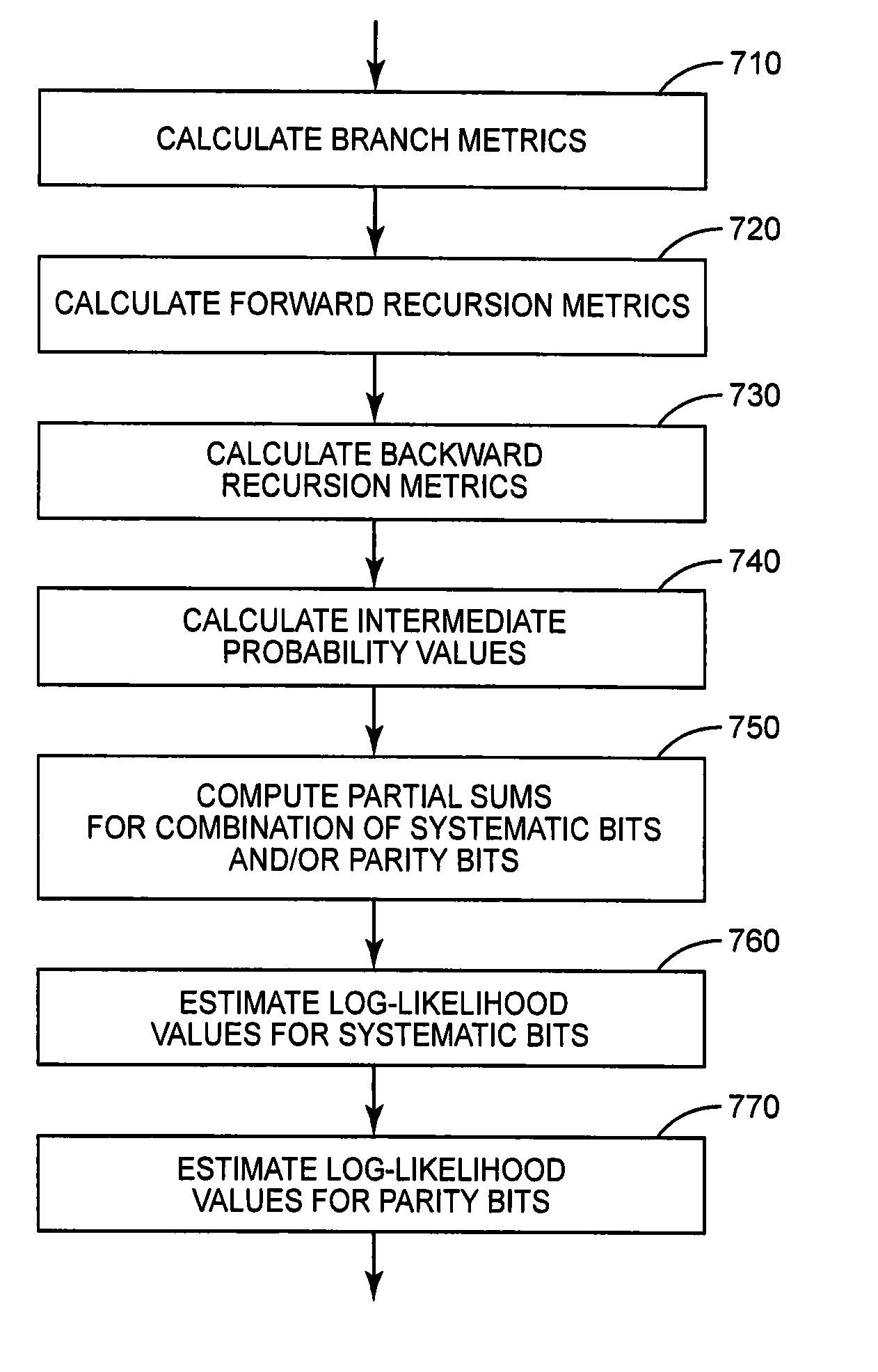
Efficient soft value generation for coded bits in a turbo decoder
ActiveUS20110055667A1Simple calculationImprove processing efficiencyCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesLog likelihoodComputer science
Techniques for generating soft values for parity bits in a convolutional decoding process are disclosed. An exemplary method comprises, for each of at least one iteration in at least one soft-input soft-output decoder, calculating intermediate probability values for each possible transition between a first plurality of candidate decoder states at a first time and a second plurality of candidate decoder states at a second time. Two or more partial sums are then computed from the intermediate probability values, wherein the partial sums correspond to possible combinations of two or more systematic bits, two or more parity bits, or at least one systematic bit and at least one parity bit. Soft values, such as log-likelihood values, are then estimated for each of at least one systematic bit and at least one parity bit of the received communications data corresponding to the interval between the first and second times, based on the partial sums.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
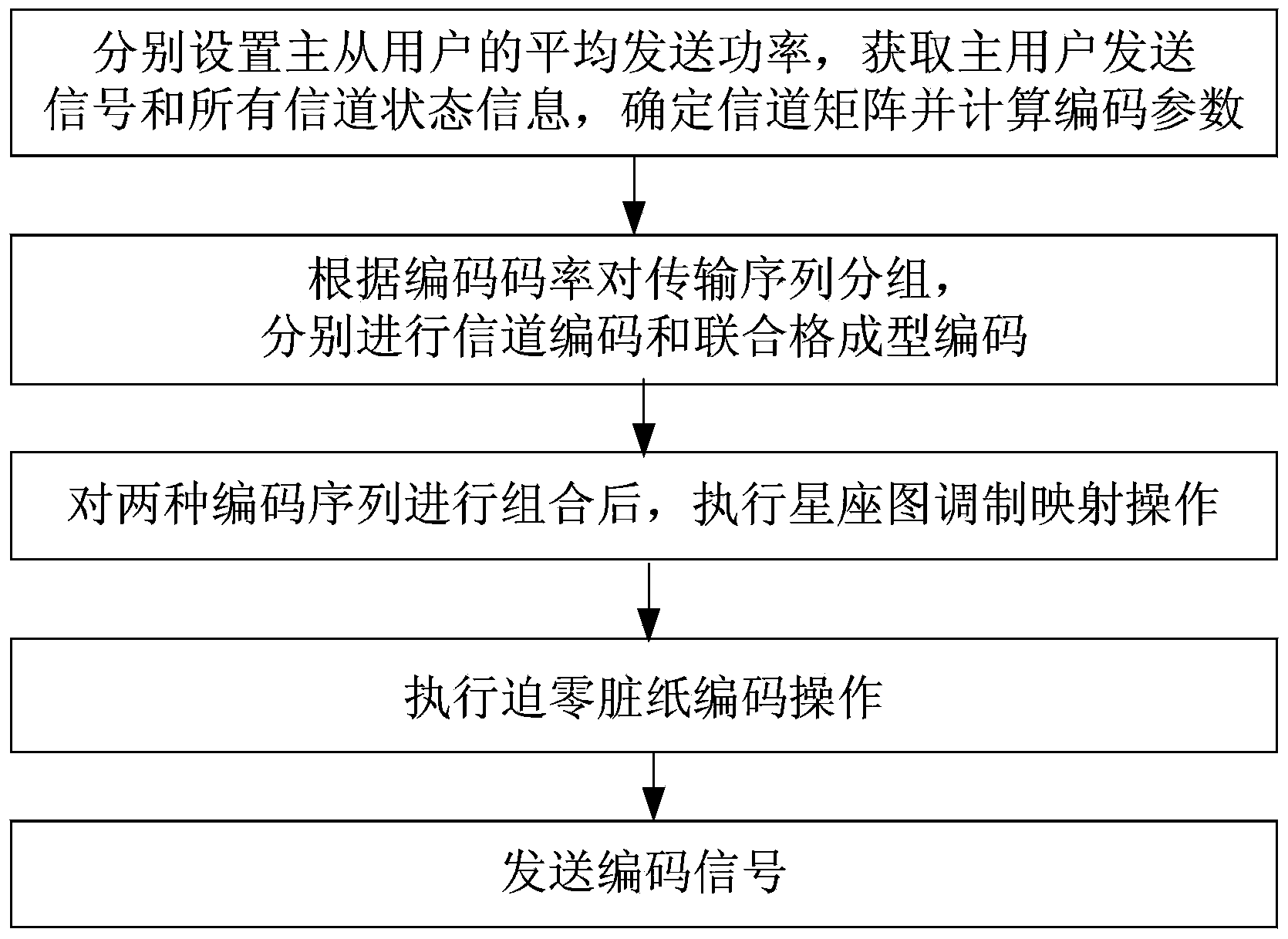
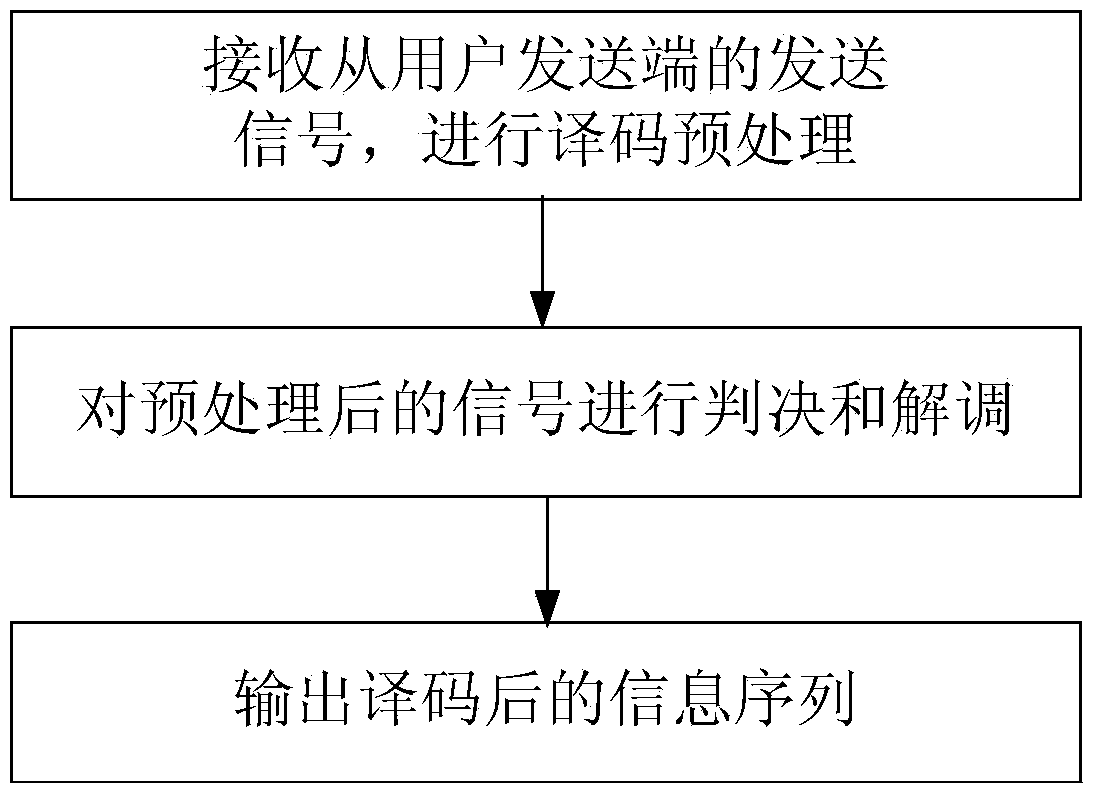
Dirty paper coding and decoding method based on joint lattice forming technology in cognitive network
ActiveCN104135347AReduce receiving bit error rateReduce complexityError preventionComputation complexitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a dirty paper coding and decoding method based on a joint lattice forming technology in a cognitive network, and the method is applicable to the occasion that a main network has only one main user and a cognitive wireless network has multiple secondary users. The method includes the specific steps that to guarantee that a signal to noise ratio of a main user receiving end is not changed, secondary user sending ends forward a sending signal of the main user while the secondary user sending ends send the corresponding signals through multiple transmitting antennas of the secondary user sending ends; grouping is conducted on signals transmitted to all secondary user receiving ends through the secondary user sending ends, channel coding