Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88results about "Power reduction by energy recovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
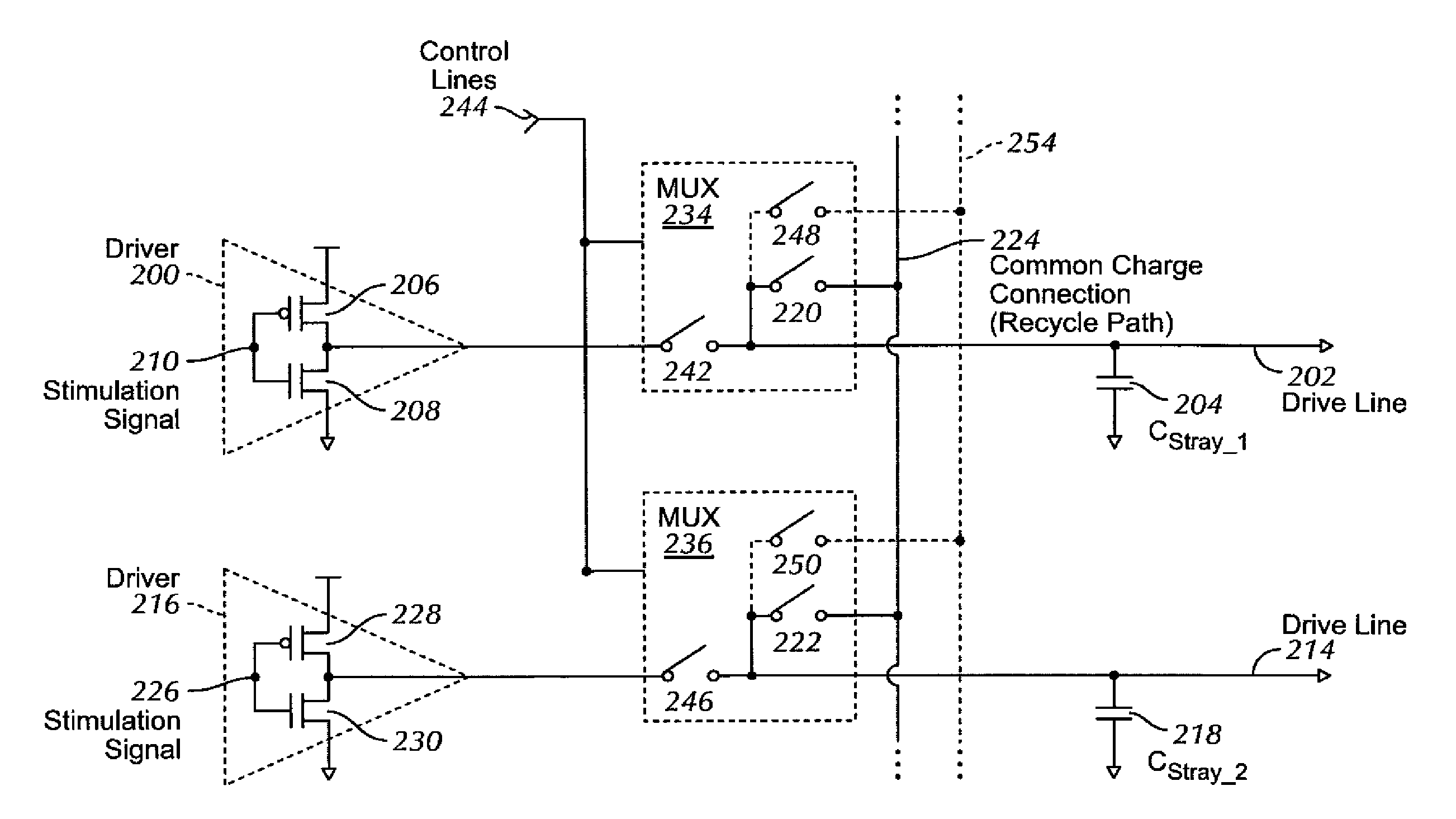
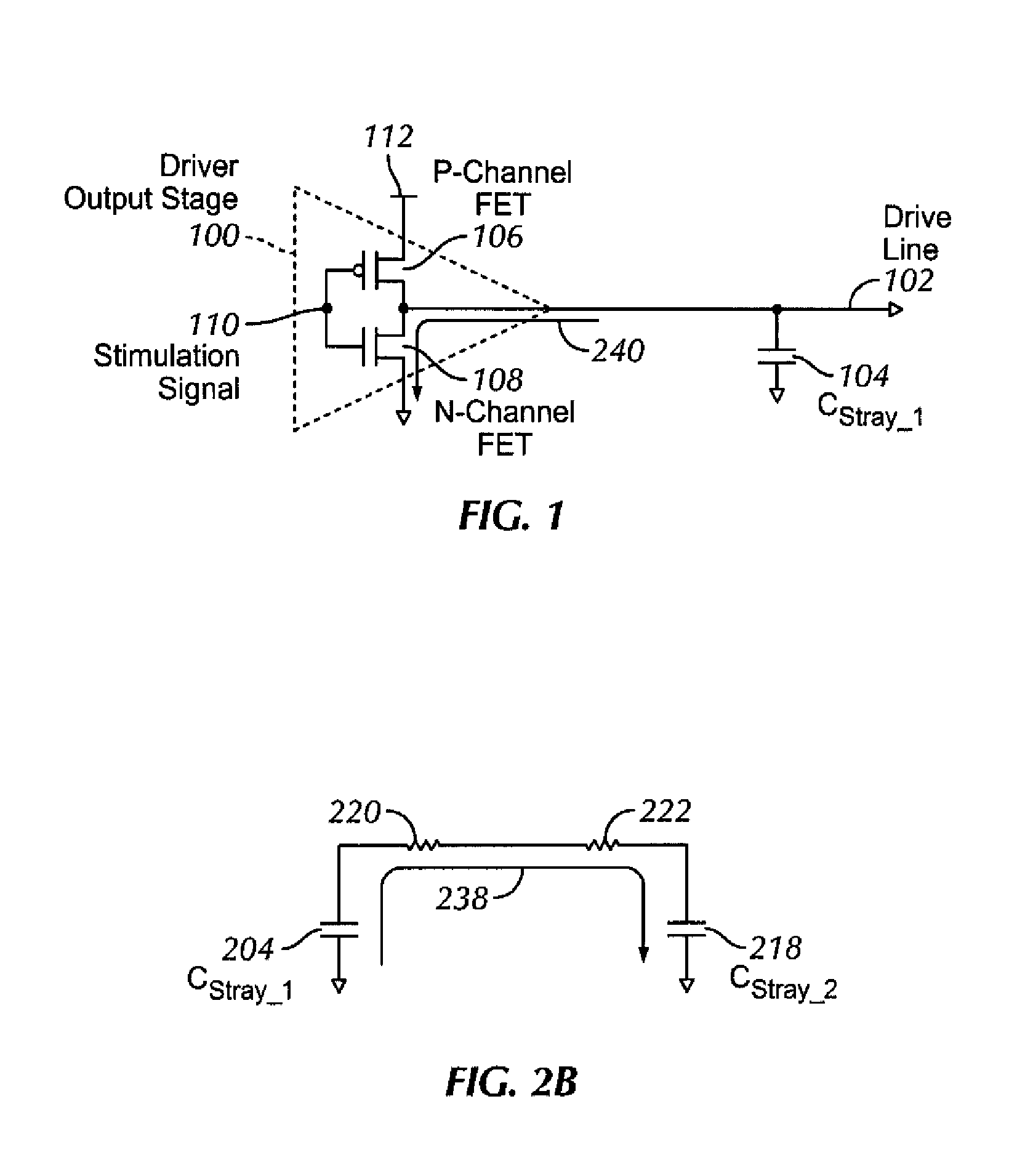
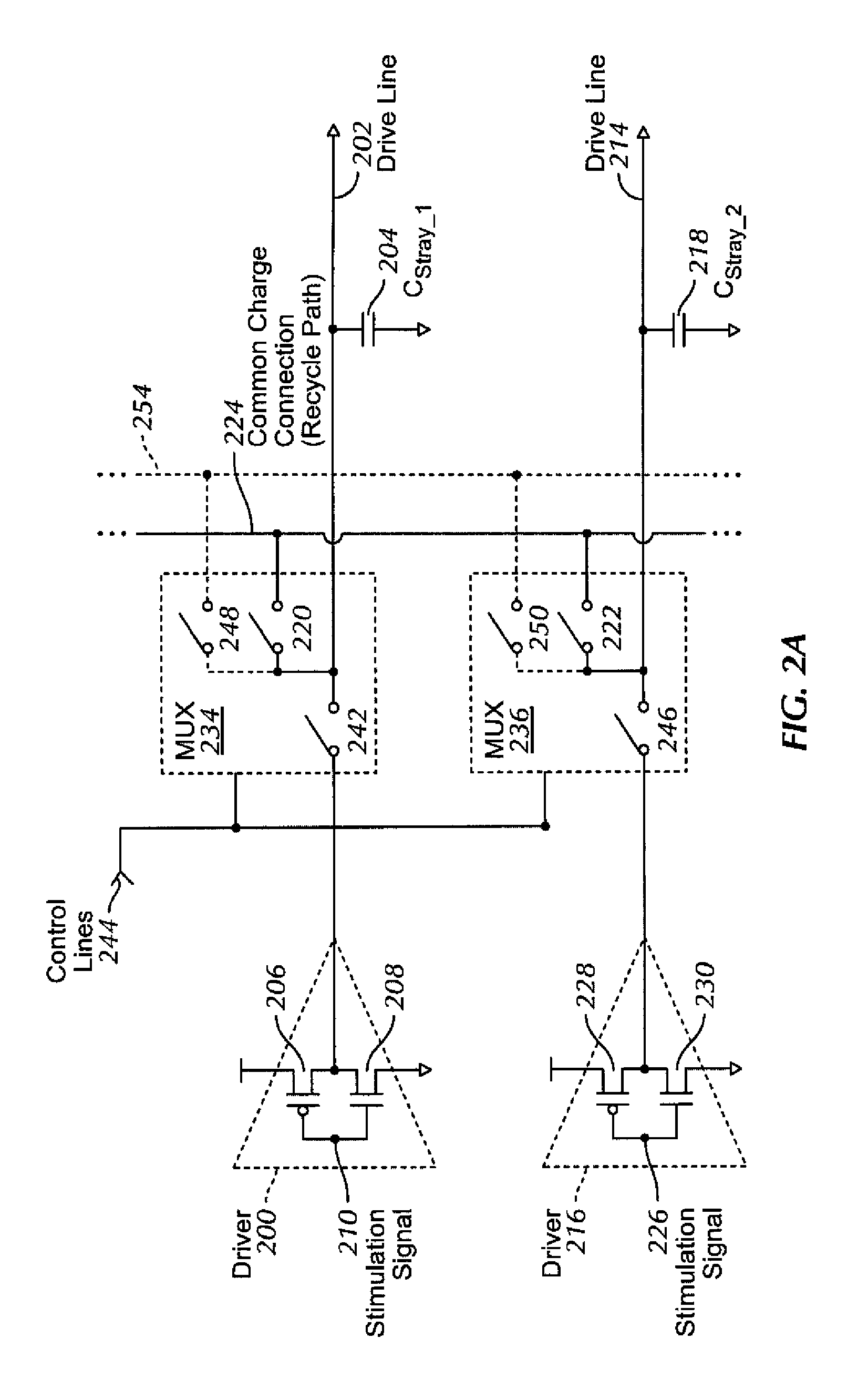
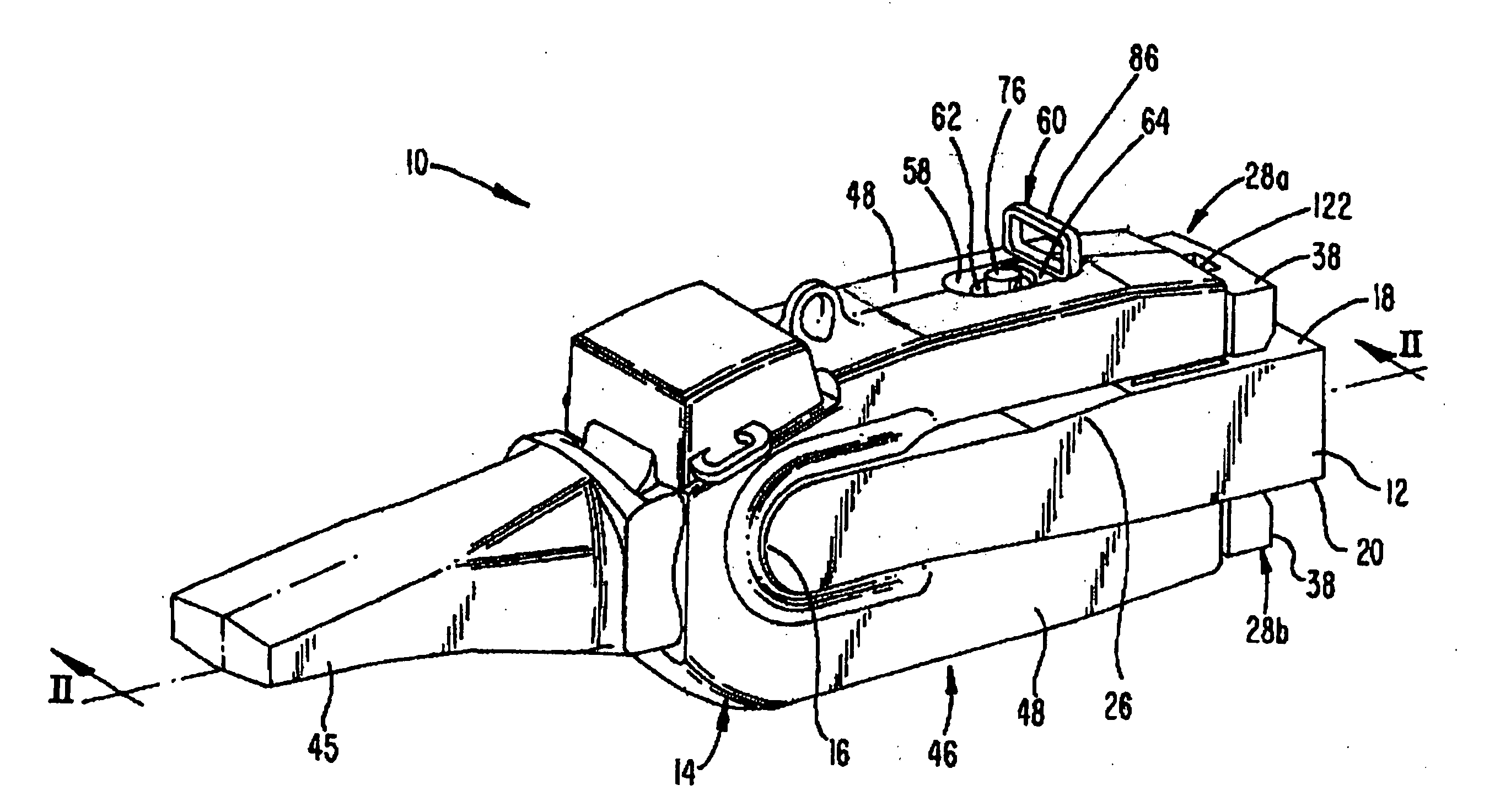
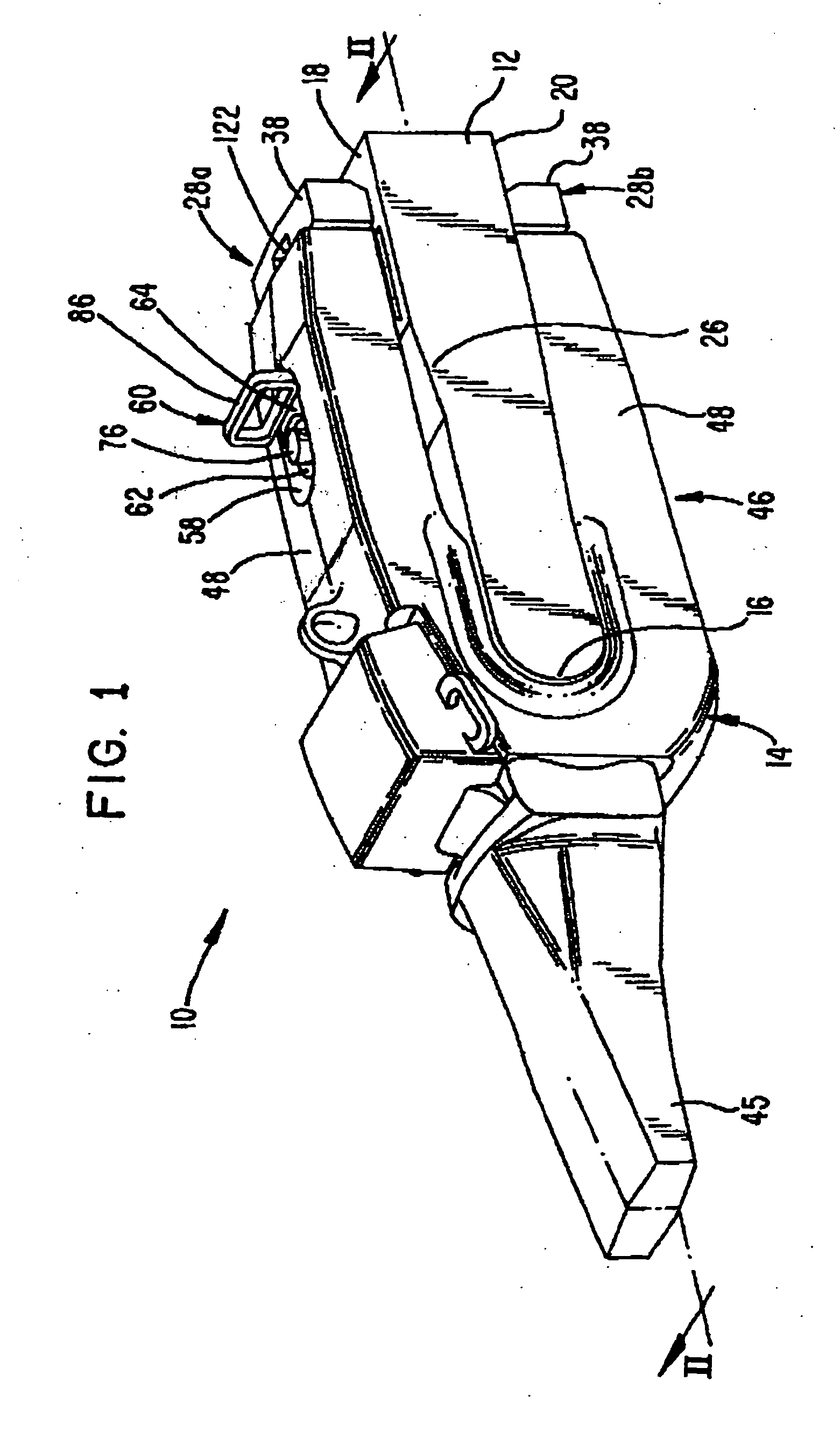
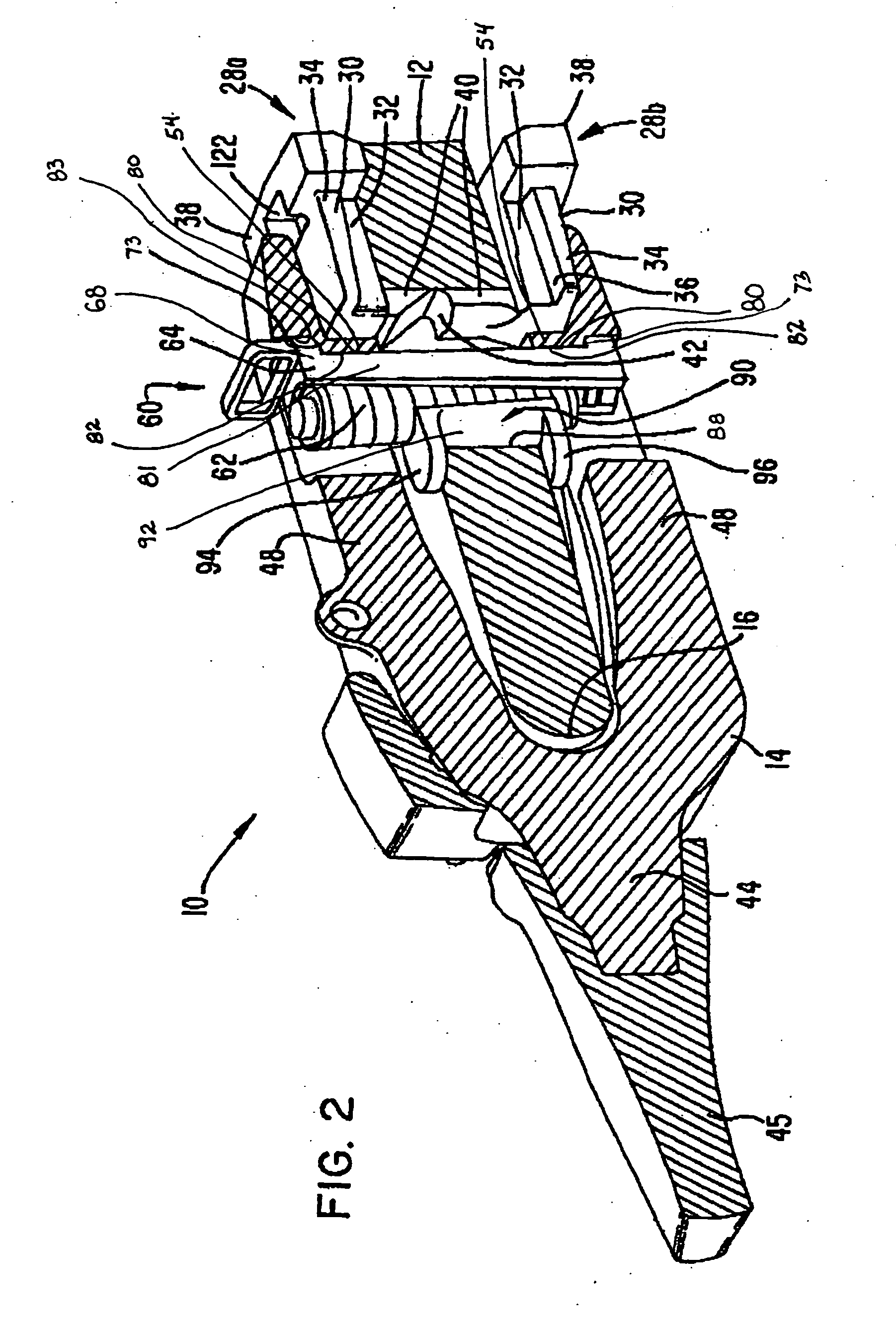
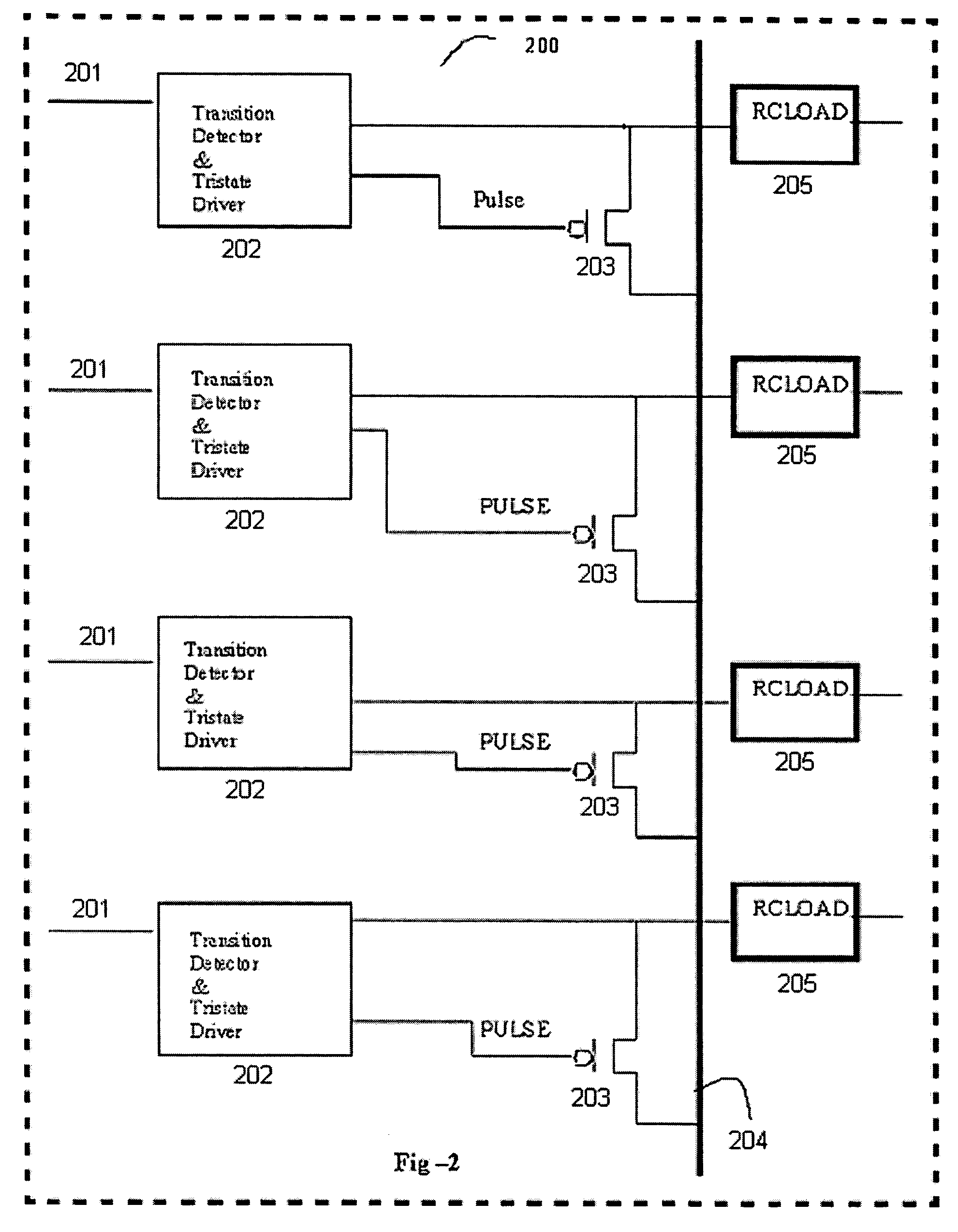
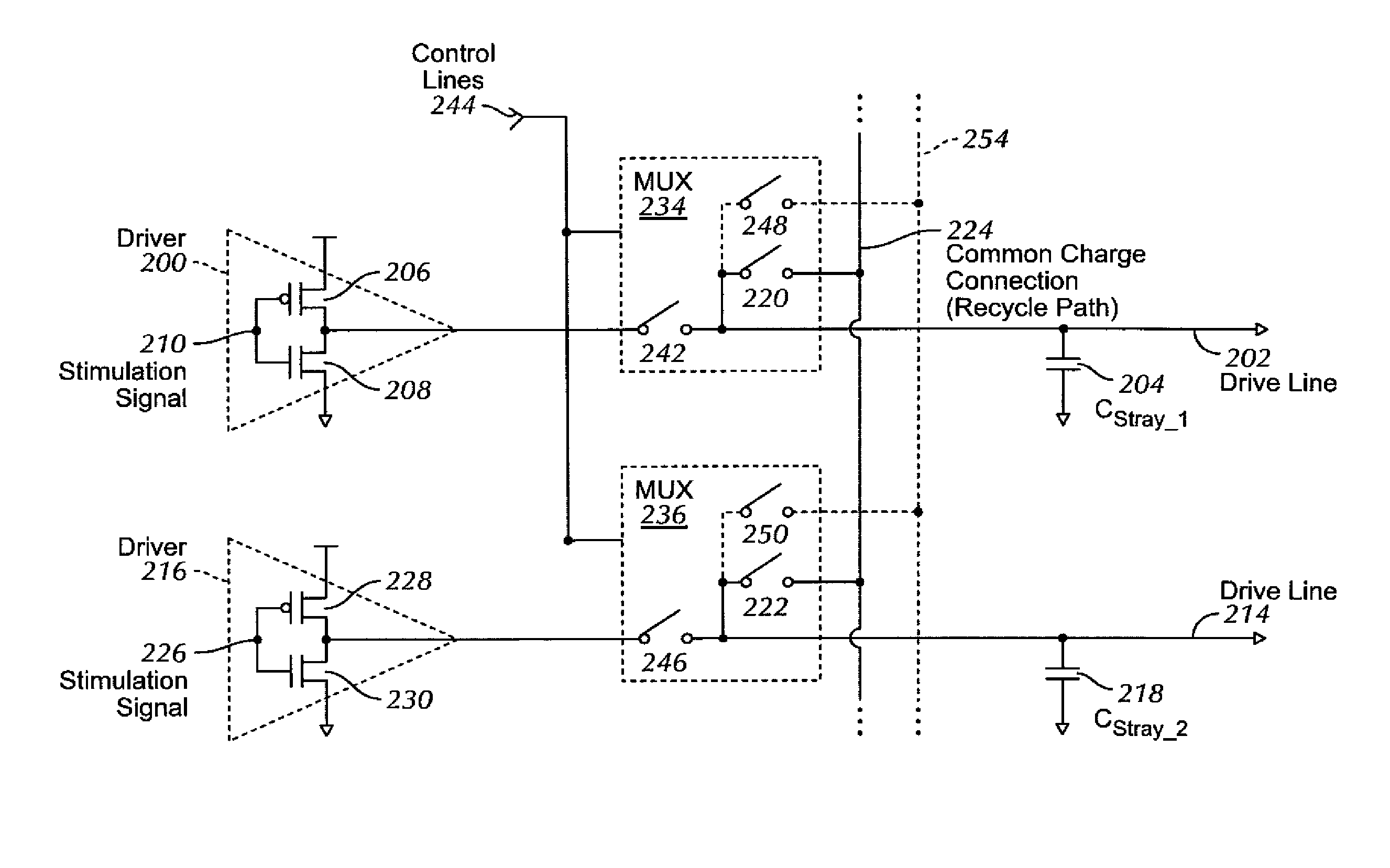
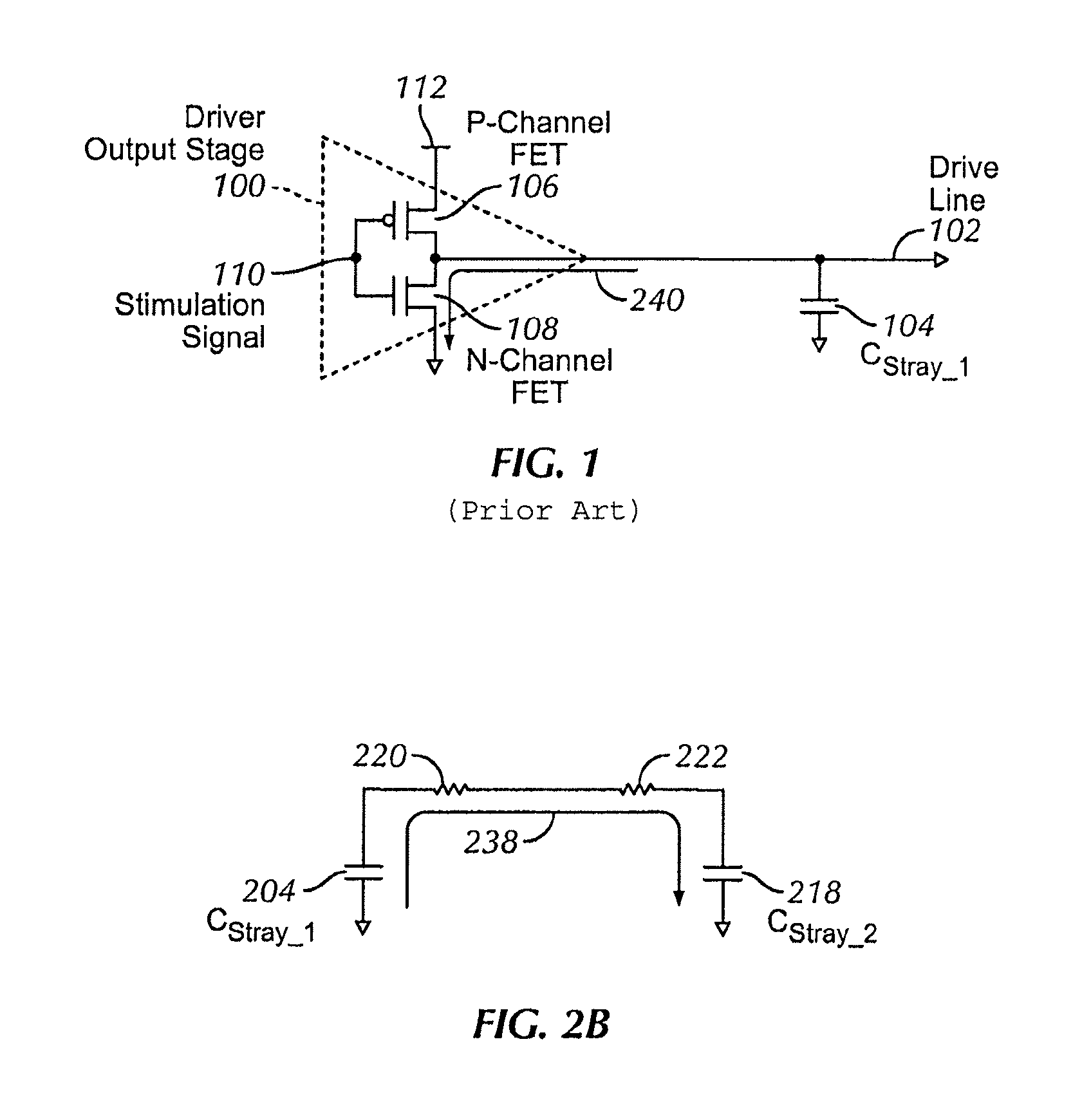
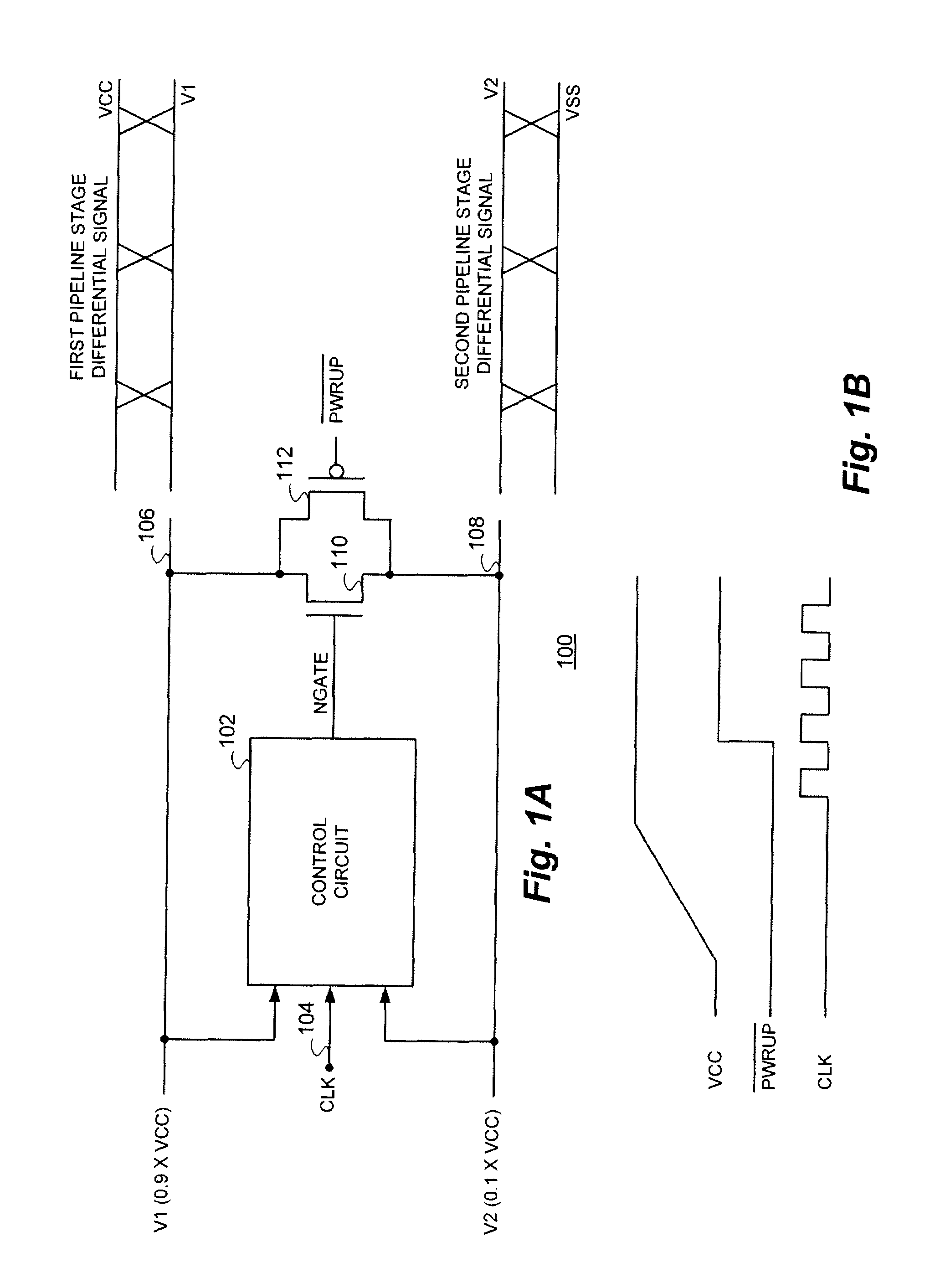
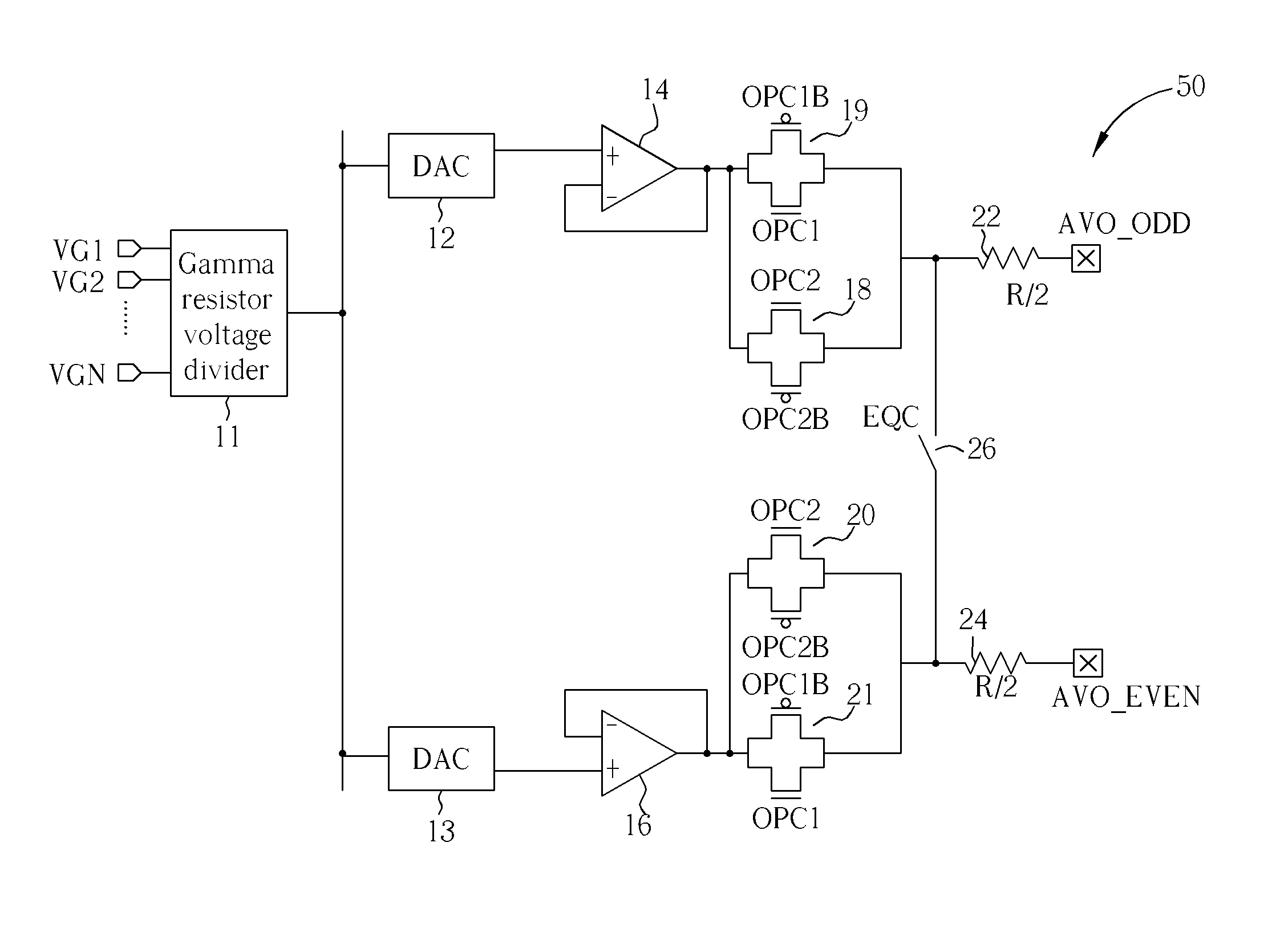
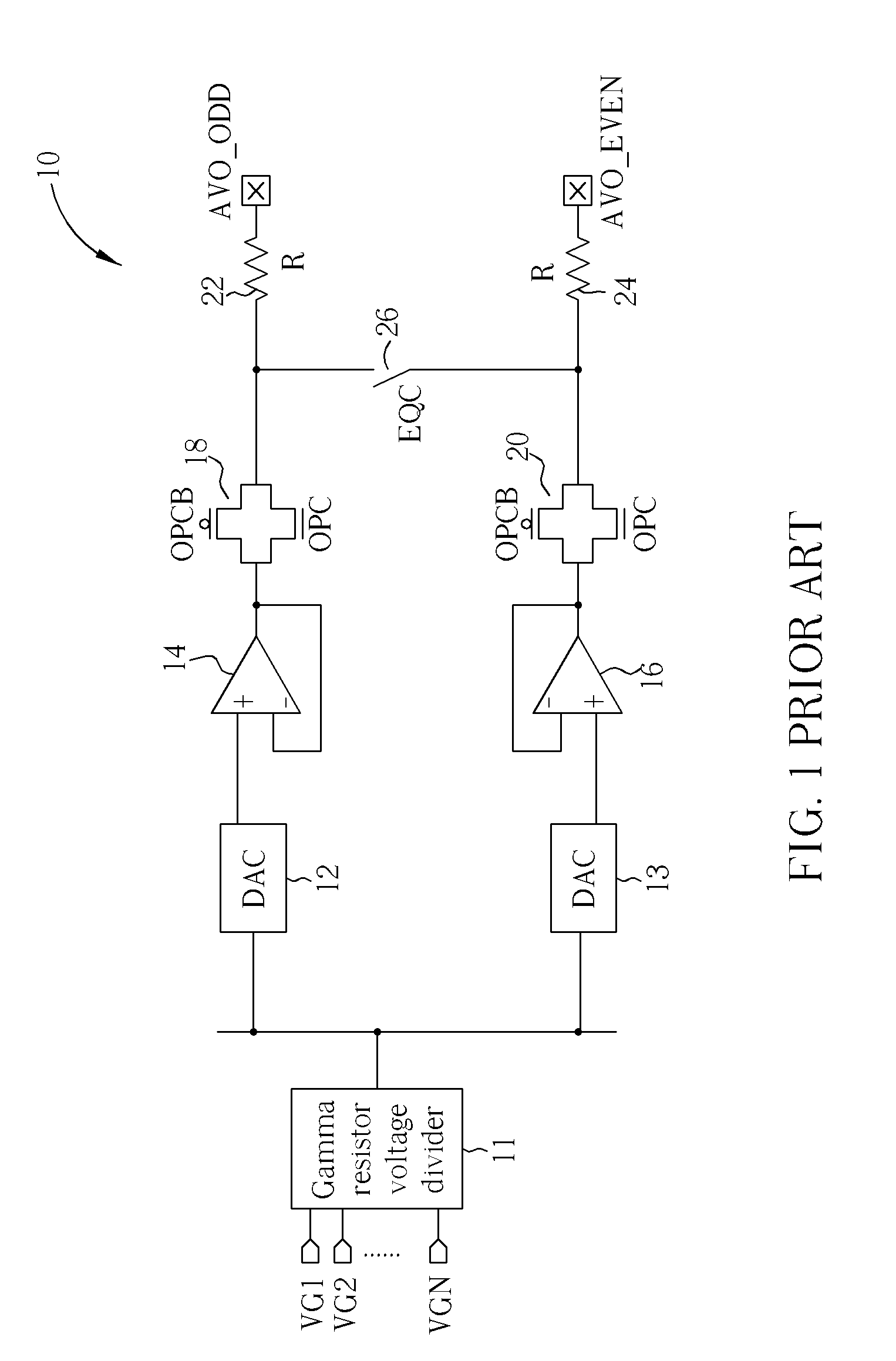
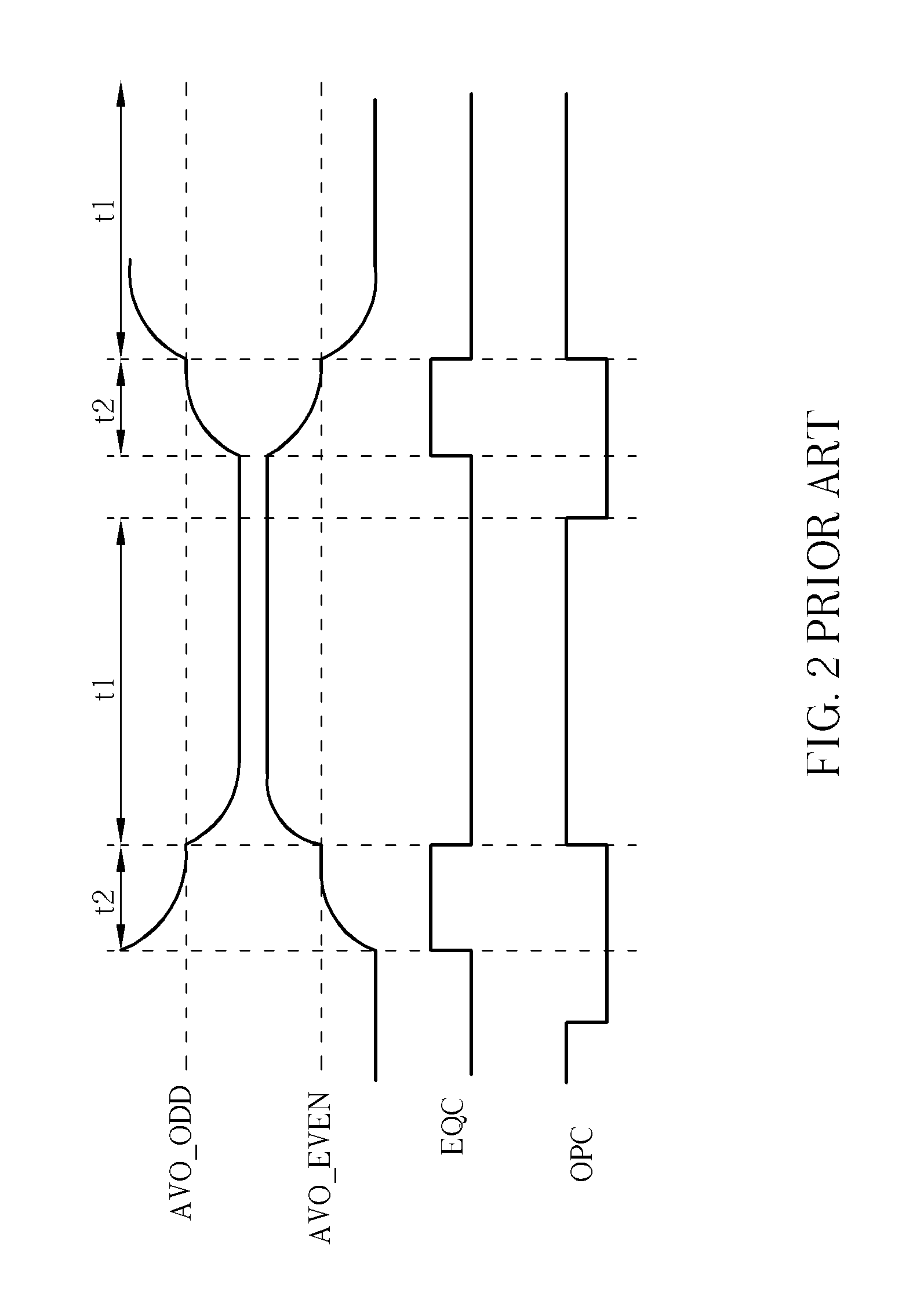
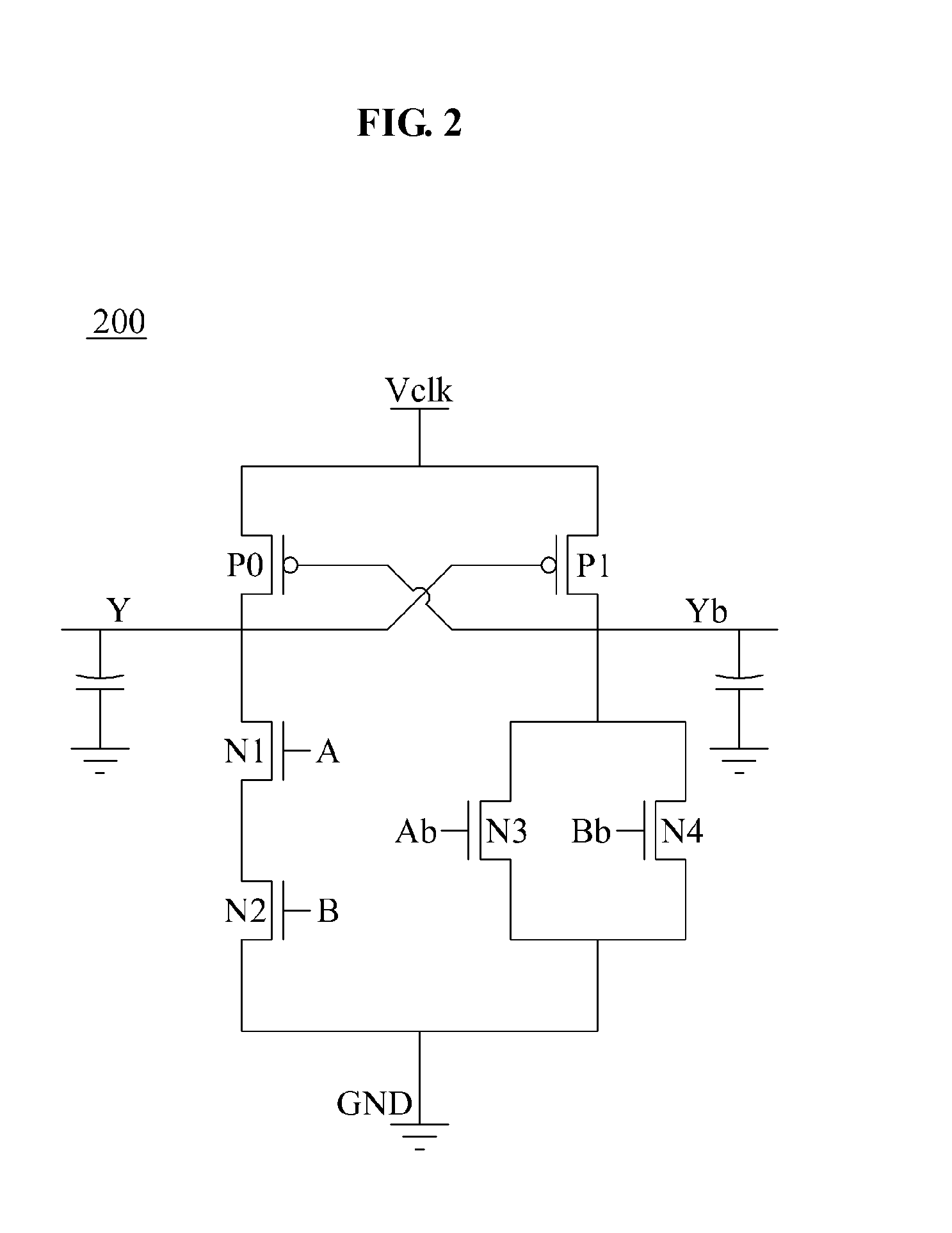
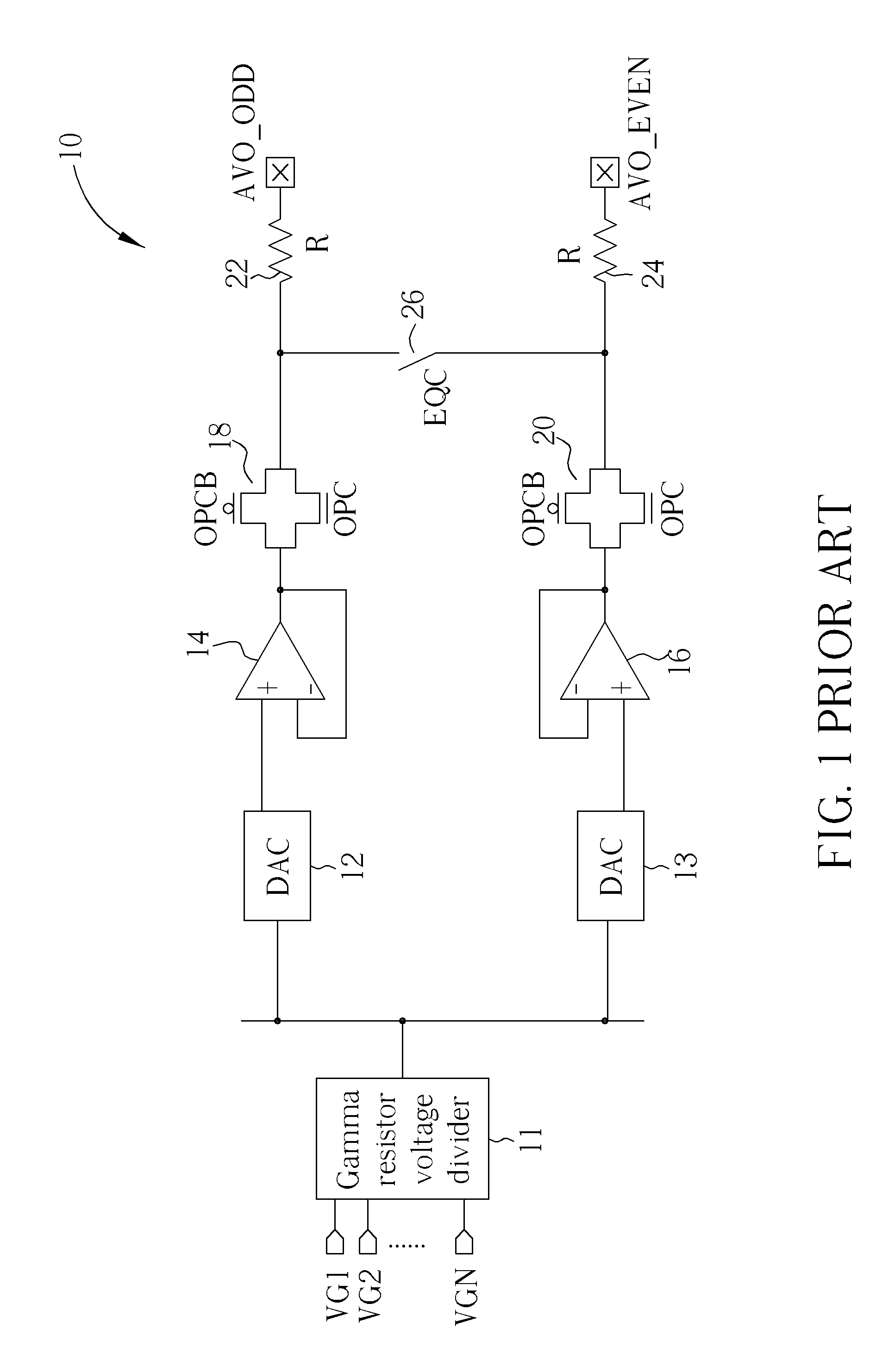
Charge recycling for multi-touch controllers
ActiveUS20090212642A1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceMaximize signalPower reduction by energy recoveryDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceMuxponder
