Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62results about How to "High force density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
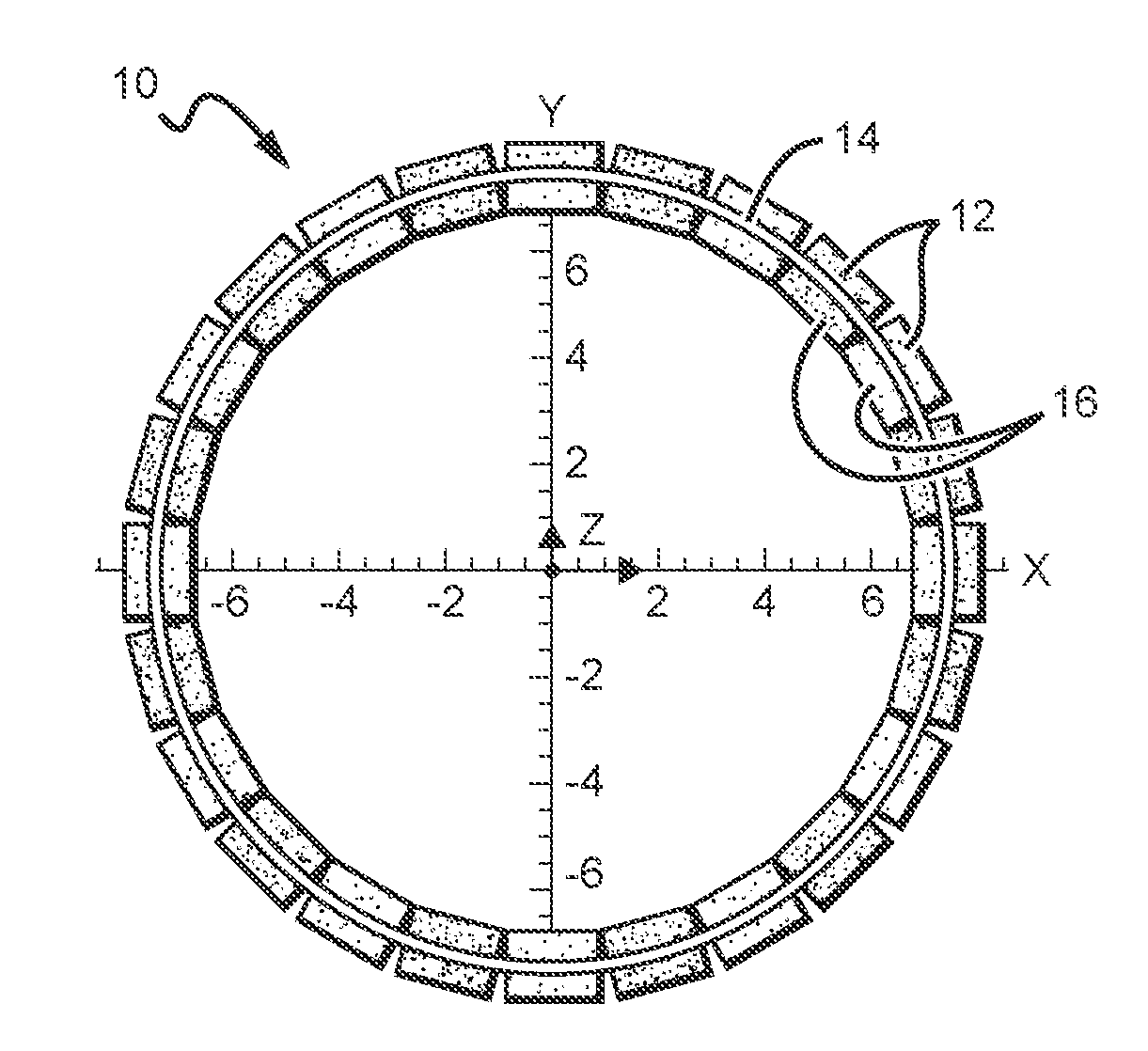
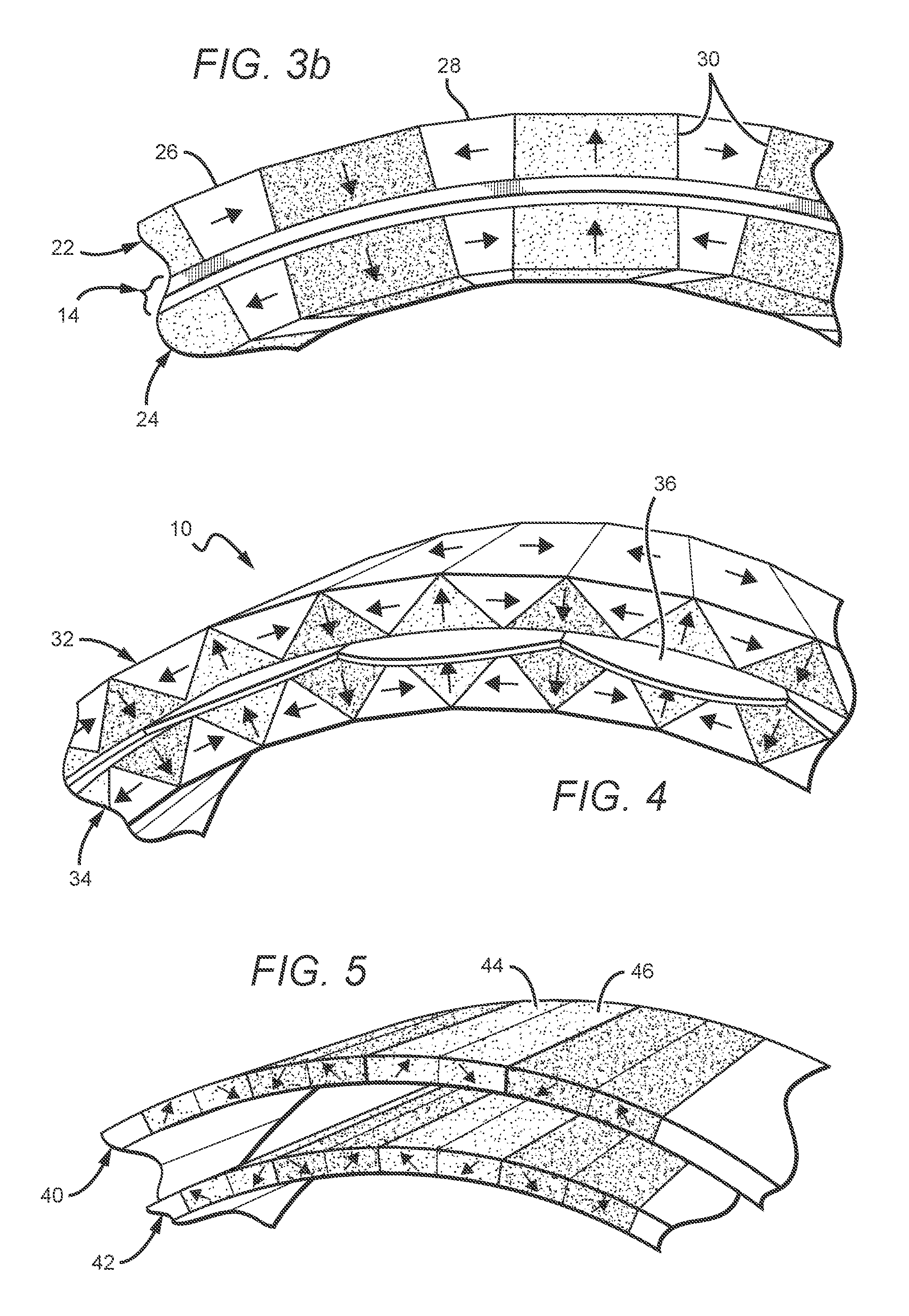
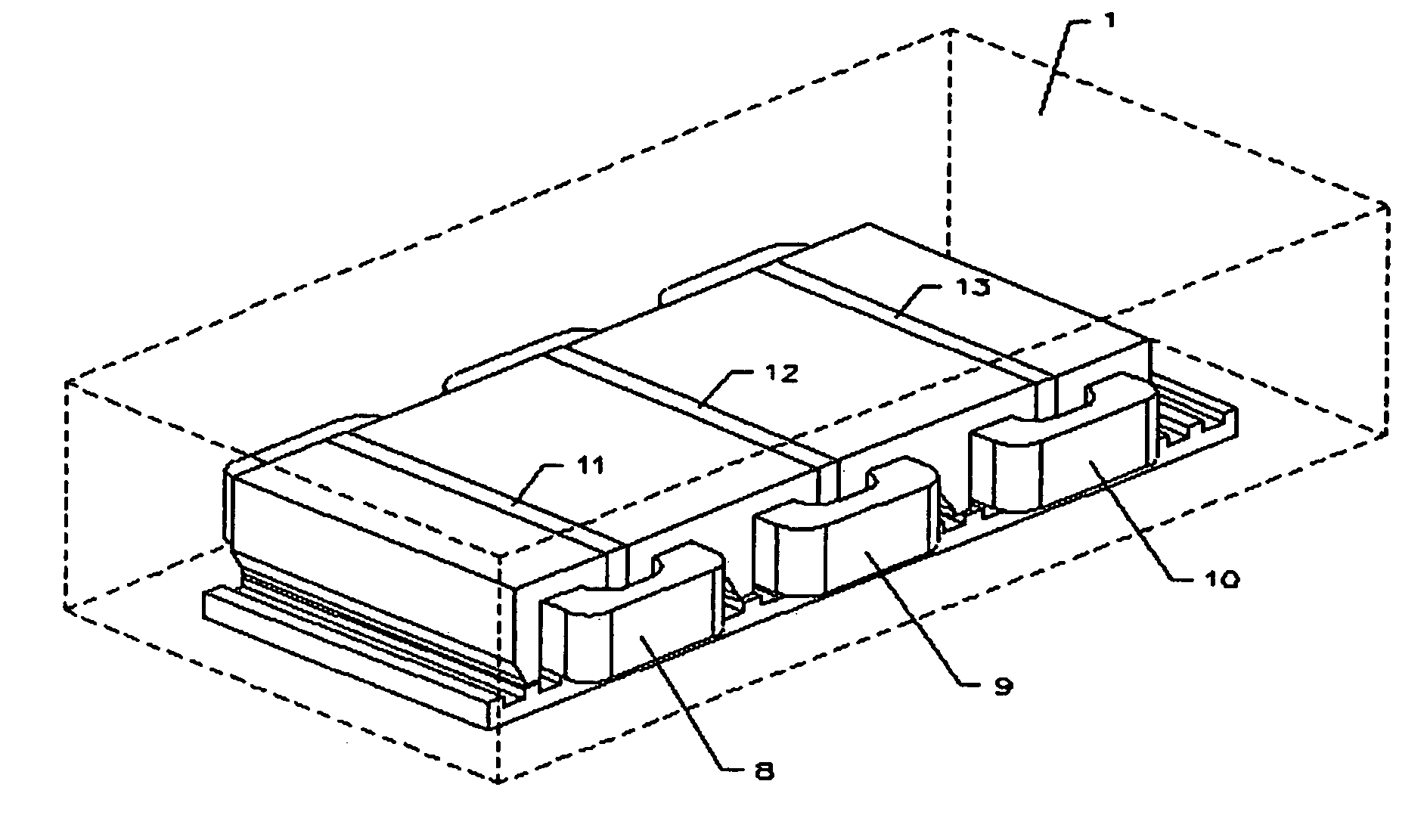
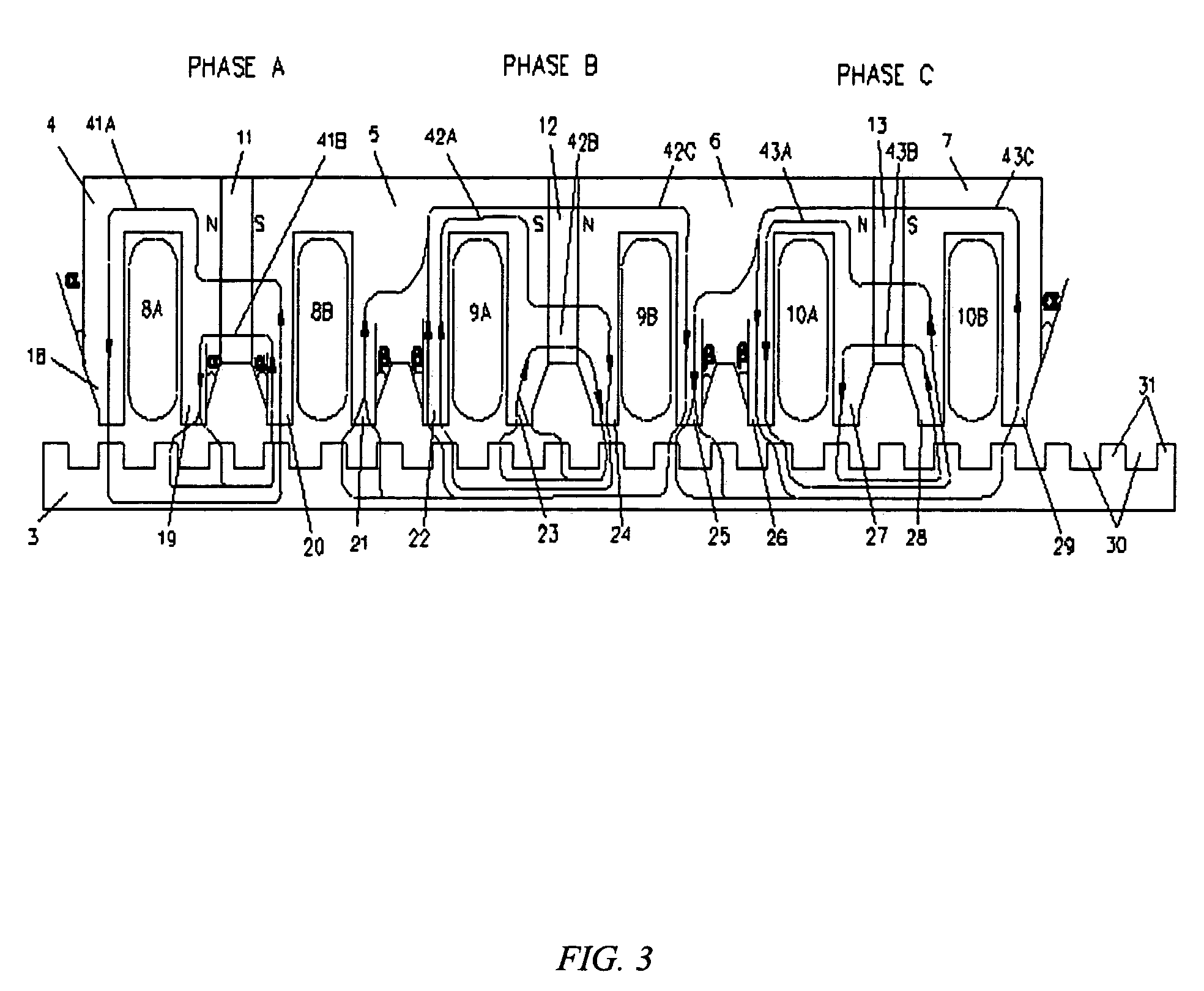
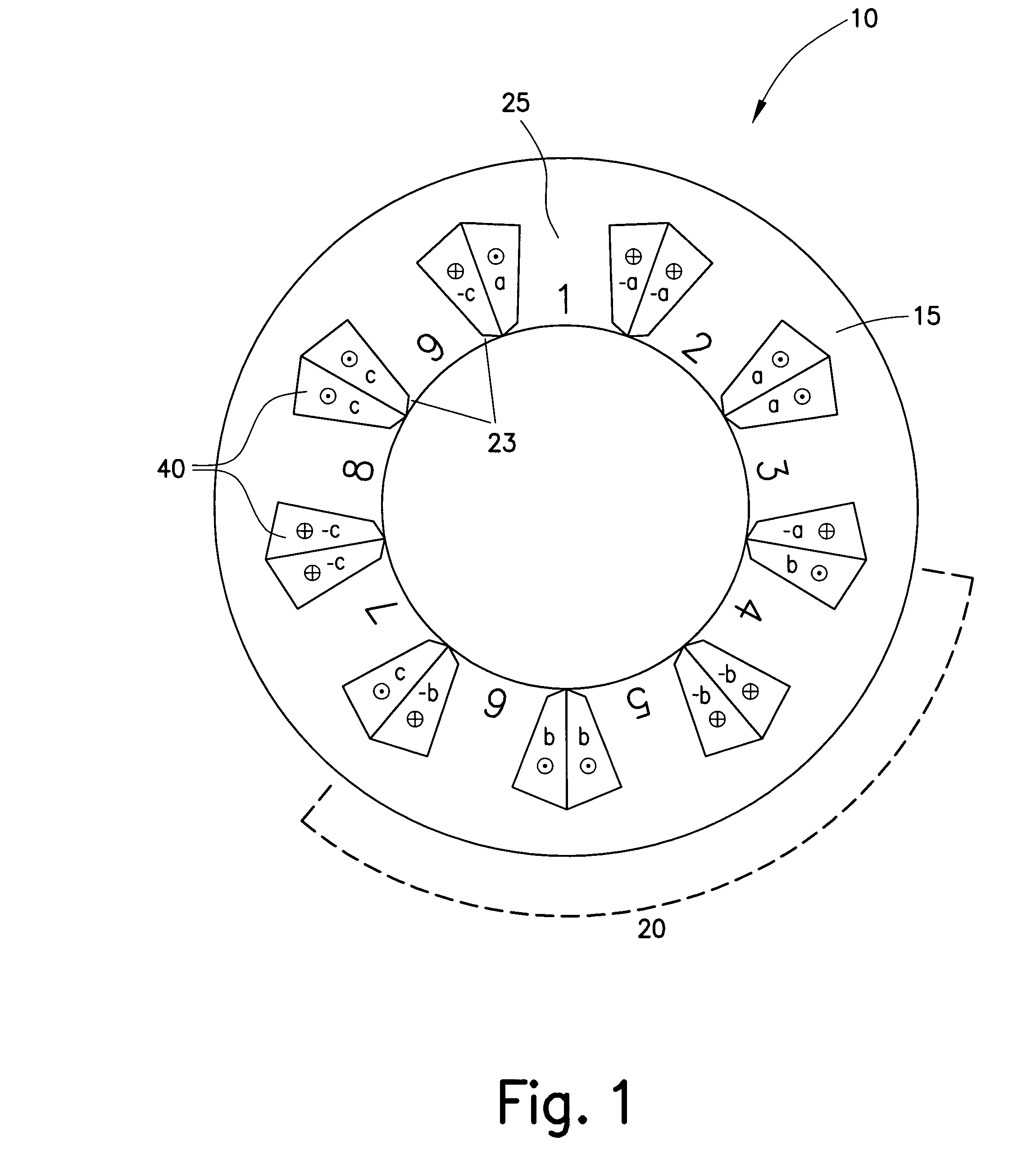
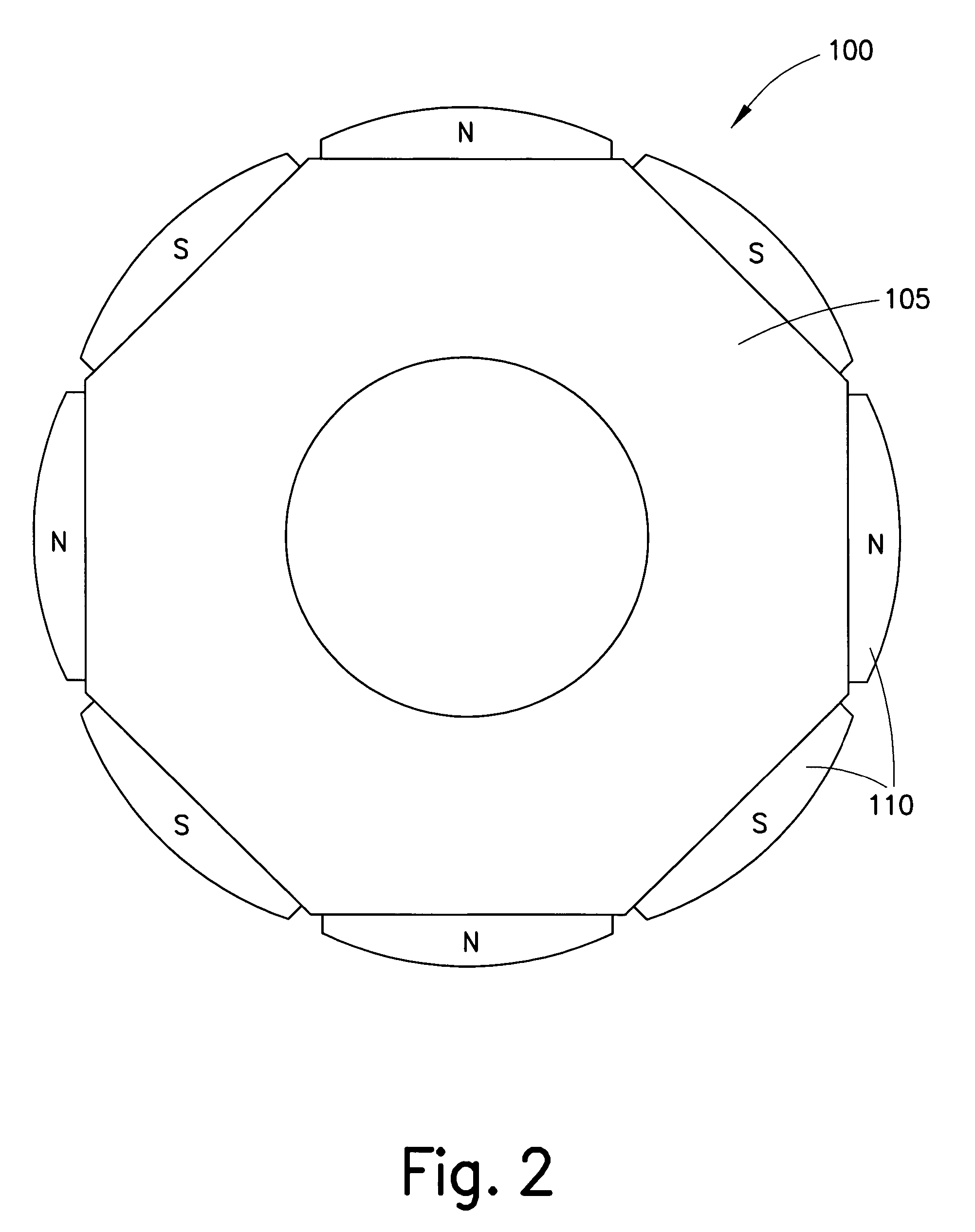
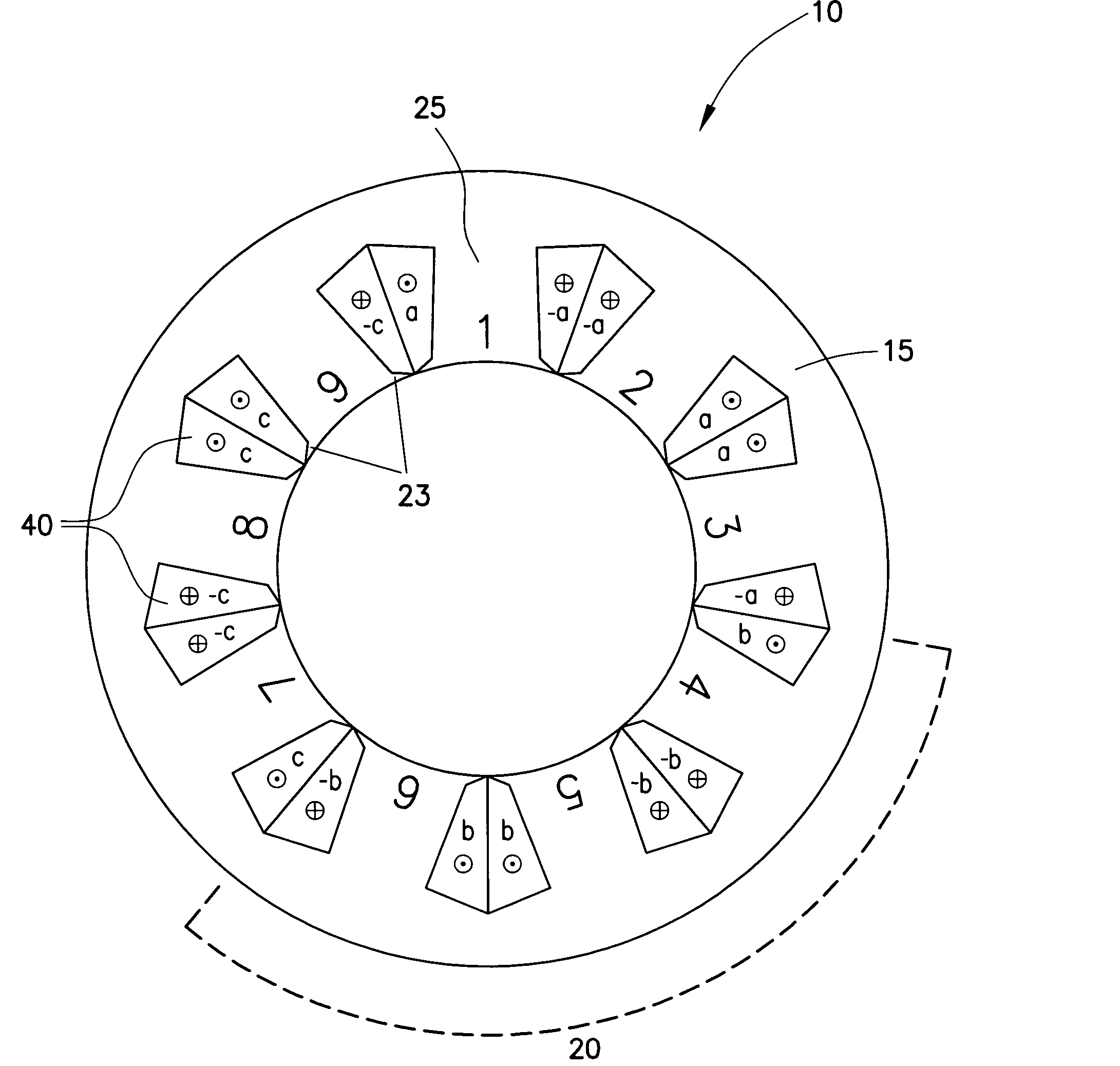
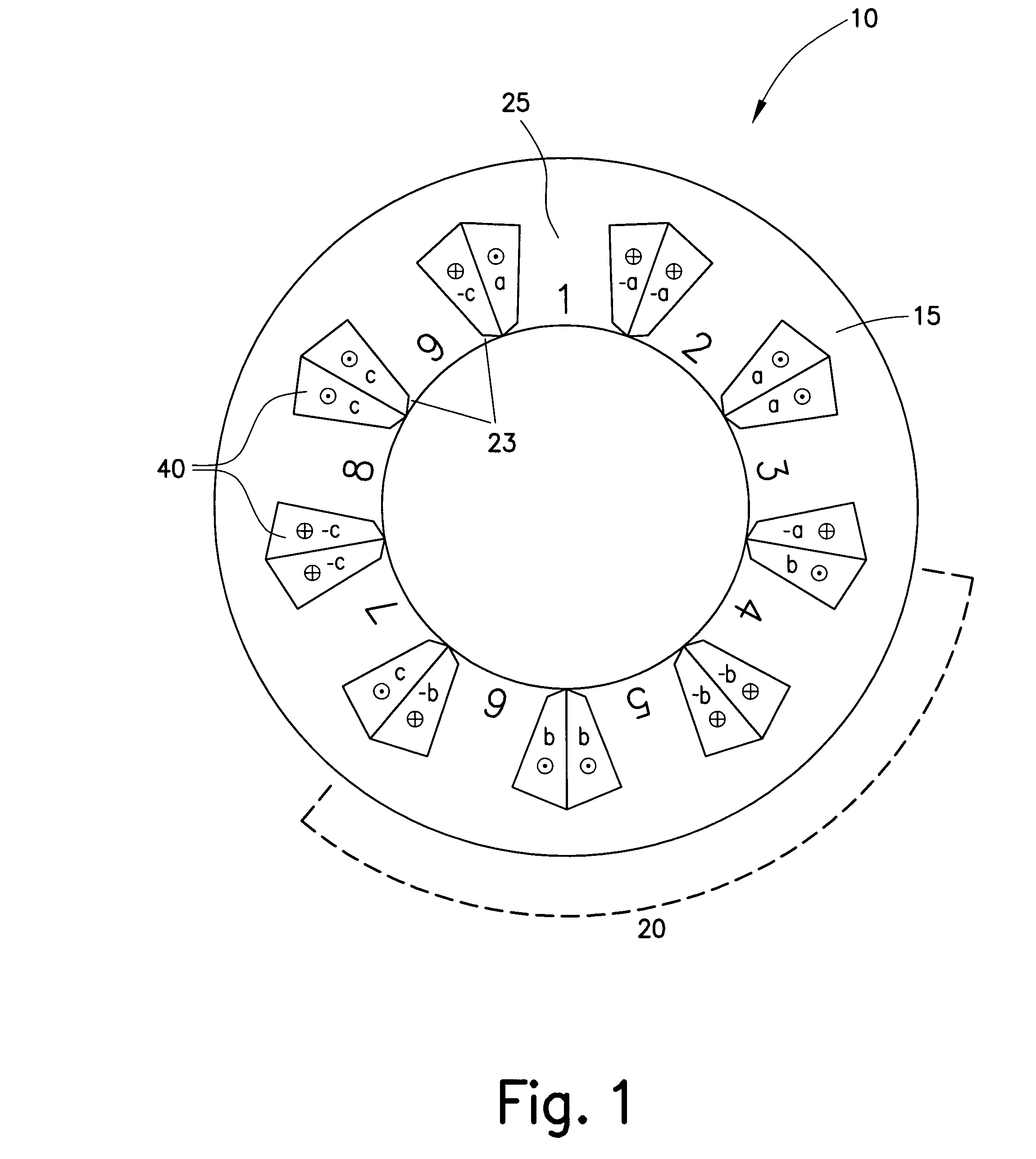
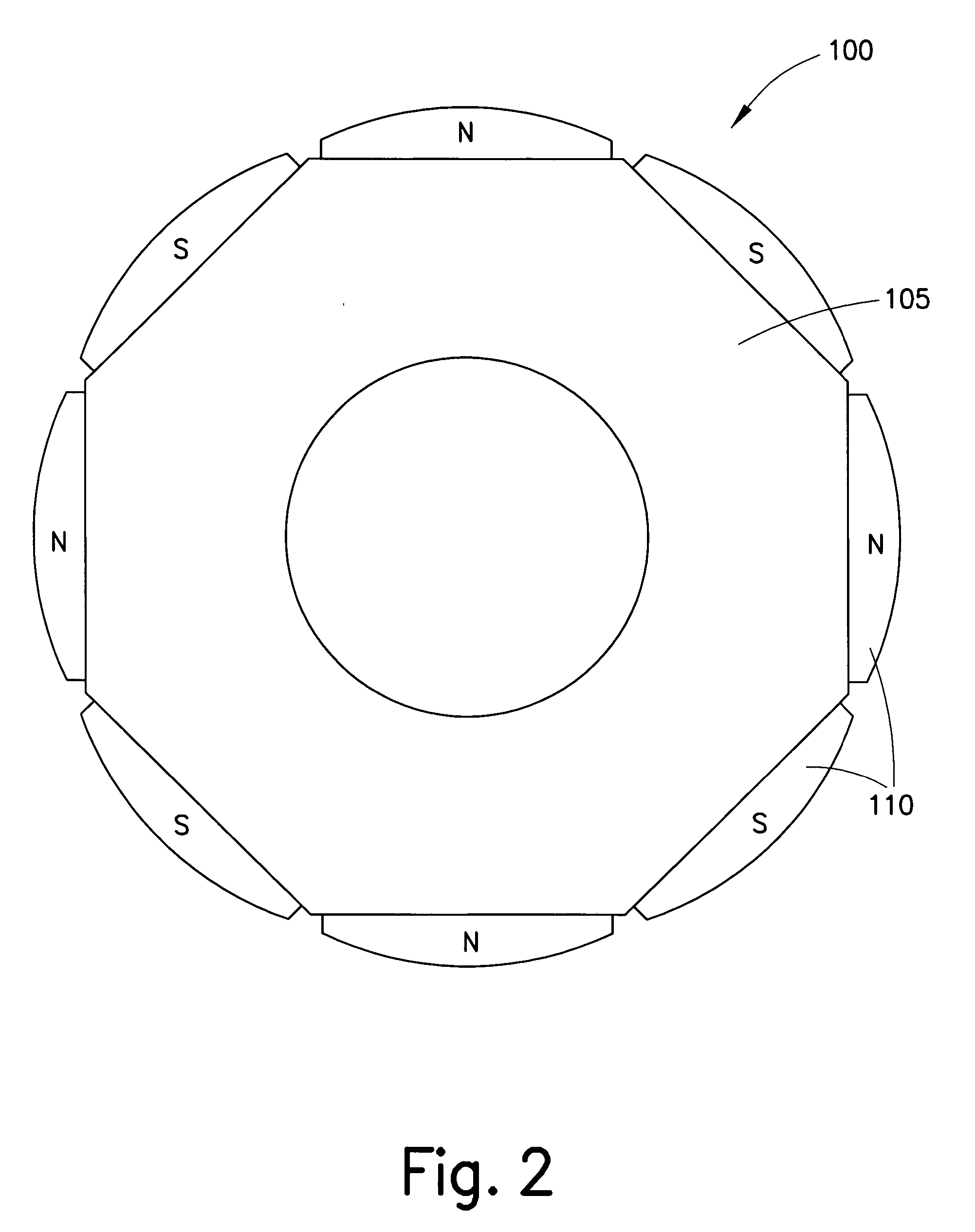
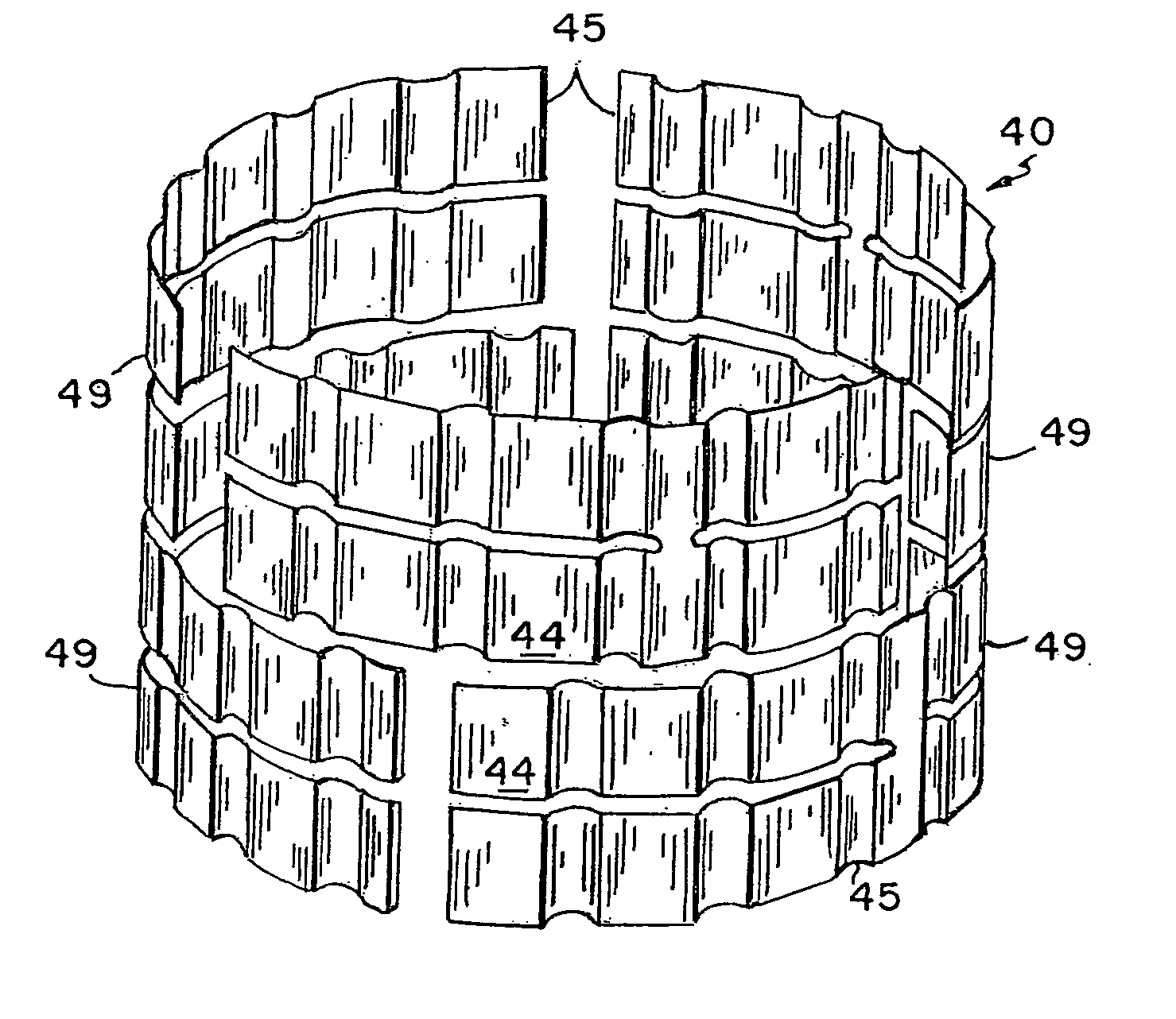
