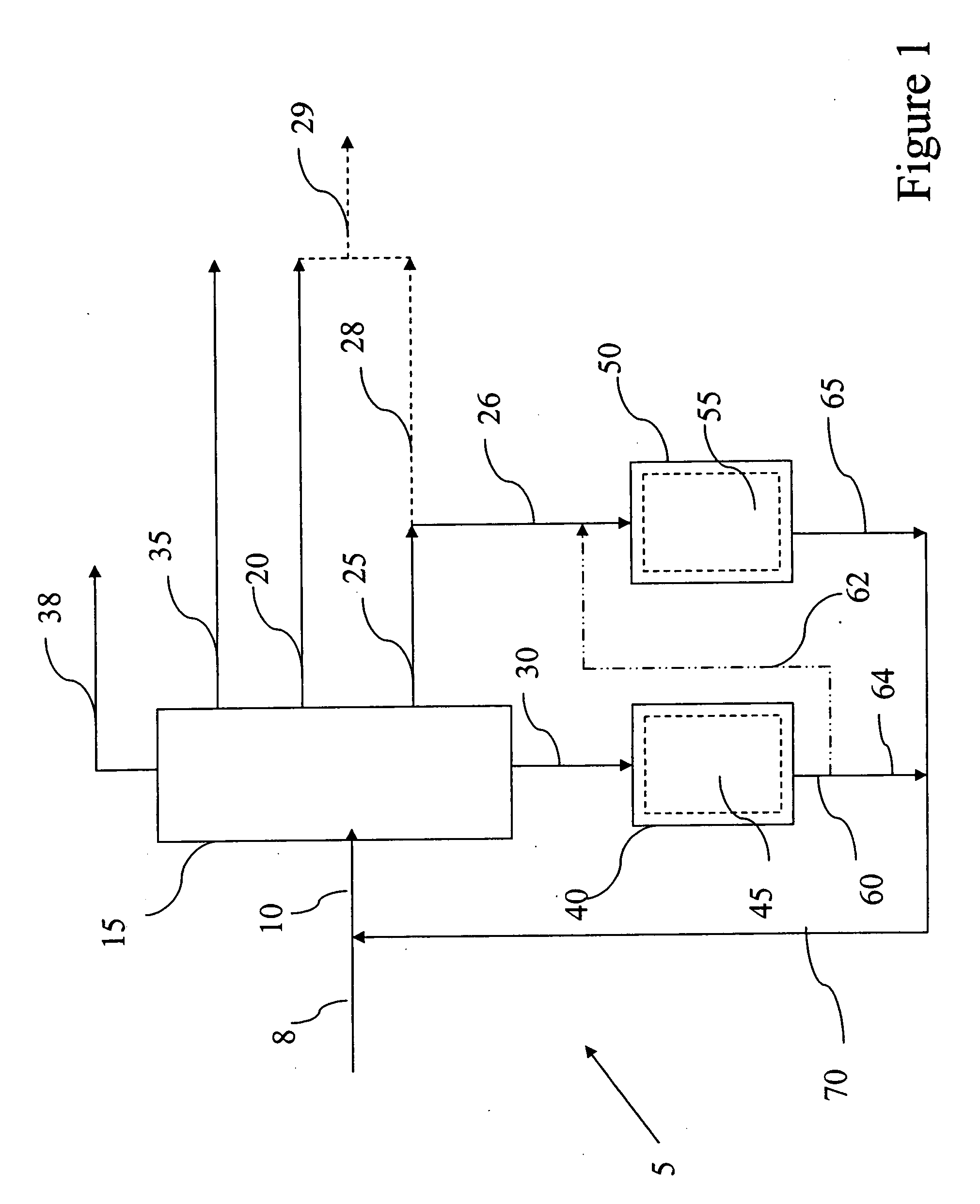
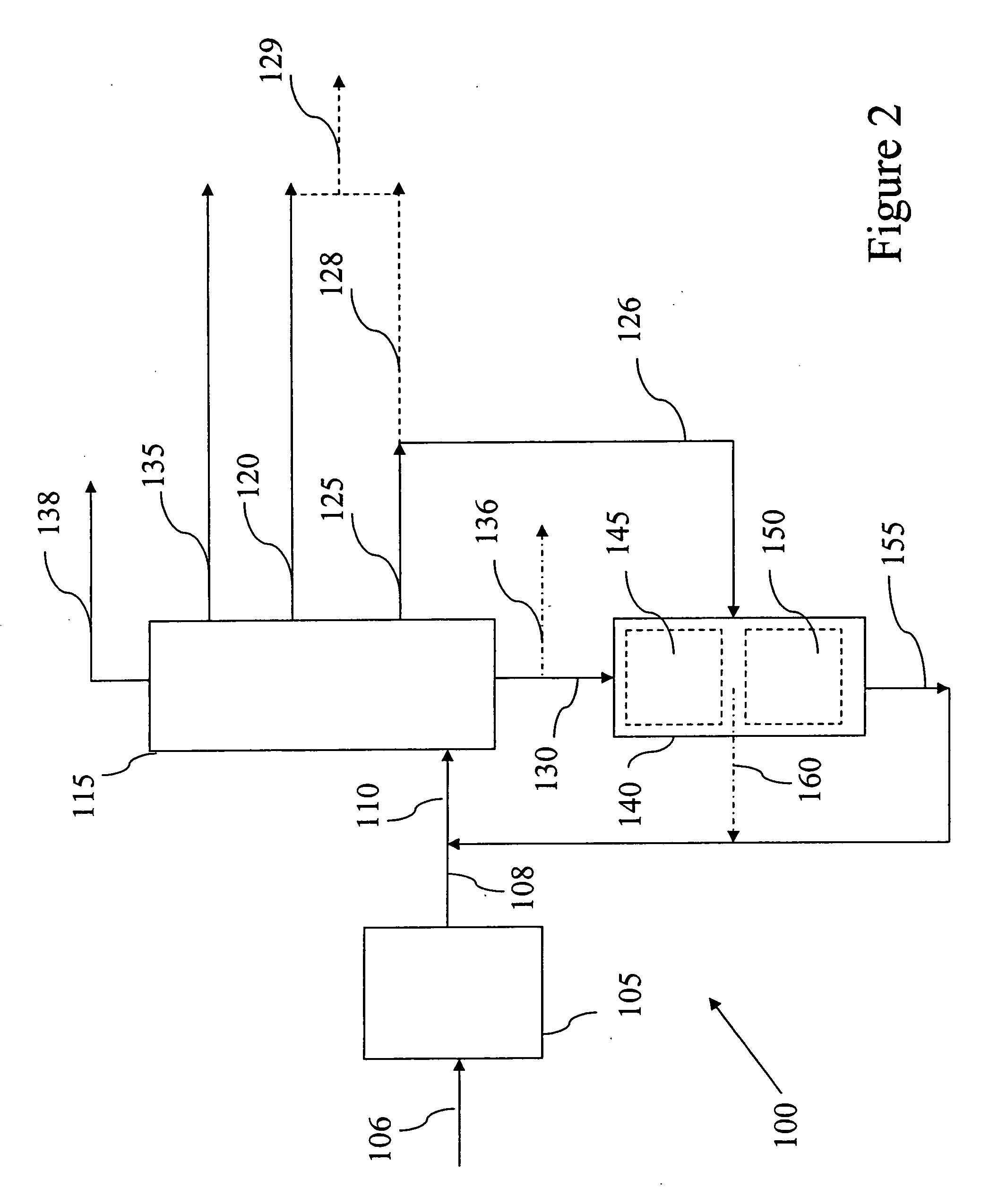
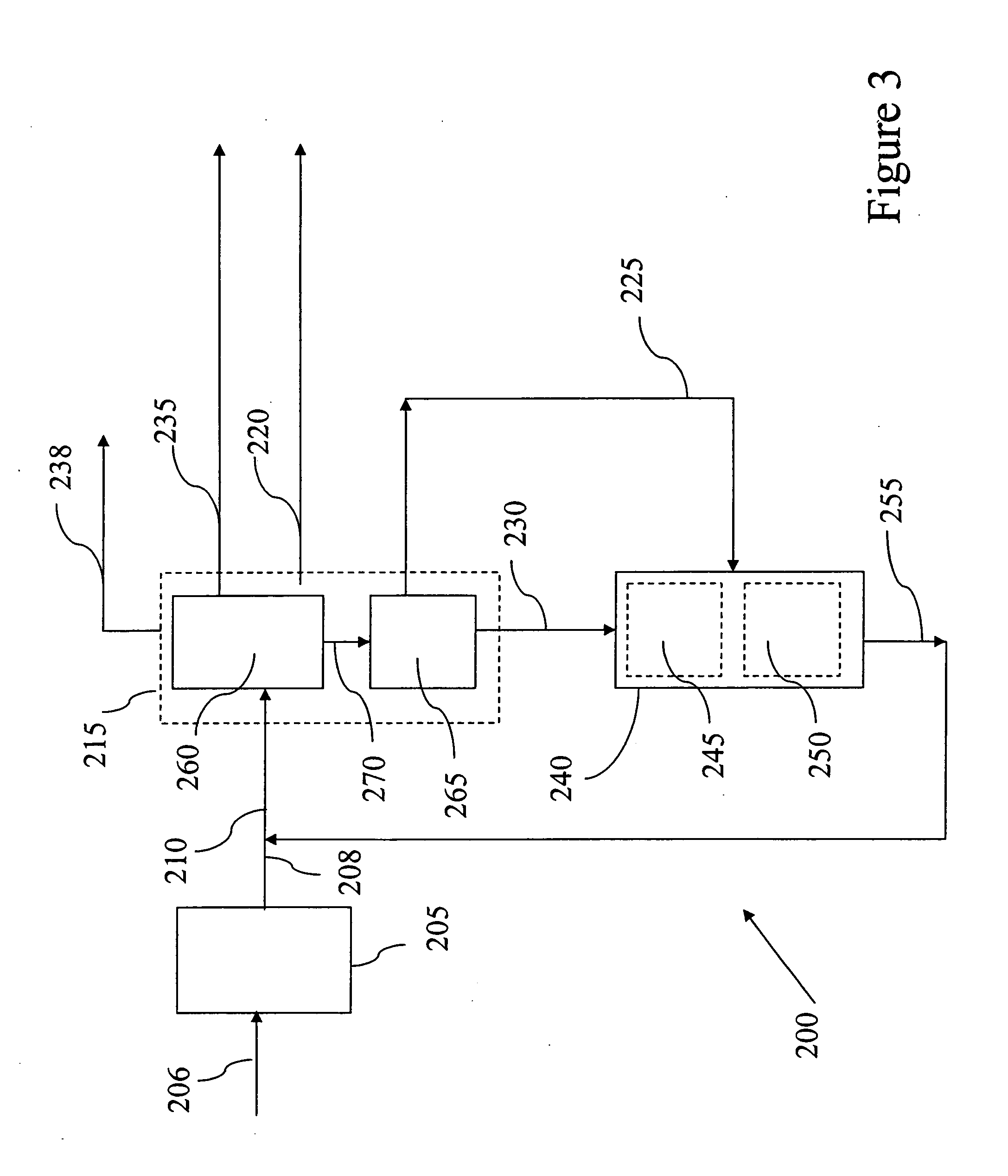
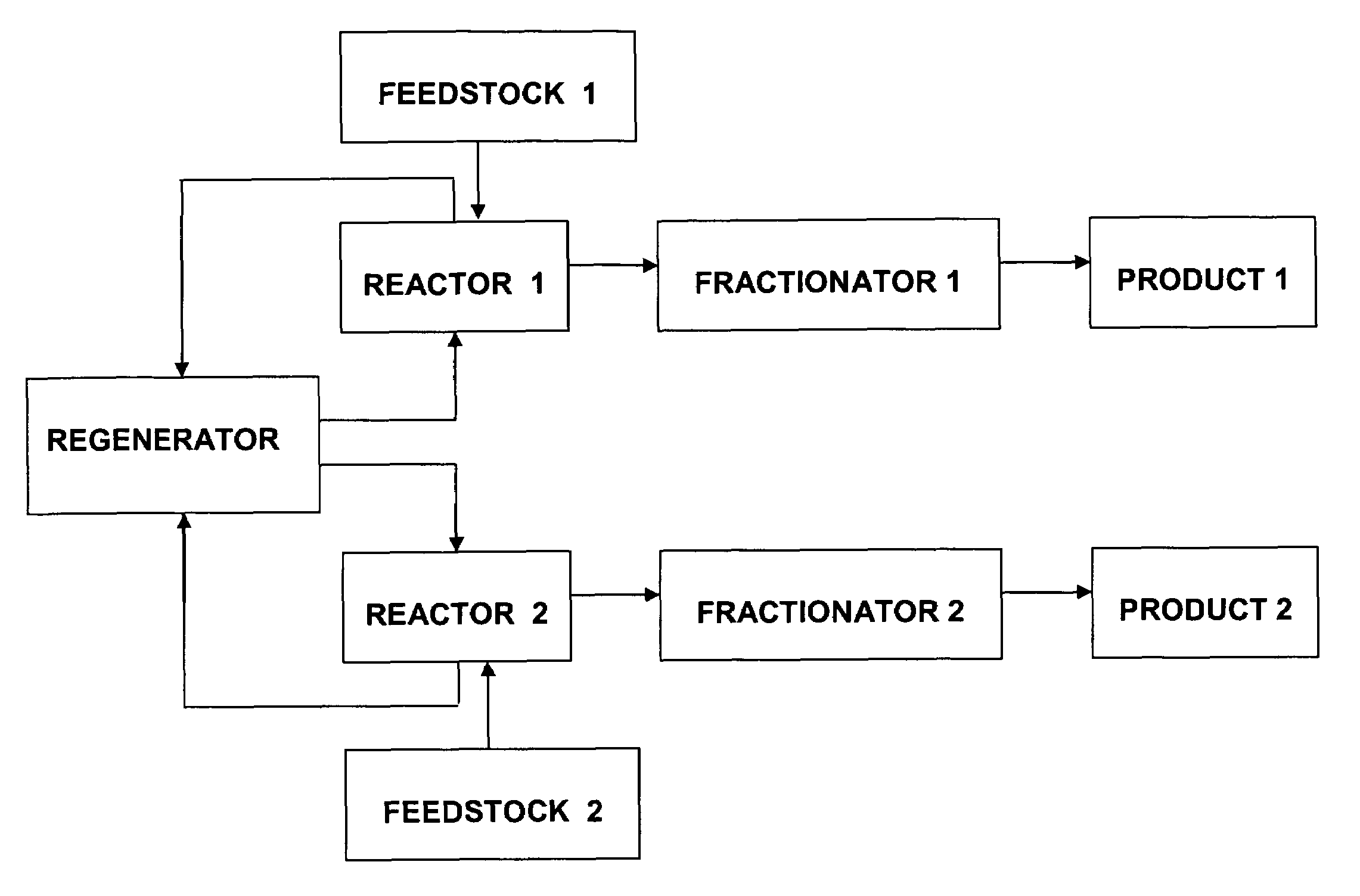
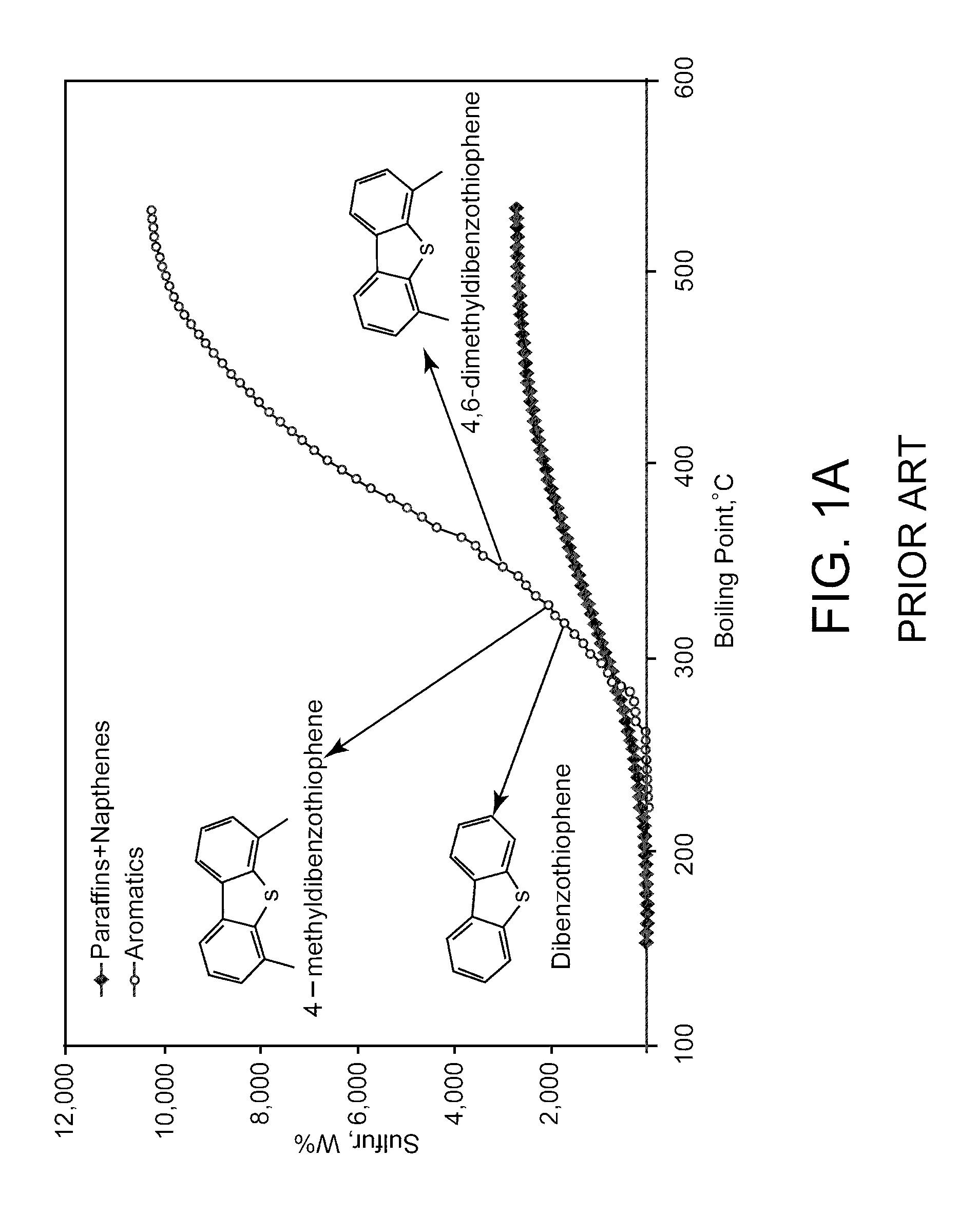
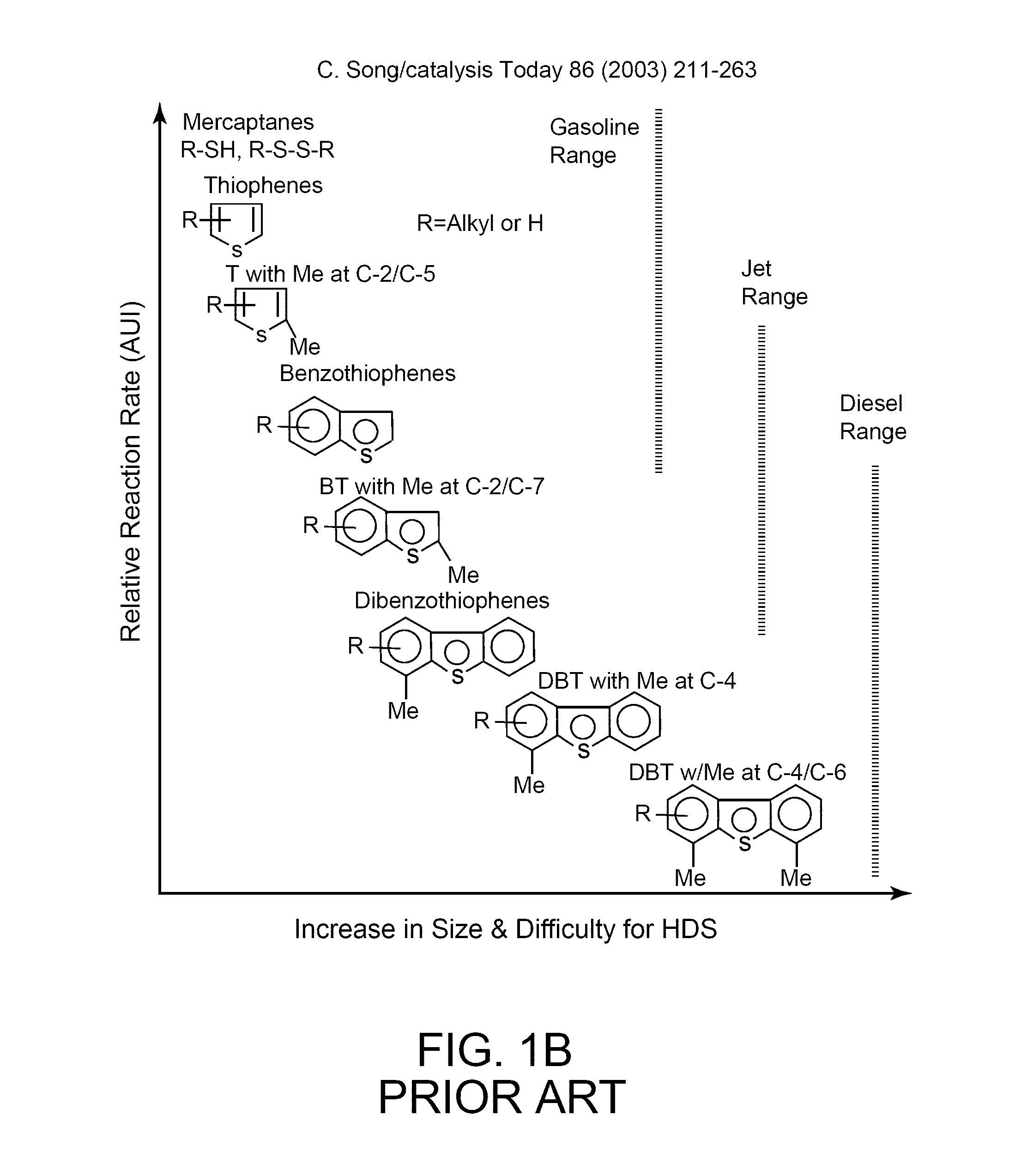
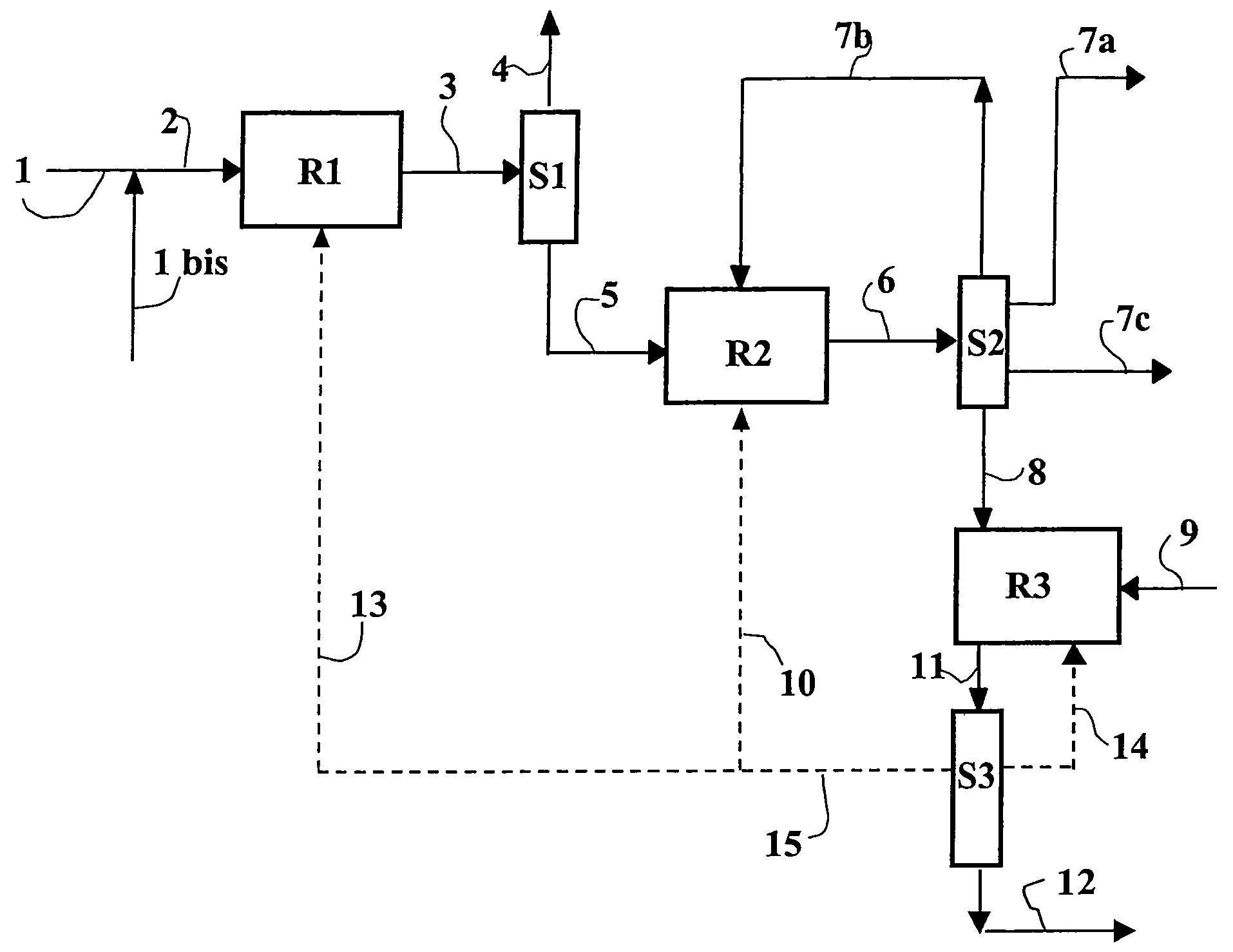
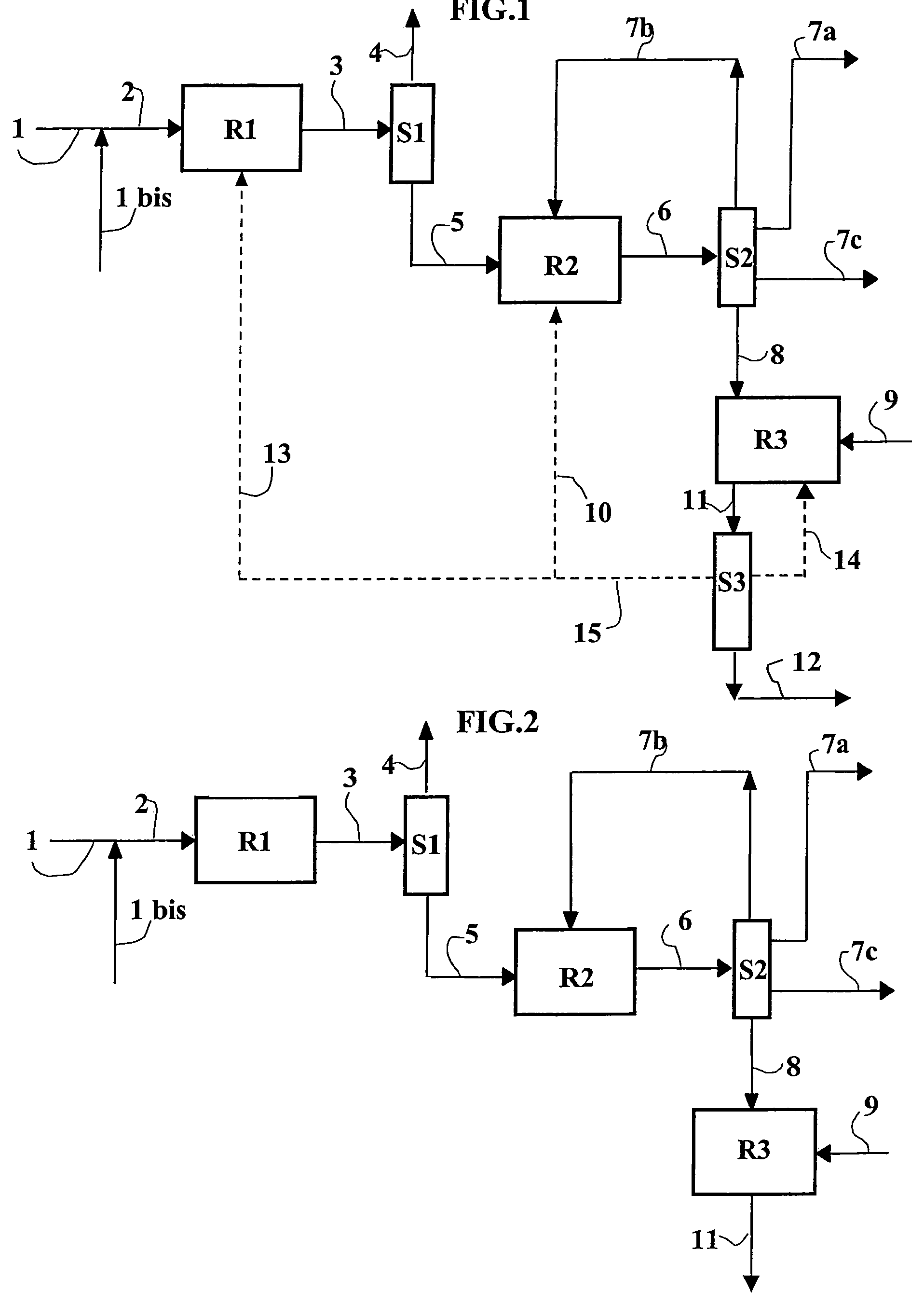
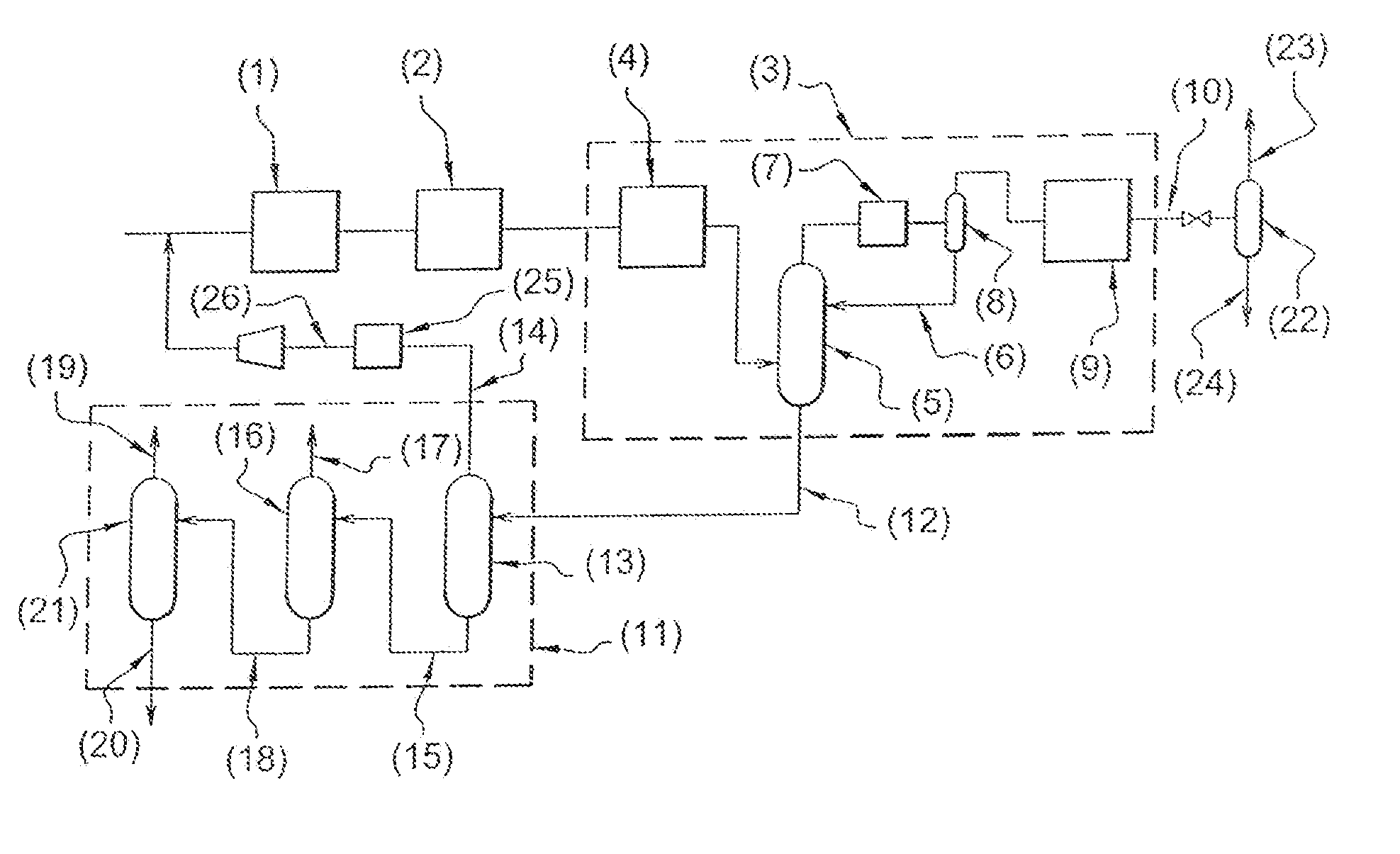
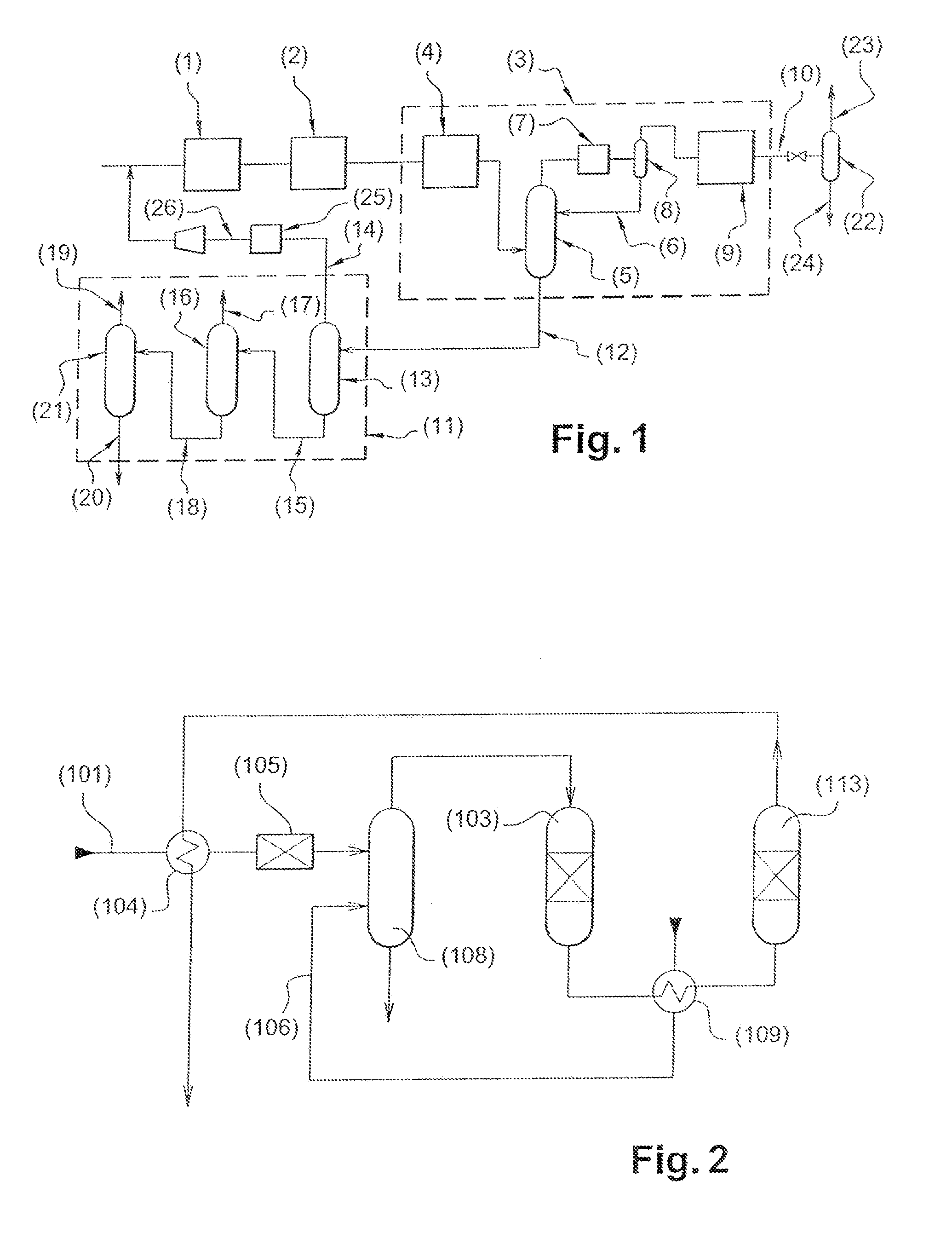
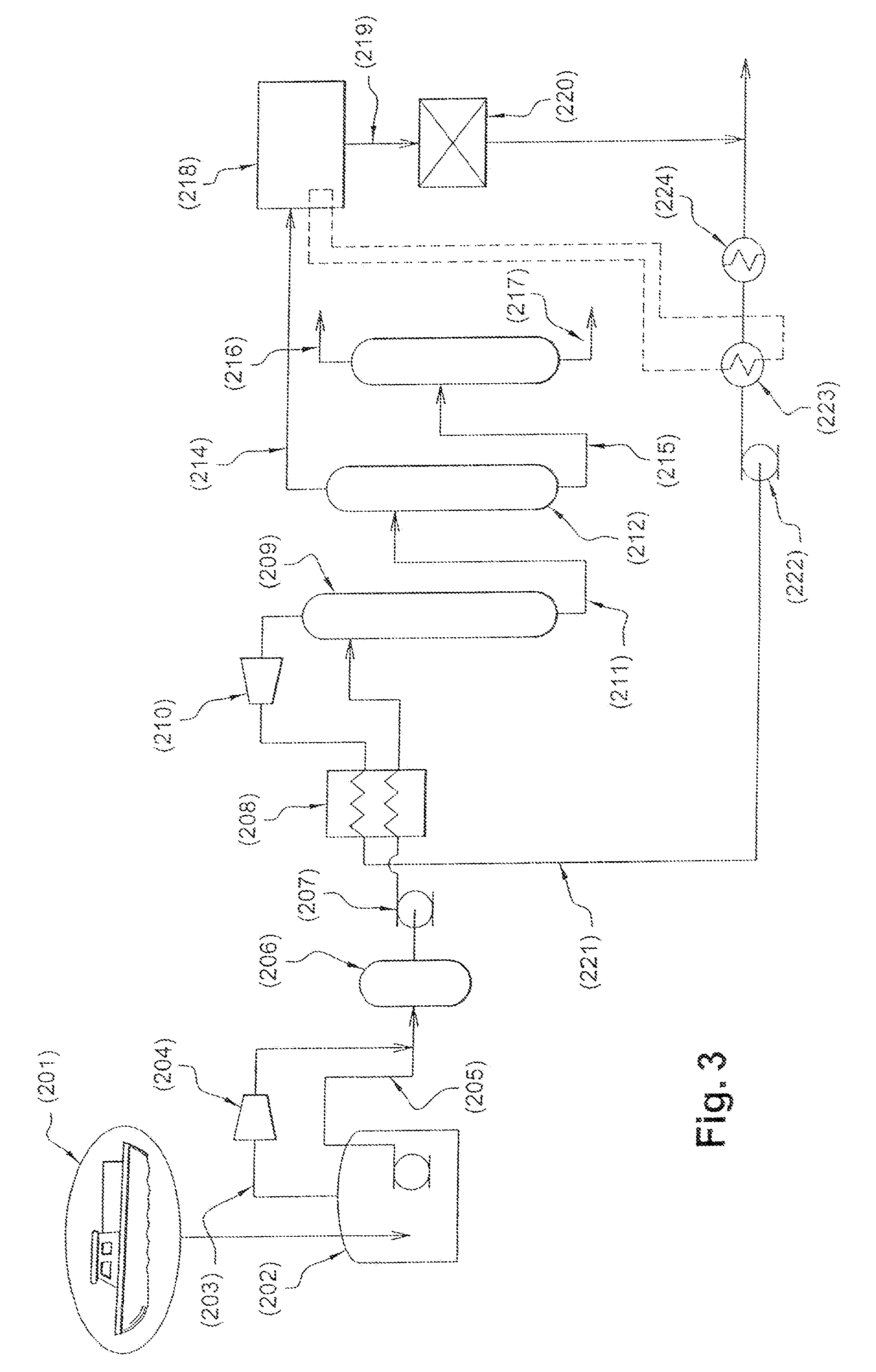
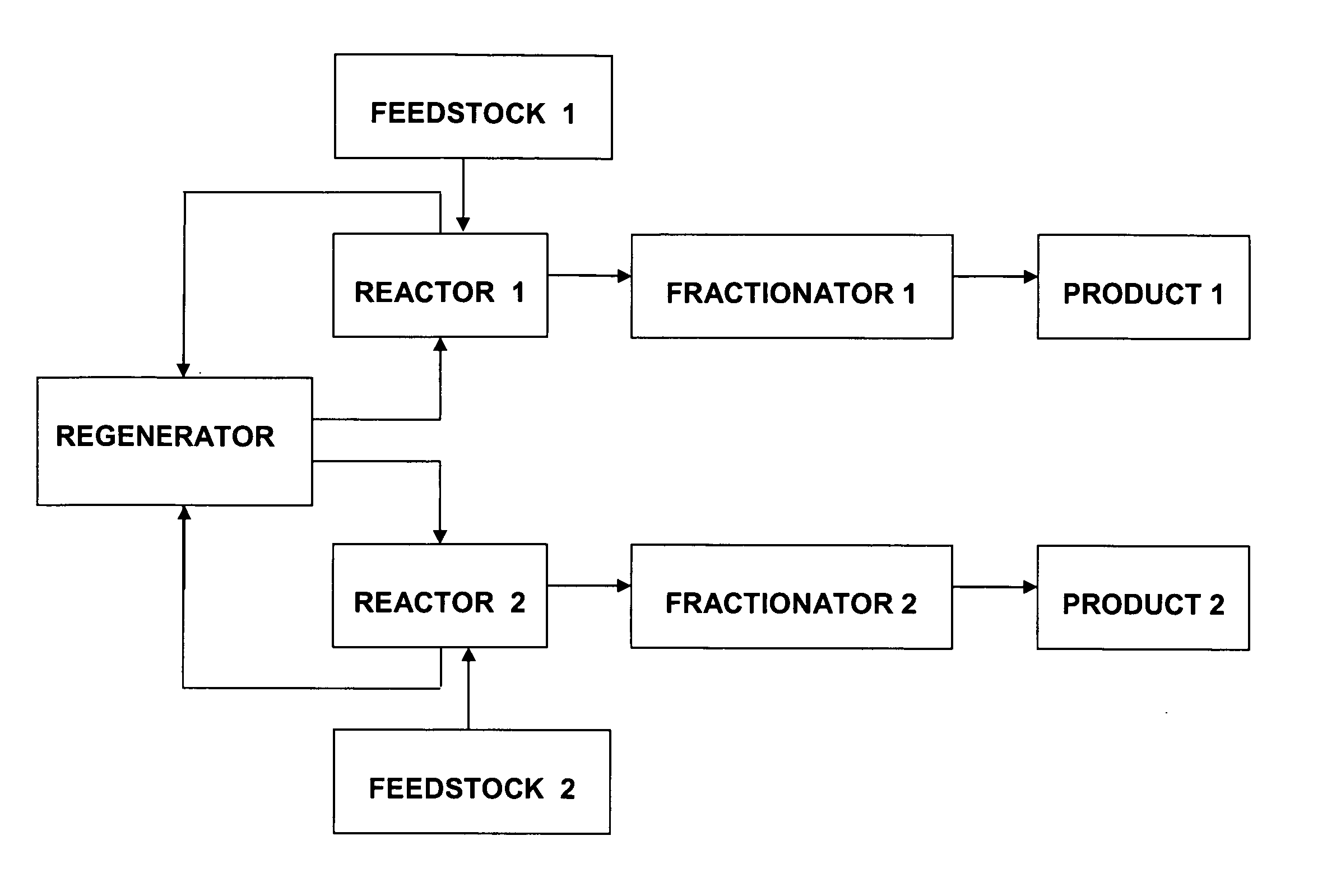
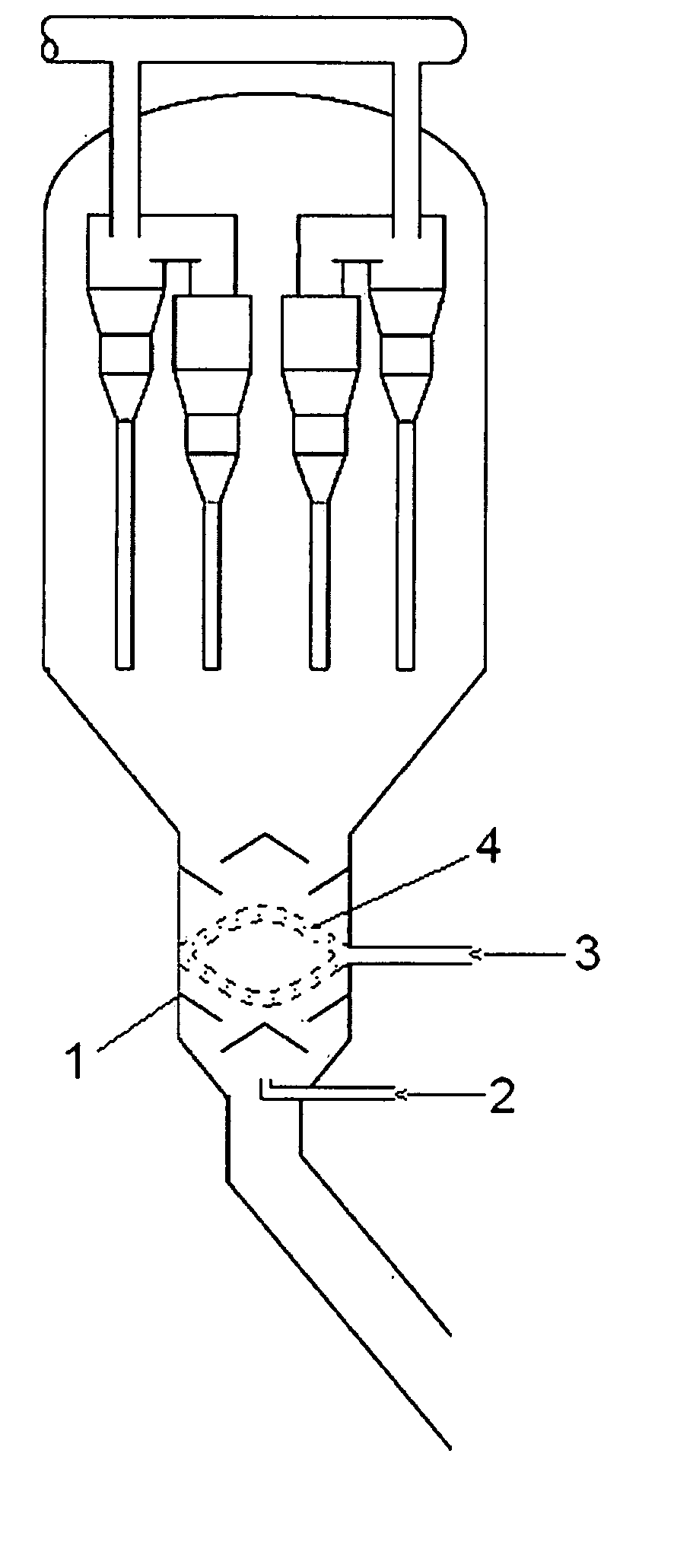
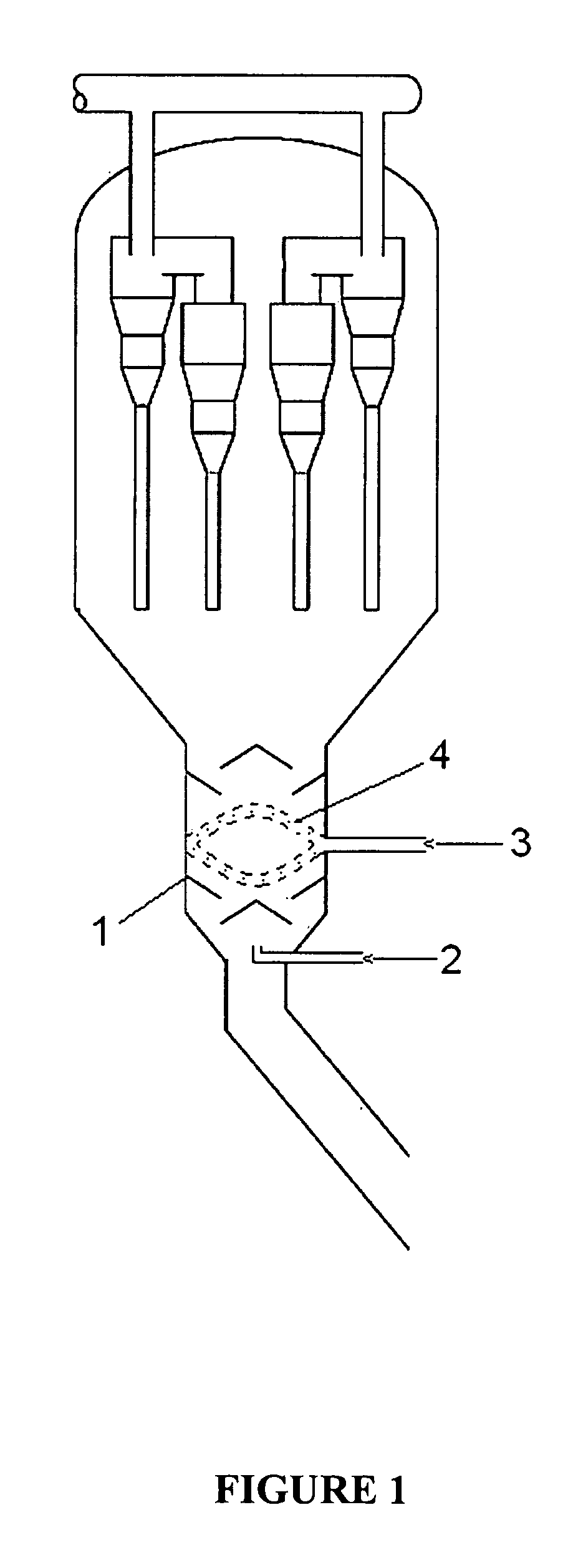
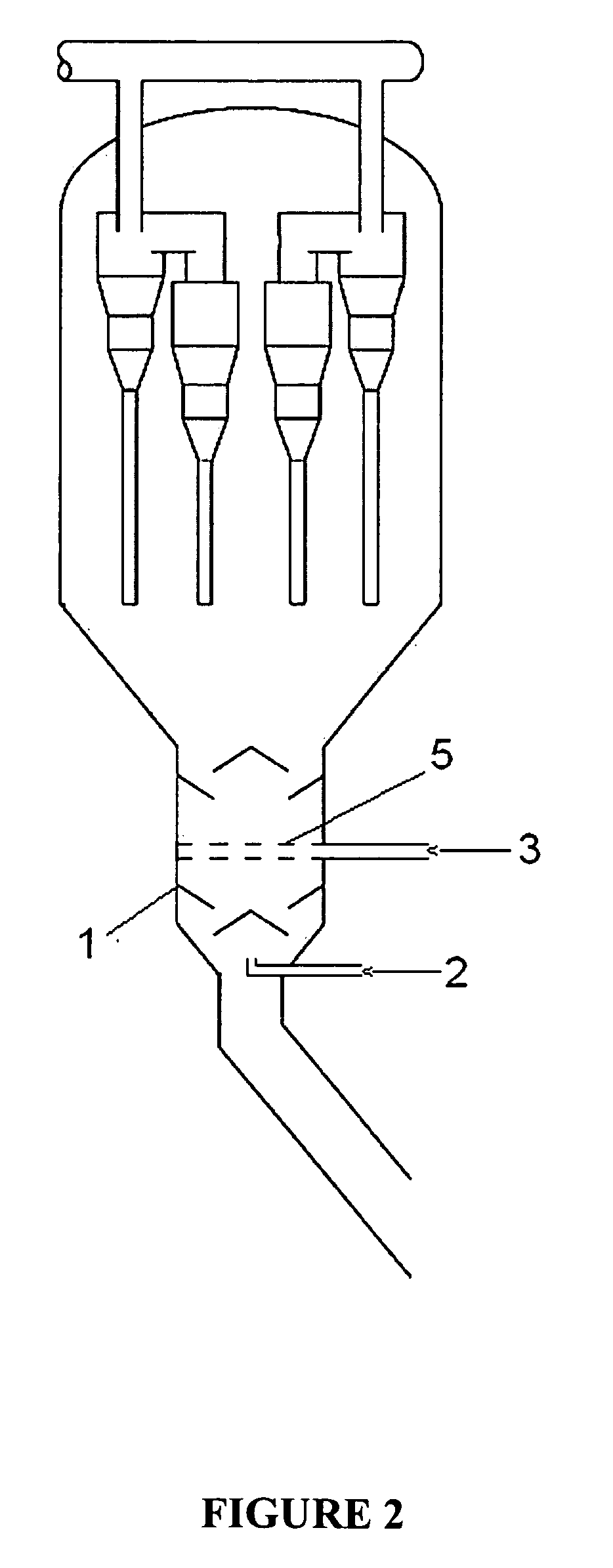
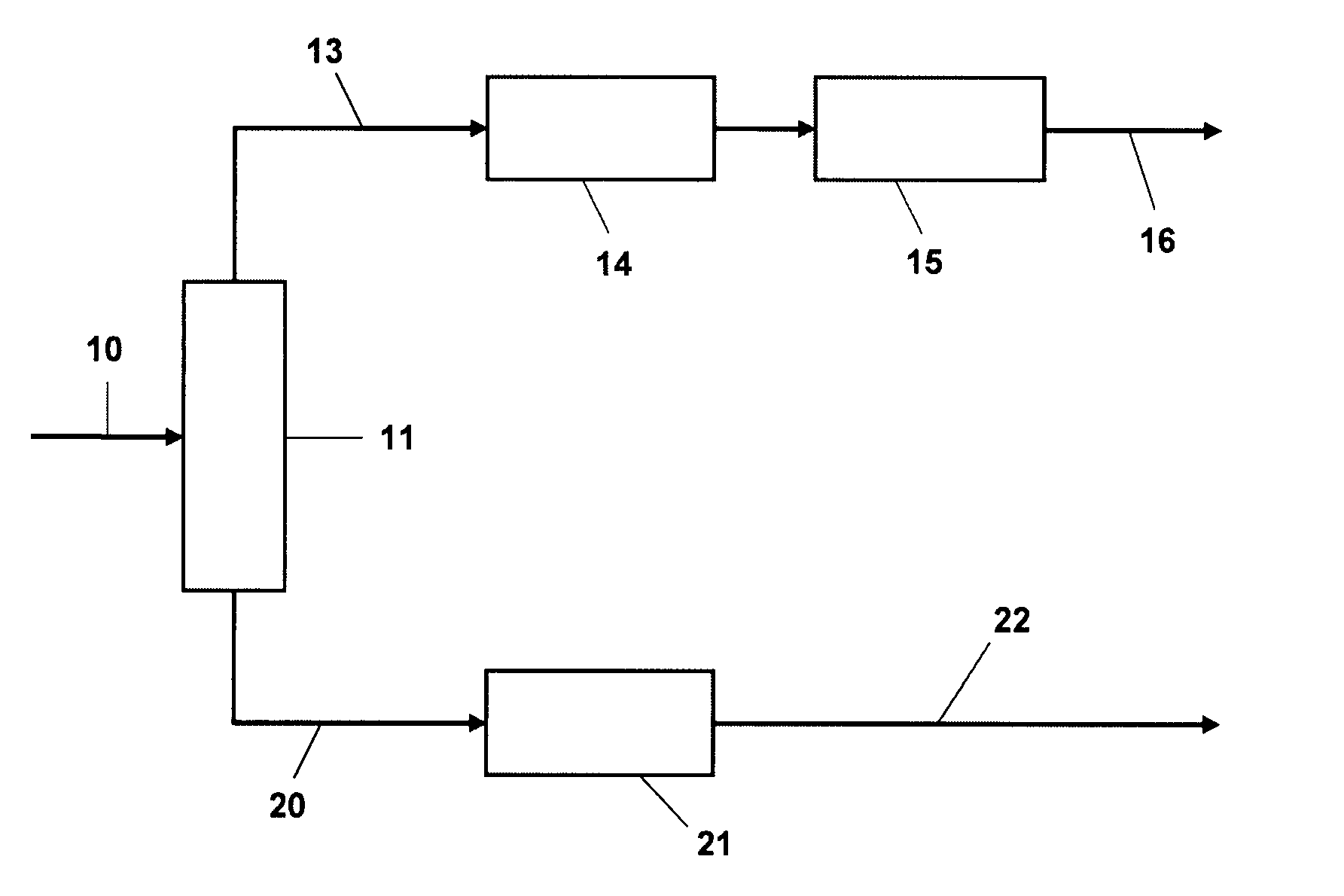
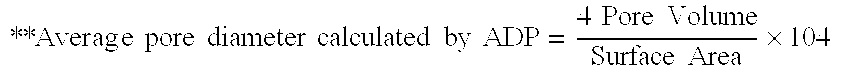Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
189results about "Treatment with plural parallel refining stages" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
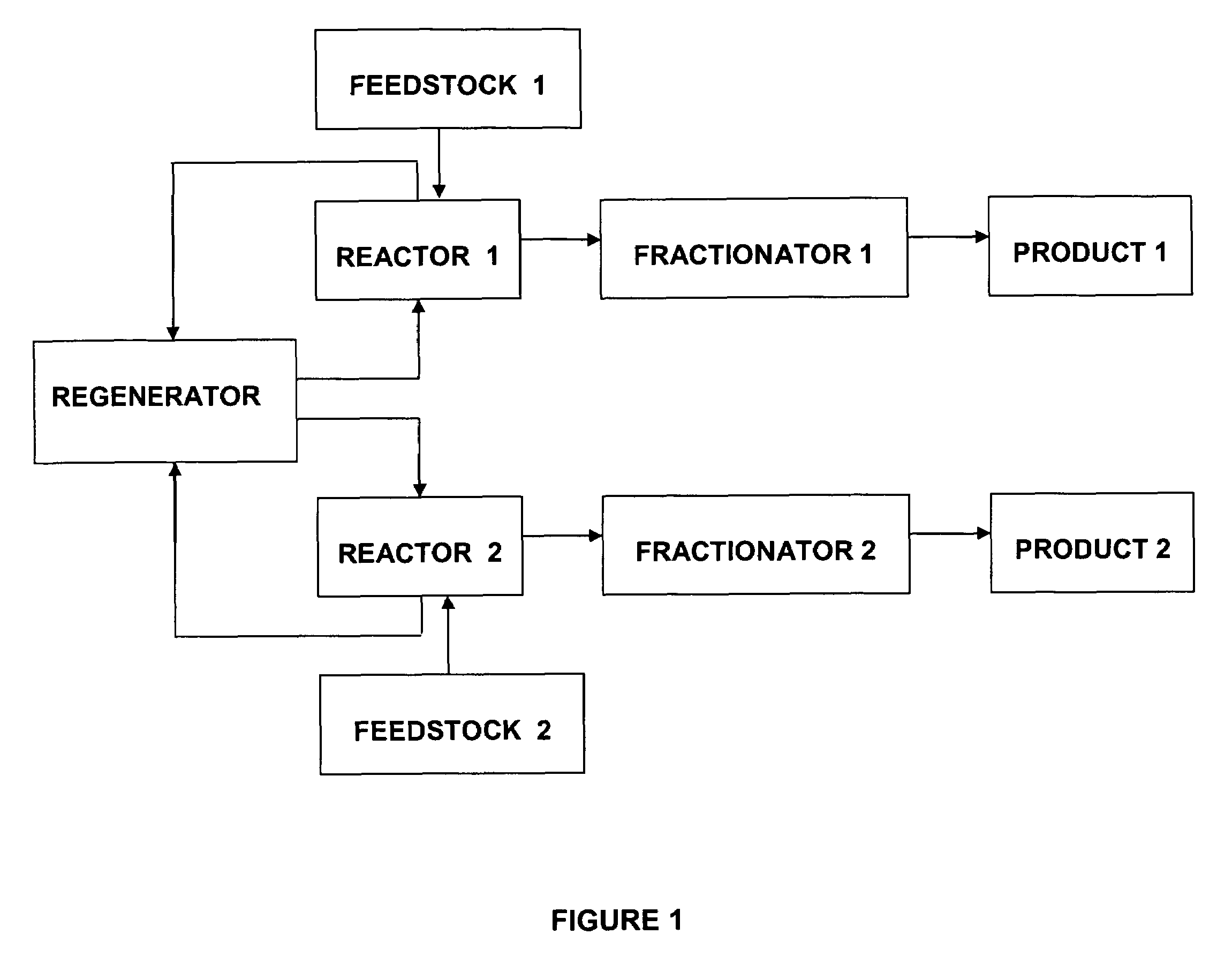
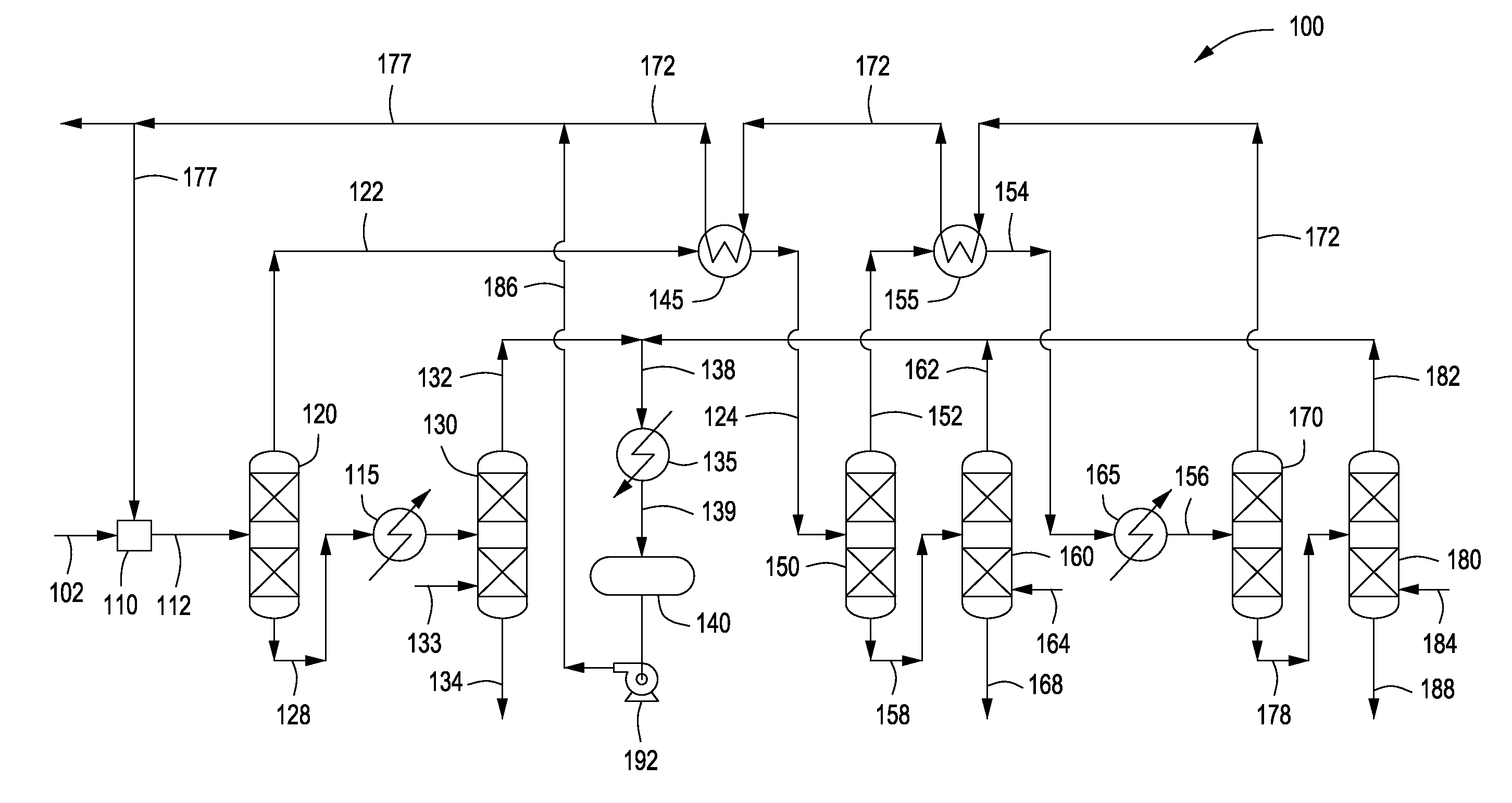
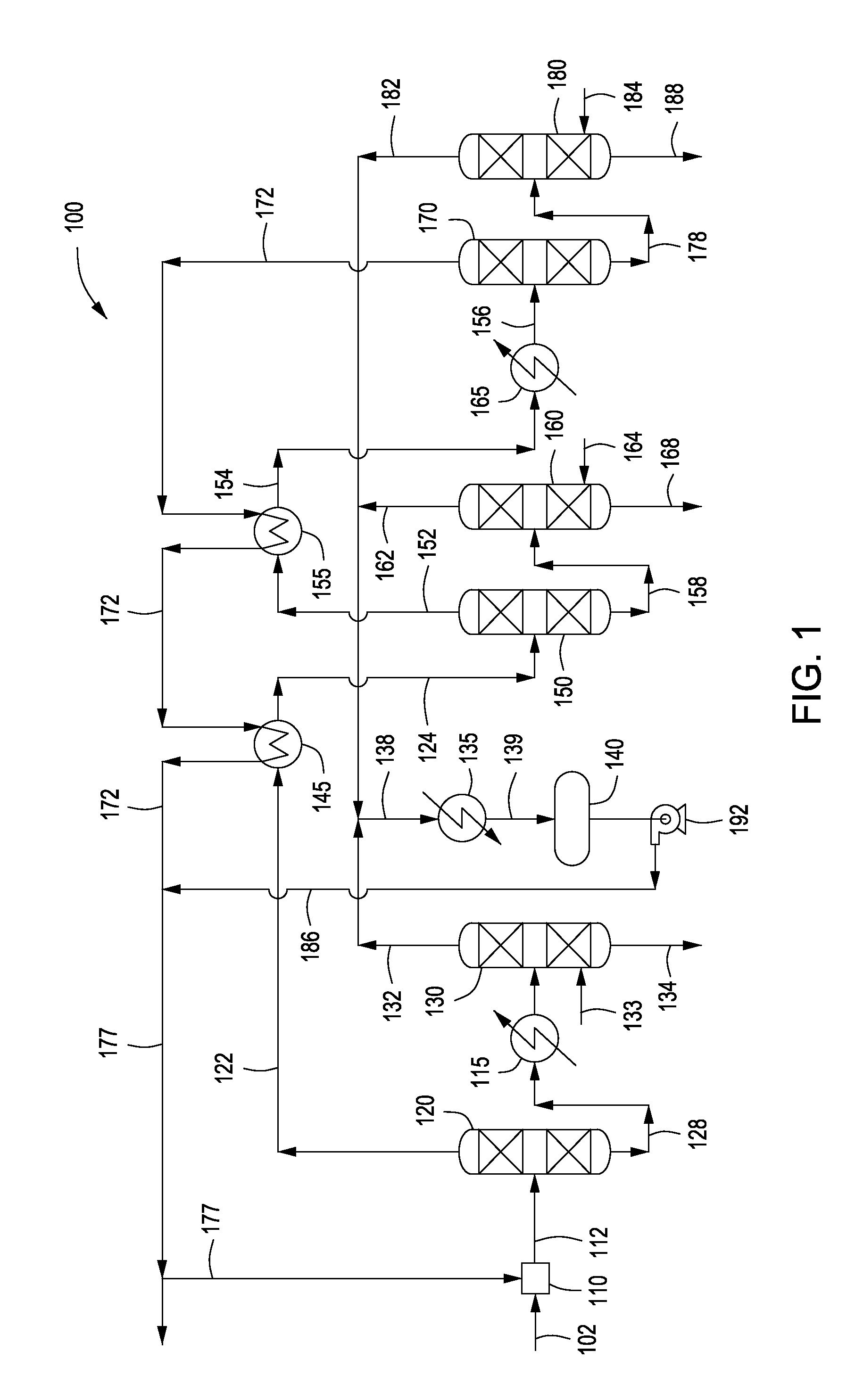
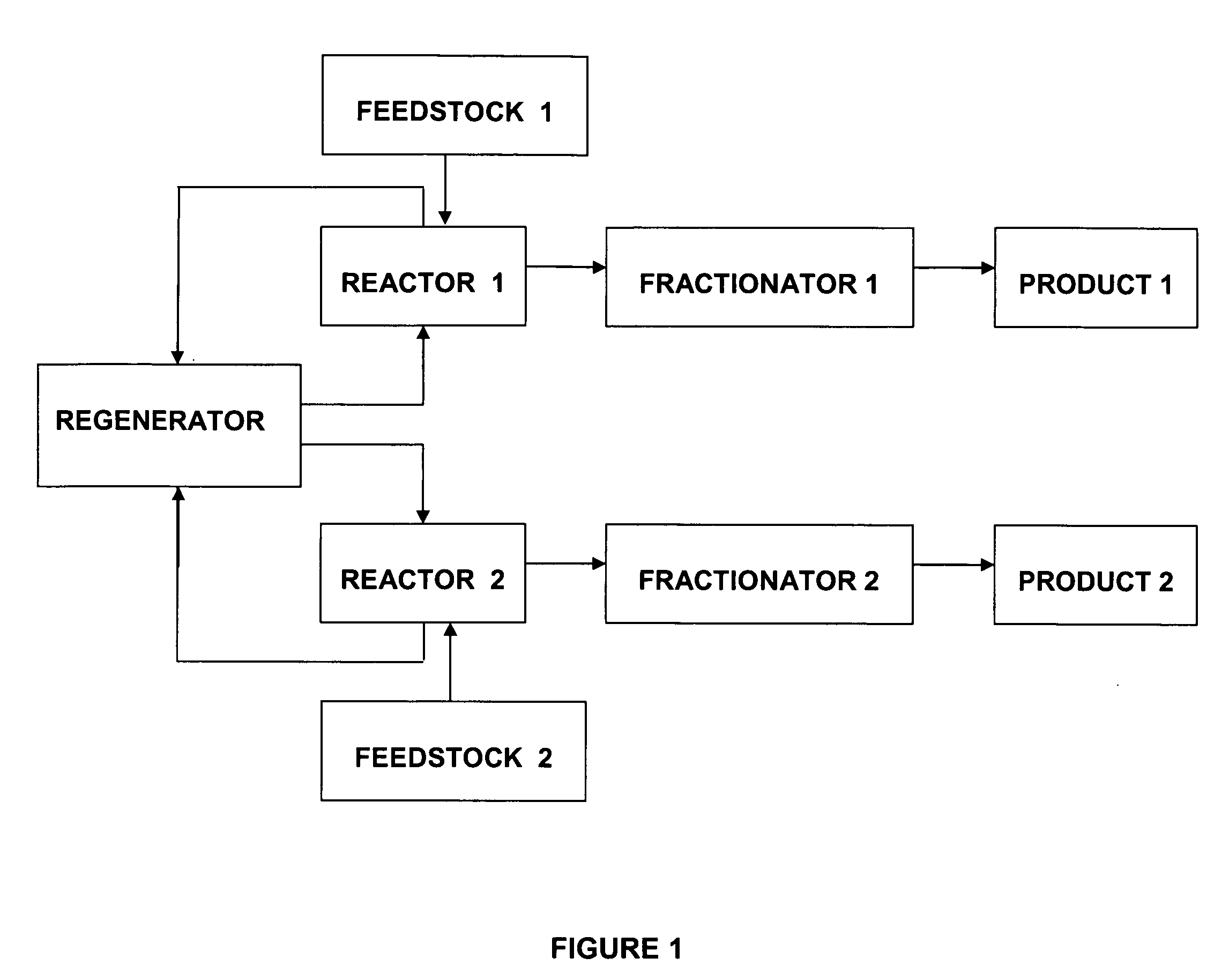
Method and apparatus for making a middle distillate product and lower olefins from a hydrocarbon feedstock
ActiveUS20060178546A1Yield maximizationCatalytic crackingCatalytic naphtha reformingPetroleum productGasoline
Disclosed is a process for making middle distillate and lower olefins. The process includes catalytically cracking a gas oil feedstock within a riser reactor zone by contacting under suitable catalytic cracking conditions within the riser reactor zone the gas oil feedstock with a middle distillate selective cracking catalyst that comprises amorphous silica alumina and a zeolite to yield a cracked gas oil product and a spent cracking catalyst. The spent cracking catalyst