and joint lattice forming coding are conduced respectively, and then a coding bit sequence is mapped into a symbol sequence and zero-forcing dirty paper coding is conducted so as to eliminate interference of other users; signals sent out by the main user are overlapped and then transmitted to multiple secondary user receiving ends through a channel by means of multiple transmitting antennas of a main user sending end so as to improve secondary user receiving performance. A traditional channel convolutional decoding method, namely signal restoring, is adopted for the secondary user receiving ends respectively. The method is simple in operation steps, lower in calculation complexity and high in practicability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Space diversity trellis interleaver system and method
InactiveUS7194048B2Effective noiseHigh data rateData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionData streamData segment
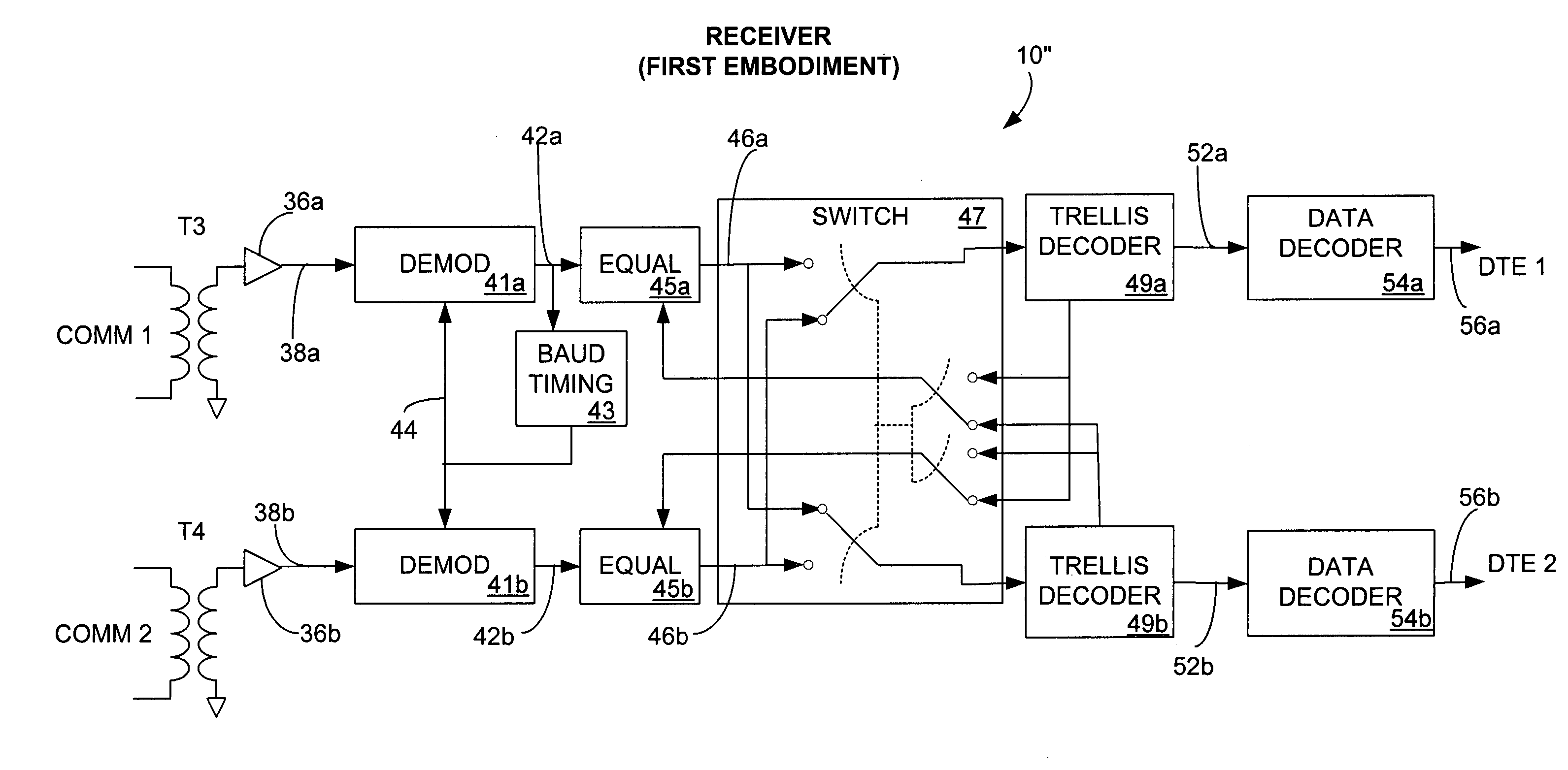
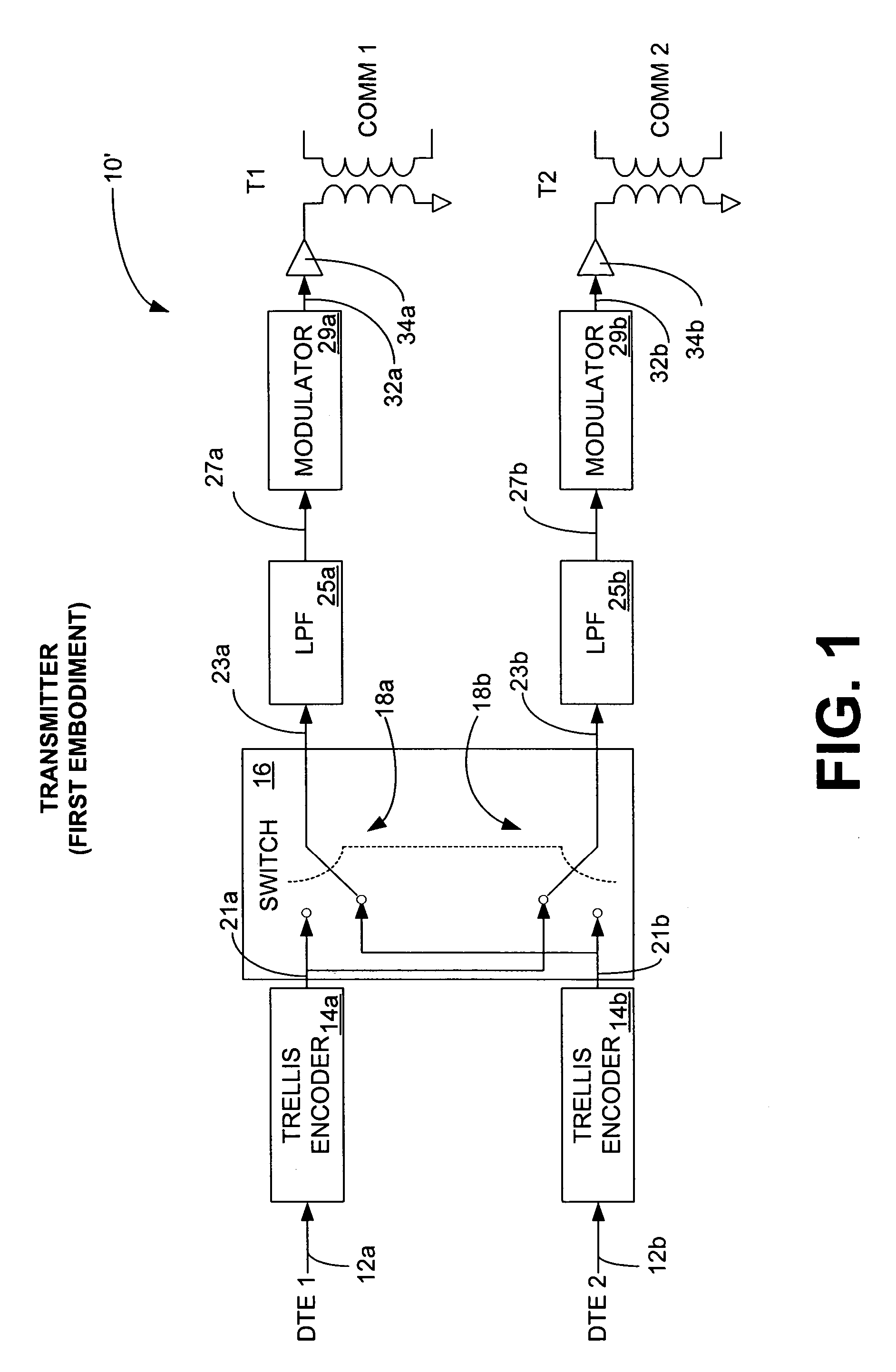
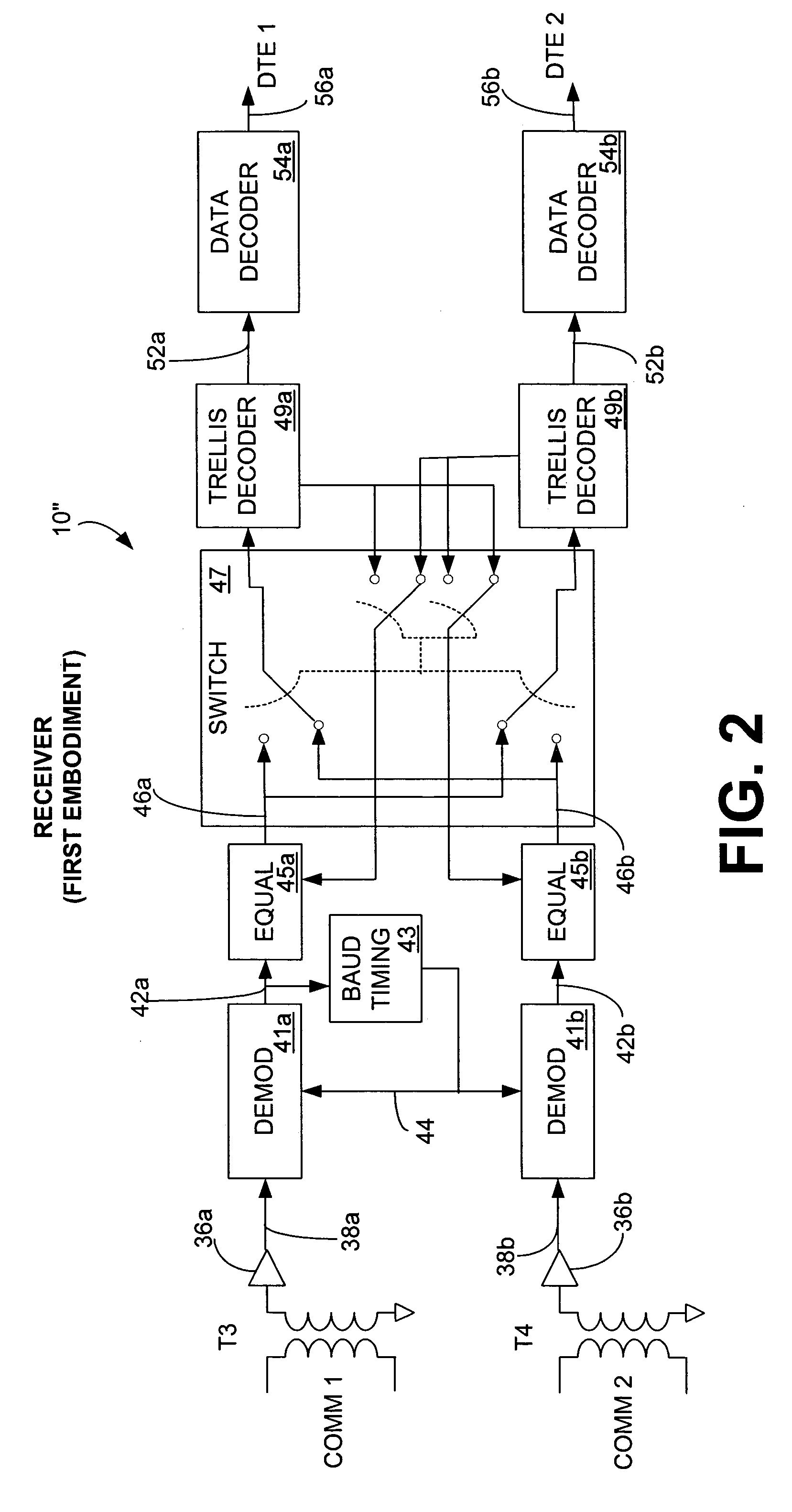
Several embodiments of a space diversity trellis interleaver system are provided for communicating data over a plurality of separate communication paths in order to inhibit distortion caused by impulse noise or other correlated noise and enhance the data transmission rate of data communications. The transmitter is designed to receive a plurality of data streams from data terminal equipment (DTE), which can be one or more devices. One or more convolutional encoders, preferably trellis encoders, encode each of the data streams. In an alternative embodiment, more than one trellis encoder is used to trellis encode each data stream. Data segments from the convolutionally encoded data streams are interleaved with a switch. The plurality of interleaved convolutionally-encoded data streams are modulated and transmitted onto a respective plurality of separate communication paths. At the receiver, the plurality of data streams is received from the separate communication paths and demodulated. The data segments are de-interleaved with a switch, and then the de-interleaved data streams are convolutionally decoded with convolutional decoders, preferably trellis decoders. The de-interleaved convolutionally decoded data streams are communicated to one or more DTEs.
