Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
361 results about "Differential line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
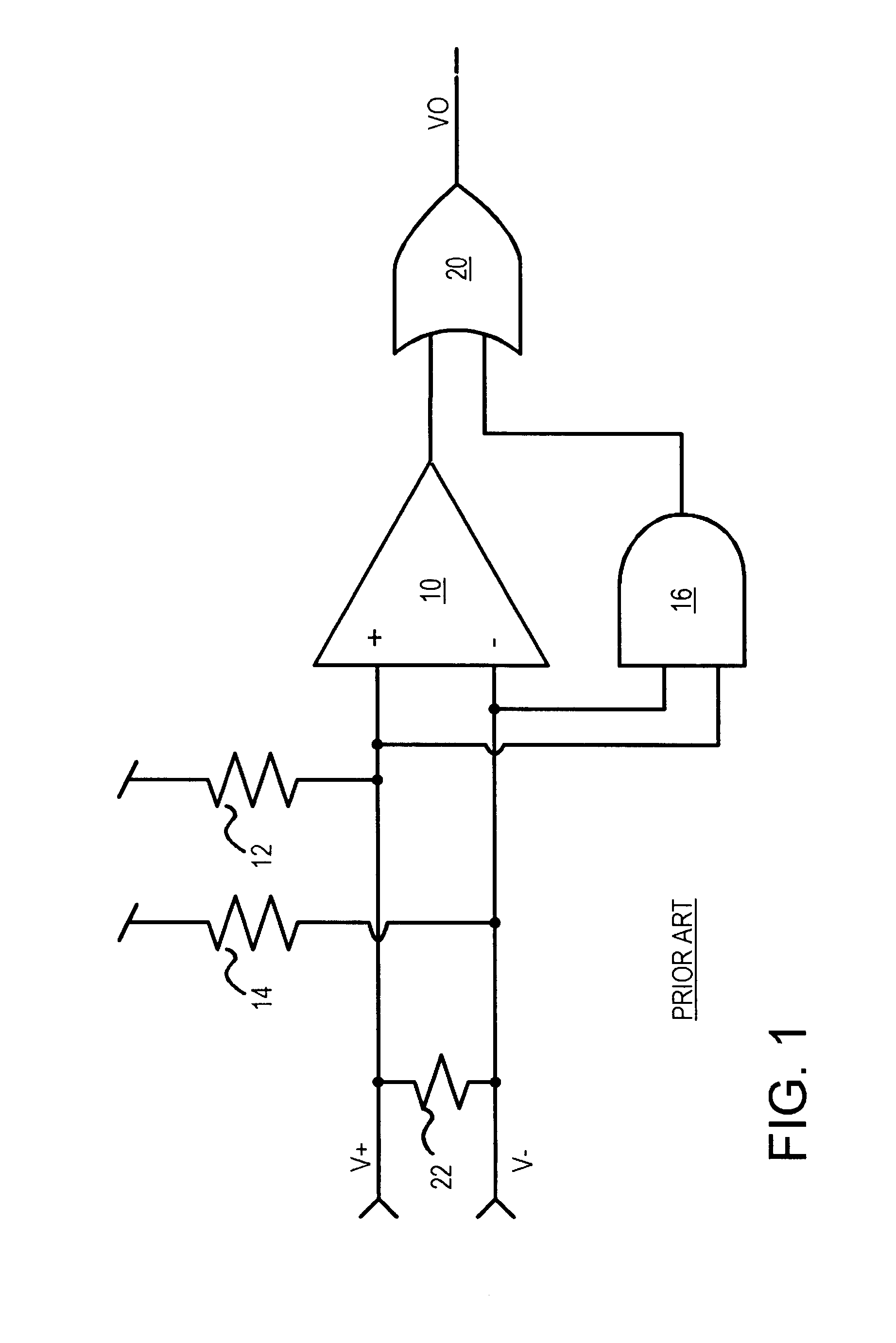
Differential line. A kind of electrical connection using two wires, one of which carries the normal signal (V) and the other carries an inverted version the signal (-V).
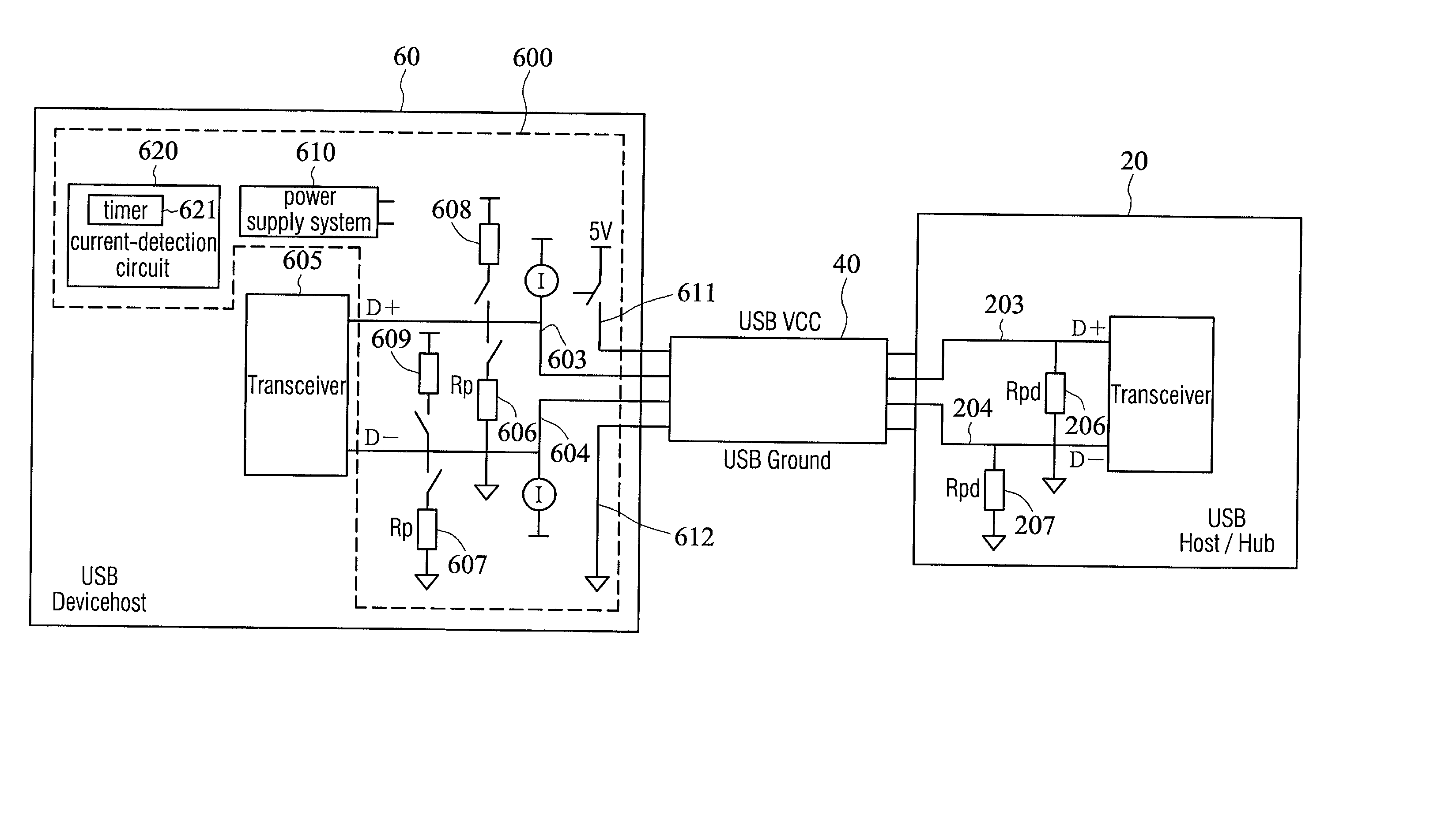
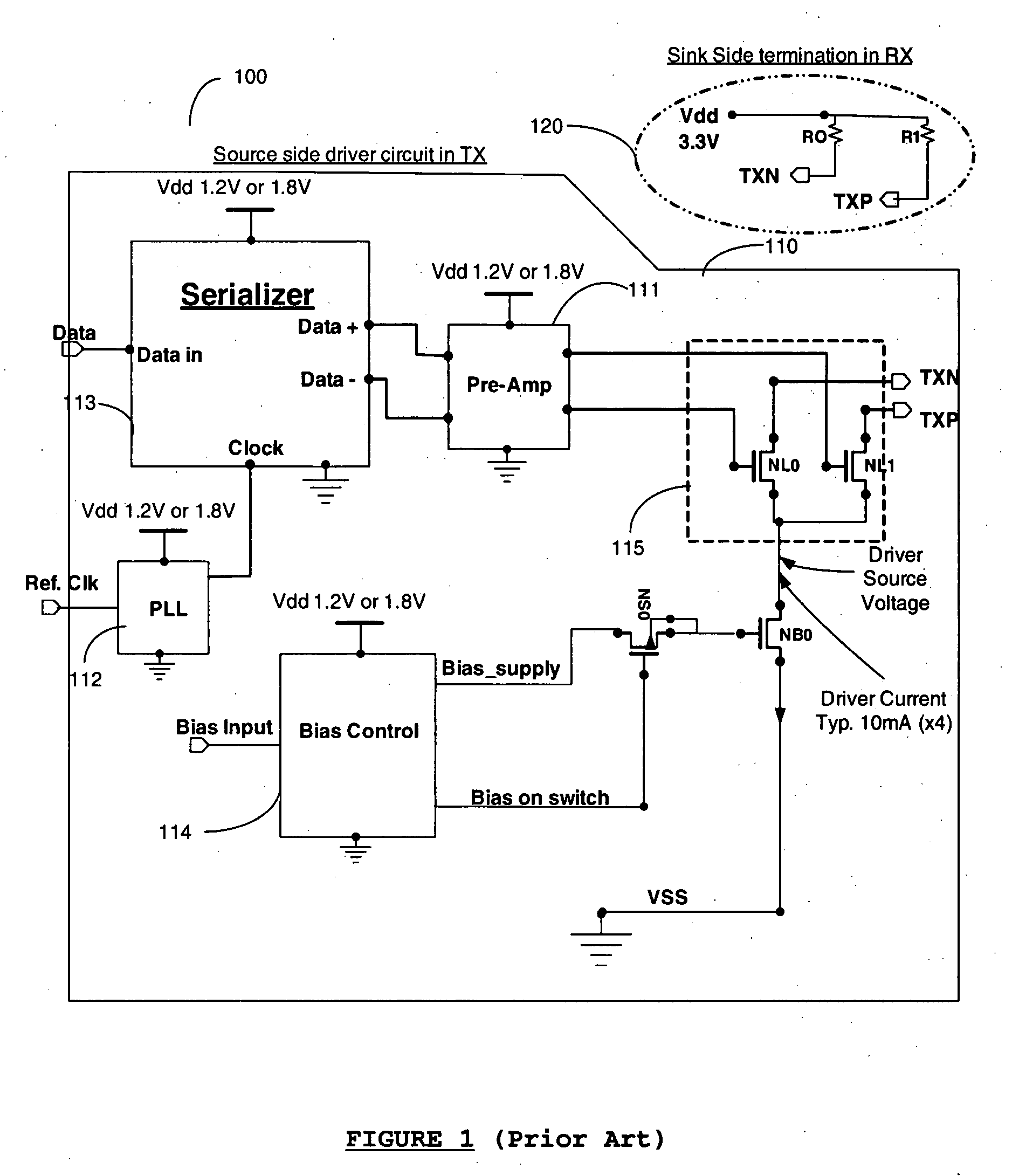
USB connection-detection circuitry and operation methods of the same
InactiveUS20020169915A1Star/tree networksInput/output processes for data processingDifferential lineDifferential signaling
A USB connection-detection circuitry and the operation method of the same are disclosed. The circuitry includes a transmitting circuit and a detecting circuit. The transmitting circuit contains a pair of differential signal lines, a pair of pull-down resistors and a pair of pull-up resistors wherein one pull-down resistor and one pull-up resistor are connected to the same differential signal line with their own individual switches. A power-related signal supplied by a power-supply system is received by the transmitting circuitry and transmitted through a differential signal line. Then, the power-related signal is grounded via a pull-down resistor. The detecting circuit is utilized to detect the power-related signals, which flow through the differential lines. When a device is connected to this connection-detection circuitry with a USB cable, the differential signal lines of the USB cable are connected with the differential signal lines of this circuitry. This results in the variation of the power-related signals, which are connected to the ground through the pull-down resistors originally. Therefore, by comparing the difference of the power-related signals before and after the connection, the connection-detection circuitry is able to automatically identify the mode of the device, which connects to the circuitry.
