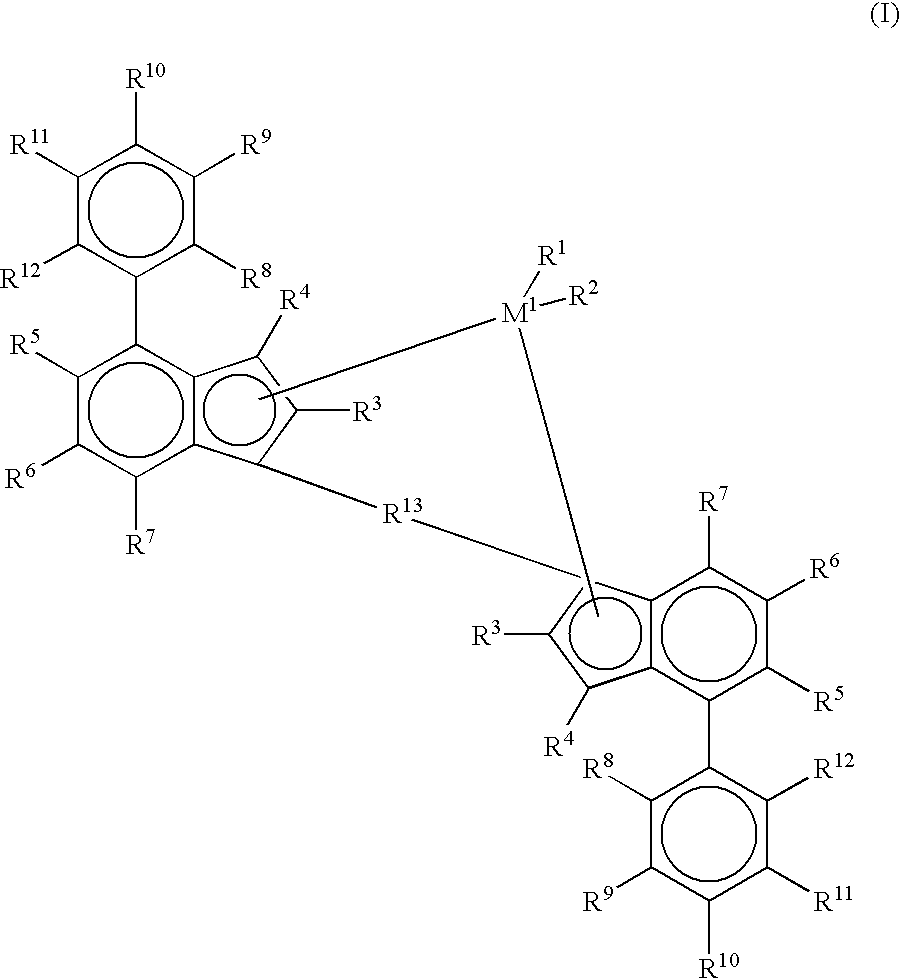
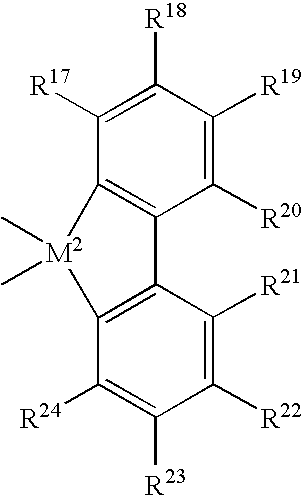
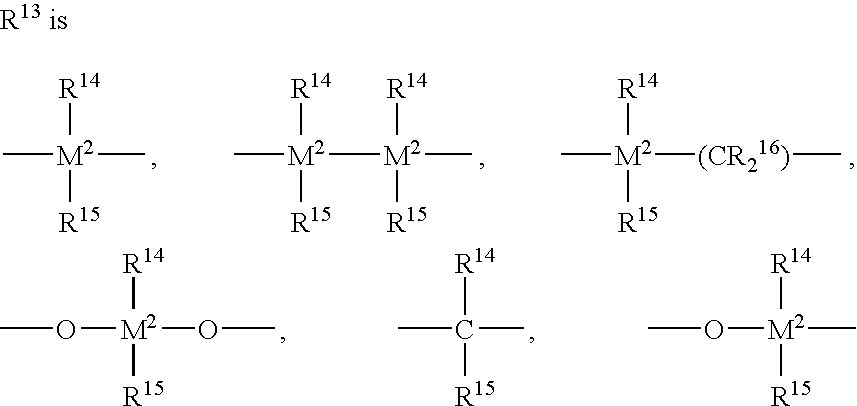Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32results about How to "High fabric strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
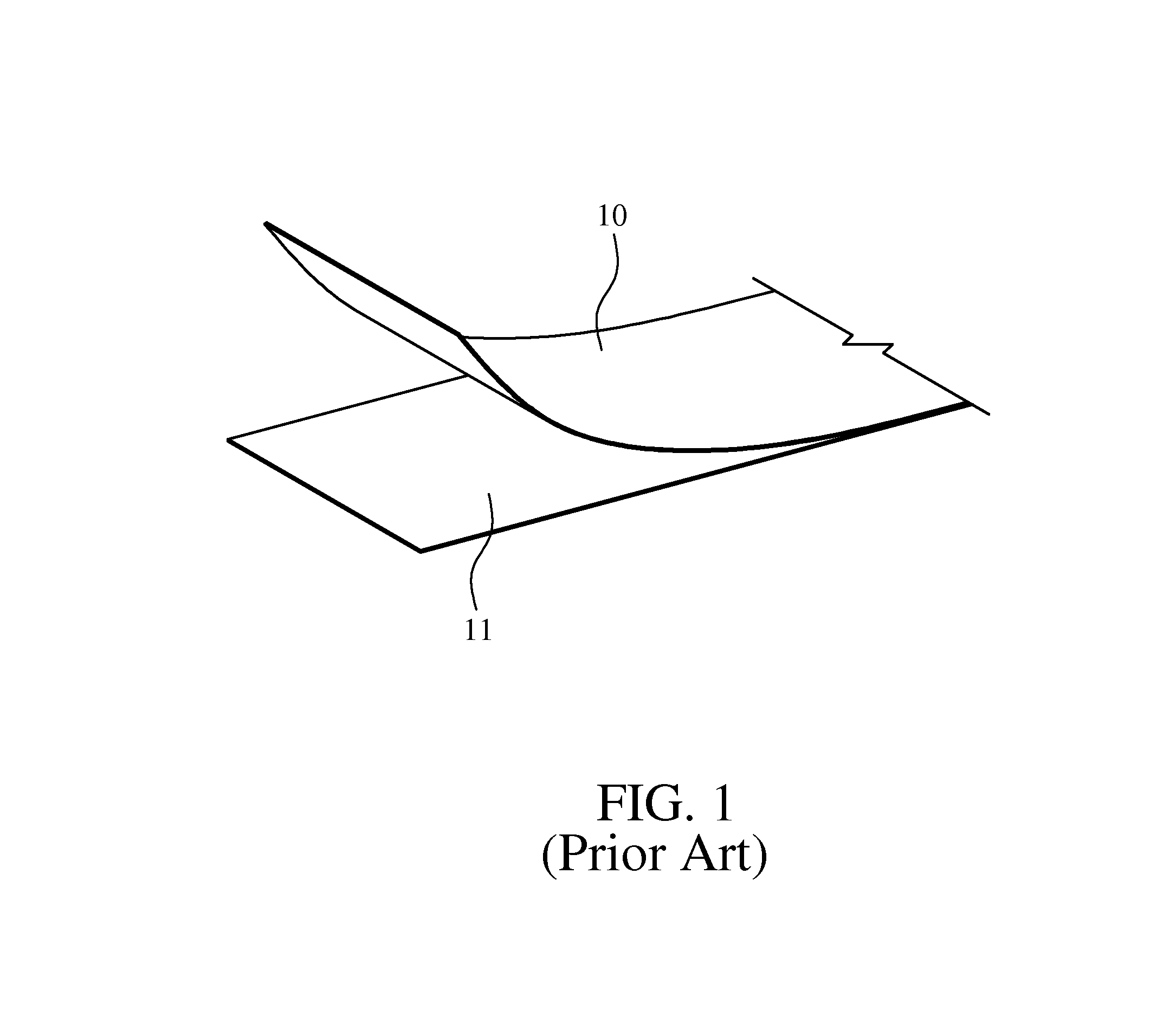
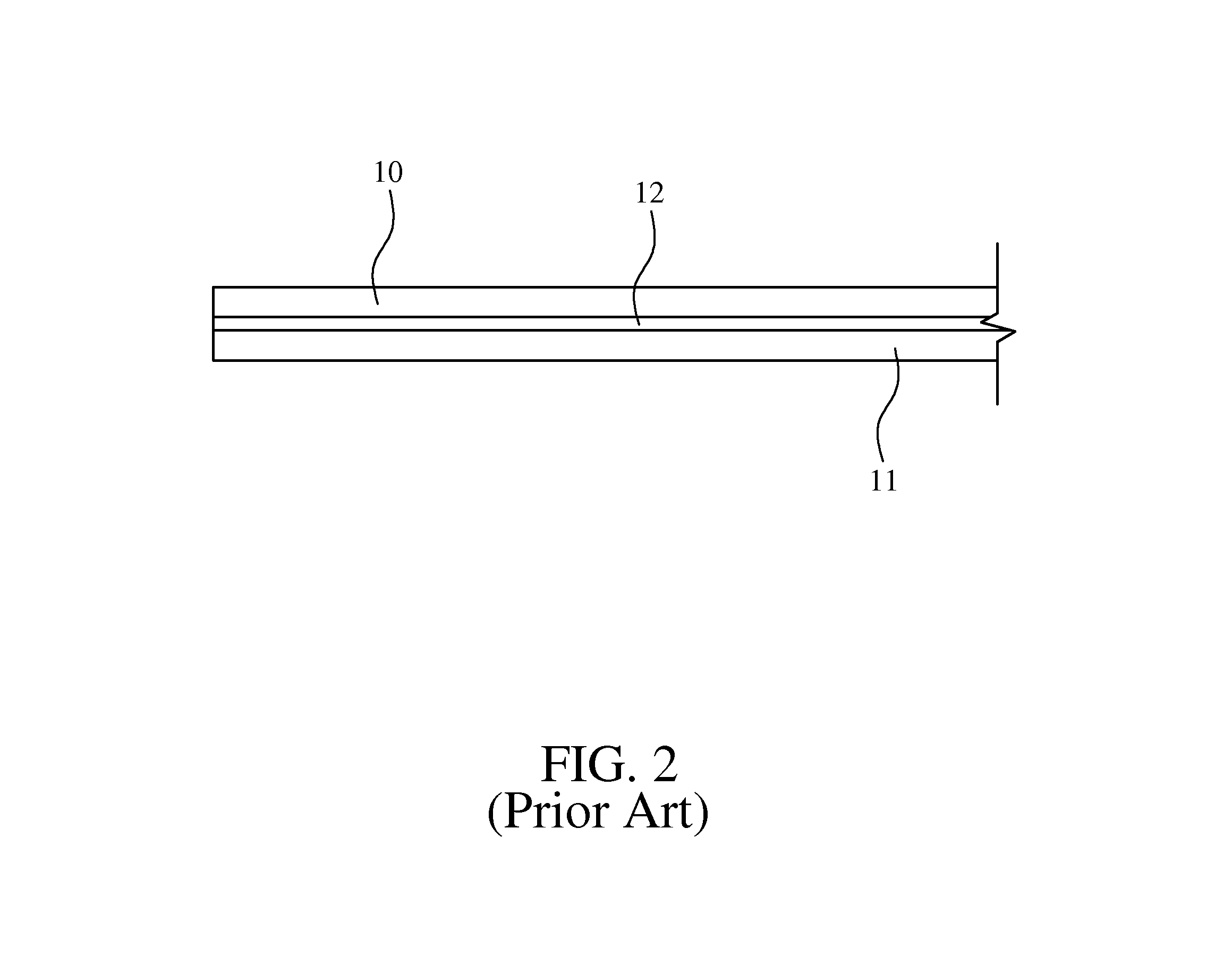
Supple penetration resistant fabric and method of making
InactiveUS6962739B1High fabric strengthStrong materialGlovesSynthetic resin layered productsBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
Owner:HIGHER DIMENSION MATERIALS INC (US)
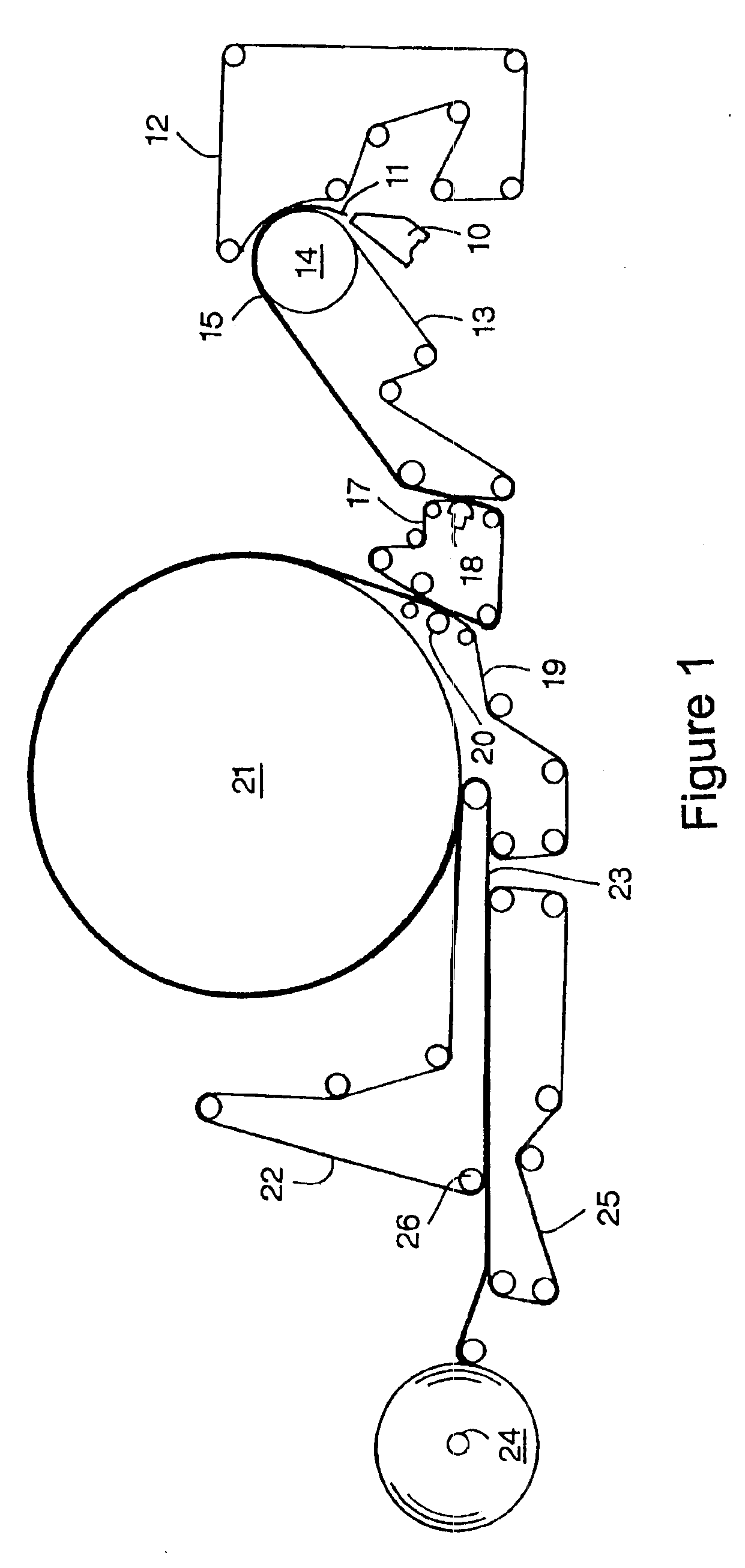
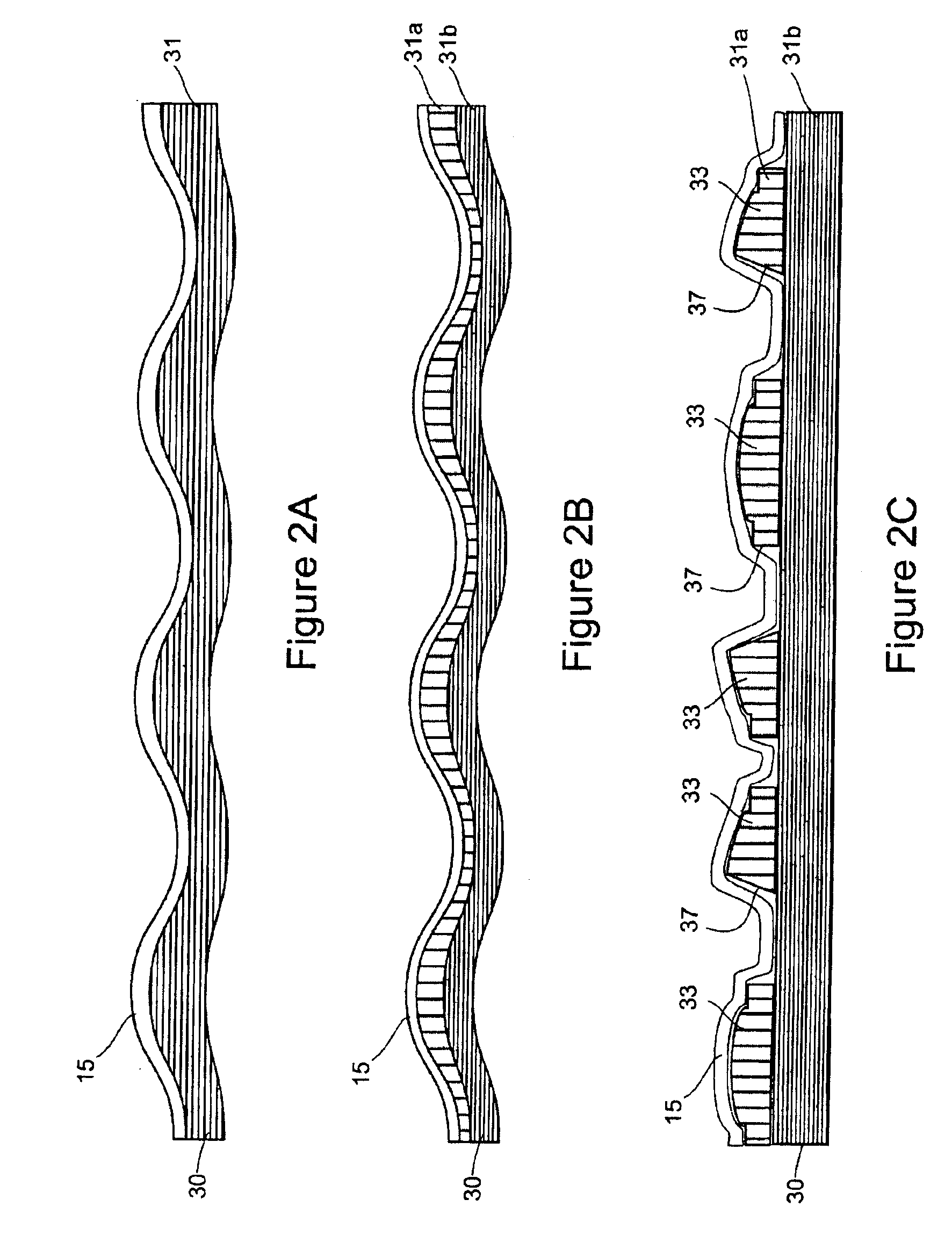
Non-woven through air dryer and transfer fabrics for tissue making
InactiveUS6878238B2High fabric strengthHigh thicknessNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperNonwoven fabricAir dryer
One embodiment of the present invention is an endless non-woven tissue making fabric having a three-dimensional texture suitable for use as a fabric for producing three-dimensional fibrous webs. The endless non-woven tissue making fabric comprises a plurality of substantially parallel adjoining sections of non-woven material. Each section of non-woven material has a width