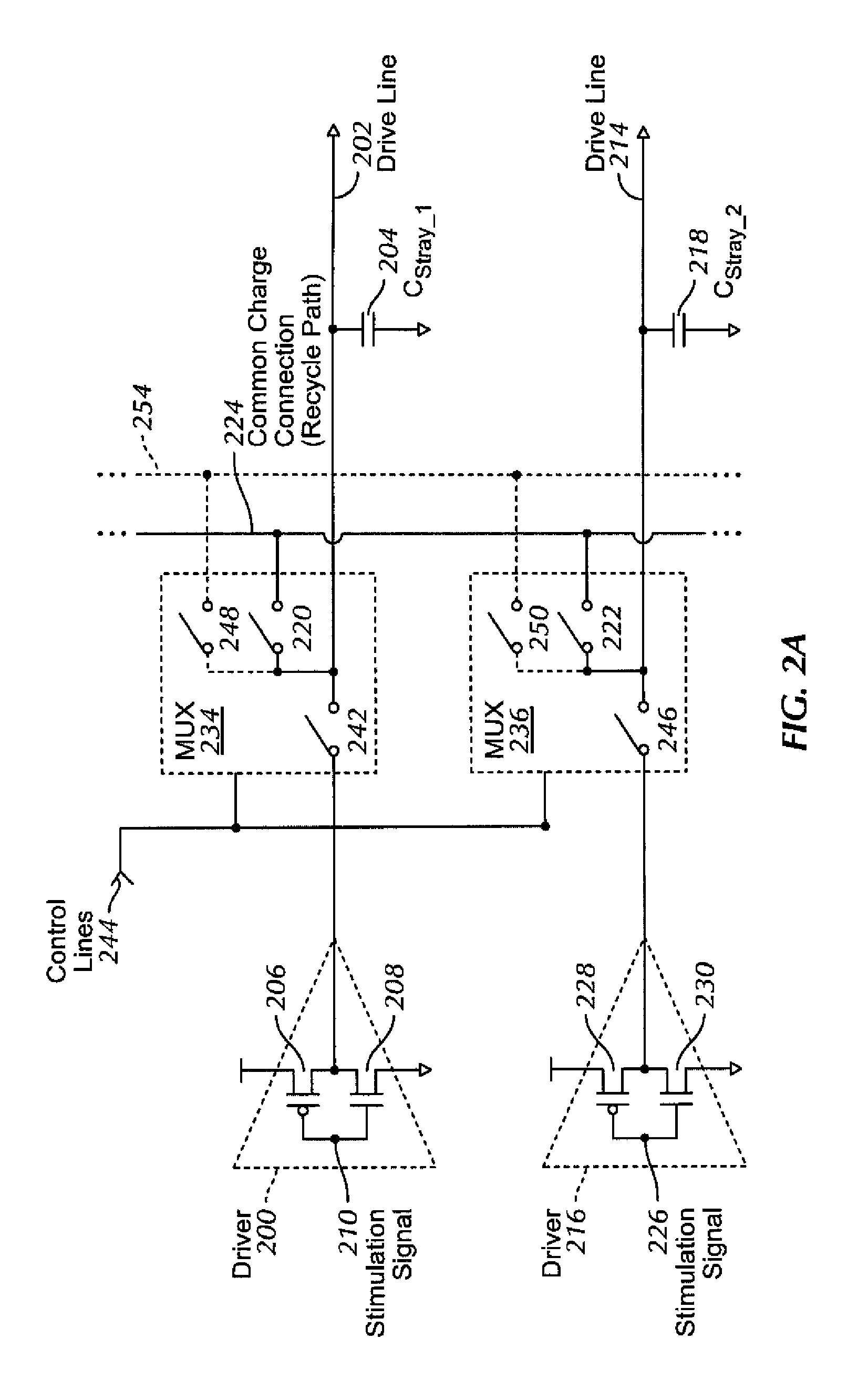
The recycling of charge when two or more of the drive lines of a touch sensor panel are being simultaneously stimulated with the in-phase and anti-phase components of a stimulation signal is disclosed. To perform charge recycling, a discharge path can be selectively formed between drive lines being stimulated with the in-phase and anti-phase components of the stimulation signal. A multiplexer can be coupled to the driver of each drive line and the common discharge path. When charge recycling is to be performed, control logic can configure the multiplexers to isolate the driver and connect the drive lines being stimulated with the in-phase component of the stimulation signal with the drive lines being stimulated with the anti-phase component of the stimulation signal. The capacitance on the charged-up drive lines can then discharge to the capacitance on the discharged drive lines.
