Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Reduce radiation load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
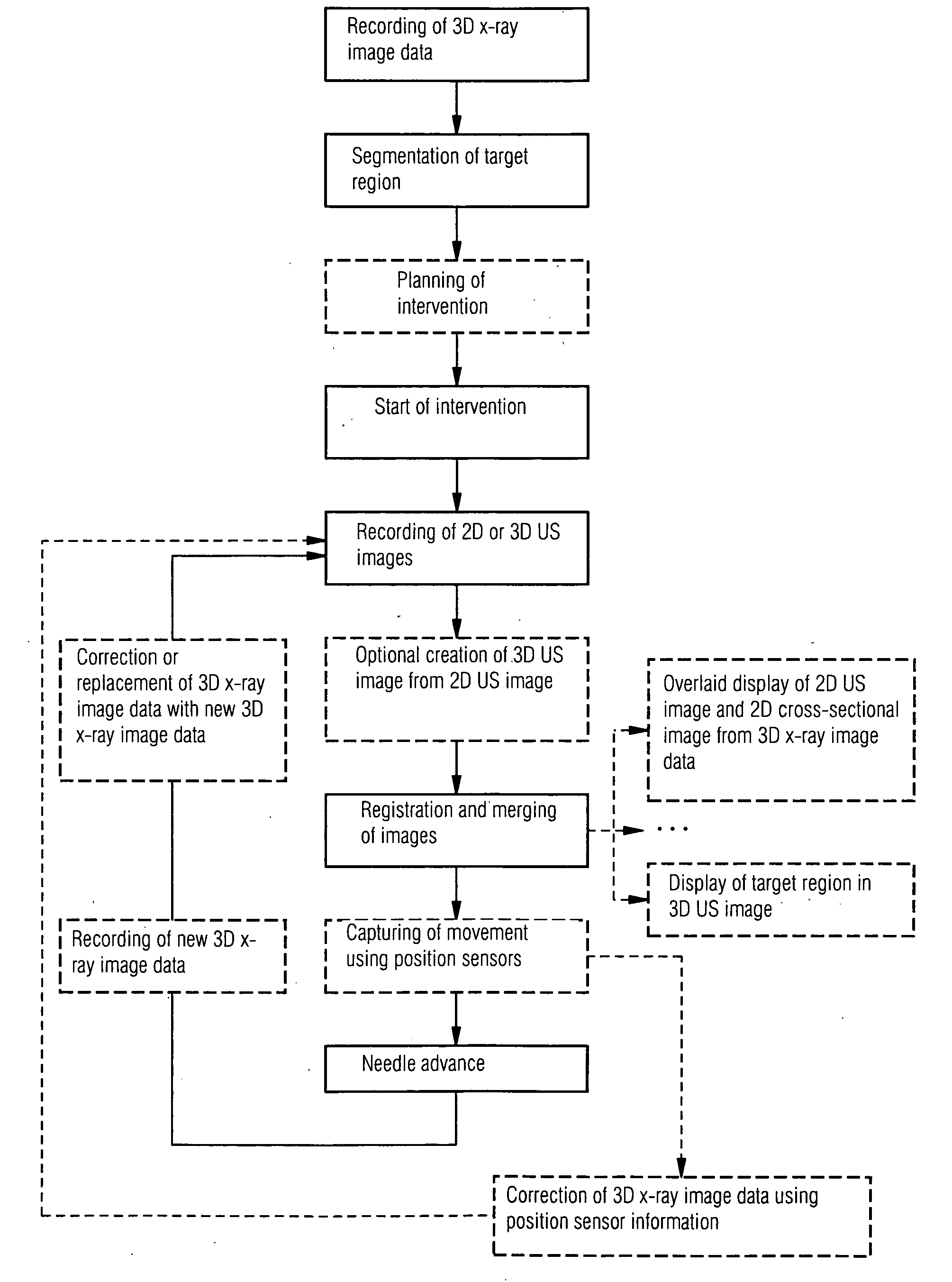
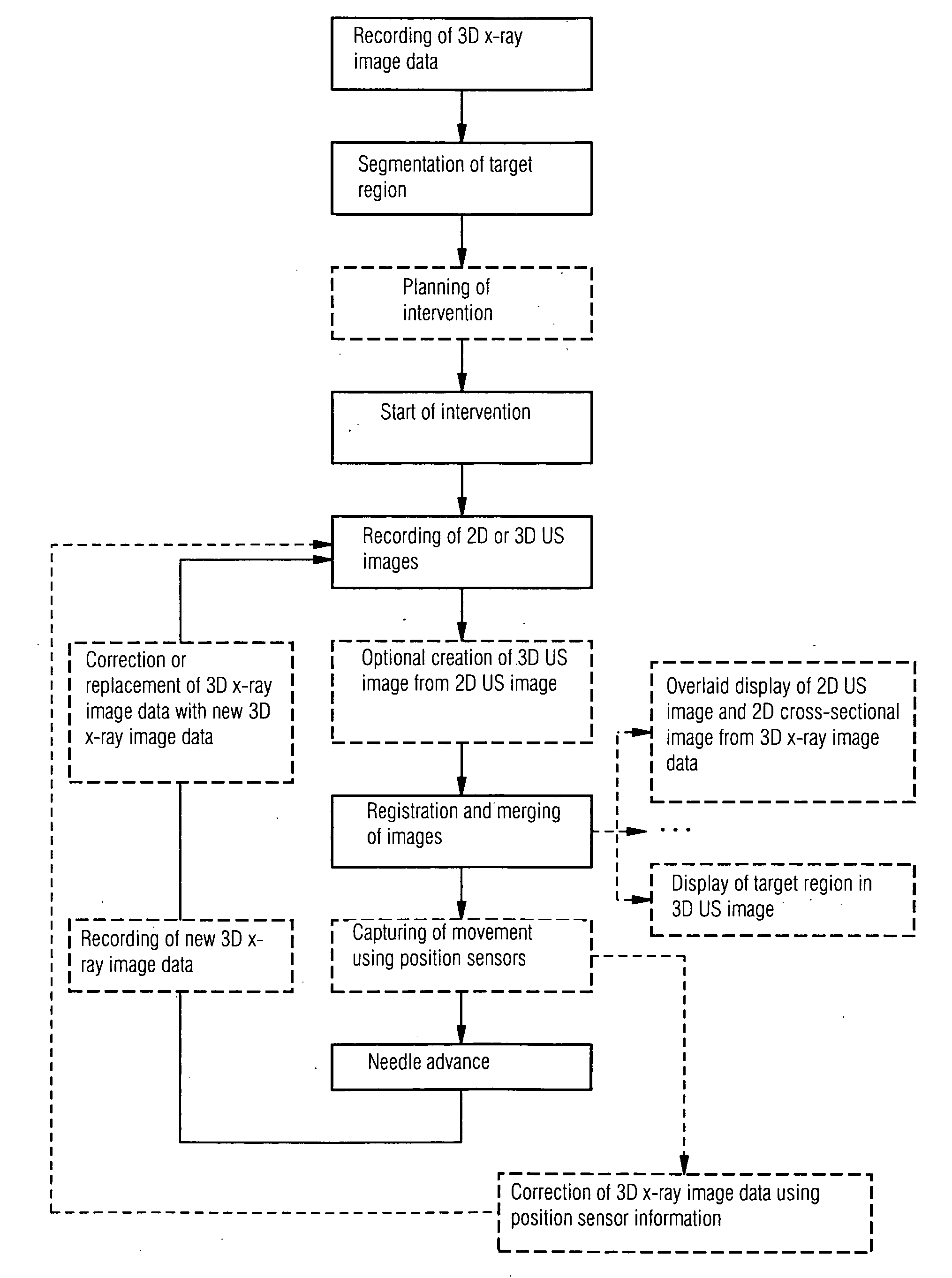
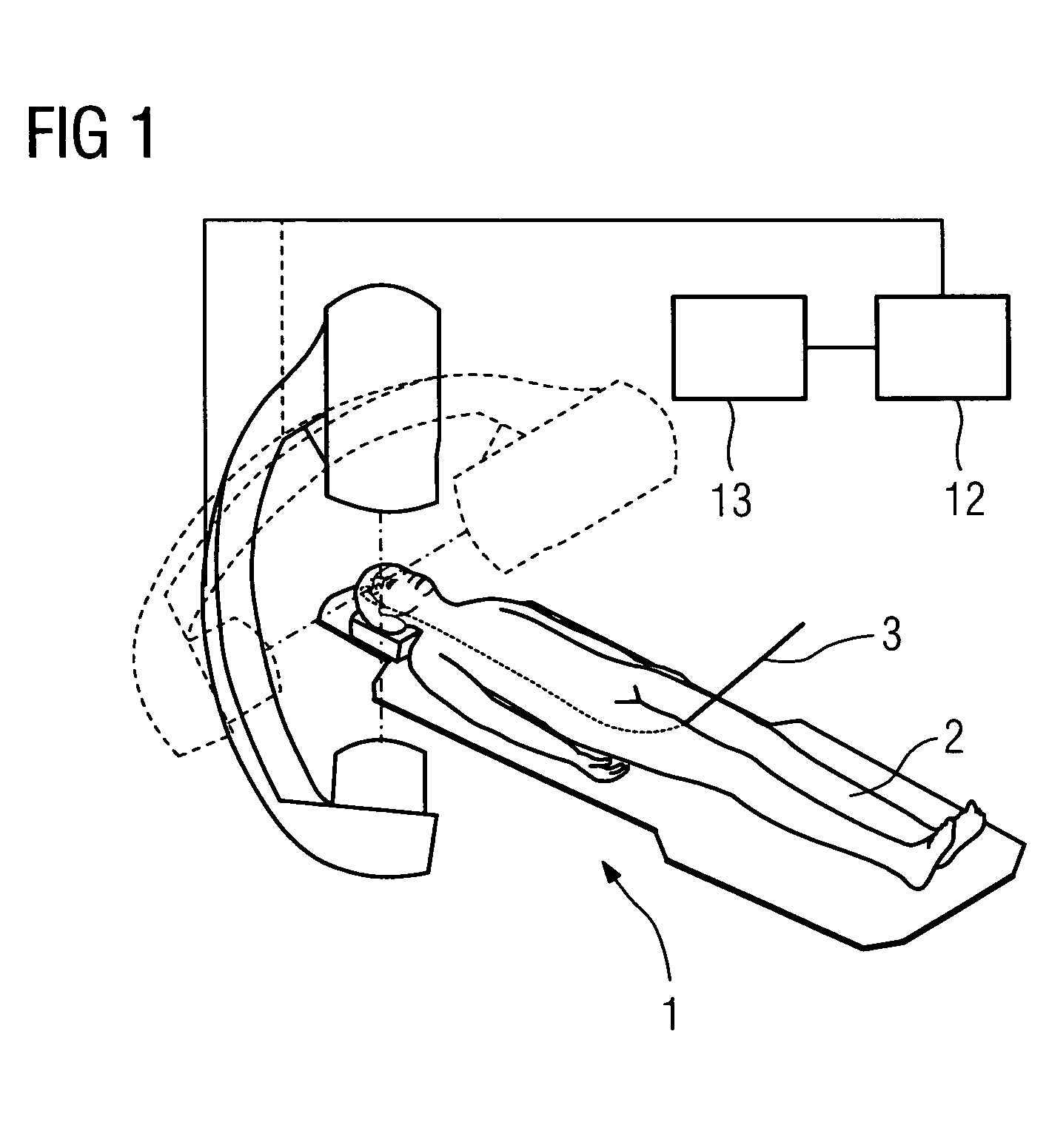
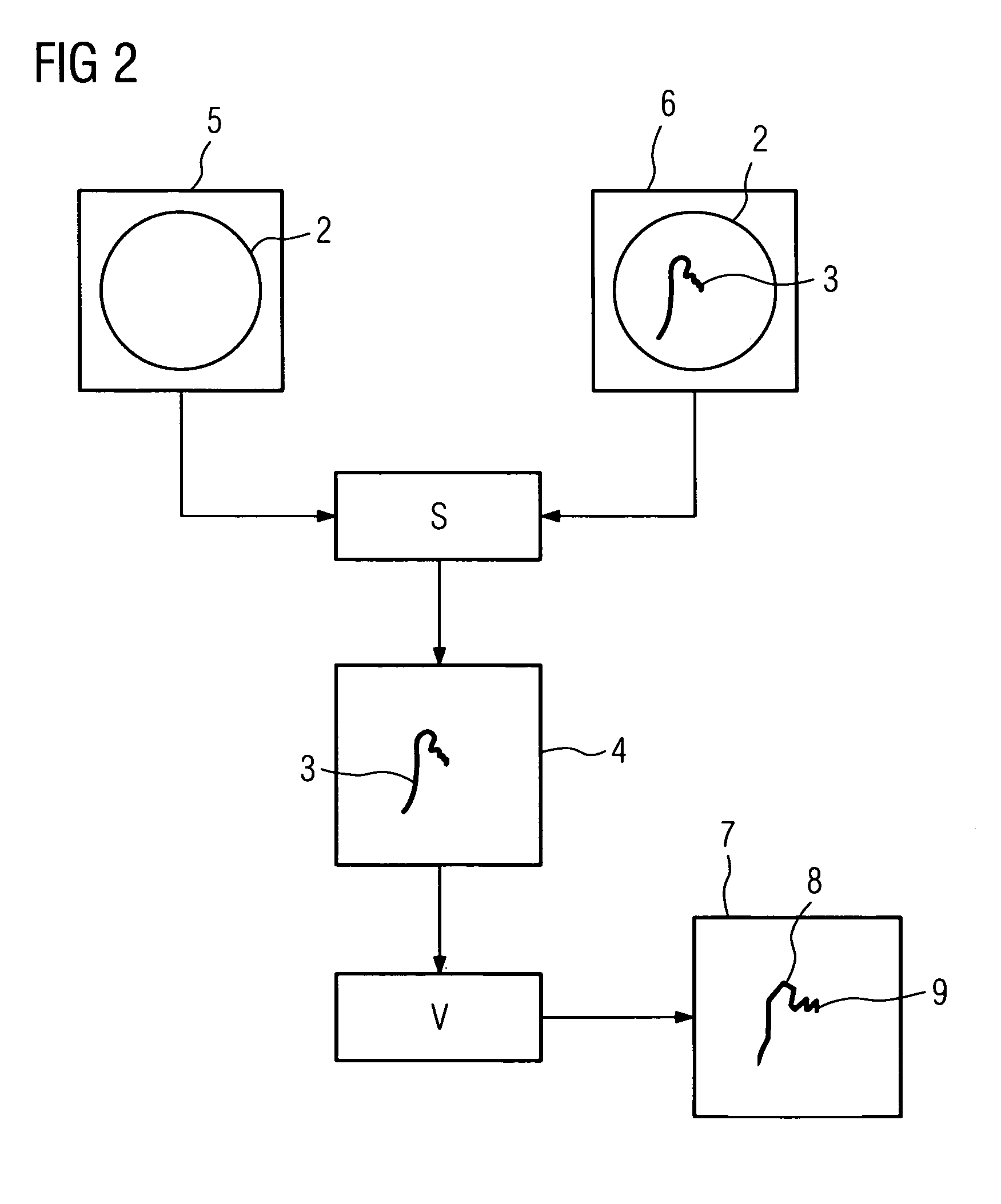
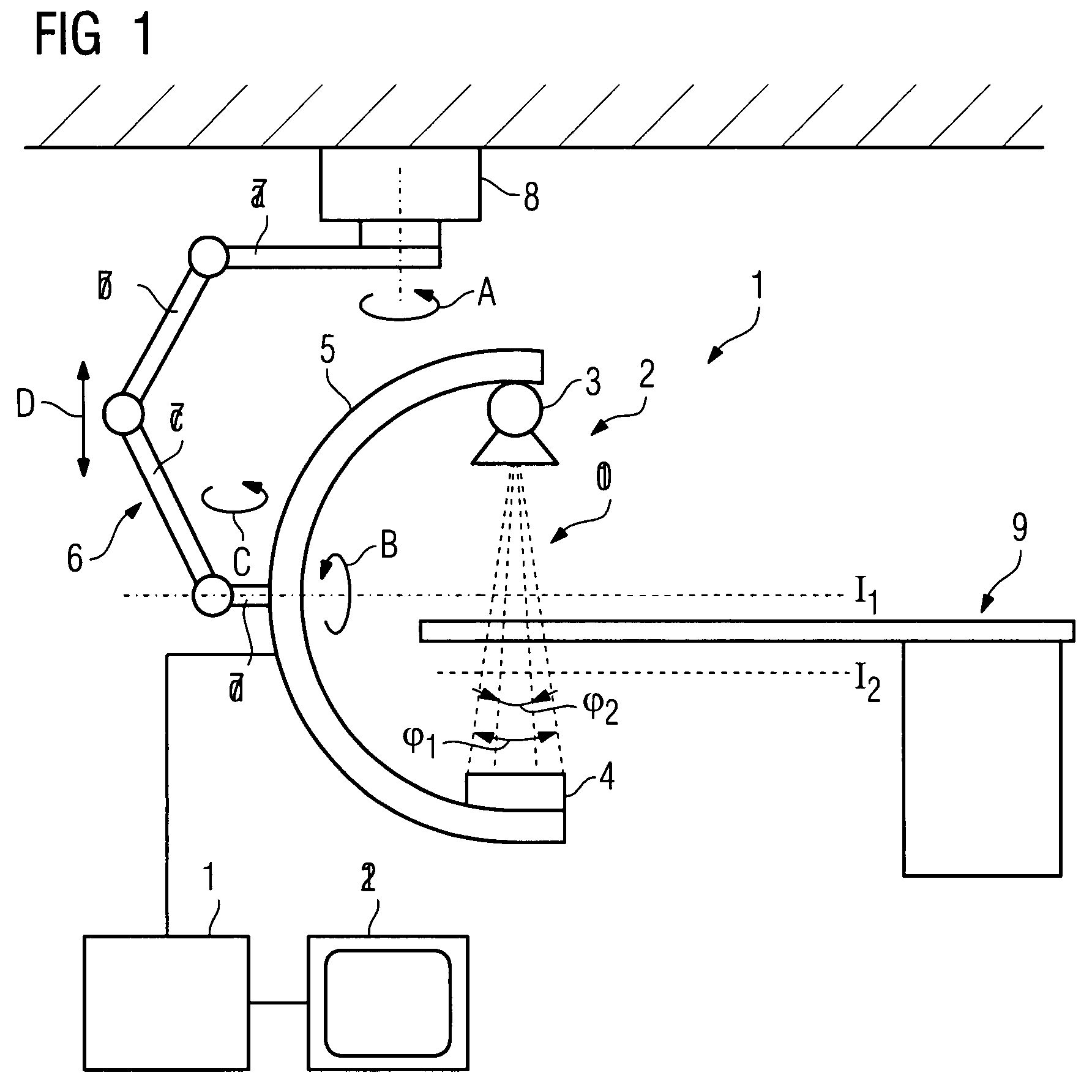
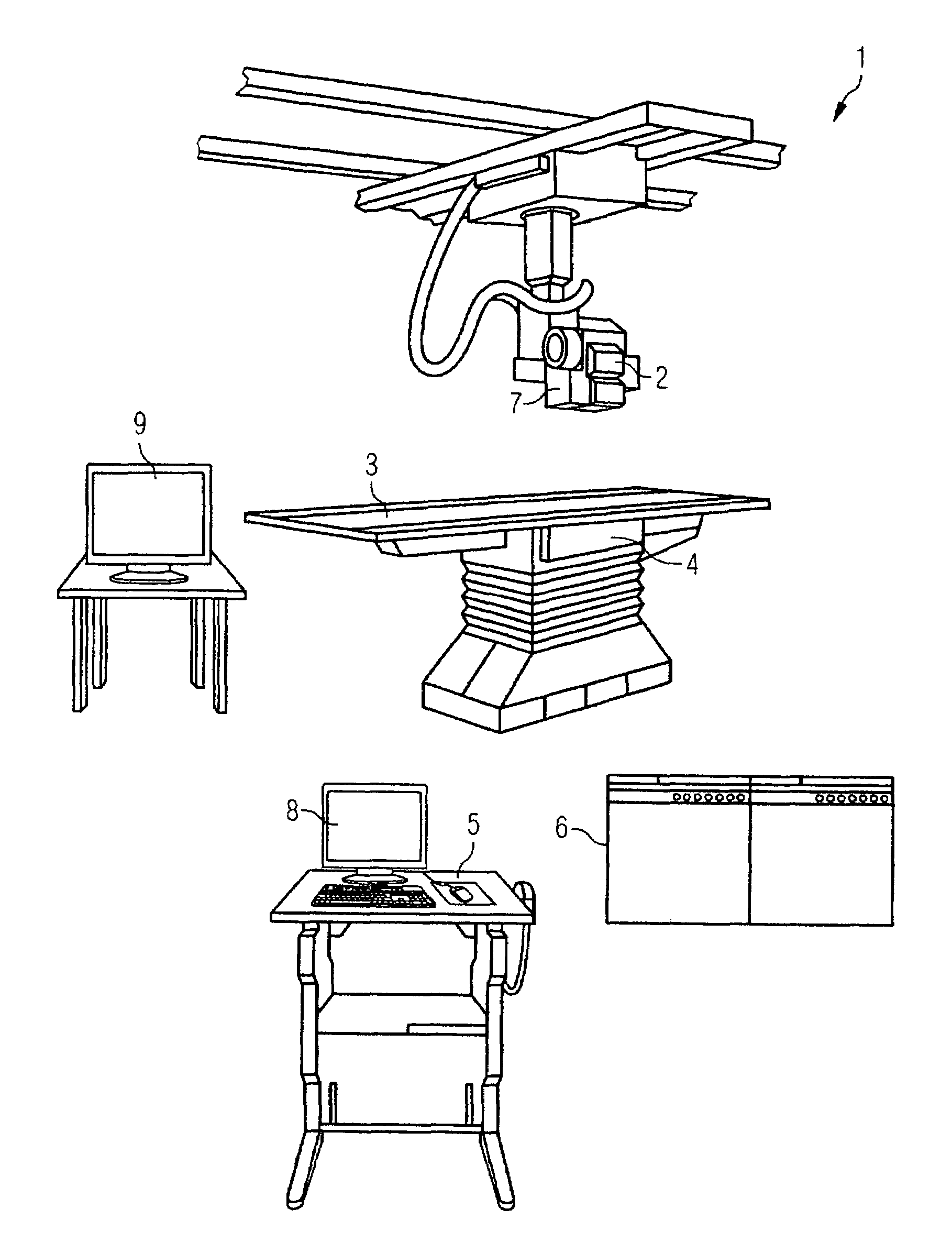
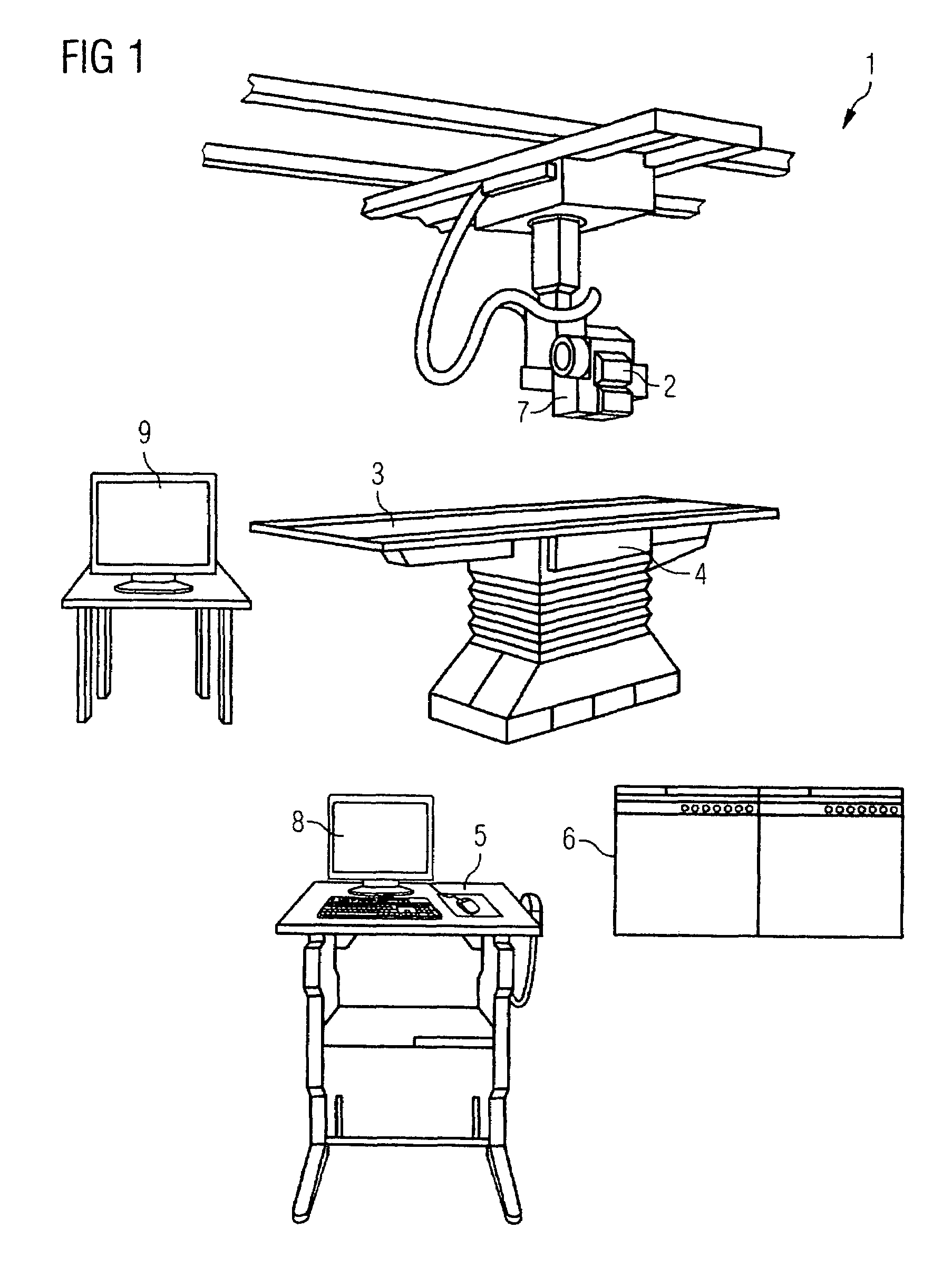
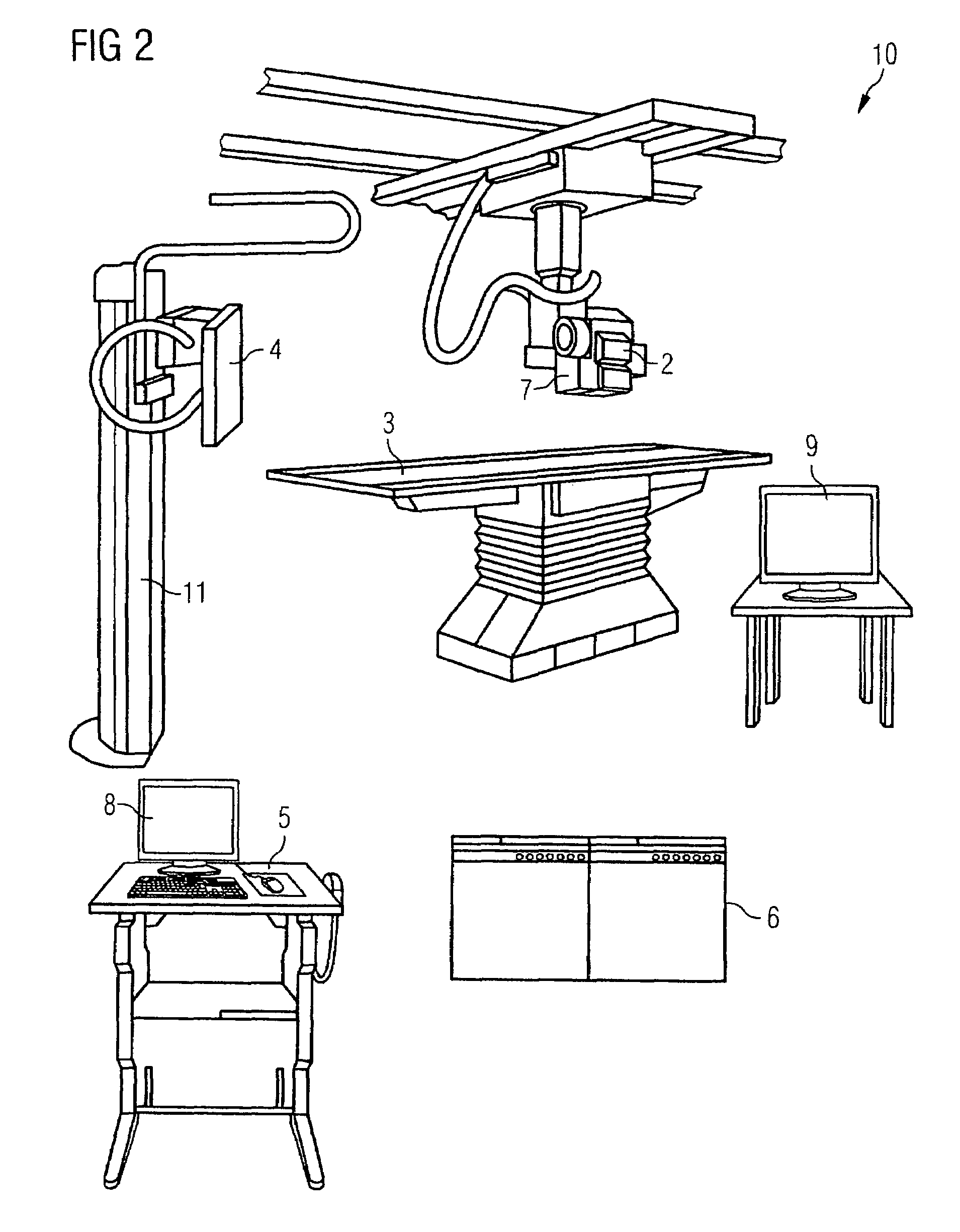
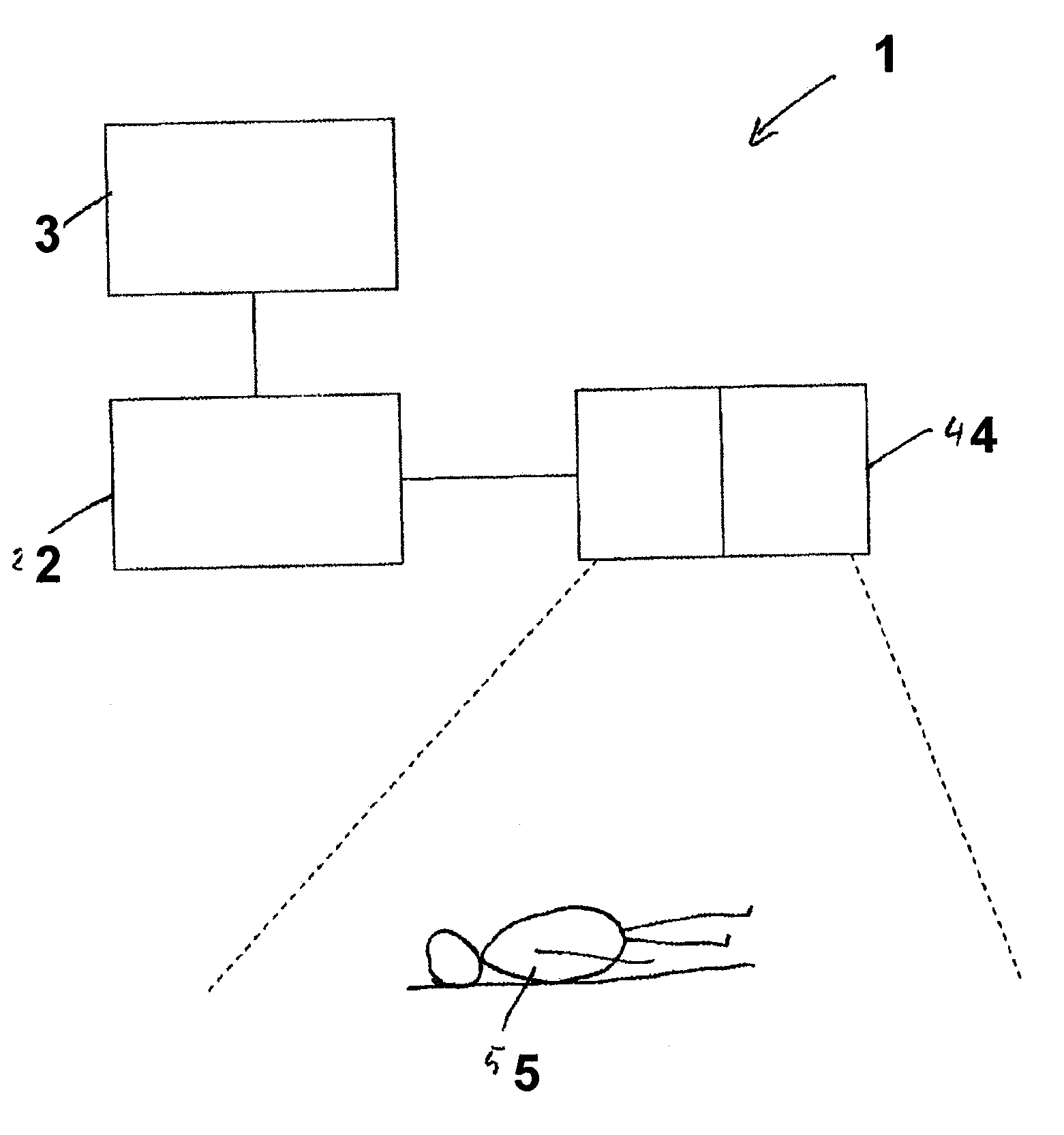
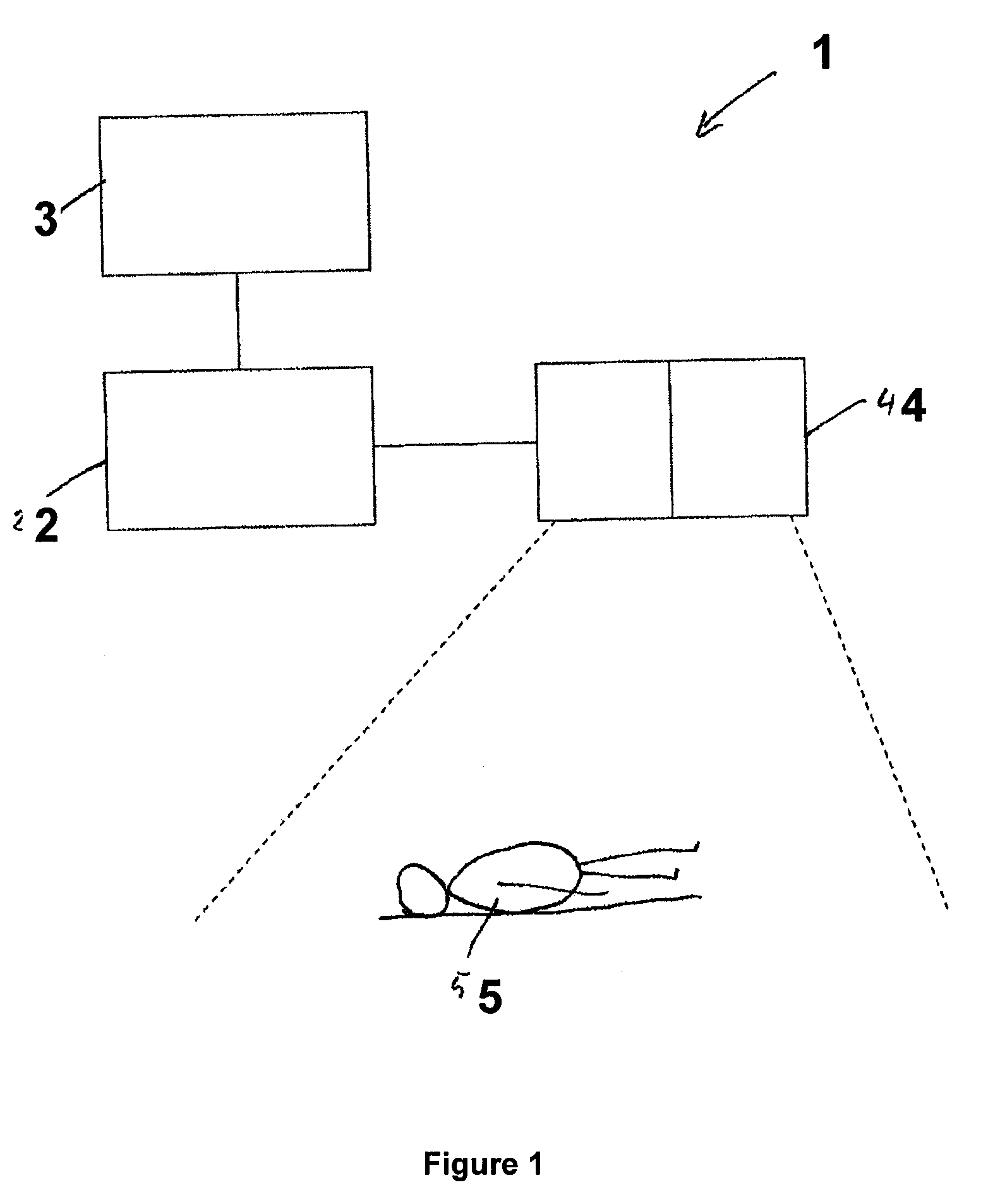
Method for assisting with percutaneous interventions
ActiveUS20090326373A1Simpler and precise registrationImprove puncture accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonification3d image
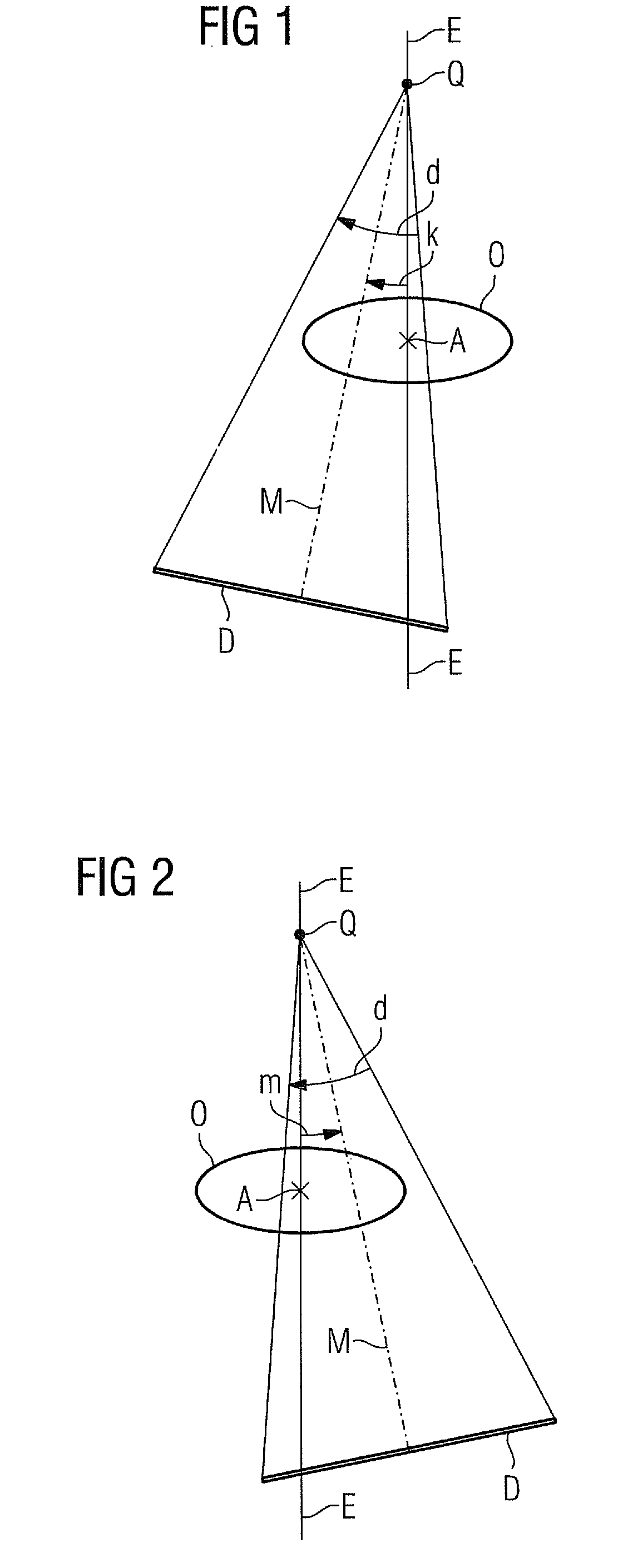
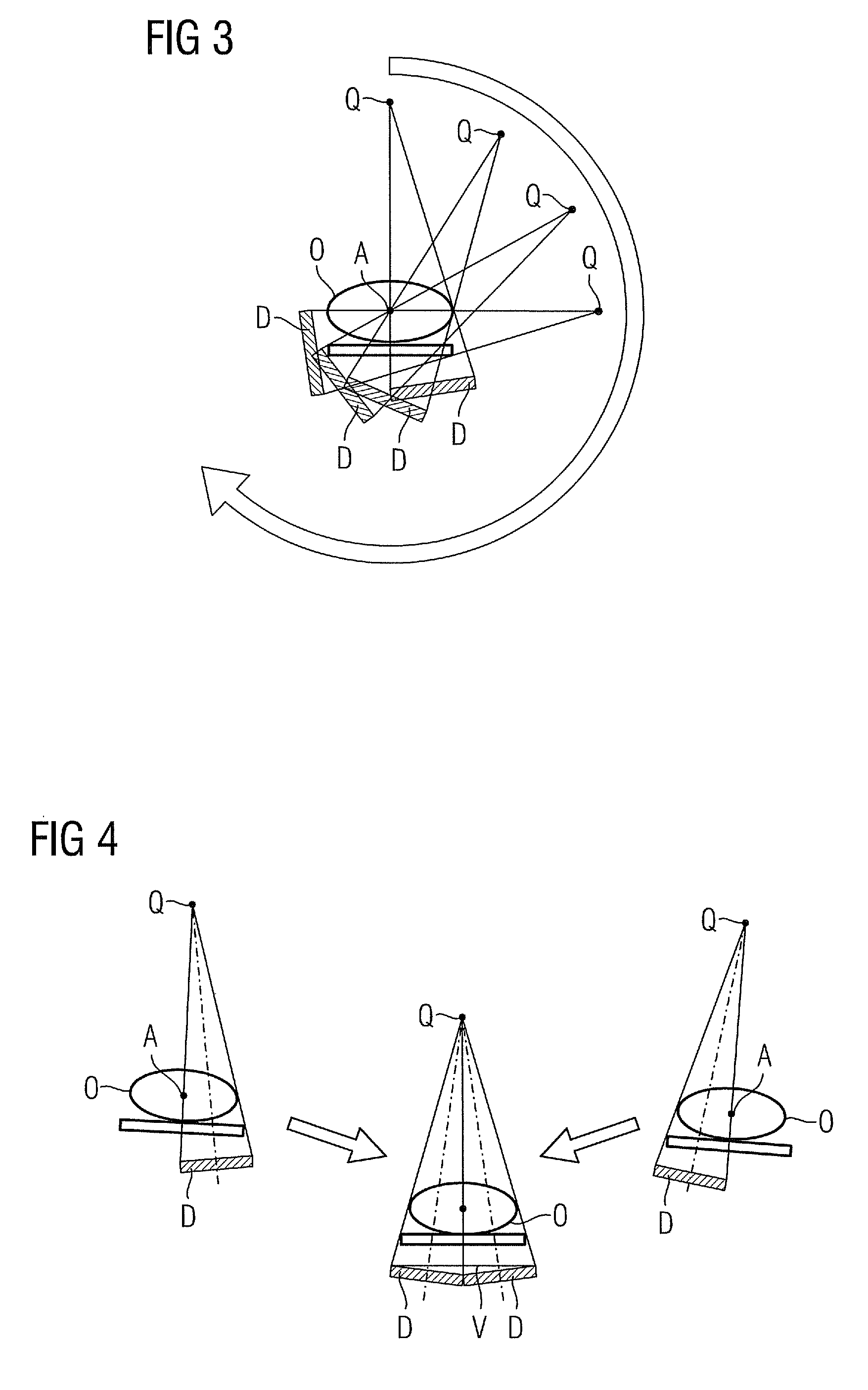
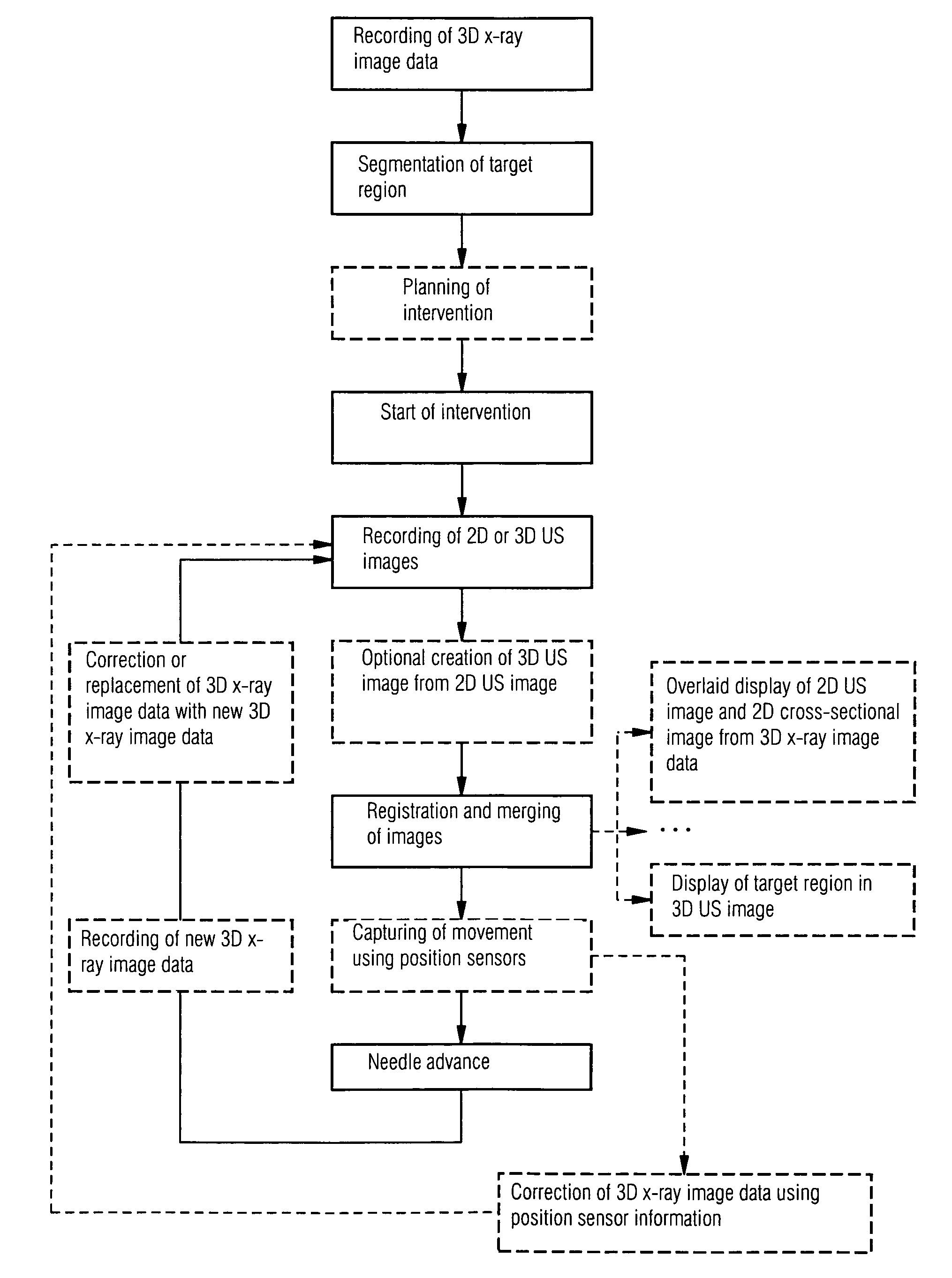
The present invention relates to a method for assisting with percutaneous interventions, wherein 2D x-ray images of an object region are recorded before the intervention using a C-arm x-ray system or a robot-based x-ray system at different projection angles and 3D x-ray image data of the object region is reconstructed from the 2D x-ray recordings. One or more 2D or 3D ultrasound images are recorded before and / or during the intervention using an external ultrasound system and registered with the 3D image data. The 2D or 3D ultrasound images are then overlaid with the 3D image data record or a target region segmented therefrom or displayed next to one another in the same perspective. The method allows a puncture or biopsy to be monitored with a low level of radiation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for the graphical representation of a medical instrument inserted at least partially into an object under examination
ActiveUS7680528B2Increase contrastImprove patient safetyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceMedical instruments
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
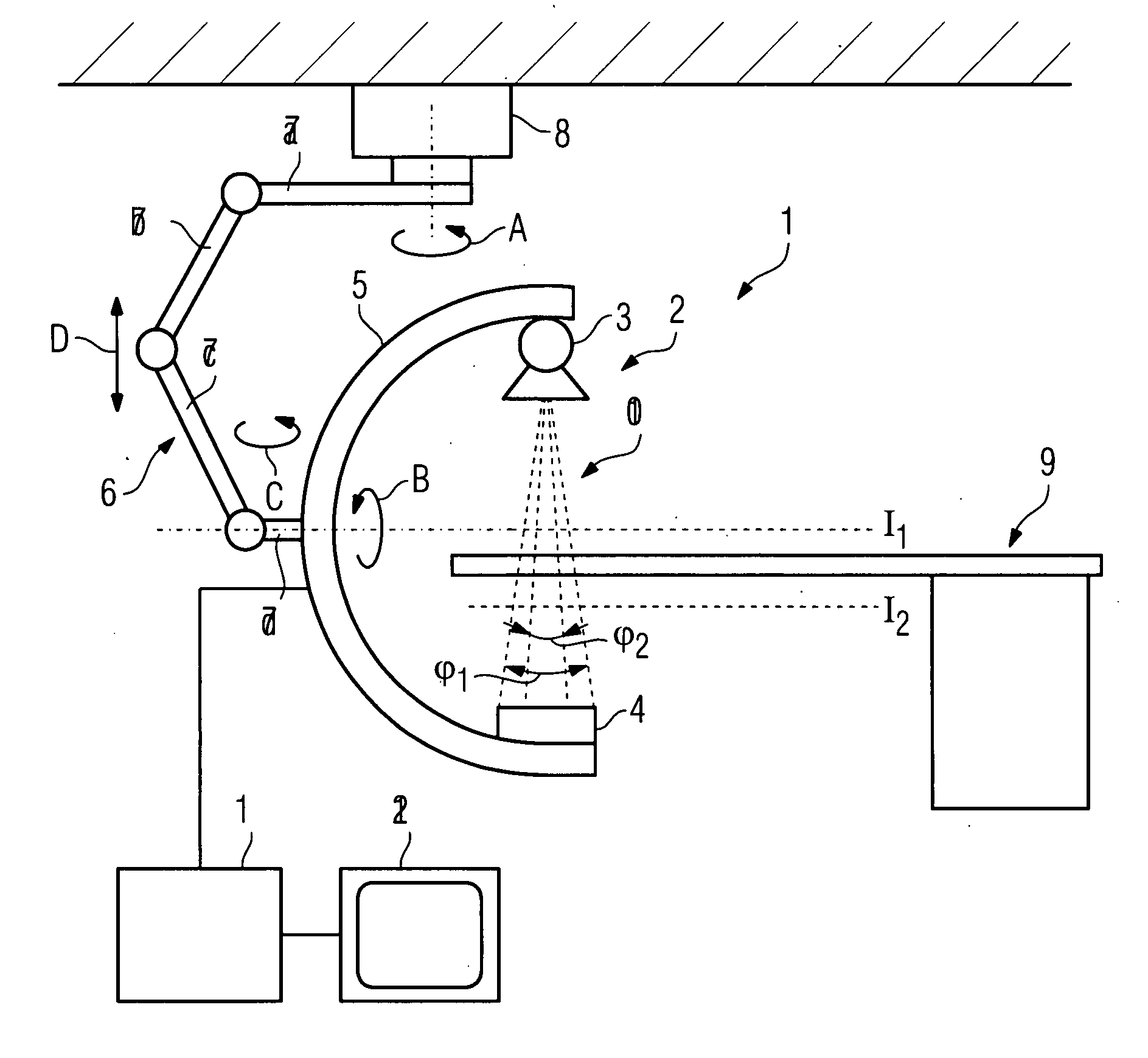
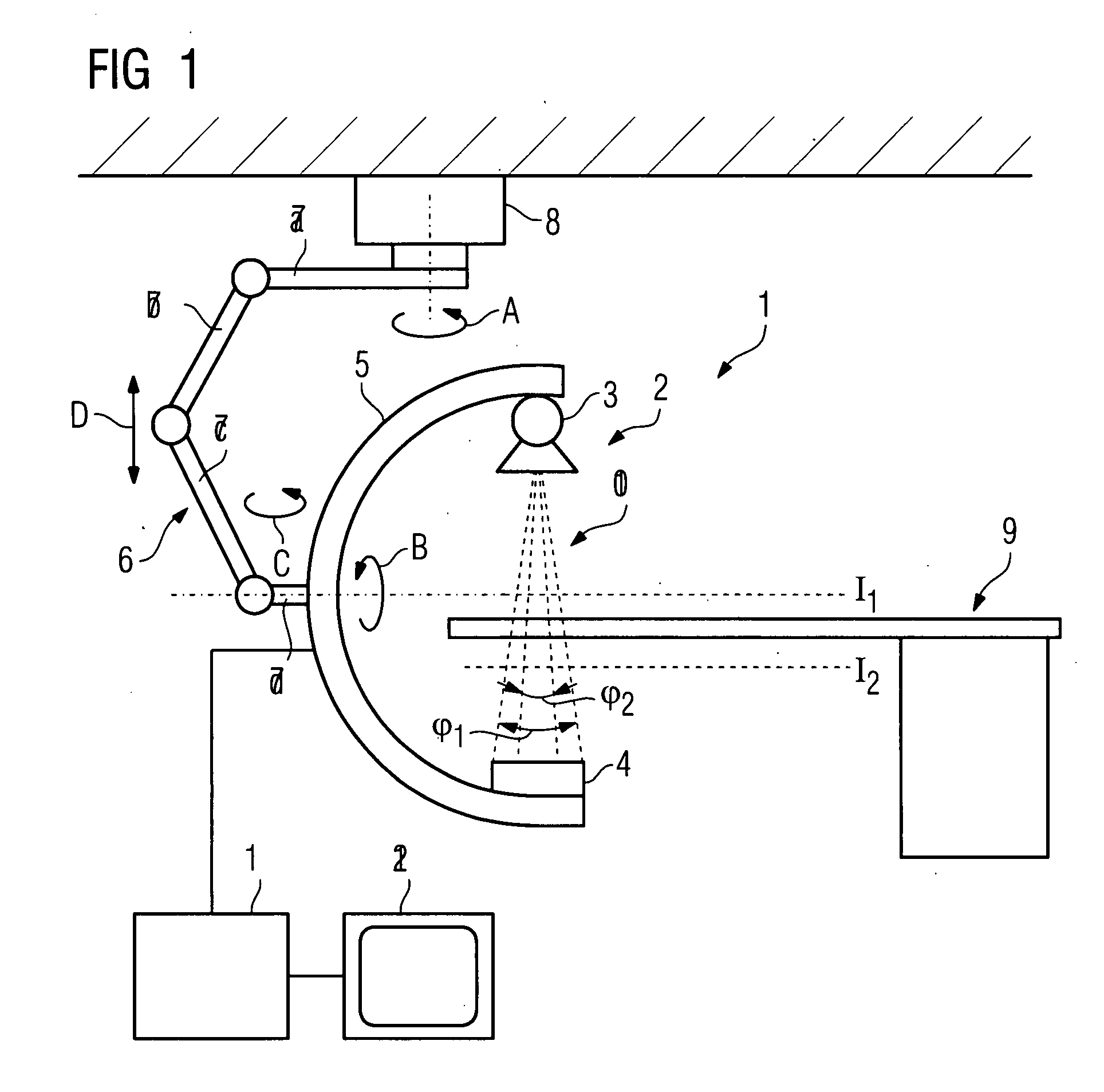
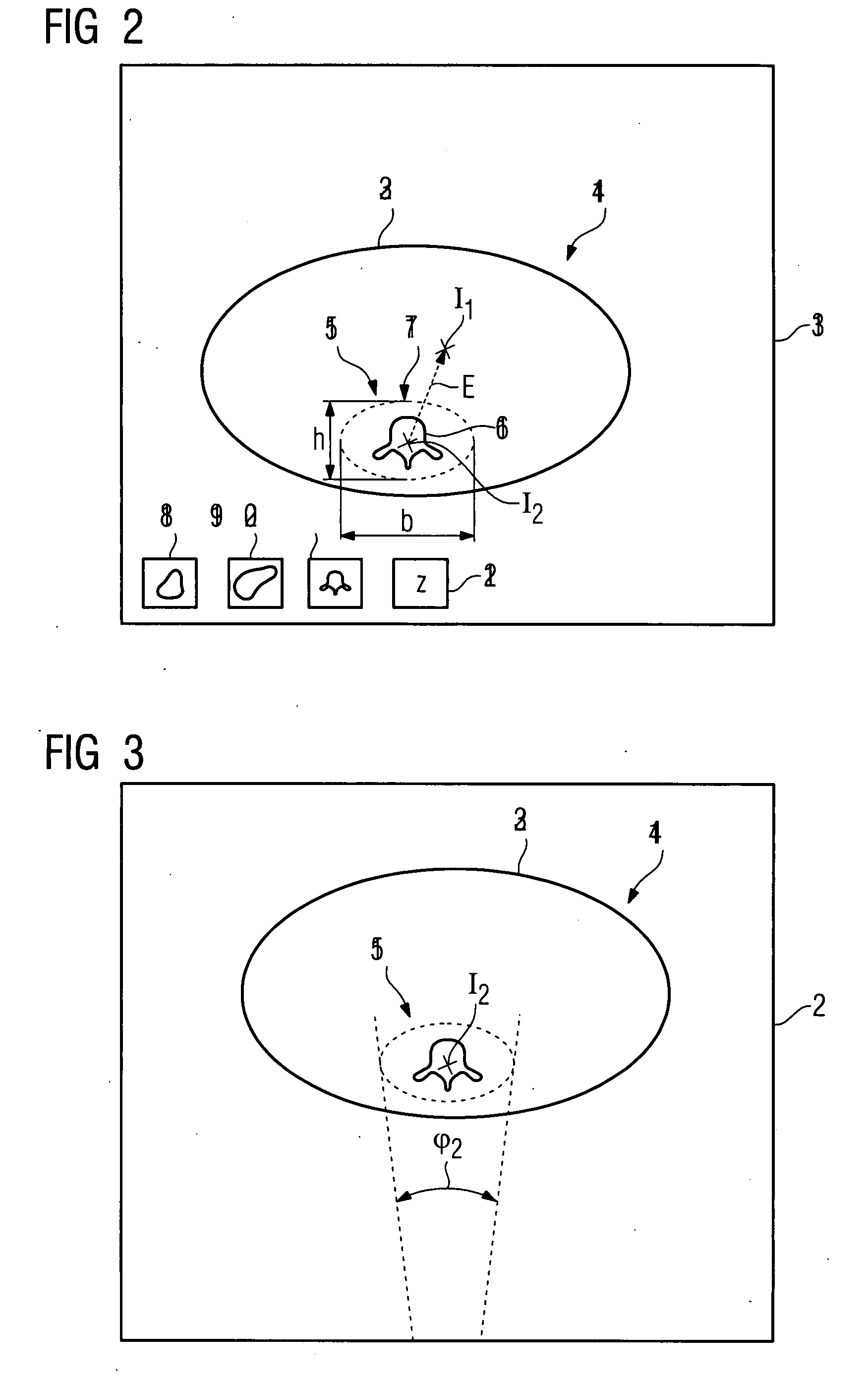
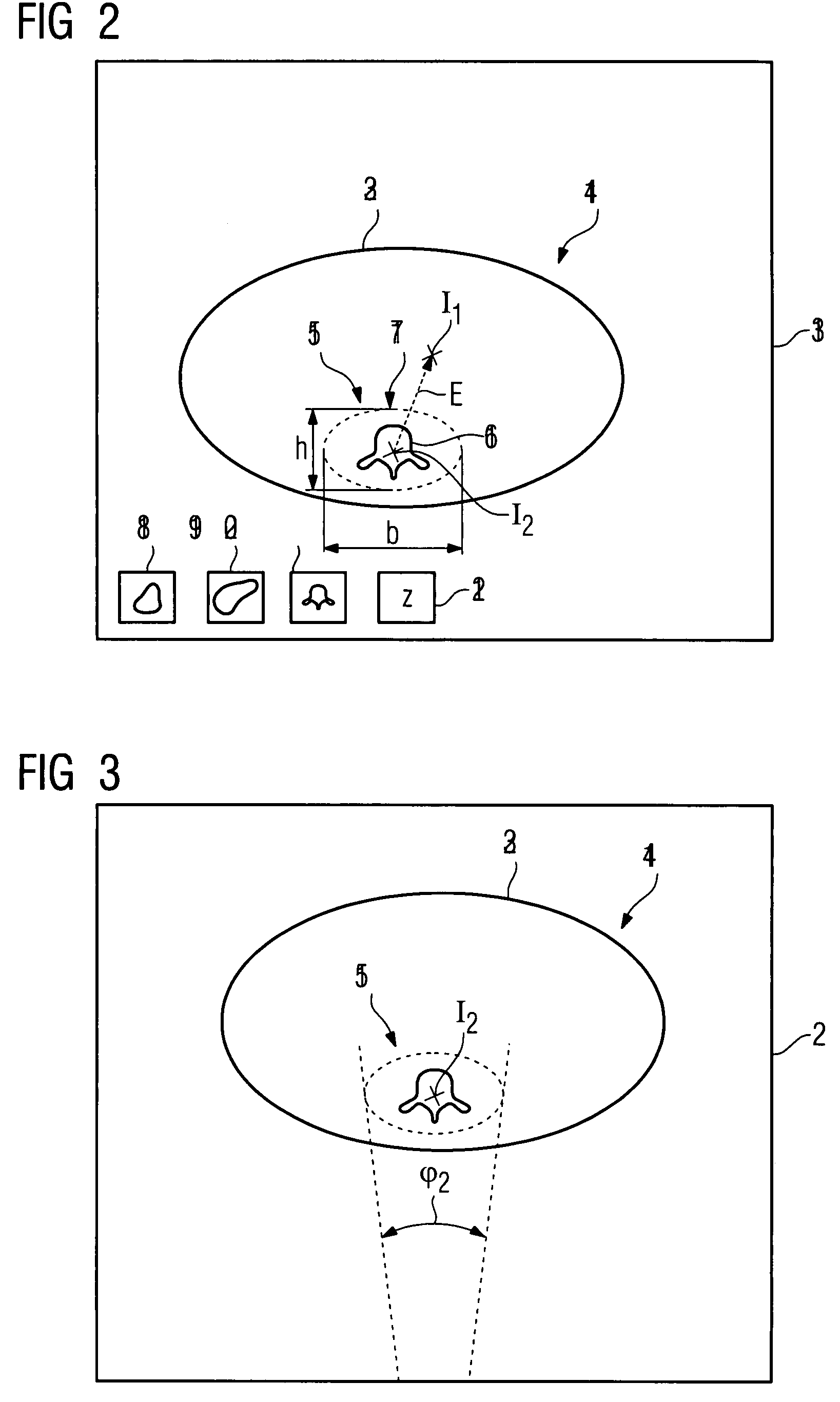
Method for recording images of a definable region of an examination object using a computed tomography facility
InactiveUS20080075225A1Low dose loadPrecise rotationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImage recordingImage resolution
There is described a method for recording images of a definable region of an examination object using an x-ray diagnostics facility for producing computed tomography recordings comprising an image recording facility comprising at least one radiation source and at least one radiation detector for the rotating recording of individual images, on the basis of, which an image suitable for outputting is produced, comprising the following steps: Recording of images of the entire examination region by rotating the image recording facility about a first isocenter with a first measuring field, a first resolution and a first dose, and generating an overview image of the examination object; Defining the region in the examination object based on the overview image and defining the location of a second isocenter as a function of the location and / or geometry of the region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Intramedullary pin tracking