substantially less than the width of the non-woven tissue making fabric. Each section of non-woven material may be joined to at least one other adjoining section of non-woven material. The non-woven tissue making fabric has a machine direction, a cross-machine direction, a tissue contacting surface and a tissue machine contacting surface. The tissue contacting surface comprises solid matter at a plurality of heights such that the tissue contacting surface of the non-woven tissue making fabric has an Overall Surface Depth of at least 0.2 mm in regions of solid matter on the tissue contacting surface.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Supercritical polymerization process and polymers produced therefrom
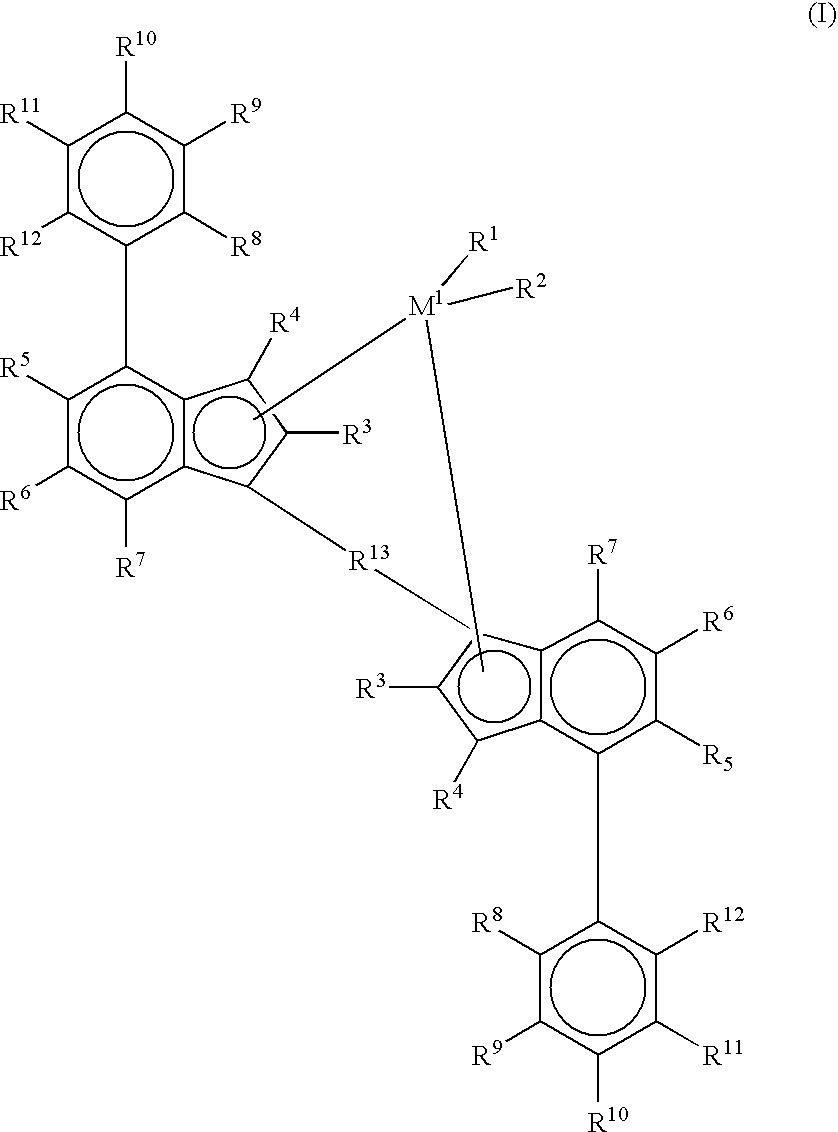
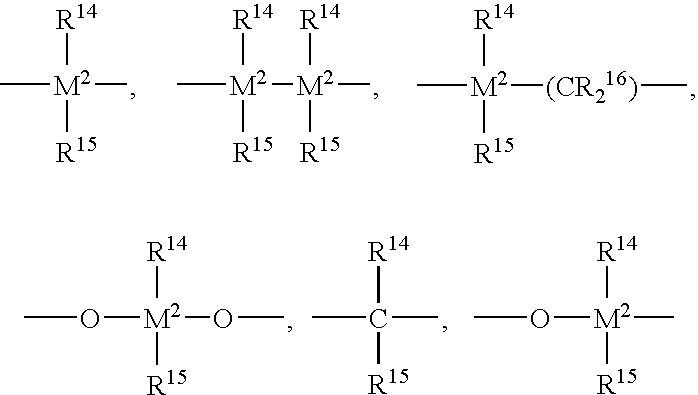
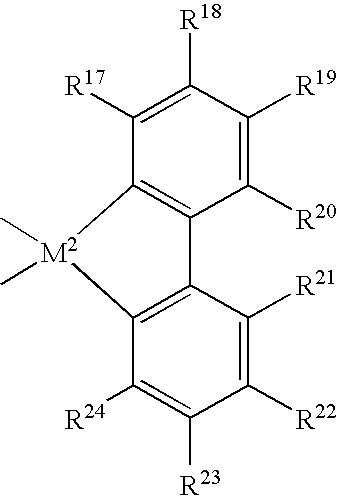
ActiveUS20040122191A1High catalytic activityDrop in molecular weightBulk chemical productionPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
This invention relates to a process to produce propylene polymers comprising contacting a metallocene catalyst compound and an activator in a reaction medium comprising propylene, from 0 to 30 volume % of one or more solvents and from 0 to 30 mole % of one or more