Owner:APPLE INC
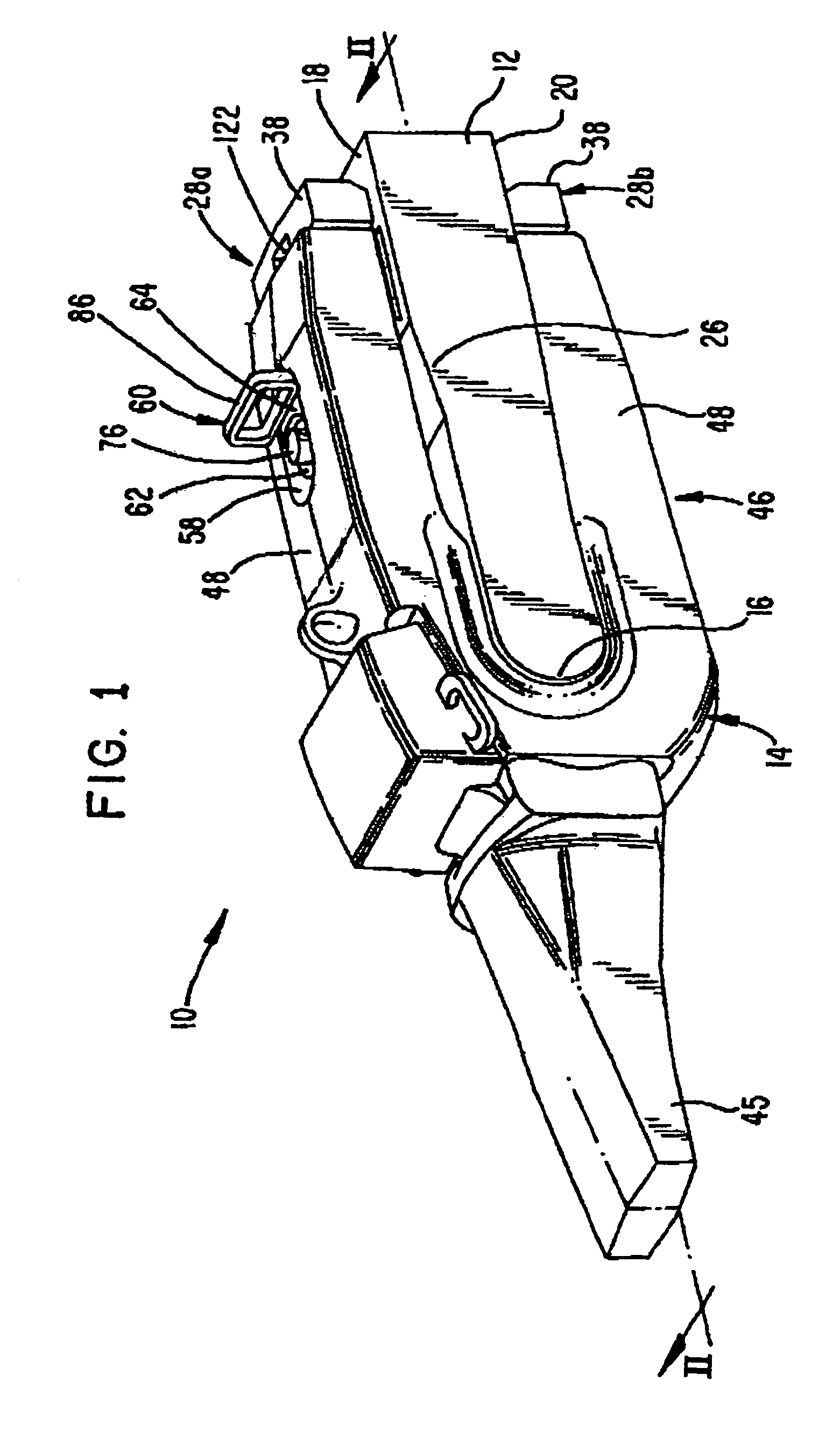
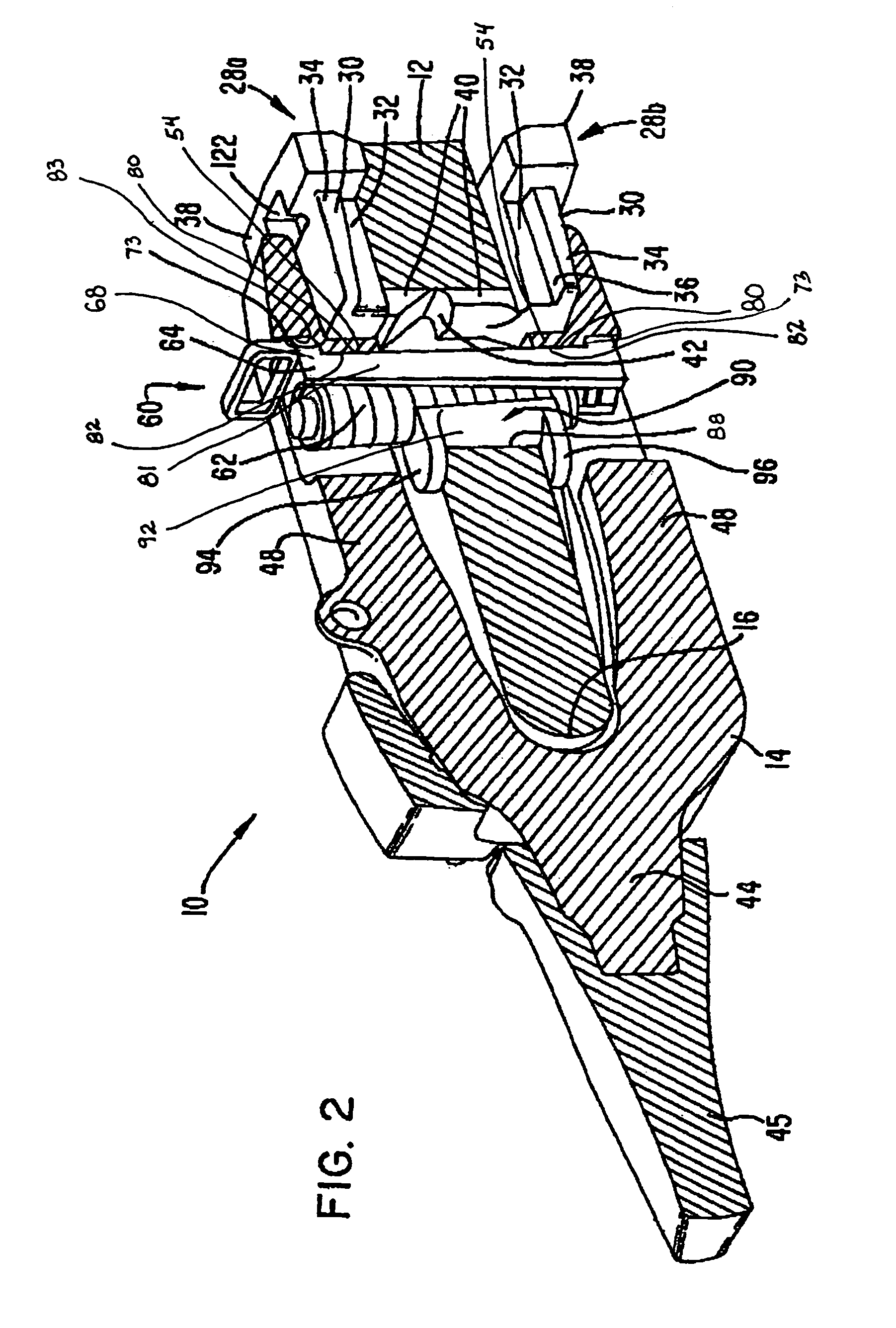
Wear assembly for an excavator
InactiveUS7299570B2Easy to installEasy to removePower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationEngineeringScrew thread
Owner:ESCO GRP LLC
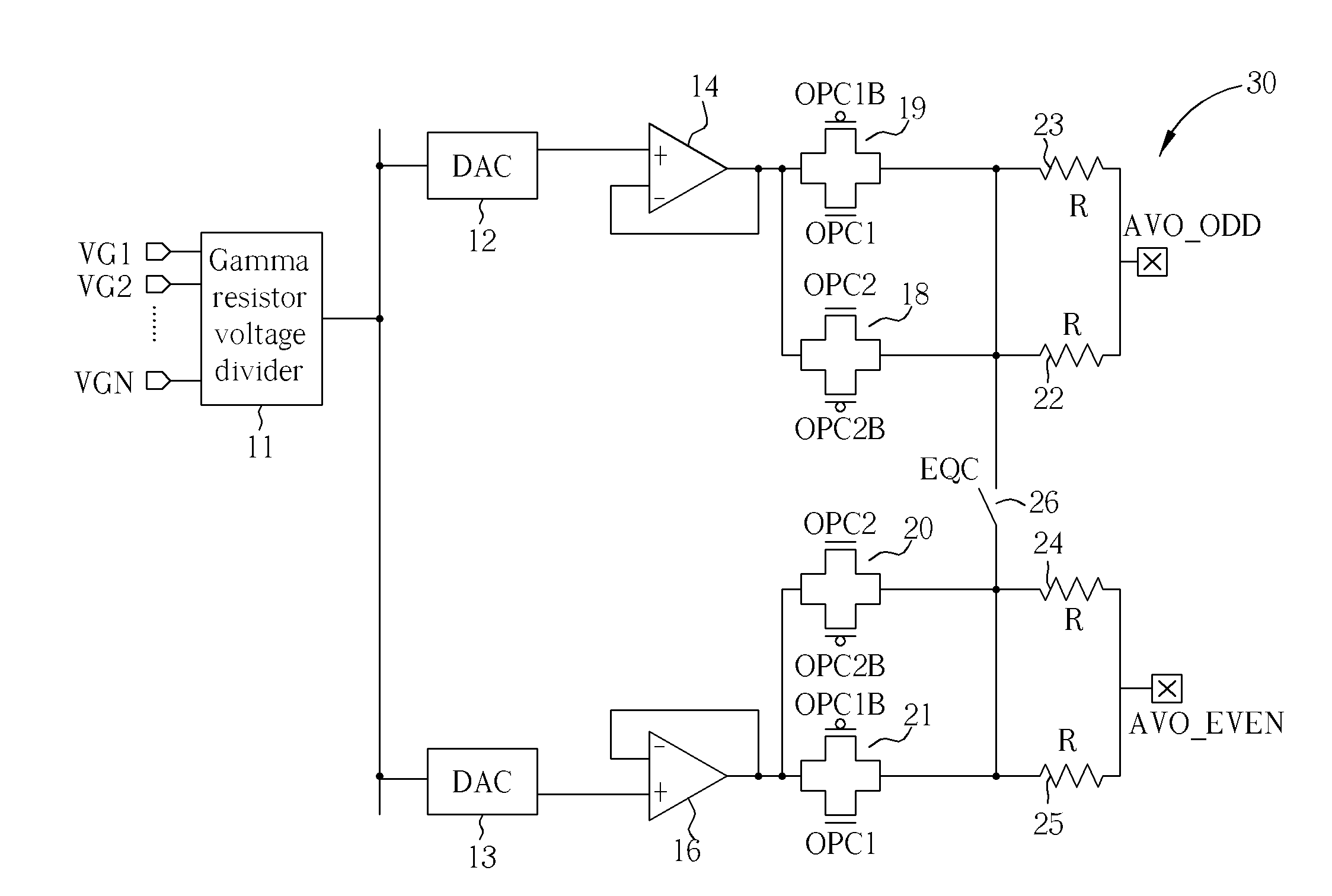
Source driver with charge sharing
ActiveUS20090015297A1Improve stabilityImprove drivabilityPower reduction by control/clock signalPower reduction by energy recoveryCharge sharingResistor
A source driver includes four output switches, two resistors, and a charge-sharing switch. The first output switch and the first resistor are coupled in series to a first output channel of the source driver. The second output switch and the second resistor are coupled in series to a second output channel of the source driver. The third output switch is coupled in parallel to the first output switch. The fourth output switch is coupled in parallel to the second output switch. The charge-sharing switch is coupled between the first resistor and the second resistor. The third output switch and the fourth output switch are controlled to adjust the resistance of the output current path of the source driver.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
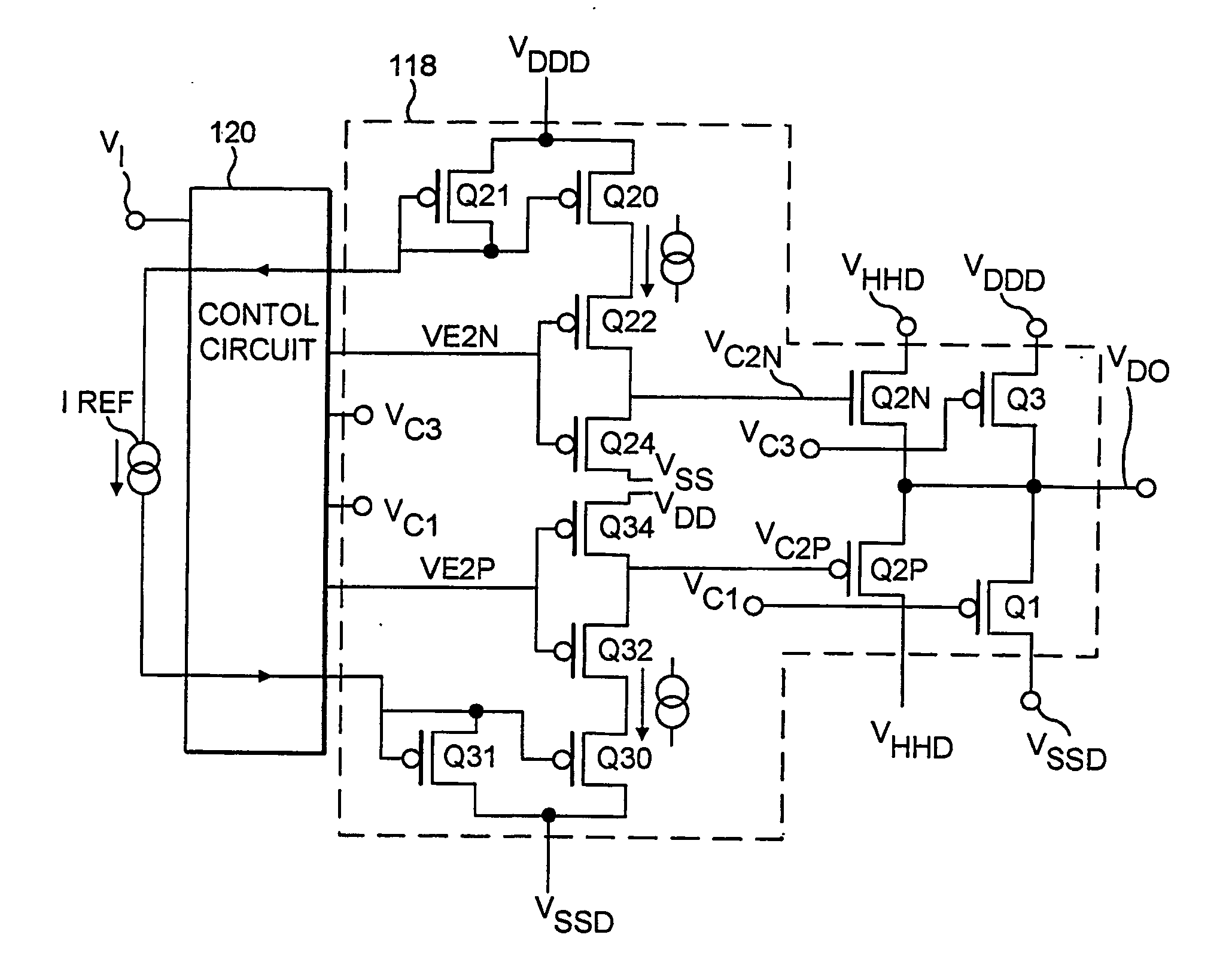
Apparatus for clocked power logic against power analysis attack
ActiveUS20120200313A1Avoid attackEliminate differencesReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by energy recoveryPower analysisParasitic capacitance
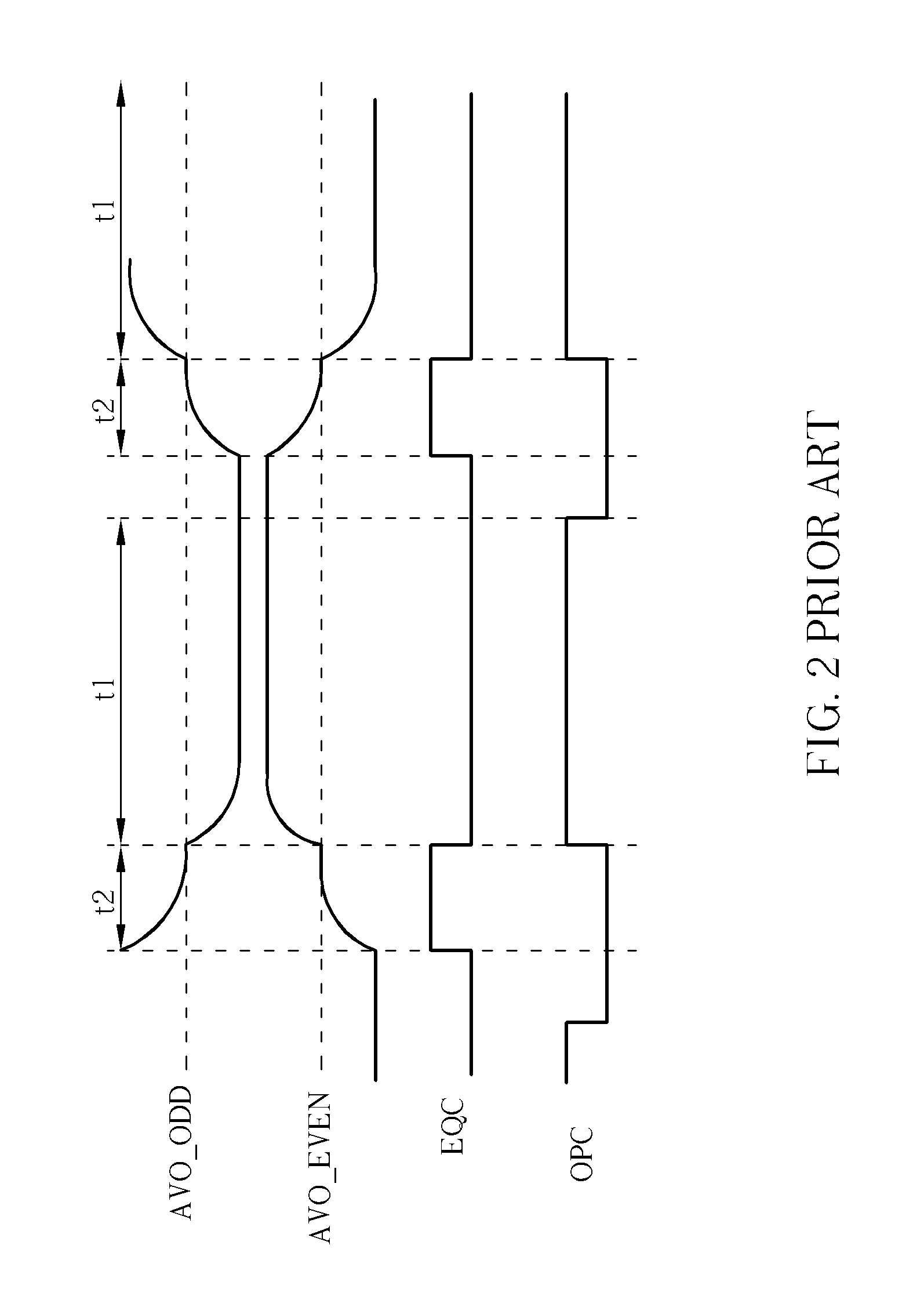
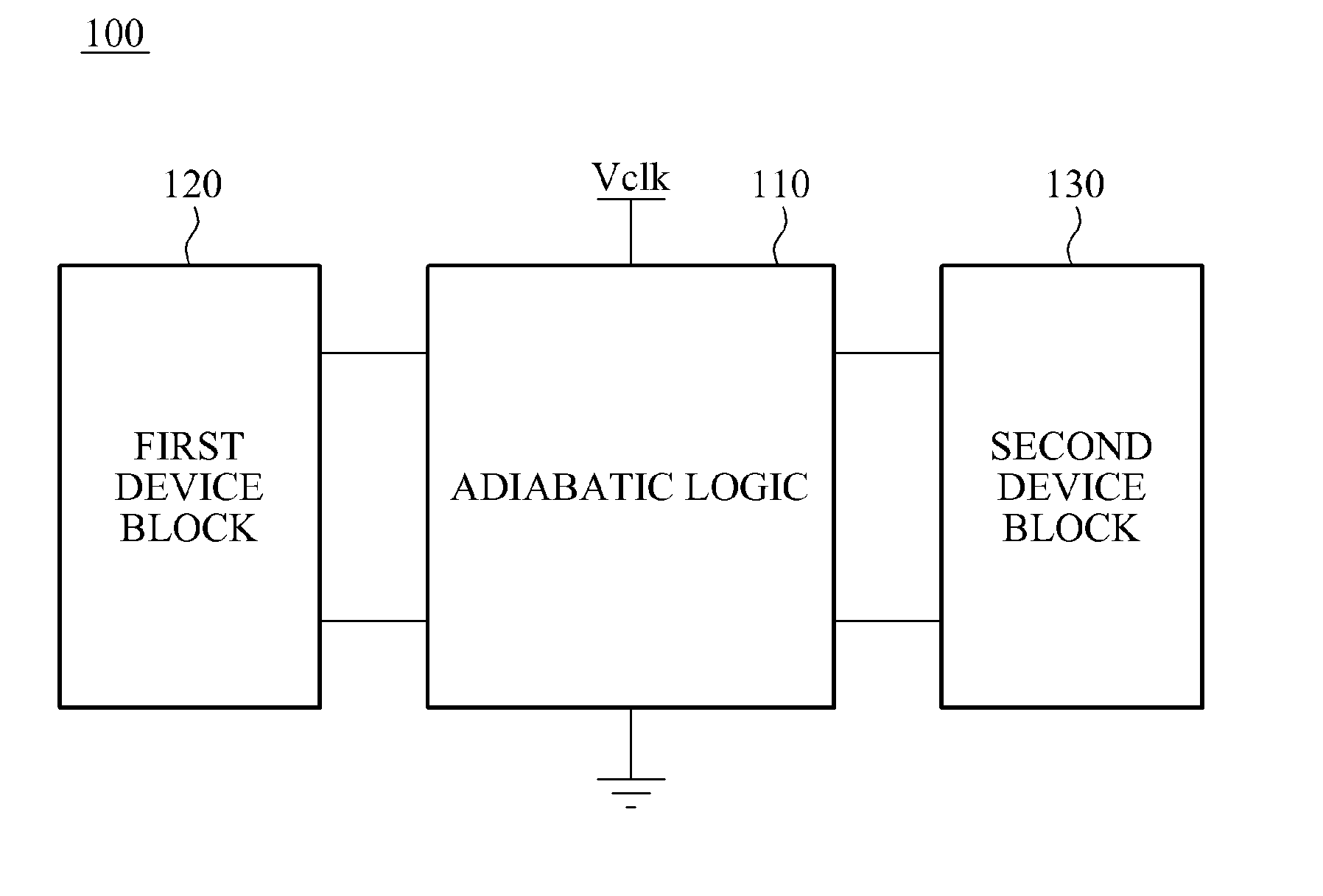
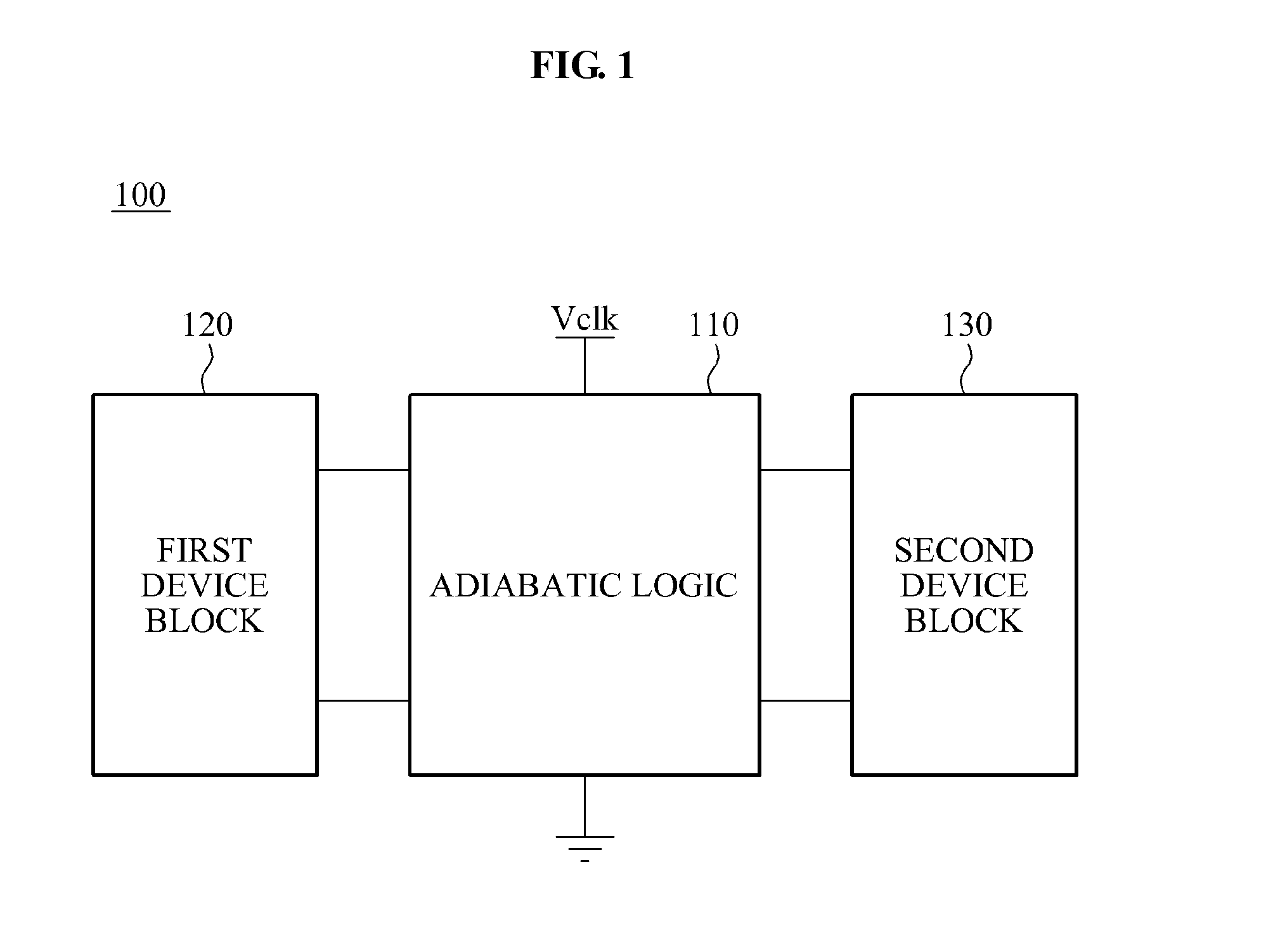
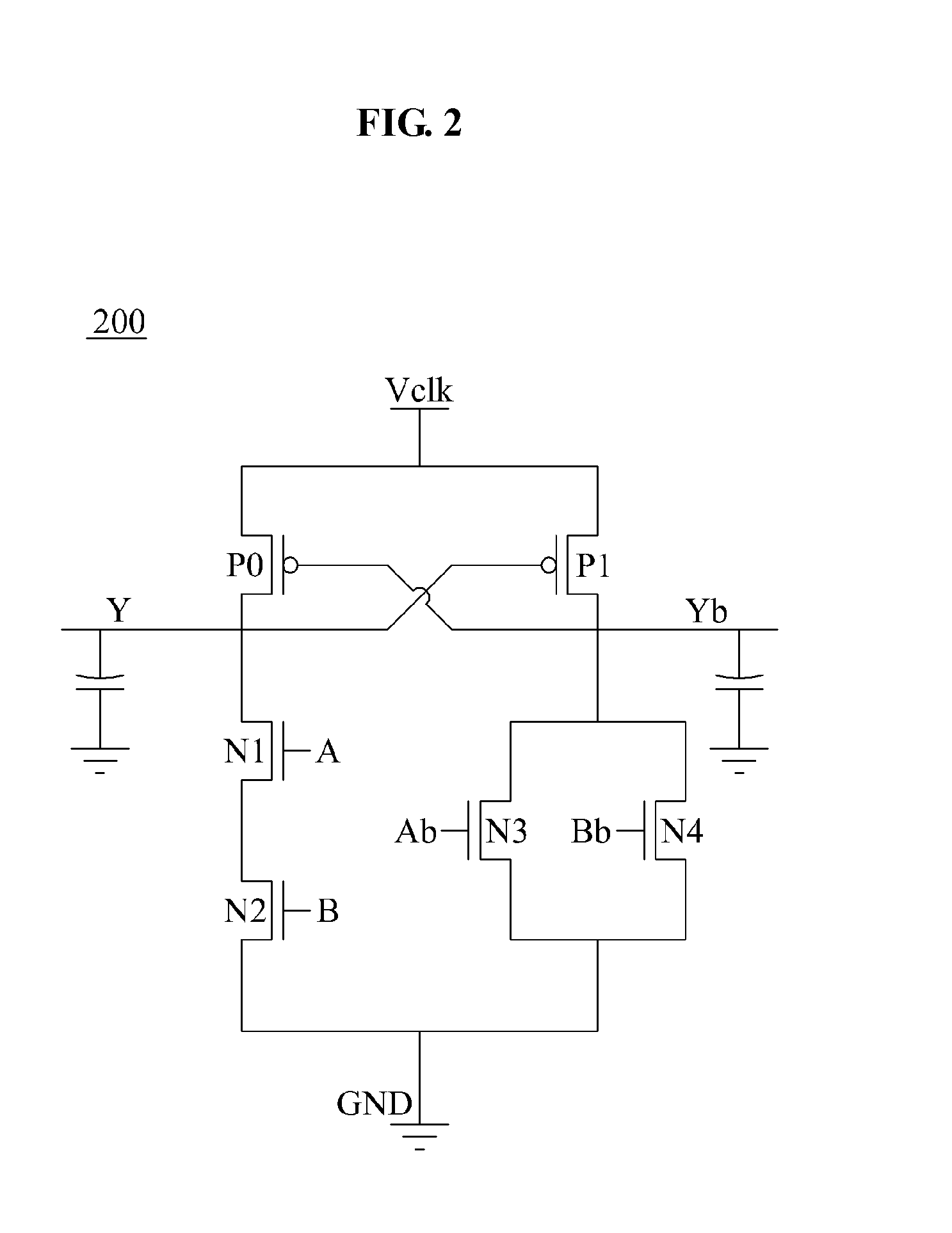
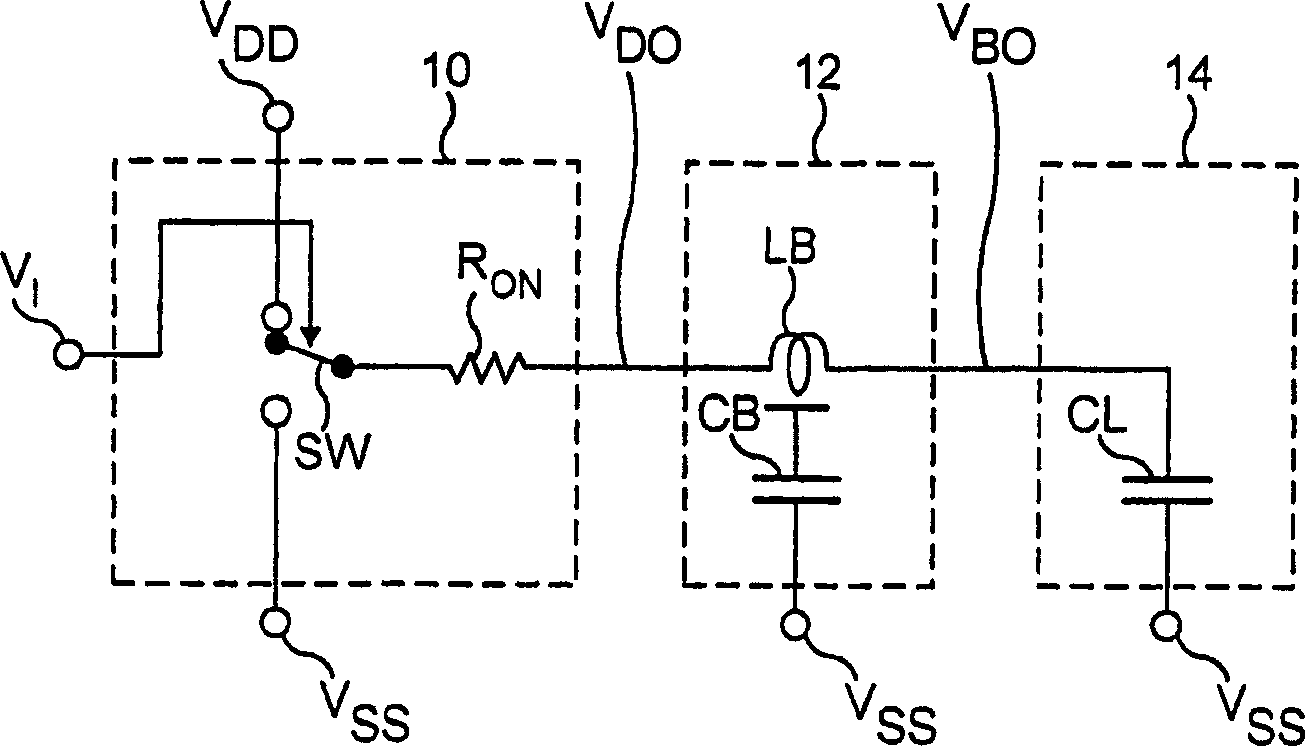
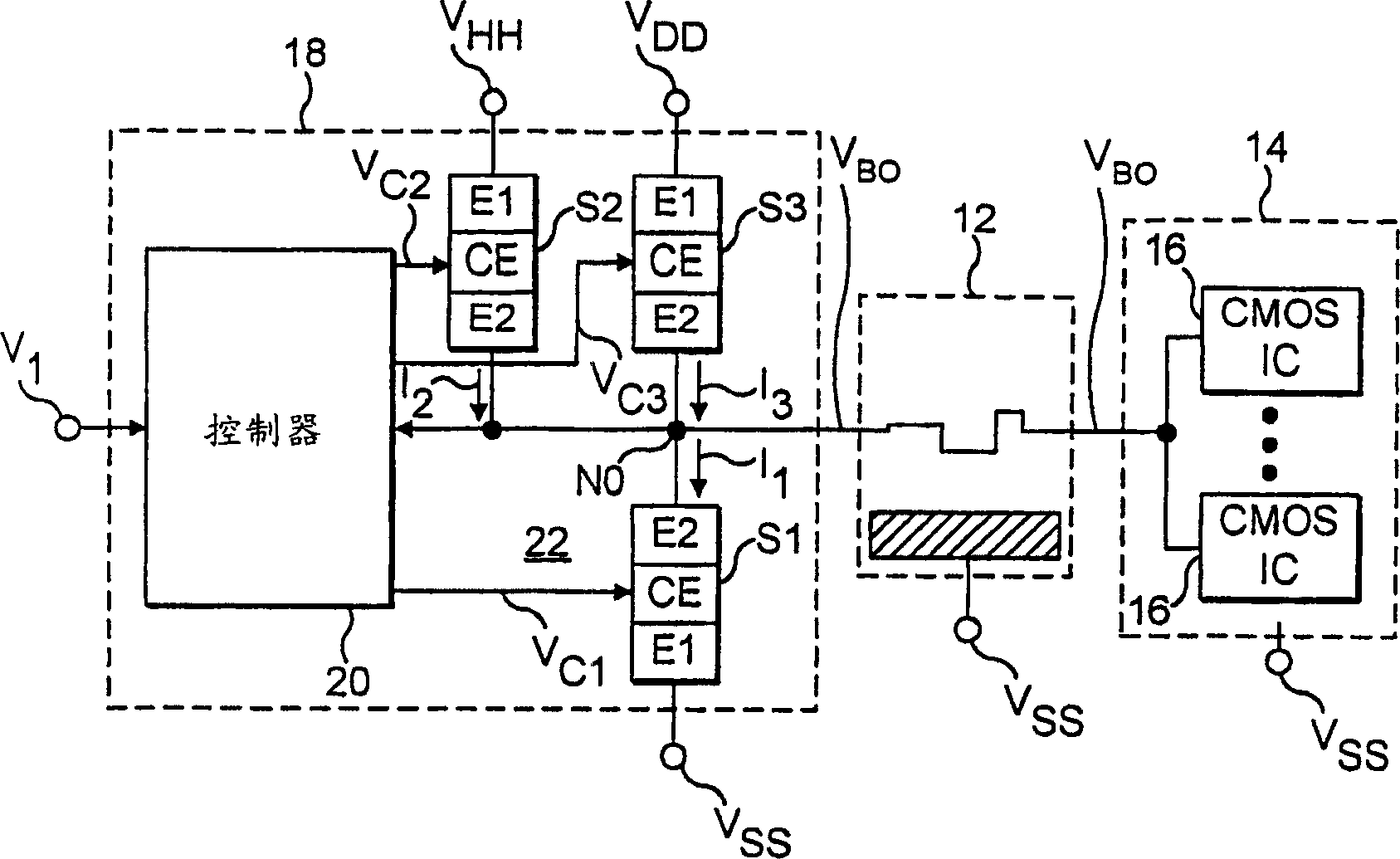
A logic apparatus secure against a power analysis attack is disclosed. The logic apparatus may include a clocked power logic to recover and reuse at least a part of charges supplied during a single clock operation; a first device block connected to the clocked power logic to remove a parasitic capacitance difference in the clocked power logic, and a second device block to readjust remaining charges in each node of the clocked power logic after a single clock operation.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
Wear assembly for an excavator
InactiveUS20060010726A1Easy to installEasy to removePower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationEngineeringExcavator
A wear assembly for attaching a wear member to a support structure that includes a wear member and a lock. The wear member includes a pair of legs to straddle the support structure, each with a hole that aligns with a hole in the support structure for receiving a lock to hold the wear member in place. Each hole includes a recess with an engagement surface facing generally away from the support structure for receiving portions of the lock. The lock includes a wedge provided with a thread formation that threadedly engages a second thread formation in the aligned holes so that rotation of the wedge axially drives the wedge.
