Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78results about How to "Avoid static friction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
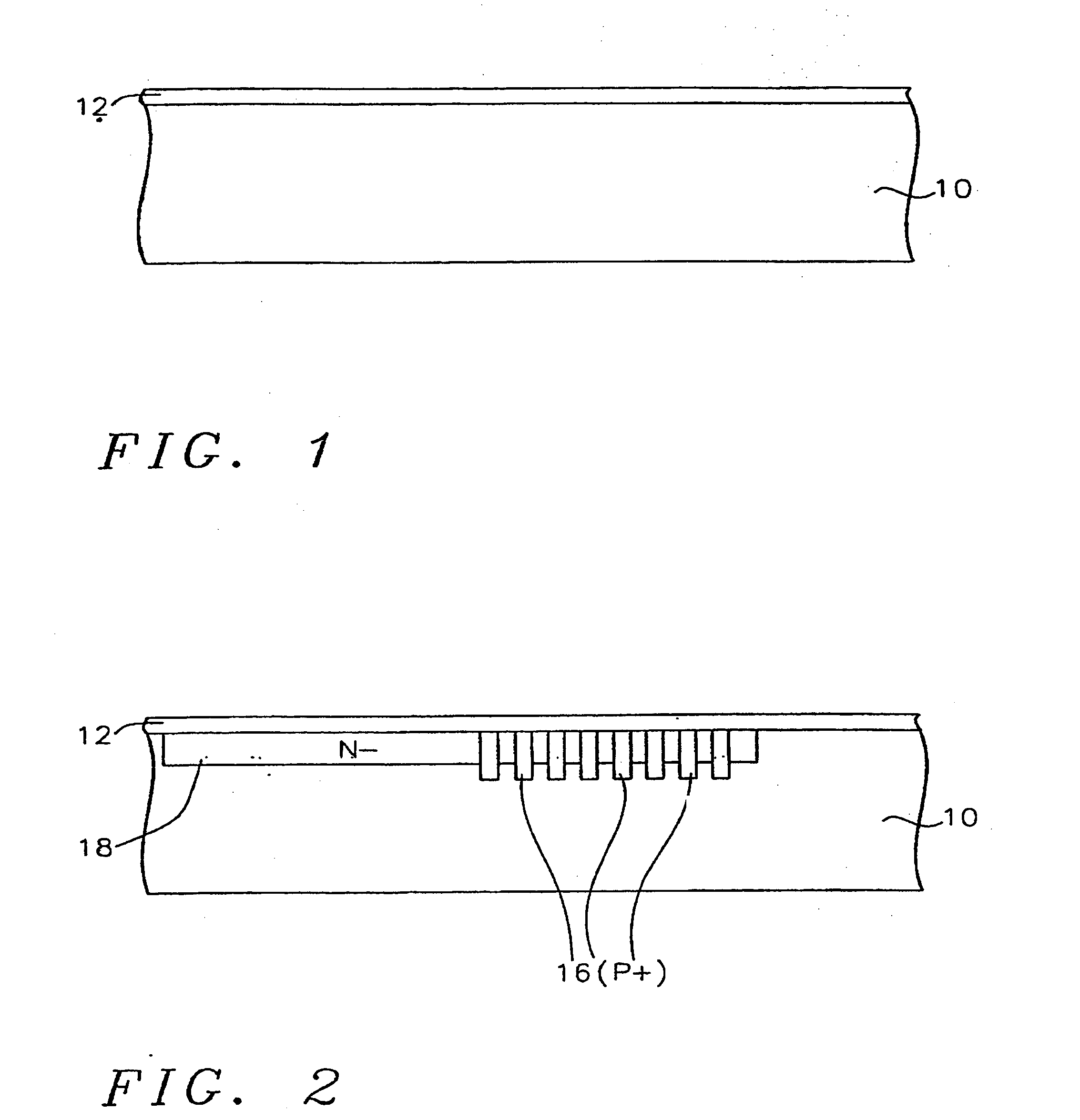
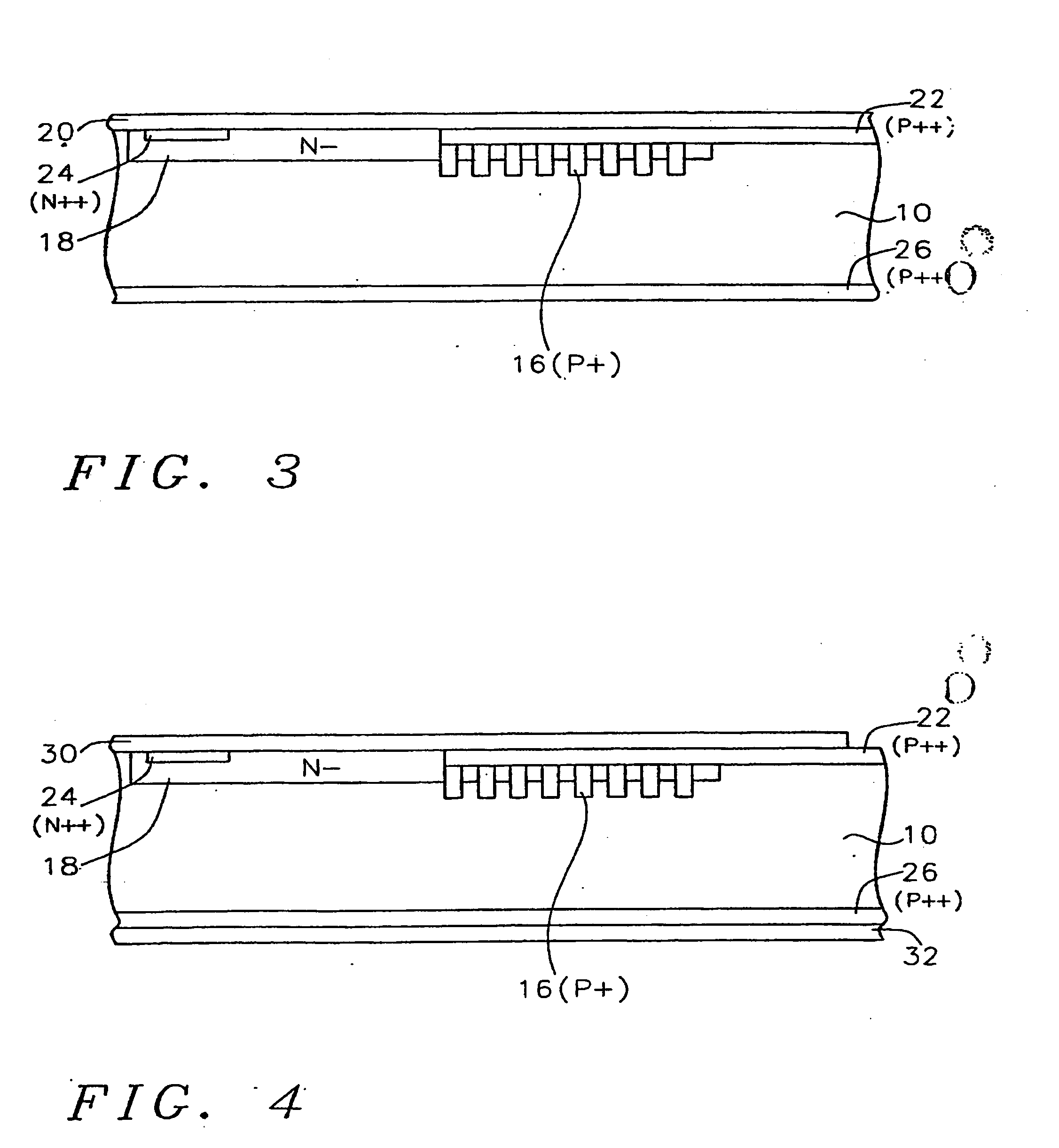
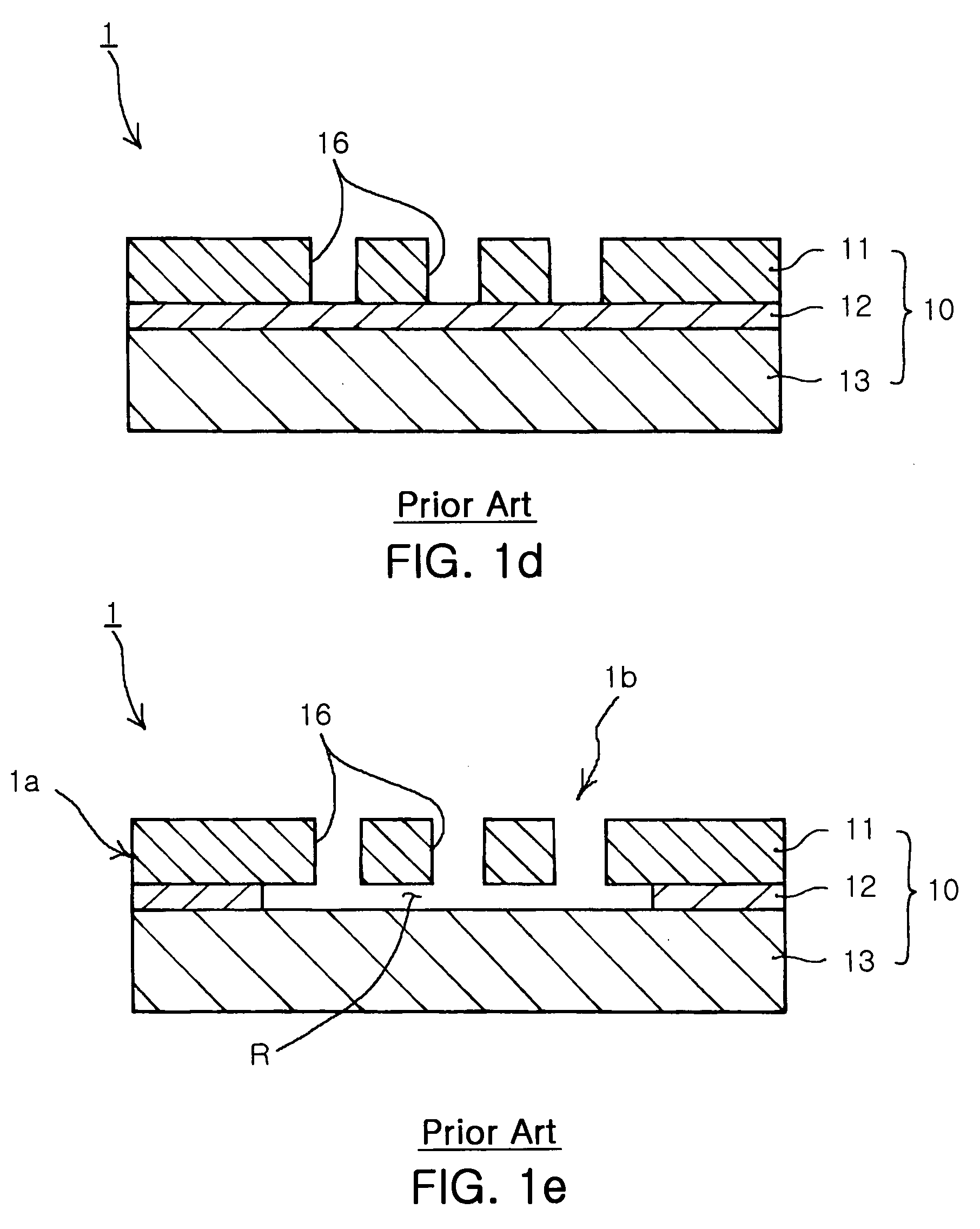
Imprint lithography template comprising alignment marks
InactiveUS6842229B2Accurately determineTimely processingLiquid crystal compositionsNanoinformaticsLithography processComputer engineering
A system of determining and correcting alignment during imprint lithography process is described. During an imprint lithographic process the template may be aligned with the substrate by the use of alignment marks disposed on both the template and substrate. The alignment may be determined and corrected for before the layer is processed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
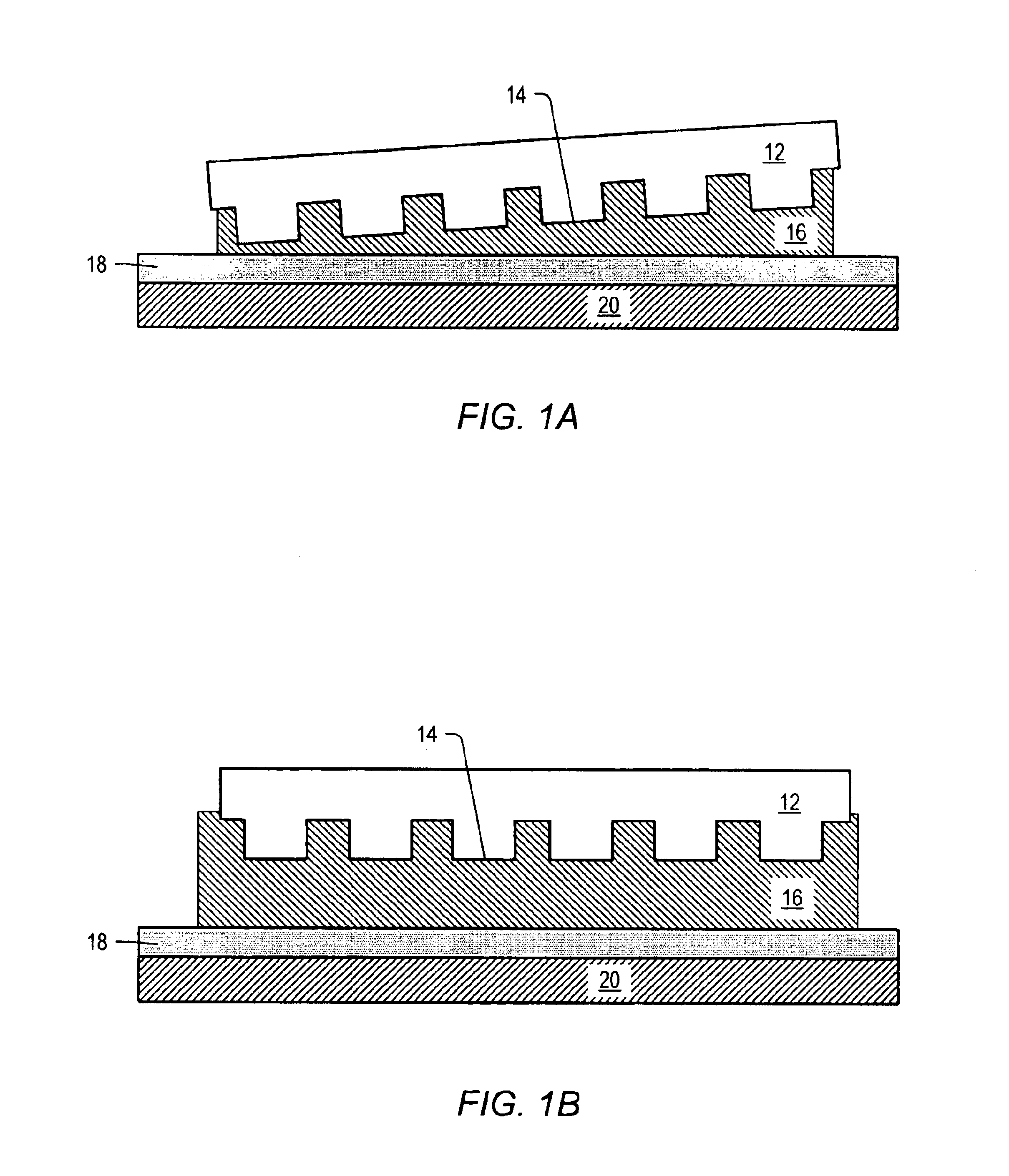
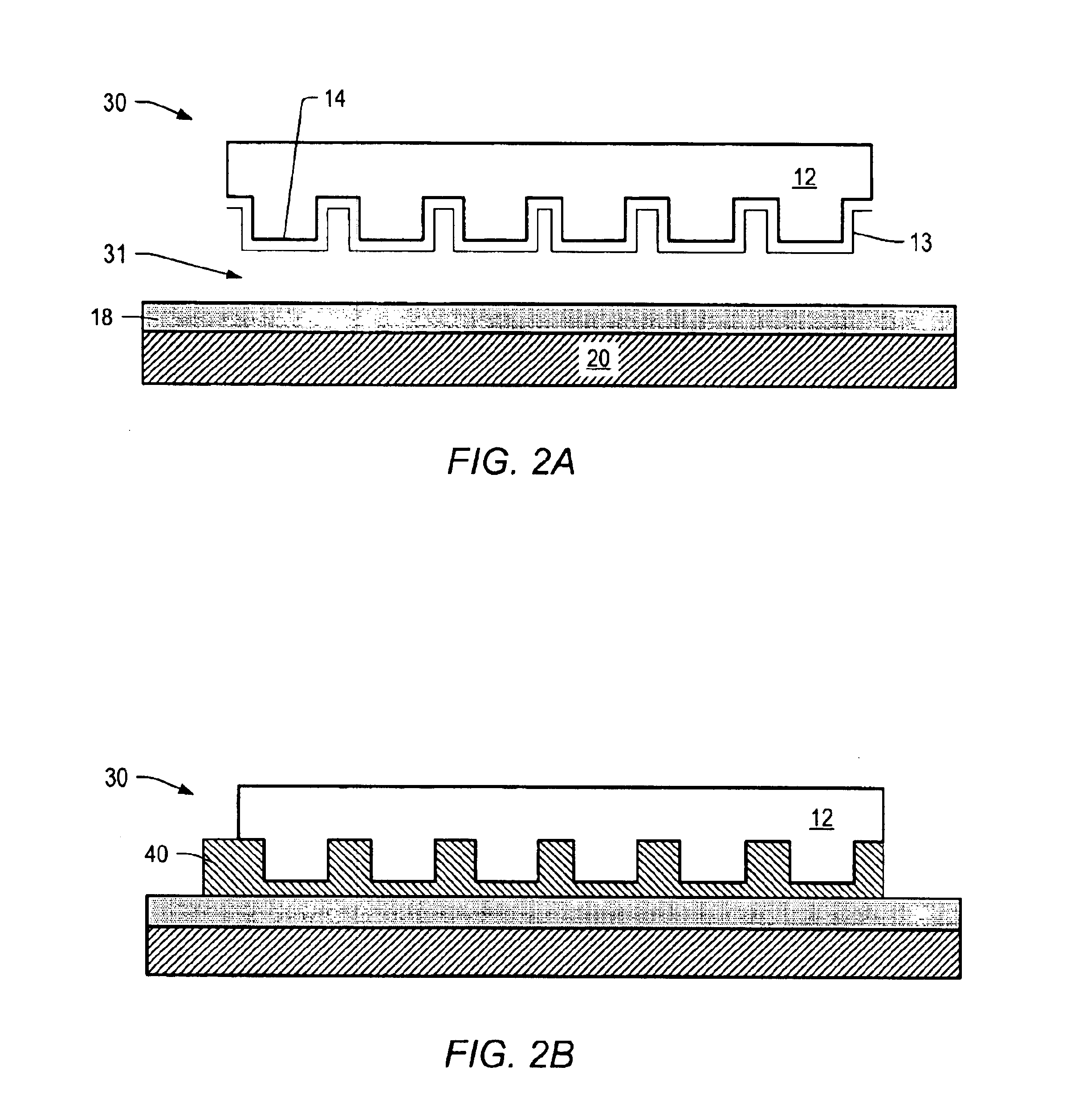
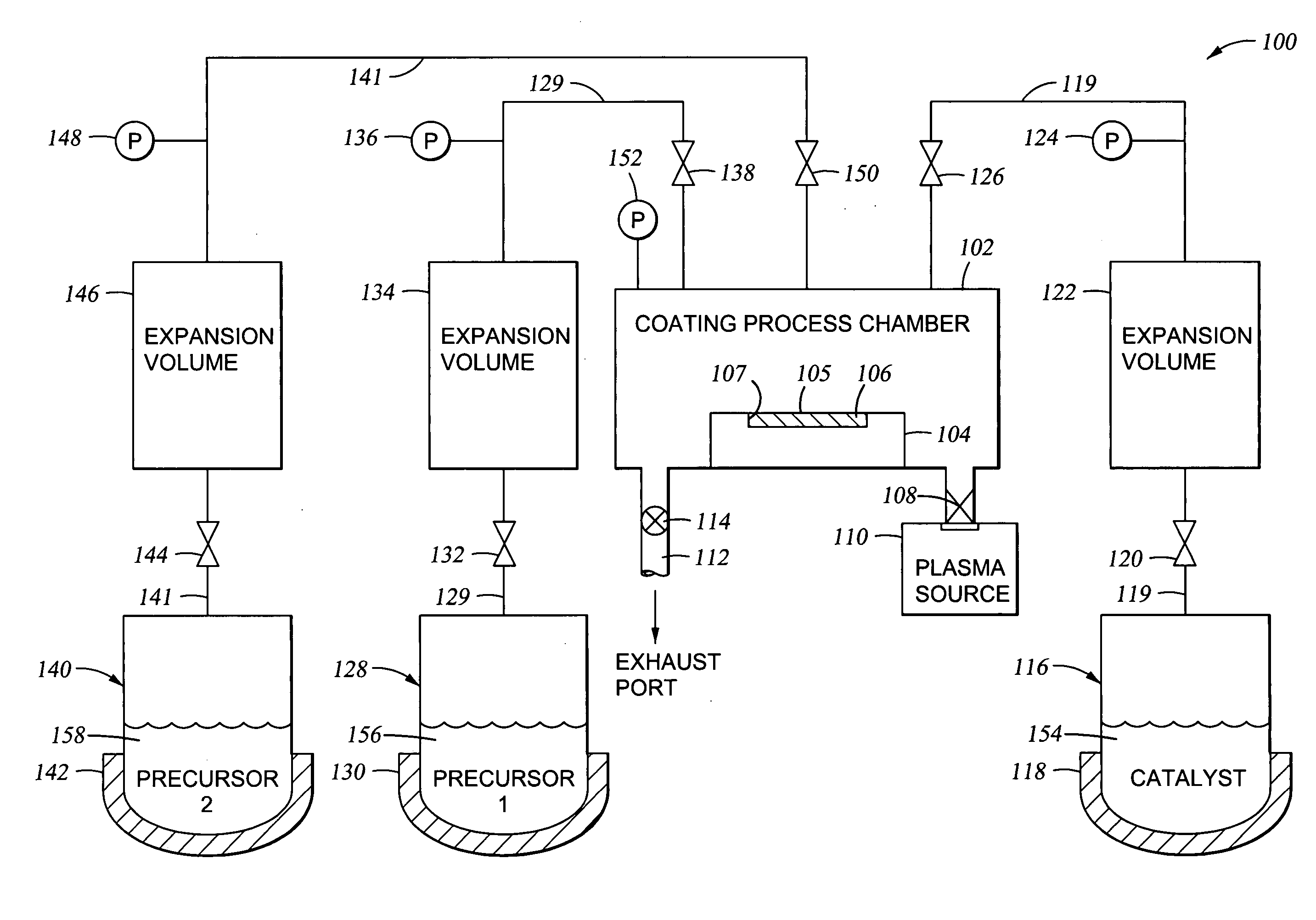
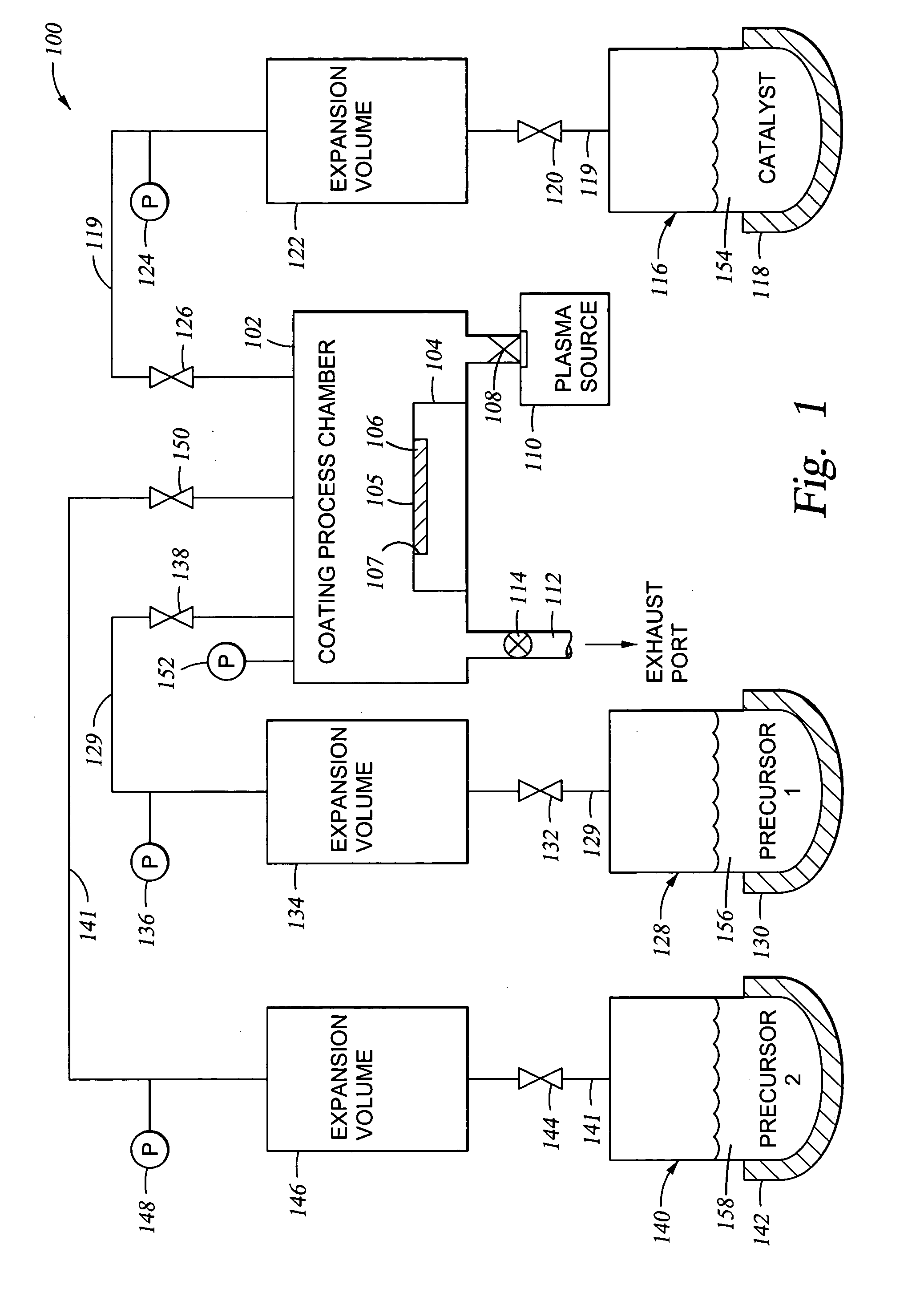
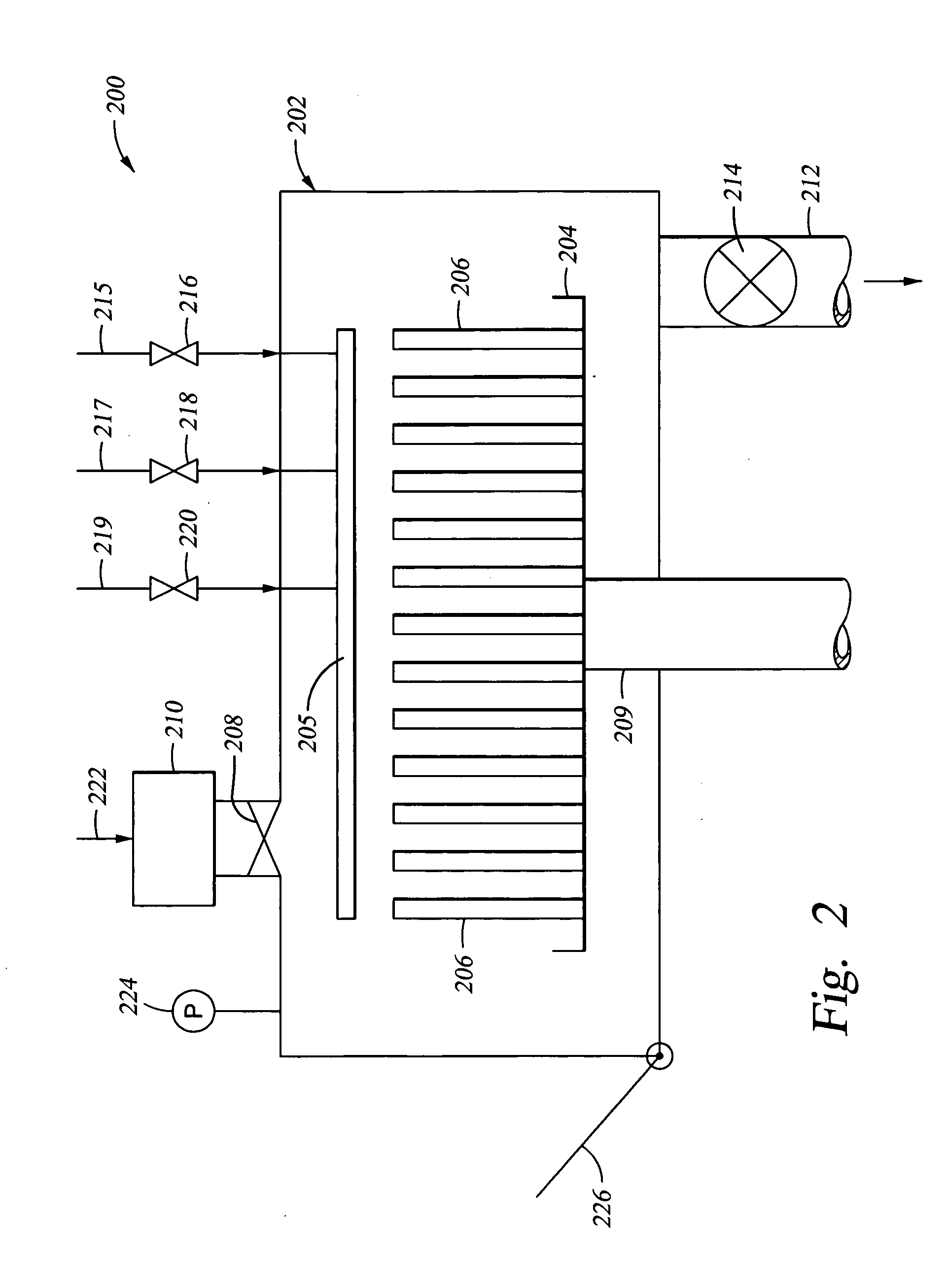
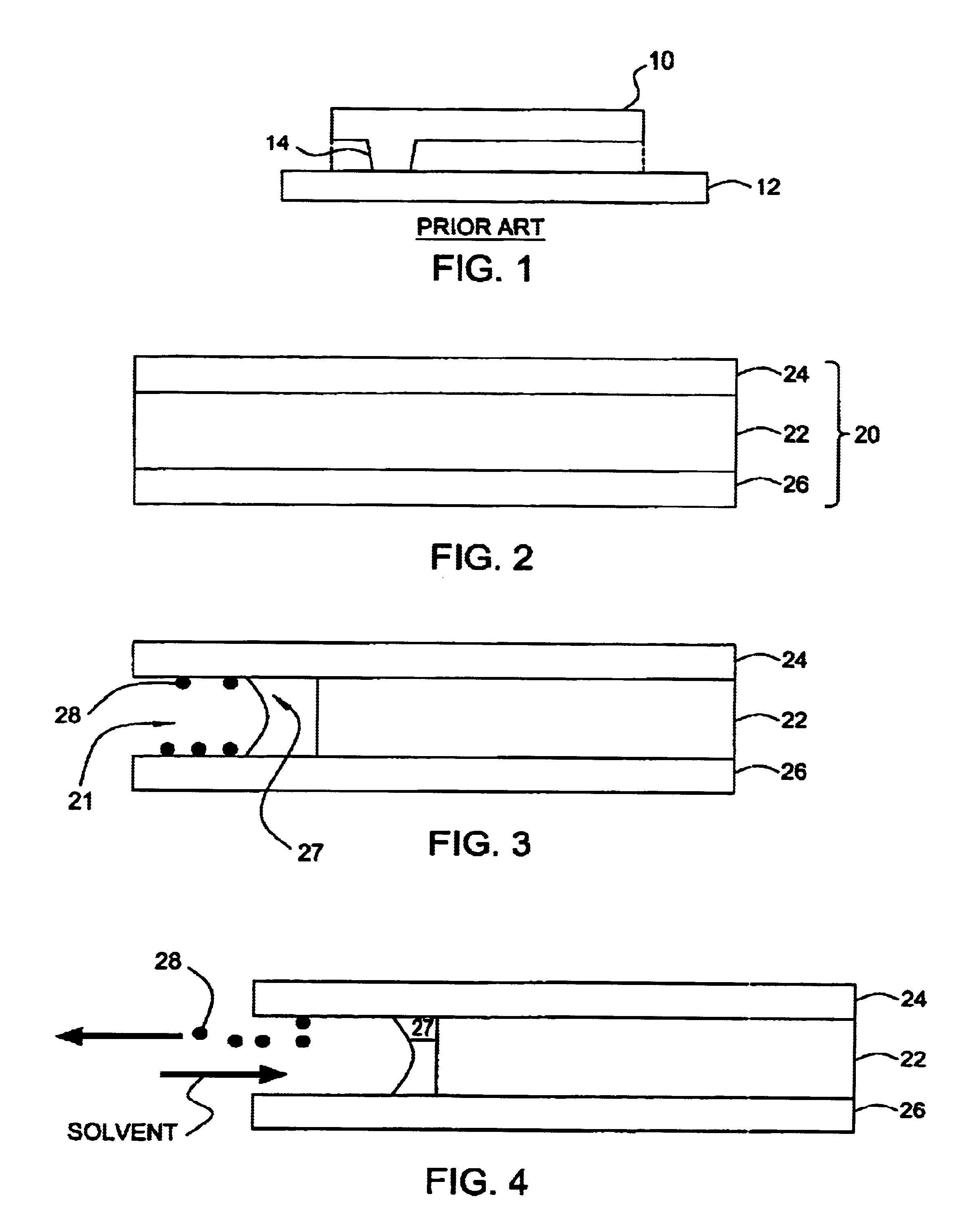
Apparatus and method for controlled application of reactive vapors to produce thin films and coatings
InactiveUS20040261703A1Prevent stictionReduce workMaterial nanotechnologyElectrical apparatusVapor phaseThin layer
A vapor phase deposition method and apparatus for the application of thin layers and coatings on substrates. The method and apparatus are useful in the fabrication of electronic devices, micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS), Bio-MEMS devices, micro and nano imprinting lithography, and microfluidic devices. The apparatus used to carry out the method provides for the addition of a precise amount of each of the reactants to be consumed in a single reaction step of the coating formation process. The apparatus provides for precise addition of quantities of different combinations of reactants during a single step or when there are a number of different individual steps in the coating formation process. The precise addition of each of the reactants in vapor form is metered into a predetermined set volume at a specified temperature to a specified pressure, to provide a highly accurate amount of reactant.
