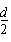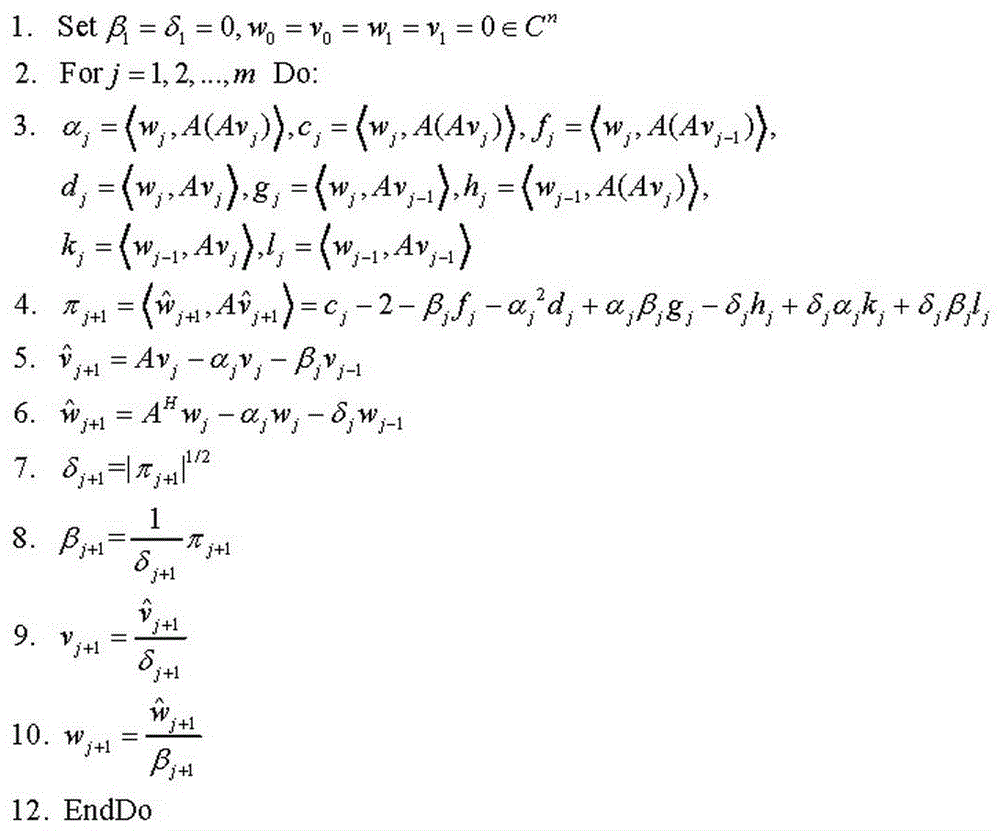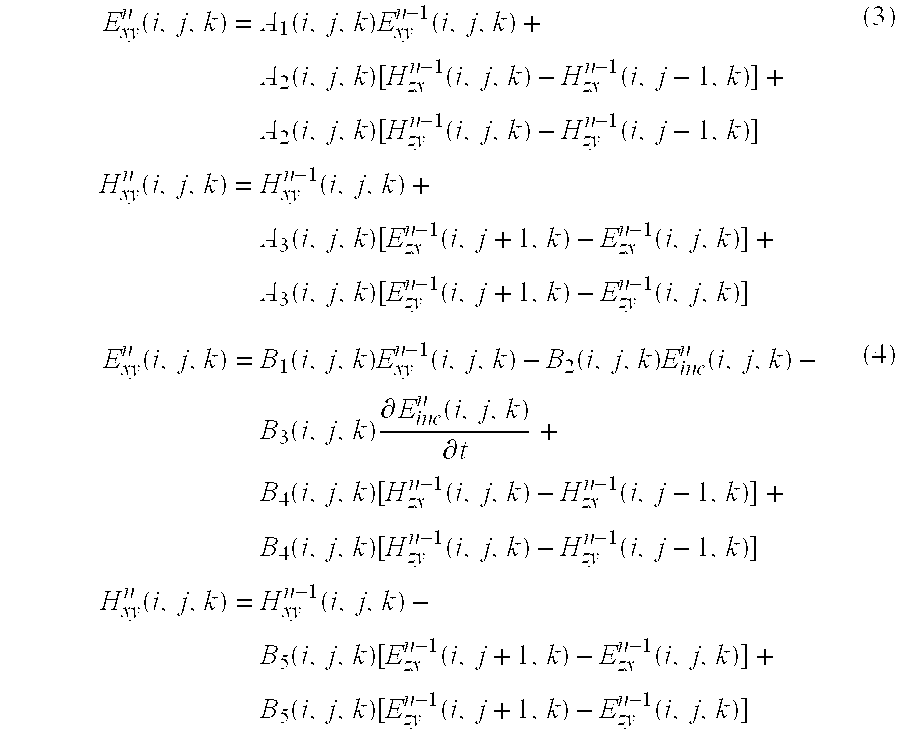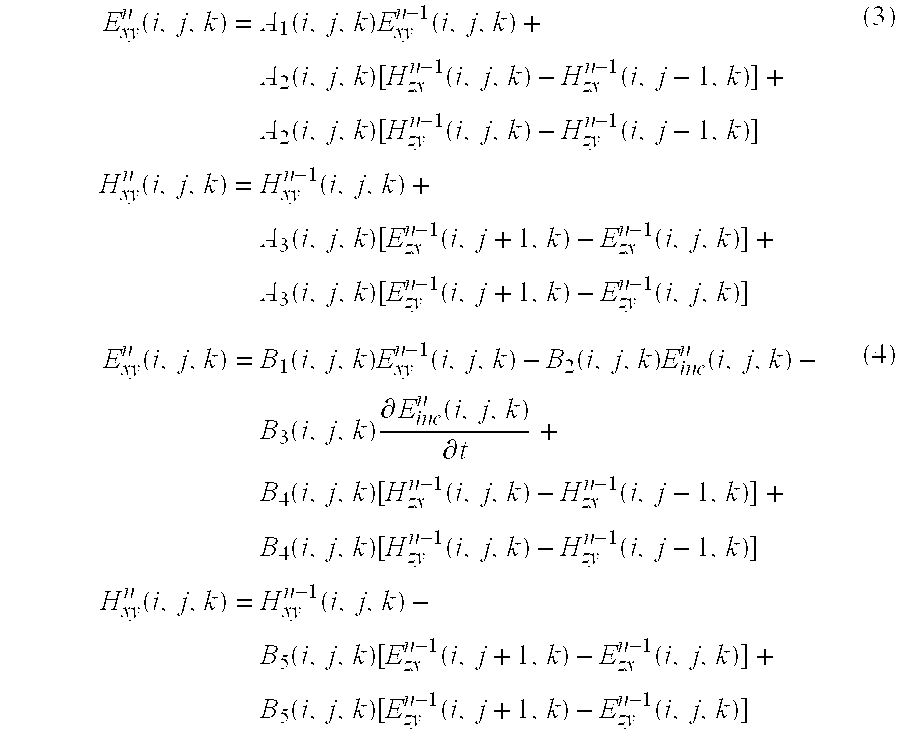Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Computational electromagnetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Computational electromagnetics (CEM), computational electrodynamics or electromagnetic modeling is the process of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic fields with physical objects and the environment.
Near-field effect error analysis method
ActiveCN104063544AResearch intuitiveSpecial data processing applicationsArray elementRadio frequency
The invention relates to a near-field effect error analysis method and belongs to the field of radio frequency simulation. Conventional work such as three-element array antenna near-field effect error analysis in China is all based on analytic methods, which are simple, but cannot achieve accurate results and be applicable in an unlimited frequency range. Therefore the near-field effect error analysis method aims to meet the requirements on high frequency and high precision in radio frequency simulation. According to practical application, the near-field effect error analysis method starts with three array element of a three-element array, develops a computational electromagnetic numerical method, combines electromagnetic simulation software to simulate the near-field effect of a three-element array antenna simultaneously, an azimuth-angle and pitch-angle near-field effect error correction table, and obtains a correct target recurrence position through near-field effect error correction. The near-field effect error analysis method is simple and easy and meets the requirements on high frequency and high precision in radio frequency simulation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
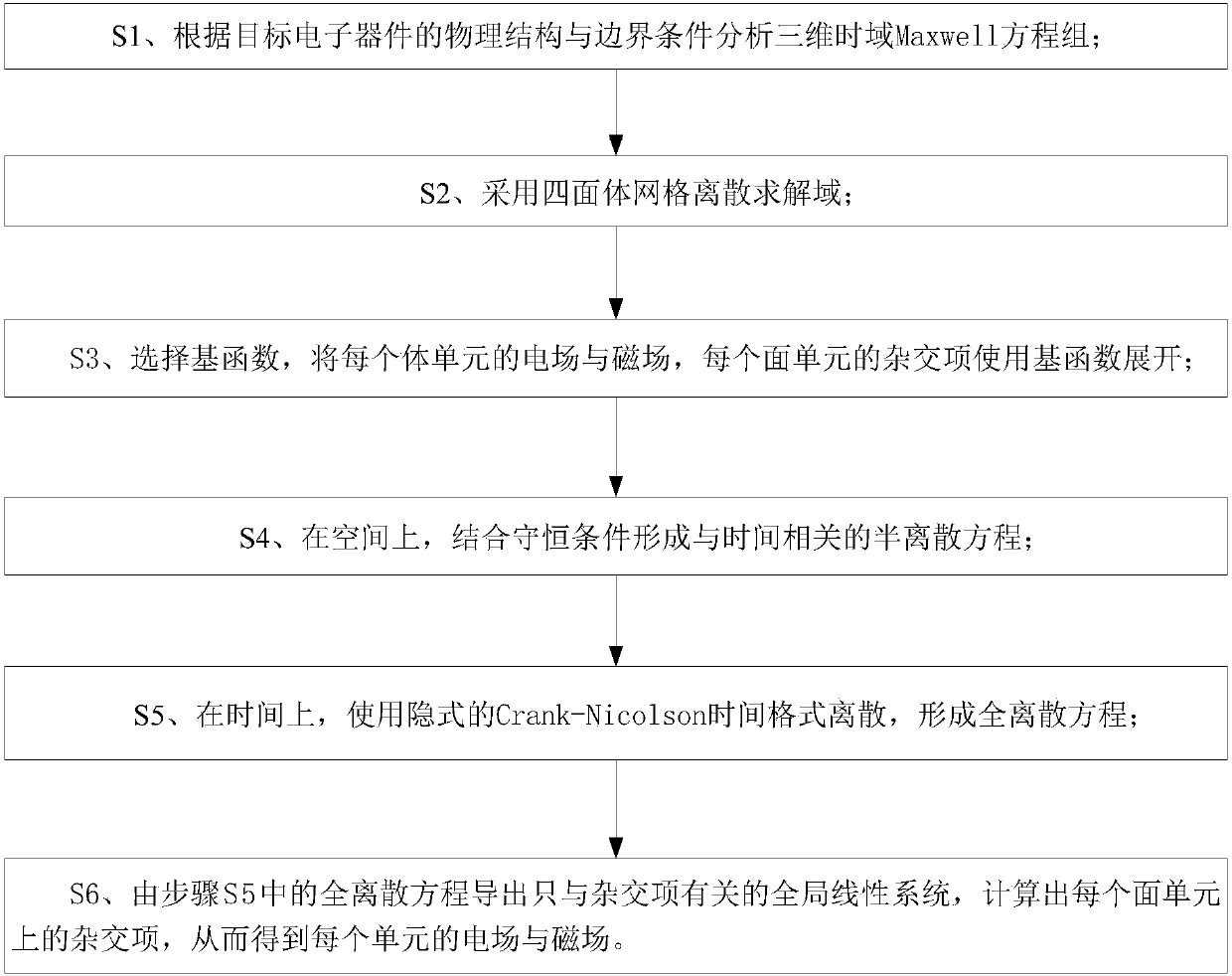
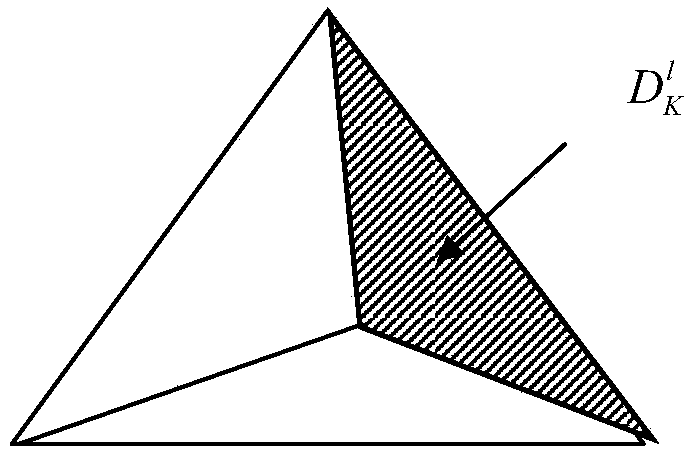
Hybrid time-domain discontinuous-Galerkin-method-based numerical method of time-domain computational-electromagnetics
InactiveCN107944141AObtaining Electromagnetic Response CharacteristicsImprove parallelismDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsElectromagnetic environmentTime domain electromagnetics
The invention discloses a hybrid time-domain discontinuous-Galerkin-method-based numerical method of time-domain computational-electromagnetics. The method is applied to the numerical-solving field oftime-domain computational-electromagnetics. A hybrid term is introduced on interface units of adjacent body units, and is used to define numerical flux of electromagnetic fields, an implicit Crank-Nicolson time format is used to disperse three-dimensional time-domain Maxwell equations, after introducing the hybrid term, to obtain a global linear system related only to the hybrid term, and the electromagnetic fields of all the units are obtained through solving for the hybrid term. Therefore, the deficiency of calculation time, memory and precision of existing time-domain electromagnetic-fieldnumerical-methods in processing multi-scale equipment under complex electromagnetic environments can be effectively avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Three-dimensional target scattering coefficient measurement method based on MIMO array technology
ActiveCN101509974ARealize three-dimensional high-resolution measurementImprove measurement efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMultiple inputElectromagnetism