Owner:SUMMIT TECH SYST LP
Meteorological data complement method based on automatic convolutional encoding and decoding algorithm
ActiveCN106446546AOvercoming the problem of oversimplificationFlexible gap fillingSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsComputer scienceConvolution
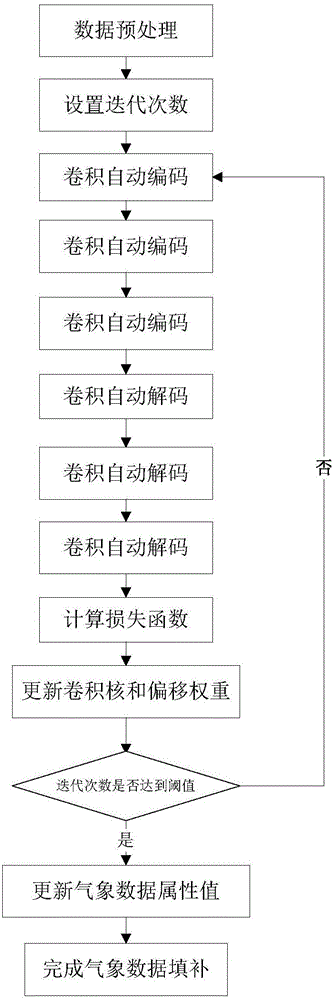
Provided is a meteorological data complement method based on automatic convolutional encoding and decoding algorithms. The method comprises the steps that meteorological data is preprocessed; the number of iterations is set; automatic convolutional encoding is conducted on a four-dimensional matrix; automatic convolutional encoding is conducted on a feature matching matrix; automatic convolutional encoding is conducted on the feature matching matrix; automatic convolutional decoding is conducted on the feature matching matrix; automatic convolutional decoding is conducted on the feature matching matrix; automatic convolutional decoding is conducted on the feature matching matrix; a loss function is calculated; a convolution kernel and an offset weight are updated; a meteorological data attribute value is updated; meteorological data complement is completed. According to the meteorological data complement method based on the automatic convolutional encoding and decoding algorithms, the problem that the precision of data complement is low is solved, and the method has the advantages of being high in robustness and missing value filling accuracy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
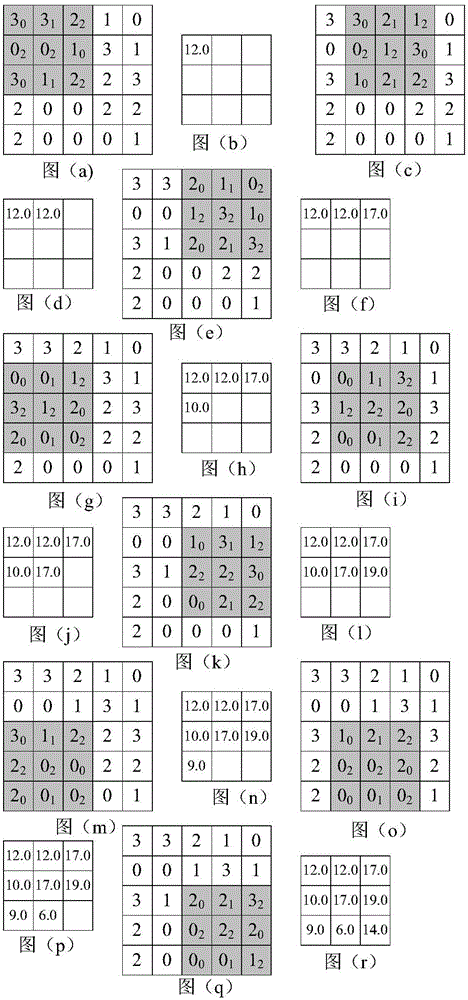
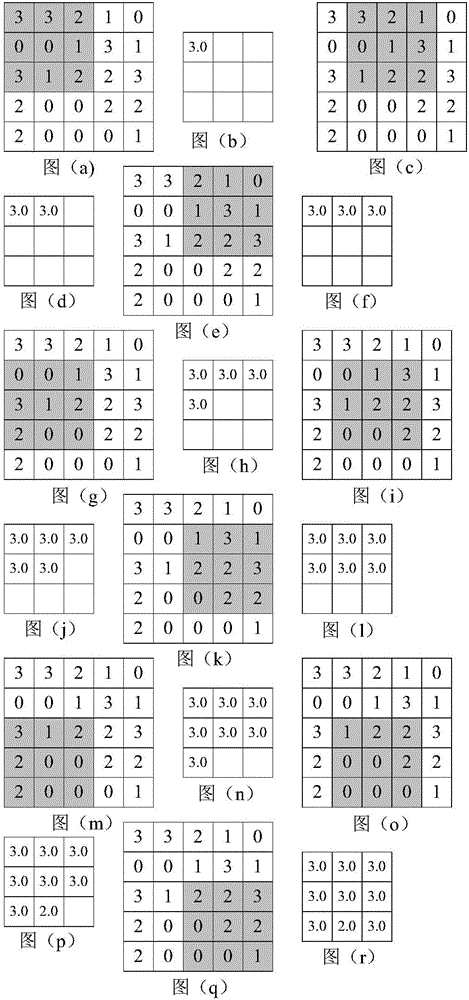
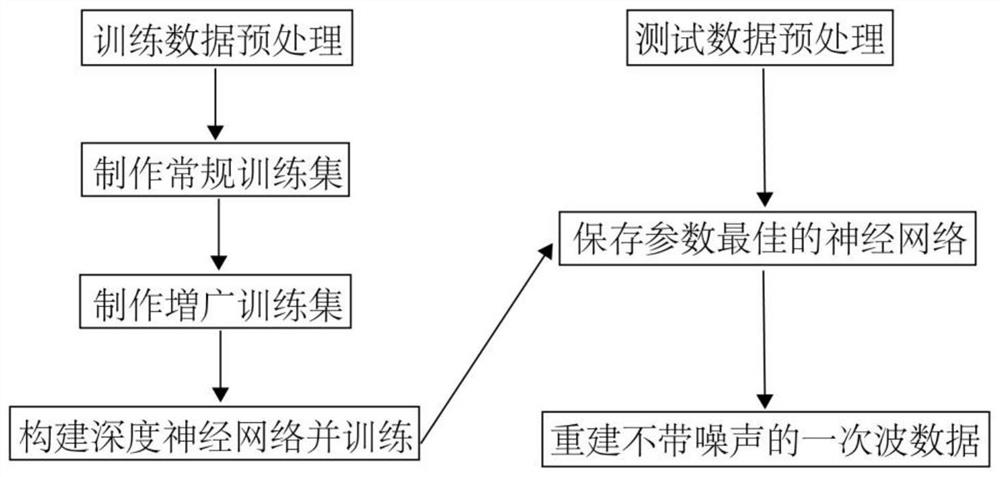
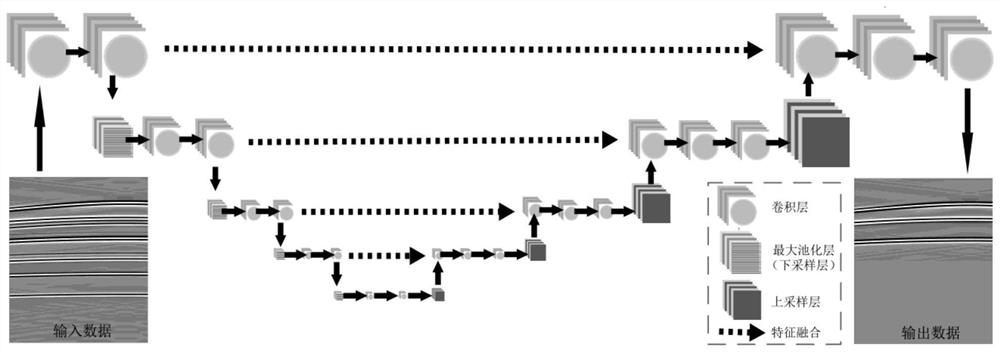
Method for suppressing seismic multiples based on data augmentation training deep neural network
ActiveCN112946749AHas generalization abilityFast and even real-time refactoringSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasData setOriginal data
The invention discloses a method for suppressing seismic multiples based on a data augmentation training deep neural network, belongs to the technical field of exploration seismic signal processing, and relates to suppression of seismic data multiples and random noise and reconstruction of primary waves. According to the method, a deep neural network with a convolutional coding process and a convolutional decoding process is designed, the convolutional coding process is used for learning and training primary wave features of seismic data in a set, and the convolutional decoding process can utilize the features to reconstruct primary waves and suppress multiples. In the training stage, original data containing multiples and data added with random noise form an augmented data set, and higher anti-noise stability can be achieved by using the data set to learn neural network parameters compared with a neural network trained only by using the original data as input data.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Butterfly processor for telecommunications
InactiveUS20020129320A1Reduction in hardwareError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer moduleComputer science
The present invention discloses a butterfly processor capable of performing convolutional decoding and LogMAP decoding in telecommunications systems. First and second add-compare-select modules are provided for receiving input path metrics. A branch metric calculator is also provided for receiving input data and extrinsic data. The branch metric calculator generates output branch metrics to each of the first and second add-compare-select modules. Each of the add-compare-select modules includes a log-sum correction means coupled to compare and select components. A controllable switch selectively couples outputs of the select components and the log-sum corrections means to enable either one of convolutional or LogMAP decoding.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Double-factor authentication method based on double convolutional and cycle encoding