Owner:APPLIED MICROSTRUCTURES
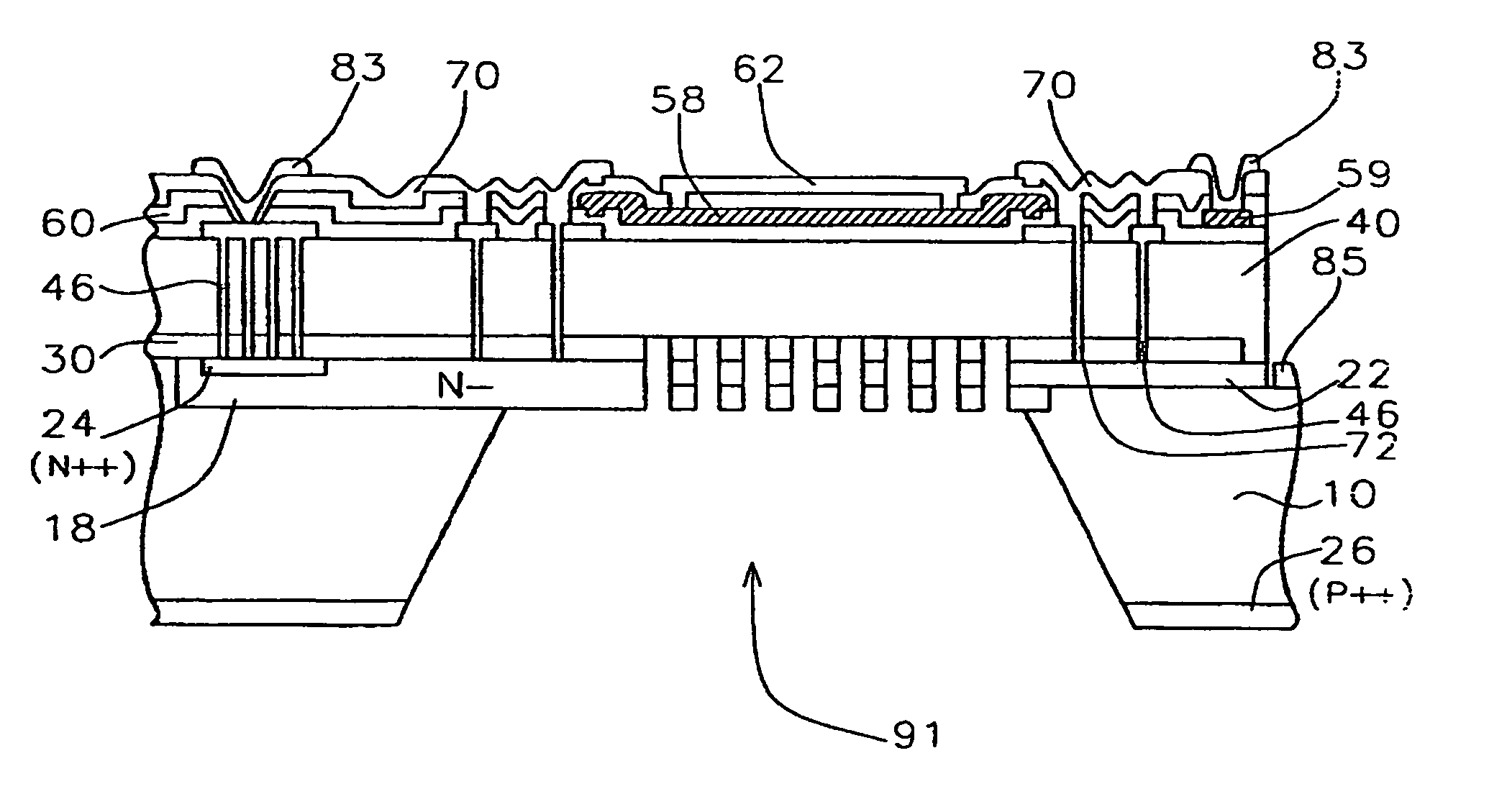
High performance silicon condenser microphone with perforated single crystal silicon backplate
InactiveUS20050005421A1High sensitivityReduce noiseSemiconductor electrostatic transducersDeaf-aid setsCapacitanceEngineering
A silicon condenser microphone is described. The silicon condenser microphone of the present invention comprises a perforated backplate comprising a portion of a single crystal silicon substrate, a support structure formed on the single crystal silicon substrate, and a floating silicon diaphragm supported at its edge by the support structure and lying parallel to the perforated backplate and separated from the perforated backplate by an air gap.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Capacitive microphone and method for making the same
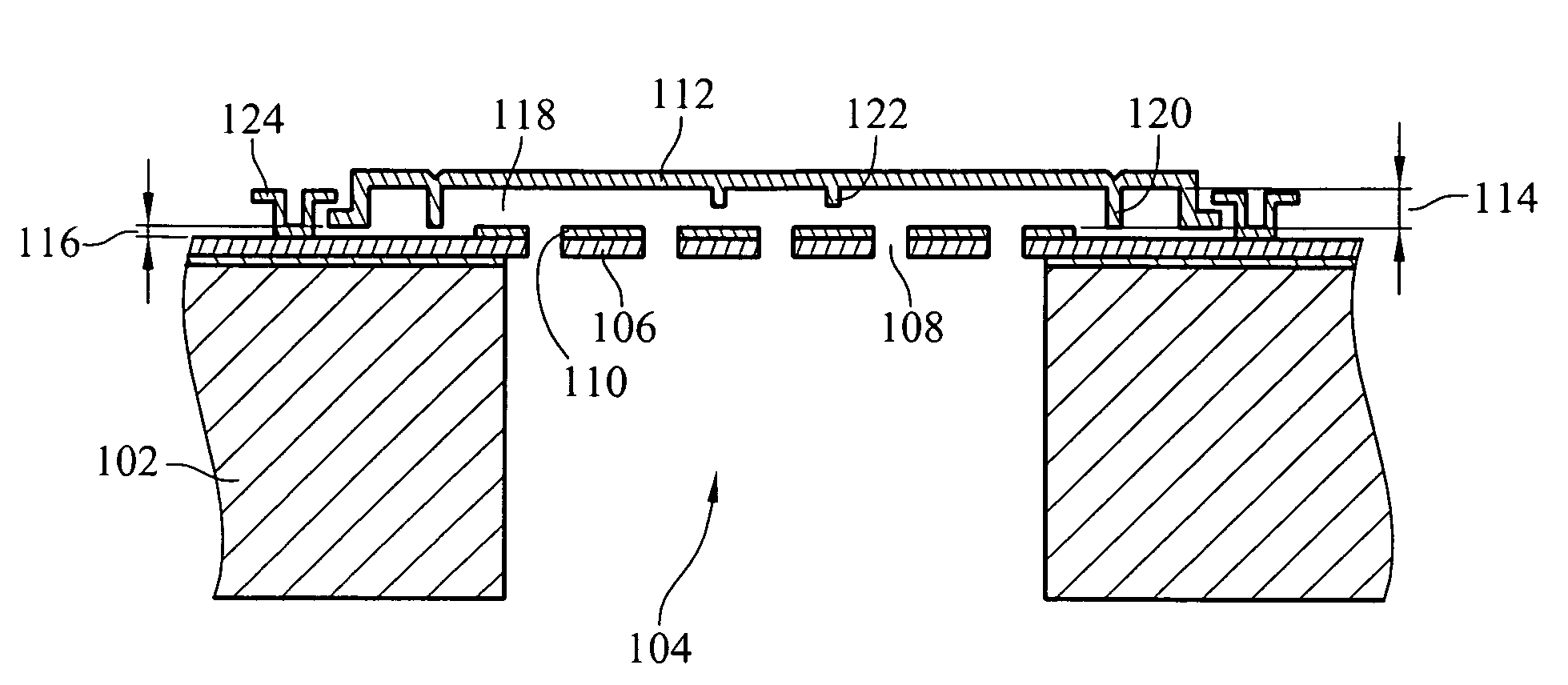
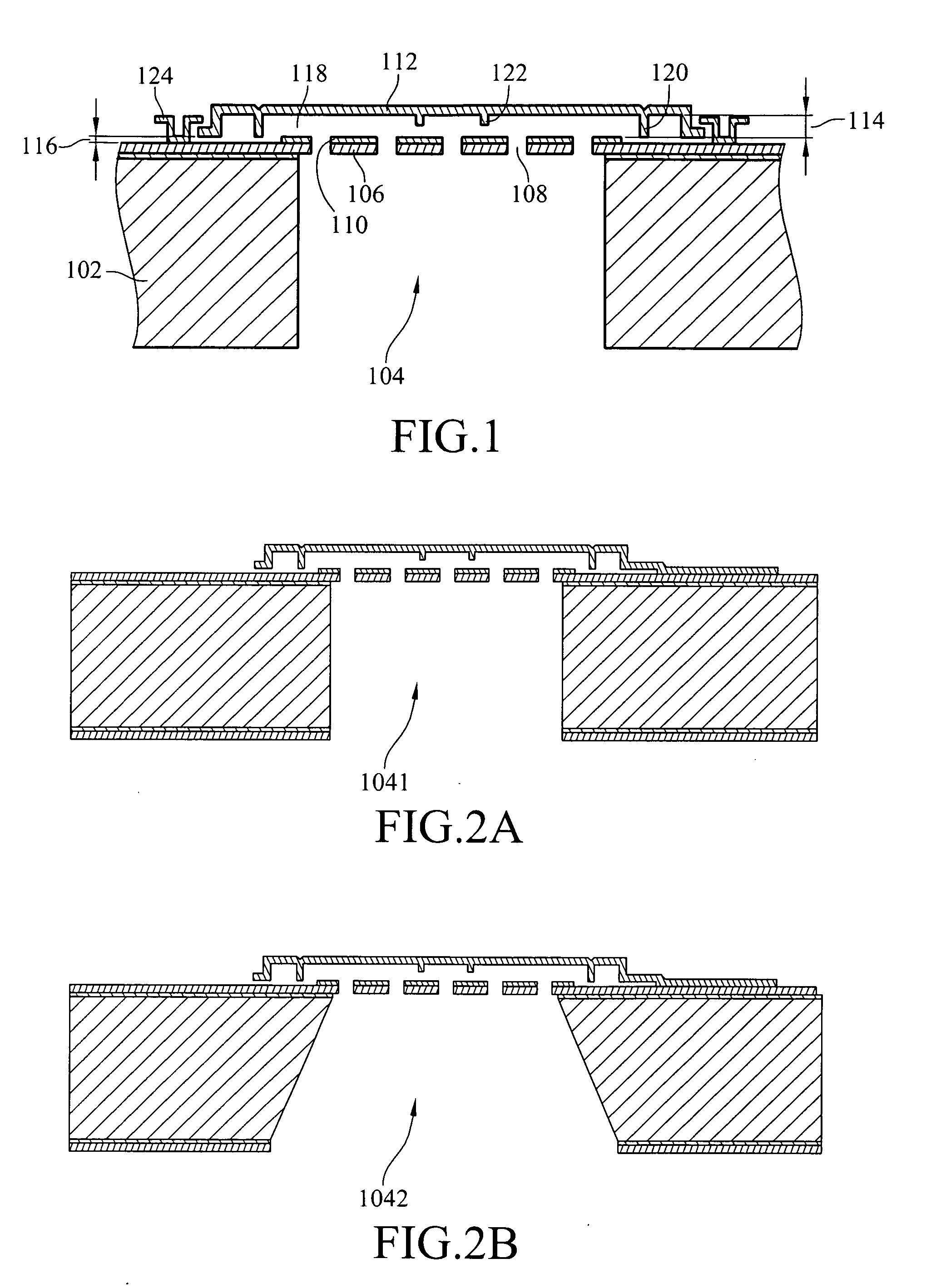
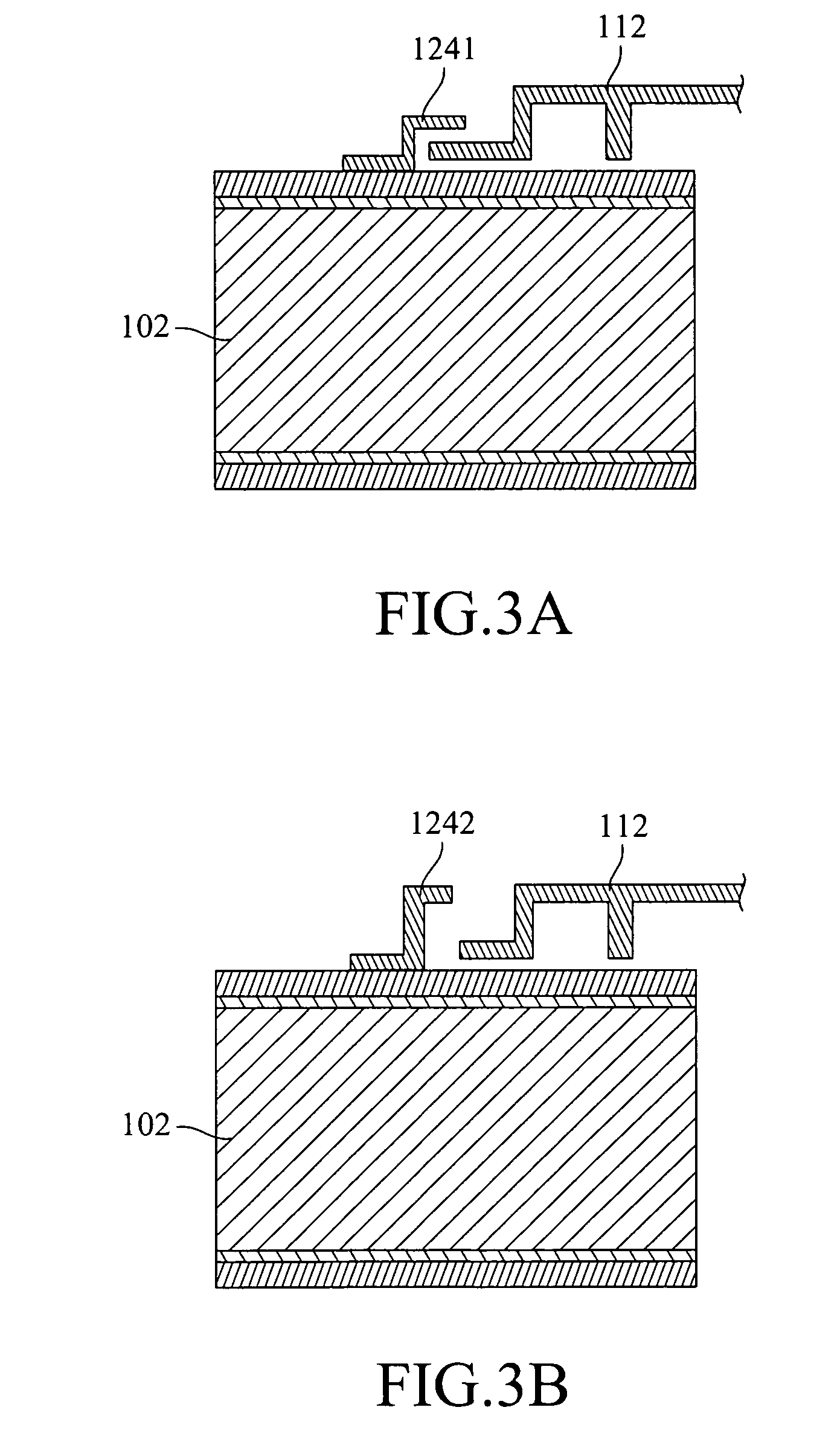
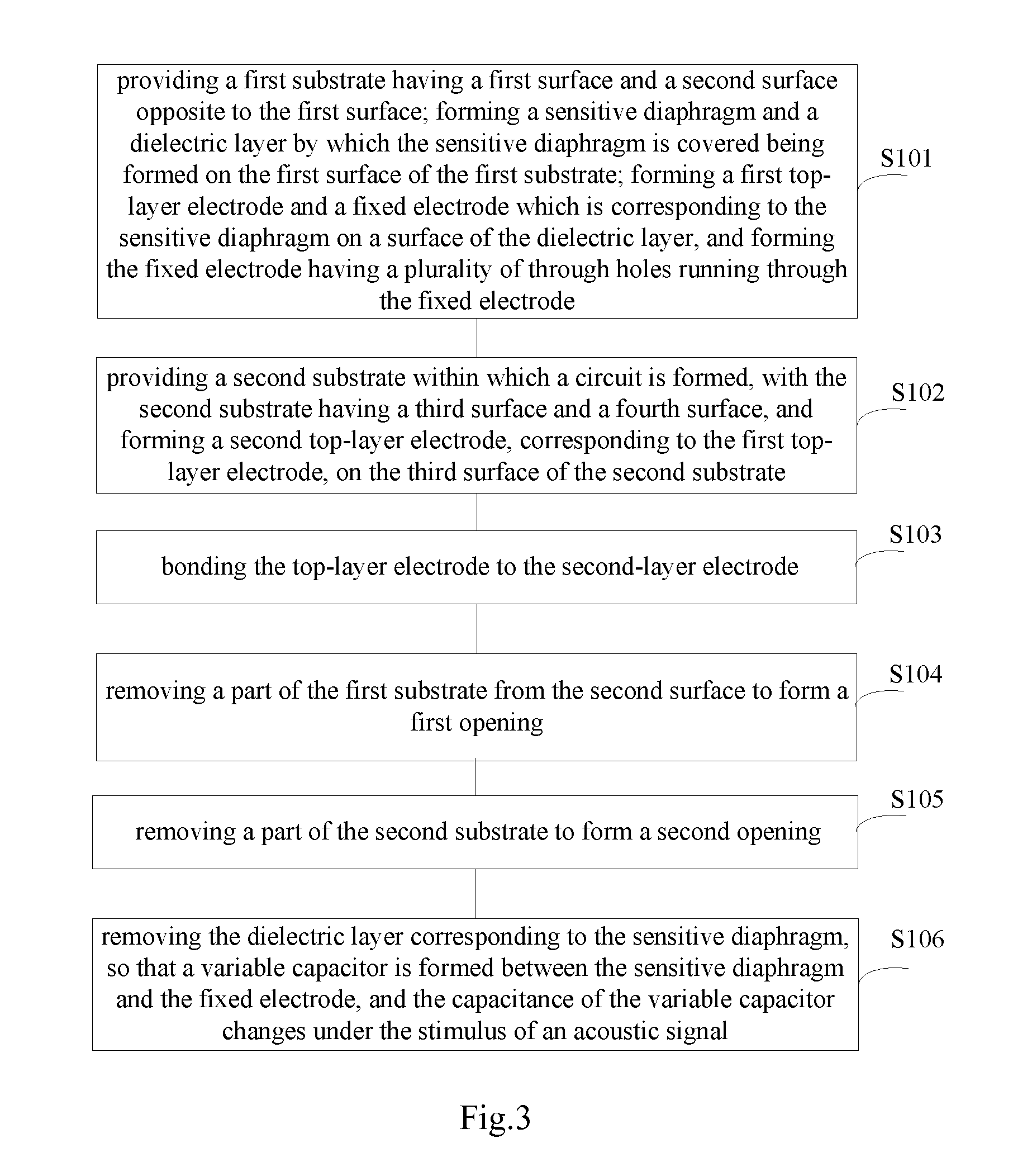
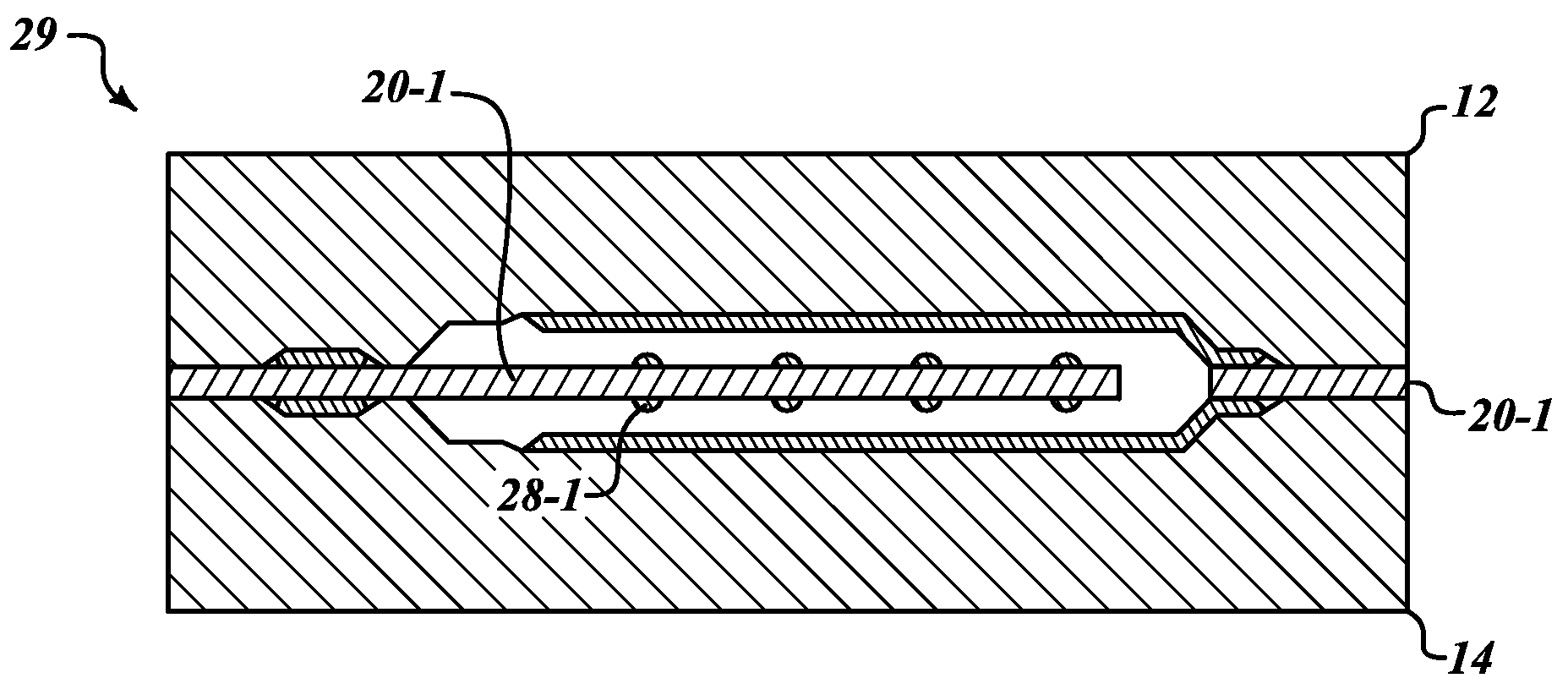
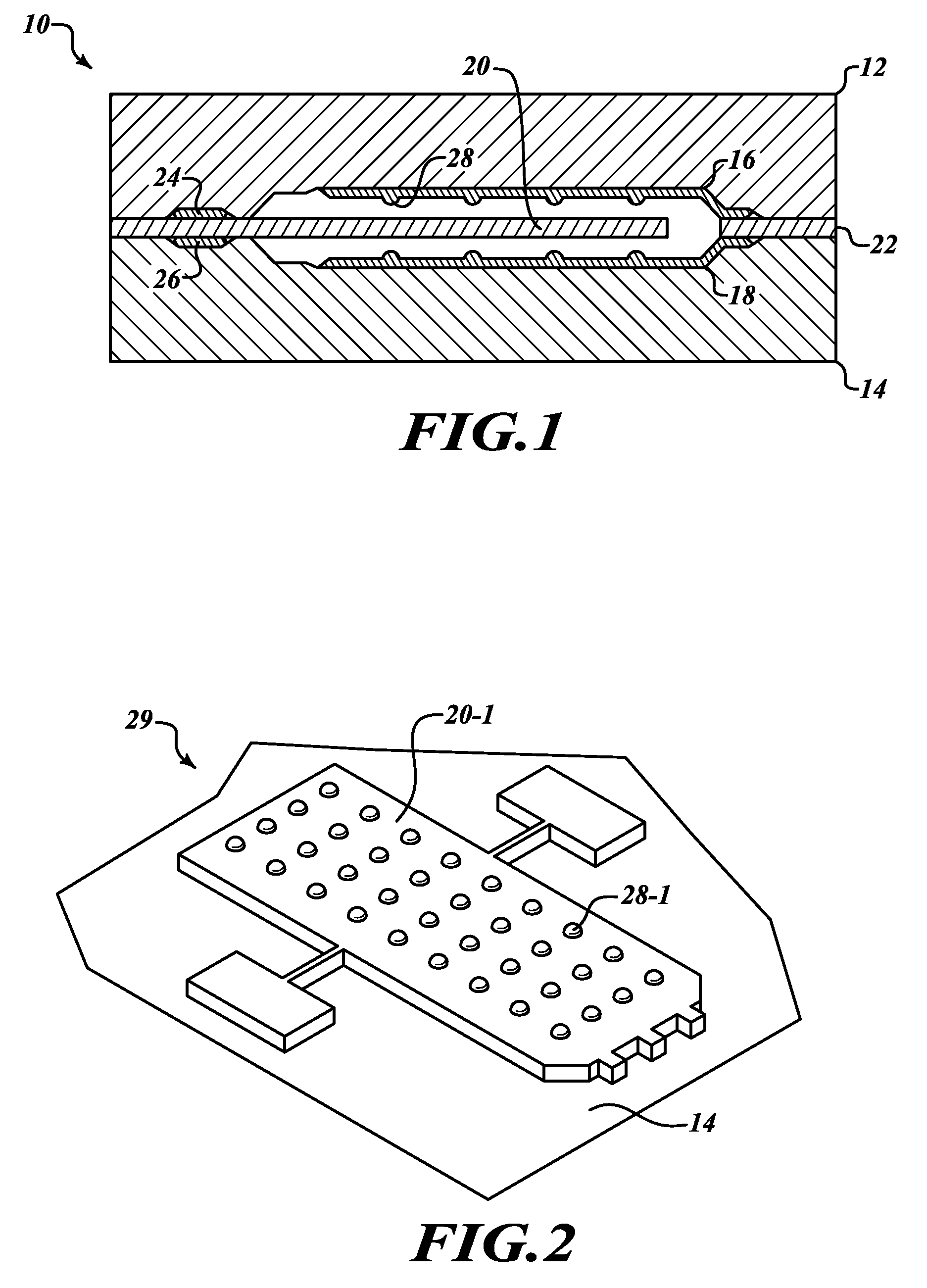
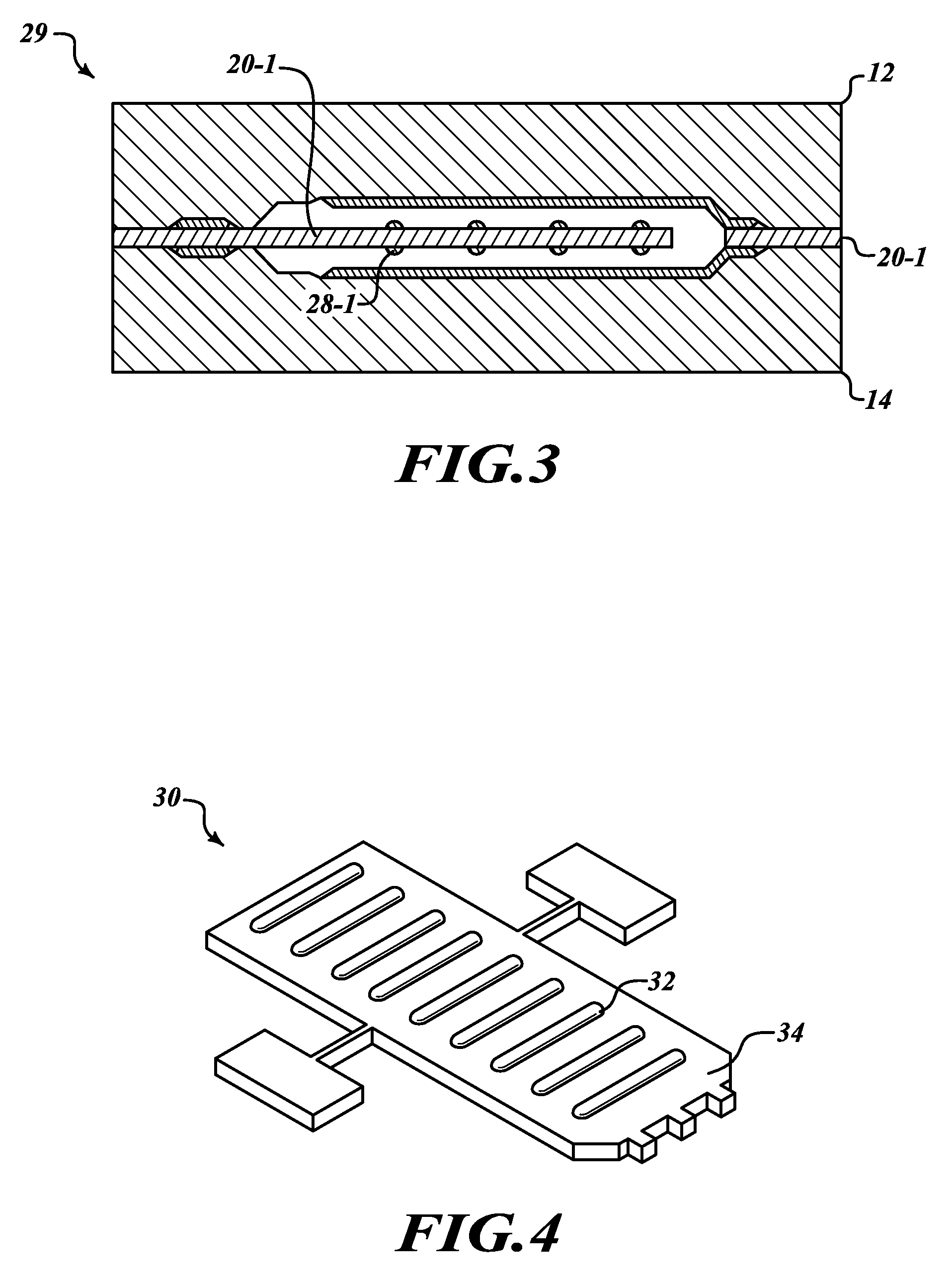
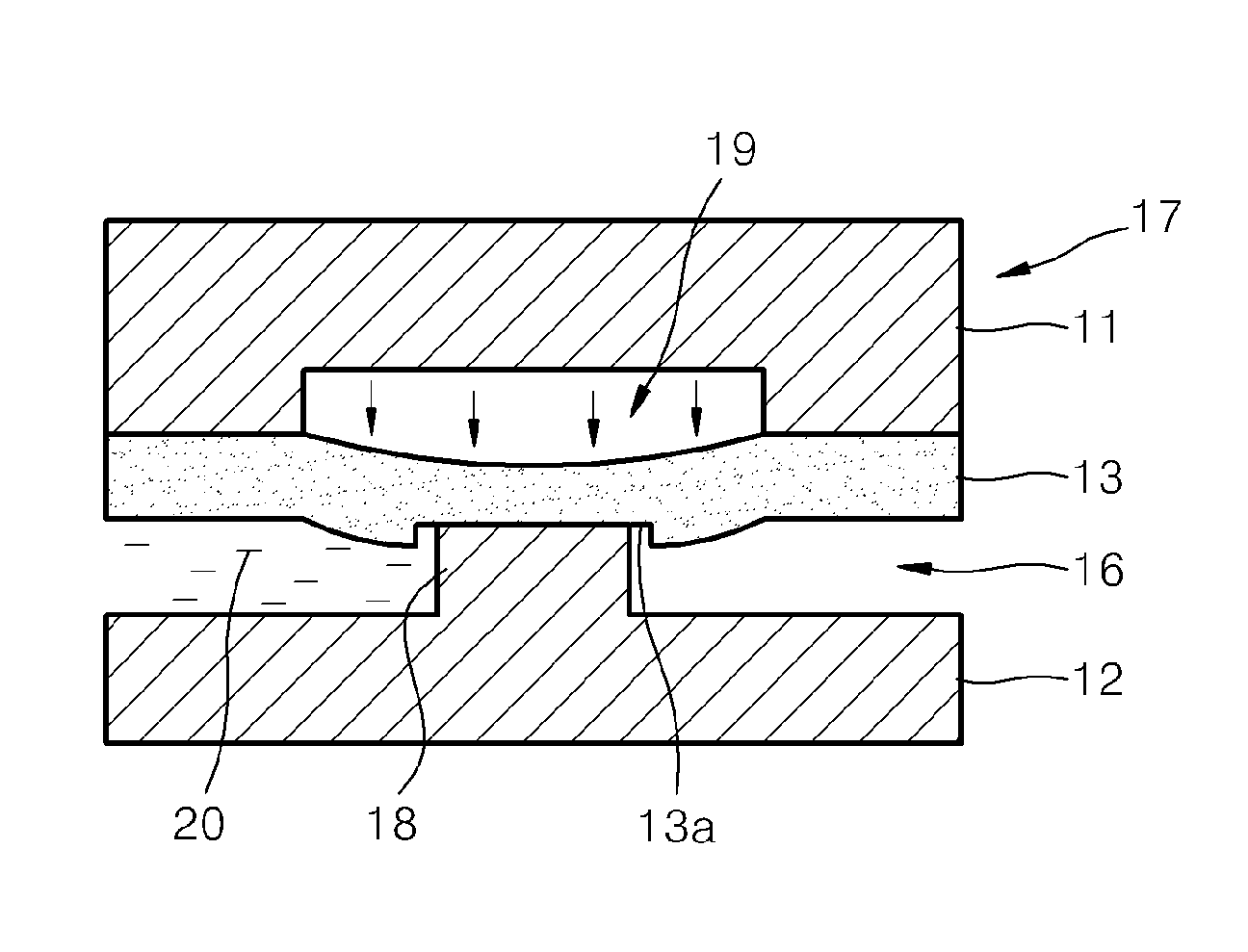
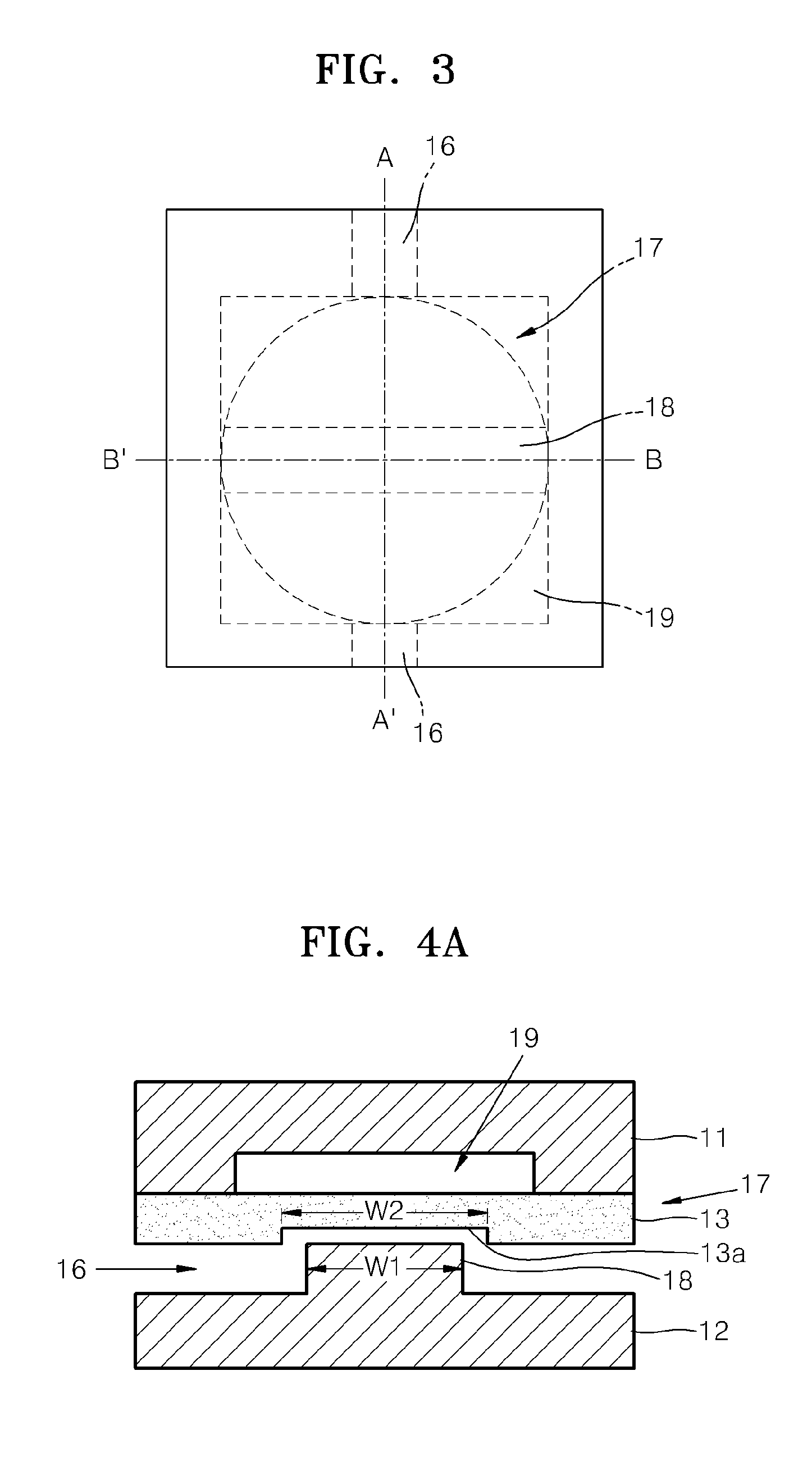
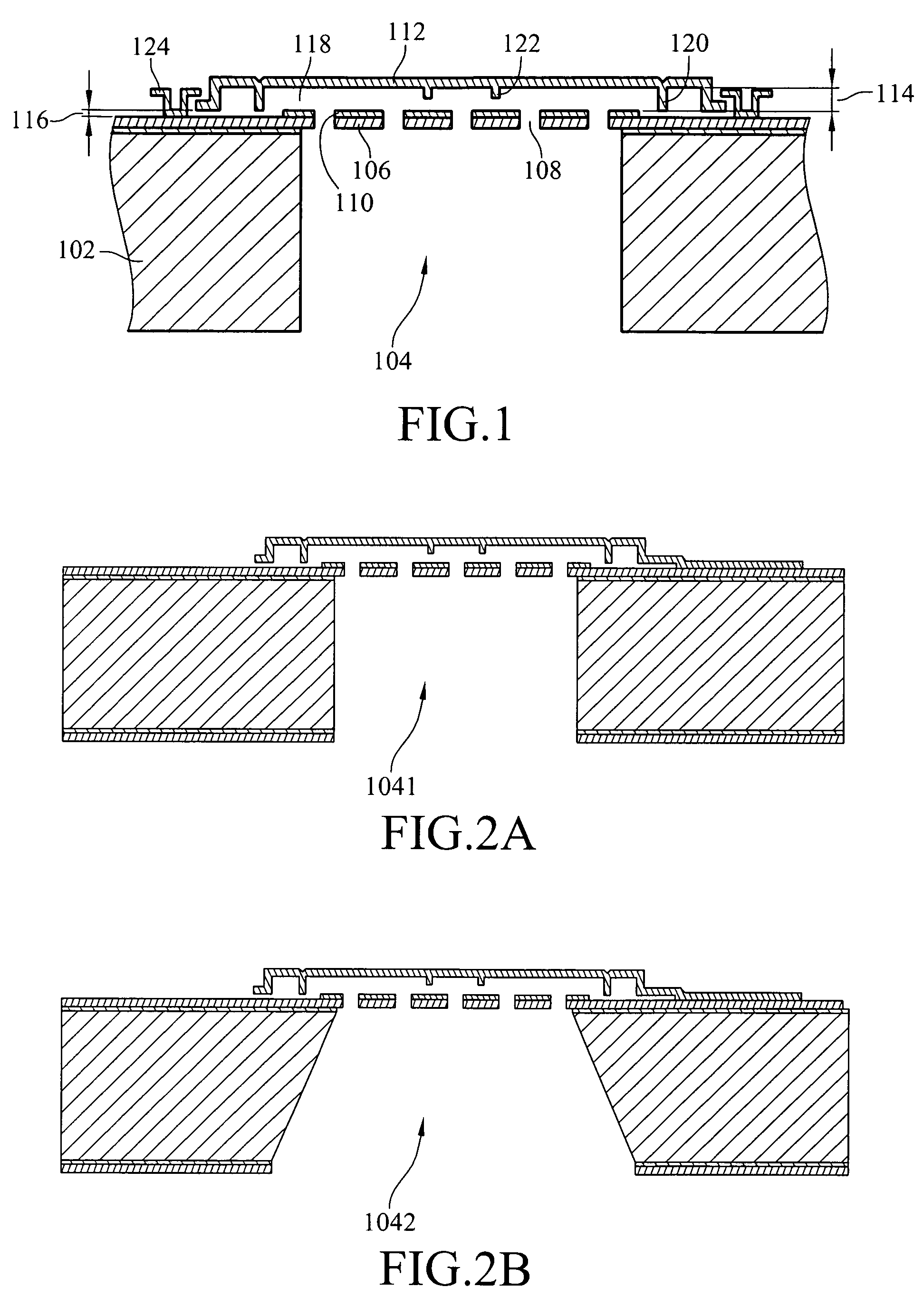
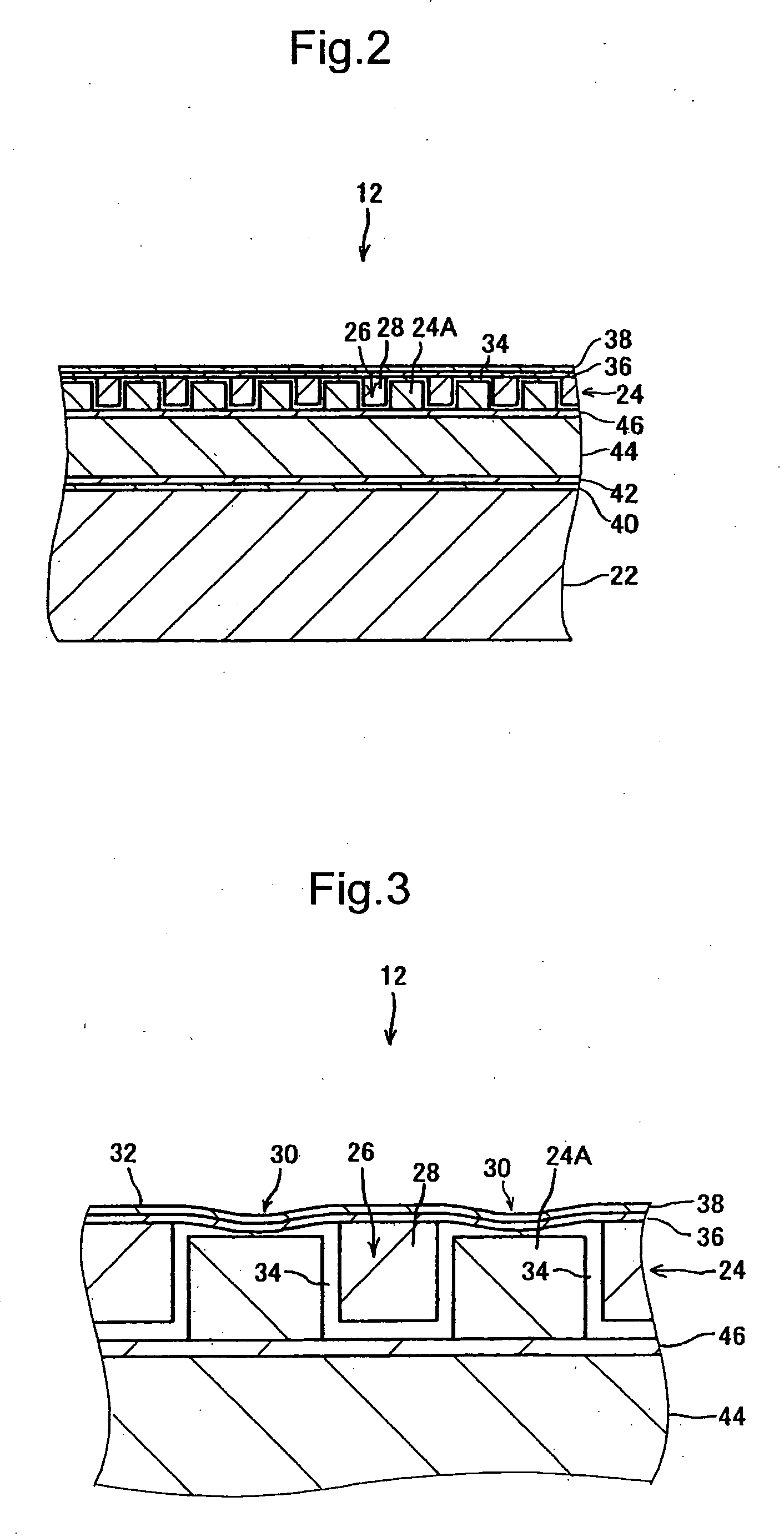
ActiveUS20070154040A1Avoid static frictionAvoid driftingElectrostatic transducer microphonesDeaf-aid setsEngineeringStiction
A capacitive microphone and method for making the same are provided. A backplate with a plurality of holes is formed on a substrate with at least one cavity, and a diaphragm is formed above the backplate. There is an air gap between the backplate and the diaphragm. The air gap and the cavity communicate with each other by each hole. The diaphragm and the backplate are separated by a first distance and a second distance which is smaller than the first distance, such that the difference is formed on the diaphragm. The second distance area is fastened through surface stiction produced by mist or other fluids.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
High performance silicon condenser microphone with perforated single crystal silicon backplate
InactiveUS7132307B2High sensitivityReduce noisePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesSemiconductor electrostatic transducersEngineeringCondenser microphone
A silicon condenser microphone is described. The silicon condenser microphone of the present invention comprises a perforated backplate comprising a portion of a single crystal silicon substrate, a support structure formed on the single crystal silicon substrate, and a floating silicon diaphragm supported at its edge by the support structure and lying parallel to the perforated backplate and separated from the perforated backplate by an air gap.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
MEMS structure and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050280106A1Avoid problemsImprove production yieldTelevision system detailsImpedence networksEngineeringGas supply
