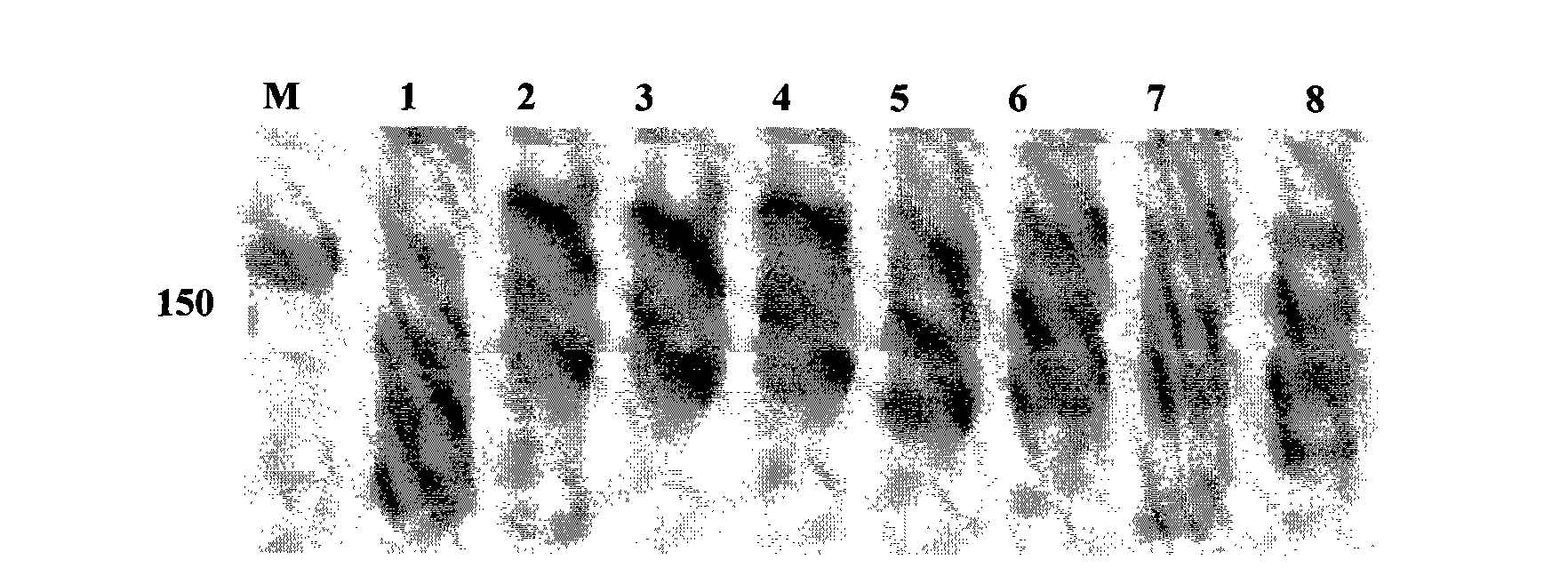
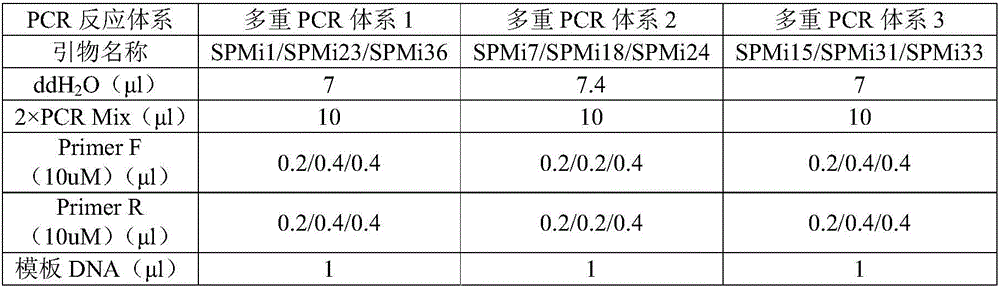
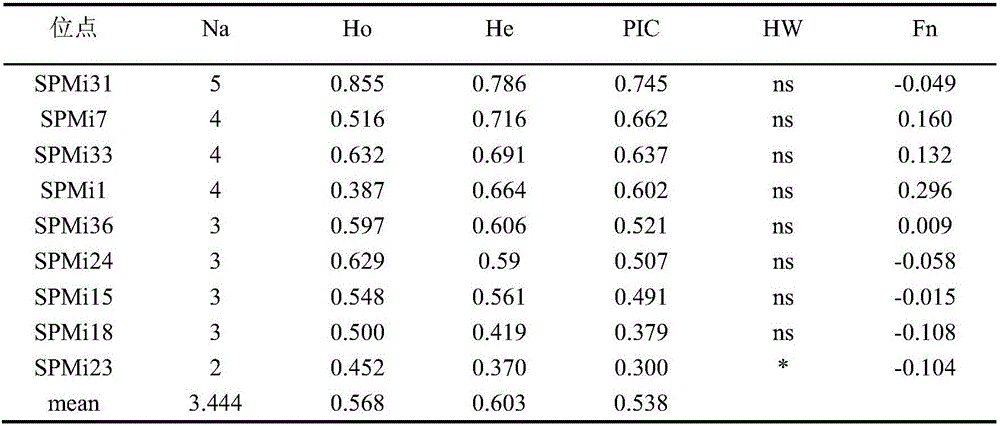
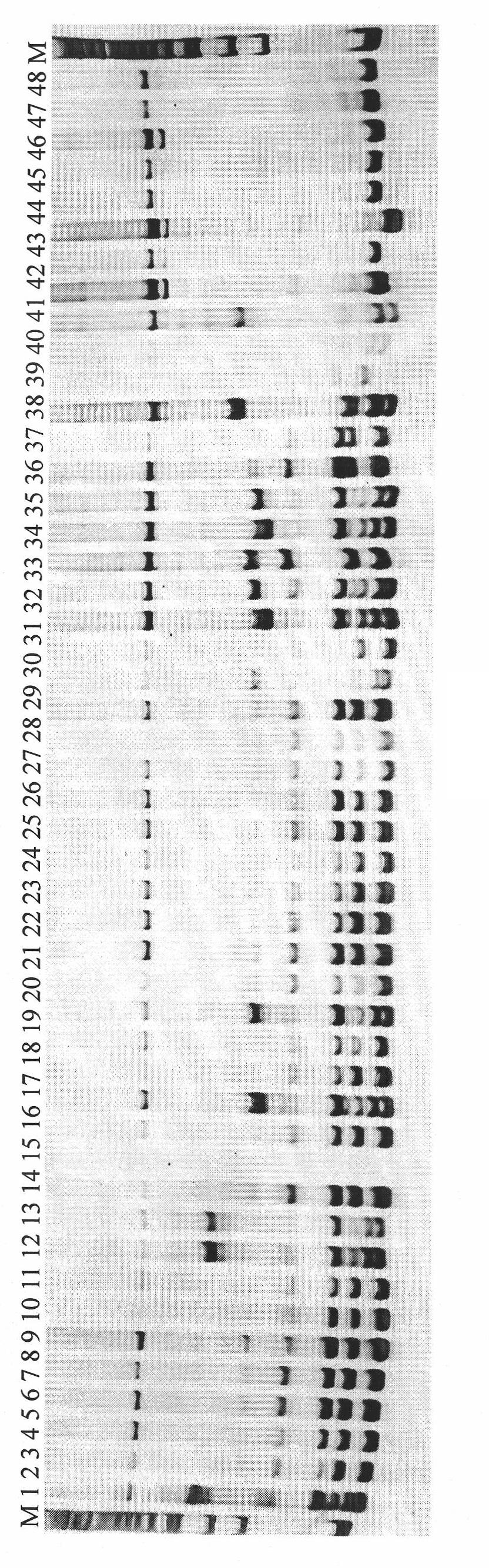
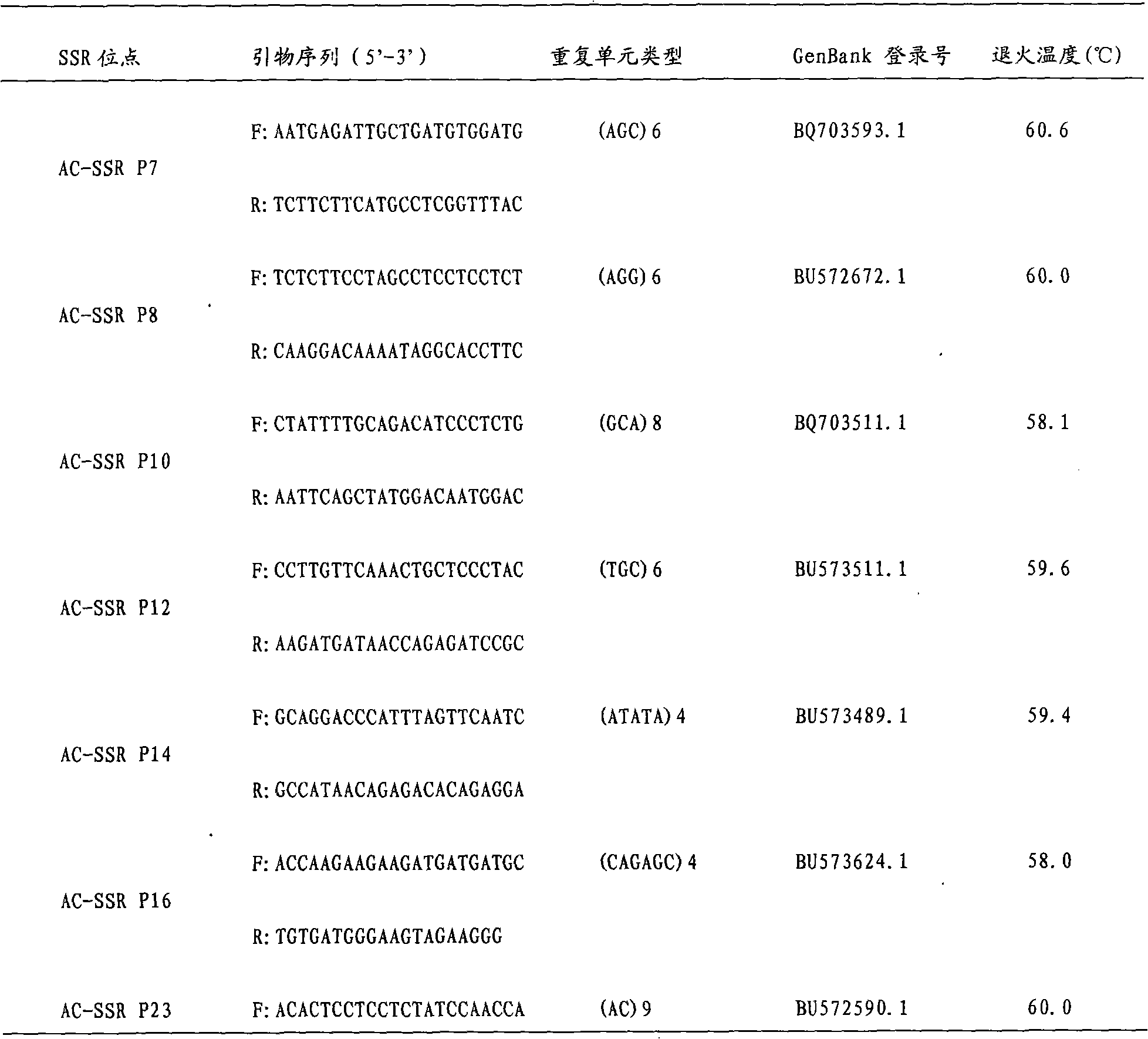
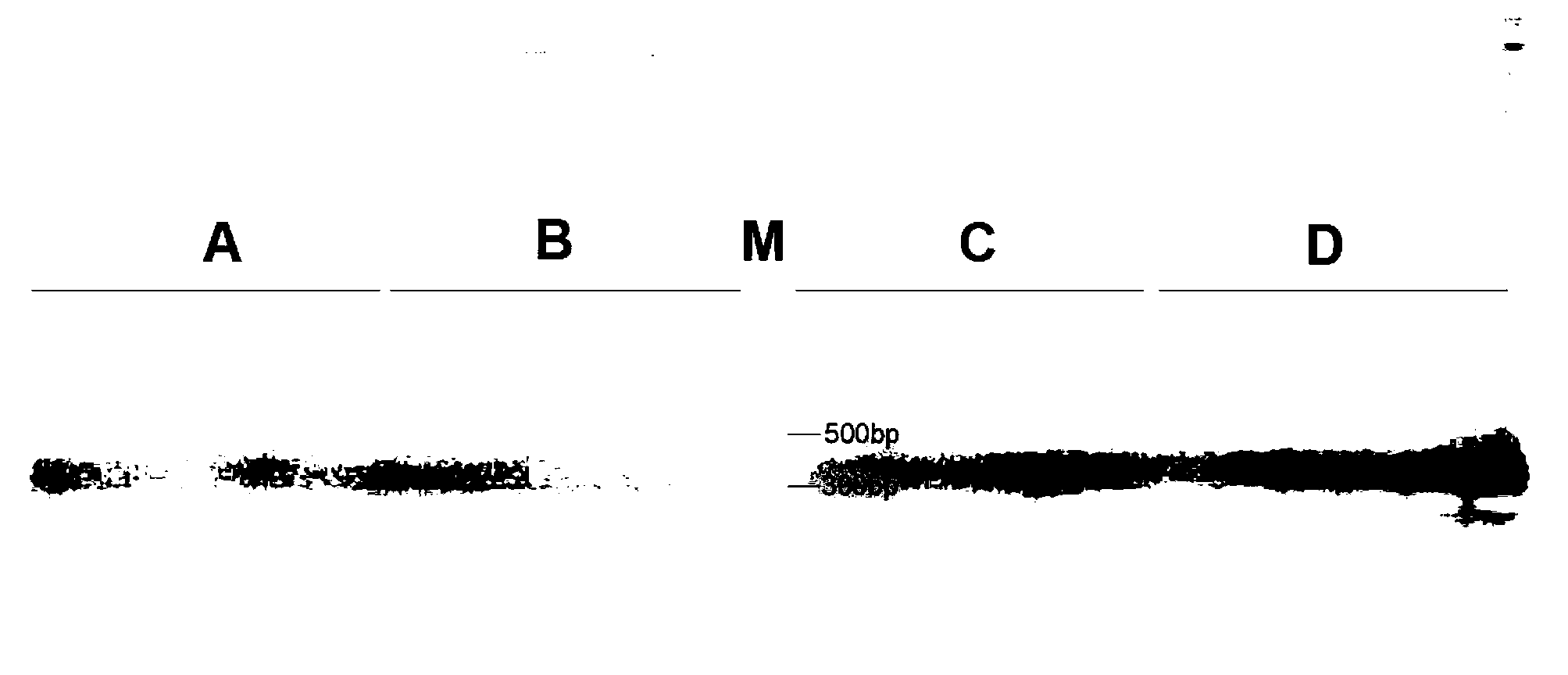
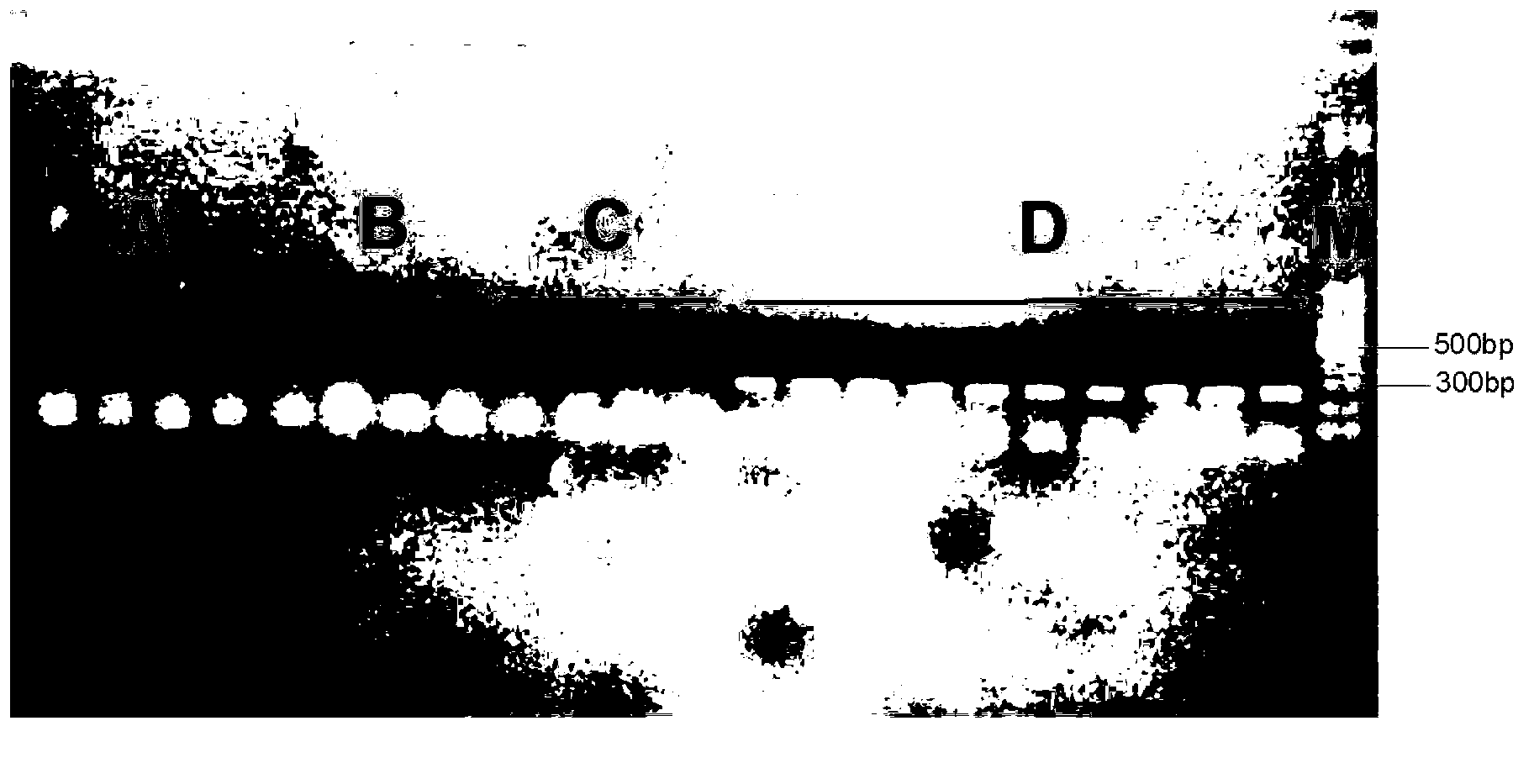
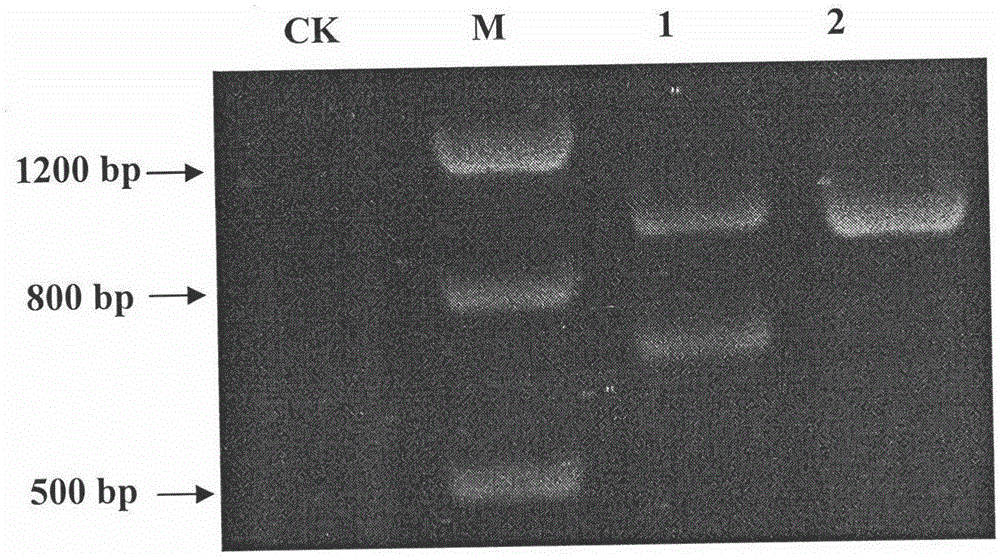
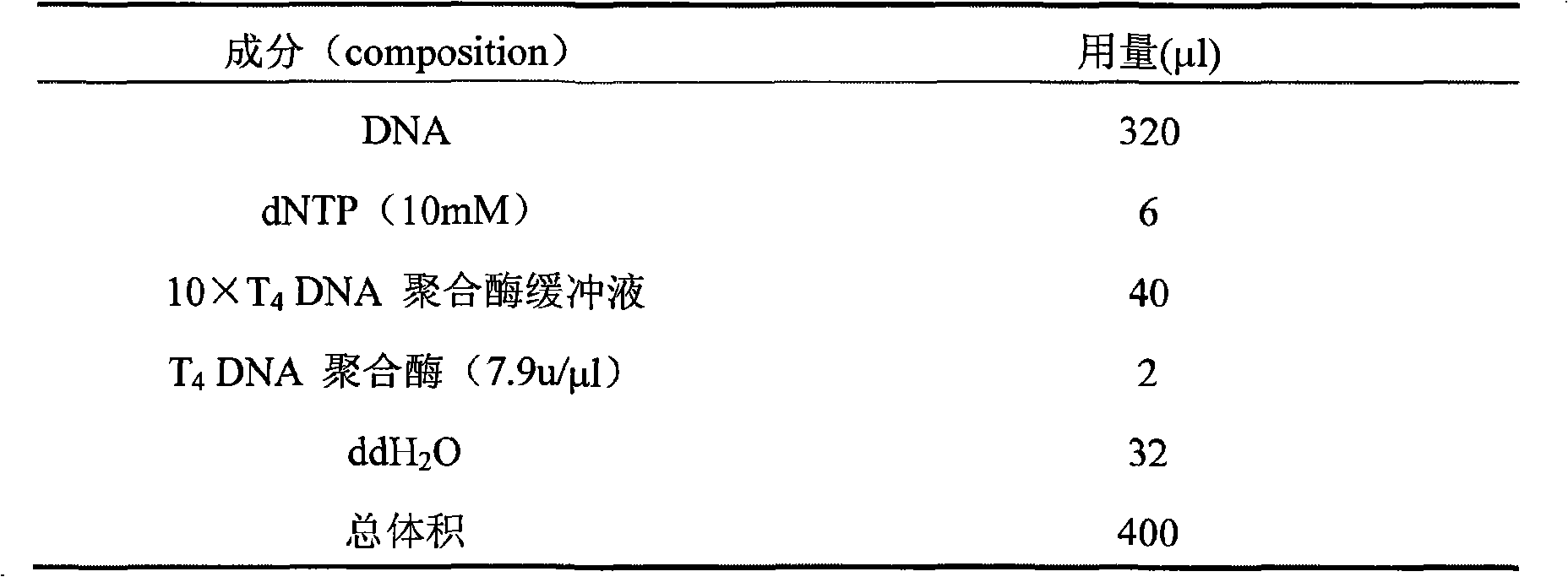
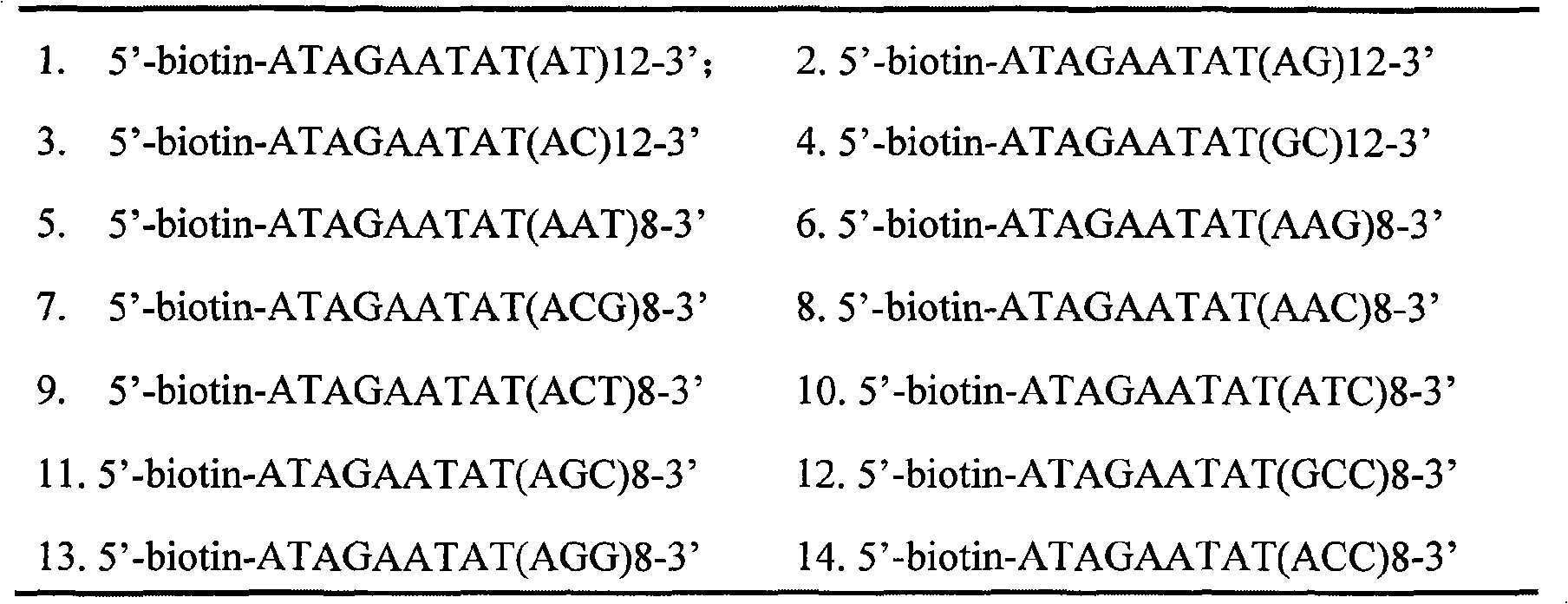
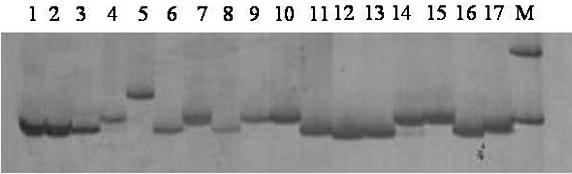
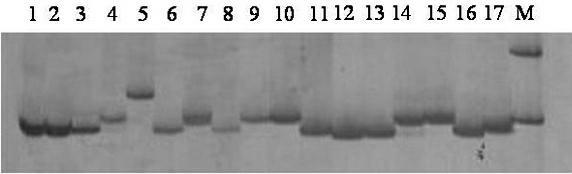
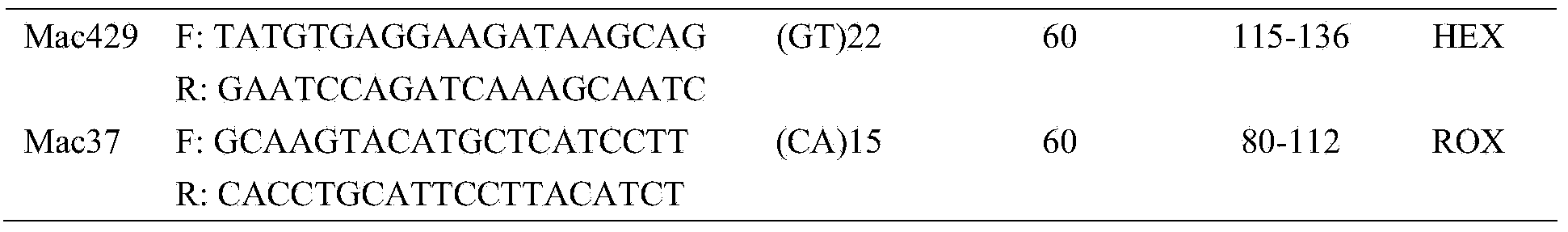
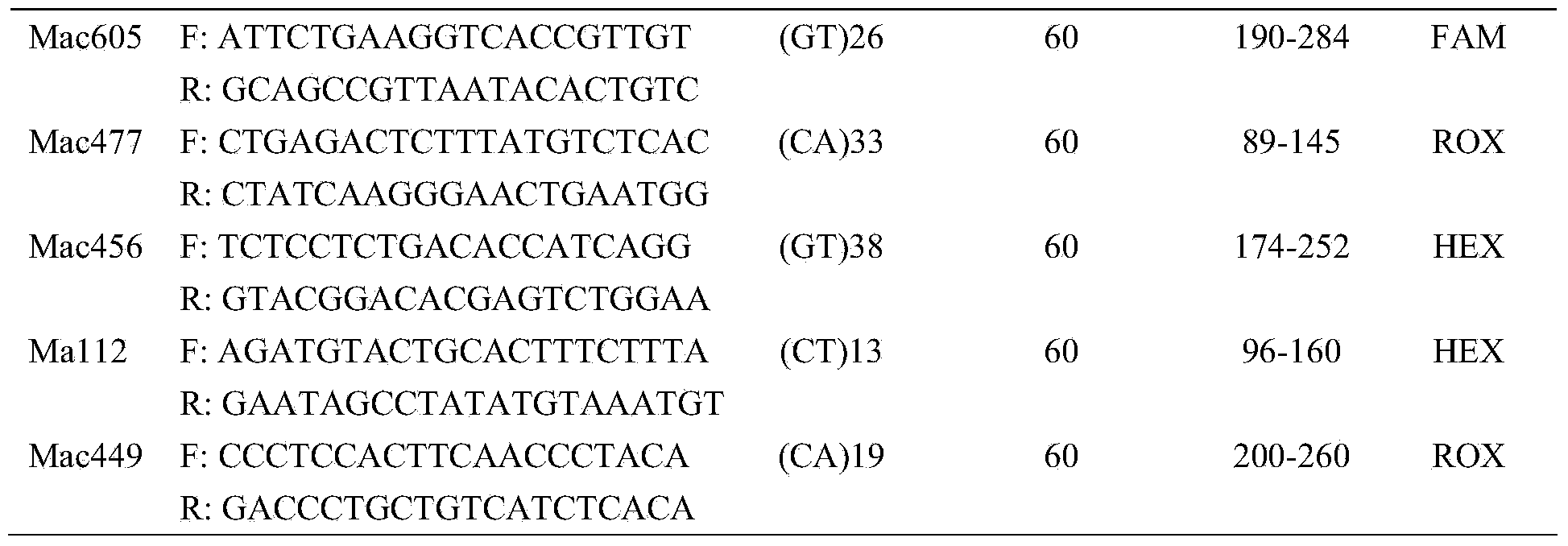
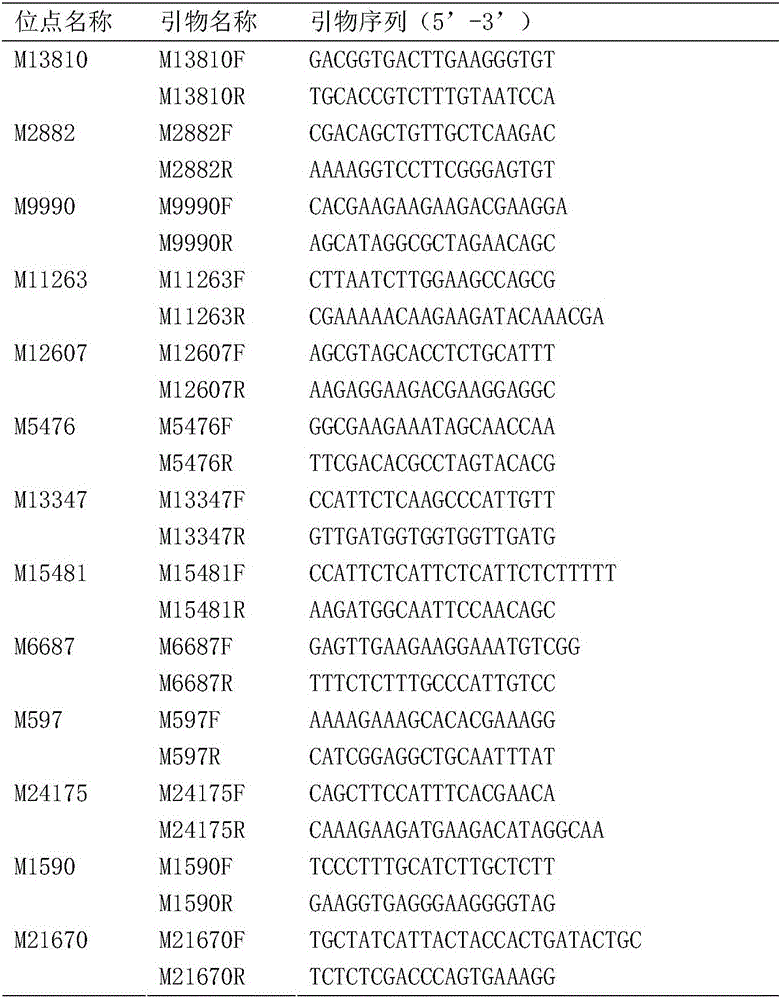
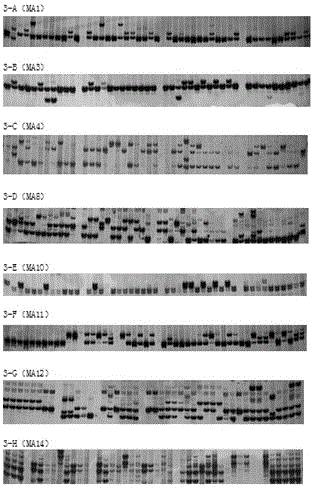
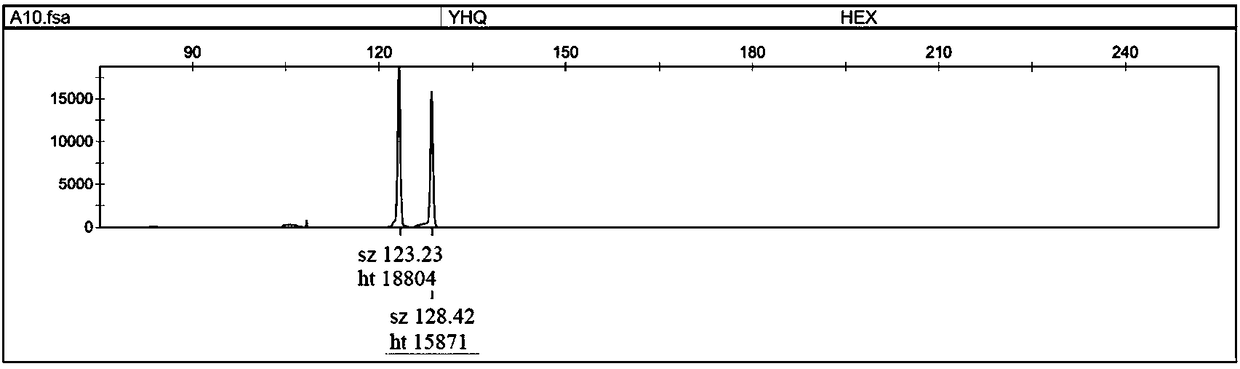
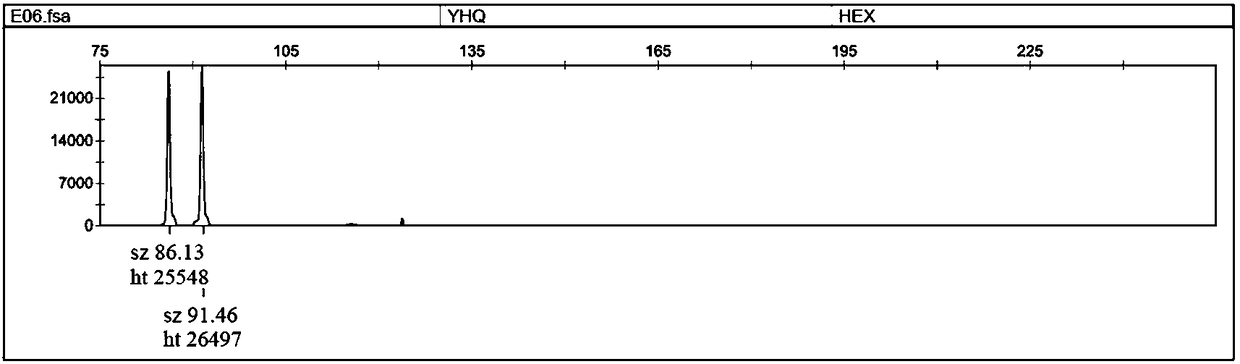
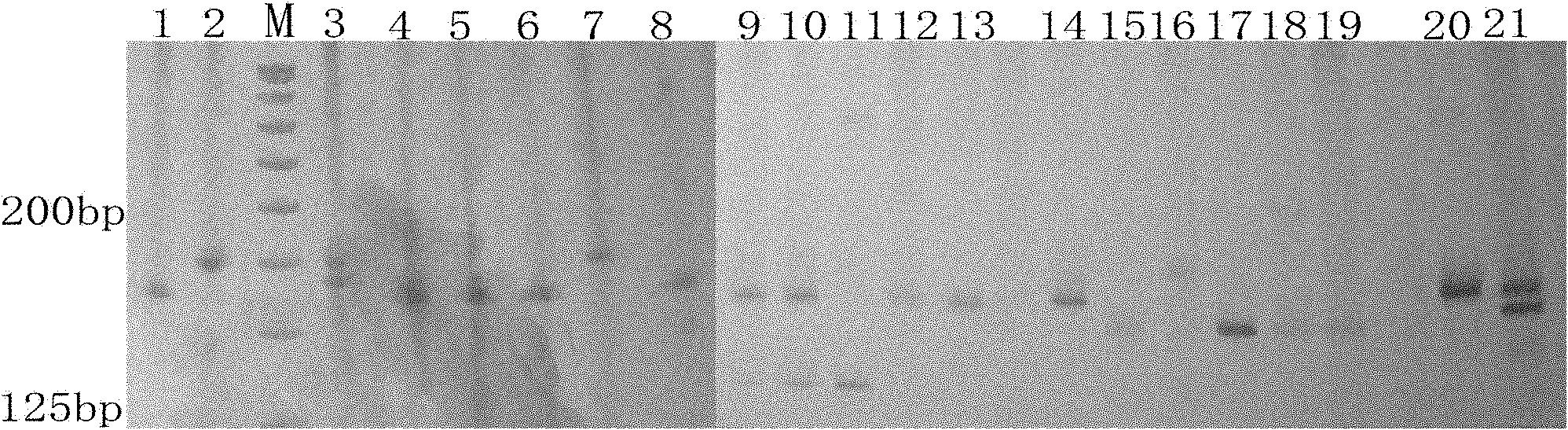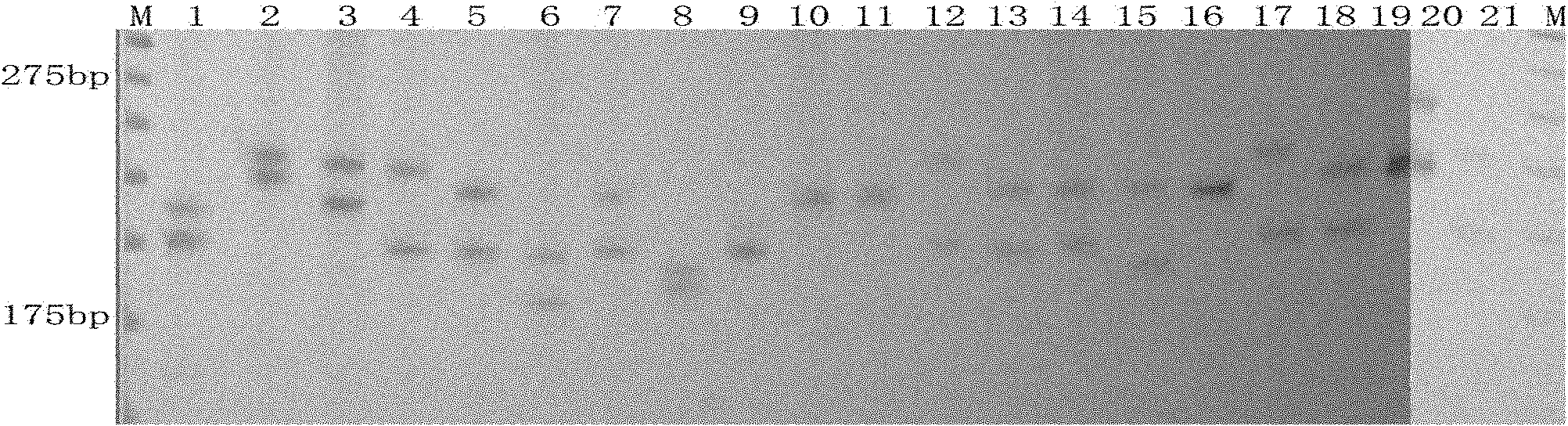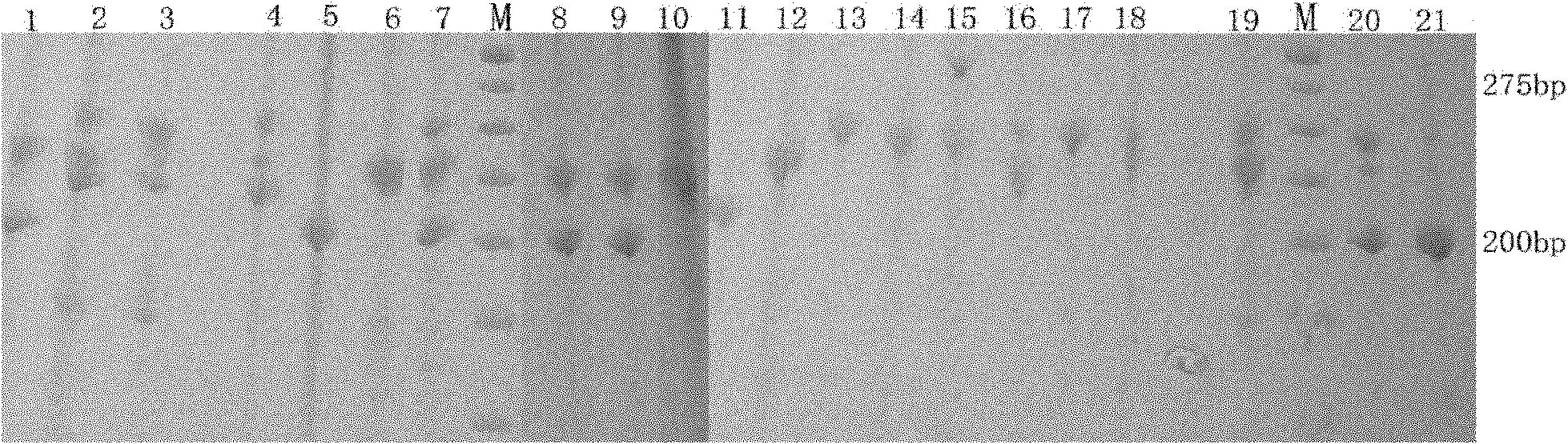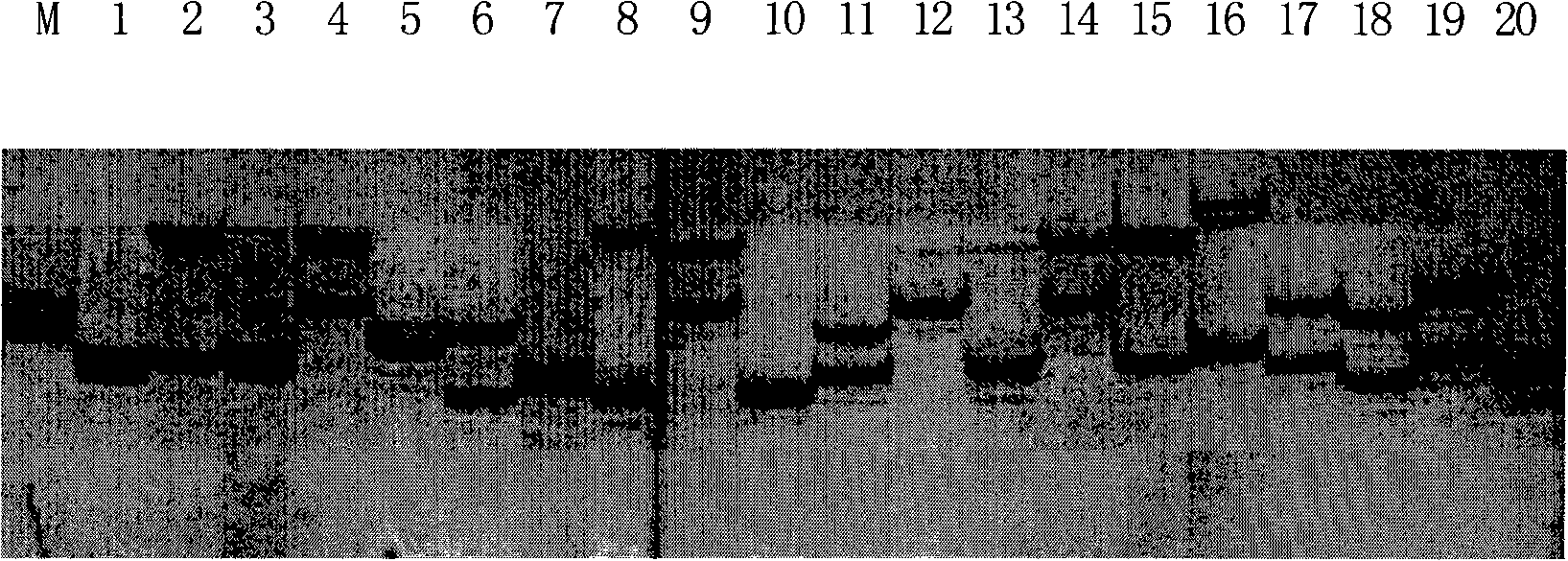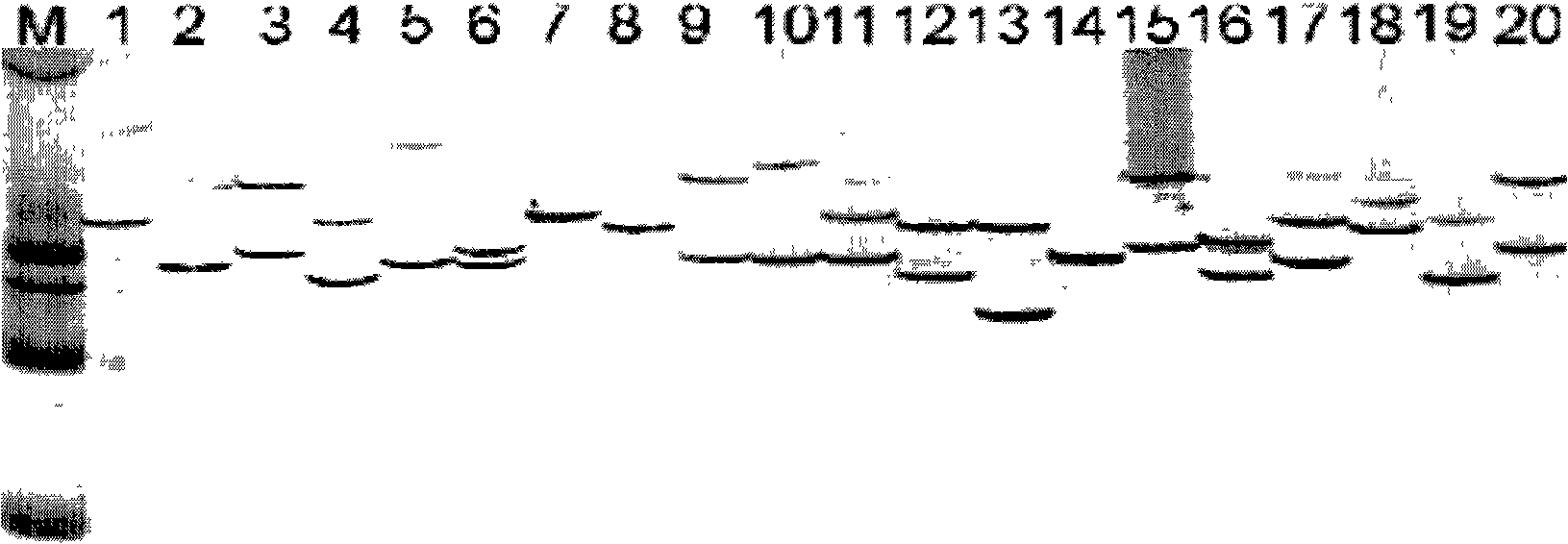Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Alphasatellite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alphasatellites are single stranded satellite DNA that are dependent on a virus for transmission. The genome is a single circular single strand DNA molecule. The first alphasatellites were described in 1999 and were associated with cotton leaf curl disease and Ageratum yellow vein disease. As begomoviruses are being characterised at the molecular level an increasing number of alphasatellites are being described.
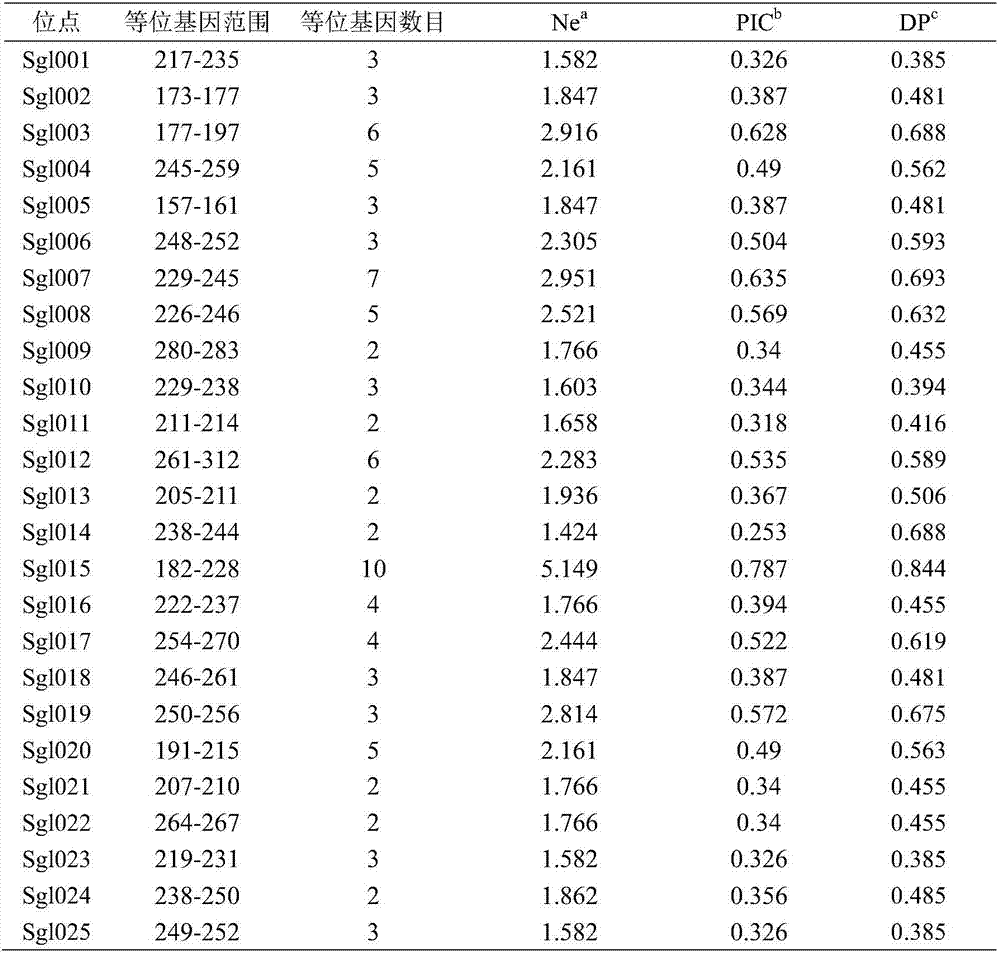
Microsatellite molecular marker of lycoris
The invention discloses a microsatellite deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecular marker of lycoris. 33 microsatellite DNA-containing clones are obtained and 10 microsatellite molecular markers with rich polymorphism, namely Lyra-1, Lyra-2, Lyra-3, Lyra-4, Lyra-5, Lyra-6, Lyra-7, Lyra-8, Lyra-9 and Lyra-10, are determined by establishing a lycoris microsatellite (CT)n enrichment library, screening and sequencing the positive clones of the microsatellite. The marker can be used for researching genetic diversity protection of the lycoris and variation and evolution relation between species and populations of lycoris plants and identifying the varieties of the lycoris; and the marker has high repeatability and is a reliable and effective molecular marker.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Cowpea chloroplast SSR molecule labeled polymorphic primers and screening method thereof, and method for identifying genetic relationship of cowpeas
ActiveCN103911372AComprehensive identificationLess prone to recombinationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenetic diversityScreening method
The invention discloses cowpea chloroplast SSR molecule labeled polymorphic primers and a screening method thereof and a method for identifying genetic relationship of cowpeas, belonging to the technical field of molecular biology of crops. The cowpea chloroplast SSR molecule labeled polymorphic primers are described in the specification. The method for identifying polymorphism of the cowpea chloroplast SSR molecule labeled primers comprises the following steps: extracting genomic DNAs of cowpeas of different varieties; mixing designed primers and the genomic DNAs and carrying out PCR amplification and electrophoretic separation; and acquiring the cowpea chloroplast SSR molecule labeled polymorphic primers. The method for identifying the genetic relationship of cowpeas comprises the following steps: extracting genomic DNA of a cowpea; carrying out PCR amplification and electrophoretic separation by using the cowpea chloroplast SSR molecule labeled polymorphic primers and recording statistical results; and carrying out genetic relationship analysis on the results. The polymorphic primers can reflect genetic information of plasmon of cowpeas and can be used for research on germplasm resource classification, genetic relationship identification, genetic diversity analysis and the like of cowpeas.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Microsatellite family identification method for ictalurus punctatus
ActiveCN107502663ASave human effortSave moneyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA paternity testingPolyculture
The invention discloses a microsatellite family identification method for ictalurus punctatus. The microsatellite family identification method comprises the following steps: (1) breeding an ictalurus punctatus family by adopting an artificial propagation method, and carrying out polyculture on 100 family descendants in one pond; (2) analyzing gene types of an ictalurus punctatus breeding group on 18 microsatellite marker sites by adopting a fluorescence marking primer and a multi-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification method; screening 10 effective microsatellite markers which have high polymorphism and are suitable for family identification; (3) optimizing a multi-PCR amplification system of the 10 microsatellite markers and analyzing gene types of the polycultured descendants on 10 microsatellite marker sites; (4) identifying a parental origin of each descendant according to the gene types of parents and the descendants. According to the microsatellite family identification method disclosed by the invention, a paternity testing method is established for the ictalurus punctatus for the first time and the identification accuracy reaches 96.6 percent; polyculture individual parents of the ictalurus punctatus can be rapidly and accurately identified. The microsatellite family identification method disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately carrying out family identification on the polyculture individual parents of the ictalurus punctatus, and the breeding effect is improved.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