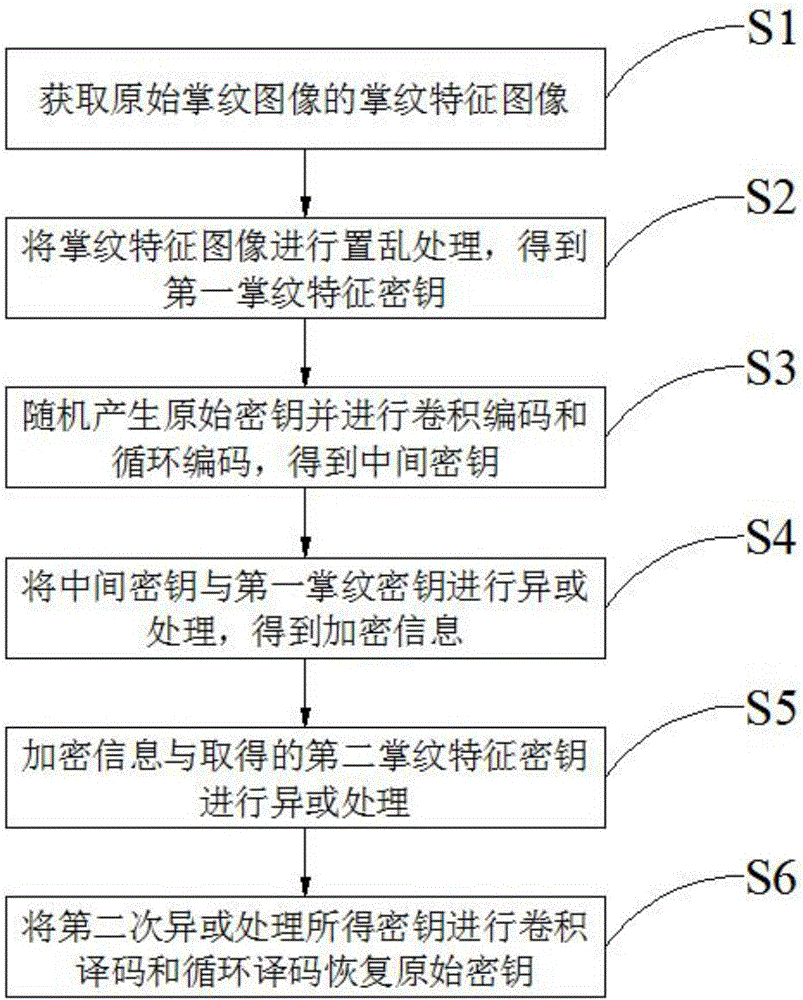
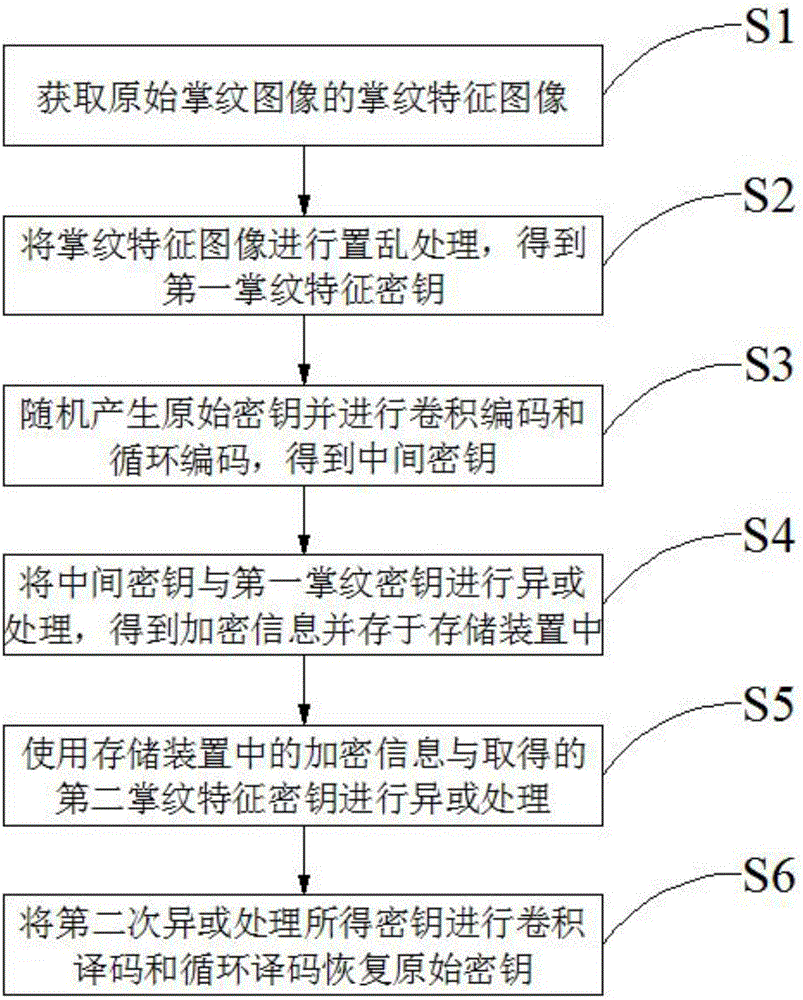
ActiveCN106789063AImprove securityImprove authentication accuracyUser identity/authority verificationMatching and classificationComputer hardwarePalm print
The invention discloses a double-factor authentication method based on double convolutional and cycle encoding, which comprises an encrypting process and a decrypting process. The encrypting process comprises the steps of: carrying out scrambling processing on a palm print feature image of an original palm print image to obtain a first palm print feature secret key; then randomly generating an original secret key, and carrying out convolutional encoding and cycle encoding processing to obtain an intermediate secret key; and carrying out exclusive-or processing on the intermediate secret key and the first palm print feature secret key to obtain encrypted information. The decrypting process comprises the steps of: carrying out exclusive-or processing on the encrypted information and a palm print feature secret key obtained again; and then carrying out convolutional decoding and cycle decoding processing to recover the original secret key. According to the double-factor authentication method disclosed by the invention, double-factor authentication of palm print biological features and a random secret key is implemented, so that security is high; and moreover, in the decrypting process, the original secret key can be completely recovered by carrying out exclusive-or processing on the encrypted information and the scrambled palm print features and then carrying out convolutional decoding and cycle decoding, so that authentication accuracy is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Channel concatenated coding and decoding method for power line carrier communication and apparatus thereof
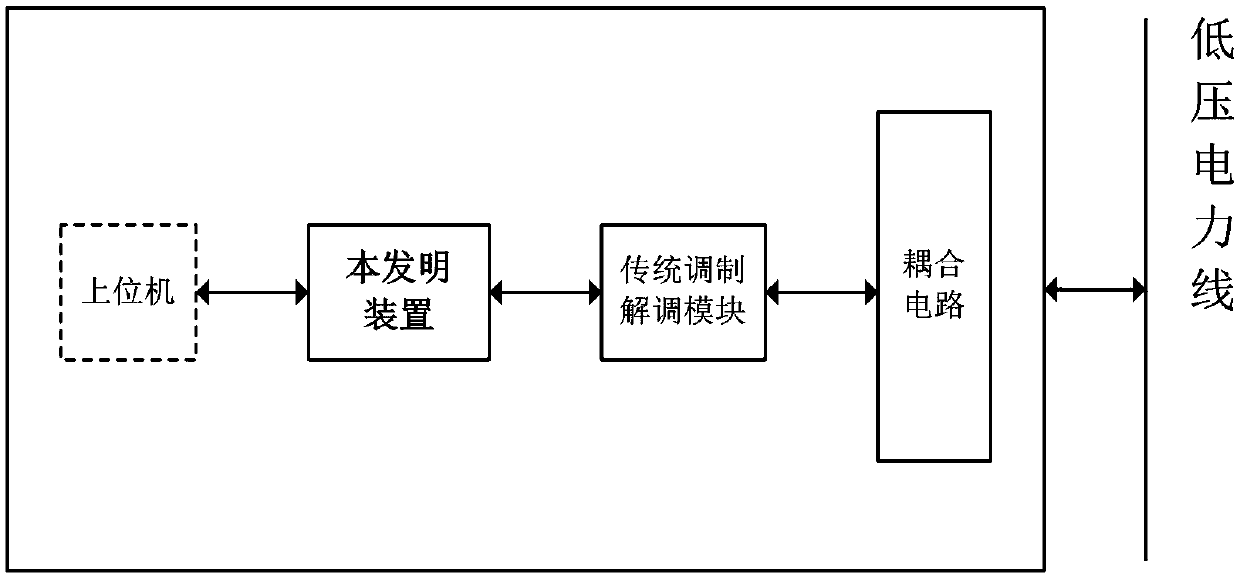
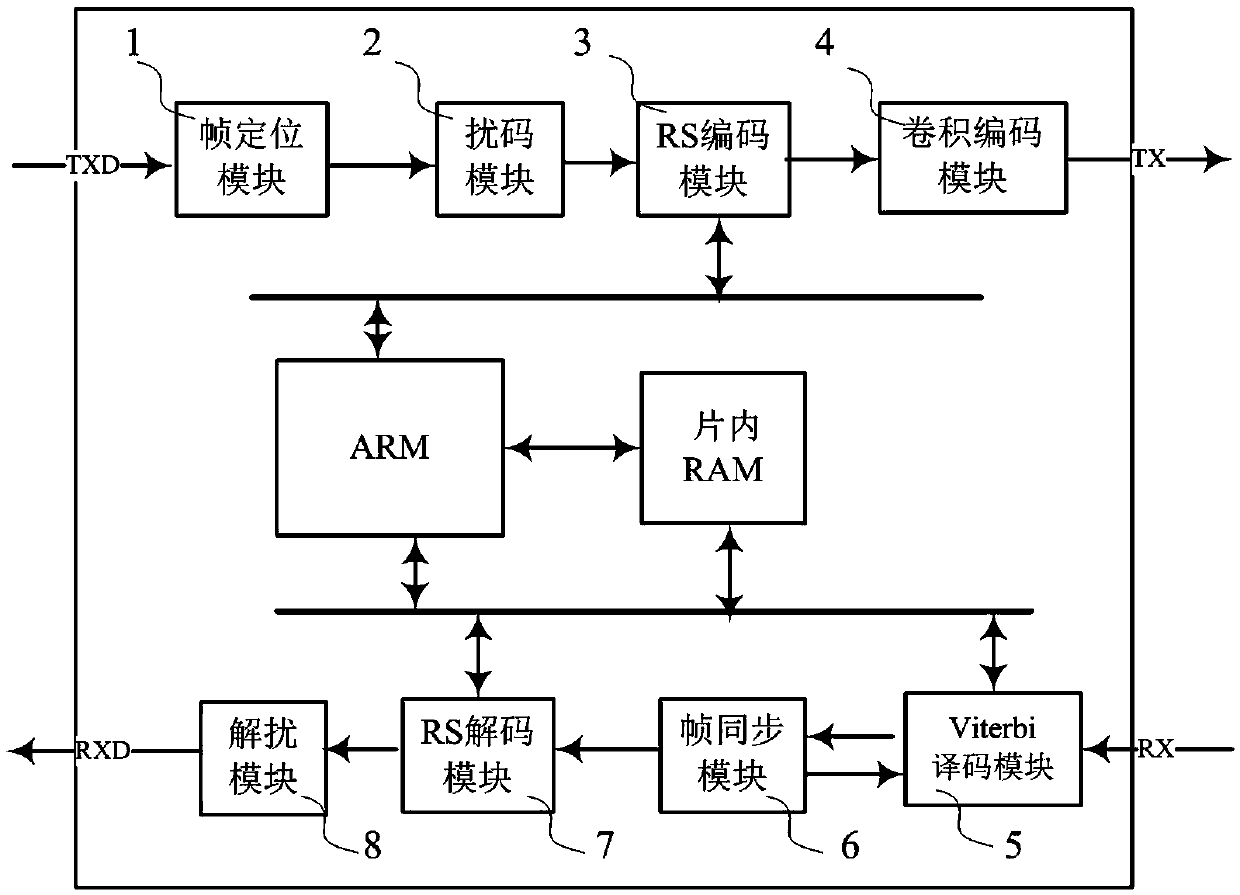
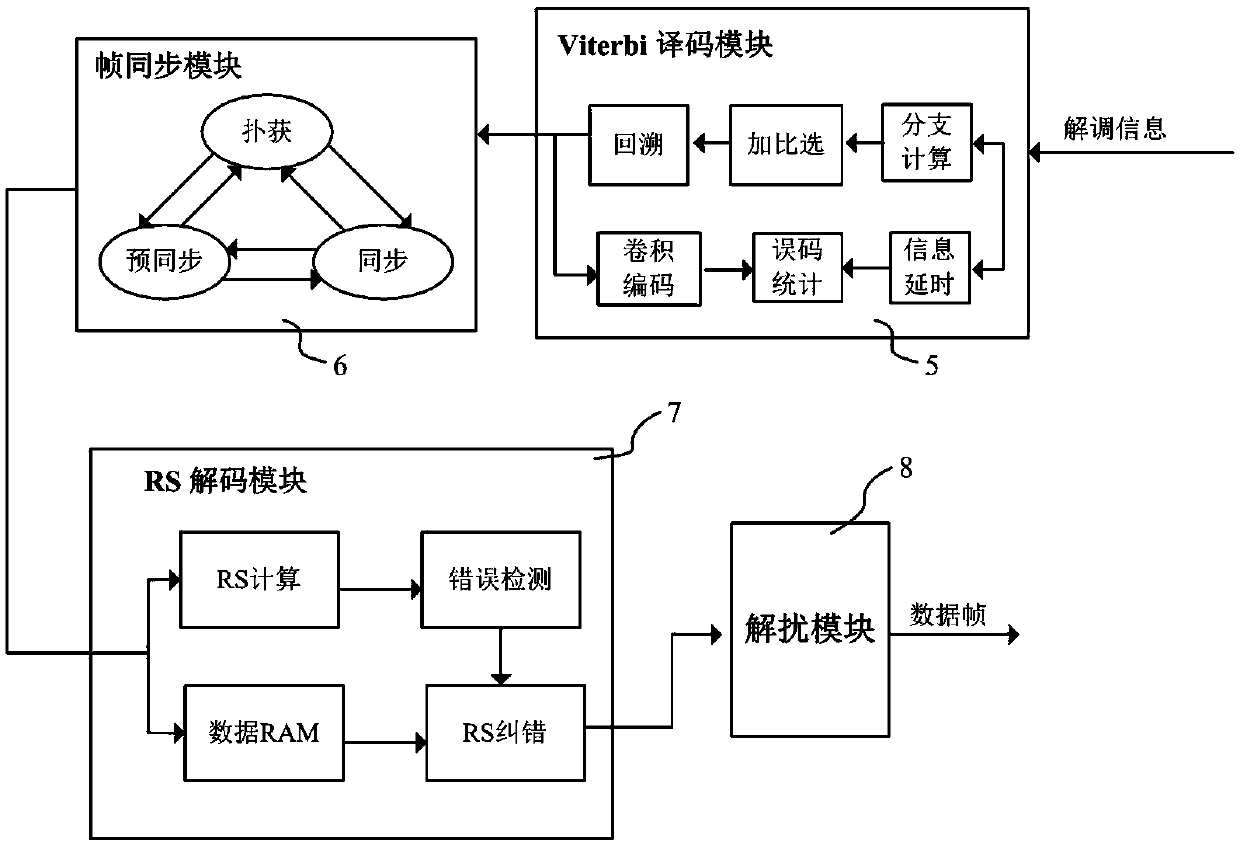
ActiveCN105515614AImprove accuracyIncrease processing rateError preventionPower distribution line transmissionCode moduleConvolutional code
The invention relates to a channel concatenated coding and decoding method for power line carrier communication and an apparatus thereof. According to the coding process, an original information frame sent from an upper computer enters a frame location module for frame head location; after location, the original information frame enters a code scrambling module for code scrambling; after code scrambling, the original information frame enters an RS coding module for RS coding; and after an RS code is output, the original information frame enters a convolutional coding module for convolutional coding, and then the code is output. According to the decoding process, demodulated baseband coding information is sent to a Viterbi decoding module for convolutional decoding; after Viterbi convolutional decoding, original rate information is recovered; a frame synchronization module searches a frame head from the original rate information so as to realize frame synchronization; after frame synchronization, RS decoding data clustering information can be determined; a synchronization result is fed back to the Viterbi decoding module simultaneously; information with the frame synchronized enters an RS decoding module for RS decoding; and finally, a descrambling module descrambles the information so as to recover the original information frame. The channel concatenated coding and decoding method can be applied to a modulation-demodulation device of power line carrier communication, and can improve the anti-interference capacity of signals in transmission, transmission quality and transmission efficiency.