A MEMS structure includes a floating space formed on the upper silicon layer by a first dry etching, and then dry etched to a predeterminded depth on the lower silicon layer by etching gas supplied through the etched holes from which the oxide film has been removed at the bottom surface thereof in a second dry etching process, so as to float the movable portion; and the oxide film for preventing electrical short circuit remaining on the lower surface of the movable portion so as to correspond to the lower silicon layer leaving the floating space therebetween.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
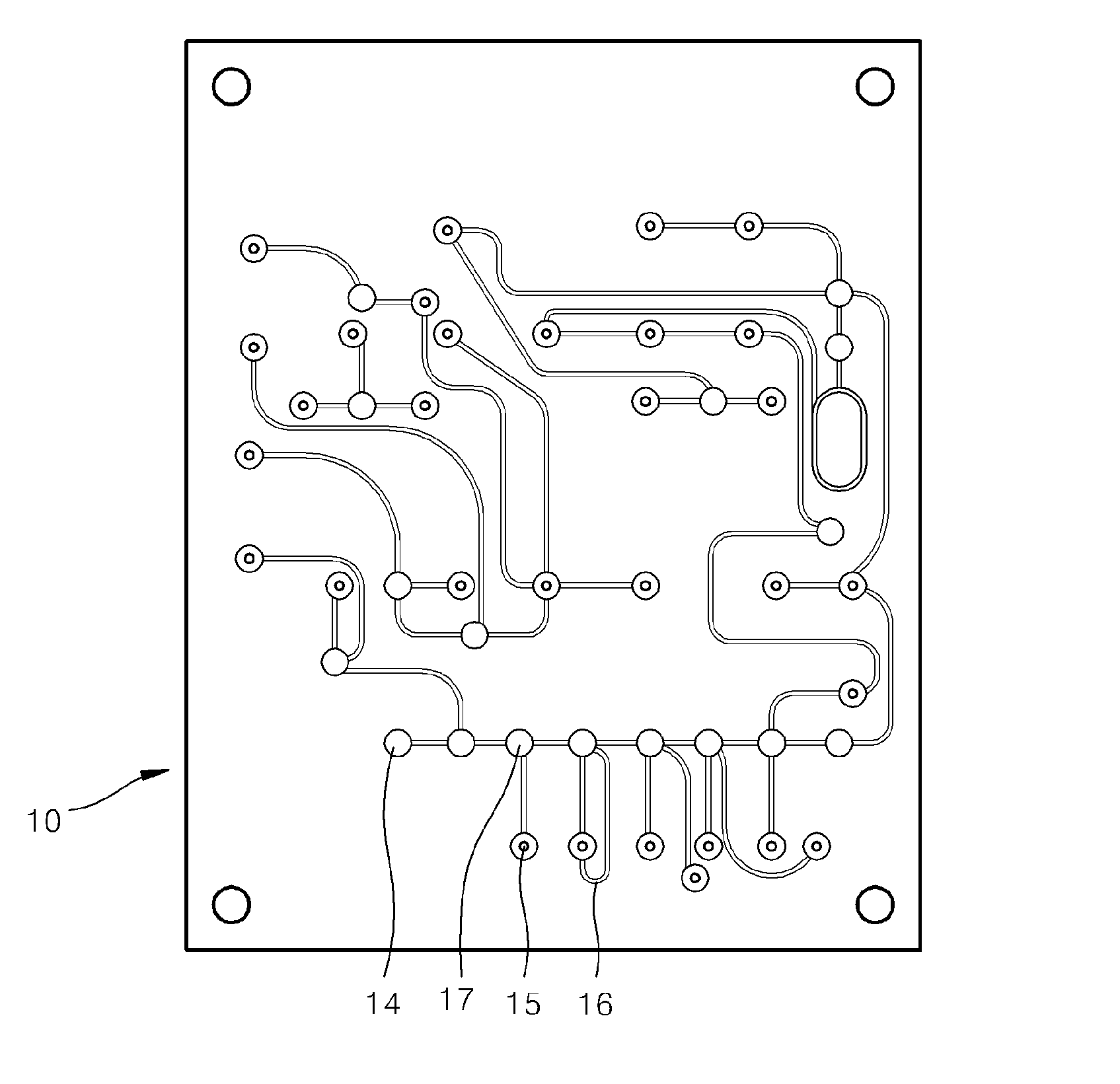
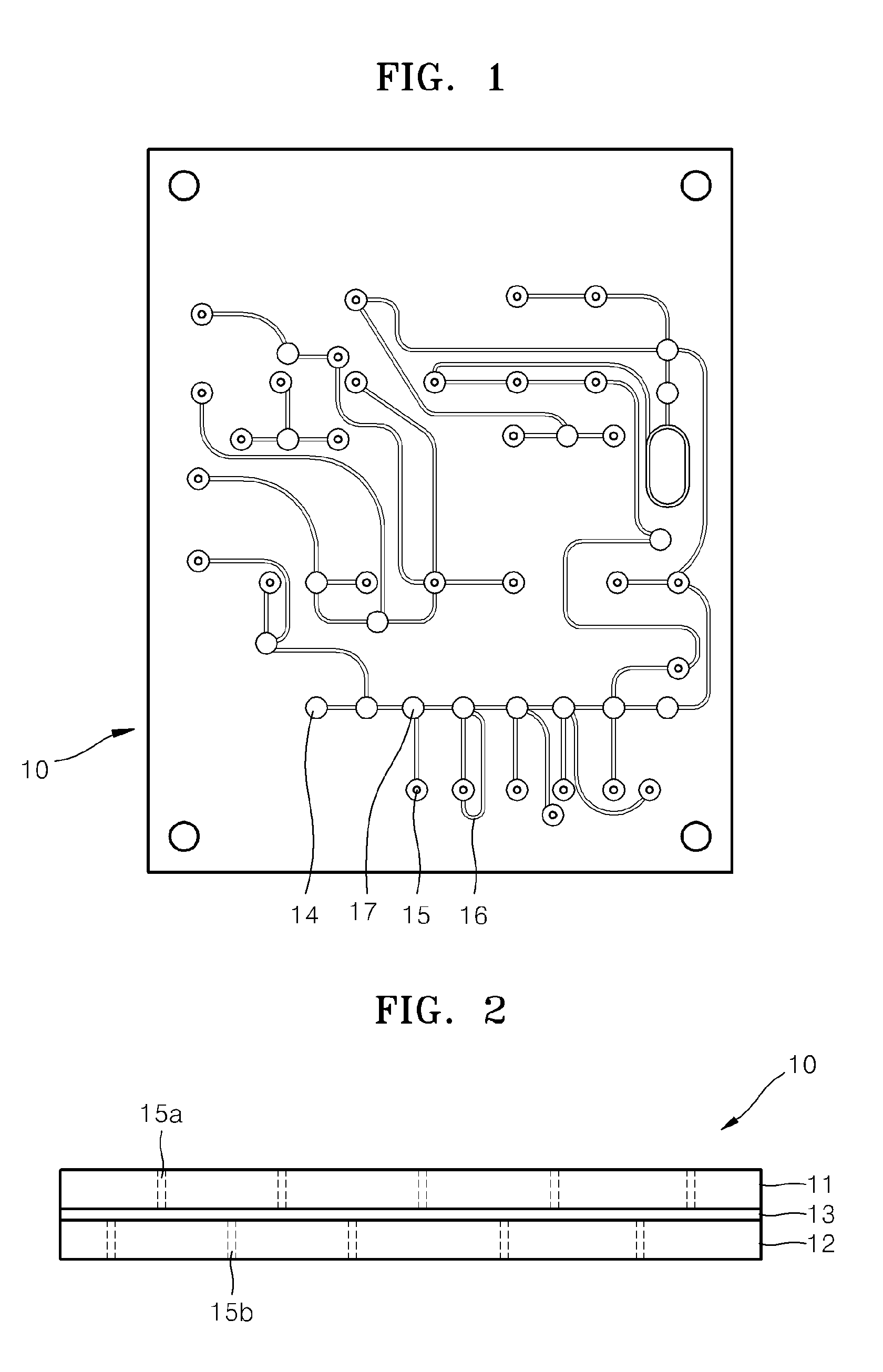
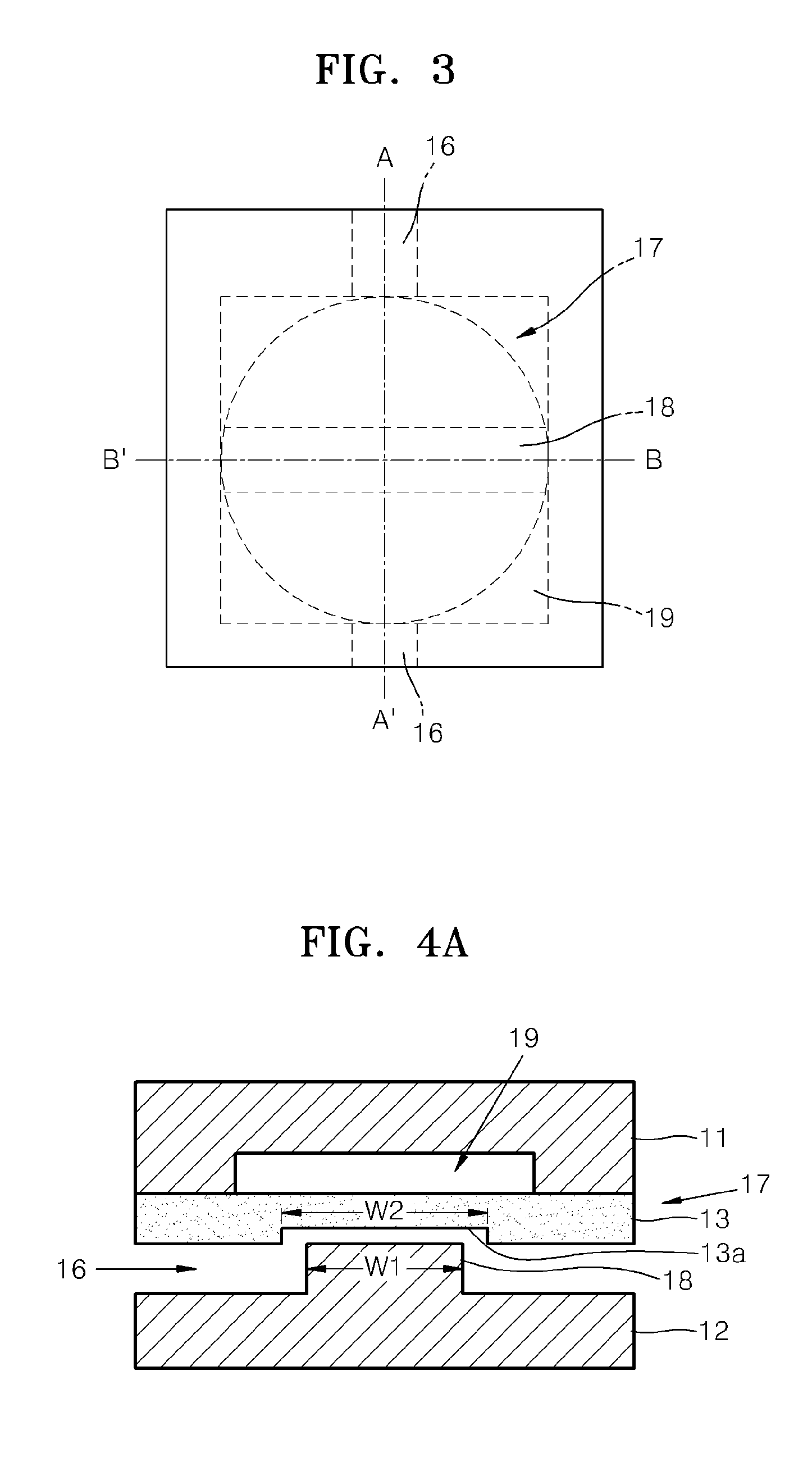
Microfluidic device having microvalve
ActiveUS20110305607A1Avoid static frictionValve arrangementsLaboratory glasswaresFine structureEngineering
A microfluidic device including a microvalve includes a first substrate, a second substrate facing the first substrate, an elastic film between the first and second substrates, a microfluidic channel on the second substrate, a valve seat of the second substrate protruding in the microfluidic channel, and a fine structure on a surface of the elastic film, facing the valve seat and which contacts the valve seat when the microvalve is operated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
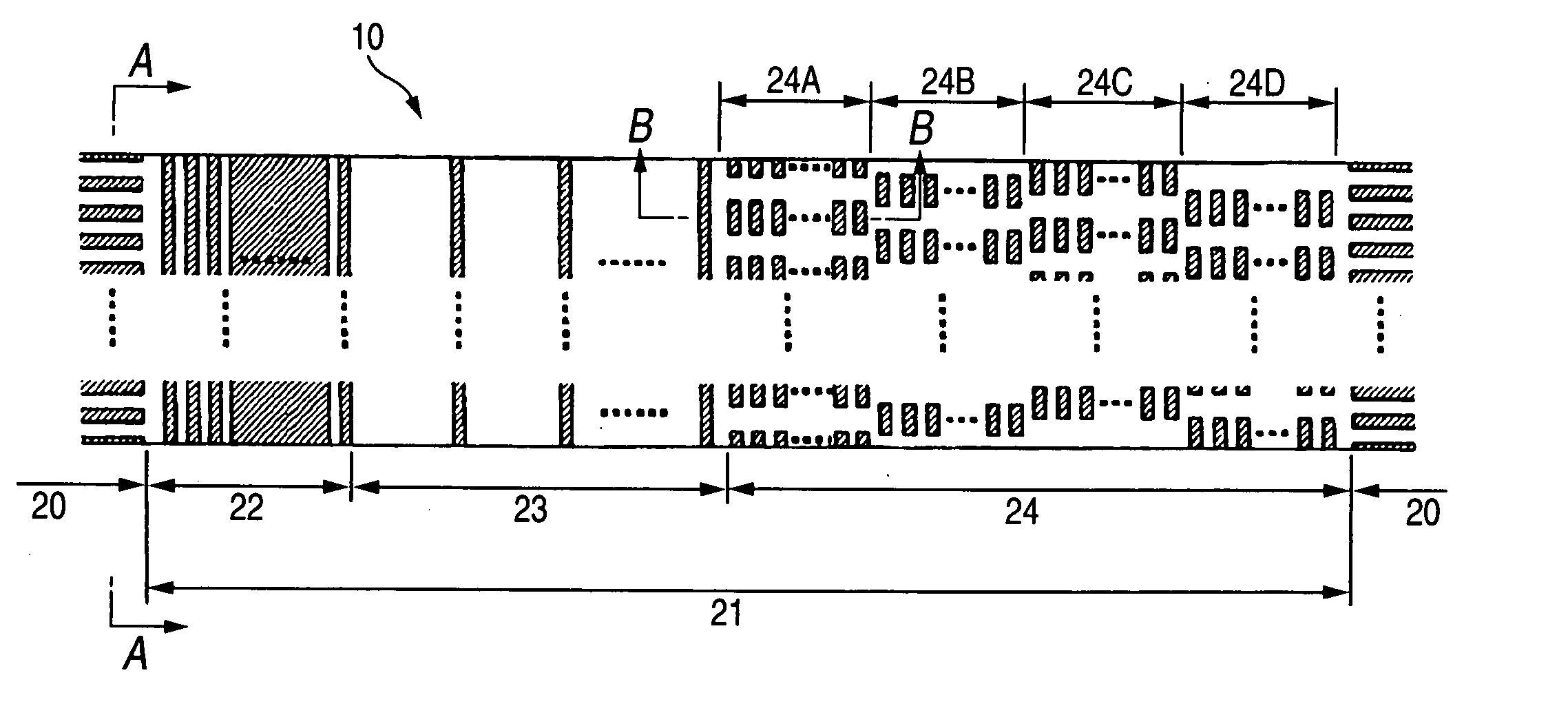
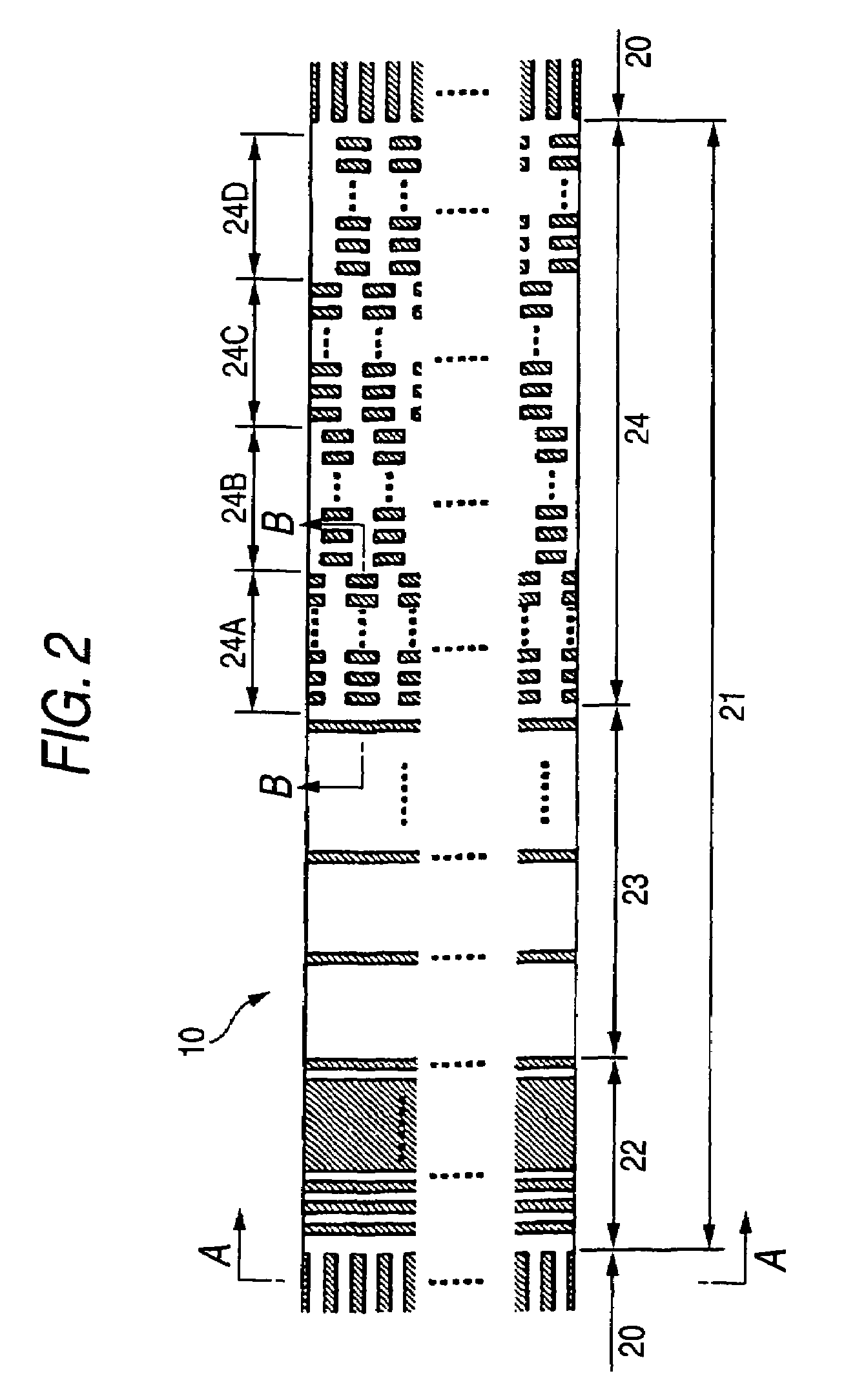
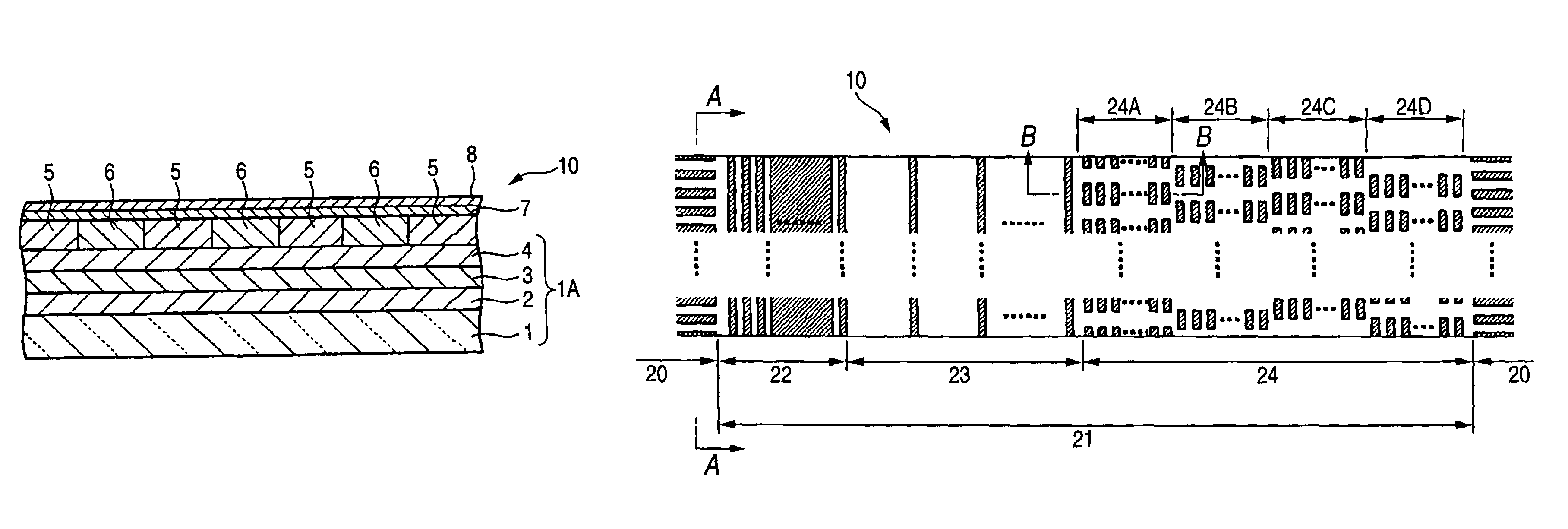
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
InactiveUS20050191526A1Cost reductionIncrease frictional resistanceMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageSurface levelEngineering
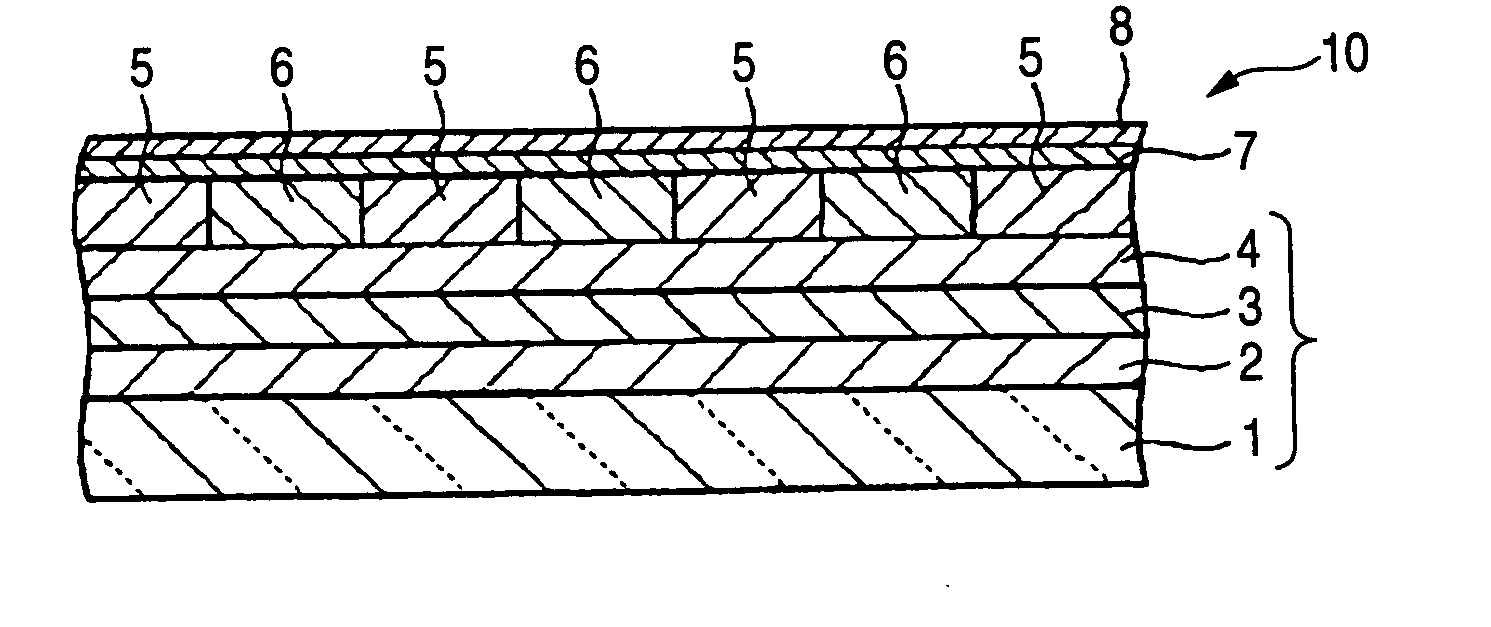
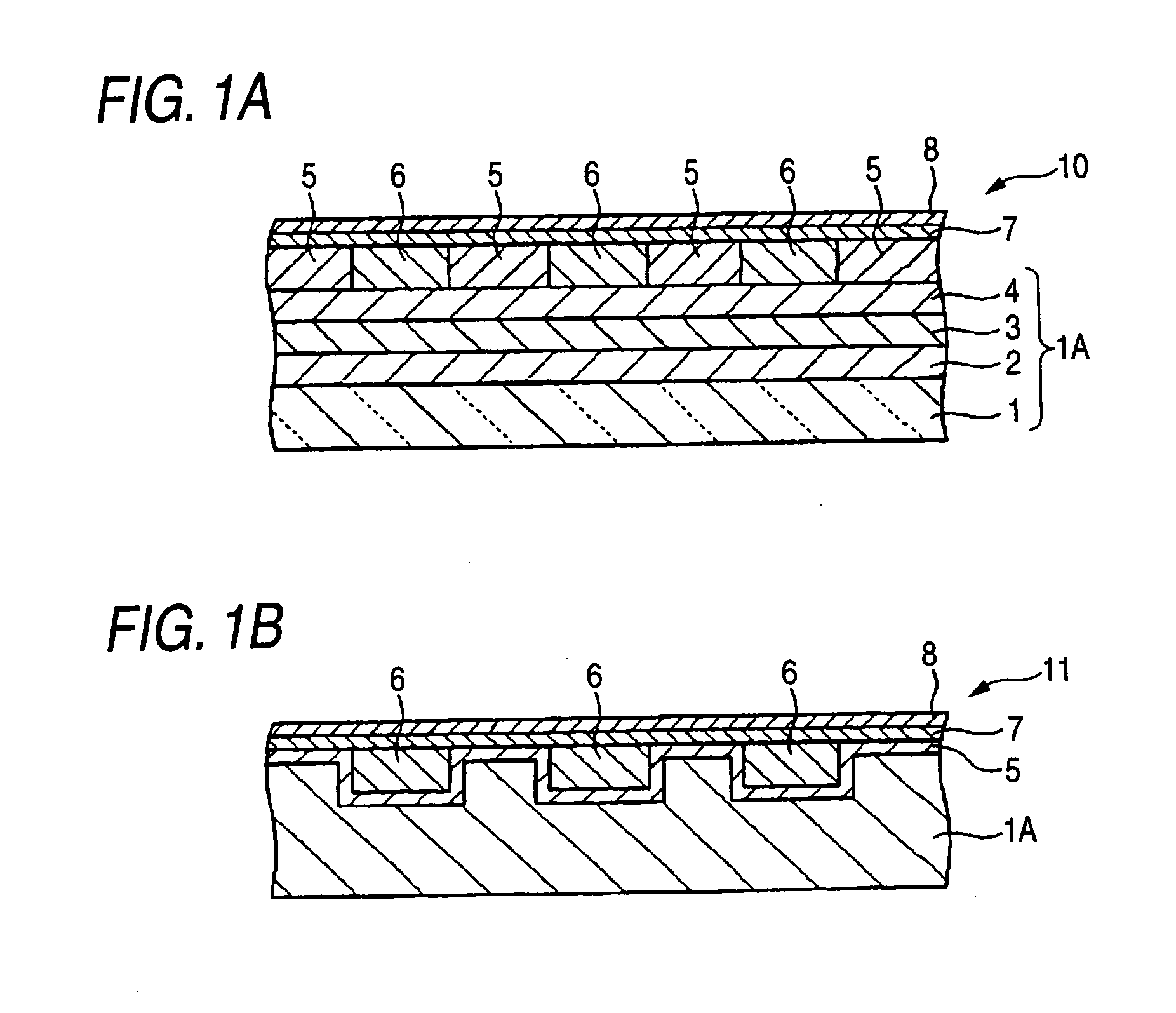
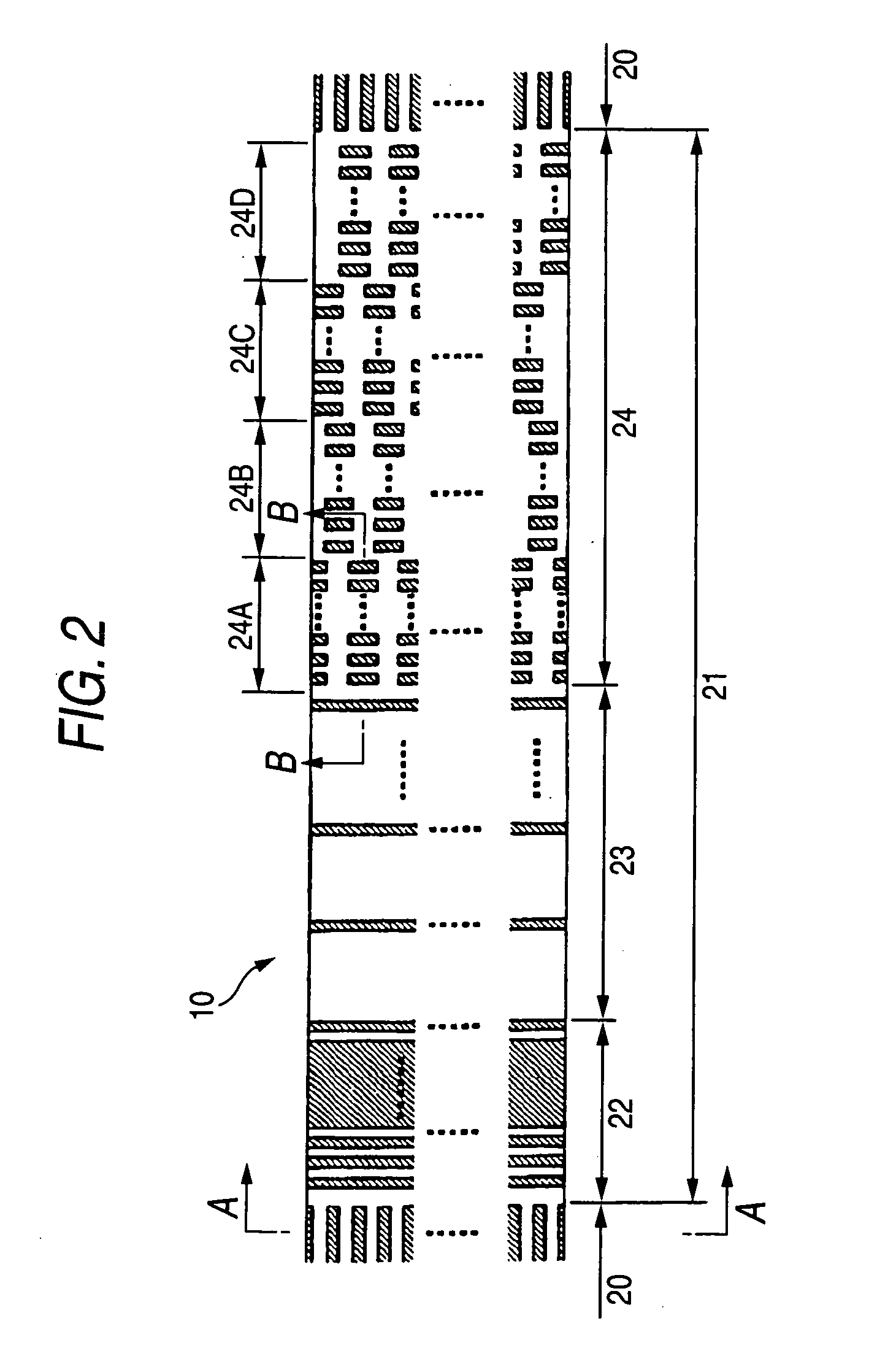
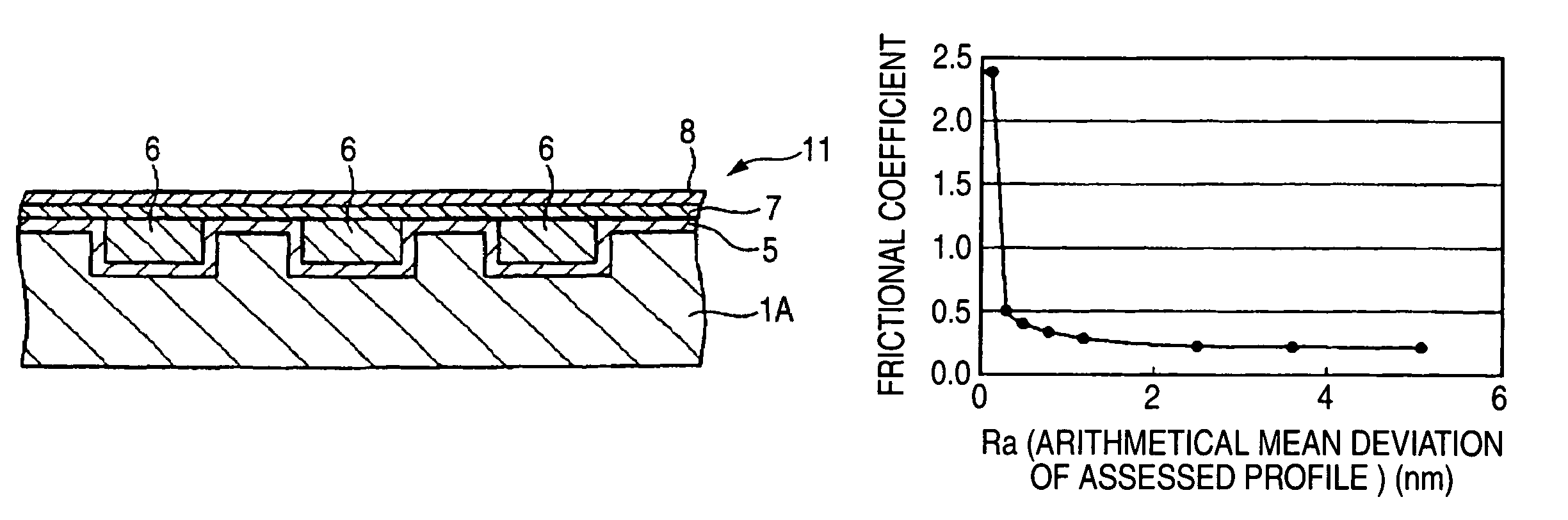
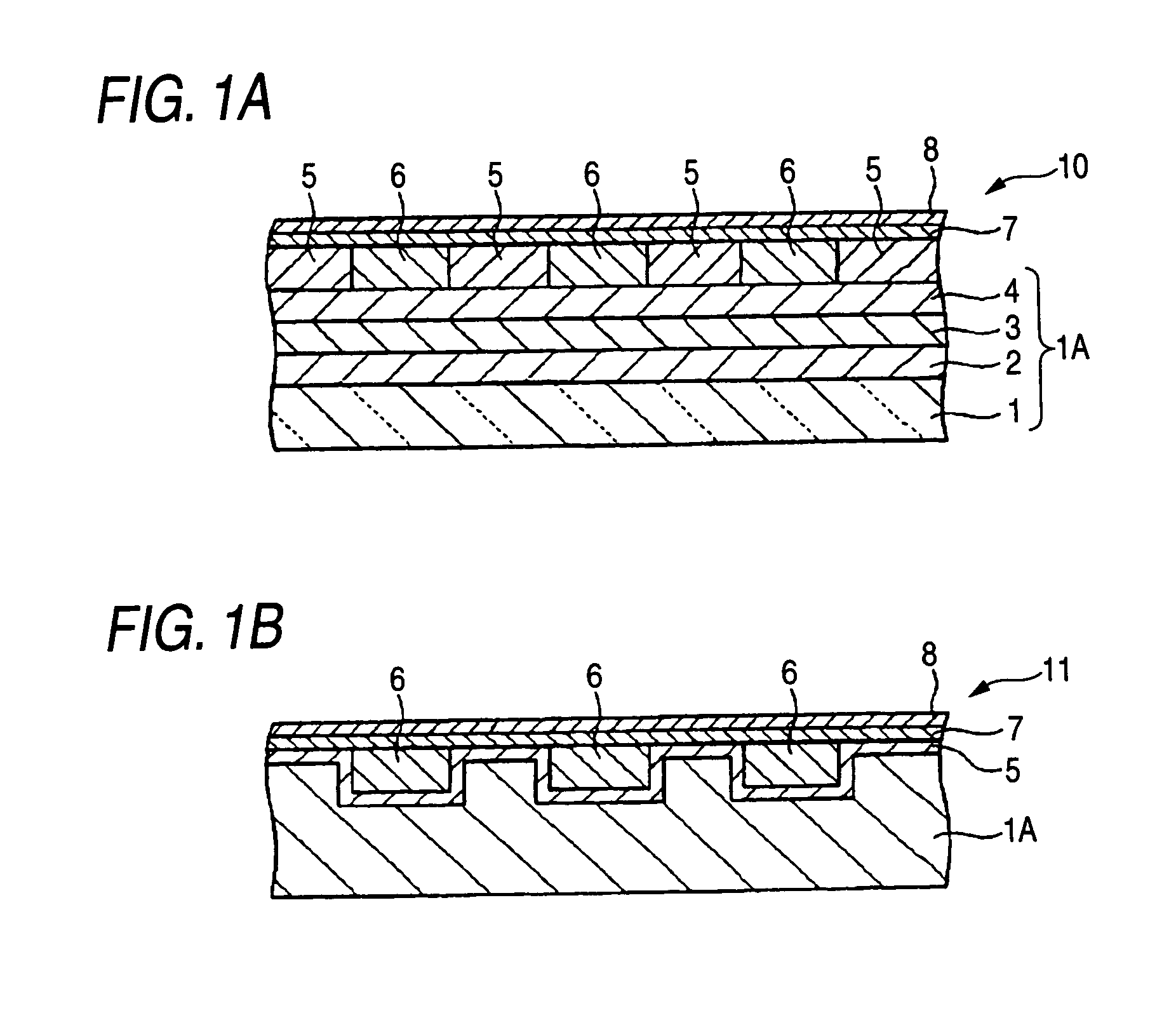
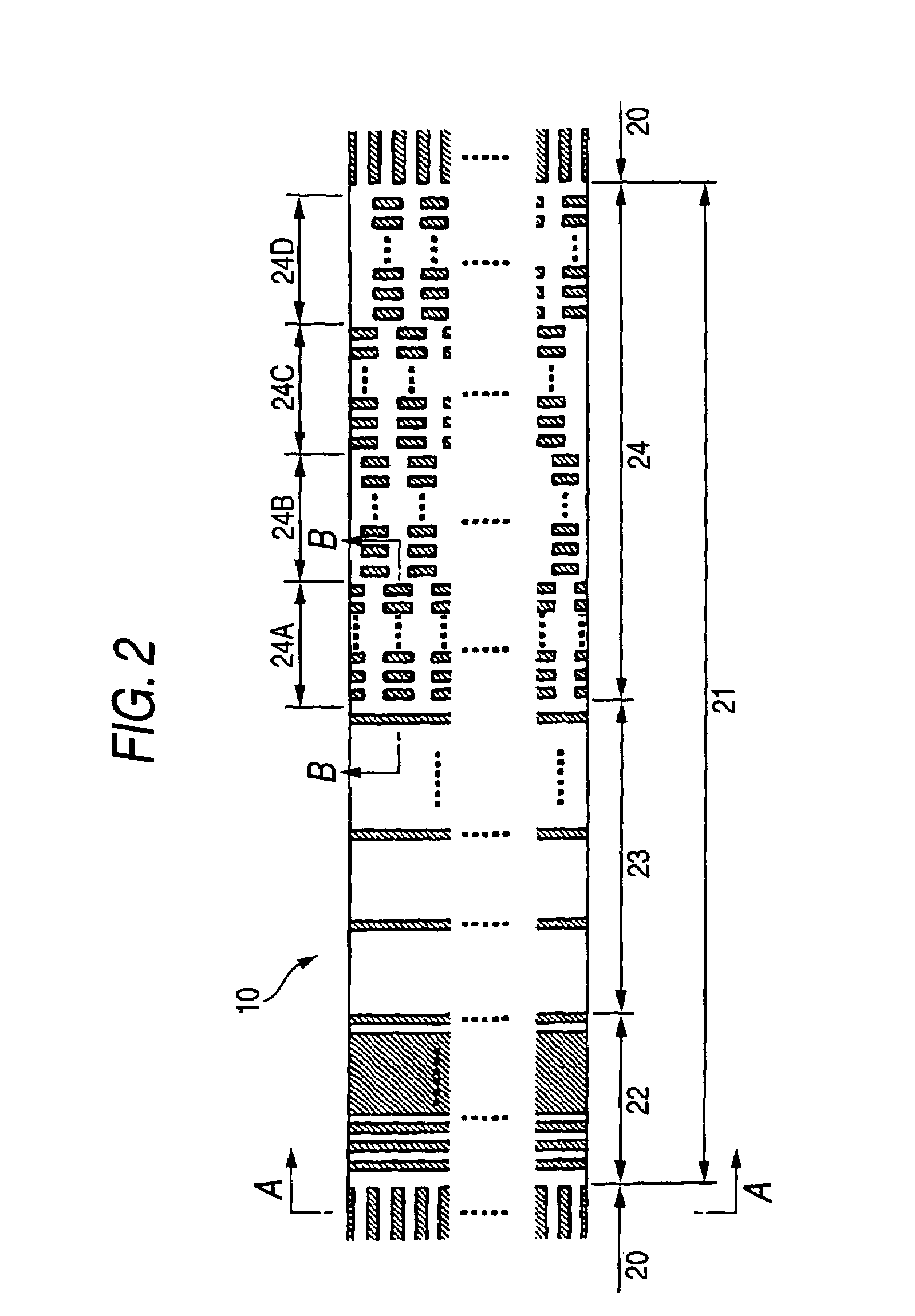
A magnetic recording medium including at least a disk substrate 1A, a magnetic recording layer 5 formed with a predetermined concavo-convex pattern on the disk substrate 1A, and a non-magnetic layer 6 filled into concave portions of the concavo-convex pattern, so as to have data track regions 20 and servo pattern regions 21. Due to the existence of concaves and convexes in the surface of each data track region 20, the foregoing problem is solved. On this occasion, arithmetical mean deviation of the assessed profile Ra of the surface of each data track region 20 is preferably not lower than 0.3 nm. The difference in surface level between each concave and each convex existing in the surface of the data track region 20 is preferably not larger than 6 nm.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
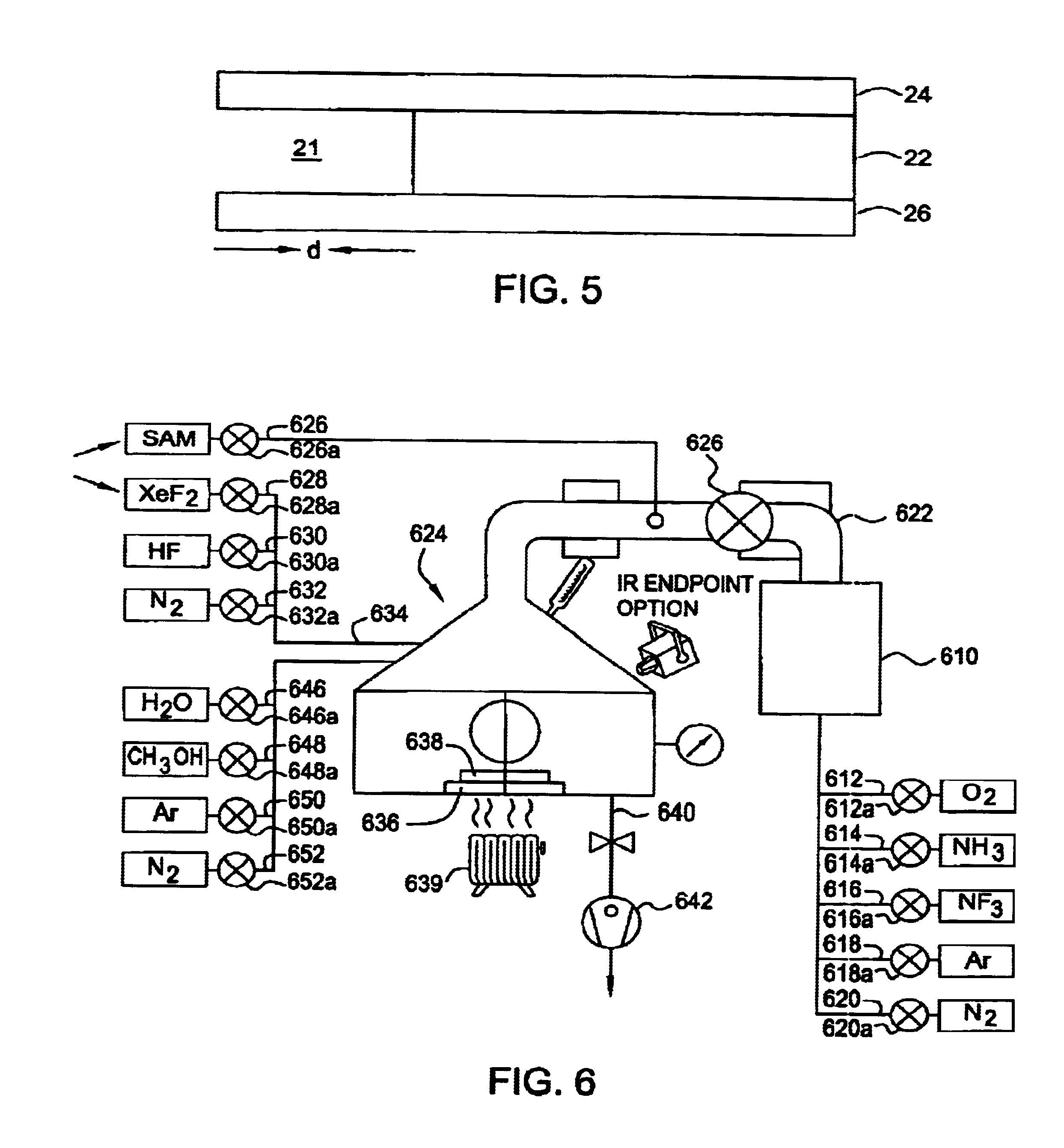
Etch process for etching microstructures
InactiveUS6936183B2Limited amountAvoid static frictionDecorative surface effectsCoupling light guidesHydrogen fluoridePhysical chemistry
A two-step method of releasing microelectromechanical devices from a substrate is disclosed. The first step comprises isotropically etching a silicon oxide layer sandwiched between two silicon-containing layers with a gaseous hydrogen fluoride-water mixture, the overlying silicon layer to be separated from the underlying silicon layer or substrate for a time sufficient to form an opening but not to release the overlying layer, and the second step comprises adding a drying agent to substitute for moisture remaining in the opening and to dissolve away any residues in the opening that can cause stiction.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