Owner:PROLIFIC TECH INC
Grounding member for cable assembly
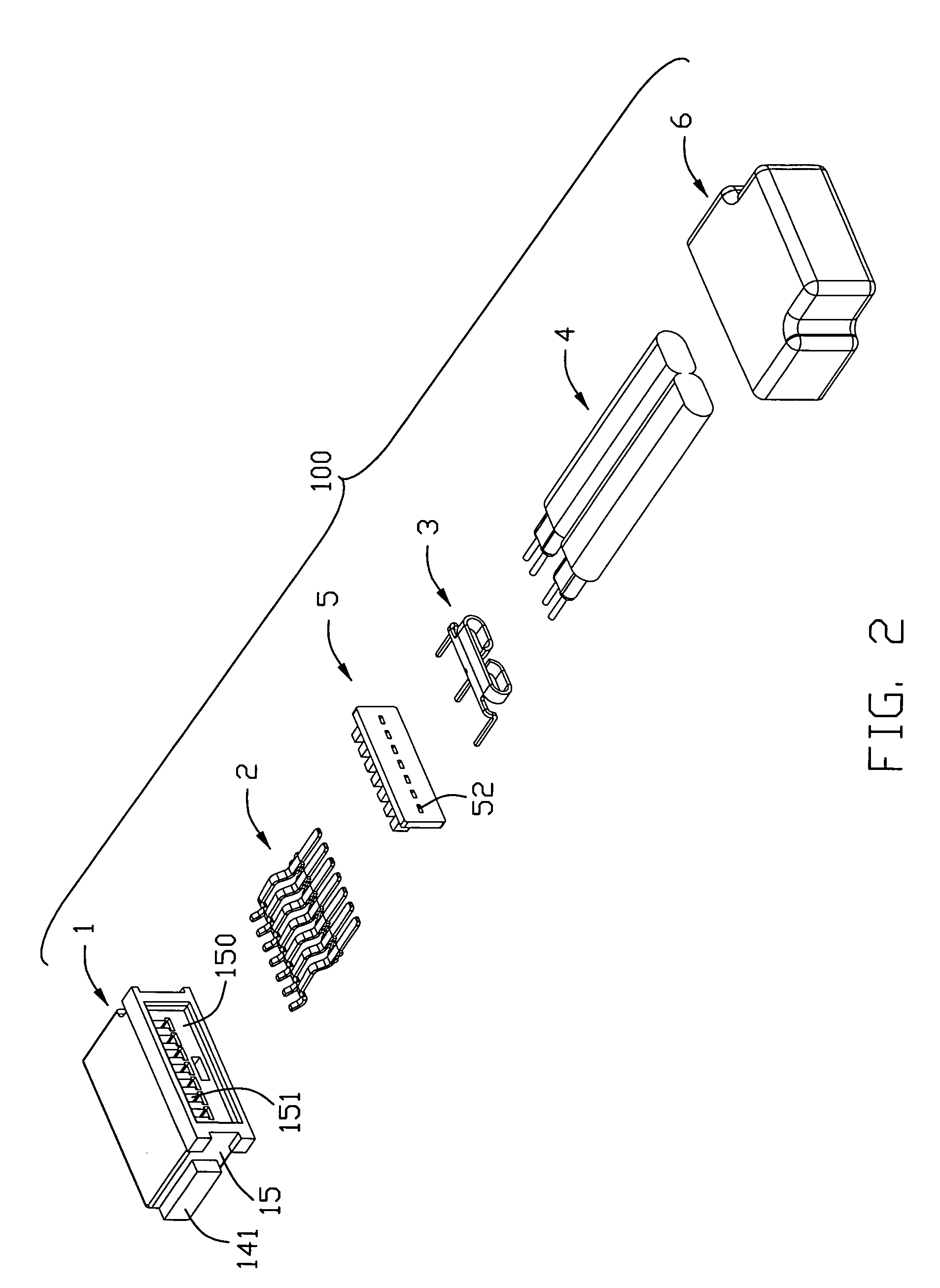
InactiveUS7819675B2Coupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsConnection contact member materialGround contactDifferential line
An cable assembly (100) includes an insulated housing (1) extending along a front-to-back direction; a plurality of contacts (2) arranged in a row and supported by the insulated housing, said contacts including three grounding contact members spaced by two pair of signal contact members; a cable (4) including two juxtaposed differential wire pairs (41) respectively enclosed by conductive shielding portions (43); a grounding member (3) including a main portion (31), three finger portions (33) extending forwardly from a front side of the main portion and two arm portions (32) formed at lateral sides of a rear segment of the main portion, said grounding member (3) securely engaged with the cable via the two arm portions thereof griping the conductive shielding portions; and the finger portions soldered to the grounding contact members, and inner conductors of the differential pairs soldered to the signal contact members, respectively.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Output controlled line driver with programmable common mode control
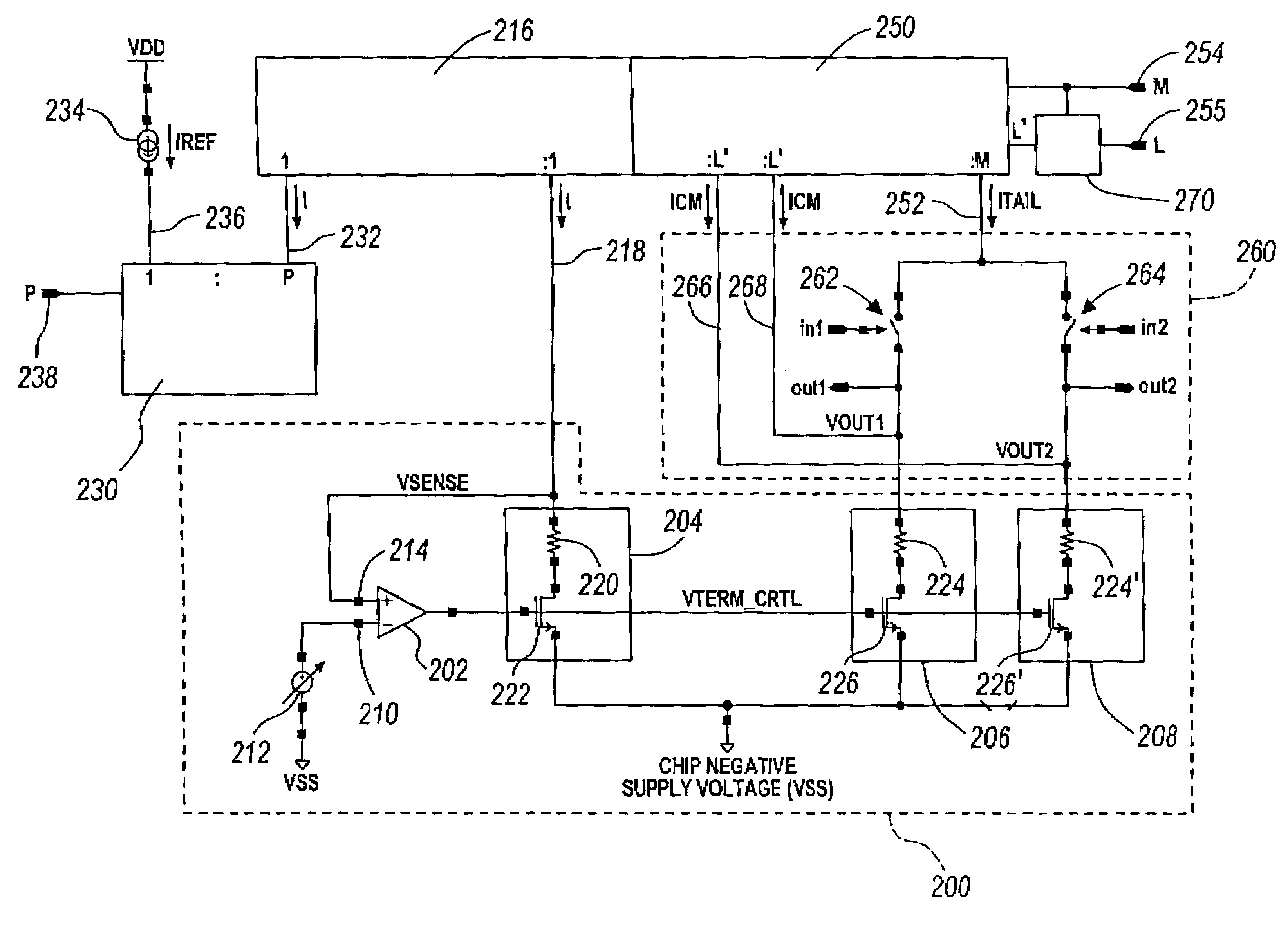
InactiveUS6504397B1Superior electrical source impedance terminationLow costReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingCMOSDifferential line
A differential line driver having integrated output termination resistors is disclosed. The termination resistors are a combination of a controlled transistor and a low precision resistor. The transistor calibrates-out the imprecision of the resistor based on a precise electrical reference. In a preferred embodiment the transistor is a CMOS transistor and the resistor is a CMOS resistor. The combination of a CMOS transistor and CMOS resistor features higher linearity and precision than a CMOS transistor alone due to the smaller effective drain-source voltage across the CMOS transistor. Moreover, the present invention discloses independent programmability of the integrated output termination resistor, the output common mode voltage, and the output amplitude. The value of the output termination resistor(s), the value of the output common mode voltage, and the value of the output amplitude are controlled independently and are continuously maintained with respect to a precise electrical reference. As a result, the value of the output termination resistance, the value of the output common mode voltage, and the value of the output amplitude are insensitive to manufacturing process tolerances and variations in temperature and supply voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
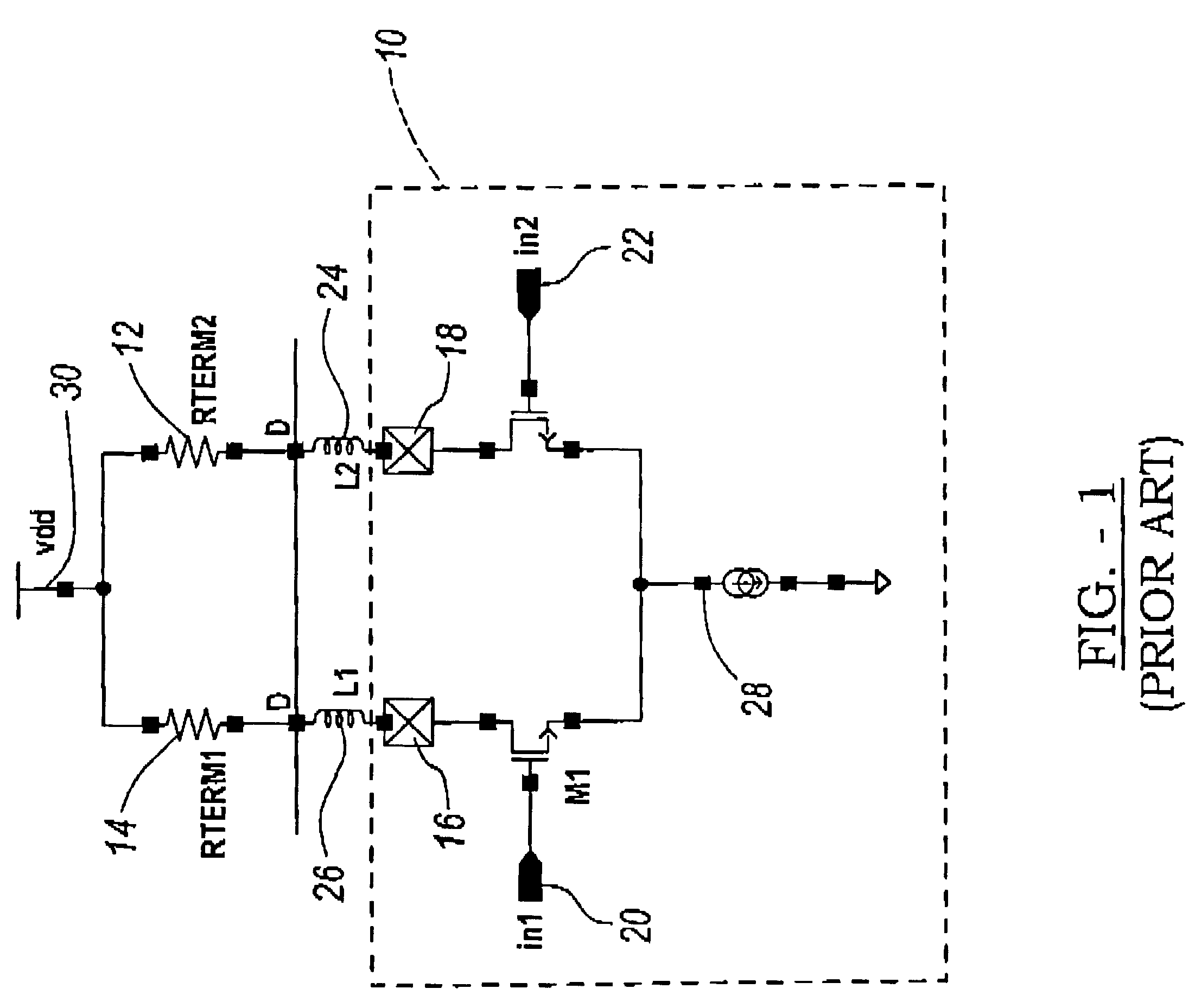
Power down mode signaled by differential transmitter's high-Z state detected by receiver sensing same voltage on differential lines
InactiveUS6593801B1Energy efficient ICTMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectricityDifferential line
A power-down signal is encoded into a differential pair of lines between two chips. When the differential transmitter powers down, it enters a high-impedance state and floats the differential lines A shunt resistor between a pair of differential lines equalize the voltages on the differential lines so they float to a same voltage when a differential transmitter is disabled and enters a high-impedance state. The condition of equal voltages on the differential lines is detected by an equal-voltage detector that generates a power-down signal when the differential lines are at equal voltages for a period of time. The period of time can be greater than the cross-over time during normal switching to prevent false power-downs during normal switching. Standard differential drivers can signal power-down using the high-impedance state, which is detected by equal voltages on the differential lines. A sensitive dual-differential amplifier and a simpler detector are disclosed.
Owner:DIODES INC
Apparatus and method for termination powered differential interface periphery
ActiveUS20080278122A1Resonant long antennasPower consumption reductionDifferential lineElectrical resistance and conductance
An apparatus and method for supplying power to the peripheral circuits of a transmitter circuit, especially an HDMI transmitter circuit, is disclosed. In an HDMI transmitter the termination resistors of the output driver are part of the receiver. DC power for the driver is supplied through these termination resistors. In prior art implementations of circuits this power, supplied by the receiver circuit, is wasted in the DC set-up circuit of the differential line driver. It is suggested to use this wasted power from the remote termination to power selected peripheral circuits of the transmitter. The use of this wasted power in the line driver for powering the peripheral circuits reduces the total system power.