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY ANYANG POWER SUPPLY +1
Method and system for correcting errors of decoded data by using UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) receiver
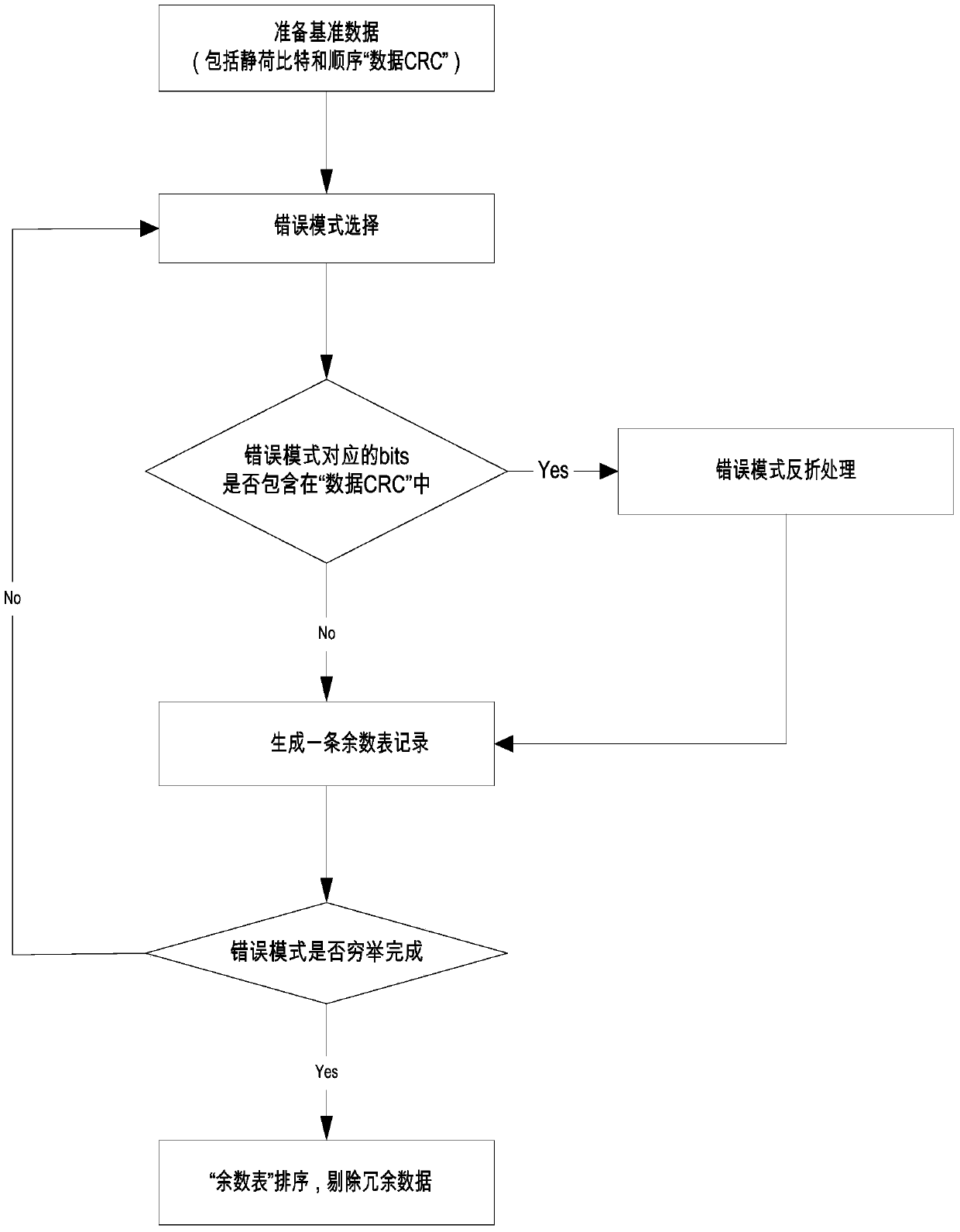
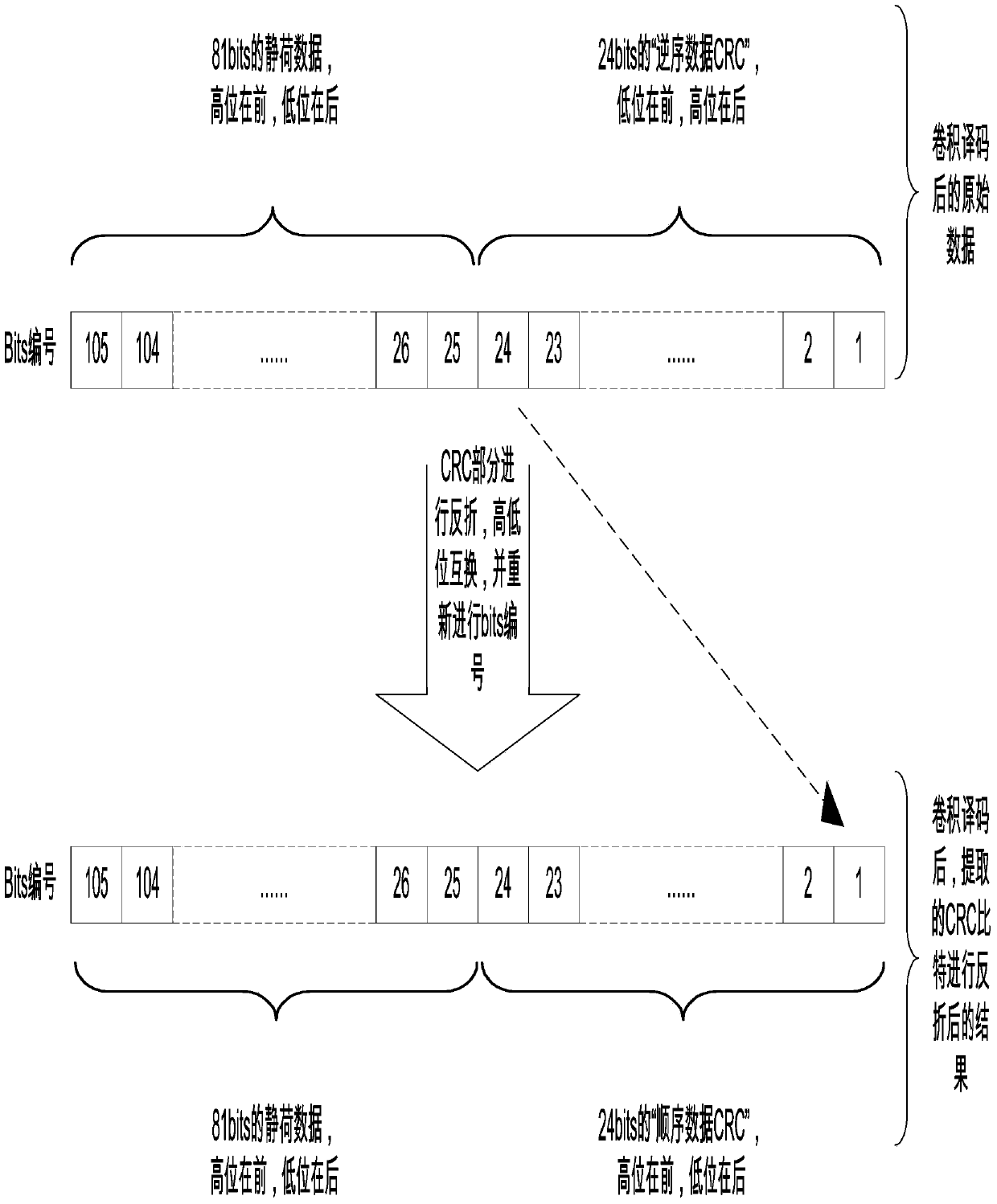
InactiveCN103746773ARe-correctionSolve the problem of not being able to provide further error correction functions on the dataError preventionNetwork packetDependability
The invention provides a method and a system for correcting errors of decoded data by using a UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) receiver. The method comprises the following steps: A, performing CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) on convolutional decoded data; B, retrieving in a remainder table. The method and the system have the beneficial effects that the remainder table is constructed by using two significant features of a convolutional decoding error result, and a corresponding error mode is obtained, so that re-correction of the decoded data is realized, and the problem that the conventional UMTS receiver cannot be used for further correcting the data after a convolutional decoding error is solved. The method provided by the invention can be implemented in the form of hardware as well as the form of a software functional module, and is not limited to the combination of hardware and software of any form. Over 50 percent of error packets in convolutional decoding error data packets can be corrected on average, the voice quality and signaling reliability are improved greatly, and the uplink capacity of the system is increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
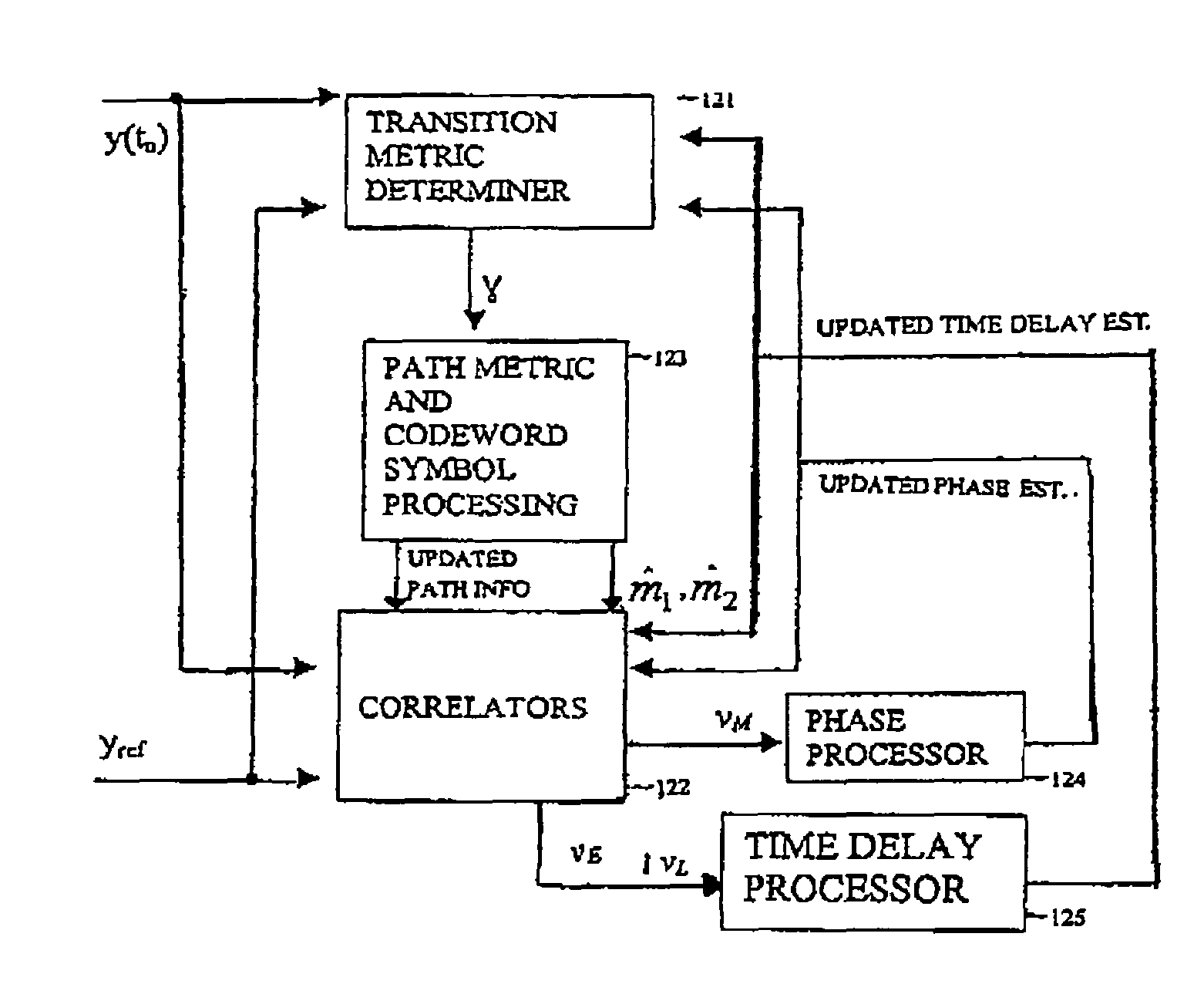
Using convolutional decoding to improve time delay and phase estimation in digital communications
ActiveUS7653155B1Error preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsComputer scienceCommunications receiver
The time delay and / or phase of a communication signal received by a digital communication receiver can be estimated based on a convolutional decoding operation that the communication receiver performs on the received communication signal. If the original transmitted communication signal has been spread according to a spreading operation, a corresponding despreading operation can be integrated into the convolutional decoding operation.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
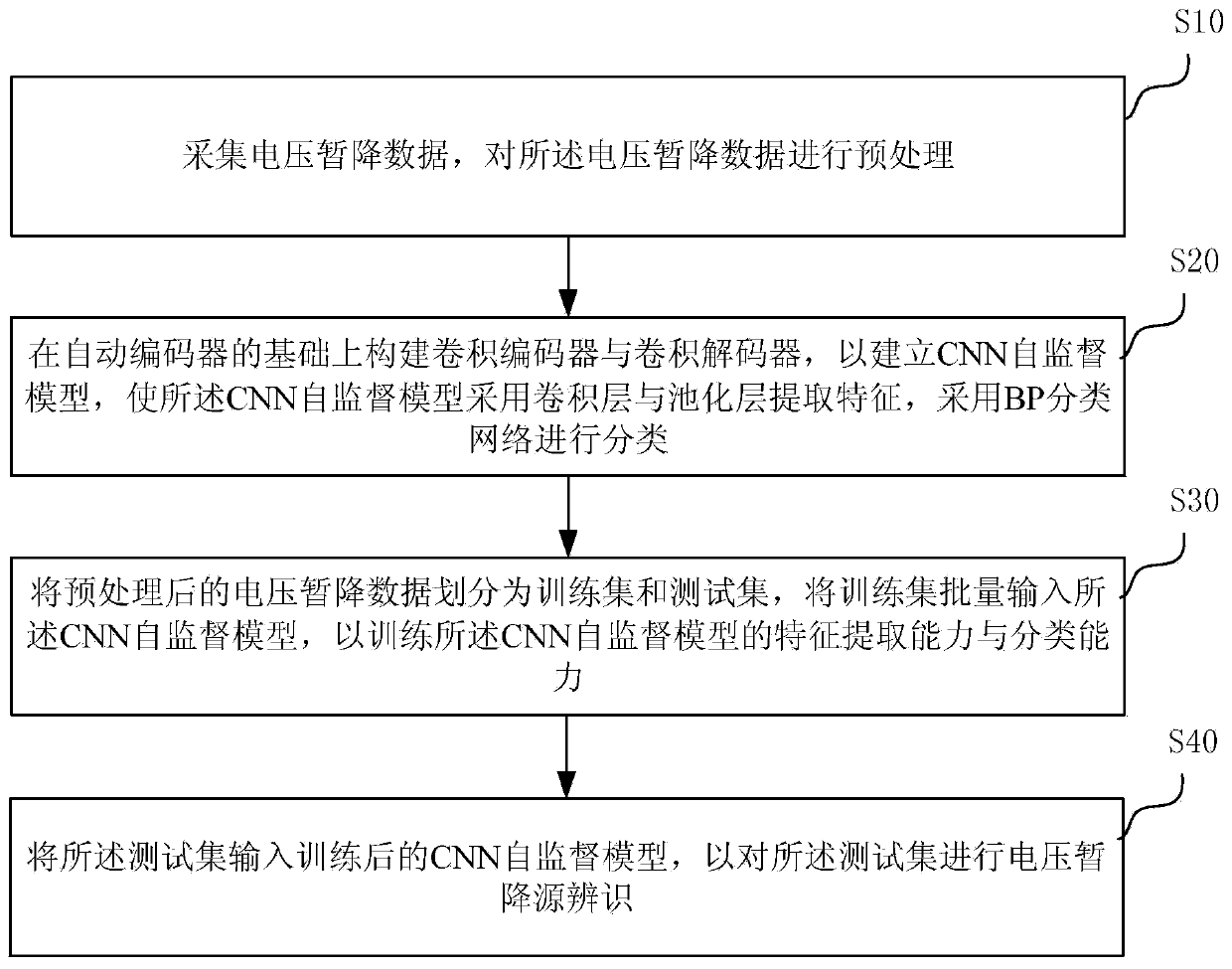
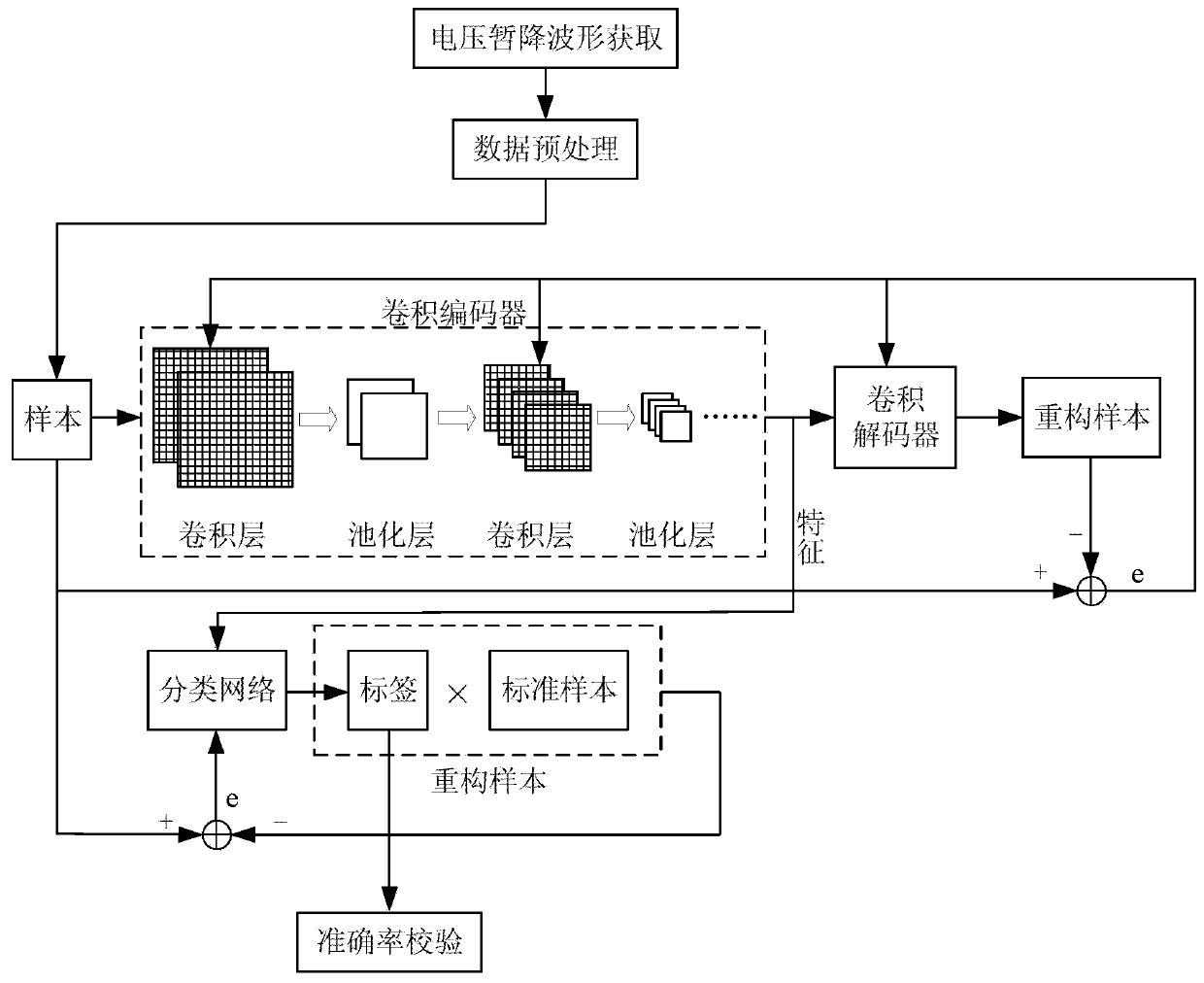
CNN-based self-supervised voltage sag source recognition method
InactiveCN110672905ATroubleshoot issues that aren't correctly identifiedCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature extractionEngineering