InactiveUS20050213239A1Reduce frictional resistanceAvoid static frictionMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageEngineeringSurface level
A magnetic recording medium including at least a disk substrate 1A, a magnetic recording layer 5 formed with a predetermined concavo-convex pattern on the disk substrate 1A, and a non-magnetic layer 6 filled into concave portions of the concavo-convex pattern, so as to have data track regions 20 and servo pattern regions 21. Due to the existence of concaves and convexes in the surface of each servo pattern region 21, the foregoing problem is solved. On this occasion, arithmetical mean deviation of the assessed profile Ra of the surface of each servo pattern region 21 is preferably not lower than 0.3 nm. The difference in surface level between each concave and each convex existing in the surface of the servo pattern region 21 is preferably not larger than 6 nm.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
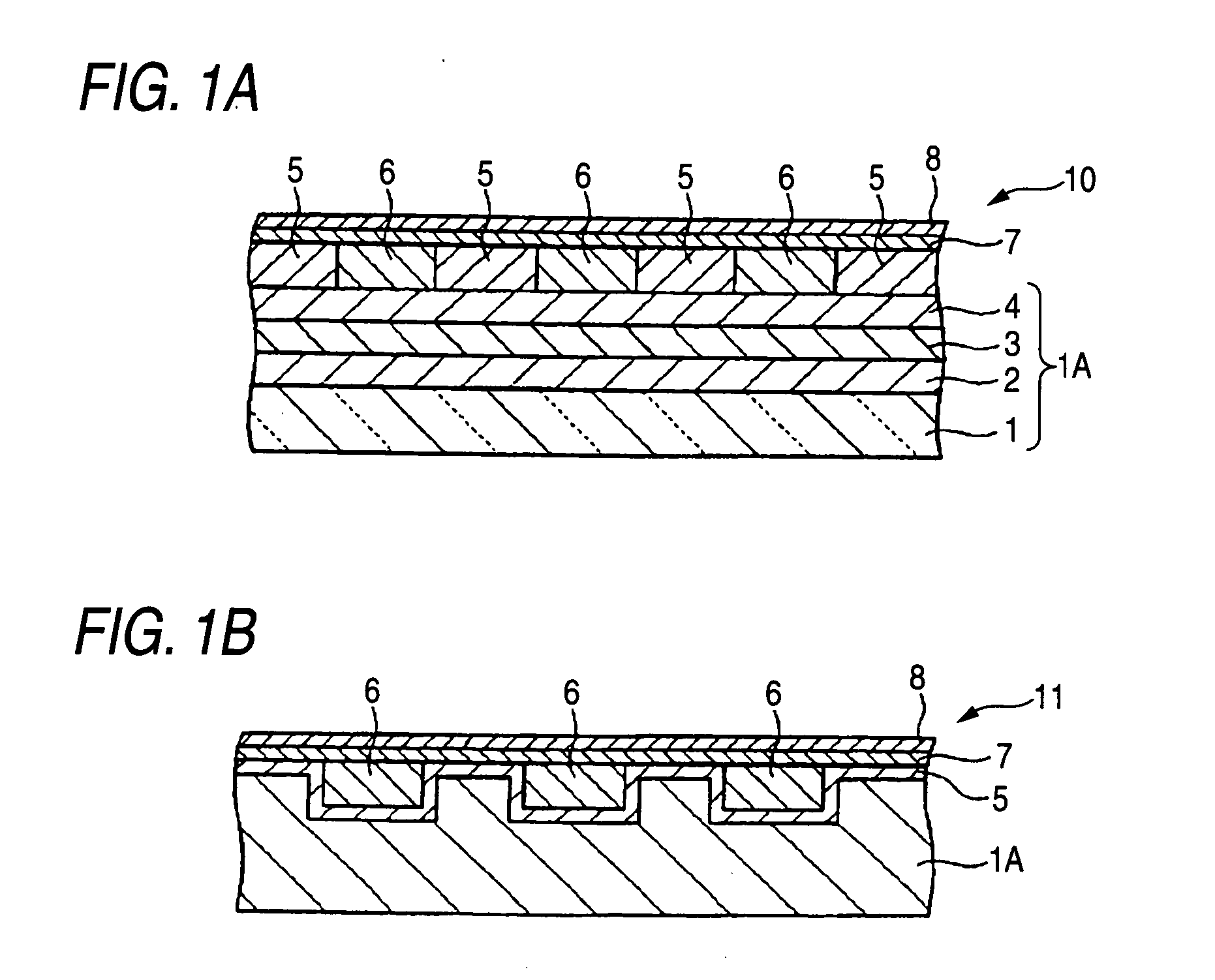
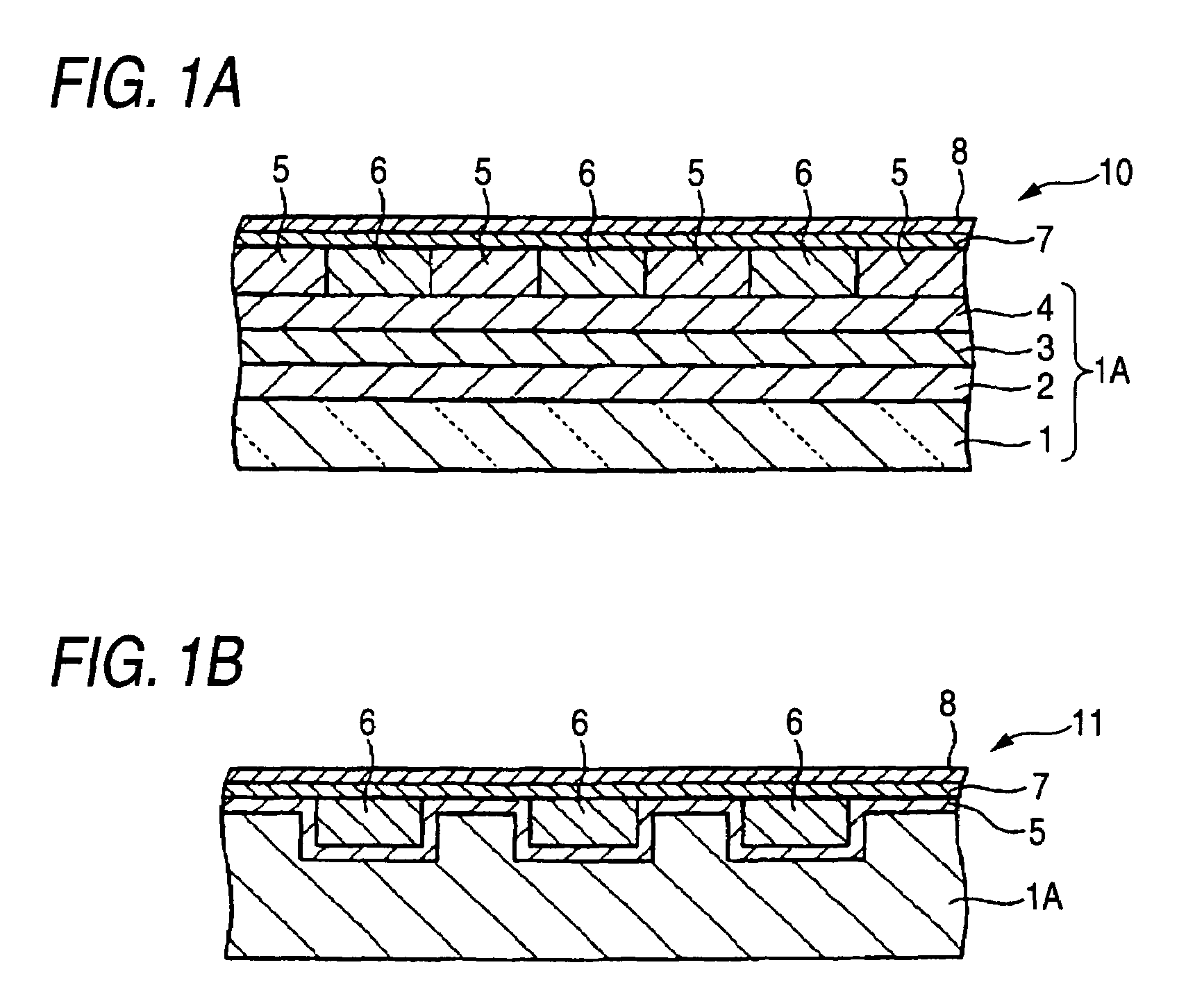
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20050196650A1Increase frictional resistanceIncrease areal densityMagnetic materials for record carriersLayered productsEngineeringNon magnetic
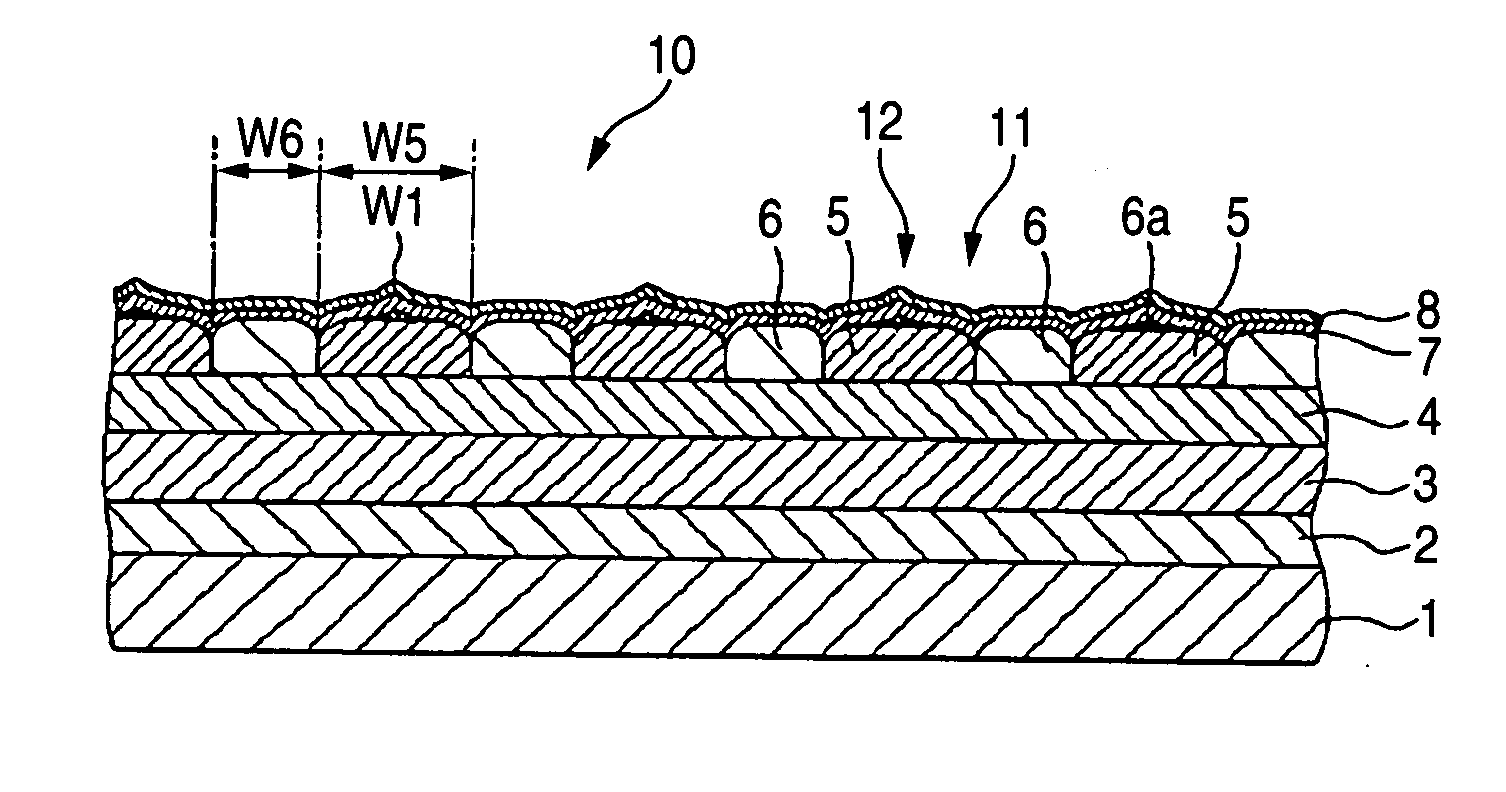
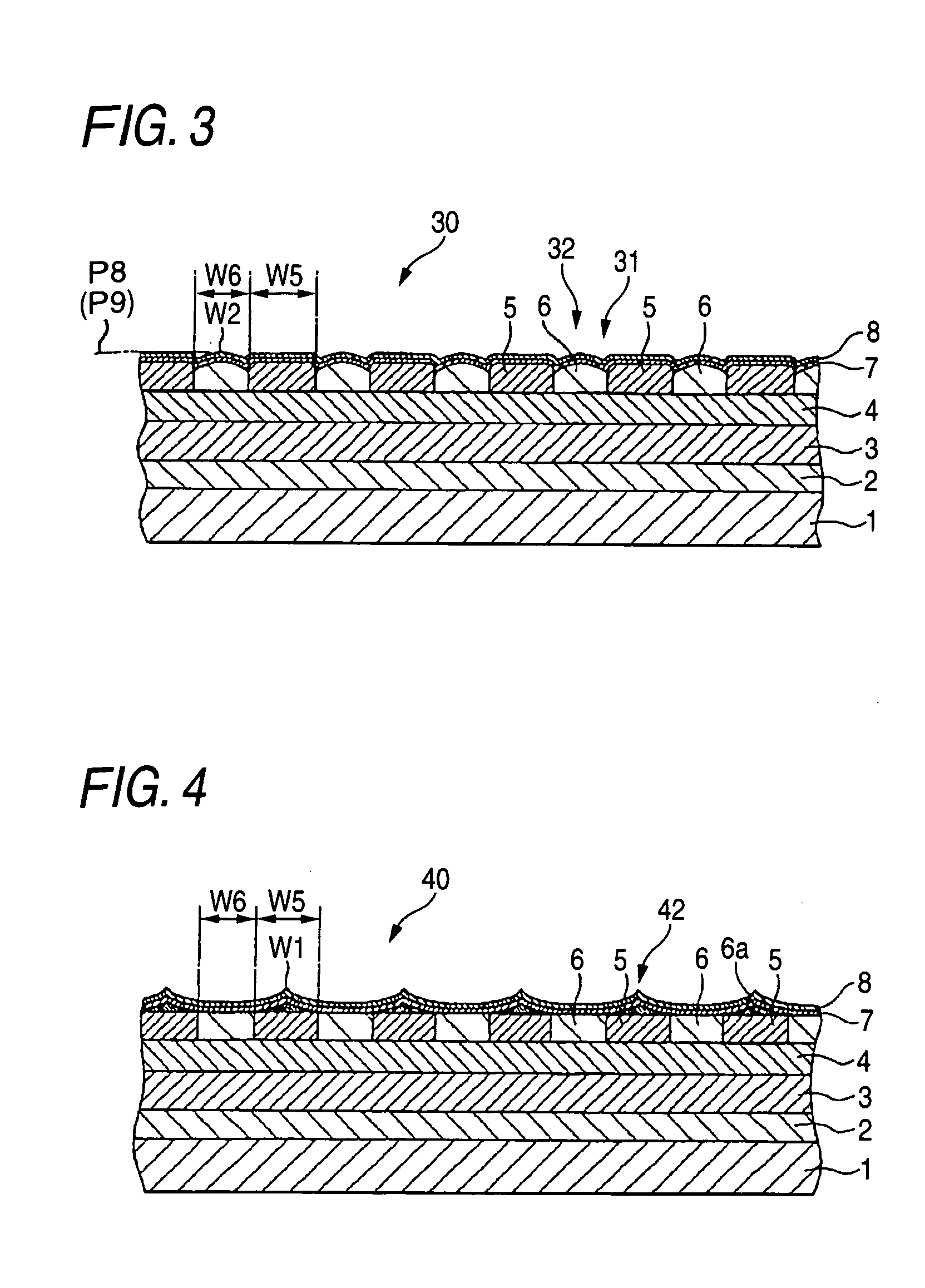
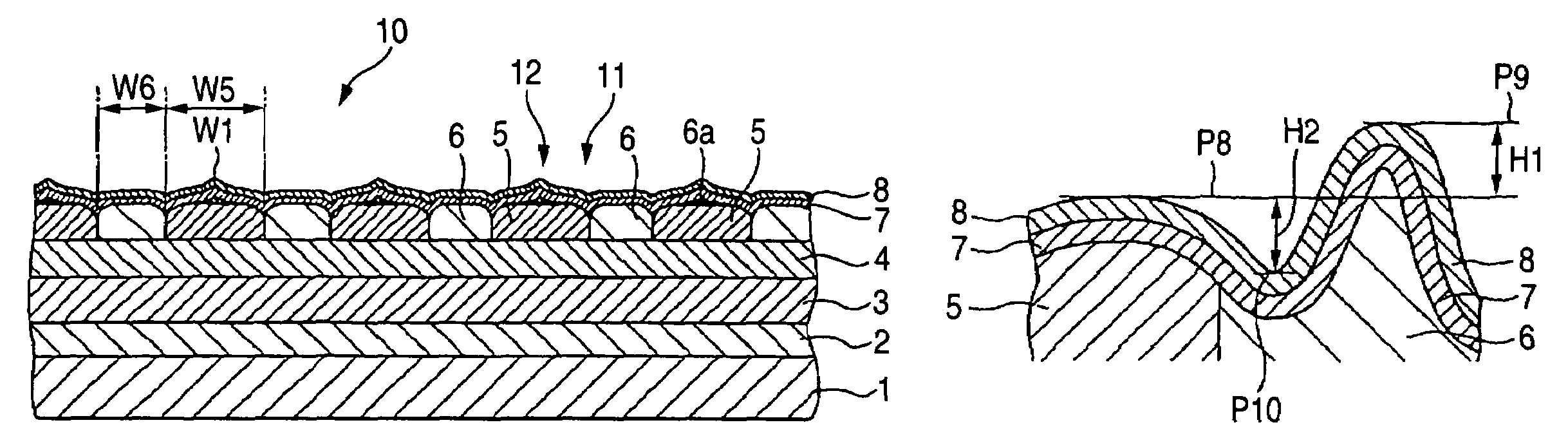
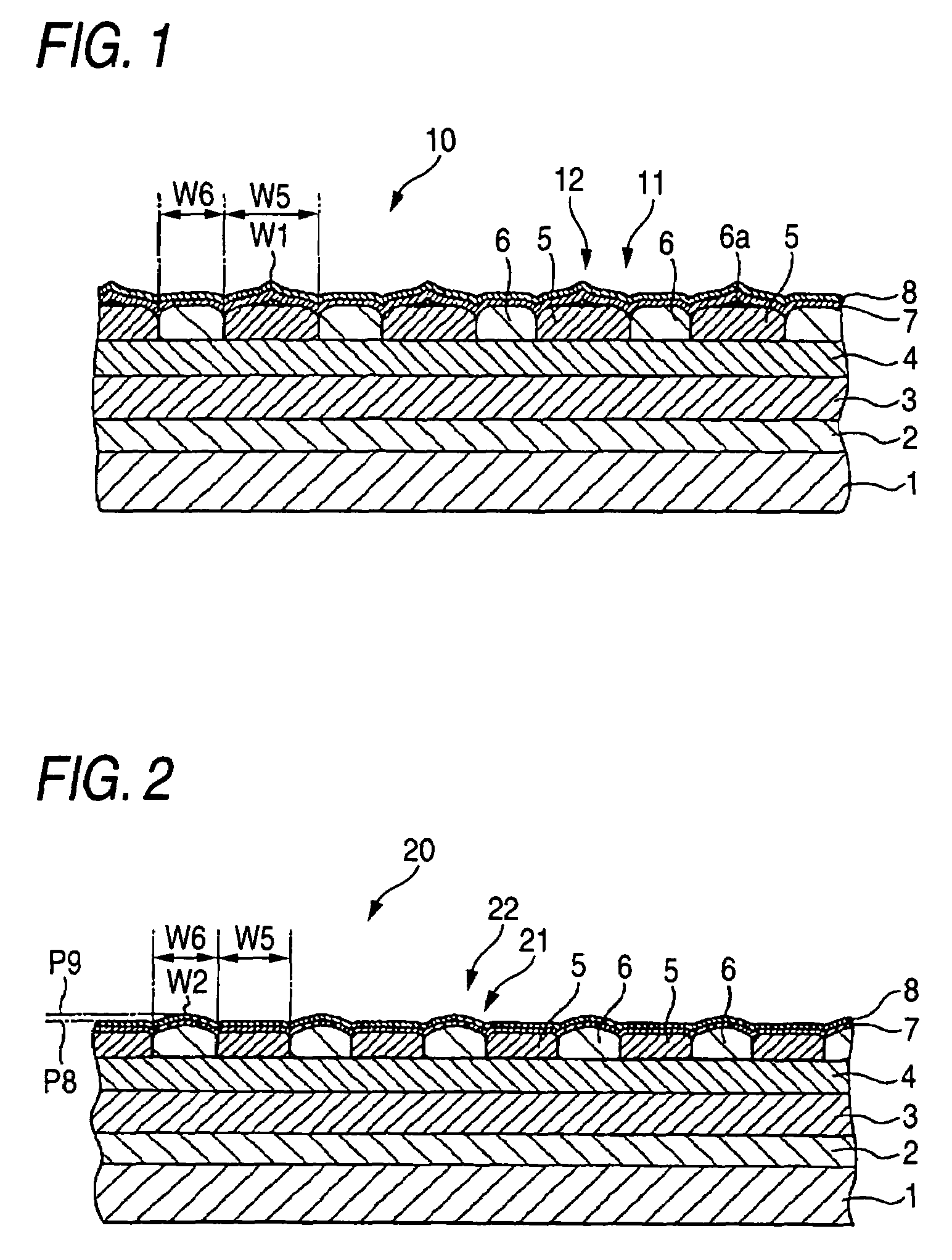
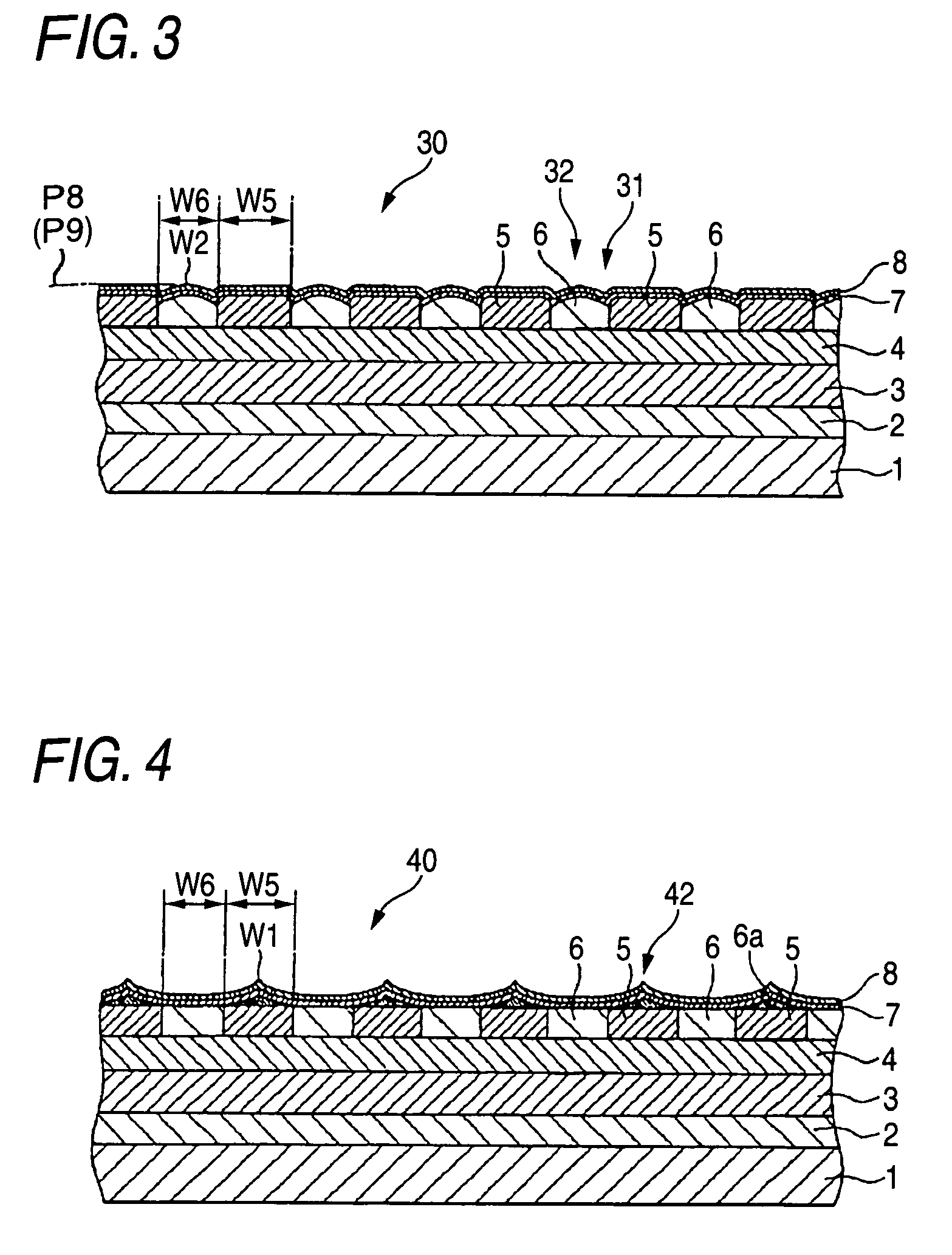
A magnetic recording medium includes at least a disk substrate 1, a magnetic recording layer 5 formed with a predetermined concavo-convex pattern on the disk substrate 1, and a non-magnetic layer 6 formed in concave portions of the concavo-convex pattern. Convex shapes made of a non-magnetic material are formed on the magnetic recording layer 5 or the non-magnetic layer 6. Each convex shape is formed, for example, into a mountain-like shape whose upper surface width (W1 or W2) is made smaller than width W5 of each convex portion of the magnetic recording layer 5 or width W6 of each concave portion where the non-magnetic layer 6 is formed.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device using a magnetic recording layer formed with a predetermined concavo-convex pattern
InactiveUS7352529B2Avoid static frictionLow in spacing lossMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageSurface levelEngineering
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
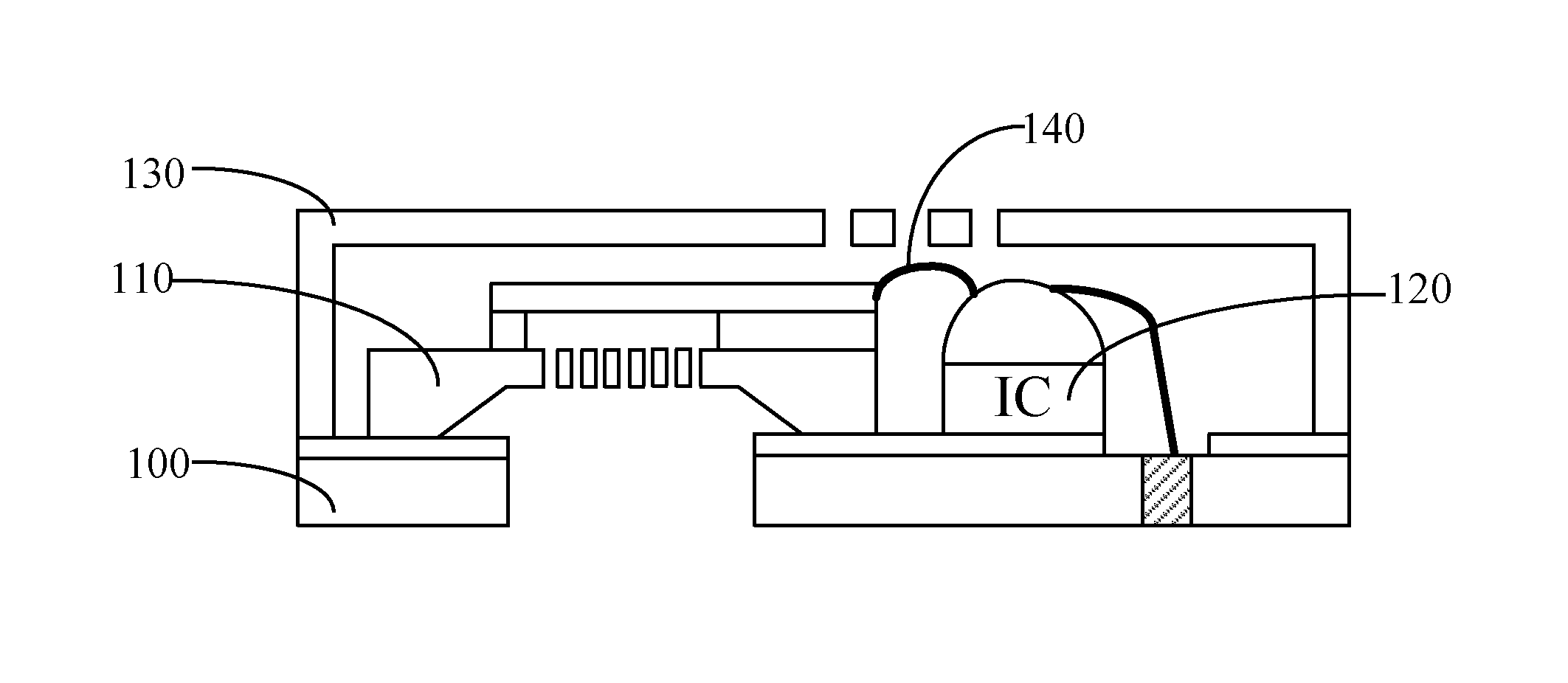
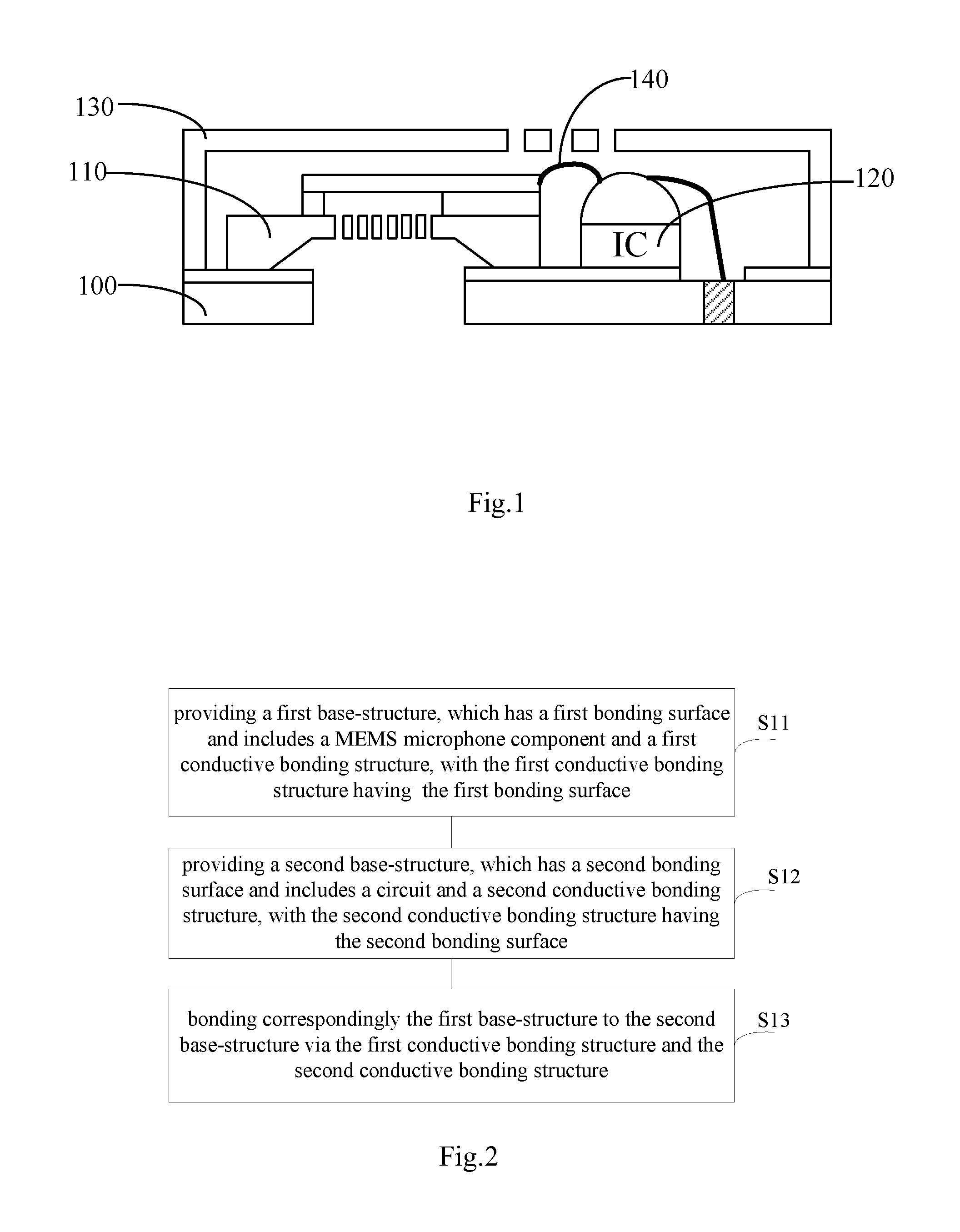
MEMS microphone and forming method therefor
ActiveUS20140003633A1Small sizeHigh performanceCooking-vessel materialsMicrophonesMems microphoneSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) microphone and a forming method therefore. The MEMS microphone comprises: a first substrate, the first substrate is provided with a first bonding face, the first substrate comprises an MEMS microphone component and a first conductive bonding structure arranged on the first bonding face, a second substrate, the second substrate is provided with a second bonding face, the second