Owner:ESCO GRP LLC
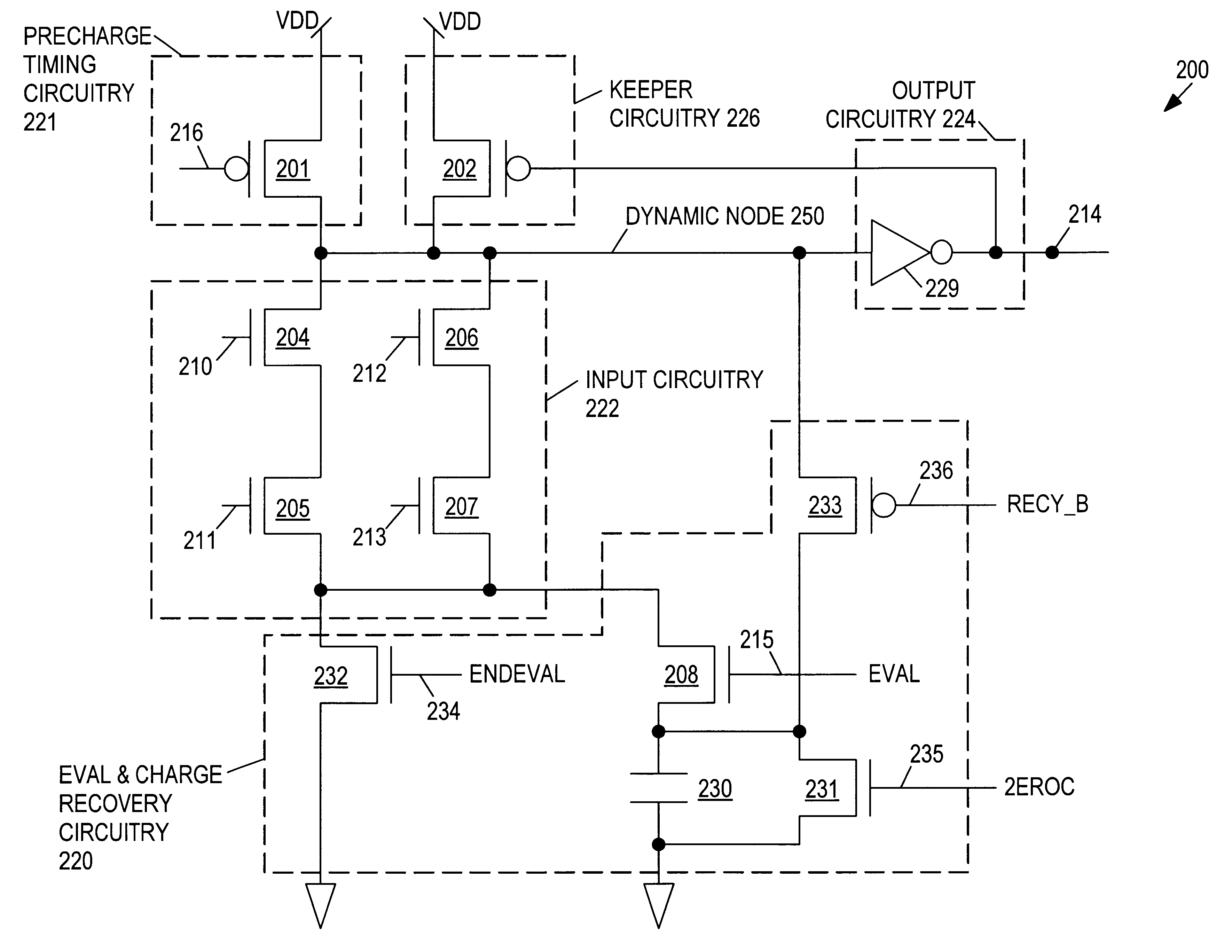
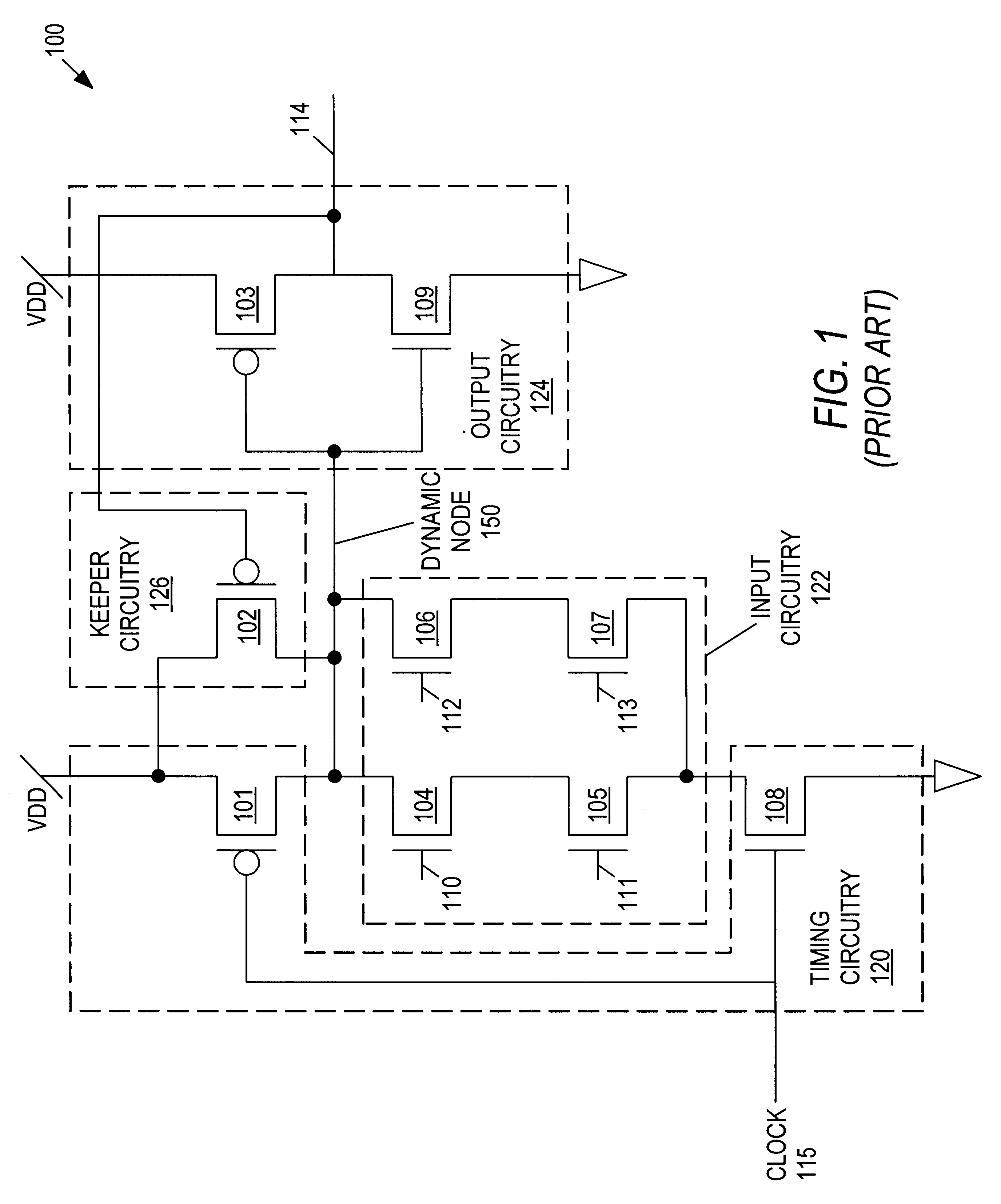
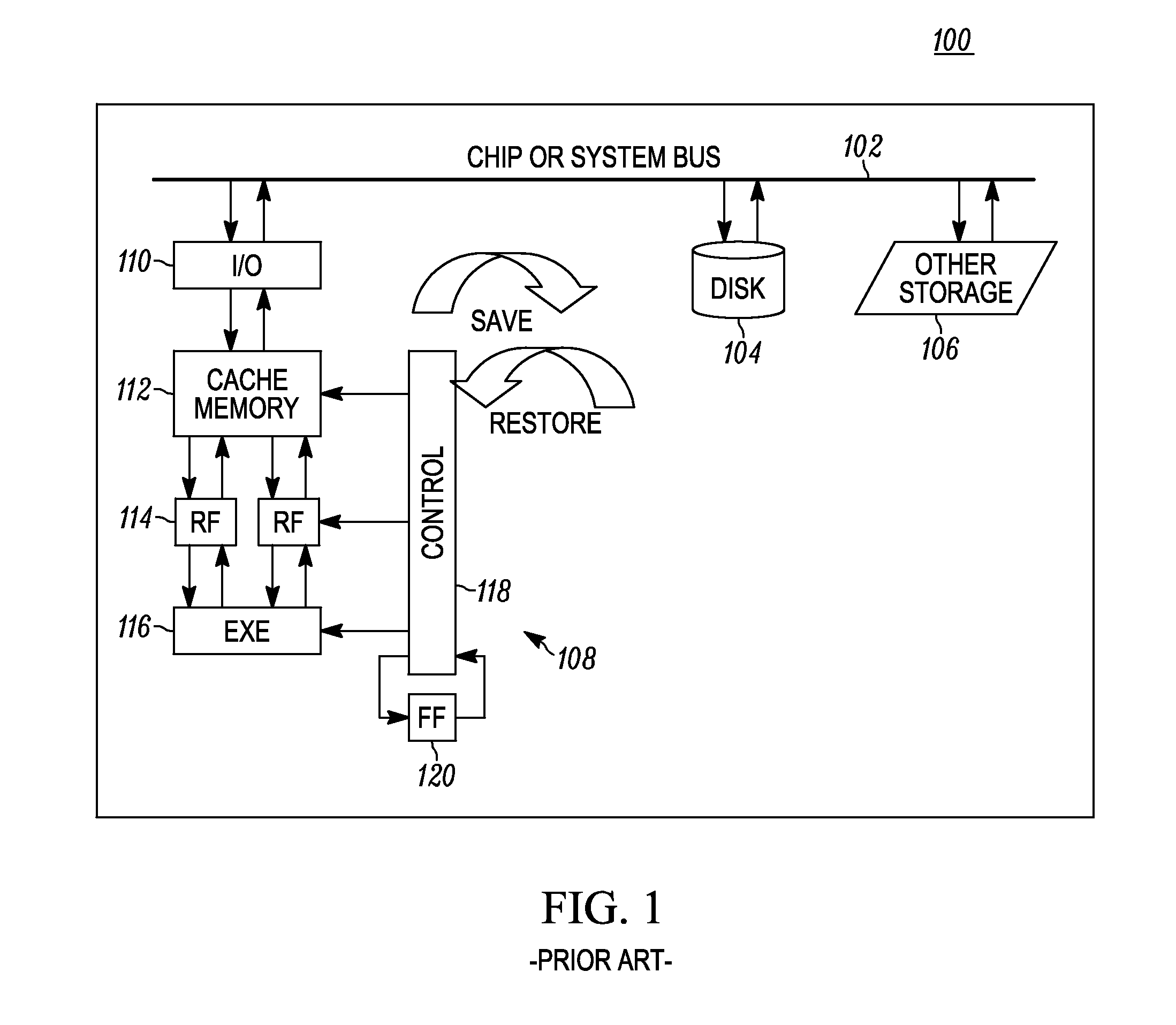
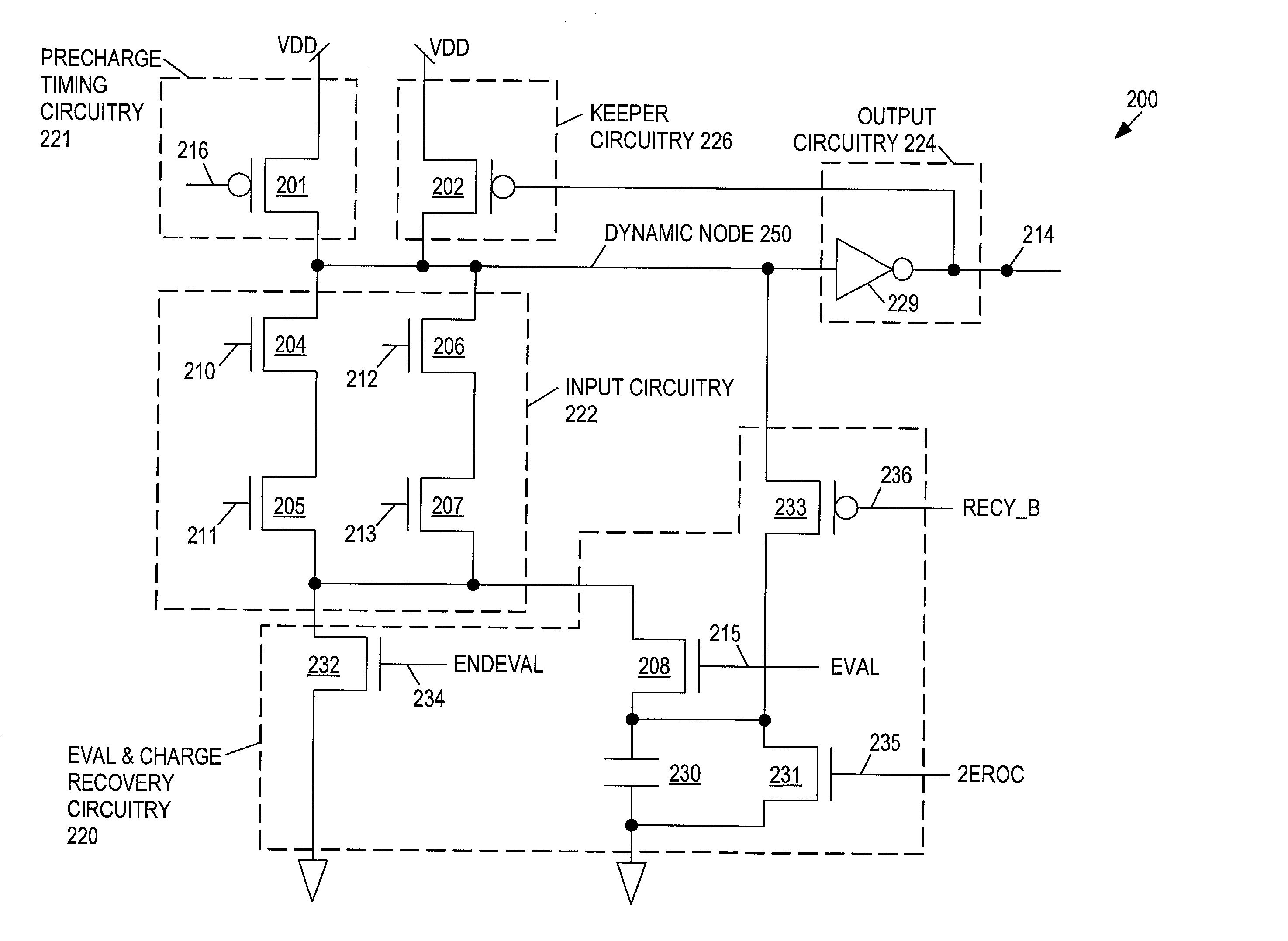
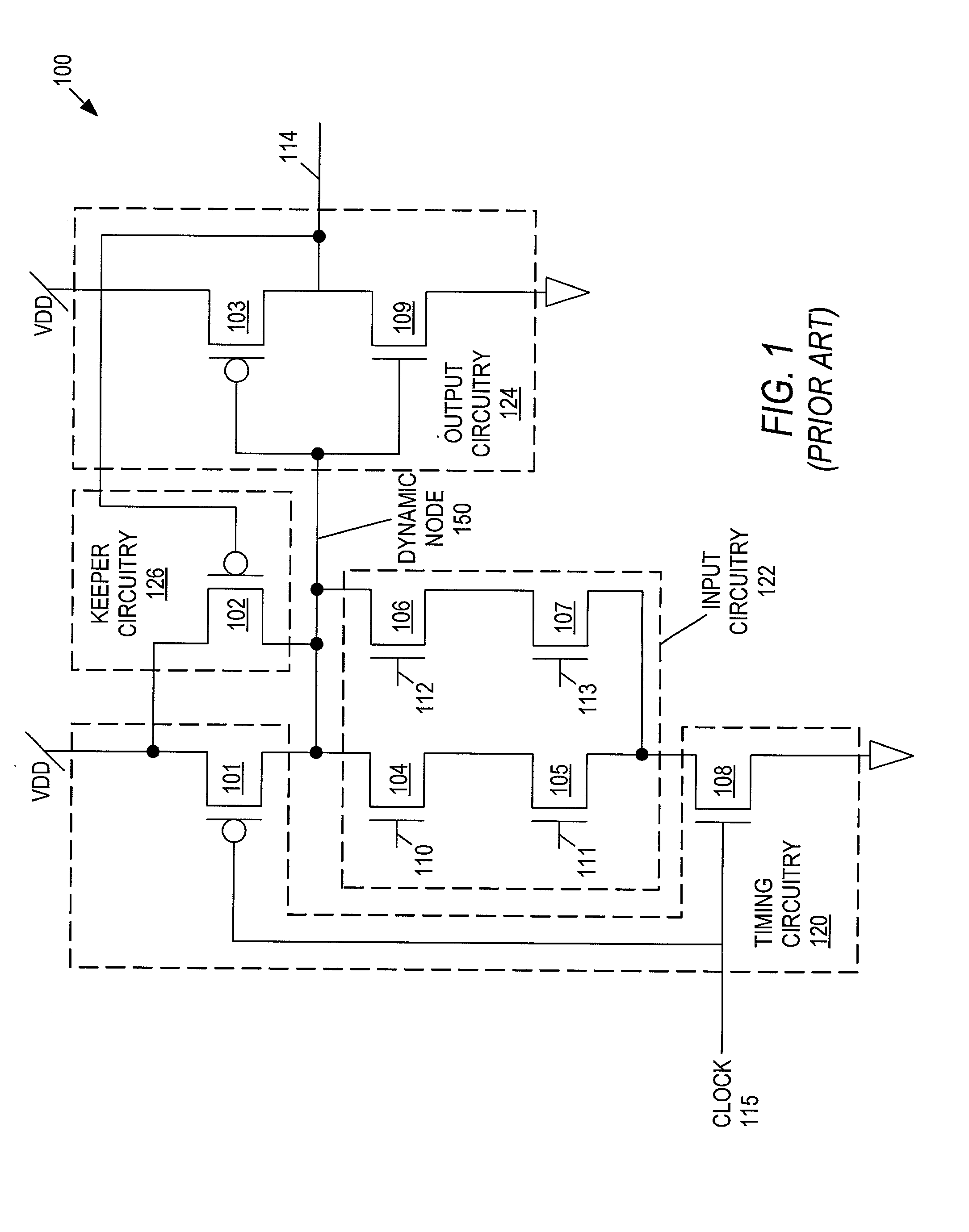
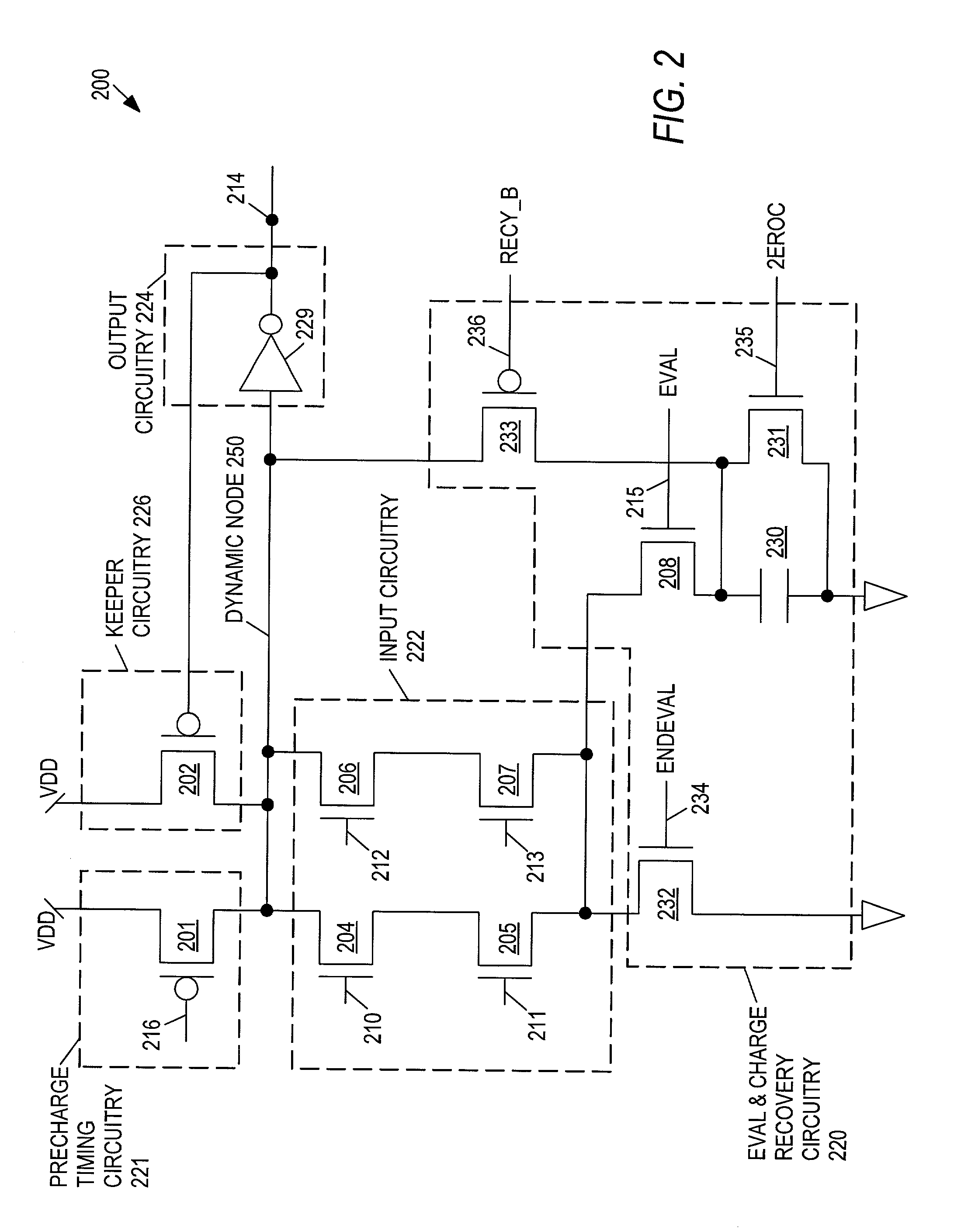
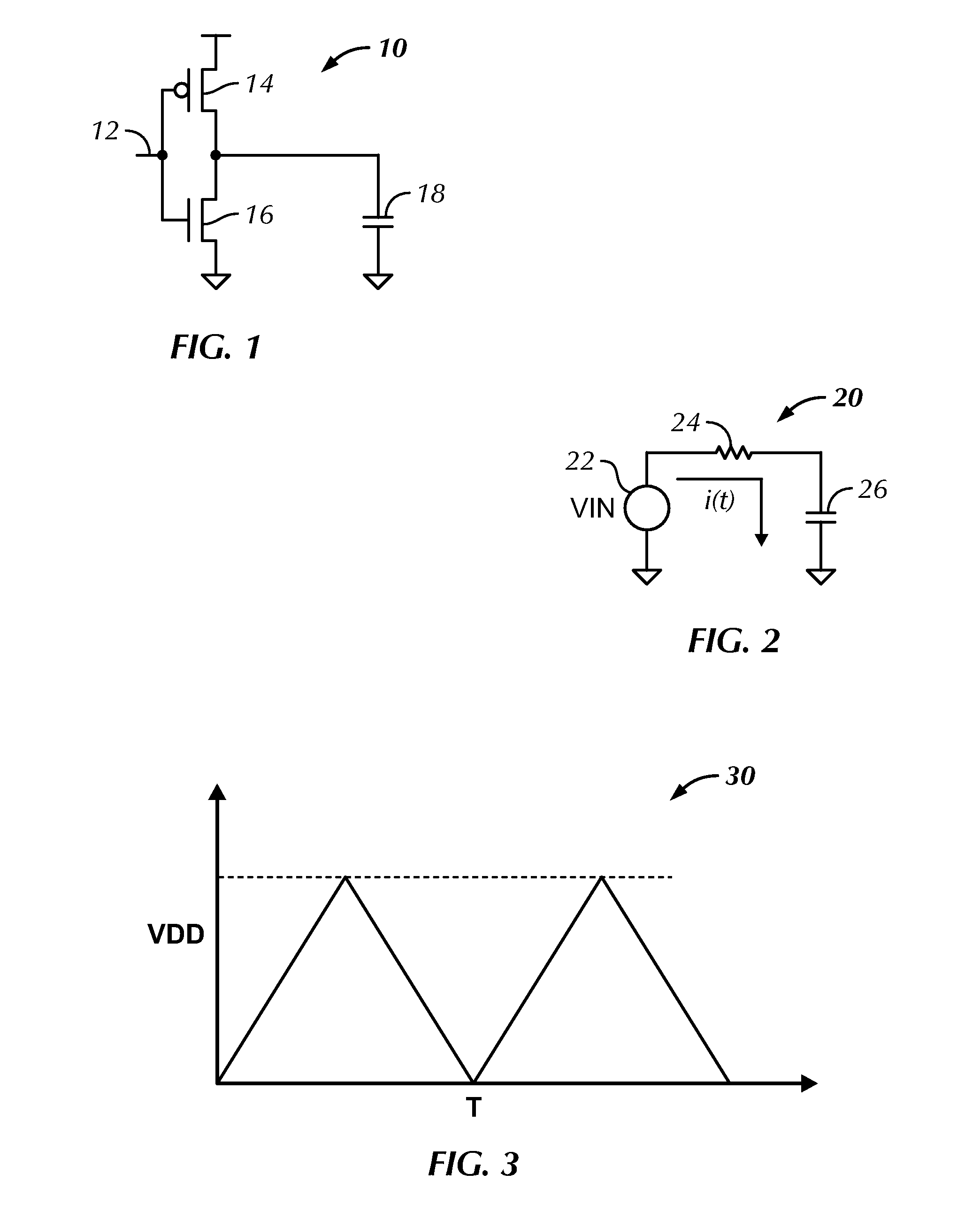
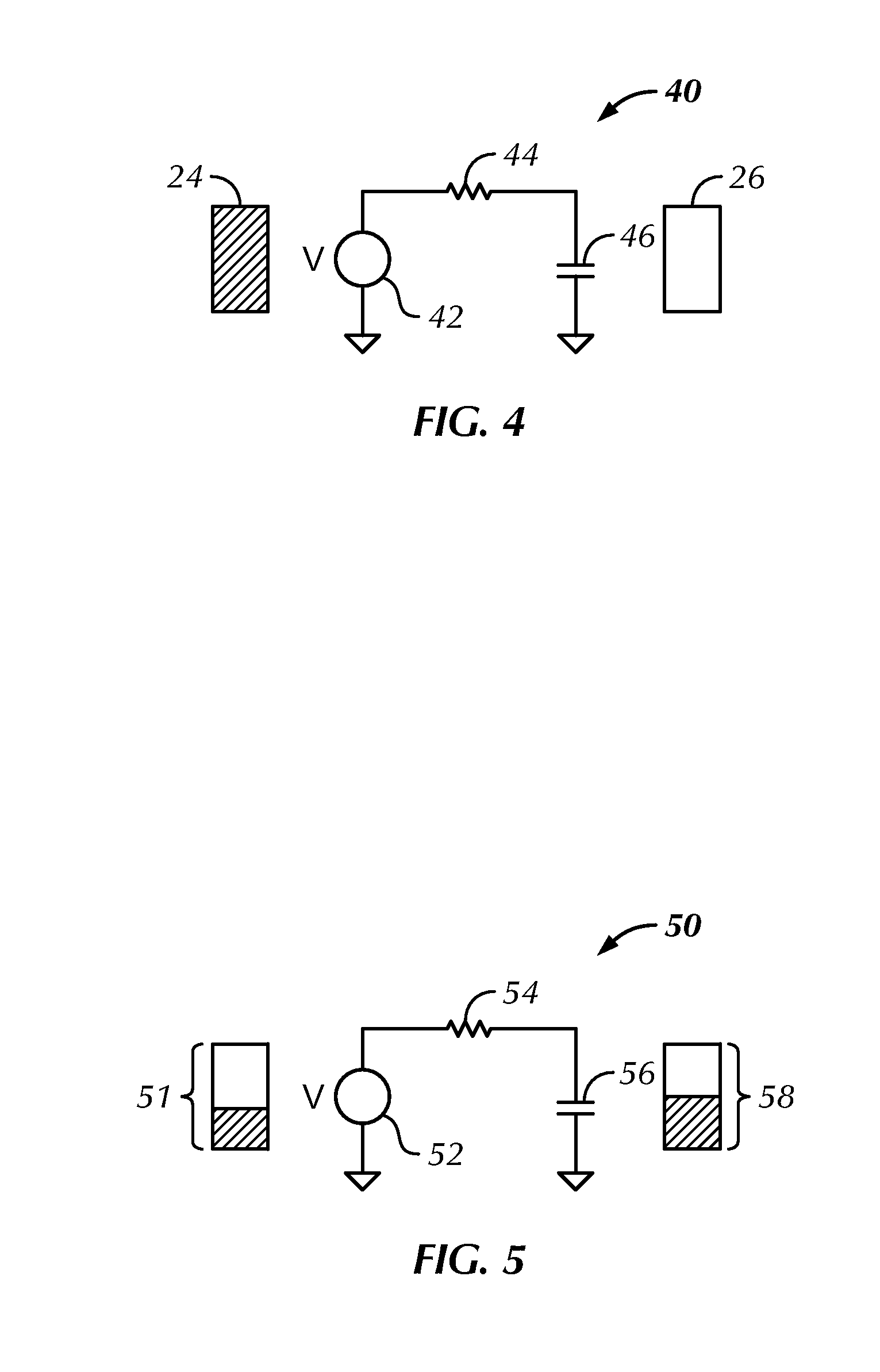
Charge recovery for dynamic circuits
InactiveUS6570408B2Power reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationEvaluation IntervalCharge recovery
In one aspect, a method for charge recovery in dynamic circuitry includes discharging a dynamic node during an evaluation interval by input circuitry coupled to the dynamic node responsive to one or more input signals. The discharging includes transferring the charge from the dynamic node to a capacitor during the evaluation time interval. The dynamic node is charged during a precharge interval by a voltage source and precharge timing circuitry coupled to the dynamic node responsive to a precharge signal. The charging includes transferring the charge from the capacitor back to the dynamic node.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
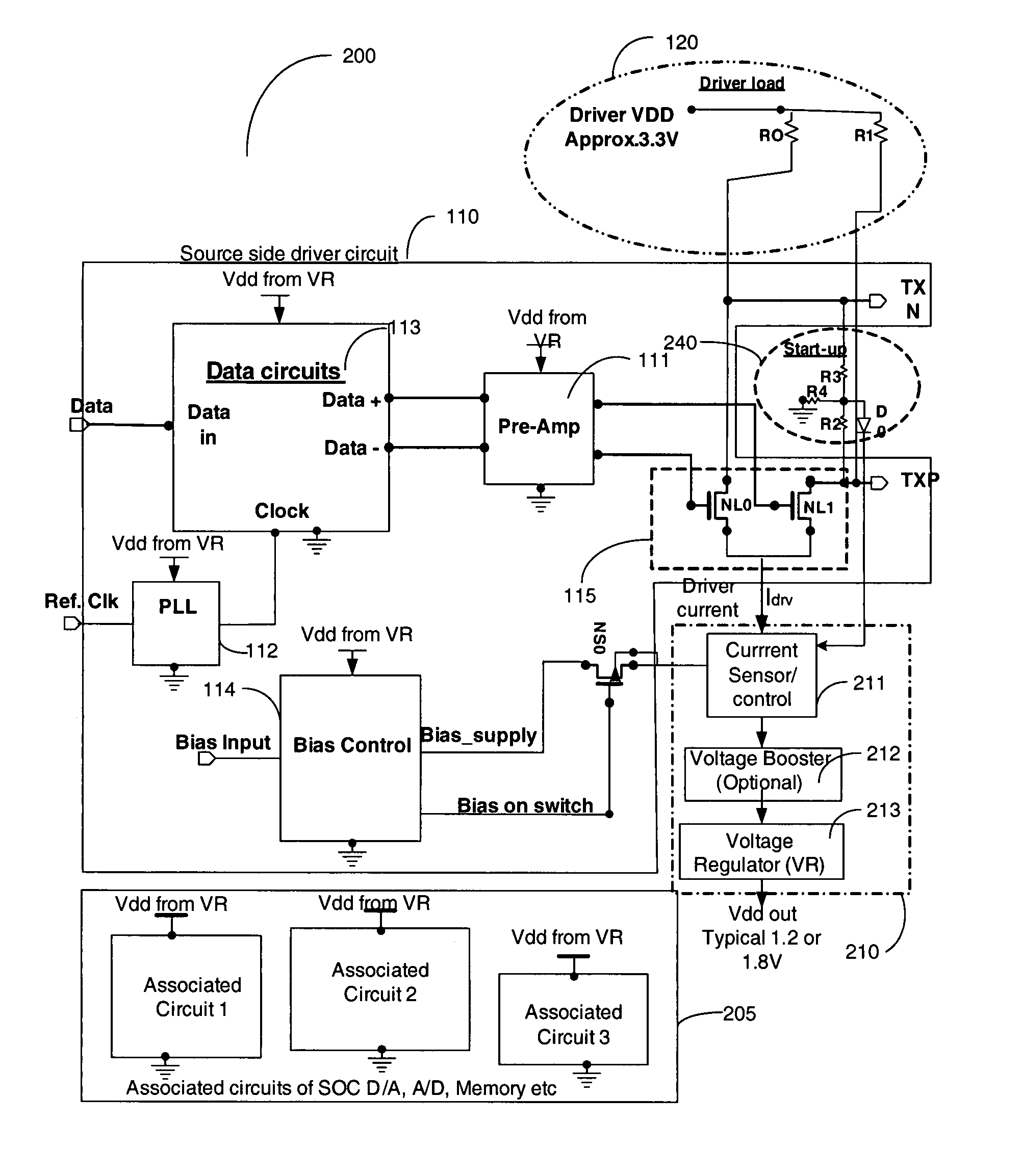
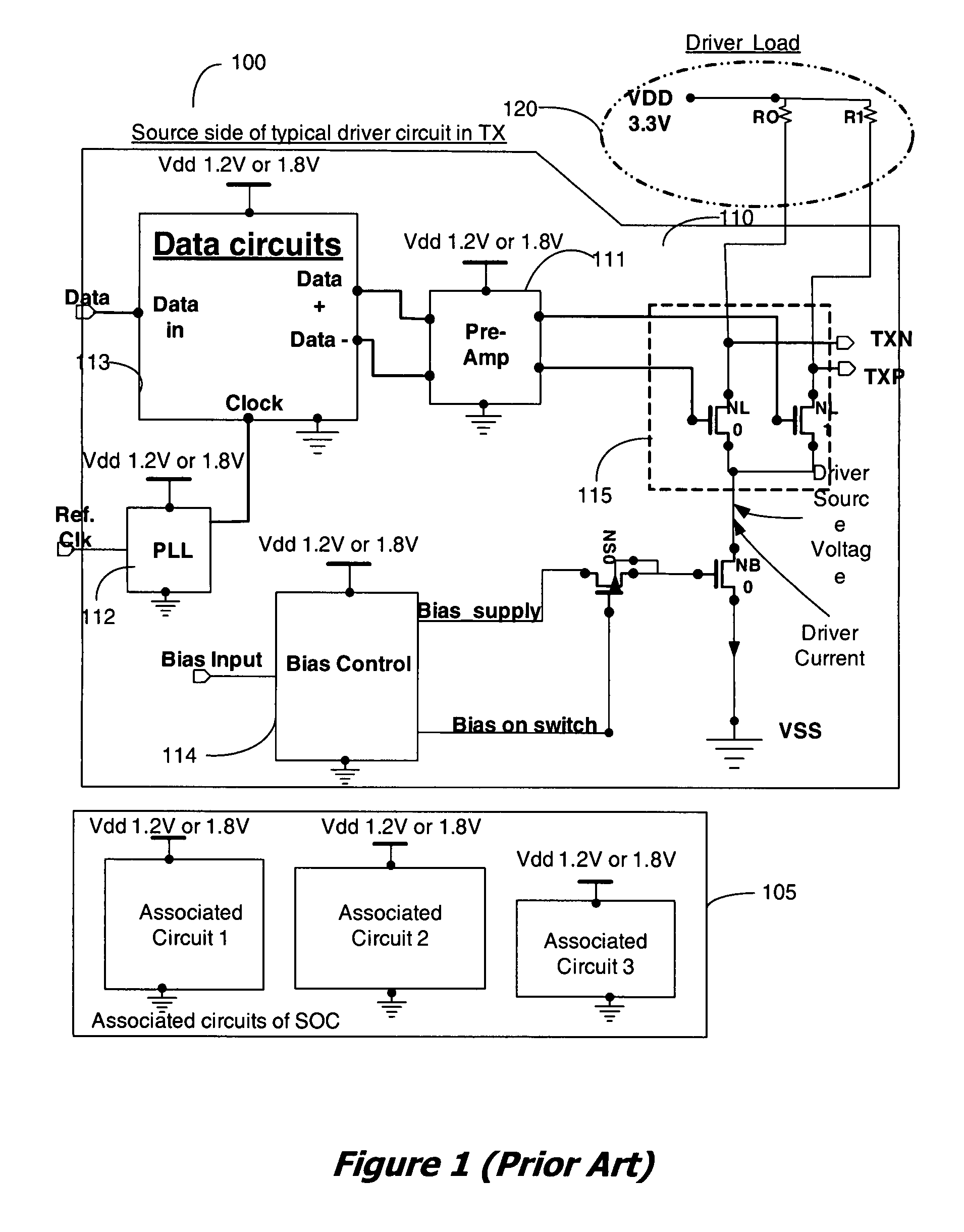
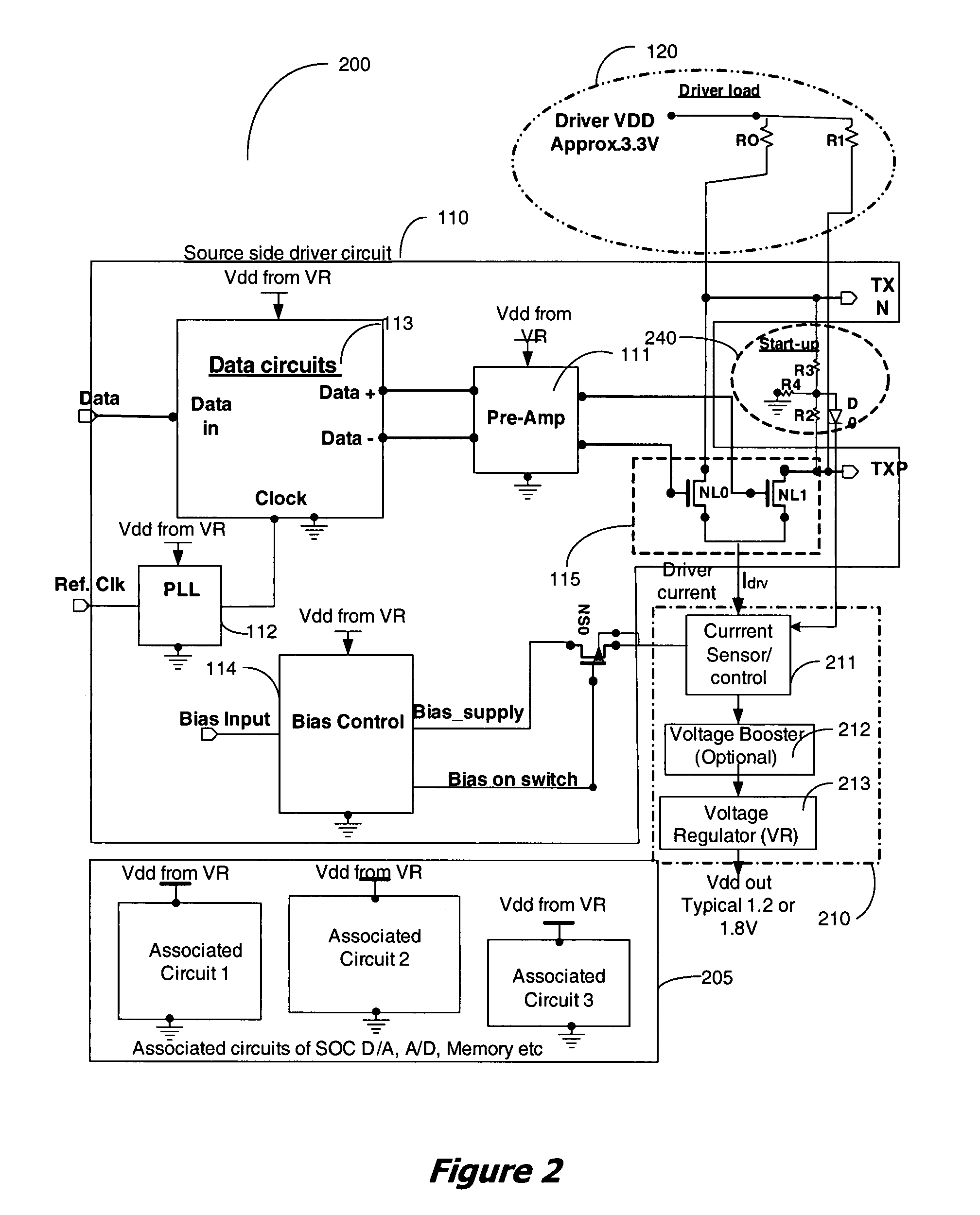
Apparatus and method for recovery of wasted power from differential drivers
InactiveUS20080278224A1Power reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationElectrical resistance and conductanceDifferential line
An apparatus and method for supplying power to circuits of an integrated circuit (IC) from the wasted power in low-swing high-speed differential line drivers used in the IC, is disclosed. In a high speed line driver the load resistors of the driver are connected to a power supply, either the local power supply or the receiver power supply. DC power for the driver is supplied through these resistors. A large portion of this power, supplied from the power supply is wasted in the DC set-up circuit of the differential line driver. It is proposed to use this wasted power to power selected circuits of an IC. The use of this wasted power from the drivers for powering the circuits reduces the overall power dissipation of the system.