is regenerated to yield a regenerated cracking catalyst. Within an intermediate cracking reactor such as a dense bed reactor zone and under suitable high severity cracking conditions a gasoline feedstock is contacted with the regenerated cracking catalyst to yield a cracked gasoline product and a used regenerated cracking catalyst. The used regenerated cracking catalyst is utilized as the middle distillate selective catalyst.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
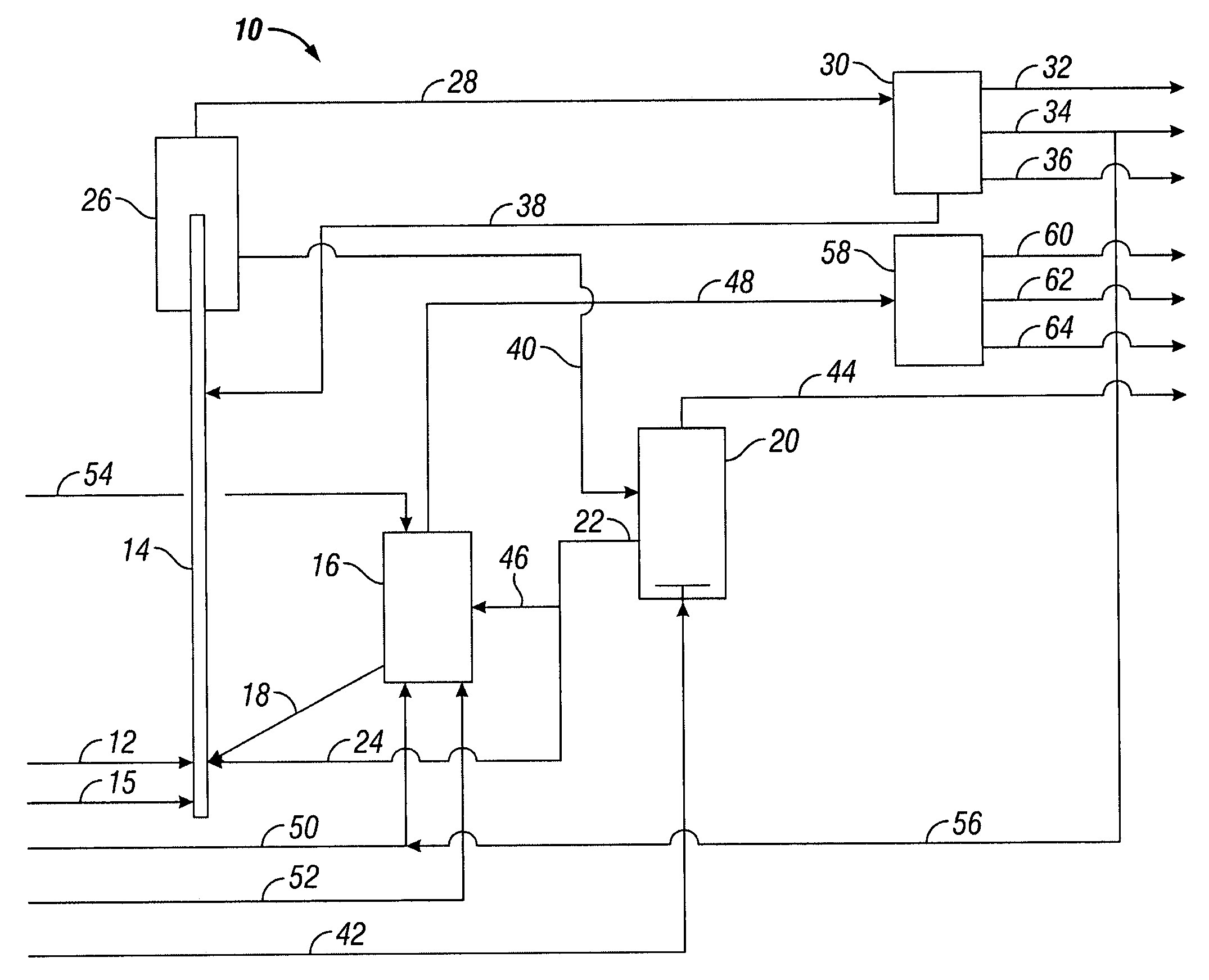
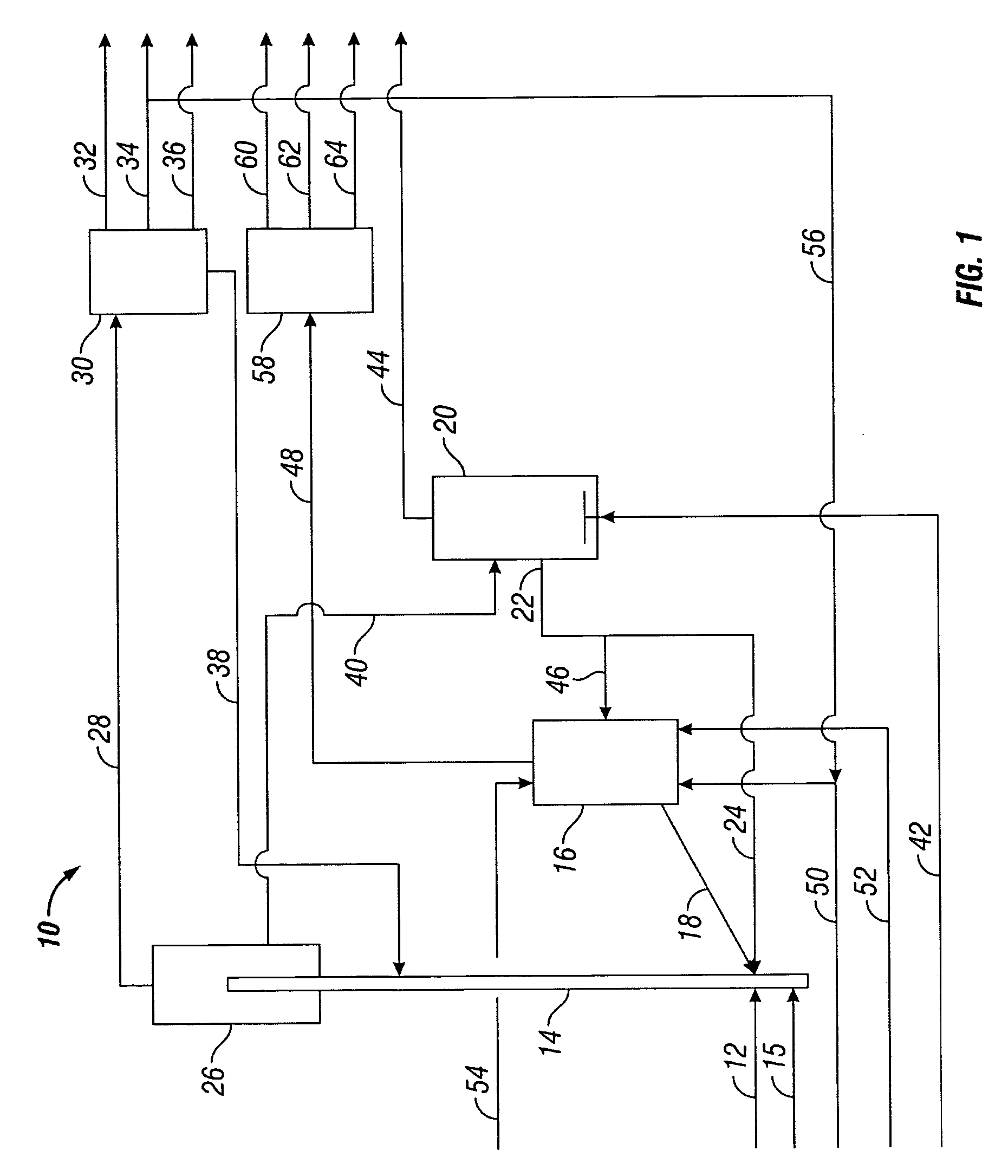
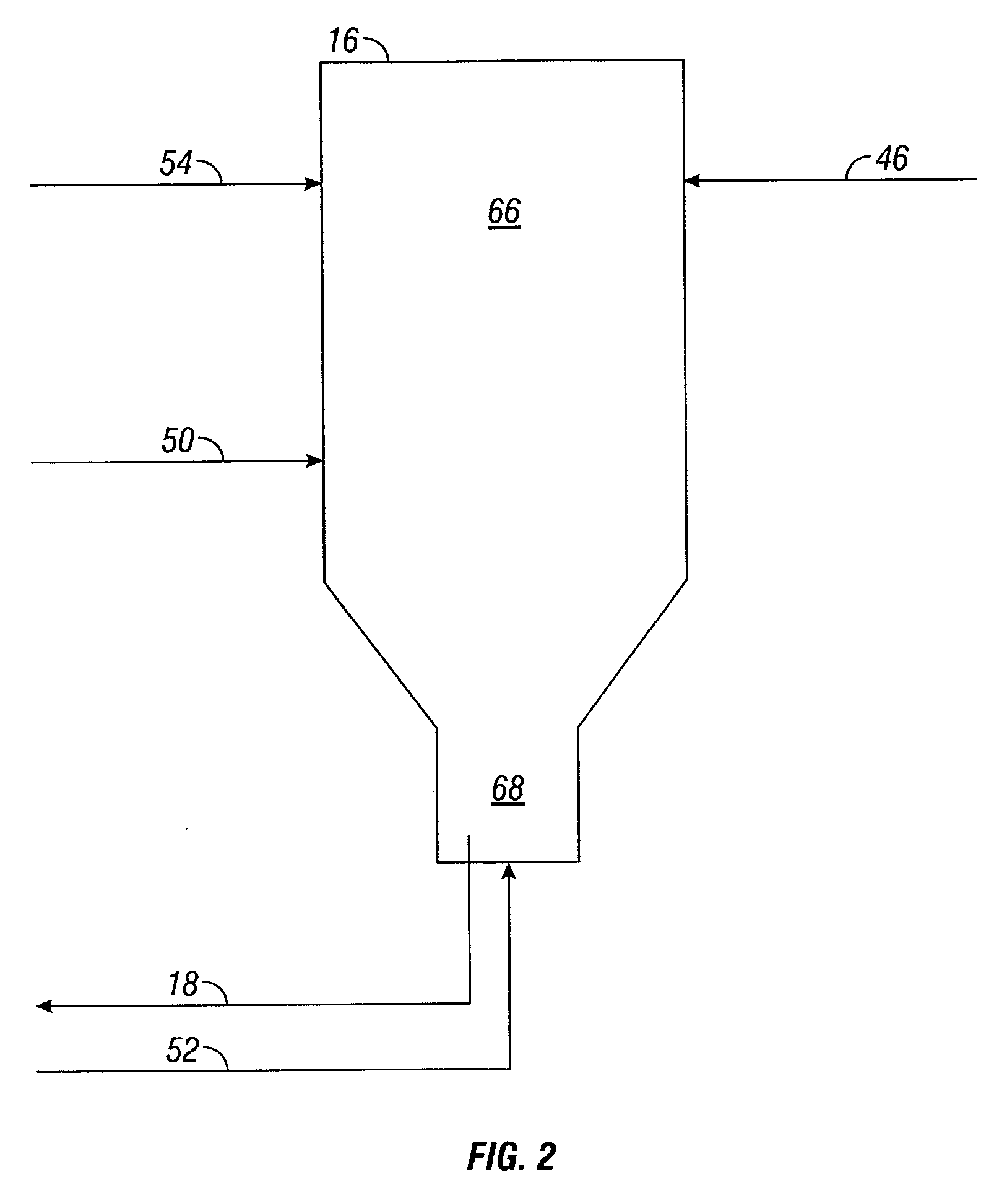
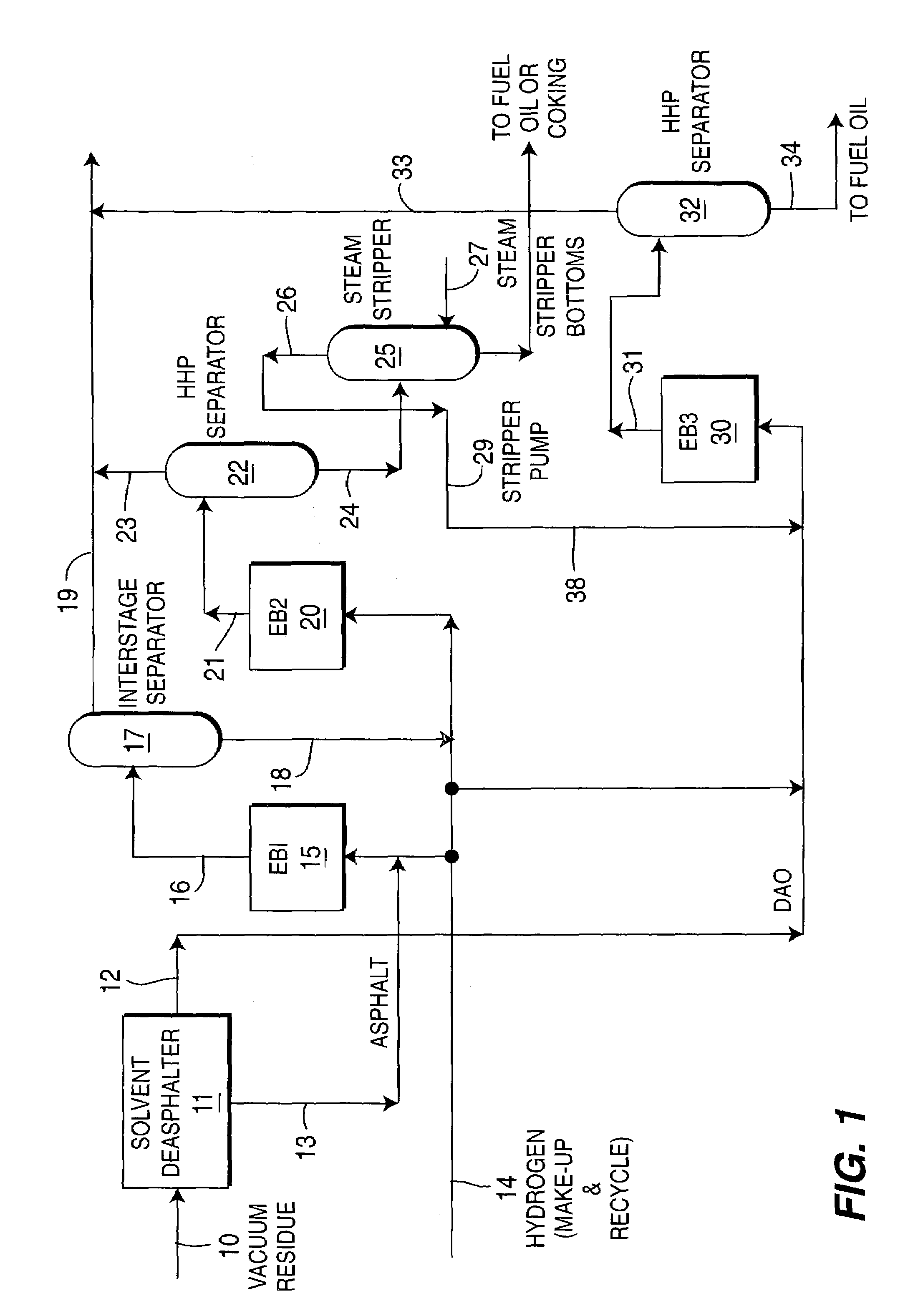
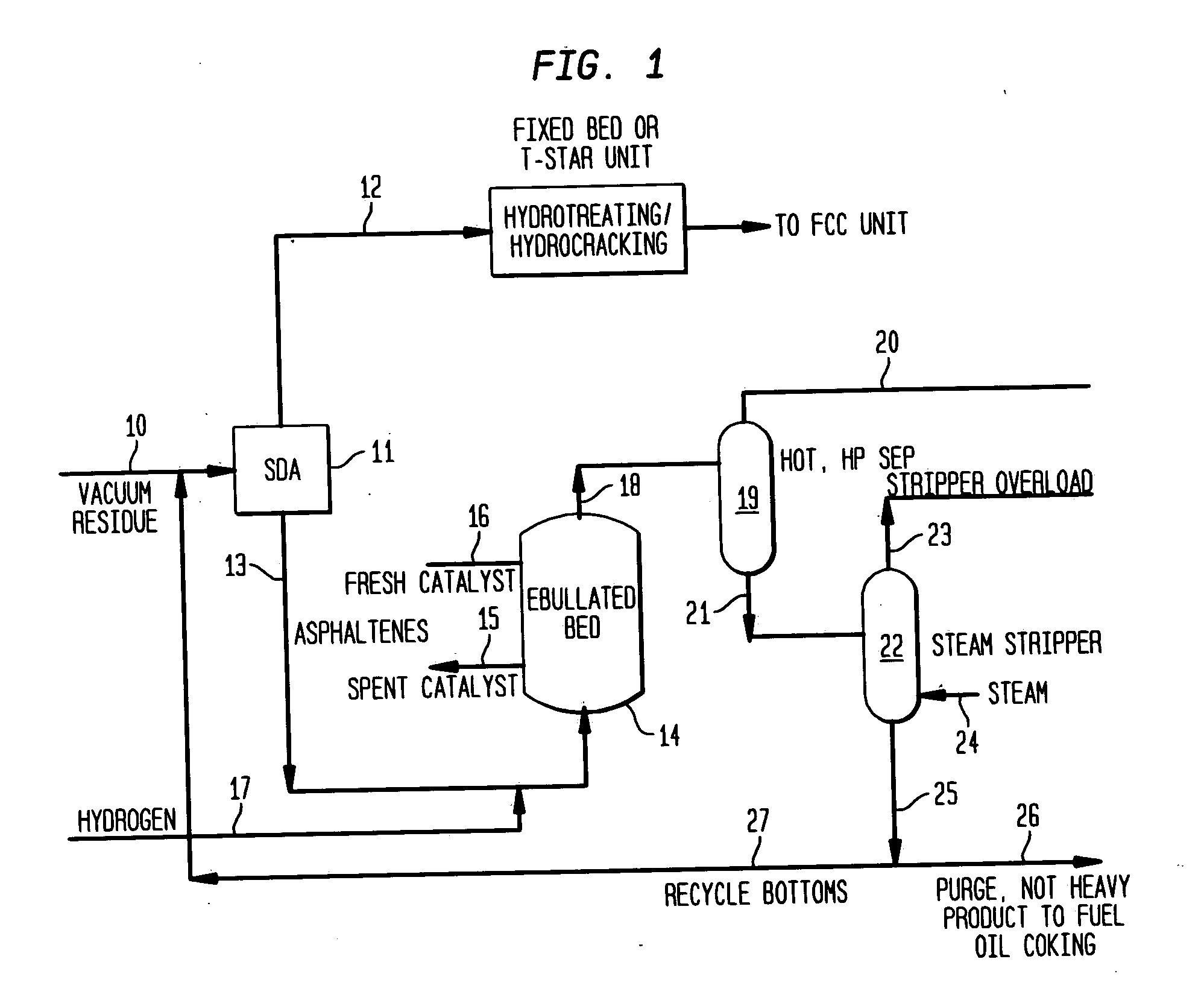
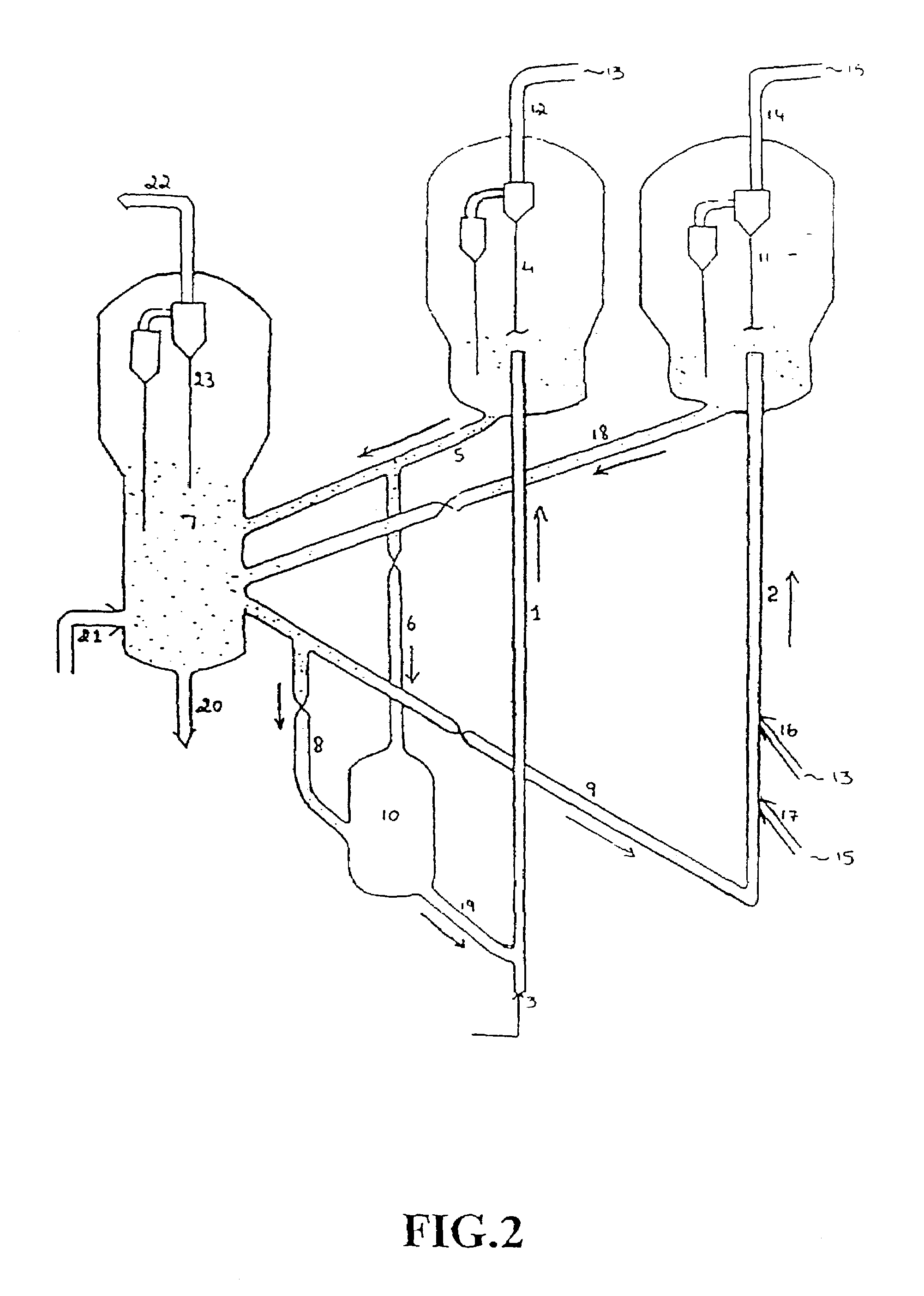
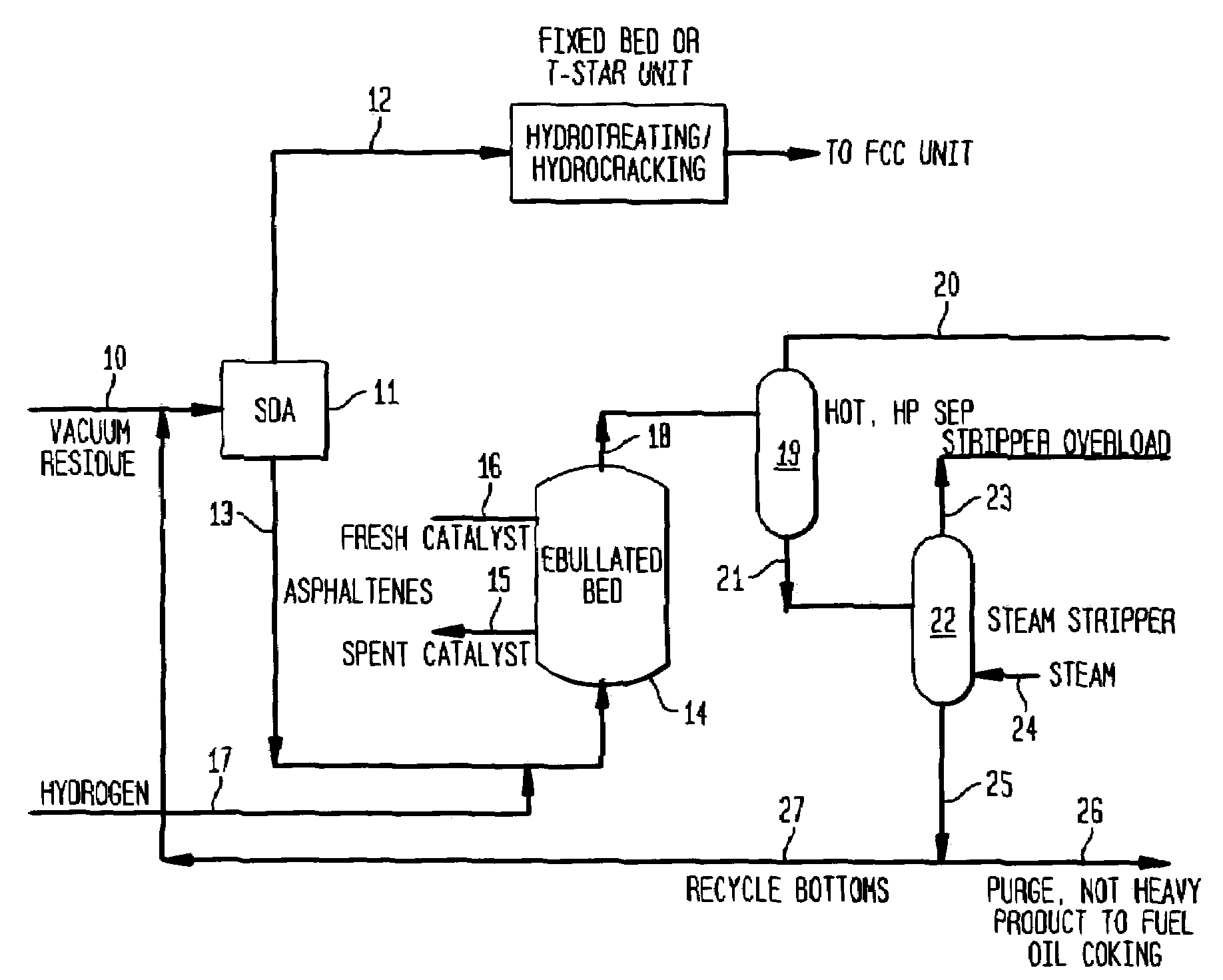
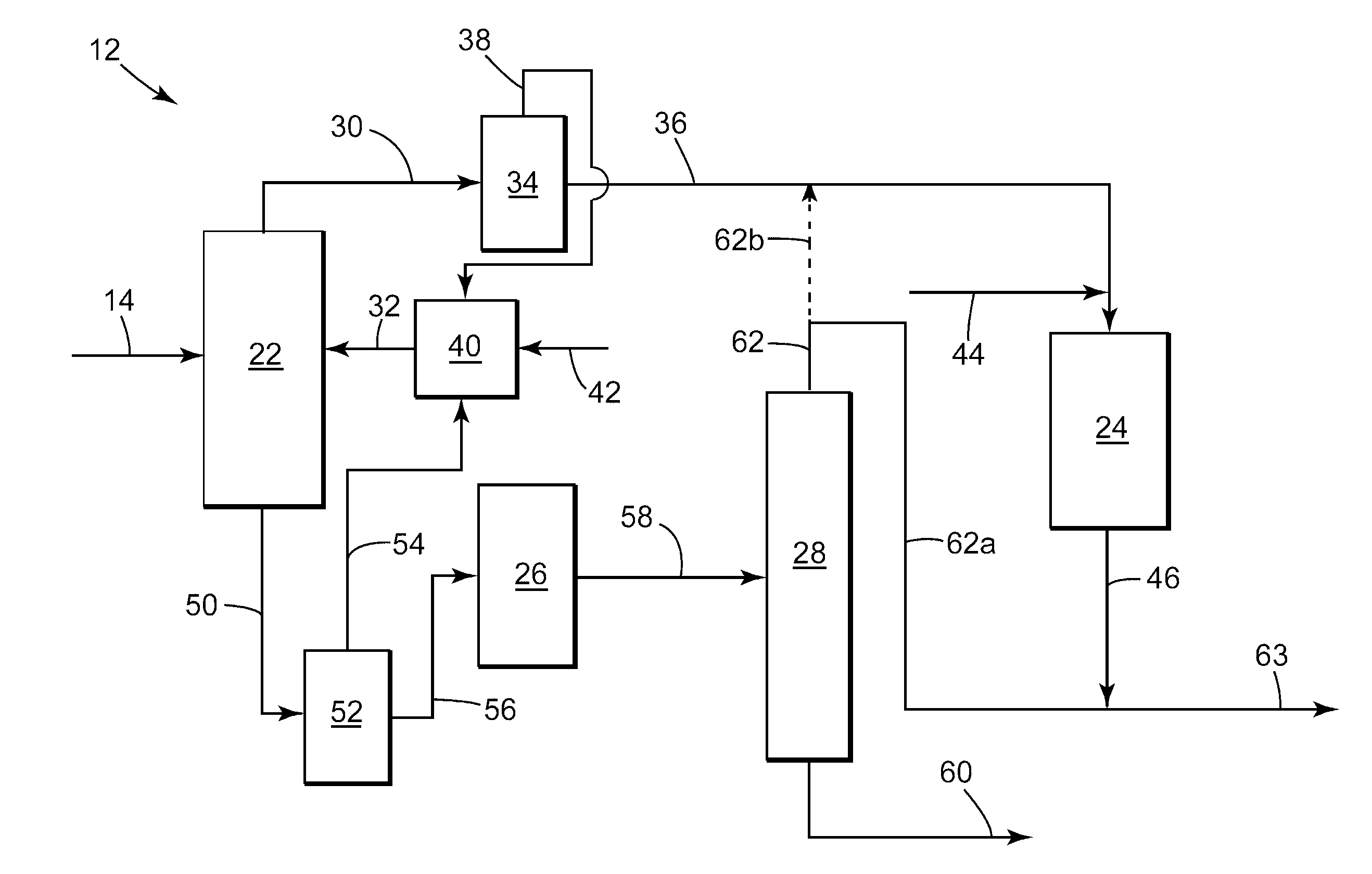
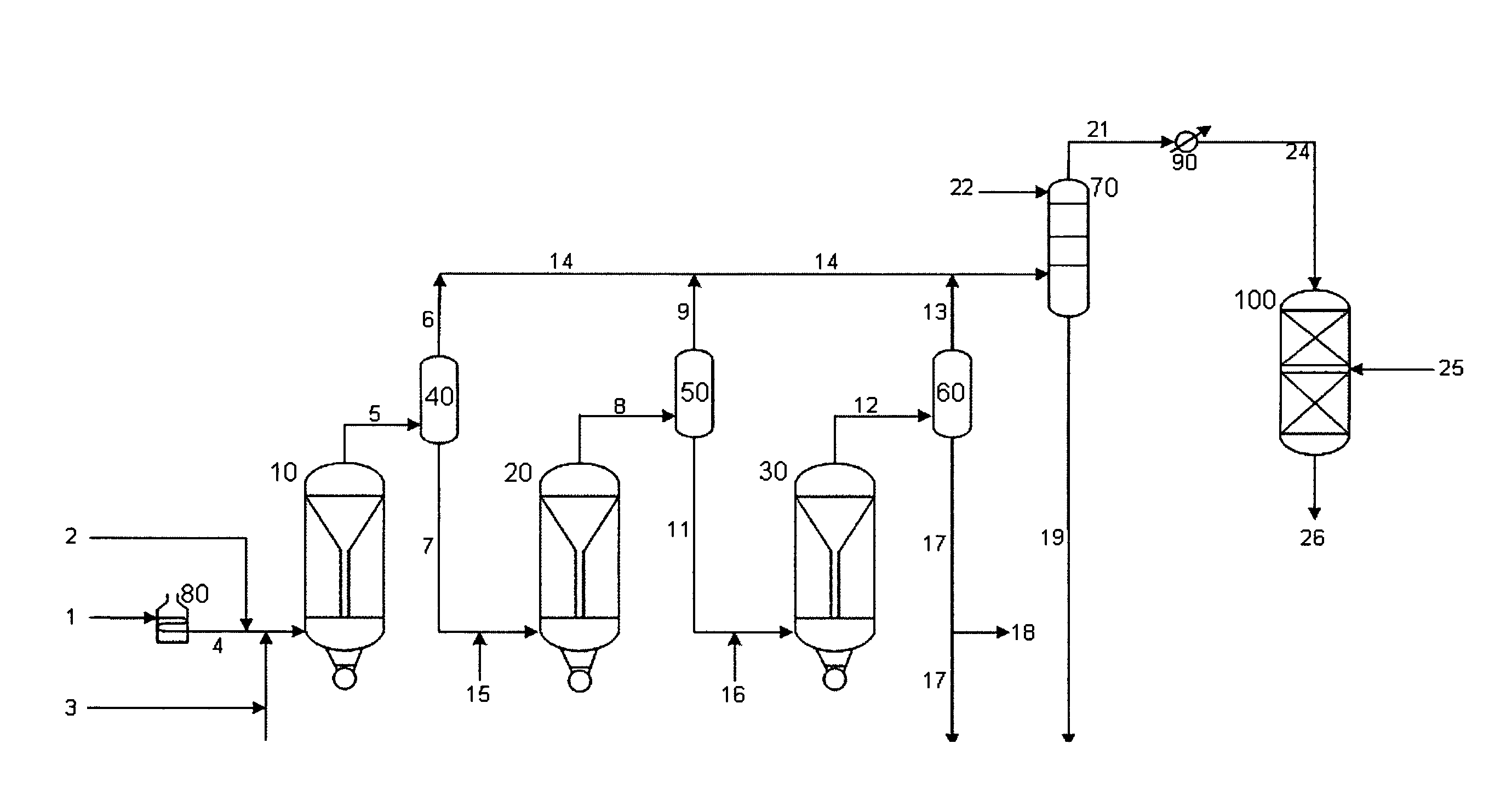
Effective integration of solvent deasphalting and ebullated-bed processing
InactiveUS7214308B2Reduced light gas yieldImprove hydrogen efficiencyTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel stages onlyReactor systemHeavy crude oil
This invention relates to a novel method for economically processing vacuum residue from heavy crude oils by selectively processing the difficult and easy components in reactors whose design and operating conditions are optimized for the specific feed. The process utilizes an integrated solvent deasphalting (SDA) / ebullated-bed design wherein the heavy vacuum residue feedstock is initially sent to an SDA unit operated with C4 / C5 solvent to achieve a high deasphalted oil (DAO) yield. The resulting SDA products, namely asphaltenes and DAO are separately treated in ebullated-bed reactor(s) systems whose design and operating conditions are optimized for a particular feedstock. The resulting net conversion, associated distillate yield and product qualities are greatly improved relative to treatment of the entire residue feedstock in a common ebullated-bed reactor system.