ActiveUS20050261700A1Minimizing invasive experience of patientPrecise NavigationSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsEngineeringReference device
A tracking device for an intramedullary pin whose spatial position is determined and / or tracked in image-guided surgery, including a reference device at a proximal end of the intramedullary pin and a medical navigation system which locates the reference device and determines the orientation of the intramedullary pin from the proximal end. A deformation detection device detects deformations of the intramedullary pin and communicates the deformations to the navigation system. Also provided is a tracking method for determining or tracking the spatial position of an intramedullary pin in image-guided surgery, and to an intramedullary pin that includes a deformation detection device.
Owner:BRAINLAB
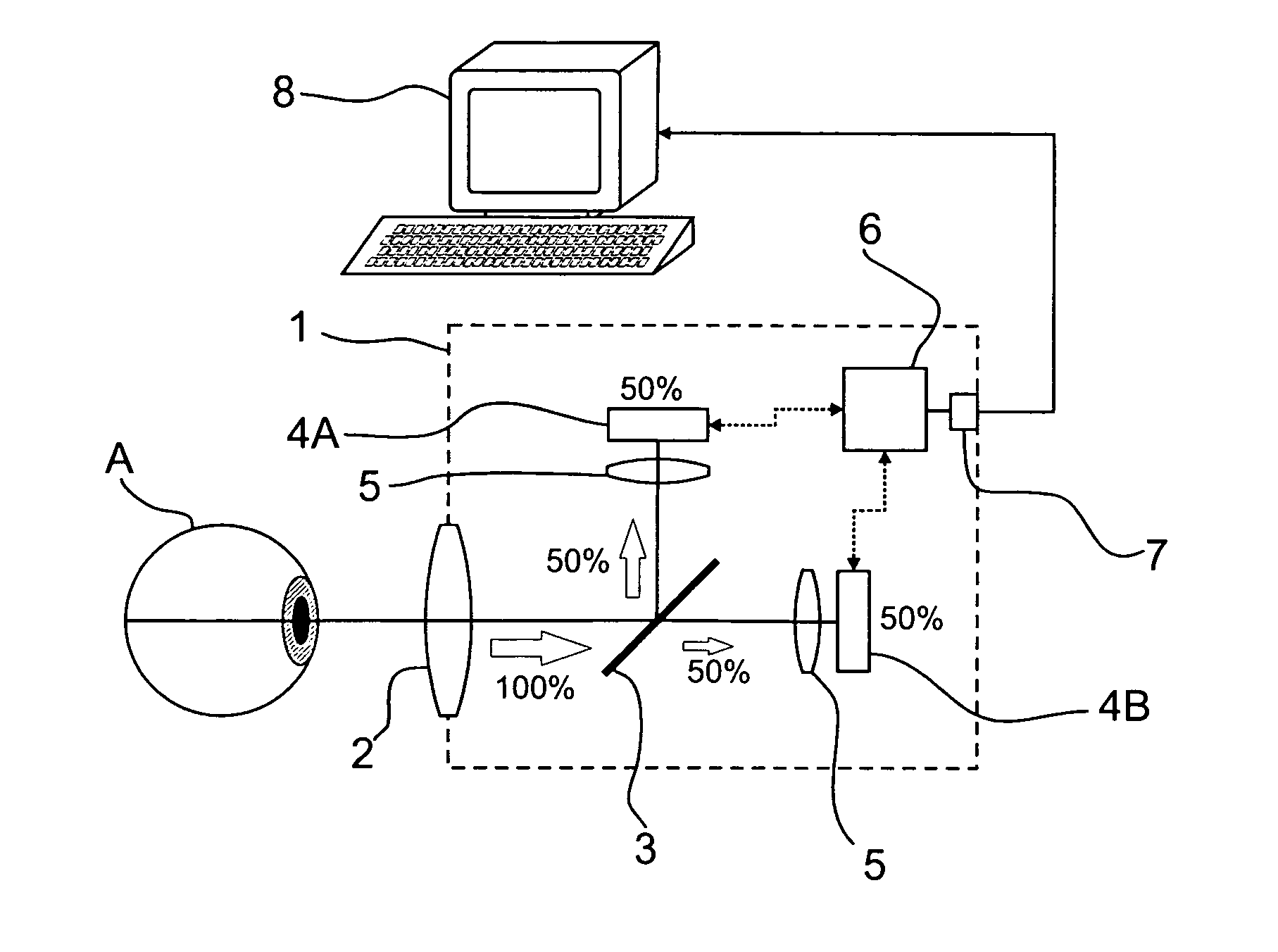
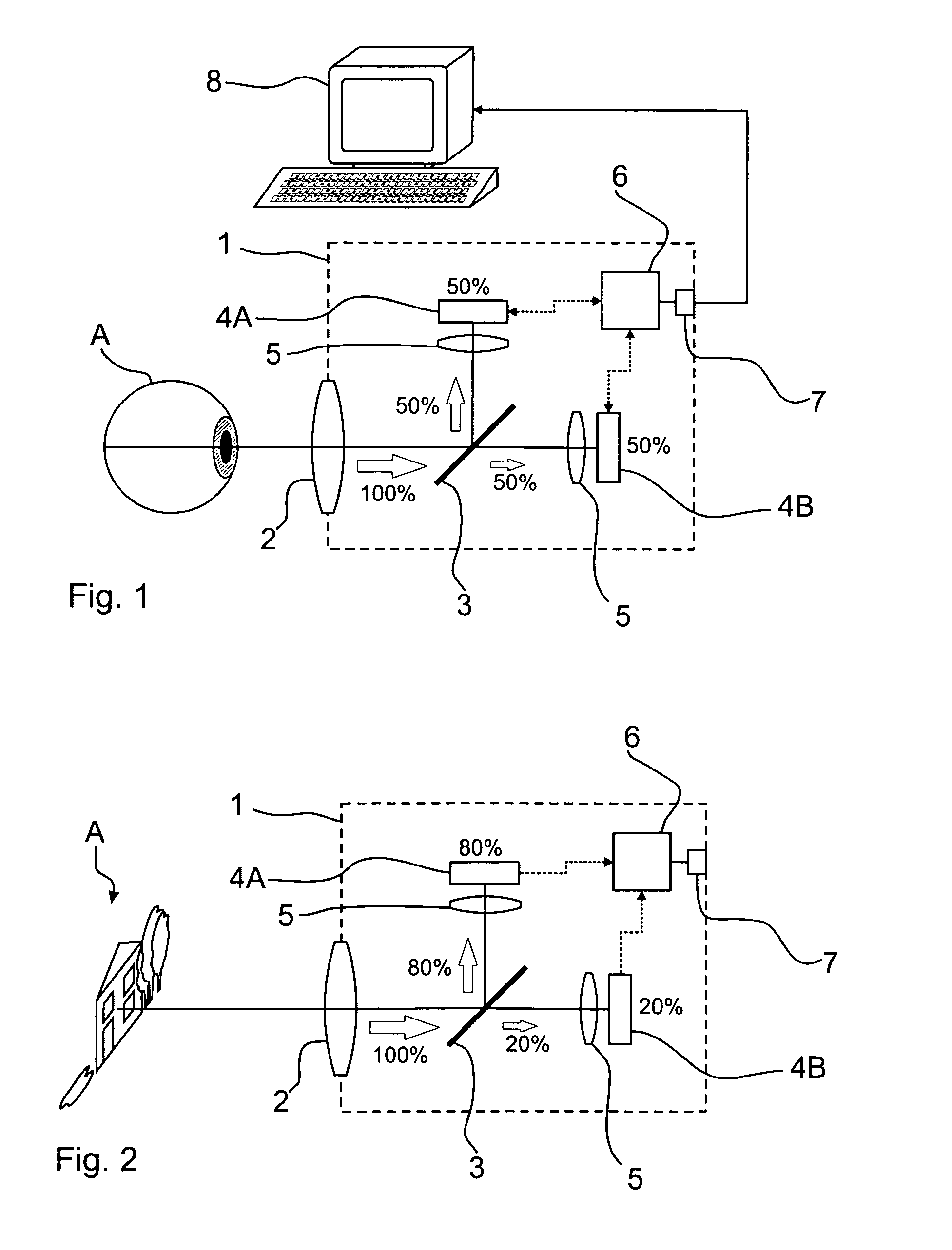
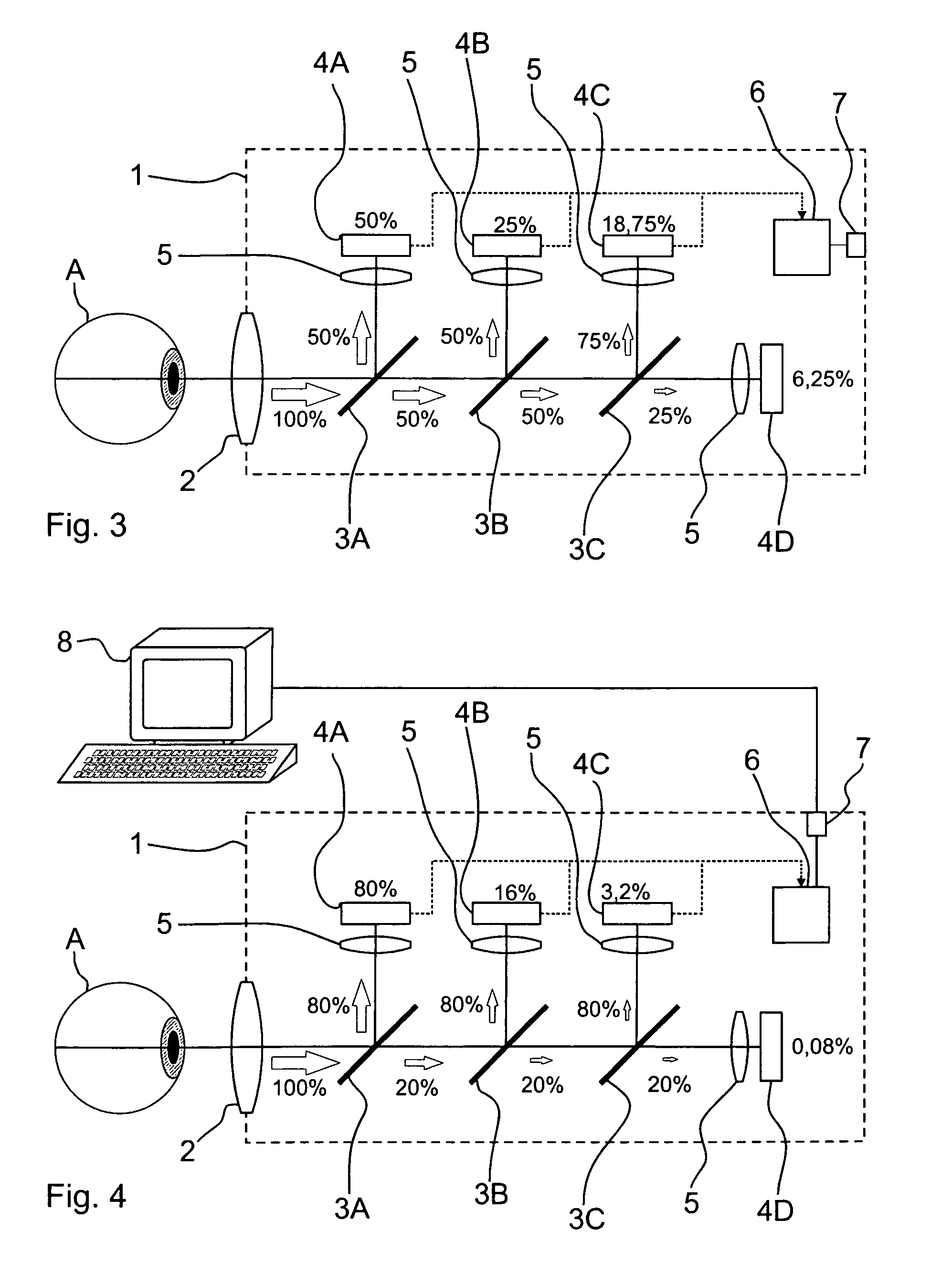
Arrangement and method for generating images with expanded dynamics
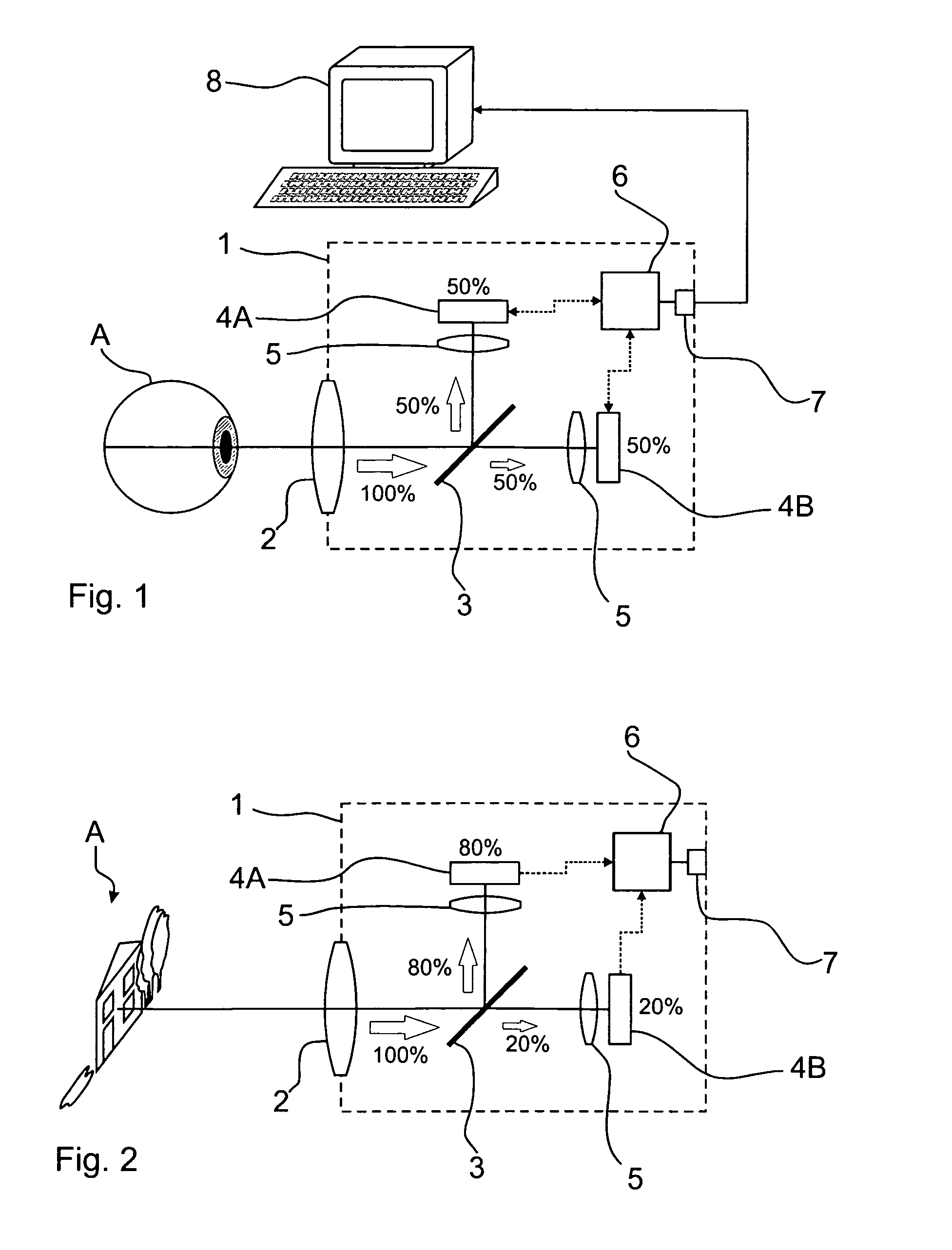
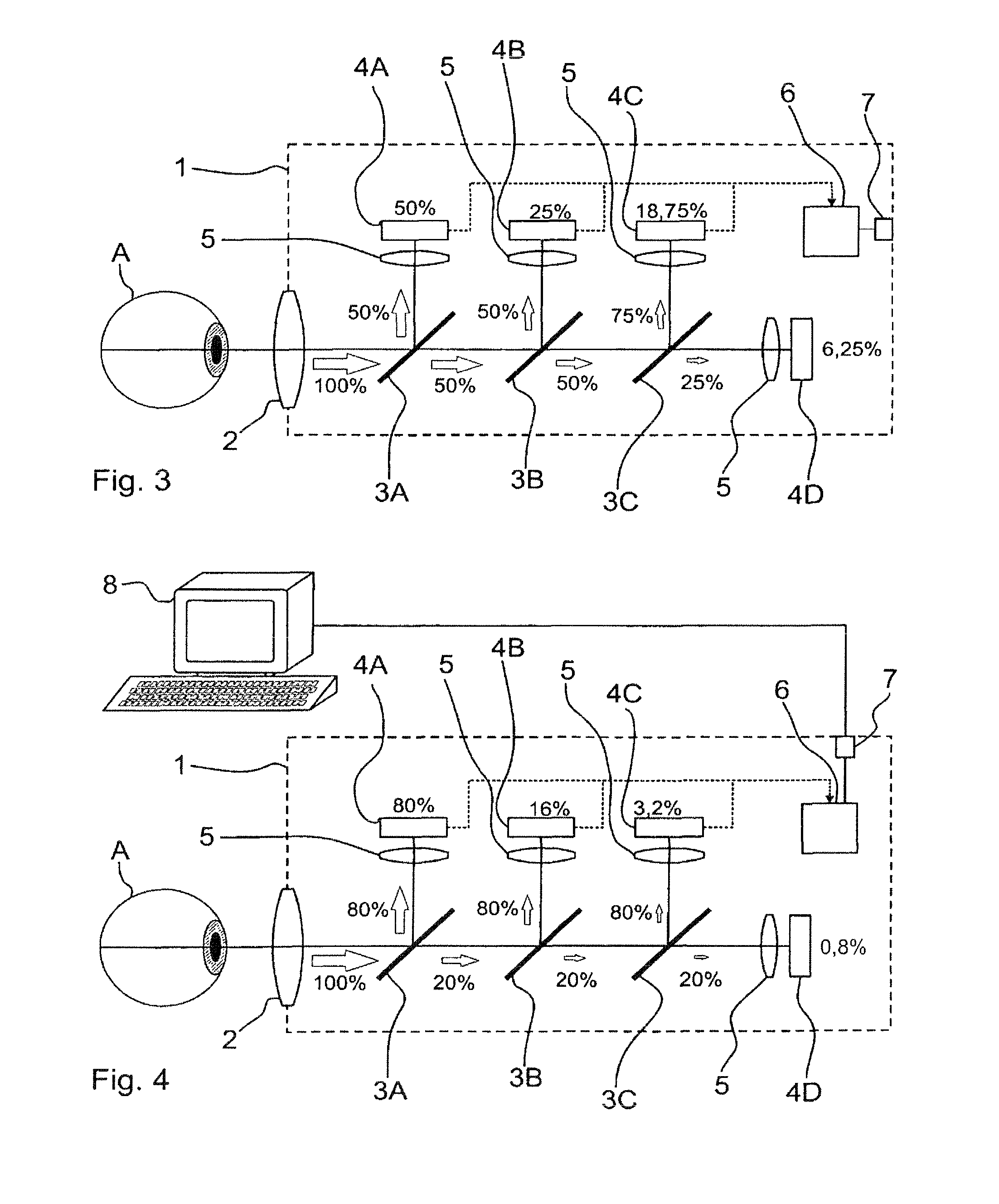
ActiveUS20100201799A1Strong computing powerImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamDynamic range
An ophthalmic device and an arrangement for generating images with expanded dynamic range and a corresponding method for generating images with expanded dynamic range have at least one beamsplitter, in particular with an asymmetric splitting ratio, and at least two image sensors, wherein the image sensors are reflected into a common imaging beam path by the at least one beamsplitter.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Method for recording images of a definable region of an examination object using a computed tomography facility
InactiveUS7500783B2Precise rotationReduce radiation loadTomographyRadiation beam directing meansSoft x rayObject based
There is described a method for recording images of a definable region of an examination object using an x-ray diagnostics facility for producing computed tomography recordings comprising an image recording facility comprising at least one radiation source and at least one radiation detector for the rotating recording of individual images, on the basis of which an image suitable for outputting is produced, comprising the following steps: Recording of images of the entire examination region by rotating the image recording facility about a first isocenter with a first measuring field, a first resolution and a first dose, and generating an overview image of the examination object; Defining the region in the examination object based on the overview image and defining the location of a second isocenter as a function of the location and / or geometry of the region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
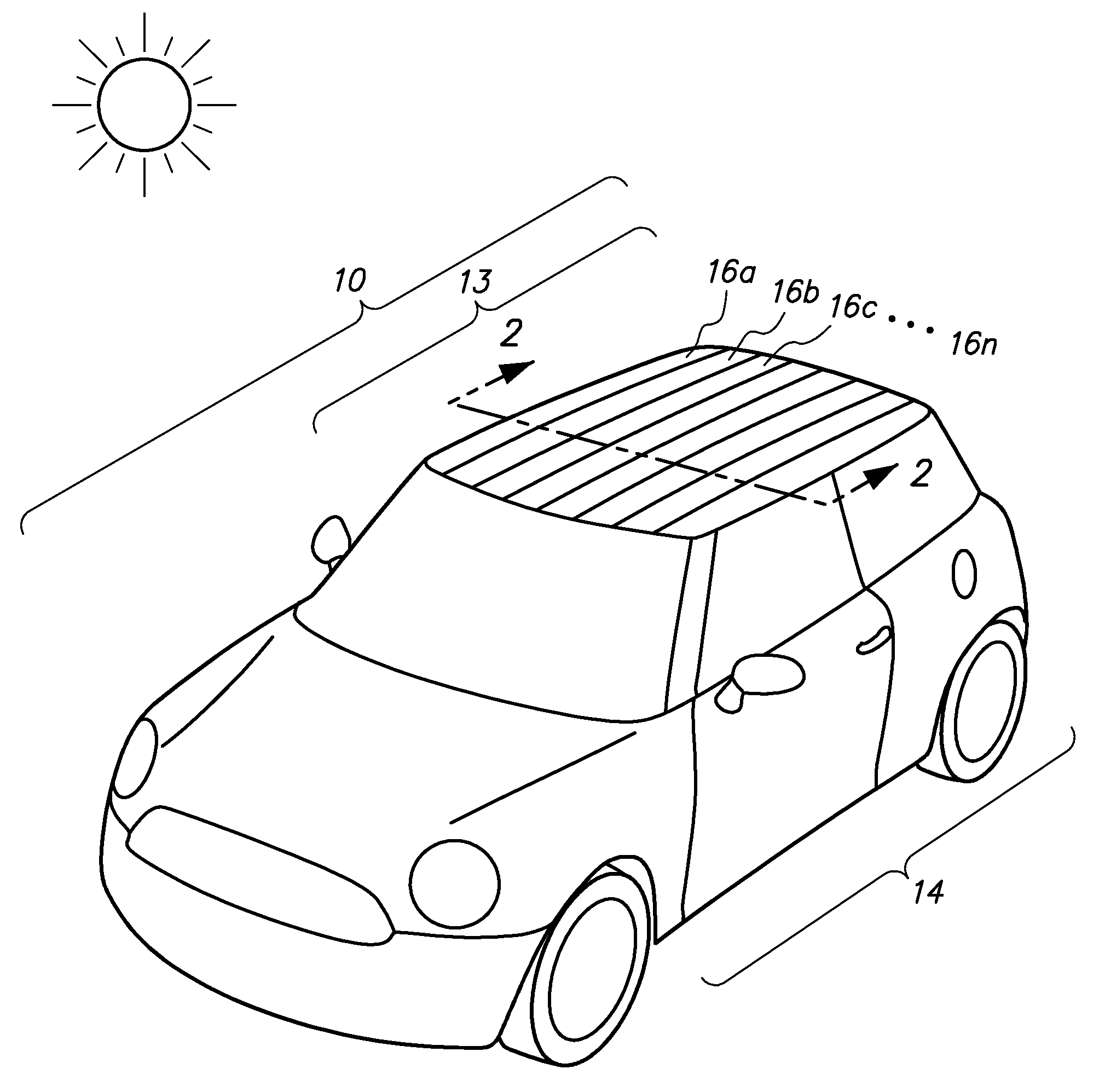
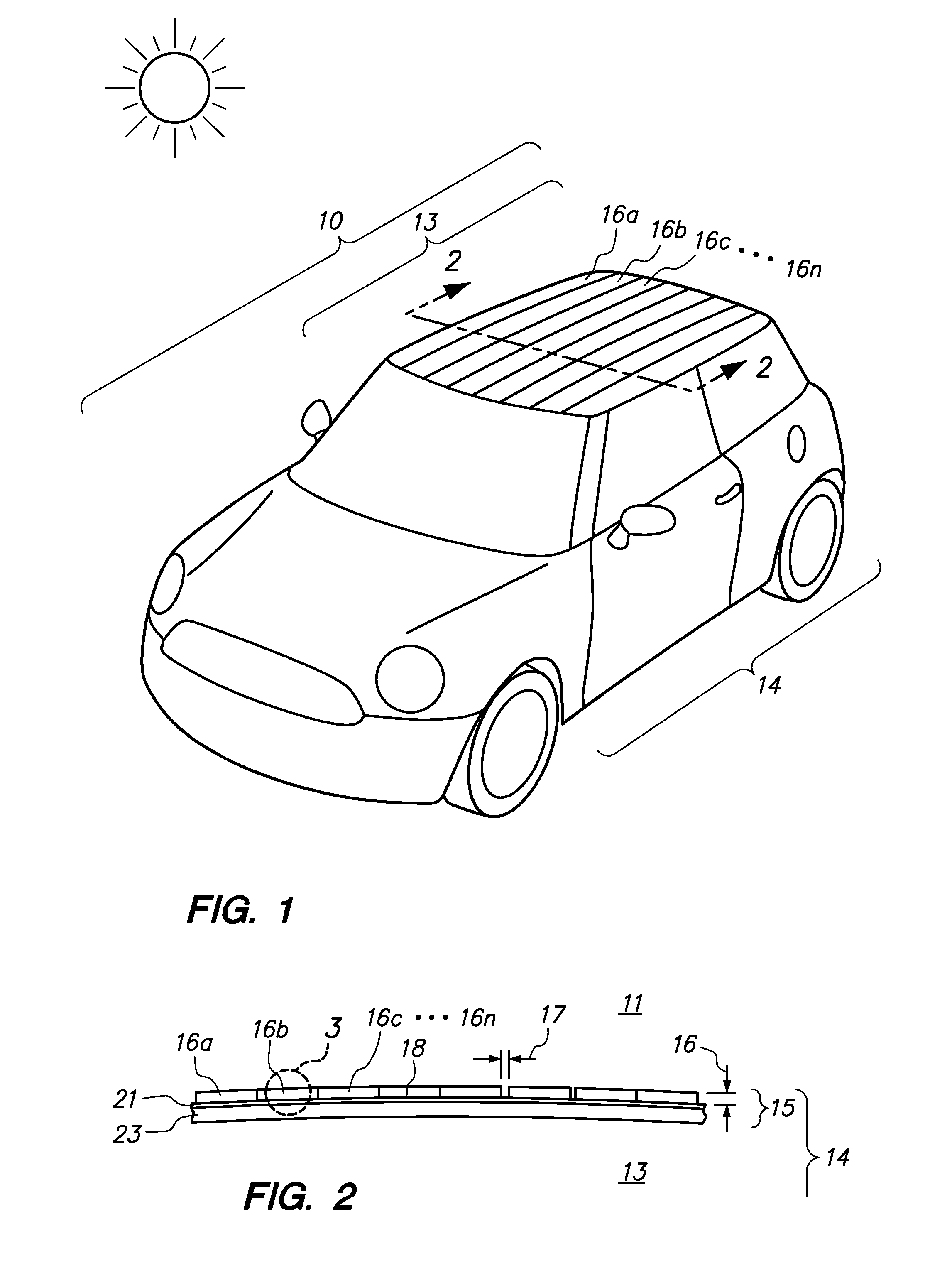
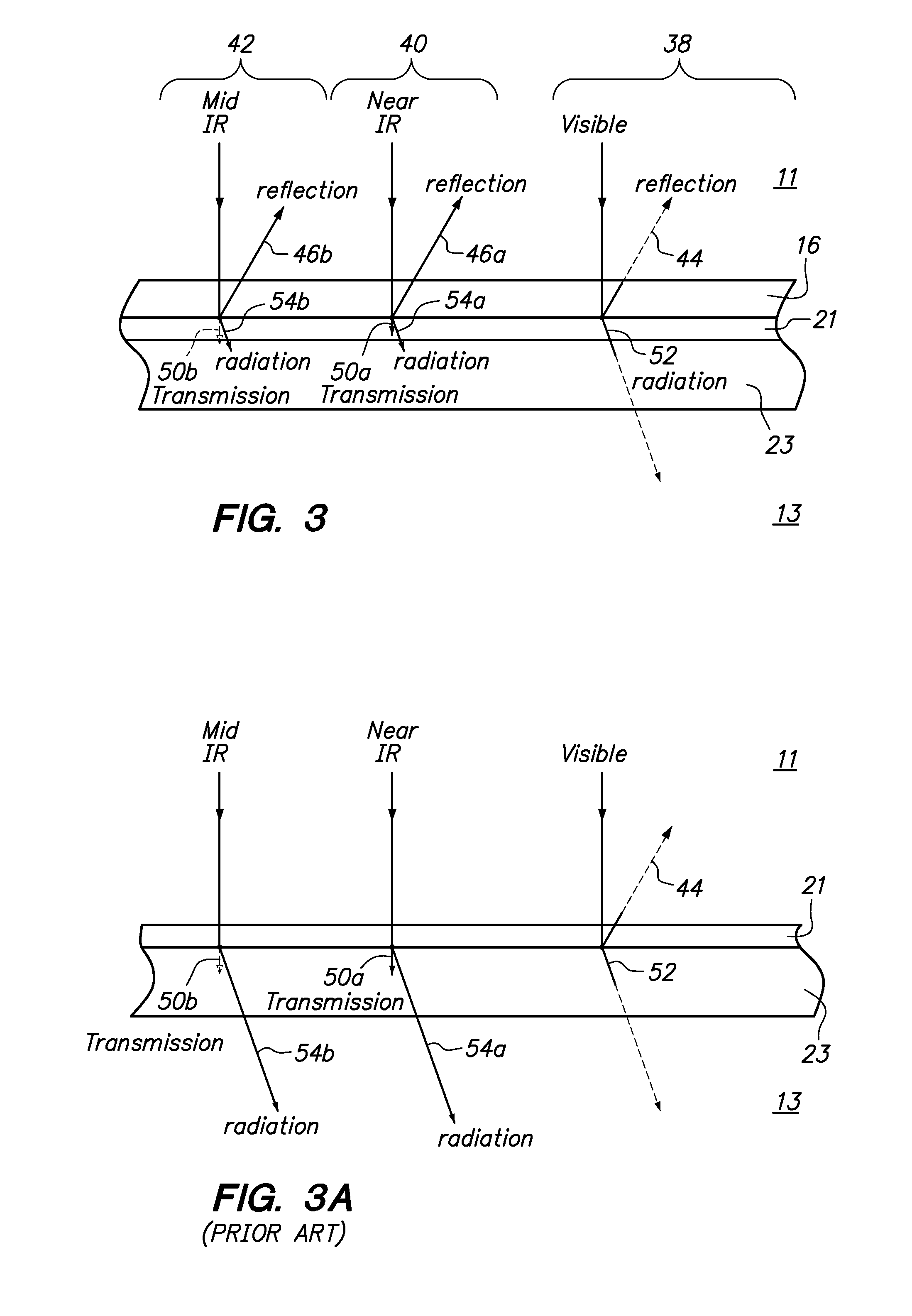
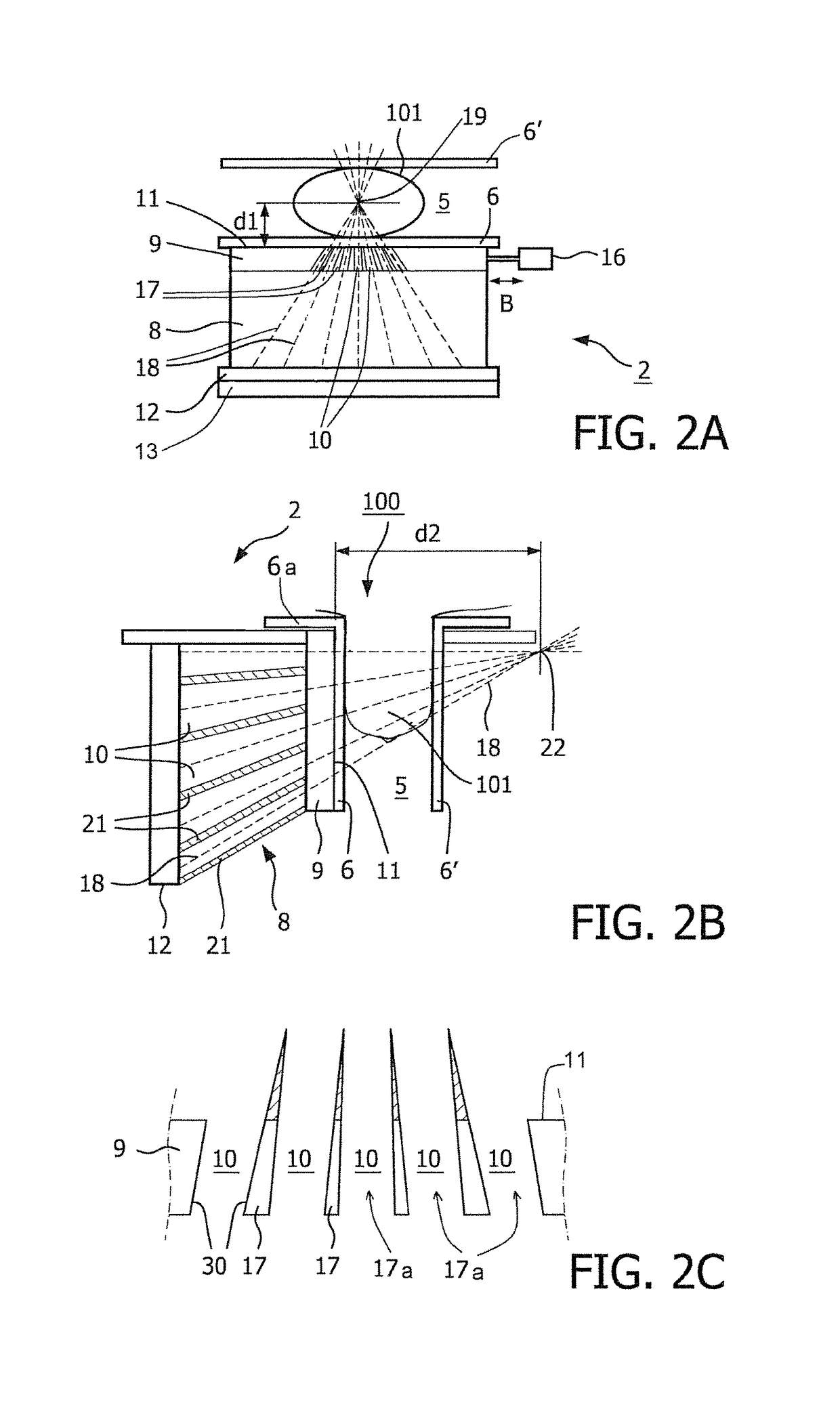