The invention provides a method for measuring the scattering coefficient of a three-dimensional target, which is based on the multiple-input and multiple-output array technology, and the method synthesizes a large two-dimensional antenna array by controlling the antenna of the multiple-input and multiple-output array to accurately move on a one-dimensional platform, and then obtaining three-dimensional high resolution distribution of the scattering coefficient of the target by being combined with the pulse compressing technology in signal processing, thus realizing three-dimensional high resolution measurement to the scattering coefficient of the target. The method overcomes the defects of large calculation amount, approximate error, difficult application and complicated target and broadband signal of the method for calculating the scattering coefficient of the target on the basis of computational electromagnetics and the defects of low resolution and being incapable of measuring large targets in the method for measuring the scattering coefficient of the target in a microwave dark room. The method is applicable to the fields of target scattering property research, stealth material / aircraft design, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
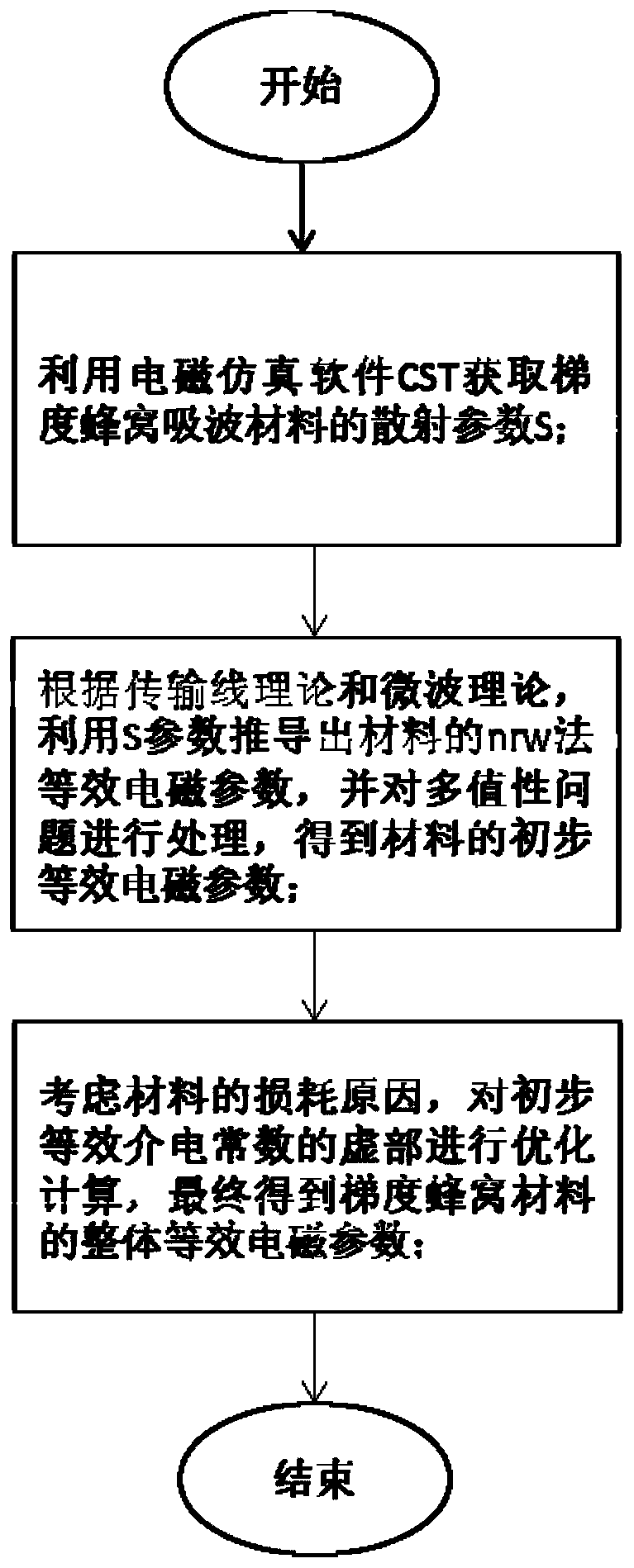
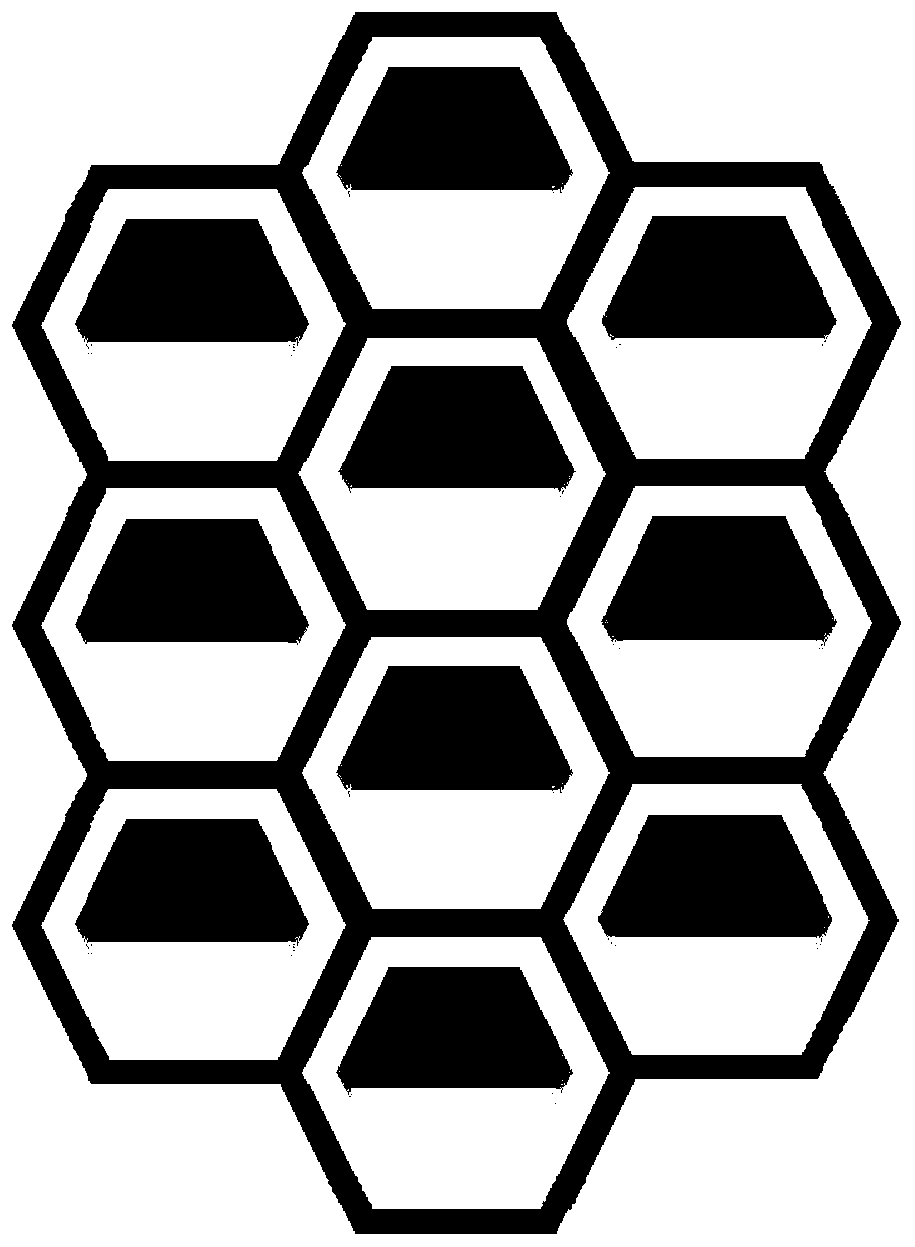
Equivalent electromagnetic parameter extraction method of gradient honeycomb wave-absorbing material
ActiveCN111259534AThe principle is simpleEasy to useDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComputational electromagnetismHoneycomb
The invention belongs to the technical field of computational electromagnetism, and particularly relates to an equivalent electromagnetic parameter extraction method of a gradient honeycomb wave-absorbing material. According to the invention, a multi-valued problem is solved by adopting an imaginary part phase compensation method; the influence of a gradient unique structure of a gradient honeycomb wave-absorbing material on equivalent parameters is considered, wherein the parameters mainly comprise the coating thickness of an electromagnetic wave incident end, the coating thickness of an electromagnetic wave emergent end, the number of gradient layers of the gradient honeycomb wave-absorbing material, the increment between the adjacent gradient coatings and other physical dimension parameters so as to extract the equivalent electromagnetic parameters of the gradient honeycomb wave-absorbing material. The technical scheme has the advantages of being simple in principle and convenient to use, and the obtained equivalent electromagnetic parameters are relatively accurate.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Design by space transformation form high to low dimensions
InactiveUS20050240612A1Improve understandingSave design spaceForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsCurve fittingHigh dimensional
A method is provided for transforming data from a high-dimensional to low-dimensional design space, and for inspecting the transformed data in such a manner as to permit effective navigation and exploration of the high-dimensional design space. Conveniently, an optimum / conditional value for a prescribed functional representation of the transformed data can be derived by visual inspection of a 2-D image map representation of the transformed data. Significantly, the invention has utility for various aircraft design applications and although this technology has been developed with reference to aircraft aerodynamic design in particular, the design space visualisation and curve-fitting technology developed is general. It should therefore be equally applicable to other disciplines such as cost analysis, structures and computational electromagnetics, in which expensive analysis tools are used to find optima for complicated design problems. It is expected to be particularly useful in multi-disciplinary design and situations where there are multiple optima in the design space.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Efficient analyzing method for superfine line structure object electromagnetic property