comonomers, under temperature and pressure conditions below the melting point of the propylene polymer and where: a) the temperature is at or above the critical temperature for the reaction medium, and the pressure is at least 500 kPa above the critical pressure of the reaction medium; or b) the temperature is 1° C. or more above the critical temperature for the reaction medium, and the pressure is at or above the critical pressure of the reaction medium; or c) the temperature is 1° C. or more above the critical temperature for the reaction medium, and the pressure is at least 500 kPa above the critical pressure of the reaction medium.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
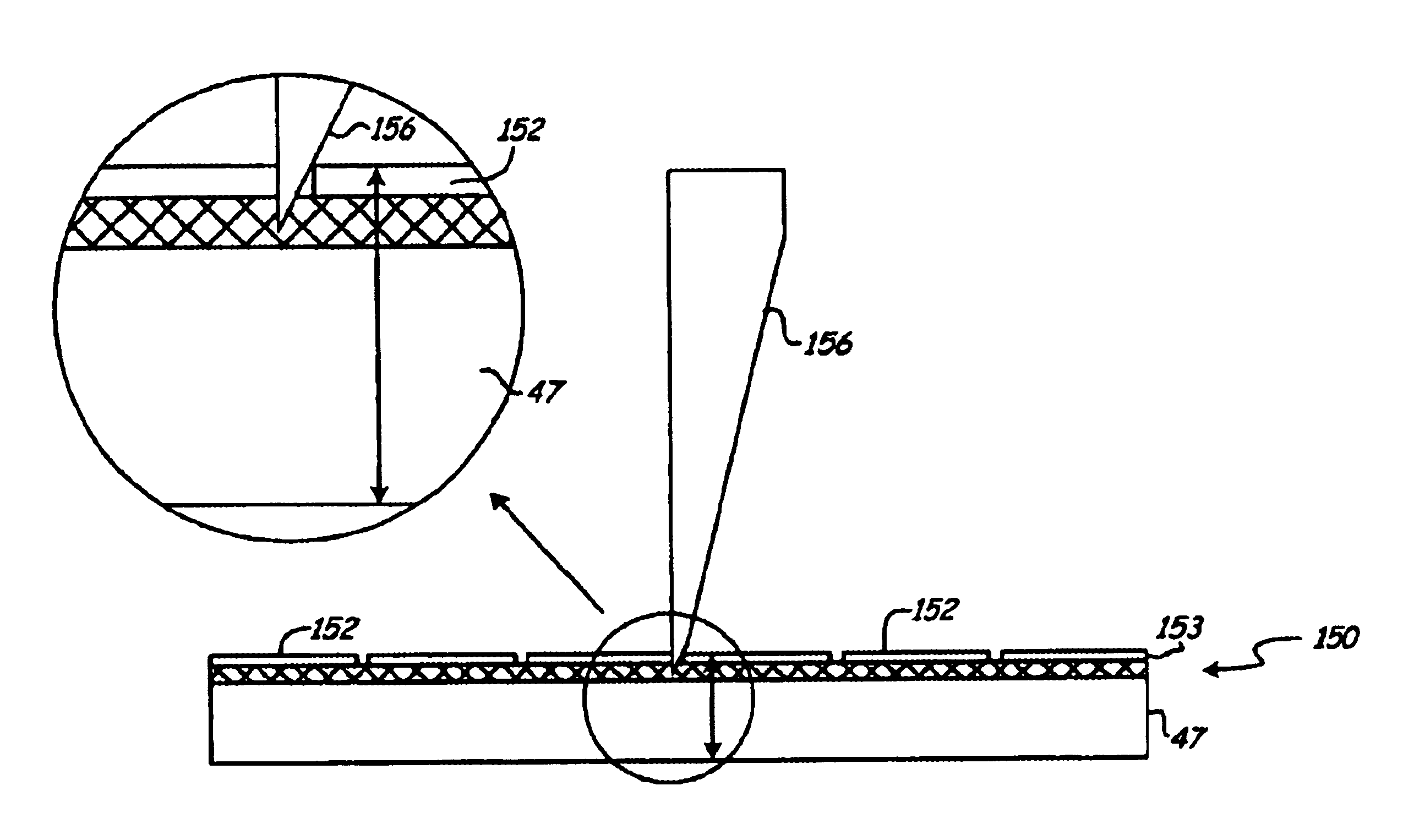
Supple penetration resistant fabric and method of making
InactiveUS20050170221A1Sustain damageGlobal supplenessGlovesSynthetic resin layered productsMedical treatmentCivil engineering
A puncture, pierce, and cut resistant fabric comprised of a plurality of sheets of plates arranged in a repeating pattern. A material interconnects the plates. The fabric is twistable, bendable, and flexible. It is constructed of substances that will withstand cutting, puncture, and piercing forces encountered in medical or other environments.