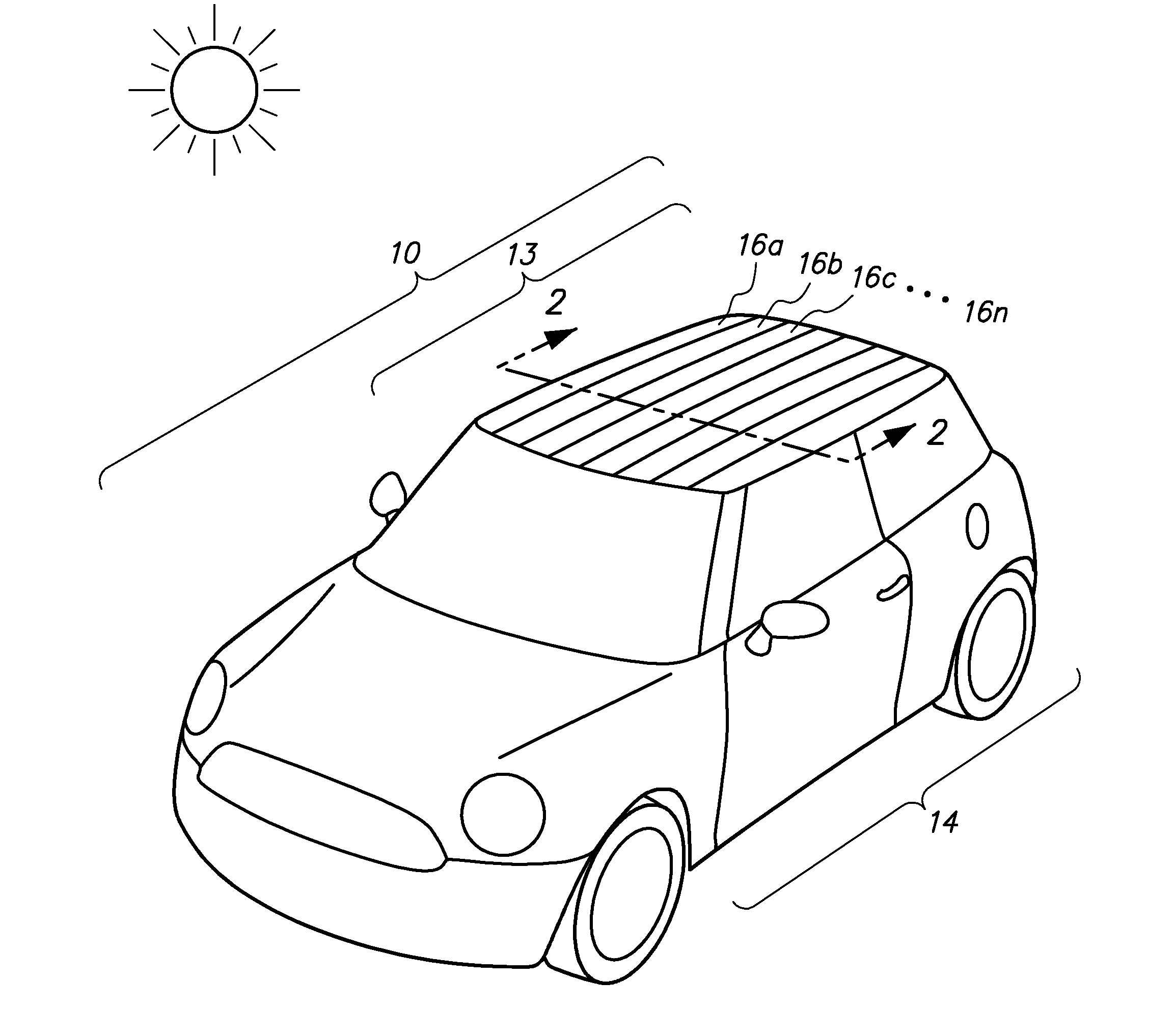
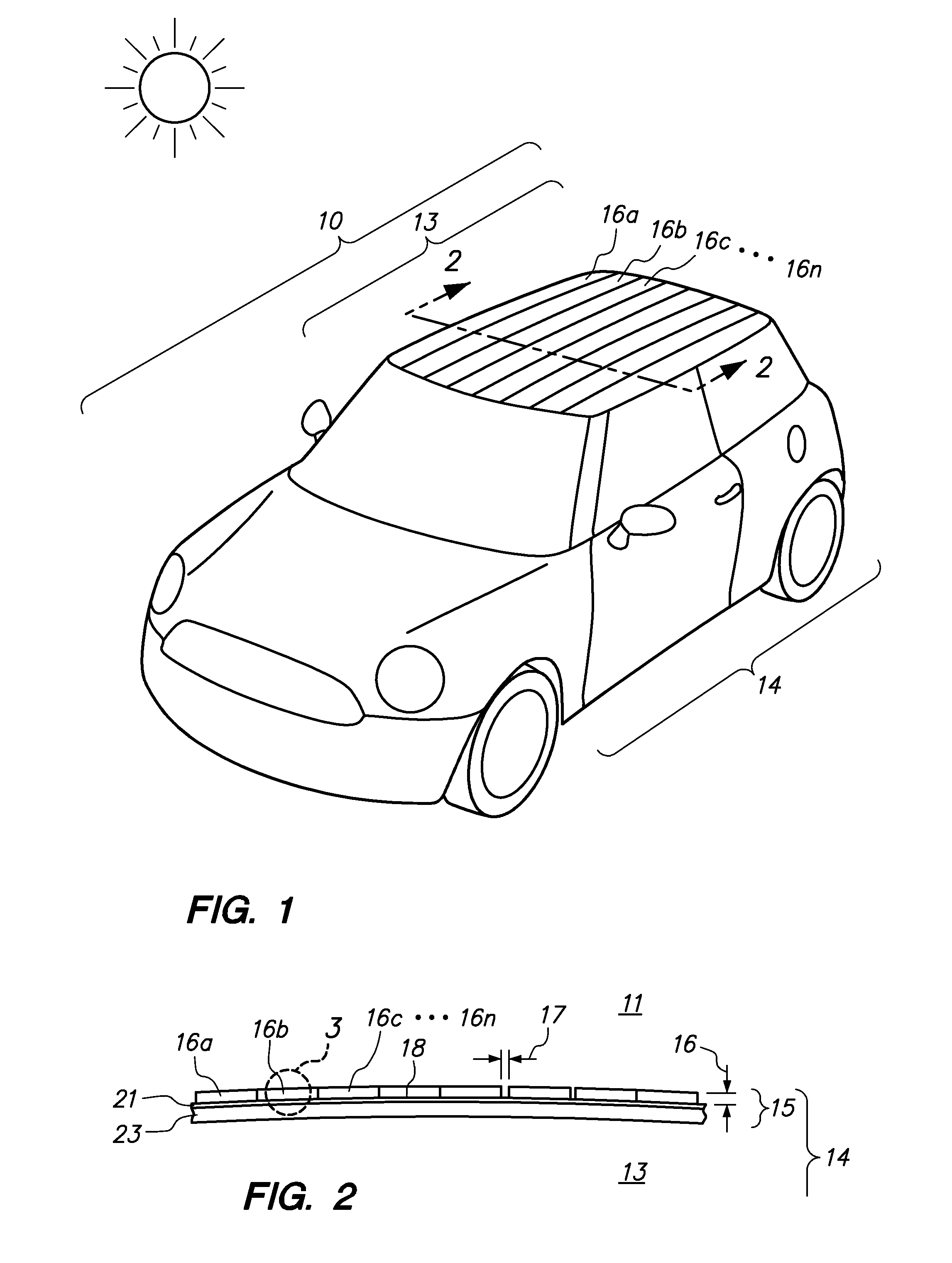
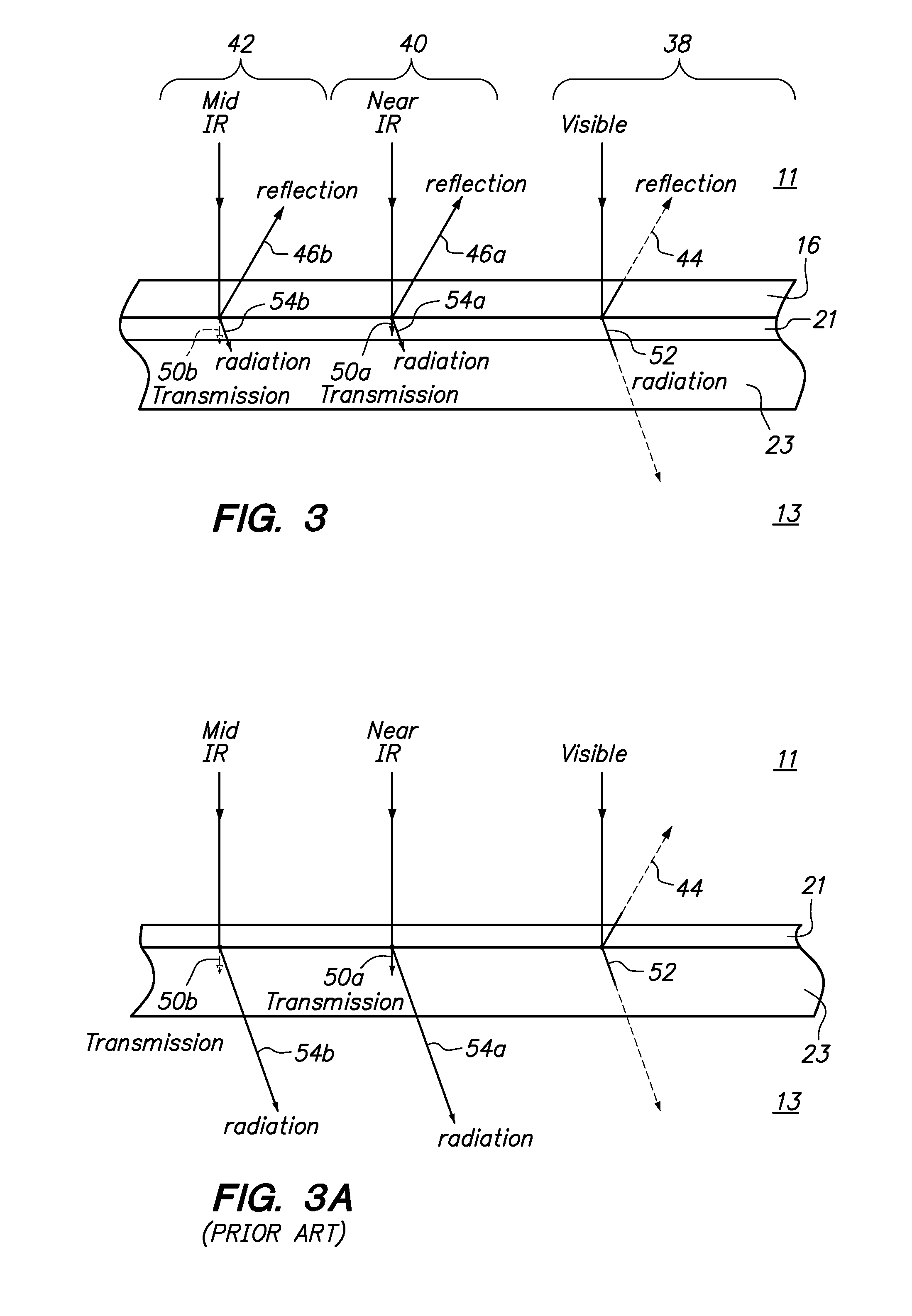
Automobiles having a radiant barrier
ActiveUS8361260B2Improve efficiencyHigh light transmittanceMirrorsLamination ancillary operationsControl systemBlack body
Owner:WILSON STEPHEN S +2
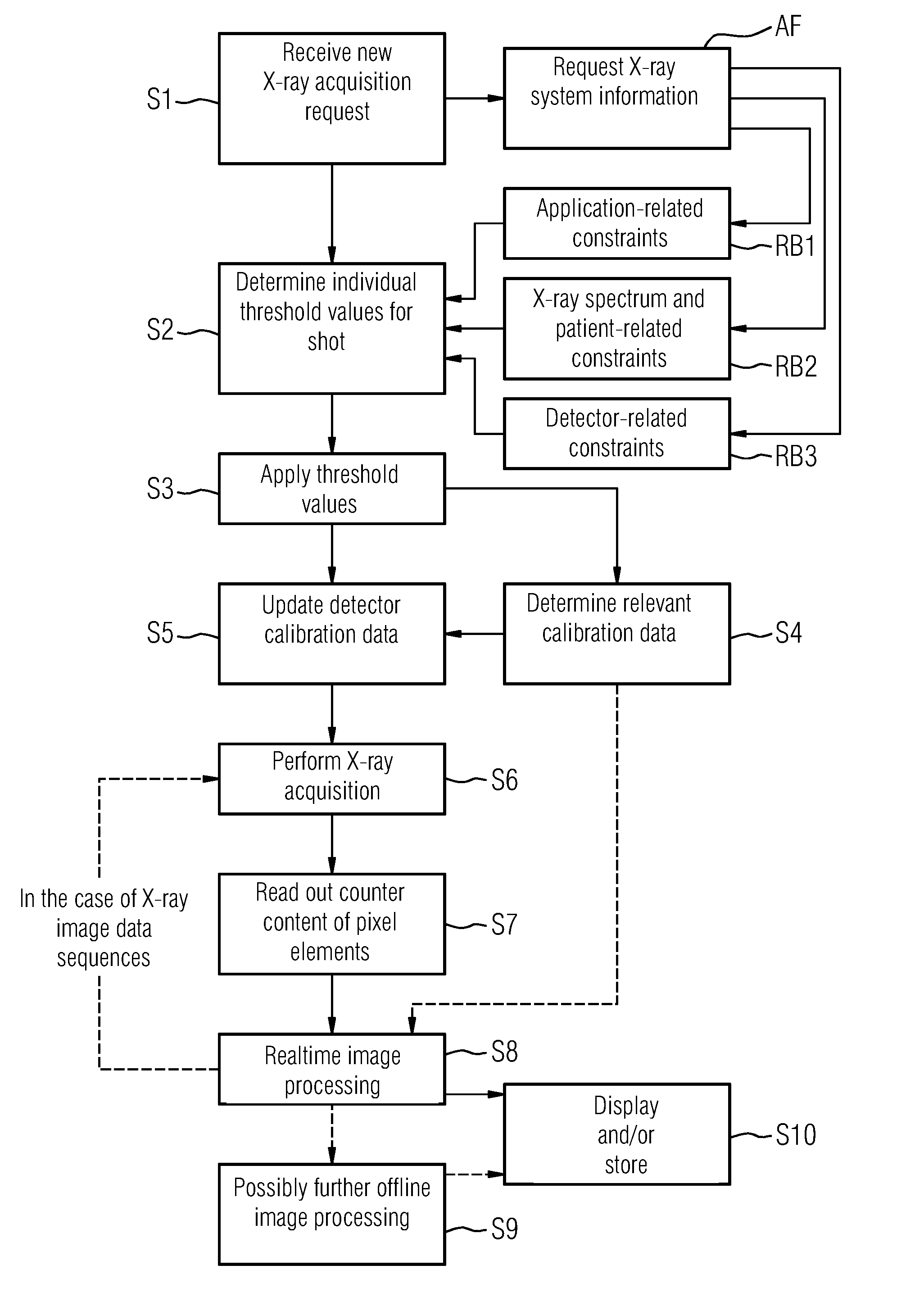
Method and System for Acquiring an X-Ray Image
InactiveUS20140270073A1Improve overall utilizationEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementSoft x rayX-ray
A method acquires an X-ray image via a counting digital X-ray detector of an X-ray system. The X-ray detector has an X-ray converter for converting X-ray radiation into an electrical signal and a matrix having a plurality of counting pixel elements. At least one variable threshold value is applied for each pixel element such that an incoming signal is counted by a memory unit in each instance that the incoming signal exceeds the threshold value. The method includes receiving a request to acquire one or more X-ray images, automatically determining one or more threshold values individually adjusted to the X-ray image(s), setting the threshold values in the X-ray detector, applying X-ray radiation while the threshold values are applied, converting X-ray quanta into count signals, storing the count signals in the X-ray detector, outputting image data representing the X-ray image from the X-ray detector, and displaying or storing the X-image.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Defining scanning parameters of a ct scan using external image capture
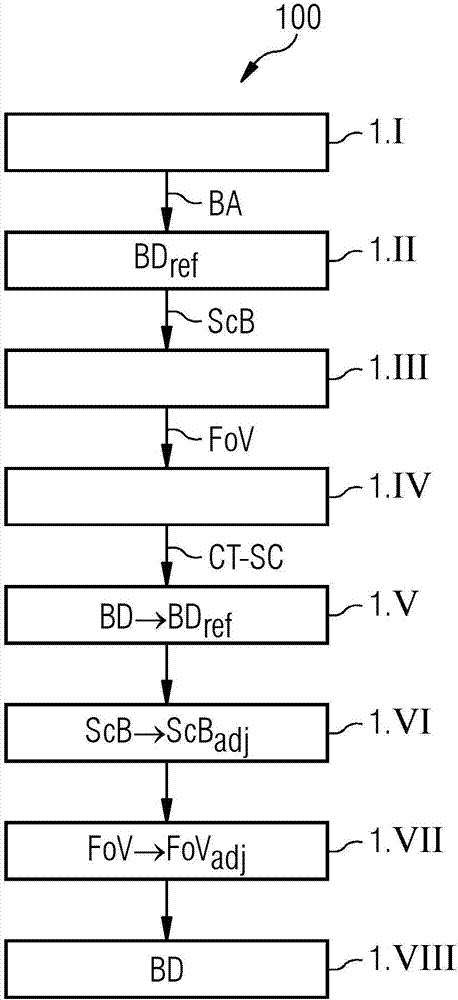
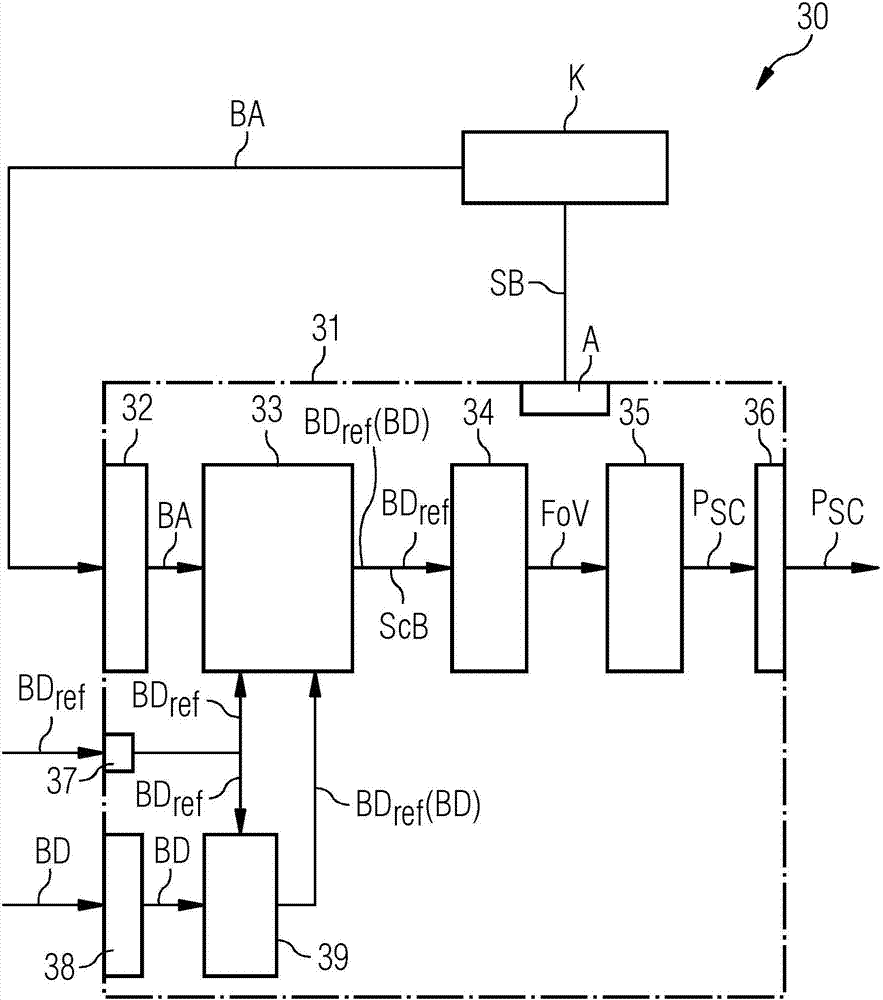
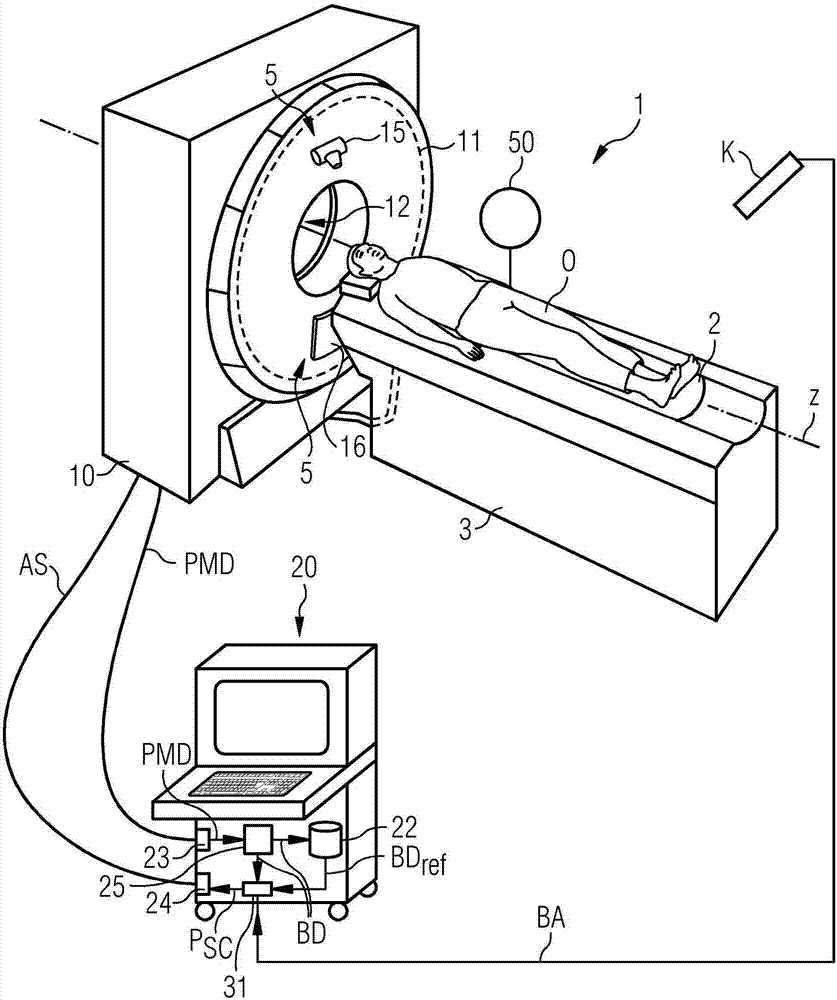
ActiveCN107334485AShorten the length of timeReduce radiation loadRadiation diagnostic device controlComputerised tomographsComputed tomographyComputer science
A method for defining scanning parameters of a CT scan of a region of interest of an examination object (O) using a CT system is described. In an embodiment of the method, external image capture of external features of the examination object is carried out using an additional image capture unit. In addition, at least one scanning parameter in the axial direction of the CT system is determined on the basis of the external image capture. Finally, a CT scan is performed using the at least one scanning parameter determined. A CT scan range defining device is additionally described. A computed tomography system is also described.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Skew chicane based betatron eigenmode exchange module
InactiveUS7858951B1Reduced footprintConsolidating the functionalities of skew-quadLaser detailsMagnetic induction acceleratorsLight beamEngineering
A skewed chicane eigenmode exchange module (SCEEM) that combines in a single beamline segment the separate functionalities of a skew quad eigenmode exchange module and a magnetic chicane. This module allows the exchange of independent betatron eigenmodes, alters electron beam orbit geometry, and provides longitudinal parameter control with dispersion management in a single beamline segment with stable betatron behavior. It thus reduces the spatial requirements for multiple beam dynamic functions, reduces required component counts and thus reduces costs, and allows the use of more compact accelerator configurations than prior art design methods.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Dynamic thermal infrared invisible composite material based on dual phase change and preparation method