Blue crab ptssr17 microsatellite DNA marker testing technique
ActiveCN101294217AEasy to detectSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatelliteGenotype
The invention relates to a detection technology by ptssr17 microsatellite DNA markers in a blue crab. The technology is characterized in that: first, genome DNA of the blue crab is extracted and diluted to reserve; second, by utilizing a ptssr17 microsatellite core sequence in a genomic library of the blue crab, specificity primers are designed at the two ends of the sequence thereof; third, the genome DNA of different geographic groups of the blue crab or individuals in a blue crab group is processed through the PCR amplification by using the primers, and PCR products are processed through the modified polyacrylamide gel detection; finally, bands which are generated in the products are utilized for analyzing so as to determine the genotype of each individual, thereby obtaining a polymorphic map on the enormous genetic variation of the blue crab in the a ptssr17 core sequence area. The polymorphic map that the ptssr17 genetic mark gene locus of the blue crab shows the enormous genetic variation can be obtained rapidly; the method is simple and convenient; the each individual genotype of the blue crab at the locus can be detected intuitively from the obtained results. The detection technology is mainly used in the genetic marks among the blue crab groups, the genealogical identification, the genetic map construction, etc.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Screening method for species group with heterosis of germany mirror carp
InactiveCN101403006AScreening results are accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatelliteCyprinus
The invention relates to a screening method of dominant hybridization species of German mirror carps and discloses a screening method of the dominant hybridization species of carps. The invention provides an effective screening method of the dominant hybridization species of the German mirror carps so as to ensure the genetic diversity of hybrids thereof, thus reducing the workloads, shortening the breeding period, decreasing the breeding cost and improving the success rate of selective breeding. The screening method includes the following steps: 1. morphological marker; 2. microsatellite molecular maker; and 3. data analysis. The method screens the dominant hybridization species of the German mirror carps by combining the morphological marker and the microsatellite molecular marker. The genetic differences between the species are dually tested and the screening results are more accurate.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
Molecule marking method for identifying tilapia nilotica, oreochromis aureus and hybridized fish thereof
InactiveCN102226220AAccurate identificationSmooth responseMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisMicrobiology
The invention relates to a molecule marking method for identifying tilapia nilotica, oreochromis aureus and hybridized fish thereof. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: selecting three pairs of specific microsatellite marked primer combinations; sampling blood or fins from tilapia to be detected; extracting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a gene group; performing multiple polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifications on the DNA of the gene group of the tilapia to be detected; performing electrophoretic separation on the PCR product with a 8.0 percent non-denatured polyacrylamide gel; dying by argentation; and photographing to record the electrophoretic results. According to the results of multiple PCR electrophoretic detection, the tilapia nilotica, the oreochromis aureus and the hybridized fish thereof can be identified. By the method, the tilapia nilotica, the oreochromis aureus and the hybridized fish thereof can be quickly and effectively identified.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Spinibarbus dneticulatus microsatellite family identification method
InactiveCN106399530AImprove efficiencyLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenetics
The method discloses a spinibarbus dneticulatus microsatellite family identification method. The method comprises carrying out artificial breeding on spinibarbus dneticulatus parents from the natural population to obtain two families, extracting a genomic DNA, designing and synthesizing a series of microsatellite primer sequences, carrying out PCR amplification on the genomic DNA, screening 9 pairs of the primers with high amplification stability, high polymorphism and high heterozygosity, combining the primers to form three multiplex PCR systems, respectively carrying out PCR amplification on the genomic DNA to obtain a multiplex PCR product, analyzing the multiplex PCR product, and determining the parents in a parent-child relationship with the individual to be detected. The method provides novel technological means for assessment of identification of the spinibarbus dneticulatus family, seed quality management and proliferation and release effects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Amygdalus communis EST (expressed sequence tag) microsatellite marker screening method
The invention relates to an Amygdalus communis EST (expressed sequence tag) microsatellite marker screening method. For the sequence of ESTs of Amygdalus communis disclosed by GeneBank, microsatellite retrieval software WebSat is used to excavate an EST microsatellite molecular marker and screen out two pairs of high-polymorphism Amygdalus communis microsatellite primer sequences. The Amygdalus communis microsatellite DNA marker is used for researches on the resource evaluation, the identification and the genetic diversity analysis of the Amygdalus communis, the construction of a genetic map, the molecular auxiliary selective breeding and the like, thereby being a reliable and effective molecular marker.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Primer and method for authenticating frankliniella occidentalis by using expressed sequence tag (EST) microsatellite markers
InactiveCN103255223ASimple and Stable Molecular MarkersSolving the Puzzle of Differentiating Western Flower ThripsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic DNAMicrosatellite
The invention relates to a primer and a method for authenticating frankliniella occidentalis by using expressed sequence tag (EST) microsatellite markers. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting the genomic DNA of thrips; (2) performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on the genomic DNA of thrips, which serves as a template; and (3) performing sepharose gel electrophoretic analysis on an enzyme-digested product prepared in the step (2). By the authentication method, simple and stable molecule markers are supplied to screening of frankliniella occidentalis and other three types of thrips and a foundation is laid for the future research on the population dynamic authentication, the biology and an invasive mechanism of frankliniella occidentalis.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for quickly and synchronously detecting tomato yellow leaf curl virus and accompanying China tomato yellow leaf curl virus satellite
InactiveCN105018649AFast sync detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSerum igeTomato yellow leaf curl virus
The invention provides a method for quickly and synchronously detecting two virus components, including the tomato yellow leaf curl virus and the accompanying China tomato yellow leaf curl virus satellite, on tomatoes, and belongs to the field of plant protection. According to the nucleotide sequence of the tomato yellow leaf curl virus and the nucleotide sequence of the China tomato yellow leaf curl virus satellite, two pairs of primers are designed, namely TYmF / TYmR and TycnbF / TycnbR, wherein the TYmF / TYmR combination is used for detecting the tomato yellow leaf curl virus, and the TycnbF / TycnbR combination is sued for detecting the China tomato yellow leaf curl virus satellite. After total DNAs are extracted from a sample, only one time of PCR is needed to achieve detection of the two components including the tomato yellow leaf curl virus and the accompanying China tomato yellow leaf curl virus satellite. The method solves the problems existing in traditional biology, serology, electron microscopy observation and other methods. Compared with the traditional method that a virus is detected through one-time PCR, the detection method reduces cost, saves time and is a special, sensitive, economical and convenient method.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES +1
Blue crab ptssr36 microsatellite DNA marker testing technique
ActiveCN101294218AEasy to detectSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatelliteGenotype
The invention discloses a detection technology by ptssr36 microsatellite DNA markers in a blue crab. The detection technology is characterized in that: first, genome DNA of the blue crab is extracted and diluted to reserve; second, by utilizing a ptssr36 microsatellite core sequence in a genomic library of the blue crab, specificity primers are designed at two ends of the sequence thereof; third, the genome DNA of different geographic groups of the blue crab or individuals in a blue crab group is processed through the PCR amplification by using the primers, and PCR products are processed through the modified polyacrylamide gel detection; finally, bands which are generated in the products are utilized for analyzing so as to determine the genotype of each individual, thereby obtaining a polymorphic map on the enormous genetic variation of the blue crab in the a ptssr36 core sequence area. The polymorphic map that the ptssr36 genetic mark gene locus of the blue crab shows the enormous genetic variation can be obtained rapidly; the method is simple and convenient; the each individual genotype of the blue crab at the locus can be detected intuitively from the obtained results. The detection technology is mainly used in the genetic marks among the blue crab groups, the genealogical identification, the genetic map construction, etc.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