The present invention discloses a CNN-based self-supervised voltage sag source recognition method. The method comprises the following steps: collecting voltage sag data, pre-processing the voltage sagdata; constructing a convolutional coder and a convolutional decoder based on an autocoder, to establish a CNN self-supervised model, so that the CNN self-supervised model extracts a feature by usinga convolution layer and a pooling layer, and performs classification by using a BP classification network; dividing the pre-processed voltage sag data into a training set and a test set, inputting the training set into the CNN self-supervised model in batches, to train a feature extraction capability and a classification capability of the CNN self-supervised model; and inputting the test set intothe trained CNN self-supervised model, to perform voltage sag source recognition on the test set. According to the method, a voltage sag source can be recognized accurately.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Viterbi decoder with adaptive traceback
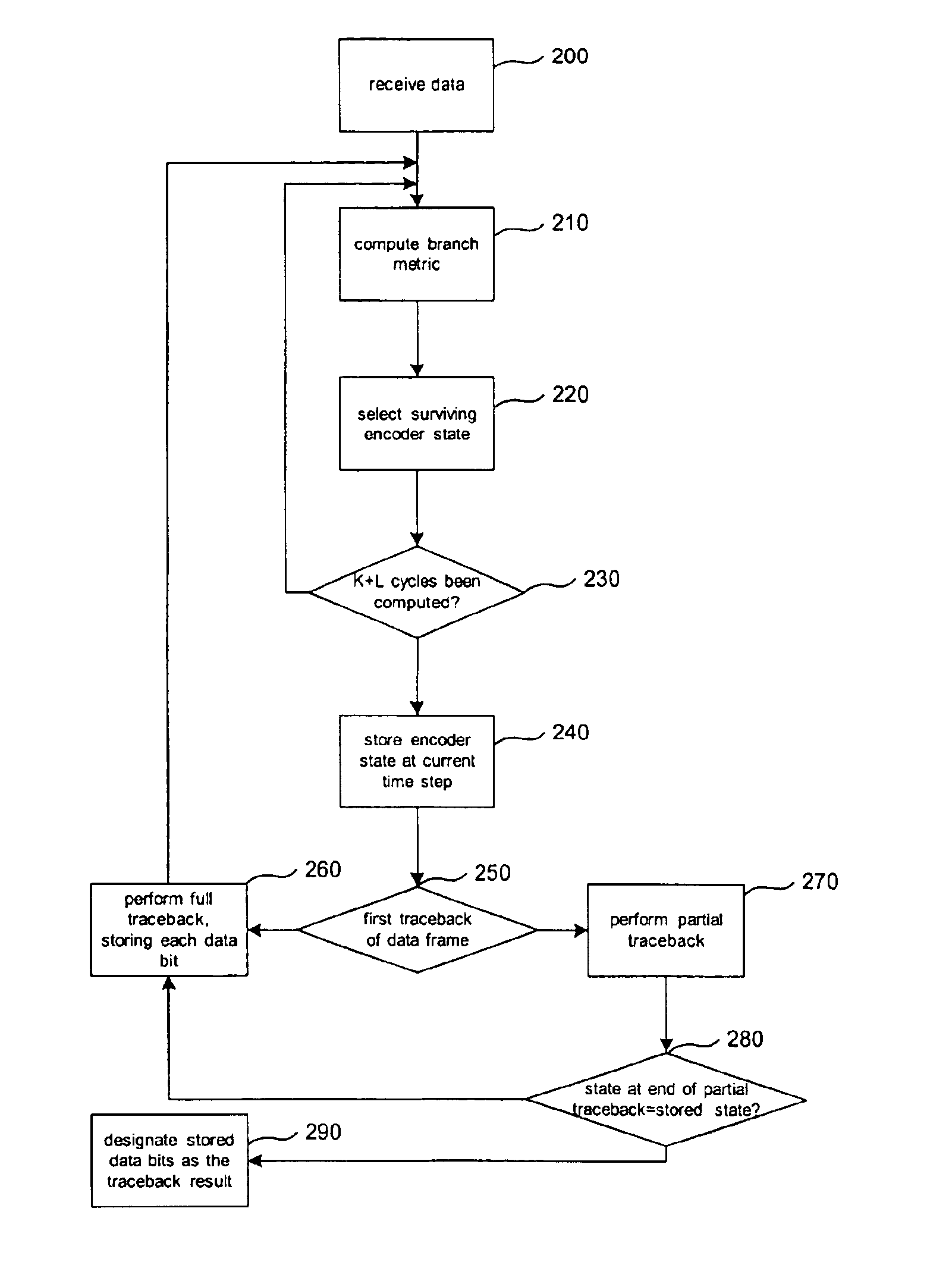
InactiveUS6842490B1Error preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsViterbi decoderComputer science
In a convolutional decoder using partial traceback, L−1 data bits of a traceback beginning at a time step T are stored, where L is the traceback length; these L−1 data bits are the data bits corresponding to the L−1 time steps backwards from time step T. The maximum likelihood encoder state for time T is also saved. (The L-th data bit is the desired data bit as in conventional convolutional decoders.) In a subsequent partial traceback preferably beginning at time T+1 that ends at time step T, the maximum likelihood encoder state for time T determined from the partial traceback is compared with the stored encoder state for time T. If they correspond to the same encoder state, the L−1 stored data bits are designated as the last L−1 data bits of the current (partial) traceback.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Algorithm for a memory-based Viterbi decoder
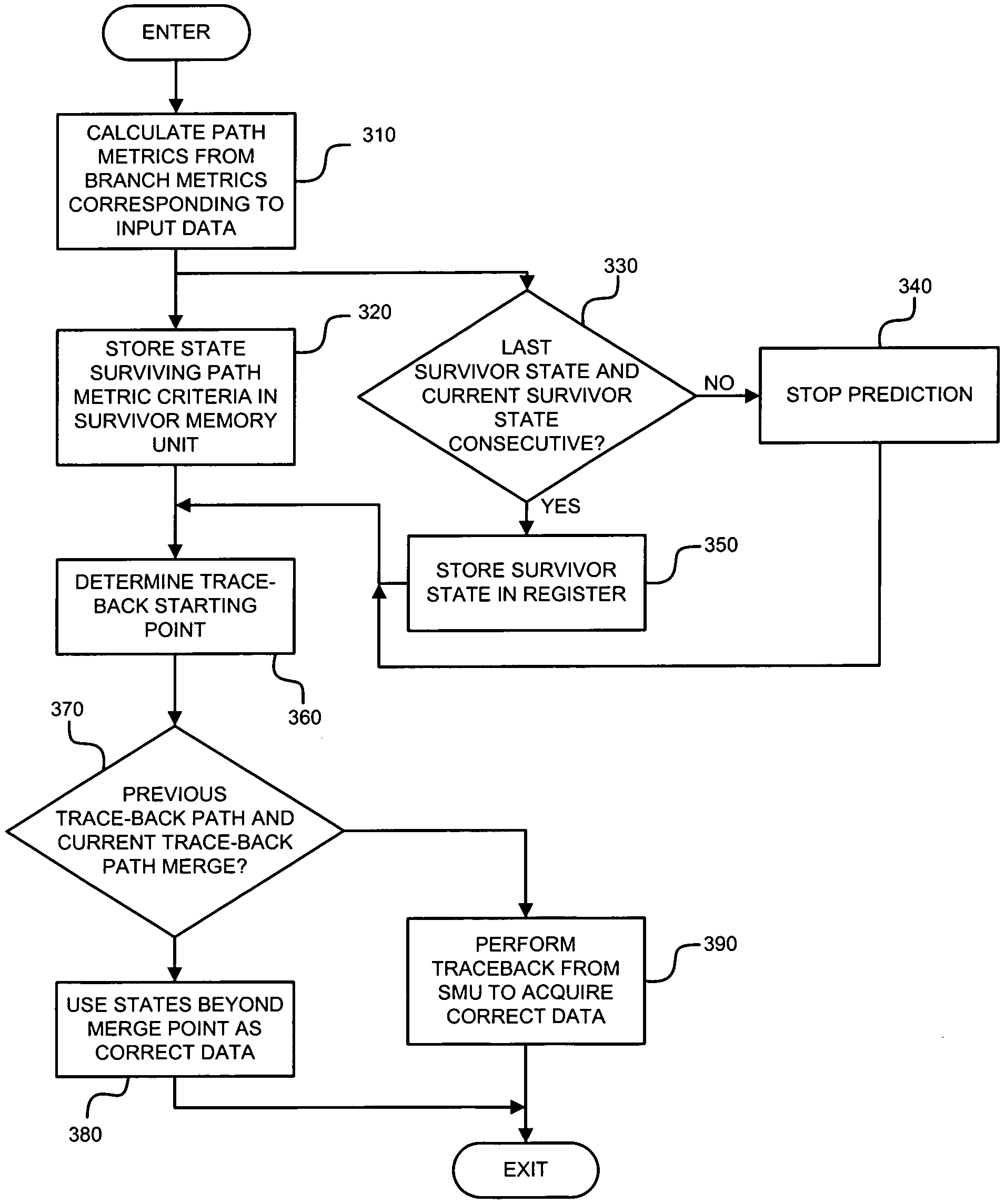
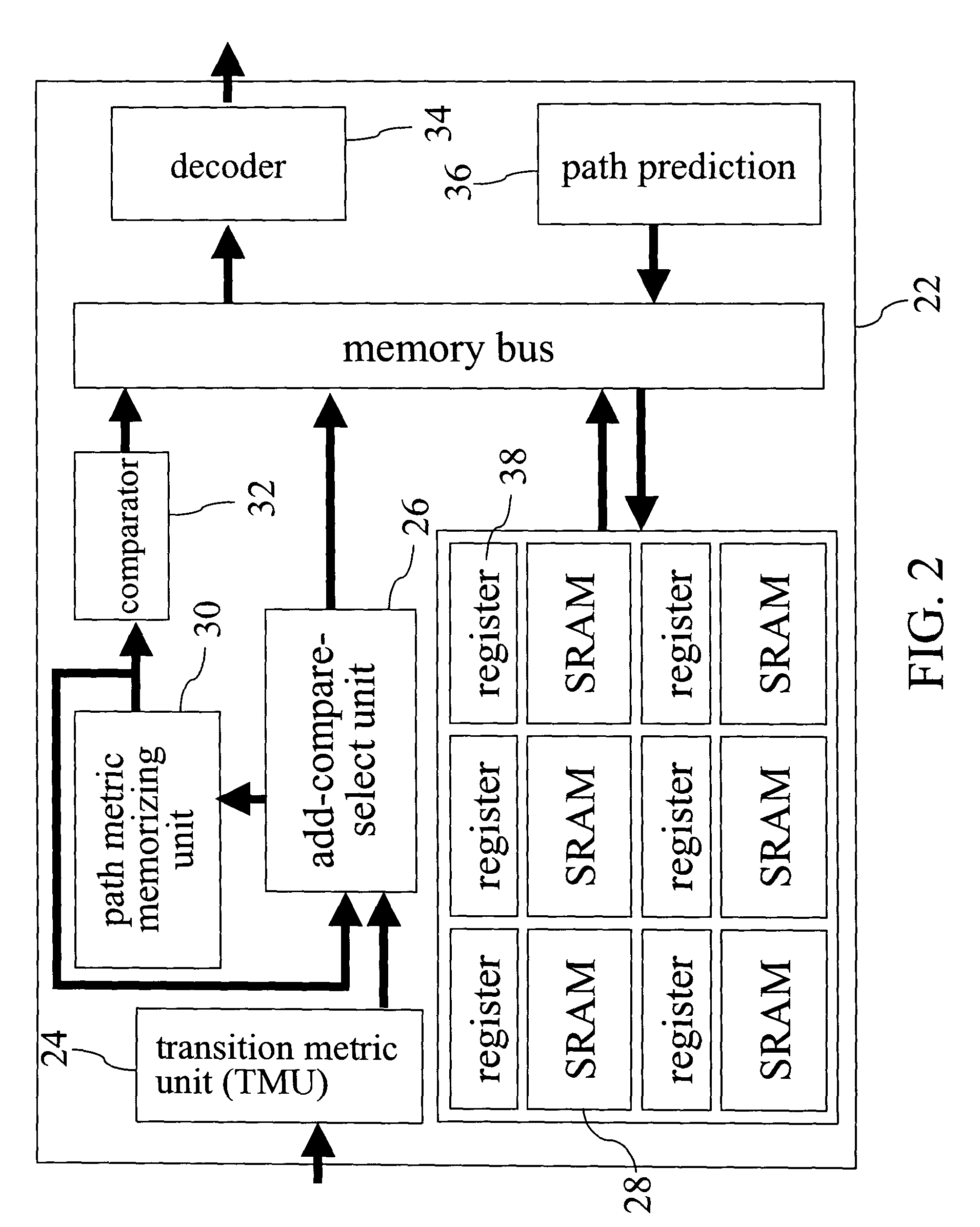
InactiveUS7263653B2Reduce in quantityReduce power consumptionData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderProcessor register
A method of convolutional decoding with a memory-based Viterbi decoder employs the property of a trace-back path; that is, the similarity between two consecutive trace-back paths becomes higher as the data error rate goes down. Therefore, the method of the invention saves the previous trace-back path into a register, and as soon as the current trace-back path is found to be the same as the previous one, the demanded