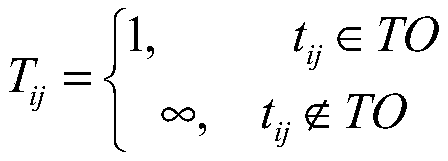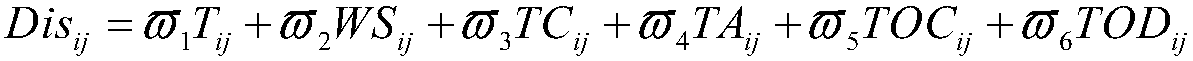A multi-satellite mission planning method based on k-means clustering
A task planning, K-means technology, applied in instruments, complex mathematical operations, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as complex calculation process and many iterations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
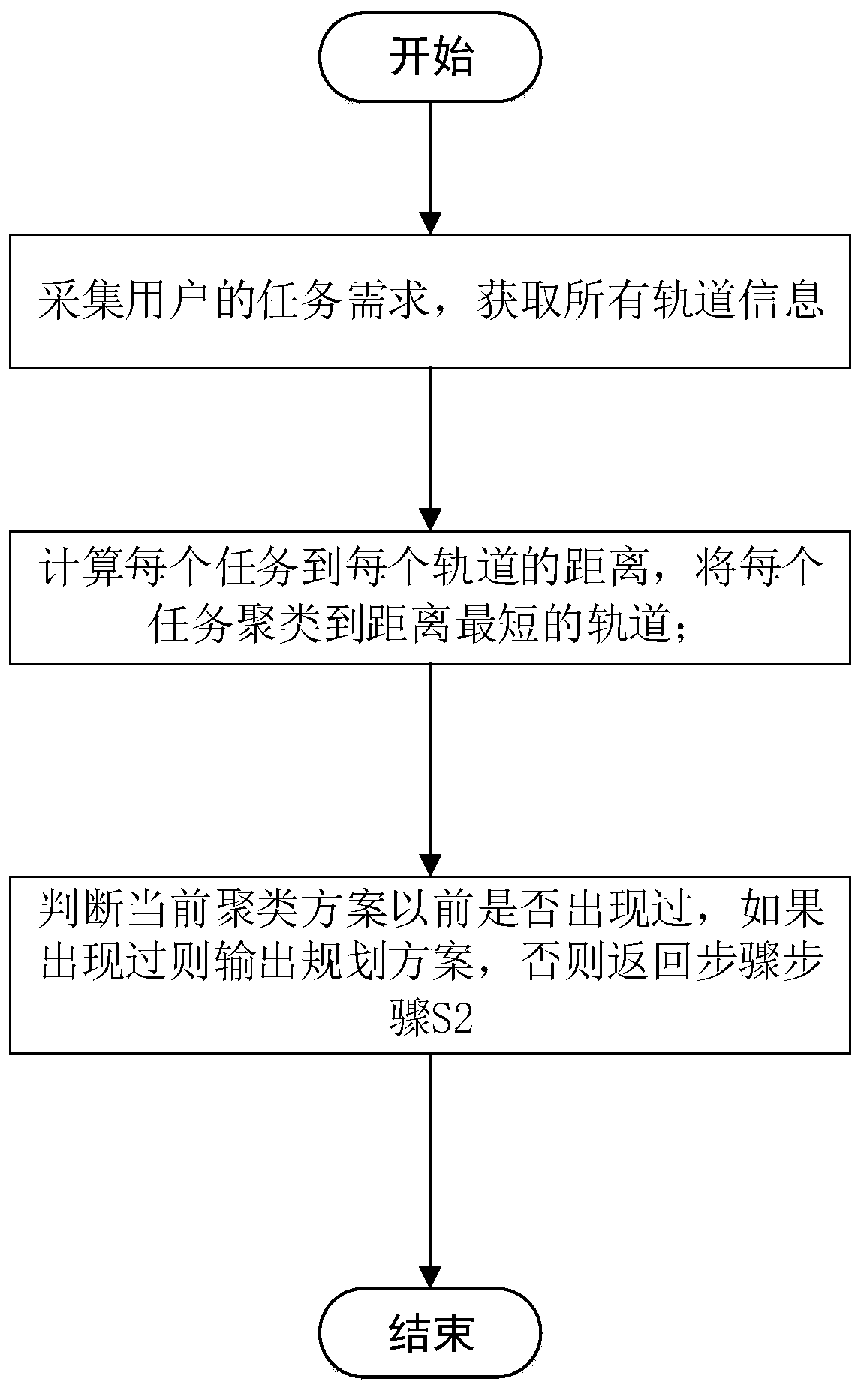
[0048] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings, but the present invention can be implemented in many different ways defined and covered by the claims.
[0049] The basic idea of the K-means clustering algorithm is to divide the N data in the data set into K classes, and the average vector from the data in each class to the center of the class is the shortest, which is also the distance from the point to the cluster point. Usually, the K-means clustering algorithm randomly selects K points as the cluster centers, calculates the distance from other points to each cluster center, and assigns each point to the class where the cluster center with the shortest distance is located. Find the center value of all data in a class to establish a new clustering point, and then continue to classify all points. After several iterations, until the clustering category of each point is stable, the K-means clustering...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com