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Isomerization/dehazing process for base oils from Fischer-Tropsch wax
InactiveUS7198710B2Hydrocarbon by hydrogenationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesWaxMolecular sieve
A method for producing lubricant base oils is provided comprising the steps of: (a) separating a feedstock into a light lubricant base oil fraction and a heavy fraction; (b) hydroisomerizing the fractions over a medium pore size molecular sieve catalyst under hydroisomerization conditions to produce an isomerized light lubricant base oil fraction having a pour point less than or equal to a target pour point of the lubricant base oils and an isomerized heavy fraction having a pour point of equal to or greater than the target pour point of the lubricant base oils and a cloud point greater than the target cloud point of the lubricant base oils; and (c) dehazing the isomerized heavy fraction to provide a heavy lubricant base oil having a pour point less than or equal to the target pour point of the lubricant base oils and a cloud point less than or equal to the target cloud point of the lubricant base oils.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
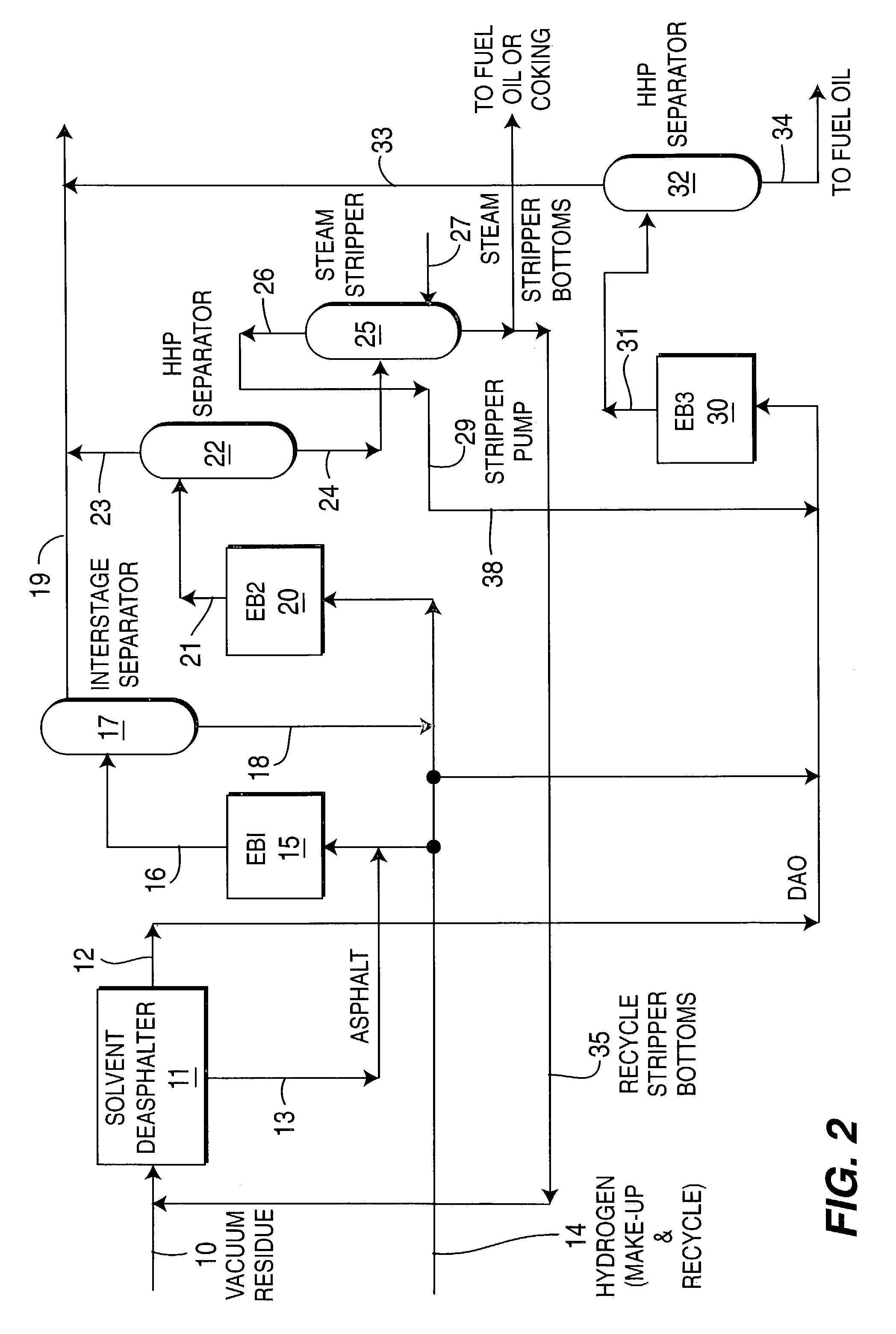
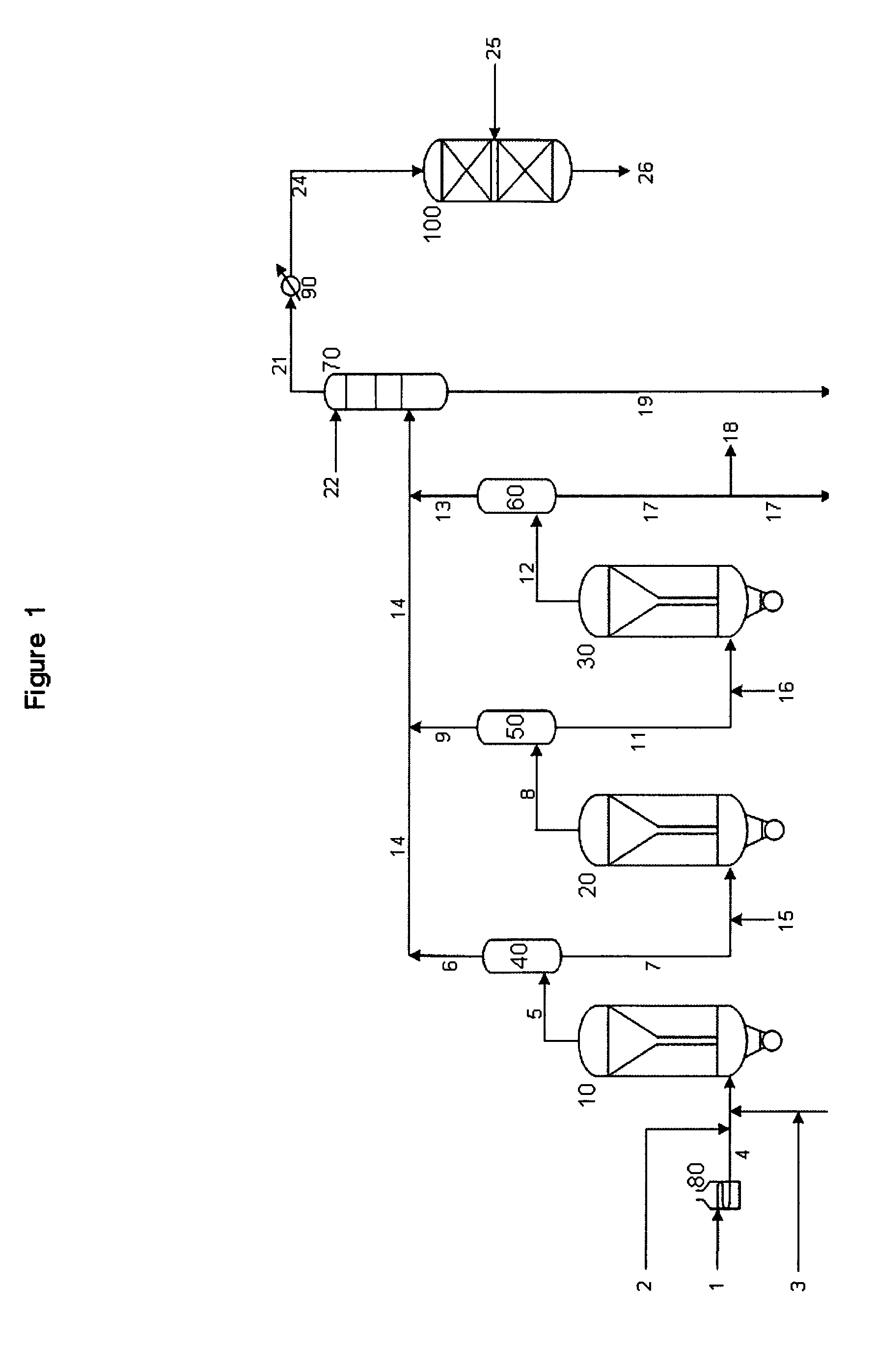
Integrated SDA and ebullated-bed process
ActiveUS20060118463A1Most efficientMinimizing chanceTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel stages onlyBiochemical engineeringFixed bed
