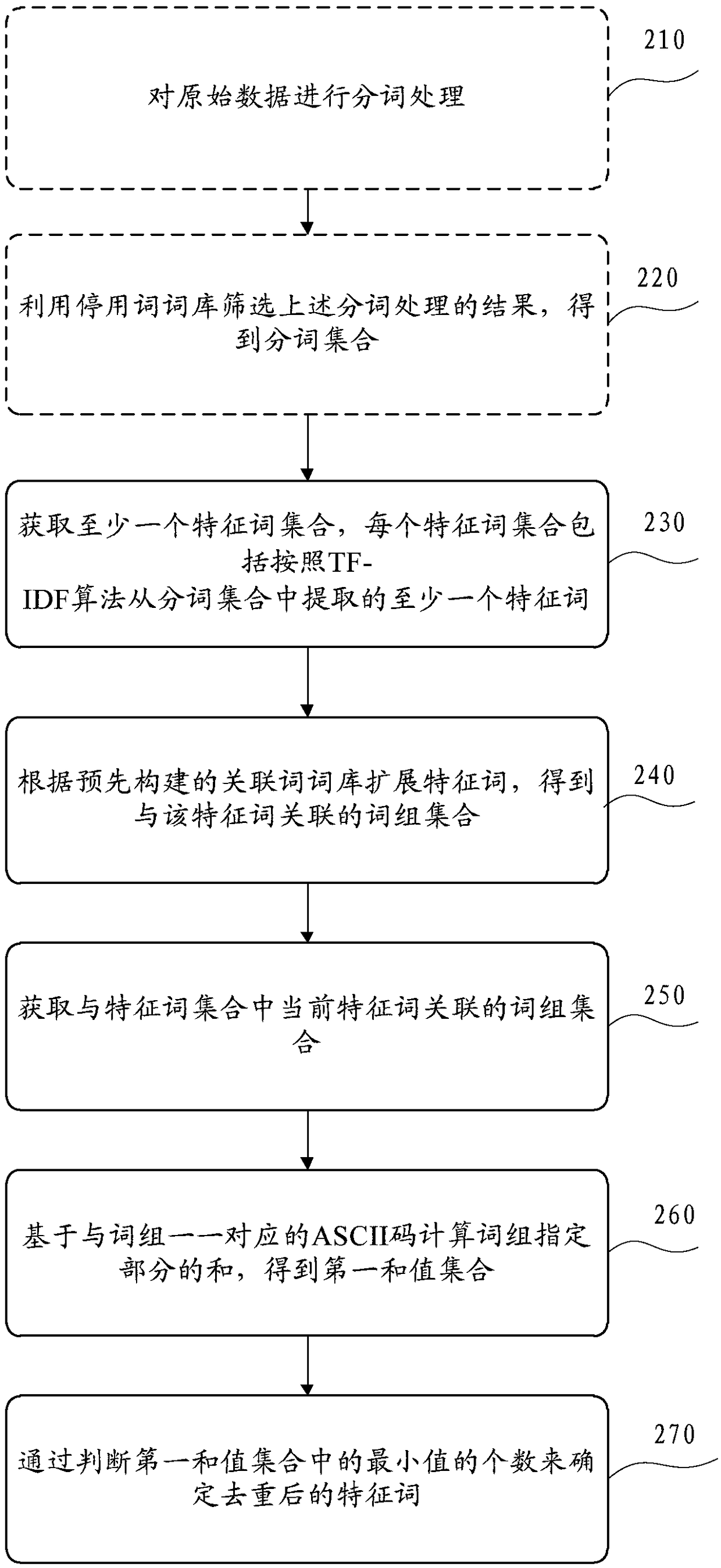
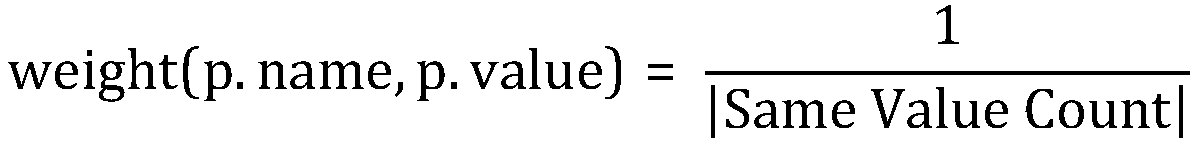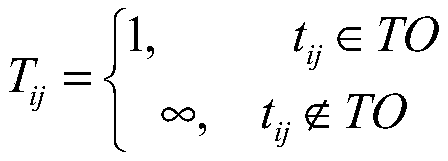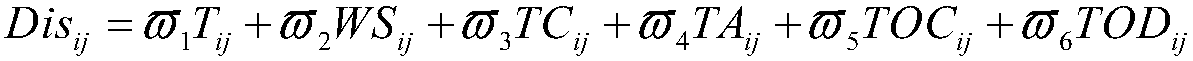Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about How to "Save computing space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
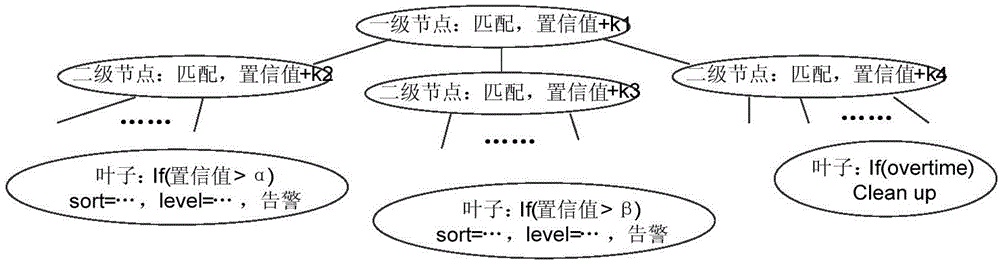
Intelligent association analysis method and intelligent association analysis device for security events
ActiveCN105376193AImprove the efficiency of correlation analysisSave computing spaceData switching networksReal time acquisitionData mining
The invention relates to an intelligent association analysis method and an intelligent association analysis device for security events. The intelligent association analysis method comprises the steps of decomposing the attribute characteristic of a security event which is acquired in real time and standardizing the attribute characteristic values; and traversing an offline generated unified inference structure by means of the standardized attribute characteristic value, thereby determining an attack type. The intelligent association analysis method and the intelligent association analysis device improve association analysis efficiency.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
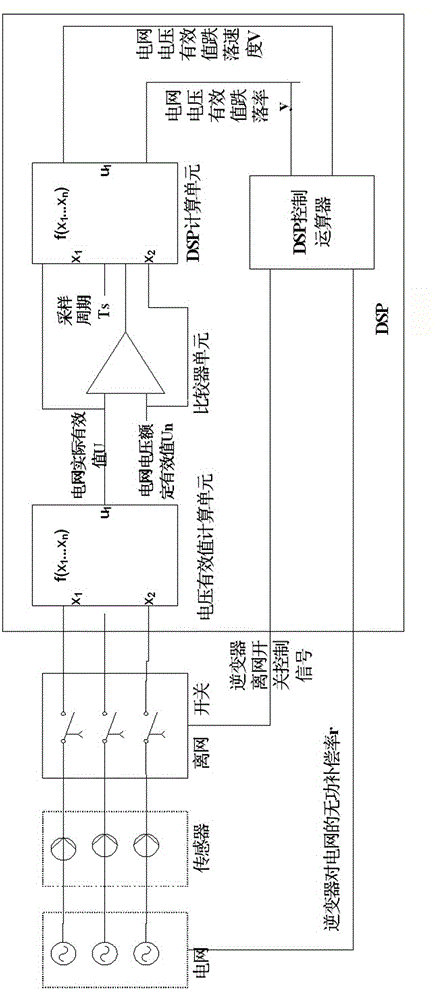
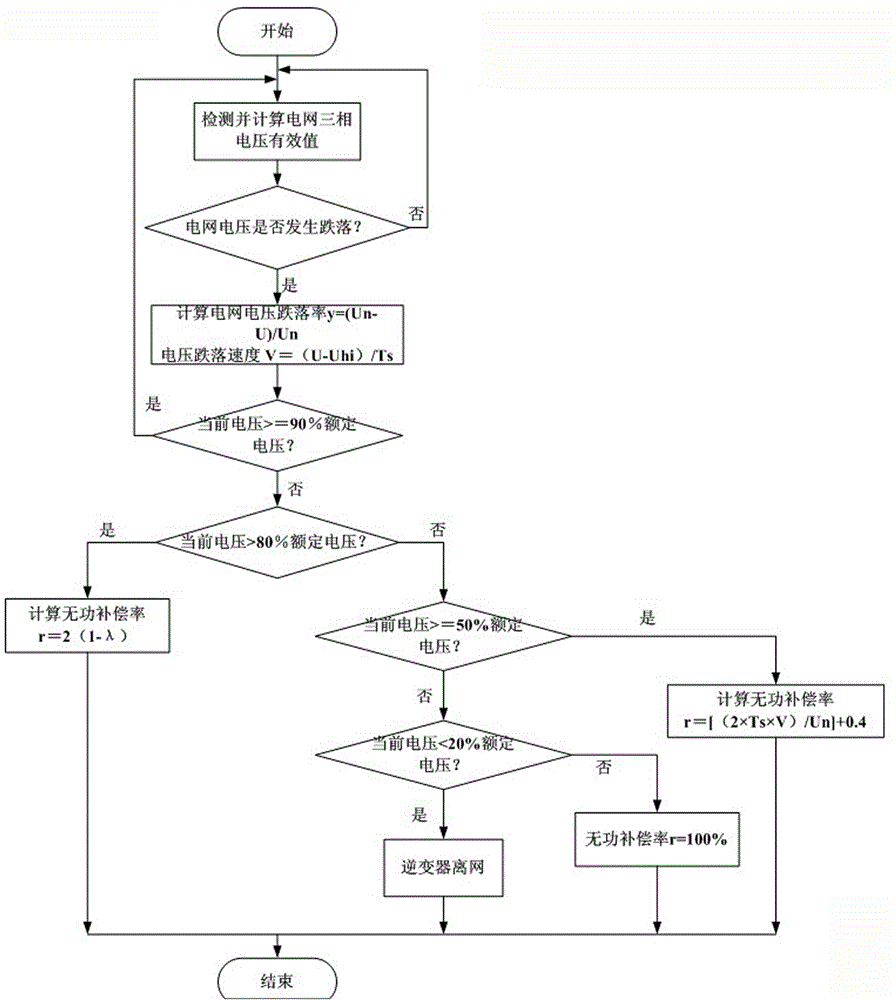
Method and device for dynamic inactive compensation control of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
ActiveCN104426152ASolve the phenomenon of false compensationImprove reliabilityReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationAc network voltage adjustmentProportion integration differentiationGrid connected inverter
The invention relates to a method for dynamic inactive compensation control of a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter. The method comprises the following steps of enabling a sensor to detect the effective value of three-phase voltage of a power grid in real time, calculating and analyzing the change degree of the effective value of the three-phase voltage of the power grid through PID (proportion integration differentiation) control, using the minimum value of the three-phase state as the control quantity, and detecting the voltage states of the power grid; when the voltage of the power grid drops, calculating the dropping rate y of the effective value of the voltage of the power grid and the dropping speed V of the voltage of the power grid; inputting the two control quantities, namely the dropping rate y of the effective value of the voltage of the power grid and the dropping speed V of the voltage of the power grid, into a DSP (digital signal processor) controller, and respectively controlling the inactive compensation rates of a photovoltaic inverter off-grid switch and the photovoltaic inverter. The method has the advantage that the inactive compensation rate of the photovoltaic inverter is controlled by two control factors, namely the voltage dropping degree and the voltage dropping speed, the mutual supplementing function of the two control factors in the sudden dropping process of the voltage of the power grid is utilized, the possible false compensation of the photovoltaic inverter on the power grid is avoided, and the reliability of inactive compensation software is improved.
Owner:CSIC HAIWEI ZHENGZHOU HIGH TECH CO LTD
Method and device for simulating diffusion process of contrast agent
ActiveCN104574503AImprove accuracySave computing space3D-image rendering3D modellingSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsMedicine
The invention provides a method and device for simulating a diffusion process of a contrast agent. The method comprises steps as follows: a three-dimensional blood vessel model is built according to a blood vessel CT scanning image; the three-dimensional blood vessel model is pre-processed; the pre-processed model is rendered to a screen, and particles are initialized; the three-dimensional blood vessel model rendered to the screen and the initialized particles are subjected to collision detection, the action force of the three-dimensional blood vessel model on the particles is calculated according to a collision detection result to obtain external force; internal force among the initialized particles is calculated according to smoothed particle hydrodynamics; the state of the particles in the three-dimensional blood vessel model rendered to the screen is updated and rendered to the screen. The method and device solve the technical problems of large calculation amount, difficulty in acquisition of parameters and low authenticity of a simulation effect with a conventional method for simulating the diffusion process of the contrast agent in the prior art, and realize the technical effects of good instantaneity, high simulation effect accuracy and simple simulation process.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
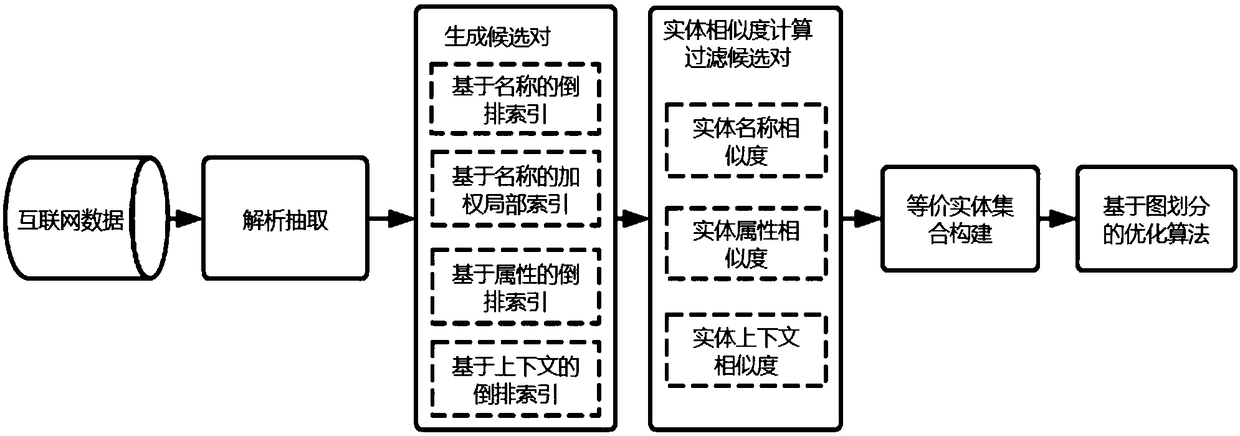
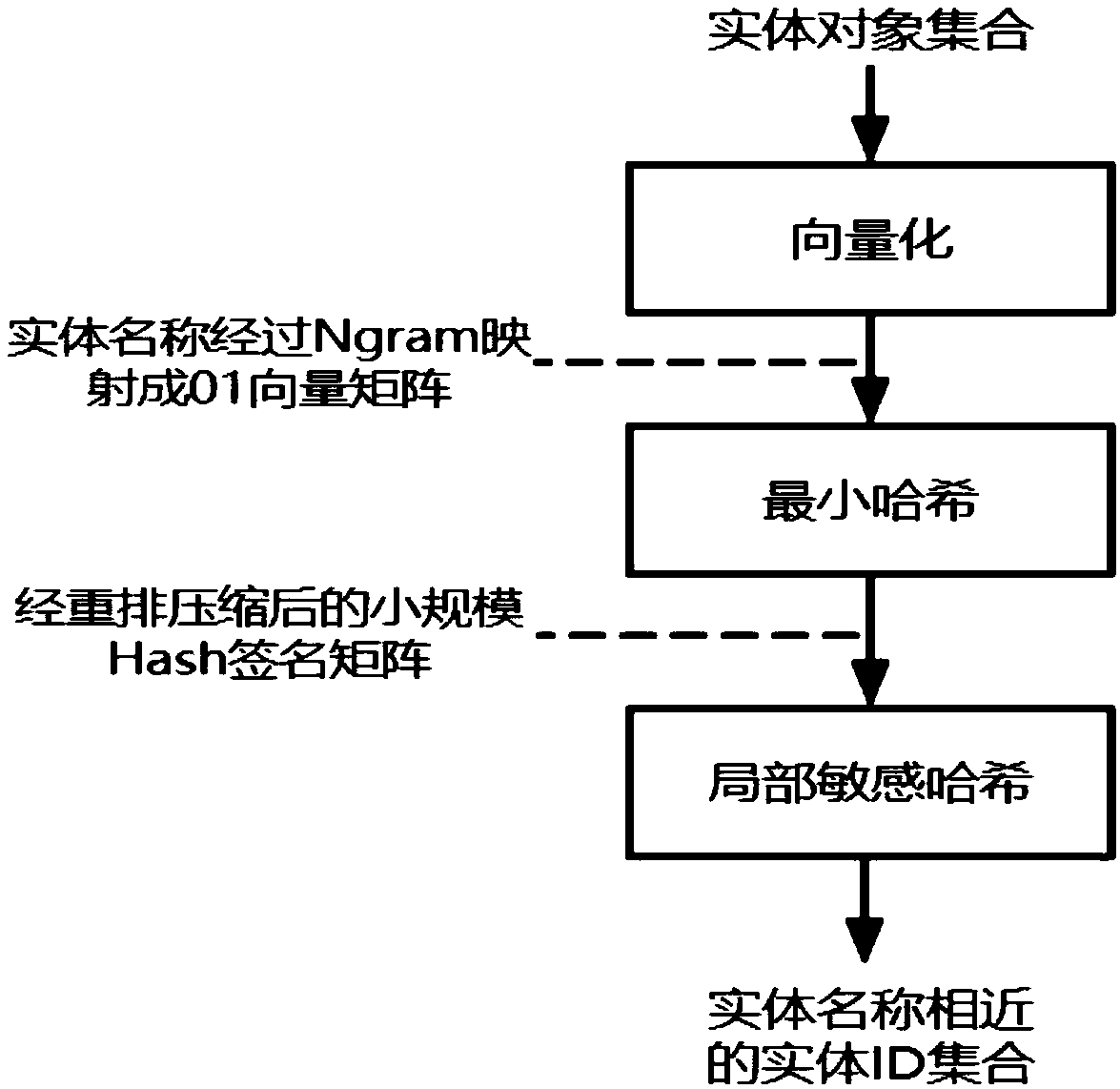
An optimization method of entity alignment based on graph partition
ActiveCN109359172AImprove accuracyQuality improvementWeb data retrievalText database indexingAlgorithmThe Internet
The invention discloses an optimization method of entity alignment based on graph partition . Candidate entity pairs are mined from all entities by composite index, and whether the candidate entity pairs are aligned or not is judged by entity similarity measurement method, and then an optimization algorithm based on graph partition is proposed to improve the accuracy of equivalent entity alignmentby utilizing the similarity relationship between entities. The method of the invention solves the entity alignment problem of the large-scale Internet data, and can accurately and completely mine theentity set equivalent to each other in the original data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