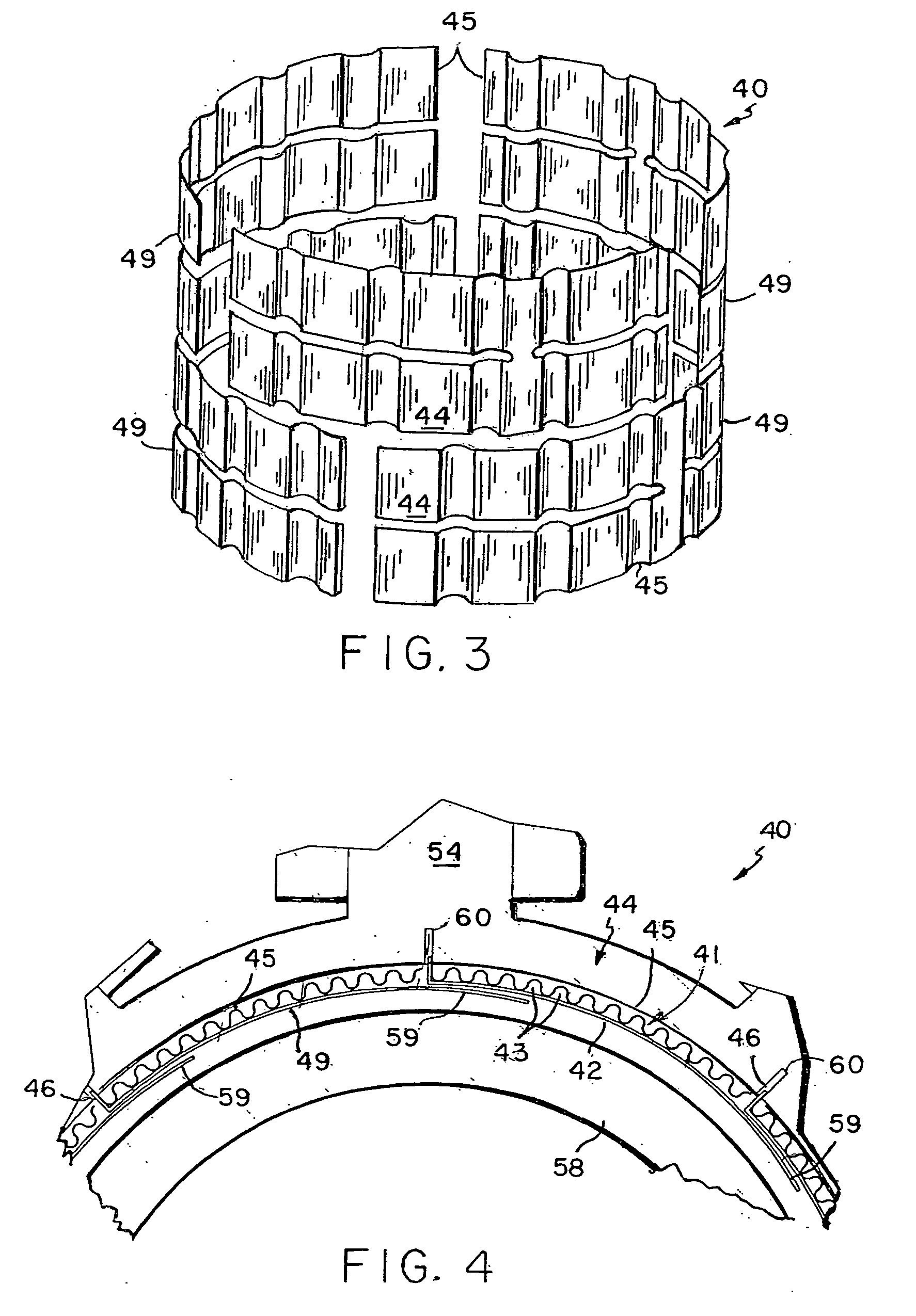
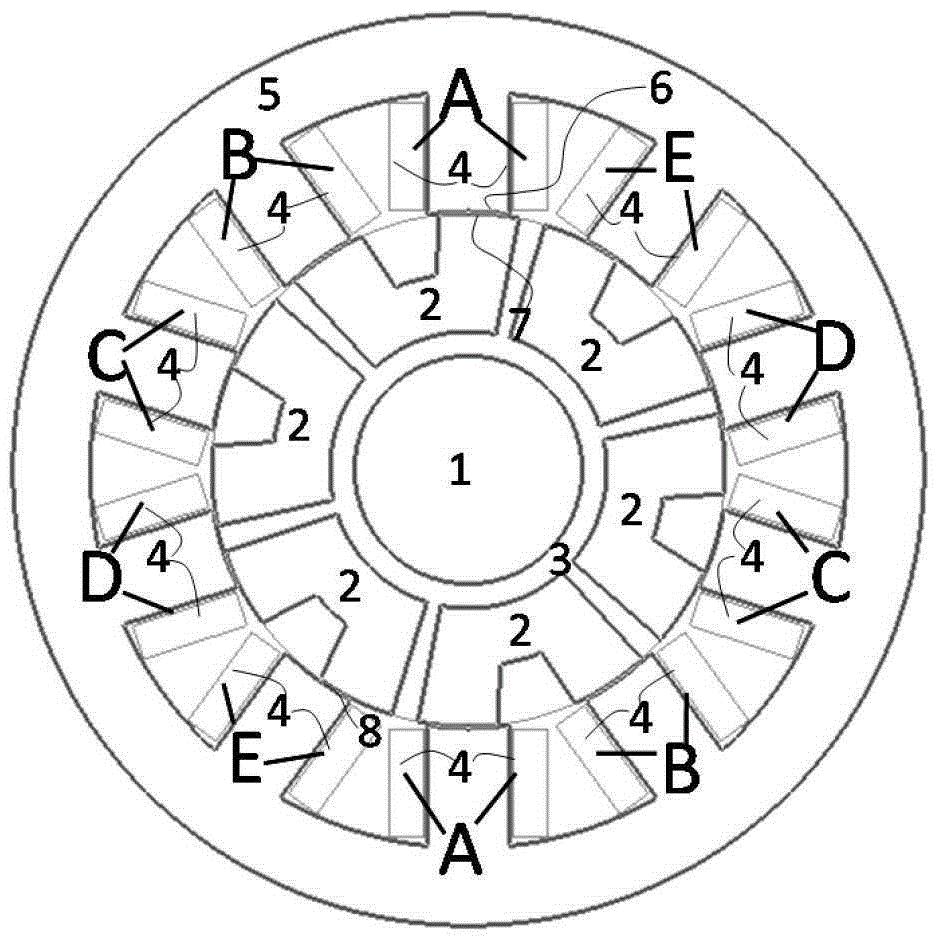
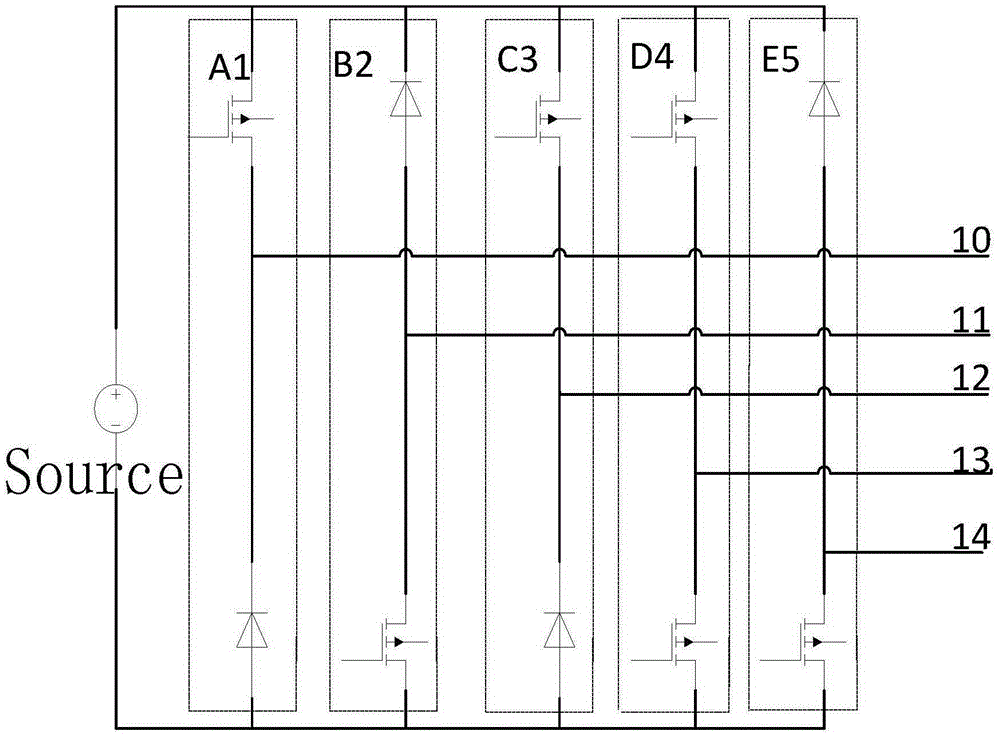
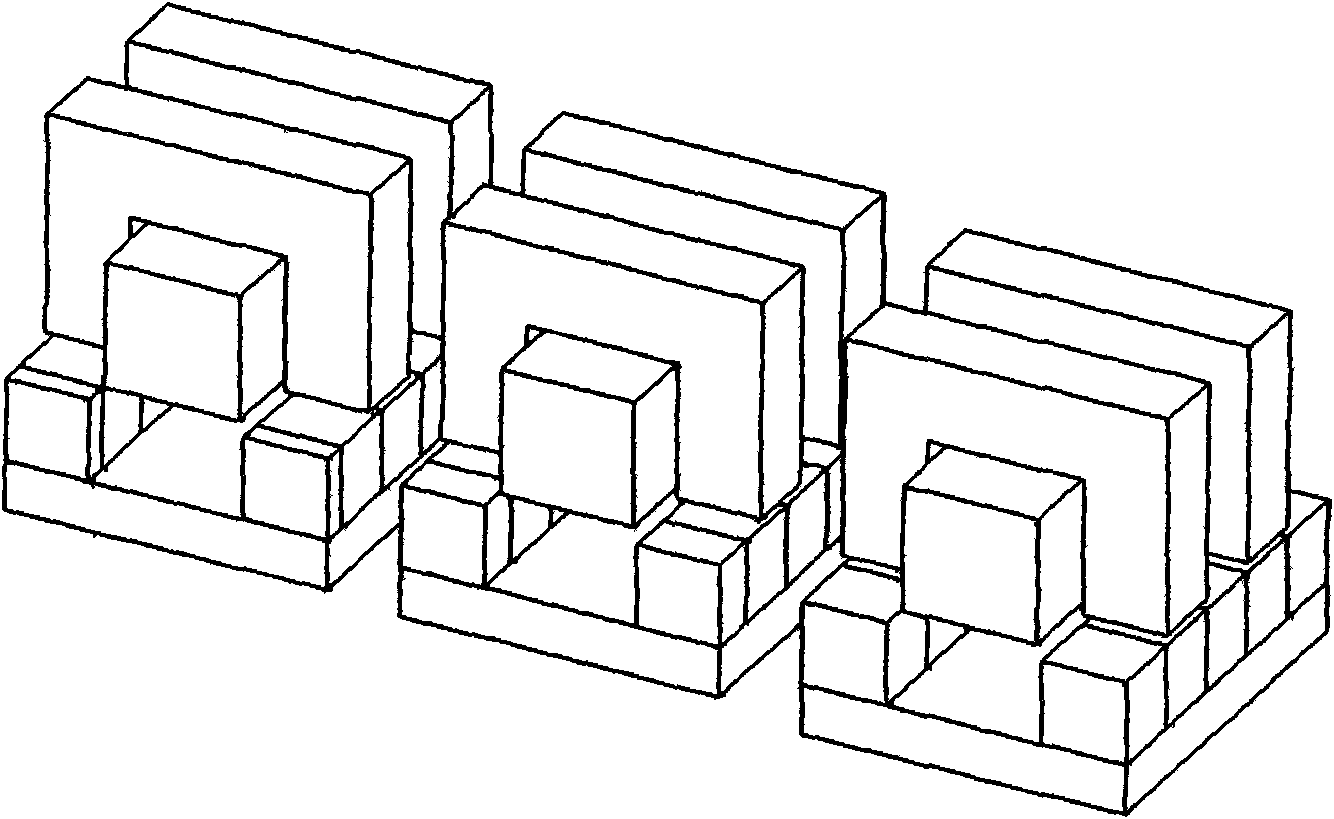
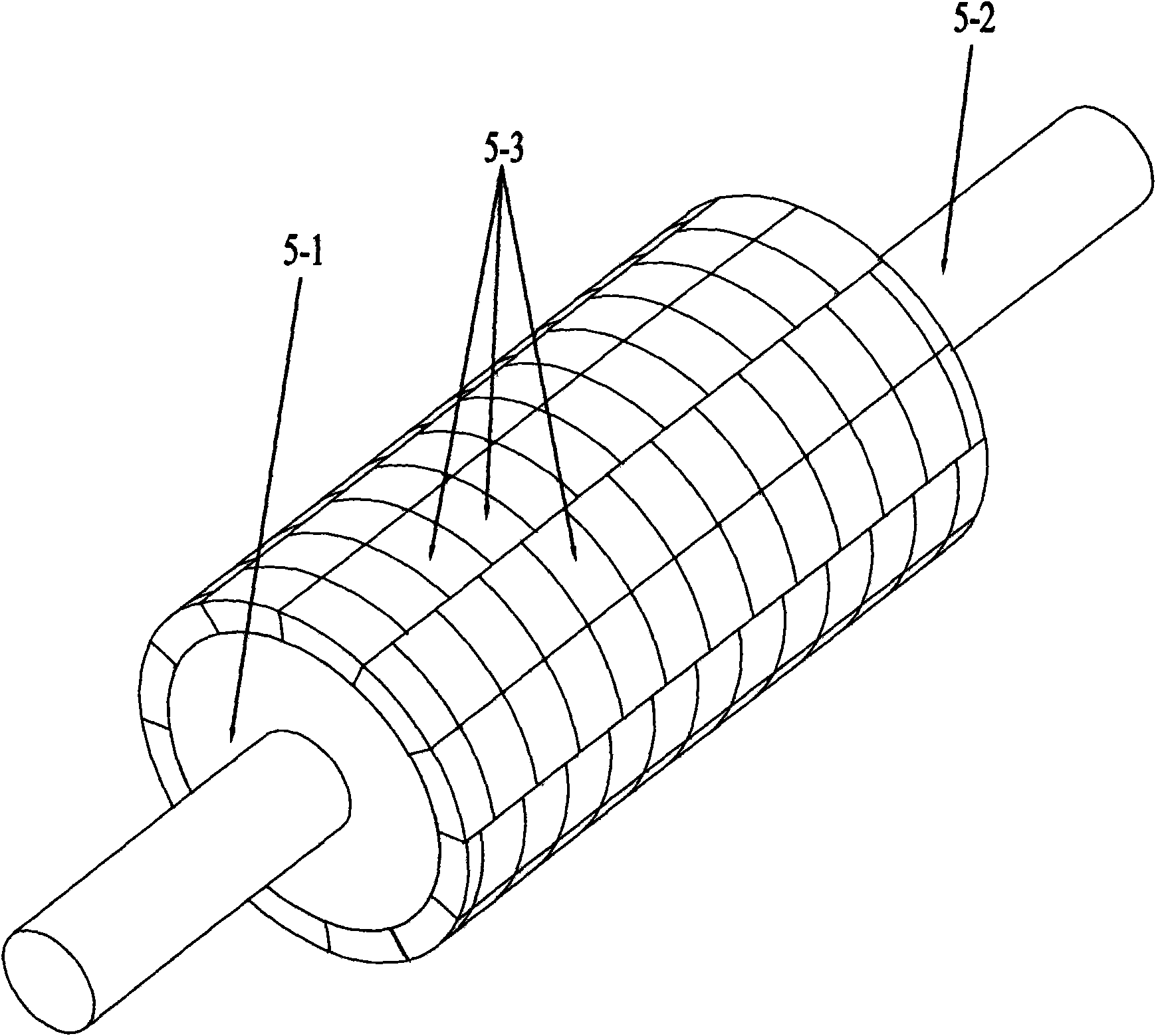
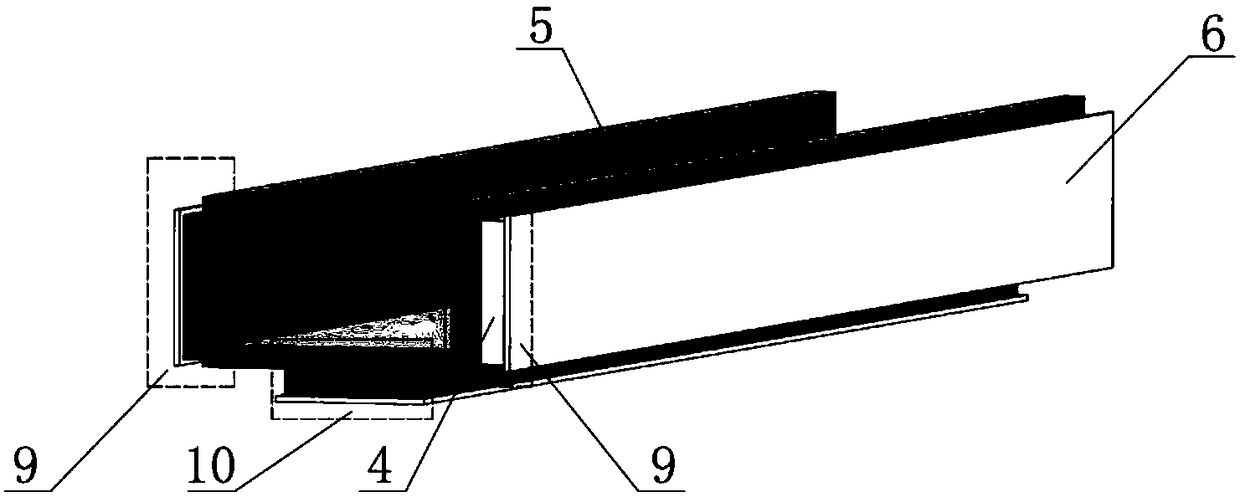
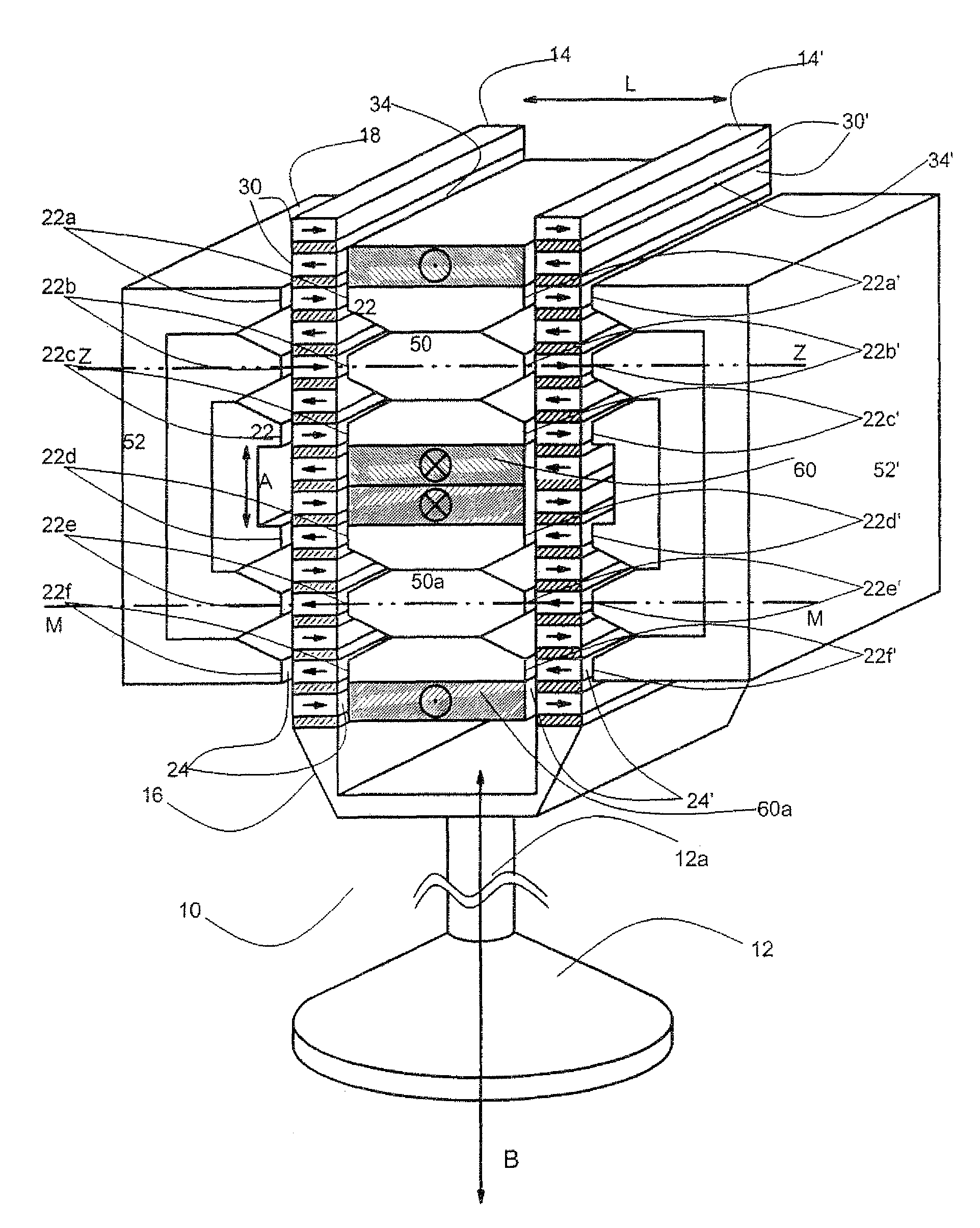
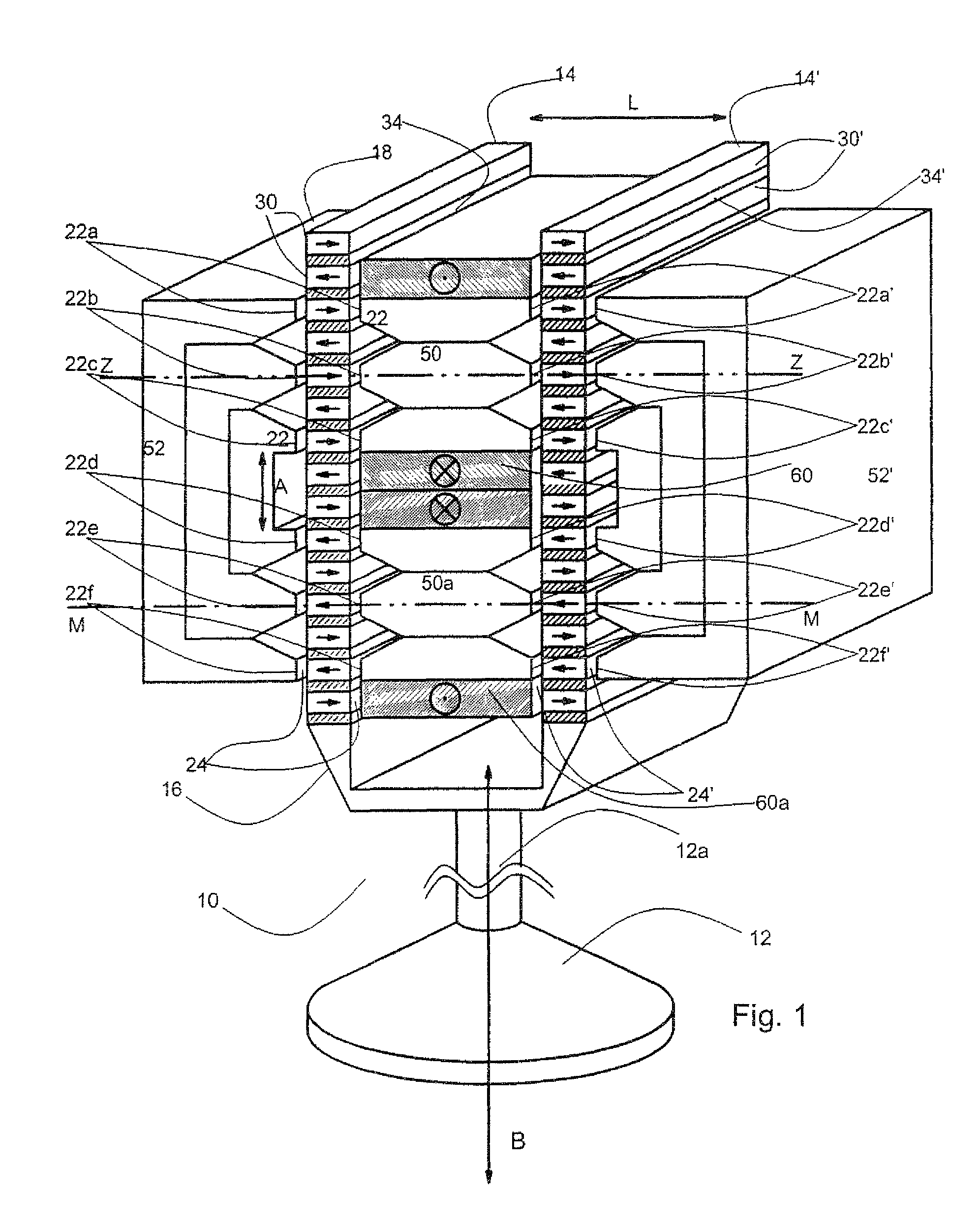
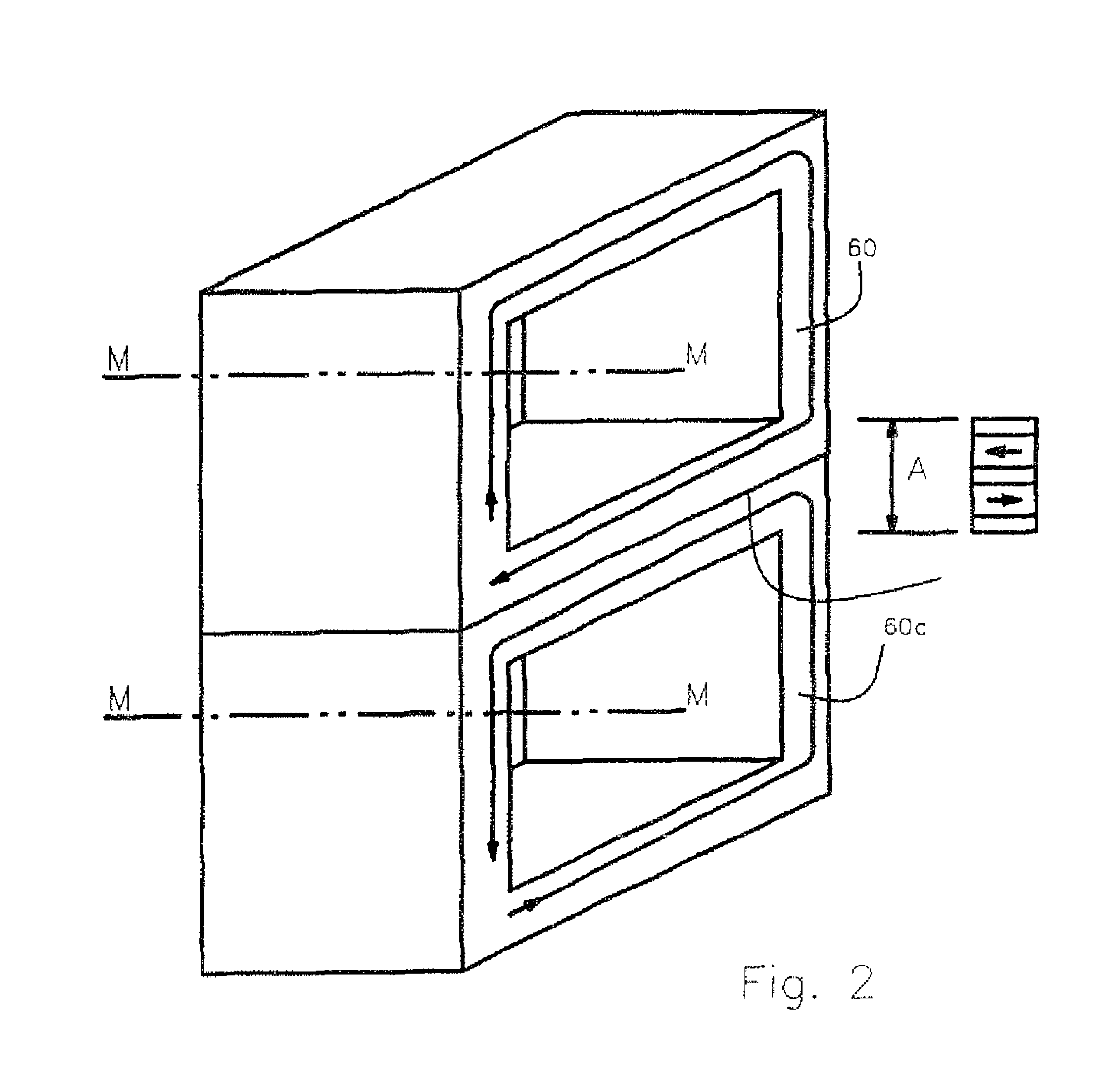
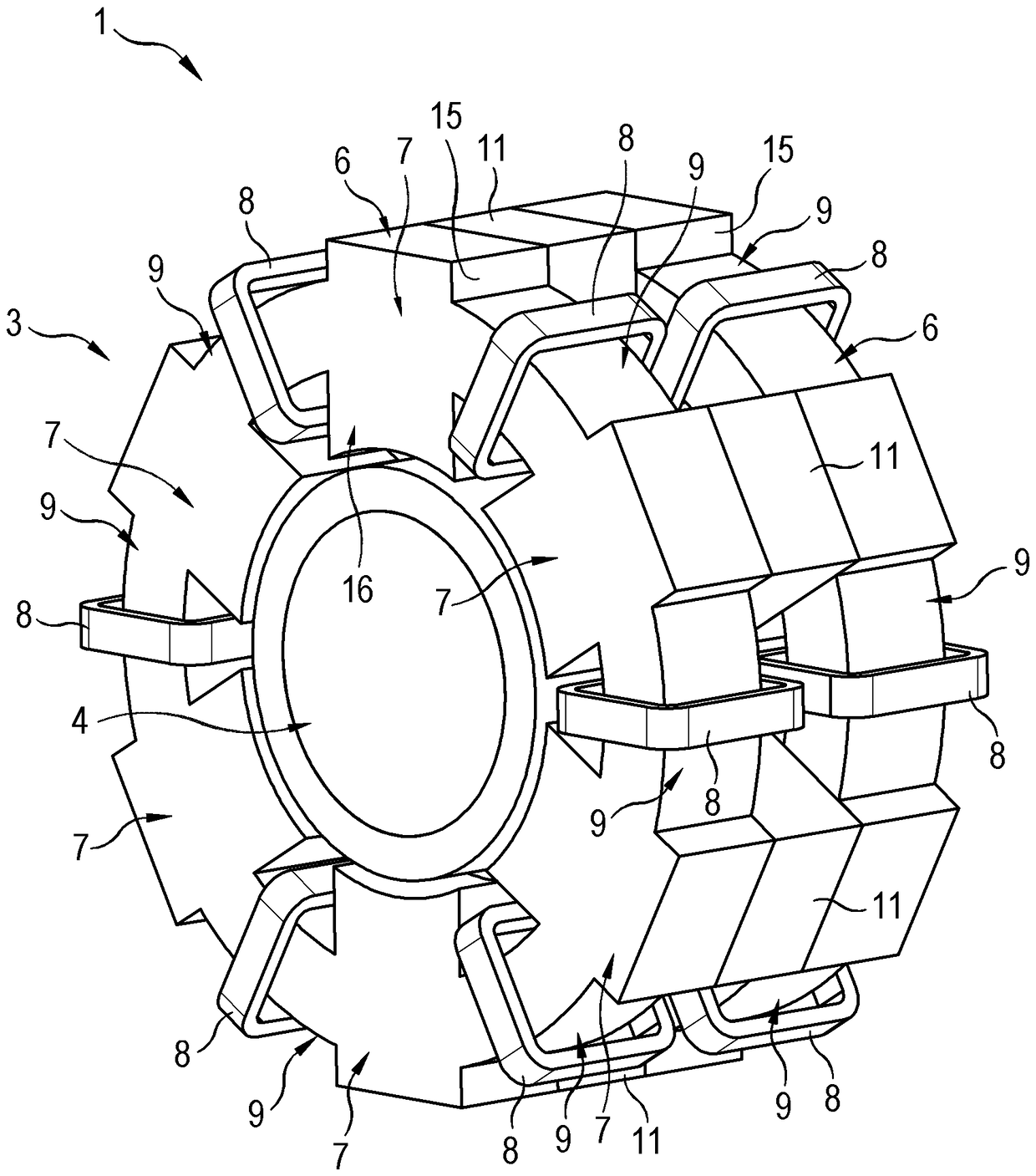
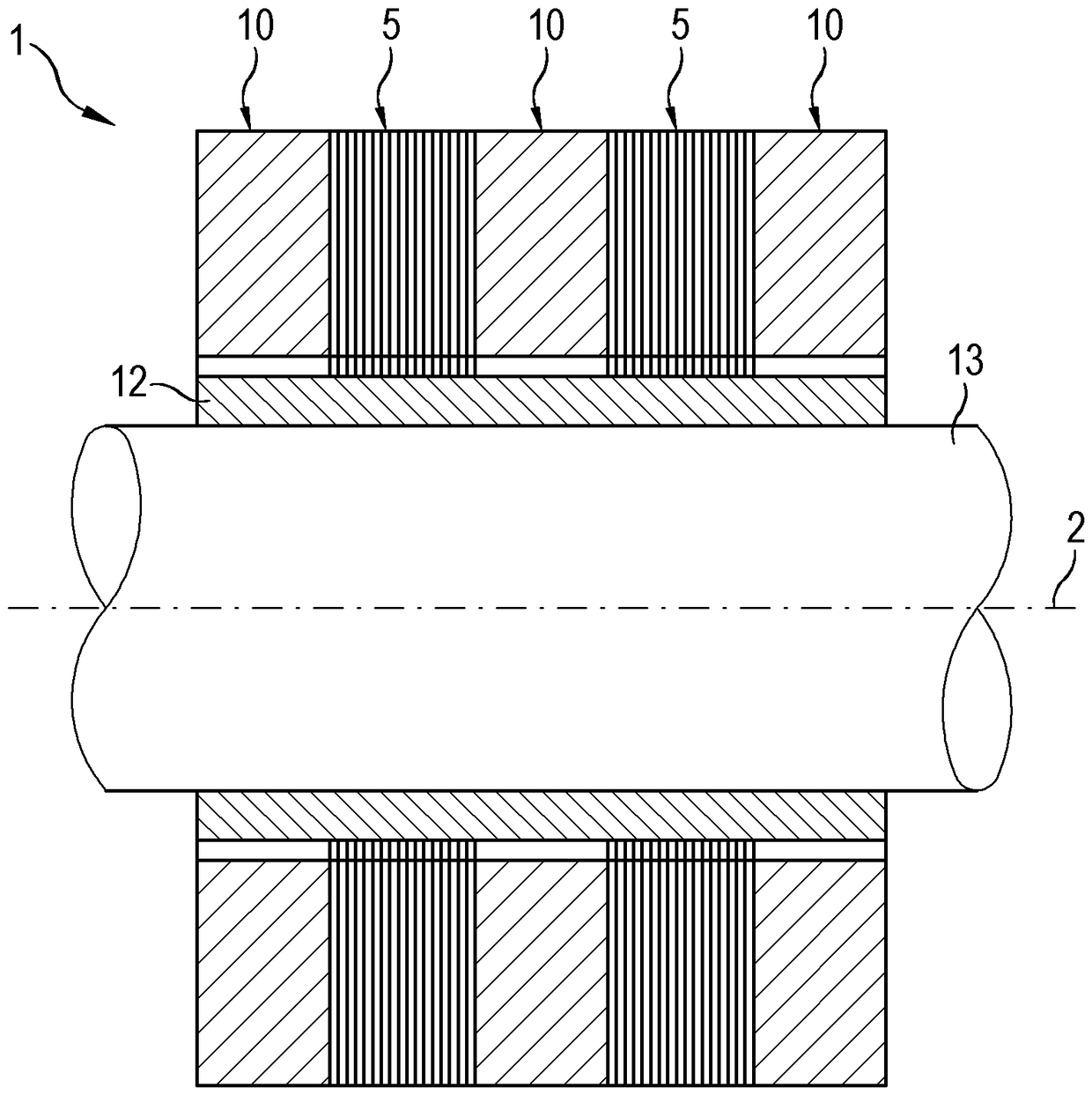
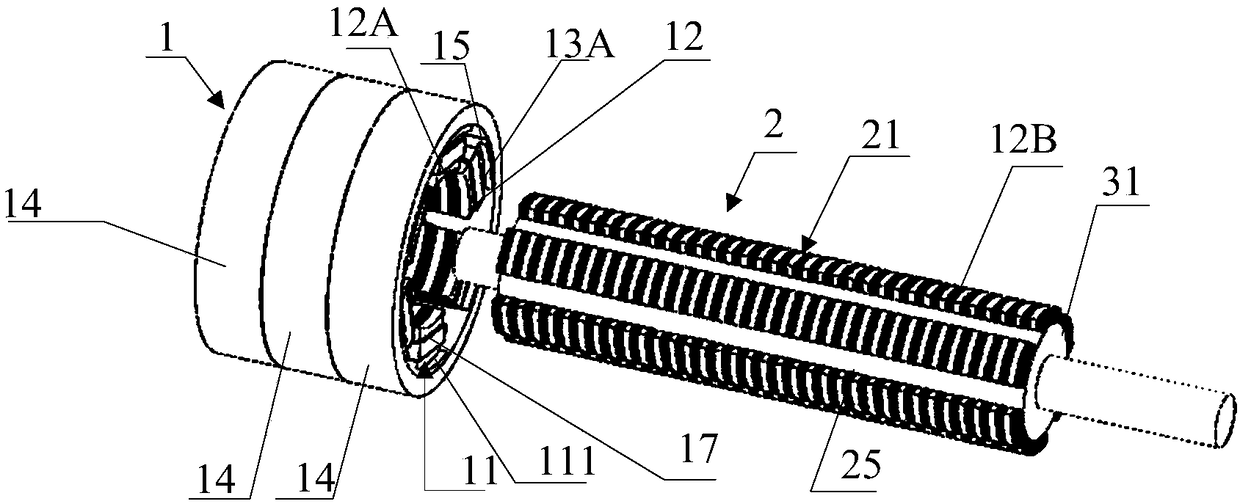
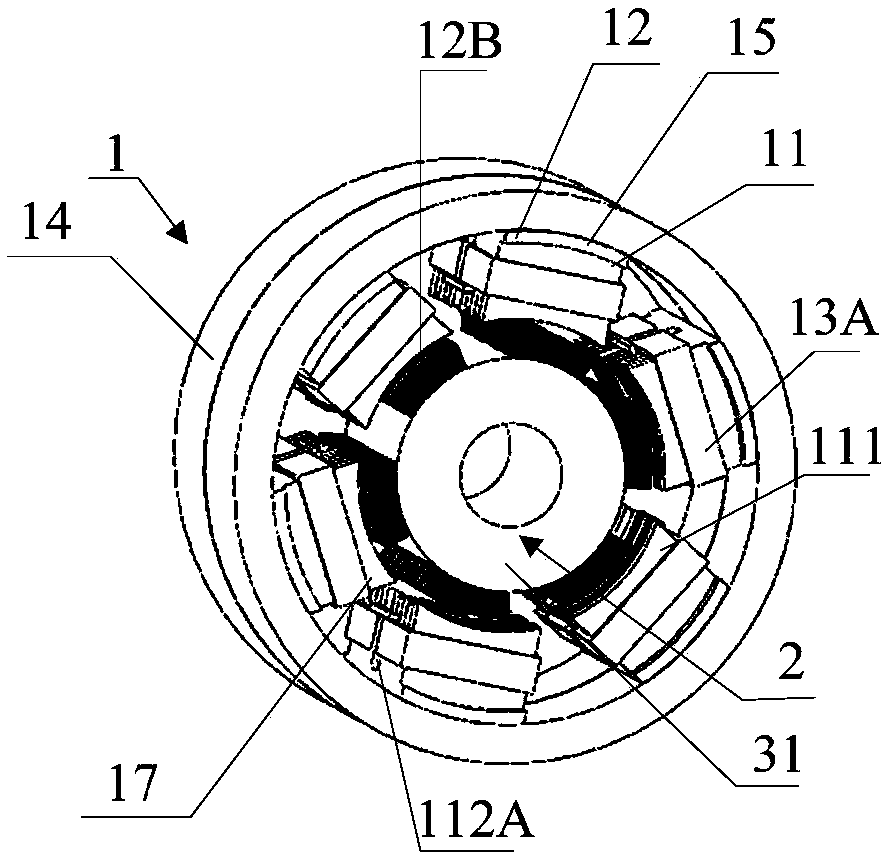
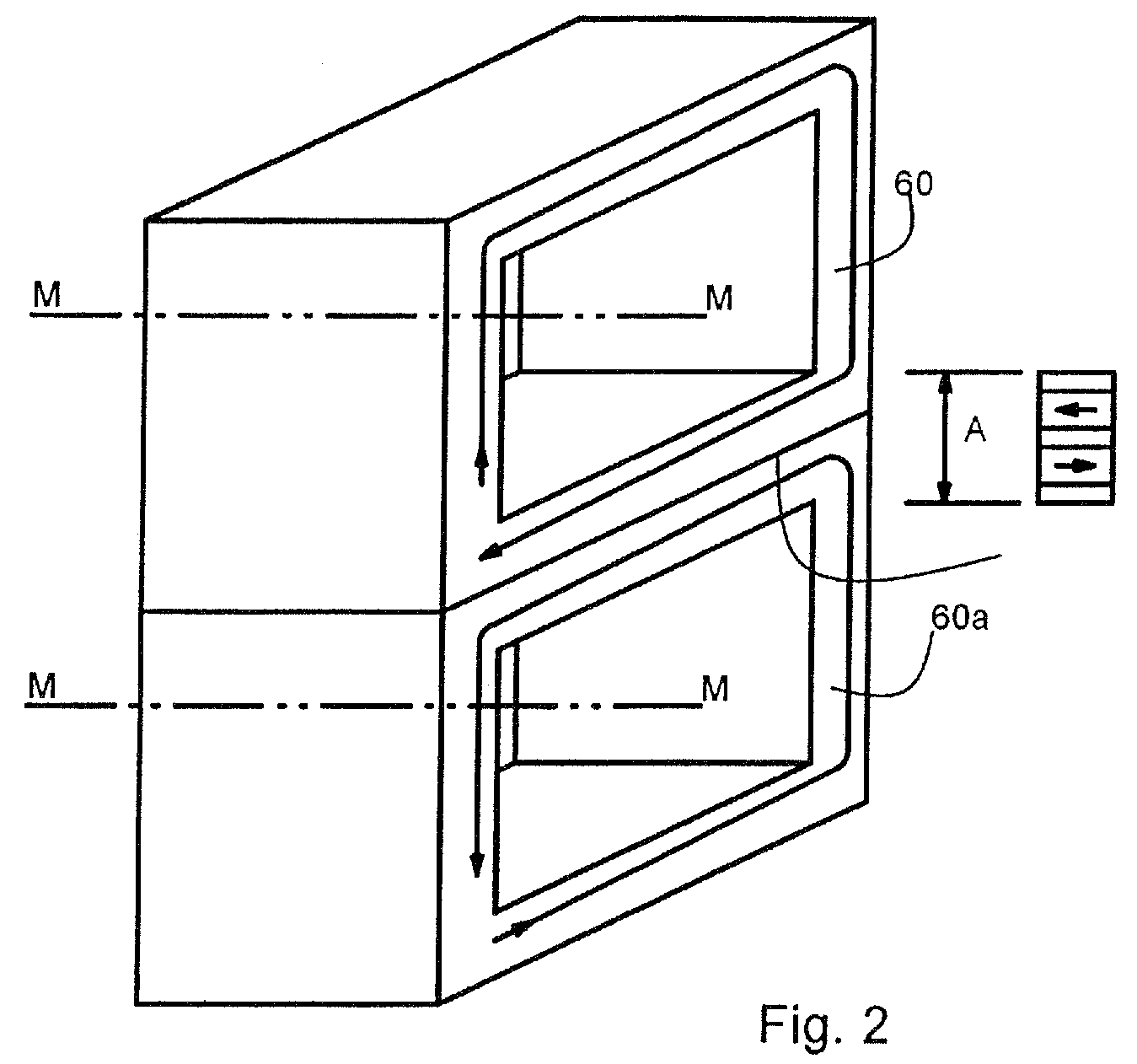
Electric Motor With Laminated Sheet Windings
ActiveUS20160126794A1High force densityWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetPower flow
An electric machine employs laminated sheets windings (LSWs) and permanent magnets which rotate about the LSWs. A ‘radial’ embodiment employs magnets which are magnetized radially and LSWs laid parallel to the rotation axis. An ‘axial’ embodiment uses axially magnetized magnets with LSWs laid radially in the plane of the motor. The magnets may be arranged as Halbach arrays. Magnets and LSWs are arranged concentrically with an air gap therebetween; the motor may employ “Large Air Gap Electric Ring” (LAGER) technology. The laminated sheets form a continuous stack of series-connected concentric metal layers; dielectric layers insulate each metal layer from its adjacent layers. Cuts arranged periodically around each LSW run parallel to the rotation axis and extend through all of the metal layers, with adjacent cuts originating on opposite sides of the LSW such that they form a serpentine path for current to flow as it flows around the winding.