Owner:HIGHER DIMENSION MATERIALS INC (US)
High temperature bulk polymerization of branched crystalline polypropylene
Branched crystalline polypropylene compositions and methods for the preparation of branched crystalline polypropylene compositions are provided. For example, described herein is a process of preparing branched crystalline polypropylene composition that comprises contacting a supported metallocene catalyst compound with a polymerization medium that comprises propylene monomers; and conducting polymerization of the propylene monomers at a temperature greater than 70° C. for a time sufficient to provide branched crystalline polypropylene that has from 0.0 wt % to 2.0 wt % ethylene and a heat of fusion of 70 J / g or more.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Non-woven through air dryer and transfer fabrics for tissue making
InactiveUS6875315B2High fabric strengthHigh thicknessNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperNonwoven fabricAir dryer
One embodiment of the present invention is an endless non-woven tissue making fabric. The endless non-woven tissue making fabric has a machine direction, cross-machine direction, a tissue machine contacting surface, a tissue contacting surface, a first side edge, and a second side edge. The non-woven tissue making fabric comprises a fabric strip of non-woven material comprising at least one layer of non-woven material. The fabric strip has a first edge, an opposing second edge, a machine direction, and a cross-machine direction. The fabric strip may be spirally wound in a plurality of contiguous turns wherein the first edge in a turn of the fabric strip extends beyond the second edge of an adjacent turn of the fabric strip, thereby forming a spirally continuous seam with adjacent turns of the fabric strip.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Polypropylene fibers and fabrics
ActiveUS20140155854A1Improve tensile propertiesHigh fabric strengthSynthetic resin layered productsMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentPolymer sciencePropylene Polymers
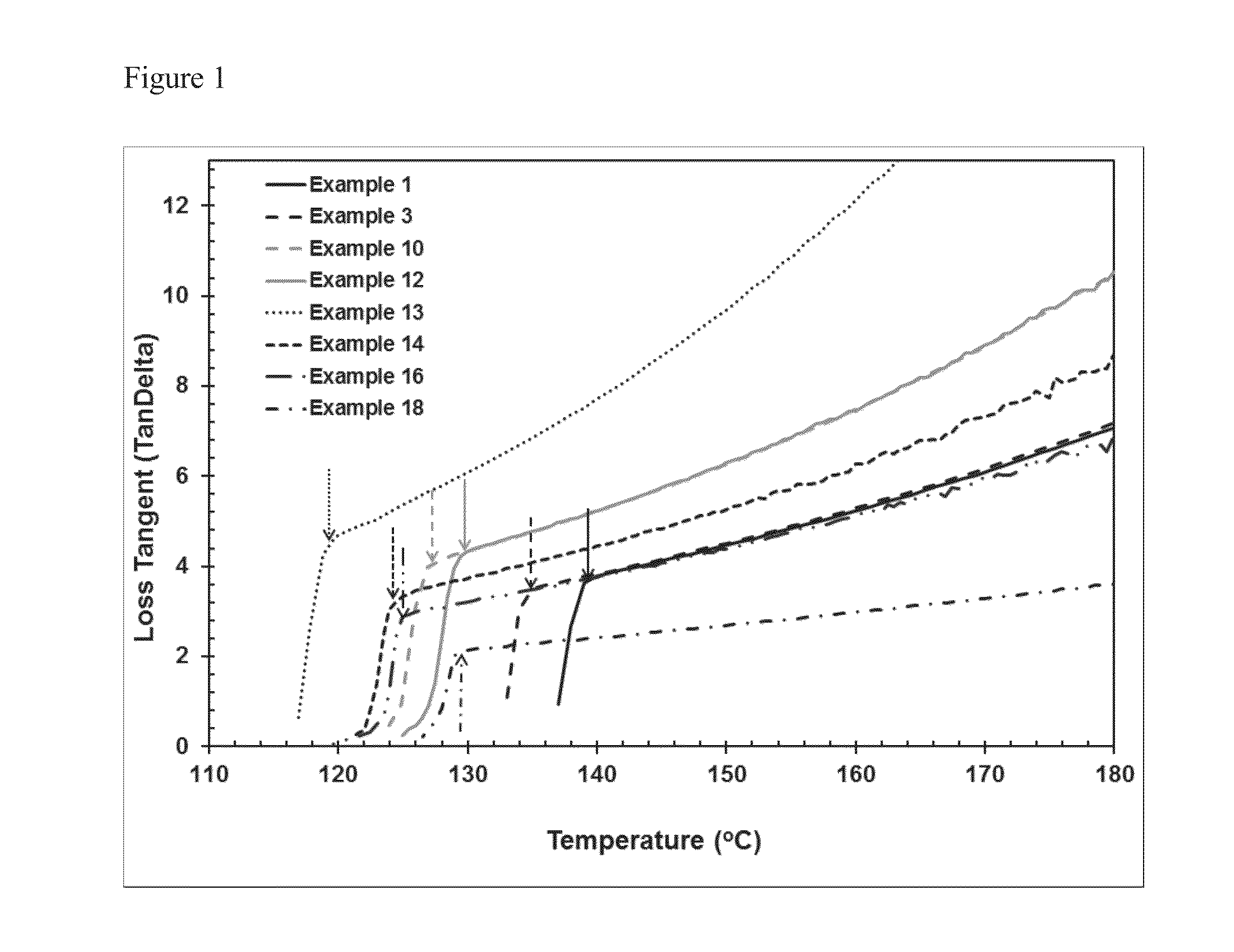
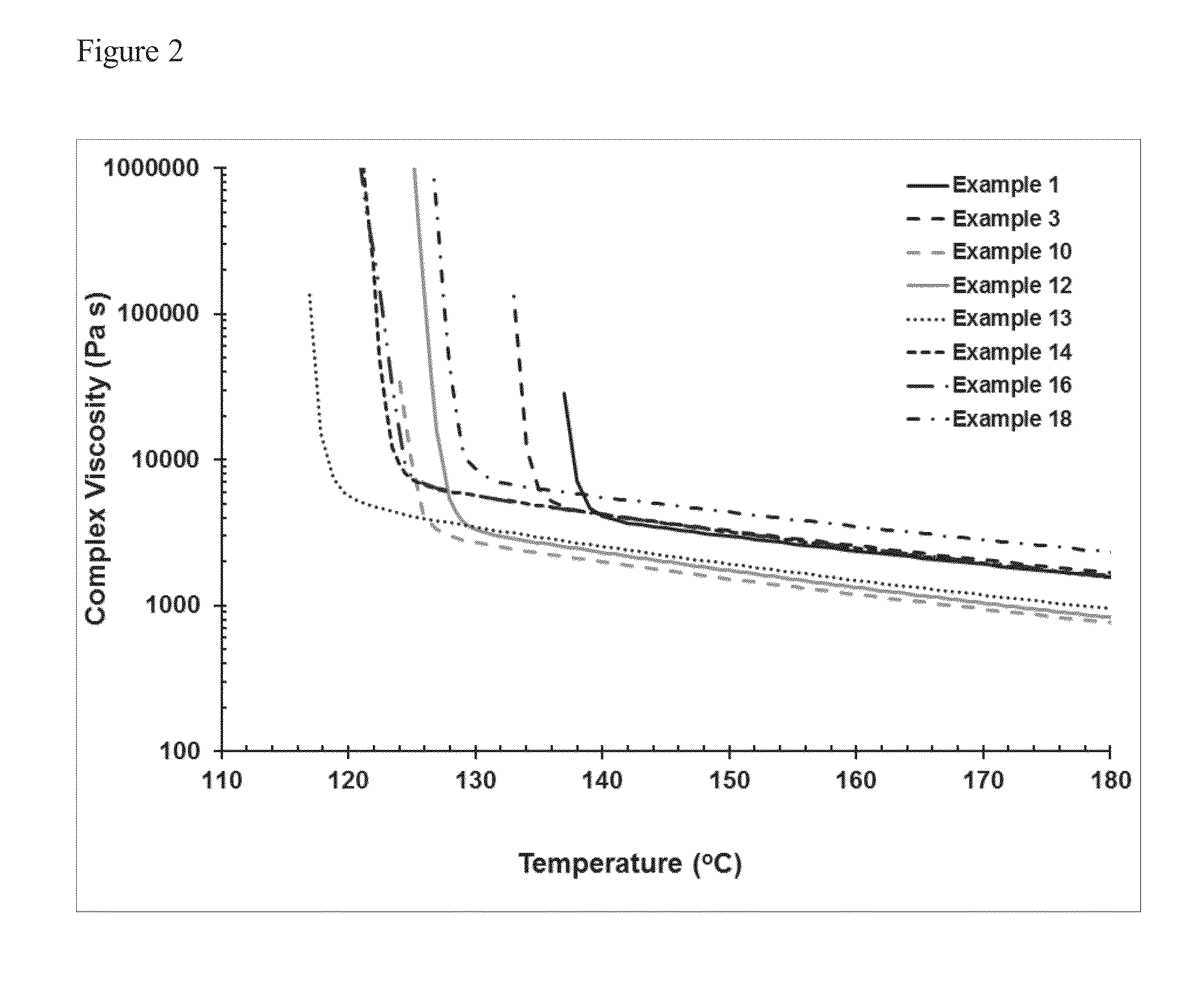
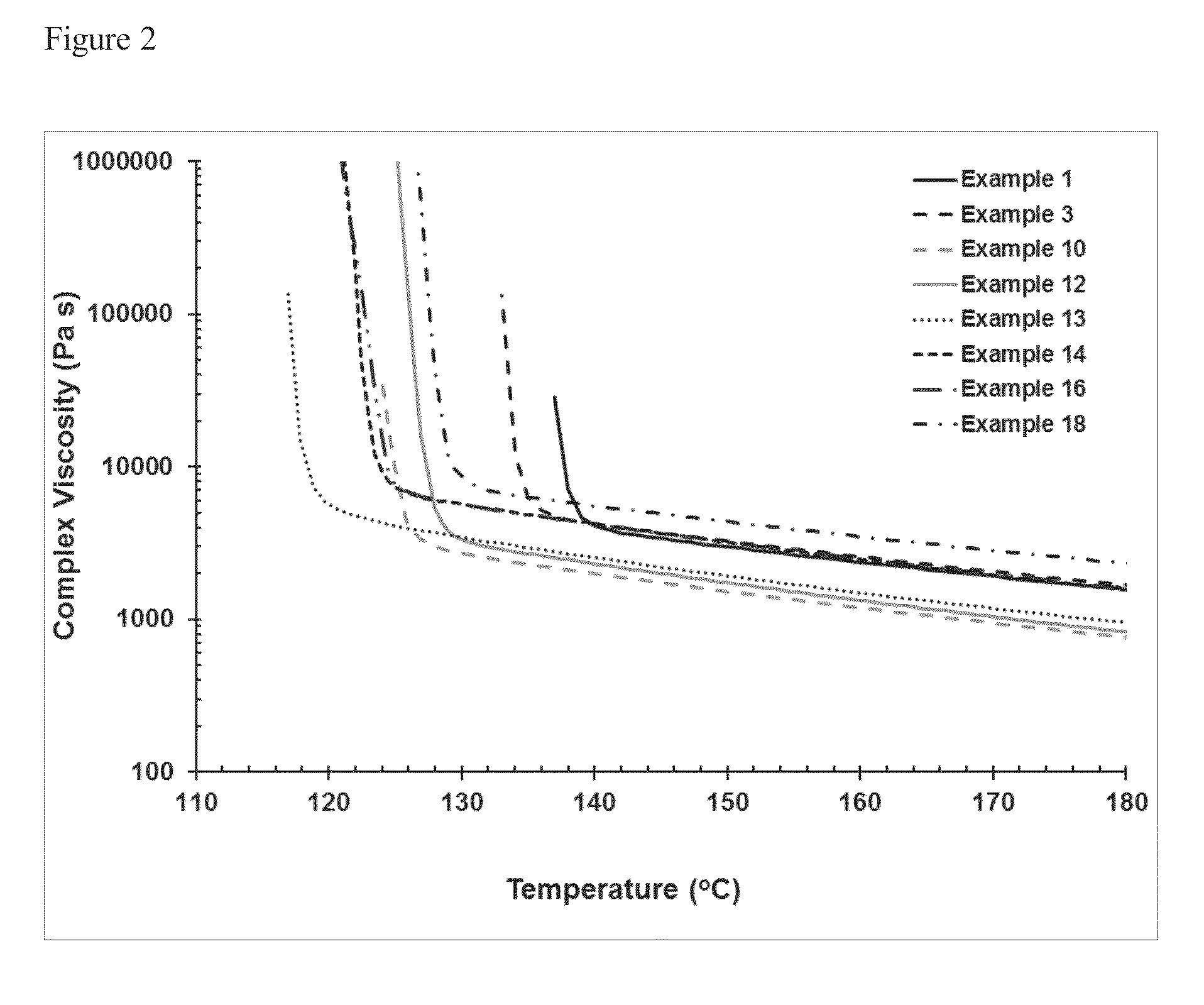
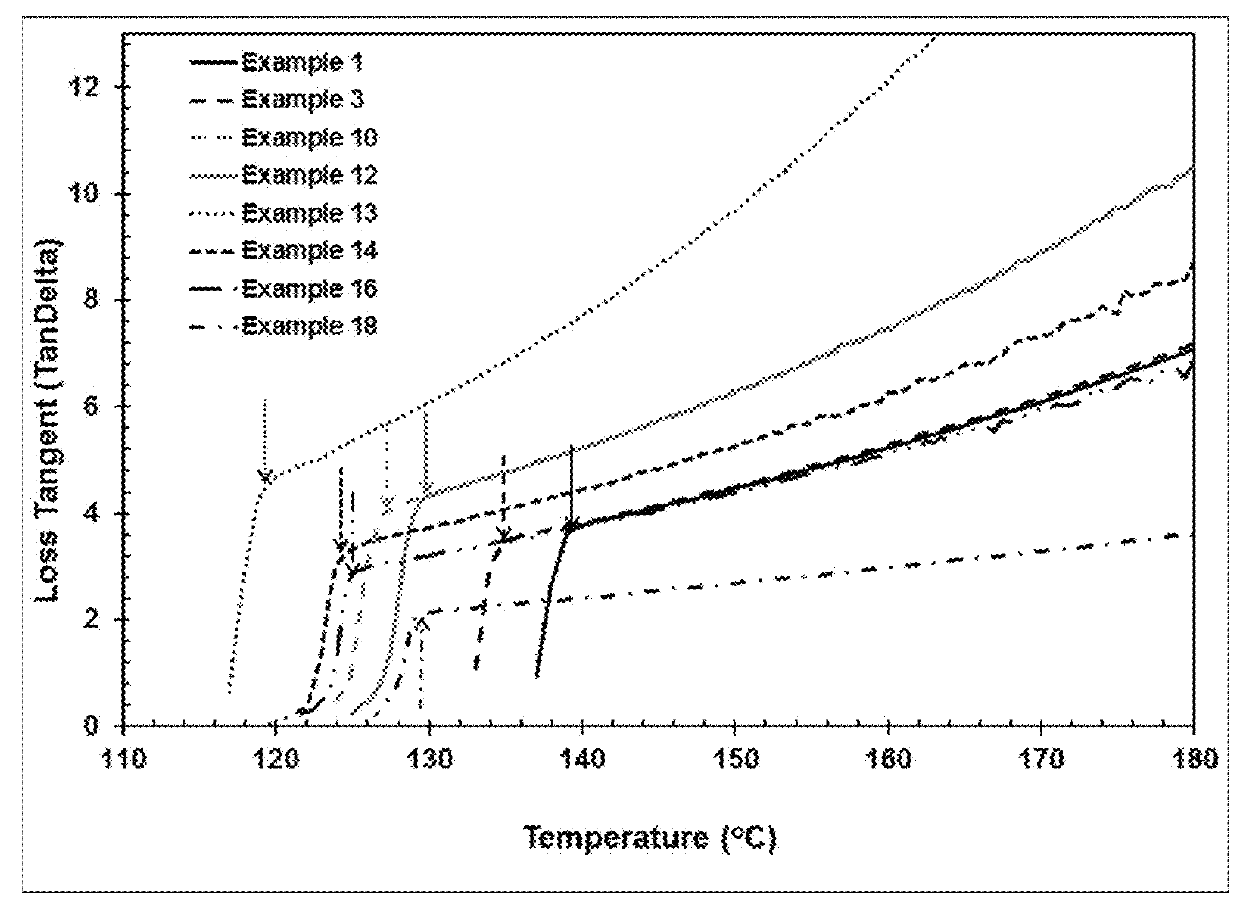
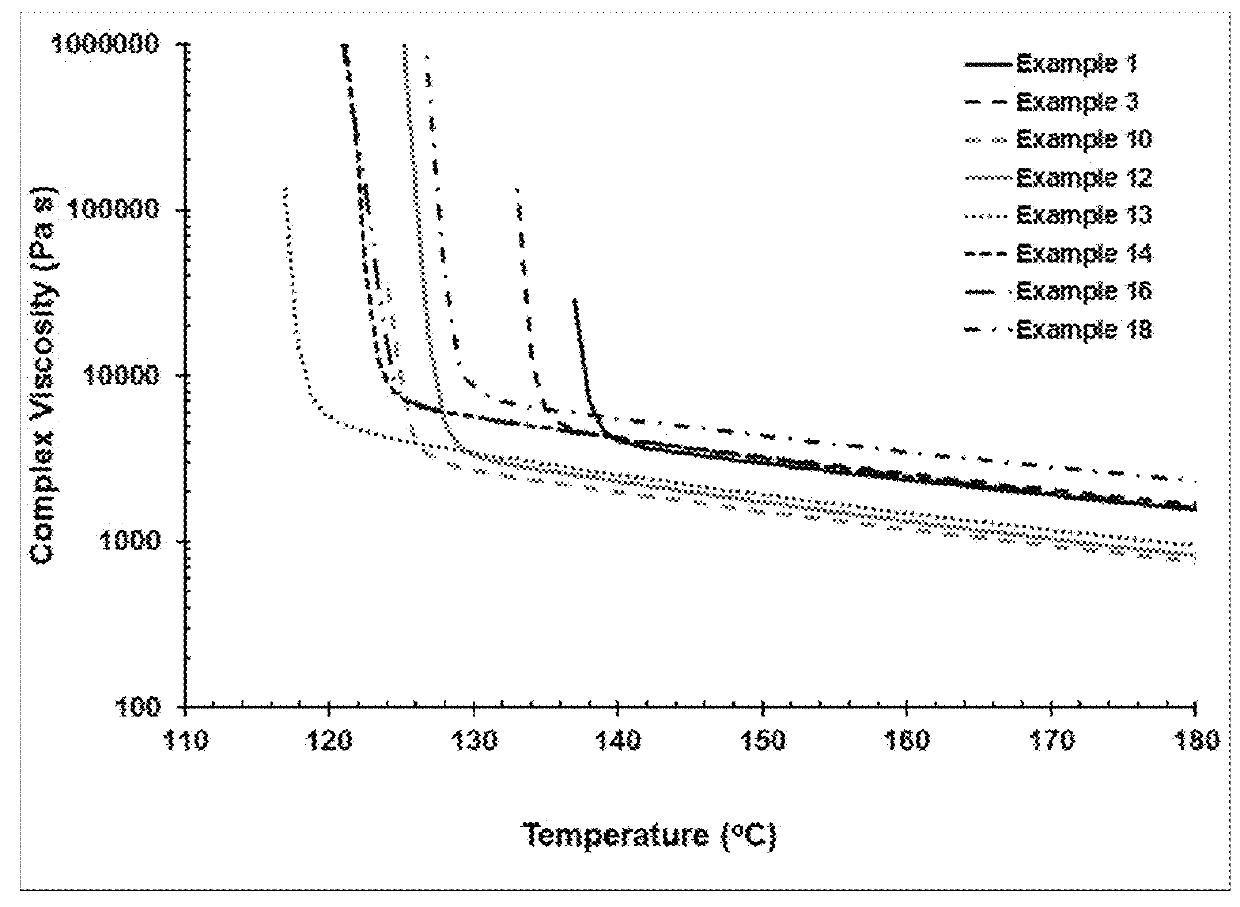
This invention relates to polypropylene fibers and fabrics containing polypropylene fibers, the fibers comprising propylene polymers comprising at least 50 mol % propylene, said polymers having: a) a melt flow rate (MFR, ASTM 1238, 230° C., 2.16 kg) of about 10 dg / min to about 25 dg / min; b) a dimensionless Stress Ratio / Loss Tangent Index R2 [defined by Eq. (8)] at 190° C. from about 1.5 to about 30; c) an onset temperature of crystallization under flow, Tc,rheol, (as determined by SAOS rheology, 190° C., 1° C. / min, where said polymer has 0 wt % nucleating agent present), of at least about 123° C.; d) an average meso run length determined by 13C NMR of at least about 55 or higher; and e) optionally, a loss tangent, tan δ, [defined by Eq. (2)] at an angular frequency of 0.1 rad / s at 190° C. from about 14 to about 70.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC +1