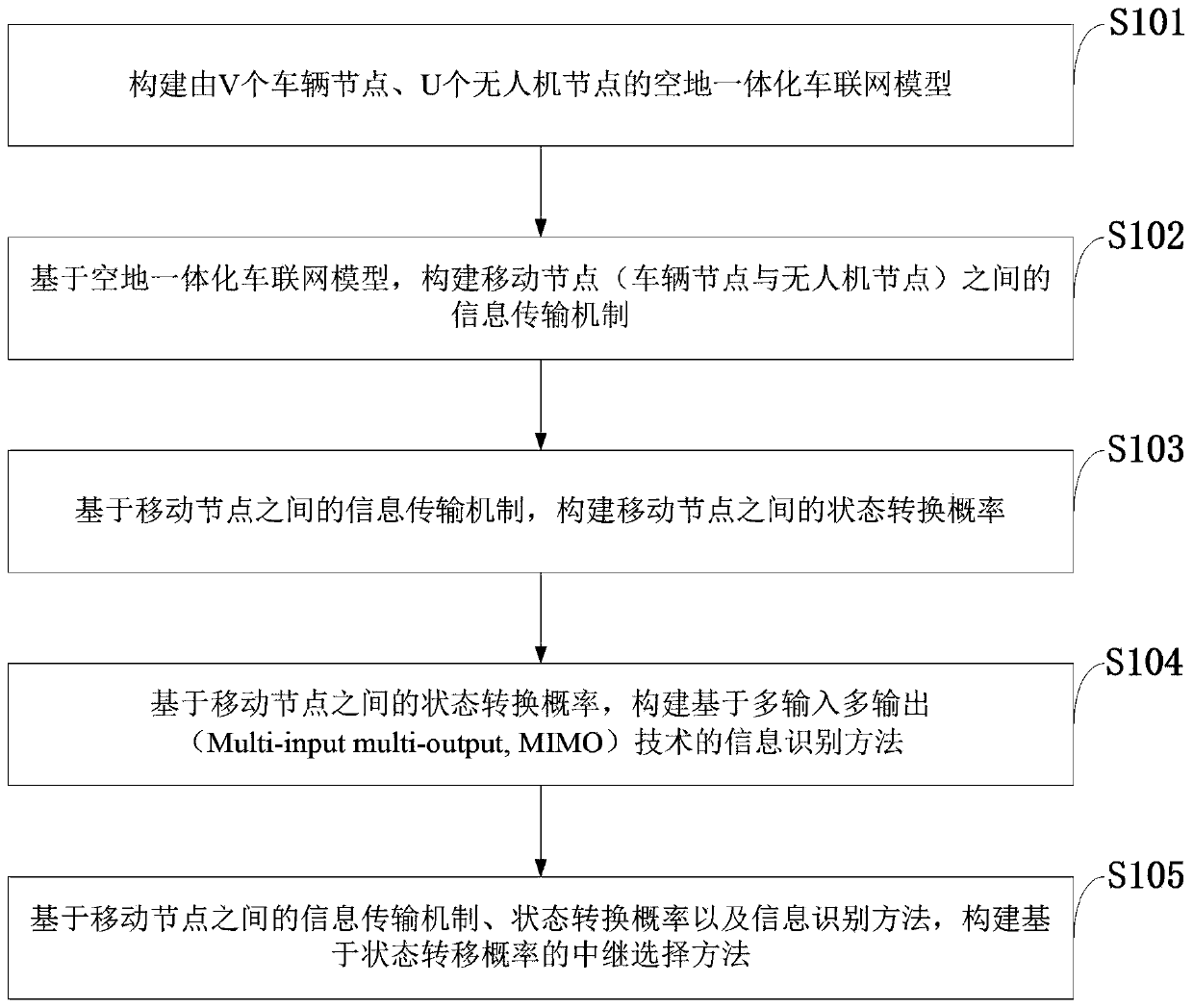
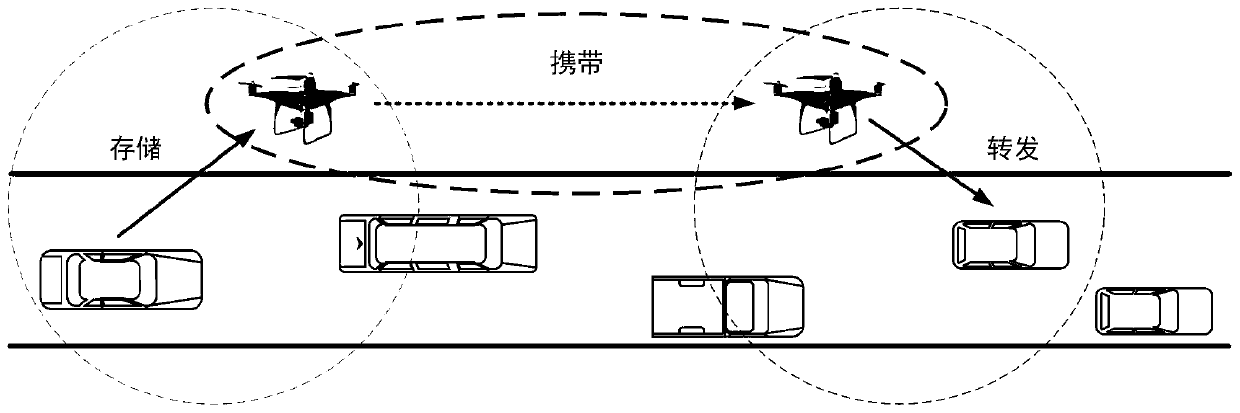
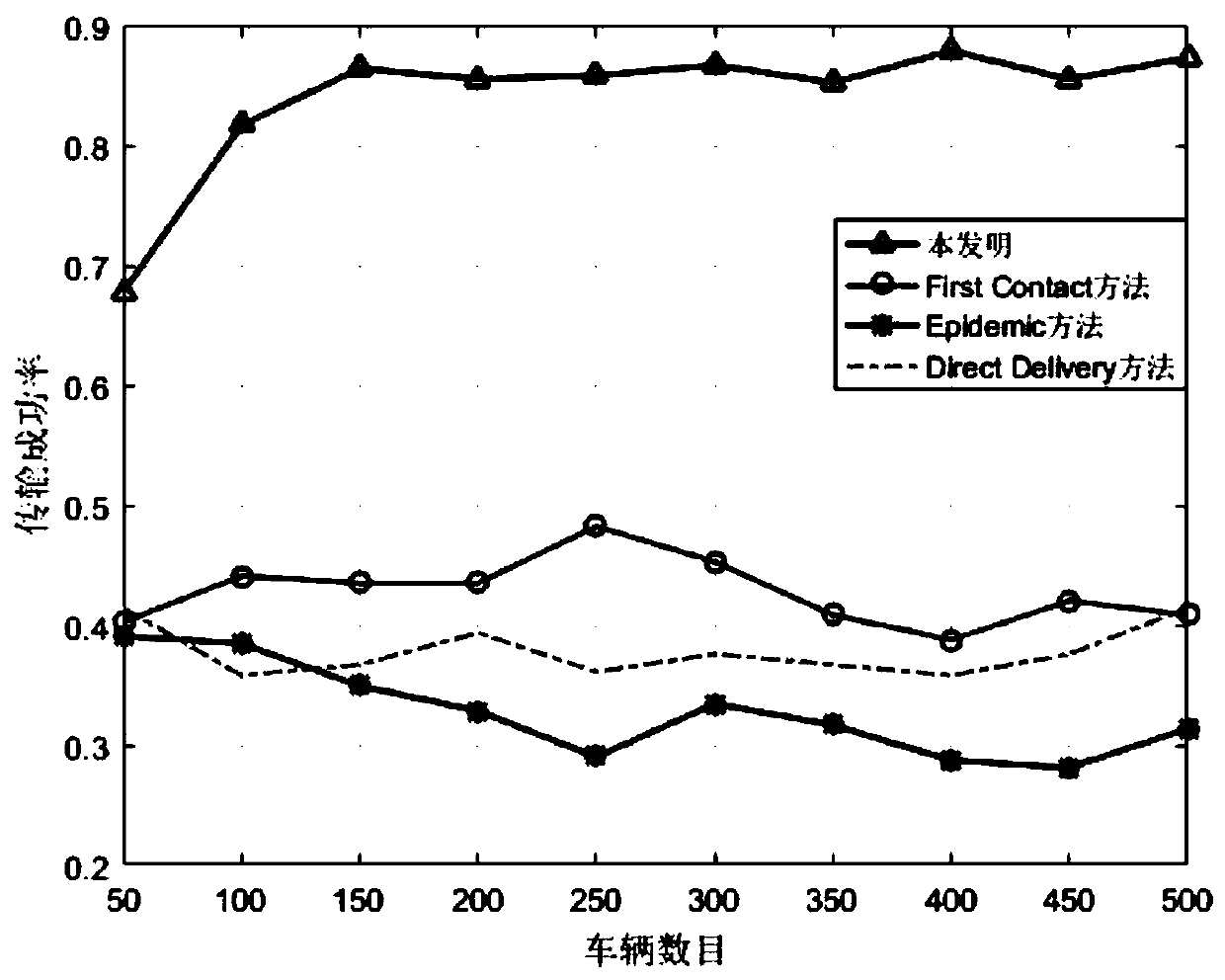
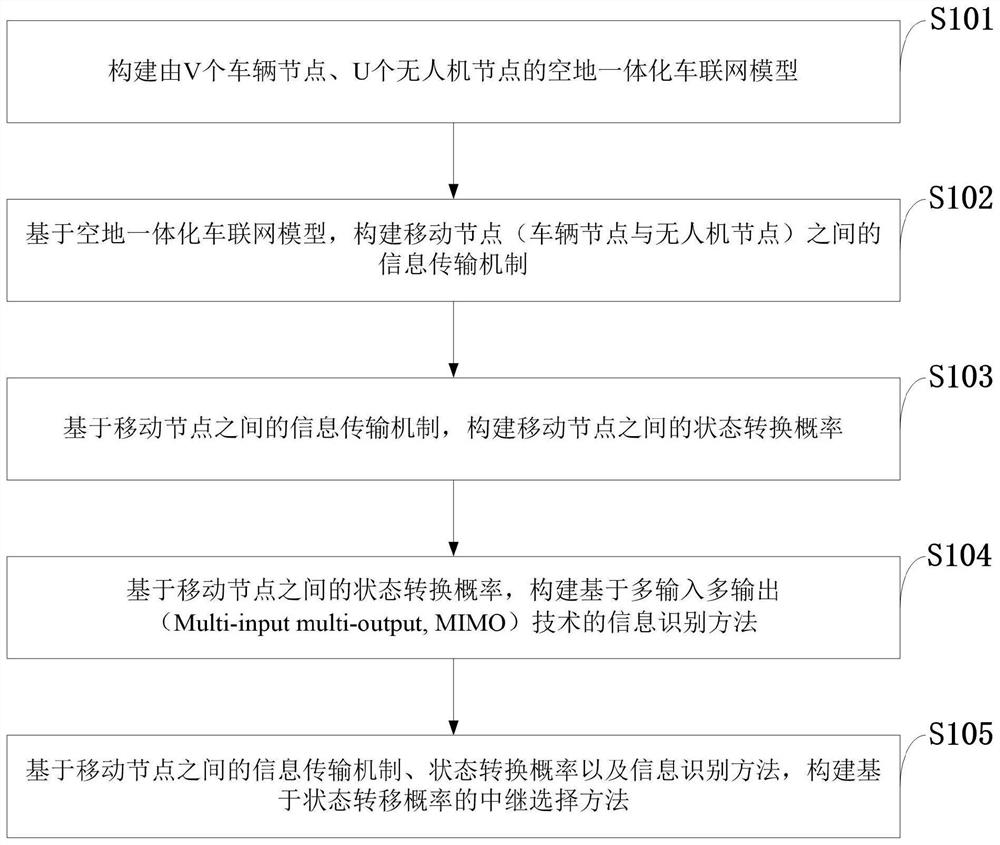
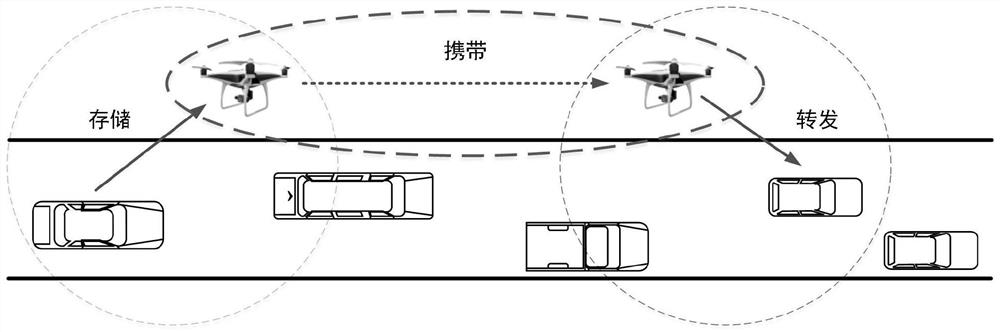
Air-ground integrated Internet of Vehicles relay selection method based on state transition probability
ActiveCN111132075AReduce the probability of collisionIncrease success rateParticular environment based servicesRadio transmissionInformation transmissionIntelligent transportation system its
The invention belongs to the technical field of air-ground integrated Internet of Vehicles communication, and discloses an air-ground integrated Internet of Vehicles relay selection method based on state transition probability. The method comprises the steps of constructing an air-ground integrated Internet of Vehicles model composed of V vehicle nodes and U unmanned aerial vehicle nodes; constructing an information transmission mechanism between the mobile nodes based on the air-ground integrated Internet of Vehicles model; constructing a state transition probability between the mobile nodesbased on the information transmission mechanism between the mobile nodes; based on the state transition probability between the mobile nodes, constructing an information identification method based ona multiple-input-multiple-output technology; and constructing a relay selection method based on the state transition probability on the basis of the information transmission mechanism between the mobile nodes, the state transition probability and the information identification method. The method can be applied to an urban intelligent traffic system, the relation among vehicles, unmanned aerial vehicles and users is enhanced, and a real-time, accurate and efficient comprehensive transportation and information transmission system is built.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
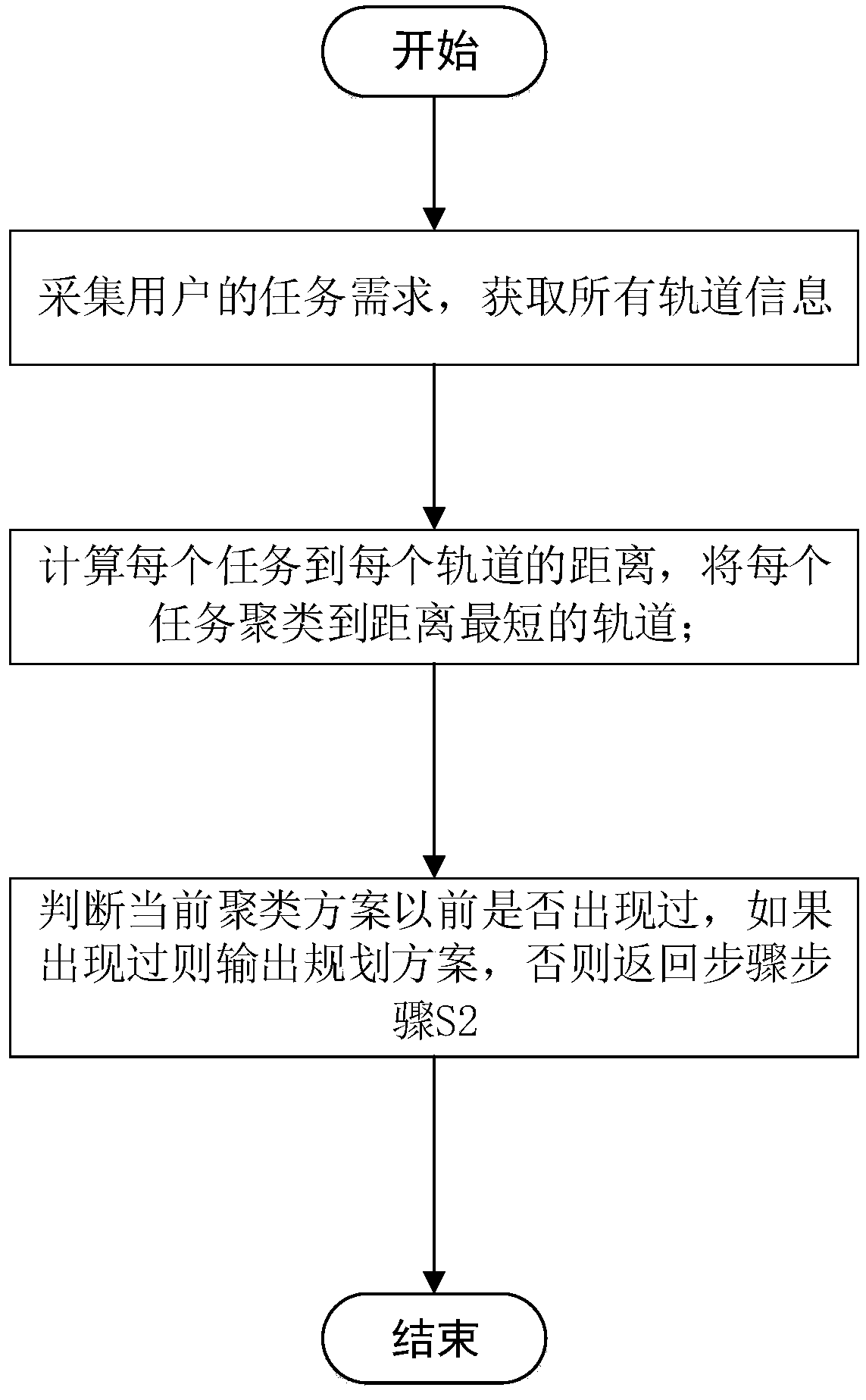
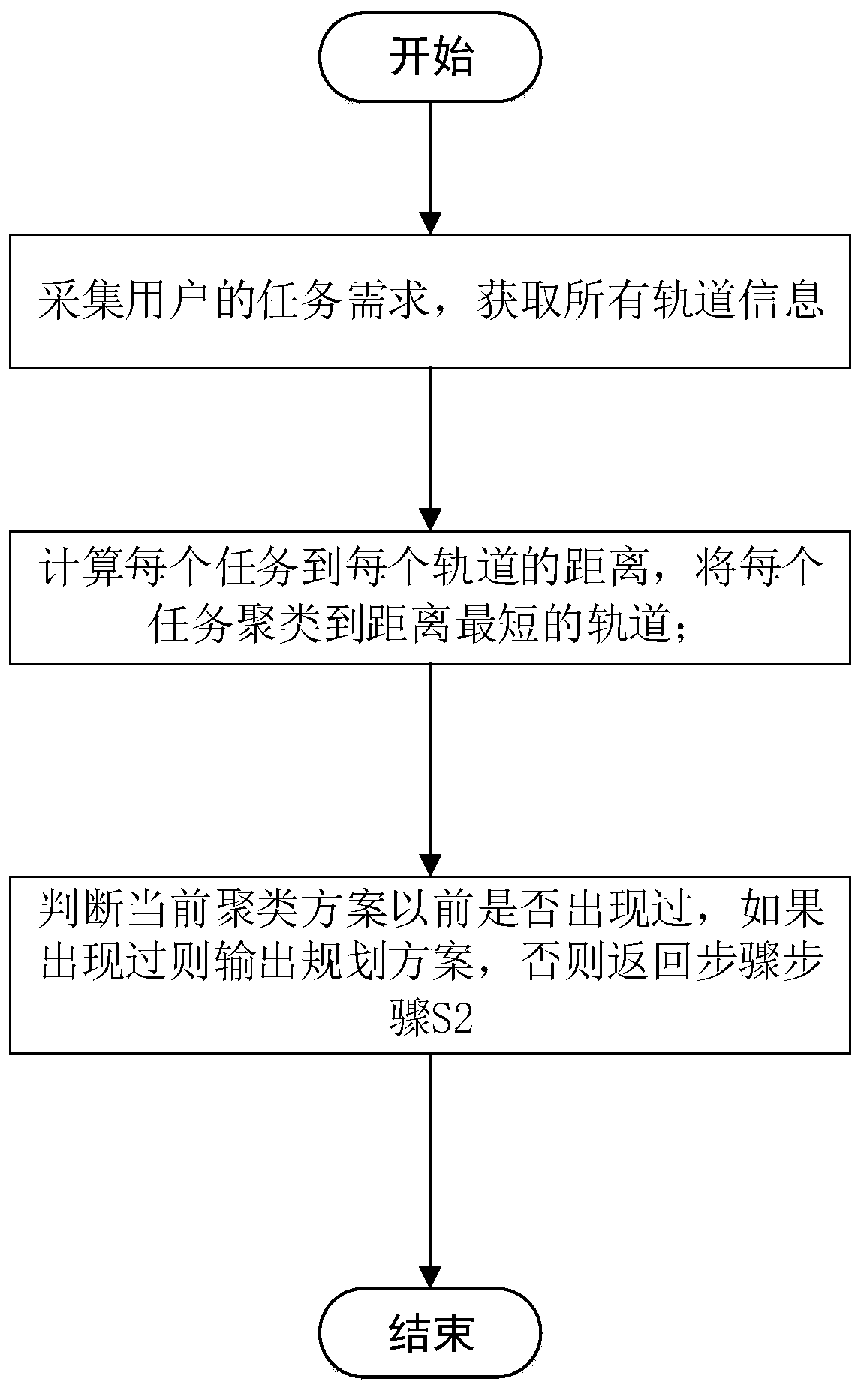
A multi-satellite task planning method based on K-means clustering
ActiveCN109002966AImprove completion rateSatisfy time complexity constraintsCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesCluster algorithmTime complexity
The invention provides a multi-satellite task planning method based on K-means clustering, the method comprises the steps of: S1, collecting task requirements of users T= {t1, t2, t3... Tn}, and obtaining an orbital working time set O= {o1, o2, o3,... Om} corresponding to each circle of sun illumination region of all currently available satellites;S 2, calculating the distance Disij between the task ti and each element oj in the set O, forming a distance set D= {di1, di2, di3... Din} between the task ti and the orbit set O, and clustering the task ti to the orbit k, Disik=Min (D) which is theshortest distance from the orbit set O; S3, judging whether the current clustering scheme sk belongs to the set S= {s1, s2, s3,... Sz}, outputting the clustering scheme sk if sk belongs to S, otherwise adding the scheme sk to the scheme set S, and returning to step S2. By analyzing the factors affecting the assignment of multi-satellite tasks and quantifying these factors and by using the K-meansclustering algorithm, a multi-satellite cooperative task assignment scheme is designed, which has fewer iterations and faster computational speed, and can meet the constraints of time complexity for large-scale optimization problems, and greatly improve the quality of imaging, and improve the completion rate of the task.
Owner:湖南国科轩宇信息科技有限公司
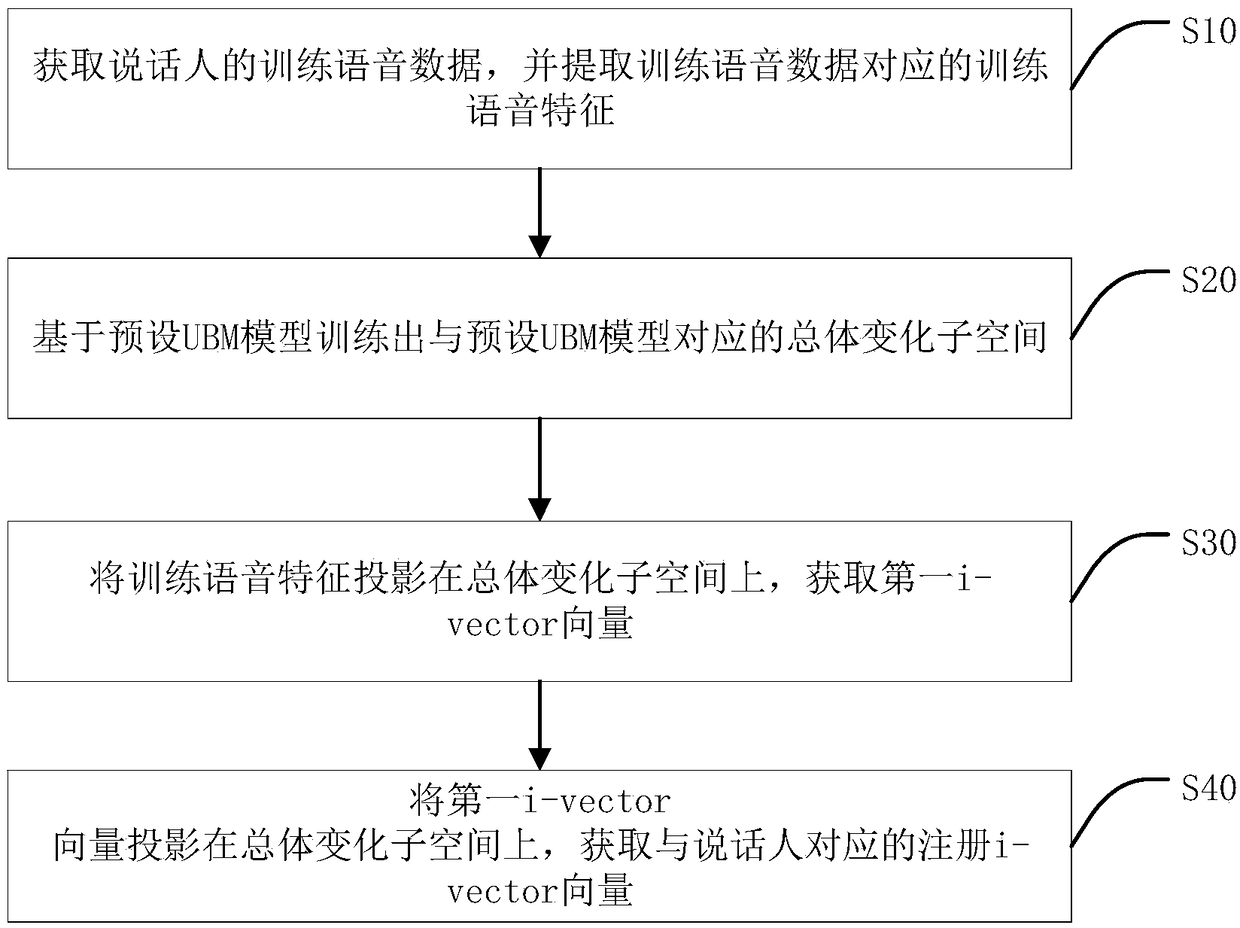
I-vector vector extraction method and apparatus, speaker recognition method and device, equipment and medium
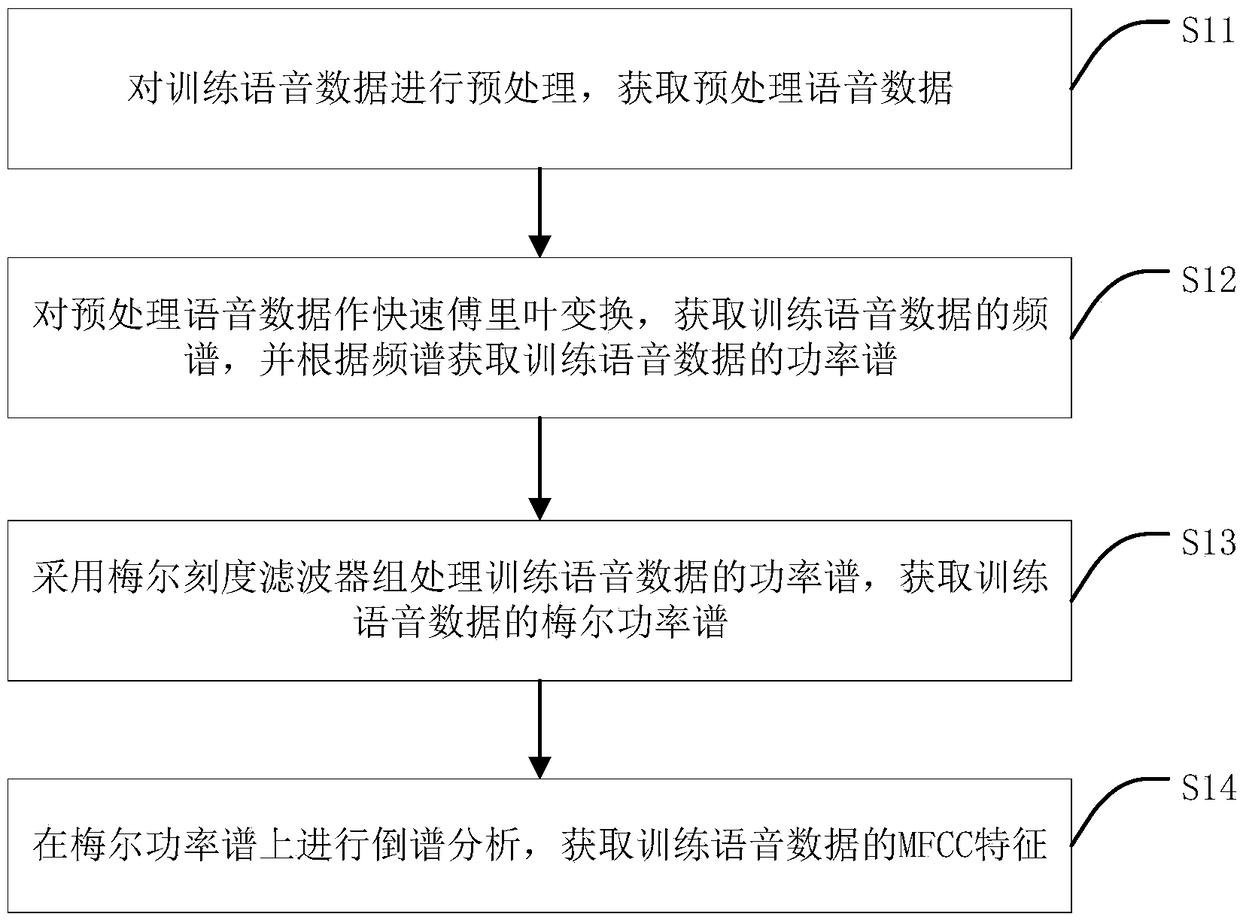
ActiveCN109065022AReduce recognition complexityImprove puritySpeech recognitionFeature dataSpeech sound
The invention discloses an i-vector vector extraction method and apparatus, a speaker recognition method and device, equipment and a medium. The i-vector vector extraction method comprises: acquiringtraining speech data of a speaker and extracting training speech features corresponding the training speech data; on the basis of a preset UBM model, training an overall changing subspace corresponding to the preset UBM model; projecting the training speech data on the overall changing subspace and acquiring a first i-vector vector; and projecting the first i-vector vector on the overall changingsubspace and acquiring a registered i-vector vector corresponding to the speaker. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the training speech feature data are projected twice, the dimension can be reduced, more noise features can be removed, and the purity of the speech feature of the speaker can be improved; and after dimension reduction, the computing space is reduced and the recognition efficiency of the speech recognition is also improved.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
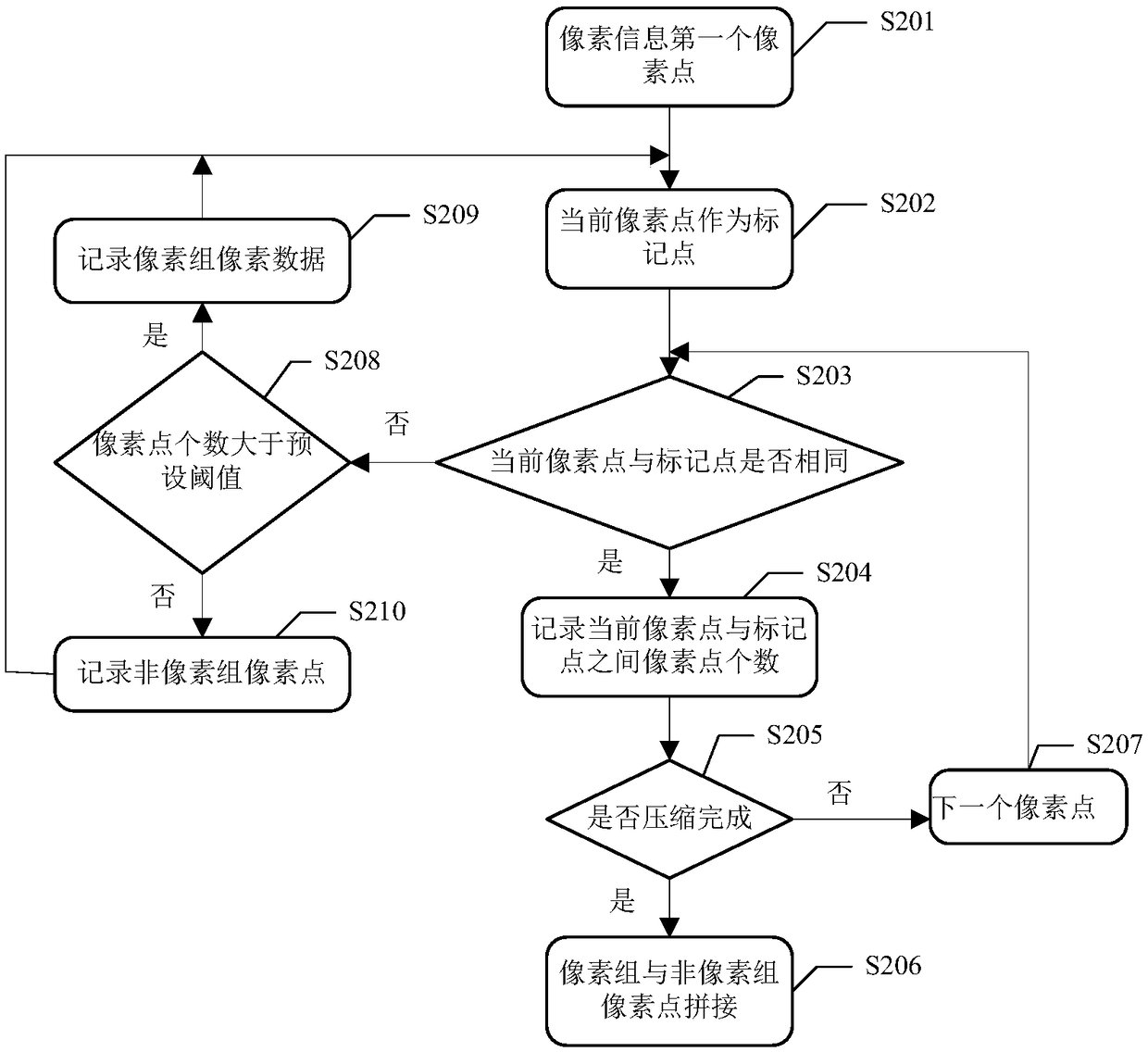
Monochrome image compression method and device, medium and electronic equipment
ActiveCN108900843ASave storage spaceImprove transmission efficiencyDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a monochrome image compression method and device, a medium and electronic equipment. The monochrome image compression method comprises the following steps: acquiring the pixel information of a target image to be compressed; dividing multiple pixel points with the same color values and continuous addresses into pixel groups according to the pixel informationof the target image to obtain at least one pixel group; and sequentially storing the pixel data of the pixel groups and storing the pixel points of a non-pixel group in the pixel information to generate the compression data of the target image. Through the adoption of the technical scheme, the space can be saved, and the compression efficiency is improved.