path is obtained. After that, the memory read operations will stop, thereby reducing the power consumption caused by memory read operations. Prior to path trace-back, the path prediction can be executed by utilizing the property that the minimum path metric and the path are consecutive. The invention reduces the number of memory access operations and power consumption by employing the mechanisms of path matching and path prediction.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Efficient soft value generation for coded bits in a turbo decoder
ActiveUS8271858B2Improve processing efficiencySimple calculationData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionLog likelihoodComputer science
Techniques for generating soft values for parity bits in a convolutional decoding process are disclosed. An exemplary method comprises, for each of at least one iteration in at least one soft-input soft-output decoder, calculating intermediate probability values for each possible transition between a first plurality of candidate decoder states at a first time and a second plurality of candidate decoder states at a second time. Two or more partial sums are then computed from the intermediate probability values, wherein the partial sums correspond to possible combinations of two or more systematic bits, two or more parity bits, or at least one systematic bit and at least one parity bit. Soft values, such as log-likelihood values, are then estimated for each of at least one systematic bit and at least one parity bit of the received communications data corresponding to the interval between the first and second times, based on the partial sums.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
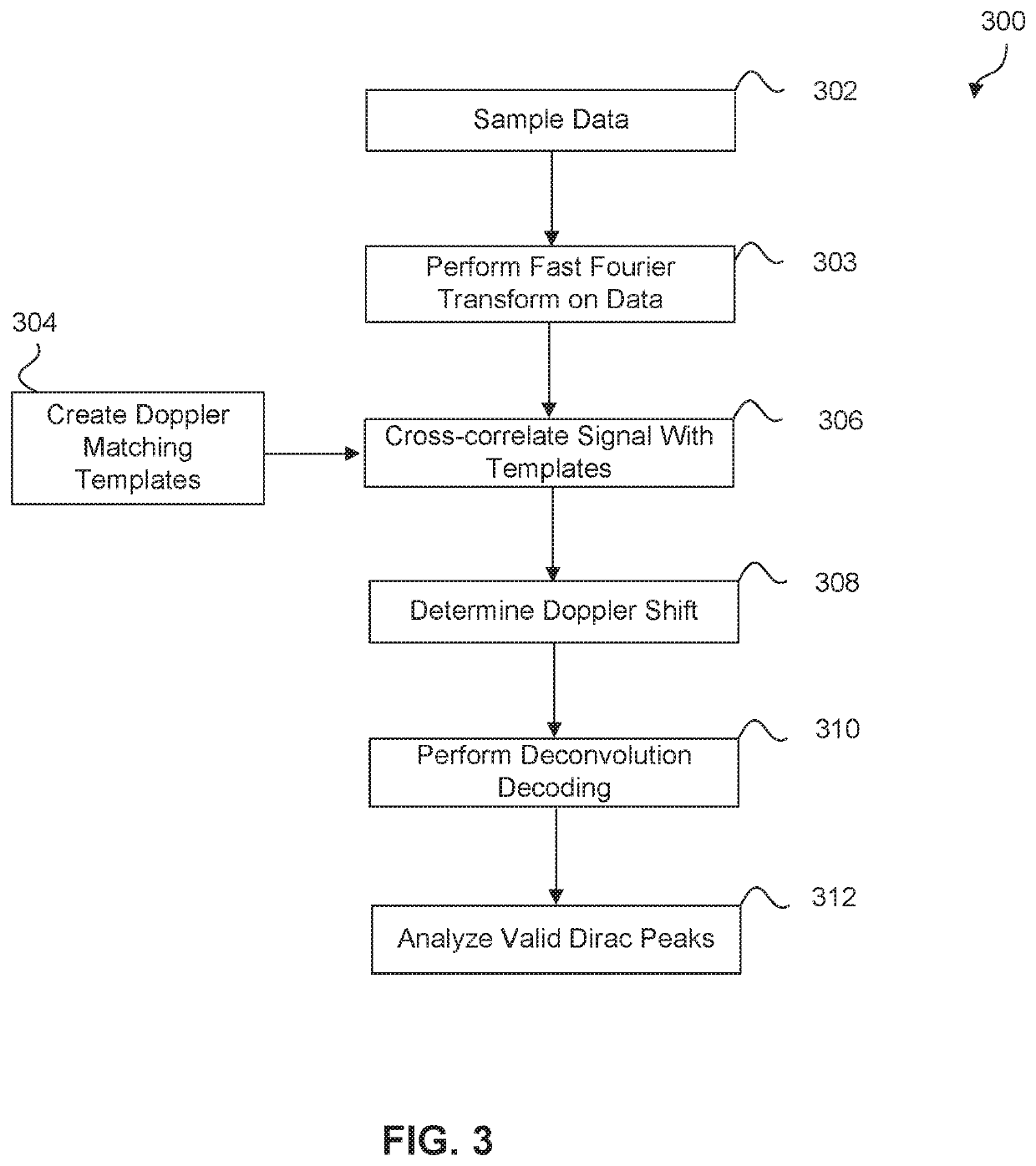
Position determination system having a deconvolution decoder
ActiveUS10670693B2Accurate modelingSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionPosition fixationEngineeringFrequency shift
The present disclosure relates to an acoustic position determination system that includes a mobile communication device and at least one base transmitter unit. The mobile communication device is configured to transmit and receive acoustic signals. Due to relative movements between the mobile communication device and the base transmitter unit, frequencies of the received signals shift due to Doppler effect. The mobile communication device is configured to compensate Doppler frequency shifts in the received acoustic signals prior to performing a deconvolution decoding process. The mobile communication device is further configured to compensate Doppler frequency shifts and perform deconvolution decoding process on acoustic signals received from multiple signal transmission paths.