Cotton and polyester bunchy heterochromatic interwoven fabric and processing process thereof
InactiveCN103184614AImprove wrinkle resistanceHigh fabric strengthMercerising of indefinite length fabricsSingeingPolyesterYarn
The invention discloses a cotton and polyester bunchy heterochromatic interwoven fabric, wherein CJ9.7 tex is adopted as warp, CJ11.6Ztex+T11.8Ztex is adopted as weft; and the fabric texture adopted is a 1 / 1 and 2 / 2 modified rib weave. According to a processing process of the cotton and polyester bunchy heterochromatic interwoven fabric, special technological conditions are adopted in processes such as spinning, weaving, and dyeing and finishing. The fabric and the processing process have the beneficial effects that a novel polyester bunchy yarn of the fabric is spun by applying the conventional polyester raw material, a heterochromatic dyeing effect is represented after the novel polyester bunchy yarn is interwoven and dyed with a cotton bunchy yarn, and a considerable effect is achieved after the two conventional fibers are interwoven through the innovative design. Because of embedding of the polyester bunchy yarn, the crease resistance of a cotton product is also improved, the strength and the washing fast-drying property of the fabric are increased and the like, low cost and good quality are realized, and the market positioning on the cost performance of the product is met. The product design has innovativeness and systematicness. During printing and dyeing processing, the heterochromatic effect of the fabric is achieved by using a cotton and polyester heterochromatic dyeing process through an improved process.
Owner:TIANJIN TIANFANG INVESTMENT HLDG
Supple penetration resistant fabric and method of making
InactiveUS20090142535A1High fabric strengthStrong materialGlovesSynthetic resin layered productsBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
A puncture, pierce, and cut resistant fabric comprised of a plurality of sheets of plates arranged in a repeating pattern. A material interconnects the plates. The fabric is twistable, bendable, and flexible. It is constructed of substances that will withstand cutting, puncture, and piercing forces encountered in medical or other environments.
Owner:HIGHER DIMENSION MATERIALS INC
Fiber for wetlaid non-woven fabric
ActiveUS20090324947A1Good fiber dispersionUniformityPaper/cardboardSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperFiber diameterNonwoven fabric
There is provided a fiber for a wetlaid non-woven fabric, said fiber can be the basis ingredient of a paper that maintains uniform mass per unit area and fiber dispersion and has unprecedented bulkiness. The fiber for a wetlaid non-woven fabric has 30 to 100 wt % of apparently crimping fibers with a fiber diameter of from 3 to 40 mum and 0 to 70 wt % of latently crimping fibers with a fiber diameter of from 3 to 40 mum.
