Cowpea chloroplast SSR molecule labeled polymorphic primers and screening method thereof, and method for identifying genetic relationship of cowpeas
A technology of polymorphic primers and molecular markers, applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA preparation, etc., can solve the problem of incomplete germplasm resources of cowpea, and achieve a comprehensive method for identifying the genetic relationship of cowpea , Small molecular weight, not easy to recombine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
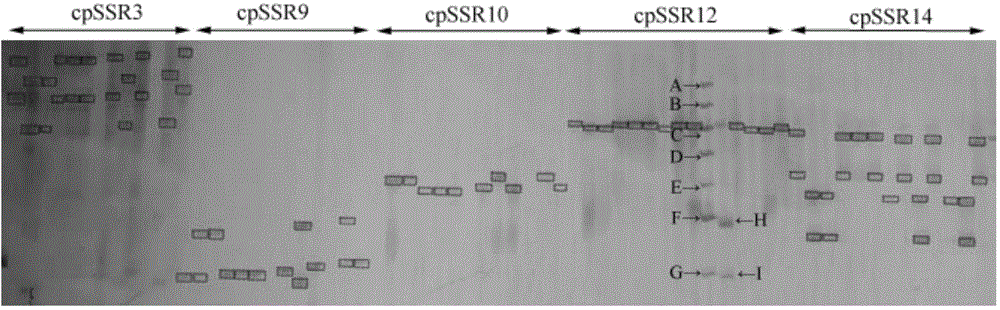
[0049] The embodiment of the present invention provides a polymorphic primer for microsatellite molecular markers of cowpea chloroplast.
[0050] 1. Polymorphic primer screening of chloroplast microsatellite molecular markers
[0051]Download the full sequence of the cowpea (V.unguiculata) chloroplast genome (NC_018051) from the GenBank public database (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ), analyze the full sequence of the cowpea chloroplast genome, and screen chloroplast microsatellite molecules sequence. Single-base microsatellites were searched using the software Tandem Repeats Finder4.04 (Benson G.Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences[J].Nucleic Acids Research,1999,27(2):573-580.); Base microsatellite molecules were analyzed using SSRhunter1.3 software (Li Qiang, Wan Jianmin. SSRHunter, the development of a localized SSR site search software [J]. Genetics, 2005, 27(5):808-810.), The search conditions are set as follows: the minimum number of repeats for a si...
Embodiment 2
[0072] The embodiment of the present invention provides a kind of method that utilizes the polymorphism primer of the cowpea chloroplast microsatellite molecular marker that embodiment one provides to identify cowpea genetic relationship, specifically as follows:
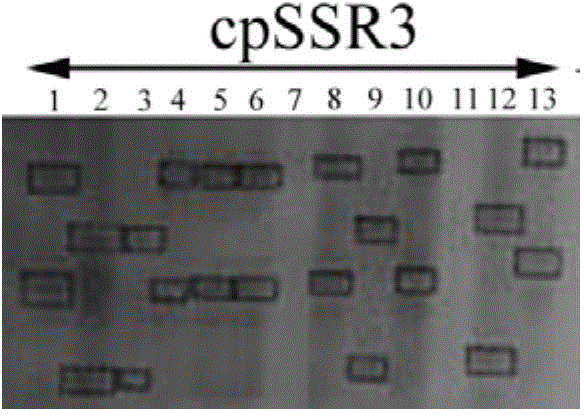
[0073] Sample: 13 parts of samples provided for testing in Example 1 of the present invention, including 10 parts of cowpea materials and 3 parts of kidney bean materials (3 parts of kidney beans are respectively codes J9, J13, B20 in Table 2 of Embodiment 1), and extract Genomic DNA of 13 samples to detect the generality of polymorphic primers of microsatellite molecular markers in cowpea chloroplasts in kidney bean.
[0074] First, the polymorphic primers of cowpea chloroplast microsatellite molecular markers provided in Example 1 of electrophoresis detection are mixed with the genomic DNA of the sample to amplify to obtain an amplified product, and the amplified product is passed through a denaturing polyacrylamid...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for analyzing the genetic diversity of cowpea by using the polymorphic primers of 5 pairs of cowpea chloroplast microsatellite molecular markers provided in Example 1 to reveal the current status of genetic diversity of the tested cowpea samples, based on 5 pairs of cowpea The polymorphic primers of chloroplast microsatellite molecular markers and the diversity information detected by 10 cowpea samples were analyzed by Popgene1.32 software, wherein:
[0081] Calculate the main genetic diversity parameters observed heterozygosity (observed heterozygosity, Ho);
[0082] Expected heterozygosity (expected heterozygosity, He);
[0083] number of alleles (Na);
[0084] Effective number of alleles (=Effective number of alleles, Ne);
[0085] Shannon coefficient (Shannon's Information index, I).
[0086] Polymorphism information index (PIC) calculation reference formula (Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW. Con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com