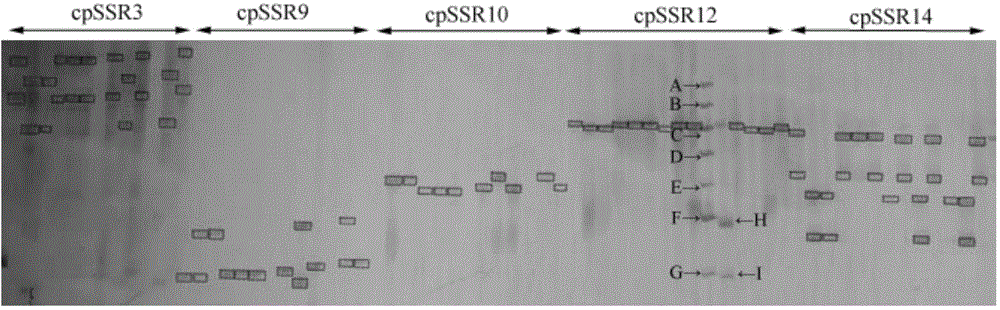
Camellia polymorphic chloroplast genome microsatellite molecular marker primers and method for screening and discriminating related species
ActiveCN109337997AEfficient developmentAvoid the Phenomenon of "Misidentification"Microbiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCapillary electrophoresisGenetic diversity
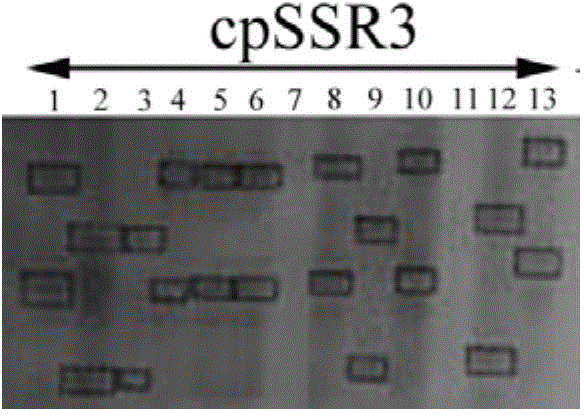
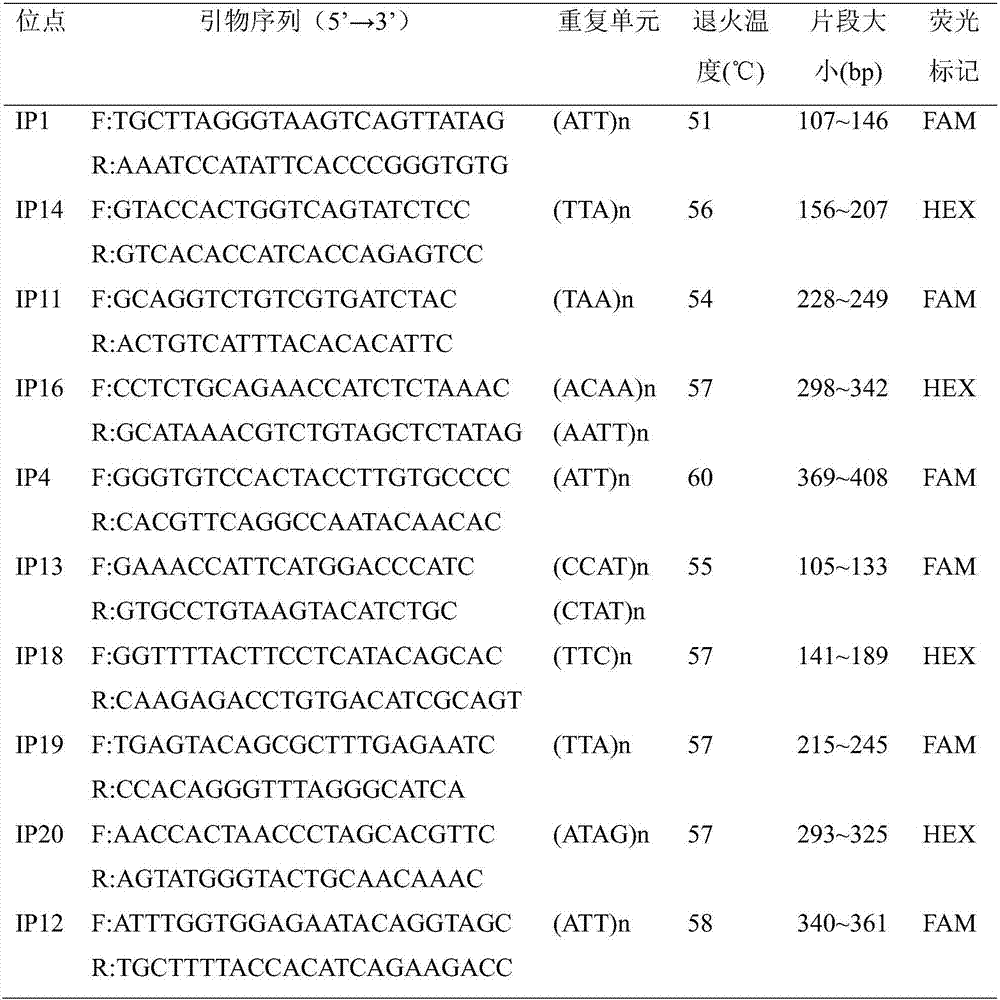
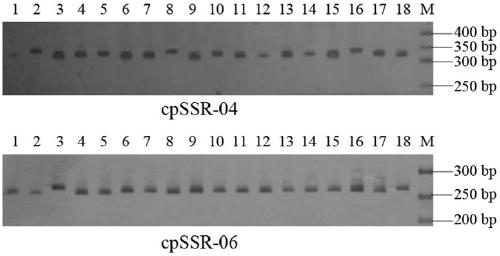
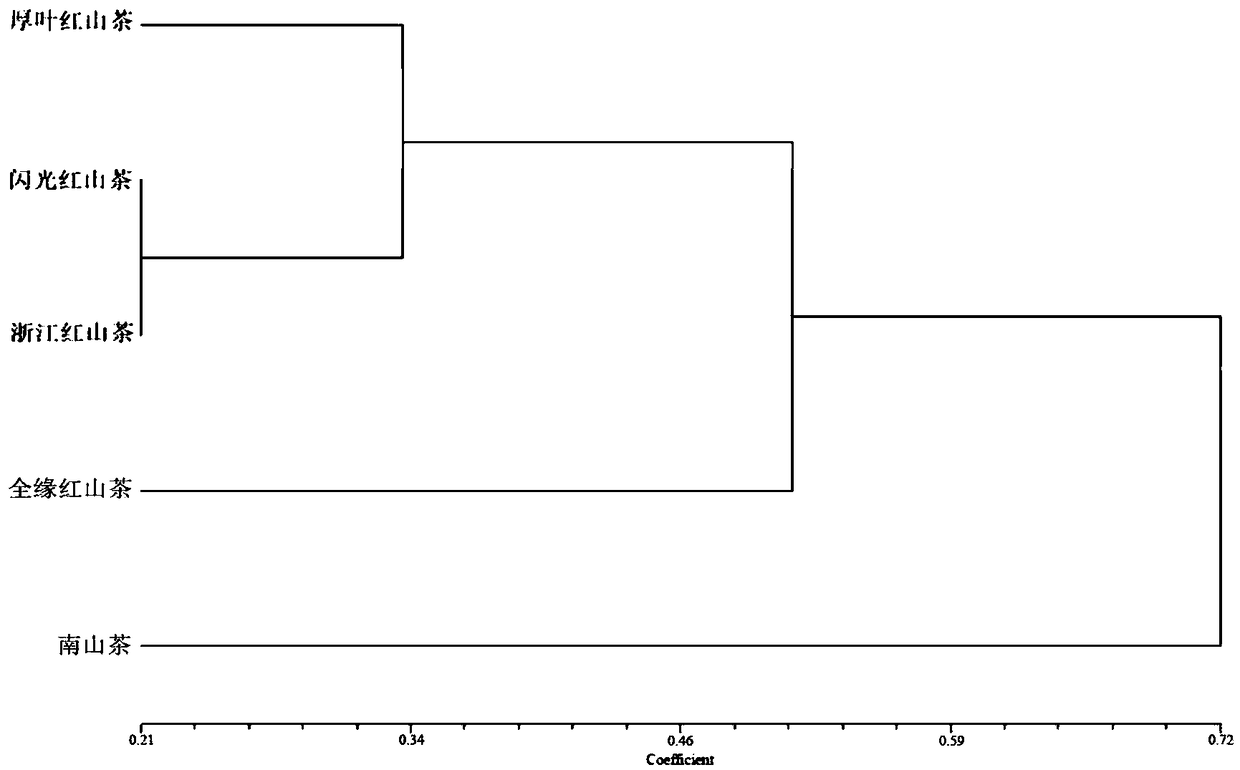
The invention belongs to the technical field of forestry molecular biology and particularly relates to camellia polymorphic chloroplast genome microsatellite molecular marker primers and a method forscreening and discriminating related species. Based on the relative consistency of camellia species chloroplast DNA sequence microsatellite sites, cpSSR primers are designed aiming at the specific microsatellite sites with interspecies variation; DNA of different camellia species is execrated, mixed with the primers and amplified and then is subjected to electrophoresis detection; finally, the 16pairs of camellia polymorphic chloroplast genome microsatellite molecular marker primers are obtained. The method for discriminating the related species comprises the following steps: extracting bothDNA of Zhejiang red camellia and DNA of related species of the Zhejiang red camellia, performing capillary electrophoresis separation by adopting the polymorphic primers, and separating and discriminating the related species according to PCR product fragments. The primer screening method provided by the invention is quick, efficient and widely applicable to other plant species with chloroplast genome sequence information; an obtained polymorphic cpSSR marker can be used for the systematic classification of camellia plants, related species discrimination, genetic diversity analysis and other studies.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
STR (short tandem repeats) molecular markers for Sporothrix globosa and applications of STR molecular markers
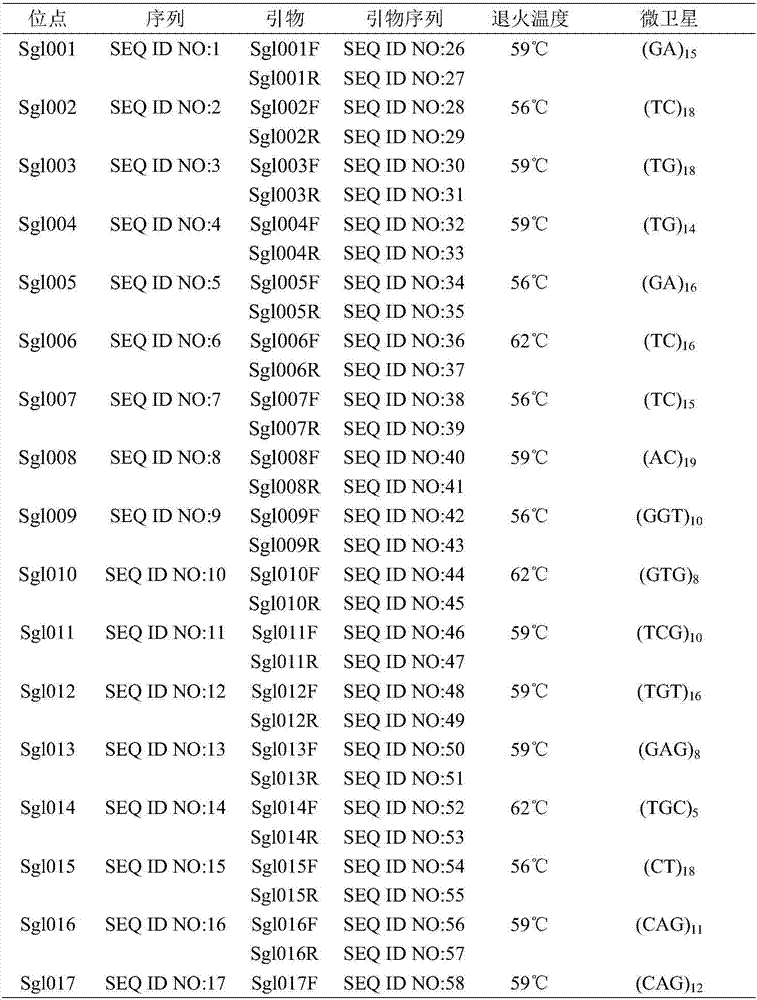
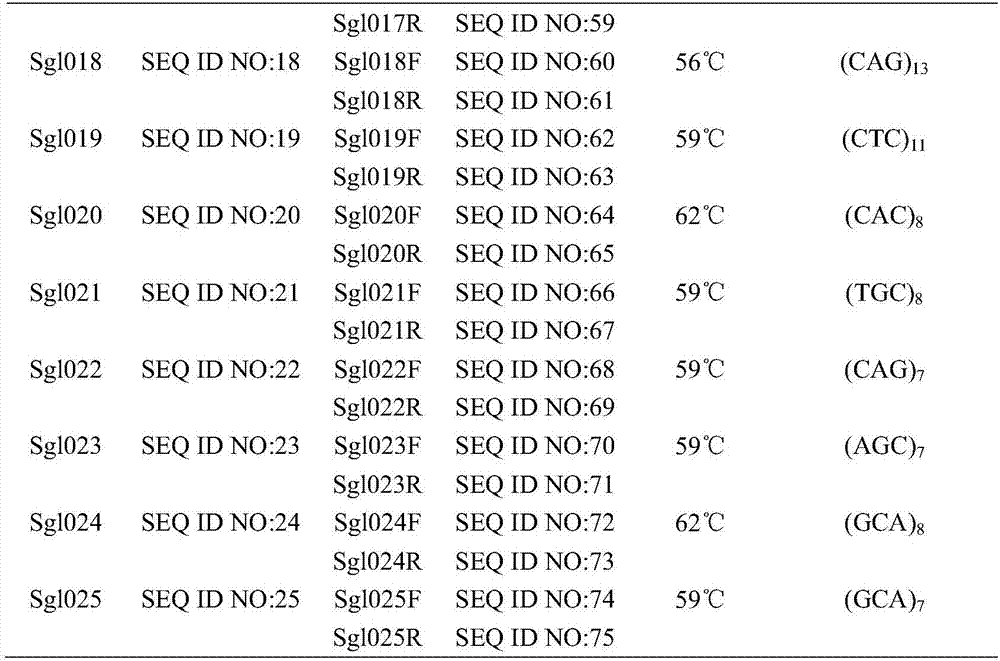
The invention relates to STR (short tandem repeats) molecular markers for Sporothrix globosa and applications of the STR molecular markers. The invention provides a microsatellite locus (STR molecular marker) combination for the Sporothrix globosa for the first time and provides a set of specific primers (SEQ ID NO:26-75) capable of efficiently amplifying Sporothrix globosa populations as well as detection conditions. The microsatellite locus combination contains 25 highly polymorphic microsatellite loci (SEQ ID NO:1-25). The set of microsatellite loci for the Sporothrix globosa not only can be applied to genetic background analysis and molecular tracing of the Sporothrix globosa, but also can be applied to molecular epidemiology, population genetics and phylogenetic analysis of the Sporothrix globosa.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Geographically-specific Plasmodium vivax molecule marker, and its application in strain tracing
PendingCN103865979AGuaranteed to be scientificTo achieve the purpose of traceabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicrosatelliteMosquito infection
The invention relates to a geographically-specific Plasmodium vivax molecule marker, and its application in strain tracing. The molecule marker includes a Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein center replication region reflecting mosquito infection differences of different media, a height polymorphism microsatellite reflecting mutation, migration and genetic drift, and a drug resistance related gene mutation reflecting the population positivity selection of drug control. Results show that each of a Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein center replication region sequence, dihydrofolate reductase SNP, dihydrobiopterin synthetase SNP, a neutral microsatellite and the like has a geographic specificity, and can be used as a classification index in tracing detection.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Method for authenticating Beijing fatty chickens by microsatellite markers
ActiveCN103374629ASimple and fast operationLow detection costMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele frequencyMicrosatellite
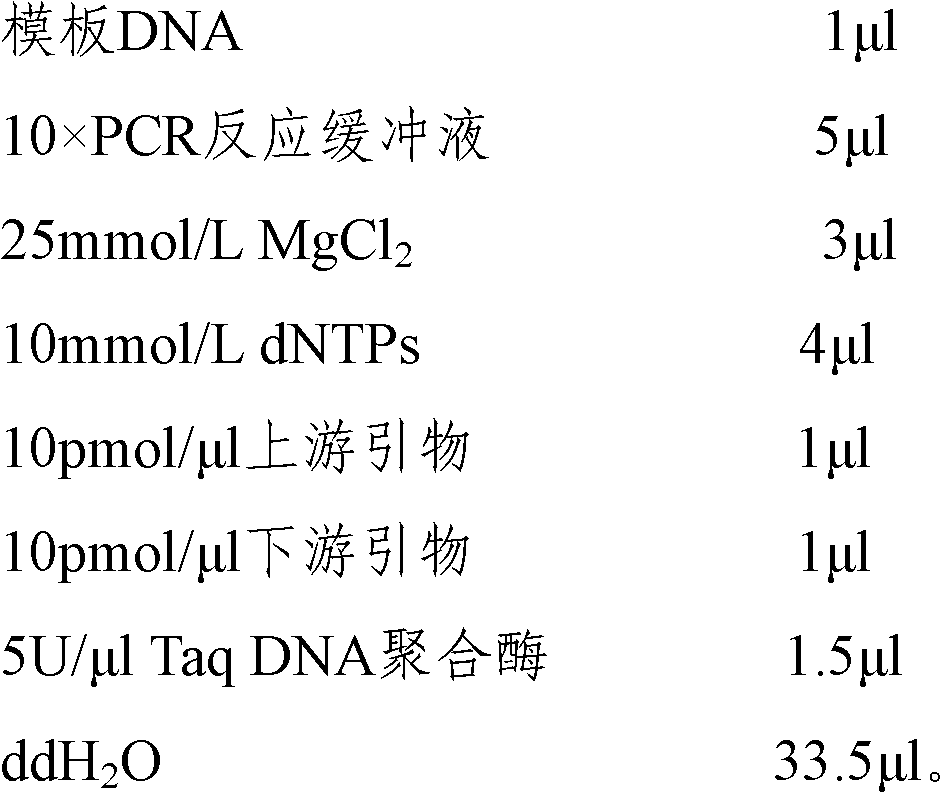
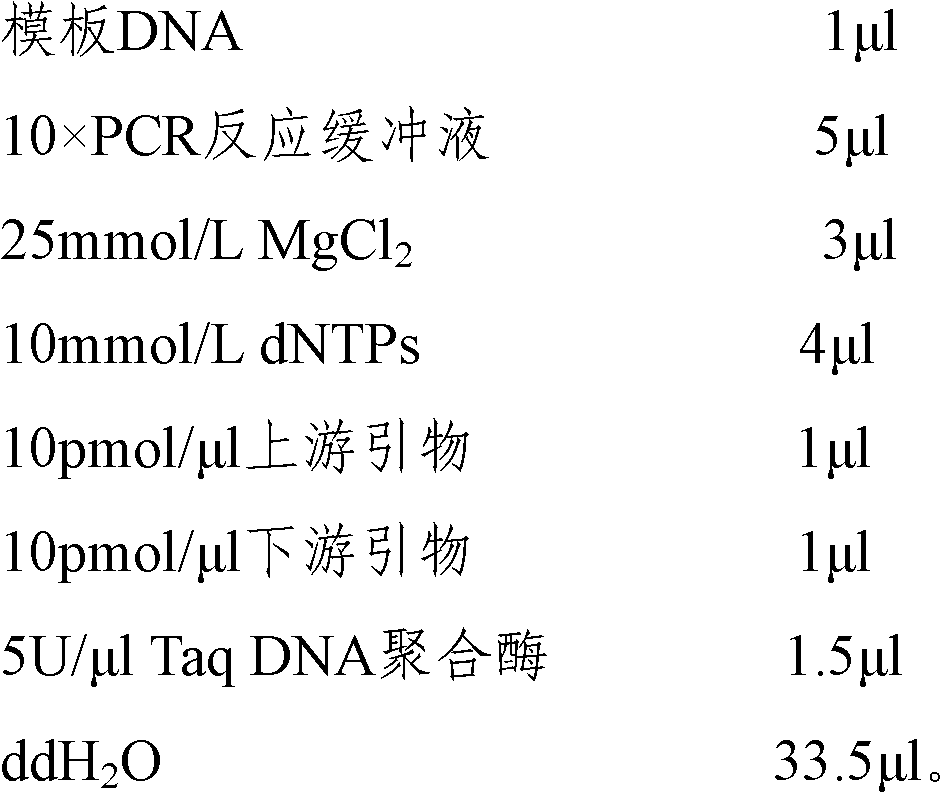
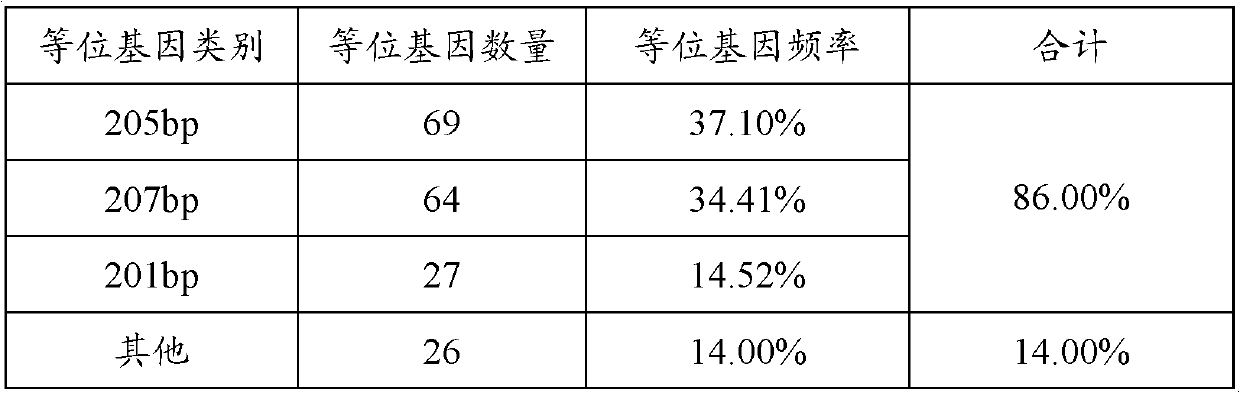