bonding substrate comprises a circuit and a second conductive bonding structure arranged on the second bonding face; the first substrate and the second substrate are oppositely fitted together via the first conductive bonding structure and the second conductive bonding structure. Embodiments of the present invention have a simple packaging technique and a compact size; the MEMS microphone packaging structure formed has a great performance on signal-to-noise ratio, and a great anti-interference capability
Owner:MEMSEN ELECTRONICS
Systems and methods for stiction reduction in MEMS devices
InactiveUS20100181652A1Avoid static frictionImprove production yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorMaterial type
Systems and methods for reducing stiction between elements of a microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) device during anodic bonding. The MEMS device includes a substrate cover with an optional conductor on its interior surface and the cover is anchored to a first portion of a sensing element. The MEMS device further includes a second portion of the sensing element separated from the substrate cover with a space and an antistiction element disposed between the second portion and cover. The antistiction element can be formed of a material type with high electrostatic resistance, to prevent stiction between MEMS device elements during anodic bonding.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method of preventing stiction of MEMS devices
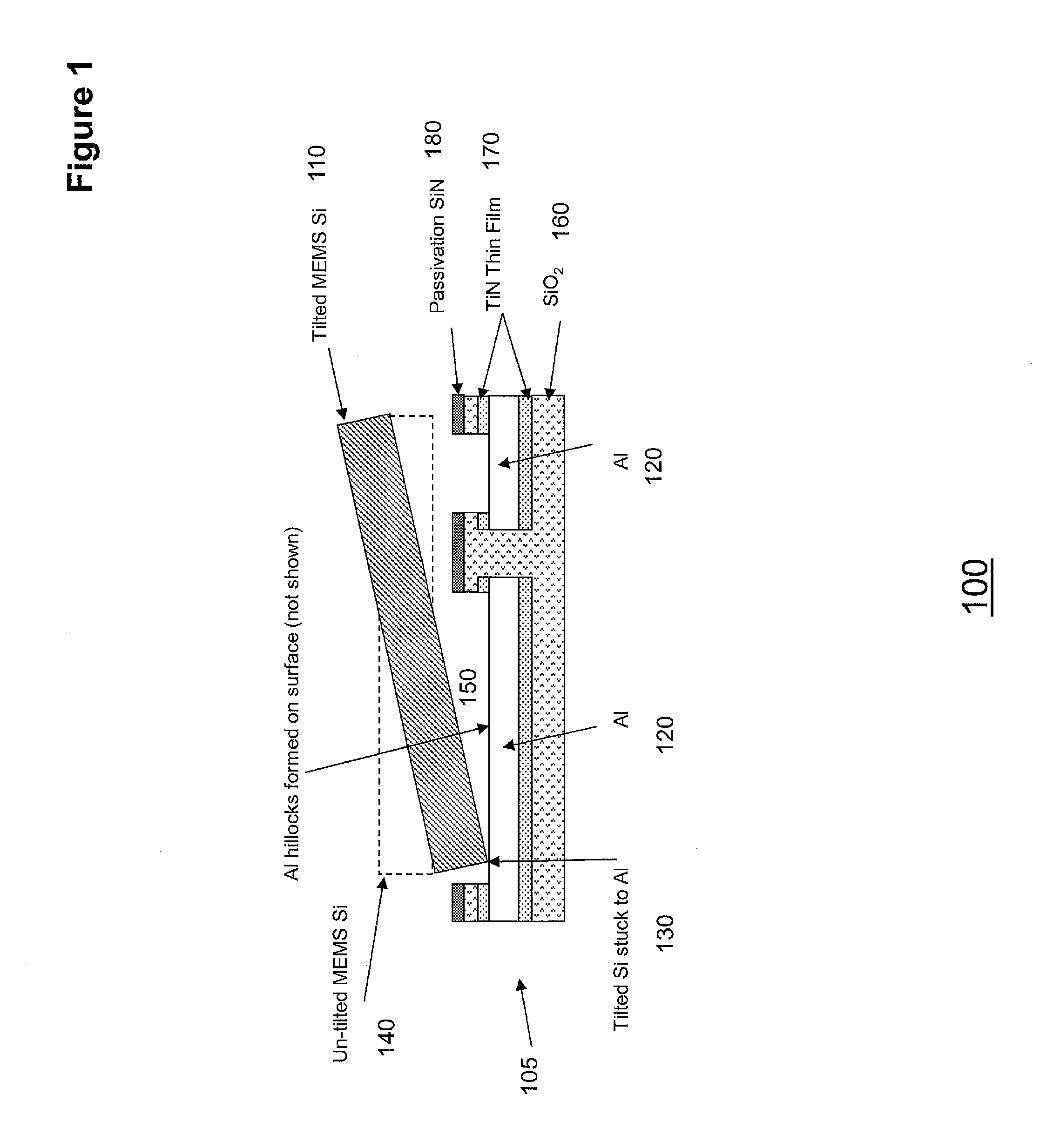
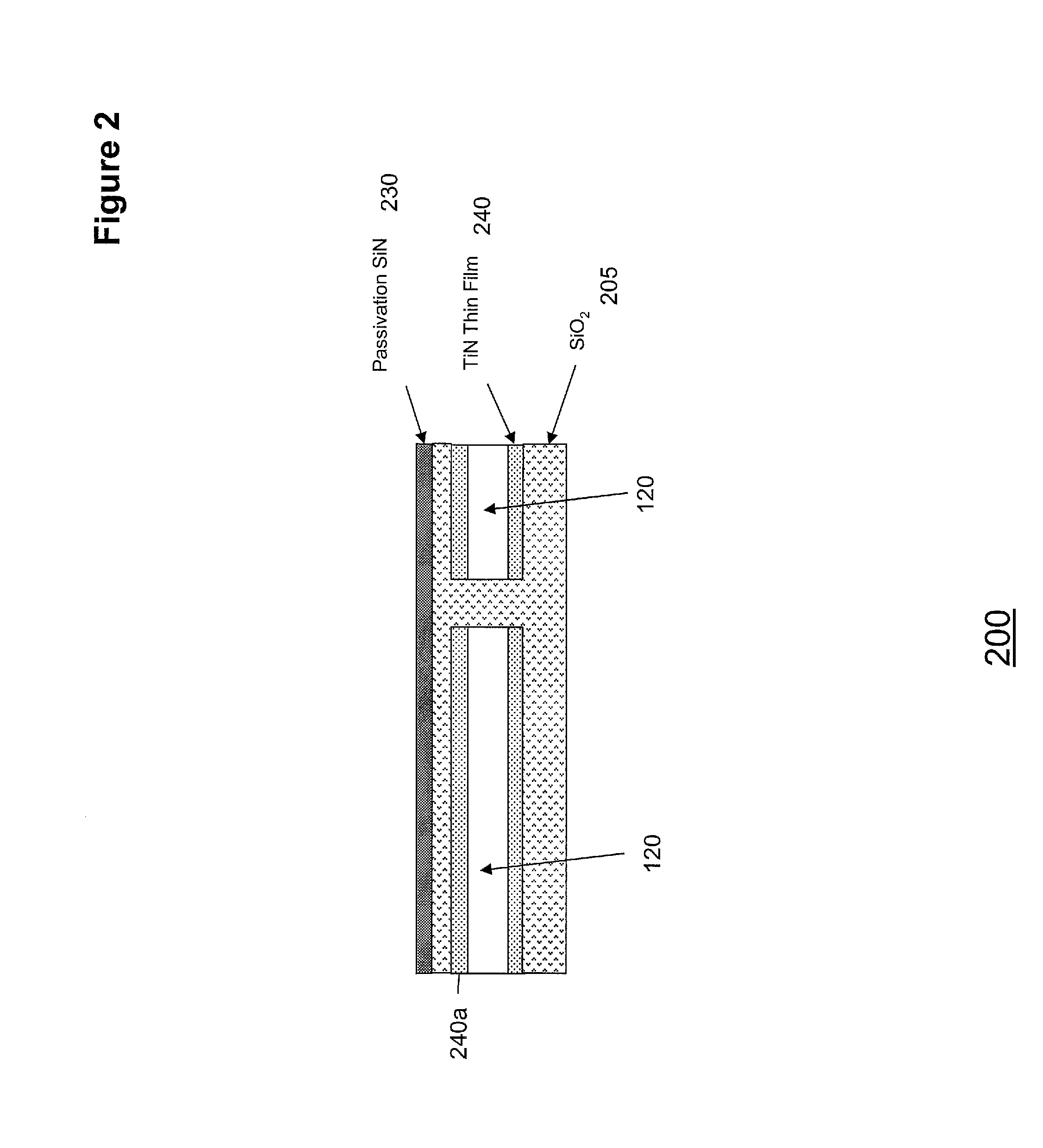
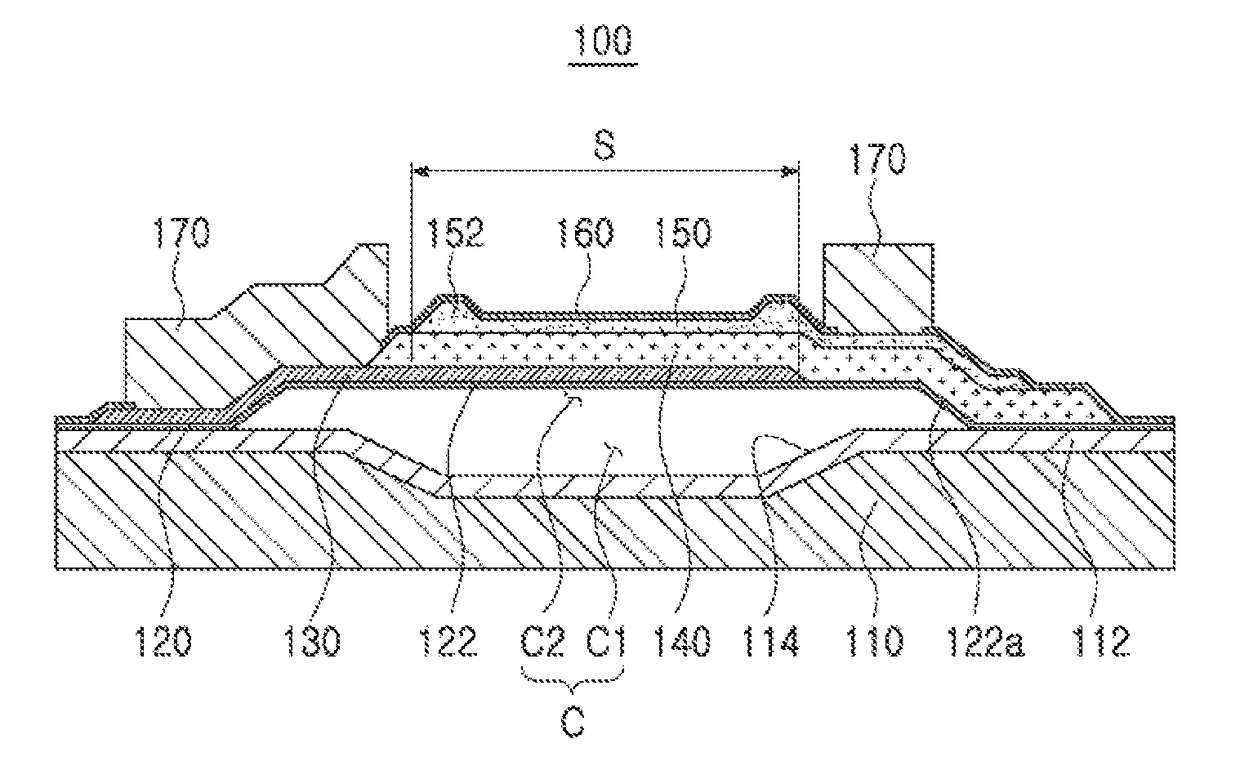
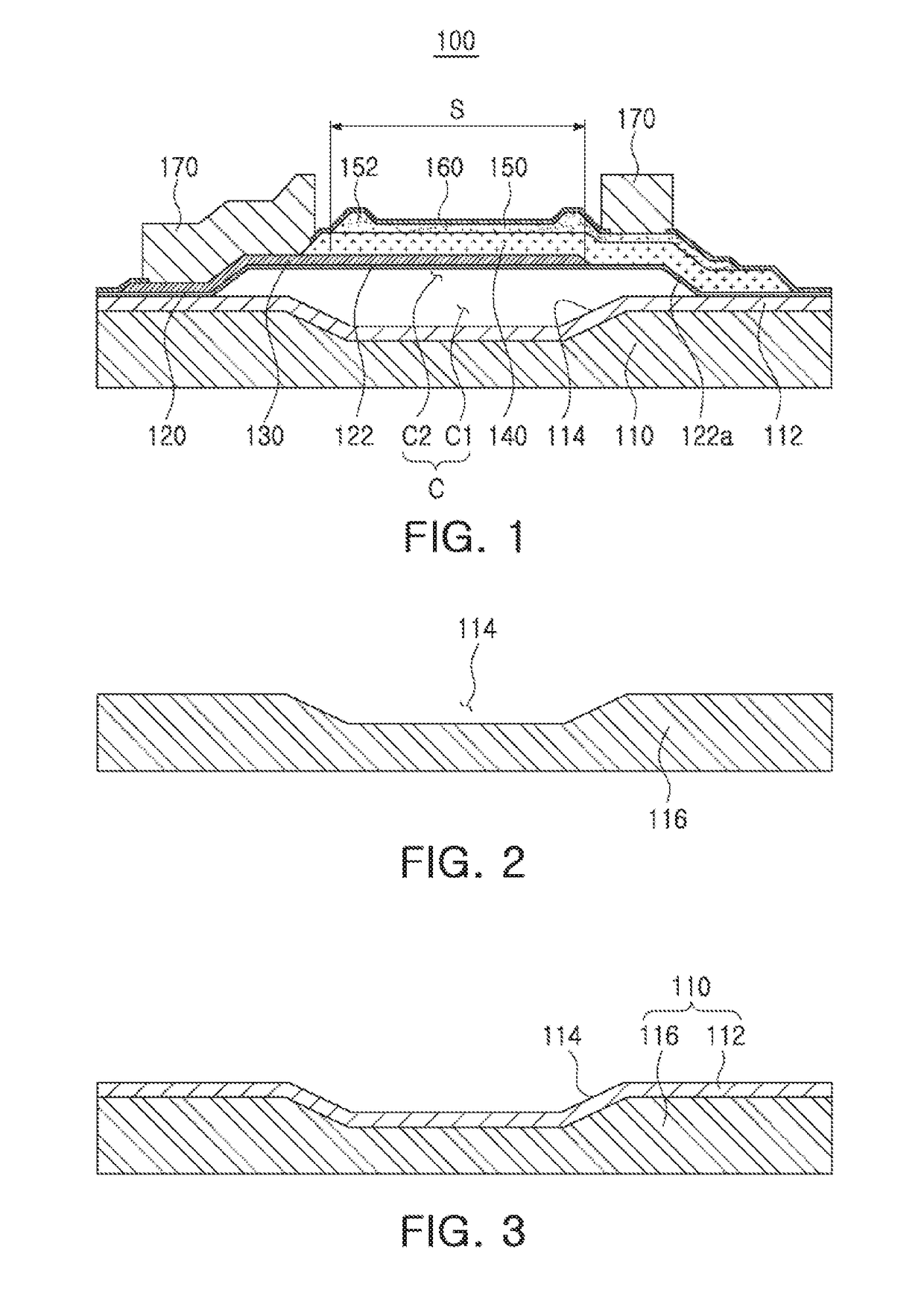
InactiveUS20120313189A1Avoid static frictionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrostructural device manufactureCMOSTitanium nitride
A method and apparatus are disclosed for reducing stiction in MEMS devices. The method comprises patterning a CMOS wafer to expose Titanium-Nitride (TiN) surface for a MEMS stop and patterning the TiN to form a plurality of stop pads on the top metal aluminum surface of the CMOS wafer. The method is applied for a moveable MEMS structure bonded to a CMOS wafer. The TiN surface and / or plurality of stop pads minimize stiction between the MEMS structure and the CMOS wafer. Further, the TiN film on top of aluminum electrode suppresses the formation of aluminum hillocks which effects the MEMS structure movement.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Bulk acoustic wave resonator and method of manufacturing the same
A bulk acoustic wave resonator includes a substrate including a cavity groove, a membrane layer disposed above the substrate and including a convex portion. And a lower electrode including a portion thereof disposed on the convex portion. The bulk acoustic wave resonator also includes a piezoelectric layer configured so that a portion of the piezoelectric layer is disposed above the convex portion, and an upper electrode disposed on the piezoelectric layer. A first space formed by the cavity groove and a second space formed by the convex portion form a cavity, the cavity groove is disposed below an active region, and the convex portion comprises an inclined surface disposed outside of the cavity groove.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Electrostatic actuator, variable capacitance capacitor, electric switch, and method for driving electrostatic actuator