Owner:ANALOGIX SEMICON
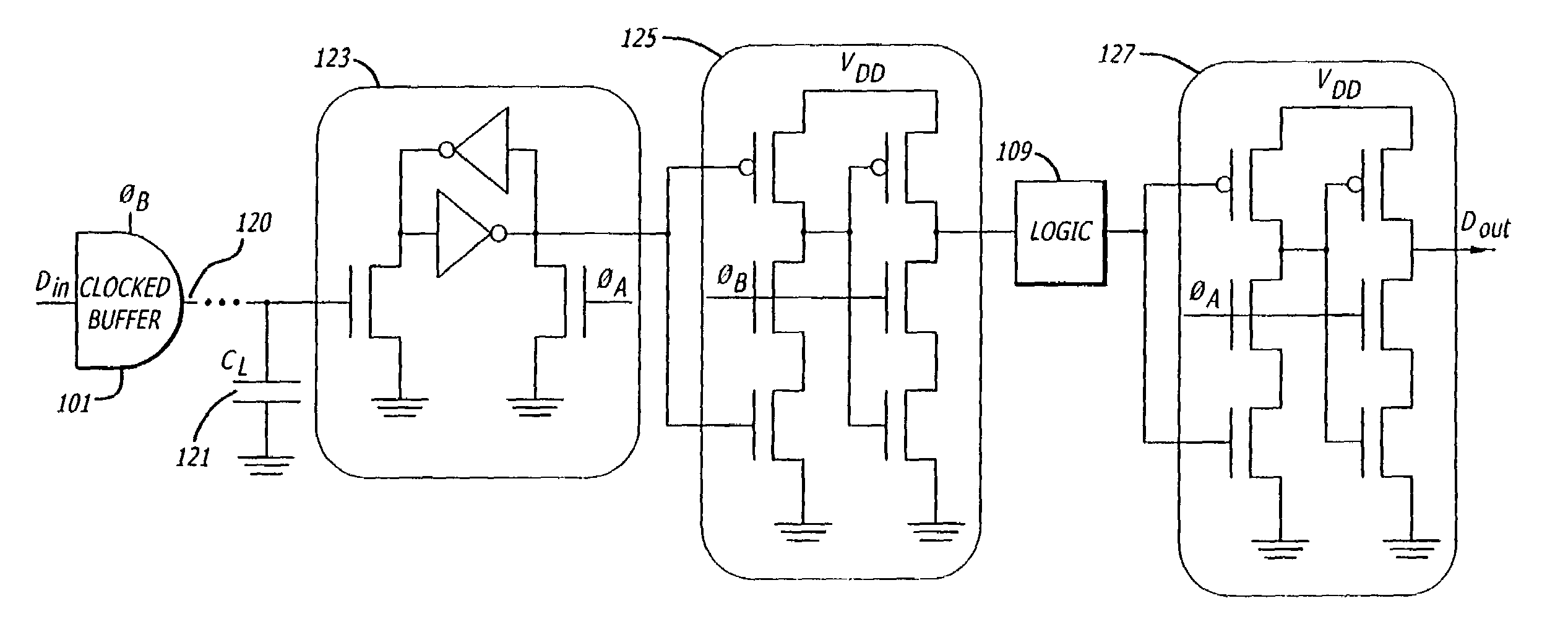
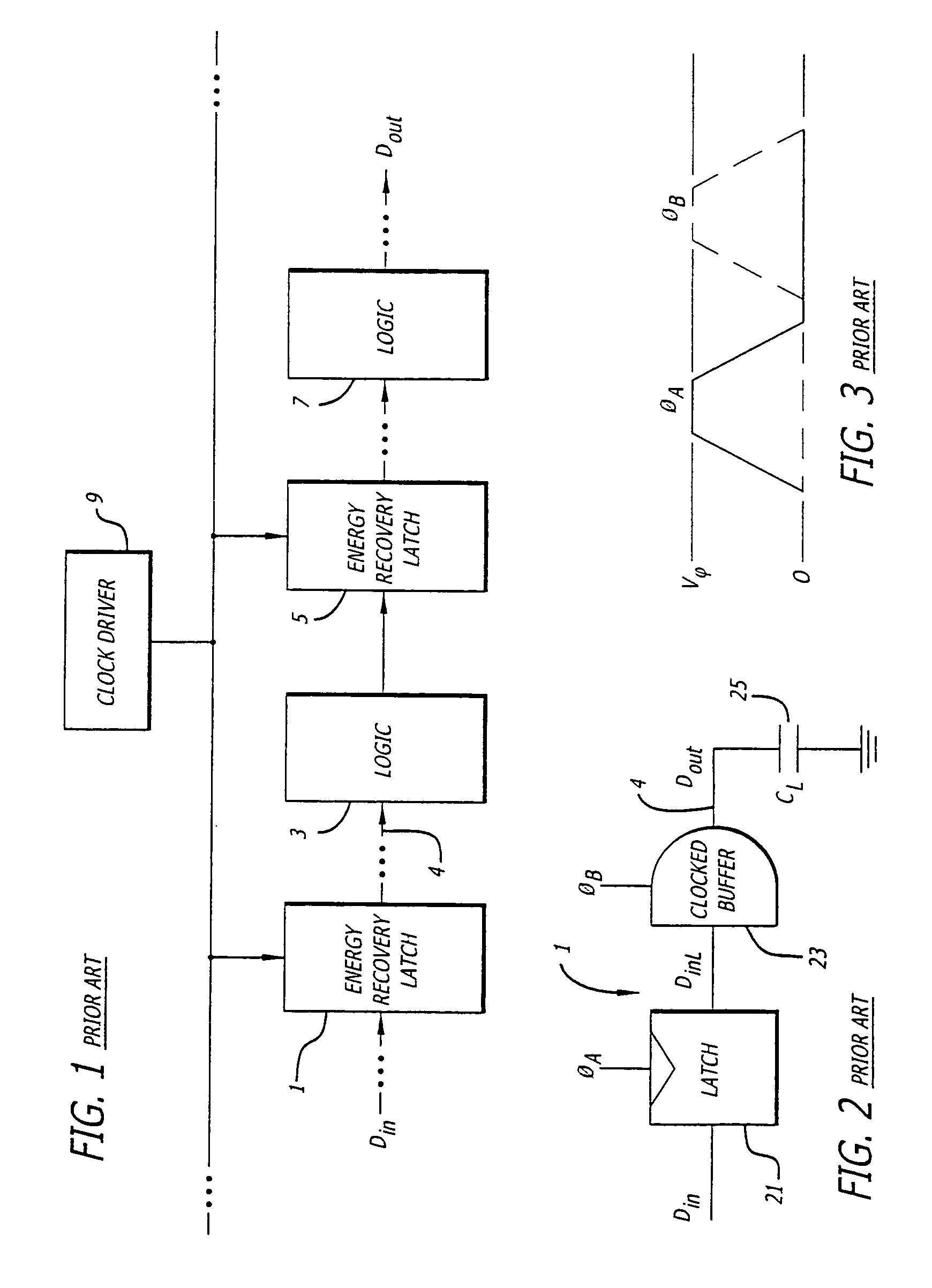
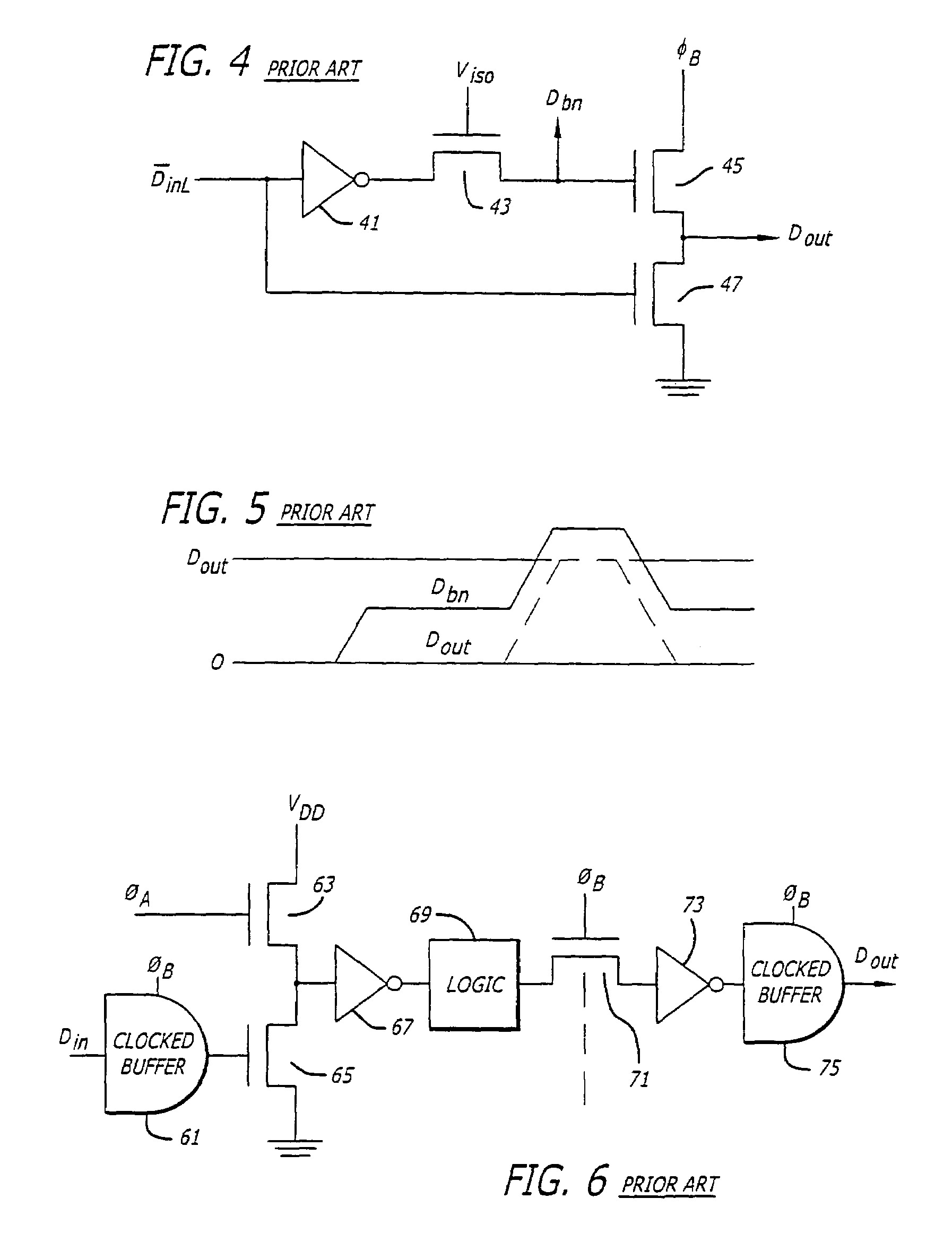
High-performance clock-powered logic
InactiveUS7005893B1Reduce energy consumptionIncrease speedReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by energy recoveryEngineeringLogic circuitry
High performance clock-powered logic runs at below supply levels and reduces the need for faster digital logic circuitry. In a preferred embodiment, a clocked buffer (101) is used to drive the signal line. The receiving end of the line is connected to a jam latch (123), preferably followed by an n-latch (125), followed by the digital logic (109), and followed by a second n-latch (127). The first n-latch is eliminated in an alternative embodiment, preferably one that uses complementary data signals.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method and system for reducing power consumption in digital circuitry using charge redistribution circuits
ActiveUS7116137B2Reduce power consumptionPower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationCharge recoveryEngineering
A method and system for reducing power consumption in digital circuits using charge redistribution include a plurality of signal lines, an intermediate floating virtual source / sink, and a charge redistribution circuit connected to each signal line that isolates the signal line from its source and connects it to the intermediate floating virtual source / sink during an idle period prior to a change of state.This charge redistribution provides steady state statistical independent advantage due to charge recycling without inserting extra complimentary lines.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PVT LTD
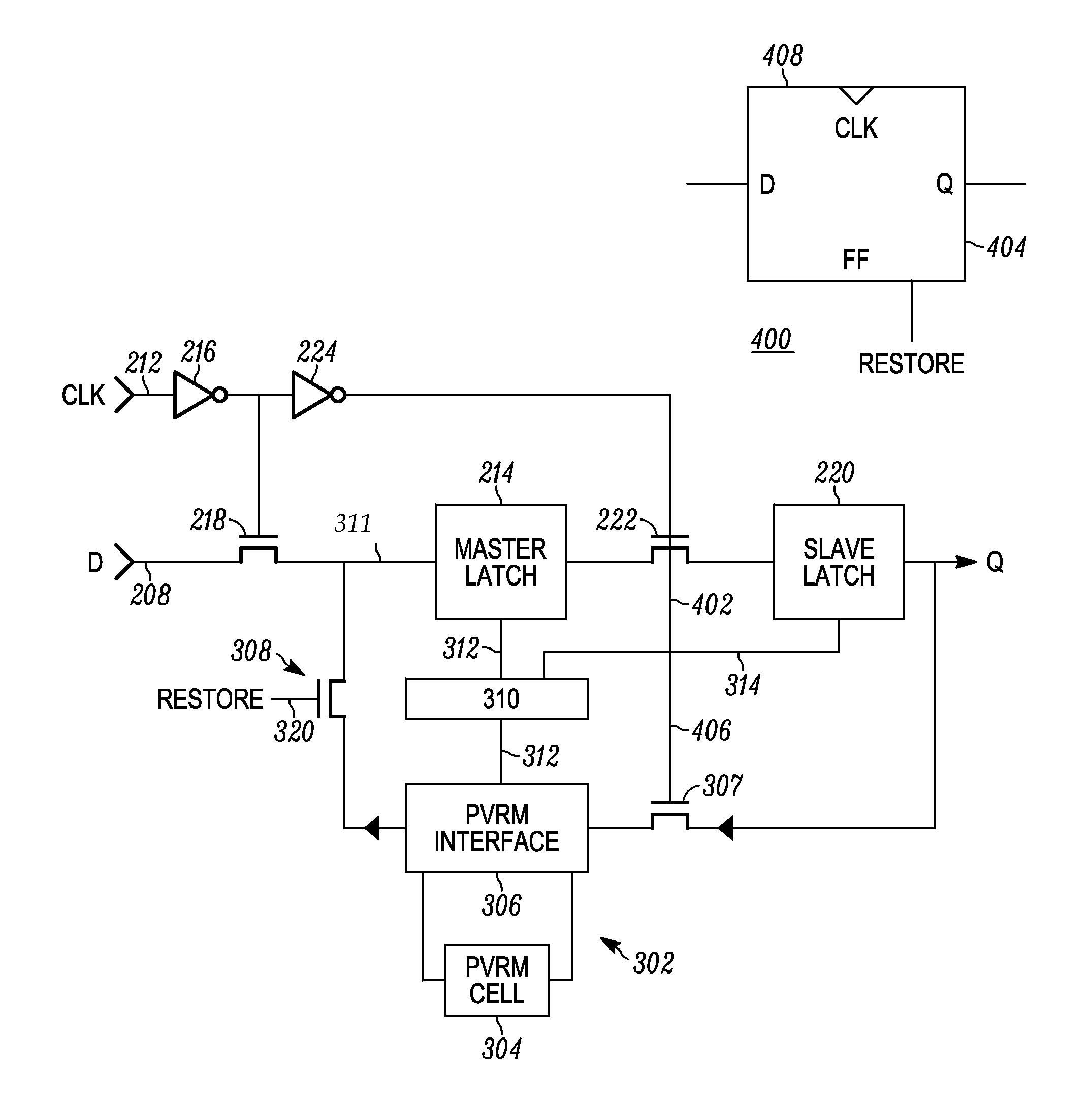
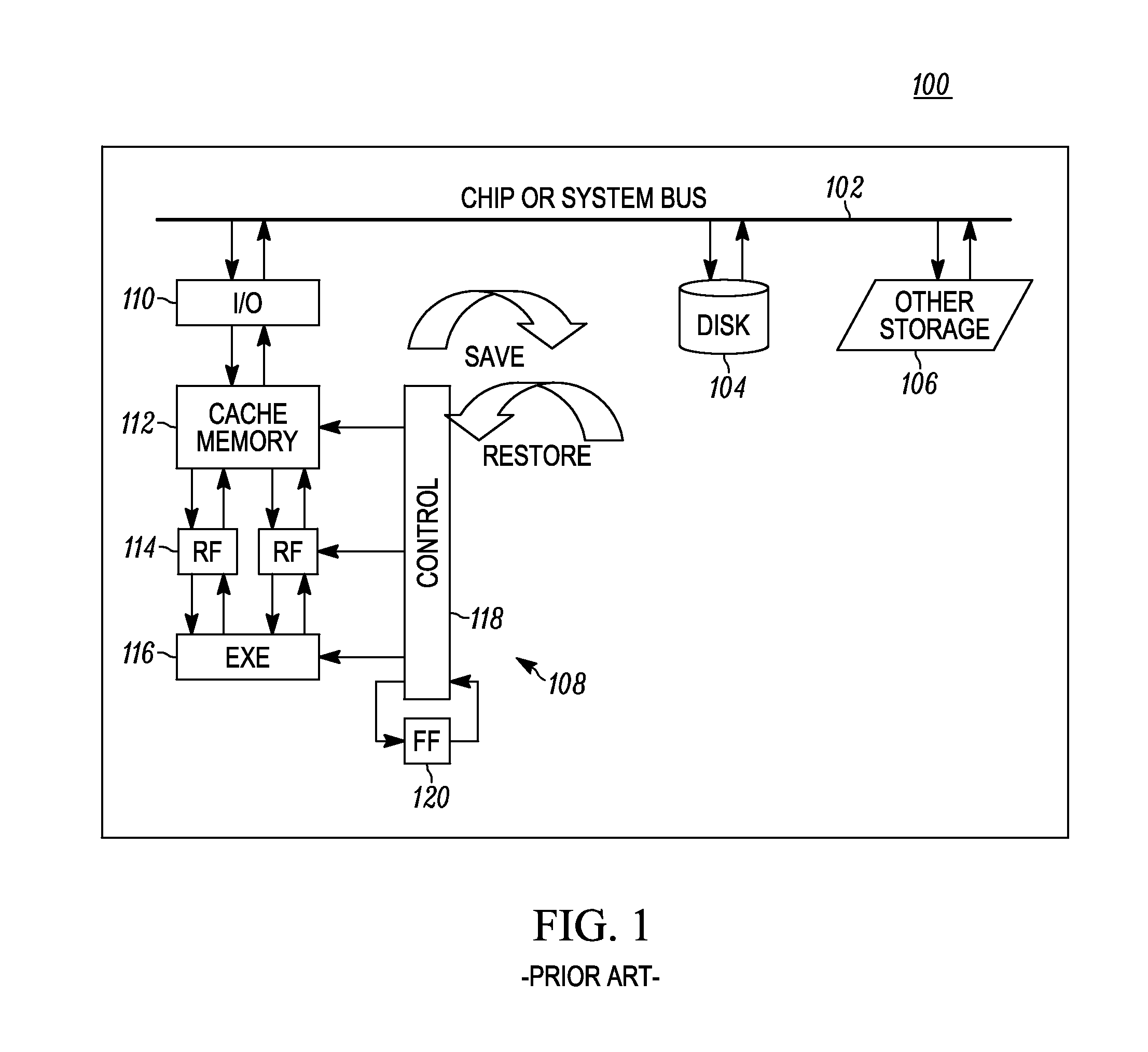
Method and apparatus for controlling state information retention in an apparatus
ActiveUS20130070515A1Power reduction by control/clock signalPower reduction by energy recoveryControl equipmentVariable resistance
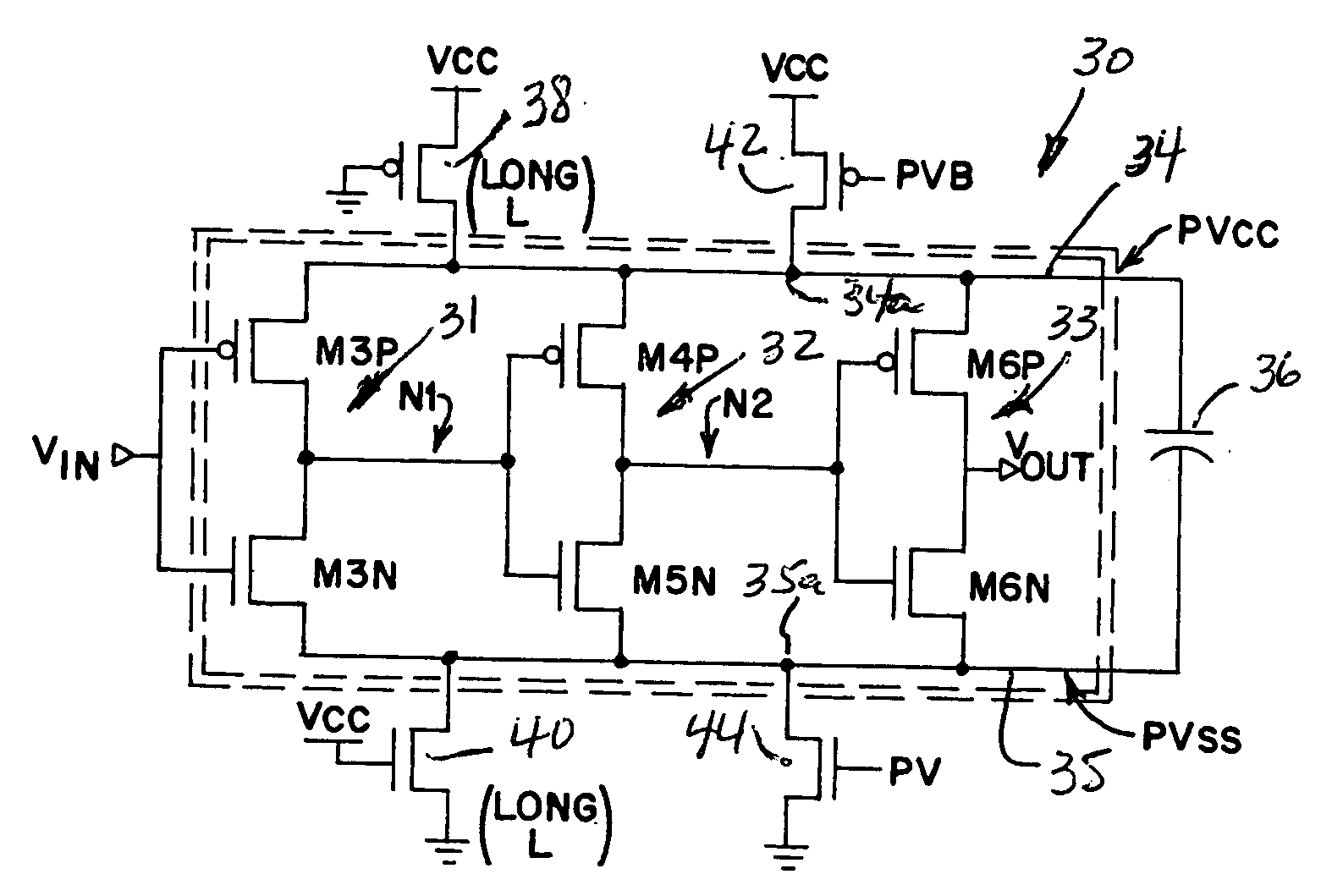
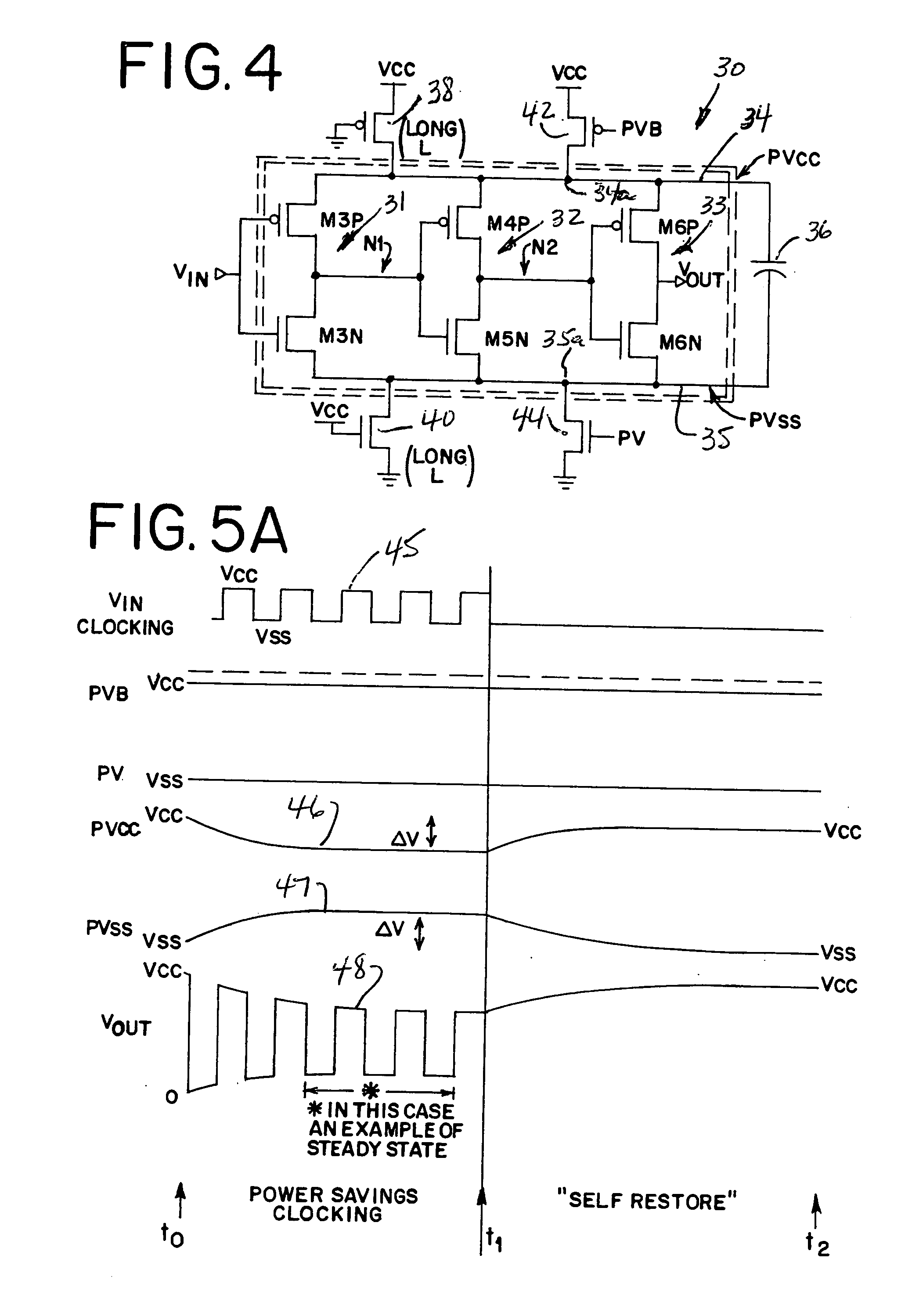
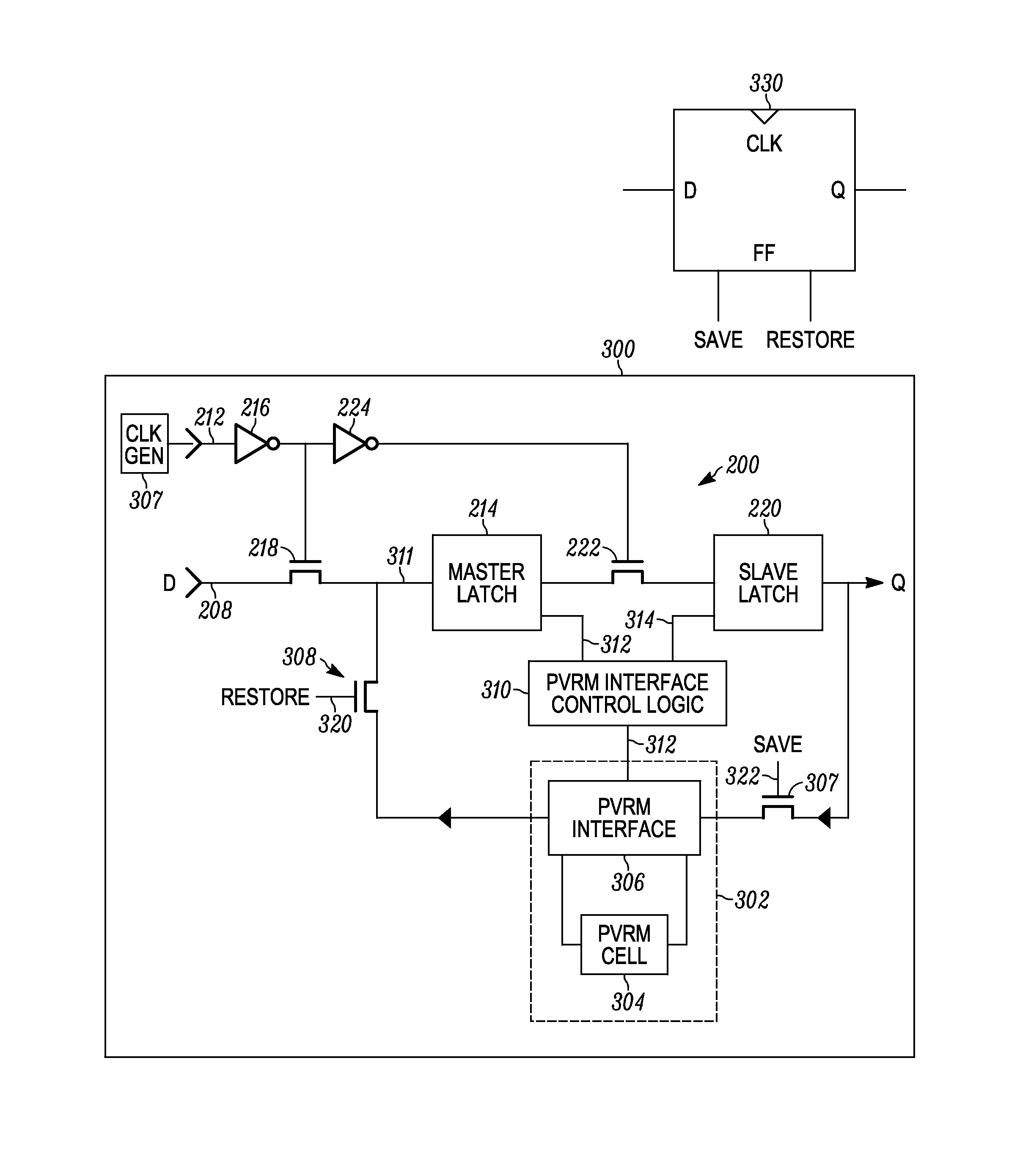
A method and apparatus for controlling state information retention determines at least a state information save or restore condition for at least one processing circuit such as one or more CPU or GPU cores or pipelines, in an integrated circuit. In response to determining the state information save or restore condition, the method and apparatus controls either or both of saving or restoring of state information for different virtual machines operating on the processing circuit, into corresponding on-die persistent passive variable resistance memory. The state information save or restore condition is a virtual machine level state information save or restore condition. State information for each of differing virtual machines is saved or restored from differing on-die passive variable resistance memory cells that are assigned on a per-virtual machine basis.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
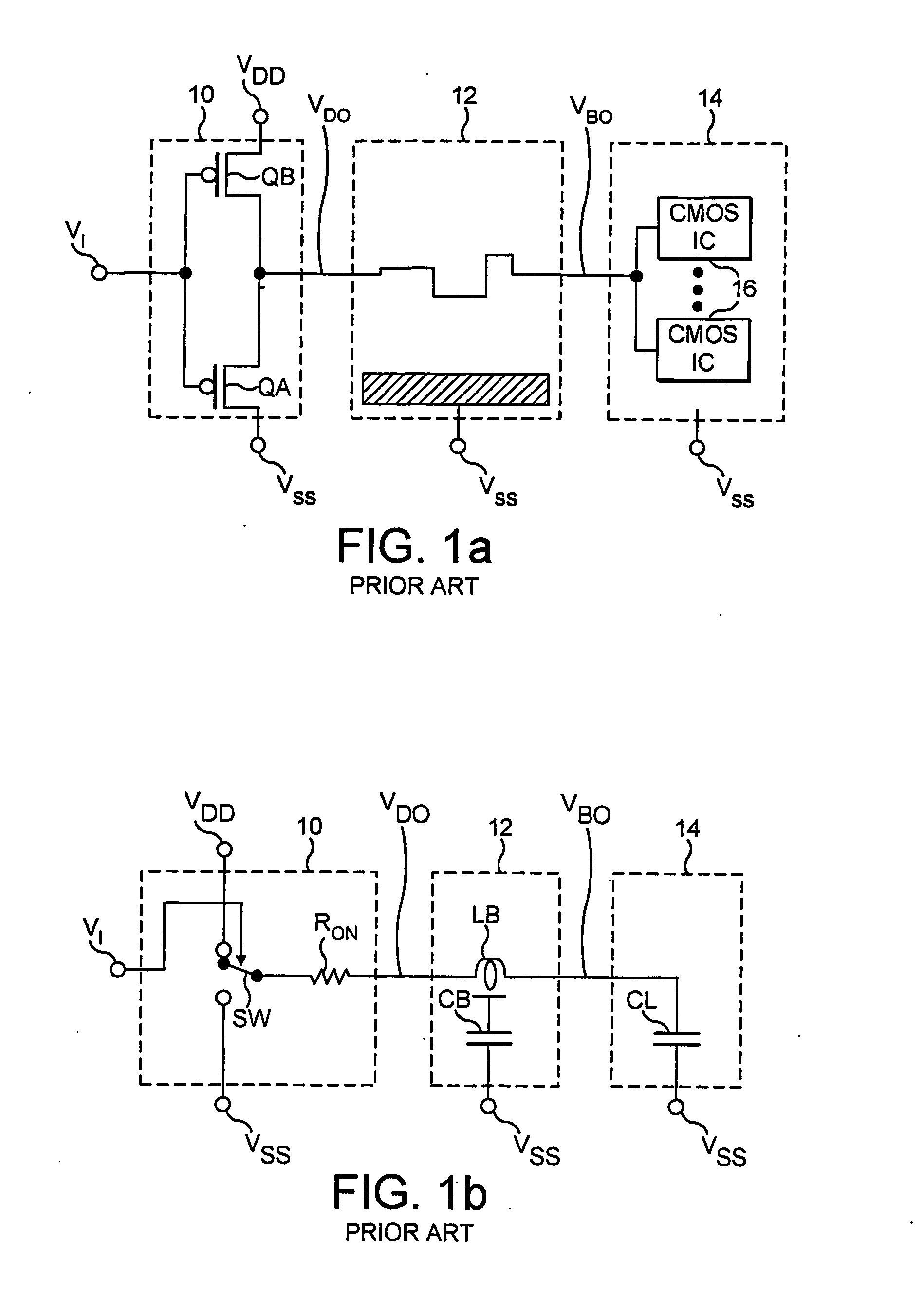
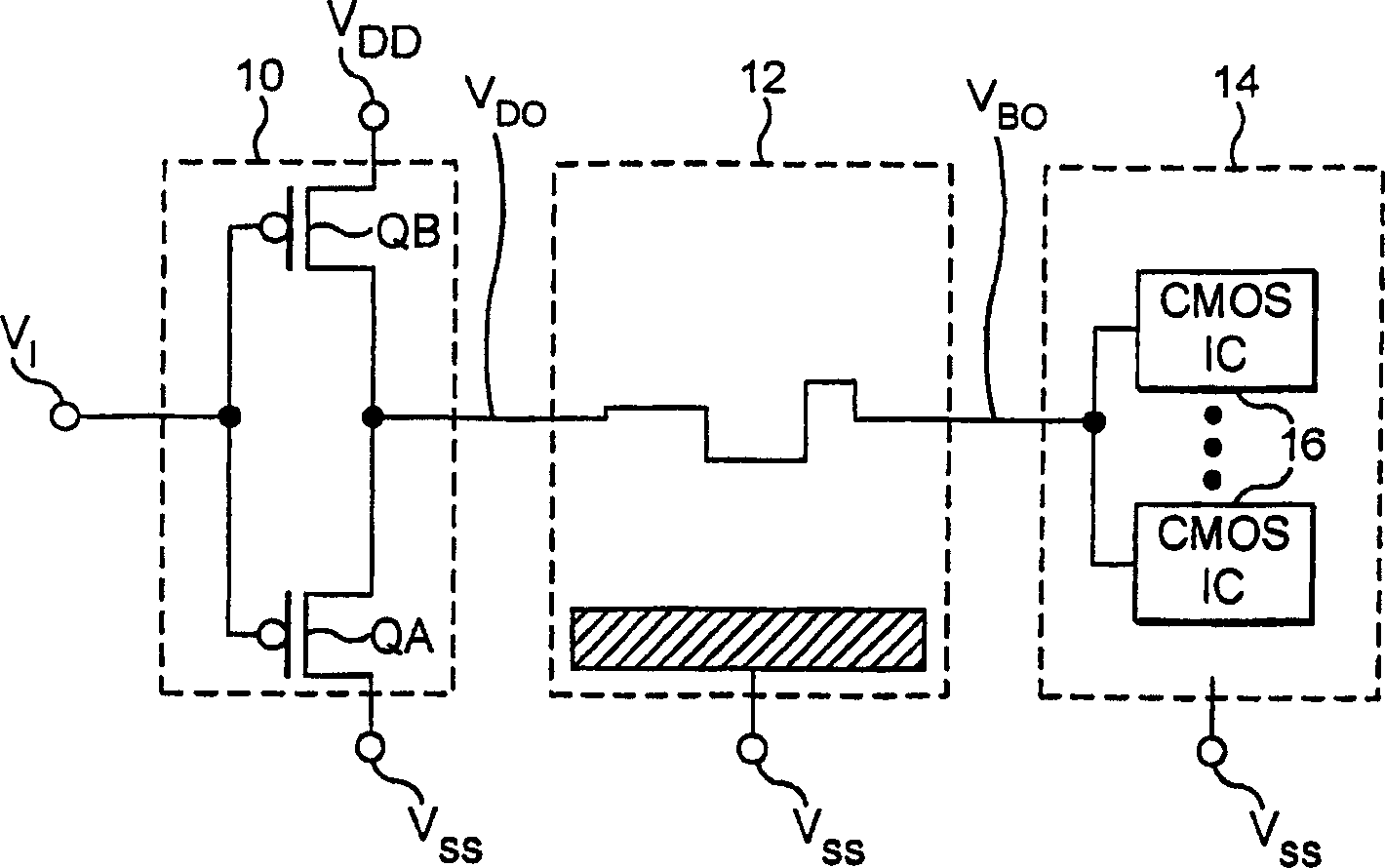
Resonant line drivers
InactiveUS20070182461A1Low signalImprove signal integrityPower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationDriver circuitCapacitance
An electronic driver circuit for comnmunicating a logic value along a conductor (12) from one part of a system (10) to another (14) by representing each of two logic values by one of two logic levels (VDD, Vss).A capacitor (CR1) reduces ground and power reference differences between a chip containing the driver and the board on which it is mounted. The capacitor also provides power and ground decoupling. According to another aspect, a controlled slew rate ramp initiates an incident or outbound wave or turn-on and circuits are described for this. The time taken to complete the controlled slew rate ramp can be adjusted. The arrangements allow reduced power consumption, whilst at the same time producing desirable signal characteristics.
