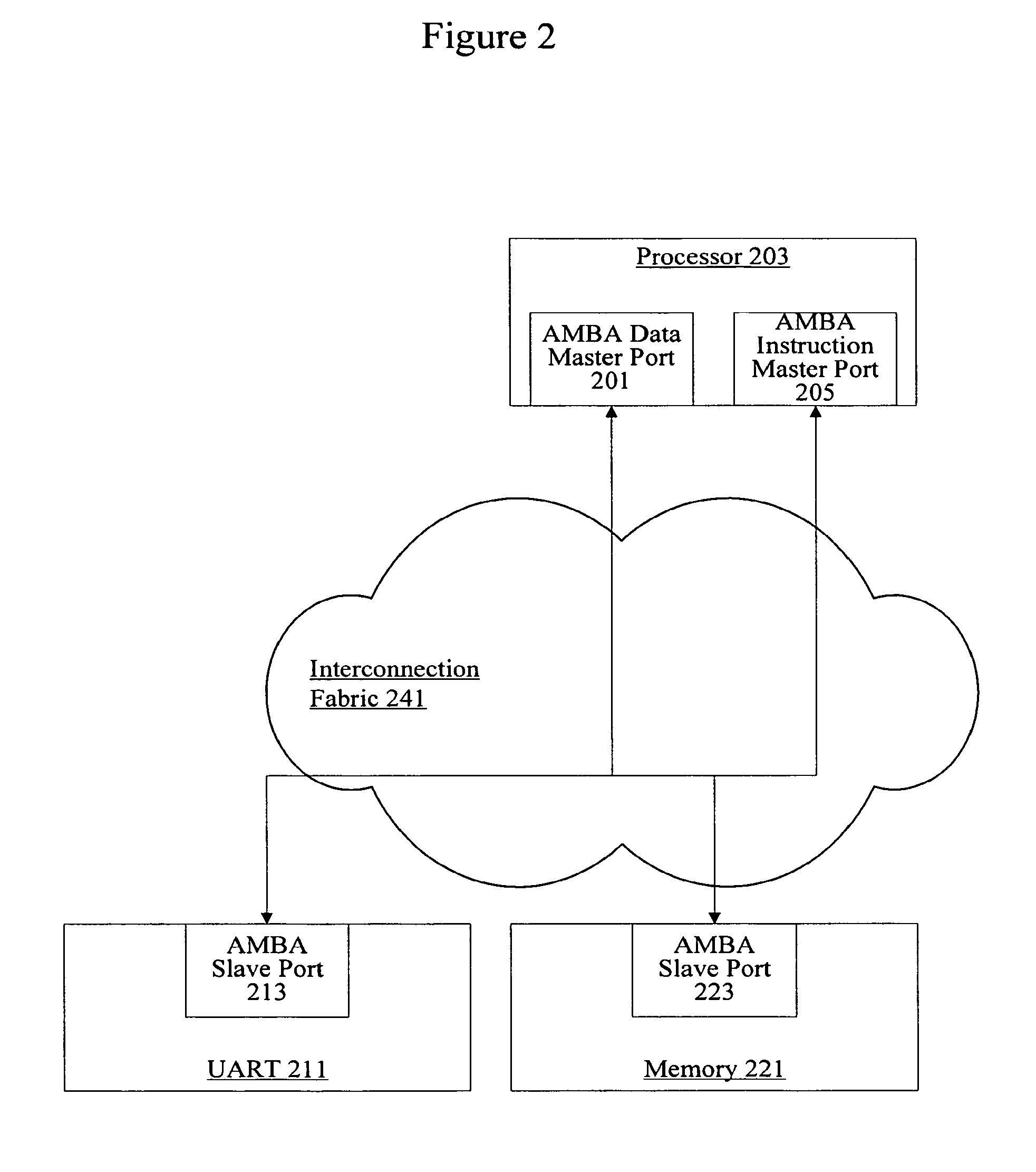
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
144 results about "Clock domain crossing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
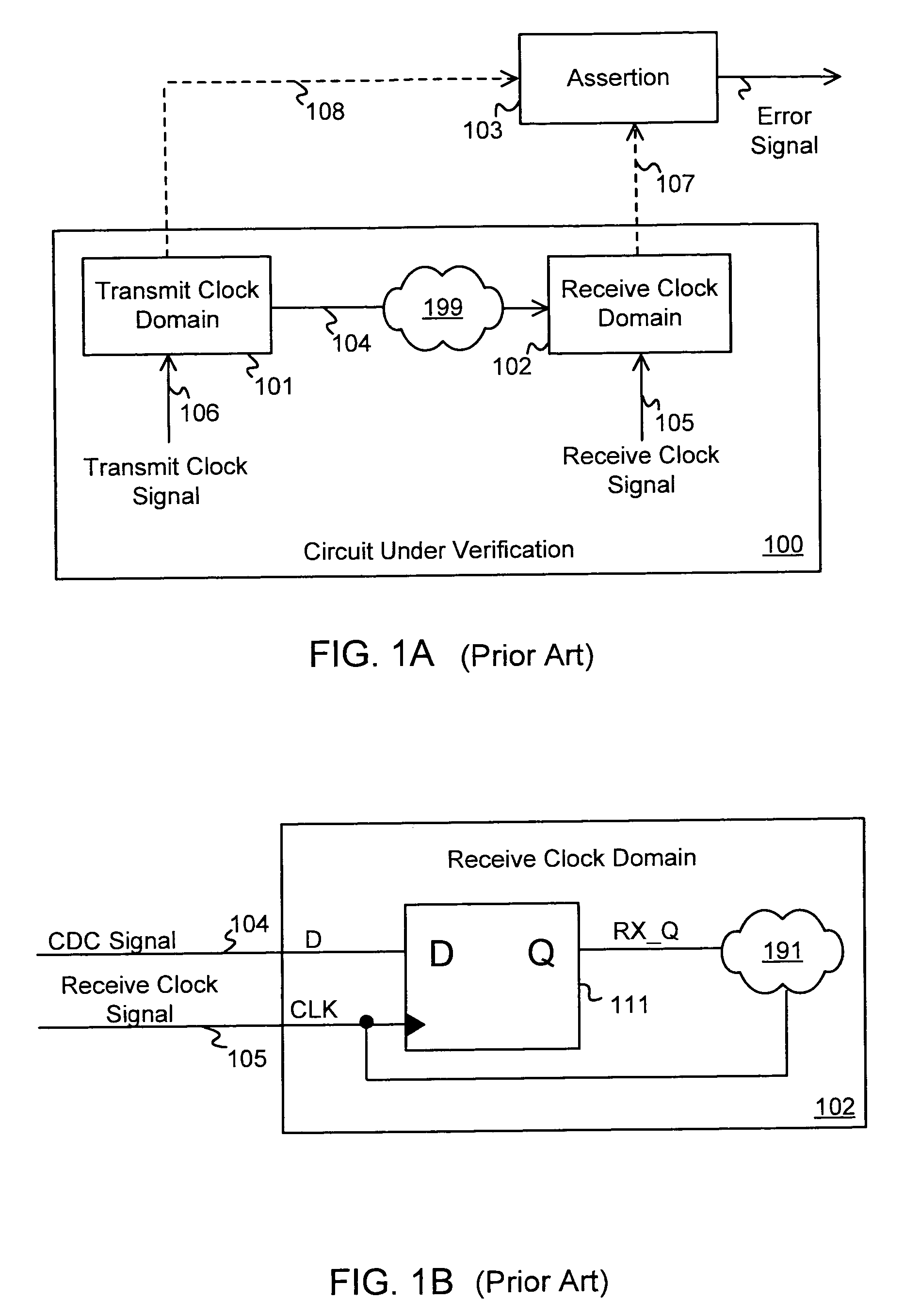
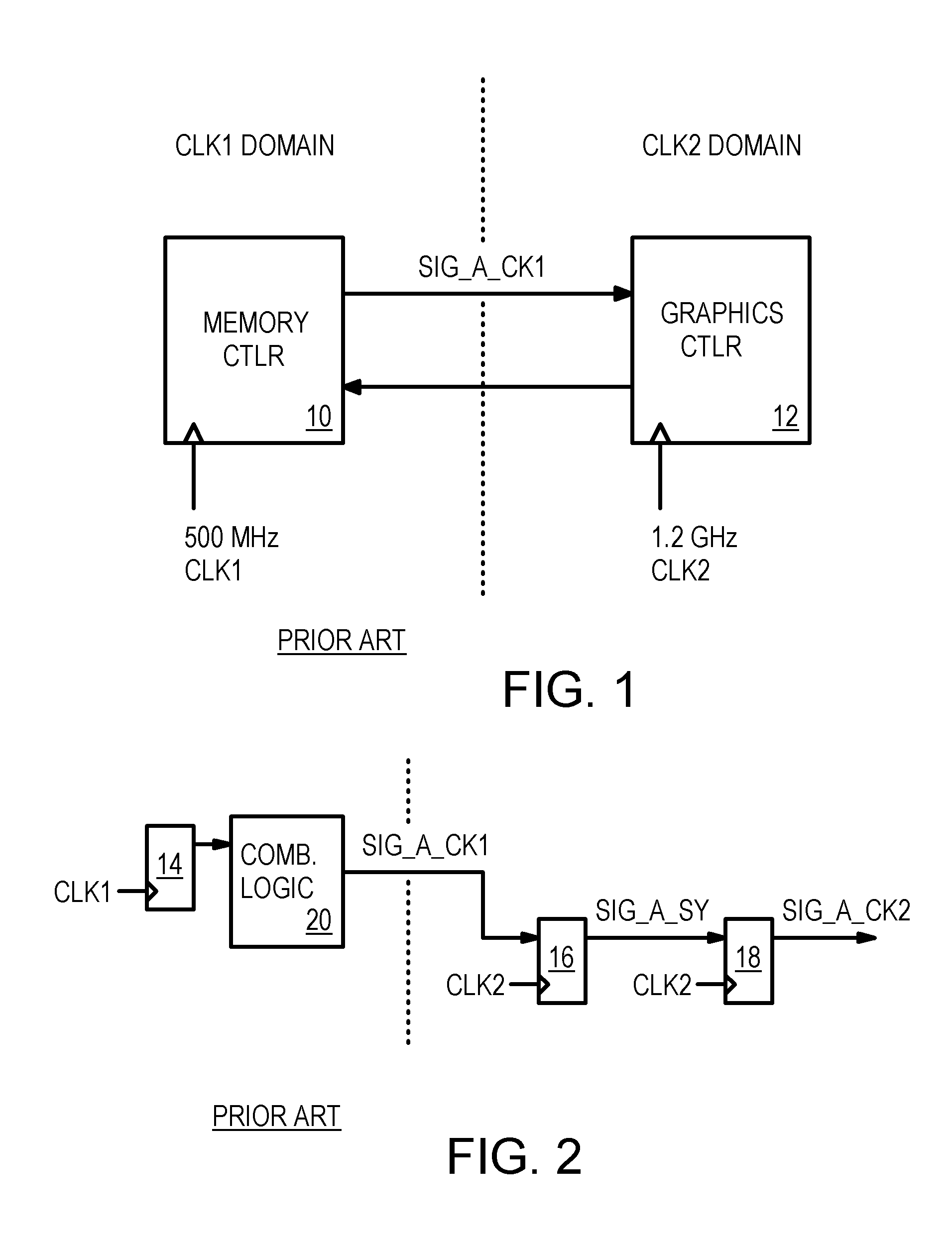
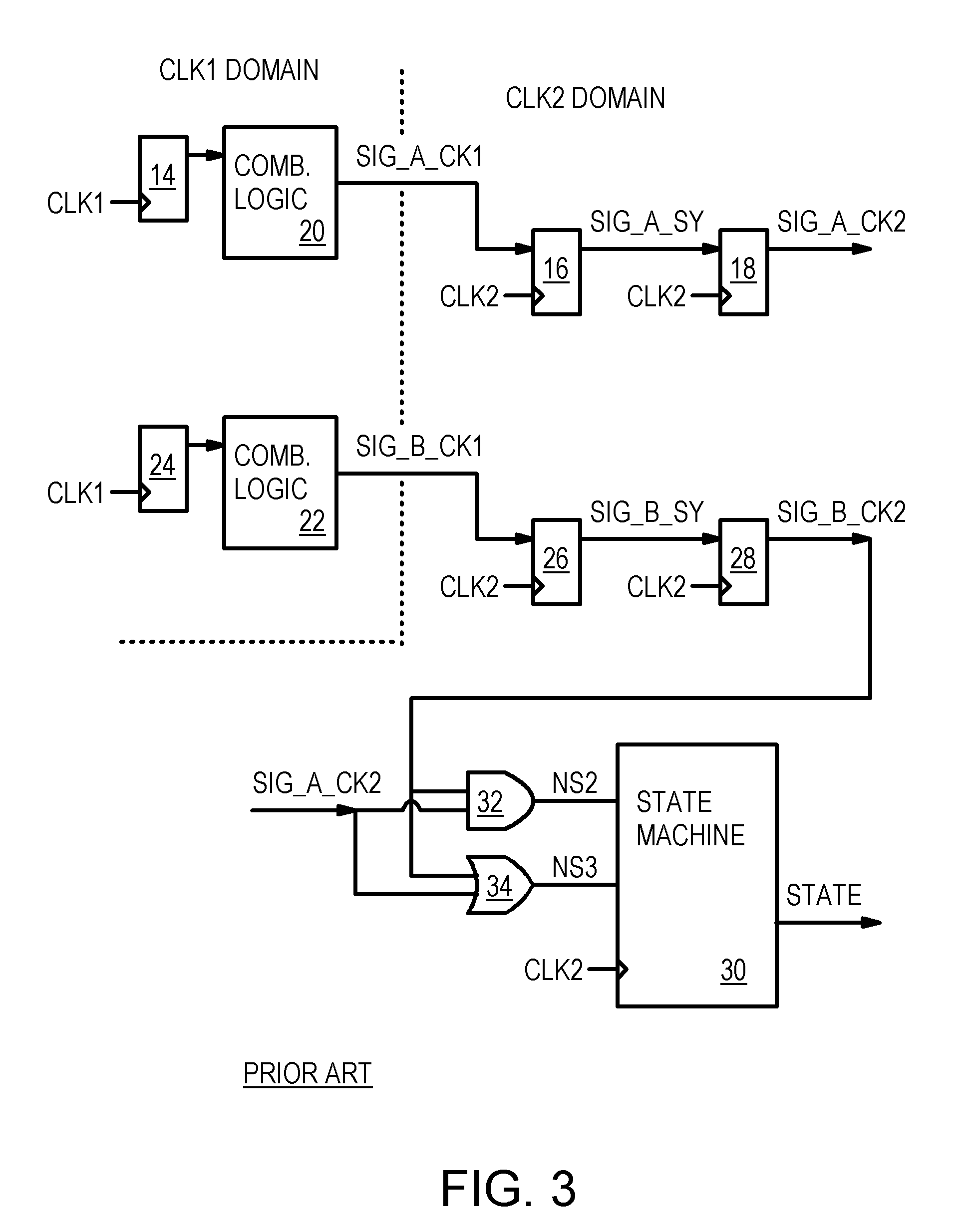
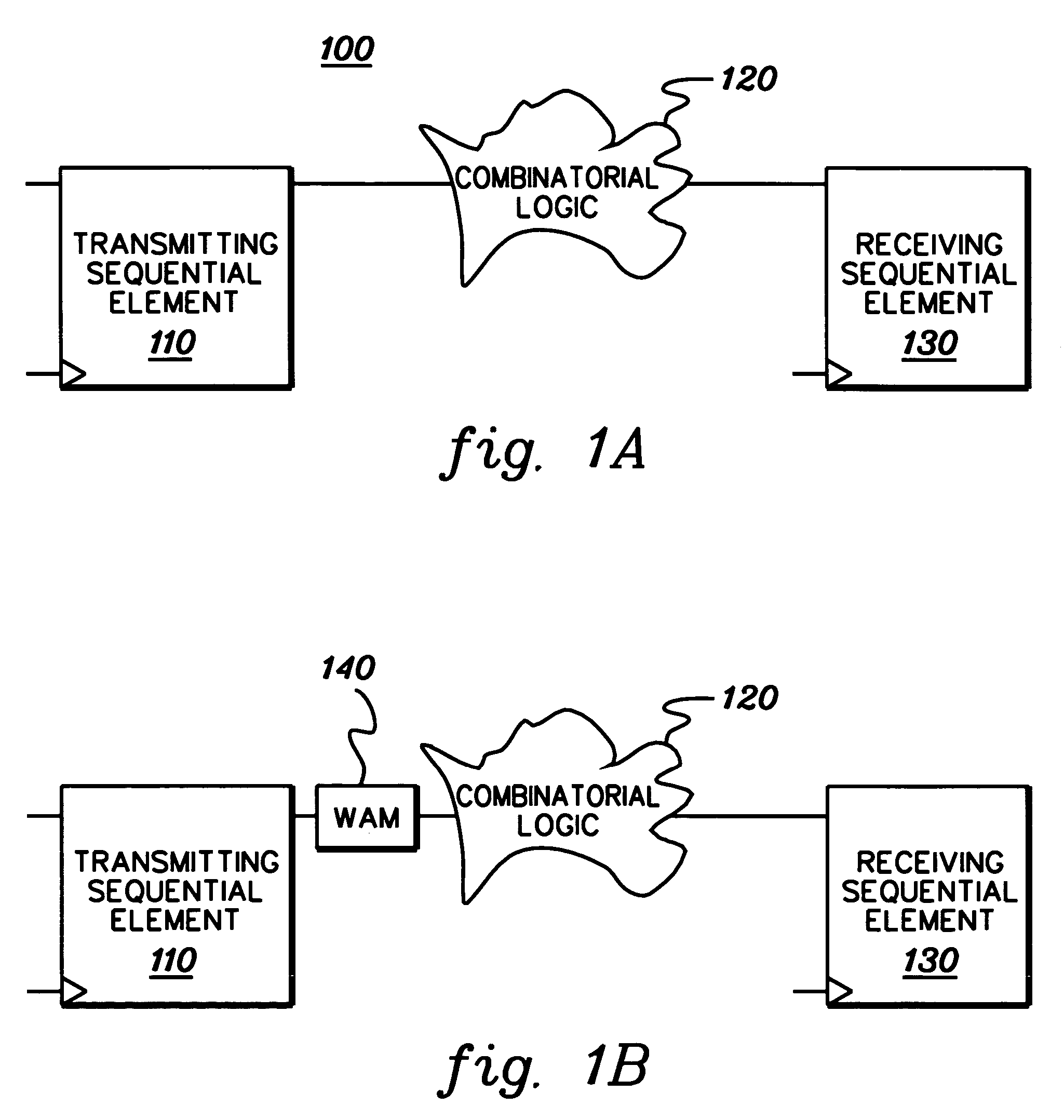
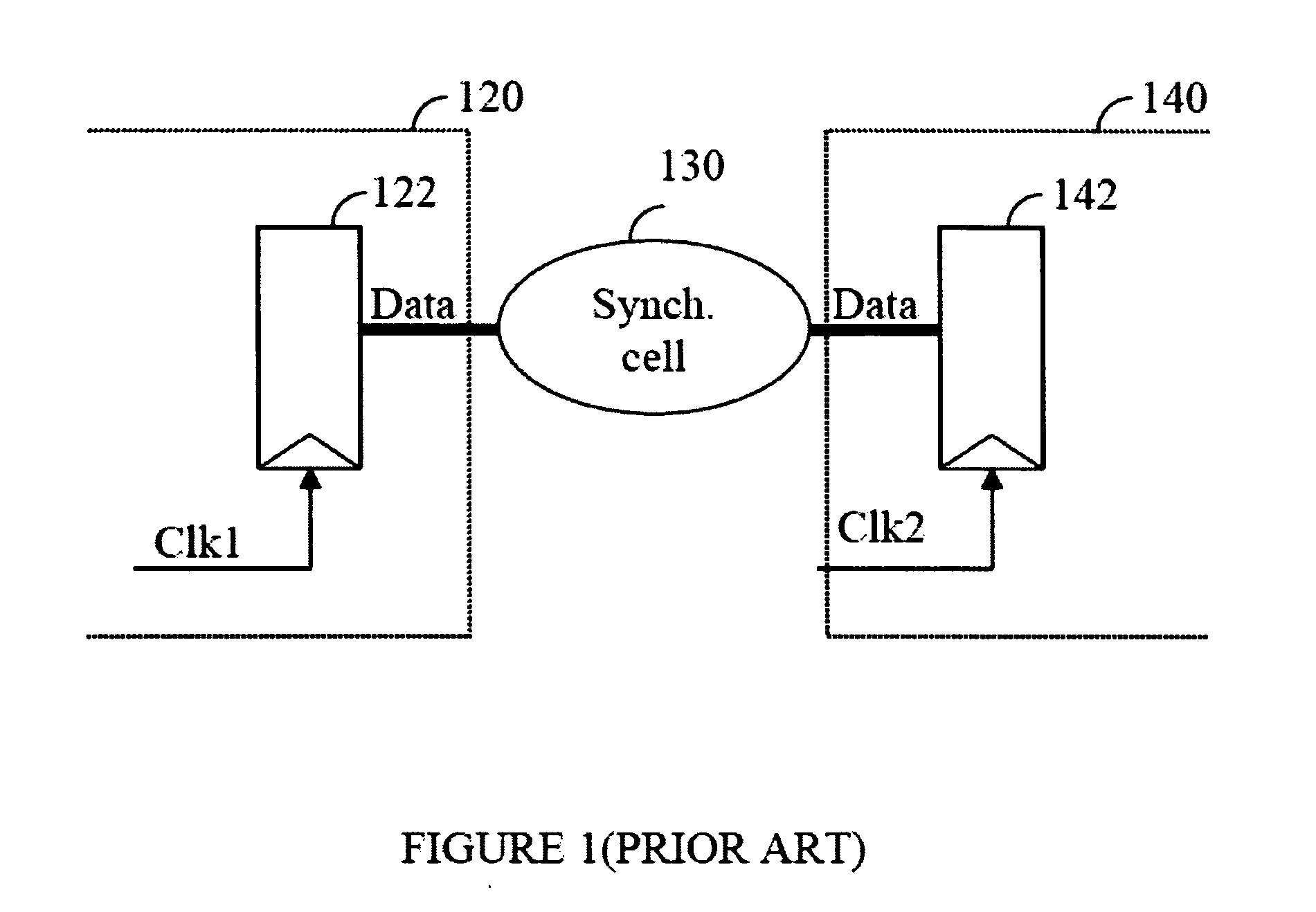
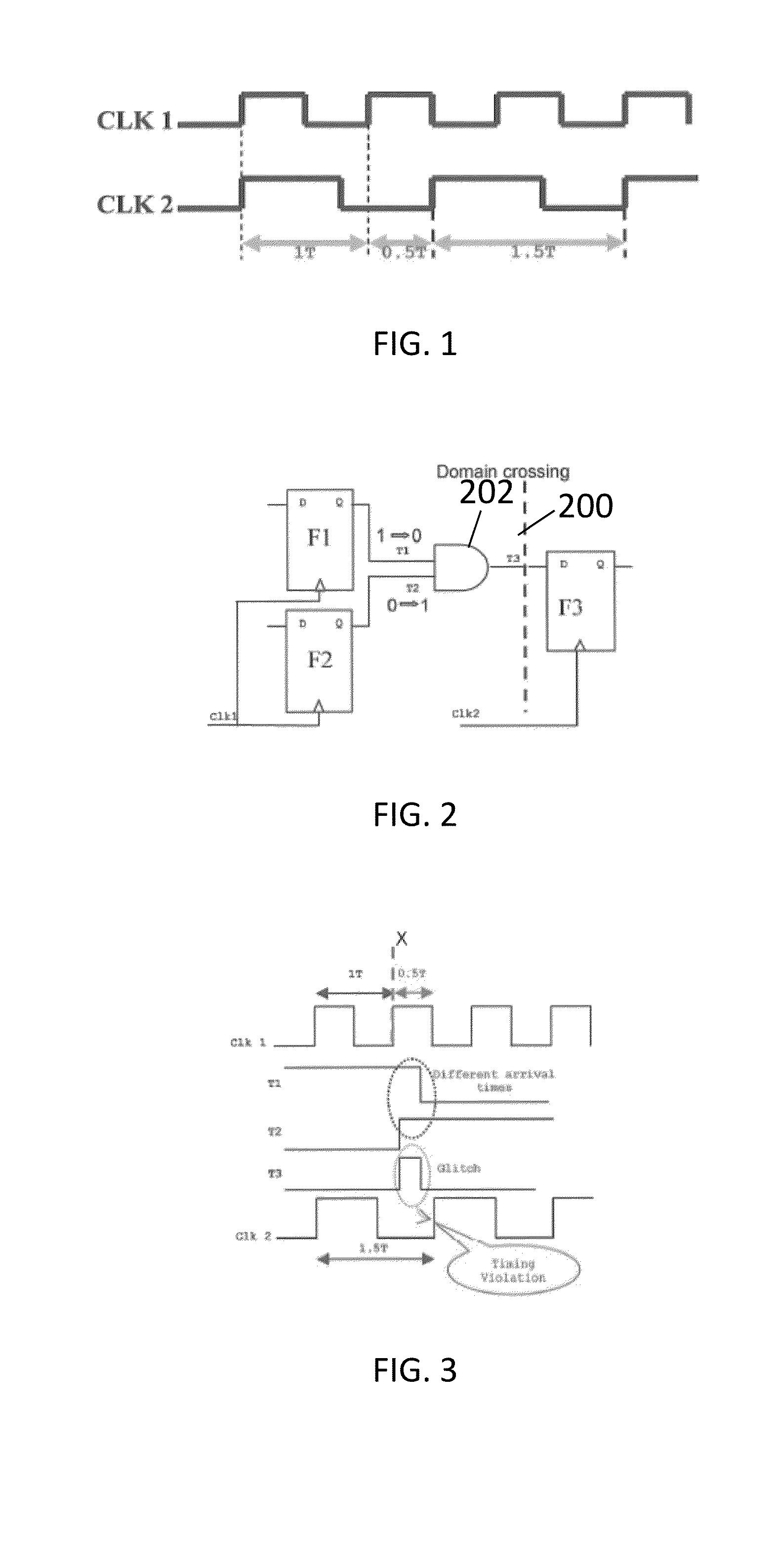
In digital electronic design a clock domain crossing (CDC), or simply clock crossing, is the traversal of a signal in a synchronous digital circuit from one clock domain into another. If a signal does not assert long enough and is not registered, it may appear asynchronous on the incoming clock boundary.