Owner:ANALOGIX SEMICON
Water pump automatic circulation assembly line
ActiveCN102284860AAccurate detectionOptimizationPump testingAssembly machinesDifferential lineEngineering
The invention discloses an automatic flow assembly line for a water pump. The automatic flow assembly line comprises a circulated flow line mainly consisting of a differential chain line and an arc flat chain line and is characterized in that the circulated flow line is provided with an automatic water pump comprehensive testing platform, an air tightness testing unit, a main sealing automatic pressing table and more than two manual placement stations. The circulated flow line is also provided with circularly delivered tool plates. The automatic water pump comprehensive testing platform, the air tightness testing unit, the main sealing automatic pressing table and the manual placement stations are respectively provided with a tool plate jacking unit and a positioning stopper. In the automatic flow assembly line for the water pump, a part to be assembled can be conveniently placed on the tool plate for corresponding installation during assembly, and different automatic tests can be performed on different stations, so the labor intensity is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:JUNHE PUMPS HLDG
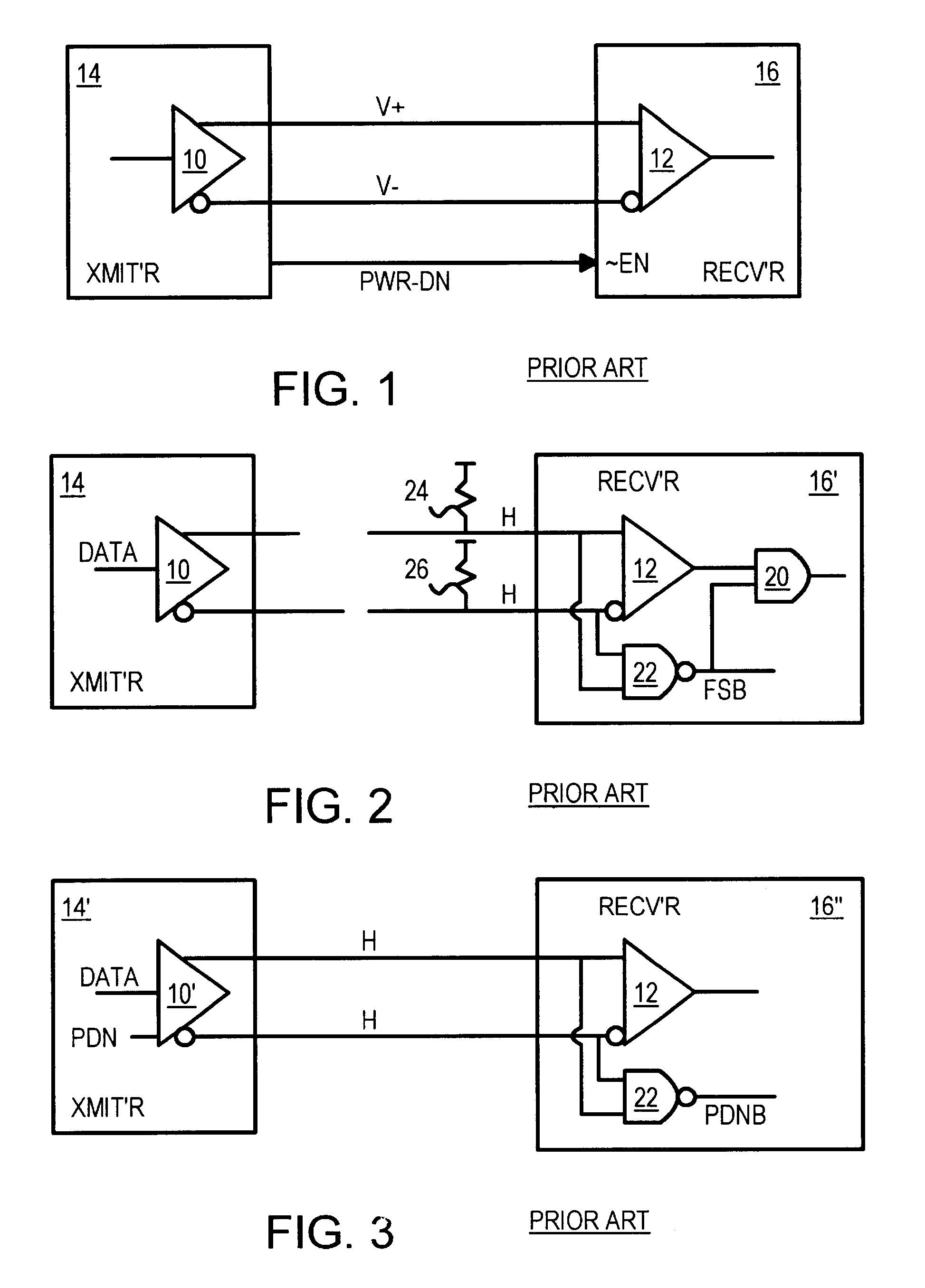
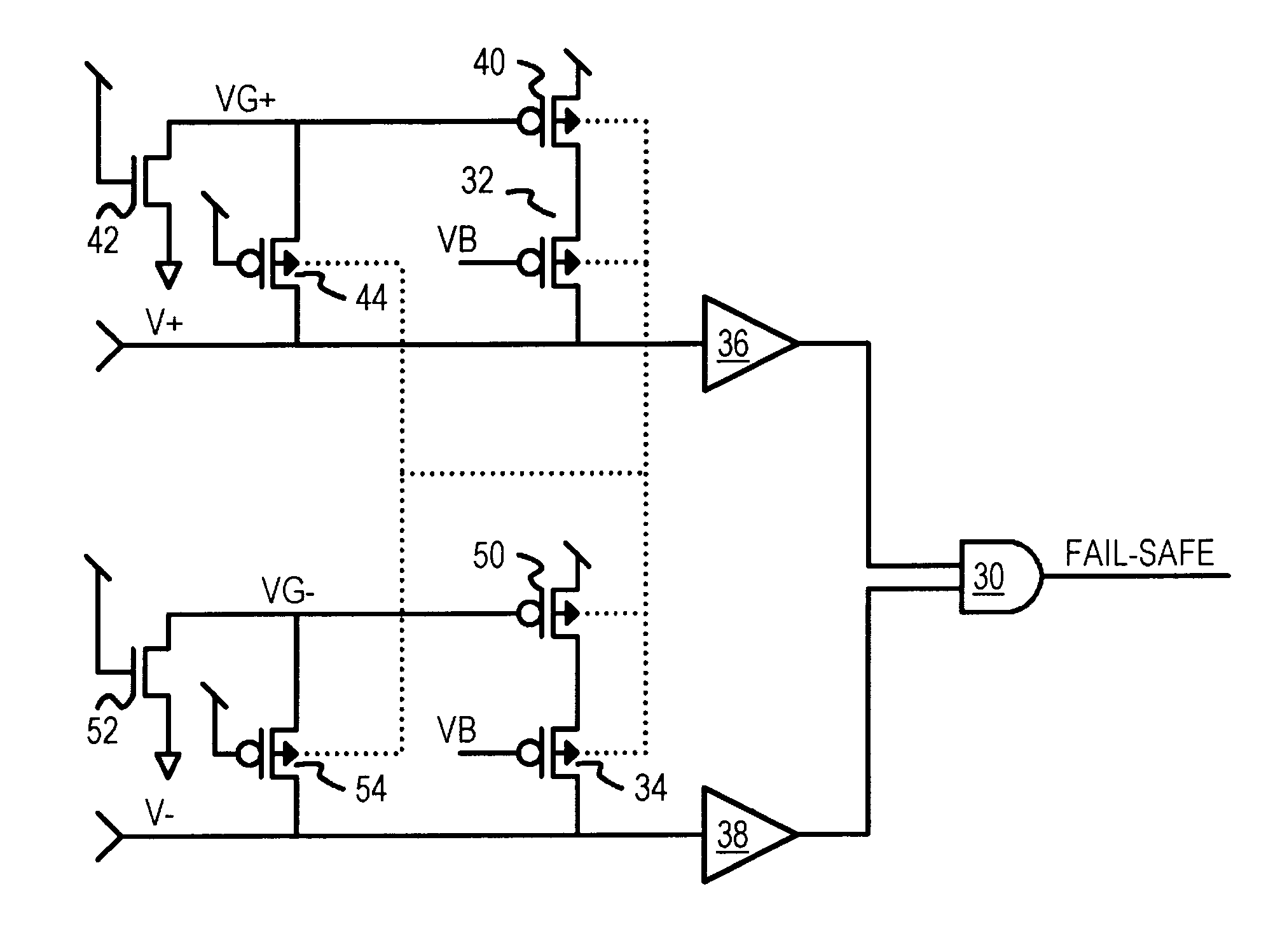
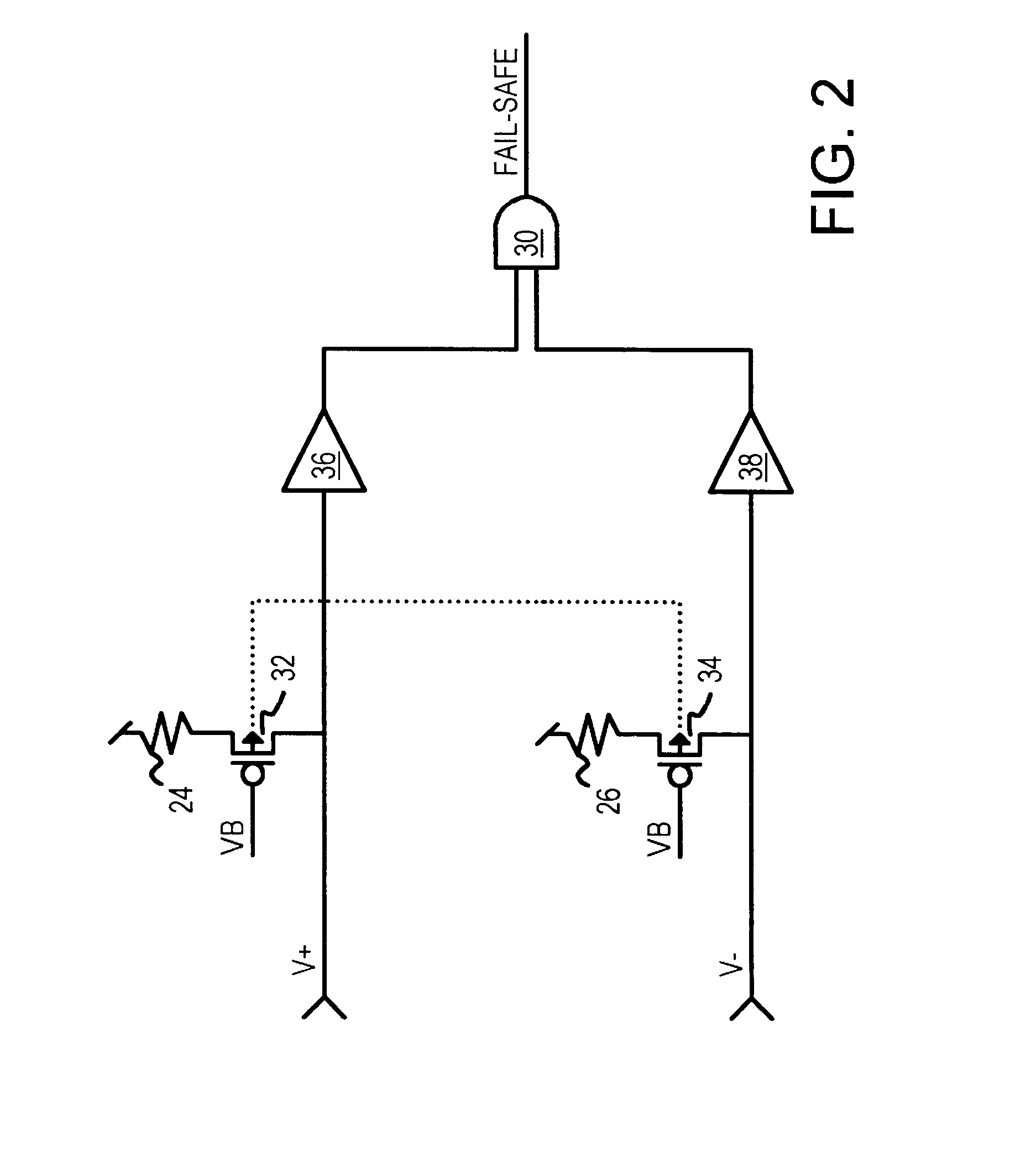
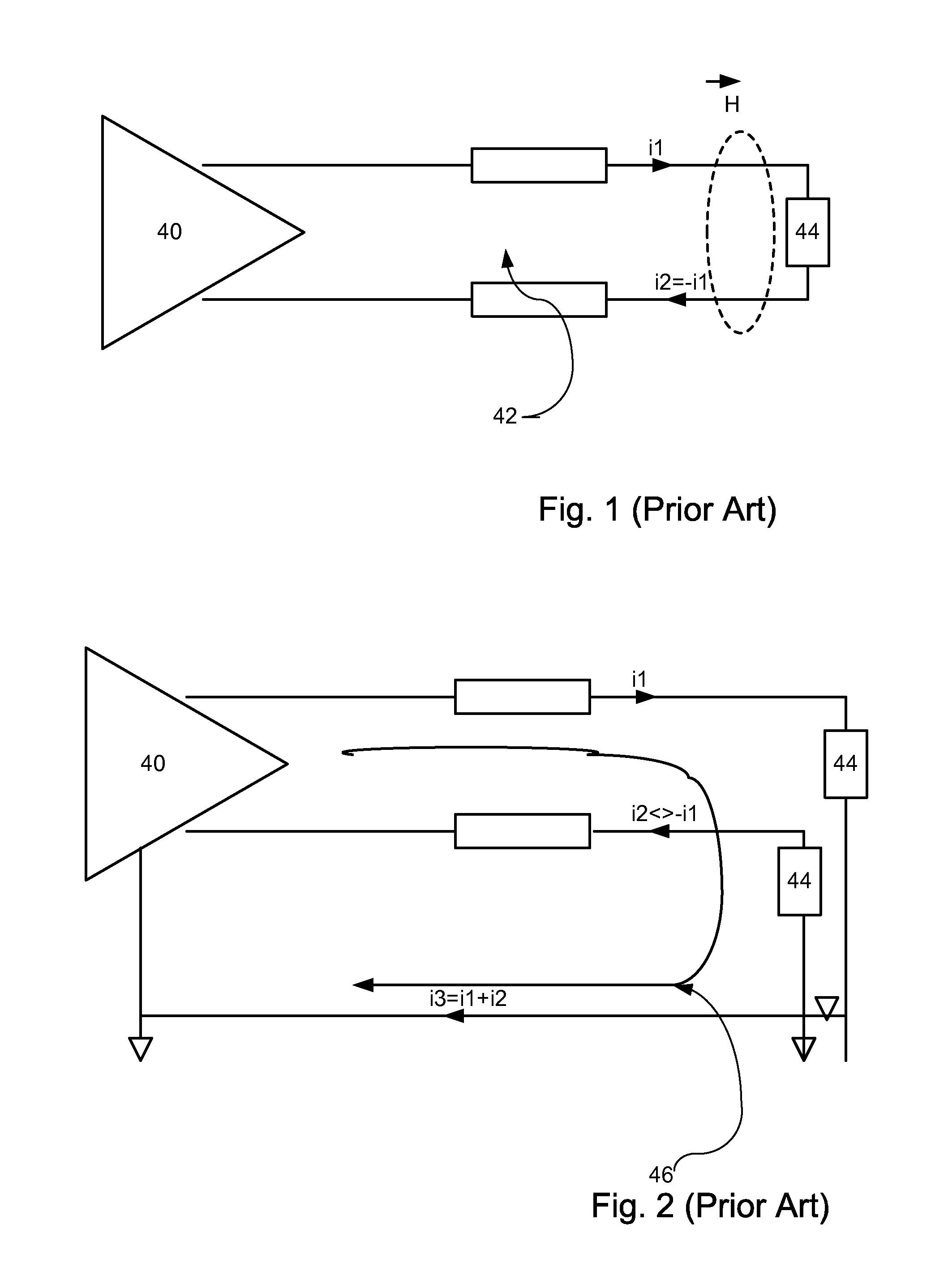
Fail-safe circuit with low input impedance using active-transistor differential-line terminators
InactiveUS6525559B1Reliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsEngineeringPull-up resistor
A fail-safe circuit for a pair of differential input lines detects when one or both lines are open. Each line has a pull-up of a switched p-channel transistor in series with a resistor or another p-channel transistor that has its effective resistance controlled by a gate bias. The gate of the switched p-channel transistor is driven to ground when power is applied to the gate of a grounding n-channel transistor. When power is off, a p-channel connecting transistor charges the gate node from the differential input line when a positive voltage is applied to the input line, such as during a leakage test. Charging the gate node prevents the switched p-channel transistor from turning on, blocking a leakage current path through the pull-up. An N-well bias circuit can be added, which connects the N-well under p-channel transistors to power or the gate node or the input line.