Owner:GREENTECH MOTORS
Linear hybrid brushless servo motor
ActiveUS20060131967A1Improve performanceReduce manufacturing costPropulsion systemsElectromagnetic couplingElectric machine
An improved linear hybrid brushless servo motor is disclosed. The motor comprises a forcer and a platen. The forcer has a plurality of stacks, permanent magnets, and coils which form a three-phase motor. The platen has a low cost ferromagnetic steel plate. The stacks, permanent magnets and phase coils of the forcer are specially designed to have the optimal electromagnetic coupling between the forcer and platen to achieve a high force density servomotor. In one embodiment, two E-shaped stacks are used to physically couple two phases to substantially minimize the unexpected cogging force and force ripple. Three other forcer configurations which achieve a three-phase, highly cost effective and high force density linear hybrid brushless servo motor are also disclosed.
Owner:BALDOR ELECTRIC COMPANY
Thrust optimization design method for tubular permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
InactiveCN102013785AHigh force densityConvenient lengthPropulsion systemsPhase differenceFinite element method
The invention discloses a thrust optimization design method for a tubular permanent magnet synchronous linear motor, which comprises: firstly, building a solid model of the motor and setting run option parameters including the length of the primary iron core of the primary iron core stator of the motor; secondly, resolving the run option parameters by using a finite element method and building a finite element geometrical model; thirdly, calculating the optimization phase difference between the end forces at the two ends of the primary iron core stator according to a formula, and regulating the length of the primary iron core to obtain the optimal length of the primary iron core, which corresponds to the optimization phase difference; and finally, obtaining the tubular permanent magnet synchronous linear motor with the smallest thrust fluctuation through magnetization by the optimal length of the primary iron core, the half-open, half-closed, round-bottom grooved tooth-groove structure and a Halbach structure. In the invention, the thrust fluctuation is minimized by relieving the influences of magnetic drag produced by an end effect and a tooth-groove effect on the thrust fluctuation; the method is simple and effective; and the calculation accuracy is high, and the motor can serve as both an electrical motor and a generator.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Linear hybrid brushless servo motor
ActiveUS7230355B2Improve performanceReduce manufacturing costPropulsion systemsElectromagnetic couplingElectric machine
An improved linear hybrid brushless servo motor is disclosed. The motor comprises a forcer and a platen. The forcer has a plurality of stacks, permanent magnets, and coils which form a three-phase motor. The platen has a low cost ferromagnetic steel plate. The stacks, permanent magnets and phase coils of the forcer are specially designed to have the optimal electromagnetic coupling between the forcer and platen to achieve a high force density servomotor. In one embodiment, two E-shaped stacks are used to physically couple two phases to substantially minimize the unexpected cogging force and force ripple. Three other forcer configurations which achieve a three-phase, highly cost effective and high force density linear hybrid brushless servo motor are also disclosed.
Owner:BALDOR ELECTRIC COMPANY
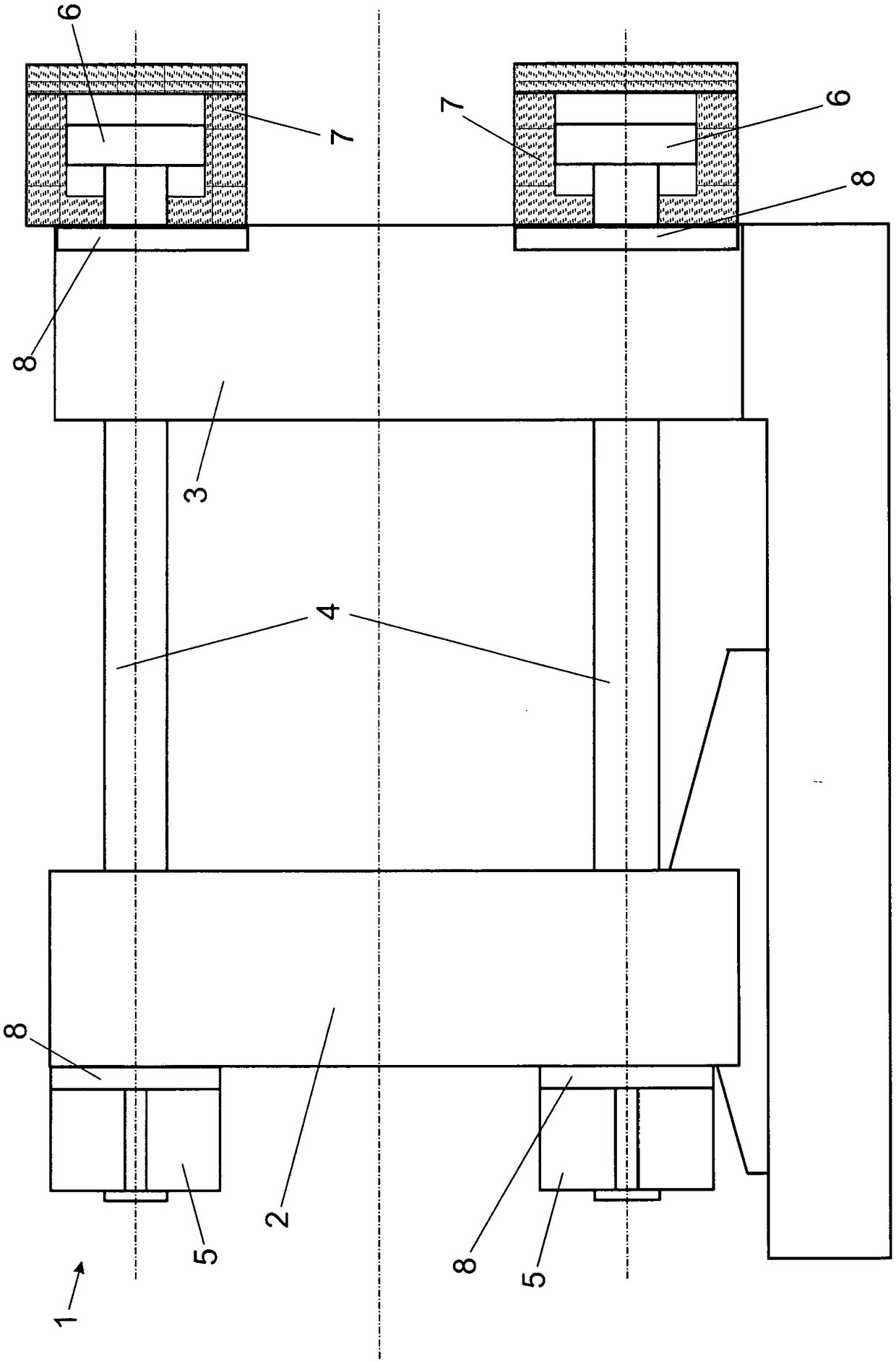
Linear Actuator in an Electric Percussion Tool
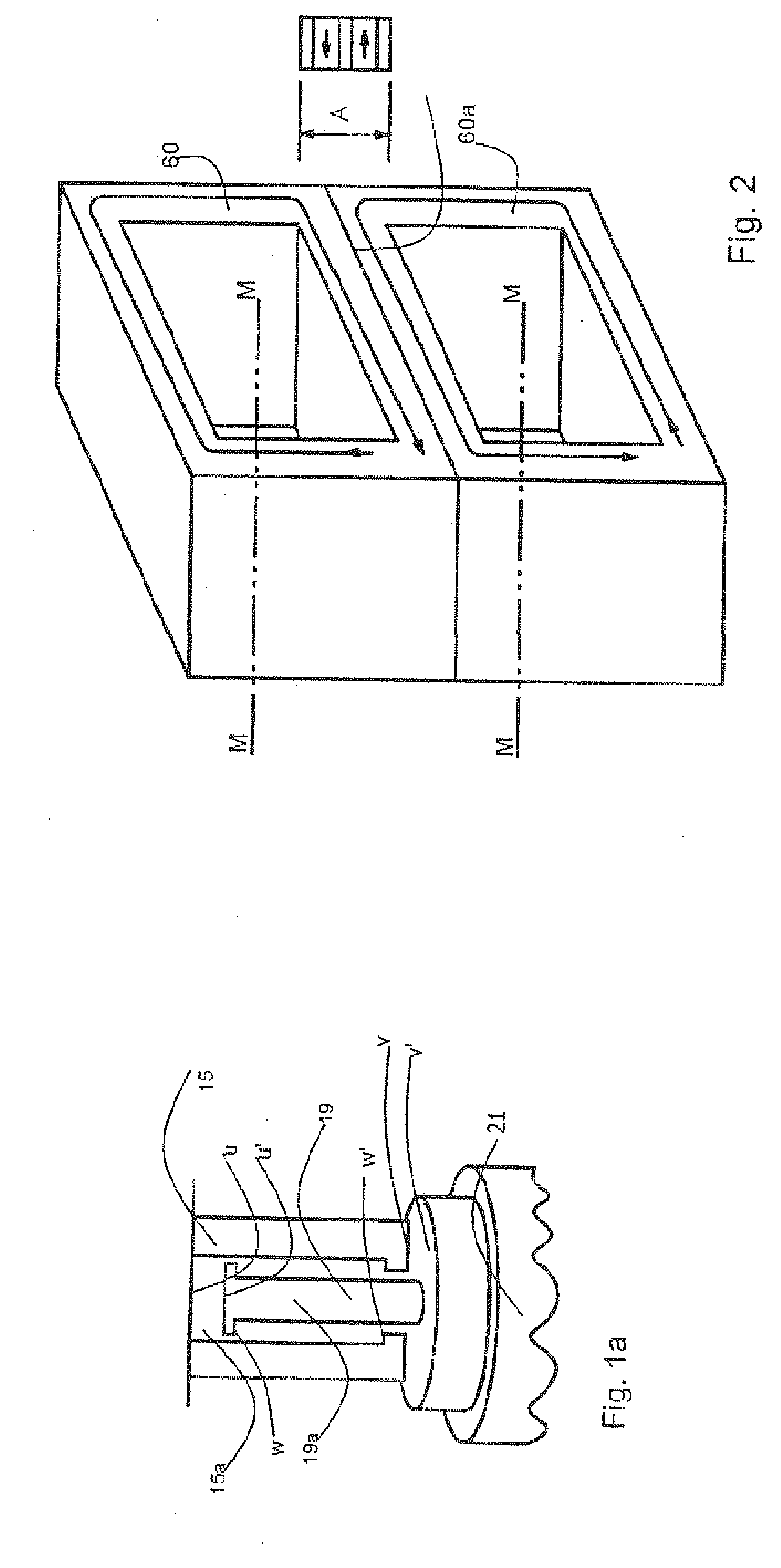
InactiveUS20080252150A1Less spatial limitationEfficient magneticallyPortable percussive toolsPropulsion systemsMechanical impactEngineering
A linear actuator in an electric percussion tool is equipped with a rotor and a stator, wherein the rotor has at least two stacks, which are arranged at a predetermined distance from one another, of superposed permanently magnetic bars, the stator is formed, at least partially, from a soft-magnetic material and has at least two pairs of teeth with mutually opposed teeth, of which each pair of teeth receives one of the two stacks between them, in each case, while forming an air gap, and wherein the stator has at least two magnetically conductive inner regions which are located between the two stacks, are arranged at a predetermined distance from one another in the direction of movement of the rotor and are at least partially surrounded, in each case, by an essentially hollow-cylindrical coil arrangement, the central longitudinal axis of which is oriented approximately transversely to the direction of movement of the rotor, and the rotor has a driving element which is able to transmit a mechanical impulse to a tool belonging to the electric percussion tool.
Owner:COMPACT DYNAMICS
Electrical induction machine and primary part
InactiveUS7560835B2Improve linearityLow leakage inductanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsAsynchronous induction motorsRotor magnetsSynchronous motor
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
Combined driving device for performing rotational motion and reciprocating linear motion and linear motor with reduced inertia