Owner:K TRONICS (SUZHOU) TECH CO LTD +1
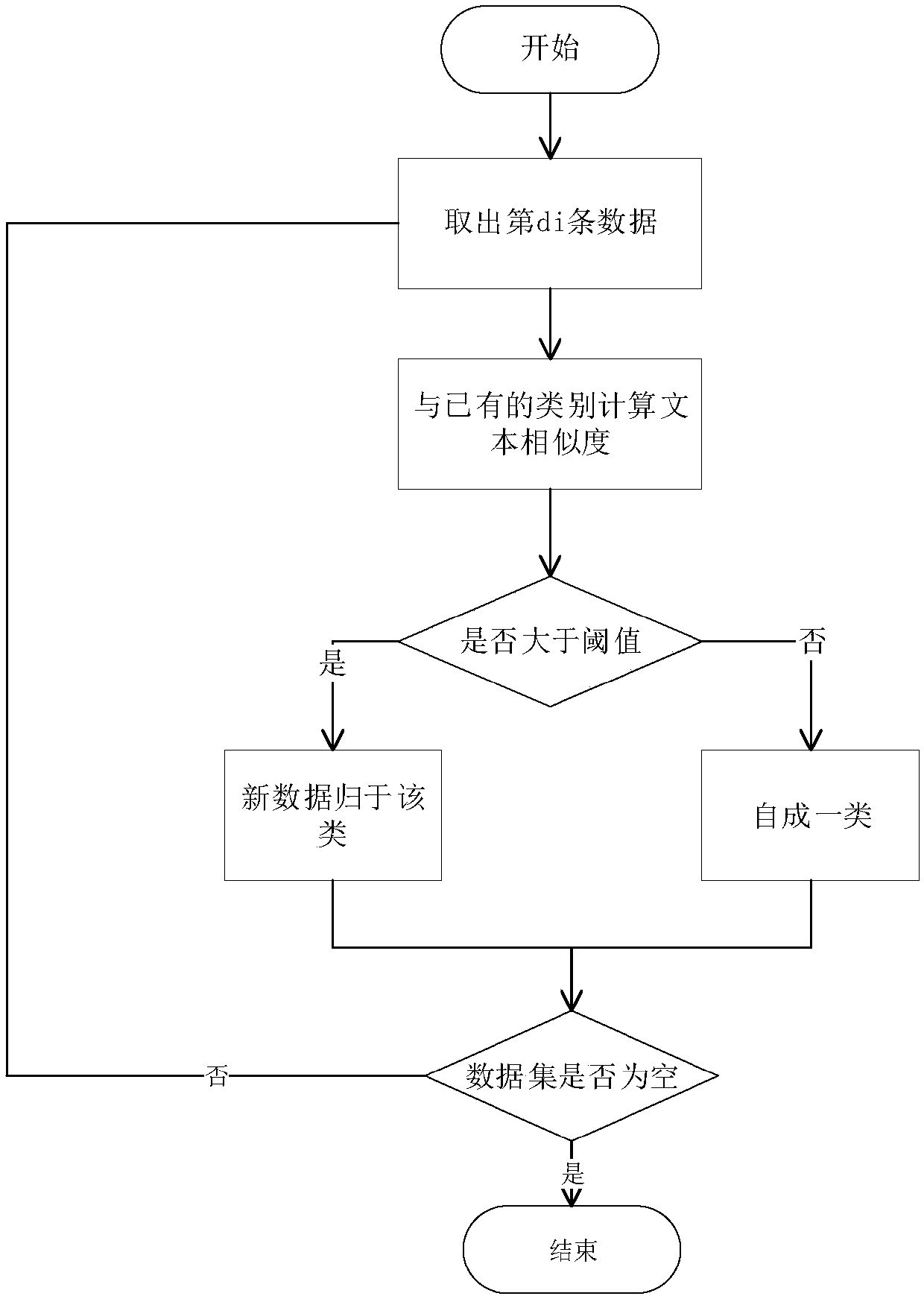
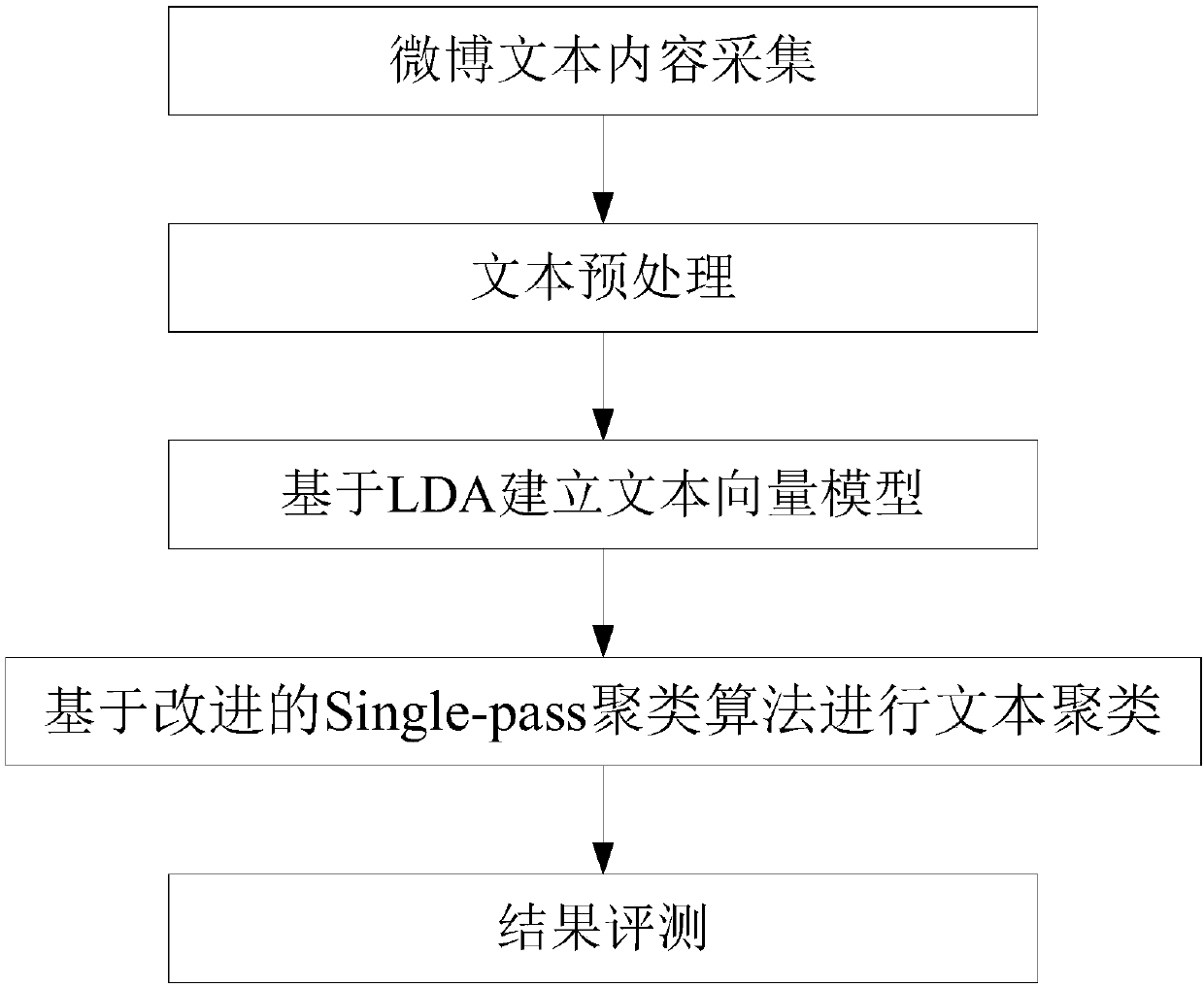
Microblog topic detection method based on improved Single-pass clustering algorithm
InactiveCN107832467AGuaranteed identityReduce the number of comparisonsData processing applicationsWeb data indexingCluster algorithmCanopy clustering algorithm
The invention discloses a microblog topic detection method based on an improved Single-pass clustering algorithm. The method includes microblog text content collection, text preprocessing, text vectormodel establishment based on LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation), text clustering based on the improved Single-pass clustering algorithm, and result evaluation. The improved Single-pass clustering algorithm includes: adding a time parameter, calculating clustering center points for category data, and inputting the data in a batch manner. According to the method and the algorithm, identity of topicsis guaranteed through adding the time parameter; the new data are compared with the clustering center points through calculating the clustering center points for the category data, thus reducing of frequency of comparing the new data with each piece of data is facilitated, and efficiency of calculation is improved; and newly input clustering center points are compared with the center points afterclustering through inputting the data in the batch manner, namely firstly clustering the data and then inputting the same, operation efficiency is improved, and operation space is saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
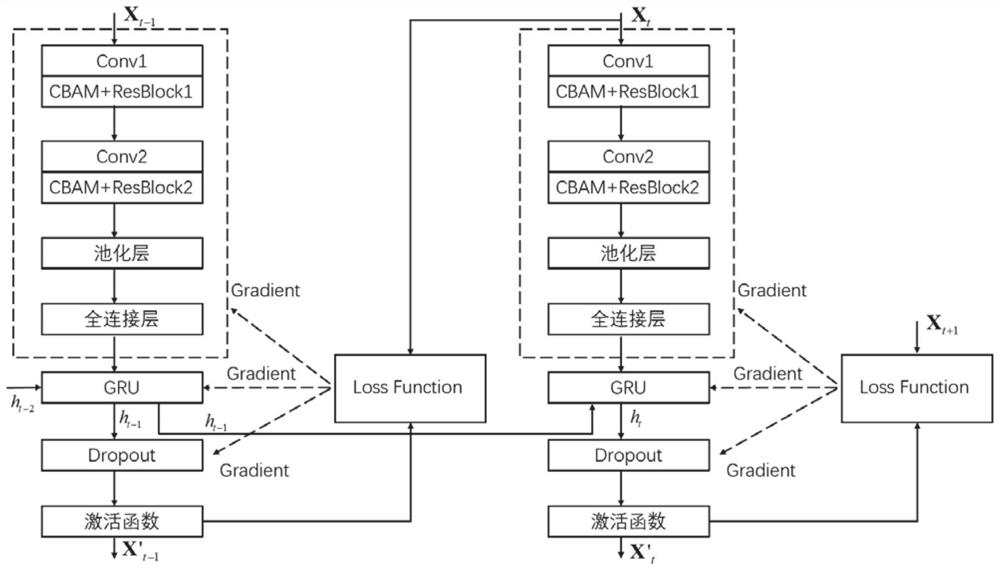
Frequency spectrum prediction sensing method based on RCS-GRU model
ActiveCN113852432AReduce lossEasy extractionTransmission monitoringNeural architecturesFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of cognitive radio, and particularly relates to a frequency spectrum prediction sensing method based on an RCS-GRU model. The method comprises the following steps: simulating a channel by adopting an M / M / N queuing theory model; combining and splicing the channel state sequences simulated in the step 1 into a matrix; establishing a convolutional neural network model based on residual CBAM, inputting the spliced channel state matrix set into the model, and extracting features of spectrum occupancy states among channels; inputting the extracted feature data set into a GRU model, mining the features of the channel state in the time sequence, performing spectrum prediction, and outputting the channel state of the next time slot; adopting an Adam optimization algorithm to set a variable learning rate optimization cross loss function to train an RCS-GRU network, and adding a dropout method in the training process; and evaluating the prediction performance of the RCS-GRU by adopting a relation curve of the false alarm prediction probability and the detection prediction probability and a root mean square error (RMSE).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Open-circuit fault diagnosis method for switching tube in half-bridge sub-module of MMC converter
ActiveCN112710950ASmall amount of calculationSave computing spaceCircuit interrupters testingCapacitive currentCapacitance
The invention discloses an open-circuit fault diagnosis method for a switching tube in a half-bridge sub-module of an MMC converter. The diagnosis method is composed of an event triggering program and an IGBT open-circuit fault diagnosis program. The IGBT open-circuit fault diagnosis program is started when the capacitive voltage of a certain half-bridge sub-module exceeds a threshold value interval set by the event triggering program; and when the capacitive current state observation value, the capacitive current theoretical value and the sub-module driving function Si of the half-bridge sub-module meet the conditions, the fault IGBT of the half-bridge sub-module can be accurately positioned. A sub-module capacitive current sensor does not need to be additionally added, and the method can be widely applied to existing MMC commercial products; capacitive current is observed in real time through a capacitive current state observer; the observation value of the capacitive current is symbolized through a symbolic function. By means of the method, the high anti-interference capacity is achieved for system parameter changes and sampling disturbance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
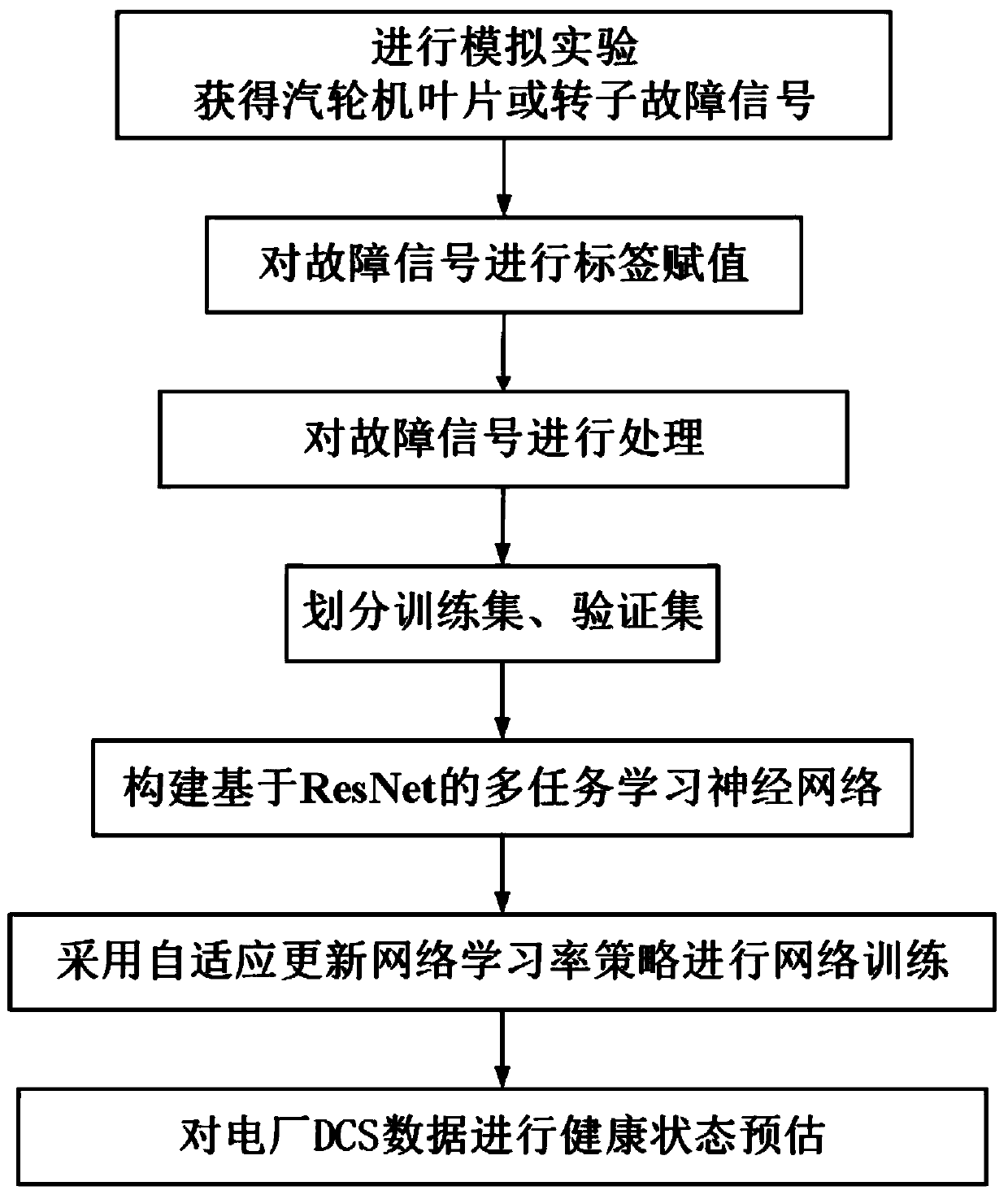
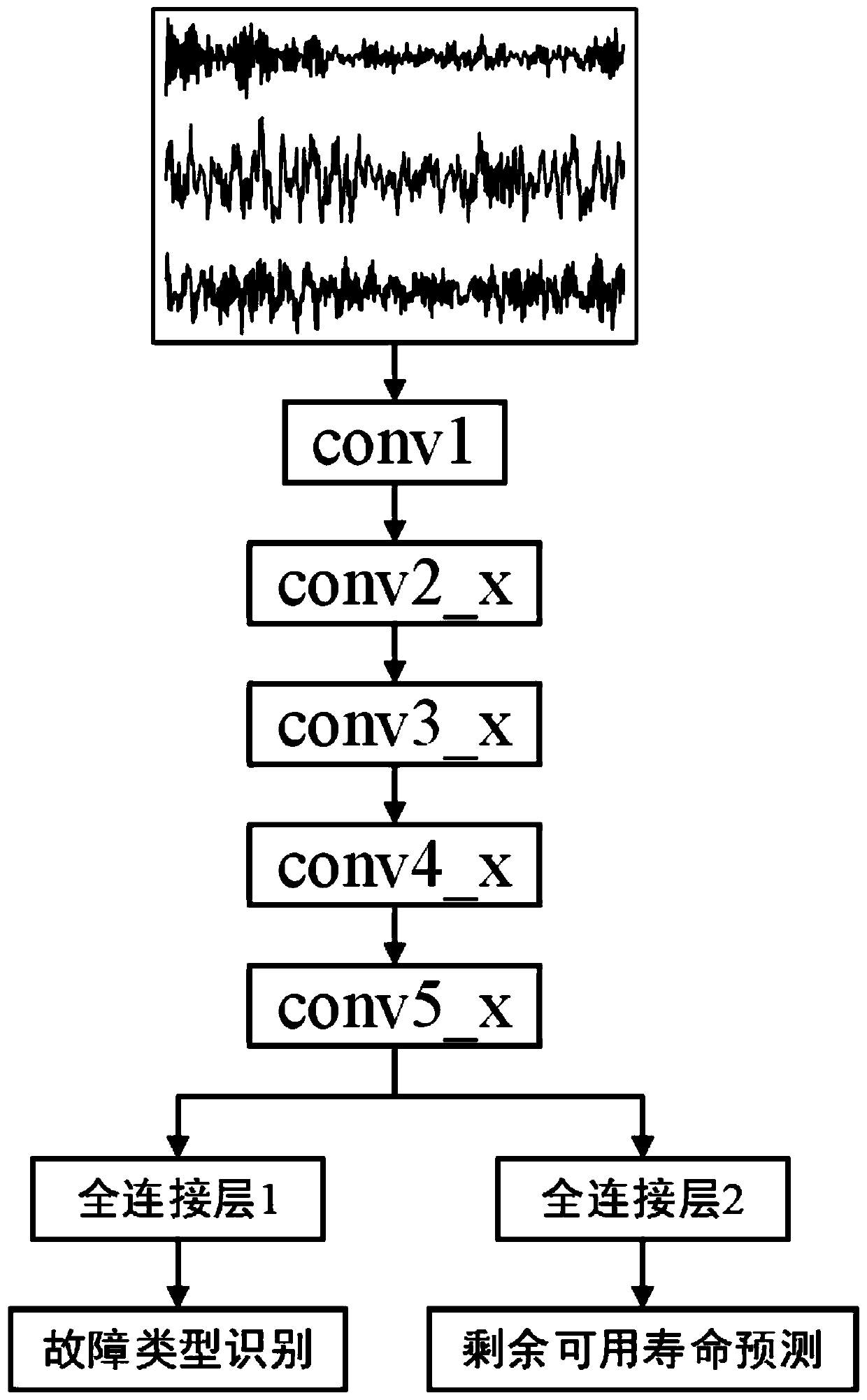
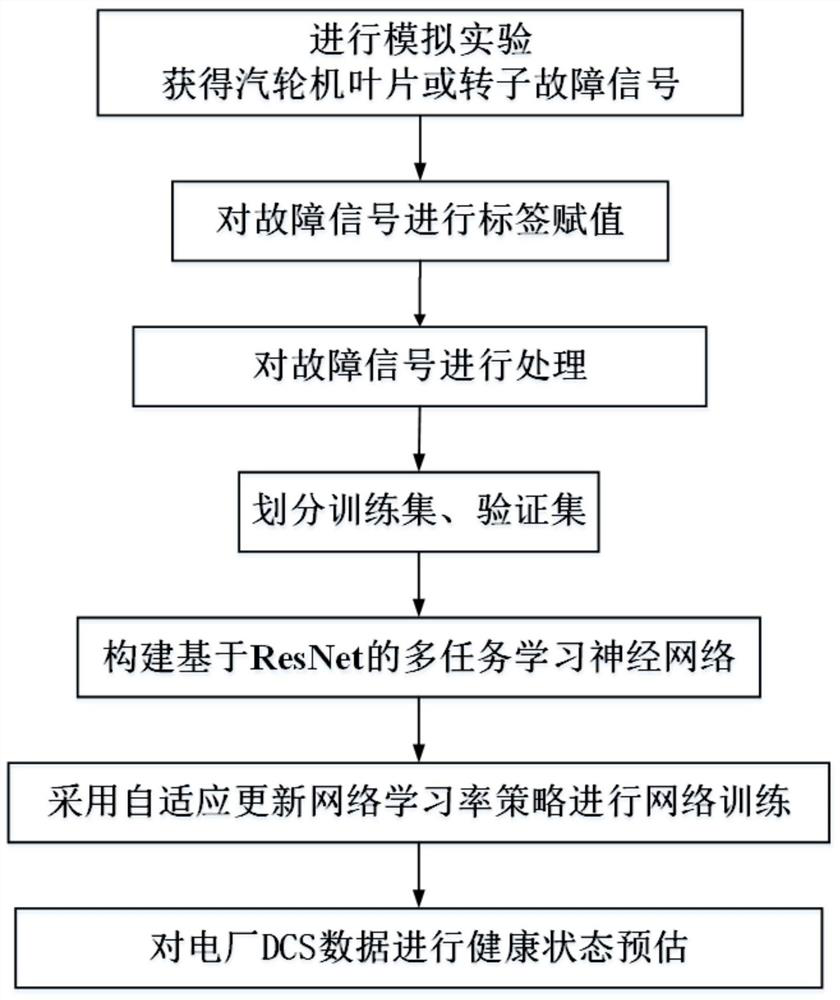
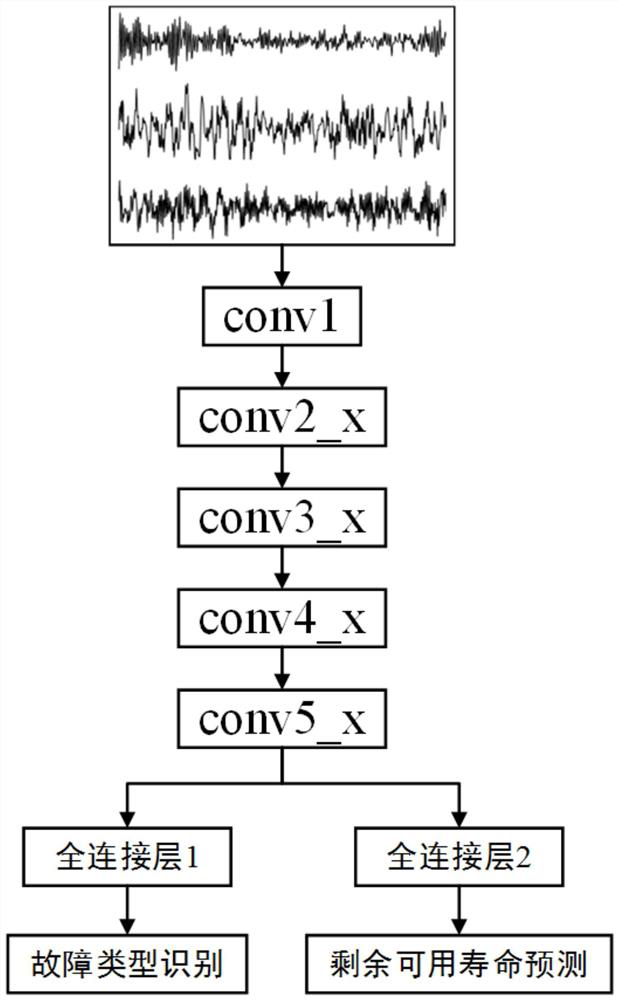
Steam turbine component health state assessment method based on ResNet
ActiveCN110046409AGuaranteed safe operationAvoid sudden failureGeometric CADCharacter and pattern recognitionData acquisitionMulti-task learning