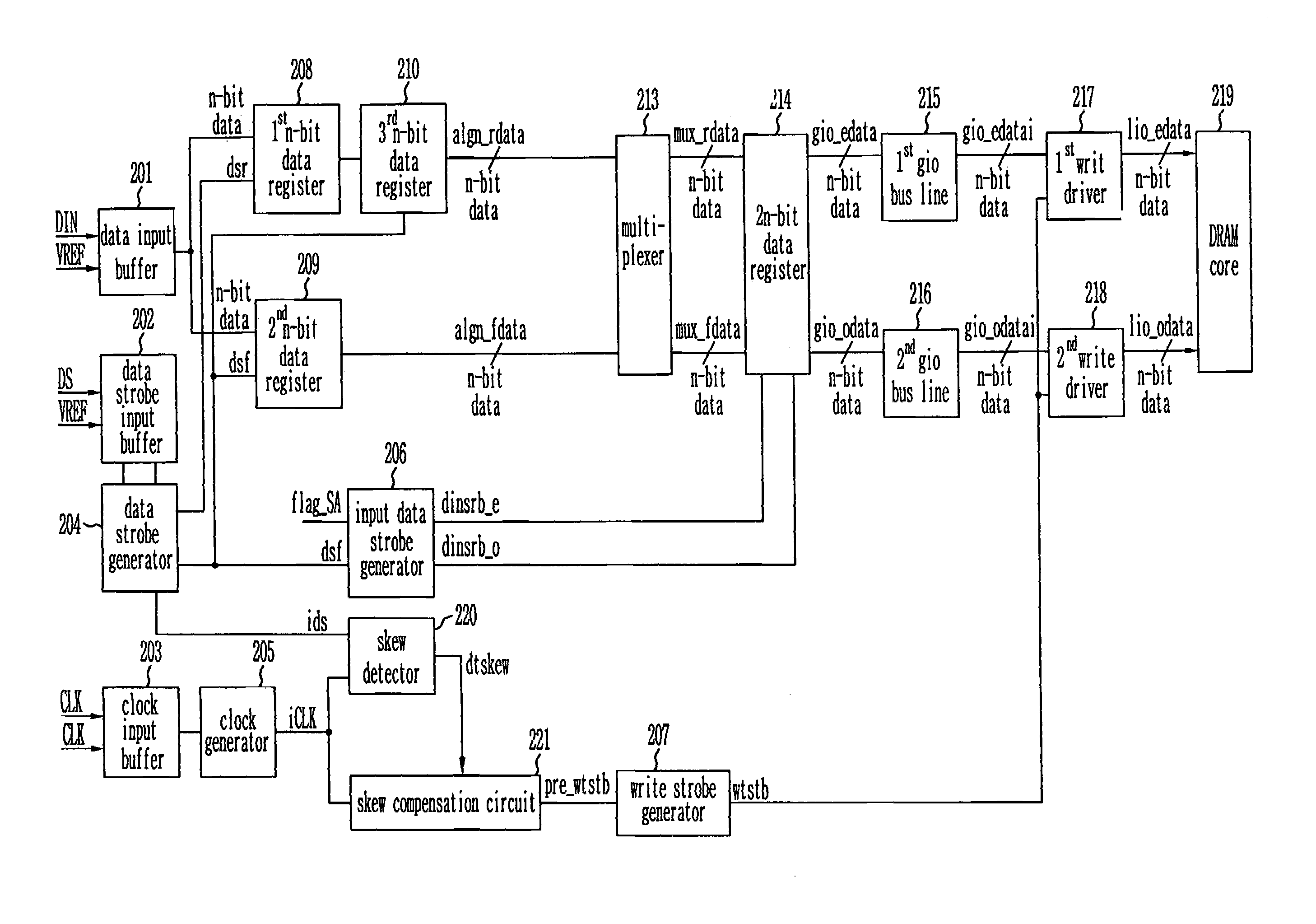
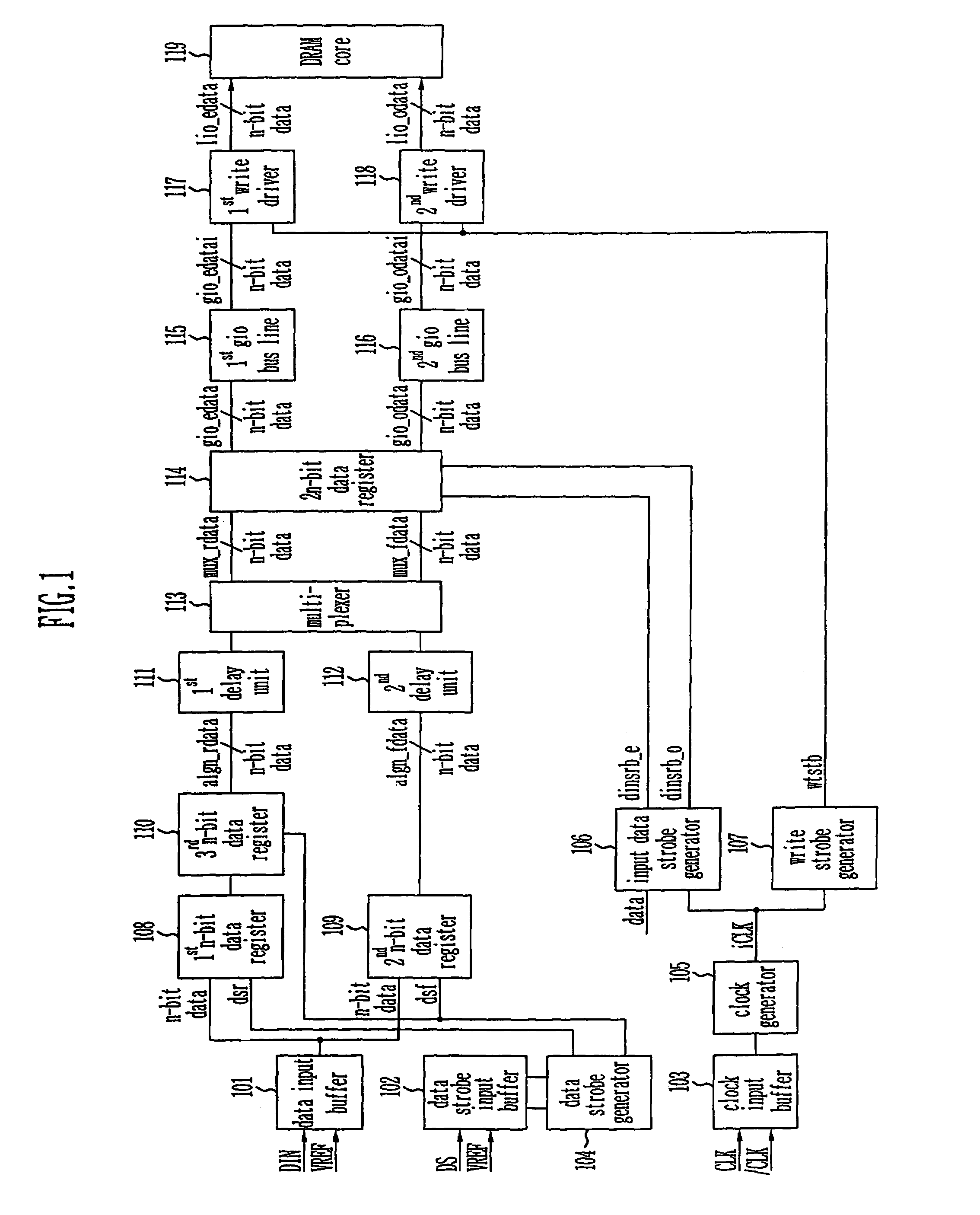
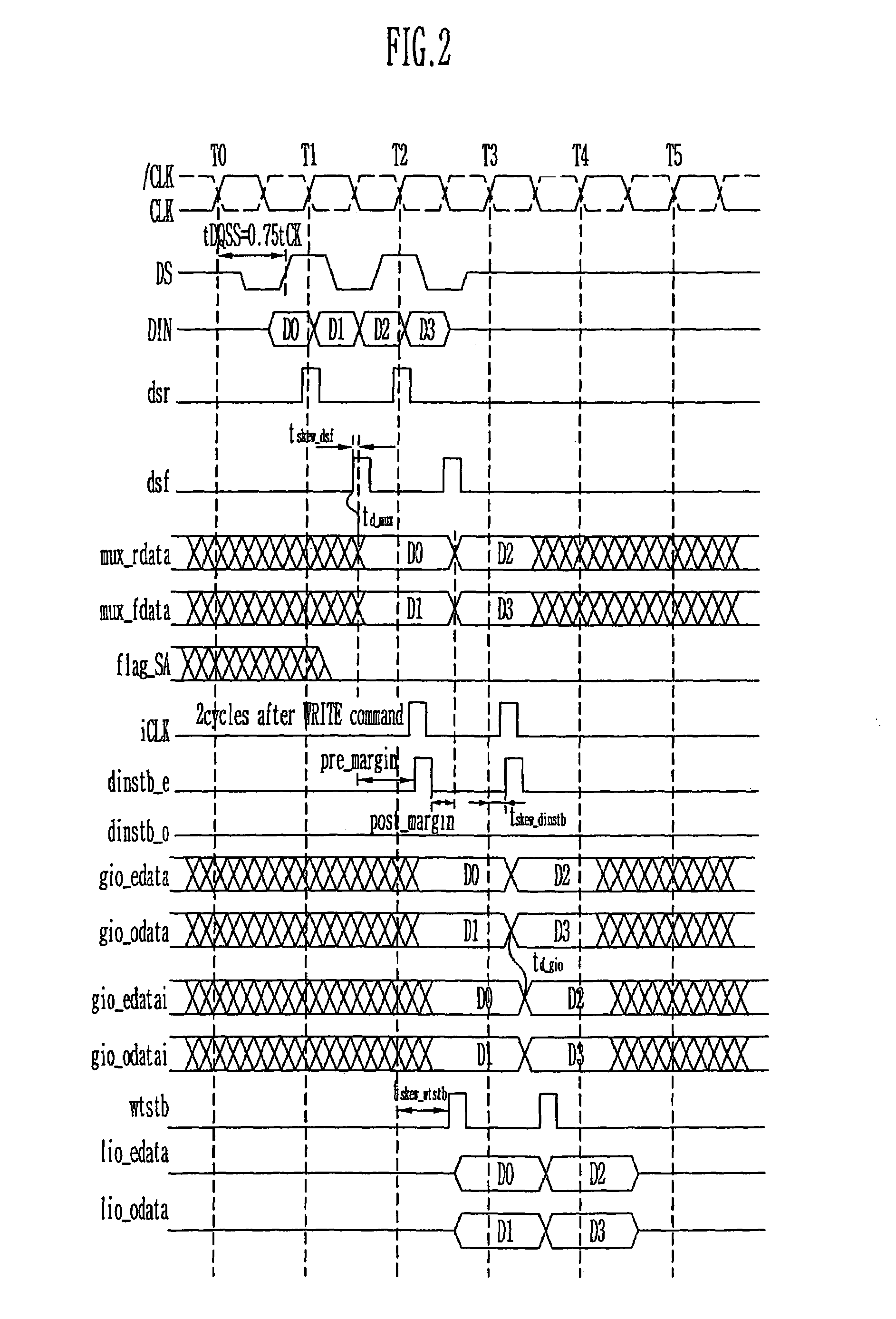
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
ActiveUS7042799B2Guaranteed uptimeTiming marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
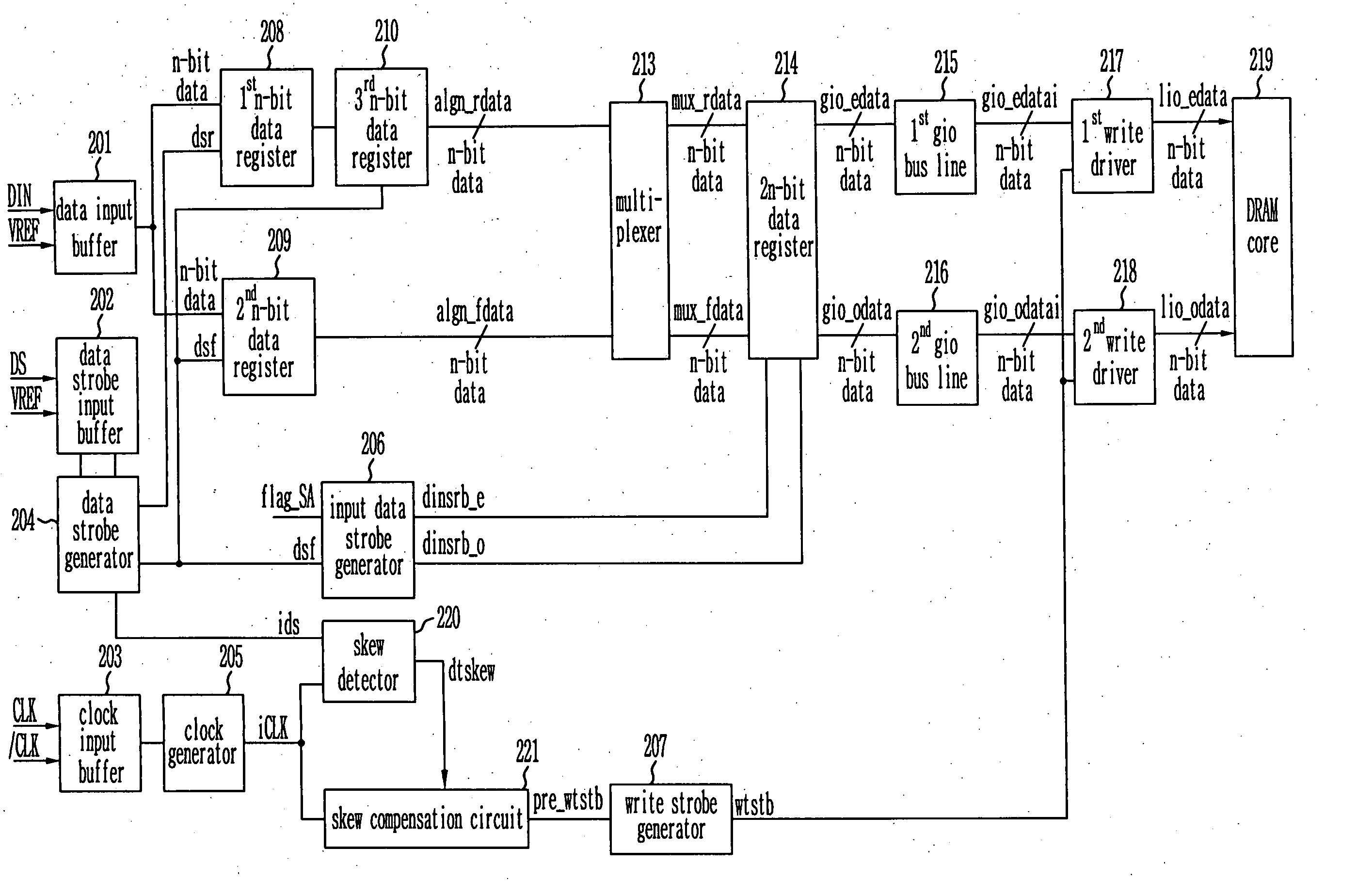
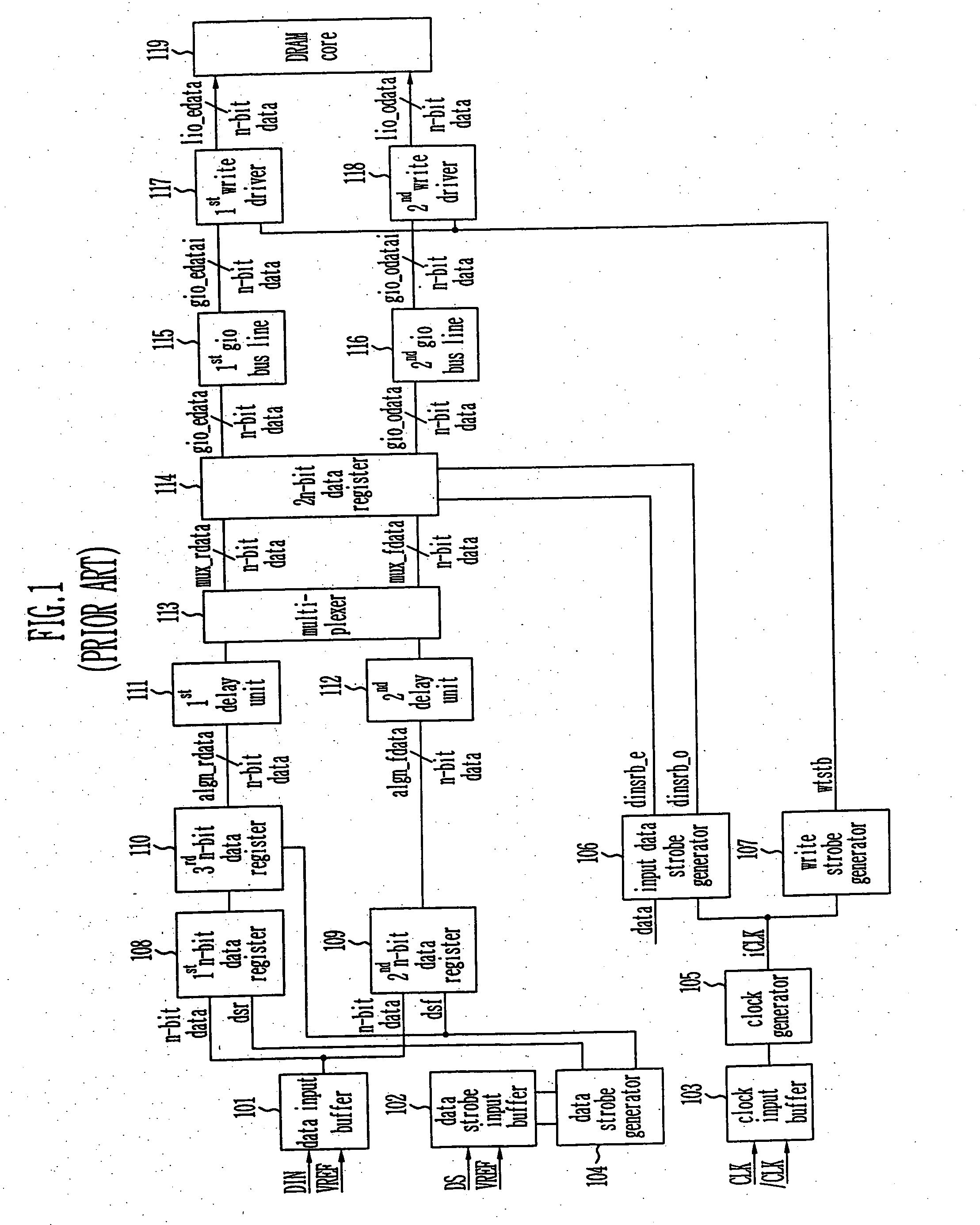
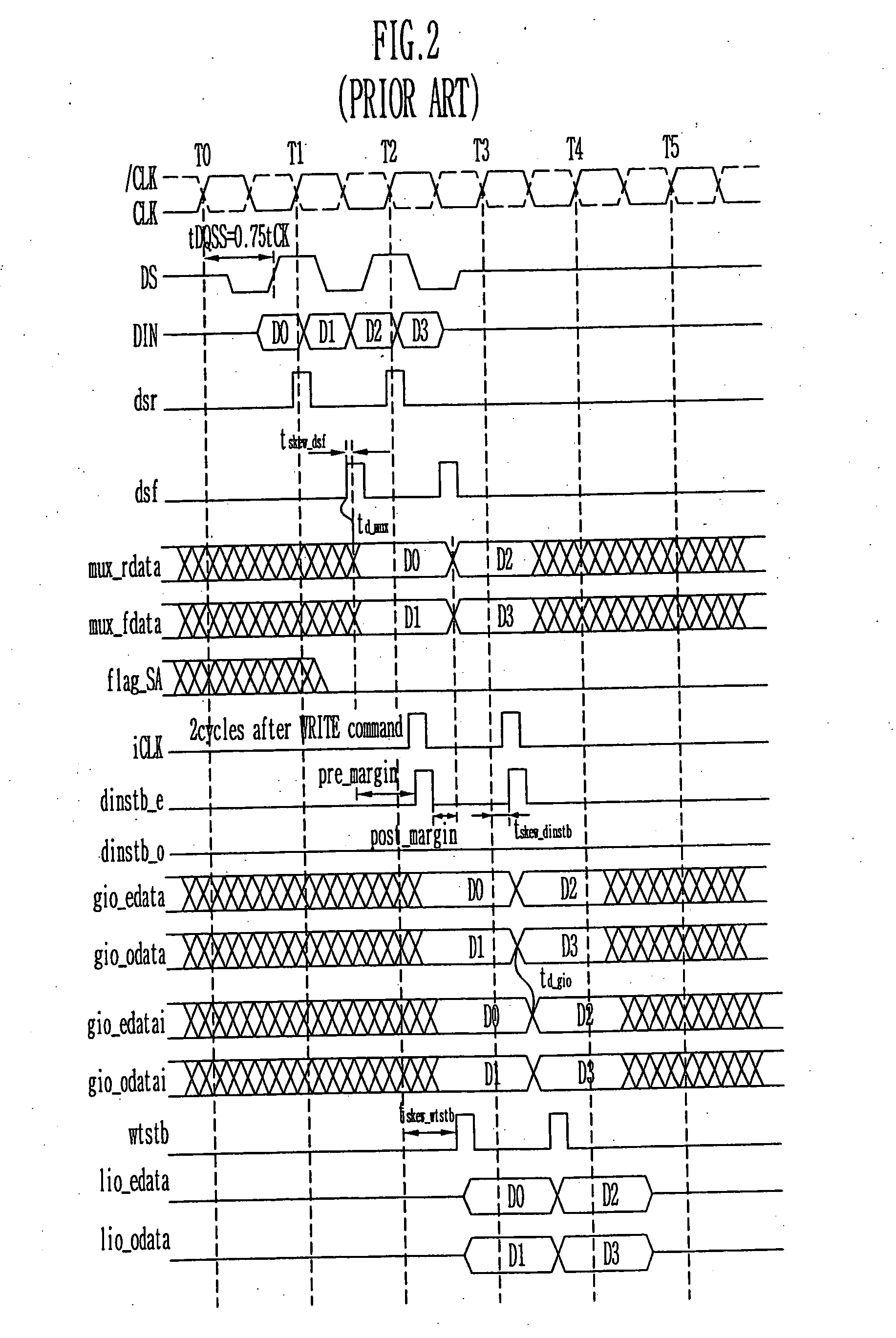
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
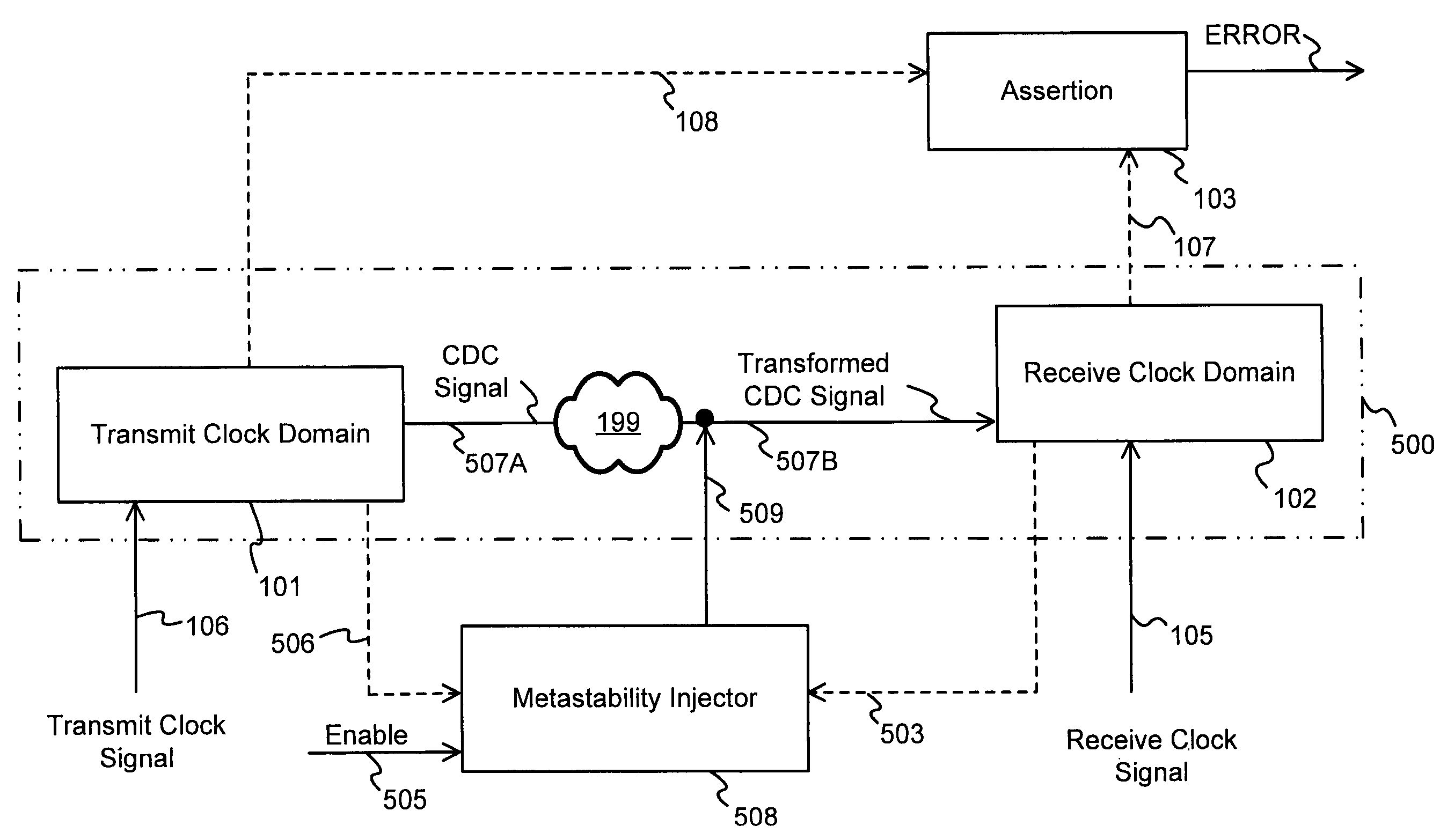
Metastability effects simulation for a circuit description
ActiveUS7356789B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareElectrical testingProcessor registerComputer science
A circuit design that contains at least two clock domains is simulated using a novel system and method for injecting the effects of metastability. The system includes detectors for detecting, during simulation, when a clock in a transmit clock domain and a clock in a receive clock domain are aligned and when the input of a register receiving a clock-domain-crossing signal is changing. The system includes coverage monitors for measuring, during simulation, statistics related to metastability injection. The system accurately models the effects of metastability by, at appropriate times during simulation, pseudo-randomly inverting outputs of registers receiving clock-domain-crossing signals. By accurately modeling the effects of metastability, errors in the circuit design can be detected while simulating a pre-existing simulation test. The simulation with metastability effects injection is repeatable and requires no modification of pre-existing RTL design files or simulation test files.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
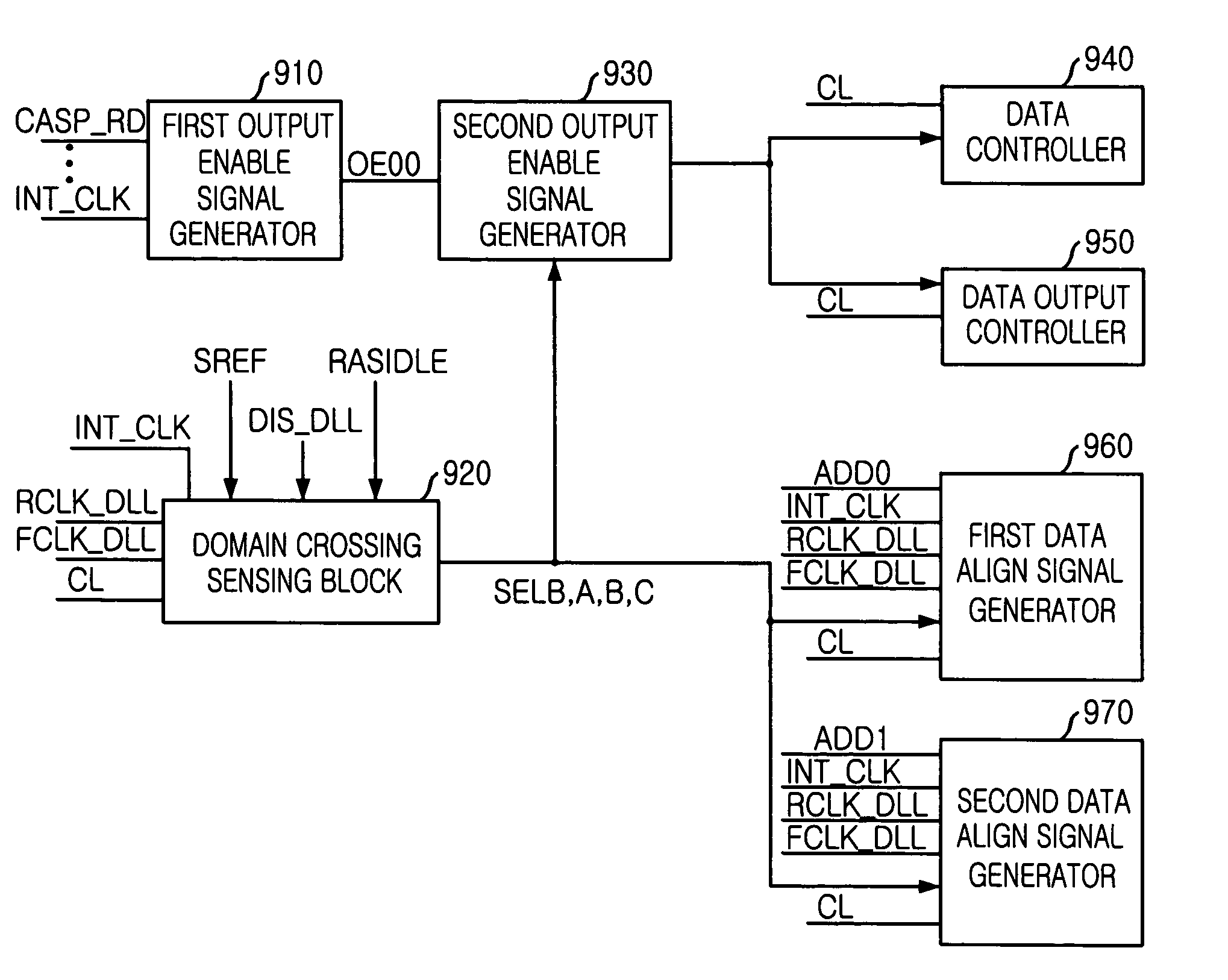
Semiconductor device for domain crossing
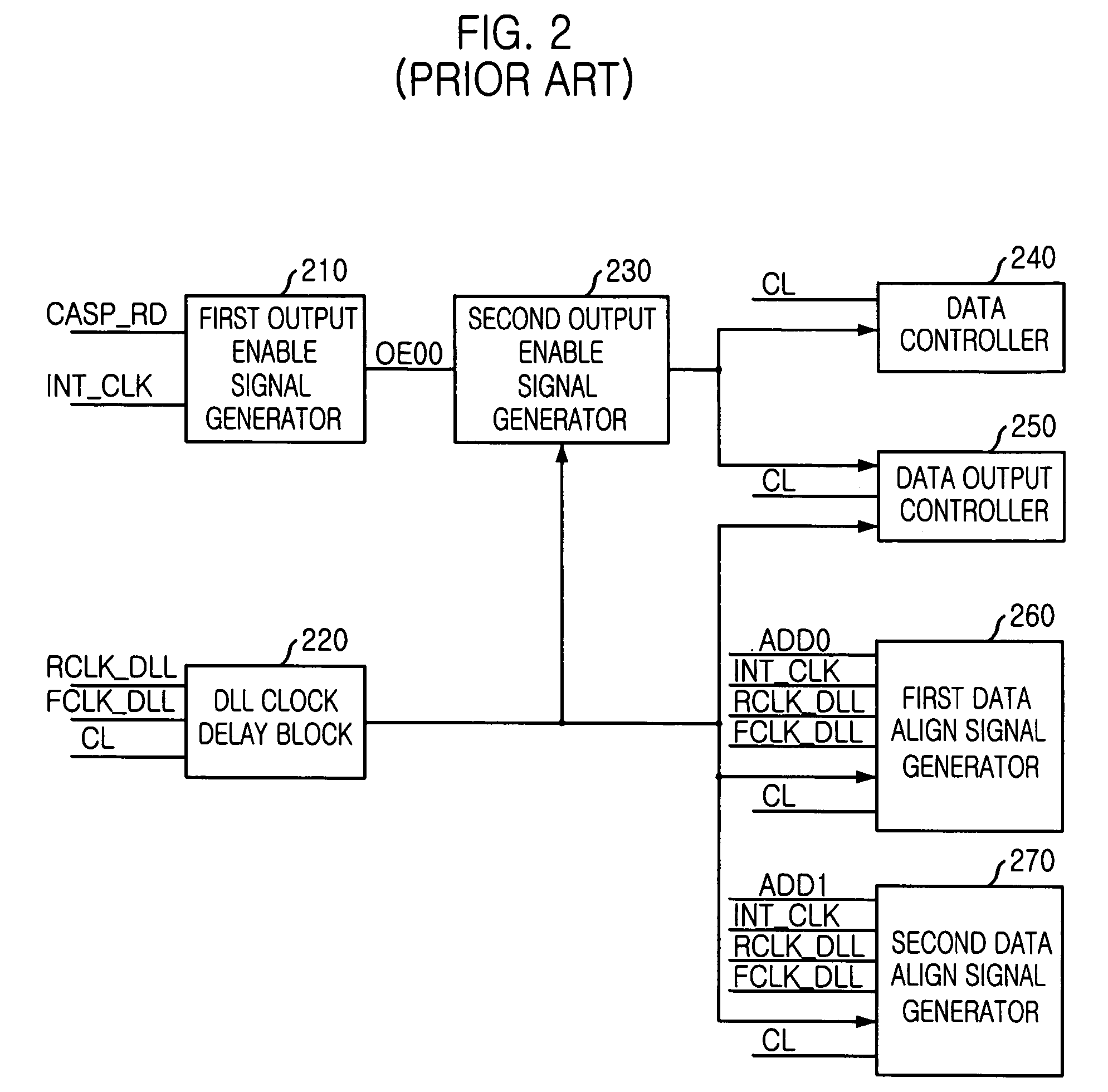
An apparatus, for use in a semiconductor device, for providing a domain crossing operation. The apparatus includes a domain crossing sensing block, in response to an operation mode signal, first and second delay locked loop (DLL) clock signals and a CAS latency, generates a plurality of selection signals. An output enable signal generator, in response to the plurality of selection signals, generates a plurality of output enable signals. A data control block, in response to the output enable signals and the CAS latency, controls a data output operation in the semiconductor device. Each of a plurality of data align block, in response to the selection signals, the first and second DLL clock signals and an address signal, aligns data corresponding to the address signal in the data output operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
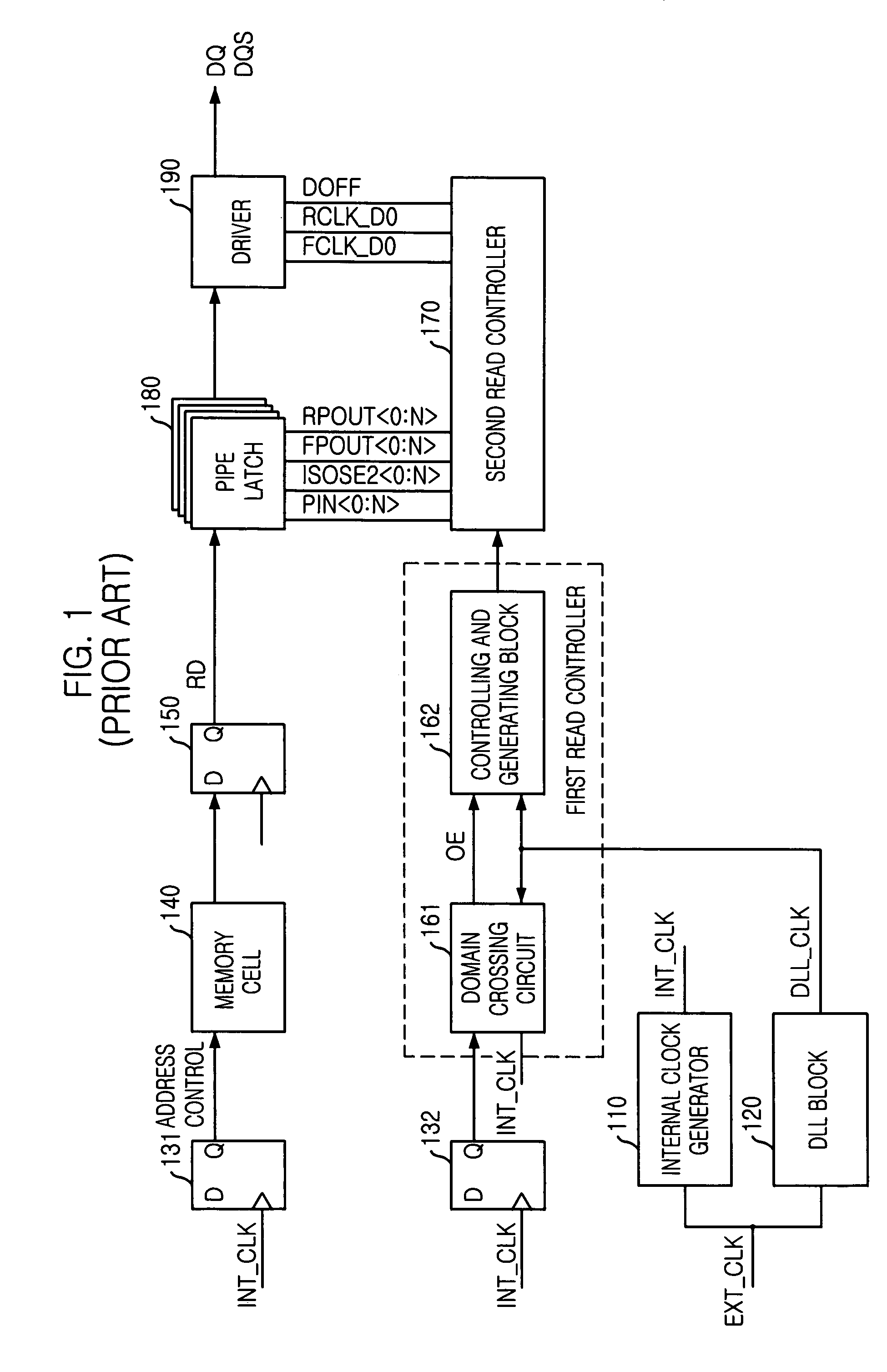
Synchronous memory read data capture
ActiveUS20080005518A1Simple and low latencyDigital storageMemory systemsLatency (engineering)Computer science
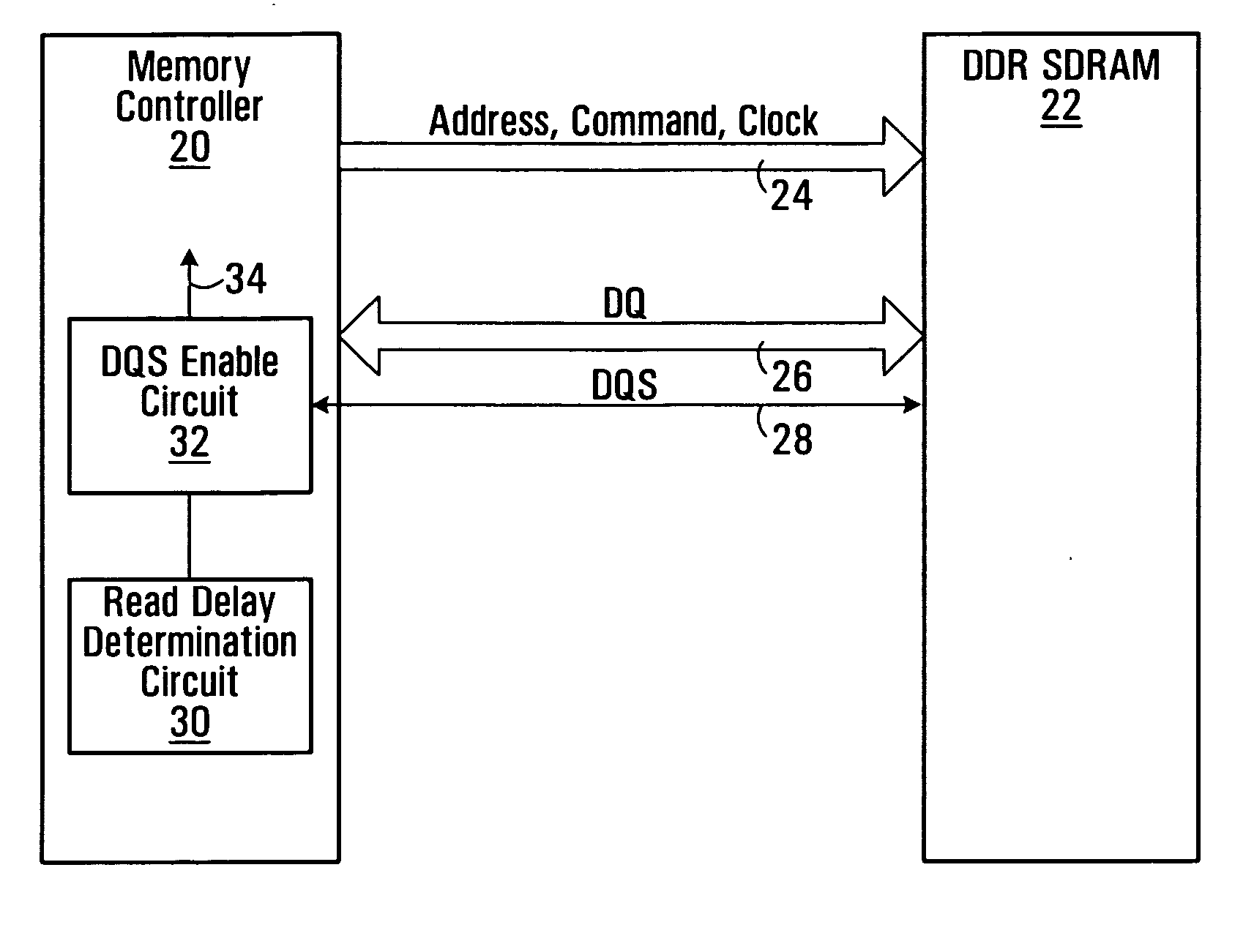
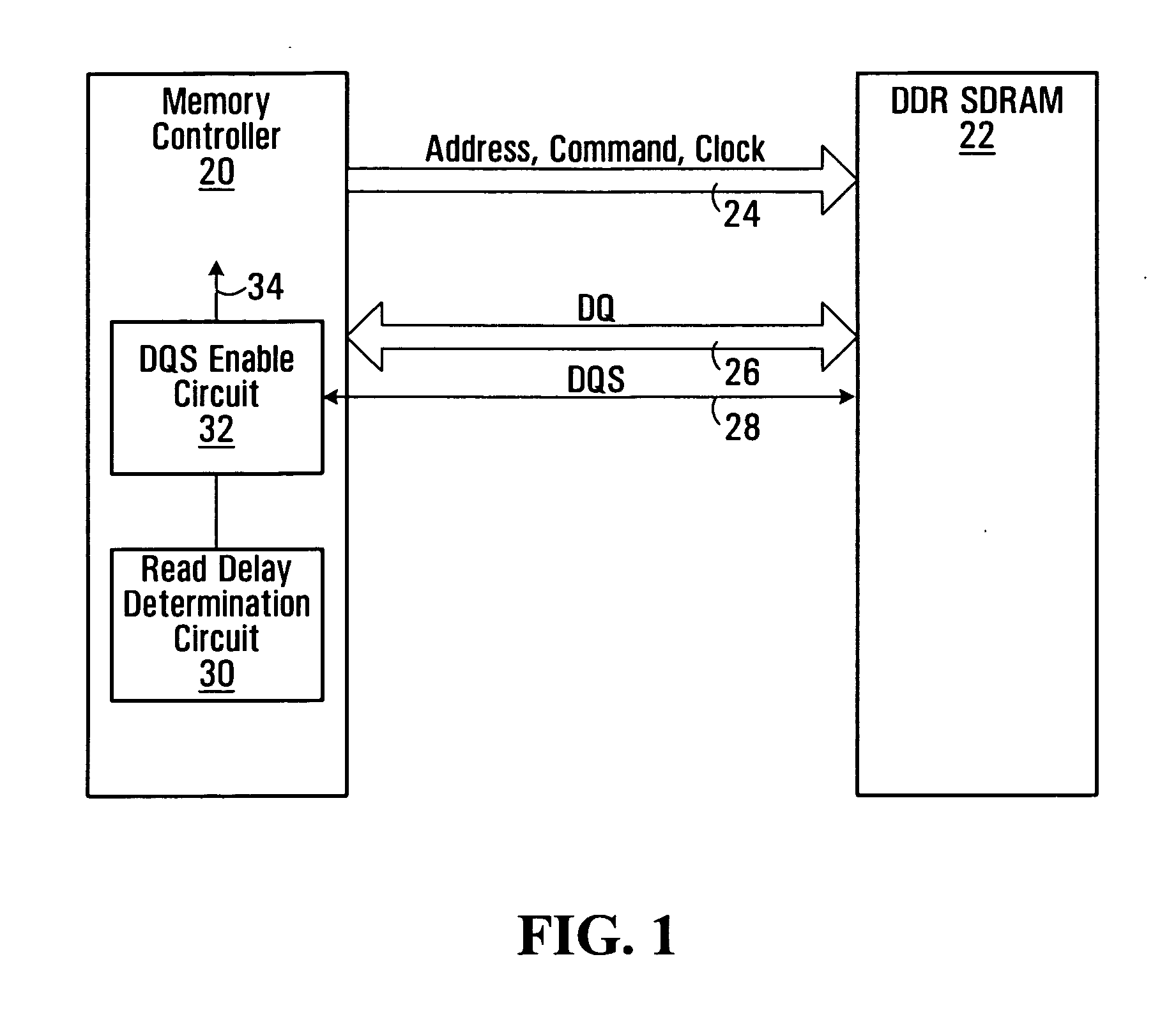
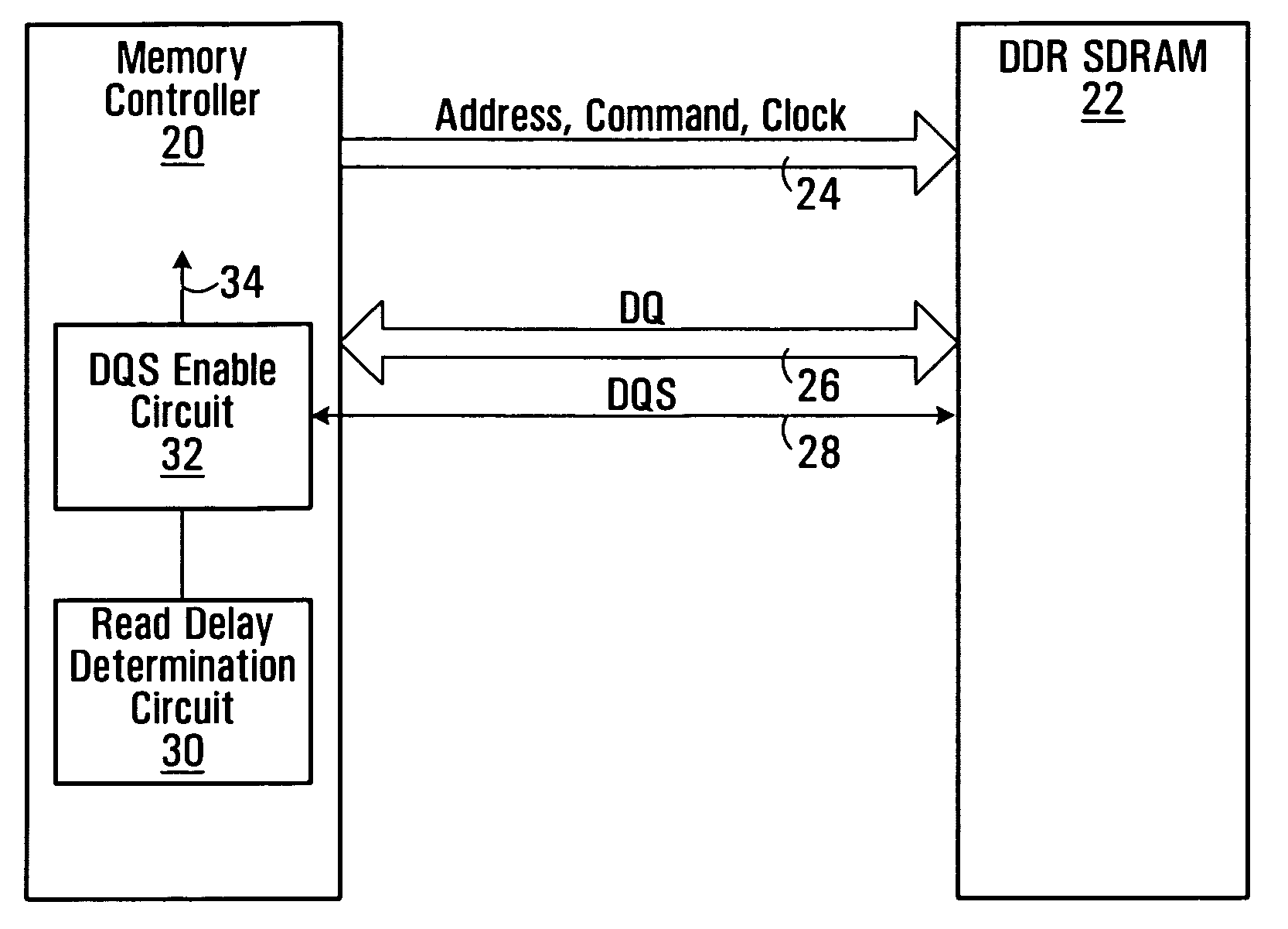
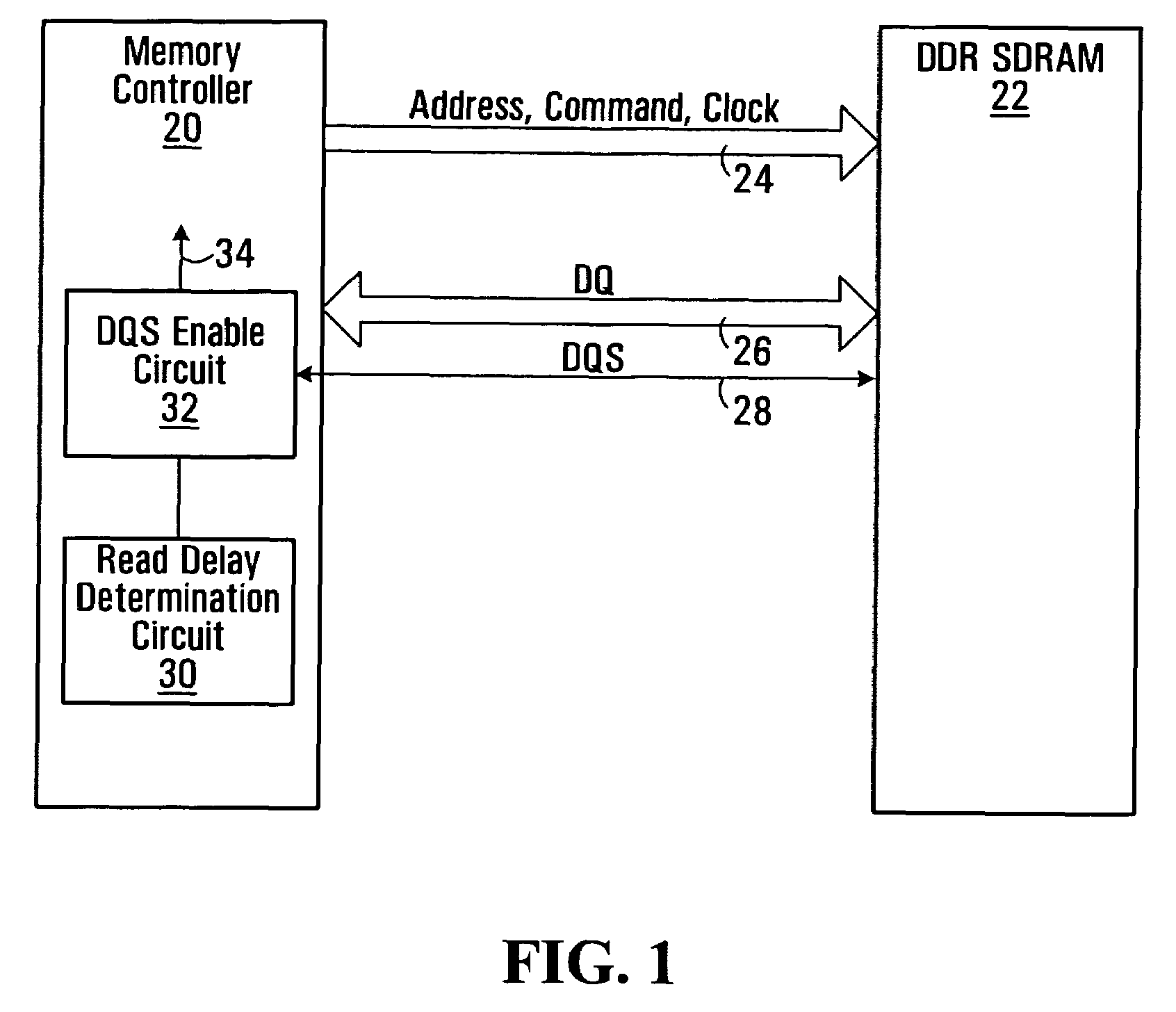
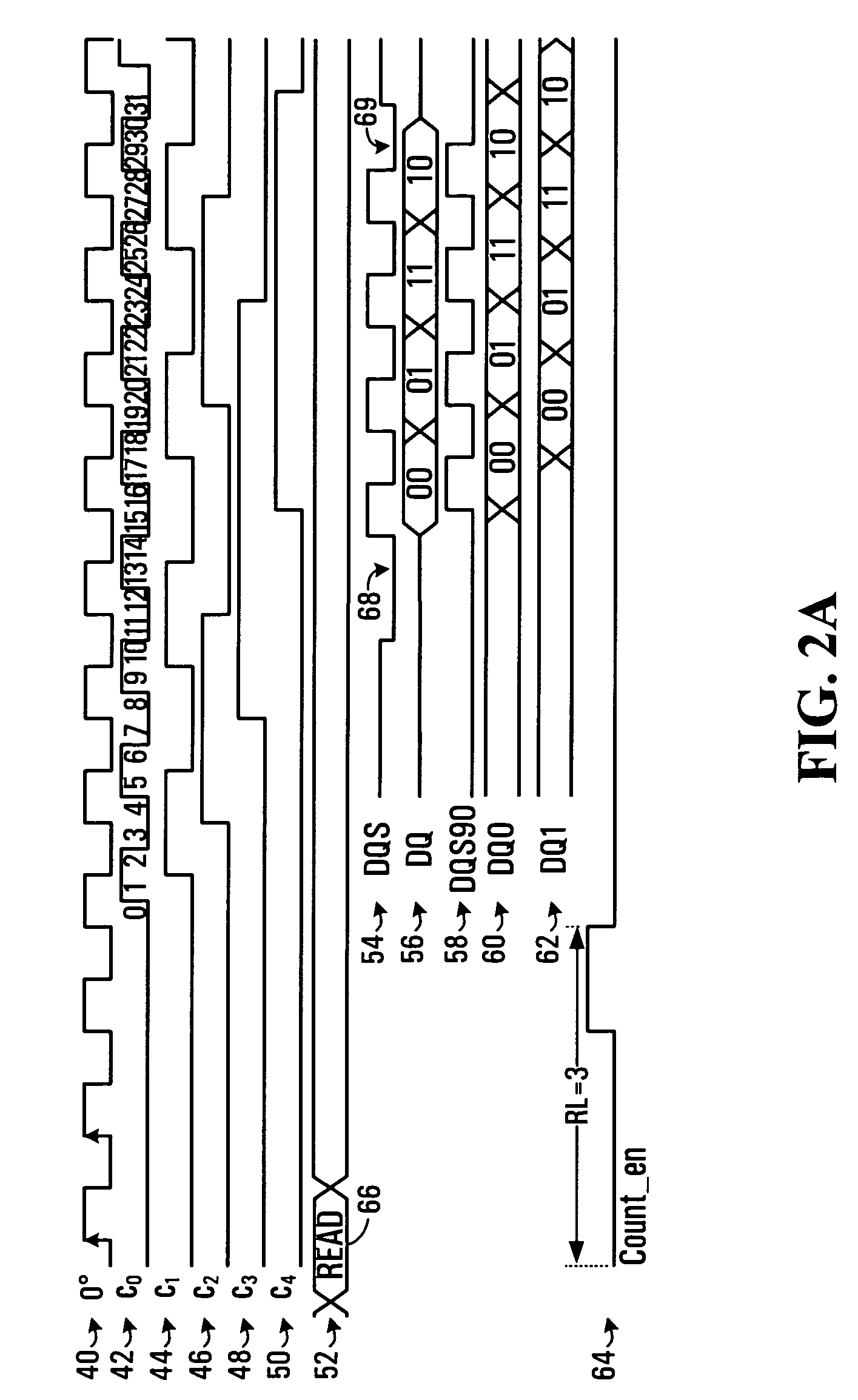
