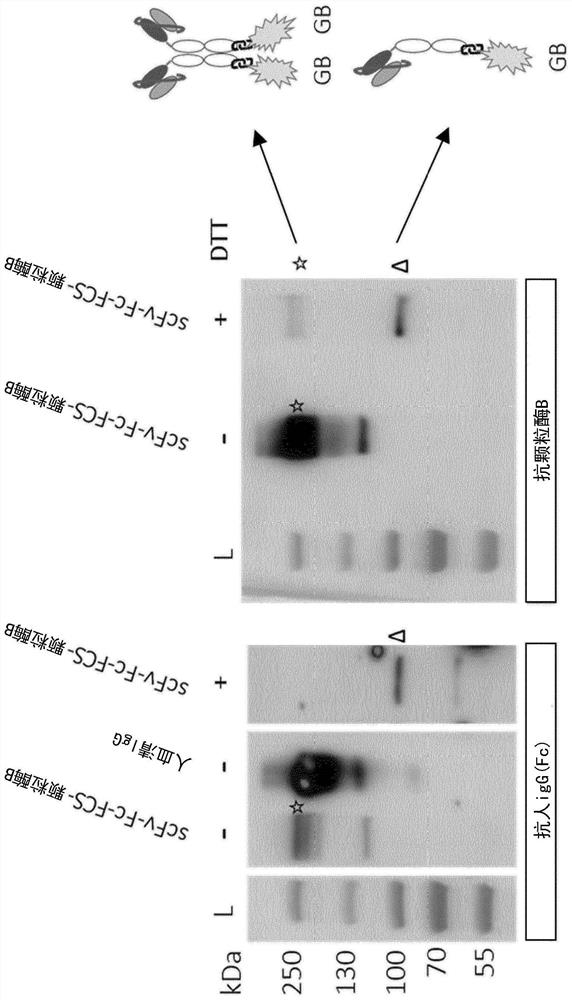
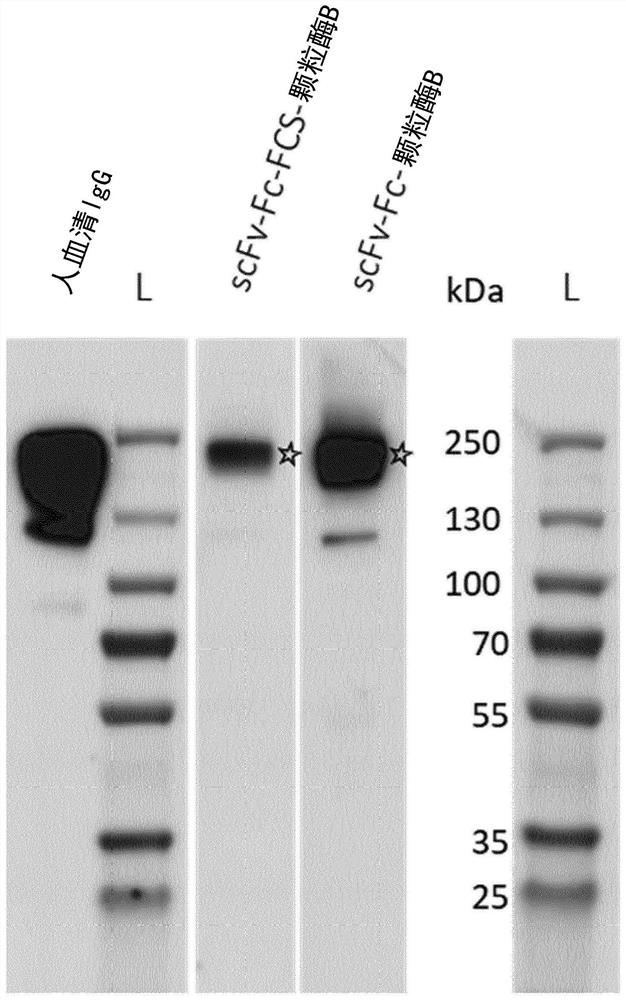
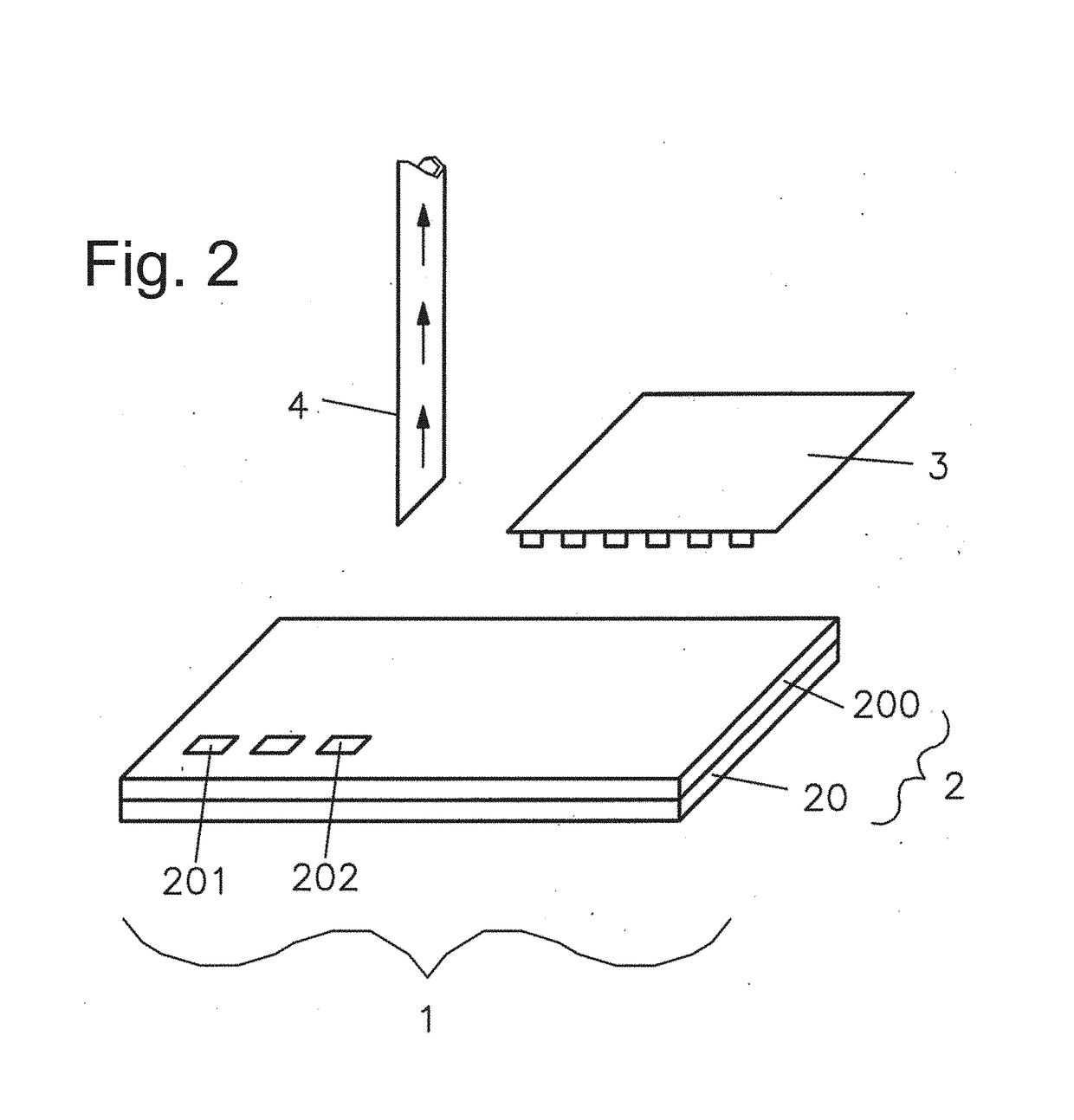
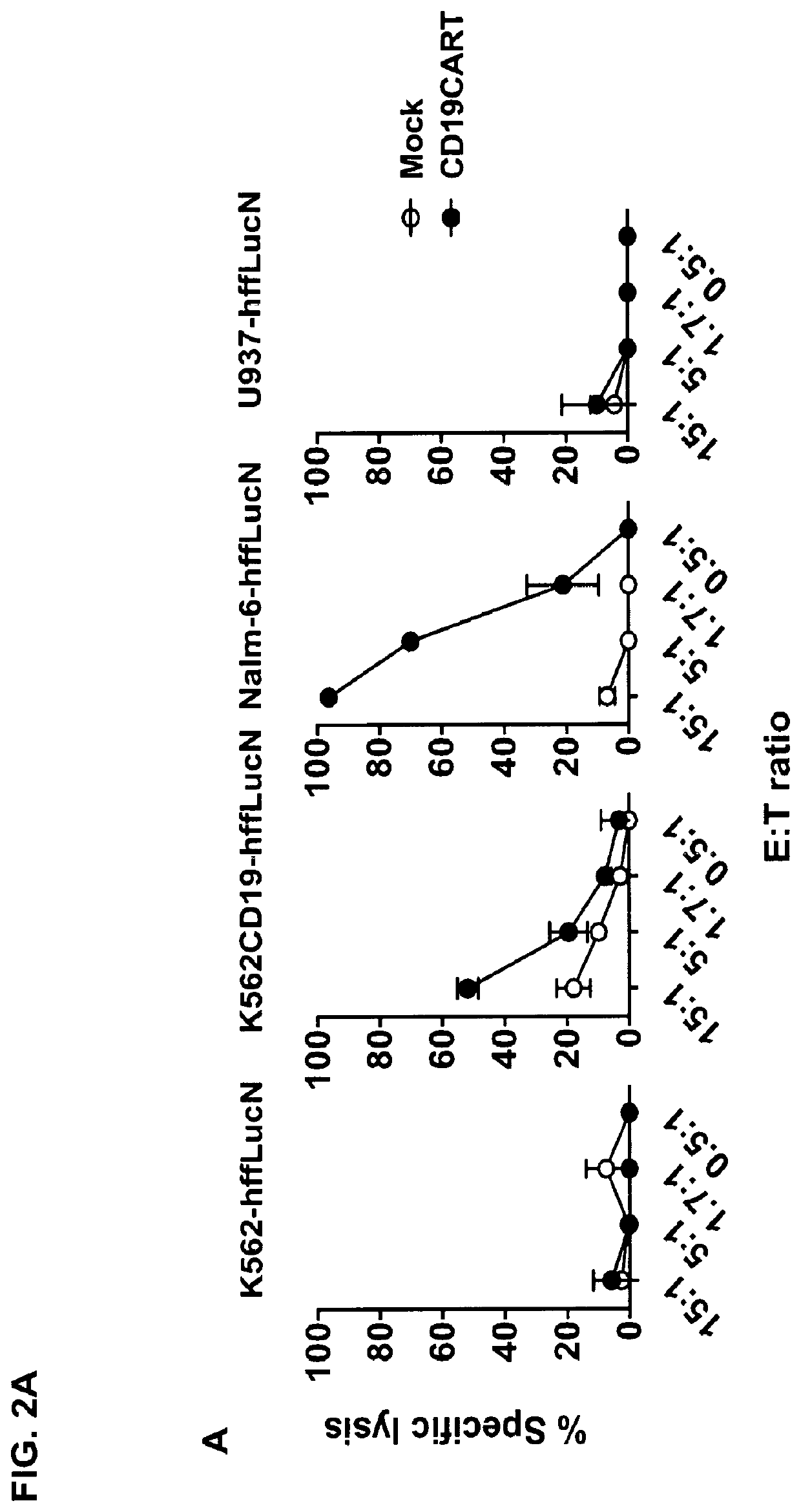
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Antibody mimetic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antibody mimetics are organic compounds that, like antibodies, can specifically bind antigens, but that are not structurally related to antibodies. Nucleic acids and small molecules are sometimes considered antibody mimetics as well, but not artificial antibodies, antibody fragments and fusion proteins composed from these.
Fibronectin ed-b antibodies, conjugates thereof, and methods of use
InactiveUS20090162372A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntibody conjugateAntibody fragments
The present invention provides anti-ED-B antibodies, antibody fragments, and antibody mimetics and such antibodies conjugated to a partner molecule, wherein the antibody or the antibody-partner molecule conjugate provides a therapeutic effect regardless of whether the ED-B-antibody or ED-B-conjugate complex is internalized within a targeted cell.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
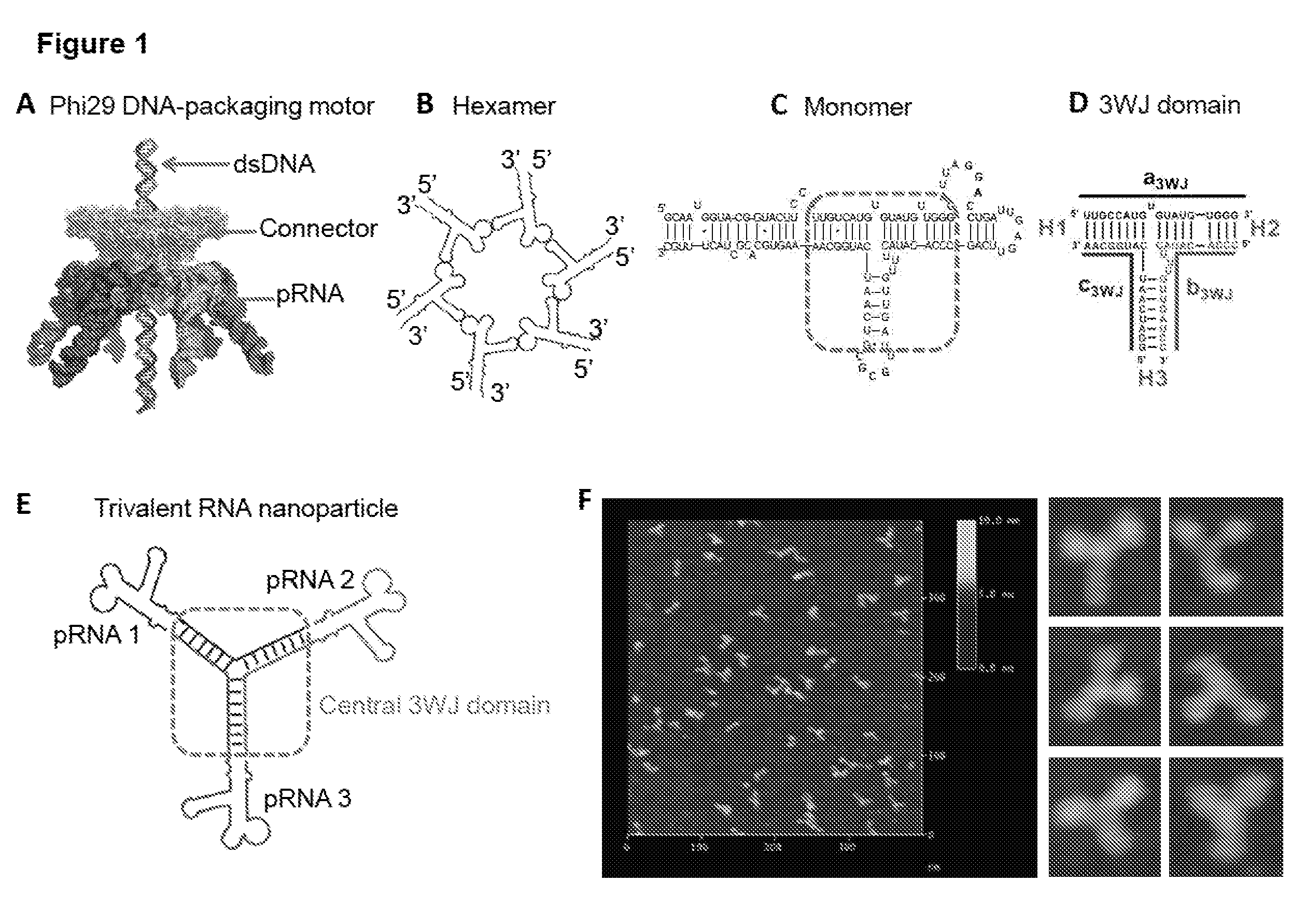
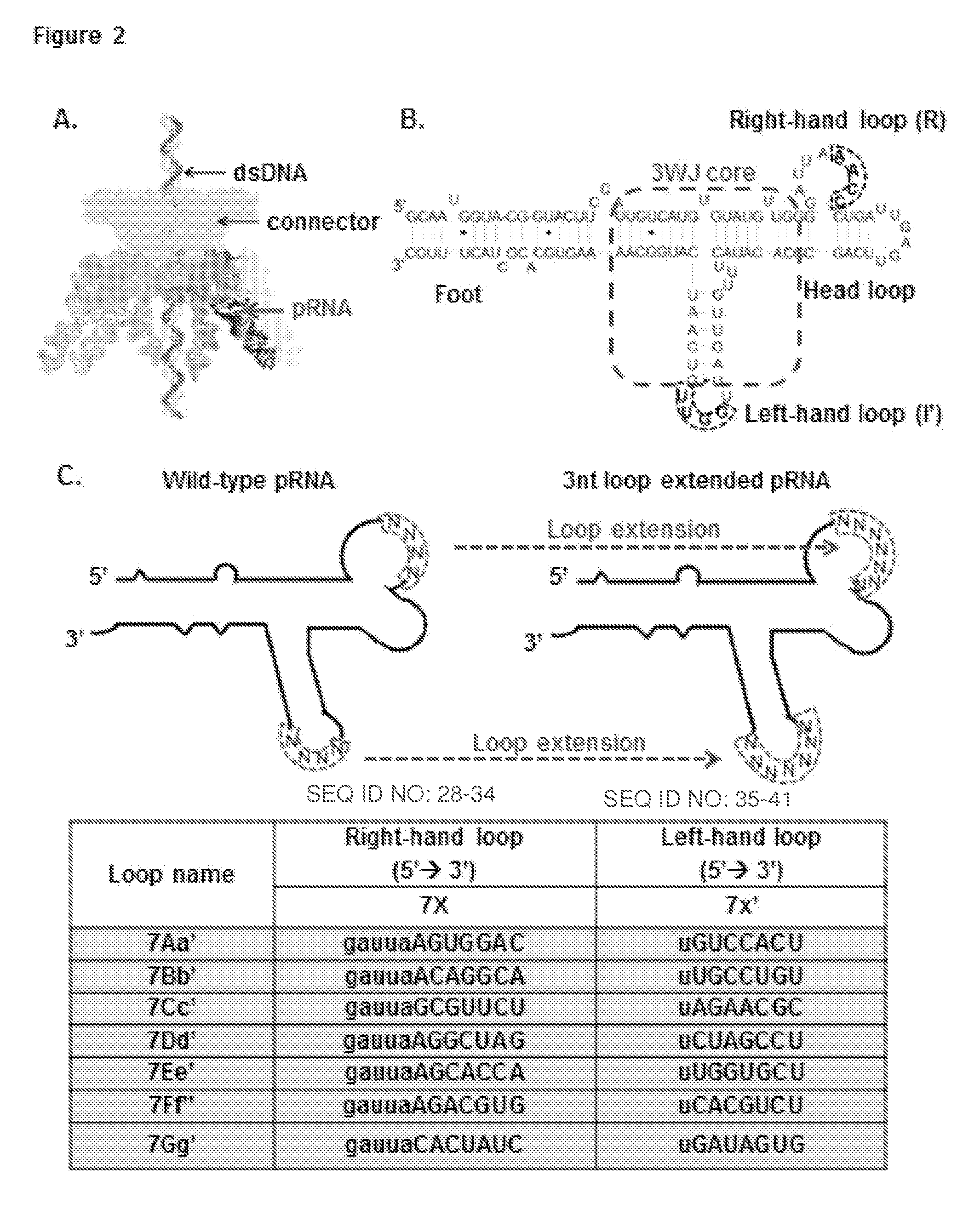
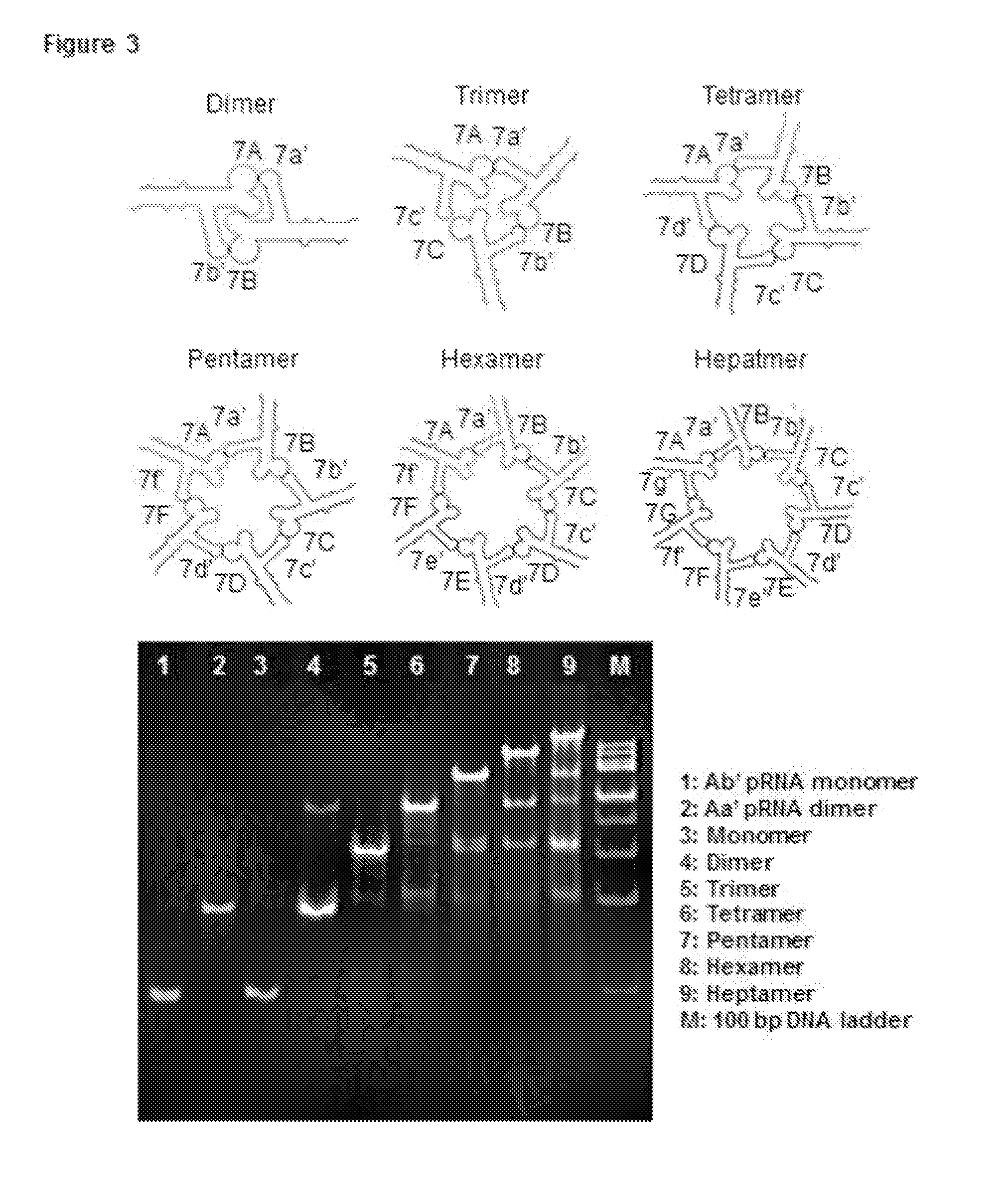
pRNA multivalent junction domain for use in stable multivalent RNA nanoparticles
Trifurcate RNA junction domains derived from phi29 pRNA are described that assemble with high affinity and that are stable in vitro and in vivo. Further expansion of trifurcated RNA domains to multiple way junction scaffolds via creative designs enable an array of toolkit to construct nanoparticle architectures with diverse shapes and angles. The scaffolds can be used to form RNA nanoparticles having a wide variety of uses, including promotion of RNA crystallization, creation of RNA aptamer with high affinity to mimic antibody, delivery of therapeutic and / or diagnostic agents such as biologically active RNA-based moieties, including siRNA, ribozymes, aptamers, and others.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
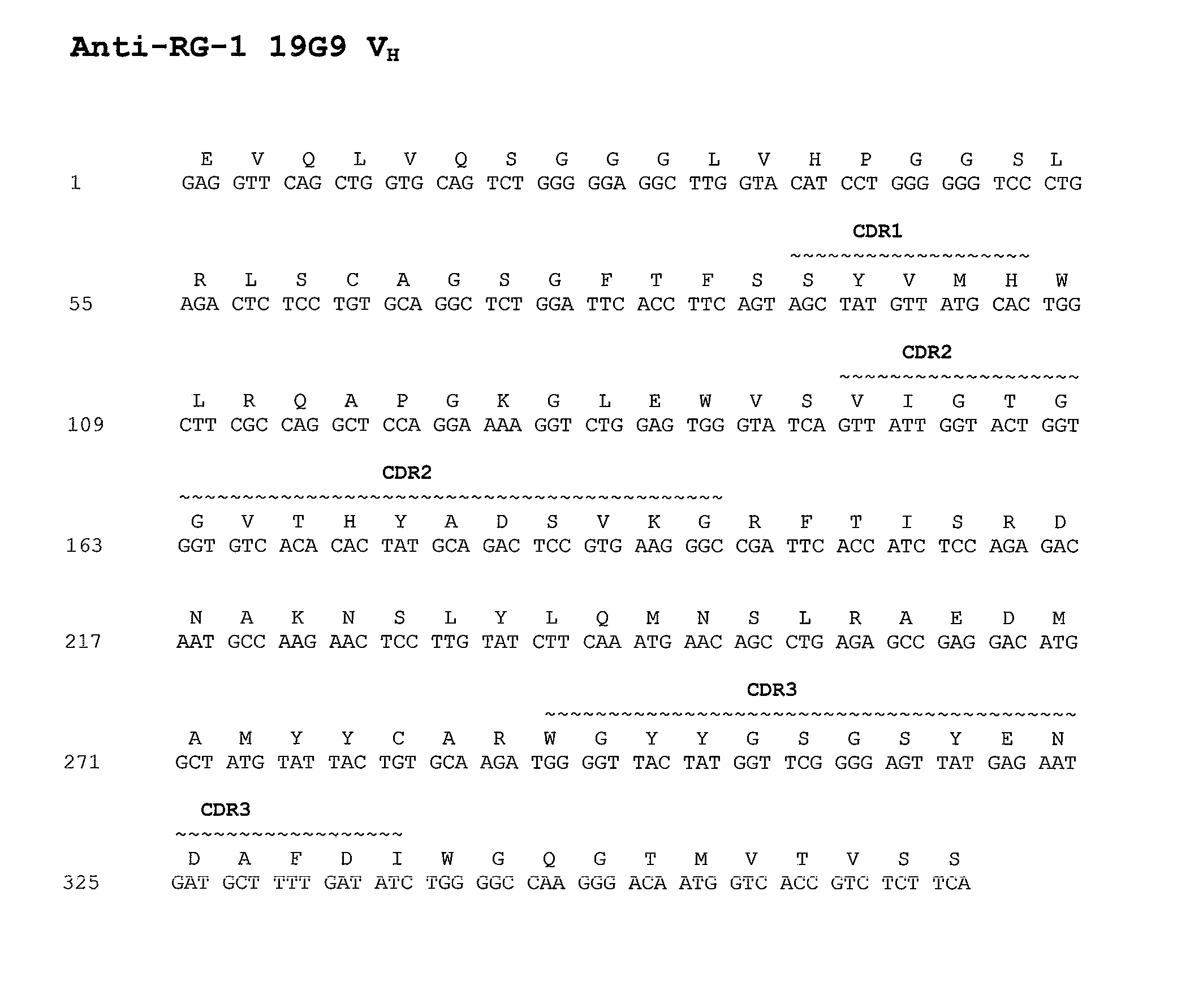
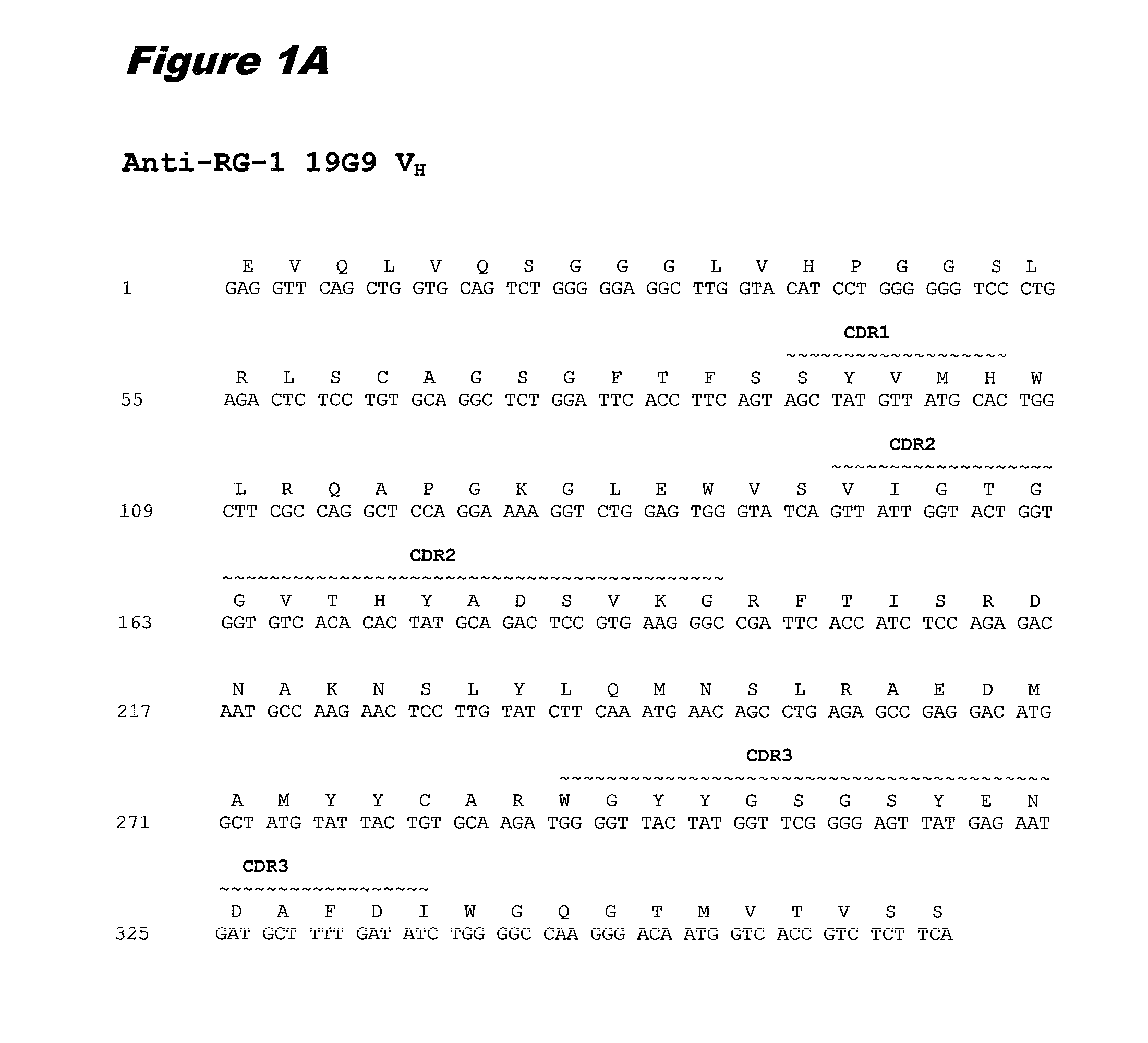
Conjugates of Anti-rg-1 antibodies
InactiveUS20110020329A1High affinityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntibody fragmentsAntibody mimetic