The invention discloses a steam turbine component health state assessment method based on ResNet, which comprises the following steps: carrying out a simulation experiment of a steam turbine component, and carrying out vibration data acquisition through a plurality of measuring points, wherein the vibration data comprises fault signal data and normal working condition data; carrying out label assignment on the fault signal data, wherein the label information comprises a fault type and residual available life; segmenting the fault signal data assigned by each label and carrying out normalization processing to obtain a sample set; dividing the sample set according to a preset proportion to obtain a training set and a verification set; training a pre-constructed ResNet-based multi-task learning neural network model through the training set by adopting a strategy of adaptively updating the network learning rate to reach a preset convergence condition, and obtaining a trained ResNet-based evaluation model; steam turbine part health state assessment is achieved through the assessment model. A multi-task learning mechanism is adopted, the fault type and the health degree of the steam turbine can be judged at the same time, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
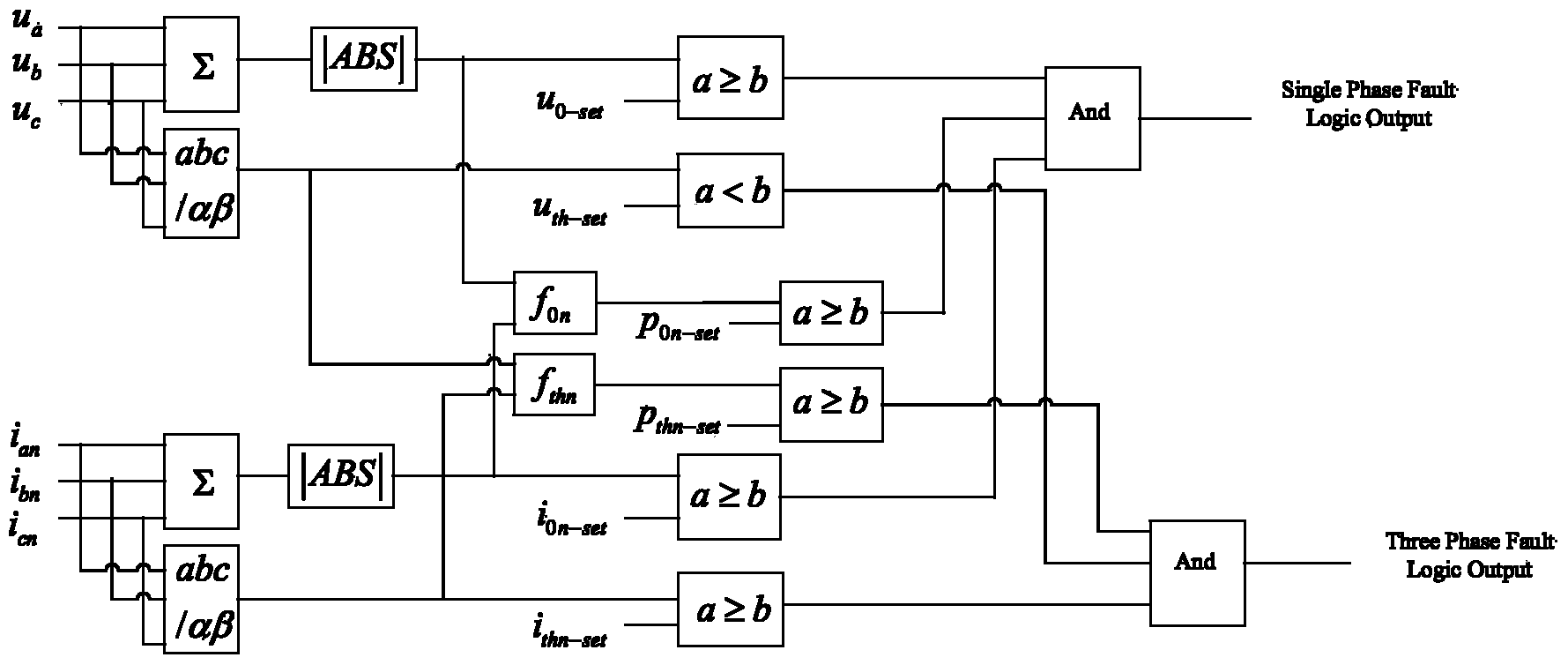
Alternating-current fault detection method for high-voltage direct-current power transmission
The invention provides an alternating-current fault detection method for high-voltage direct-current power transmission. The alternating-current fault detection method for high-voltage direct-current power transmission comprises the following steps of obtaining the three-phase voltage of a current conversion bus and three-phase currents of outgoing lines of the current conversion bus; obtaining a voltage zero-sequence component value and a rotating vector amplitude of the current conversion bus according to the three-phase voltage of the current conversion bus, and obtaining current zero-sequence component values and rotating vector amplitudes of the outgoing lines of the current conversion bus according to the three-phase currents of outgoing lines of the current conversion bus; obtaining power zero-sequence component values and power rotating vector amplitudes of the outgoing lines of the current conversion bus; comparing the values and the amplitudes with the set values and the set amplitudes respectively to obtain the fault detection result. The alternating-current fault detection method for high-voltage direct-current power transmission is high in speed and accuracy, and meets the requirement of high-voltage direct-current power transmission for fault detection, and valuable information is provided for the defense commutation failure of a control system for high-voltage direct-current power transmission.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +3
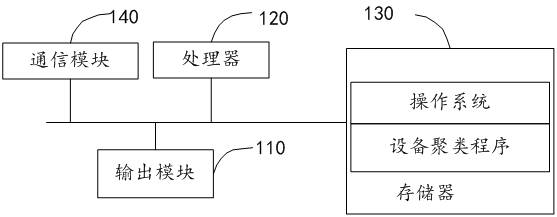
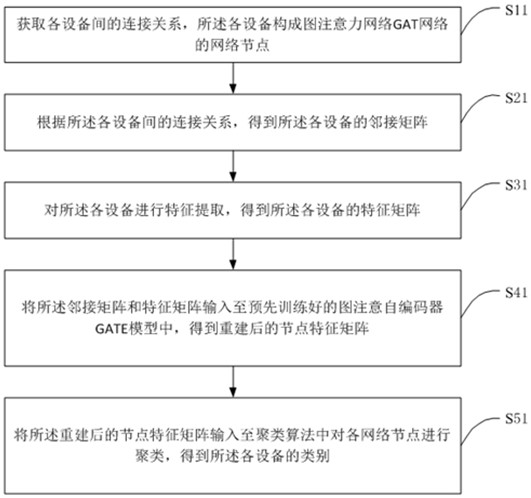
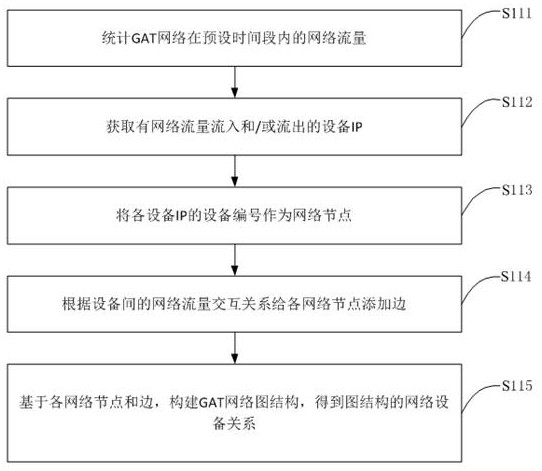
Equipment clustering method, terminal equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN114841296ASave computing spaceCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesCluster algorithmAlgorithm
The invention discloses a device clustering method, a terminal device and a storage medium, and the device clustering method comprises the steps: obtaining a connection relationship between devices, the devices forming network nodes of a GAT network; obtaining an adjacent matrix of each device according to the connection relationship among the devices; performing feature extraction on each device to obtain a feature matrix of each device; inputting the adjacent matrix and the feature matrix into a pre-trained graph attention auto-encoder GATE model to obtain a reconstructed node feature matrix; and inputting the reconstructed node feature matrix into a clustering algorithm to cluster each network node to obtain the category of each device. The invention provides an equipment clustering scheme which does not need to update the node features of the whole graph and re-calculate the whole graph under the condition that the equipment nodes are increased, so that a large amount of calculation space is saved.
Owner:北京六方云信息技术有限公司 +1
Depthwise fast convolution system based on image processing, and image recognition method
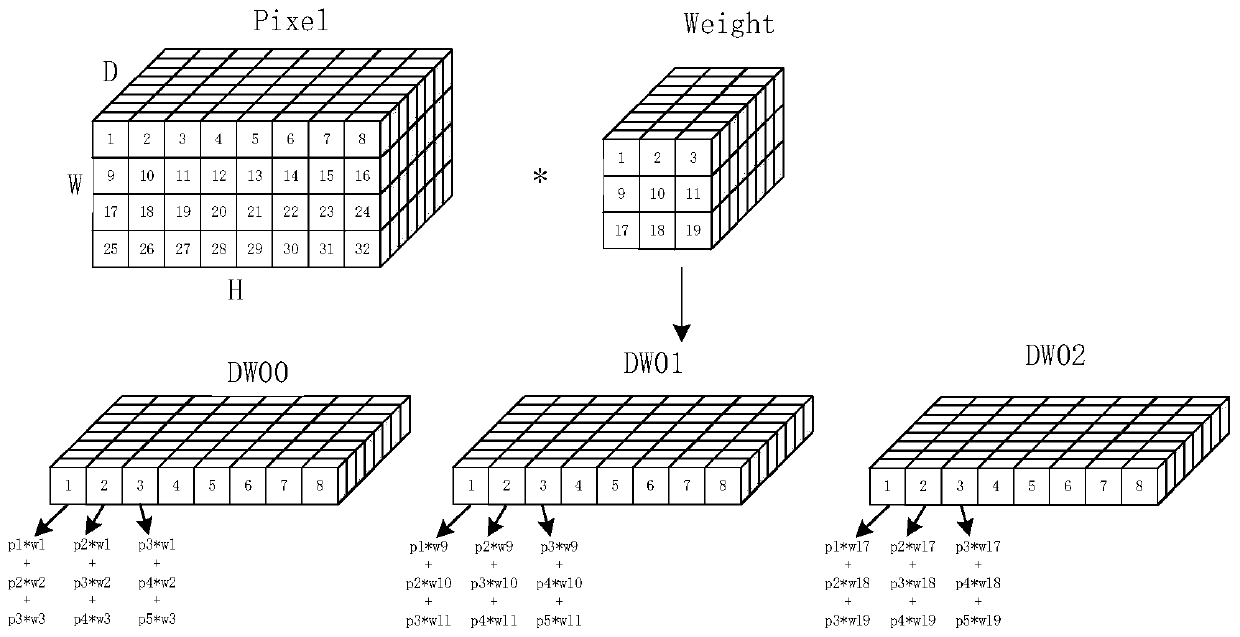
PendingCN111260598AAvoid repeated readingIncrease profitImage enhancementNeural architecturesPattern recognitionImaging processing
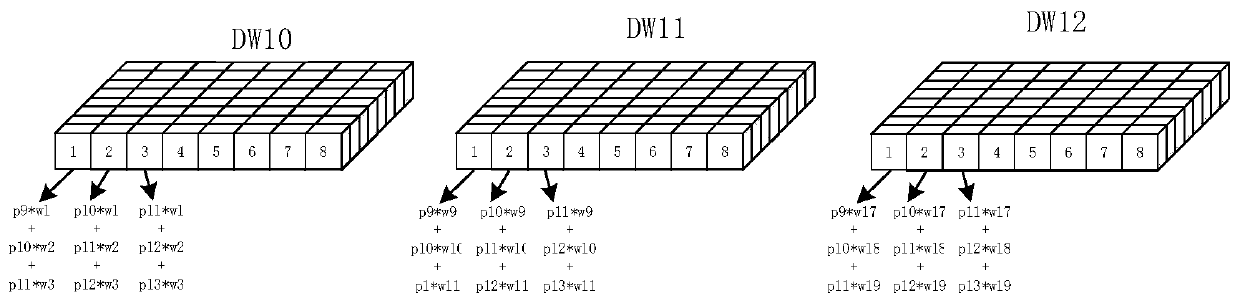
The invention discloses a Depthwise fast convolution system based on image processing. The Depthwise fast convolution system comprises an image pixel reading unit and a DW convolution calculation unit. The image pixel reading unit can store an image to be processed into the storage unit in a multi-dimensional form; and the DW convolution calculation unit reads the image data in rows and then performs multiply-accumulate calculation with the convolution kernels of the three rows to obtain calculation results of all pixel points. According to the system, a rapid algorithm of image convolution isrealized, the process of repeatedly reading the image storage unit can be reduced, the calculation space used by convolution is reduced, and the result of image convolution can be rapidly and accurately obtained.