Owner:FIBERVISIONS LP +1
Polypropylene fibers and fabrics
ActiveUS9322114B2Improve tensile propertiesExcellent combination of tensile property and textural propertyMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentAbsorbent padsPolymer sciencePropylene Polymers
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC +1
Conductive fabric
InactiveUS20150004372A1High fabric strengthImprove insulation performanceCellulosic plastic layered productsInsulated cablesEngineeringConductive yarn
In a conductive fabric that includes conductive yarn and non-conductive yarn, a fabric end edge in a region that includes an end portion of at least a portion of the conductive yarn is provided in a position recessed farther to an inside of a fabric surface than a fabric end edge in another region. The end portion of the at least a portion of the conductive yarn is provided to the inside of the fabric surface.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
Diene-modified propylene copolymers
Certain specific embodiments of the inventions will now be discussed. For example, a process of preparing a copolymer composition that includes a diene-modified polypropylene copolymer is described, which process includes: contacting a metallocene catalyst compound with a polymerization medium that includes at least a propylene monomer and an alpha, internal non-conjugated diene monomer; and conducting polymerization of the monomers in the presence of the metallocene catalyst compound for a time sufficient to provide a diene-modified polypropylene random copolymer that includes monomeric units derived from each of the monomers, and having from 0.0 wt % to 2.0 wt % ethylene and a heat of fusion of 25 J / g or more.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Non-woven through air dryer and transfer fabrics for tissue making
InactiveUS20060081349A1High thicknessHigh weightNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperNonwoven fabricAir dryer
One embodiment of the present invention is an endless non-woven tissue making fabric having a three-dimensional texture suitable for use as a fabric for producing three-dimensional fibrous webs. The endless non-woven tissue making fabric comprises a plurality of substantially parallel adjoining sections of non-woven material. Each section of non-woven material has a width substantially less than the width of the non-woven tissue making fabric. Each section of non-woven material may be joined to at least one other adjoining section of non-woven material. The non-woven tissue making fabric has a machine direction, a cross-machine direction, a tissue contacting surface and a tissue machine contacting surface. The tissue contacting surface comprises solid matter at a plurality of heights such that the tissue contacting surface of the non-woven tissue making fabric has an Overall Surface Depth of at least 0.2 mm in regions of solid matter on the tissue contacting surface.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
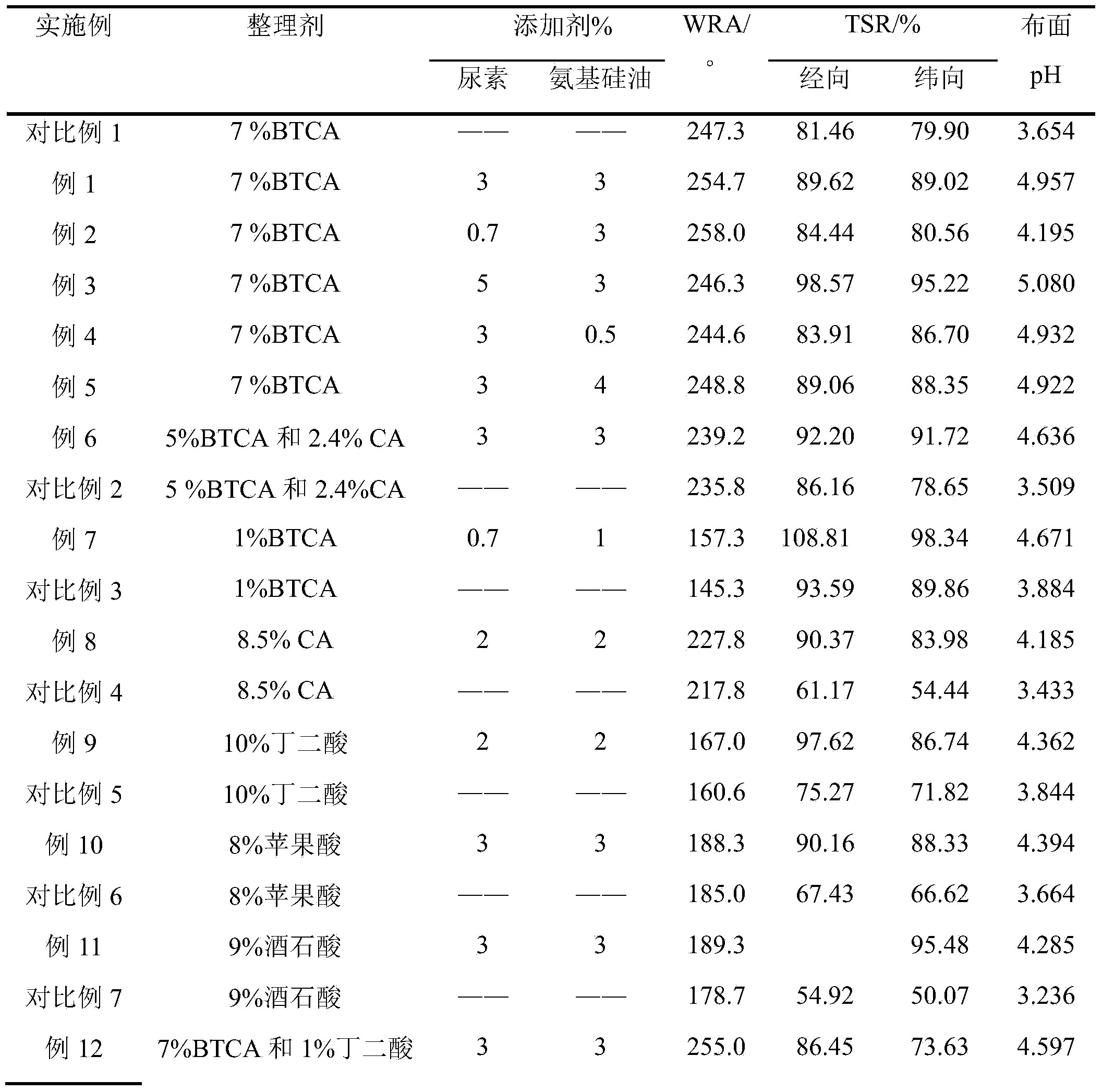
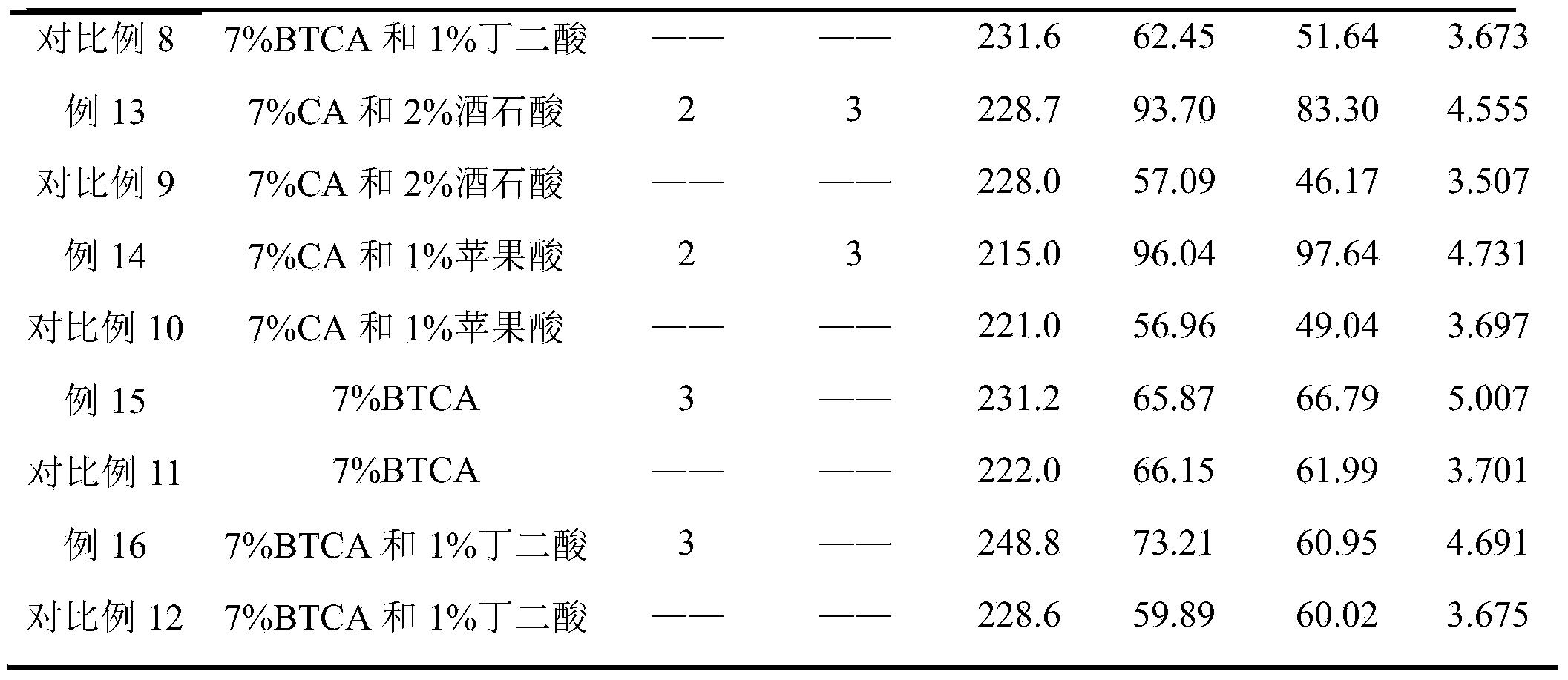
Polybasic carboxylic acid non-ironing process washing-free method adopting urea as additive
The invention relates to a polybasic carboxylic acid non-ironing process washing-free method adopting urea as an additive. The method comprises the steps as follows: a finishing solution is prepared and contains components in percentage by weight as follows: 1%-10% of a polybasic carboxylic acid formaldehyde-free non-ironing finishing agent, 1%-4.6% of a catalyst sodium hypophosphite and 0.7%-5% of urea; and a fabric is soaked twice and rolled twice in the finishing solution, the solution retention rate is in a range of 80%-110%, and then the fabric is dried at the temperature of 80-100 DEG C for 2-10 min and baked at the temperature of 150-180 DEG C for 1-5 min finally. The method is simple to operate, the washing procedure after the cotton fabric is finished by polybasic carboxylic acid is omitted, the enterprise cost can be saved, and industrial production is easy to perform; and by means of the obtained non-ironing product, the wrinkle recovery angle and the tearing strength retention rate of the fabric are improved compared with a common formaldehyde-free non-ironing product, further, the pH value of the finished cloth surface is increased to be higher than 4.0, requirements of GB 18401-2010 are met.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Branched diene-modified crystalline polypropylene terpolymers
Certain specific embodiments of the invention will now be discussed. For example, a process of preparing a polymer composition that includes a branched crystalline diene-modified polypropylene random terpolymer is described, which process includes: contacting a metallocene catalyst compound with a polymerization medium that includes at least a propylene monomer, a first diene monomer, and a second diene monomer; and conducting polymerization of the monomers in the presence of the metallocene catalyst compound for a time sufficient to provide a branched crystalline diene-modified polypropylene random terpolymer that includes monomeric units derived from each of the monomers, and having from 0.0 wt % to 2.0 wt % ethylene and a heat of fusion of 30 J / g or more
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Light-weight high-strength fabric for fencing protective clothing and preparation process thereof
ActiveUS20180163329A1High strengthProtection strengthWeft knittingLayered productsFiberAfter treatment
A light-weight high-strength fabric for fencing protective clothing uses UHMWPE fibers with fiber number of 360-420D and high-strength terylene silks with fiber number of 460-540D as raw materials. The fabric is prepared through the steps of batching, twisting, weaving, and after-treatment. The resulting fabric has less defects due to improvements in fabric formula and weaving techniques, etc. The puncture strength of the fabric can reach 3300N, and the mass per unit area can be reduced to 600 g / m2.