InactiveCN102780380AReduce weightSmall inertiaMagnetic circuit rotating partsMechanical energy handlingEngineeringLinear motion
Motive power of a combined driving device or a linear motor should be improved, and accordingly a combined driving device for performing rotational motion and reciprocating linear motion is provided that possesses a rotary motor (1) and a linear motor (2) and an operating shaft (3). The operating shaft (3) can be rotated by the rotary motor (1) to perform rotational motion and can perform linear motion by the linear motor (2); the operating shaft (3) possesses an output side (4). The rotary motor (1) is more closely arranged on the output side (4) of the operating shaft (3) than the linear motor (2). Accordingly the operating shaft (3) can be designed to be shorter. The measure of improving motive power is to reduce rotor quality of the linear motor (2).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
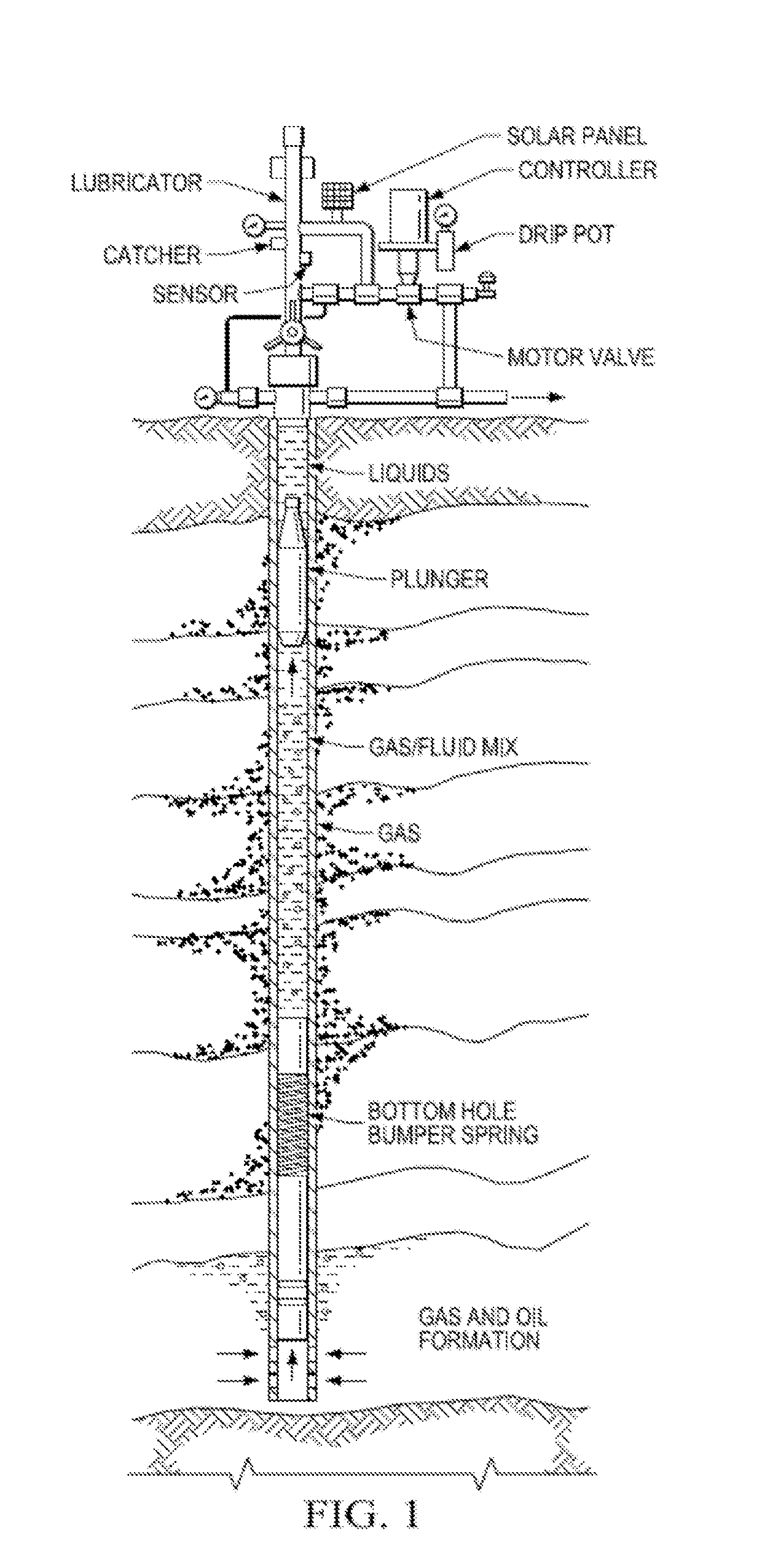
Linear induction motor plunger lift
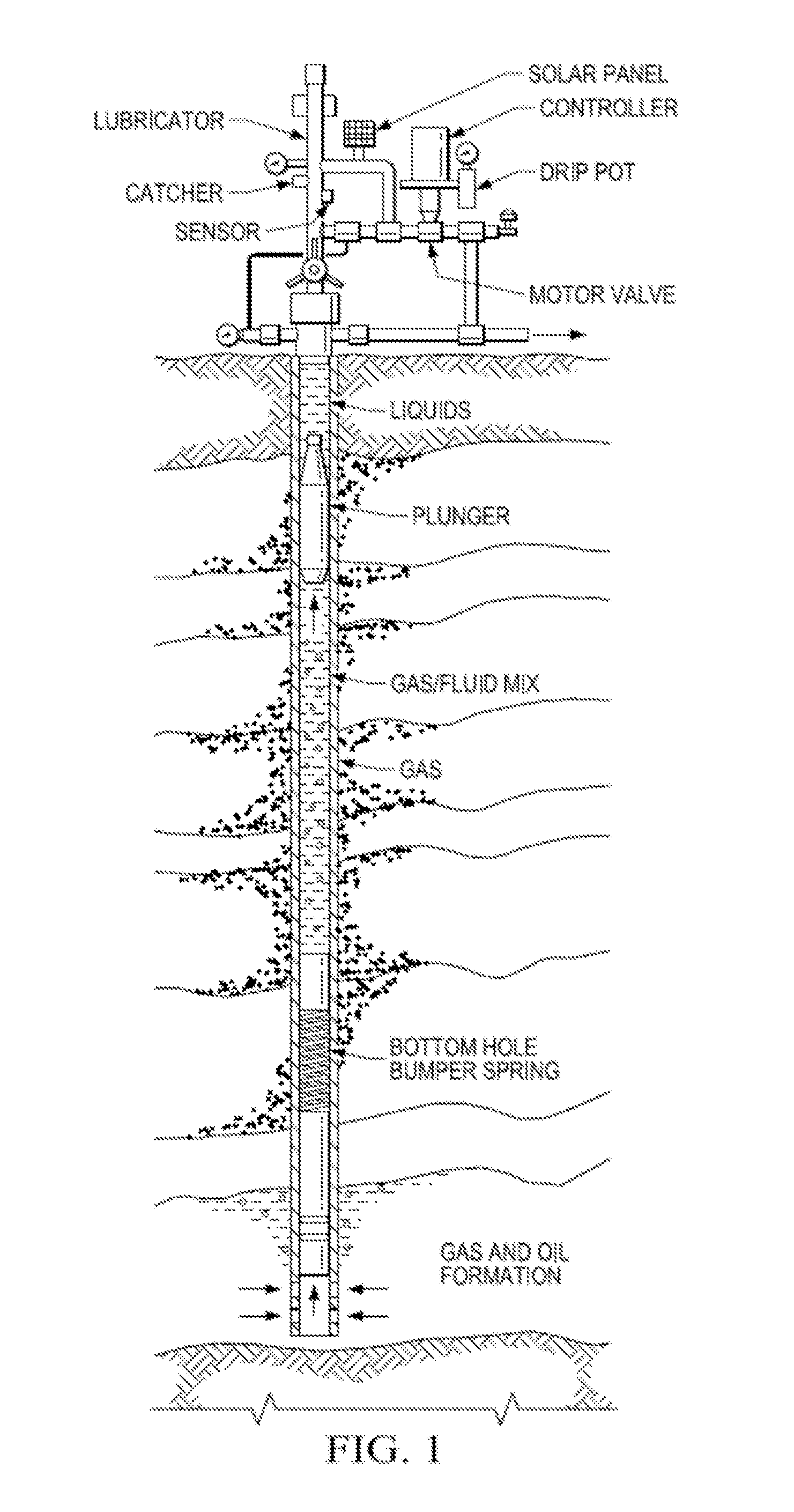
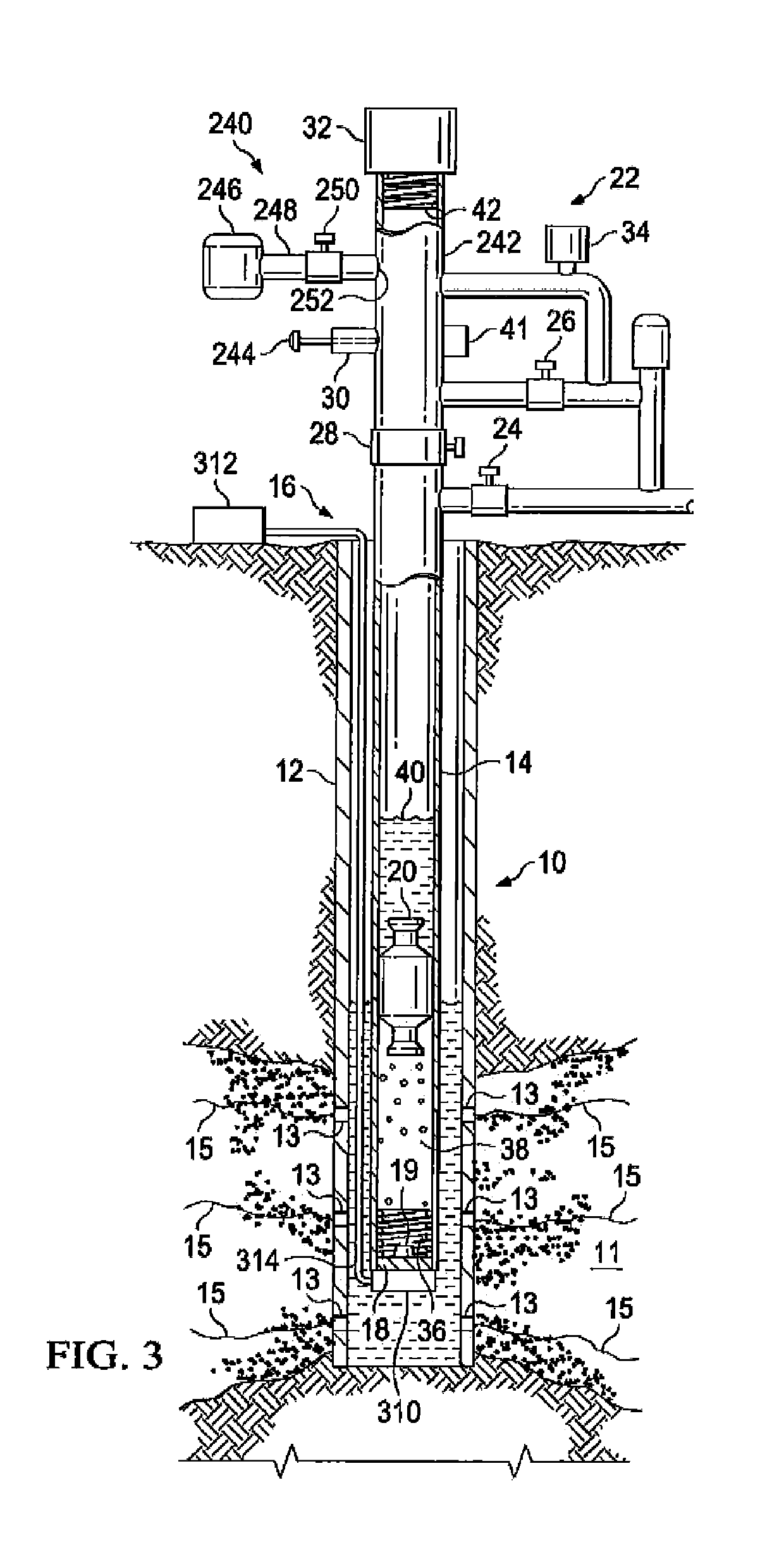
ActiveUS20160312589A1Little strengthLess energy efficientFluid removalElectric machineElectromotive force
A plunger lift system that uses a linear induction motor instead of gas or fluid pressure to lift the plunger. Electrical voltage is applied to electromagnets installed along the tubing of a wellbore that will induce magnets contained within a special plunger that is introduced inside the tubing to move it and allow it to lift liquids with a piston-like action. The electromotive force may be adjusted by varying the applied voltage as needed to lift the column of liquid from the wellbore or the current reversed to accelerate and optimize plunger descent.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Electrical induction machine and primary part
InactiveUS20060125338A1Improve linearityLow leakage inductanceSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorRotor magnets
A primary part of an electrical induction machine, especially a synchronous motor or a linear motor, includes a plurality of modules which each have teeth situated in a row having at least partially encircling slots, in the slot of each tooth a coil is wound around this tooth, and the coils of a single module are connected to a single phase of a rotary current network. The number of modules in the primary part is equal to the number of current phases or an integral multiple thereof. A single module includes an uneven number of teeth but at least three teeth, and teeth directly adjacent to one another of a single module include coils that have an opposite winding direction, which generates an opposite magnetic field polarity at the teeth. An electrical induction machine, especially a synchronous motor or a linear motor, includes a primary part and a secondary part, working together with the primary part via an air gap, which may have permanent magnets as rotor magnets.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
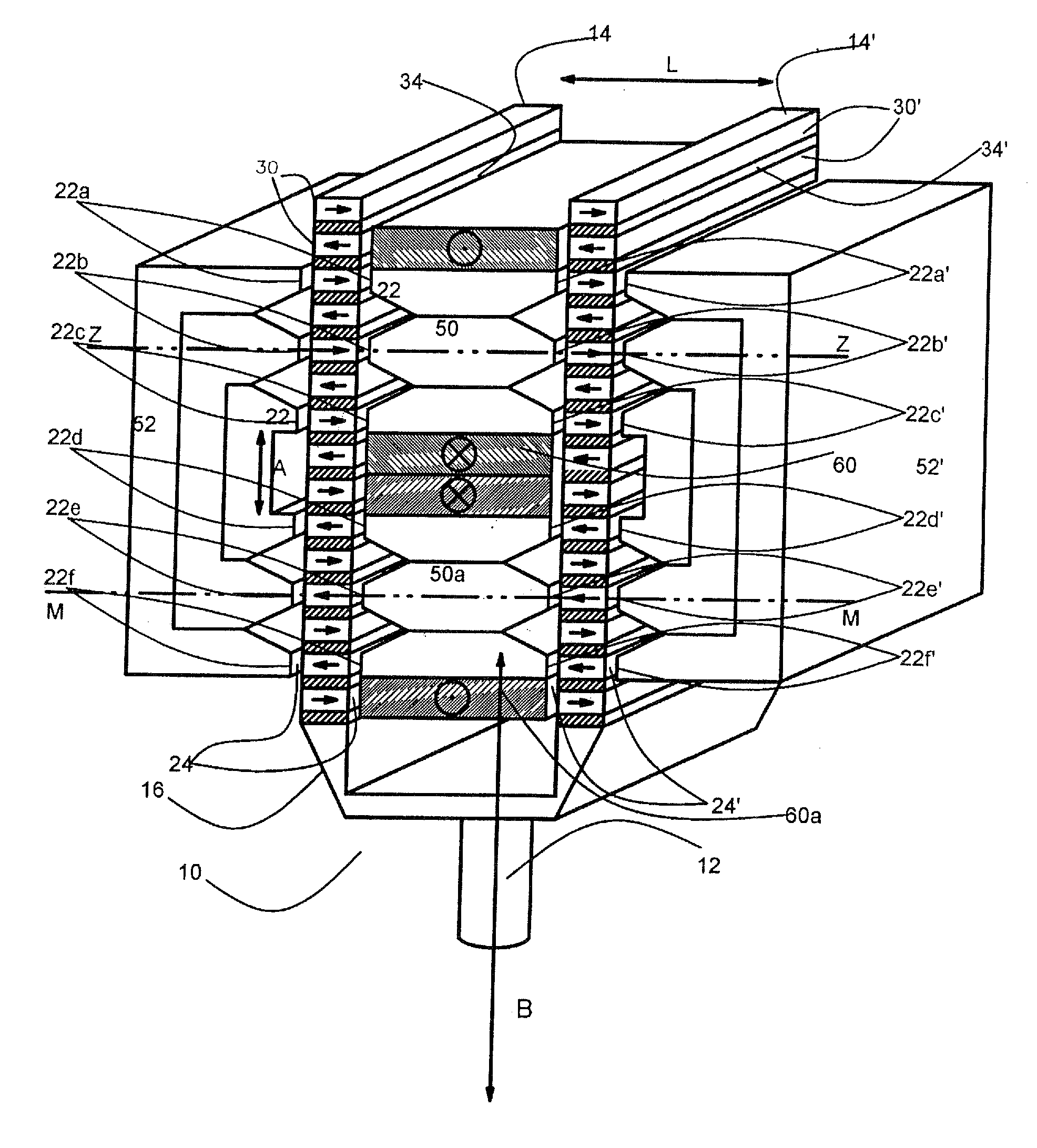
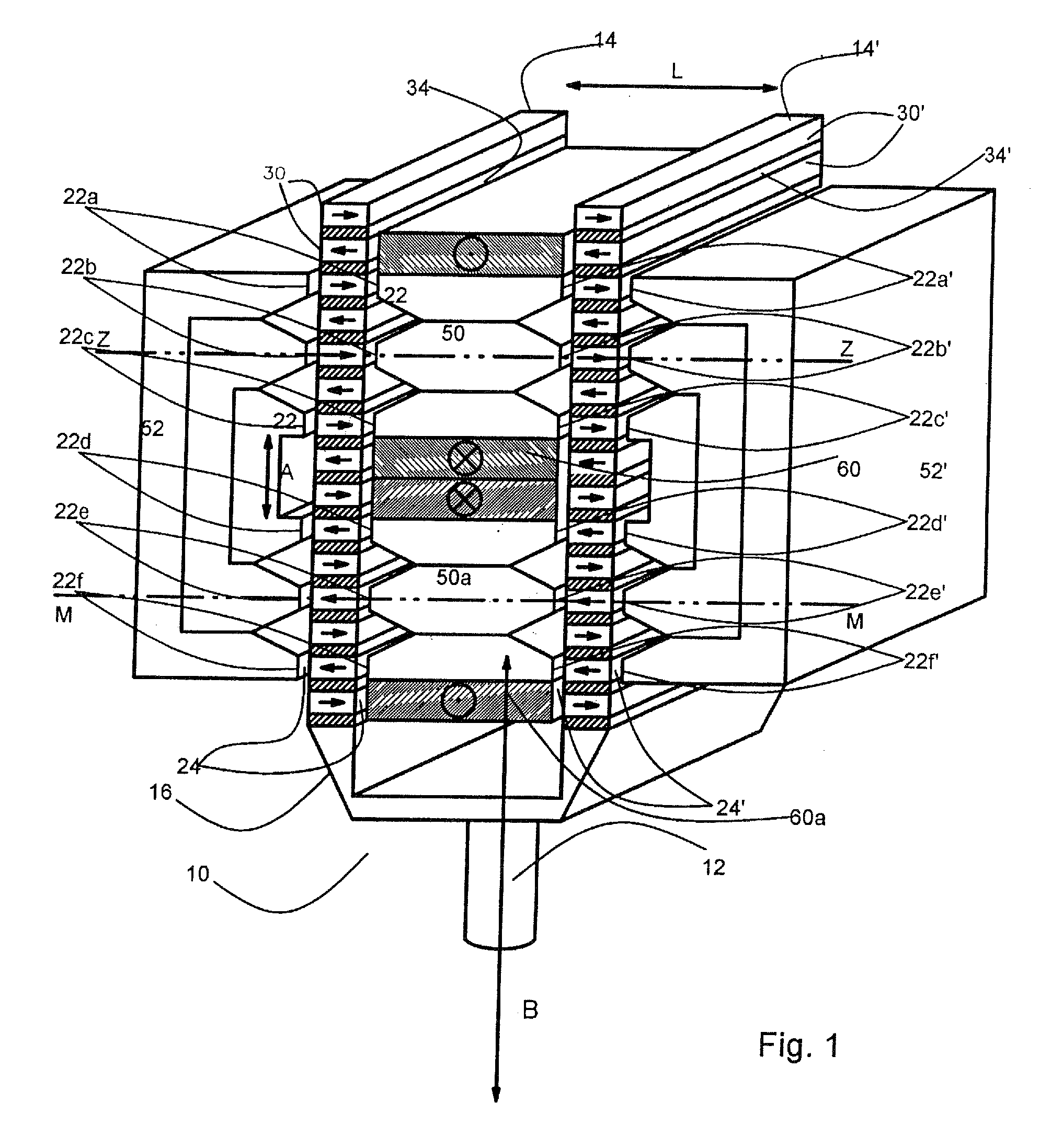
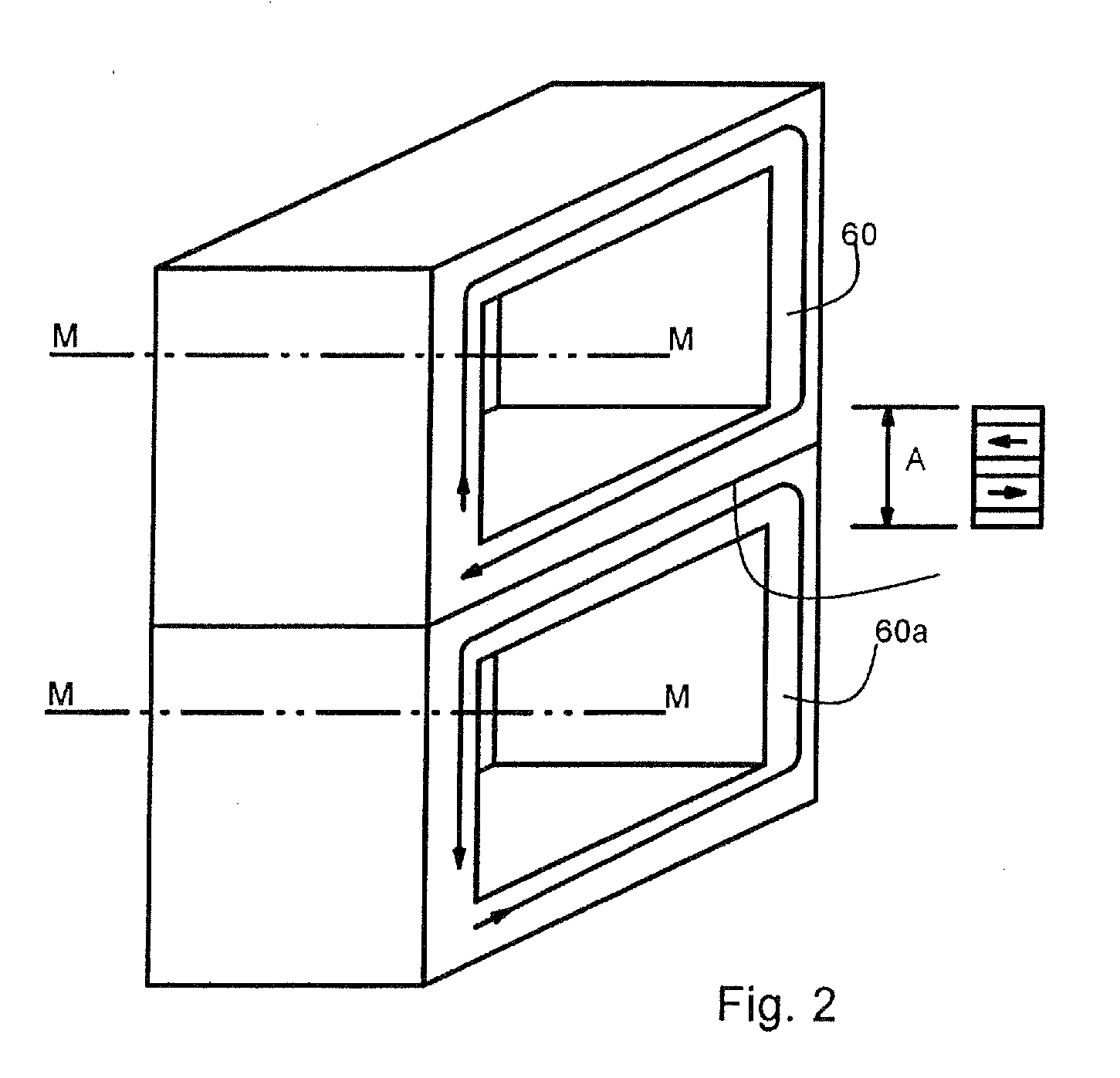
Integrated magnetic/foil bearing and methods for supporting a shaft journal using the same
An integrated bearing system (10) for supporting a rotatable shaft journal (58). The system (10) comprises a foil bearing (40) in combination with a magnetic field generating device (50) that produces a magnetic bearing capability to the rotatable shaft journal (58). The foil bearing (40) is integrated into the magnetic field generating device (50), leaving an air gap between the shaft journal (58) and the foil bearing (10). Under normal operating conditions, the magnetic field generating device (50) and the foil bearing (10) each provide a portion of the support to the shaft journal (58).
Owner:PERFECT GALAXY INT
Gas exchange valve drive for a valve-controlled combustion engine
InactiveUS20030111029A1Higher magnetomotive forceLess space restrictionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMachines/enginesStator coilEngineering
The gas exchange valve drive for a valve-controlled combustion engine has a hollow cylindrical rotor to be coupled with a valve member and a stator, with the rotor comprising permanent-magnetic rings concentrically arranged one above the other, the stator being at least partially constructed of a soft magnetic material and comprising at least one tooth facing towards the rotor, the stator comprising a radially inner magnetically conductive area and a radially outer magnetically conductive area, with the rings of the rotor being arranged between the inner area and the outer area of the stator, and the outer area of the stator in at least one partial section being designed with a C-shaped cross-section and comprising at least one stator coil. In the radially inner magnetically conductive area of the stator and / or in the radially outer magnetically conductive area of the stator at least one tooth is formed in the direction of movement of the rotor, whose dimension in the direction of movement of the rotor is essentially the same as the dimension of a permanent-magnetic ring in the direction of movement of the rotor, so that in a predetermined position of the rotor the at least one tooth of the stator is in alignment with one permanent-magnetic ring.