ActiveUS20150116893A1Prevent stictionEasily controlElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCapacitor with electrode distance variationCapacitanceElectrostatic actuator
An electrostatic actuator includes: a fixed driving electrode that is disposed on a silicon substrate; a movable driving electrode that is disposed so as to face the fixed driving electrode and approaches the fixed driving electrode with an electrostatic force generated between the movable driving electrode and the fixed driving electrode; and a pair of spacers that comes in contact with the movable driving electrode in an approaching state in which the fixed driving electrode and the movable driving electrode approach each other and forms a prescribed air gap between the fixed driving electrode and the movable driving electrode, wherein each of the spacers has a spacer electrode portion that comes in contact with the movable driving electrode via an insulator and has the same potential as one of the electrodes at least in the approaching state.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Microfluidic device having microvalve
A microfluidic device including a microvalve includes a first substrate, a second substrate facing the first substrate, an elastic film between the first and second substrates, a microfluidic channel on the second substrate, a valve seat of the second substrate protruding in the microfluidic channel, and a fine structure on a surface of the elastic film, facing the valve seat and which contacts the valve seat when the microvalve is operated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Capacitive microphone and method for making the same
ActiveUS7912235B2Avoid static frictionAvoid driftingElectrostatic transducer microphonesDeaf-aid setsEngineeringCapacitive microphone
A capacitive microphone and method for making the same are provided. A backplate with a plurality of holes is formed on a substrate with at least one cavity, and a diaphragm is formed above the backplate. There is an air gap between the backplate and the diaphragm. The air gap and the cavity communicate with each other by each hole. The diaphragm and the backplate are separated by a first distance and a second distance which is smaller than the first distance, such that the difference is formed on the diaphragm. The second distance area is fastened through surface stiction produced by mist or other fluids.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Propulsion assembly for endoscope
InactiveUS20130158353A1Reduce frictionAvoid damageGastroscopesOesophagoscopesEngineeringMechanical engineering
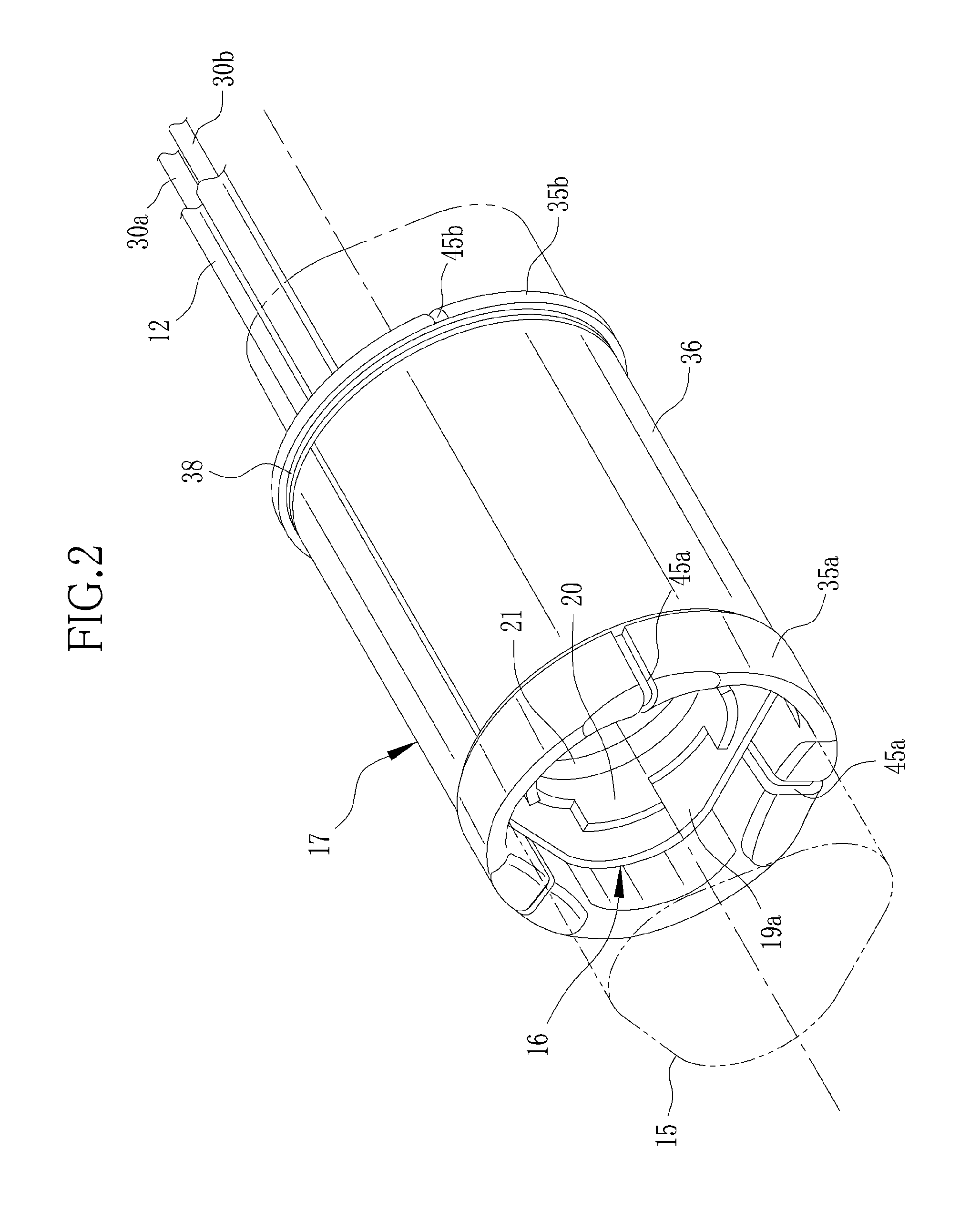