InactiveCN104112044AFind out quicklySpecial data processing applicationsCurrent distributionAnalysis method
The invention provides an efficient analyzing method for a superfine line structure object electromagnetic property, and belongs to the field of analyzing of a computational electromagnetic moment method. A section wavelet serves as a primary function in the moment method, fast wavelet transform is used, a sparse matrix can be obtained through calculation, and therefore the defects caused by a dense matrix are overcome, and a effect more accurate and efficient than that of traditional analyzing can be obtained. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an object is placed in an appropriate geometry coordinate system, and an electric field integral equation to which the surface current conforms is listed; secondly, the section wavelet serves as the primary function to carry out expansion on an unknown current; thirdly, geometry mapping is established and is substituted into an original matrix equation; fourthly, the matrix equation is solved; fifthly, the current distribution is obtained through solving, and the scattering problem is dealt with to obtain far field distribution. The method can serve as an efficient and accurate means for studying a wire antenna, and plays a significant role.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
FETD (finite-element time-domain) Analog simulation method based on parallel algorithm
ActiveCN107247686AGuaranteed calculation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingParallel algorithmFinite element time domain
The invention discloses an FETD (finite-element time-domain) analog simulation method based on a parallel algorithm and belongs to the field of computational electromagnetics. According to the method, loop iteration solving of an equation is achieved by replacing conventional serial computation by parallel computation based on existing algorithms; in the parallel solving process, a matrix is introduced to convert an equation set in order to overcome dependent relationship of three adjacent moment unknown quantities in a time marching equation, so that paralleling is made feasible. The method enables the problem of low loop iteration solving efficiency of a time marching equation in FETD to be solved at the premise of ensuring computation precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
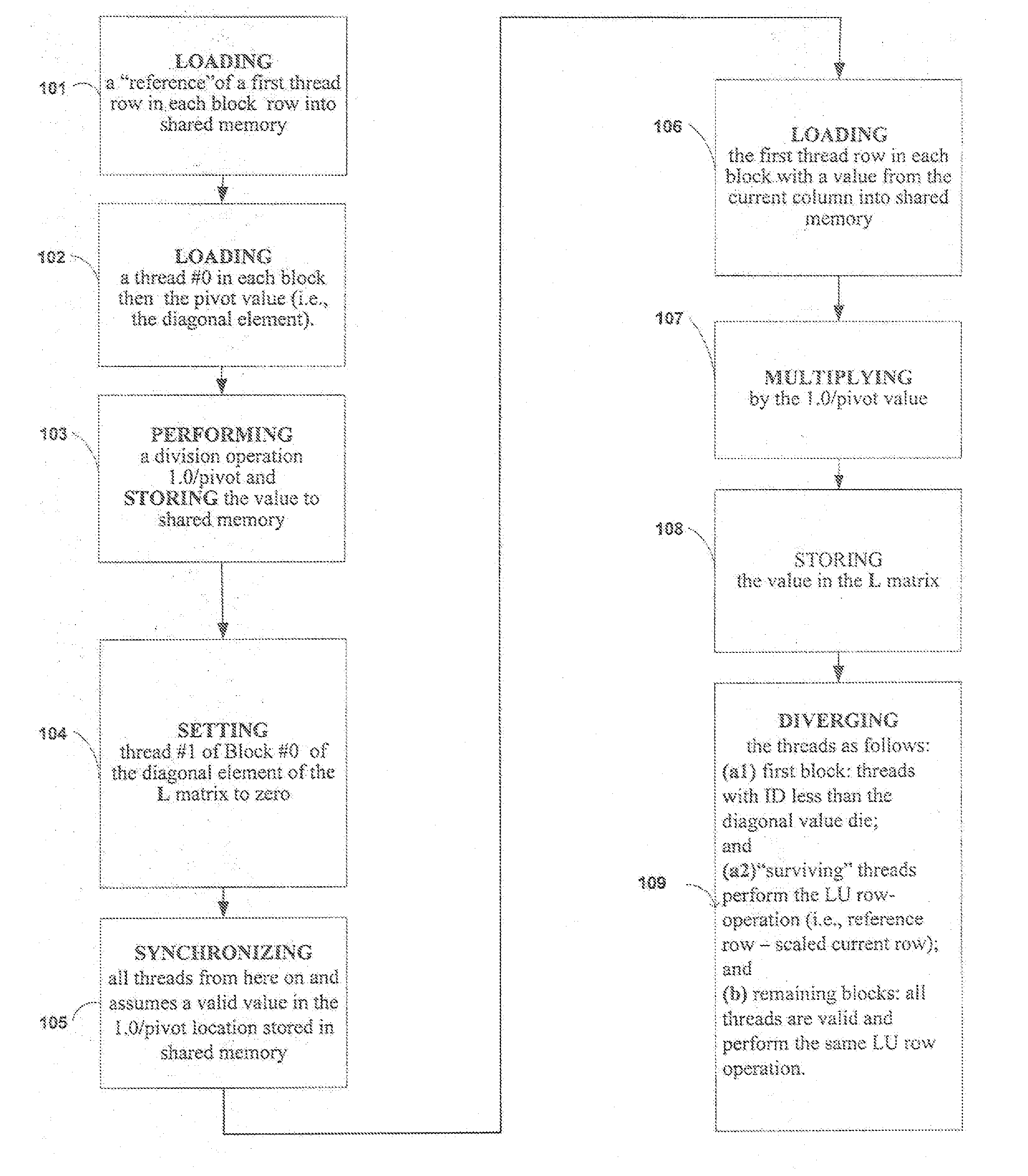
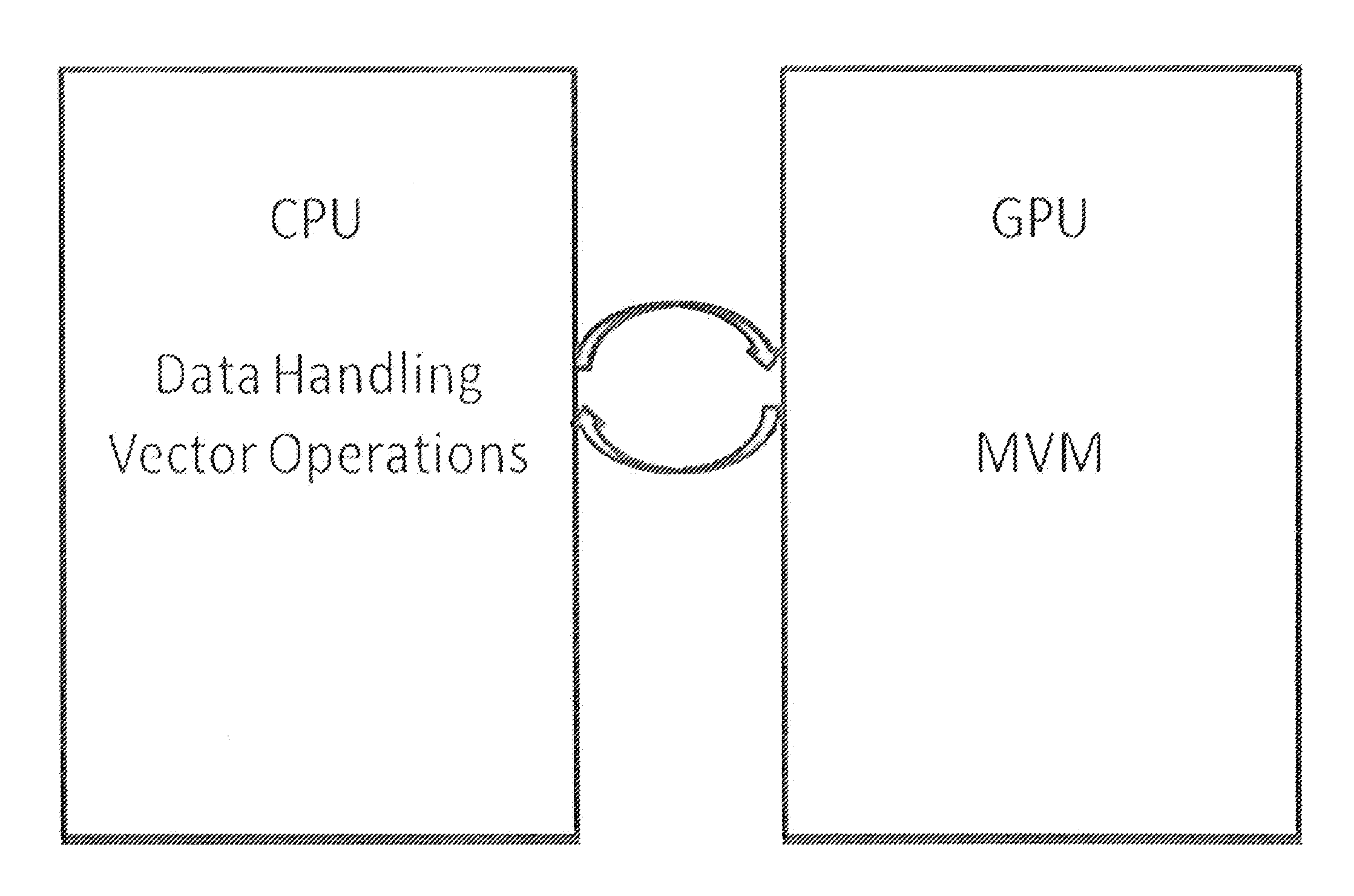
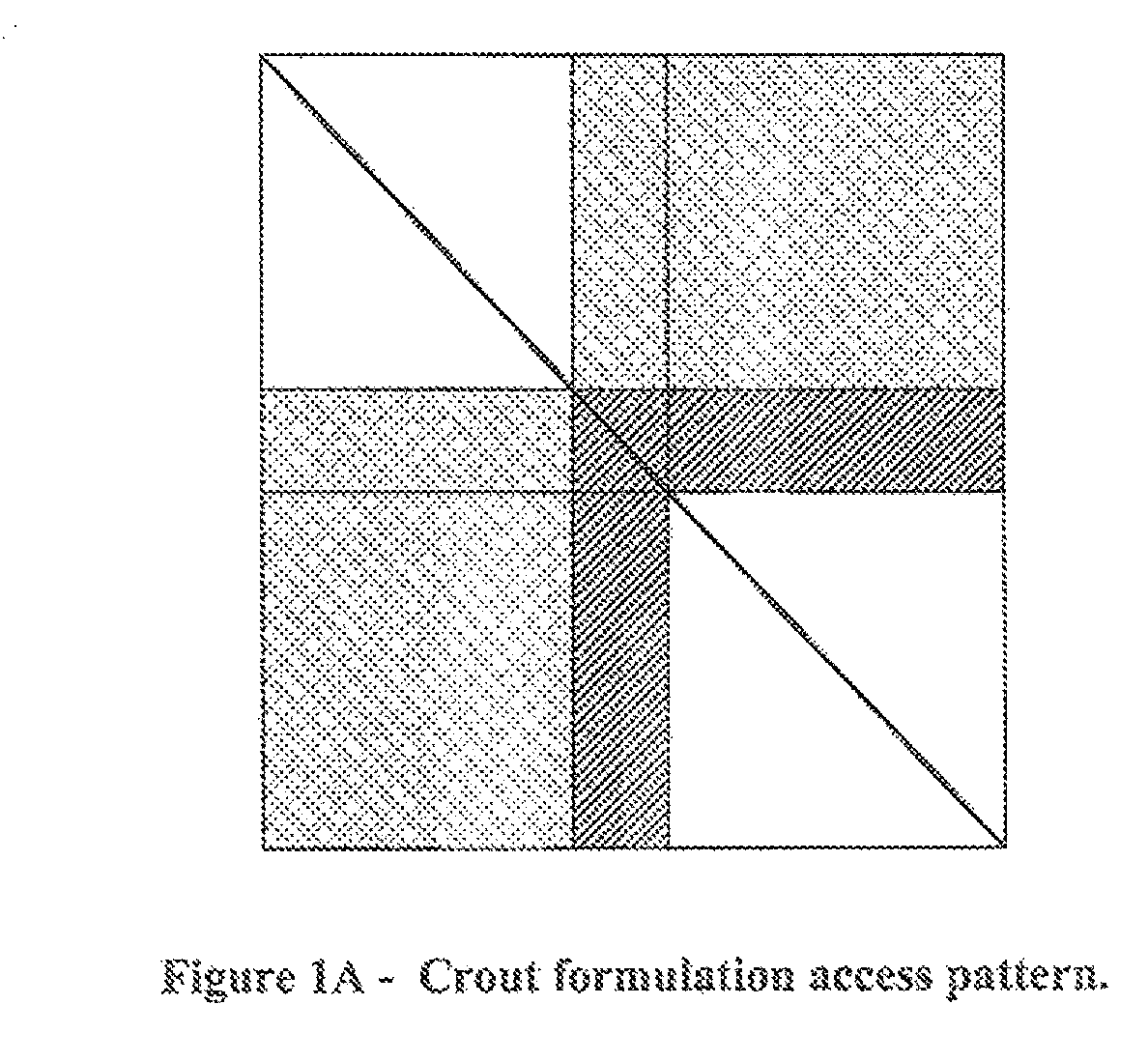
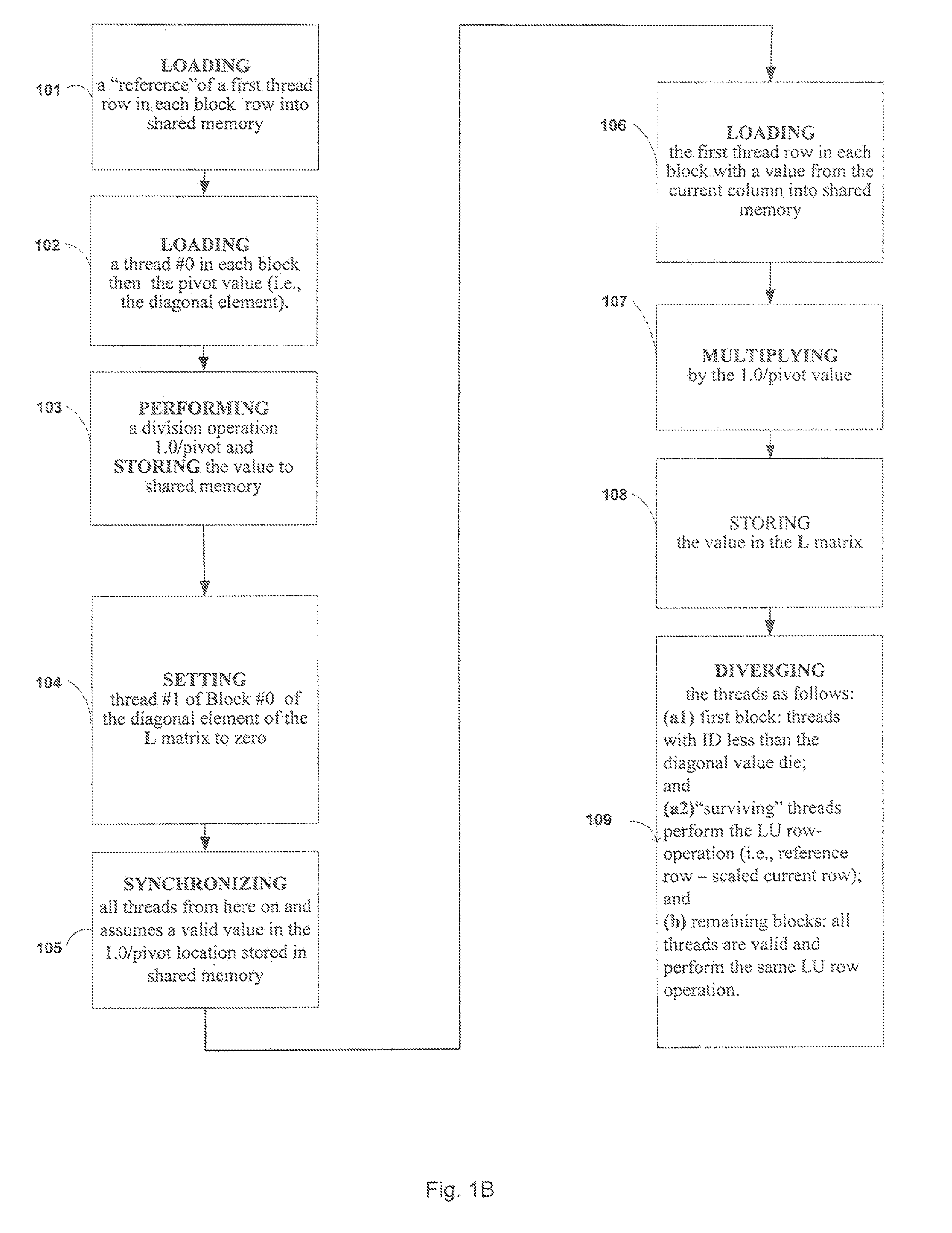
Method for Using a Graphics Processing Unit for Accelerated Iterative and Direct Solutions to Systems of Linear Equations
ActiveUS20100318593A1Simple methodIncrease rangeComplex mathematical operationsComputation using denominational number representationGraphicsComputational science