Anti-RG-1 antibodies, antibody fragments, or antibody mimetics conjugated to partner molecules, such as drugs, radioisotopes, and cytotoxins, wherein the partner molecule exerts its effect regardless of whether the RG-1 bound conjugate is internalized within a targeted cell, are useful for treating cancers.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
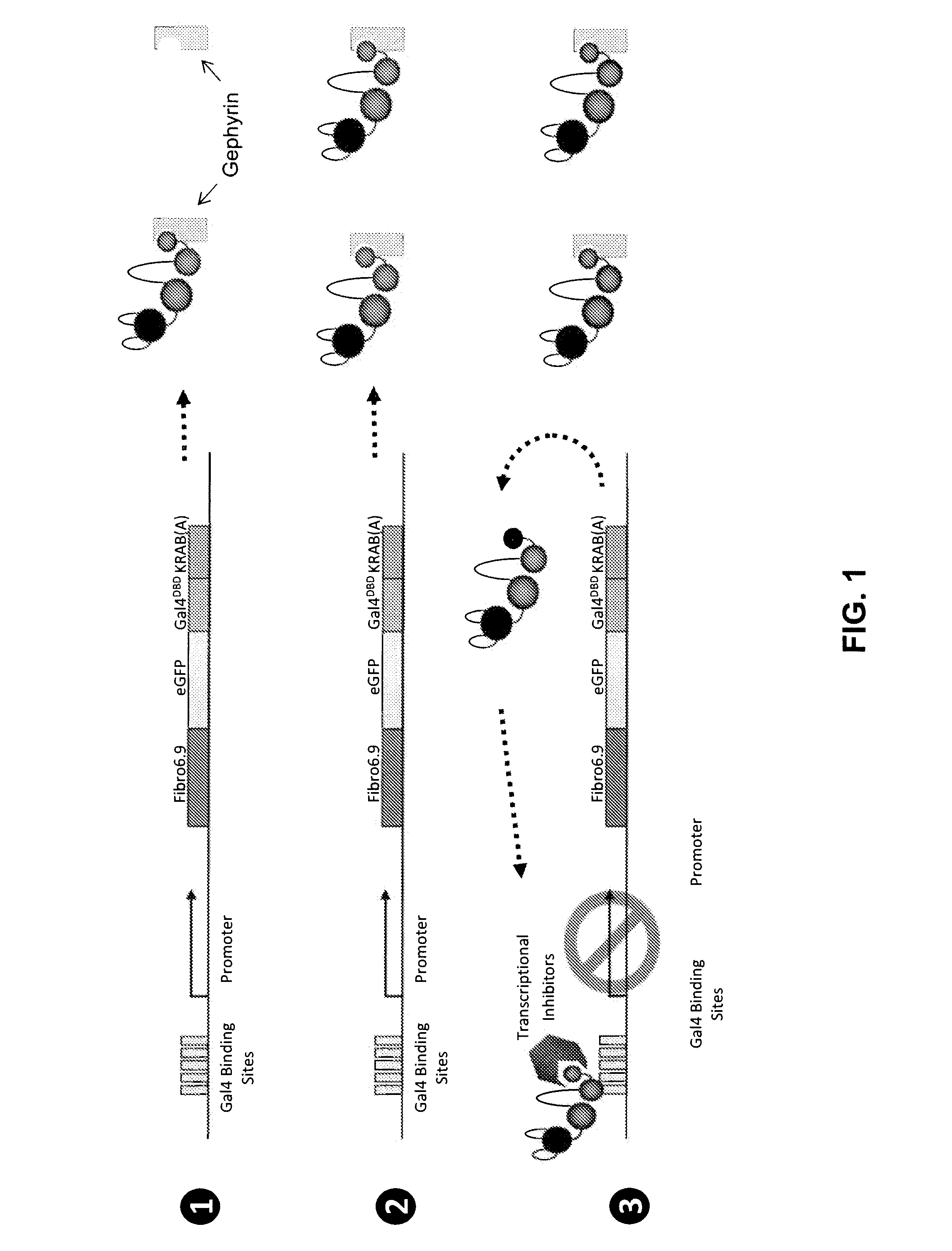
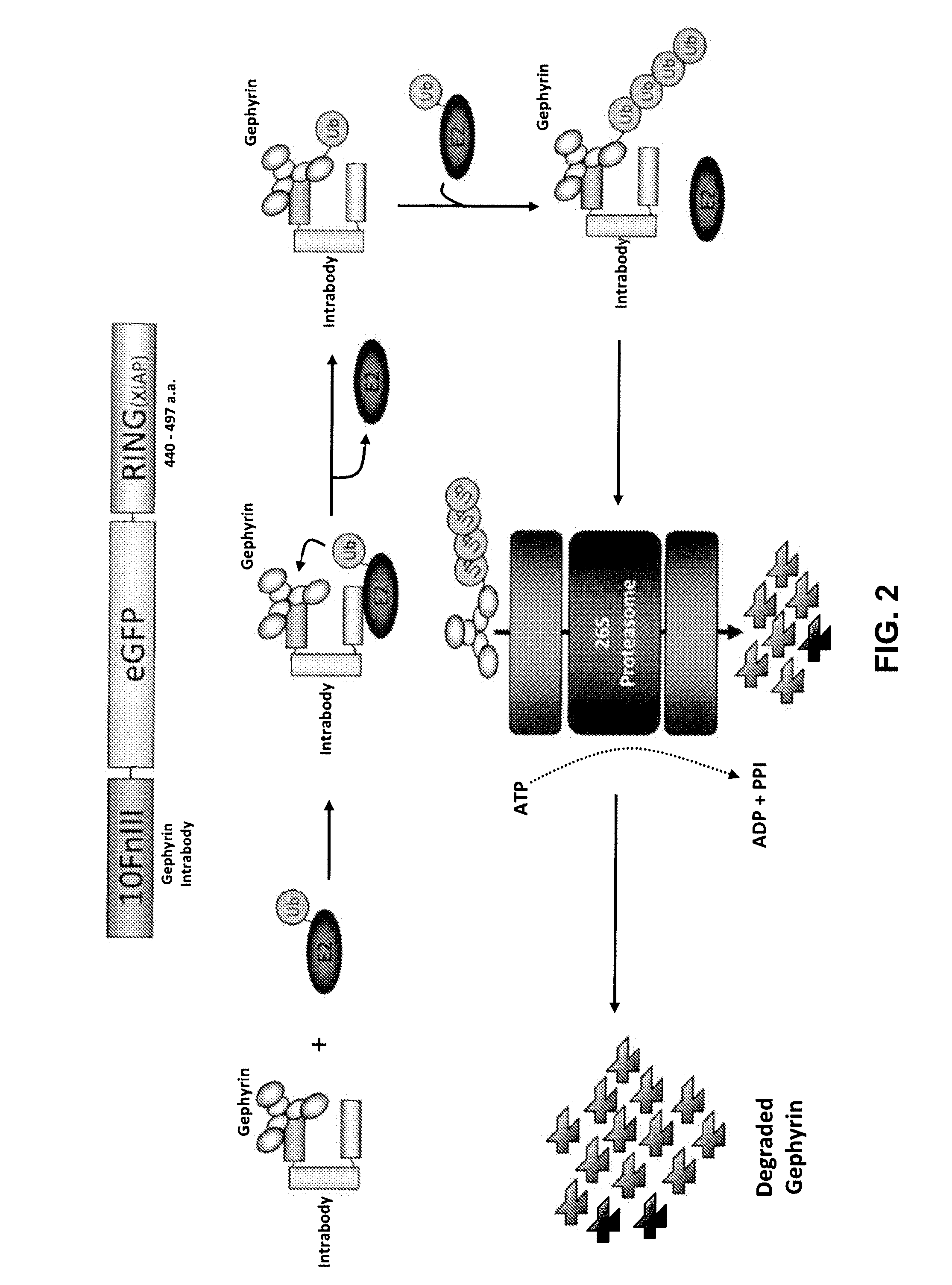
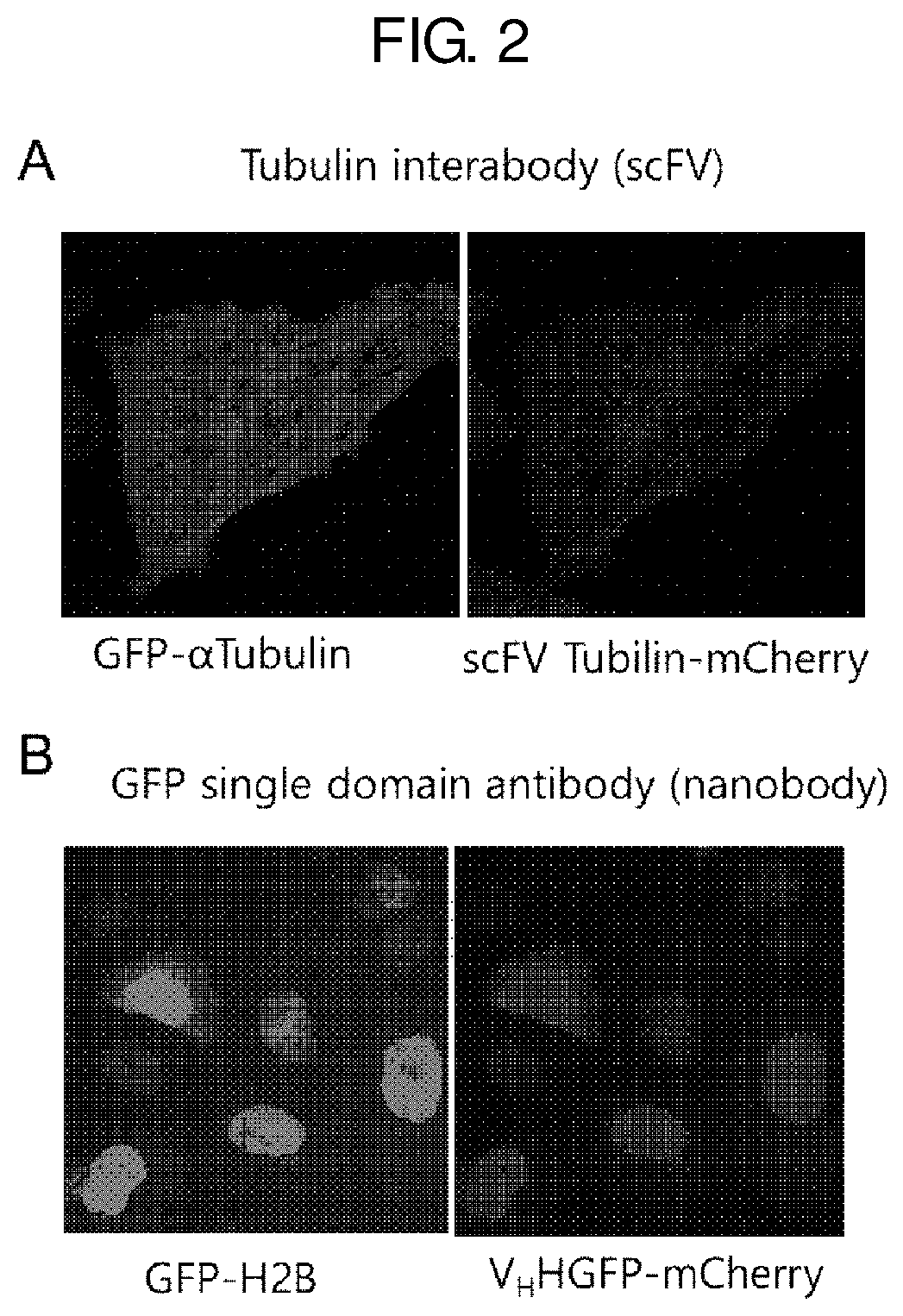
Antibody and antibody mimetic for visualization and ablation of endogenous proteins
ActiveUS20140287426A1Remove background noiseEfficient identificationFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenProtein target
Provided are compositions and methods for labeling an endogenous protein, in particular, in a live cell, or for ablating an endogenous or target protein. The compositions relate to a fusion protein having a binding moiety such as an antibody, an antigen binding fragment of an antibody or an antibody mimetic that recognizes the endogenous or target protein.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Novel polypeptide for resisting tumors caused by EB (Epstein-Barr) viruses, and application and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102101888ALow immunogenicityImprove securityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibody mimetic
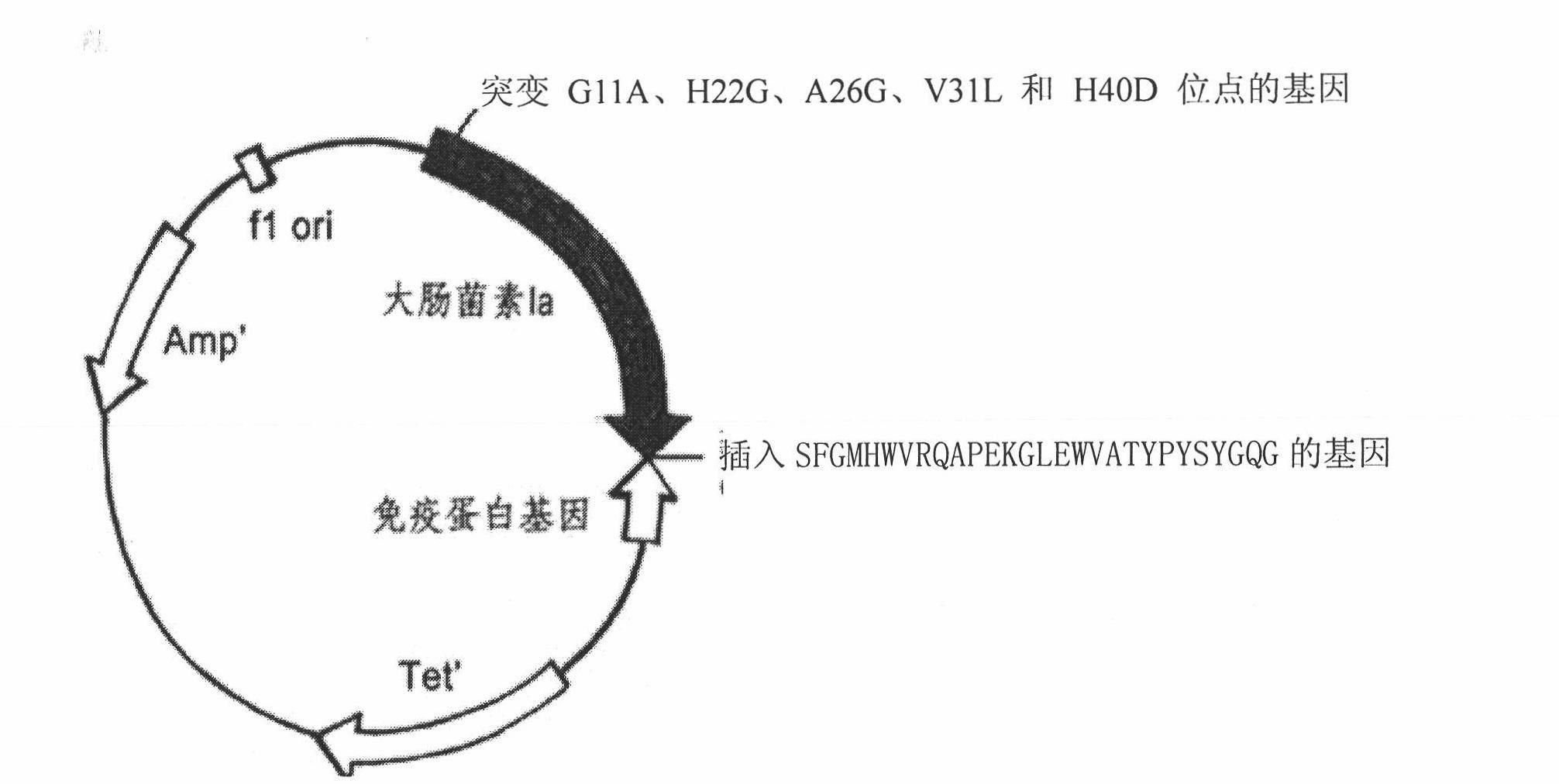
The invention relates to a novel polypeptide for resisting tumors caused by EB (Epstein-Barr) viruses, and application and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of antineoplastic medicaments. The novel polypeptide is composed of a colicine allosteric polypeptide capable of forming ion channels, and an antibody polypeptide for resisting EB viruses or a mimic antibody polypeptide ofan anti-EB virus antibody, wherein the colicine allosteric polypeptide capable of forming ion channels is formed by mutating amino acid residues G11A, H22G, A26G, V31L and H40D with wild type colicine E1, Ia, Ib, A, B and N or a peptide chain of aqueous pore canal domain thereof; and the amino acid sequence of the anti-EB virus antibody is identical to that of a monoclonal antibody secreted by ATCC HB-168 hybridoma. The invention provides an improved medicament, which has the advantages of strong lethality, high safety, high specificity and low sensitization possibility, for treating tumors caused by EB viruses, and a preparation method thereof.