The invention provides a method for authenticating Beijing fatty chickens by microsatellite markers. The method comprises the following steps of: performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) multiplication and sequencing on an LEI0070 microsatellite seat by taking a gene group of a chicken to be authenticated as a template and 5'-TGCGGAGAGCAATTAGTCTGC-3' and 5'-GGAAAACAATCACTGCCTCG-3' as primers, counting the frequencies of allelic genes on the microsatellite seat according to a sequencing result, and if the sum of the frequencies of three allelic genes, namely 201 bp, 205 bp and 207 bp, is over 75 percent, authenticating the chicken to be authenticated as the Beijing fatty chicken. The method has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, low detection cost and high accuracy.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chinese hamster microsatellite genetic marker and screening method thereof
InactiveCN101328500AImprove standardizationImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRestriction enzyme digestionScreening method
The invention relates to an animal DNA molecule heredity mark technique, in particular to a Chinese hamster microsatellite heredity mark and a selecting method thereof to solve the problems that the report on the Chinese hamster microsatellite mark is not presented and the method for selecting the microsatellite mark that the DNA genome is broken down by the restriction enzyme digestion has a plurality of problems. The Chinese hamster genome DNA is extracted and is broken down by ultrasonic, and the DNA segment is reclaimed by electrophoresis. A Chinese hamster genome microsatellite enriched library is established, positive cloning vectors are selected from the library for sequencing. 17 microsatellite marks are obtained by selection. According to the microsatellite repetitive sequence, a primer is designed and 17 pairs of primers are selected for the heredity detection. When the method is used, the PCR amplification is performed on genome DNA of different individuals in a colony or of different colonies of Chinese hamster by using the 17 pairs of the primers. The electrophoresis detection is performed on the amplification product. According to the detection data and a map, the gene of each individual is determined. The method has good stability, high repetitiveness, strong comparability and simple operation.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Flax micro-satellite DNA mark
The invention discloses a flax micro-satellite DNA mark and provides a DNA sequence of 25 flax micro-satellite loci and an enlarging method for enlarging the primer sequence of the 25 flax micro-satellite loci. The 25 flax micro-satellite loci are used for classifying flax species, analyzing the genetic affinity and marking auxiliary culturing. With favorable repetitiveness, the flax micro-satellite DNA mark is a reliable and effective molecular mark.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microsatellite marker relevant with tachysurus fulvidraco growth characteristics and detection and application thereof
ActiveCN106167825AIncrease genetic diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a microsatellite marker relevant with tachysurus fulvidraco growth characteristics and detection and application thereof. That is, four microsatellite loci are found on a tachysurus fulvidraco GH sequence, the microsatellite loci are amplified by screening specific primers, relevance between the microsatellite loci and growth traits is analyzed, and dominant genotypes favorable for the growth traits are found. Results indicate that three loci are remarkably or extremely remarkably relevant with the growth traits, a locus GA is remarkably relevant with body weight, body length, standing height and body thickness and is extremely remarkably relevant with total length and depth of caudal peduncle, wherein CD is a dominant genotype; a locus TCTT is remarkably relevant with head length and depth of caudal peduncle, wherein BD is a dominant genotype; and a locus AC is remarkably relevant with body thickness and head length, wherein DD is a dominant genotype. The four microsatellite loci obtained by primer amplification have high genetic diversity and are remarkably or extremely remarkably relevant with the growth traits. The microsatellite marker is of great significance for molecular breeding practice.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for identifying fx151 genetic variation map by using litopenaeus vannamei boone fx151 microsatellite DNA marker
InactiveCN101967519AGood polymorphismImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatelliteGenotype
The invention discloses a method for identifying an fx151 genetic variation map by using a litopenaeus vannamei boone fx151 microsatellite Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) marker, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: extracting a litopenaeus vannamei boone genome and diluting for later use, designing specific primers at two ends of a sequence by utilizing a litopenaeus vannamei boone fx151 microsatellite DNA core sequence, performing Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification on genomes DNA of different groups or individuals in the groups of the litopenaeus vannamei boone by using the primers, and performing denaturing polyacrylamide gel detection on a PCR product; and performing silver staining development by utilizing stripes generated by the product and analyzing, and determining a genotype of each individual to obtain a polymorphic genetic variation map of the litopenaeus vannamei boone at a fx151 genetic marker gene locus. The method can rapidly obtain the polymorphic map of the litopenaeus vannamei boone fx151 genetic marker gene locus which presents high genetic variation, is convenient and simple, and the obtain result can intuitively detect the genotype of each individual litopenaeus vannamei boone.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Detection method of ecssr1024 microsatellite dna marker in white shrimp