This invention relates to a novel integrated method for economically processing vacuum residue from heavy crude oils. This is accomplished by utilizing a solvent deasphalter (SDA) in the first step of the process with a C3 / C4 / C5 solvent such that the DAO product can thereafter be processed in a classic fixed-bed hydrotreater or hydrocracker. The SDA feed also includes recycled stripper bottoms containing unconverted residue / asphaltenes from a downstream steam stripper unit. The asphaltenes from the SDA are sent to an ebullated-bed reactor for conversion of the residue and asphaltenes. Residue conversion in the range of 60-80% is achieved and asphaltene conversion is in the range of 50-70%. The overall residue conversion, with the DAO product considered non-residue, is in the range of 80 W %-90 W % and significantly higher than could be achieved without utilizing the present invention.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Multi stage selective catalytic cracking process and a system for producing high yield of middle distillate products from heavy hydrocarbon feedstocks
InactiveUS7029571B1MinimizeImproving cetane qualityTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCatalytic crackingFluidized bedPetroleum
According to this invention, there is provided a process and apparatus for catalytic cracking of various petroleum based heavy feed stocks in the presence of solid zeolite catalyst and high pore size acidic components for selective bottom cracking and mixtures thereof, in multiple riser type continuously circulating fluidized bed reactors operated at different severities to produce high yield of middle distillates, in the range of 50–65 wt % of fresh feed.