Owner:MIDAS GREEN
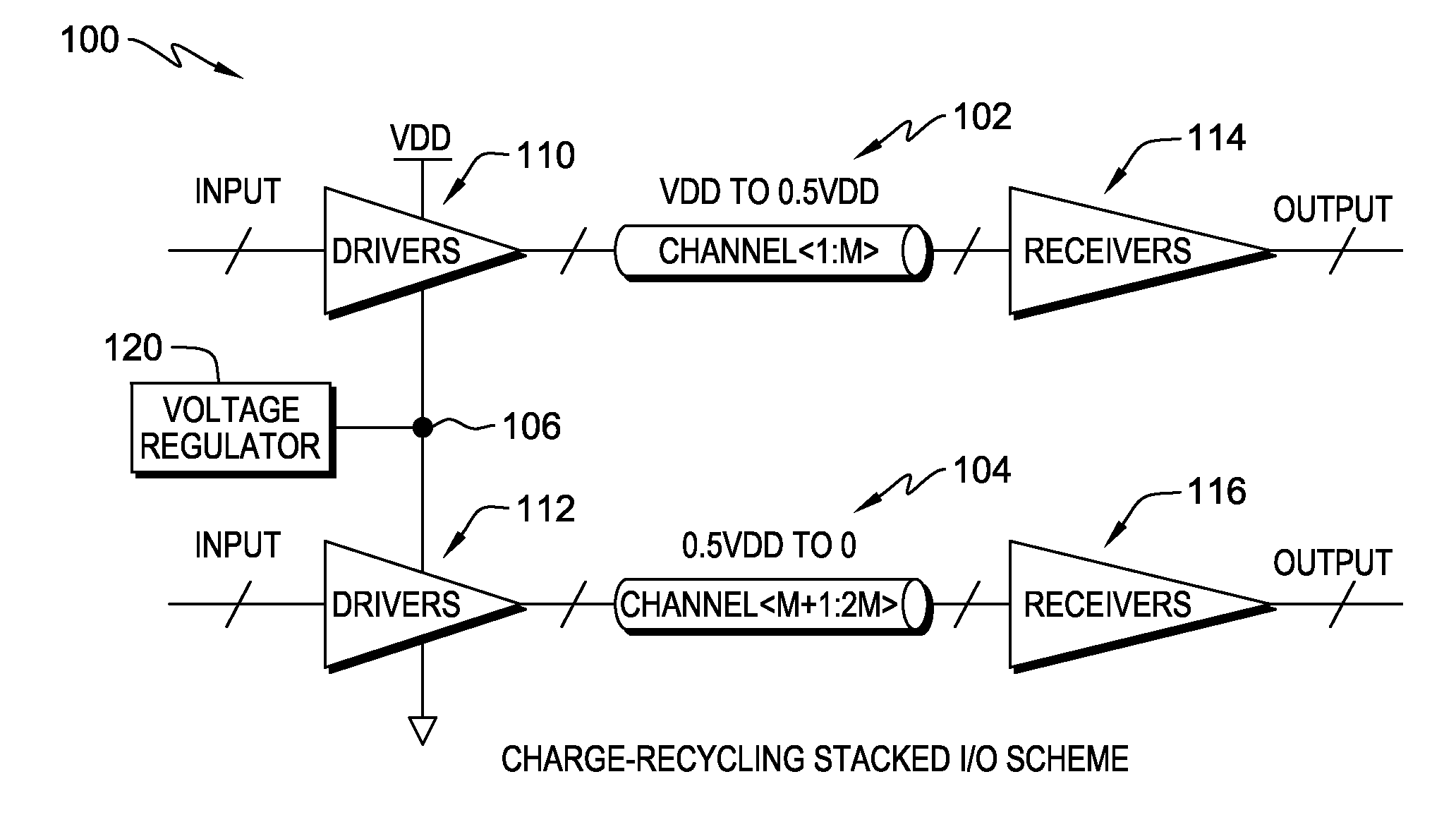
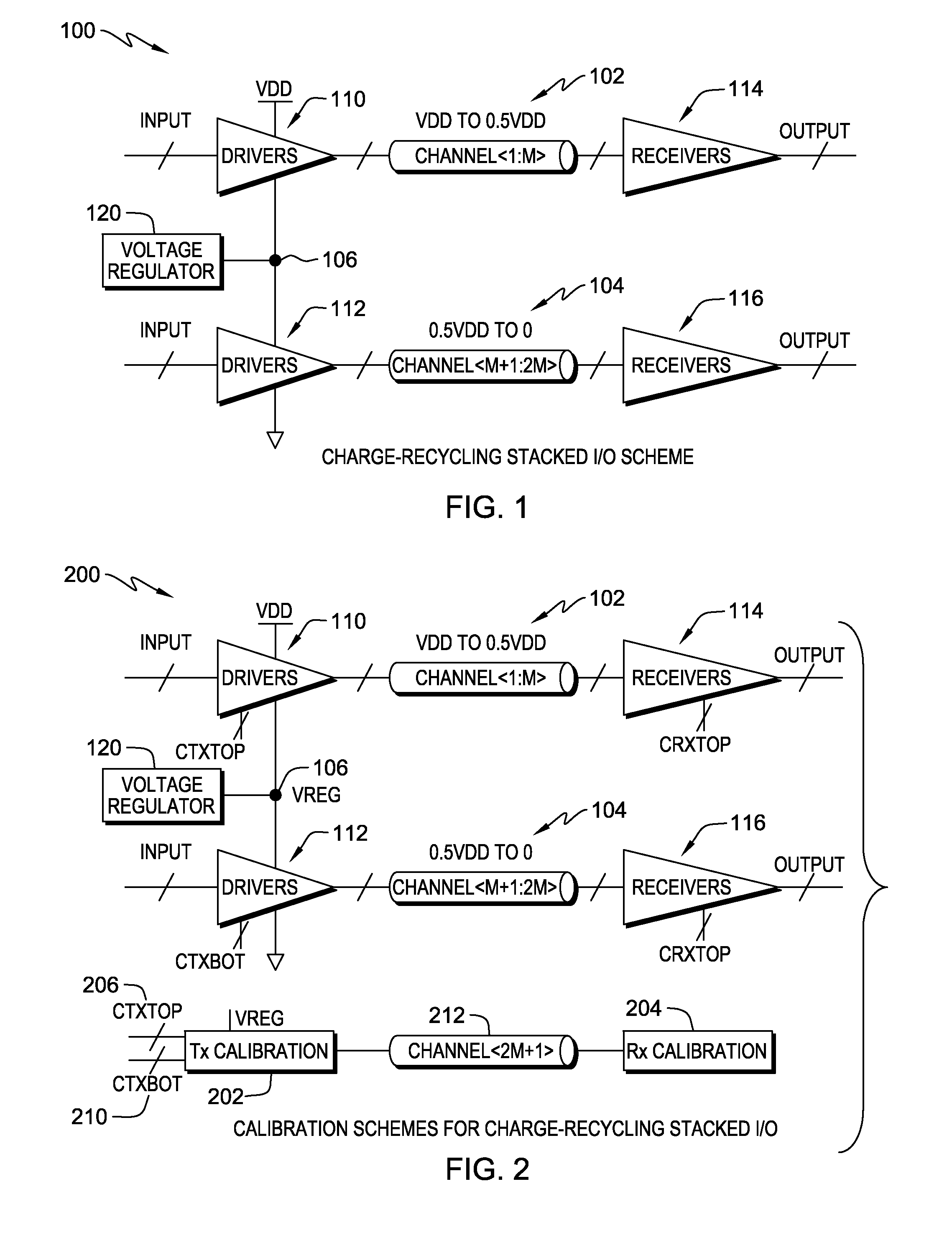
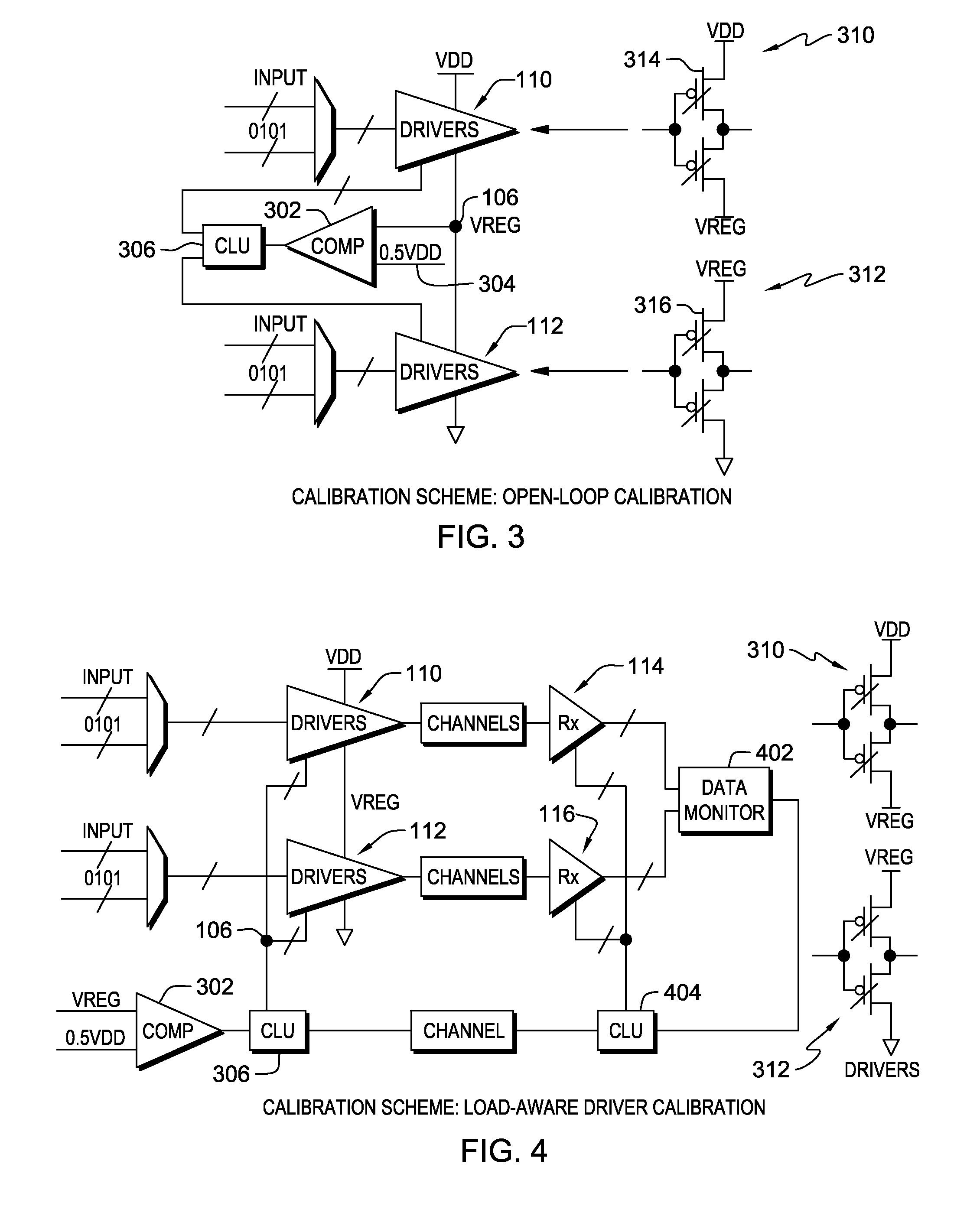
Calibration schemes for charge-recycling stacked voltage domains
ActiveUS20140176198A1Reduced strengthHigh strengthPower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationVoltage regulationEngineering
A method and system are disclosed for calibrating a mid-voltage node in an integrated circuit including an input-output circuit having charge-recycling stacked voltage domains including at least first and second voltage domains. In one embodiment, the method comprises transmitting data through the input-output circuit, including transmitting a first portion of the data across the first voltage domain, and transmitting a second portion of the data across the second voltage domain. The method further comprises measuring a specified characteristic of the data transmitted through the input-output circuit; and based on the measured specified characteristic, adjusting a voltage of said mid-voltage node to a defined value. The voltage of the mid-voltage node may be adjusted to accomplish a number of objectives, for example, to achieve a desired trade-off between power and performance, or so that the two voltage domains have the same performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
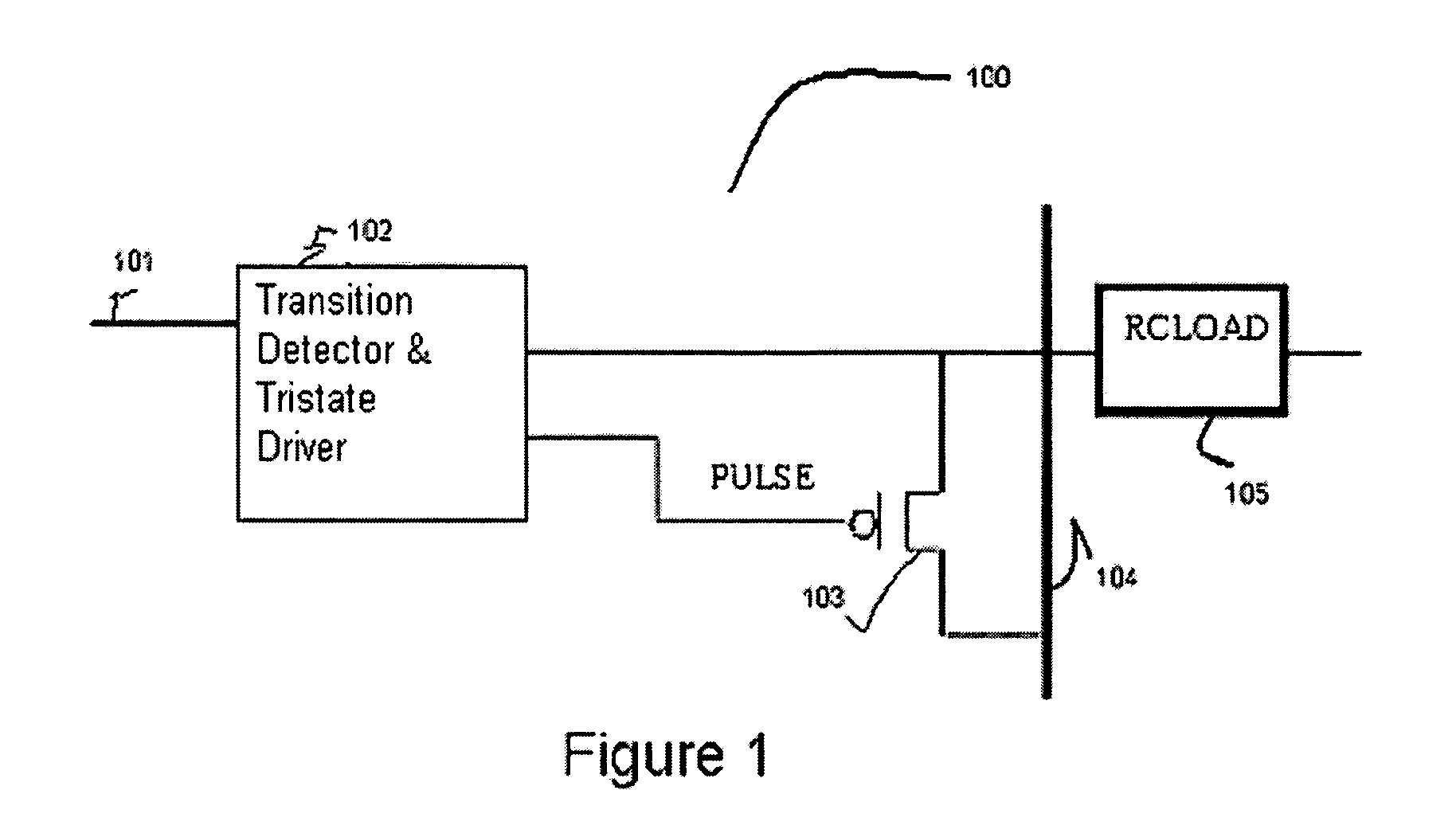
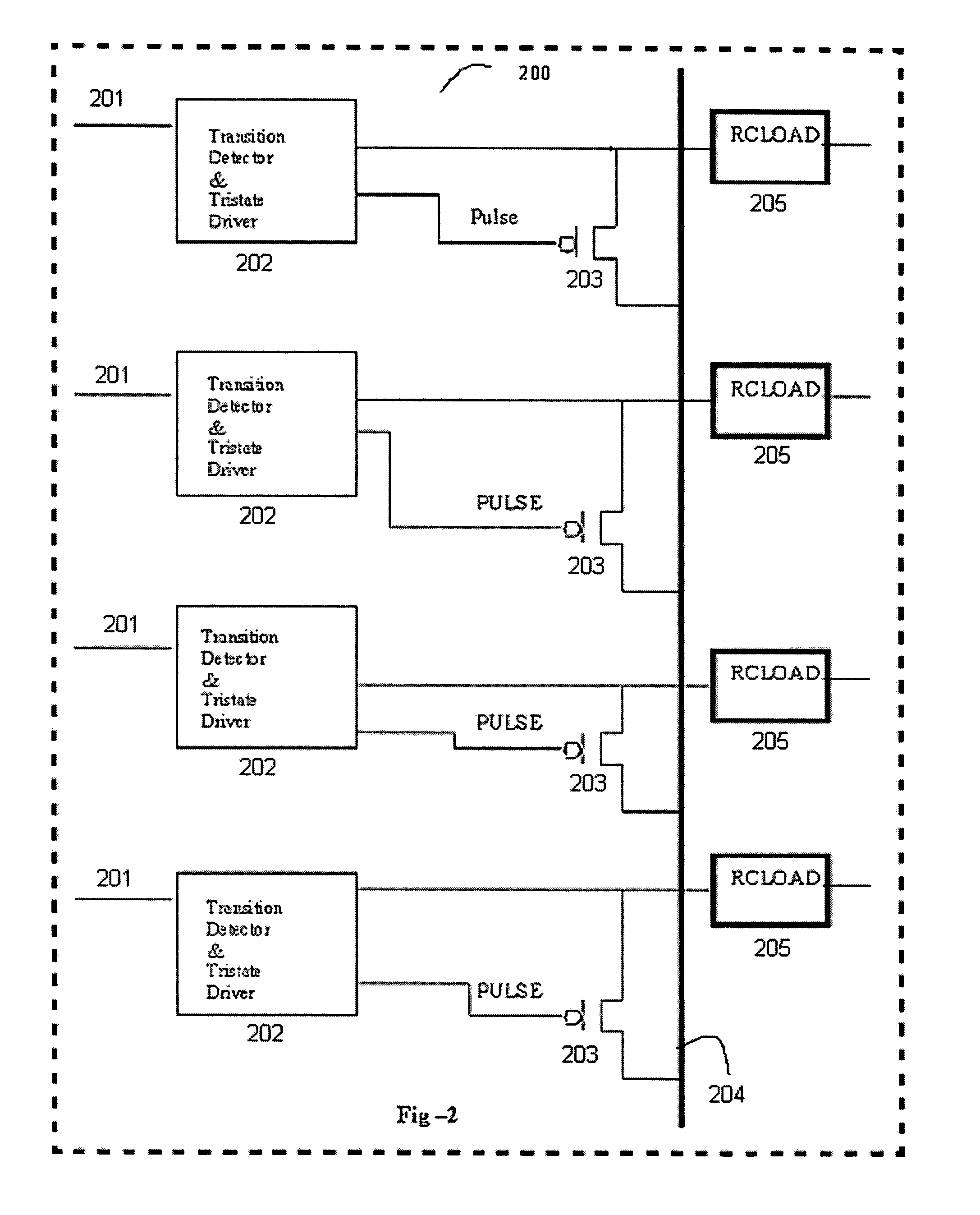
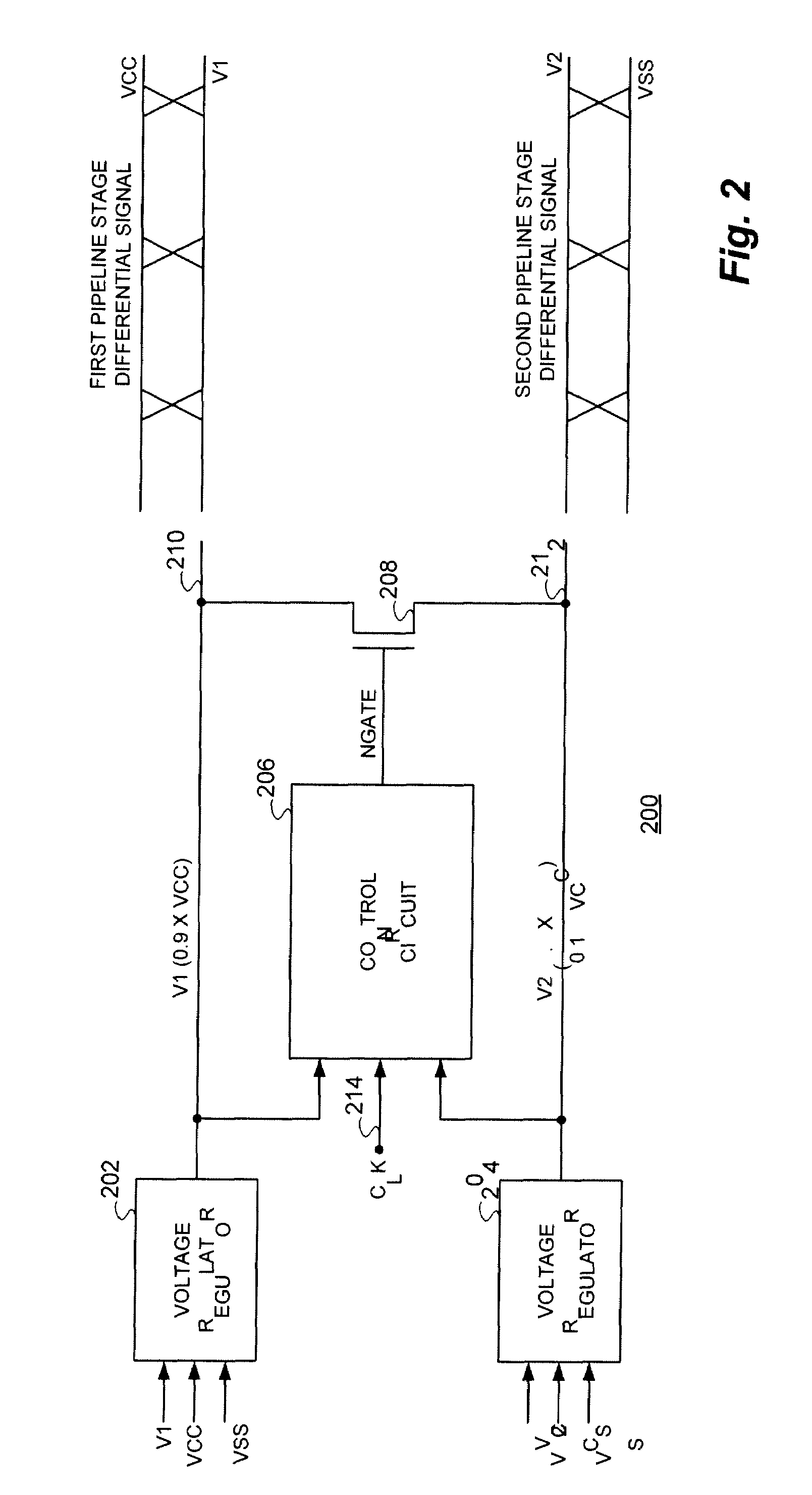
Charge recycling for multi-touch controllers
ActiveUS8432364B2Reduce electromagnetic interferenceMaximize signalPower reduction by energy recoveryDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceMultiplexer
Owner:APPLE INC
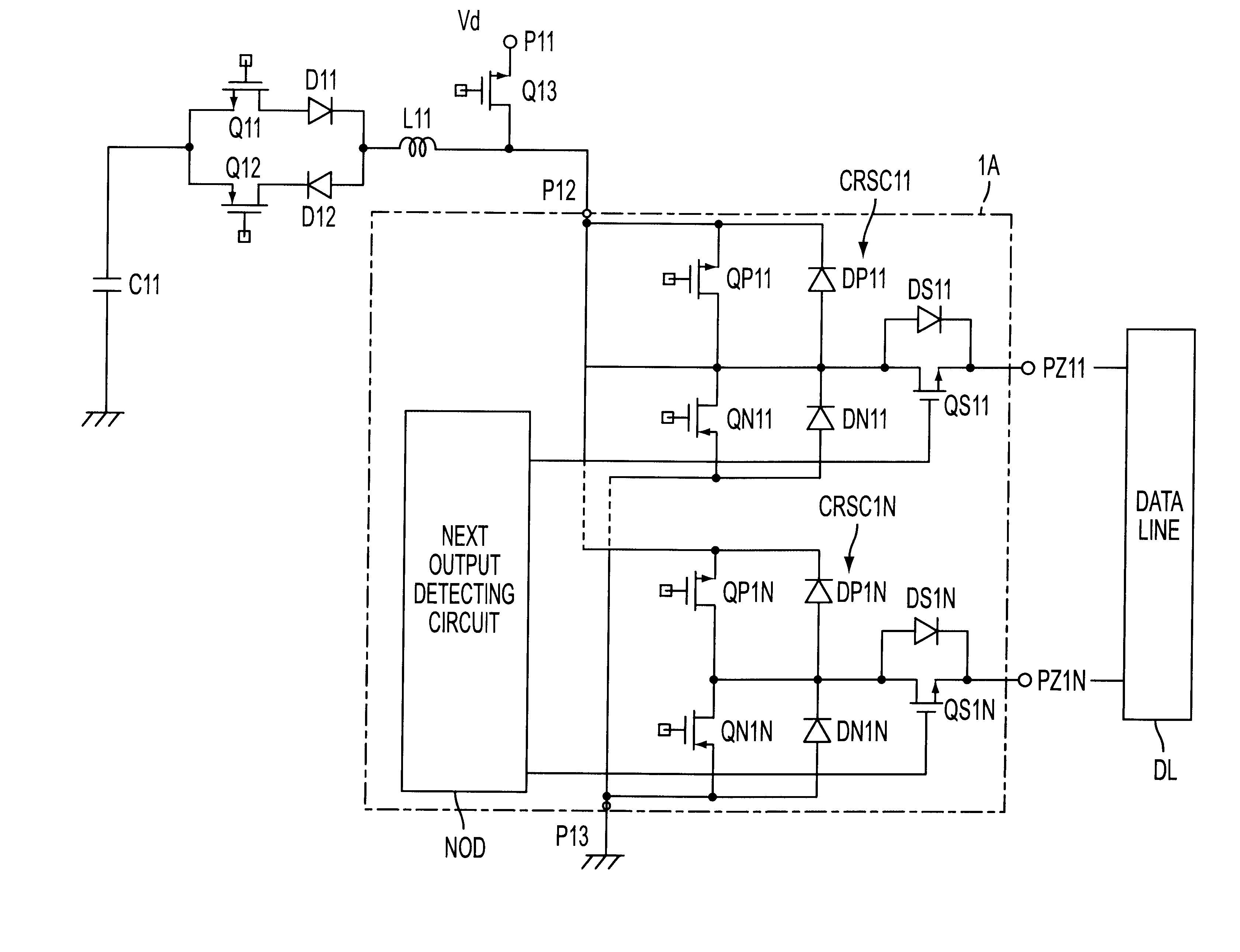
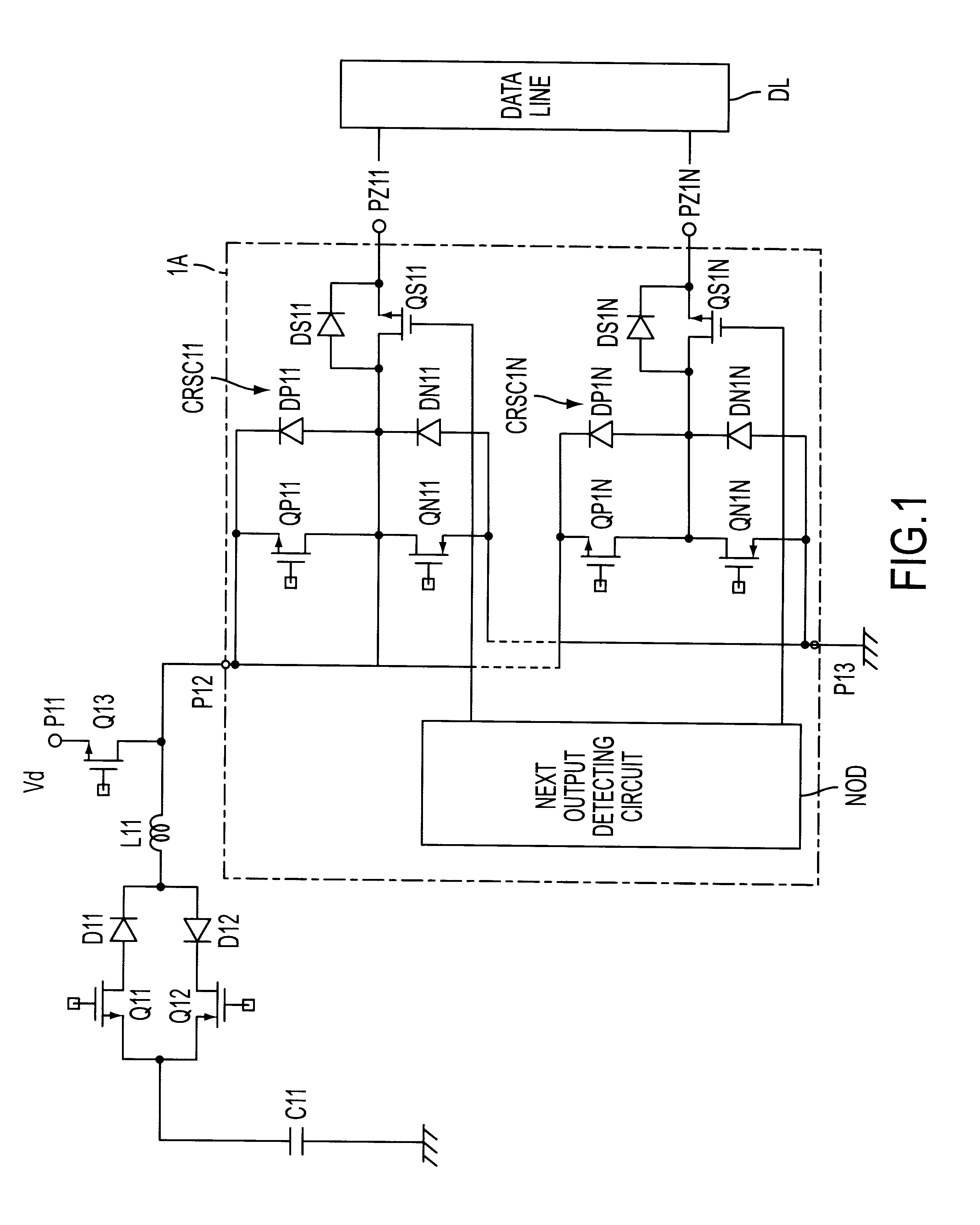
Data line drive device
InactiveUS6249279B1Increase in IC areaSimple and inexpensive and effective mannerPower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationStatic ChargesDriving circuit
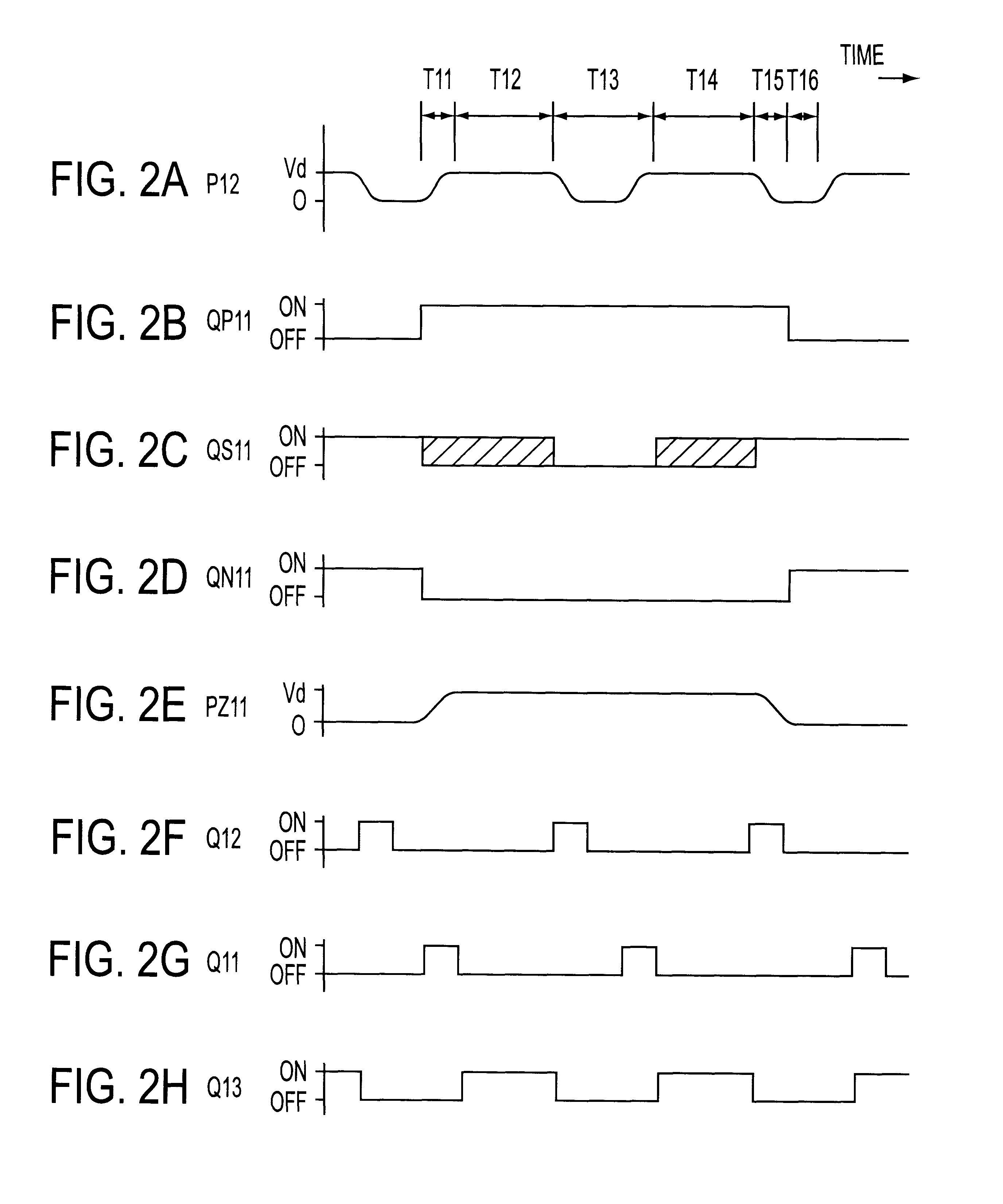
For saving power by recovery and reuse of charge on data lines of a matrix display panel, a data line drive device, has a simplified circuit configuration. The device comprises a matrix display panel having a plurality of data lines DL; a data line drive circuit 1A for driving said data lines DL, including a plurality of switch units QP1i, QN1i (i=1 to N) interposed between a data voltage applying terminal P12 and each of said data lines DL; electrostatic charge storage means C11, L11 for storing electrostatic charge on said data lines, which is connected to said data drive circuit 1A; and a switch QS1i for recovering the charge, having a parasitic diode DS1i which is interposed between said data line drive circuit 1A and each of said data lines, said charge recovering switch QS1i being brought into a conductive state when the charge on the data lines is recovered to said charge storing means C11, L11.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Low power consumption logic cell
ActiveUS20170179954A1Capacitance varyPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCapacitanceElectrical battery
The invention relates to a logic cell for an integrated circuit including at least one first variable-capacitance capacitor having first and second main electrodes separated by an insulating region, and a third control electrode capable of receiving a control voltage referenced to a reference node of the cell to vary the capacitance between the first and second main electrodes, the third electrode being coupled to a node of application of a first logic input signal of the cell, and the first and second electrodes being respectively coupled to a node of application of a cell power supply voltage and to a node for supplying a logic output signal of the cell.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Line reflection reduction with energy-recovery driver
InactiveUS6946868B2Reduce ringingIncrease power consumptionInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsEnergy recoveryCapacitor