ActiveCN102277438ASimple methodAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementExopalaemon carinicaudaMicrosatellite
The invention provides a method for detecting an EcSSR1024 microsatellite DNA marker in exopalaemon carinicauda, which comprises: extracting genomic DNA of the exopalaemon carinicauda and diluting the genomic DNA for later use; designing specific primers at the two ends of the core sequence of an EcSSR1024 microsatellite; performing the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the genomicDNA of the exopalaemon carinicauda by using the primers, and detecting the product of the PCR amplification; and analyzing by using strips appeared in the product, and obtaining the polymorphic map of a highly-genetic variation in the core sequence area of the EcSSR1024 in the exopalaemon carinicauda. By using the primers and detection method, which are provided by the invention, the genetic variation in the core area of the EcSSR1024 microsatellite in each individual of exopalaemon carinicauda can be detected, and the polymorphic map of the highly-genetic variation in a genetic marker gene locus in the EcSSR1024 in exopalaemon carinicaud can be obtained quickly. The method is suitable to be used in population genetic marking, genealogical identification, genetic map construction and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Microsatellite family identifying method for diploid misgurnus anguillicaudatus and application of method
InactiveCN103966316AIncrease the number ofMeet the Genealogy AnalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicrosatelliteGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a microsatellite family identifying method for diploid misgurnus anguillicaudatus. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a full-sib family of diploid misgurnus anguillicaudatus; extracting parent and descendant genomic DNA of the diploid misgurnus anguillicaudatus; screening of polymorphism microsatellite marks and synthesizing a primer; conducting PCR amplification on the parent and descendant DNA samples adopting fluorescent PCR reaction; analyzing the parent genetype and the descendant genetype. The method is multiple in selected microsatellite locus allele number, high in polymorphism, and stable and reliable in PCR products; the probability of helping a descendant individual to find the natural male parent and the natural female parent utilizing the microsatellite locus is 97.8% and 99.6% respectively; the integral identification success rate is as high as 97.4%; requirements of family tree analysis and family management in heredity and breeding of the diploid misgurnus anguillicaudatus can be met fully; powerful technical guarantee is provided for molecular breeding research of the species.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
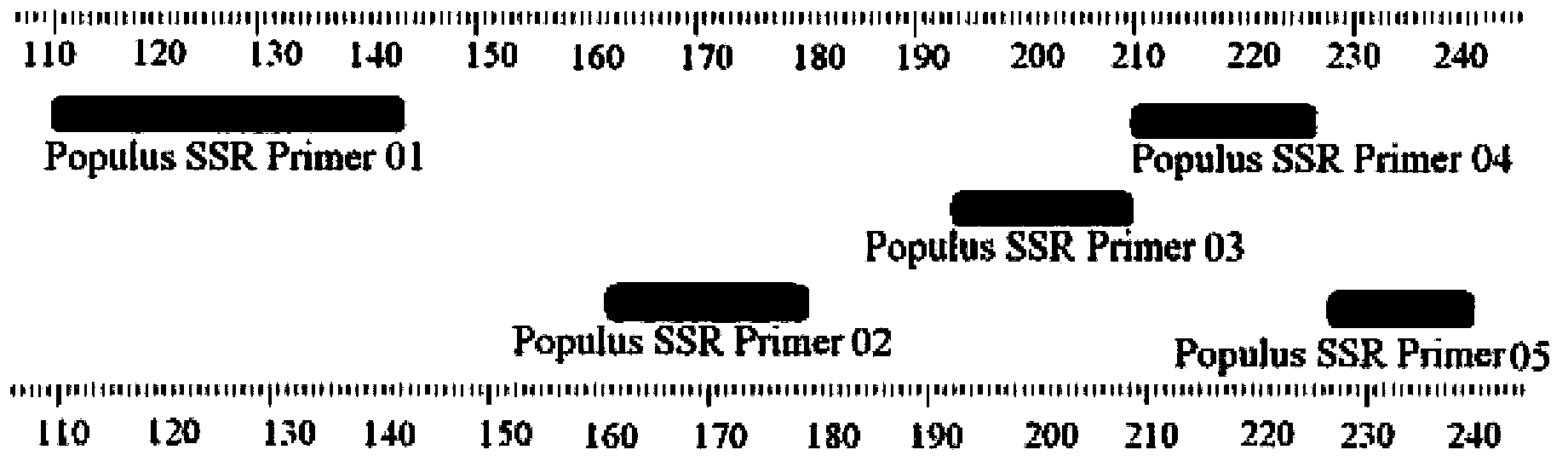
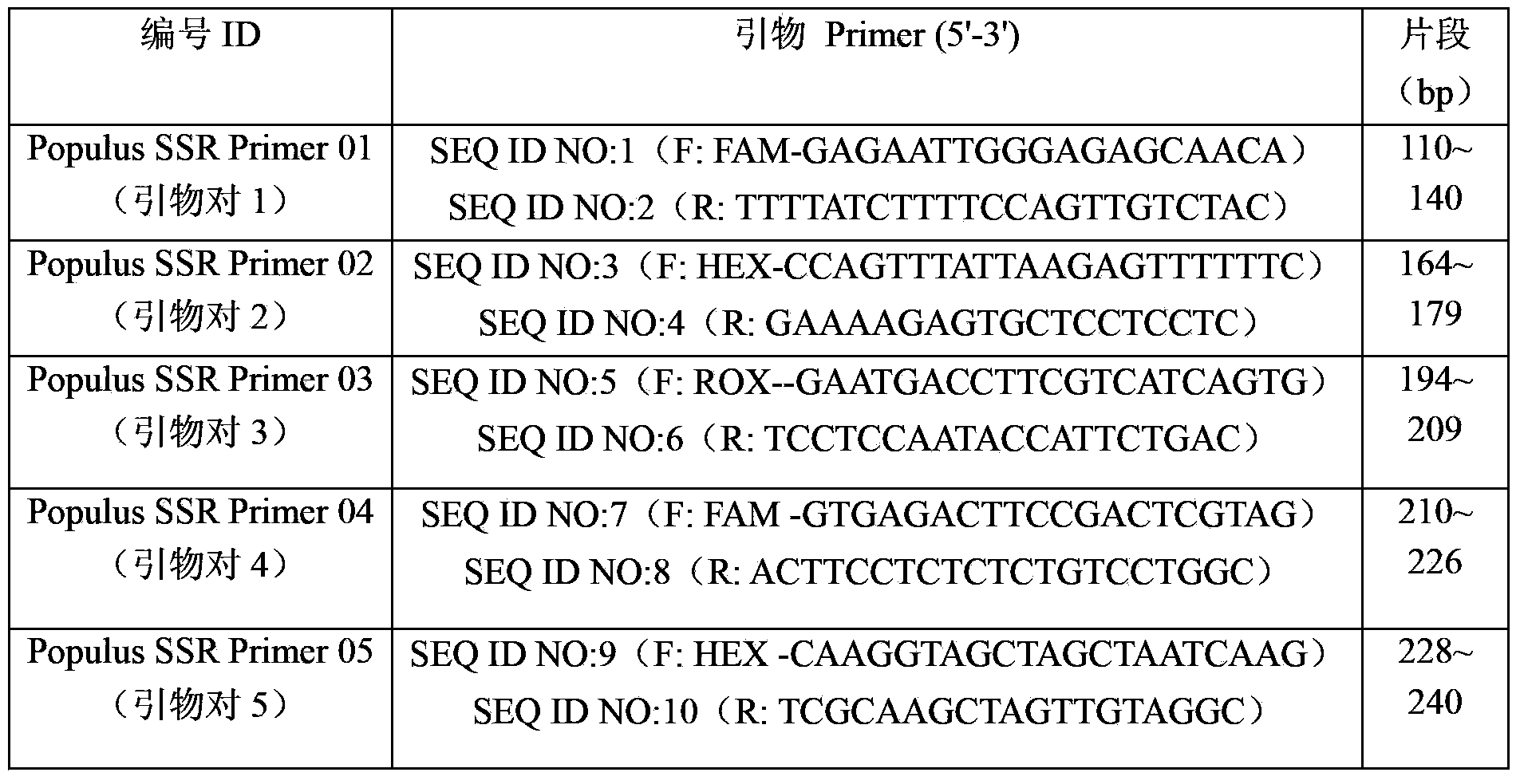
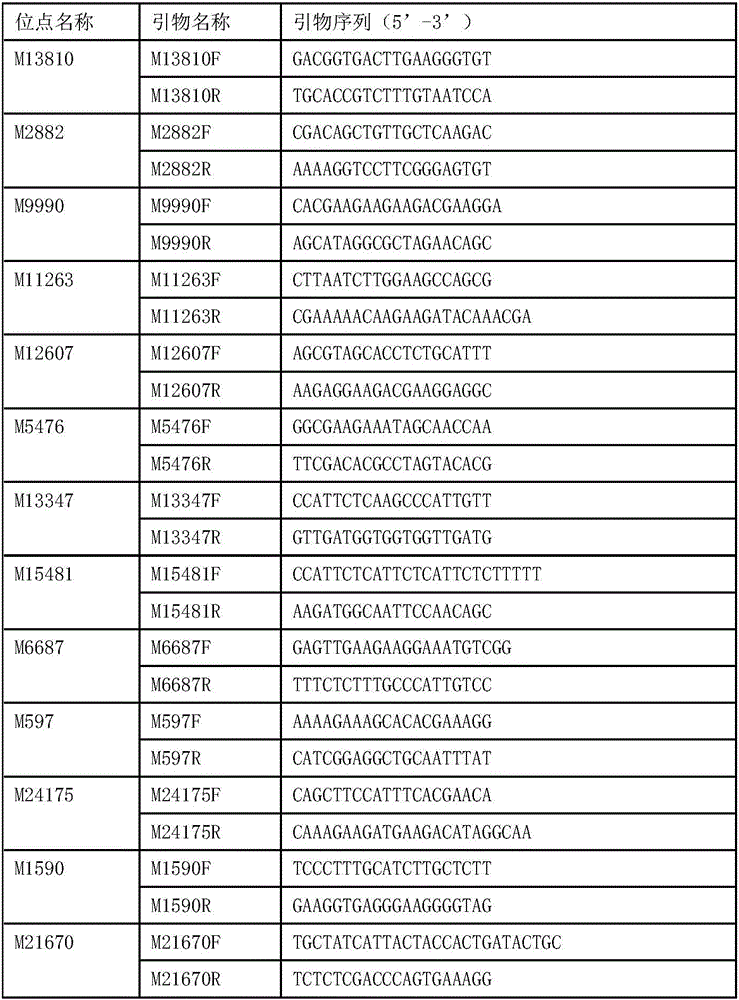
Identification method and identification kit for genetic relationships among different species among sections of populus
An identification method and an identification kit for genetic relationships among different species among sections of populus are disclosed. The method includes following steps of: S1) subjecting populus to genetic typing by adoption of polymorphic microsatellite DNA primer pairs, and constructing microsatellite DNA finger-prints of individuals in the species; and S2) subjecting populus to be identified to genotype amplification by adoption of the polymorphic microsatellite DNA primer pairs, and determining the genetic relationships of the populus to be identified according to the microsatellite DNA finger-prints, wherein the polymorphic microsatellite DNA primer pairs comprise a primer pair 1, a primer pair 2, a primer pair 3, a primer pair 4 and a primer pair 5. By application of the technical scheme, the microsatellite DNA finger-prints are constructed by utilization of the five pairs of polymorphic microsatellite DNA primers which are high in polymorphism and free of interaction between each two, and then genetic relationships of the populus among sections are determined through the microsatellite DNA finger-prints. The method is rapid, efficient, stable and suitable for different growth periods of the populus.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Sebastes schlegeli microsatellite DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) molecular marker
InactiveCN103484454AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStructure analysisMicrosatellite