Owner:SONITOR TECH
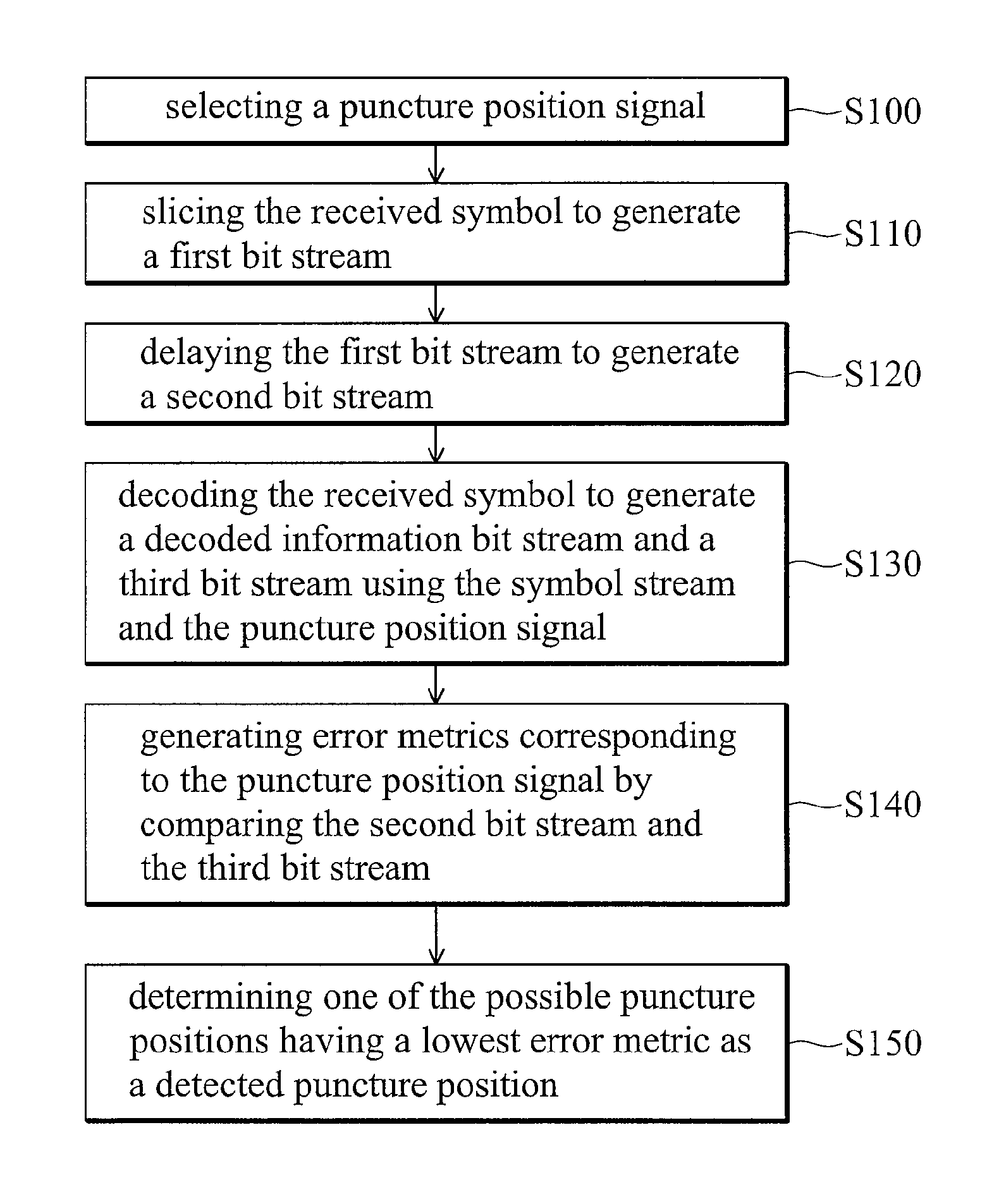
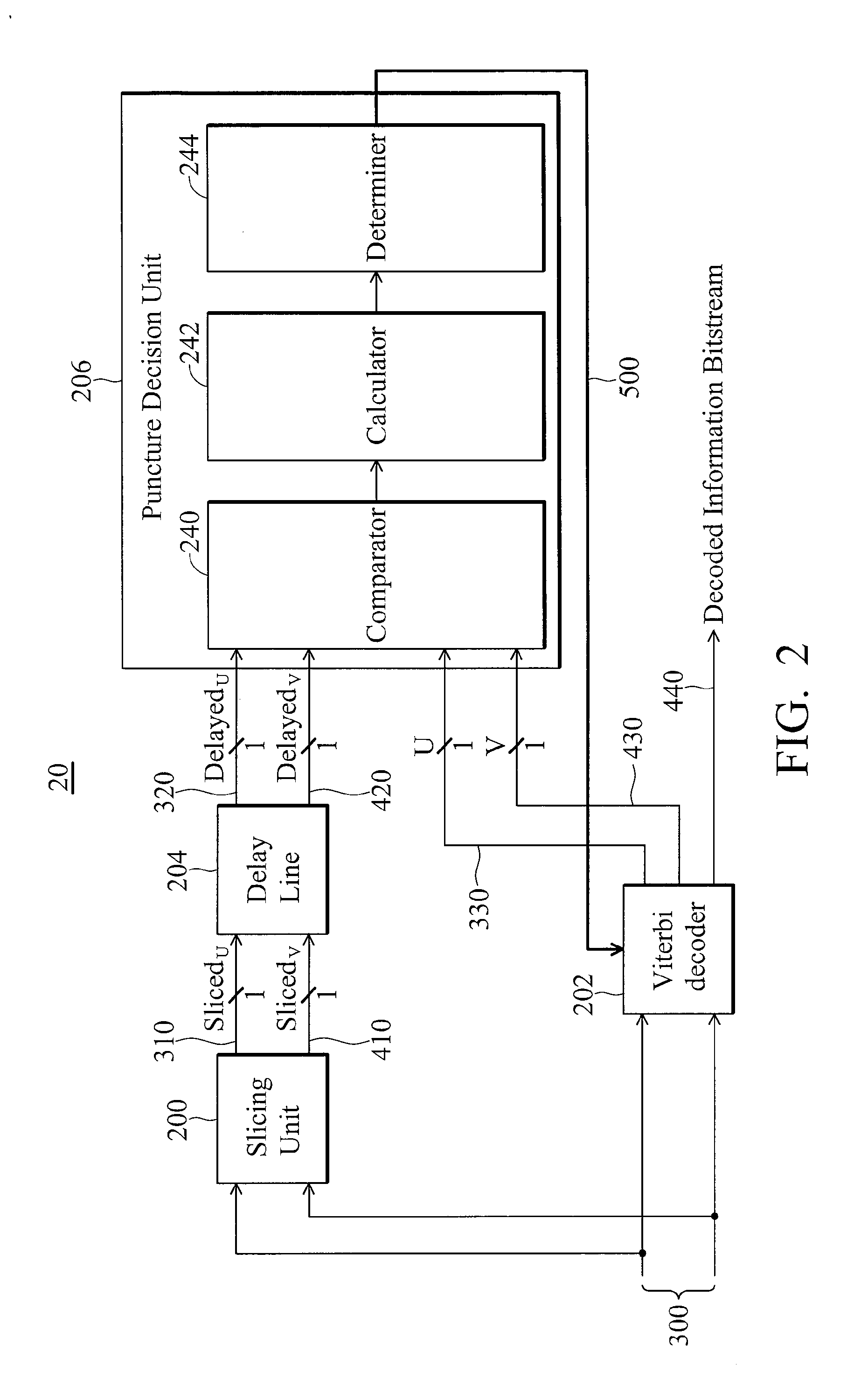
Apparatus and method for detecting puncture position in a symbol stream encoded by punctured convolutional coding scheme
ActiveUS7590925B2Complicates designData representation error detection/correctionError correction/detection using trellis codingDecision unitEmbedded system
An apparatus and method for determining a puncture position for a de-puncturing process. A stream of received symbols that corresponds to a code is received. A slicing unit slices the stream of received symbols to determine representative bits of the code to form a first bit stream. A delay line delays the first bit stream to generate a second bit stream. A convolutional decoder de-punctures and decodes the received symbol to generate a third bit stream. A puncture decision unit, coupled to the delay line and the convolutional decoder, selects the puncture position with one of possible puncture positions, and delivers the puncture position signal indicating the puncture position, and compares the second bit stream and the third bit stream to generate an error metric corresponding to the puncture position, and determines one of the possible puncture positions according to the error metric as a detected puncture position.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
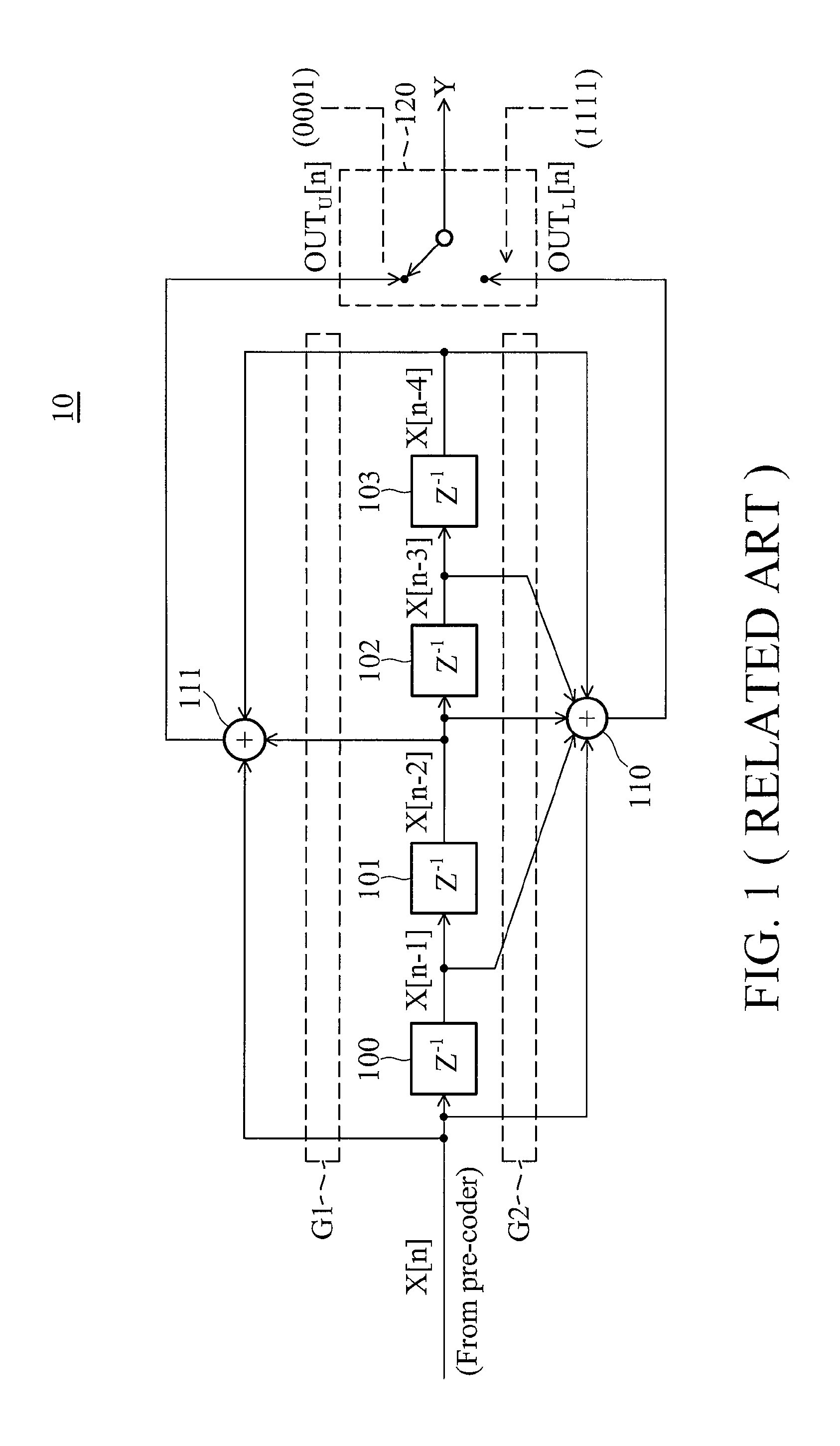
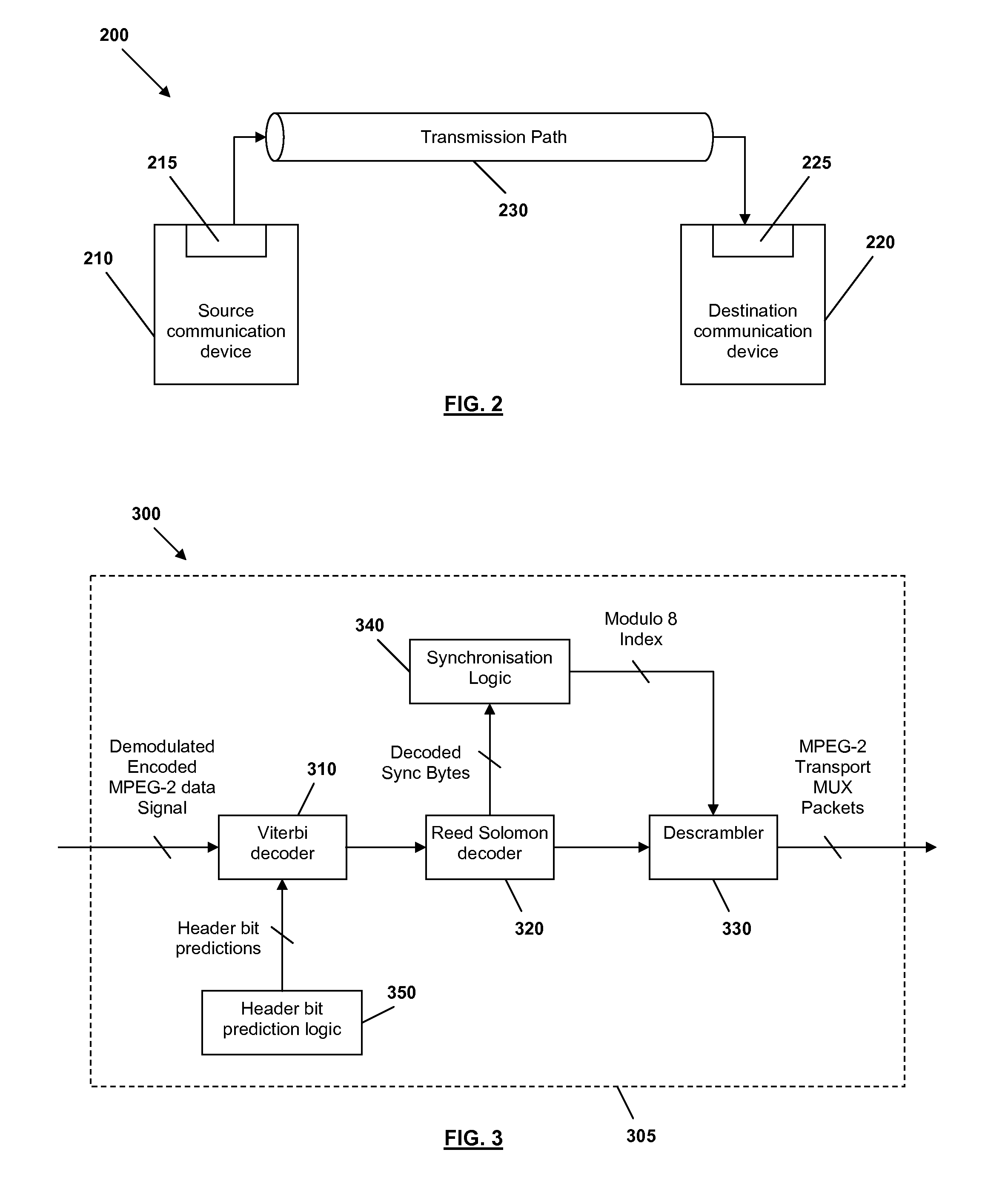
Method and apparatus for decoding received data signals
InactiveUS20100316117A1Joint error correctionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData signalConvolution
Decoding logic is arranged to receive an encoded data signal. The decoding logic comprises a convolutional decoder arranged to perform convolutional decoding on the encoded data signal, to produce a decoded data signal. The decoding logic comprises header bit prediction logic arranged to predict a value for at least one header bit within the decoded data signal, and to provide the predicted value for the at least one header bit to the convolutional decoder to be applied during convolutional decoding.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com