A method of snap-shot data training to determine the optimum timing of the DQS enable signal in a single read operation is provided. This is accomplished by first writing a Gray code count sequence into the memory and then reading it back in a single burst. The controller samples the read burst at a fixed interval from the time the command was issued to determine the loop-around delay. A simple truth table lookup determines the optimum DQS enable timing for normal reads. Advantageously, during normal read operations, the first positive edge of the enabled DQS signal is used to sample a counter that is enabled every time a command is issued. If the counter sample changes, indicating timing drift has occurred, the DQS enable signal can be adjusted to compensate for the drift and maintain a position centered in the DQS preamble. This technique can also be applied to a system that uses the iterative approach to determining DQS enable timing on power up. Another embodiment of the invention is a simple, low latency clock domain crossing circuit based on the DQS latched sample of the counter.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Hierarchical Verification Of Clock Domain Crossings
ActiveUS20100242003A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime domainComputer architecture
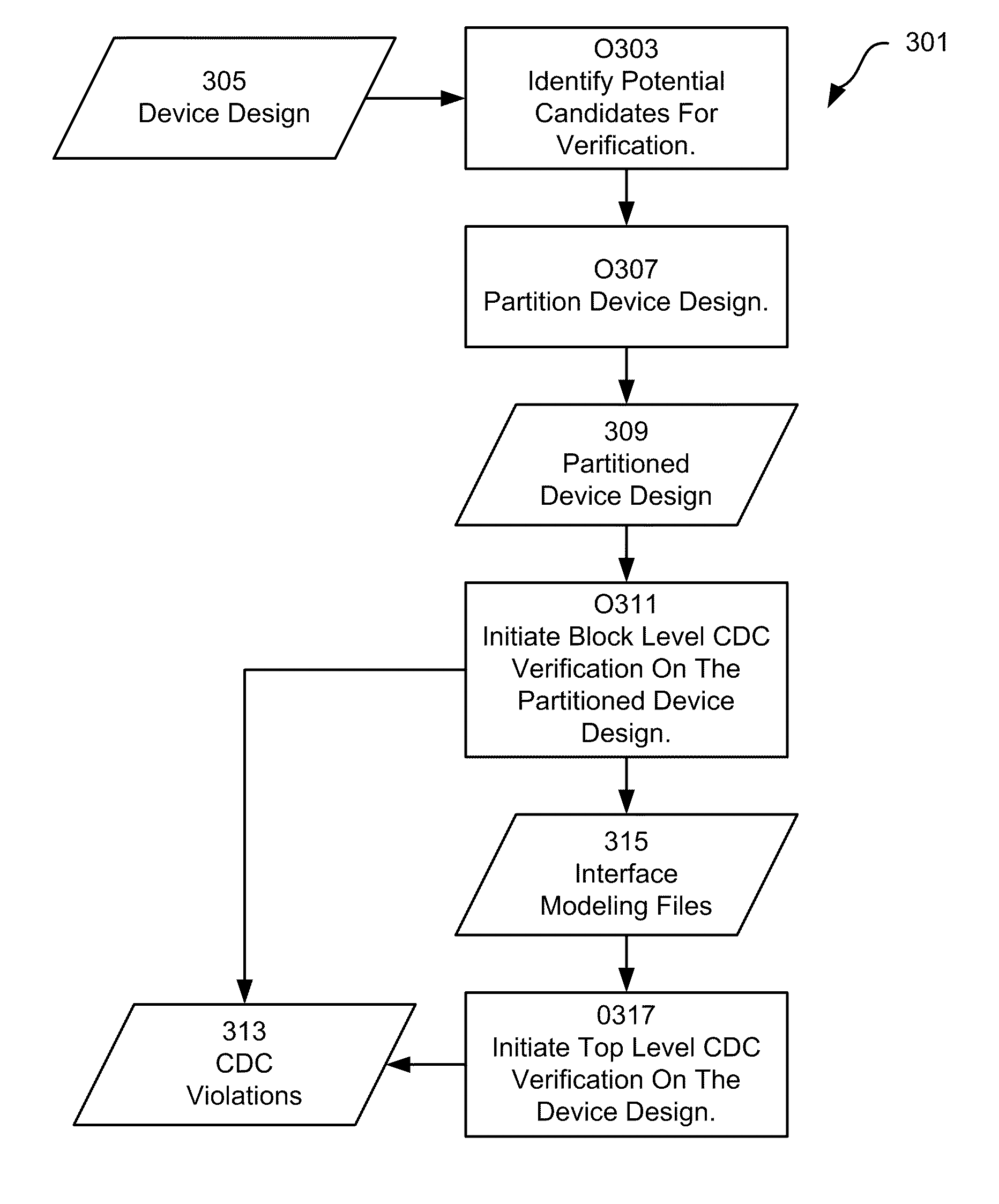
The invention provides for the hierarchical verification of clock domain crossings. In various implementations of the invention, a device design is partitioned into blocks. Subsequently, a block level clock domain crossing verification process is performed on selected ones of the blocks. Verification interface files are generated by the block level clock domain crossing process. After which, a top level clock domain crossing verification process is performed over the entire design. In various implementations, the top level clock domain crossing verification process utilizes the verification interface files to verify clock domain crossing signals between blocks. Additionally, in some implementations, blocks not verified during block level verification are verified during top level verification. With some implementations of the invention, the device design is partitioned based input from a user of the implementation. Furthermore, in various implementations, the specific clock domain crossing verification checks employed during block level verification and top level verification are specified by a user of the implementation.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Methodology for verifying multi-cycle and clock-domain-crossing logic using random flip-flop delays
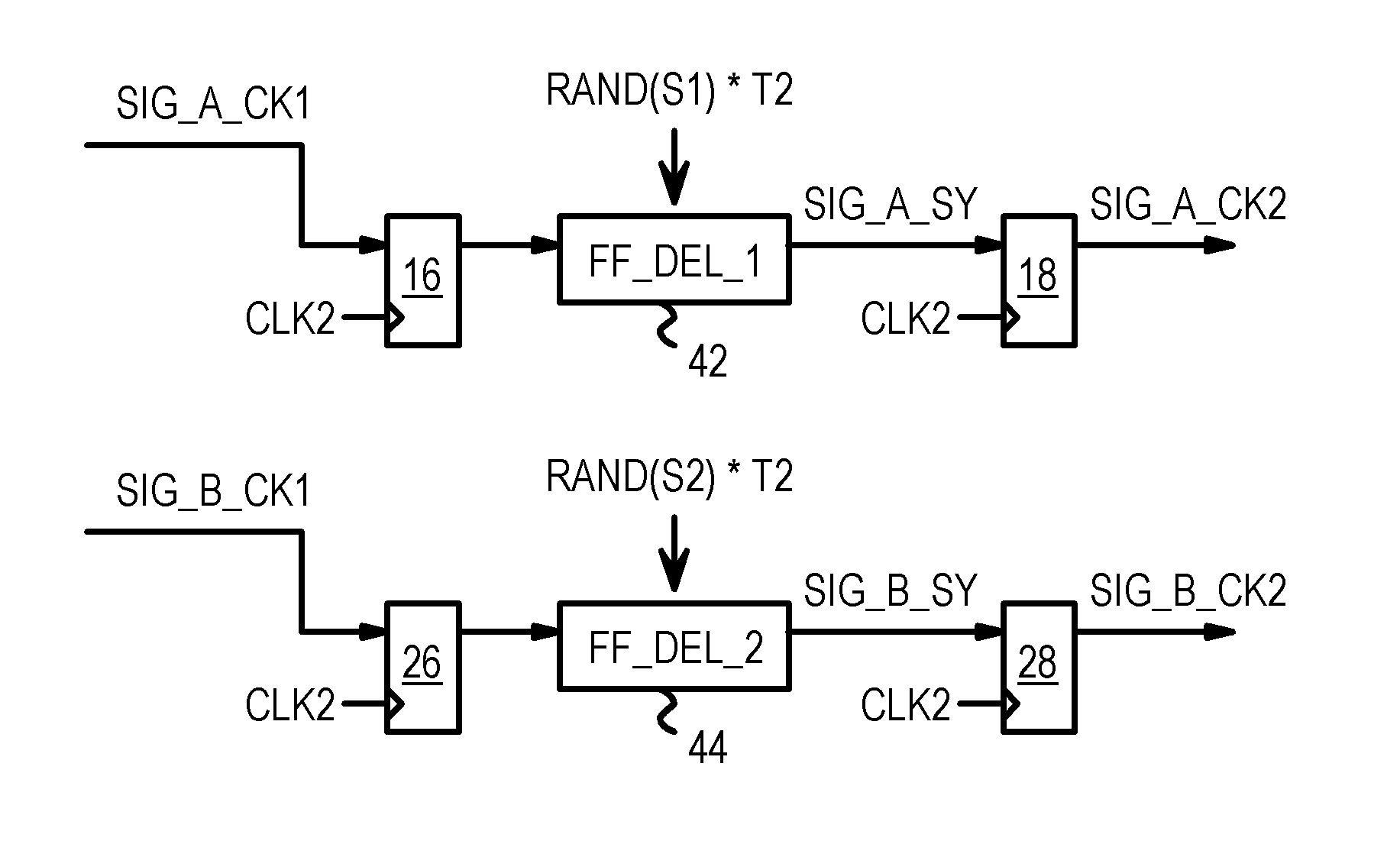
A design tool inserts randomized delays into synchronizers for signals crossing from one clock domain to another. Rather than having a wide range of random delays to select from, each synchronizer's randomized delay is selected from only two possibilities. An added delay of either zero or one clock period of the new domain's clock is added as the randomized delay. The randomized delay causes the re-synchronized domain-crossing signal to become available either in the expected cycle or in the cycle following the expected cycle. Logic hazards caused by the domain-crossing signal can be detected and the possible results simulated. The synchronizer can be a series of two flip-flops, with the random delay added to the first flip-flop. Randomized delays of either one or none added periods of the clock can also be added to multi-cycle signals within one clock domain that have two or more clock cycles to propagate.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
ActiveUS20050141331A1Stable data write operationGuaranteed uptimeRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
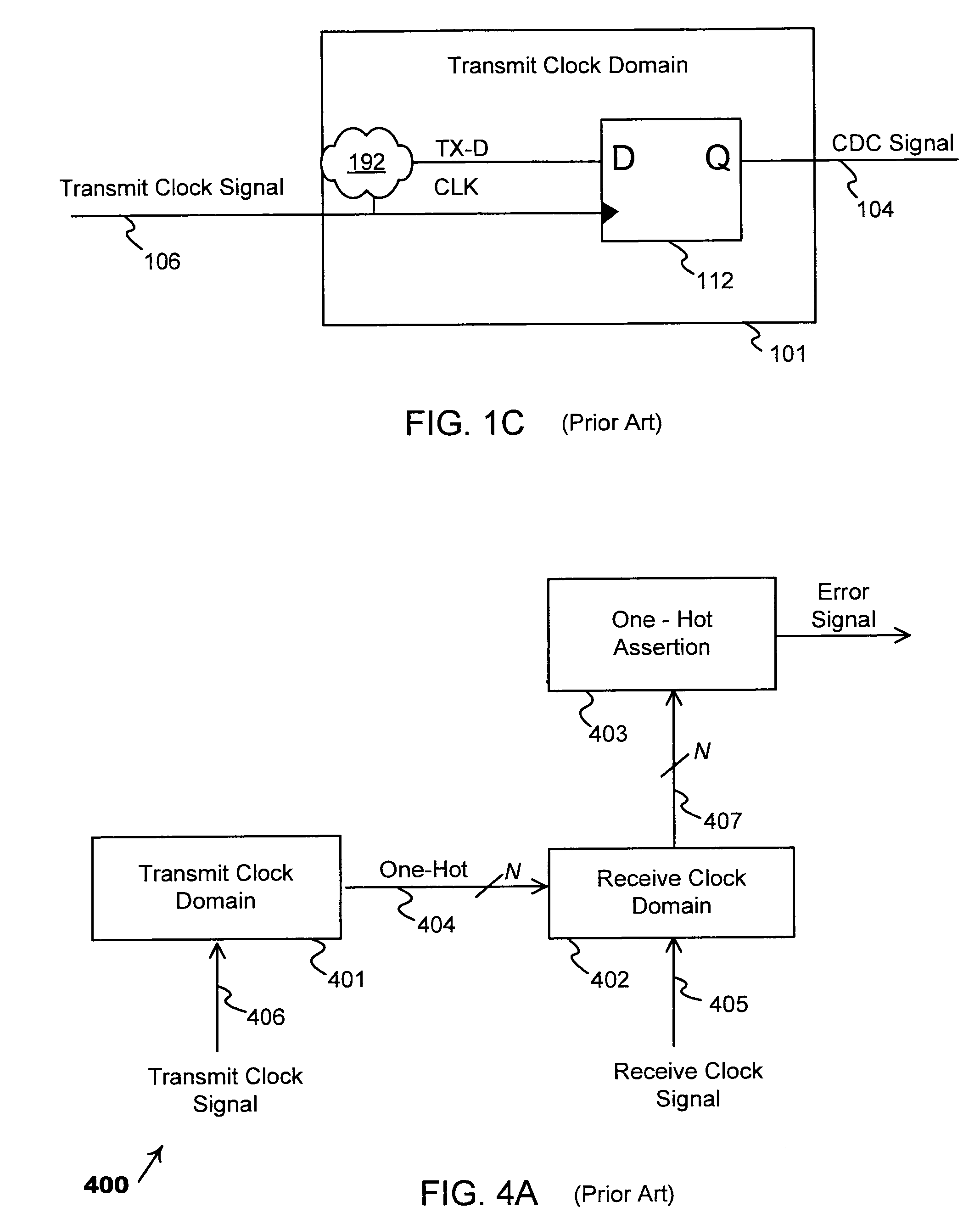