Owner:DIODES INC
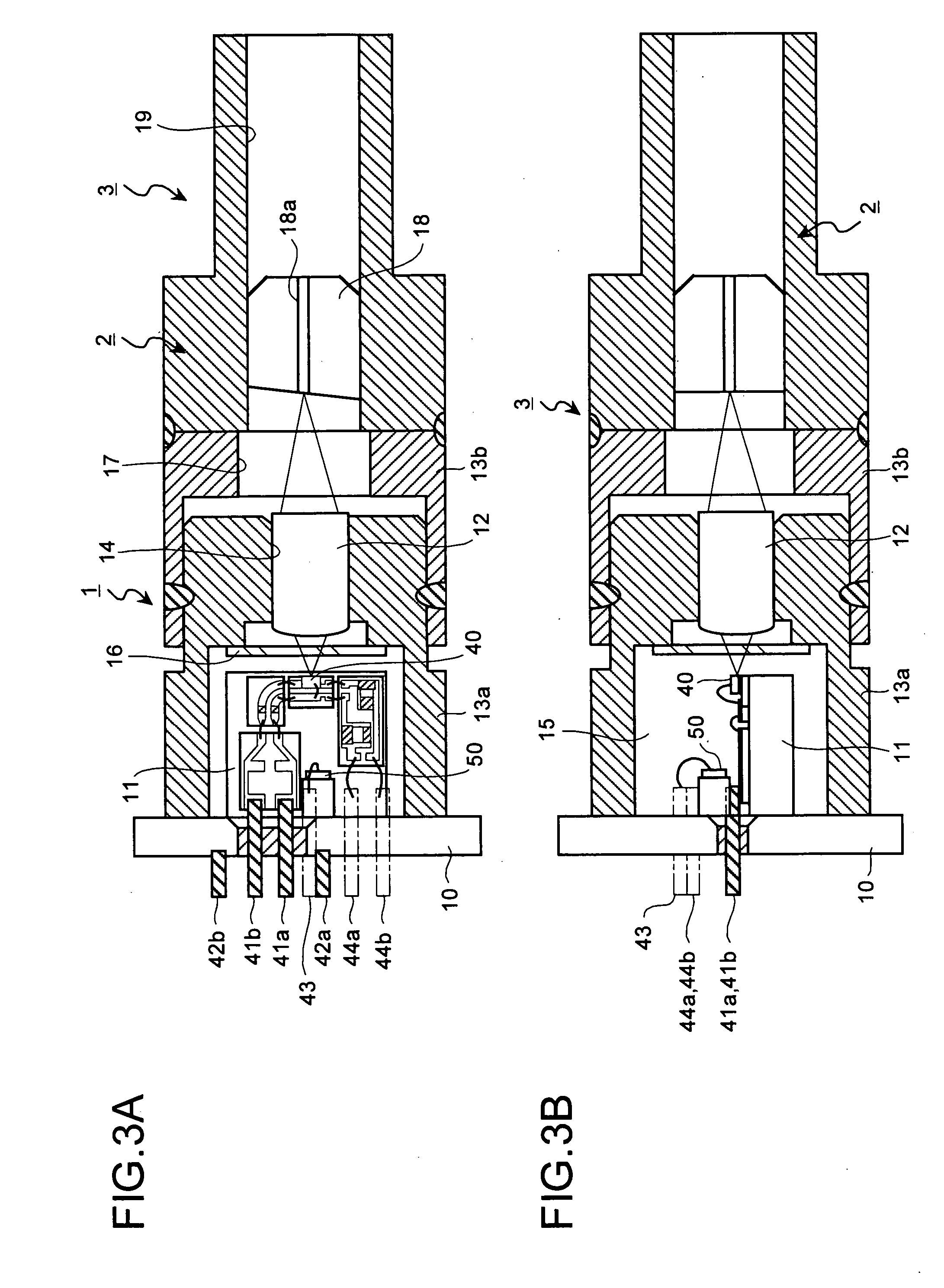
Optical semiconductor package
Includes a stem with a hole, a dielectric sealed into the hole of the stem and including a pair of pin insertion holes, and a pair of high frequency signal pins that penetrate and fit into the pair of pin insertion holes of the dielectric, and constituting differential lines connected to an optical semiconductor element.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
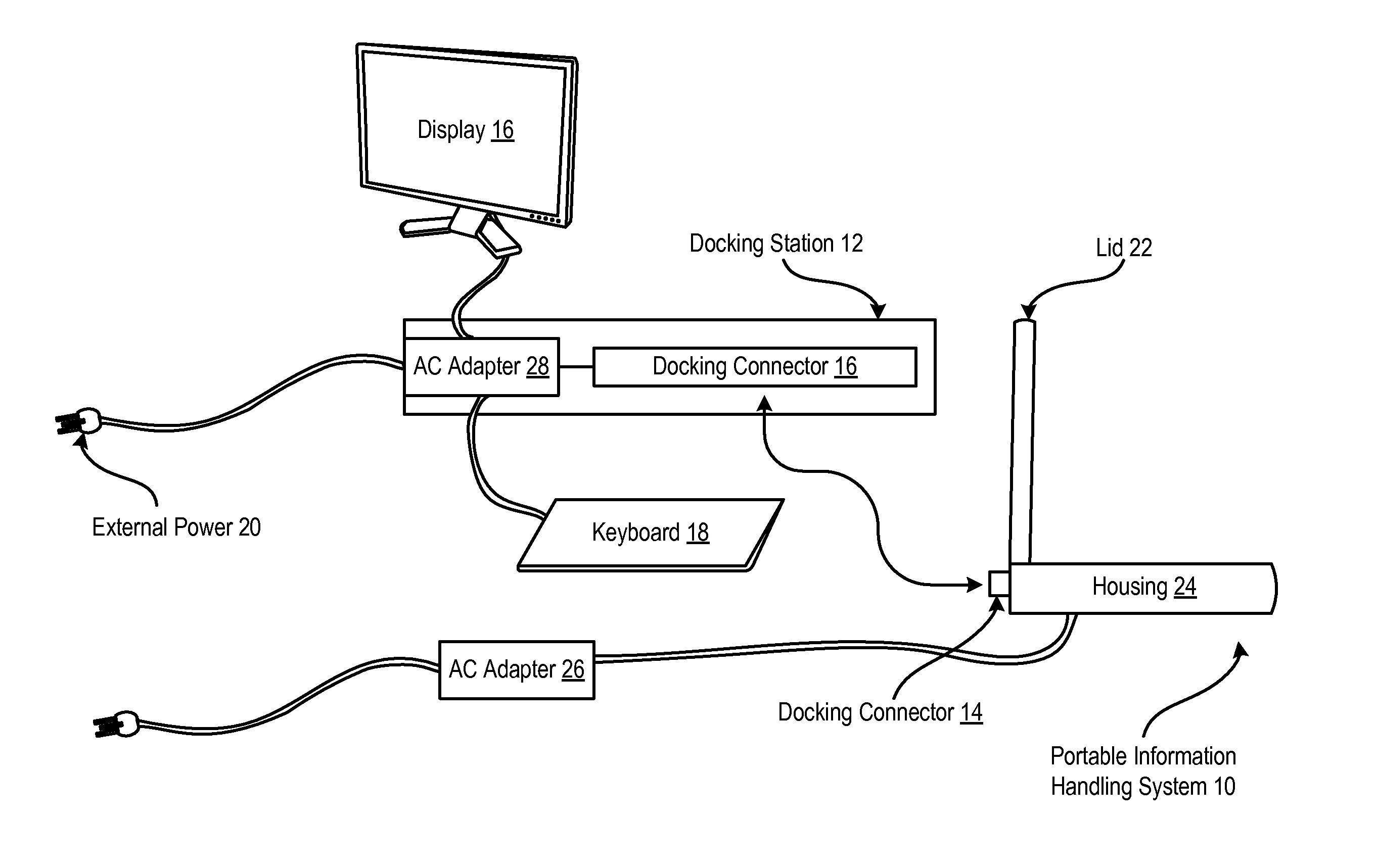
System and Method for Powering Docked Portable Information Handling System
ActiveUS20090033287A1Low costReduce disadvantagesBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsPower sensorDifferential line
A portable information handling system powered through a docking station charges an internal battery based on available power sensed at the docking station and communicated to a charger of the information handling system. A dock sensor on the information handling system selectively interfaces a local power sensor if the information handling system is not docked or a docking station sensor if the information handling system is docked. Available power sensed at the docking station is communicated to a battery charger of the information handling system by a differential wire pair interfaced through a docking connector.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
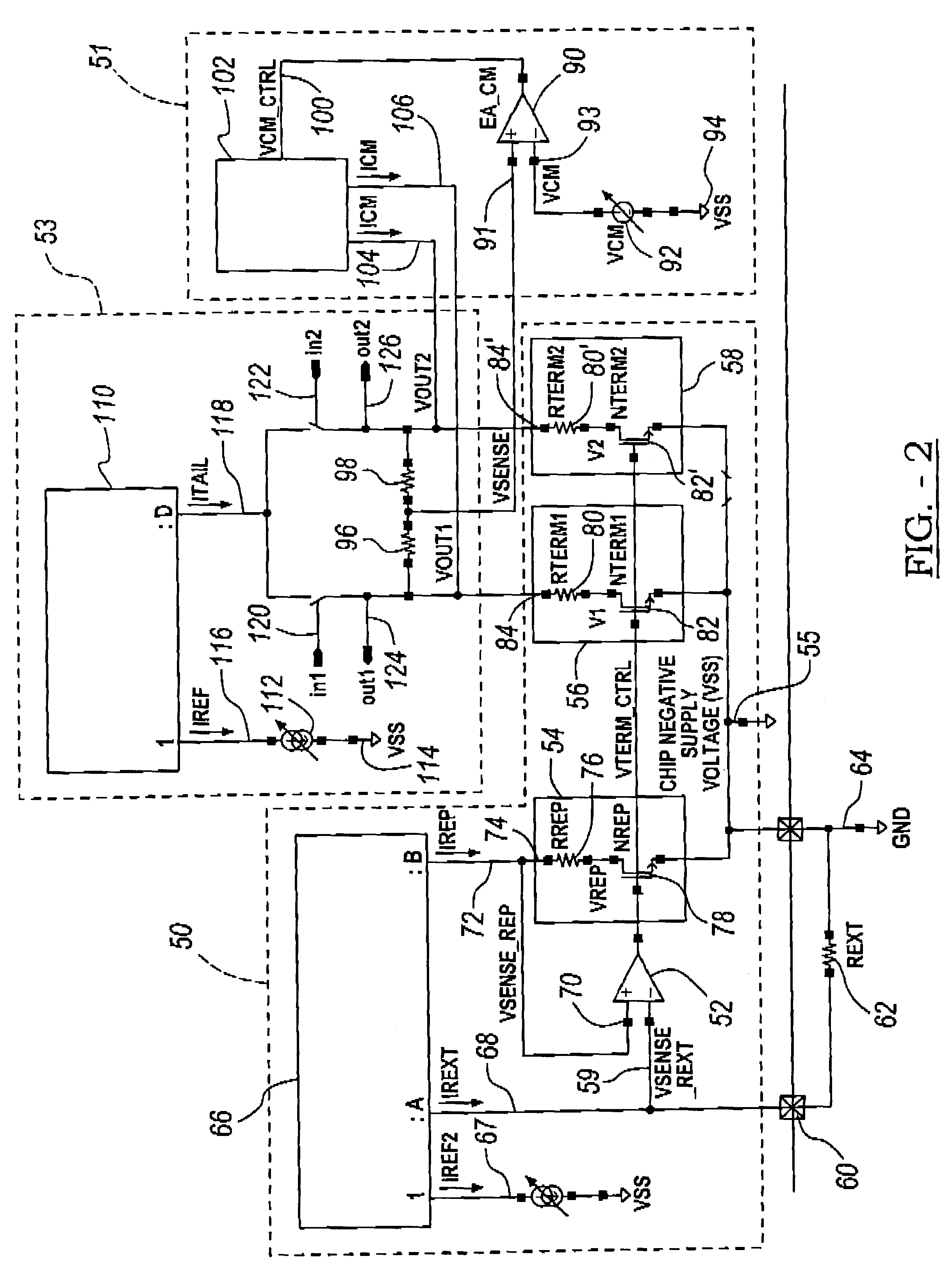
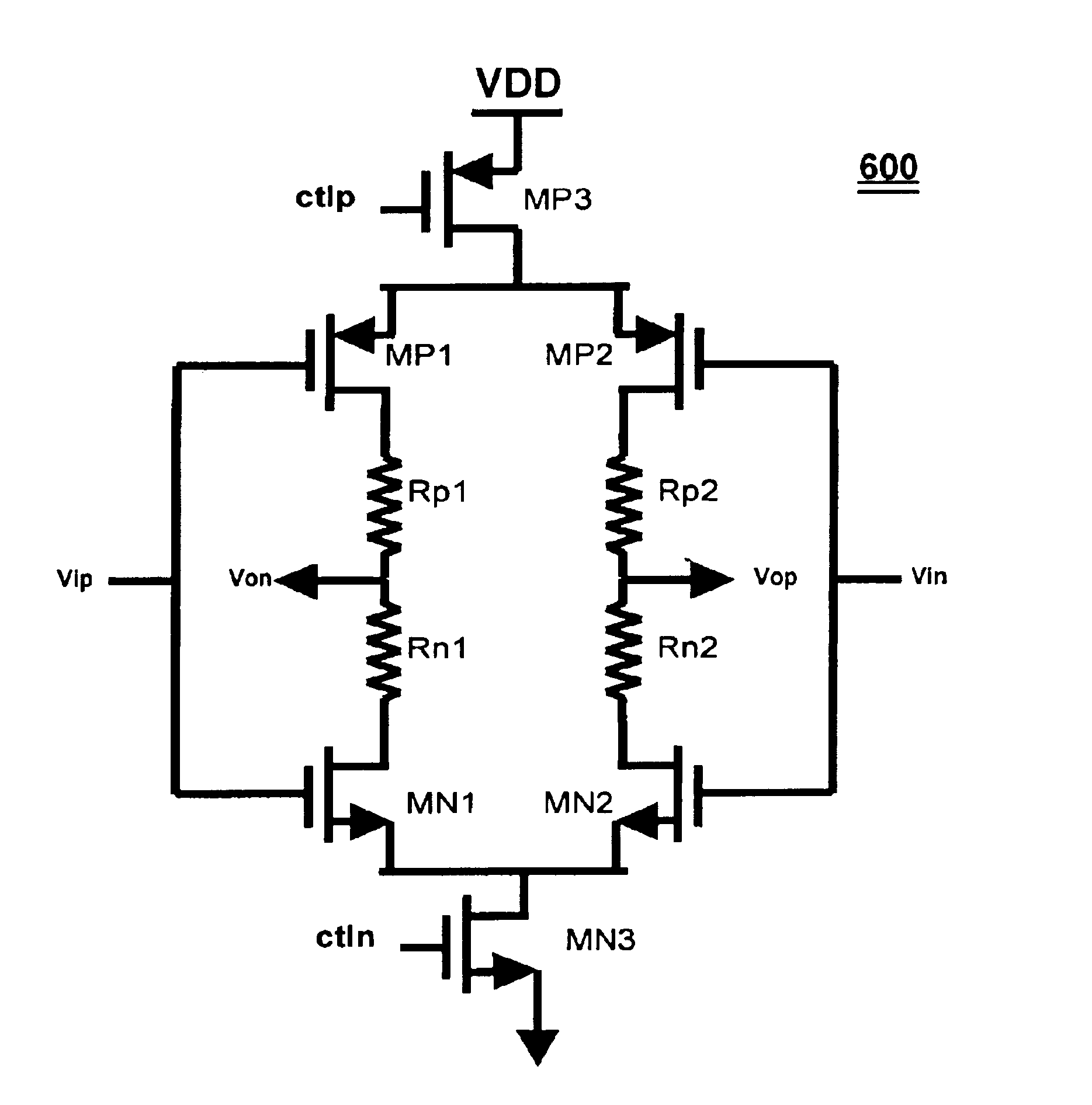
Series terminated CMOS output driver with impedance calibration
InactiveUS6894543B2Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsCMOSDifferential line
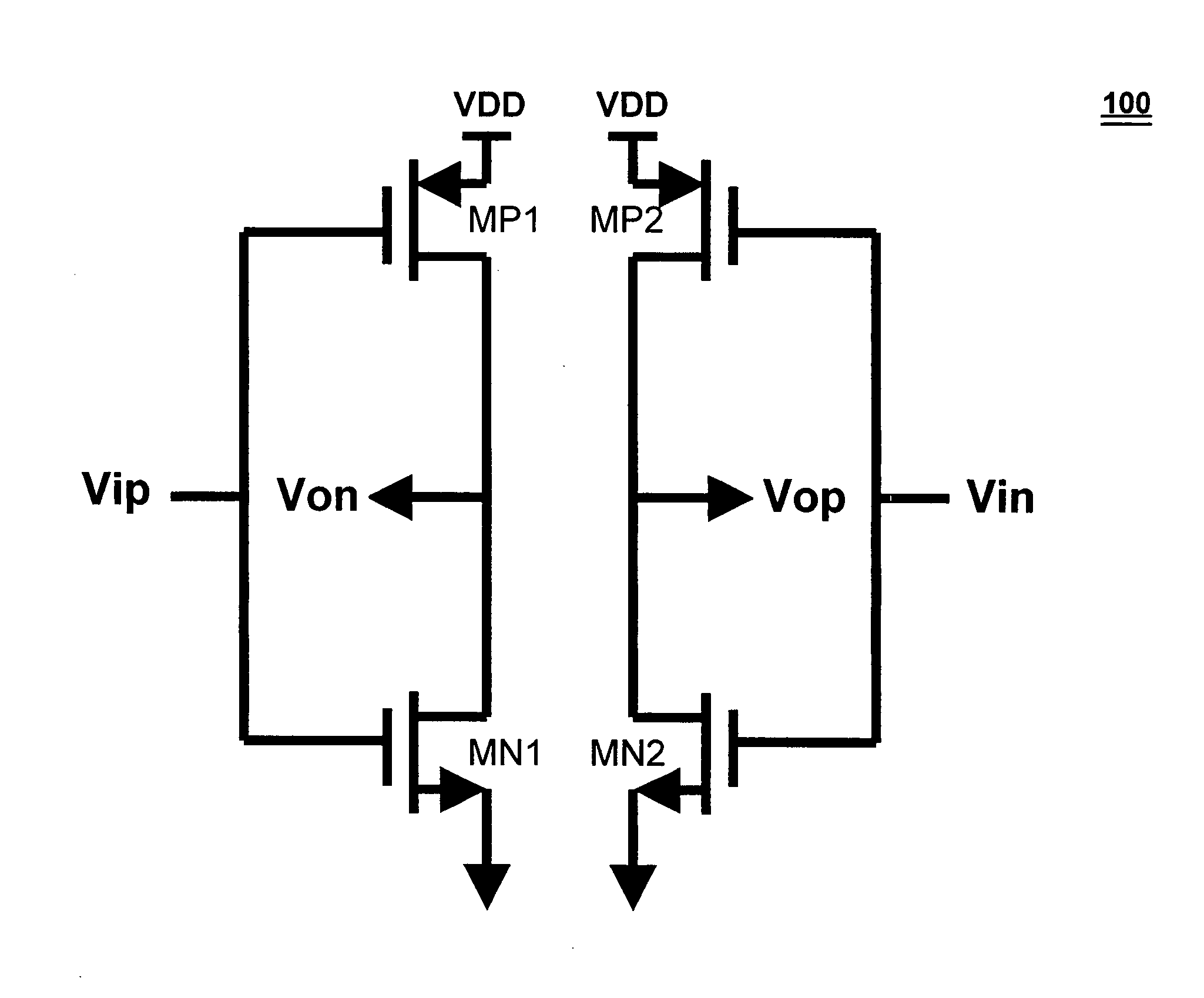
A differential line driver includes a plurality of driver cells. Control logic outputs positive and negative control signals to the driver cells so as to match a combined output impedance of the driver cells at (Vop, Von). Each driver cell includes an input Vip and an input Vin, an output Vop and an output Von, a first PMOS transistor and a first NMOS transistor having gates driven by the input Vip, and a second PMOS transistor and a second NMOS transistor having gates driven by the input Vin. A source of the first PMOS transistor is connected to a source of the second PMOS transistor. A source of the first NMOS transistor is connected to a source of the second NMOS transistor. First and second resistors are connected in series between the first PMOS transistor and the first NMOS transistor, and connected together at Von. Third and fourth resistors are connected in series between the second PMOS transistor and the second NMOS transistor, and connected together at Vop. A first output switch is driven by a corresponding positive control signal and connected between a supply voltage and the sources of the first and second PMOS transistors. A second output switch driven by a corresponding negative control signal and connected between a ground and the sources of the first and second PMOS transistors.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
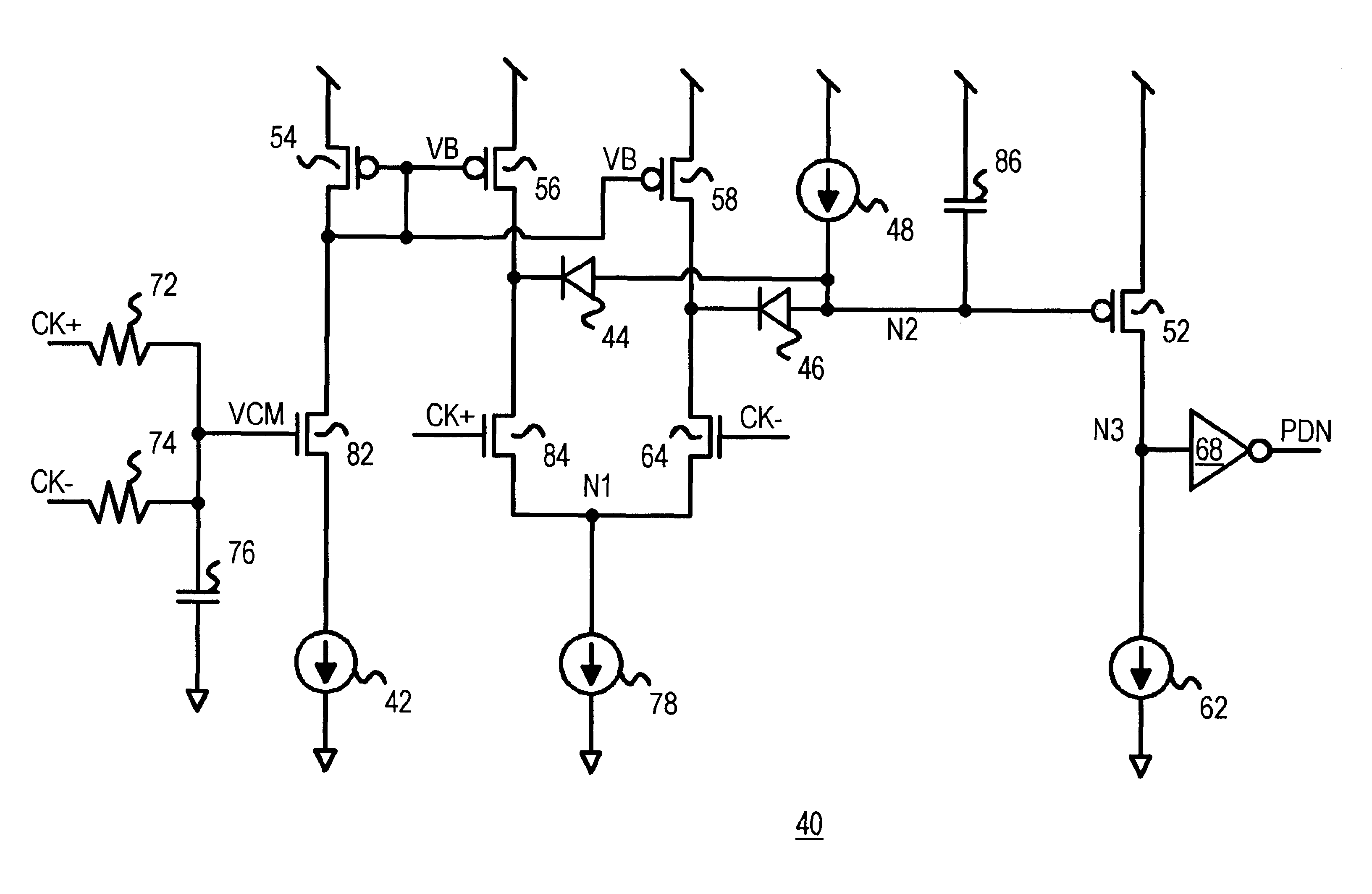
Clock presence detector comparing differential clock to common-mode voltage
InactiveUS6791369B1Energy efficient ICTMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDifferential lineReverse current