Owner:AMERICAN PHEROMYCIN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO
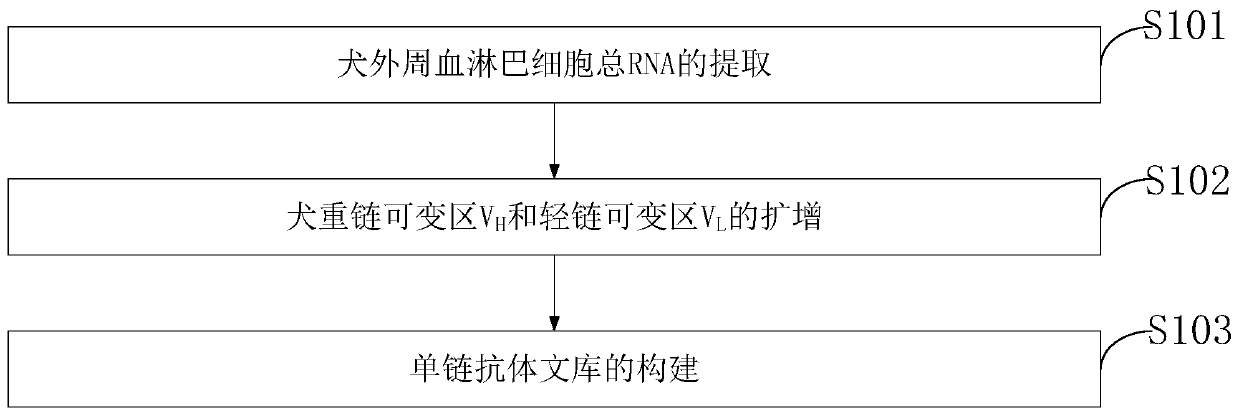
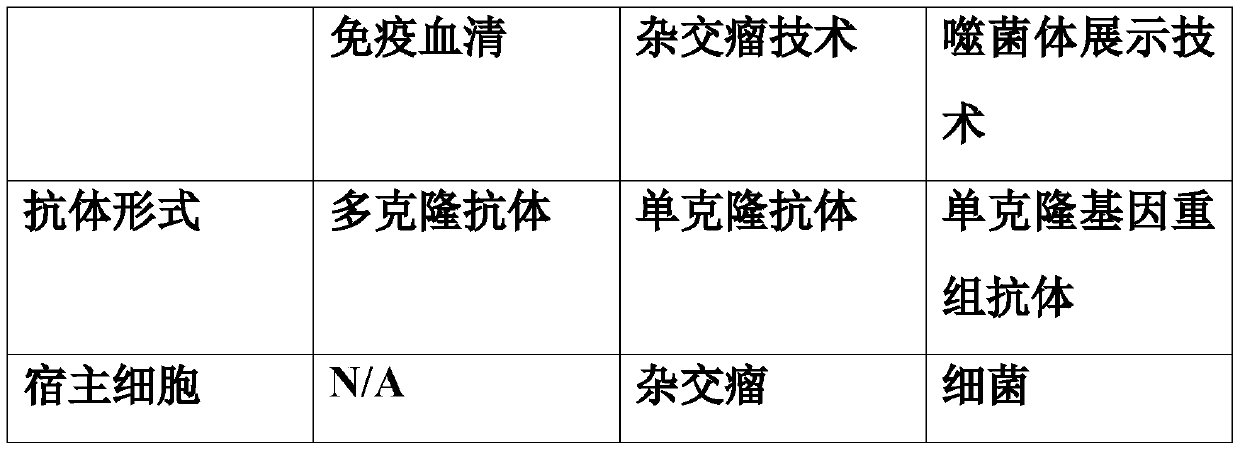
Canine-derived anti-canine parvovirus antibody, antibody library and construction method thereof
ActiveCN110964103ARapid productionSimple and fast operationPeptide librariesImmunoglobulins against virusesNucleotideAntibody mimetic
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and discloses a canine-derived anti-canine parvovirus antibody, an antibody library and a construction method thereof. The canine-derived anti-canine parvovirus antibody is a heavy chain variable region with an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 or a light chain variable region with an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2. The nucleotide sequence of DNA molecule of the heavy chain variable region is SEQ ID NO: 3. The nucleotide sequence of DNA molecule of the light chain variable region is SEQ ID NO: 4. Compared with a monoclonal antibody produced by immune animals, the phage display technology of the invention has the advantages of fast production, simple operation and higher efficiency, can be adopted to produce canine-derived antibodies, and has higher utilization value. According to the invention, by constructing the phage display antibody library, the process of antibody generation can be simulated in vitro, andantibodies against any antigen can be screened.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
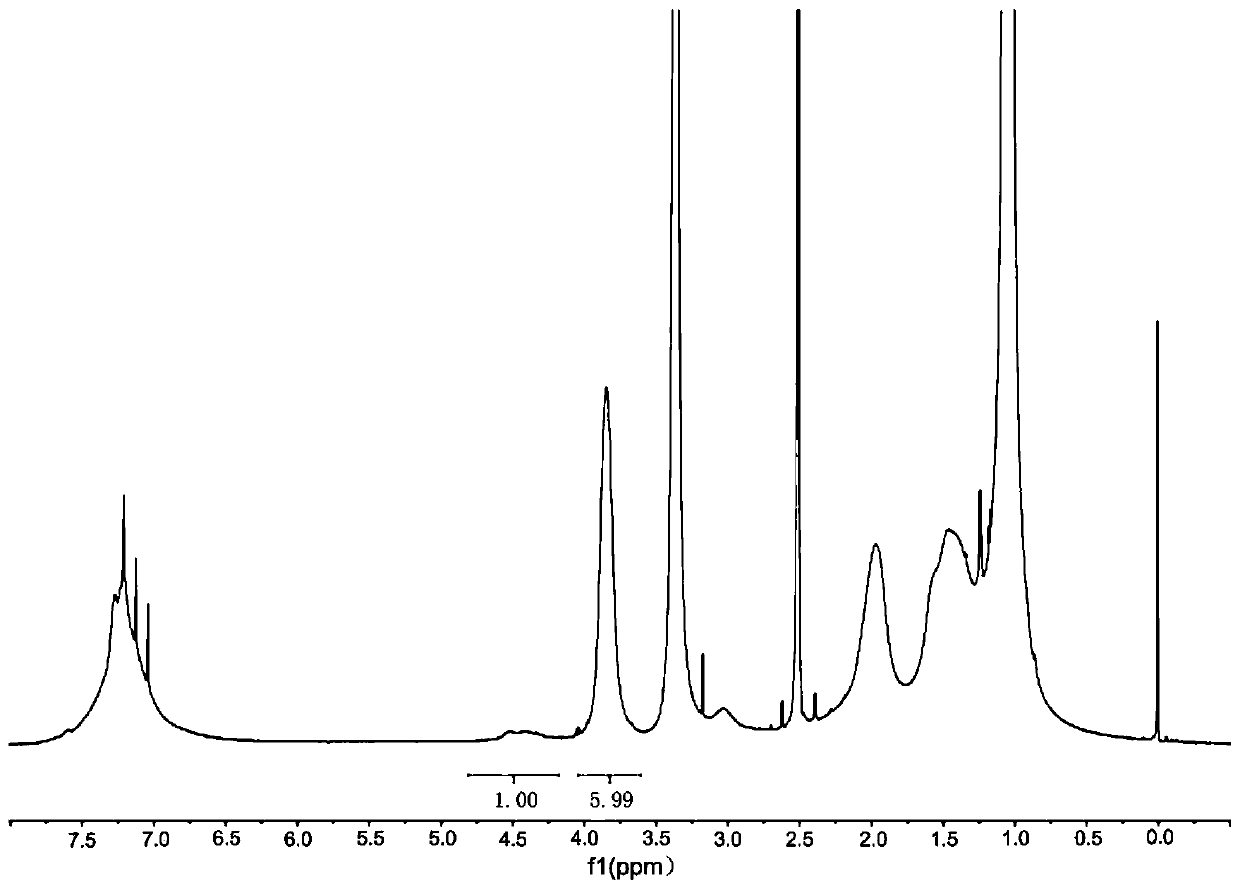
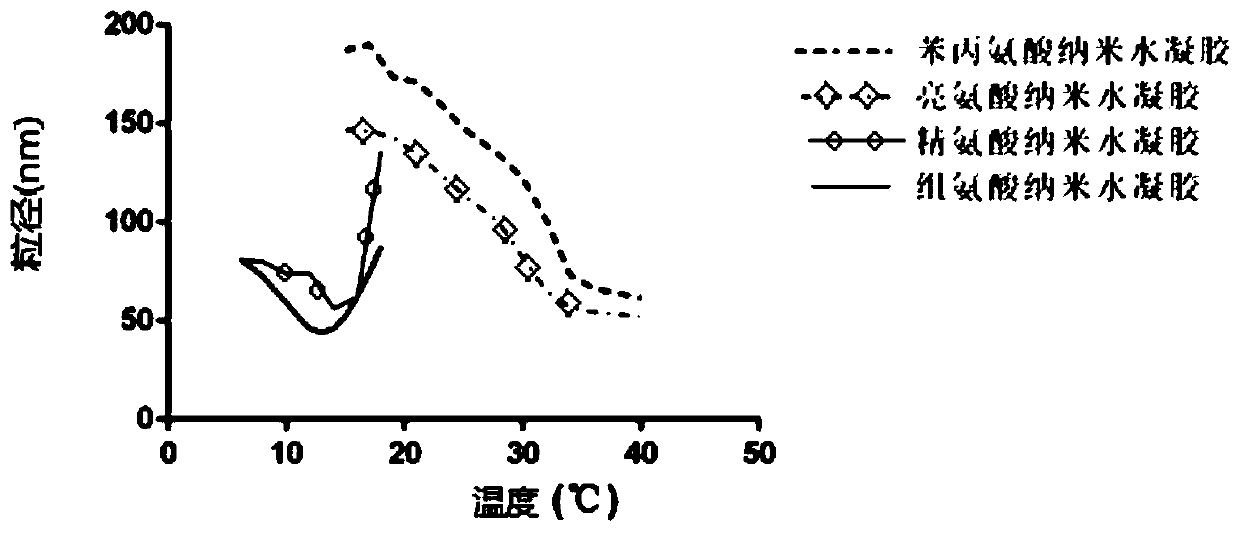
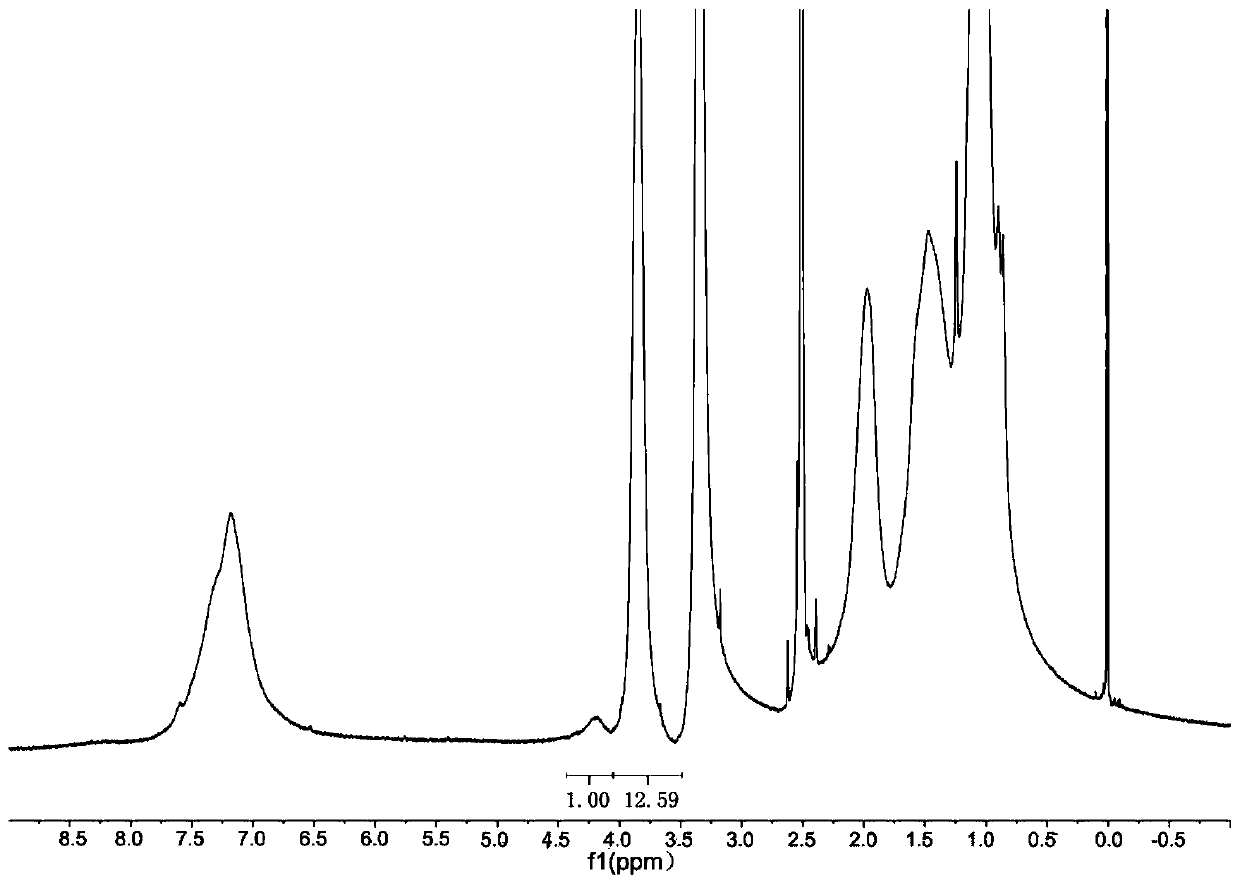
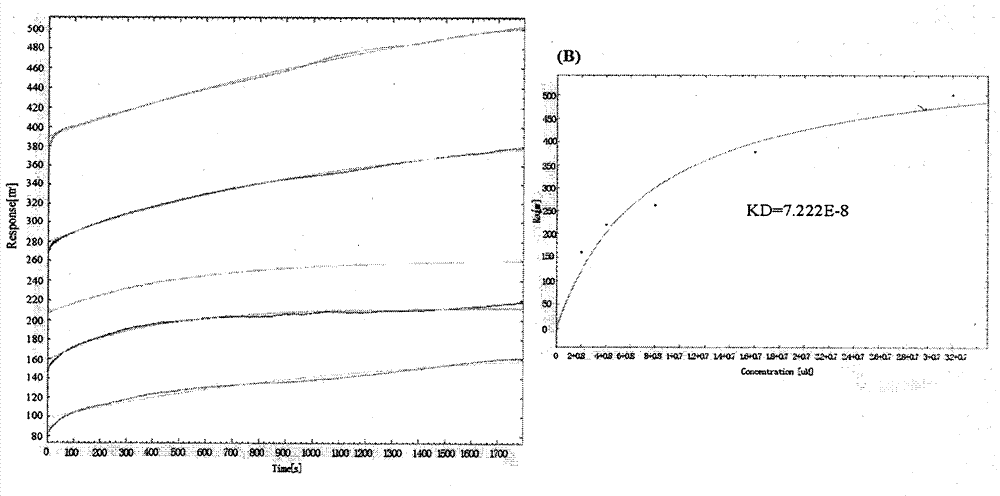
Amino acid nano hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110684150AStrong specificityImprove performanceSerum albuminPeptide preparation methodsPolymer scienceAmino acid side chain
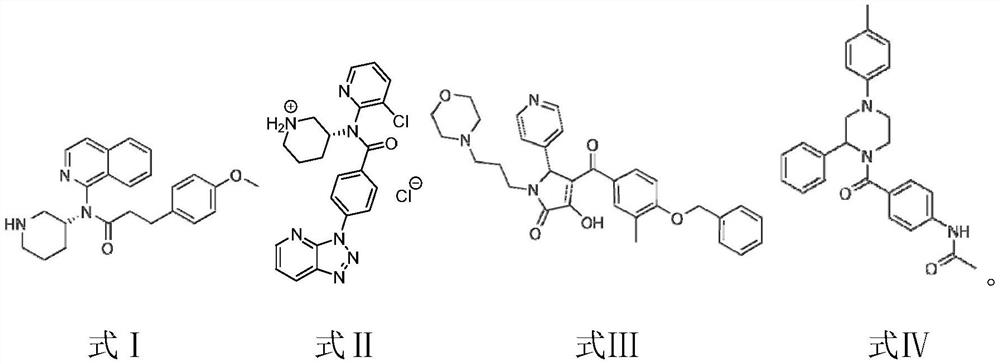
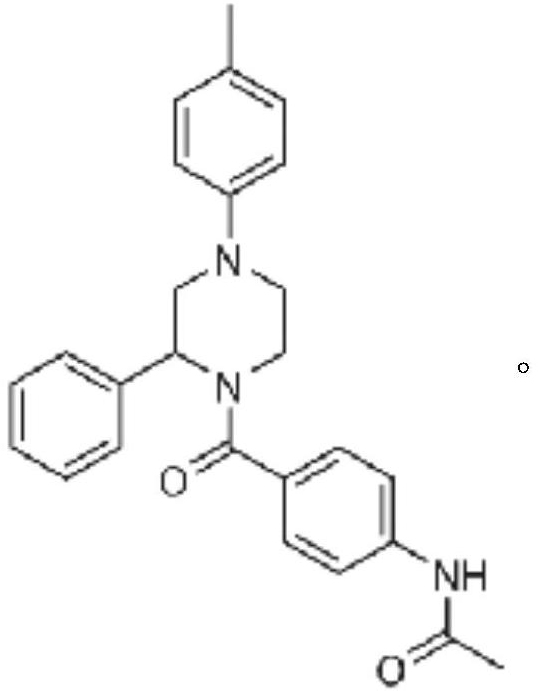
The invention discloses an amino acid nano hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid nano hydrogel has an amino acid side chain, has interactions similar to natural protein-natural protein with protein, has specific recognition capabilities for human serum protein and biomarkers such as beta-amyloid protein, brain natriuretic peptide and a gastrin release peptide precursor, and can be adopted to adsorb a target protein. The amino acid nano hydrogel is capable of improving the recognition capability of a polymer, is simple in preparation method, mild in reaction condition, has a temperature response property, and has the potential of being developed into an artificial simulated antibody or protein purification high polymer material with stable properties. The amino acid nano hydrogel is a polymer A or a polymer B, wherein the polymer A consists of segments of a formula (I), a formula (II) and a formula (III) shown in the description; and the polymer B consists of segments of a formula (IV), a formula (II), a formula (V) and a formula (III) shown in the description.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Screening method for paraquat simulation antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN104513316AAffect specific recognitionAffect spatial conformationImmunoglobulinsBiological testingLipocalinAntibody screens
Belonging to the field of biotechnologies, the invention relates to a screening method for a paraquat simulation antibody and application thereof. The simulation antibody is screened out from a ribosome display Lipocalin simulation antibody library and is subjected to soluble functional expression. The invention also relates to a method of screening the paraquat simulation antibody by a ribosome display technology. The paraquat simulation antibody screened out in the invention can be used for paraquat residual monitoring and development of a kit for rapid detection of pesticide paraquat residual.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
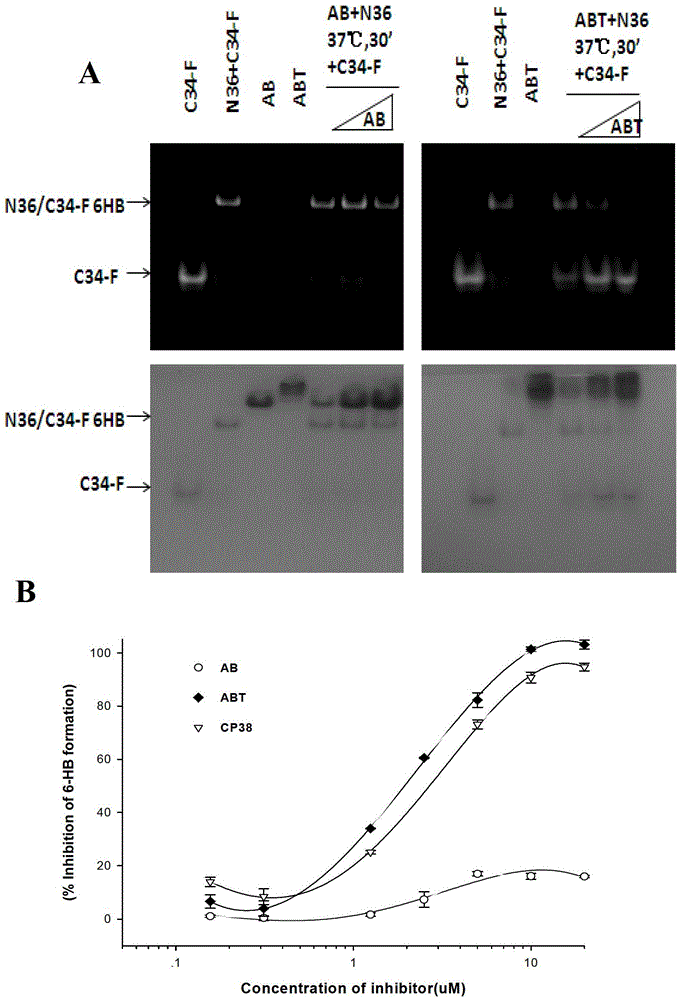
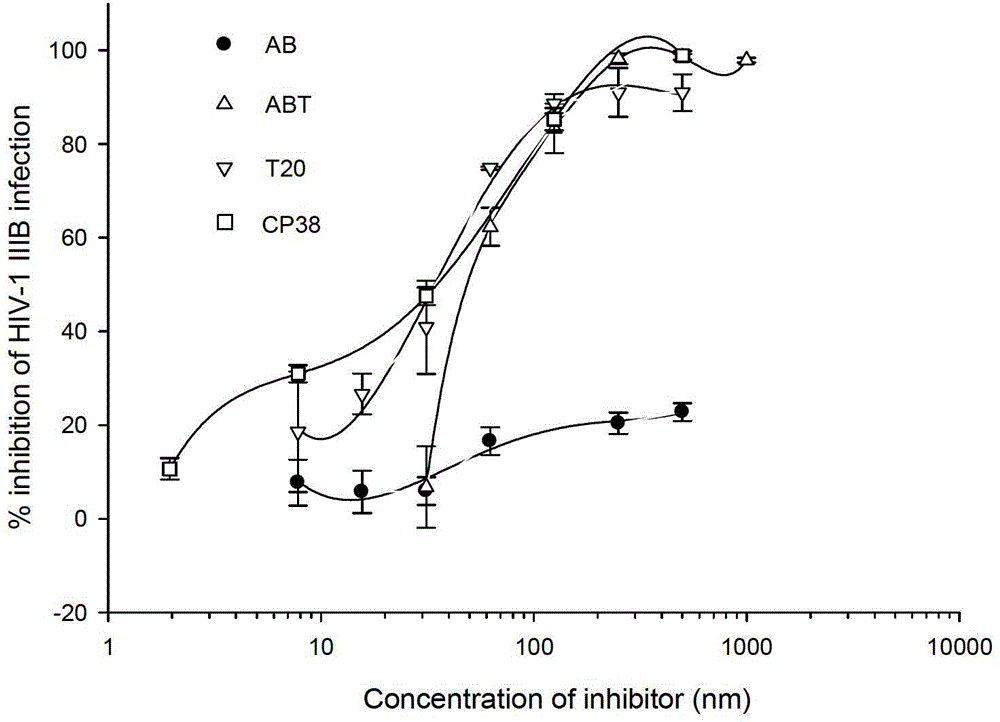
Long-acting HIV-1 membrane fusion inhibitor
ActiveCN103755810ABiological effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The invention relates to a polymer for long-acting inhibition of HIV-1 membrane fusion. The polymer for long-acting inhibition of HIV-1 membrane fusion comprises two or three parts. The first part is a HIV-1 membrane fusion-inhibition polypeptide part and the second part is an antibody mimetic part capable of bonding with serum albumin thereby prolonging a half life of the polymer in vivo. A connection molecule can be arranged between the above two parts and improve HIV-1 inhibition activity of the polymer. The polymer can block virus-induced cell fusion in vivo for a long time.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Carbohydrate binding module and use thereof
InactiveCN103097411AMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesEpitopeCarbohydrate-binding protein
The present invention provides a method of inhibiting HIV infection of a subject, comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of an antibody mimetic of carbohydrate binding module (CBM) which specifically binds to an epitope on HIV glycoprotein. The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of an antibody mimetic of carbohydrate binding module and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides a method of inhibiting HIV infection of the subject preventionally or therapically comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of an antibody mimetic of carbohydrate binding module (CBM) which specifically binds to an epitope on HIV glycoprotein
Owner:张大慈
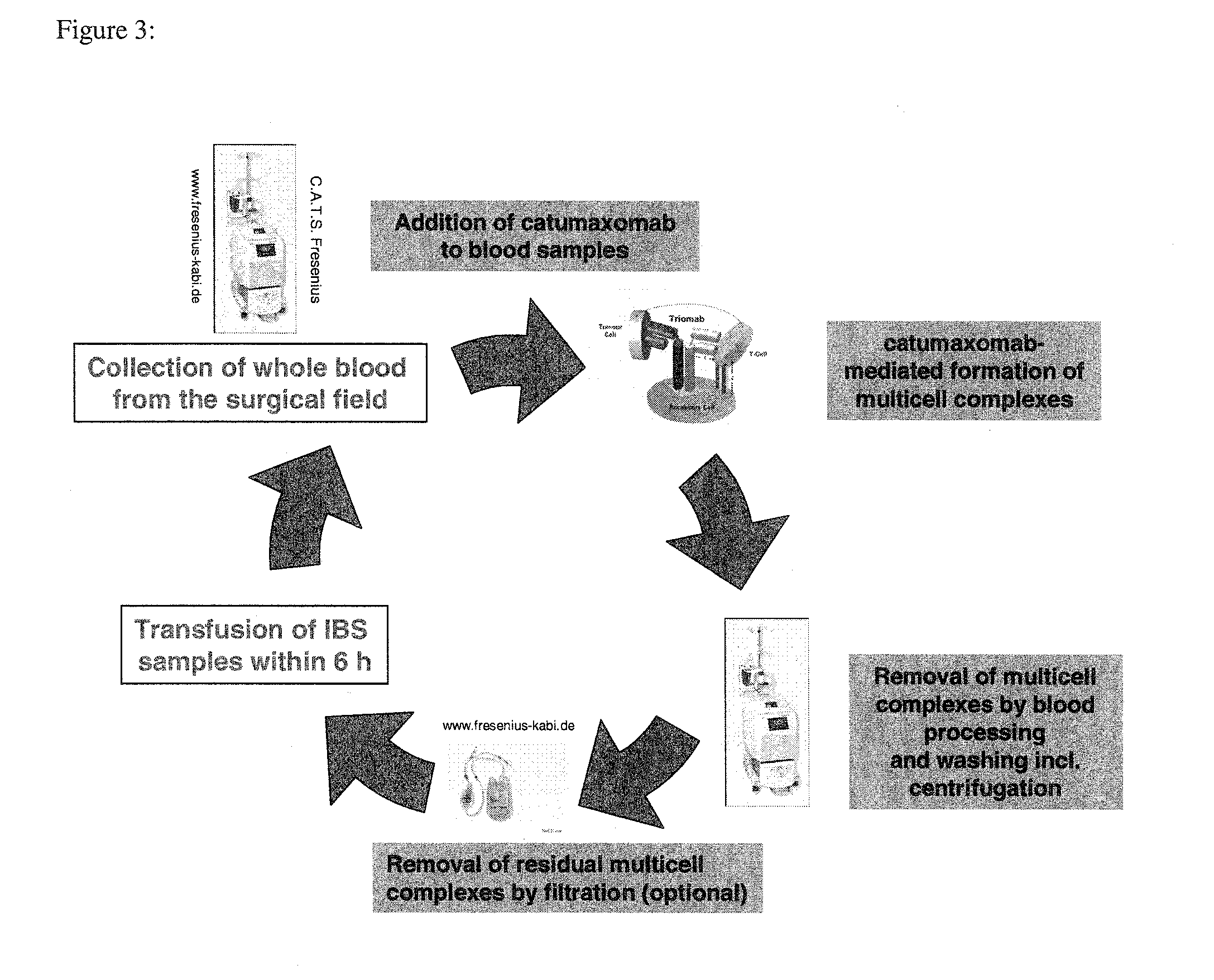
Removal of tumor cells from intraoperative autologous blood salvage
The invention relates to a method performed ex vivo for removal of tumor cells from intraoperatively collected blood salvage, to antibodies and scaffold proteins which mimic antibodies for use in said ex vivo method, to the use of said ex vivo method for removal of tumor cells from intraoperatively collected blood salvage followed by reintroducing the so obtained purified blood salvage or of concentrates of erythrocytes purified by said method to a patient from whom said intra-operatively collected blood was obtained, as well as to blood salvage or a concentrate of erythrocytes, both obtainable by said method for reinfusion to said patient.
Owner:LINDIS BLOOD CARE GMBH
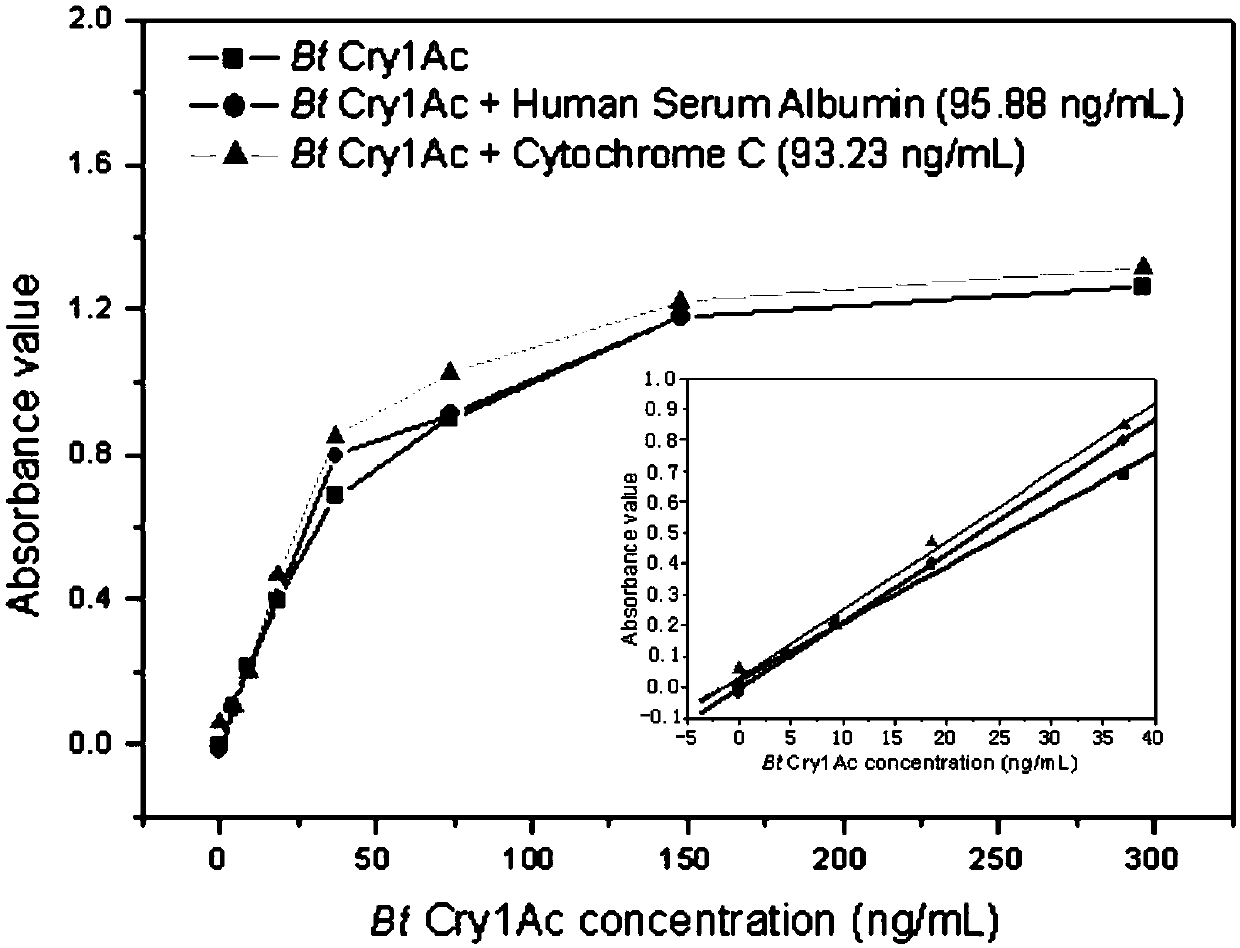
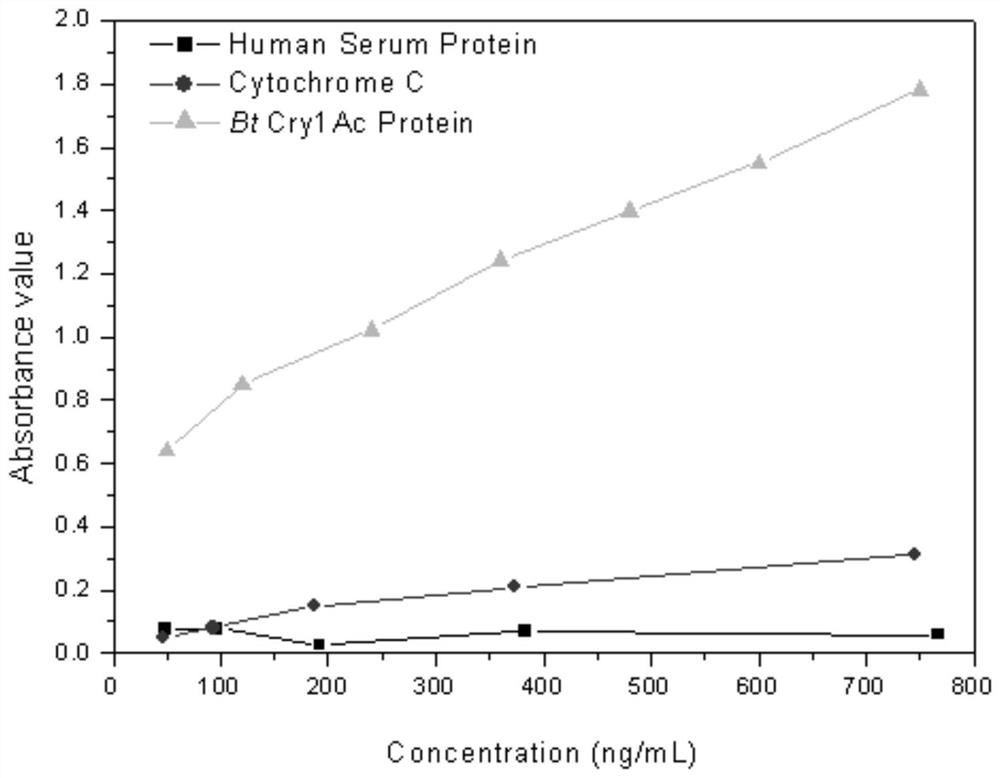
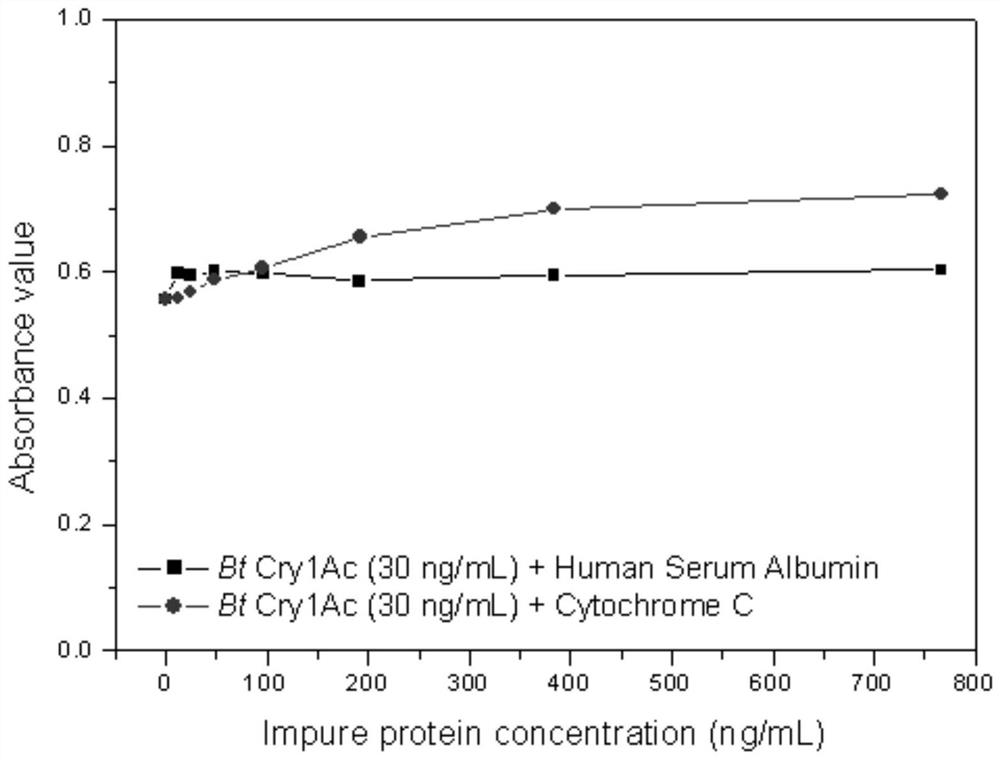
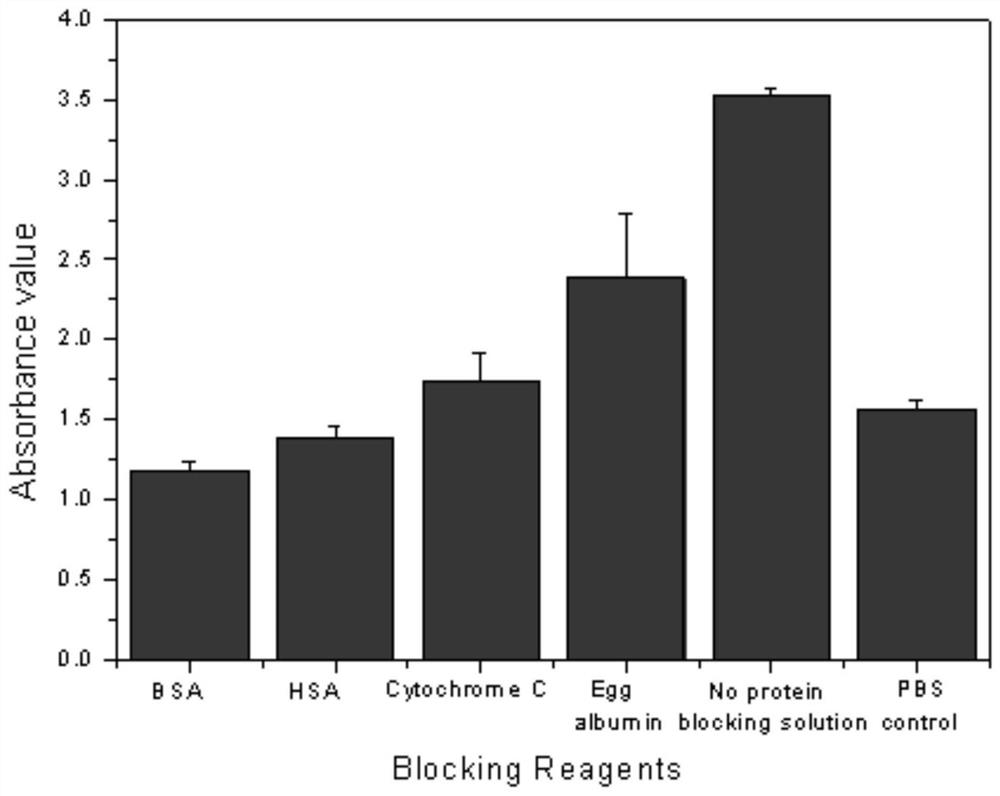
Biotin-labeled polymer nanoparticle simulated antibody and application thereof in Bt protein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
The invention discloses a biotin-labeled polymer nanoparticle simulated antibody. The antibody refers to polymer nanoparticles prepared by simulating a molecular recognition mechanism between a Bt Cry1Ac protein and a brush border membrane receptor cadherin Bt-R1 in tobacco hornworms, and reacting a synthetic acrylamide-polypeptide-amide monomer and other coexistence monomers and biotin-labeled monomers. The polypeptide comprises an amino acid sequence NITIHITDTNNK, and the coexistence monomers refer to acrylamide and / or acrylate compounds. The invention further discloses a Bt enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit and a detection method established based on the biotin-labeled polymer nanoparticle simulated antibody. The Bt protein detected by the method is diversified in type, wide in application range, low in cost and small in workload. Meanwhile, the advantages of the traditional biological antibody based enzyme linked immunosorbent assay such as excellent specificity, high accuracyand simplicity and convenience in operation are remained, and the defects that the natural antibody is difficult to prepare, high in cost, poor in environmental tolerance, easy to inactivate and harshin preservation and reaction conditions and the like are overcome.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Binding proteins to inhibitors of coagulation factors
InactiveUS20140050743A1Neutralize effectExtended half-lifeAnimal cellsBacteriaAntibody fragmentsAntidote
The present invention relates to the identification and use of antigen-binding regions, antibodies, antigen-binding antibody fragments and antibody mimetics, neutralizing the anti-coagulant effect of an anticoagulant in vitro and / or in vivo. Antibodies and functional fragments of the invention and antibody mimetics can be used to specifically reverse the pharmacological effect of an anticoagulant e.g. a FXa inhibitor for therapeutic (antidote) and / or diagnostic purposes. The invention also provides nucleic acid sequences encoding foregoing molecules, vectors containing the same, pharmaceutical compositions and kits with instructions for use.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Method of producing a binder-toxin fusion protein in a plant cell or a whole plant
ActiveCN113728107APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifEgg immunoglobulinsAntibody fragmentsNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method of producing a binder-toxin fusion protein comprising at least, one protein binder selected from the group consisting of an antibody, an antibody fragment or derivative retaining target binding capacity, or an antibody mimetic, optionally, a peptide linker, and at least one protein toxin or protein protoxin. The method comprises the steps of: contacting a plant cell or a whole plant with a nucleic acid construct comprising in operational linkage at least the following (A) at least one polynucleotide encoding for the protein binder, or a target binding chain or domain thereof, and either B1) a polynucleotide encoding for a cleavable peptide linker and a polynucleotide encoding for a protein toxin, or B2) a polynucleotide encoding for a protein protoxin, which protoxin comprises a cleavable domain for activation thereof, allowing the construct to integrate into the nucleus of the plant cell, or of one or more cells of the whole plant, and expressing the fusion protein encoded by the nucleic acid construct (Fig. 7).