Asynchronous Scheme for Clock Domain Crossing
ActiveUS20110204932A1Pulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsComputer scienceControl logic
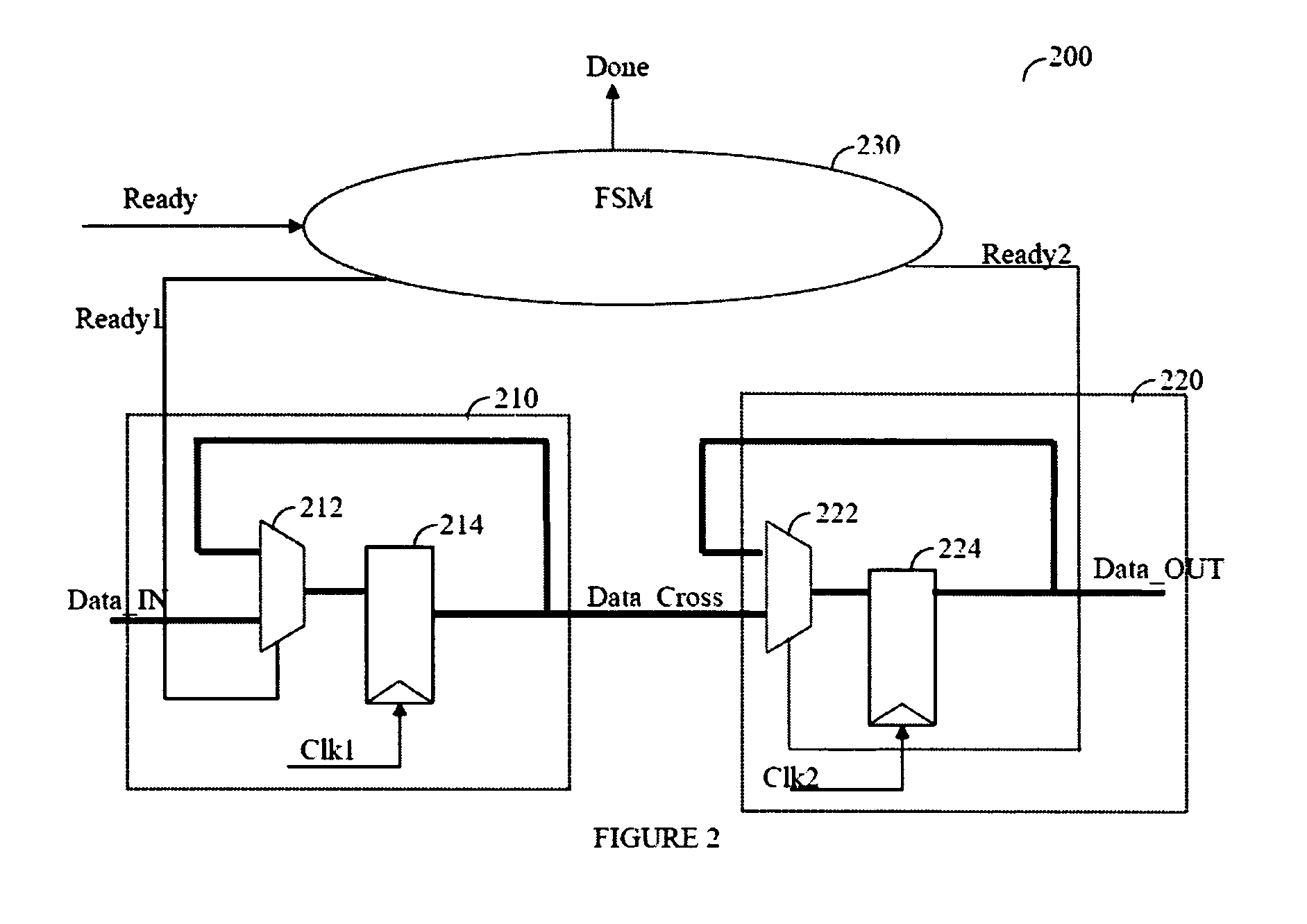
Apparatus and methods for clock domain crossing between a first clock domain and a second clock domain. The apparatus comprises a first control logic element for processing a handshake signal and producing a first arbiter input signal. Concurrently a second control logic element processes a second handshake signal and produces a second arbiter input signal. Exemplary embodiments include exactly one arbiter element inputting the first arbiter input signal, inputting the second arbiter input signal, outputting a first clocking signal to the first sequential element and outputting a second clocking signal to the second sequential element. For managing metastability by controlling the timing of the clocking inputs of the sequential devices, the apparatus includes a first controllable lock delay element selected to satisfy the setup constraint of the second sequential element, and a second controllable lock delay element selected to satisfy the hold constraint of the second sequential element.
Owner:INPHI +1
Formal Verification Of Clock Domain Crossings
ActiveUS20100199244A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designClock domain crossingFormal specification
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Formal verification of clock domain crossings
ActiveUS8271918B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designComputer scienceFormal specification
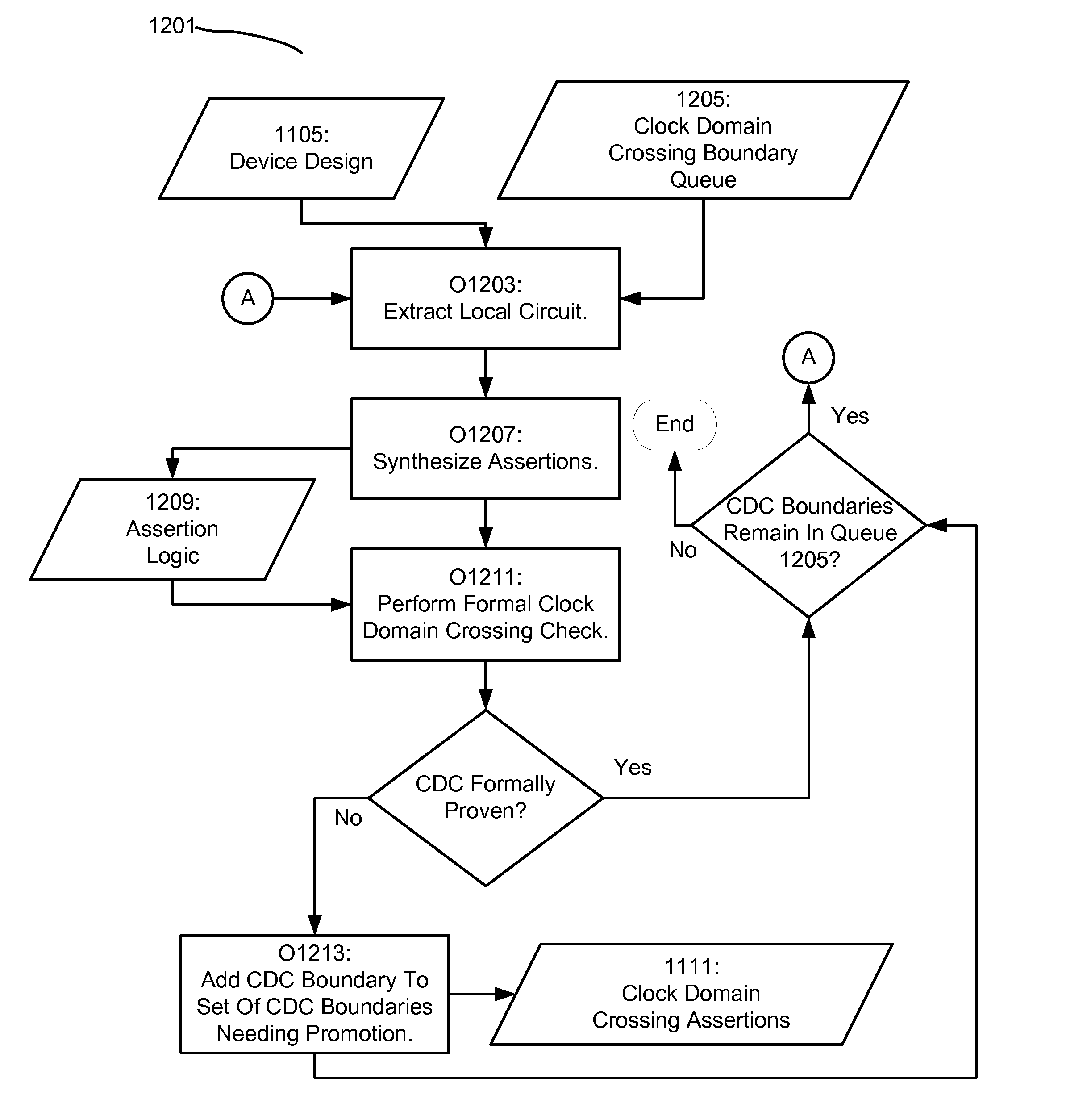
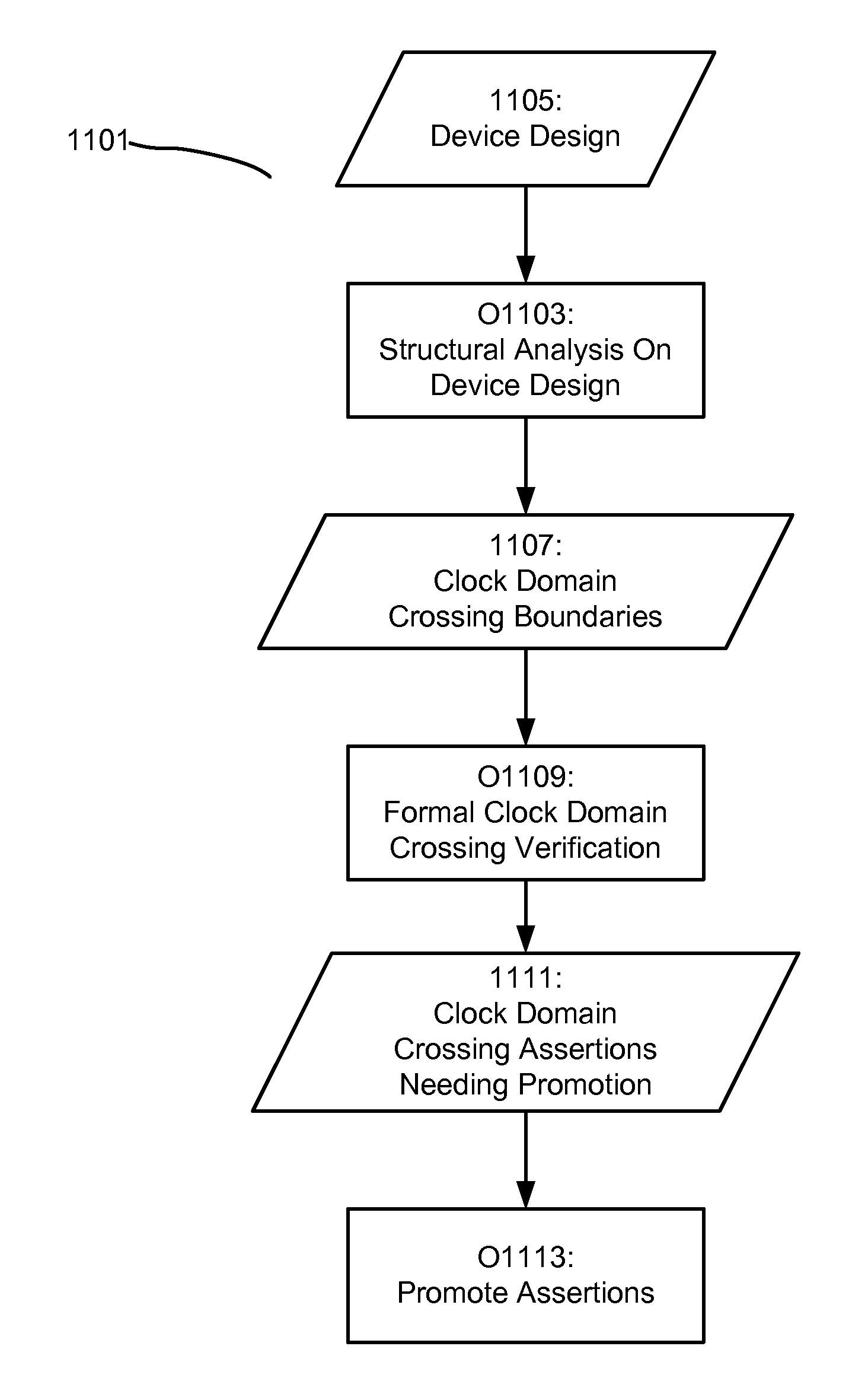
Methods and apparatus for performing automated formal clock domain crossing verification on a device are detailed. In various implementations of the invention, a device may be analyzed, wherein the clock domain crossing boundaries are identified. Subsequently, a formal clock domain crossing verification method may be applied to the identified clock domain crossing boundaries, resulting in clock domain crossing assertions being identified. After which the identified assertions may be promoted for post clock domain crossing analysis. With various implementations of the invention, a formal clock domain crossing method is provided, wherein the device components near an identified clock domain crossing are extracted. Assertions may then be synthesized and verified based upon the extracted components. Various implementations of the invention provide for clock domain crossing verification to be performed iteratively, wherein a larger and larger selection of the device is extracted during formal verification. Additionally, various implementations of the present invention provide that the clock domain crossing verification operate on the fly during a device verification procedure. With further implementations, a bit-blasted approach to clock domain crossing verification may be provided during formal verification.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method for clock synchronization validation in integrated circuit design
ActiveUS7073146B2Synchronisation information channelsGenerating/distributing signalsComputer scienceCircuit design
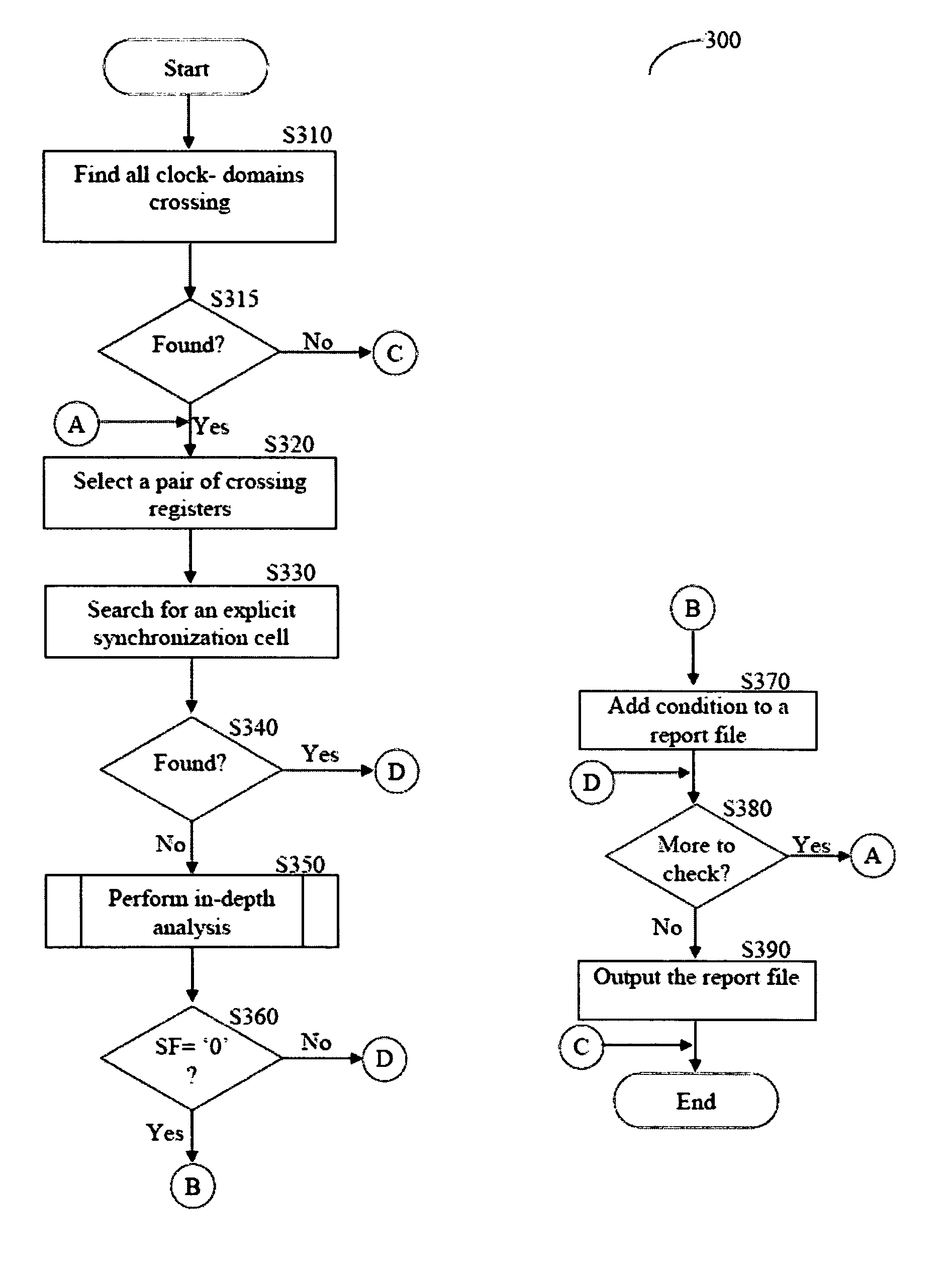
Unsynchronized clock-domain crossings in the design of integrated circuit are detected by searching for clock-crossing domains. For each clock-crossing that does not include an explicit synchronization cell, an analysis determines if the clock is stable crossing the domains.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Design tool clock domain crossing management