ActiveCN109181650AGive full play to the temperature control abilityActive and quick responsePretreated surfacesCamouflage devicesSupport matrixNanoparticle coating
The invention discloses a dynamic thermal infrared invisible composite material based on dual phase change and a preparation method and especially relates to a VO2 / mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer composite material and a preparation method, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of infrared invisible materials. The VO2 / mica based phase change heat-accumulation thinlayer composite material is composed of a VO2 nanoparticle coating and a mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer, wherein the mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer is composed of stearic acid and a vanadium-extracted mica matrix according to the mass ratio of (3 to 5) to (5 to 7). The preparation method comprises the following step: preparing VO2 nanoparticles from vanadium-extracted mica by adopting a roasting and acid leaching technology; taking the vanadium-extracted mica as a supporting matrix and embedding to a phase change functional body to prepare the mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer; and coating the mica based phase change heat-accumulation thin layer with the VO2 nanoparticles to obtain a dual phase change composite material. The dynamic thermal infrared invisible composite material based on the dual phase change, provided by the invention, can be used for cooperatively strengthening the thermal infrared invisible performance and can be applied to a thermal infrared invisible technology.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for recording an examination object
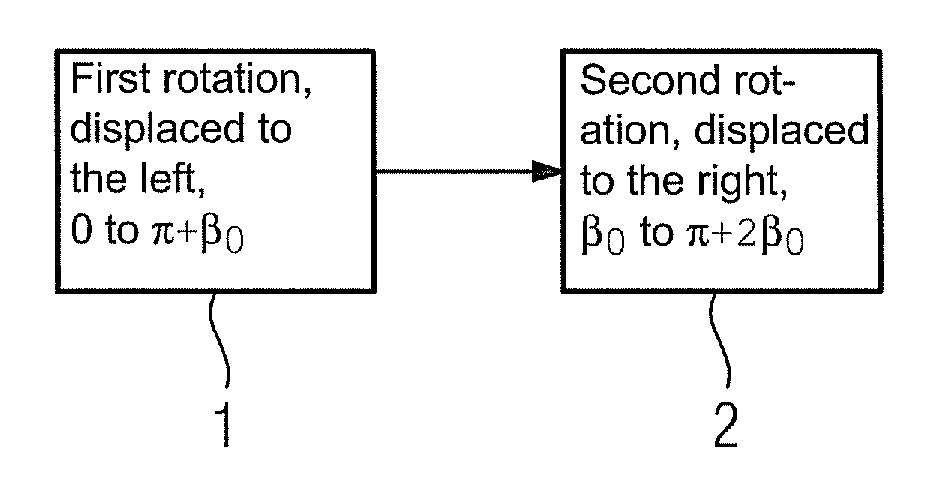
InactiveUS7986762B2Radiation loading on the examination object as lowReduce radiation loadMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRayAtomic physics
A method is provided for recording an examination object using an x-ray recording system having an x-ray source and an x-ray detector rotatable about a common axis of rotation. X-ray detector is displaced in a first direction enclosing a first angle k between a perpendicular bisector from x-ray source to x-ray detector and a plane running through x-ray source and containing the axis, k≠0. First x-ray images are recorded in angular positions of x-ray source and x-ray detector displaced in the first direction in a first rotation. X-ray detector is displaced in a second direction enclosing a second angle m between the bisector and the plane, m≠0 and is on an opposite side from k. Starting points of the rotations are differed by an angle of displacementβ0=k+m+d2,where d is the detector fan angle. Starting points and finishing points of the rotations are spanned by π+β0.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for assisting with percutaneous interventions