A propulsion assembly for an endoscope includes a support sleeve and a barrel unit. An endless track device is disposed to extend along inner and outer surfaces of the barrel unit, for endlessly moving in an axial direction of an elongated tube of the endoscope, and contacting a wall of a body cavity, for propulsion of the elongated tube. Worm wheels are disposed on the support sleeve, for driving the endless track device by engagement therewith. Plural idler rollers are disposed on the inner surface of the barrel unit in a rotatable manner, for keeping the endless track device movable in driving of the worm wheels. An guide projection is formed on the endless track device. A guide groove is formed in the barrel unit, for receiving the guide projection, to guide the endless track device on the barrel unit in the axial direction.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Arch breaking device for storage bin
InactiveCN102431741ASimple structureEasy to useLarge containersAutomatic controlProgrammable logic controller
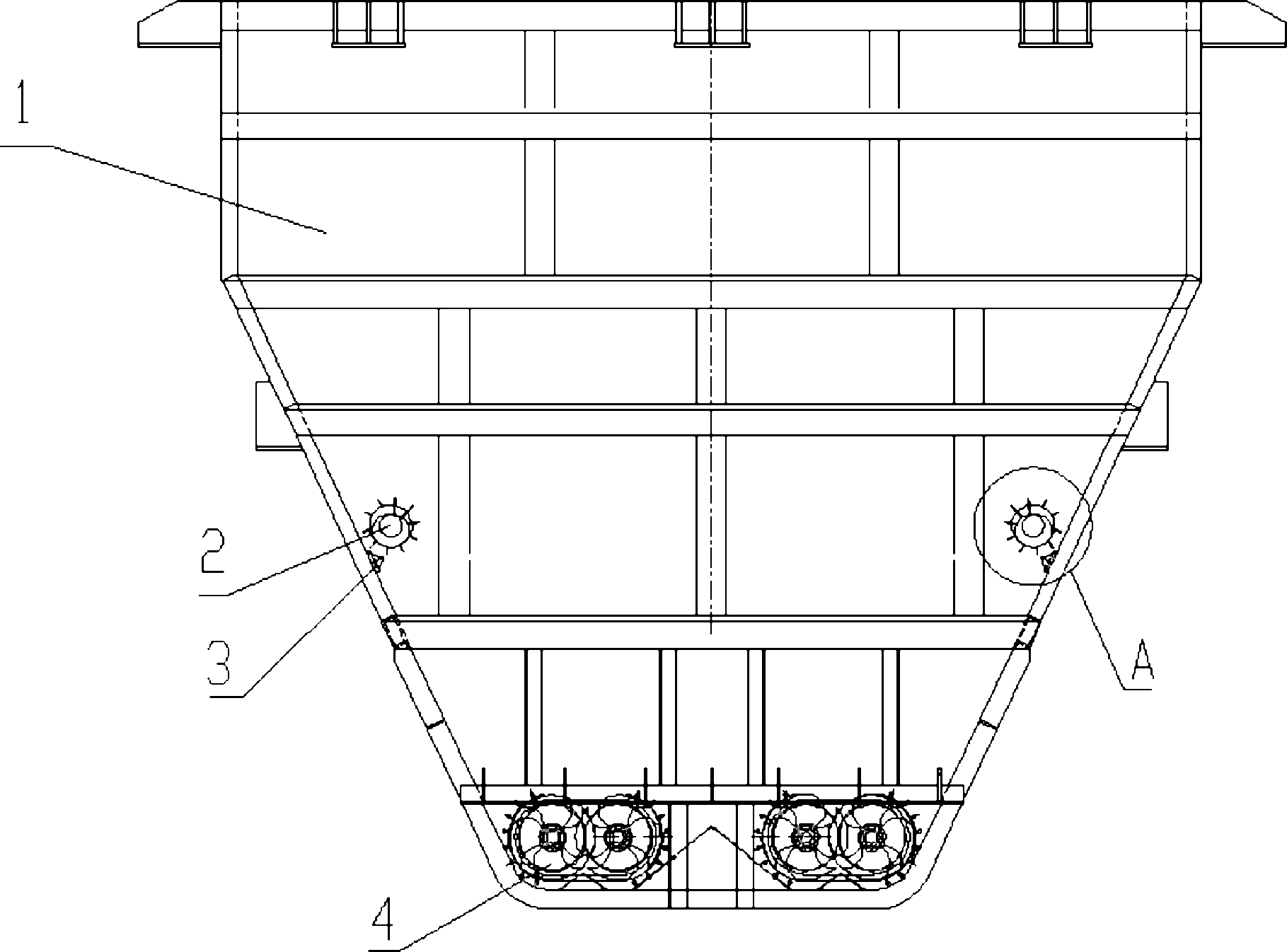
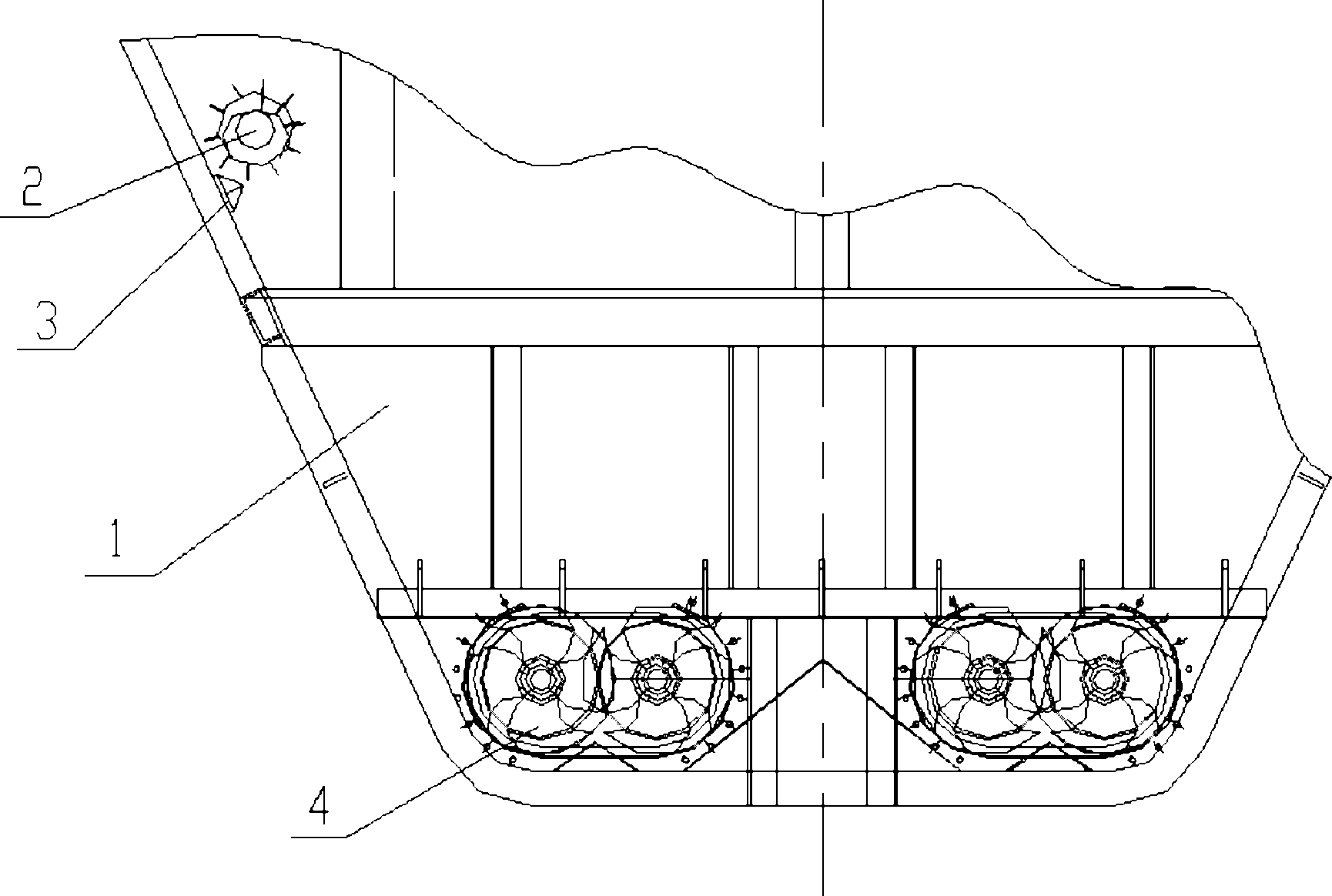
The invention provides an arch breaking device for a storage bin, comprising double-end helical teeth, disk type compression air convection devices and a helical conveyor, wherein the double-end helical teeth are fixedly installed on the inclined wall of the storage bin symmetrically by a shaft; a group of disk type compression air convection devices is evenly arranged on the storage bin wall below the double-end helical teeth by taking a storage bin axis as a center; the disk type compression air convection devices are connected with an external air pump; the air pump is connected with a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller); and a discharge opening at the bottom of the storage bin is provided with multiple groups of helical conveyors. The arch breaking device for the storage bin, disclosed by the invention, is used for breaking a material arch in the storage bin by combining with the double-end helical teeth and the disk type compression air convection devices and has the advantages of simple structure, safety and convenience for use, complete arch breakage, safety, energy saving, high automatic control degree and no damage to the storage bin.
Owner:新疆天物生态环保股份有限公司
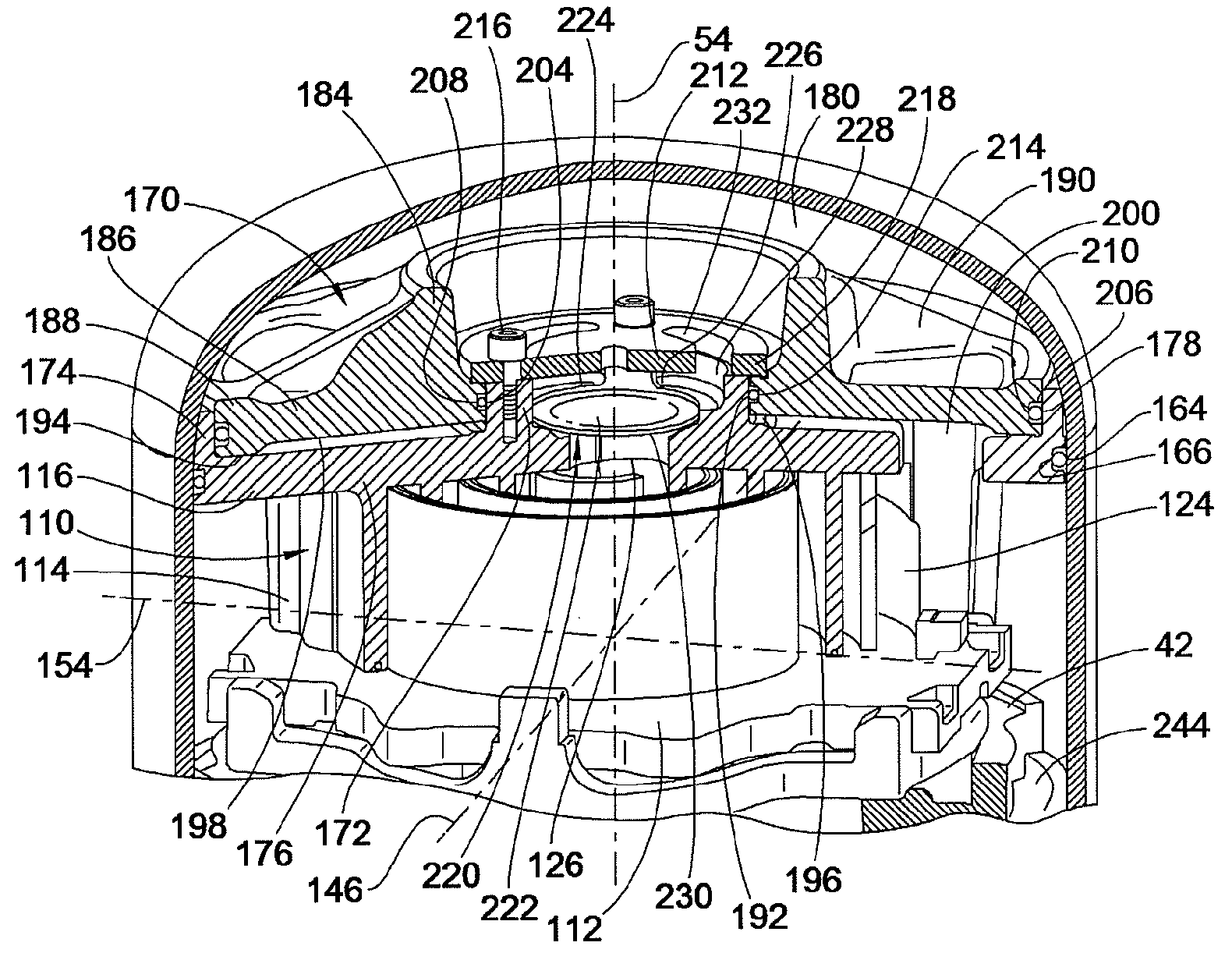
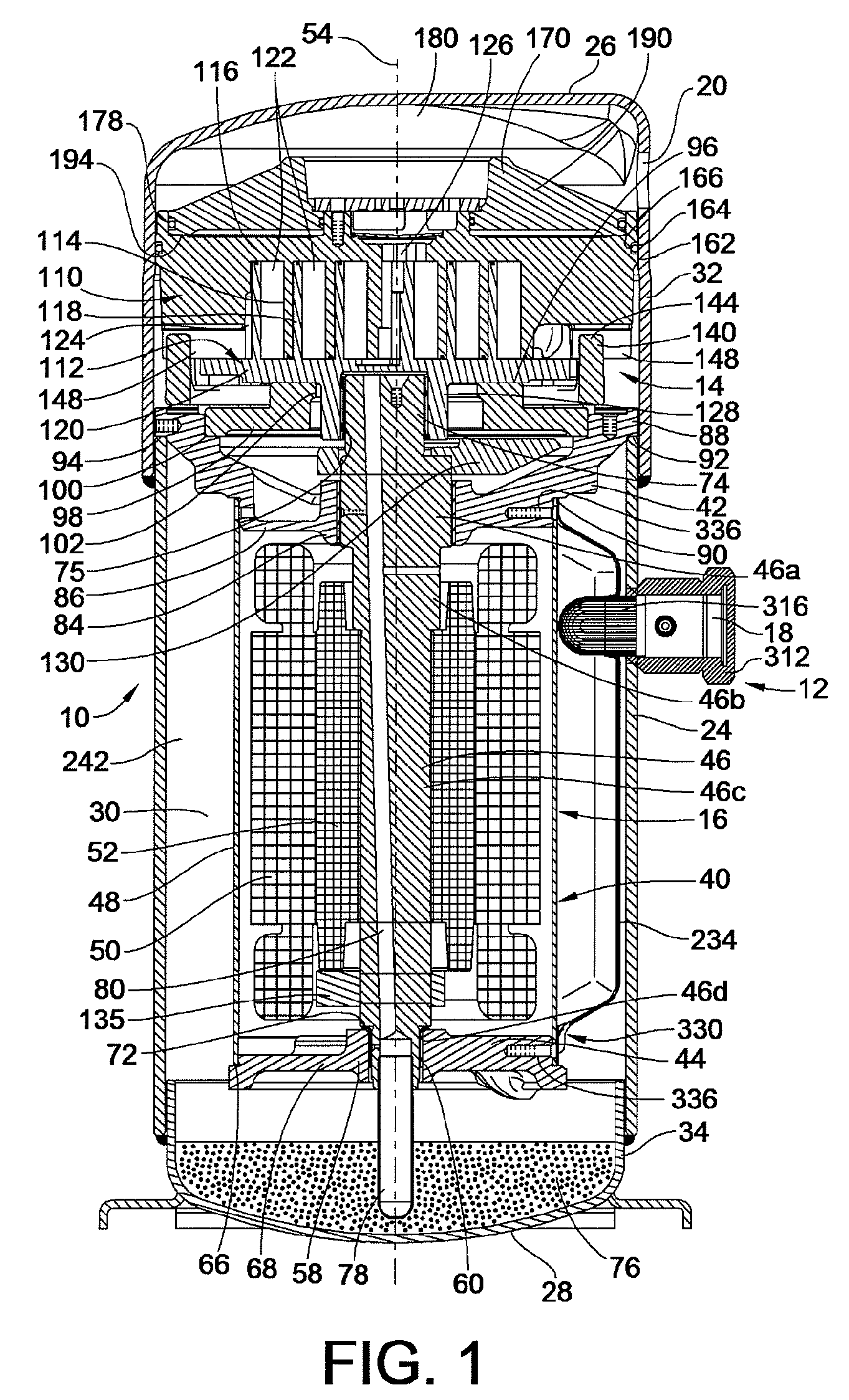
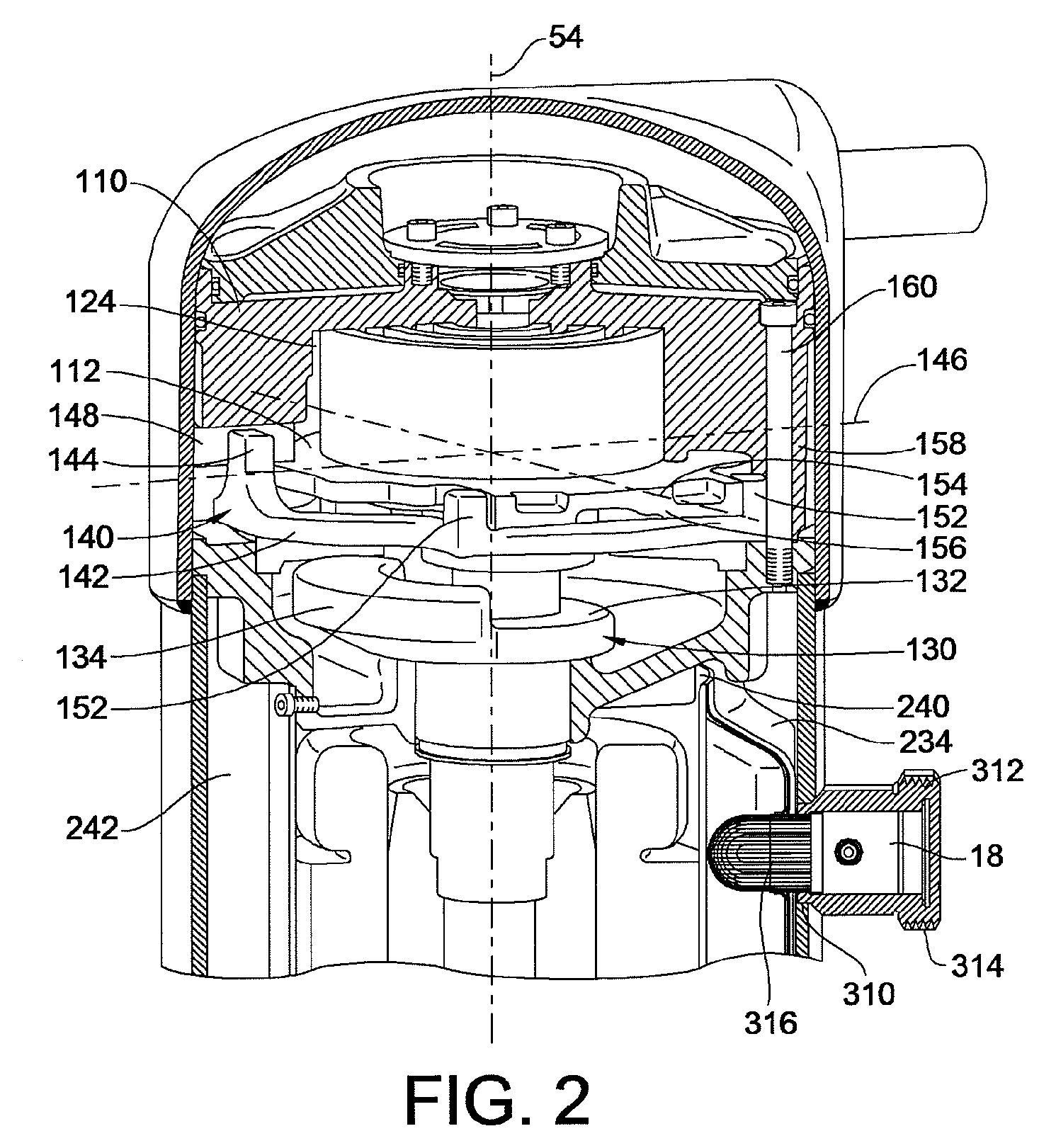
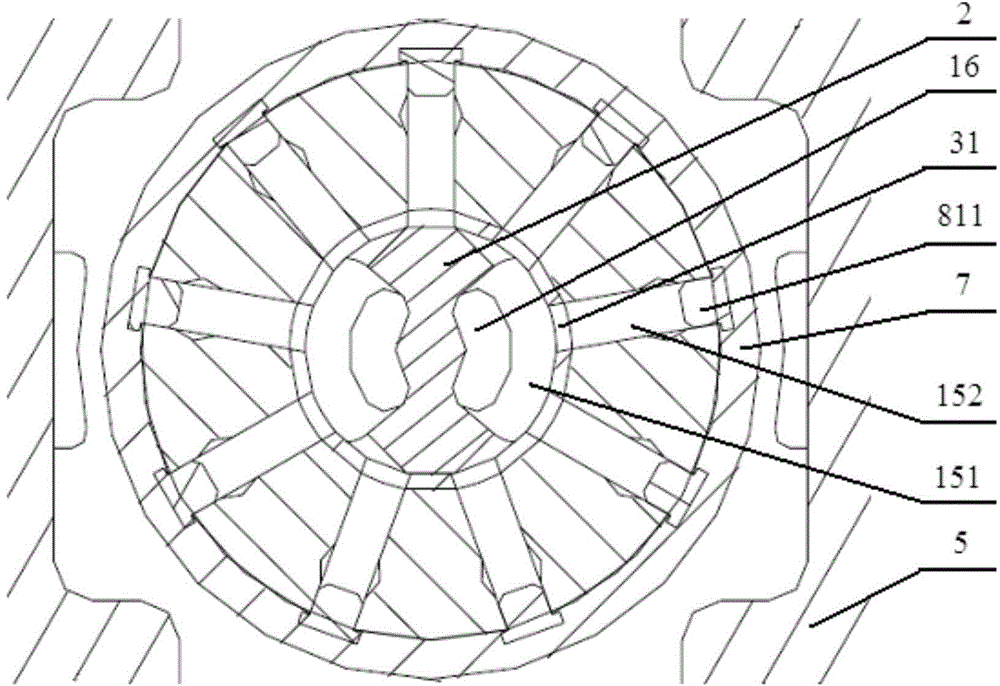
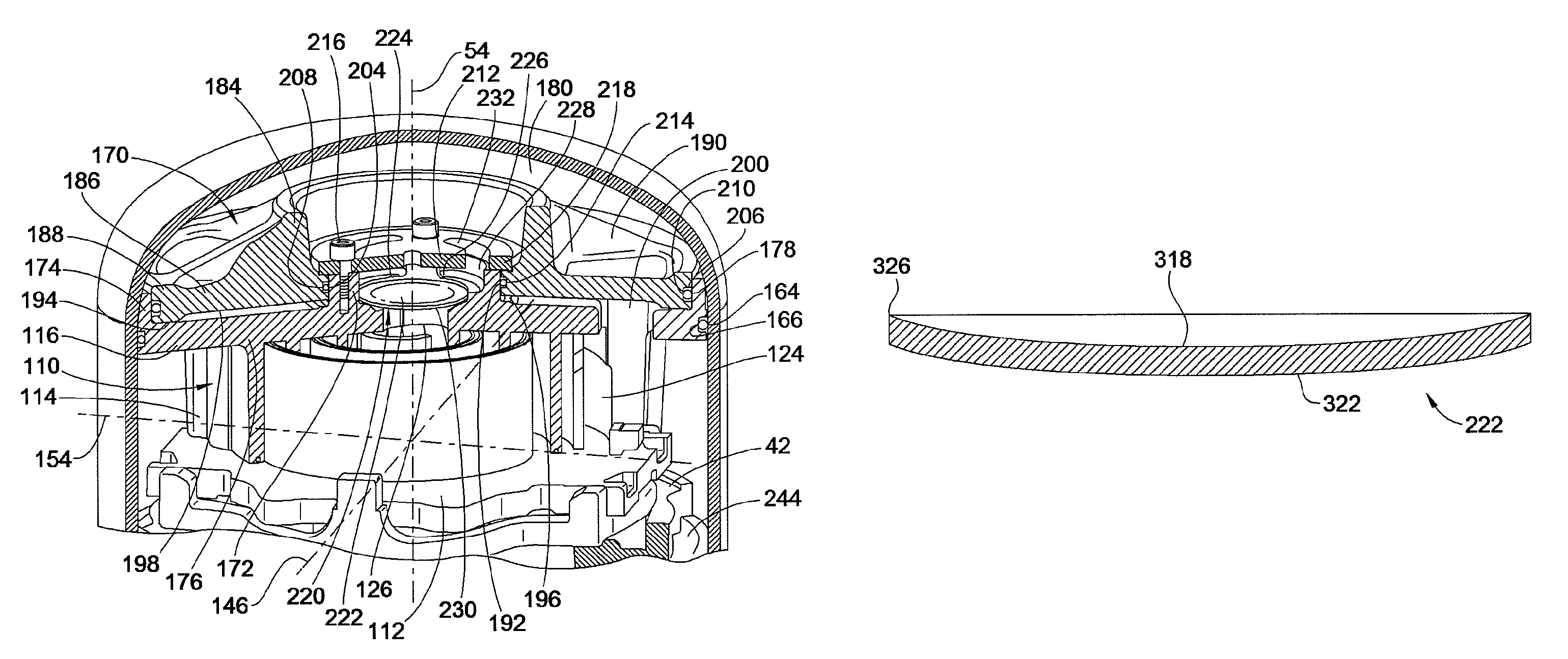
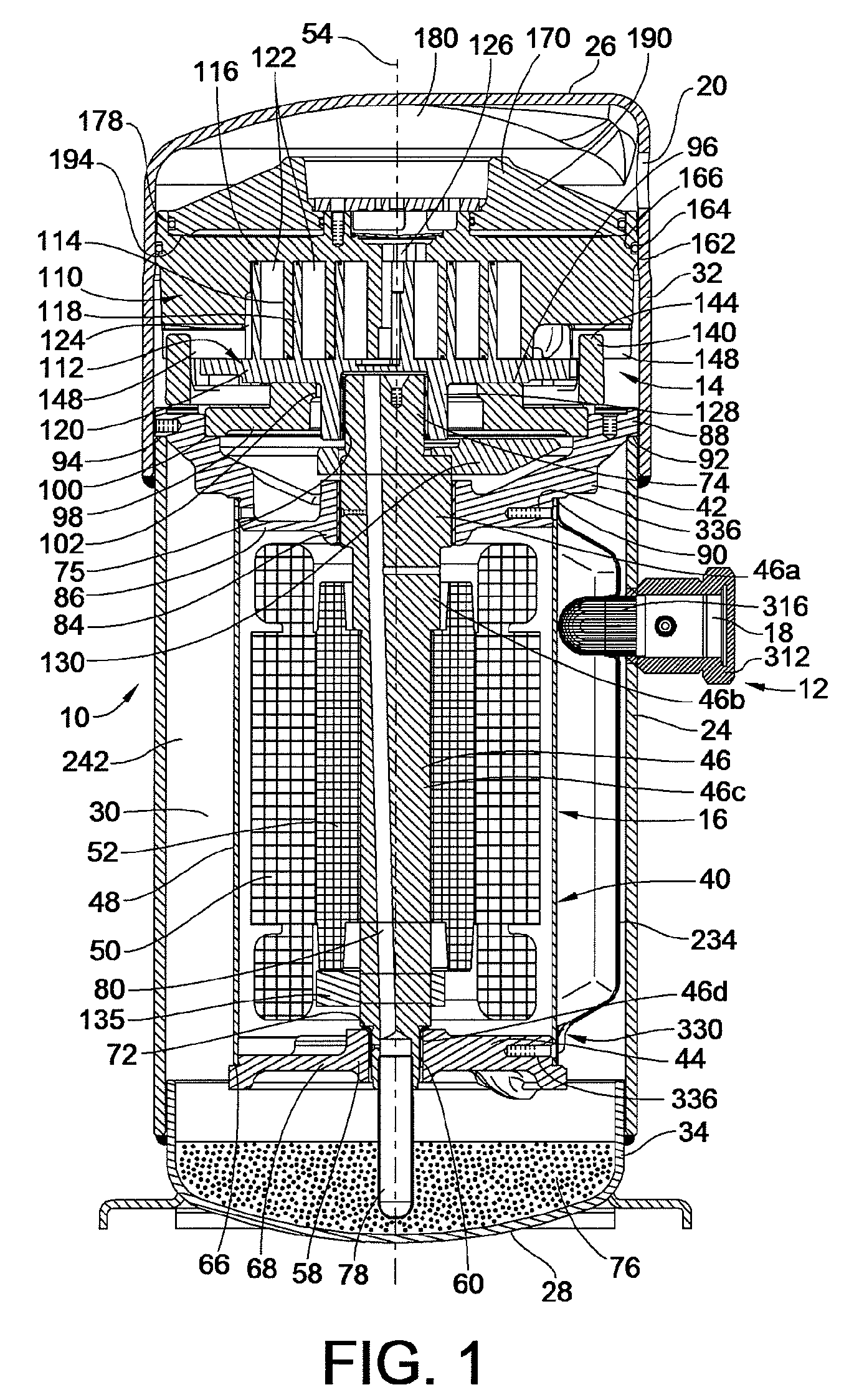
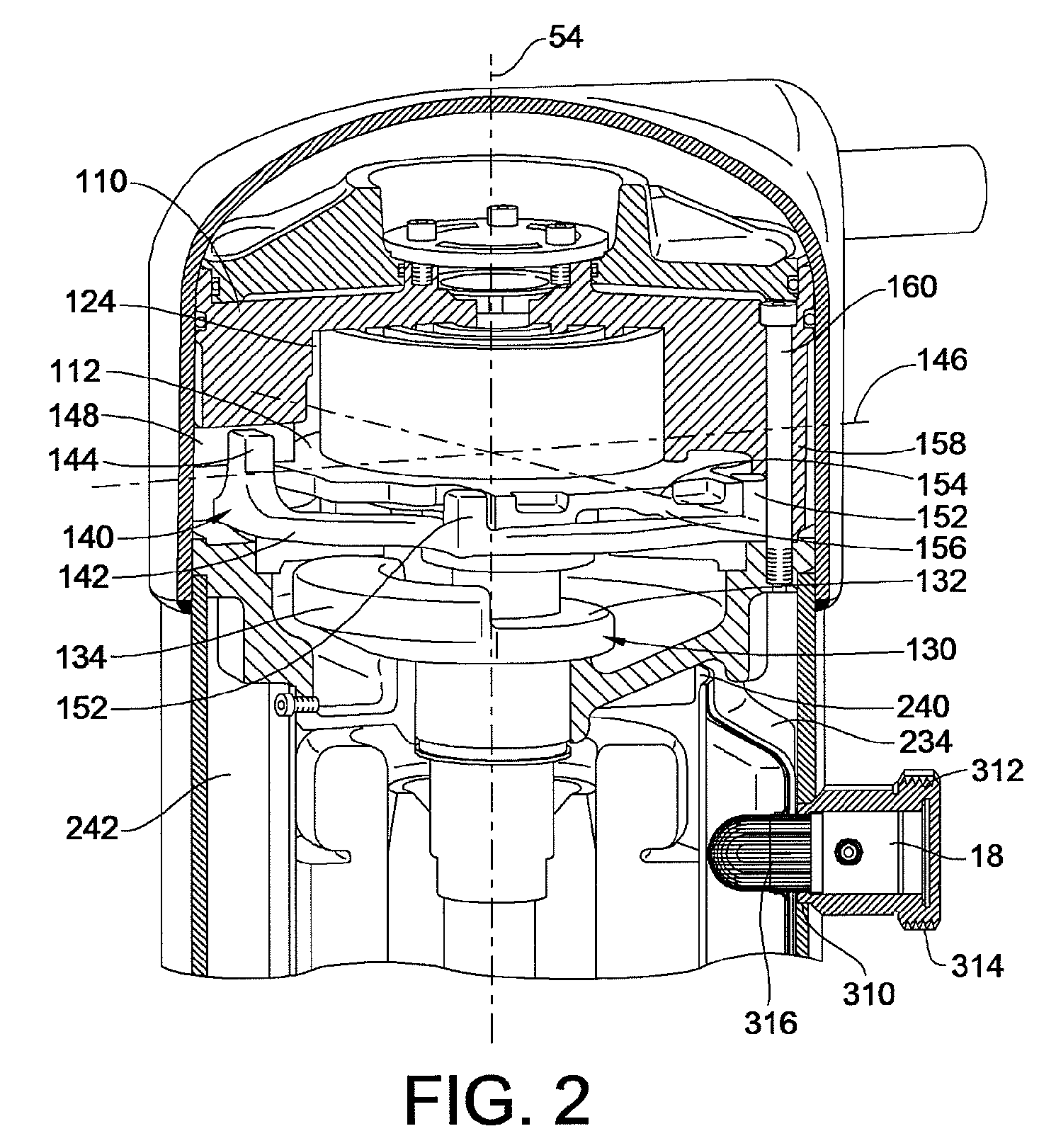
Contoured Check Valve Disc and Scroll Compressor Incorporating Same
ActiveUS20100254842A1Easy to optimizeInhibition releaseRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsEngine of arcuate-engagement typeCheck valveMinimal contact
A check valve is provided which may be integrated into a scroll compressor that prevents static cohesion sticking forces between a valve disc member and a retainer member of the check valve housing. Such static cohesion sticking forces may be particularly generated due to oil mist generation in such scroll compressors which create a thin lubricant film between the valve disc and the stop plate of the check valve housing, creating suction type static cohesion when dislodgment of the valve disc away from the stop plate is attempted. A relief region is created between the retainer and the valve disc creating a minimal contact surface area that greatly reduces and / or eliminates such static cohesion sticking forces. For example, the valve disc may be dished to have a concave surface that faces the retainer element provided by the stop plate.