Owner:ATB治疗公司
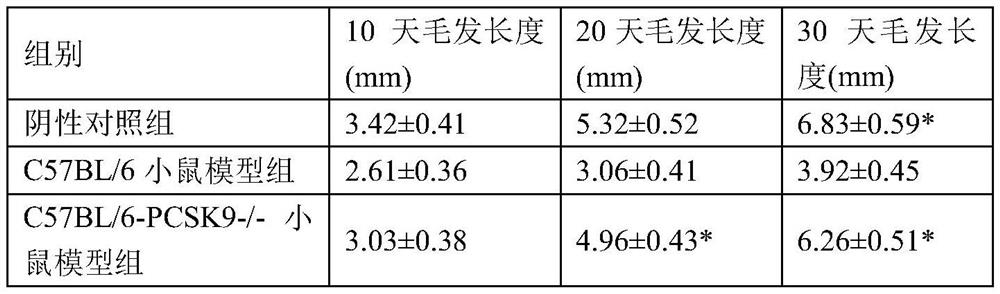
Application of PCSK9 inhibitor in preparation of products for promoting hair growth
ActiveCN113876955AGood curative effectImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseSubtilisin
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biology, and particularly relates to an effect of a proprotein convertase subtilisin / kexin type 9 (PCSK9) in promotion of hair growth and application of a PCSK9 inhibitor in preparation of products for treating alopecia diseases. The PCSK9 inhibitor is characterized in that the PCSK9 inhibitor is a PCSK9 small molecule compound or a PCSK9 interfering RNA or a PCSK9 monoclonal antibody or a PCSK9 mimic peptide or a PCSK9 mimic antibody protein or a PCSK9 antisense oligonucleotide or a PCSK9 vaccine, and the PCSK9 inhibitor is applied to preparation of the products for treating the alopecia diseases. Systematic or external PCSK9 inhibitor products can be further developed and are used for treating the alopecia diseases. The products are remarkable in curative effect and small in adverse reaction.
Owner:陈敏
Long-acting HIV-1 (Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1) membrane fusion inhibitor
InactiveCN103333255ABiological effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibody mimetic
The invention relates to long-acting inhibiting polymer for HIV-1 (Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1) membrane fusion. The long-acting inhibiting polymer is characterized by comprising two or three parts, wherein the former two parts are respectively a polypeptide part for inhibiting the HIV-1 membrane fusion and a simulative antibody part which can be combined with serum albumin so as to prolong the half-life period of the polymer in vivo; the middle of the two parts can also be additionally provided with a connecting molecule for improving the activity of the polymer in inhibiting HIV-1. The polymer can be used for preventing a cell fusion effect mediated by virus in vivo for a long term.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Antibody and antibody mimetic for visualization and ablation of endogenous proteins
ActiveUS9746475B2Remove background noiseEfficient identificationConnective tissue peptidesFusion with DNA-binding domainAntigenProtein target
Provided are compositions and methods for labeling an endogenous protein, in particular, in a live cell, or for ablating an endogenous or target protein. The compositions relate to a fusion protein having a binding moiety such as an antibody, an antigen binding fragment of an antibody or an antibody mimetic that recognizes the endogenous or target protein.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Immobilization of cells or virus particles on protein structures using a microfluidic chamber
InactiveUS20180024134A1Improve binding efficiencyStrong specificityLaboratory glasswaresRecovery/purificationSurface markerAntibody fragments
The present invention relates to methods for the immobilization of cells or virus particles of interest expressing one or more predetermined surface marker(s) on defined spots on a solid support, comprising the steps of providing a biological fluid sample suspected of containing cells or virus particles of interest; labeling the cells or virus particles of interest with antibodies, antibody fragments or antibody mimetics directed against the one or more predetermined surface marker(s) and carrying a first binding agent; and contacting the labeled cells or virus particles of interest with a solid support (biochip), said solid support comprising an array of defined isolated spots of a solid support-bound second binding agent, wherein the first and second binding agents can bind to each other. The present invention further relates to devices for the isolation of cells or virus particles of interest expressing one or more predetermined surface marker(s).
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH +1
Binding proteins to inhibitors of coagulation factors
The present invention relates to the identification and use of antigen-binding regions, antibodies, antigen-binding antibody fragments and antibody mimetics, neutralizing the anti-coagulant effect of an anticoagulant in vitro and / or in vivo. Antibodies and functional fragments of the invention and antibody mimetics can be used to specifically reverse the pharmacological effect of an anticoagulant e.g. a FXa inhibitor for therapeutic (antidote) and / or diagnostic purposes. The invention also provides nucleic acid sequences encoding foregoing molecules, vectors containing the same, pharmaceutical compositions and kits with instructions for use.
Owner:BAYER IP GMBH
Method of selecting for antibodies
PendingCN110382548APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCompound screeningAntibody mimeticMammalian cell