Presence or absence of a differential clock is detected. The voltage of each differential clock line is compared to the common-mode voltage and integrated over time by a capacitor. The capacitor is discharged during the portions of the clock cycle that the differential line is over the common-mode voltage. If the clock stops pulsing the capacitor is charged by a current source to activate a clock-loss signal. The clock-loss detector is ideal for high-frequency operation since each differential clock line is applied to only one transistor gate. The common-mode voltage generates a bias voltage for a differential amplifier that receives the true and complement differential clock lines. Diodes prevent capacitor charging by reverse current flow from the differential amplifier when the clock is inactive. The averaged peak voltage or envelope of the differential input signals is detected.
Owner:DIODES INC
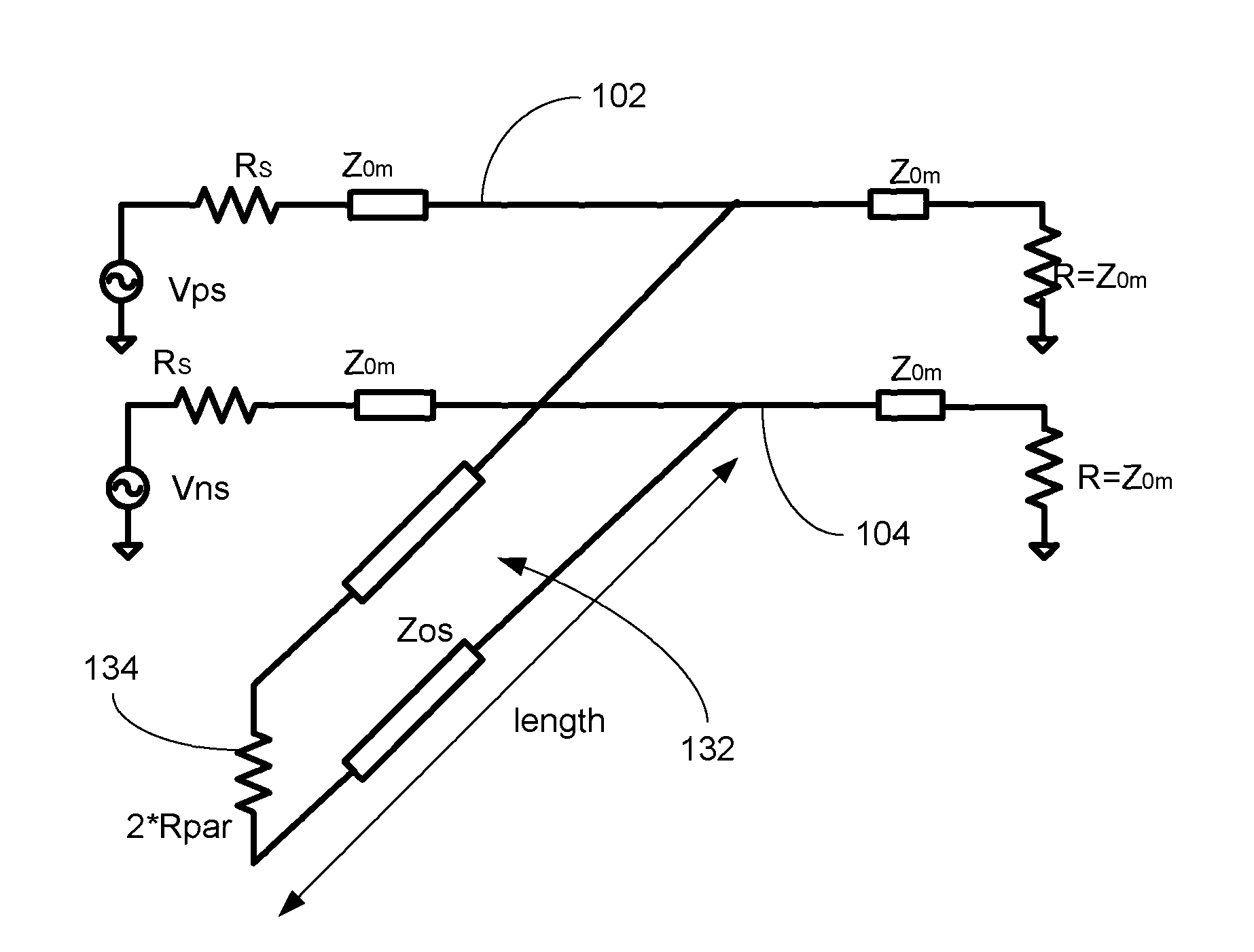
Loaded parallel stub common mode filter for differential lines carrying high rate digital signals
The present invention provides a novel structure that can be used to filter certain selected frequencies of common mode signals. The structure comprises a stub connected in parallel to a transmission line with termination at the end. It is suitable for implementation on printed circuit boards or backplanes, but it can be also used within the chip, either on die or package substrate. The structure can be also used as an equalizer, and can be used in designing an analog equalizer for high-speed circuits.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
Signal transmission system, and signal transmission line
ActiveCN1617120ATransistorElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential lineDifferential signaling
Owner:大冢宽治
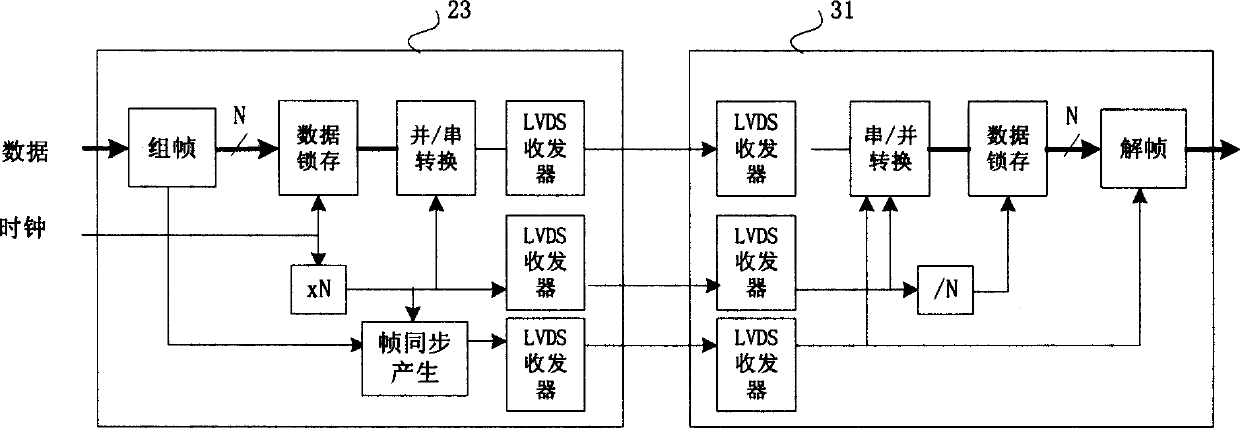
A baseband data transmission apparatus and frame synchronization method thereof
InactiveCN1571412AHigh speed transmissionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlSynchronous/start-stop systemsDifferential lineDifferential signaling
The invention relates to a base band data transmission installation and its frame synchronization method. It includes framing machine, serializer, deserialiser, deframing machine, synchronizing frame inserting controller. The serializer and the deserialiser are physically connected by low pressure high speed differential line. The framing machine is used to form the user data to user data frame with the same length. Meanwhile, the synchronizing frame inserting controller inserted synchronizing frame to free frame position periodically, the user data frame and the synchronizing frame are formed to parallel data. The serializer transforms the parallel data after framing to serial data by coding, and transforms to differential signal and transmits out by the low pressure high speed differential line. After the deserialiser transforms the received differential signal to single end signal, the serial data will be transformed to parallel data. The deframing machine finds the frame boundary according to the frame synchronization information contained in the received parallel data, then, each of the received frame data will be distributed to the after stage unit to use. The advantage of the installation and method of the invention is that the band width took up is small, the transmission efficiency is high, and the cost of the frame synchronization is reduced.