Methods for increasing the processing speed of computational electromagnetic methods, such as the Method of Moments (MoM), may involve using efficient mapping of algorithms onto a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) architecture. Various methods may provide speed / complexity improvements to either or both of: (1) direct solution via Lower-Upper (LU) factorization; and (2) iterative methods (e.g., Generalized Minimal Residual (GMRES) method).
Owner:EM PHOTONICS
Method for realizing truncated boundaries of anisotropic perfectly matched layers under Cartesian coordinate systems
ActiveCN107944214AStable truncation boundaryThe stable truncation boundary has the expressionInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsPerfectly matched layerComputational physics
The invention relates to a method for realizing truncated boundaries of anisotropic perfectly matched layers under Cartesian coordinate systems. The method is established under a Cartesian coordinatesystem, appearances of anisotropic perfectly matched layers in three-dimensional problems are spheres, and appearances of anisotropic perfectly matched layers in two-dimensional problems are circles,so that the sizes of grids are consistent, instable factors do not occur, residual grids can be truncated, the calculated amount is decreased, the calculation efficiency is improved, and the problem that square anisotropic perfectly matched layers under existing Cartesian coordinate system are low in calculation efficiency and complicated in calculation; and the appearances of the spheres are combined with square grids, so that stability and high efficiency are provided. Through a formula (as shown in the specification), parameters of truncated parameters of spherical anisotropic perfectly matched layers are designed to be used in programs of computational electromagnetics, so that the effect of simulating anechoic chamber wave-absorbing materials in limited calculation areas can be realized.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Truncation boundary for impedance matching layer
The invention discloses a truncation boundary for an impedance matching layer, and efficient computational domain truncation is realized. The shape of a three-dimensional impedance matching layer is a spherical boundary, and 47.64% of calculated amount can be saved; the shape of a two-dimensional impedance matching layer is a circular boundary, and 21.64% of calculated amount can be saved; and the parameters of the impedance matching layer on the truncation boundary, and the number of grids of the impedance matching layer are designed. According to the truncation boundary for the impedance matching layer, example verification shows that electromagnetic waves propagated to the truncation boundary can be effectively absorbed; and in addition, the impedance matching layer can be used for a method for calculating time domain finite difference of electromagnetism, but not limited to the method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TECH & EDUCATION TEACHER DEV CENT OF CHINA VOCATIONAL TRAINING & GUIDANCE
Transparent excitation source implementation method applied to finite-difference time-domain method
ActiveCN107016174AAvoid timeImprove Simulation Computing EfficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainPerfectly matched layer