A system and method for reducing reflections in a transmission line and for recovering energy from the load in the transmission during the process. At least three drive signal levels are utilized. The transition from the second level to the third level during a rising transition and the transition from the second level to the first level during a falling transition is timed to coincide with the arrival of the reflected signal from the immediately-preceding transition. A capacitor is advantageously used as the source for the intermediate drive signal levels and advantageously facilitates energy recovery and conservation.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Short-circuit charge-sharing technique for integrated circuit devices
ActiveUS7649406B2Easy enabling and disablingPower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationControl circuitCharge sharing
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
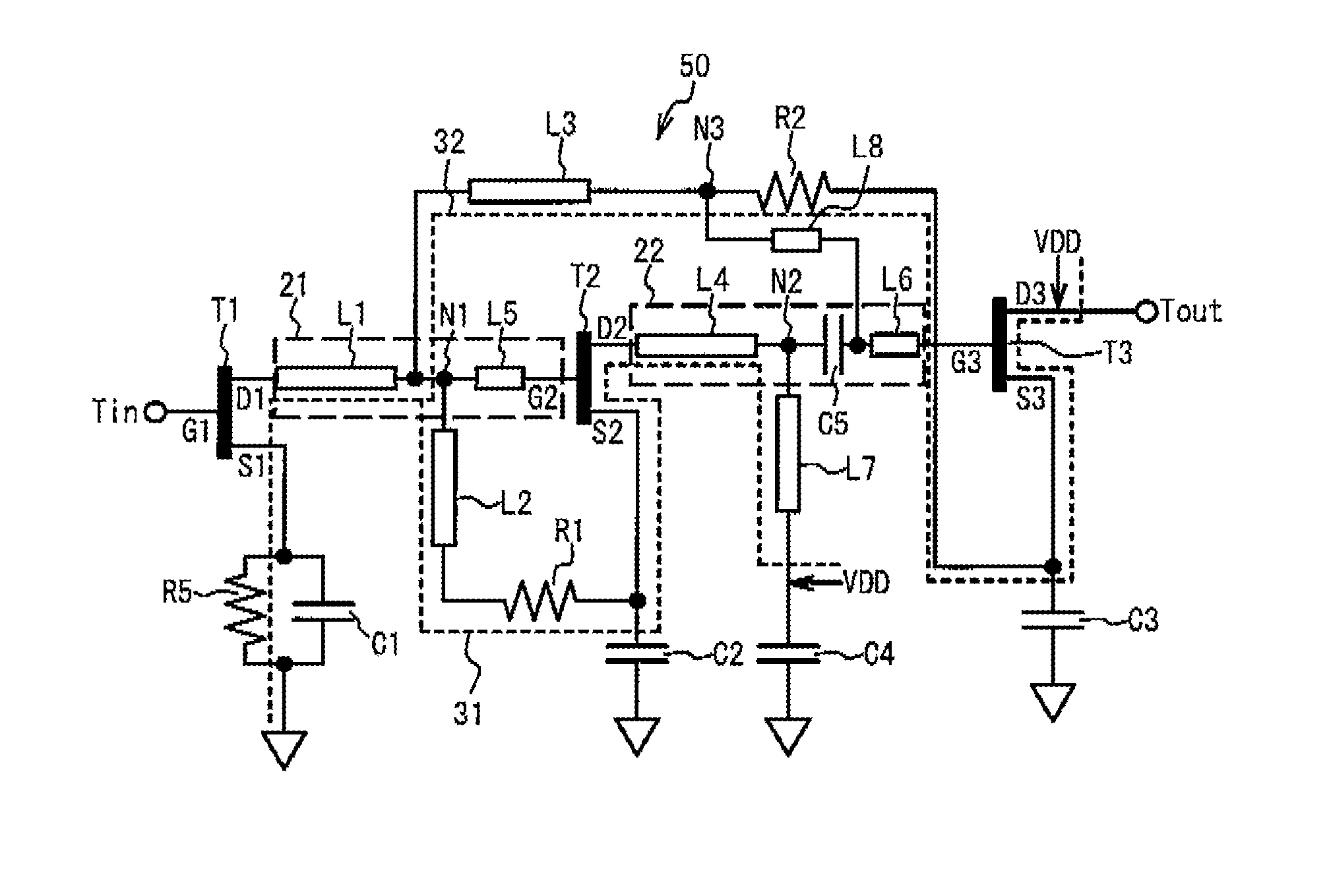
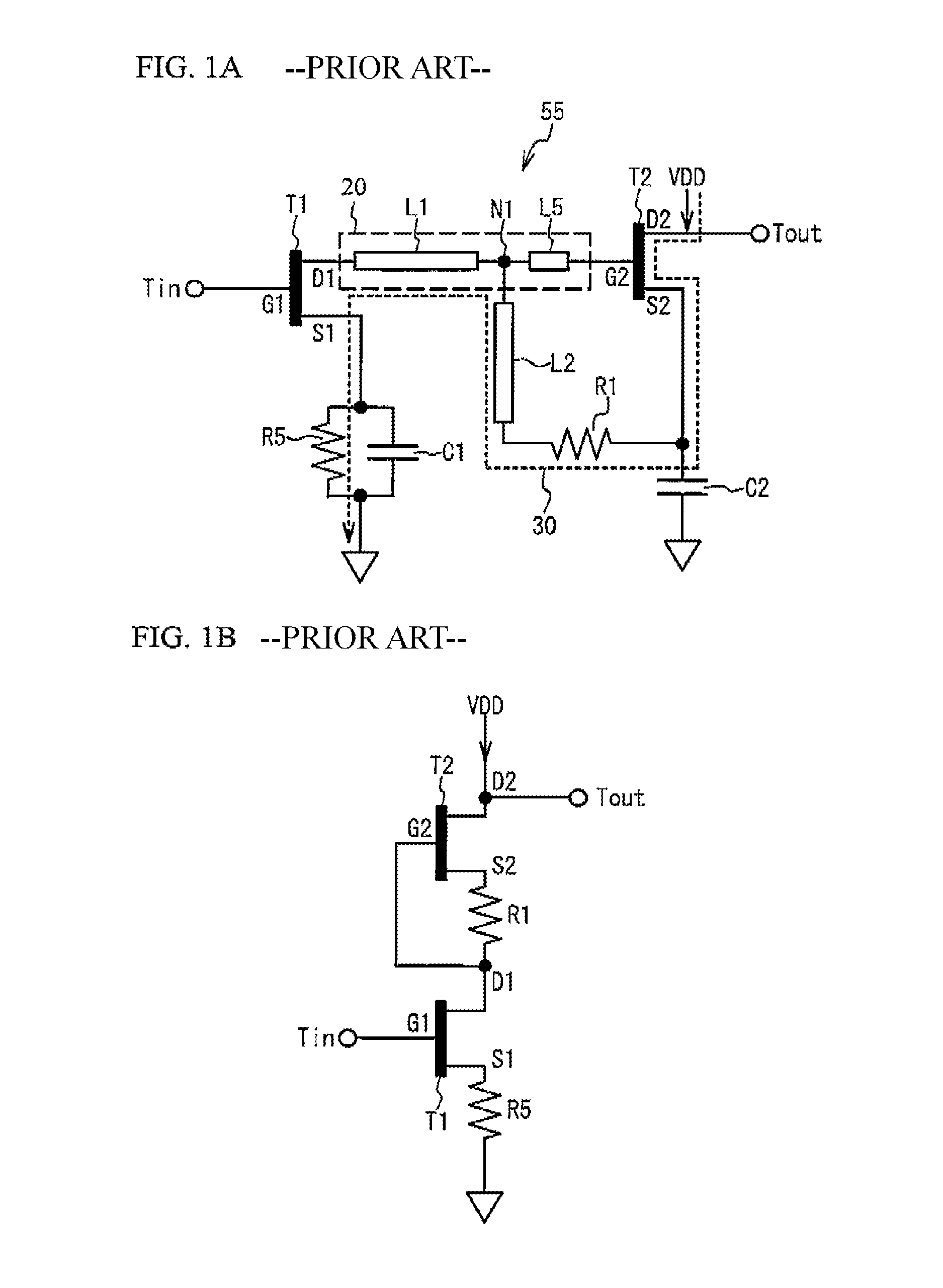
Electronic circuit
ActiveUS8508302B2Low electrical power voltageImprove performanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower flowCoupling
An electronic circuit includes: first through third transistors having a control terminal, first and second terminals; a first direct current path supplying a direct current having passed through between the first terminal and the second terminal of at least one of the second transistor and the third transistor to the second terminal of the transistor at former position compared to the transistor through which the direct current passed; a second direct current path that is different from the first direct current path and supplies a direct current having passed through between the first terminal and the second terminal of at least one of the second transistor and the third transistor to the second terminal of the transistor at former position compared to the transistor through which the direct current passed; and a common coupling point coupling the first direct current path and the second direct current path in common.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) driver circuits using shared-charge recycling charge pump structures
ActiveUS8334708B1Reduce power consumptionSacrificing output voltage levelReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by energy recoveryTransfer cellCapacitance
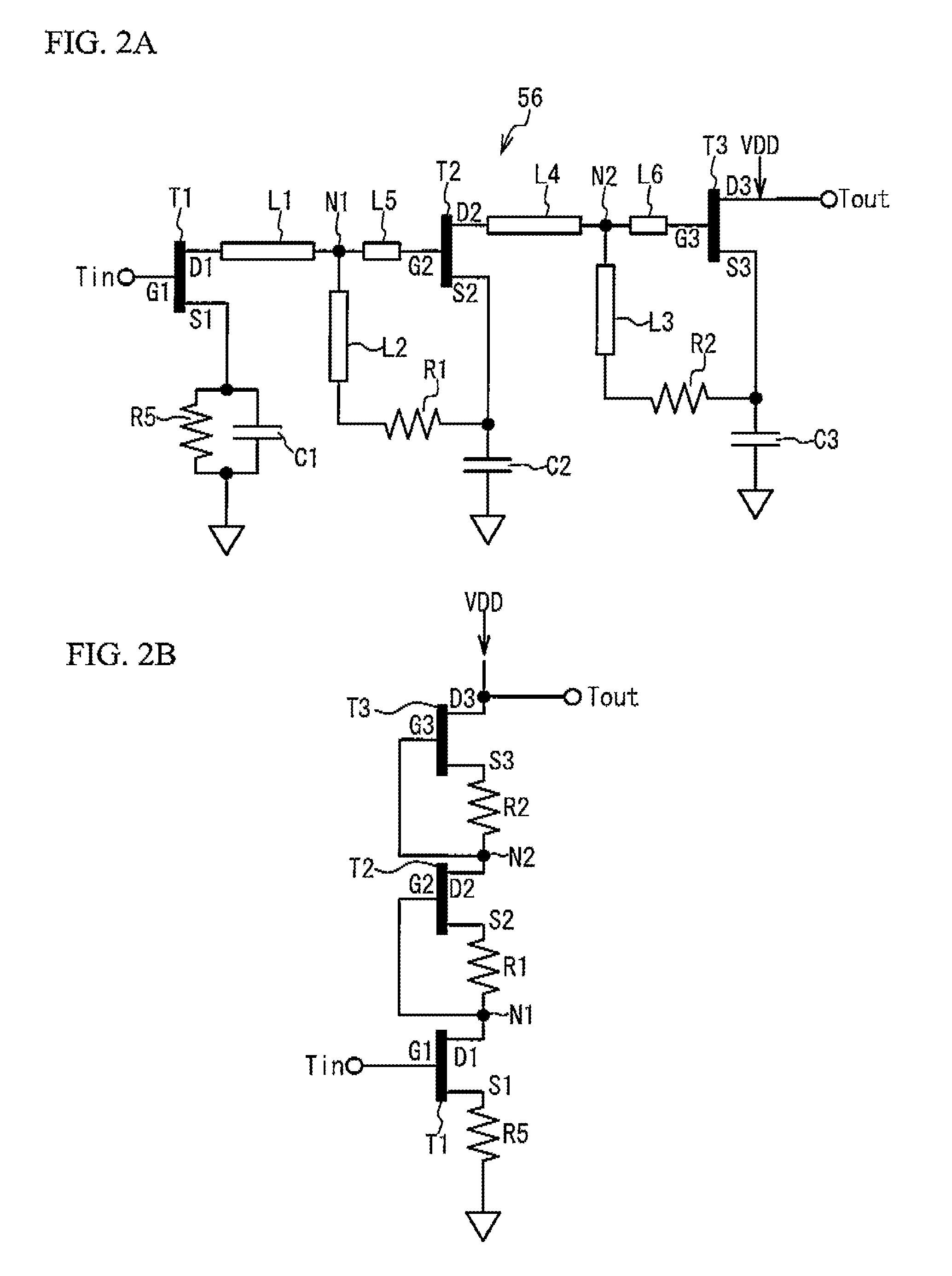
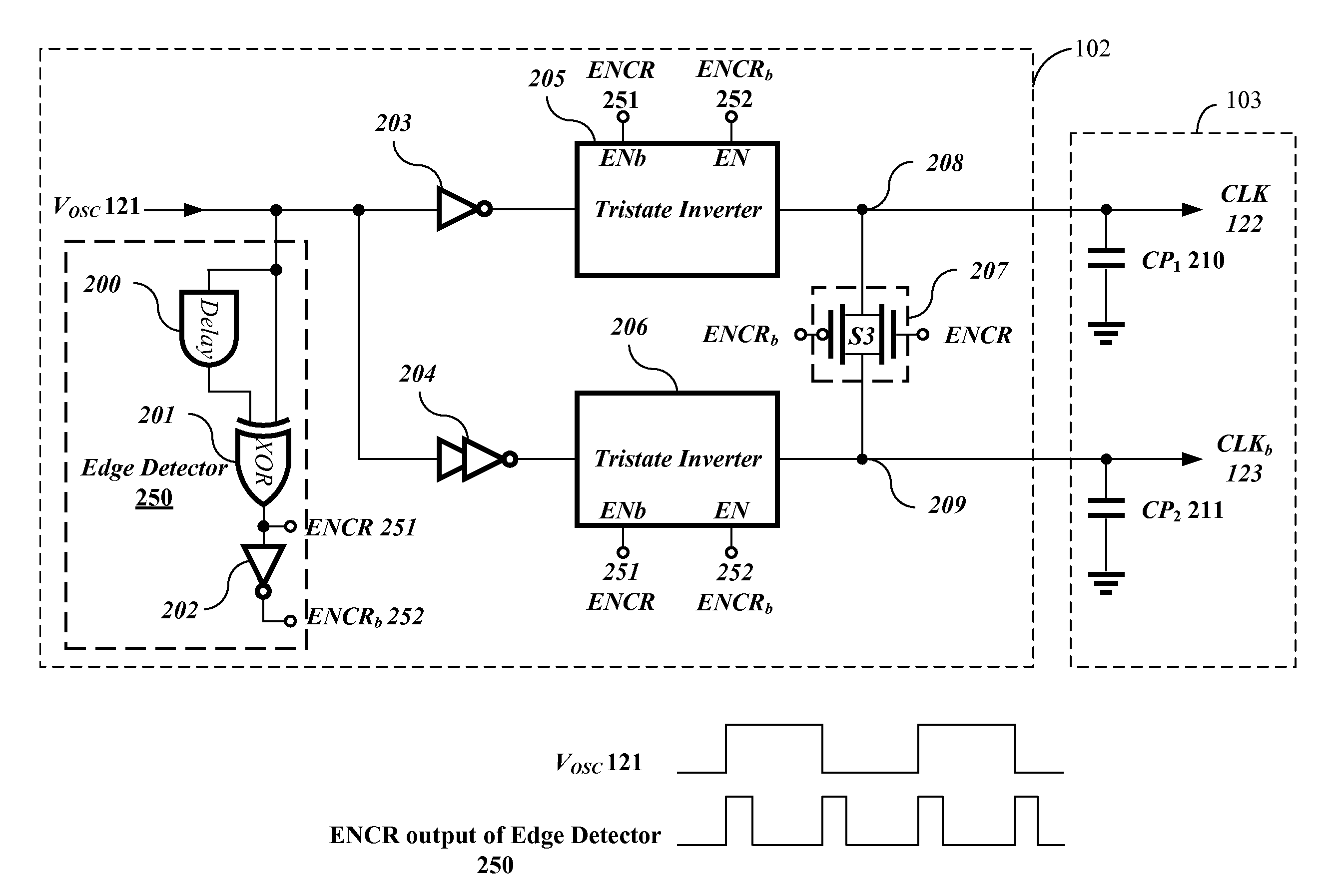
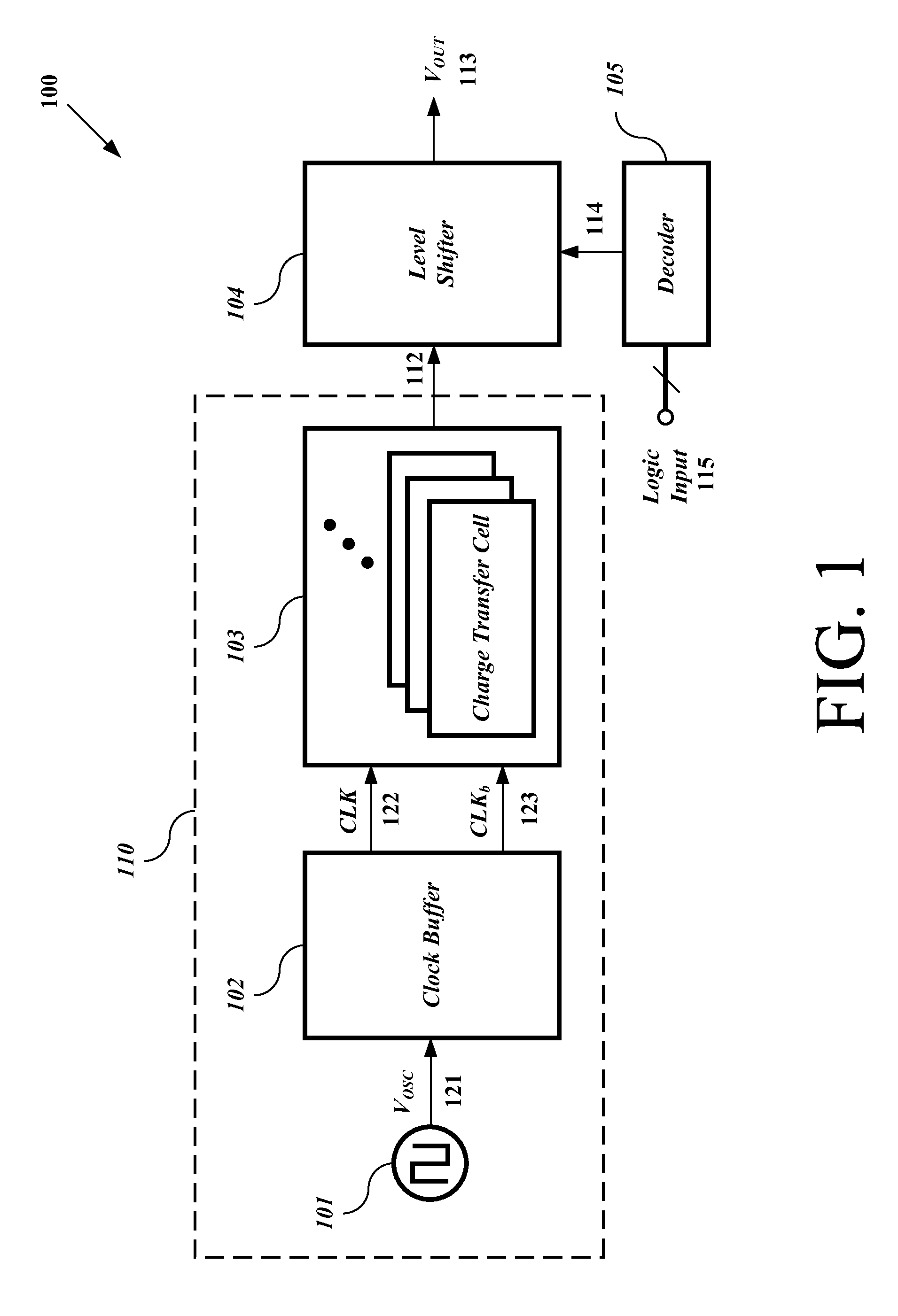
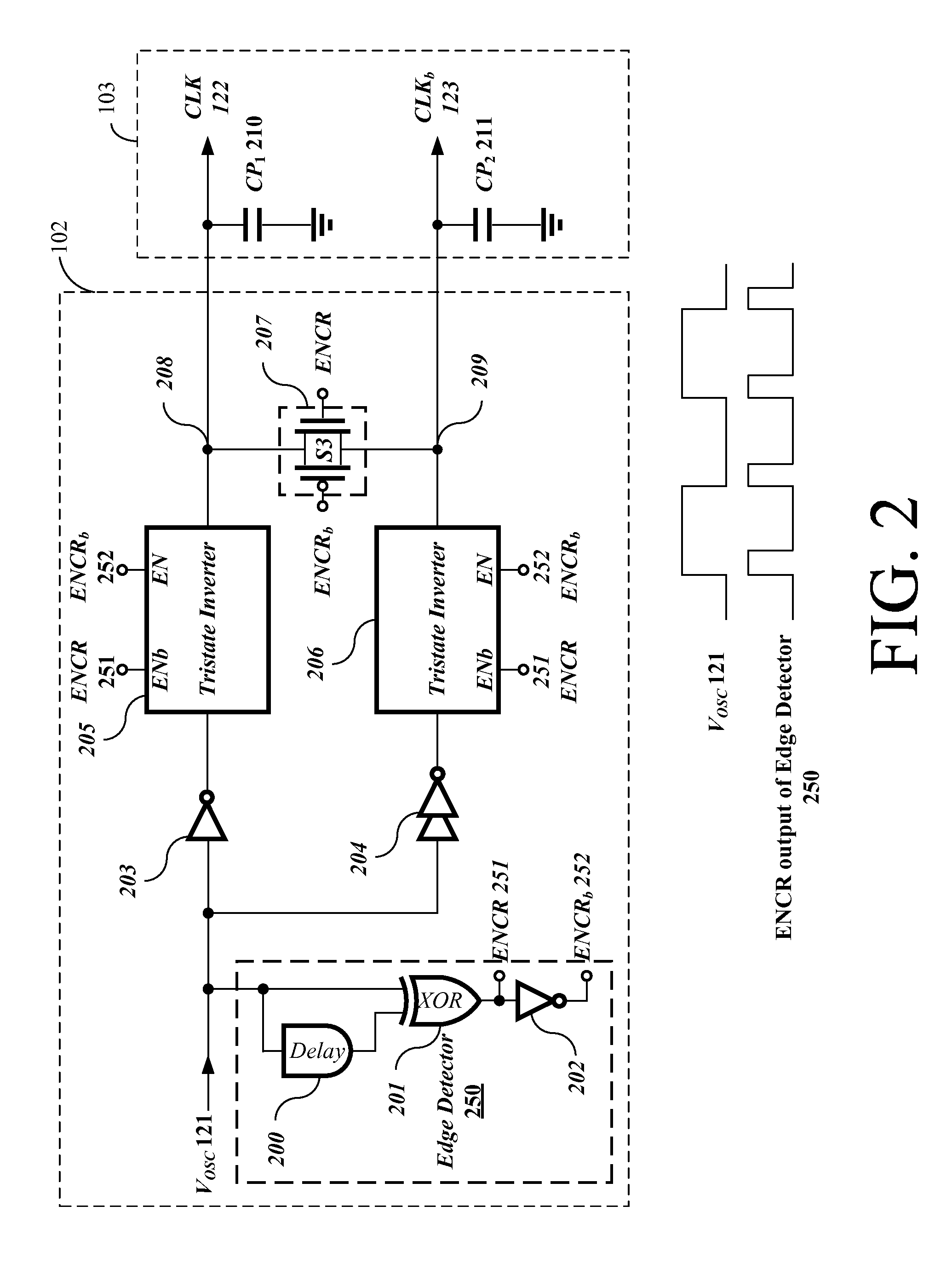
Example driver circuits can utilize shared-charge recycling charge pump structures. In particular, an example shared-charge recycling process may be applied to a clock buffer and charge transfer cells of the charge pump in a driver circuit. An example recycling process may include recycling of shared charges between the capacitors / capacitances in the charge transfer cells. An example recycling process may use the charges in one or more capacitors to charge one or more other capacitors before the charges are wasted or otherwise discharged to ground. Such recycling may significantly reduce the power consumption of the charge pump while still providing a high output voltage level, according to an example embodiment of the invention.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Source driver with charge sharing
ActiveUS7884653B2Improve stabilityImprove drivabilityPower reduction by control/clock signalPower reduction by energy recoveryPower flowEngineering
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Improvements to resonant line drivers
InactiveCN1813404APower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationDriver circuitElectrical conductor
The present invention provides an electronic driver circuit for communicating a logic value along a conductor (12) from one part of a system (10) to another (14) by representing each of two logic values by one of two logic levels (VDD, VSS). A capacitor (CR1) reduces ground and power reference differences between a chip containing the driver and the board on which it is mounted. The capacitor also provides power and ground decoupling. According to another aspect, a controlled slew rate ramp initiates an incident or outbound wave or turn-on and circuits are described for this. The time taken to complete the controlled slew rate ramp can be adjusted. The arrangements allow reduced power consumption, whilst at the same time producing desirable signal characteristics.