Owner:中科南京人工智能创新研究院
Factory processing flow recommendation method based on singular value decomposition
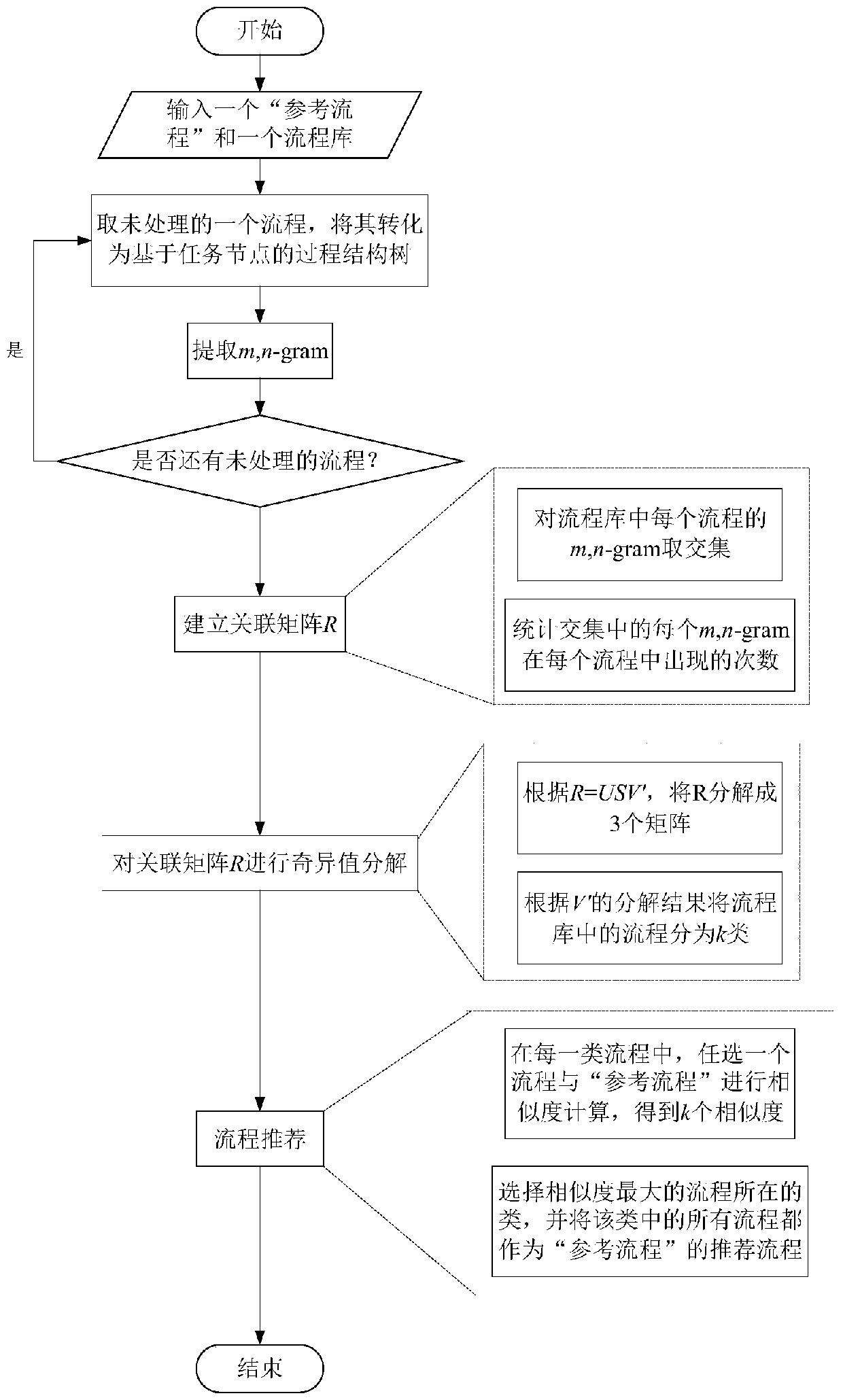
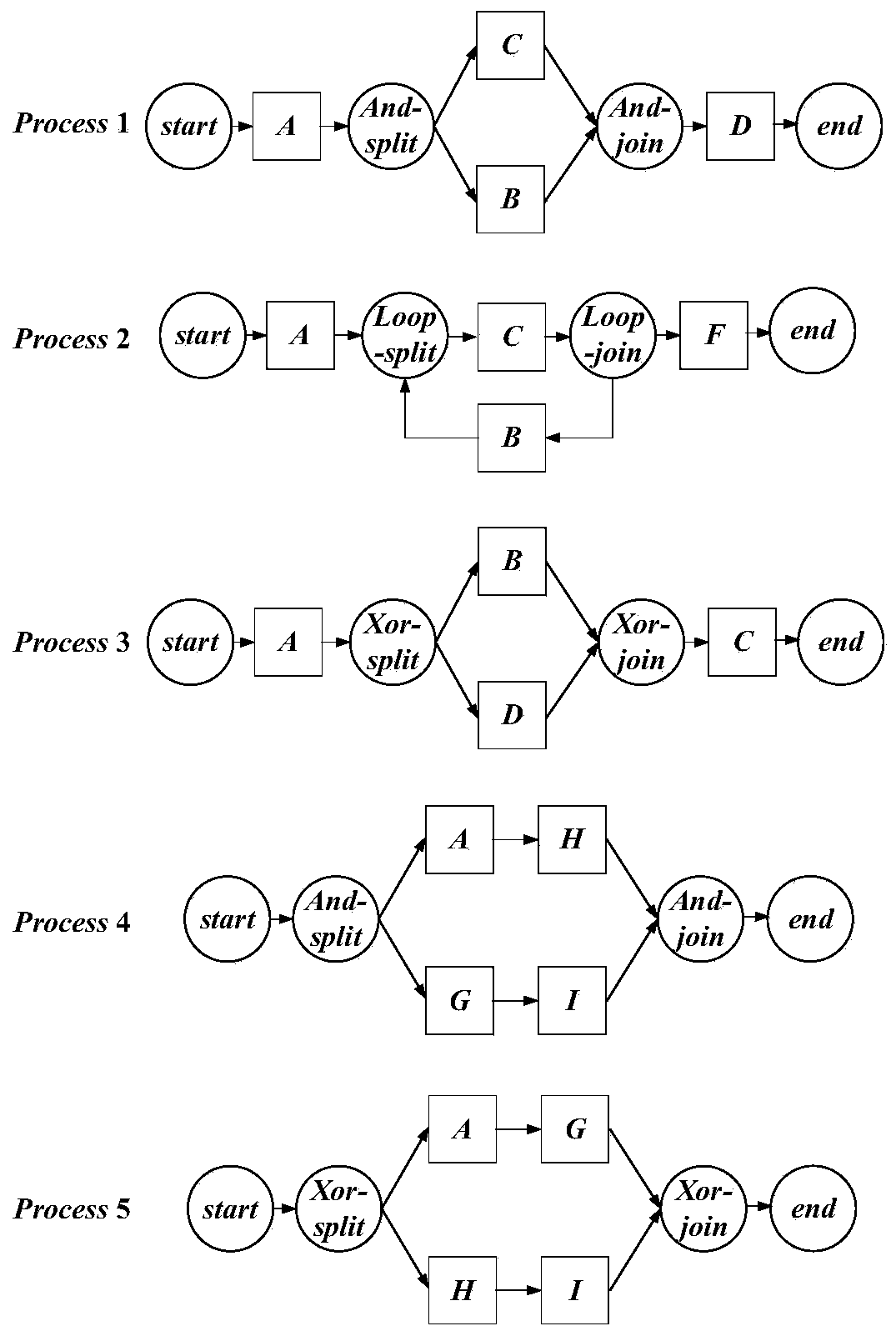
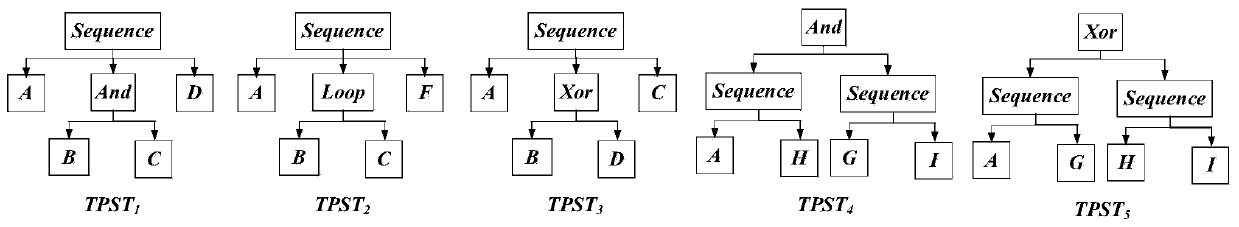
ActiveCN111008783AImprove efficiencyReduce the number of similarity calculationsOffice automationResourcesSingular value decompositionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a factory processing flow recommendation method based on singular value decomposition. The method comprises the steps of converting a factory processing flow 'reference flow 'which is being modeled and all factory processing flows in a flow library into corresponding process structure trees based on task nodes; extracting an m, n-gram set of the TPST corresponding to each processing flow in the flow library, wherein one m, n-gram represents a partial structure and behavior characteristics of one processing flow; taking a union set of the m, n-gram set of each factory processing flow in the flow library, and establishing an incidence matrix based on all the processing flows in the flow library; performing singular value decomposition on the incidence matrix, and dividing flows in the flow library into a plurality of classes according to a decomposition result; selecting any processing flow from each class of flow to be subjected to similarity calculation with the'reference flow', and using all the flows in the class of flow with the highest similarity as recommendation flows of the 'reference flow'. According to the invention, the most recommended flow of the 'reference process can be obtained only through one-time calculation, so that the calculation space is greatly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
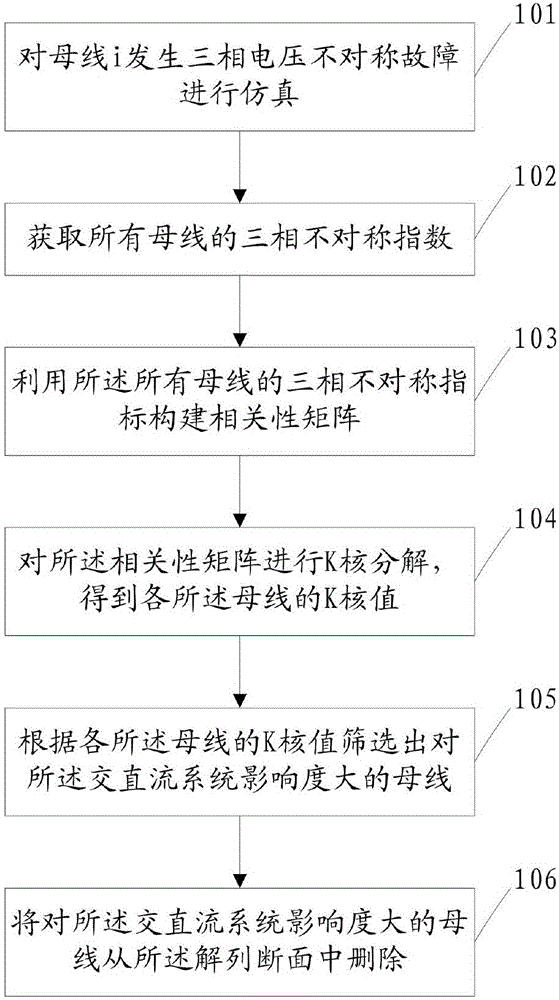
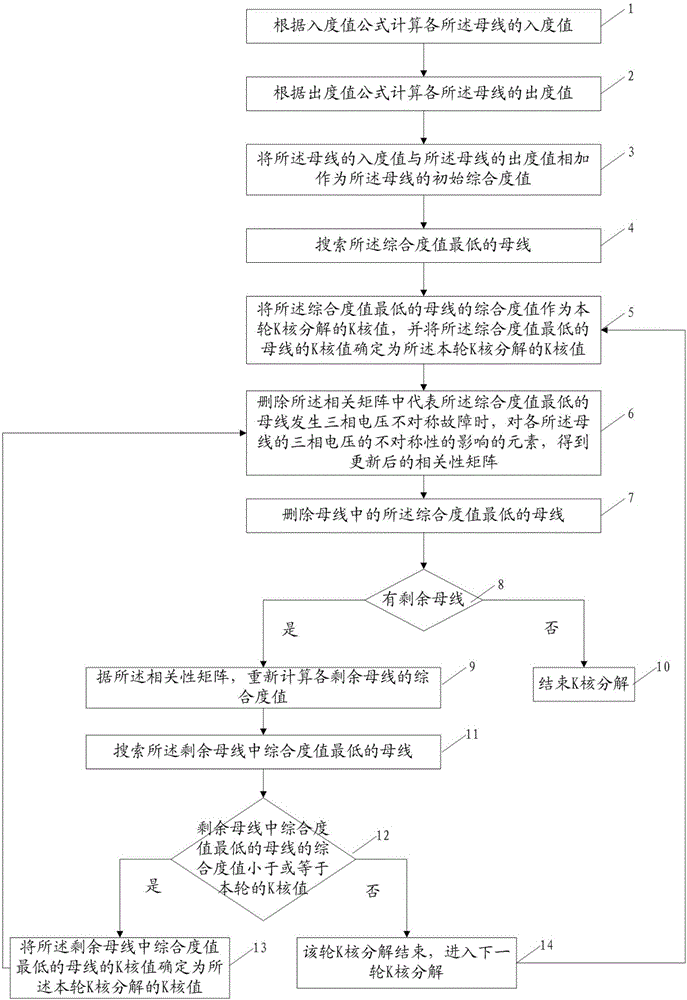
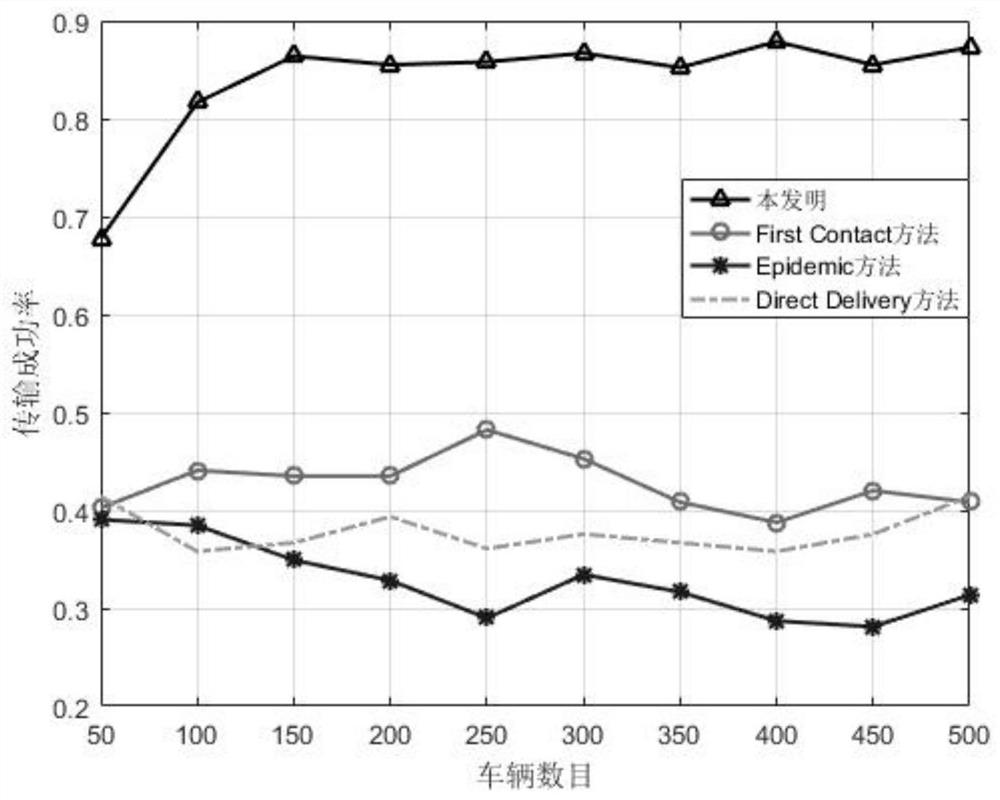
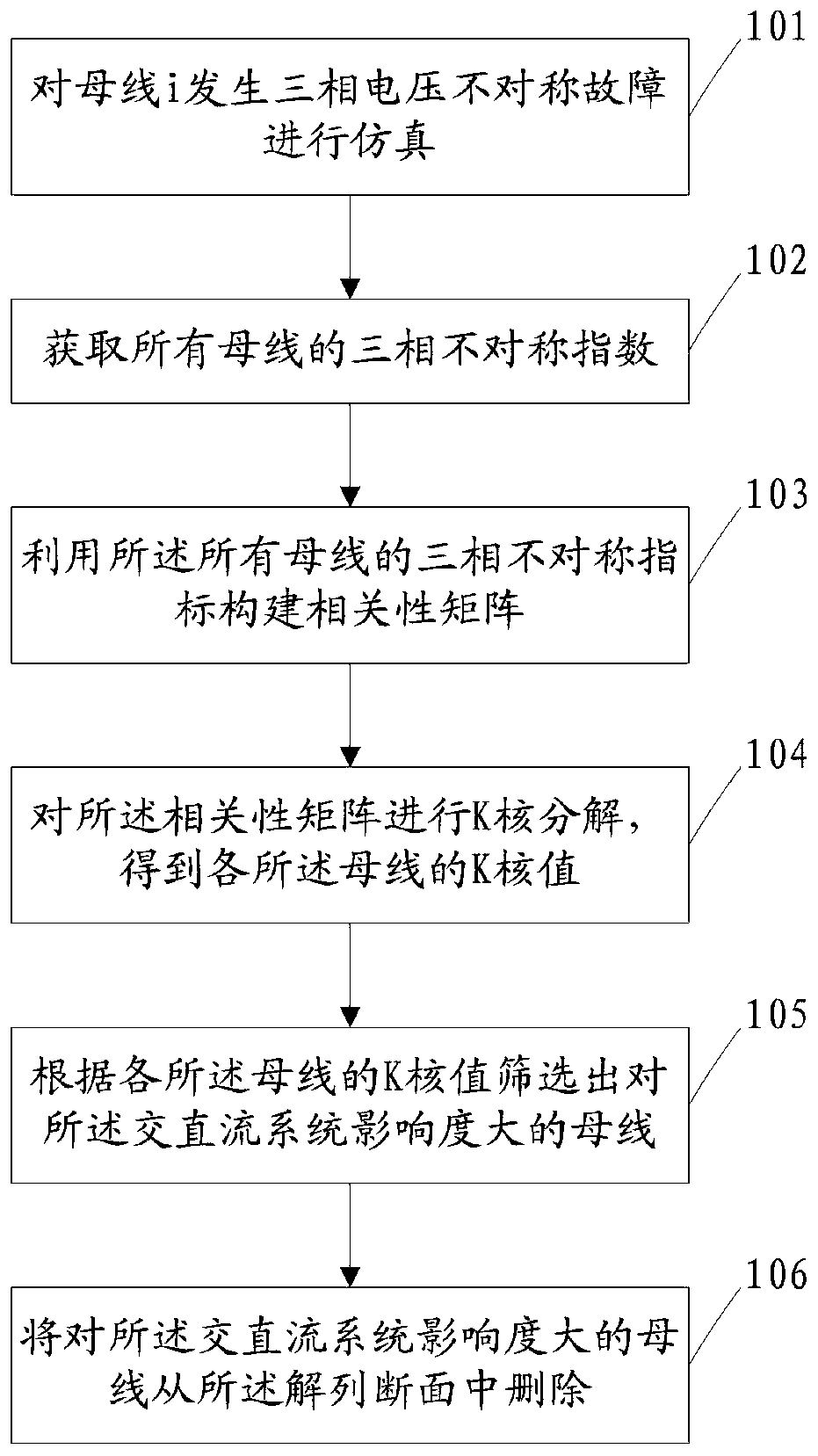
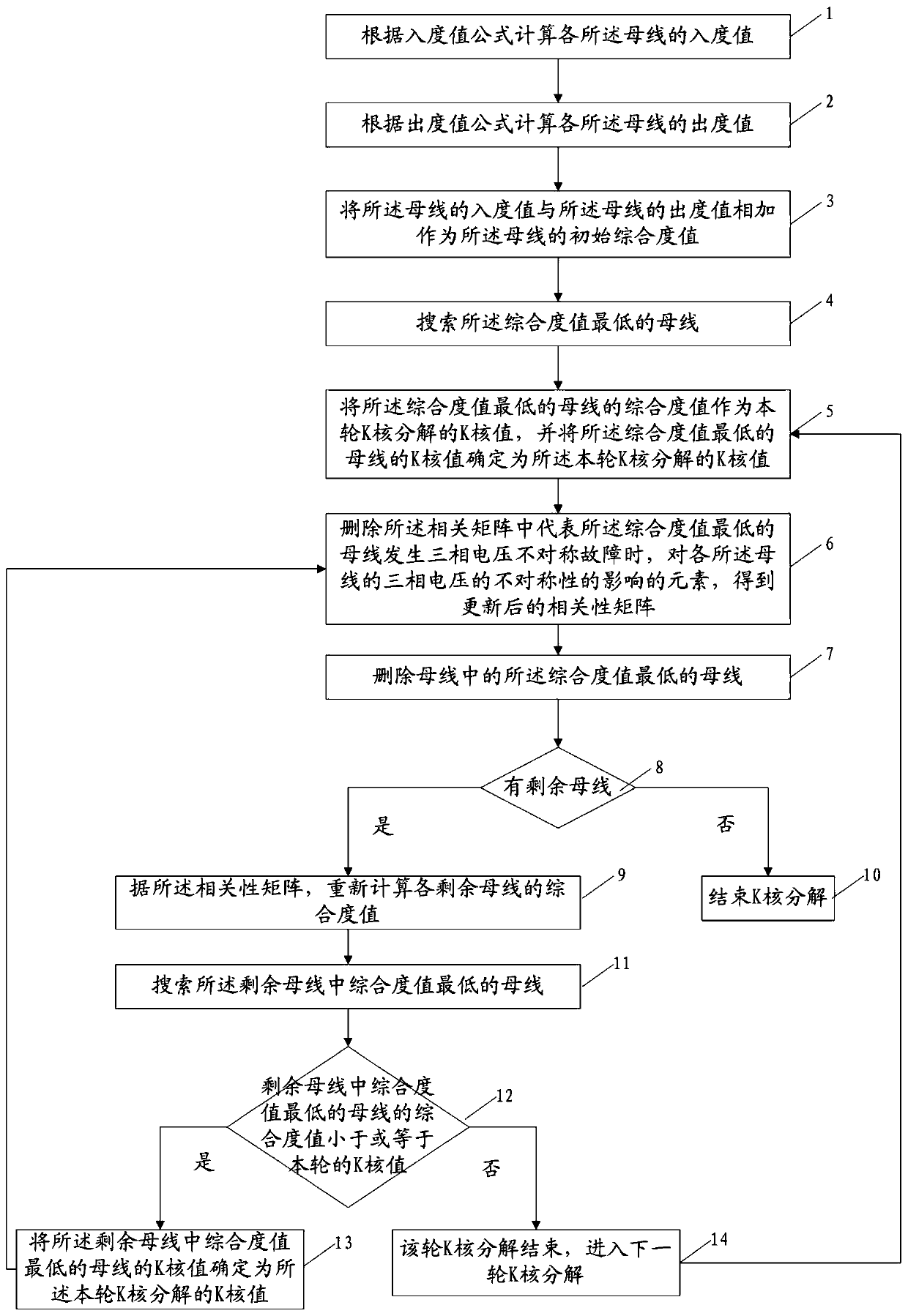
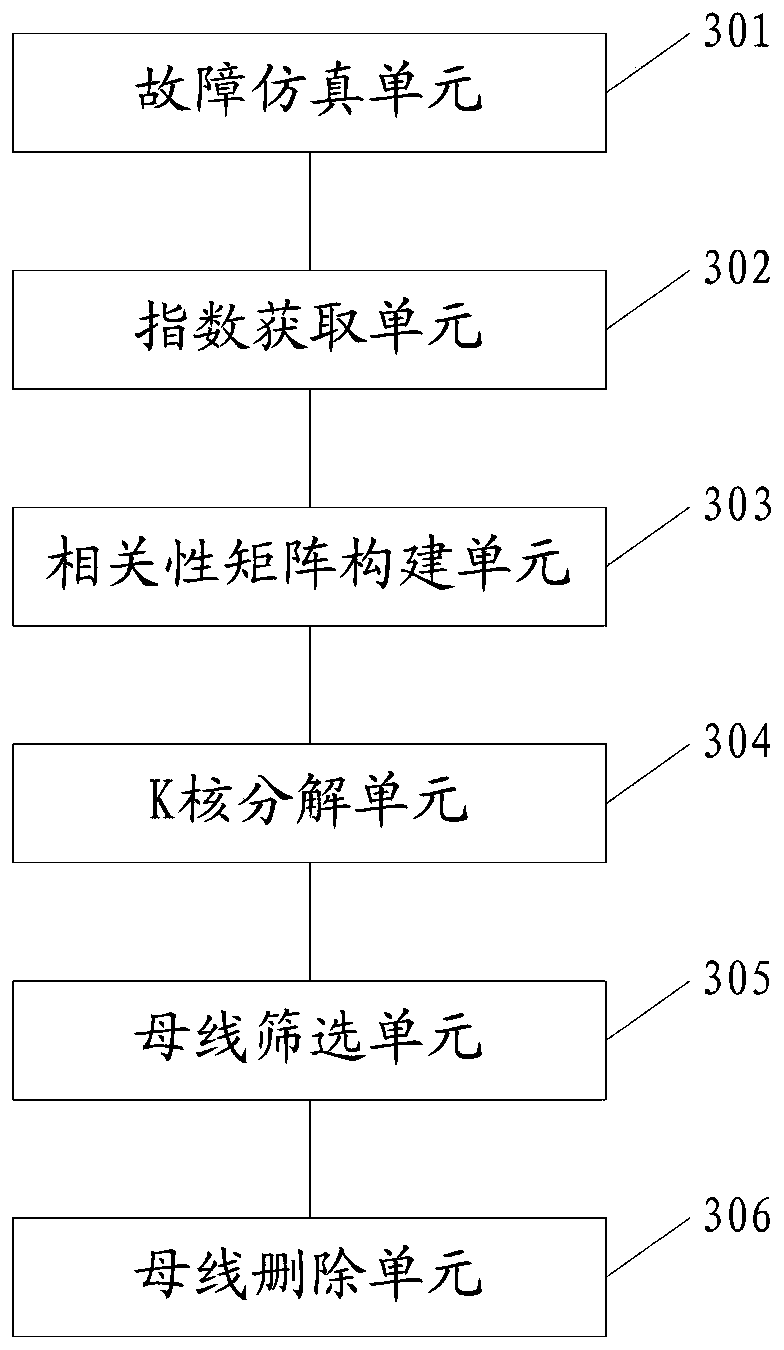
Splitting surface pre-screening method and splitting surface pre-screening system applied to alternating-current/direct-current system
ActiveCN106446471AAvoid the risk of instabilitySave computing spaceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionPre screening
The invention discloses a splitting surface pre-screening method and a splitting surface pre-screening system applied to an alternating-current / direct-current system. The splitting surface pre-screening method includes simulating asymmetrical faults in three-phase voltage of a bus bar i; acquiring three-phase asymmetric indexes of all bus bars; constructing a correlation matrix according to the three-phase asymmetric indexes of all the bus bars; subjecting the correlation matrix to K-core decomposition so as to obtain a K-core value of each bus bar; screening out the bus bar with the maximum degree of influence on the alternating-current / direct-current system according to the K-core value of each bus bar; deleting the bus bar with the maximum degree of influence on the alternating-current / direct-current system from a splitting surface composed of multiple lines, and splitting the alternating-current / direct-current system according to the splitting surface. The splitting surface pre-screening method and the splitting surface pre-screening system applied to the alternating-current / direct-current system have the advantages that on one hand, stability of the alternating-current / direct-current system subjected to splitting control is guaranteed, and on the other hand, the size of a splitting surface search space is decreased, so that operation time is saved and operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Data abnormal mutation point detection algorithm based on limited accompanying group mechanism
InactiveCN111695634AImprove accuracySave computing spaceCharacter and pattern recognitionReal-time dataData stream
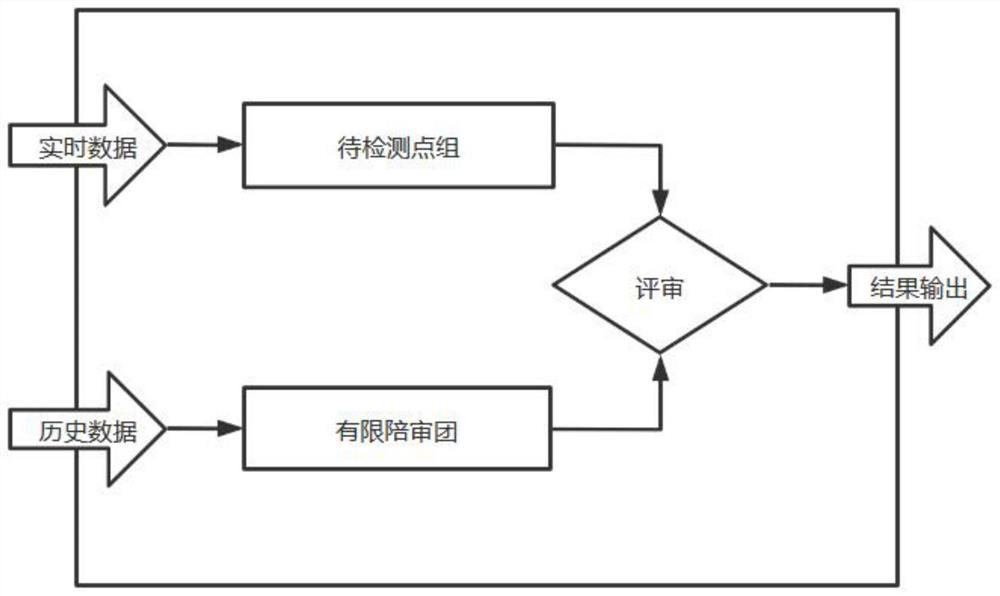
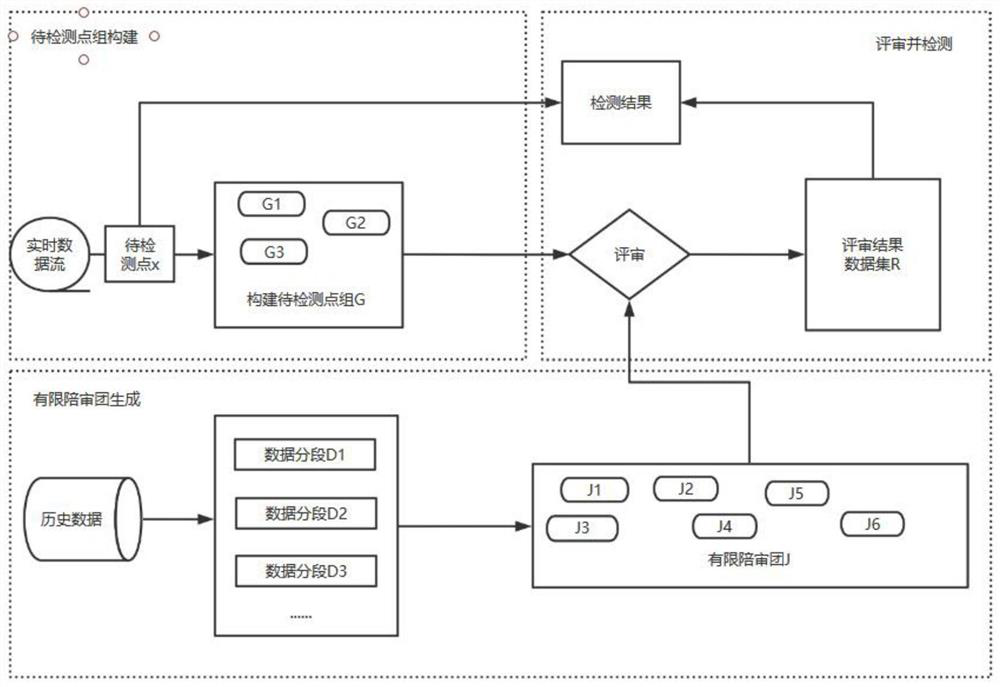
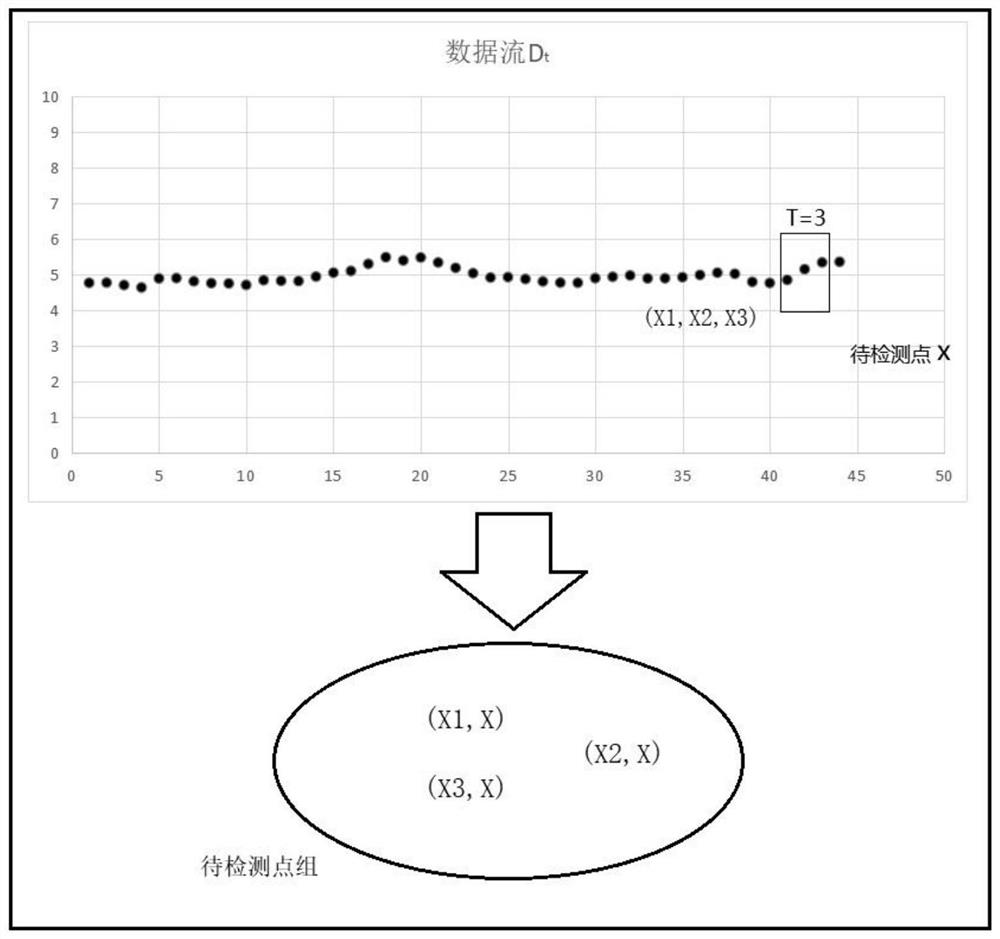
The invention discloses a novel abnormal mutation point detection method, and particularly relates to a data abnormal mutation point detection algorithm based on a limited accompanying group mechanism. A finite accompanying group mechanism is utilized to help to efficiently and accurately identify and detect the mutation points in the industrial data stream. According to the method, a limited accompanying group thought is provided, and effective identification and detection of abnormal mutation points of the data stream are realized by selecting a limited high-quality accompanying group and constructing a to-be-detected point group. The algorithm has low delay, and abnormal mutation points can be timely identified in real-time data streams.