Owner:YUAN MINGFU +1
Method for controlling mixtures especially for fabric processing
InactiveUS7448102B2Save time and costHigh fabric strengthOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTextile treatment machine partsHigh rateProcess engineering
Owner:TUBULAR TEXTILE LLC
High-density carbon fiber needled felt and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110747578AIncrease sliding resistanceHigh fabric strengthWoven fabricsNon-woven fabricsFiberHigh density
The invention discloses a high-density carbon fiber needled felt, which is formed by stacking and needling structural units, each comprising a carbon fiber mesh base and a carbon fiber stretch fabric.The carbon fiber fabric prepared with stretch fibers replaces common carbon fiber fabric, the thickness of the carbon fiber fabric is reduced, the rebound in the needling process caused by gaps amongthe carbon fibers is reduced, and therefore, the overall density and mechanical strength of the carbon fiber needled felt are improved. In addition, the service life of a felting needle for the high-density carbon fiber needled felt can be extended.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANNIAO HIGH TECH
Cotton-viscose blended fabric reactive dyeing production process
The invention relates to printing and dyeing methods, particularly to a cotton-viscose blended fabric reactive dyeing production process. The cotton-viscose blended fabric reactive dyeing production process is applicable to new production processes of dyeing cotton-viscose woven fabrics with an overflow dyeing machine. The cotton-viscose blended fabric reactive dyeing production process is implemented according to the following steps of fabric sample selection, technical process design, gray fabric singeing, alkali desizing design and washing, setting of pretreatment formulas and processes andreactive dye dying formulas and processes, sample vat dyeing, setting of dyeing, oiling and setting processes, after-finished product pre-shrinking, and finished product inspection. The cotton-viscose blended fabric reactive dyeing production process changes the dye yield and the color saturation of cotton fiber of cotton-viscose fabric non-mercerizing processes, ensure consistent dye yield of cotton fiber and viscose fiber, solves the problem of color difference between the cotton fiber and the viscose fiber, and meanwhile, reduces damage of dyeing processes to the viscose fiber and greatlyimproves the strength of fabrics and the quality of products to meet the increasingly strict requirements of clients on quality.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HANGMIN STOCK
Double-faced woven fabric
InactiveUS20130008553A1Improve structural strengthAttractive appearanceMulti-ply fabricsWoven fabricEngineering
A double-faced woven fabric includes a first and a second weave unit interlocked to each other at a plurality of stitching points. The first weave unit includes a plurality of interlaced first warp and weft threads to define a first face, and the second weave unit includes a plurality of interlaced second warp and weft threads to define a second face, which is not coplanar with the first face. The stitching points are formed by crossing the first warp threads over predetermined second weft threads, so that the stitching points are always covered by float second warp threads adjacent to the stitching points. The double-faced woven fabric with the interlocked first and second weave units has largely increased fabric strength and can present different textures, colors or patterns on the first and the second face to thereby provide good applicability.
Owner:SOLARTEX CORP
Non-Weft Cloth, Manufacturing Method Therefor, And Non-Weft Cloth Product
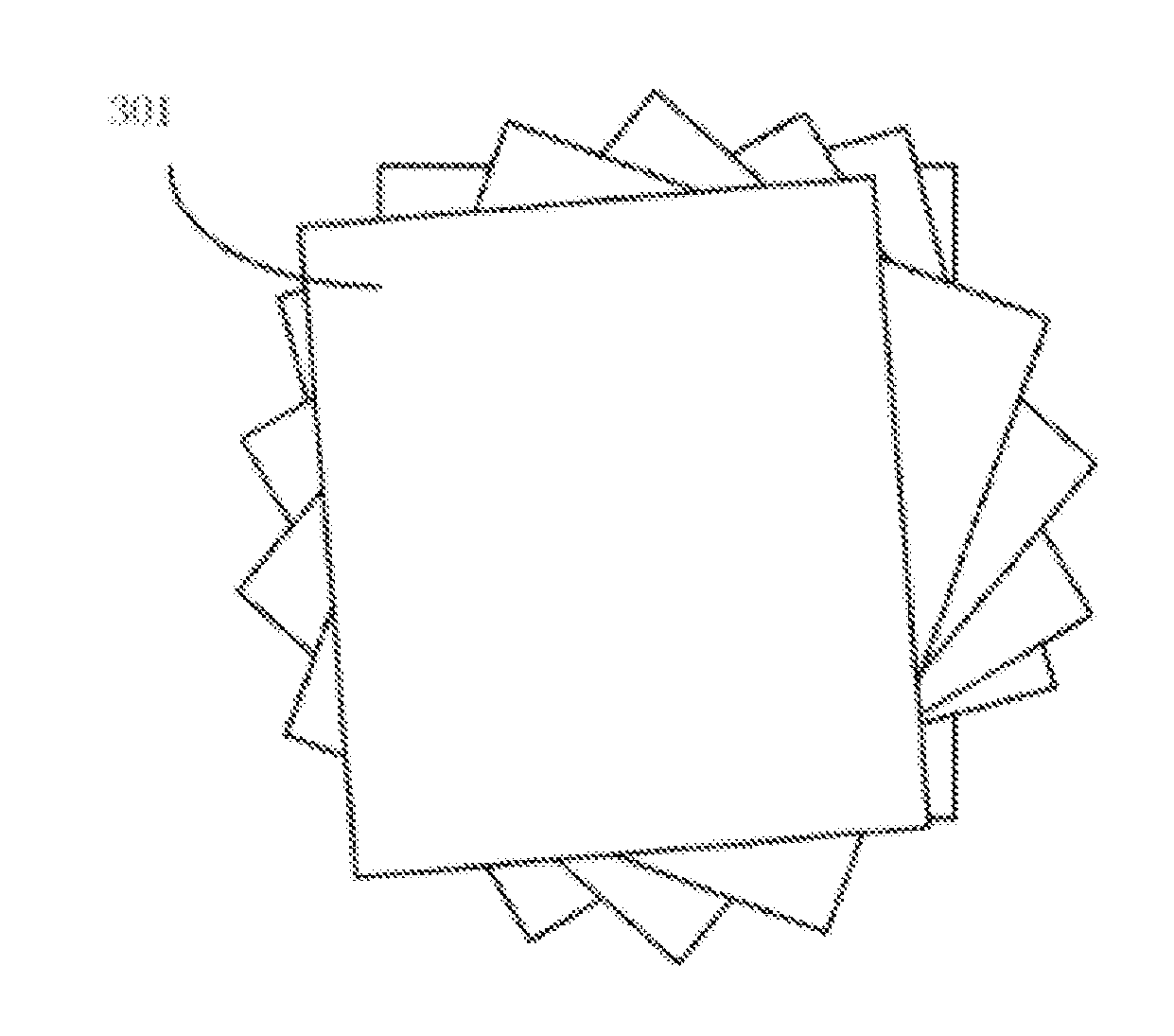
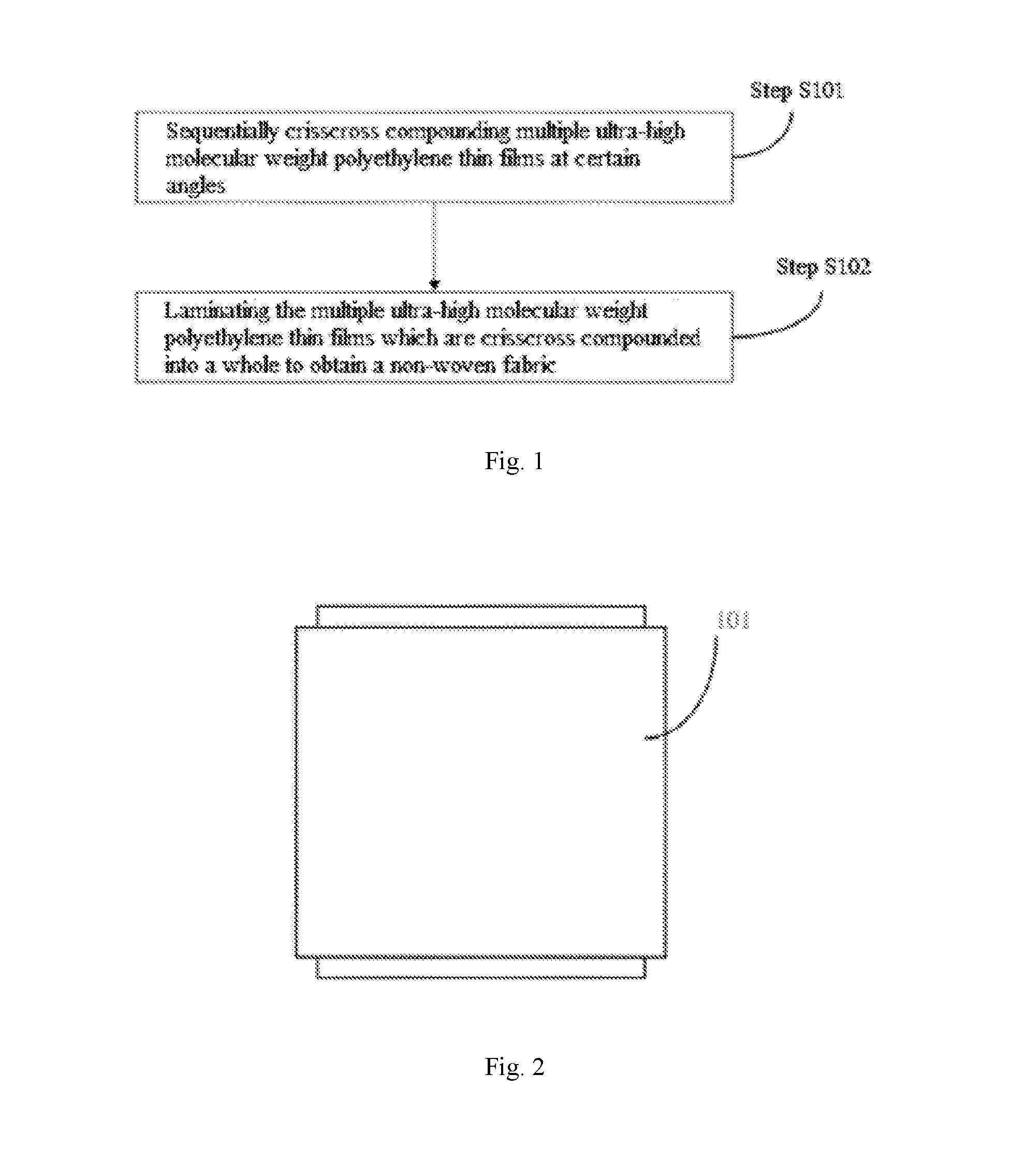
InactiveUS20160136926A1Low costHigh fabric strengthLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentUltimate tensile strengthBearing surface
The invention relates to a non-weft cloth, a manufacturing method thereof and a non-weft cloth product. The method comprises: crisscross compounding and laminating multiple ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene thin films at certain angles into a whole to obtain the non-weft cloth; and as macromolecular straight chain structures in the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene thin films are uniformly distributed, the probability of causing damages to the interior of the thin films in the manufacturing process of the non-weft cloth is relatively low, the defects of breaking, distortion, intertwining, knotting, non-uniform arrangement and the like can be avoided, when the non-weft cloth prepared on the basis of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene thin films is subject to external force impact, the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene thin films are stressed as a whole, and force-bearing points can be diffused to force-bearing surfaces rapidly to effectively transfer energy, thereby improving the strength of the non-weft cloth and improving the bulletproof performance and other protection performances thereof.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU ZHONGYUAN DEFENSE MATERIAL
Polypropylene fibers and fabrics
InactiveUS20160053419A1Improve tensile propertiesExcellent combination of tensile property and textural propertyMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentBaby linensPolymer sciencePropylene Polymers
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC +1
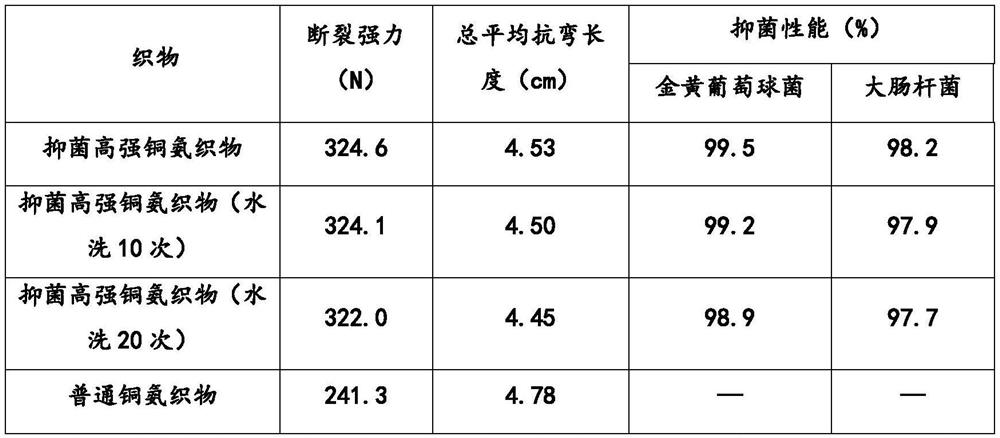
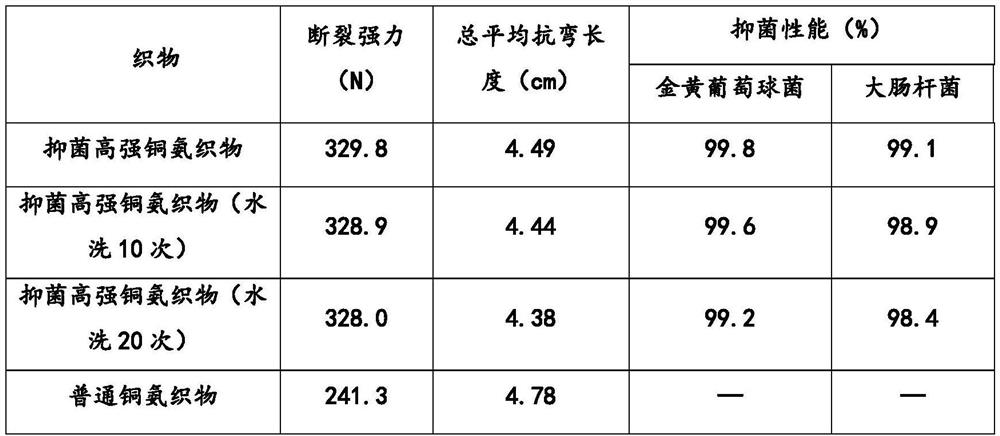
Spinning solution and preparation method thereof and antibacterial copper ammonia fabric and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112647143AGood antibacterial effectEasy to useArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsSpinning solutions preparationSpinningGraphene
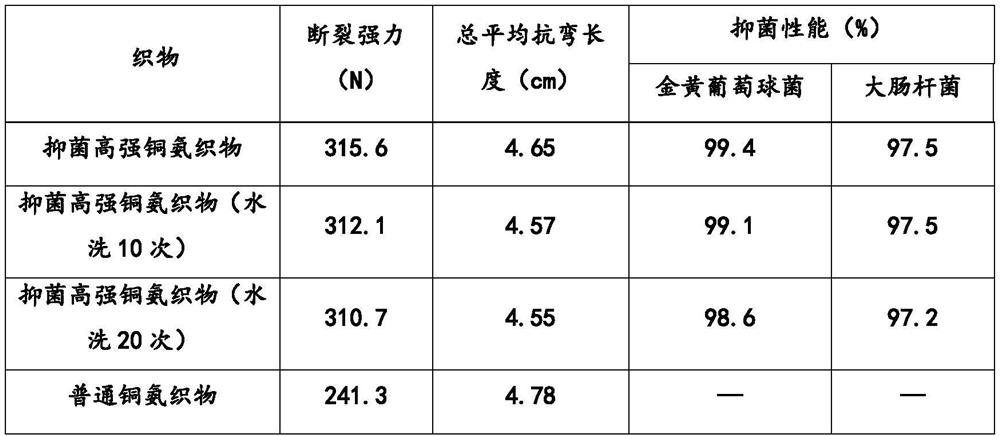