Owner:COMPACT DYNAMICS
Clutch for coupling a car door of an elevator car with a landing door of an elevator system
InactiveUS7255203B2Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyWing operation mechanismsWing fastenersElevator systemCoupling
A clutch couples a car door of an elevator car with a landing door of an elevator system, wherein the car door is movable with respect to the elevator car by a first actuator. The clutch includes at least one coupling element and a second actuator. The coupling element is movable with respect to the car door between a first position and a second position by the second actuator such that the coupling element engages with the landing door when the elevator car is within a landing zone and the coupling element is moved towards the second position, thereby establishing the coupling of the car door with the landing door. The second actuator is a linear motor.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
Block-based switched reluctance motor with short end part and short magnetic circuit and control circuit thereof
InactiveCN105391263AReduce copper consumptionShort magnetic circuitMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsPhysicsConductor Coil
The invention discloses a block-based switched reluctance motor with a short end part and a short magnetic circuit and a control circuit thereof. The motor comprises a motor stator and a block-based motor rotor; the stator comprises a stator core and a winding; a rotor part comprises rotor overlaid cores and a non magnetic framework; a plurality of stator teeth are uniformly distributed on the stator core; the stator winding is of a concentrated winding structure and wound on the stator teeth; the rotor overlaid cores are uniformly distributed at the inner side of the stator teeth and embedded in the non magnetic framework; a rotating shaft is arranged at the center of the non magnetic framework; during the running process of the motor, the motor at least has two electrified phases which are adjacent to each other; the route of the magnetic field inside the motor comprises the stator teeth of the two adjacent phases, as well as a stator yoke part, the rotor overlaid core and an air gap between the stator teeth of the two adjacent phases. When the motor disclosed by the invention runs, two adjacent phases are powered on and off at the same time, the width of the air gap magnetic field of the more is improved, the output torque of the motor is improved, and the force density of the motor is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
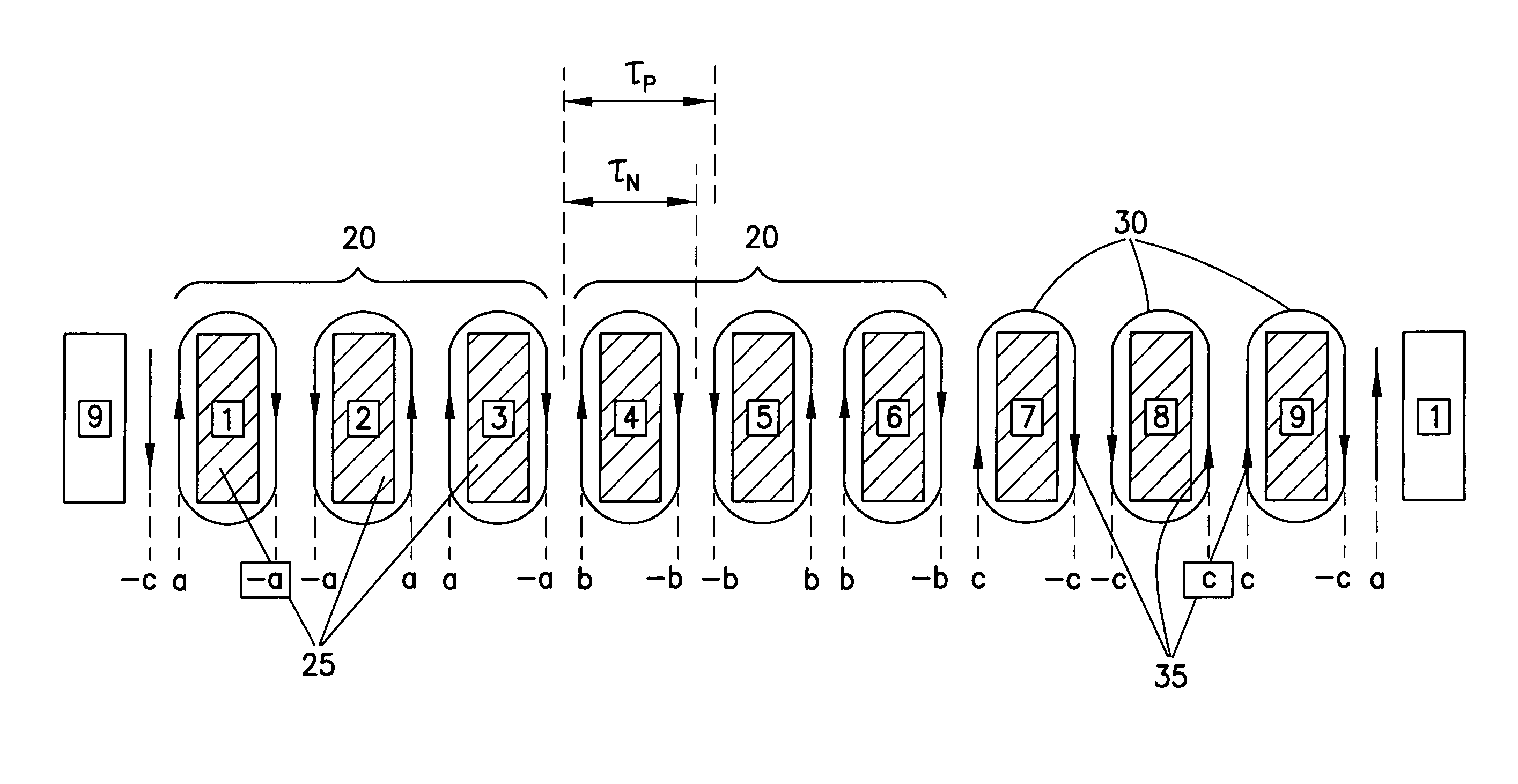
Multiphase transverse magnetic field permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
InactiveCN101604898ASimple processing technologyHigh force densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsPropulsion systemsPhysicsPole number
The invention provides a multiphase transverse magnetic field permanent magnet linear synchronous motor, which relates to a linear synchronous motor and aims to solve the problems that the prior transverse magnetic field motor has a complex structure and higher processing technological requirement. A stator component consists of n magnetic iron core rings, n-1 non-magnetic support rings and armature windings, wherein the n magnetic iron core rings and the n-1 non-magnetic support rings are arranged and overlaid alternately along the axial direction to prepare a stator core, the armature windings are encircled on I-shaped stator teeth of the magnetic iron core rings along the axial direction, the outer surface of a cylindrical mover iron core is provided with permanent magnet strips which have the same number with the pole number of motors and consist of permanent magnets along the axial direction, and the adjacent two-phase permanent magnet strips are arranged at a distance which is 2 / m times of the staggered polar distance Tau, wherein m is the phase number of the motors, and the permanent magnet strips consist of a plurality of permanent magnets which have opposite magnetization directions and are arranged alternately along the axial direction. The multiphase transverse magnetic field permanent magnet linear synchronous motor not only has simple structure and processing technique, but also has the advantages of high force density and high control characteristic, and can be widely applied in the fields of national economy, national defence and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Clutch for coupling a car door of an elevator car with a landing door of an elevator system
InactiveUS20050126860A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyWing operation mechanismsWing fastenersElevator systemCoupling
A clutch couples a car door of an elevator car with a landing door of an elevator system, wherein the car door is movable with respect to the elevator car by a first actuator. The clutch includes at least one coupling element and a second actuator. The coupling element is movable with respect to the car door between a first position and a second position by the second actuator such that the coupling element engages with the landing door when the elevator car is within a landing zone and the coupling element is moved towards the second position, thereby establishing the coupling of the car door with the landing door. The second actuator is a linear motor.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
Permanent magnet levitation linear electromagnetic propelling system
ActiveCN108382264AEliminates stringent precision requirements for constructionEasy to controlRailway vehiclesElectric propulsionLevitationElectric machine
The invention provides a permanent magnet levitation linear electromagnetic propelling system and relates to a motor, in particular to a magnetic levitation linear motor. The system aims at solving the problems that a magnetic field formed by superconducting magnets is serious in flux leakage, the magnetic field shielding difficulty is large, and the levitation control difficulty of the normal conducting magnetic levitation technology is large. The system comprises a drive control subsystem and a linear motor subsystem. The drive control subsystem comprises a power converter unit and a controller. The linear motor subsystem comprises a stator and a rotor, the stator is fixed to the ground, and the rotor is fixed to a prying vehicle and moves relative to the stator; the stator comprises a levitation-guide winding and a propelling winding; the levitation-guide winding a unilateral levitation-guide primary unit; and the propelling winding comprises a bilateral propelling primary unit. A special levitation and guide control device is not needed; and no leaking magnetic field exists on a vehicle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Linear Actuator
InactiveUS20080284259A1Increase magnetomotive forceMinimum (ohmic) lossesMagnetic circuitMachines/enginesEngineeringLinear actuator
A linear actuator is provided with a rotor and a stator. The rotor comprises at least two stacks of permanently magnetic rods one over another, the stacks being arranged at a predetermined distance from each other. The stator is at least partly produced from a soft magnetic material, and comprises at least two pairs of teeth with teeth opposite each other, each pair of teeth receiving one of the two stacks between them while forming an air gap. The stator has at least two magnetically conducting inner areas which are located between the two stacks and arranged at a predetermined distance from each other in the direction of motion of the rotor. The inner areas are each at least partially surrounded by a substantially hollow cylindrical coil arrangement, the central longitudinal axis of which is oriented substantially transversely to the direction of motion of the rotor.
Owner:COMPACT DYNAMICS
Gas exchange valve actuator for a valve-controlled internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7841309B2Less spatial limitationEfficient magneticallyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMachines/enginesValve actuatorExternal combustion engine
A gas exchange valve actuator for a valve-controlled internal combustion engine is equipped with a rotor, which is to be coupled to a valve member, and a stator, wherein the rotor has at least two stacks, which are arranged at a predetermined distance from one another, of superposed permanently magnetic bars, and the stator is formed, at least partially, from a soft-magnetic material and has at least two pairs of teeth with mutually opposed teeth, of which each pair of teeth receives one of the two stacks between them in each case, while forming an air gap, and wherein the stator has at least two magnetically conductive inner regions which are located between the two stacks and arranged at a predetermined distance from one another in the direction of movement of the rotor and which are at least partially surrounded, in each case, by an essentially hollow-cylindrical coil arrangement, the central longitudinal axis of which is oriented approximately transversely to the direction of movement of said rotor.
Owner:COMPACT DYNAMICS
Rapid deflection mirror driven by Maxwell force
ActiveCN111427148AHigh force densityHigh accuracy of rotation angleMagnetic circuit rotating partsOptical elementsLoop controlSteering angle
The invention discloses a rapid deflection mirror driven by a Maxwell force. The deflection mirror comprises a reflector, a Maxwell force actuator, a flexible support system, an angle detection systemand an outer frame assembly, wherein the reflector is installed in a center of a reflector support, the Maxwell force actuator includes a ring armature and four electromagnetic units, the ring armature is fixedly connected with the reflector support, each electromagnetic unit is composed of a permanent magnet, a coil winding and a stator core, and the four electromagnetic units form four permanent magnet magnetic circuits and eight alternating current magnetic circuits; the flexible support system mainly includes a flexible diaphragm and an axial flexible piece, recovery torque is provided for an actuating torque to achieve angle control, the flexible diaphragm supports the ring armature on four side surfaces, and the axial flexible piece supports the ring armature in the center of a lower end; and four non-contact capacitance displacement sensors in the angle detection system are uniformly distributed in four directions to detect a steering angle of the reflector in real time and generate angle feedback control and angle closed-loop control. The deflection mirror is high in force density, compact in structure and convenient to machine and manufacture.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Active radial magnetic bearing with a yoke coil
A radial magnetic bearing includes an axis, a stator and a rotor, where the stator includes at least two stator assemblies axially spaced from one another, where each of the stator assemblies includesa magnetically soft core, where at least one of the stator assemblies comprises one said magnetically soft core with several radially projecting teeth arranged distributed in the circumferential direction, and several coils likewise arranged distributed in the circumferential direction, and where two respective teeth of the magnetically soft core that are successive in the circumferential direction are connected to each other by way of a connecting section of the core. The magnetic bearing includes a permanent magnet assembly disposed axially between the two magnetically soft cores. At leastone said stator arrangement with several coils arranged distributed in the circumferential direction, the magnetically soft core of which includes several radially projecting teeth arranged distributed in the circumferential direction, is embodied such that one of the respective connecting sections is wound with one of the respective coils.
Owner:麦克森国际股份公司
Cylinder linear motor
InactiveCN108377083ASimple structureLow costReciprocating/oscillating/vibrating magnetic circuit partsPropulsion systemsProtein secondary structureLinear motor
The invention relates to a cylinder linear motor. The cylinder linear motor comprises a primary structure, a secondary structure, multiple sets of thirteenth salient pole structures, multiple third permanent magnets, multiple fourth permanent magnets, multiple first windings and multiple second windings, wherein the primary structure and the secondary structure are cylindrical structures, the primary structure is sleeved outside the secondary structure, the primary structure and the secondary structure are coaxially arranged, the multiple fourth permanent magnets are mounted on an outer wall of the secondary structure, one ends of the thirteenth salient pole structures are mounted on an inner wall of the primary structure, and the multiple third permanent magnets, the multiple first windings and the multiple second windings are mounted on the multiple sets of thirteenth salient pole structures. The windings are arranged on the static side of the primary structure, so the structure of the secondary structure is made to be simple, cost is reduced, moreover, the secondary structure is disposed in the sea water, corrosion to the magnet windings is avoided, maintenance is convenient, reliability is high, the permanent magnets used for having the auxiliary effect are all arranged on the secondary structure, and the magnetic field of the linear motor is further improved.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Magneto-optical trap method and apparatus
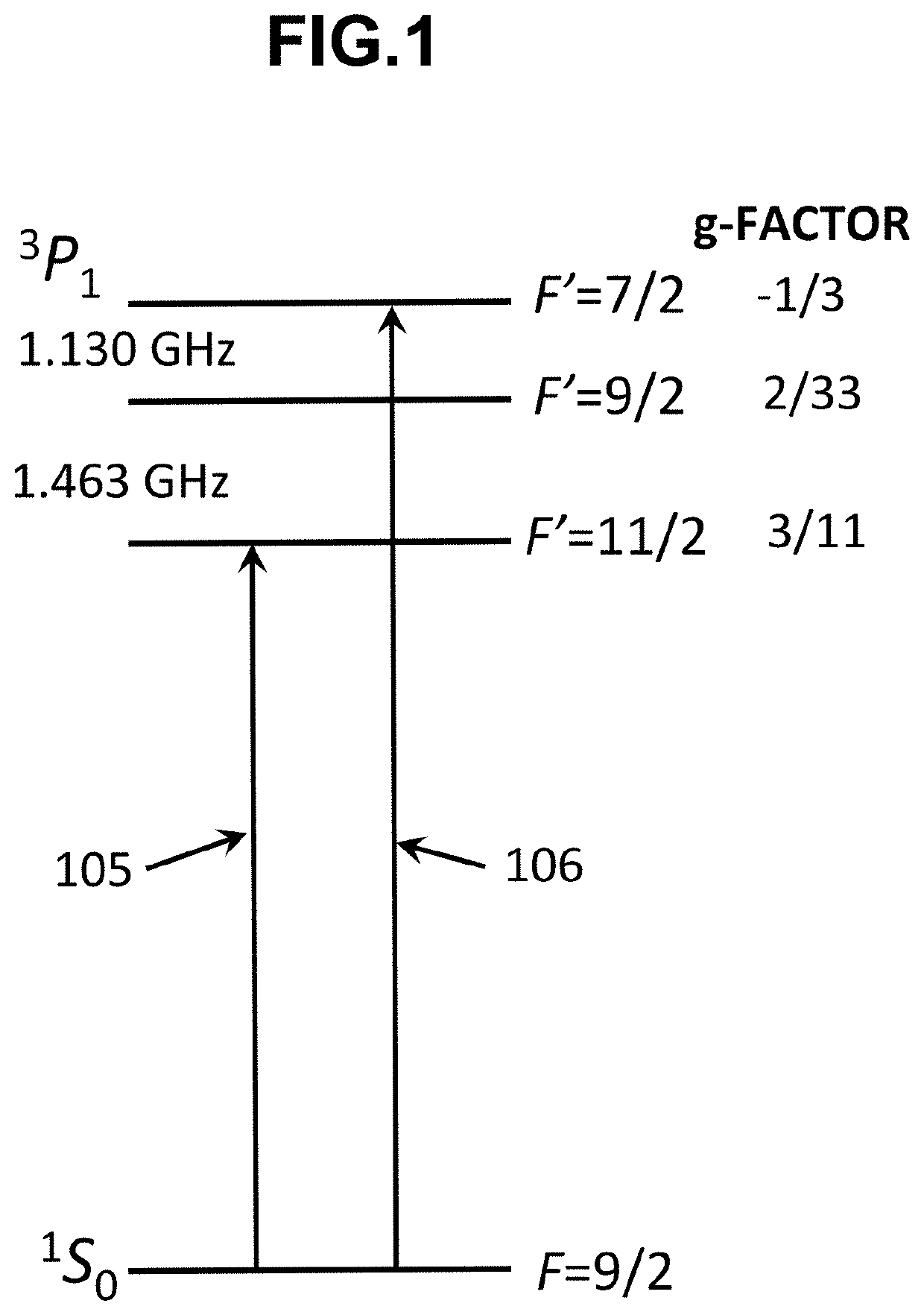
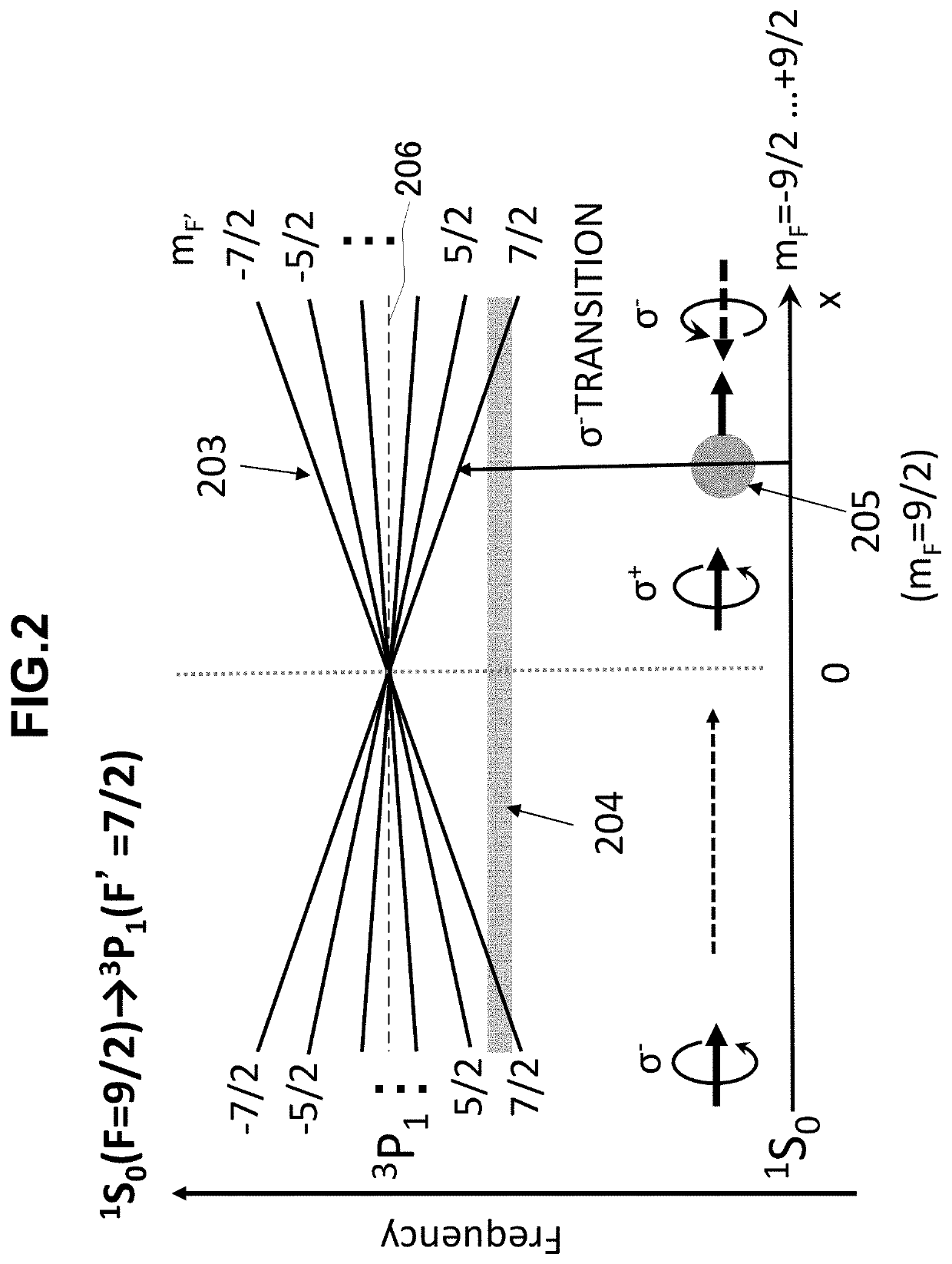
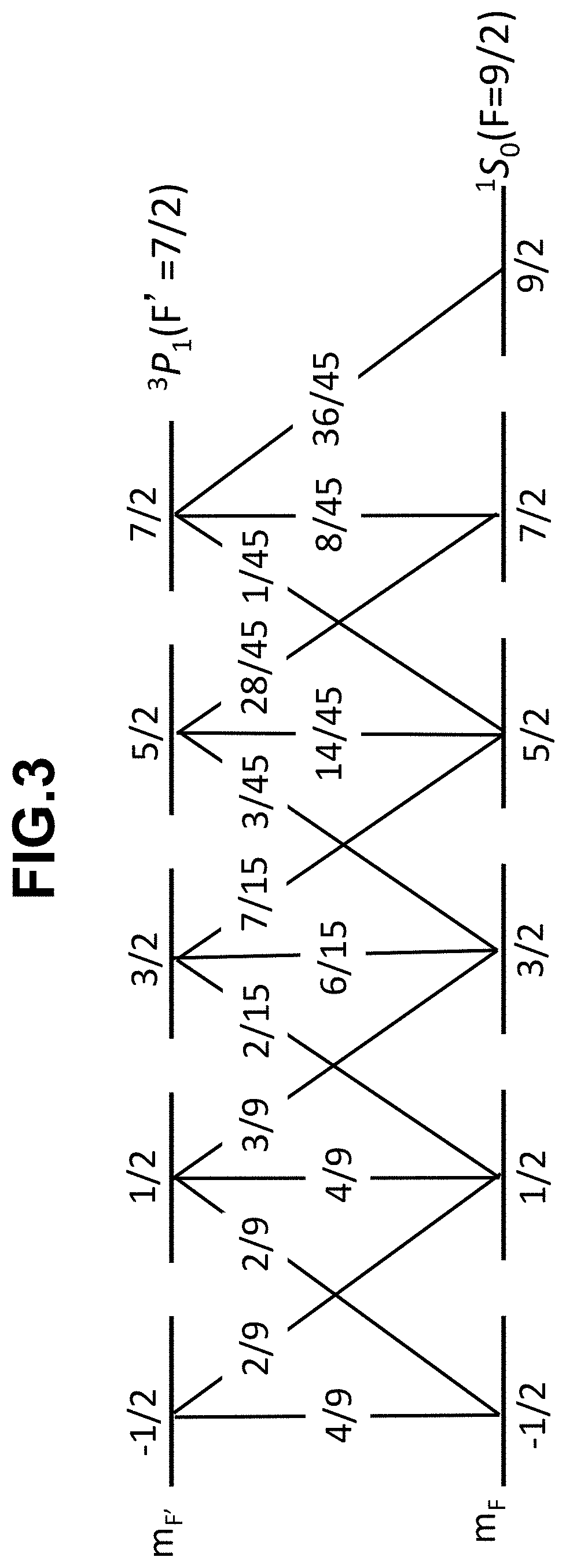
PendingUS20200275547A1Increase atomic densityHigh force densityMasersNeutron particle radiation pressure manipulationHelmholtz coilExcited state
A magneto-optical trap apparatus includes a vacuum vessel for encapsulating an atom to be trapped, an anti-Helmholtz coil for applying a magnetic field to an inside of the vacuum vessel, a laser device for generating a laser beam, and an irradiation device for irradiating the generated laser beam from a plurality of directions. The laser beam includes a first laser beam detuned from a first resonance frequency when the atom transits from a total angular momentum quantum number F in a ground state to a total angular momentum quantum number F′=F+1 in an excited state, and a second laser beam detuned from a second resonance frequency when the atom transits from the total angular momentum quantum number F in the ground state to a total angular momentum quantum number F′=F−1 in the excited state, among transitions from J=0 in a ground state to J′=1 in an excited state.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP +1
Linear actuator
InactiveUS7989991B2Avoid runningHigh force densityMagnetic circuit stationary partsMachines/enginesEngineeringLinear actuator
A linear actuator is provided with an armature and a stator. The armature has at least two stacks of permanently magnetic rods one over another, the stacks being arranged at a predetermined distance from each other. The stator is at least partly produced from a soft magnetic material, and comprises at least two pairs of teeth with teeth opposite each other, each pair of teeth receiving one of the two stacks between them while forming an air gap. The stator has at least two magnetically conducting inner areas which are located between the two stacks and arranged at a predetermined distance from each other in the direction of motion of the armature. The inner areas are each at least partially surrounded by a substantially hollow cylindrical coil arrangement, the central longitudinal axis of which is oriented substantially transversely to the direction of motion of the armature.