The invention discloses a sebastes schlegeli microsatellite DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) molecular marker. The molecular marker comprises construction of sebastes schlegeli microsatellite (CA) 16 and (GA) 16 enriched libraries and screening and sequencing of a microsatellite sequence-containing positive clone and determines 10 microsatellite markers SS101, SS102, SS103, SS104, SS105, SS106, SS107, SS108, SS109 and SS110 with rich polymorphism. The invention provides 10 sebastes schlegeli new microsatellite sites and a primer sequence and an amplification method for amplifying the 10 microsatellite sites; the molecular marker can be applied to population genetic structure analysis, paternity identification, molecular marker-assisted selection and the like of the sebastes schlegeli, and is a reliable and effective molecular marker.
Owner:AQUATIC PROD RES INST SHANDONG PROV
Molecular marker combination for Litopenaeus vannamei germplasm identification and application thereof
ActiveCN105861729AOvercoming the inability to identify Litopenaeus vannamei germplasmOvercoming germplasm problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceUnknown Source
The invention relates to a germplasm identification technology in the field of aquatic animal genetic breeding, in particular to a molecular marker combination for Litopenaeus vannamei germplasm identification and application thereof. The molecular marker combination is formed by 13 pairs of high-polymorphism microsatellite locus primers. A method for germplasm identification is established with the 13 pairs of high-polymorphism microsatellite markers, microsatellite typing is carried out on existing foreign imported germplasms including but not limited to the Zhengda breed, the SIS breed, the Kona Bay breed and the Molokai breed, and domestic artificially-selected germplasms including but not limited to the Kehai-1 breed and the Guihai-1 breed, molecular databases of different germplasm resources are established with obtained typing data, and different germplasms are identified with the molecular markers. The germplasm sources of Litopenaeus vannamei with unknown sources can be identified by comparing panel typing results with the established databases of different germplasm resources. The method for accurately identifying different germplasm materials of Litopenaeus vannamei with the molecular means has great significance on tracing, evaluation, protection and utilization of different germplasms.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting ES15 microsatellite markers of Chinese shrimps
ActiveCN101880721ASimple methodIntuitive genotypeMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryMicrosatellite
The invention relates to a method for detecting ES15 microsatellite markers of Chinese shrimps. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting genome DNA of the Chinese shrimps first; designing specific primers at both ends of a sequence of a cDNA library by utilizing the microsatellite core sequence in the cDNA library of the Chinese shrimps; performing PCR amplification on the genome DNA of individuals in different geographic groups of the Chinese shrimps or Chinese shrimp groups, and performing denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic separation on obtained PCR products to obtain a high-genetic variation polymorphism map presented by the Chinese shrimps in an ES15 core sequence area; and analyzing stripes of the map to obtain a genotype of each individual of the Chinese shrimps in ES15 loci. Through the method, a hereditary variation map of the ES15 loci of the Chinese shrimps can be obtained quickly, the genotype of each individual of the Chinese shrimps can be detected visually, and the method is simple and convenient; and the method is mainly applied to group genetic markers, genealogical authentication, the construction of genetic maps and the like of the Chinese shrimp.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for space mutation breeding of maize strong heterosis cross combination parent
InactiveCN103250626AImprovement periodImprove efficiencyPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceHeterosis
The invention discloses a method for space mutation breeding of a maize strong heterosis cross combination parent. The method includes the steps of: using a recoverable satellite to carry a maize inbred line or hybrid; recovering the primary seed and conducting monoseeding without thinning out seedlings, and performing selfing totally; subjecting a first generation of selfing to ear row planting, first selecting a good ear row, then selecting a good single plant from the good ear row to undergo selfing; increasing the planting group of a second generation of selfing, increasing the selection pressure, and further carrying out optimum selecting from the best to perform selfing; for a third generation of selfing, employing diallel crossing to prepare a combination, and letting a mutant line undergo selfing continuously; and identifying the cross combination by multipoint planting, and selecting mutant strains with good comprehensive performance and the cross combination with high specific combining ability through combining ability analysis. By improving the prior art, the method provided in the invention shortens, improves the period of inbred lines, and accelerates breeding of new varieties.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Biological control agent for plants