The invention belongs to the technical field of computational electromagnetics, and particularly relates to a transparent excitation source implementation method applied to the finite-difference time-domain method. A Yee network is used, two electric field excitation sources are added to an excitation source grid, and a feedback electric field is reduced, so that the excitation sources are equivalent to hard sources and transparent. Perfectly matched layer absorbing boundary truncated waveguide structures are added in an input port and an output port to be suitable for first-dimensional, second-dimensional and third-dimensional structures. According to the method, extra computation needs to be conducted only on electromagnetic field components on the surfaces of the excitation sources, compared with other methods, the required auxiliary calculation amount is very small, and influences on calculation efficiency can be ignored. The method is transparent, time for auxiliary calculation is avoided for waveguide type calculation simulation problems, an incident field and a scattering field are efficiently obtained, and the method has a good effect on improving the simulation calculation efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
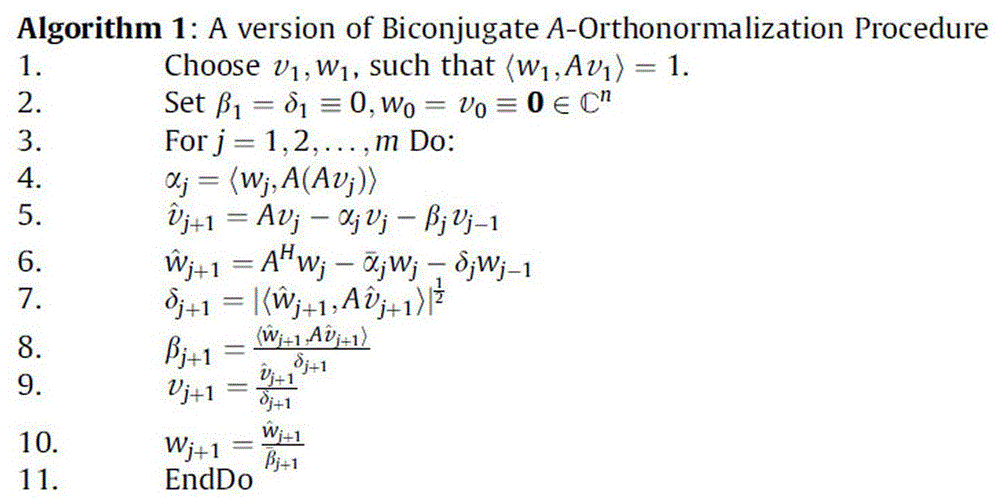
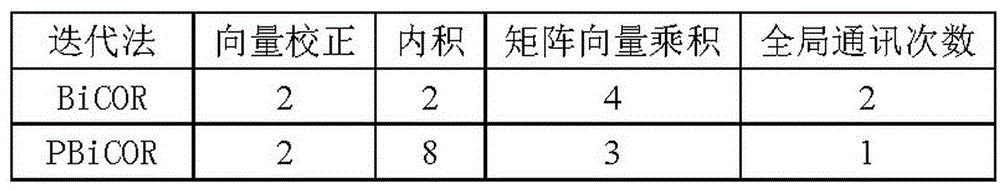
PBiCOR method suitable for distributed parallel computing
InactiveCN105045565AParallel communication performance improvementReduced number of global communicationsInterprogram communicationConcurrent instruction executionMessage deliveryThe Internet
The invention provides a PBiCOR method suitable for distributed parallel computing, and effectively solves the problem that global communications of distributed memory parallel machines influence each other. The scheme is that a parallel machine is assumed to be provided with P processors, each processor is provided with a local memory module and a corresponding processing unit, and the processing units are connected through the internet. An SPMD model is assumed to be adopted, that is to say, all the processing units execute same programs, and when one processing unit needs data of a remote processing unit, the operation must be completed through message delivery. According to the method, the number of global communications is reduced, thereby effectively improving parallel communication performance of the PBiCOR method; and the method has better parallelism and scalability, increases communication performance improvement ratio, and certainly provides a theoretical basis for the fields of petroleum reservoir simulation, weather forecast, computational fluid dynamics, computational electromagnetics, astrophysics, inertial confinement fusion (ICF) two-dimensional numerical simulation and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF AERONAUTICS
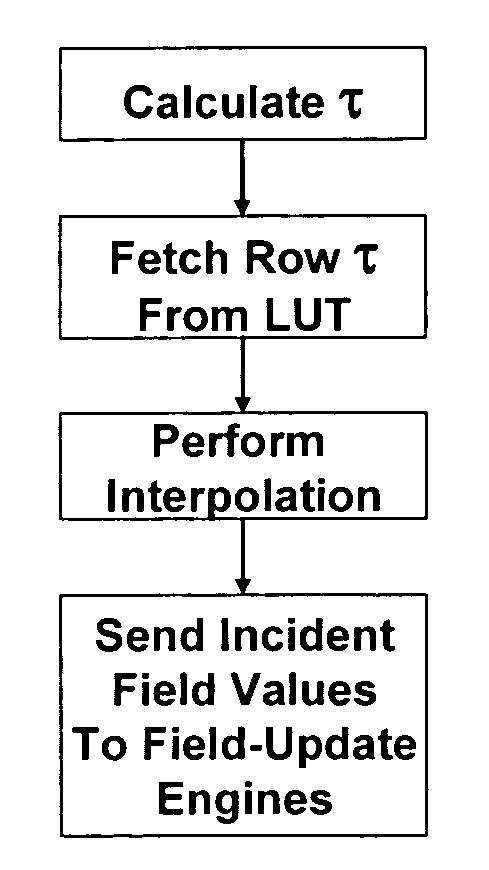
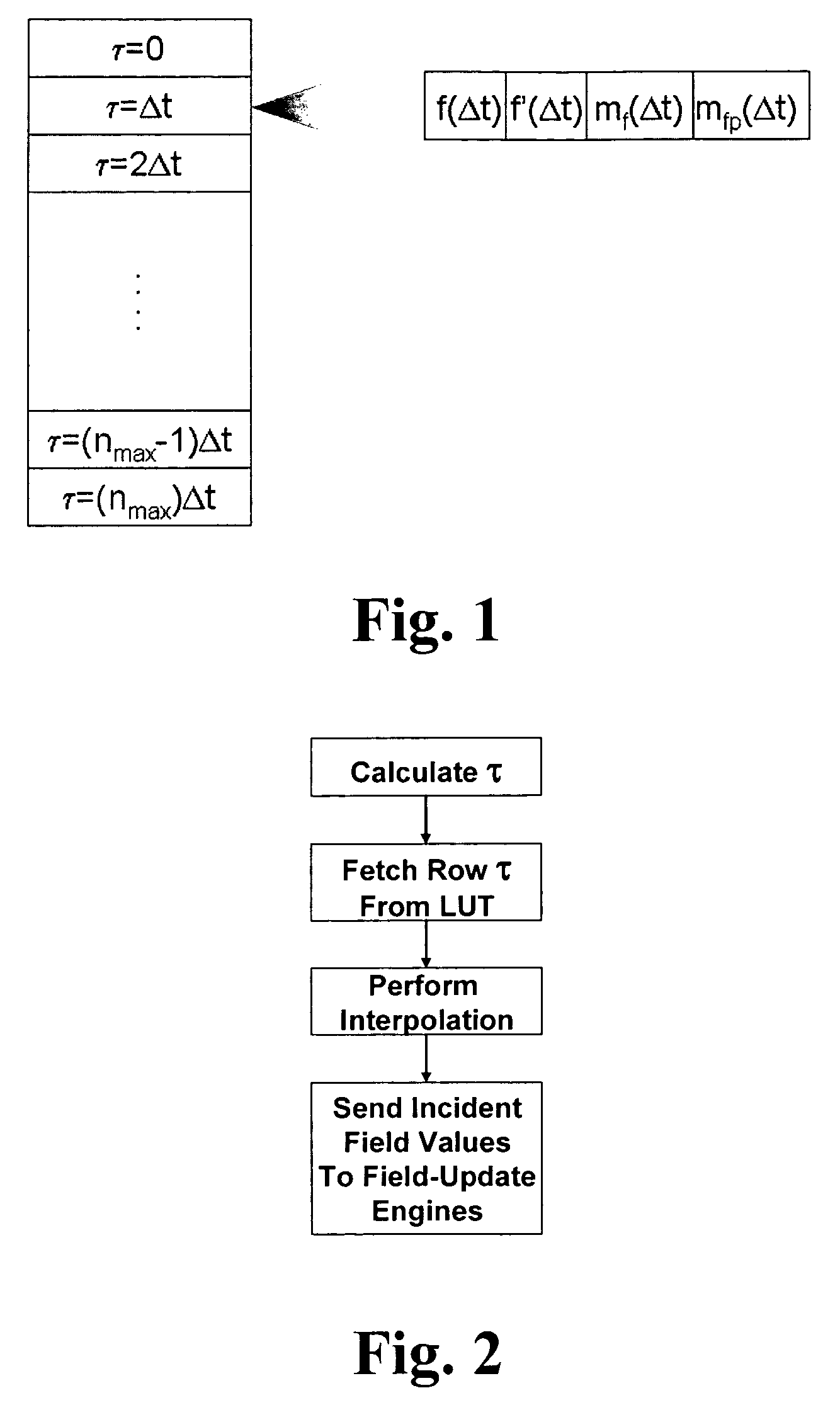
Reformulation of the finite-difference time-domain algorithm for hardware-based accelerators
InactiveUS20050273479A1Easy to implementDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsTime domainFdtd algorithm
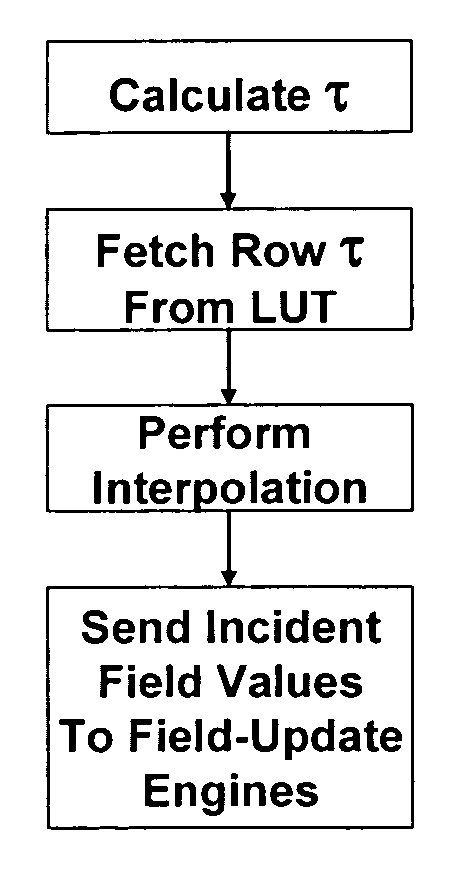
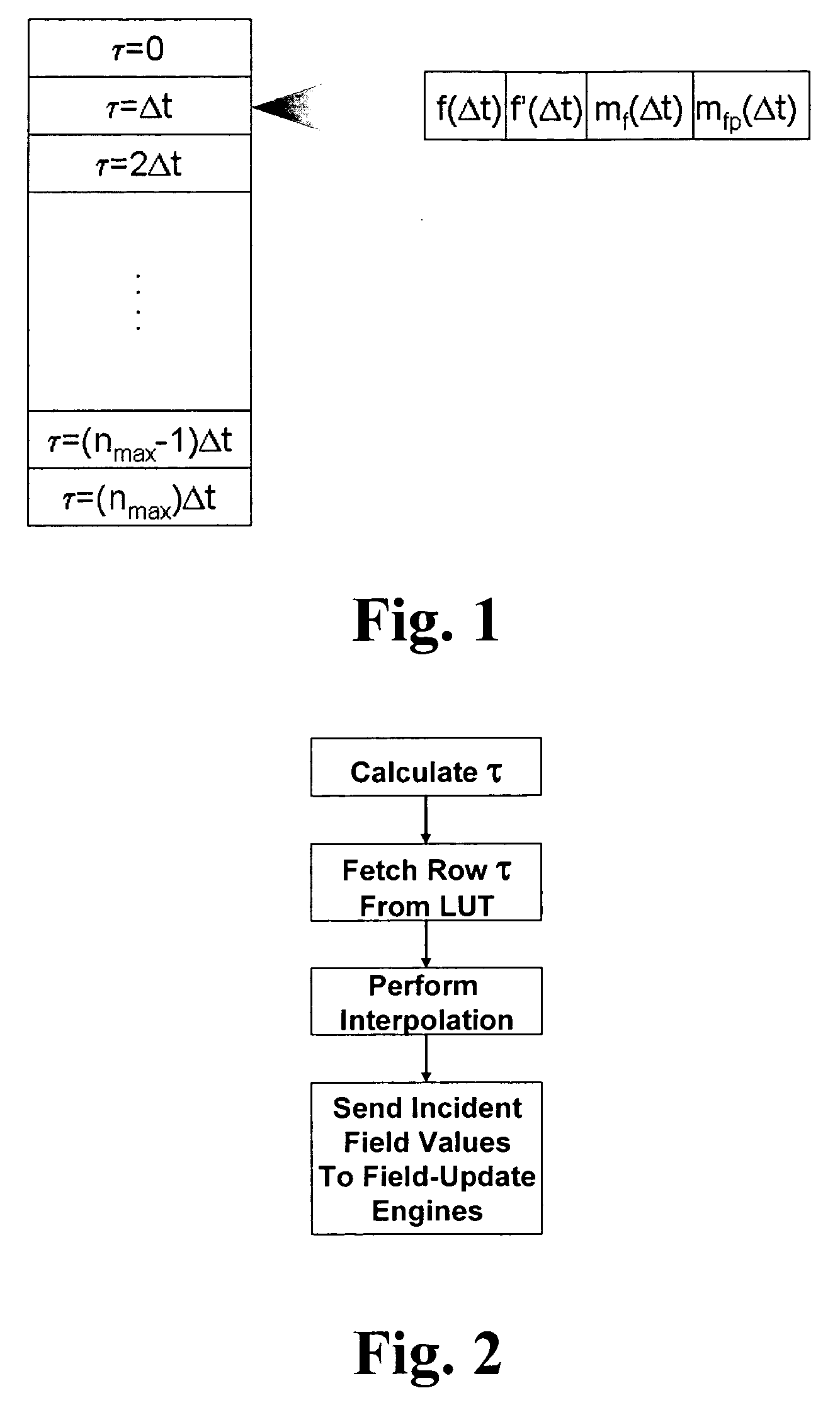
A hardware-based acceleration platform for computational electromagnetic algorithms, specifically the finite-difference time-domain (“FDTD”) method, comprises reformulating the FDTD algorithm in order to make it more hardware friendly. This reformulation makes use of split fields at every node in the mesh, and combines total- and scattered-field formulations into a single, hybrid formulation. By precomputing coefficients for the nodes in the mesh, it is possible for a single set of equations to support plane waves, point sources, PML ABCs, and PEC walls. In the method sources are determined by means of a lookup table, rather than through direct hardware computations. All of these modifications enable the hardware designer to much more easily develop an FDTD accelerator.