InactiveUS7779286B1Improve efficiencyEfficient managementCAD circuit designGenerating/distributing signalsTime domainComputer science
Methods and apparatus are provided for allowing efficient clock domain crossing management in programmable chip systems. Components associated with different clock domains can be analyzed. Clock domain crossing components are automatically selected from a library of clock domain crossing components to allow connection between disparate clock domains. Clock domain crossing components can be shared, chained, and intelligently selected for increased efficiency.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
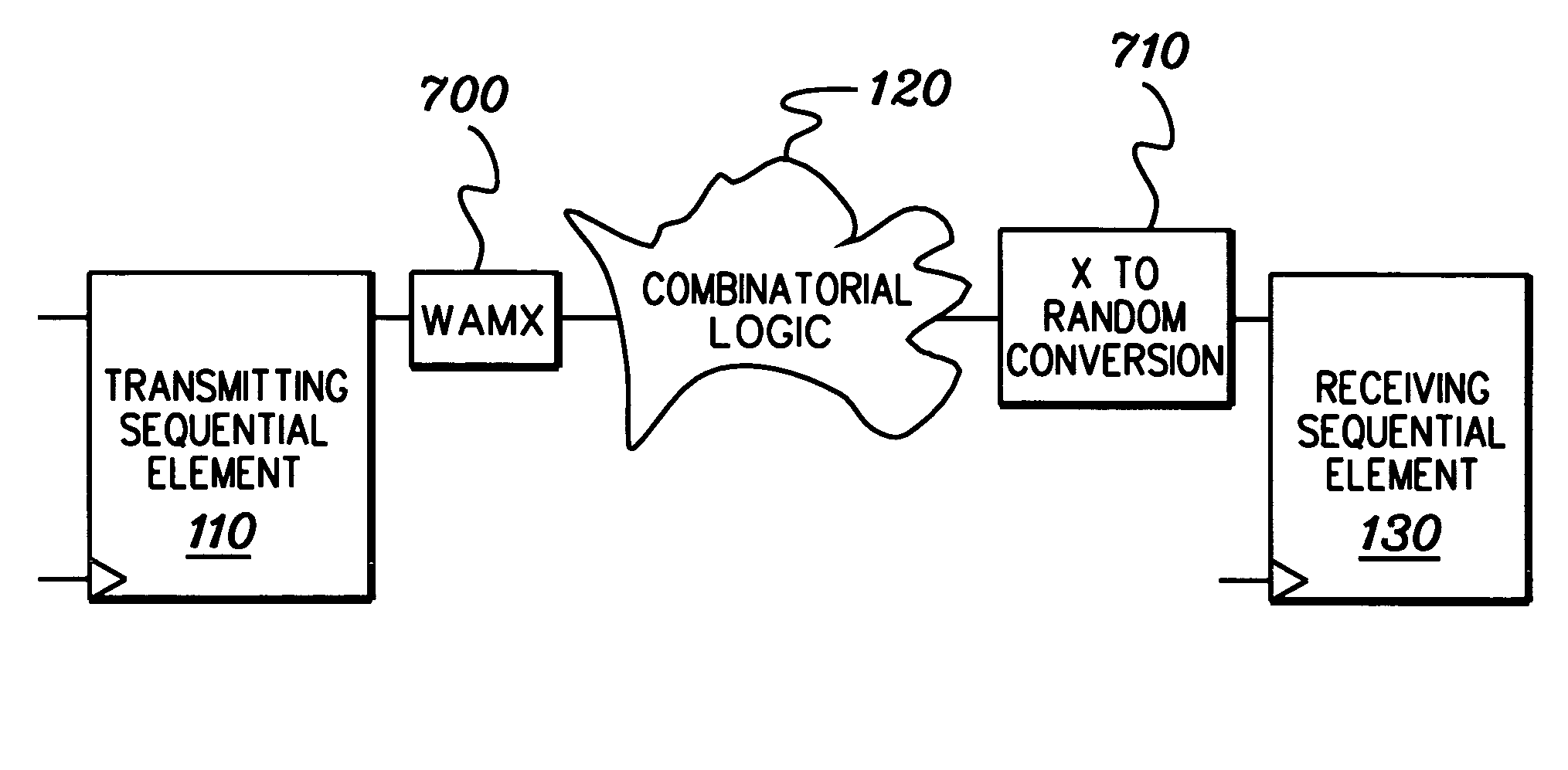
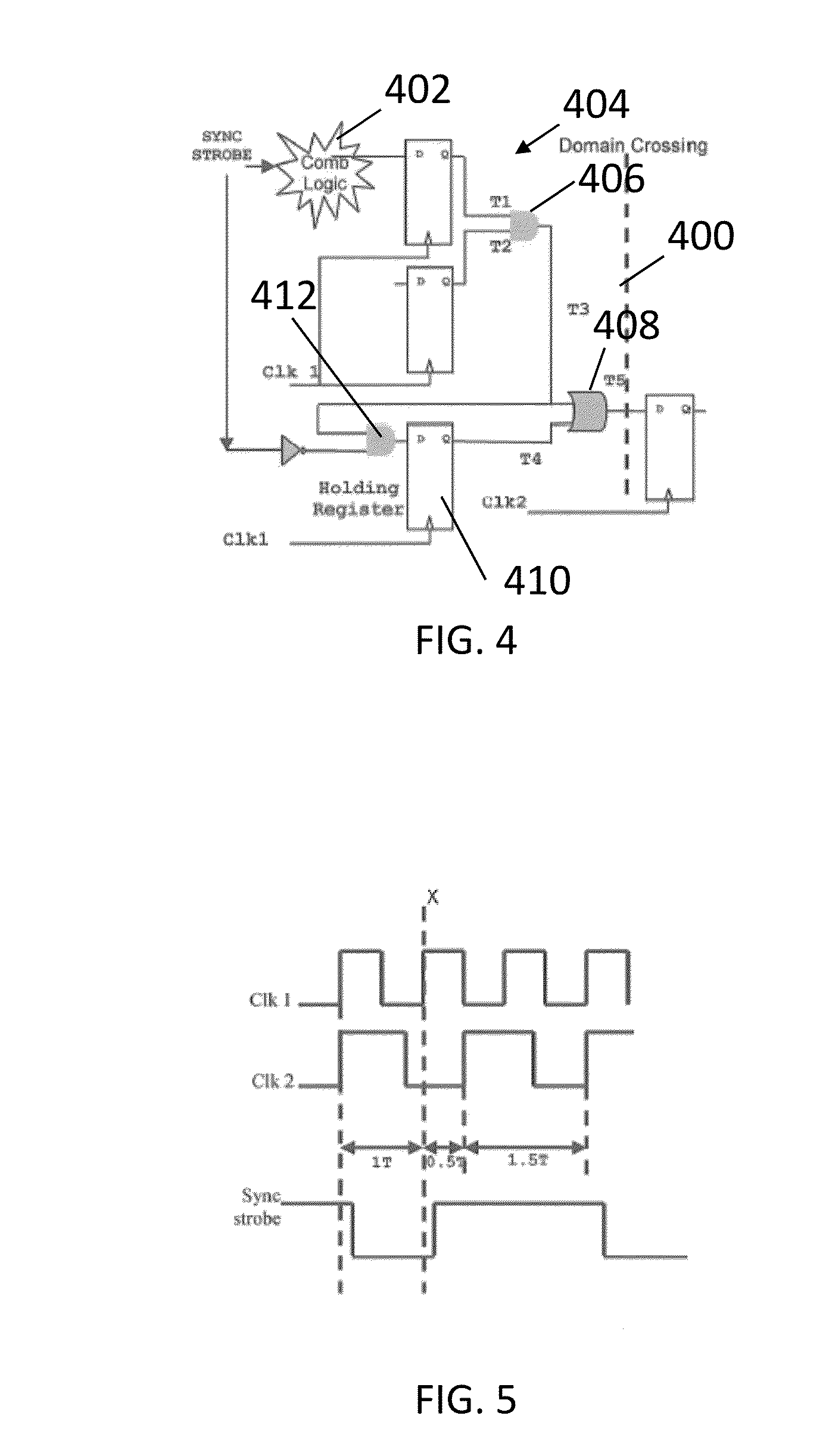
Method, apparatus, and computer program product for facilitating modeling of a combinatorial logic glitch at an asynchronous clock domain crossing
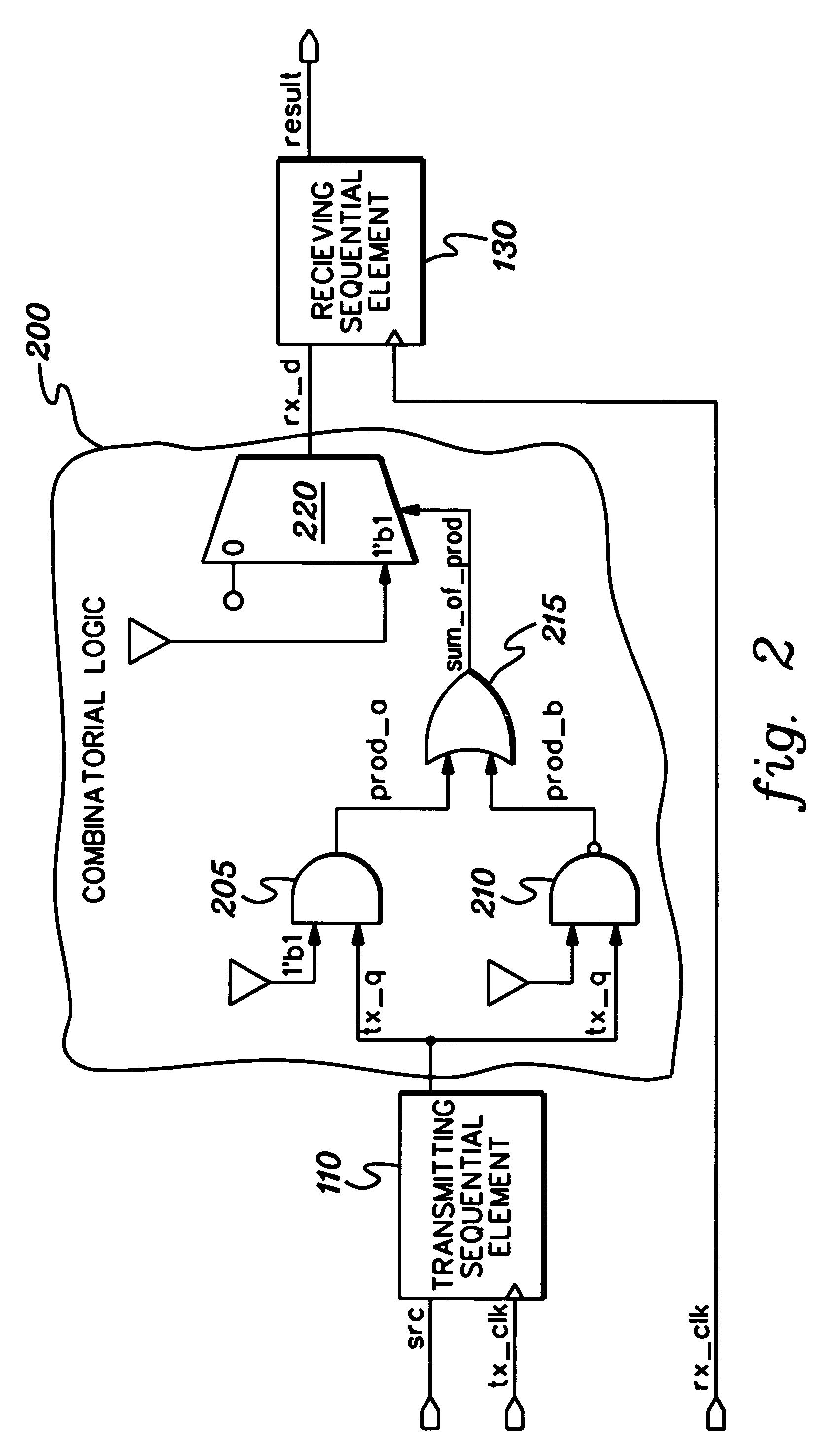
InactiveUS7333926B2Inserting of the simulation value of X into the combinatorial logic can be facilitatedFacilitate automatic propagation of the simulation value XDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationLogic modelingPath generation
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for facilitating combinatorial logic modeling at an asynchronous clock domain crossing. The modeling technique employs a simulation value of X in combinatorial logic at the asynchronous clock domain crossing of a circuit being modeled to facilitate modeling of a potential combinatorial logic glitch at the crossing during metastability periods thereof. Employing the simulation value of X includes: generating one or more equivalent functional equations for one or more combinatorial paths through the combinatorial logic at the crossing; propagating the simulation value of X through the combinatorial logic using the at least one equivalent functional equation; and then converting the simulation value of X at an output of the combinatorial logic of the asynchronous clock domain crossing to a random logic value for further propagation within the circuit being modeled.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
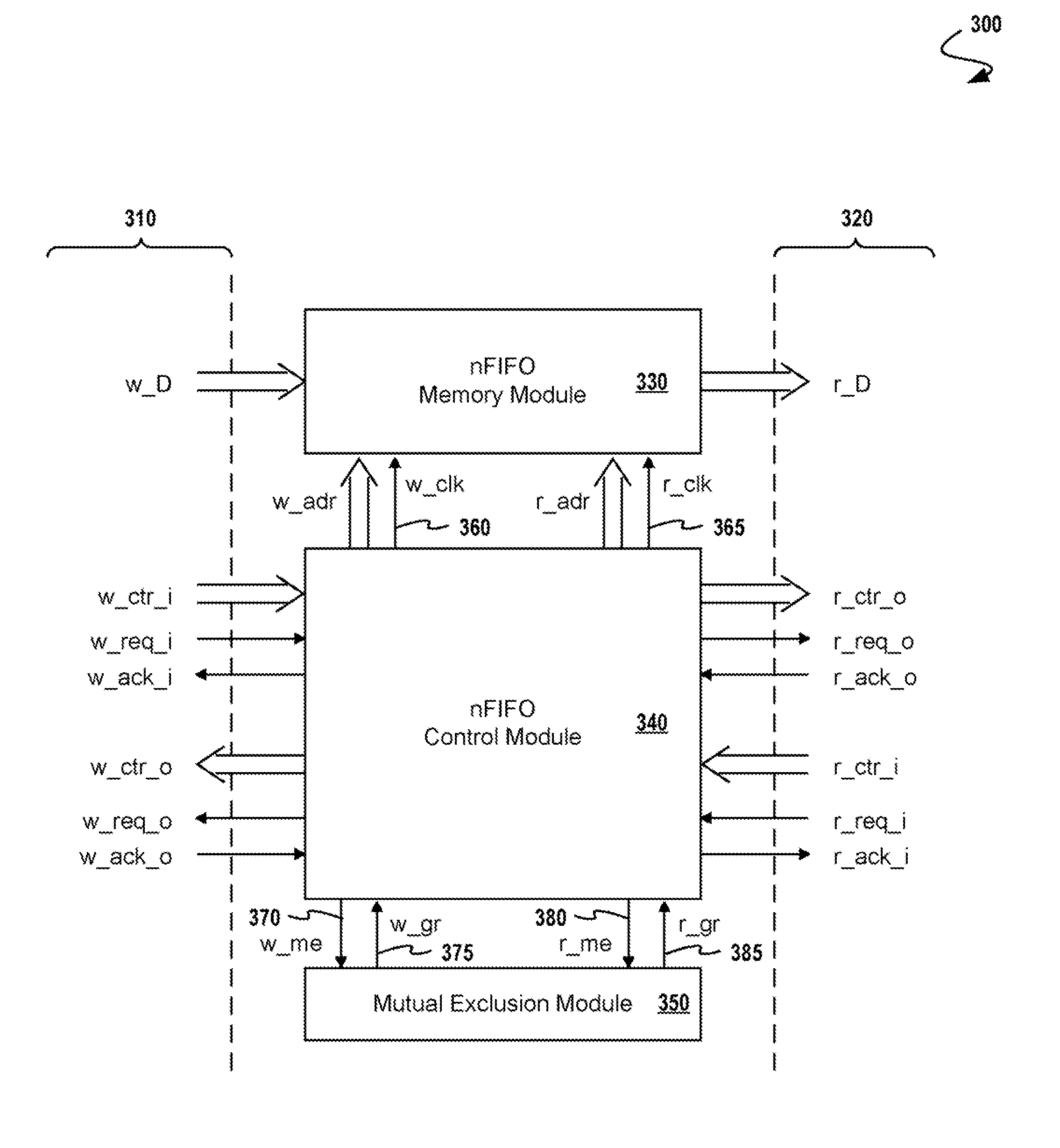
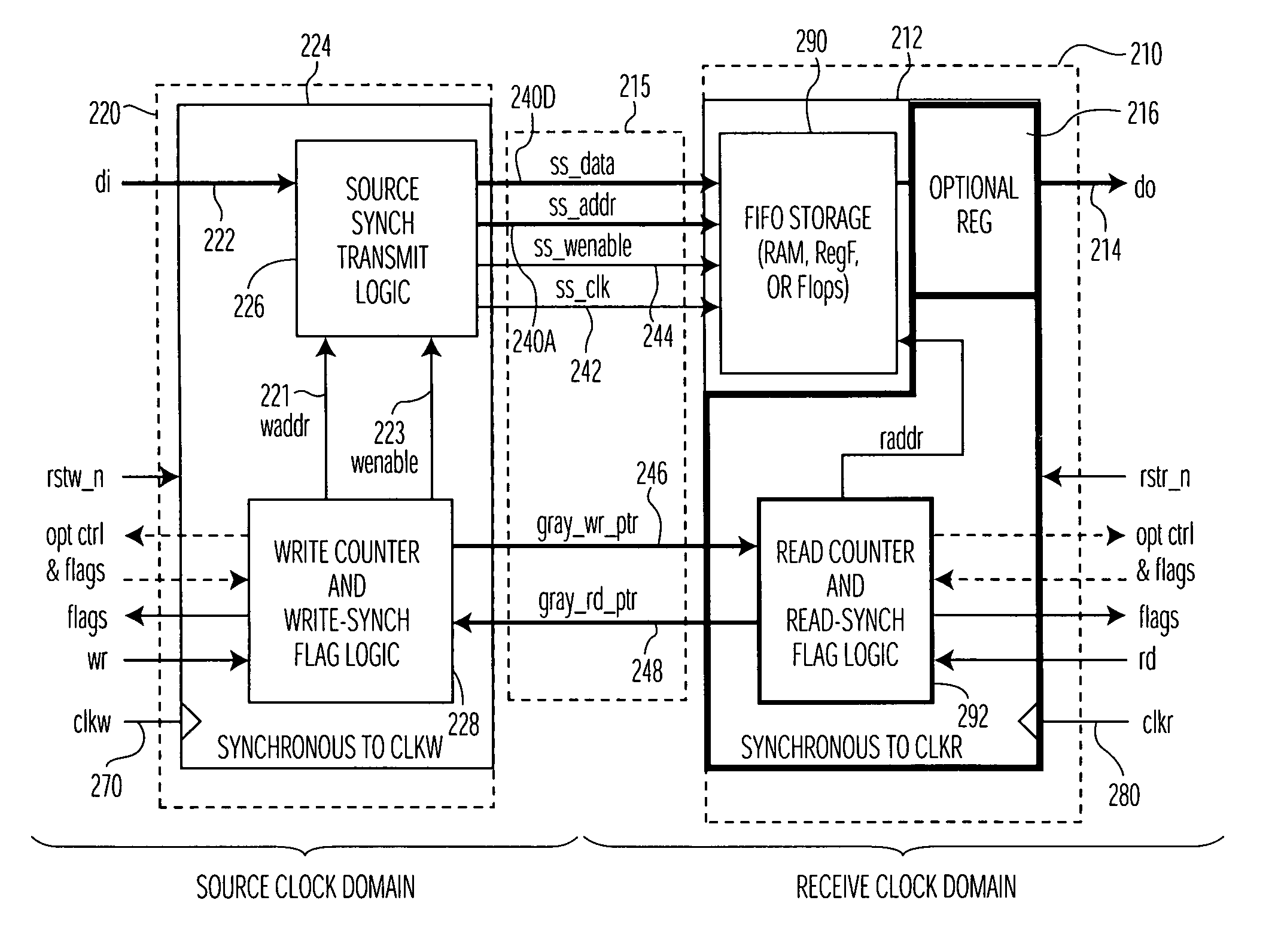
Clock domain crossing FIFO
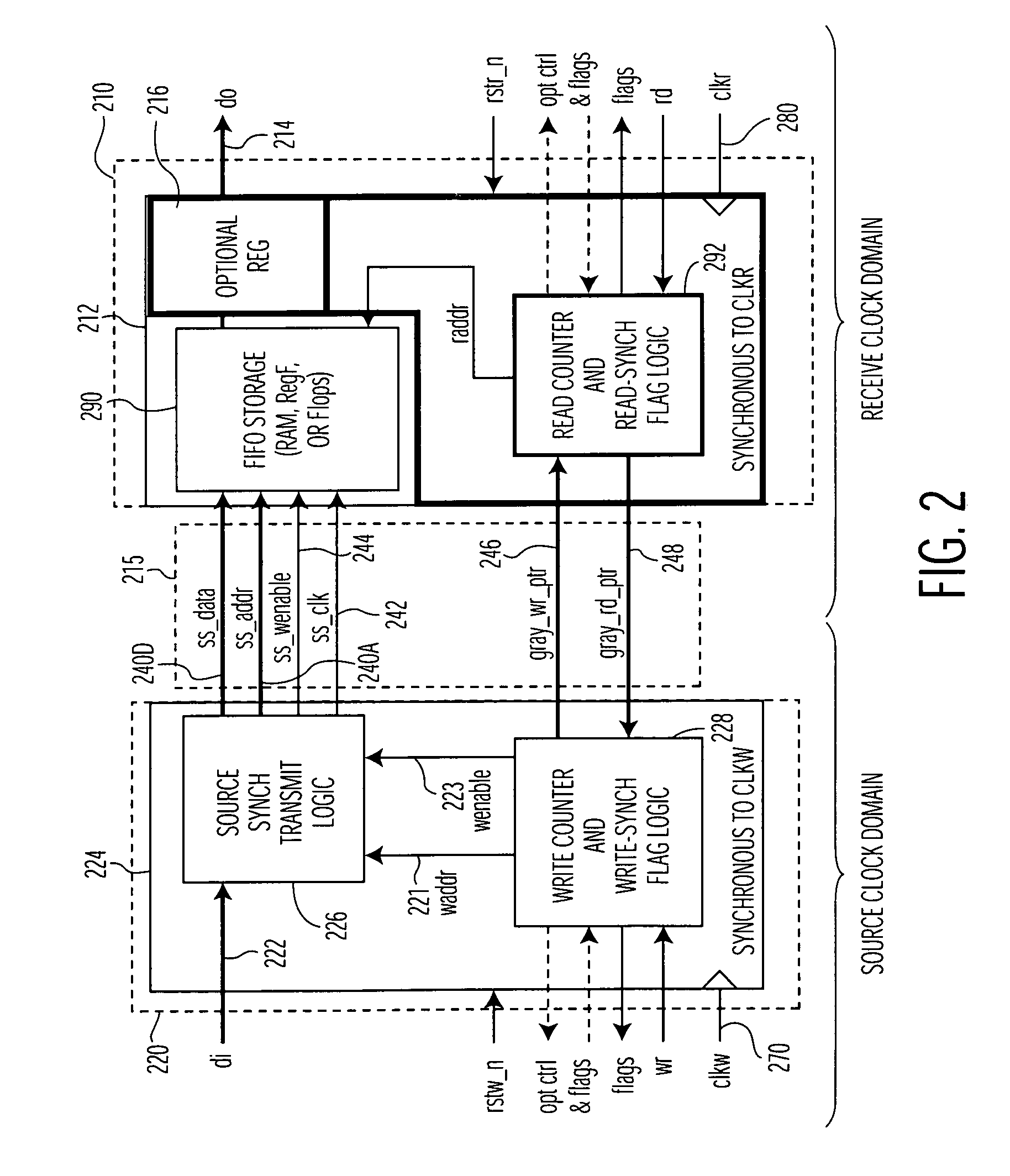
A method and arrangement of passing data from a source clock domain to a non-synchronous receive clock domain are provided. A first processing circuit, located in the source clock domain, links write-address information with the data, and a clock generator generates a transmit clock signal in the source clock domain synchronous with a source clock. The first processing circuit transmits the clock signal and the data with the linked write-address information to a second processing circuit in the receive clock domain. In the receive clock domain, the second processing circuit writes the data at an address designating a storage element corresponding to the linked write-address information. The second processing circuit clocks the data into the storage element synchronous with the accompanying transmit clock signal responsive to a write enable signal from the source clock domain, and reads the data out of the storage element synchronous with a receive domain clock.