The invention relates to a spinning solution and a preparation method thereof and an antibacterial copper ammonia fabric and a preparation method thereof. The spinning solution is prepared from a copper ammonia spinning solution and an additive solution, and the additive solution is prepared from 1,3-propylene glycol and graphene powder dissolved in the 1,3-propylene glycol. According to the spinning solution, 1,3-propylene glycol and graphene powder are added into the copper ammonia spinning solution for the first time, the two substances are added into the copper ammonia spinning solution according to a strict proportion, the processed copper ammonia fabric has excellent antibacterial performance, the fabric strength can be improved by 30% or above, and the use performance of the fabric is greatly improved.
Owner:WUJIANG DEYI FASHIONS CLOTHS
Propylene Polymers
ActiveUS20150307699A1High fabric strengthIncrease line speedMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentThin material handlingStress ratioPolymer chemistry
This invention relates to propylene polymers comprising at least 50 mol % propylene, said polymers having: a) a melt flow rate (MFR, ASTM 1238, 230° C., 2.16 kg) of 10 dg / min to 25 dg / min; b) a Dimensionless Stress Ratio / Loss Tangent Index R2 at 190° C. from 1.5 to 28; c) an onset temperature of crystallization under flow, Tc,rheol (as determined by SAOS rheology, 190° C., 1° C. / min, where said polymer has 0 wt % nucleating agent present), of at least 131° C.; d) an average meso run length determined by 13C NMR of at least 90 or higher; and e) optionally, a loss tangent, tan δ, (defined by Eq. (2)) at an angular frequency of 0.1 rad / s at 190° C. from 14 to 70.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Industrial fabric
ActiveUS20180094366A1Stable structureImprove consistencyConveyorsMachine wet endEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
An industrial fabric is a web woven from warp yarns made of monofilaments and weft yarns made of monofilaments. The warp yarns are of a double-layer structure. One of warp yarn basic units comprises four sub-units, two sub-units being located on an upper layer, the other two sub-units being located on a lower layer. The warp yarns on the upper layer and the warp yarns on the lower layer are vertically overlapped, wherein at least two sub-units comprise two parallel narrow warp yarns. Upper warp yarns and lower warp yarns are identical in texture structure, or one surface is identical to the other surface after rotating by 180 degrees. The industrial fabric is stable in structure and good in overall consistency. The upper surface is good in flatness, the surface is free from defects, and the quality and intensity of the fabric are improved.
Owner:ANPING XINPENG MESH BELT LTD
Light-weight high-strength fabric for fencing protective clothing and preparation process thereof
A light-weight high-strength fabric for fencing protective clothing uses UHMWPE fibers with fiber number of 360-420 D and high-strength terylene silks with fiber number of 460-540 D as raw materials. The fabric is prepared through the steps of batching, twisting, weaving, and after-treatment. The resulting fabric has less defects due to improvements in fabric formula and weaving techniques, etc. The puncture strength of the fabric can reach 3300 N, and the mass per unit area can be reduced to 600 g / m2.
Owner:YUAN MINGFU +1
Fiber for wetlaid non-woven fabric
ActiveUS10161064B2High fabric strengthUniform areaPaper/cardboardSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperPolymer scienceAdditive ingredient
There is provided a fiber for a wetlaid non-woven fabric, said fiber can be the basis ingredient of a paper that maintains uniform mass per unit area and fiber dispersion and has unprecedented bulkiness. The fiber for a wetlaid non-woven fabric has 30 to 100 wt % of apparently crimping fibers with a fiber diameter of from 3 to 40 μm and 0 to 70 wt % of latently crimping fibers with a fiber diameter of from 3 to 40 μm.
Owner:FIBERVISIONS LP +1
Celestial-axis glass fabric and weaving method thereof
InactiveCN109667036AImprove stabilityHigh fabric strengthWoven fabricsGlass fabricPulp and paper industry
The invention provides celestial-axis glass fabric and a weaving method thereof, and the celestial-axis glass fabric comprises warps and wefts. The celestial-axis glass fabric is characterized in thatthe warps comprise two thick warps and one fine warp, the wefts comprise two thick wefts, the two thick warps are arranged side by side, the two thick wefts are arranged side by side, the two thick warps and the two thick wefts are woven into gridding cloth, the fine warp is positioned between the two thick warps, and the fine warp and the two thick warps are arranged side by side, the fine warpis crossed and woven with the two thick warps for clamping the two thick wefts between the fine warp and the two thick warps. For the fabric, the fine warp is arranged between the two thick warps sideby side, and the fine warp is crossed with the thick warps for clamping the thick wefts between the fine warp and the two thick warps, so that the wefts are fixed and do not deviate, and therefore, stability of fabric is improved, and fabric strength is improved.
Owner:浙江鸿燕新材料有限公司
Filtering material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974169BRich varietyIncrease productionOther chemical processesFiltration separationPolymer scienceO-chlorophenol
The invention discloses a filtering material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: placing a double-component island fiber into emulsion formed by mixing o-chlorophenol, a surfactant and water; treating under an oscillation condition; washing by pure water; and after carrying out tentering, drying and hot-rolling treatment to obtain the filtering material. An emulsion treating technology is used for completely splitting the island fiber and the specific surface area is enlarged; and an obtained superfine fiber textile has excellent adsorption and separation function, and filtering effect. Compared with a melt-blown non-woven fabric, the island double-component fiber has the advantages of multiple varieties of fibers, large output, developed production process, great brute force and the like; and the filtering material can be applied to an ultra-cleaning filtering and cleaning field and has a popularization and application prospect.
Owner:嘉善泰力蜂窝制品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com