ActiveUS8099155B2Reduce radiation loadSimplify spaceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonification3d image
The present invention relates to a method for assisting with percutaneous interventions, wherein 2D x-ray images of an object region are recorded before the intervention using a C-arm x-ray system or a robot-based x-ray system at different projection angles and 3D x-ray image data of the object region is reconstructed from the 2D x-ray recordings. One or more 2D or 3D ultrasound images are recorded before and / or during the intervention using an external ultrasound system and registered with the 3D image data. The 2D or 3D ultrasound images are then overlaid with the 3D image data record or a target region segmented therefrom or displayed next to one another in the same perspective. The method allows a puncture or biopsy to be monitored with a low level of radiation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Radiography device for recording dynamic processes and associated recording method
ActiveUS7596206B2Reduce loadReduce radiation loadRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusIntervention measuresFlat detector
There is described a radiography device for recording dynamic processes and an associated recording method. The radiography arrangement is used to examine patients using an x-ray source, a digital flat detector with a single shot recording function and an operating console for controlling and recording purposes, with the flat detector also being able to display an image sequence at a rate of up to 5 Hertz, which allows the positioning of the region to be examined or the monitoring of pseudo-interventional interventions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
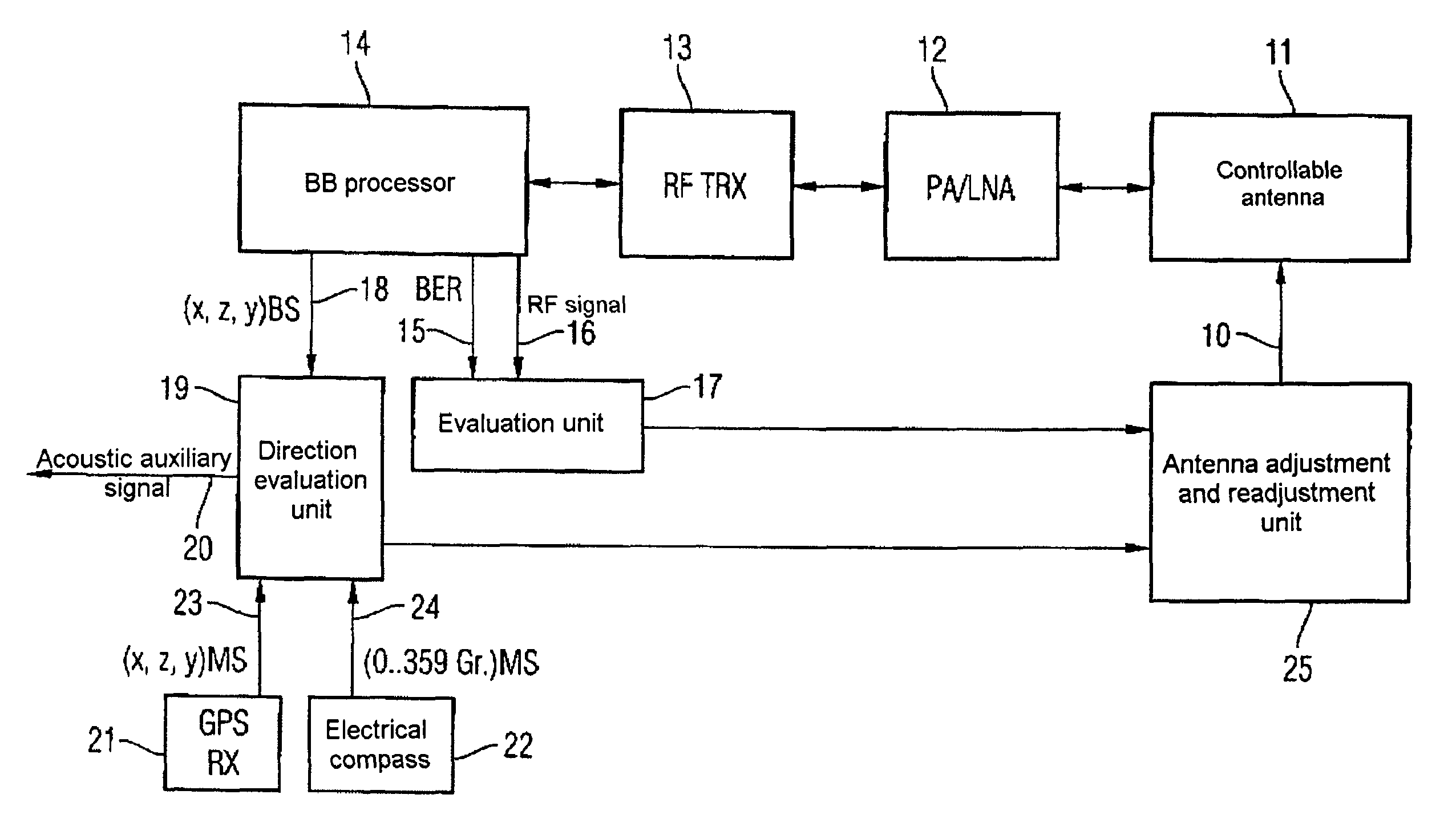
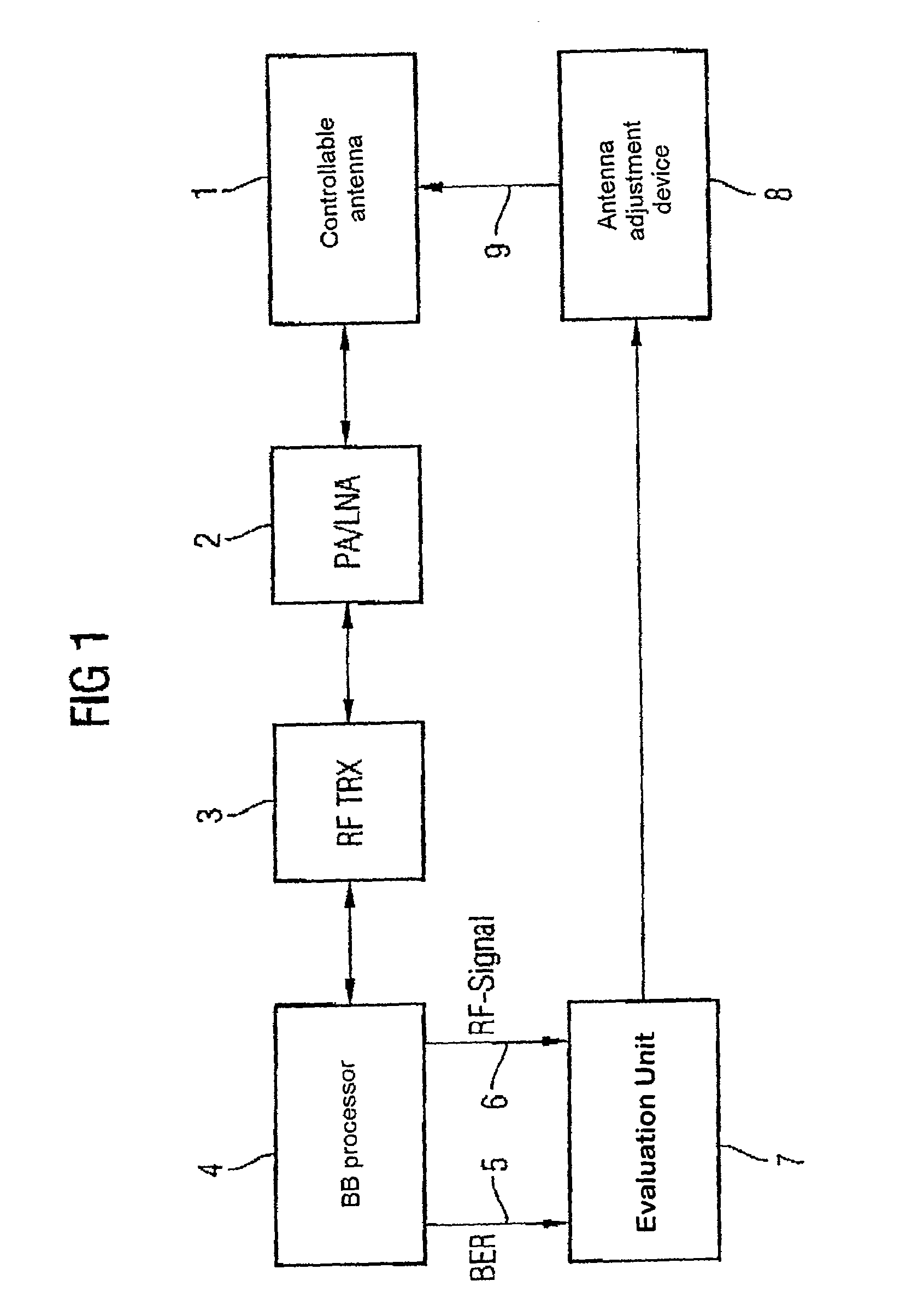
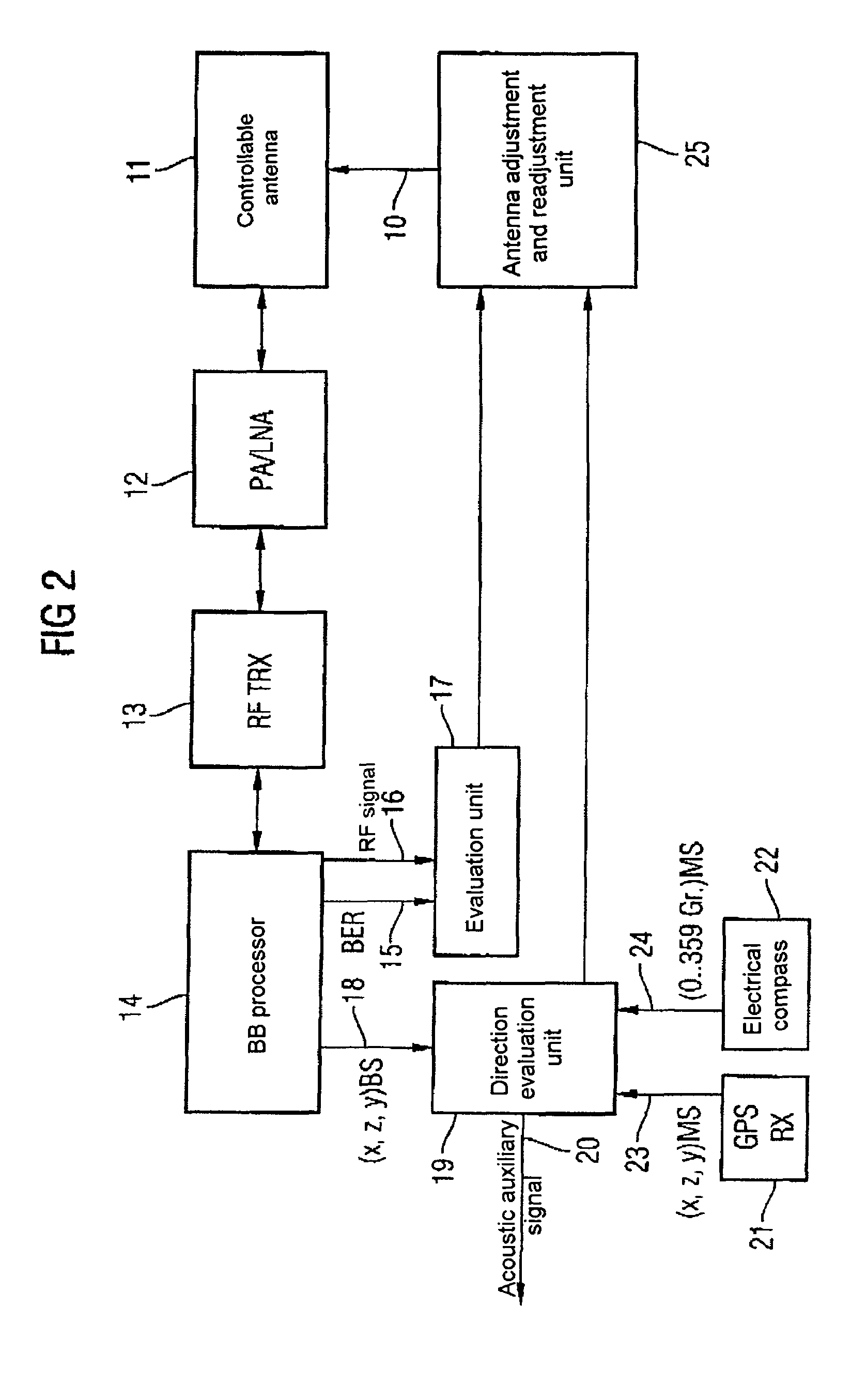
Method for reducing the radiation load by a mobile radio terminal with directional emission, and a mobile radio terminal with directional emission
InactiveUS7551890B2Reduce radiation loadPower emittedAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentSignal qualityMobile station
In a method for alignment of an antenna (1) with an adjustable directional characteristic in a mobile station in a mobile radio system, the alignment process is based on determination of two variables as a function of the direction, with the first variable being characteristic of the signal strength (6) and the second variable being characteristic of the signal quality (5, 15), and their evaluation (7). Furthermore, it is possible to make use of position information and alignment information relating inter alia to satellite-based navigation systems, and to take account of the alignment of the user.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
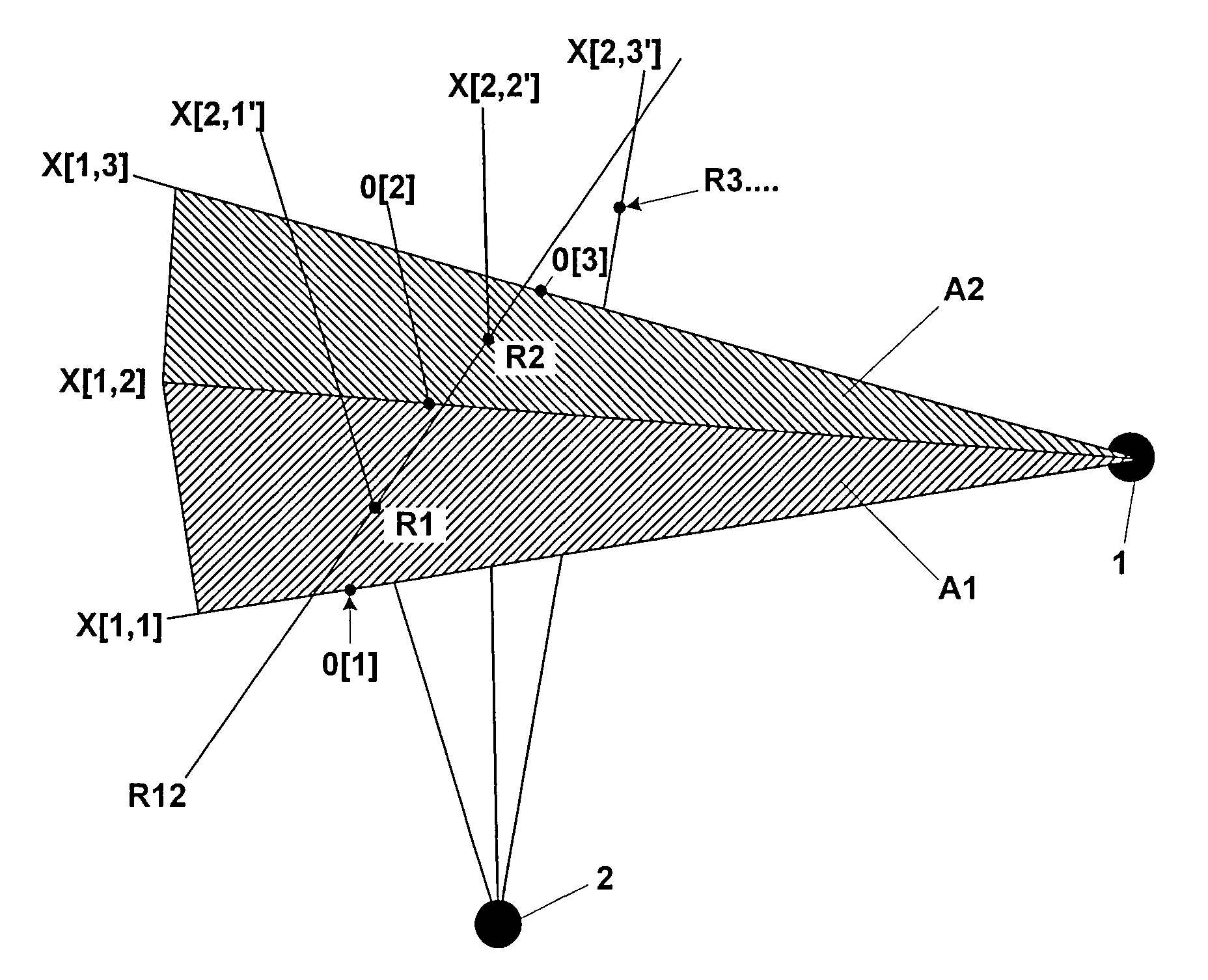
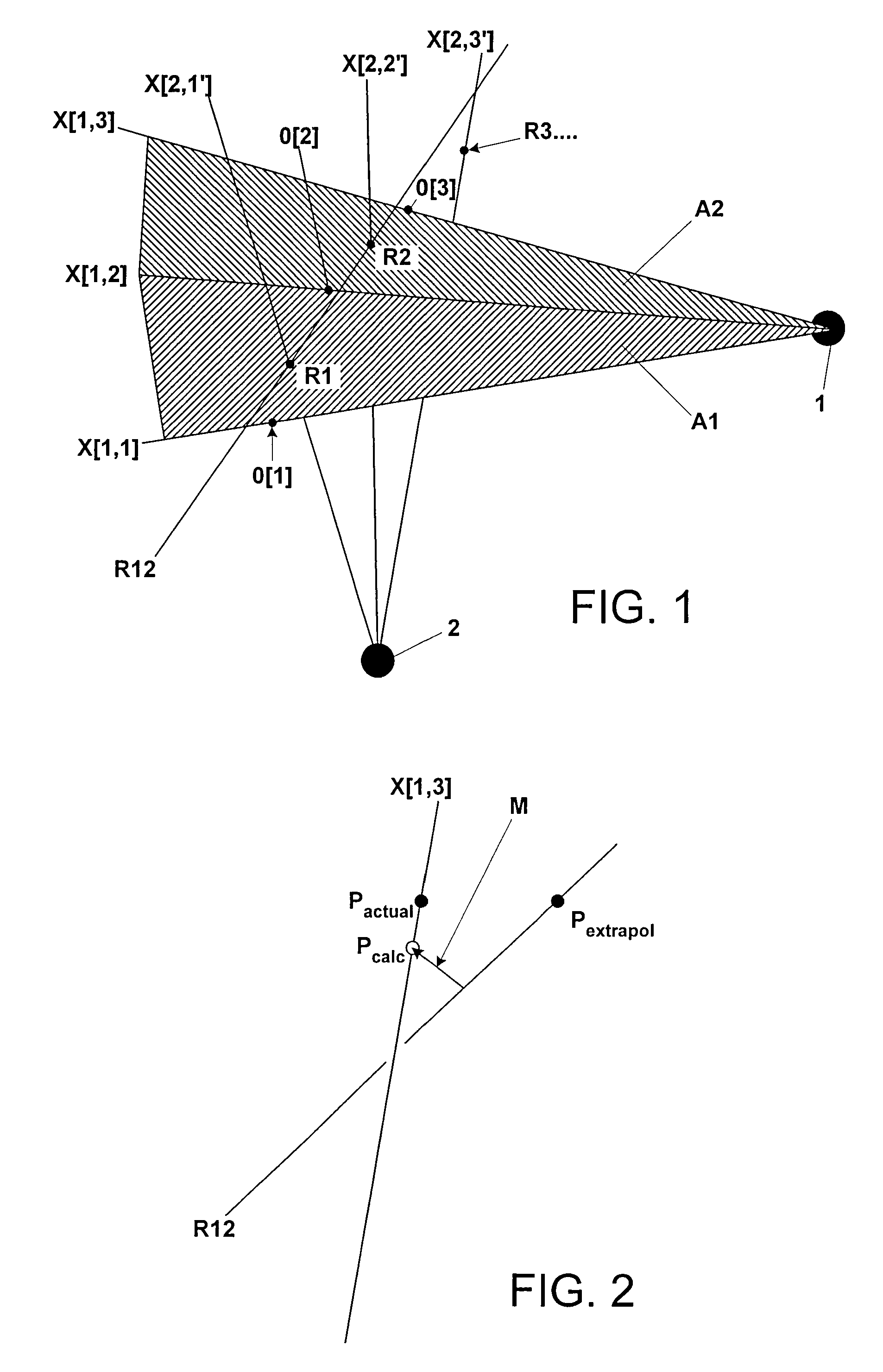
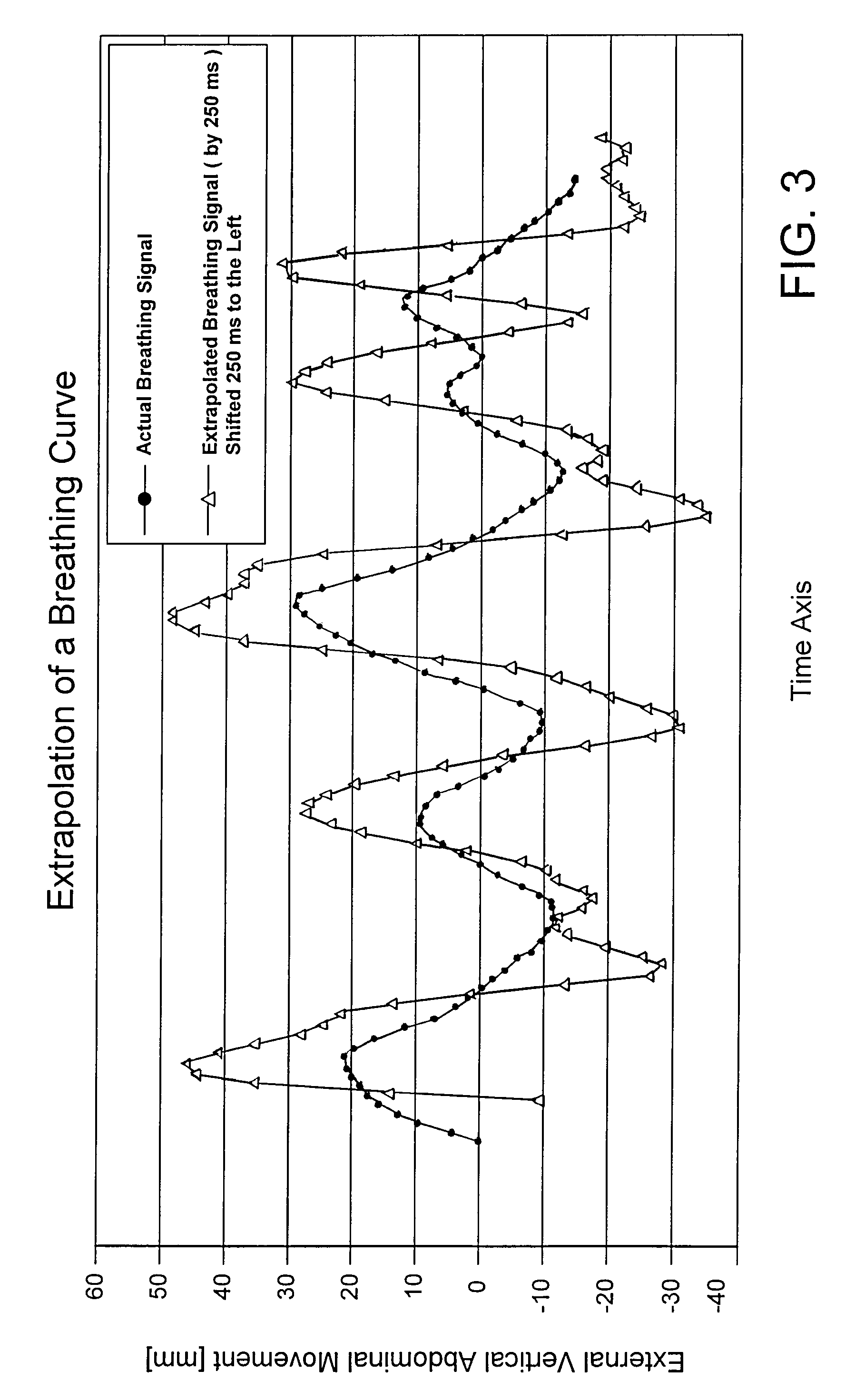
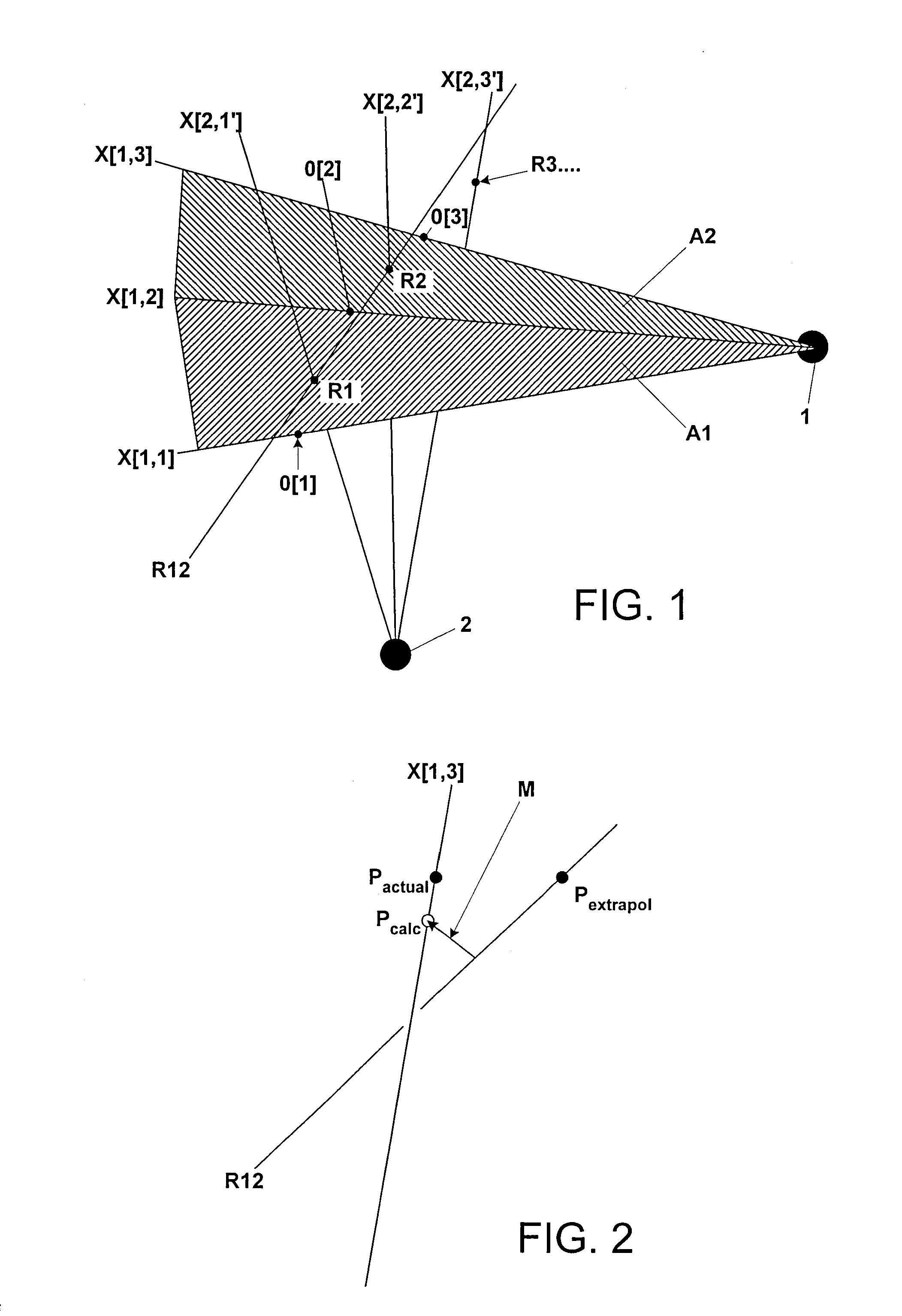
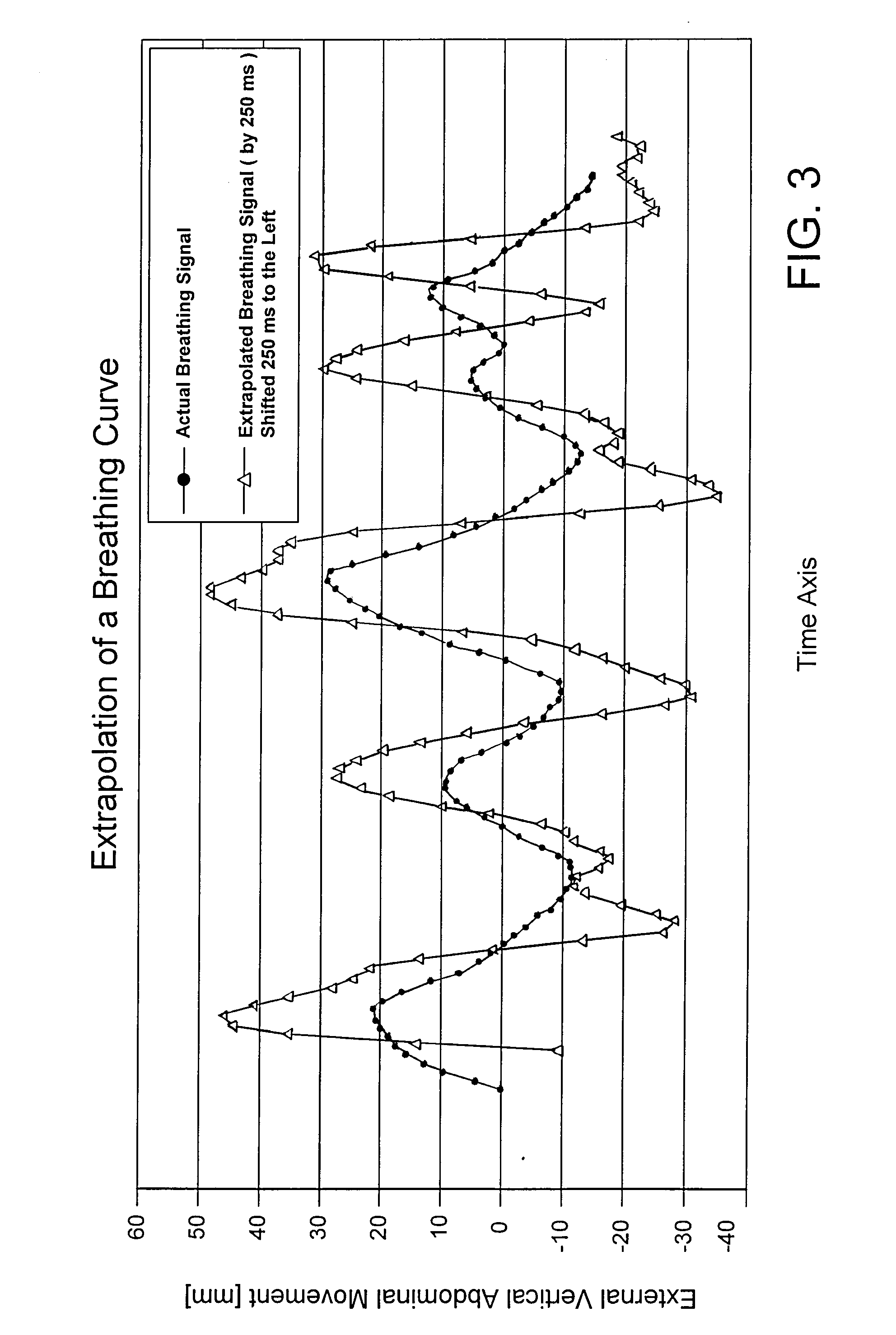