Owner:INDIAN OIL CORPORATION
Production of Transportation Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090229172A1Reduce first amountMinimize the numberBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionNaphthaHigh pressure hydrogen
A process has been developed for producing a diesel boiling point range product and an aviation boiling point range product from renewable feedstocks such as plant and animal oils. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating and deoxygenating to provide a hydrocarbon fraction which is then isomerized and selectively cracked to form the diesel boiling point range product and the aviation boiling point range product. A portion of the diesel boiling point range product, aviation boiling point range product, naphtha product, LPG, or any combination thereof can be optionally used as a rectification agent in the selective hot high pressure hydrogen stripper to decrease the amount of product carried in the stripper overhead.
Owner:UOP LLC
Hydroprocessing methods and apparatus for use in the preparation of liquid hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20050205462A1Easy to prepareEnhancing yield and cold-flow propertyTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel stages onlyWaxProduction rate
The present invention is generally related towards enhancing the yield and / or cold-flow properties of certain hydrocarbon products, increasing the degree of isomerization in a diesel product and / or increasing the production rate of a diesel product. The embodiments generally include reducing the residence time of lighter hydrocarbon fractions during hydrocracking, thereby decreasing secondary cracking, by various configurations of introducing at least two hydrocarbon feedstreams of different boiling ranges at different entry points in a hydrocracking unit. A method further includes forming a hydrocarbons stream comprising primarily C5+ Fischer-Tropsch hydrocarbon products; fractionating hydrocarbons stream to form at least a wax fraction and an intermediate fraction which serve as separate feedstreams to a hydrocracking unit comprising at least two hydroconversion zones. One embodiment comprises the use of a bifunctional catalyst in one of the hydrocracking zones so as to favor hydroisomerization of hydrocarbons to favor the formation of branched paraffins boiling in the diesel range.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Catalytic cracking process for the production of diesel from vegetable oils
The present invention relates to a thermo catalytic process to produce diesel oil from vegetable oils, in refineries which have two or more Catalytic Cracking (FCC) reactors. At least one reactor processes heavy petroleum or residue in conventional operation conditions while at least one reactor processes vegetable oils in proper operation conditions to produce diesel oil. This process employs the same catalyst employed in the FCC process, which processes conventional feedstocks simultaneously. This process transforms high heat content raw materials into fuel hydrocarbons. It may improve efficiency for the obtainment of highly pure products and may not yield glycerin, one by-product of the transesterification process. The diesel oil produced by said process may have superior qualities and / or a cetane number higher than 40. Once cracking conditions occur at lower temperatures, it may form a less oxidized product, which is consequently purer than those obtained by existent technology.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Process and apparatus for upgrading FCC product with additional reactor with catalyst recycle
InactiveUS6866771B2Increase undesirable crackingLower catalytic temperatureTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCatalytic crackingCracking reactionChemistry
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for jointly producing propylene and petrol from a relatively heavy charge
ActiveUS20050121361A1Increase in severityReaction can be limitedCatalytic crackingOrganic chemistry methodsOligomerBoiling point
A process for conversion of a hydrocarbon feedstock comprising a relatively heavy main feedstock with a boiling point above approximately 350° C., and a relatively light secondary feedstock with a boiling point below approximately 320° C., wherein, the main feedstock, representing at least 50 wt. % of the hydrocarbon feedstock, is cracked in a fluidized-bed reactor in the presence of a cracking catalyst, the secondary feedstock is cracked in a fluidized bed with the same cracking catalyst, separately or mixed with the main feedstock, said secondary feedstock comprising oligomers with at least 8 carbon atoms of light olefins with 4 and / or 5 carbon atoms.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Fluid cat cracking with high olefins production
InactiveUS20020189973A1Maximize lightThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyNaphthaOrganic chemistry
The propylene production of a fluid catalytic cracking unit employing a large pore zeolite cracking catalyst, produces more propylene by adding a naphtha cracking riser and a medium pore zeolite catalytic component to the unit, and recycling at least a portion of the naphtha crackate to the naphtha riser. The large pore size zeolite preferably comprises a USY zeolite and the medium pore size is preferably ZSM-5. Propylene production per unit of naphtha feed to the naphtha riser is maximized, by using the 60-300° F. naphtha crackate as the feed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for upgrading heavy oil using a reactor with a novel reactor separation system
ActiveUS7431822B2Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyLiquid productHydrogen
Applicants have developed a new residuum full hydroconversion slurry reactor system that allows the catalyst, unconverted oil, hydrogen, and converted oil to circulate in a continuous mixture throughout an entire reactor with no confinement of the mixture. The mixture is separated internally, within one of more of the reactors, to separate only the converted oil and hydrogen into a vapor product while permitting the unconverted oil and the slurry catalyst to continue on into the next sequential reactor as a liquid product. A portion of the unconverted oil is then converted to lower boiling point hydrocarbons in the next reactor, once again creating a mixture of unconverted oil, hydrogen, converted oil, and slurry catalyst. Further hydroprocessing may occur in additional reactors, fully converting the oil. The oil may alternately be partially converted, leaving a concentrated catalyst in unconverted oil which can be recycled directly to the first reactor.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
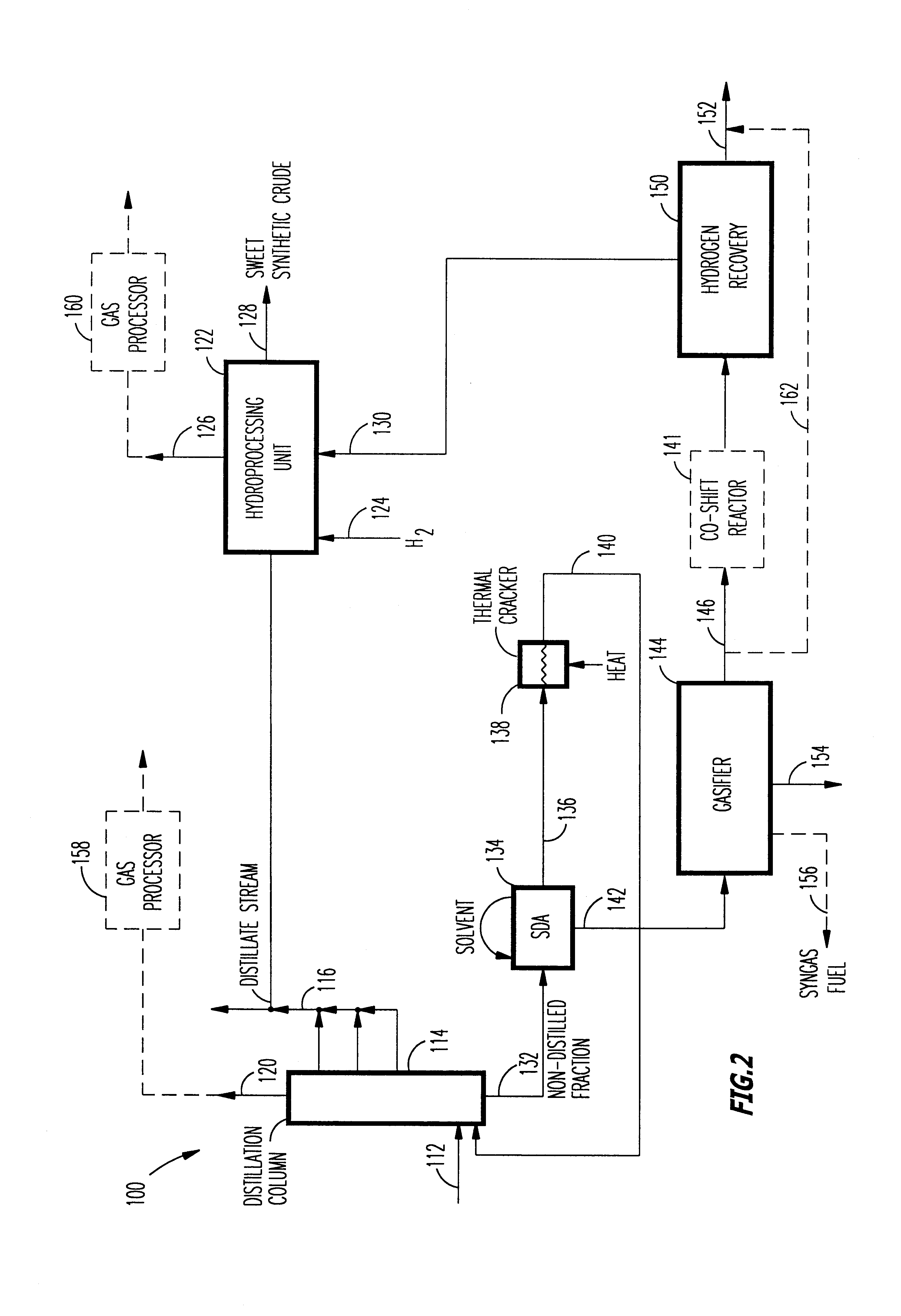
Method of and apparatus for upgrading and gasifying heavy hydrocarbon feeds
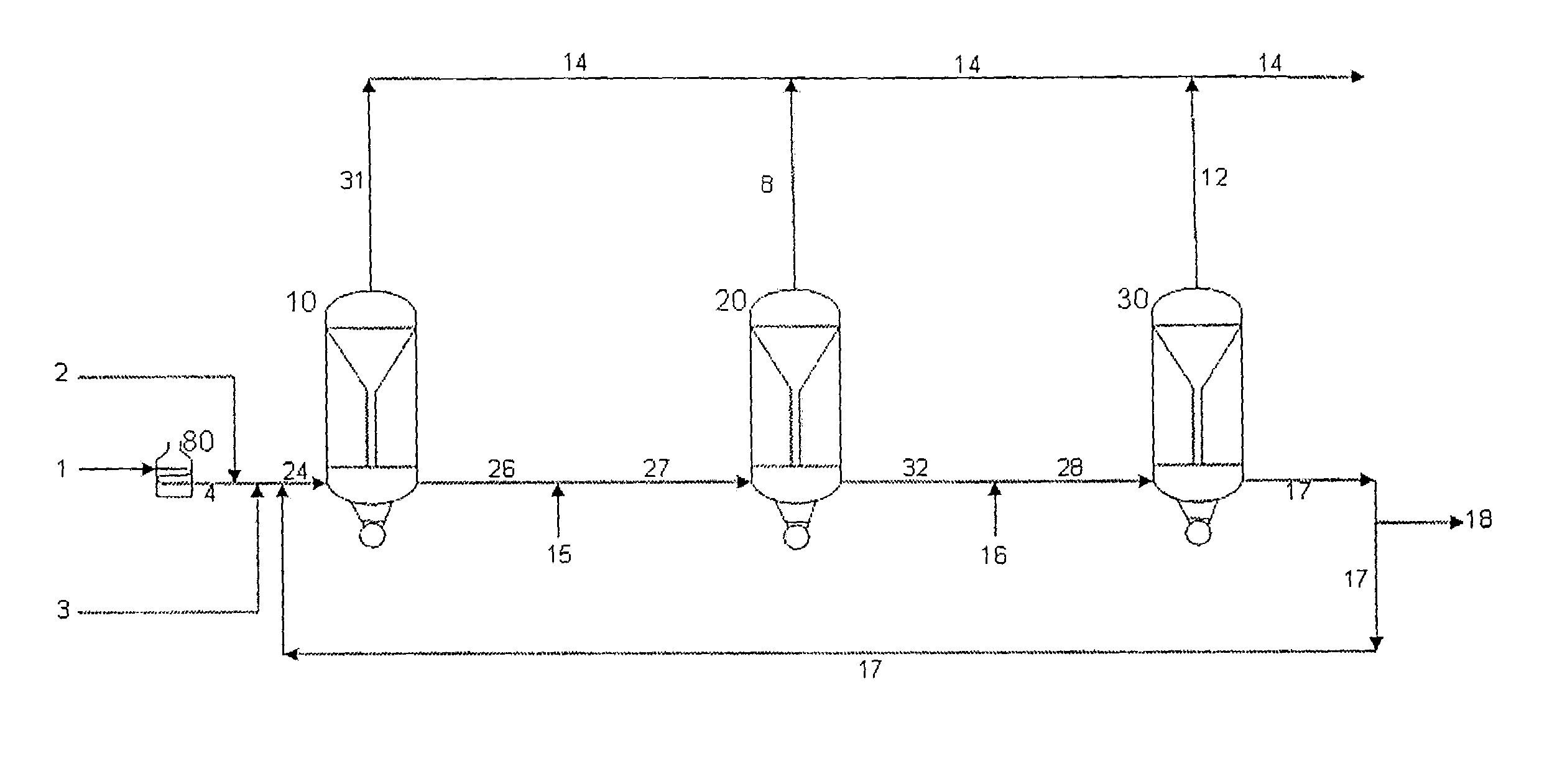
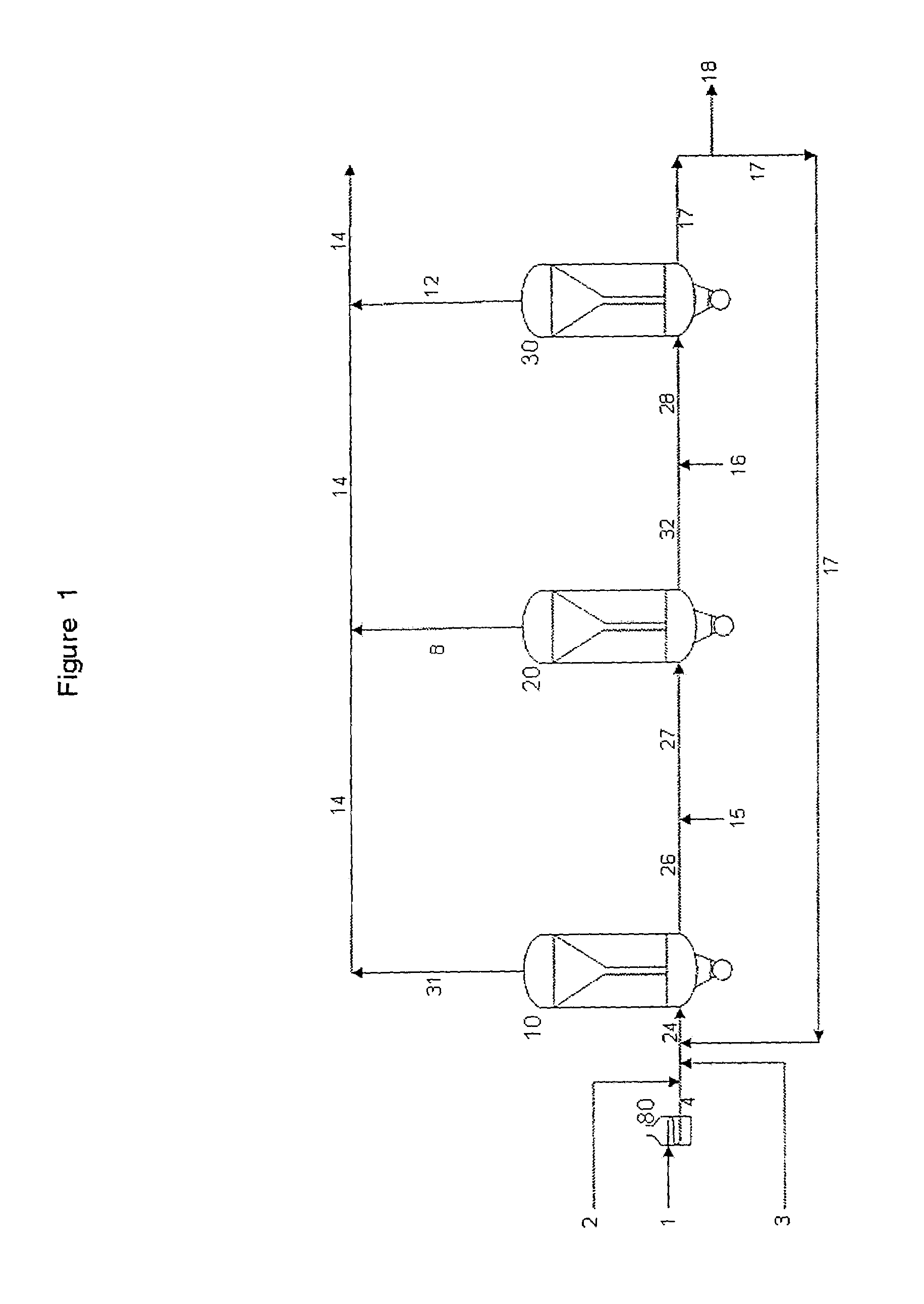
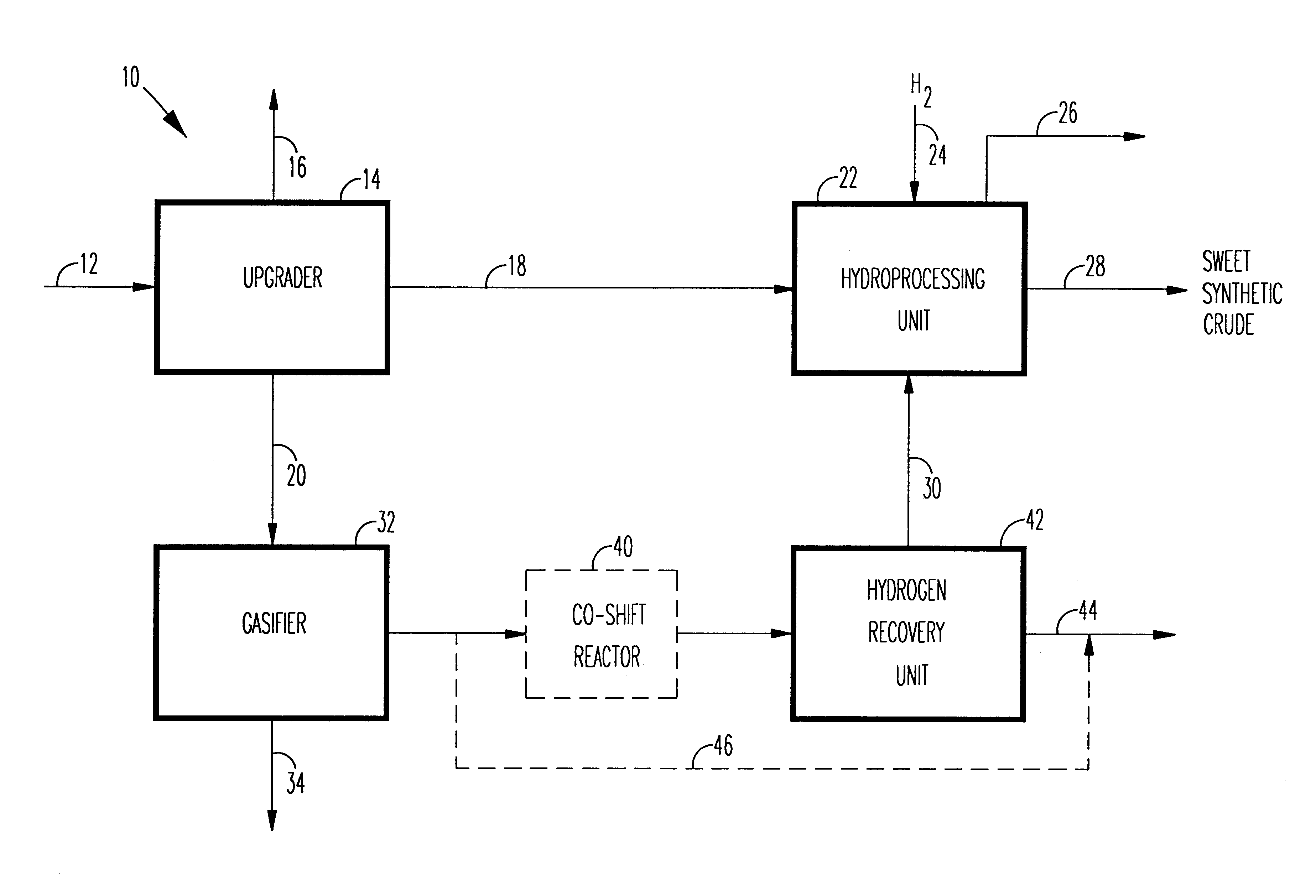
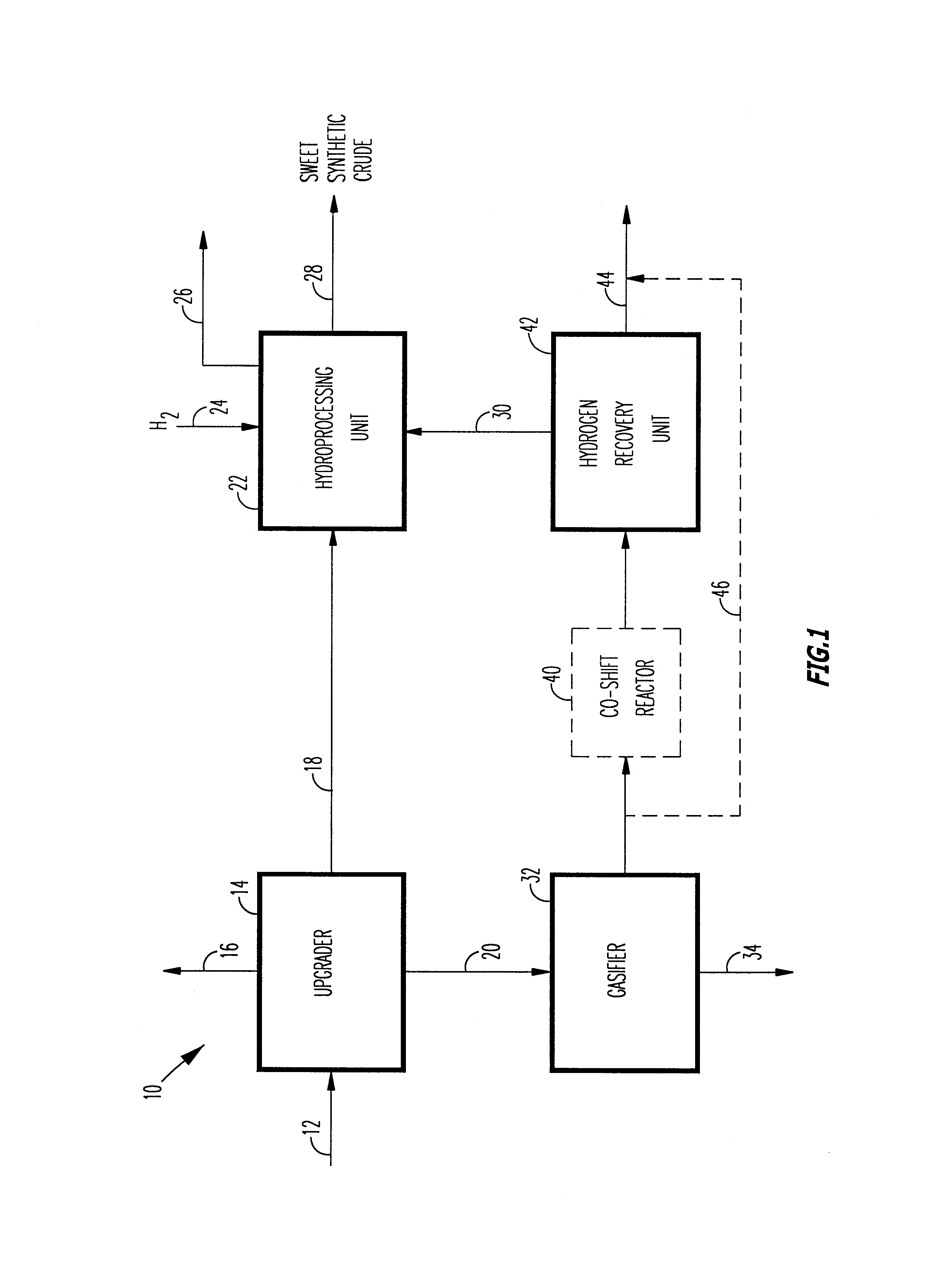
A novel apparatus for producing sweet synthetic crude from a heavy hydrocarbon feed comprising: an upgrader for receiving said heavy hydrocarbon feed and producing a distillate fraction including sour products, and high-carbon content by-products; a gasifier for receiving the high-carbon content by-products and producing synthetic fuel gas and sour by-products; a hydroprocessing unit for receiving the sour by-products and hydrogen gas, thereby producing gas and sweet crude; and a hydrogen recovery unit for receiving said synthetic fuel gas and producing further hydrogen gas and hydrogen-depleted synthetic fuel gas, said further hydrogen gas being supplied to said hydroprocessing unit.