Owner:MIDAS GREEN
Apparatus for clocked power logic against power analysis attack
ActiveUS8390311B2Reliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by energy recoveryPower analysisParasitic capacitance
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Apparatus and method for recovery of wasted power from differential drivers
InactiveUS8035359B2Power reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationDifferential lineElectric force
An apparatus and method for supplying power to circuits of an integrated circuit (IC) from the wasted power in low-swing high-speed differential line drivers used in the IC, is disclosed. In a high speed line driver the load resistors of the driver are connected to a power supply, either the local power supply or the receiver power supply. DC power for the driver is supplied through these resistors. A large portion of this power, supplied from the power supply is wasted in the DC set-up circuit of the differential line driver. It is proposed to use this wasted power to power selected circuits of an IC. The use of this wasted power from the drivers for powering the circuits reduces the overall power dissipation of the system.
Owner:ANALOGIX SEMICON
Apparatus and methods for saving power and reducing noise in integrated circuits
InactiveUS20060077002A1Save powerReduce power consumptionPower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationElectronic switchCapacitor
The power saving and noise reducing circuit includes a first impedance disposed between a positive voltage supply and a positive voltage terminal of the electronic circuitry, a second impedance disposed between a negative voltage supply and a negative voltage terminal of the electronic circuitry, and a capacitor disposed between the positive voltage terminal and negative voltage terminal of the electronic circuitry, the electronic circuitry operating from a pseudo voltage supply across the capacitor. The impedances may be current sources. High speed switching currents are recirculated to and from the capacitor to save power. Electronic switching noise is also substantially reduced.
Owner:WHITE RICHARD T
Method and apparatus for direct backup of memory circuits
InactiveUS20130070513A1Power reduction by control/clock signalPower reduction by energy recoveryEngineeringActive memory
An integrated circuit employs at least one active memory circuit and at least one memory state backup circuit wherein the at least one memory state backup circuit includes at least one passive variable resistance memory cell and at least one passive variable resistance memory cell interface that are used to backup data from the active memory circuit to the PVRM cell. Data is then placed back into the active memory circuit from the PVRM cell during a restore operation. The PVRM cell interface is operative to read the PVRM cell in response to a restore signal. PVRM cell interface control logic is operative to remove power to the PVRM cell after backup of the data to the PVRM cell from the active memory circuit. A PVRM cell (e.g., a bit cell) is added to each memory circuit that stores state information on an integrated circuit.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Charge recovery for dynamic circuits
InactiveUS20030034801A1Power reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationCharge recoveryHemt circuits
In one aspect, a method for charge recovery in dynamic circuitry includes discharging a dynamic node during an evaluation interval by input circuitry coupled to the dynamic node responsive to one or more input signals. The discharging includes transferring the charge from the dynamic node to a capacitor during the evaluation time interval. The dynamic node is charged during a precharge interval by a voltage source and precharge timing circuitry coupled to the dynamic node responsive to a precharge signal. The charging includes transferring the charge from the capacitor back to the dynamic node.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
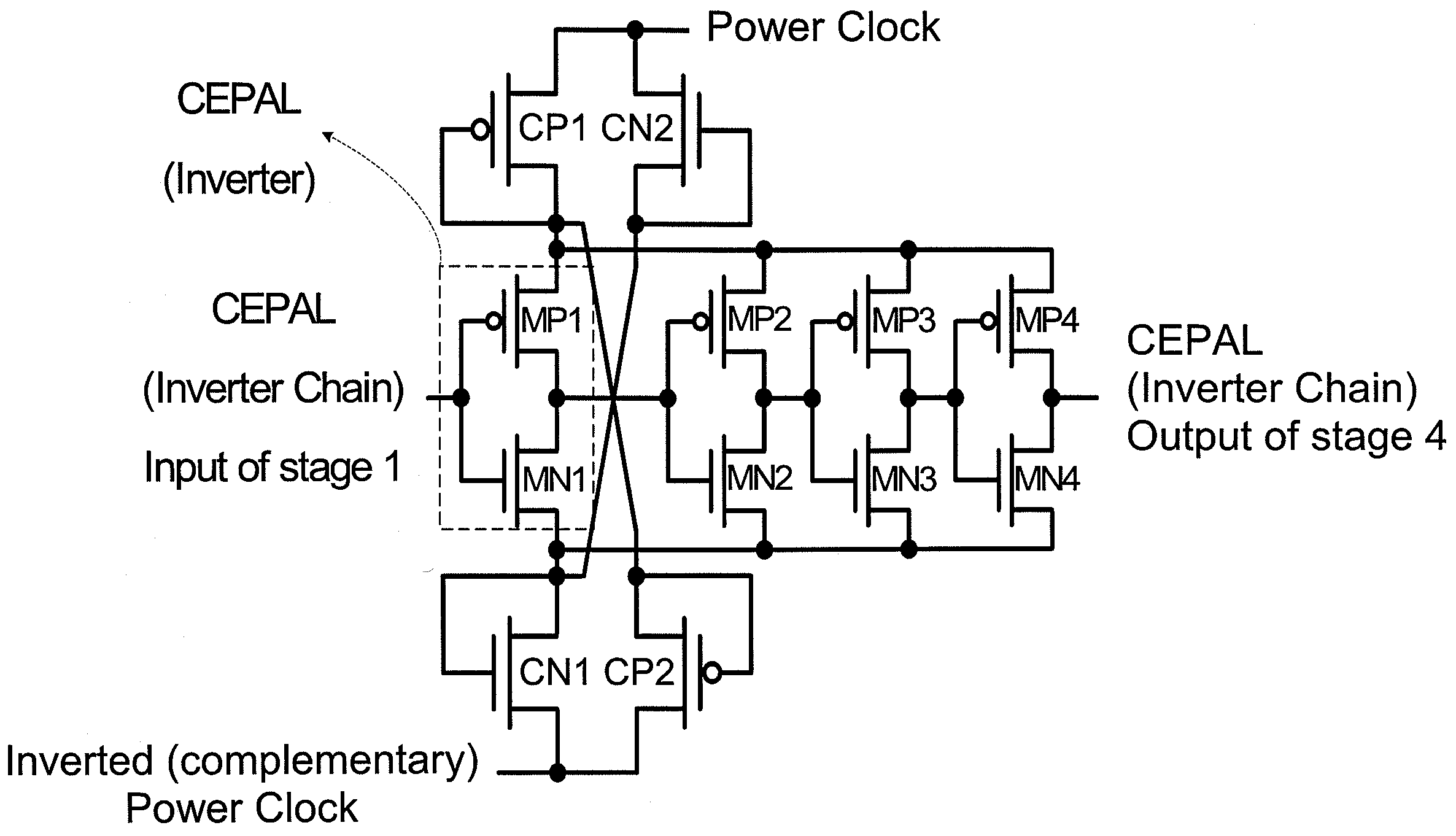
Complementary Energy Path Adiabatic Logic
InactiveUS20100073029A1Improve reliabilityImprove throughputLogic circuits characterised by logic functionPower reduction by energy recoveryAdiabatic logicClock network
A complementary energy path adiabatic logic (CEPAL) includes an evaluation network and a power clock network. The evaluation network is a logic circuit composed of P-type MOS transistors and N-type MOS transistors. The power clock network includes a P-type and N-type MOS transistors and additional P-type and N-type MOS transistors, with each of the transistors involved in the power clock network acting as an active diode.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Source driver with charge sharing
ActiveUS7928954B1Improve stabilityImprove drivabilityPower reduction by control/clock signalPower reduction by energy recoveryElectricityCharge sharing
A source driver includes an output buffer for outputting a driving signal; a first current path coupled between the output buffer and a data line; and a second current path coupled in parallel to the first current path. During a first driving period, the output buffer utilizes both the first current path and the second current path to drive the data line. During a second driving period, the output buffer utilizes only the first current path to transmit the driving signal so as to improve the stability of the source driver.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
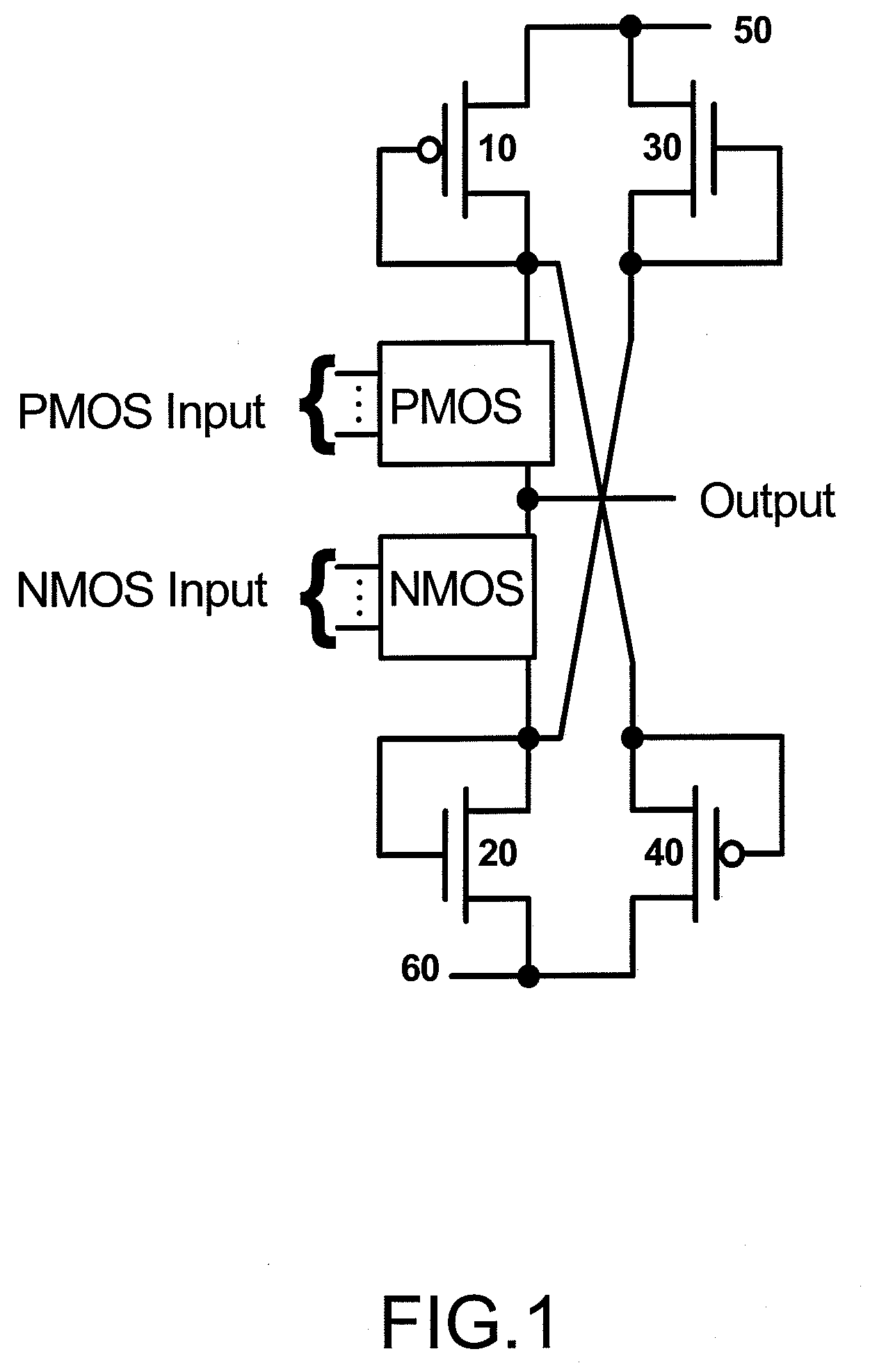
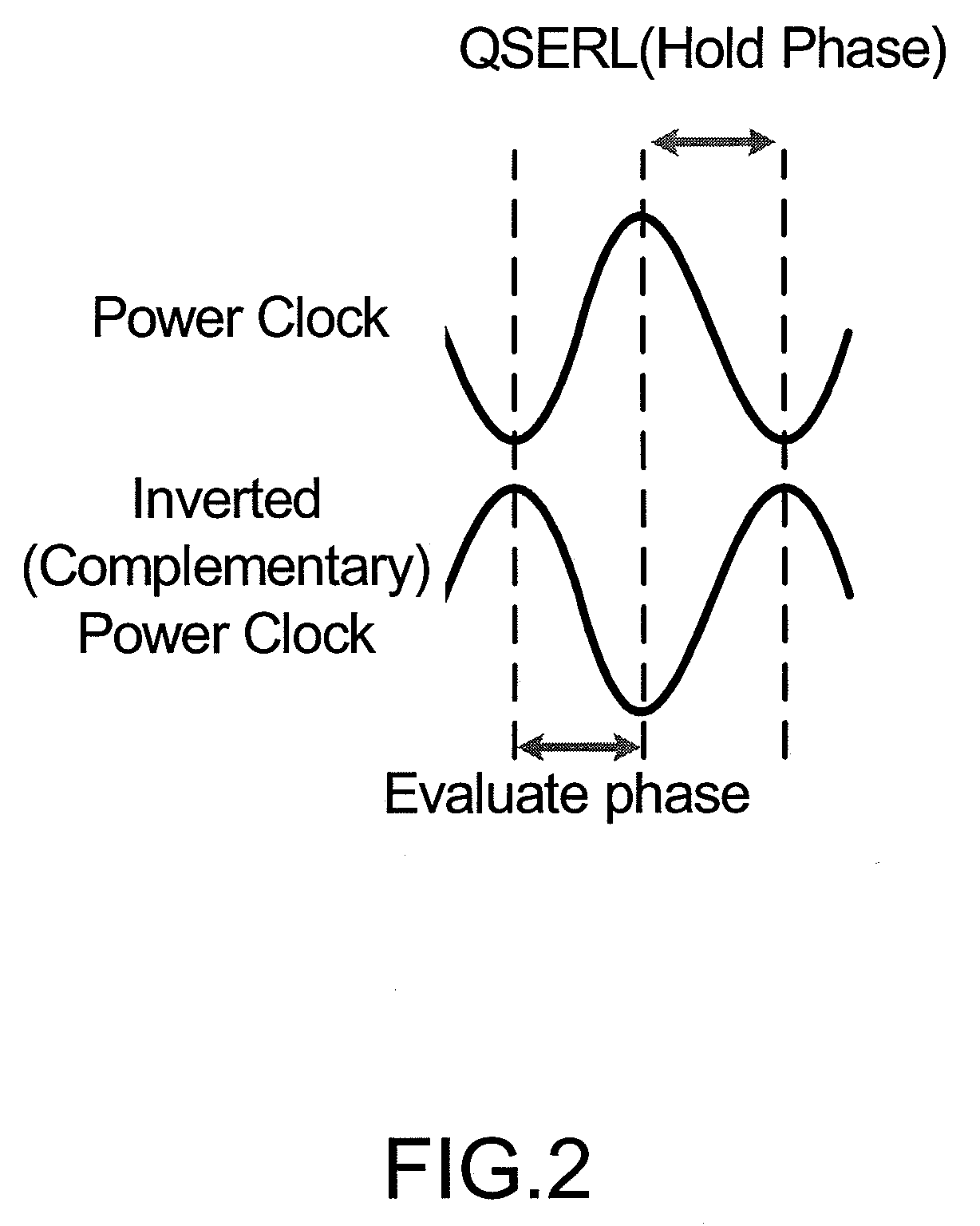
Charge recycling a 1 of N NDL gate with a time varying power supply
InactiveUS8450991B2Logic circuits characterised by logic functionPower reduction by energy recoveryPhase shift controlPower flow
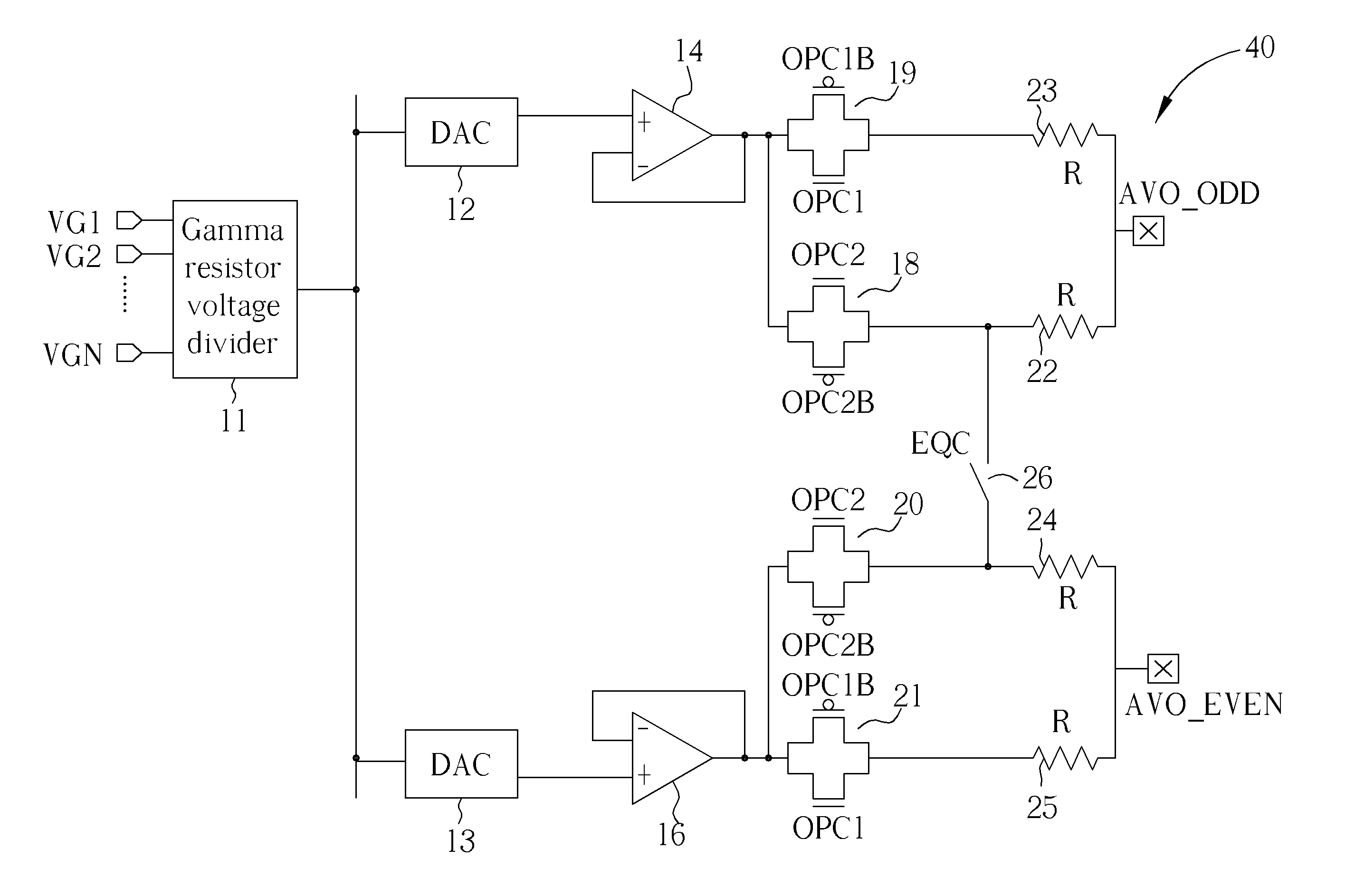
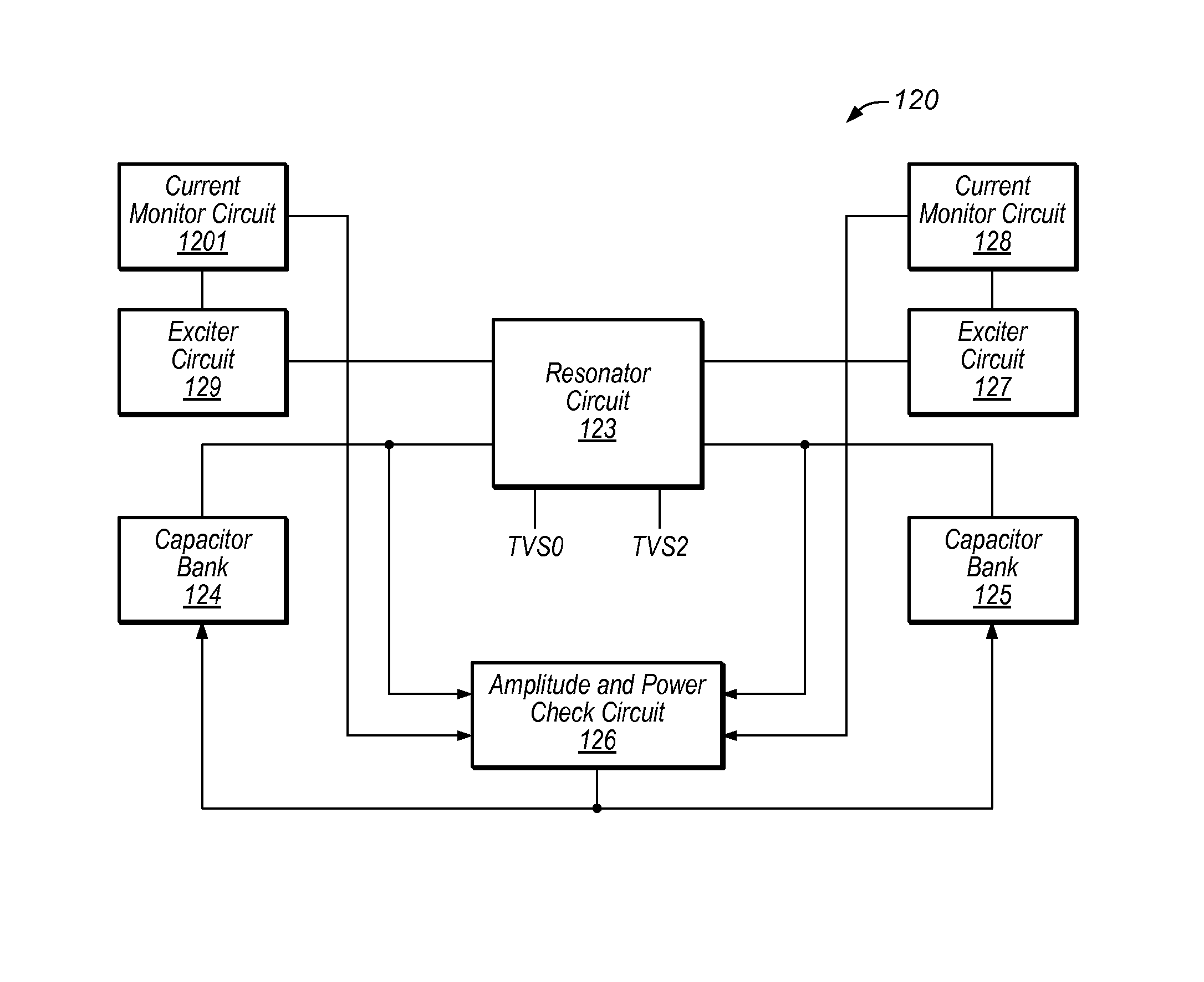
This disclosure describes an invention that is a basic charge recycling gate 70 that includes a precharge node 75, a output charging network 78, an output pre-charge and null propagate network 77, an evaluation network 76, a first time varying power supply TVS0, a second time varying power supply TVS2, and a keeper circuit 79. Additionally, this disclosure describes an invention that is a time varying power supply 130 that includes a resonator circuit 131, an amplitude and power check circuit 135, one or more overshoot and an undershoot voltage clamps 1105 and 112, exciter circuits 137 and 136, and current monitor circuits 138 and 139. In addition, the invention includes frequency self tuning with the amplitude and power check circuit 135, capacitor banks 132 and 134, and the inductor tap select controller 133. Amplitude self tuning is provided by the amplitude sample and compare circuit 144. Further, a phase shift control circuitry 150 is also provided. And, distributed control switching circuitry 160 for power management is also provided.
Owner:APPLE INC
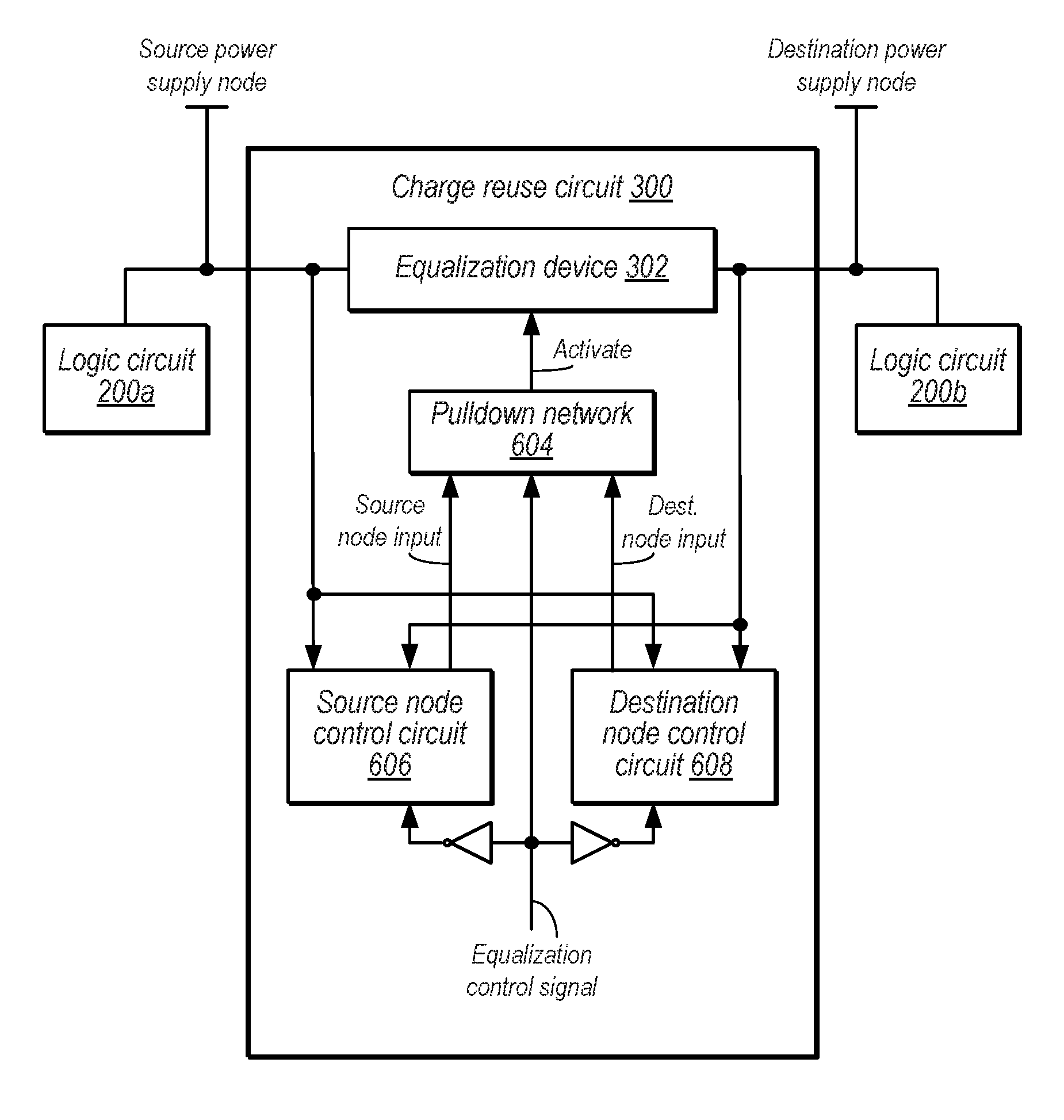
Integrated circuit power reduction through charge
ActiveUS9584122B1Avoid couplingPower reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationIntegrated circuitEngineering
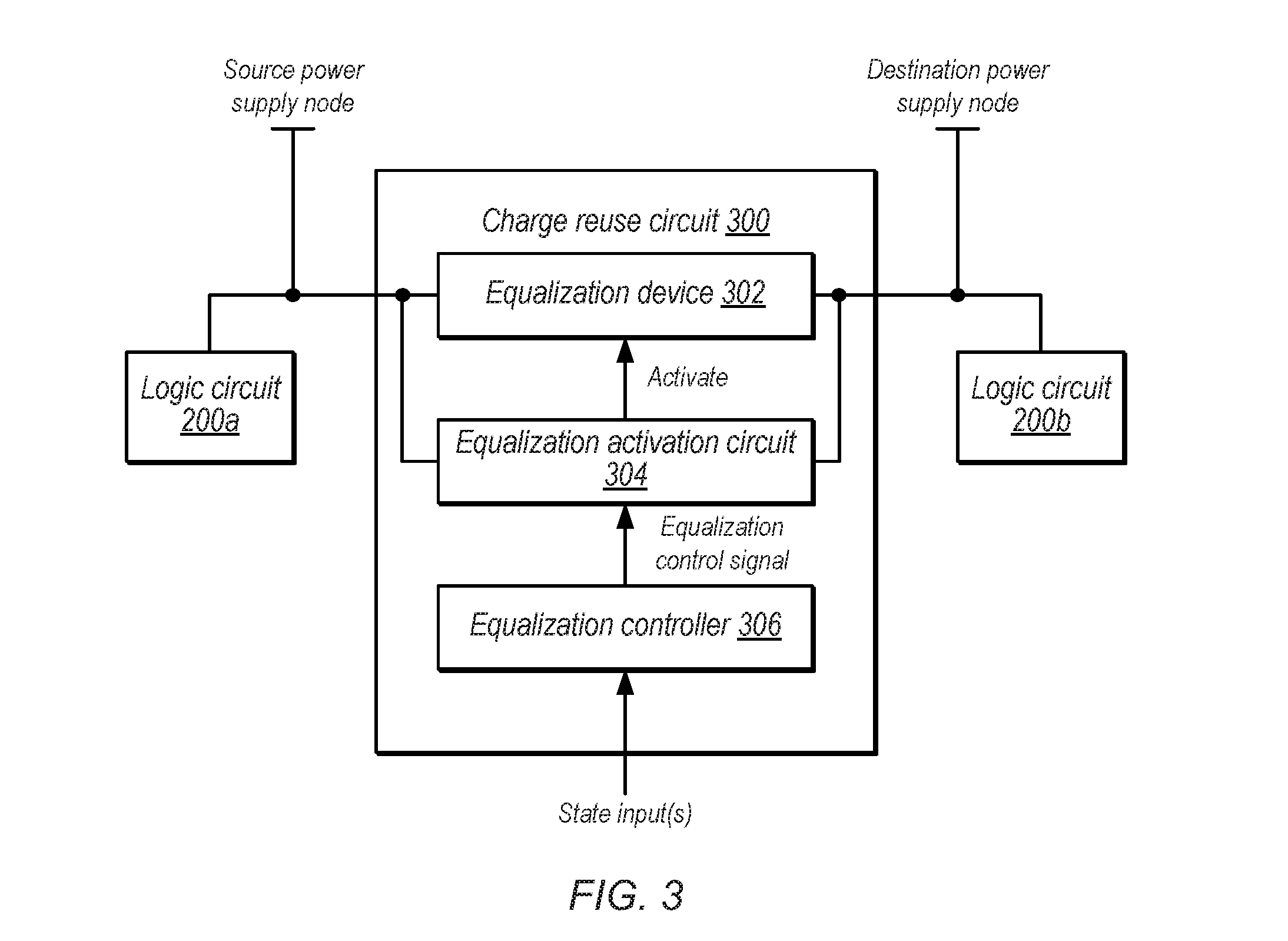
Techniques for charge reuse in an integrated circuit. A processor may include a first logic circuit coupled to a source power supply node, a second logic circuit coupled to a destination power supply node, and a charge reuse circuit that selectively transfers charge from the first logic circuit to the second logic circuit. The charge reuse circuit may include an equalization device that selectively couples the source power supply node to the destination power supply node, and an equalization activation circuit that activates the equalization device in response to detecting assertion of an equalization control signal and further detecting that a voltage differential between the source power supply node and the destination power supply node is above a threshold value. The equalization activation circuit also prevents coupling of either the source power supply node or the destination power supply node to ground during activation of the equalization device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Popular searches
Apparatus without intermediate ac conversion Electric pulse generator Pulse duration/width modulation Input/output processes for data processing Electric variable regulation Soil-shifting machines/dredgers Electronic switching Cathode-ray tube indicators Voltage/current interference elimination Oscillations generators
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com