Owner:JIANGSU FRONTIER ELECTRIC TECH +2
Rotor-wing unmanned aerial vehicle, its abnormal landing processing device and processing method
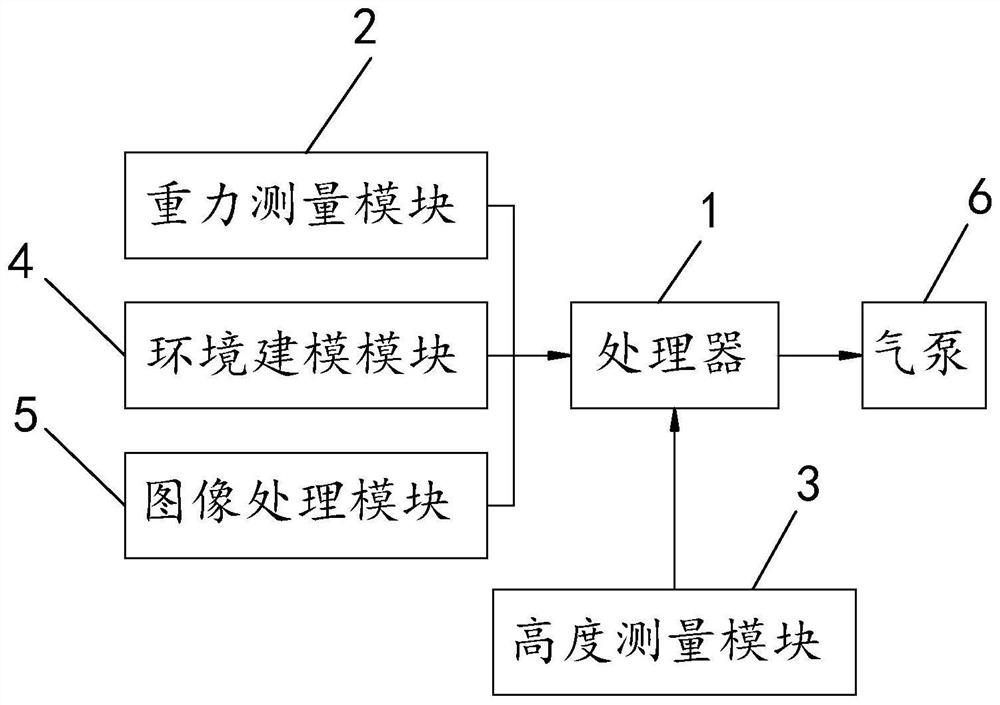
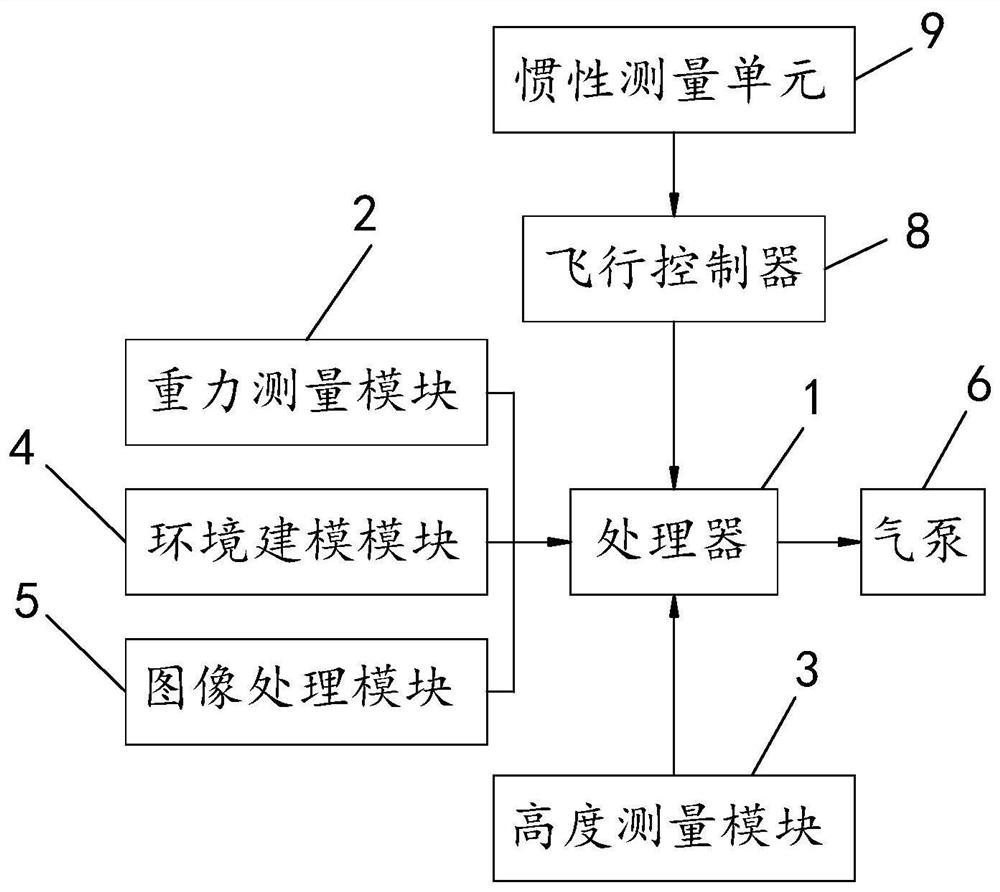
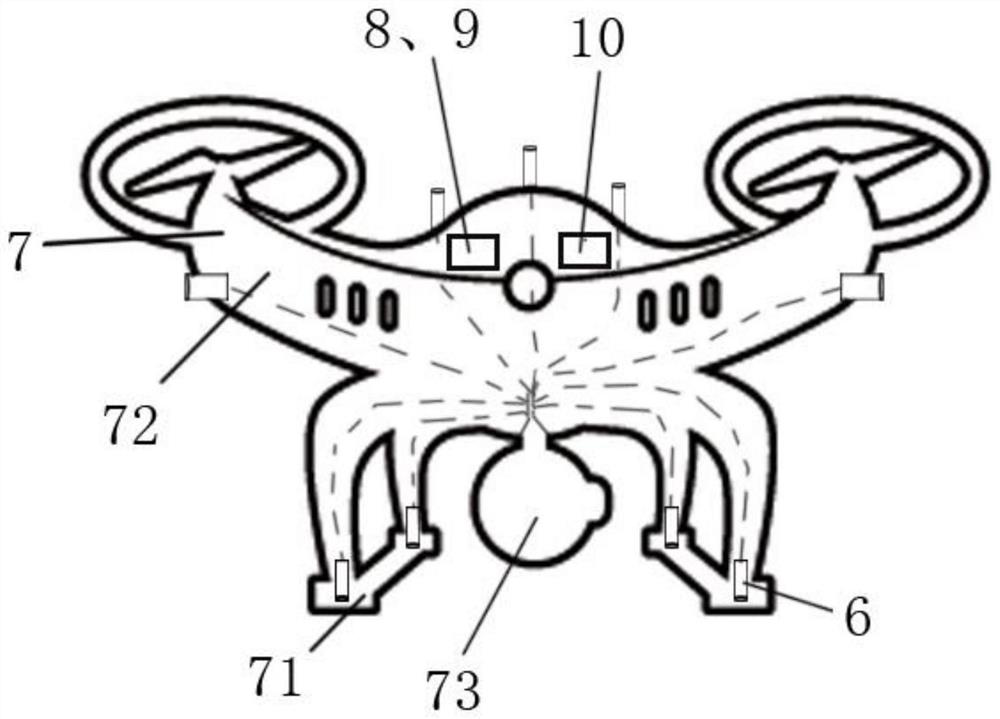
ActiveCN107145158BPlay a buffer roleImprove securityPosition/course control in three dimensionsRotocraftUncrewed vehicleGravity center
The present invention involves a rotor drone, its abnormal landing treatment device and treatment method, which includes anomalous treatment unit used to deal with an abnormal treatment unit for handling drones.The abnormal processing unit includes the processor, the gravity measurement module connected to the processor, and the height measurement module connected to the processor.High information; the landing unit is connected to the processor. When the processor determines the drone abnormality, the processor controls the landing unit according to the receiving drone's flight high.When the invention has abnormal conditions in the drone, it can independently judge the land orientation of the drone, and start the landing unit in a timely manner for the landing and buffer, effectively reduce the body damage caused by the drone abnormal landing, reduce the cost of use, increase the cost of use, increase the improvementThe safety of drones.
Owner:QINGDAO ACADEMY OF INTELLIGENT IND
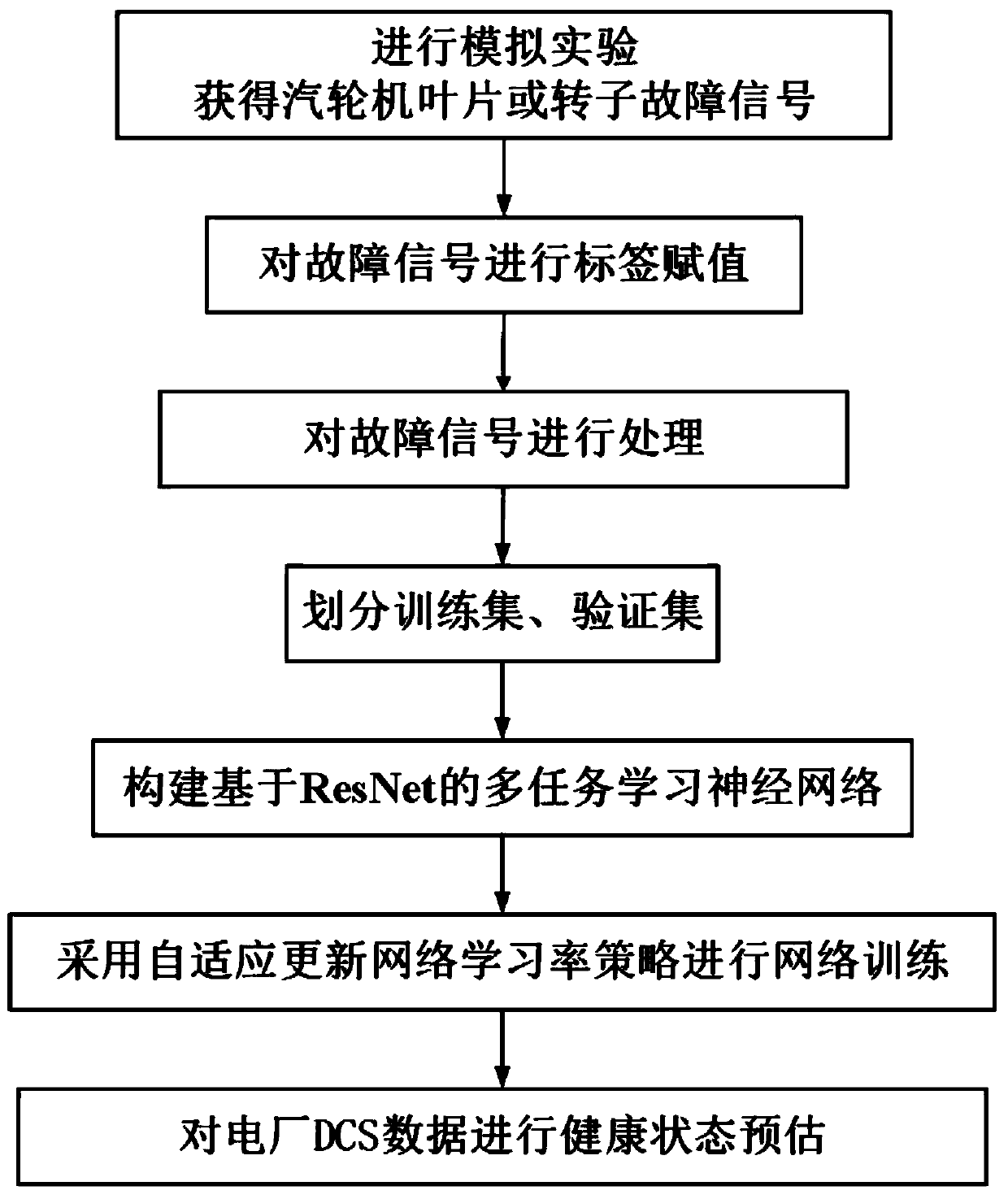
A resnet-based health status assessment method for steam turbine components
ActiveCN110046409BGuaranteed safe operationAvoid sudden failureGeometric CADCharacter and pattern recognitionData packData acquisition
The invention discloses a ResNet-based method for assessing the health status of steam turbine components, which includes: performing a simulation experiment on steam turbine components, and collecting vibration data through multiple measuring points; the vibration data includes fault signal data and normal working condition data; the fault signal The data is tagged; the tag information includes the fault type and remaining usable life; the fault signal data after each tag assignment is segmented and normalized to obtain a sample set; the sample set is divided according to a preset ratio to obtain a training set and verification Set; adopt the strategy of adaptively updating the network learning rate, train the pre-built multi-task learning neural network model based on ResNet through the training set, and obtain the trained evaluation model based on ResNet to the preset convergence condition; realize the steam turbine through the evaluation model Component health assessment. The invention adopts a multi-task learning mechanism, can simultaneously judge the fault type and the health degree of the steam turbine, and has high accuracy.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Motor target prediction torque obtaining method and motor control system
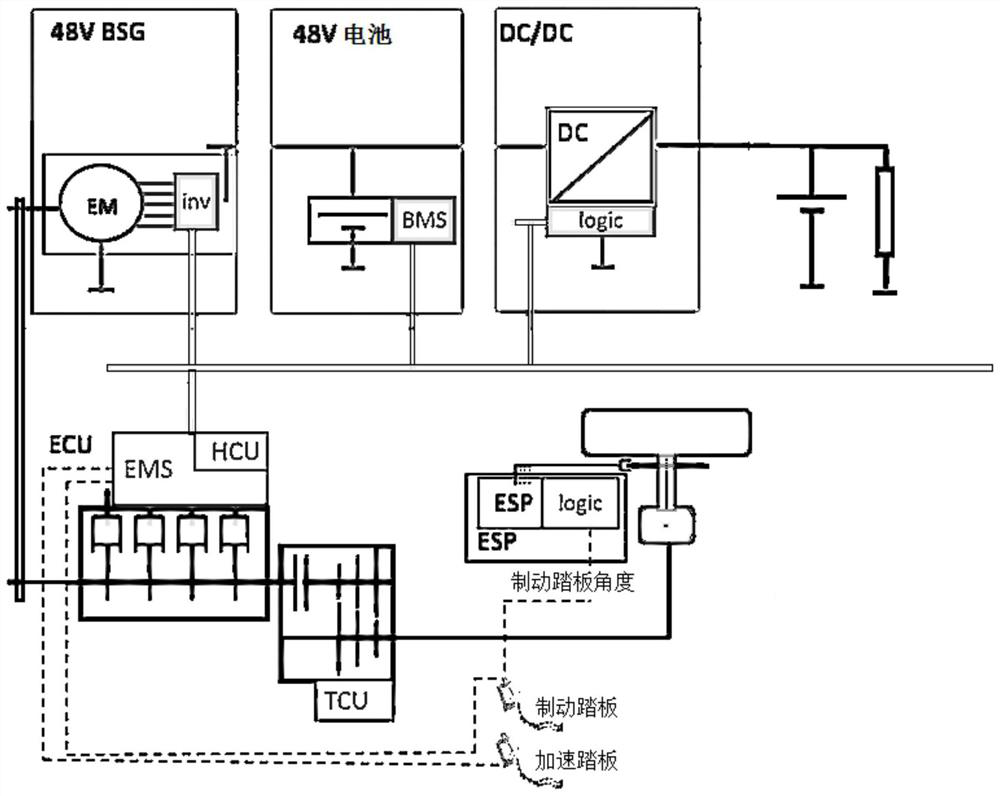
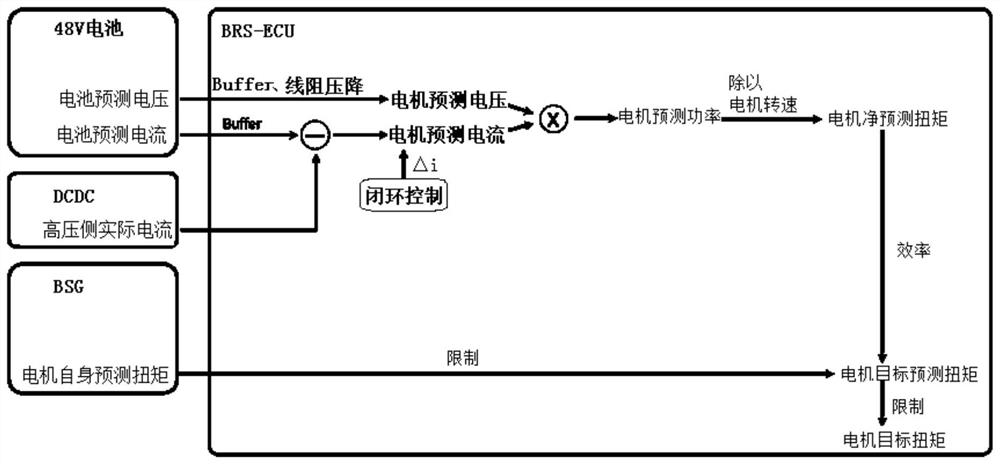
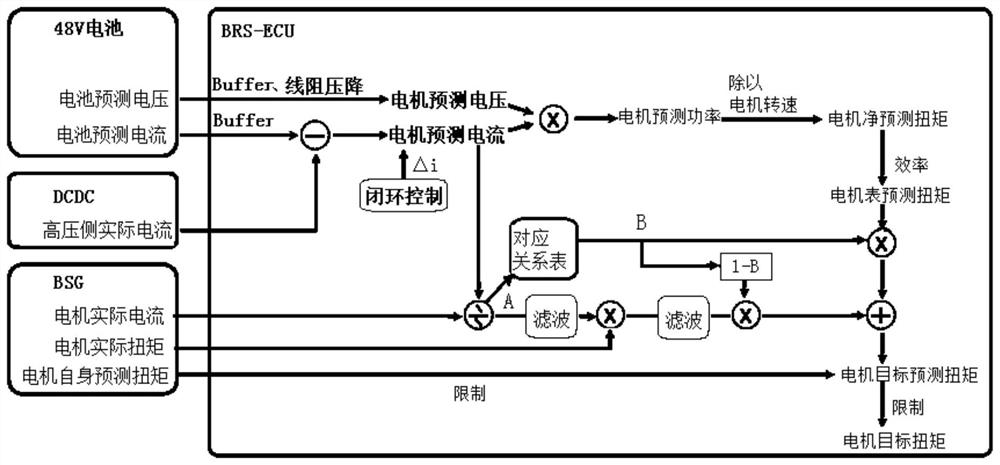
ActiveCN113078855ACalculation method is simpleImprove protectionDC motor speed/torque controlMotor parameters estimation/adaptationElectrical batteryMotor efficiency
The invention discloses a motor target prediction torque obtaining method. The method comprises calibrating an A / B corresponding relation table and a motor efficiency table; calculating according to the motor predicted voltage uppred and the motor predicted current ipred to obtain motor predicted power Ppred, and checking a motor efficiency table according to the motor predicted power Ppred and the motor rotating speed n to obtain motor predicted efficiency eta pred; obtaining a motor table prediction torque Tqpred, map according to the motor prediction power Ppred, the motor rotation speed n and the motor prediction efficiency eta pred; calculating to obtain A according to the motor predicted current ipred and the motor actual current iact; checking an A / B corresponding relation table according to A to obtain B; and according to the predicted torque Tqpred, map of the motor table and the actual torque Tqact, A and B of the motor, obtaining the target predicted torque Tqpred of the motor, nammely Tqpred = Tqpred, map * B + A * Tqact * (1-B). The invention further discloses a motor control system. The precision of the target prediction torque Tqpred of the motor is improved, meanwhile, the calculation amount is reduced, the calculation space of the controller is saved, and it is avoided that the service life of the battery is shortened due to over-current of the battery.