Owner:EM PHOTONICS
Three-dimensional high resolution target scattering coefficient measurement method based on bore diameter synthesizing technology
The invention provides a method for measuring the scattering coefficient of a three-dimensional high-resolution target, which is based on the aperture synthesis technology, and the method synthesizes a large two-dimensional antenna array by controlling the antenna to accurately move in a two-dimensional space, and then obtains three-dimensional high resolution distribution of the scattering coefficient of the target by being combined with the pulse compressing technology in signal processing, thus realizing three-dimensional high resolution measurement to the scattering coefficient of the target. The method overcomes the defects of large calculation amount, approximate error, difficult application and complicated target and broadband signal of the method for calculating the scattering coefficient of the target on the basis of computational electromagnetics and the defects of low resolution and being incapable of measuring large targets in the method for measuring the scattering coefficient of the target in a microwave dark room. The method is applicable to the fields of target scattering property research, stealth material / aircraft design, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Electromagnetic interference analyzing method of moving object on random rough sea surface
InactiveCN103902818AAccurate Analysis and PredictionImprove the closenessSpecial data processing applicationsElectromagnetic interferenceClassical mechanics
The invention relates to an electromagnetic interference analyzing method of a moving object on the random rough sea surface. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that 1, electromagnetic scattering of the random rough sea surface is calculated in a layered mode; 2, a computational electromagnetic method is adopted, the moving boundary condition is set, and composite electromagnetic radiation of the moving object and the random rough sea surface is calculated; 3, composite electromagnetic radiation of the layered random rough sea surface and a target on the random rough sea surface is calculated.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
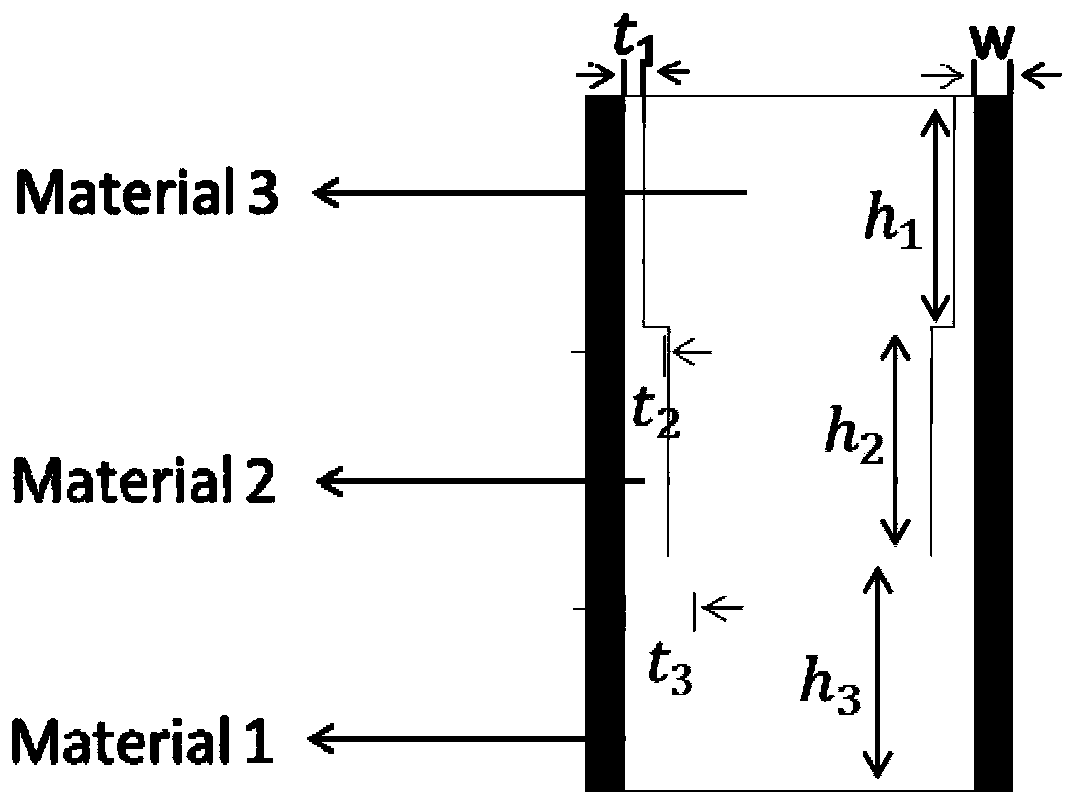
Deduction calculation method for equivalent electromagnetic parameters of rubber plate type wave-absorbing material
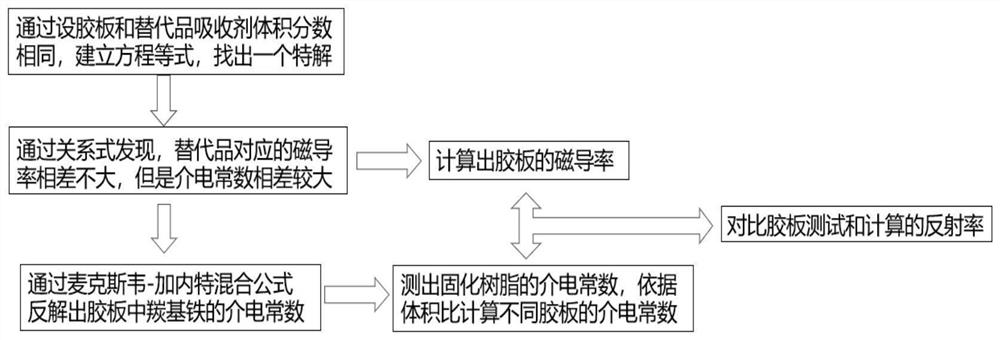
ActiveCN113960512AShort preparation cycleShort processResistance/reactance/impedencePermeability measurementsComputational electromagnetismEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of computational electromagnetism, and particularly relates to a deduction calculation method for equivalent electromagnetic parameters of a rubber plate type wave-absorbing material. The method comprises the following steps of introducing a theory that the volume ratio is consistent and the magnetic conductivity is consistent and a Maxwell Gardt mixed formula into the electromagnetic parameter calculation of the rubber plate type wave-absorbing material, and combining a reflectivity calculation formula to quickly obtain the electromagnetic parameter of the corresponding rubber plate type wave-absorbing material according to the obtained electromagnetic parameter of the corresponding substitute. The manufacturing period of the mixed substitute of the paraffin and the absorbent is shorter than that of a rubber plate, so that the process of manufacturing the rubber plate is omitted, and the problem of long time consumption for obtaining the electromagnetic parameters of the rubber plate type wave-absorbing material in the process of preparing the rubber plate wave-absorbing material in the prior art is solved. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention shortens the manufacturing time of the rubber plate material object.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Analytical verification method of inverse discrete fourier transform for electromagnetic field propagation in waveguides
ActiveCN109460598ACorrect mistakesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsInverse discrete fourier transformValidation methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of computational electromagnetics, in particular to an inverse discrete Fourier transform analytical verification method for propagating an electromagneticfield in a waveguide during a waveguide structure simulation calculation process. The invention corrects the error that the amplitude of the electromagnetic wave propagates infinitely in the waveguide when the signal frequency is less than the cutoff frequency by modifying the calculation formula of the waveguide propagation constant in the analytical verification method of the inverse discrete Fourier transform, and provides a complete analytical verification method suitable for describing any frequency range in the waveguide.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radome electromagnetic performance analysis method considering heat effect
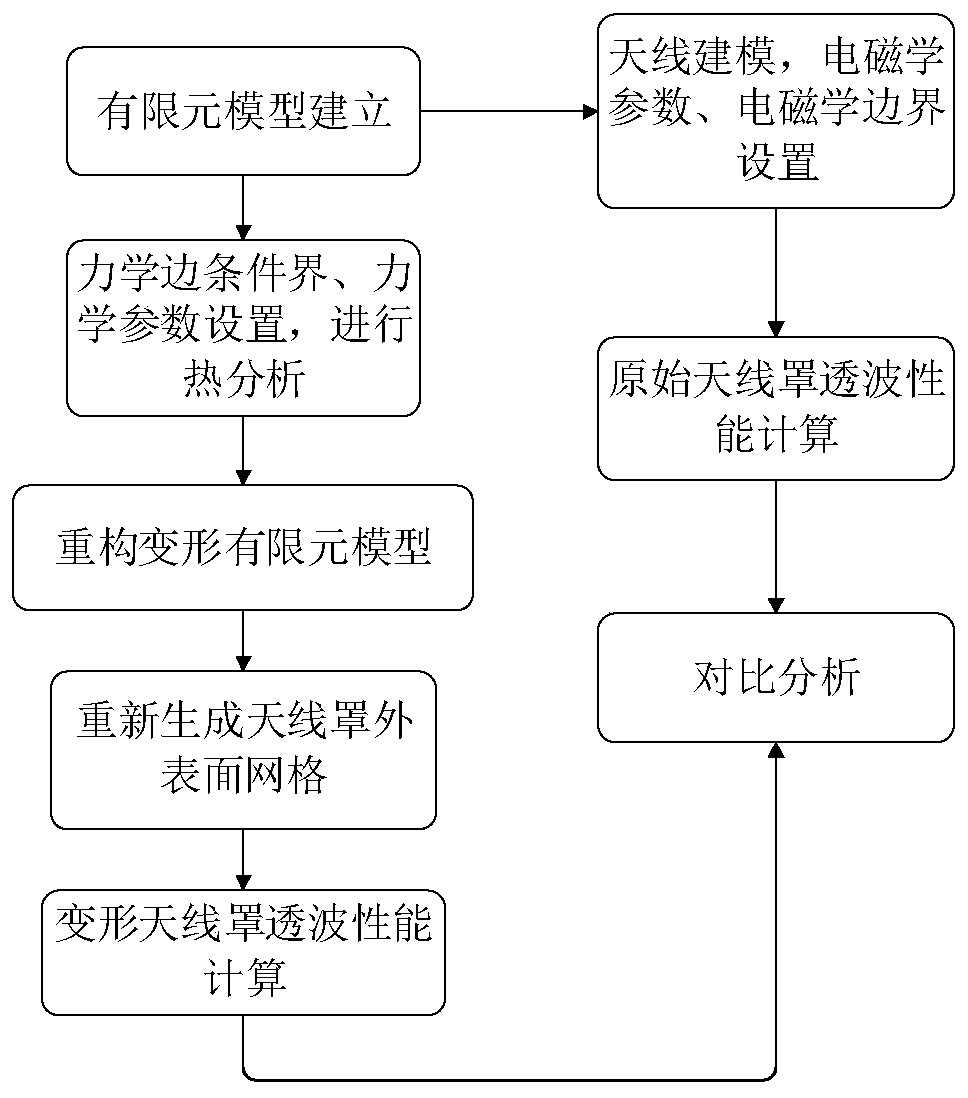
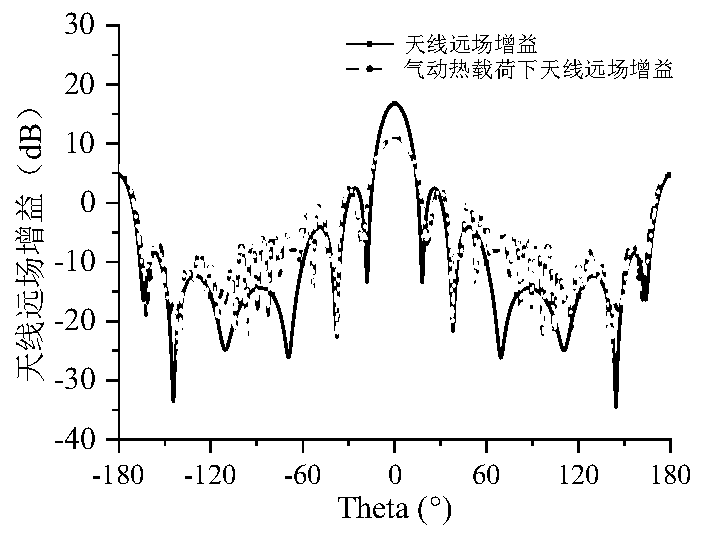
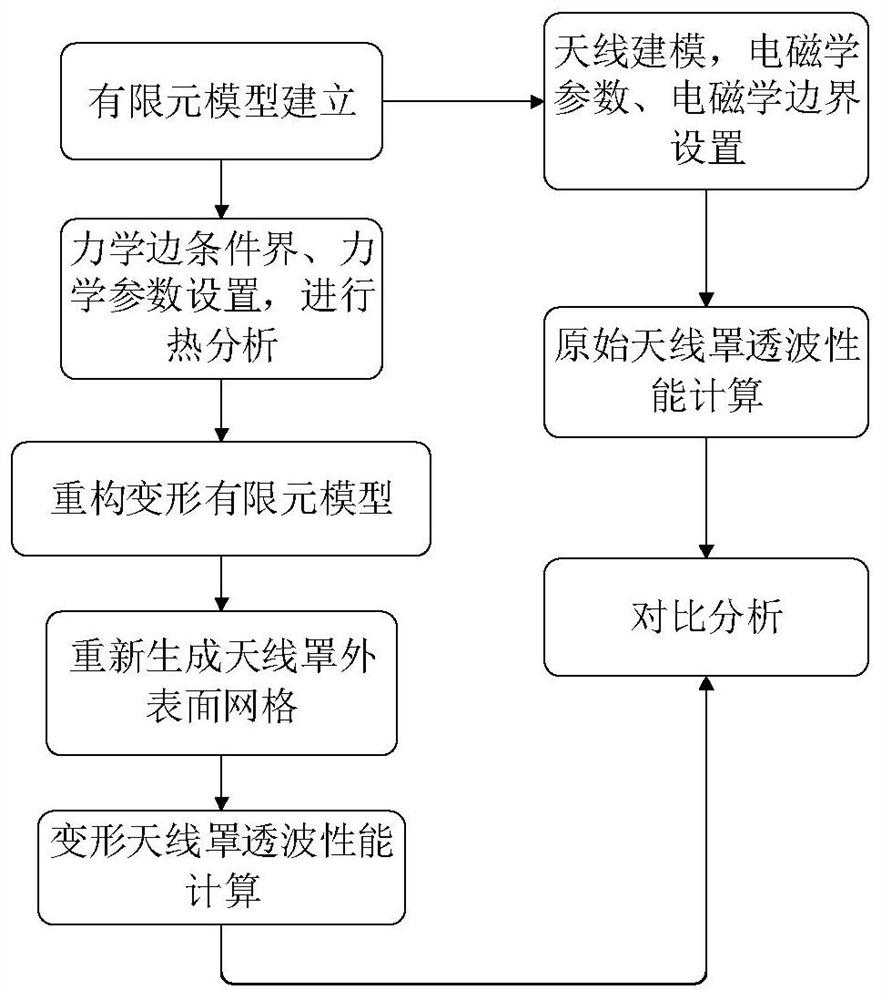
ActiveCN111274726ABreaking through the boundaries of disciplinesShorten the iteration cycleDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelEngineering
The invention provides a radome electromagnetic performance analysis method considering a heat effect. The method mainly comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a radome mechanical calculationelectromagnetism calculation finite element model; s2, adding material attributes to the mechanical finite element model established in the step S1, and applying a temperature load and boundary conditions; s3, solving the static problem, and extracting node displacement; s4, reconstructing a finite element model of deformation under a temperature load based on the node displacement extracted in S3; s5, reconstructing the finite element model deformed in the step S4 based on HyperMesh software to obtain an electromagnetic calculation finite element model; s6, electromagnetic medium parameter setting and antenna modeling of the electromagnetic calculation finite element model established in the S5 are completed, and analysis of the wave-transparent performance of the radome under the temperature load is completed; and S7, electromagnetic medium parameter setting and antenna modeling of the electromagnetic calculation finite element model established in the step S1.2 are completed, and original state radome wave transmission performance analysis is completed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
An Analysis Method of Radome Electromagnetic Performance Considering Thermal Effect
ActiveCN111274726BBreaking through the boundaries of disciplinesShorten the iteration cycleDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelEngineering
The invention provides a radome electromagnetic performance analysis method considering a heat effect. The method mainly comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a radome mechanical calculationelectromagnetism calculation finite element model; s2, adding material attributes to the mechanical finite element model established in the step S1, and applying a temperature load and boundary conditions; s3, solving the static problem, and extracting node displacement; s4, reconstructing a finite element model of deformation under a temperature load based on the node displacement extracted in S3; s5, reconstructing the finite element model deformed in the step S4 based on HyperMesh software to obtain an electromagnetic calculation finite element model; s6, electromagnetic medium parameter setting and antenna modeling of the electromagnetic calculation finite element model established in the S5 are completed, and analysis of the wave-transparent performance of the radome under the temperature load is completed; and S7, electromagnetic medium parameter setting and antenna modeling of the electromagnetic calculation finite element model established in the step S1.2 are completed, and original state radome wave transmission performance analysis is completed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Perfect matching layer method of hyperbolic metamaterial based on time domain finite difference
PendingCN114417667AVerify validitySolve the problem of not being able to absorb electromagnetic waves in hyperbolic materialsDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingParticle physicsFdtd algorithm
The invention discloses a hyperbolic metamaterial perfect matching layer method based on time domain finite difference, and belongs to the field of computational electromagnetic simulation. Comprising the following steps: 1) setting simulation parameters of an FDTD algorithm; 2) determining simulation precision and the number of discrete grids; 3) adding a sine wave source into the hyperbolic medium; 4) updating electric field and magnetic field components; 5) drawing magnetic field distribution, and analyzing stability; and 6) data post-processing: if the result of the field quantity of the magnetic field obtained in the step 5) is not convergent or the error is large, the PML is unstable, and the PML needs to be corrected. The problem that electromagnetic waves propagated in a hyperbolic material have numerical divergence in frequency domain PML simulation of traditional PML and COMSOL is solved, the problem that the frequency domain PML in the time domain traditional PML and COMSOL cannot absorb the electromagnetic waves in the hyperbolic material is solved, high stability is shown, and a numerical result further verifies the effectiveness of a PML improvement technology.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for solving electromagnetic scattering of electric large object through wavelet moment method of centroid segmentation
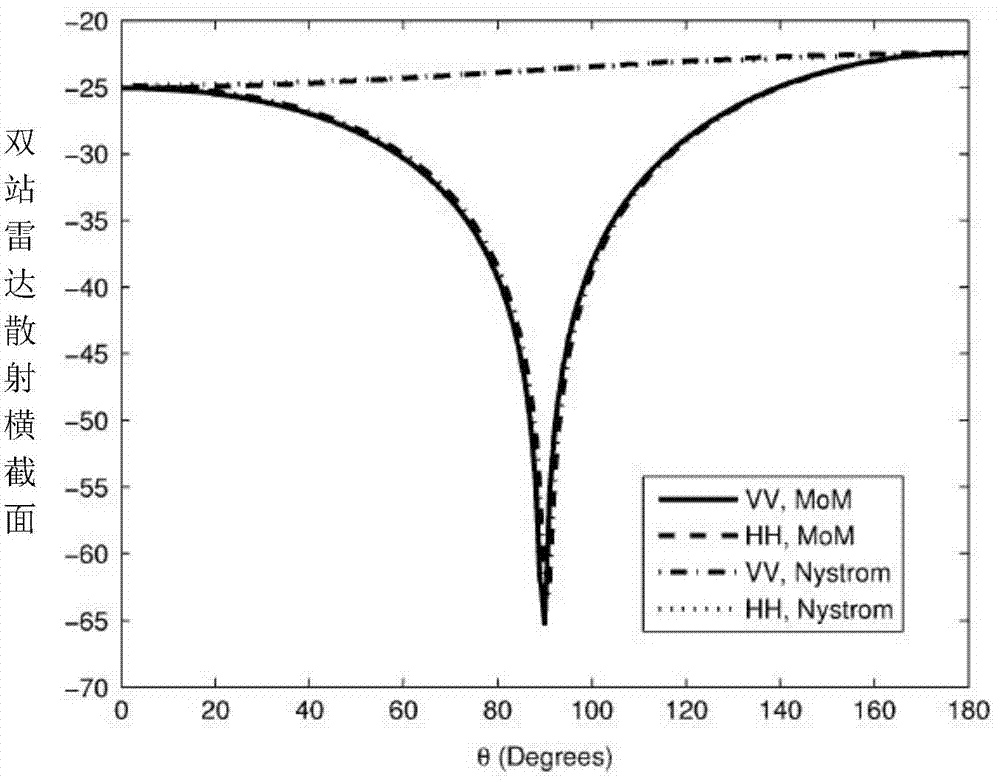
ActiveCN110765412AQuick solveReduce computing timeComplex mathematical operationsVanishing momentsTarget surface
The invention discloses a method for solving electromagnetic scattering of an electric large object through a wavelet moment method of centroid segmentation, and belongs to the field of computationalelectromagnetism in electromagnetic engineering. For aiming at problems in calculating electromagnetic scattering of an electrically large-size conductor target, formed matrix complexity, computational volume, errors are easy to occur; firstly, triangular discretization is carried out on a target surface by utilizing an RWG basis function; each original triangle is divided into nine same sub-triangles; nine same sub-triangles are efficiently filled with impedance matrix elements by adopting a centroid segmentation method; and further an impedance matrix without singularity in calculating is obtained; secondly, a sparse matrix generated by discrete wavelet transform is acted on the efficiently filled impedance matrix, and the dense impedance matrix is sparsified by using the multi-resolution and vanishing moment characteristics of a wavelet basic body, thereby reducing the calculation time. Simulation proves that the method provided by the invention can be used for quickly calculating the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the electrically large object under the condition of ensuring the calculation precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
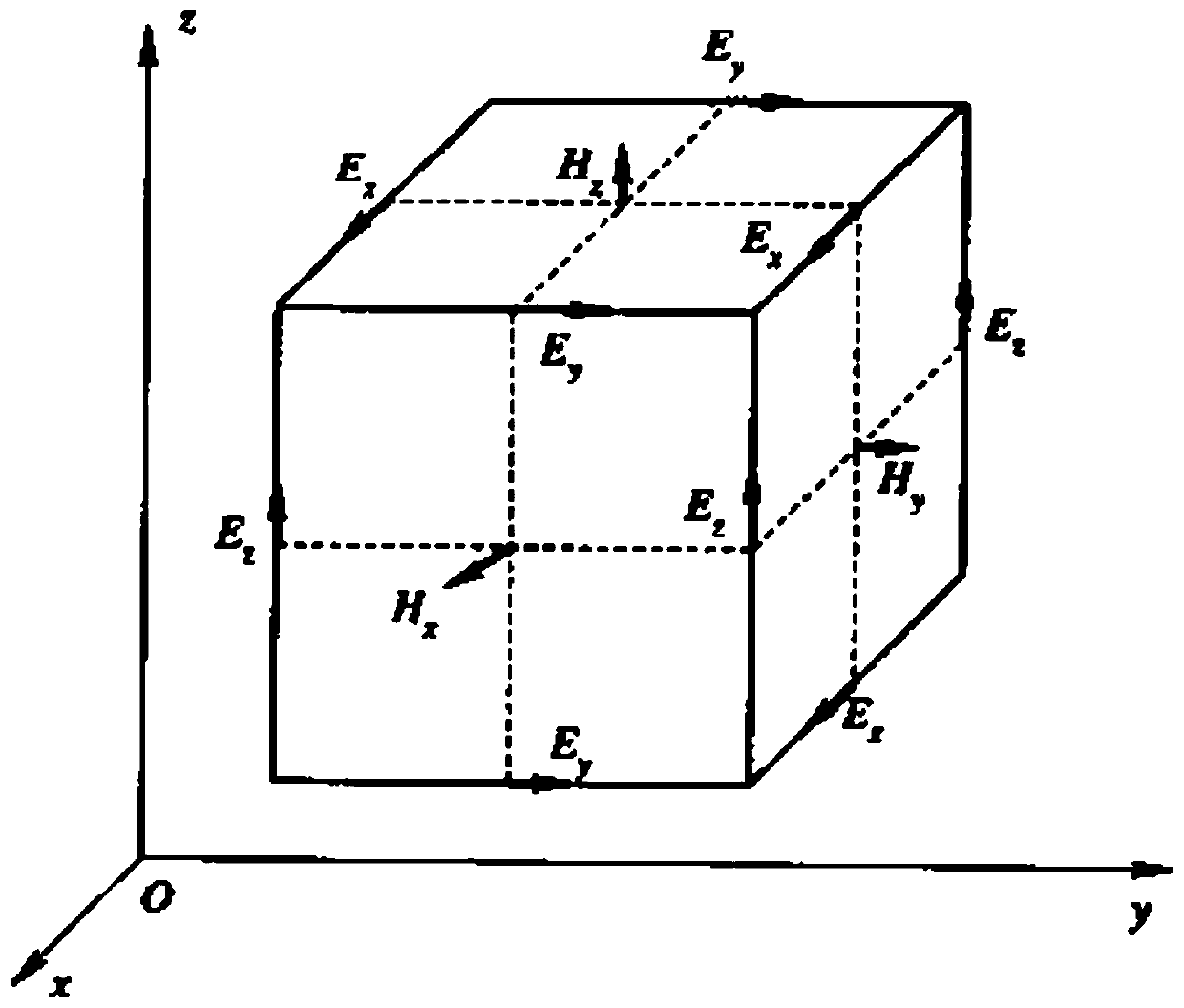
A NUMERICAL METHOD BASED ON FUNCTION APPROXIMATION FOR ADAPTIVE 3D MICROWAVE TUBE INPUT-OUTPUT WINDOW MODEL REDUCTION
ActiveCN107526869BAvoid complexityImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention belongs to the field of computational electromagnetism numerical solution, and provides a numerical method for reducing the order of a three-dimensional microwave tube input and output window model based on function approximation adaptive error analysis. The three-dimensional eigenanalysis of the microwave tube is carried out through the vector finite element method, and the complex The electromagnetic problem is converted into a mathematical large-scale matrix function equation, and a series of reductions are performed on the equation, that is, the Chebyshev function is used to approximate, combined with the error analysis of the eigenvalues, adaptively select the interpolation point, and divide the convergence of the entire frequency band interval, the expanded subspace of the reduced-order model is obtained, and the final S-parameters can be obtained through post-processing, so as to realize the optimization simulation of the full-band adaptation of the microwave tube.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A FETD Simulation Method Based on Parallel Algorithm
ActiveCN107247686BGuaranteed calculation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComputational scienceConcurrent computation
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A leapfrogadi-fdtd method based on GPU parallelism
ActiveCN107526887BShorten the time periodAvoid time costDesign optimisation/simulationProcessor architectures/configurationComputational sciencePERQ
The invention belongs to the field of computational electromagnetics and high-performance computing, and is specifically a Leapfrog ADI‑FDTD method based on GPU parallelism. The present invention adopts Yee grid, by applying GPU parallel computing technology to the Leapfrog ADI-FDTD algorithm containing CPML absorption boundary, forming the Leapfrog ADI-FDTD algorithm containing CPML absorption boundary based on GPU parallel acceleration, while maintaining Leapfrog ADI-FDTD algorithm While the FDTD algorithm and CPML absorb the excellent characteristics of the boundary, it greatly improves the calculation efficiency, greatly saves calculation time, reduces the time period and cost of numerical simulation experiments, and meets the high-efficiency requirements of related scientific research or device design.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for using a graphics processing unit for accelerated iterative and direct solutions to systems of linear equations
ActiveUS8495120B2Simple methodIncrease rangeComplex mathematical operationsComputation using denominational number representationComputational scienceGraphics
Methods for increasing the processing speed of computational electromagnetic methods, such as the Method of Moments (MoM), may involve using efficient mapping of algorithms onto a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) architecture. Various methods may provide speed / complexity improvements to either or both of: (1) direct solution via Lower-Upper (LU) factorization; and (2) iterative methods (e.g., Generalized Minimal Residual (GMRES) method).