Owner:晋江市高新技术开发办公室
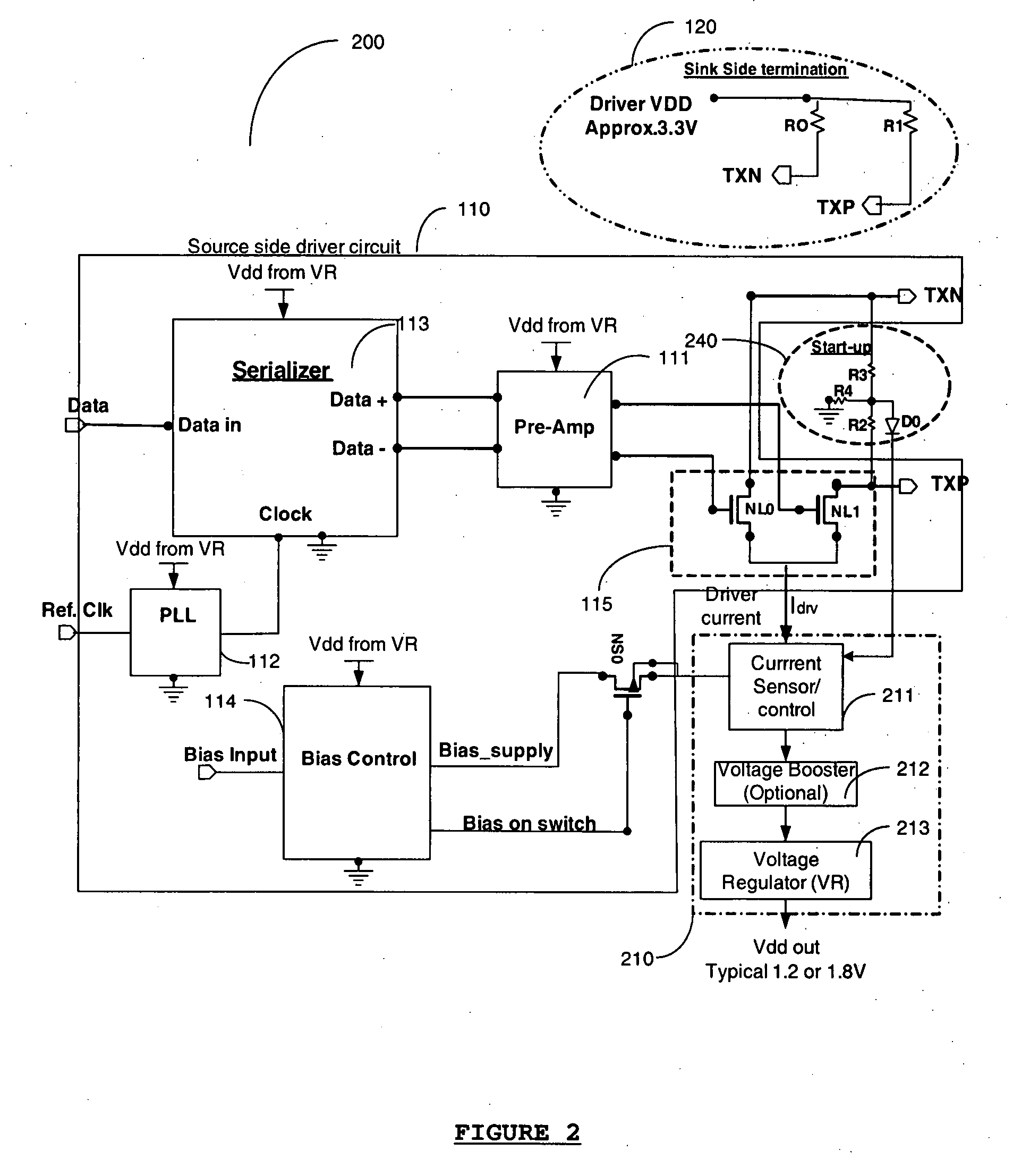
Apparatus and method for recovery of wasted power from differential drivers
InactiveUS20080278224A1Power reduction by energy recoveryPower reduction by adiabatic operationElectrical resistance and conductanceDifferential line
An apparatus and method for supplying power to circuits of an integrated circuit (IC) from the wasted power in low-swing high-speed differential line drivers used in the IC, is disclosed. In a high speed line driver the load resistors of the driver are connected to a power supply, either the local power supply or the receiver power supply. DC power for the driver is supplied through these resistors. A large portion of this power, supplied from the power supply is wasted in the DC set-up circuit of the differential line driver. It is proposed to use this wasted power to power selected circuits of an IC. The use of this wasted power from the drivers for powering the circuits reduces the overall power dissipation of the system.
Owner:ANALOGIX SEMICON
Transmission lines for CMOS integrated circuits
InactiveUS7101778B2Reduce signal delayReduction in skew and crosstalkSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSignal delay
Improved methods and structures are provided for impedance-controlled low-loss lines in CMOS integrated circuits. The present invention offers a reduction in signal delay. Moreover, the present invention further provides a reduction in skew and crosstalk. Embodiments of the present invention also provide the fabrication of improved transmission lines for silicon-based integrated circuits using conventional CMOS fabrication techniques. One method of the present invention provides transmission lines in an integrated circuit. Another method includes forming transmission lines in a memory device. The present invention includes a transmission line circuit, a differential line circuit, a twisted pair circuit as well as systems incorporating these different circuits all formed according to the methods provided in this application.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Low loss interconnect structure for use in microelectronic circuits
InactiveUS6909127B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDifferential lineDifferential signaling
A low loss on-die interconnect structure includes first and second differential signal lines on one of the metal layers of a microelectronic die. One or more traces may also be provided on another metal layer of the die that are non-parallel (e.g., orthogonal) to the differential signal lines. Because the traces are non-parallel, they provide a relatively high impedance return path for signals on the differential signal lines. Thus, a signal return path through the opposite differential line predominates for the signals on the differential lines. In one application, the low loss interconnect structure is used within an on-die salphasic clock distribution network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Optical semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050067698A1Improve wavinessLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDifferential lineDevice material
The present invention includes a first conductor line connected to one end of an optical semiconductor element (20), and supplying an electric signal to this optical semiconductor element (20); a second conductor line connected to the other end of the optical semiconductor element (20), and supplying an electric signal to this optical semiconductor element (20); a first inductance element (21a) connected to the one end of the optical semiconductor element (20), and cutting off the electric signal at a high frequency; and a second inductance element (21b) connected to the other end of the optical semiconductor element (20), and cutting off the electric signal at the high frequency, wherein the first and the second conductor lines constitute differential lines.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
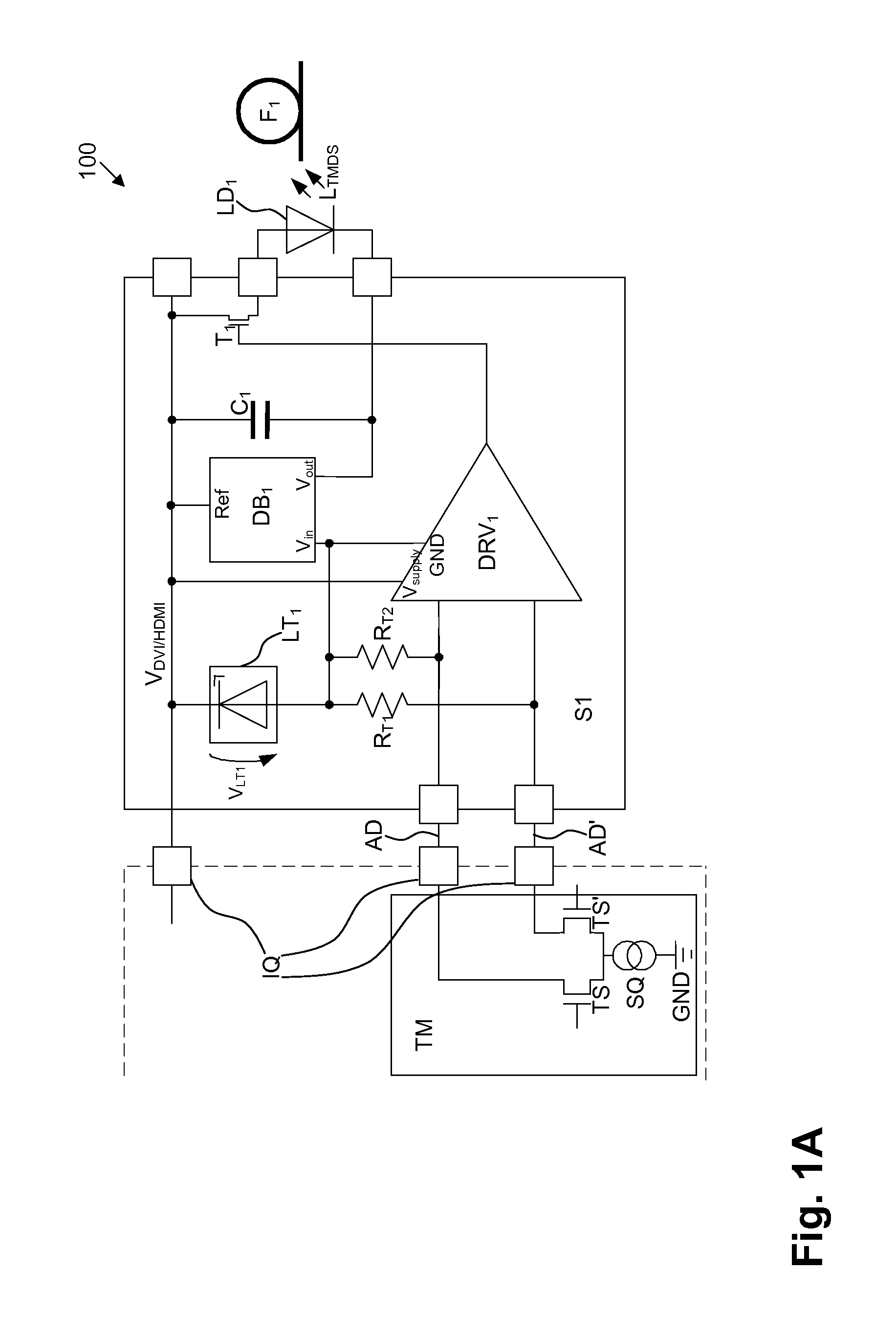
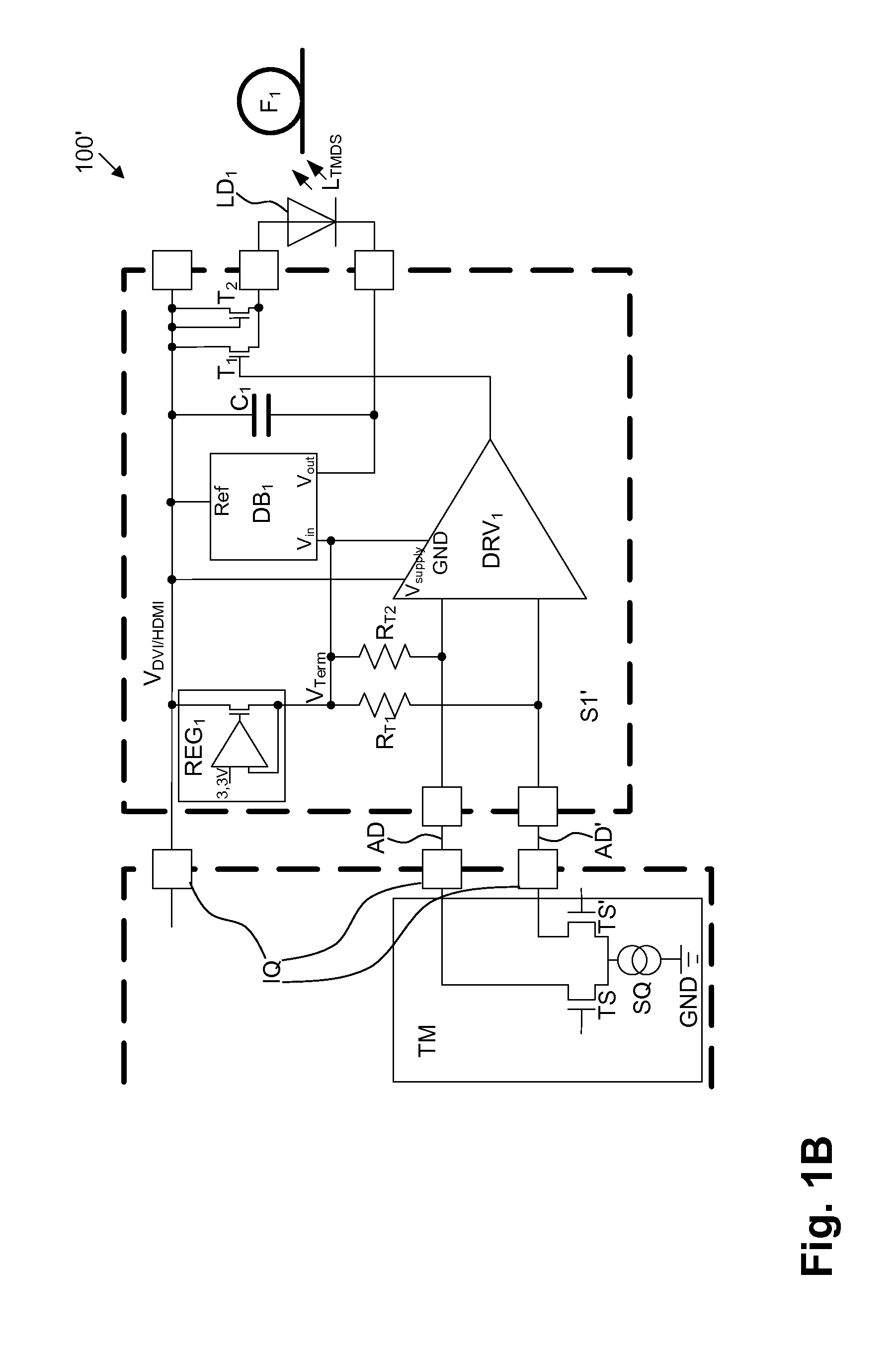
Circuit arrangement and method for transmitting TMDS encoded signals
ActiveUS8824898B2Cheap for transmissionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDriver circuitDifferential line
For providing circuit arrangement and method for transmitting signals from a data source to a data sink, the signals being TMDS encoded, the driver circuit is supplied by a connection interface, connected upstream, assigned to data source, with supply voltage, electrical TMDS encoded signals are electro-optically converted by an LED connected downstream of the driver circuit and coupled into an optical fiber as light supplied with TMDS encoded signals, the direct current portion supplied from TMDS transmitter to connection interface, to data source, is converted by driver circuit to a modulated signal current for controlling LED. Light supplied with TMDS encoded signals decoupled out from optical fiber by light-absorbing element, opto-electrically converted and supplied to transimpedance converter circuit connected downstream of light-absorbing element and upstream of connection interface assigned to data sink, transimpedance converter circuit being supplied by direct voltage portion being applied to differential pair of wires.
Owner:SILICON LINE
Differential signal routing line distributing system and differential signal routing line distributing method
InactiveCN103366023AReduce common mode noiseComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsDifferential lineSignal routing
A layout method for the creation of a differential pair for the transmission of signals generates a differential pair between a differential signal sender and a differential signal receiver in a layout of a PCB. Differential signals are transmitted via two wires. A plurality of vertical lines are created on the differential pair. Junctions of the vertical lines and the two wires are defined as pairs of points. A first length between one terminal of the differential signal sender and one point of each pair of points and a second length between the other terminal of the differential signal sender and the other point of each pair of points are calculated. If any difference between the first length and the second length does not fall within an allowable range, the lengths of the two wires are adjusted.