Owner:NXP BV
Method for clock synchronization validation in integrated circuit design
ActiveUS20050097484A1Simple methodSynchronisation information channelsGenerating/distributing signalsComputer scienceClock synchronization
Unsynchronized clock-domain crossings in the design of integrated circuit are detected by searching for clock-crossing domains. For each clock-crossing that does not include an explicit synchronization cell, an analysis determines if the clock is stable crossing the domains.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
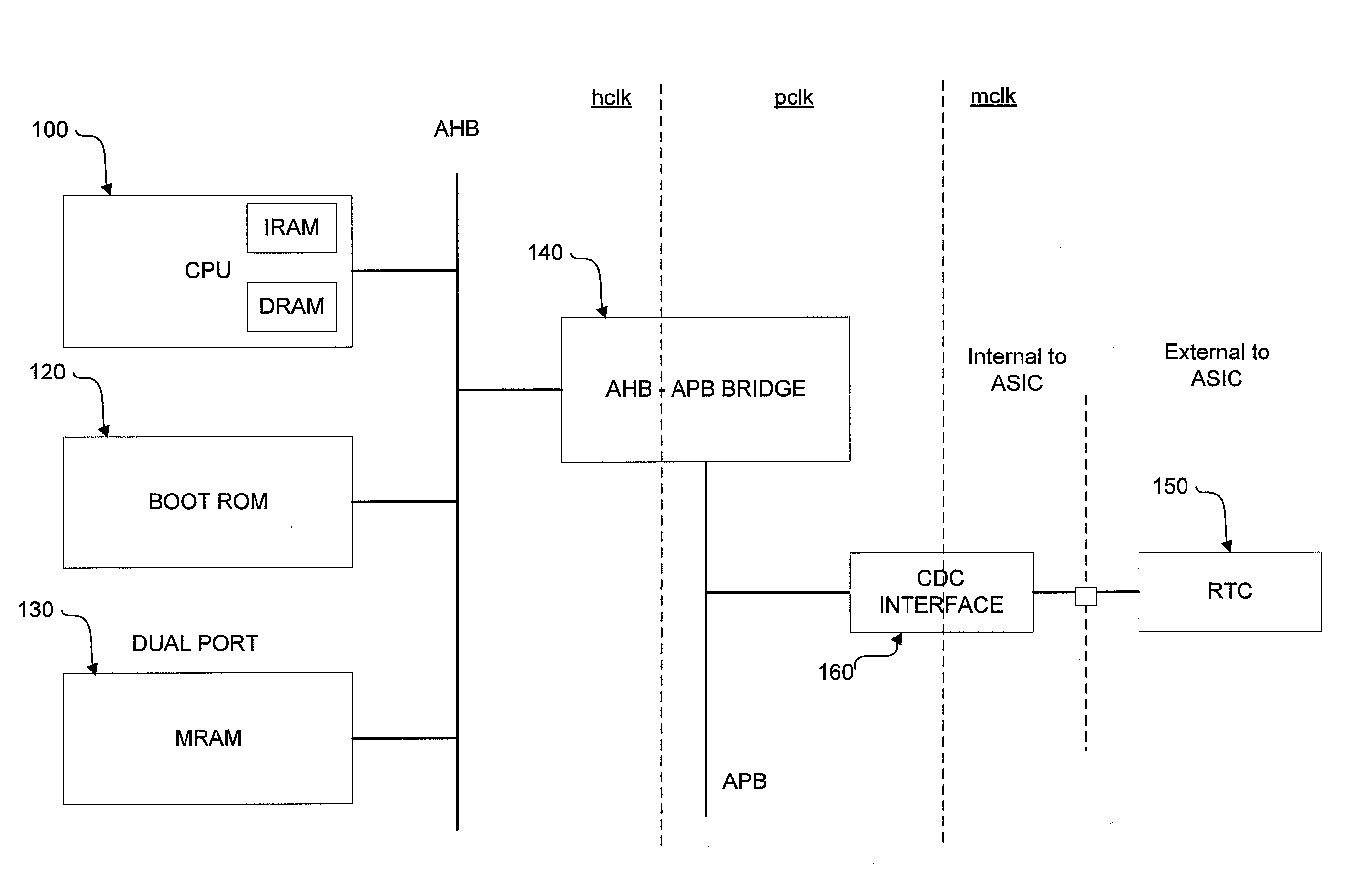
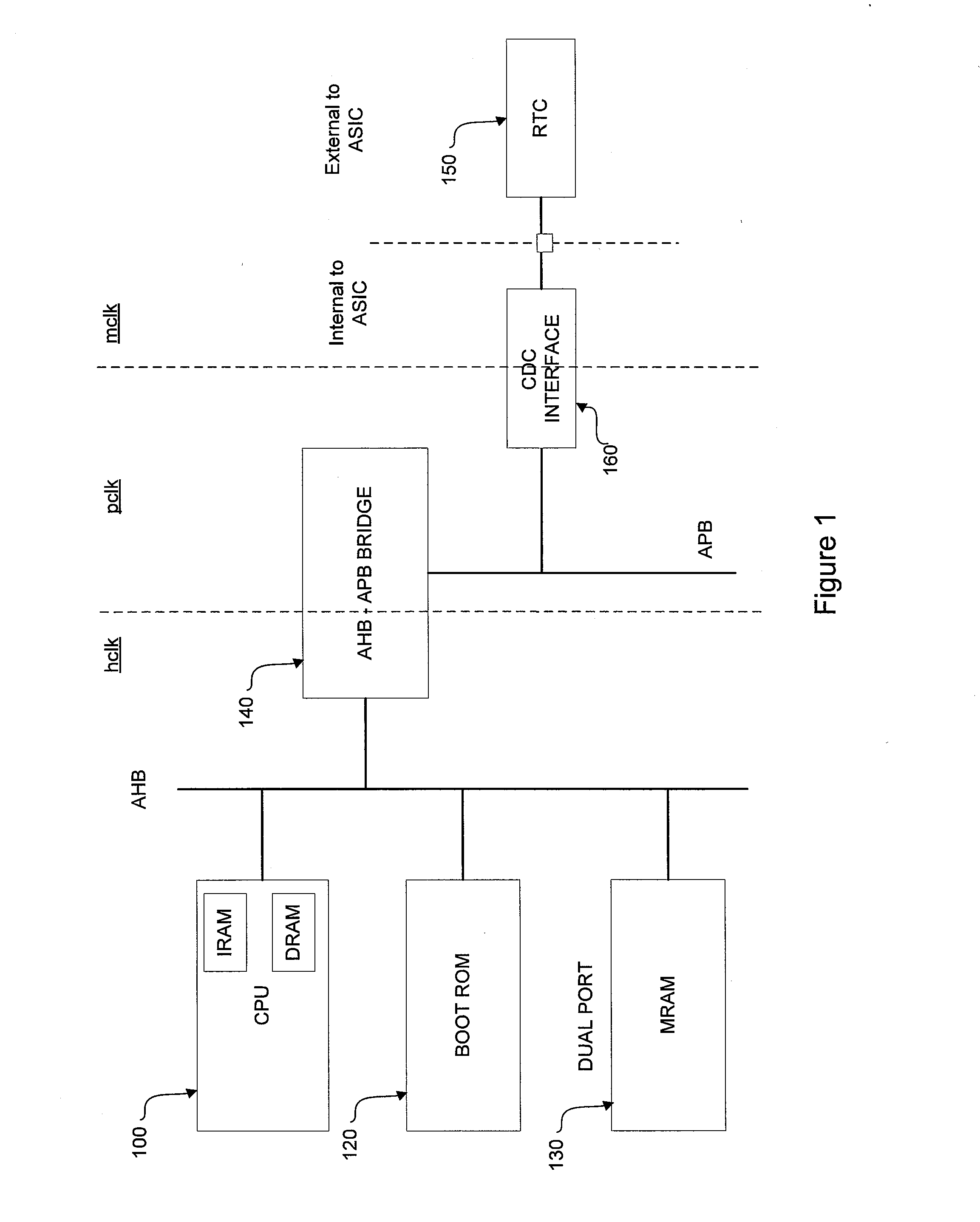
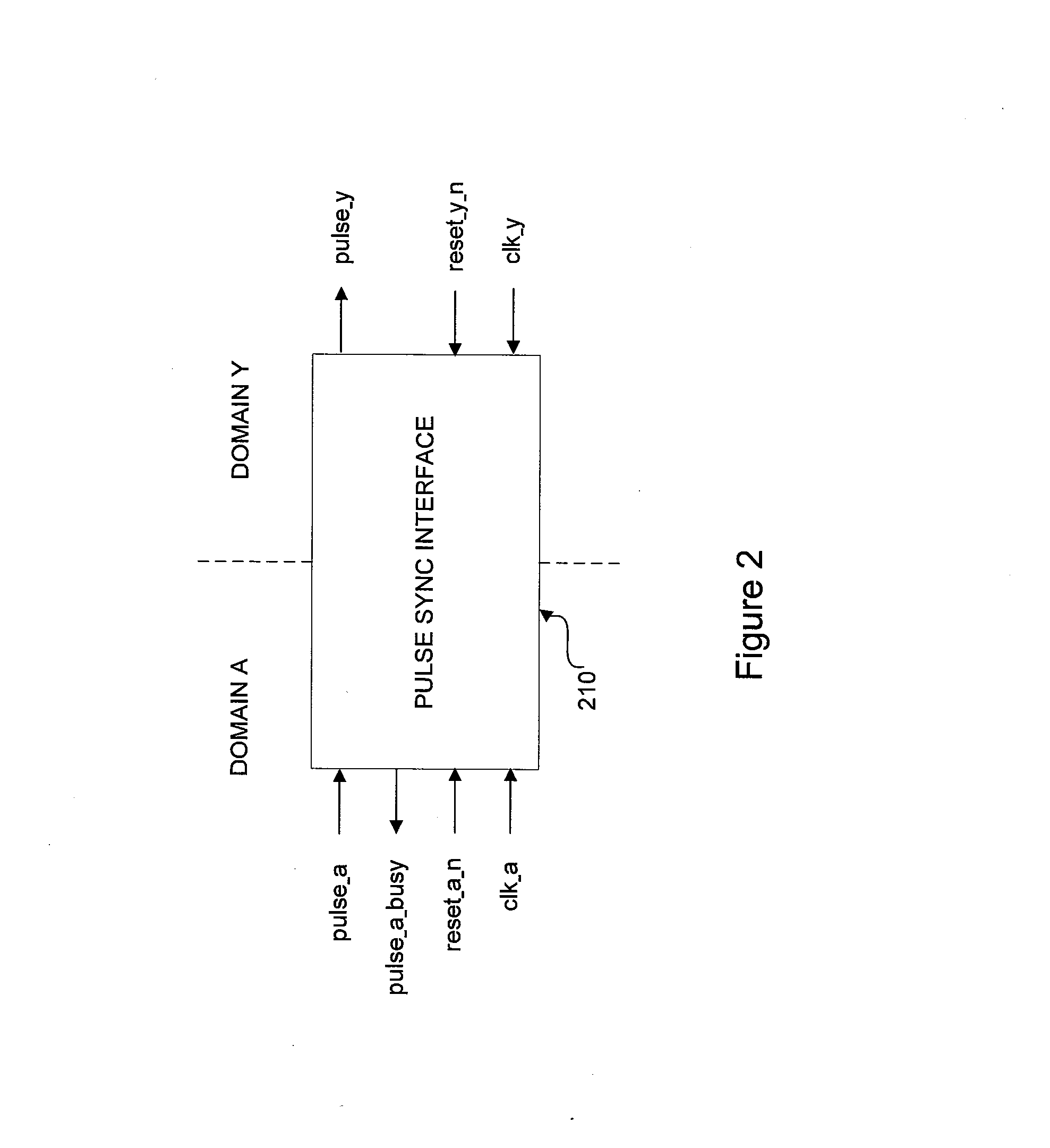
Clock domain crossing interface
ActiveUS20130013950A1Generating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple useClock domain crossingProcessor register
A flexible and scalable bi-directional CDC interface is set forth between clock domains in a SoC device. The interface comprises a pulse sync circuit for receiving a pulse synchronized to the source clock domain and in response outputting a busy signal to the source clock domain and outputting the pulse synchronized to said destination clock domain; an input register for latching data from said source clock domain in response to a transition of said source clock in the event said busy signal is not active and preventing said data from being latched in the event said busy signal is active so as not to corrupt previously latched data; and an output register for receiving said pulse from said pulse sync circuit and in response latching said pulse from said input register on a transition of said destination clock.
Owner:PSION
Apparatus and Method for Achieving Glitch-Free Clock Domain Crossing Signals
ActiveUS20130132760A1Generating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple useProcessor registerComputer science
A computer implemented method includes identifying in an original circuit output signals that drive domain crossing logic separating a first clock domain from a second clock domain. A revised circuit is formed with a register attached to the domain crossing logic. The register receives an output signal and a synchronization signal that precludes the output signal from transitioning at selected clock cycle intervals.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
FPGA (field programmable gate array) based USB3.0 interface module
InactiveCN104881388AVersatilityHigh speed data transmissionElectric digital data processingFpga implementationsData transmission
The invention discloses an FPGA (field programmable gate array) based USB3.0 interface module, and relates to a USB3.0 interface module in order to realize compatibility with a USB2.0 high-speed interface as well as high-speed data transmission between a computer and an FPGA. According to the interface module, the FPGA is adopted to realize logic control, and the high-speed data transmission is realized through data read-write operation of synchronous slave equipment FIFO (first input first output) in a chip FX3; the interface module control logic comprises a USB3.0 transmitting module, a USB3.0 receiving module, an FIFO transmitting module for clock domain crossing operation and an FIFO receiving module for the clock domain crossing operation. The FPGA based USB3.0 ultrahigh-speed interface is compatible with the USB2.0 high-speed interface, and the high-speed data transmission between the computer and the FPGA is realized.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
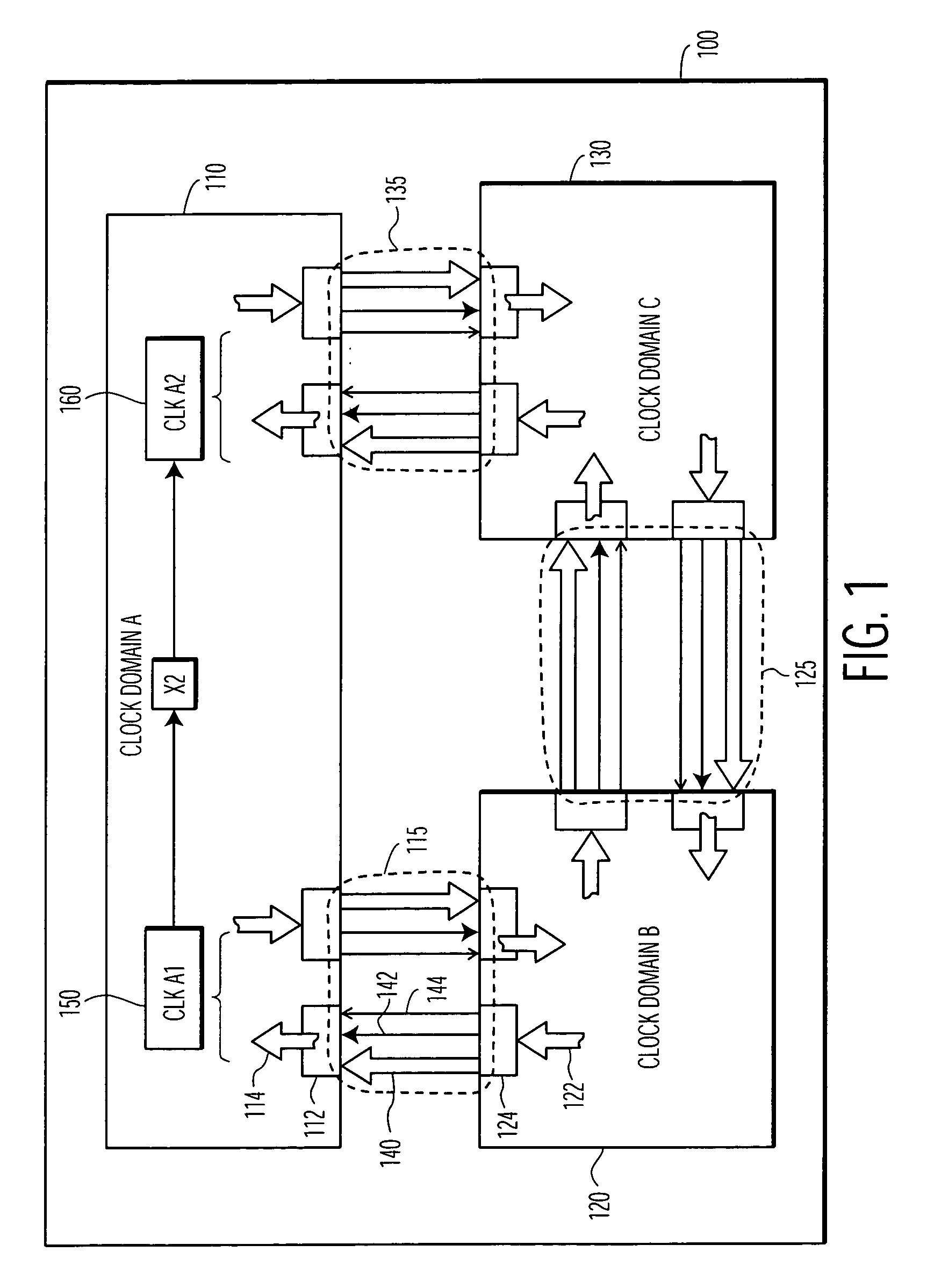
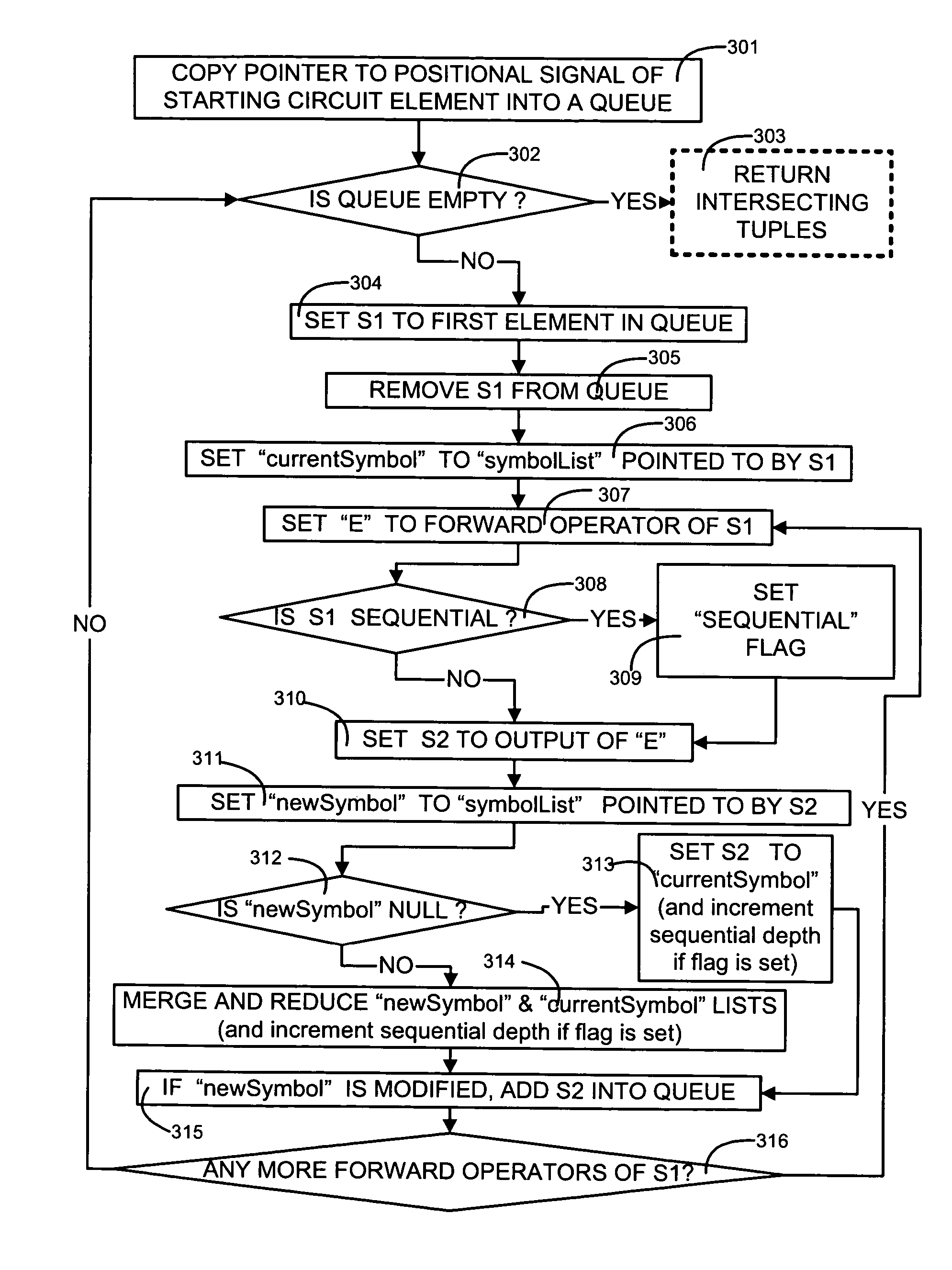
Tuple propagator and its use in analysis of mixed clock domain designs
ActiveUS20050273735A1Electronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareAlgorithmPropagator
Names of signals are propagated through a circuit design inside tuples, with each tuple including at least a signal name and a sequential depth. A tuple being propagated is added to a list of zero or more tuples currently identified with a circuit element, unless a tuple of the same signal name is already present in the list. If already present in the list, then propagation of that tuple is stopped. Propagation of tuples may also be stopped depending on user-defined limits, e.g. on sequential depth. Tuple propagation may be used, depending on the embodiment, to identify features of interest in the circuit design, e.g. (a) a point of convergence of differently clocked signals, (b) location of gray coders, and (c) location of synchronizers, by appropriate identification of circuit elements from which tuple propagation is to start, and by appropriate checks on lists of tuples that result from tuple propagation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Device and method for processing clock-domain-crossing asynchronous data, chip and operating method of chip
InactiveCN102510281AGood precisionGood synchronizationPrintingLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsLogical operationsData signal
The invention provides a device and a method for processing clock-domain-crossing asynchronous data, a chip and an operating method of the chip. The device comprises a first data sampling unit, a second data sampling unit, a logical operation unit and a clock signal synchronization unit, wherein the first data sampling unit acquires data and obtains a first data signal in a first clock domain; the second data sampling unit acquires the data and obtains a second data signal in a second clock domain; the logical operation unit receives the first data signal and the second data signal and performs logical operation; the clock signal synchronization unit samples a first clock signal in the first clock domain and / or a second clock signal in the second clock domain to obtain a first synchronous clock signal and / or a second synchronous clock signal; and at least one of the first data sampling unit and the second data sampling unit acquires the data under the first synchronous clock signal and / or the second synchronous clock signal. The method comprises the following steps of: synchronizing clock signals in other clock domains by using a reference clock signal; and sampling the data. By the invention, data synchronism can be ensured, and the processing accuracy of the data is improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI TIANWEI TECH DEV CO LTD