Non-diagnostic stereoscopic x-ray tracking of moving objects in the context of radiotherapy and radiosurgery, with time-offset image recording
ActiveUS7400700B2Avoid damaging healthy tissueSpecifically irradiateX-ray/infra-red processesSterographic imagingSoft x rayRadiosurgery
A non-diagnostic, stereoscopic x-ray tracking apparatus and method for tracking moving objects in the context of radiotherapy and radiosurgery includes using two x-ray tubes to alternately and repeatedly record x-ray images of an object along two different viewing lines through the target area of an irradiating apparatus. The viewing lines intersect at a known angle, wherein an extrapolated object trajectory is ascertained by determining surfaces and intersecting points. Further, a minimum transversal from the object trajectory onto a current viewing line is ascertained, wherein the three-dimensional position of the tracked object is approximated at the point at which the object trajectory meets the viewing line.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material based on dual phase change and preparation method thereof
PendingUS20210324254A1Reduce surface temperatureReduce radiant energyPretreated surfacesCamouflage devicesRoscoeliteNanoparticle coating
A dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material based on dual phase change is a VO2 / mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer composite material composed of a VO2 nanoparticle coating and a mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer, wherein the mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer consists of stearic acid and a vanadium-extracted mica substrate in a mass ratio of 3-5:5-7. The composite material based on dual phase change is prepared by extracting vanadium from vanadium mica using a roasting and acid leaching process to prepare VO2 nanoparticles and a vanadium-extracted mica, embedding a phase change functional body into the vanadium-extracted mica as a support substrate to prepare a mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer, and coating the VO2 nanoparticles on the mica-based phase change thermal storage thin layer. The dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material can synergistically reinforce thermal infrared stealth performance.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Intramedullary pin tracking
ActiveUS8382759B2Minimizing experience of patientPrecise NavigationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisIntramedullary rodReference device
A tracking device for an intramedullary pin whose spatial position is determined and / or tracked in image-guided surgery, including a reference device at a proximal end of the intramedullary pin and a medical navigation system which locates the reference device and determines the orientation of the intramedullary pin from the proximal end. A deformation detection device detects deformations of the intramedullary pin and communicates the deformations to the navigation system. Also provided is a tracking method for determining or tracking the spatial position of an intramedullary pin in image-guided surgery, and to an intramedullary pin that includes a deformation detection device.