Owner:DONGYING POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +2
Grounding member for cable assembly
InactiveUS20090197467A1Coupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsConnection contact member materialDifferential lineGround contact
An cable assembly (100) includes an insulated housing (1) extending along a front-to-back direction; a plurality of contacts (2) arranged in a row and supported by the insulated housing, said contacts including three grounding contact members spaced by two pair of signal contact members; a cable (4) including two juxtaposed differential wire pairs (41) respectively enclosed by conductive shielding portions (43); a grounding member (3) including a main portion (31), three finger portions (33) extending forwardly from a front side of the main portion and two arm portions (32) formed at lateral sides of a rear segment of the main portion, said grounding member (3) securely engaged with the cable via the two arm portions thereof griping the conductive shielding portions; and the finger portions soldered to the grounding contact members, and inner conductors of the differential pairs soldered to the signal contact members, respectively.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Lowpass-bandstop common mode filter for differential lines carrying high rate digital signals
ActiveUS7812693B1Current interference reductionUnbalanced current interference reductionDifferential lineHigh rate
The present invention provides a novel structure that can be used to make a common mode filter. Only the common mode will be attenuated and the differential mode will not be attenuated. This structure can be implemented in a number of ways, a specific embodiment using strip-line and slot-line junctions is very compact and well-suited to use with multilayer PCBs, and does not require any extra components. It can be designed to attenuate certain discrete frequencies, by designing the poles of the transfer function to be at these frequencies.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
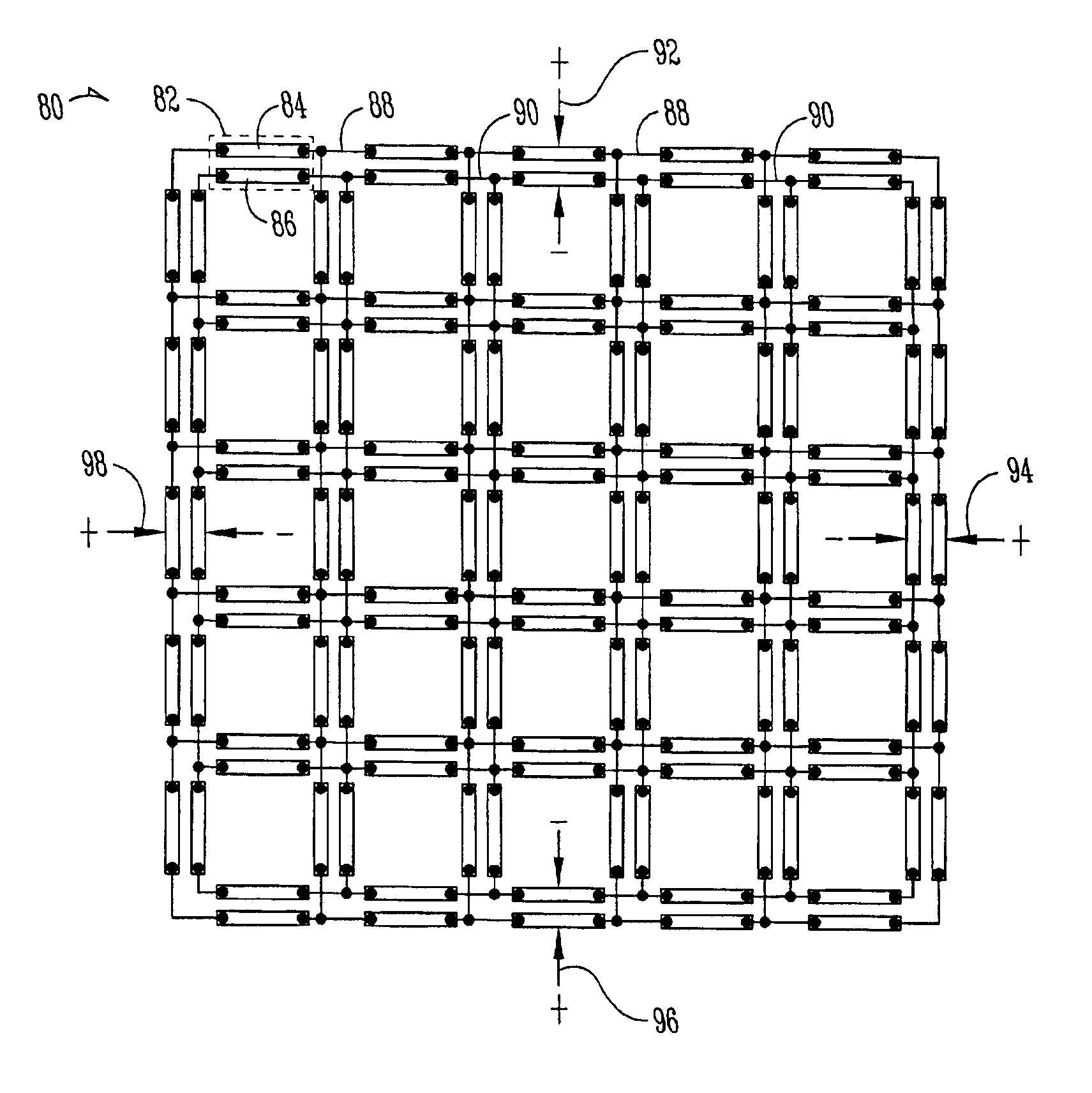
Coupling cancellation scheme
ActiveUS7830221B2Multiple-port networksElectrical connection printed elementsDifferential lineCoupling
Methods and apparatus are disclosed, such as those involving an interconnection layout for an integrated circuit (IC). One such layout includes a plurality of differential pairs of lines. Each differential pair has two lines including one or more parallel portions extending substantially parallel to each other. Each pair also includes a shield line. Each of the shield lines includes one or more parallel portions interposed between the parallel portions of one of the pairs of differential lines. One or more of the shield lines are electrically connected to a voltage reference, such as ground. This layout is believed to reduce or eliminate intra-pair coupling as well as inter-pair coupling.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Parallel wiring and integrated circuit
ActiveUS20050056455A1Excellent crosstalk robustnessFlat/ribbon cablesWaveguidesDifferential lineIntegrated circuit
A parallel wiring according to the present invention includes a plurality of differential lines juxtaposed in a reference direction, wherein each differential line includes two wiring lines which are substantially parallel to each other, and the two wiring lines oppose each other obliquely with respect to the reference direction.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Wiring method of differential signal line and PCB
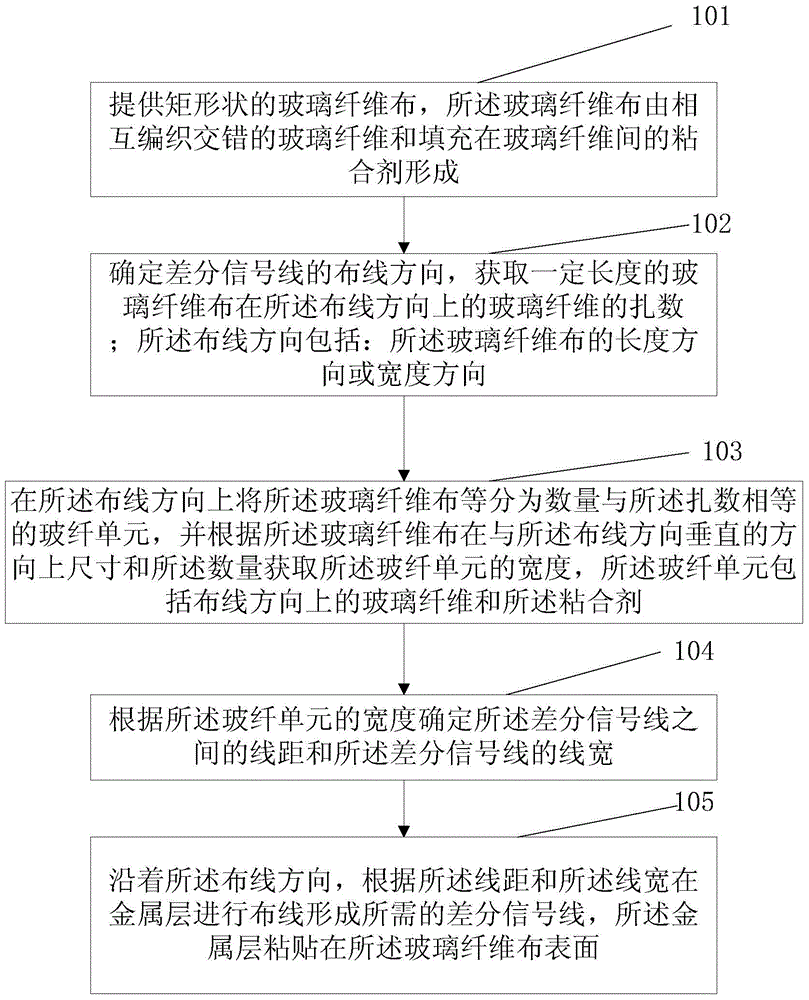
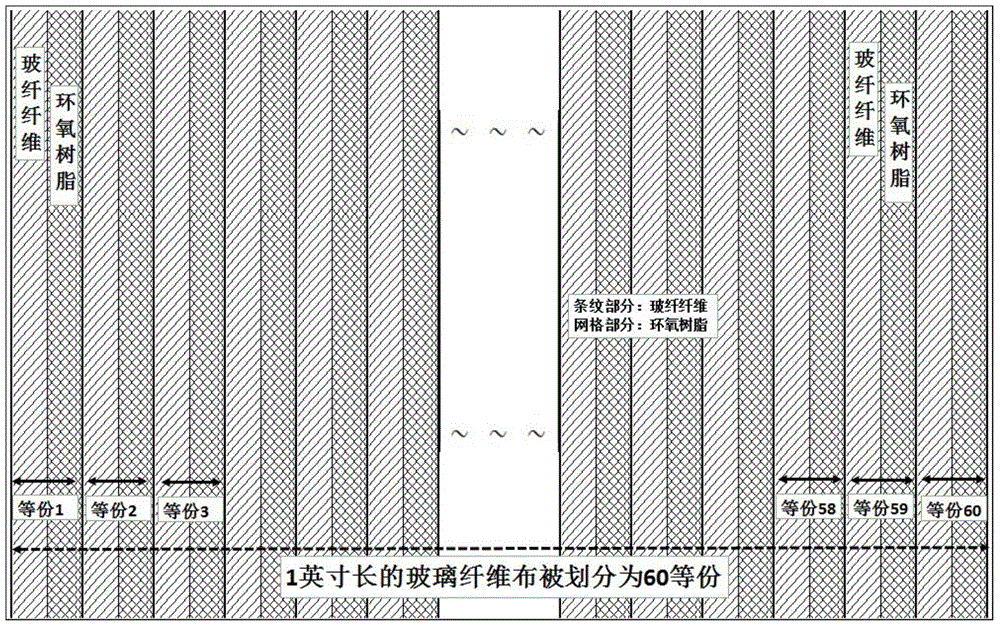
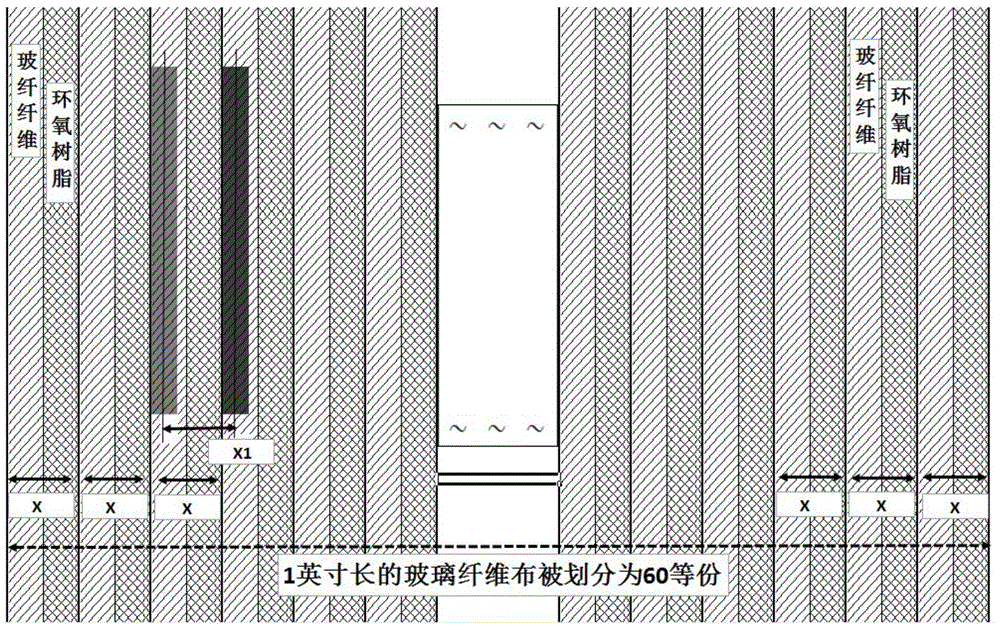
ActiveCN105704931APracticalImprove signal qualityPrinted circuit aspectsConductive pattern formationDifferential lineAdhesive
The invention discloses a wiring method of a differential signal line and a PCB. The wiring method includes: rectangular fiberglass fabrics are provided, and the fiberglass fabrics are formed by fiberglass mutually woven in a staggered manner and adhesives filled between the fiberglass; the wiring direction of the differential line is determined, and the bundle number of the fiberglass of the fiberglass fabrics in the direction is obtained; the wiring direction comprises the length direction or the width direction of the fiberglass fabrics; the fiberglass fabrics are divided into fiberglass units with the number equal to the bundle number in the wiring direction, the width of the fiberglass units is obtained according to the dimension and the quantity of the fiberglass fabrics in the direction vertical to the wiring direction, and the fiberglass units comprise fiberglass in the wiring direction and the adhesives; the line distance and the line width of the differential signal line are determined according to the width of the fiberglass units; and wiring is performed on a metal layer along the wiring direction according to the line distance and the line width to form the required differential signal line, and the metal layer is pasted on the surface of the fiberglass fabrics. According to the method, the problems of high cost, large occupied wiring space, and long wiring time of the conventional control differential signal delay wiring method are solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
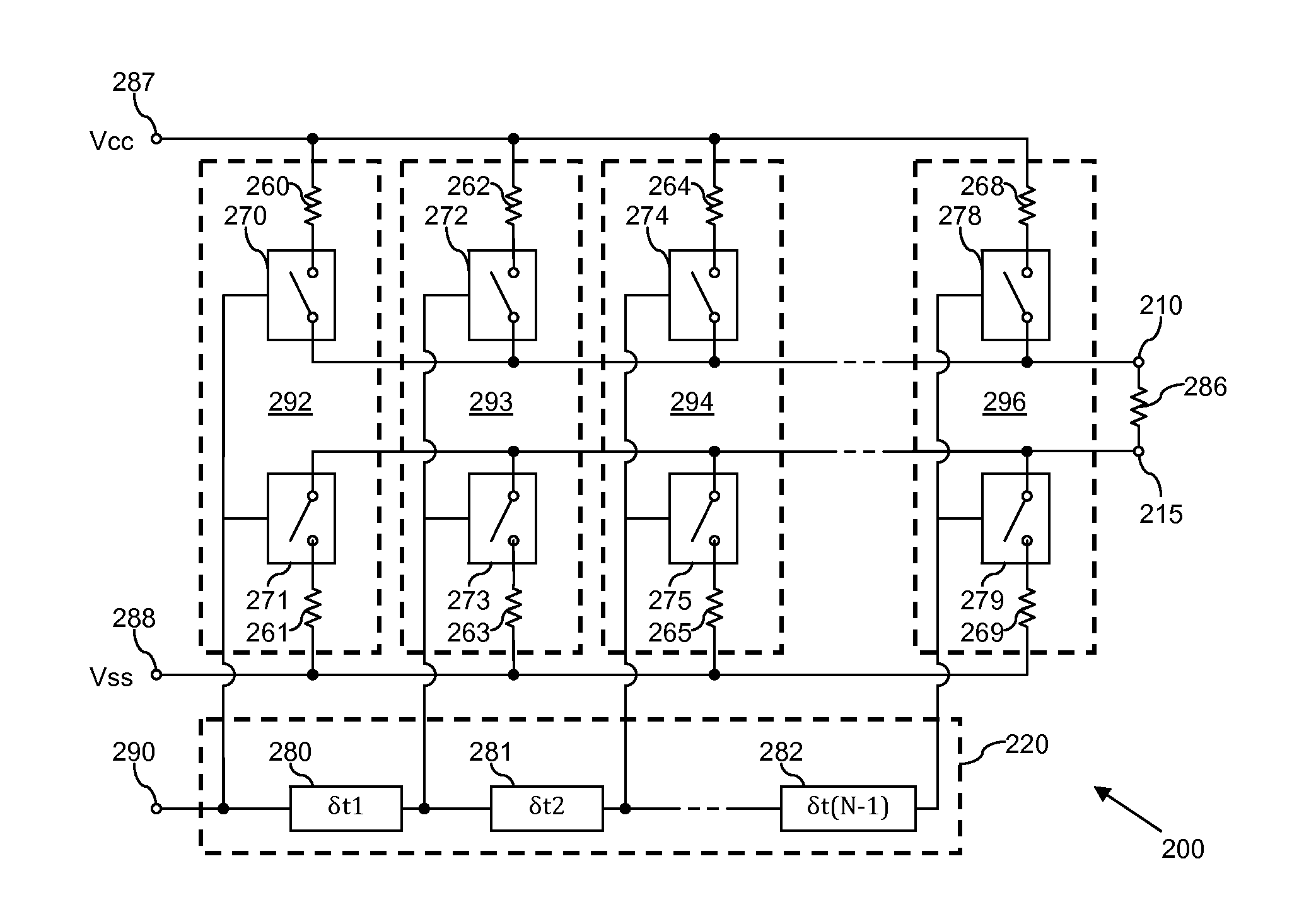
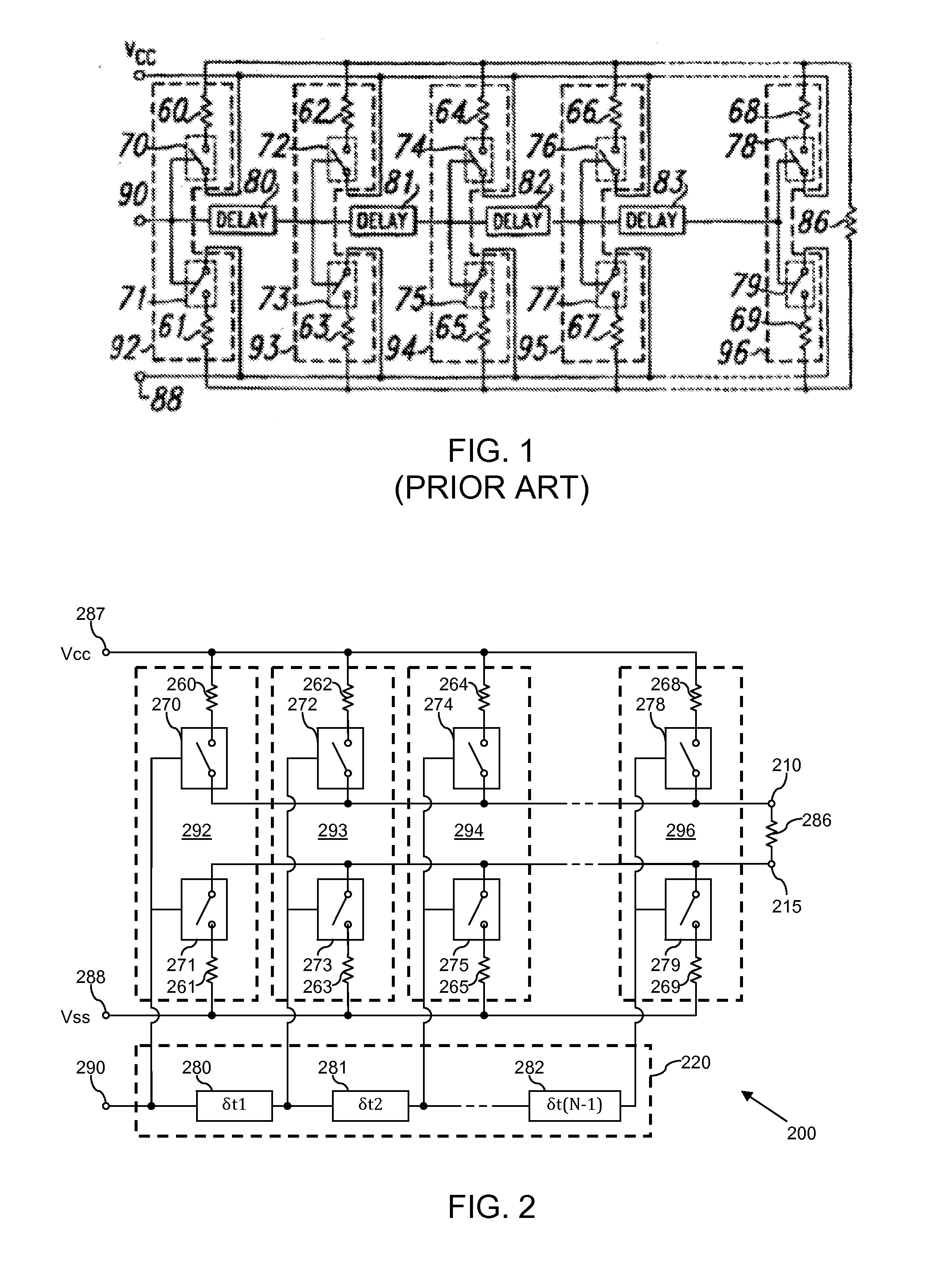
Differential line driver circuit and method therefor
A differential line driver circuit comprising a plurality of driver stages is described. Each driver stage is operably coupled to at least one output of the line driver circuit and arranged to receive at least one control signal and to drive at least one output signal on the at least one output of the line driver circuit in accordance with the at least one control signal received thereby. The line driver circuit further comprises at least one delay component arranged to receive the at least one control signal, and to sequentially propagate the at least one control signal to the driver stages with time delays between the propagation of the at least one control signal to sequentially adjacent driver stages. The delay component is arranged to sequentially propagate the at least one control signal to the driver stages such that such that the at least one control signal is propagated with at least one of: a progressively increasing time delay between sequentially adjacent driver stages; and a progressively decreasing time delay between sequentially adjacent driver stages.