Owner:BITZER KUEHLMASCHINENBAU GMBH
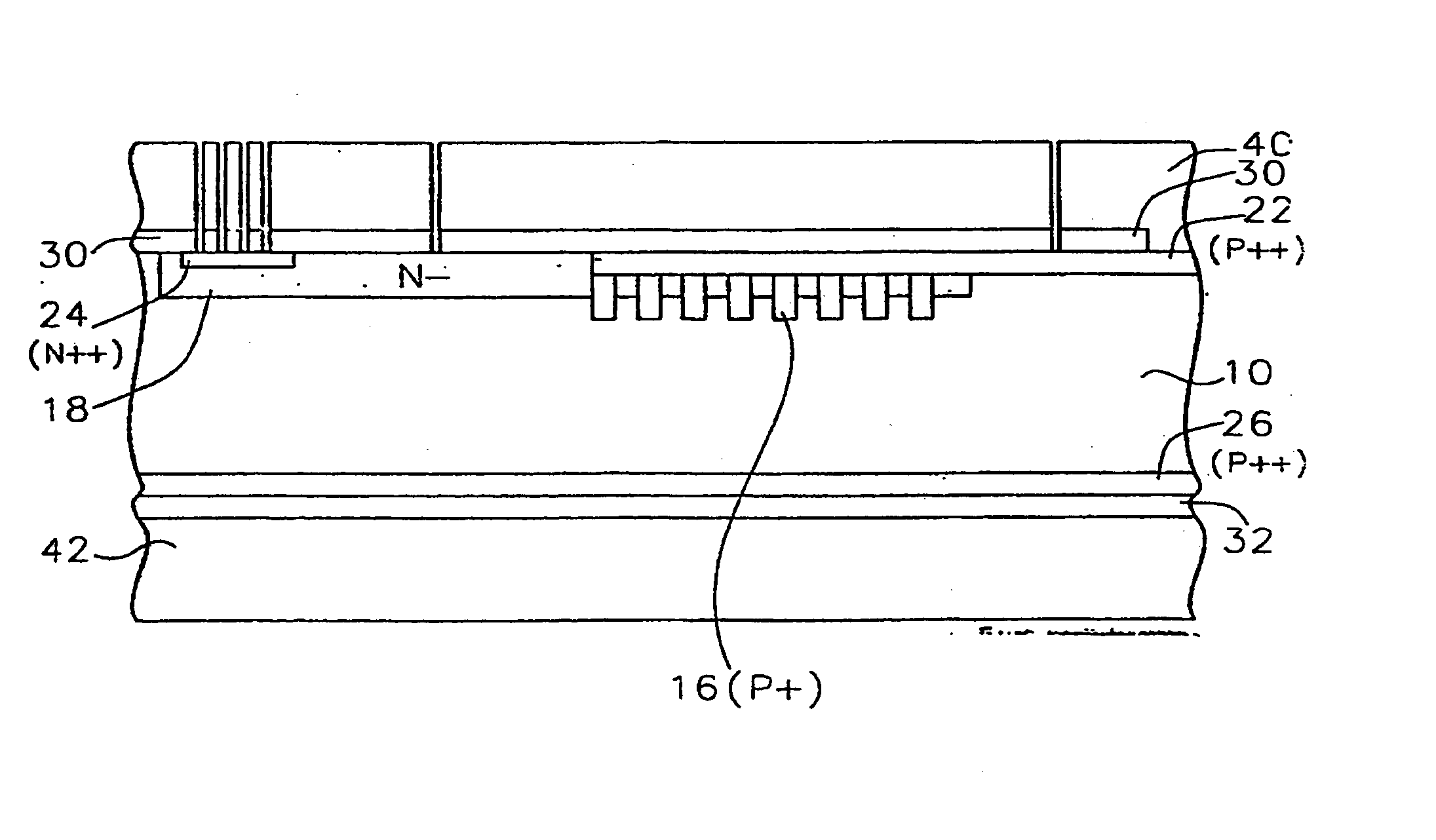
Magnetic recording medium having servo and data track regions with different arithmetical mean deviations
InactiveUS7423842B2Avoid static frictionLow in spacing lossMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageGraphicsSurface level
A magnetic recording medium including at least a disk substrate 1A, a magnetic recording layer 5 formed with a predetermined concavo-convex pattern on the disk substrate 1A, and a non-magnetic layer 6 filled into concave portions of the concavo-convex pattern, so as to have data track regions 20 and servo pattern regions 21. Due to the existence of concaves and convexes in the surface of each data track region 20, the foregoing problem is solved. On this occasion, arithmetical mean deviation of the assessed profile Ra of the surface of each data track region 20 is preferably not lower than 0.3 nm. The difference in surface level between each concave and each convex existing in the surface of the data track region 20 is preferably not larger than 6 nm.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20060172154A1Increase areal densityImprove reliabilityProtective coatings for layersMagnetic materials for record carriersRecording layerRecording media
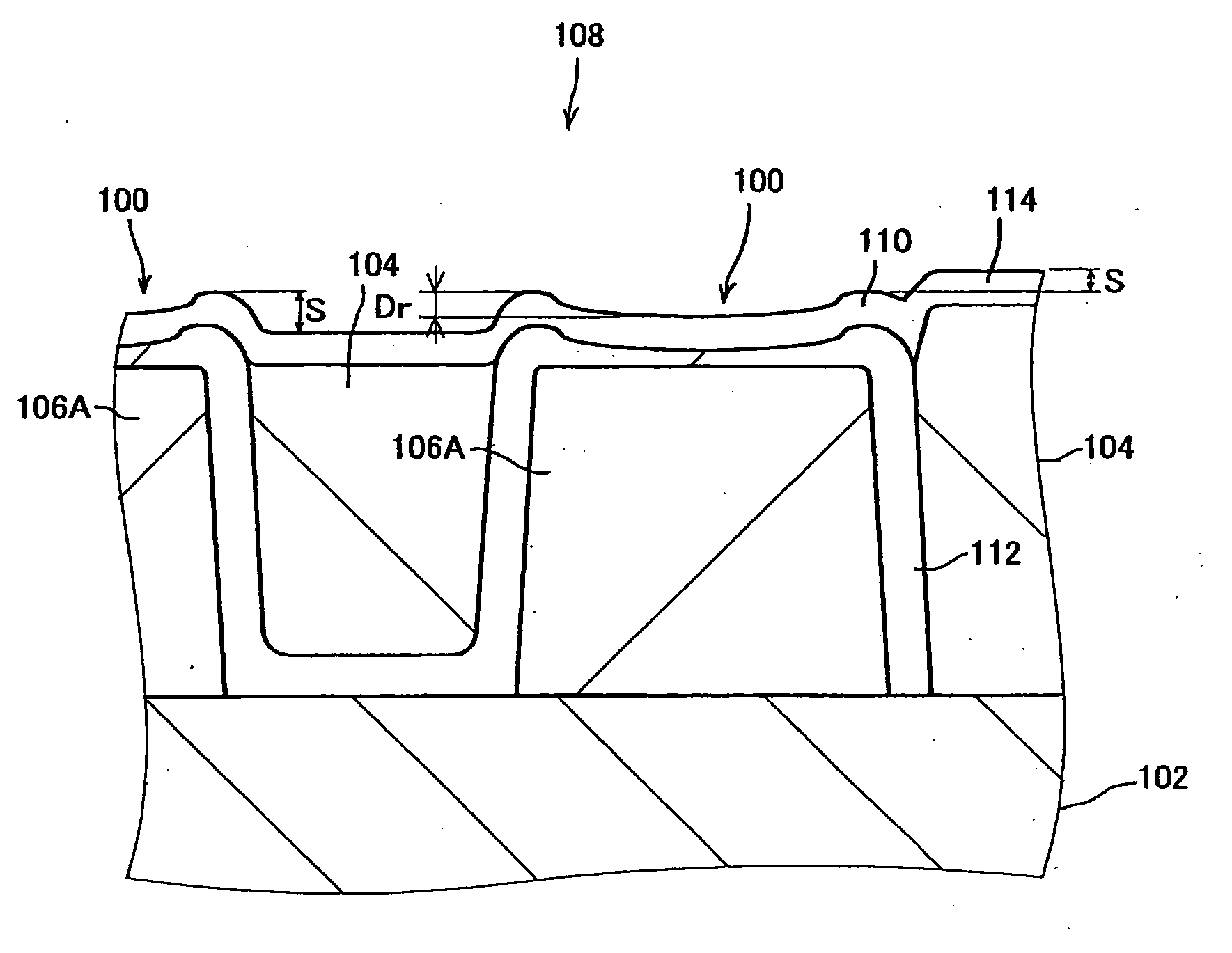
The magnetic recording medium includes: recording elements formed as the convex portions of the recording layer formed in the predetermined concavo-convex pattern over a substrate; and a filling elements with which a concave portions between the recording elements are filled. A surface concave portion is formed in a surface of the magnetic recording medium above the recording element. The surface concave portion has a cross-sectional shape of which a portion corresponding to a center of the recording element lying thereunder in a width direction thereof is recessed deepest toward the substrate, and has a width monotonically increasing with increase of a distance from the substrate.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
MEMS structure and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS7074635B2Preventing electrical short circuitImprove production yieldTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGas supplySilicon
A MEMS structure includes a floating space formed on the upper silicon layer by a first dry etching, and then dry etched to a predeterminded depth on the lower silicon layer by etching gas supplied through the etched holes from which the oxide film has been removed at the bottom surface thereof in a second dry etching process, so as to float the movable portion; and the oxide film for preventing electrical short circuit remaining on the lower surface of the movable portion so as to correspond to the lower silicon layer leaving the floating space therebetween.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Magnetic recording medium including disk substrate, magnetic layer, and non-magnetic layer
InactiveUS7438982B2Avoid static frictionProtective coatings for layersMagnetic materials for record carriersRecording layerNon magnetic
A magnetic recording medium includes at least a disk substrate, a magnetic recording layer formed with a predetermined concavo-convex pattern on the disk substrate, and a non-magnetic layer formed in concave portions of the concavo-convex pattern. Convex shapes made of a non-magnetic material are formed on the magnetic recording layer or the non-magnetic layer. Each convex shape is formed, for example, into a mountain-like shape whose upper surface width is made smaller than a width of each convex portion of the magnetic recording layer or a width of each concave portion where the non-magnetic layer 6 is formed.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Synchronization system and method for changing a gear
ActiveCN105556151AFriction does not appearImprove synchronicityMechanical actuated clutchesGearing controlGear wheelSynchronization system
The invention provides a synchronization system and method for changing a gear. The invention relates to a synchronization system (10) for a change-speed gearbox comprising a synchronizing body (12) which is assigned to a gearbox shaft, and comprising a first and a second synchronizing ring (32, 34, 36, 38), which are assigned to a first and a second gear wheel (28, 30) respectively. Furthermore, the synchronizing ring (10) has a sliding sleeve (26) and at least one pressure piece (18), which is displaceably arranged on the synchronizing body (12) and is able to exert an axial compressive force on the corresponding synchronizing ring (32, 34, 36, 38). Moreover, the synchronizing ring (10) has a resilient actuating element (20), which acts between the sliding sleeve (26) and the pressure piece (18), a latching recess (50) for the neutral position and a ventilation contour (54) being provided on the sliding sleeve (26). The ventilation contour (54) can interact with the actuating element (20) in such a way that, when the sliding sleeve (26) is moved in order to engage with one of the gear wheels (28, 13), the pressure piece (18) is loaded away from the corresponding synchronizing ring (32, 34, 36, 38). The ventilation contour (54) has an axial length which is no more than twice the idle stroke of the sliding sleeve (26) between the neutral position and the position in which the corresponding synchronizing ring (32, 34, 36, 38) presses against a frictional surface assigned thereto.
Owner:HOERBIGER ANTRIEBSTECHN HLDG
Quantified and axial plunger pump
ActiveCN104948409AImprove volumetric efficiencyReduce volumePositive-displacement liquid enginesMulti-cylinder pumpsRadial piston pumpWorking pressure
The invention provides a quantified and axial plunger pump. The plunger pump is a radial flow distribution pump and comprises a transmission shaft, a cylinder, a flow distribution sleeve, a flow distribution shaft and an inclined disc, wherein the transmission shaft is driven by external force to rotate, the cylinder, the flow distribution sleeve and the flow distribution shaft are connected with the transmission shaft, and the inclined disc enables the plunger pump to output fluid in a quantified mode. The cylinder, the flow distribution sleeve, the flow distribution shaft and the transmission shaft are coaxially arranged. Compared with a traditional radial plunger pump, the plunger pump has the main advantages of being simple in structure, small in size and light in weight; compared with a traditional axial plunger pump, the plunger pump has the main advantages that the rotation speed of the pump can be substantially increased, working pressure can be substantially increased, the nominal flow rate can be multiplied, or at equal working pressure, the volume efficiency of the pump is remarkably improved, and noise can be lowered by more than10 db.
Owner:湖南力威液压设备股份有限公司
Contoured check valve disc and scroll compressor incorporating same
ActiveUS8328543B2Prevent cohesionAvoid static frictionRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsEngine of arcuate-engagement typeEngineeringCheck valve
A check valve is provided which may be integrated into a scroll compressor that prevents static cohesion sticking forces between a valve disc member and a retainer member of the check valve housing. Such static cohesion sticking forces may be particularly generated due to oil mist generation in such scroll compressors which create a thin lubricant film between the valve disc and the stop plate of the check valve housing, creating suction type static cohesion when dislodgment of the valve disc away from the stop plate is attempted. A relief region is created between the retainer and the valve disc creating a minimal contact surface area that greatly reduces and / or eliminates such static cohesion sticking forces. For example, the valve disc may be dished to have a concave surface that faces the retainer element provided by the stop plate.
Owner:BITZER KUEHLMASCHINENBAU GMBH
Method for regulating the current through an electromagnetic actuator
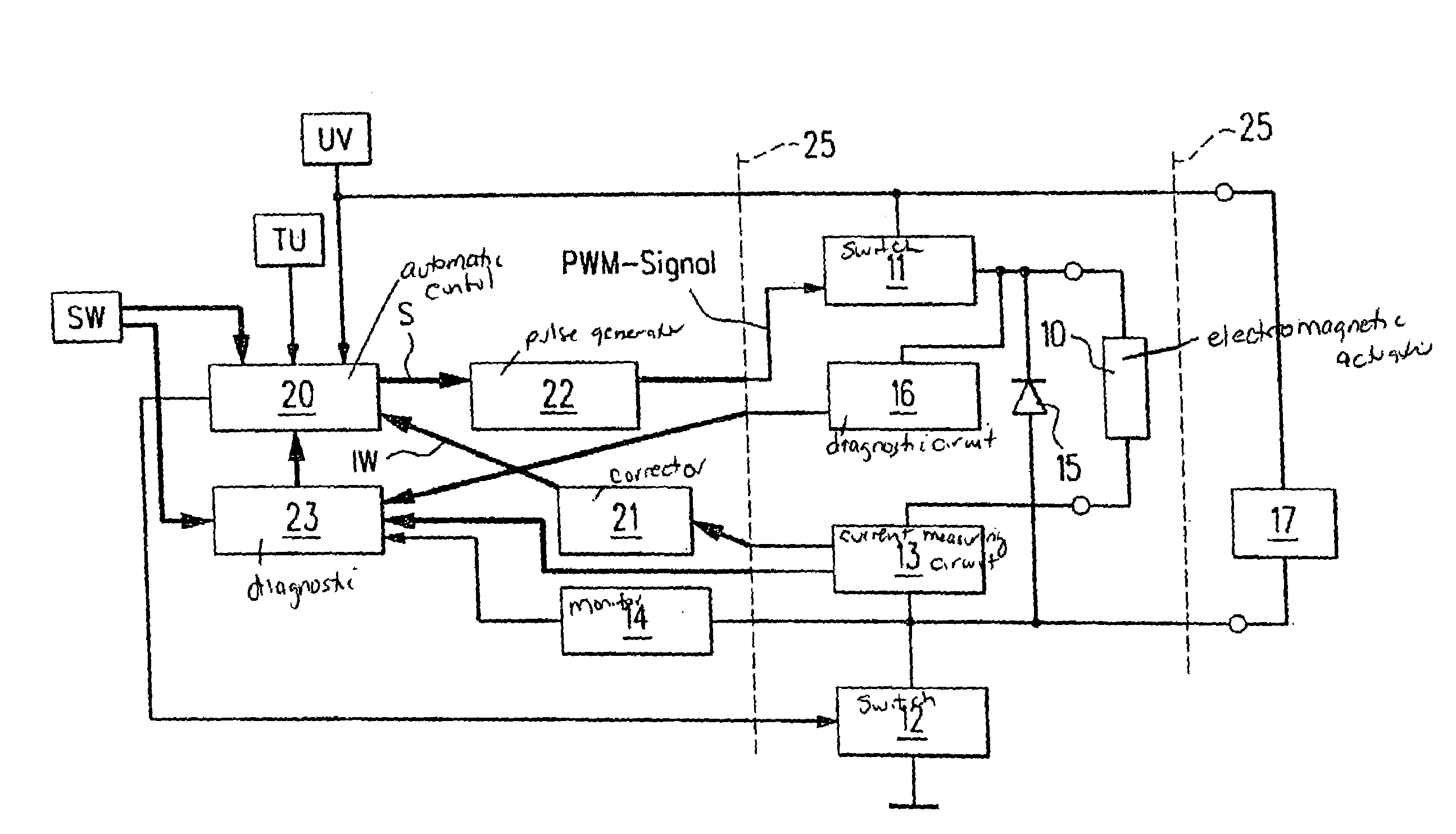
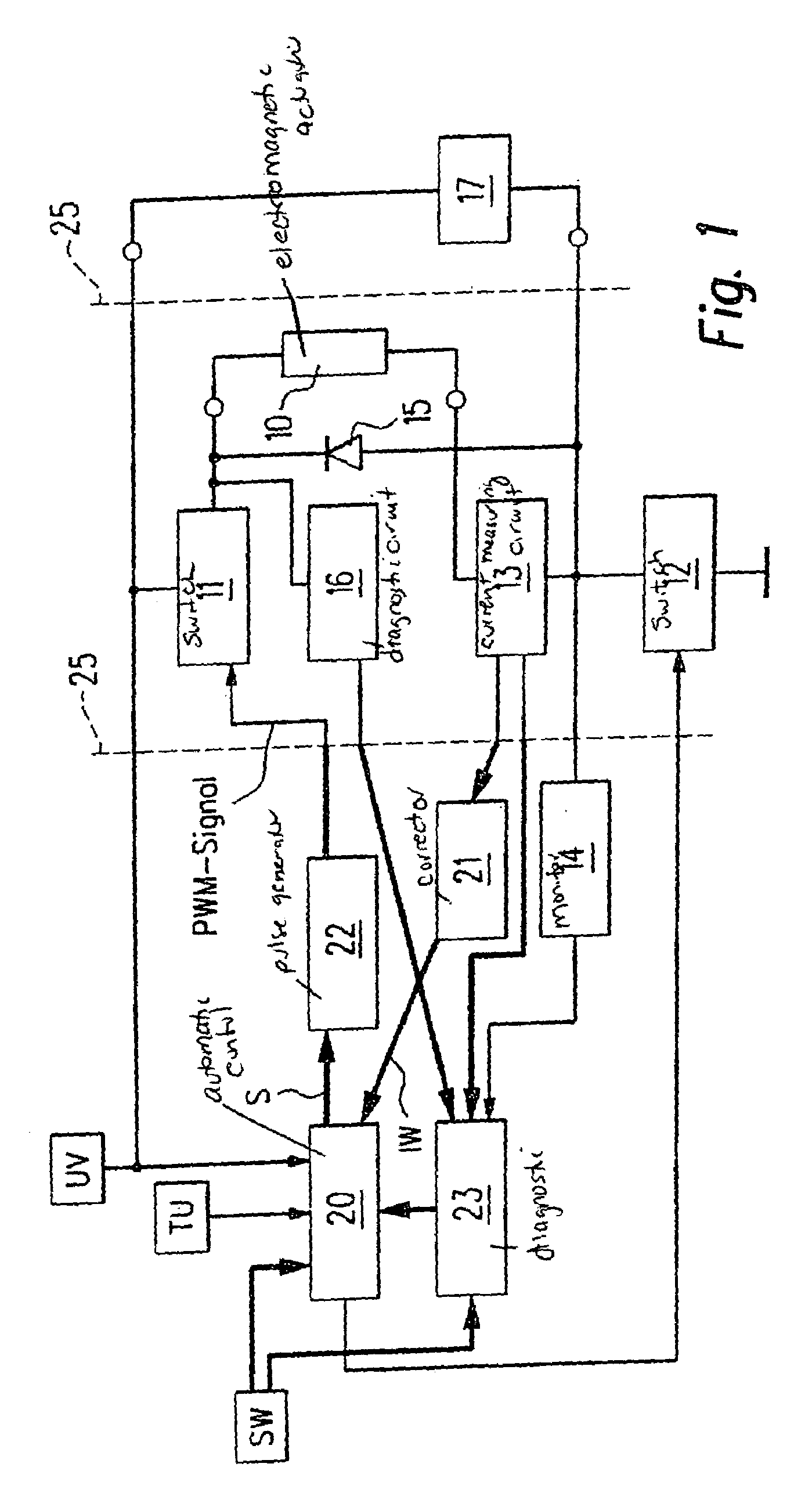
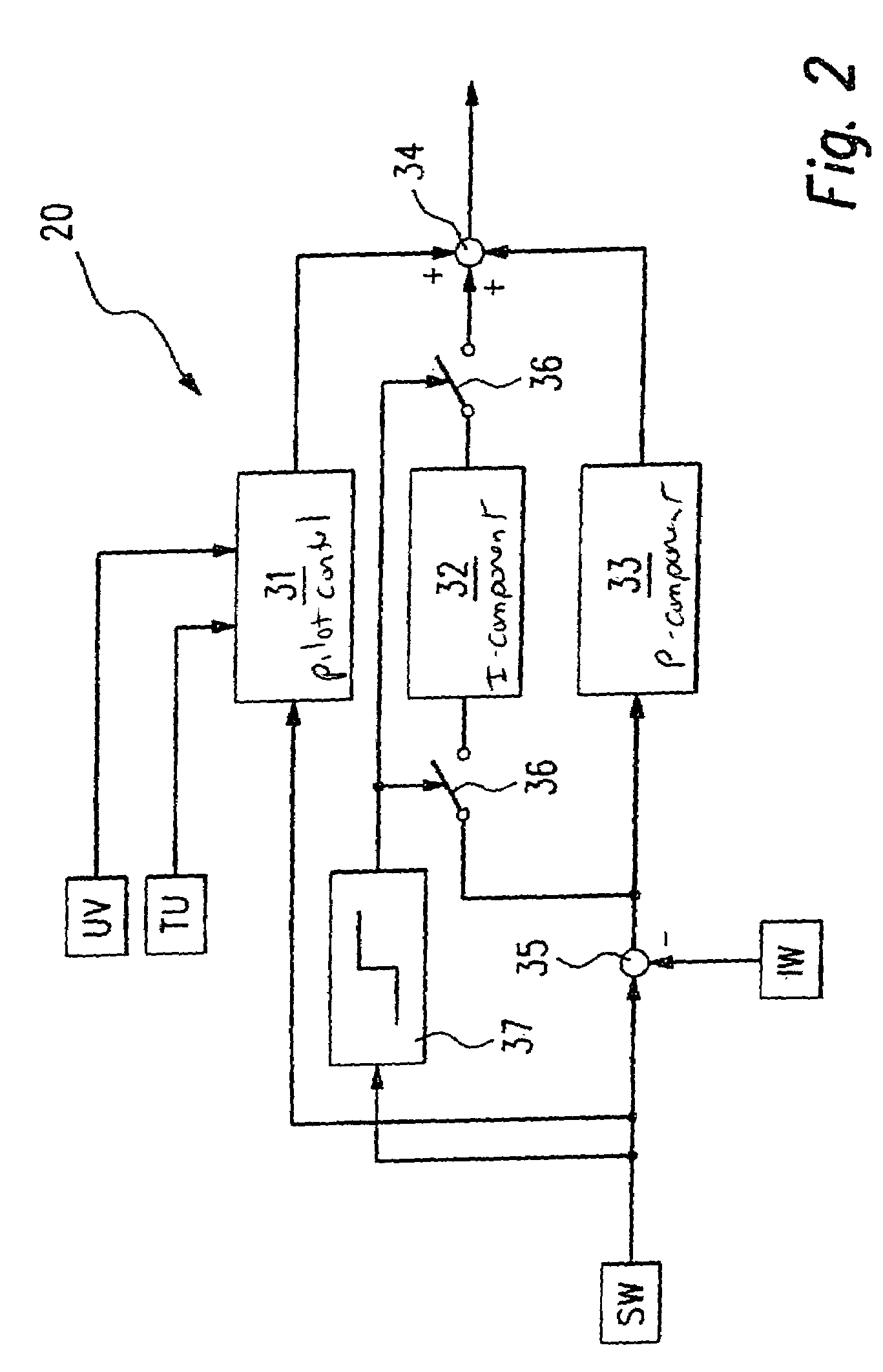
InactiveUS7206180B2High control precisionReduce a so-called seating bounce of the electromagnetic actuatorAC motor controlElectrical controlSwitching cycleFlyback diode
A method for regulating the current through an electromagnetic actuator. The actuator, a first switch and a current-measuring circuit form a series circuit. A free-wheeling diode is parallel-connected to the actuator. The first switch is closed and opened by a control and a pulse generator using a PWM signal (PWM=pulse width modulation) in such a way that the current flowing through the actuator and measured by the current-measuring circuit is regulated to a setpoint value (SW). The time duration of one on and off switching cycle of the PWM signal is altered, and a so-called dither function in the form of a low-frequency oscillation is superimposed on the PWM signal.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com