Owner:EM PHOTONICS
Reformulation of the finite-difference time-domain algorithm for hardware-based accelerators
InactiveUS7340695B2Easy to implementDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsTime domainLookup table
A hardware-based acceleration platform for computational electromagnetic algorithms, specifically the finite-difference time-domain (“FDTD”) method, comprises reformulating the FDTD algorithm in order to make it more hardware friendly. This reformulation makes use of split fields at every node in the mesh, and combines total- and scattered-field formulations into a single, hybrid formulation. By precomputing coefficients for the nodes in the mesh, it is possible for a single set of equations to support plane waves, point sources, PML ABCs, and PEC walls. In the method sources are determined by means of a lookup table, rather than through direct hardware computations. All of these modifications enable the hardware designer to much more easily develop an FDTD accelerator.
Owner:EM PHOTONICS
Fusion and Optimization Method of Mesh Model of Ship and Wake
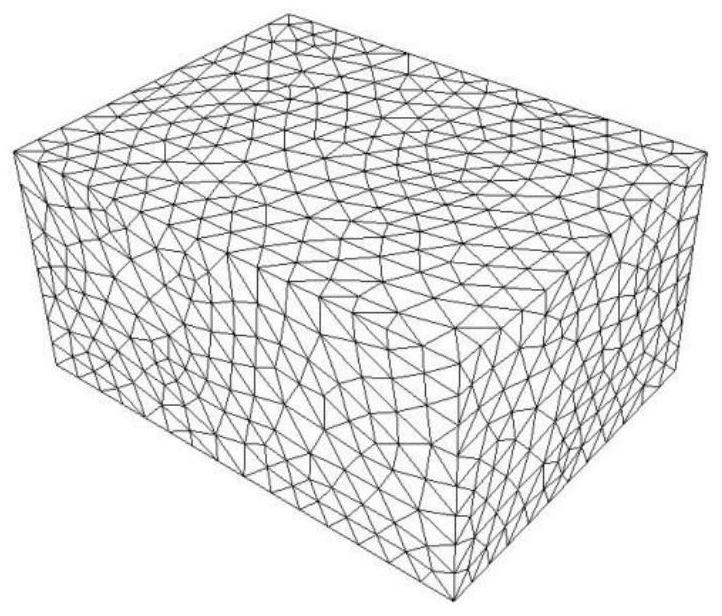
ActiveCN106649992BEfficient fusionNo strings attachedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPoint cloudGrid density
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Analytical Verification Method of Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform for Electromagnetic Field Propagation in Waveguide
ActiveCN109460598BCorrect mistakesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware engineeringEngineering
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Integrated development environment to establish a digital thread in the lifecycle of a structural product
ActiveUS11416646B2Traceable, accurate, reusable and efficientImproved meshingGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationPERQGraphical user interface
An apparatus for designing a structural product includes memory to store computer-readable program code for an integrated development environment to establish a digital thread in a lifecycle of the structural product, and processing circuitry to execute the computer-readable program code. The apparatus is thereby caused to generate a graphical user interface from which the integrated development environment is accessible to cause the apparatus to generate an electromagnetic effects (EME) model of the structural product from authoritative data including a solid model of the structural product, and parameterize the EME model with one or more electrical properties. The apparatus is caused to produce a computational electromagnetics (CEM) model of the structural product from the parameterized EME model, perform a CEM analysis from the CEM model to generate a corresponding solution is generated, and post-process the corresponding solution.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for analyzing electromagnetic radiation characteristics of piezoelectric ceramic material
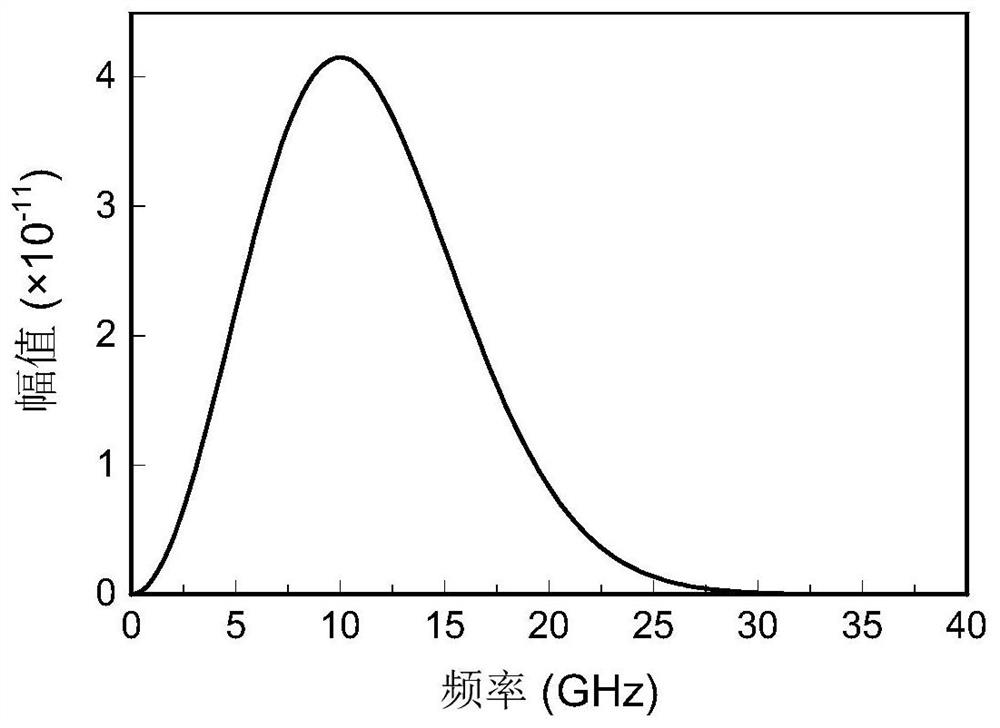
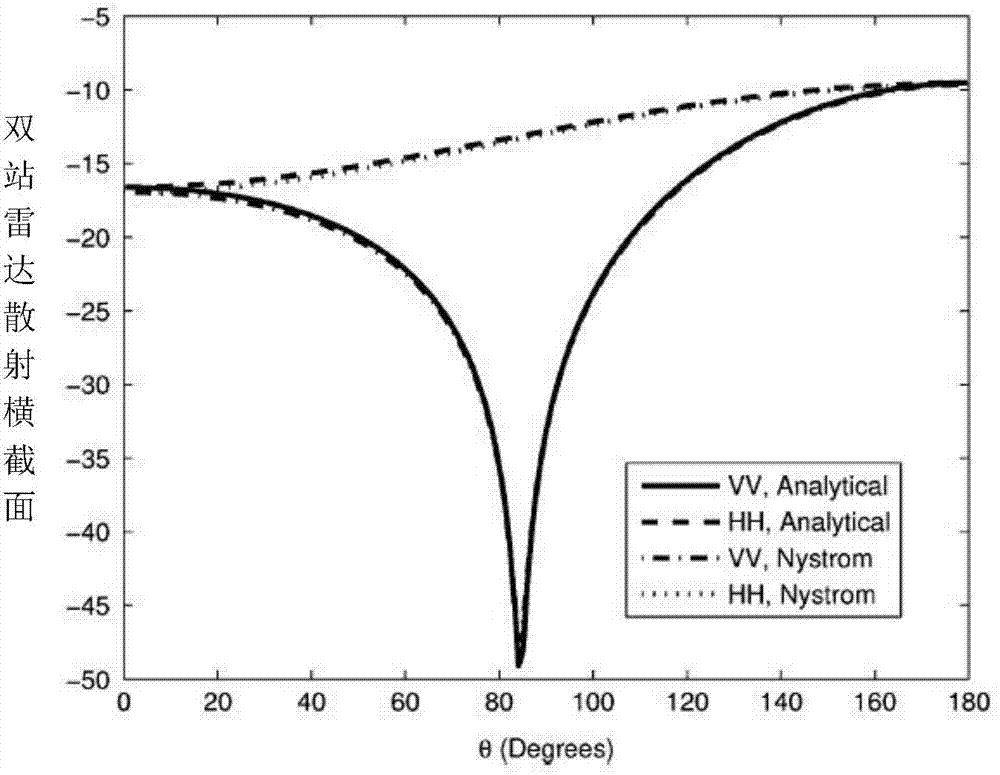
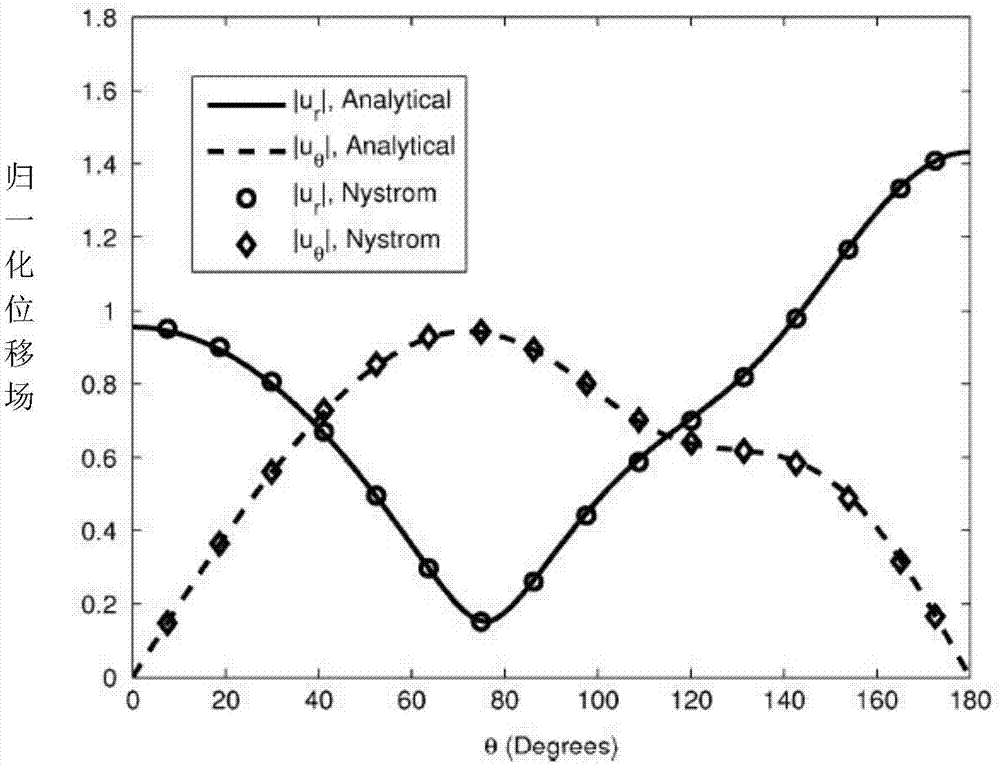
The invention provides a method for analyzing the electromagnetic radiation characteristics of a piezoelectric ceramic material and belongs to the field of computational electromagnetic analysis. According to the method for analyzing the electromagnetic radiation characteristics of the piezoelectric ceramic material, the interaction process between induction elastic waves and electromagnetic waves under the action of microwaves is accurately described by solving coupled Maxwell equations and an elastic wave equation. The method is different from a traditional method that coupled equations are deduced in a partial differential equation mode. By the adoption of the method, an excitation source of elastic waves is taken as electromagnetic force, generated induction elastic waves are taken as an excitation source and influence original electromagnetic waves in turn, the electromagnetic wave portion and the elastic wave portion of an integral equation are deduced based on the Huygens equivalence principle and the extinction theorem, the electromagnetic wave portion and the elastic wave portion are coupled through the excitation source, and the Nystrom method is introduced to solve the coupled integral equations for the first time. The piezoelectric ceramic is a polycrystal having the piezoelectric performance and is an important part of information functional ceramic. The method for analyzing the electromagnetic radiation characteristics of the piezoelectric ceramic material has quite important significance in research and development of a high-performance high-precision piezoelectric ceramic material.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com