Owner:ORMAT IND LTD
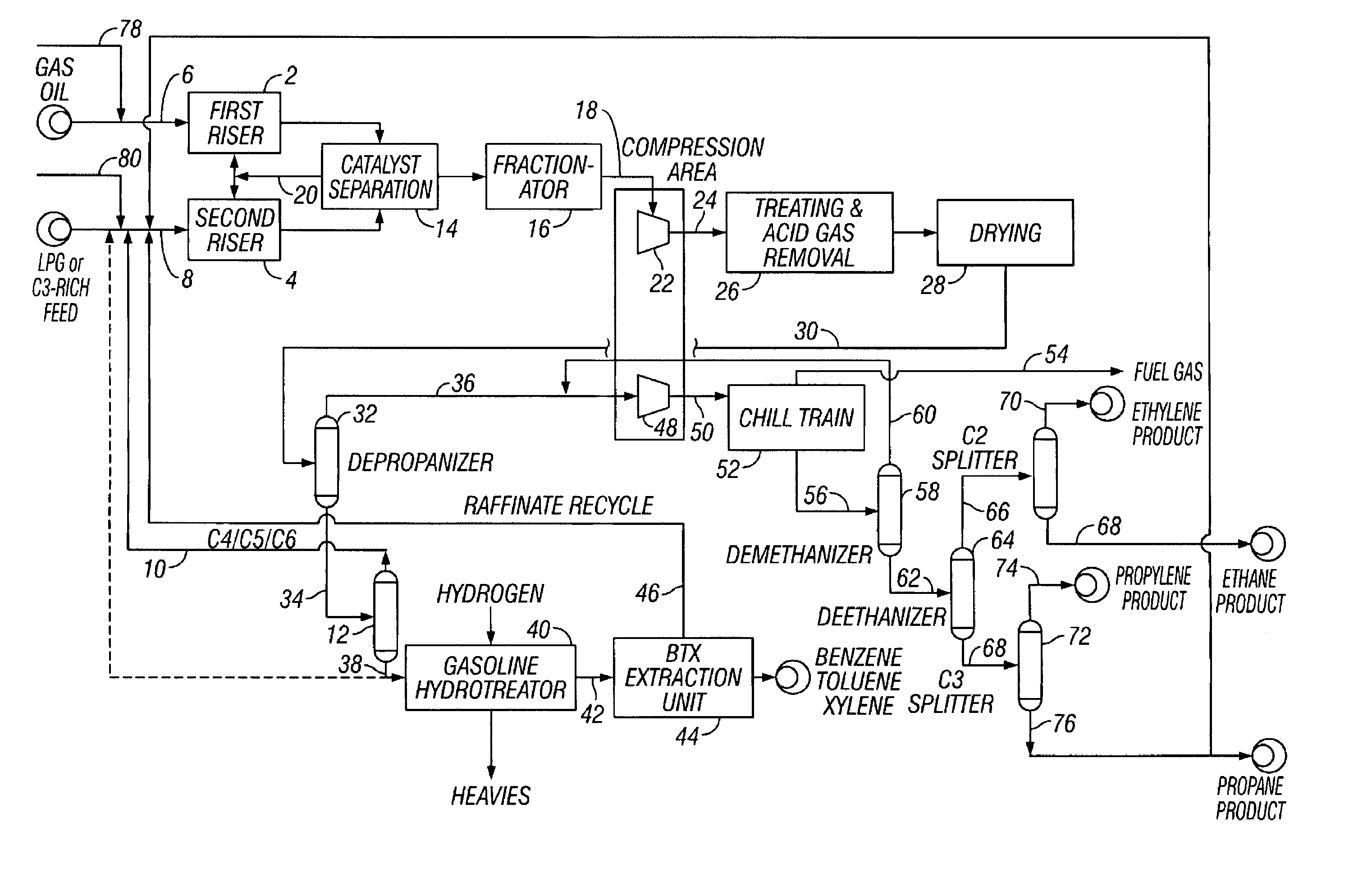
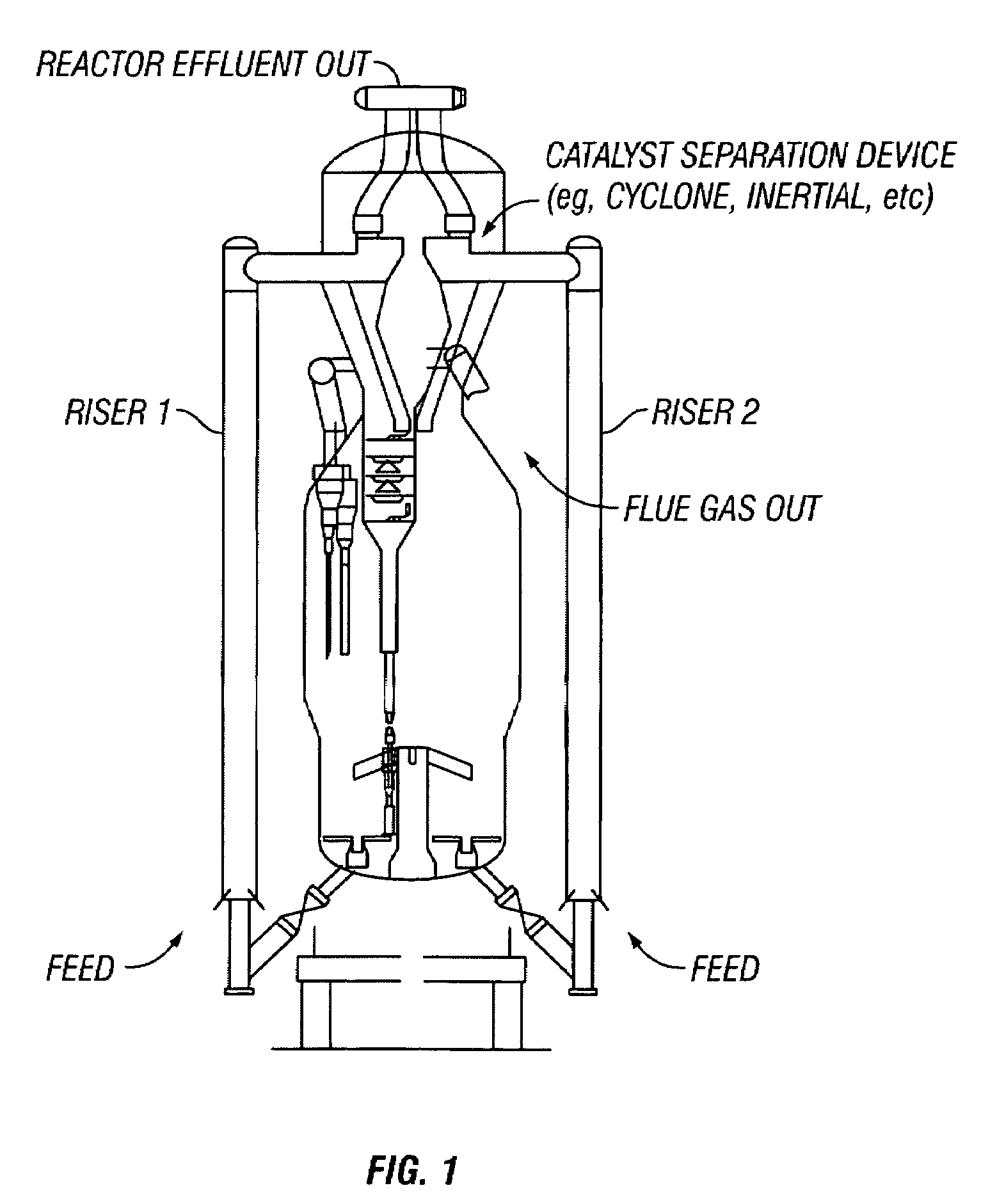
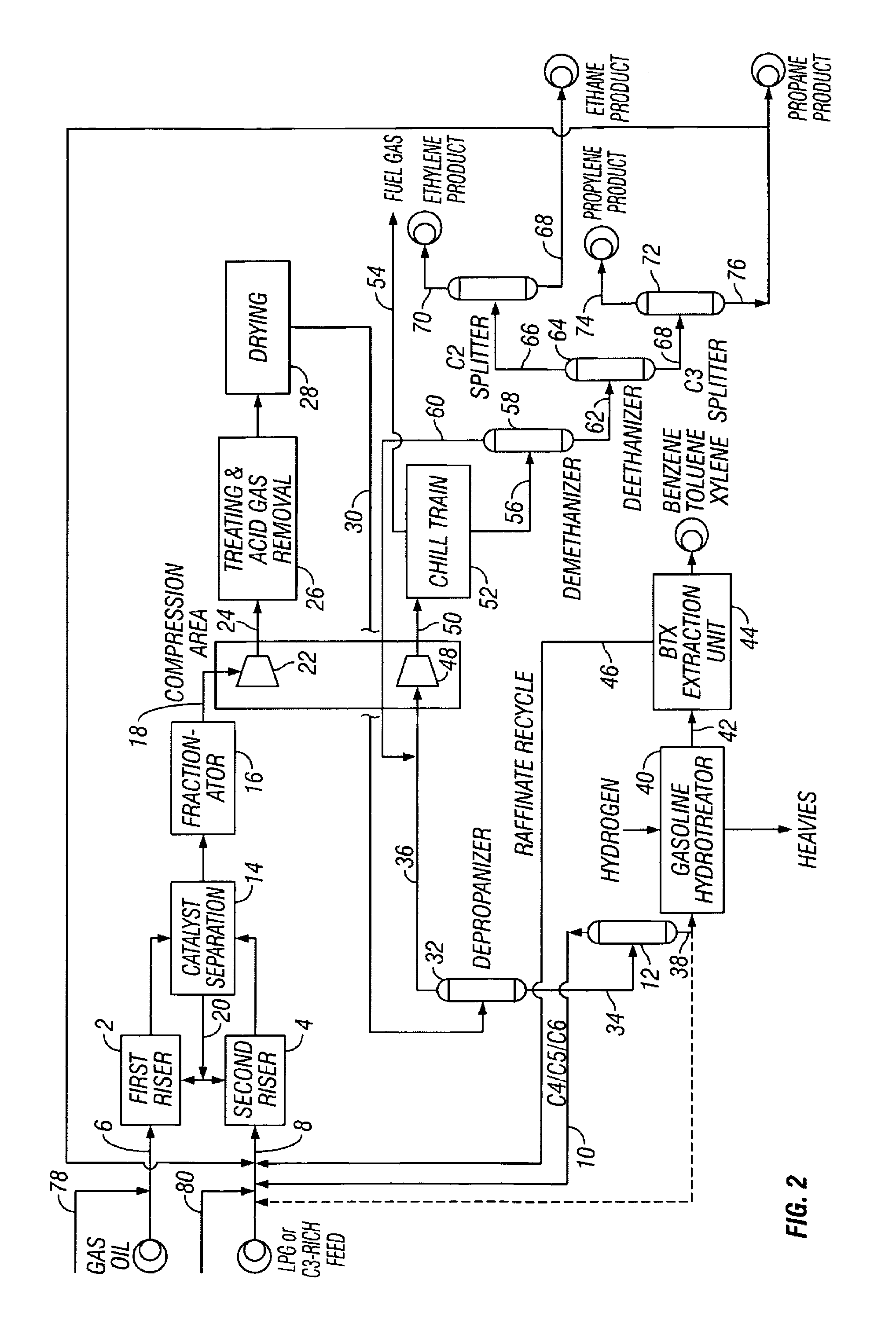
FCC process for converting C3/C4 feeds to olefins and aromatics
ActiveUS7611622B2Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCatalytic crackingEngineeringAlkene
A dual riser FCC process for converting C3 / C4-containing feedstocks to aromatics. First and second hydrocarbon feeds (5, 6) are supplied to the respective first and second risers (2, 4) in a dual-riser FCC unit with a gallium enriched catalyst to make an effluent rich in ethylene, propylene and aromatics. The first riser (2) is operated at less severe conditions than the second riser (4) and can receive a relatively heavy feed such as gas oil. The feed to the second riser (4) includes propane, for example LPG, propane recycle from the C3 splitter (72), etc. The FCC catalyst can include gallium to promote aromatics formation.
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
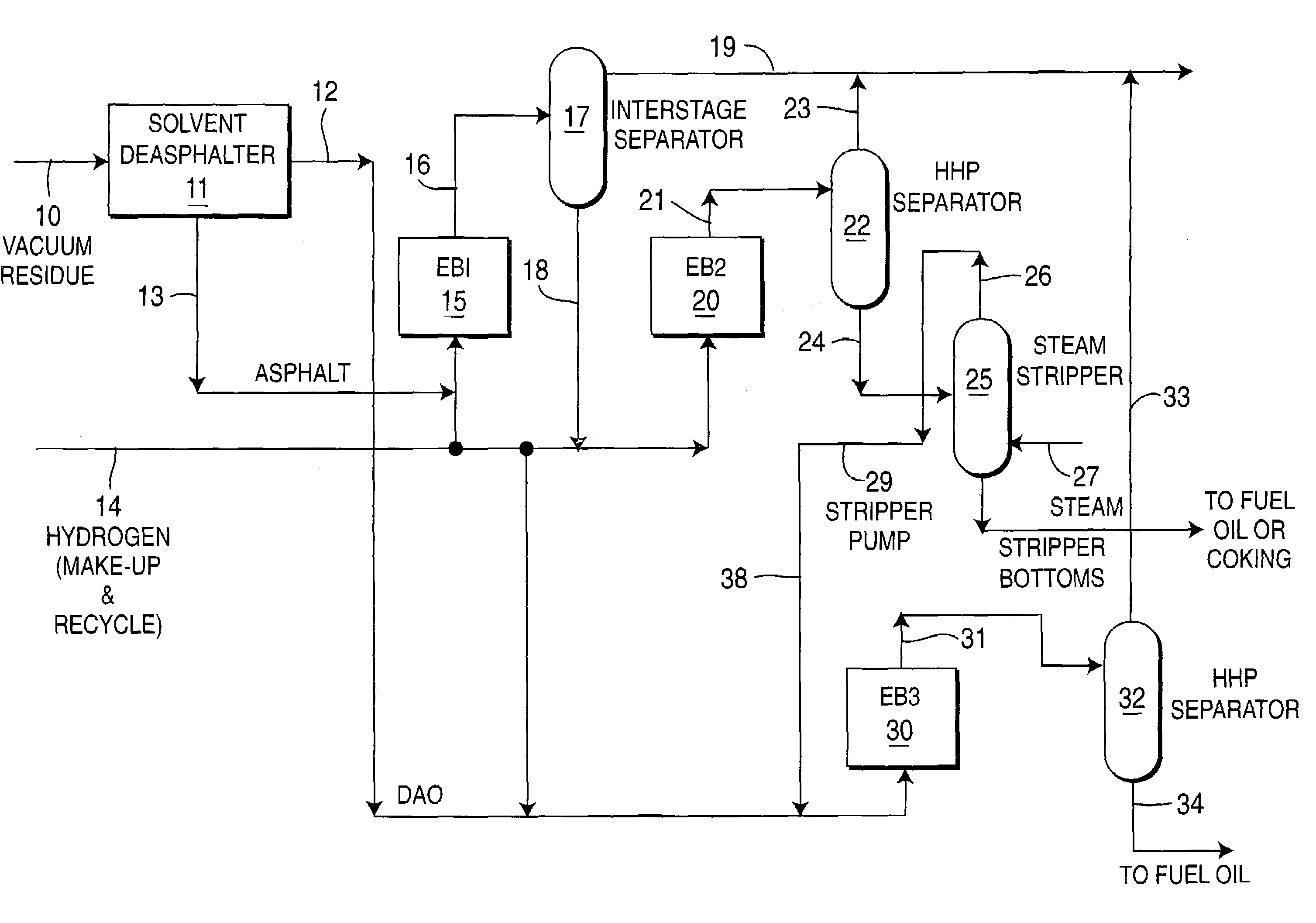
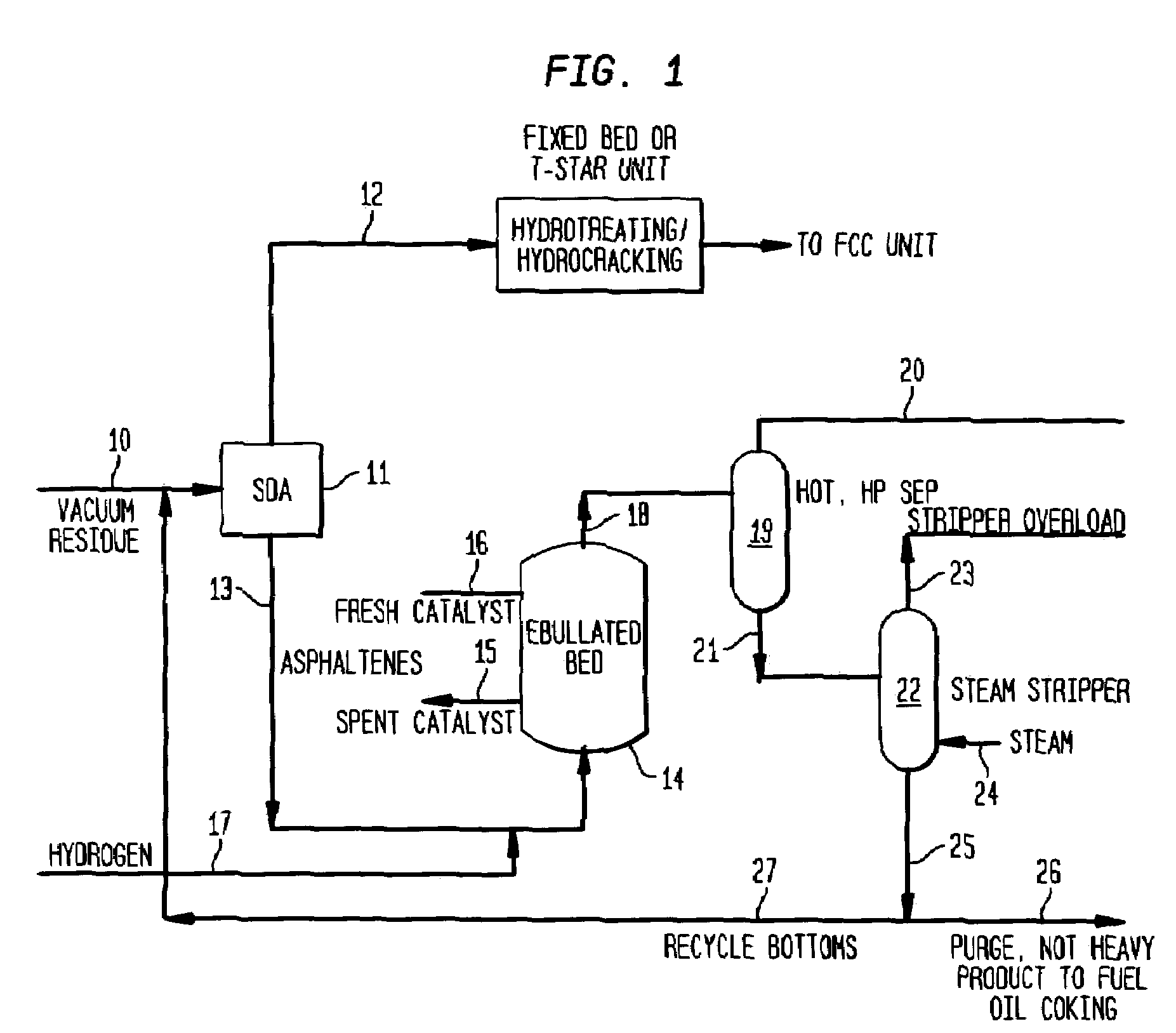
Integrated SDA and ebullated-bed process
ActiveUS7279090B2Wide pore catalystMost efficientTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel stages onlyBiochemical engineeringFixed bed
This invention relates to a novel integrated method for economically processing vacuum residue from heavy crude oils. This is accomplished by utilizing a solvent deasphalter (SDA) in the first step of the process with a C3 / C4 / C5 solvent such that the DAO product can thereafter be processed in a classic fixed-bed hydrotreater or hydrocracker. The SDA feed also includes recycled stripper bottoms containing unconverted residue / asphaltenes from a downstream steam stripper unit.The asphaltenes from the SDA are sent to an ebullated-bed reactor for conversion of the residue and asphaltenes. Residue conversion in the range of 60-80% is achieved and asphaltene conversion is in the range of 50-70%. The overall residue conversion, with the DAO product considered non-residue, is in the range of 80 W %-90 W % and significantly higher than could be achieved without utilizing the present invention.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for producing synthetic naphtha fuel and synthetic naphtha fuel produced by that process
InactiveUS6475375B1Treatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel stages onlyNaphthaEngineering
The invention provides a process for the production of a synthetic naphtha fuel suitable for use in compression ignition (CI) engines, the process including at least the steps of hydrotreating at least a fraction of a Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis reaction product of CO and H2, or a derivative thereof, hydrocracking at least a fraction of the FT synthesis product or a derivative thereof, and fractionating the process products to obtain a desired synthetic naphtha fuel characteristic. The invention also provides a synthetic naphtha fuel made by the process as well as a fuel composition and a Cloud Point depressant for a diesel containg fuel composition, said fuel composition and said depressant including the synthetic naphtha of the invention.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD +1
Process for upgrading heavy oil using a highly active slurry catalyst composition
ActiveUS20070138057A1Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyHydrogenSlurry reactor
The instant invention is directed to a new residuum full hydroconversion slurry reactor system that allows the catalyst, unconverted oil and converted oil to circulate in a continuous mixture throughout an entire reactor with no confinement of the mixture. The mixture is partially separated in between the reactors to remove only the products and hydrogen, while permitting the unconverted oil and the slurry catalyst to continue on into the next sequential reactor where a portion of the unconverted oil is converted to lower boiling point hydrocarbons, once again creating a mixture of unconverted oil, converted oil, and slurry catalyst. Further hydroprocessing may occur in additional reactors, fully converting the oil. The oil may alternately be partially converted, leaving a highly concentrated catalyst in unconverted oil which can be recycled directly to the first reactor.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Integrated hydroprocessing and fluid catalytic cracking for processing of a crude oil
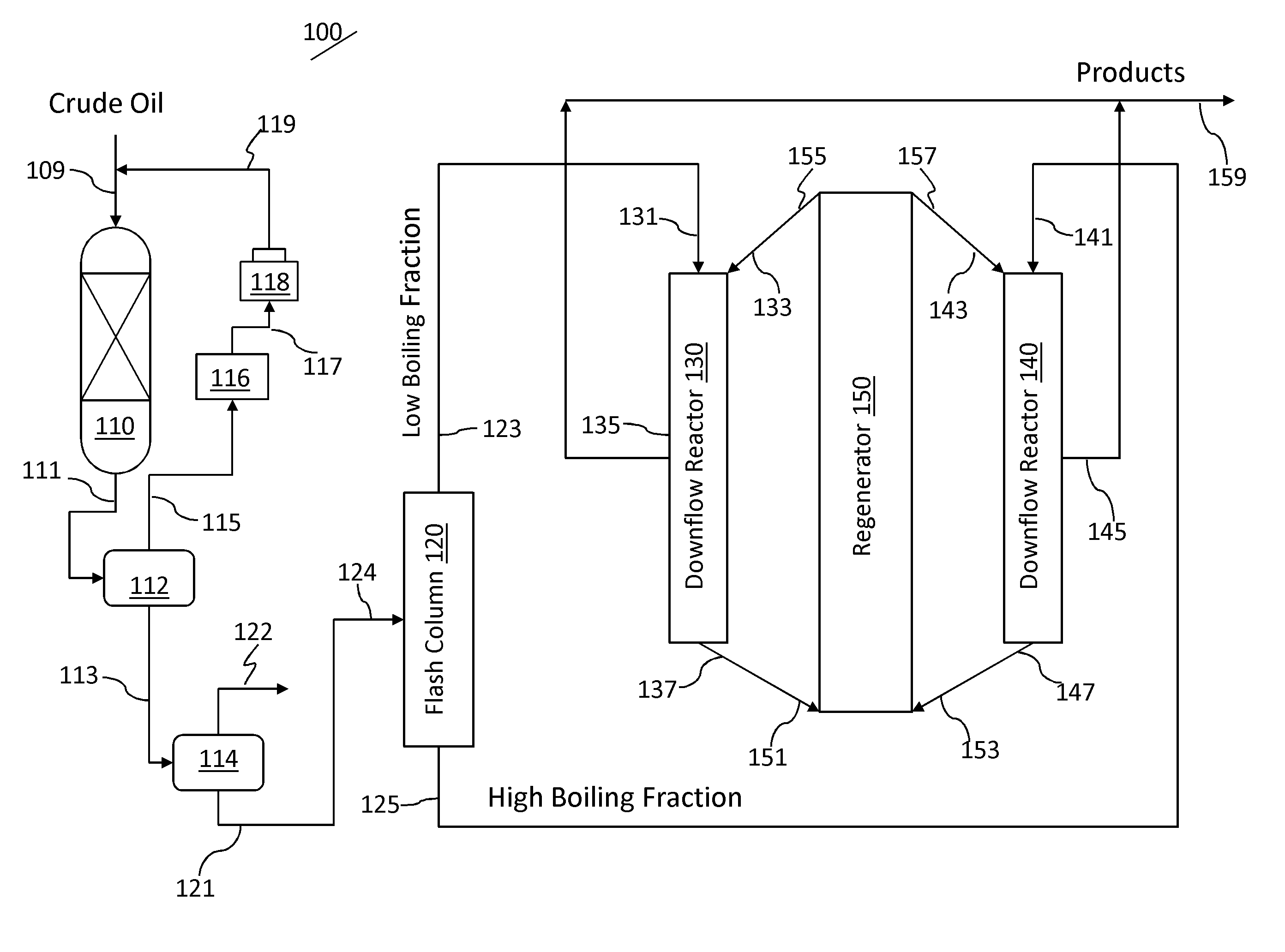
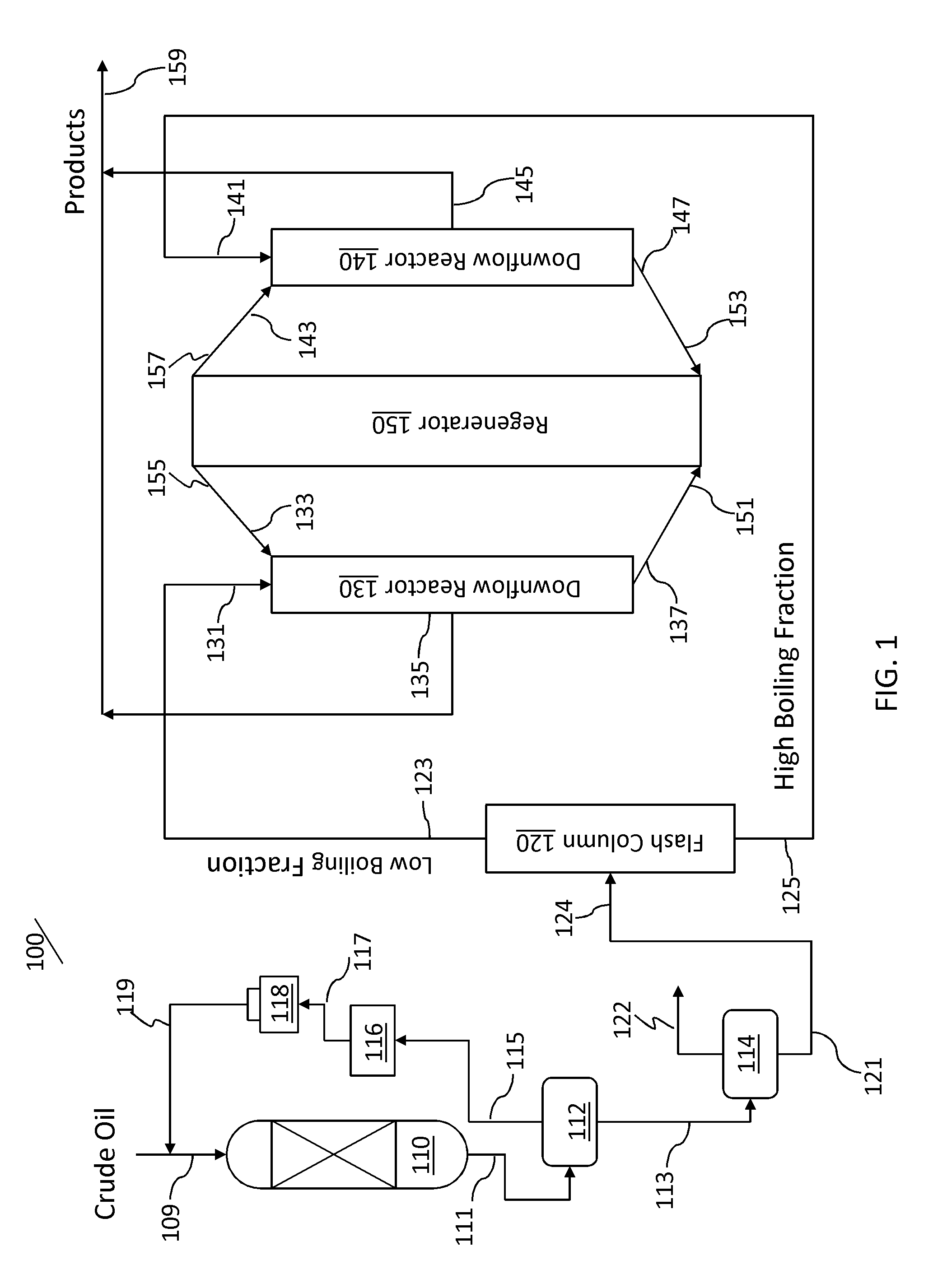
ActiveUS9096806B2Catalytic crackingTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyHydrogenBoiling point
An integrated hydroprocessing and fluid catalytic cracking process is provided for the direct processing of a crude oil to produce olefinic and aromatic petrochemicals. Crude oil and hydrogen are charged to a hydroprocessing zone operating under conditions effective to produce a hydroprocessed effluent having a reduced content of contaminants, an increased paraffinicity, reduced Bureau of Mines Correlation Index, and an increased American Petroleum Institute gravity. The hydroprocessed effluent is separated into a low boiling fraction and a high boiling fraction. The low boiling fraction is cracked in a first downflow reactor of a fluid catalytic cracking unit in the presence of a predetermined amount of catalyst to produce cracked products and spent catalyst, and the high boiling fraction is cracked in a second downflow reactor of the fluid catalytic cracking unit in the presence of a predetermined amount of catalyst to produce cracked products and spent catalyst. Spent catalyst from both the first and second downflow reactors are regenerated in a common regeneration zone, and first and second cracked product streams are recovered.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
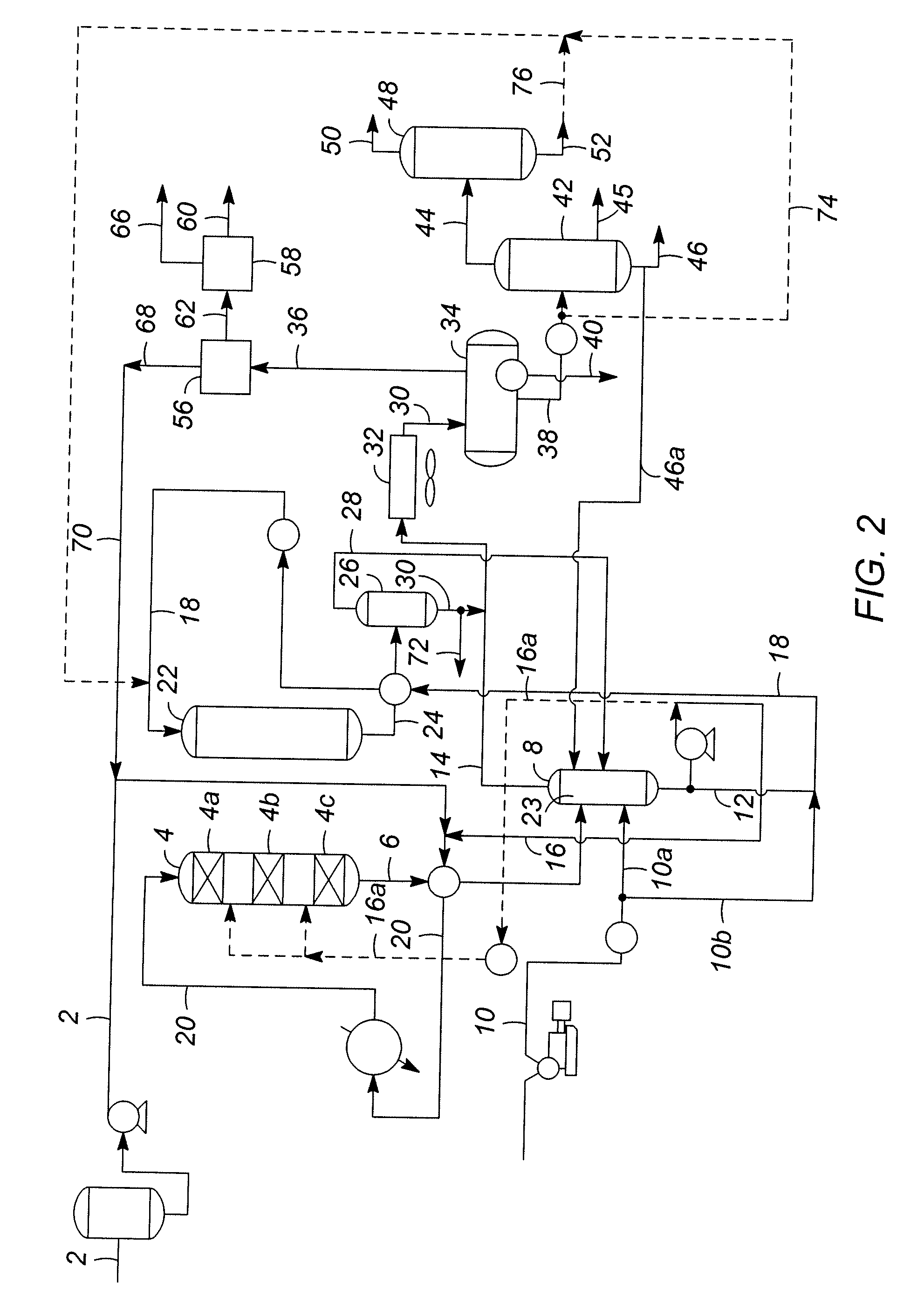
Deep desulfurization method for catalytically cracked gasoline
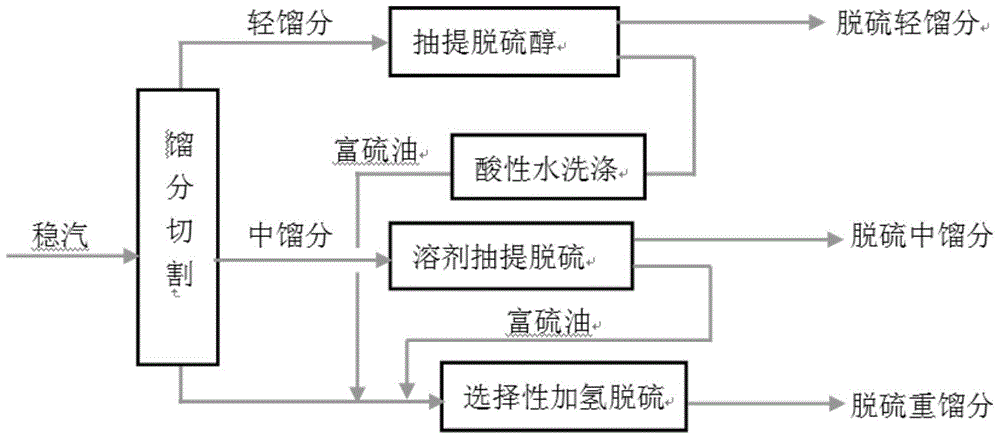
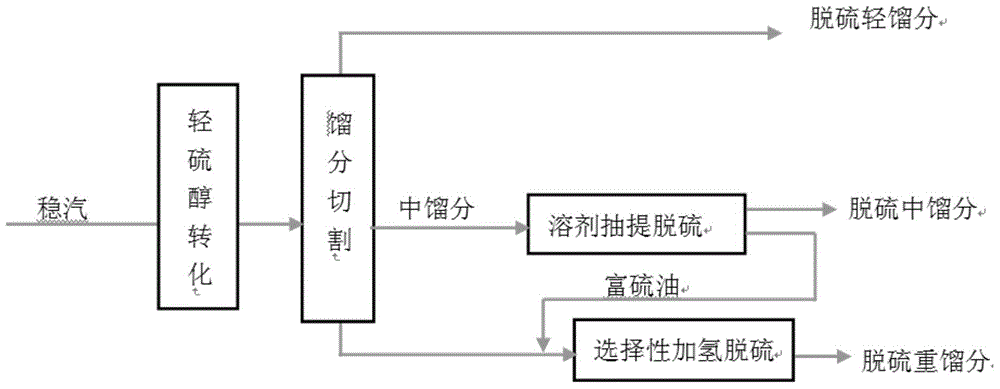
ActiveCN103555359AWide applicabilityReduce sulfur contentTreatment with plural parallel refining stagesTreatment with hydrotreatment processesSulfurGasoline
The invention provides a gasoline fraction solvent extraction desulfurization method comprising the steps of enabling a gasoline fraction to enter from the lower middle part of an extraction tower, enabling a solvent to enter from the top of the extraction tower, filling saturated C5 into a reflux device at the bottom of the extraction tower, controlling the temperature of the top of the extraction tower at 55-100 DEG C, the temperature of the bottom of the extraction tower at 40-80 DEG C, the pressure of the top of the extraction tower at 0.2-0.7MPa, the solvent to gasoline fraction ratio at 1.0-5.0 and the saturated C5 to gasoline fraction feeding ratio at 0.1-0.5, ejecting the extracted and desulfurized gasoline fraction out of the extraction tower, and washing to obtain a desulfurized gasoline fraction; discharging the solvent from the bottom of the extraction tower, separating a C5-contained light component, a sulfur-rich component, water and the solvent, returning the light component to the reflux device of the extraction tower, returning the water to the washing step, and returning the solvent to the top of the extraction tower, wherein sulfides, aromatic hydrocarbons and the C5 are extracted by the solvent. The invention also provides a deep desulfurization method for catalytically cracked gasoline. The solvent extraction desulfurization method is flexibly combined with the traditional desulfurization technology used by an enterprise, so that the deep desulfurization is realized, and meanwhile, the octane value loss of the gasoline fraction is remarkably reduced.