Owner:UNITED AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS SYST
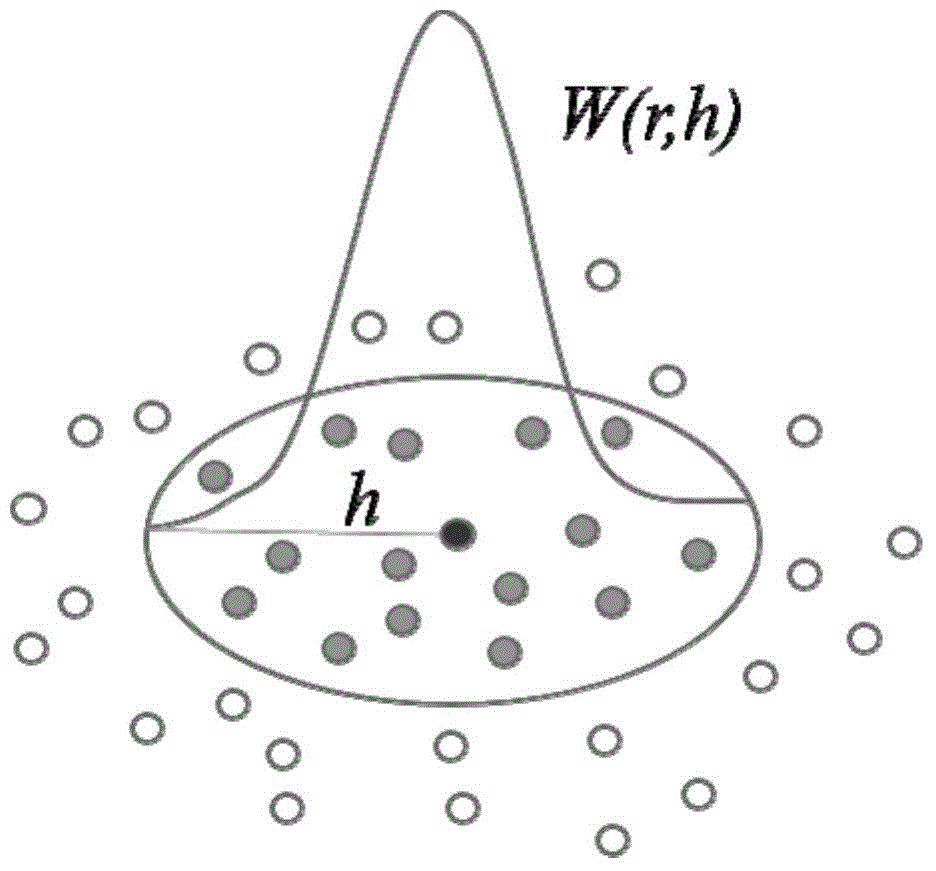
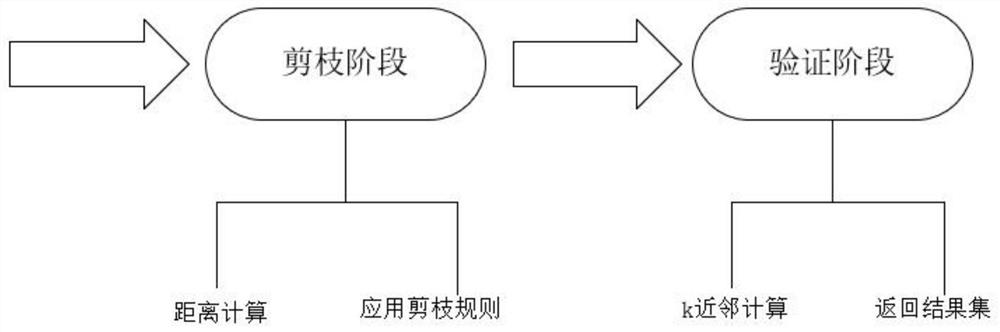
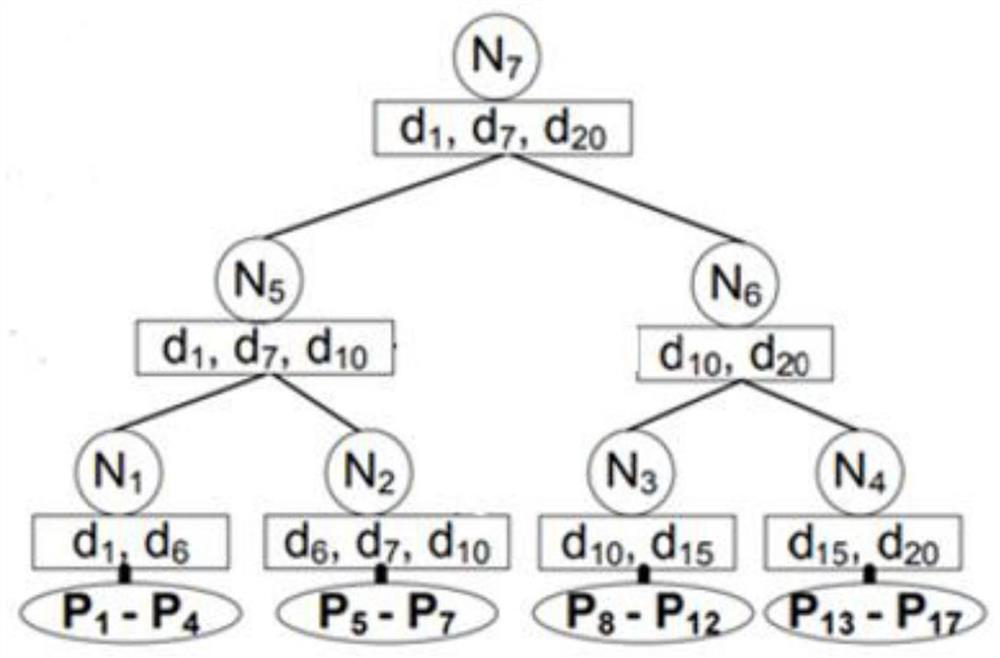
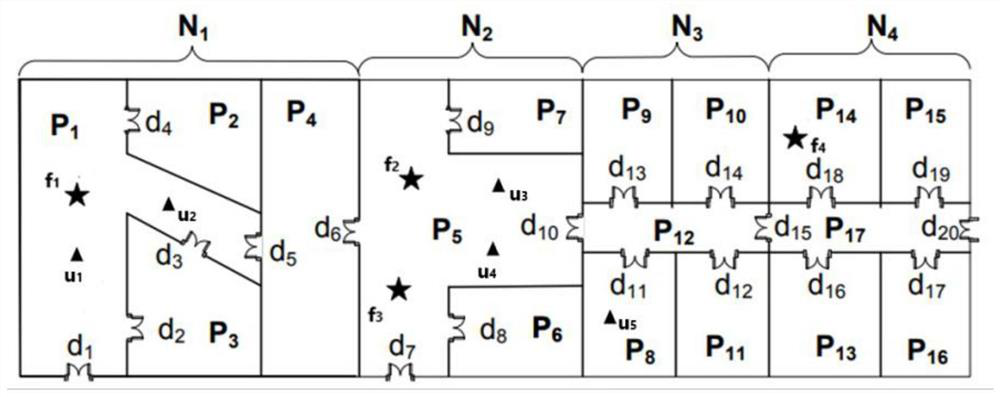
Indoor space reverse k neighbor query method and application thereof
PendingCN114860856ASave computing spaceQuick calculationGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsNear neighborRoomba
The invention discloses an indoor space reverse k-nearest neighbor query method, which utilizes indoor space information and a corresponding VIP tree structure to simplify calculation of an indoor distance and traverse different rooms, and utilizes user point information and equipment point information to prune and verify a reverse k-nearest neighbor of a query point. The method specifically comprises the following steps: screening candidate nodes and necessary nodes from leaf nodes of a VIP tree by using a pruning algorithm; verifying the users in the candidate nodes by using a verification algorithm, and judging whether the users are reverse k neighbors of the query point or not; and directly adding the user points contained in the required nodes into the result set. According to the method, some very effective pruning rules are designed by determining the distance ranges between equipment points and different spaces by utilizing the characteristics of indoor spaces, and a pruning verification framework is adopted to reduce the calculation space and reduce unnecessary calculation according to the pruning rules, so that the purpose of quickly calculating the reverse k-nearest neighbor of a query point is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
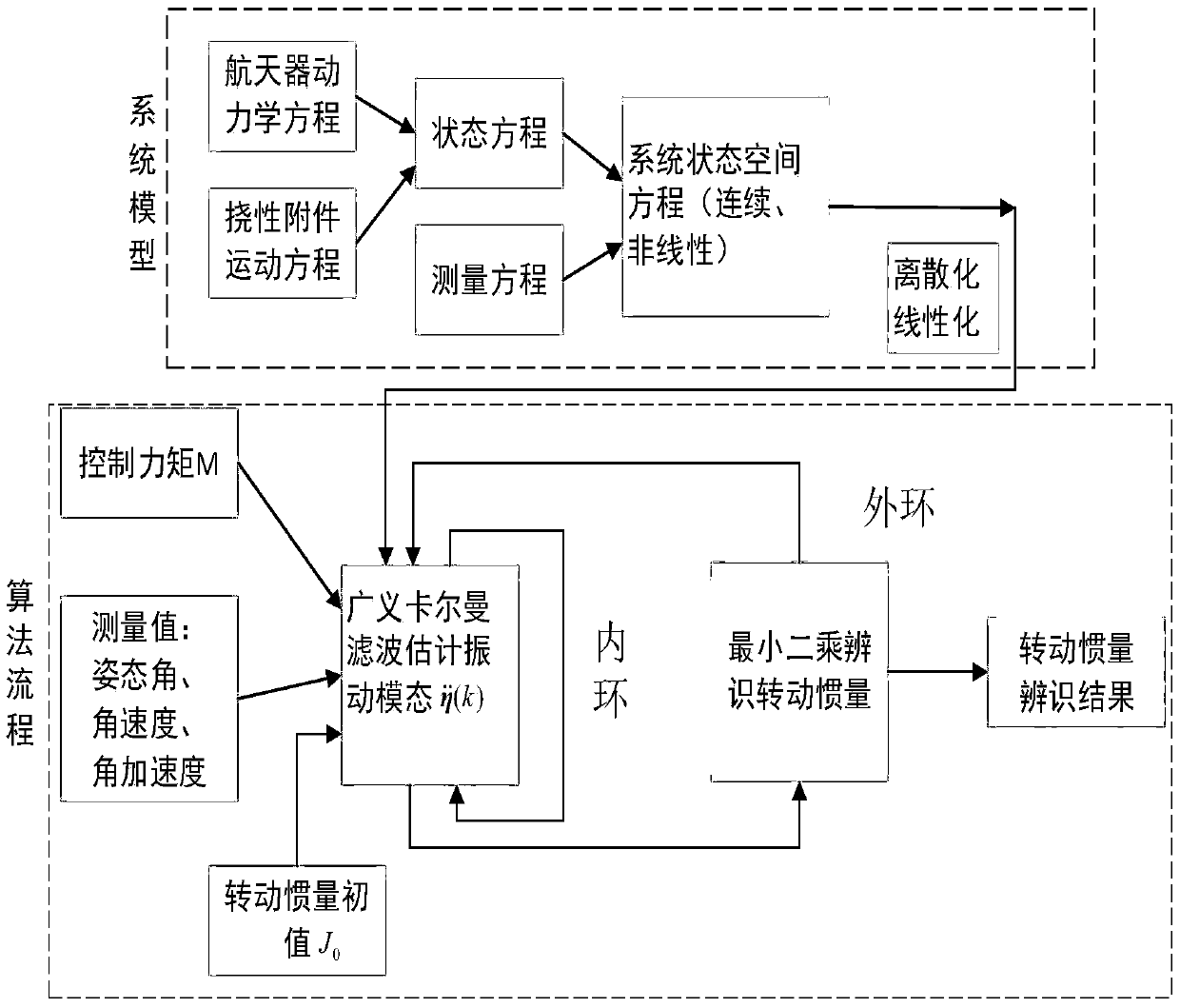
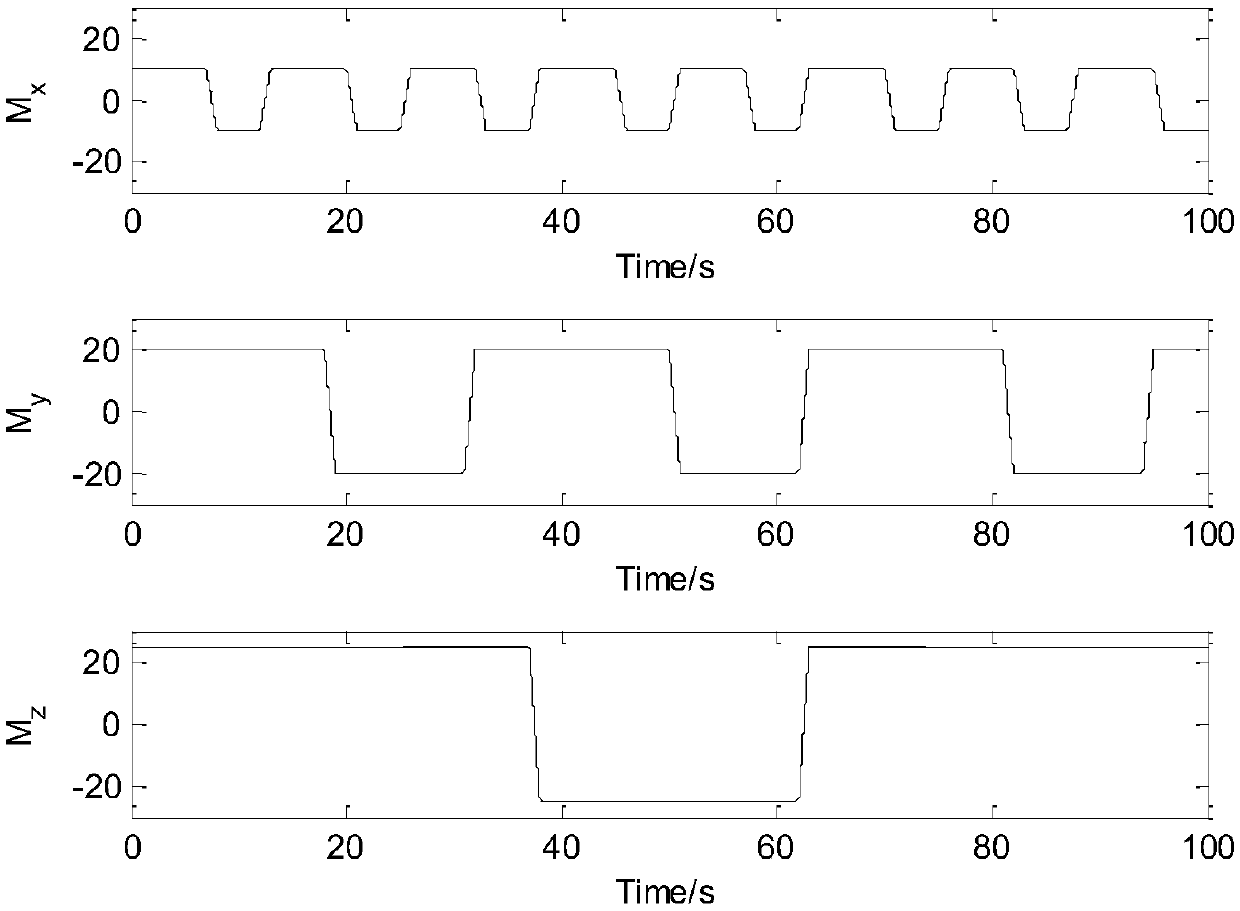
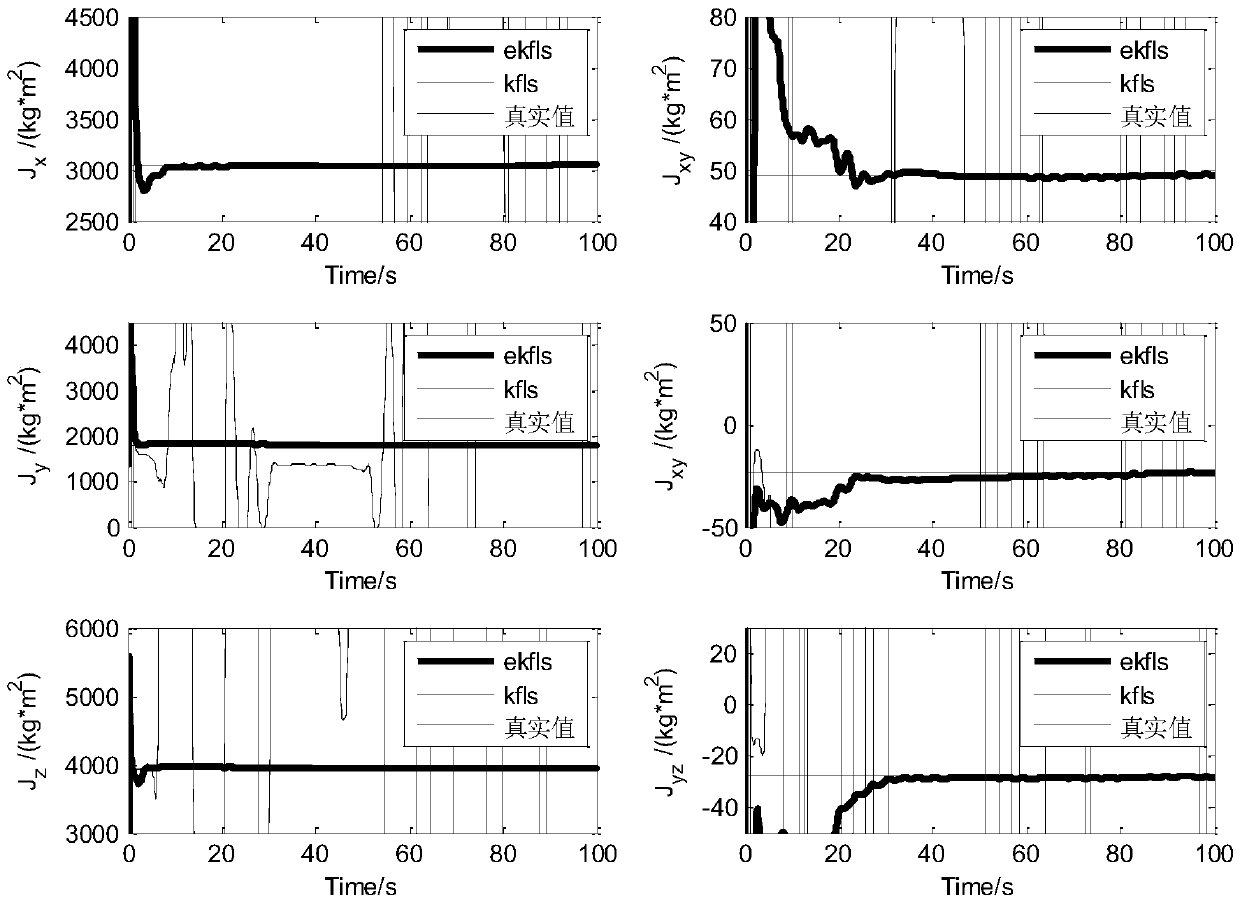
A method for on-orbit identification of moment of inertia of spacecraft with flexible attachments under large-angle maneuvering
InactiveCN107036761BSave computing spaceFast operationStatic/dynamic balance measurementGyroscopeDynamic equation
The invention discloses a method for in-orbit identification of moment-of-inertia of spacecraft with flexible attachment in a large angle maneuver, and the method comprises the following steps: S1) according to the altitude dynamic equation of the spacecraft and the motion equation of the flexible attachment, establishing a nonlinear system dynamic model; S2) using the angular velocity data collected by a gyroscope and the control moment data of the spacecraft maneuvering and utilizing the generalized Kalman filter algorithm to estimate the vibration mode of the flexible attachment and its derivatives; S3) writing the attitude dynamic equation of the satellite with the flexible attachment in the form of least squares; using the second derivative (described in the abstract) of vibration mode estimated in S2 and using the least squares algorithm to identify the moment-of-inertia of the satellite; and S4) mutually calling the vibration mode estimated from the generalized Kalman filter algorithm in S2 and the moment-of-inertia identified from the lease squares in S3; repeating S2 and S3 steps; and through the combination and the recursion of the generalized Kalman filter and least squares method, obtaining the identification value for the moment-of-inertia.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
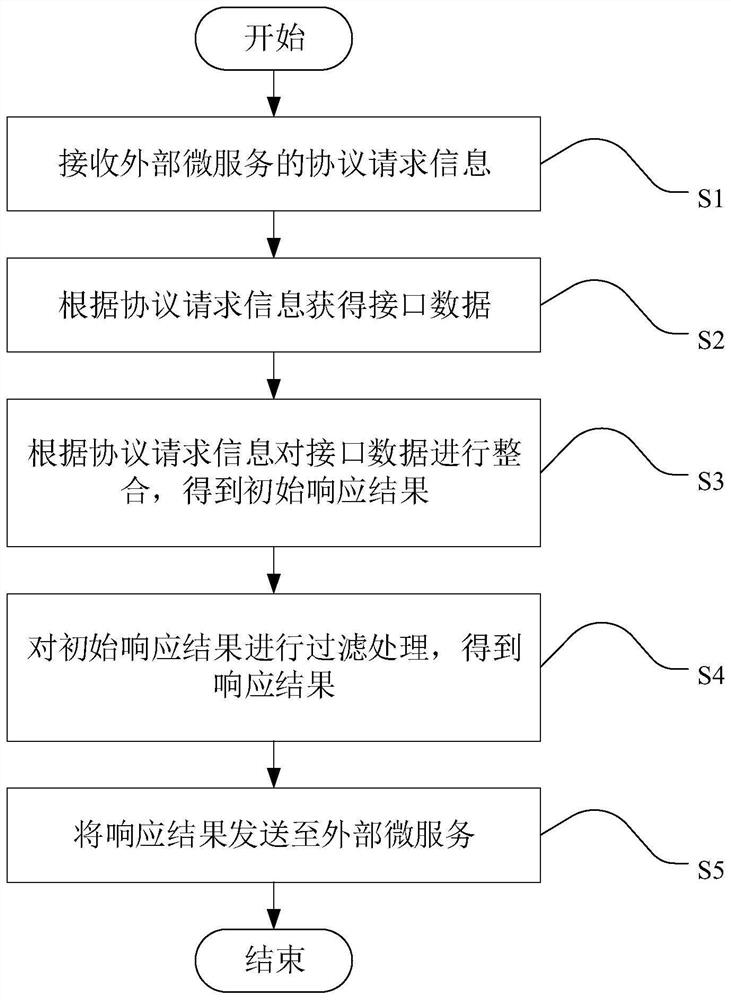
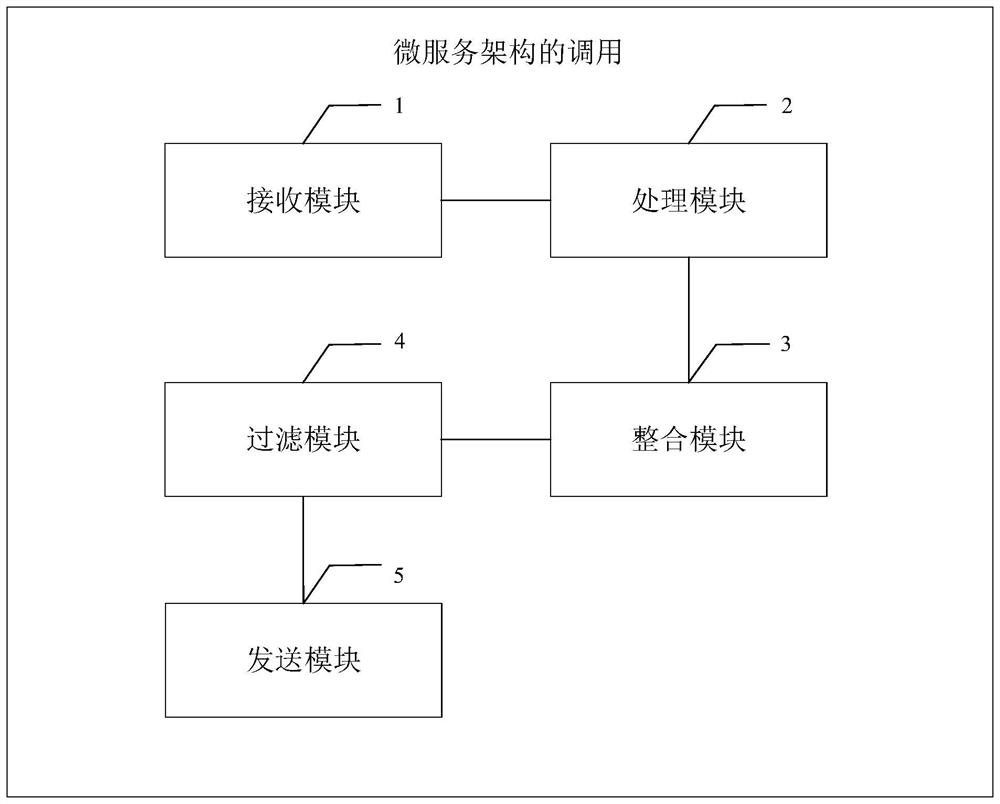
Microservice architecture calling method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114238178ASimple callReduce maintenance costsElectric digital data processingSoftware engineeringMicroservices
The embodiment of the invention provides a micro-service architecture calling method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: receiving protocol request information of an external micro-service; obtaining interface data according to the protocol request information; integrating the interface data according to the protocol request information to obtain an initial response result; filtering the initial response result to obtain a response result; and sending a response result to the external micro-service. By implementing the embodiment of the invention, a plurality of interfaces with single functions can be freely combined together for calling, so that the calling of multiple interfaces is simplified, and the maintenance cost is reduced.