Owner:BRAINLAB
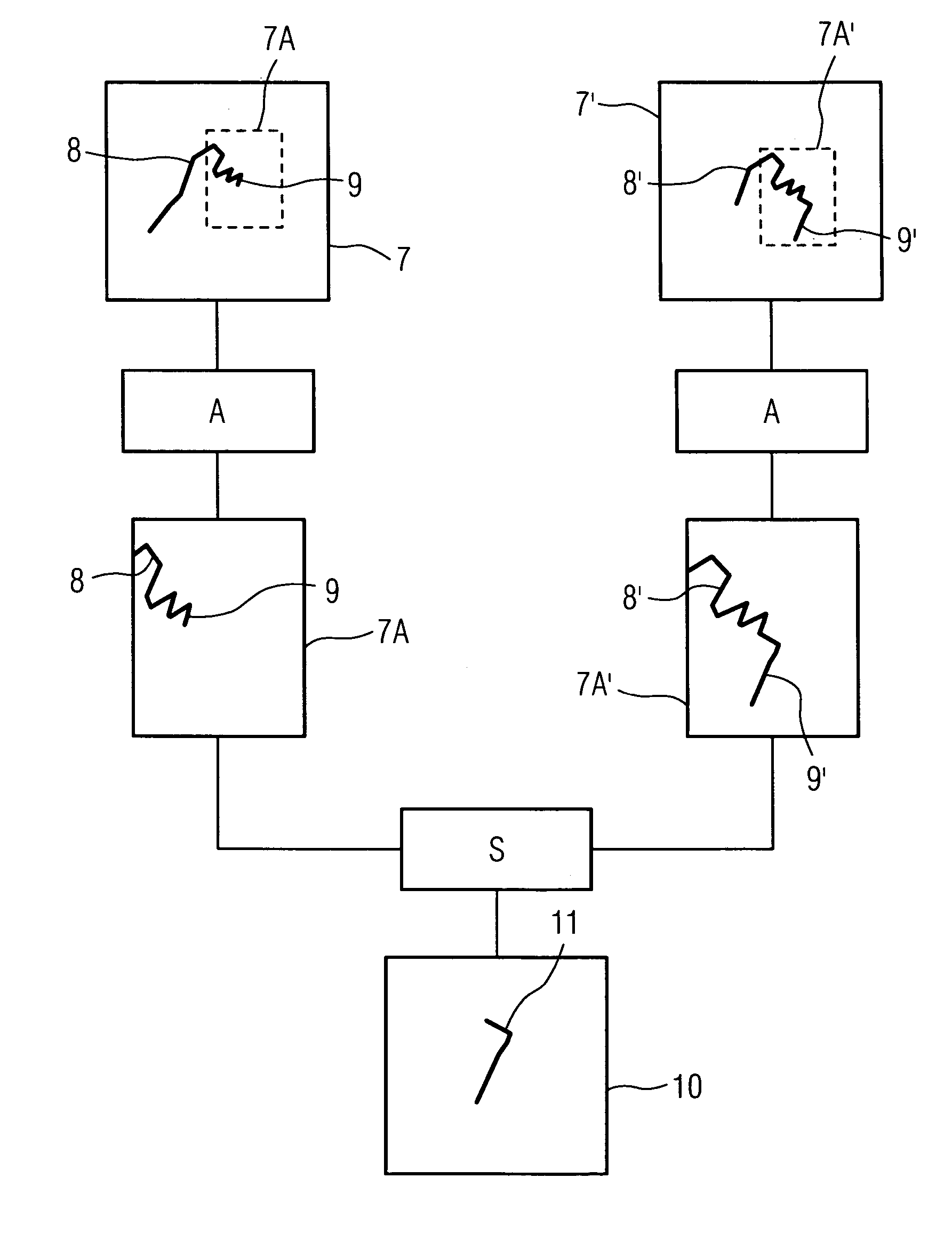
Method for ascertaining the position of a medical instrument in a body
InactiveUS20090326369A1Small sizeReduce radiation loadSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgeryBlood vessel
The present invention relates to a method for ascertaining the position of the head of a medical instrument in a vascular system, wherein the instrument can be inserted into the vascular system of a body and describes a path at least partially inside the vascular system, and the position of the instrument head is calculated from structural data, length data and the relative position between a reference point and the vascular system, wherein the instrument is guided past the reference point, the structural data represents the structure of the vascular system, and the length data represents the length of the path between the reference point and the instrument head.
Owner:BRAINLAB
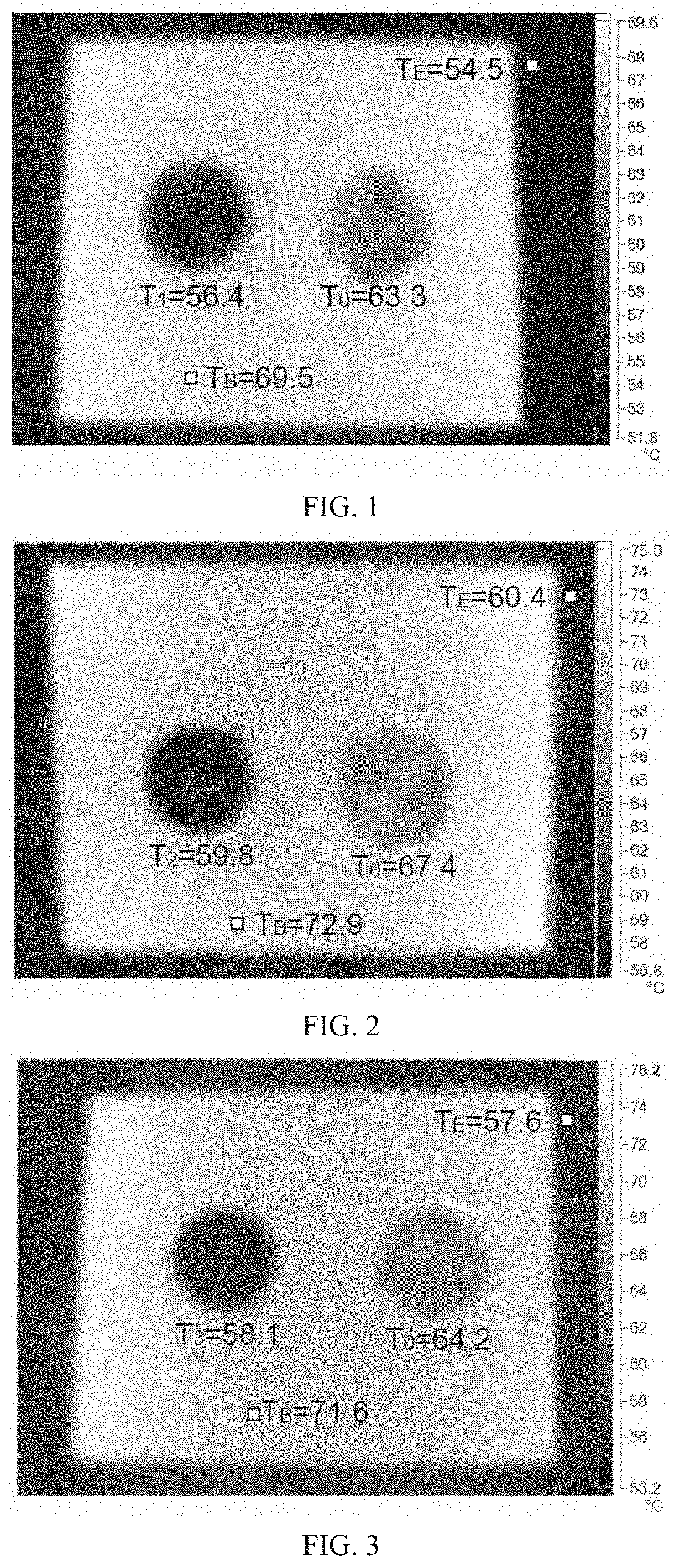
Scanning of a human body part with high-energy radiation emitted by the body part
ActiveUS20170020467A1Reduce radiation loadLow costRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsHigh energyCompression device
A scanner for scanning a body part of a human, such as, for example, a breast of a woman includes a supporting part for the upper body of a human, a receiving space for the body part to be scanned, possibly a compression device for pressing against the body part introduced into the receiving space, and a camera which is arranged to form an image of the body part introduced into the receiving space and pressed against by the compression device, with the aid of high-energy radiation emitted by the body part. The camera includes a collimator having a movable collimator part which has an incident surface facing towards the receiving space. The collimator defines and delimits an astigmatic, two-dimensional collection of radiation channels for the high-energy radiation.
Owner:MILABS BV
Radiography device for recording dynamic processes and associated recording method
ActiveUS20070286334A1Reduce loadReduce radiation loadRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusFlat detectorX-ray
There is described a radiography device for recording dynamic processes and an associated recording method. The radiography arrangement is used to examine patients using an x-ray source, a digital flat detector with a single shot recording function and an operating console for controlling and recording purposes, with the flat detector also being able to display an image sequence at a rate of up to 5 Hertz, which allows the positioning of the region to be examined or the monitoring of pseudo-interventional interventions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Non-diagnostic stereoscopic x-ray tracking of moving objects in the context of radiotherapy and radiosurgery, with time-offset image recording
ActiveUS20070230655A1Avoid damaging healthy tissueSpecifically irradiateX-ray/infra-red processesSterographic imagingRadiosurgerySoft x ray
A non-diagnostic, stereoscopic x-ray tracking apparatus and method for tracking moving objects in the context of radiotherapy and radiosurgery includes using two x-ray tubes to alternately and repeatedly record x-ray images of an object along two different viewing lines through the target area of an irradiating apparatus. The viewing lines intersect at a known angle, wherein an extrapolated object trajectory is ascertained by determining surfaces and intersecting points. Further, a minimum transversal from the object trajectory onto a current viewing line is ascertained, wherein the three-dimensional position of the tracked object is approximated at the point at which the object trajectory meets the viewing line.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Scanning of a human body part with high-energy radiation emitted by the body part
ActiveUS9610051B2Reduce radiation loadLow costRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsHuman bodyHigh energy
A scanner for scanning a body part of a human, such as, for example, a breast of a woman includes a supporting part for the upper body of a human, a receiving space for the body part to be scanned, possibly a compression device for pressing against the body part introduced into the receiving space, and a camera which is arranged to form an image of the body part introduced into the receiving space and pressed against by the compression device, with the aid of high-energy radiation emitted by the body part. The camera includes a collimator having a movable collimator part which has an incident surface facing towards the receiving space. The collimator defines and delimits an astigmatic, two-dimensional collection of radiation channels for the high-energy radiation.
Owner:MILABS BV
A dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material based on double phase transition and its preparation method
ActiveCN109181650BGive full play to the temperature control abilityActive and quick responsePretreated surfacesCamouflage devicesRoscoeliteNanoparticle coating
The invention discloses a dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material and a preparation method based on double phase transition; especially a VO 2 / Mica-based phase change heat storage thin-layer composite material and preparation method; belongs to the technical field of thermal infrared stealth material preparation; the VO 2 / Mica-based phase change heat storage thin-layer composite material is made of VO 2 The nanoparticle coating is composed of a mica-based phase-change heat storage thin layer, and the mica-based phase-change heat storage thin layer is composed of stearic acid and a vanadium-extracted mica matrix in a mass ratio of 3-5:5-7. The present invention adopts roasting acid leaching process to extract vanadium from vanadium mica and prepare VO 2 Nanoparticles, the mica after vanadium extraction is used as the support matrix to embed the phase change functional body to prepare the mica-based phase-change heat storage thin layer, and the mica-based phase-change heat storage thin layer is coated with VO 2 Nanoparticles, made double phase change composite material. The dynamic thermal infrared stealth composite material based on the double phase transition of the present invention can realize synergistic enhancement of thermal infrared stealth performance, and can be applied to thermal infrared stealth technology.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Automobiles Having a Radiant Barrier
ActiveUS20110013272A1Improve efficiencyHigh light transmittanceCovering/liningsMirrorsControl systemBlack body
An automobile or vehicle having a high efficiency solar control system is provided. The automobile may have a painted surface and a film mounted to its exterior side. The film may reflect solar radiation in the near and mid infrared ranges yet allow high transmission of light in the visible range such that the painted panel may be seen. The film may have a layer of silver which reflects the solar radiation in the near and mid infrared ranges. Since the silver is susceptible to oxidation and turns the silver into a black body which absorbs the near and mid infrared radiation, the film may be designed to slow the rate of oxidation of the silver layer to an acceptable level. The silver layer may be sandwiched between the glass which does not allow oxygen to diffuse there through and reach the layer of silver and a stack of sacrificial layers having a certain thickness which slows down the rate of oxygen diffusion to an acceptable level.