Owner:HEBEI REFINING TECH CO LTD
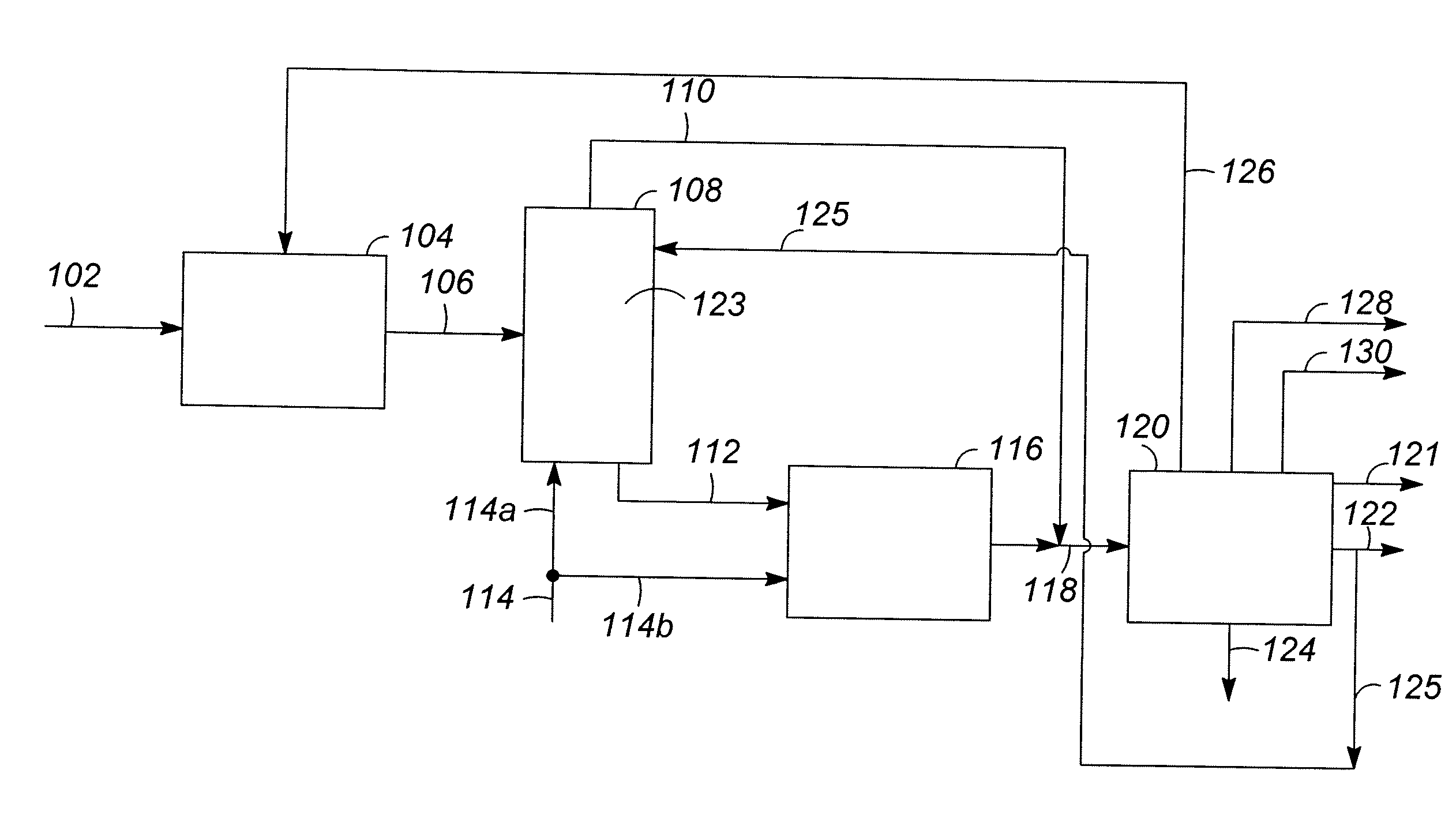
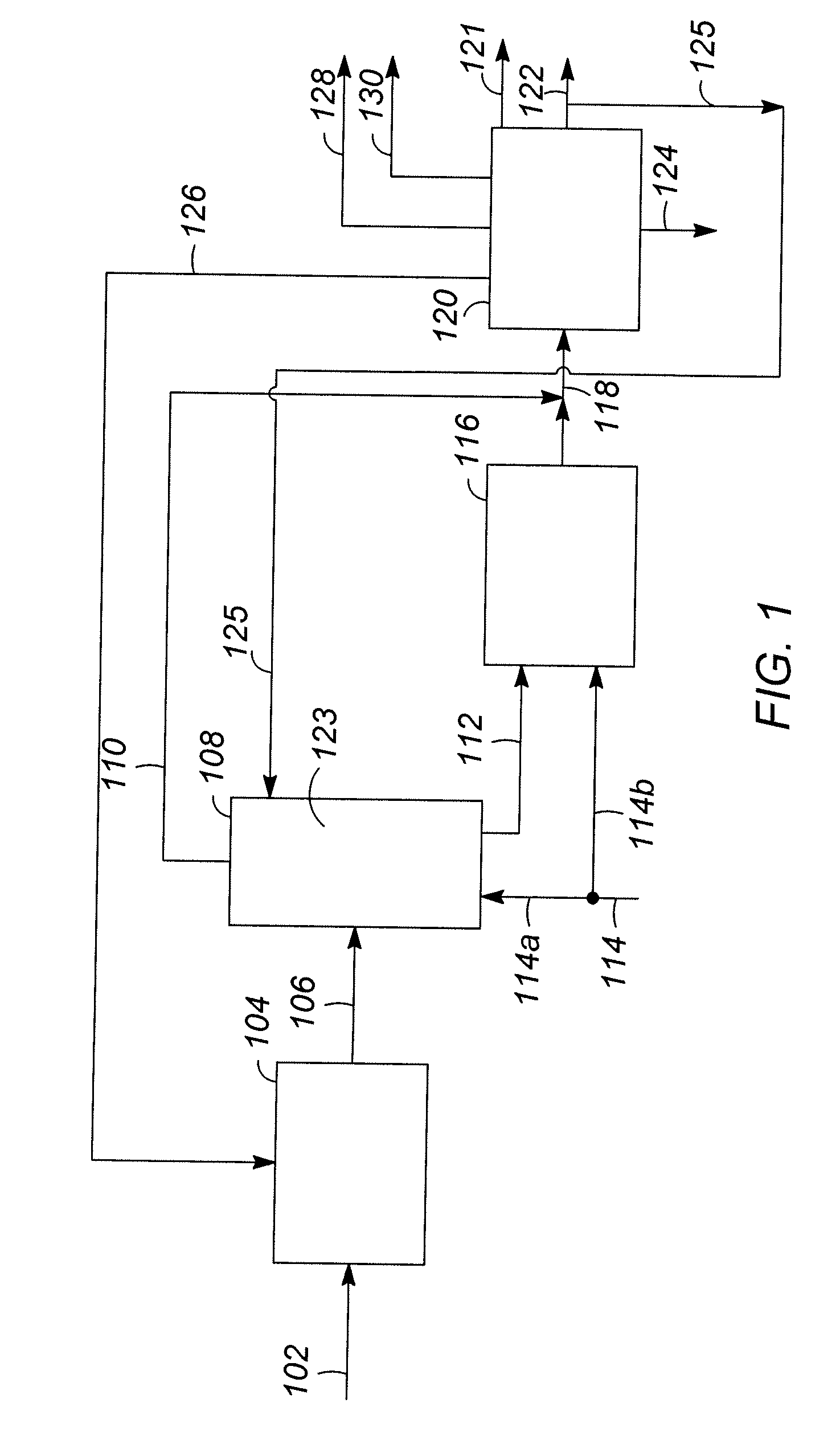
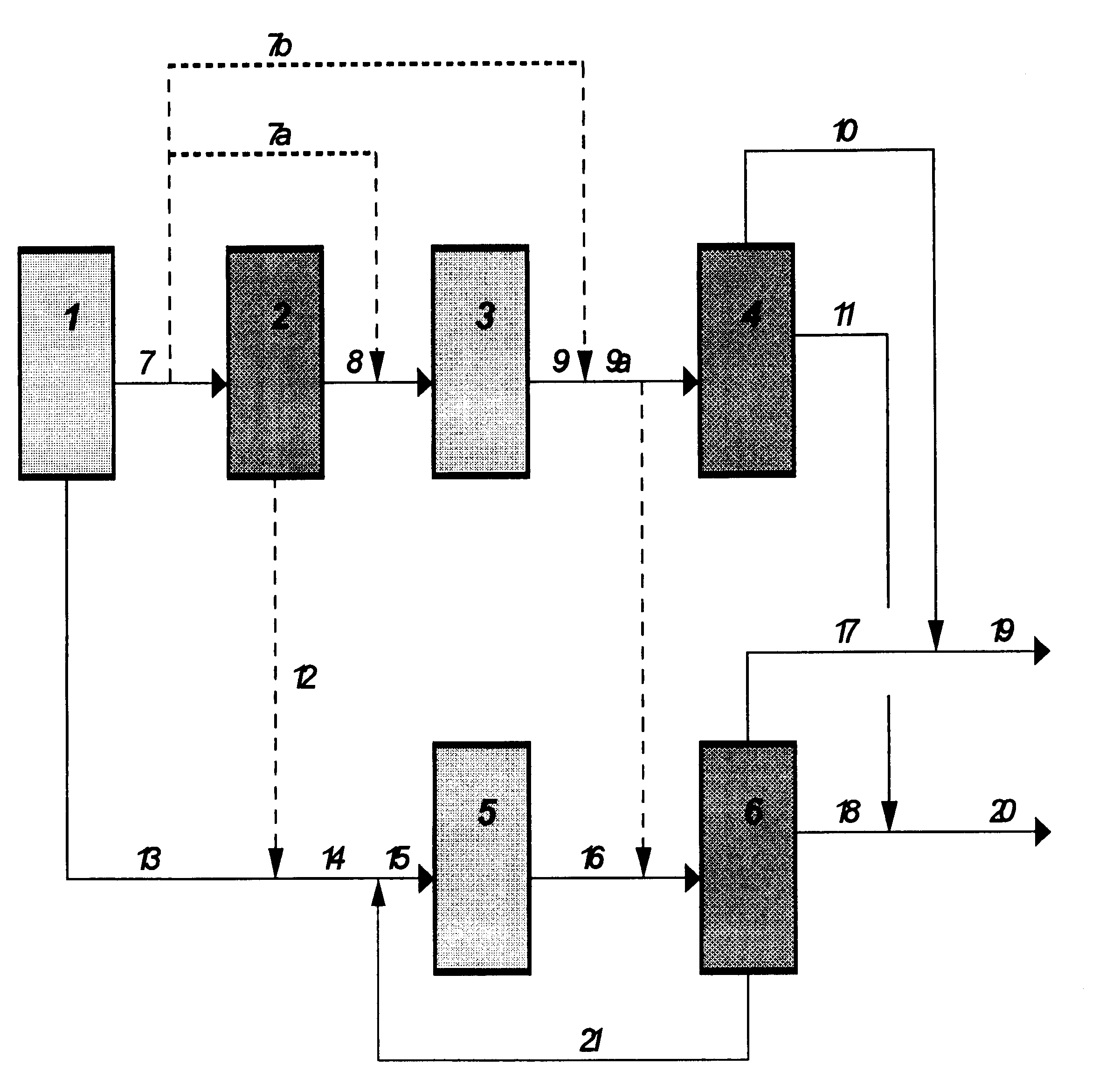
Integrated in-line pretreatment and heavy oil upgrading process
ActiveUS7431831B2Lower capital expenditureImprove product qualityTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyContinuous reactorSlurry reactor
A new residuum full hydroconversion slurry reactor system has been developed that allows the catalyst, unconverted oil, products and hydrogen to circulate in a continuous mixture throughout an entire reactor with no confinement of the mixture. The mixture is partially separated in between the reactors to remove only the products and hydrogen while permitting the unconverted oil and the slurry catalyst to continue on into the next sequential reactor. In the next reactor, a portion of the unconverted oil is converted to lower boiling point hydrocarbons, once again creating a mixture of unconverted oil, products, hydrogen and slurry catalyst. Further hydroprocessing may occur in additional reactors, fully converting the oil. The oil may alternately be partially converted, leaving a highly concentrated catalyst in unconverted oil which can be recycled directly to the first reactor. The slurry reactor system is, in this invention, preceded by an in-line pretreating step, such as hydrotreating or deasphalting. Following the slurry reactor system, fully converted oil may be subsequently hydrofinished for the removal of hetoroatoms such as sulfur and nitrogen.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
System for upgrading of heavy hydrocarbons
Systems and methods for processing one or more hydrocarbons are provided. One or more hydrocarbons can be selectively separated to provide one or more heavy deasphalted oils. At least a portion of the heavy deasphalted oil can be cracked using a fluidized catalytic cracker to provide one or more lighter hydrocarbon products.
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
Integrated desulfurization and denitrification process including mild hydrotreating of aromatic-lean fraction and oxidation of aromatic-rich fraction
ActiveUS20120152804A1Improve overall utilizationCost-effective processTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyRefining with oxygen compoundsNitrogenOrganonitrogen compounds
Deep desulfurization of hydrocarbon feeds containing undesired organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds to produce a hydrocarbon product having low levels of sulfur-containing and nitrogen-containing compounds, is achieved by first subjecting the entire feed to an extraction zone to separate an aromatic-rich fraction containing a substantial amount of the refractory organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds and an aromatic-lean fraction containing a substantial amount of the labile organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds. The aromatic-lean fraction is contacted with a hydrotreating catalyst in a hydrotreating reaction zone operating under mild conditions to convert the labile organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds. The aromatic-rich fraction is oxidized to convert the refractory organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds to oxidized organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds. These oxidized organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds are subsequently removed, producing a stream containing reduced levels of organosulfur and organonitrogen compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method for jointly producing propylene and petrol from a relatively heavy charge
ActiveUS7374662B2Increase in severityReaction can be limitedCatalytic crackingOrganic chemistry methodsOligomerFluidized bed
A process for conversion of a hydrocarbon feedstock comprising a relatively heavy main feedstock with a boiling point above approximately 350° C., and a relatively light secondary feedstock with a boiling point below approximately 320° C., wherein,the main feedstock, representing at least 50 wt. % of the hydrocarbon feedstock, is cracked in a fluidized-bed reactor in the presence of a cracking catalyst,the secondary feedstock is cracked in a fluidized bed with the same cracking catalyst, separately or mixed with the main feedstock, said secondary feedstock comprising oligomers with at least 8 carbon atoms of light olefins with 4 and / or 5 carbon atoms.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
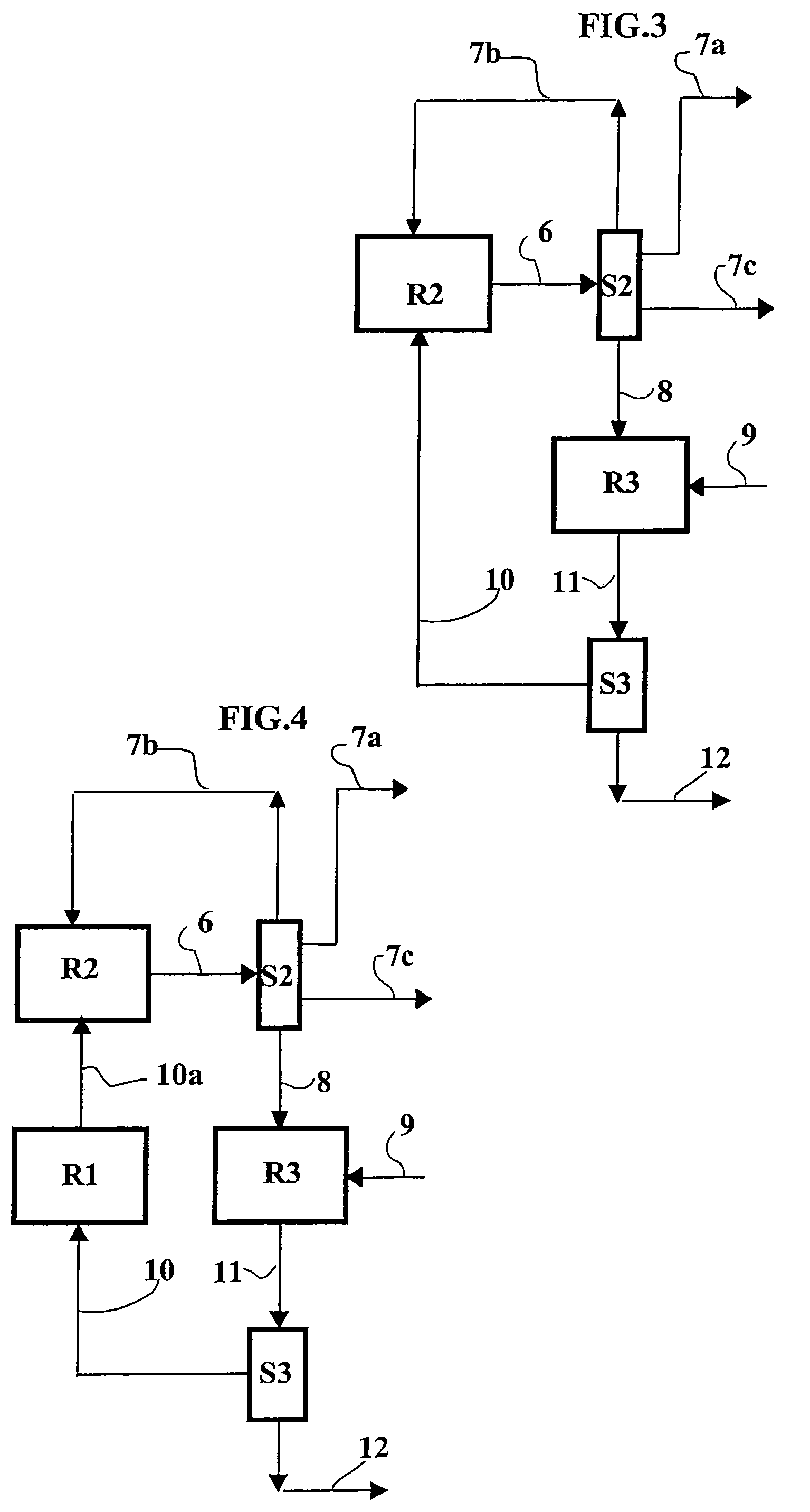
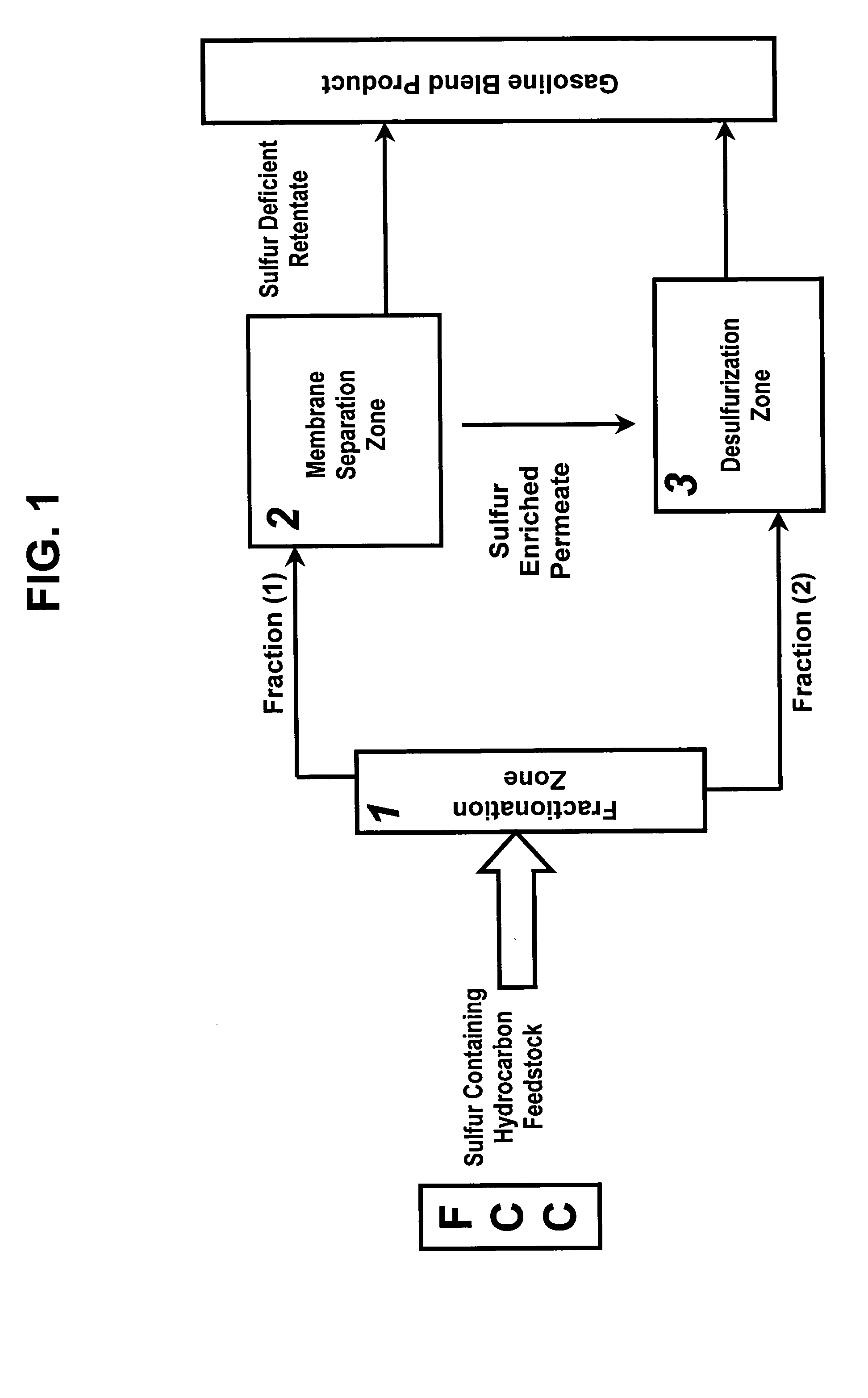
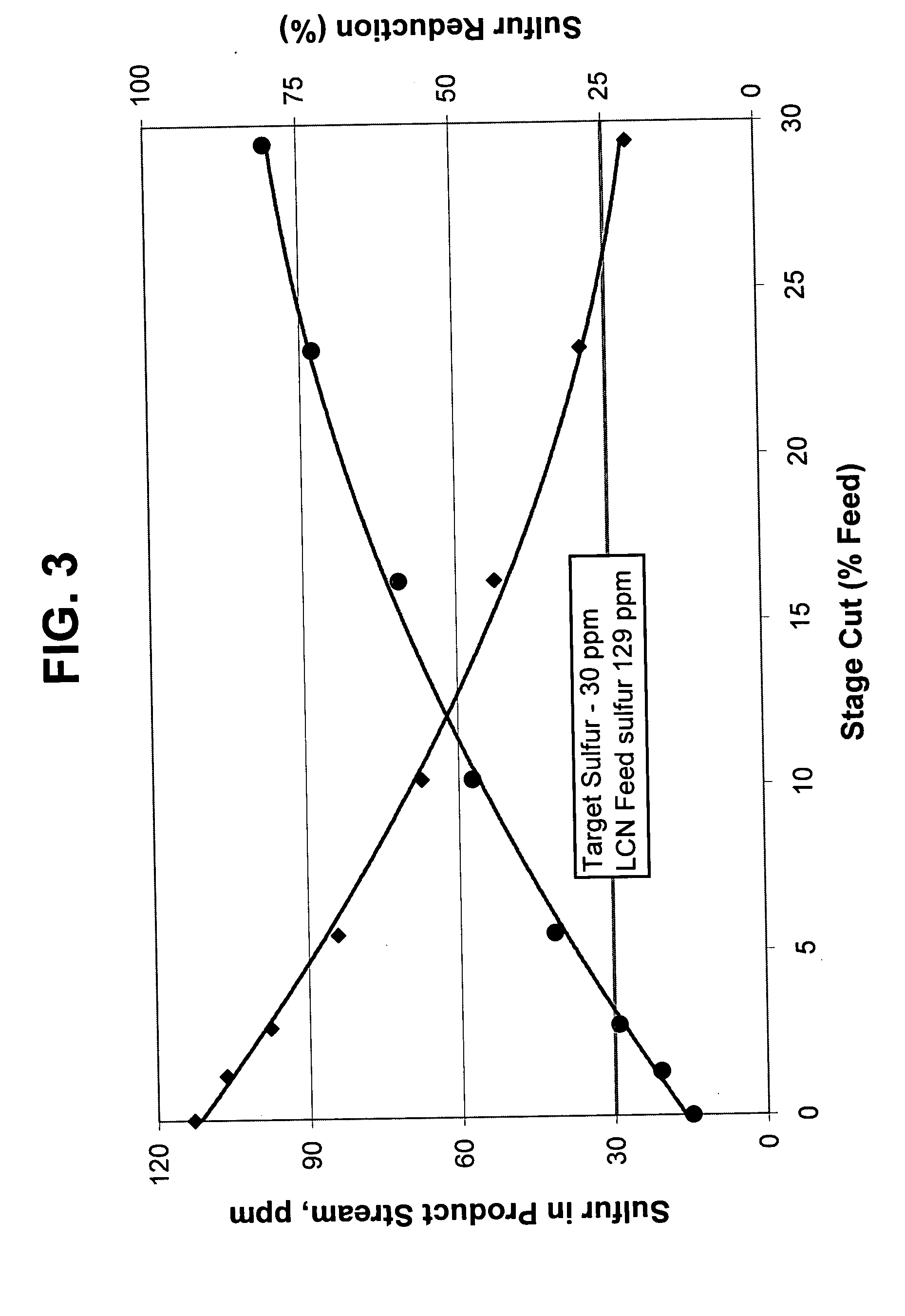
Method of reducing sulfur in hydrocarbon feedstock using a membrane separation zone
ActiveUS20050067323A1Reduce sulfur contentEasy to operateTreatment with plural serial refining stagesTreatment with plural parallel refining stagesNaphthaHydrodesulfurization
A membrane is used in combination with fractionation and hydrodesulfurization to reduce the sulfur content of hydrocarbon feeds, preferably sulfur-containing naphtha feeds. A membrane separation zone is employed to treat a fraction of effluent from a fractionation zone containing sulfur-containing non-aromatic hydrocarbons to produce a sulfur rich permeate and sulfur deficient retentate. The sulfur rich permeate and a second fraction of the fractionation zone, which contains sulfur-containing aromatic hydrocarbons, are further treated in a hydrodesulfurization zone. The stream from the hydrodesulfurization zone and the sulfur deficient retentate from the membrane separation zone are then processed as low sulfur hydrocarbon streams, especially those streams being processed in the manufacture of gasoline when the initial hydrocarbon stream is naphtha from a fluidized catalytic cracking unit.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
Method for adjusting the high heating value of gas in the LNG chain
The subject of the invention is a method for treating a natural gas containing ethane, comprising the following stages: (a) extraction of at least one part of the ethane from the natural gas; (b) reforming of at least one part of the extracted ethane into a synthesis gas; (c) methanation of the synthesis gas into a methane-rich gas; and (d) mixing of the methane-rich gas with the natural gas. Installation for implementing this method.