Owner:LINKDOC TECH BEIJING CO LTD
A multi-satellite mission planning method based on k-means clustering
ActiveCN109002966BImprove completion rateSatisfy time complexity constraintsComplex mathematical operationsCluster algorithmRound complexity
The present invention provides a multi-satellite mission planning method based on K-means clustering, S1, collecting the user's mission requirements T={t 1 ,t 2 ,t 3 ...t n}, to obtain the set of orbital working hours of each sunlit area corresponding to all currently available satellites O={o 1 ,o 2 ,o 3 ,...o m}. S2, computing task t i to each element o in the set O j The distance Dis ij , forming a task t i The distance set D={d to the orbital set O i1 , d i2 , d i3 ... d in}, the task t i Clustering to the shortest orbital k,Dis ik =Min(D); S3, judging the current clustering scheme s k Whether it belongs to the set S={s 1 ,s 2 ,s 3 ,...s z}, if s k ∈S then output the clustering scheme s k , otherwise the scheme s k Add to the scheme set S, and return to step S2. The present invention quantifies these factors by analyzing the factors affecting multi-satellite task allocation, and combines the K-means clustering algorithm to plan a multi-satellite collaborative task allocation scheme, with fewer iterations and fast calculation speed, which can meet large-scale optimization problems Constrains the time complexity of the algorithm, and greatly improves the quality of imaging and the completion rate of tasks.
Owner:湖南国科轩宇信息科技有限公司
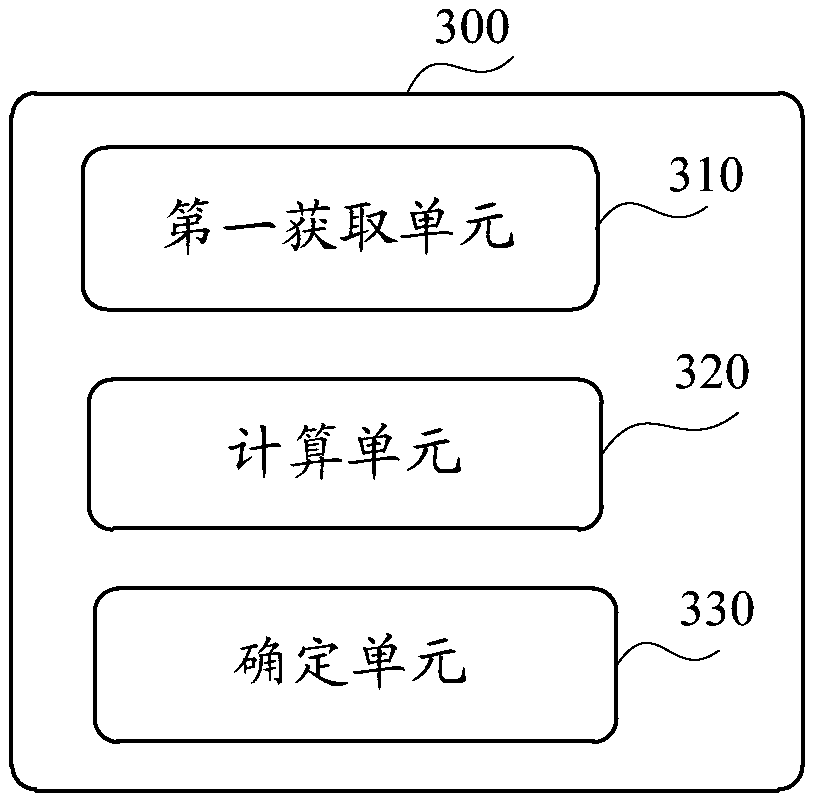
De-duplication method, device, apparatus and storage medium thereof for feature word
PendingCN109062898AReduce computational complexityImprove generalizationNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionComputation complexity
A method, a device, an apparatus, and a storage medium for de-duplication of feature word are disclosed. The method includes: acquiring a set of phrases associated with a current feature word in the set of feature words; calculating a sum of a specified part of a phrase based on an ASCII code corresponding to the phrase one by one to obtain a first set of sum values; the deduplicated feature wordsbeing determined by judging the number of minimum values in the first set of sum values. According to the technical proposal of the embodiment of the present application, by calculating the sum of ASCII codes, the feature words with the same meaning are de-duplicated, thereby reducing the computational complexity of the current feature word de-duplication method, saving computational space, and significantly improving the generalization ability of the current feature words to the text.
Owner:DONGJUN NEW ENERGY CO LTD
A relay selection method for air-ground integrated vehicle networking based on state transition probability
ActiveCN111132075BReduce the probability of collisionIncrease success rateParticular environment based servicesRadio transmissionInformation transmissionIntelligent transportation system its
The invention belongs to the technical field of air-ground integrated vehicle networking communication, discloses a relay selection method based on state transition probability of air-ground integrated vehicle networking, and constructs an air-ground integrated vehicle networking model consisting of V vehicle nodes and U UAV nodes ; Based on the air-ground integrated vehicle networking model, construct the information transmission mechanism between the mobile nodes; based on the information transmission mechanism between the mobile nodes, construct the state transition probability between the mobile nodes; Based on the state transition probability between mobile nodes, an information identification method based on multiple input and multiple output technology is constructed; based on the information transmission mechanism, state transition probability and information identification method between the mobile nodes, a relay selection based on state transition probability is constructed method. The invention can be applied to urban intelligent transportation systems, strengthen the connection among vehicles, drones and users, and create a real-time, accurate and efficient comprehensive transportation and information transmission system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A method and system for decoupling section pre-screening applied to AC and DC systems
ActiveCN106446471BAvoid the risk of instabilitySave computing spaceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionAsymmetry Index
The invention discloses a splitting surface pre-screening method and a splitting surface pre-screening system applied to an alternating-current / direct-current system. The splitting surface pre-screening method includes simulating asymmetrical faults in three-phase voltage of a bus bar i; acquiring three-phase asymmetric indexes of all bus bars; constructing a correlation matrix according to the three-phase asymmetric indexes of all the bus bars; subjecting the correlation matrix to K-core decomposition so as to obtain a K-core value of each bus bar; screening out the bus bar with the maximum degree of influence on the alternating-current / direct-current system according to the K-core value of each bus bar; deleting the bus bar with the maximum degree of influence on the alternating-current / direct-current system from a splitting surface composed of multiple lines, and splitting the alternating-current / direct-current system according to the splitting surface. The splitting surface pre-screening method and the splitting surface pre-screening system applied to the alternating-current / direct-current system have the advantages that on one hand, stability of the alternating-current / direct-current system subjected to splitting control is guaranteed, and on the other hand, the size of a splitting surface search space is decreased, so that operation time is saved and operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Oil pump controller
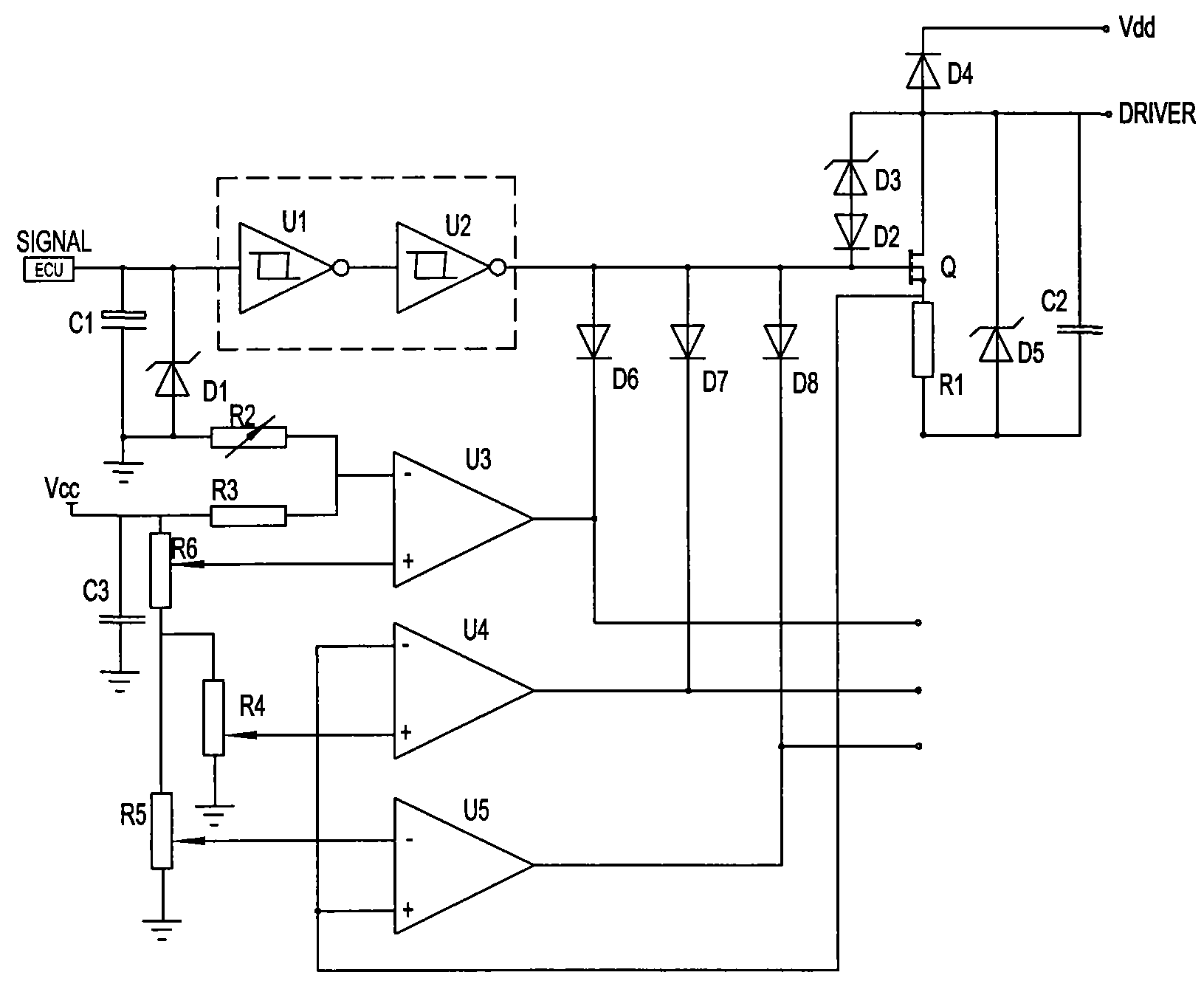
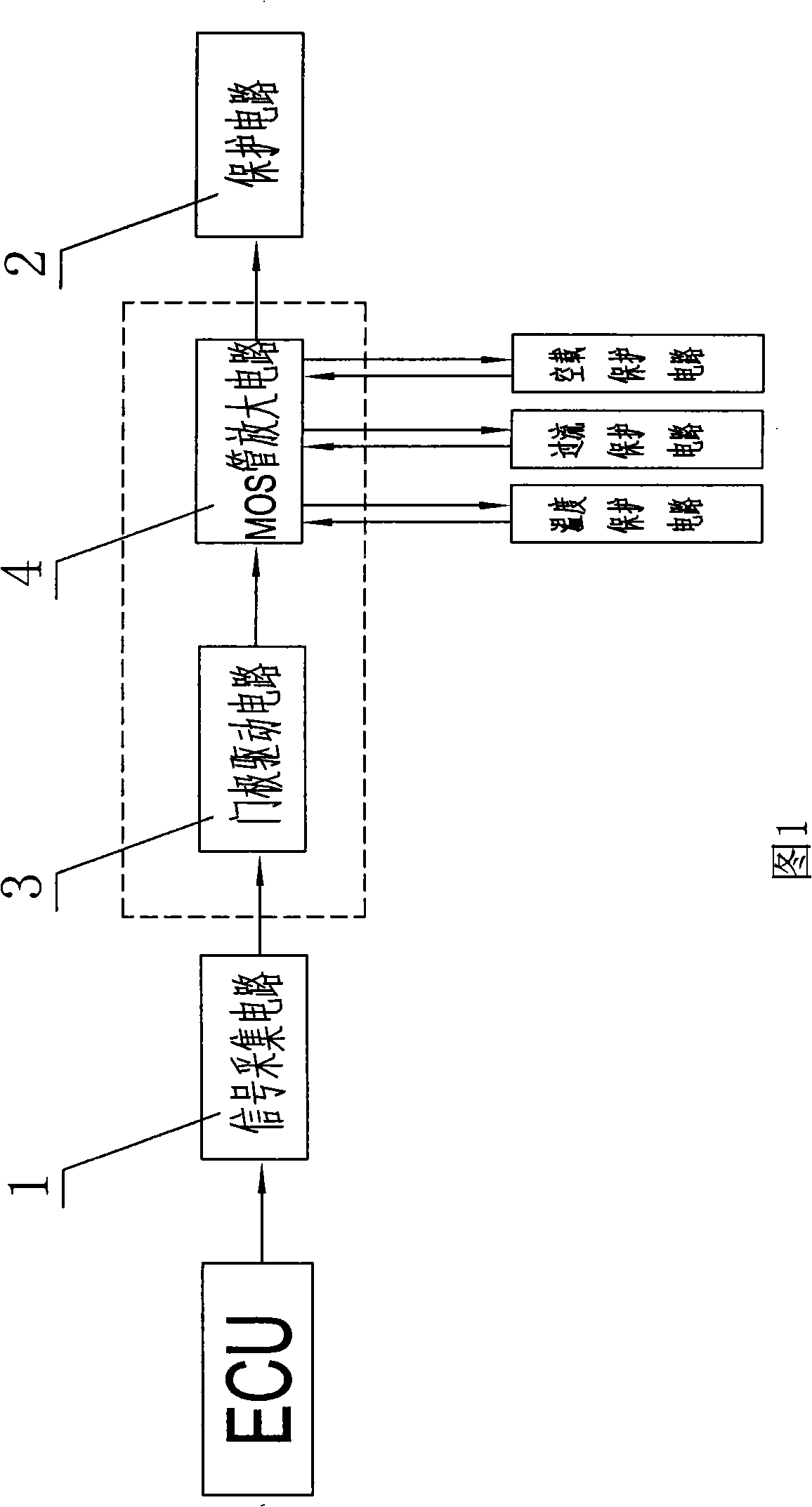
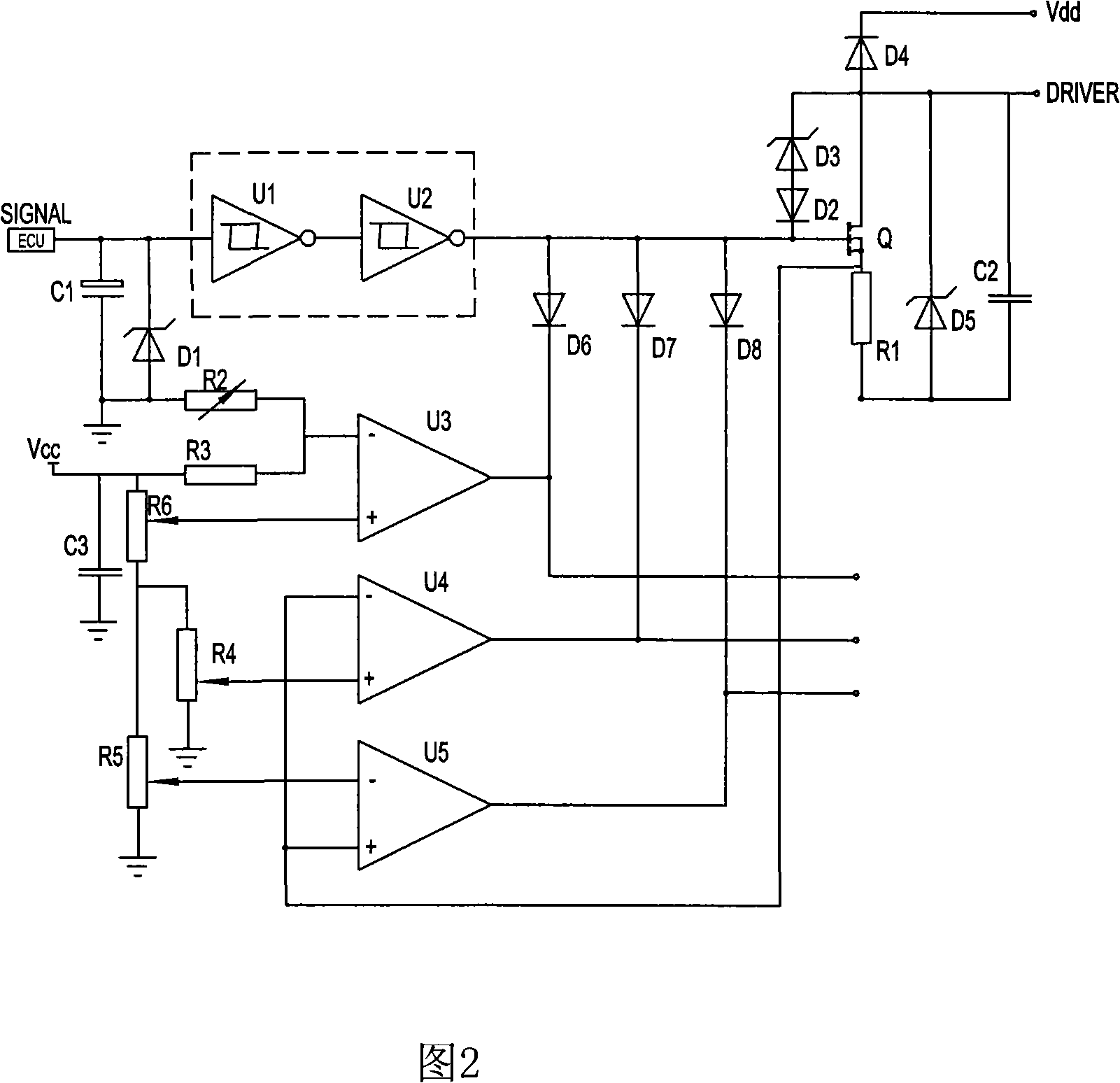
InactiveCN101338715BSave computing spaceReduce cooling burdenMachines/enginesLiquid fuel feedersDriver circuitEngineering
The present invention discloses an oil pump controller which consists of a signal collecting circuit, a signal transformation circuit and a protective circuit and is characterized in that the signal transformation circuit consists of a gate drive circuit and an MOS pipe amplifying circuit, wherein, the signal collecting circuit obtains an oil pump start instruction and transports the oil pump start instruction to the gate drive circuit; the gate drive circuit transforms the oil pump start instruction and sends the oil pump start instruction to the MOS pipe amplifying circuit; the MOS pipe amplifying circuit amplifies the oil pump start instruction and generates a drive signal; the MOS pipe amplifying circuit is provided with a switch pipe, the drain electrode of which outputs the oil pumpstart instruction to the protective circuit. The oil pump controller is also provided with a temperature protective circuit, an overcurrent protective circuit and an non-load protective circuit. The oil pump controller has the obvious effects of reducing the cost, low heat, reducing surge current, increasing various kinds of safety protection measures and providing the oil pump safe operation with effective safeguard. The oil pump controller reduces ECU head dissipation load and improves ECU working efficiency.
Owner:力帆科技(集团)股份有限公司
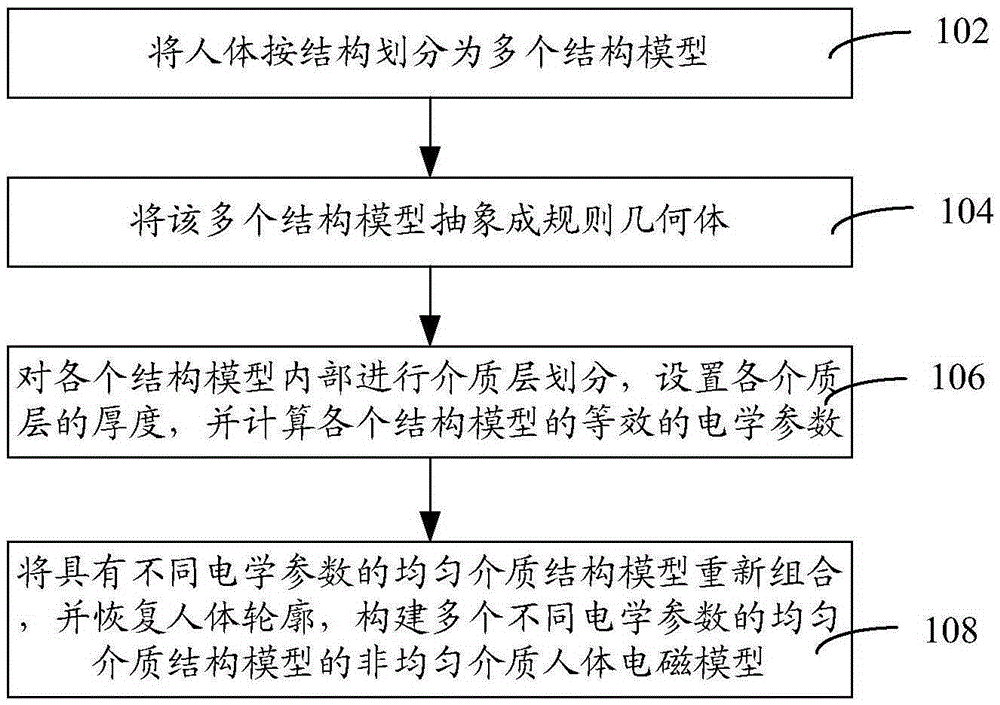
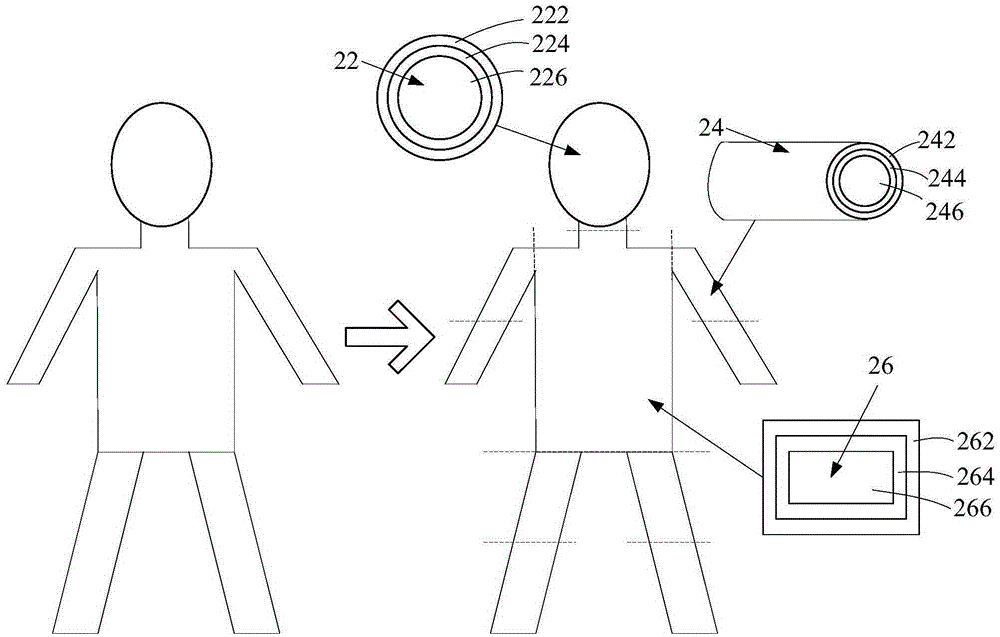
Human body communication channel modeling method and system based on heterogeneous medium
The invention relates to a human body communication channel modeling method based on a non-uniform medium and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps that a human body is divided into multiple structural models according to the structure; the multiple structural models are abstracted into regular geometries; medium layer division is performed in the internal parts of all the structural models, thickness of all medium layers is arranged, and equivalent electrical parameters of all the structural models are computed; and the uniform medium structural models with different electrical parameters are recombined and a human body contour is recovered so that multiple non-uniform medium human body electromagnetic models of the uniform medium structural models with different electrical parameters are constructed. According to the aforementioned human body communication channel modeling method based on the non-uniform medium and the system thereof, the non-uniform medium human body electromagnetic models of the uniform medium structural models with different electrical parameters are constructed so that accuracy is high in comparison with unified uniform medium human body models. Besides, all the structural models are equivalent to the uniform medium structural models so that subsequent computation is simplified and computation space is saved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com