Owner:COMPACT DYNAMICS
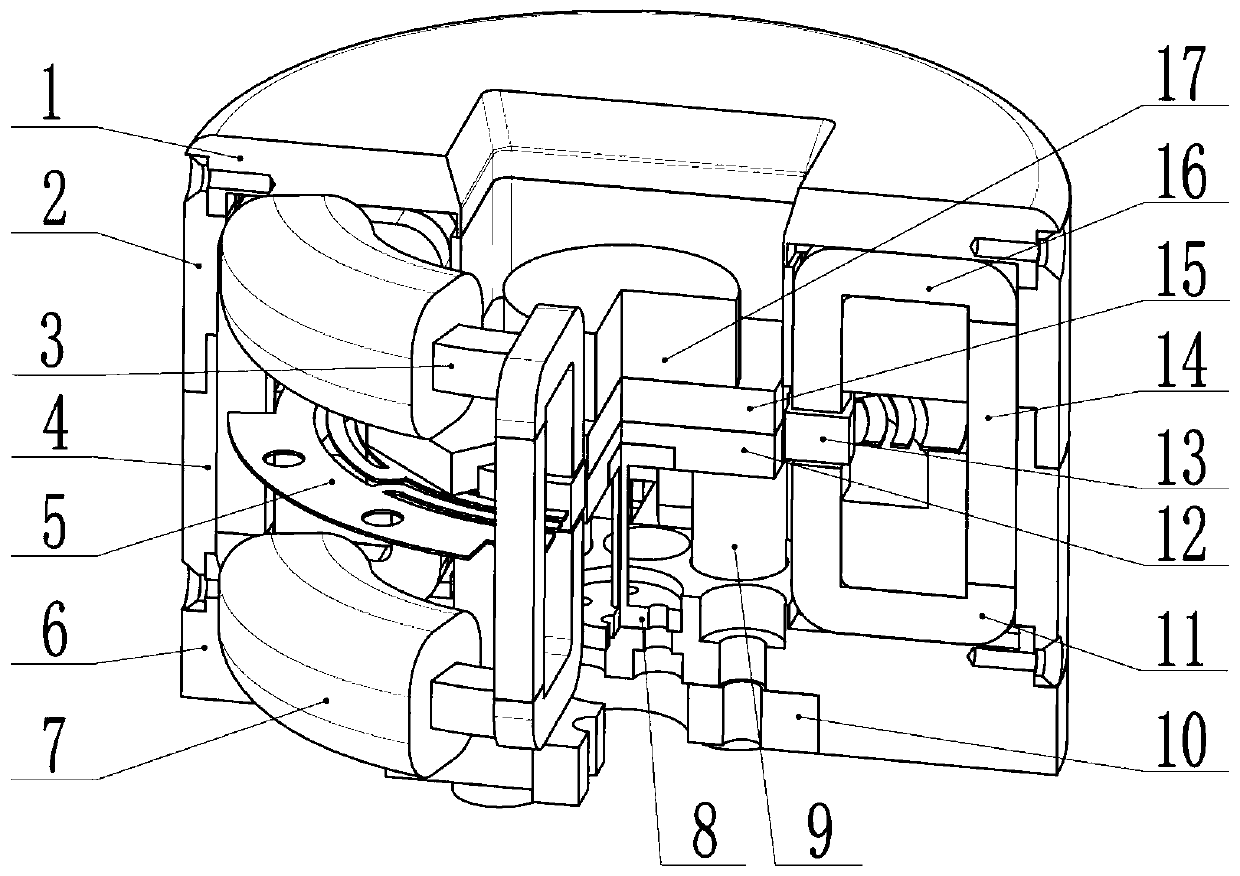
Dual-plate-type die closing unit used for moulding machine
The invention relates to a dual-plate-type die closing unit used for a moulding machine, which is used for applying a die closing force to at least two moulding mold parts and includes: a first and asecond mold clamping boards which can move relative to each other; a pull rod which penestrates through the first and a second mold clamping boards and moves relative to the same; a locking apparatus,by which the pull rod can be locked with the first mold clamping board and / or a piston-cylinder unit; the piston-cylinder unit which is configured to apply at least one part of a die closing force asa part of a die closing force apparatus and / or enable the pull rod to move relative to the first and / or second mold clamping boards as a part of a mold height adjustment apparatus, wherein the die closing force apparatus includes an active material configured to apply a part of the die closing force under effect of electromagnetic field and / or temperature varying, and / or, the mold height adjustment apparatus includes the active material, which is configured to determine extension size of defining the mold height of the active material under the effect of the electromagnetic field and / or temperature varying.
Owner:ENGEL AUSTRIA
Linear induction motor plunger lift
ActiveUS10246976B2Improve dynamic performanceImprove reliabilityFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringElectromotive force
A plunger lift system that uses a linear induction motor instead of gas or fluid pressure to lift the plunger. Electrical voltage is applied to electromagnets installed along the tubing of a wellbore that will induce magnets contained within a special plunger that is introduced inside the tubing to move it and allow it to lift liquids with a piston-like action. The electromotive force may be adjusted by varying the applied voltage as needed to lift the column of liquid from the wellbore or the current reversed to accelerate and optimize plunger descent.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Flux-switching transverse flux permanent magnet linear motor
InactiveCN104811001AReduce dosageHigh force densityDynamo-electric machinesTransverse fluxPermanent magnet linear motor
The invention relates to a flux-switching transverse flux permanent magnet linear motor which comprises two C-shaped stators and at least one rotor. Two ends of each rotor are arranged in the two stators respectively, a plurality of strip teeth are arranged on three faces of the inner walls of the stators, the rotors comprise connecting plates, three projecting pole structures are arranged at two ends of the connecting plates respectively, each projecting pole structure comprises two U-shaped teeth and two L-shaped teeth, the two U-shaped teeth are arranged at intervals, the two L-shaped teeth are arranged on one opposite side of the two U-shaped teeth respectively, the two L-shaped teeth and the U-shaped teeth adjacent to the L-shaped teeth are opposite, permanent magnets are arranged among the L-shaped teeth and the U-shaped teeth and between the two U-shaped teeth respectively, and each permanent magnet and unilateral U-shaped teeth and / or L-shaped teeth of two sides of the permanent magnet are encircled through an armature winding. The flux-switching transverse flux permanent magnet linear motor solves the problems of high permanent magnet consumption, serious magnetic flux leakage and poor heat dissipation effect of a traditional flux permanent magnet linear motor, and is simple in structure, easy to mount and high in reliability.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Cylindrical linear motor
InactiveCN108494219AAvoid demagnetizationLow costReciprocating/oscillating/vibrating magnetic circuit partsPropulsion systemsElectric machineLinear motor
The invention relates to a cylindrical linear motor, which comprises a primary structure, a secondary structure, multiple groups of fourth salient pole structures, multiple permanent magnets and multiple windings, wherein both the primary structure and the secondary structure are cylindrical; the primary structure sleeves the secondary structure; the secondary structure and the primary structure are arranged coaxially; the multiple permanent magnets are arranged on the inner wall of the primary structure; one end of each fourth salient pole structure is arranged on the inner wall of the primary structure; and the multiple permanent magnets and the windings are arranged on the multiple fourth salient pole structures. Through arranging the permanent magnets and the windings at the stationaryside of the primary structure, the secondary structure is simple and the cost is reduced; and besides, the secondary structure is put in sea water, corrosion of the permanent magnets and the windingsdoes not happen, the maintenance is convenient, and the reliability is high.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Double stator permanent magnet cursor linear motor and design method for increasing magnetic field modulation effect
ActiveUS20180301968A1Improve magnetic propertiesReduce contentSynchronous machinesMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineFinite element method
Disclosed is a double-stator linear vernier permanent magnet (DS-LVPM) motor and method to increase the magnetic field modulation effect. The motor contains a primary, and first and second secondaries on both sides of the primary, spaced by an air gap. The motor secondary includes modulation teeth. The primary is bilaterally symmetrical, and permanent magnets (PM) are embedded in the yoke of the primary core elements. The design solves the inherent problem of flux leakage at the end of PMs for conventional VPM motors, so as to improve utilization of PMs, thereby increasing thrust density of the motors. Additionally, the motor secondaries are laminated by silicon steel sheet, which saves PM material and significantly reduces cost for linear long stroke applications. By adjusting PM structure parameters, the design can use finite element method (FFM) to calculate repeatedly to get PM structure parameters corresponding to maximum electromotive force (EMF).
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Segmented electrical machine
ActiveUS20190081532A1Reduced space requirementsFast response timeAssociation with control/drive circuitsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineMagnetic reluctance
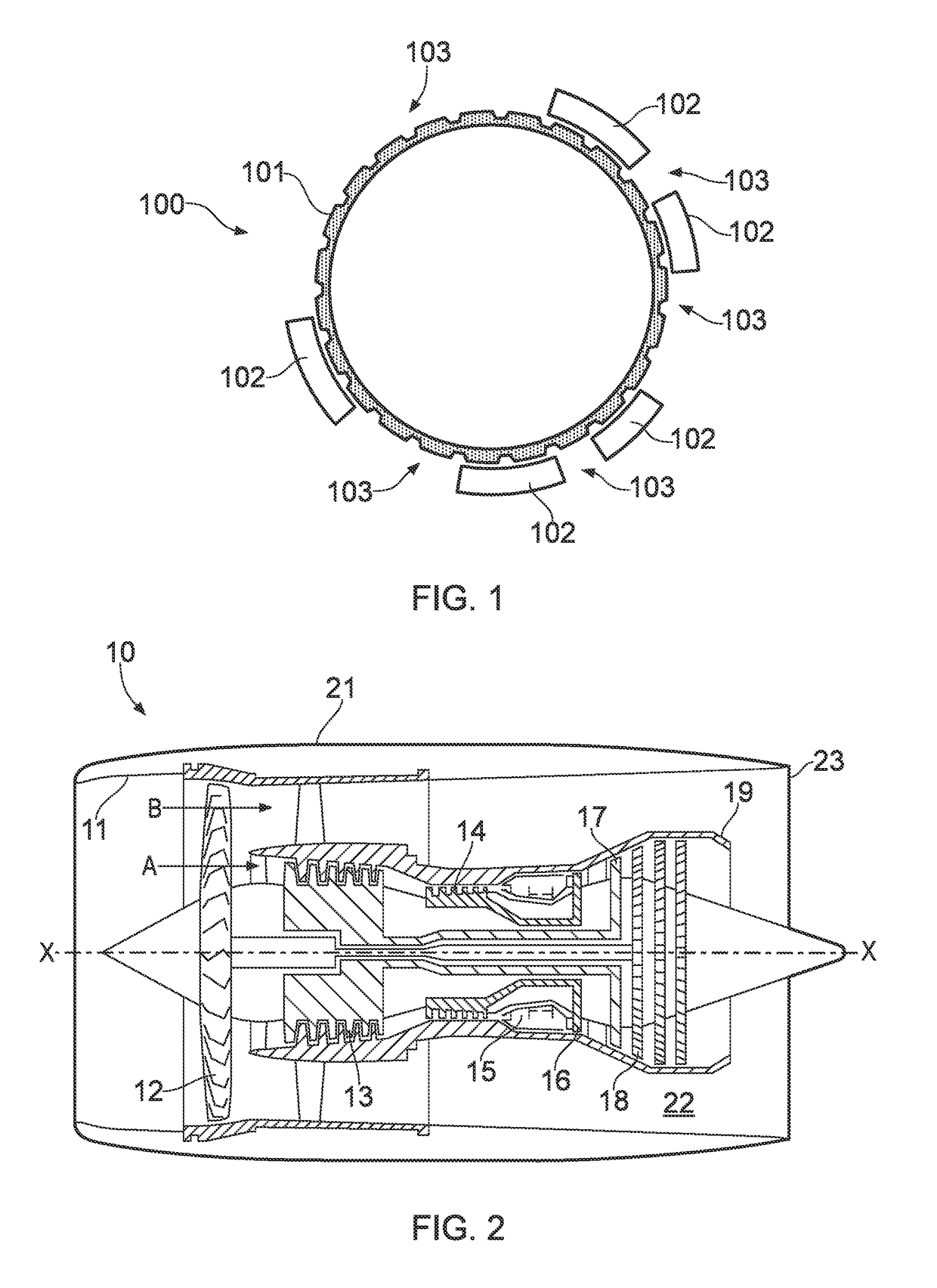
An electrical machine has a variable reluctance rotor, and a stator formed as an annular array of stator segments. The reluctance of the rotor-to-stator magnetic flux path varies with rotor position whereby the stator segments are magnetically energizable to rotate the rotor. The stator segments are arranged in the array such that, when energized to rotate the rotor, they produce an unbalanced force on the rotor. The machine further has a compensator including one or more balancing segments which are configured to be magnetically energizable to produce a balancing force on the rotor which balances the unbalanced force. The reluctance of the rotor-to-compensator magnetic flux path is substantially invariant with rotor position.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Linear motor
ActiveCN106849605AImprove driving abilityImprove stabilityPropulsion systemsElectric machineEngineering
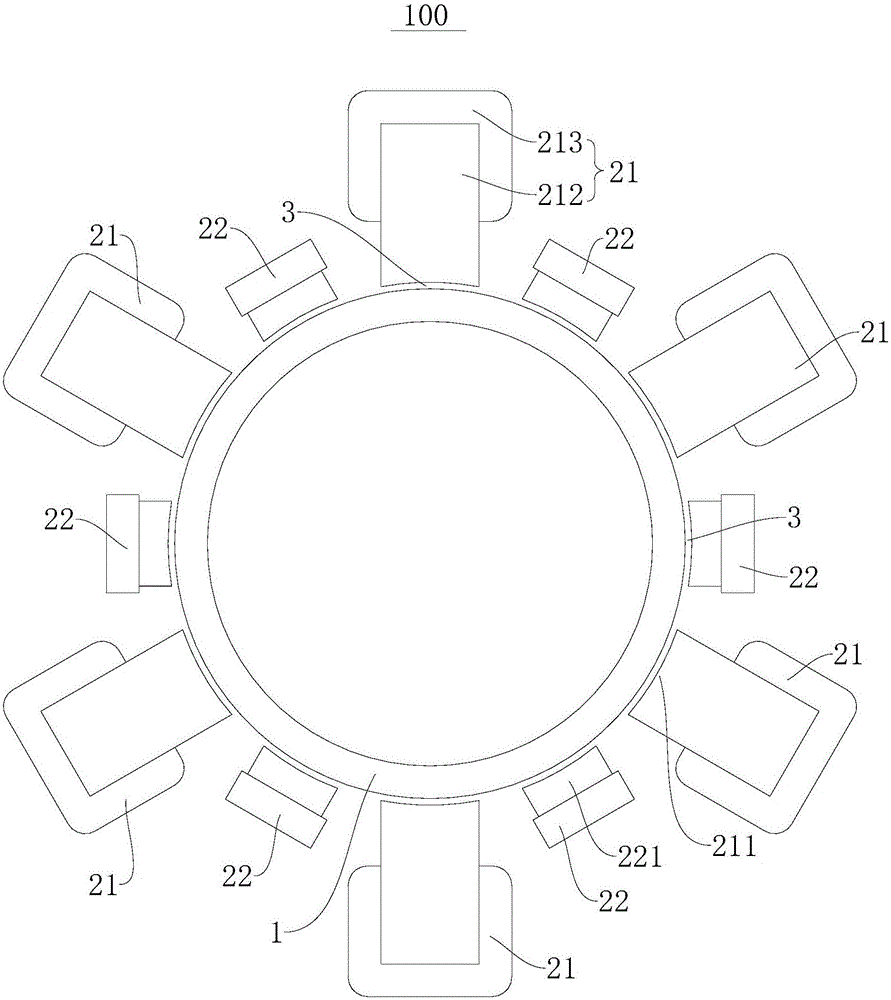
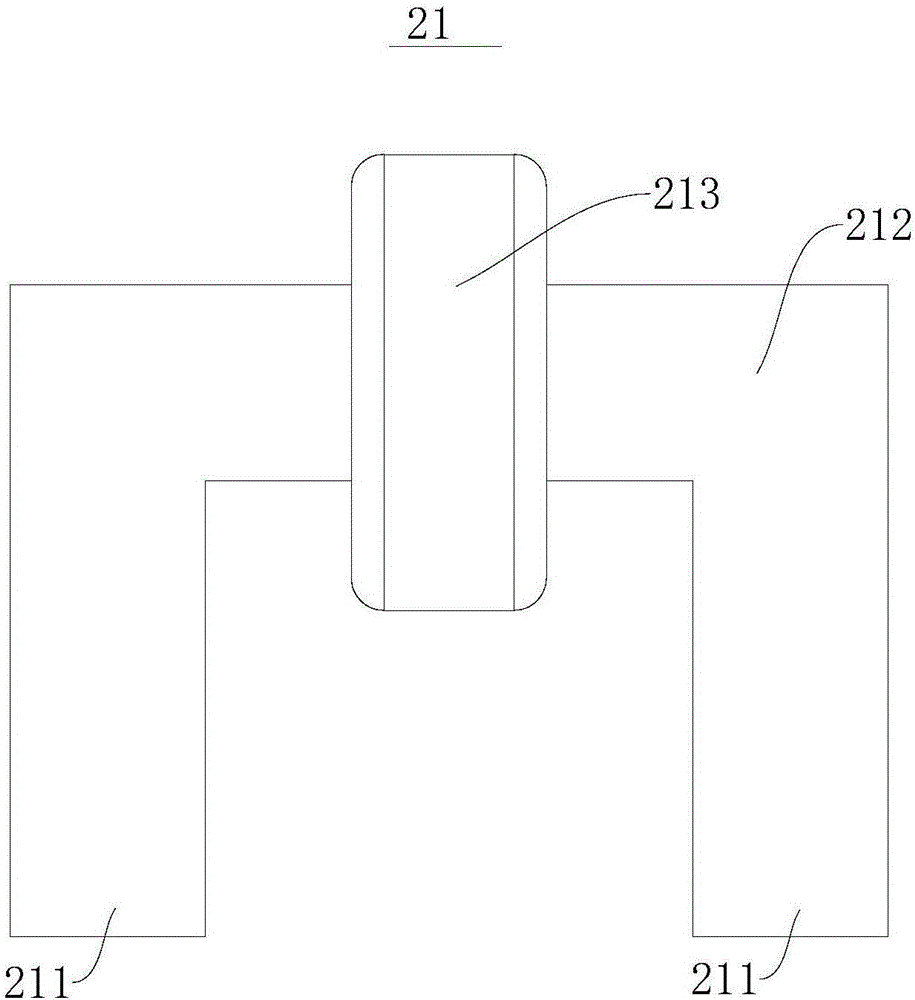
The invention discloses a linear motor. The linear motor comprises a motor secondary part and a motor primary part. The motor secondary part comprises a magnetic conductive magnetic resistance side, the magnetic resistance side comprises a plurality of annular magnetic resistance iron cores distributed at intervals, the motor primary part and the motor secondary part are arranged in a spaced mode to form an air gap, the motor primary part comprises a plurality of winding excitation sides and a plurality of permanent magnet sides, the winding excitation sides are distributed at intervals in the peripheral direction of the magnetic resistance iron cores and are applicable to induction to generate a magnetic field, the multiple winding excitation sides and the multiple permanent magnet sides are arranged in a staggered mode in the peripheral direction of the magnetic resistance iron cores, and the permanent magnet excitation sides and the winding excitation sides are matched. According to the linear motor, the motor primary part can be pushed to move in the laying direction of the magnetic resistance iron core of the motor primary part, the force density is large, and the linear motor is suitable for various linear direct-dive occasions.
Owner:WELLING WUHU MOTOR MFG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com