Owner:WILSON STEPHEN S +2
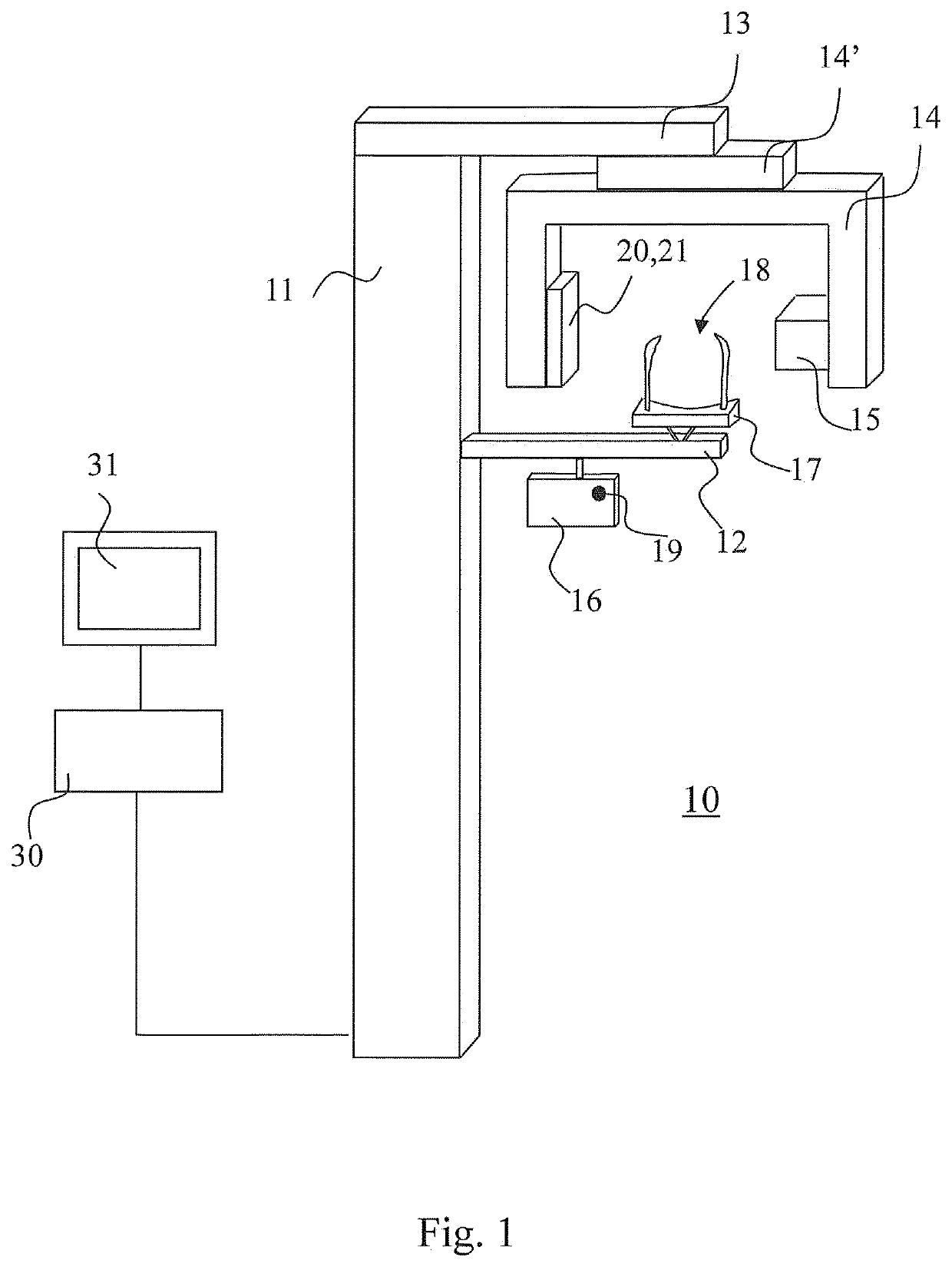
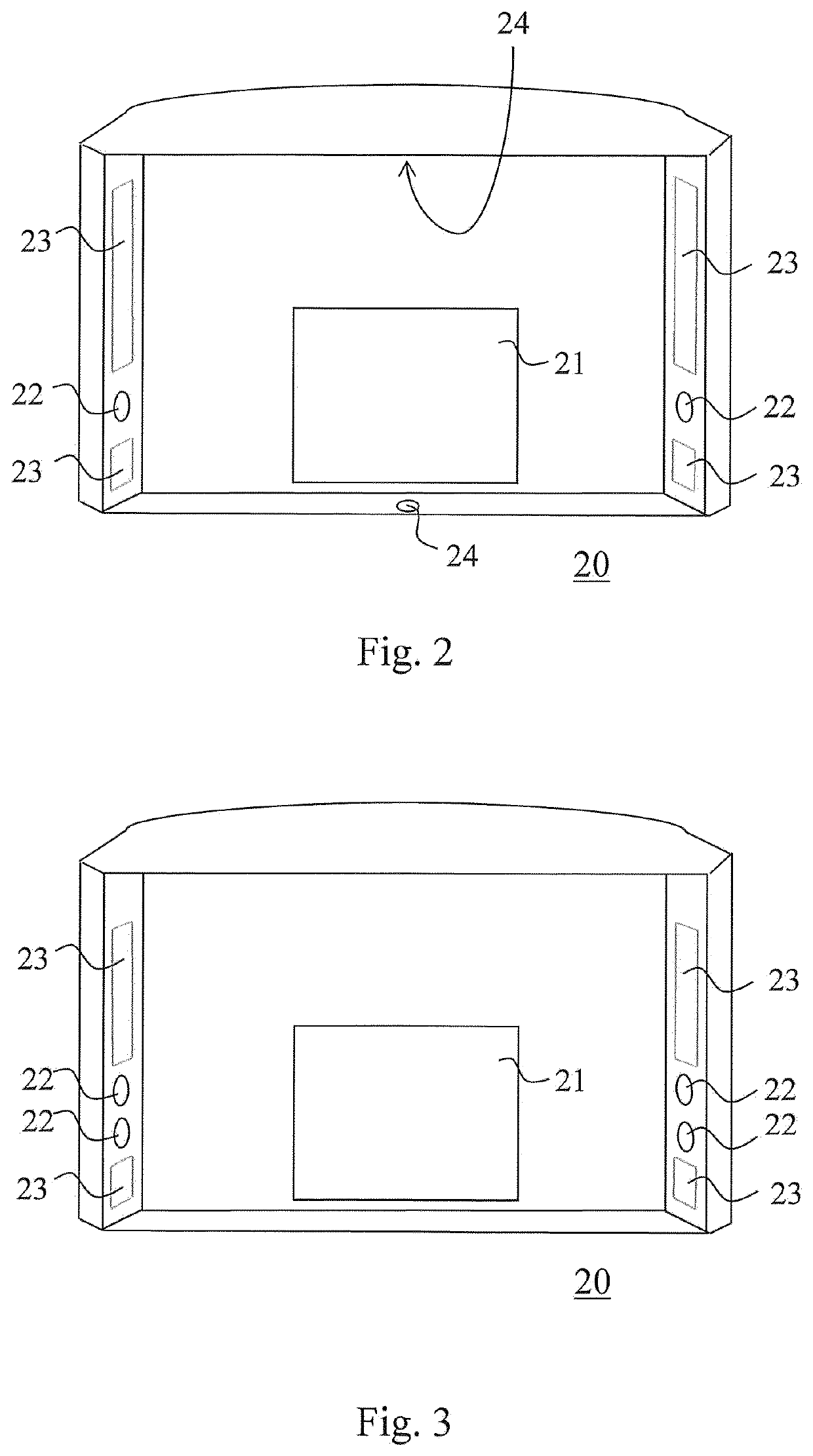
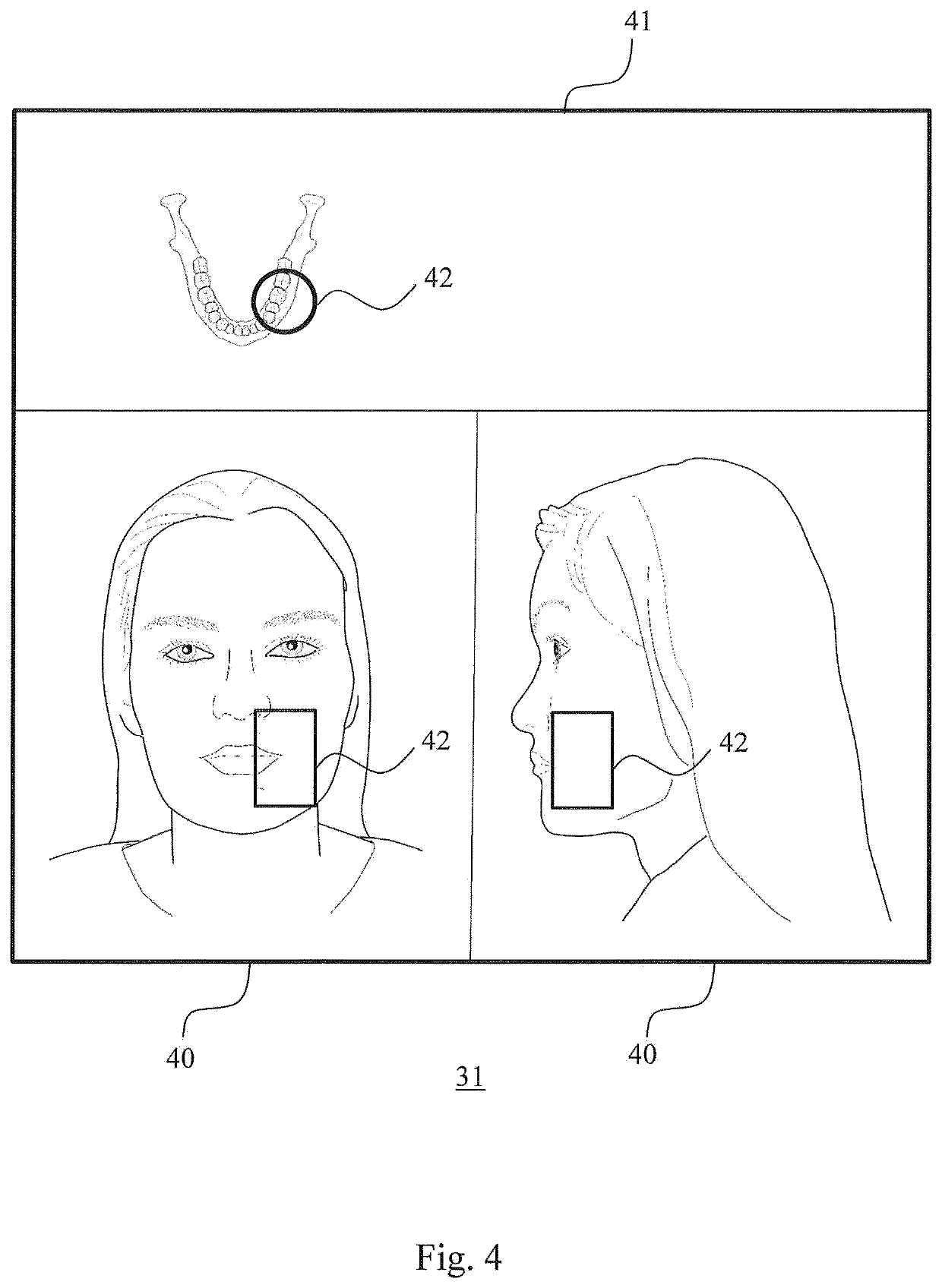
Computed tomography and positioning of a volume to be imaged
ActiveUS20200085387A1Reduce radiation loadComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical structuresComputed tomography
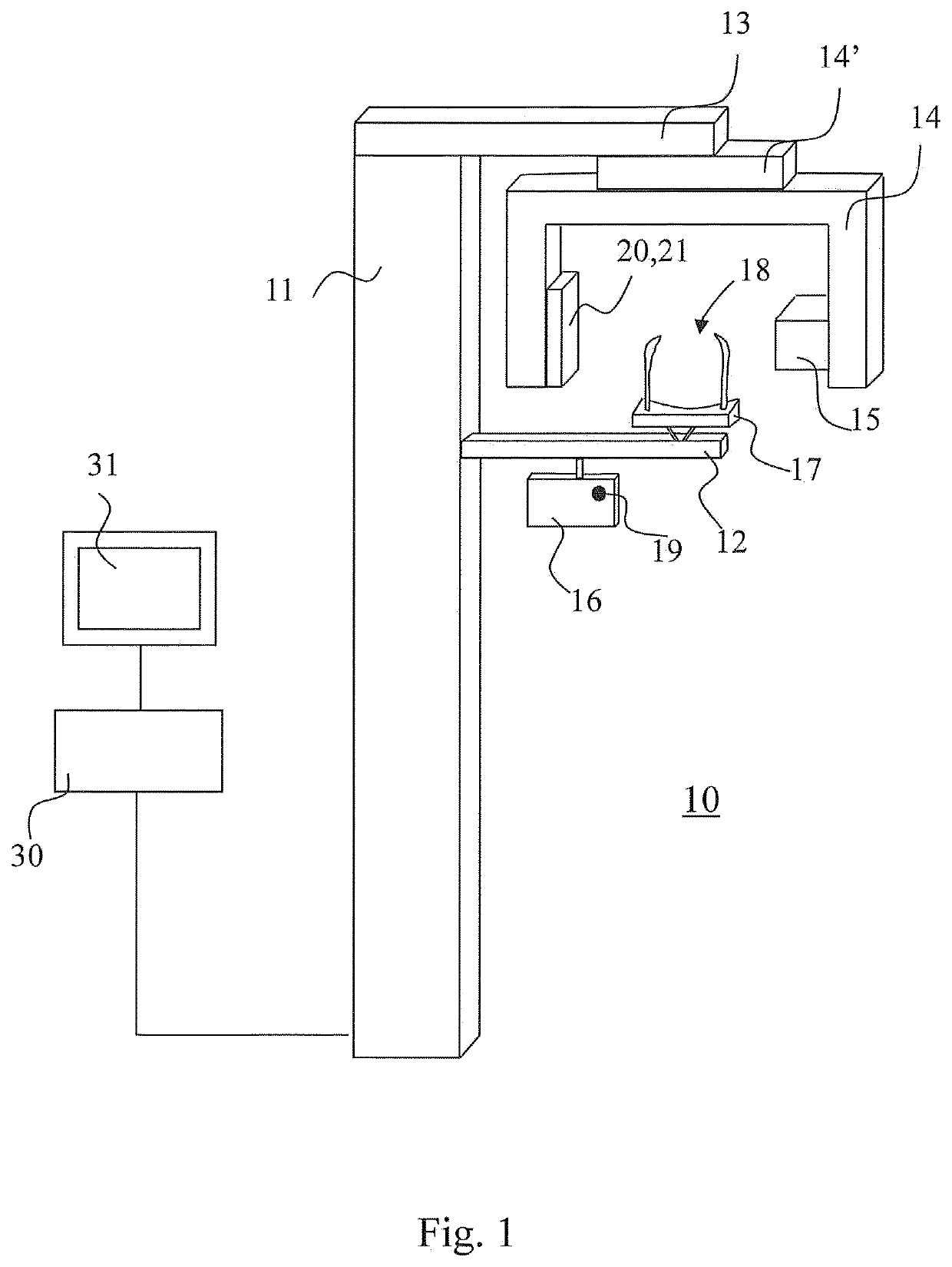
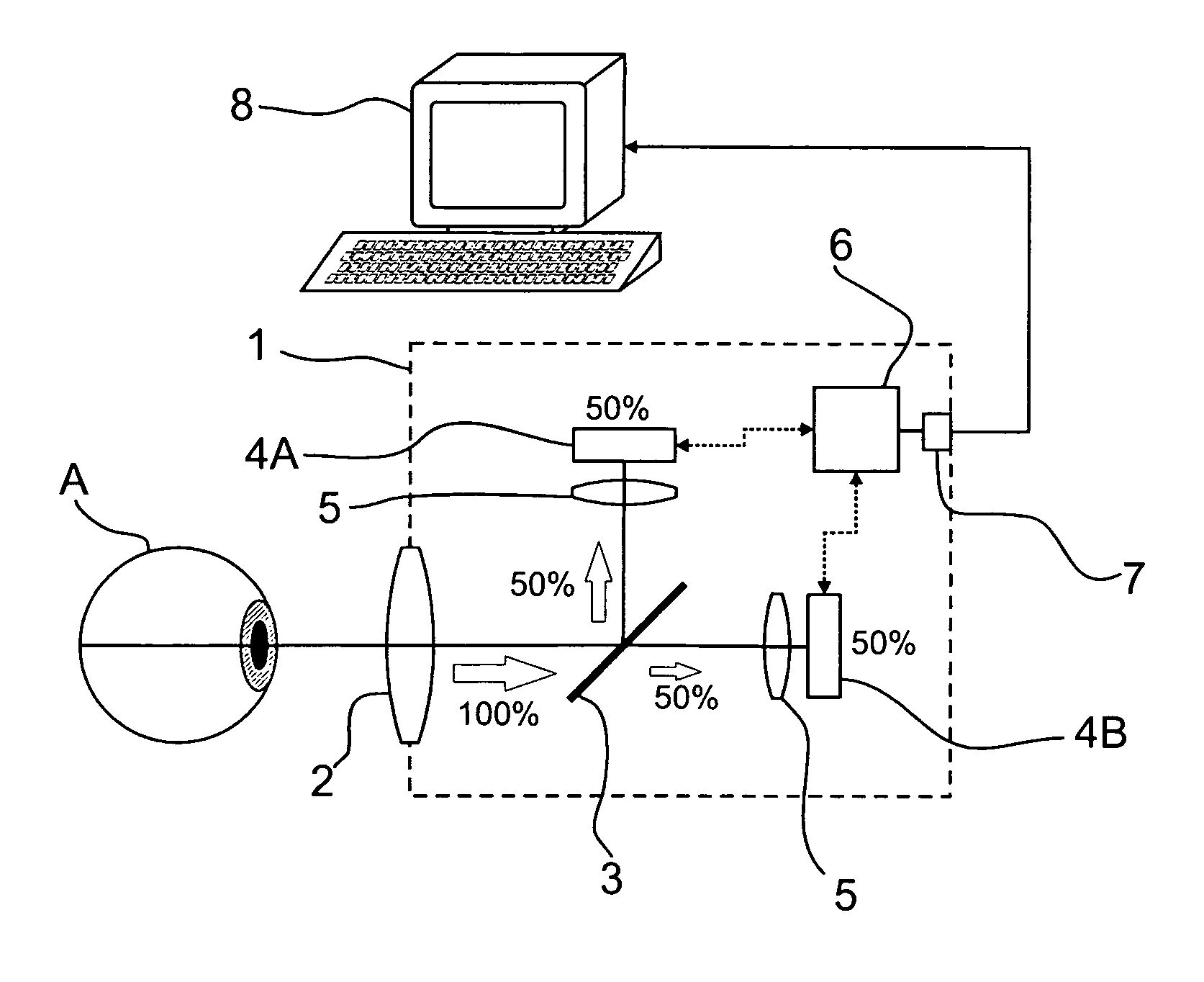
The invention relates to positioning a volume to be imaged for computed tomography imaging. According to the invention, at least two optical cameras (22) are used for taking a photo or for live imaging an anatomy from different directions. A volume positioning indicator (42) is shown in connection with these images, the volume positioning indicator (42) indicating the location of the volume within the area imaged by the cameras (22) to get imaged by the computed tomography imaging apparatus (10).
Owner:PLANMECA
Computed tomography and positioning of a volume to be imaged
ActiveUS11259761B2Reduce radiation loadComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical structuresComputed tomography
The invention relates to positioning a volume to be imaged for computed tomography imaging. According to the invention, at least two optical cameras (22) are used for taking a photo or for live imaging an anatomy from different directions. A volume positioning indicator (42) is shown in connection with these images, the volume positioning indicator (42) indicating the location of the volume within the area imaged by the cameras (22) to get imaged by the computed tomography imaging apparatus (10).
Owner:PLANMECA
Arrangement and method for generating images with expanded dynamics
ActiveUS8542273B2Reduce radiation loadIncrease motivationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamDynamic range
An ophthalmic device and an arrangement for generating images with expanded dynamic range and a corresponding method for generating images with expanded dynamic range have at least one beamsplitter, in particular with an asymmetric splitting ratio, and at least two image sensors, wherein the image sensors are reflected into a common imaging beam path by the at least one beamsplitter.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Energy-saving window with vacuum layer combined with convection layer and installation and use method of energy-saving window
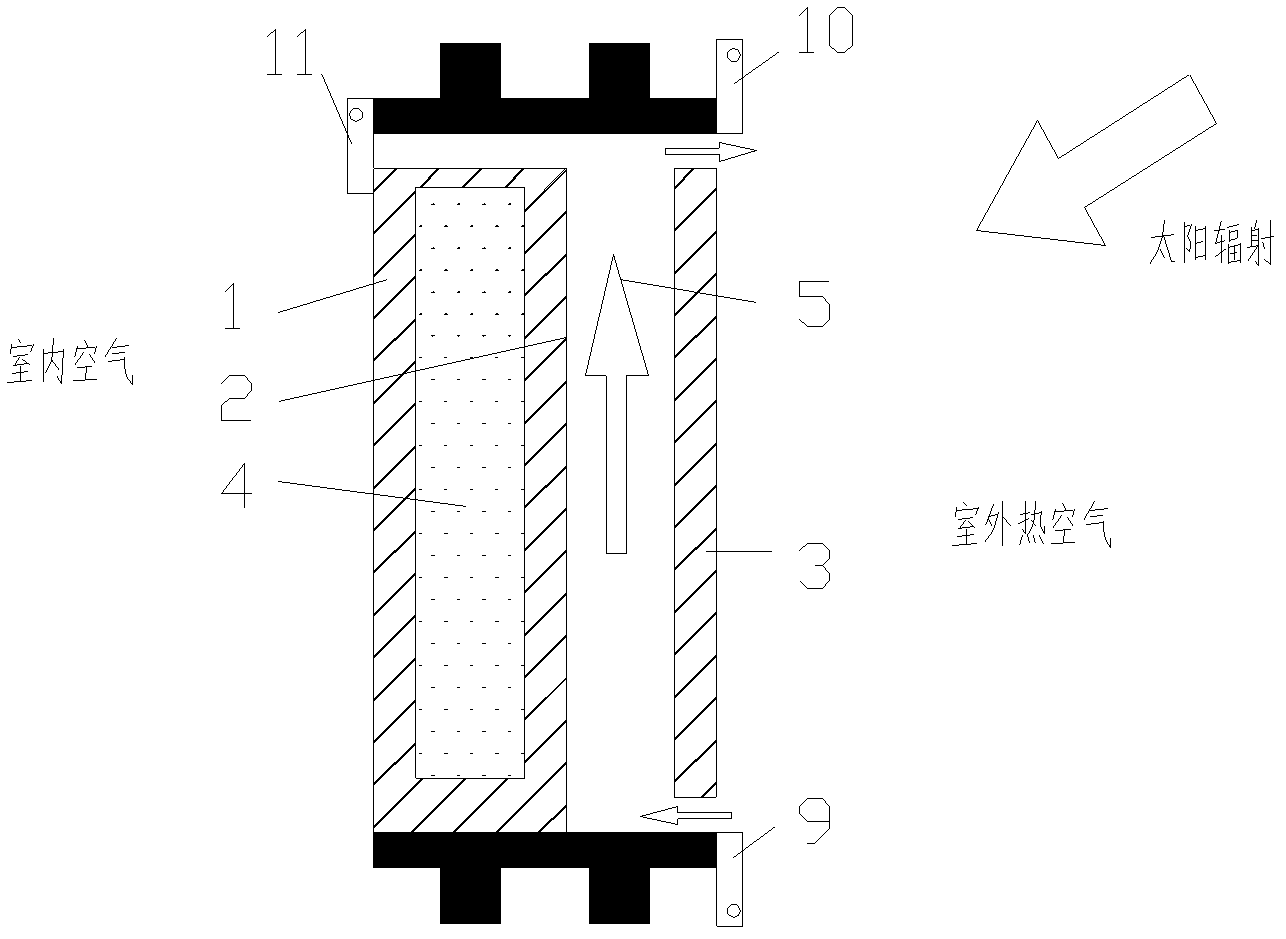
InactiveCN102518373BReduce radiationReduce radiation loadClimate change adaptationWindows/door improvementEngineeringEnergy conservation
The invention belongs to the field of energy conservation of buildings, and particularly relates to an energy-saving window with a vacuum layer combined with a convection layer and an installation and use method of the energy-saving window. The energy-saving window comprises vacuum interlayer outside glass, middle glass, convection interlayer outside glass, a vacuum interlayer and the ventilating convection layer. A vacuum interlayer upper ventilating pore groove and a vacuum interlayer upper ventilating pore groove opening and closing plate are arranged between an upper window frame and the upper portion of the vacuum interlayer; a convection interlayer upper ventilating pore groove and a convection interlayer upper ventilating pore groove opening and closing plate are arranged between the upper window frame and the upper portion of the convection interlayer outside glass; and a convection interlayer lower ventilating pore groove and a convection interlayer lower ventilating pore groove opening and closing plate are arranged between a lower window frame and the lower portion of the convection interlayer outside glass. Indoor all-year reasonable radiation, convection and vacuum heat insulation effects are realized by means of opening or closing the different ventilating pore grooves, so that the requirement of energy conservation of buildings is met.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process and arrangement for confocal microscopy
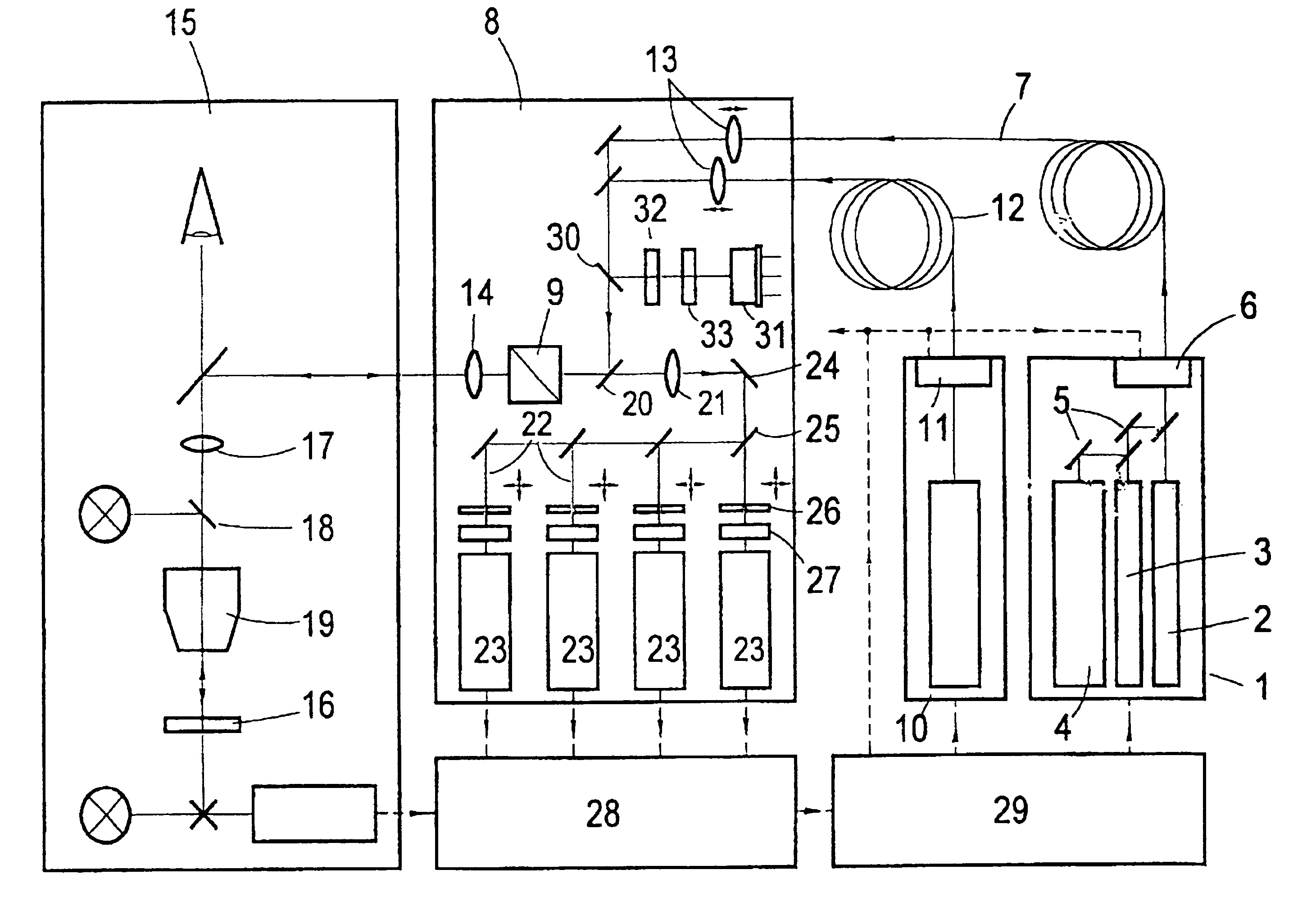
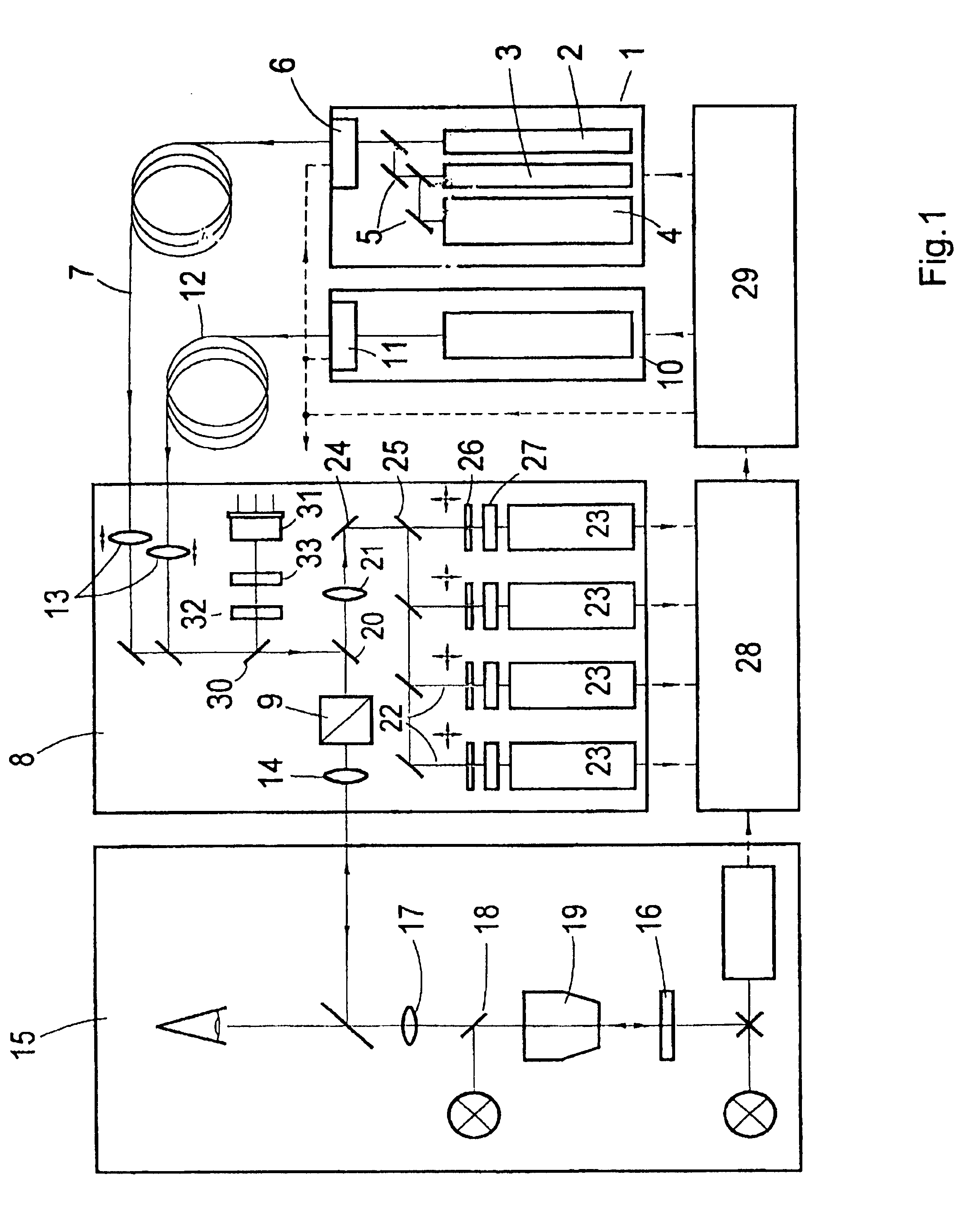
InactiveUSRE41666E1Precise image evaluationReduce radiation loadRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLaser scanning microscopeOptoelectronics
A process for confocal microscopy is disclosed in which laser light is coupled into a microscope beam path, directed successively with respect to time onto different locations of a specimen, and an image of the scanned plane is generated from the light reflected and emitted by the irradiated locations. A change in the spectral composition and in the intensity of light isare carried out during the deflection of the laser beam from location to location, while the deflection continues in an uninterrupted manner. In this way , so that at least two adjacent locations of the specimen located next to one another are acted upon by light with different spectral characteristics and by laser radiation of different intensity. By periodically interrupting the coupling in of the laser light during the deflection of the microscope beam path, it is made possible that only selected portions of the image field are acted upon by the laser radiation. A laser scanning microscope for carrying out this process is also disclosed. A laser scanning microscope for carrying out this process is also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com