Owner:TOTAL PUTEAUX FR
Catalytic cracking process for the production of diesel from vegetal oils
ActiveUS20070007176A1Increase cetane numberCatalytic crackingCatalytic naphtha reformingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesTransesterification
The present invention comprises a thermo catalytic process to produce diesel oil from vegetal oils, in refineries which have two or more Catalytic Cracking (FCC) reactors. At least one reactor processes heavy gasoleum or residue in conventional operation conditions while at least one reactor processes vegetal oils in proper operation conditions to produce diesel oil. This process employs the same catalyst employed in the FCC process, which processes conventional feedstocks simultaneously. This process transforms high heat content raw materials into fuel hydrocarbons. It shows excellent efficiency for the obtention of highly pure products and do not yield glycerin, one by-product of the transesterification process. The diesel oil produced by said process presents quality superior and cetane number higher than 40. Once cracking reactions occur at lower temperatures, it forms less oxidized product, which is consequently purer than those obtained by existent technology are.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Integrated heavy oil upgrading process and in-line hydrofinishing process
ActiveUS7708877B2Low viscosityTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlySlurry reactorBoiling point
A new residuum full hydroconversion slurry reactor system has been developed that allows the catalyst, unconverted oil and converted oil to circulate in a continuous mixture throughout an entire reactor with no confinement of the mixture. The mixture is partially separated in between the reactors to remove only the converted oil while permitting the unconverted oil and the slurry catalyst to continue on into the next sequential reactor where a portion of the unconverted oil is converted to lower boiling point hydrocarbons, once again creating a mixture of unconverted oil, converted oil, and slurry catalyst. Further hydroprocessing may occur in additional reactors, fully converting the oil. The oil may alternately be partially converted, leaving a highly concentrated catalyst in unconverted oil which can be recycled directly to the first reactor. Fully converted oil is subsequently hydrofinished for the nearly complete removal of hetoroatoms such as sulfur and nitrogen.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process and device to optimize the yield of fluid catalytic cracking products
ActiveUS20060021909A1Not compromise conventional stripping efficiencyCatalytic crackingTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyThermodynamicsPtru catalyst
A process and device to optimize the yield of fluid catalytic cracking products through a reactive stripping process are disclosed. One or more hydrocarbon streams (3) are introduced in an intermediary region of the stripper (1) of a fluid catalytic cracking unit (FCC), from a device that allows a homogeneous distribution with adequate dispersion. This / these stream(s) react(s) with the catalyst of FCC, although its activity is reduced due to the adsorption of hydrocarbons in the reaction zone, generating products that improve and / or change the global distribution of products, providing a refinery profile adequate to meet quality demands and requirements.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Process for benzene reduction and sulfur removal from FCC naphthas
InactiveUS20080116112A1Reduce saturationLess attentionTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyMolecular sieve catalystsAlkyl transferBenzene
A process for the removal of sulfur compounds and benzene of a catalytically cracked petroleum naphtha comprising benzene, organic sulfur compounds and olefins, by fractionating the cracked naphtha into a relatively low boiling range, olefinic, light catalytic naphtha (LCN) and an olefinic heavy catalytic naphtha (HCN) which boils above the range of the LCN the boiling ranges of the LCN and the HCN being defined by a cut point selected to maintain most of the benzene in the cracked naphtha in the LCN together with olefins in the boiling range of the LCN. The LCN is subjected to an optional non-hydrogenative desulfurization step followed by a fixed bed alkylation step in which the benzene in the LCN is alkylated with the olefins contained in this fraction. The HCN is treated by a similar an alkylation step using the olefins contained in this fraction to alkylate the sulfur compounds, forming alkylated products which boil above the gasoline boiling range. The LCN and HCN are then fractionated to remove light ends and higher boiling sulfur reaction products (disulfides, alkylated thiophenes) boiling above the gasoline boiling range.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
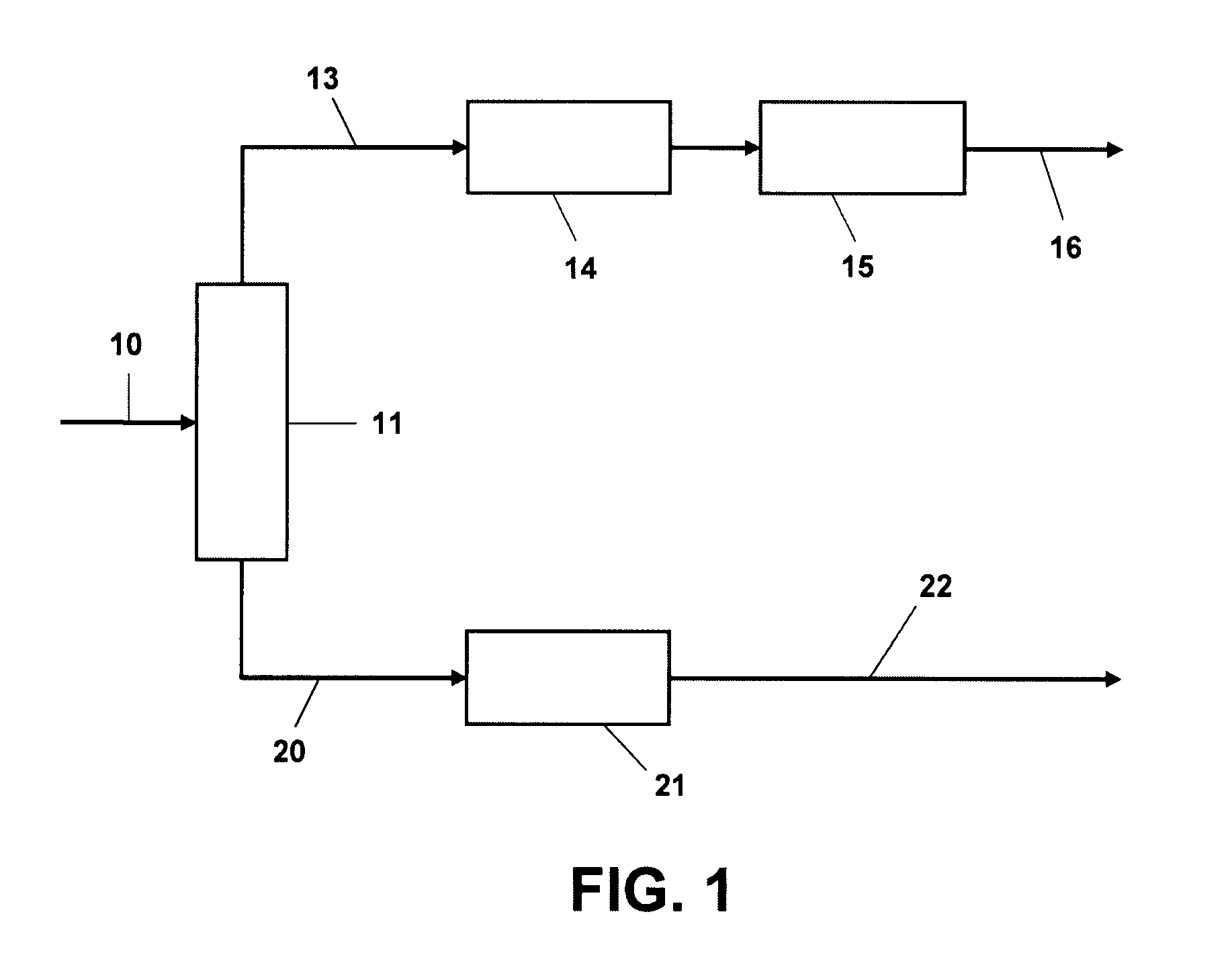
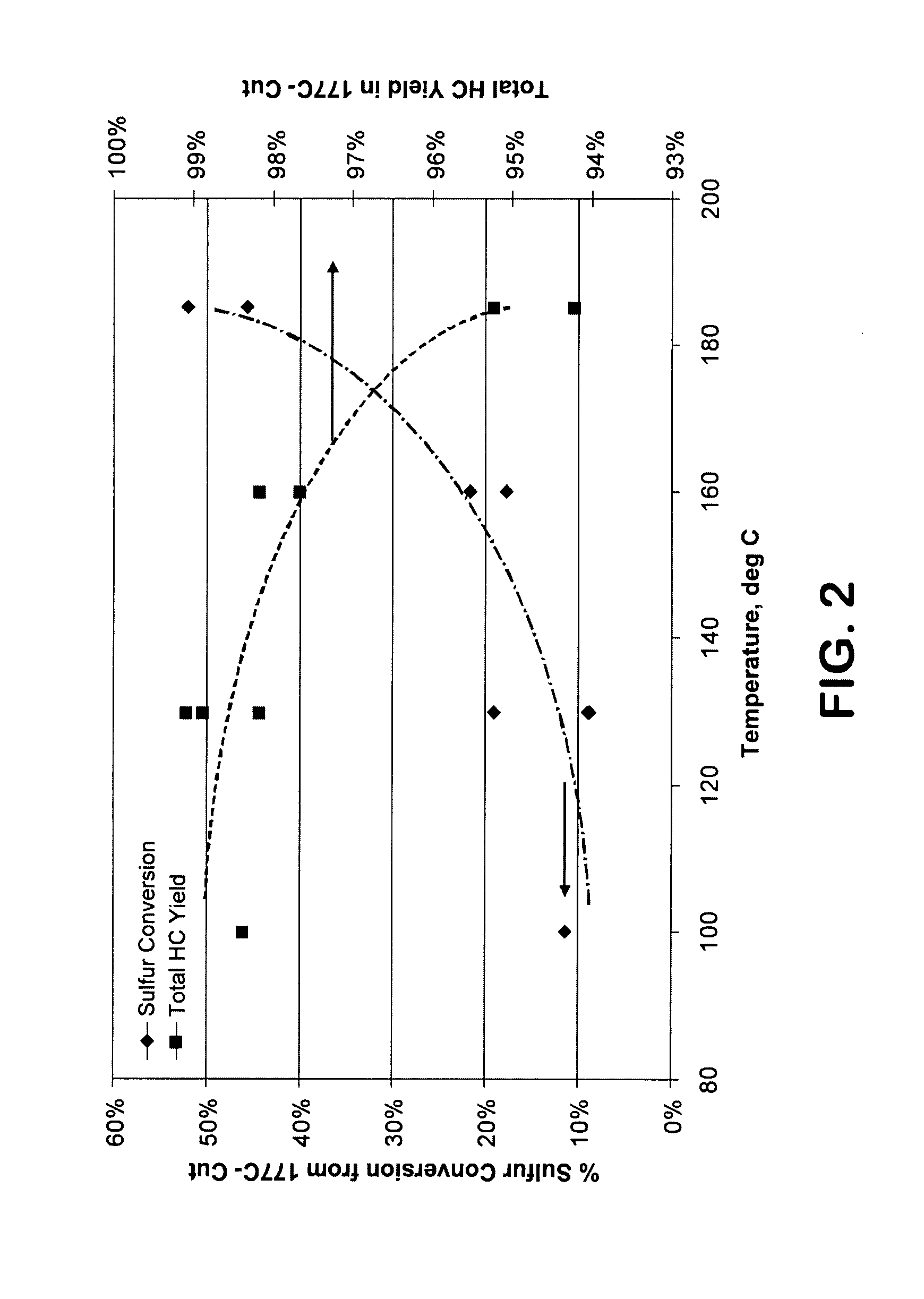
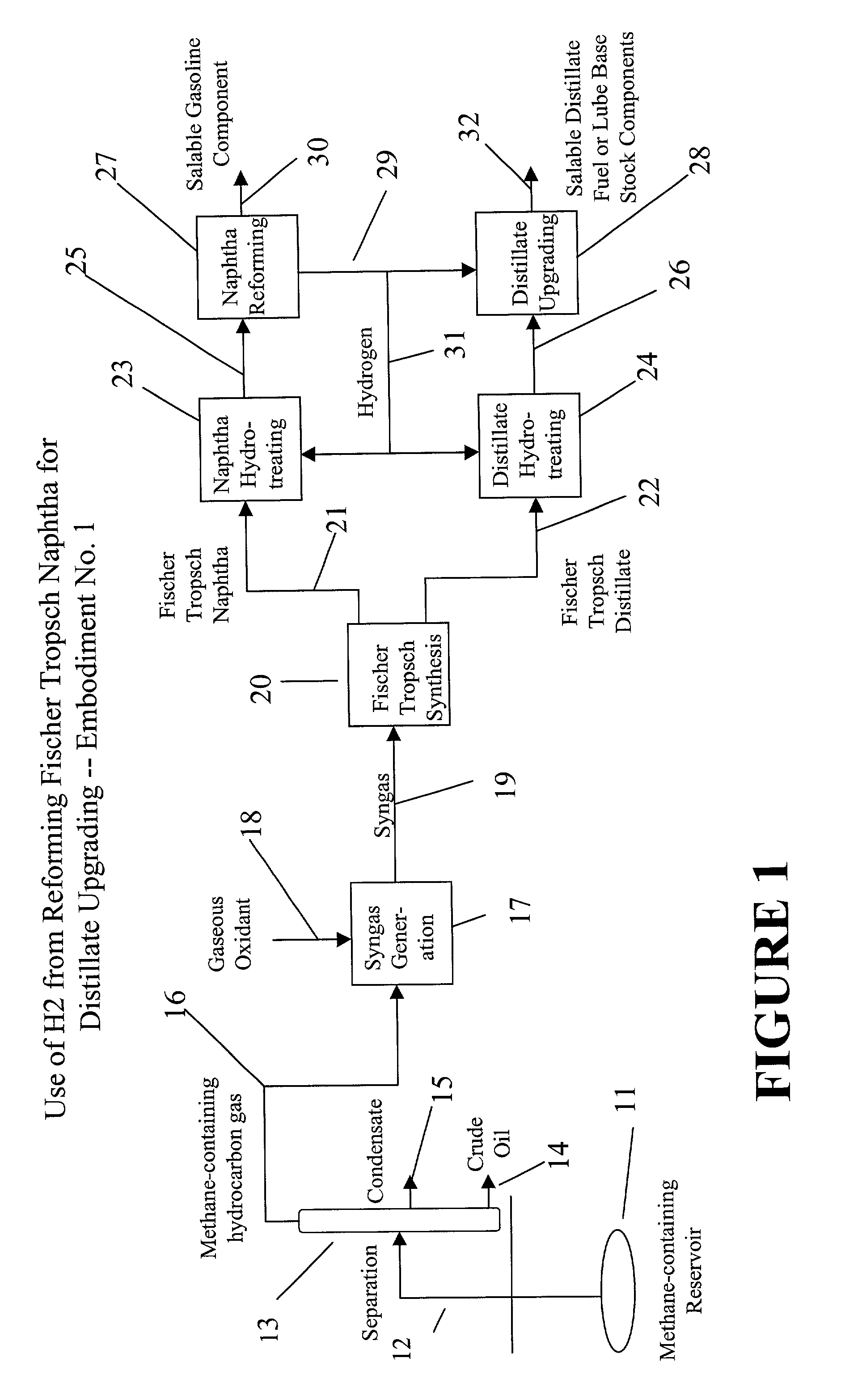
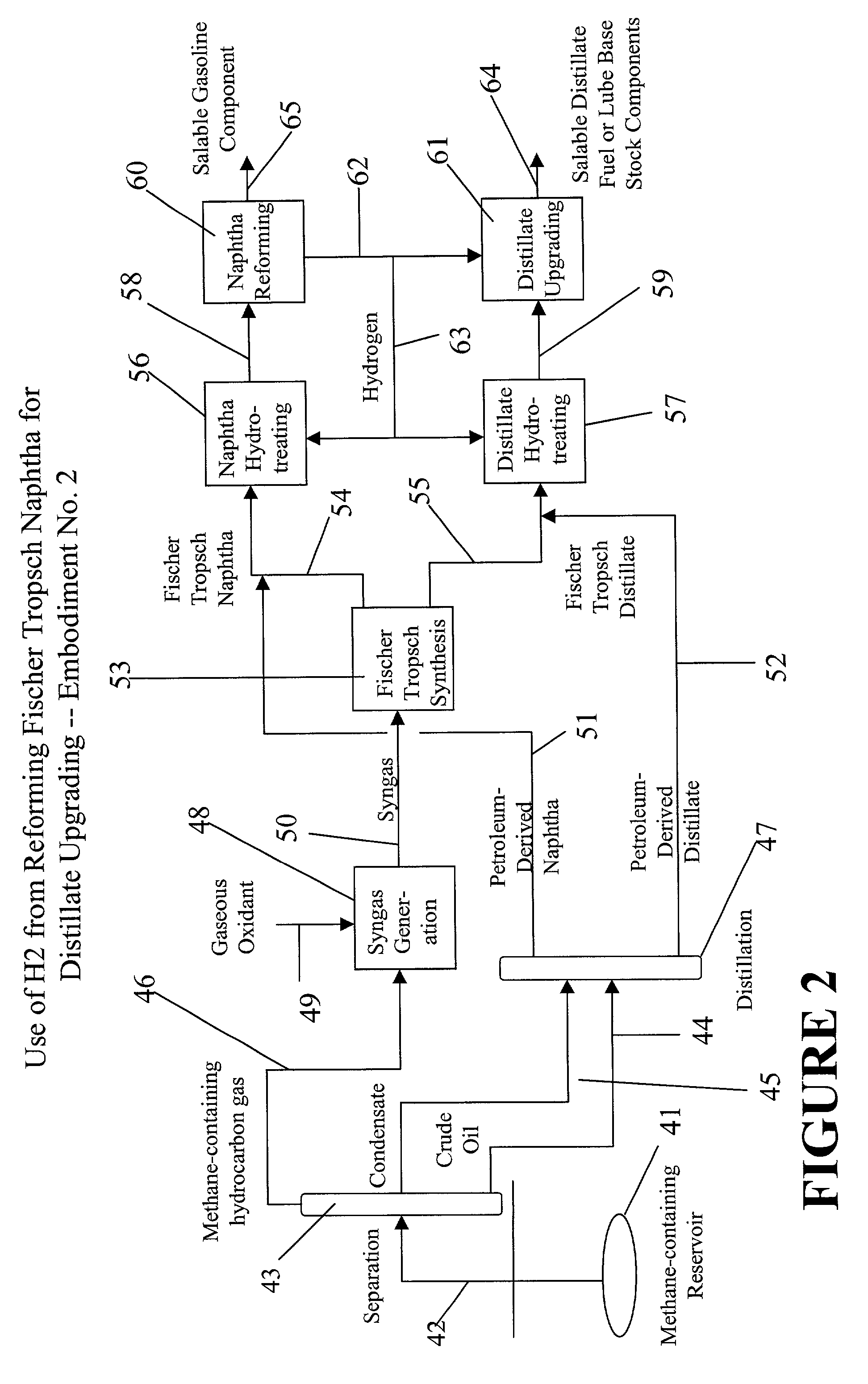
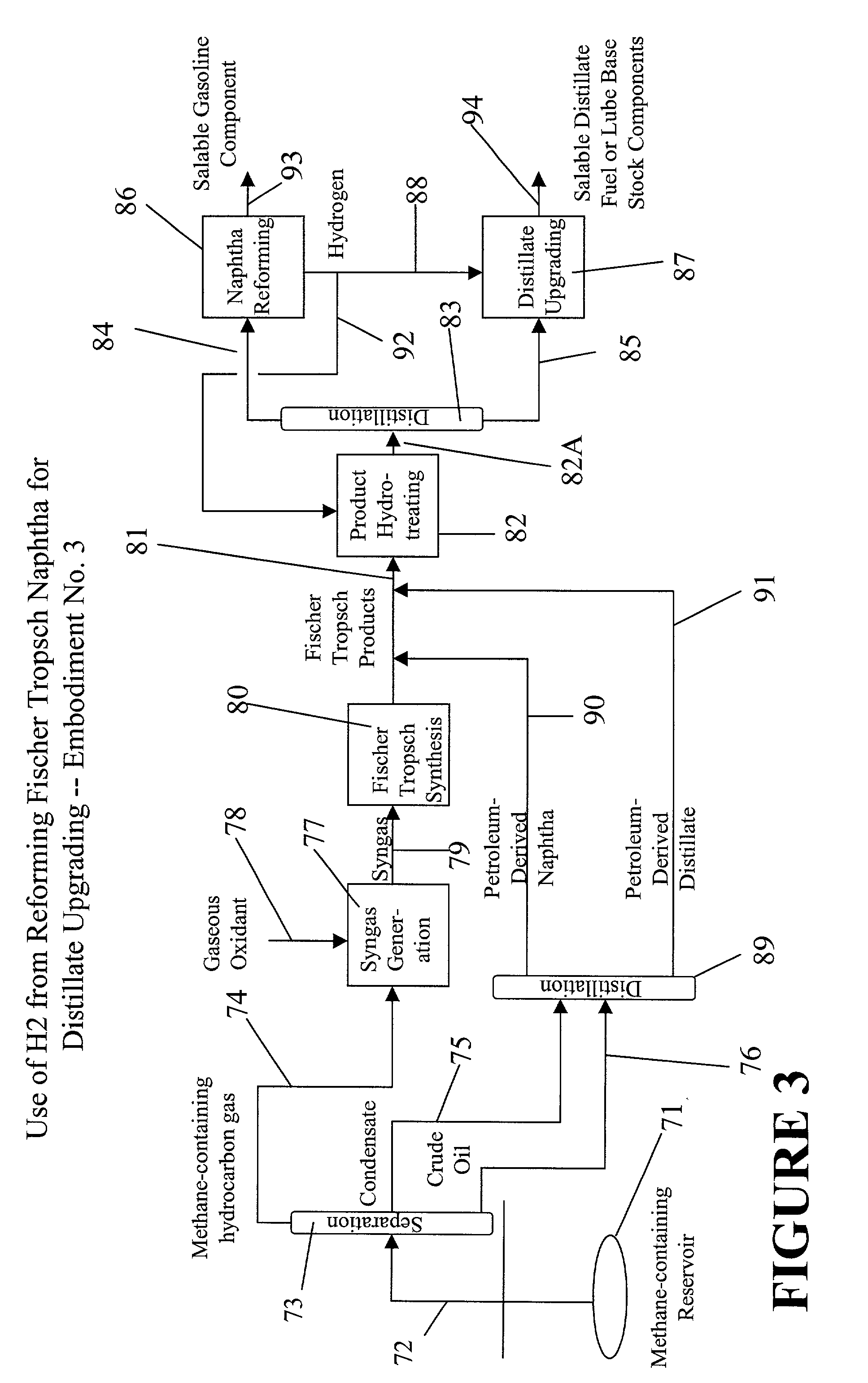
Upgrading fischer-tropsch and petroleum-derived naphthas and distillates
InactiveUS20030141220A1Inexpensively upgradedCheap offerTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel stages onlyHydrogenNaphtha
A process for upgrading at least one of a Fischer-Tropsch naphtha and a Fischer-Tropsch distillate to produce at least one of a gasoline component, a distillate fuel or a lube base feedstock component. The process includes reforming a Fischer-Tropsch naphtha to produce hydrogen by-product and a gasoline component with a research octane rating of at least about 80. The process further includes upgrading a Fischer-Tropsch distillate using the hydrogen by-product to produce a distillate fuel and / or a lube base feedstock component.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com