The present invention relates to a method for identifying specific binding partners (e.g. antibodies or antibody mimetics) which bind to a desired target polypeptide. In particular, the method involves expressing a library of antibodies or antibody mimetics in a population of mammalian cells, wherein each cell in the population of cells displays the target polypeptide on the outer surface of the cell, and identifying or isolating cells within the population of cells to which antibodies or antibody mimetics are bound.
Owner:OXFORD GENETICS
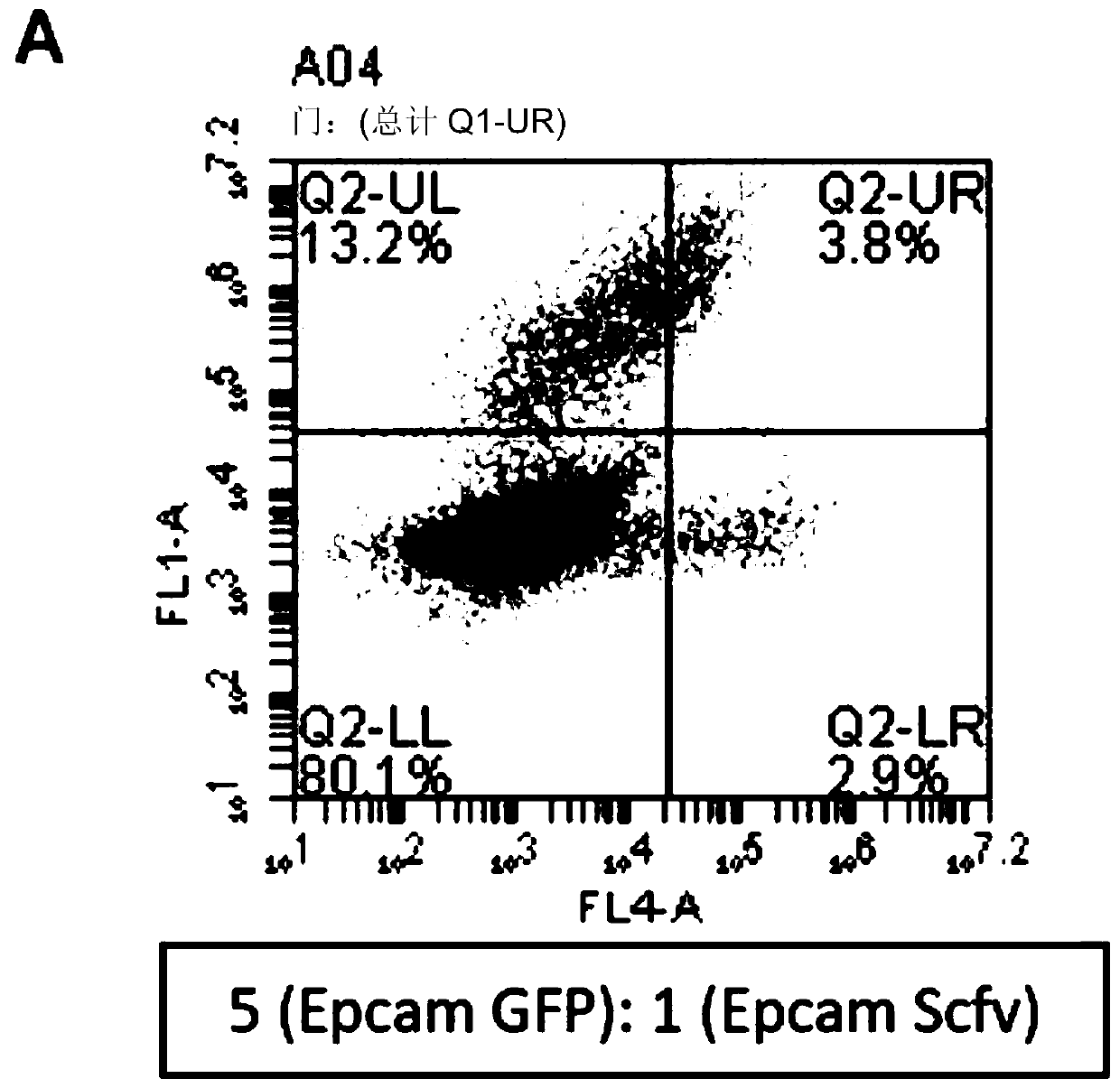
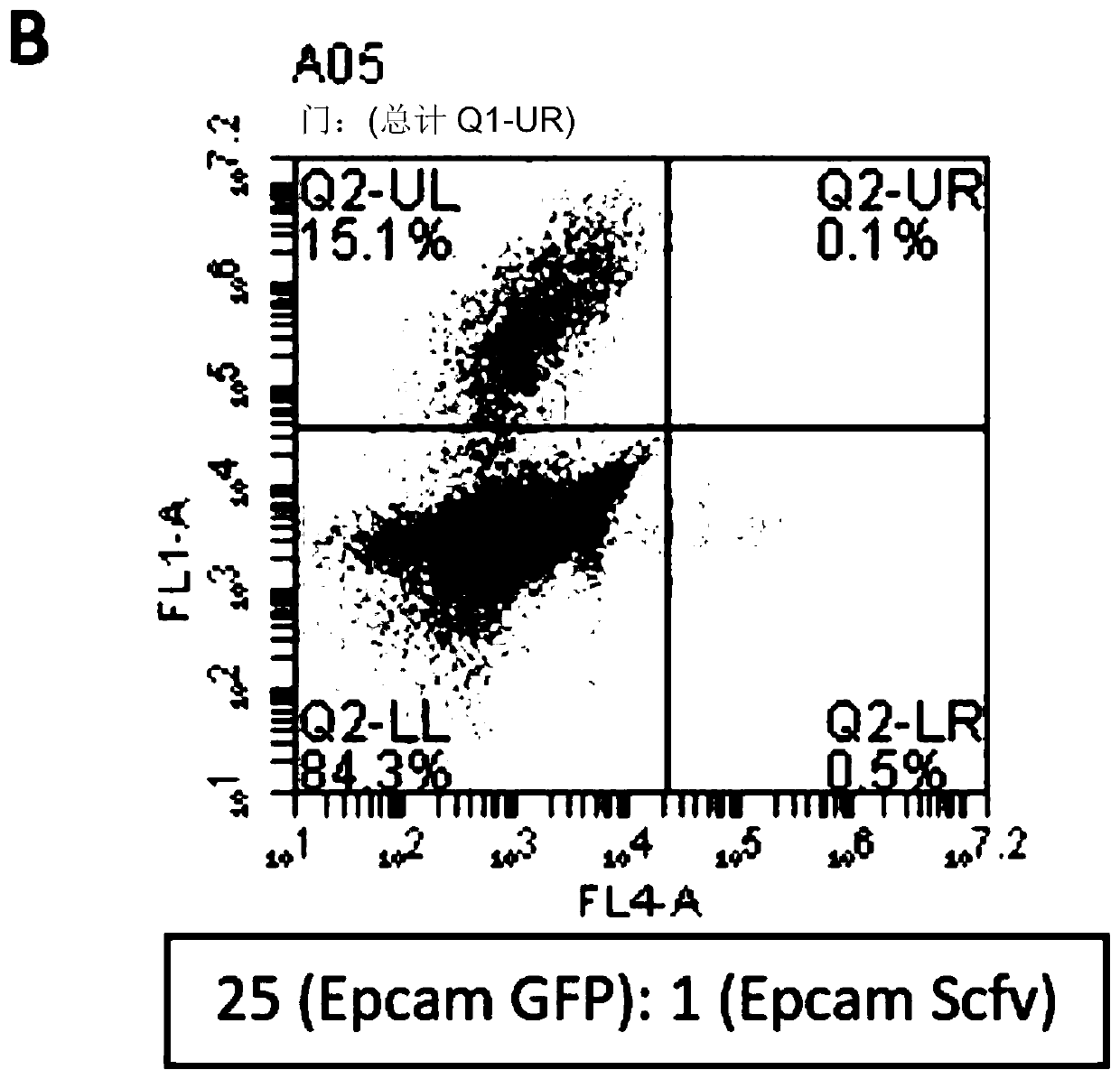
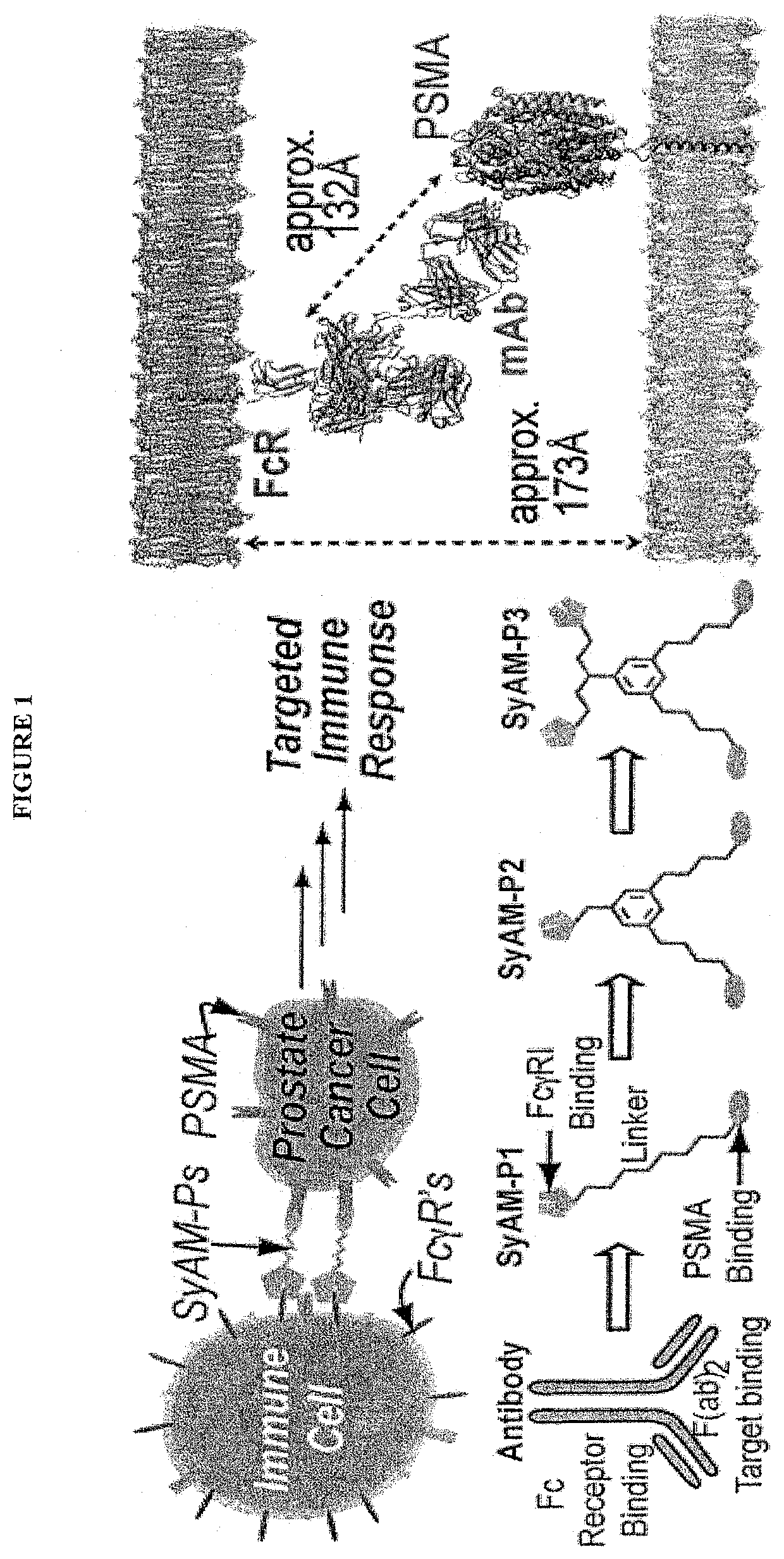
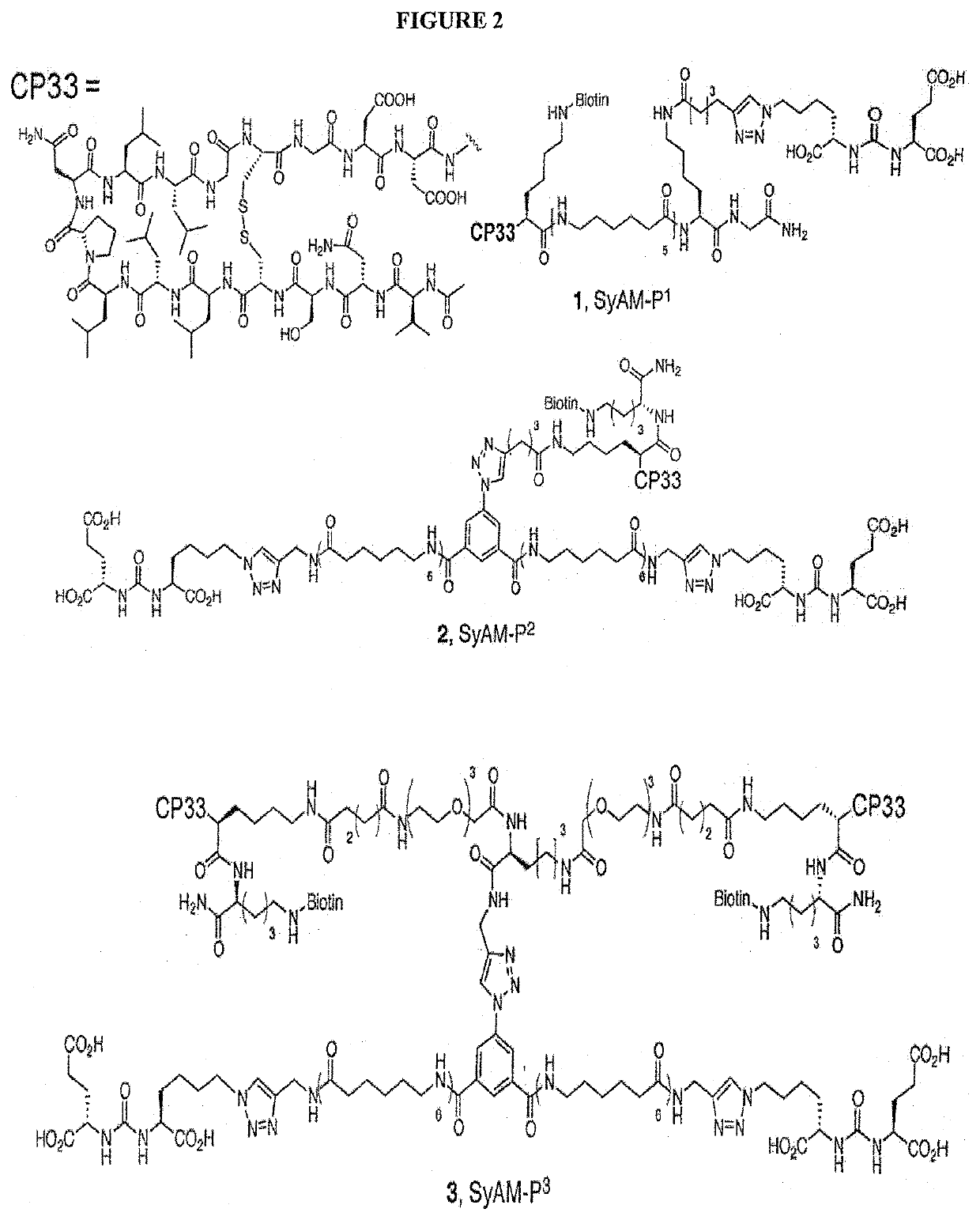
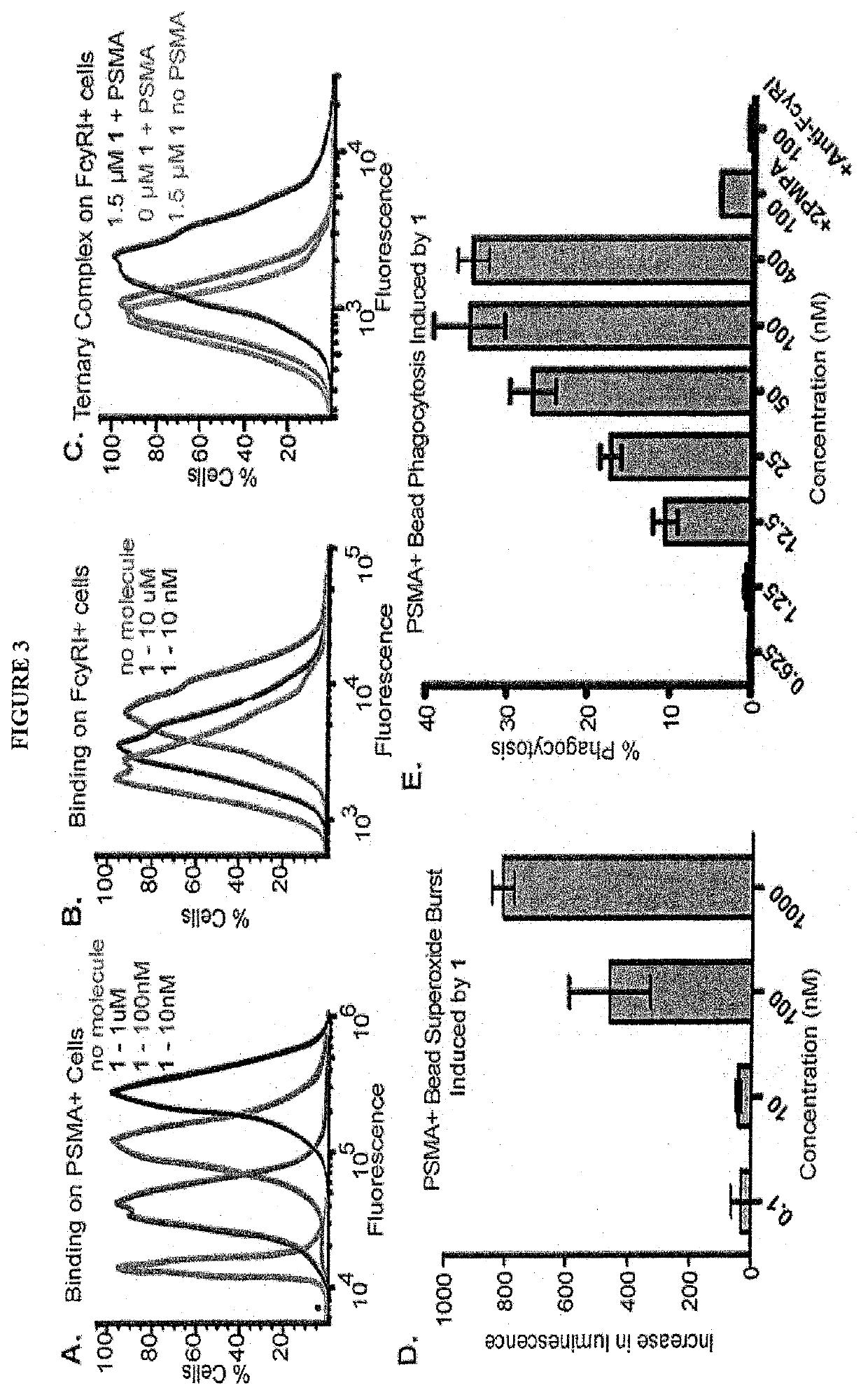
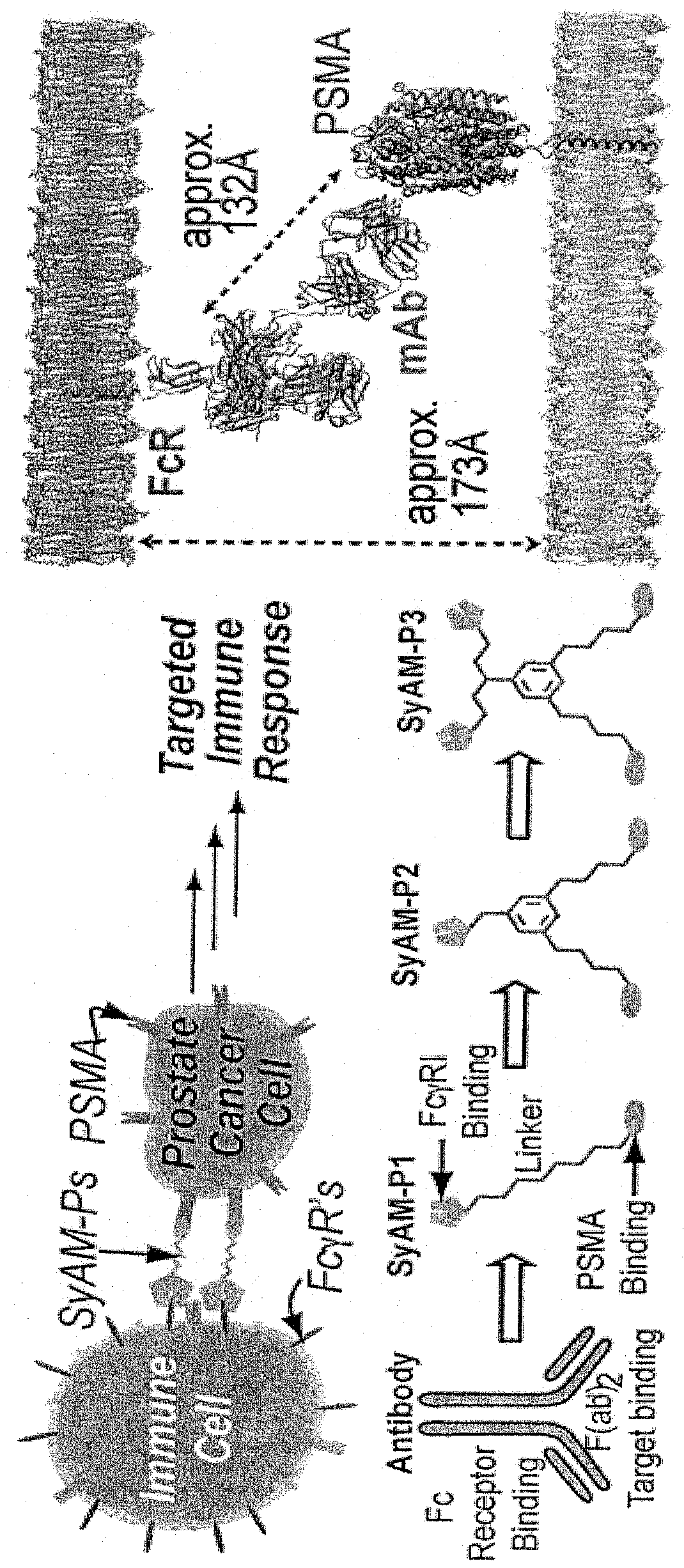
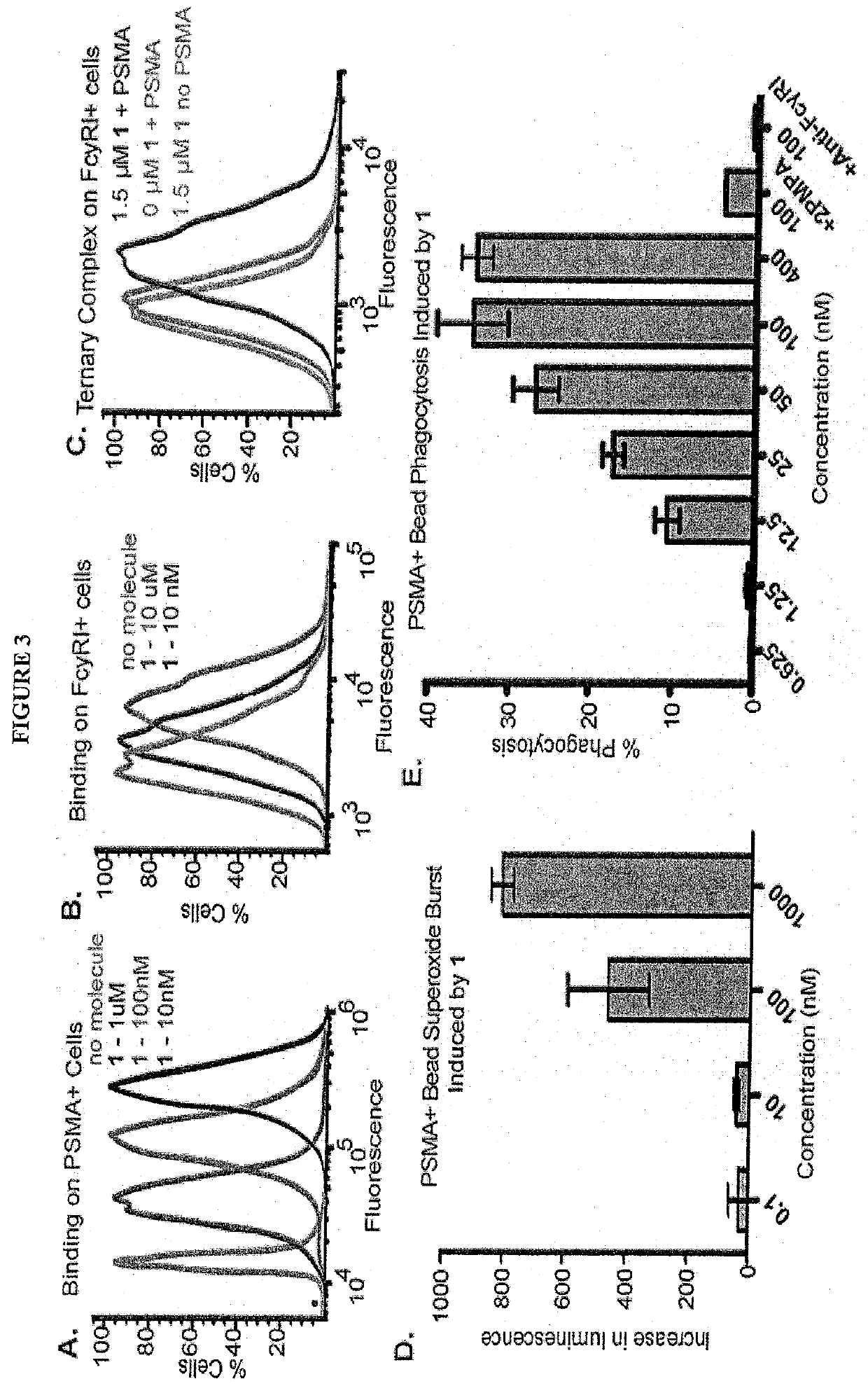
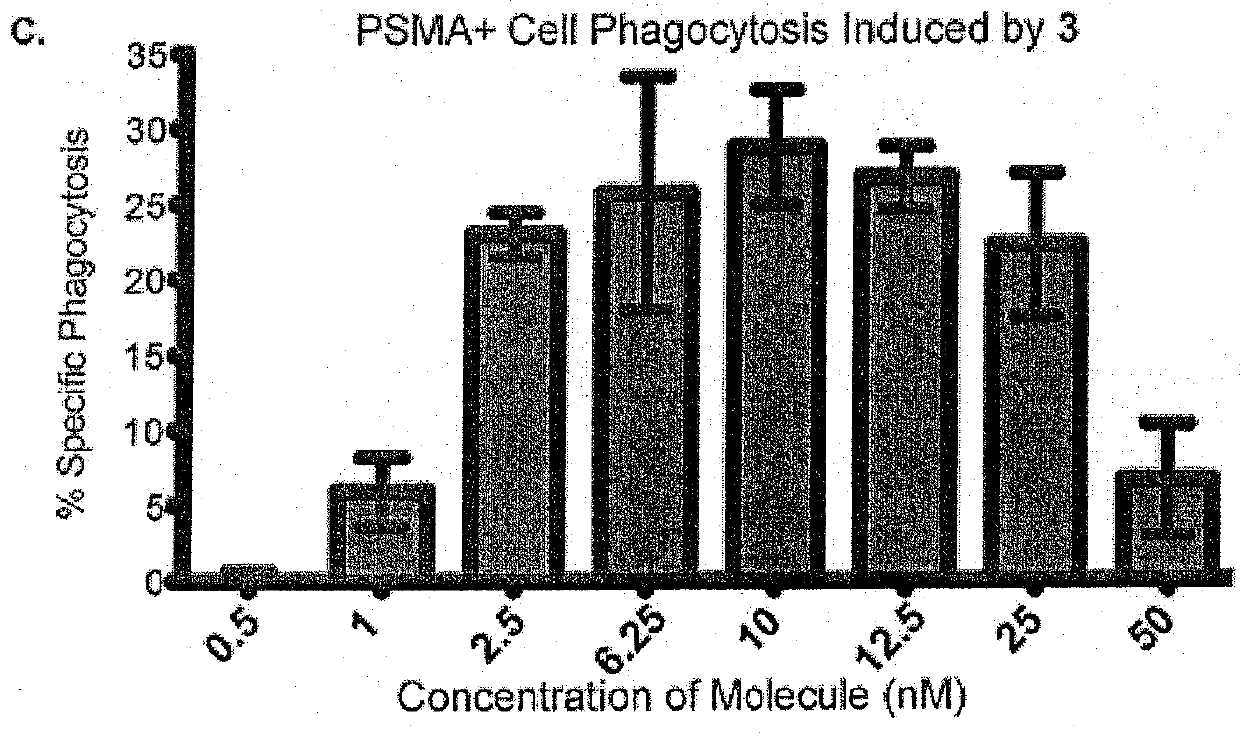
Synthetic antibody mimetic compounds (SyAMs) targeting cancer, especially prostate cancer
ActiveUS10912836B2Inhibit and reduce likelihoodOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryProstate cancer cellAntigen
The present invention relates to compounds which function as antibody mimetic compounds. These compounds are bifunctional / multifunctional compounds which contain at least one cancer cell binding moiety which selectively binds to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and a FC receptor binding moiety which modulates an FC immune receptor, preferably a FcγRI receptor. Compounds according to the present invention bind selectively to cancer cells which upregulate PSMA and through that interaction, place the Fc receptor binding moiety of the compound in proximity to a Fc receptor, preferably a FcγRI receptor, which can modulate (preferably, upregulate) a humoral response in a patient to cancer cells. Through this biological action of the compounds according to the present invention, cancer cells, including metastatic cancer cells, especially prostate cancer cells can be immune regulated, resulting in the favorable therapy of cancer in a patient. Methods of using these compounds to treat cancer and / or reduce the likelihood of metastasis of cancer are additional aspects of the present invention.
Owner:YALE UNIV
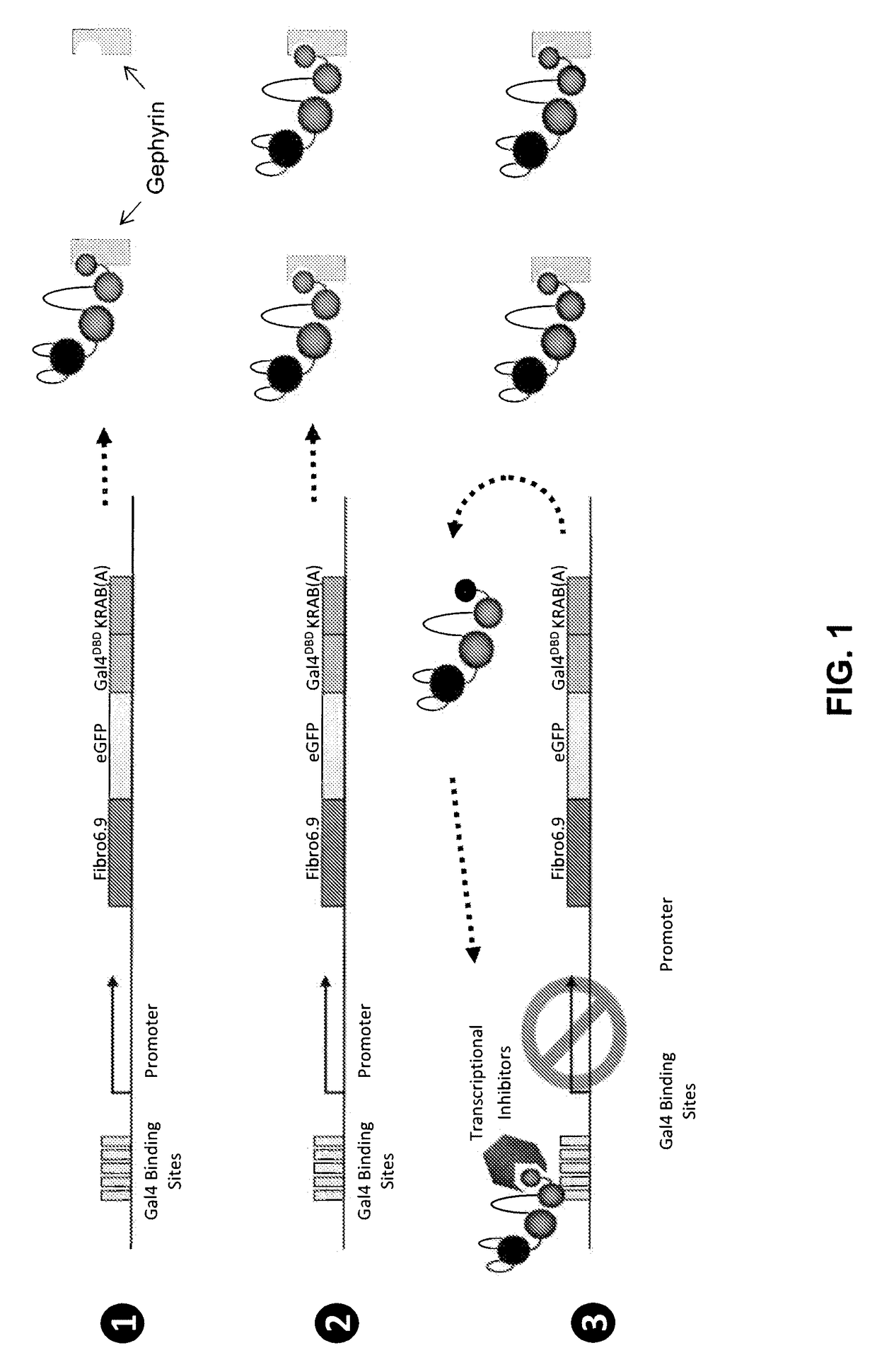
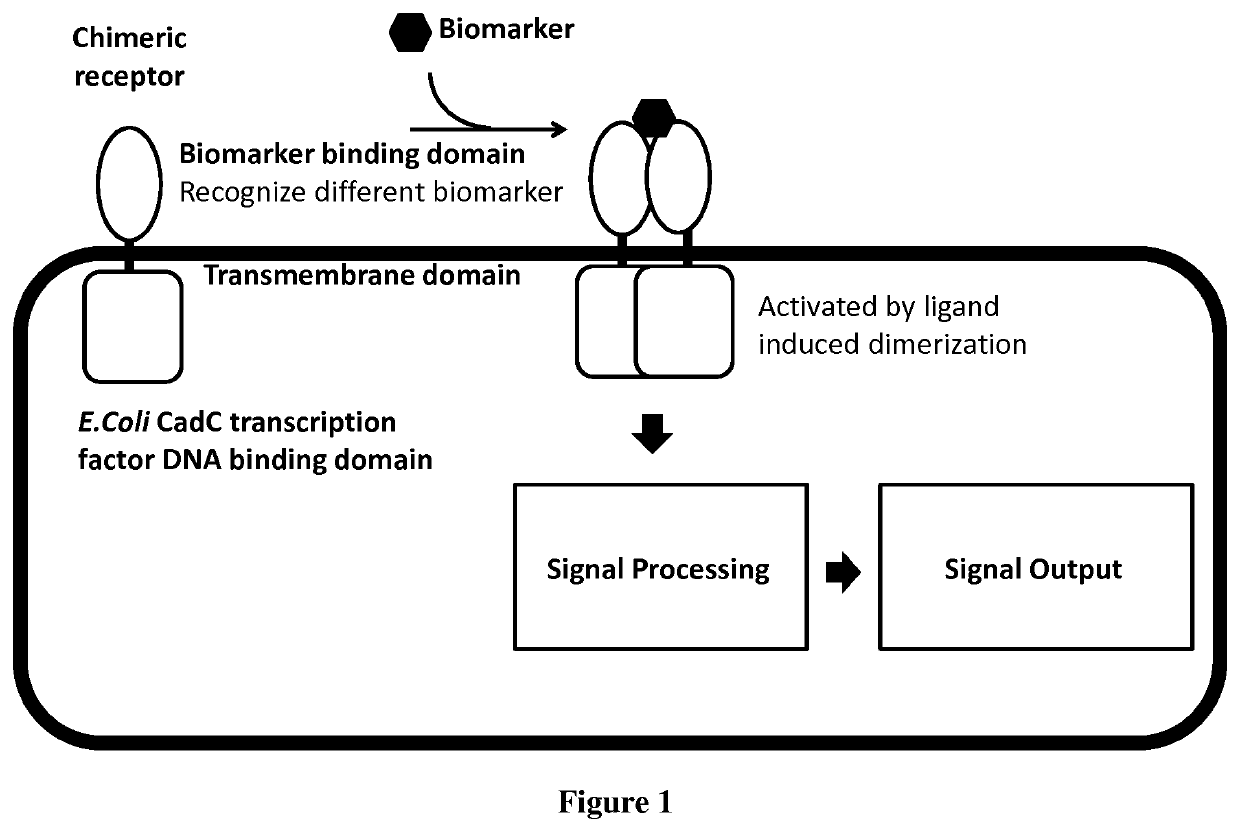
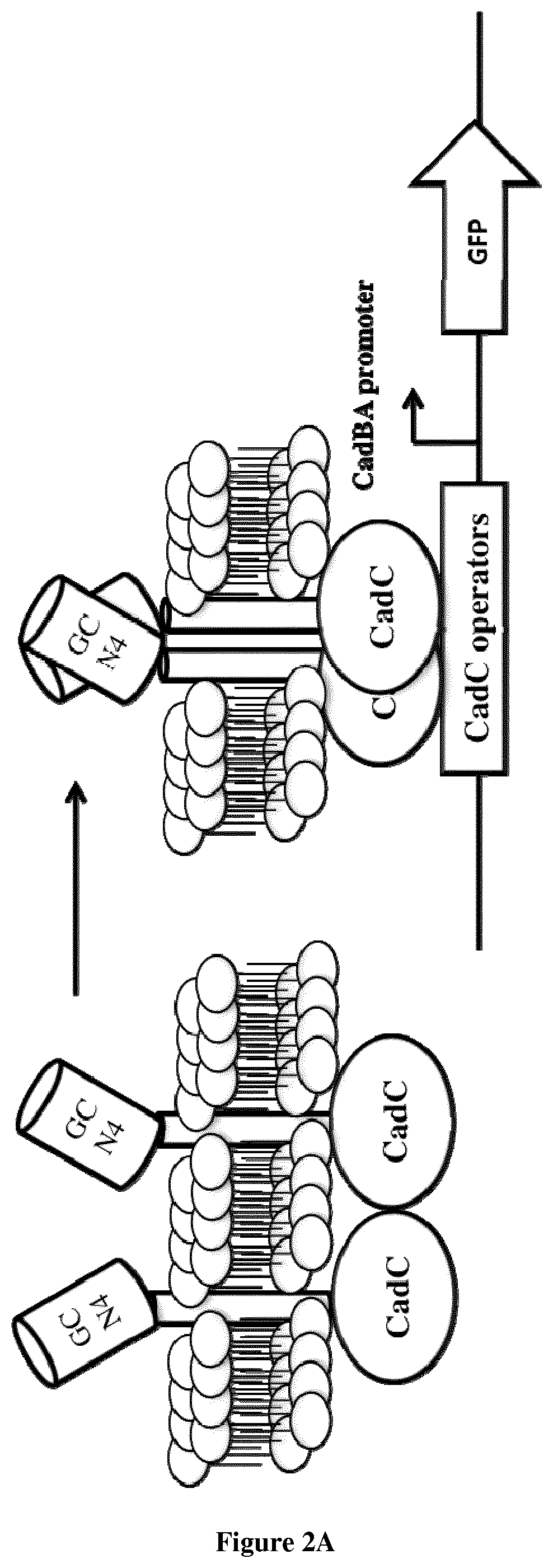
Chimeric receptor for use in whole-cell sensors for detecting analytes of interest
PendingUS20200096507A1Prevent steric hindrancesEasy to insertFusion with DNA-binding domainImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDNA-binding domainHeavy chain
The present invention relates to chimeric receptors that can be used in whole-cell sensors for detecting analytes of interest. The inventors showed that the DNA binding domains and downstream gene expression can be activated via dimerization of an artificial dimerization composed of a single chain variable domain. They demonstrated for the first time that an artificial bacterial receptor using an antibody-like domain can be activated and produce a transcriptional output upon ligand-binding. In particular, the present invention relates to a chimeric receptor polypeptide comprising: i) a first DNA binding domain, ii) at least one binding domain selected from the group consisting of heavy chain variable domain, camelid VHHs, or antibody mimetics having specificity for an analyte, and iii) a linker between the DNA binding domain and the binding domain.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
A biotin-labeled polymer nanoparticle mimic antibody and its application in bt protein ELISA
The invention discloses a biotin-labeled polymer nanoparticle simulated antibody. The antibody refers to polymer nanoparticles prepared by simulating a molecular recognition mechanism between a Bt Cry1Ac protein and a brush border membrane receptor cadherin Bt-R1 in tobacco hornworms, and reacting a synthetic acrylamide-polypeptide-amide monomer and other coexistence monomers and biotin-labeled monomers. The polypeptide comprises an amino acid sequence NITIHITDTNNK, and the coexistence monomers refer to acrylamide and / or acrylate compounds. The invention further discloses a Bt enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit and a detection method established based on the biotin-labeled polymer nanoparticle simulated antibody. The Bt protein detected by the method is diversified in type, wide in application range, low in cost and small in workload. Meanwhile, the advantages of the traditional biological antibody based enzyme linked immunosorbent assay such as excellent specificity, high accuracyand simplicity and convenience in operation are remained, and the defects that the natural antibody is difficult to prepare, high in cost, poor in environmental tolerance, easy to inactivate and harshin preservation and reaction conditions and the like are overcome.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
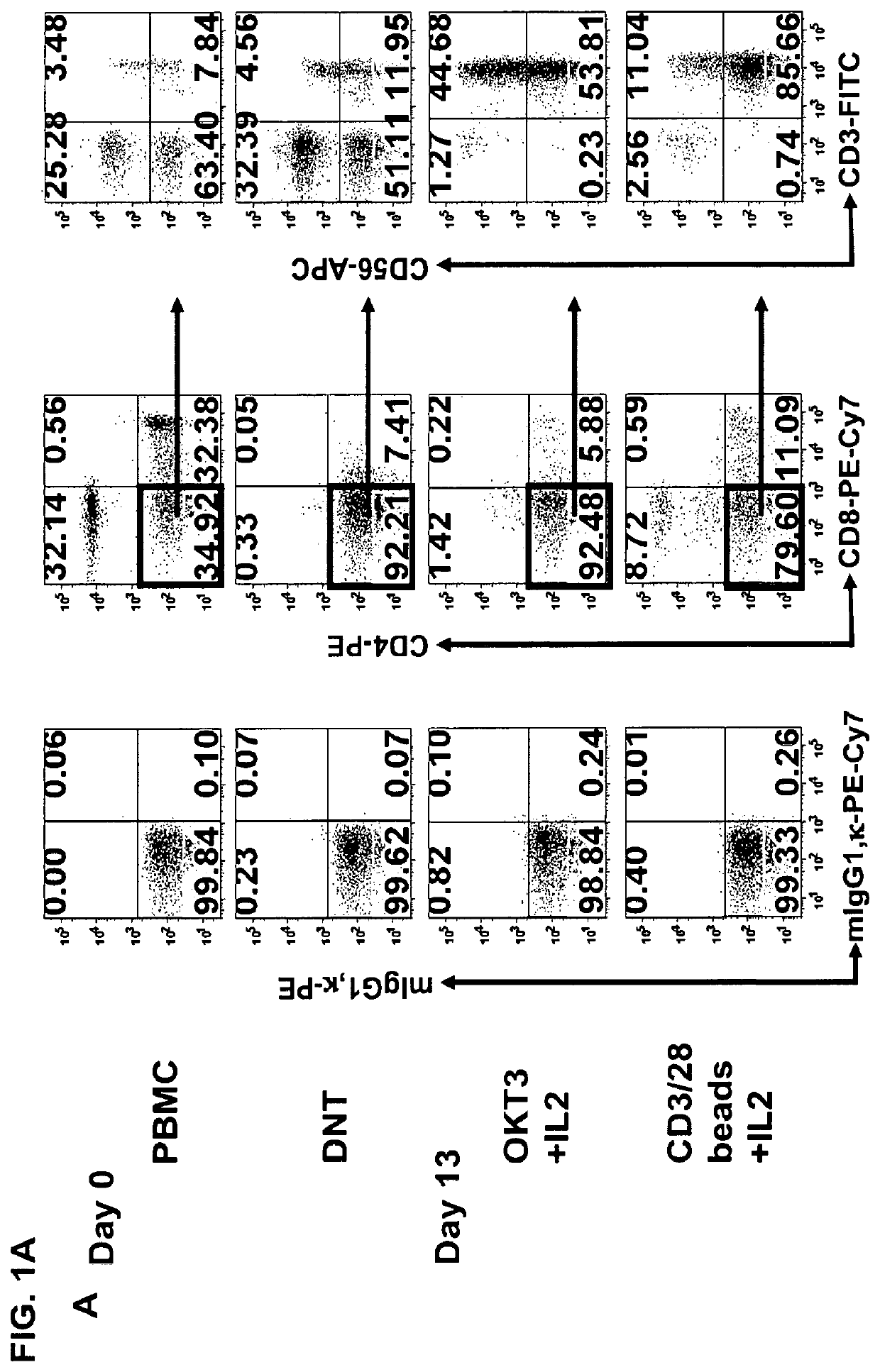
Type iii nkt cells and related compositions and methods
PendingUS20220249562A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorsSomatic cell