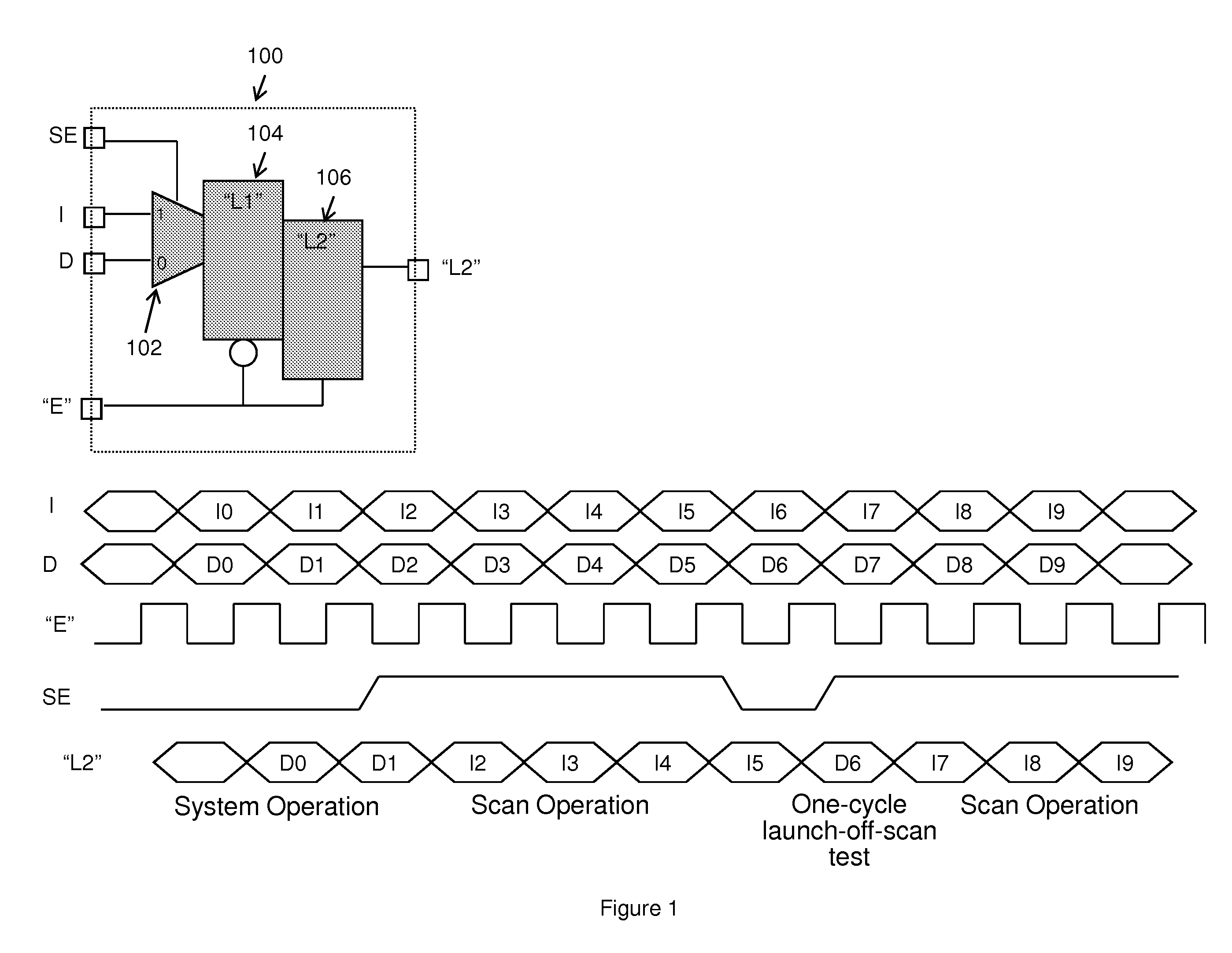
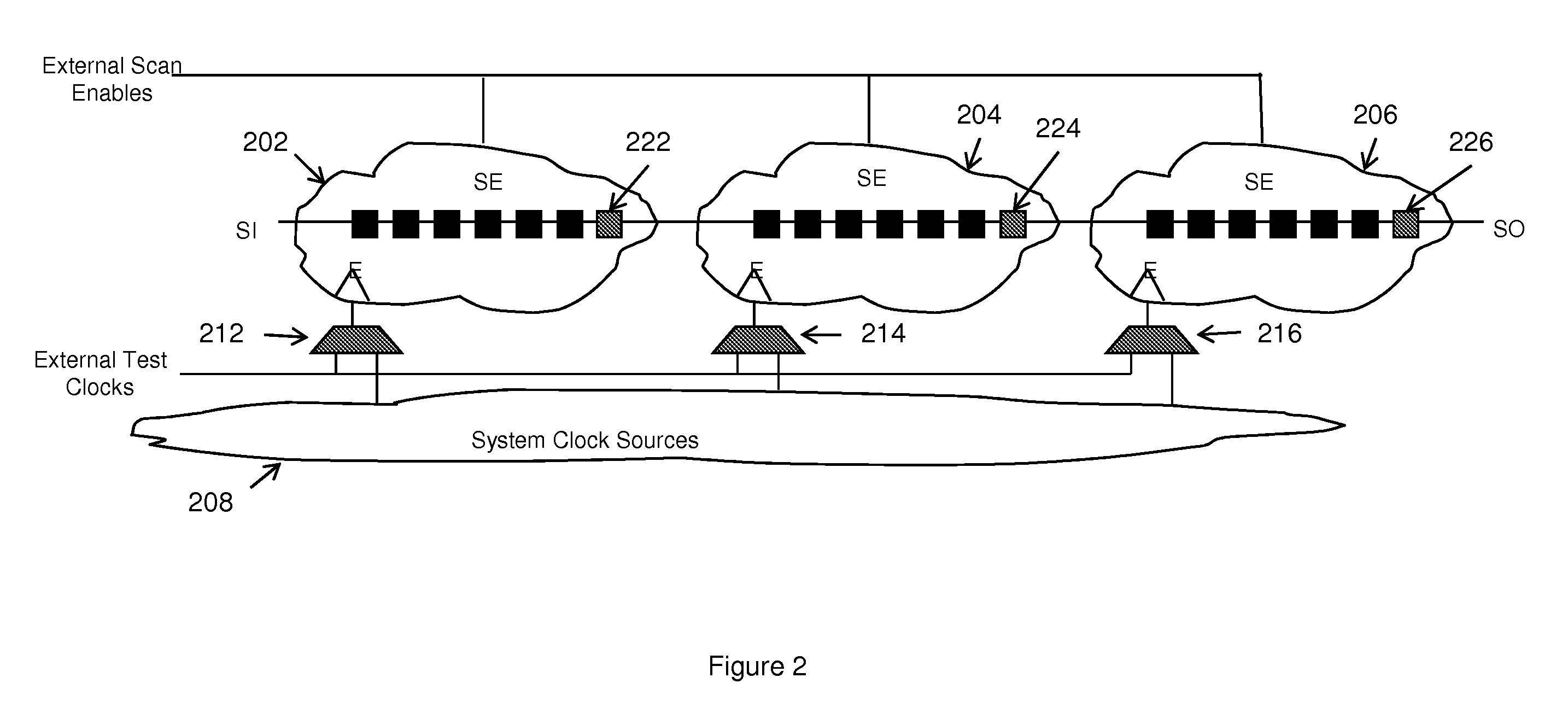
Avoiding race conditions at clock domain crossings in an edge based scan design
A structure, system, and method block clock inputs to clock domains (using a computer). While the clock domain inputs are blocked, the structure, system, and method perform a first timing test only of signals that are transmitted within the clock domains (using the computer) by only observing latches that receive signals from sources within the clock domains. The structure, system, and method also unblock the clock inputs to the clock domains (using the computer). While the clock domain inputs are unblocked, the structure, system, and method perform a second timing test only of signals that are transmitted between the clock domains by only observing latches that receive signals from other clock domains.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
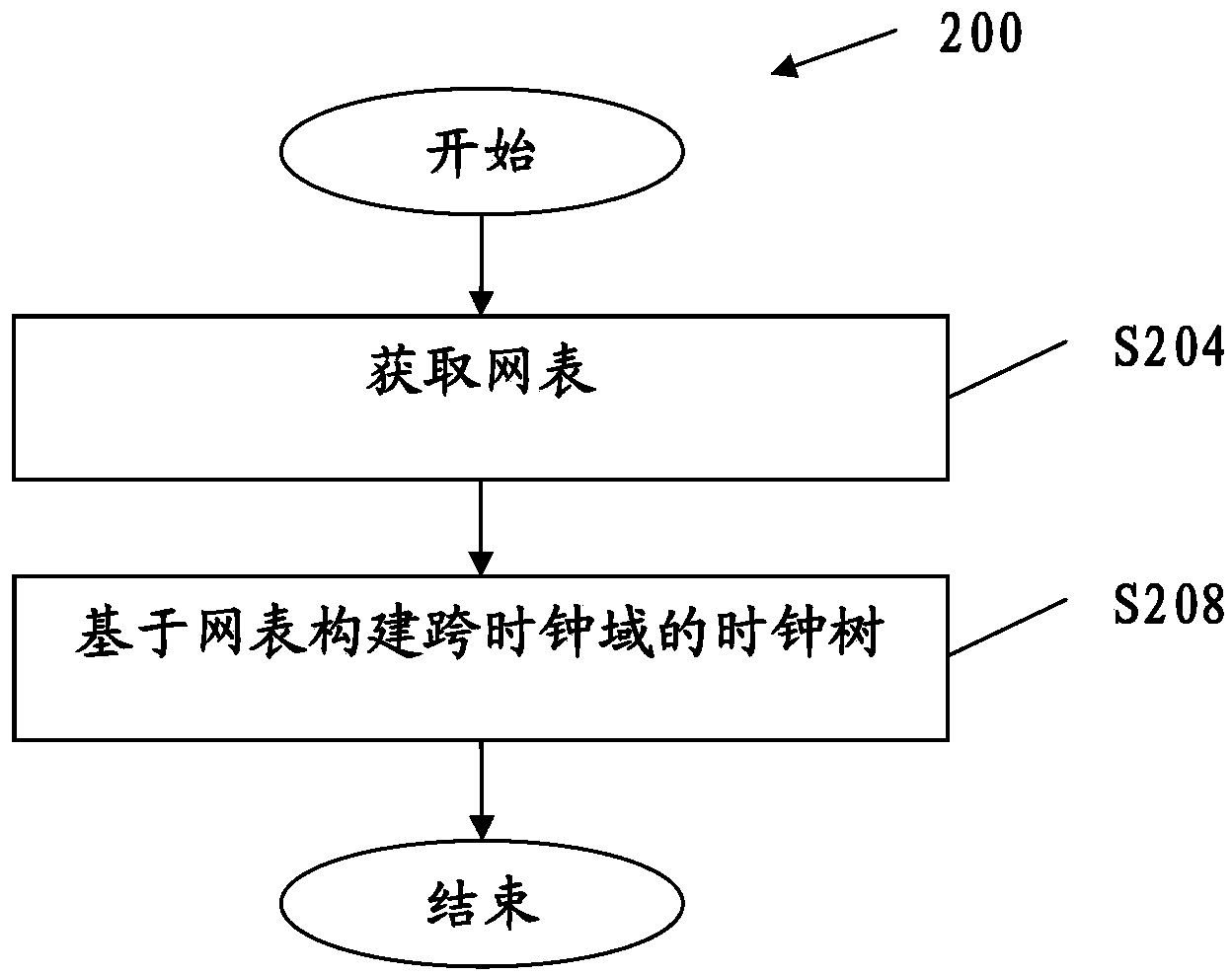
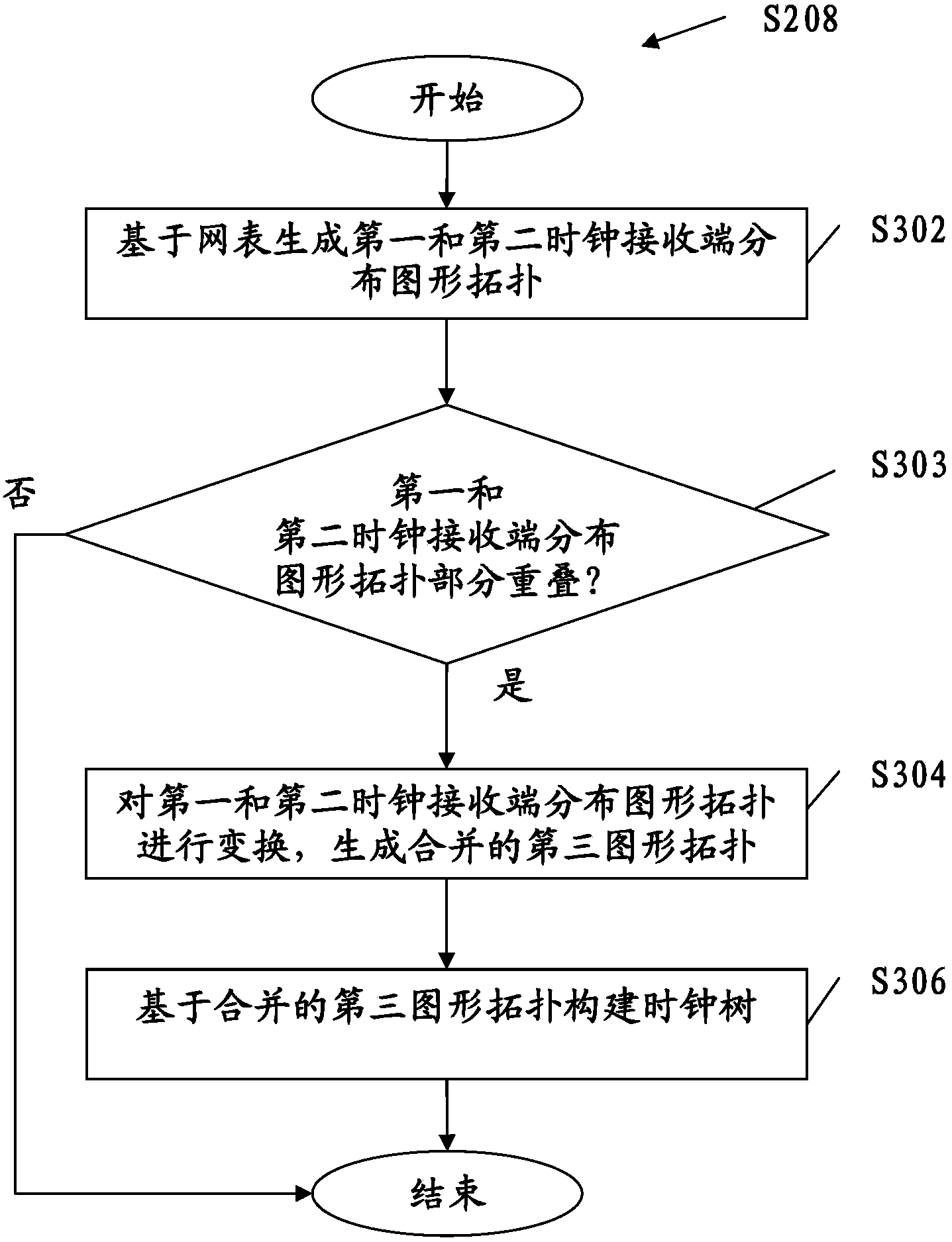
Clock-domain-crossing clock tree building method, clock-domain-crossing clock tree building system, integrated circuit and manufacturing method
InactiveCN104077427AImprove performanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsTheoretical computer science
Disclosed is a method and system for clock tree construction across clock domains, an integrated circuit and fabrication method thereof. A method for clock tree construction includes acquiring a netlist describing an integrated circuit (IC), comprising data for describing physical locations and logic connections of clock sinks belonging to multiple clock domains on the pattern of the IC, and constructing the clock tree across clock domains based on the netlist, such that clock cells belonging to different clock domains can share more physical locations. Accordingly, clock trees can be constructed across clock domains to improve IC performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
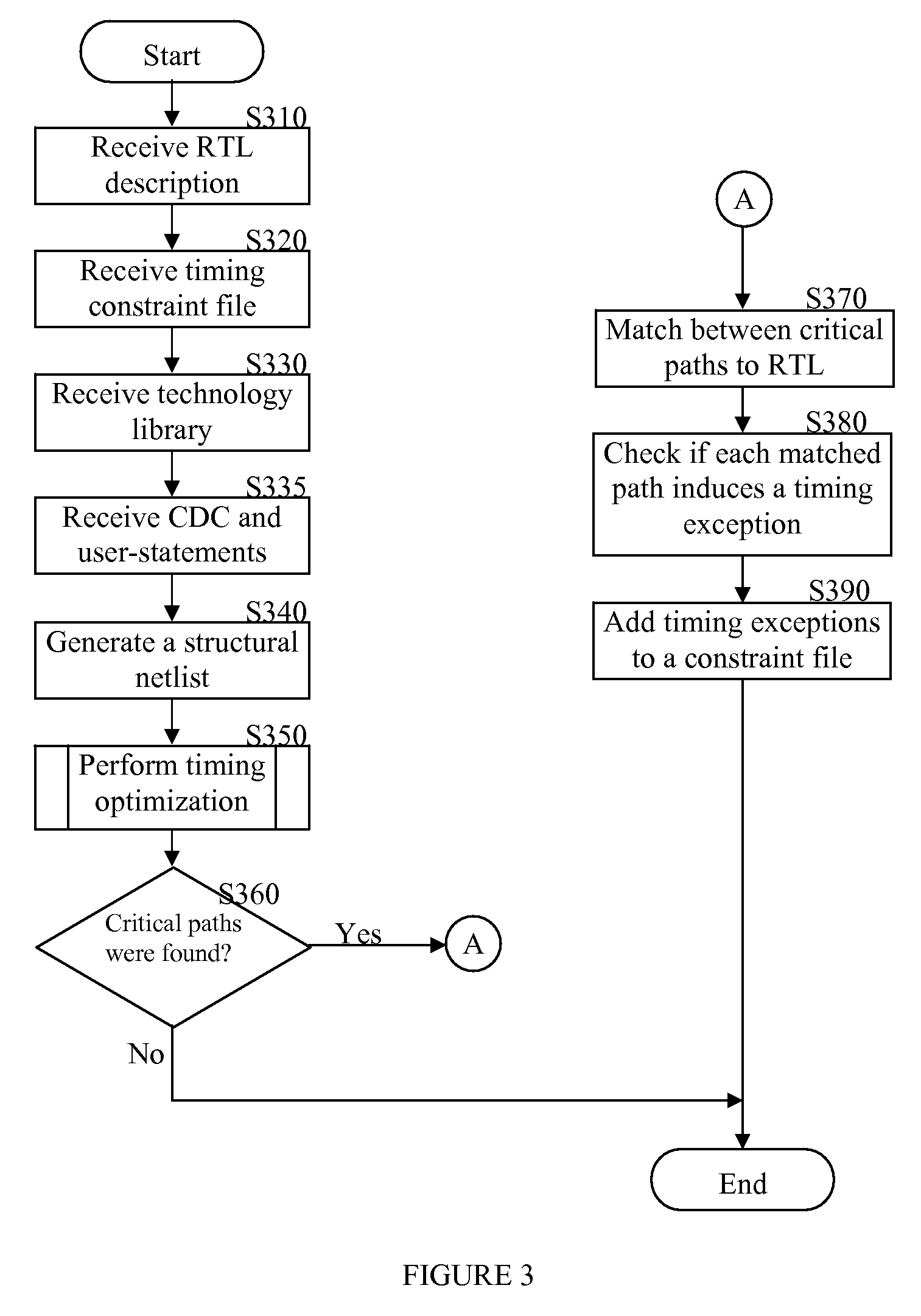
Method for generating timing exceptions
InactiveUS20080201671A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFalse pathComputer science
A method for generating timing exceptions for integrated circuit (IC) designs is disclosed. The method includes synthesizing an input RTL description into a gate-level netlist mapped to a technology library; detecting timing critical paths in the netlist; and determining for each detected timing critical path whether it induces timing exceptions. The timing exceptions generated by the disclosed method include, but are not limited to, multi-cycle paths, clock domain crossing false paths, asynchronous false paths, functional false paths, combinational false paths, sequential false paths, timing false paths, and the like.
Owner:ATRENTA
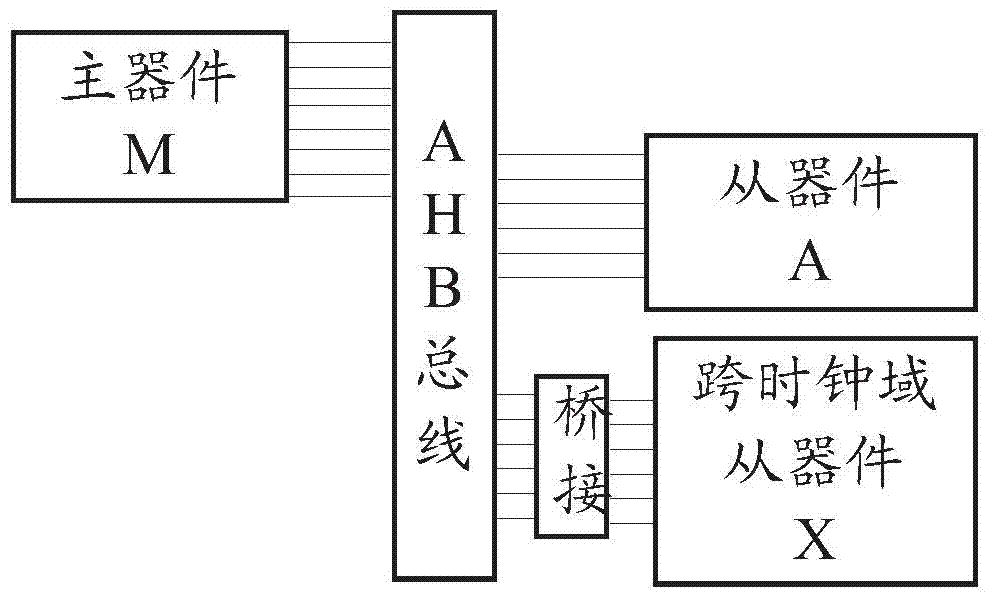
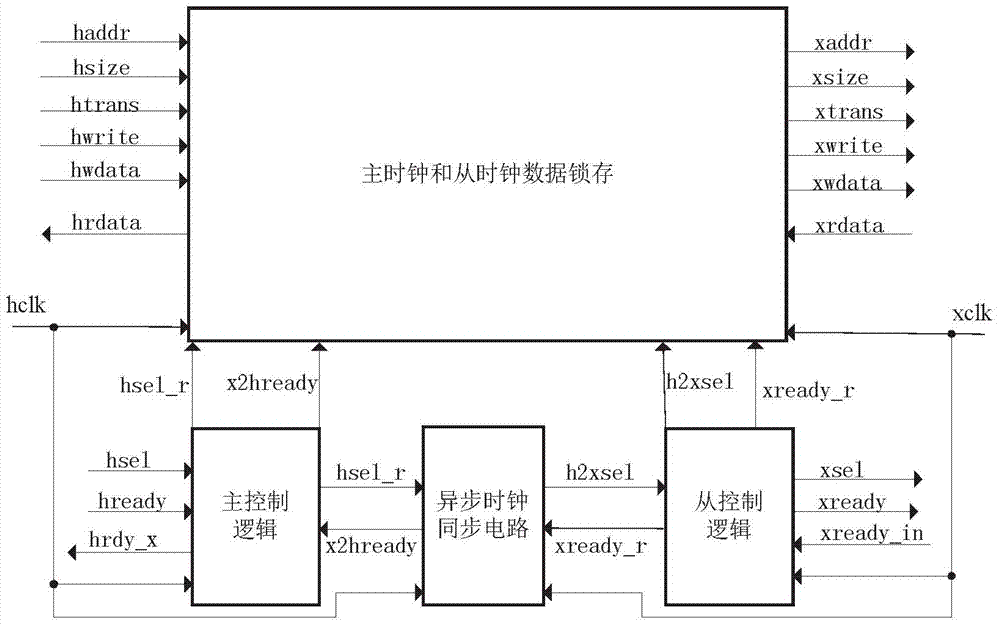
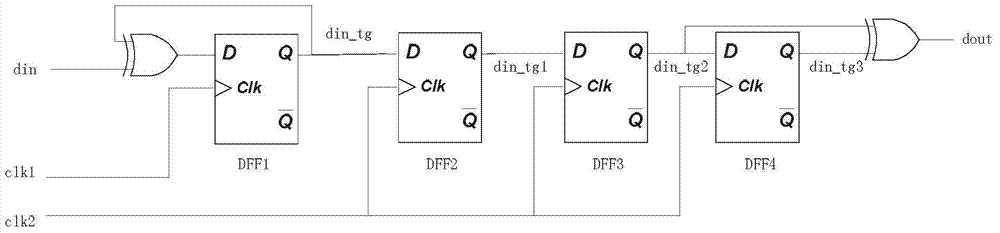
Clock domain crossing AHB (advanced high-performance bus) bridging method and device
ActiveCN104850524AAvoid lossGuaranteed normal transmissionElectric digital data processingControl signalSlave clock
The invention discloses a clock domain crossing AHB (advanced high-performance bus) bridging method and device. The device comprises a master control logic module, a slave control logic module, a master clock and slave clock data latching module and an asynchronous pulse and synchronous circuit module. The master control logic module generates a bus control signal of a master clock domain according to a bus signal of a master device; the master control logic module generates a response signal fed back to the master device according to a slave device bus signal sampled in the master clock domain and latched by a slave clock domain; the slave control logic module generates a bus control signal of the slave clock domain according to a response signal of a slave device and a master device bus signal sampled in the slave clock domain and latched by the master clock domain; when the bus control signal is effectively enabled, the master clock and slave clock data latching module latches and samples synchronous data; the asynchronous pulse and synchronous circuit module synchronizes clock domain crossing signals to an opposite-party clock domain. The clock domain crossing AHB bridging method and device have the advantage that the master and slave devices can implement the AHB protocol under any frequency.
Owner:DATANG MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +1
Static analysis of VLSI reliability
ActiveUS8707229B1Reduce probabilityCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatic timing analysisIntegrated circuit layout
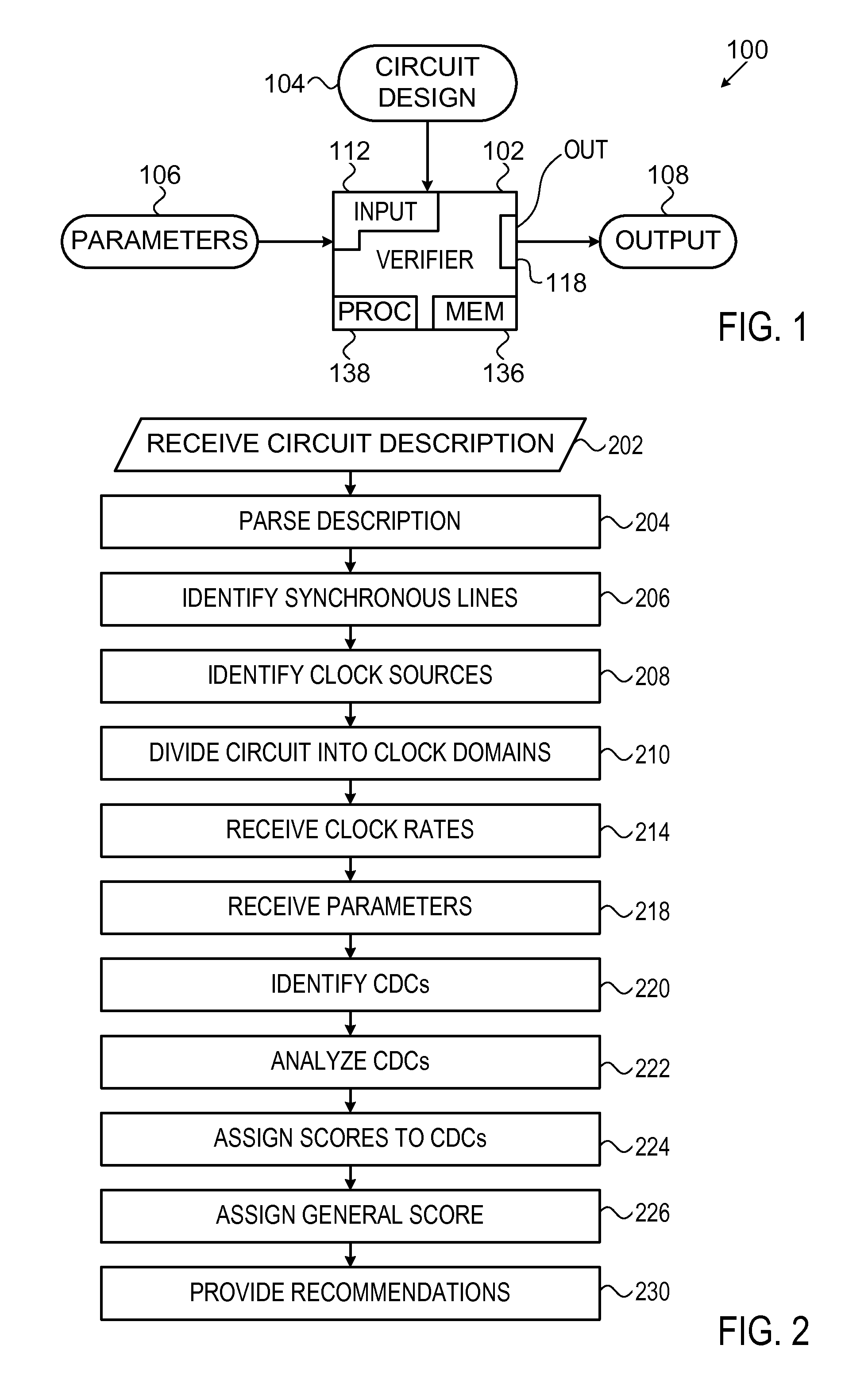
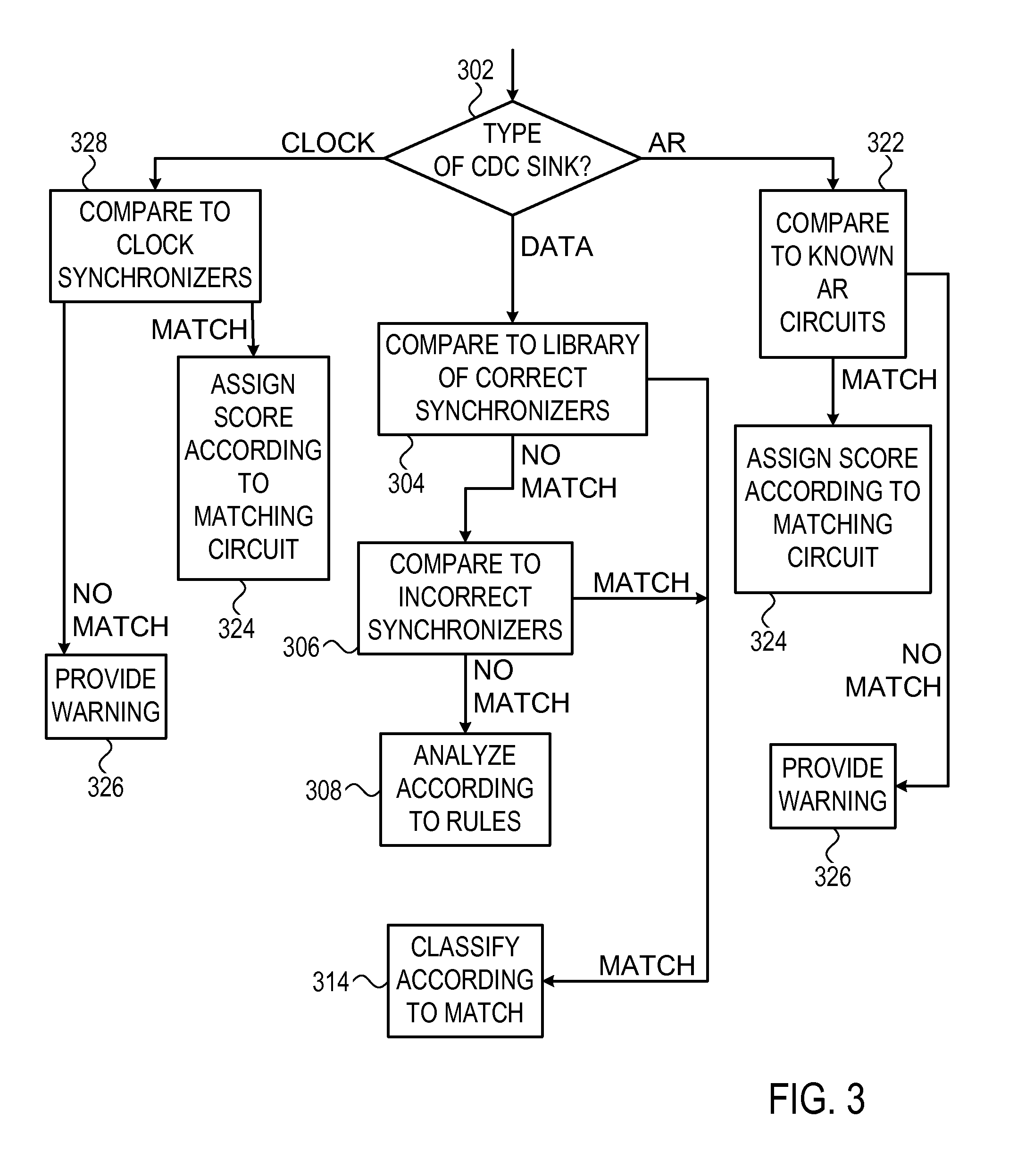
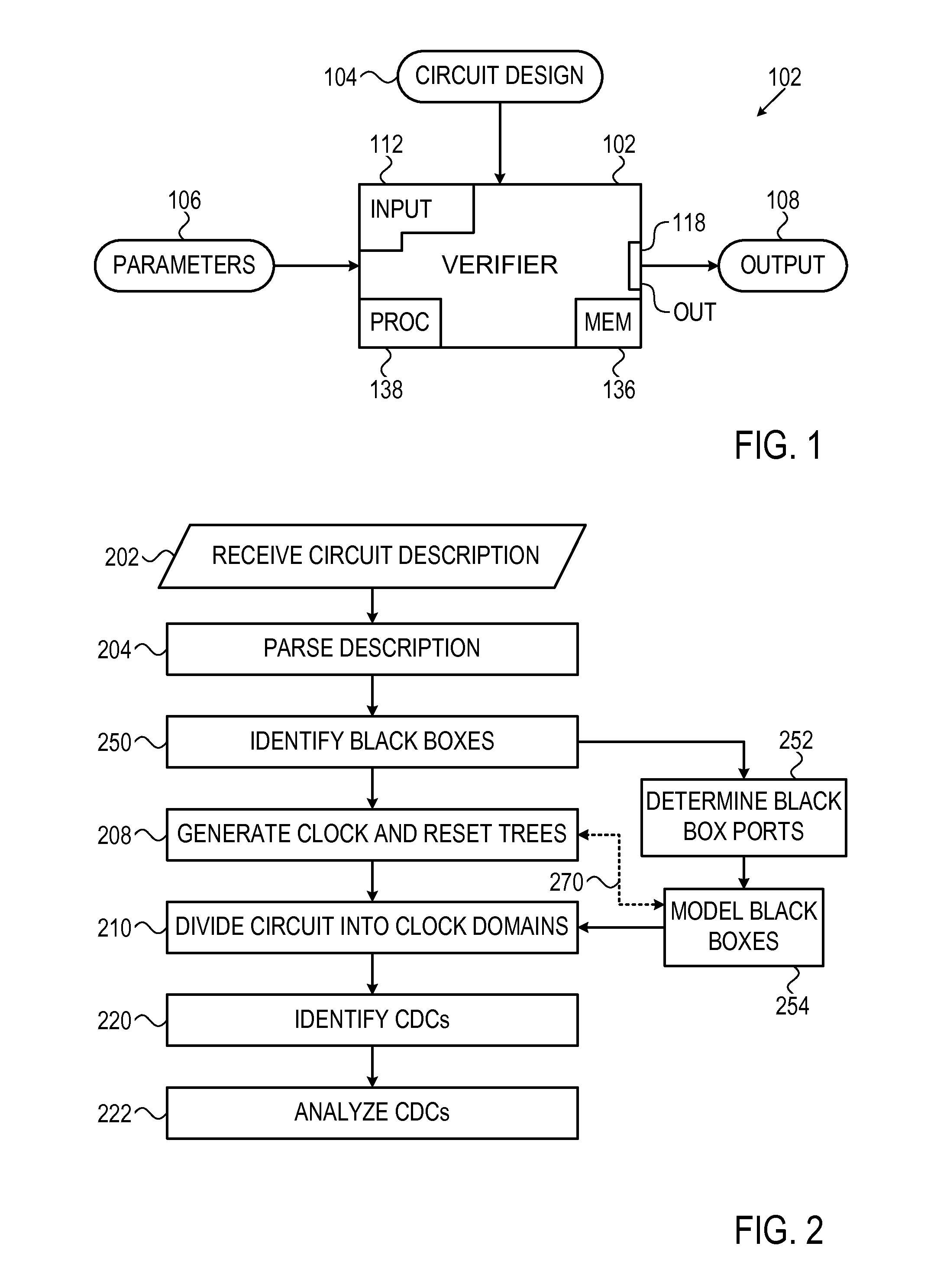
A circuit verifier having an input interface configured to receive descriptions of integrated circuits and a processing unit configured to scan through a description of an integrated circuit received through the input interface in order to identify clock domain crossings in the circuit and to provide a numerical score for each of the identified clock domain crossings.