Owner:NXP USA INC
System and method for arranging differential signal wire
InactiveCN102339332AReduce common mode noiseCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsDifferential lineDifferential signaling
The invention discloses a system for arranging a differential signal wire. The system runs on a computer which comprises a wire arranging tool. The system comprises an establishing module and an adjusting module, wherein the establishing module is used for establishing a differential wire pair between a signal transmitting end and a signal receiving end by using the wire arranging tool; a perpendicular line is drawn on the boundary between a non-parallel region and a parallel region of a differential wire pair lead-out region; two intersection points between the perpendicular line and the differential wire pair refer to points at the same position; a perpendicular line is drawn from a bent position on a wire of the differential wire pair lead-out region to a position passing through an element; intersection points between the perpendicular line and the differential wire pair refer points at the same position; and the adjusting module is used for adjusting the wire of a differential signal when the difference value of the wire distance between the pin of the signal transmitting end and one pair of points at the same position is not in a standard range. The invention further provides a method for arranging a differential signal wire. According to the invention, tight coupling of the differential signal wire can be realized.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
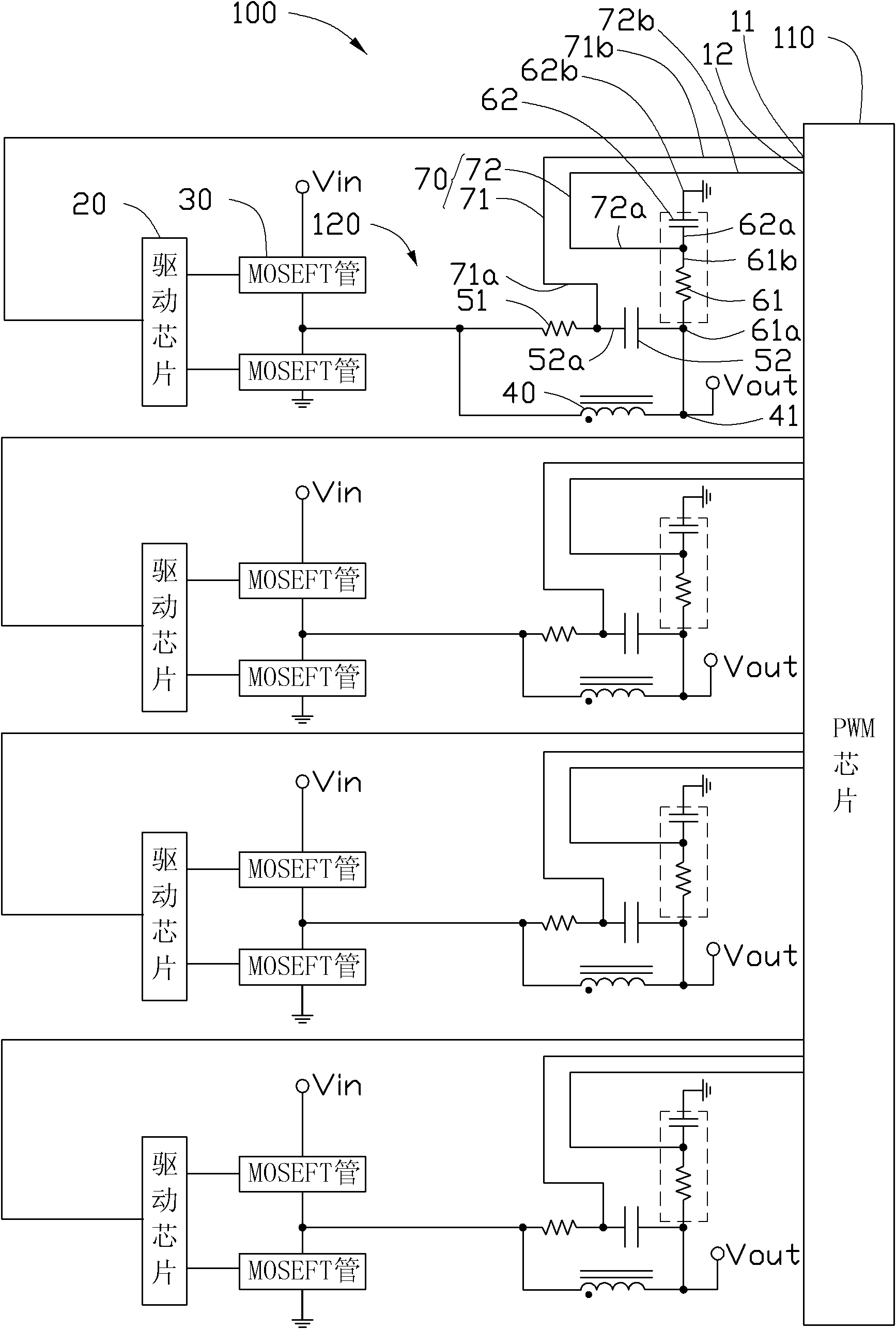
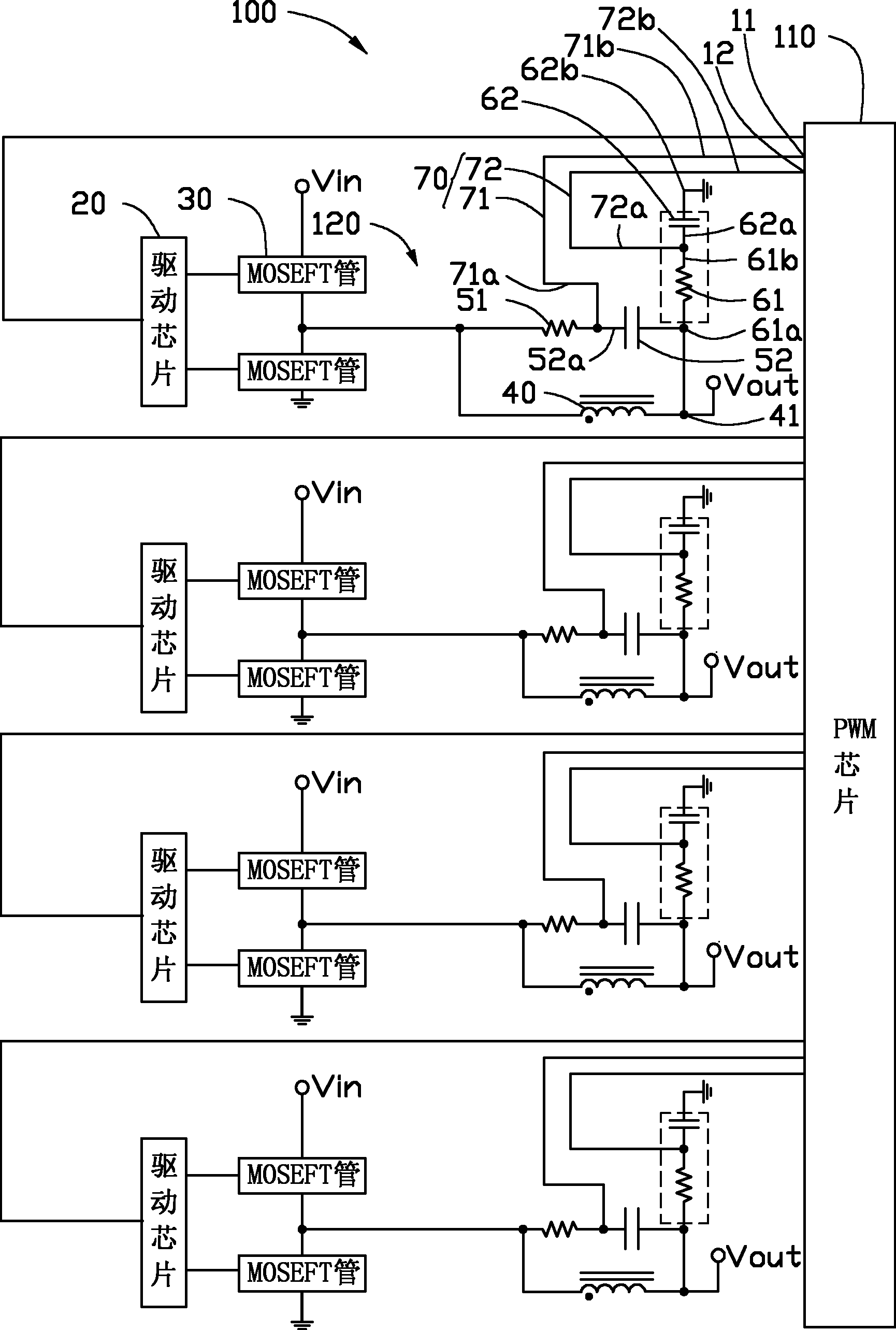
Multiphase power supply circuit
InactiveCN102609066AImprove accuracyExtended sampling timeVolume/mass flow measurementApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceElectricity
A multiphase power supply circuit comprises a PWM (pulse-width modulation) chip and a plurality of sub-circuits. Each sub-circuit comprises an inductor, a first resistor, a first capacitor, a differential line pair, a second resistor and a second capacitor. The first resistor and the first capacitor in each sub-circuit are serially connected, and then are parallelly connected with the inductor in the sub-circuit. The differential line pair in each sub-circuit comprises a first differential line and a second differential line. The first differential line in each sub-circuit is connected between a joint of the corresponding first resistor and the corresponding first capacitor and a terminal of a current sensor of the PWM chip. One end of the second resistor in each sub-circuit is electrically connected to a joint of the corresponding capacitor and the corresponding inductor, one end of the second resistor in each sub-circuit is serially connected with the corresponding second capacitor while the other end of the second capacitor is ground, the second differential line in each sub-circuit is electrically connected between a joint of the corresponding second resistor and the corresponding second capacitor and another terminal of a current sensor of the PWM chip, and the ratio of capacitances of the second capacitors of the sub-circuits is equal to that of lengths of the corresponding differential line pairs. The circuit can prolong sampling time of the long differential line pairs, and increases sampling accuracy.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Transmission lines for CMOS integrated circuits
InactiveUS7554829B2Reduce signal delayReduction in skew and crosstalkSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
Improved methods and structures are provided for impedance-controlled low-loss lines in CMOS integrated circuits. The present invention offers a reduction in signal delay. Moreover, the present invention further provides a reduction in skew and crosstalk. Embodiments of the present invention also provide the fabrication of improved transmission lines for silicon-based integrated circuits using conventional CMOS fabrication techniques. One method of the present invention provides transmission lines in an integrated circuit. Another method includes forming transmission lines in a memory device. The present invention includes a transmission line circuit, a differential line circuit, a twisted pair circuit as well as systems incorporating these different circuits all formed according to the methods provided in this application.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Series terminated CMOS output driver with impedance calibration
InactiveUS20050127958A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDifferential lineCMOS
A differential line driver includes a plurality of driver cells. Control logic outputs positive and negative control signals to the driver cells so as to match a combined output impedance of the driver cells at (Vop, Von). Each driver cell includes an input Vip and an input Vin, an output Vop and an output Von, a first PMOS transistor and a first NMOS transistor having gates driven by the input Vip, and a second PMOS transistor and a second NMOS transistor having gates driven by the input Vin. A source of the first PMOS transistor is connected to a source of the second PMOS transistor. A source of the first NMOS transistor is connected to a source of the second NMOS transistor. First and second resistors are connected in series between the first PMOS transistor and the first NMOS transistor, and connected together at Von. Third and fourth resistors are connected in series between the second PMOS transistor and the second NMOS transistor, and connected together at Vop. A first output switch is driven by a corresponding positive control signal and connected between a supply voltage and the sources of the first and second PMOS transistors. A second output switch driven by a corresponding negative control signal and connected between a ground and the sources of the first and second PMOS transistors.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com