The present disclosure relates to type III natural killer T (NKT) cells (e.g., CD3+CD56+ type III NKT cells), pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of preparation and use thereof, in particular use of them as therapeutic agents for the treatment various cancers. Modified type III NKT cells, e.g., to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), a T cell receptor (TCR), a T cell receptor mimic antibody (TCRm), or a combination thereof, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of preparation and use thereof, are also disclosed.
Owner:AKESO THERAPEUTICS INC
A kind of novel antibiotic containing antibody mimetic and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN101633699BImprove permeabilityLow immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsComplementarity determining regionAntibiotic Y
The present invention belongs to field of biology and medicine, and especially relates to a novel antibiotic comprising a mimetic antibody, its preparation methods and uses thereof. The novel antibiotic comprising comprising an antibody mimetic and a colicin,or comprising an antibody mimetic and a channel-forming domain of a colicin, the antibody mimetic covalently bonded to the carboxyl end of the polypeptide of the colicin or the channel-forming domain of the colicin, wherein the colicin is selected from a group consisting of colicin E1, Ia, Ib, A, B, N; wherein said antibody mimetic being yielded by fusing two complementarity determining regions (CDRs), V H CDR 1 ) and V L CDR through a cognate framework region (V H FR 2 ) of an immunoglobulin; wherein the immunoglobulin specifically recognizes bacterium porins. Its antibacterial ability is a thousandfold powerful than normal antibiotics. Due to its unique action mechanism, drug resistance resulted in mutation can hardly be acquired by pathogenic bacteria. And the antibiotic will not hurt normal human cells when it kills pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, it can be used for manufacturing antibacterial medicament of killing Diplococcus intracellularis, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:PHEROMONICIN BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
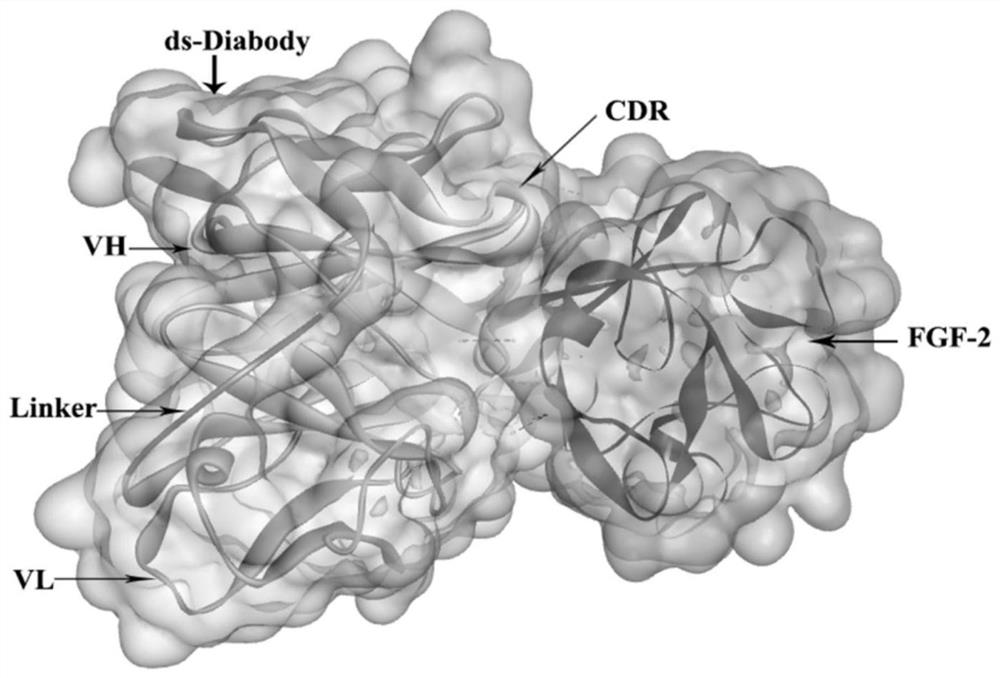
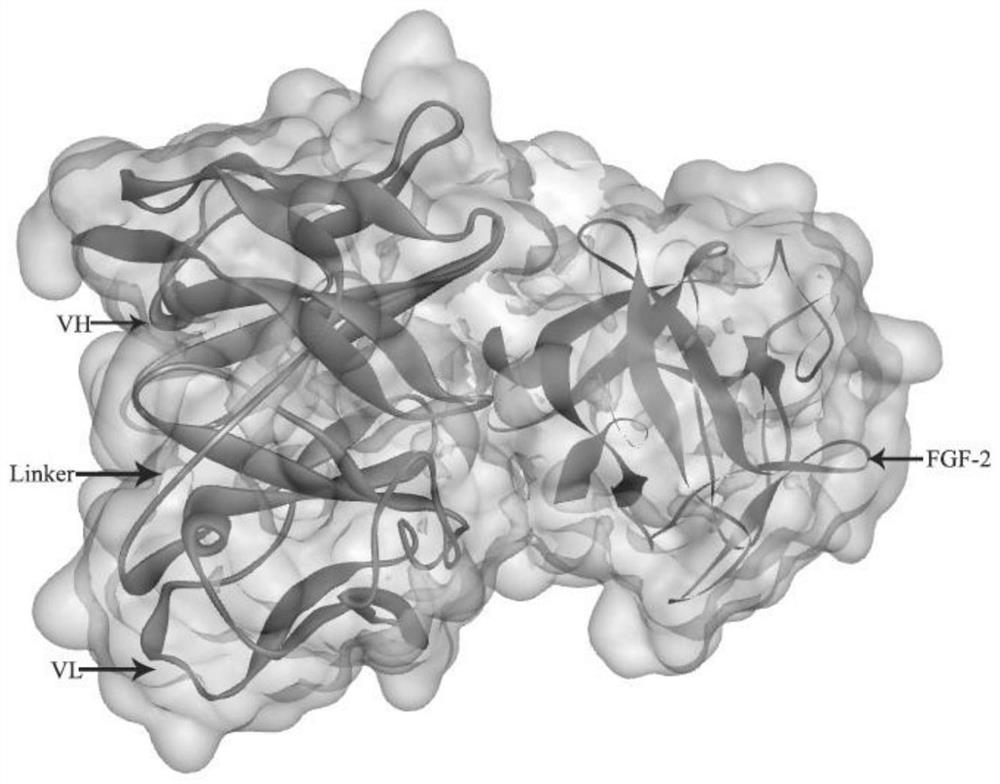
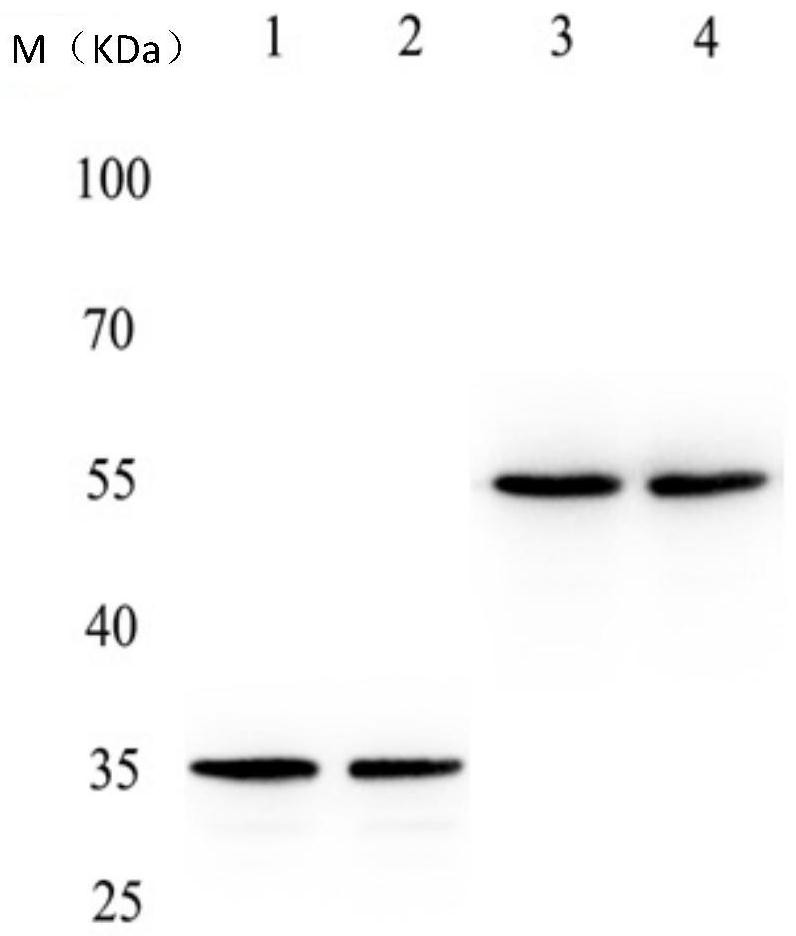
A high-affinity anti-fgf-2 disulfide bond-stabilized human double-chain antibody and its application
ActiveCN107880125BPromote growthEasy transferDigestive systemImmunoglobulins against growth factorsDisulfide bondingAntigen
The invention discloses a high-affinity anti-FGF-2 human-derived double-chain antibody with a stable disulfide bond and application. The human-derived double-chain antibody comprises a light-chain variable region shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 and a heavy-chain variable region shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. According to the high-affinity anti-FGF-2 human-derived double-chain antibody, a molecular structure is usedfor simulating a space structure of an antibody ds-Diabody and an antigen, and the stability is analyzed through thermodynamics; an antibody structure is optimized and modified to obtain the high-affinity anti-FGF-2 human-derived double-chain antibody with the stable disulfide bond; compared with an unmodified anti-FGF-2 human-derived ds-Diabody, the combination activity is improved by 3 times and the high-affinity anti-FGF-2 human-derived double-chain antibody with the stable disulfide bond has higher affinity; the antibody belongs to a small molecular antibody and has good tissue permeability; the disulfide bond is introduced so that the stability of the antibody can be improved; the antibody can be used for effectively inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and inhibiting the growth and transferring of tumors. Therefore, the human-derived double-chain antibody provided by the invention has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Synthetic antibody mimetic compounds (SYAMS) targeting cancer, especially prostate cancer
ActiveUS20190209696A1Reduce the possibilityInhibit and reduce likelihoodOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAntigenFc(alpha) receptor
The present invention relates to compounds which function as antibody mimetic compounds. These compounds are bifunctional / multifunctional compounds which contain at least one cancer cell binding moiety which selectively binds to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and a FC receptor binding moiety which modulates an FC immune receptor, preferably a FcγRI receptor. Compounds according to the present invention bind selectively to cancer cells which upregulate PSMA and through that interaction, place the Fc receptor binding moiety of the compound in proximity to a Fc receptor, preferably a FcγRI receptor, which can modulate (preferably, upregulate) a humoral response in a patient to cancer cells. Through this biological action of the compounds according to the present invention, cancer cells, including metastatic cancer cells, especially prostate cancer cells can be immune regulated, resulting in the favorable therapy of cancer in a patient. Methods of using these compounds to treat cancer and / or reduce the likelihood of metastasis of cancer are additional aspects of the present invention.