Owner:VSYNC CIRCUITS
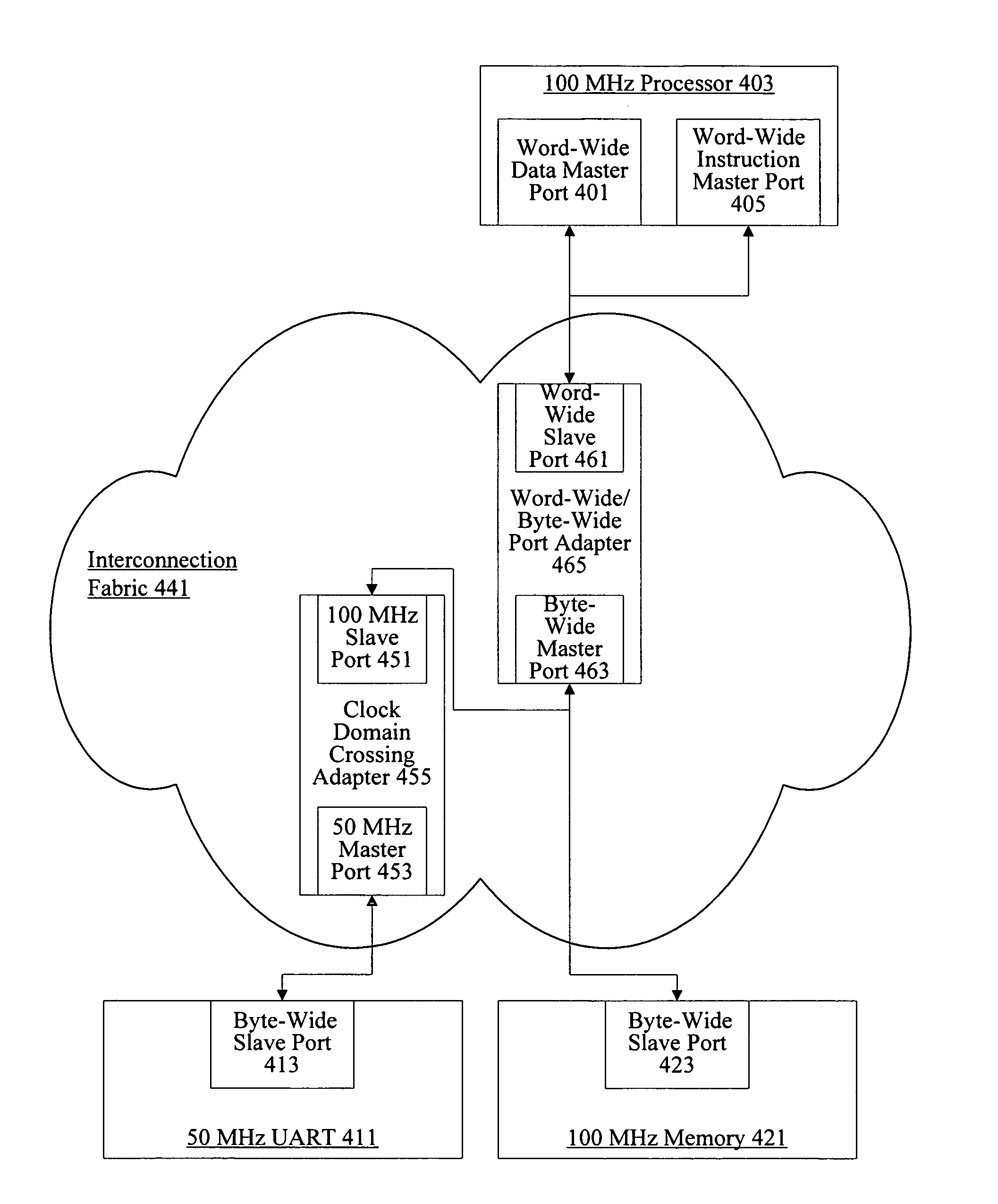
Selection of port adapters for clock crossing boundaries
InactiveUS8286025B1Improve efficiencyEfficient managementCAD circuit designGenerating/distributing signalsTime domainComputer science
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Synchronous memory read data capture
ActiveUS7685393B2Simple and low latencyDigital storageMemory systemsTruth valueLatency (engineering)
A method of snap-shot data training to determine the optimum timing of the DQS enable signal in a single read operation is provided. This is accomplished by first writing a Gray code count sequence into the memory and then reading it back in a single burst. The controller samples the read burst at a fixed interval from the time the command was issued to determine the loop-around delay. A simple truth table lookup determines the optimum DQS enable timing for normal reads. Advantageously, during normal read operations, the first positive edge of the enabled DQS signal is used to sample a counter that is enabled every time a command is issued. If the counter sample changes, indicating timing drift has occurred, the DQS enable signal can be adjusted to compensate for the drift and maintain a position centered in the DQS preamble. This technique can also be applied to a system that uses the iterative approach to determining DQS enable timing on power up. Another embodiment of the invention is a simple, low latency clock domain crossing circuit based on the DQS latched sample of the counter.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
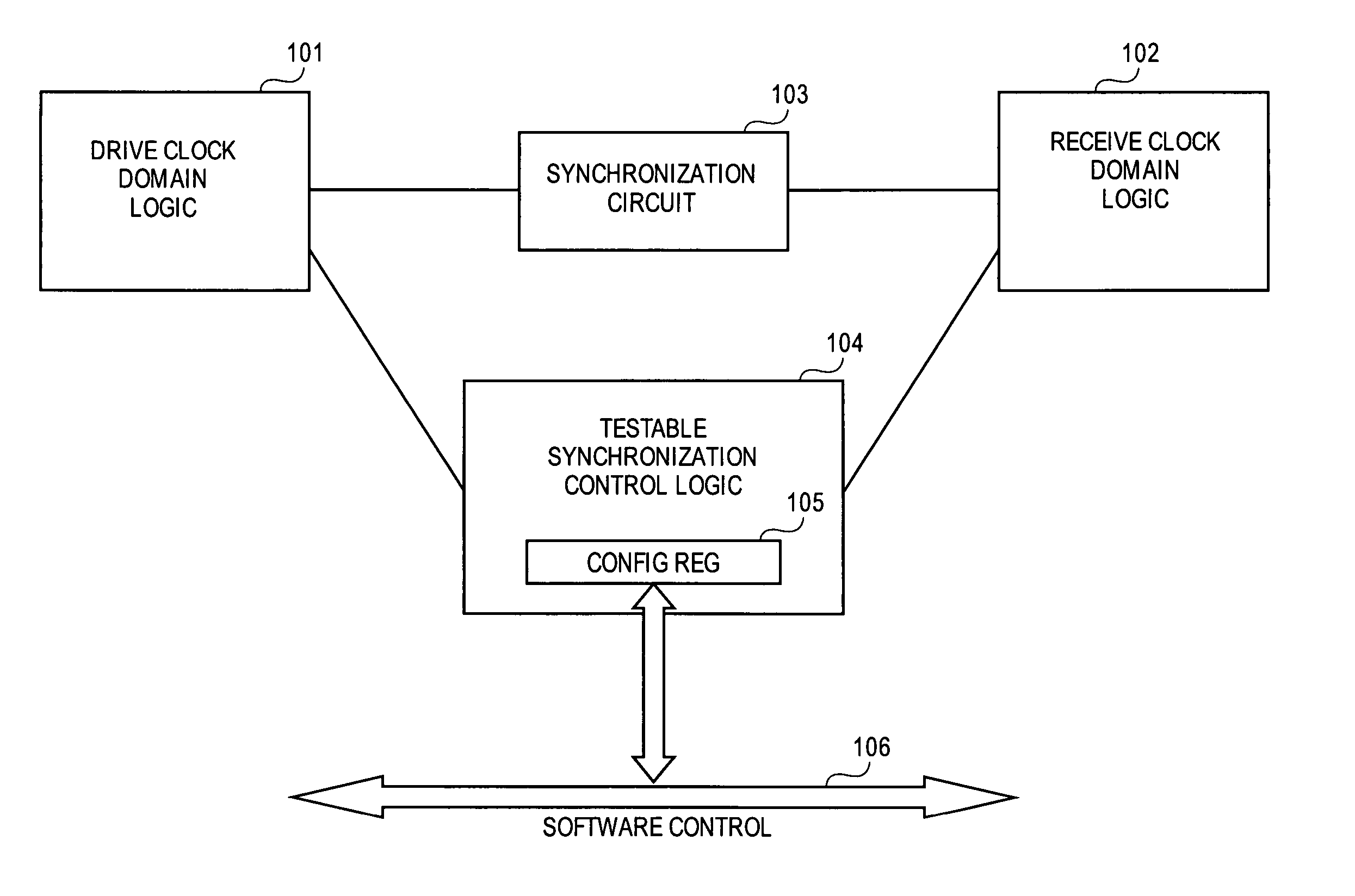
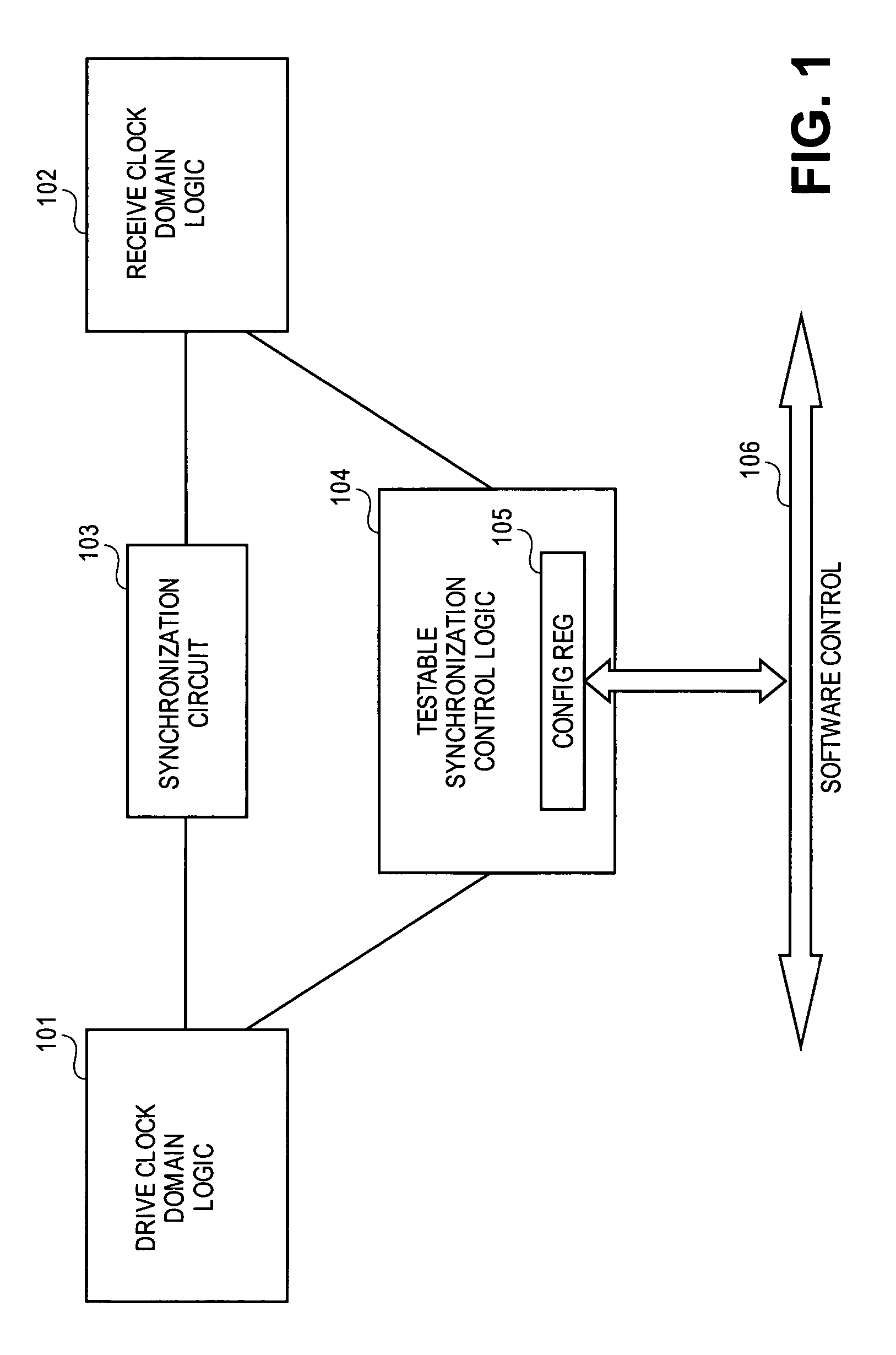
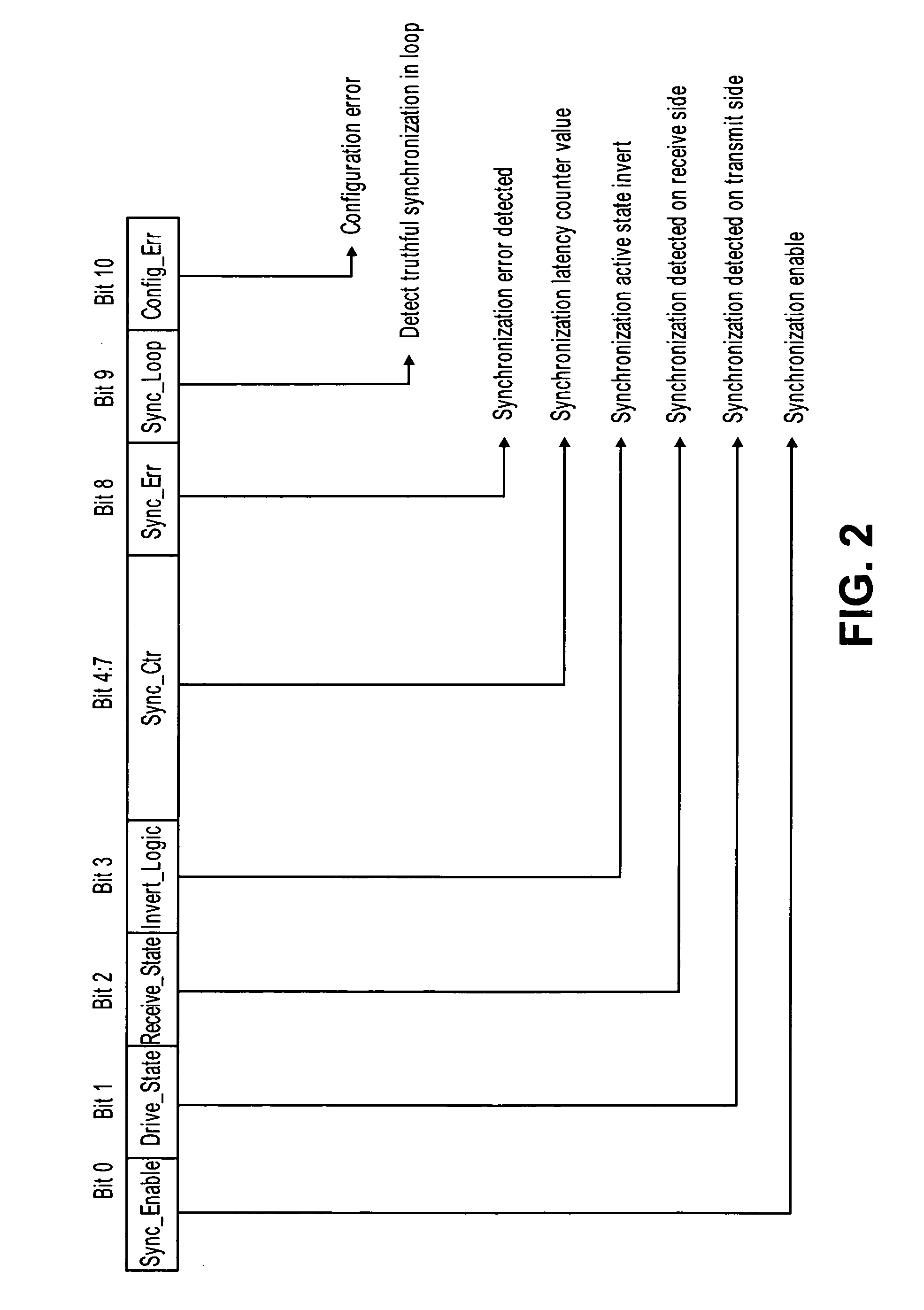
Testable design methodology for clock domain crossing
InactiveUS20070130492A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionComputer scienceDesign methods
A design methodology to debug synchronization of a signal crossing clock domains. A testable synchronization control logic utilizes a programmable register to set parameters to test signals traversing from one clock domain to another clock domain across a synchronization circuit. The register is programmed with a latency value that corresponds to a correct synchronization timing for the clock domain crossing. Other bit entries in the register provide setting of other debug parameters and indications of monitored results.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
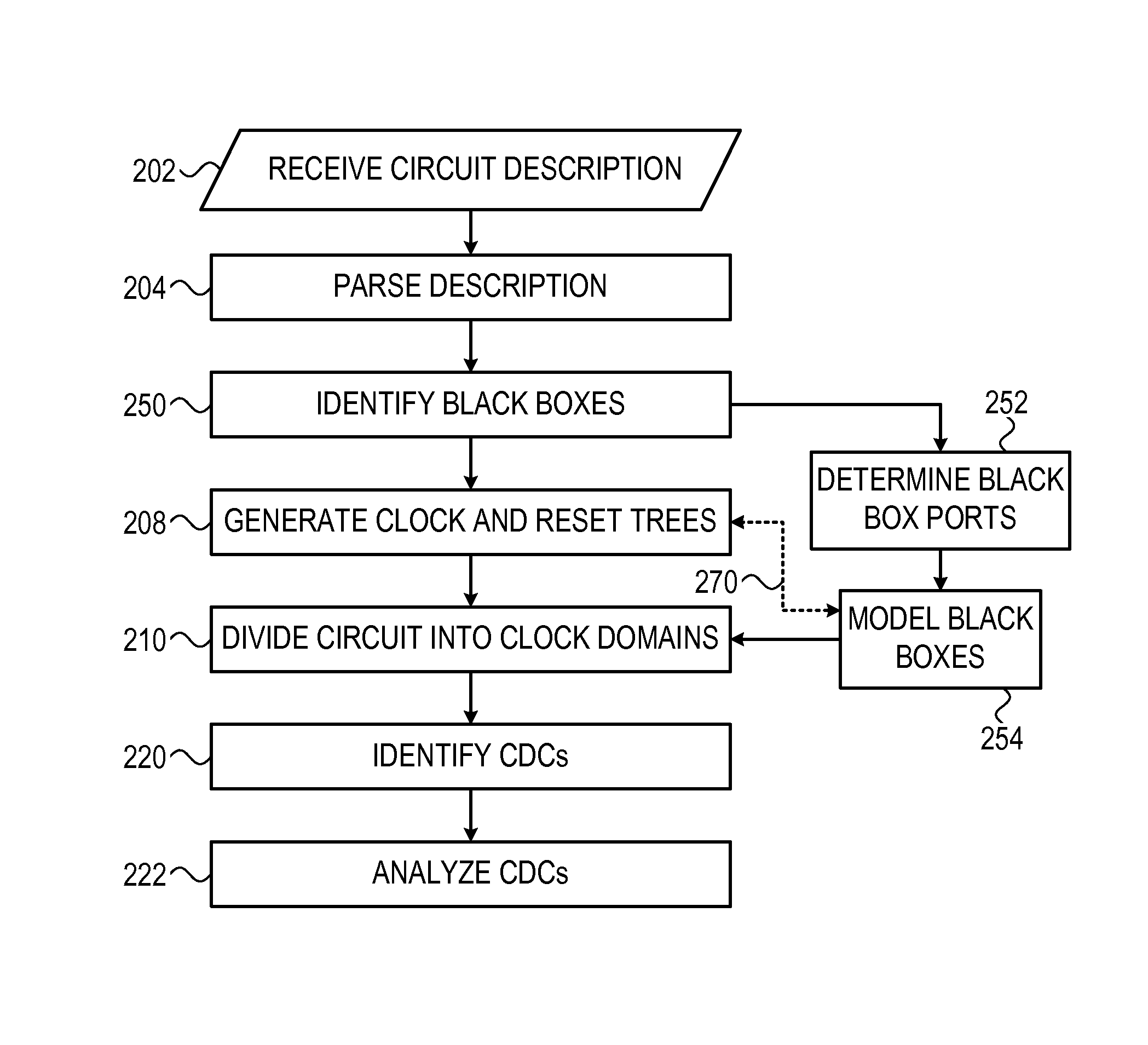
VLSI black-box verification
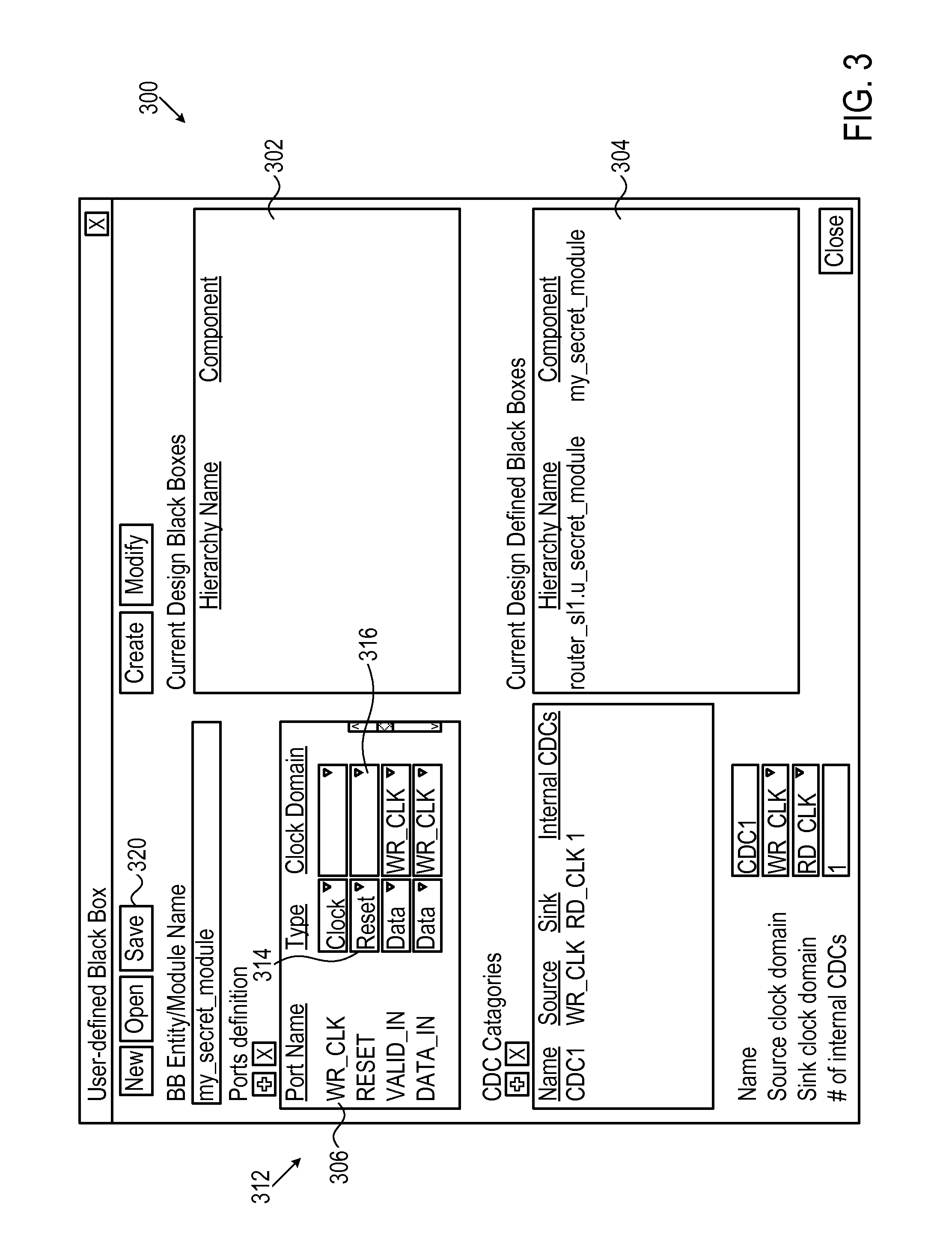
ActiveUS8661383B1Reduced processing resourceElectrical testingComputer aided designComputer scienceIntegrated circuit
A circuit verifier scans through a description of an integrated circuit to identify black-boxes in the description. The verifier assigns the identified black-boxes to clock domains and identifies clock domain crossings, in which a black-box assigned to a first clock domain is connected to an element belonging to a second clock domain. In some cases the verifier identifies signal reconvergence through black-boxes.
Owner:VSYNC CIRCUITS
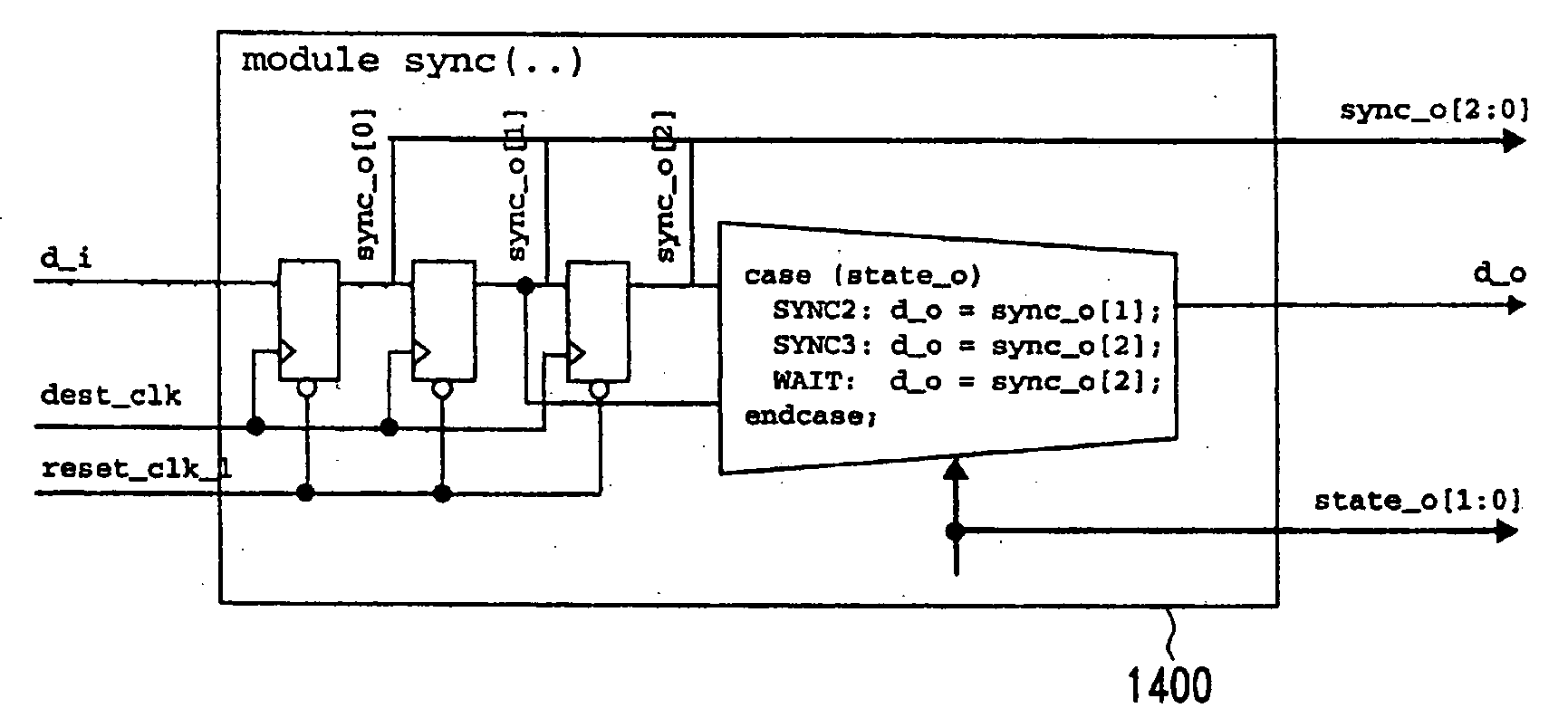
Dynamic synchronizer simulation
InactiveUS20070129923A1Modelling behaviourBetter modelling real-silicon behaviourAnalogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designComputer scienceSilicon
A synchronizer module is provided that may be used to facilitate the simulation of circuitry having clock domain crossing signals. A multiple-stage synchronizer may be used where at least one of the multiple synchronizer stages is dynamically enabled and disabled. The synchronizer module may have a delay unit for selectively applying a variable delay. This may allow for better modelling the real-silicon behaviour for simulation purposes to detect signal synchronization problems earlier in the flow, for instance during RTL (Register Transfer Level) design.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com