A biological control agent for plants and a method of inoculating the plants with the biological control agent in order protect against plant disease are provided. The treatment method consists of inoculating the plant with a strain of cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), referred to as the KU1 strain, having an associated viral satellite RNA of SEQ ID NO: 1. Particularly, the KU1 strain may be used to protect plants against a particular viral strain of CMV, referred to as the KU2 strain, characterized by the associated viral satellite RNA of SEQ ID NO: 2, which causes tomato necrosis. Additionally, the KU1 strain may be used to protect against potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTV), which causes tomato stunting, fusarium wilt disease in the tomato (caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Lycopersicae), and leaf spotting disease in the tomato (caused by Alternaria alternate).
Owner:KUWAIT UNIV
Rhizoctonia solani kuha SSR mark, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106399508AEfficient enrichmentRapid enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesRestriction enzyme digestionMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a rhizoctonia solani kuha SSR mark, as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular organism. The rhizoctonia solani kuha SSR mark comprises 8 groups of primer pairs, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting genome DNA of rhizoctonia solani kuha; secondly, obtaining a DNA fragment through restriction enzyme digestion total NDA; thirdly, ensuring that a biotin labeled probe is cross-fertilized with a target fragment; fourthly, enriching a DNA fragment containing an SSR sequence through a magnetic bead; fifthly, amplifying and purifying the DNA fragment containing the SSR sequence; sixthly, performing clone sequencing on the DNA fragment; seventhly, designing an SSR primer through an SSR flanking sequence, which is used for amplifying a microsatellite fragment of a locus. The rhizoctonia solani kuha SSR mark is high in primer specificity, stable in amplification, simple in operation, short in period and low in cost, meanwhile has the advantages of rich codominant inheritance and polymorphism, and can be applied to analysis of the genetic diversity of rhizoctonia solani kuha.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
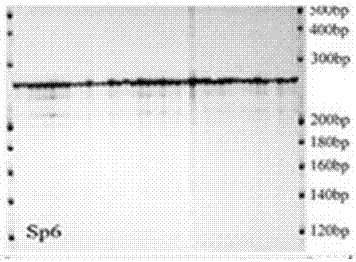
Method for detecting spirodela polyrrhiza Sp6 microsatellite marker by means of specific primers
ActiveCN107058477AEasy to detectSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic diversityMicrosatellite
The invention provides a method for detecting a spirodela polyrrhiza Sp6 microsatellite marker by means of specific primers. The detection method comprises the steps of 1, conducting material pretreatment, wherein a spirodela polyrrhiza sample is acquired, cultured, packaged and dried for use; 2, extracting spirodela polyrrhiza genomic DNA; 3, designing the specific primers: microsatellite node Sp6 specific primers: F: GAACCTTAATATGCGACCAAG R: CAAGAAAGTCAAATACAGCGG; 4, conducting PCR amplification on genomic DNA of spirodela polyrrhiza individuals in different proles by means of the primers; and 5, conducting preliminary screening on a PRC product, adding loading buffer, and conducting vertical electrophoresis analysis on denatured polyacrylamide gel after denaturing, so as to obtain a polymorphic map about large genetic diversity of spirodela polyrrhiza in an Sp6 core sequence area. By the adoption of the method, the polymorphic map about large genetic diversity of a spirodela polyrrhiza Sp6 genetic marker locus can be obtained fast. The method is simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Alligator sinensis microsatellite polymorphic site and identification method and specific primer sequence thereof
ActiveCN108588240AStrong resolutionEconomic Paternity TestMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA paternity testingMicrosatellite
The invention provides an alligator sinensis microsatellite polymorphic site and an identification method and specific primer sequences thereof. On this basis, thirteen pairs of specific primer sequences are screened, and the sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.26. The method for identifying the alligator sinensis microsatellite polymorphic site comprises the steps that an alligator sinensis genome is adopted to screen microsatellite sites and high-quality primers, sequencing read data of the alligator sinensis genome is compared to an alligator sinensis reference genome to identify INDEL, according to an INDEL identification result and a microsatellite screening result, the microsatellite sites with polymorphism are screened out. The provided thirteen pairs of specific primers are all polymorphic sites and have stronger resolution capability. The set of microsatellite primers can be economically, quickly and accurately used for the paternity test of the alligator sinensis, thereby being conductive to performing phylon reconstruction and information perfecting on alligator sinensis population, so that a scientific management scheme is formulated to guide the later protection work of the alligator sinensis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com