Owner:YALE UNIV
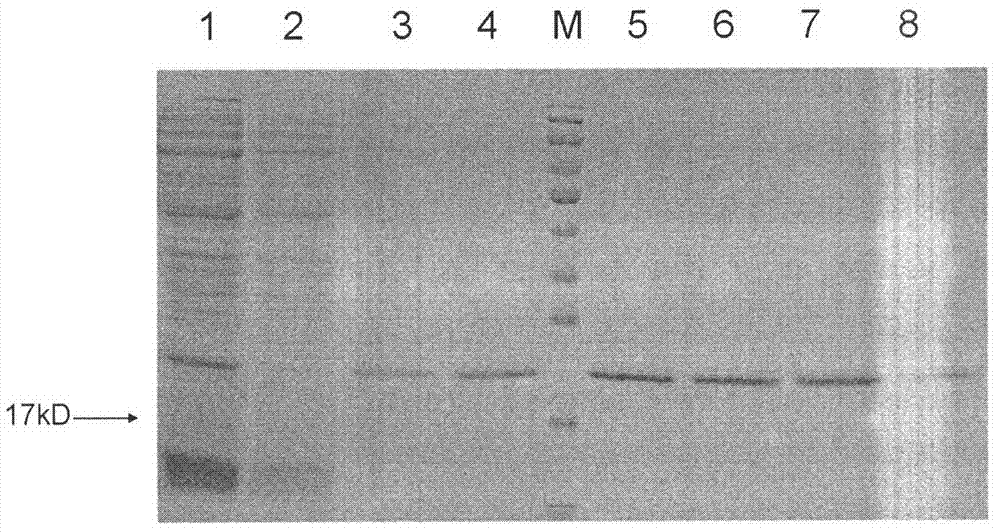
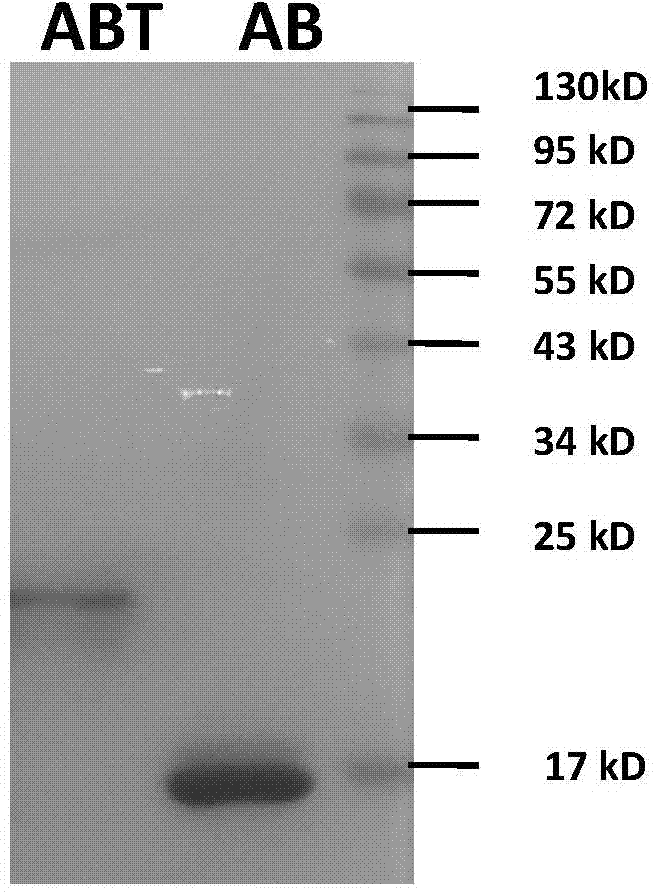
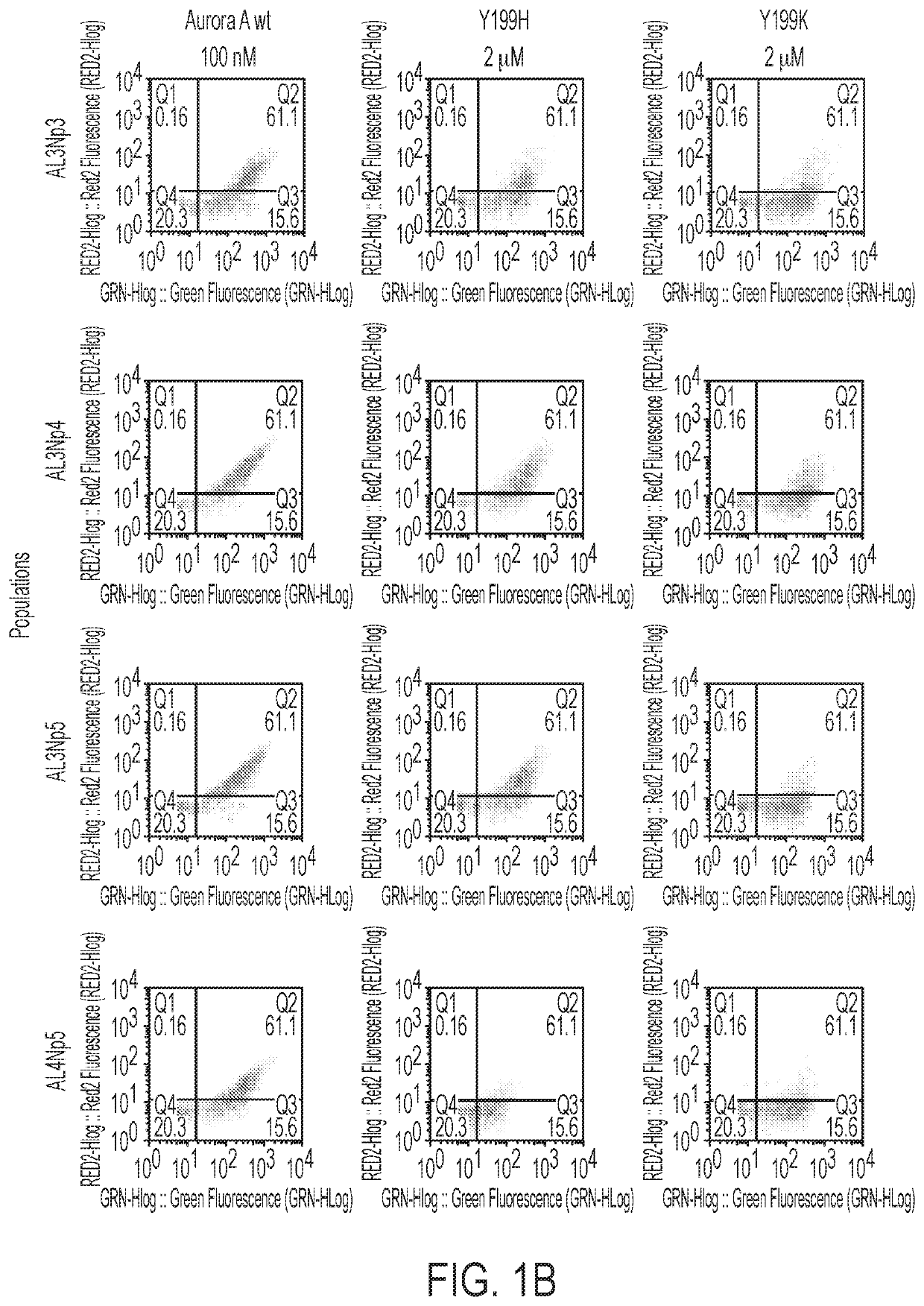
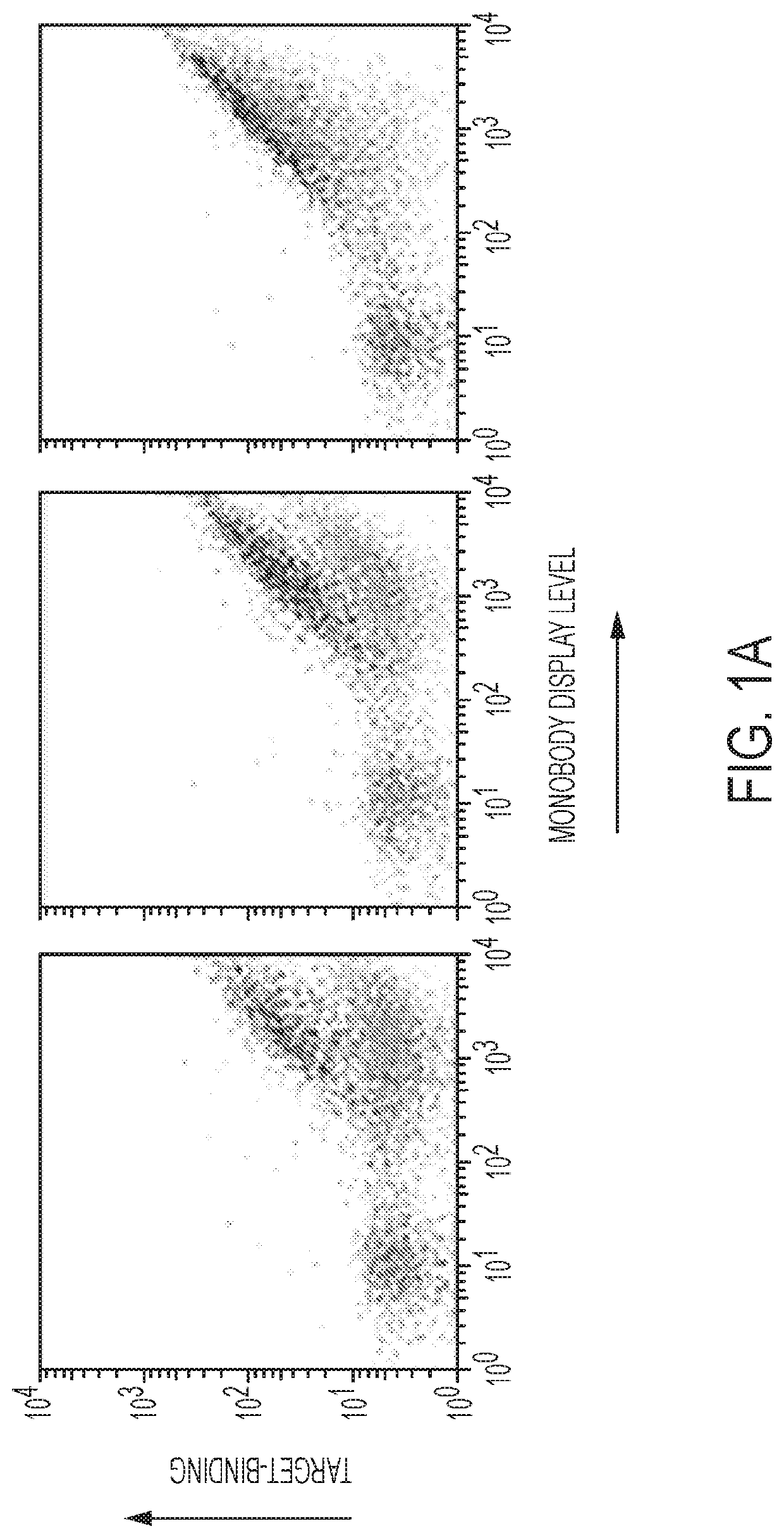
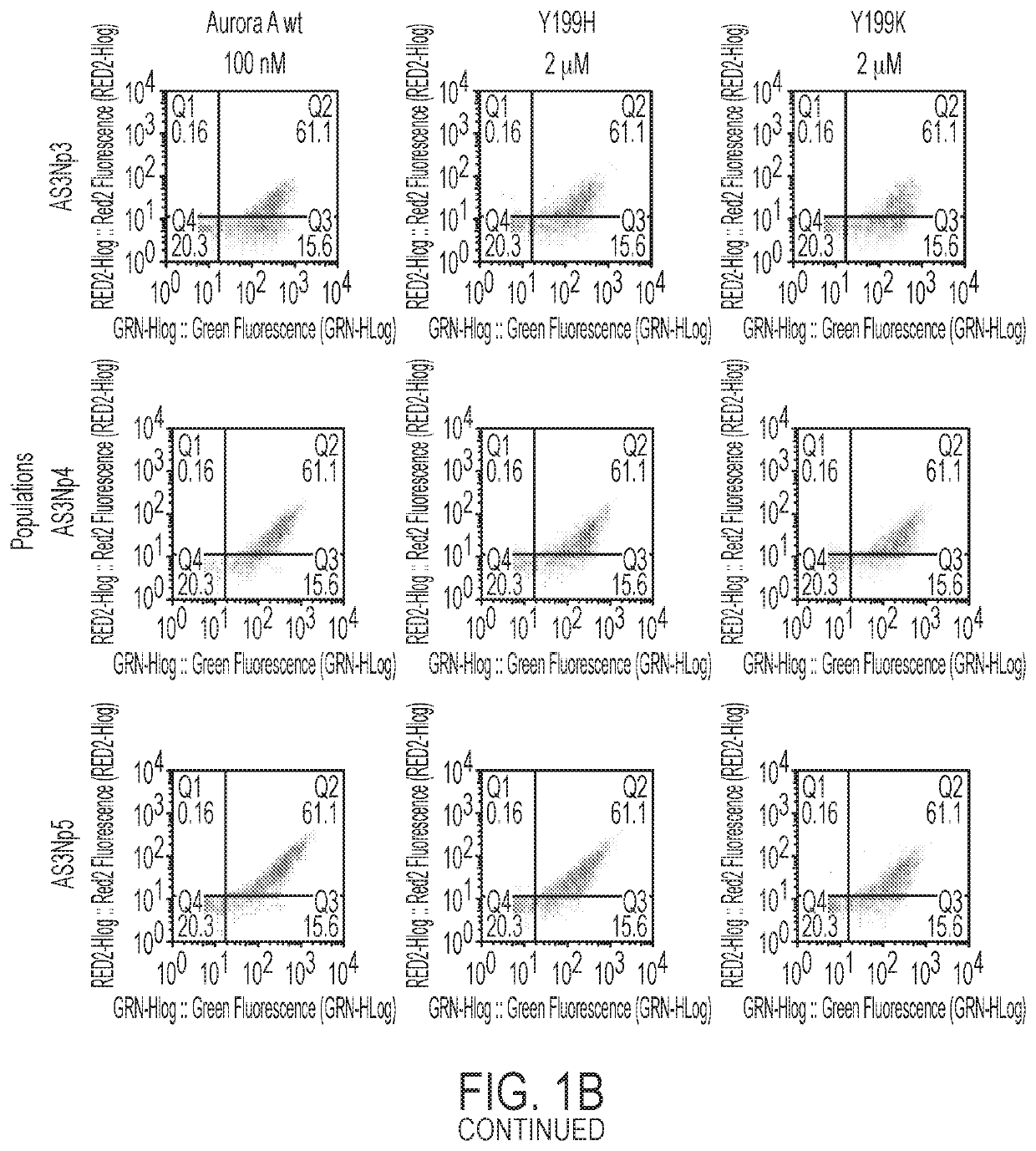
Compositions and methods for modulating kinase activity
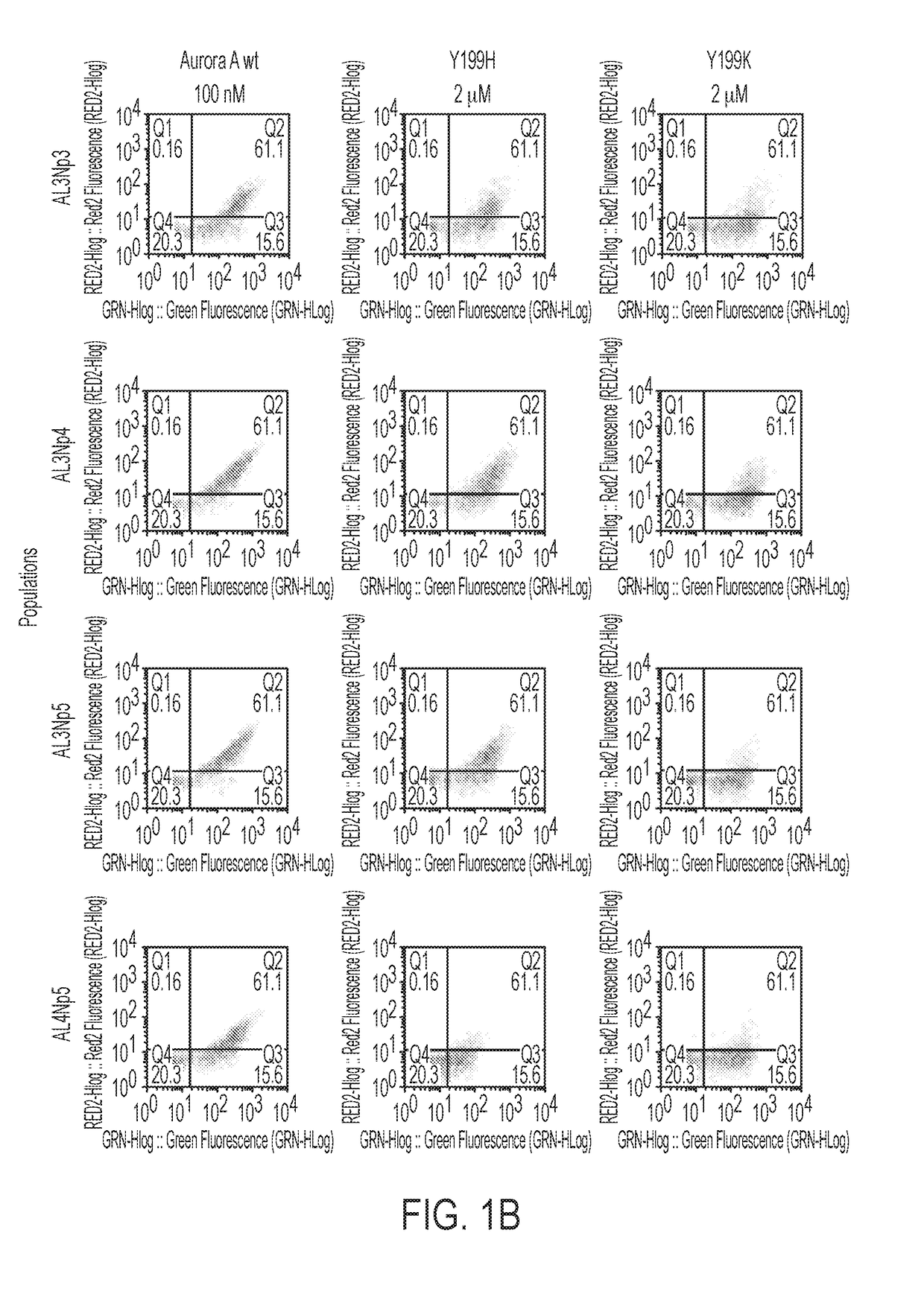
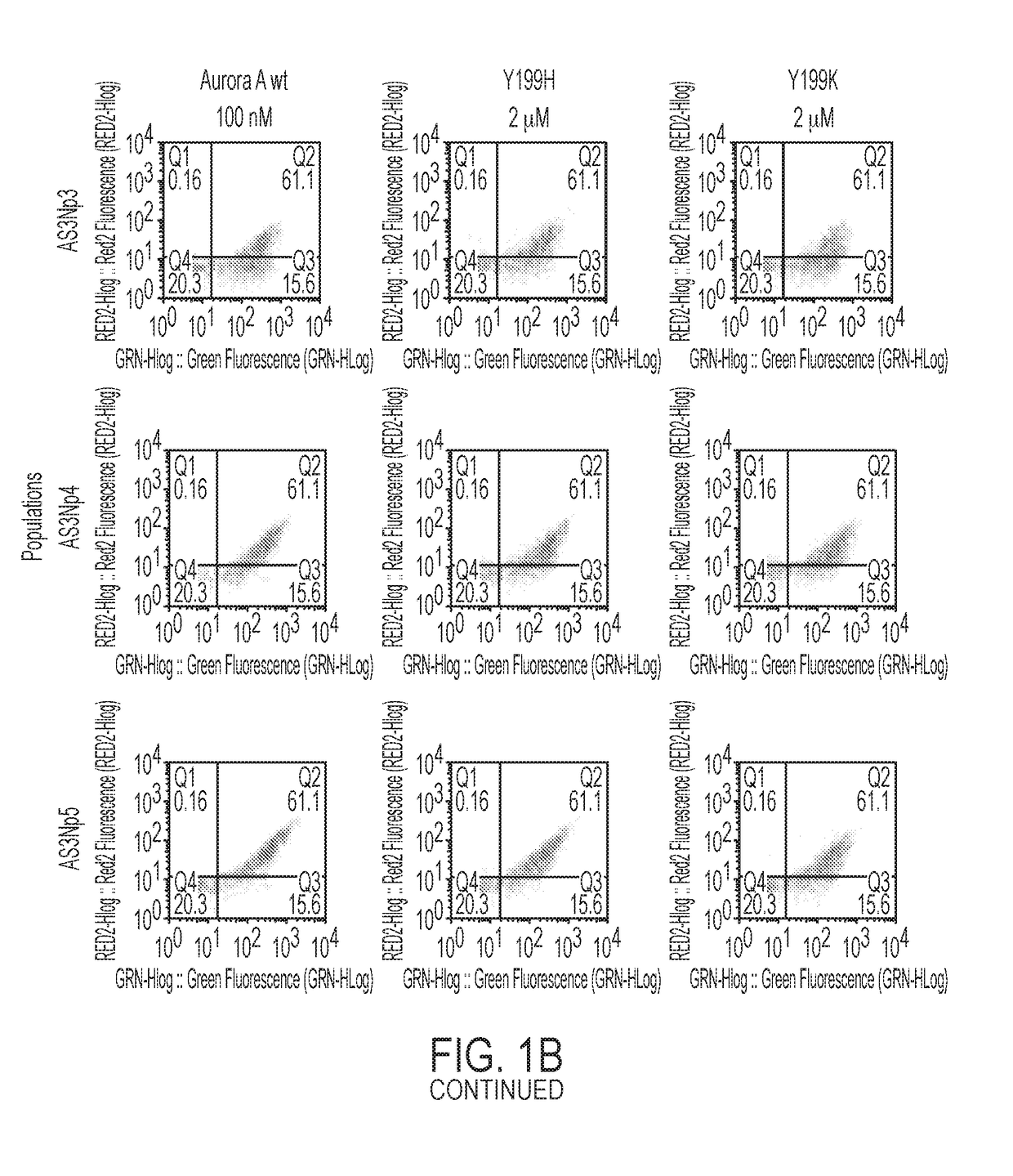
ActiveUS20180334510A1Increase Aurora A kinase activityPrevent proliferationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCompound screeningAntigenKinase activity
The present invention features an antibody mimetic, or an antigen binding fragment thereof, that specifically binds to an allosteric site of Aurora A kinase, therapeutic compositions comprising this antibody mimetic, and the use of the monobody to modulate Aurora A kinase for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
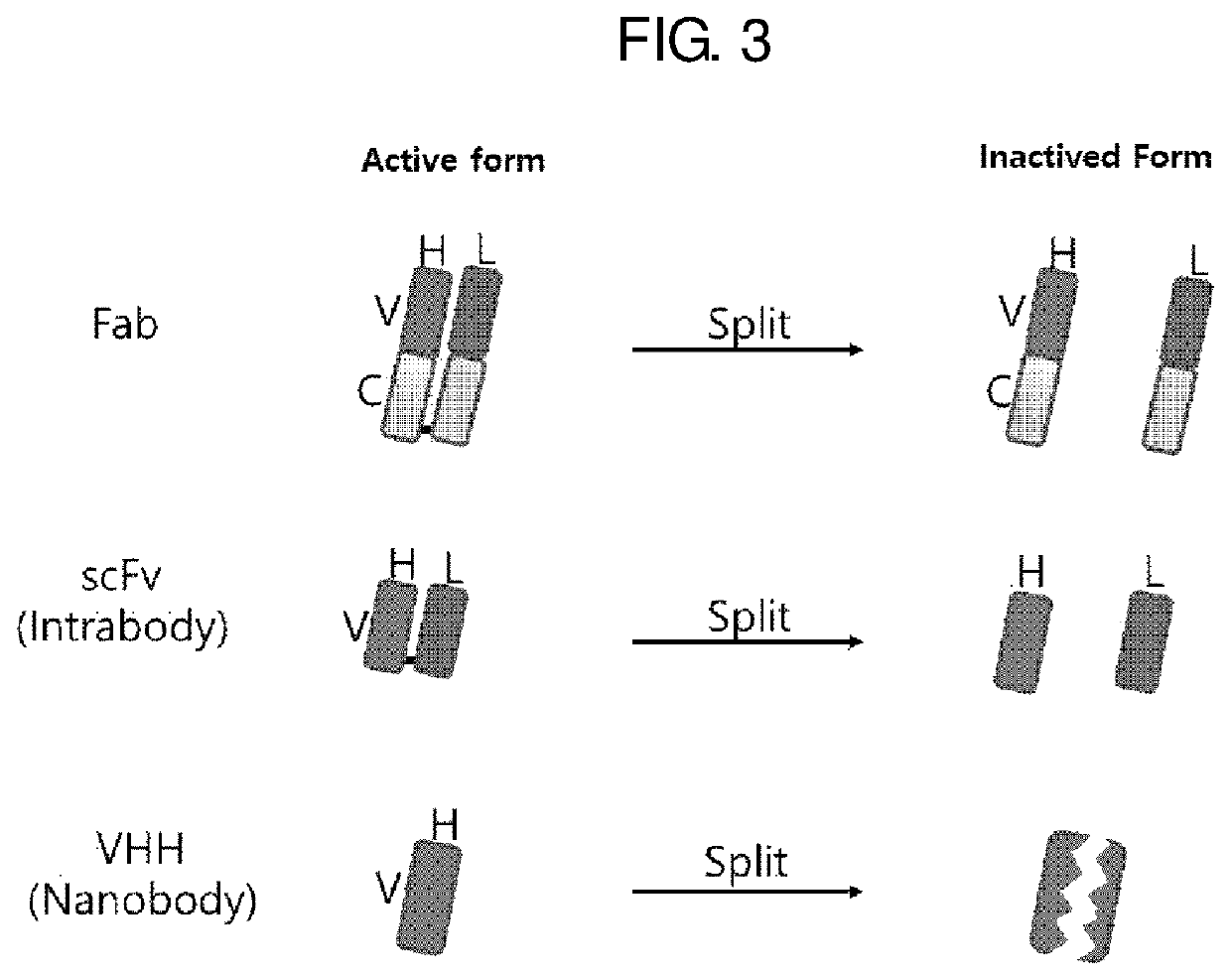
Antibody mimetic capable of being activated reversibly and uses thereof
ActiveUS11155604B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesBiochemistry
The present invention relates to the preparation of an antibody analogue capable of being activated reversibly, and uses thereof, and provides a fusion protein comprising an inactive first fragment of an antibody analogue is fused to a stimulus-induced dimerization protein.
Owner:INST FOR BASIC SCI
Compositions and methods for modulating kinase activity
ActiveUS11104741B2Prevent proliferationReduced survivalPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCompound screeningAntigenKinase activity
The present invention features an antibody mimetic, or an antigen binding fragment thereof, that specifically binds to an allosteric site of Aurora A kinase, therapeutic compositions comprising this antibody mimetic, and the use of the monobody to modulate Aurora A kinase for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com